Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
730results about "Crankshaft bearings" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
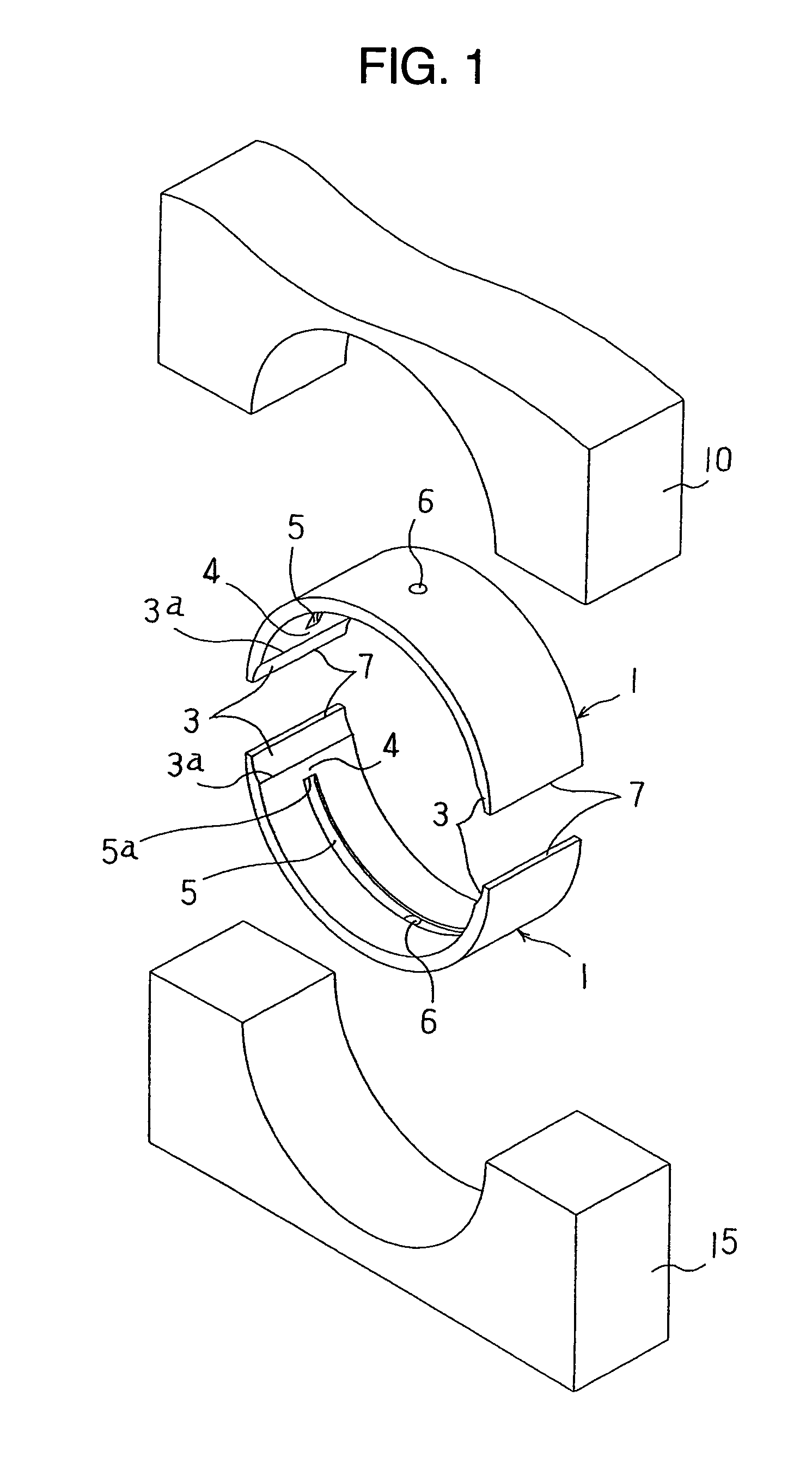
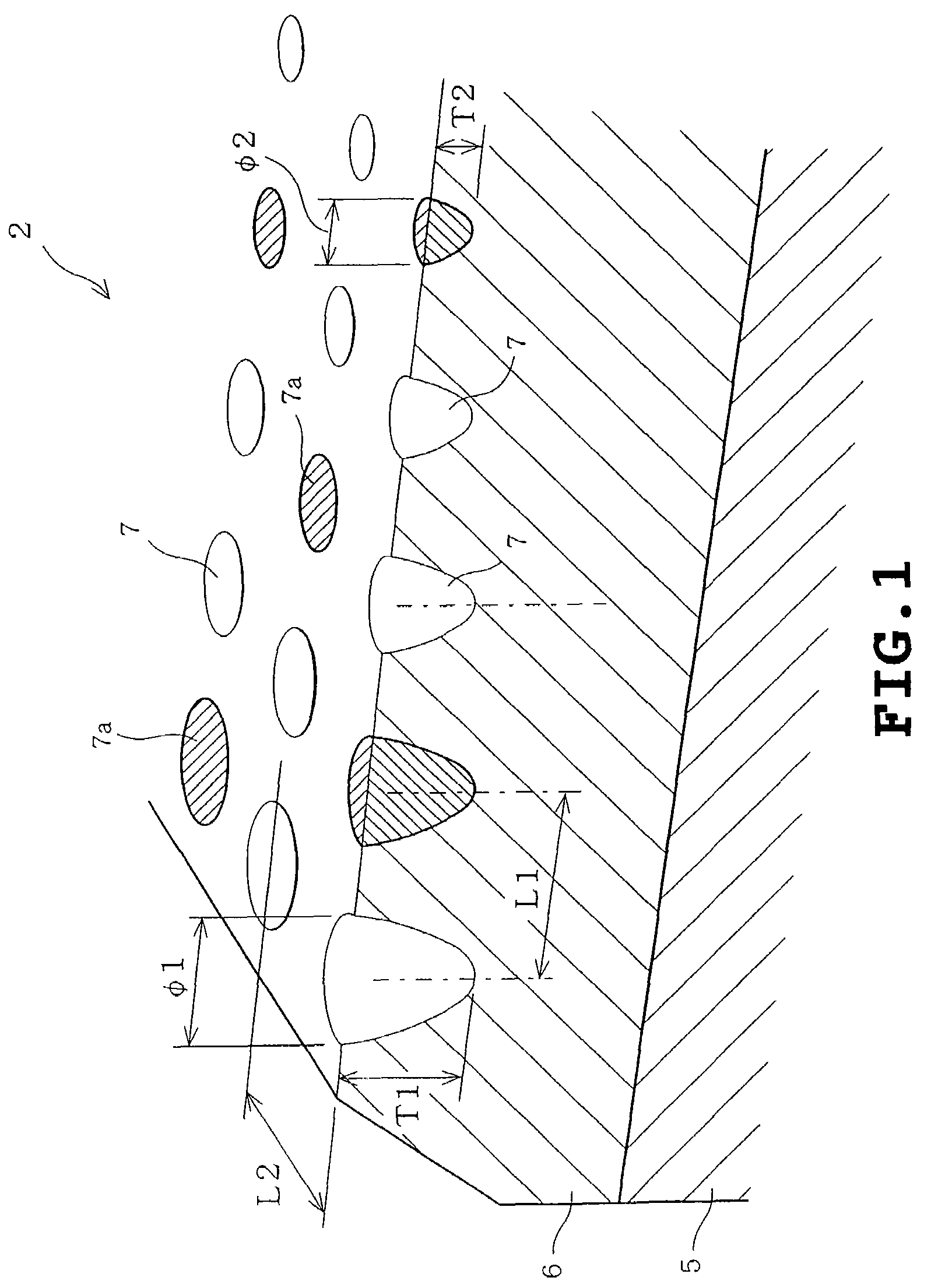
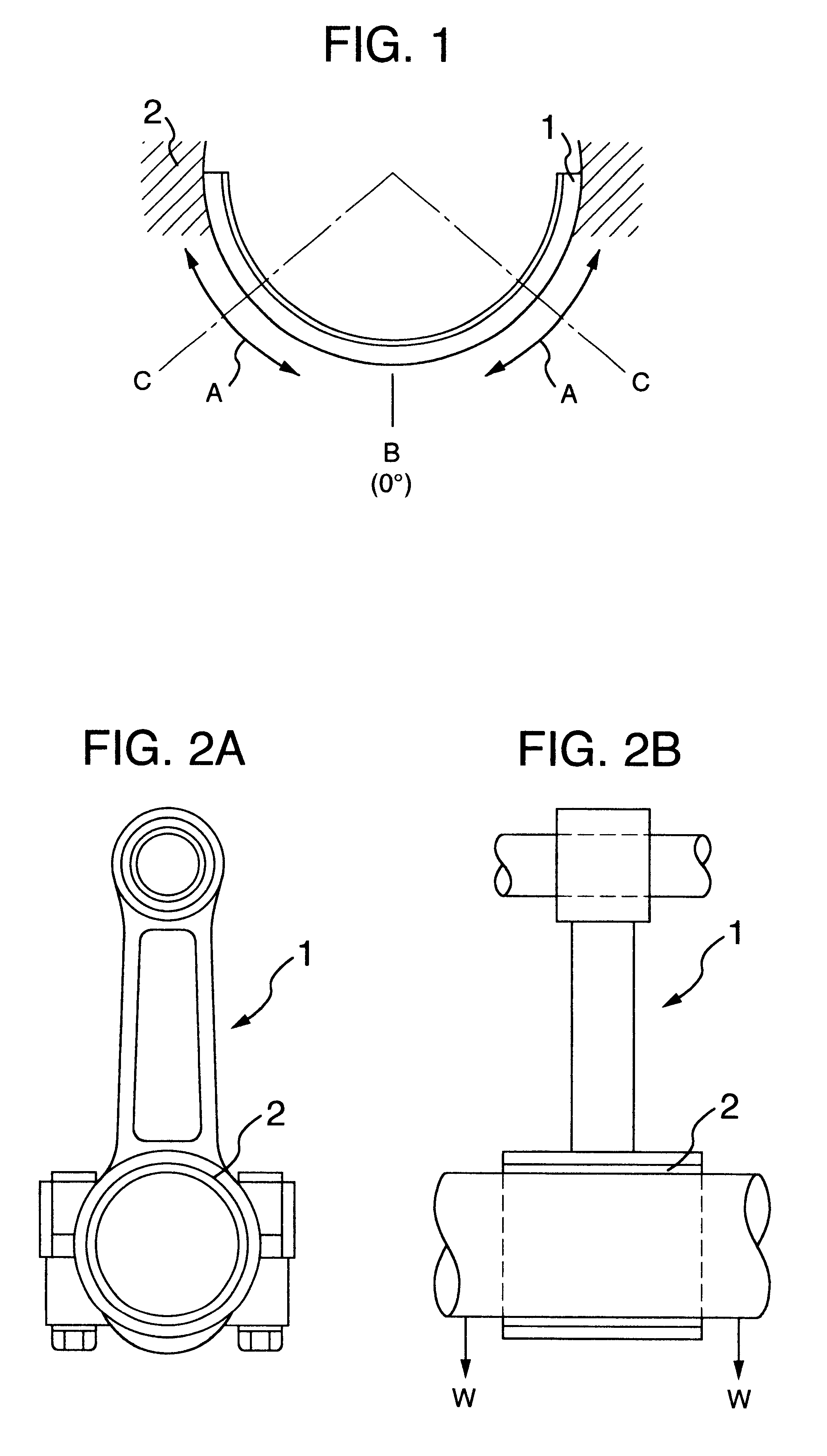
Sliding bearing and its production method
A sliding bearing, which comprises a lining and a bismuth or bismuth-alloy overlay having improved compatibility and fatigue resistance is provided. The overlay is characterized by the following orientation. The relative ratio of the X-ray diffraction intensity I[hkl] of the bismuth or bismuth-alloy overlay defined below satisfies the following conditions (a) and (b):(a) the relative ratio of the X-ray diffraction intensity I[hkl] of planes other than the {012} planes is from 0.2 to 5 times as high as the ratio of the X-ray diffraction intensity I[012], namely, 0.2I[012]<=I[hkl]<=5I[012](b) the relative ratio of the X-ray diffraction intensity I[hkl] of three or more planes other than {012} planes ranges from 0.5 to 2 times as high as the ratio of the X-ray diffraction intensity I[012], namely, 0.5I[012]<=2I[012].
Owner:TAIHO INDUSTRIES CO LTD +2
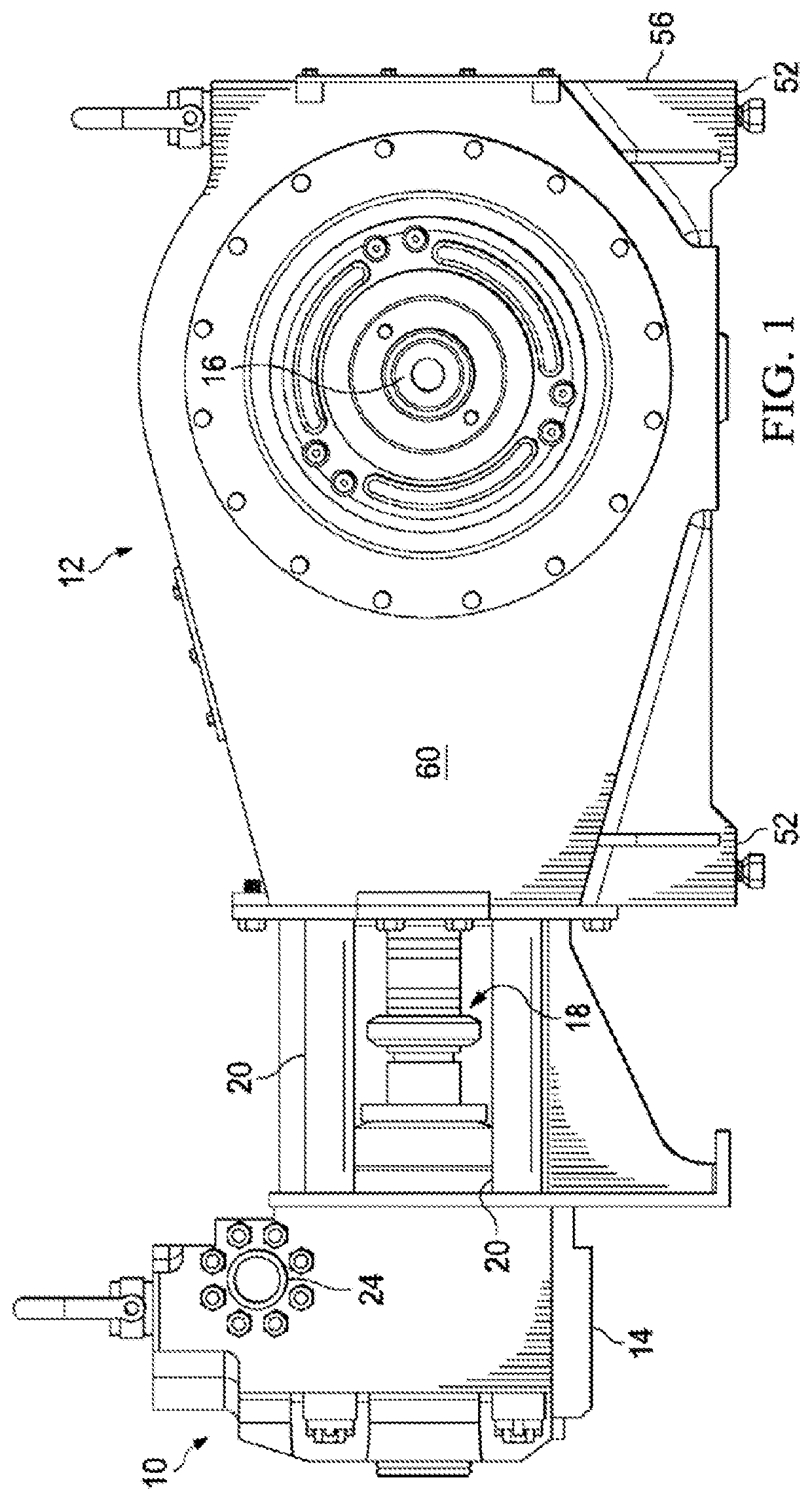
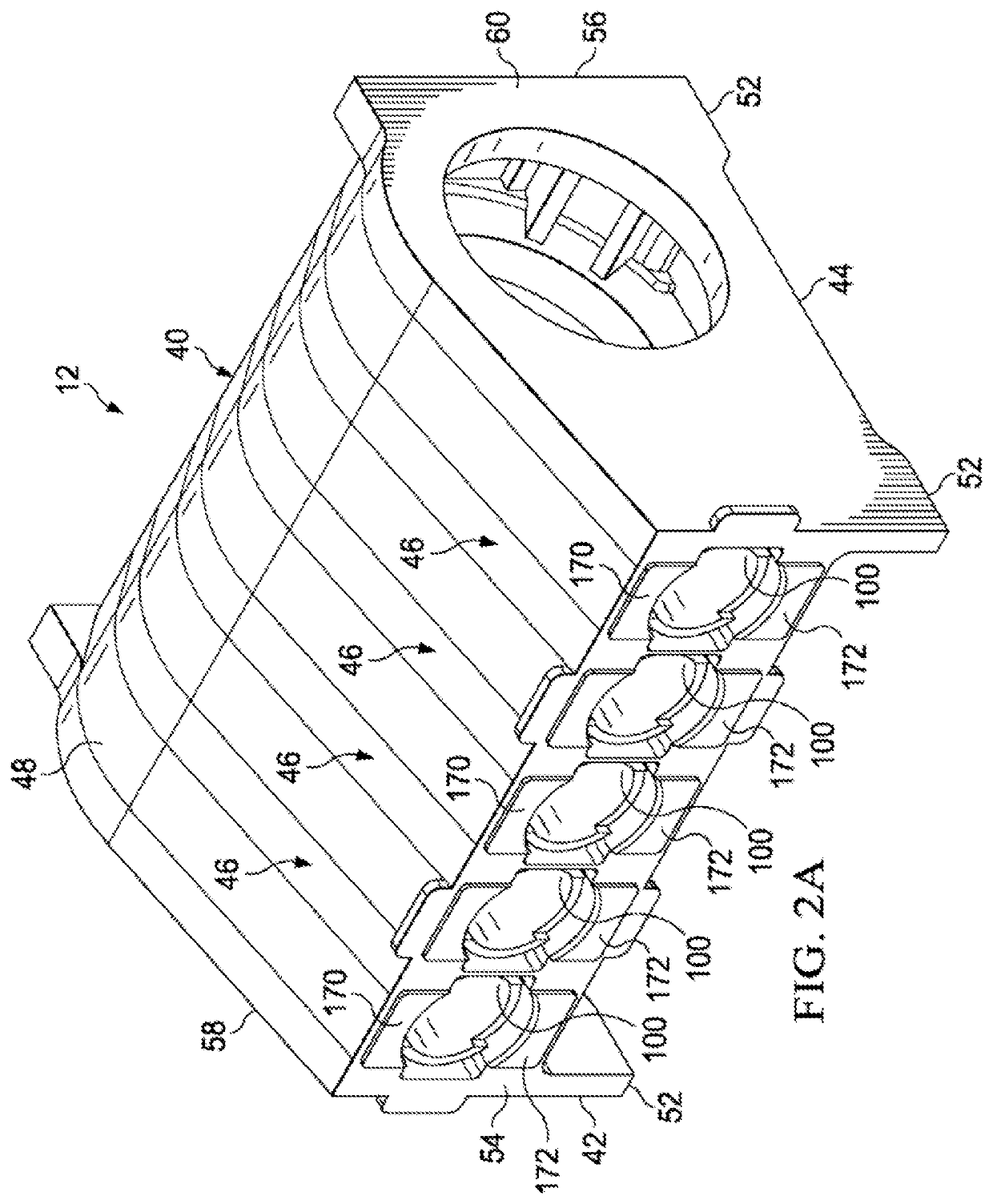
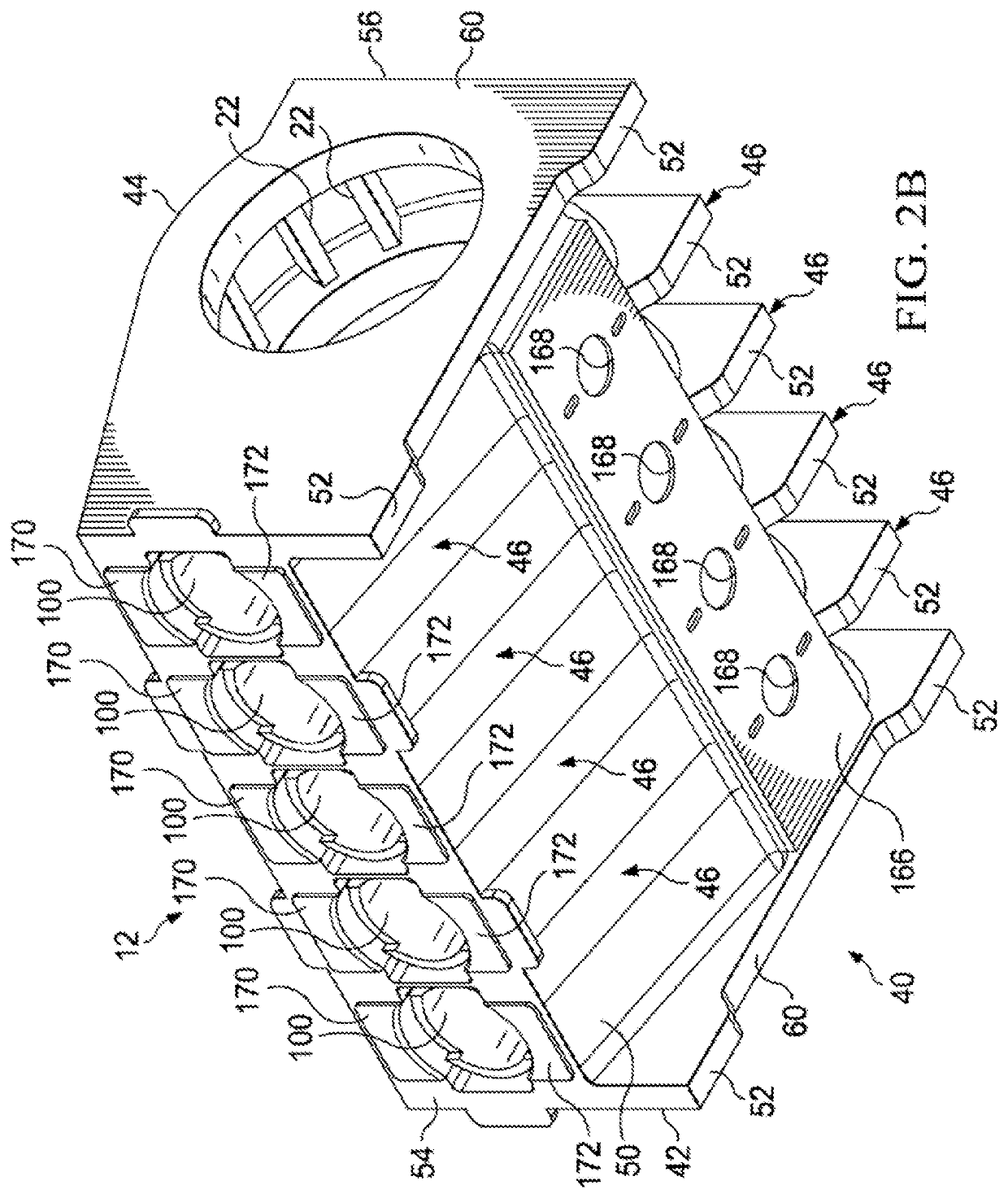
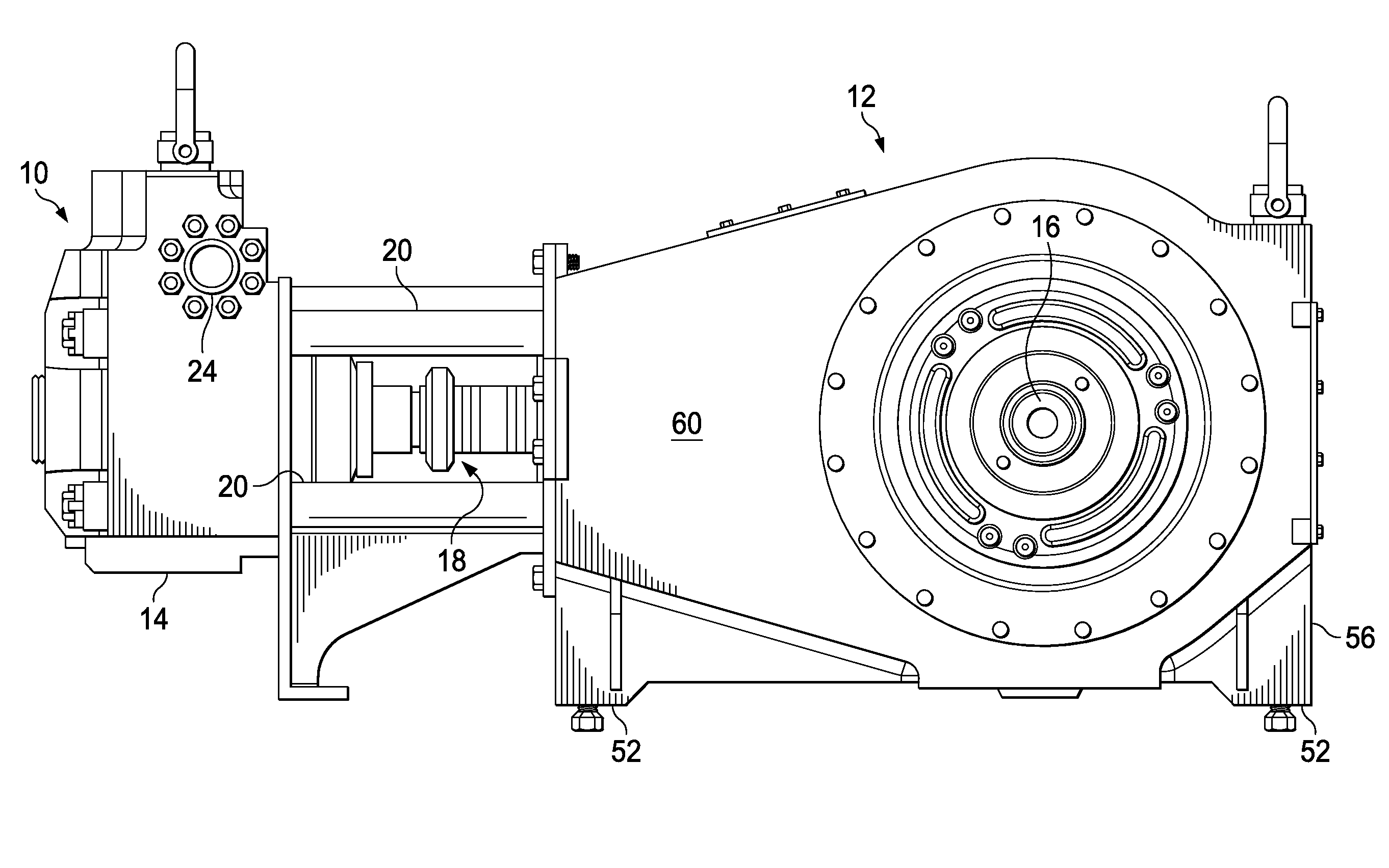
Support for Reciprocating Pump
A gearbox is coupled to a power end housing of a reciprocating pump, where the gearbox includes at least one support member having a first end securely affixed to the gearbox, and the at least one support member having a second end securely affixed to an immobile part of the reciprocating pump for supporting the gearbox and resisting movement of the gearbox relative to the reciprocating pump.
Owner:SPM OIL & GAS INC
System and method for reinforcing reciprocating pump
ActiveUS20160025082A1Resistance to movementPositive displacement pump componentsCrankshaft bearingsEngineeringRelative motion
A drive system for a fluid end of a reciprocating pump assembly including a drive member and a power end housing having a crankshaft rotatably disposed therein. The assembly includes a gearbox secured to the power end housing, the gearbox operatively connecting the drive member to the crankshaft for rotation thereof. The assembly further includes at least one arm member extending between the gearbox and the power end housing, the at least one arm member positioned to resist relative movement between the gearbox and the power end housing.
