Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Large fov" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
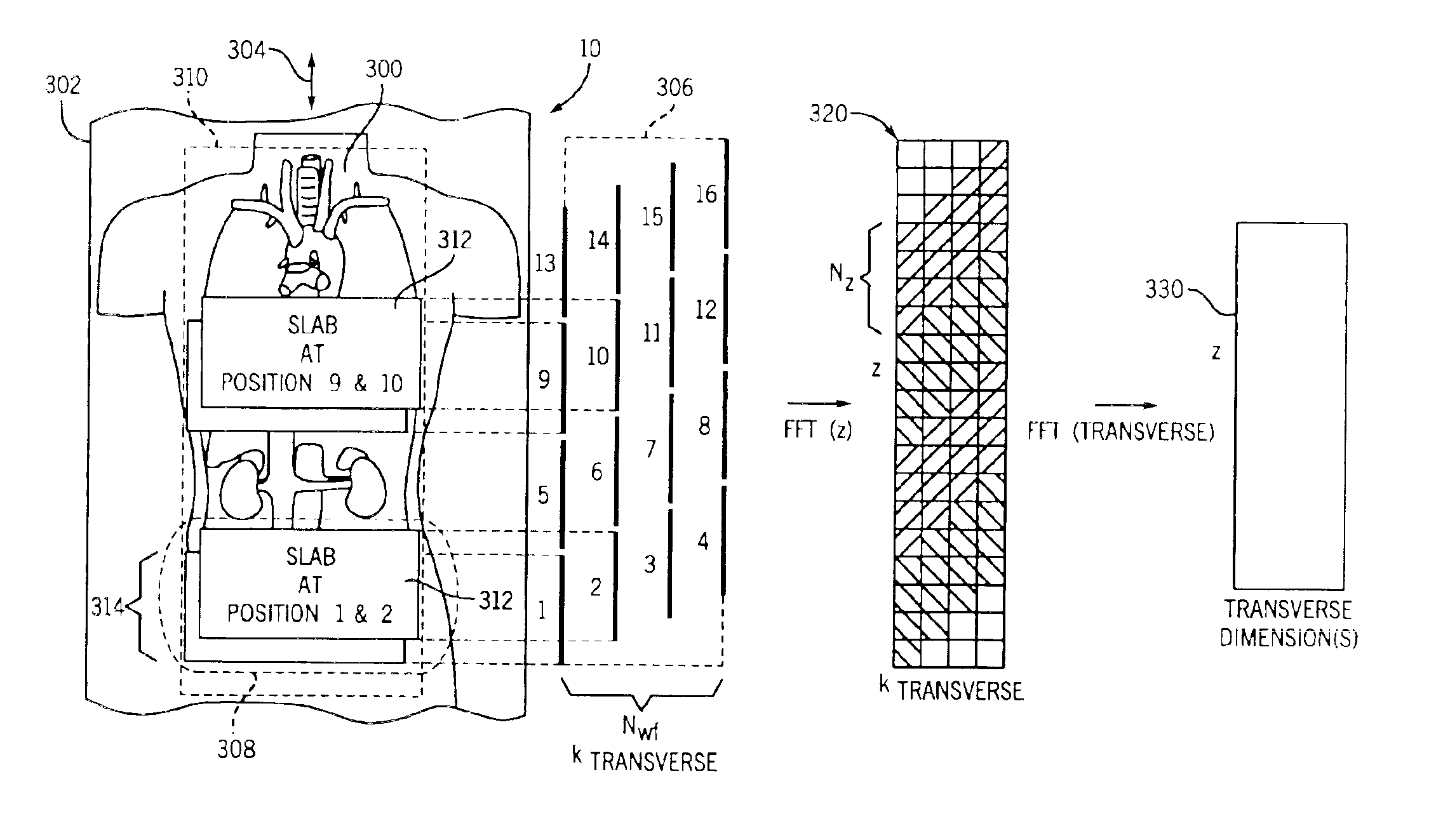
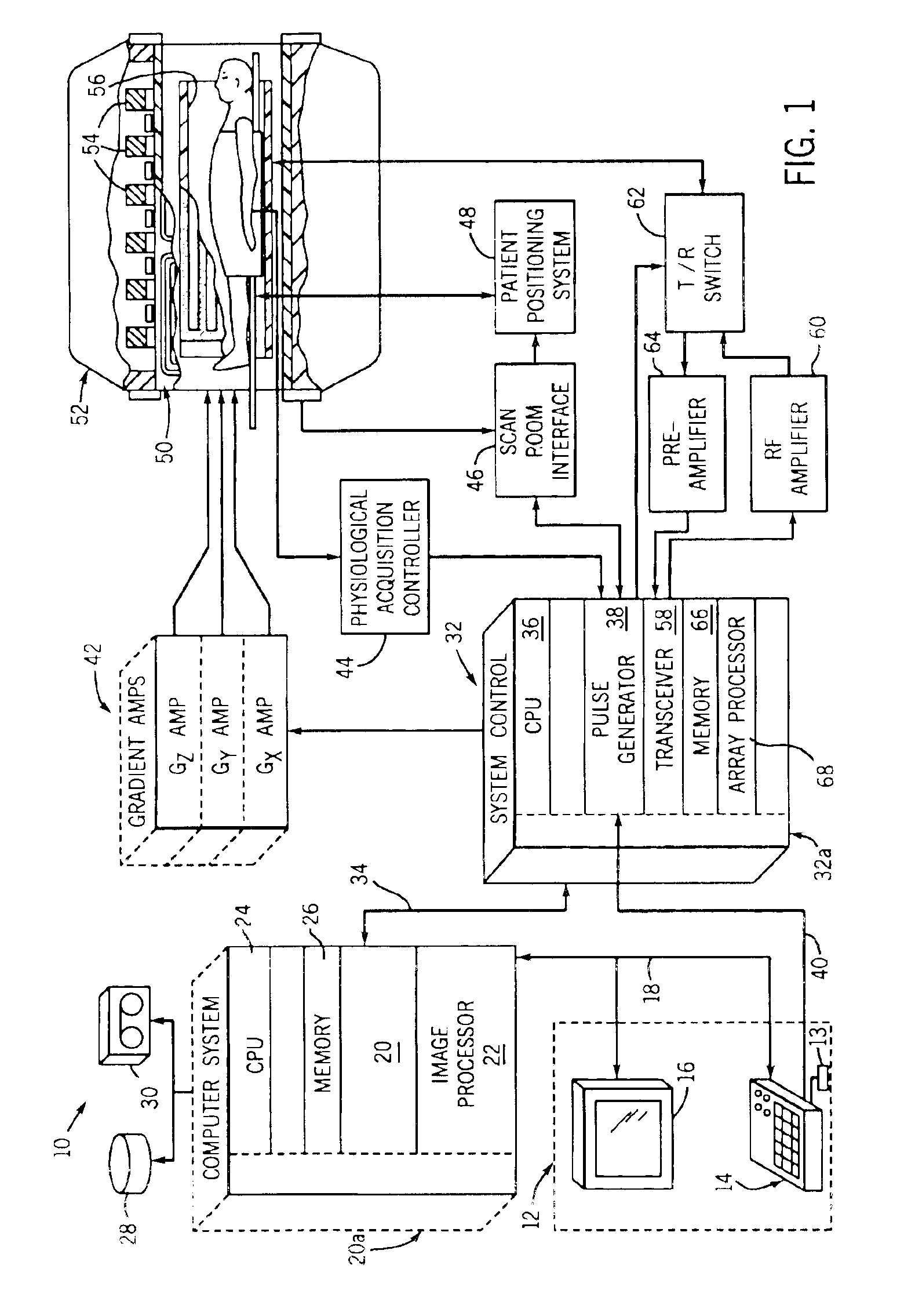
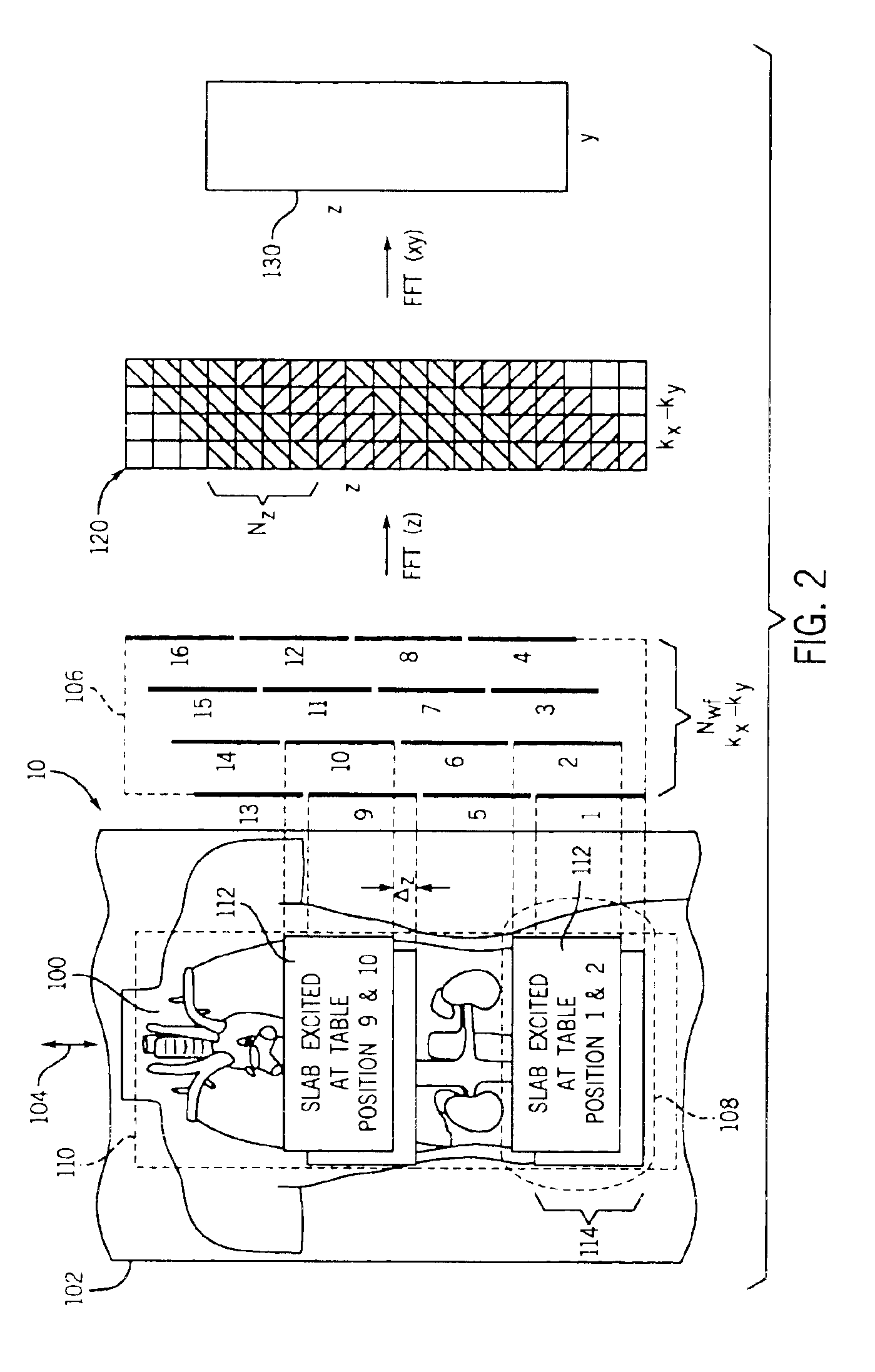
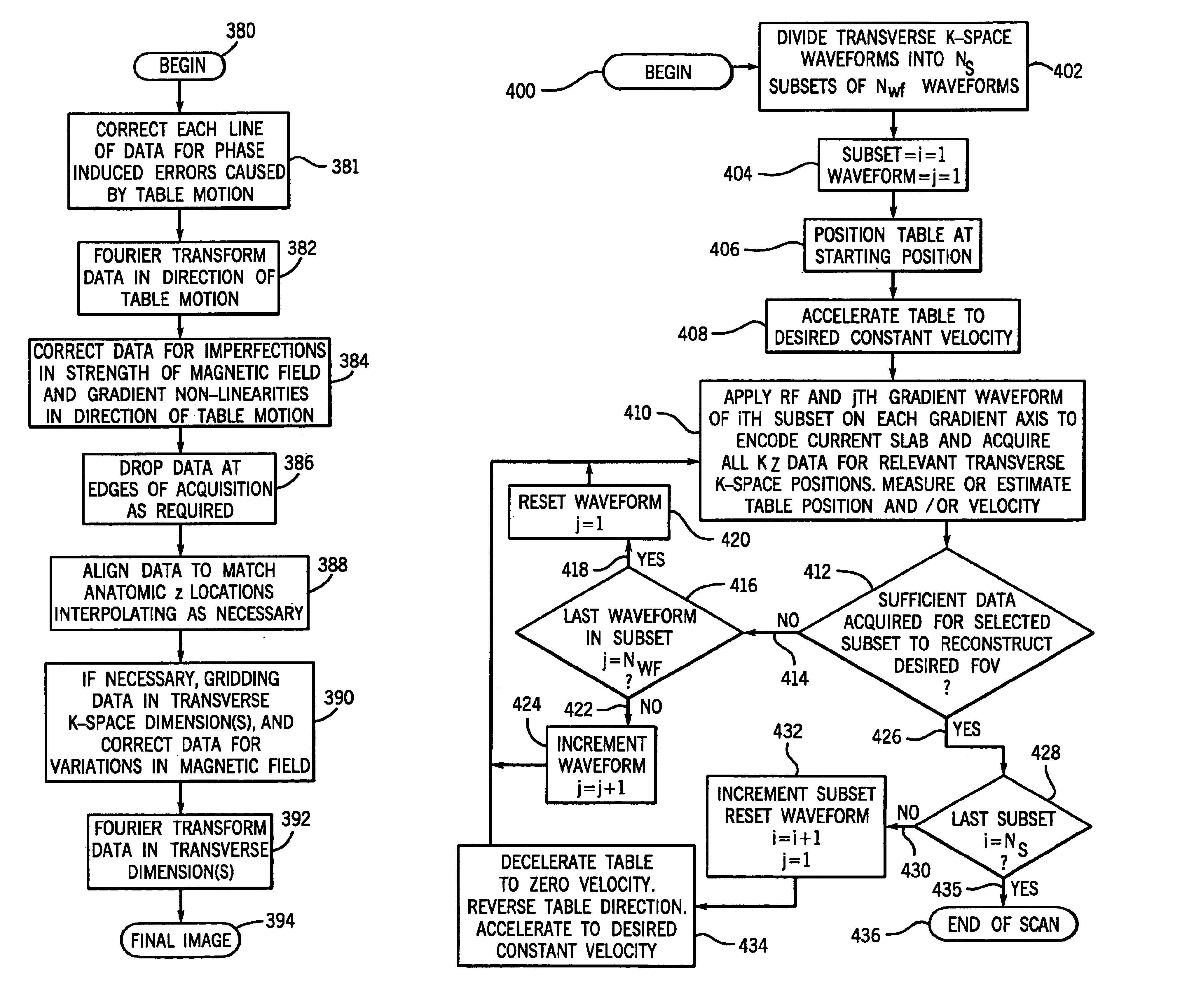
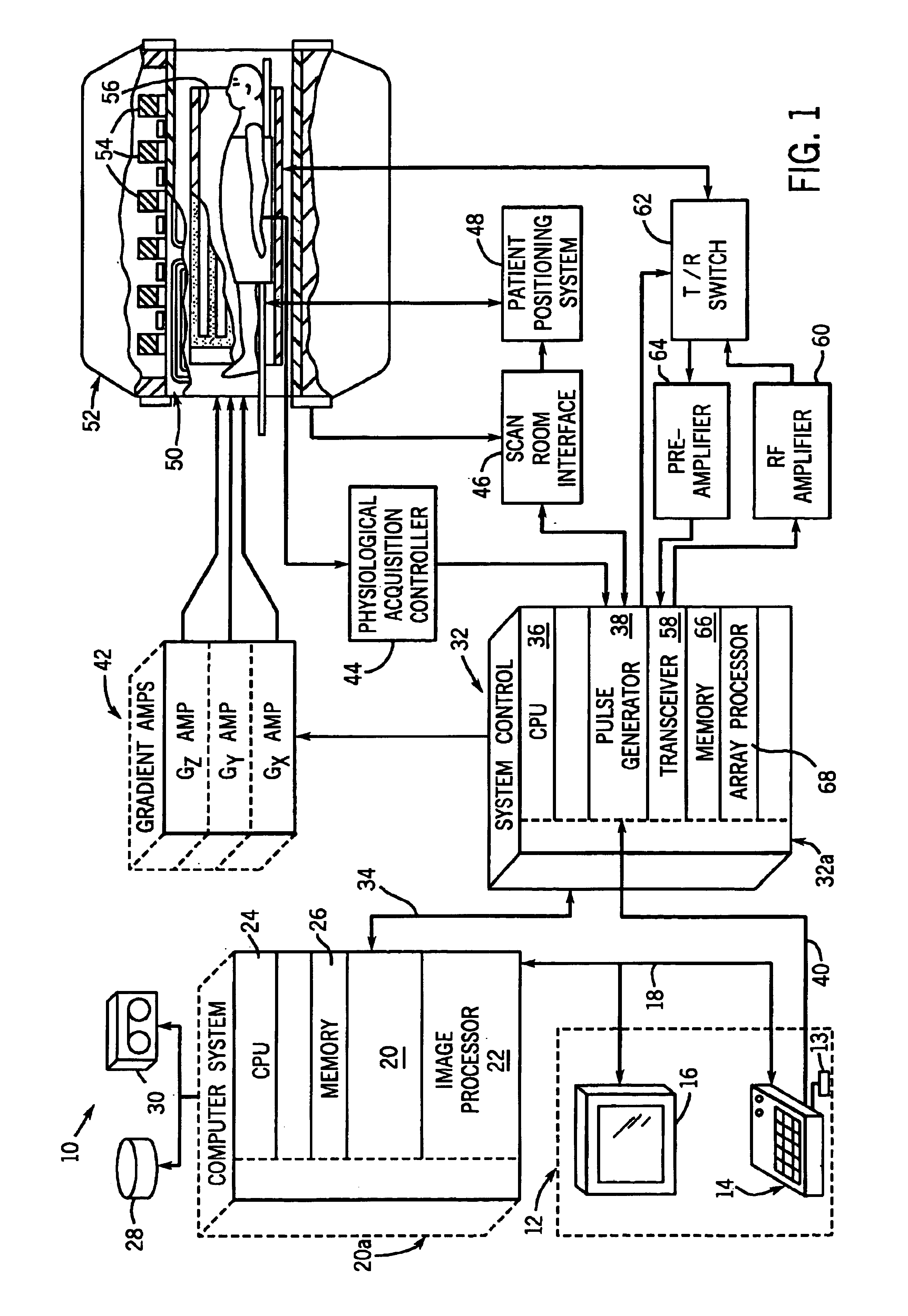
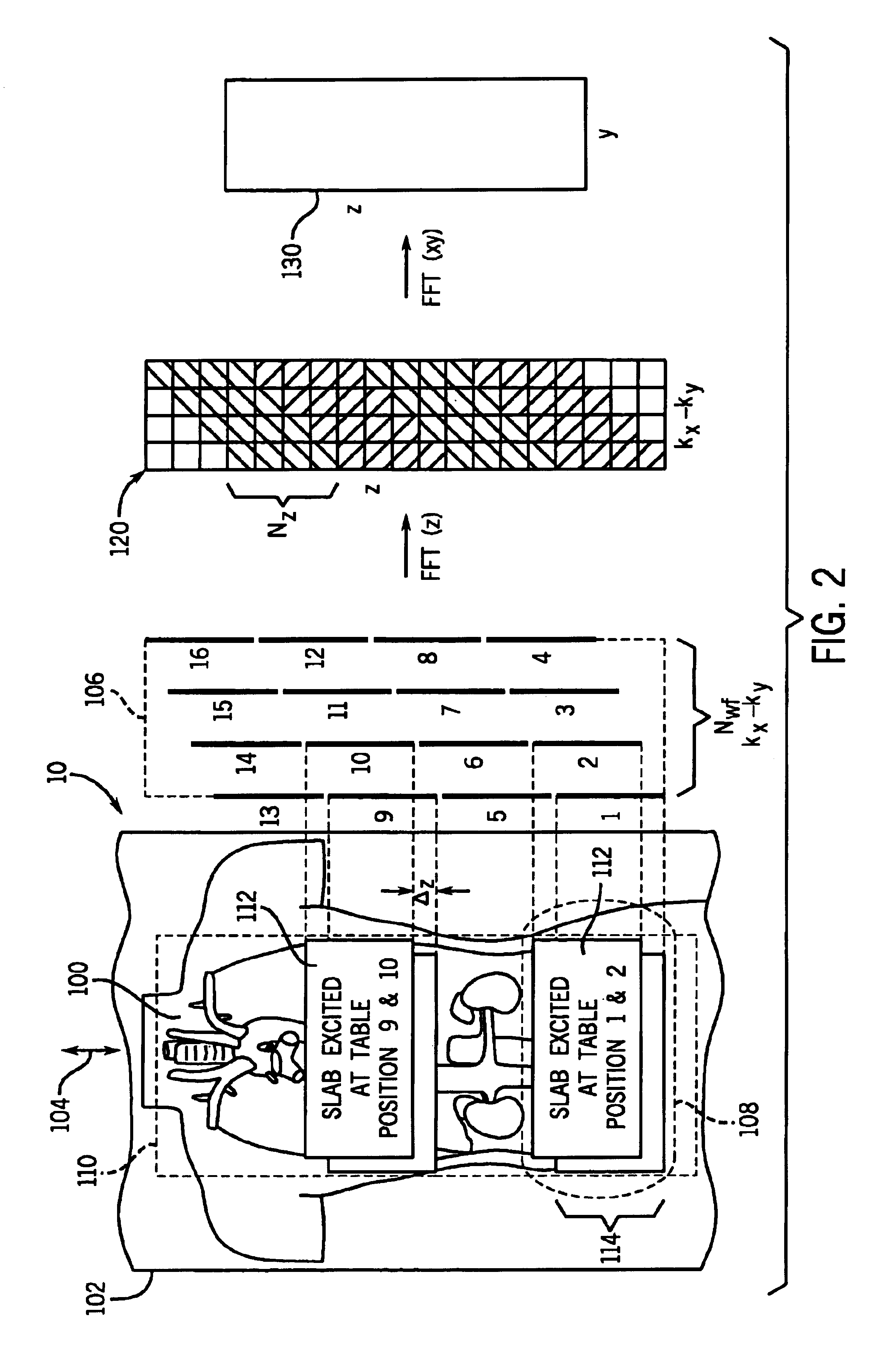
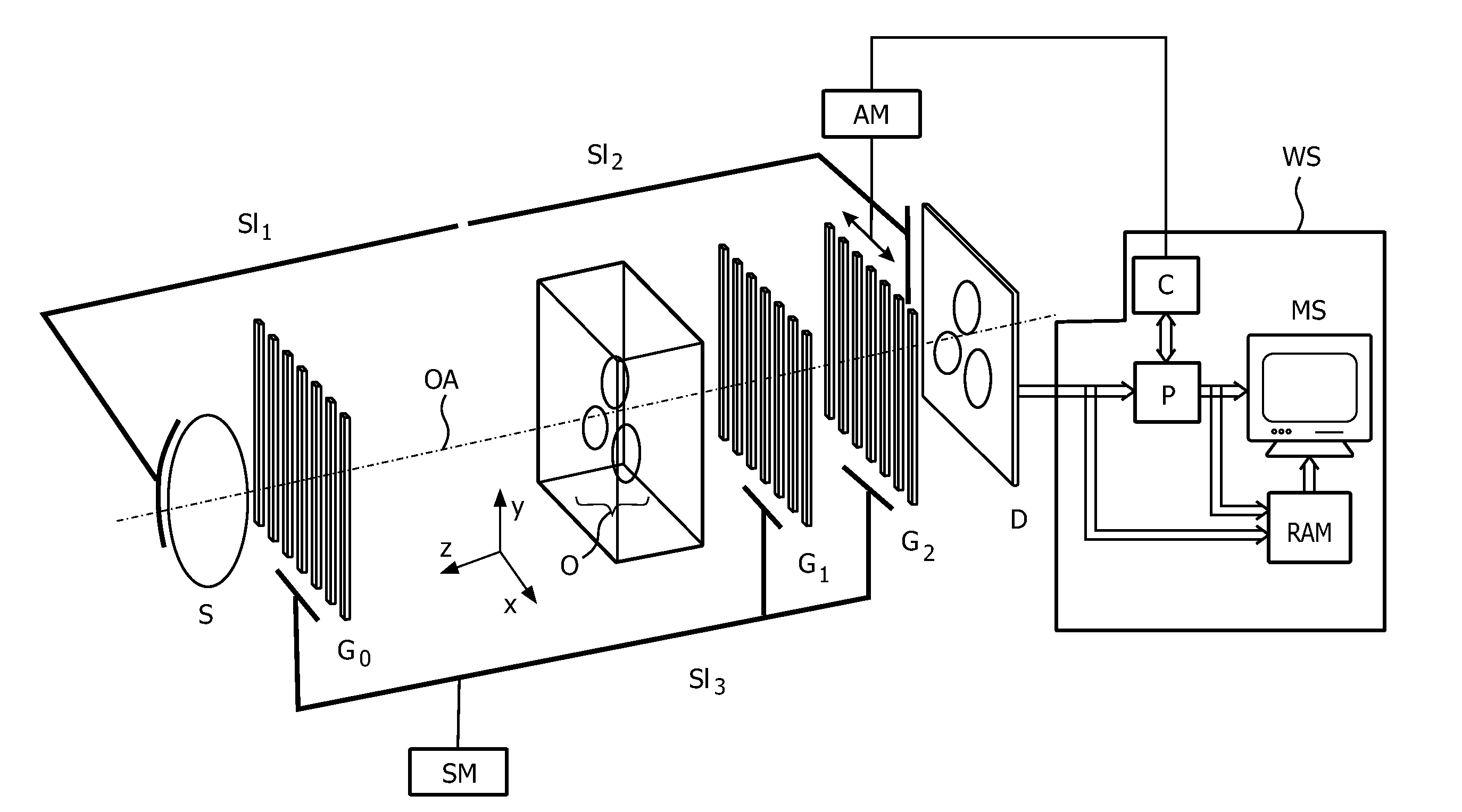
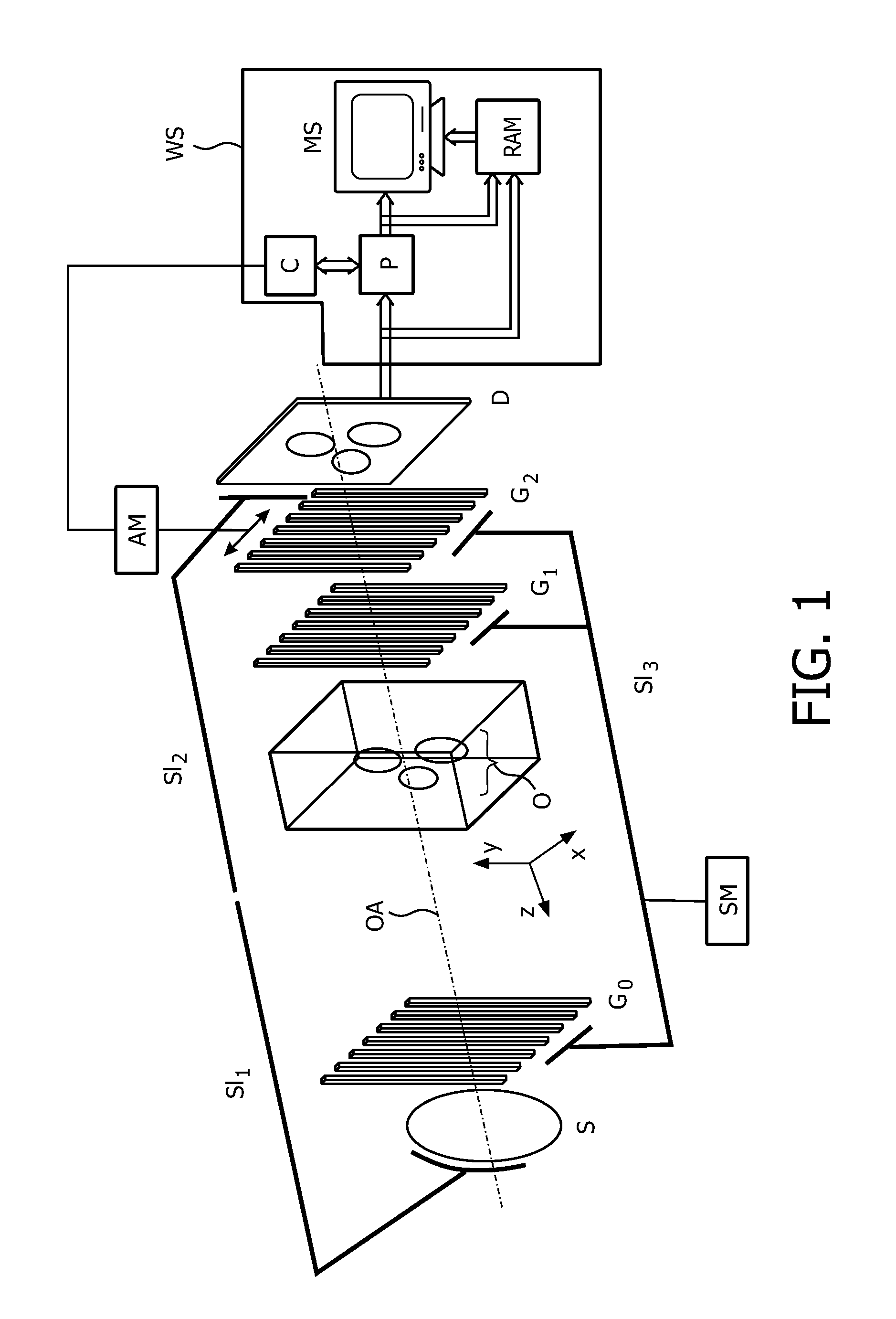
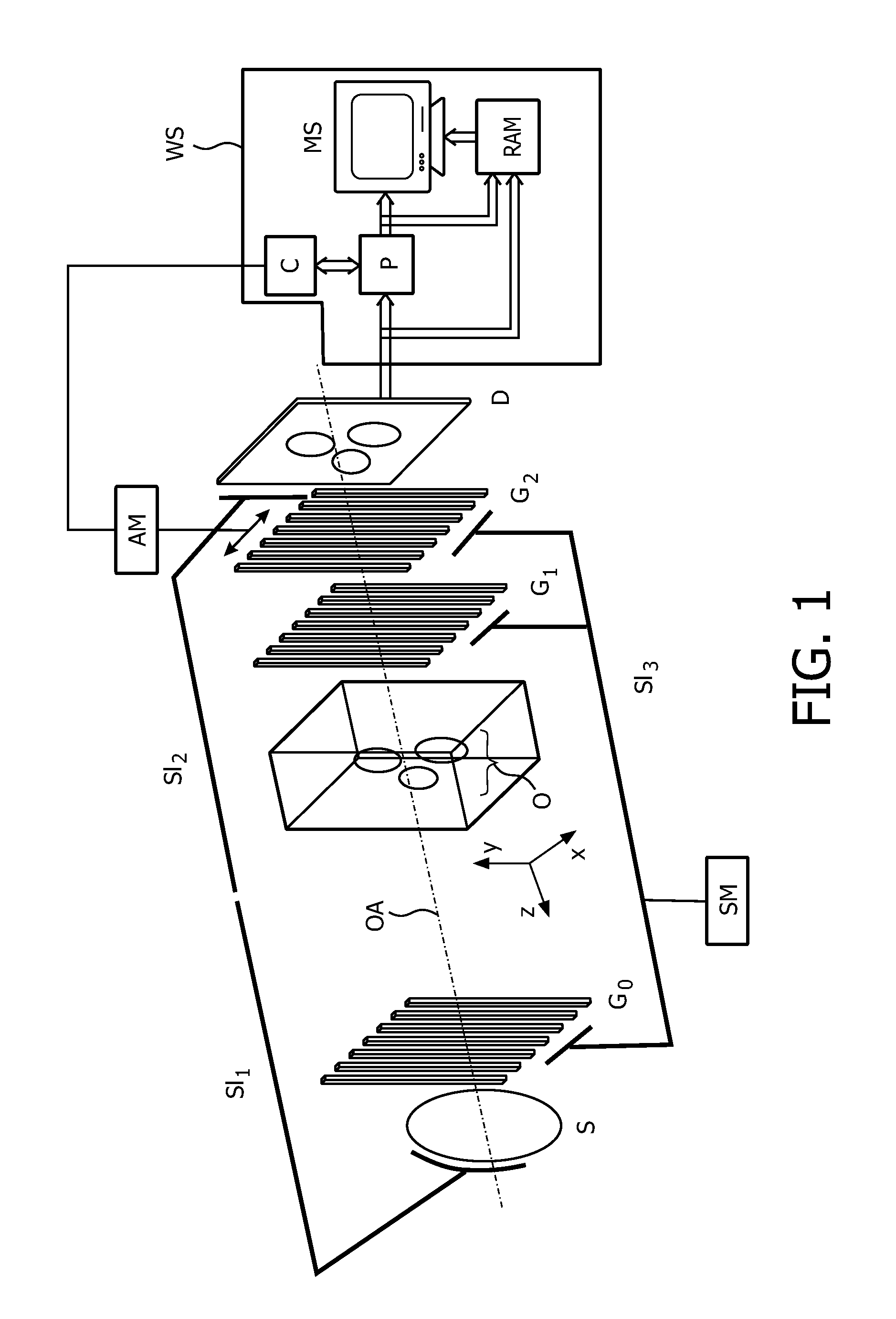
Moving table MRI with frequency-encoding in the z-direction
InactiveUS6897655B2Expand coverageShorten the timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLarge fovAcquisition time
A system and method are disclosed using continuous table motion while acquiring data to reconstruct MR images across a large FOV without significant slab-boundary artifacts that reduces acquisition time. At each table position, full z-encoding data are acquired for a subset of the transverse k-space data. The table is moved through a number of positions over the desired FOV and MR data are acquired over the plurality of table positions. Since full z-data are acquired for each slab, the data can be Fourier transformed in z, interpolated, sorted, and aligned to match anatomic z locations. The fully sampled and aligned data is then Fourier transformed in remaining dimension(s) to reconstruct the final image that is free of slab-boundary artifacts.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Moving table MRI with frequency-encoding in the z-direction
InactiveUS6891374B2Expand coverageShorten the timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLarge fovComplete data
A system and method are disclosed using continuous table motion while acquiring data to reconstruct MR images across a large FOV without significant slab-boundary artifacts that reduces acquisition time. At each table position, full z-encoding data are acquired for a subset of the transverse k-space data. The table is moved through a number of positions over the desired FOV and MR data are acquired over the plurality of table positions. Since full z-data are acquired for each slab, the data can be Fourier transformed in z, interpolated, sorted, and aligned to match anatomic z locations. The fully sampled and aligned data is then Fourier transformed in remaining dimension(s) to reconstruct the final image that is free of slab-boundary artifacts.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
