Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Vibrational resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A vibration resonance occurs when equipment or a product is exposed to an external forced vibration occurring at one or more of its natural frequencies. The resulting product response vibration is amplified and can be huge! Vibration resonances can cause severe damage to products and significantly shorten their life.
Solid state surface catalysis reactor
InactiveUS6916451B1Physical/chemical process catalystsPhotovoltaicsChemical reactionElectric generator
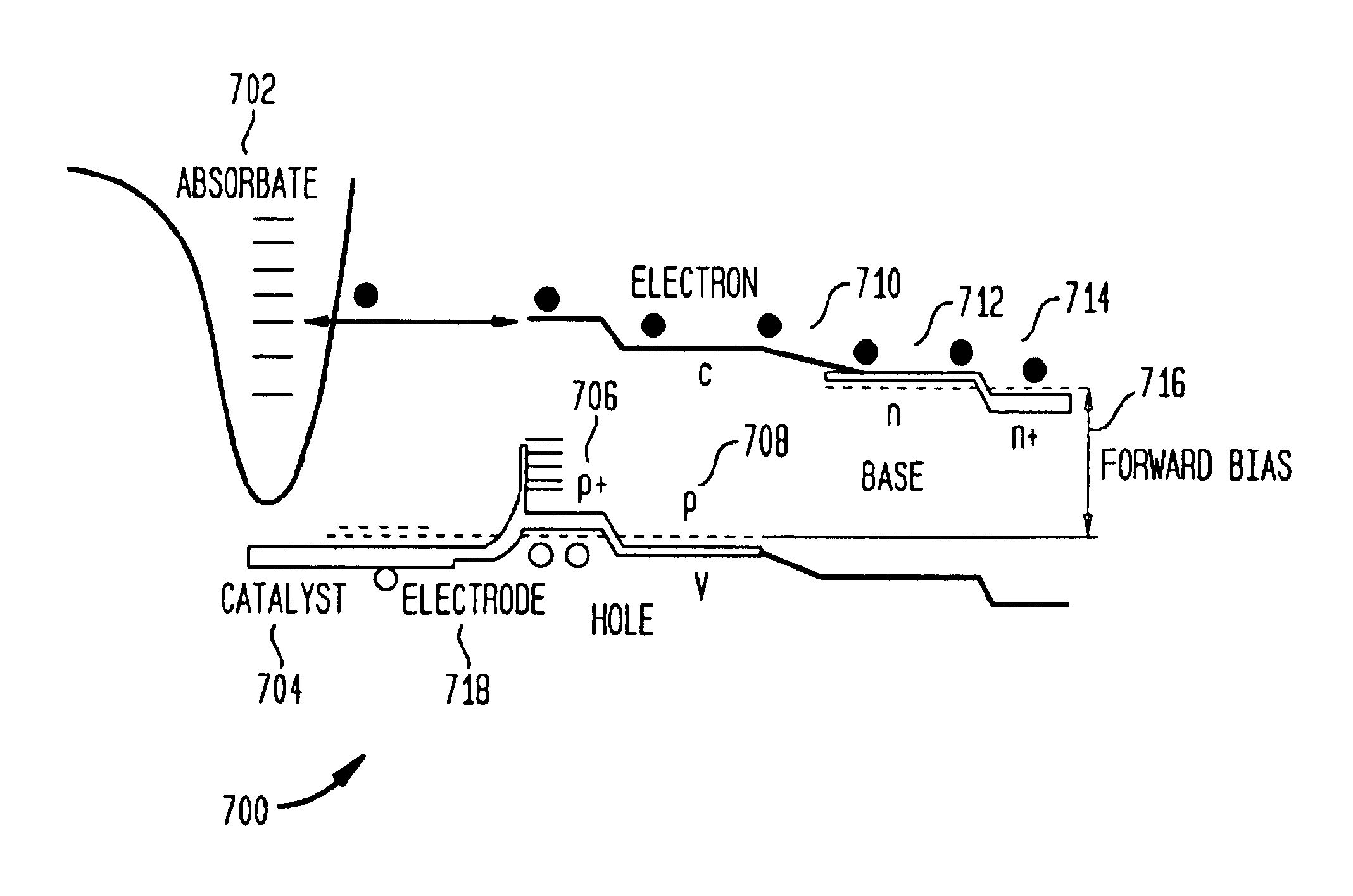
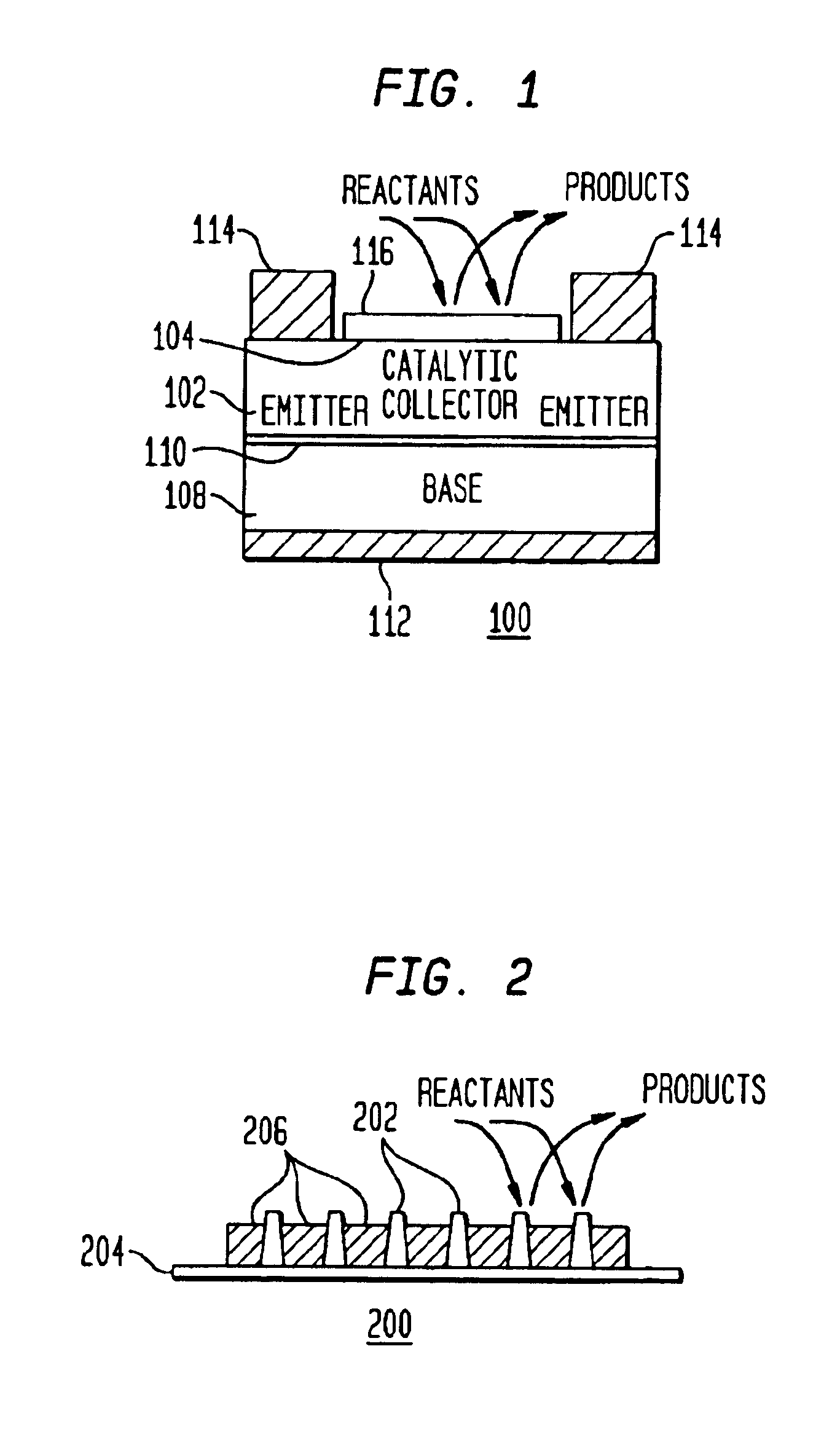
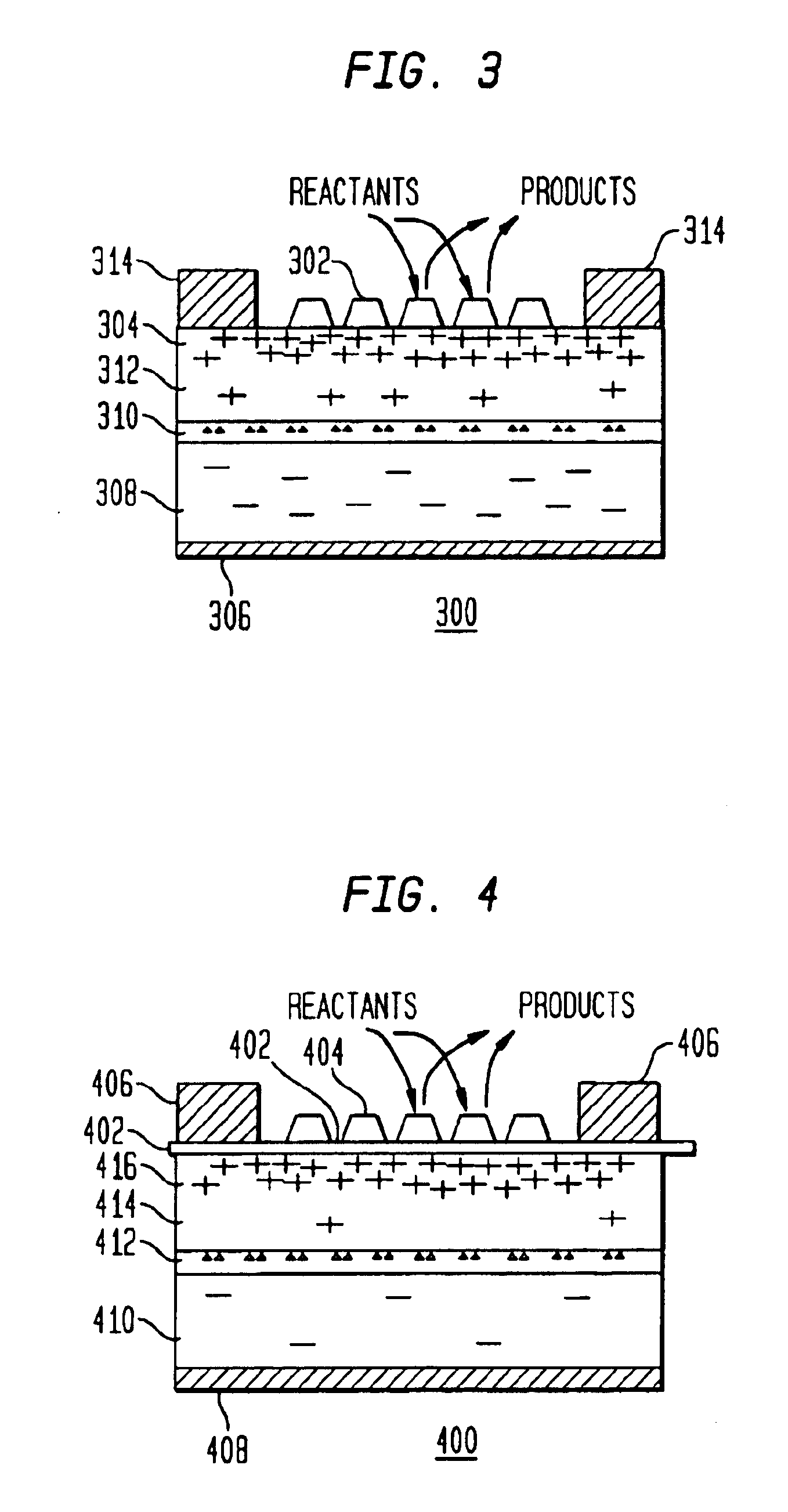
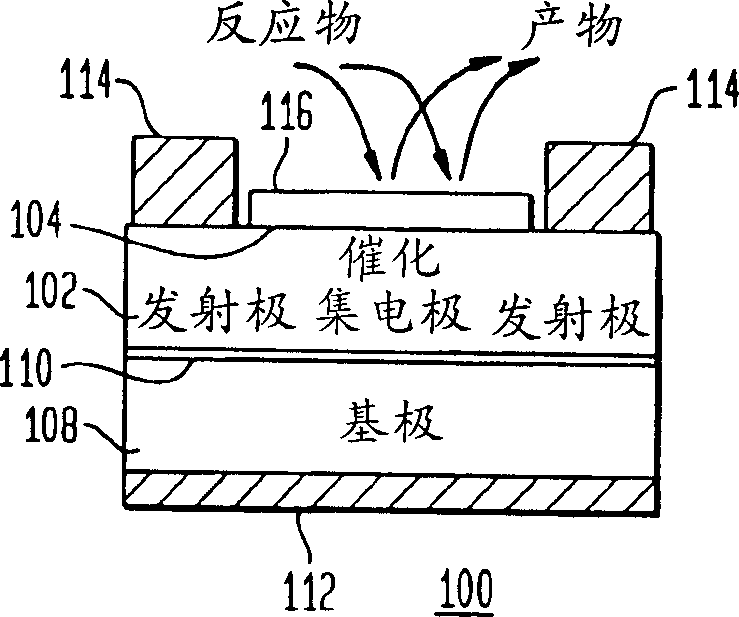
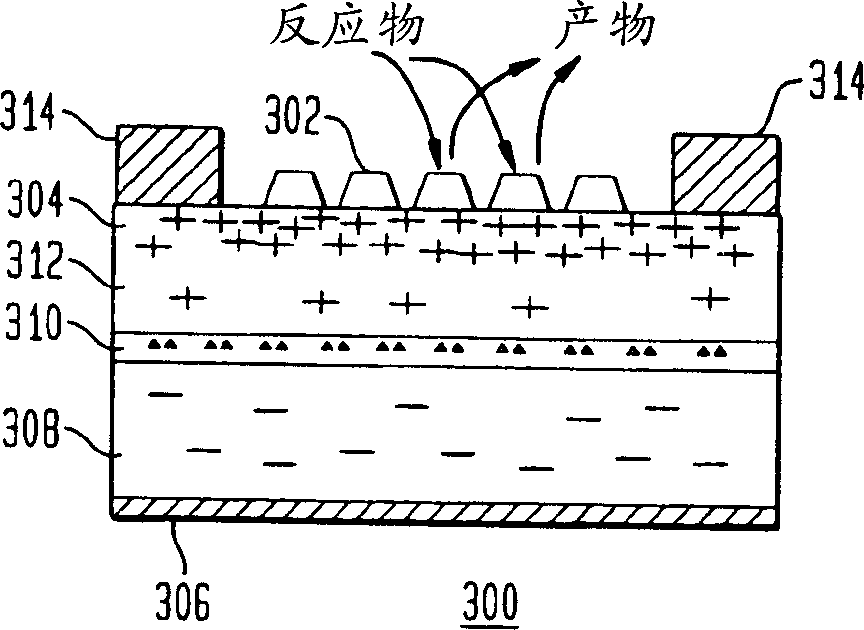
A method and apparatus to stimulate chemical reactions on a catalyst surface using electricity, and the reverse process to convert energy released from chemical reactions into electricity. A reversible emitter generates electrons which are injected into reactants on the catalyst surface, exciting chemically reactive vibrational resonances. Hot electrons created in the emitter region of a semiconductor junction diffuse to the co-located collector region and catalyst surface. Catalyst clusters or films bonded on the collector surface transfer the hot electrons to or from the catalyst surface having adsorbed reactants. The dimension of the catalyst-collector is less than the energy mean free path of hot electrons. The hot electrons excite reactant vibrations before thermalizing with the substrate lattice thereby accelerating reactions. The hot electrons are also generated by the same reactions on a catalyst surface. The method and apparatus is reversible and may be operated as an electric generator using chemical reactions.
Owner:NEOKISMET L L C
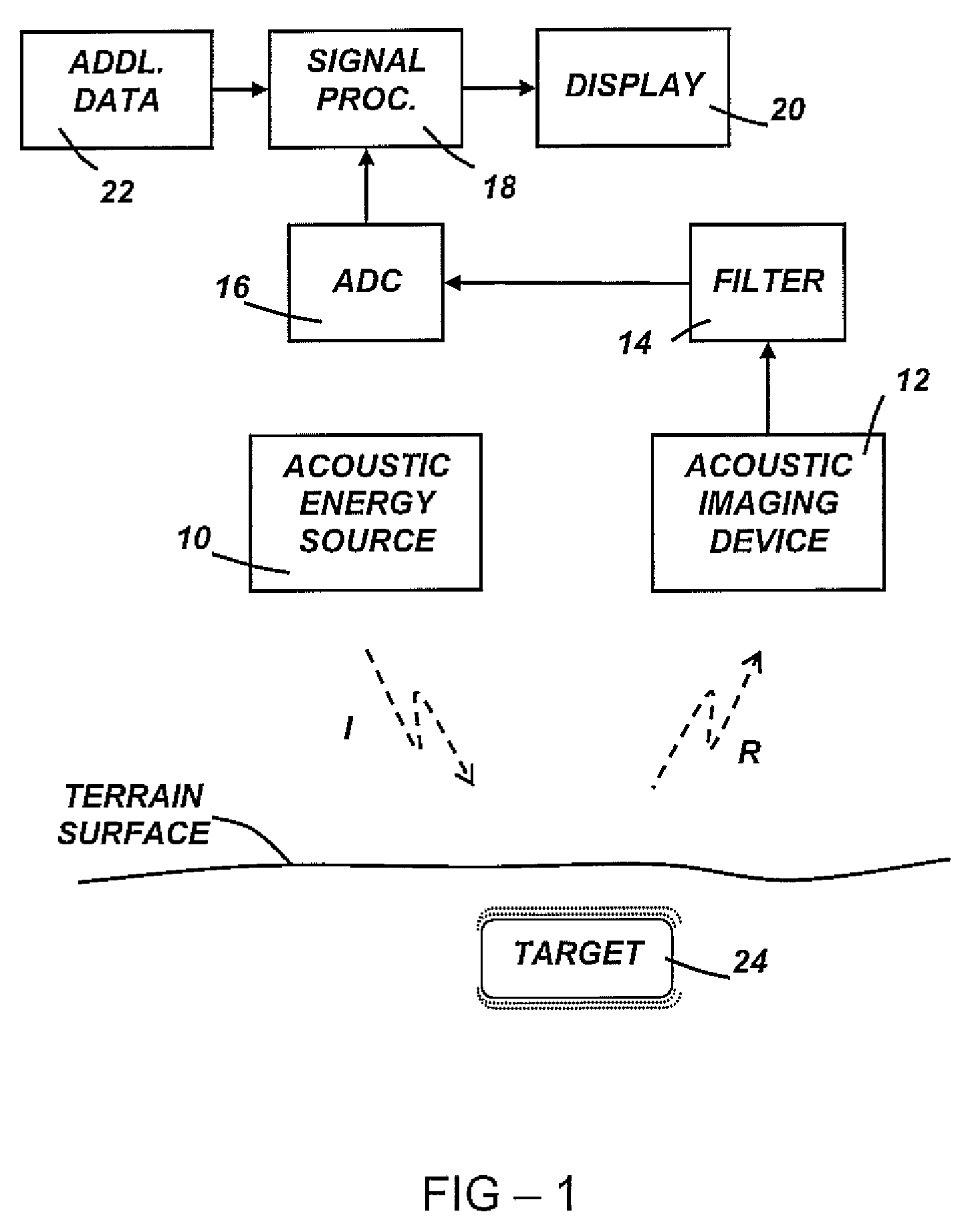
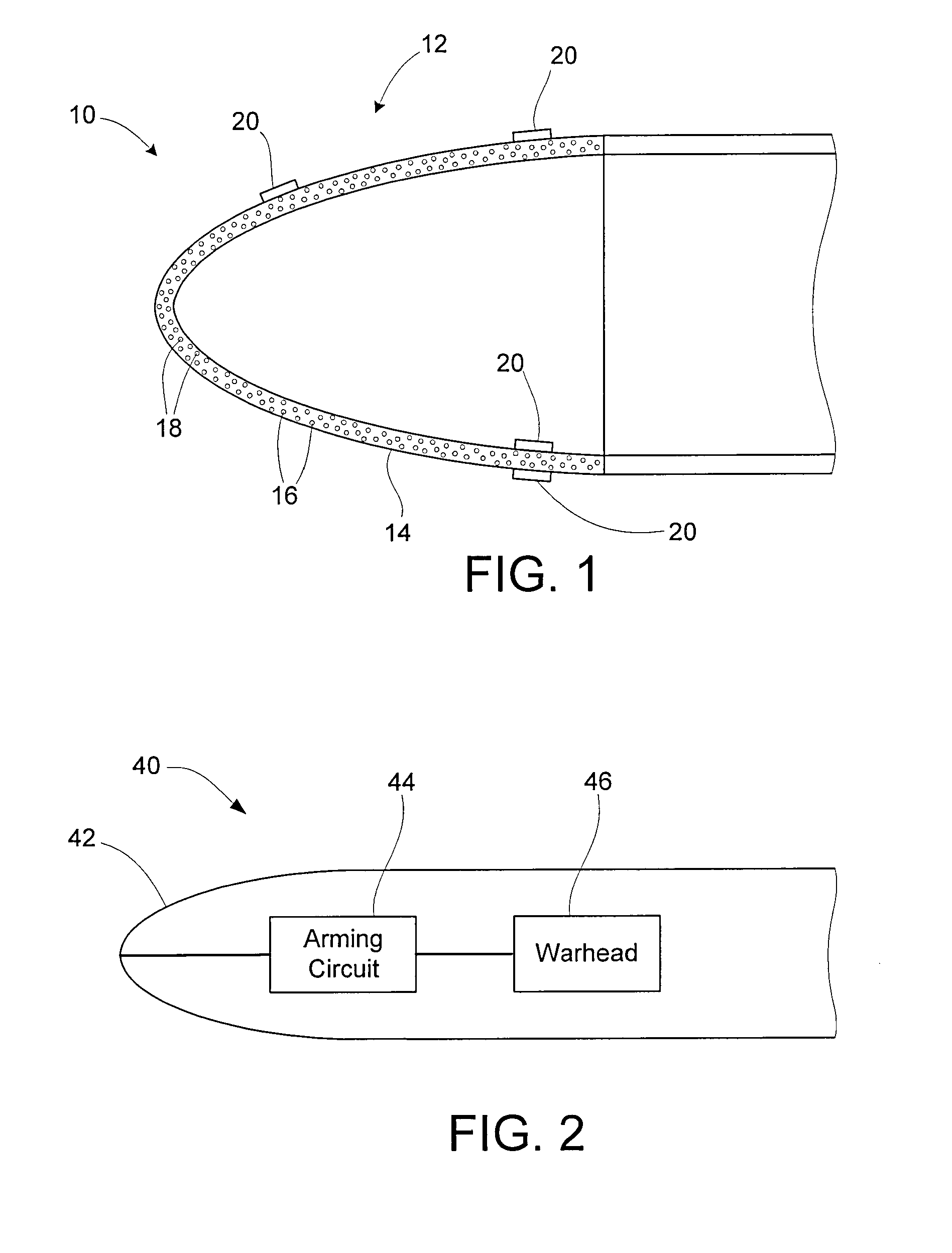
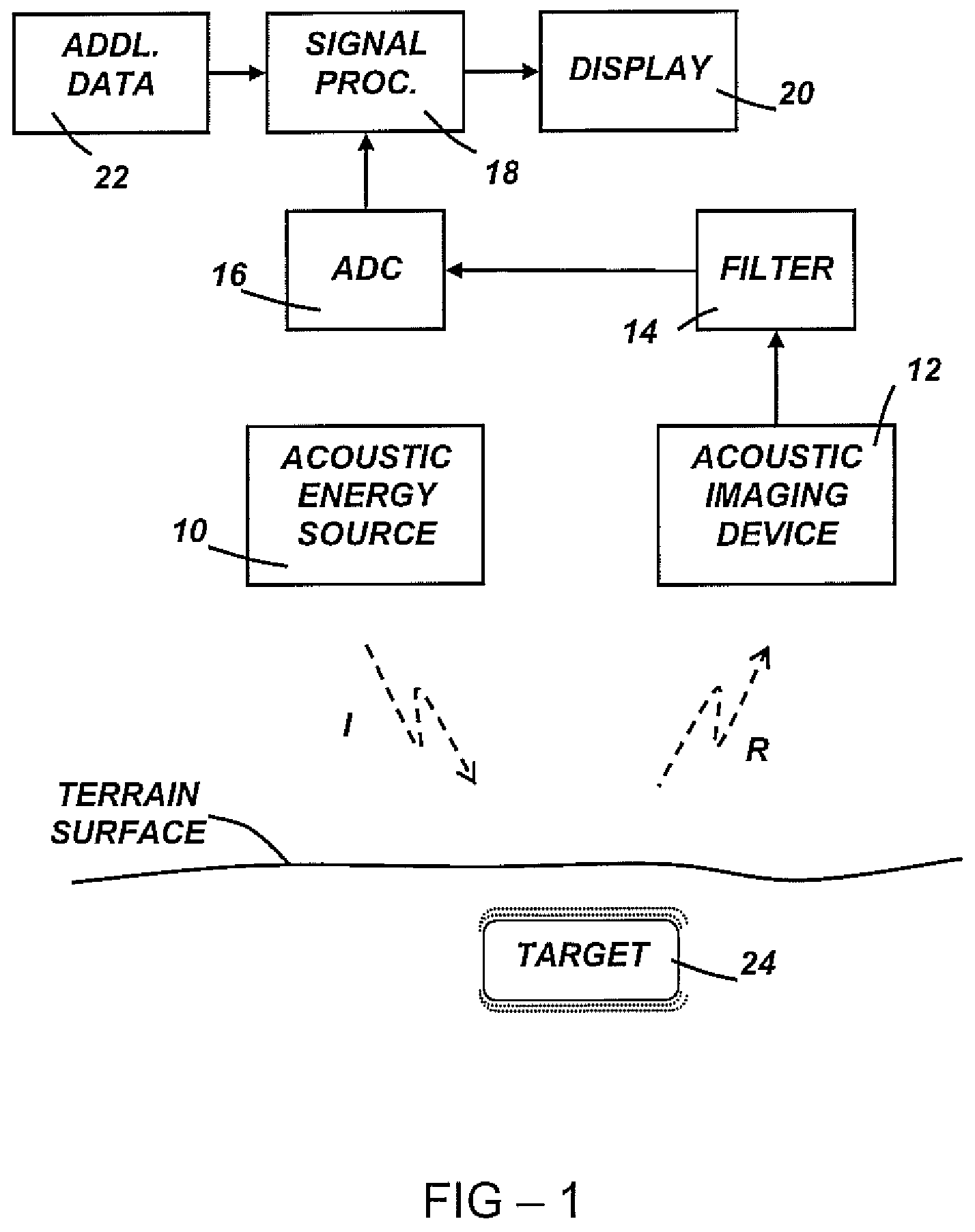
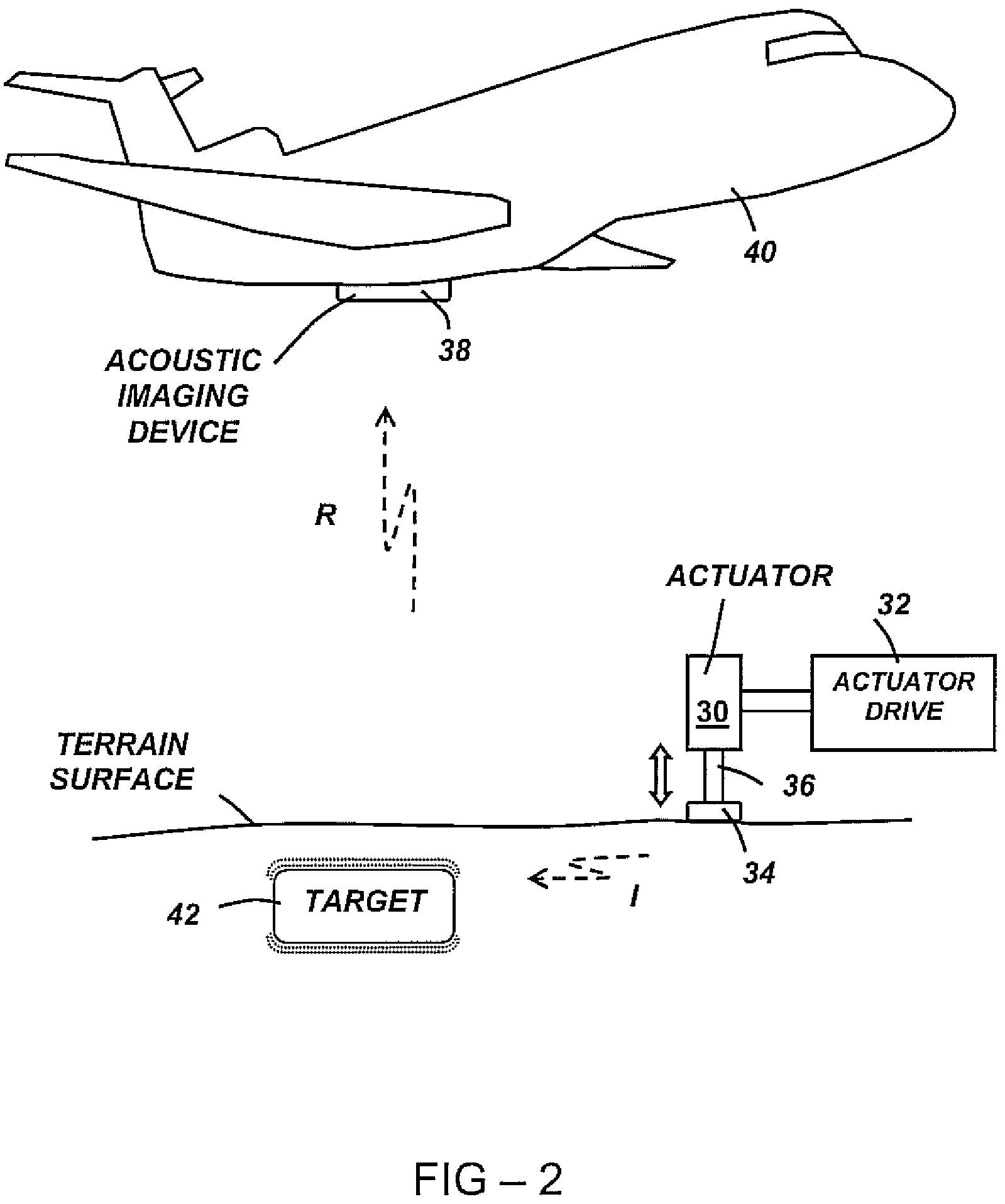
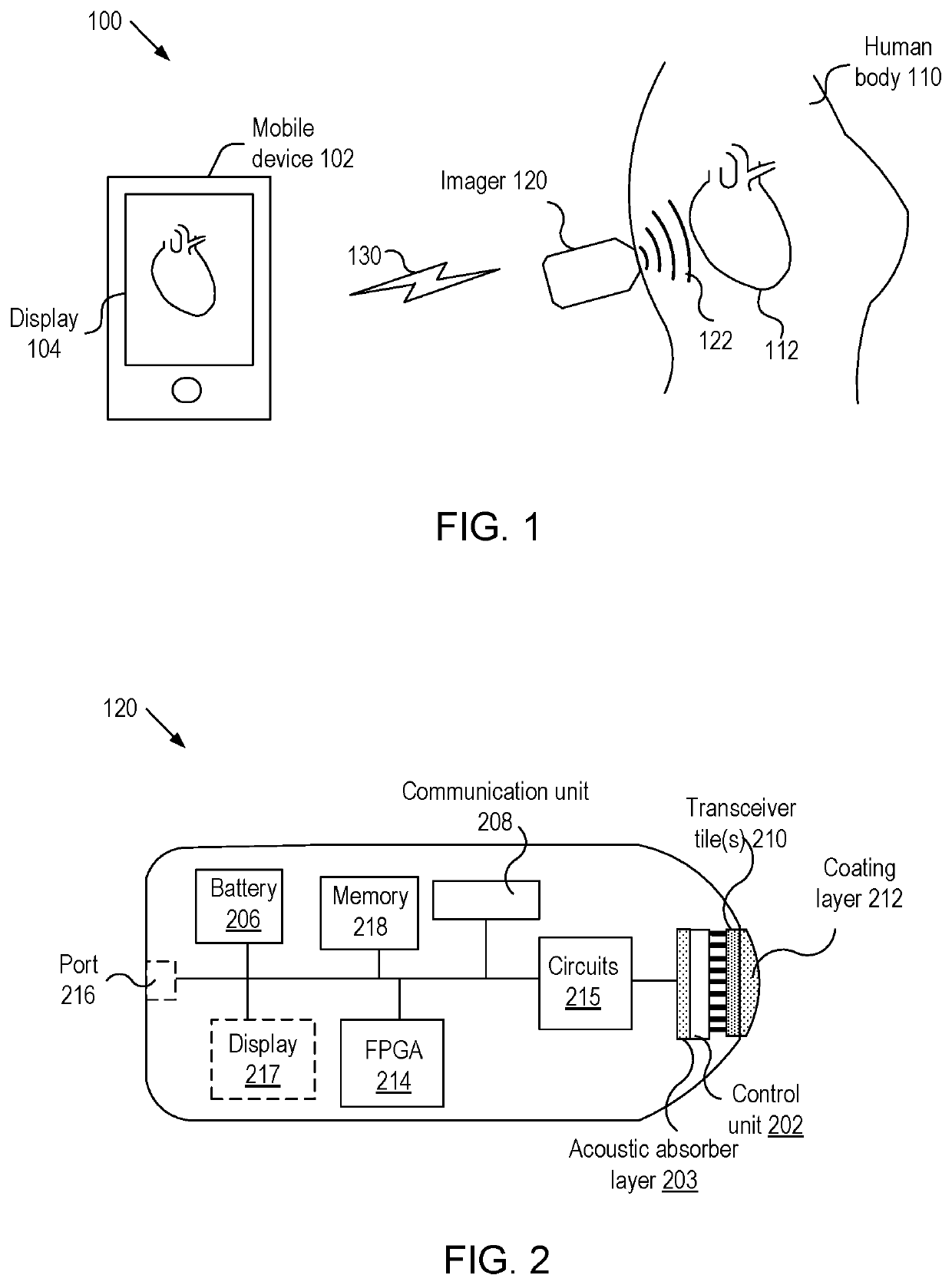
Object detection using acoustic imaging
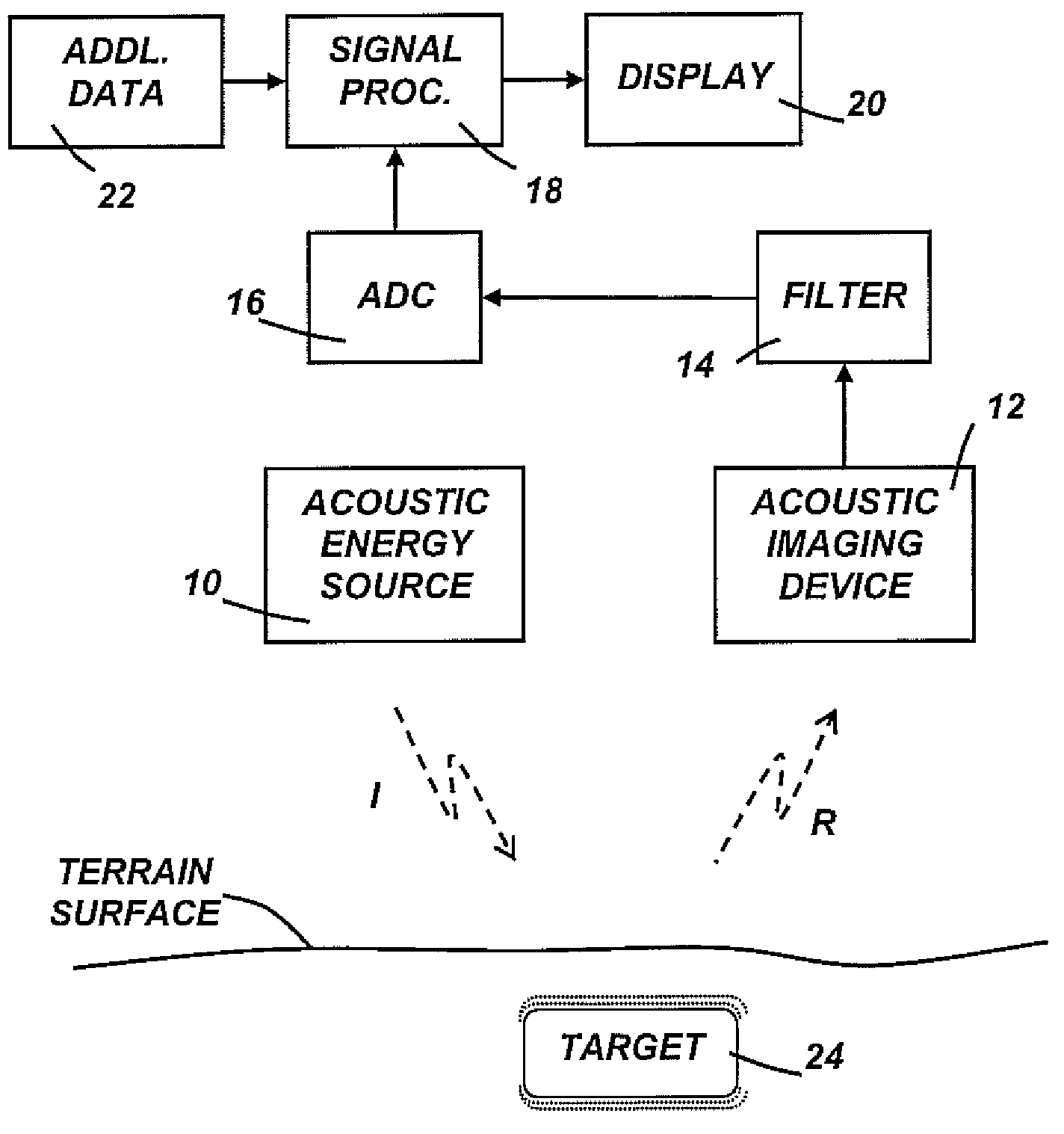
