Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
589 results about "Acoustic frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
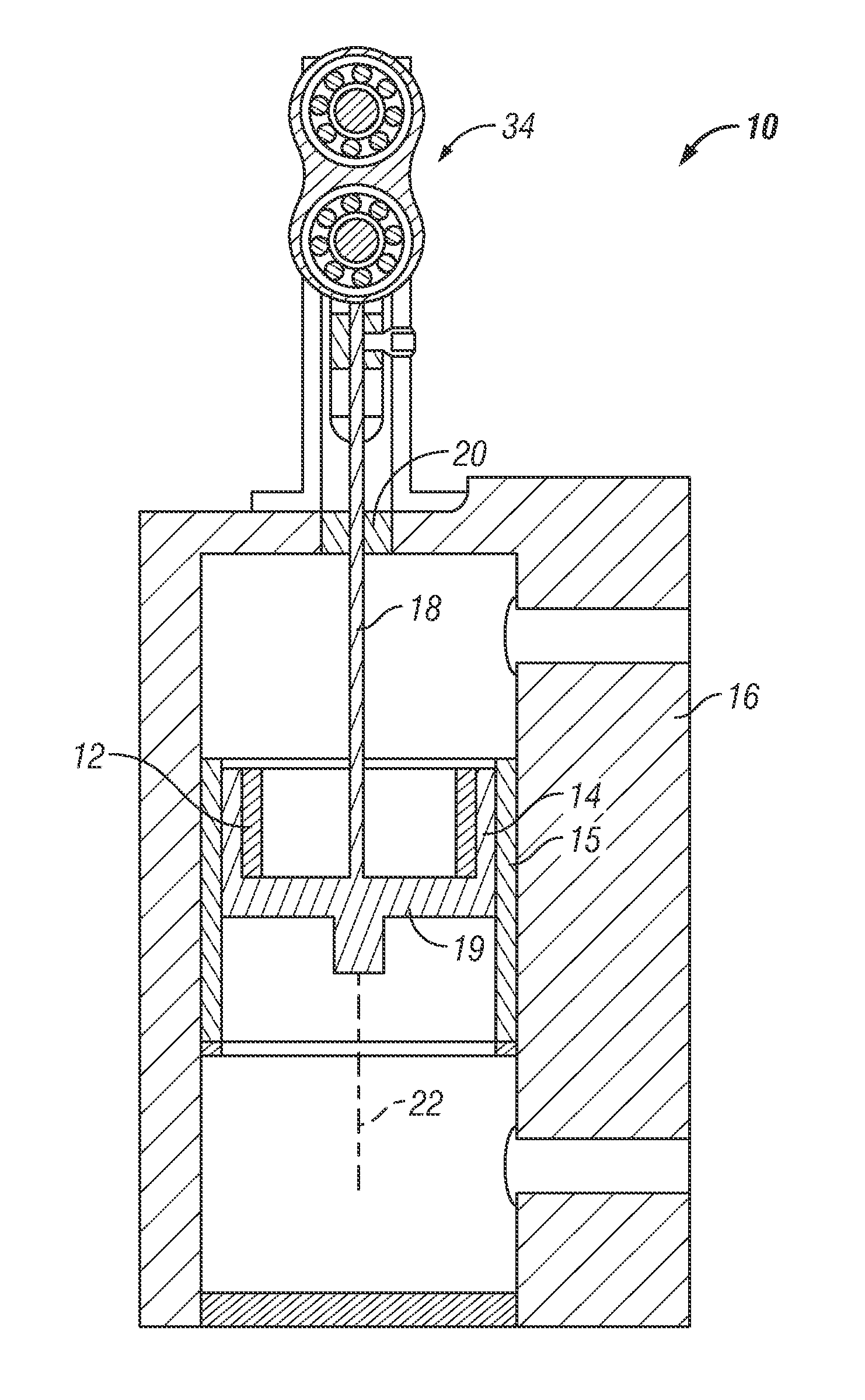
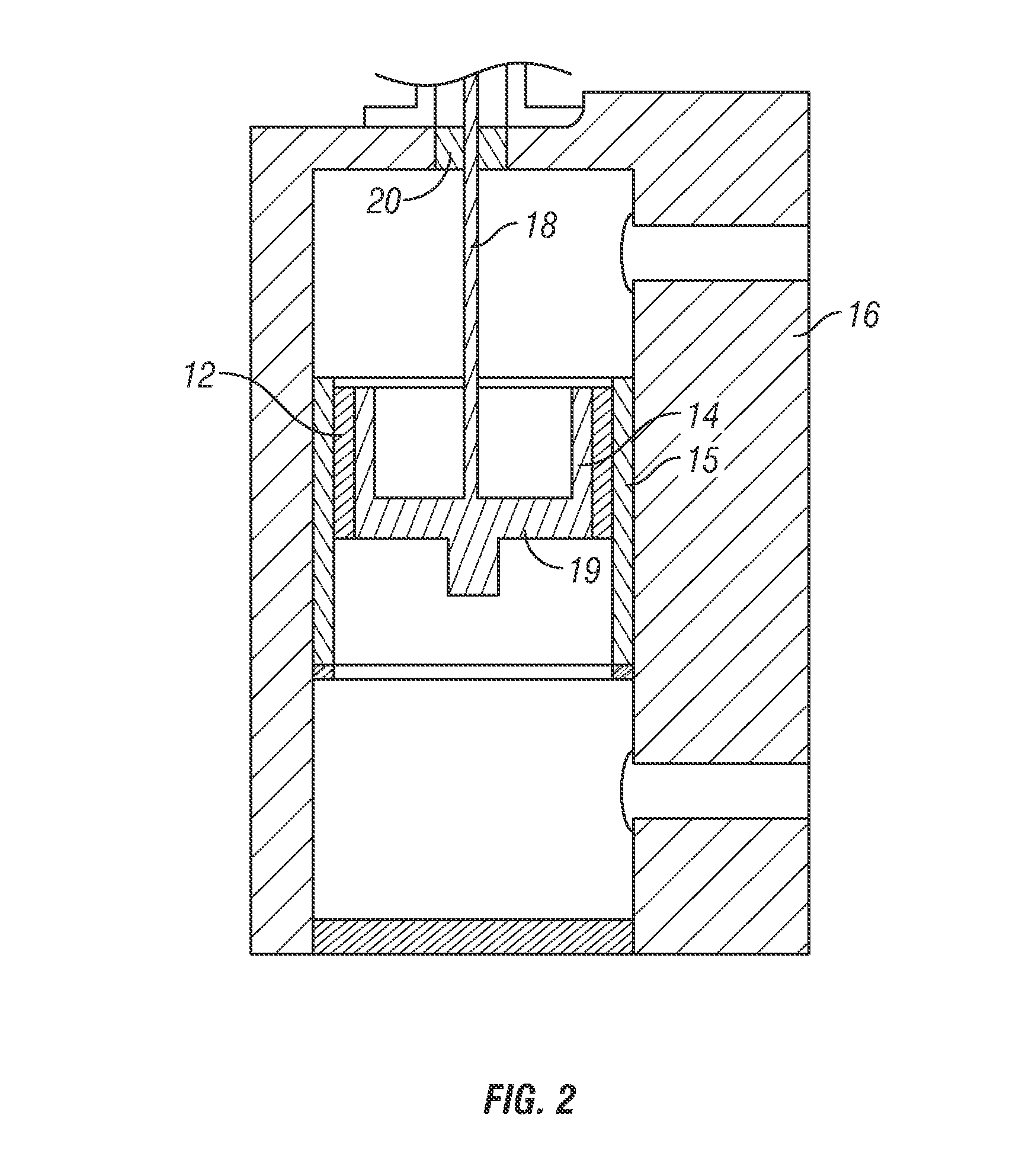
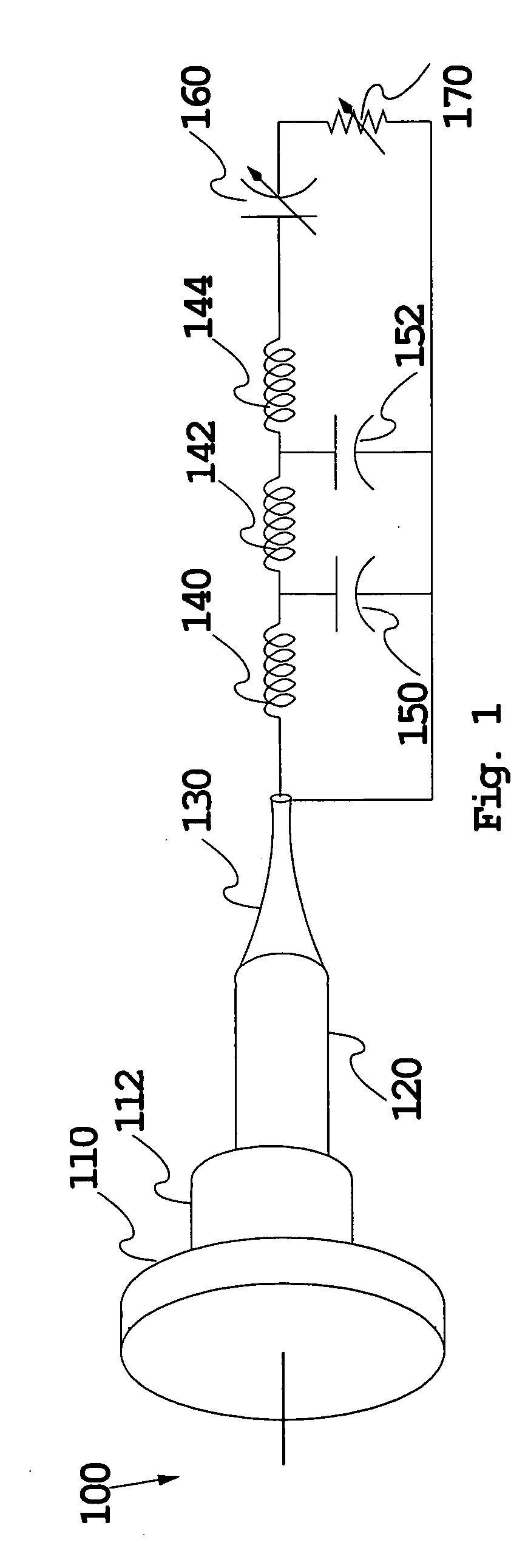
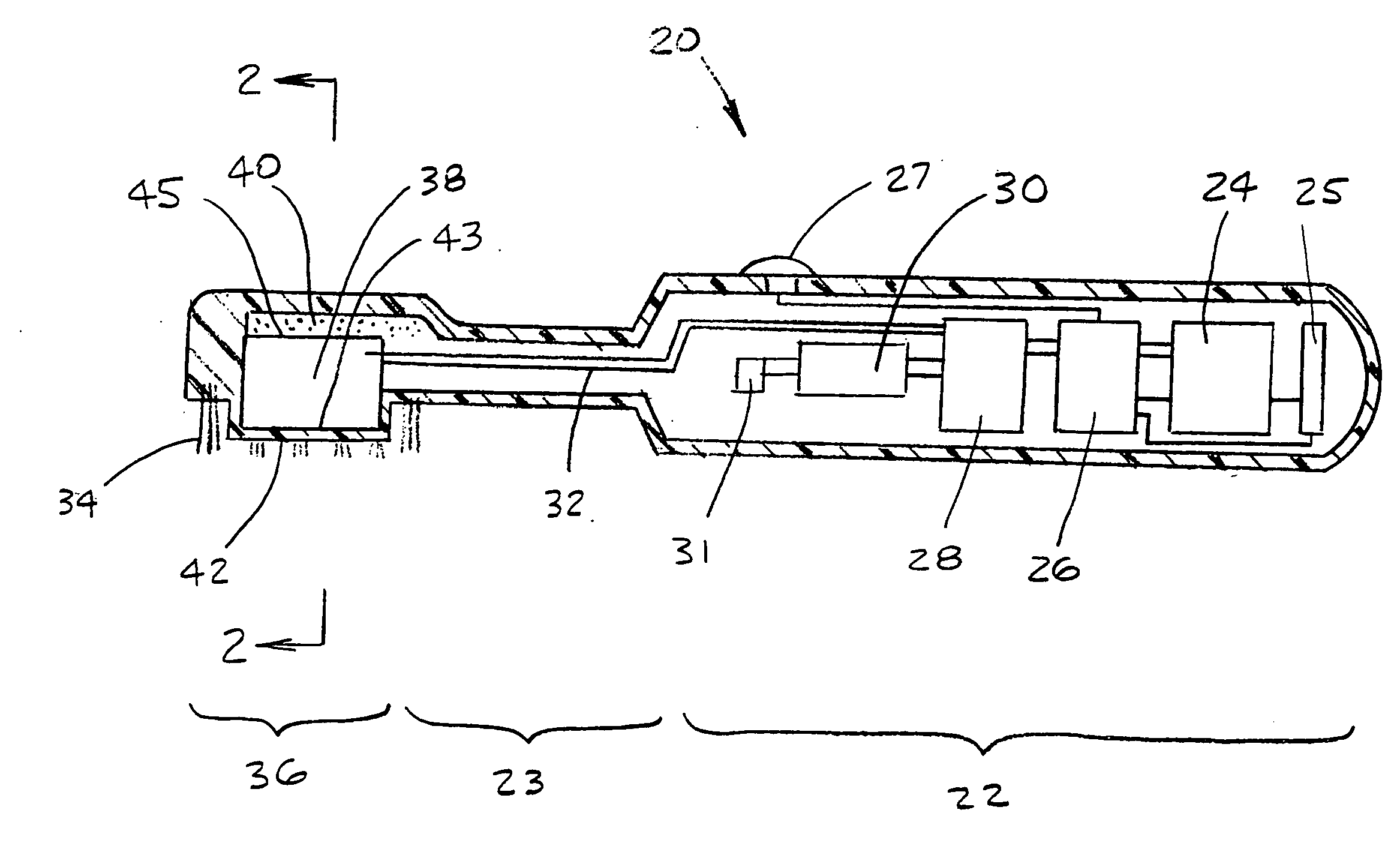
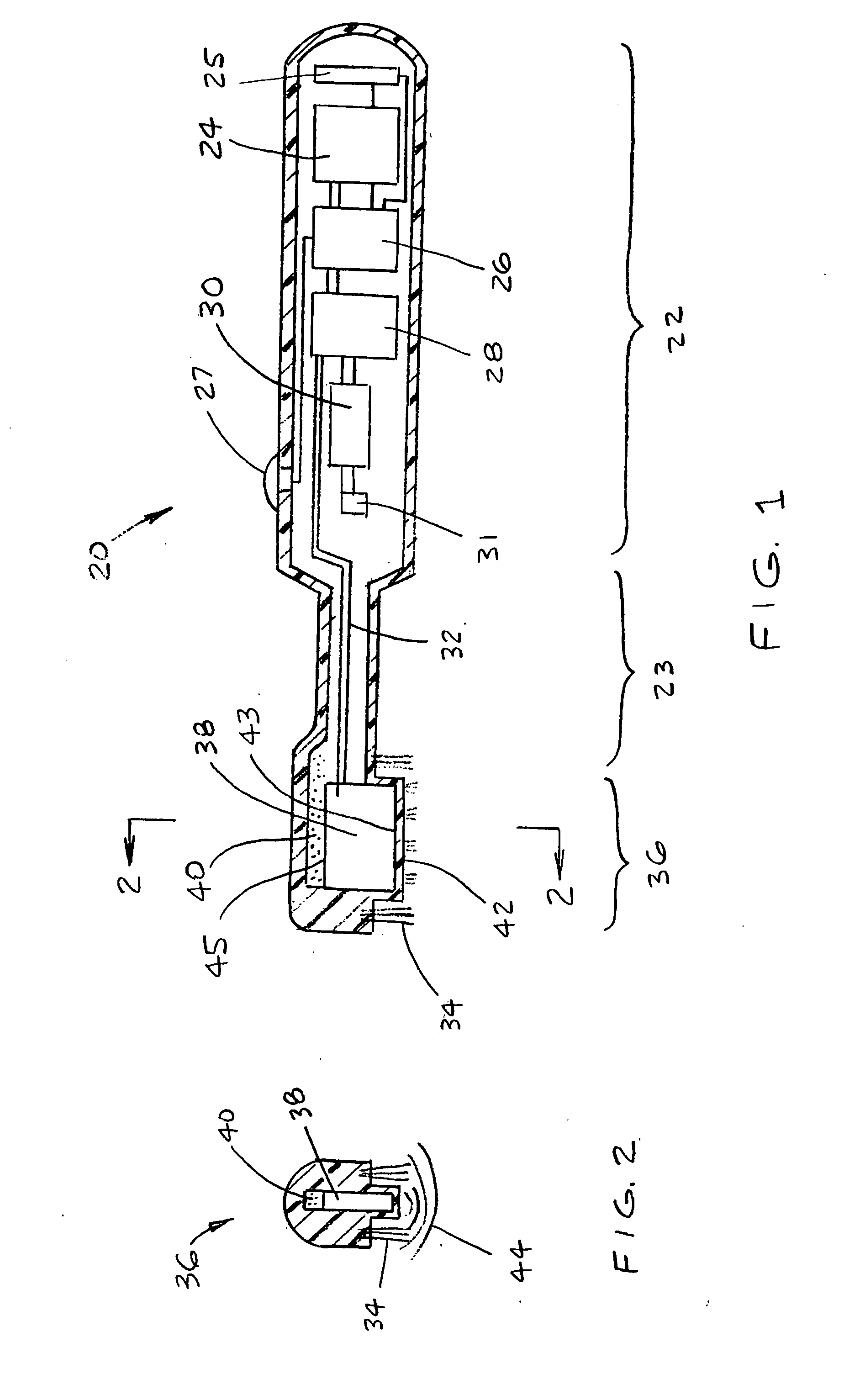
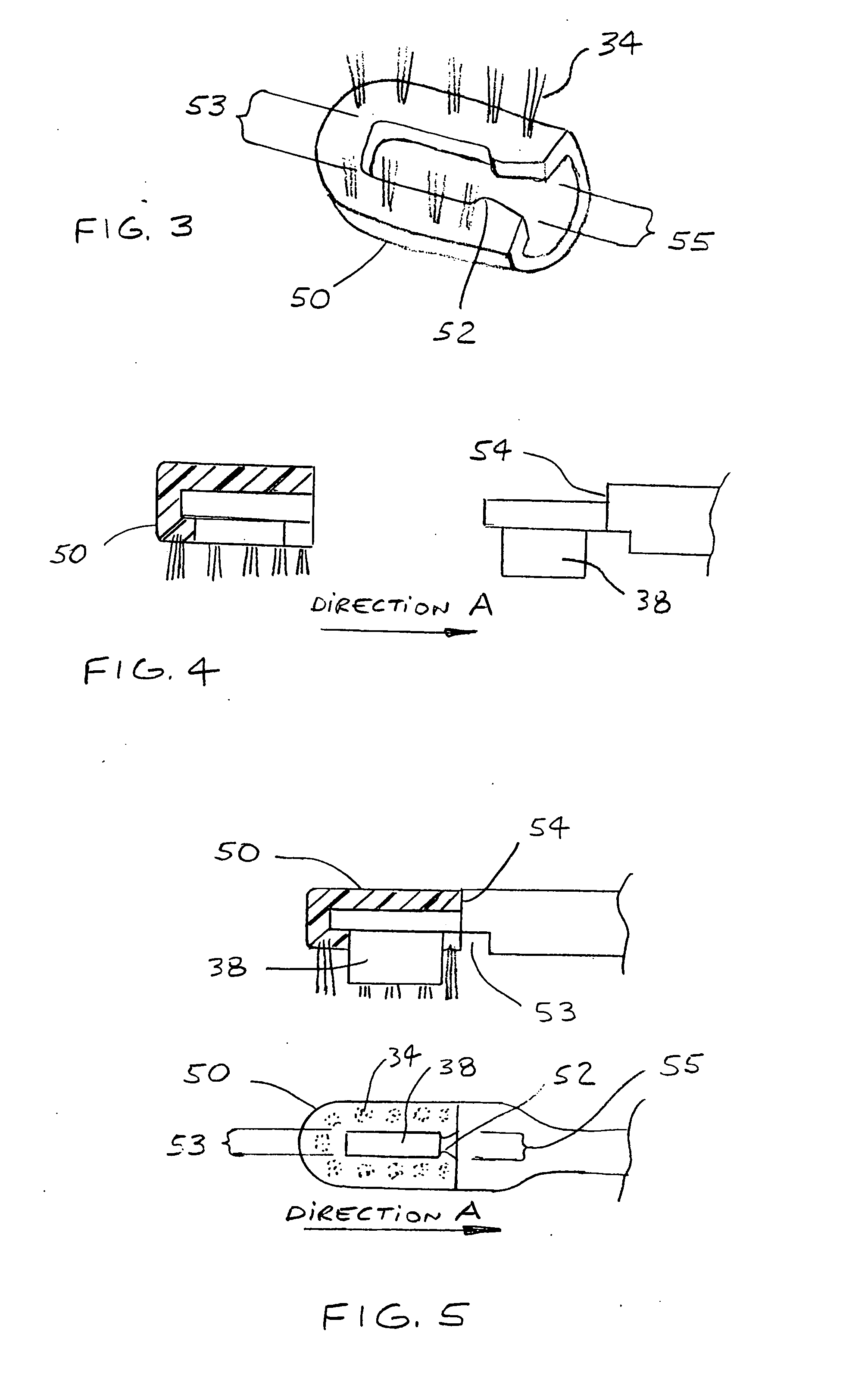
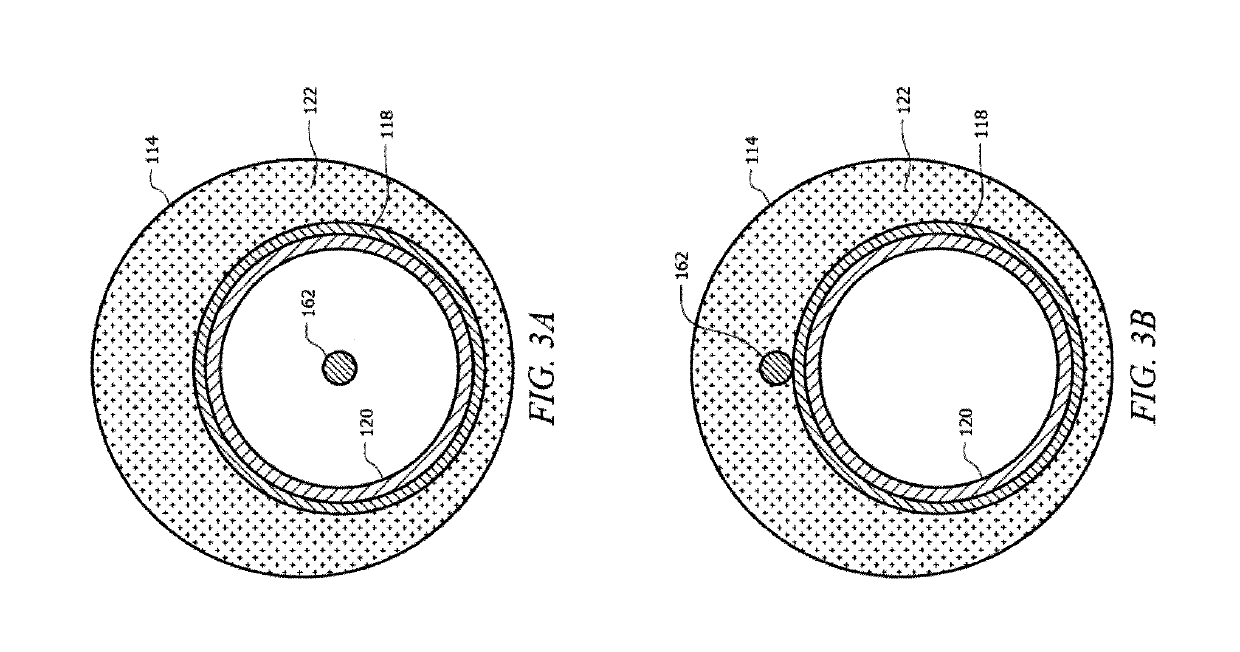
Acoustic device
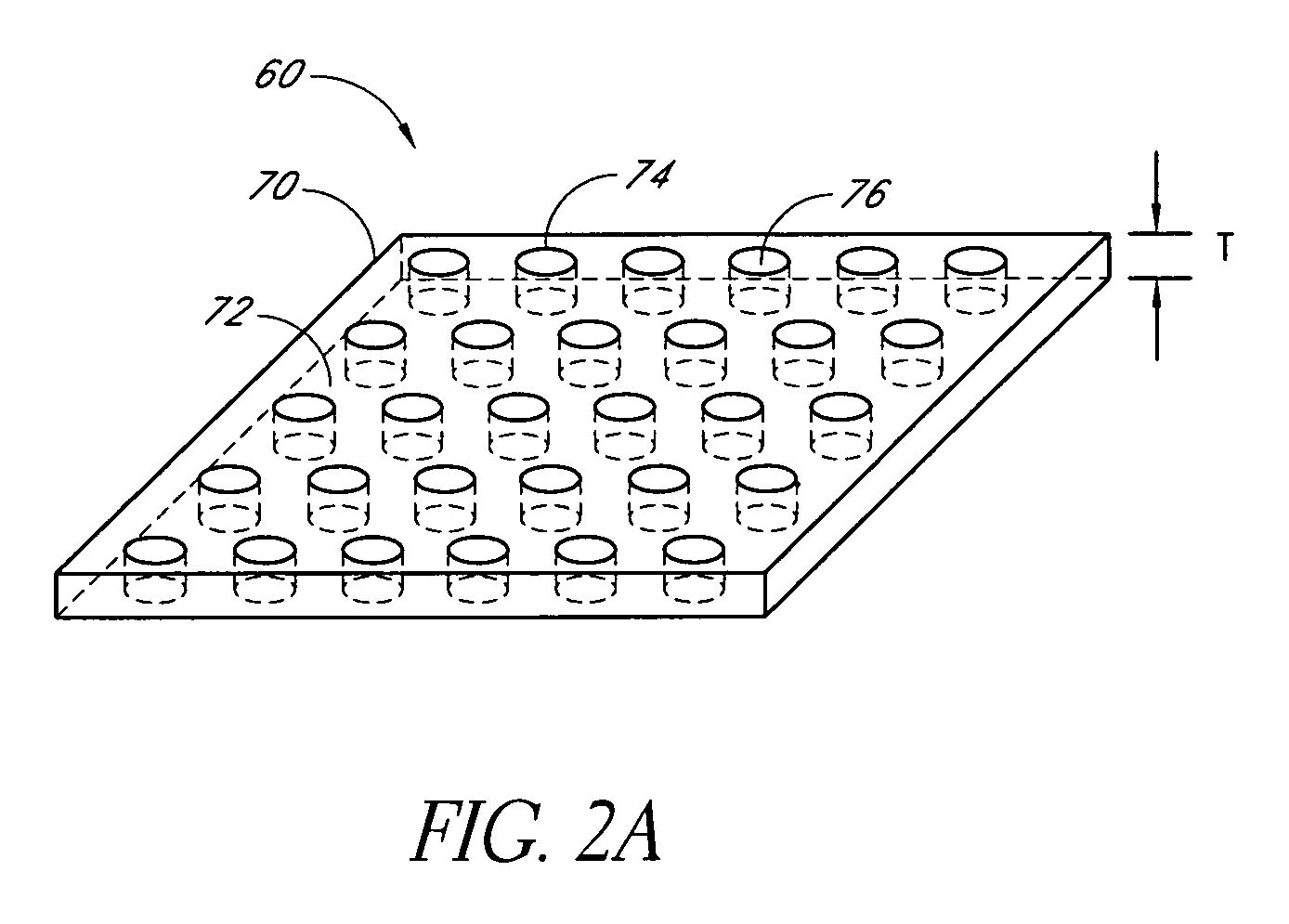
InactiveUS6332029B1Spread fastGood effectTelevision system detailsElectrophonic musical instrumentsEngineeringBending stiffness
Acoustic device including a member extending transversely of its thickness and capable of sustaining bending waves at least over an intendedly consequentially acoustically active area of the transverse extent of said member, the member having, by reason of orderly design methodology disclosed and claimed, a distribution of resonant modes of its natural bending wave vibration at least over said area that is dependent on values of particular parameters of said members, including geometrical configuration and directional bending stiffness(es), which values have been selected to predetermine said distribution of natural resonant modes being consonant with required achievable acoustic action of said member for operation of said device over a desired operative acoustic frequency range.
Owner:NEW TRANSDUCERS LTD
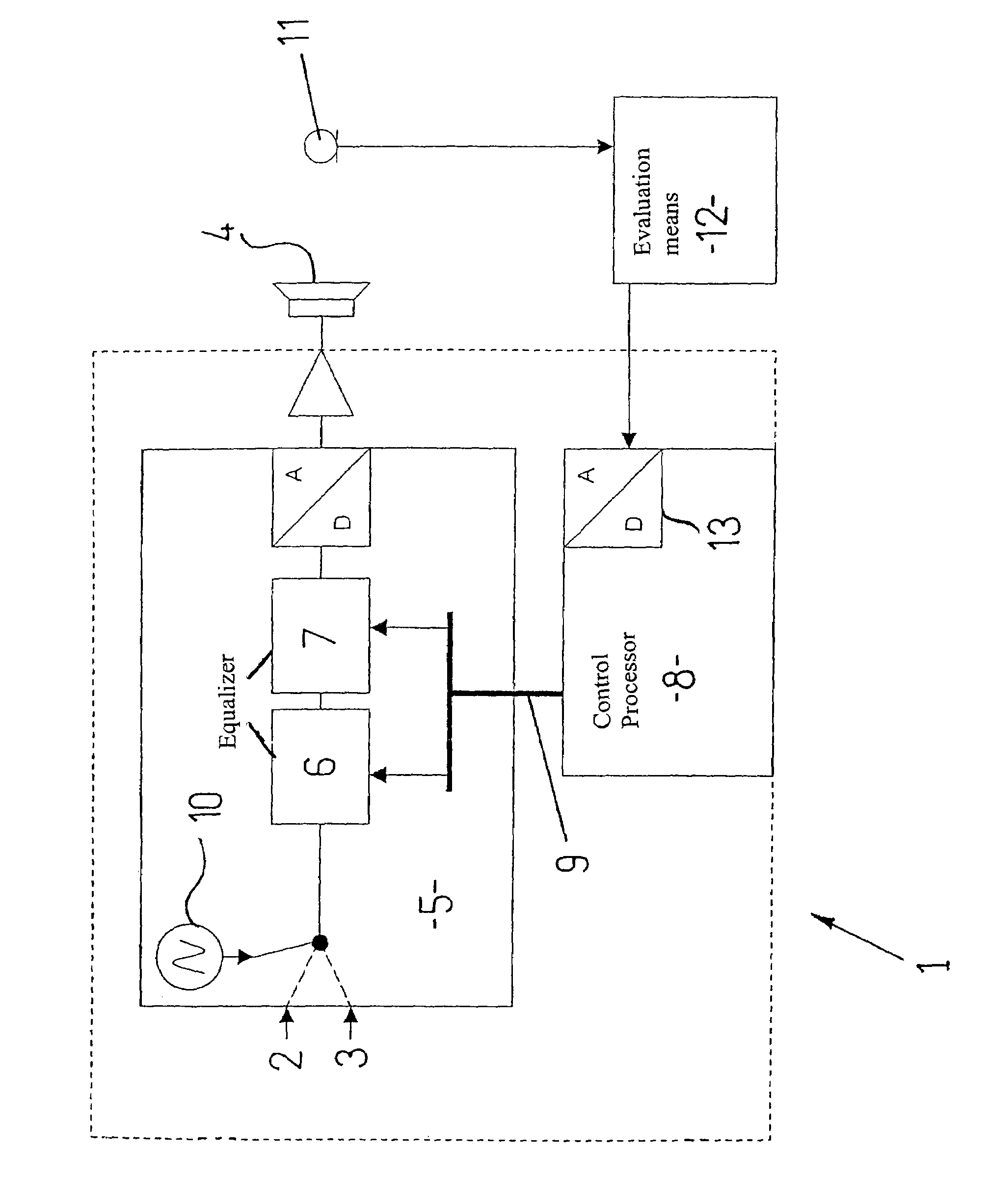
Method for automatically adjusting the filter parameters of a digital equalizer and reproduction device for audio signals for implementing such a method
InactiveUS7289637B2Reduce spendingFrequency response correctionTransmissionUltrasound attenuationEngineering
A method is proposed for automatically adjusting the filter parameters—center frequency, quality and amplification or attenuation—of at least one digital equalizer which is a component of a reproduction device for audio signals in a vehicle passenger compartment. To that end, first of all, the acoustical frequency response of the passenger compartment is ascertained. The inadequacies in the acoustics of the passenger compartment in the form of local maxima and minima in the measured frequency response are then determined. On this basis, the filter parameters are adjusted automatically so that at least a portion of these inadequacies is compensated. A reproduction device for audio signals for implementing this method is also proposed.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
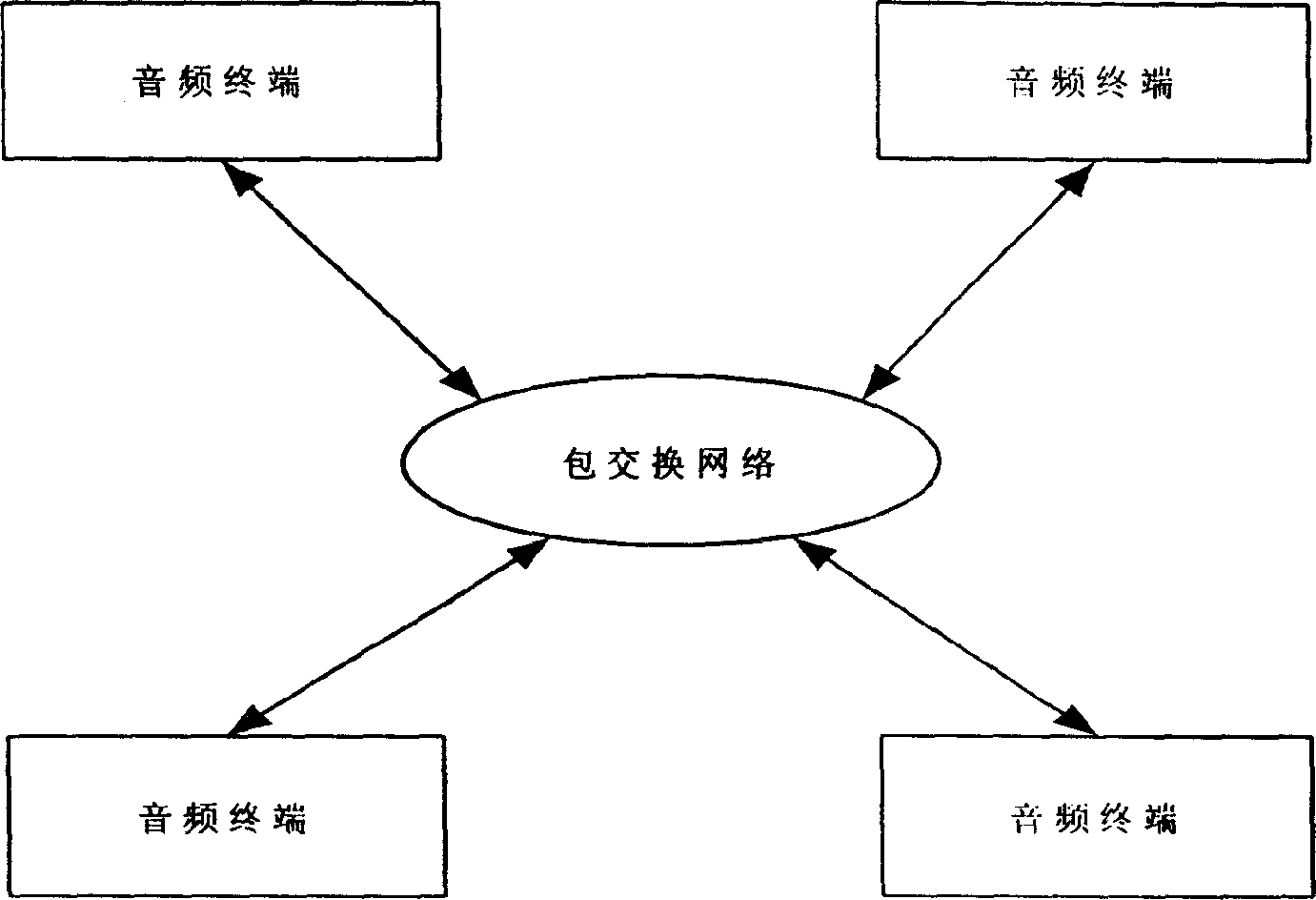
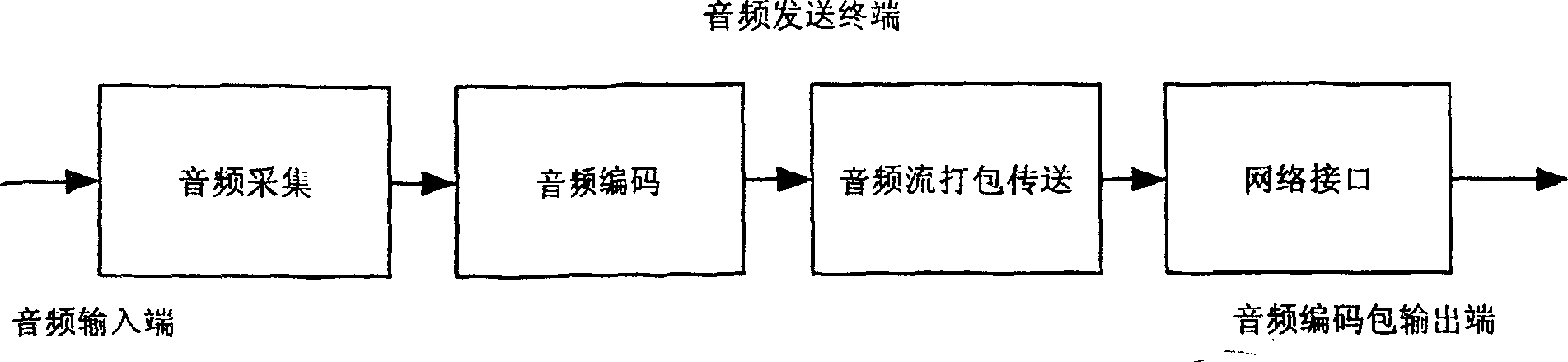
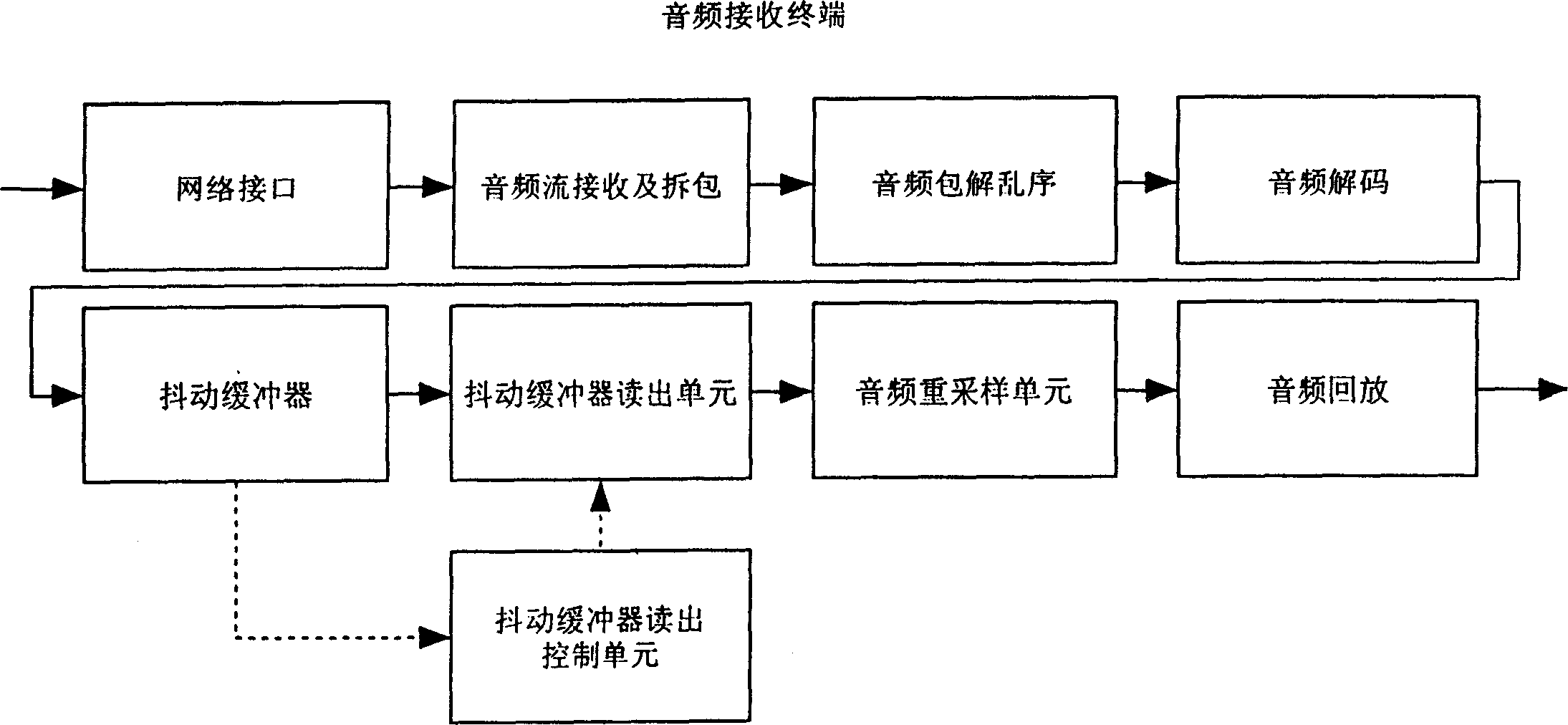