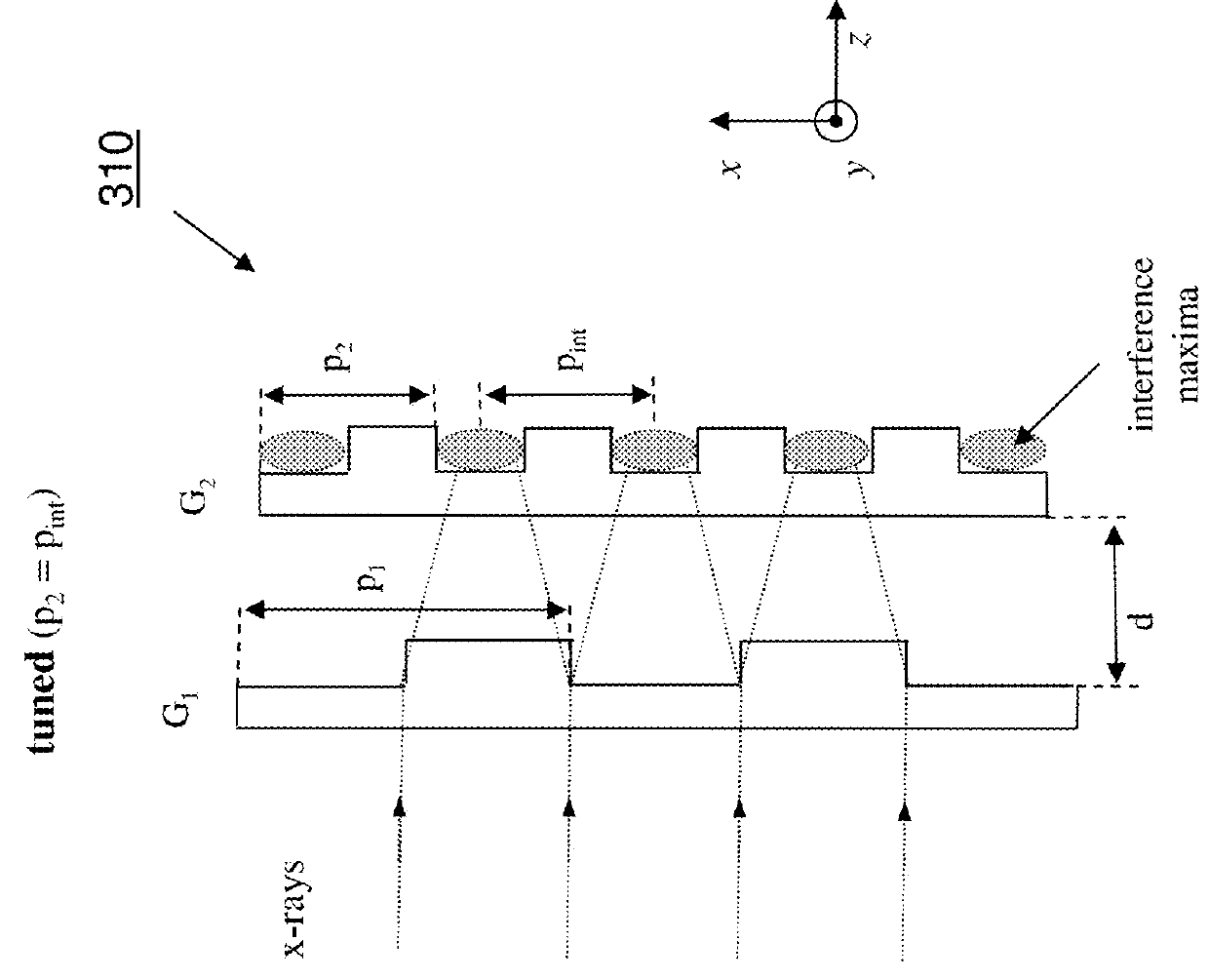
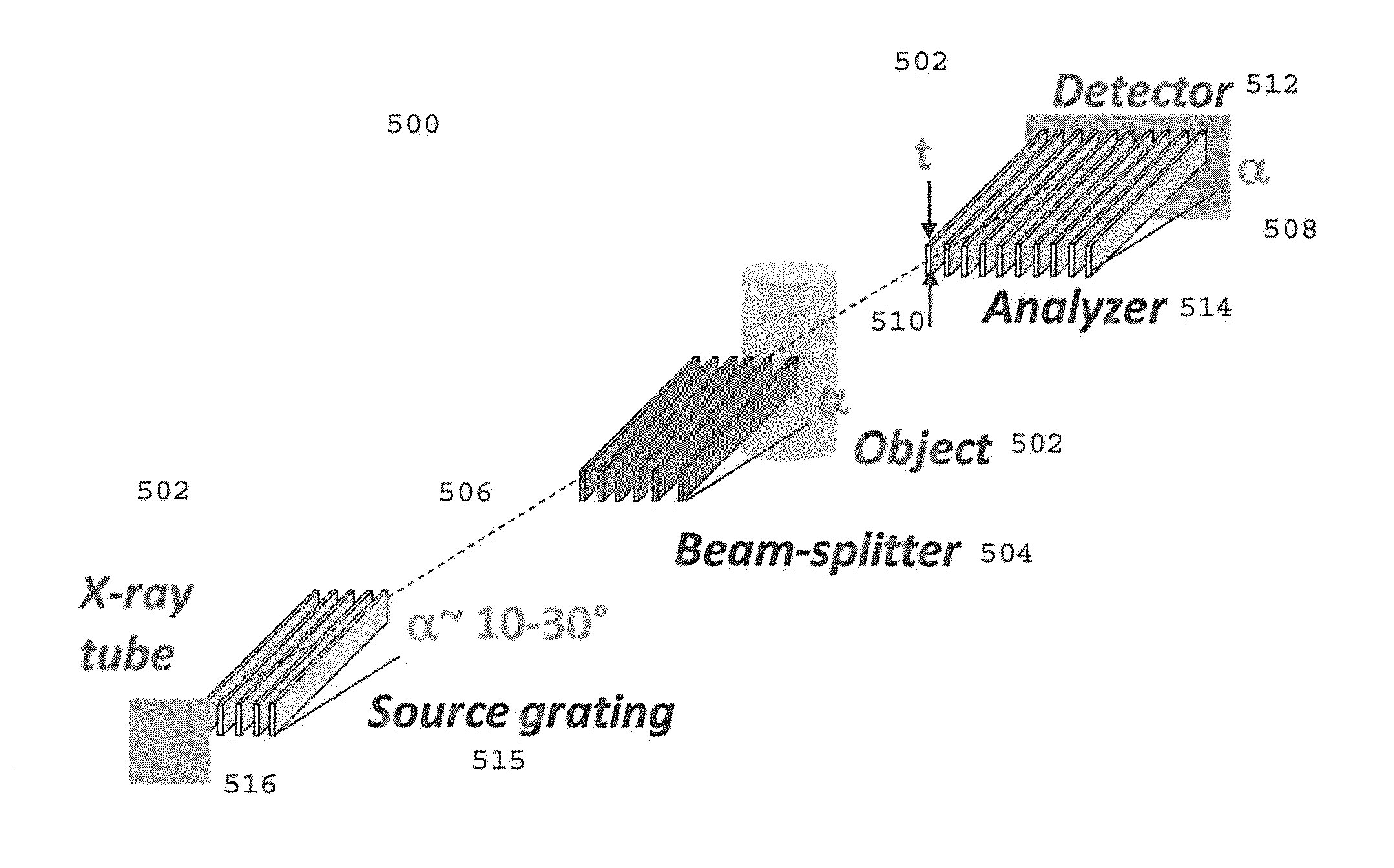
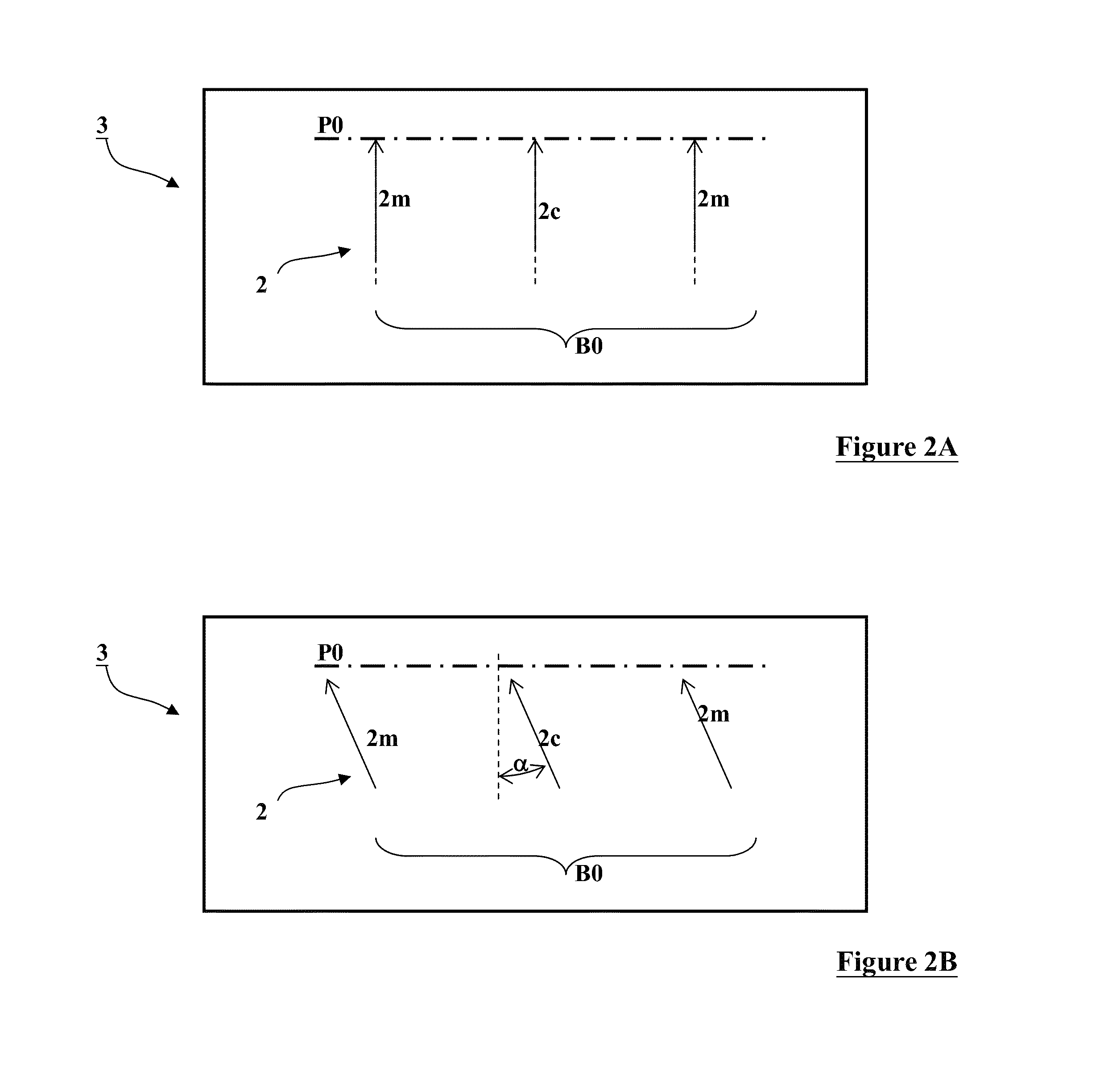
Large FOV phase contrast imaging based on detuned configuration including acquisition and reconstruction techniques
ActiveUS9357975B2Reduce disadvantagesAchieve effectImaging devicesRadiation diagnostic device controlLarge fovDigital imaging
Embodiments of methods and apparatus are disclosed for obtaining a phase-contrast digital imaging system and methods for same that can include an x-ray source for radiographic imaging; a beam shaping assembly, an x-ray grating interferometer including a phase grating and an analyzer grating; and an x-ray detector; where the source grating, the phase grating, and the analyzer grating are detuned and a plurality of uncorrelated reference images are obtained for use in imaging processing with the detuned system.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Architectures for cardiac CT based on area x-ray sources
InactiveUS7388940B1Improve time resolutionReducing conebeam artifactMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingLarge fovDetector array
A CT imaging system includes a rotatable gantry having an opening to receive an object to be scanned having a small field-of-view (FOV) inside a large FOV. A plurality of area sources is attached to the rotatable gantry, each area source includes a plurality of x-ray emission sources, wherein the plurality of area sources are configured to emit x-rays toward the object. A plurality of x-ray detector arrays is attached to the gantry and positioned such that at least a first detector array and a second detector array each receive x-rays that pass through at least the entire small FOV of the object.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Large field of view modulating retro reflector (MRR) for free space optical communication