Embodiments of the present invention include methods and apparatus for the detection of objects using acoustic imaging. Vibrational resonance characteristics of man-made objects may be significantly different from those of the surrounding natural materials, allowing an acoustic image to highlight the position of the object, even if the object is concealed from visual imaging.
Owner:FEV ENGINE TECH
Structural material with piezoelectric material particles
ActiveUS20080179993A1Vibration measurement in solidsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesElectricityStructural health monitoring
A load-bearing structural member has a continuous structural material with piezoelectric material particles mixed in throughout. The structural material may be any of a variety of suitable materials, such as polymer materials, composite materials, ceramic materials, or concrete. The piezoelectric material particles may be used for evaluating the soundness of the structural member, such as in quality control or structural health monitoring processes. The structural member may include one or more conductive pickups used for receiving signals from the structural member. The signals may be induced by introducing ultrasonic signals or vibrational resonance signals into the structural member. The response from such induced signals may be used for quality control purposes or structural health monitoring. Piezomagnetic, electro-strictive, or magneto-strictive material particles may also be spread throughout the structural material, to amplify and otherwise enhance the signals from the piezoelectric material particles.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Object detection using acoustic imaging
Embodiments of the present invention include methods and apparatus for the detection of objects using acoustic imaging. Vibrational resonance characteristics of man-made objects may be significantly different from those of the surrounding natural materials, allowing an acoustic image to highlight the position of the object, even if the object is concealed from visual imaging.
Owner:FEV ENGINE TECH
Device and method for stimulated raman detection
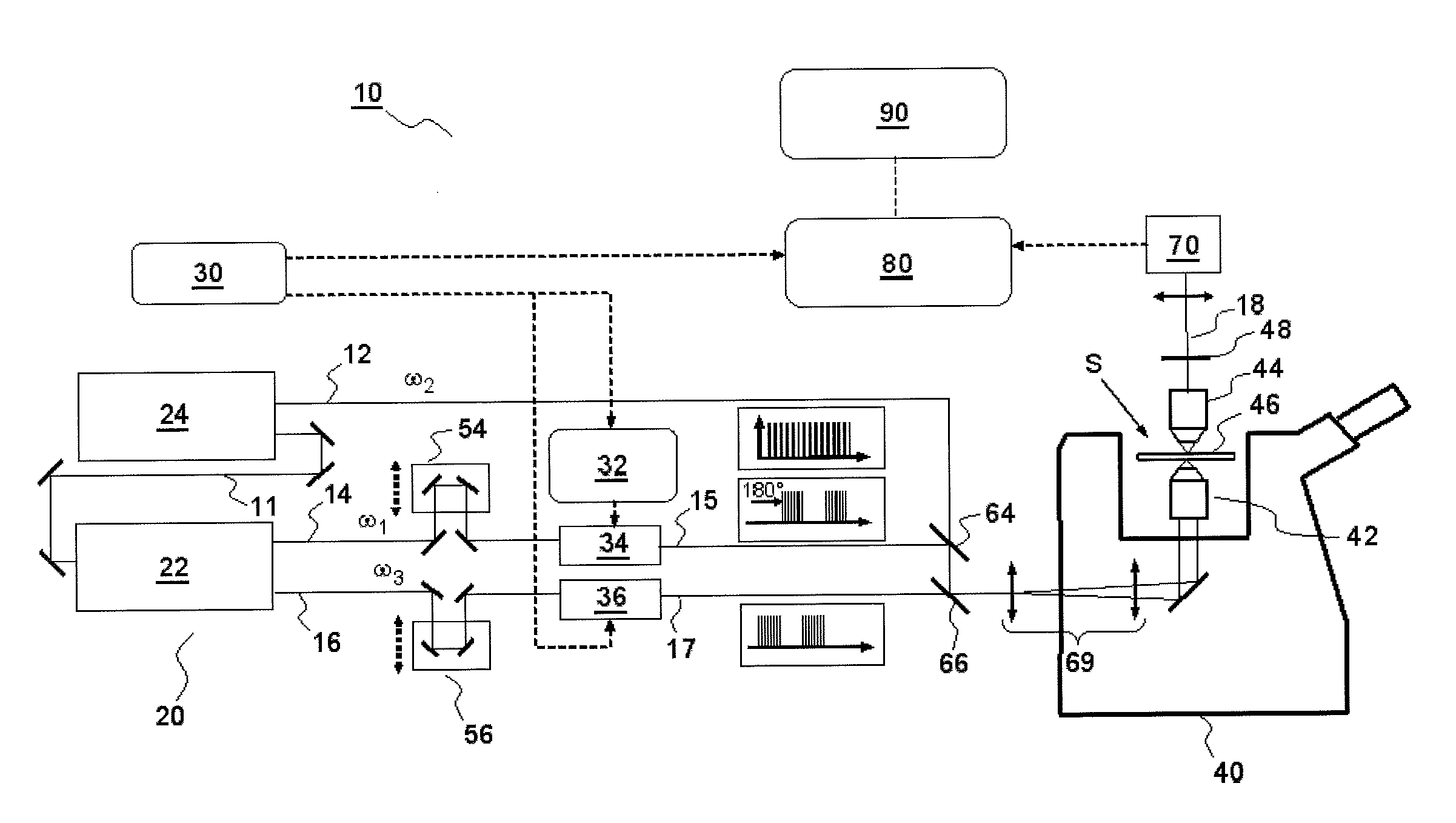
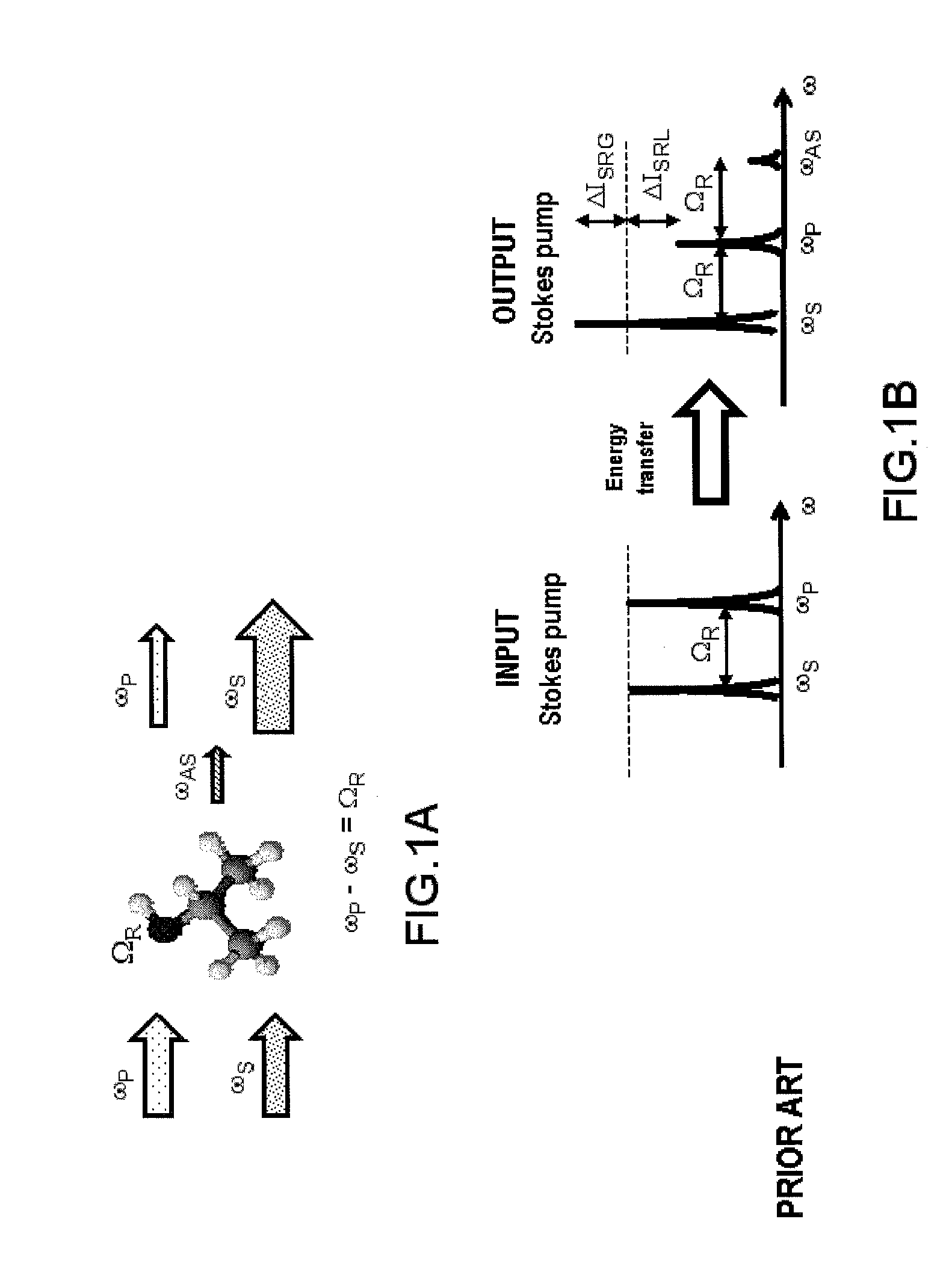
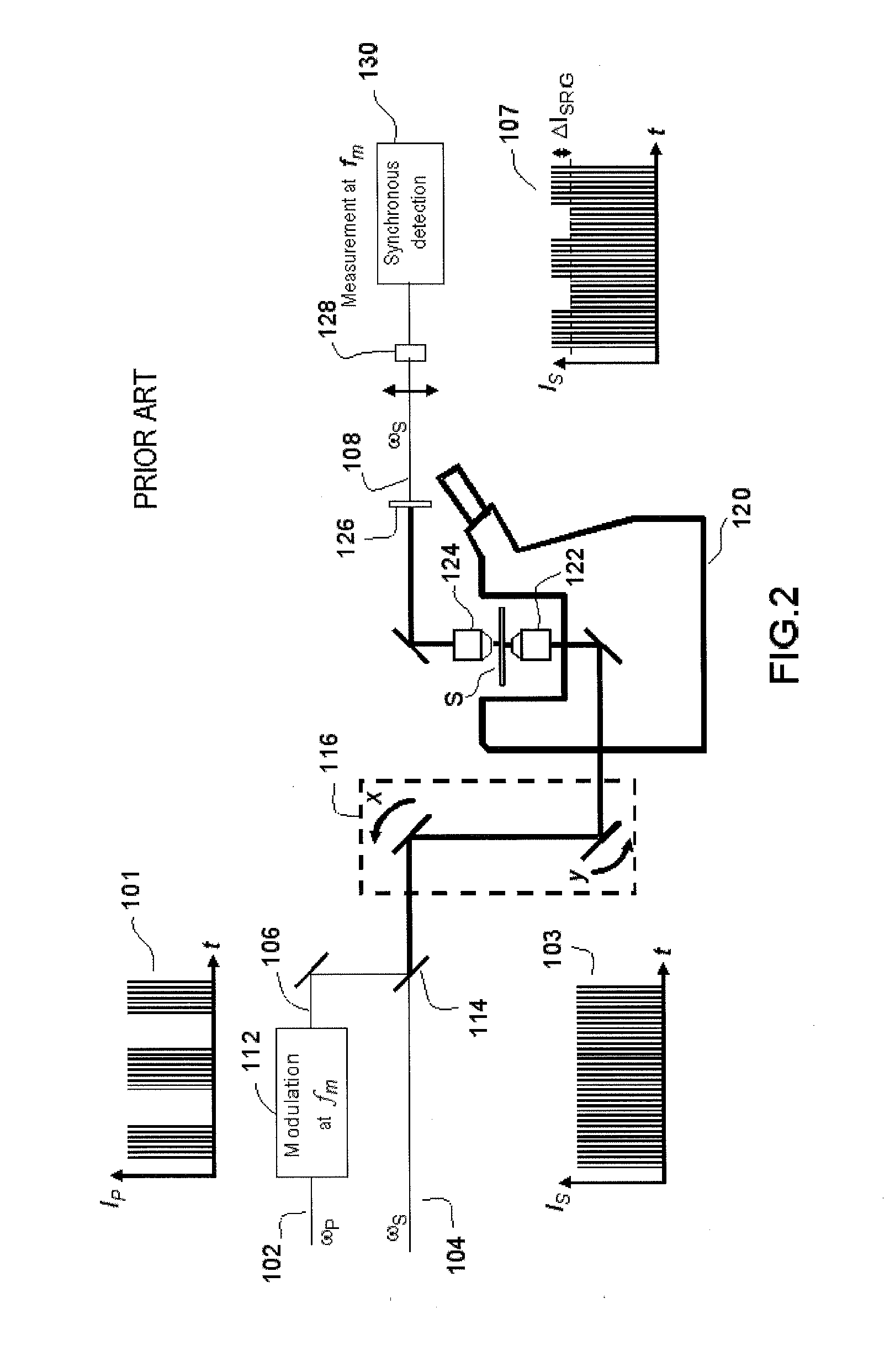