Method for processing acoustic frequency flow playback in network terminal buffer
InactiveCN1464685ASpeed up or slow down playbackContinuous and smooth playbackSpecial service provision for substationTelephonic communicationComputer hardwareNetwork termination
The invention discloses a method for processing audio stream playback in the network terminal buffer zone for solving the problem of voice pausing and jamming in the network communication. The aim of the invention is achieved by performing real time audio (e.g. voice) communication on the packet-switching network (e.g. IP network), arranging a shake buffer zone on the receiving end, after the receiving end receives the audio package, it first performs decoding based on the normal sequence, then places it into the shake buffer zone, when the shake buffer zone is to be filled, lower the sampling rate to the audio data to realize the fast playback of the audio data stream, when the shake buffer zone is to be empty, raise the sampling rate to the audio data to realize the low speed playback of the audio data stream, when the audio data in the shake buffer is within the normal range, playback the audio stream with the original sampling rate.
Owner:优创科技(深圳)有限公司
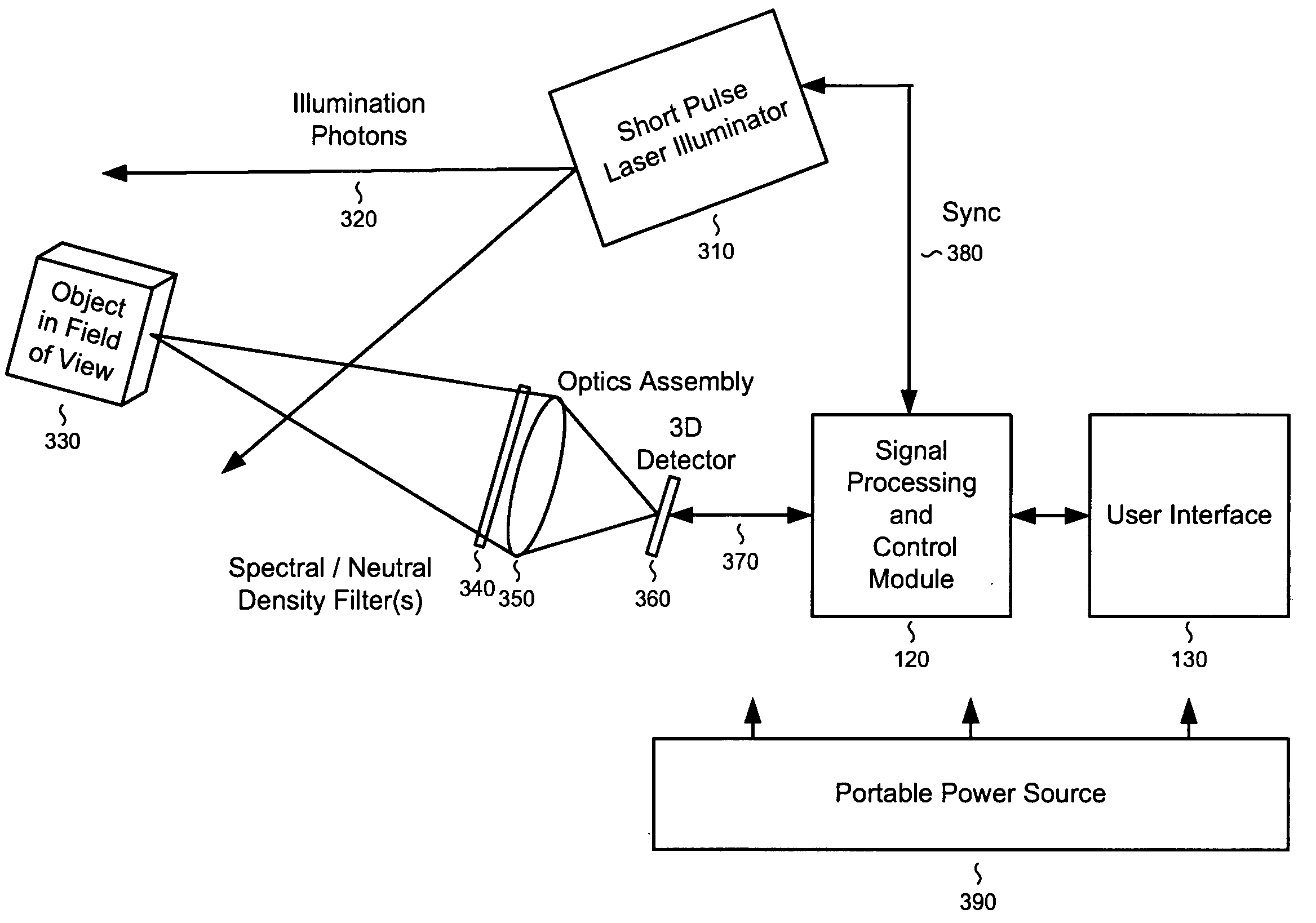
Systems and methods for laser radar imaging for the blind and visually impaired
InactiveUS20080309913A1Improve accuracyAccurate informationOptical rangefindersSolid-state devicesVisually impairedRadar systems
A 3D imaging ladar system comprises a solid state laser and geiger-mode avalanche photodiodes utilizing a scanning imaging system in conjunction with a user interface to provide 3D spatial object information for vision augmentation for the blind. Depth and located object information is presented acoustically by: 1) generating an audio acoustic field to present depth as amplitude and the audio image as a 2D location. 2) holographic acoustical imaging for a 3D sweep of the acoustic field. 3) a 2D acoustic sweep combined with acoustic frequency information to create a 3D presentation.A system to fuse data derived from a three dimensional imaging ladar system with information from a visible, ultraviolet, or infrared camera systems and acoustically present the information in a four or five dimensional acoustical format utilizing three dimensional acoustic position information, along with frequency, and modulation to represent color, texture, or object recognition information is also provided.
Owner:FALLON JAMES JOHN
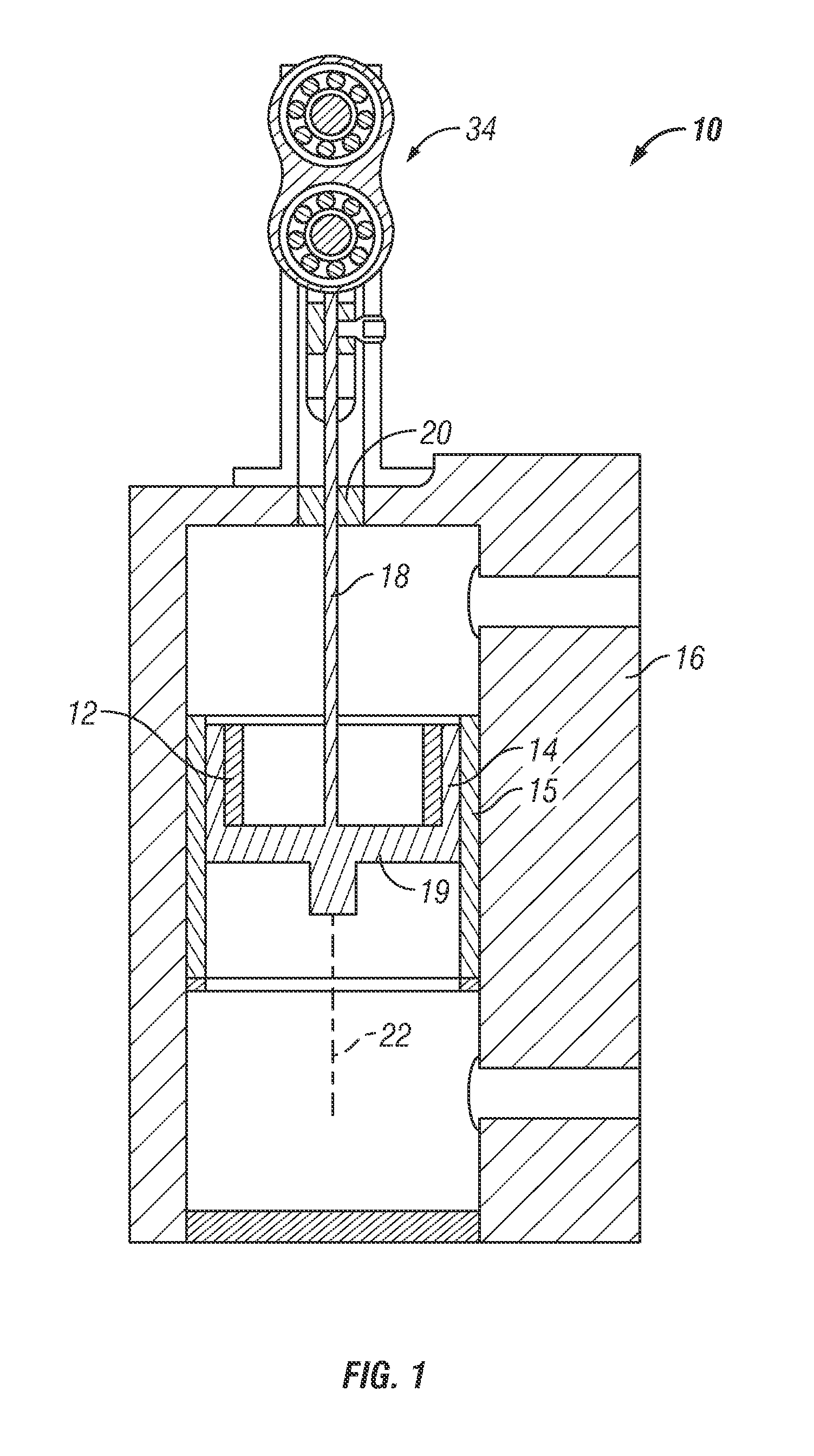
Acoustic device