A modulating retro-reflector (MRR) can be configured to provide a large field of view. The MRR can include a solid corner cube reflector (CCR) manufactured of a material having a high index of refraction at the desired operating wavelength. CCRs made from high index materials such as InP or Si, have an index of refraction of approximately 3.48 at an operating wavelength of approximately 1550 nm and can provide a conical Field of View (FOV) of greater than ±60 degrees compared to less than ±30 degrees for CCRs made from BK-7. Each CCR can include one or more elements configured to modulate an optical signal incident on the CCR. A retro-modulating transponder can use fewer large FOV MRRs to support communication over a predetermined incident optical span compared to narrower FOV MRRs resulting in lower cost, smaller size, weight and power requirements.
Owner:CUBIC CORPORATION
Large fov phase contrast imaging based on detuned configuration including acquisition and reconstruction techniques
ActiveUS20150182178A1Achieve effectReduce disadvantagesImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationLarge fovDigital imaging
Embodiments of methods and apparatus are disclosed for obtaining a phase-contrast digital imaging system and methods for same that can include an x-ray source for radiographic imaging; a beam shaping assembly, an x-ray grating interferometer including a phase grating and an analyzer grating; and an x-ray detector; where the source grating, the phase grating, and the analyzer grating are detuned and a plurality of uncorrelated reference images are obtained for use in imaging processing with the detuned system.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
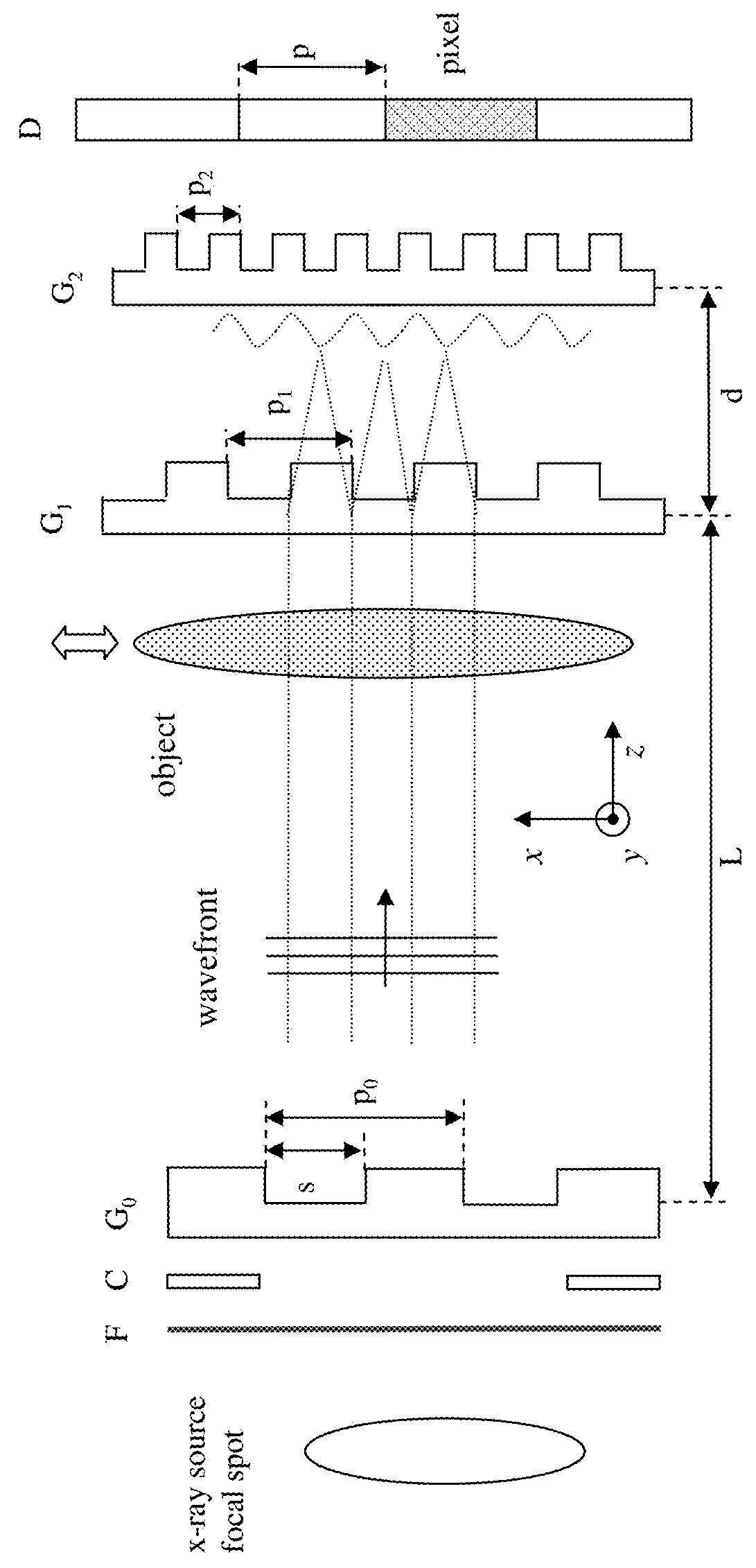
Phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS20120243658A1High contrast-to-noise ratioReduce exposureRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusLarge fovGrating
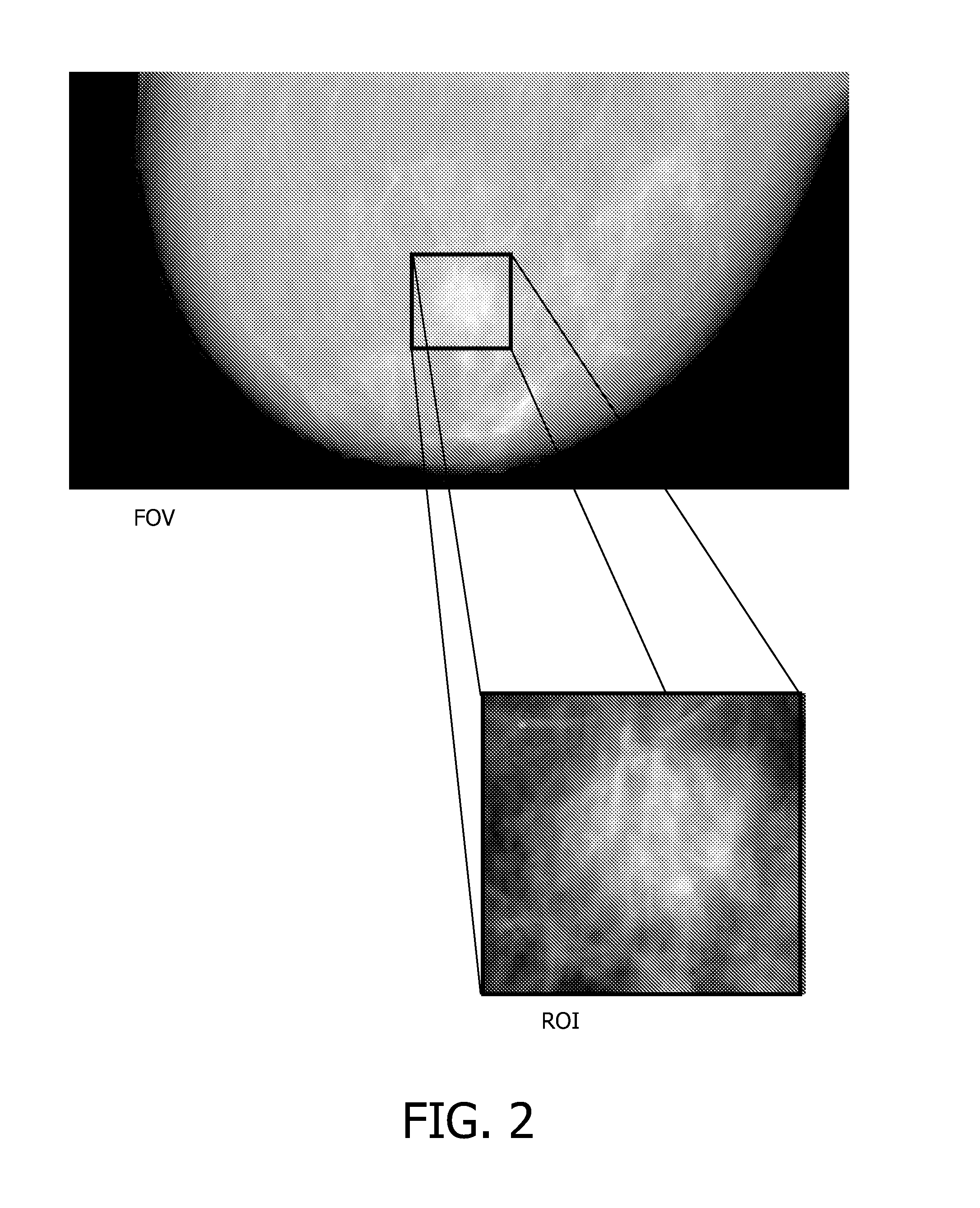
X-ray devices for Phase Contrast Imaging (PCI) are often built up with the help of gratings. For large field-of-views (FOV), production cost and complexity of these gratings could increase significantly as they need to have a focused geometry. Instead of a pure PCI with a large FOV, this invention suggests to combine a traditional absorption X-ray-imaging system with large-FOV with an insertable low-cost PCI system with small-FOV, The invention supports the user to direct the PCI system with reduced FOV to a region that he regards as most interesting for performing a PCI scan thus eliminating X-ray dose exposure for scanning regions not interesting for a radiologist. The PCI scan may be generated on the basis of local tomography.