Owner:SPM OIL & GAS INC
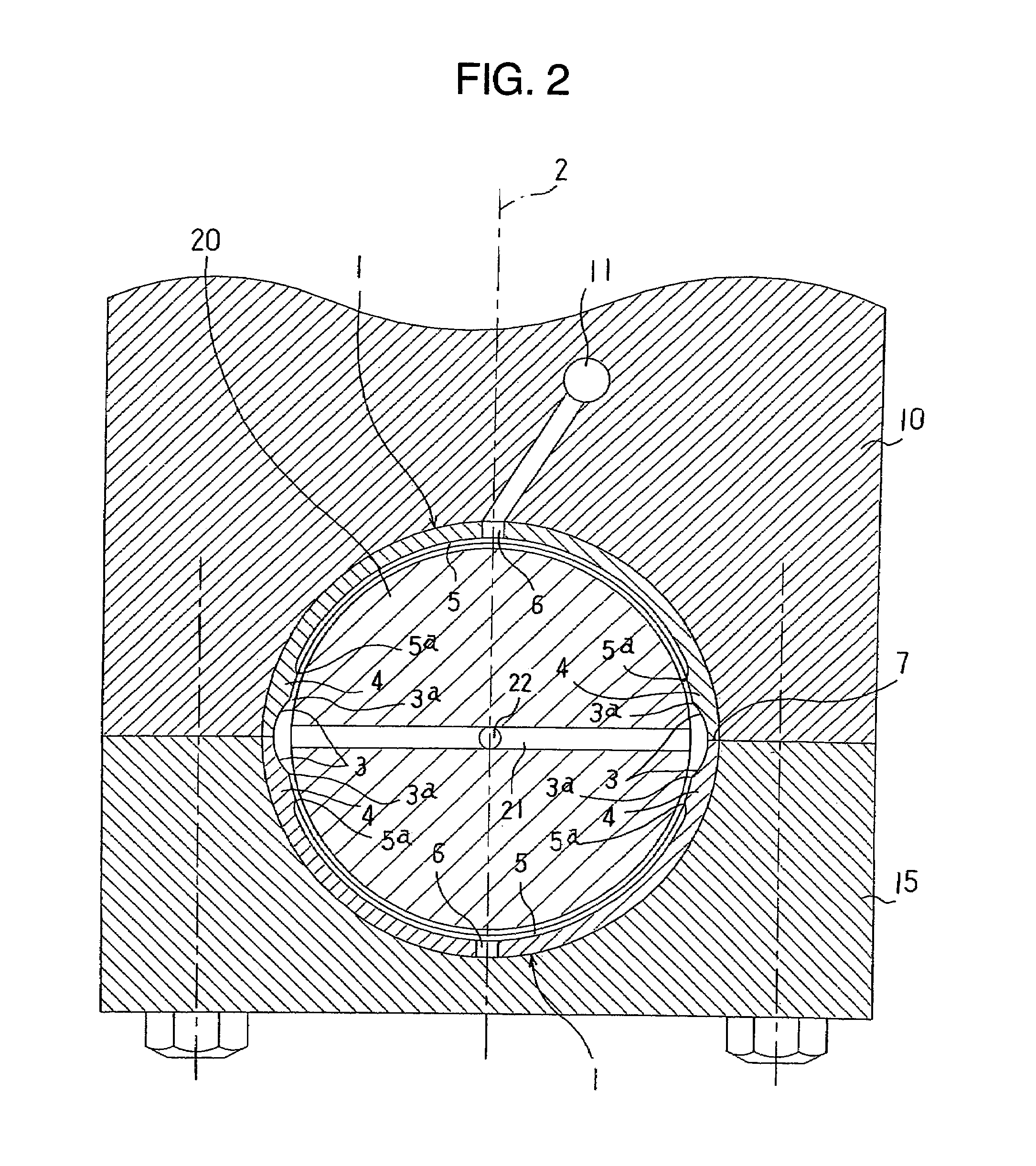
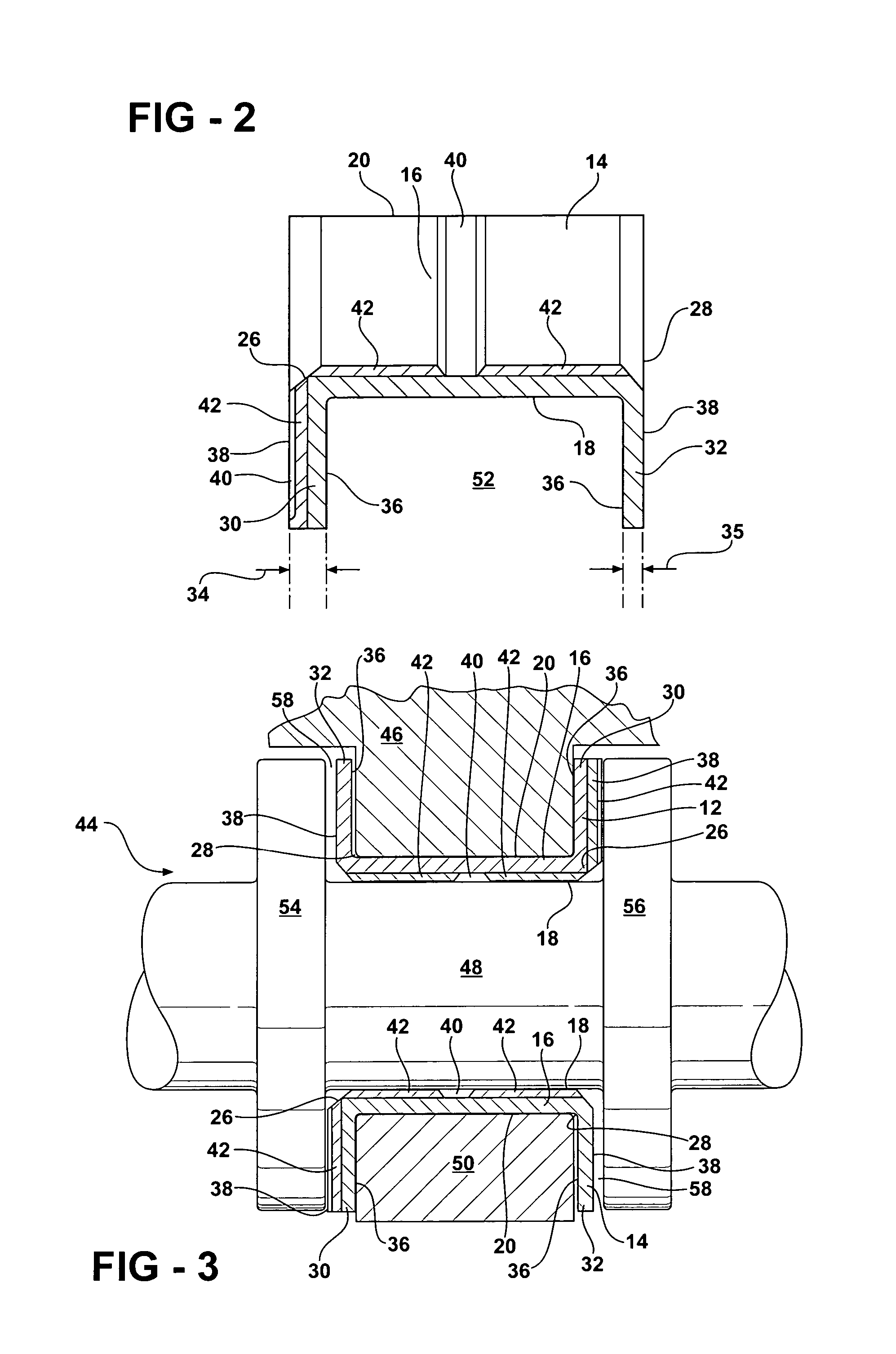
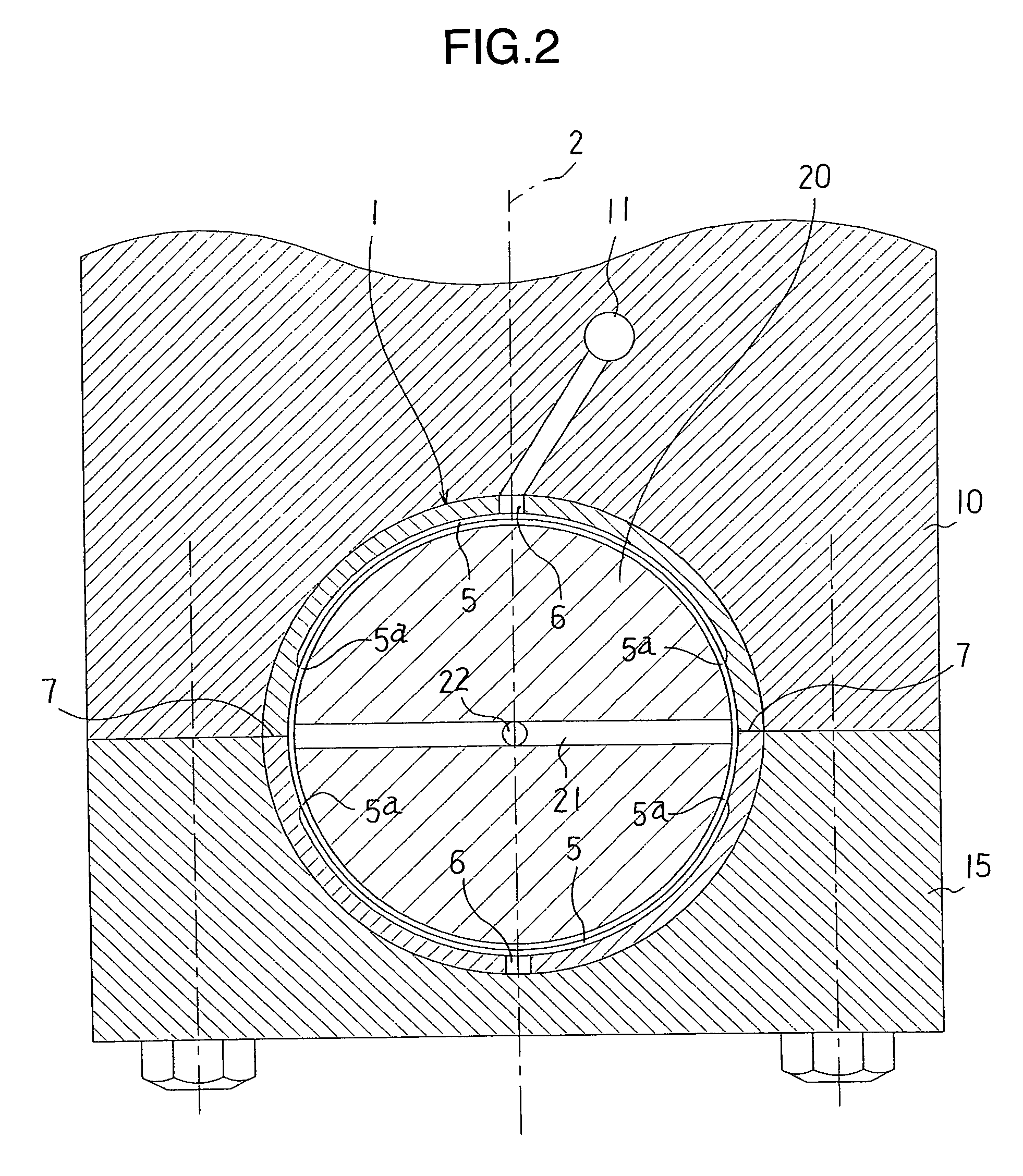
Sliding bearing for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20110058761A1Reduced conformabilityIncrease load capacityCrankshaft bearingsShaftsEngineeringInternal combustion engine
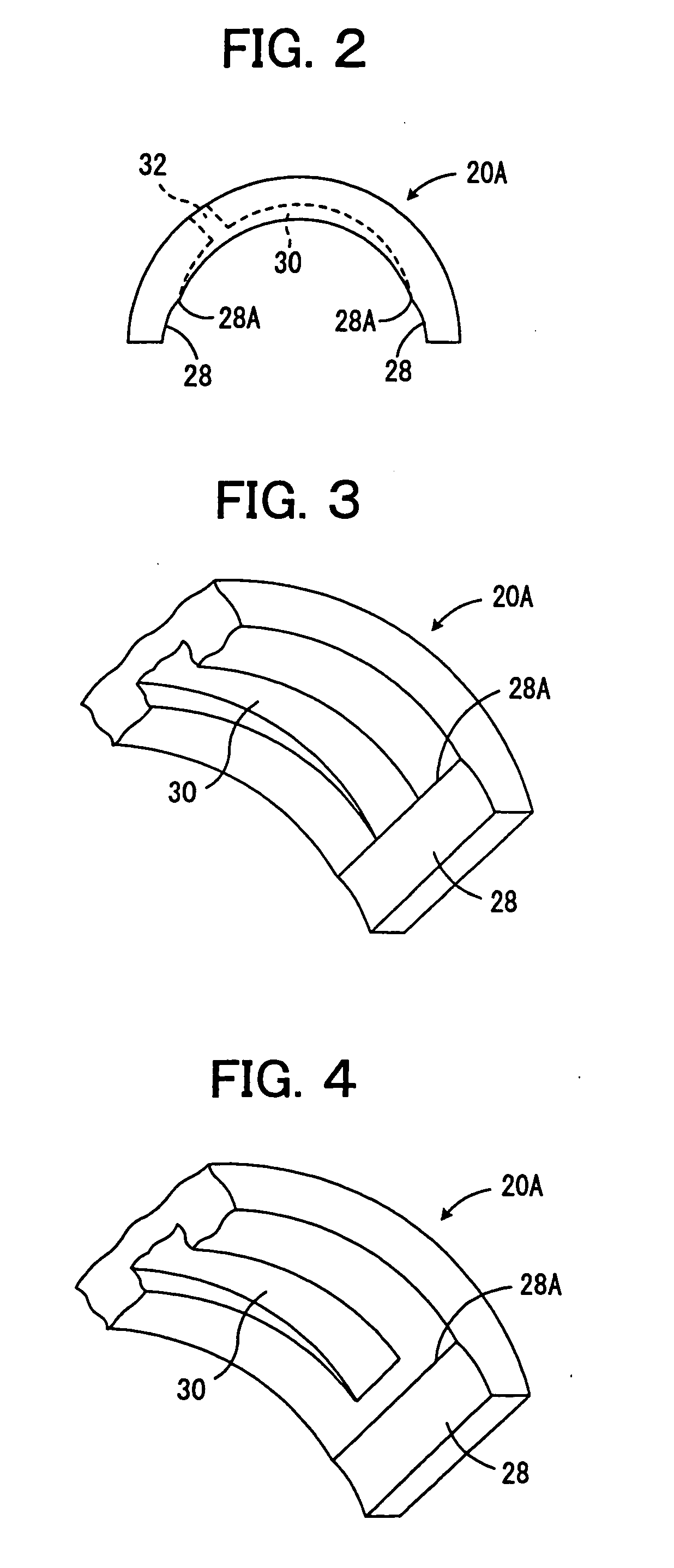
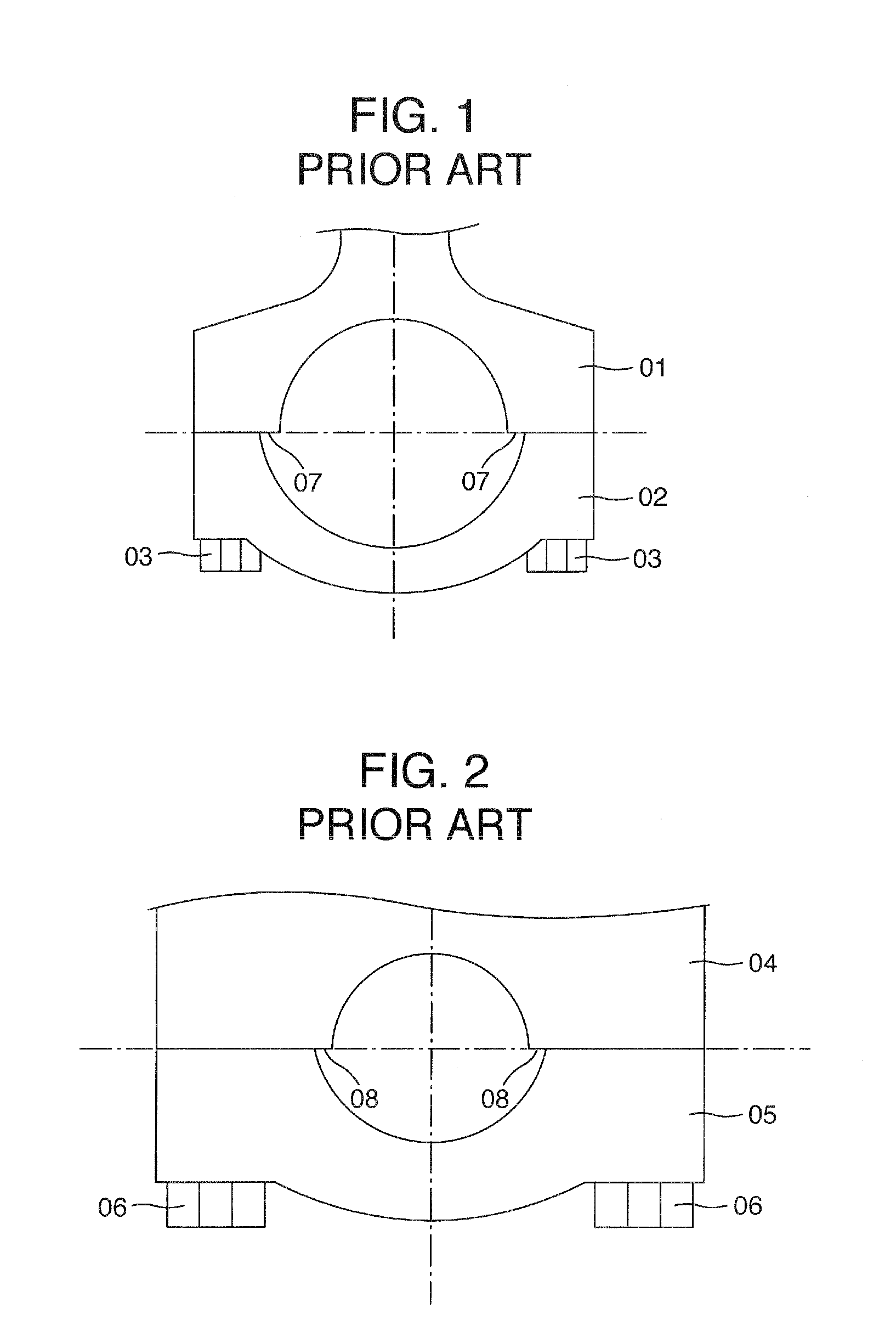
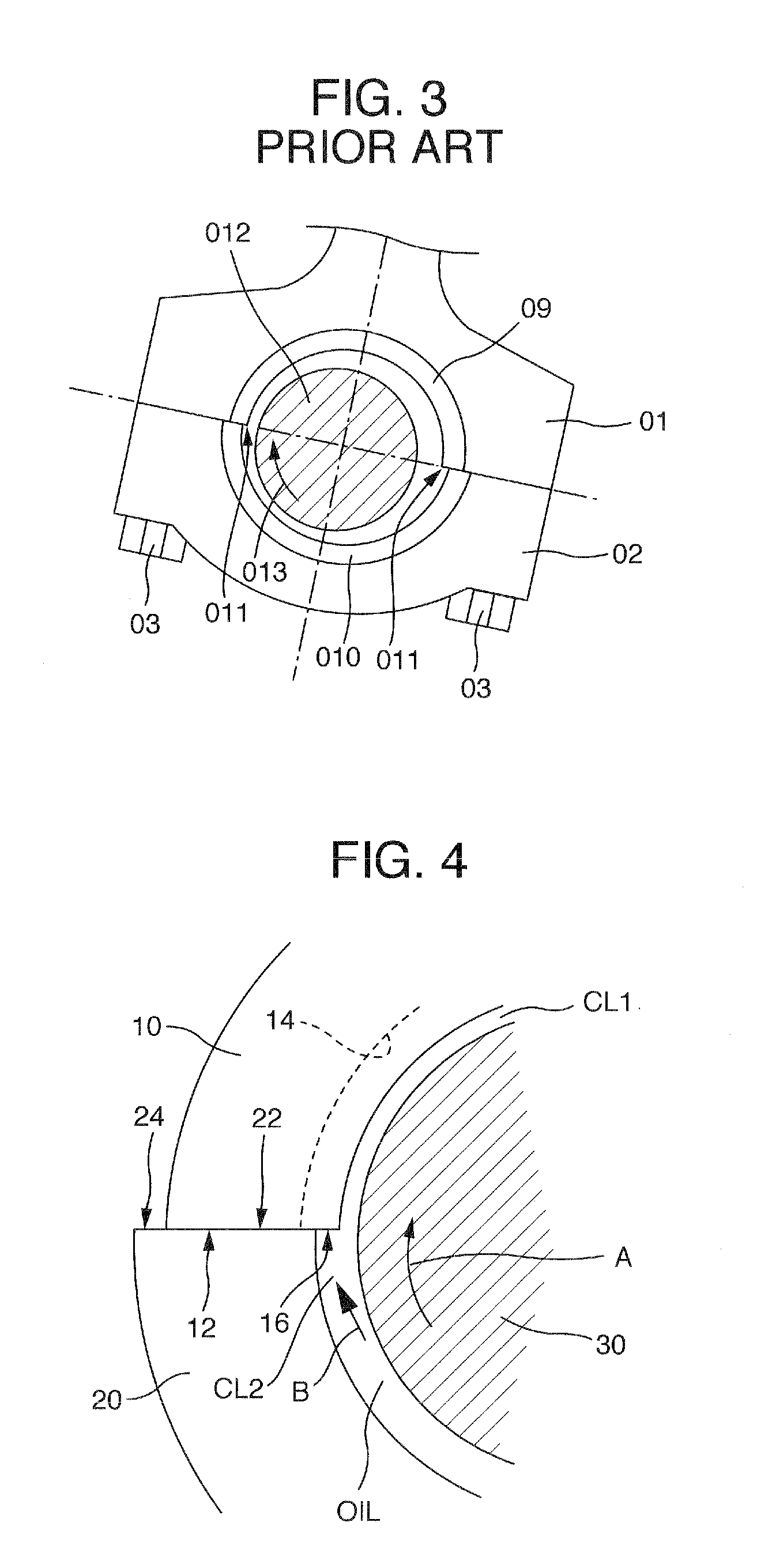
Disclosed is a sliding bearing for an internal combustion engine for supporting a crankshaft including a pair of semi-cylindrical bearings combined with each other into a cylindrical body. Each of inner circumferential surfaces of the respective semi-cylindrical bearings includes first and second curved surfaces following two kinds of arcs with different curvatures. The first curved surface is in a region including a circumferential central portion of the inner circumferential surface. The second curved surfaces are in remaining two regions of the inner circumferential surface. The circumferential oil groove and the axial groove communicate with each other. The circumferential grooves of the second curved surfaces and the axial groove communicate with each other. The groove bottoms of the circumferential grooves of the second curved surfaces are displaced to a side of the bearing inner circumferential surface from a groove bottom of the axial groove.
Owner:DAIDO METAL CO LTD
Lightened Rotating Member and Method of Producing Same
InactiveUS20140196570A1Reduce inertiaReducing balanceCrankshaftsRoller bearingsEngineeringMain bearing
A lightened rotating member for a machine. The lightened member includes a plurality of radially machined penetrations within at least one main bearing support journal of the rotating member. The plurality of penetrations is formed around the circumference of the main bearing journal face, with the penetration centerline directed radially toward the rotating member's axial centerline. An even number of penetrations may be utilized with minimal adverse effect on the balance of the rotating member. Odd numbers of penetrations may require subsequent rebalancing. The rotating member may be any rotating member that utilizes one or more main bearing support journals.
