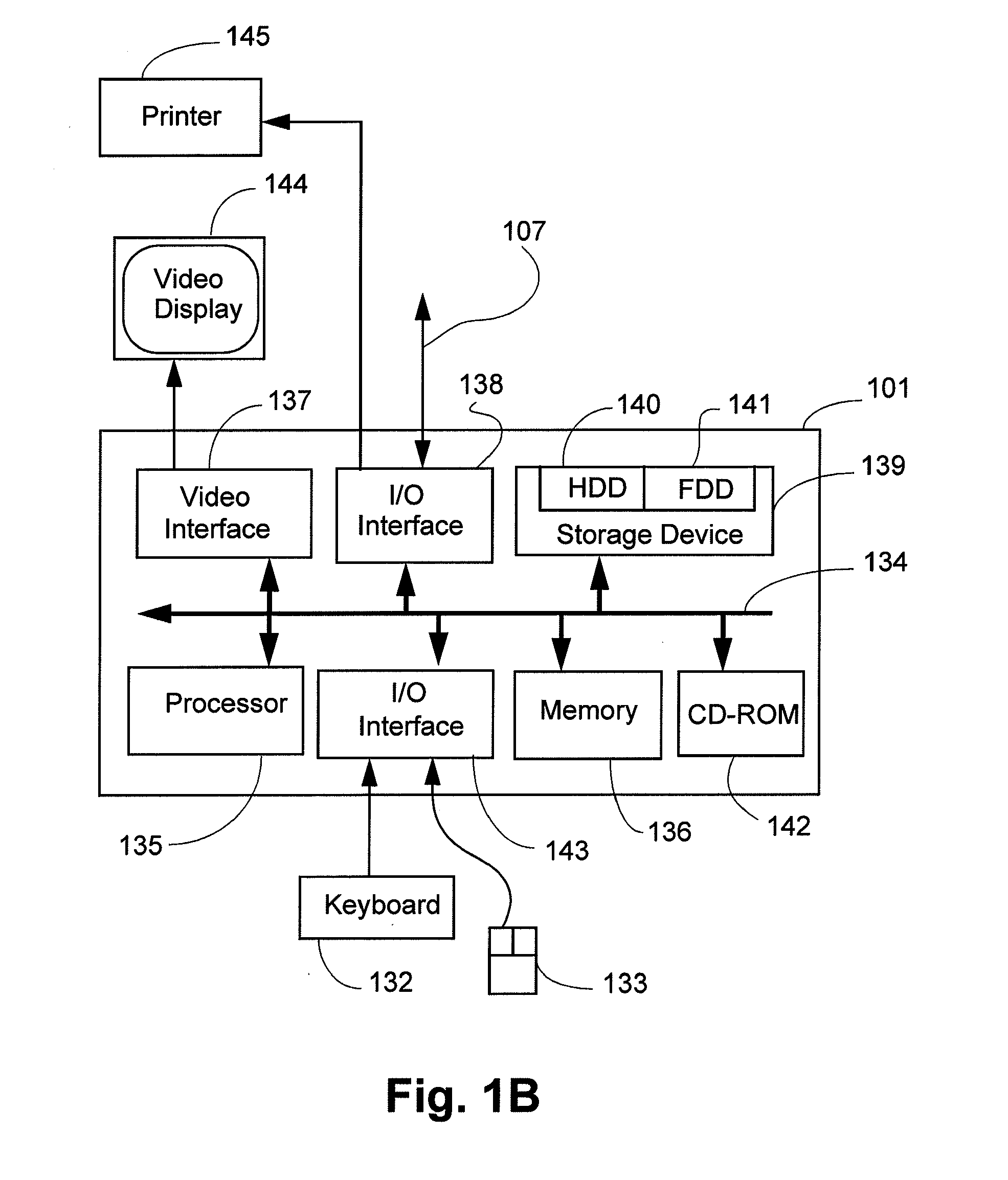
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4581 results about "Object function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
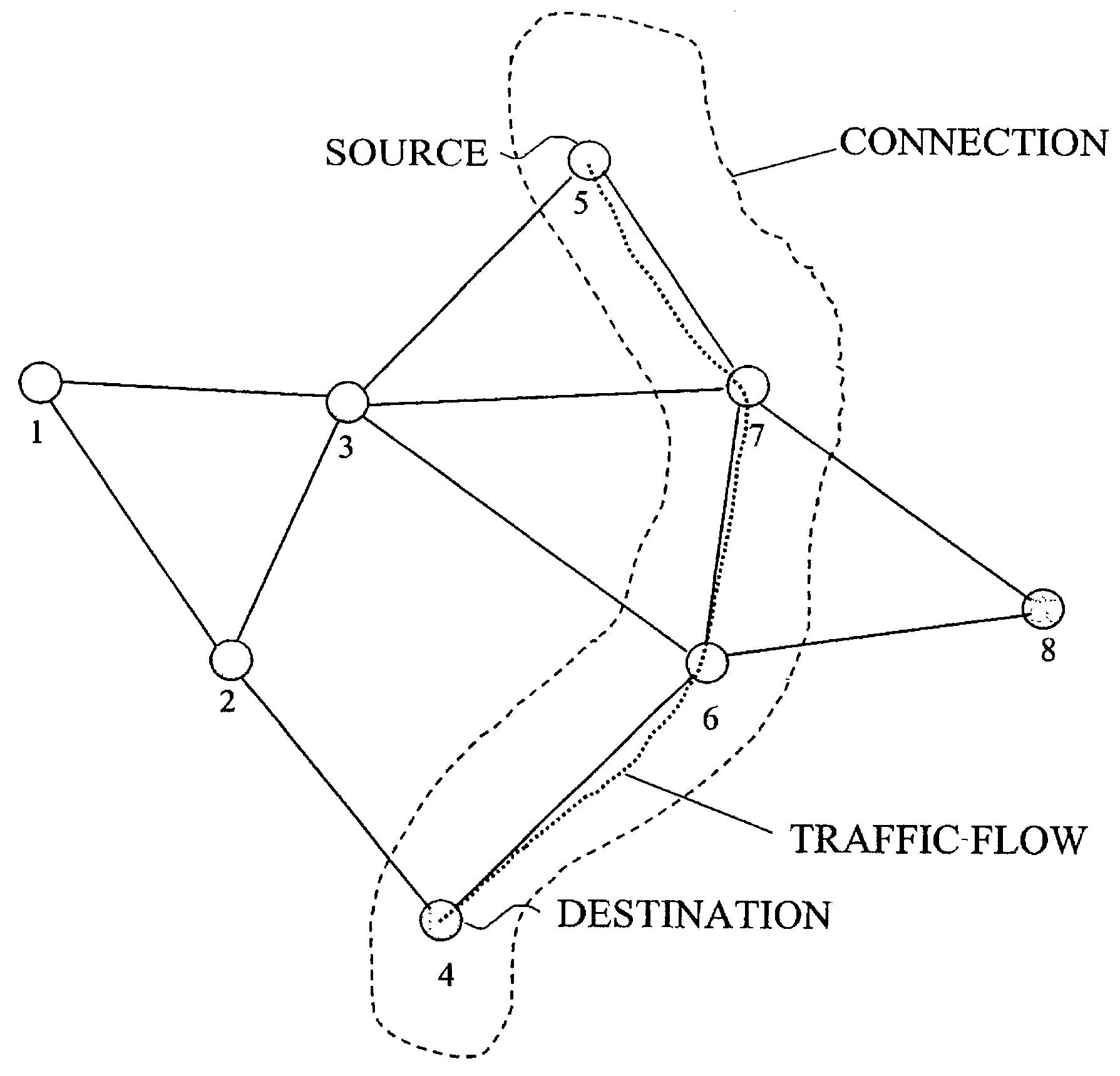
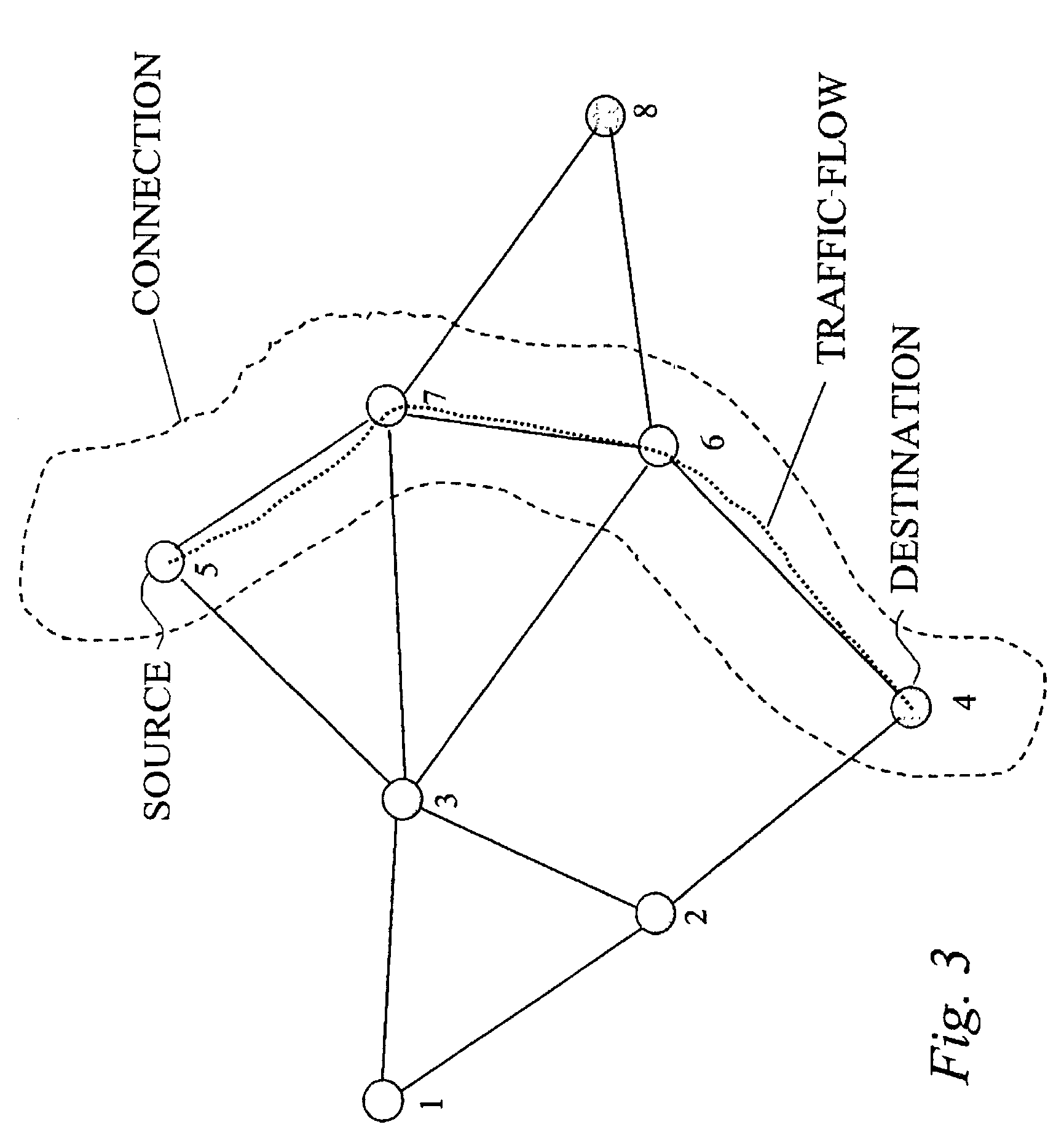
Cross-layer integrated collision free path routing
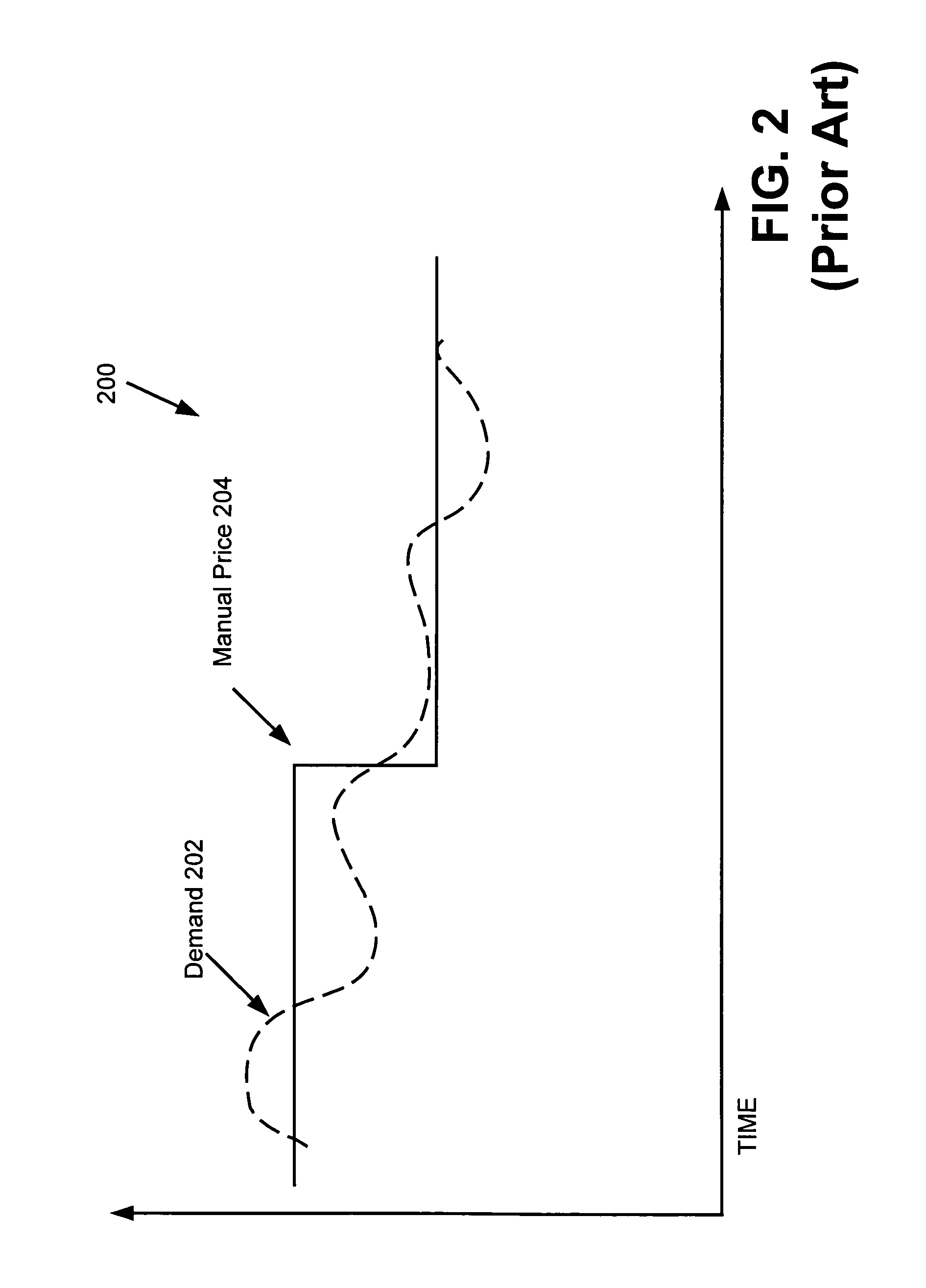
InactiveUS7339897B2Increase profitEnergy efficient ICTPower managementQuality of serviceSelf adaptive
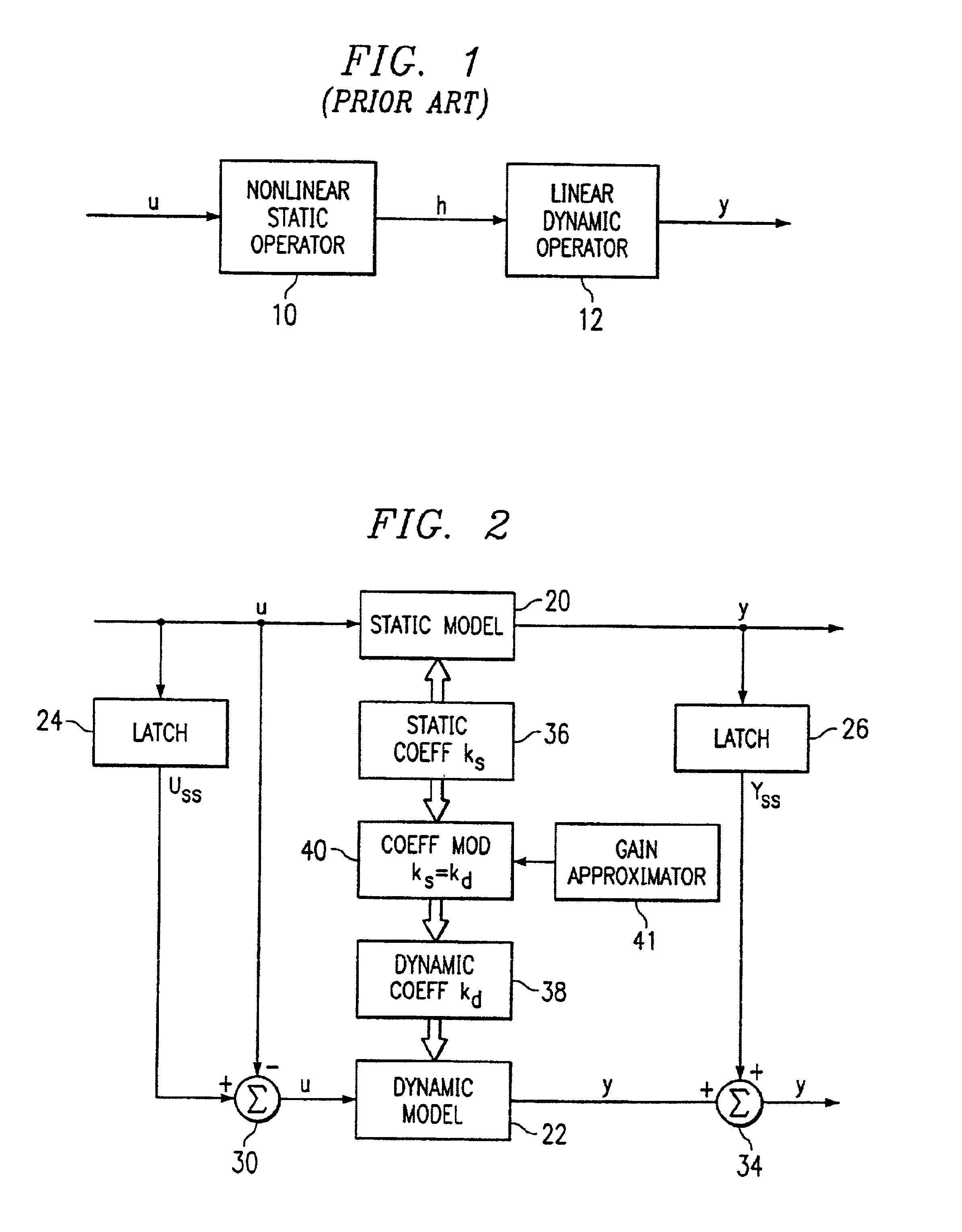
A true cross-layer integration of functions is provided on several protocol layers within a network, thus providing a unified approach to Quality of Service (QoS) provisioning in a multihop network. In the unified approach, connections are preferably determined by integrated optimization of a given objective function with respect to connection parameters on at least three protocol layers within the network. Preferably, the optimization involves routing (path selection), channel access as well as adaptation of physical link parameters. By incorporating physical connection parameters together with properly designed constraints, the issue of interference can be carefully considered. It is thereby possible to determine connection parameters that ensure substantially non-interfering communication with respect to existing connections as well as the new connection.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
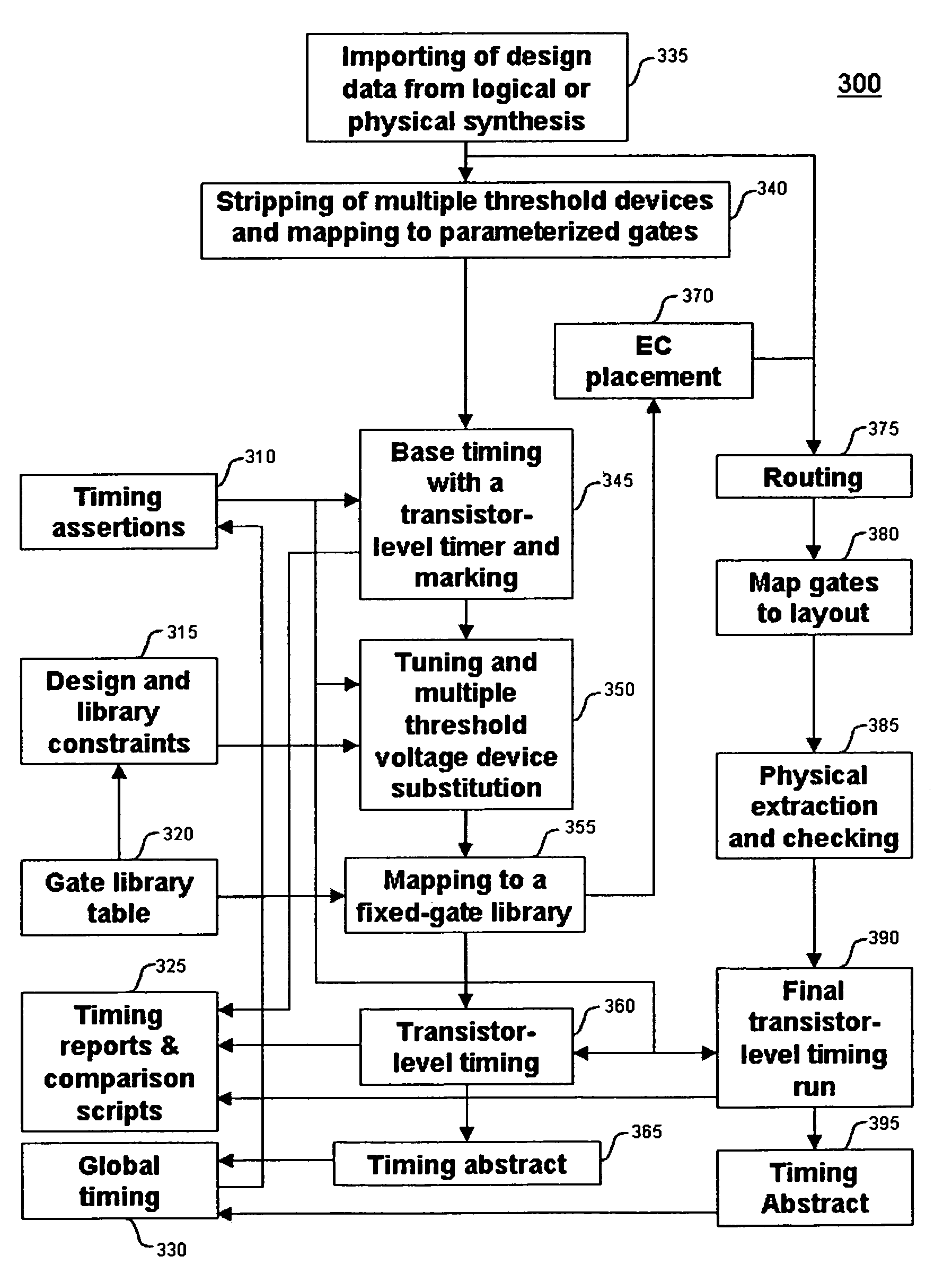
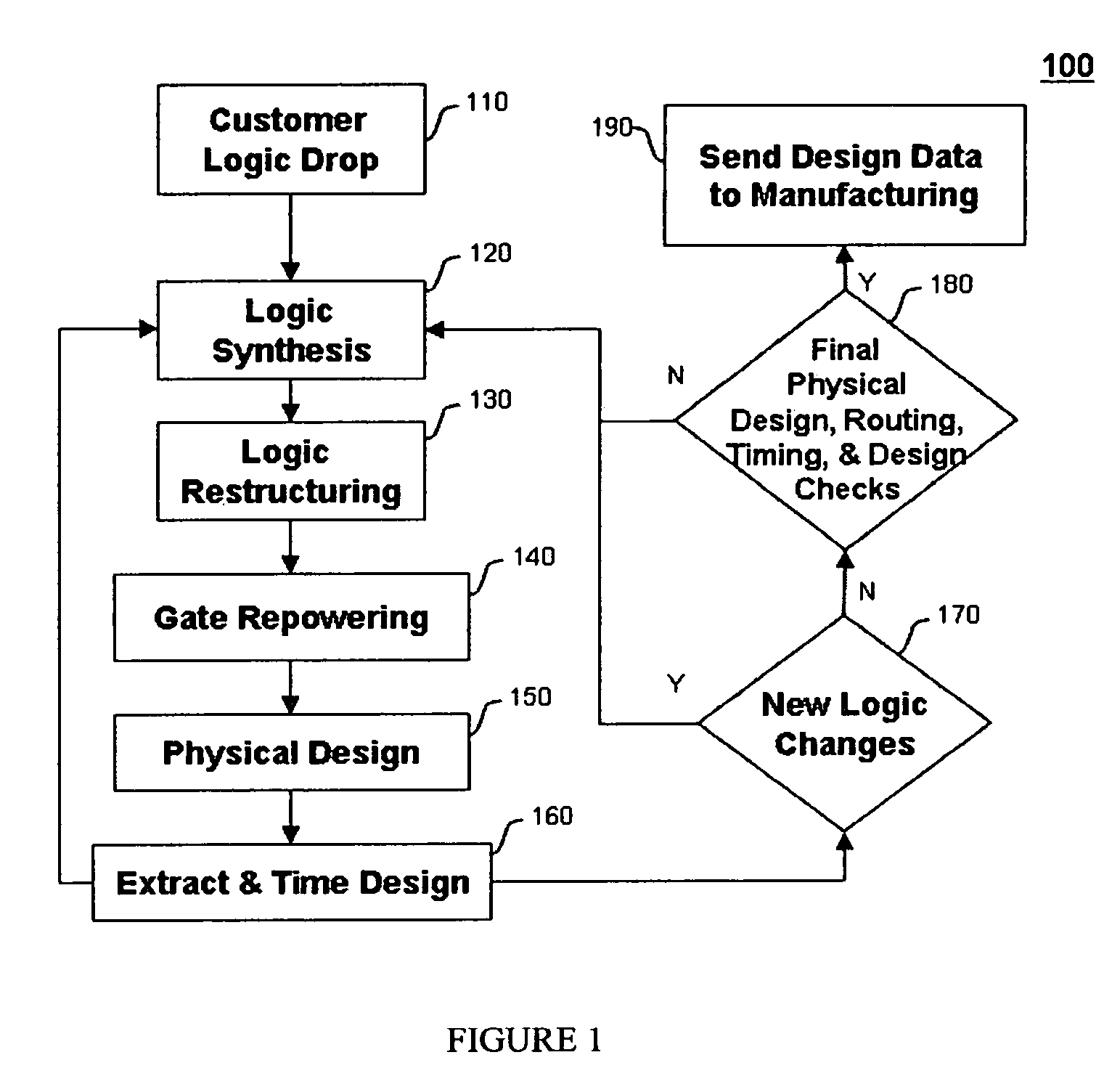
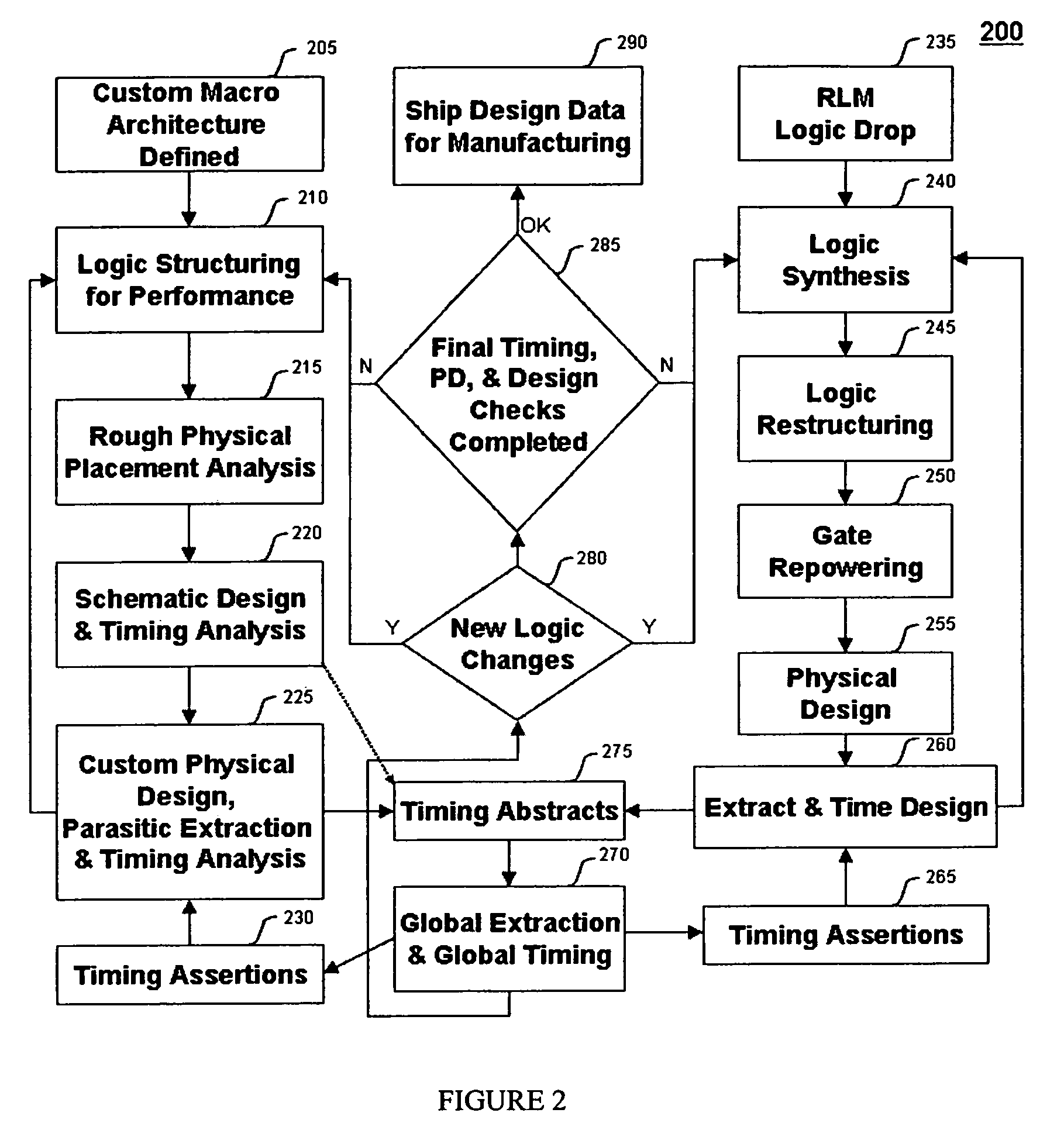
Method for tuning a digital design for synthesized random logic circuit macros in a continuous design space with optional insertion of multiple threshold voltage devices
InactiveUS7093208B2Efficient and effective methodologyError minimizationDigital storageComputer aided designContinuous designCritical section
