Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
304 results about "Molecular beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
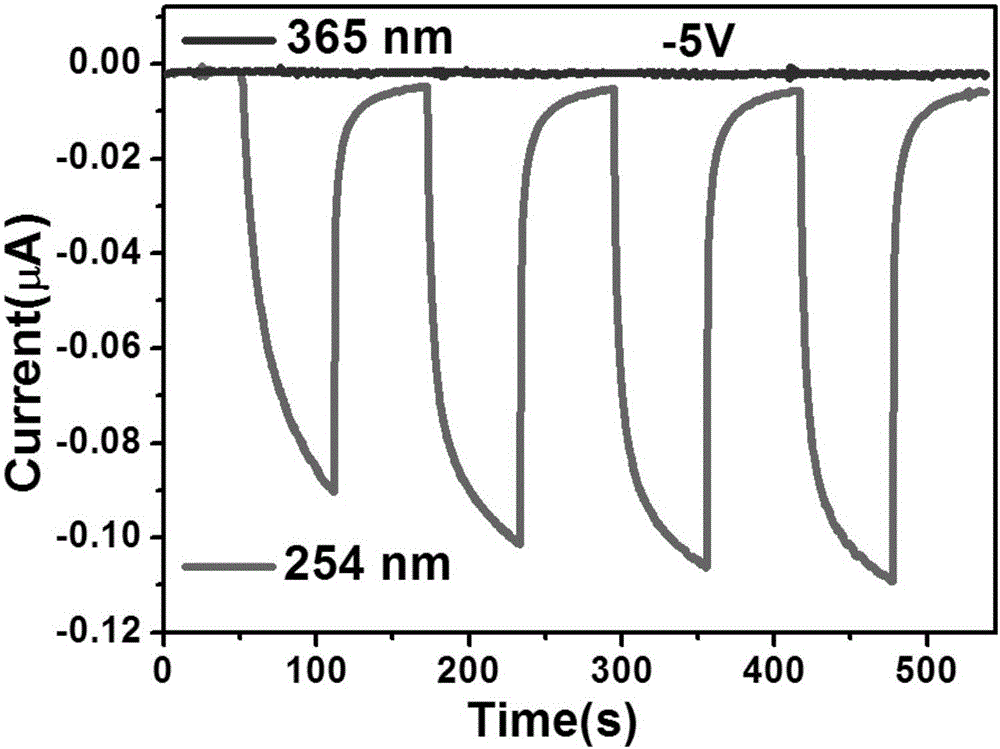
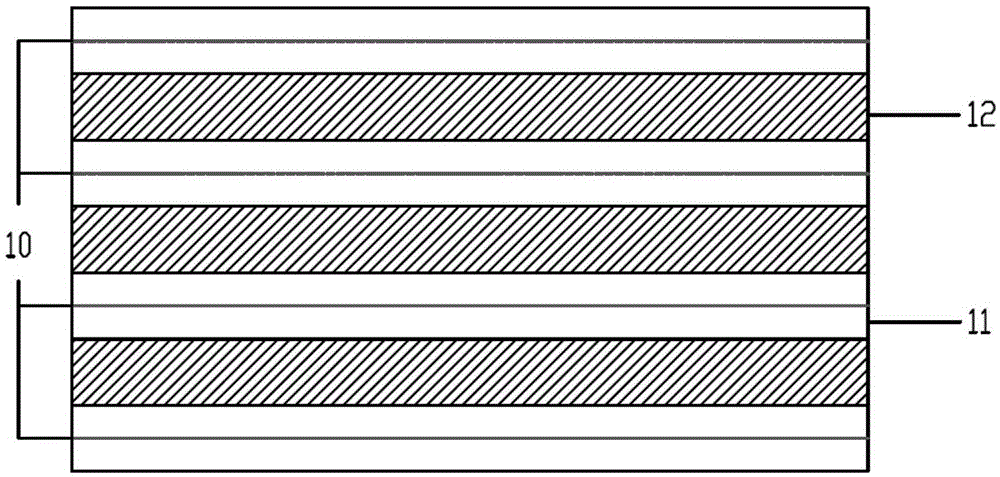
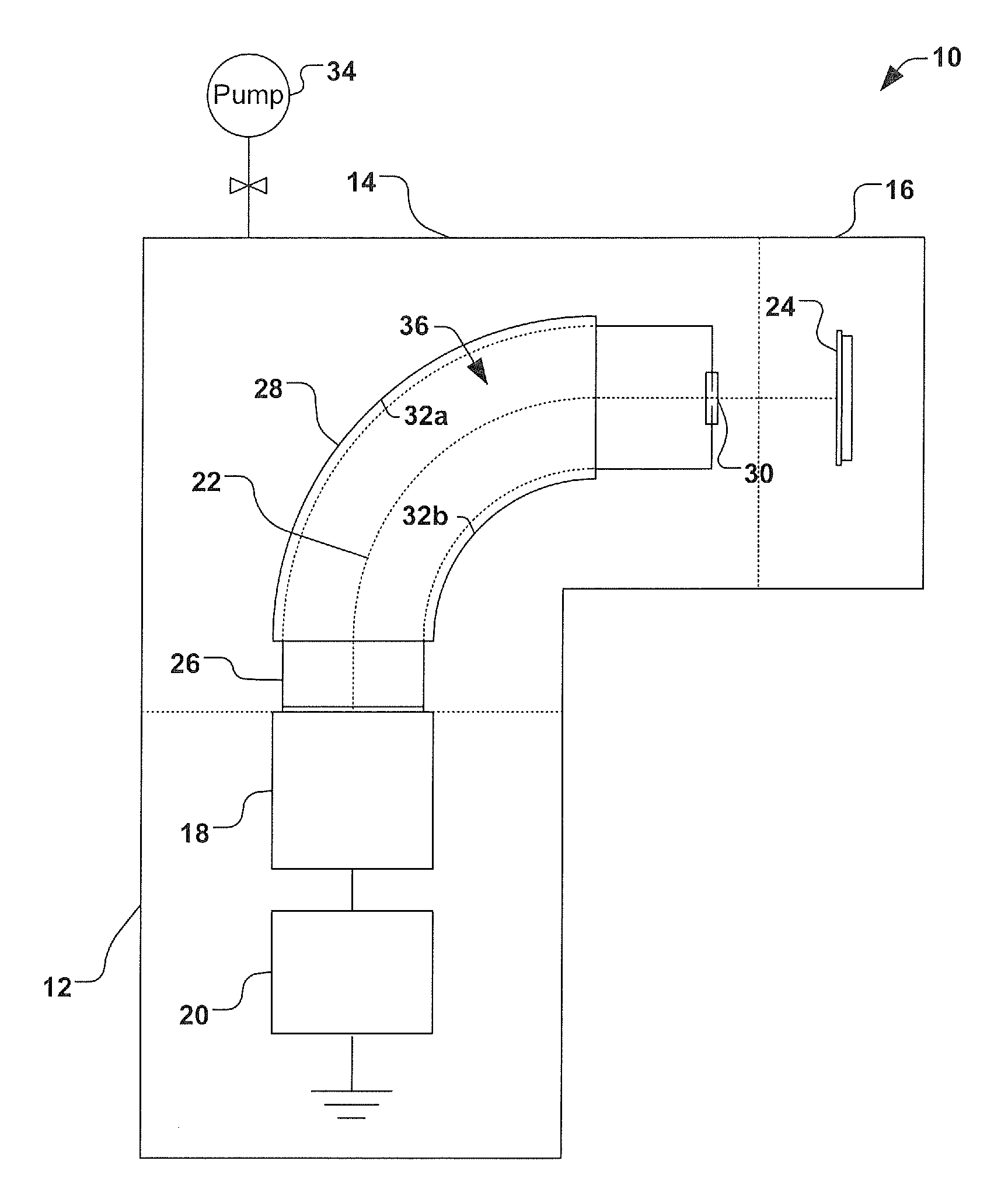
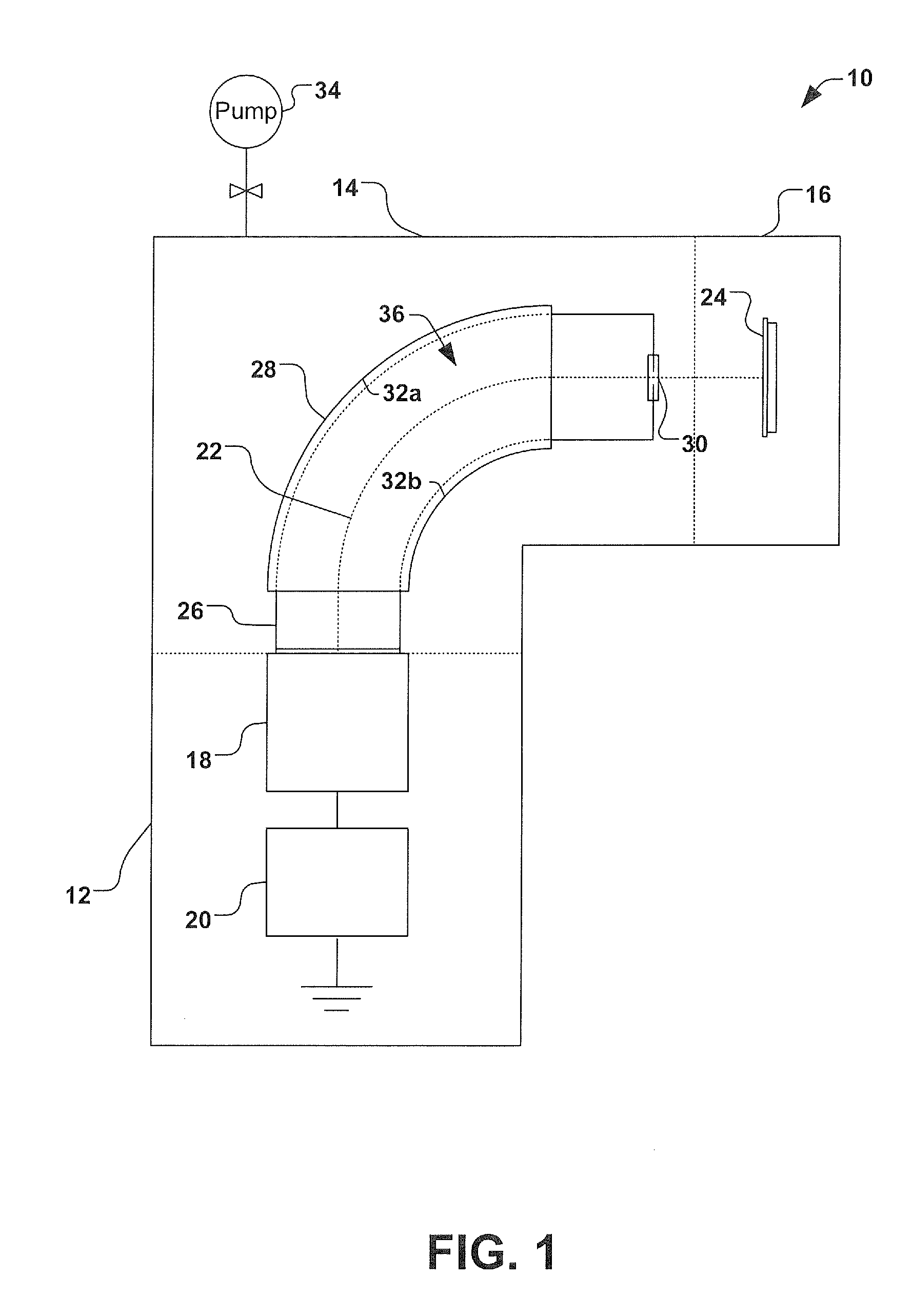
A molecular beam is produced by allowing a gas at higher pressure to expand through a small orifice into a chamber at lower pressure to form a beam of particles (atoms, free radicals, molecules or ions) moving at approximately equal velocities, with very few collisions between the particles. Molecular beam is useful for fabricating thin films in molecular beam epitaxy and artificial structures such as quantum wells, quantum wires, and quantum dots. Molecular beams have also been applied as crossed molecular beams. The molecules in the molecular beam can be manipulated by electrical fields and magnetic fields. Molecules can be decelerated in a Stark decelerator or in a Zeeman slower.
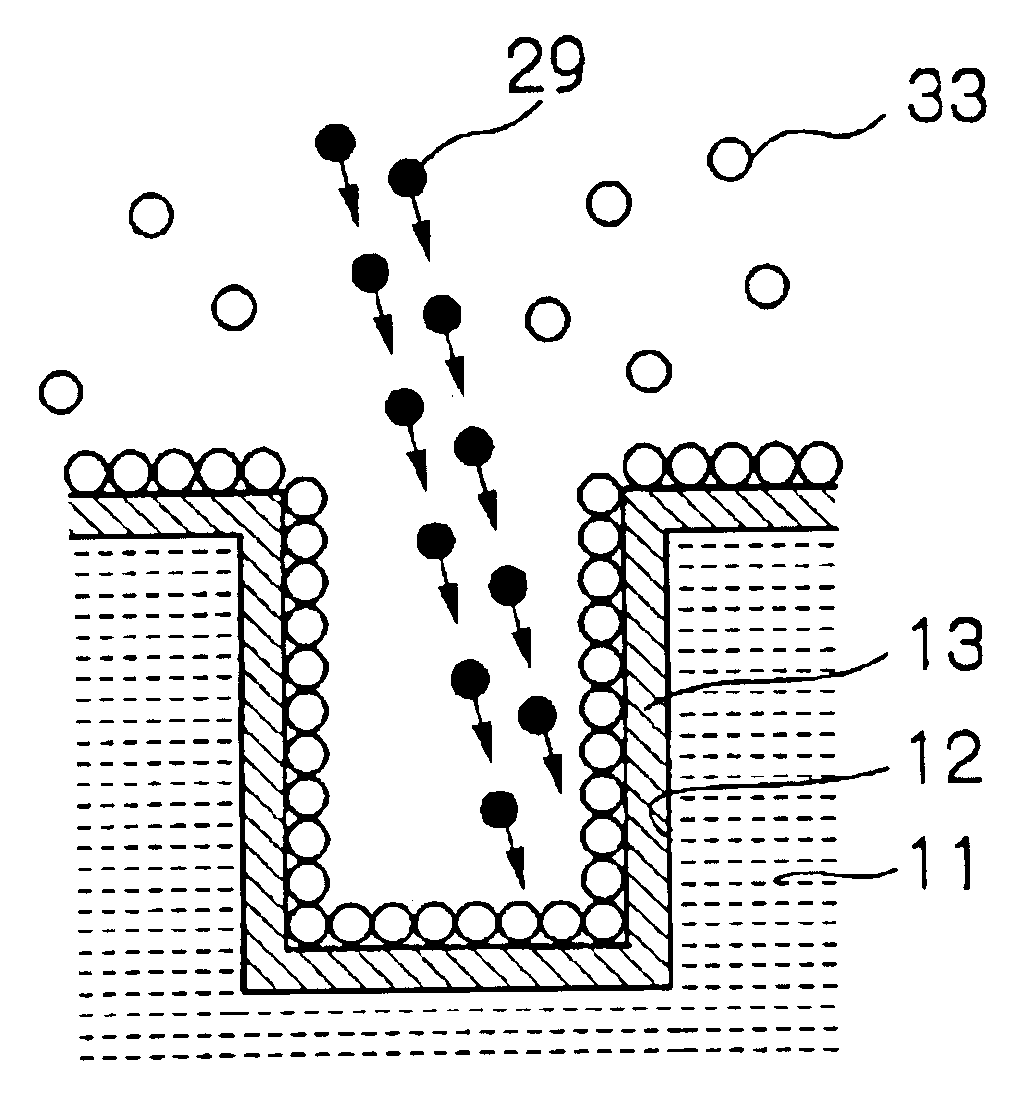
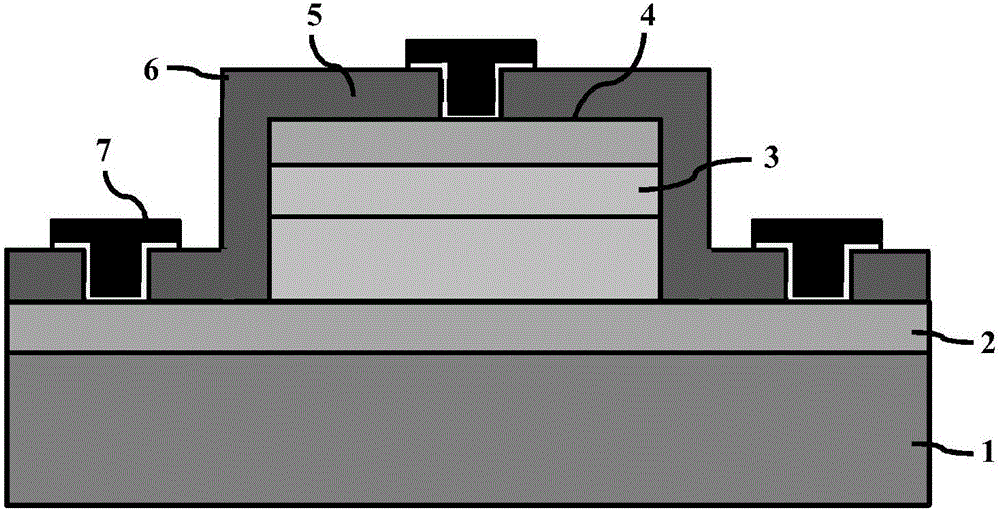
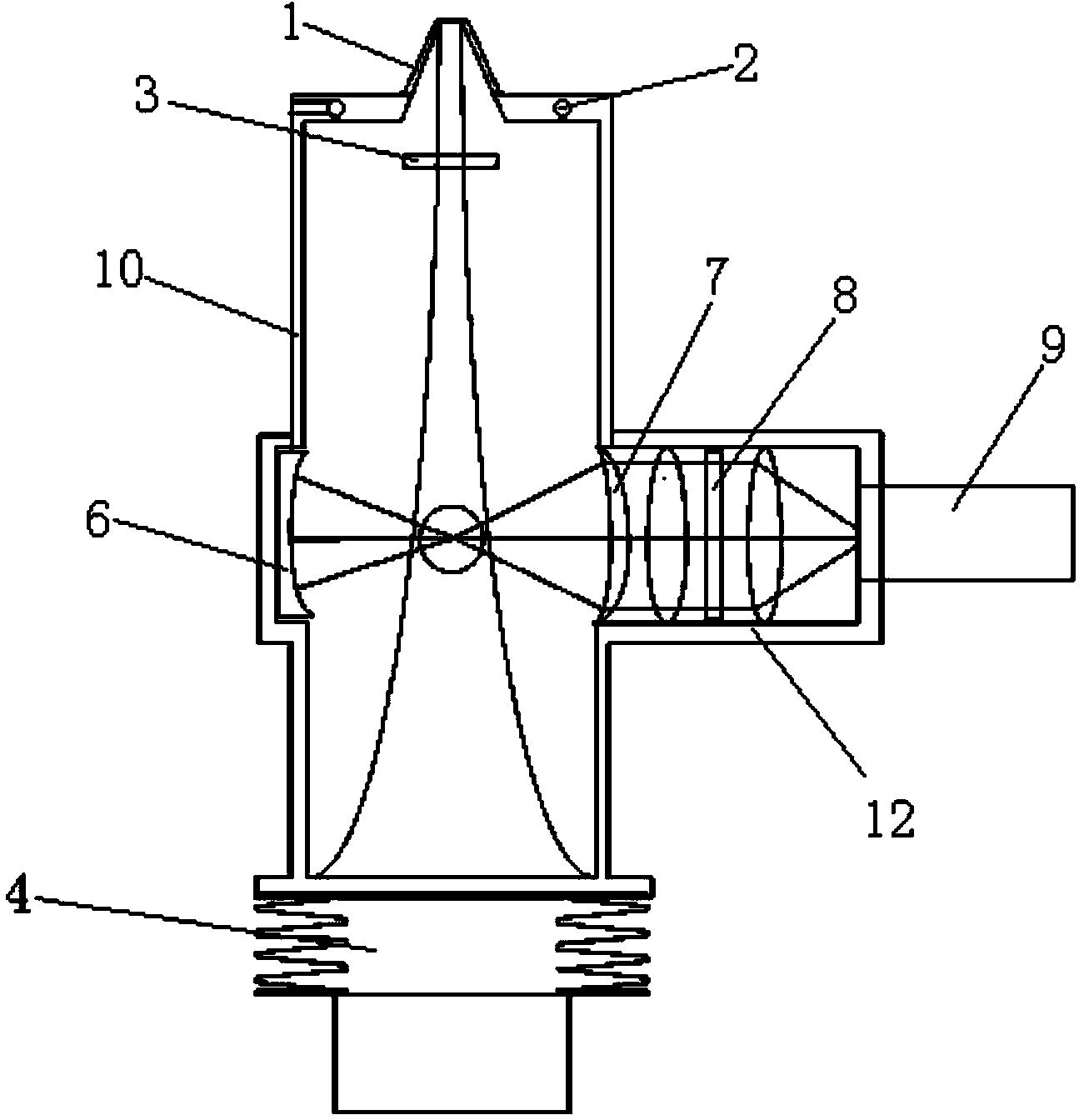
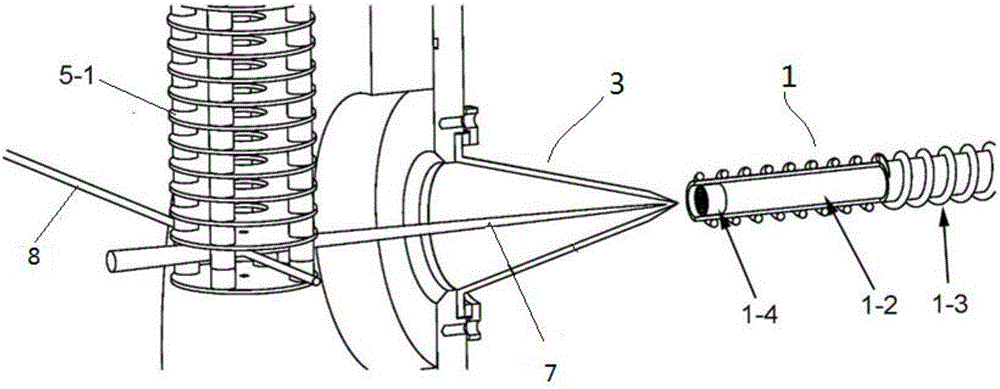
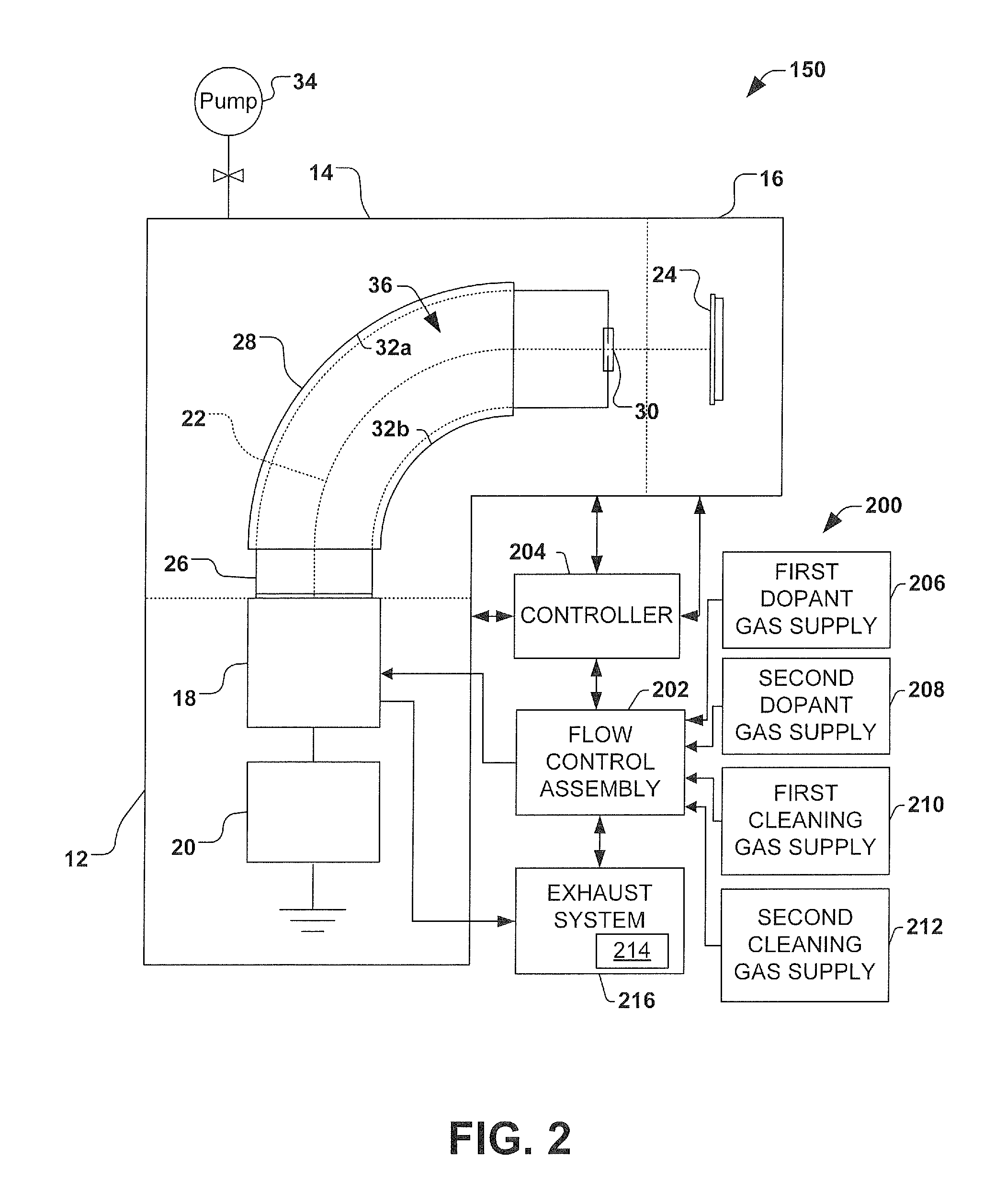
Coating, modification and etching of substrate surface with particle beam irradiation of the same
InactiveUS6921722B2Favorable adhesion (bond) strengthBonding strengthElectric discharge heatingElectric discharge tubesEtchingAtomic beam
There is provided a method of performing a surface treatment, such as coating, denaturation, modification and etching, on a surface of a substrate. The method comprises the steps of bringing a surface treatment gas into contact with a surface of a substrate, and irradiating the surface of the substrate with a fast particle beam to enhance an activity of the surface and / or the surface treatment gas, thereby facilitating a reaction between the surface and the gas. The fast particle beam may be selected from a group consisting of an electron beam, a charged particle beam, an atomic beam and molecular beam. For example, during a coating operation, chemical deposition of predetermined component elements of the gas onto the surface is effected and a predetermined portion of the surface of the substrate is irradiated with a particle beam to form a coating layer on the predetermined portion.