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS9084528B2Reducing X-ray dose exposureReduce intensityRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusLarge fovGrating
X-ray devices for Phase Contrast Imaging (PCI) are often built up with the help of gratings. For large field-of-views (FOV), production cost and complexity of these gratings could increase significantly as they need to have a focused geometry. Instead of a pure PCI with a large FOV, this invention suggests to combine a traditional absorption X-ray-imaging system with large-FOV with an insertable low-cost PCI system with small-FOV, The invention supports the user to direct the PCI system with reduced FOV to a region that he regards as most interesting for performing a PCI scan thus eliminating X-ray dose exposure for scanning regions not interesting for a radiologist. The PCI scan may be generated on the basis of local tomography.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method for a compact display
ActiveUS20170019602A1Well formedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEye reliefLarge fov
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Objective Lens System for Fast Scanning Large FOV
The device includes a beam source for generating an electron beam, a beam guiding tube passed through an objective lens, an objective lens for generating a magnetic field in the vicinity of the specimen to focus the particles of the particle beam on the specimen, a control electrode having a potential for providing a retarding field to the particle beam near the specimen to reduce the energy of the particle beam when the beam collides with the specimen, a deflection system including a plurality of deflection units situated along the optical axis for deflecting the particle beam to allow scanning on the specimen with large area, at least one of the deflection units located in the retarding field of the beam, the remainder of the deflection units located within the central bore of the objective lens, and a detection unit to capture secondary electron (SE) and backscattered electrons (BSE).