A Digital Design Method which may be automated is for obtaining timing closure in the design of large, complex, high-performance digital integrated circuits. The methodincludes the use of a tuner on random logic macros that adjusts transistor sizes in a continuous domain. To accommodate this tuning, logic gates are mapped to parameterized cells for the tuning and then back to fixed gates after the tuning. Tuning is constrained in such a way as to minimize “binning errors” when the design is mapped back to fixed cells. Further, the critical sections of the circuit are marked in order to make the optimization more effective and to fit within the problem-size constraints of the tuner. A specially formulated objective function is employed during the tuning to promote faster global timing convergence, despite possibly incorrect initial timing budgets. The specially formulated objective function targets all paths that are failing timing, with appropriate weighting, rather than just targeting the most critical path. Finally, the addition of multiple threshold voltage gates allows for increased performance while limiting leakage power.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
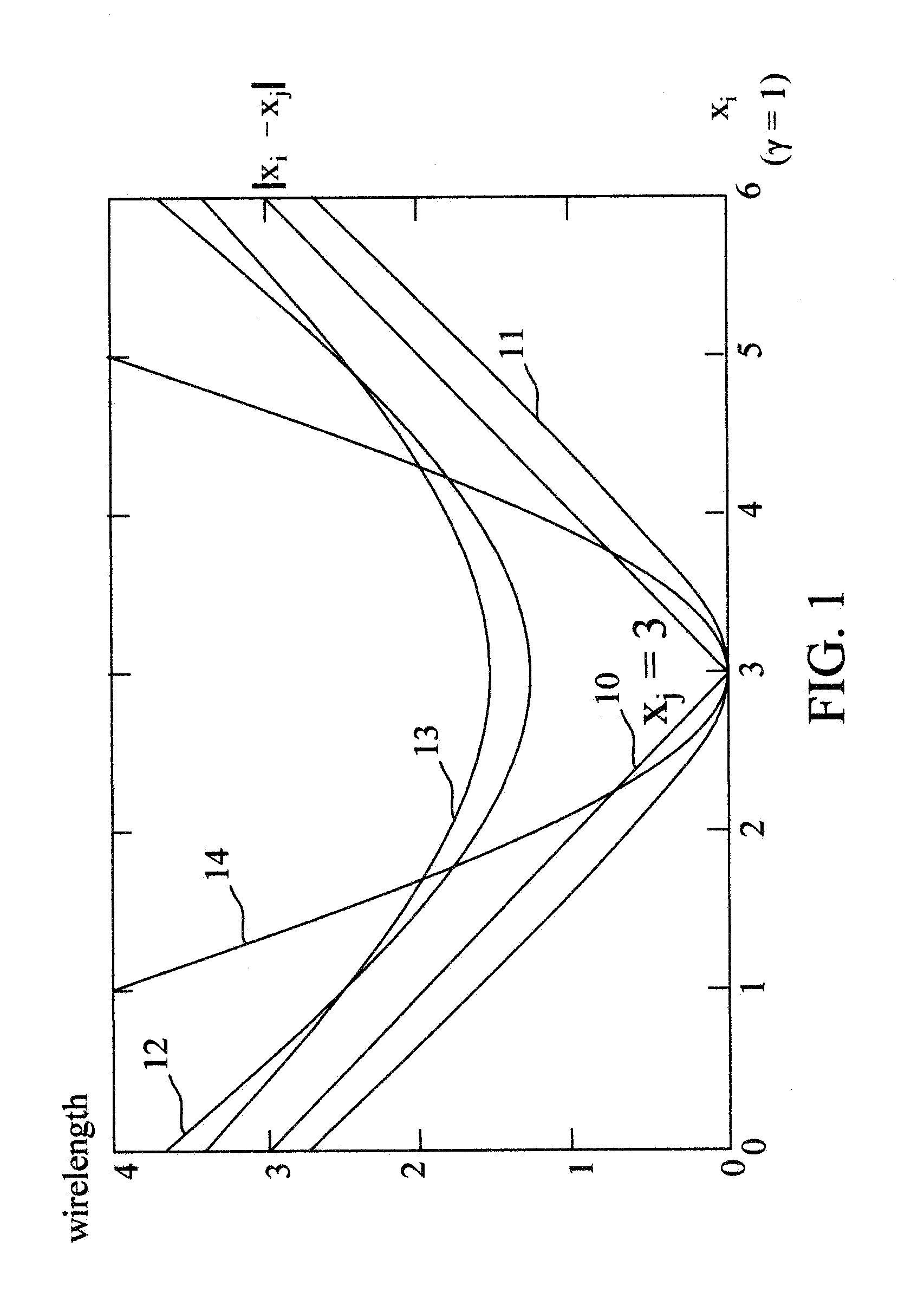
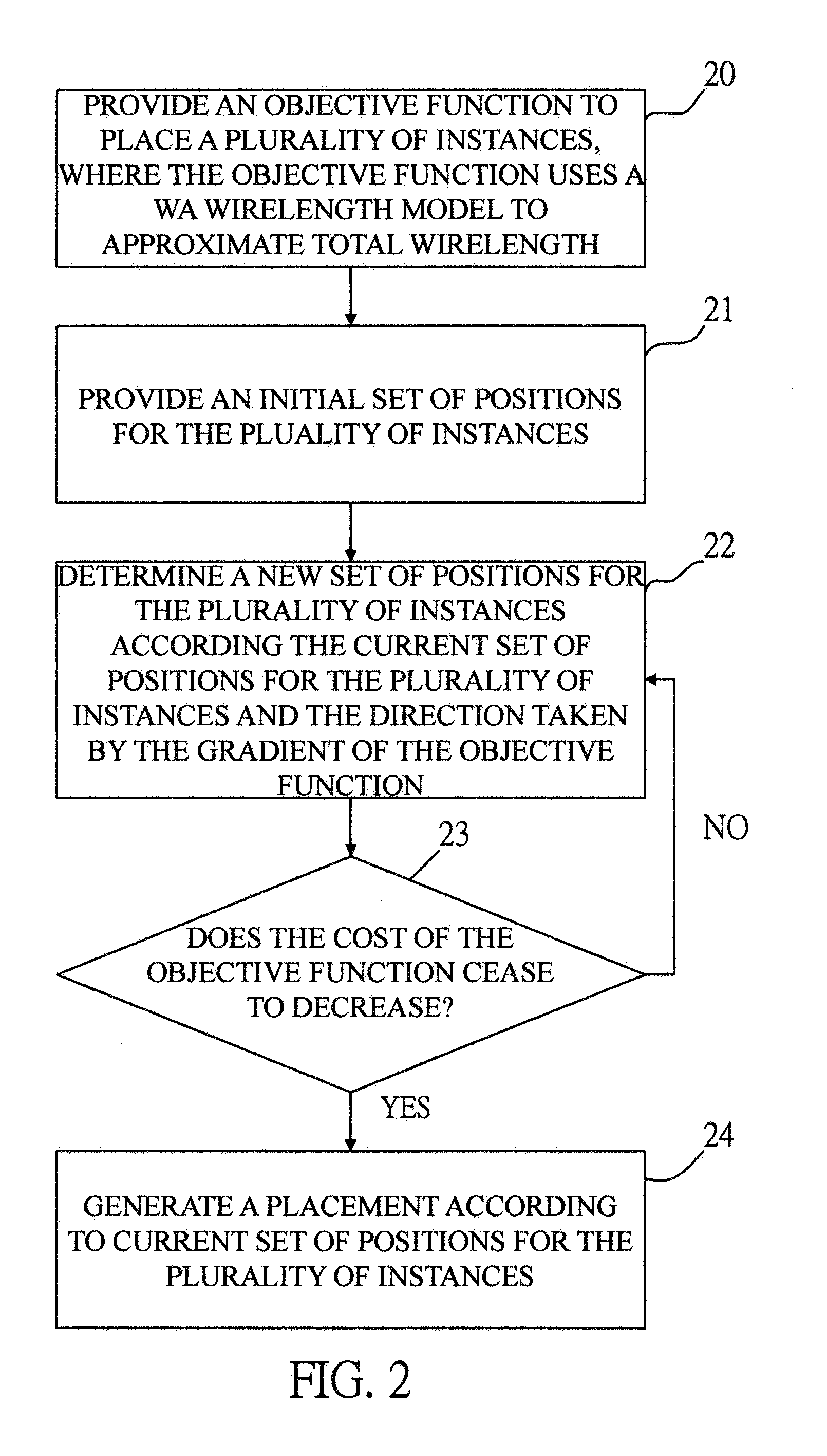
Method of analytical placement with weighted-average wirelength model
ActiveUS20130097574A1Quality improvementInsufficient improvementComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer scienceObject function
A computer-implemented method to generate a placement for a plurality of instances for an integrated circuit (IC) by utilizing a novel weighted-average (WA) wirelength model, which outperforms a well-known log-sum-exp wirelength model, to approximate the total wirelength. The placement is determined by performing an optimization process on an