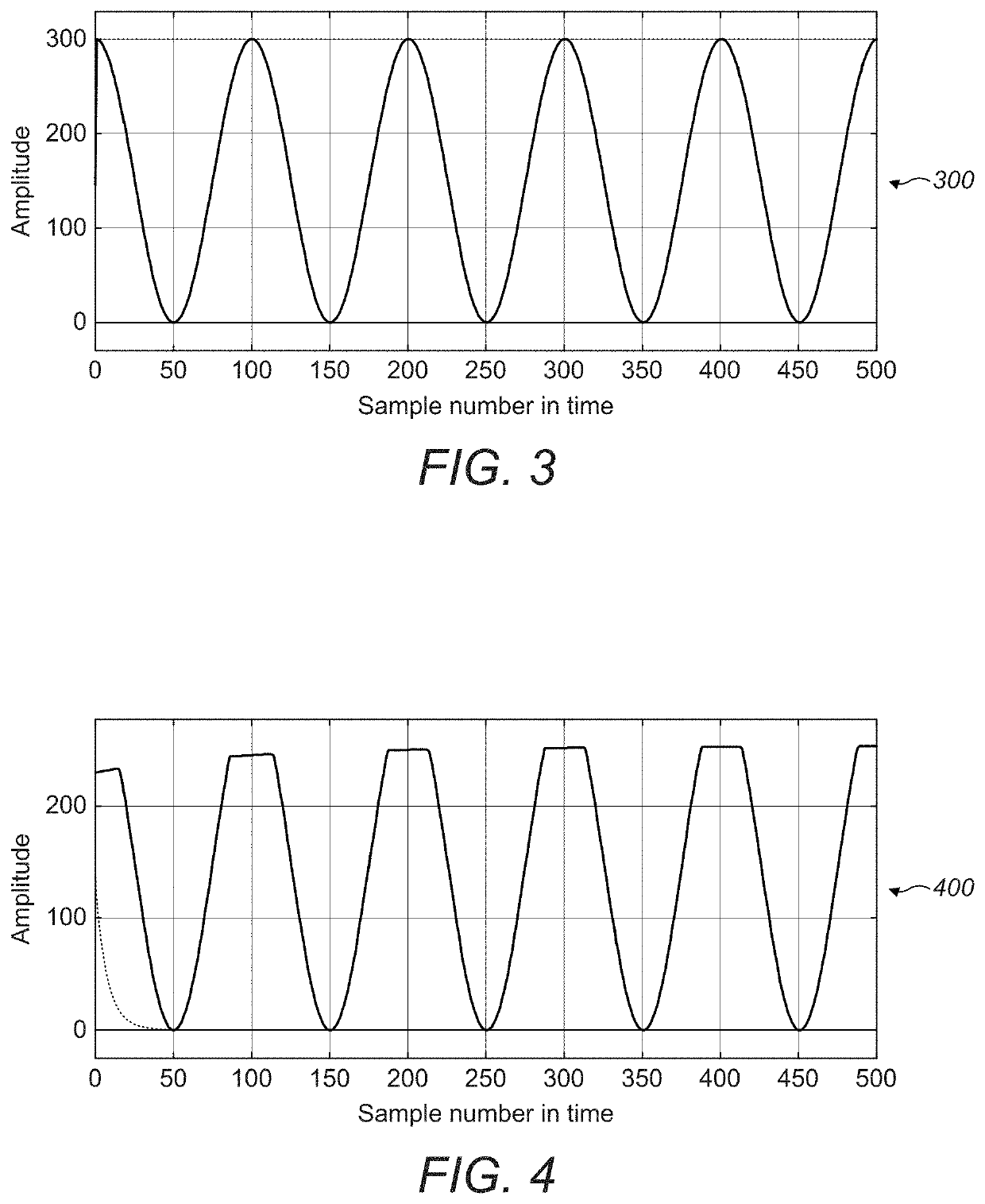
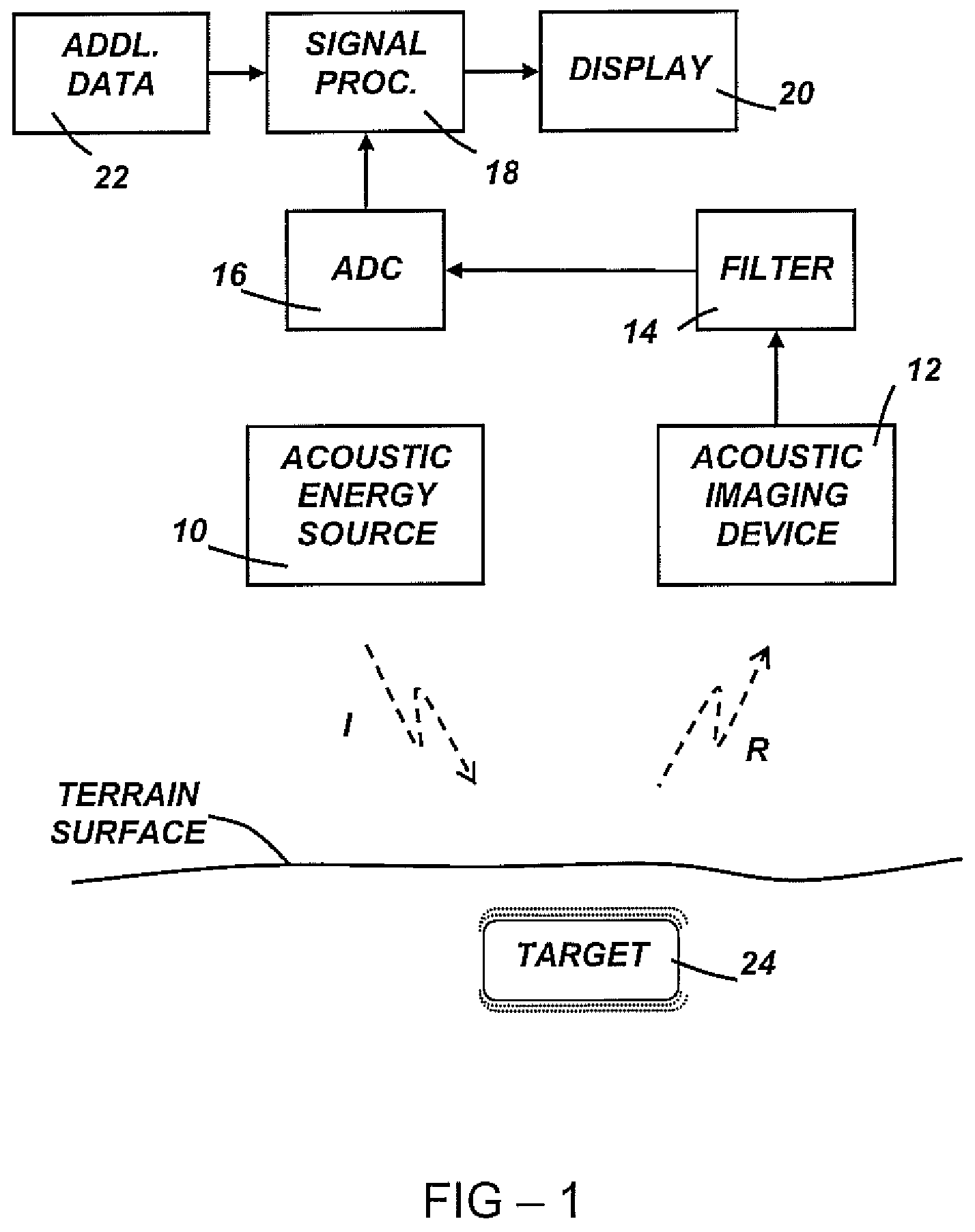
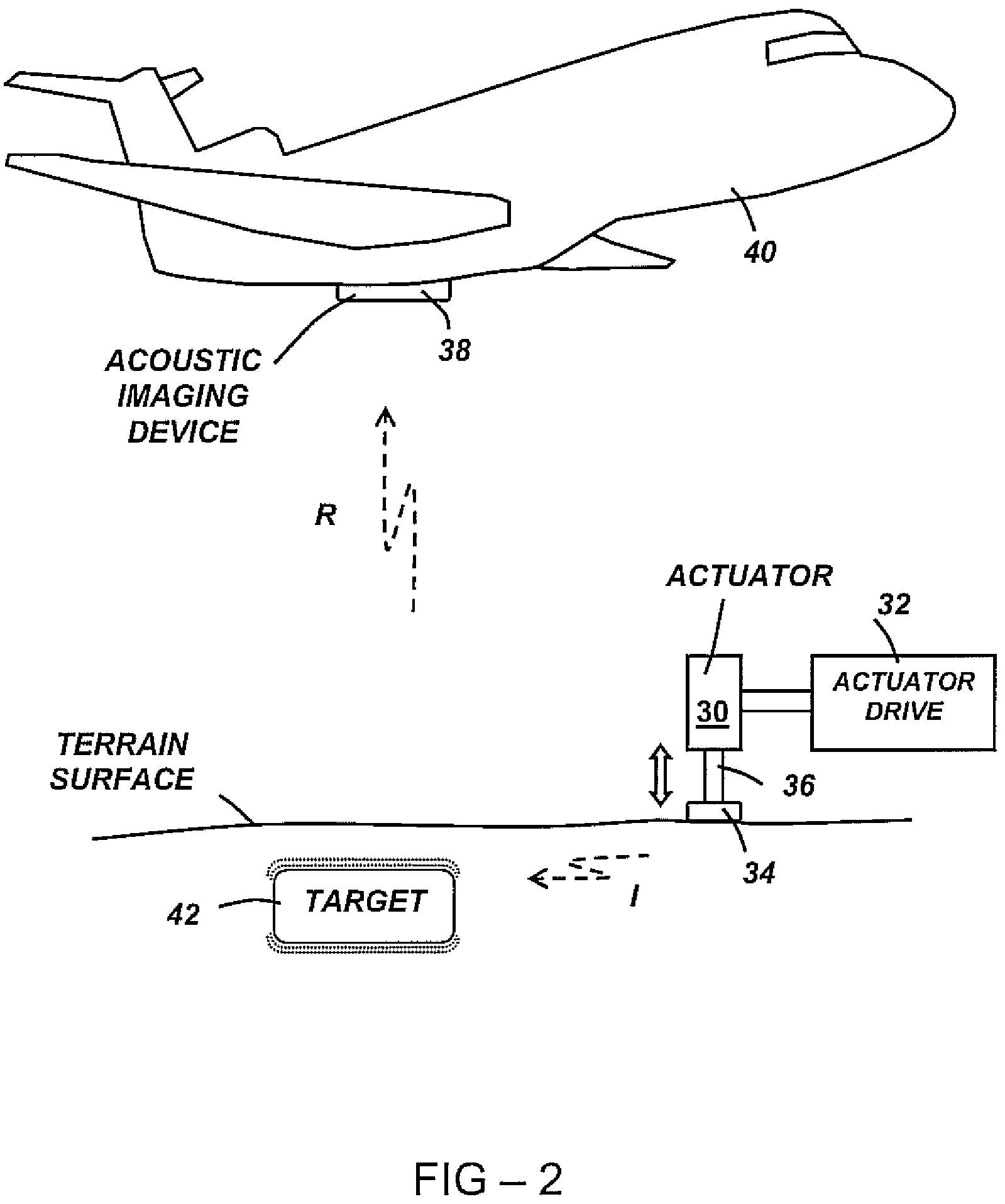
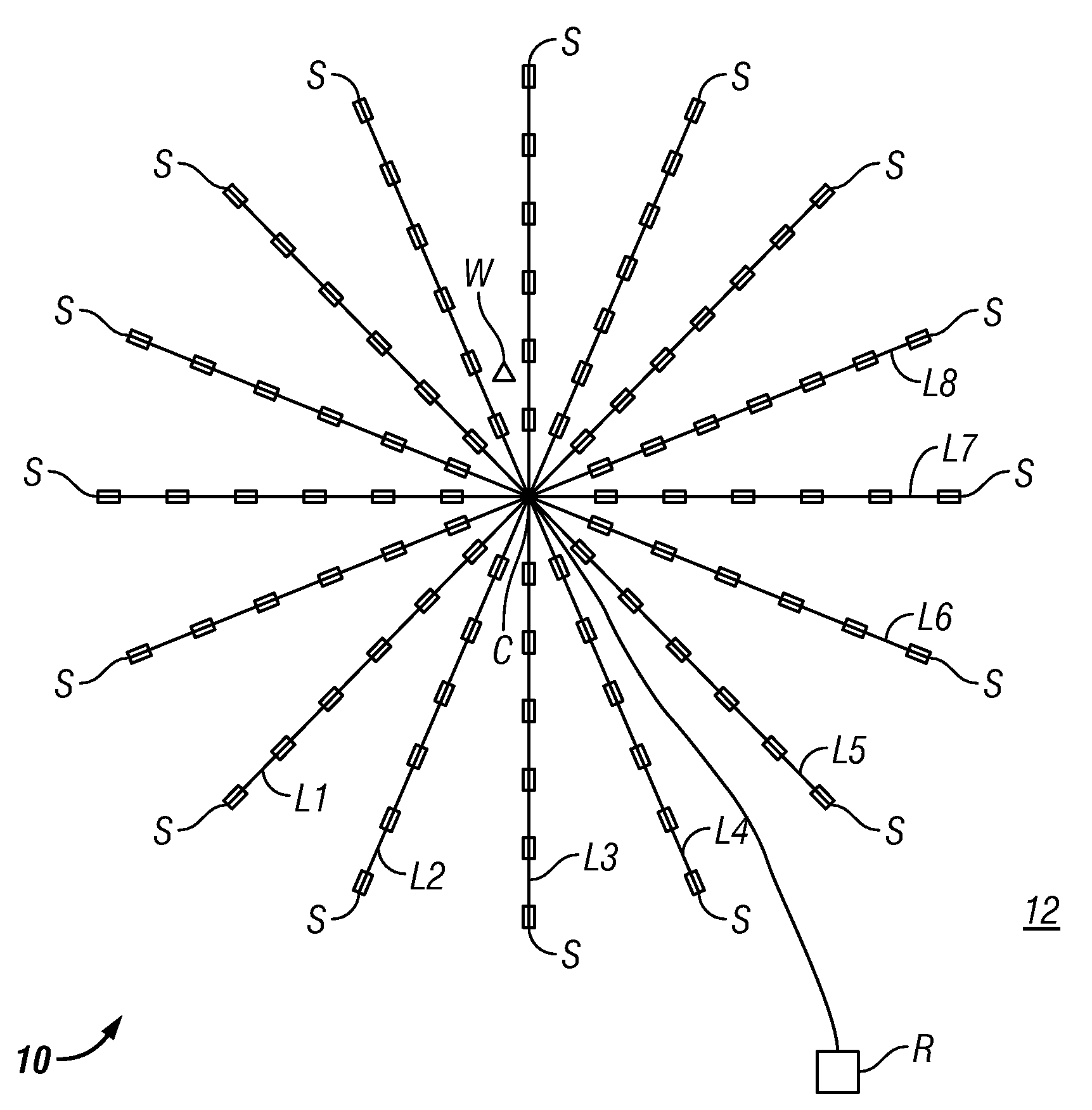
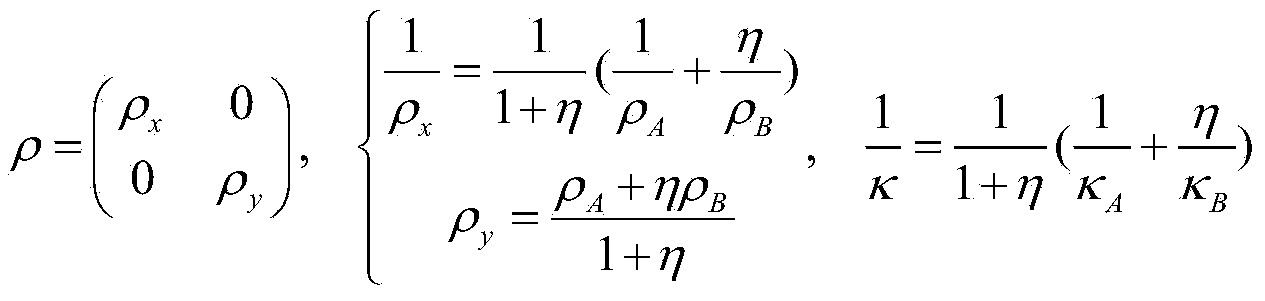Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
126 results about "Acoustical imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
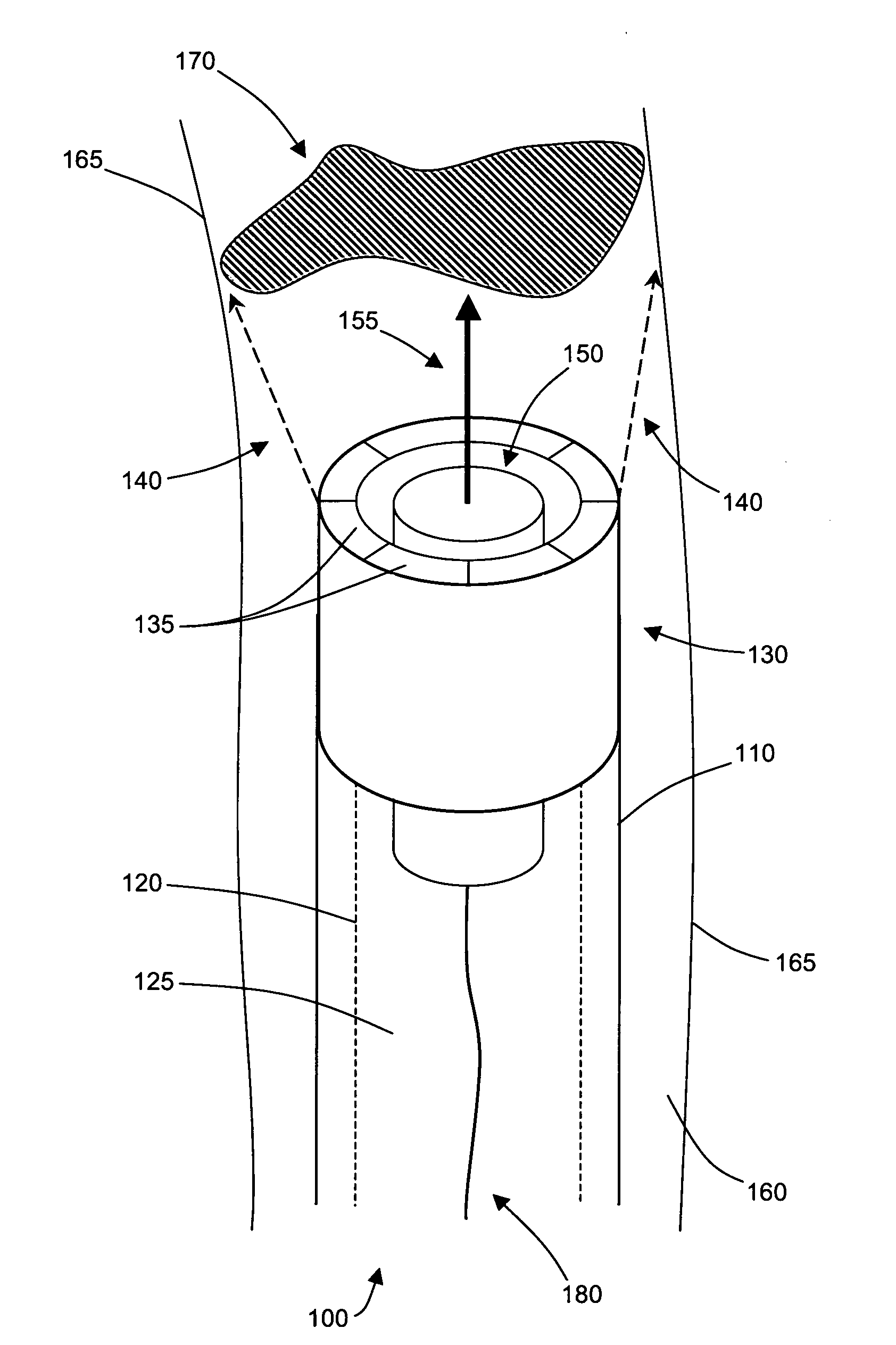
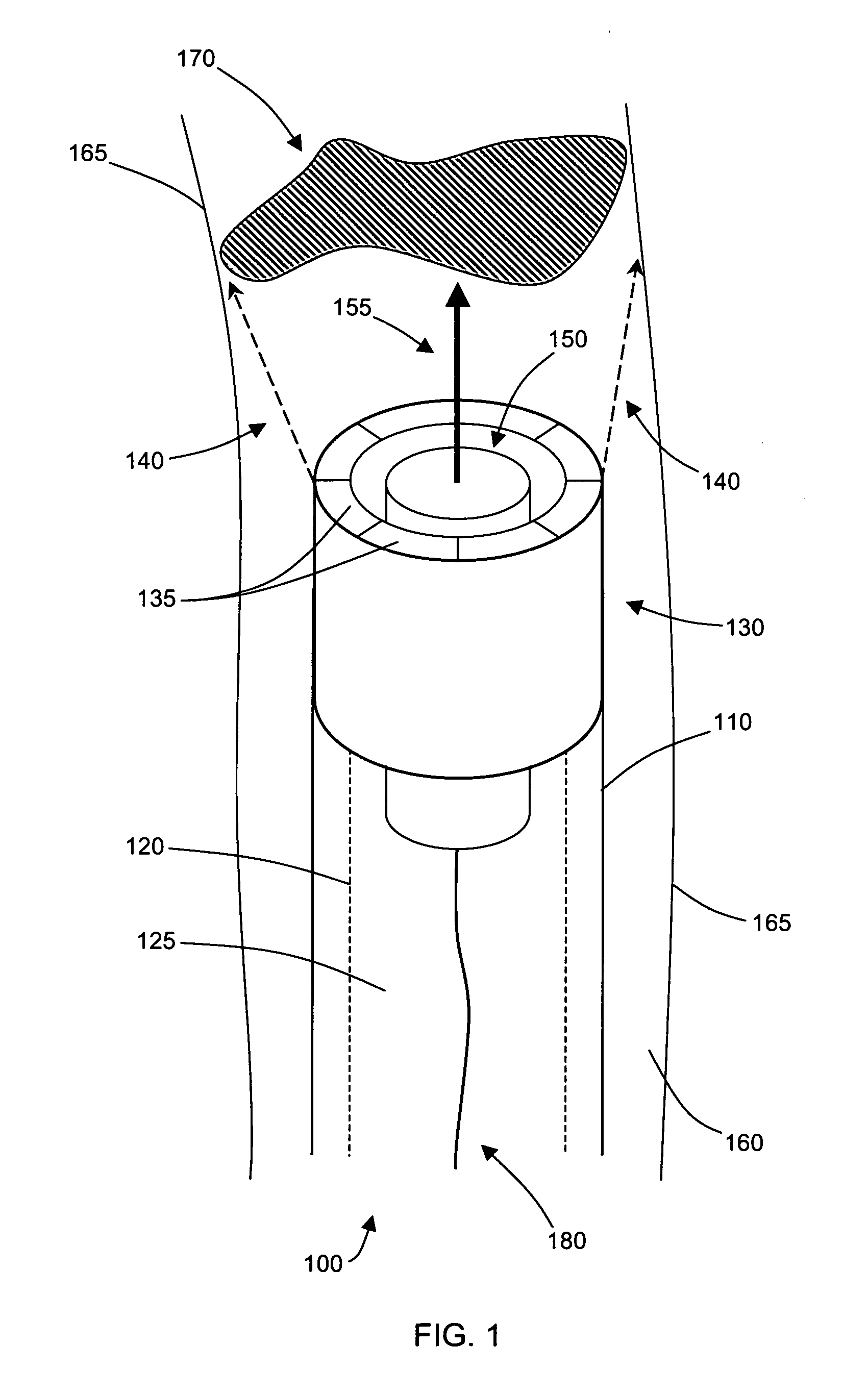
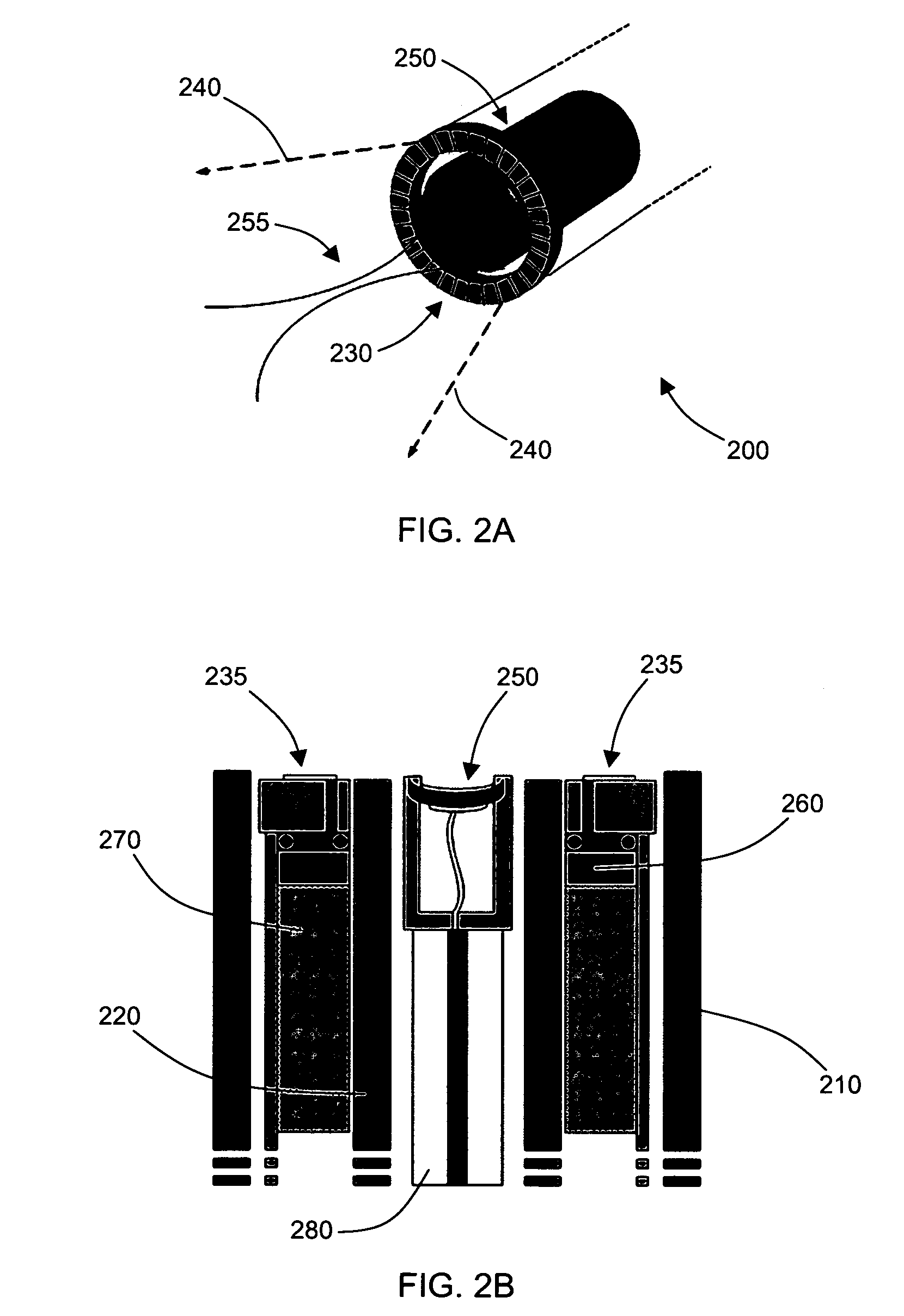
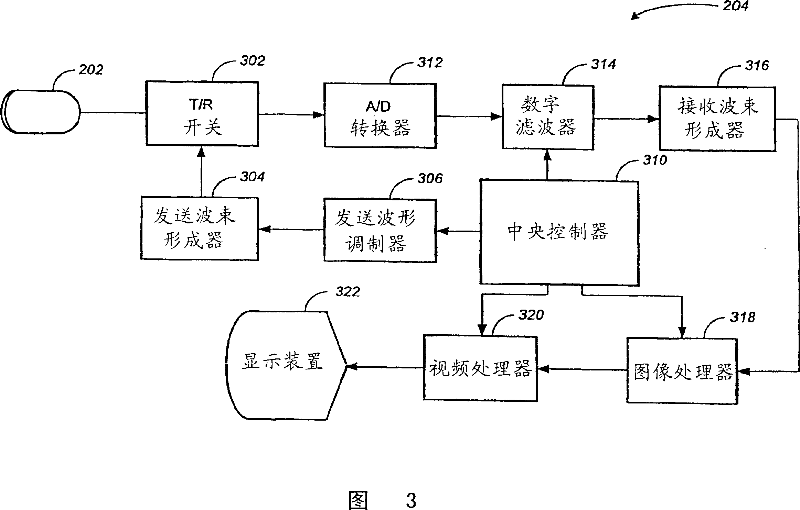
Image-guided delivery of therapeutic tools duing minimally invasive surgeries and interventions
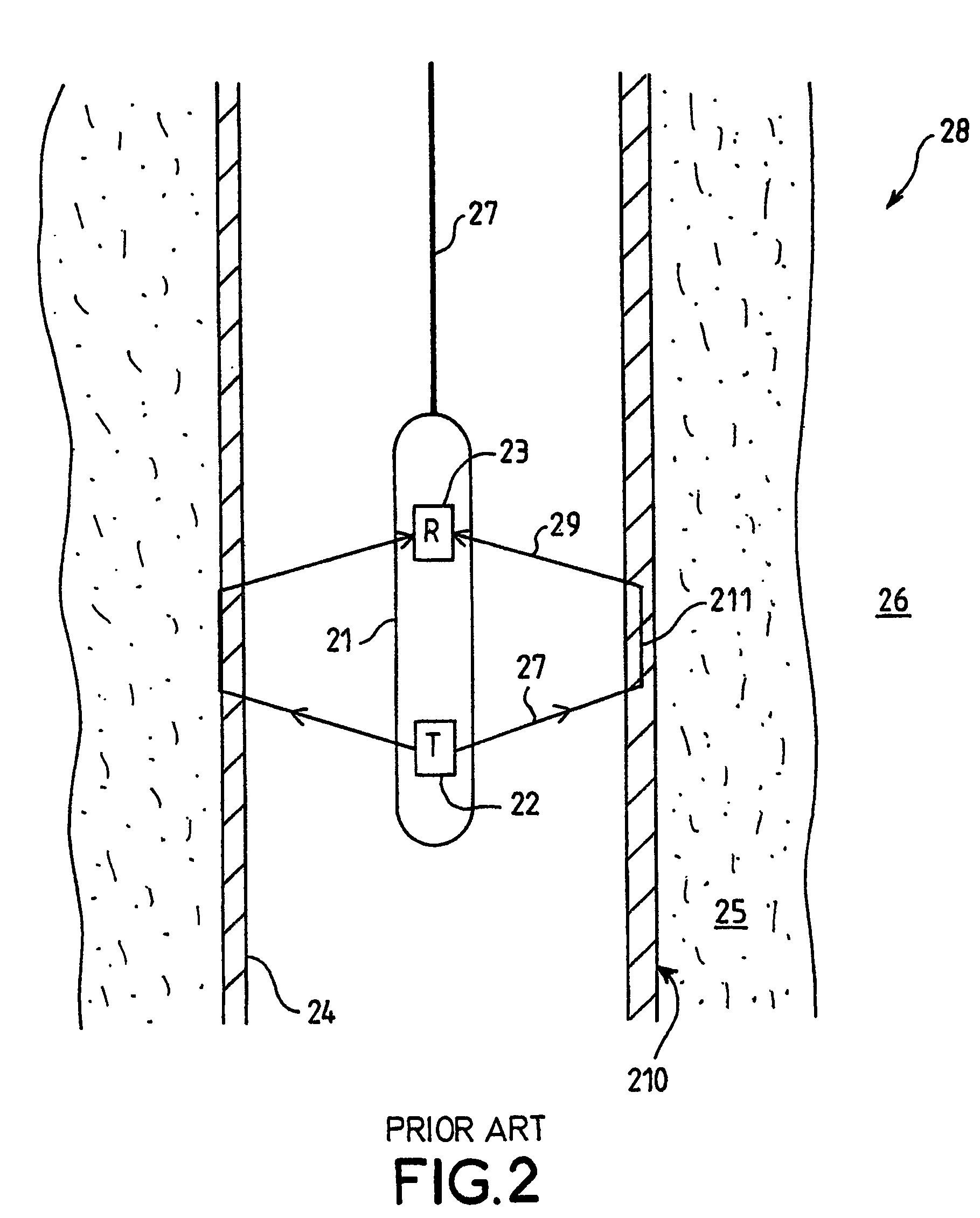
InactiveUS20080221448A1Enhance the imageMinimally invasiveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCapacitanceUltrasonic sensor
Imaged-guided therapy for minimally invasive surgeries and interventions is provided. An image-guided device includes an elongate tubular member, such as a catheter, an annular array of capacitive micromachined ultrasound transducers (cMUTs) for real-time three-dimensional forward-looking acoustic imaging, and a therapeutic tool. The therapeutic tool is positioned inside an inner lumen of the elongate tubular member and can be a device for tissue ablation, such as a high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) device or a laser. The HIFU device is operable at high frequencies to have a sufficiently small focus spot, thus a high focal intensity. The imaging annular array is also operable at high frequencies for good acoustic imaging resolution. The high resolution forward-looking imaging array, in combination with the high frequency HIFU transducer, provides a single image-guided therapy device for precise tissue ablation and real-time imaging feedback.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Acoustic imaging by nonlinear low frequency manipulation of high frequency scattering and propagation properties
ActiveUS20060052699A1Easy to measureFrame rateOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryLinearityAcoustical imaging
Acoustic imaging provides images with reduced reverberation noise and images of nonlinear scattering and propagation parameters of the object. The received signal from transmitted dual frequency band acoustic pulse complexes is processed with overlapping high and low frequency pulses. The high frequency pulse is used for image reconstruction and the low frequency pulse manipulate the nonlinear scattering and / or propagation properties of the high frequency pulse. The scattered signal from a single dual band pulse complex for filtering in the fast time (depth time) domain provides a signal with suppression of reverberation noise with 1st harmonic sensitivity and increased spatial resolution. Through filtering in the pulse number coordinate and corrections for nonlinear propagation delays, a linear back scattering signal with suppressed pulse reverberation noise, a nonlinear back scattering signal, and quantitative nonlinear forward propagation and scattering parameters are extracted.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
Systems and methods for laser radar imaging for the blind and visually impaired