Owner:FTS INT SERVICES
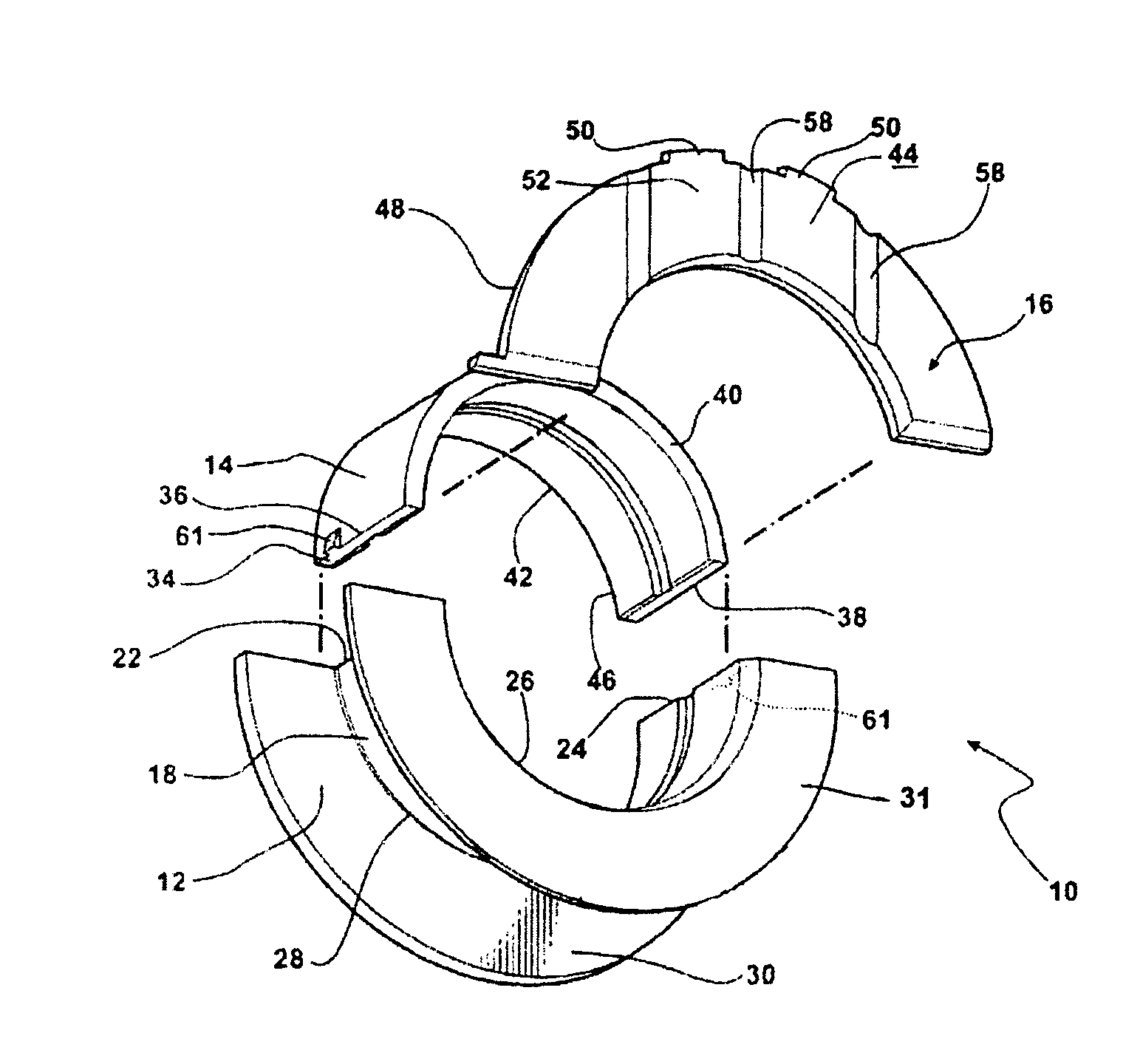
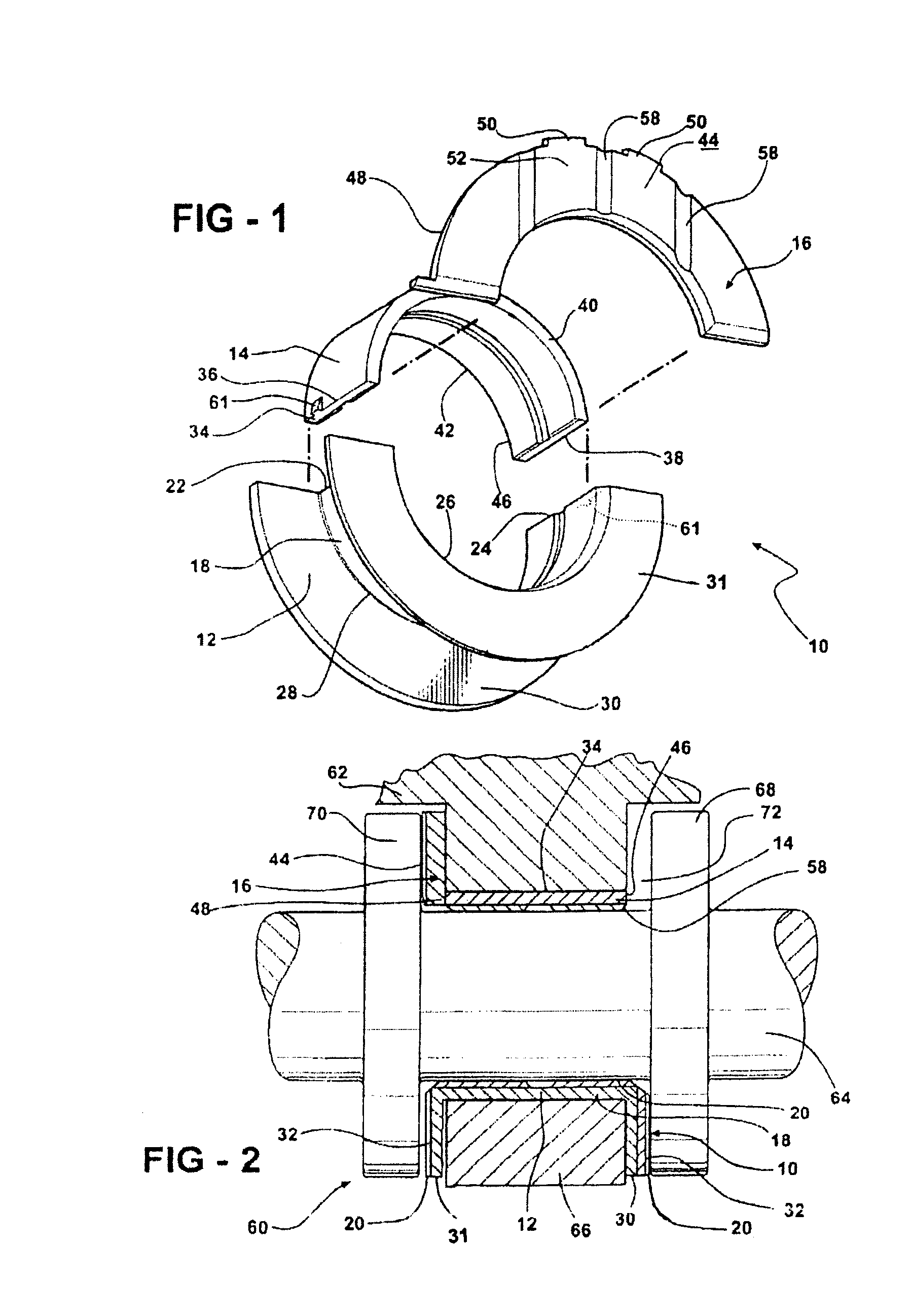
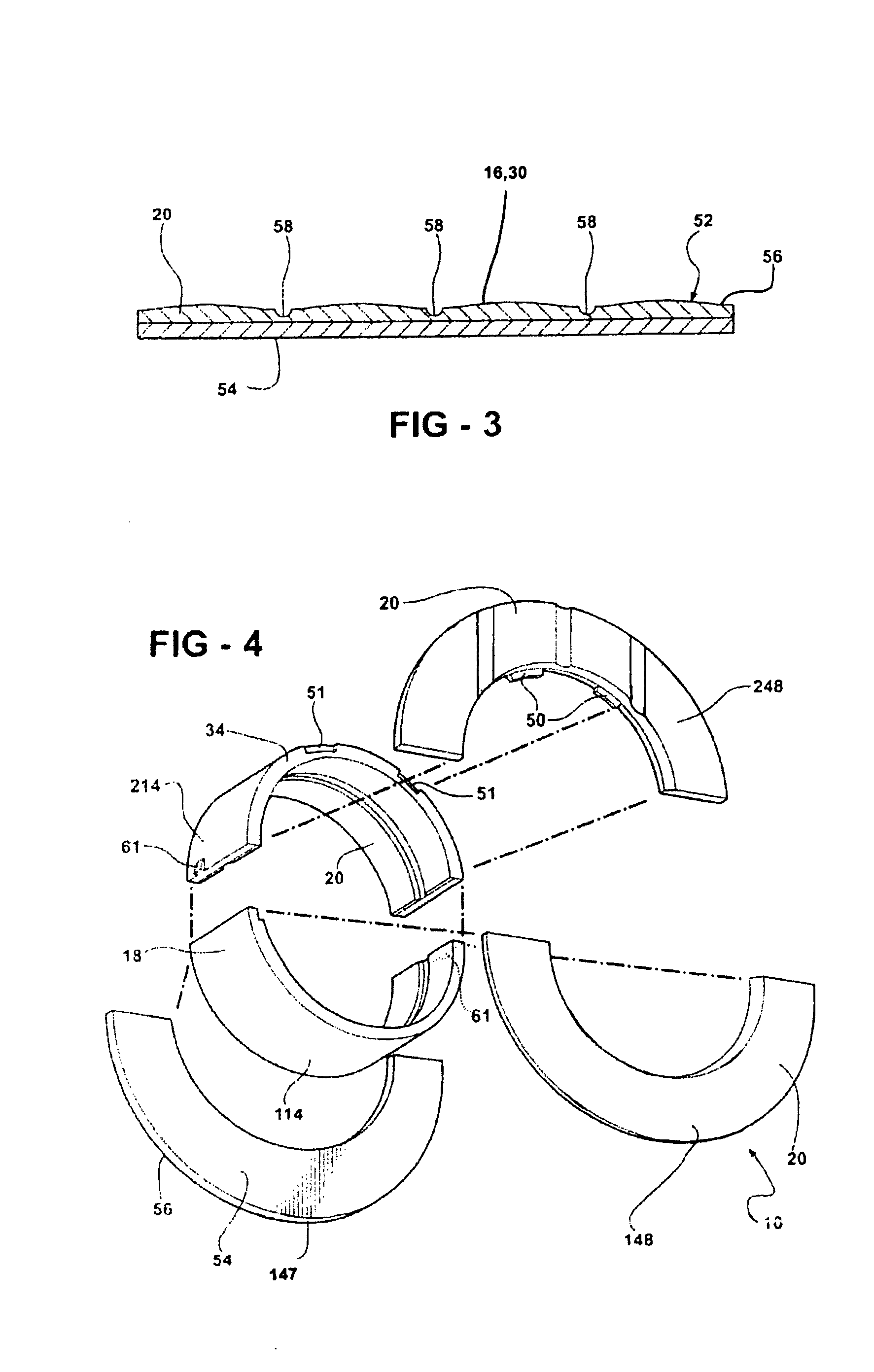
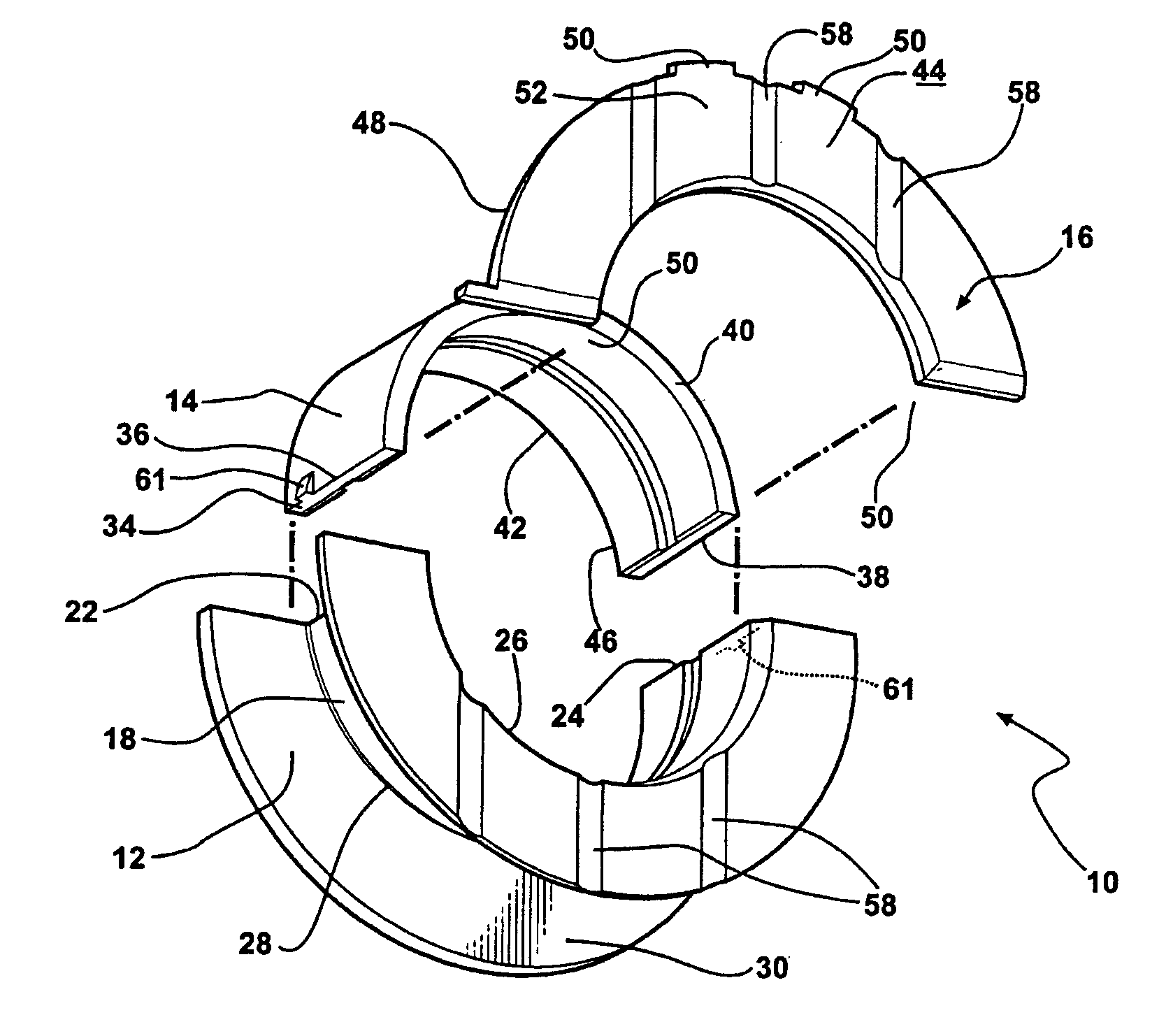
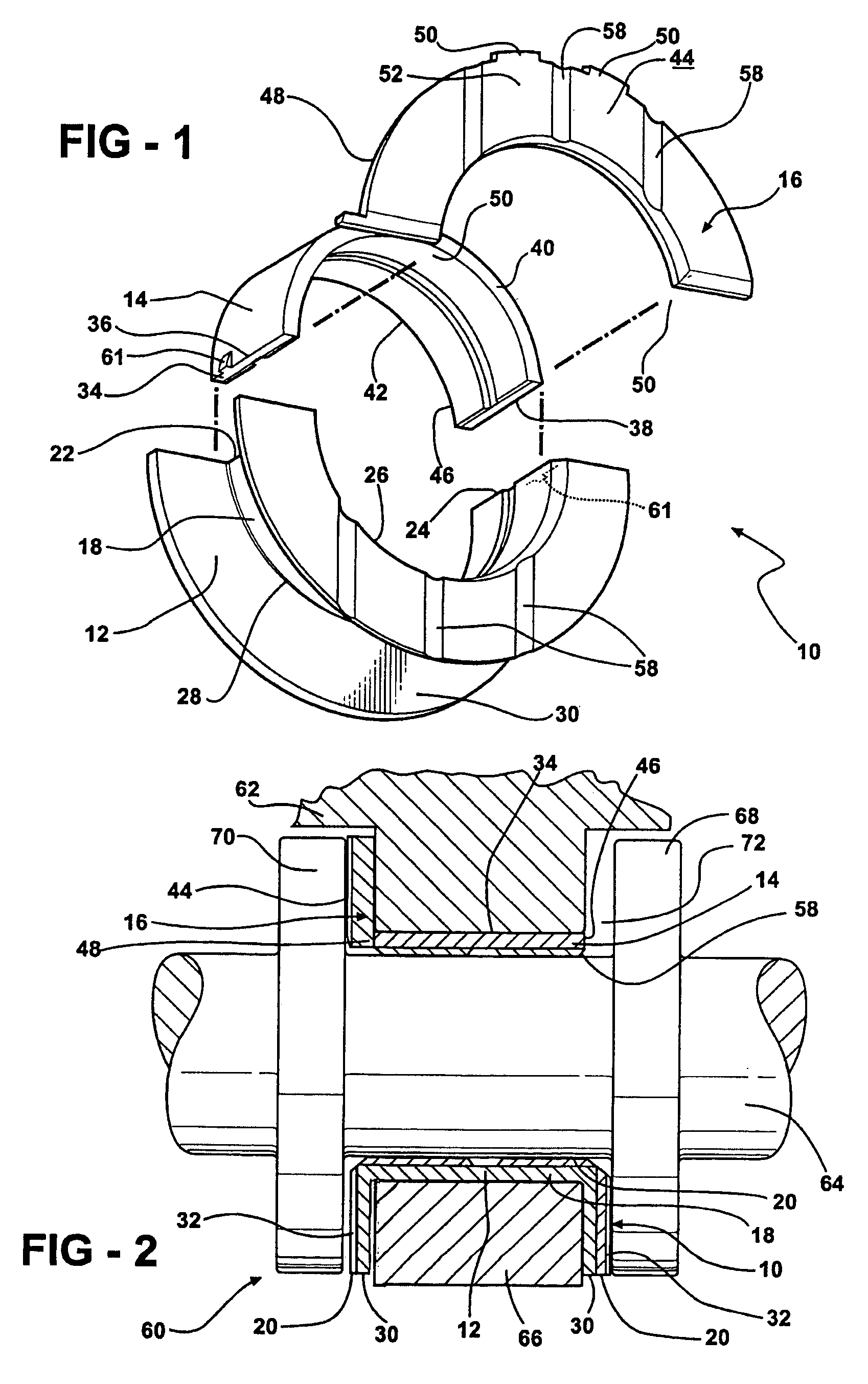
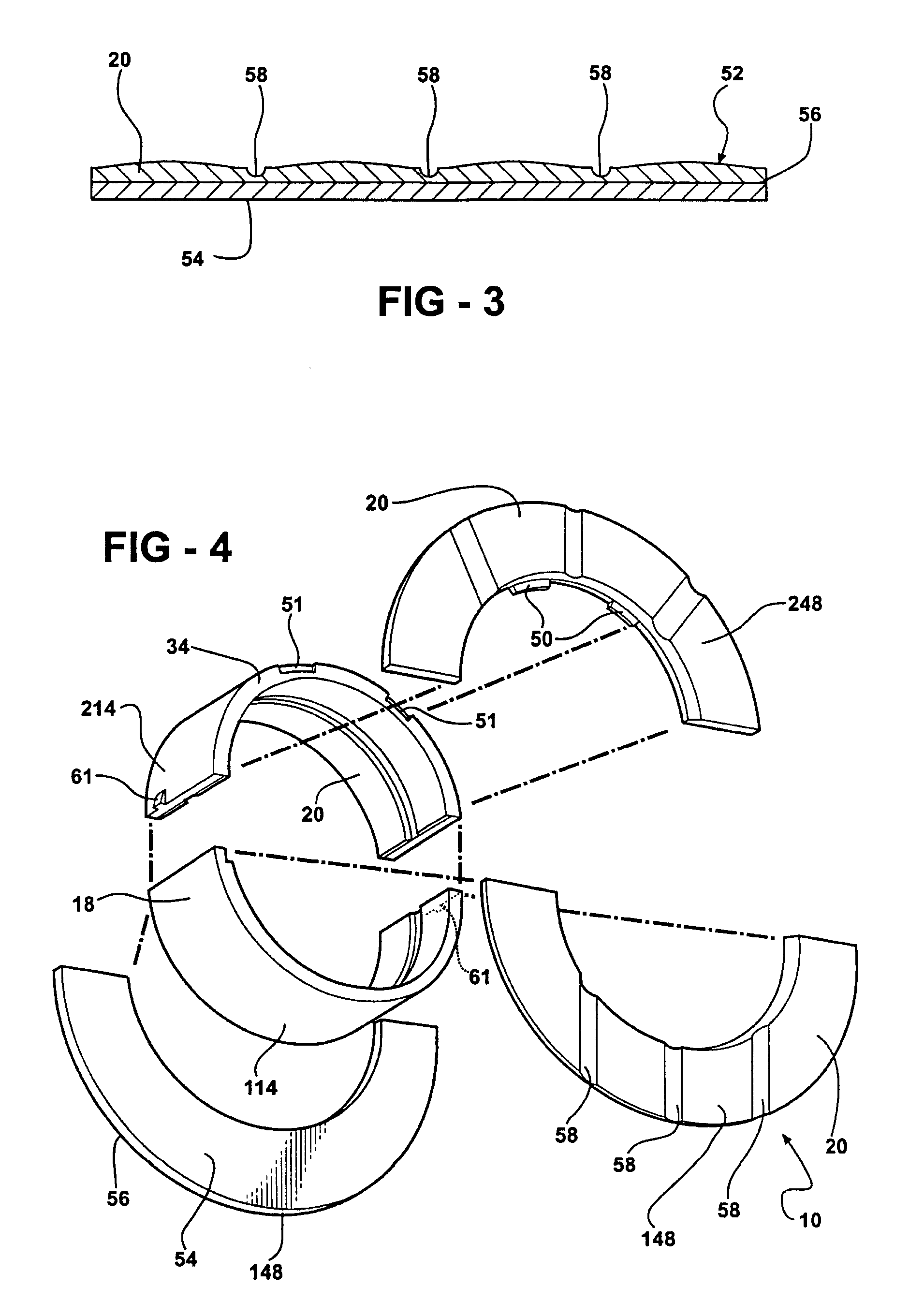
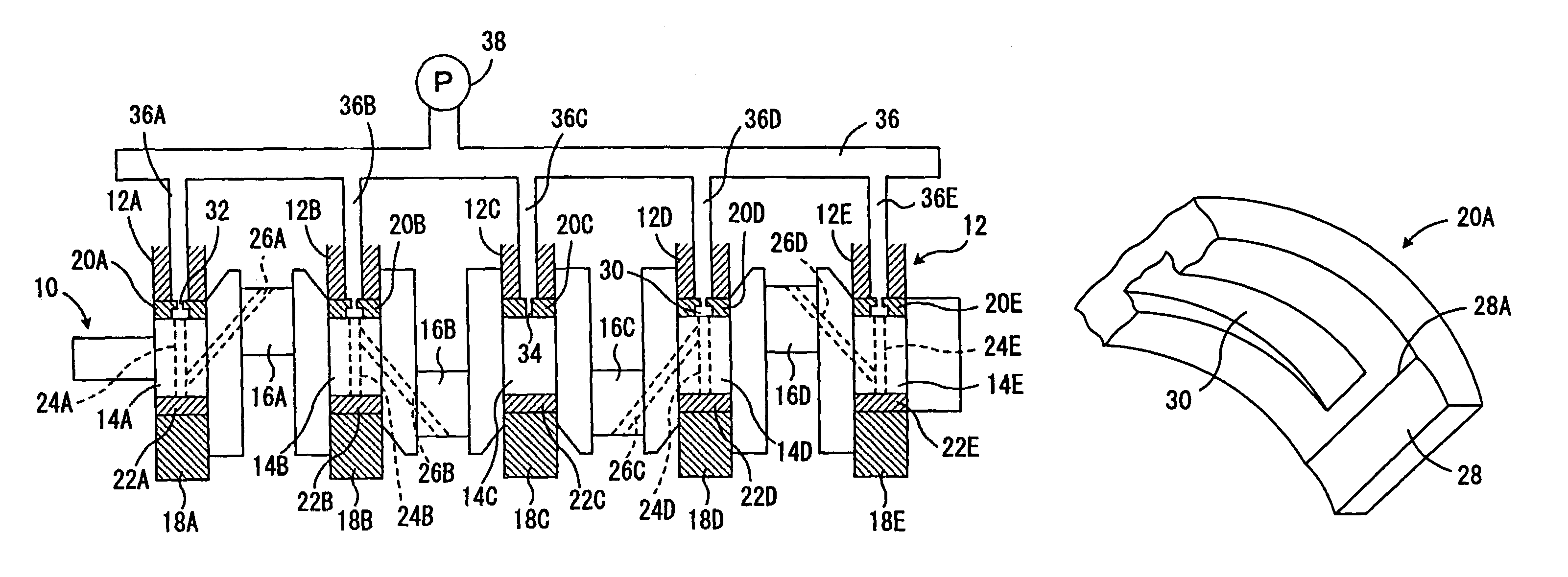
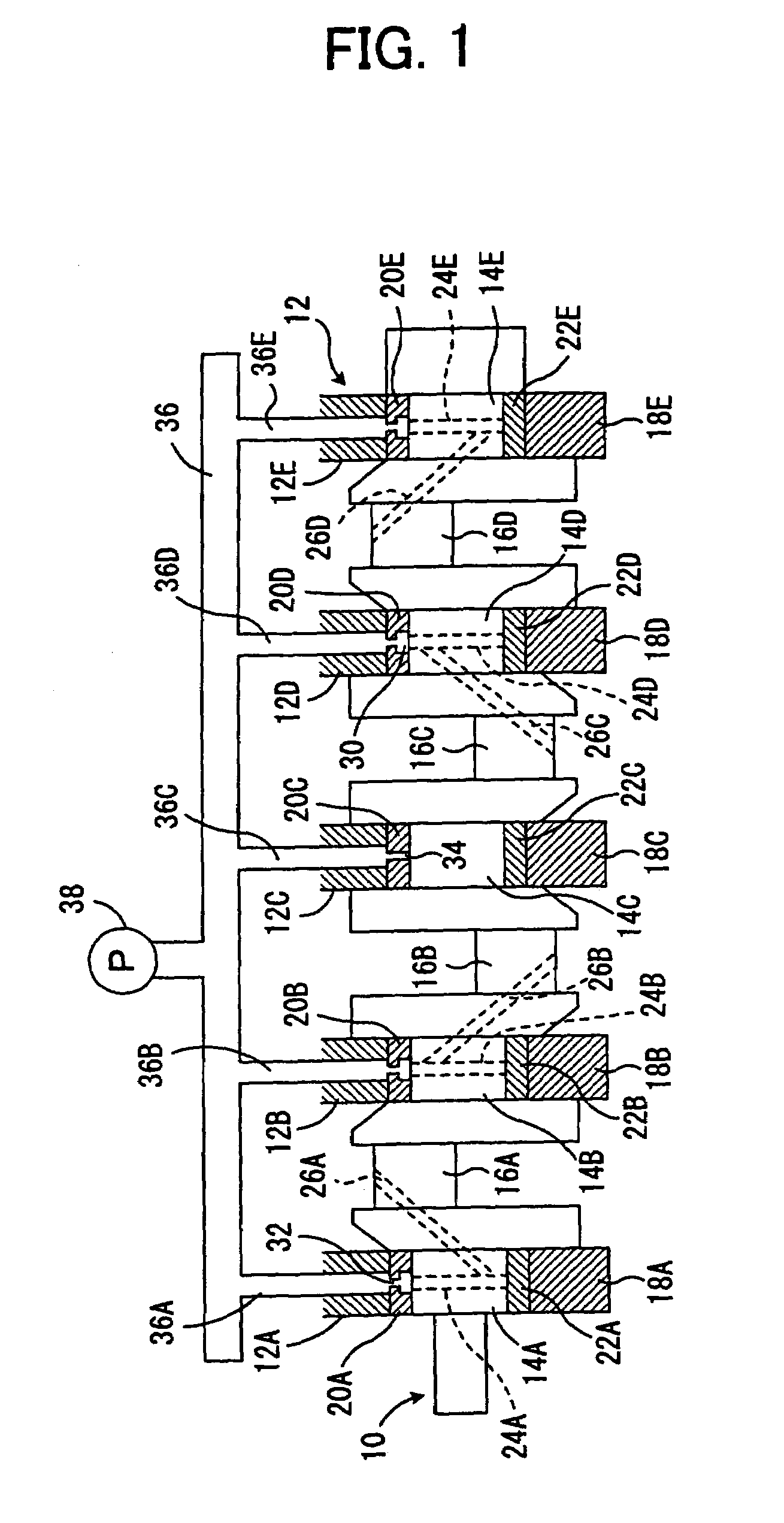
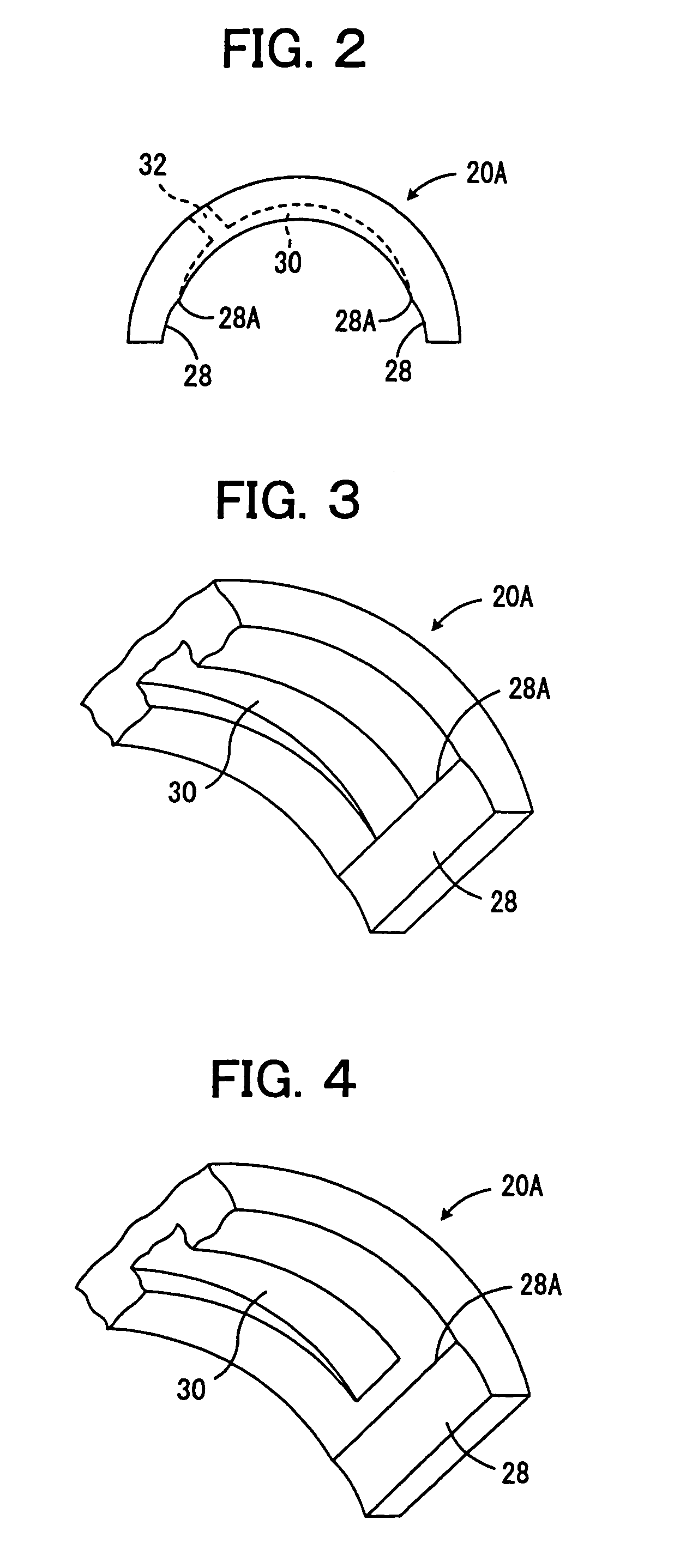
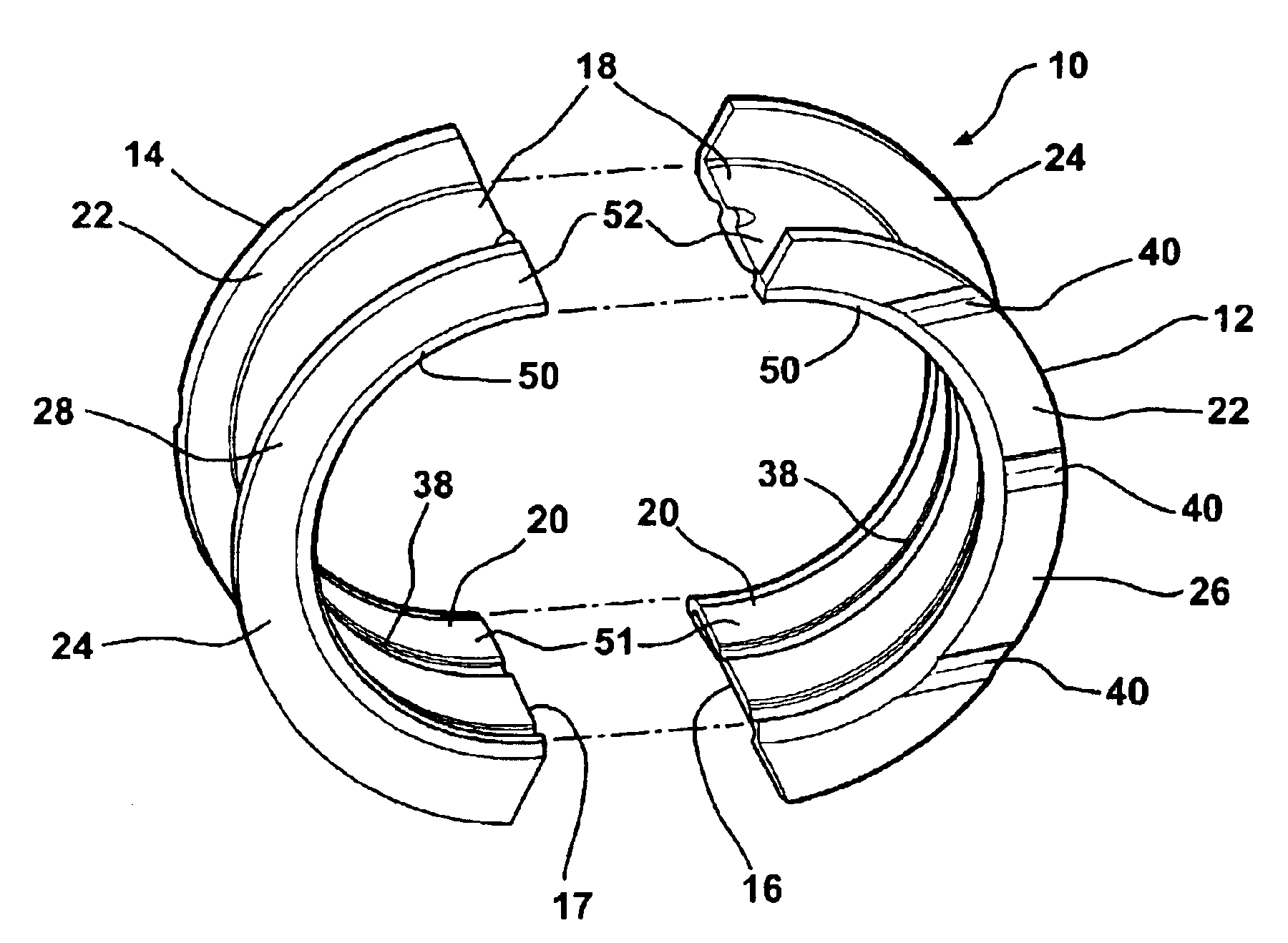
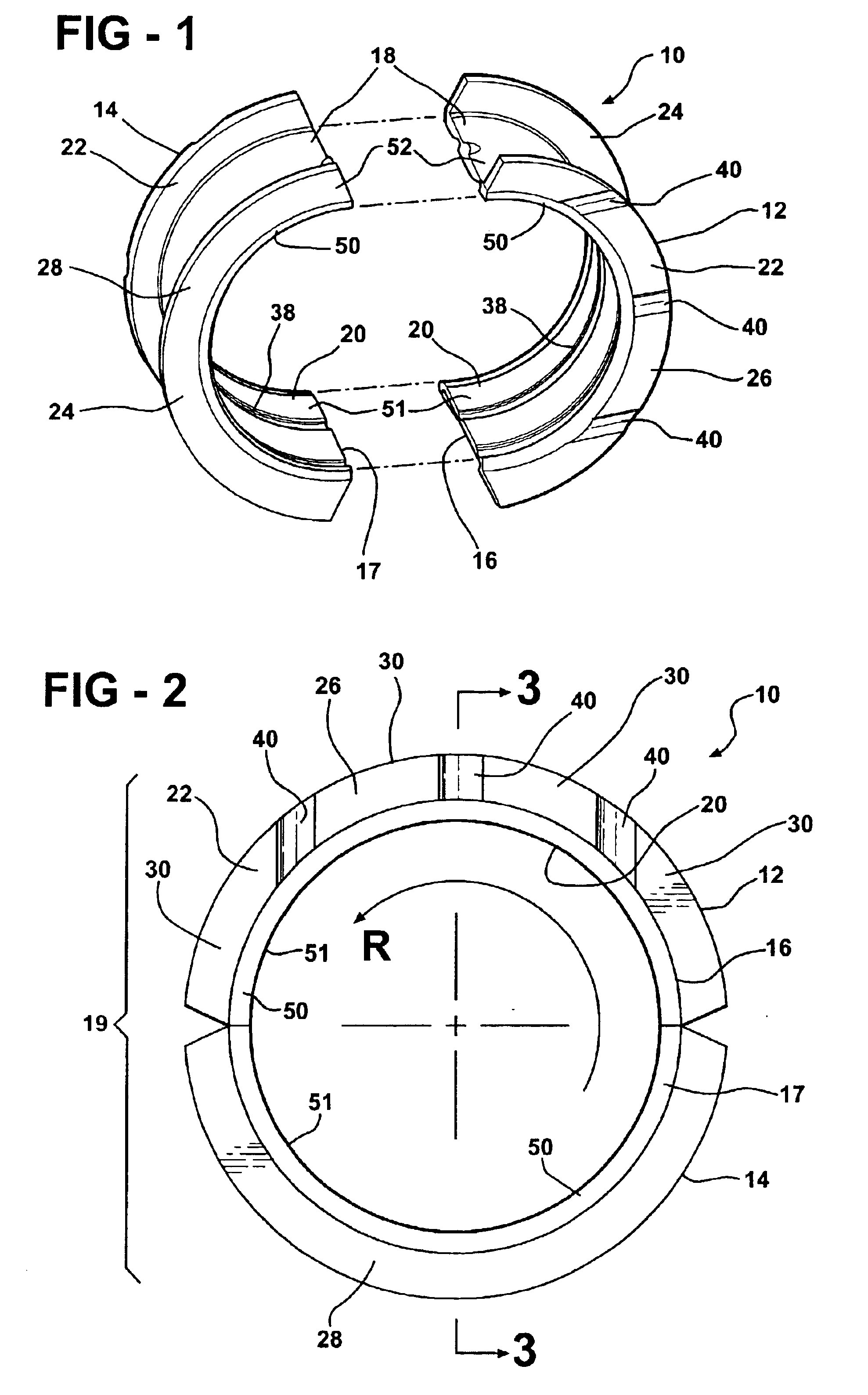
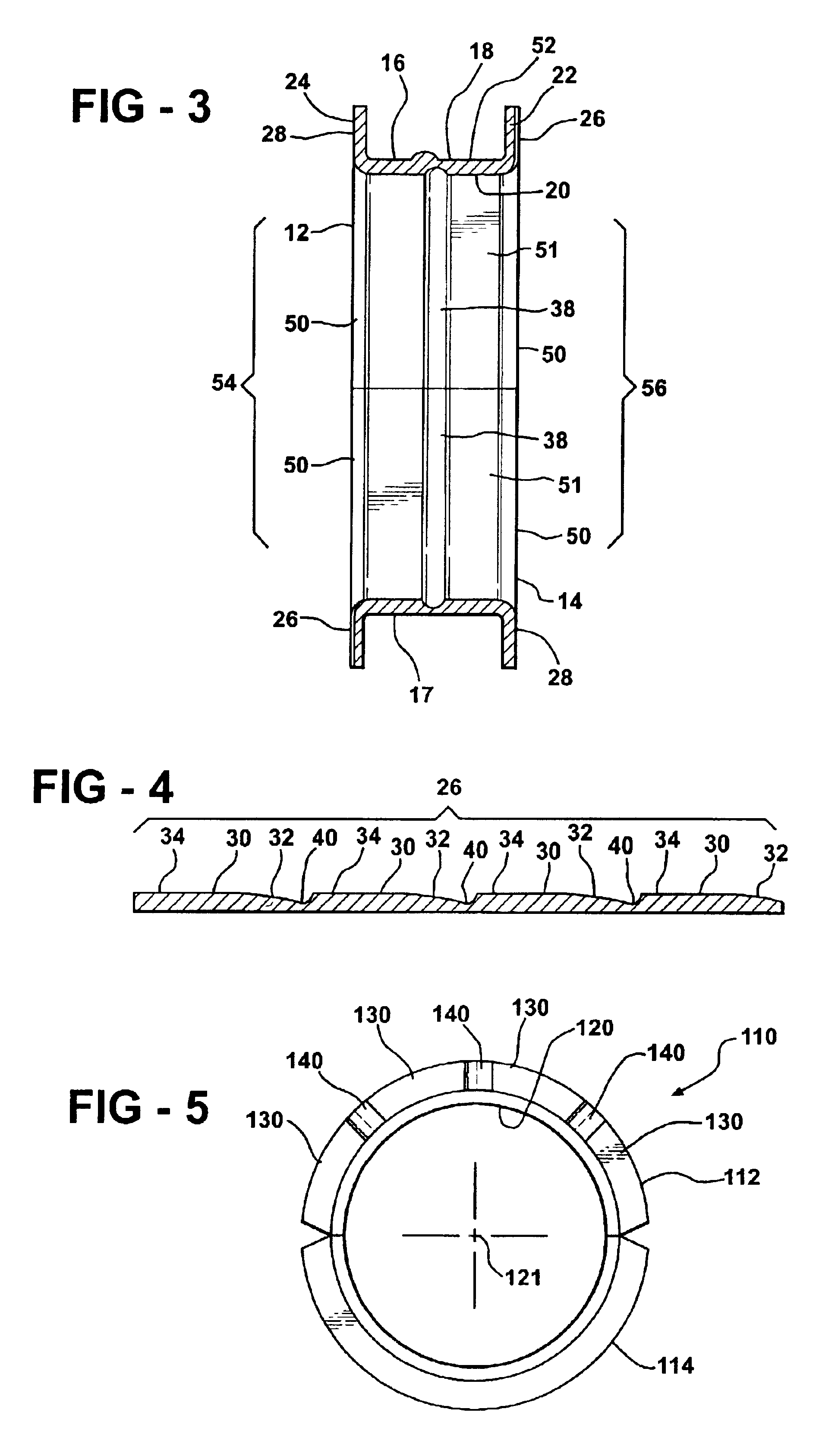
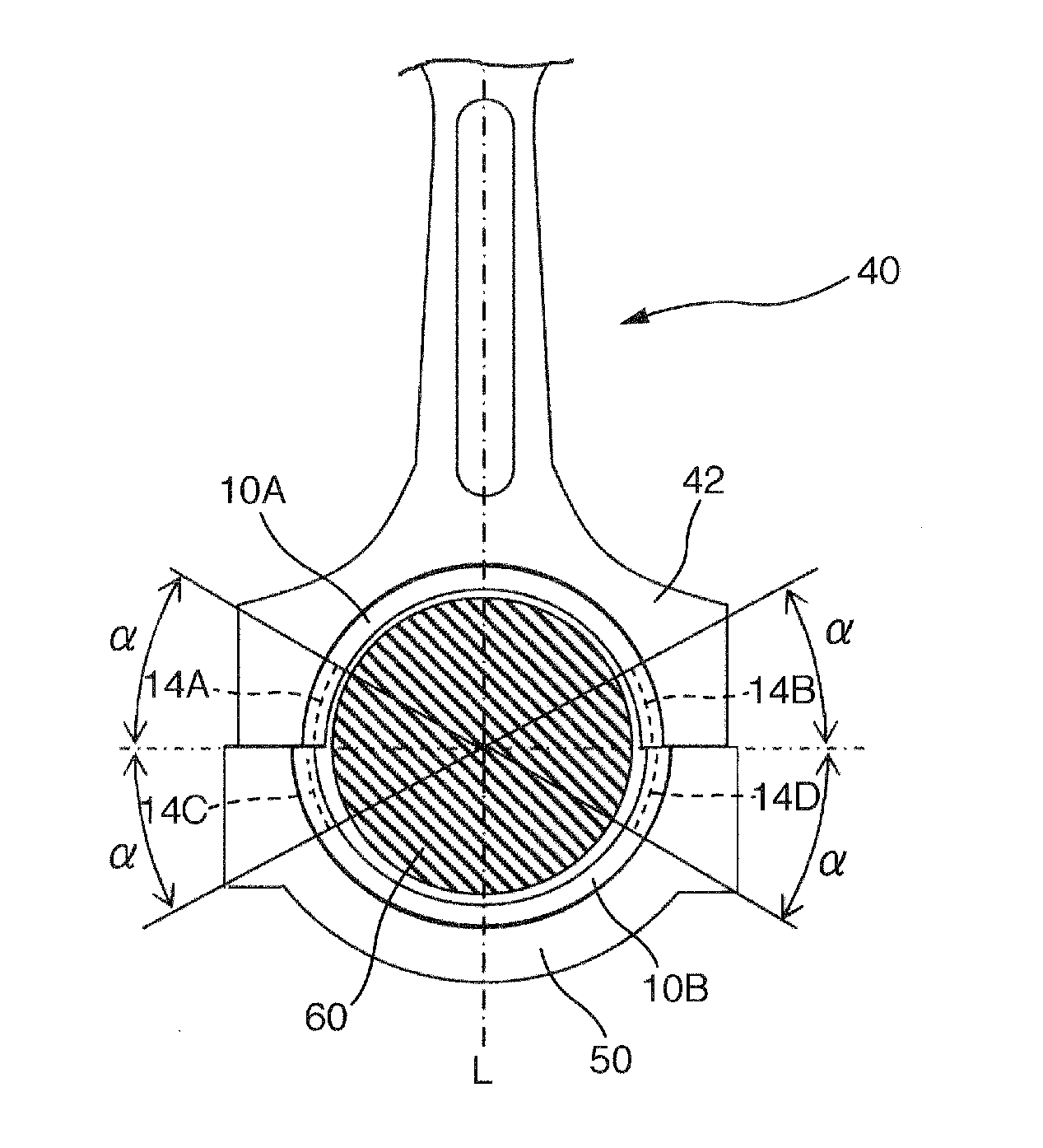
Thrust bearing assembly
InactiveUS7134793B2Reduce manufacturing costExpensive to manufactureBearing assemblyCrankshaft bearingsThrust bearingFree edge
The subject invention provides a thrust bearing assembly having only three thrust flanges in total. One portion of the thrust bearing assembly comprises a main bearing having an arcuate bearing shell with a concave inner surface and a convex outer surface. A thrust washer having hydrodynamic features abuts one of the edges of the main bearing and extends radially outwardly from the outer surface thereof forming a thrust surface. The other of the edges of the main bearing is free of a flange. The free edge of the main bearing is preferably spaced inward from other thrust surfaces and the edge has a substantially narrower width than the other thrust surfaces. The other portion of the assembly may include a traditional thrust bearing having one thrust flange with hydrodynamic features and another thrust flange free of hydrodynamic features, both extending radially outwardly therefrom or may include another main bearing abutting a pair of thrust washers, one having hydrodynamic features and one free of hydrodynamic features, extending radially outwardly from the other main bearing. In either configuration, the thrust flange or thrust washer that is free of hydrodynamic features is opposite the thrust washer having hydrodynamic features of the main bearing.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WORLD WIDE LLC
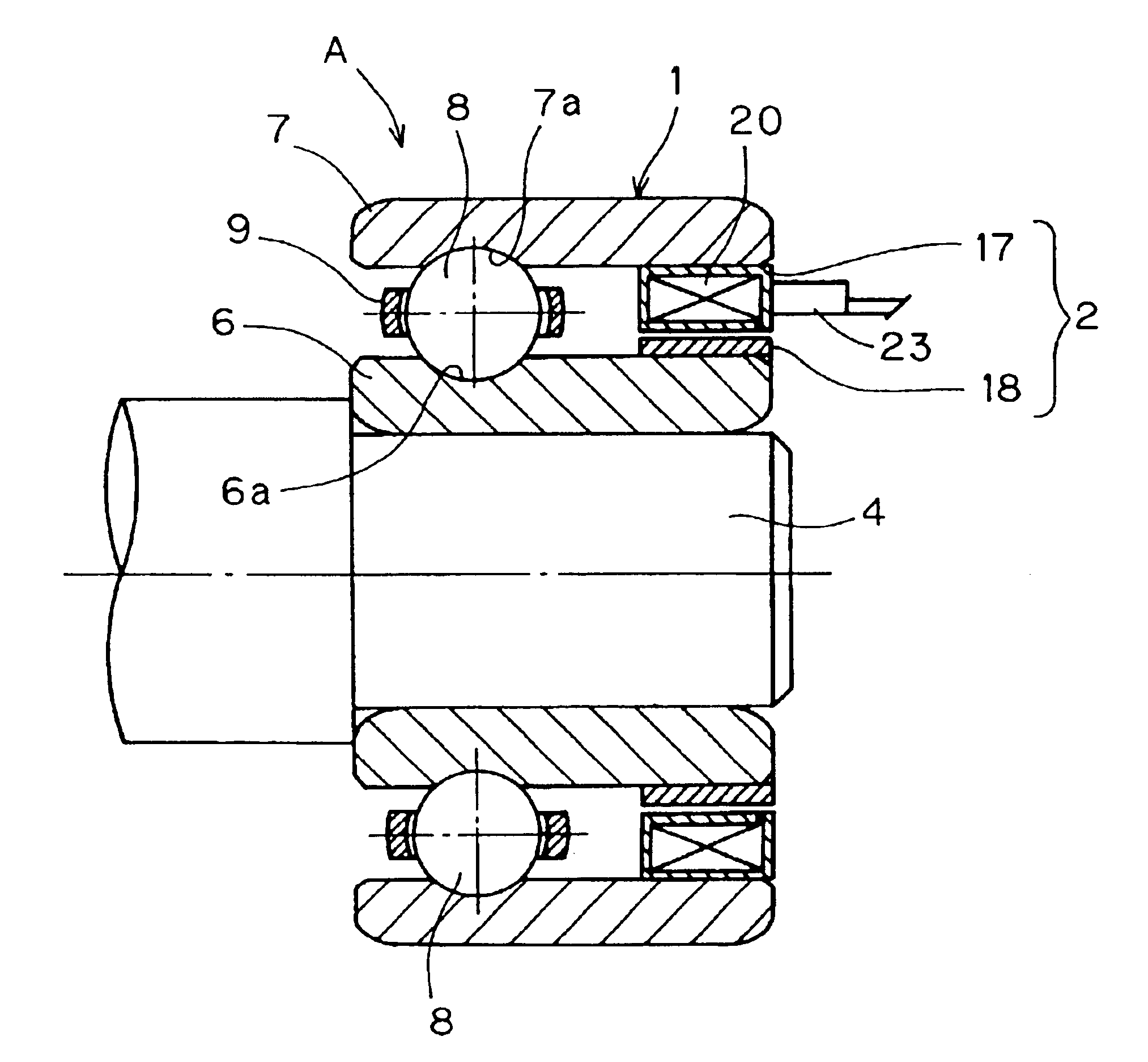
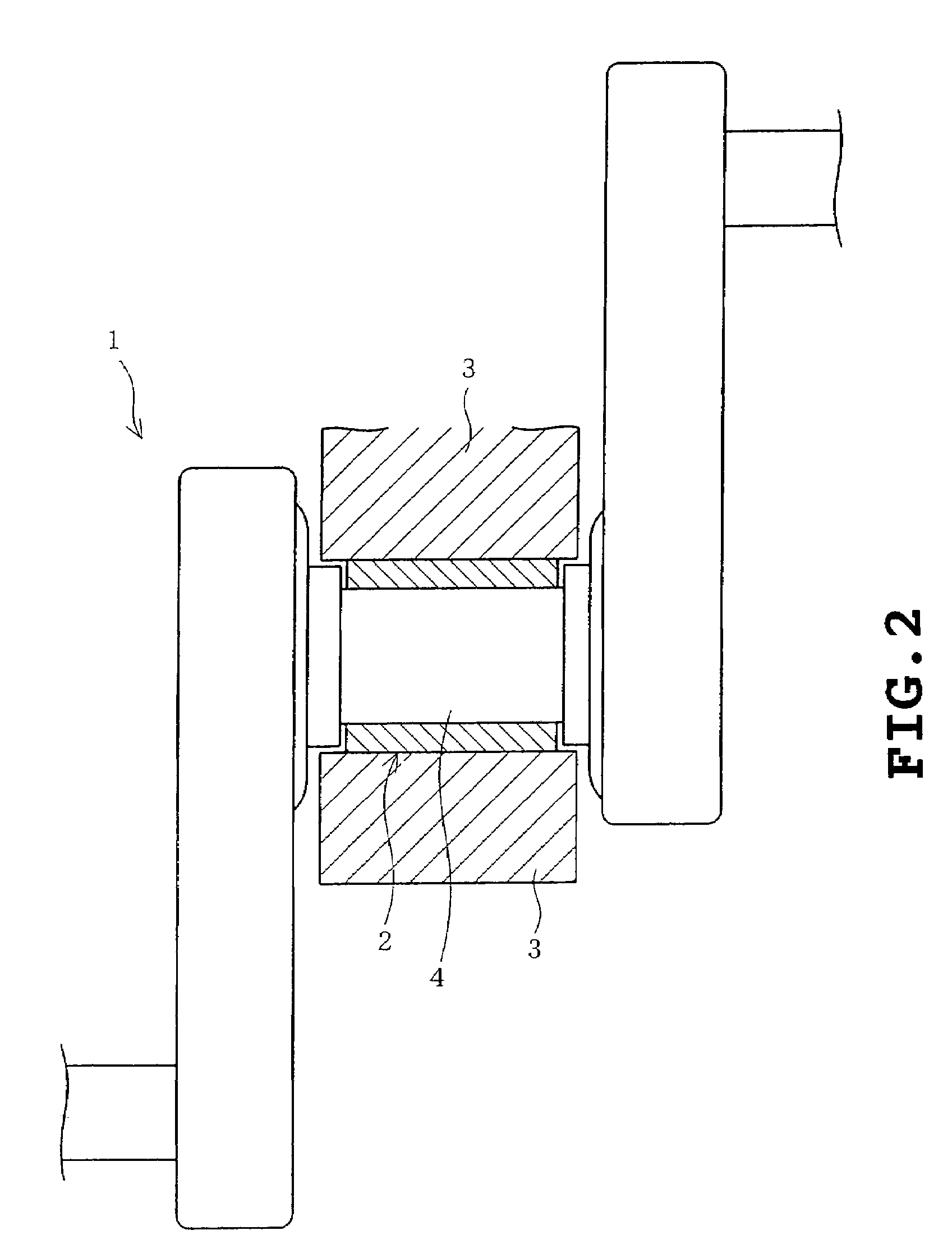
Bearing assembly with electric power generator
InactiveUS6838794B2Small sizeEasy to mergeBearing assemblyBall bearingsEngineeringGenerating capacity
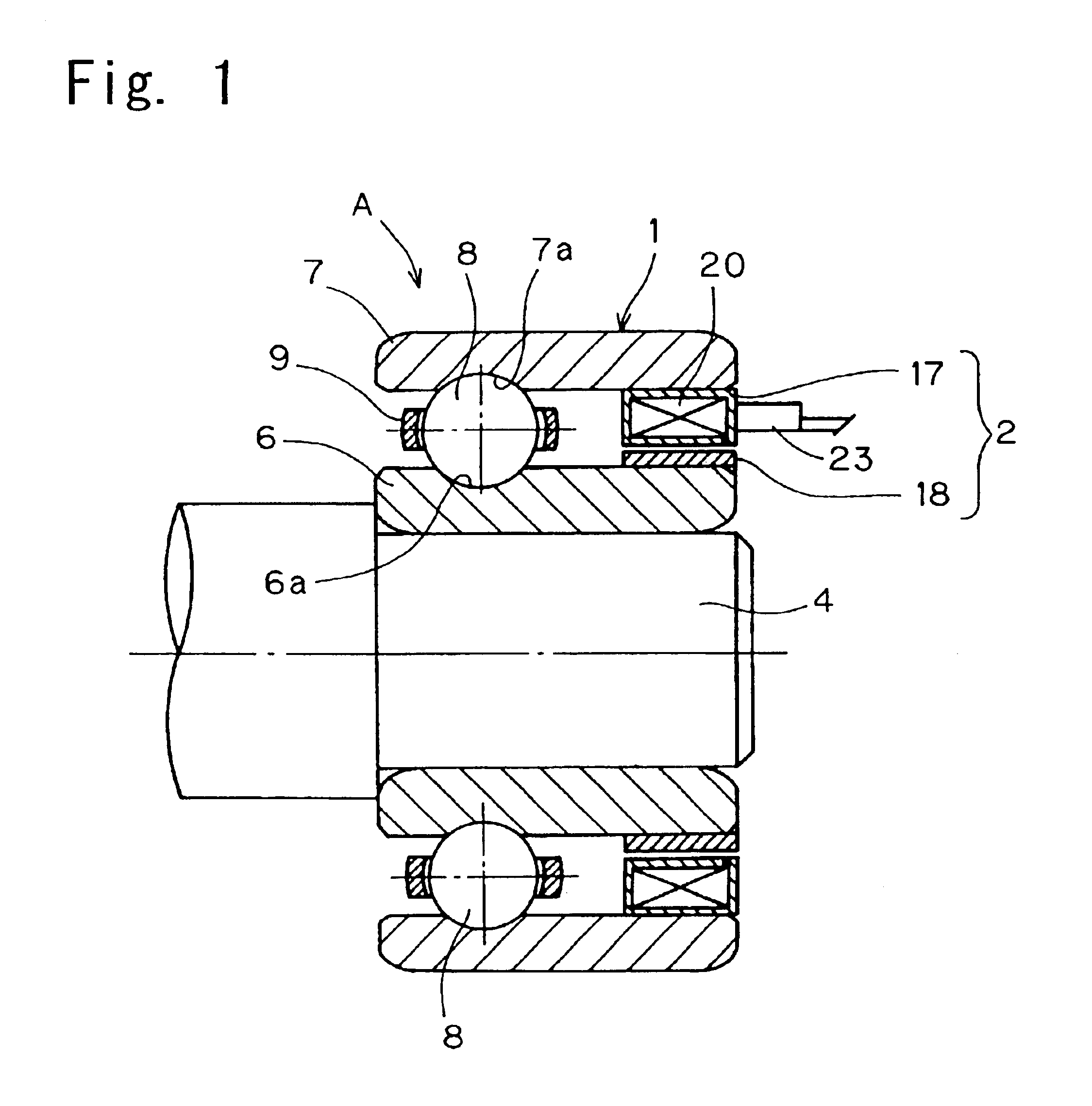
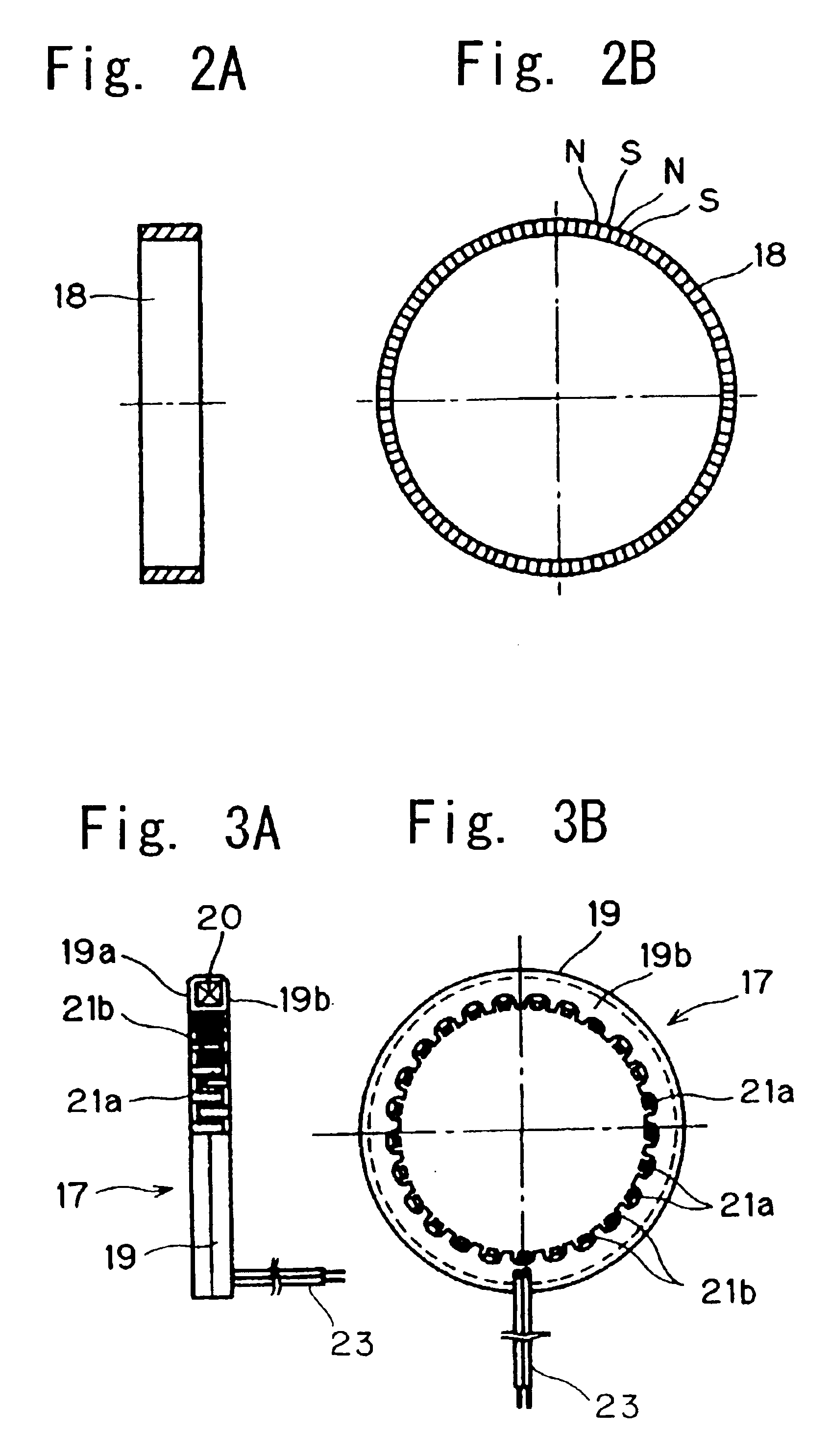
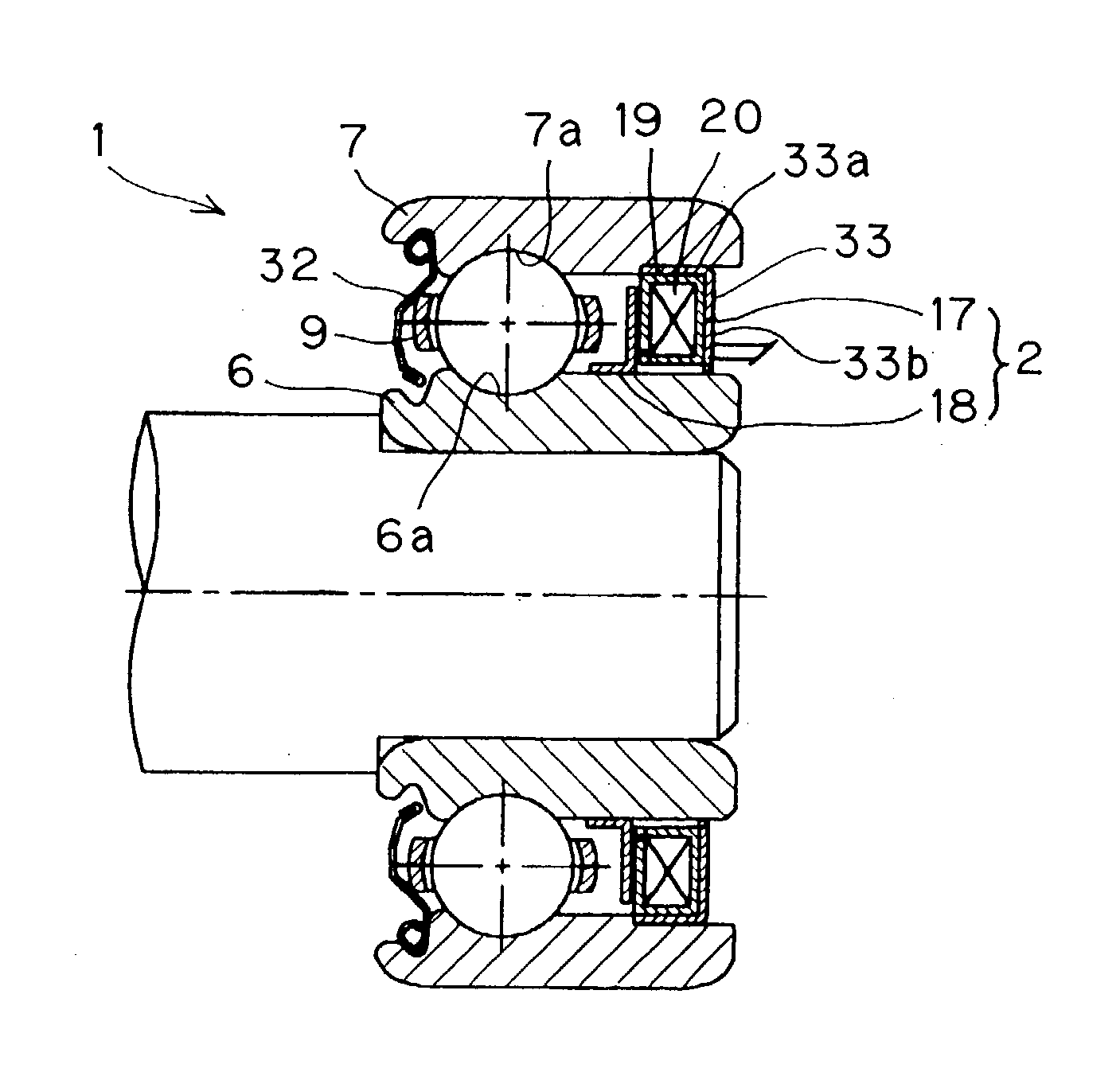