objective function which includes a wirelength function approximated by the WA wirelength model. The method can be extended to generate a placement for a plurality of instances for a three-dimensional (3D) integrated circuit (IC) which considers the sizes of through-silicon vias (TSVs) and the physical positions for TSV insertion. With the physical positions of TSVs determined during placement, 3D routing can easily be accomplished with better routed wirelength, TSV counts, and total silicon area.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
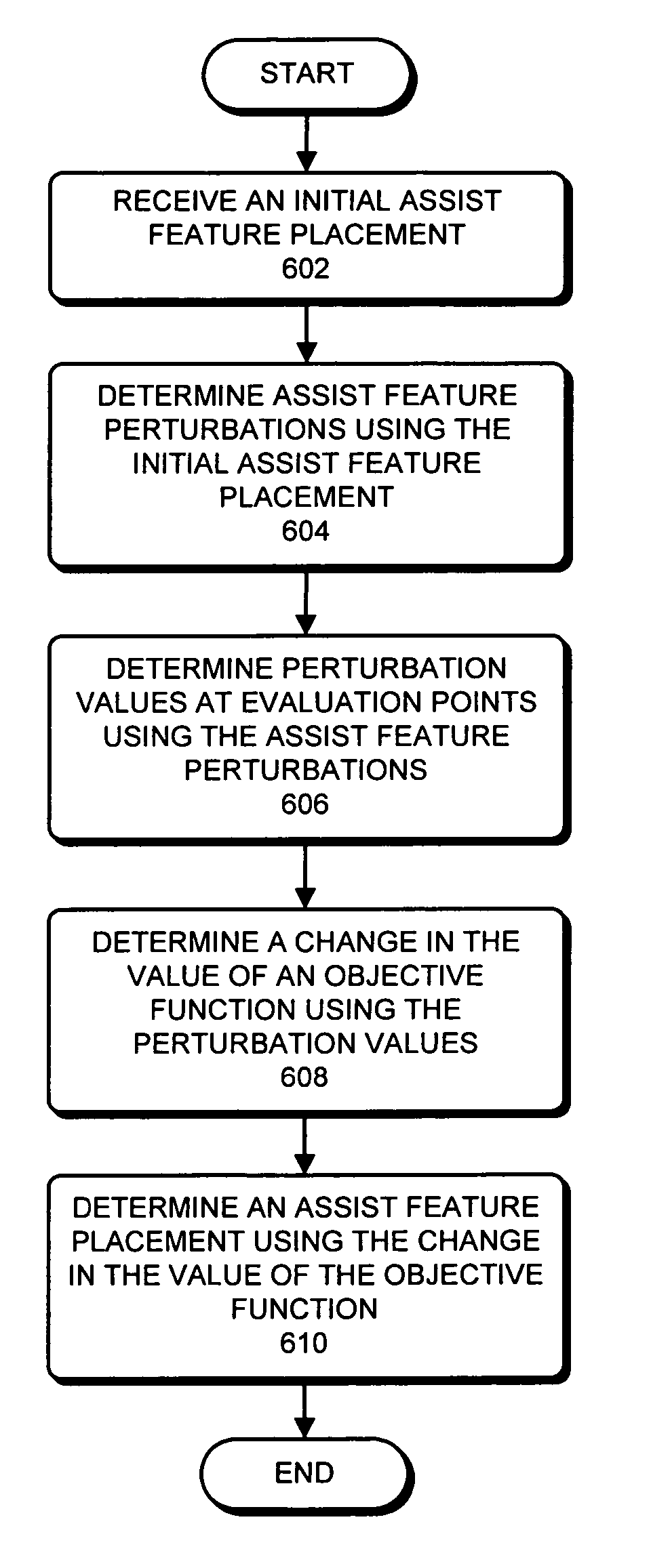
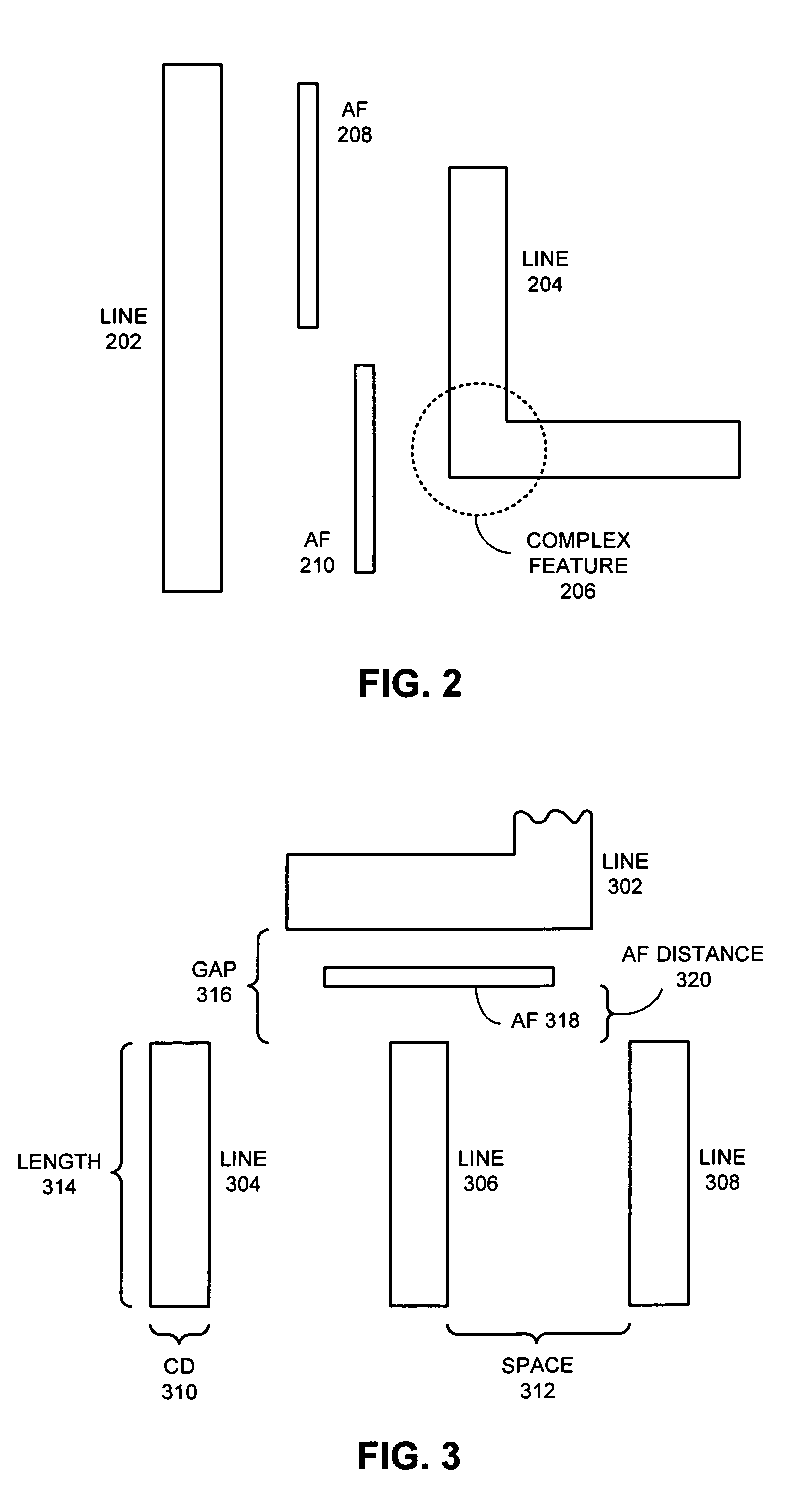
Assist feature placement using a process-sensitivity model
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
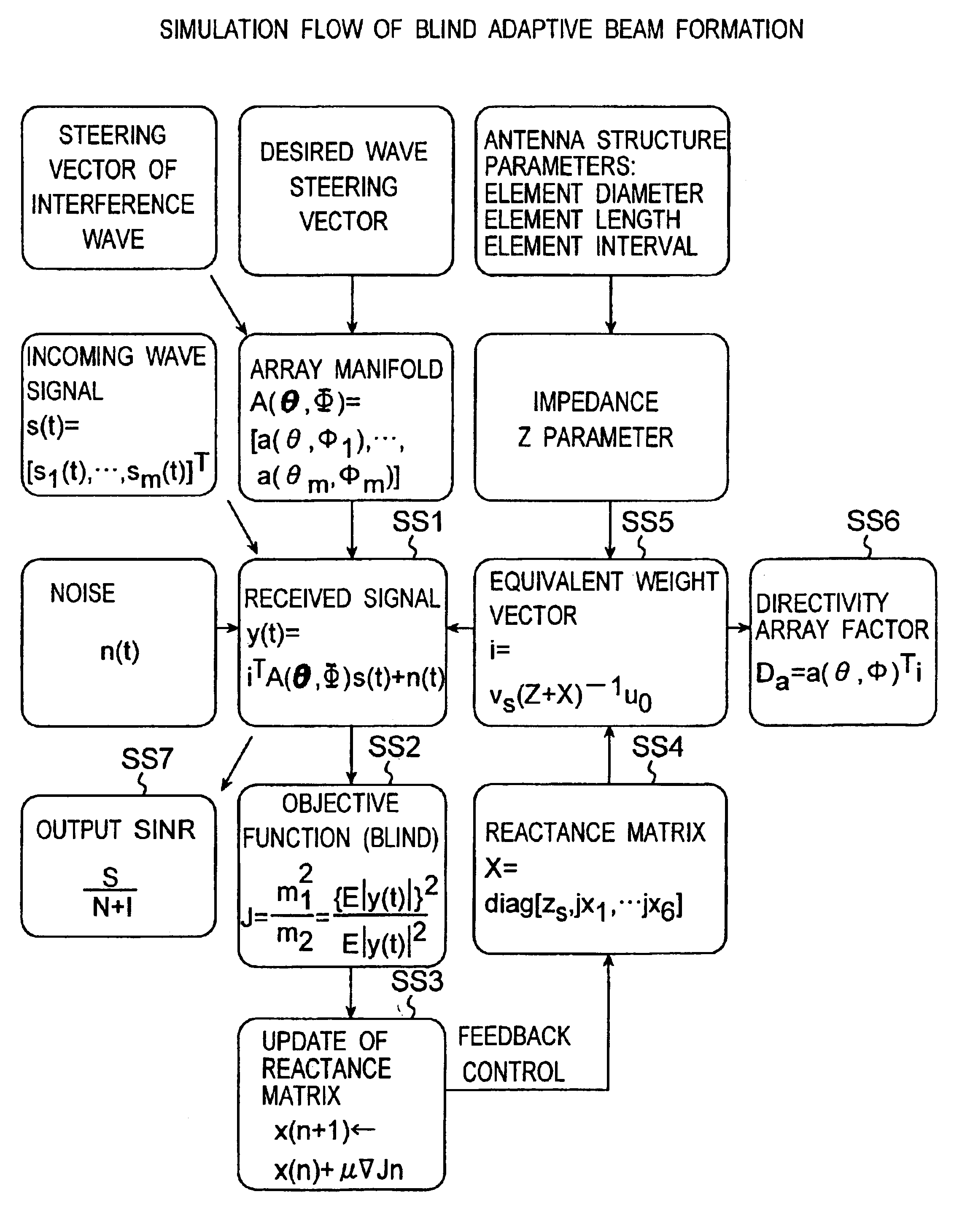
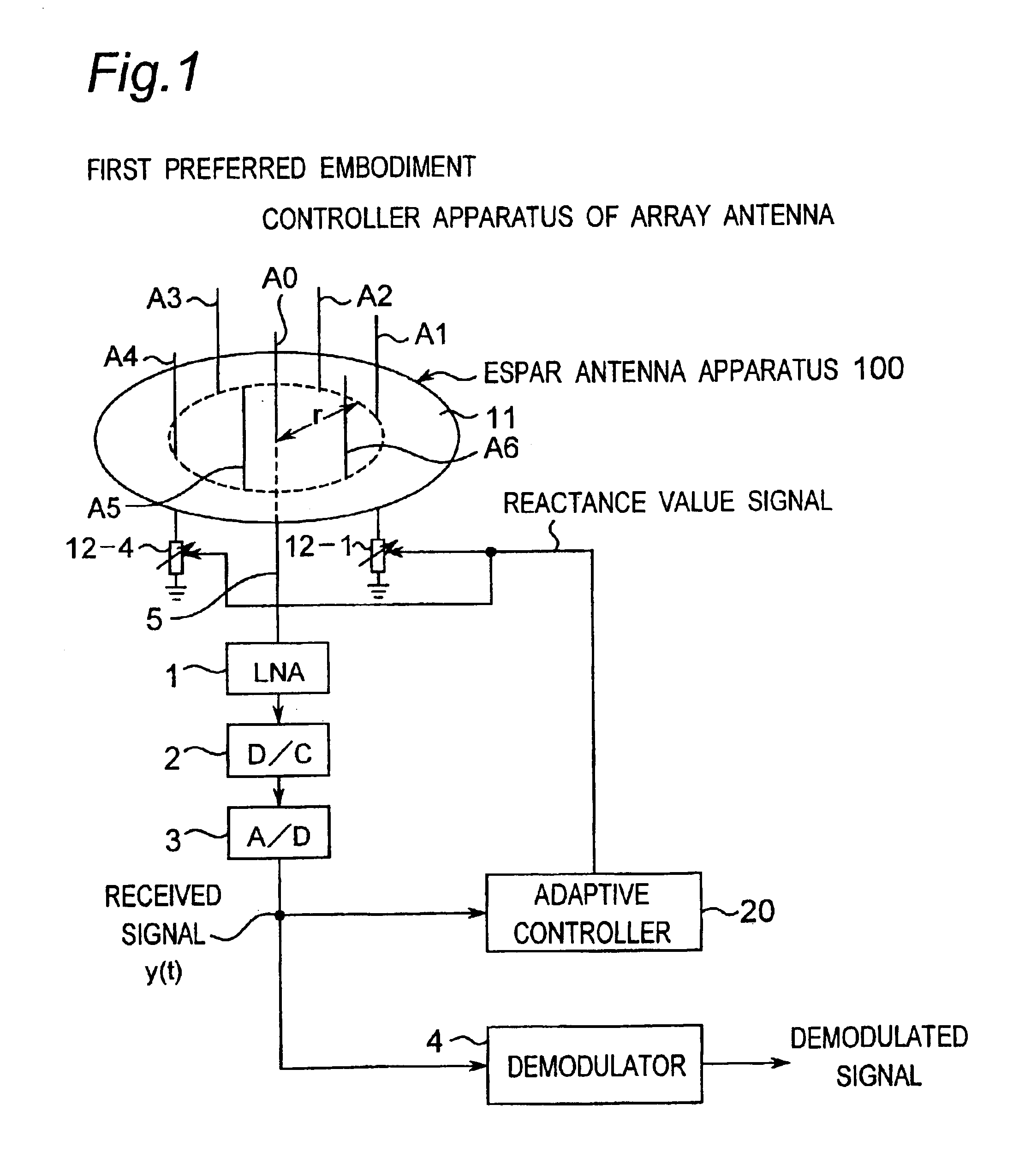
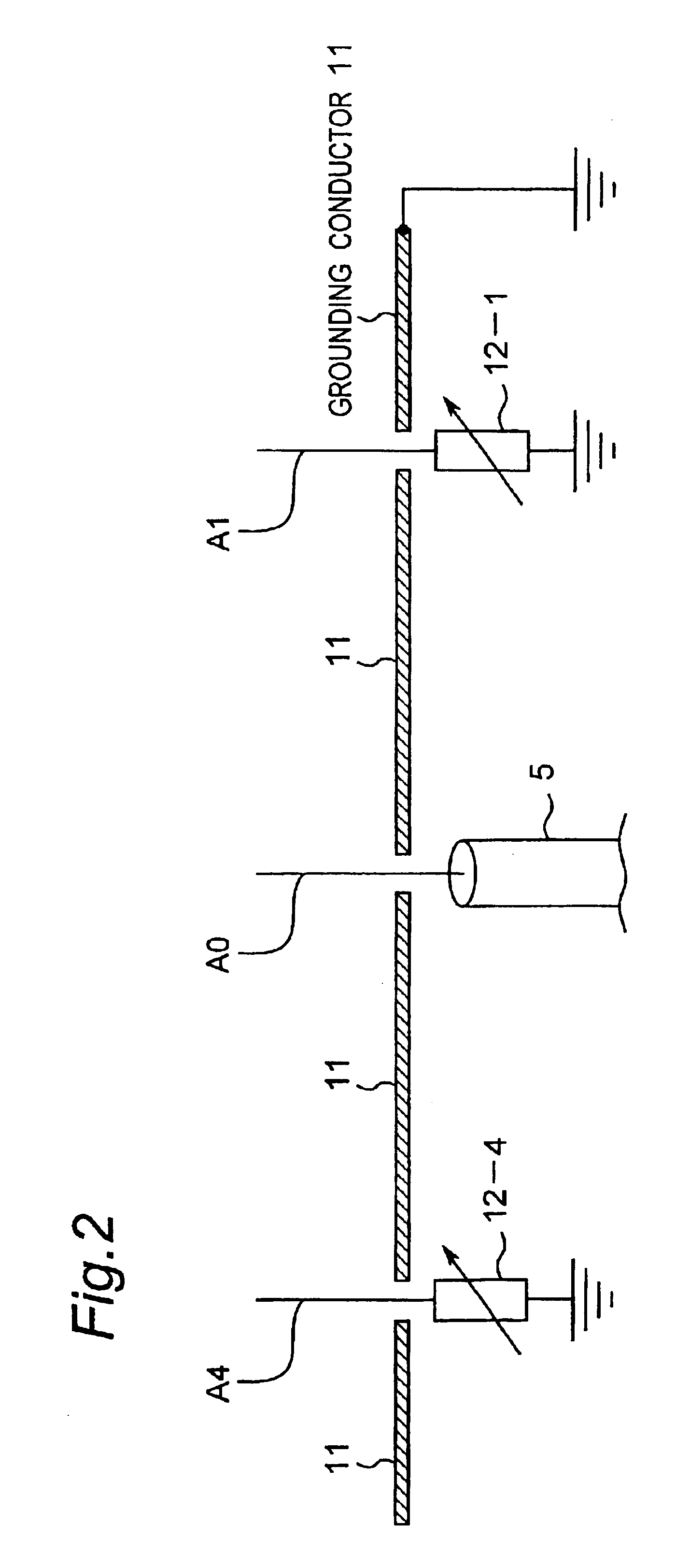
Method for controlling array antenna equipped with a plurality of antenna elements, method for calculating signal to noise ratio of received signal, and method for adaptively controlling radio receiver
InactiveUS7057573B2Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsAmplitude-modulated pulse demodulationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Radio reception
Based on a received signal y(t) received by a radiating element of an array antenna including the single radiating element and a plurality of parasitic elements, an adaptive controller calculates and sets a reactance value of a variable reactance element for directing a main beam of the array antenna in a direction of a desired wave and directing nulls in directions of interference waves so that a value of an objective function expressed by only the received signal y(t) becomes either one of the maximum and the minimum by using an iterative numerical solution of a nonlinear programming method.