InactiveUS20020027999A1Spread fastAccelerate buildingTelevision system detailsElectrophonic musical instrumentsEngineeringBending stiffness
Acoustic device including a member extending transversely of its thickness and capable of sustaining bending waves at least over an intendedly consequentially acoustically active area of the transverse extent of said member, the member having, by reason of orderly design methodology disclosed and claimed, a distribution of resonant modes of its natural bending wave vibration at least over said area that is dependent on values of particular parameters of said members, including geometrical configuration and directional bending stiffness(es), which values have been selected to predetermine said distribution of natural resonant modes being consonant with required achievable acoustic action of said member for operation of said device over a desired operative acoustic frequency range.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Pump piston assembly with acoustic dampening device
InactiveUS20130081536A1Reduces and eliminates squeaking noiseReduce noisePositive displacement pump componentsCylindersReciprocating motionEngineering
A pump piston assembly has a pump cylinder, at least one hollow piston slidably mounted for reciprocating motion in the pump cylinder, the piston having an inner surface of a first diameter and an outer surface of a second diameter, and a liner sleeve of a different material from the piston mounted on the inner or outer surface of the piston with a close or friction fit to the diameter of the piston surface on which it is mounted. The liner sleeve is of an acoustic dampening material which has a lower acoustic frequency than the piston material and is configured to absorb harmonic acoustic vibrations resulting from reciprocation of the piston in the cylinder.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
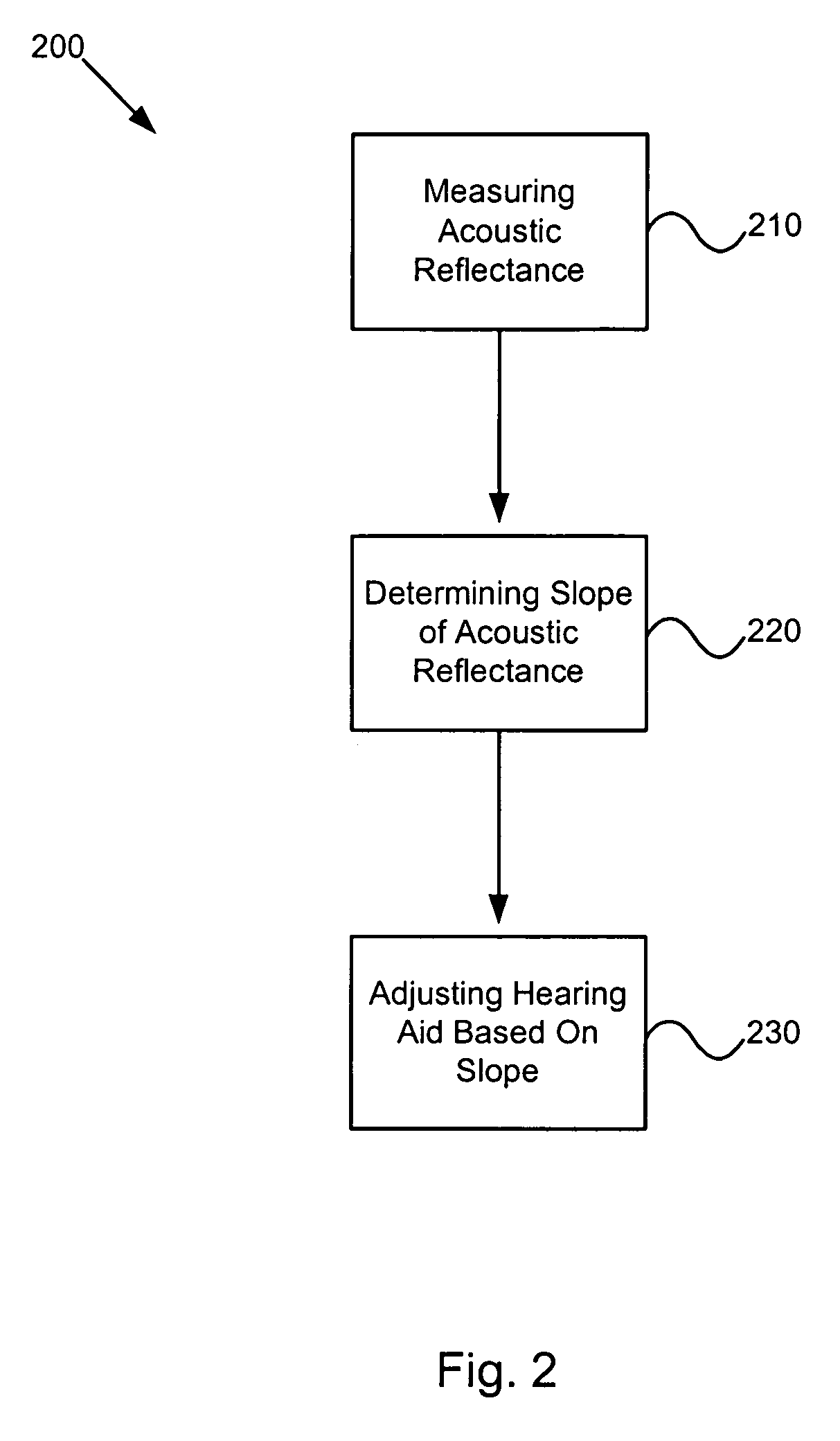
System and method for automatically adjusting hearing aid based on acoustic reflectance
Method and system for automatically adjusting a hearing aid. The method includes measuring an acoustic reflectance associated with an ear canal as a function of an incident pressure and an acoustic frequency, processing information associated with the measured acoustic reflectance, determining a reflectance slope based on, at least, information associated with the measured acoustic reflectance, and adjusting, at least, one parameter associated with the hearing aid based on, at least, information associated with the reflectance slope. The reflectance slope is associated with a reflectance component varying with the incident pressure.