ActiveUS20160047750A1Suppress artifactsArtifact dueRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringMolecular vibrationSynchronous detection
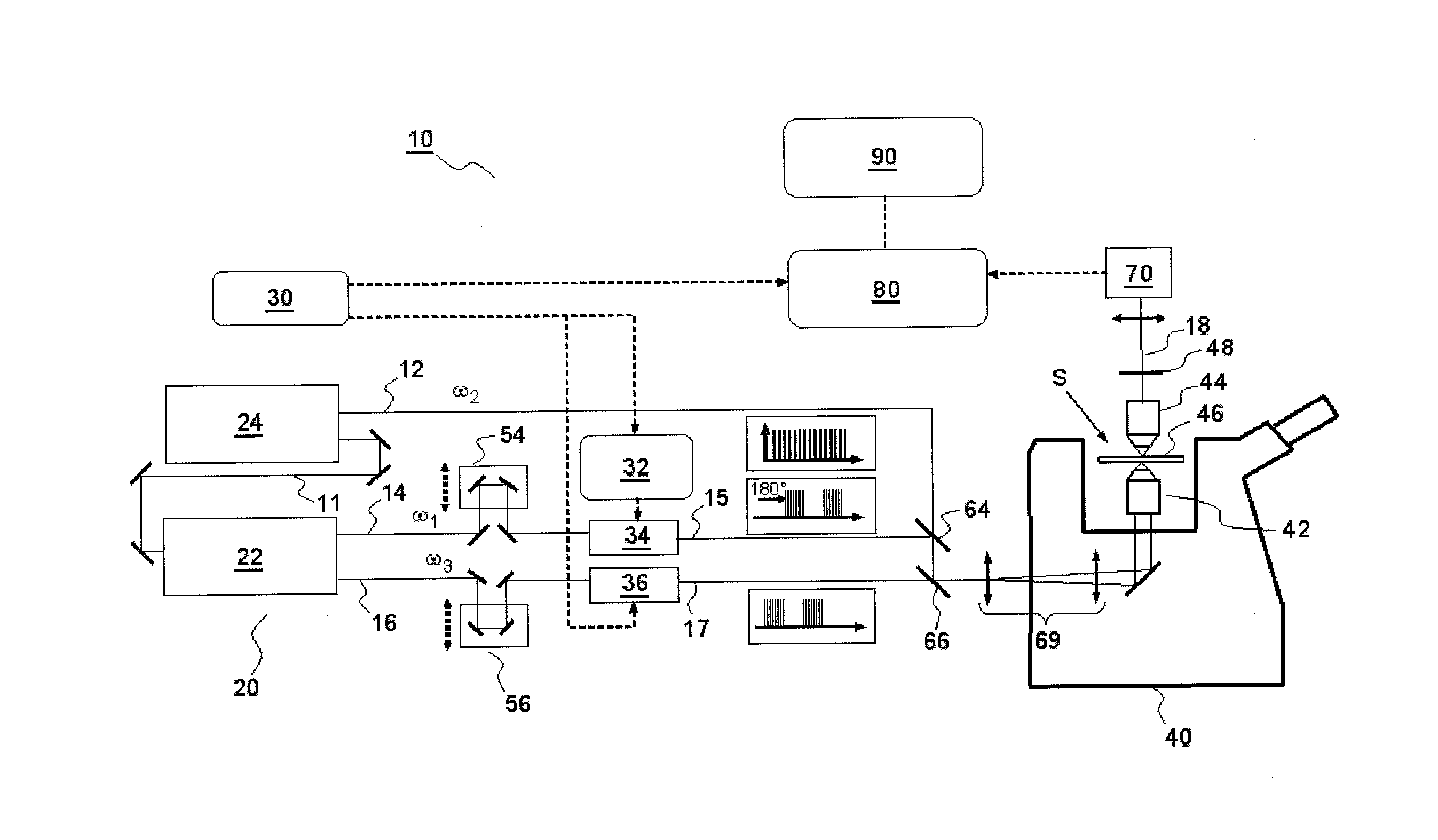
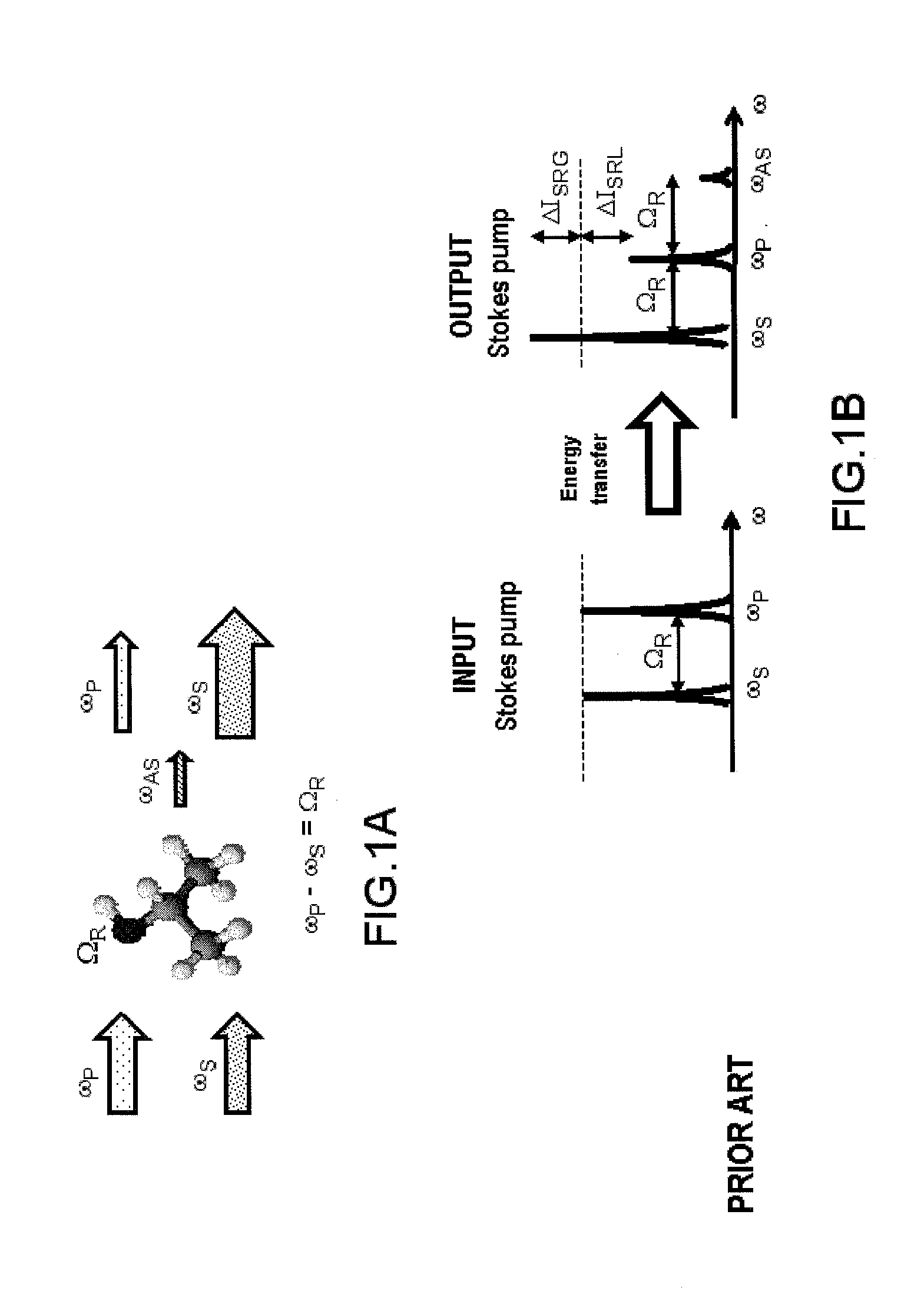
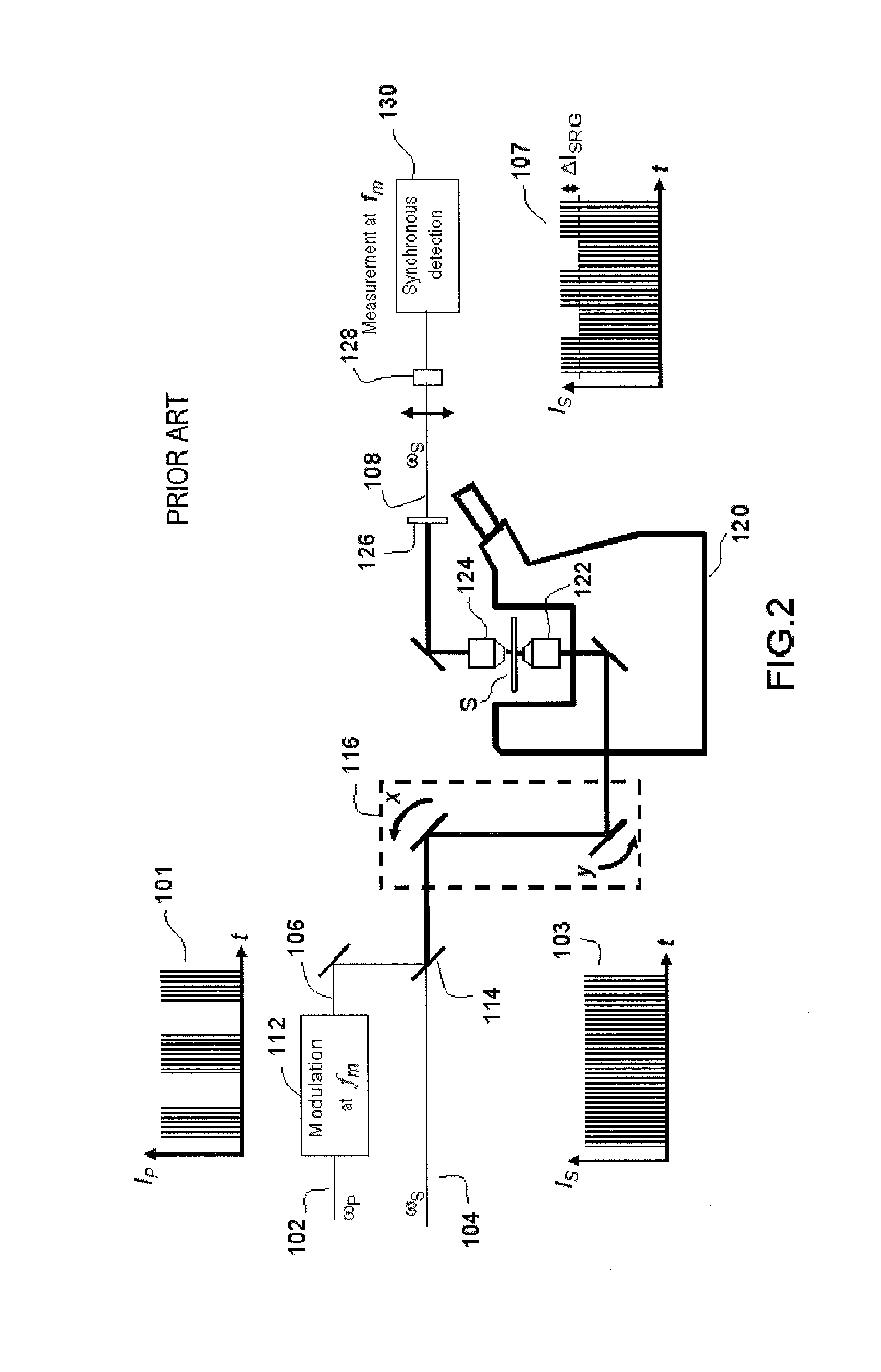
According to one aspect, the invention relates to a device for detecting a resonant non-linear optical signal of Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) type induced in a sample. The device comprises electro-optical means for making interact in the sample, at a first modulation frequency, trains of light pulses of angular frequencies ω1 and ω2 and, at a second modulation frequency, trains of light pulses of angular frequencies ω2 and ω3, such that ω2−ω1=ω3−ω2=ΩR where ΩR is a molecular vibrational resonant angular frequency of the sample. Moreover, the device comprises means for synchronous detection at the first and second modulation frequencies of non-linear optical signals resulting from the interaction of the light pulses in the sample, and electronic processing means making it possible to obtain, from electronic signals resulting from the synchronous detection, a signal characterizing the molecular vibrational resonance of the sample.
Owner:UNIV DE PROVENCE D AIX MARSEILLE I +1
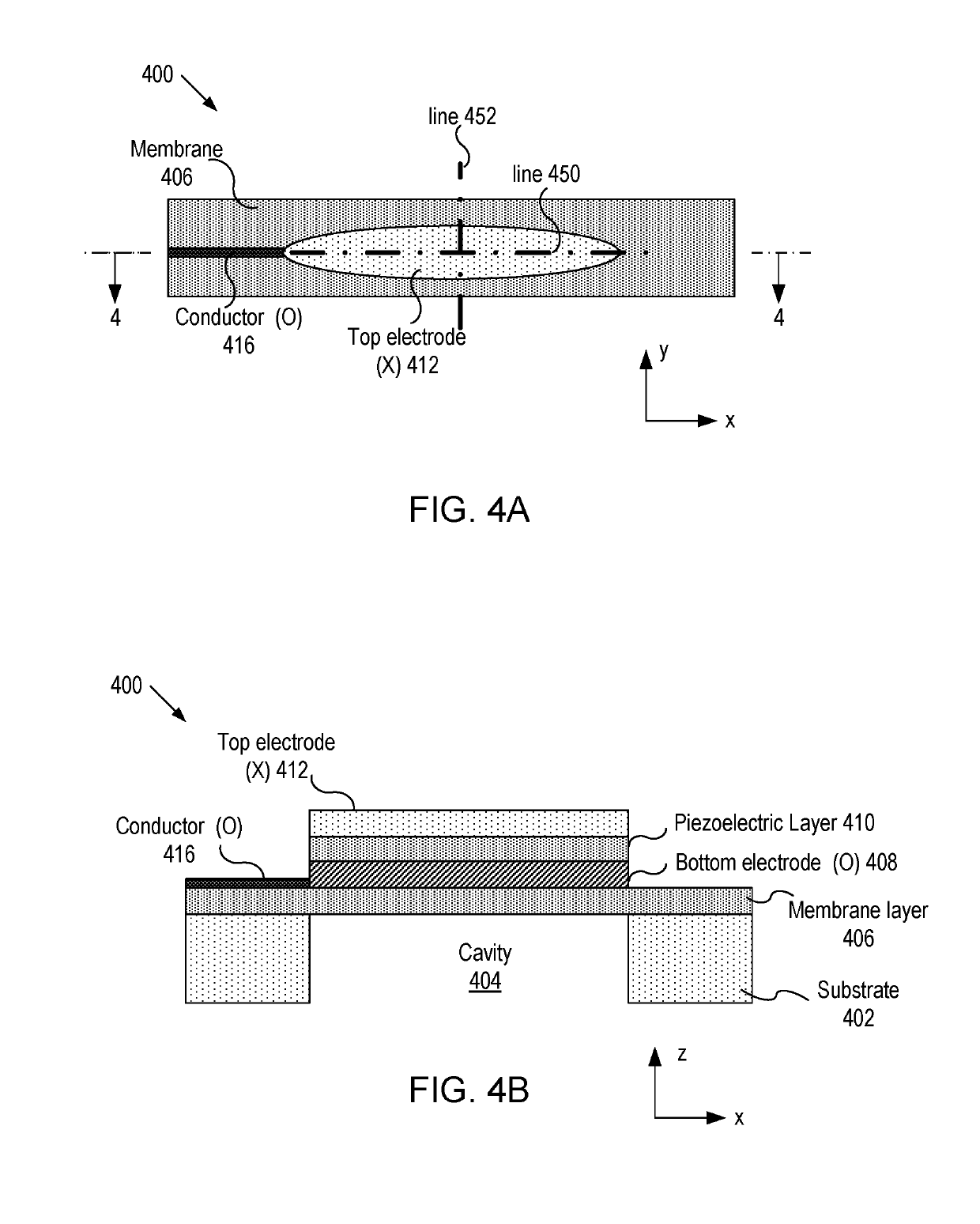
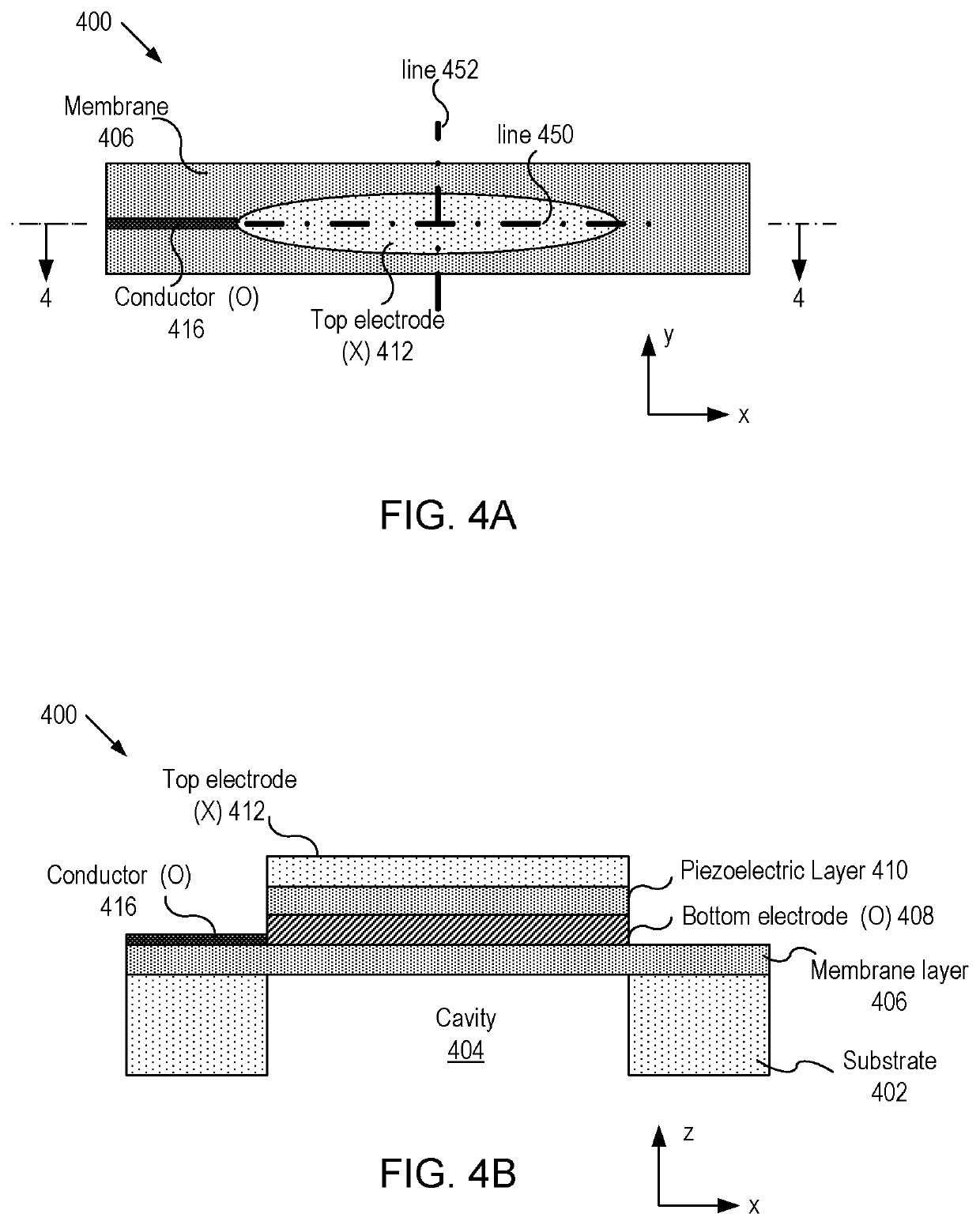
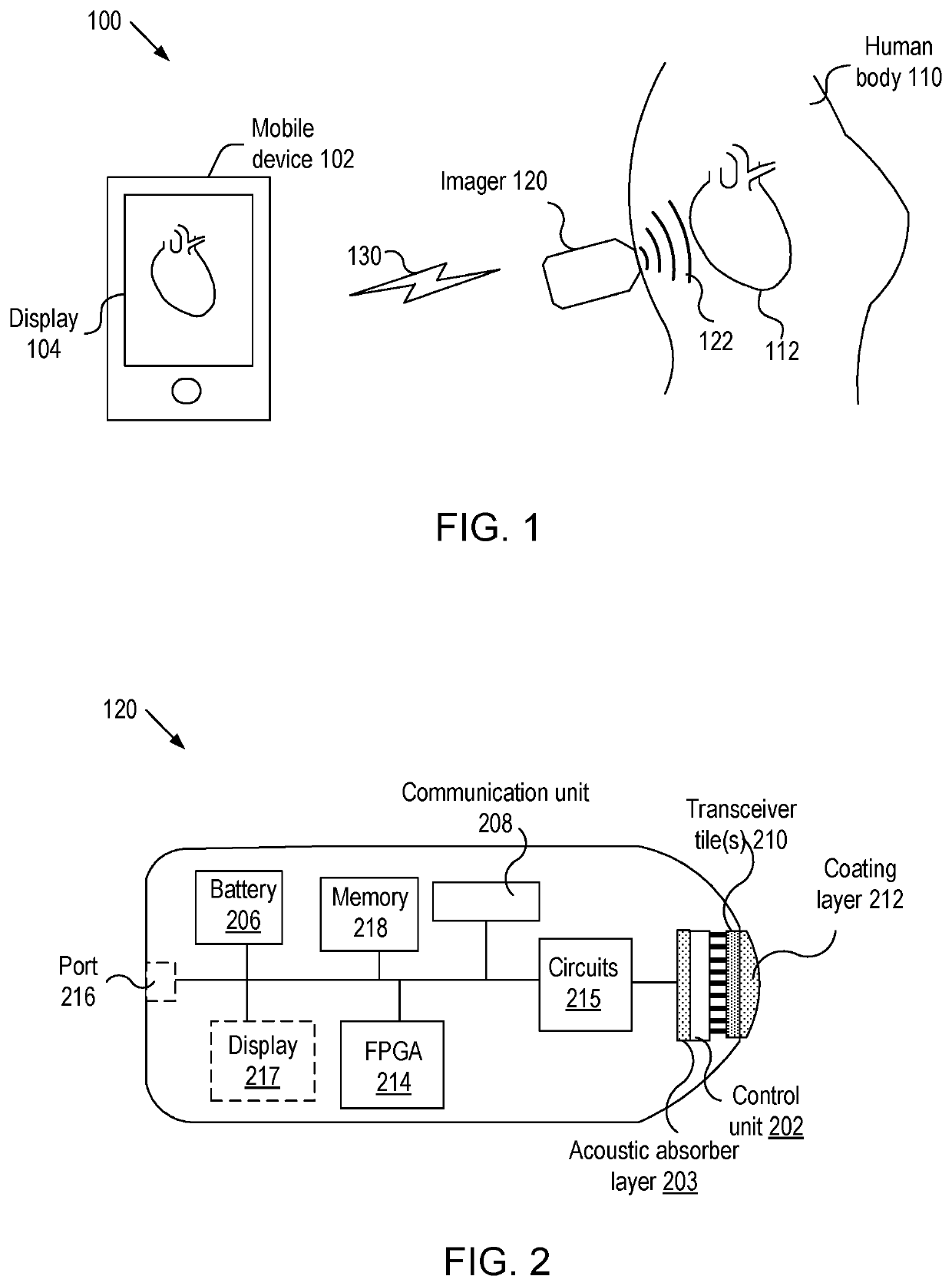
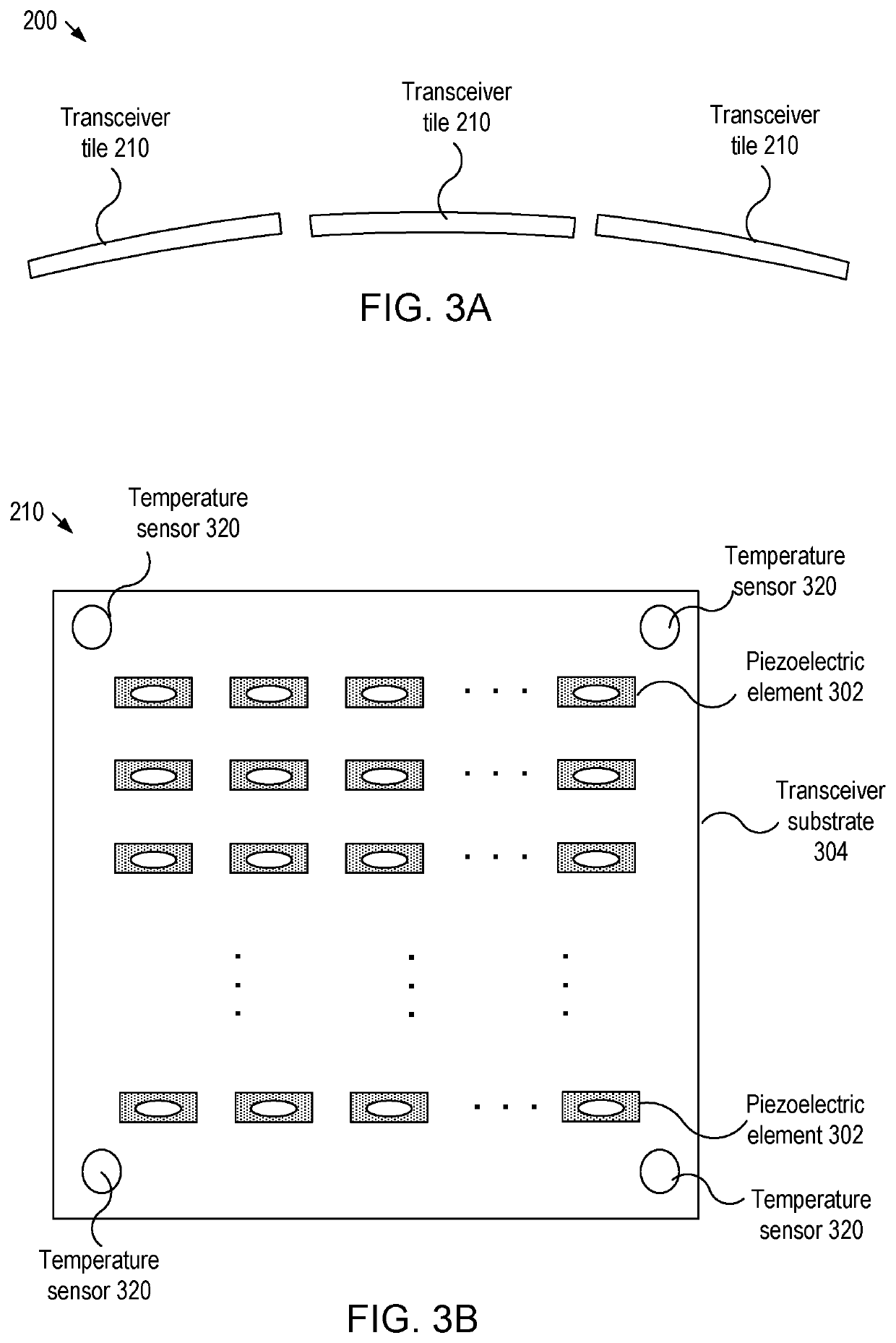
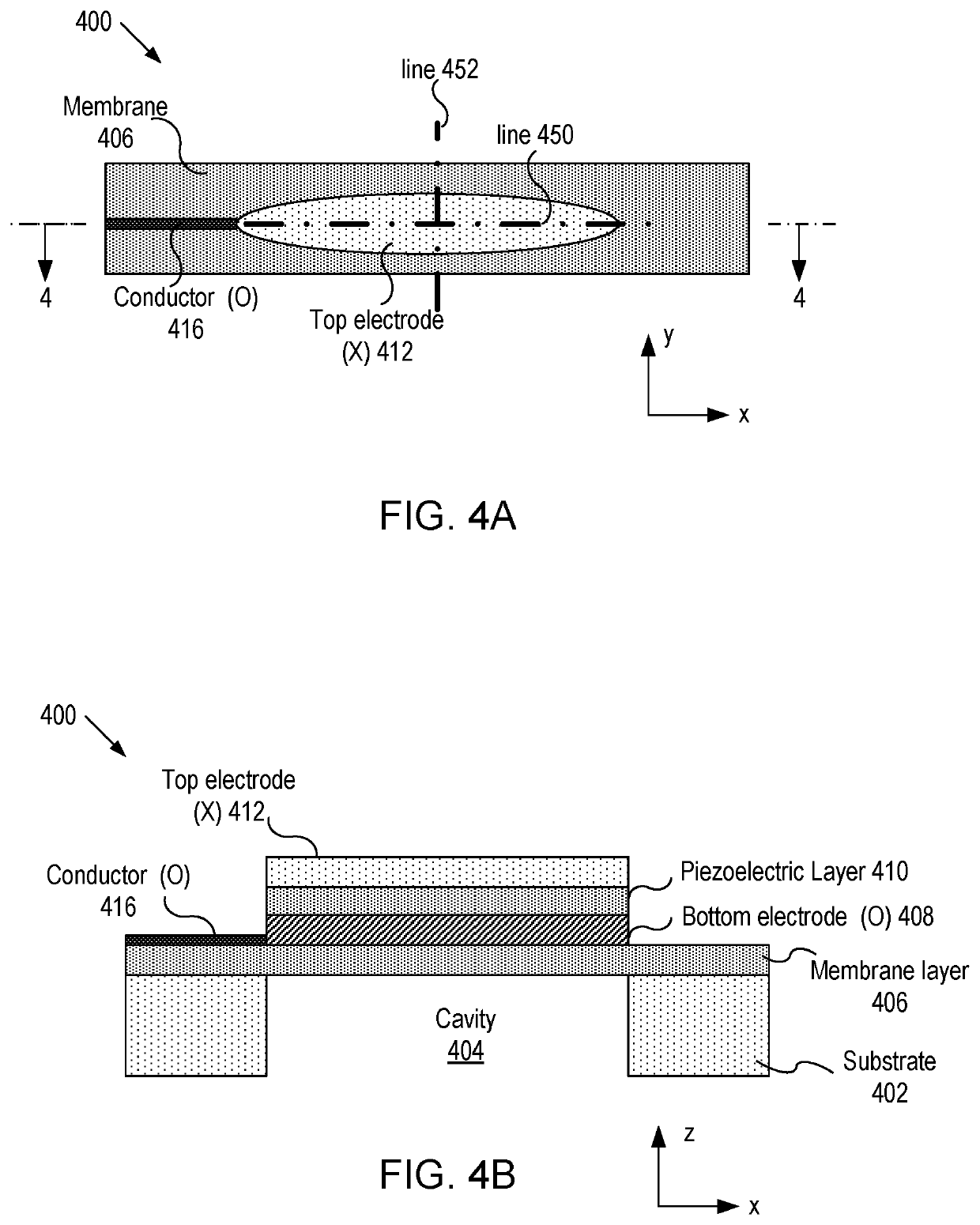
Imaging devices having piezoelectric transceivers
ActiveUS20190316958A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorTransceiver
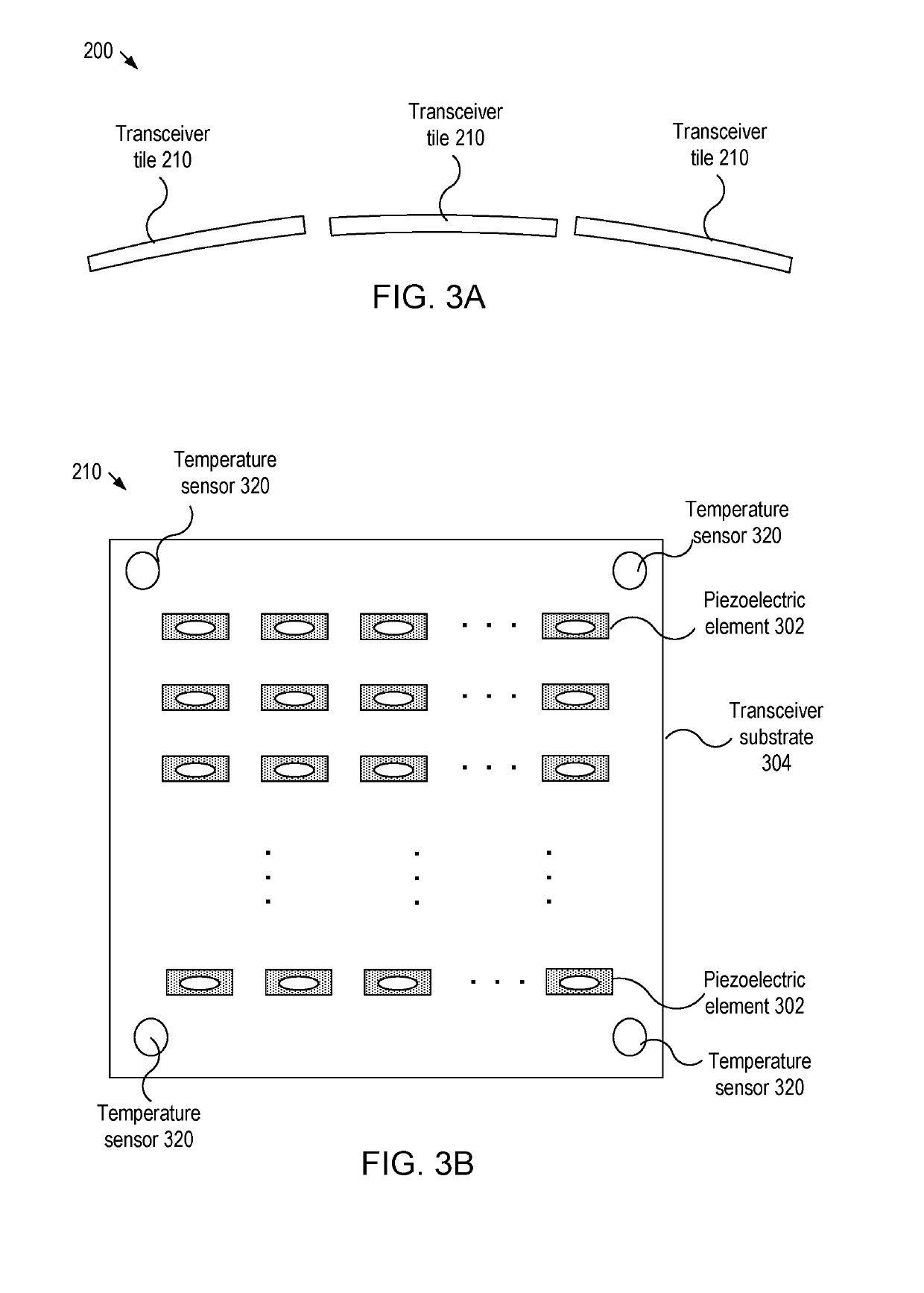
A micromachined ultrasonic transducer (MUT). The MUT includes: a substrate; a membrane suspending from the substrate; a bottom electrode disposed on the membrane; a piezoelectric layer disposed on the bottom electrode and an asymmetric top electrode is disposed on the piezoelectric layer. The areal density distribution of the asymmetric electrode along an axis has a plurality of local maxima, wherein locations of the plurality of local maxima coincide with locations where a plurality of anti-nodal points at a vibrational resonance frequency is located.