Owner:EBARA CORP
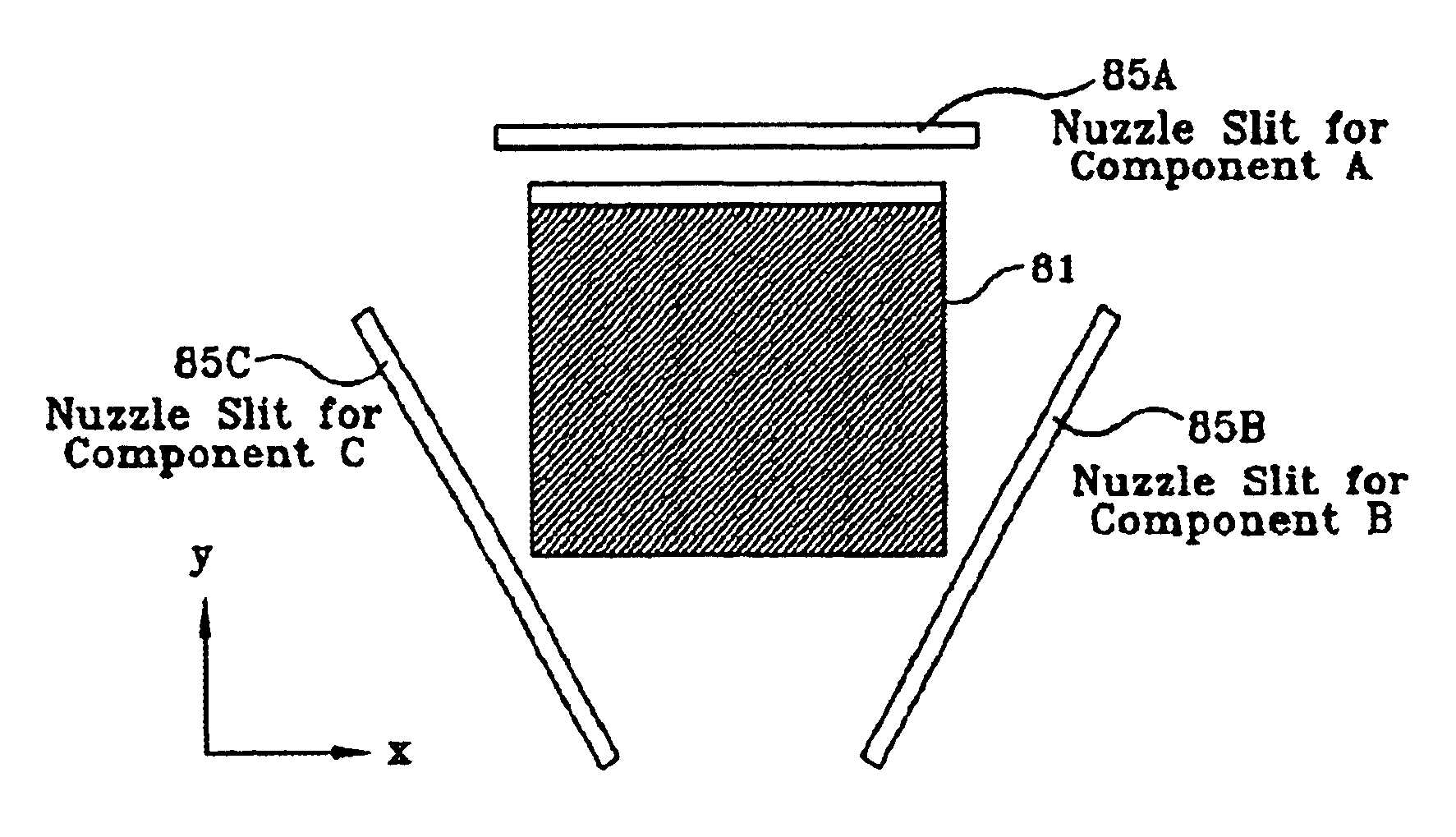
Combinatorial synthesis of material chips
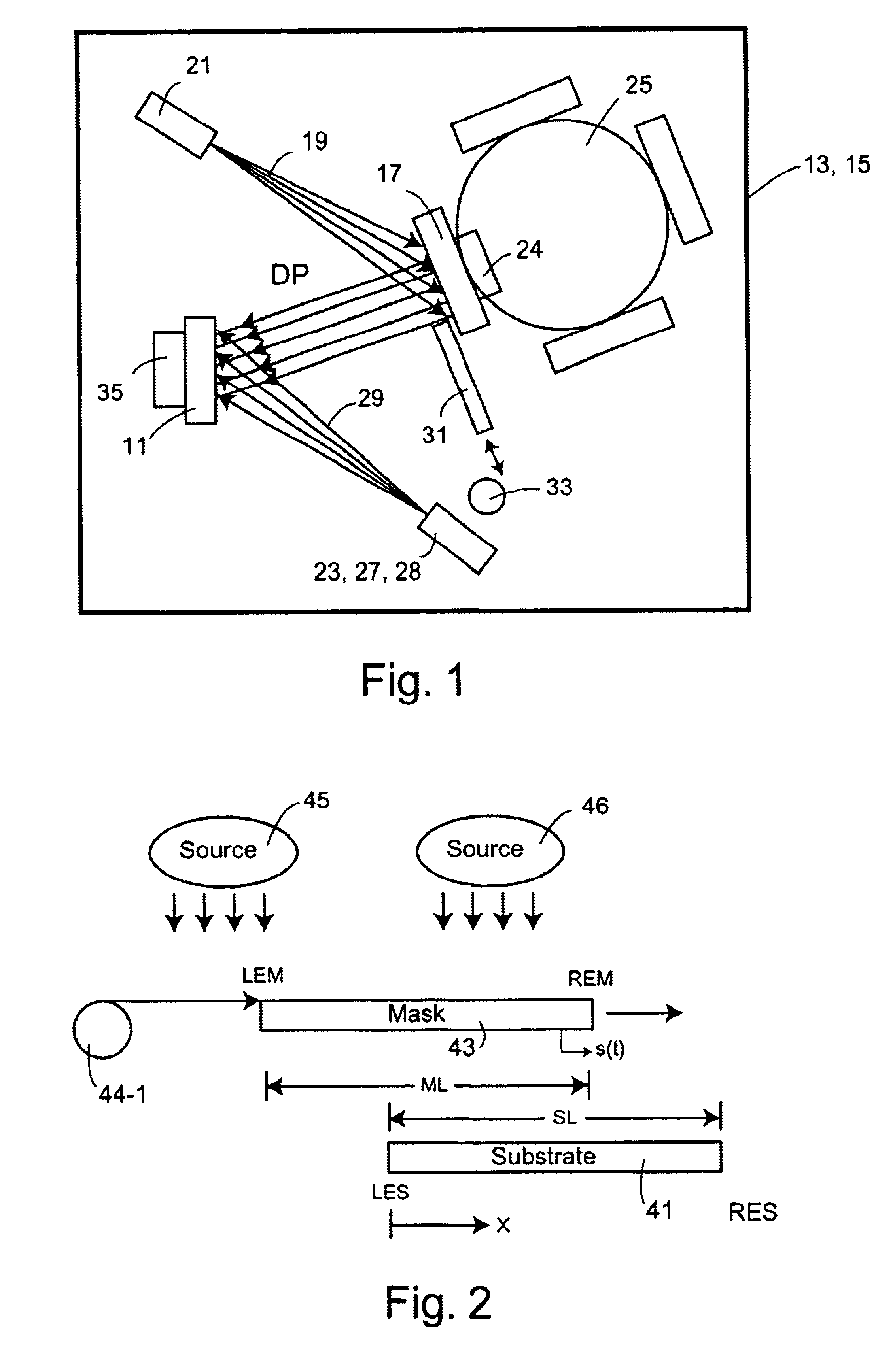
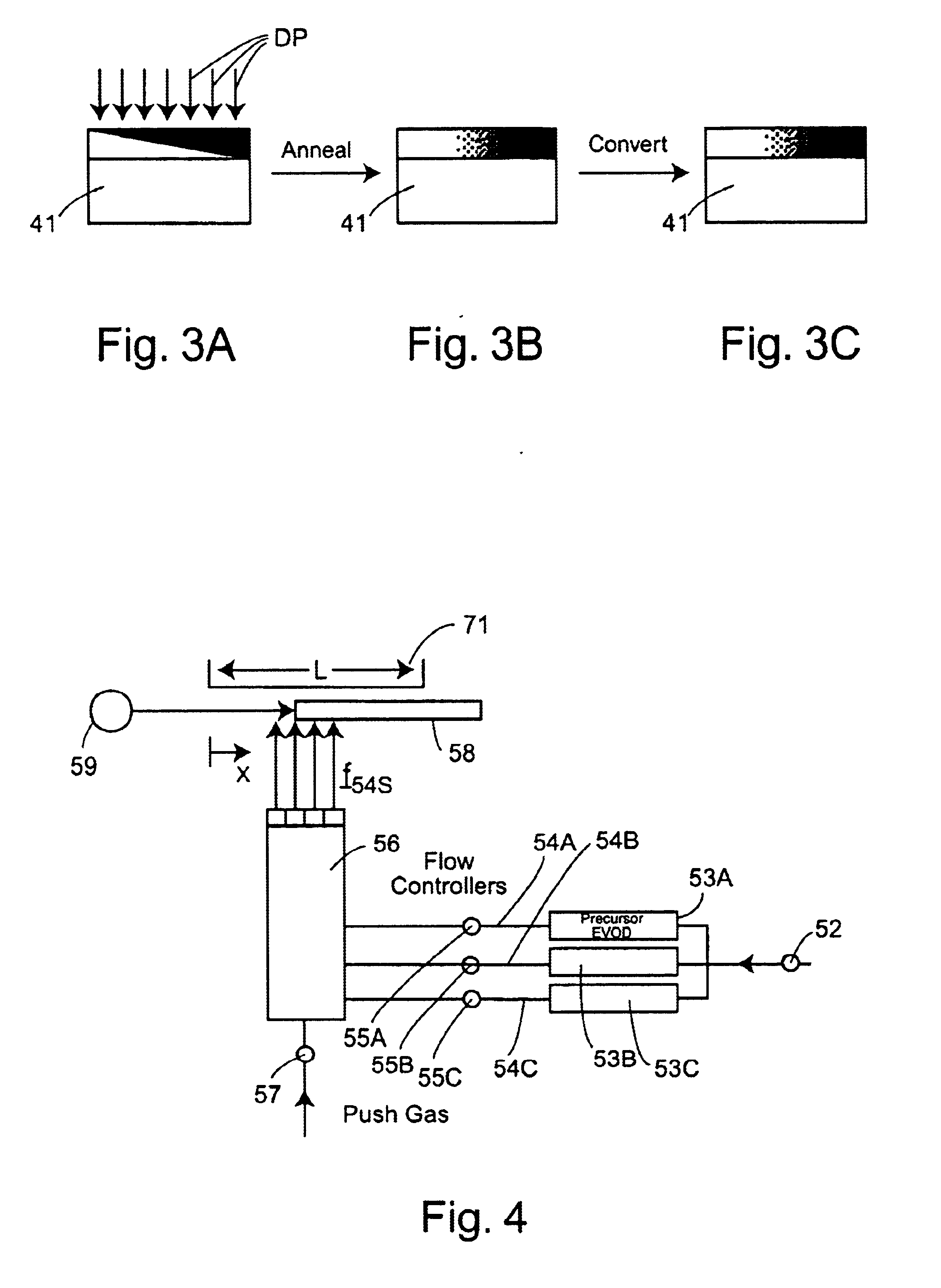
InactiveUS6911129B1Promote exchangeReduce the temperatureCellsSequential/parallel process reactionsEngineeringCombinatorial synthesis
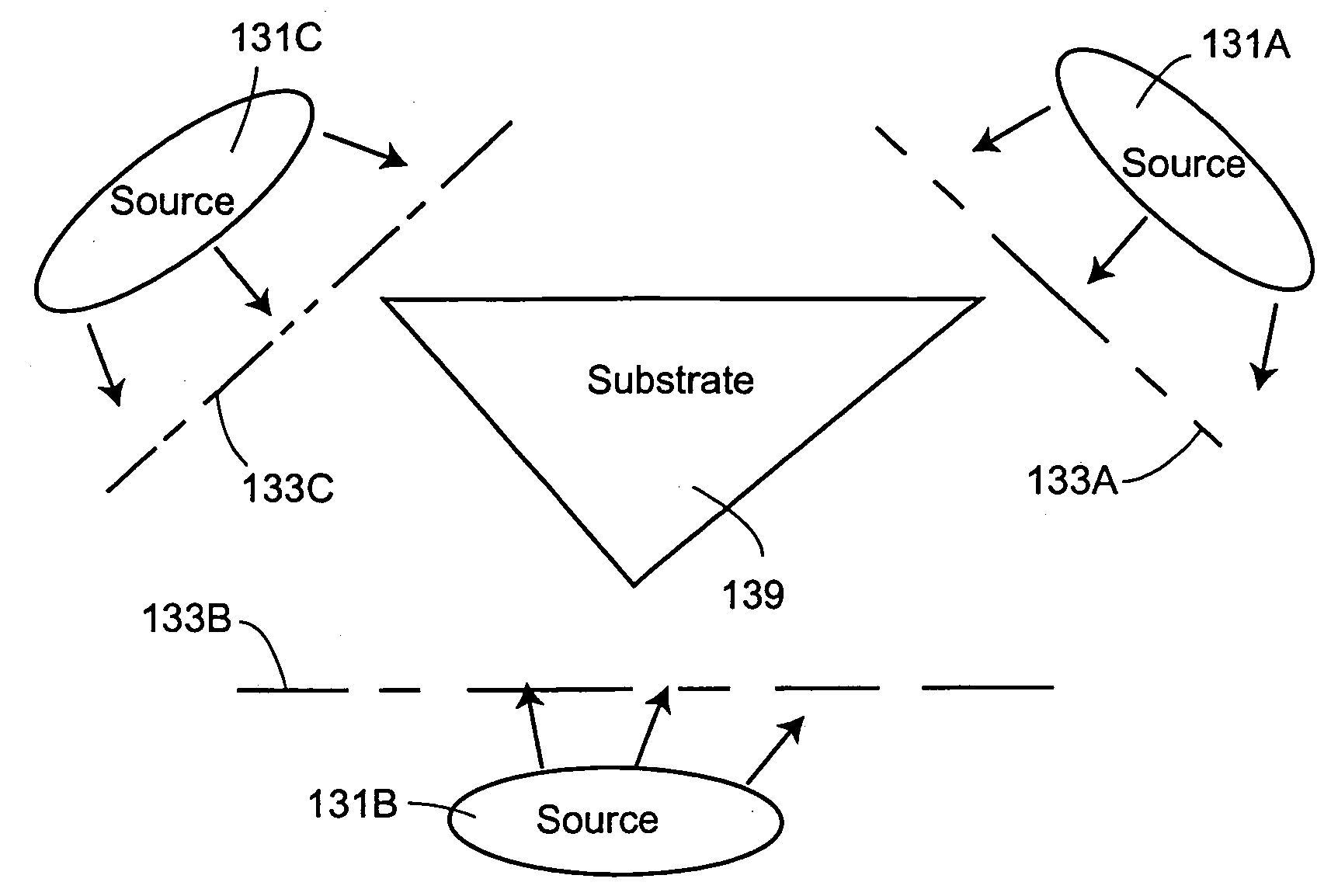
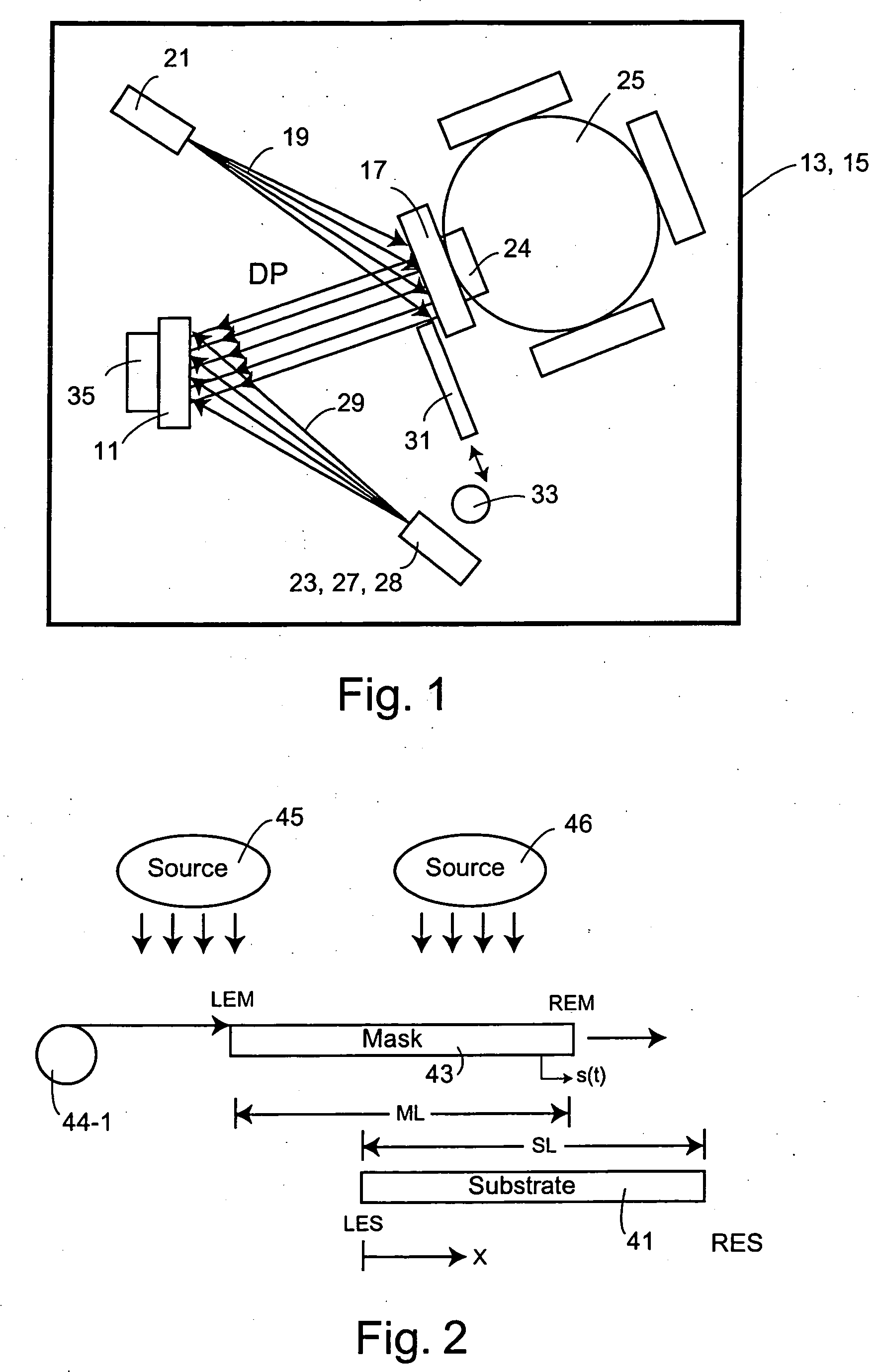
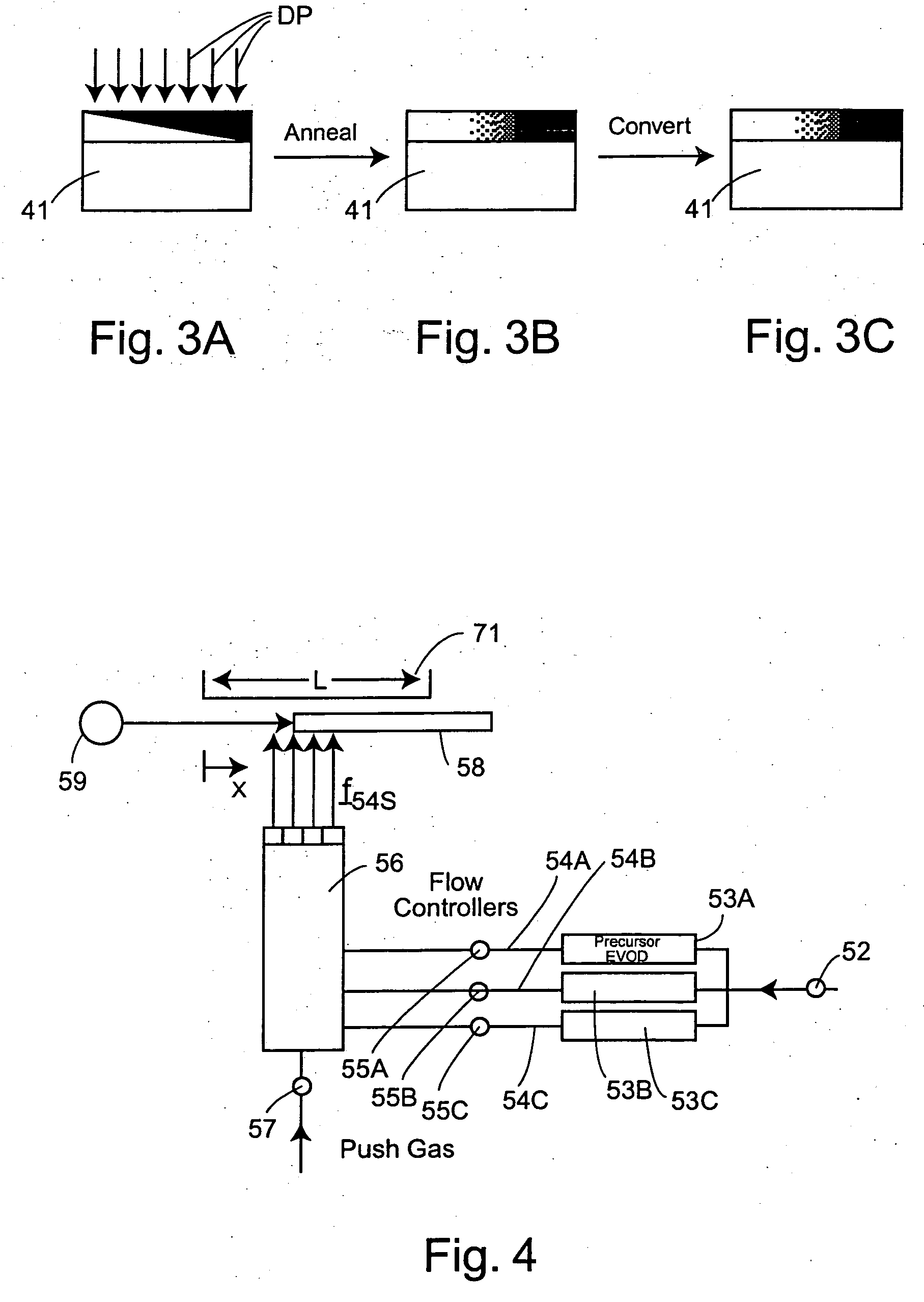
Systems and methods for providing in situ, controllably variable concentrations of one, two or more chemical components on a substrate to produce an integrated materials chip. The component concentrations can vary linearly, quadratically or according to any other reasonable power law with one or two location coordinates. In one embodiment, a source and a mask with fixed or varying aperture widths and fixed or varying aperture spacings are used to produce the desired concentration envelope. In another embodiment, a mask with one or more movable apertures or openings provides a chemical component flux that varies with location on the substrate, in one or two dimensions. In another embodiment, flow of the chemical components through nuzzle slits provides the desired concentrations. An ion beam source, a sputtering source, a laser ablation source, a molecular beam source, a chemical vapor deposition source and / or an evaporative source can provide the chemical component(s) to be deposited on the substrate. Carbides, nitrides, oxides halides and other elements and compounds can be added to and reacted with the deposits on the substrate.
Owner:INTEMATIX
Mass spectrometer method and apparatus for analyzing a sample in a solution
InactiveUS7247495B2Fast and reliable identificationHigh sensitivityComponent separationSamples introduction/extractionSpray nozzleMass analyzer
The invention provides a mass spectrometric method for analyzing a sample in a solution, including the steps of directing a flow of a solution containing sample compounds to be analyzed towards a supersonic nozzle having an input end and an output end; vaporizing the solution and sample prior to its expansion from the output end of said supersonic nozzle; allowing expansion of the vaporized sample and solution from said supersonic nozzle into a vacuum system, forming a supersonic molecular beam with vibrationally cold sample molecules; ionizing the vaporized sample compounds with electrons while contained as vibrationally cold molecules in said supersonic molecular beam; mass analyzing the ions formed from said sample compounds; detecting said ions formed from said sample compounds after mass analysis, and processing the data obtained from the resulting mass spectral information, for identifying and / or quantifying the chemical content of said sample. The invention also provides apparatus for analyzing a sample in a solution.