Owner:ATR ADVANCED TELECOMM RES INST INT
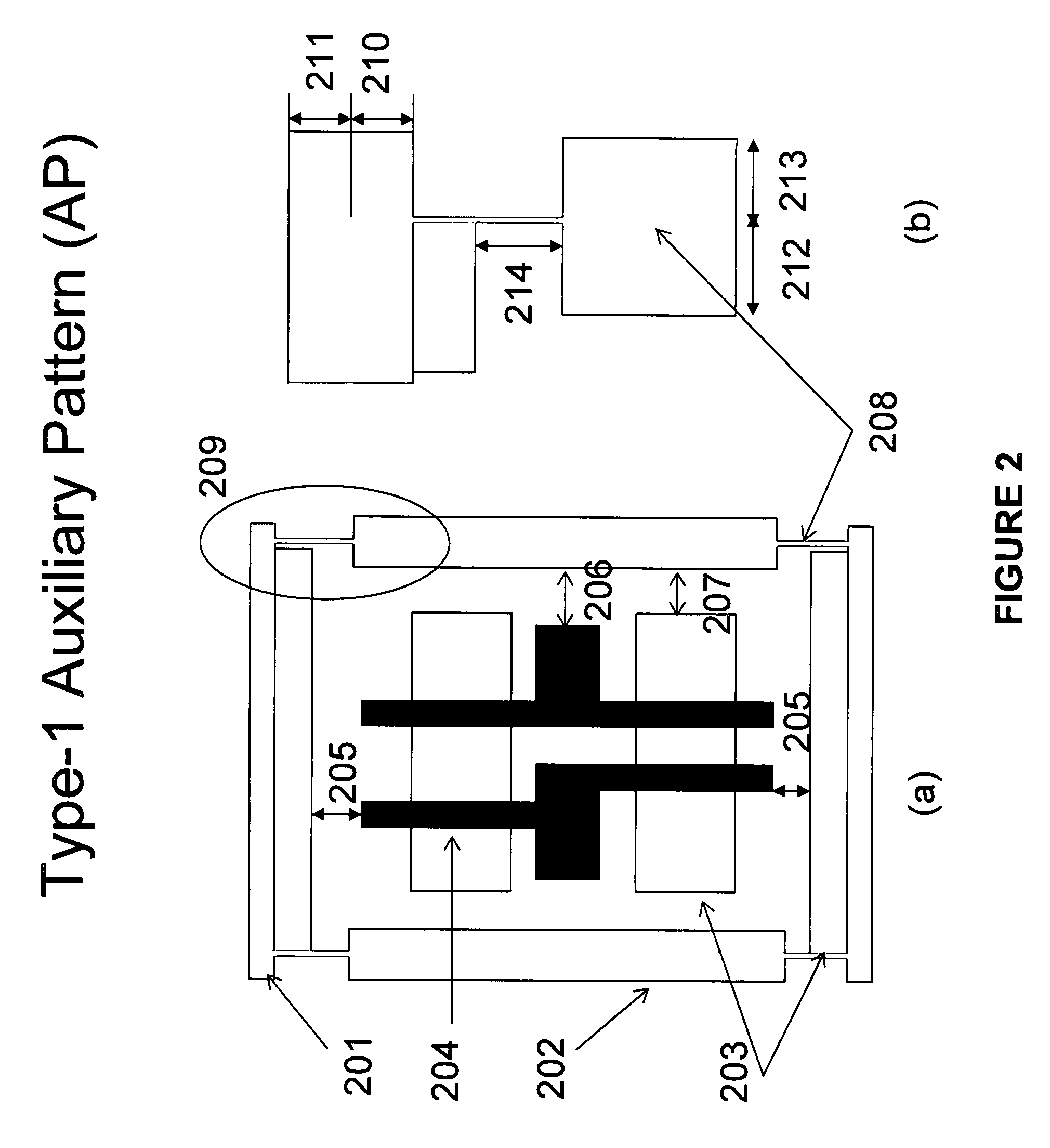
Method, apparatus and system for designing an integrated circuit including generating at least one auxiliary pattern for cell-based optical proximity correction
InactiveUS7873929B2Reduce running timeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCell basedObject function
Method and apparatus for designing an integrated circuit. A new layout is generated for at least one standard cell that incorporates an auxiliary pattern on a gate layer to facilitate cell-based optical proximity correction. An original placement solution is modified for a plurality of standard cells to permit incorporation of cells containing auxiliary patterns while improving an objective function of a resulting placement solution for the plurality of standard cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
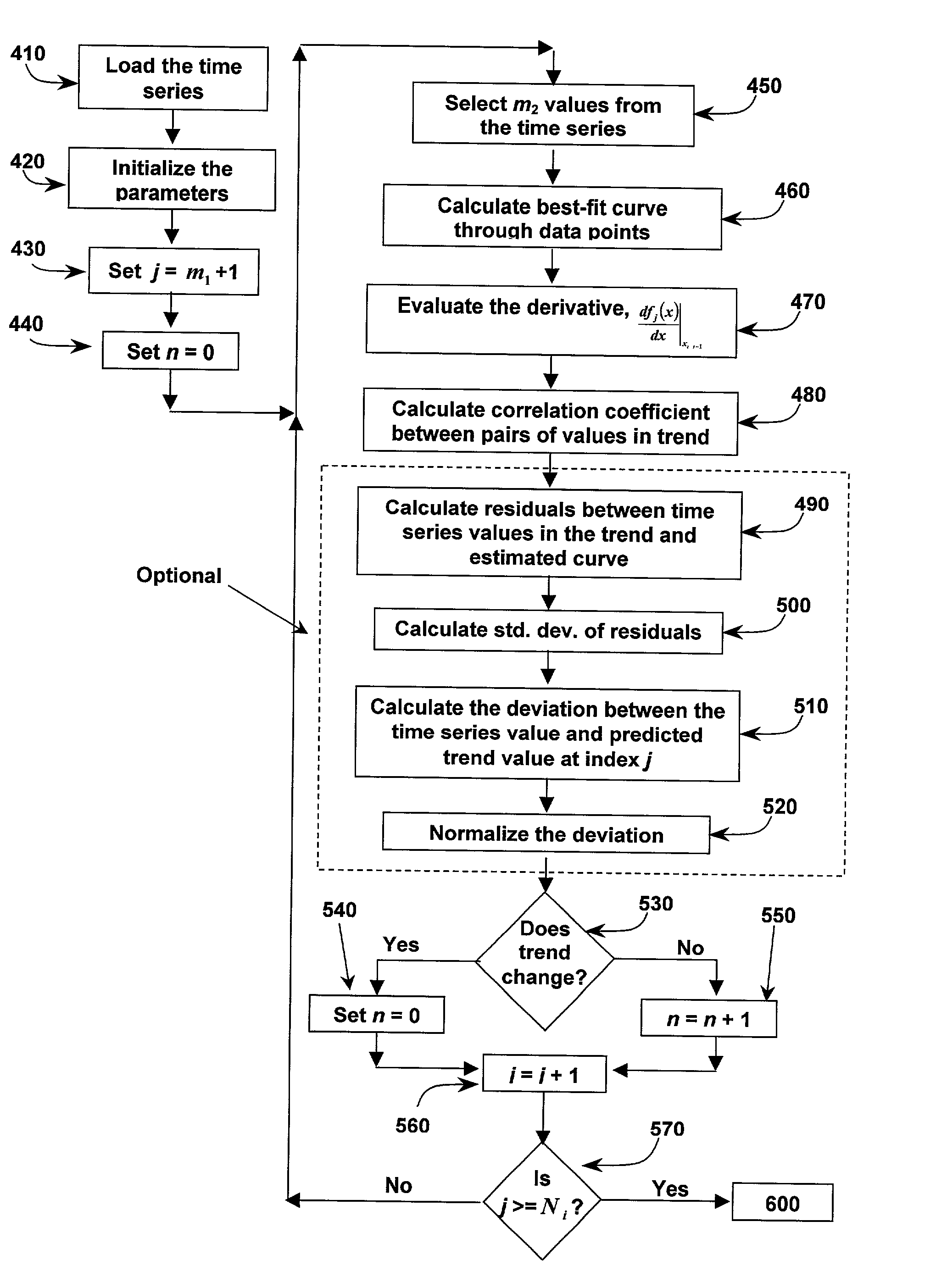
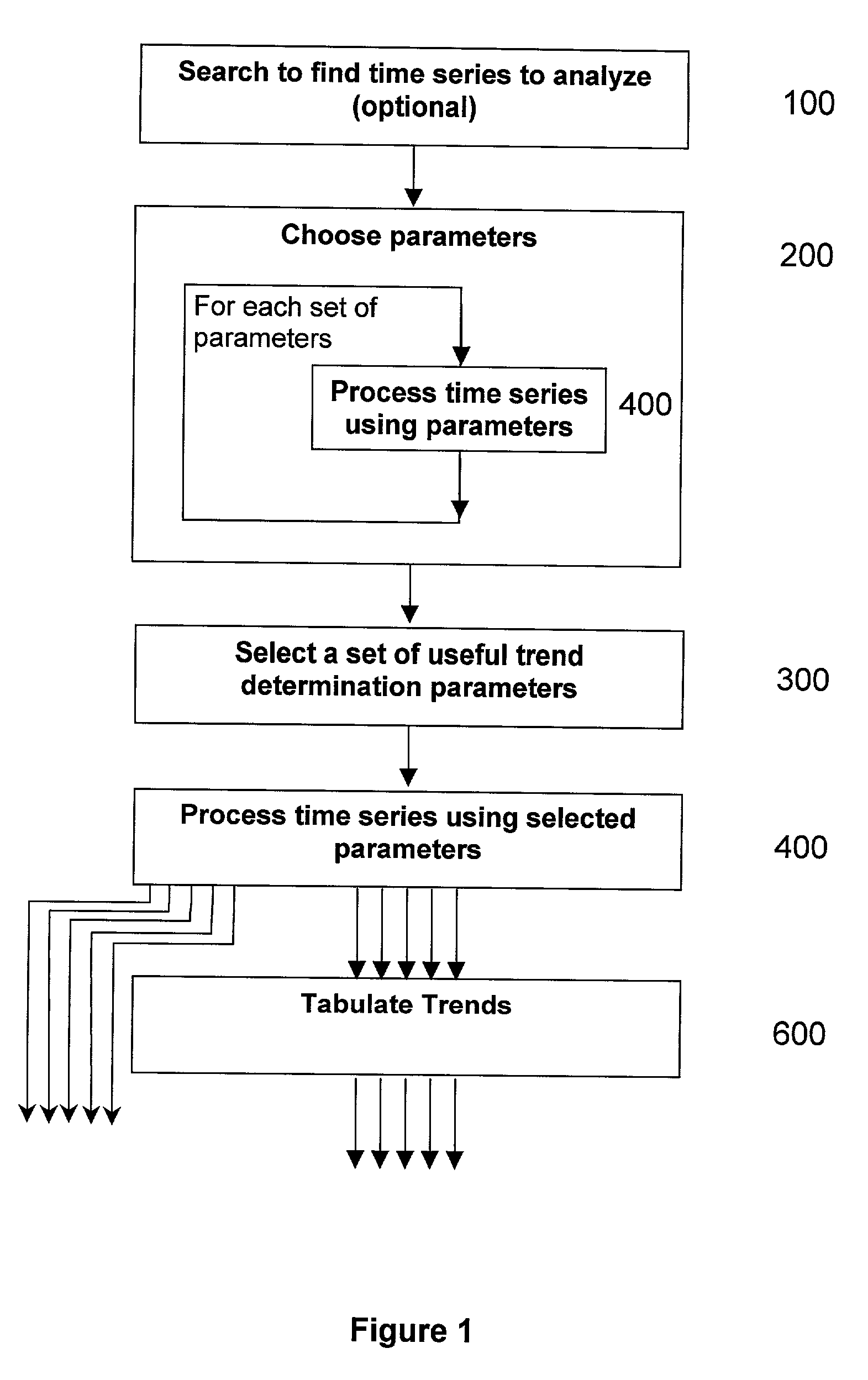
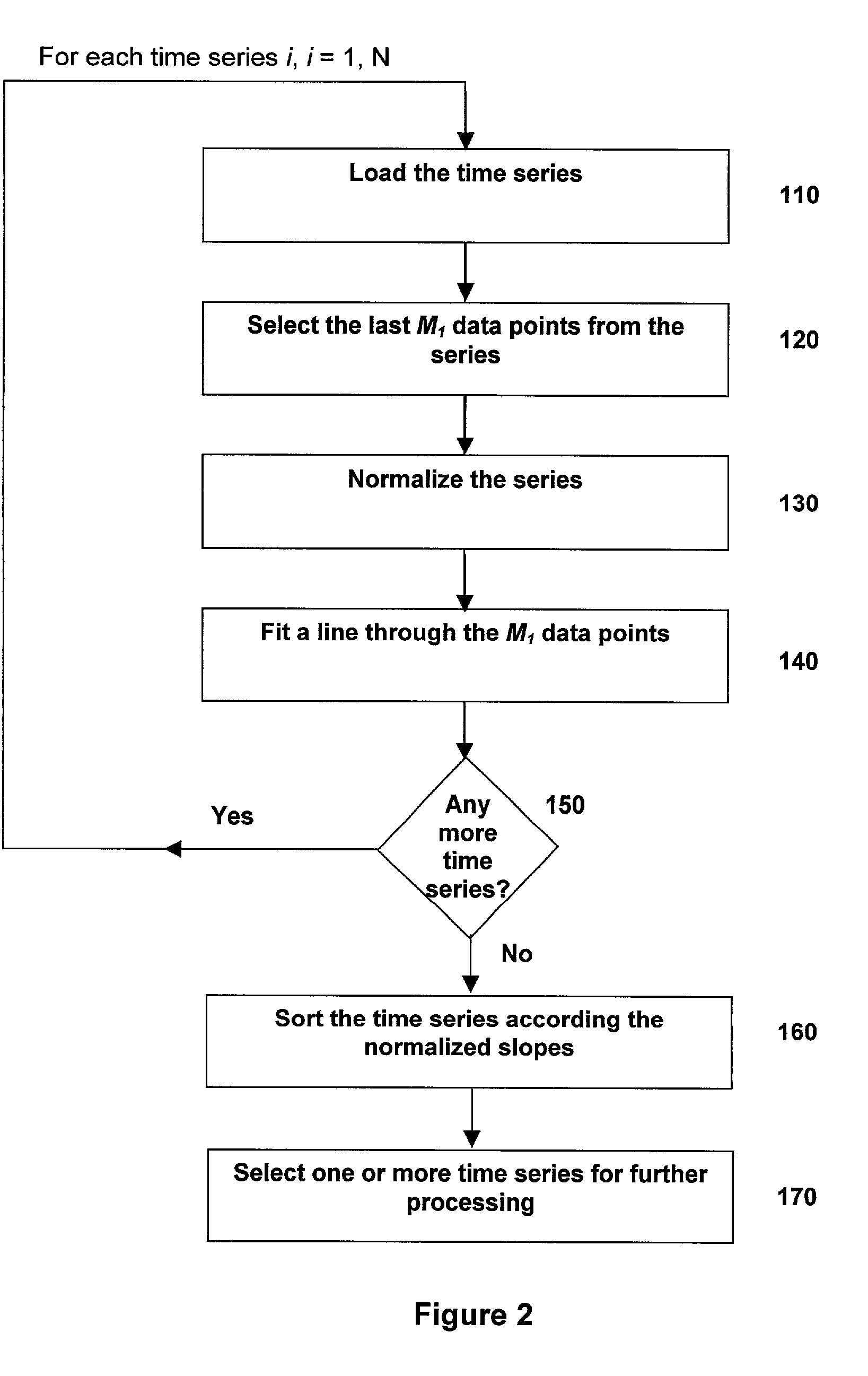
Method and system to identify discrete trends in time series
A signal processing system and method for breaking a time series into piece-wise discrete trends and determining whether new data represents the continuation of a trend. The method identifies and utilizes at least one set of trend determination parameters, which have favorable trend fit characteristics relative to other possible sets of parameters. In a semi-automated embodiment, the error and trend length characteristics are cross-plotted for multiple sets of possible parameters, and one or more of the parameter sets is selected from the graph. In an automated embodiment, an objective function is formulated from the characteristics, and an optimization technique is applied to identify one or more good parameter sets.
Owner:BOERNER SEAN T
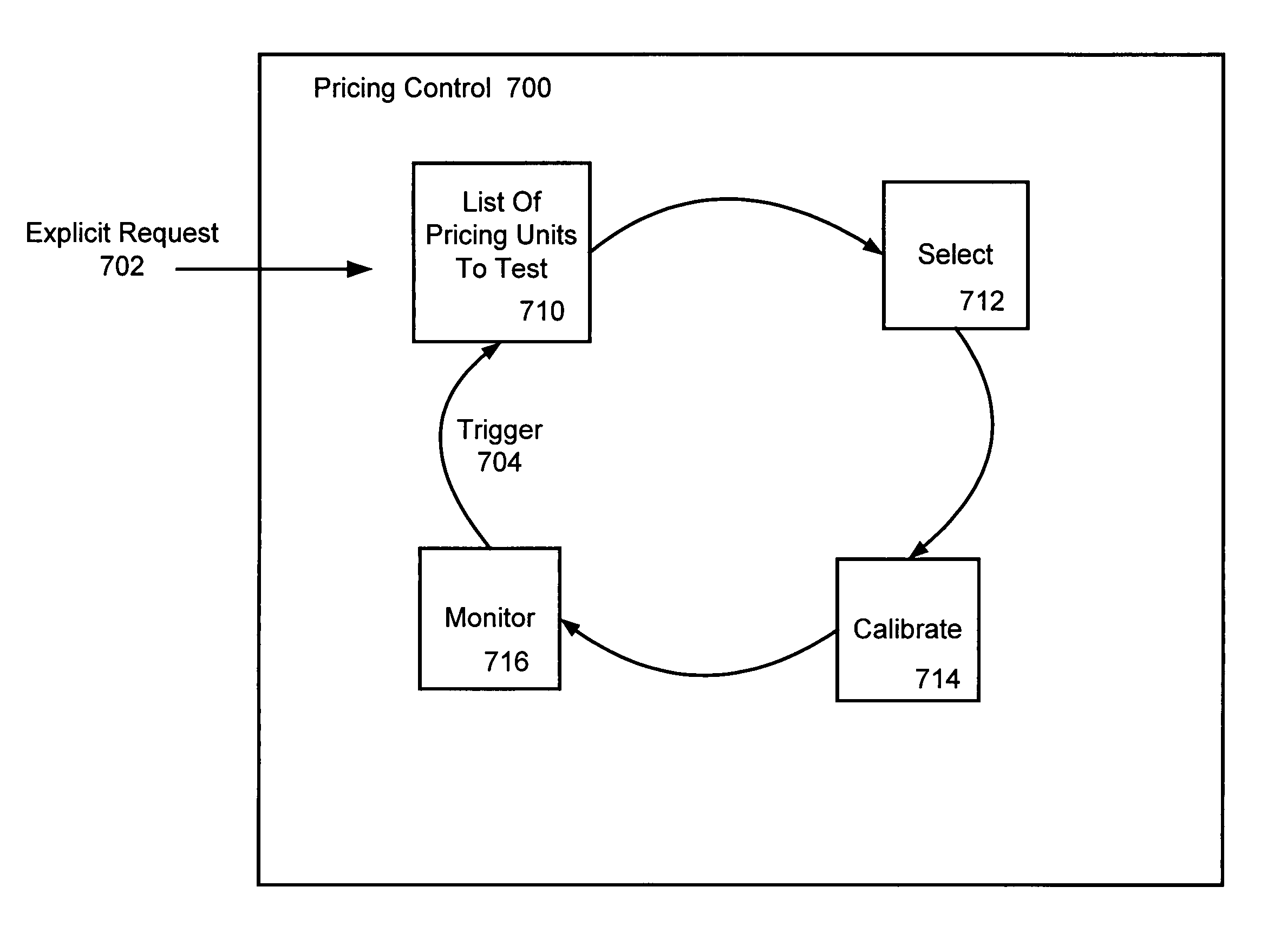
Method and apparatus for automatic pricing in electronic commerce
InactiveUS7970713B1Increased cost of testingReduce testing costsMarket predictionsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsE-commerceMajorization minimization
Owner:OIP TECH
Strategic planning and optimization system
InactiveUS6988076B2Improve usabilityLow costReservationsForecastingEnterprise modellingObject function
A software method for strategic planning and optimization allows a user to model an enterprise to visualize an effect of an auxiliary goal, such as price image, on a primary goal of the enterprise. A primary goal of the enterprise is selected, and is represented by a primary objective function which, in turn, depends upon a set of operational variables. The auxiliary goal is represented by a constraint function that depends upon a subset of the operational variables. An effective objective function is constructed by combining the primary objective function and the constraint function, and the effective objective function is optimized to yield a set of operational decisions that optimize the primary objective function while concurrently satisfying the constraint function. The set of operational decisions are provided to a user, the operational decisions enabling the enterprise to achieve the primary goal and satisfy the auxiliary goal.