Owner:EXO IMAGING INC
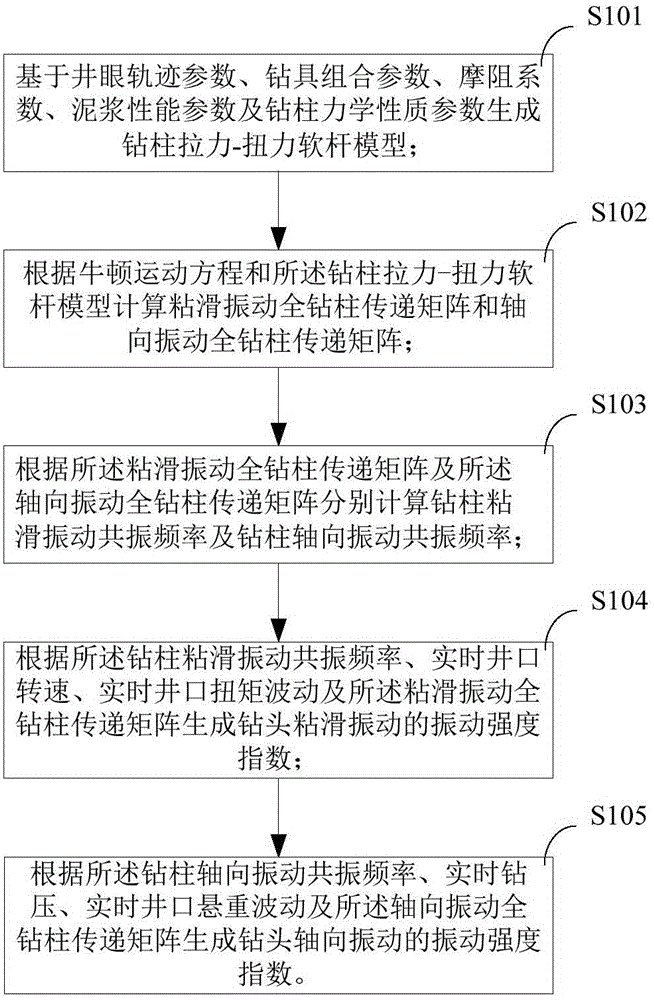
Downhole vibration monitoring method
ActiveCN105986803AAvoid damageImprove rock breaking efficiencyAutomatic control for drillingVibration amplitudeTransfer matrix
The invention provides a downhole vibration monitoring method. The method includes the steps that a drill stem tension-torsion soft-string model is generated on the basic of well track parameters, drilling assembly parameters, coefficients of friction resistance, mud performance parameters and drill stem mechanical property parameters; a stick-slip vibration drill stem transfer matrix and an axial vibration drill stem transfer matrix are calculated according to the Newton motion equation and the drill stem tension-torsion soft-string model; the stick-slip vibration resonant frequency of the drill stem and the axial vibration resonant frequency of the drill stem are calculated according to the stick-slip vibration drill stem transfer matrix and the axial vibration drill stem transfer matrix; the vibration strength index of stick-slip vibration of a drill bit is generated according to the stick-slip vibration resonant frequency of the drill stem, the real-time well mouth rotation speed, the well mouth torque fluctuation and the stick-slip vibration drill stem transfer matrix; and the vibration strength index of axial vibration of the drill bit is generated according to the axial vibration resonant frequency of the drill stem, the real-time drilling pressure, the well mouth hanging load fluctuation and the axial vibration drill stem transfer matrix. By means of the method, the downhole vibration amplitude can be judged visually and quantificationally.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
Non-invasive fluid density and viscosity measurement
ActiveUS8166801B2Maintain integrityFlow propertiesSpecific gravity measurementNon invasiveVibrational resonance
The noninvasively measurement of the density and viscosity of static or flowing fluids in a section of pipe such that the pipe performs as the sensing apparatus, is described. Measurement of a suitable structural vibration resonance frequency of the pipe and the width of this resonance permits the density and viscosity to be determined, respectively. The viscosity may also be measured by monitoring the decay in time of a vibration resonance in the pipe.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
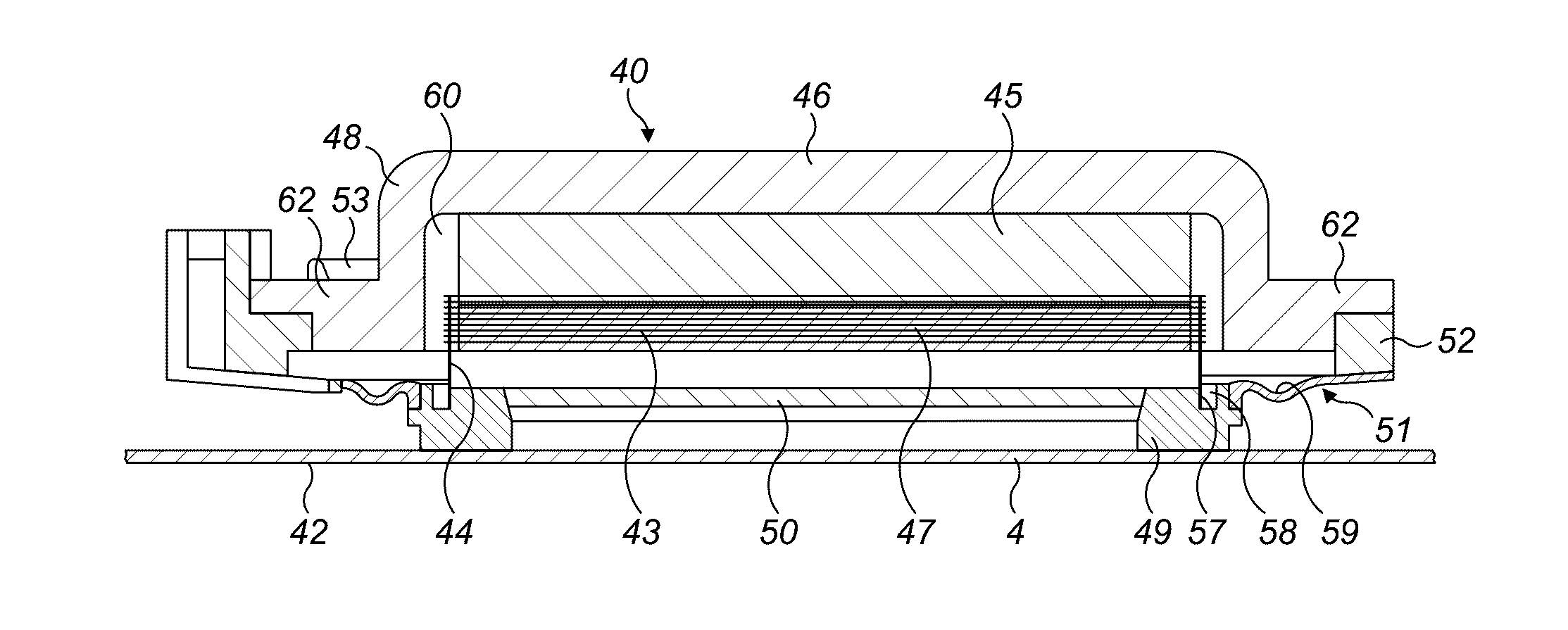
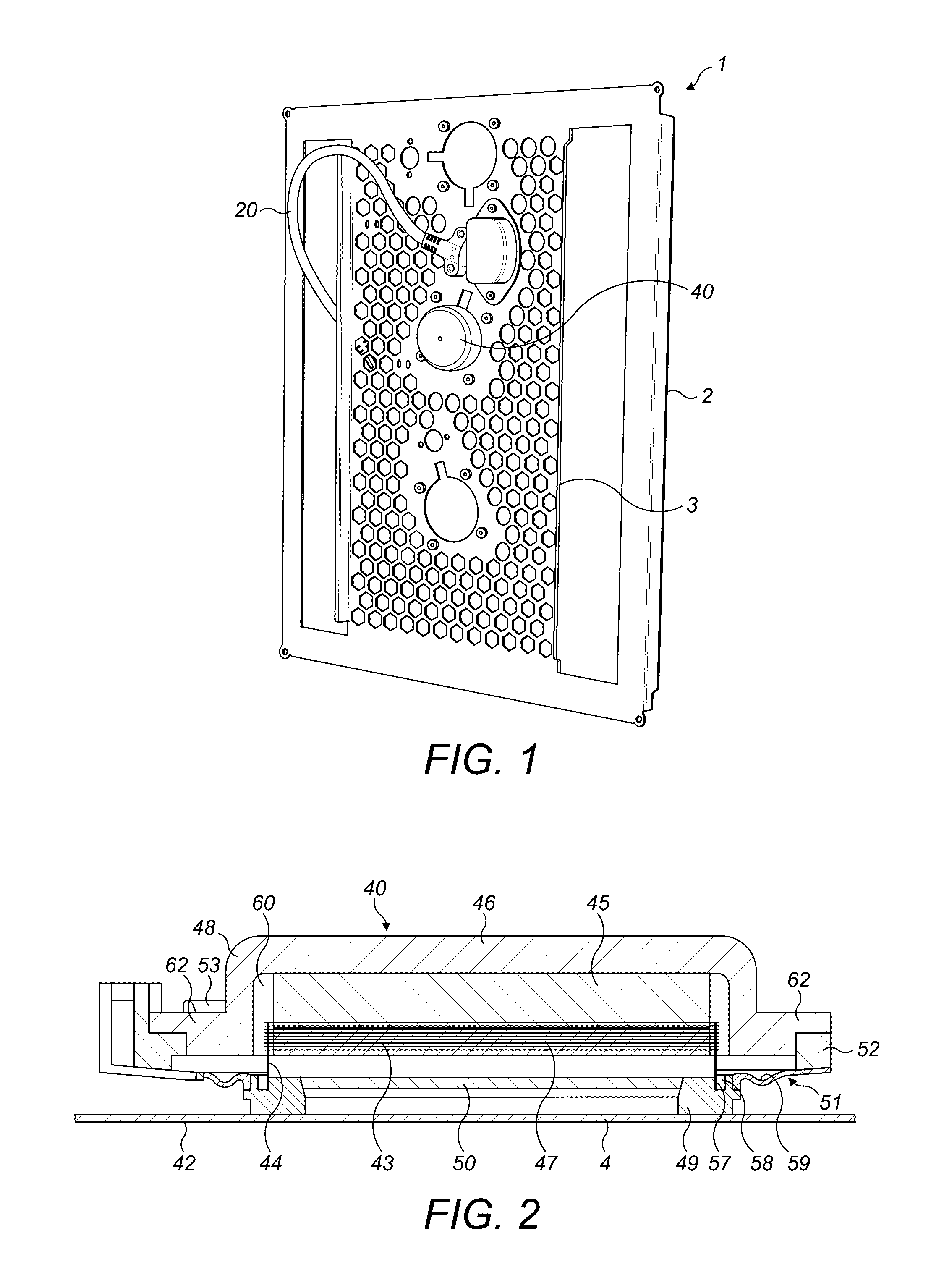
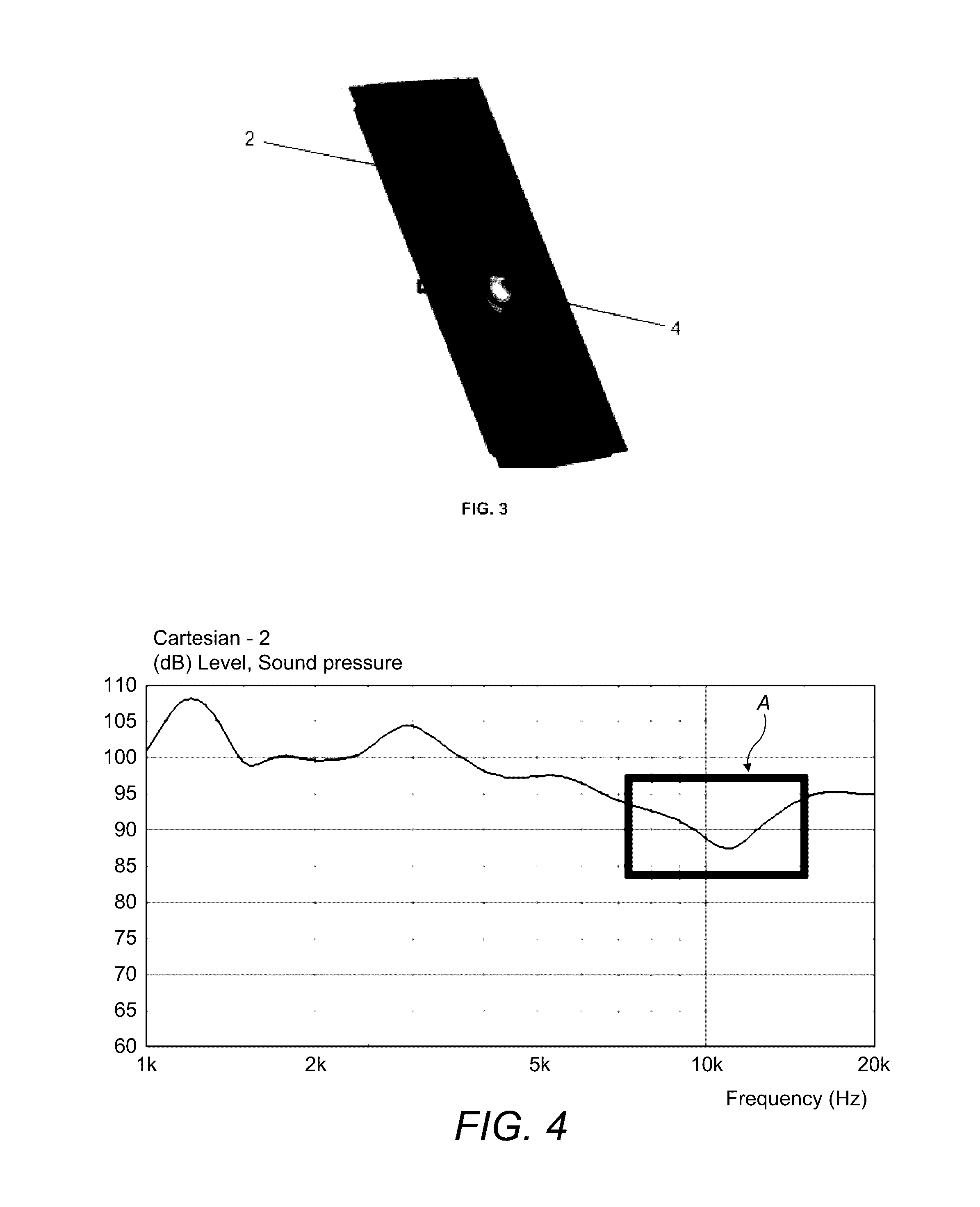
Distributed mode louspeaker damping oscillations within exciter feet
ActiveUS20160360313A1Improve performanceIncrease amplitudeBending wave transducersDiaphragm dampingEngineeringLoudspeaker
There is provided a flat panel loudspeaker comprising a resonant panel, an exciter comprising a foot generally cylindrical in shape, coupled to the resonant panel and defining an inner region of the resonant panel. The exciter is drivable to vibrate the resonant panel via the foot, whereby to produce a sound. A stiffness of the resonant panel in the inner region is greater than a stiffness of the resonant panel in a region of the resonant panel outside the inner region. Additionally or alternatively, the flat panel loudspeaker further comprises a damping member in contact with the inner region of the resonant panel and arranged inside the foot to generally brace against the vibration of the resonant panel so as to damp a response of the resonant panel in the inner region to a vibration from the exciter.