InactiveUS20080309913A1Improve accuracyAccurate informationOptical rangefindersSolid-state devicesVisually impairedRadar systems
A 3D imaging ladar system comprises a solid state laser and geiger-mode avalanche photodiodes utilizing a scanning imaging system in conjunction with a user interface to provide 3D spatial object information for vision augmentation for the blind. Depth and located object information is presented acoustically by: 1) generating an audio acoustic field to present depth as amplitude and the audio image as a 2D location. 2) holographic acoustical imaging for a 3D sweep of the acoustic field. 3) a 2D acoustic sweep combined with acoustic frequency information to create a 3D presentation.A system to fuse data derived from a three dimensional imaging ladar system with information from a visible, ultraviolet, or infrared camera systems and acoustically present the information in a four or five dimensional acoustical format utilizing three dimensional acoustic position information, along with frequency, and modulation to represent color, texture, or object recognition information is also provided.
Owner:FALLON JAMES JOHN
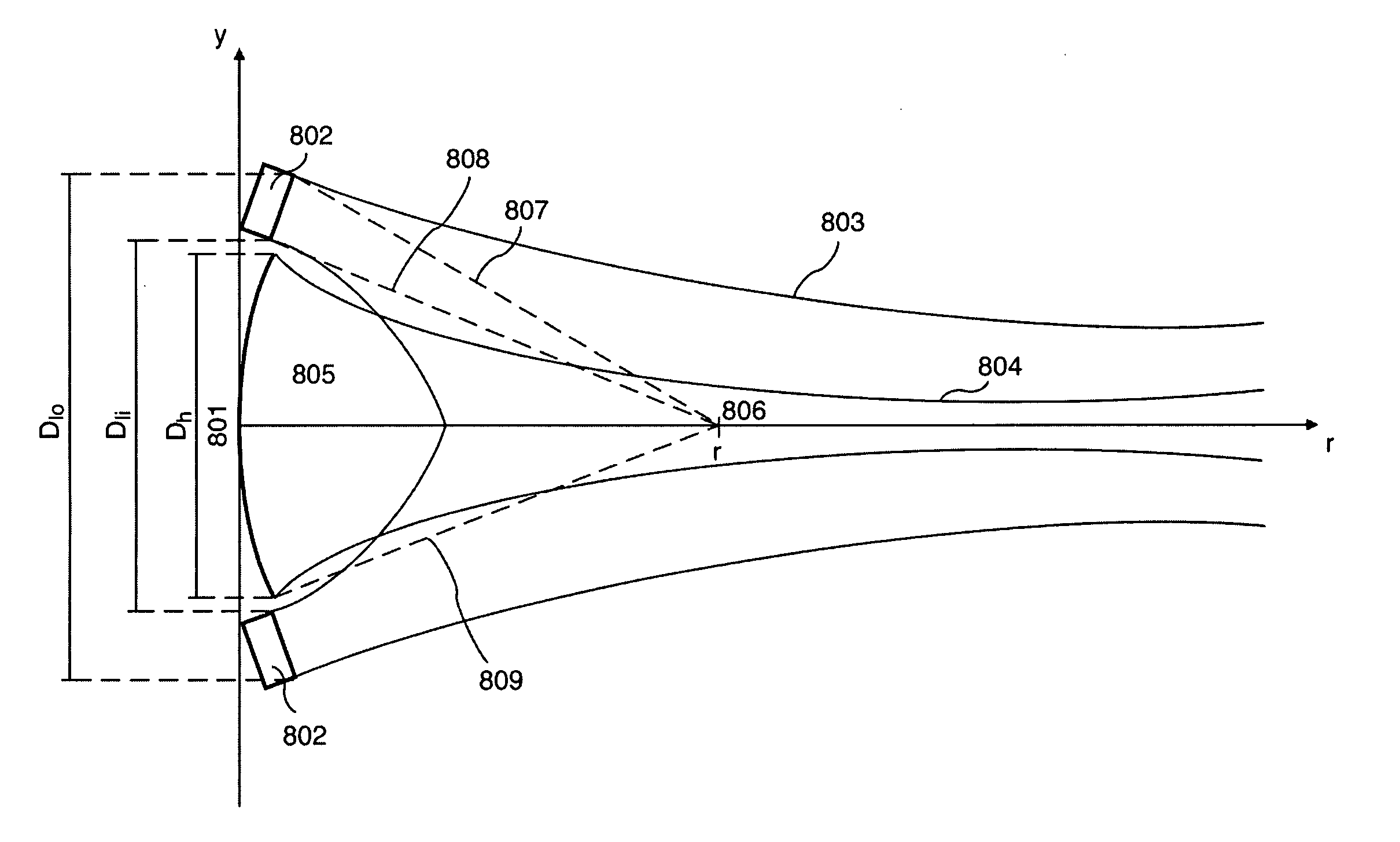
Acoustic imaging probe incorporating photoacoustic excitation
Various embodiments of the present invention provide for a photoacoustic imaging probe for use in a photoacoustic imaging system, whereby the probe is comprised of a cohesive composite, acoustic lens incorporating aspheric geometry and exhibiting low or practically no measurable dispersion of acoustic waves constructed of at least one material with a low acoustic impedance and attenuation and a relatively low acoustic velocity and at least one other material with a low acoustic impedance and attenuation and a relatively high acoustic velocity. The probe is housed in a conduit filled with a low acoustic velocity and low acoustic impedance fluid such as water or mineral oil. The lens may be designed as a telecentric lens, an acoustic zoom lens, a catadioptric lens, or a reflective lens. The lens focuses acoustic waves on an acoustic imager which detects the image. The acoustic imager may be designed as a 2 dimensional array of transducers. Research to date indicates that within the range of acoustic frequencies of interest, 1 MHz-50 MHz and preferable 2 MHz-10 MHz, there exists little velocity variation within the materials of interest, and the lens design approach may currently be considered to be essentially monochromatic. The acoustic waves can be generated when an emitting light source illuminates a test subject comprising materials that generate acoustic waves at differing intensities and / or frequencies when illuminated with light, for example tissue containing blood vessels, wherein the blood vessels excite and generate an acoustic pulse. The probe has an acoustic window made of a material with low acoustic impedance which allows the acoustic pulse to enter the probe without distortion and then may be reflected by a mirror onto the acoustic lens. The probe may include the emitting light source and an optical window to allow light emitting from said light source to illuminate the test subject.