Owner:SAP AG
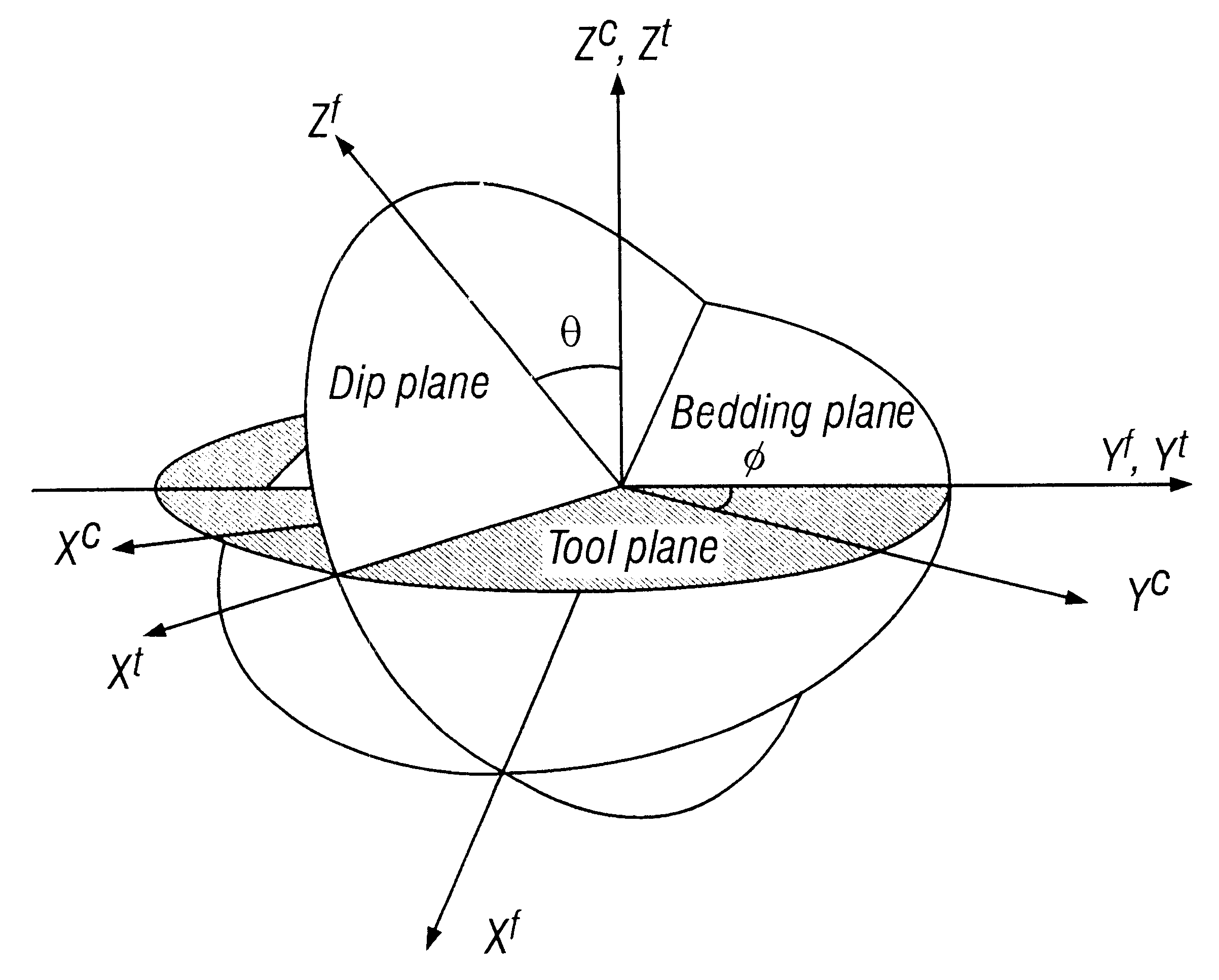
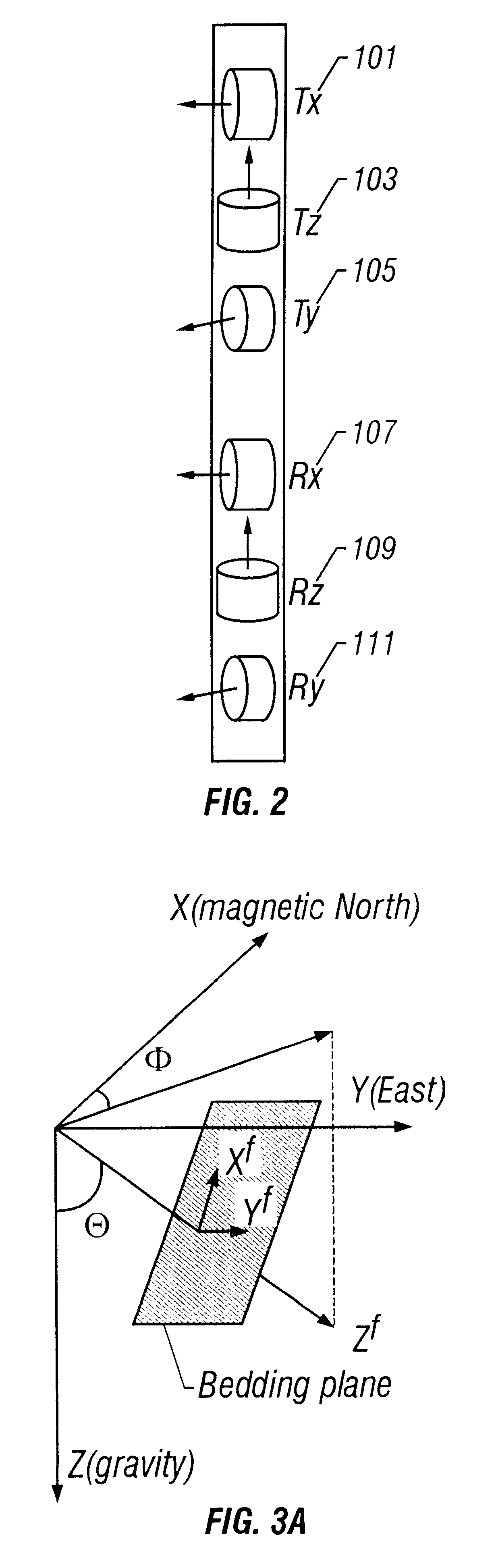
Simultaneous determination of formation angles and anisotropic resistivity using multi-component induction logging data
InactiveUS6643589B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingHorizontal and verticalObject function
Measurements made by a multicomponent logging tool in a borehole are inverted to obtain horizontal and vertical resistivities and formation dip and azimuth angles of a formation traversed by the borehole. The inversion is performed using a generalized Marquardt-Levenberg method. In this generalized Marquardt-Levenberg method, a data objective function is defined that is related to a difference between the model output and the measured data. The iterative procedure involves reducing a global objective function that is the sum of the data objective function and a model objective function related to changes in the model in successive iterations. In an alternate embodiment of the invention, the formation azimuth angle is excluded from the iterative process by using derived relations between the multicomponent measurements.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
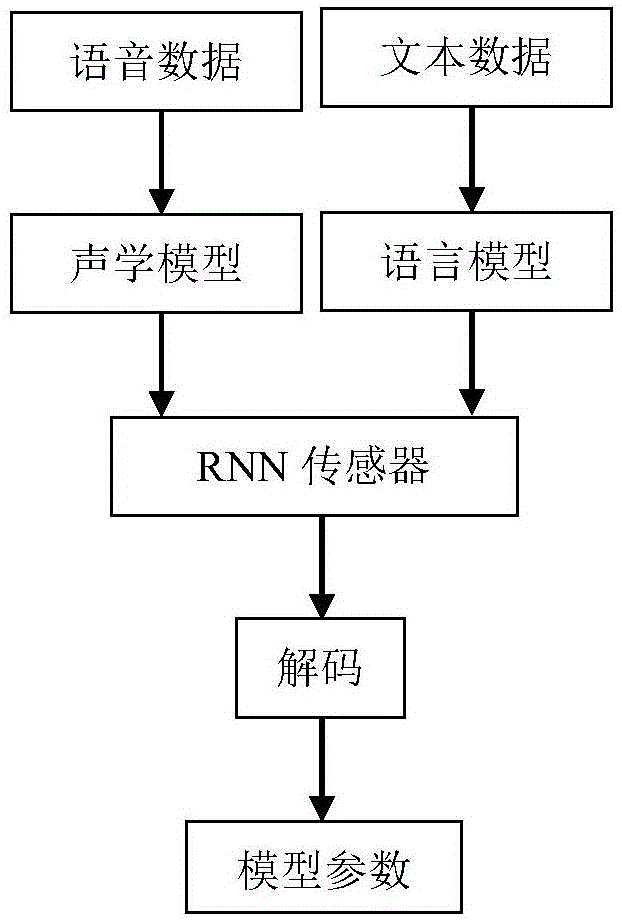
Voice identification method using long-short term memory model recurrent neural network
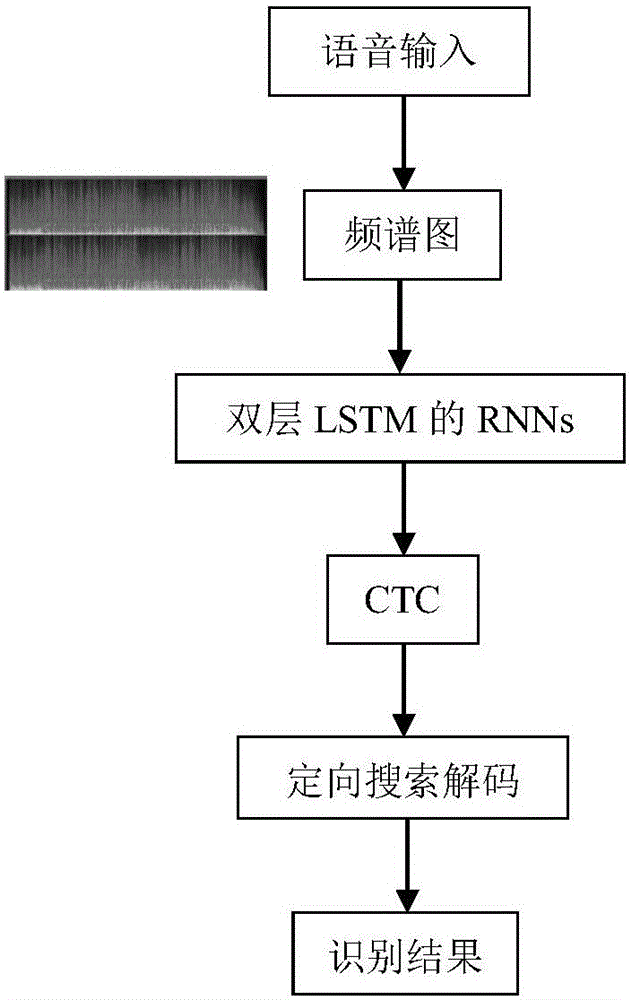
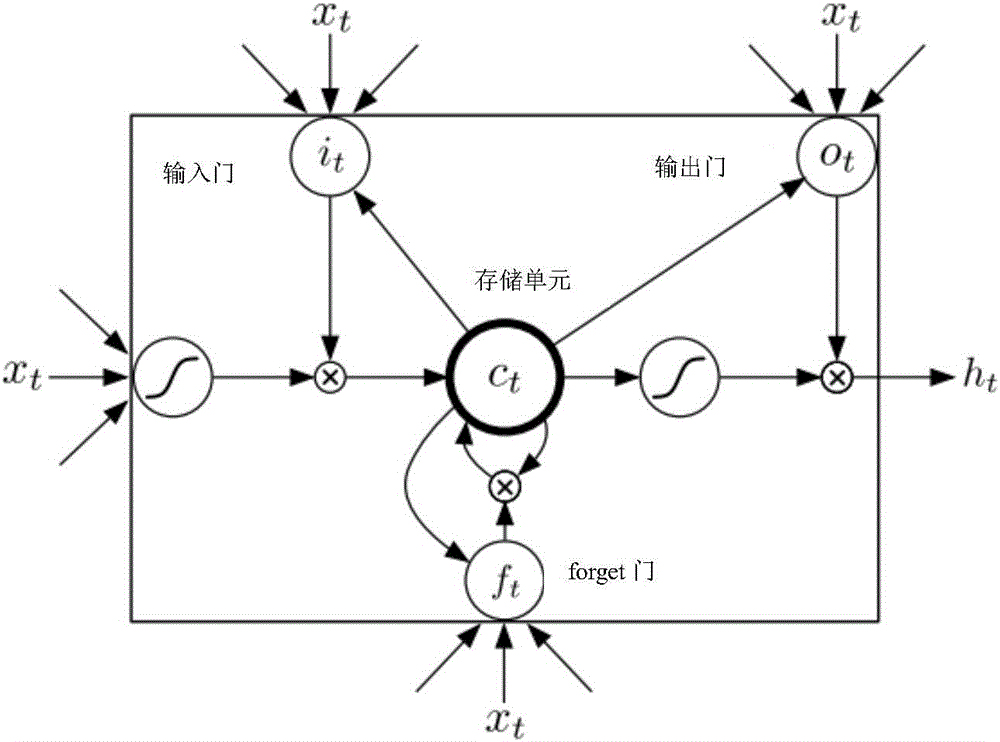
The invention discloses a voice identification method using a long-short term memory model recurrent neural network. The voice identification method comprises training and identification. The training process comprises steps of introducing voice data and text data to generate a commonly-trained acoustic and language mode, and using an RNN sensor to perform decoding to form a model parameter. The identification process comprises steps of converting voice input to a frequency spectrum graph through Fourier conversion, using the recursion neural network of the long-short term memory model to perform orientational searching decoding and finally generating an identification result. The voice identification method adopts the recursion neural network (RNNs) and adopts connection time classification (CTC) to train RNNs through an end-to-end training method. These LSTM units combining with the long-short term memory have good effects and combines with multi-level expression to prove effective in a deep network; only one neural network model (end-to-end model) exits from a voice characteristic (an input end) to a character string (an output end) and the neural network can be directly trained by a target function which is a some kind of a proxy of WER, which avoids to cost useless work to optimize an individual target function.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
Document layout method
InactiveUS20090307583A1Natural language data processingOther printing apparatusGraphicsGraphical user interface
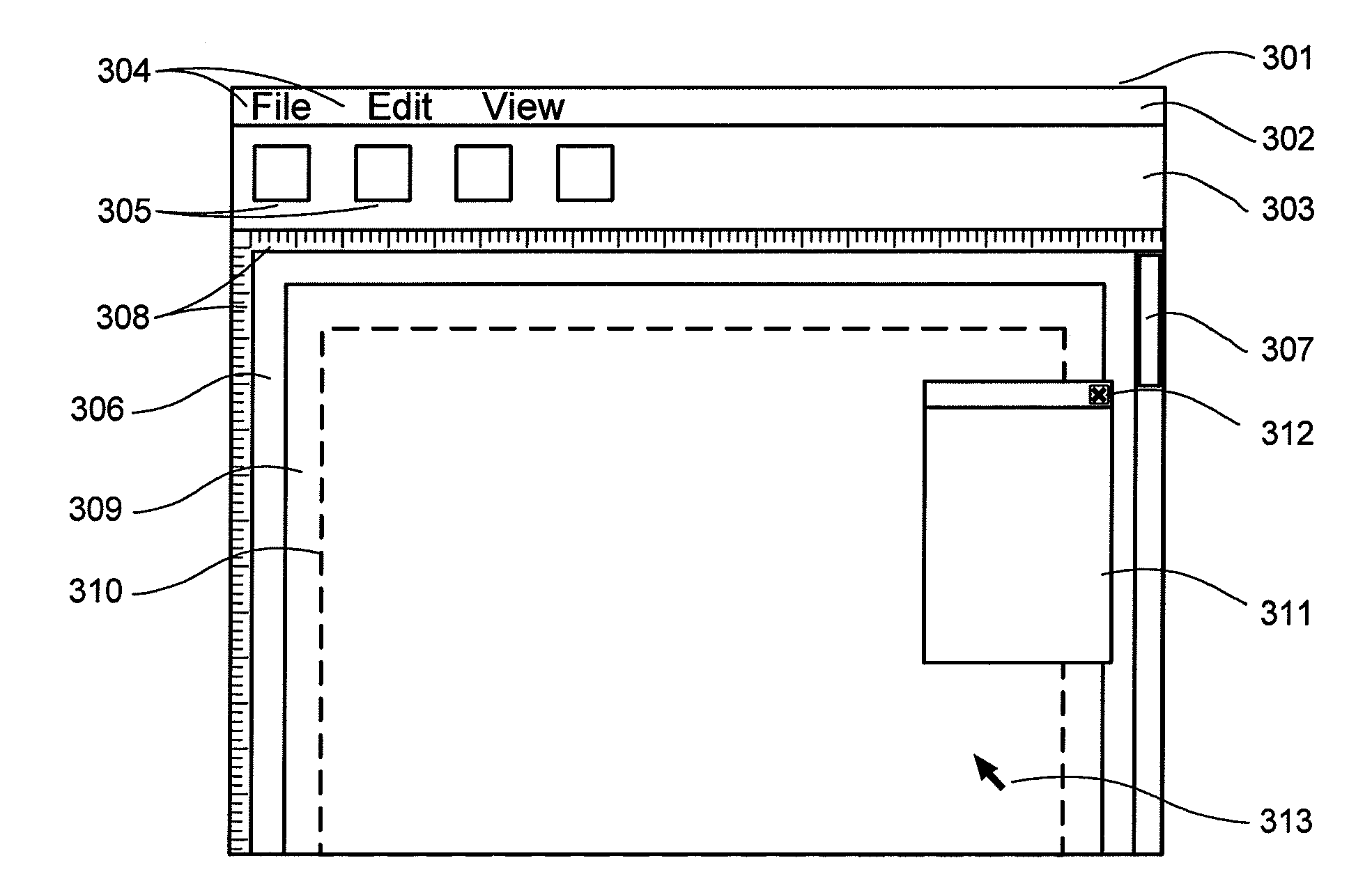
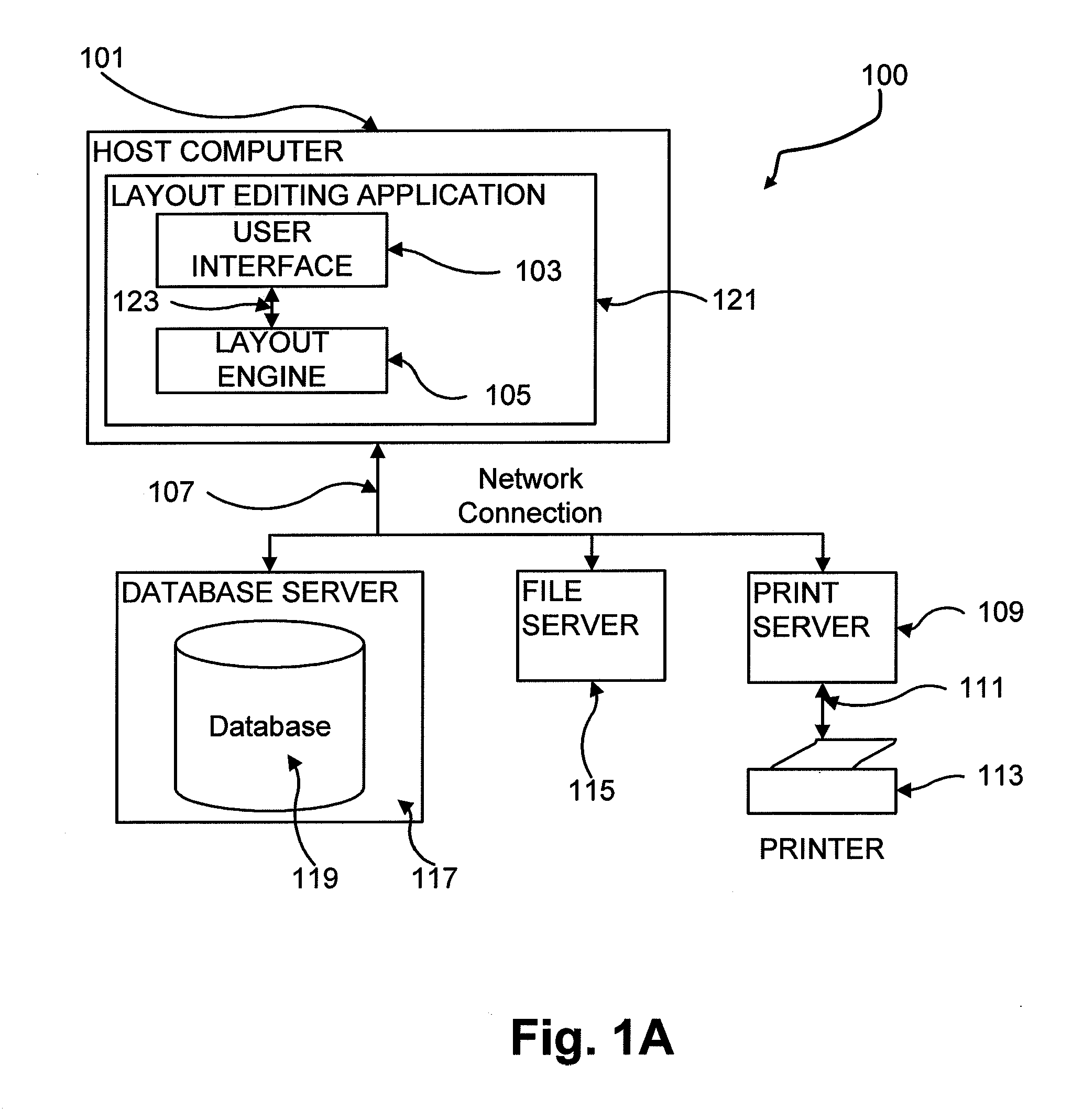
Methods and apparatus for variable document printing are disclosed in which a graphical user interface is configured to allow user manipulation of layout rules associated with content containers within a template for variable document generation. One method involves laying out (626) container objects (407, 408) forming part of a template (624) intended for a variable data document. The objects each have a rectangular boundary in two-dimensional space, and the method comprises detecting an operation (628, 2800) to modify a position of at least one edge of at least one of the objects. Then, rules of association between edges of the objects having a corresponding orientation to the one edge are identified. A position of at least the one edge is then modified whilst observing the rules of association between all the correspondingly oriented edges. Finally an objective function derived from the rules of association between the correspondingly oriented edges is minimized (3009) to thereby balance a layout of the objects in at least the dimension of modification. Other methods involve maintaining the objective function for a group of edges, the addition and removal of constraints in respect of correspondingly oriented edges, the removal, addition and then removal of constraints in modifying the width of a container, the calculation of text container sizes, and the creation of tables, particularly for text containers.