Owner:AMINA TECH
Steel automotive drive shaft with carbon fiber liner
A new and improved composite rotary steel drive shaft comprises a radially outer steel tubular member and a radially inner carbon fiber tubular liner which is adhesively bonded upon the inner peripheral wall surface of the radially outer steel tubular member wherein the carbon fiber tubular liner is characterized by or exhibits a relatively high modulus of elasticity. As a result of the adhesive bonding of the radially inner carbon fiber tubular liner upon the inner peripheral wall surface of the radially outer steel tubular member, the torsional stiffness properties of the resulting composite rotary steel drive shaft are dramatically increased to such a degree that high-performance, high-speed rotary operation of the same, within the range of ten thousand revolutions per minute (10,000 RPM), is enabled without the composite rotary drive shaft experiencing any undesirable deflections, or any detrimental vibrational resonance, as has been characteristic of conventional rotary drive shafts. In addition, in view of the fact that the radially outer member of the composite rotary steel drive shaft comprises a radially outer steel tubular member, the resulting composite rotary steel drive shaft is considered to be a steel rotary drive shaft and is therefore acceptable to, and is able to be sanctioned by various professional automotive racing authorities.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
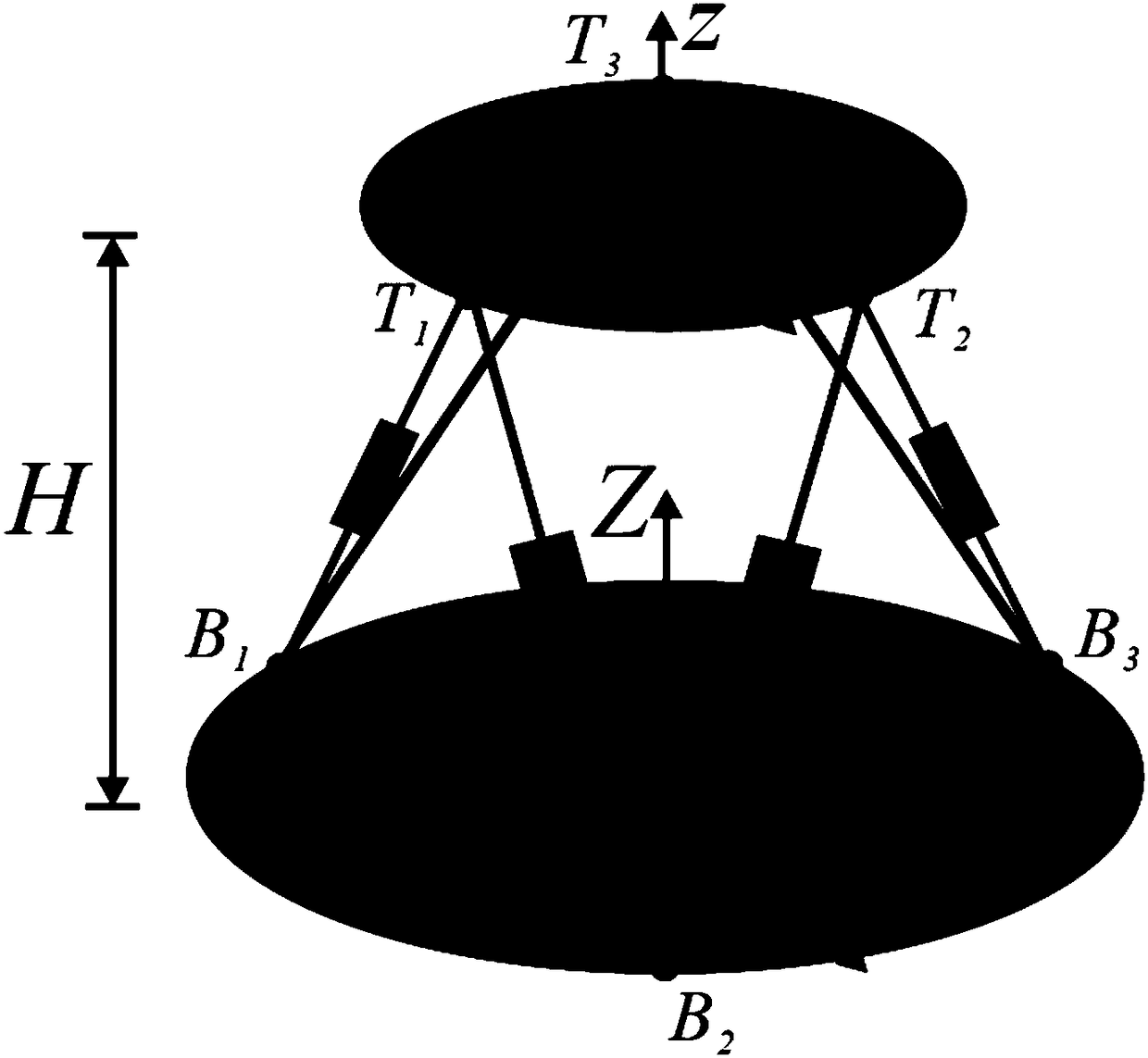
Six-degree-of-freedom ultralow frequency vibration isolation device based on zero stiffness system and control system thereof
ActiveCN108253084ASolve Vibration ProblemsSolve the impactNon-rotating vibration suppressionControl systemNon linear dynamic
The invention discloses a six-degree-of-freedom ultralow frequency vibration isolation device based on a zero stiffness system and a control system thereof, and relates to the fields of multi-degree-of-freedom low frequency, ultralow frequency and even zero-frequency vibration isolation and micro vibration simulation experiments. The six-degree-of-freedom ultralow frequency vibration isolation device based on the zero stiffness system is formed by connecting a supporting platform, a basic platform and a vibration isolation module. The vibration isolation module comprises an upper connecting rod, a lower connecting rod, a columnar shell, a vertical spring, a horizontal spring and a connecting assembly between the springs. The upper end of the upper connecting rod is connected with the supporting platform. The lower end of the upper connecting rod penetrates through an upper end cover of the columnar shell and is connected with the connecting assembly between the springs. The upper end of the lower connecting rod is fixedly connected with a lower end cover of the columnar shell. The lower end of the lower connecting rod is connected with the basic platform. The vibration isolation module meets the characteristic of zero stiffness. In combination with a gravity environment self-adapting control system, an isolated object is in a suspended state. Low frequency, ultralow frequency and even zero-frequency full-band vibration immune and isolation performance can be realized, and the problem of the multicoupling technique of multi-degree-of-freedom ultralow frequency, vibration resonance and non-linear dynamics is solved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
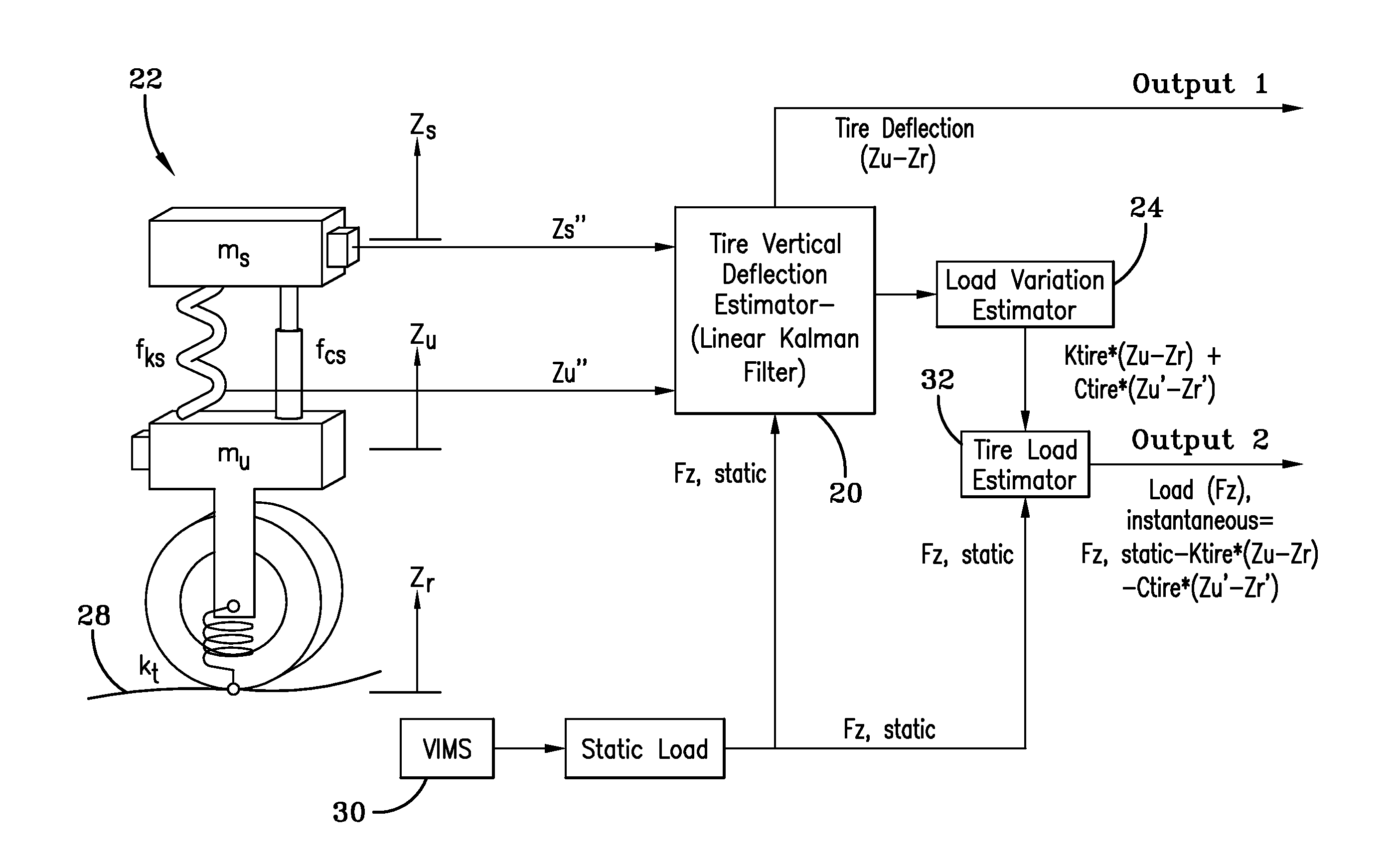
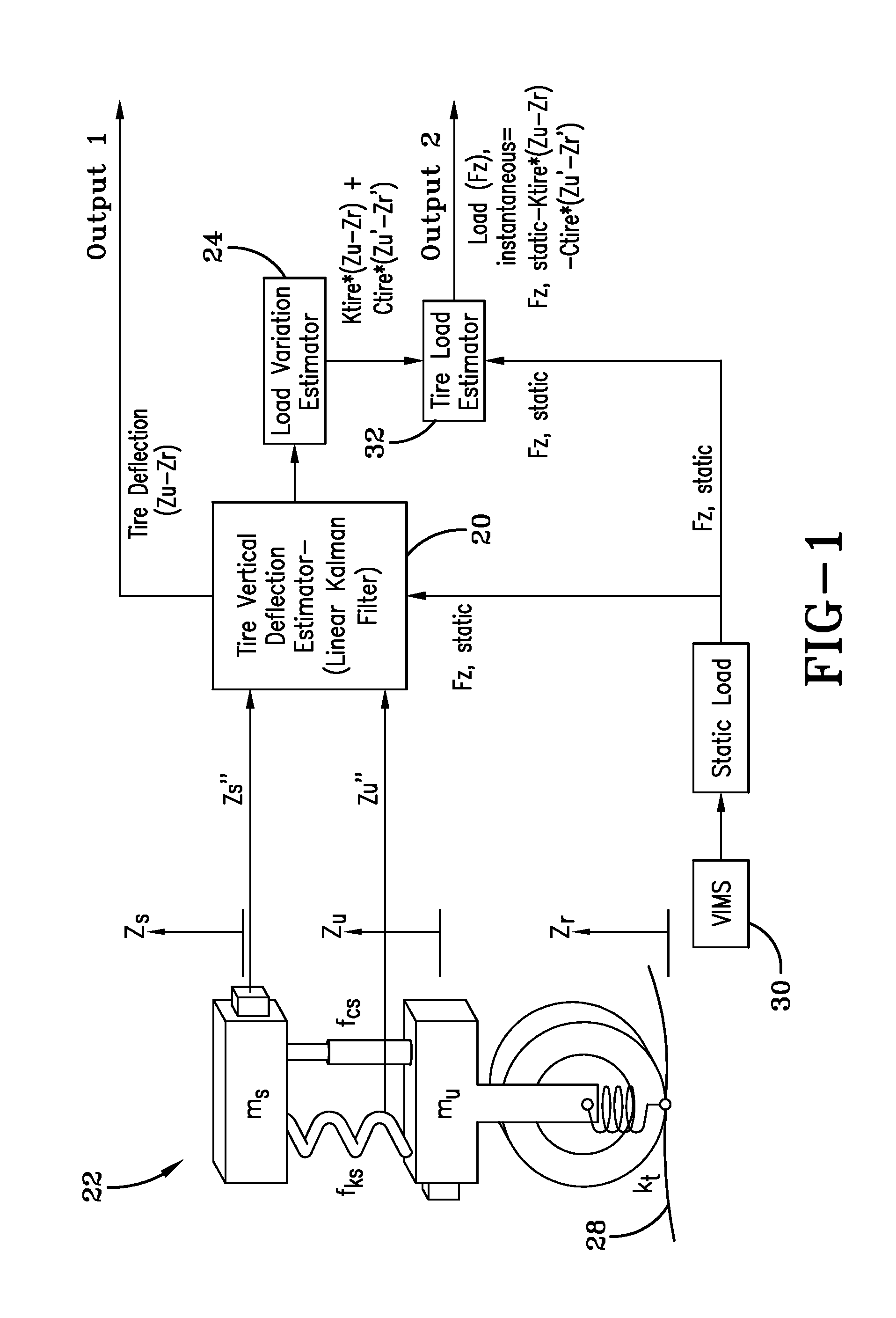