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Wearable display
InactiveUS20180172981A1Improving cosmetic appearanceReduce overall chromatic aberrationStatic indicating devicesProjectorsLarge fovDisplay device
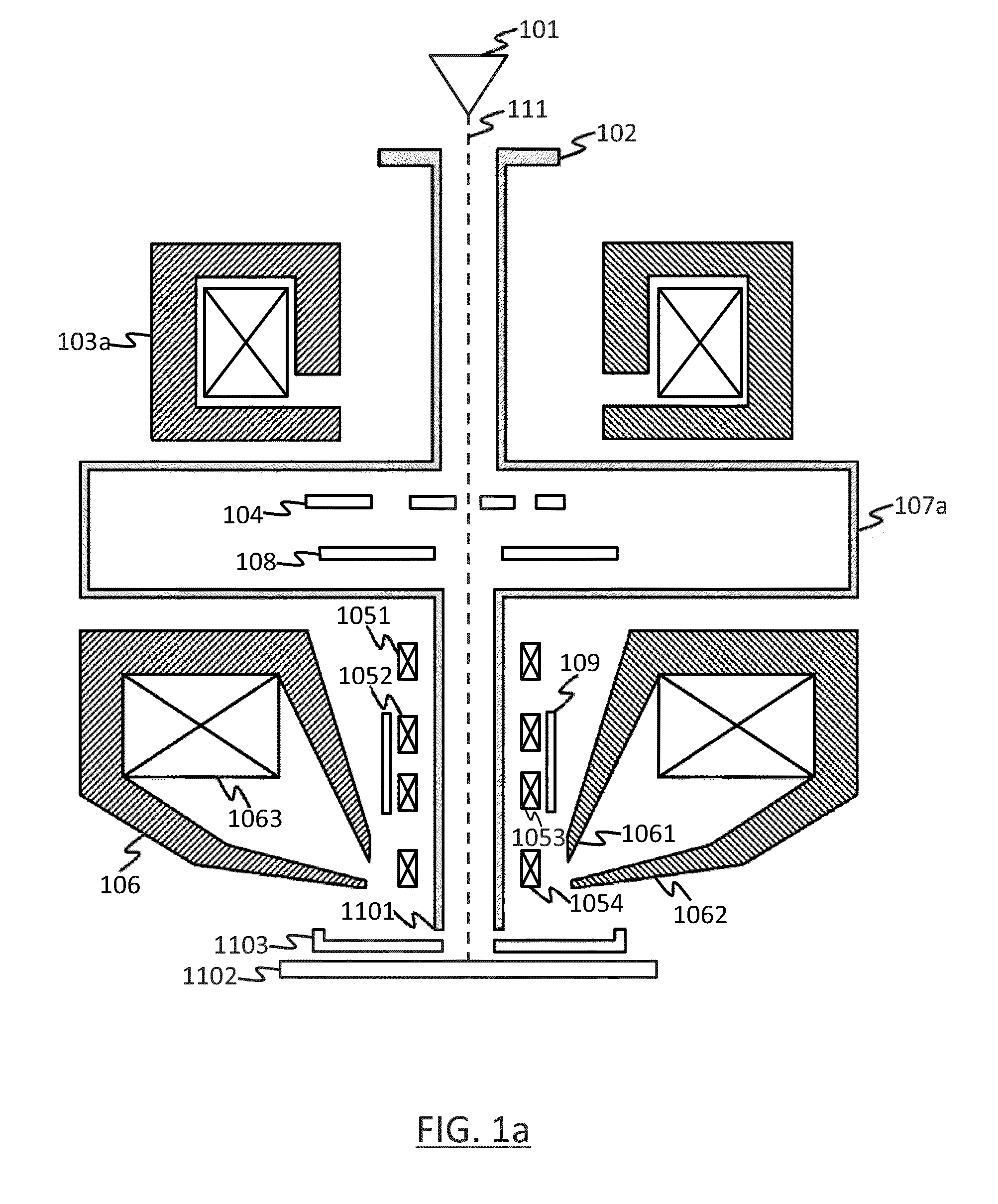
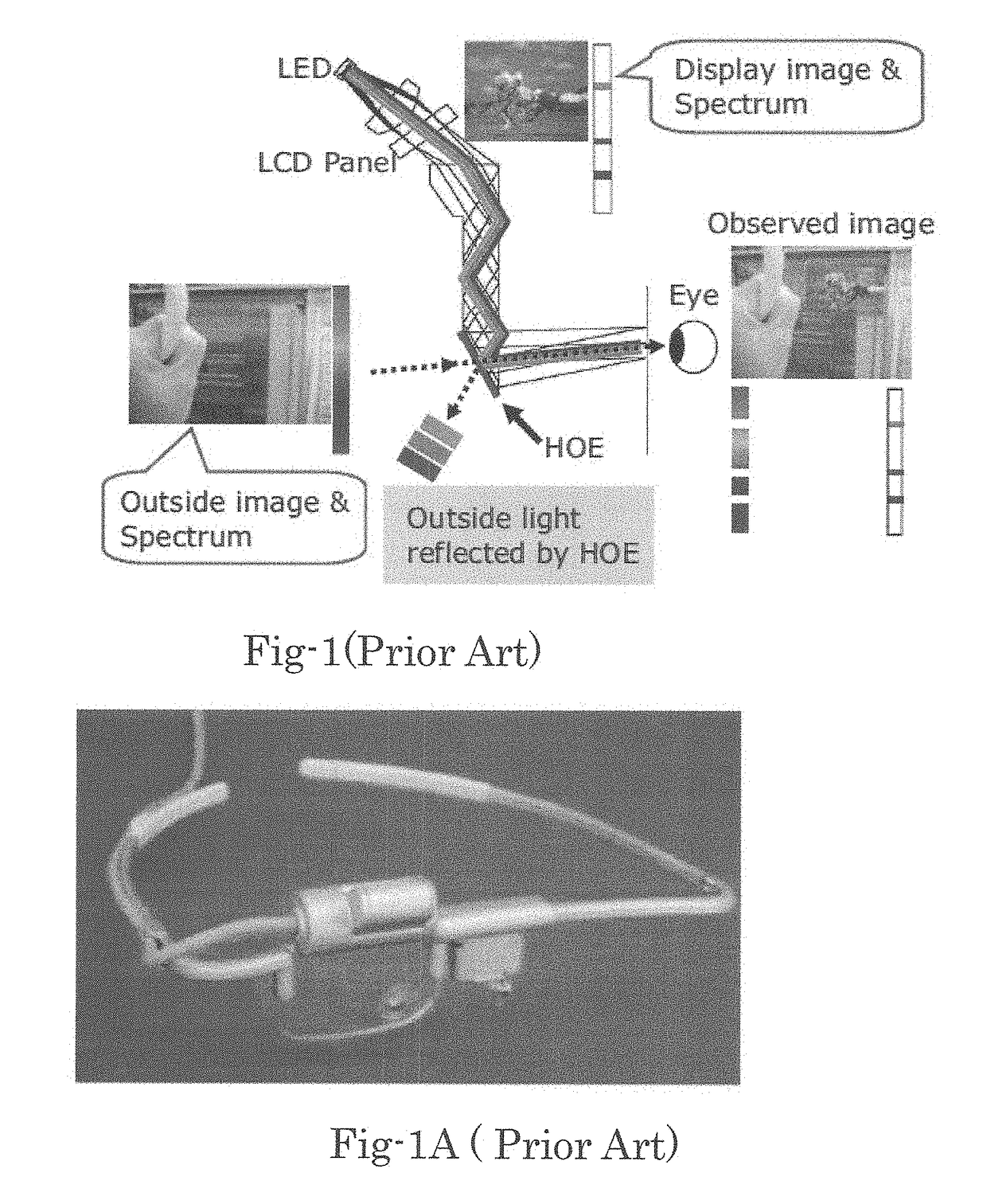
An image display system including tangential outgoing projected light combined with holographic optical element is disclosed. This invention enables very small compact wearable display suitable eyewear display with complete stealth characteristic, electronic vision control and very high solution having large FOV and Eye Box.
Owner:ISHII FUSAO
Large-FOV (field of view) short-range laser radar and vehicle
PendingCN108802763ASimple structureEasy production and adjustmentElectromagnetic wave reradiationLarge fovBlind zone
The invention discloses large-FOV (field of view) short-range laser radar. The laser radar comprises a laser transmitting module, a laser receiving module and a rotating structure, wherein the laser transmitting module comprises a laser used for transmitting outgoing laser beams, a control circuit used for controlling the laser to work as well as a one-dimensional galvanometer used for changing light path direction of the outgoing laser beams in the vertical direction; the laser receiving module is used for receiving reflection laser to execute target detection, and the reflection laser is aroused by the outgoing laser beams reflected by the one-dimensional galvanometer under action of an external obstacle; the rotating structure is used for driving the laser transmitting module and the laser receiving module to rotate horizontally. The invention further discloses a vehicle. The large-FOV short-range laser radar is arranged at the front end of the vehicle. Short-range detection blind zone can be reduced, the structure is simple, production, installation and adjustment are convenient, and production cost is reduced greatly.
Owner:HESAI TECH CO LTD
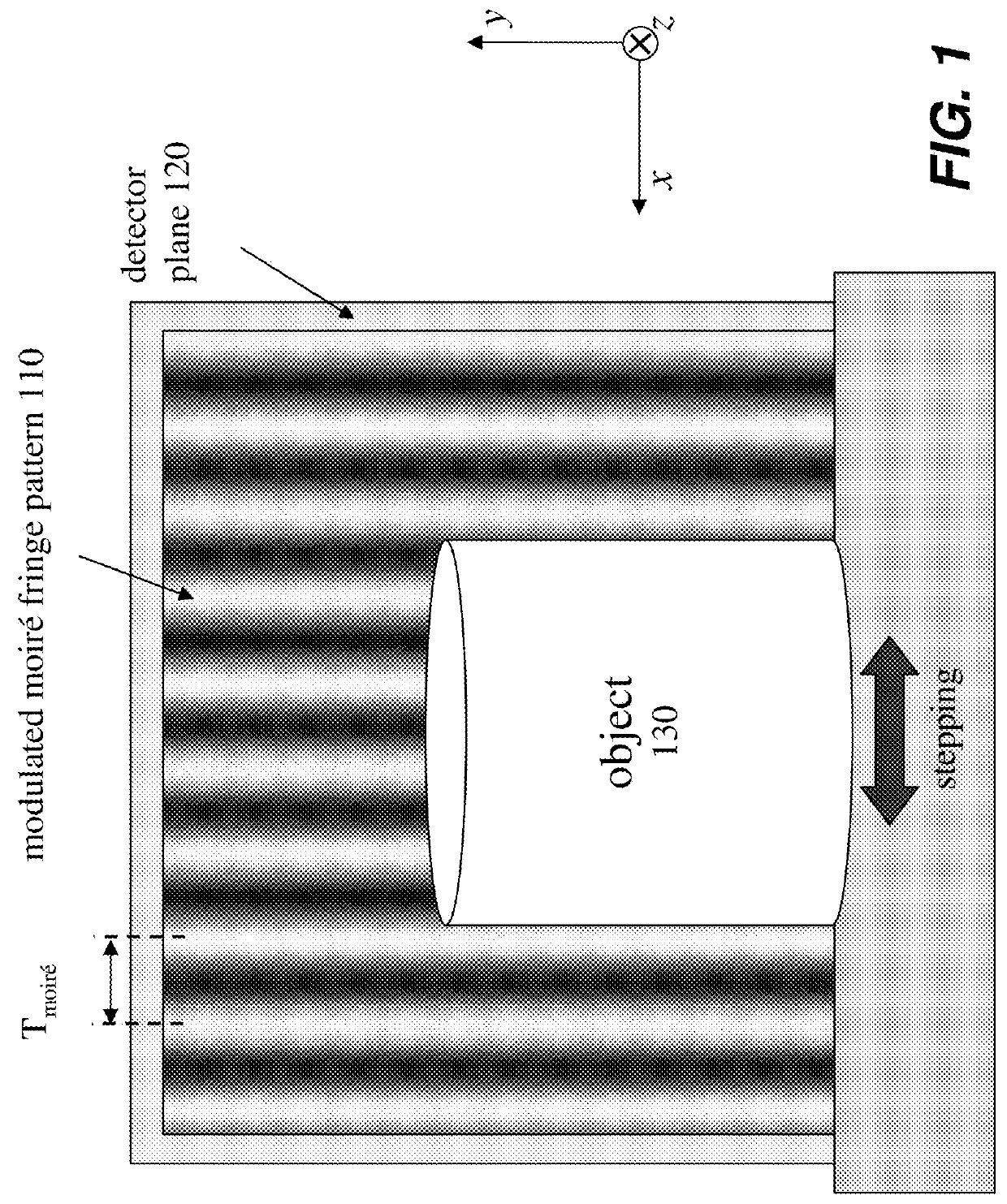
Large field of view grating interferometers for x-ray phase contrast imaging and ct at high energy
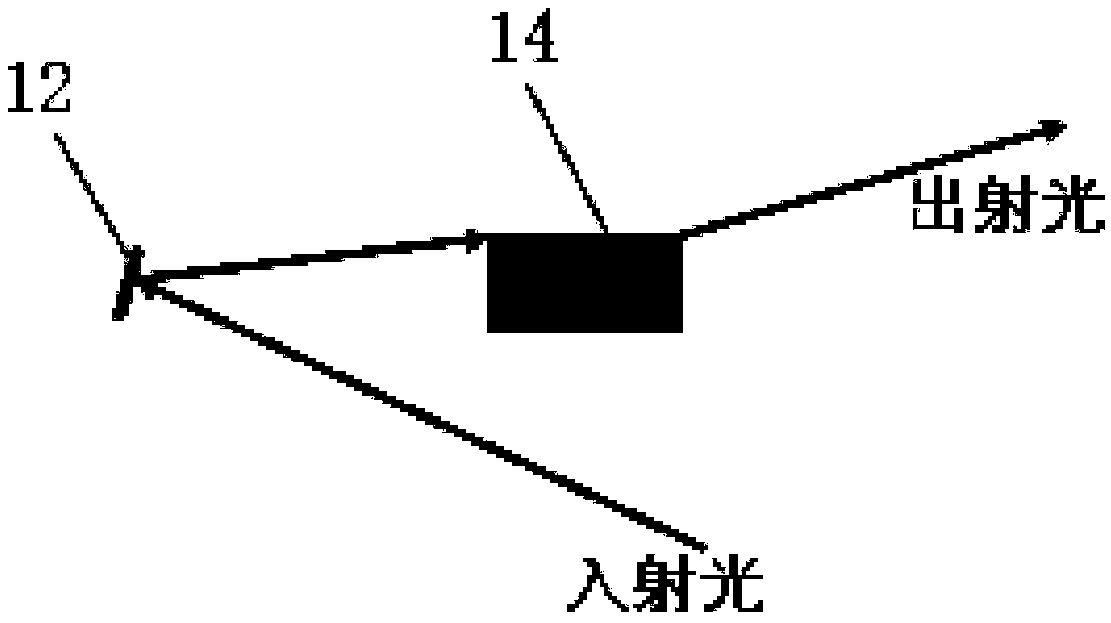
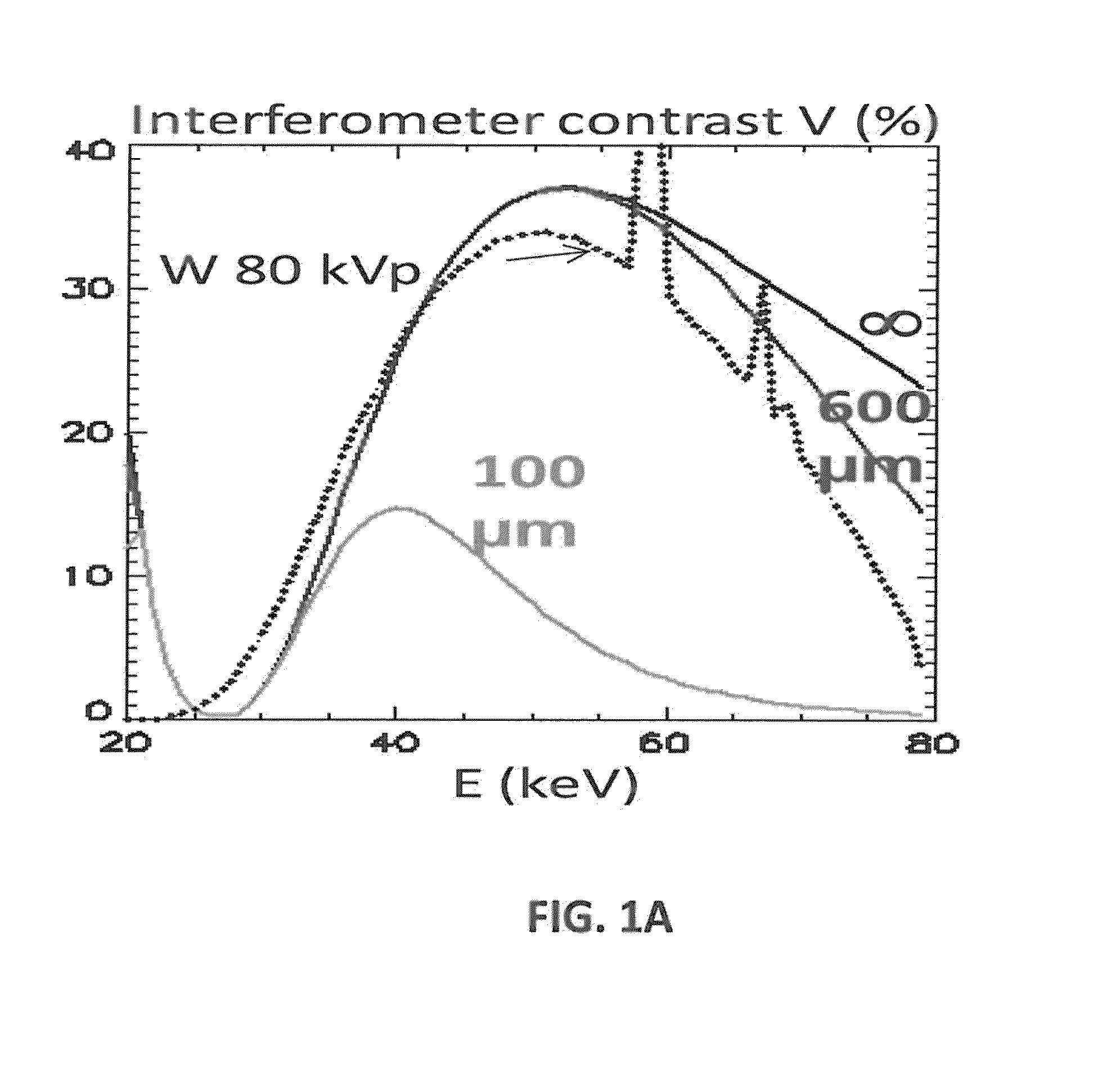
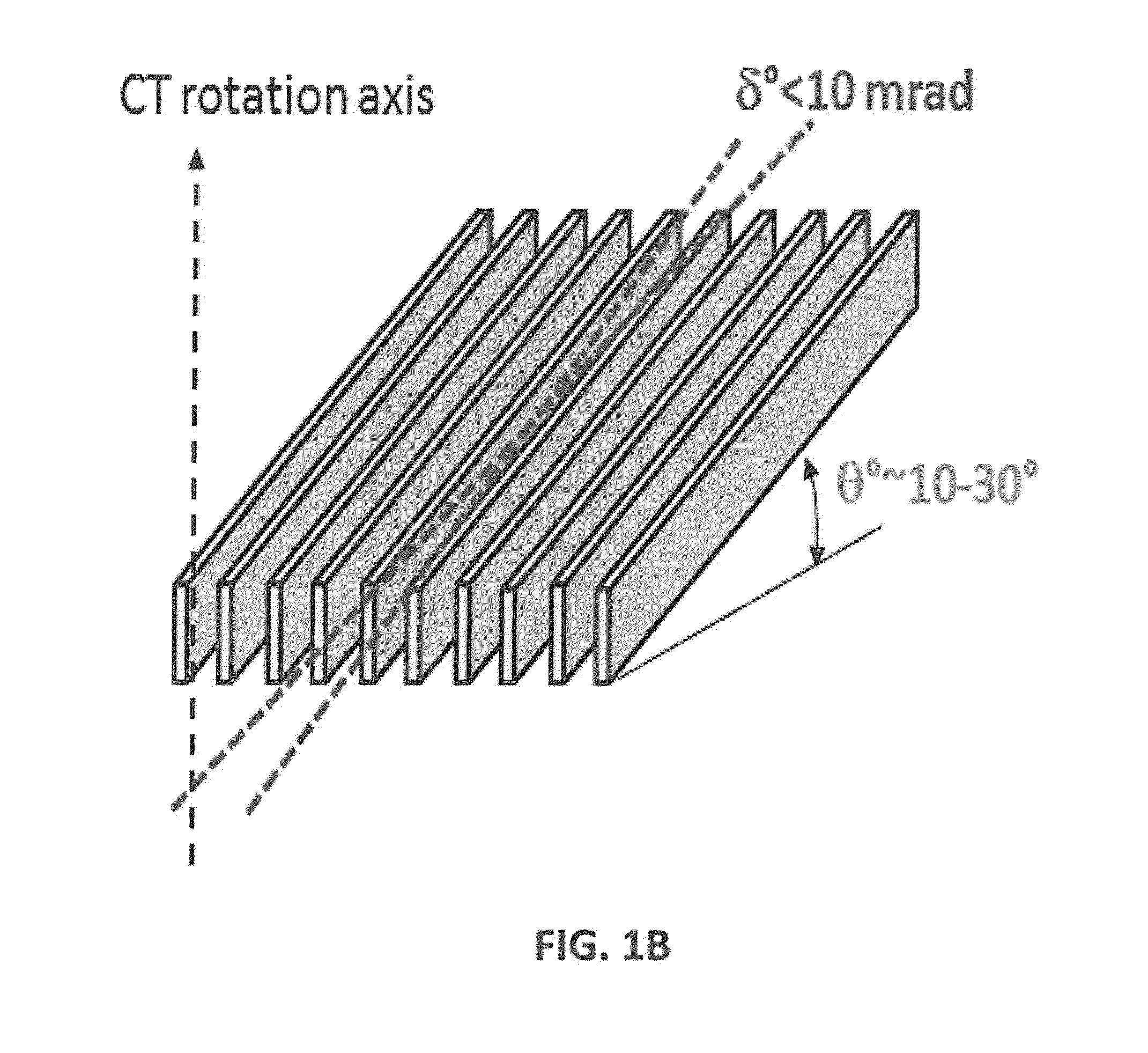