Owner:AMIRAV AVIV
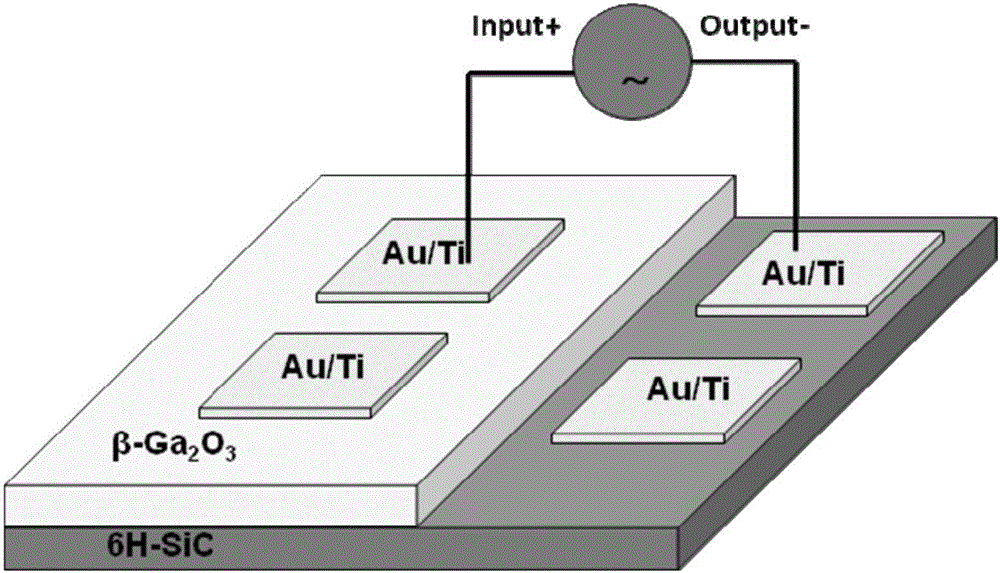
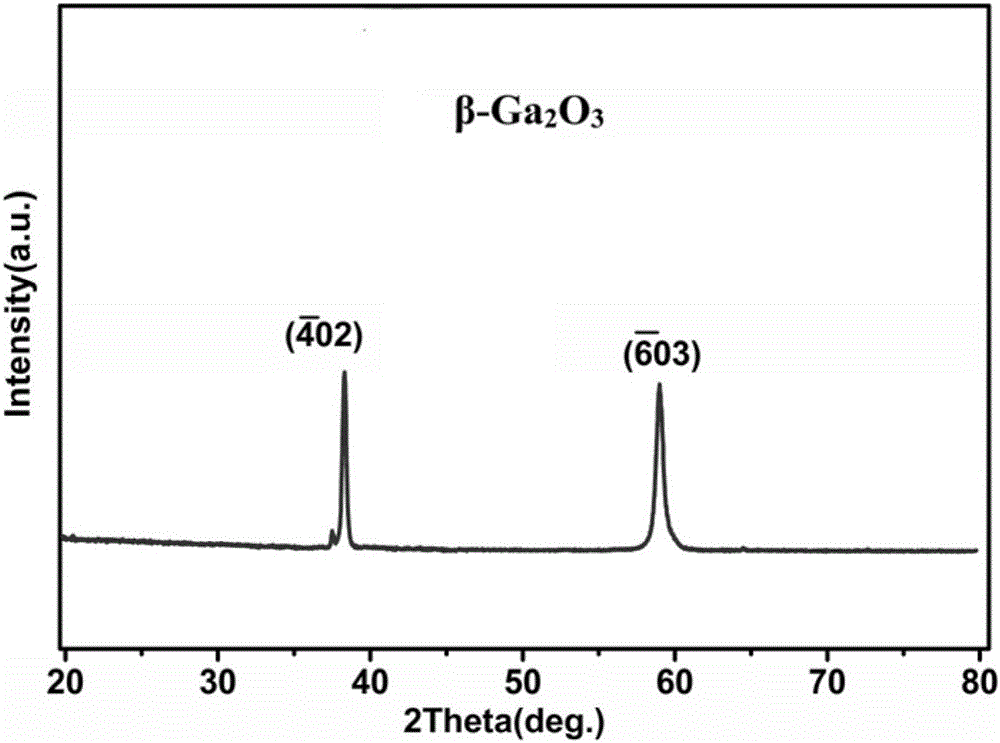
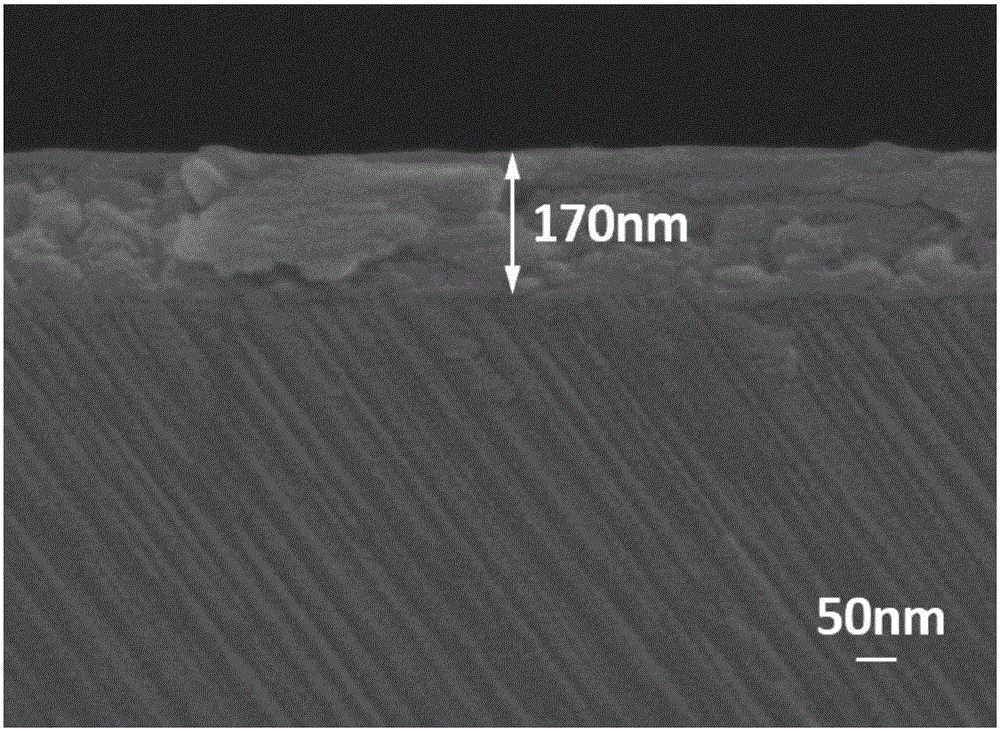
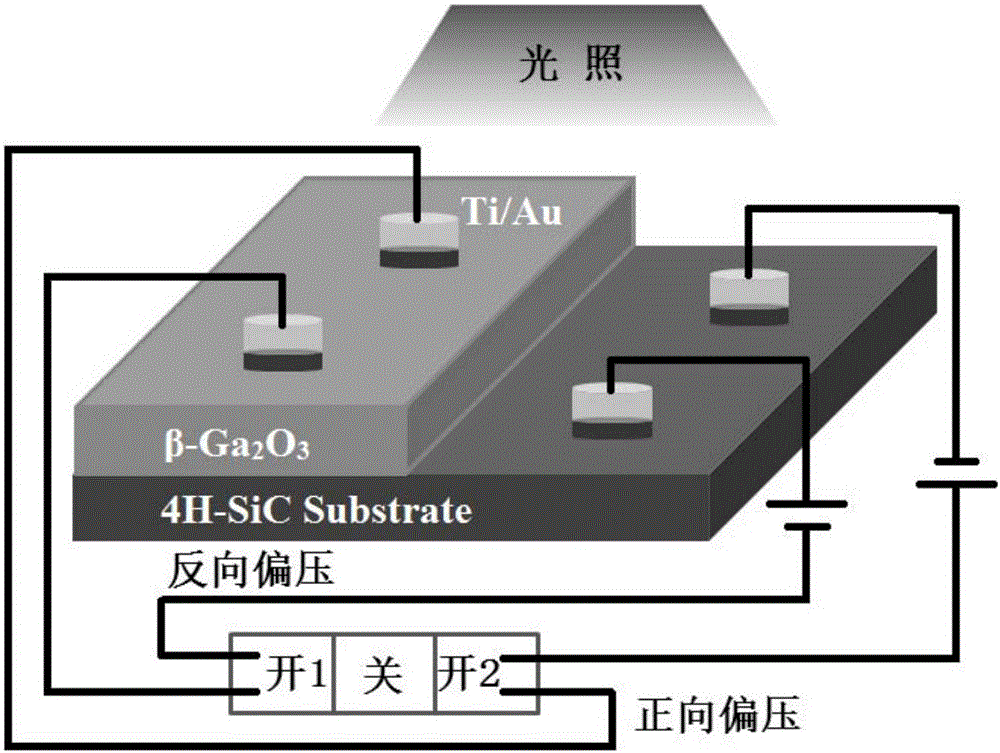
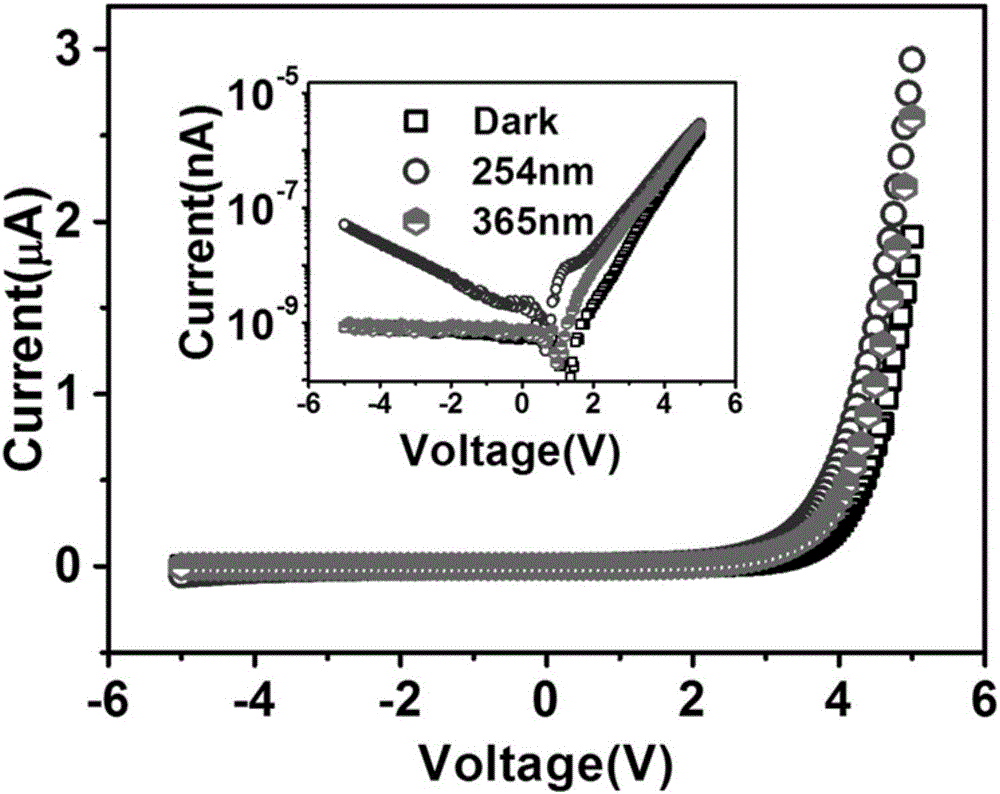
Visible-blind ultraviolet detector based on Beta-Ga2O3/SiC heterojunction thin film and fabrication method of visible-blind ultraviolet detector
ActiveCN105742398AStrong process controllabilityEasy to operateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionUltraviolet detectors
The invention relates to an ultraviolet detector, in particular to a visible-blind ultraviolet detector based on a Beta-Ga2O3 / SiC heterojunction thin film and a fabrication method of the visible-blind ultraviolet detector. According to the fabrication method, a layer of Beta-Ga2O3 thin film is deposited on an n-type 6H-SiC substrate by a laser molecular beam epitaxial technique, and then a layer of Ti / Au thin film is deposited on the n-type 6H-SiC substrate and the Beta-Ga2O3 thin film through a mask by a radio frequency magnetron sputtering to be used as an electrode. The fabricated visible-blind ultraviolet detector has the advantages of stable performance, response sensitivity, small dark current and high potential application; and moreover, the fabrication method has the characteristics of high process controllability, simplicity in operation, high universality, restorability of repeated test and the like, and has great application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Capillary separated vaporization chamber and nozzle device and method
There is provided a capillary separated vaporization chamber and nozzle method and device for improved electron ionization liquid chromatography mass spectrometry of samples in a supersonic molecular beam. The device includes a vaporization chamber located upstream of a supersonic nozzle; a capillary separating the vaporization chamber and the supersonic nozzle, means for spray formation from sample in a flowing liquid; a vacuum system into which the supersonic nozzle induces supersonic expansion of the vaporized sample compounds and solvent vapor, for forming a supersonic molecular beam with vibrationally cold sample molecules and vaporized solvent; flythrough electron ionization ion source; mass analyzer; an ion detector and means for data processing of the resulting mass spectral information, for identifying and / or quantifying the chemical content of the sample.