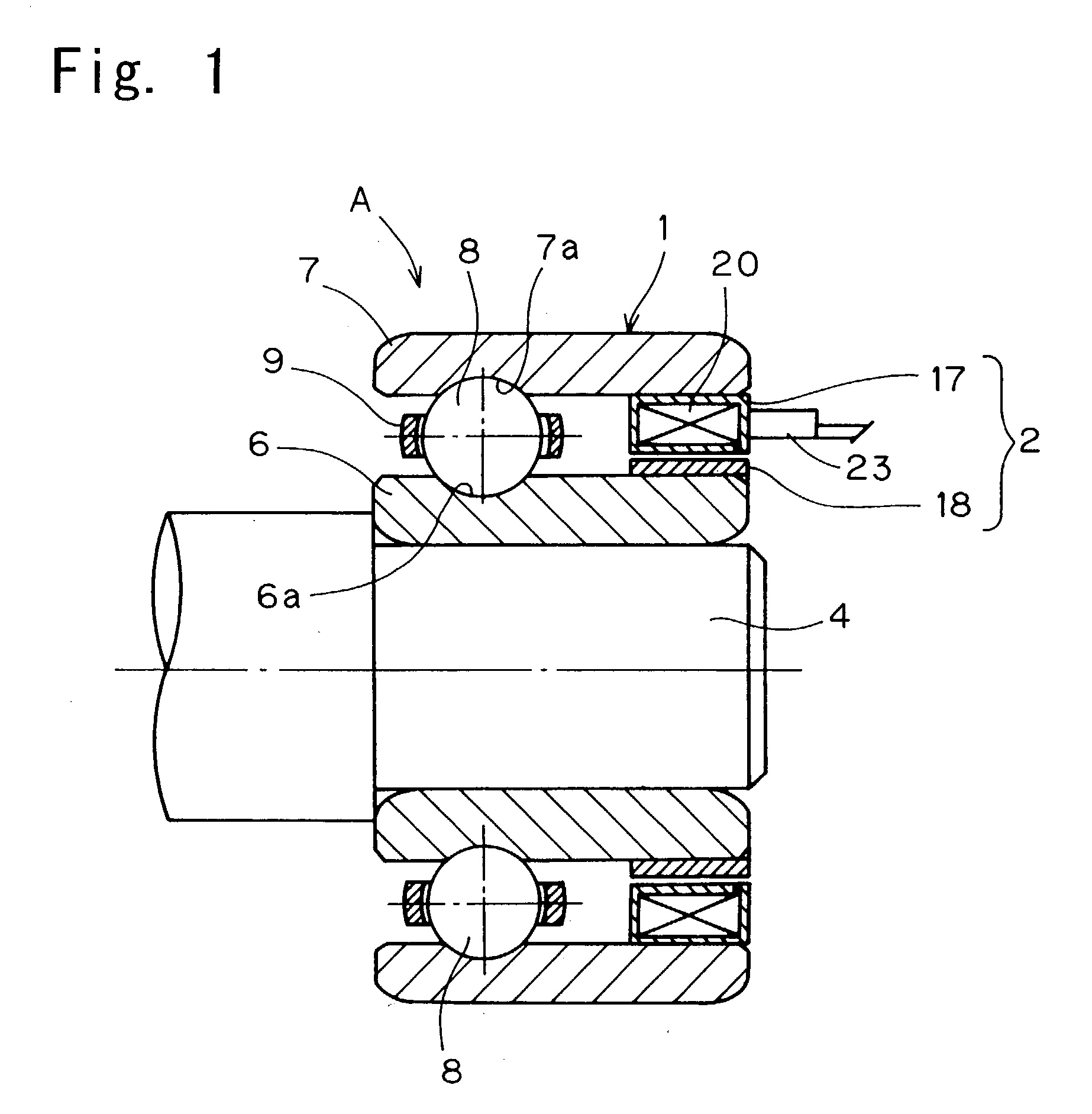
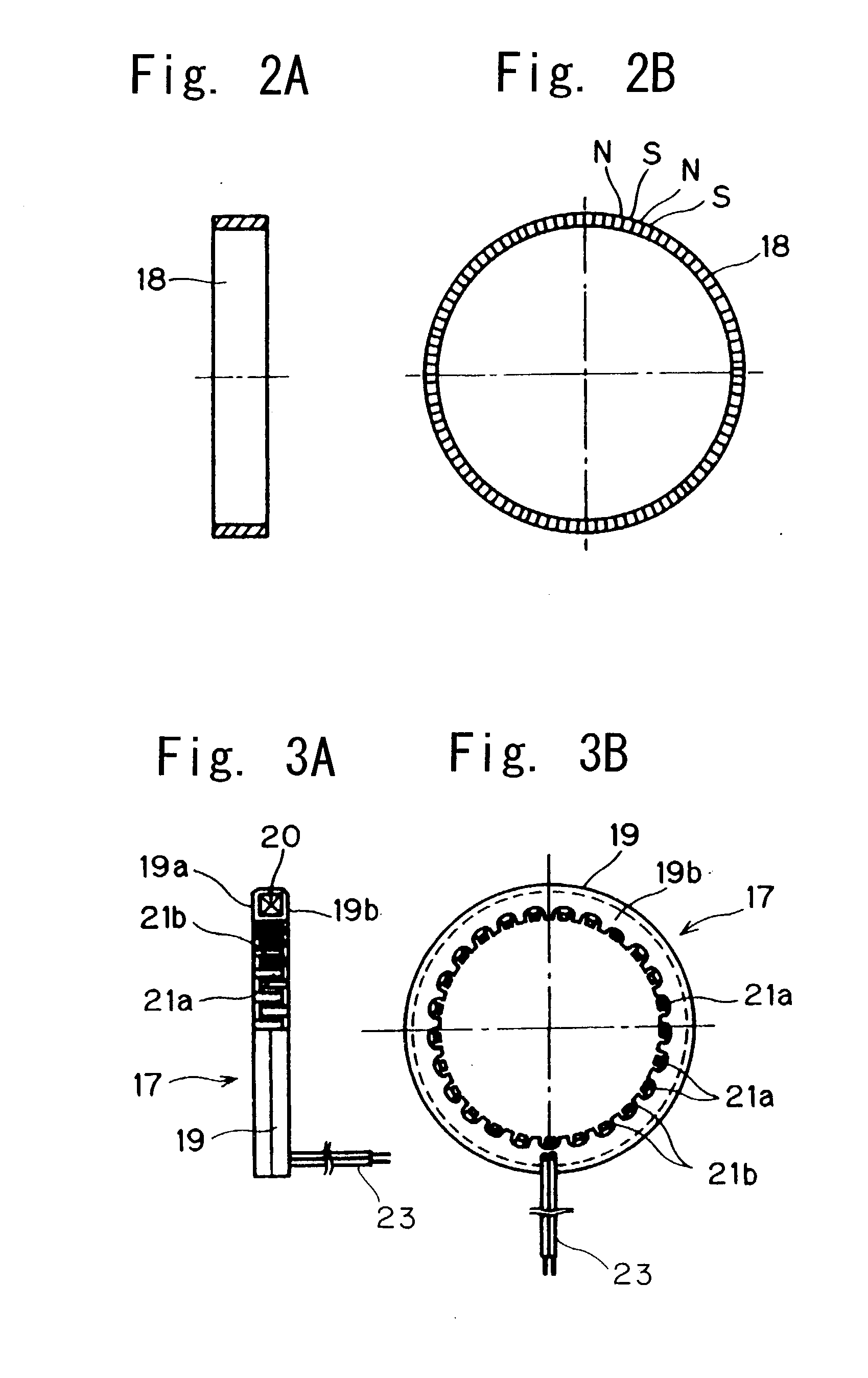
To provide a bearing assembly having an electric power generating capability, that can be assembled compact in size and easily incorporated in a drive transmission system of an internal combustion engine, the bearing assembly having an electric power generating capability includes a rolling bearing 1 including an outer race 7 and an inner race 6 rotatable relative to the outer race 7, and an electric power generator 2 interposed between the inner and outer races 6 and 7 for generating an electric power by a rotation of the inner race 6 relative to the outer race 7. This bearing assembly may be used as a bearing in the drive transmission system of the internal combustion engine for rotatably supporting, for example, a crankshaft 4.
Owner:NTN CORP
Copper-based bearing material and sliding bearing for internal combustion engines
InactiveUS6025081AEasy to slideFree cutting propertyConnecting rod bearingsCasingsCombustionInternal combustion engine
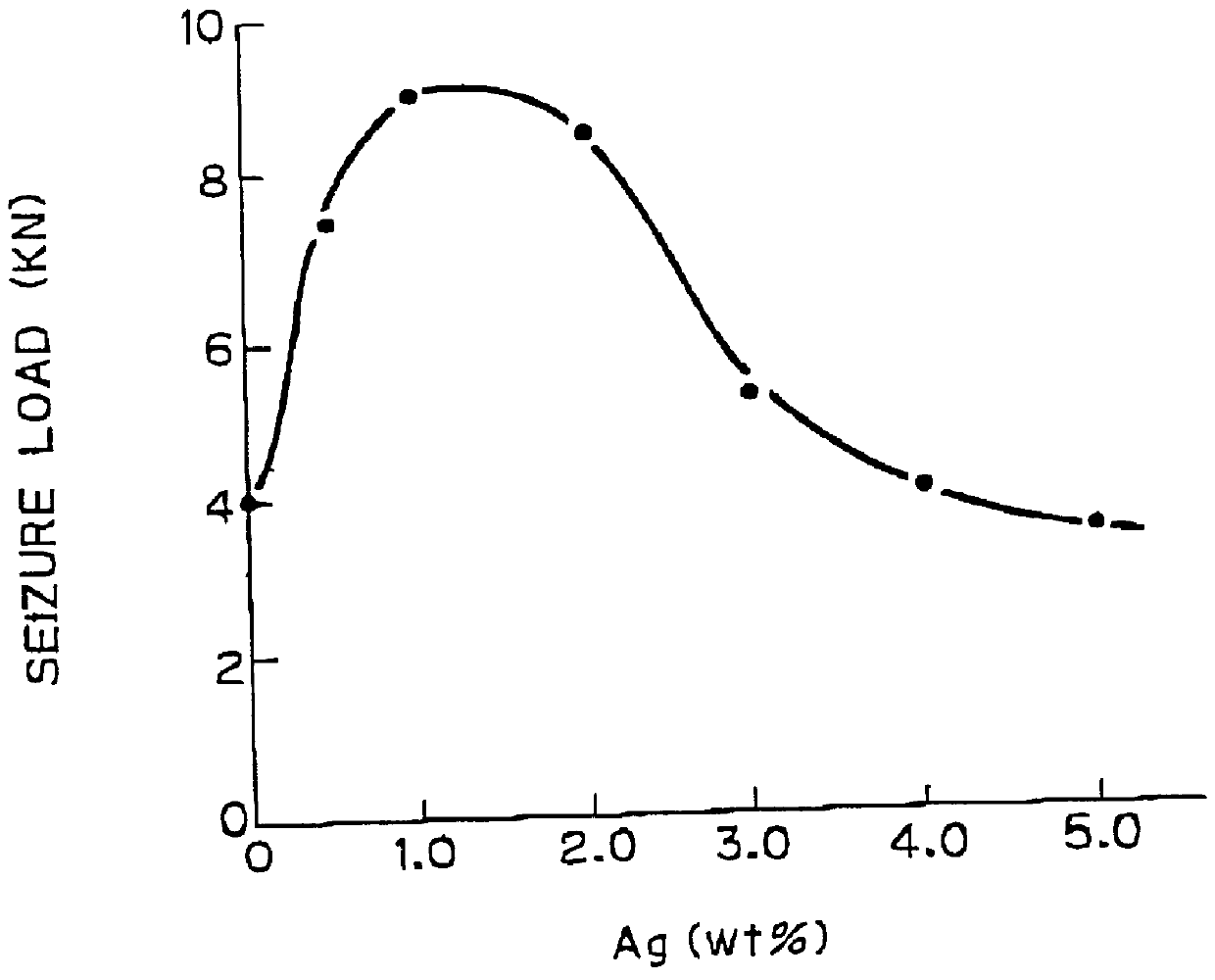
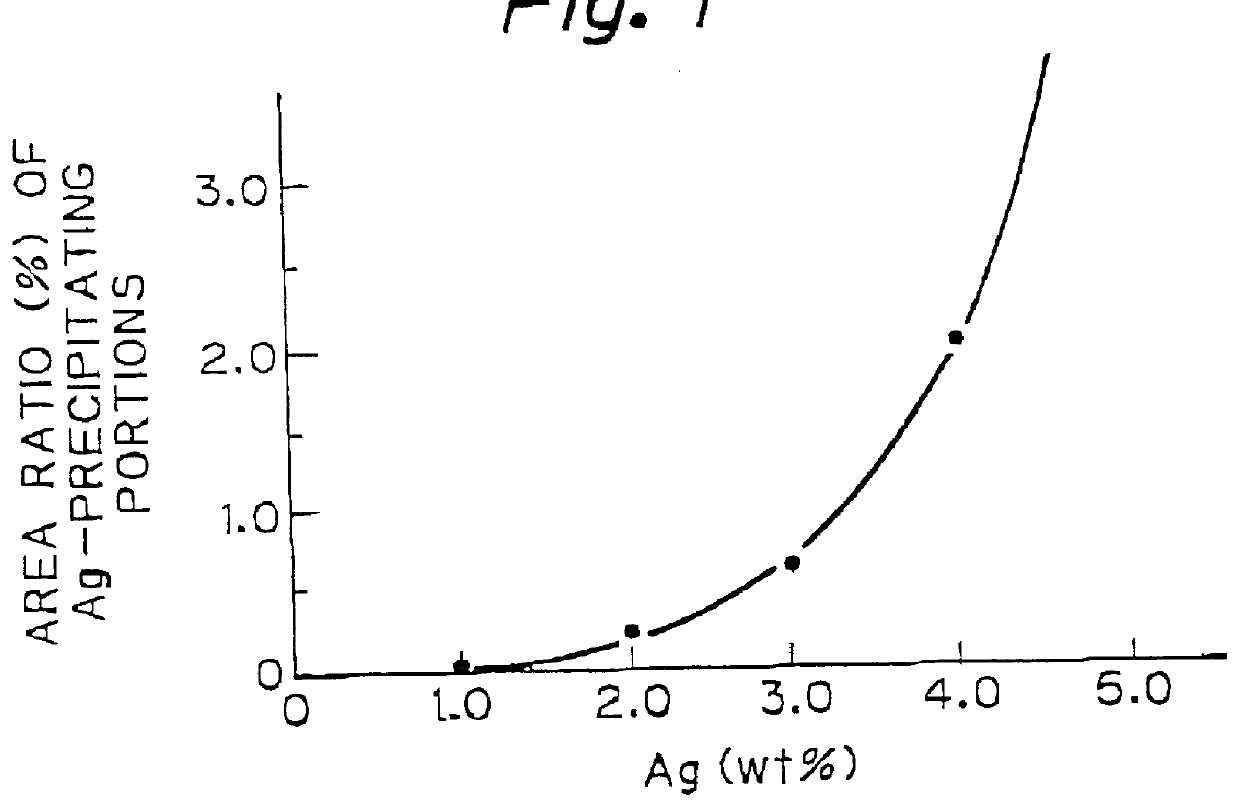
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 03118 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 8, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 8, 1998 PCT Filed Oct. 25, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 15695 PCT Pub. Date May 1, 1997The copper-based sliding material has improved seizure resistance, even if it is free of Pb, and enables thinning of the overlay. The copper alloy provided consists of from 0.1 to 2% of Ag, from 1 to 10% of Sn, and the balance consisting of Cu and unavoidable impurities and, further said Ag and Sn do not essentially form the secondary phases but are in complete or essentially solid-solution state in the Cu matrix.
Owner:TAIHO INDUSTRIES CO LTD
Bearing assembly
A bearing assembly comprises a bearing race received in a bore of a housing comprising a deformable housing material. The bearing race includes one or more recesses formed on a surface thereof disposed proximate the housing. Each recess receives housing material that has been deformed locally therein after the bearing race is received in the bore to prevent both rotational and axial motion of the bearing race relative to the housing.
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
Slide bearing
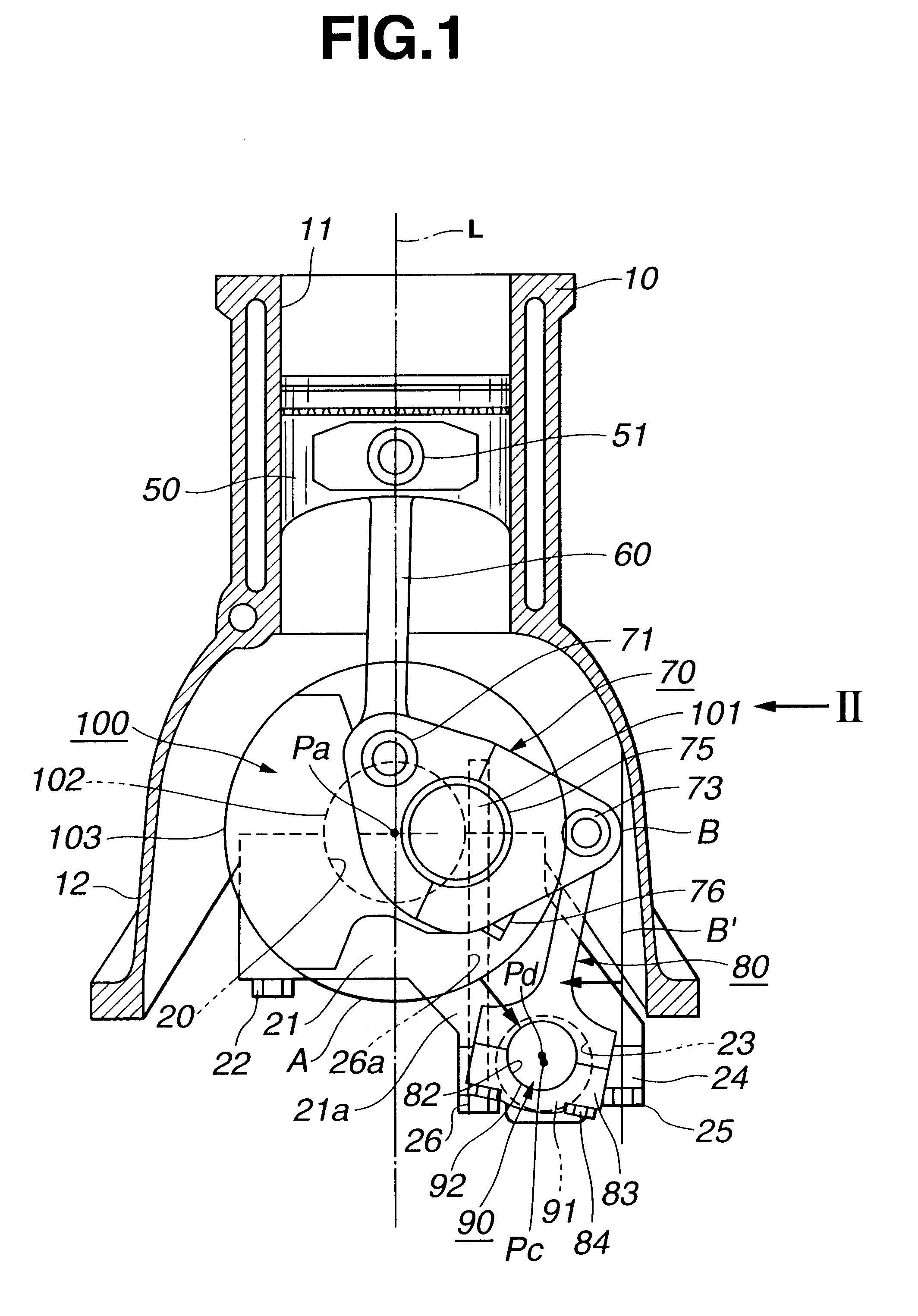
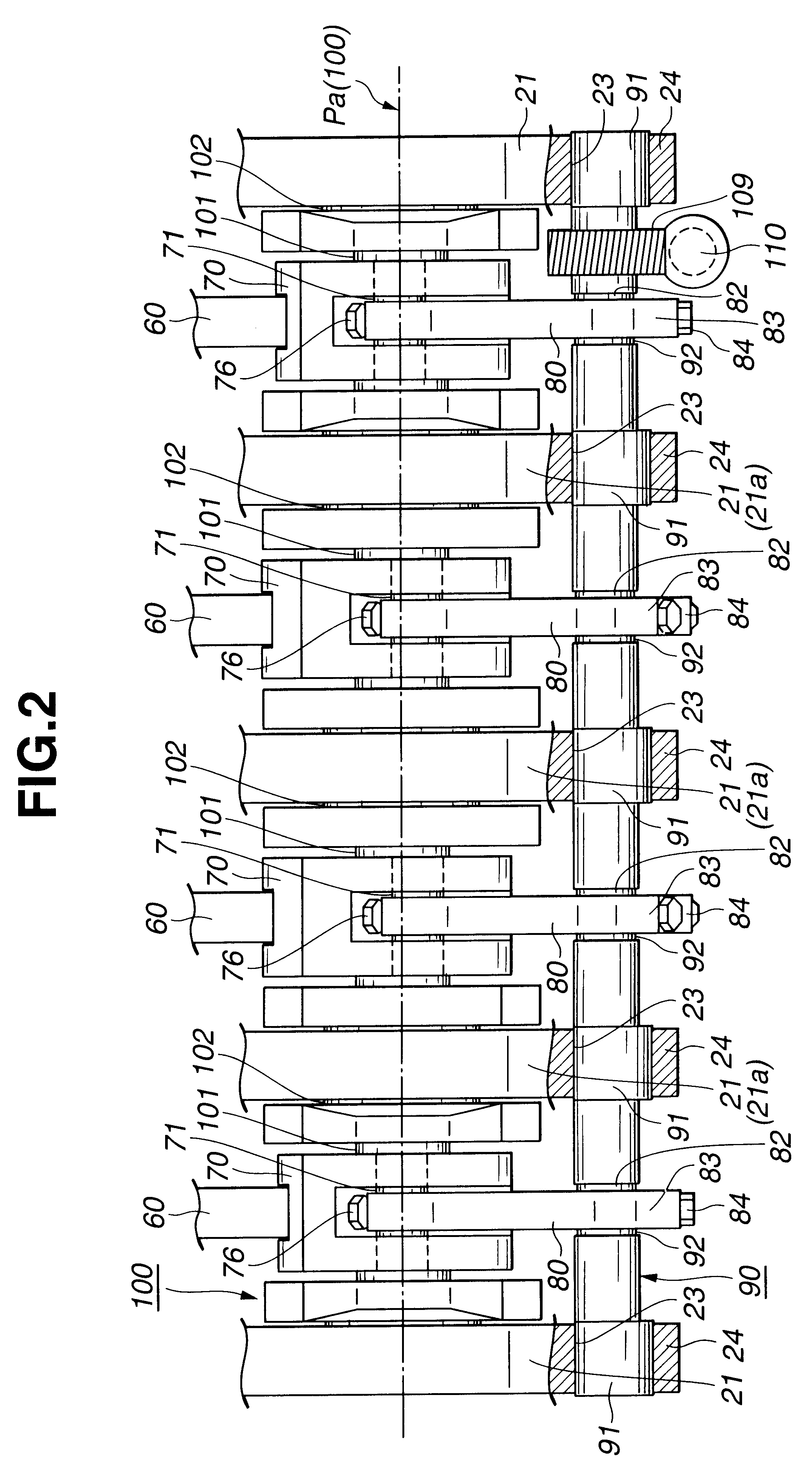