Owner:ARNOLD STEPHEN C
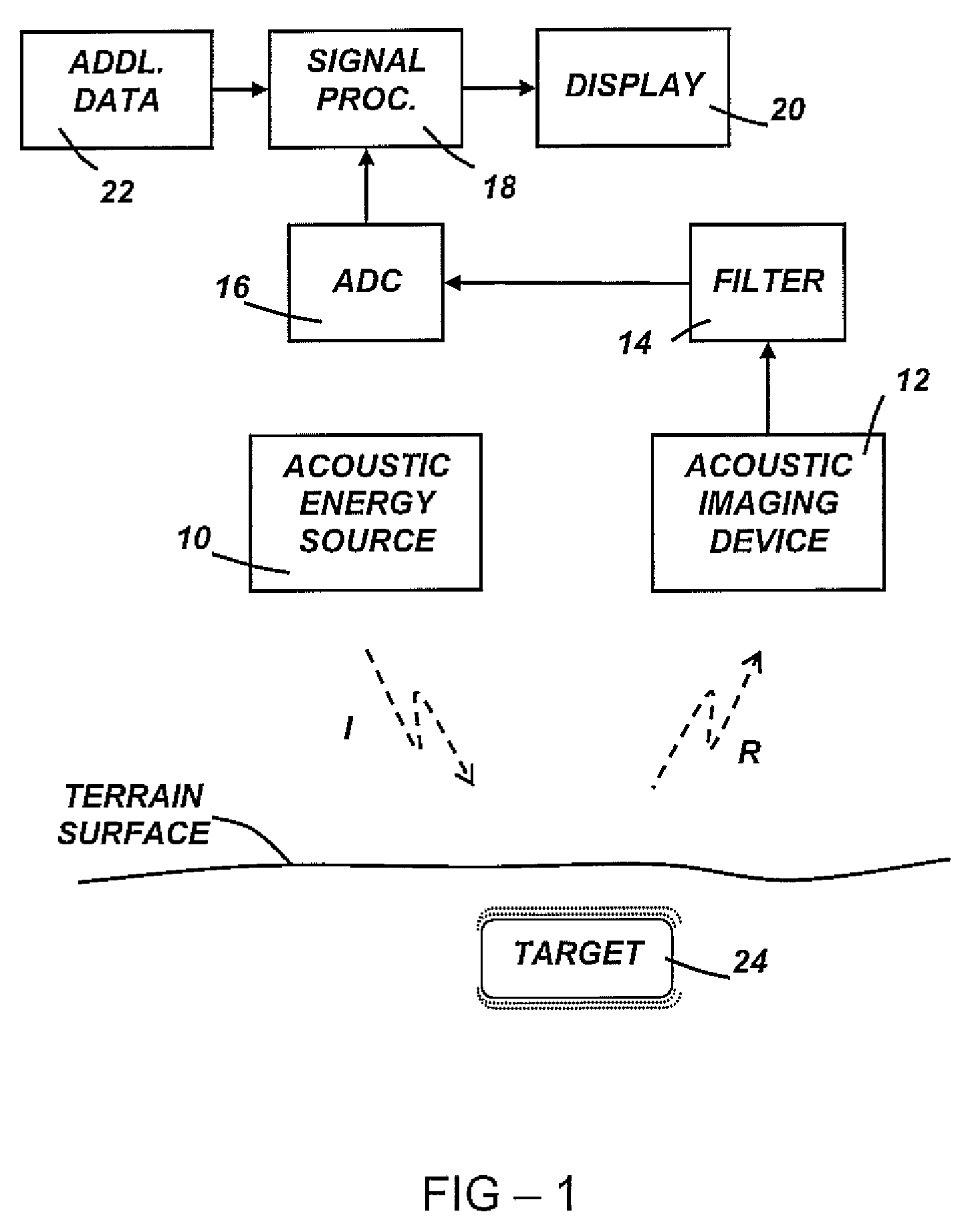
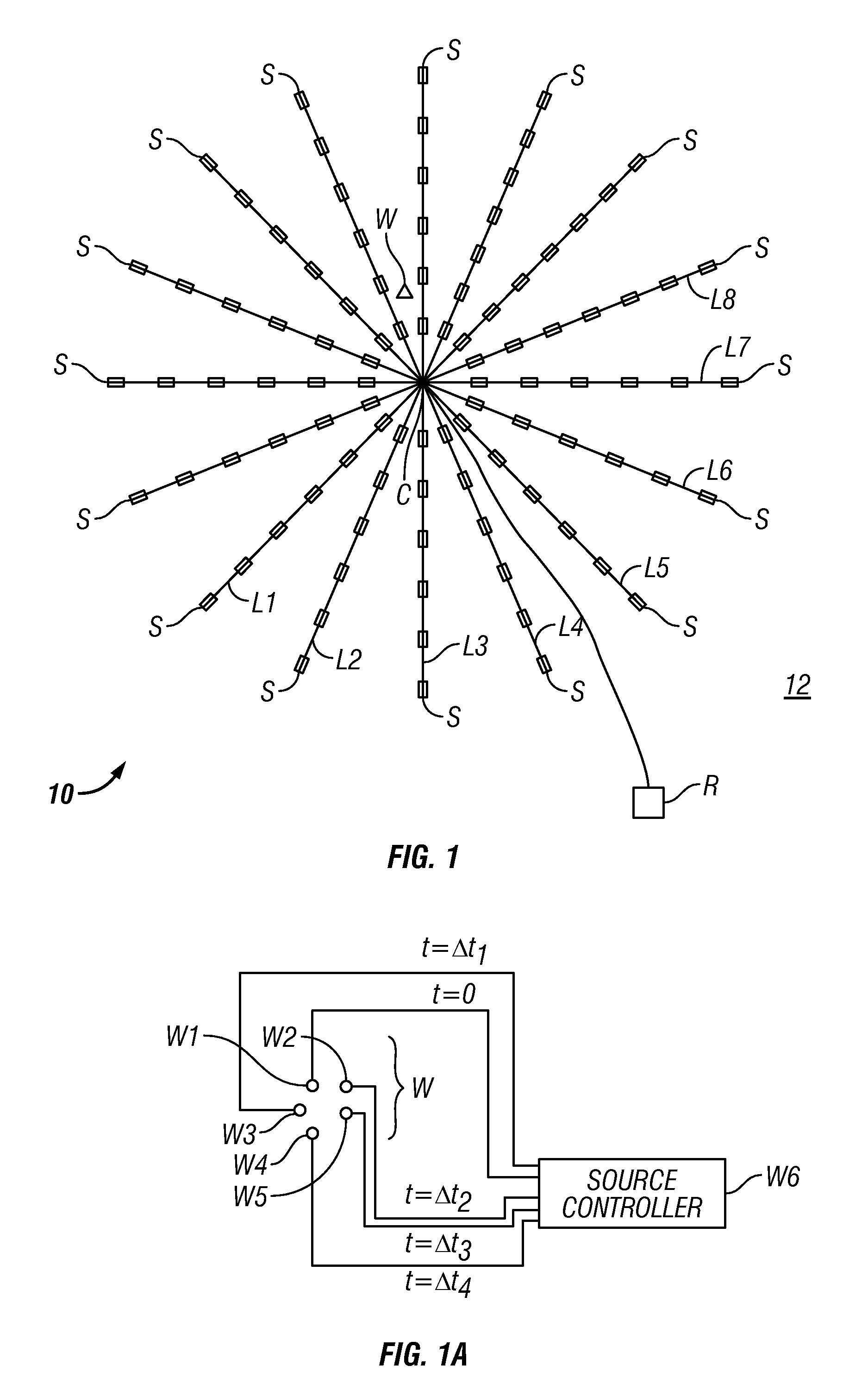
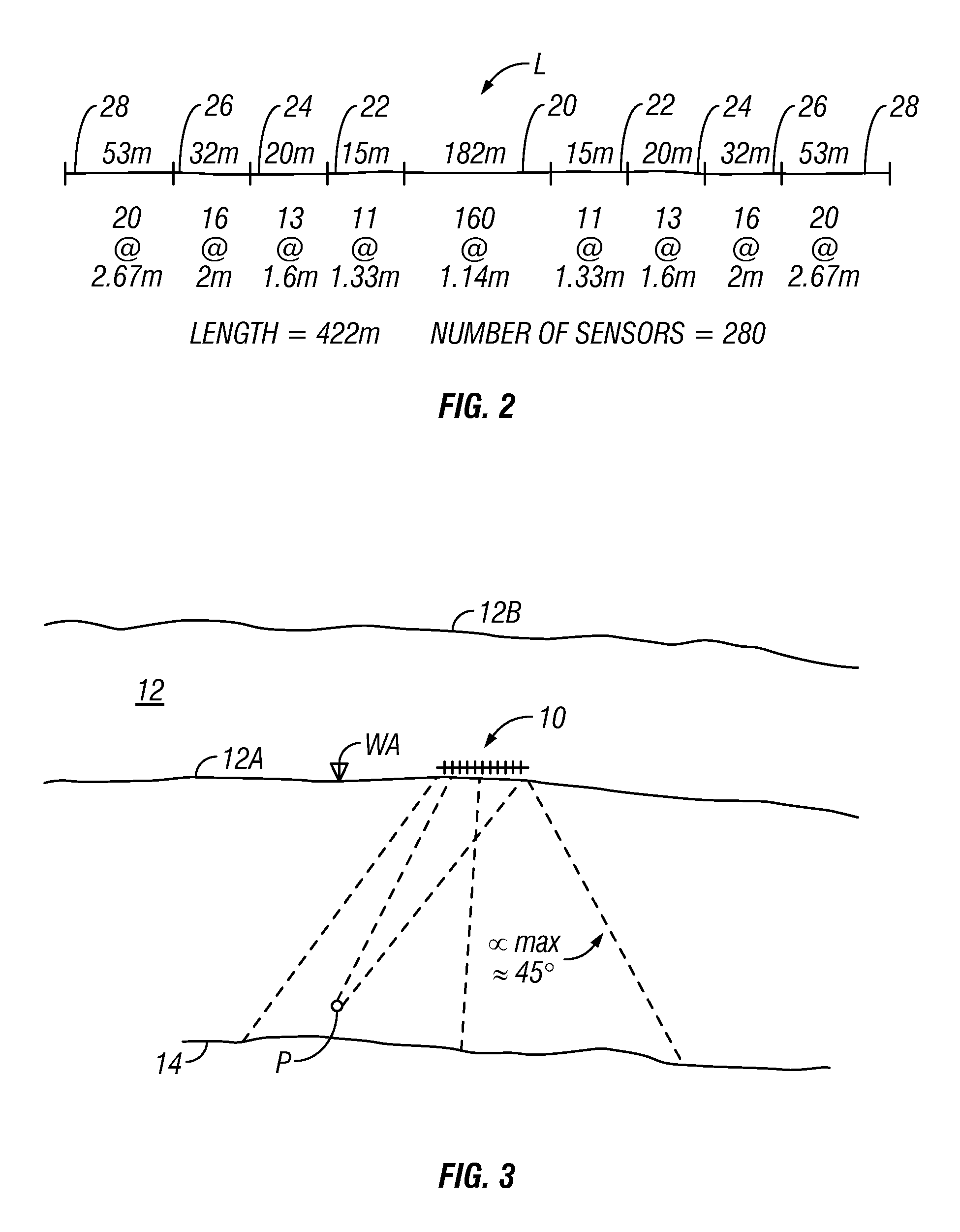
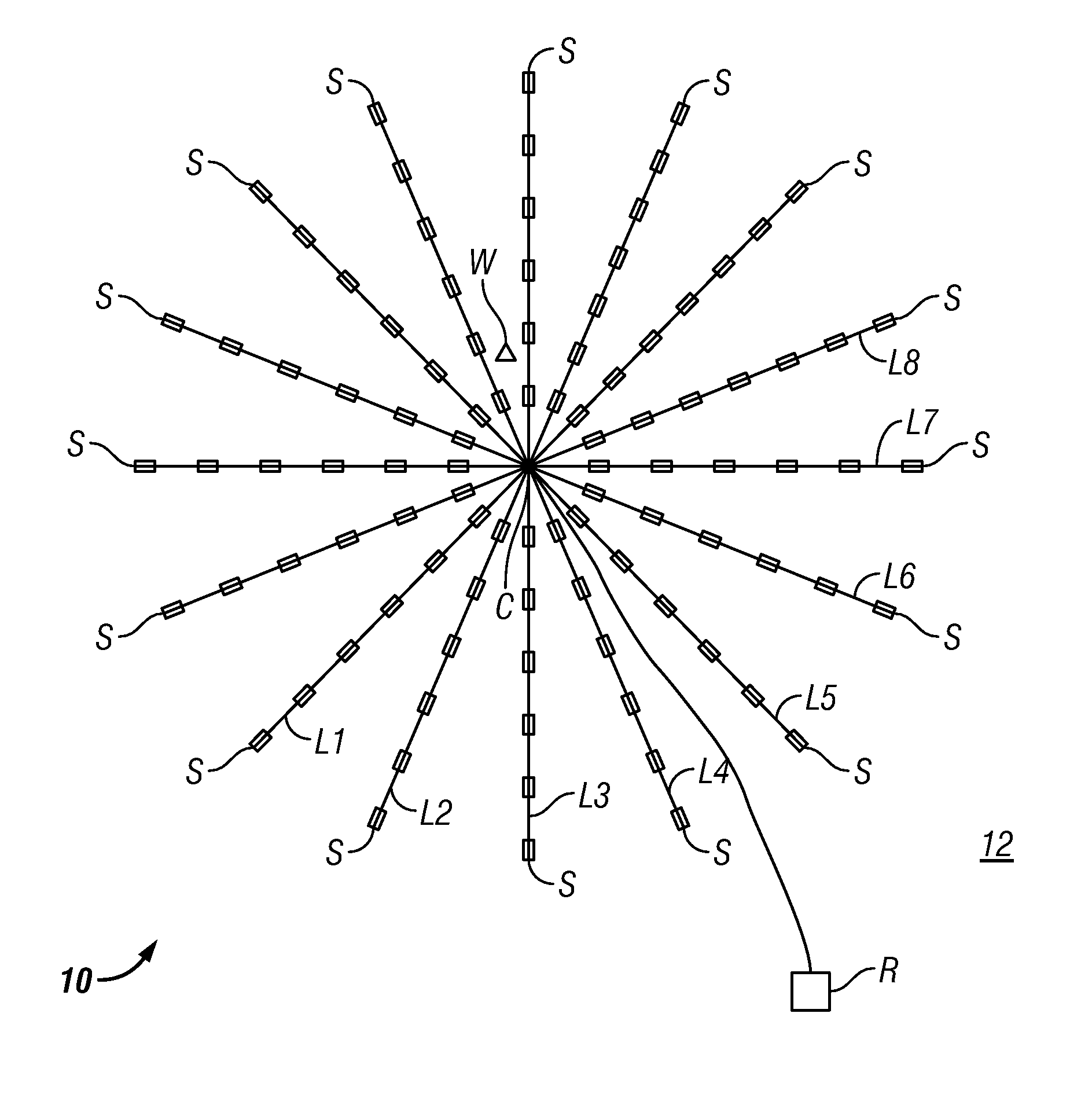
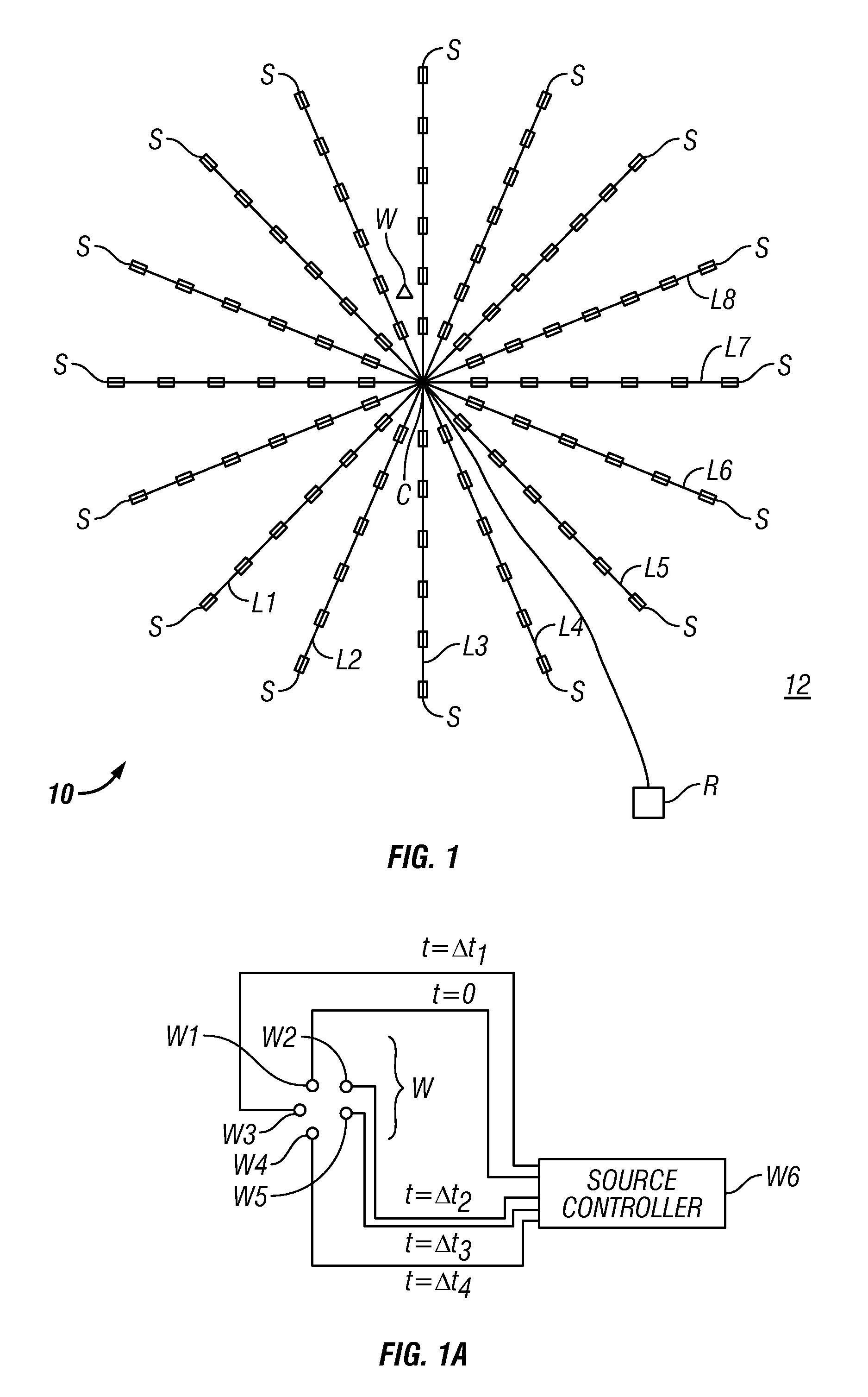
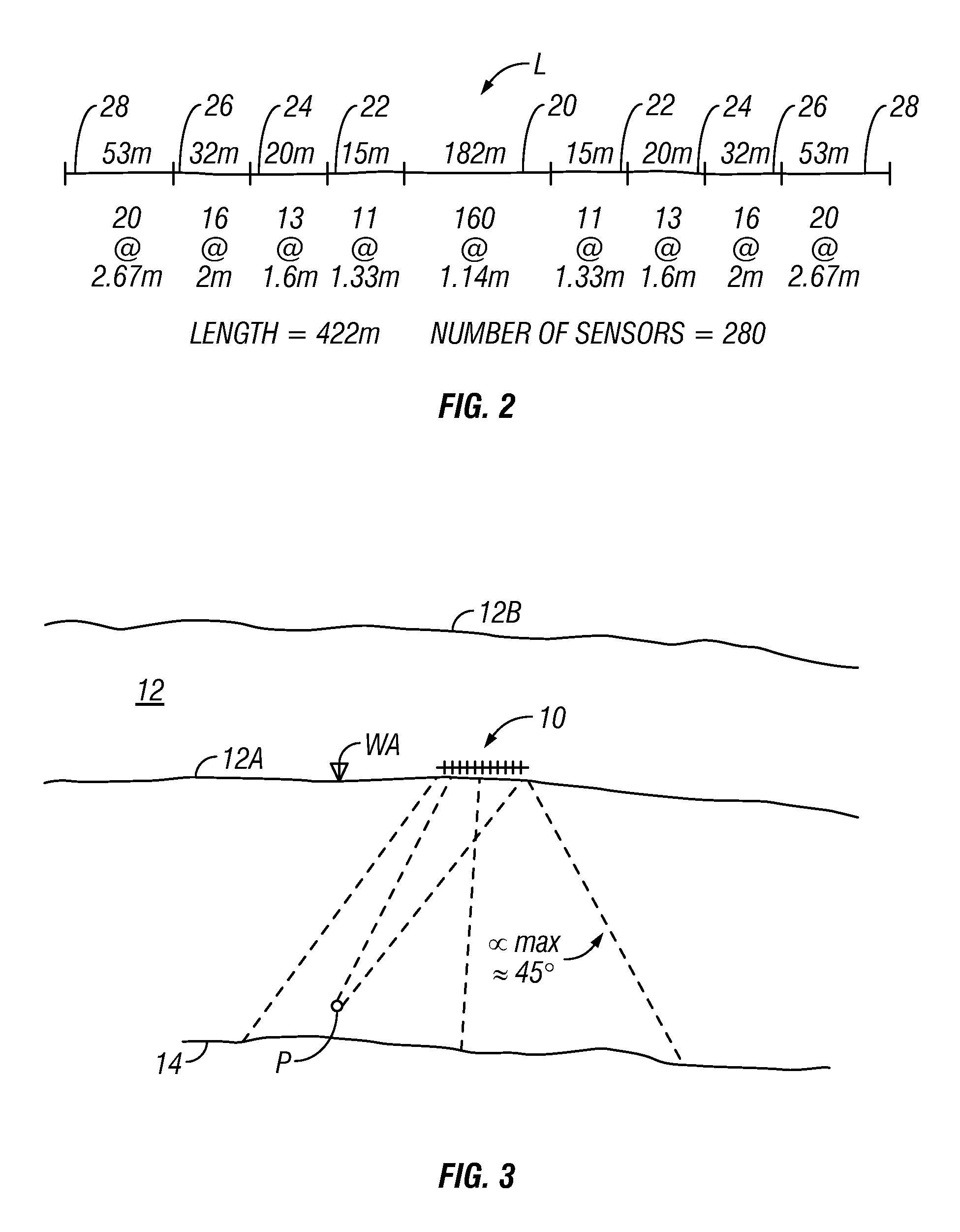
Method for acoustic imaging of the earth's subsurface using a fixed position sensor array and beam steering
A method for seismic surveying includes disposing a plurality of seismic sensors in a selected pattern above an area of the Earth's subsurface to be evaluated. A seismic energy source is repeatedly actuated proximate the seismic sensors. Signals generated by the seismic sensors, indexed in time with respect to each actuation of the seismic energy source are recorded. The recorded signals are processed to generate an image corresponding to at least one point in the subsurface. The processing includes stacking recordings from each sensor for a plurality of actuations of the source and beam steering a response of the seismic sensors such that the at least one point is equivalent to a focal point of a response of the plurality of sensors.
Owner:ACOUSTIC ZOOM
Object detection using acoustic imaging
Embodiments of the present invention include methods and apparatus for the detection of objects using acoustic imaging. Vibrational resonance characteristics of man-made objects may be significantly different from those of the surrounding natural materials, allowing an acoustic image to highlight the position of the object, even if the object is concealed from visual imaging.
Owner:FEV ENGINE TECH
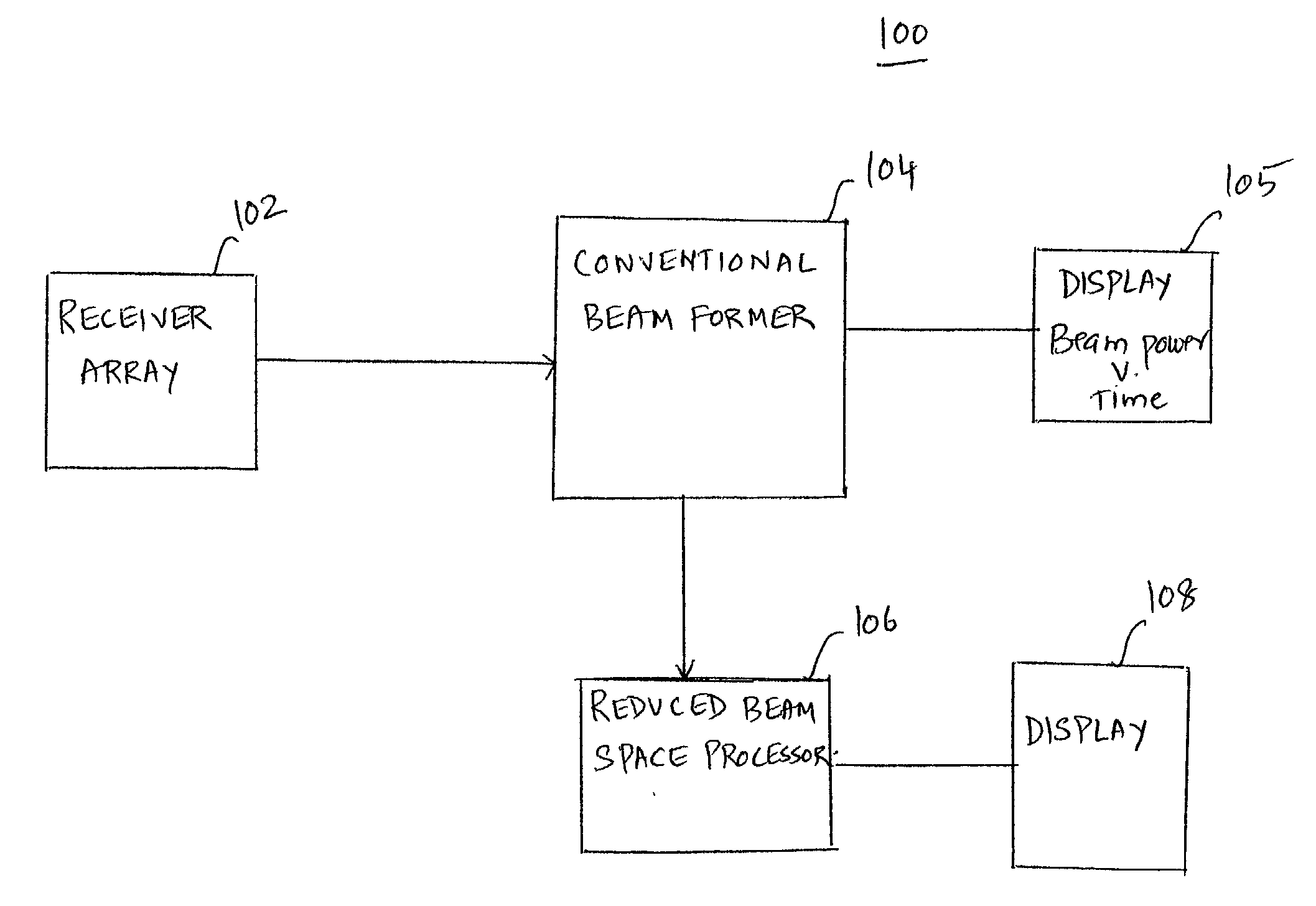
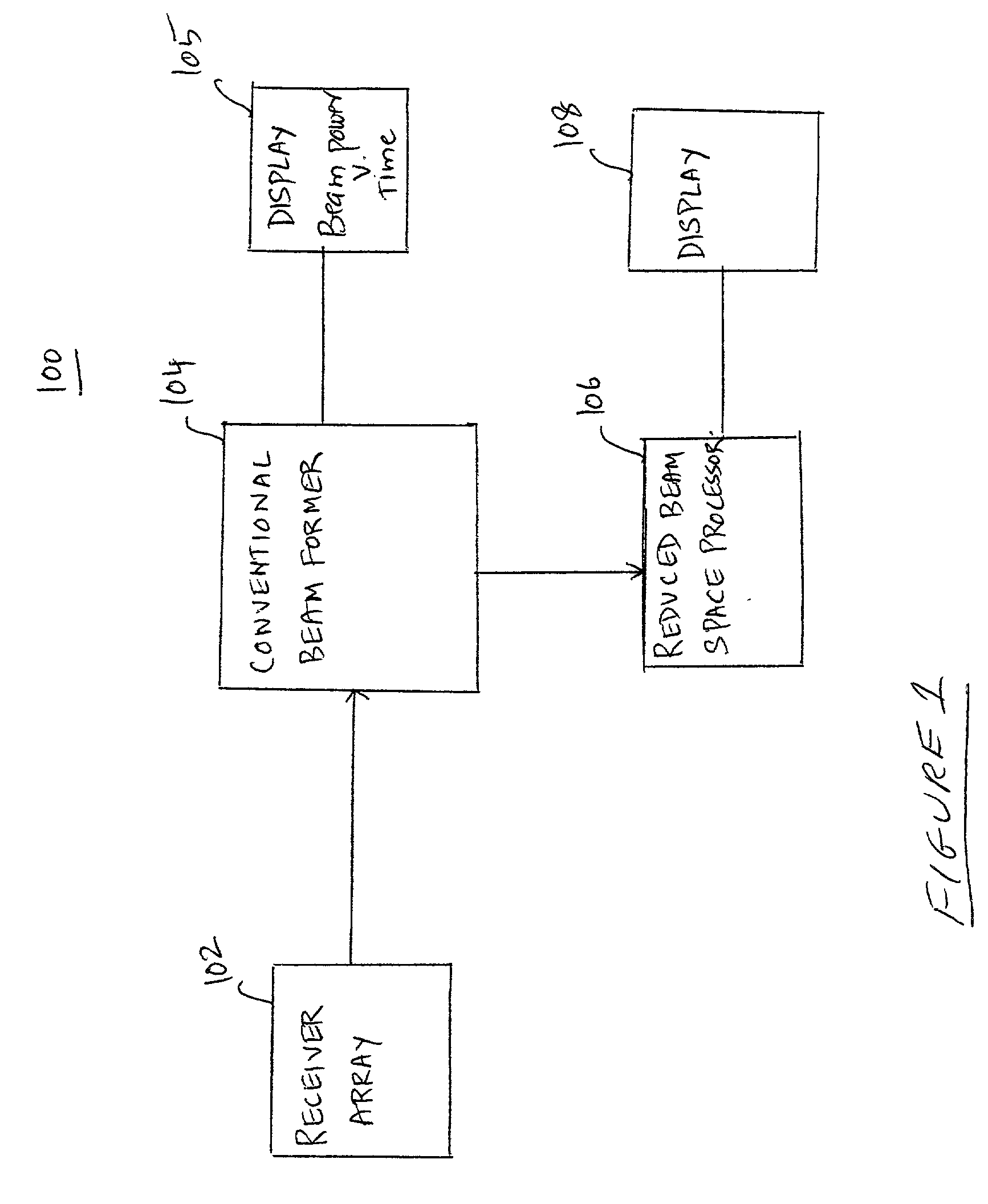
Method and apparatus for passive acoustic imaging using a horizontal line array
InactiveUS20030231547A1Direction/deviation determination systemsPhotographyRadarThree-dimensional space
An apparatus for processing passive acoustic signals received on a horizontal line array that were either emitted from an underwater object or echo returned from an object, is proposed to display a radar-like range-bearing image of the object, thereby showing the location of the object relative to the receiver horizontal line array. The range-bearing images can be created at different water depth to search for an underwater object in a three-dimensional space. The method includes receiving an acoustic signal from the target, determining a beam covariance matrix, determining a replica field for a range-bearing of the target, determining a replica beam from the replica field; and processing the beam covariance matrix and the replica beam to determine range-bearing ambiguity surface and estimate depth ambiguity for selected peaks of the ambiguity surface.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
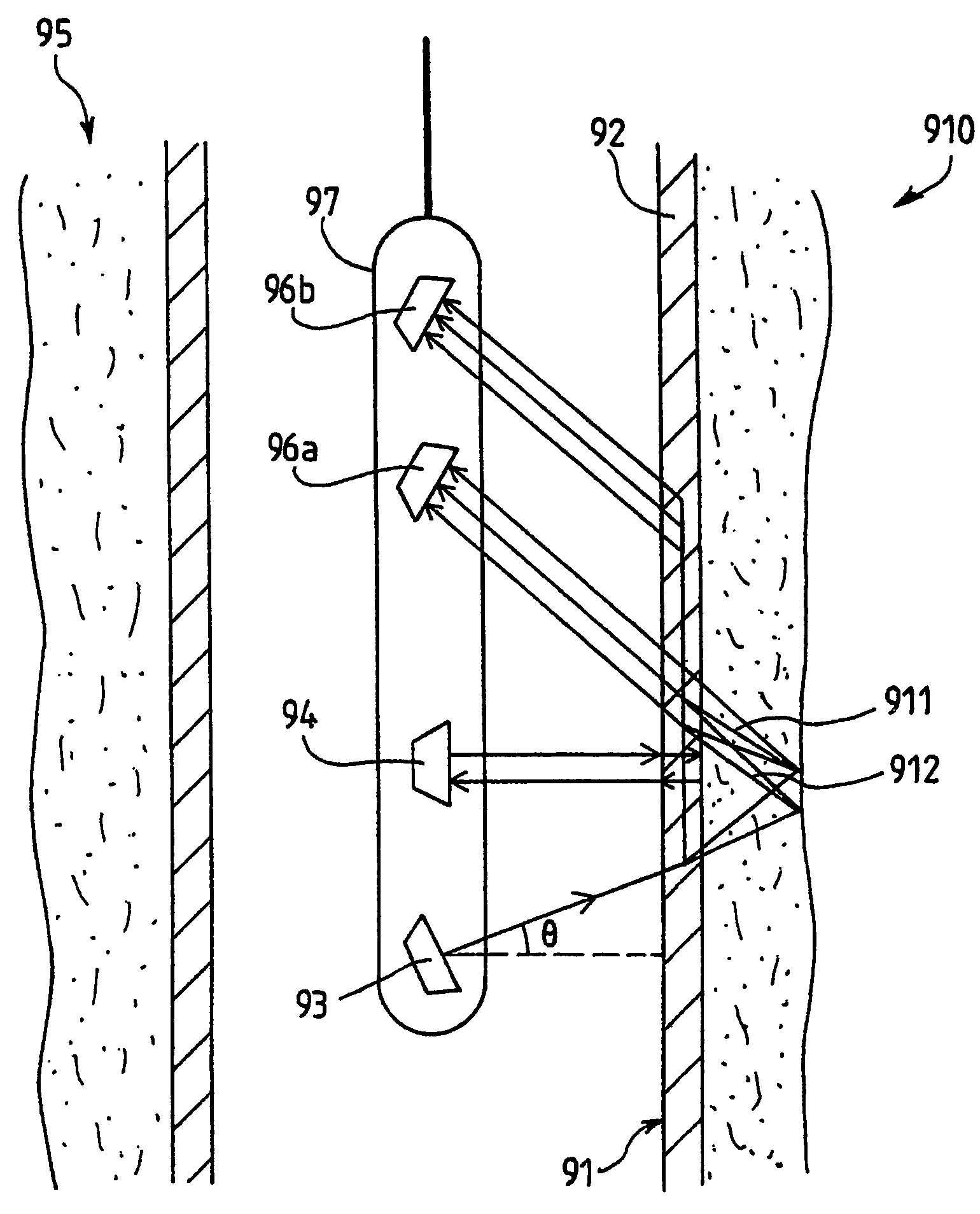
Underwater high-resolution side-looking acoustic imaging system and method thereof
InactiveCN101825709AImprove surveying and mapping efficiencyAcoustic wave reradiationAcoustical imagingRadio frequency