Owner:MIMOSA ACOUSTICS
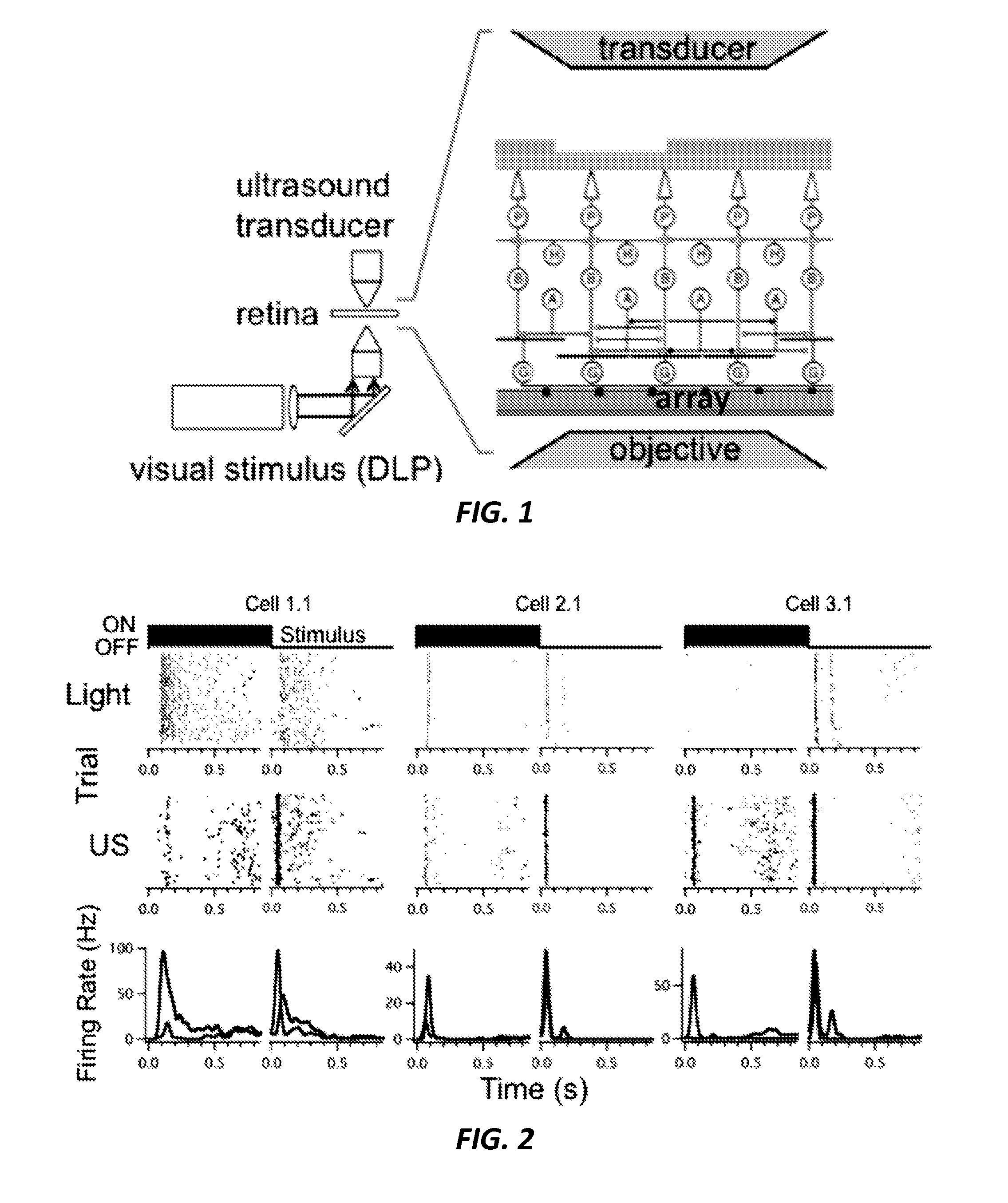
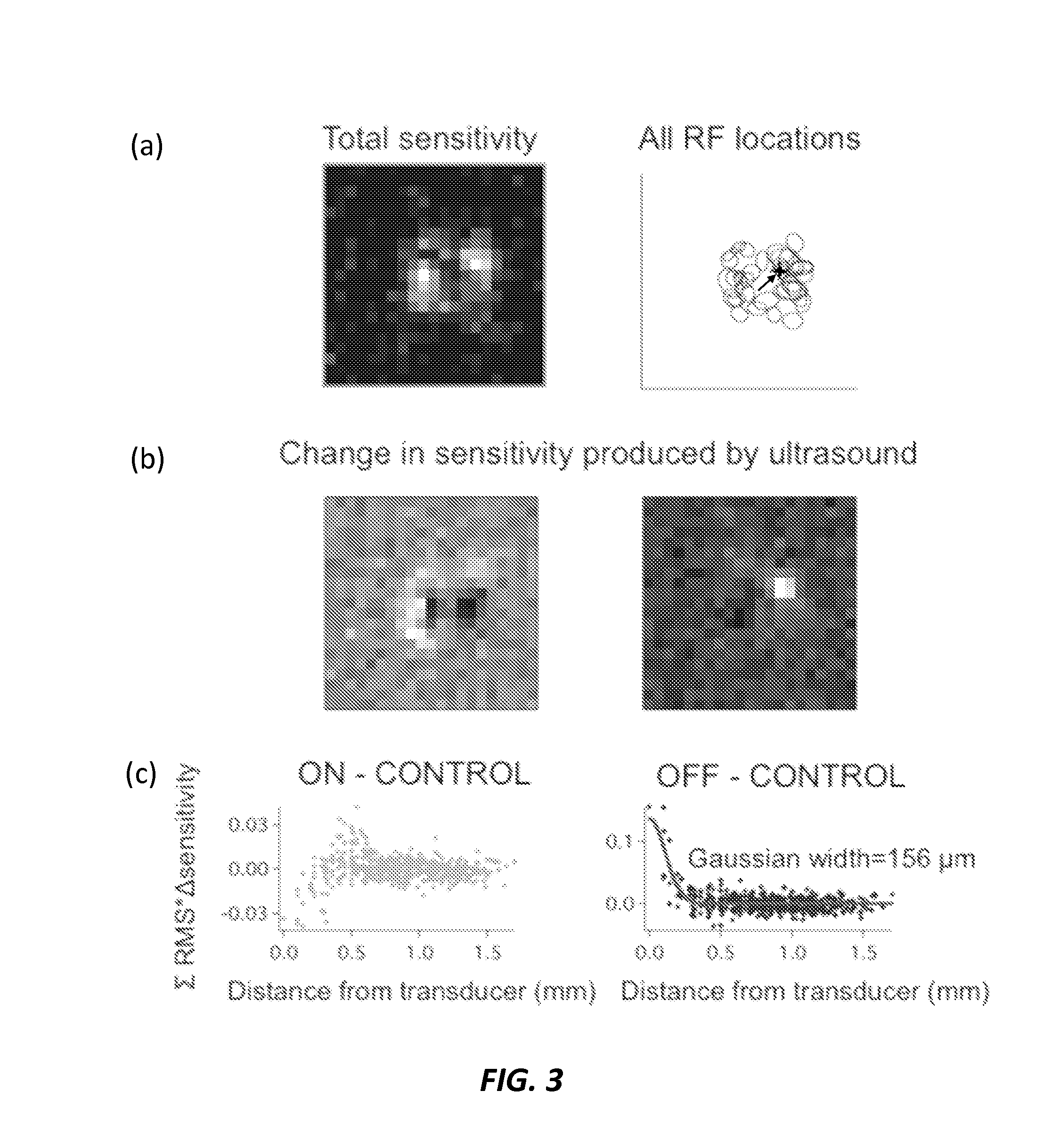
Noninvasive Ultrasound-Based Retinal Stimulator: Ultrasonic Eye
A retinal stimulation and prosthetic device is provided that includes at least one ultrasonic transducer having a focused ultrasonic signal, where the focused ultrasonic signal includes an acoustic frequency, a spot size, a temporal pattern, a pulse duration and a power capable of stimulating retinal neurons when the at least one ultrasonic transducer is disposed proximal to an eye.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
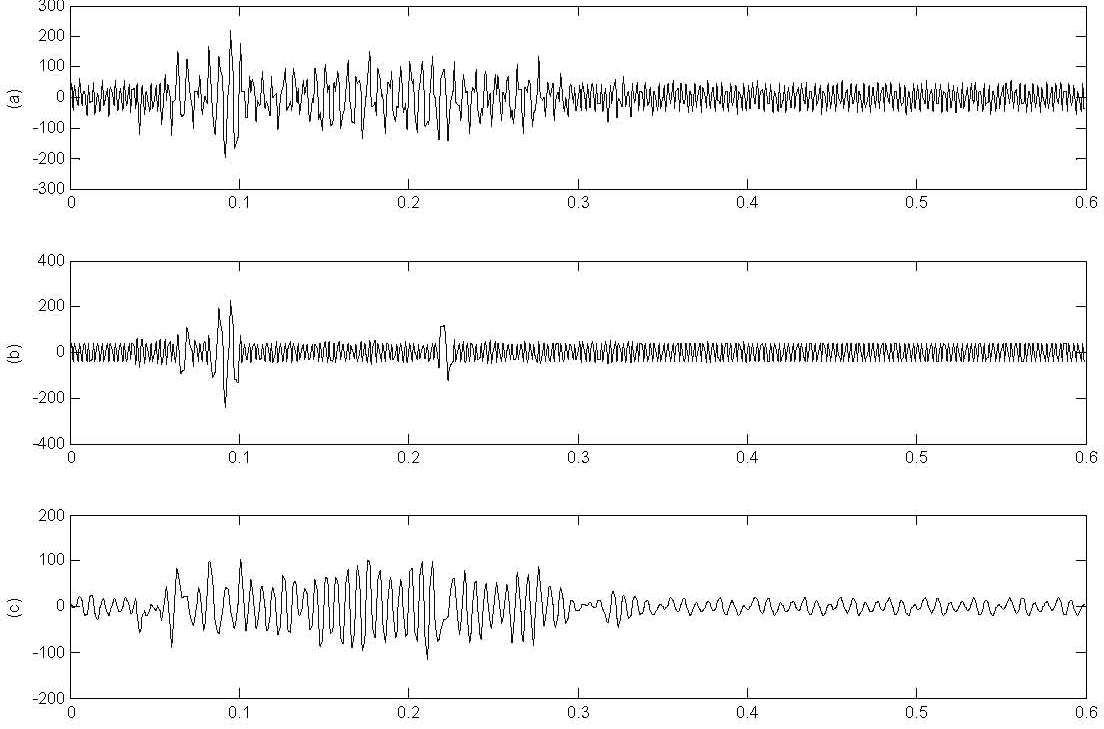
Vibration and audio signal-based high-speed train track defect detecting method
ActiveCN101900708AReflect damage informationEasy to analyzeAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalLinear correlationEngineering
The invention discloses a vibration and audio signal-based high-speed train track damage detecting method, belongs to the field of signal detection and processing as well as safety monitoring, and solves the problems of low detection speed and single detection method in the conventional train track damage detection. The method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring vibration signals and audio signals of a train track through sensors arranged at train track detection points; 2, respectively extracting information characteristics included in the vibration signals and the audio signals; 3, respectively obtaining a nonlinear correlation curve of the vibration signals and a nonlinear correlation curve of the audio signals by using a nonlinear correlation analysis method; 4, respectively analyzing the information of the two nonlinear correlation curves obtained in the step 3 so as to respectively obtain minimum values of the two nonlinear correlation curves; and 5, carrying out data fusion on the two minimum values and corresponding information thereof so as to obtain a damage coefficient, and looking up a table to obtain the damage degree according to the coefficient. The method is suitable for detecting the damage on railway train tracks and monitoring the safety operation of trains.
Owner:哈尔滨工业大学高新技术开发总公司
Portable Dialysis Access Monitor Device
InactiveUS20110054352A1Effectively save medical resourceImprove medical qualityStethoscopeTelemetric patient monitoringFistulaMonitor equipment
A portable dialysis access monitor device, comprising: an electronic monitor device and a server. The electronic monitor device includes a first microprocessor, an acoustic detector, a touch screen, a first storage device, a diagnostic programming module, an alarm device and a power supply device. The first microprocessor collects acoustic frequency signals, sound signals and thrill signals detected from a dialytic fistula. If signal difference is greater than a predetermined threshold value, the electronic monitor device provides a warning by the alarm device. The server includes a second microprocessor, a second storage device and a mobile internet. The server receives and analyzes the acoustic frequency signals, the sound signals and the thrill signals detected from the dialytic fistula by utilizing the second microprocessor to get an analyzed result. The server transmits the analyzed result to the electronic monitor device by utilizing the mobile internet.
Owner:KO PO JEN +2
Extended reach ultrasonic toothbrush with improvements
InactiveUS20090211042A1Increase reachImprove the level ofGum massageTooth pluggers/hammersBristleMaximum level
An ultrasonic toothbrush for daily oral hygiene application is disclosed, having an ultrasound transducer in direct contact with the fluids in the oral cavity, without ultrasound energy attenuation between the transducer and the fluids in the oral cavity. Maximum level of ultrasound energy coupled to the fluids within the oral cavity and to the teeth and gums and periodontal pockets, achieving maximum loosening of soft plaque. Toothbrush configurations of ultrasonically enhanced manually operated toothbrushes and motorized toothbrushes having lateral direction sonic frequency vibrating brush heads emitting ultrasonic energy are disclosed. To generate the sonic frequency lateral vibration of the brush head, a motion transducer is utilized. Removable and user replaceable brush heads are described. In the various configurations low voltage DC energy supplied by a battery is converted to ultrasonic frequency DC current to activate the ultrasonic transducer. All configurations are utilizing bristle tufts to effectively dislodge plaque loosened by the ultrasonic waves from the surfaces of teeth and gums.