ActiveUS20100046869A1Reduces amount of lubricantAvoid damageCrankshaftsConnecting rod bearingsEngineeringMechanical engineering
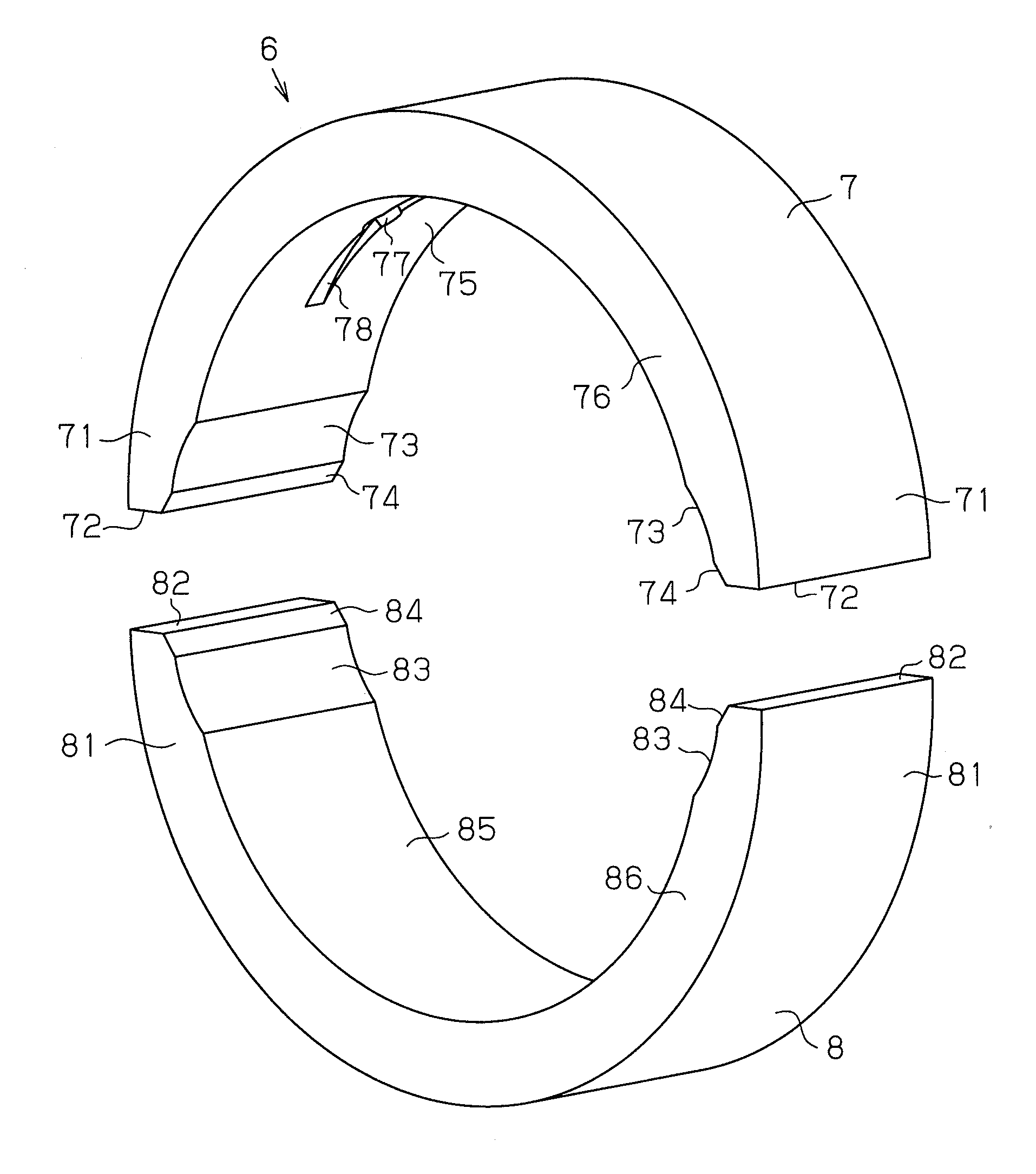
A crank bearing is disclosed that includes a semicircular upper bearing and a semicircular lower bearing, which can be split from each other. The upper bearing includes a first oil passage for introducing engine oil from the outside to a gap between the crank bearing and a crank journal, and a second oil passage for permitting the engine oil to flow in the circumferential direction of the crank bearing. The first oil passage includes an inner circumference opening, which is open to the inner circumference of the main bearing. The upper bearing includes a non-undercut portion in which no oil passage is formed on the trailing side of the inner circumference opening in the rotational direction of the crank journal. A chamfer oil passage for discharging the engine oil in the second oil passage to the outside from the axial direction of the crank bearing is provided in at least one of the lower bearing and a region on the proceeding side of the circumference opening in the rotational direction of the crank journal.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Plain bearing
Owner:DAIDO METAL CO LTD
Oil-feeding device for engine crankshaft
InactiveUS20050263125A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease frictionCrankshaftsCasingsEngineeringCylinder block
An oil-feeding device for a crankshaft where the amount of lubricant oil leaking from supporting areas of main journal portions is reduced without increasing friction of bearing members against the main journal portions. The oil-feeding device for a crankshaft includes upper bearing members and lower bearing members. The upper and lower bearing members have a half hollow cylindrical shape, are provided with crush relief portions at both ends, and jointly encompass main journal portions of a crank shaft. The upper bearing members have circumferentially extending oil grooves provided in the faces opposite the main journal portions, the grooves penetrating through oil passages of a cylinder block. The lower bearing members do not have oil grooves. The oil grooves do not extend in the crush relief portions, and therefore the leakage of lubricant oil, fed to the oil grooves, to the areas of the crush relief portions is suppressed.