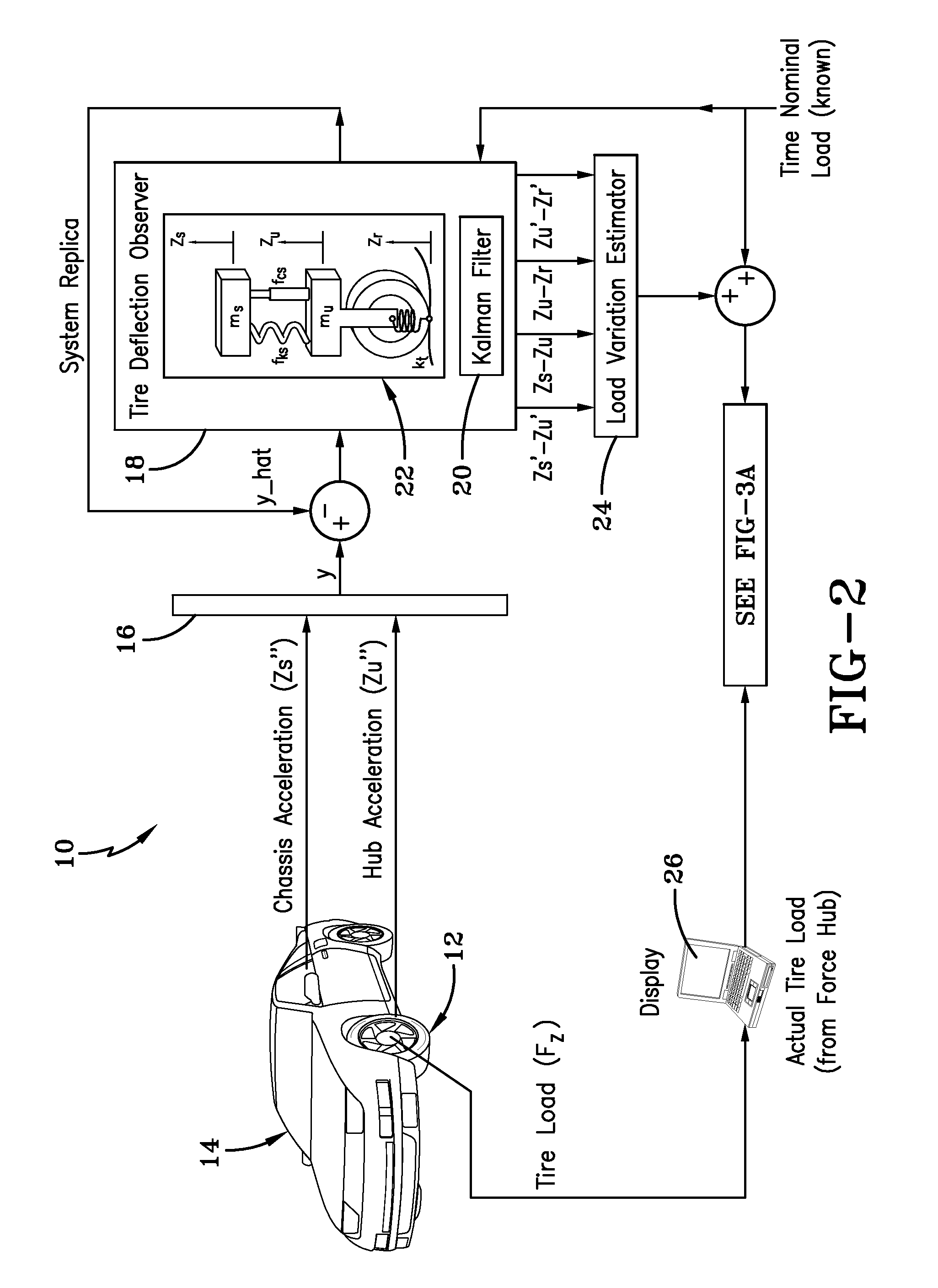
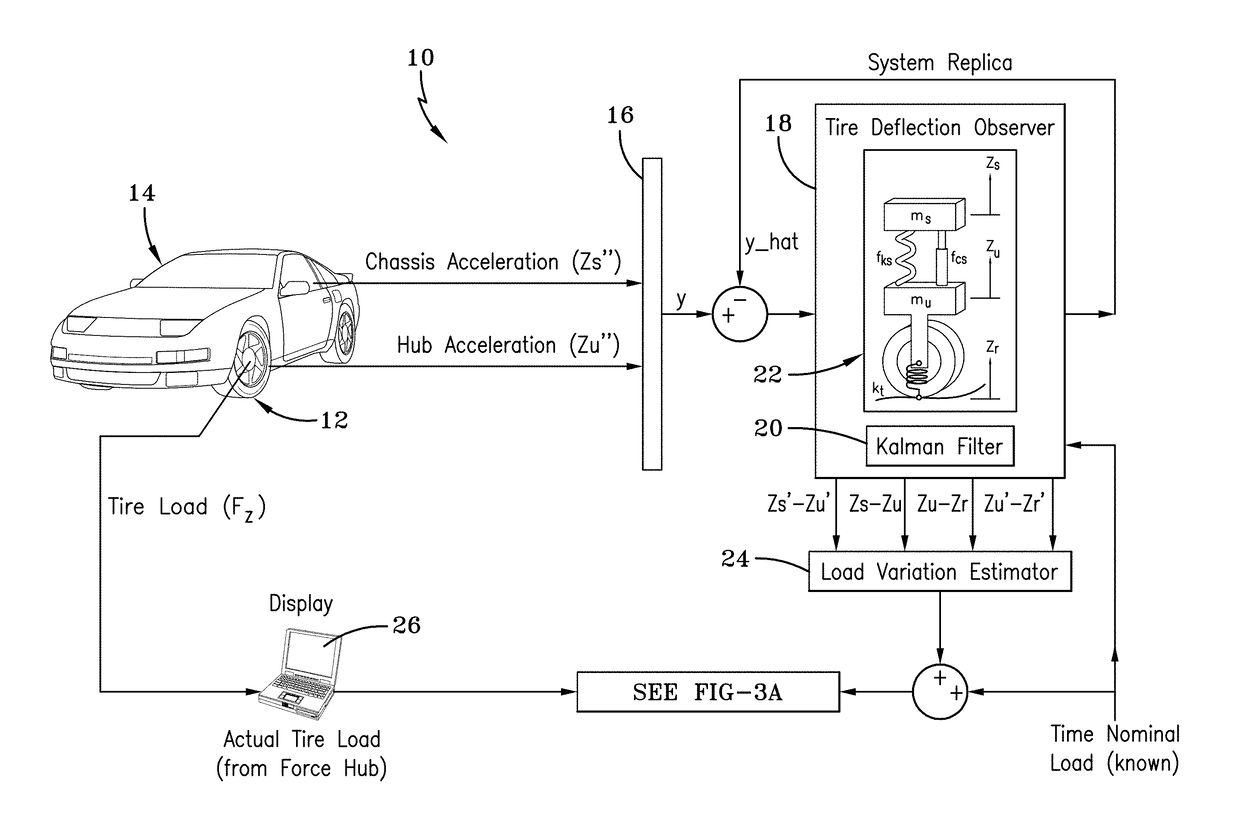
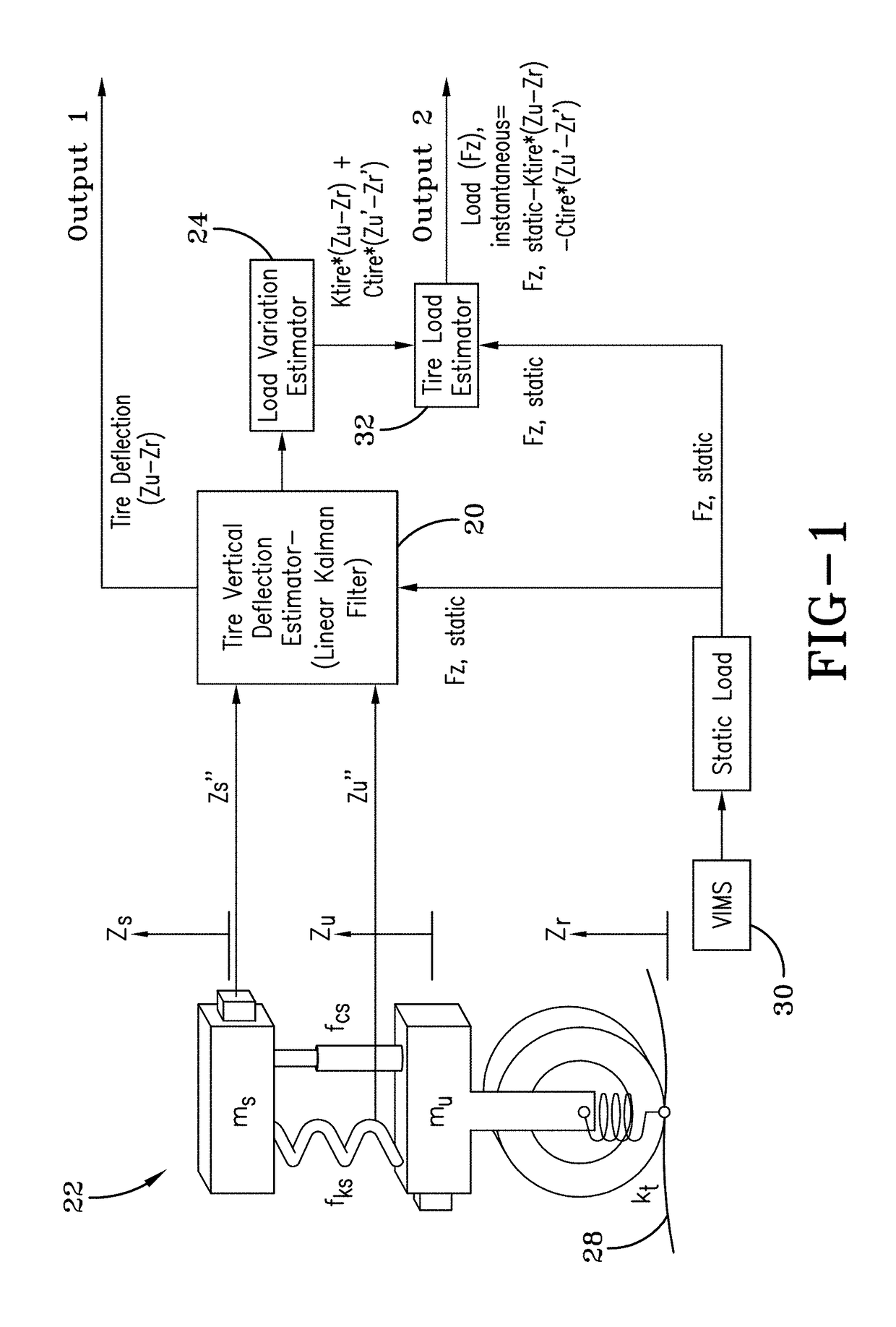
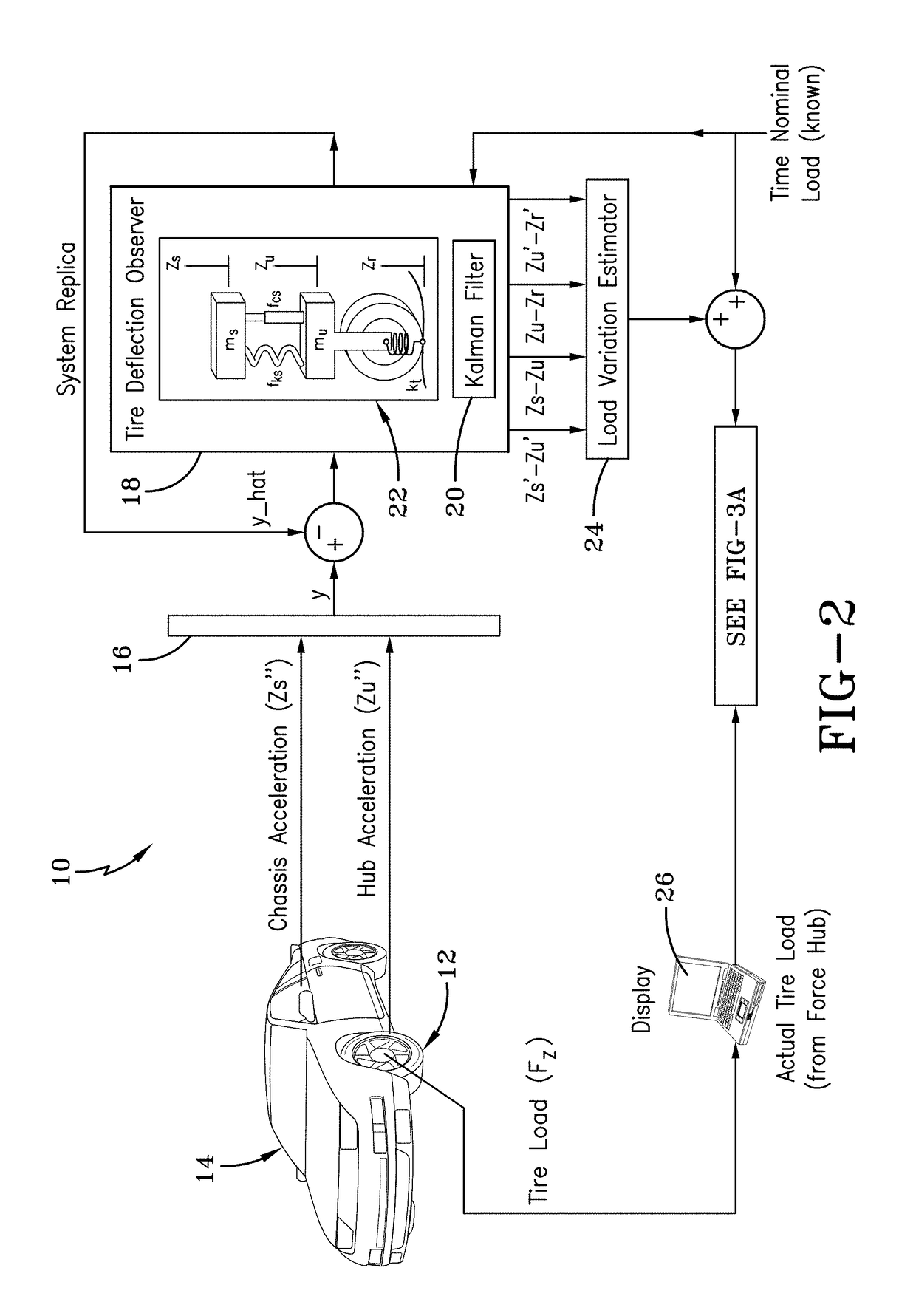
Vehicle loading condition detection system and method
A system and method estimating a vehicle tire load identifies a change in vehicle loading condition by measuring vibration resonant frequency peaks (bounce mode and / or pitch mode) of the unsprung mass. Signals required include the chassis vertical acceleration and / or chassis pitch rate obtained from commercially available sensors mounted to the vehicle. An observer model receives the inertial signal(s) and generates a dynamic load estimation based upon observed frequency change in the sprung mass natural frequency.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Controlling surface chemistry on solid substrates
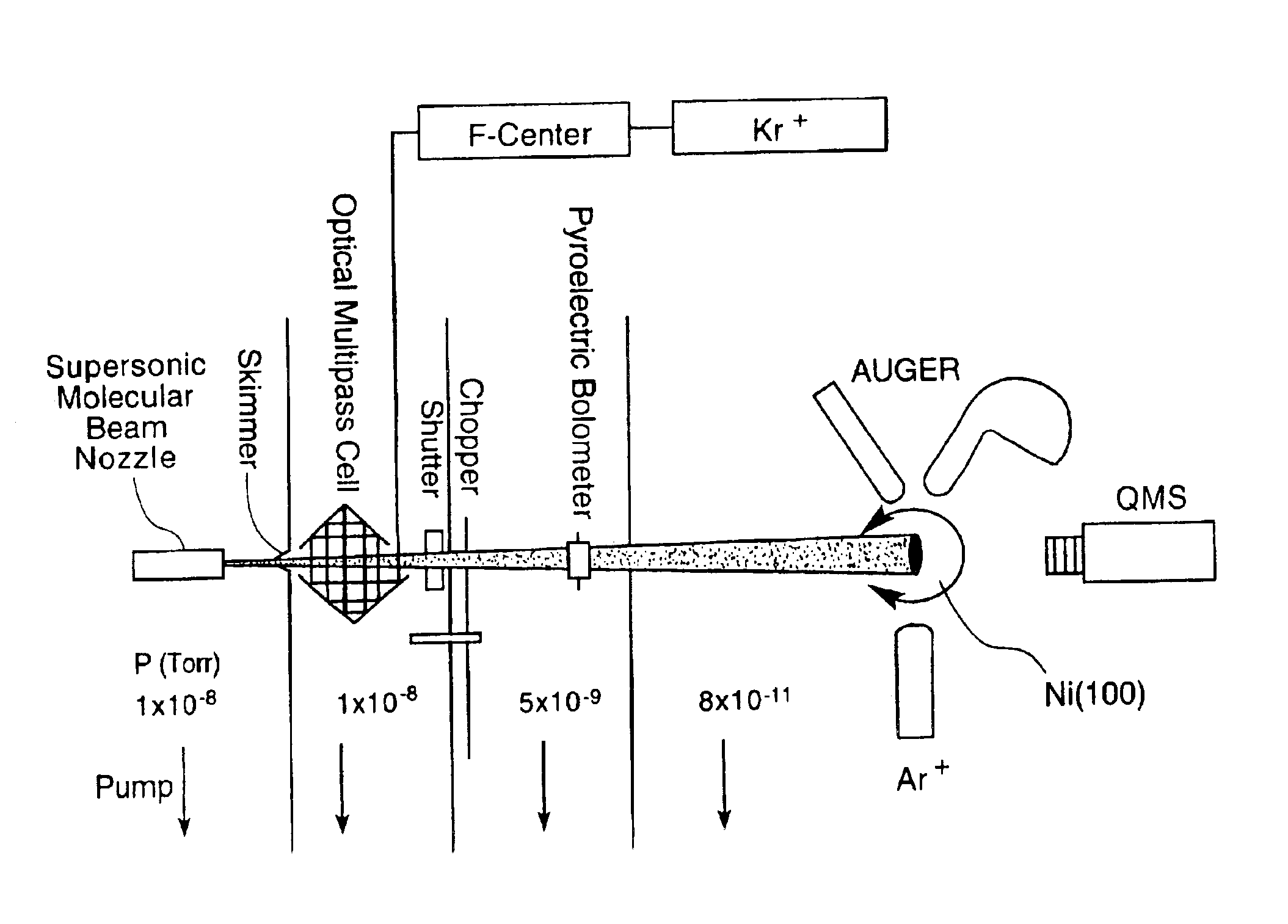
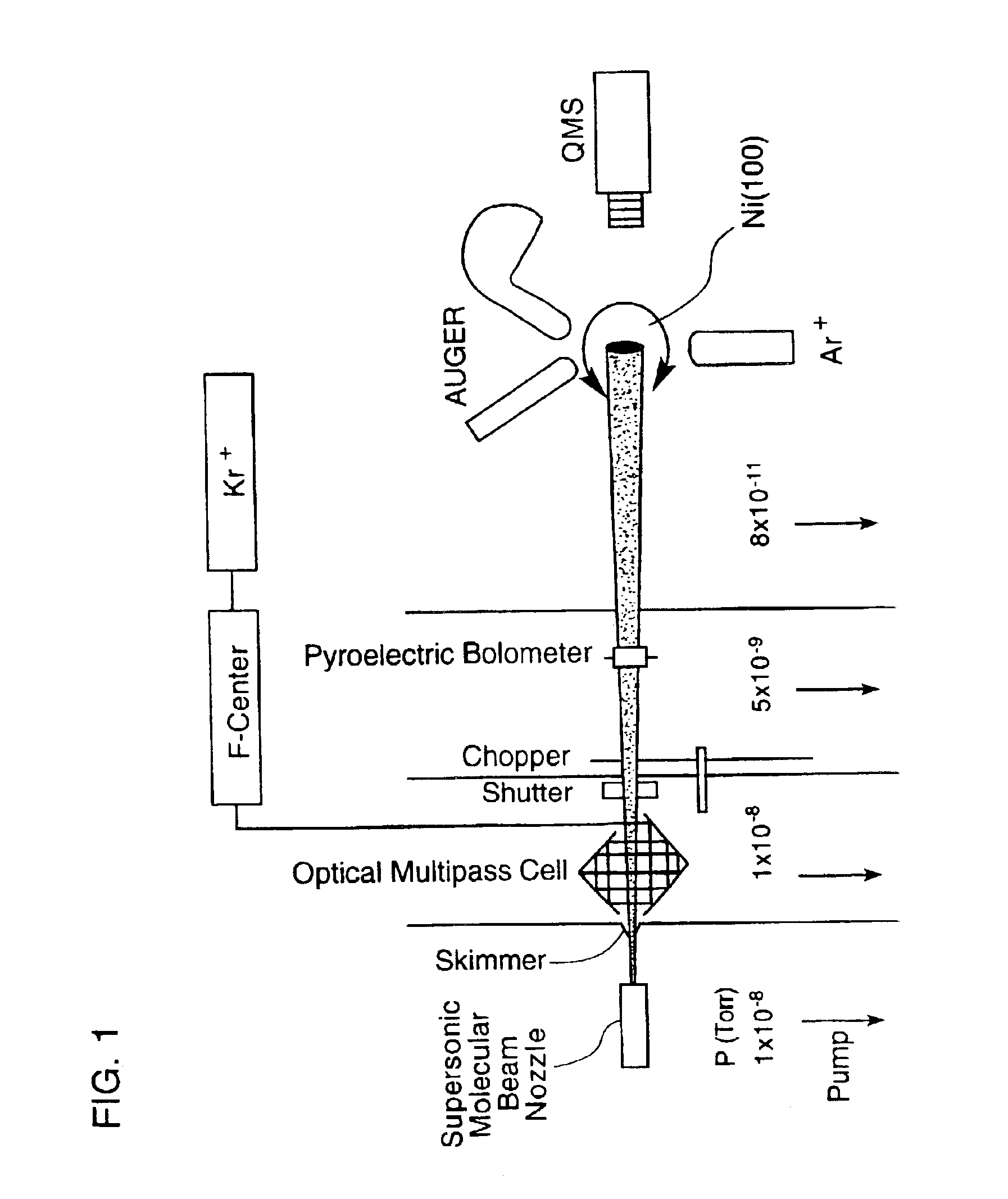
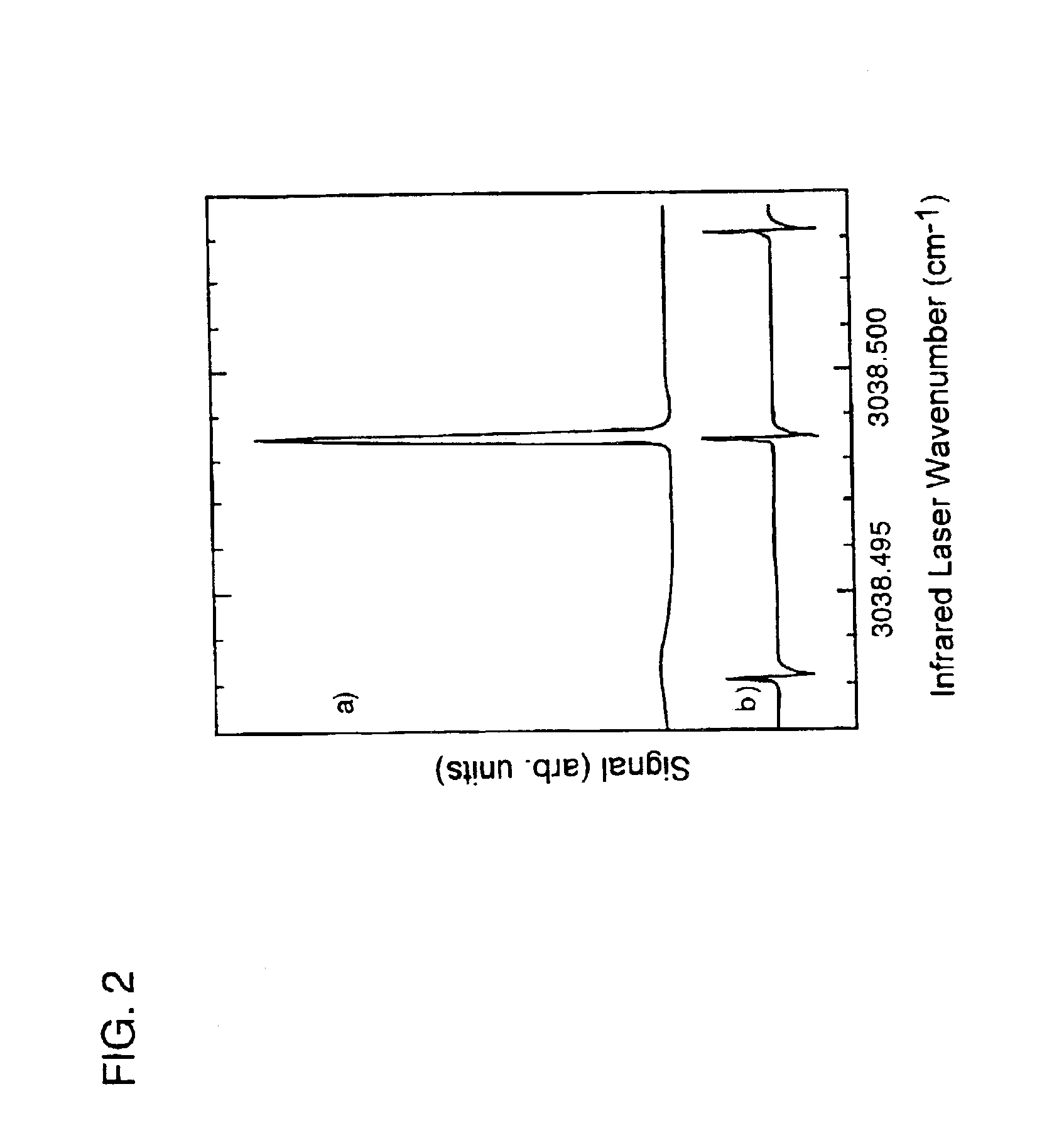
InactiveUS6951827B2Avoid low surface temperaturesReduce needPolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsSolid substrateLaser beams
By exposing precursor molecules traveling in a molecular beam to a narrow bandwidth laser beam (hu) tuned to a vibrational resonance frequency of the molecules and aimed orthogonal to the molecular beam (FIG. 6A), only those molecules having velocity (va) along trajectory (A) orthogonal to the laser beam are excited, becoming several orders of magnitude more reactive, affording a high degree of control over precise locations of reactions of molecules. Controlling a reaction on a surface of a solid substrate, includes; (a) obtaining a precursor molecule that includes (or can be reacted to form) species to be reacted with the substrate; (b) creating a molecular beam (eg., supersonic) that includes the precursor molecule; (c) vibrationally exciting the molecule with the laser beam tuned to a vibrational resonance frequency of the molecule; and (d) causing the exciting molecule to impinge on the substrate, enabling reactions (deposition, etching . . . ) of the species with the substrate.
Owner:TUFTS UNIV
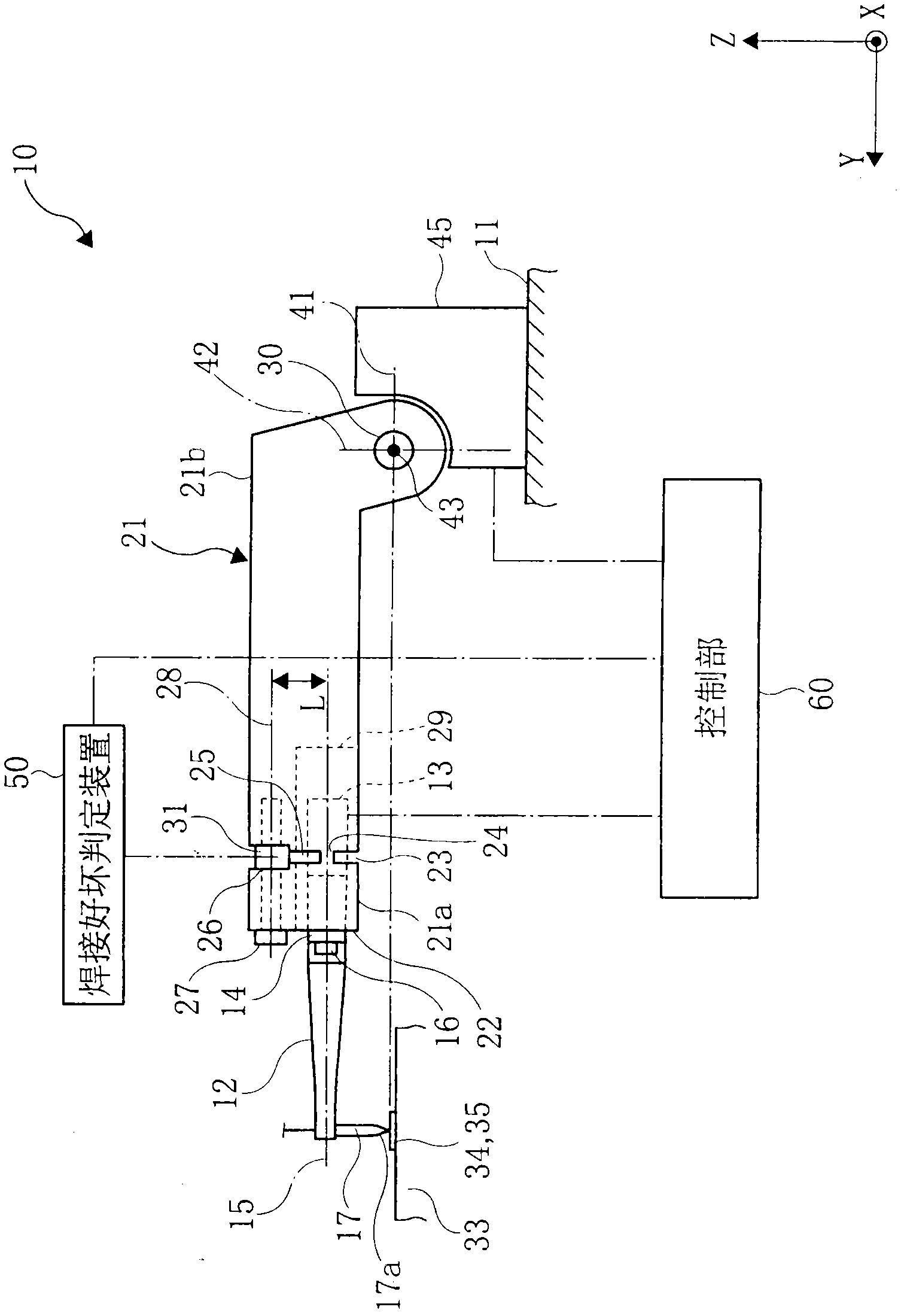
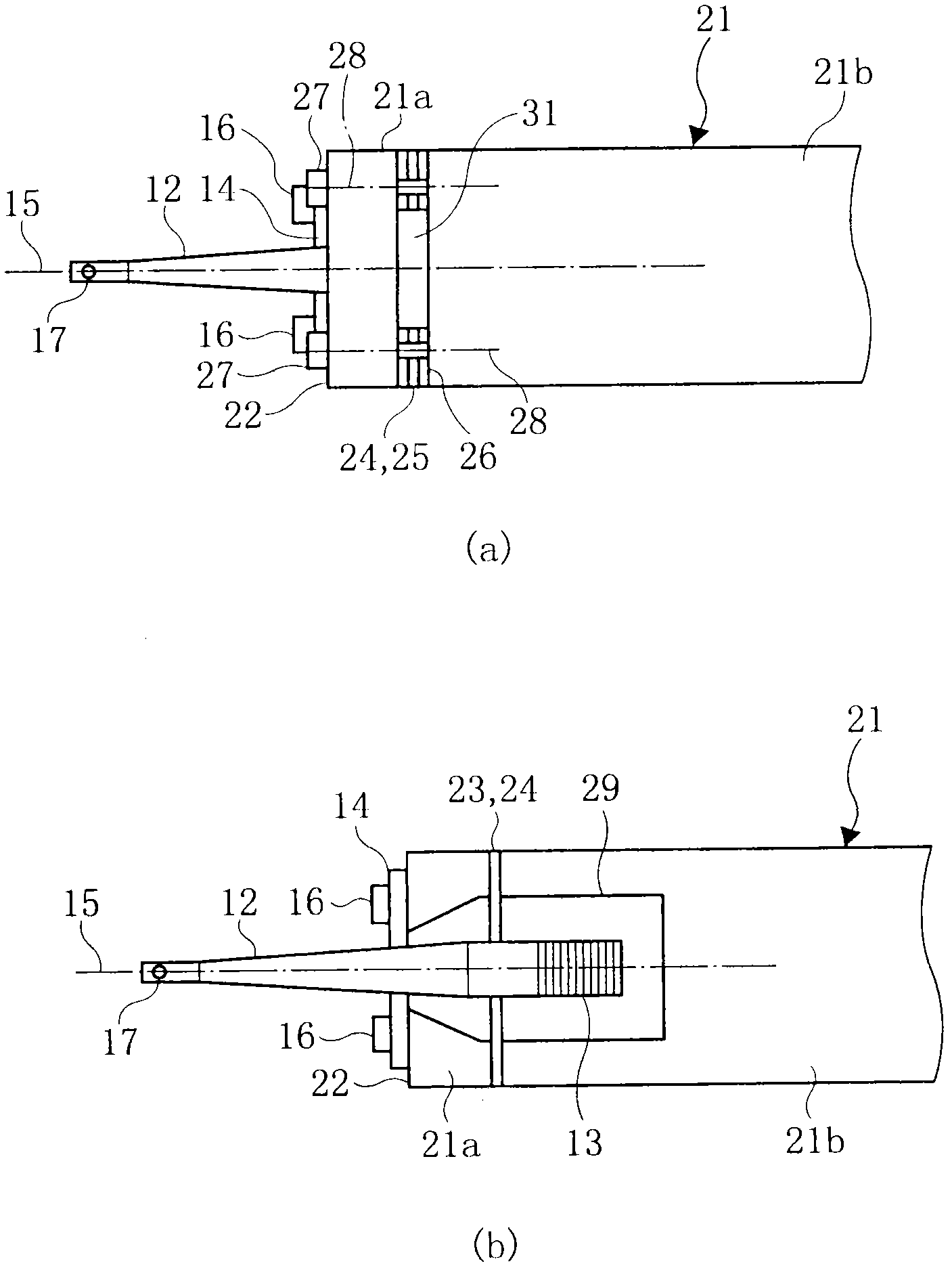
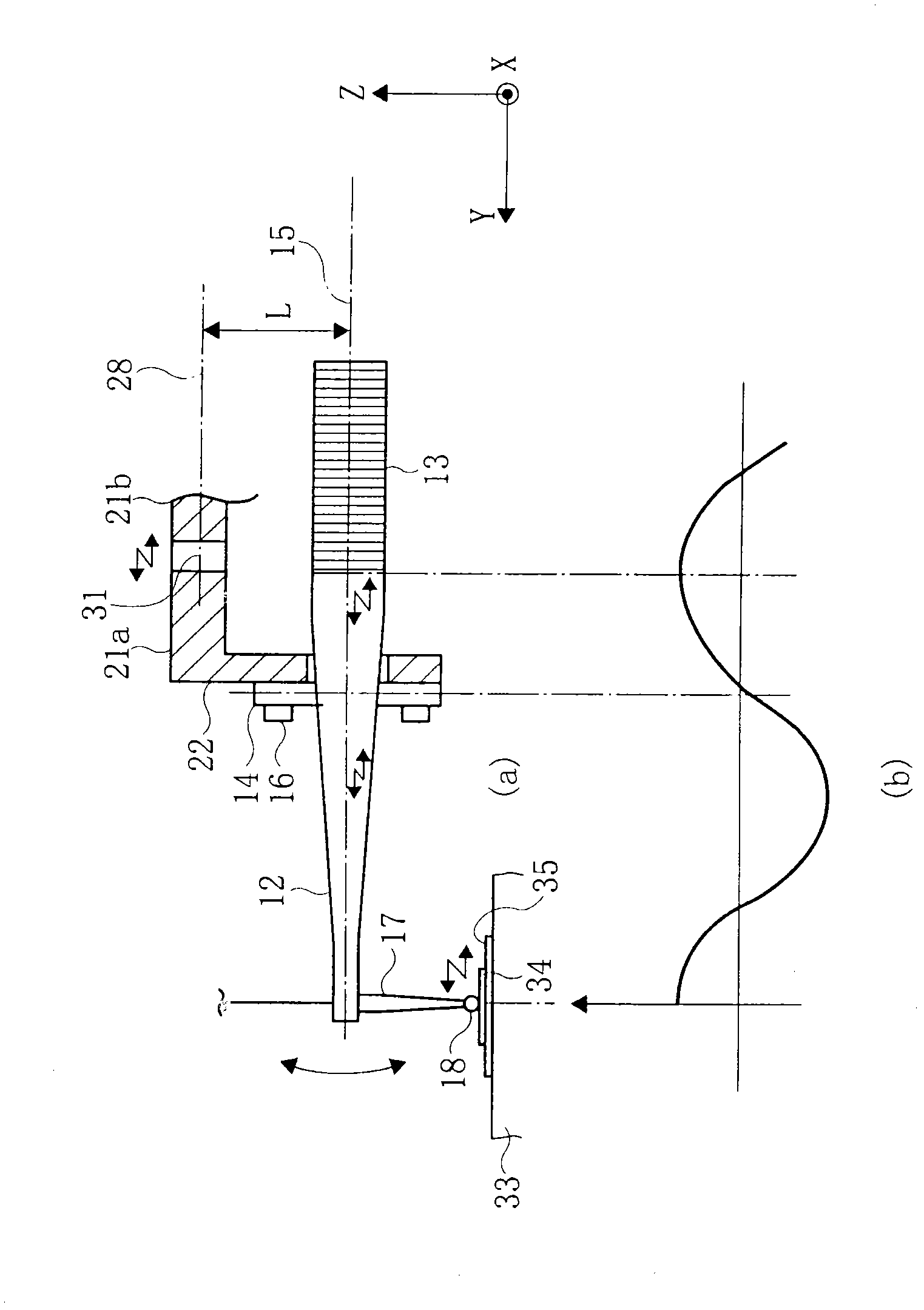
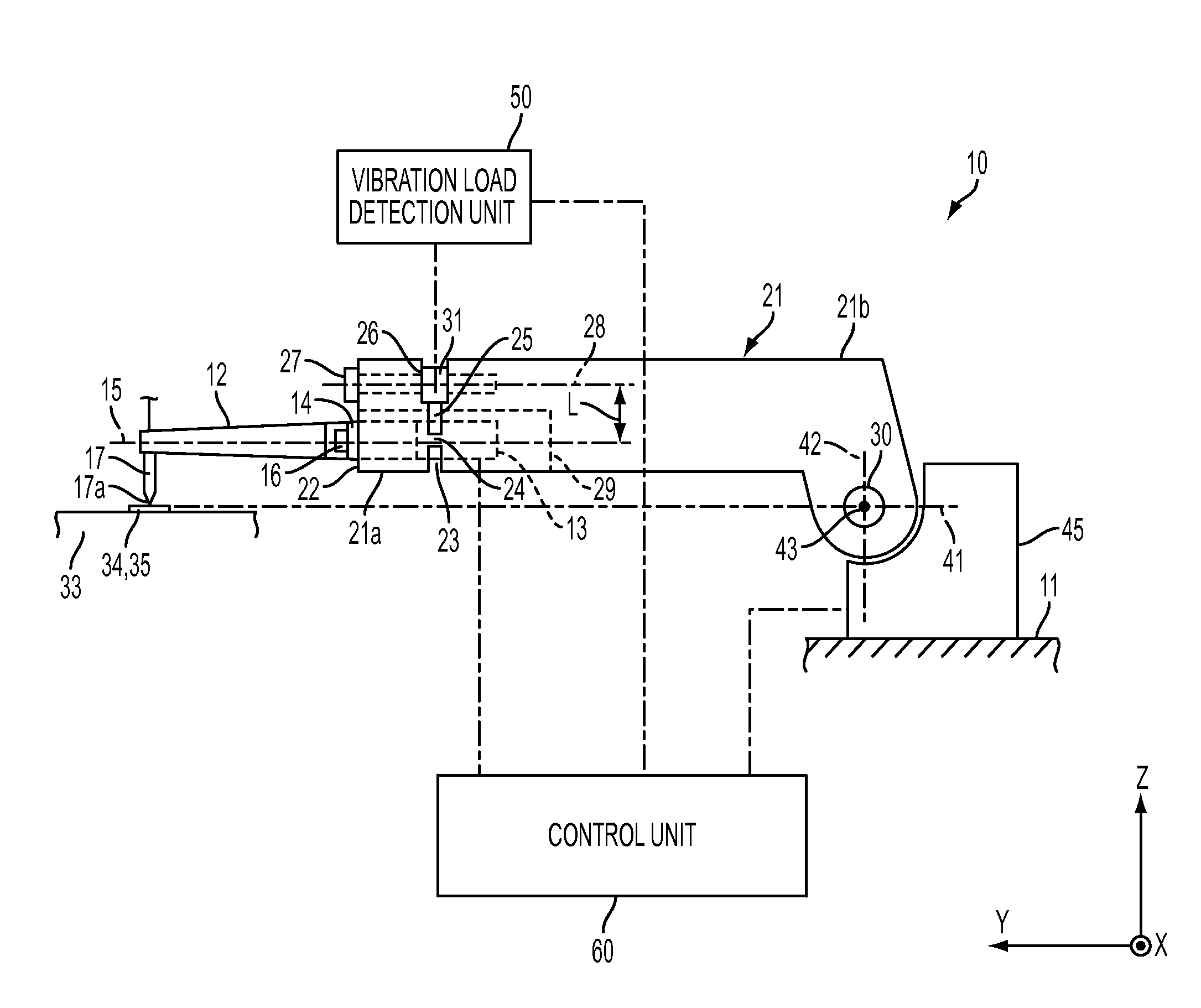
Method for judging pass/fail of bonding, apparatus for judging pass/fail of bonding, and bonding apparatus
ActiveCN102099903ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringLongitudinal vibration
An apparatus for judging pass / fail of bonding for a bonding apparatus comprises an ultrasonic horn performing longitudinal vibration in the direction of the central axis by resonating with the vibration of an ultrasonic vibrator; a capillary fixed to the antinode of vibration of the ultrasonic horn; a flange provided at the node of vibration of the ultrasonic horn; a bonding arm; and a load sensor fixed between the center of rotation of the bonding arm and the flange fixing surface while being offset in the direction approaching to and receding from a bonding object from the central axis of the ultrasonic horn in the longitudinal direction. The load sensor continuously detects the load applied to a bonding tool in the direction approaching to and receding from the bonding object at the time of bonding, the maximum value of detected load is set as an impact load and then pass / fail judgment is made on bonding based on the impact load. Consequently, the pass / fail judgment is made on bonding while bonding is being performed.