The invention provides an underwater high-resolution side-looking acoustic imaging system. The system comprises a transmitting array, a receiving array and a receiver, wherein the receiver comprises a signal conditioning and acquisition functional module, a data transmission module and a data processing module, the signal conditioning and acquisition functional module is used for filtering and amplifying underwater acoustic signals and converting analog signals into digital signals, the data processing module also comprises a memory module, an image reconstruction module, a movement error estimation and compensation processing module and an image display module. The system is characterized in that: the transmitting array is a transmitting array group which consists of two transmitting arrays, and is used for transmitting acoustic signals with different frequency bands, and each transmitting array is driven by a transmitter. The invention also puts forward a method for utilizing the transmitting array group to carry out underwater high-resolution side-looking acoustic imaging. The invention has the advantages that: the limitation of the length of a plurality of sub-arrays of a sonar array on the moving speed is reduced, and thereby the surveying efficiency of the imaging system is increased.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
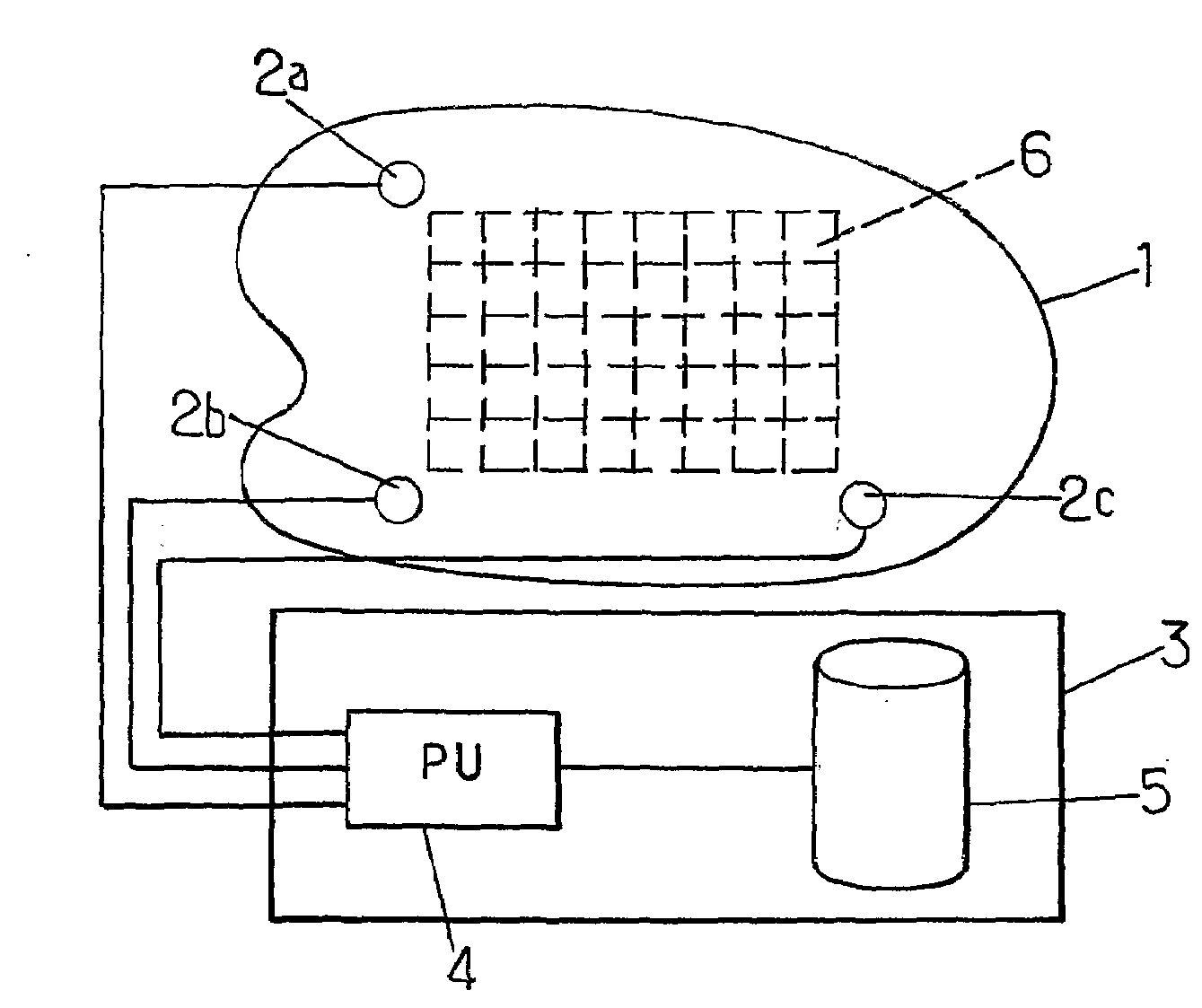
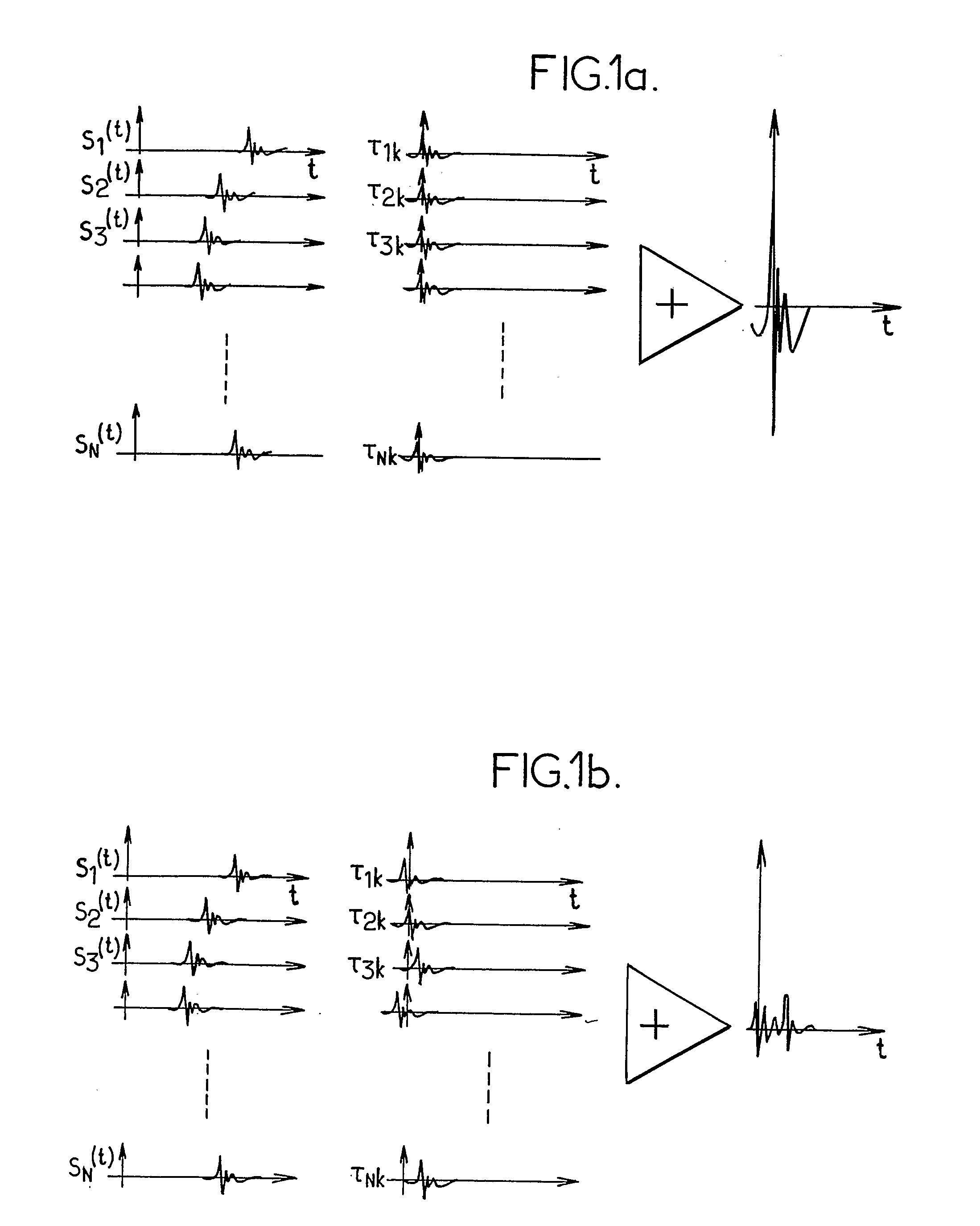
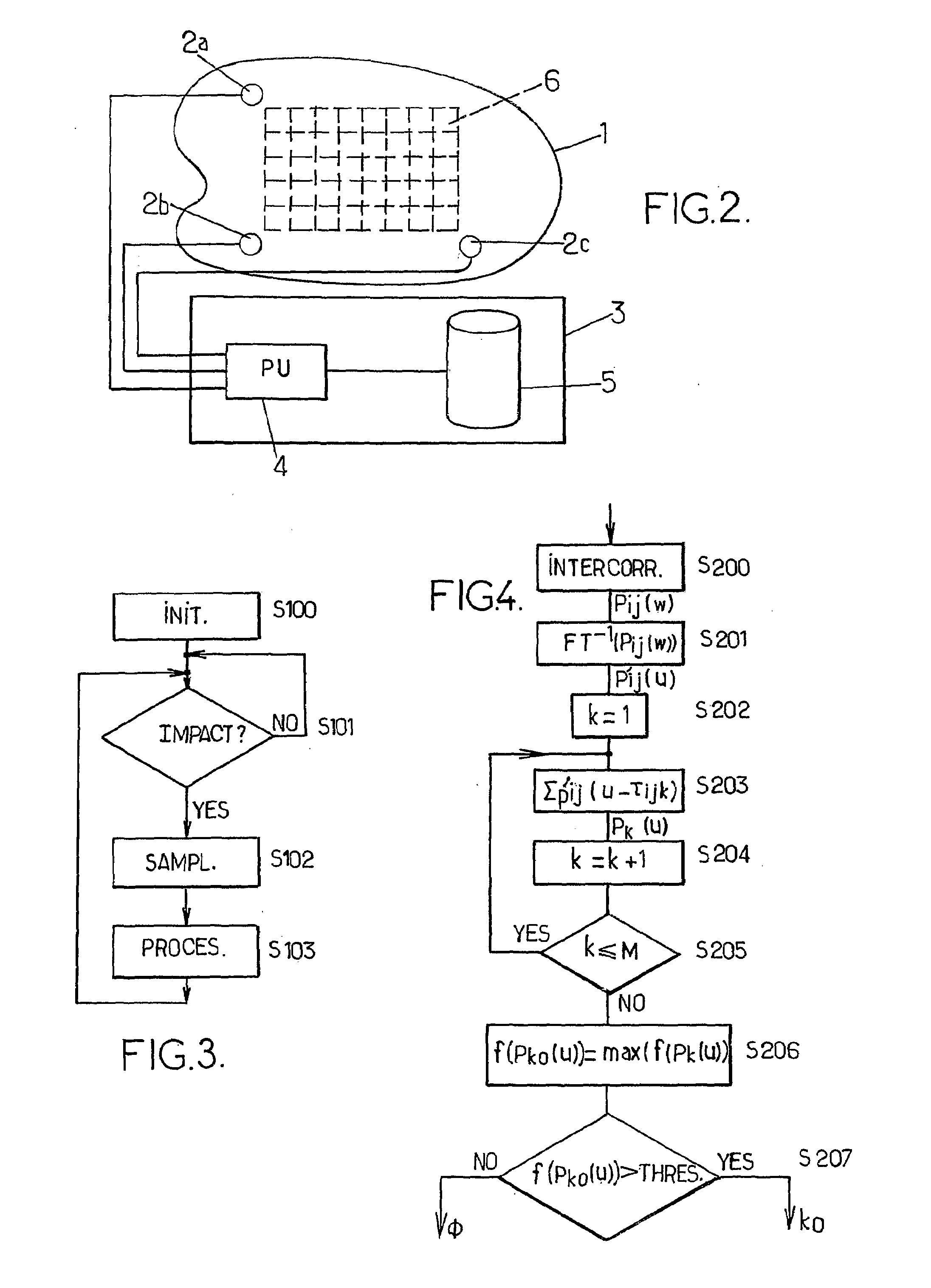
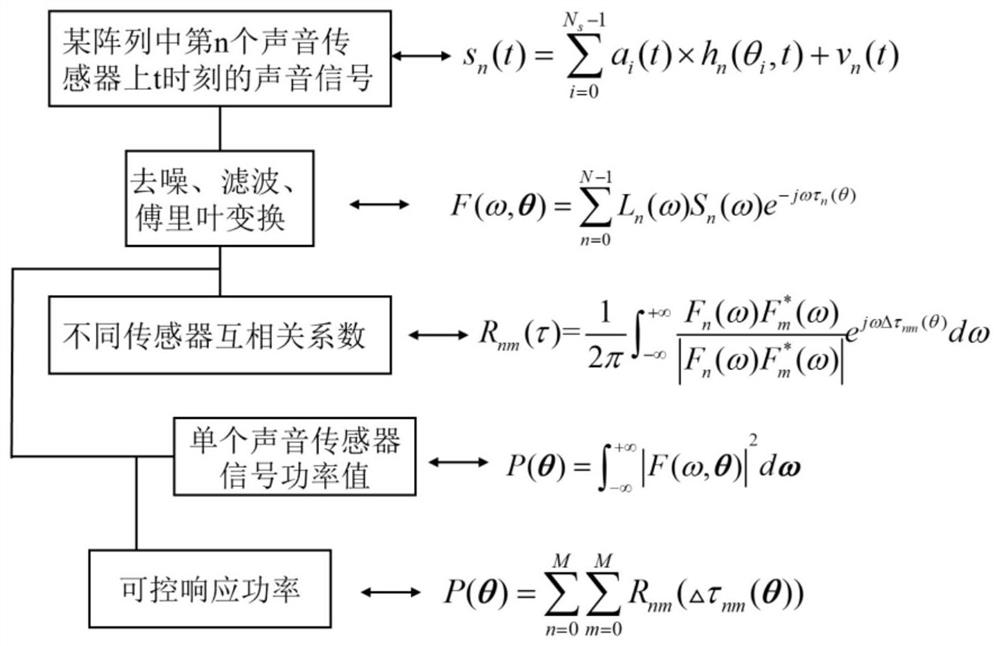
Method For Determining The Location Of Impacts By Acoustic Imaging
ActiveUS20090122028A1Material analysis using acoustic emission techniquesProcessing detected response signalAcoustical imagingComputer science
A method for determining the location of an impact on a surface (1) comprising N acoustic sensors (2a, 2b, 2c), transmitting a sensed signal si(t) to a processing unit (4) comprises the following steps (a) computing P intercorrelation products (b) calculating P inverse Fourier transforms p′ij (u) (c) computing for each area k, Pk(u)=ΣP′ij (u−τijk); d) finding k0, where a characterizing value of Pk0 (u) is greater than a given threshold value.
Owner:ELO TOUCH SOLUTIONS INC
Driving techniques for phased-array systems
ActiveUS10943578B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical vibrations separationEngineeringAcoustical imaging
Various techniques for driving phased array systems are described, specifically intended for acoustic phased arrays with applications to mid-air haptics, parametric audio, acoustic levitation and acoustic imaging, including a system: 1) that is capable of mitigating the effect of the changes in the air to provide a consistent haptic experience; 2) that produces trap points in air; 3) that defines phased-array optimization in terms of vectors for the production of more consistent haptic effects; 4) that defines one or more control points or regions in space via a controlled acoustic field; 5) that uses a reduced representation method for the construction of acoustic basis functions; 6) that performs efficient evaluation of complex-valued functions for a large quantity of throughput; 7) that generates a Krylov sub-space of a matrix; and 8) that maximizes an objective described by different control points and / or regions to those used to create the acoustic basis functions.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
Object detection using acoustic imaging
Embodiments of the present invention include methods and apparatus for the detection of objects using acoustic imaging. Vibrational resonance characteristics of man-made objects may be significantly different from those of the surrounding natural materials, allowing an acoustic image to highlight the position of the object, even if the object is concealed from visual imaging.