A device and method of the present disclosure provides large field-of-view Talbot-Lau phase contrast CT systems up to very high X-ray energy. The device includes microperiodic gratings tilted at glancing incidence and tiled on a single substrate to provide the large field-of-view phase contrast CT system. The present disclosure is a simple, economical, and accurate method for combining multiple GAIs into a larger FOV system, capable of performing phase-contrast tomography (PC-CT) on large objects. The device and method can be applied to medical X-ray imaging, industrial non-destructive testing, and security screening.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Intelligent positioning method for small ceramic tiles based on multi-feature fusion
InactiveCN106504262AGuaranteed edgeImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisLarge fovCcd camera
The invention discloses an intelligent positioning method for small ceramic files based on multi-feature fusion. The intelligent positioning method comprises the steps of S1, image acquisition; S2, image preprocessing; S3, feature extraction, S4, image target determination; and S5, ceramic file positioning. In the step of image acquisition, an image is acquired through a high-speed linear array CCD camera. In the step of image preprocessing, gray processing is firstly performed on the image, then filtering and denoising processing is carried out, the filtered image is segmented by adopting an edge detection algorithm, the profile of the small ceramic tile is extracted, and then a profile diagram of the ceramic tile is acquired. In the step of feature extraction, corresponding primitive features are generated based on geometric features of the ceramic tile profile in the profile diagram in the step S2; and a logical AND operation is performed by using a filtered image and the profile mask diagram in the step S2, transferring an operation result diagram into an HSV color space, and color features are generated; and combination features are generated according to the primitive features and the color features. The intelligent positioning method realizes high-precision positioning for the small ceramic tiles at a large FOV (Field of View), thereby providing accurate positioning data for visual inspection and robot grasping. In addition, multiple segmentation units can operate concurrently in a multi-threaded system, and the real-time performance of the system is improved.