Owner:SHINKAWA CO LTD
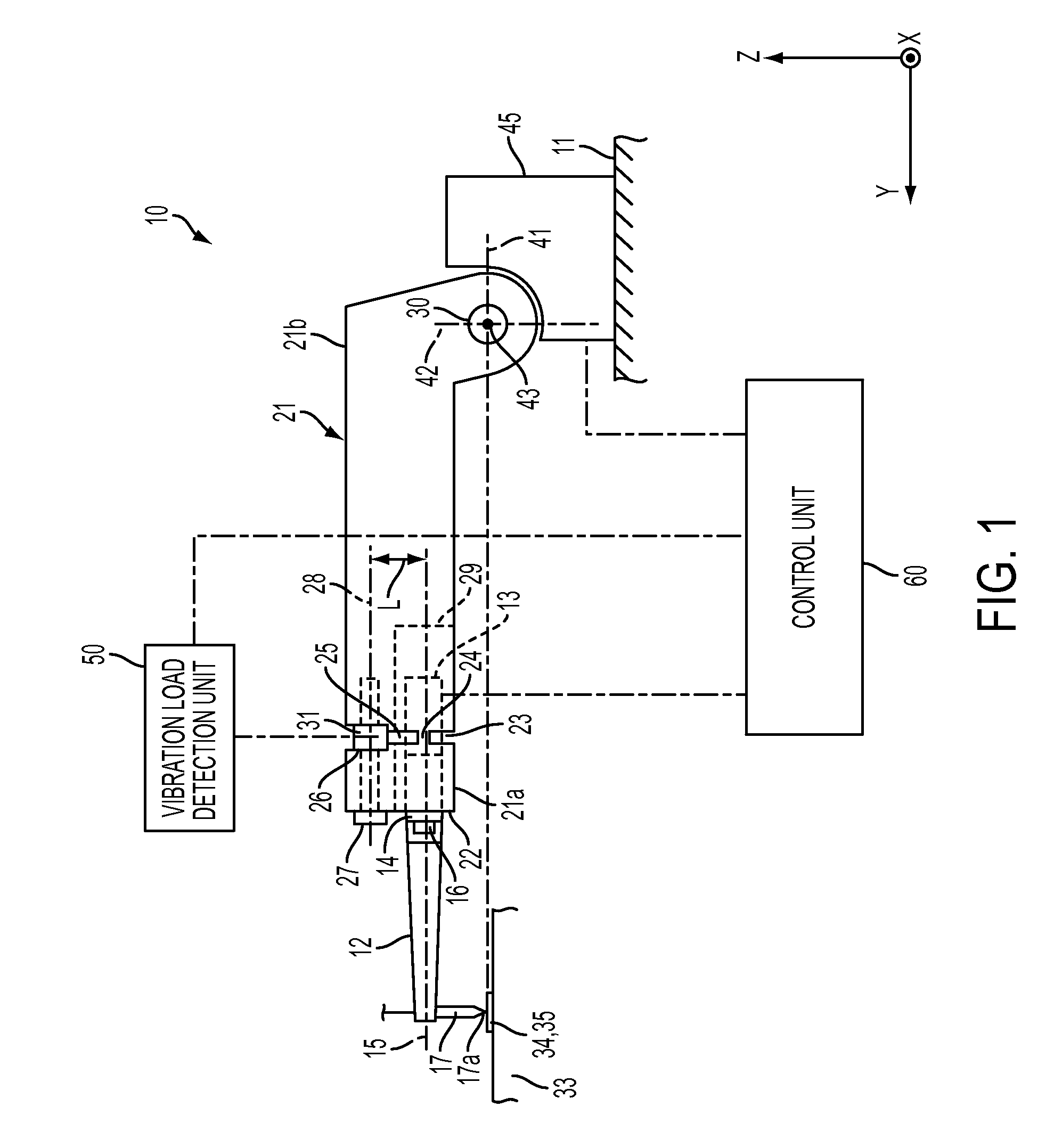
Bonding apparatus
ActiveUS20110155789A1Simple structureWelding/cutting auxillary devicesSolid-state devicesCentre of rotationUltrasound
A bonding apparatus includes an ultrasonic horn configured to vibrate longitudinally in resonance with the vibration of an ultrasonic vibrator; a capillary attached at an anti-node of the vibration of the ultrasonic horn; a flange provided at a node of the vibration of the ultrasonic horn; a bonding arm; a load sensor attached between the center of rotation of the bonding arm and a flange mounting surface; and a vibration load detection unit for extracting a signal obtained by causing a signal that is detected with the load sensor to pass a signal within a frequency range around the vibrational frequency of the ultrasonic vibrator through a band-pass filter, whereby the bonding apparatus can detect the vibration load at a tip end of the capillary in the direction along the central axis of the ultrasonic horn with a simple structure.
Owner:SHINKAWA CO LTD
Imaging devices having piezoelectric transceivers
ActiveUS20200225082A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorTransceiver
A micromachined ultrasonic transducer (MUT). The MUT includes: a substrate; a membrane suspending from the substrate; a bottom electrode disposed on the membrane; a piezoelectric layer disposed on the bottom electrode and an asymmetric top electrode is disposed on the piezoelectric layer. The areal density distribution of the asymmetric electrode along an axis has a plurality of local maxima, wherein locations of the plurality of local maxima coincide with locations where a plurality of anti-nodal points at a vibrational resonance frequency is located.
Owner:EXO IMAGING INC
Device and method for stimulated Raman detection
According to one aspect, the invention relates to a device for detecting a resonant non-linear optical signal of Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) type induced in a sample. The device comprises electro-optical means for making interact in the sample, at a first modulation frequency, trains of light pulses of angular frequencies ω1 and ω2 and, at a second modulation frequency, trains of light pulses of angular frequencies ω2 and ω3, such that ω2−ω1=ω3−ω2=ΩR where ΩR is a molecular vibrational resonant angular frequency of the sample. Moreover, the device comprises means for synchronous detection at the first and second modulation frequencies of non-linear optical signals resulting from the interaction of the light pulses in the sample, and electronic processing means making it possible to obtain, from electronic signals resulting from the synchronous detection, a signal characterizing the molecular vibrational resonance of the sample.
Owner:UNIV DAIX MARSEILLE +1
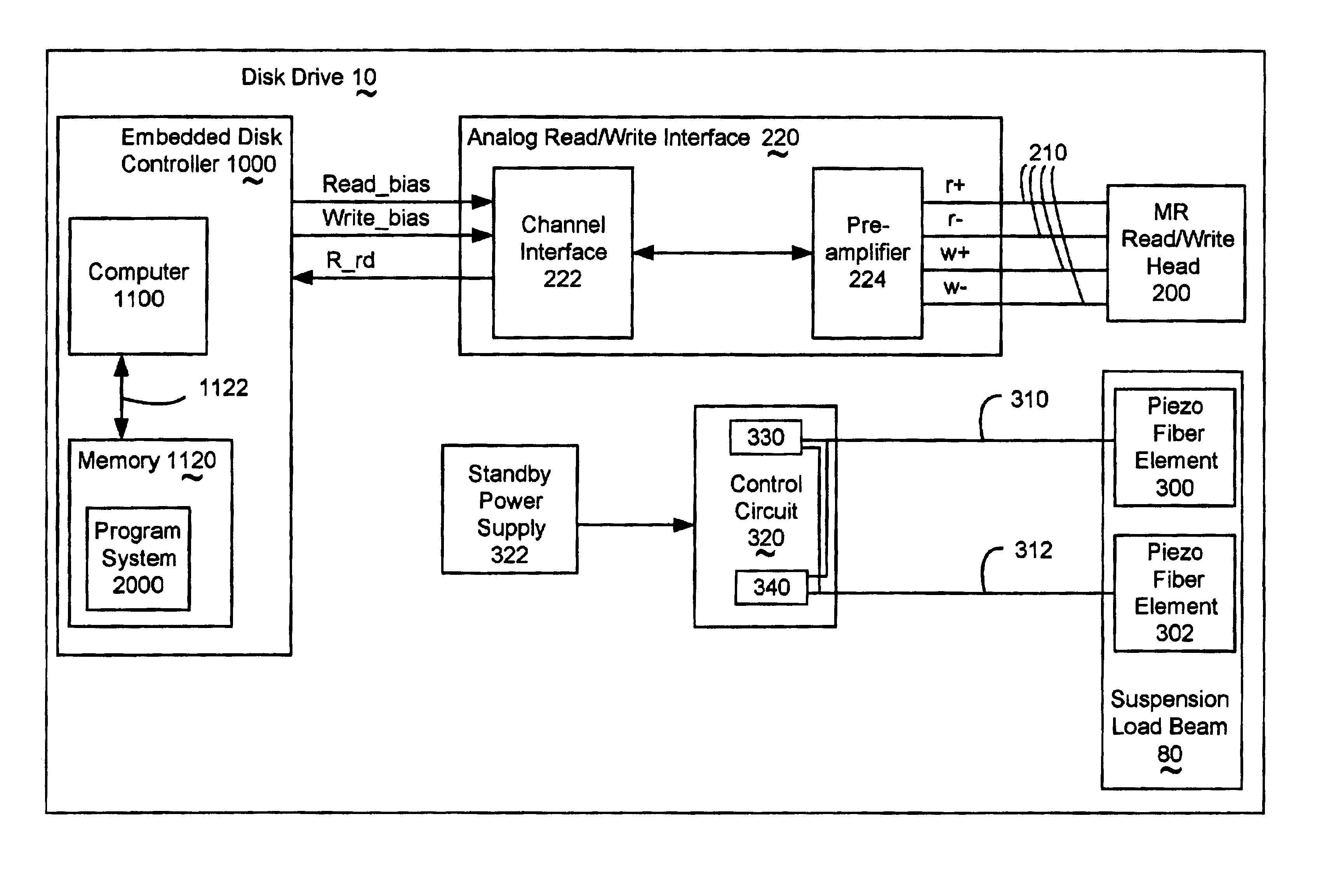
Method and apparatus actively damping mechanical vibration and shock in head suspensions of a disk drive
InactiveUS6909571B2Electrical connection between head and armTrack finding/aligningEngineeringVibrational resonance
The invention includes a method of attenuating resonance frequency modes in head suspensions, which does not significantly increase the weight of the head suspension. The invention provides a way to control the head deflection from the disk surface, which helps minimize damage from head slapping. The invention includes a basic head suspension infrastructure for which vibration resonance can be predictably controlled.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Imaging devices having piezoelectric transceivers
ActiveUS10648852B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorTransceiver
A micromachined ultrasonic transducer (MUT). The MUT includes: a substrate; a membrane suspending from the substrate; a bottom electrode disposed on the membrane; a piezoelectric layer disposed on the bottom electrode and an asymmetric top electrode is disposed on the piezoelectric layer. The areal density distribution of the asymmetric electrode along an axis has a plurality of local maxima, wherein locations of the plurality of local maxima coincide with locations where a plurality of anti-nodal points at a vibrational resonance frequency is located.
Owner:EXO IMAGING INC
Solid state surface catalysis reactor
InactiveCN1409651APhysical/chemical process catalystsEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesChemical reactionElectric generator
A method and apparatus to stimulate chemical reactions on a catalyst surface (116) using electricity, and the reverse process to convert energy released from chemical reactions into electricity. A reversible emitter (102) generates electrons which are injected into reactants on the catalyst surface (116), exciting chemically reactive vibrational resonances. Hot electrons created in the emitter region of a semiconductor junction (110) diffuse to the co-located collector region and catalyst surface (116). Catalyst clusters or films bonded on the collector surface transfer the hot electrons to or from the catalyst surface (116) having adsorbed reactants. The dimension of the catalyst-collector (104) is less than the energy mean free path of hot electrons. The hot electrons excite reactant vibrations before thermalizing with the substrate lattice thereby accelerating reactions. The hot electrons are also generated by the same reactions on a catalyst surface. The method and apparatus is reversible and may be operated as an electric generator using chemical reactions.
Owner:NEOKISMET L L C
Infrared Mueller matrix acquisition and preprocessing system and method
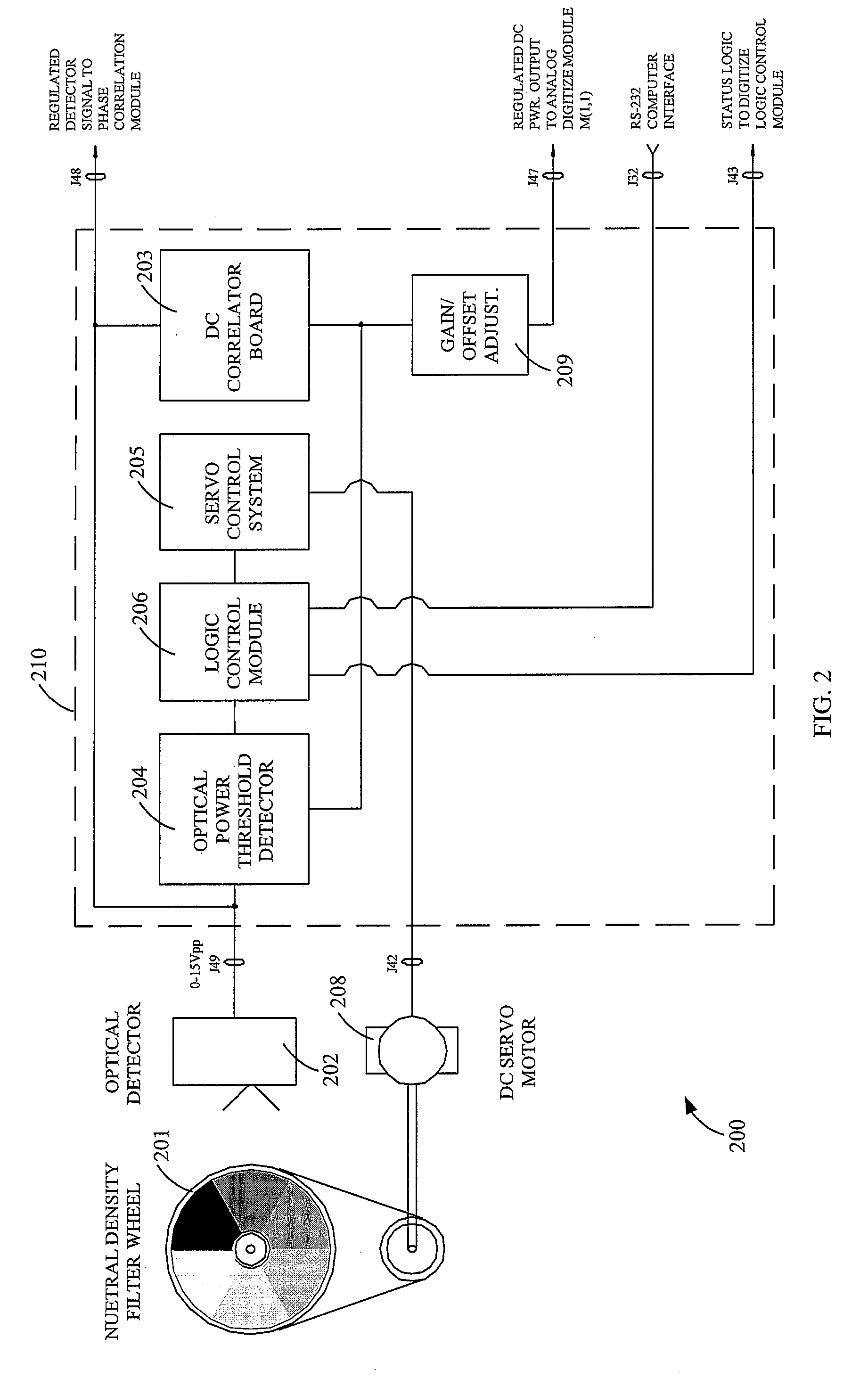
InactiveUS7737399B1Improve throughputRadiation pyrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesMiddle infraredData acquisition
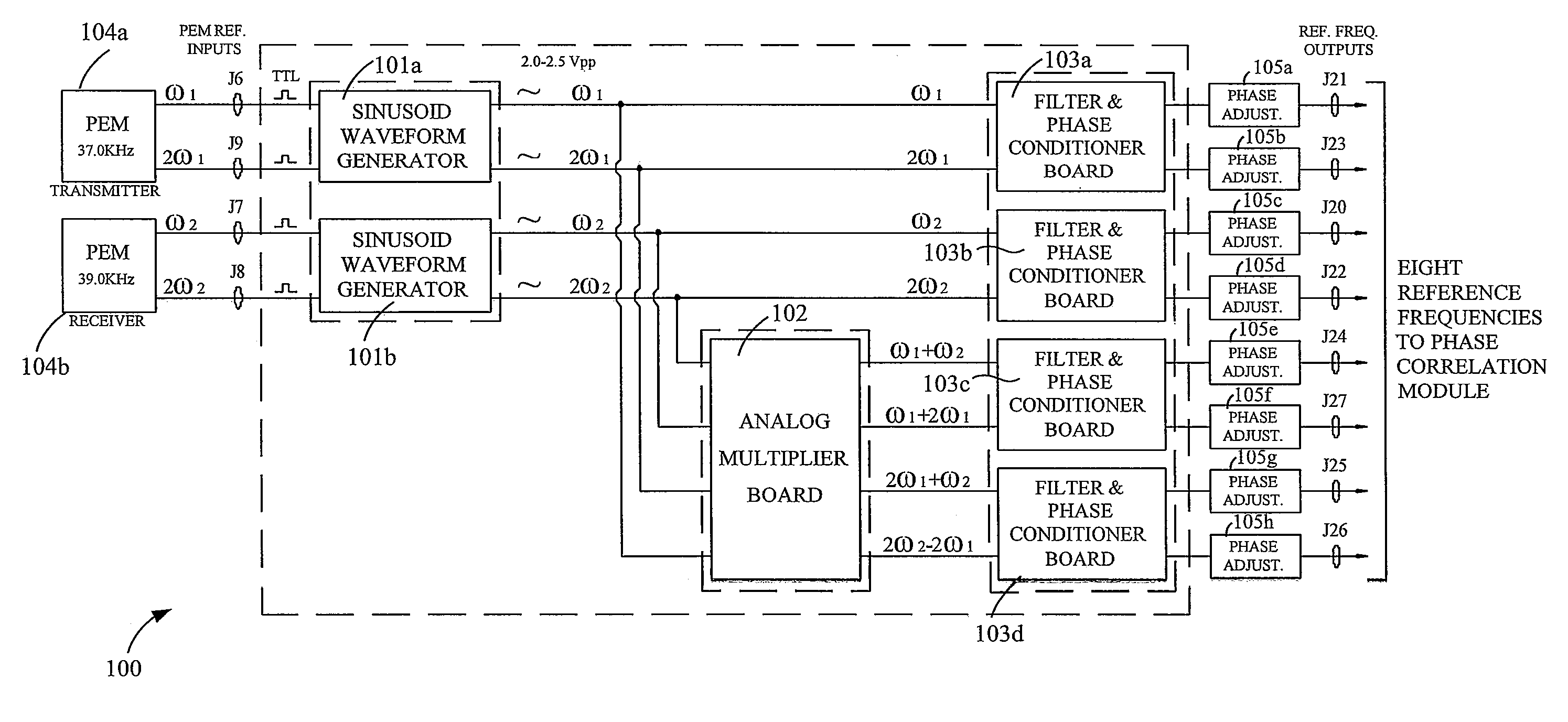
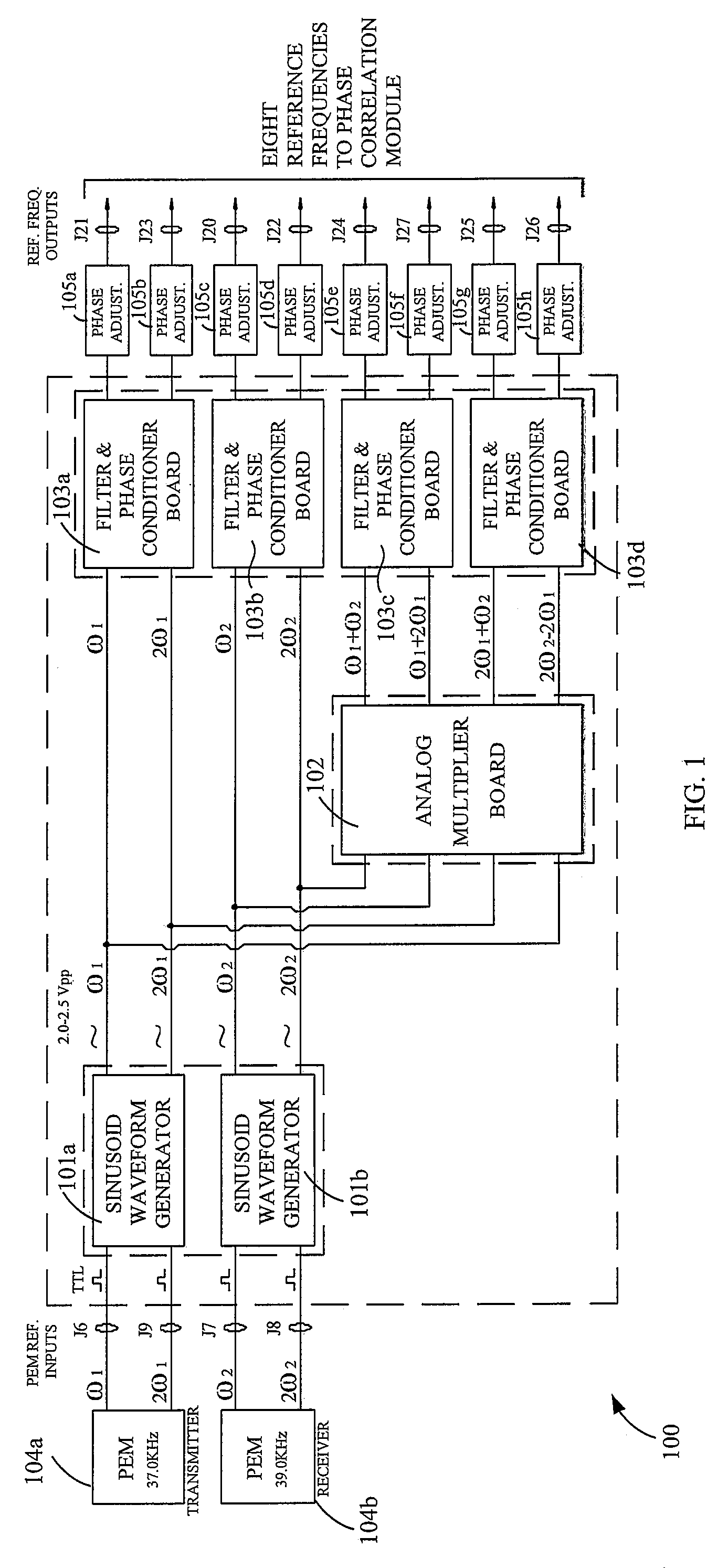
An analog Mueller matrix data acquisition system (AMMS) acquiring middle-infrared Mueller (M) matrices of backscattering surfaces. The M-elements are measured by means of an active photopolarimetric sensor. The AMMS records nine M-elements simultaneously in groups of four modulo 2 incident continuous-wave CO2 laser beams—one incident beam is tuned to a fundamental molecular absorption cross-section by the aerosol of detection interest (analytic wavelength λa) while the other beam is detuned off that resonance band (reference wavelength λr) and in the closest vicinity to λa. Accordingly, those ΔM elements exhibiting susceptible behavior to the aerosol analyte, driven on-then-off its molecular vibrational resonance band, cues an identification event thus providing detection decision information. The AMMS is comprised of PEM reference frequency synthesizer, optical power regulation, data digitizer, and computer interface components in an interfaced and integrated framework that governs all operations of M-elements production by the photopolarimetric sensor.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Recoilless speaker system
ActiveUS8201659B2Accurate and strong soundReduce vibrationTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsElectrical apparatus casings/cabinets/drawersMiniaturizationEngineering
The present invention provides a recoilless speaker system capable of reducing adversely affecting vibration and generating an accurate and strong sound, and contributing to the realization of lighter weight, miniaturization and lower cost related to manufacturing, and also capable of being installed in a suspended state and generating sound even under zero gravity as long as air exists.The present invention includes a symmetrical and tubular resonance wall and a pair of or two or more pairs of vibration units symmetrically arranged on both left and right sides of the resonance wall, where the vibration units that form a pair are configured to vibrate synchronously with each other, the resonance wall is made from a flexible material so as to resonate to the vibration, a sound absorbing member is arranged in a tubular form along the inner wall of the resonance wall, and vibration suppressing materials are held at the sound absorbing member and / or the vibration unit.