Owner:FEV ENGINE TECH
Method for acoustic imaging of the earth's subsurface using a fixed position sensor array and beam steering
A method for seismic surveying includes disposing a plurality of seismic sensors in a selected pattern above an area of the Earth's subsurface to be evaluated. A seismic energy source is repeatedly actuated proximate the seismic sensors. Signals generated by the seismic sensors, indexed in time with respect to each actuation of the seismic energy source are recorded. The recorded signals are processed to generate an image corresponding to at least one point in the subsurface. The processing includes stacking recordings from each sensor for a plurality of actuations of the source and beam steering a response of the seismic sensors such that the at least one point is equivalent to a focal point of a response of the plurality of sensors.
Owner:ACOUSTIC ZOOM
Multimode acoustic imaging in cased wells
A well casing is insonified with a first acoustic wave in a first mode that may be any mode of a set including: extensional mode, thickness mode, flexural mode. A first echo is received at a first acoustic transducer for receiving, a first signal is produced and a first measurement is extracted from the first signal. The casing is then insonified with a second acoustic wave in a second mode that may be any mode of the set of modes but is distinct from the first mode. A second echo is received at a selected second acoustic transducer for receiving and a second signal is produced. A second measurement is extracted from the second signal. The zone behind the casing of the well is evaluated from a combination of the first measurement and the second measurement.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Synthetic aperture ultrasound system
InactiveUS20160270763A1Organ movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSynthetic aperture sonarSonification
Systems, devices, and methods for synthetic aperture acoustic imaging, range-Doppler measurements, and therapies are disclosed. One synthetic aperture acoustic system includes a waveform generation and processing device and an acoustic probe device that are designed to enable generation, transmission, reception, and processing of coherent, spread-spectrum, instantaneous-wideband, coded waveforms in synthetic aperture ultrasound (SAU) applications.
Owner:DECISION SCI MEDICAL CO LLC
Method for acoustic imaging of the earth's subsurface using a fixed position sensor array and beam steering
A method for seismic surveying includes disposing a plurality of seismic sensors in a selected pattern above an area of the Earth's subsurface to be evaluated. A seismic energy source is repeatedly actuated proximate the seismic sensors. Signals generated by the seismic sensors, indexed in time with respect to each actuation of the seismic energy source are recorded. The recorded signals are processed to generate an image corresponding to at least one point in the subsurface. The processing includes stacking recordings from each sensor for a plurality of actuations of the source and beam steering a response of the seismic sensors such that the at least one point is equivalent to a focal point of a response of the plurality of sensors.