Owner:TAIHO INDUSTRIES CO LTD
Bearing assembly with electric power generator
InactiveUS20030173844A1Small sizeAssemblage can advantageously be improvedBearing assemblyBall bearingsEngineeringInternal combustion engine
To provide a bearing assembly having an electric power generating capability, that can be assembled compact in size and easily incorporated in a drive transmission system of an internal combustion engine, the bearing assembly having an electric power generating capability includes a rolling bearing 1 including an outer race 7 and an inner race 6 rotatable relative to the outer race 7, and an electric power generator 2 interposed between the inner and outer races 6 and 7 for generating an electric power by a rotation of the inner race 6 relative to the outer race 7. This bearing assembly may be used as a bearing in the drive transmission system of the internal combustion engine for rotatably supporting, for example, a crankshaft 4.
Owner:NTN CORP
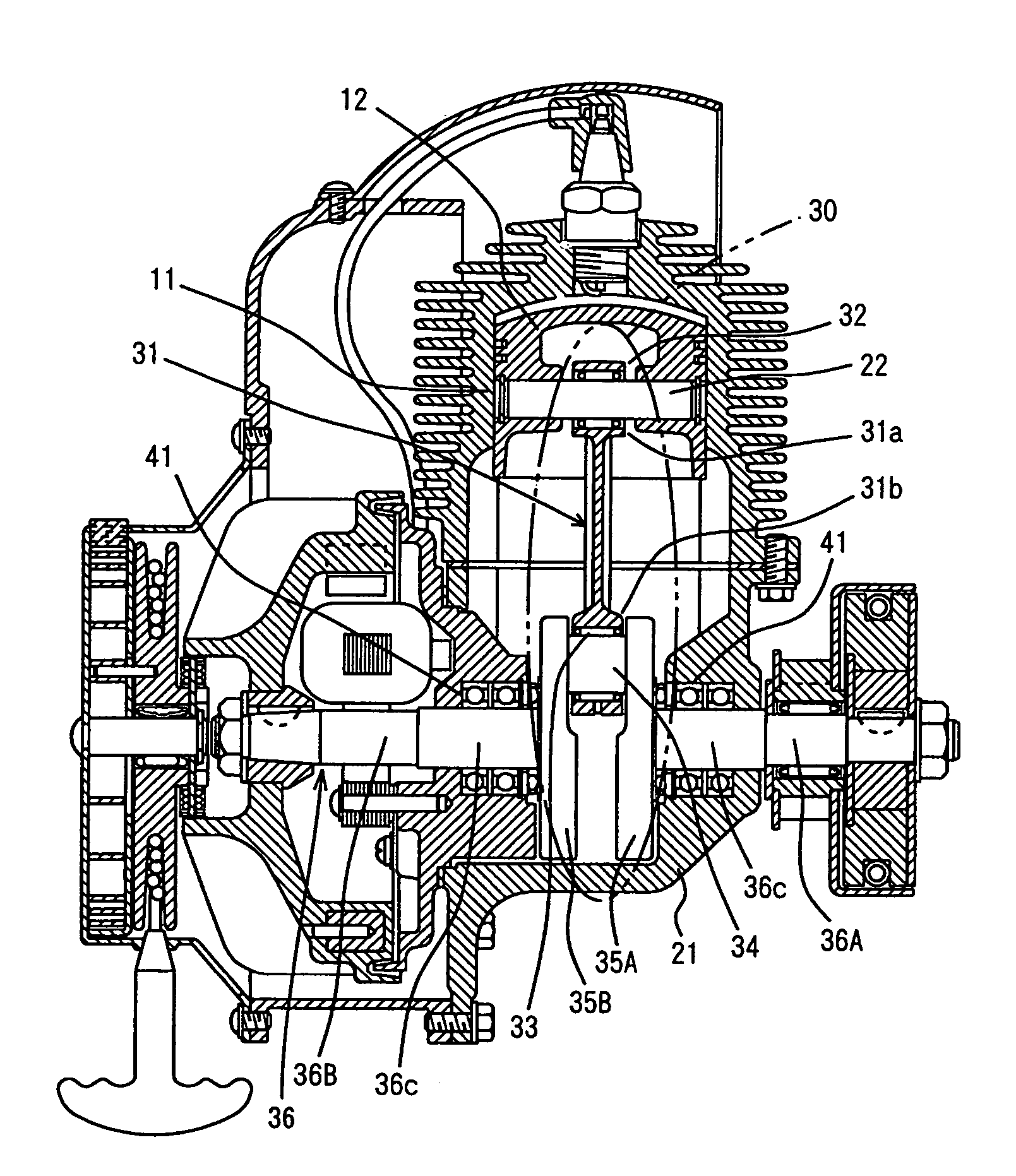
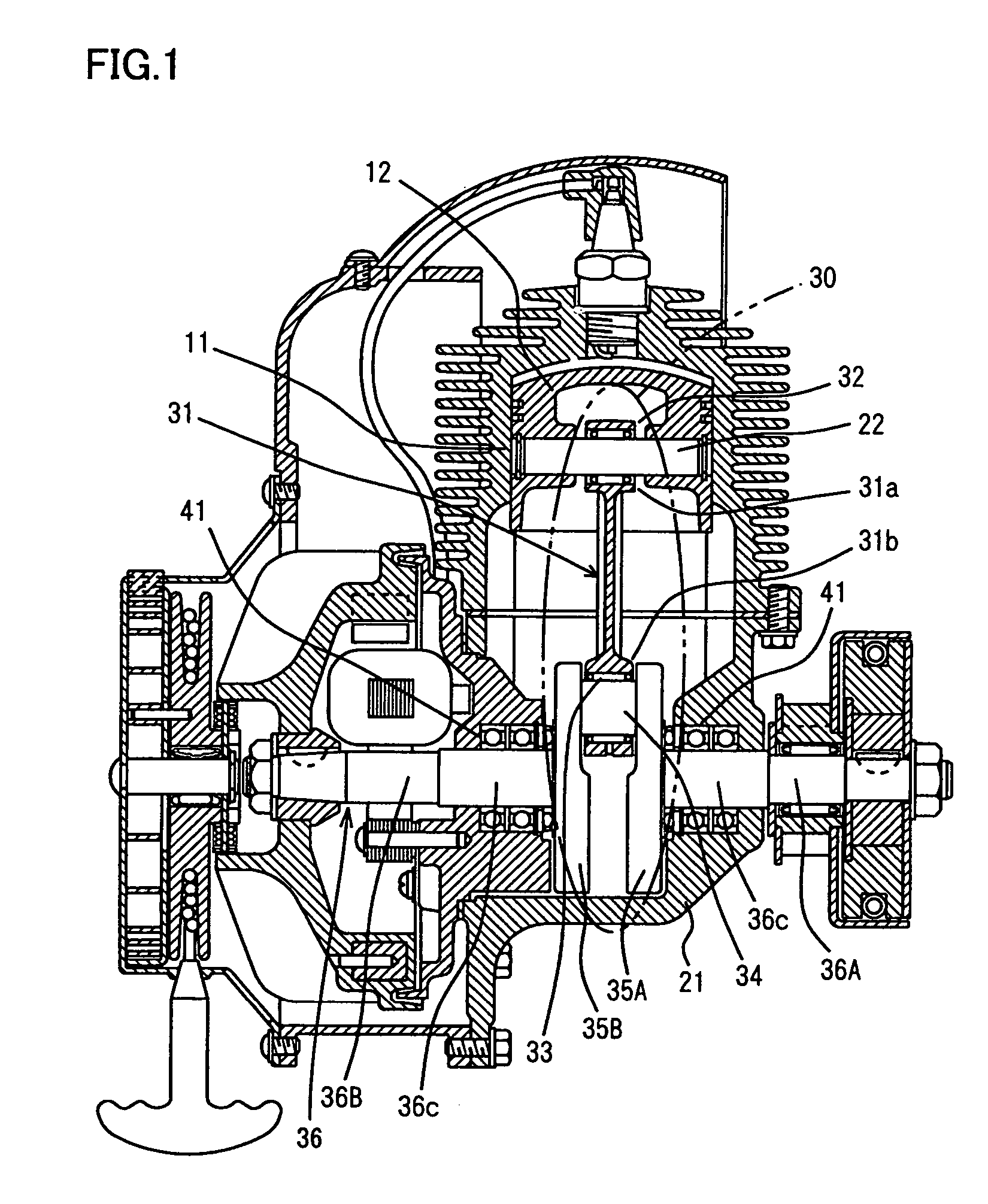
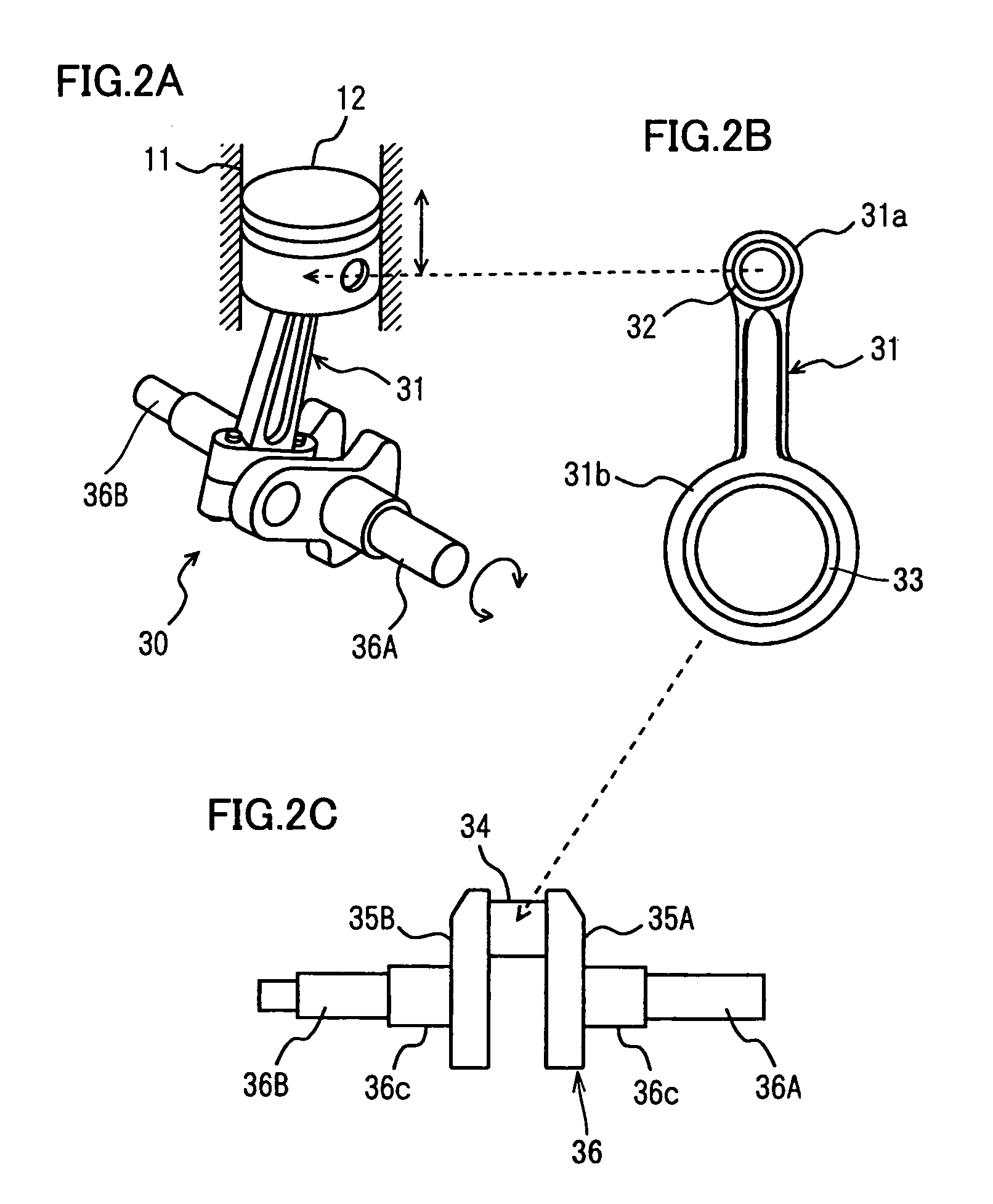
Internal combustion engine with variable compression ratio mechanism
An internal combustion engine is constructed to include a variable compression ratio mechanism. The mechanism has the following structure. An upper link has one end pivotally connected to a piston pin of a piston of the engine. A lower link is pivotally disposed on a crank pin of a crankshaft of the engine and has one part pivotally connected to the other end of the upper link. A control shaft extends substantially in parallel with the crankshaft. A control link has an end pivotally connected to the other part of the lower link. The other end of the control link is connected to the control shaft through an eccentric bearing structure, so that rotation of the control shaft about its axis induces a pivoting of the lower link about the crank pin varying the stroke of the piston.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Internal combustion engine with variable compression ratio mechanism
An internal combustion engine is constructed to include a variable compression ratio mechanism. The mechanism has the following structure. An upper link has one end pivotally connected to a piston pin of a piston of the engine. A lower link is pivotally disposed on a crank pin of a crankshaft of the engine and has one part pivotally connected to the other end of the upper link. A control shaft extends substantially in parallel with the crankshaft. A control link has an end pivotally connected to the other part of the lower link. The other end of the control link is connected to the control shaft through an eccentric bearing structure, so that rotation of the control shaft about its axis induces a pivoting of the lower link about the crank pin varying the stroke of the piston.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Thrust bearing
A thrust bearing assembly includes an upper thrust bearing and a lower thrust bearing for use in an engine assembly of a vehicle and which, are preferably, identically configured. The upper and lower thrust bearings each include an arcuate bearing shell with a concave inner surface and a convex outer surface and each may be formed with a pair of axially spaced flanges extending radially outwardly of the bearing shells. The flanges may be formed as one piece with the bearing shell and the thickness of one of the flanges is greater than that of the other of the flanges. The thicker flanges are load bearing and preferably contoured, whereas the thinner flanges are not. The bearings are installed with the thick flange of each bearing matched radially opposite the thin flange of the companion bearing to minimize fatigue and failure normally attributed to repeated seating and unseating of the bearing assemblies having flanges of equal thickness caused by changing bending loads imparted by a shaft.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WORLD WIDE LLC
Support structure in crank mechanism and component constituting crank mechanism
InactiveUS7147382B2High strengthSuppressing an increase in rate of secular dimensional changeCrankshaftsConnecting rodsAustenite grainReciprocating motion
A component of a crank mechanism is incorporated in the crank mechanism that converts reciprocating motion of a piston to rotary motion by means of a crank pin, a crank arm and a crank shaft via a connecting bar, and has a hydrogen content of no more than 0.5 ppm, austenite crystal grains of a grain size number exceeding 10, or a fracture stress value of no less than 2650 MPa. Thus, a support structure in and a component of a crank mechanism ensuring a long fatigue life, high anti-crack strength, and a reduced rate of secular dimensional change to improve dimensional stability, can be obtained.
Owner:NTN CORP
Caged roller assembly and reduction gear unit using the same
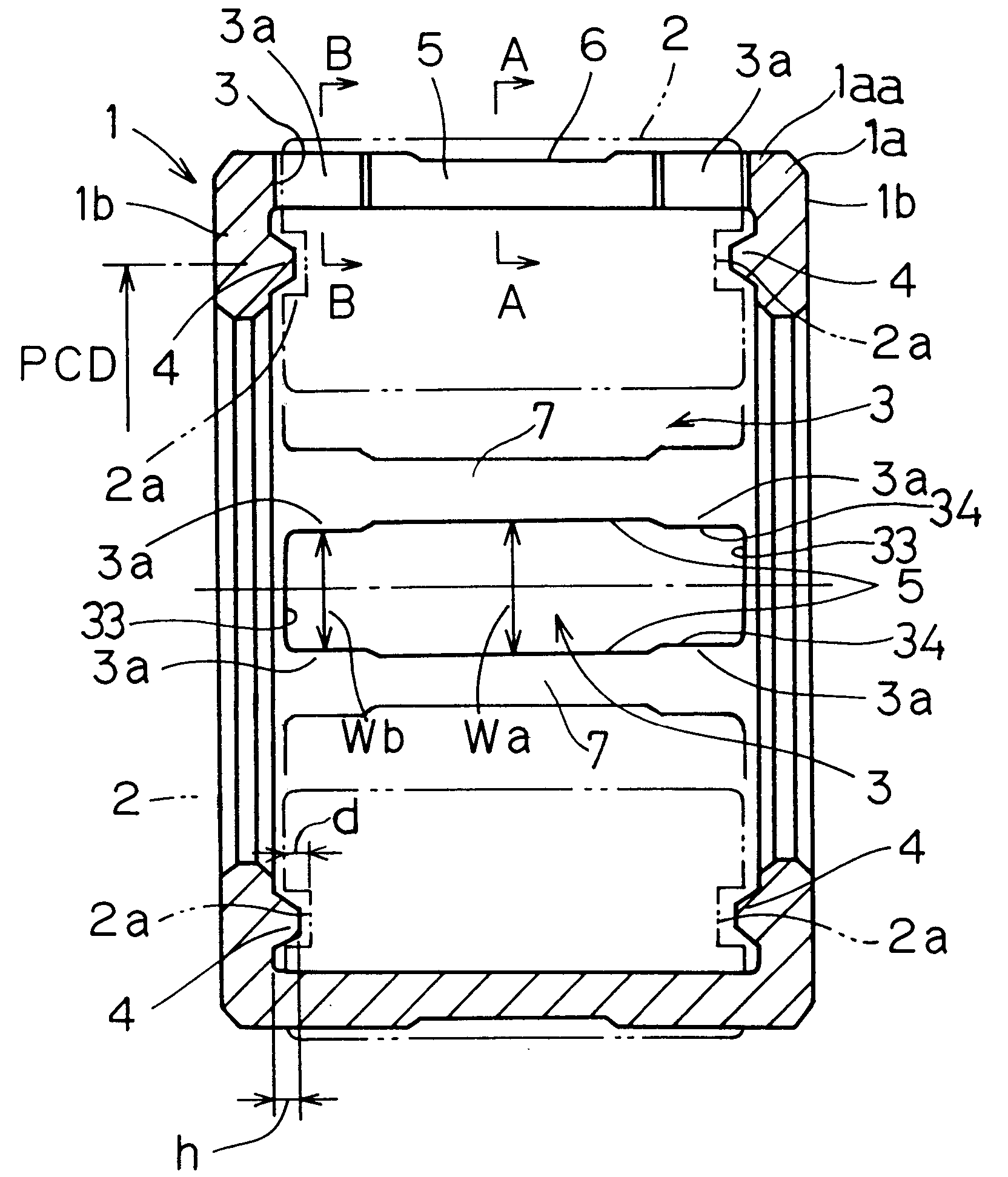
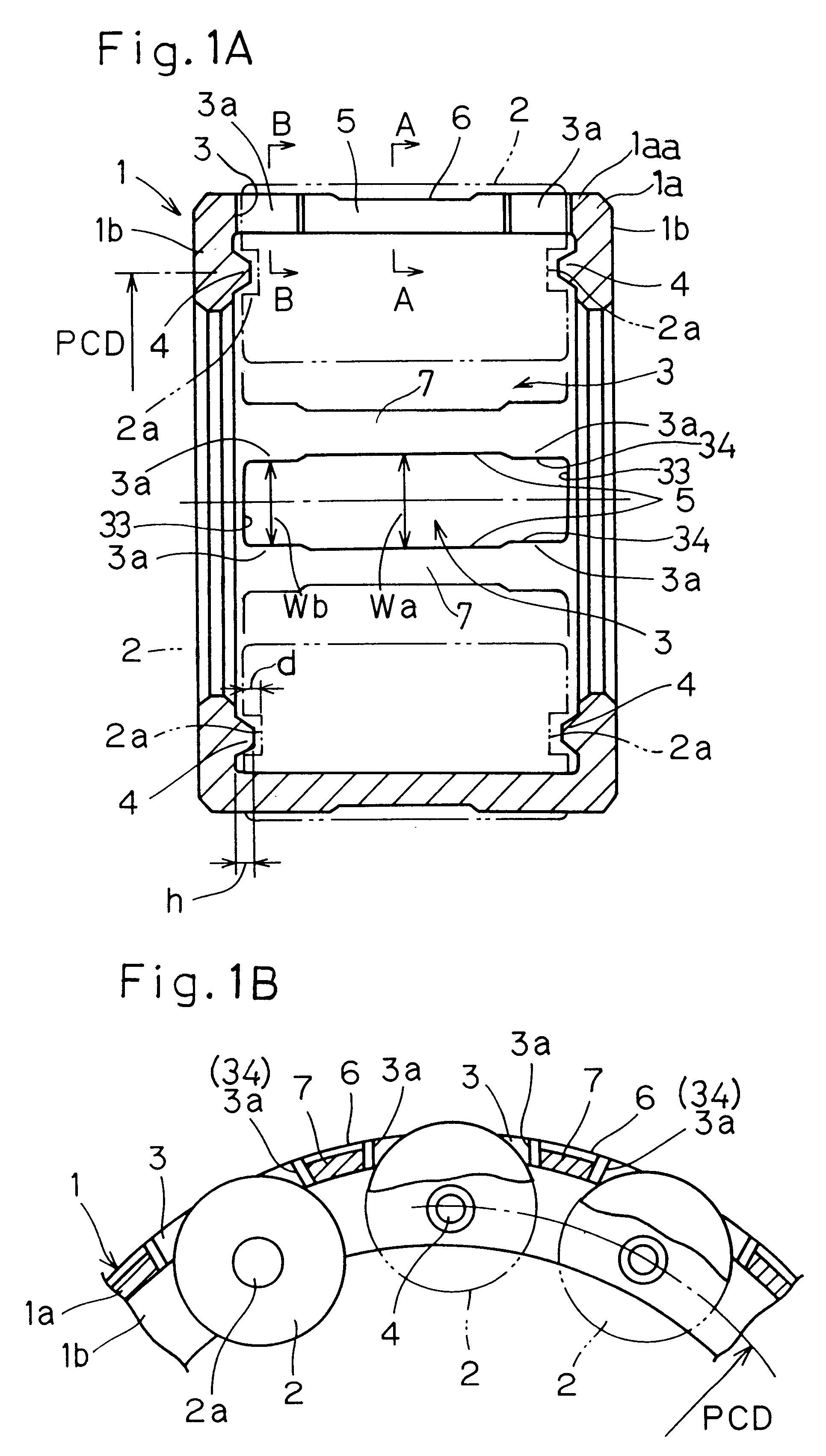
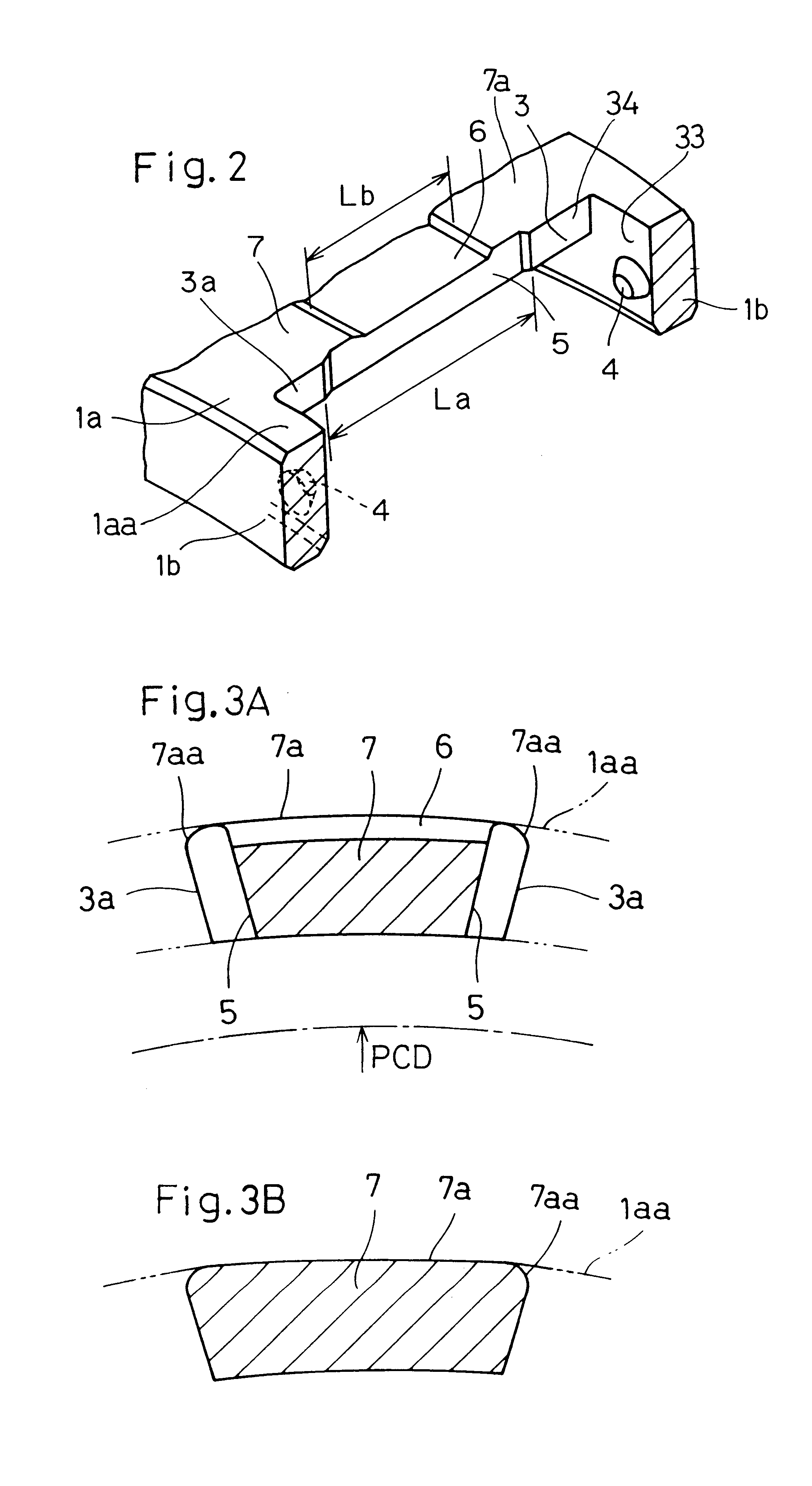
To provide a caged roller assembly having a large load bearing capacity within a limited space, substantially free from a problem associated with separation of rollers from a roller retainer in either direction radially outwardly or inwardly of the roller retainer, and excellent in assemblability while a skewing of the roller is prevented, the caged roller assembly includes a roller retainer (1) and a plurality of rollers (2). The roller retainer (1) includes a circumferential ring body (1a) of a diameter greater than the pitch circle PCD depicted by longitudinal axes of the rollers (2), and a pair of annular collars or flanks (1b) lying perpendicular to the circumferential ring body (1a). A bearing boss (4) for each roller (2) is formed in each of the annular flank (1b) on one hand, and a bearing recess (2a) is defined in each of opposite end faces of each roller (2) for operatively receiving the respective bearing bosses (4) to thereby rotatably support the associated roller (2) in a non-detachable fashion.