Owner:AMIRAV AVIV
Fast gas chromatograph method and device for analyzing a sample
ActiveUS20120085148A1Component separationDispersed particle separationCapillary gas chromatographyGas phase
In a fast gas chromatograph (GC) method and device for obtaining fast gas chromatography analysis, a capillary gas chromatography column is inserted into a resistively heated metal tube located mostly outside a standard gas chromatograph oven, which may serve as a heated transfer line to a flexible column that enters the resistively heated metal tube from its injector and exits into its detector. The fast GC device enables less than one minute full range temperature programming and cooling back analysis cycle time. The fast GC according to one embodiment is combined with mass spectrometry with supersonic molecular beams for the provision of fast analysis cycle time together with highly informative mass spectral information for improved sample analysis and identification.
Owner:AMIRAV AVIV
Lithium ion battery pentabasic high-entropy oxide nano-film as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN107994228AWith charge and discharge performanceMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesHigh energyCopper oxide
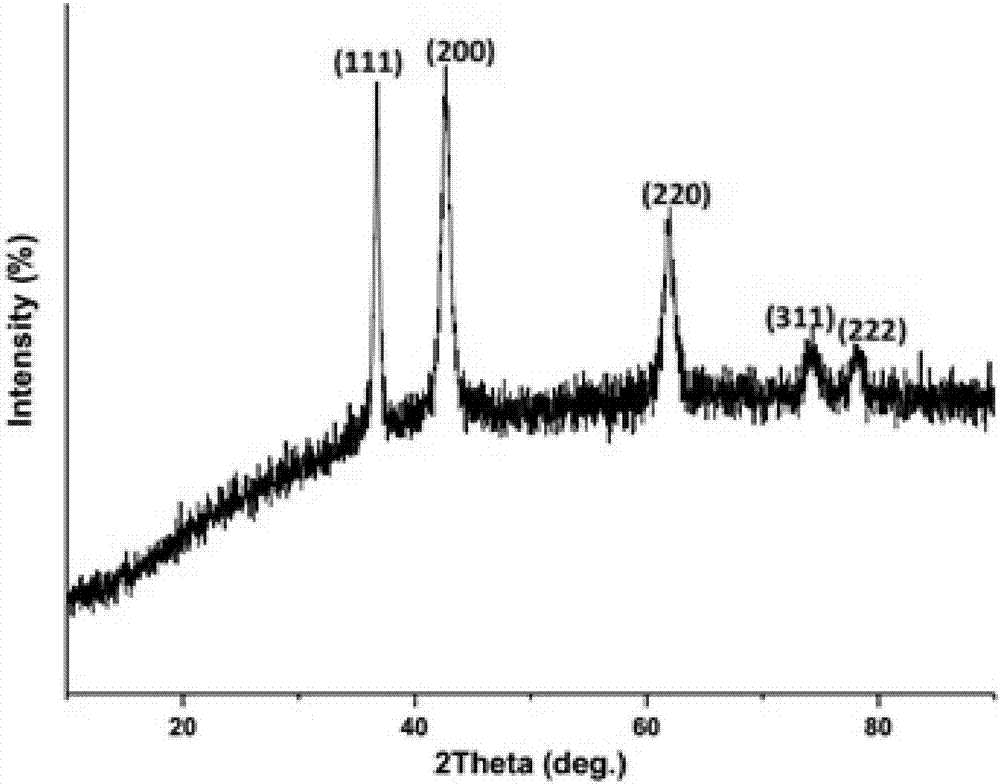
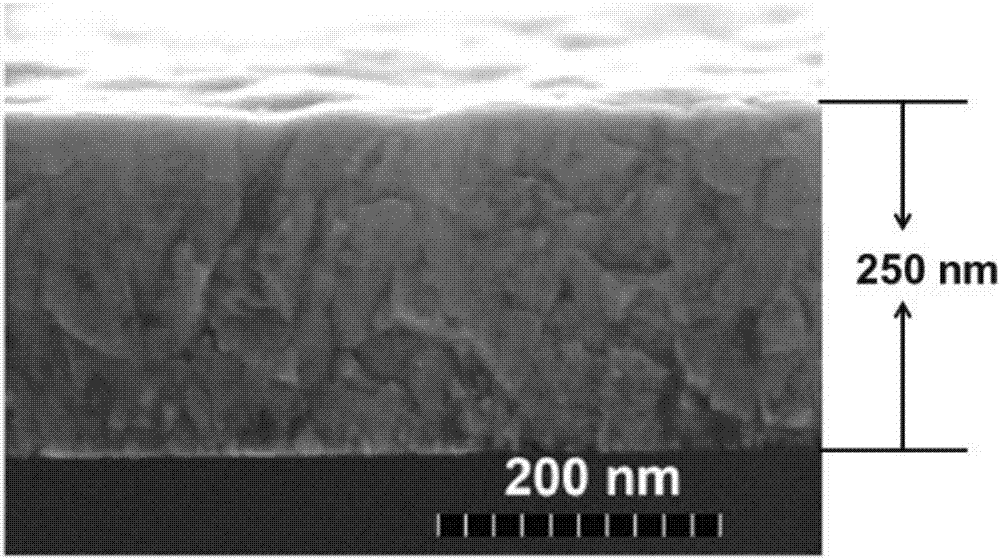
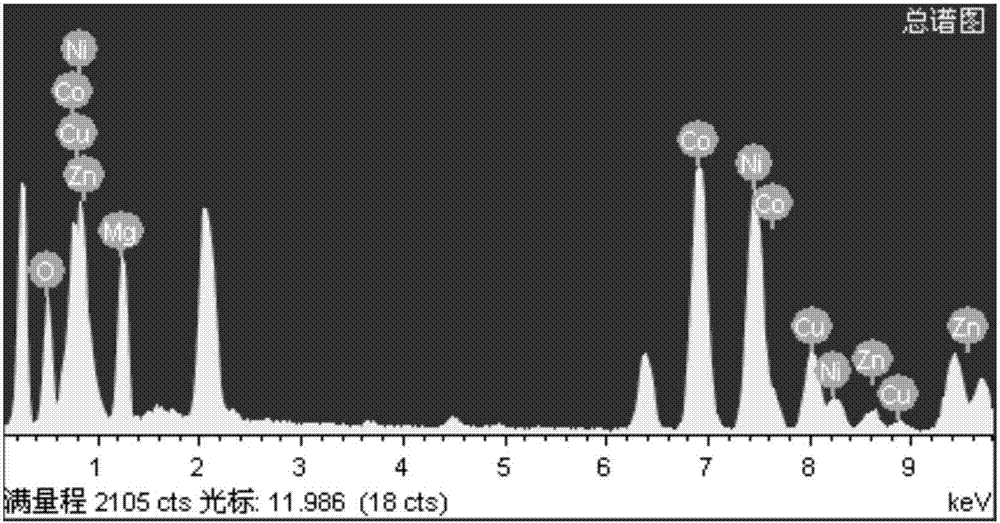
The invention discloses a lithium ion battery pentabasic high-entropy oxide nano-film as well as preparation and application thereof. The used initial raw materials comprise magnesium oxide, cobalt oxide, nickel oxide, copper oxide and zinc oxide, wherein the molar ratio of the magnesium oxide to the cobalt oxide to the nickel oxide to the copper oxide to the zinc oxide is (2-2.5):(1.5-2):(2-3):(1.5-2):(1.5-2). The pentabasic high-entropy oxide film is prepared in the following steps: performing high-energy ball milling on the oxide, uniformly mixing to prepare a target material for laser molecular beam epitaxial deposition, focusing pulse laser generated by a laser through a lens, entering the target material and performing deposition. The pentabasic high-entropy oxide nano-film is applied to a negative electrode material of the lithium ion battery and has excellent circulating characteristic and high stability. The preparation method has the characteristics of simple process, low cost and no pollution.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS ENG CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Making method for IV-VI semiconductor single crystal film and the heterogeneous structure
InactiveCN101106092AQuality improvementPrecise and controllable thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFrom condensed vaporsBeam sourceUltra-high vacuum
The invention discloses a method to produce IV-VI semiconductor single-crystal thin film and the hetero-structure thereof. Under the condition of accurately controlled ultra-high vacuum, IV-VI atom and molecular beams vaporized from a beam source furnace encounter a clean single-crystal liner surface with good crystal surface orientation, and atom and molecular reaching the surface of the liner form high-quality single-crystal thin film after processes such as attachment, transition, and crystallization on the surface of liner. Through the accurate control of growth conditions, such as beam runoff and linear temperature, extended IV-VI compounds grow on the surface of linear by a molecular layer and a molecular layer. The method can grow IV-VI semiconductor hetero-structures, including quantum-well and super-lattice. The production cost is low, and the quality is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Pulsed flow modulation gas chromatography mass spectrometry with supersonic molecular beams method and apparatus
ActiveUS20080302959A1Time-of-flight spectrometersComponent separationVapor phase chromatographyMass chromatography
There is provided a pulsed flow modulation gas chromatograph mass spectrometer with supersonic molecular beams apparatus and method for improved sample analysis. The apparatus includes a gas chromatograph with an injector for the analysis of sample compounds, a first analytical column in the gas chromatograph, a sample storage, a gas pulse generator, a pressure generator, a conduit for transferring the sample compounds into a second analytical column having a different polarity than the polarity of the first analytical column, a second gas pulse generator, a transfer line for transferring the sample compounds into a supersonic nozzle, a member for adding a makeup gas to the output gas flow of the second analytical column before the supersonic nozzle, an element for reducing the flow rate of the added makeup gas, a supersonic nozzle for the expansion of the sample with the combined second analytical column and added makeup gas, a fly-through electron ionization ion source, a mass analyzer, an ion detector for the detection of the ions of the sample compounds after their mass analysis, a data processor and presenter, and a repeater for repeating the cycle of the first gas pulse of relatively high flow rate followed by the second gas pulse of intermediate flow rate.
Owner:AMIRAV AVIV
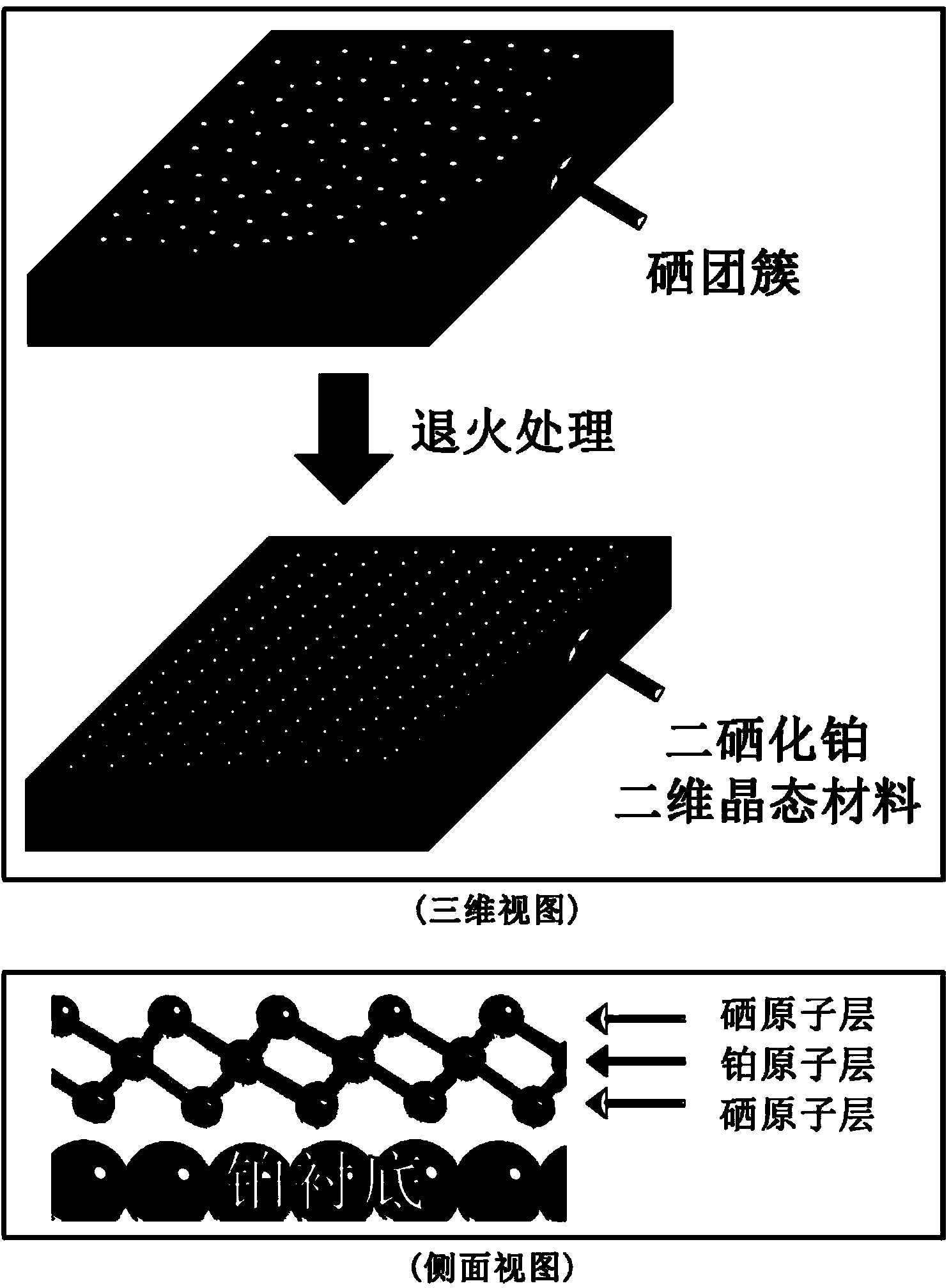
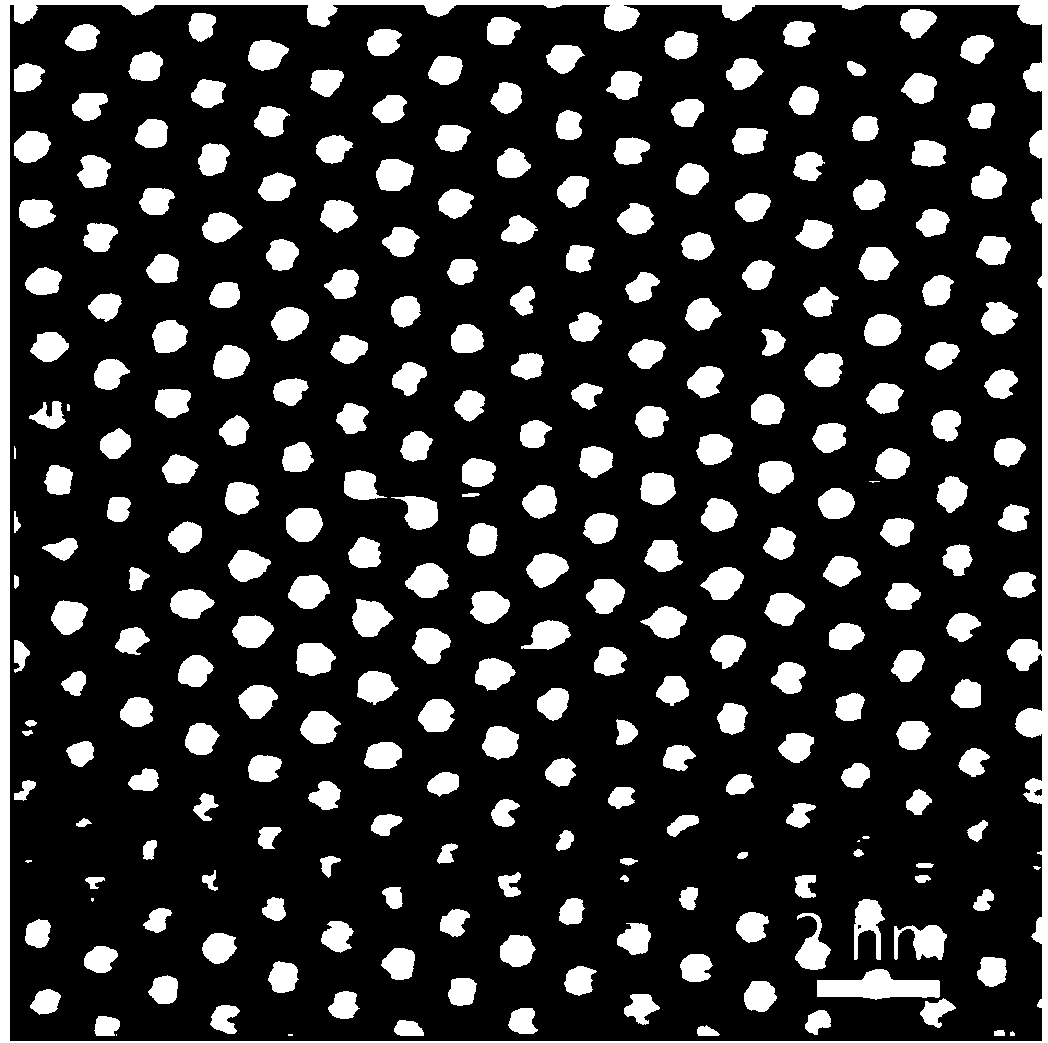
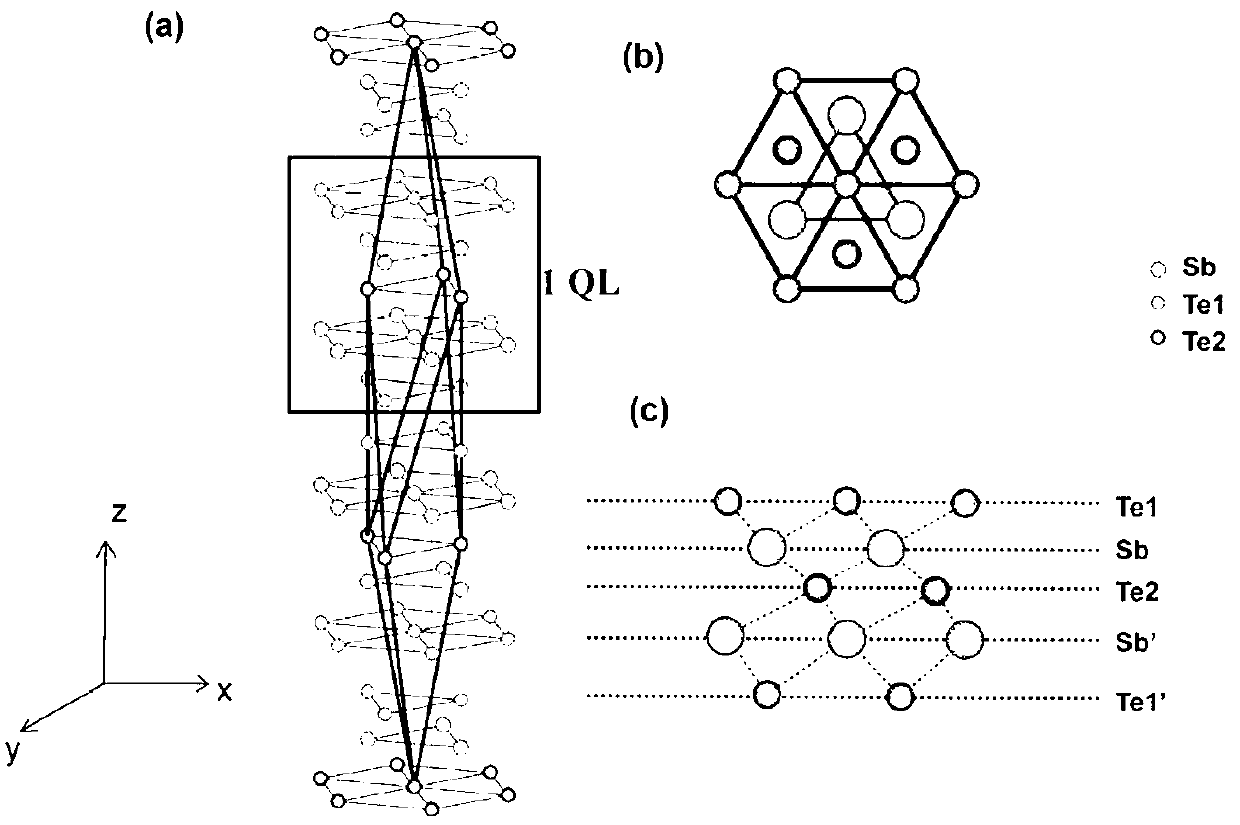
Platinum diselenide crystal material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104233214ABroaden the field of studyImprove electronic propertiesVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingTitanium diselenideSe element
The invention discloses a platinum diselenide crystal material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) under a vacuum environment, evaporating and depositing a proper amount of high purity selenium on a metal platinum substrate; and 2) carrying out an annealing treatment, so that selenium atoms covering the surface of the substrate and platinum atoms on the substrate interact to form a two-dimensional ordered crystalline state membrane structure in a sandwich arrangement of selenium-platinum-selenium so as to obtain the platinum diselenide crystal material. The inorganic two-dimensional crystalline state material is a new member of a transitional metal disulfide compound family, expands the field of research on non-carbon based two-dimensional crystal materials, and has a wide application potential in future information electronics and apparatus development and research. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the platinum diselenide two-dimensional crystalline state material with a big area and a high quality is grown on a molecular beam epitaxial method, so that the electronic properties of the platinum diselenide crystalline state material and related applications and development are favorably researched.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Field effect transistors, methods of fabricating a carbon-insulating layer using molecular beam epitaxy and methods of fabricating a field effect transistor