Owner:QUANZHOU INST OF EQUIP MFG
Energy filter for charged particle beam apparatus
ActiveUS9000395B2Improve uniformityIncrease contrastStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationLarge fovDevice form
This invention provides a method for improving performance of a reflective type energy filter for a charged particle beam, which employs a beam-adjusting lens on an entrance side of a potential barrier of the energy filter to make the charged particle beam become a substantially parallel beam to be incident onto the potential barrier. The method makes the energy filter have both a fine energy-discrimination power over a large emission angle spread and a high uniformity of energy-discrimination powers over a large FOV. A LVSEM using this method in the energy filter can obviously improve image contrast. The invention also provides multiple energy-discrimination detection devices formed by using the advantages of the method.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Polarization multiplexing waveguide display device
InactiveCN110824613AHigh diffraction efficiencyImprove efficiencyOptical waveguide light guideColor imageLarge fov
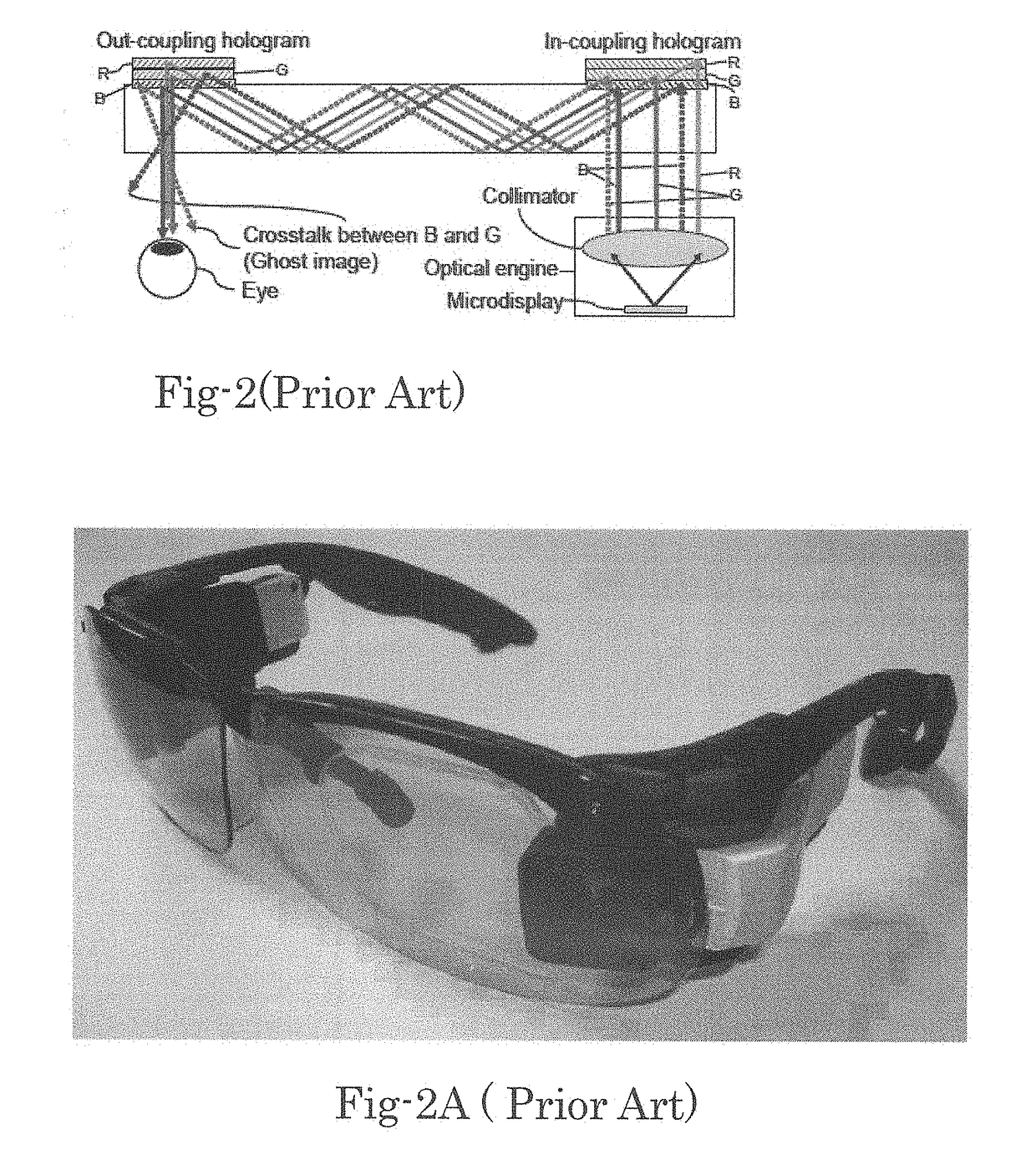
The invention discloses a polarization multiplexing waveguide display device composed of an in-coupling device, an out-coupling device and a waveguide. By using a color polarizing volume holographic grating as a coupling device of the waveguide, compared with the traditional holographic coupling grating, the novel grating adopts the self-assembly effect and anisotropy of liquid crystals, has highdiffraction efficiency and large diffraction angles, can work at a wide wavelength and angular bandwidth, and has polarization selectivity. In combination with the disclosed double-layer waveguide structure, the invention is applied to near-eye display applications, and can realize color image transmission with large FOV, high transparency and high efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Energy Filter for Charged Particle Beam Apparatus
ActiveUS20140284476A1Improve uniformityIncrease contrastStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationLarge fovDevice form
This invention provides a method for improving performance of a reflective type energy filter for a charged particle beam, which employs a beam-adjusting lens on an entrance side of a potential barrier of the energy filter to make the charged particle beam become a substantially parallel beam to be incident onto the potential barrier. The method makes the energy filter have both a fine energy-discrimination power over a large emission angle spread and a high uniformity of energy-discrimination powers over a large FOV. A LVSEM using this method in the energy filter can obviously improve image contrast. The invention also provides multiple energy-discrimination detection devices formed by using the advantages of the method.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Ultra-large FOV (Field Of View) static polarized Fourier transform imaging spectrometer
InactiveCN102012267ALarge field of viewReduce volumeInterferometric spectrometryLarge fovBeam splitter
The invention relates to an ultra-large FOV (Field Of View) static polarized Fourier transform imaging spectrometer comprising a front telescope system, a polarizer, an FOV compensation-type polarized beam splitter, a polarization analyzer, an imaging lens group and a detector which are coaxially and sequentially arranged, wherein the detector is connected with a signal collecting and processing system. The invention introduces two Savart polarizers which respectively have positive and negative interference fringe distortion to form the polarized beam splitter so that the positive interference fringe distortion and the negative interference fringe distortion can mutually counteract so as to enlarge the FOV angle. The invention has the advantages of small size, light weight, simple and compact structure, no motion part, large FOV, great luminous flux, high detection sensitivity, noise-signal ratio and wavelength accuracy and wide spectral detection range.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Optical system for head-mounted display system
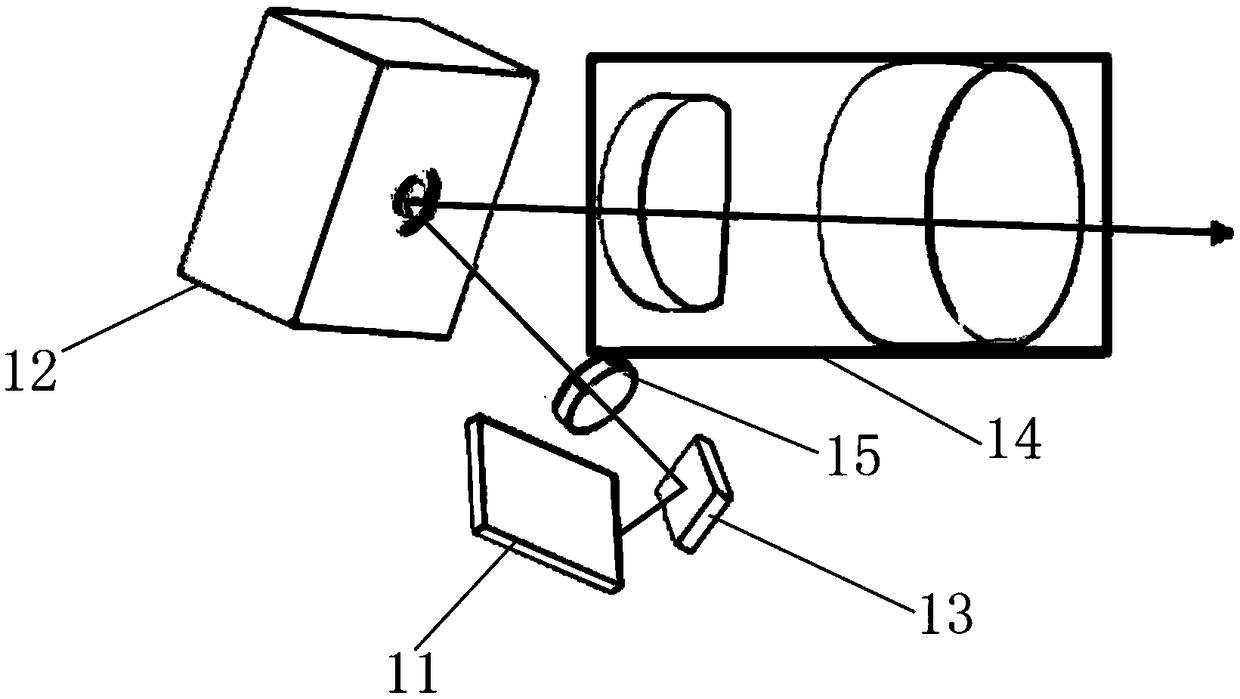
Systems and methods for providing optical systems which utilize double Fresnel lenses on curved surfaces for use with display systems, such as silicon-based micro display systems (e.g., OLED micro displays) used with head mounted display (HMD) systems. The optical systems disclosed herein may implement multiplexing or blending to provide a smooth profile transition and reduce aberrations between zones or fields (e.g., small FOV angles, large FOV angles) of a Fresnel surface which is defined by multiple Fresnel patterns or functions. An optical system for a micro display is provided which utilizes double Fresnel lenses on curved surfaces to shorten the focal length while maintaining a good shape factor for moldability and aberration control.
Owner:VALVE
Phase contrast imaging
ActiveCN102781327AQuality improvementMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation diagnosticsLarge fovGrating
X-ray devices for Phase Contrast Imaging (PCI) are often built up with the help of gratings. For large field-of-views (FOV), production cost and complexity of these gratings could increase significantly as they need to have a focused geometry. Instead of a pure PCI with a large FOV, this invention suggests to combine a traditional absorption X-ray imaging system with large-FOV with an insertable low-cost PCI system with small-FOV, The invention supports the user to direct the PCI system with reduced FOV to a region that he regards as most interesting for performing a PCI scan thus eliminating X-ray dose exposure for scanning regions not interesting for a radiologist. The PCI scan may be generated on the basis of local tomography.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Architectures for cardiac ct based on area x-ray sources
InactiveUS20080123804A1Improve time resolutionReducing conebeam artifactMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingLarge fovX-ray
A CT imaging system includes a rotatable gantry having an opening to receive an object to be scanned having a small field-of-view (FOV) inside a large FOV. A plurality of area sources is attached to the rotatable gantry, each area source includes a plurality of x-ray emission sources, wherein the plurality of area sources are configured to emit x-rays toward the object. A plurality of x-ray detector arrays is attached to the gantry and positioned such that at least a first detector array and a second detector array each receive x-rays that pass through at least the entire small FOV of the object.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
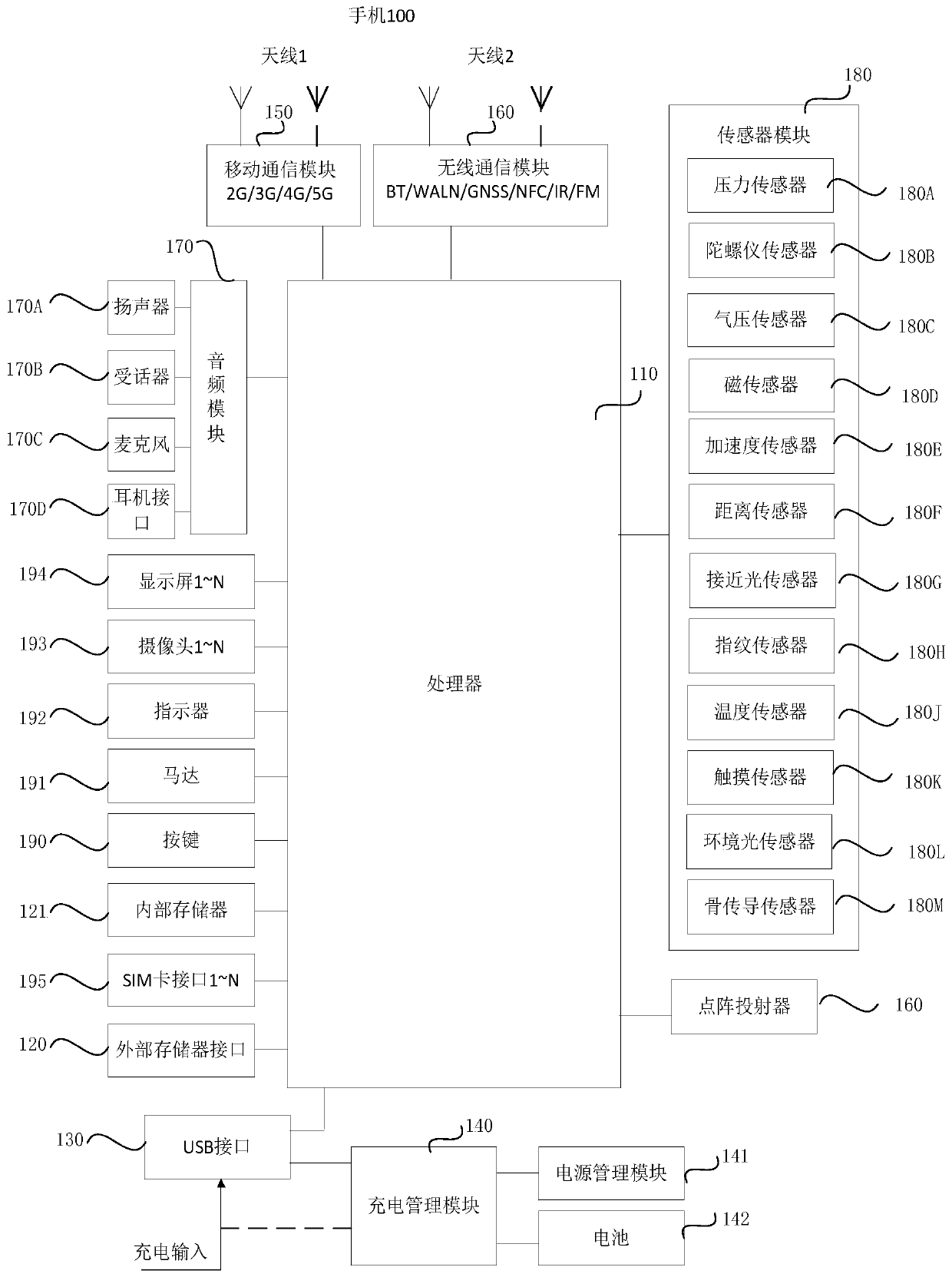
Image shooting method and electronic equipment
The invention provides an image shooting method and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps: detecting a first operation, starting a first camera and a second camera in the electronic equipment, and displaying a framing interface; inputting a first image acquired by the first camera and a second image acquired by the second camera into a first fusion network to obtain a first output image; pasting image information on the first image to a first area on the first output image to obtain a third image, and inputting the second image into a second fusion network to obtain asecond output image; and pasting the image information of the second area on the second output image to a third area on a third image to obtain a fourth image, the third area being an area other thanthe first area on the third image. In the mode, in the image obtained by fusing the small fov image and the large fov image through the electronic equipment, the definition of different areas is consistent. A fusion boundary cannot appear, and the image shooting quality can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
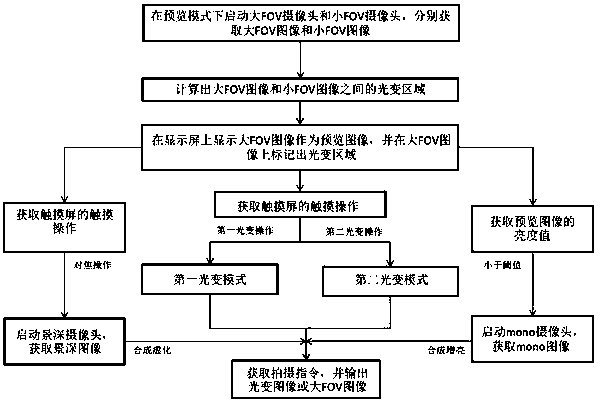
Multi-camera shooting method and shooting terminal, and readable storage medium
InactiveCN108833768APrevent losing the targetPrevent the problem of composition offsetTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLarge fovMulti camera
The invention discloses a multi-camera shooting method and shooting terminal, and a readable storage medium. The shooting method comprises: a large FOV camera and a small FOV camera are started in a preview mode and a large FOV image and a small FOV image are obtained respectively; a light-changing region between the large FOV image and the small FOV image is calculated; the large FOV image is displayed as a preview image on a display screen and a light-changing area is marked on the large FOV image; a touch operation of a touch screen is acquired; if the obtained touch operation is a preset first light-changing operation, switching to a first light-changing mode is carried out; if the obtained touch operation is a preset second light-changing operation, switching to a second light-changing mode is carried out; and a shooting instruction is obtained and a light-changing image or the large FOV image is outputted. Therefore, a problem of losing of a shot target or composition shift occurrence after optical zooming is solved; and the user is able to carry out optical zooming shooting conveniently.
Owner:TRULY OPTO ELECTRONICS
Novel millimeter-wave radar signal processing method
The invention provides a radar signal processing method which comprises the steps: arranging a millimeter wave radar virtual antenna array, wherein periodic deviation exists between the actual phase difference and the measurement phase difference when the azimuth angle is larger than the measurement azimuth angle of the virtual antenna; measuring the phase difference, and calculating a fuzzy azimuth angle according to a phase method angle measurement principle; substituting the fuzzy azimuth angle into a pitch compensation phase difference formula to obtain a pitch compensation phase difference, compensating the antenna array element by utilizing the pitch compensation phase difference, and then obtaining a pitch angle according to the phase method angle measurement principle; substituting the pitch angle into a pitch compensation phase difference formula to obtain a direction-dimensional pitch compensation phase difference, performing phase compensation on the antenna array element by utilizing the direction-dimensional pitch compensation phase difference, and then obtaining an unambiguous azimuth angle according to the phase method angle measurement principle; and comparing the fuzzy azimuth angle with the non-fuzzy azimuth angle, and obtaining a true value of the pitch angle when the two angles are equal. The large FOV and the high angle resolution can be achieved without additionally increasing the number of antennas, and the contradiction between the angle resolution and the azimuth angle range is effectively reconciled.