Owner:CANON KK
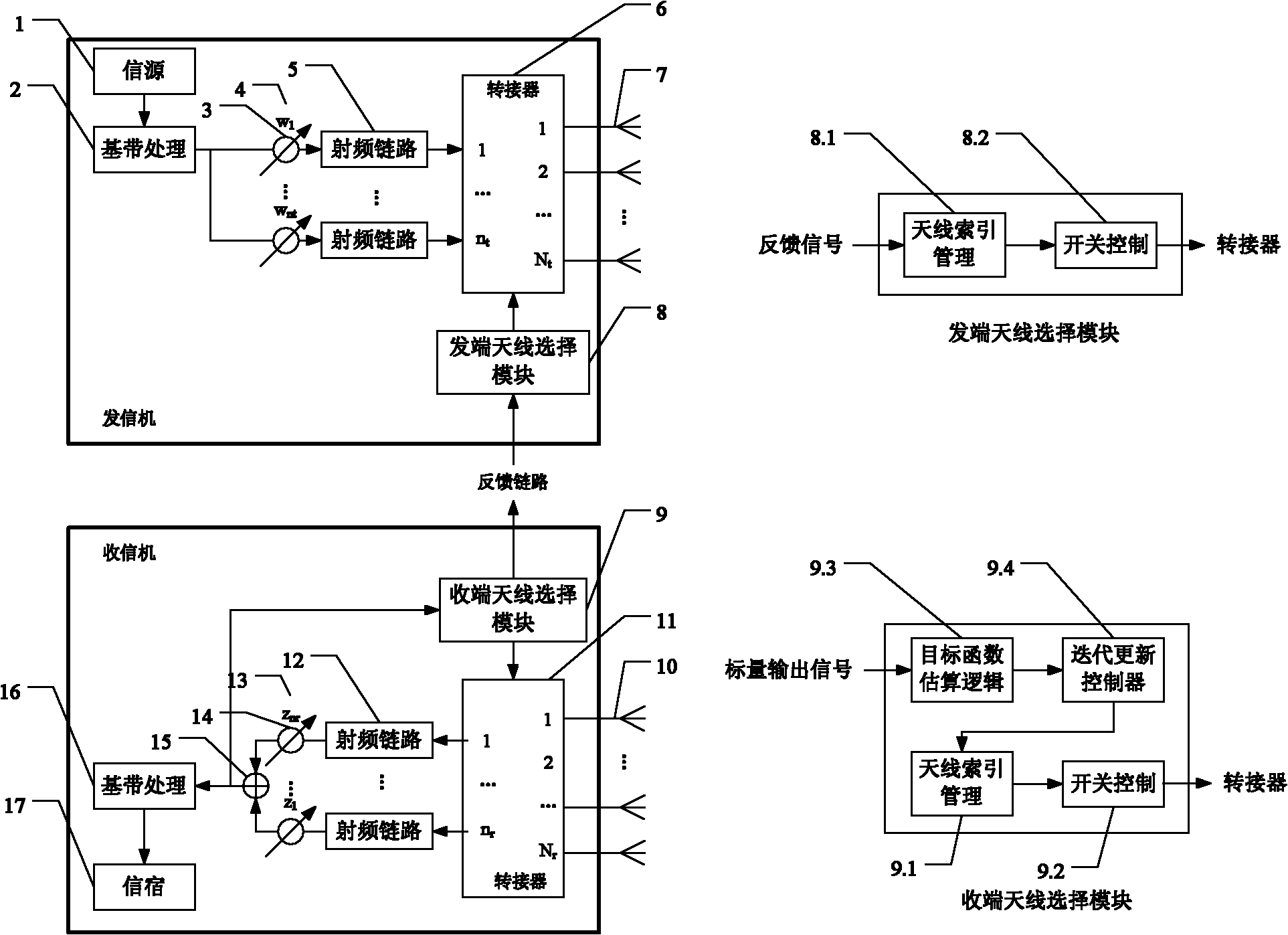
MIMO system and application method thereof for adaptive antenna selection
InactiveCN101867402AReduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionData transmissionSelf adaptive
The invention discloses an MIMO system and an application method thereof for adaptive antenna selection. The MIMO system comprises a transmitter, a receiver and a wireless channel; the process of the antenna selection which is realized in the MIMO system adopts an iterative feedback structure; a subset is selected quickly from a large amount of antenna sets by using the characteristic of 60 GHz channel without accurate channel estimation, so that a subchannel corresponding to an antenna subarray is optimal in the sense of a defined target function; and high speed data transmission is performed by using the selected optimal antenna subarray. The invention provides the rapid and efficient application method for the MIMO system along with low cost, and solves the technical problems of high complexity and low efficiency of the traditional antenna selection method in the large-scale the MIMO system. An experiment proves that: the adopted method can obtain good performance only through several iterations and low computational complexity; and the system can better support the application of the large-scale the antenna array.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
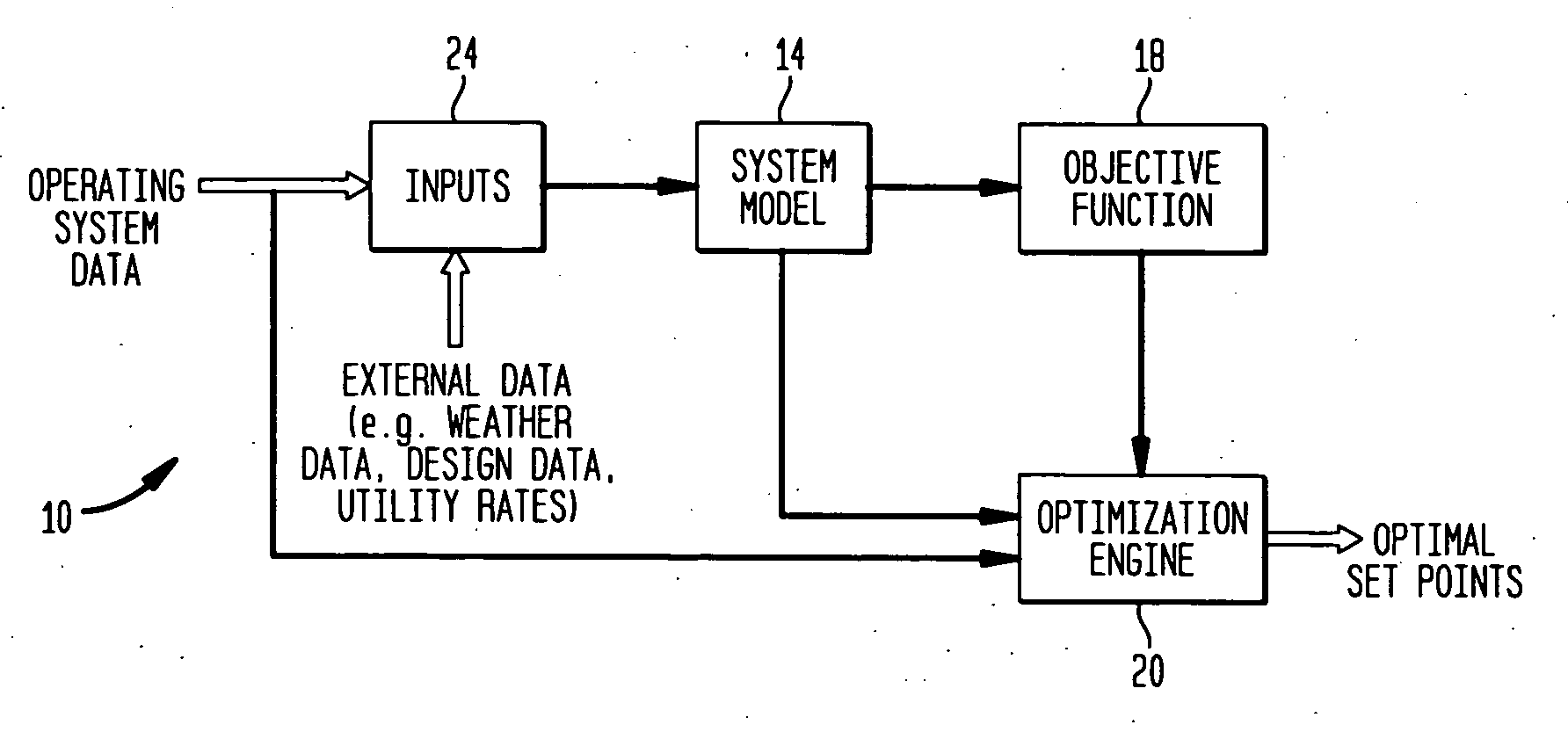
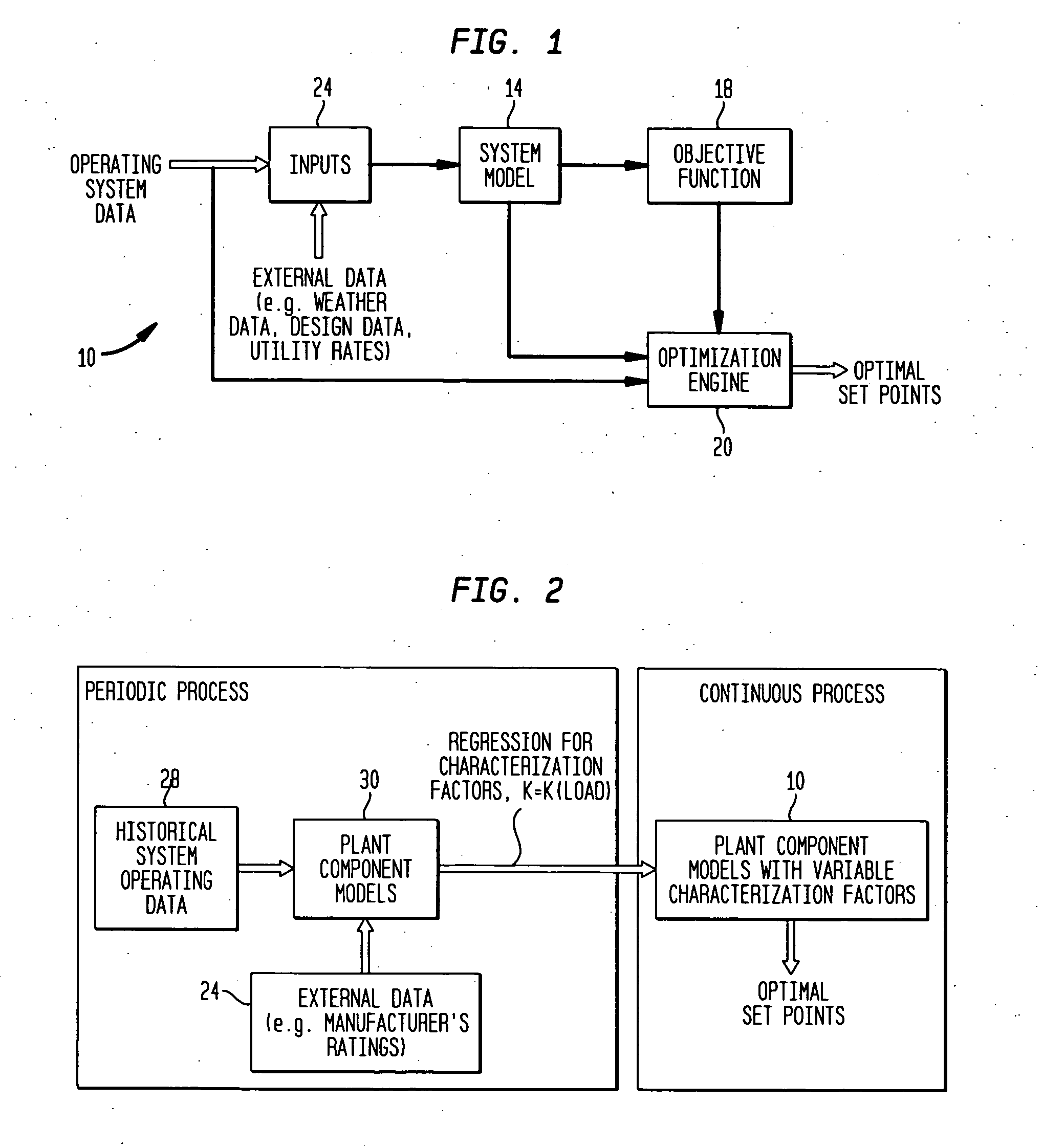
System and method for optimizing global set points in a building environmental management system
InactiveUS20050192680A1Point to optimizationReduce operating costsSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlFuzzy ruleComponent modeling
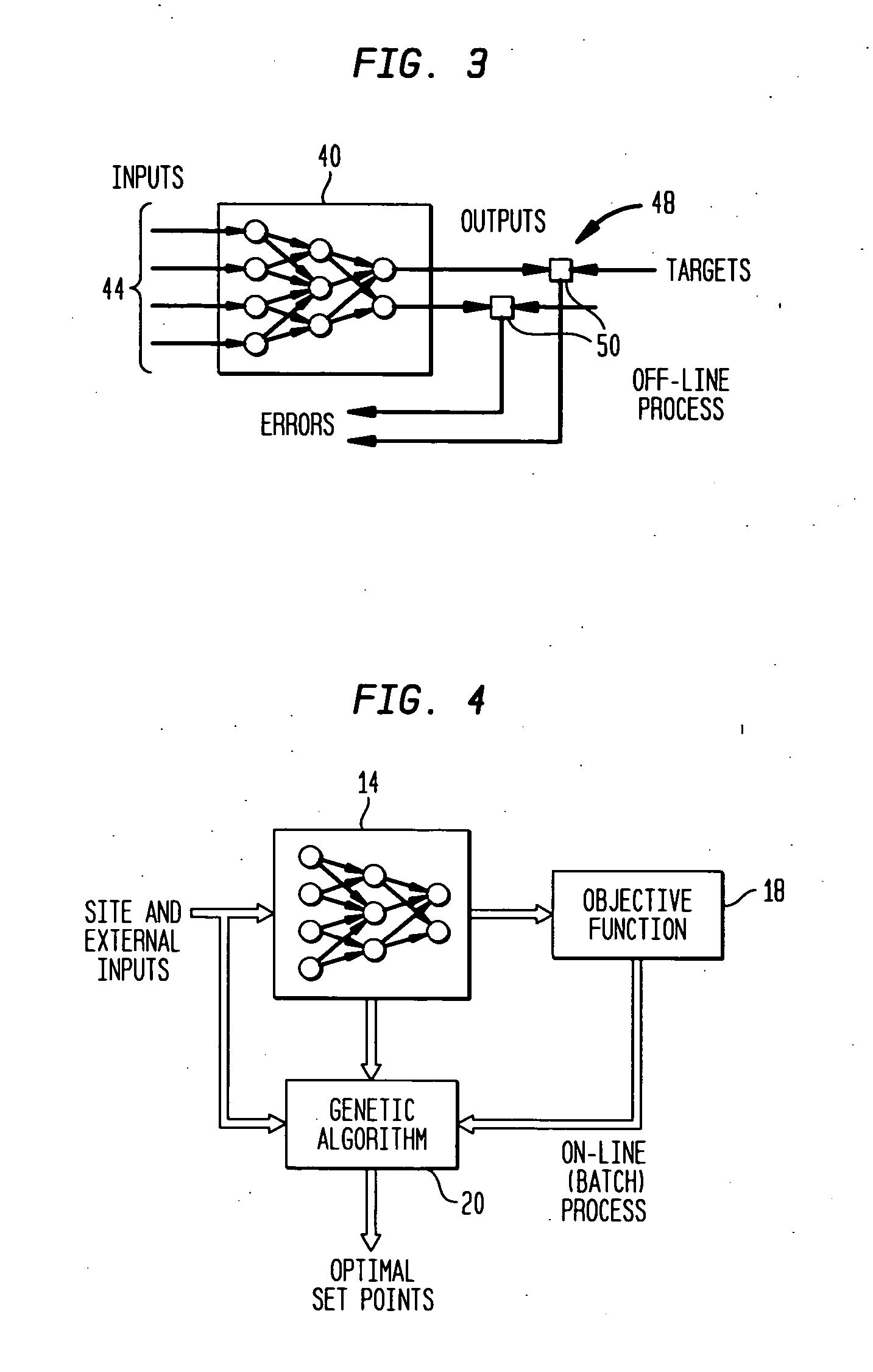
A system generates optimal global set points for an environmental management system. The system comprises a system model for modeling components of a thermal plant, an objective function for modeling a parameter of the thermal plant, and an optimization engine for optimizing the parameter modeled by the objective function. The system model is coupled to an input data collector for receiving building data and weather data corresponding to a particular site. The system model includes models for thermal plant system components that may be implemented using classical models or artificial intelligence models. Classical models are those models that are implemented using linear programming, unconstrained non-linear programming, or constrained non-linear programming methodologies. The artificial intelligence models are those models that may be implemented using a fuzzy expert control system with crisp and fuzzy rules, genetic algorithms for optimization, or neural networks.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
Health cost calculator/flexible spending account calculator
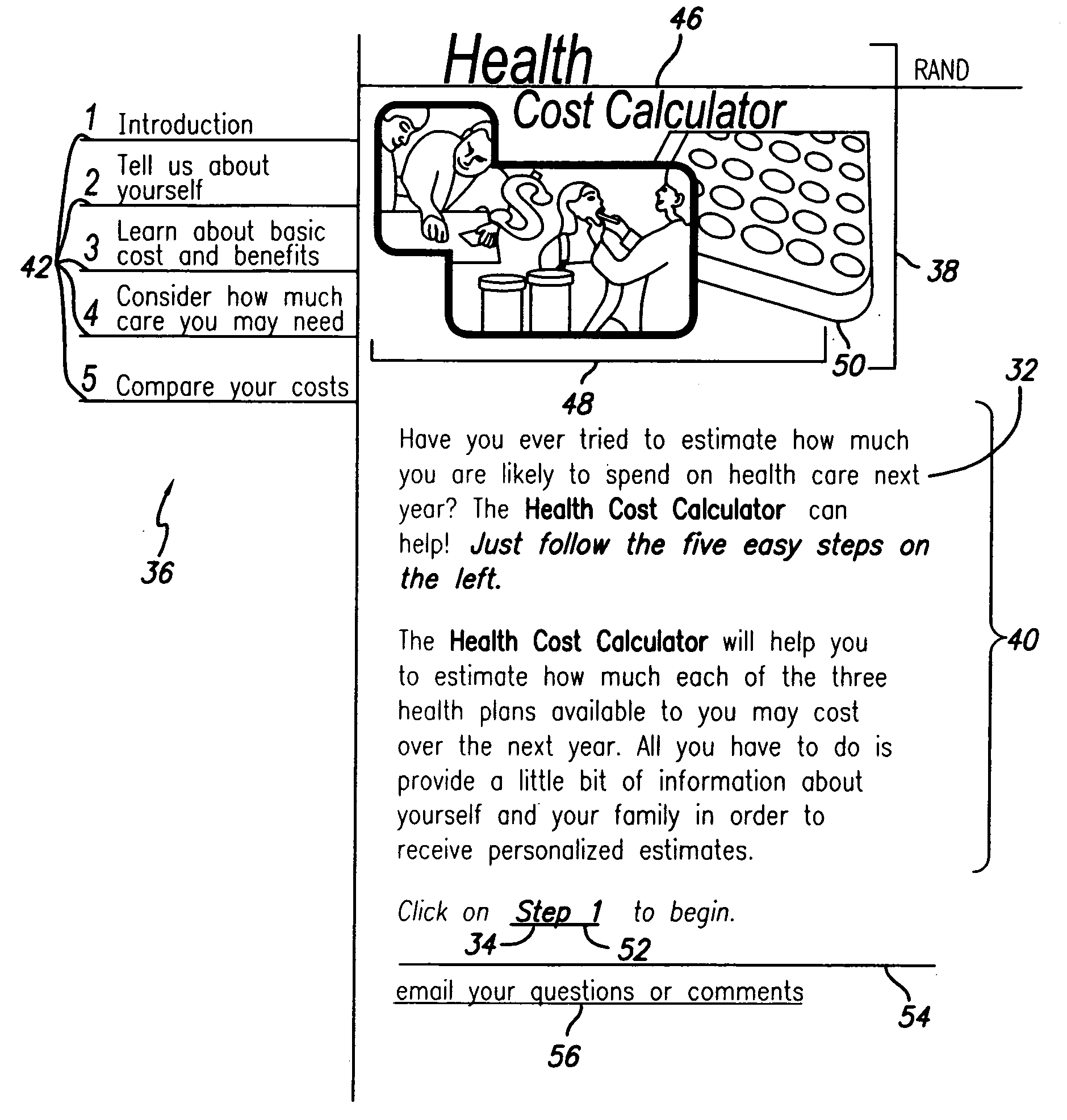
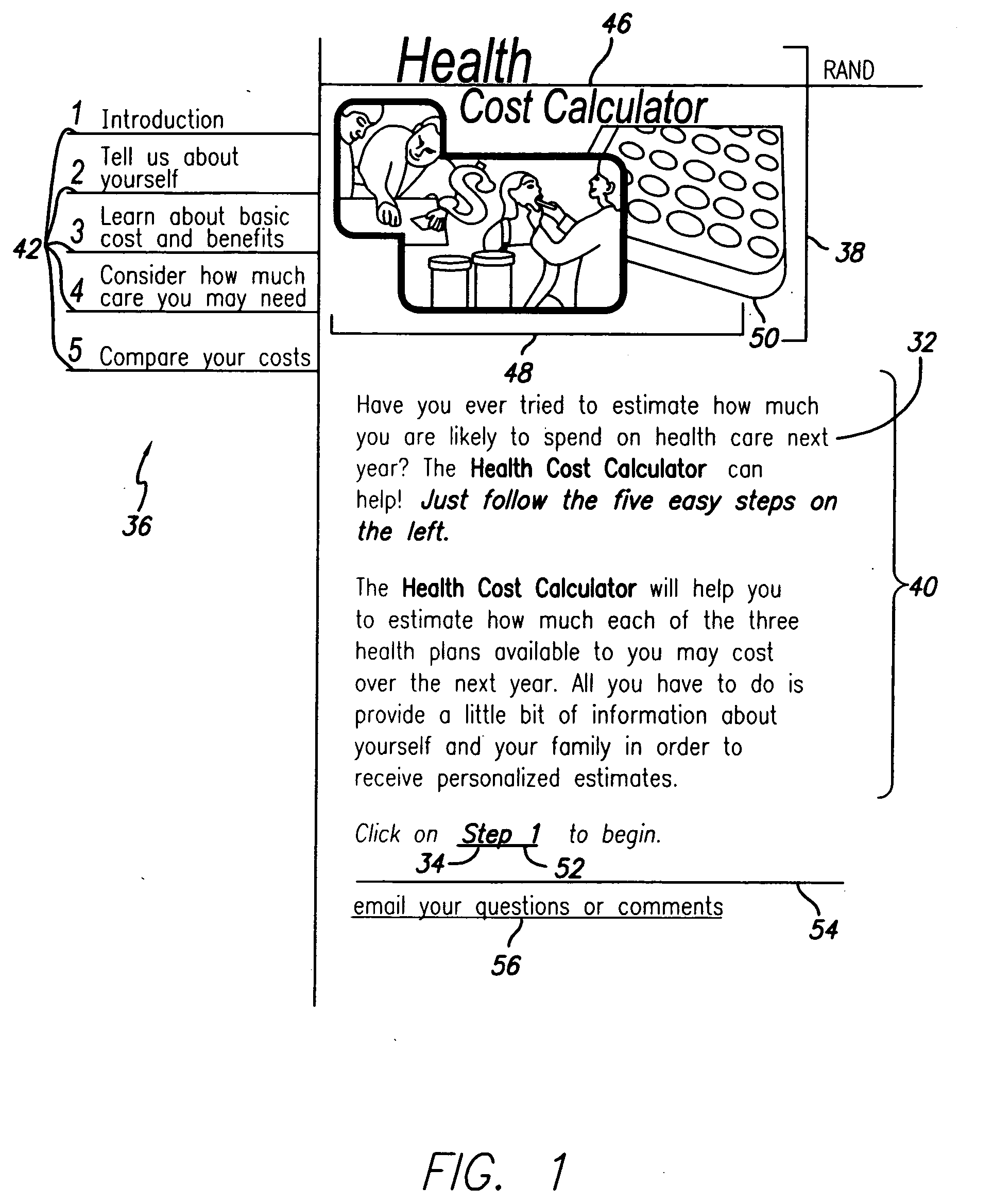
A method and system of providing comparative cost information for health insurance plans. Claims files are generated for the reference population of real historical patients for each the plans. Information is presented to users on the distribution of out-of-pocket costs for health care that users are likely to incur in the coming year, based on the parameters of health plans, information on the user and his / her household, and the actual health care use and costs for a reference population comparable to the users. Information is presented to users on optimal contributions to their flexible spending account for health care in the coming year and solving a dynamic numerical model based on users' objective function; solutions are based on the parameters of health plans, information on the user and his / her household, and the actual health care use and costs for a reference population comparable to the user.