ActiveUS20110121409A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDiamond-like carbonField-effect transistor
Field effect transistors, methods of fabricating a carbon insulating layer using molecular beam epitaxy and methods of fabricating a field effect transistor using the same are provided, the methods of fabricating the carbon insulating layer include maintaining a substrate disposed in a molecular beam epitaxy chamber at a temperature in a range of about 300° C. to about 500° C. and maintaining the chamber in vacuum of 10−11 Torr or less prior to performing an epitaxy process, and supplying a carbon source to the chamber to form a carbon insulating layer on the substrate. The carbon insulating layer is formed of diamond-like carbon and tetrahedral amorphous carbon.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
A method for making IV-VI sector semiconductor single crystal film on CdZnTe underlay
InactiveCN101236905AQuality improvementClear interfaceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFrom condensed vaporsBridgman methodGas phase
The invention provides a method for preparing an IV-VI semiconductor single crystal thin film on a CdZnTe substrate, wherein, in a molecular beam epitaxy(MBE) device, by adopting an MBE growth method and utilizing molecular beam sources of different IV-VI compounds and under different growth temperatures(200 to 425DEG C), the single crystal thin film is epitaxially grown on the CdZnTe single crystal substrate materials; the CdZnTe substrate has a general formula of Cd1-xZnxTe, wherein X is equal to 0 to 0.3; the single crystal thin film grows by the vertical Bridgman method or vapor transport method, is cut along the (111) crystal orientation or (100) crystal orientation, is mechanically polished by Al2O3 powder and then is chemically polished by the bromine-methanol, the concentration of which is 1 percent. The method for preparing an IV-VI semiconductor single crystal thin film on a CdZnTe substrate has the advantages of being capable of realizing the controllable growth of device structures such as hetero junction, quantum well and superlattice, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
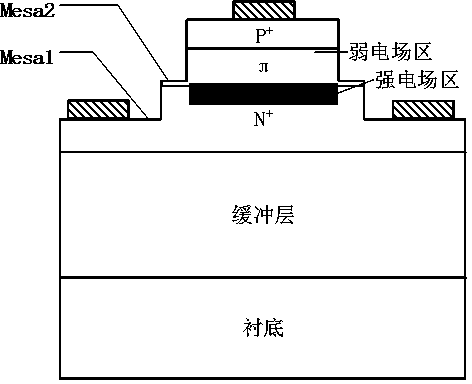
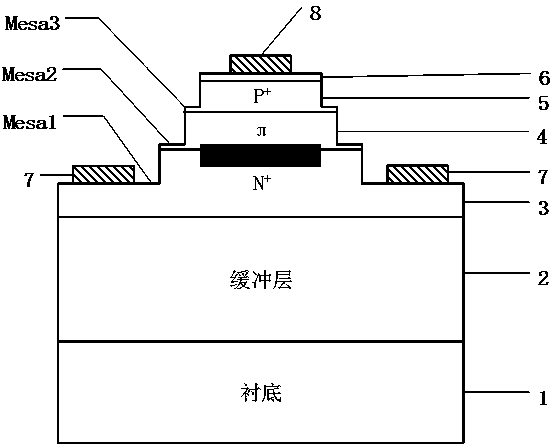
Three-mesa p-Pi-n structured III-nitride semiconductor avalanche photodetector and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104282793AAvoid premature breakdownSolve the problem of reverse premature breakdownFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesPhotodetectorElectrode Contact
The invention relates to the technical field of detectors, in particular to a three-mesa p-Pi-n structured III-nitride semiconductor avalanche photodetector and a preparation method of the three-mesa p-Pi-n structured III-nitride semiconductor avalanche photodetector. The three-mesa p-Pi-n structured III-nitride semiconductor avalanche photodetector comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, an n-type doping nitride ohmic electrode contact layer, a Pi-type nitride active layer, a p-type doping nitride layer, a p-type heavy-doping nitride ohmic contact layer, n-type ohmic contact electrodes and a p-type ohmic contact electrode, wherein the buffer layer, the n-type doping nitride ohmic electrode contact layer, the Pi-type nitride active layer, the p-type doping nitride layer and the p-type heavy-doping nitride ohmic contact layer are sequentially grown on the substrate through epitaxial growth methods such as a molecular beam epitaxial method or an organometallic chemical vapor deposition epitaxial method; the n-type ohmic contact electrodes are manufactured on the n-type layer, and the p-type ohmic contact electrode is manufactured on the p-type layer. The three-mesa p-Pi-n structured III-nitride semiconductor avalanche photodetector can solve the problems that a traditional p-i-n structured device leaks a large number of currents and the edge of the traditional p-i-n structured device can be broken through easily in advance; moreover, a three-mesa structure conducts double-suppression protection on edge electric fields of a strong electric field region and a weak electric field region of a p-Pi-n structured device, so that the edge electric field is effectively prevented from being broken through in advance.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
GeSn-GeSi material based heterogeneous phototransistor and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN105789347ANarrow detection wavelengthNarrow detection wavelength rangeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCMOSHeterojunction
The invention discloses a GeSn-GeSi material based heterogeneous phototransistor and a fabrication method thereof. A collector and an emitter of the transistor both adopt a GeSi material, a light absorption region and a base region both adopt a GeSn material, an emitter region, the base region, the light absorption region and a collector region are sequentially and vertically arranged, and a passivation layer encircles the peripheries of the emitter region, the base region, the light absorption region and the collector region. According to the fabrication method of the transistor, the GeSn material is grown by a low-temperature solid-source molecular beam epitaxial process, and the fabrication method is a standard complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) fabrication method. The GeSn material with a high light absorption coefficient forms heterojunctions in the light absorption region, the GeSi emitter region and the collector region, the light sensitivity and light current during detection of an infrared light signal by the transistor are improved, and the GeSn-GeSi material based heterogeneous phototransistor has high light absorption rate.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Preparation method of topological insulator structure