Owner:ROBERT T BOCK CONSULTANCY
Dual-frequency coaxial earphones with shared magnet
ActiveUS20100046783A1Minimized dimensionSolve the real problemTransducers for sound channels pluralityFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsDual frequencyEngineering
A dual-frequency coaxial earphone has a shared magnet, which is interposed between a top board of a outer yoke and an outer disk of a inner yoke, wherein the outer yoke and the inner yoke each has a different polarity. A low-frequency voice coil of a low-frequency speaker part extends axially into and between an annular wall of the outer yoke and the outer disk of the inner yoke. An inner sleeve of the inner yoke extends into a first central opening of the outer yoke. Therefore, a high frequency of the high-frequency speaker part can pass through the inner sleeve so as to energize a central diaphragm of the low-frequency speaker part and to form a same phase as, and to output frequency synchronously with, the low-frequency speaker part. As such, the problem of intermodulation of distortion for the high and low acoustic frequencies can be solved, and that dimension of the earphone can be minimized.
Owner:JETVOX ACOUSTIC
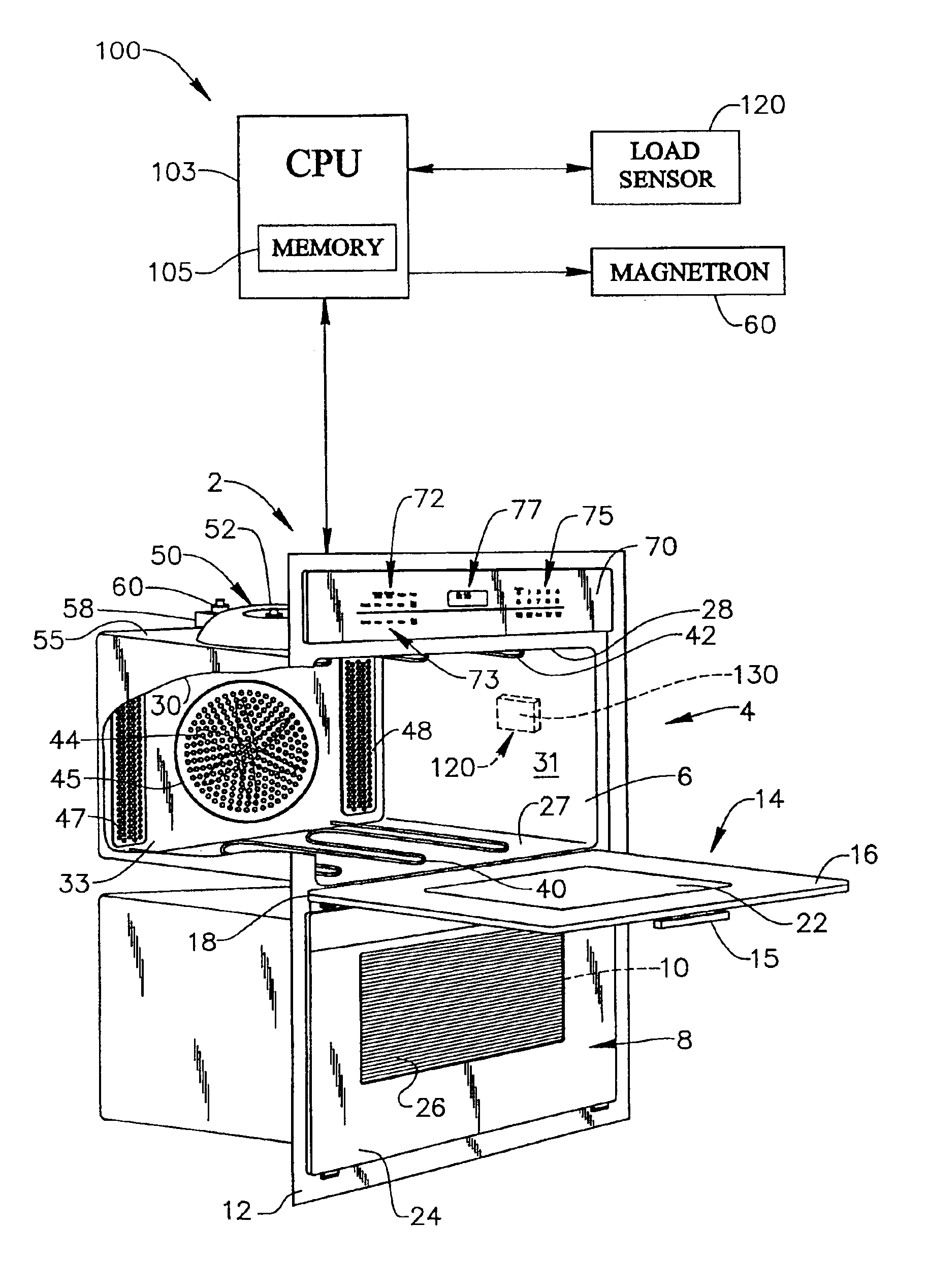
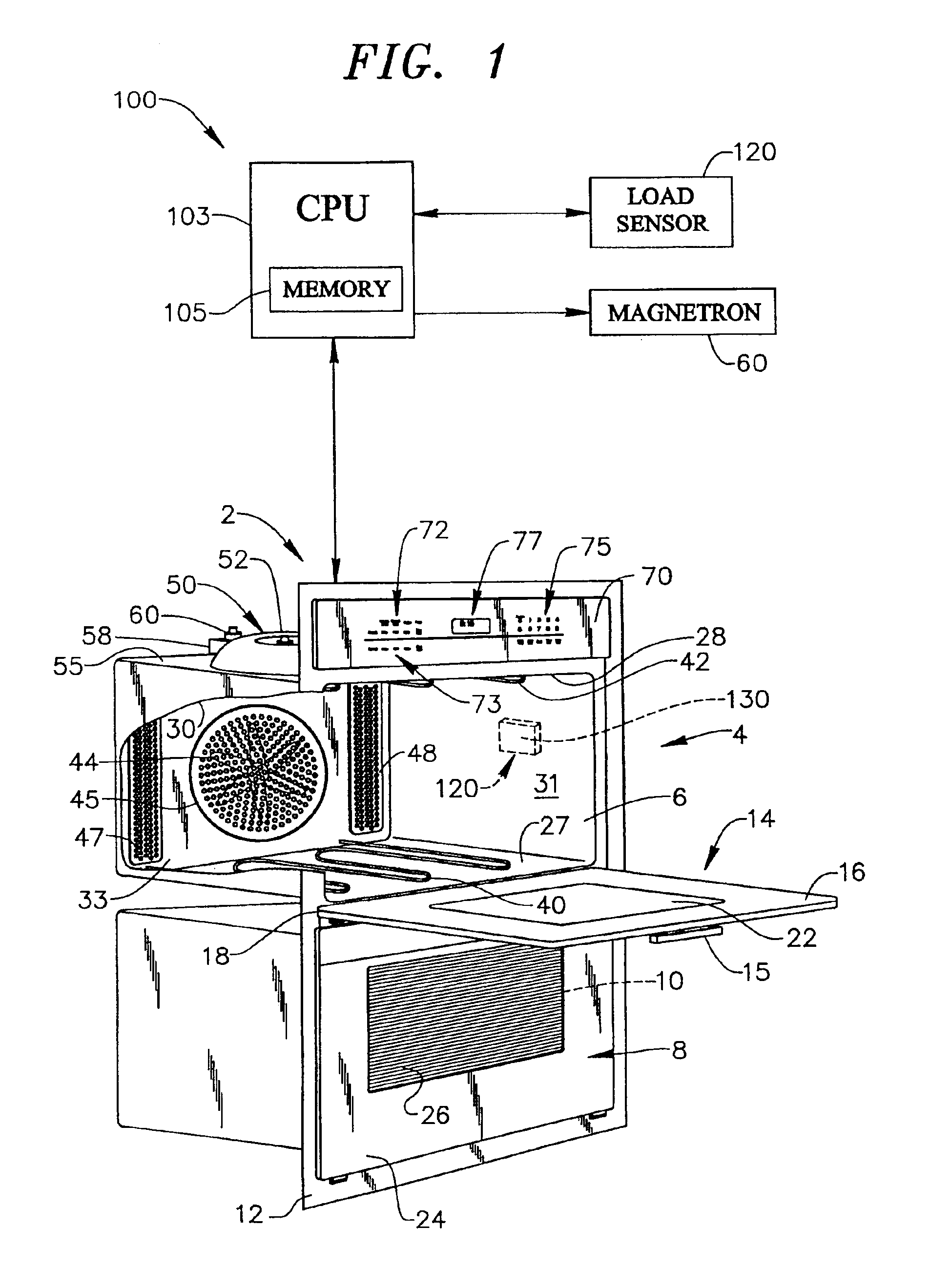
System for sensing the presence of a load in an oven cavity of a microwave cooking appliance
A microwave cooking appliance includes an oven cavity, a magnetron and a load sensing system. The load sensing system is used to detects the presence of a load in the oven cavity by introducing a high frequency energy burst into the oven cavity, with the energy burst being reflected back. A controller, based on a time period between emitted and reflected signals, determines whether a load is present in the oven cavity. If no load is present, operation of the magnetron is terminated. Preferably, the high frequency energy burst is an ultrasonic acoustic frequency energy burst in a range between approximately 10 kHz and 100 kHz.
Owner:ACP OF DELAWARE
Acoustic imaging probe incorporating photoacoustic excitation
Various embodiments of the present invention provide for a photoacoustic imaging probe for use in a photoacoustic imaging system, whereby the probe is comprised of a cohesive composite, acoustic lens incorporating aspheric geometry and exhibiting low or practically no measurable dispersion of acoustic waves constructed of at least one material with a low acoustic impedance and attenuation and a relatively low acoustic velocity and at least one other material with a low acoustic impedance and attenuation and a relatively high acoustic velocity. The probe is housed in a conduit filled with a low acoustic velocity and low acoustic impedance fluid such as water or mineral oil. The lens may be designed as a telecentric lens, an acoustic zoom lens, a catadioptric lens, or a reflective lens. The lens focuses acoustic waves on an acoustic imager which detects the image. The acoustic imager may be designed as a 2 dimensional array of transducers. Research to date indicates that within the range of acoustic frequencies of interest, 1 MHz-50 MHz and preferable 2 MHz-10 MHz, there exists little velocity variation within the materials of interest, and the lens design approach may currently be considered to be essentially monochromatic. The acoustic waves can be generated when an emitting light source illuminates a test subject comprising materials that generate acoustic waves at differing intensities and / or frequencies when illuminated with light, for example tissue containing blood vessels, wherein the blood vessels excite and generate an acoustic pulse. The probe has an acoustic window made of a material with low acoustic impedance which allows the acoustic pulse to enter the probe without distortion and then may be reflected by a mirror onto the acoustic lens. The probe may include the emitting light source and an optical window to allow light emitting from said light source to illuminate the test subject.
Owner:ARNOLD STEPHEN C
Photonic crystal structure sensor
ActiveUS7630589B2Improve temperature stabilitySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansCrystal structurePhotonic crystal structure
An acoustic sensor and a method of fabricating an acoustic sensor are provided. The acoustic sensor includes at least one photonic crystal structure and an optical fiber having an end optically coupled to the at least one photonic crystal structure. The acoustic sensor further includes a structural portion mechanically coupled to the at least one photonic crystal structure and to the optical fiber. The at least one photonic crystal structure, the optical fiber, and the structural portion substantially bound a region having a volume such that a frequency response of the acoustic sensor is generally flat in a range of acoustic frequencies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
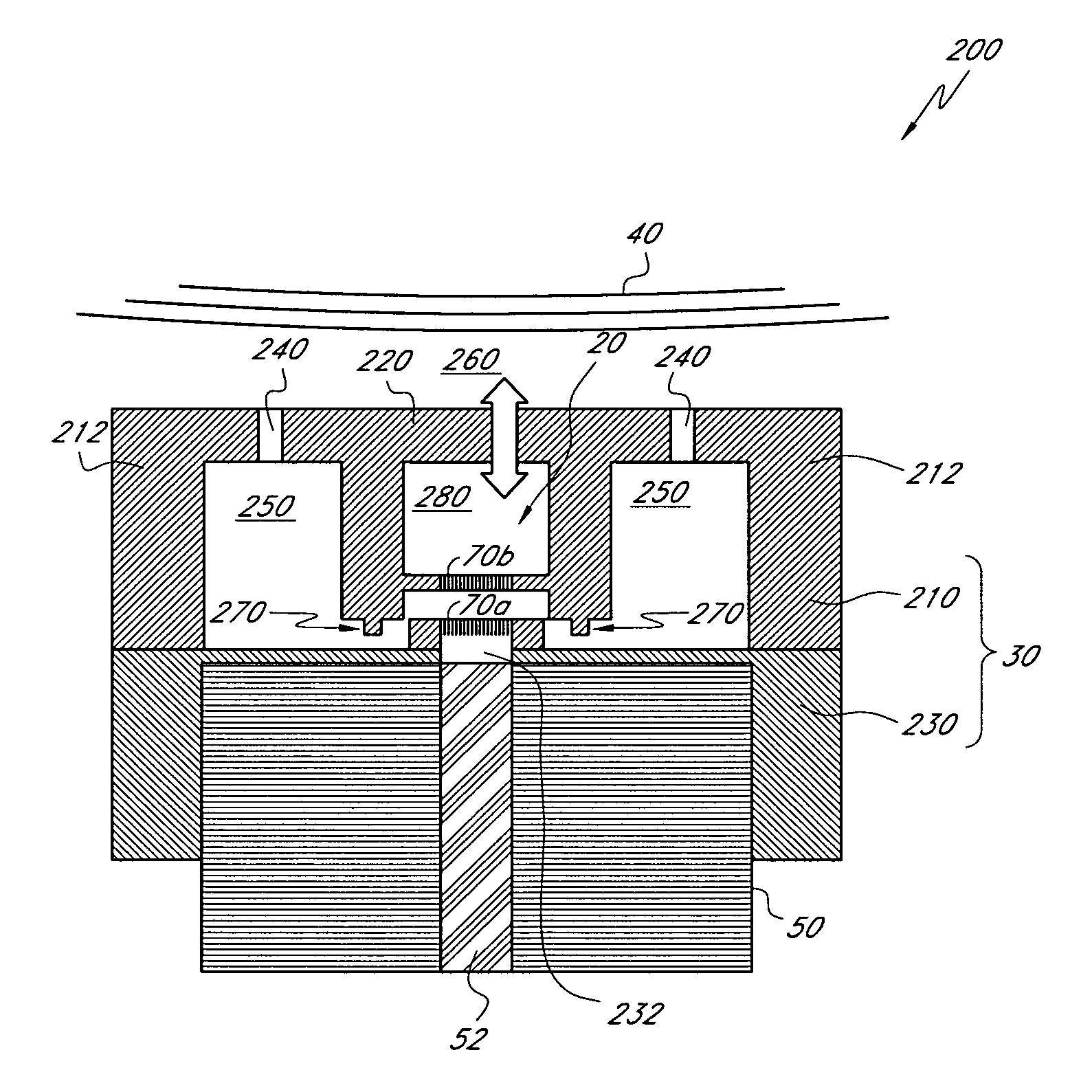
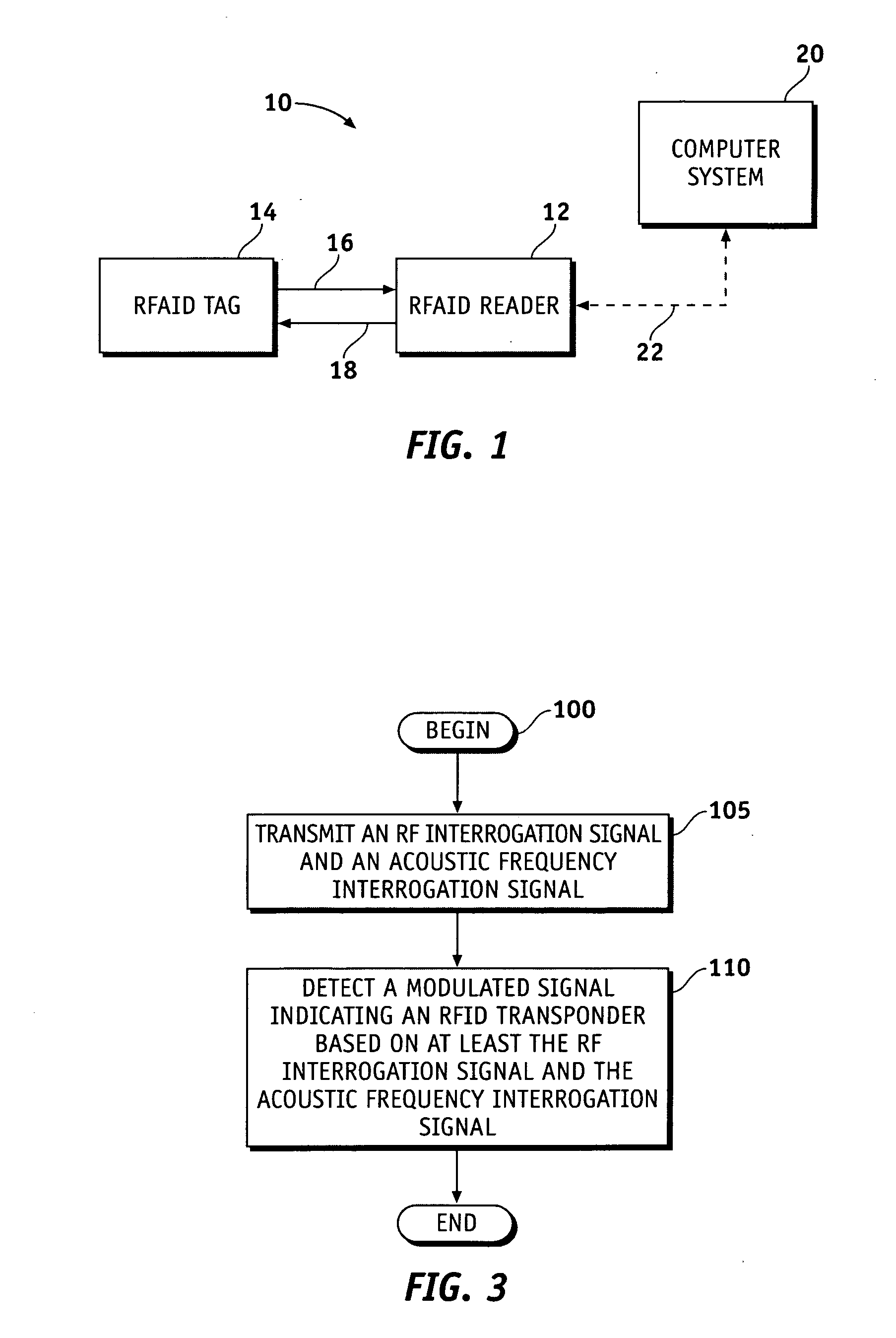
Mode-diveristy RFAID tag and interrogator system and method for identifying an RFAID transponder