Owner:SCHOENBAUM MICHAEL +1
System and methods for image segmentation in N-dimensional space
ActiveUS20080317308A1Improve accuracyImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisVolumetric dataAlgorithm
A system and methods for the efficient segmentation of globally optimal surfaces representing object boundaries in volumetric datasets is provided. An optical surface detection system and methods are provided that are capable of simultaneously detecting multiple interacting surfaces in which the optimality is controlled by the cost functions designed for individual surfaces and by several geometric constraints defining the surface smoothness and interrelations. The graph search applications use objective functions that incorporate non-uniform cost terms such as “on-surface” costs as well as “in-region” costs.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Method of operating a fast scanning mirror
ActiveUS8752969B1Reduce frictionRapid responseAngle measurementAdditive manufacturing apparatusObject structureLight beam
The mirror has a base, inner stage, reflector, controller, and mechanical subsystems pivotally supporting stage and reflector: subsystem #1, the stage (about one rotation axis, relative to the base); subsystem #2, the reflector (about another axis, relative to the stage). Stage and reflector each rotate on respective jewel, ceramic or other refractory bearings. Controller establishes stage / base and reflector / stage angles. Subsystems include respective bearings. The method includes (1) using the two-axis mechanism to receive, and measure an incident angle of, incident rays from an external object; (2) then using that mechanism to direct a radiation beam from a laser source toward the external object, responsive to incident rays. Optionally step (1) operates the mirror at peak acceleration, or minimum response time, as function of mirror thickness; and provides two- to three-millimeter mirror thickness. Optionally step (2) directs the beam to disrupt object function or impair object structure.
Owner:ARETE ASSOCIATES INC
Method and apparatus for training a system model with gain constraints
InactiveUS7058617B1Maintain sensitivitySimulator controlDigital computer detailsData setTheoretical computer science
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
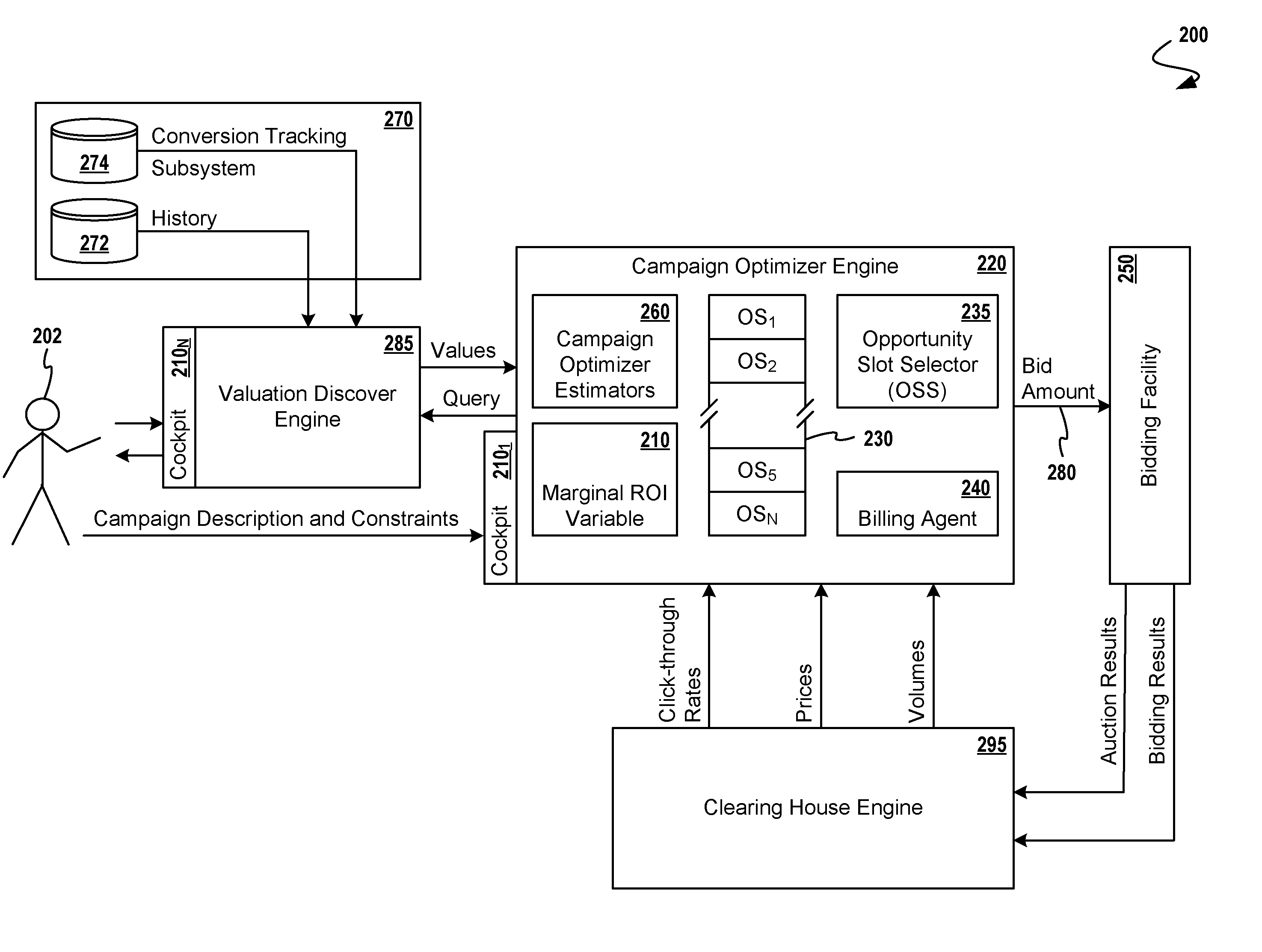
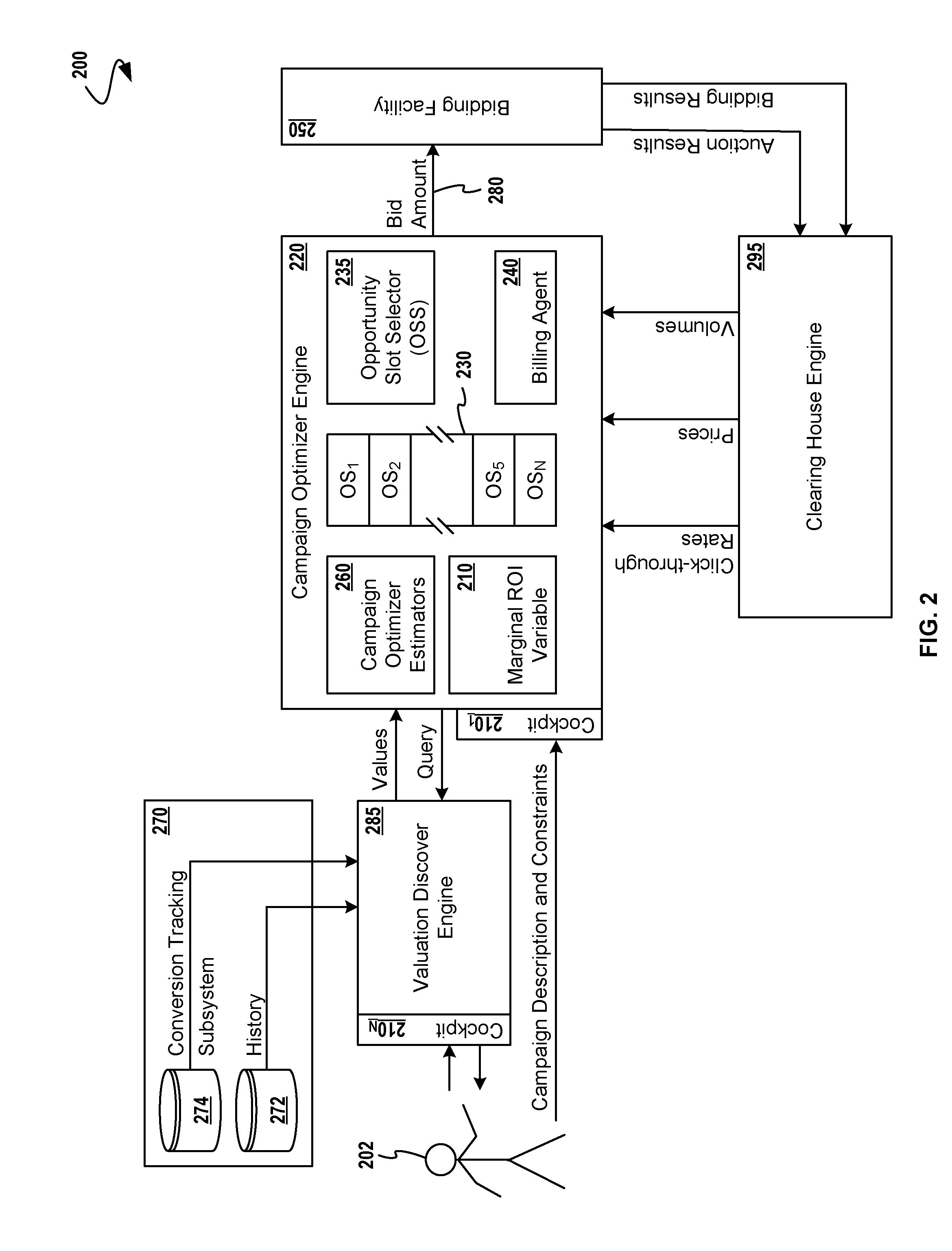
Automatic Campaign Optimization for Online Advertising Using Return on Investment Metrics
A method for optimizing quantitative return-on-investment performance in an online advertising campaign. The advertising campaign has a finite campaign period and a finite spending budget within a system that includes a bidding facility for bidding on a plurality of advertising slots. The method seeks to optimize performance of the campaign according to an objective function that includes a marginal return on investment variable, which variable is maintained throughout a series of iterations. Techniques are disclosed for capturing campaign parameters and constraints from advertisers, and mathematical techniques are used in determining a selected advertising slot upon which to bid at each iteration. A tracking system provides a history of winning bids and forecast of inventory. After bidding, the value of the marginal return on investment variable is changed based on the results of the bidding. The next bidding operations are based on the value of the marginal return on investment variable.
Owner:OATH INC
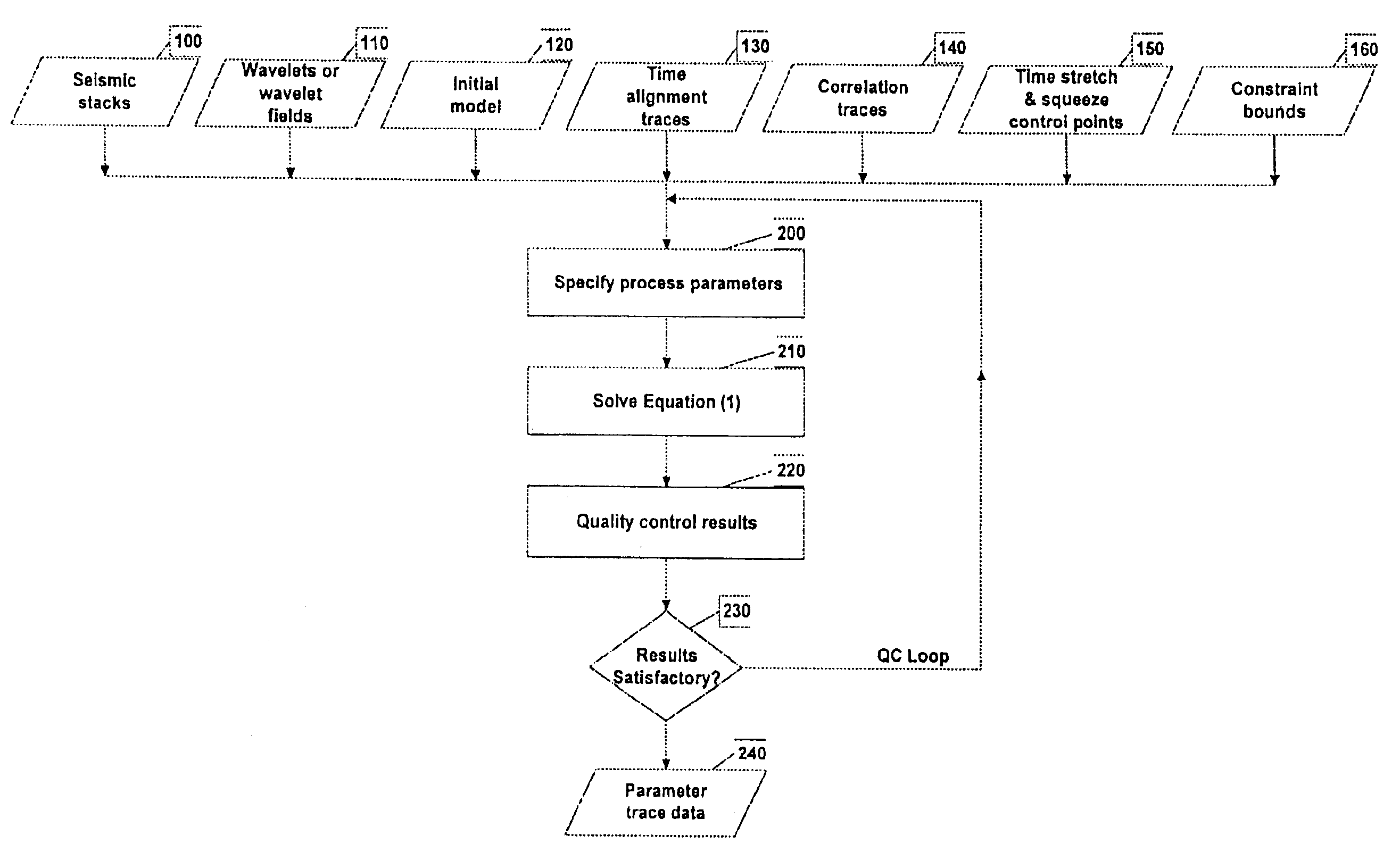
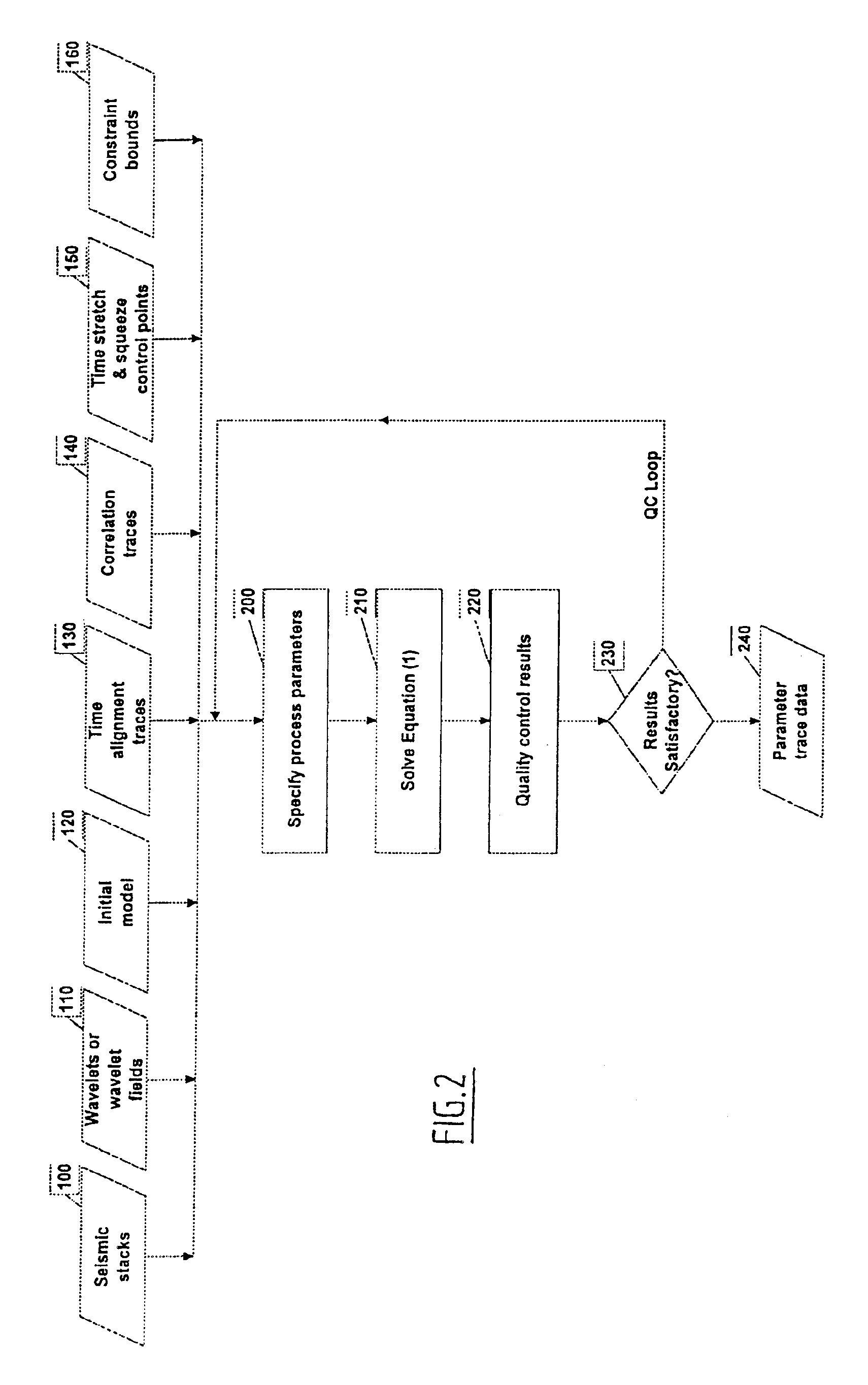
Method of estimating elastic and compositional parameters from seismic and echo-acoustic data
InactiveUS6876928B2Improve resolving power and robustnessSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsComputer scienceObject function
A method for determining from measured reflection data on a plurality of trace positions, a plurality of subsurface parameters. The method includes the steps of: preprocessing the measured reflection data into a plurality of partial or full stacks; specifying one or more initial subsurface parameters defining an initial subsurface model; specifying a wavelet or wavelet field for each of the partial or full stacks of the measured reflection data; calculating synthetic reflection data based on the specified wavelets and the initial subsurface parameters; optimizing an objective function, including the weighted difference between measured reflection data and synthetic reflection data for a plurality of trace positions simultaneously; and outputting the optimized subsurface parameters. A device for implementing this method is also included.
Owner:CGG SERVICES NL
Dynamical methods for solving large-scale discrete and continuous optimization problems
InactiveUS7050953B2Easy to solveSimple methodDigital computer detailsComputation using non-denominational number representationLocal optimumDynamic method
Dynamical methods for obtaining the global optimal solution of general optimization problems having closed form or black box objective functions, including the steps of first finding, in a deterministic manner, one local optimal solution starting from an initial point, and then finding another local optimal solution starting from the previously found one until all the local optimal solutions starting from any initial point are found, and then finding from said points the global optimal solution.