ActiveCN102995117AReduce concentrationRealization of Quantized Anomalous Hall EffectPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesStrontium titanateSurface cleaning
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
In-situ osteoplastic active calcium phosphate cement and its prepn and application
The present invention discloses an in-situ osteoplastic active calcium phosphate cement and its preparation process and application. Sodium alginate, collagen, hydrocellulose, polypeptide molecular beam, etc. are used to embed BMP, FGF, TGF-beta and other composite to maintain the activity of bioactive factor. Embedded bioactive factor is made to compound with CPC powder and mix with curing liquid to form paste capable of being moulded at will and self hardened in human body environment and humidity. Inside body, the bioactive factor can induce formation of blood vessel and new bone, formation of active tissue and functional reconstruction. The used CPC cured body may be used as calcium source and phosphorus source for forming new bone and speeding bone tissue formation. The present invention is applied for filling and repairing of bone.
Owner:SHANGHAI REBONE BIOMATERIALS
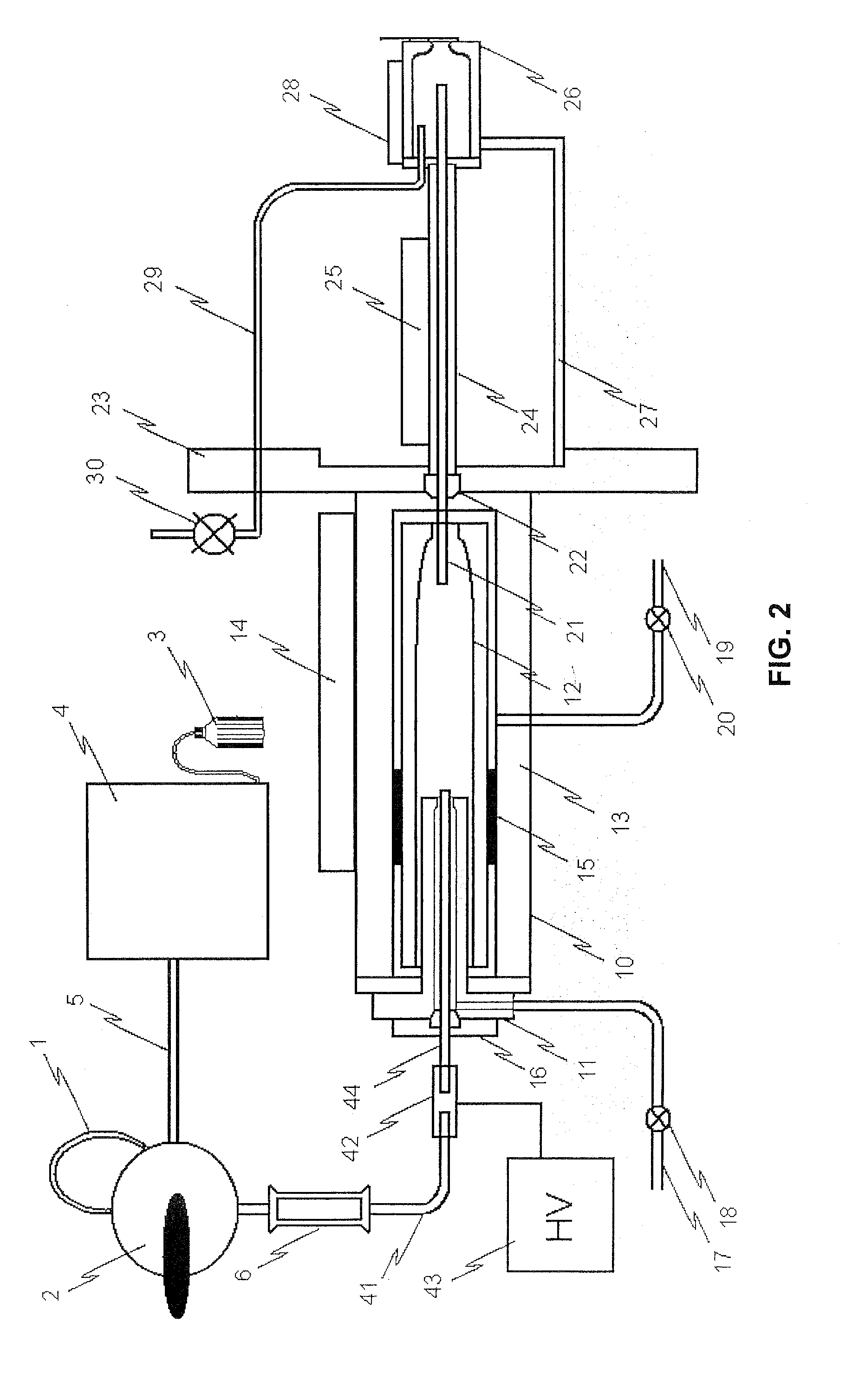
Method and apparatus for generation of molecular beam
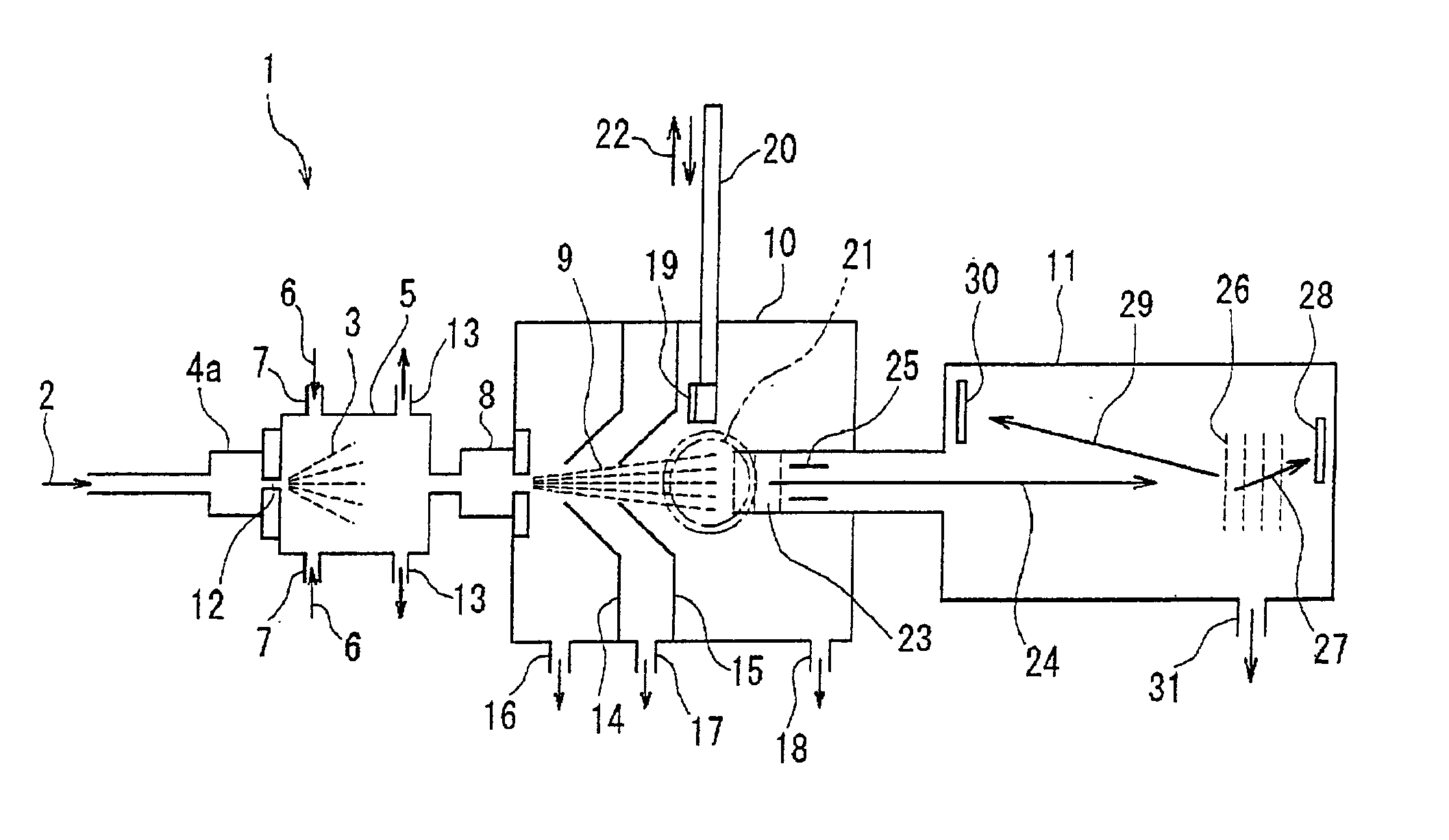
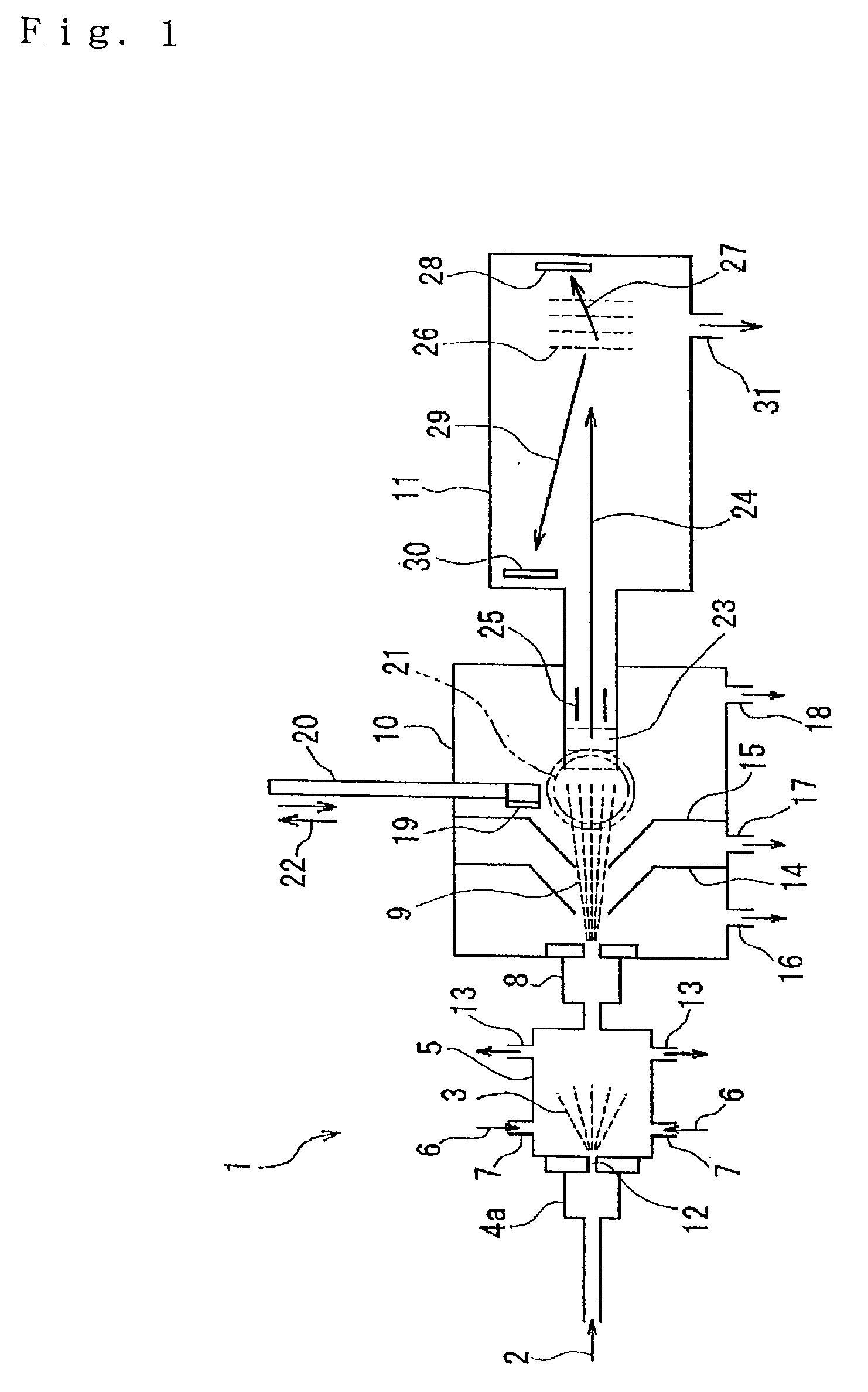
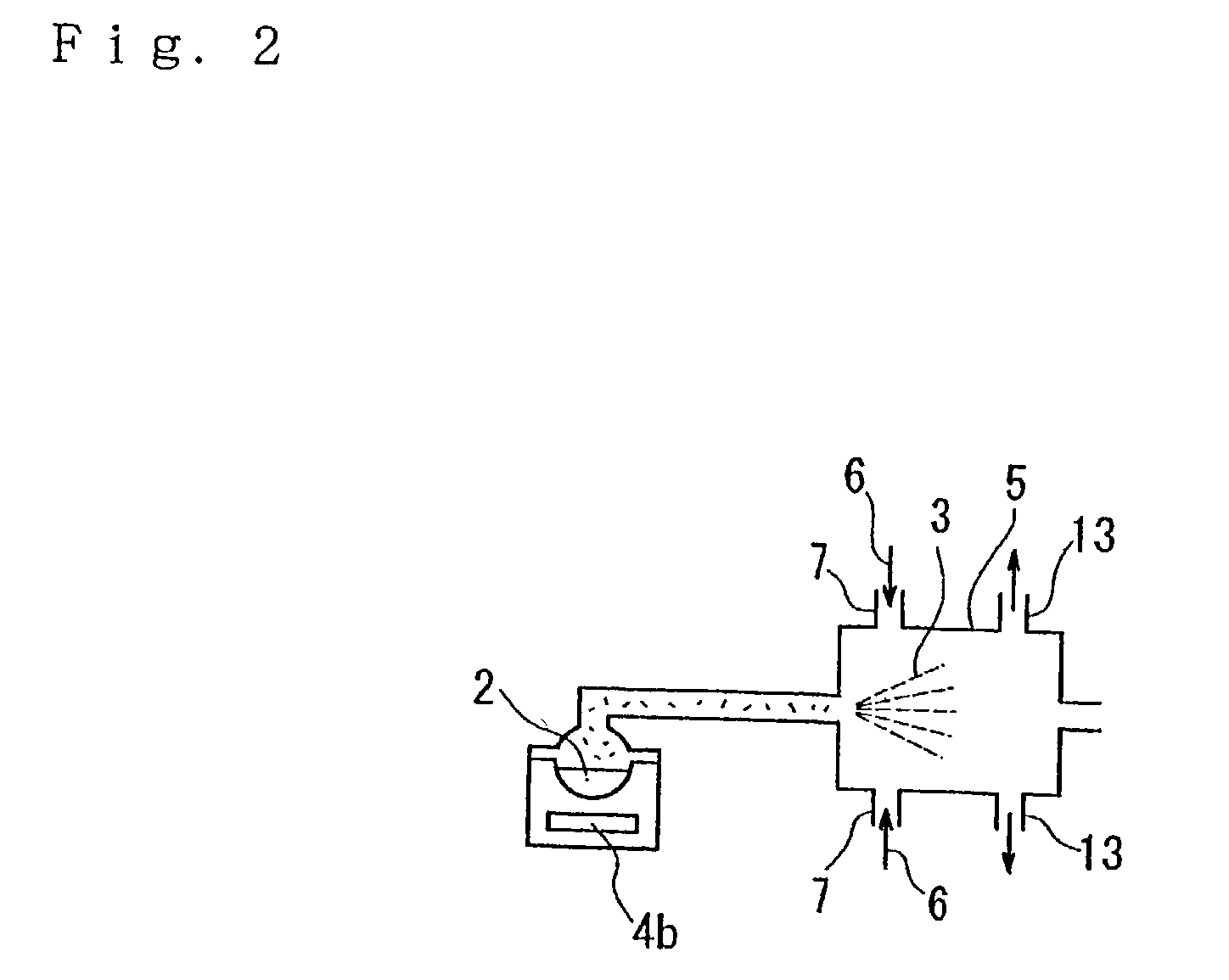
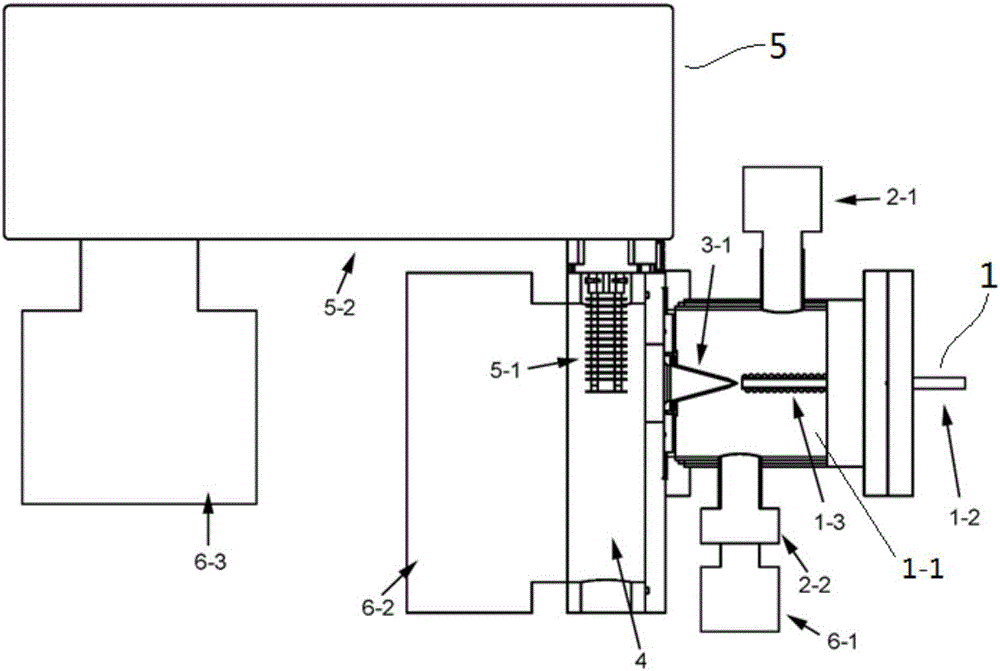
InactiveUS20030168592A1Easy to prepareImprove film qualityLaser detailsSamples introduction/extractionSolvent moleculeMolecular cluster
Here is disclosed a method for generation of a molecular beam from a sample solution, comprising steps of operating a spray-in device to introduce the sample solution in atomized state into a spray chamber, impinging a suitable gas on the sample solution in atomized state or heating the sample solution in atomized state to generate solute molecules deprived of solvent molecules, and then ejecting these solute molecules through an orifice into a low air pressure chamber. The apparatus as well as the method according to the present invention enable to generate a molecular beam for a variety of molecules, particularly for the neutral molecules which can be decomposed by heating at a high temperature or those which can not be sublimated or vaporized even by heating at a high temperature, as long as the sample solutions are prepared. Due to the method as well as the apparatus according to the invention, it is possible to conduct the mass spectroscopy studies and also other spectroscopic analyses about the molecules and the molecular clusters containing in the molecular beam generated in this manner, for example, by irradiating laser beams. It is possible to also possible to deposit the molecules on a substrate.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Manufacturing method of passivated InAs/GaSb secondary category superlattice infrared detector
InactiveCN102569521AReduce dark currentROA increaseFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCooking & bakingManufacturing technology
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of a passivated InAs / GaSb secondary category superlattice infrared detector. The method comprises the following steps that: a metal organic chemical vapor deposition method or a molecular beam epitaxial method is employed to enable a buffer layer, a secondary superlattice layer, an intrinsic secondary superlattice light absorption layer, an N type secondary superlattice layer, and an N type ohmic contact layer to be successively grown on a substrate, so that an epitaxial wafer is formed; a wet etching method or a dry etching method is employed to carry out corrosion or etching on the epitaxial wafer; a spin coating machine is used to coat a resin material on the surface of the etched epitaxial wafer; exposure is carried out; medium baking and developing are carried out as well as an upper electrode and light entering window and lower electrode windows are formed on the resin material-coated epitaxial wafer; an electrode material is manufactured; photoetching is carried out on the electrode material to form upper electrodes and lower electrodes. According to the invention, a passivated infrared detector that is manufactured by the provided manufacturing method has low dark currents and ROA is increased; besides, the method has characteristics of simple manufacturing technology, strong passivation film strength and good passivation effect and the like.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing cuprous oxide film
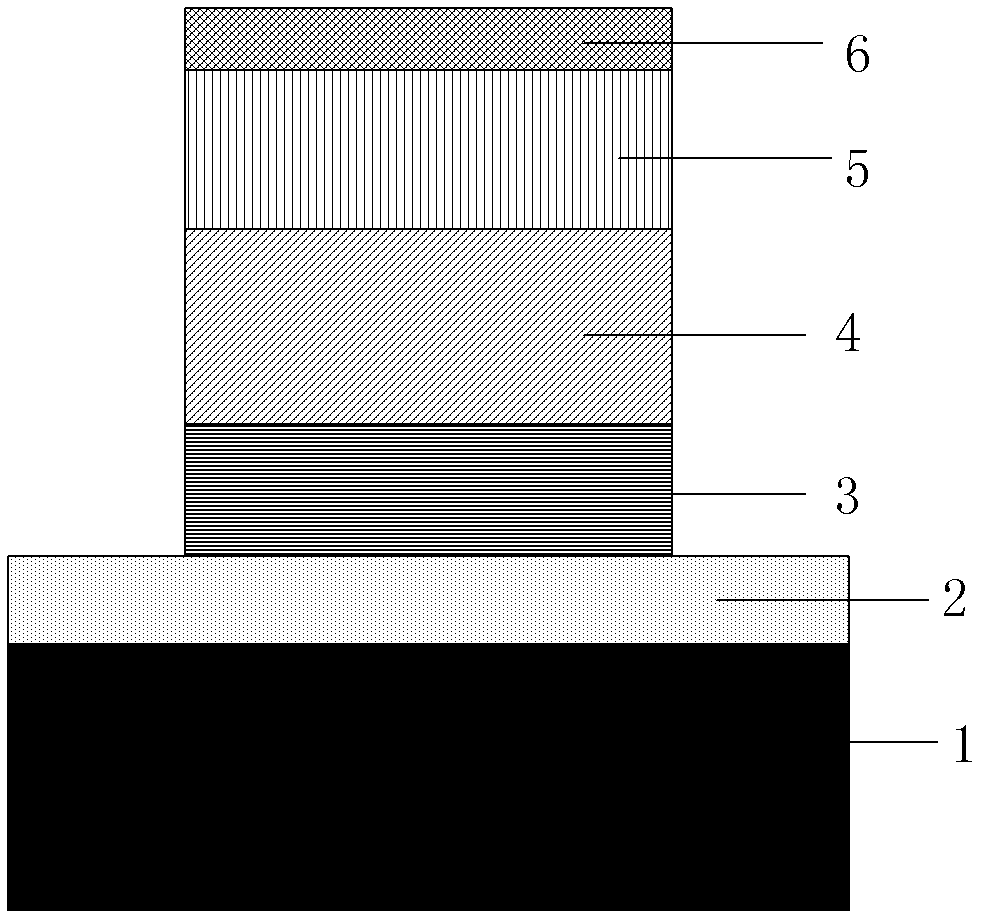
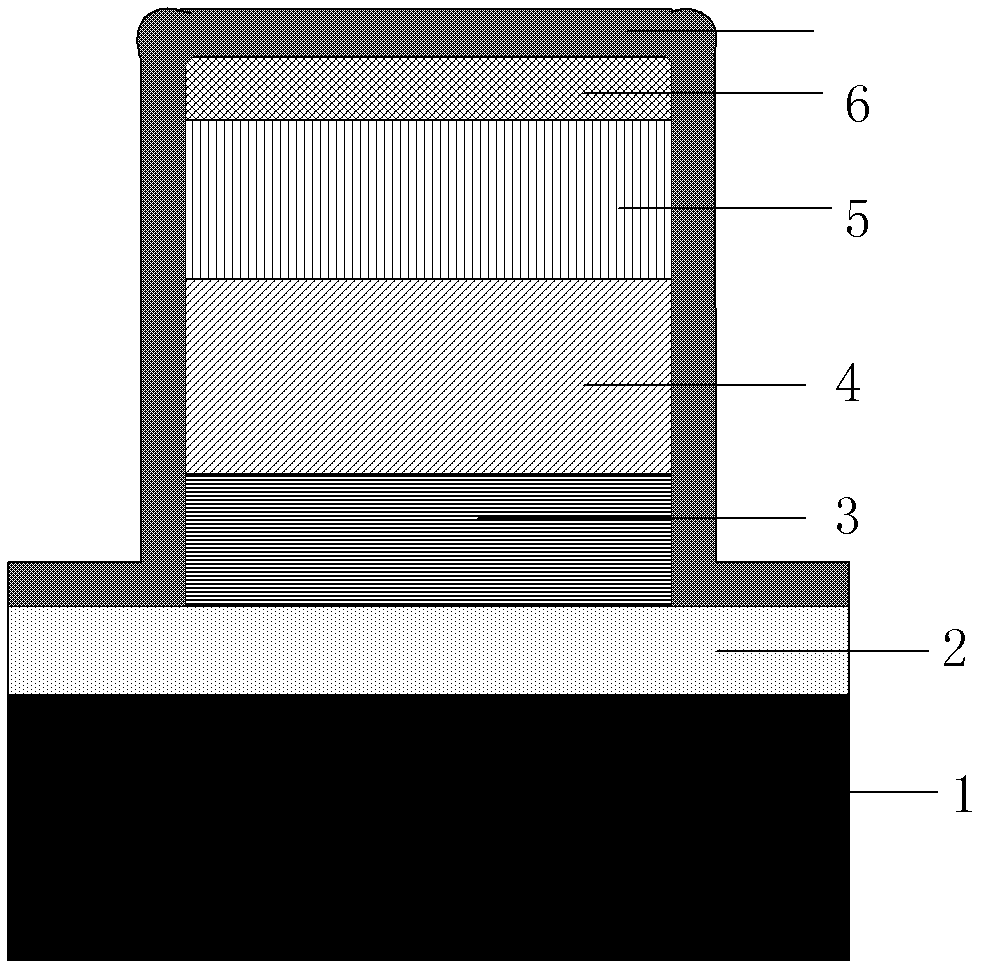
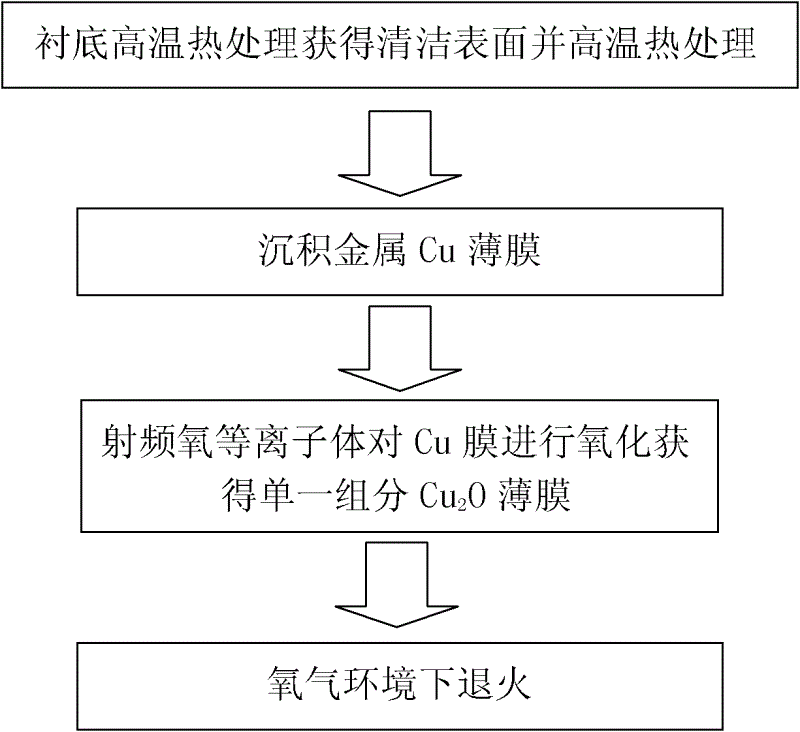
InactiveCN102623521AShorten the timeQuality improvementFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSingle crystalRadio frequency
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cuprous oxide film. The method comprises the following steps: step (1), selecting a monocrystal substrate and carrying out cleaning, and then introducing the cleaned monocrystal substrate into an ultrahigh vacuum film preparation system; step (2), carrying out heat treatment on the monocrystal substrate under the ultrahigh vacuum situation so as to remove surface impurities thereof; step (3), depositing a Cu film on the substrate surface processed in the step (2) under the condition that the air pressure is less than or equal to 10<-8>mbar, wherein the temperature of the substrate is in a range from 0 DEG C to 700 DEG C; step (4), carrying out oxidation treatment on the Cu film by utilizing radio frequency oxygen plasma; and step (5), carrying out annealing for 10 to 30 mins at the temperature of 600 to 900 DEG C and then reducing the temperature to a room temperature and taking the film out. According to the invention, growth of the Cu film with high quality is realized by utilizing an ultrahigh vacuum molecular beam epitaxial technology and a strong oxidizing property of an active oxygen atom. And the prepared Cu2O monocrystal film is expected to be applied in fields including a solar thin-film cell and an optoelectronic device and the like.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fluorescent pool for atmosphere Hox free radical real-time measurement
InactiveCN103674911ARealize online monitoringAcquisition stableFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceShielding gas