Owner:NTN CORP
Sliding member
InactiveUS7399122B2Prevent slidingAvoid it happening againCrankshaftsCrankshaft bearingsEngineeringMechanical engineering
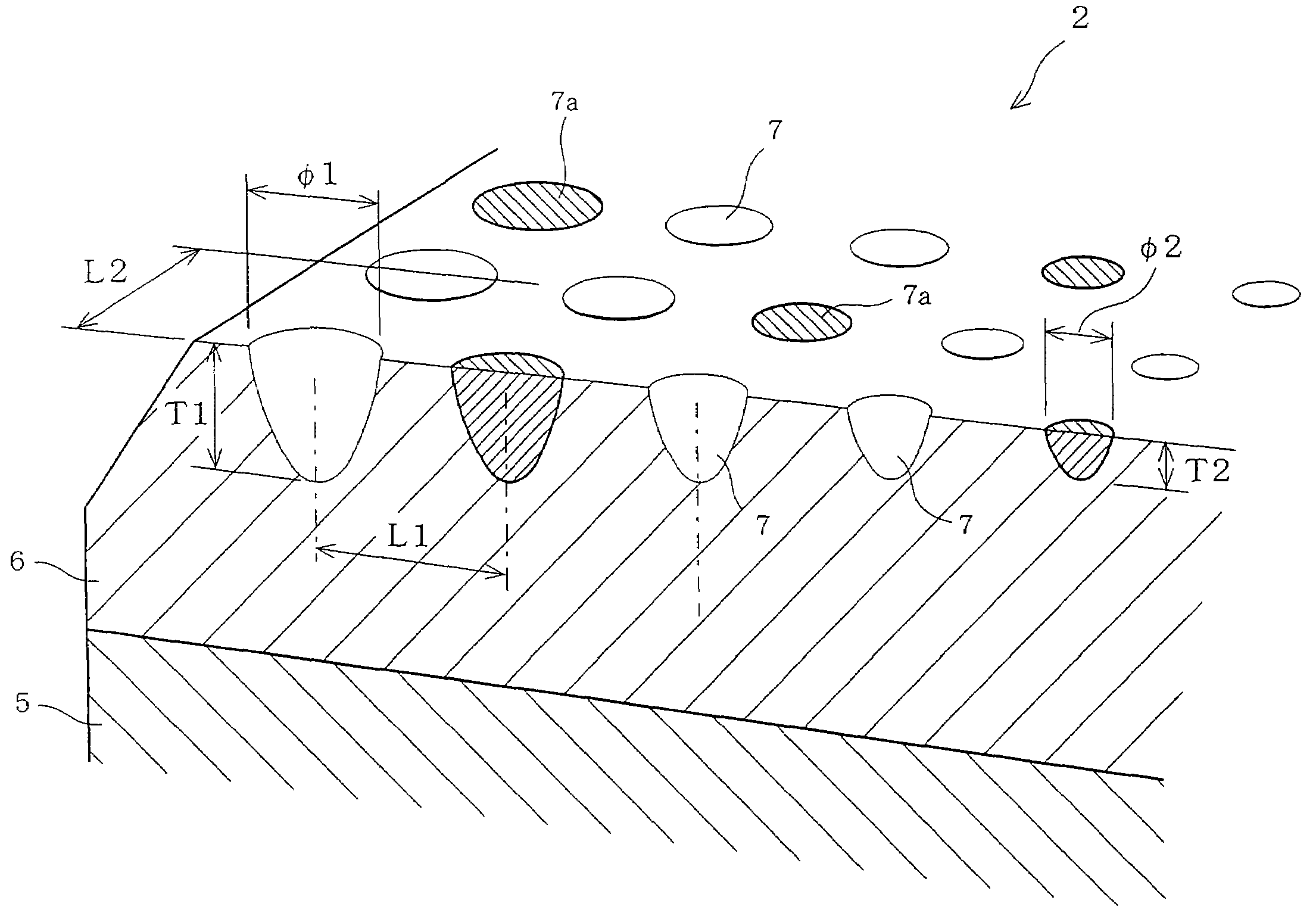
In order to improve conformability of a sliding surface of a sliding member in an early state of sliding, there is provided a sliding member in which a plurality of holes are formed on a sliding surface, and the diameters (or the opening area) of the holes on the sliding surface are arranged so as to become gradually large as it gets closer to both ends in an axial direction from the center side in the axial direction. This feature decreases the pressurized area as it gets closer to the ends of the sliding surface so that it wears at an early stage, whereby a conformed surface following the deflection of a mating member is provided.
Owner:DAIDO METAL CO LTD
Main bearing for engine with high belt load
InactiveUS20120294558A1Easy to wearFully lubricatedCrankshaft bearingsBearing componentsUltimate tensile strengthHybrid vehicle
A main bearing (20) for supporting a rotating crankshaft (56) includes an upper shell (22) and a lower shell (24). An upper inner surface (32) of the upper shell (22) has an oil supply groove (26) extending circumferentially therealong, an oil stem groove (28) extending obliquely from the oil supply groove (26), and a pair of oil distribution grooves (30) extending from the oil stem groove (28) along and parallel to the oil supply groove (26) to present an F-shape along the upper inner surface (32) of the main bearing (20). The oil grooves (26, 28, 30) provide for improved lubrication of the main bearing (20) at startup and when the engine is idle or stopped, especially in electric and hybrid vehicles. The main bearing (20) also has exceptional strength and load bearing capacity.
Owner:TENNECO
Roller bearing
A roller bearing for rotatably supporting a rotating shaft of an internal combustion engine between a main body and a cap of the internal combustion engine. The roller bearing including: a plurality of rollers; a retainer which is cirumferentially splittable and supports the plurality of rollers; and an outer race which is cirumferentially splittable and forms a raceway surface for the plurality of rollers. The retainer is split into a plurality of retaining members. The outer race is split into a plurality of race plates. At least one of the race plates is provided with one of a projection and a cavity to be engaged with one of the main body and the cap to restrict a relative movement between the one of the race plates and the one of the cylinder head and the cap.
Owner:NSK LTD
Thrust bearing assembly
InactiveUS20060034556A1Reduce manufacturing costLow costBearing assemblyCrankshaft bearingsThrust bearingFree edge
The subject invention provides a thrust bearing assembly having only three thrust flanges in total. One portion of the thrust bearing assembly comprises a main bearing having an arcuate bearing shell with a concave inner surface and a convex outer surface. A thrust washer having hydrodynamic features abuts one of the edges of the main bearing and extends radially outwardly from the outer surface thereof forming a thrust surface. The other of the edges of the main bearing is free of a flange. The free edge of the main bearing is preferably spaced inward from other thrust surfaces and the edge has a substantially narrower width than the other thrust surfaces. The other portion of the assembly may include a traditional thrust bearing having one thrust flange with hydrodynamic features and another thrust flange free of hydrodynamic features, both extending radially outwardly therefrom or may include another main bearing abutting a pair of thrust washers, one having hydrodynamic features and one free of hydrodynamic features, extending radially outwardly from the other main bearing. In either configuration, the thrust flange or thrust washer that is free of hydrodynamic features is opposite the thrust washer having hydrodynamic features of the main bearing.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WORLD WIDE LLC
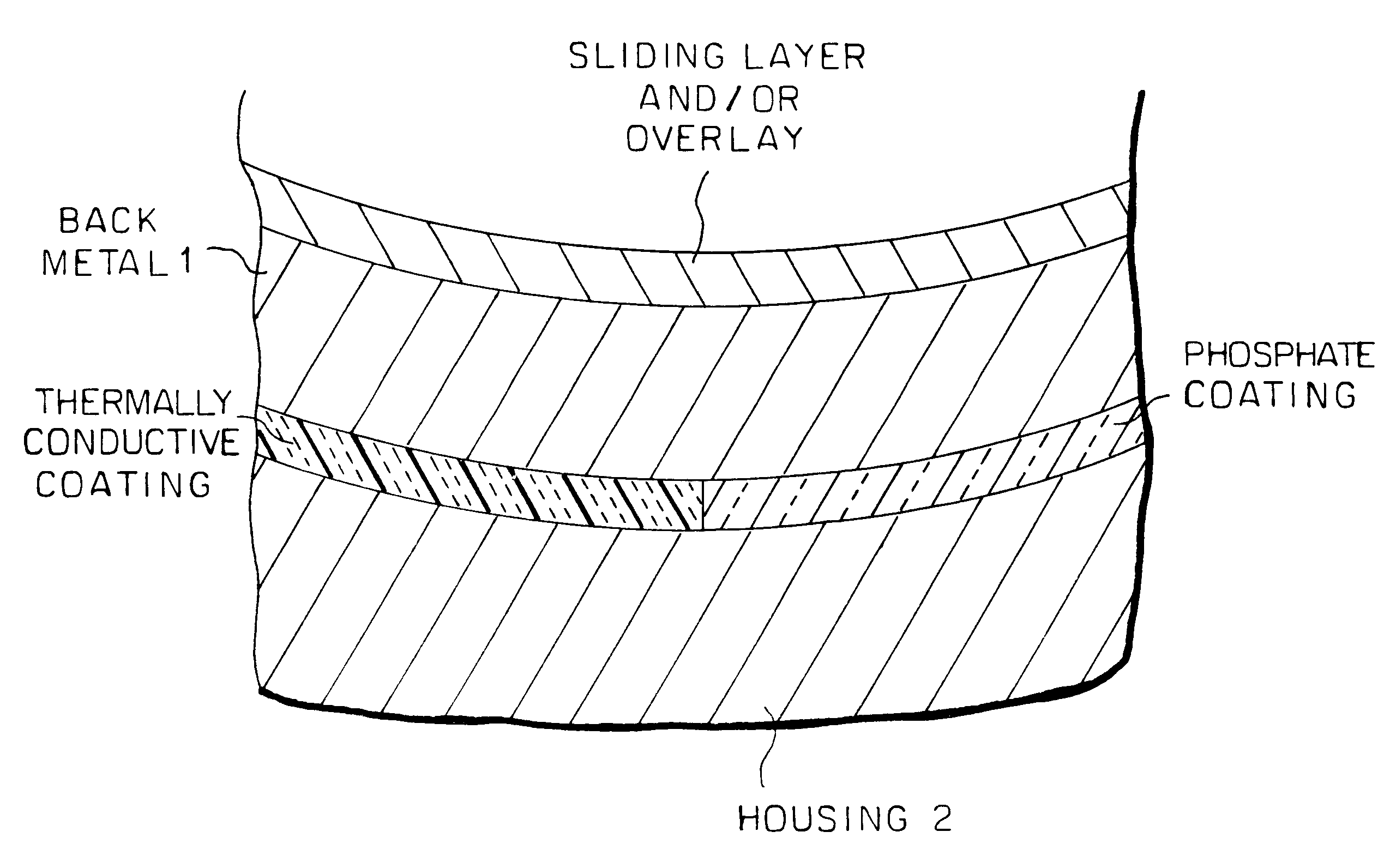
Sliding bearing and sliding bearing structure
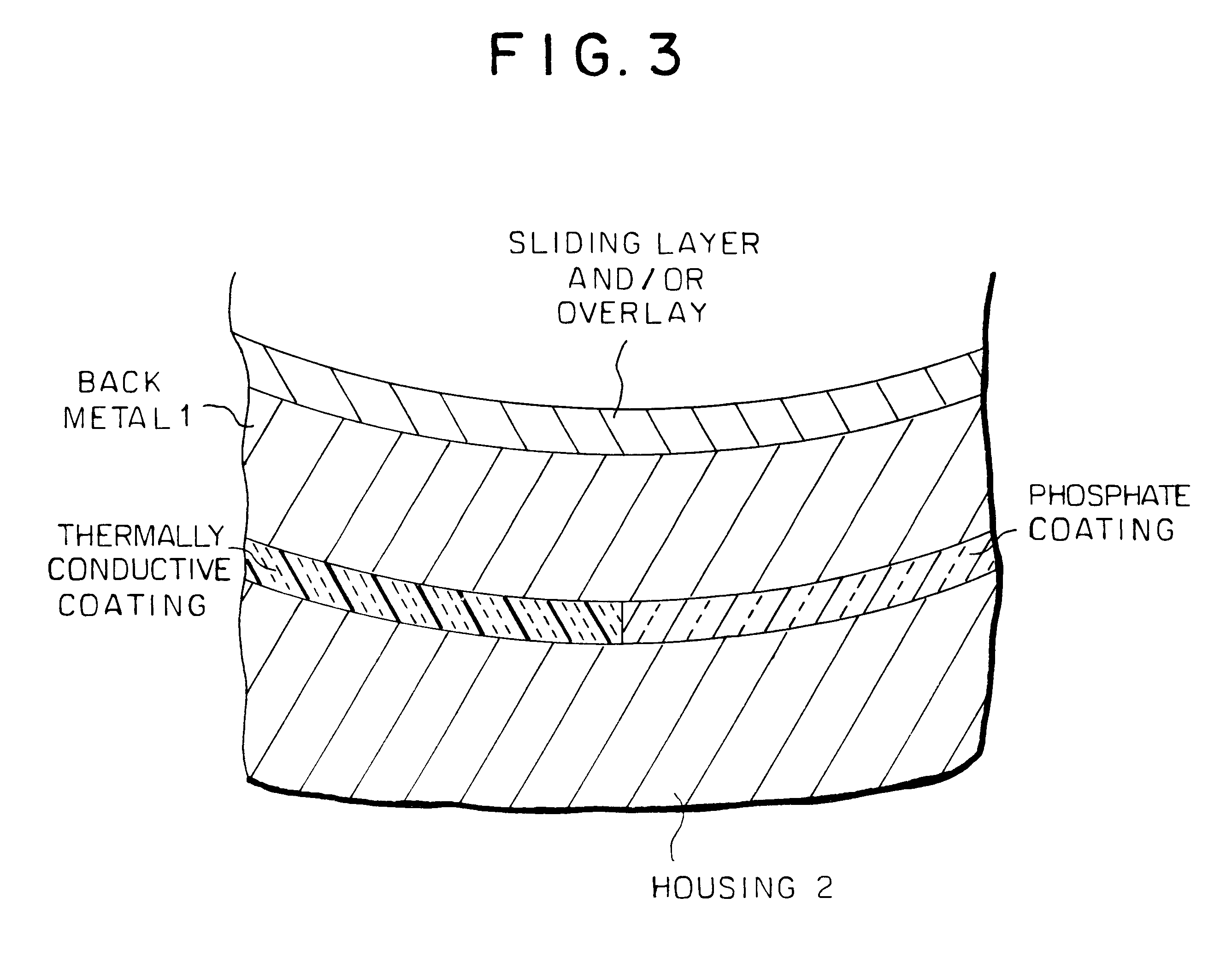
InactiveUS6357918B1Improve the immunityGood anti-occlusion performanceConnecting rod bearingsCrankshaft bearingsElectrical conductorFretting wear
There is disclosed a sliding bearing provided with a sliding bearing layer and a back metal layer bonded to the outer face of the sliding bearing layer, the back face of which back metal layer being coated with a phosphate coating at a portion where fretting wear is apt to occur while coated with a coating of a thermally good conductor at another portion where no phosphate coating is provided, whereby seizure resistance as well as fretting resistance is improved because the dispersing of heat can be improved by the coating of the thermally good conductor.
Owner:DAIDO METAL CO LTD
Sliding bearing
ActiveUS20050213859A1Avoid deformationPrevent leakageCrankshaft bearingsShaftsEngineeringMechanical engineering
There is provided a sliding bearing, which can continuously enhance conformability even when deformation by high oil film pressure in the vicinity of a central part of the sliding bearing occurs. The sliding bearing includes crownings which are each formed in an inclined shape toward an outer peripheral surface from an inner peripheral surface, at end parts in an axial direction, of an inner peripheral surface of a sliding bearing, so that even when the region in the vicinity of the central part of the sliding bearing 1 receives the oil film pressure and deforms in the recessed shape so as for both the end parts in the axial direction to locally contact a shaft, conformability can be enhanced not only at an early stage of use of the sliding bearing but also continuously by relief by the crownings.
Owner:DAIDO METAL CO LTD
Oil-feeding device for an engine crankshaft
InactiveUS7281854B2Reduce the amount requiredIncrease frictionCrankshaftsCrankshaft bearingsCylinder blockMechanical engineering
An oil-feeding device for a crankshaft where the amount of lubricant oil leaking from supporting areas of main journal portions is reduced without increasing friction of bearing members against the main journal portions. The oil-feeding device for a crankshaft includes upper bearing members and lower bearing members. The upper and lower bearing members have a half hollow cylindrical shape, are provided with crush relief portions at both ends, and jointly encompass main journal portions of a crank shaft. The upper bearing members have circumferentially extending oil grooves provided in the faces opposite the main journal portions, the grooves penetrating through oil passages of a cylinder block. The lower bearing members do not have oil grooves. The oil grooves do not extend in the crush relief portions, and therefore the leakage of lubricant oil, fed to the oil grooves, to the areas of the crush relief portions is suppressed.
Owner:TAIHO INDUSTRIES CO LTD
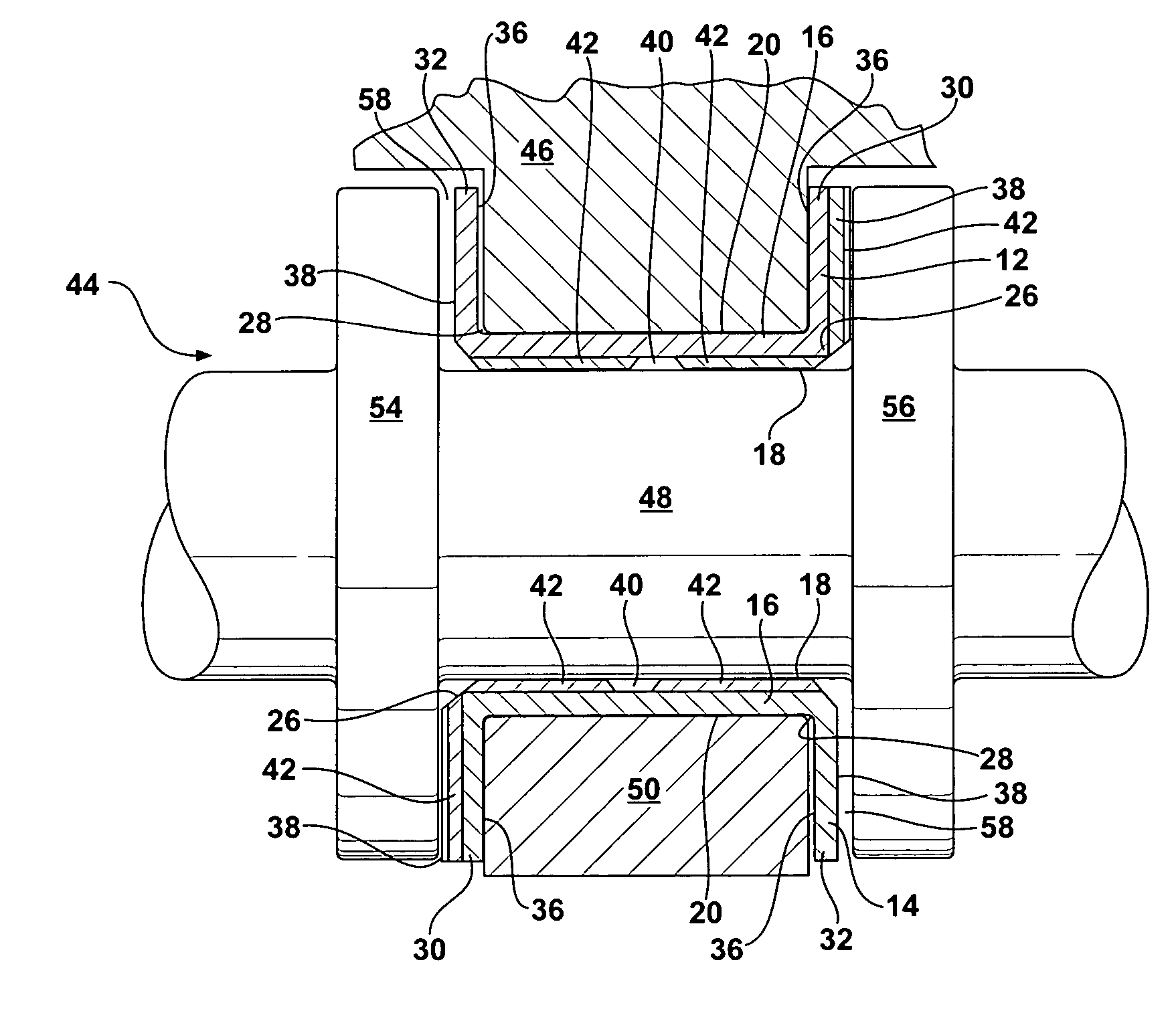
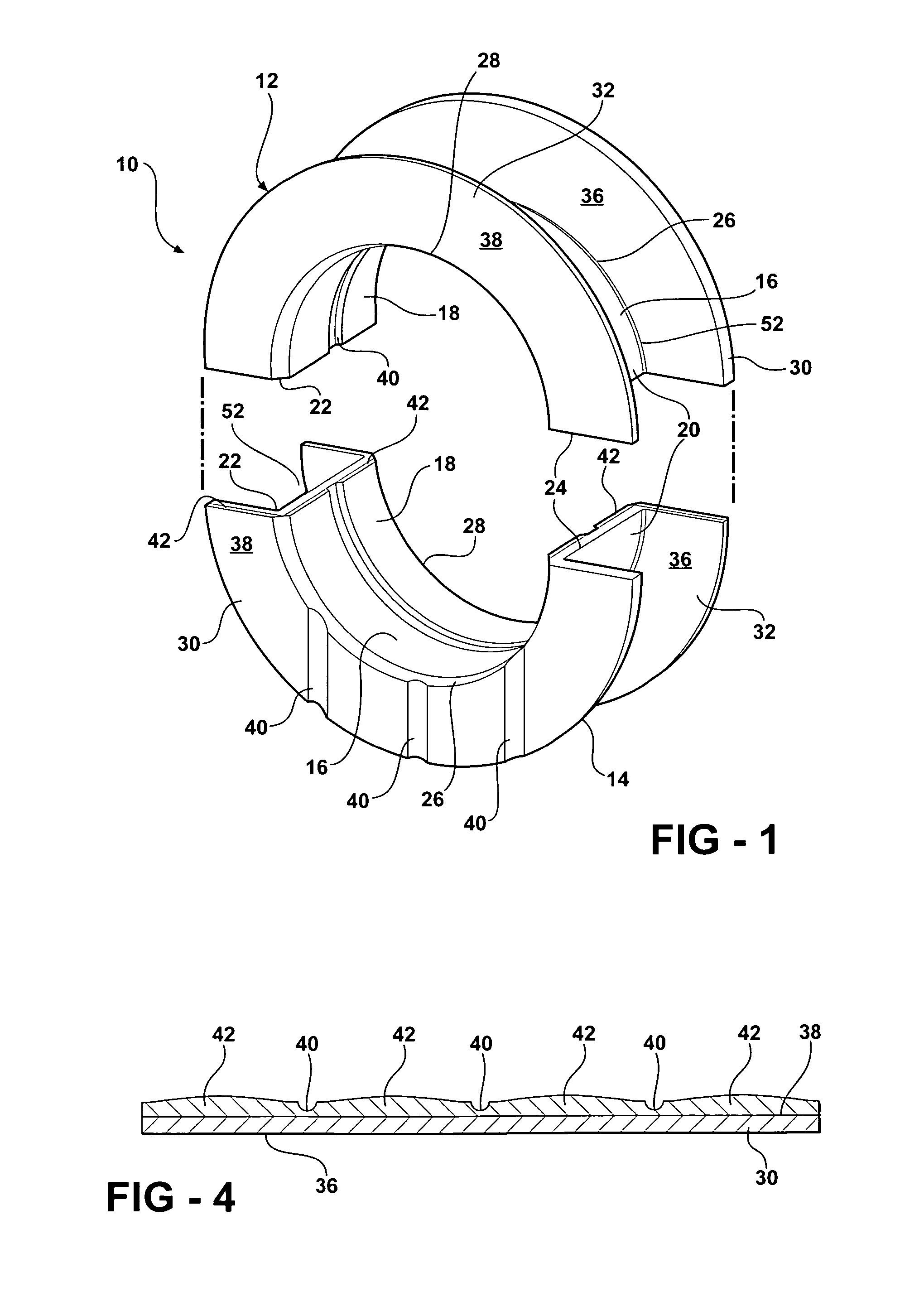
Flange bearing
InactiveUS6921210B2Few manufacturing stepFew stepsCrankshaft bearingsBearing componentsExternal combustion engineEngineering
An engine bearing for an internal combustion engine has a pair of separately constructed bearing halves comprising a pair of arcuate shells having a pair of laterally spaced flanges extending generally radially outwardly from each shell. Each pair of laterally spaced flanges comprises a pair of thrust faces facing generally away from one another with one of the thrust faces comprising an undulating contoured surface and the other thrust face having a generally planar non-contoured surface. The engine bearing is assembled having the contoured surface of one engine bearing half abutting the non-contoured surface of the other engine bearing half so that the engine bearing has generally opposite sides comprising both contoured and non-contoured surfaces.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WORLD WIDE LLC
Sliding bearing for internal combustion engine and sliding bearing device
InactiveUS20100119181A1Increase stiffnessInhibition effectConnecting rod bearingsCrankshaft bearingsHigh stiffnessEngineering
Disclosed is a sliding bearing consisting of a pair of semi-cylindrical bearings for supporting a crankshaft or a crank pin in an internal combustion engine. The sliding bearing is incorporated in a split-type bearing housing. One of the semi-cylindrical bearings being incorporated in at least one of the pair of housing halves, which one housing half has a relatively higher stiffness, is provided with a number of circumferential grooves on an inner surface of the semi-cylindrical bearing so as to extend circumferentially along the inner surface of the semi-cylindrical bearing. The circumferential grooves existing at least one circumferential end region of the inner surface of the semi-cylindrical bearing have a depth of not less than 10 μm, the circumferential end region including a circumferential bearing end face orientating a direction opposite to the rotation direction of the shaft or pin.