Owner:ACOUSTIC ZOOM
Manufacturing process or in service defects acoustic imaging using sensor array
ActiveUS20050209791A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesCharacter and pattern recognitionSensor arrayTomography
A mobile platform is provided which has at least one component having an array of distributed piezoelectric transmitters and an associated array of distributed receivers. The receivers are configured to receive ultrasonic transmissions from the transmitters. Data from the receivers is stored in memory and processed through an algebraic reconstruction tomography algorithm which forms an image of the defect within the component. An algorithm is used to determine the position and size of the defect.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
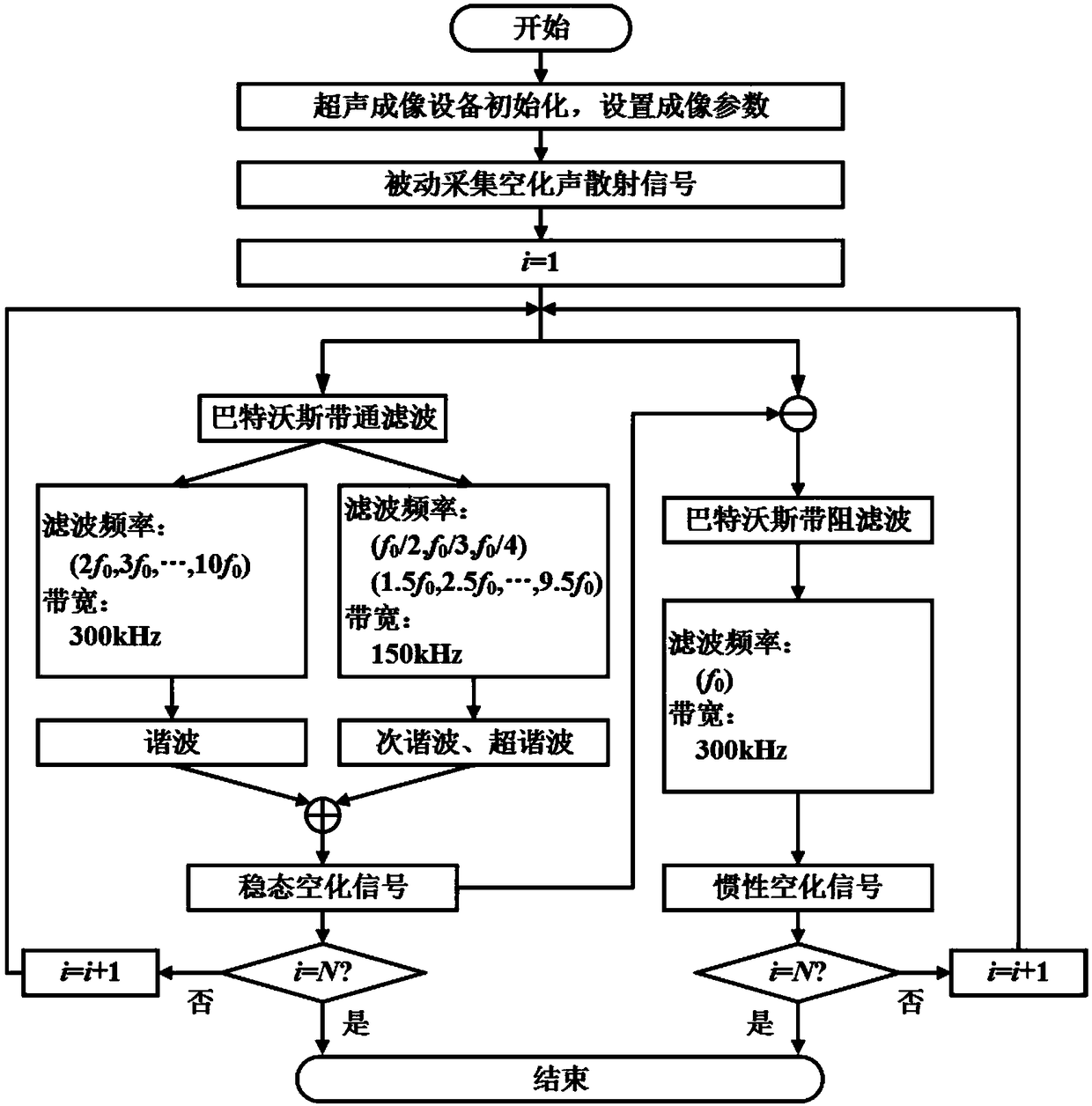
Real-time high-resolution spatio-temporal distribution imaging method and system for focused ultrasonic cavitation
ActiveCN109431536ASteady state resolutionImprove resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic cavitationSonification
The invention provides a real-time high-resolution spatio-temporal distribution imaging method and system for focused ultrasonic cavitation. A cavitation acoustic scattering signal is filtered to obtain a steady state and an inertial cavitation signal; an existing passive acoustic imaging algorithm is modified based on a high-resolution coherence coefficient to obtain a high-resolution steady state and an inertial cavitation image; the cavitation image is screened, the additional cavitation energy is removed, the steady state and an inertial cavitation feature image are obtained through the principal component analysis, and on the basis, the spatio-temporal distribution of the steady state and the inertial cavitation is obtained. The method can solve the problems that active ultrasound imaging can only obtain cavitation microbubble distribution and cannot obtain the spatio-temporal distribution of a cavitation activity, and passive acoustic imaging is poor in resolution and lacks effective cavitation spatio-temporal distribution calculation methods, provide an effective means for cavitation transient physics process researches and focused ultrasound therapy evaluation, and lay thefoundation for the clinical application of ultrasound-guided and monitored focused ultrasound therapy systems.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
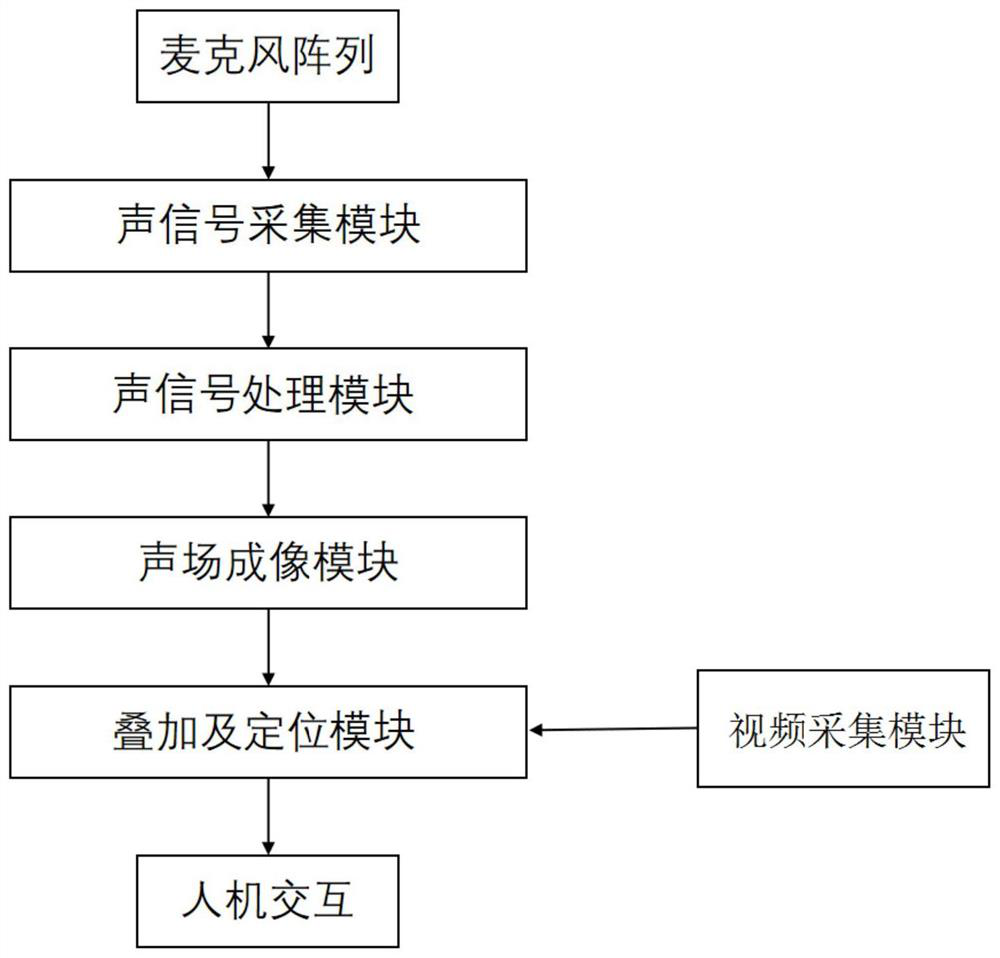
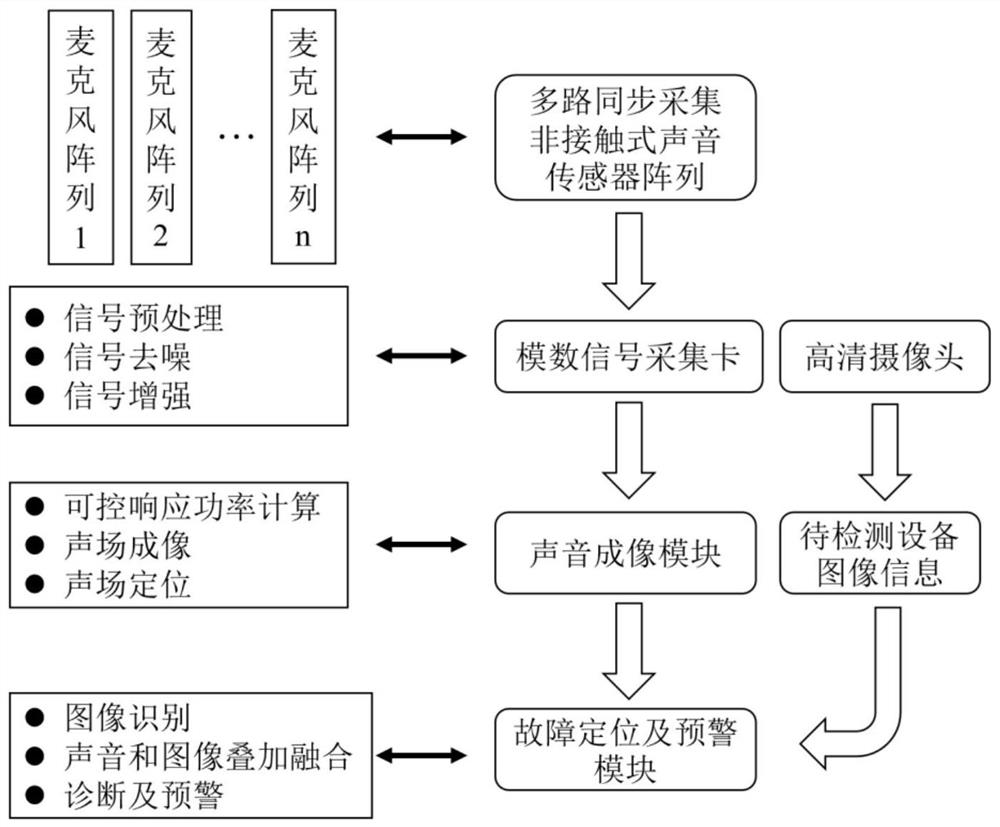
GIS equipment mechanical fault detection system and method based on acoustic imaging
ActiveCN113267330AReduce sidelobeImprove anti-interference abilityMachine part testingPosition fixationSound sourcesEngineering
The invention provides a GIS equipment mechanical fault detection system and method based on acoustic imaging, and the system comprises an acoustic signal collection module, an acoustic signal processing module, a sound field imaging module, a video collection module, a superposition positioning output module, and a man-machine interaction terminal. The sound signal acquisition module comprises a microphone array with a non-uniform spiral arrangement structure and an analog-to-digital conversion module, and is used for acquiring multichannel sound signals. According to the detection method, collected sound signals are processed through spectral subtraction, sound field models including a measuring point plane measuring point model and a sound source focus point model are constructed based on an array, then an intermediate structure is obtained through calculation of a beam forming algorithm, iterative calculation is carried out in combination with a deconvolution DAMAS algorithm, a sound field cloud distribution diagram is output, the image data synchronously acquired with the sound signal are overlapped and fused, and a sound field effect picture is output.
Owner:STATE GRID CHONGQING ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
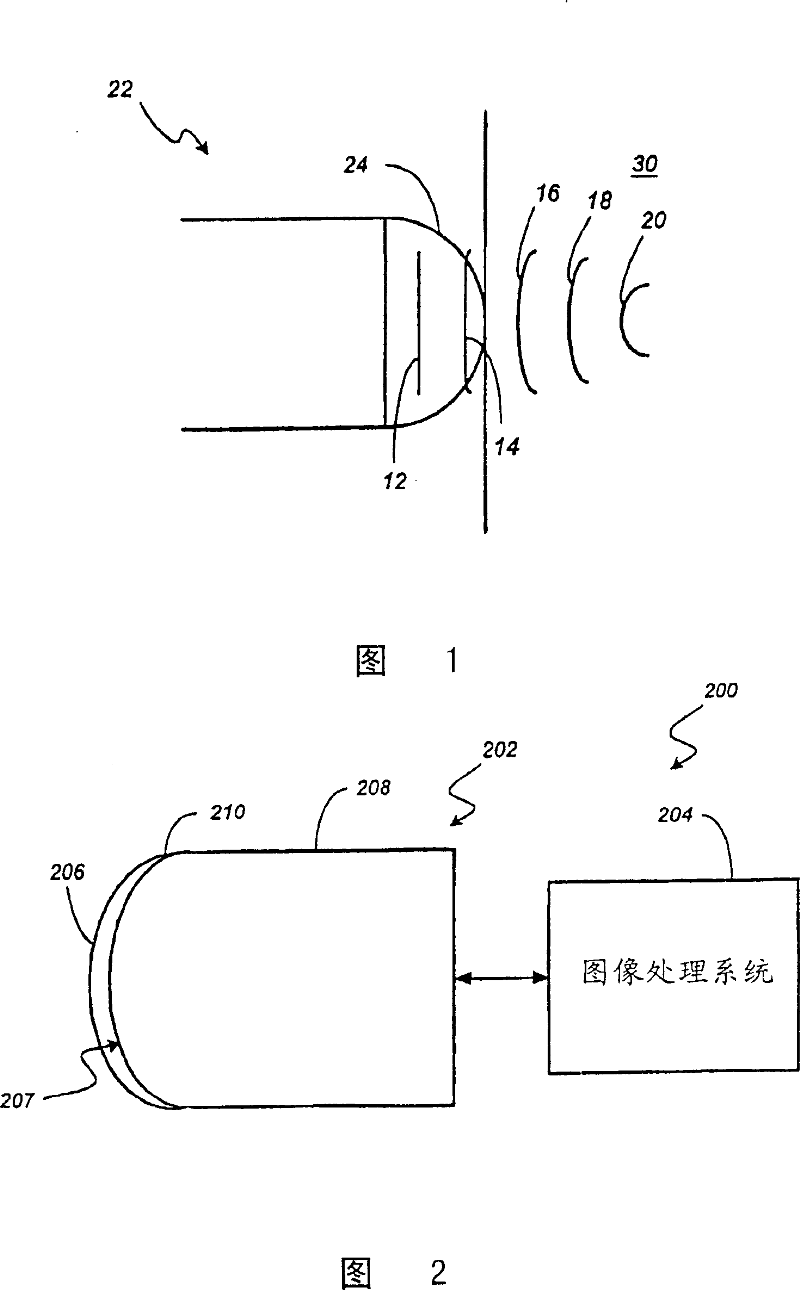
Ultrasound transducer
InactiveCN100354651CMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesBlood flow measurement devicesUltrasound imagingRepetitive motion injury
An acoustic imaging system is described. A preferred system includes a protective cover configured to mate with a transducer body. The transducer includes a two-dimensional transducer element matrix array formed by a plurality of individually controllable transducer elements. The protective cover is superposed above the two-dimensional matrix array and is transparent to incident acoustic energy. Preferably, the protective cover is shaped to reduce patient discomfort and repetitive motion injuries to sonographers. Alternative embodiments comprise a shaped two-dimensional transducer element matrix array. Methods for improved ultrasound imaging are also provided.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Single channel scanning acoustic microscope with multiple focused ultrasonic transducers
ActiveUS20140116143A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationUltrasonic sensorTime delays
A single channel scanning acoustic microscope that increases the throughput of the acoustic imaging system by connecting a multi-transducer assembly in parallel to a single channel electronic circuit. The single channel scanning acoustic microscope includes multiple transducers configured to generate a time delay for individual ultrasonic waves generated by each transducer, wherein a pulse generator simultaneously sends a pulse signal to the multi-transducer assembly.