The invention discloses a fluorescent pool for atmosphere Hox free radical real-time measurement. The fluorescent pool comprises a gas flow tube, a laser tube, and a fluorescence detection tube. A vacuum pump is used to extract the gas to be detected into the gas flow tube through a pinhole-shaped molecular beam splitter; an N2 shielding gas inlet is formed in the side of the gas inlet of the gas flow tube to ensure the sampling stability and low loss. 308 nm laser emitted and tuned by a laser is guided in the laser tube, and OH free radicals in the gas to be detected in the center of the fluorescent pool is excited to generate fluorescence; a plurality of diaphragms are mounted in the laser tube to reduce influence of laser stray light; a lens assembly and a reflector collect the excited fluorescent signals; the fluorescent signals pass through an optical filter and are detected through a photomultiplier; NO gas is introduced in the gas flow tube through an NO annular intake tube; the HO2 free radicals are converted to OH free radicals, and then the HO2 free radicals are compared and measured. The fluorescent pool can respectively measure the concentration of the OH free radicals and the HO2 free radicals, and can be applied to measurement and study of the concentration of HOx which is an important radical for the atmosphere oxidability.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
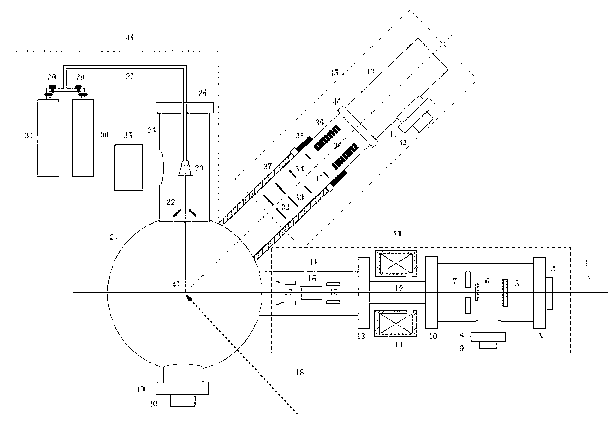
Molecular four-dimensional imaging system
InactiveCN102830095AImprove analytical abilityEasy to parseTube electron sourcesAnalysis by material excitationIonMolecular beam
The invention discloses a molecular four-dimensional imaging system based on femtosecond electron diffraction. The molecular four-dimensional imaging system comprises a femtosecond electronic gun system, an ultrasonic molecular beam system, a sample room, an ion velocity imaging system, a vacuum system and a relevant correction regulating system. Femtosecond electronic impulse is obtained by high-voltage electrode acceleration and magnetic lens focus; and direct and real-time molecular diffraction images can be obtained by the action of the electronic impulse and ultrasonic molecular beams. Auxiliary analysis information such as velocity distribution and angular distribution parameters of dissociation fragments can be obtained by integrating ion velocity imaging technology, so that electronic diffraction images of complicated molecular dynamic processes can be analyzed and identified better. The four-dimensional imaging system has relatively high time resolution capability and spatial resolution capability, can analyze four-dimensional dynamic images with femtosecond time resolution and atomic-scale spatial resolution conveniently under the assist of the ion velocity imaging technology.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
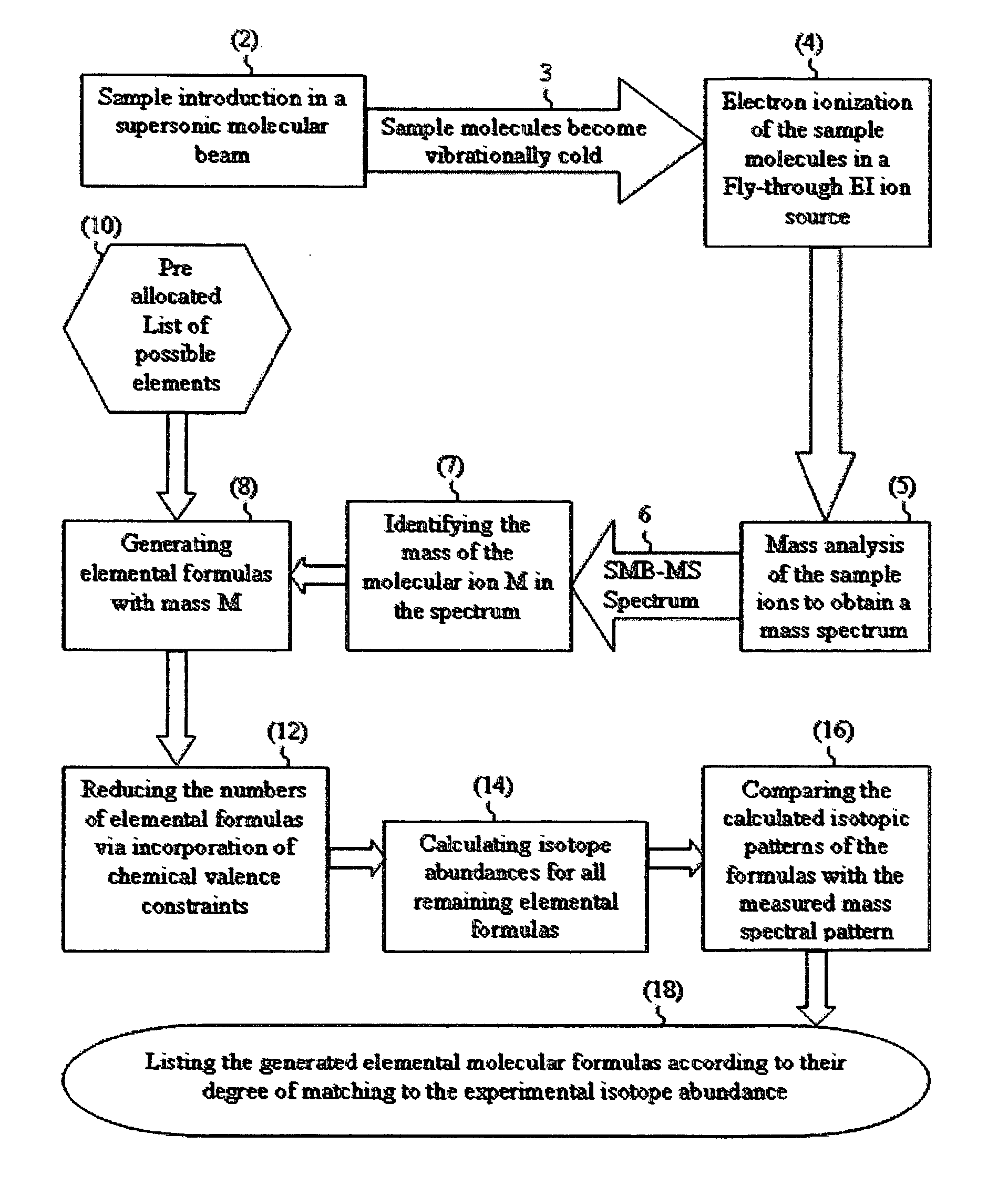
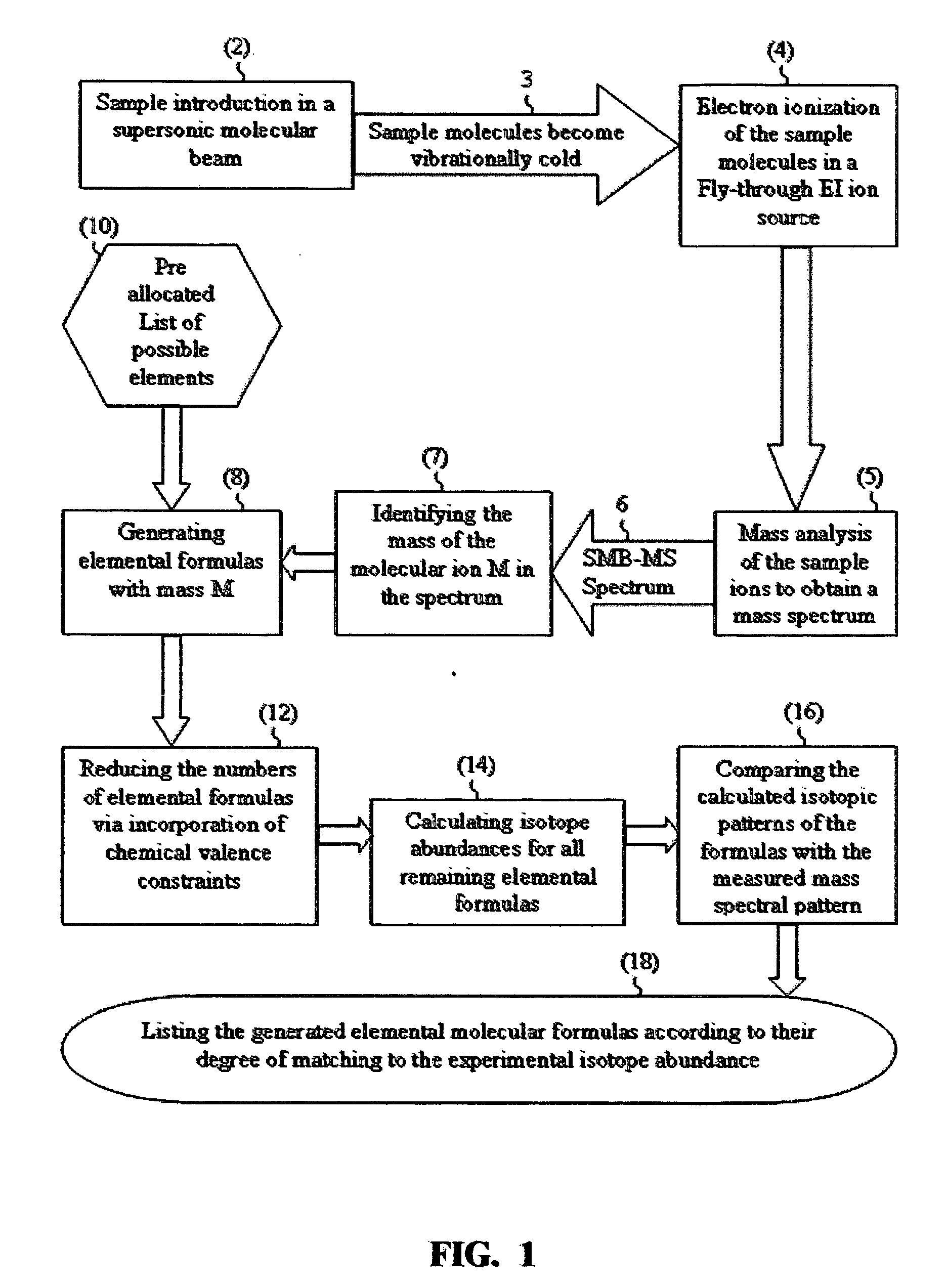
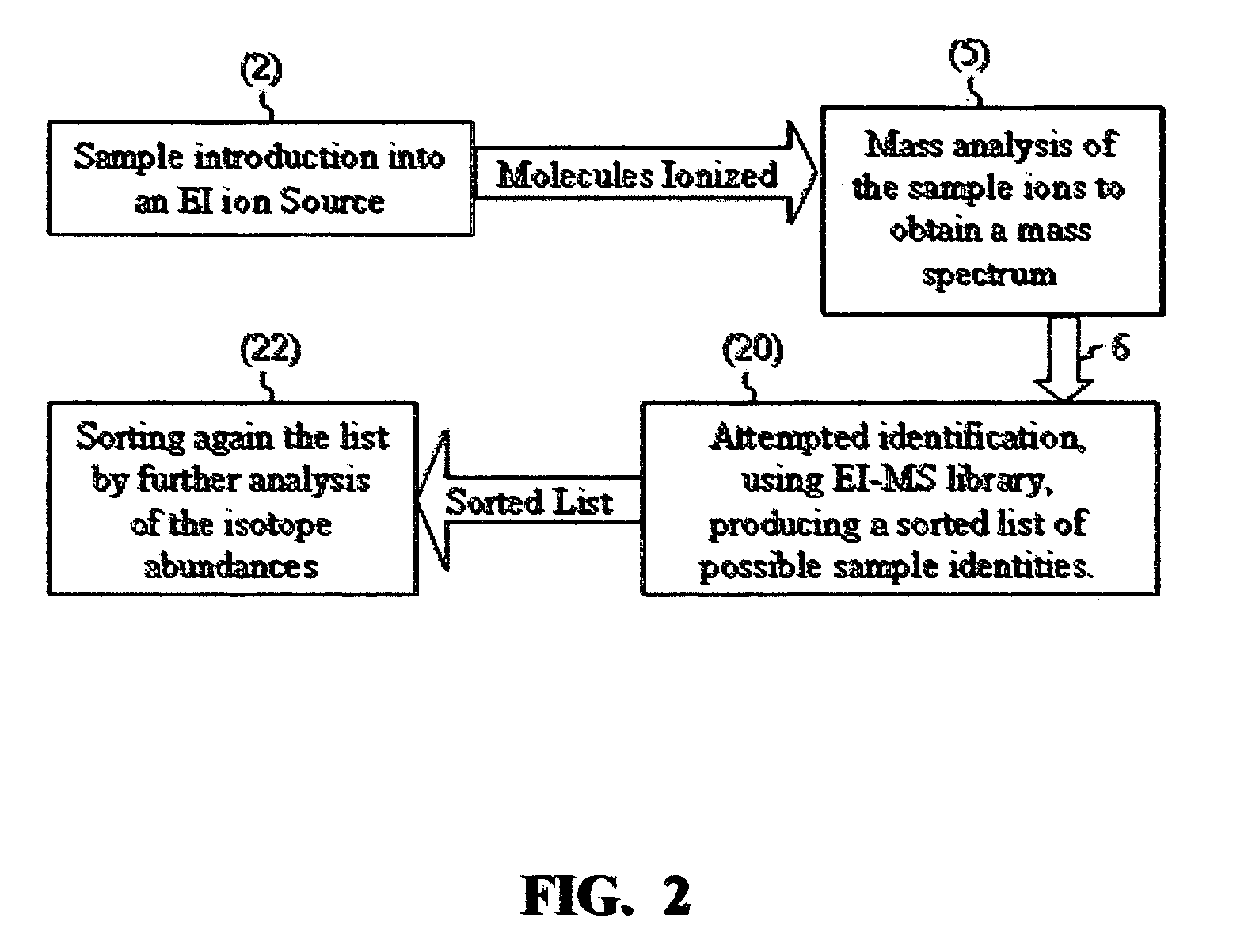
Mass spectrometric based method for sample identification
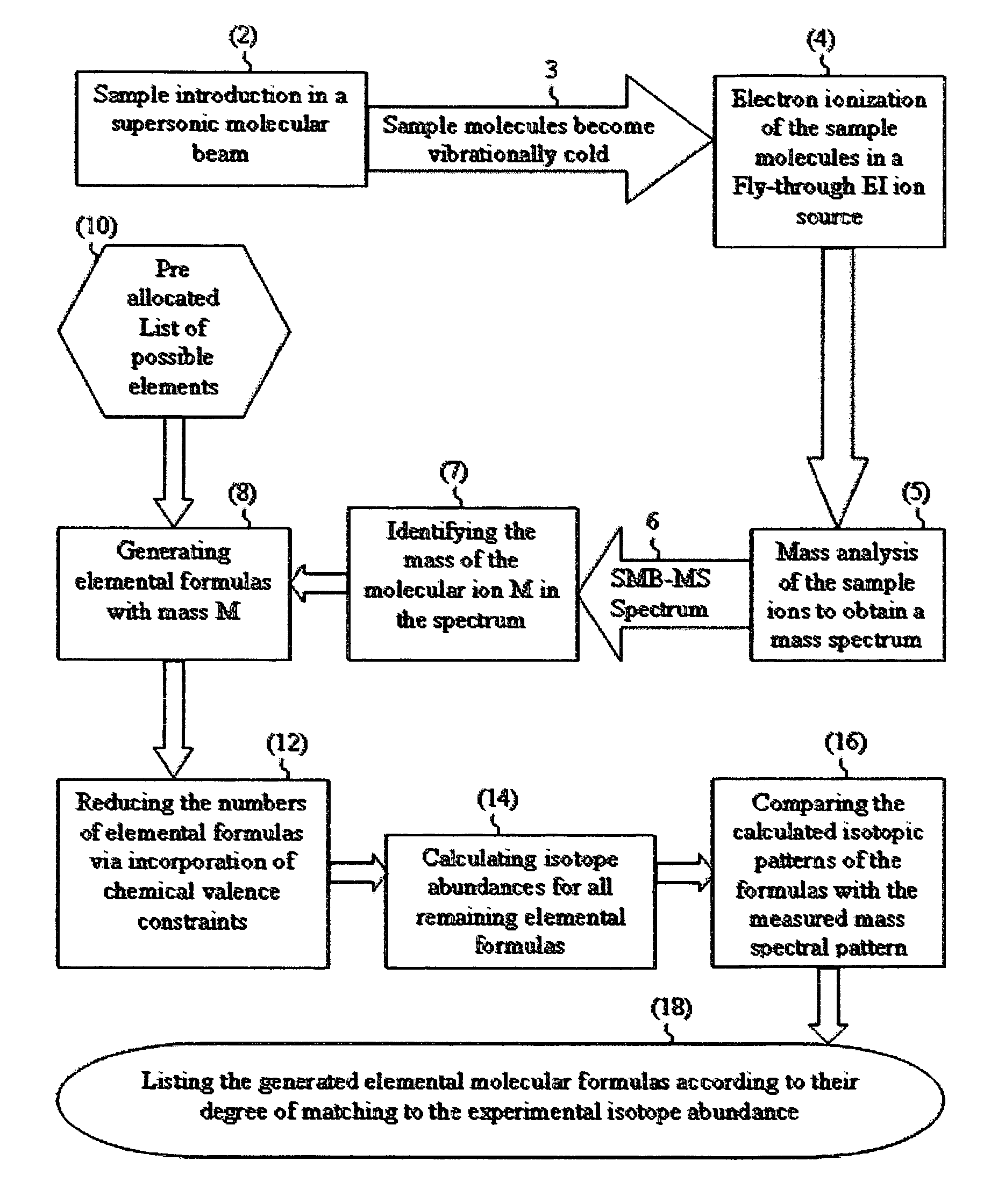
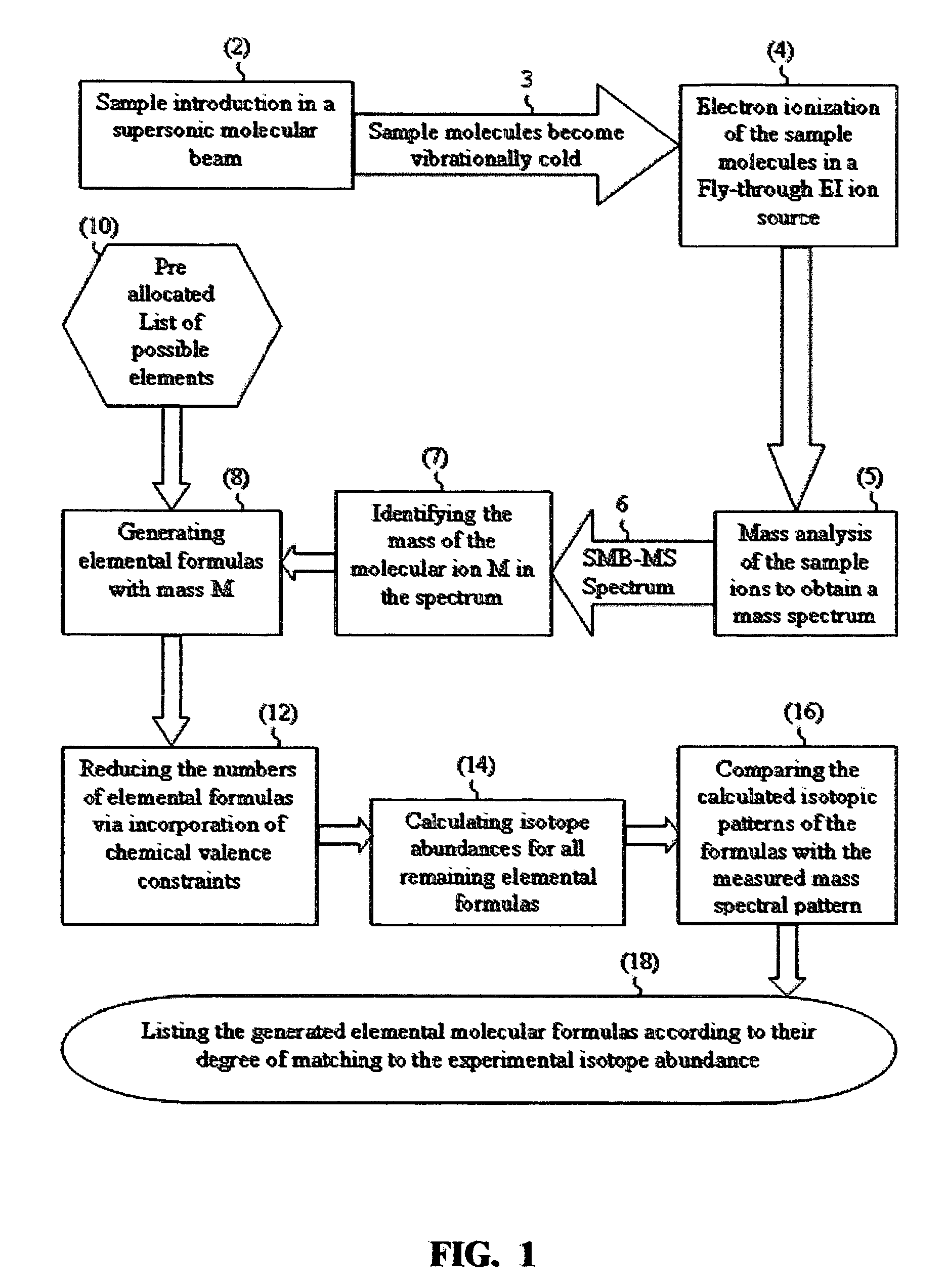
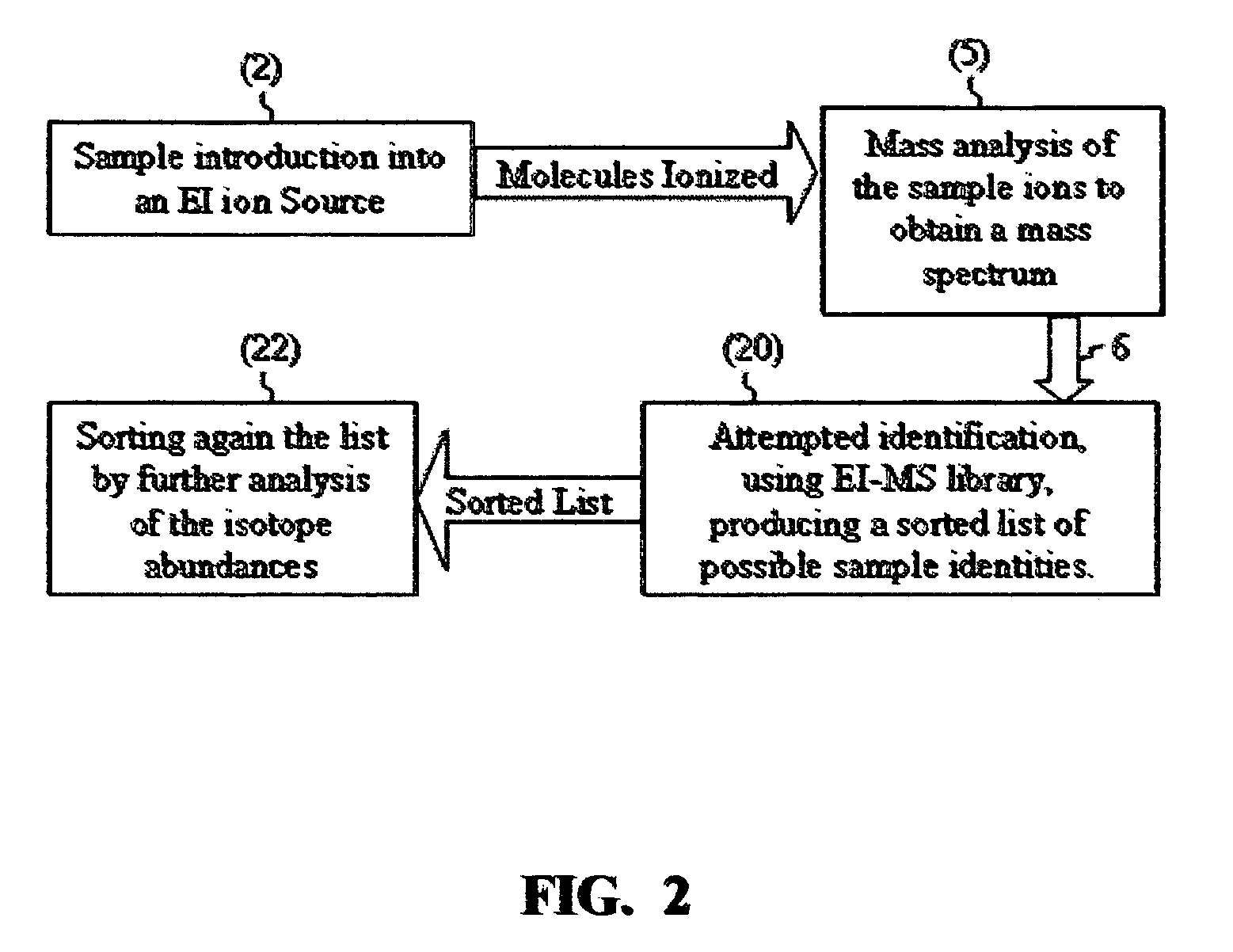
ActiveUS7345275B2Reduce in quantityMeasurement arrangements for variableDigital computer detailsIsotopeMass analyzer
There is provided a mass spectrometric based method for sample identification, including the steps of introducing sample compounds into a vacuum chamber of a mass spectrometer in a seeded supersonic molecular beam, ionizing with electrons the sample compounds, being vibrationally cold molecules, in the supersonic molecular beam during their flight through an electron ionization ion source, mass analyzing the ionized sample compounds with a mass analyzer of a mass spectrometer to obtain a mass spectrum of at least one compound in the sample, identifying the molecular ion group of isotopomers in the mass spectrum, generating various molecular elemental formulas from the identified molecular ion and a pre-allocated list of elements, reducing the number of the molecular elemental formulas by the incorporation of chemical valence considerations and constraints, calculating isotope abundances for the generated elemental formulas, comparing the calculated isotope abundances with the experimentally obtained mass spectral isotope abundance, and listing the generated elemental formulas according to their degree of matching to the experimentally obtained mass spectral isotope abundance.
Owner:AMIRAV AVIV +1
Device for in-situ detection of catalytic reaction intermediate and product and detection method
InactiveCN105717189AReal-timeRealize analysisMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansVacuum pumpingControl system
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Monolithically-integrated multi-functional ultraviolet/solar blind ultraviolet two-color detector and fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN105870225AStrong process controllabilityEasy to operateFinal product manufacturePhotometry for measuring UV lightRadio frequency magnetron sputteringHigh pressure
The invention relates to an ultraviolet / solar blind ultraviolet two-color detector, in particular to a monolithically-integrated multi-functional ultraviolet / solar blind ultraviolet two-color detector and a fabrication method thereof. A layer of gallium oxide thin film is deposited on a silicon carbide substrate by a laser molecular beam epitaxial technology, and then a layer of titanium / gold thin film is deposited on the silicon carbide substrate and the gallium oxide thin film by a mask plate through a radio frequency magnetron sputtering technology to be used as an electrode. The monolithically-integrated multi-functional two-color ultraviolet detector fabricated according to the method has the advantages of reaction sensitivity, performance stability and low dark current, the functions of ultraviolet flame detection and ultraviolet intensity detection of a solar blind region can be separately achieved in different voltage modes, and the monolithically-integrated multi-functional two-color ultraviolet detector can be used for detecting fire alarm, high-voltage line corona and solar ultraviolet intensity; and moreover, the fabrication method has the characteristics of high process controllability, high universality, restorability of repeated tests and great application prospect, and is simple to operate.