Owner:北京理工睿行电子科技有限公司 +1
Shooting method and shooting terminal of multi-camera, and readable storage medium
The invention discloses a shooting method and shooting terminal of multi-camera, and a readable storage medium. The shooting method of the multi-camera comprises the following steps: acquiring a shooting mode; if the acquired shooting mode is an IR mode, starting a RGB-IR switching camera and an IR transmitter, and turning on an IR optical filter on the RGB-IR switching camera, thereby acquiring an IR image; starting the RGB-IR switching camera and a RGB camera if the acquired shooting mode is an optical variable mode, and turning off the IP optical filter on the RGB-IR switching camera, thereby respectively acquiring a small FOV image and a large FOV image, wherein the field of view angle of the RGB-IR switching camera is less than that of the RGB camera. Through the shooting method disclosed by the invention, the IR mode and the optical variable mode can be realized by adopting a RGB-IR switching camera with small field of view angle and the RGB camera with the large field of view angle.
Owner:TRULY OPTO ELECTRONICS
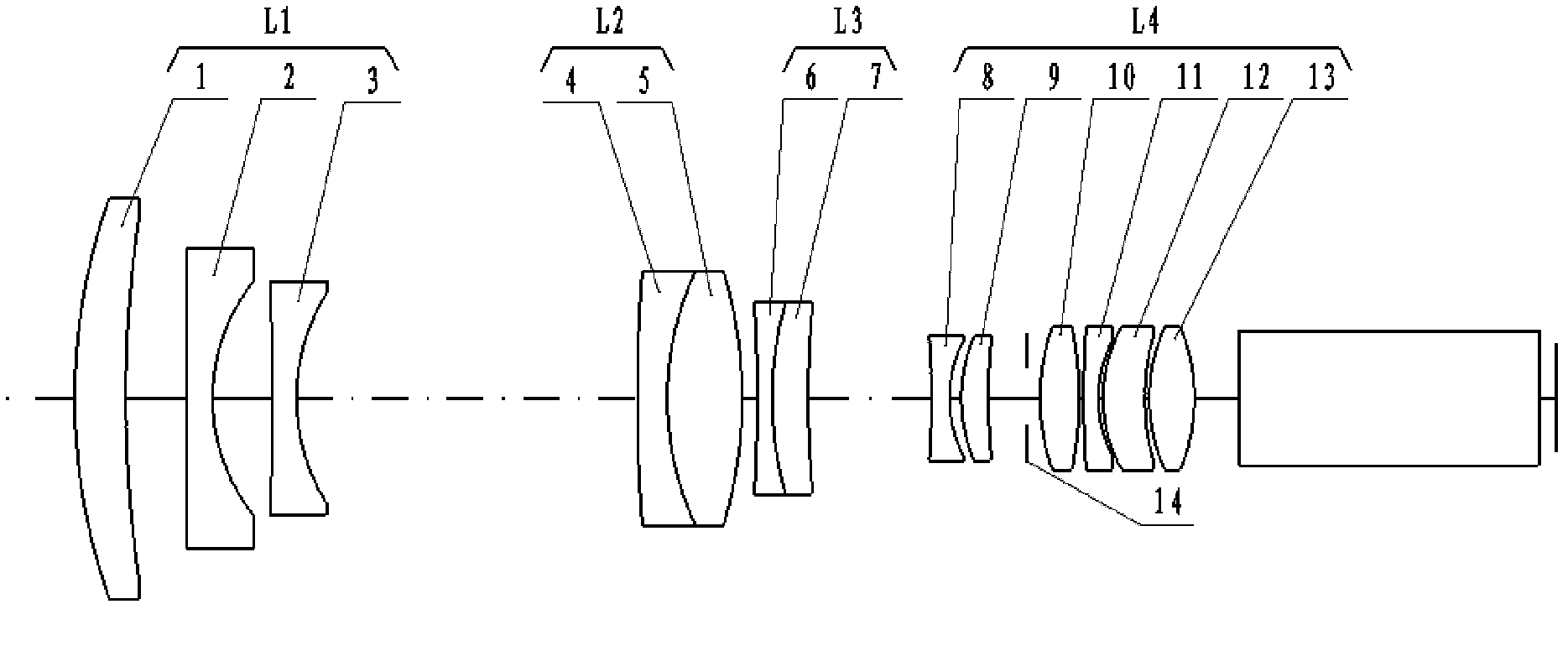
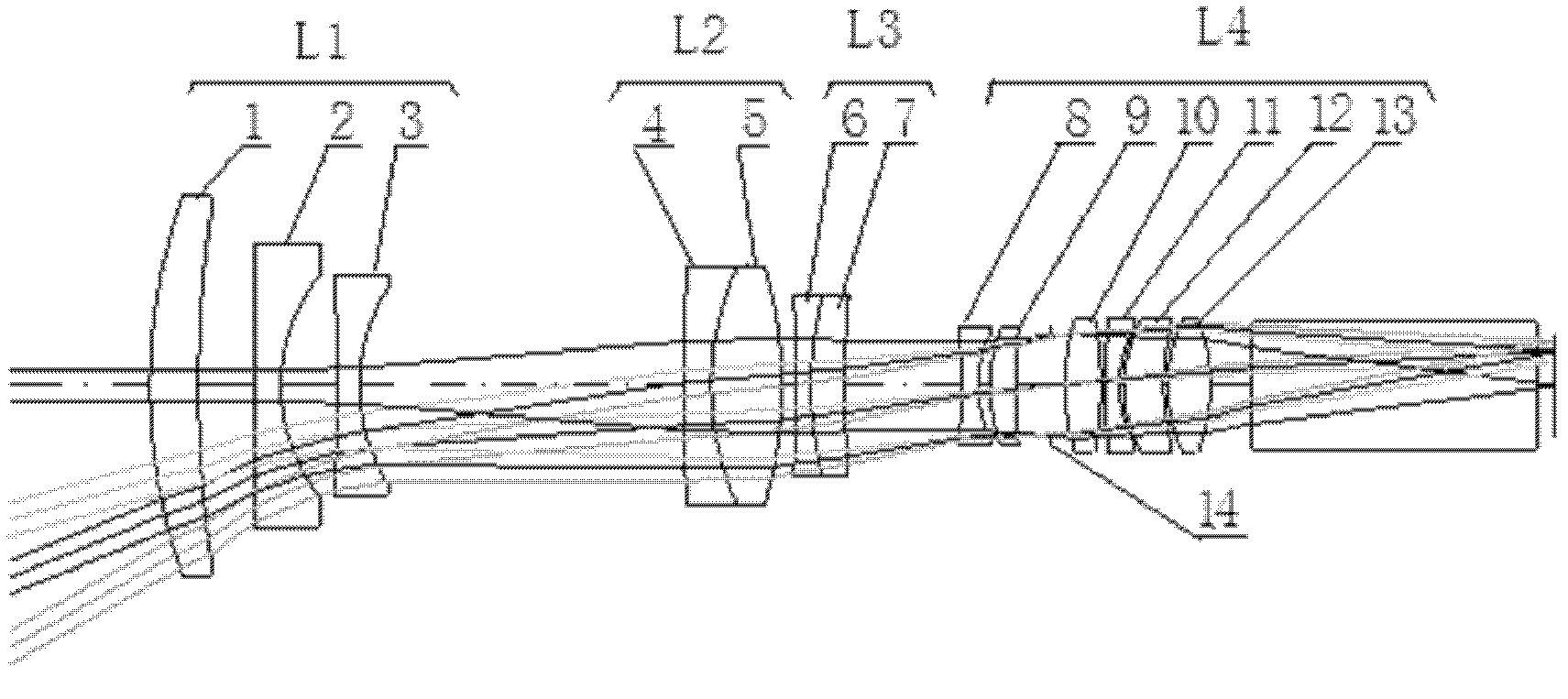
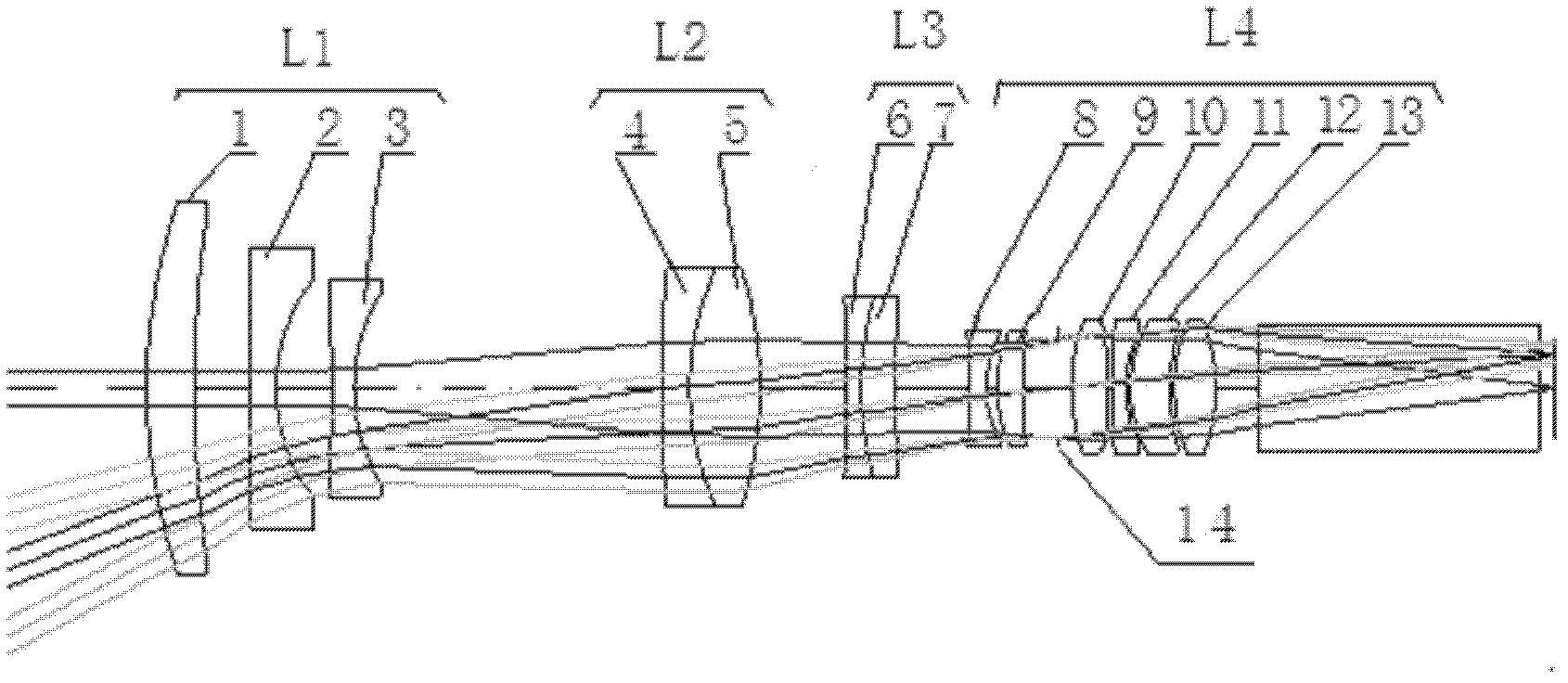
High-resolution large-fov (field of view) zoom projection lens
ActiveCN102590992AHigh transfer functionHigh resolutionDiffraction gratingsMountingsLarge fovHigh resolution imaging
The invention relates to a high-resolution large-fov (field of view) zoom projection lens. An optical system lens group comprises a front compensation lens group, a variable-magnification lens group, a rear compensation lens group and a rear fixed lens group which are arrayed in sequence along the optical axis from a screen to an image plane DMD (digital micro-mirror device) chip; the variable-magnification lens group is the positive focal-length group component; the front compensation lens group and the rear compensation lens group are the negative focal-length group components; the rear fixed lens group is the positive focal-length group component; the front compensation lens group comprises three lenses; the variable-magnification lens group comprises two lenses; the rear compensation lens group comprises two lenses; the rear fixed lens group comprises six lenses; and the rear fixed lens group is provided with a diaphragm. The focal power of each lens group is distributed reasonably, and the high-resolution large-fov zoom projection lens has a compact structure, a large fov, a high resolution and a good image forming effect, can achieve a significant effect when being used for projecting images on a 2-4k DMD chip based large screen, adopts the materials being easy to process and is suitable for bath production.
Owner:HUBEI JIUZHIYANG INFRARED SYST CO LTD
Objective lens system for fast scanning large FOV
The device includes a beam source for generating an electron beam, a beam guiding tube passed through an objective lens, an objective lens for generating a magnetic field in the vicinity of the specimen to focus the particles of the particle beam on the specimen, a control electrode having a potential for providing a retarding field to the particle beam near the specimen to reduce the energy of the particle beam when the beam collides with the specimen, a deflection system including a plurality of deflection units situated along the optical axis for deflecting the particle beam to allow scanning on the specimen with large area, at least one of the deflection units located in the retarding field of the beam, the remainder of the deflection units located within the central bore of the objective lens, and a detection unit to capture secondary electron (SE) and backscattered electrons (BSE).
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Energy-discrimination detection device
This invention provides a method for improving performance of a reflective type energy filter for a charged particle beam, which employs a beam-adjusting lens on an entrance side of a potential barrier of the energy filter to make the charged particle beam become a substantially parallel beam to be incident onto the potential barrier. The method makes the energy filter have both a fine energy-discrimination power over a large emission angle spread and a high uniformity of energy-discrimination powers over a large FOV. A LVSEM using this method in the energy filter can obviously improve image contrast. The invention also provides multiple energy-discrimination detection devices formed by using the advantages of the method.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Long cavity laser sensor for large FOV auto-tracking
The presently disclosed technique presents laser-based method and apparatus for use in remote sensing. In general, objects within a field of view are lased by a long cavity laser apparatus. Returns are detected, captured, and processed to identify actual objects of interest. These can then be communicated to a user. Over time, the actual objects of interest can be auto-tracked.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Large field of view grating interferometers for x-ray phase contrast imaging and ct at high energy
A device and method of the present disclosure provides large field-of-view Talbot-Lau phase contrast CT systems up to very high X-ray energy. The device includes microperiodic gratings tilted at glancing incidence and tiled on a single substrate to provide the large field-of-view phase contrast CT system. The present disclosure is a simple, economical, and accurate method for combining multiple GAIs into a larger FOV system, capable of performing phase-contrast tomography (PC-CT) on large objects. The device and method can be applied to medical X-ray imaging, industrial non-destructive testing, and security screening.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com