Owner:IMAI KAZUMICHI
Structural material with piezoelectric material particles
ActiveUS7411338B1Vibration measurement in solidsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesStructural health monitoringQuality control
A load-bearing structural member has a continuous structural material with piezoelectric material particles mixed in throughout. The structural material may be any of a variety of suitable materials, such as polymer materials, composite materials, ceramic materials, or concrete. The piezoelectric material particles may be used for evaluating the soundness of the structural member, such as in quality control or structural health monitoring processes. The structural member may include one or more conductive pickups used for receiving signals from the structural member. The signals may be induced by introducing ultrasonic signals or vibrational resonance signals into the structural member. The response from such induced signals may be used for quality control purposes or structural health monitoring. Piezomagnetic, electro-strictive, or magneto-strictive material particles may also be spread throughout the structural material, to amplify and otherwise enhance the signals from the piezoelectric material particles.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Vehicle loading condition detection system and method
ActiveUS10048170B2Error minimizationTyre measurementsApparatus for force/torque/work measurementIn vehiclePeak value
A system and method estimating a vehicle tire load identifies a change in vehicle loading condition by measuring vibration resonant frequency peaks (bounce mode and / or pitch mode) of the unsprung mass. Signals required include the chassis vertical acceleration and / or chassis pitch rate obtained from commercially available sensors mounted to the vehicle. An observer model receives the inertial signal(s) and generates a dynamic load estimation based upon observed frequency change in the sprung mass natural frequency.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
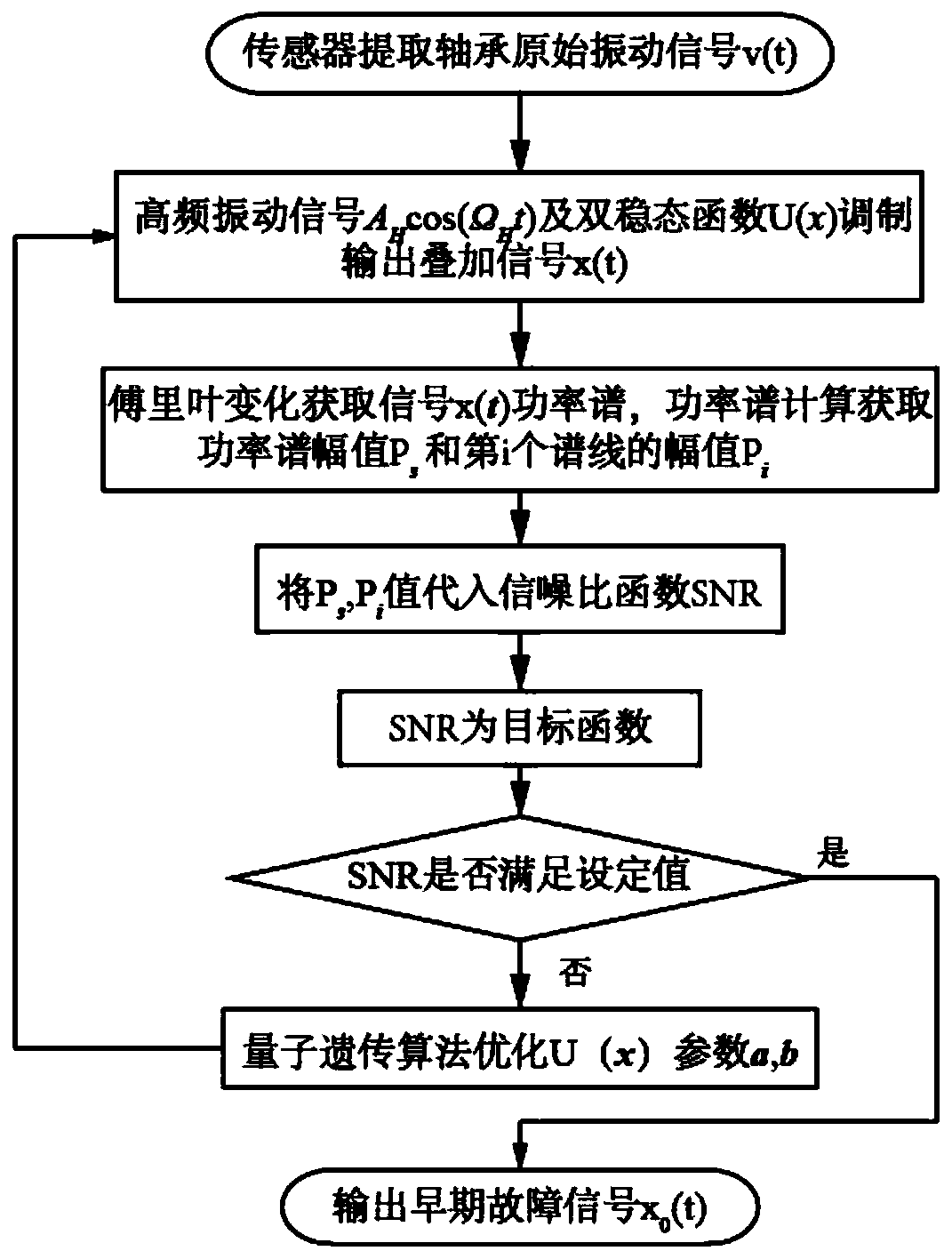
Bearing fault early diagnosis method based on adaptive frequency shift variable scale resonance technology
ActiveCN111220386AExcellent fault detection resultsEliminate distractionsMachine part testingPattern recognitionEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of bearing fault diagnosis, and discloses a bearing fault early diagnosis method based on an adaptive frequency shift variable-scale vibration resonance technology. The method comprises the steps of firstly extracting an original vibration signal of a bearing, then processing the vibration signal of the bearing by a signal processing function to generate a superposed signal, and then optimizing the superposed signal by using a quantum genetic algorithm to adjust the parameters of a bistable situation function with the purpose of improving the signal-to-noise ratio, so that a waveform is outputted better. The method has the beneficial effects that the steady-state function parameters can be quickly optimized by utilizing the acquired signals through the quantum genetic algorithm, and the signal-to-noise ratio of the output signals is improved, so that the bearing fault characteristic signals are enhanced by utilizing the noise, the bearing fault is effectively detected, and the detection effect is superior to that of a traditional maximum correlation spectrum kurtosis deconvolution method.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
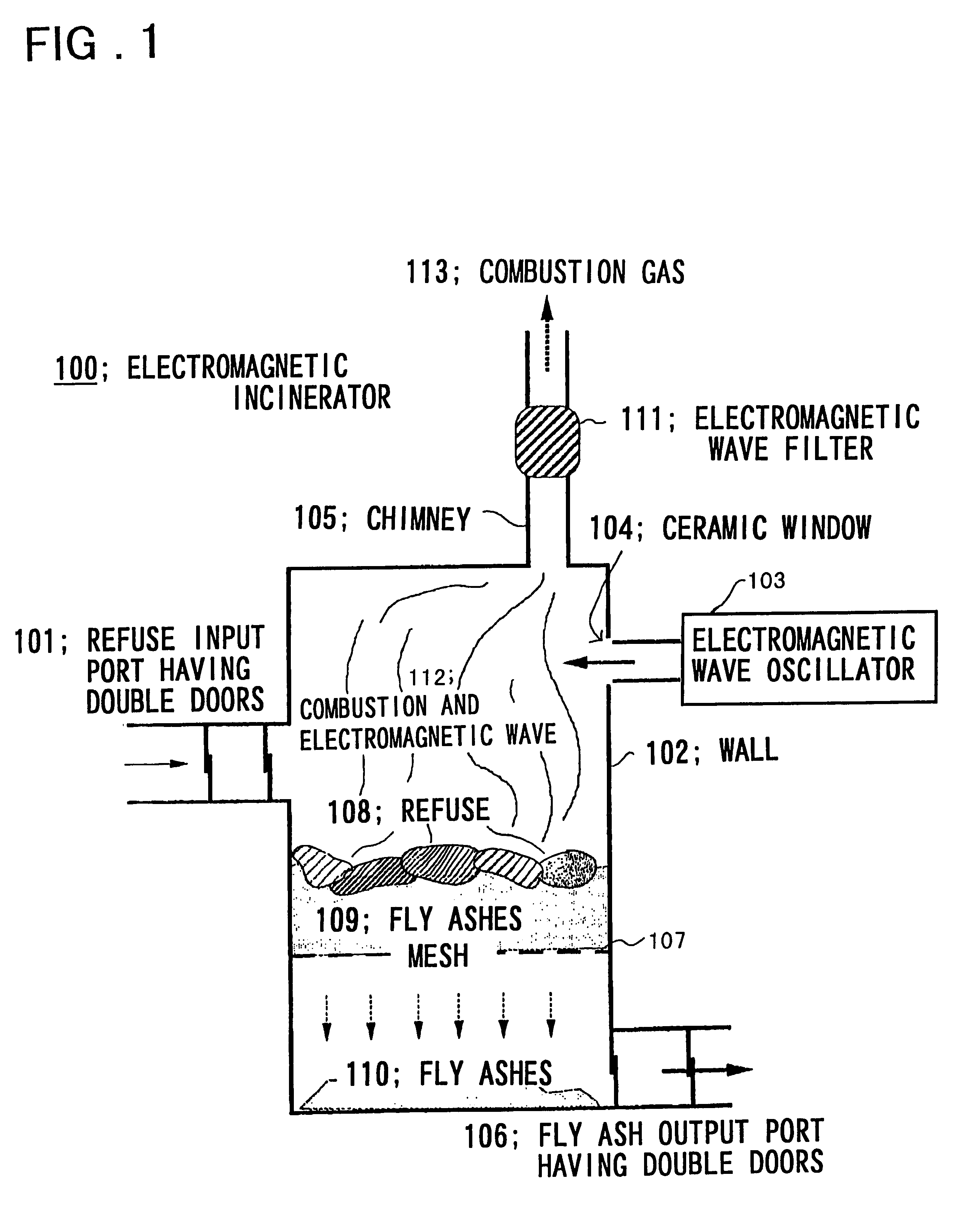
Process and apparatus for treating dioxins
InactiveUS6503463B2Improve efficiencyLow costDispersed particle separationOrganic decompositionEngineeringPolychlorinated Dibenzo-p-dioxins
A process and apparatus assuring low costs and high efficiency in practicing refuse incineration. A applying electromagnetic wave of a frequency band resonant with rotation or vibration of a specific substance e.g., dioxins molecule, thereby to heat the dioxins molecule selectively up to high temperature to remove the dioxins molecule by decomposition.
Owner:Y Y L
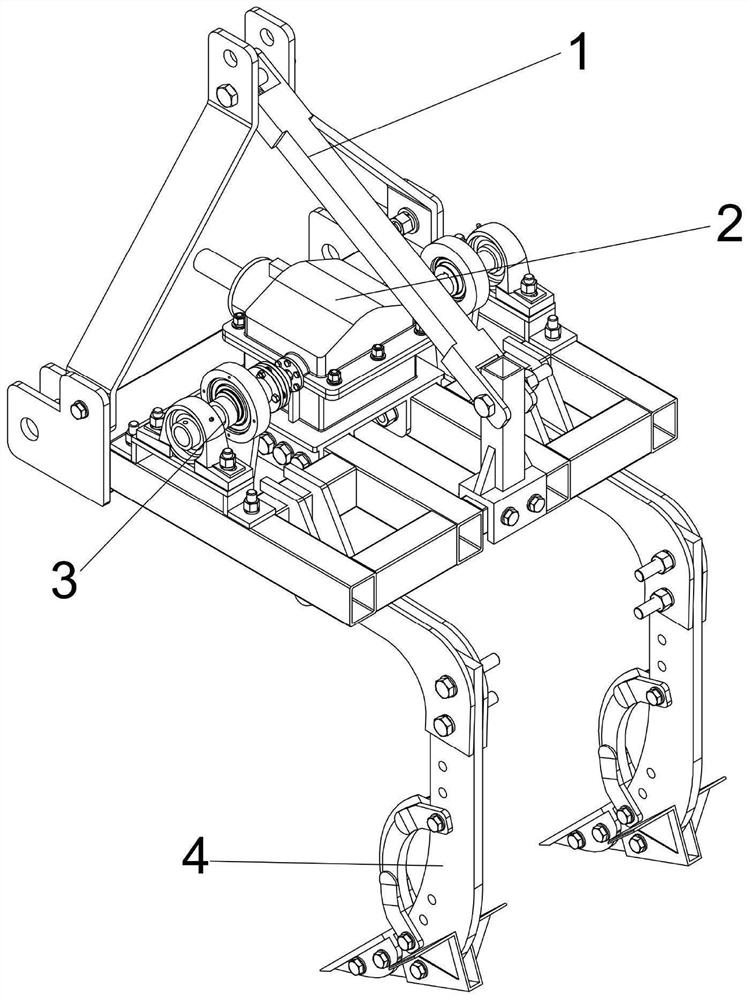
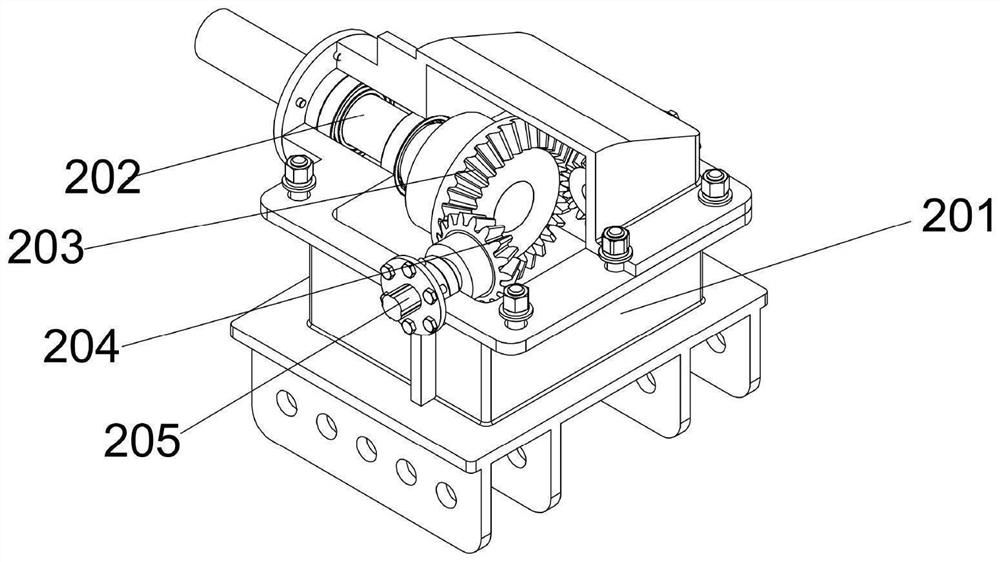
A vibrating subsoiler
The invention discloses a vibrating subsoiler, which comprises a subsoiling platform, a coaxial reverse transmission mechanism, a vibrating and swinging transmission mechanism and a subsoiling shovel with a soil breaker; On the platform, and connected with the power source of the tractor in front, two of the vibration and swing transmission mechanisms are installed on the subsoiling platform, and the two vibration and swing transmission mechanisms are respectively arranged on the coaxial reverse transmission mechanism. The two sides are respectively connected with two output shafts on both sides of the coaxial reverse transmission mechanism, and a subsoiler shovel with a soil breaker is installed at the bottom of each vibration and swing transmission mechanism. The invention can effectively reduce the resistance in the subsoiling process of the subsoiling shovel, overcome the problems of coaxial and coaxial axial force superposition and unidirectional vibration resonance in the existing subsoiling shovel, and solve the problem of the soil breaker of the subsoiling shovel for different depths The adaptability of the plow bottom layer is relatively poor, and it cannot be well adapted to the problem of deep loosening of different soil properties.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Pump body applied to compressor and compressor
PendingCN114776560AReduce noiseHigh working reliabilityPositive displacement pump componentsCrankshaft bearingsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The pump body comprises a crankshaft and an air cylinder, the crankshaft penetrates through the air cylinder, and the air cylinder is provided with a first end and a second end which are opposite to each other; the first supporting bearing is arranged at the first end and sleeves the crankshaft; the second supporting bearing is arranged at the second end and sleeves the crankshaft; the third supporting bearing is arranged on the side, away from the air cylinder, of the second supporting bearing, and the third supporting bearing is connected with the second supporting bearing and arranged on the crankshaft in a sleeving mode. Therefore, the crankshaft is supported by the first supporting bearing, the second supporting bearing and the third supporting bearing at the same time, the supporting rigidity of the crankshaft is effectively improved, the inherent frequency of crankshaft whirling vibration is moved out of the unbalanced radial electromagnetic force fundamental frequency range in the rotating speed interval of the compressor, crankshaft whirling vibration resonance is eliminated, and the noise of the compressor is reduced; the stress state of each supporting bearing can be improved, eccentric wear of the crankshaft is relieved, and the working reliability of the compressor is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEIZHI COMPRESSOR
A six-degree-of-freedom ultra-low frequency vibration isolation device and its control system based on a zero-stiffness system
ActiveCN108253084BSolve Vibration ProblemsSolve the impactNon-rotating vibration suppressionNon linear dynamicZero frequency
The invention discloses a six-degree-of-freedom ultralow frequency vibration isolation device based on a zero stiffness system and a control system thereof, and relates to the fields of multi-degree-of-freedom low frequency, ultralow frequency and even zero-frequency vibration isolation and micro vibration simulation experiments. The six-degree-of-freedom ultralow frequency vibration isolation device based on the zero stiffness system is formed by connecting a supporting platform, a basic platform and a vibration isolation module. The vibration isolation module comprises an upper connecting rod, a lower connecting rod, a columnar shell, a vertical spring, a horizontal spring and a connecting assembly between the springs. The upper end of the upper connecting rod is connected with the supporting platform. The lower end of the upper connecting rod penetrates through an upper end cover of the columnar shell and is connected with the connecting assembly between the springs. The upper end of the lower connecting rod is fixedly connected with a lower end cover of the columnar shell. The lower end of the lower connecting rod is connected with the basic platform. The vibration isolation module meets the characteristic of zero stiffness. In combination with a gravity environment self-adapting control system, an isolated object is in a suspended state. Low frequency, ultralow frequency and even zero-frequency full-band vibration immune and isolation performance can be realized, and the problem of the multicoupling technique of multi-degree-of-freedom ultralow frequency, vibration resonance and non-linear dynamics is solved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
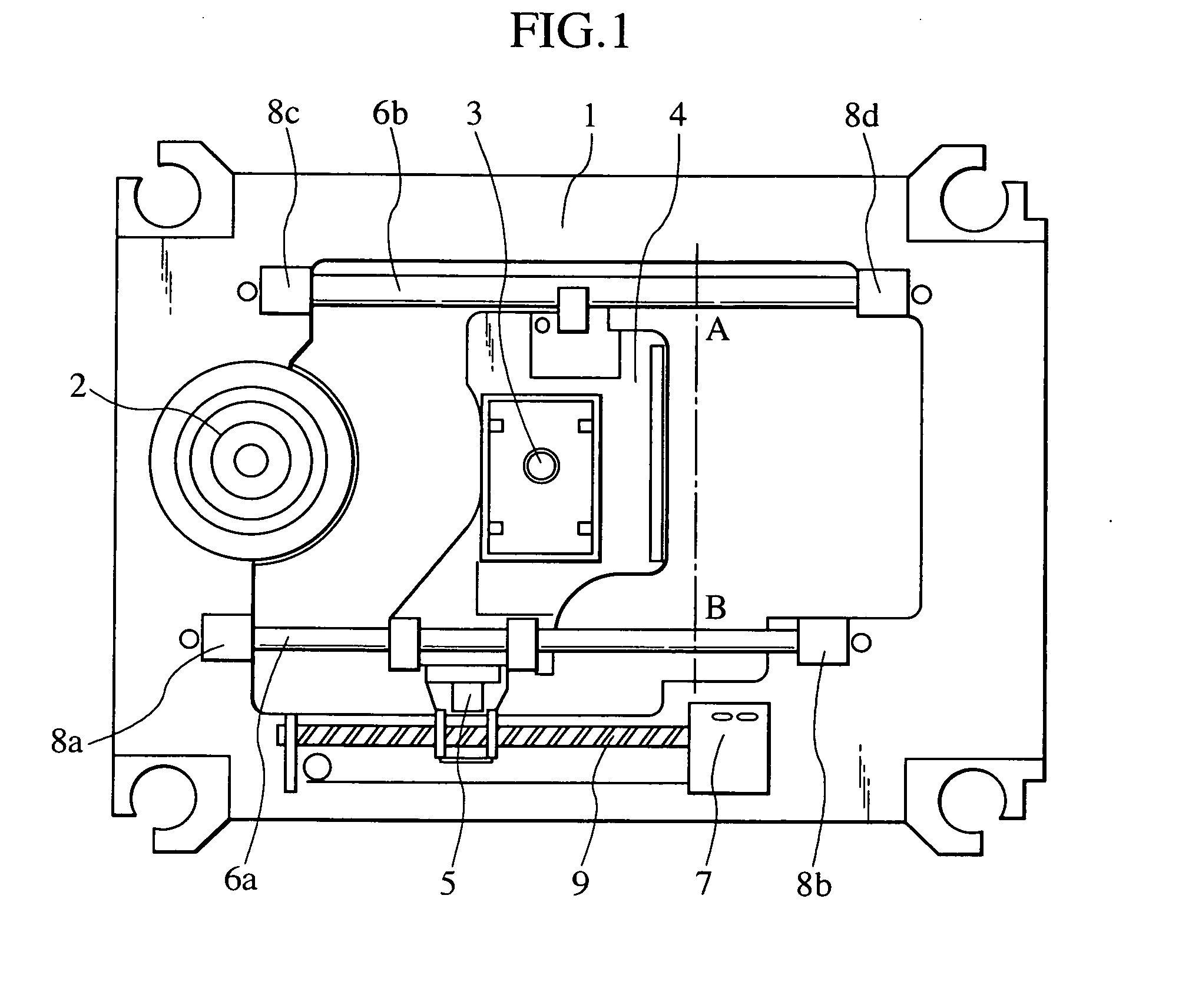
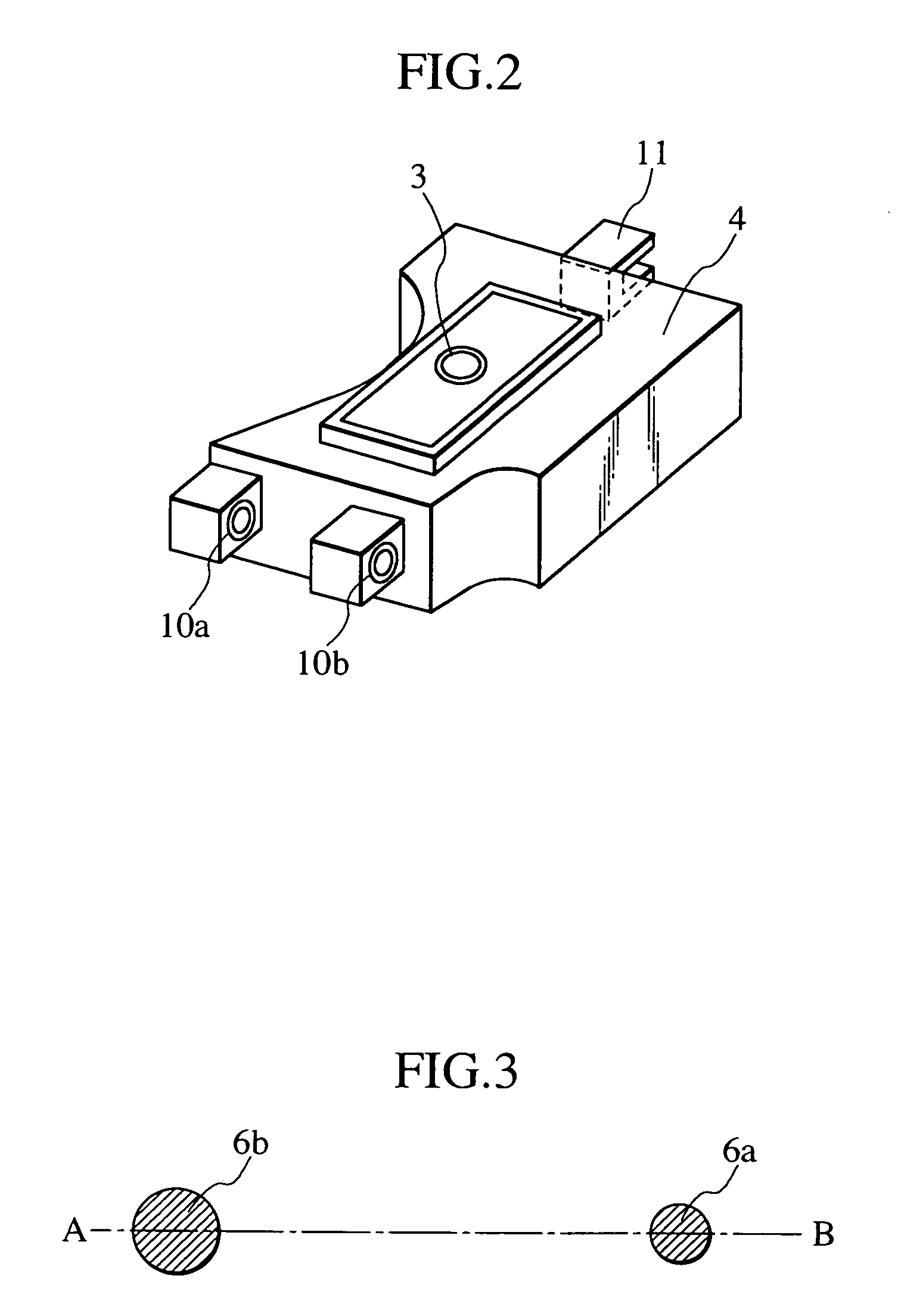
Optical disc apparatus
InactiveUS20070127324A1Avoid positioningSuppressing the vibrational resonance of the guide shaftsRecord information storageOptical recording/reproducingOptical pickupEngineering
An optical disc apparatus includes a main guide shaft and a subsidiary guide shaft disposed so as to guide movement of a sliding base which holds an optical pickup. The optical pickup enables information recording and reproducing operations on an optical disc. The main guide shaft and the subsidiary guide shaft are configured so as to suppress vibrational resonance caused between the main guide shaft and the subsidiary guide shaft.
Owner:HITACHI-LG DATA STORAGE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com