ActiveUS20060267772A1Sensing by pneumatic/hydraulic meansMemory record carrier reading problemsTransducerEngineering
Methods and apparatus are provided for mode diversity radio frequency identification (RFAID). The apparatus comprises a first transducer configured to receive a first radio frequency (RF) signal, a second transducer configured to receive an acoustic signal, and an impedance modulator coupled to the first transducer and the second transducer and configured to emit a signal identifying an RFAID tag when the first transducer receives the first RF signal and / or the second transducer receives the acoustic signal. The method comprises transmitting an RF signal and an acoustic frequency signal, and detecting a first modulated signal indicating an RFAID transponder. The first modulated signal is based on one of the RF signal and the acoustic signal.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
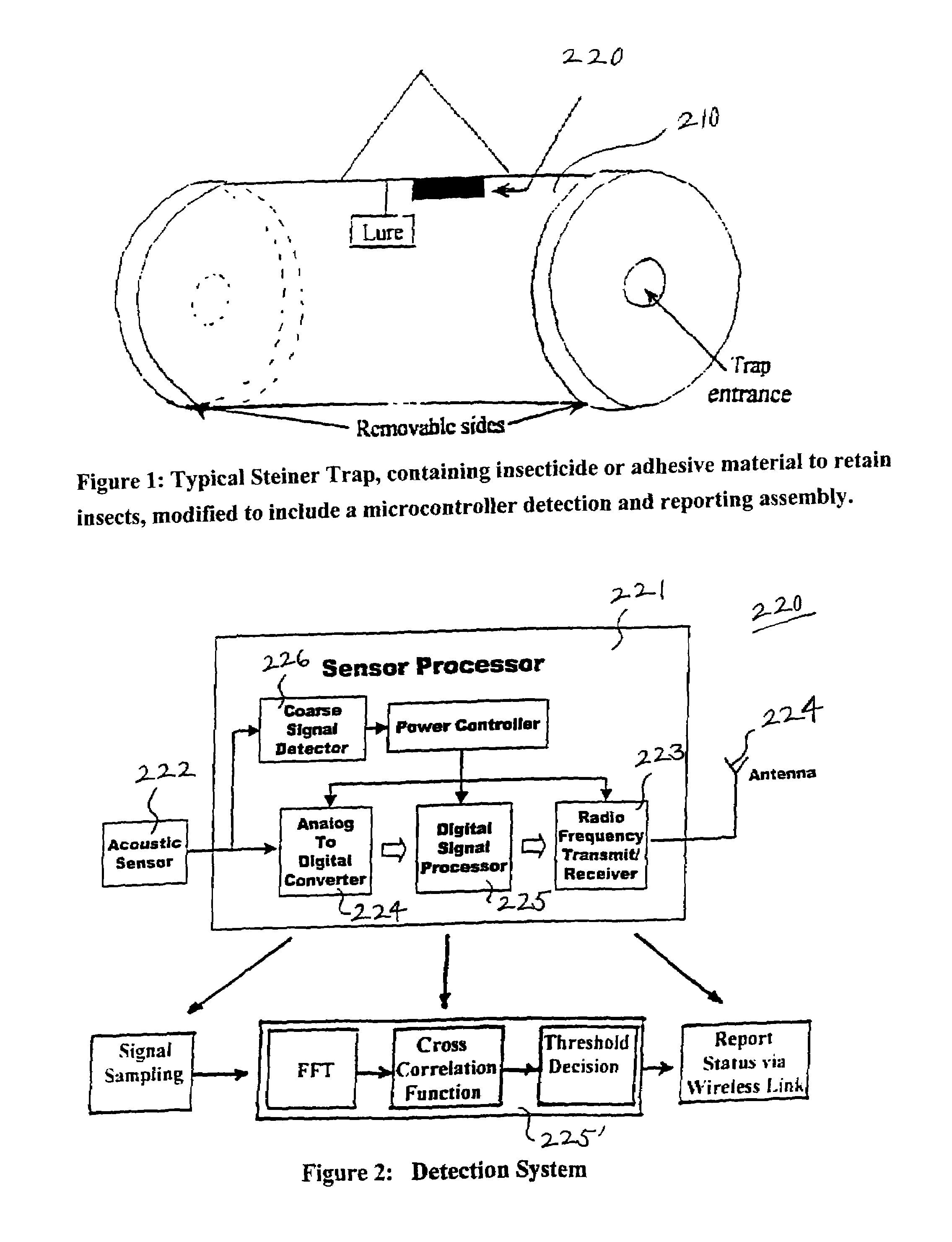
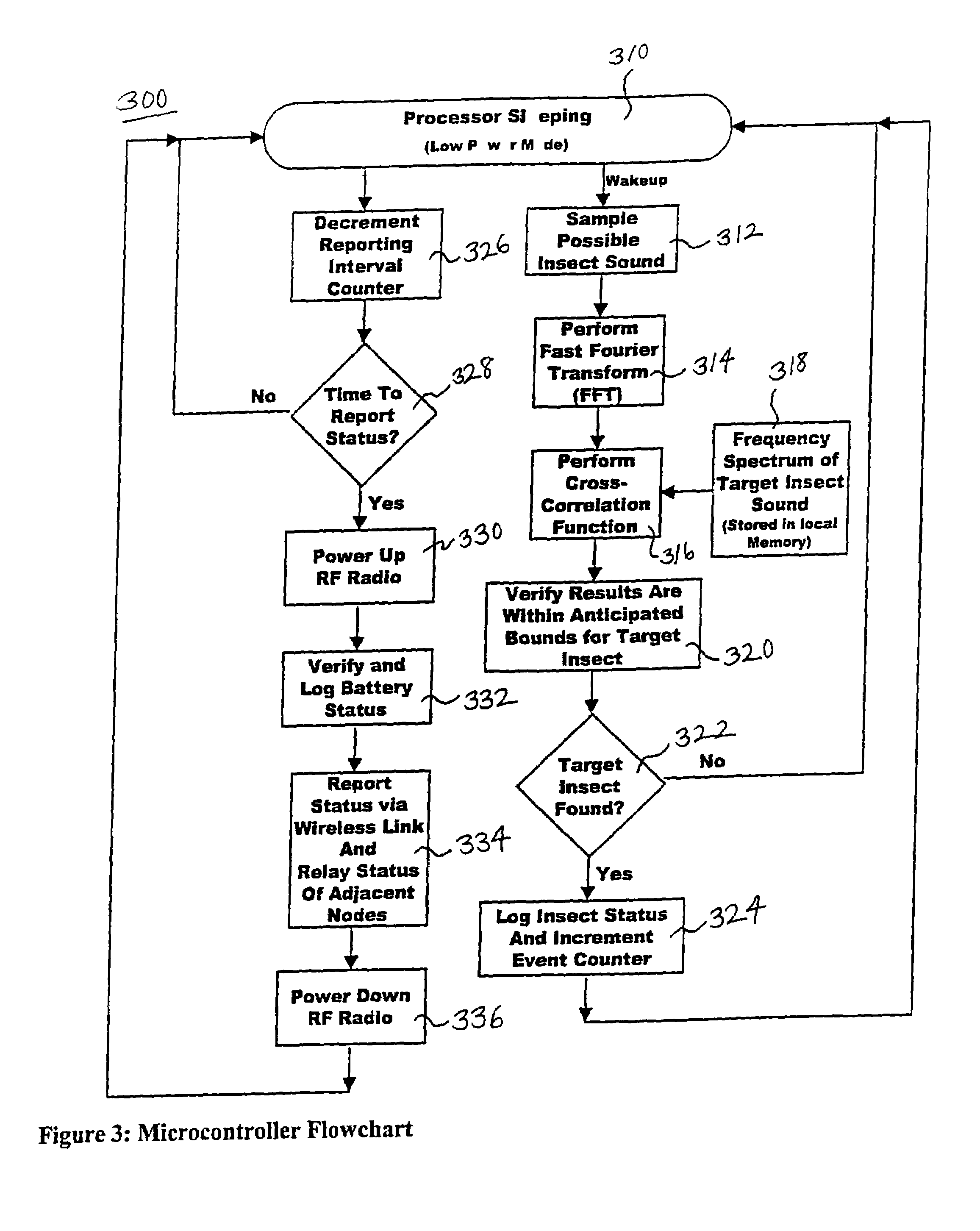
Method and system for remotely detecting trapped insects
InactiveUS7020996B2Effective meanAccurate detectionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsMicrocontrollerDecoy
Detection and monitoring of flying insects of a given species can be facilitated by placing inside a lure-baited trap a microcontroller assembly that can sense and discriminate the presence of that species, usually by the sound it makes and then sending a positive report to a central monitoring station by satellite, internet, or antennae transmission. The central monitoring station receives the putative identifications of the targeted insect species, matched with the locations of traps responding positively, and then maps the locations of the positive trap responses. Additional features include: identification of insect species by a characteristic acoustic frequency range, a pattern stored in the microcontroller and / or the central monitoring station; use of multi-lure traps; periodic transfer of test signals from the central monitoring station to remote detection stations to verify that the system is working properly; and use of the microcontroller sensor assembly without traps to monitor sound-emitting life forms at sites attractive to targeted species.
Owner:BEROZA MORTON
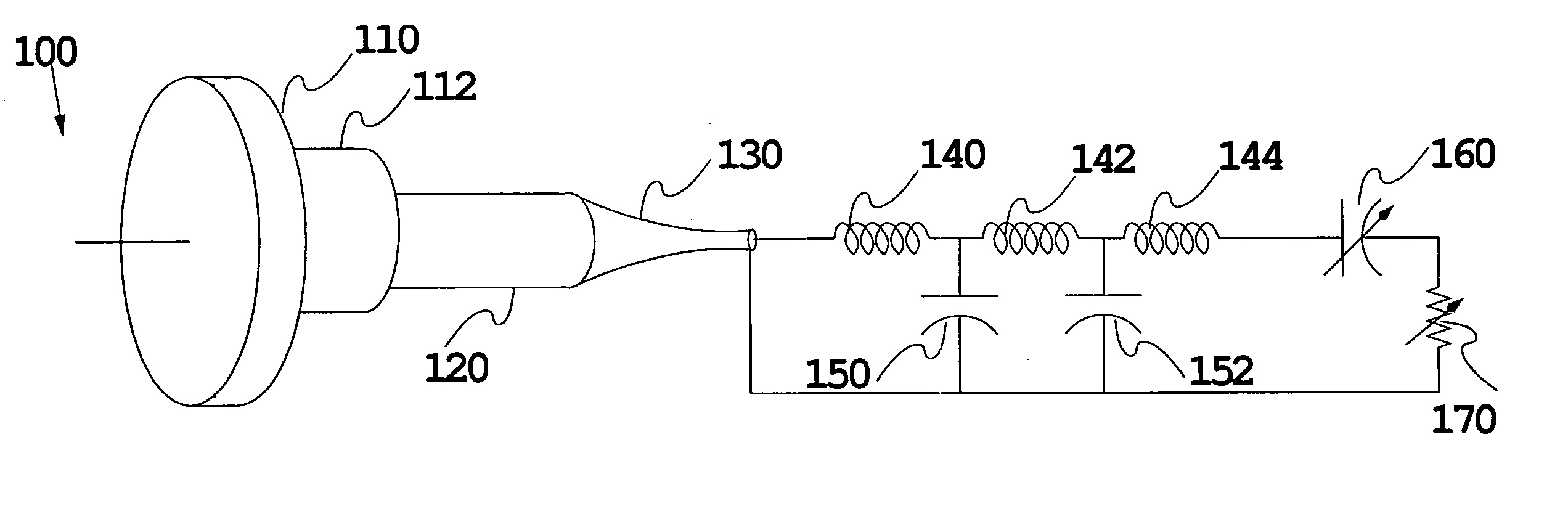
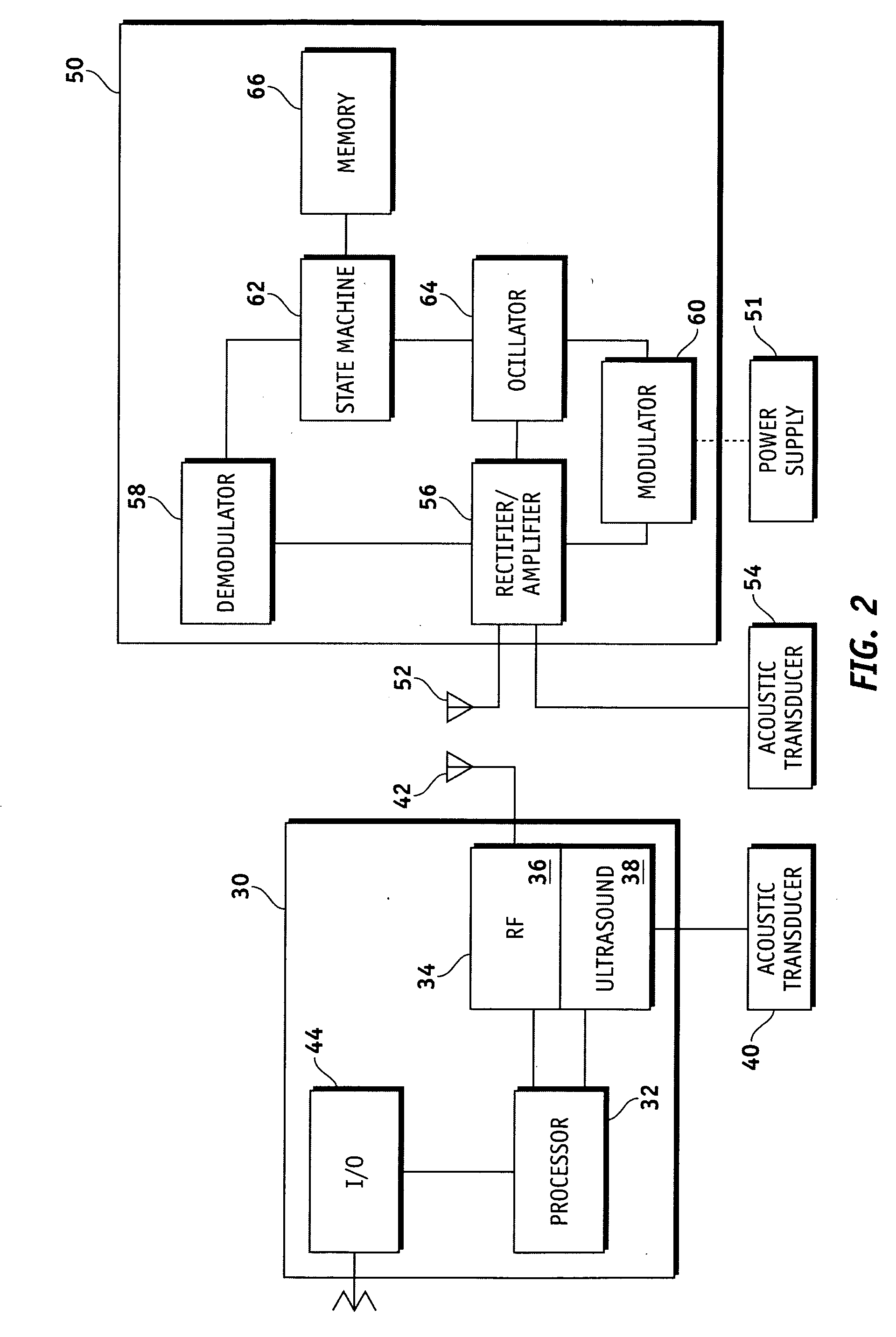
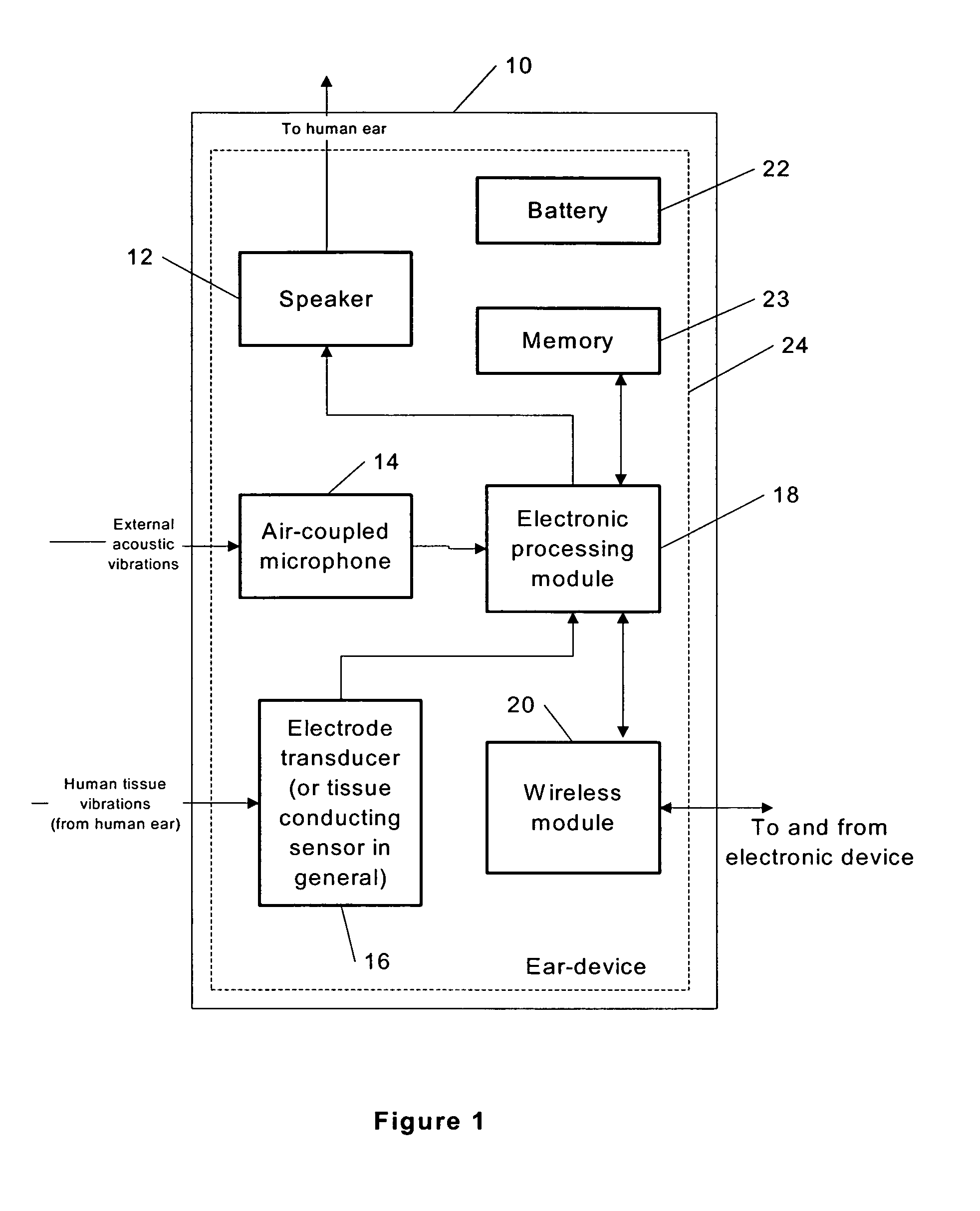
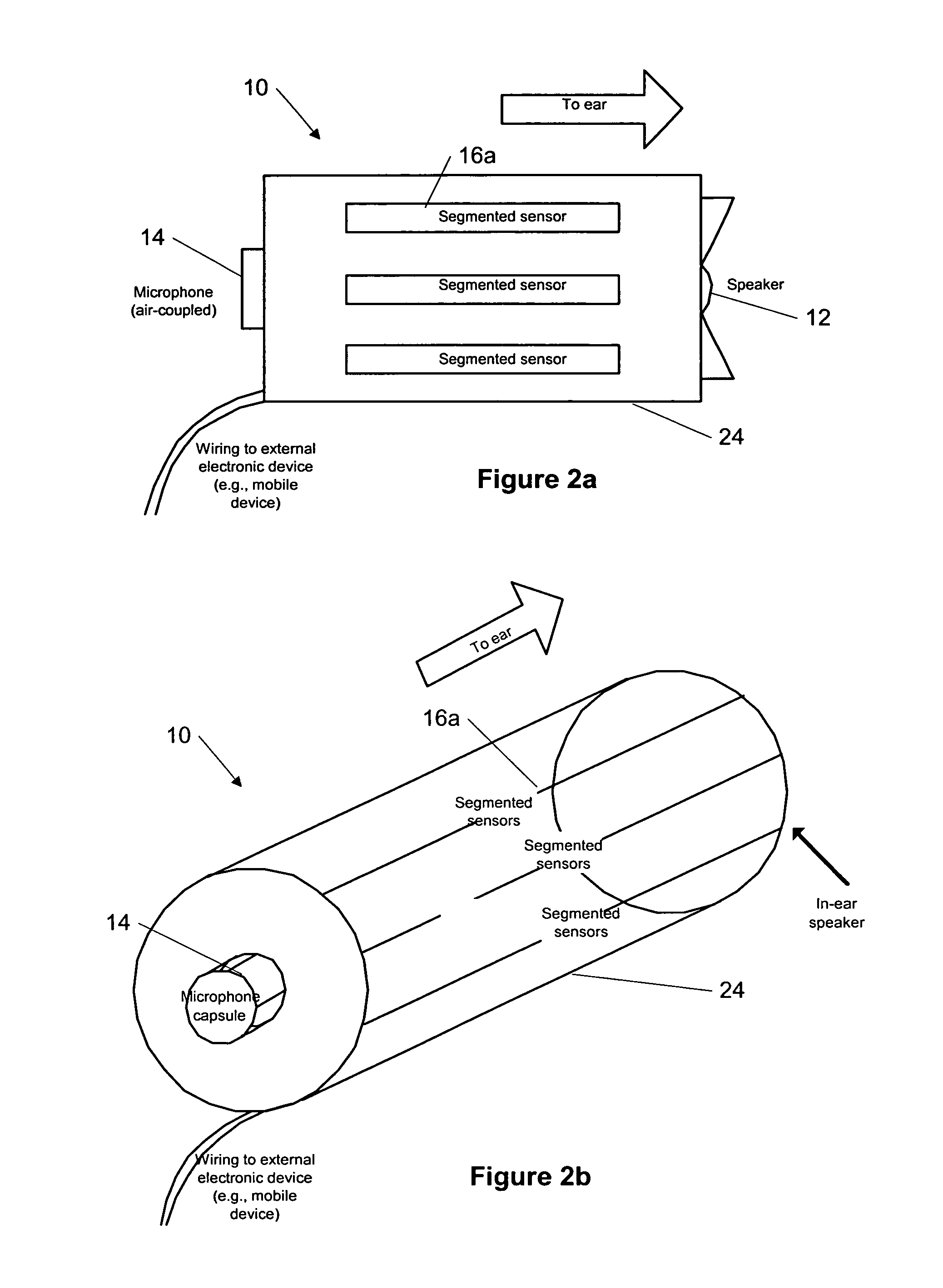
Ear-mounted transducer and ear-device
The specification and drawings present a new method, apparatus and software product for providing flexible audio communication solutions using ear-devices utilizing, e.g., electrode transducers with one or more sensors comprising a surface resonator cavity sensitive to a predetermined acoustic frequency range for using, for example, in headsets and hearing aids. The ear-device can be configured for inserting it into a human ear for a handsfree operation and the sensors can be configured to detect human tissue vibrations using the surface resonator cavity. The acoustic communication solutions with these ear-devices may include: providing two-way communications in normal conditions as well as in noisy conditions, providing protection of hearing, recording the true sound field bin-aurally, providing a playback capability, providing volume enhancement and equalization for persons with hearing defects, etc.
Owner:RPX CORP
Dual-frequency coaxial earphones
ActiveUS20090279729A1Small sizeIntra aural earpiecesFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsPhase cancellationDual frequency
A dual-frequency coaxial earphone includes a frame, a shared yoke, a high frequency speaker part, and a low frequency speaker part. The high frequency speaker part and the low frequency speaker part are coaxially arranged at inside and outside of the shared yoke, and are coaxial with a central opening of the frame. Further, a permanent magnet of the higher frequency speaker part is contrary, in polarity, to an annular magnet of the low frequency speaker part. Therefore, acoustic frequency of the low frequency speaker part can be phase-countered by passing thereof through an acoustic annular recess, so that the acoustic frequency of the low frequency speaker part has the same phase as the acoustic frequency of the high frequency speaker part and both then are output synchronally. The high frequency speaker part and the low frequency speaker part can then be separated, in acoustic frequency, from each other. This will effectively solve the problem of intermodulation of distortion for the high and low acoustic frequencies, and reduce the size of the earphone to more compact.
Owner:JETVOX ACOUSTIC
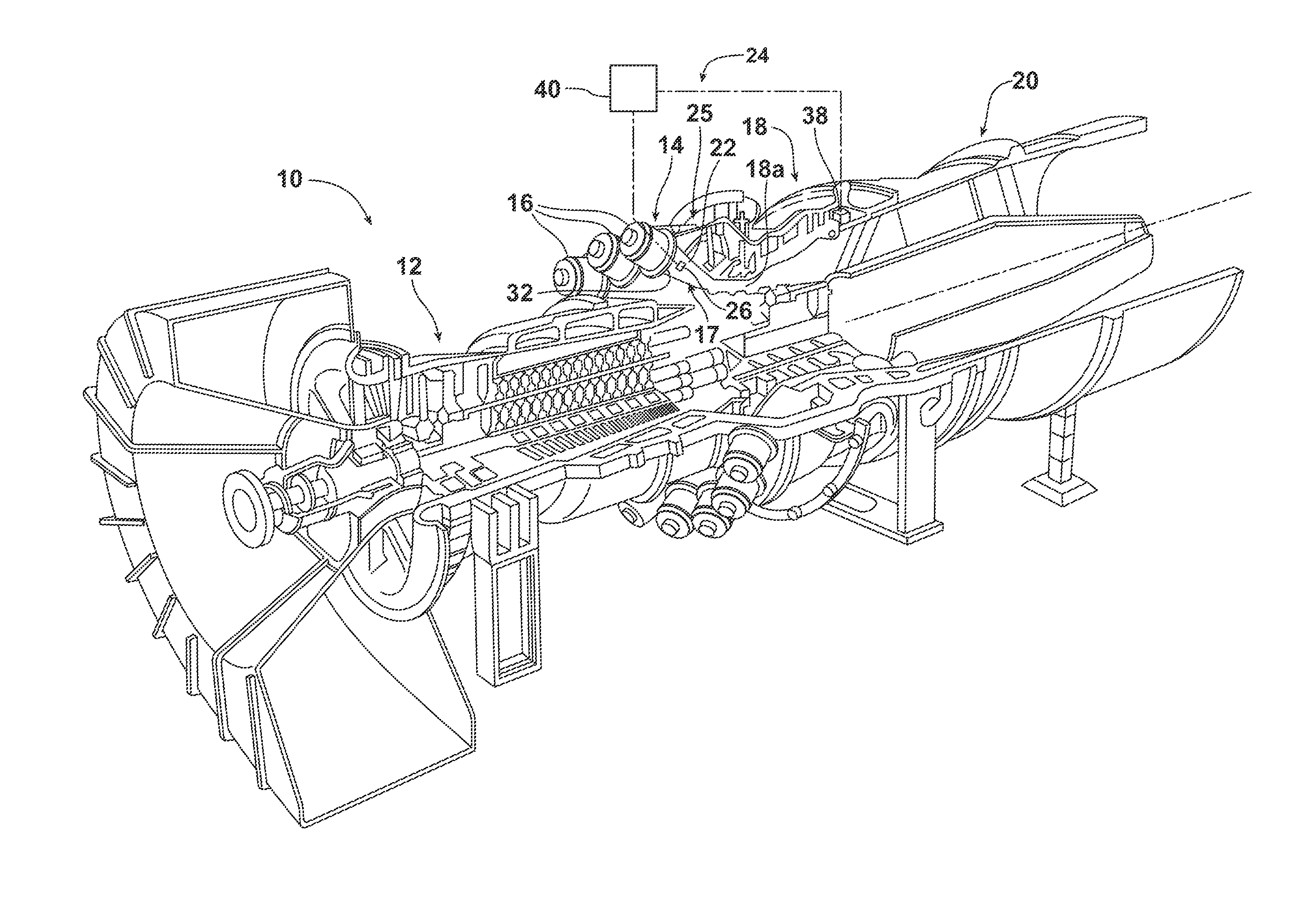
Temperature measurement in a gas turbine engine combustor
InactiveUS20140278200A1Thermometer detailsTemperature measurement in motorsCombustorCombustion chamber