Owner:NORDSON CORP
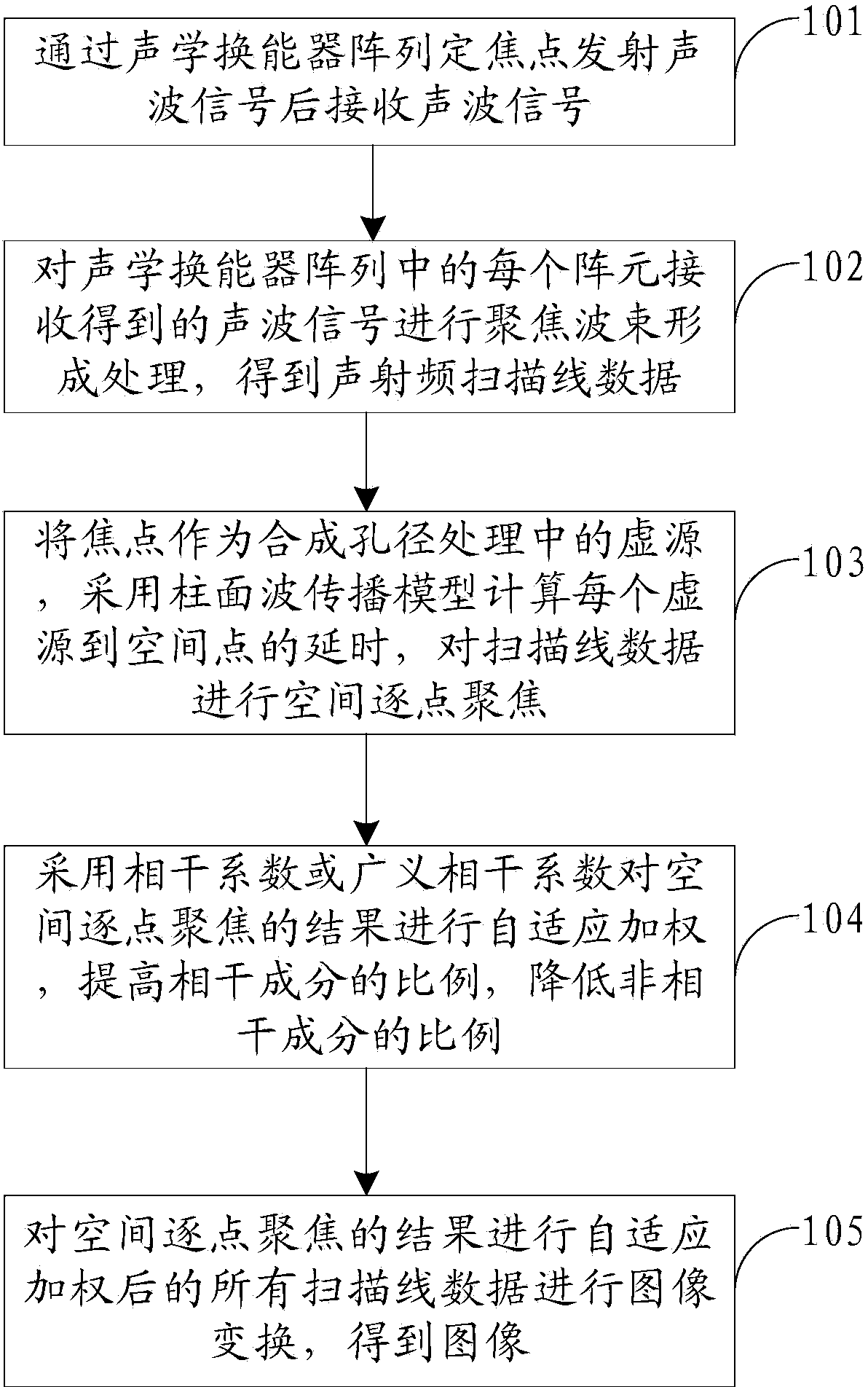
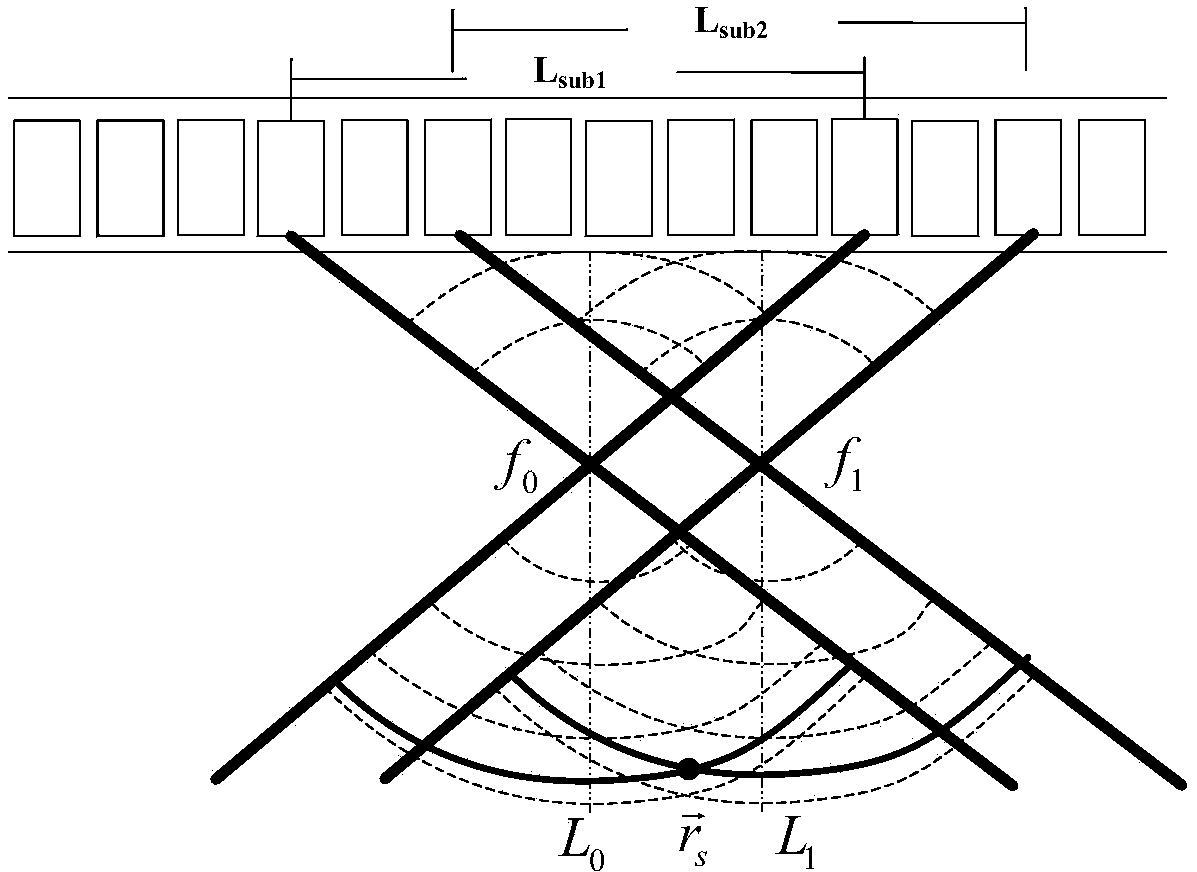
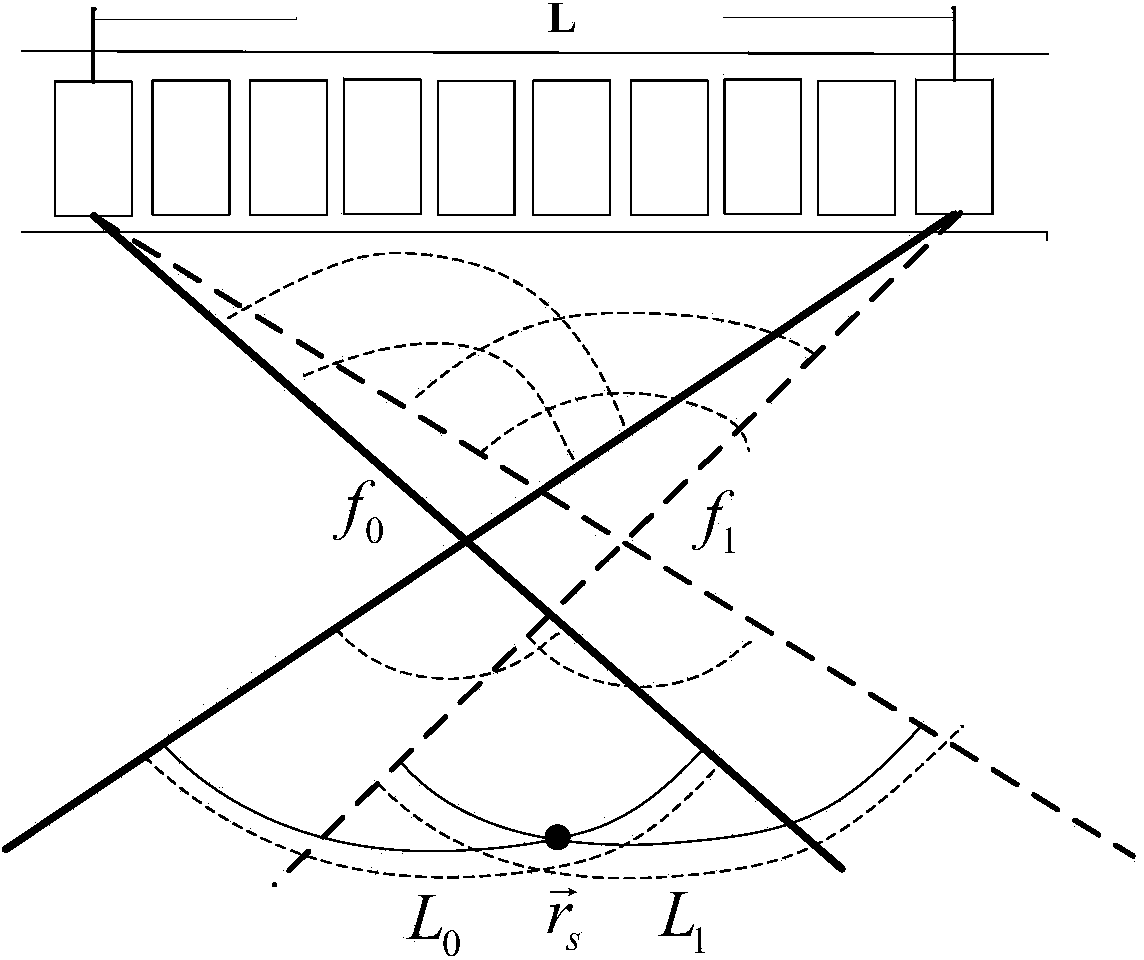
Self-adaptive acoustic imaging method
InactiveCN103969651AReduce sidelobeImprove Acoustic Imaging QualityAcoustic wave reradiationImaging qualityArray element
The invention relates to a self-adaptive acoustic imaging method. The method includes the steps that acoustic wave signals are received after being transmitted at fixed focuses through an acoustic transducer array; focusing beamforming processing is carried out on the acoustic wave signals received by each array element in the acoustic transducer array to obtain acoustic radio frequency scanning line data; the focuses are used as virtual sources in synthetic aperture processing, tine delay from each virtual source to the spatial point is calculated by means of a cylindrical wave propagation model, and spatial point-by-point focusing is carried out on the scanning line data; self-adaptive weighting is conducted on the result of the spatial point-by-point focusing by the adoption of correlation coefficients or generalized correlation coefficients, the proportion of coherent components is increased, and the proportion of incoherent component is reduced; image transformation is carried out on all the scanning line data after self-adaptive weighting conducted on the result of the spatial point-by-point focusing to obtain images. According to the method, the lateral resolution and contrast ratio which are identical in depth are achieved, the number of sidelobes is effectively reduced, and therefore all-round improvement in acoustic imaging quality is achieved.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
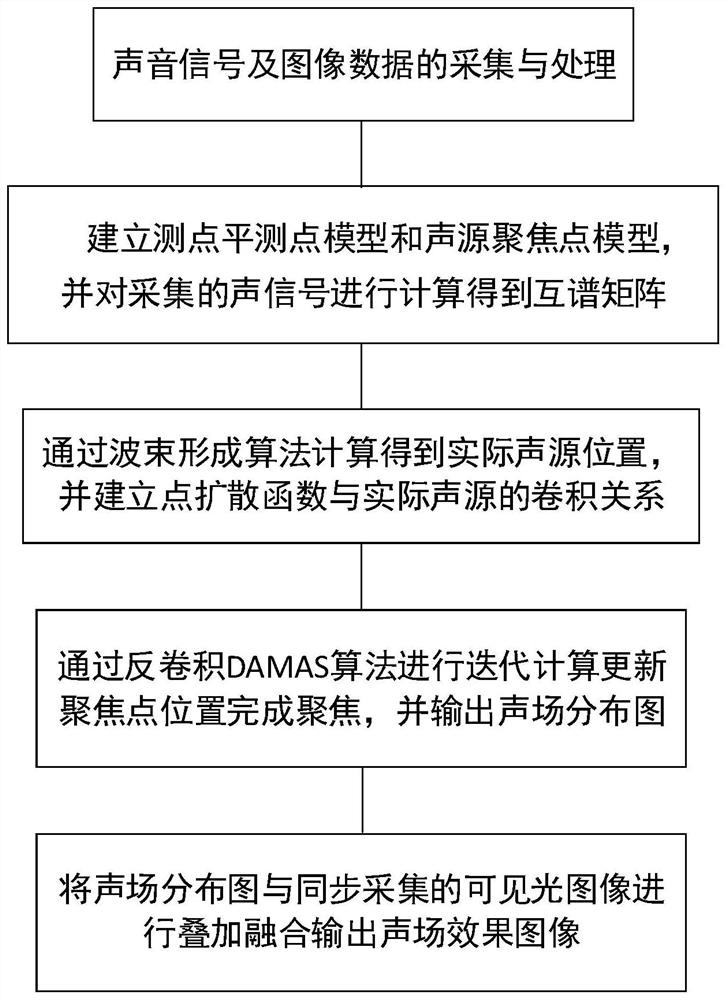
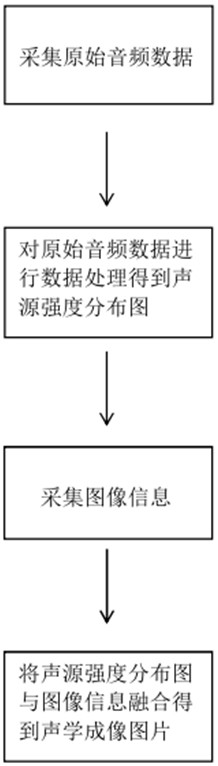
Acoustic imaging method
ActiveCN112017688AThe result is accurateDoes not cause large differences in intensity distribution resultsSpeech analysisDistribution matrixSound sources
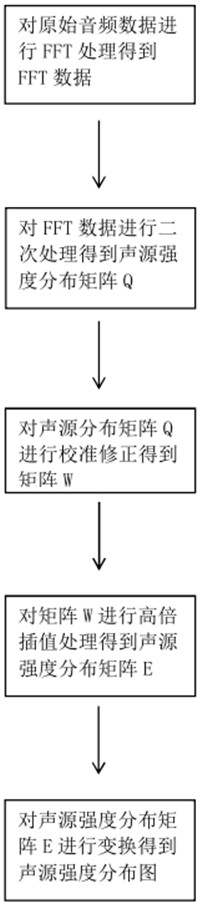
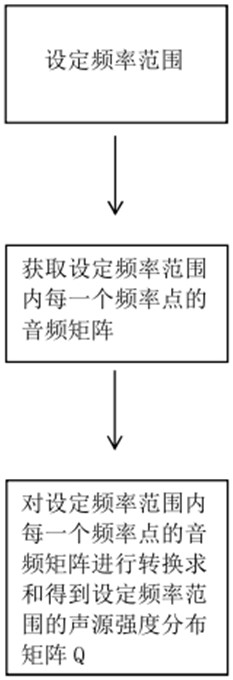
The invention relates to an acoustic imaging method, which solves the problems that general noise detection needs large computing power and cannot be adjusted to adapt to systems with different computing power conditions. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring original audio data through a microphone; performing data processing on the original audio data to obtain a sound source intensity distribution diagram; collecting image information through a camera; and fusing the sound source intensity distribution diagram with the image information to obtain an acoustic imaging picture. The beneficial effects of the invention are that: the method achieves the visualization and materialization of the sound intensity through the combination of the sound source intensity distributiondiagram and the photographed image; a correction matrix is adopted to calibrate and correct the calculation deviation of the sound source intensity distribution matrix, and unnecessary interference iseliminated, so that the result is more precise; high-power interpolation processing is carried out after FFT processing, so that the computing power pressure is reduced, and meanwhile, the resolutionratio is also ensured; the simplified and optimized process can also be realized by using a small and light carrier device, and can be suitable for more application scenes.
Owner:杭州兆华电子股份有限公司
Lens structure body of acoustical super lens, acoustical super lens and imaging device thereof
InactiveCN103913787AIncrease contrastThere is no local resonance phenomenonMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLensAudio power amplifierImaging quality
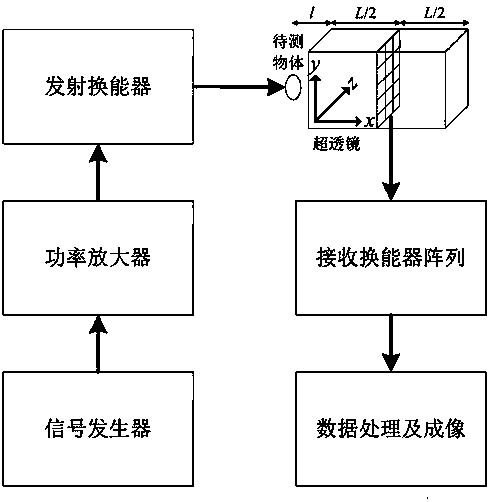
The invention provides a lens structure body of an acoustical super lens, the acoustical super lens and an imaging device thereof. The acoustical super lens comprises the lens structure body and light media, the imaging device of the acoustical super lens comprises a signal generator, a power amplifier, a transmitting transducer, the acoustical super lens and a receiving transducer array, the signal generator is connected with the power amplifier through a transmission line, the power amplifier is connected with the transmitting transducer through a transmission line, the front face of the lens structure body is a lens receiving face of the acoustical super lens, the lens receiving face of the acoustical super lens right faces the signal emission direction of the transmitting transducer, the receiving transducer array comprises a plurality of receiving transducers, and the receiving transducers are arranged at the geometric center of a square through hole of the acoustical super lens. According to the lens structure body of the acoustical super lens, the acoustical super lens and the imaging device thereof, high-resolution acoustical imaging can be conducted on an object at a certain distance, and evanescent waves can be well received, amplified and used for improving imaging quality.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Photoacoustic microscope and method for monitoring breaking of microvesicles in biological tissue
PendingCN106943120AIncrease contrastHigh resolutionOrgan movement/changes detectionCatheterPhotoacoustic microscopyMicro imaging
The invention discloses a photoacoustic microscope. The photoacoustic microscope comprises a microscope system, a signal collection control system and a driving system. The invention further discloses a method for monitoring breaking of microvesicles in biological tissue with the use of the photoacoustic microscope. The photoacoustic imaging is combined with features of high contrast ratio of optical imaging and high resolution ratio of acoustic imaging. Due to low scattering properties of acoustic signal transmission in tissue, deeper penetration degree is obtained compared with a conventional optical imaging method. There is no need to slicing tissue and the method is non-invasive so that long-term monitoring is achieved. Photoacoustic microscope imaging equipment helps achieve imaging of multiple anatomical positions.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Electric conductivity rebuilding method for magnetocaloric acoustical imaging
ActiveCN104473640AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Scalar potential
The invention relates to an electric conductivity rebuilding method for magnetocaloric acoustical imaging. The electric conductivity rebuilding method is based on a magnetocaloric acoustical imaging principle. An exciting coil is used for exerting MHz current excitation on a conducting object, joule heat is generated in the conducting object, and further, ultrasonic signals are generated. An ultrasonic transducer is used for receiving the ultrasonic signals, the received ultrasonic signals are processed and collected, and then, an electric conductivity image of the conducting object is obtained by adopting an electric conductivity image rebuilding algorithm. The electric conductivity rebuilding method comprises the concrete steps that 1, firstly, high-signal-to-noise-ratio magnetocaloric acoustical signals are obtained; 2, the obtained magnetocaloric acoustical signals are used for rebuilding to obtain thermal sound source distribution of the conducting object; 3, the thermal sound source distribution and a one-order magnetic vector space component are used, and a non-linear finite element solution method is adopted for rebuilding a scalar potential space component; 4, the rebuilt scalar potential space component is used for rebuilding the electric conductivity.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sound source imaging method based on microphone array
PendingCN113176538ARealize visualizationImaging Intuition and ImagePosition fixationPhase correctionSound sources
The invention provides a sound source imaging method based on a microphone array, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, forming a multi-channel microphone array through a multi-arm spiral array, and enabling the number of channels to be N; S2, collecting original audio data of N channels through a microphone array; S3, performing phase correction on the original audio data; S4, processing the corrected audio data to obtain a complex matrix R '; S5, determining coordinates of each point on the scanning surface according to the coordinates of the microphone array; S6, calculating a guide vector from the scanning surface to the array surface, and obtaining a sound source intensity distribution diagram of the scanning surface according to the cross-spectrum matrix R; and S7, carrying out superposition processing on the sound source intensity distribution diagram and the video image to obtain a real-time acoustic imaging diagram. The problem that the positioning result of the existing sound source positioning method is easily interfered by external factors is solved through audio data correction and video superposition.