Owner:DAIDO METAL CO LTD
Lead-free bearing
A lead-free bearing includes a bronze matrix powder metal bearing layer bonded to a steel backing a fully densified. The bearing material has about 8 to 12% by weight tin, about 1 to less than 5% by weight bismuth, and about 0.03 to 0.08% by weight phosphorus, with the balance being copper. The tin is soluable in the copper to yield the bronze matrix, and the bismuth exists as finely dispersed, undissolved islands through the matrix. Such bearings exhibit physical properties comparable to or better than those of traditional bronze-lead bearings and improved wear in seizure properties.
Owner:CITIGROUP GLOBAL MARKETAB
Needle roller bearing, crank shaft supporting structure, and split method of outer ring of needle roller bearing
InactiveUS20070116393A1Smooth rollingAvoid troubleCrankshaft bearingsShaftsNeedle roller bearingEngineering
A needle roller bearing comprises an outer ring having a plurality of outer ring members split by split lines extending in the axial direction of the bearing, and a plurality of needle rollers arranged on the track surface of the outer ring so that they can roll. The outer ring is split by a load applied to its end surface in the direction crossing the end surface.
Owner:NTN CORP
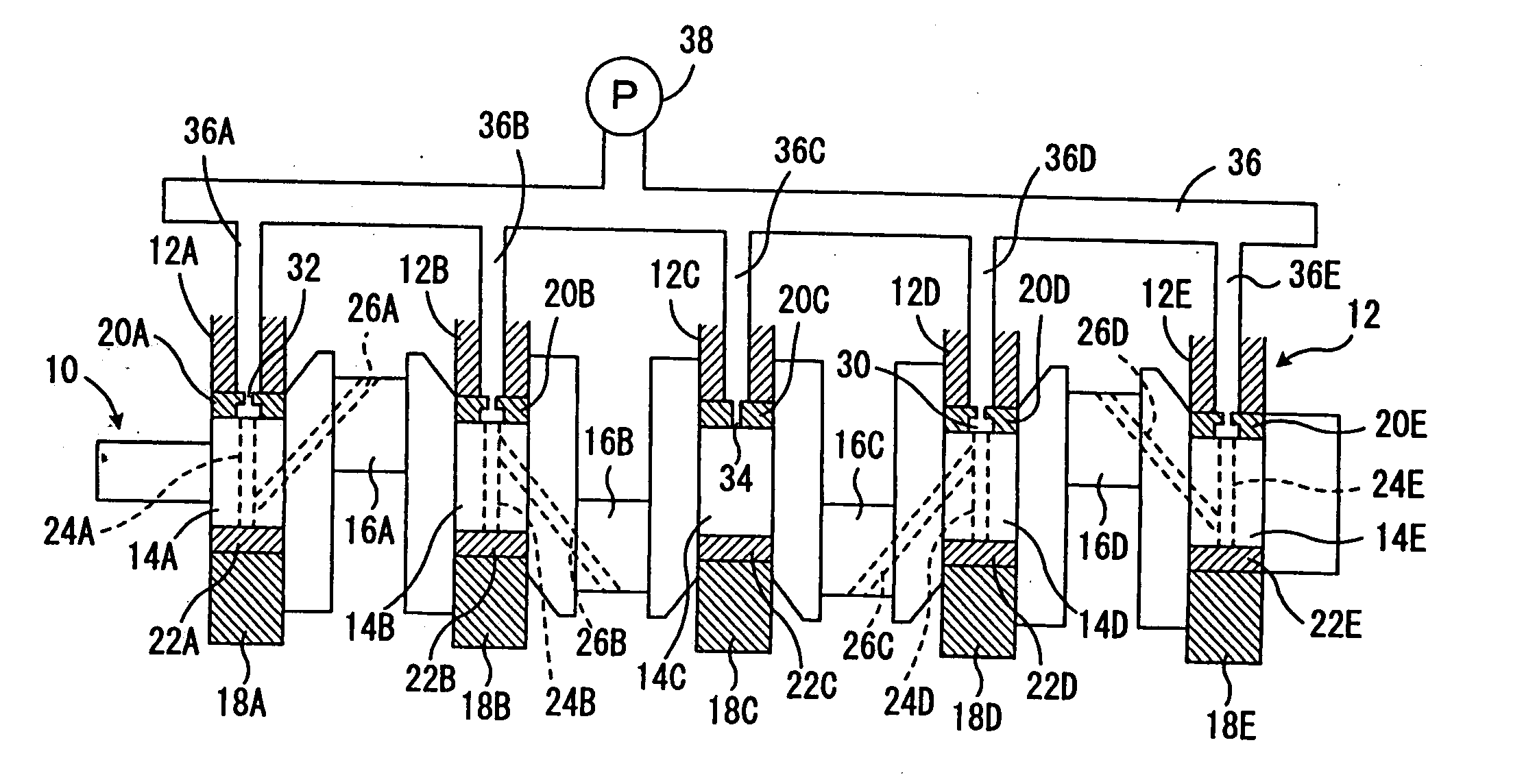
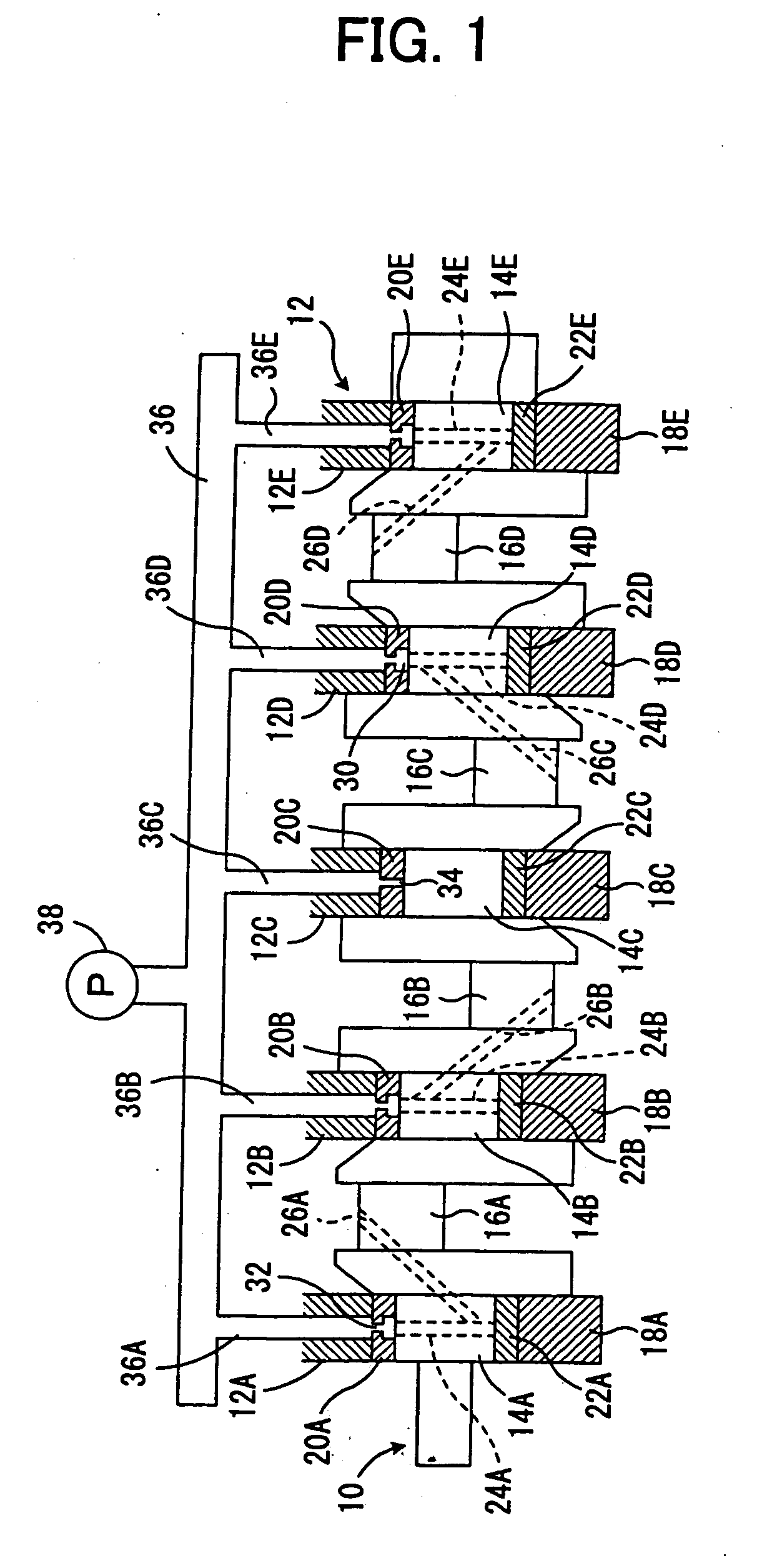
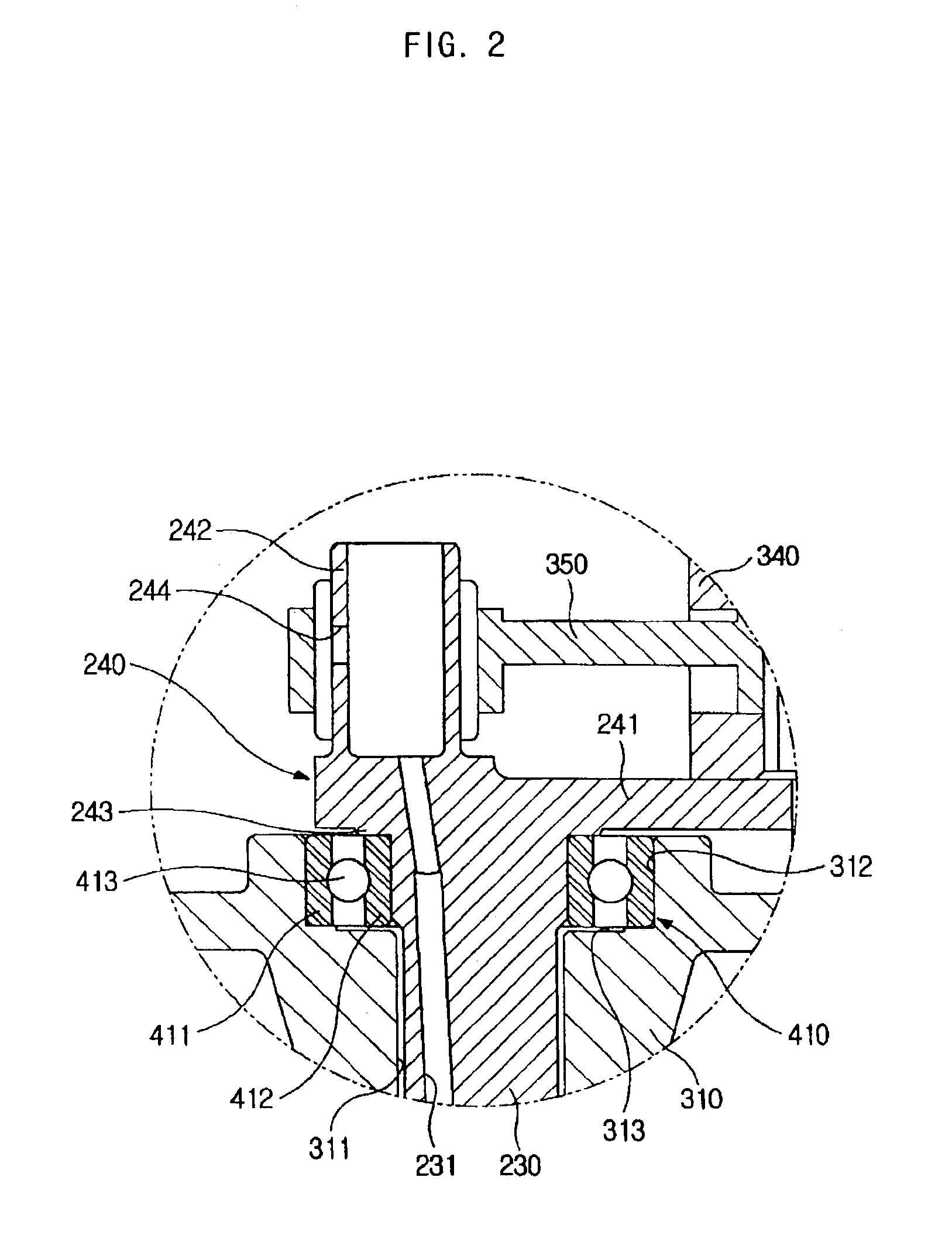
Hermetic reciprocating compressor
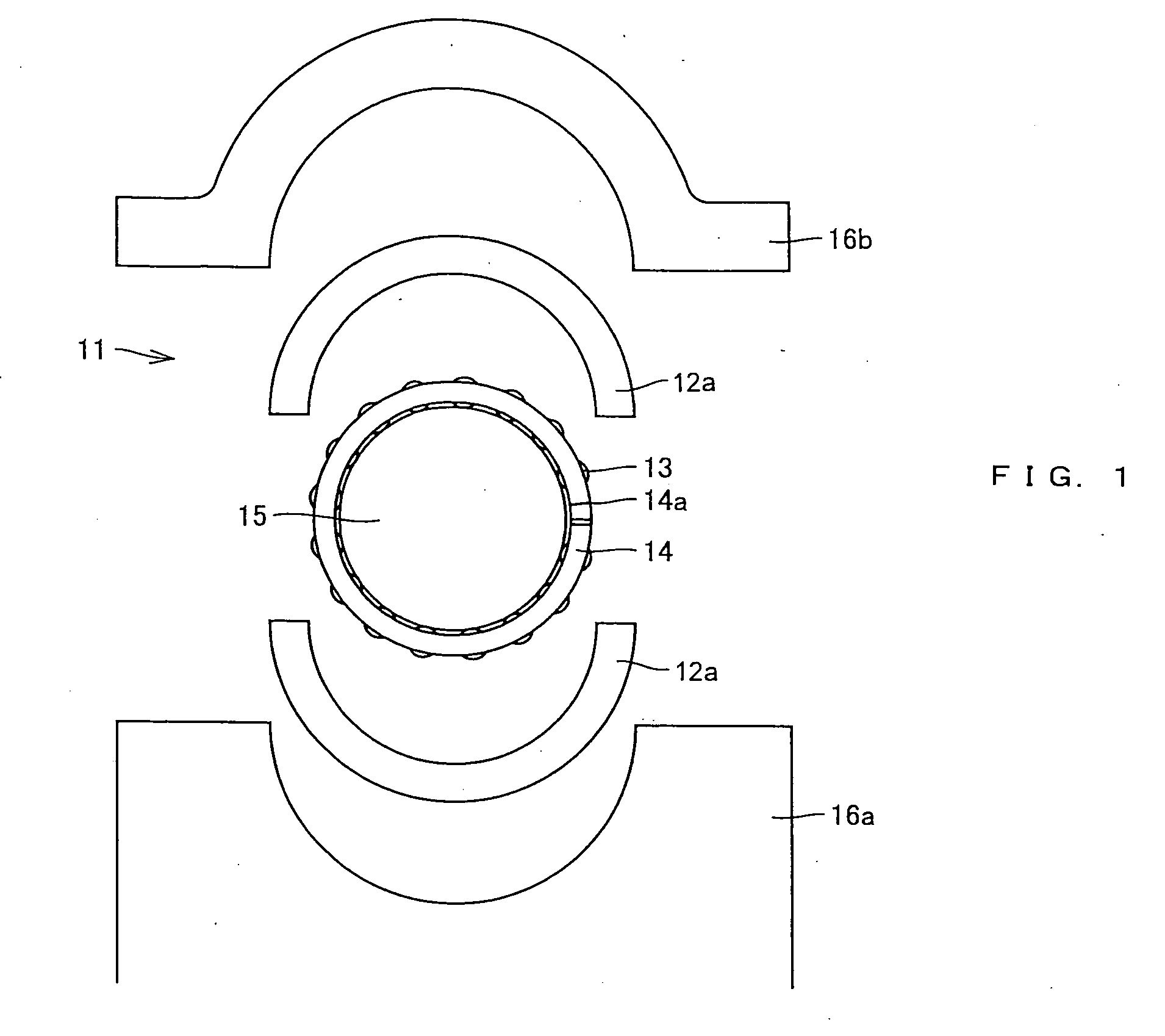
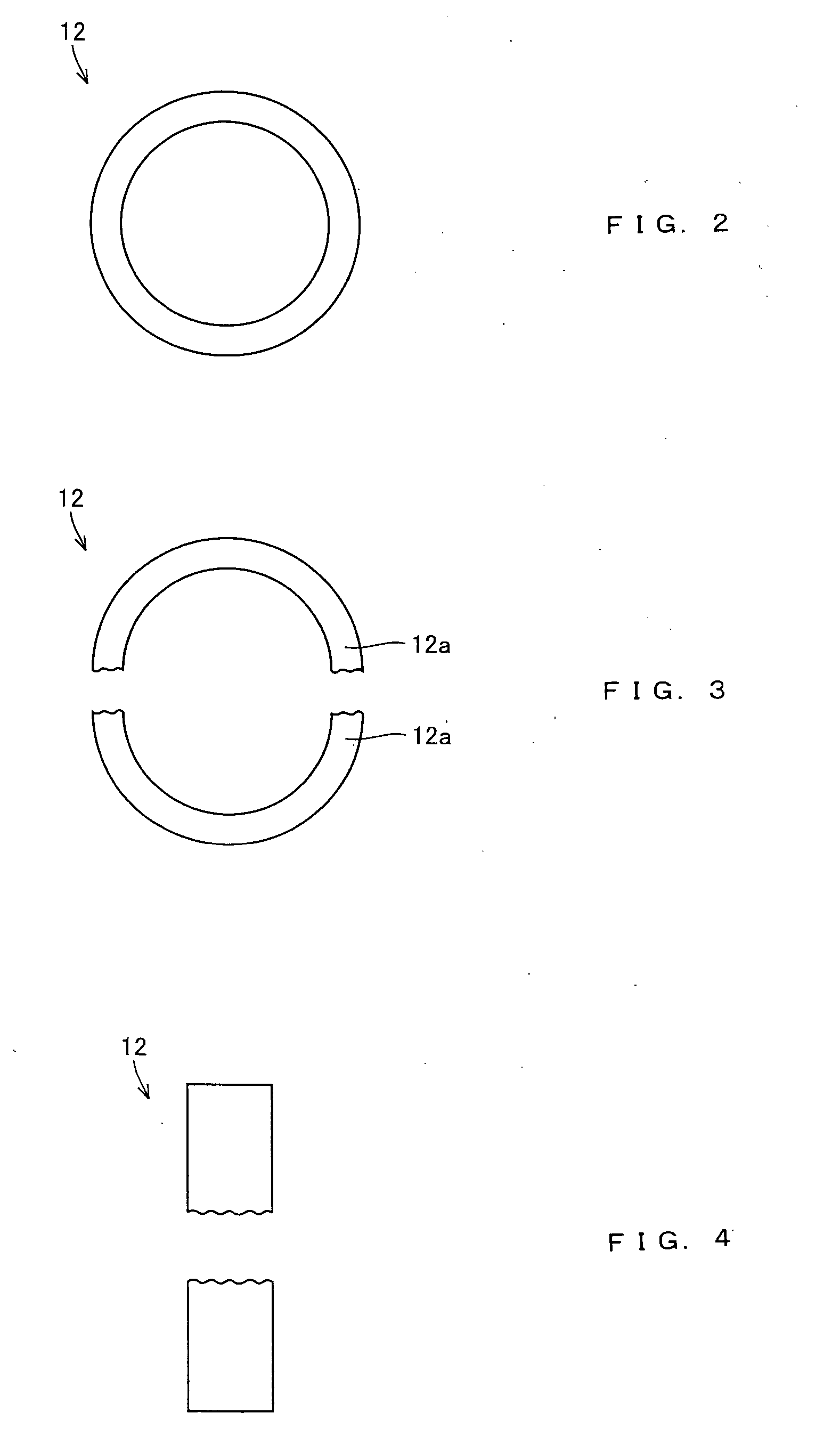
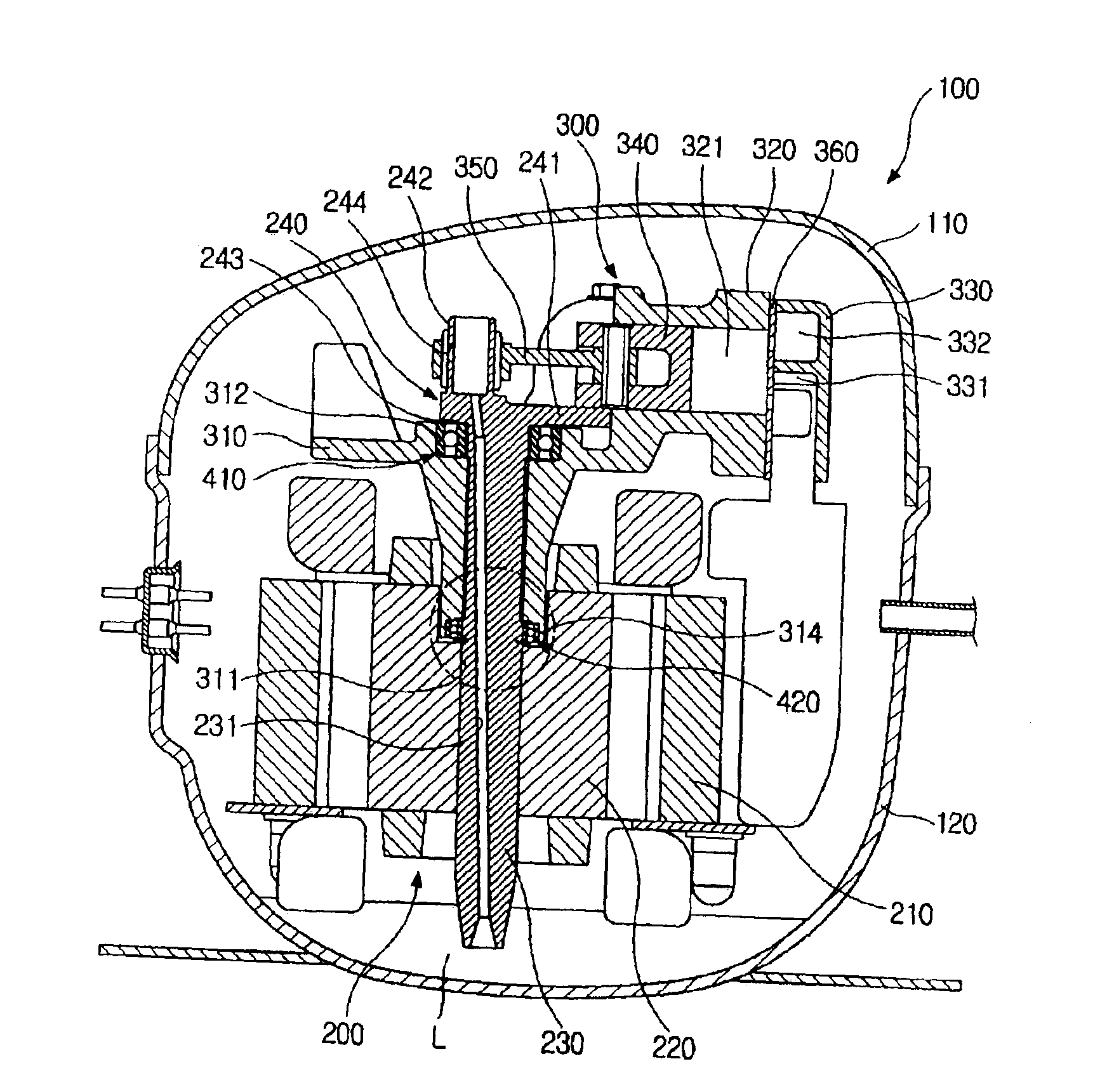
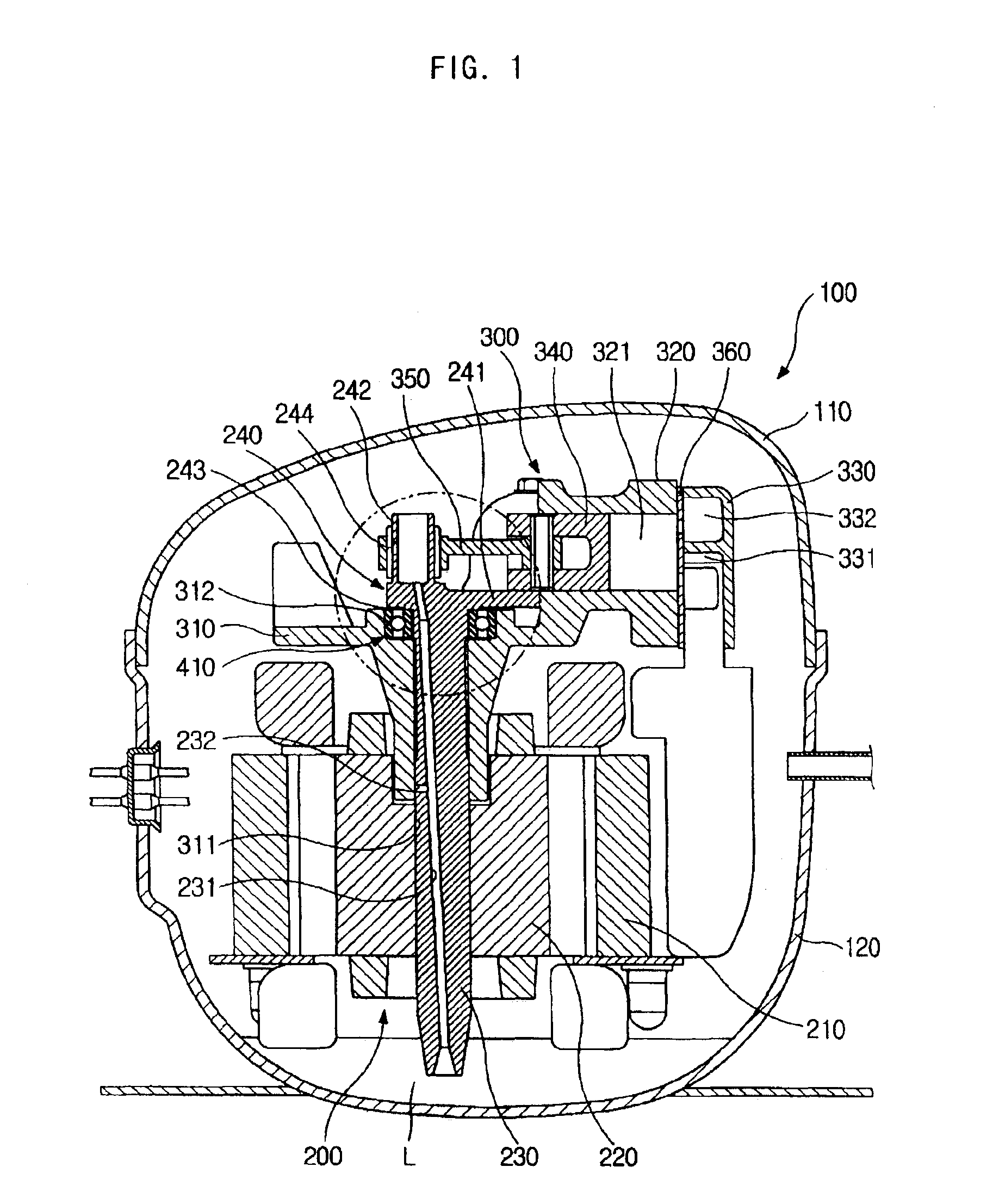
InactiveUS6948418B2Reduce noiseImprove compression efficiencyRolling contact bearingsPositive displacement pump componentsReciprocating motionEngineering
A hermetic reciprocating compressor, in which a bearing structure to support a rotating shaft is improved to minimize frictional contact between the parts of the compressor, thus reducing noise of the compressor and improving compression efficiency of the compressor. In the hermetic reciprocating compressor, a first annular bearing seat is formed around an upper edge of a shaft bore of a frame to seat therein a first radial bearing which sustains loads of a rotating shaft. The first radial bearing is a self-aligning radial bearing which allows the rotating shaft to self-align due to a clearance angle of the first radial bearing, even when a desired perpendicular arrangement of the shaft bore relative to a cylinder block is not formed, due to a mechanical tolerance of the frame. The first radial bearing sustains both axial loads of the rotating shaft and horizontal loads acting in the rotating shaft due to rectilinear reciprocation of a piston, thus reducing the losses caused by friction between the rotating shaft and the frame. In addition, since the rotating shaft self-aligns due to the first radial bearing, it is possible to reduce the losses caused by friction between a compression chamber and the piston and between the rotating shaft and the frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG GWANGJU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com