A method and system for determining a temperature of a working gas passing through a passage to a turbine section of a gas turbine engine. The method includes identifying an acoustic frequency at a first location in the engine upstream from the turbine section, and using the acoustic frequency for determining a first temperature value at the first location that is directly proportional to the acoustic frequency and a calculated constant value. A second temperature of the working gas is determined at a second location in the engine and, using the second temperature, a back calculation is performed to determine a temperature value for the working gas at the first location. The first temperature value is compared to the back calculated temperature value to change the calculated constant value to a recalculated constant value. Subsequent first temperature values at the first location may be determined based on the recalculated constant value.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Device and Methods for Targeting of Transcranial Ultrasound Neuromodulation by Automated Transcranial Doppler Imaging
InactiveUS20150151142A1Overcome deficienciesReduce amountSurgeryChiropractic devicesSonificationBlood vessel
Methods and systems for transcranial ultrasound neuromodulation as well as targeting such neuromodulation in the brain are disclosed. Automated transcranial Doppler imaging (aTCD) of blood flow in the brain is performed and one or more 3-dimensional maps of the neurovasculature are generated. Ultrasound energy is delivered transcranially in conjunction to induce neuromodulation. One or more brain regions for neuromodulation are targeted by using brain blood vessel landmarks identified by aTCD components. The landmarks are used for initial targeting of the neuromodulation to one or more brain regions of interest and / or for maintaining neuromodulation targeting despite user or device movements. Acoustic contrast agents may be employed to generate broadband ultrasound waves locally at the site of target cells. Transcranial ultrasound neuromodulation may be achieved by having confocal ultrasound waves differing in acoustic frequency by a frequency effective for neuromodulation interfere to generate vibrational forces in the brain that induce neuromodulation.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Taste cell sensor using surface acoustic wave resonator and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104089996AReduce volumePractical and convenientMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial electrochemical variablesTaste cellControllability
The invention relates to a taste cell sensor using a surface acoustic wave resonator. The taste cell sensor includes the surface acoustic wave resonator, which is encapsulated in a metal shell by vacuum. The surface acoustic wave resonator adopts ST cut quartz as a piezoelectric substrate material, is prepared by a photolithography process, the emitted surface acoustic frequency is 433MHZ. The taste cell sensor also includes a silk-screen printing carbon electrode, which is in series connection with the surface acoustic wave resonator. The silk-screen printing carbon electrode is firstly modified by amino acid and then coated with an NCI-H716 cell suspension solution. The taste cell sensor provided by the invention has the advantages of small volume, practicability and convenience, fast electrode response, high sensitivity, good batch repeatability, low cost and the like, can achieve high frequency, and can realize rapid real-time detection. The preparation method has the characteristics of simple preparation process, small material consumption, high process repeatability and controllability, and is convenient for batch production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
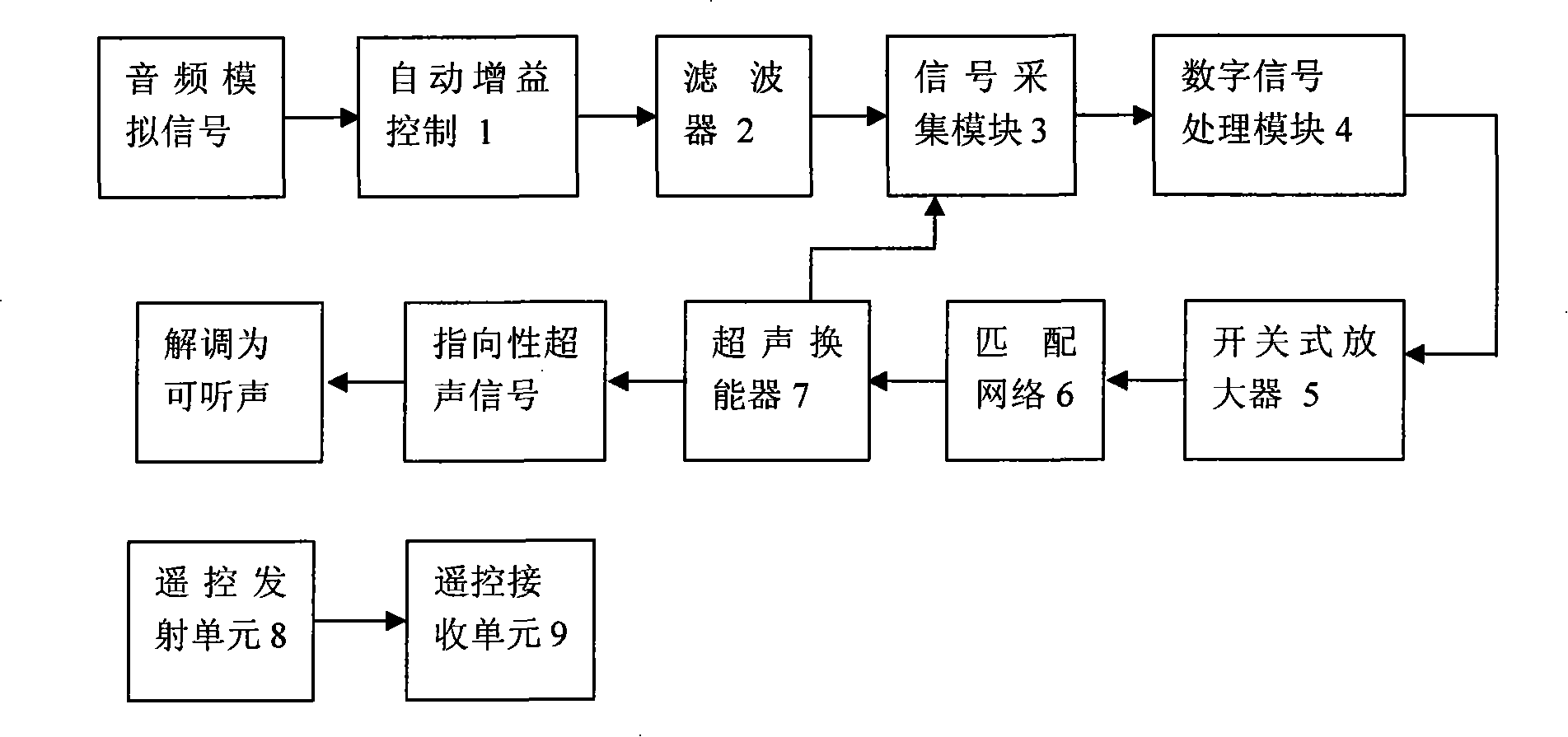
Method for numeral sound signal processing and digital type sound frequency directional loudspeaker
InactiveCN101203062AImplement video extensionRealize remote controlSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionTransducer circuitsDigital signal processingSound sources
The invention discloses a digital audio directional loudspeaker and a digital audio signal processing method. An automatic gain control module adjusts the amplitude of a sound source signal; then, a filter filters out elements beyond a audio signal belt so as to reduce noises; a signal input module changes an audio analog signal into a digital signal; the processing of approximate square root algorithm or other algorithms to the audio digital signal is finished in the digital signal processing module; two state levels are output into a switch type power amplifier to match with the network to assure impedance matching; an ultrasonic transducer is used for changing an electric signal into a sound pressure signal. The ultrasonic signal which is emitted from the transducer carries the input audio signal information, does the nonlinear interaction in the air and is demodulated into audible sound. A remote control receiving unit receives orders sent by a remote control transmission unit to control parameters such as point angle, volume, transmission distance, sound effect and point sound, etc.