Owner:东港智科产业园有限公司
Molecular beam epitaxy growing method of high-speed vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
ActiveCN105337166AReduce the impactReduce spreadLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserDelta doping
The invention provides a molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) growing method of a high-speed vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser. The method comprises the steps that deoxidation pretreatment is conducted on a GaAs substrate, and epitaxial growth of a GaAs buffer layer, a lower DBR, an active region, an oxidation confinement layer and an upper DBR is sequentially achieved; in the growth process, the active region is clamped between the upper DBR and the lower DBR, and a delta-doping method is adopted by the potential barrier middle position of the active region, wherein a doping source adopts carbon (C), and growth is stopped for a period of time under the protection of As after delta-doping is completed. By means of the method, the technical problems of reducing a threshold, increasing differential gain and reducing nonlinear gain compression are solved, and the good effects of reducing optical losses, decreasing line width and increasing output power and intrinsic bandwidth are achieved.
Owner:WUHAN TELECOMM DEVICES
Method and apparatus for cleaning residue from an ion source component
InactiveUS20110108058A1Electric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingHydrocotyle bowlesioidesFluorocarbon
Some techniques disclosed herein facilitate cleaning residue from a molecular beam component. For example, in an exemplary method, a molecular beam is provided along a beam path, causing residue build up on the molecular beam component. To reduce the residue, the molecular beam component is exposed to a hydro-fluorocarbon plasma. Exposure to the hydro-fluorocarbon plasma is ended based on whether a first predetermined condition is met, the first predetermined condition indicative of an extent of removal of the residue. Other methods and systems are also disclosed.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
Mass spectrometric based method for sample identification
ActiveUS20060284068A1Reduce in quantityDigital computer detailsMeasurement arrangements for variableIsotopeElemental formula
There is provided a mass spectrometric based method for sample identification, including the steps of introducing sample compounds into a vacuum chamber of a mass spectrometer in a seeded supersonic molecular beam, ionizing with electrons the sample compounds, being vibrationally cold molecules, in the supersonic molecular beam during their flight through an electron ionization ion source, mass analyzing the ionized sample compounds with a mass analyzer of a mass spectrometer to obtain a mass spectrum of at least one compound in the sample, identifying the molecular ion group of isotopomers in the mass spectrum, generating various molecular elemental formulas from the identified molecular ion and a pre-allocated list of elements, reducing the number of the molecular elemental formulas by the incorporation of chemical valence considerations and constraints, calculating isotope abundances for the generated elemental formulas, comparing the calculated isotope abundances with the experimentally obtained mass spectral isotope abundance, and listing the generated elemental formulas according to their degree of matching to the experimentally obtained mass spectral isotope abundance.
Owner:AMIRAV AVIV +1
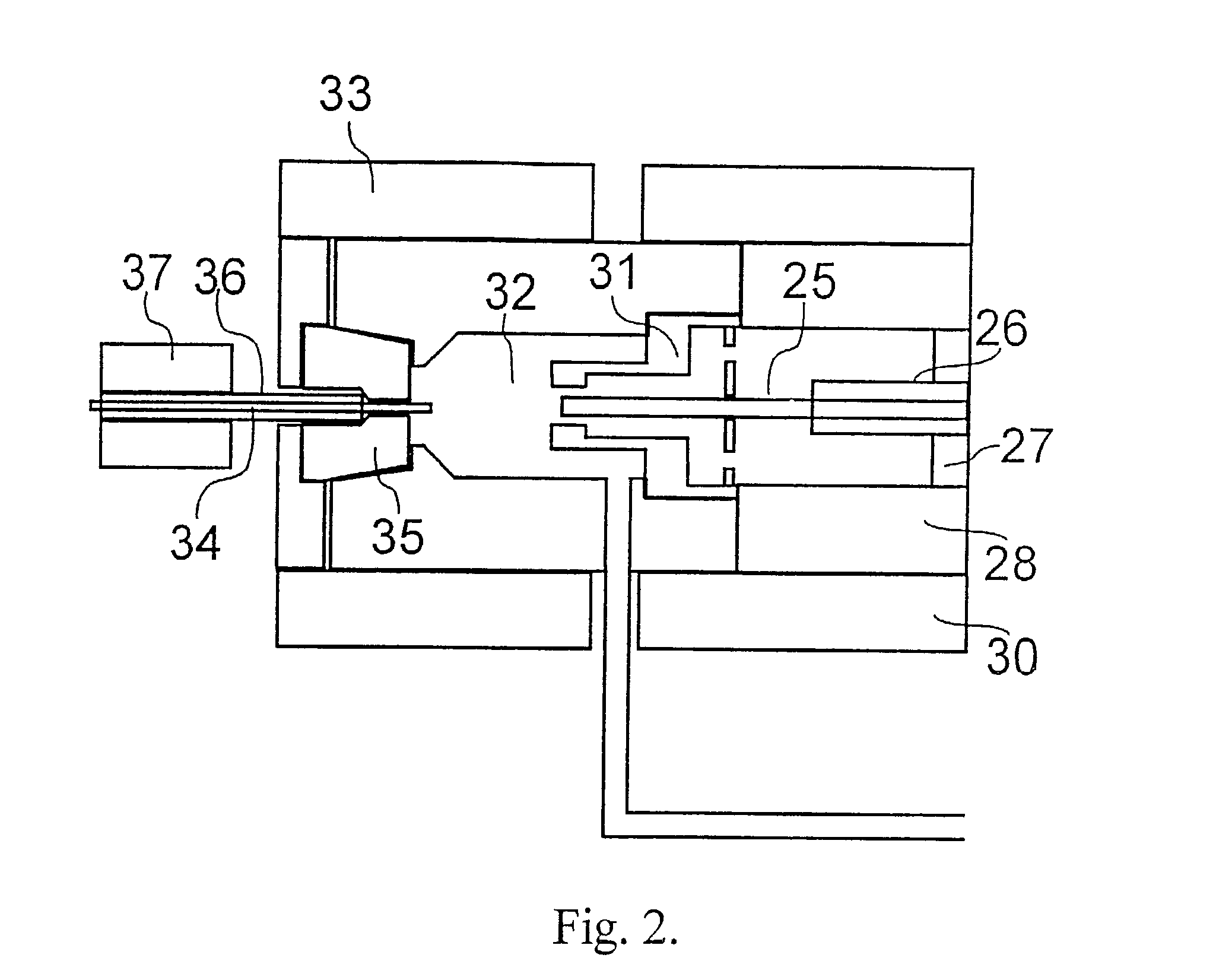
Molecular beam source apparatus for film deposition and method for depositing film by molecular beam
InactiveCN1393575AImprove qualityIncrease profitPolycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingCrucibleEffusion
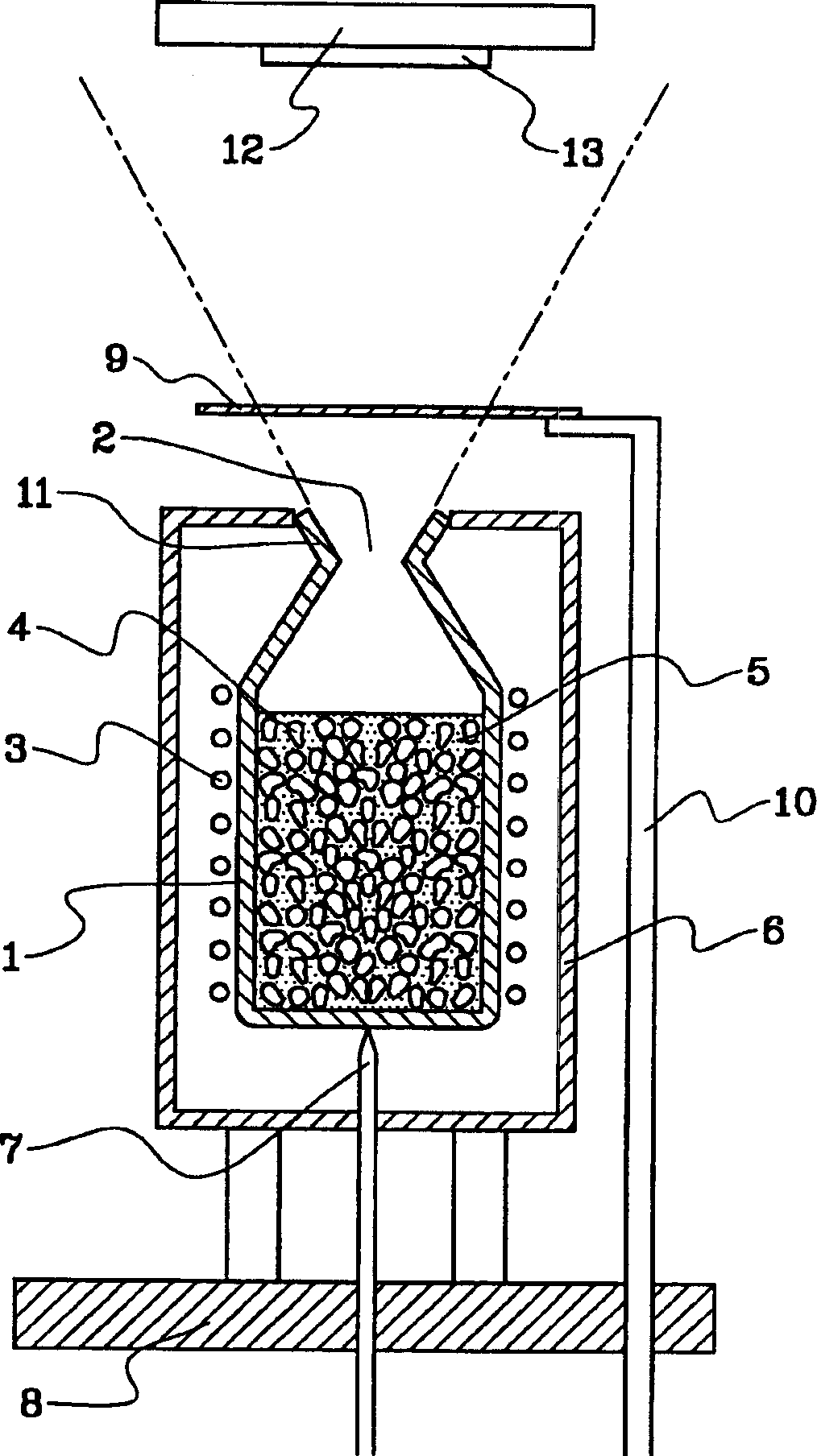
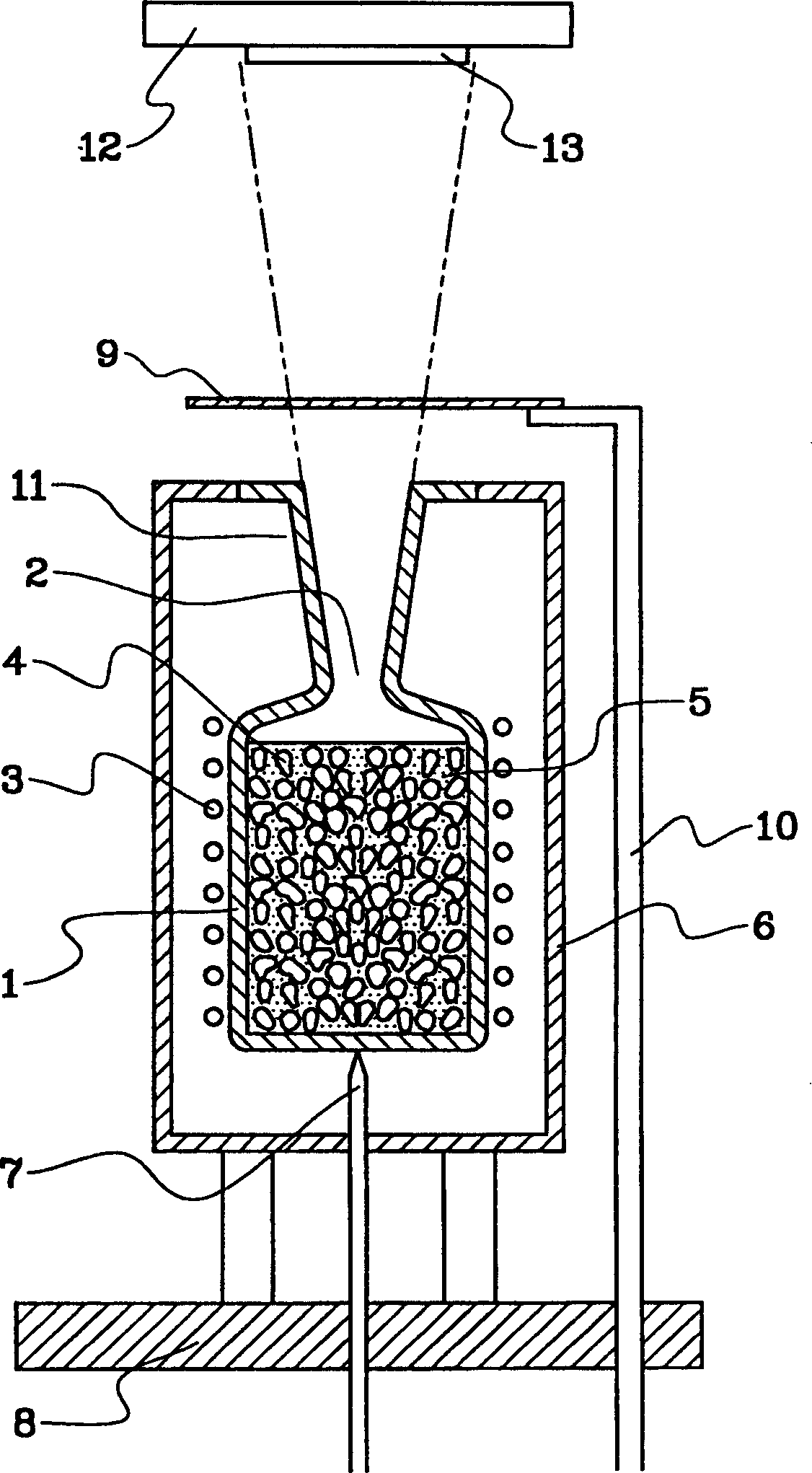
A molecular beam epitaxy effusion cell, in which effusion material 5 is heated to melt down to be evaporated, so as to generate vapor molecule for growth of a thin film thereof upon a solid body surface, comprises: a crucible 1 for containing the effusion material 5 therein; and a heating means for heating the effusion material 5 contained within the crucible 1, wherein in the crucible 1 is contained heat conduction medium 4, being stable thermally and chemically and having heat conductivity higher than that of the effusion material 5, such as of pyrolytic boron nitride (PBN), together with the effusion material 5.
Owner:CHOSHU IND
Back shining type ZnO base ultraviolet imaging solid state focal plane detection array and its preparation
InactiveCN101055881AFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndium bumpUltraviolet lights
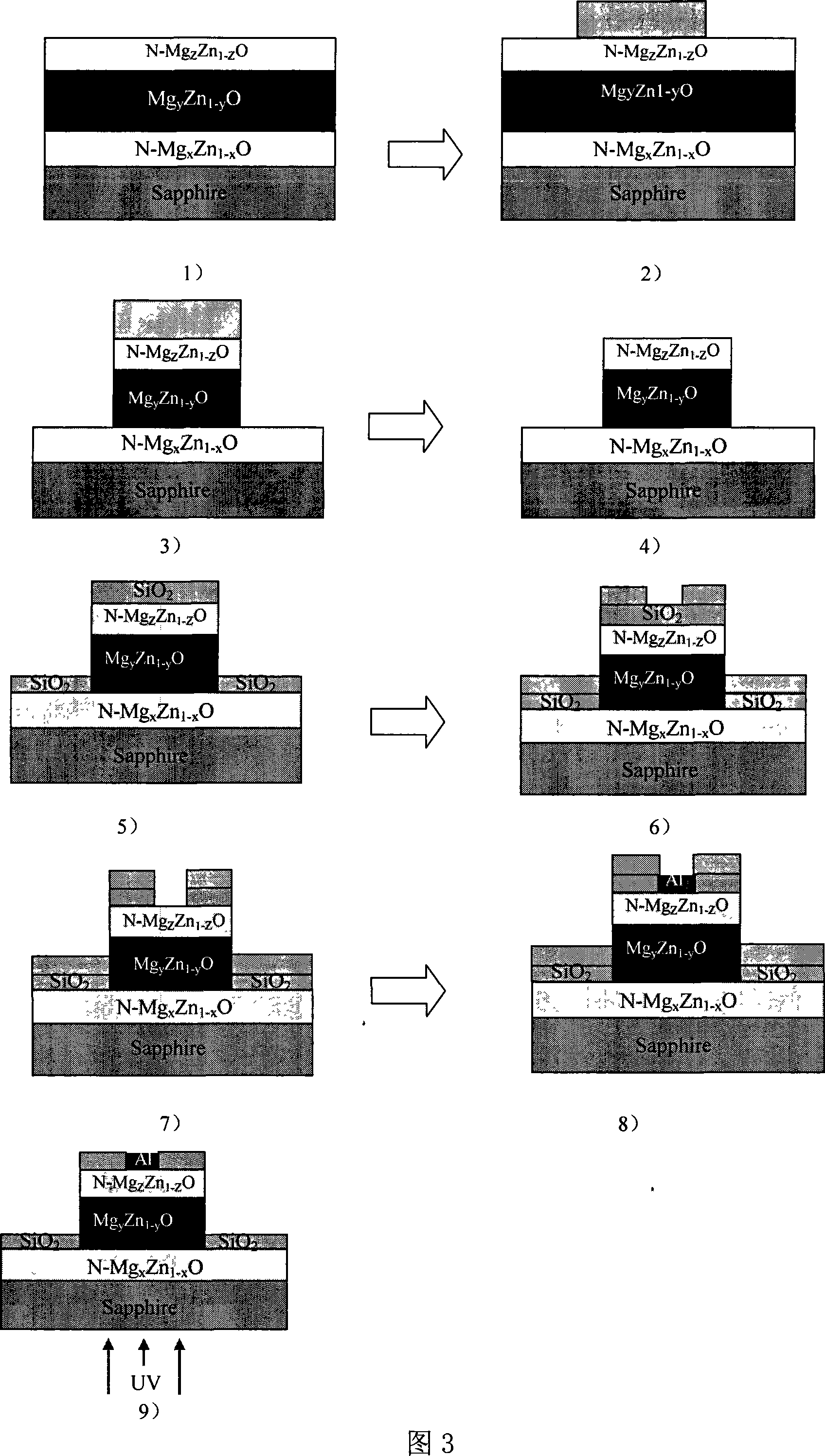
The invention relates to a backlight ZnO-based ultraviolet imaging solid focal plane surveying array and preparation, which on the sapphire (0001)substrate of double-face polishing, uses laser molecular beam to epitaxially grow a MgxZn1-xO(BexZn1-xO) nesa heavily doped with Al, then epitaxially growing a MgyZn1-yO layer without adulterant, sensitive to ultraviolet light. Then a MgzZn1-zO ohm contact epitaxial layer heavily doped with Al is gengerated on the upper surface. An array pixel cell structure is formed by using a photoetching and ICP ion etching method, then uses RF magnetron sputtering to plate a SiO2 passivation layer, based on the etched graph. An Al contact of electrodes etched by reactive ion uses a method of evaporation plated film to form a metallic contact, for rapid annealing activation of an ultraviolet sensitive active layer to form an ohm contact, thus getting a backlight ZnO-based ultraviolet imaging solid focal plane surveying array. The invention and the matched Si-CMOS readout circuit chip are interconnected through indium bumps, which are put on the focal plane of the ultraviolet lens, added with the corresponding image processing, memory circuit and software to form a complete ultraviolet imaging device.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Combinatorial synthesis of material chips
InactiveUS20050166850A1Promote exchangeLarge area uniformityLiquid surface applicatorsSequential/parallel process reactionsEngineeringCombinatorial synthesis
Systems and methods for providing in situ, controllably variable concentrations of one, two or more chemical components on a substrate to produce an integrated materials chip. The component concentrations can vary linearly, quadratically or according to any other reasonable power law with one or two location coordinates. In one embodiment, a source and a mask with fixed or varying aperture widths and fixed or varying aperture spacings are used to produce the desired concentration envelope. In another embodiment, a mask with one or more movable apertures or openings provides a chemical component flux that varies with location on the substrate, in one or two dimensions. In another embodiment, flow of the chemical components through nuzzle slits provides the desired concentrations. An ion beam source, a sputtering source, a laser ablation source, a molecular beam source, a chemical vapor deposition source and / or an evaporative source can provide the chemical component(s) to be deposited on the substrate. Carbides, nitrides, oxides, halides and other elements and compounds can be added to and reacted with the deposits on the substrate.
Owner:INTEMATIX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com