Owner:HANGZHOU AIHUA INSTR
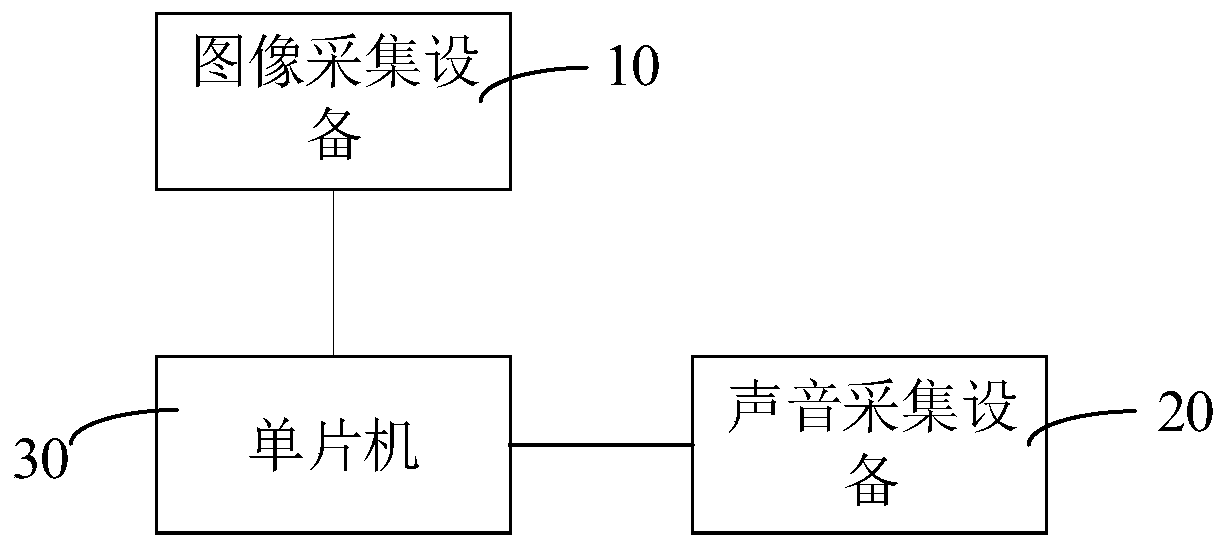
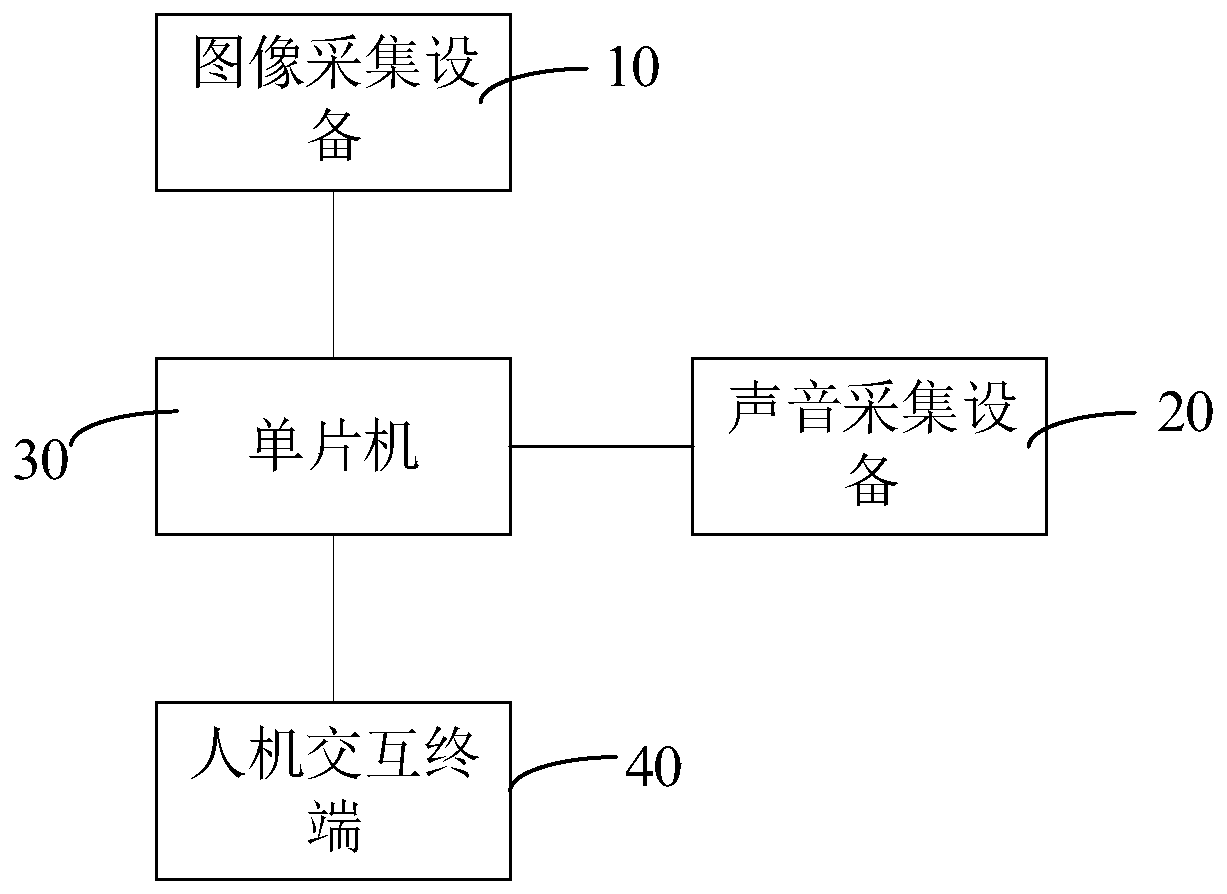
Acoustic imaging apparatus, method, device and system for detecting abnormal sound of transformer
InactiveCN111308395AEasy to moveOptimize layoutSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementTransformers testingSound sourcesSound image
The invention relates to an acoustic imaging apparatus, method, device and system for detecting abnormal sound of a transformer. The acoustic imaging apparatus for detecting the abnormal sound of thetransformer comprises an image acquisition apparatus, a sound acquisition apparatus and a single-chip microcomputer which is connected with the image acquisition apparatus and the sound acquisition apparatus. The single-chip microcomputer acquires an acoustic emission plane of the transformer and performs gridding processing on the acoustic emission plane to obtain each grid node; the single-chipmicrocomputer acquires sound propagation time delay from each grid node to each acoustic sensor, and performs reconstruction processing on the sound wave signal according to the sound propagation timedelay to obtain a reconstructed sound wave signal; the single-chip microcomputer carries out superposition processing on the reconstructed sound wave signal and the initial sound wave signal to obtain an acoustic cloud atlas; and generates an abnormal sound image of the transformer according to the acoustic cloud picture and the optical image information. The position and intensity information ofa sound source point can be visually obtained, so that the abnormal sound position is obtained. The single-chip microcomputer is used for acoustically imaging the abnormal sound of the transformer, and the problem that traditional equipment is high in cost is solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU
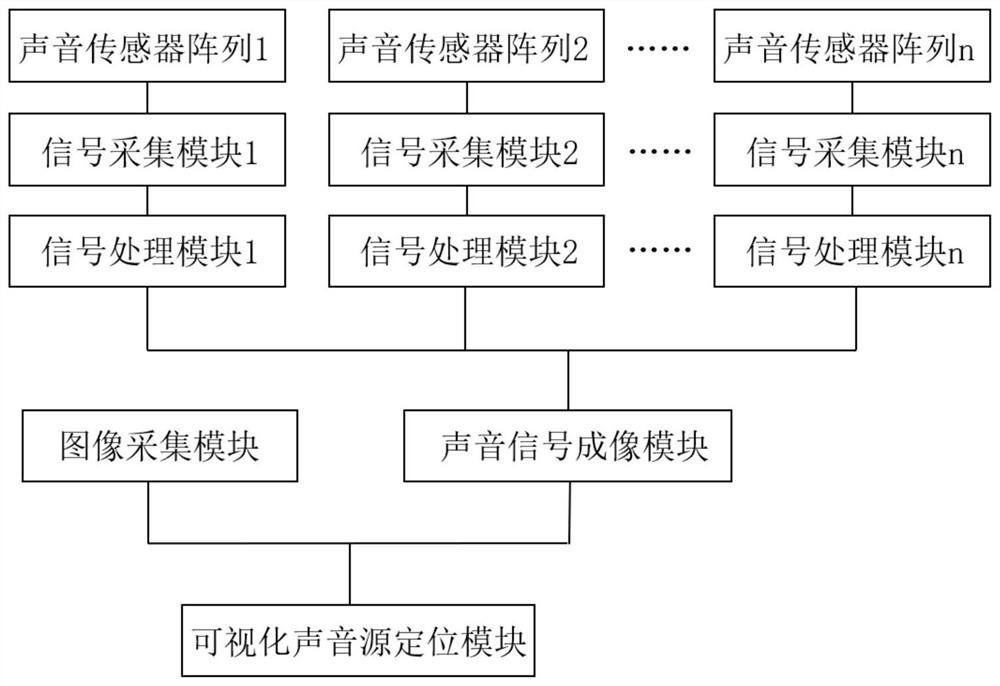
Acoustic imaging positioning system and method for intelligent monitoring of transformer substation domain faults
PendingCN114414963AImprove detection efficiencyImprove positioning efficiencyTesting dielectric strengthCircuit arrangementsSensor arraySound sources
The invention belongs to the technical field of power equipment fault detection of acoustic imaging, and discloses an acoustic imaging positioning system for transformer substation domain fault intelligent monitoring, which comprises a sound acquisition module, and is characterized in that the sound acquisition module comprises a plurality of sound sensor arrays; the signal processing module is used for judging whether the digital signal is a fault sound signal or a background noise signal, and if the digital signal is judged to be an abnormal fault signal, removing the background noise signal in the abnormal fault signal to obtain an effective signal; the sound signal imaging module is used for calculating and analyzing the effective signals to obtain sound signal characteristics and obtaining a sound position distribution array diagram corresponding to the sound sensor array; the image acquisition module is used for acquiring visual image data of each device; and the visual sound source positioning module is used for performing overlay analysis on the sound position distribution array diagram and visual image data to determine a sound fault position. The problems that an existing state monitoring device is high in system integration and technical complexity and not visual in detection result are solved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
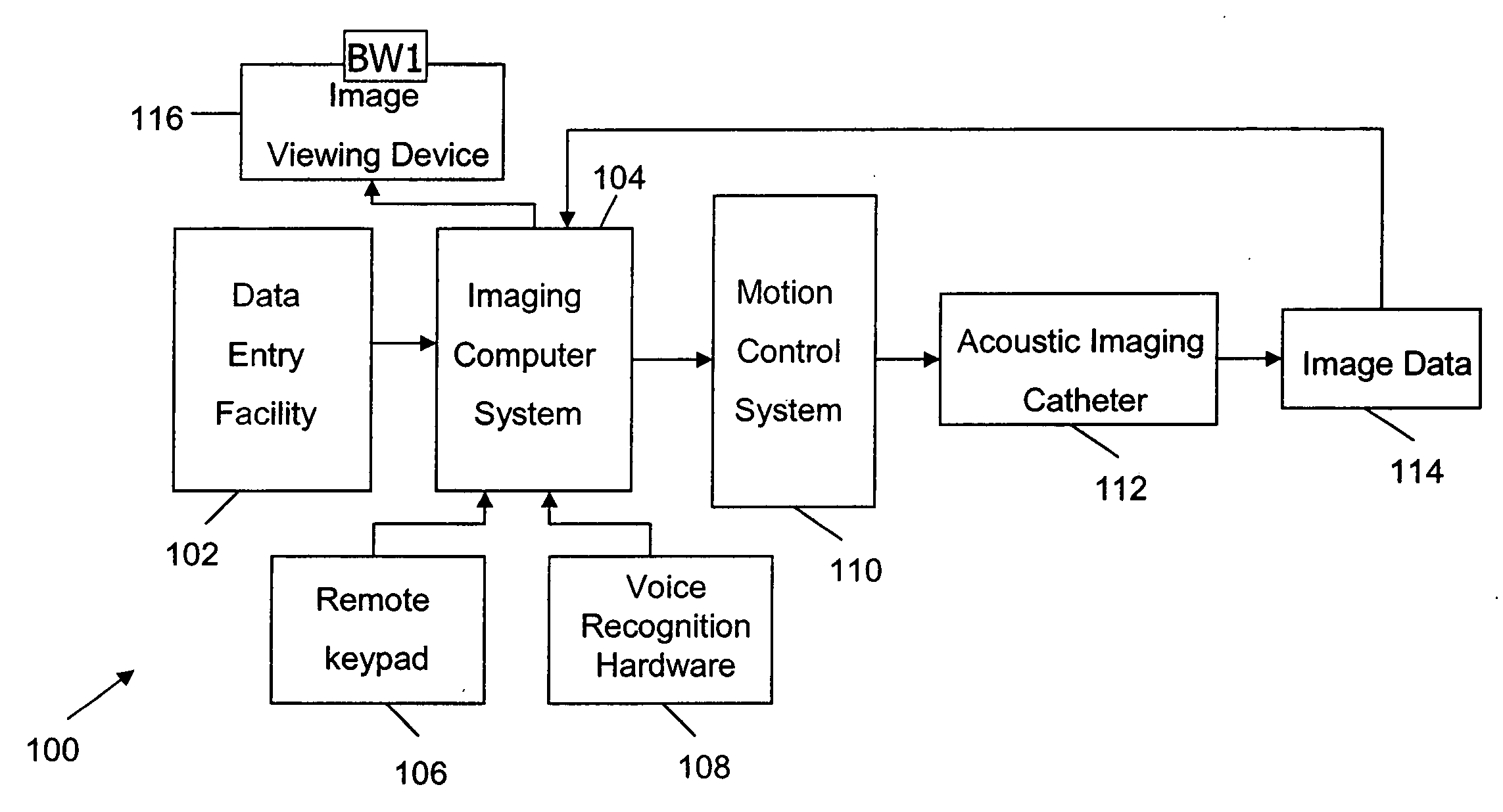
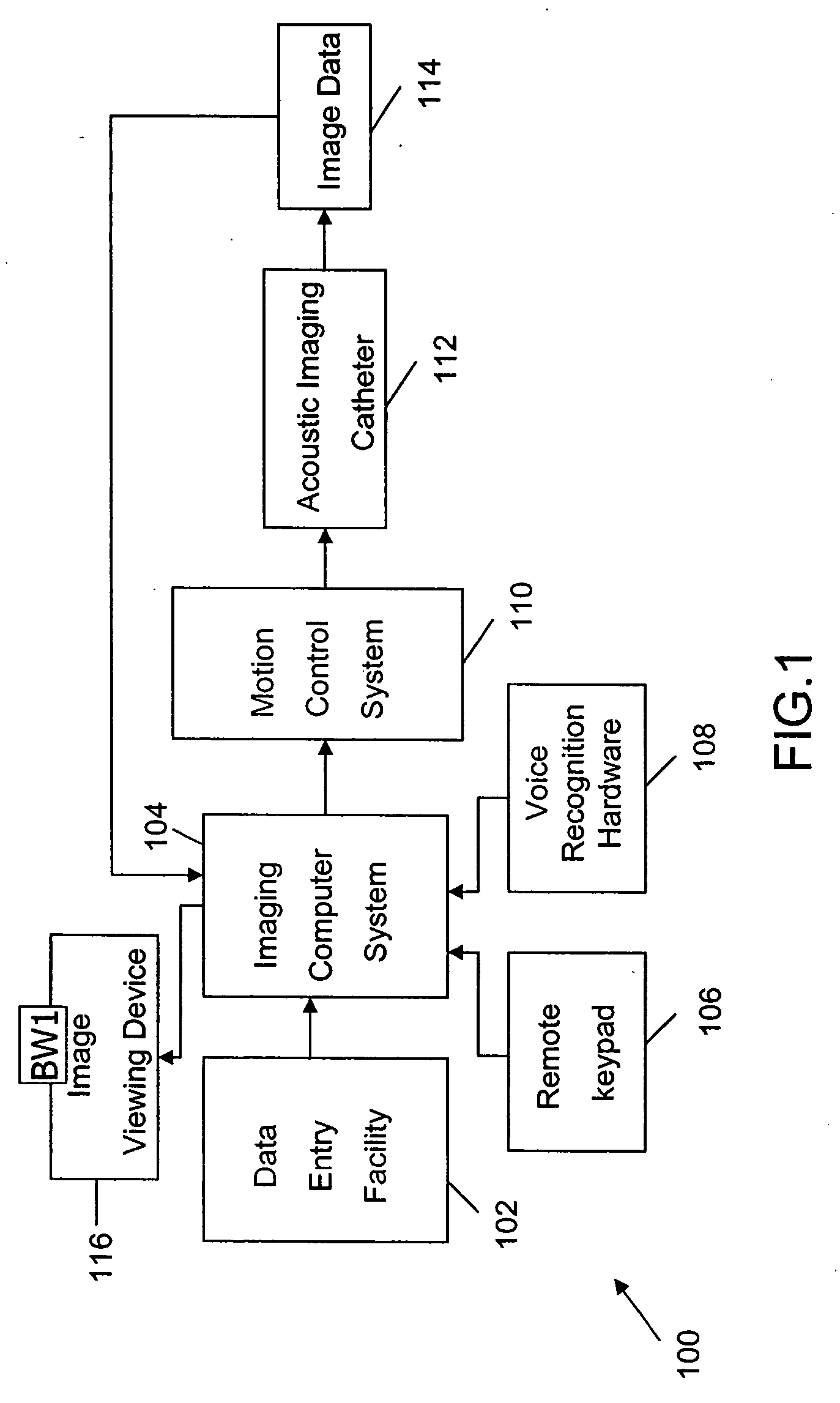
Transurethral ultrasonic imaging system
InactiveUS20060247529A1Reduce in quantityHelp positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterSonificationMedicine
An ultrasound scanning system and methods of using the same. In one preferred form, an ultrasound scanning system comprises an acoustic imaging catheter comprising an ultrasonic transducer, a motion control system and an imaging computer system for imaging a patient's genitourinary system. In another preferred form, an ultrasound scanning system is used for imaging a patient's prostate gland.
Owner:FRW 1
Three-dimensional scanning acoustic imaging device
InactiveCN103969652AReduce complexityLow costAcoustic wave reradiationAcoustical imagingSafety monitoring
The invention discloses a three-dimensional scanning acoustic imaging device and belongs to the field of underwater engineering mapping, and particularly the three-dimensional scanning acoustic imaging device is composed of an underwater machine rotary table, an acoustic imaging unit and an auxiliary measuring device. An acoustic multi-beam ranging principle is adopted as the basic principle of the device, a transmitting transducer array transmits sound beams which are narrow in the horizontal direction and wide in the perpendicular direction to irradiate a detection area, the transmitting transducer array conducts beam forming processing on received multi-channel signals to form multiple receiving beams which are quite narrow in the perpendicular direction, the arriving time of the echo of each receiving beam is calculated, the position of a space target can be calculated according to the direction of the beams, one perpendicular scanning line of an underground scene can be obtained through each time of receiving and transmitting, 360-degree rotary scanning is conducted on the horizontal plane through the underwater machine rotary table, finally, a three-dimensional point cloud image of the specific underwater area is formed, and therefore a three-dimensional structure of the underwater scene is visually reflected. The device can be widely applied to multiple fields of underwater structural object detection, bridge underwater detection, ocean platform underwater safety monitoring and the like.
Owner:BEIJING HYDRO TECH MARINE TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com