Owner:徐利梅
Photonic crystal structure sensor
ActiveUS20080226217A1Improve temperature stabilitySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansCrystal structurePhotonic crystal structure
An acoustic sensor and a method of fabricating an acoustic sensor are provided. The acoustic sensor includes at least one photonic crystal structure and an optical fiber having an end optically coupled to the at least one photonic crystal structure. The acoustic sensor further includes a structural portion mechanically coupled to the at least one photonic crystal structure and to the optical fiber. The at least one photonic crystal structure, the optical fiber, and the structural portion substantially bound a region having a volume such that a frequency response of the acoustic sensor is generally flat in a range of acoustic frequencies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Headphone for spatial sound reproduction
ActiveUS20060204016A1Small space requirementEasy to useTransducers for sound channels pluralityHeadphones for stereophonic communicationHuman earEngineering
The invention concerns a headphone and a compatible recording device for spatial sound reproduction provided with two earphones, each earphone having a support defining at least partly a cap-like surface comprehensively covering the listener's ear. Each earphone includes at least five speakers arranged on said support. The speakers are adapted to reproduce an acoustic field, such that it is perceived as being continuous by the human ear, for acoustic frequencies lower than a given maximum frequency.
Owner:A VOLUTE
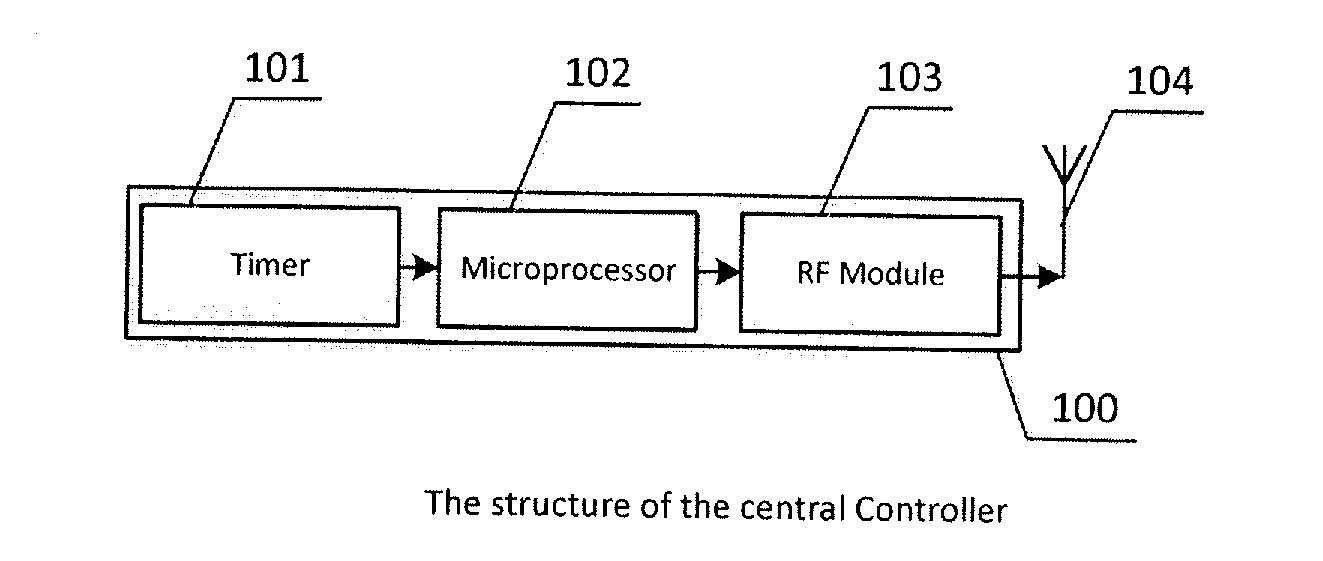
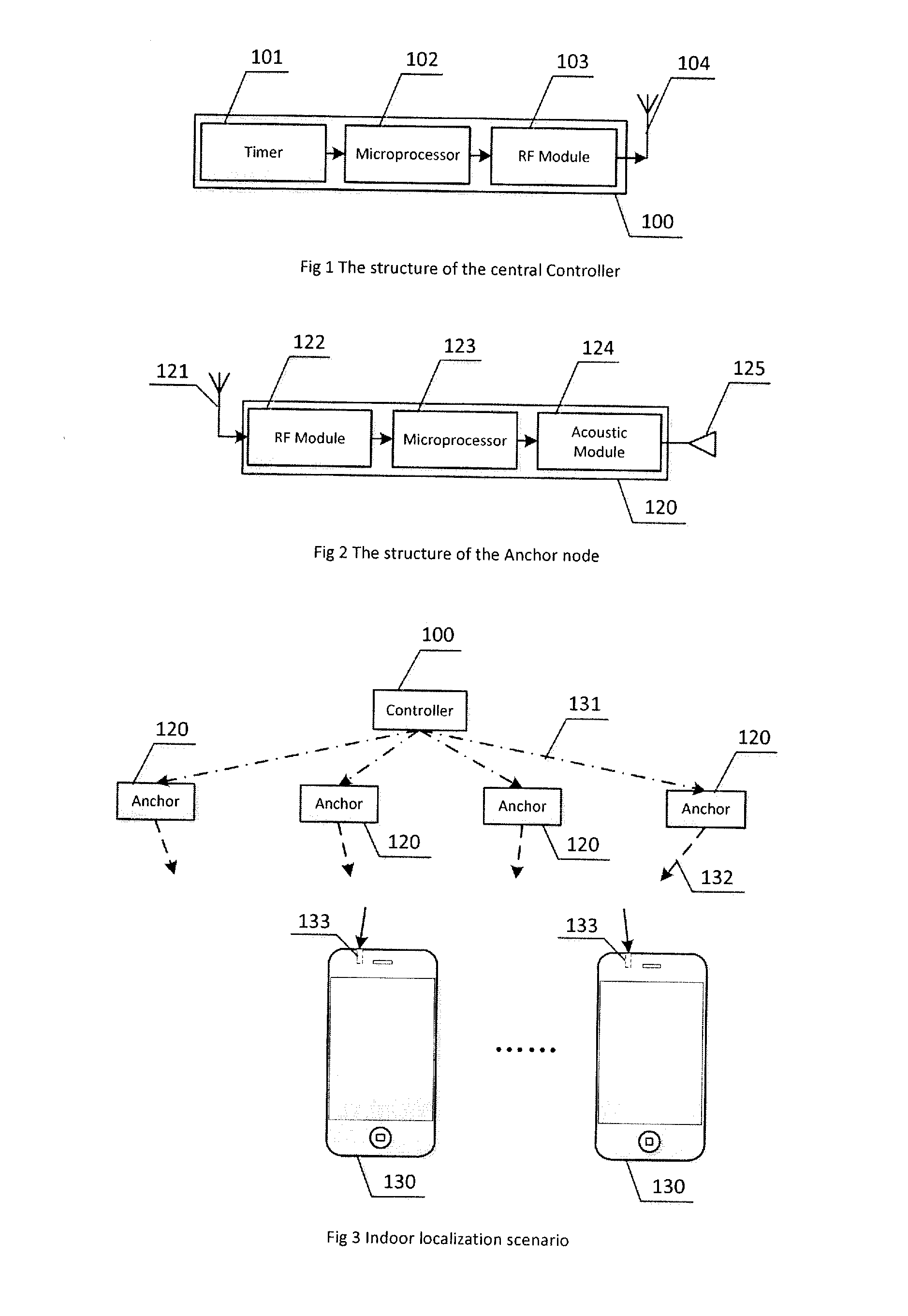
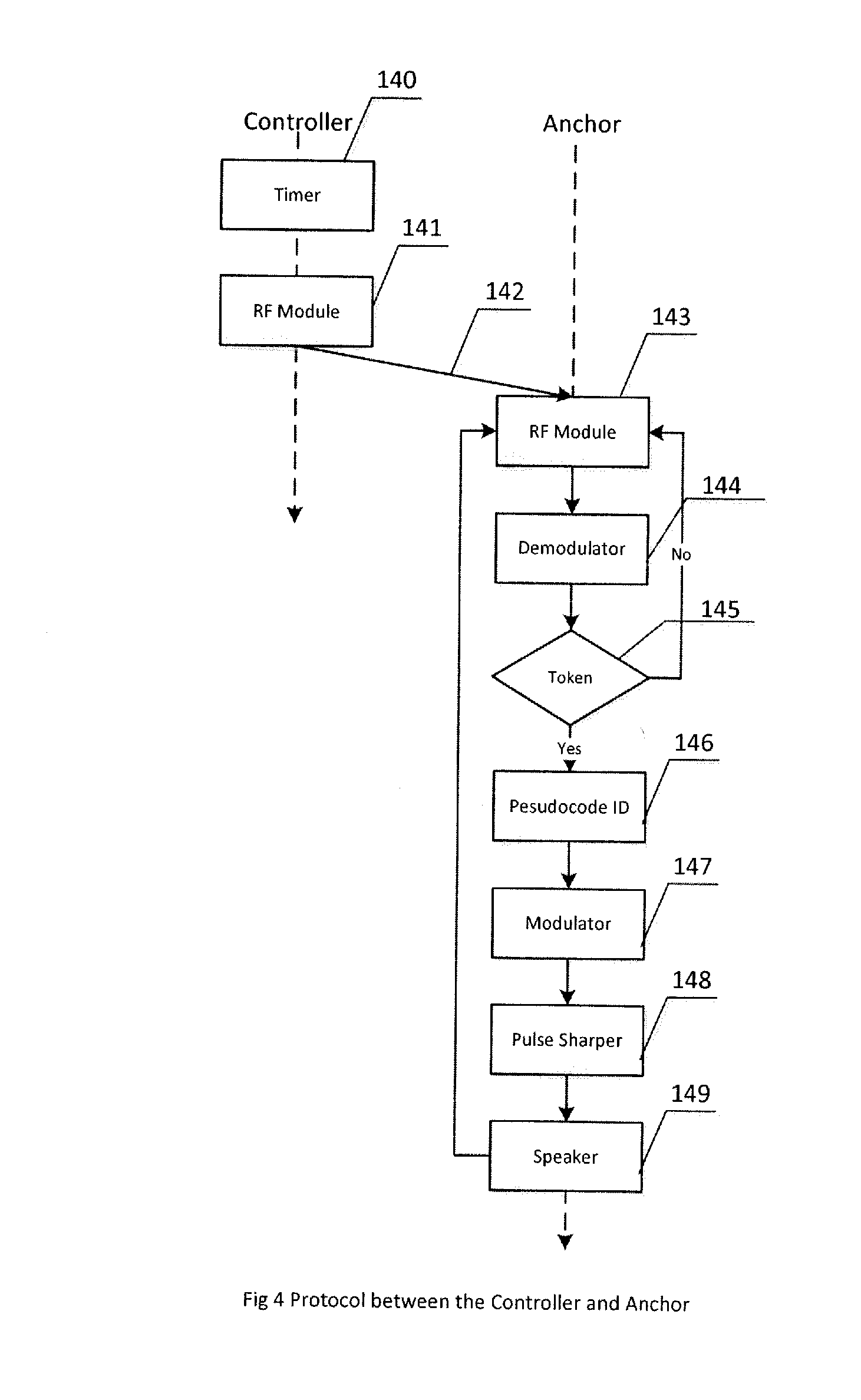
Apparatus, method, and software systems for smartphone-based fine-grained indoor localization
Techniques for accurate, low-complexity, scalable indoor localization. Low-complexity anchor nodes generate acoustic beacon signals, which are passively detectable by a mobile device, which may be unmodified smartphones operating in an acoustic frequency range. The acoustic beacon signals are modulated via codes in a boundary band of audio and ultrasound frequencies, imperceptible to humans yet detectable via a voice microphone of an unmodified smartphone. An application on the mobile device passively captures the acoustic beacon signals and determines relative distances to the anchor nodes. Localization and distance update techniques, implemented on the mobile device and / or a remote server, determines and updates in real-time the location of the mobile device. The system may be scalable to support any number of mobile devices. Based on the tracked location, the indoor localization system may provide indoor location-based-services (LBS) to the mobile devices, and transmit to the mobile device information relevant to its location.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Array micro audio directional transducer
InactiveCN101583062AEnsure consistencyHighly directional audible signalPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsSonificationTransducer
The invention provides an array micro audio directional transducer, belonging to the technical field of ultrasound, in particular to the technical field of transducer. The transducer comprises the following working steps: a plurality of micro transducer units are arranged on a support frame evenly or unevenly for transmitting ultrasound modulated by audible signals; the ultrasound is self modulation in air to generate audible sound with high directivity. The transducer unit consists of four parts, namely, a top electrode, a bottom electrode, radiating materials and a base. The surface of the support frame is coated with plus-minus electrodes to connect with all plus-minus electrodes of the transducer units. The number of the array micro audio directional transducer units can be changed according to the requirements of directivity, sound pressure level and other parameters. The transducer features high conversation efficiency in electro mechanics, strong directivity, good stability, changeable array structure and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Howling detecting and suppressing apparatus, method and computer program product
InactiveUS7133529B2Easy constructionImprove sound qualityTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSignal processingTime segmentEngineering
Herein disclosed a howling detecting and suppressing apparatus for detecting and suppressing howling sound components comprising: a frequency dividing processing section for converting a plurality of sound time signal segments each corresponding to a time segment into a plurality of sound frequency signal segments each corresponding to a frequency segment; a howling suppressing section for respectively adjusting gains for said sound frequency signal segments converted by said frequency dividing processing section to generate howling-suppressed sound frequency signal segments; a howling detecting section for judging whether a howling sound component is present or not for each of said howling-suppressed sound frequency signal segments generated by said howling suppressing section to detect howling sound frequency signal segments each in which it is judged that said howling sound component is present and non-howling sound frequency signal segments each in which it is judged that said howling sound component is not present; and a frequency synthesizing processing section for synthesizing said howling-suppressed sound frequency signal segments suppressed by said howling suppressing section to generate howling-suppressed sound time signal segments, whereby said howling suppressing section is operative to respectively adjust gains for said sound frequency signal segments converted by said frequency dividing processing section by changing the gains of said howling sound frequency signal segments detected by said howling detecting section and passing through said non-howling sound frequency signal segments detected by said howling detecting section.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Detecting Downhole Events Using Acoustic Frequency Domain Features
A method of detecting an event within a wellbore includes obtaining a sample data set, determining a plurality of frequency domain features of the sample data set, comparing the plurality of frequency domain features with an event signature, determining that the plurality of frequency domain features matches the thresholds, ranges, or both of the event signature, and determining the presence of the event within the wellbore based on determining that the plurality of frequency domain features match the thresholds, ranges, or both of the event signature. The sample data set is a sample of an acoustic signal originating within a wellbore including a fluid. The sample data set is representative of the acoustic signal across a frequency spectrum. The event signature includes a plurality of thresholds, ranges, or both corresponding to the plurality of frequency domain features.
Owner:BP EXPLORATION OPERATING CO LTD
Millimeter wave sensor used to optimize performance of a beamforming microphone array
A method for operating a beamforming microphone array for use in a predetermined area comprising: receiving acoustic audio signals at each of a plurality of microphones, converting the same to an electrical mic audio signal, and outputting each of the plurality of electrical mic audio signals; generating a user location data signal by a wave sensor system, and outputting the user location data signal, wherein the user location data signal includes location information of one or more people within the predetermined area; receiving both the user location data signal and plurality of mic audio signals at an adaptive beamforming device; adapting one or more beams by the adaptive beamforming device based on the user location data signal and plurality of output electrical mic audio signals wherein each of the one or more beams acquires sound from one or more specific locations in the predetermined area; and performing acoustic echo cancellation on each of the one or more beams output from the adaptive beamforming device.
Owner:CRESTRON ELECTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com