Owner:BIGWOOD SYST
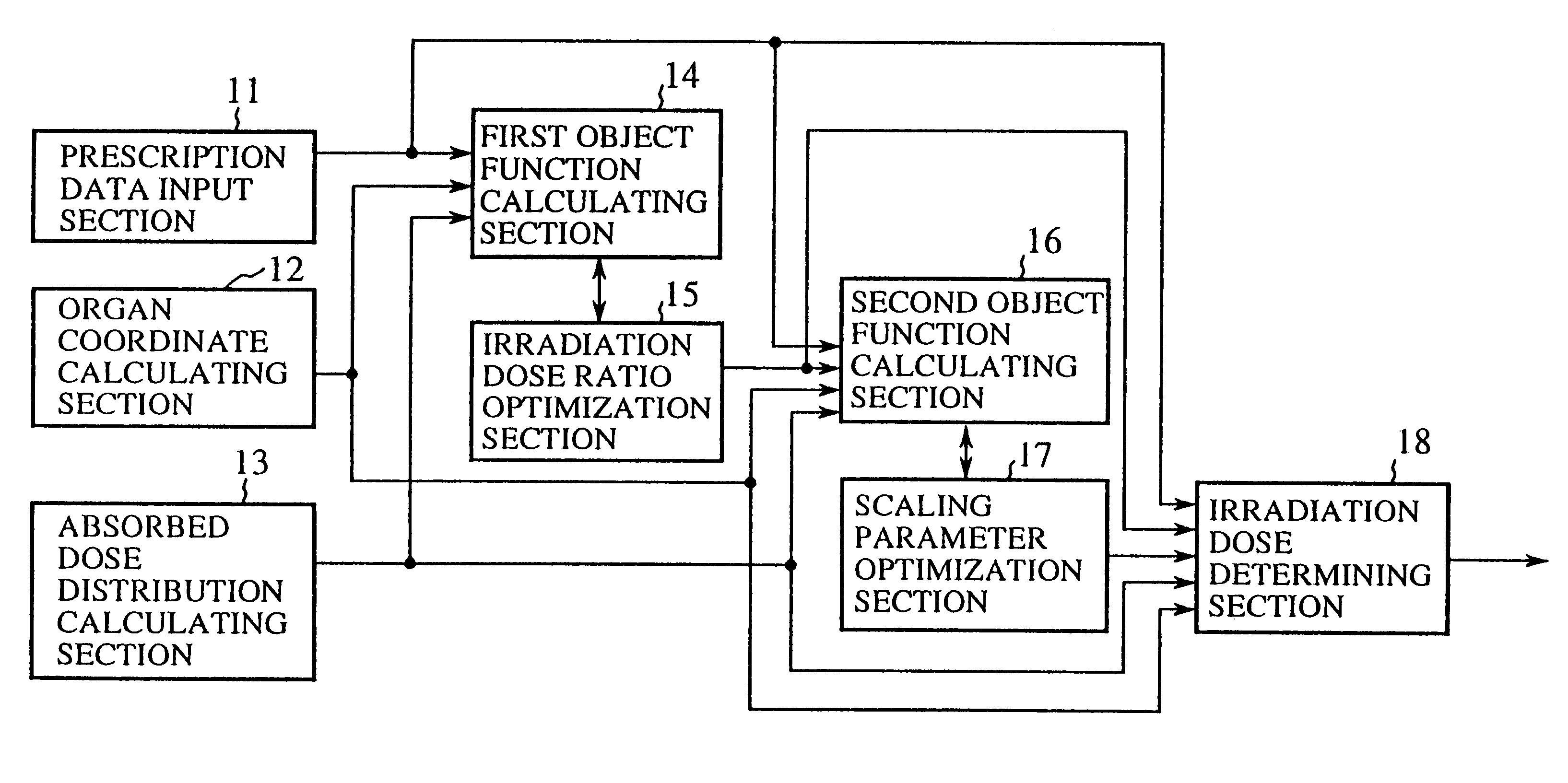
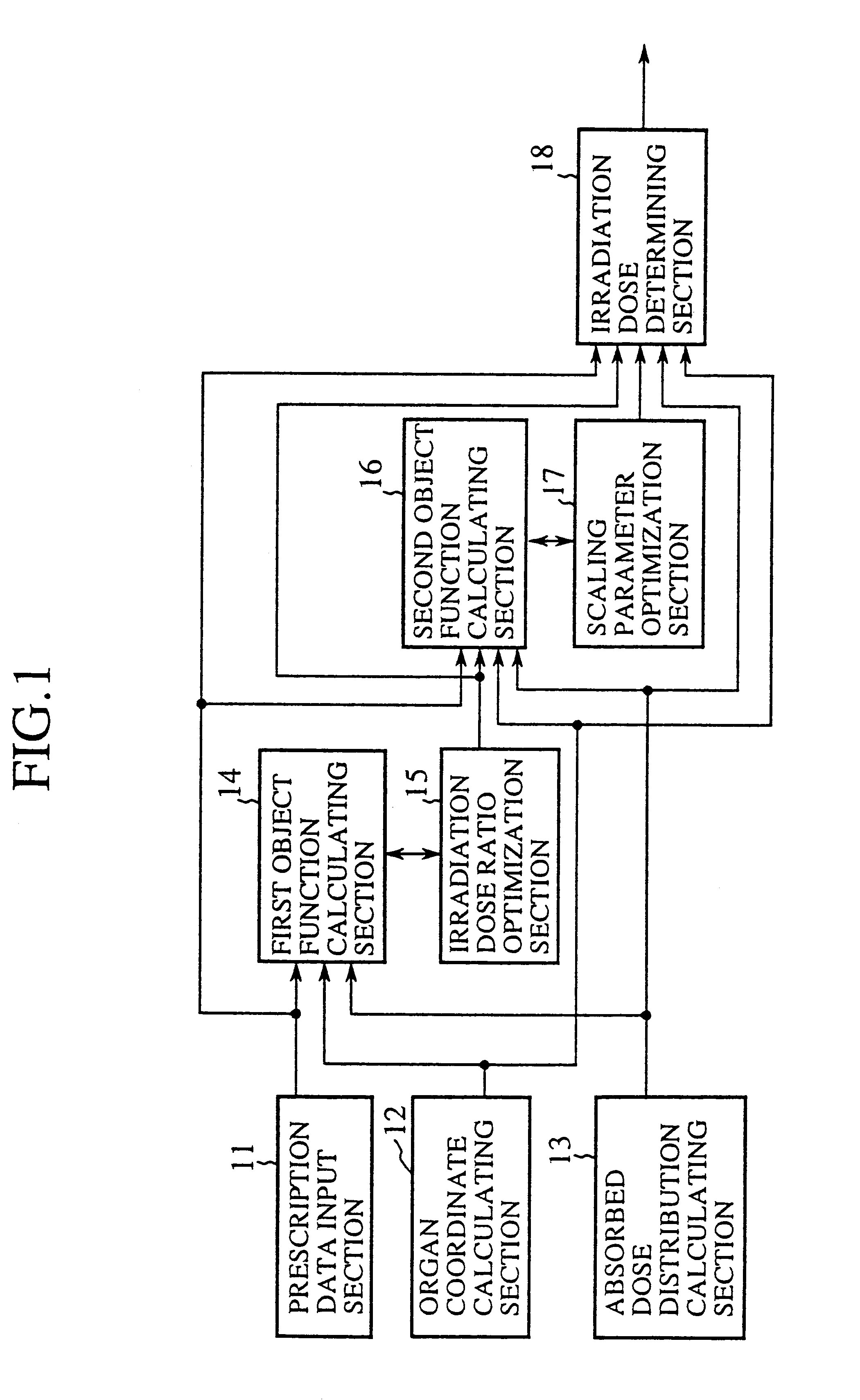
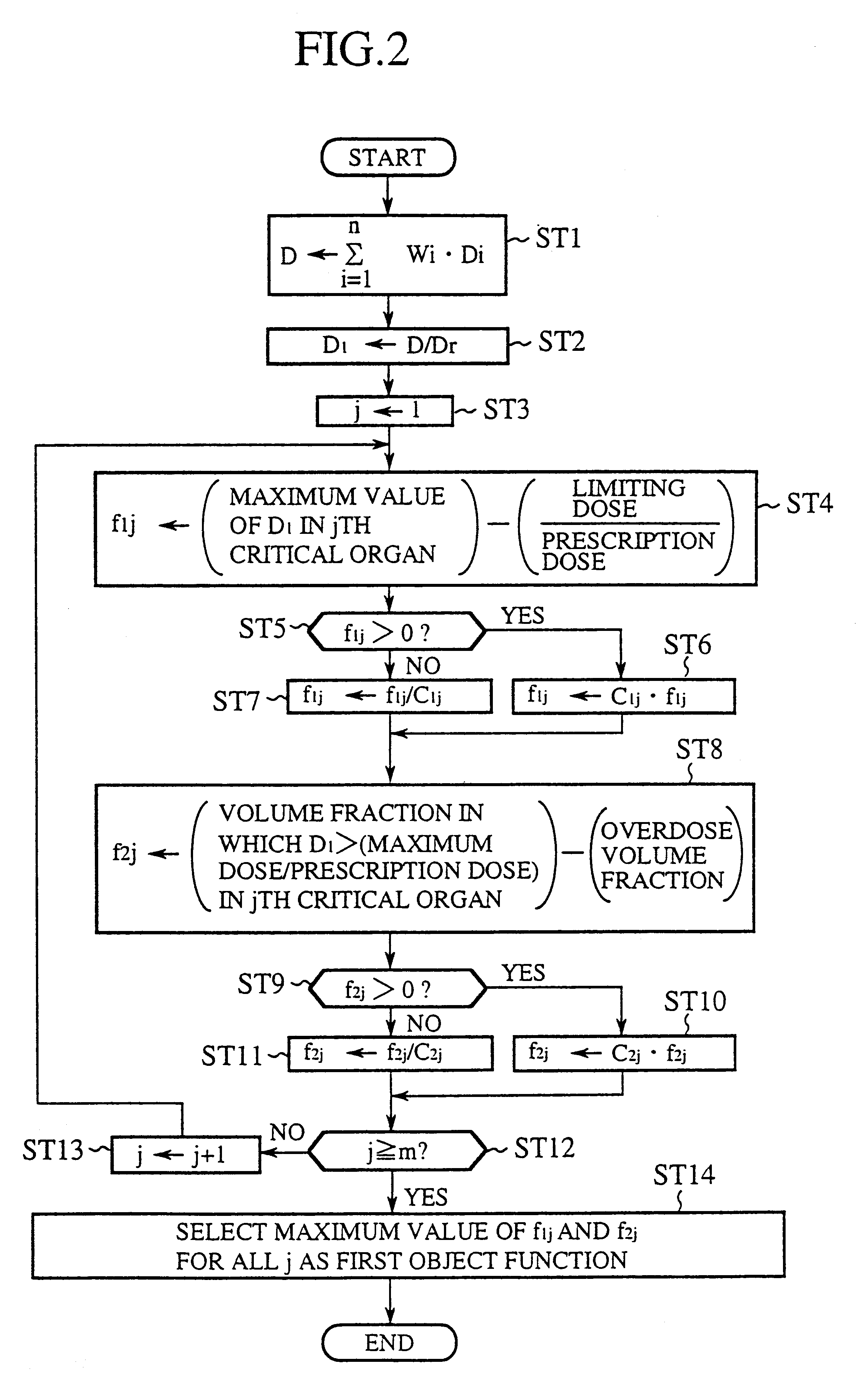
Irradiation dose calculation unit, irradiation dose calculation method and recording medium
An irradiation dose calculating unit can solve a problem of a conventional irradiation dose calculating unit in that since irradiation doses from portals are empirically determined, it is likely that optimum irradiation doses are not established for a target and a critical organ. A prescription data input section is used for a physician to input prescription data designating doses to a target and a critical organ. First and second object function calculating sections each calculate predefined indices, and obtain a first object function representing the level of satisfaction for the critical organ and a second object function representing the level of satisfaction for the target and critical organ. The irradiation doses from the portals are calculated based on these object functions such that the prescription data are satisfied.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
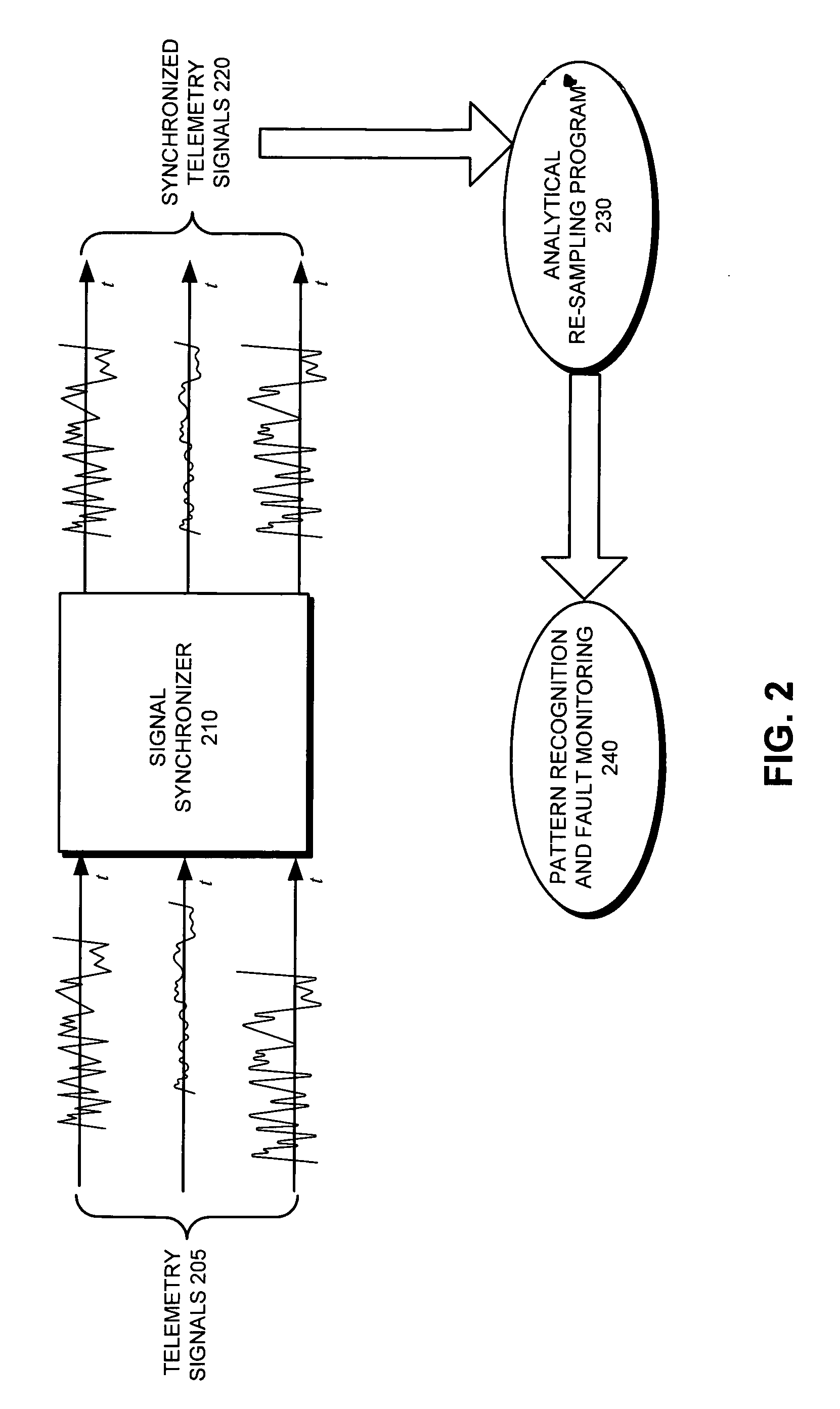
Optimizing synchronization between monitored computer system signals
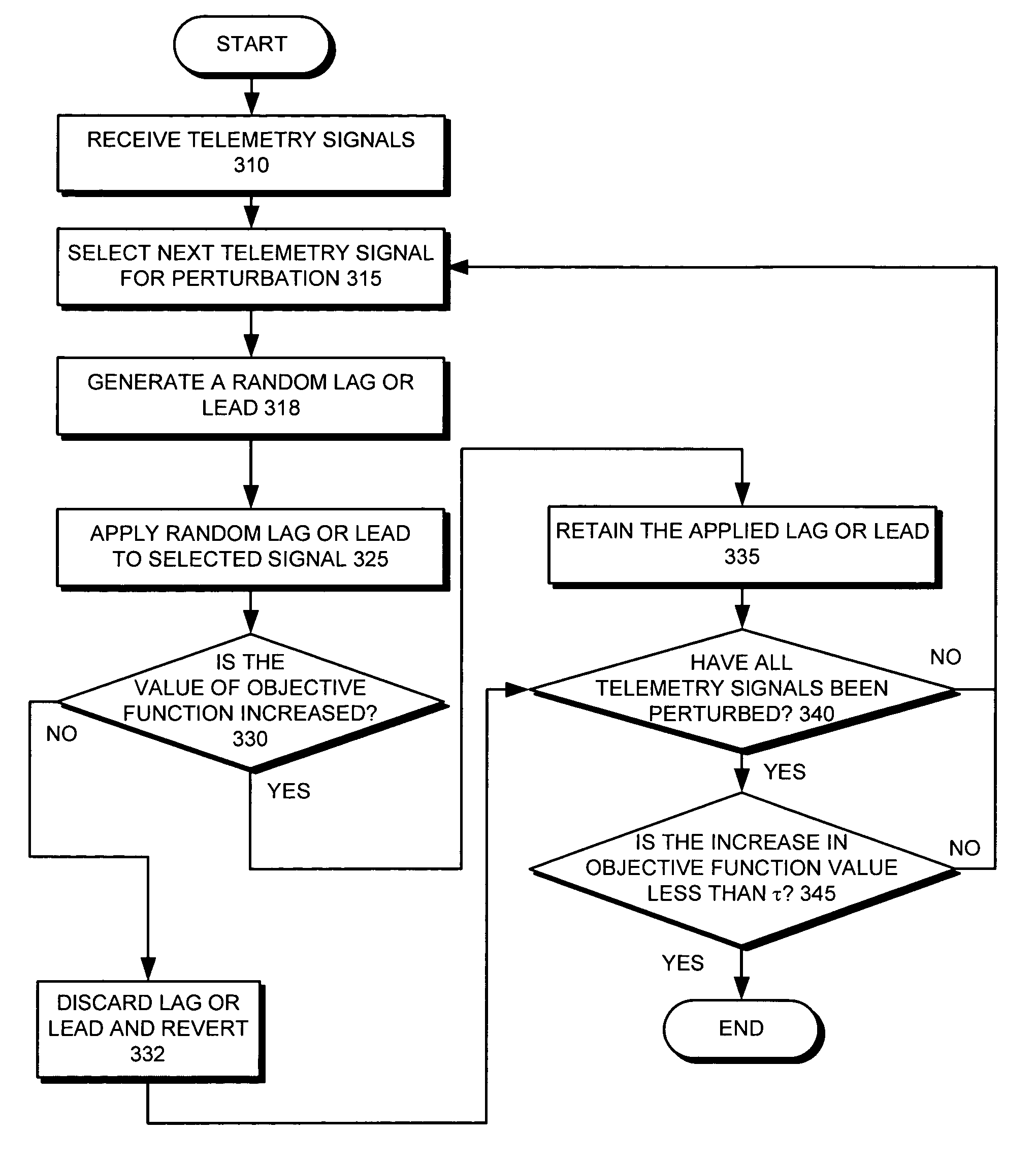
ActiveUS7391835B1Good synchronizationIncrease valueDetecting faulty hardware by remote testMultiple digital computer combinationsComputerized systemComputer science
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that optimizes synchronization between monitored signals in a computer system. During operation, the system receives a number of monitored signals. The system then forms a number of signal pairs by grouping each signal with every other signal. Next, the system optimizes synchronization between the signals by iteratively perturbing the timing of each signal in an attempt to increase the value of an objective function which reflects the overall synchronization between all the signals.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
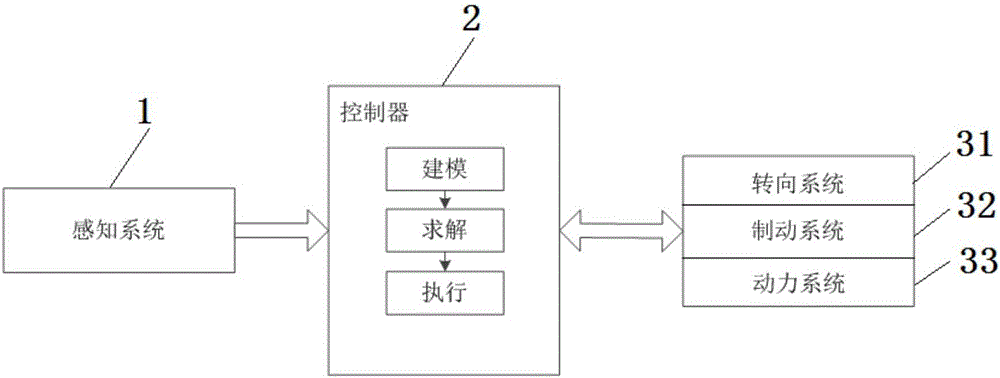
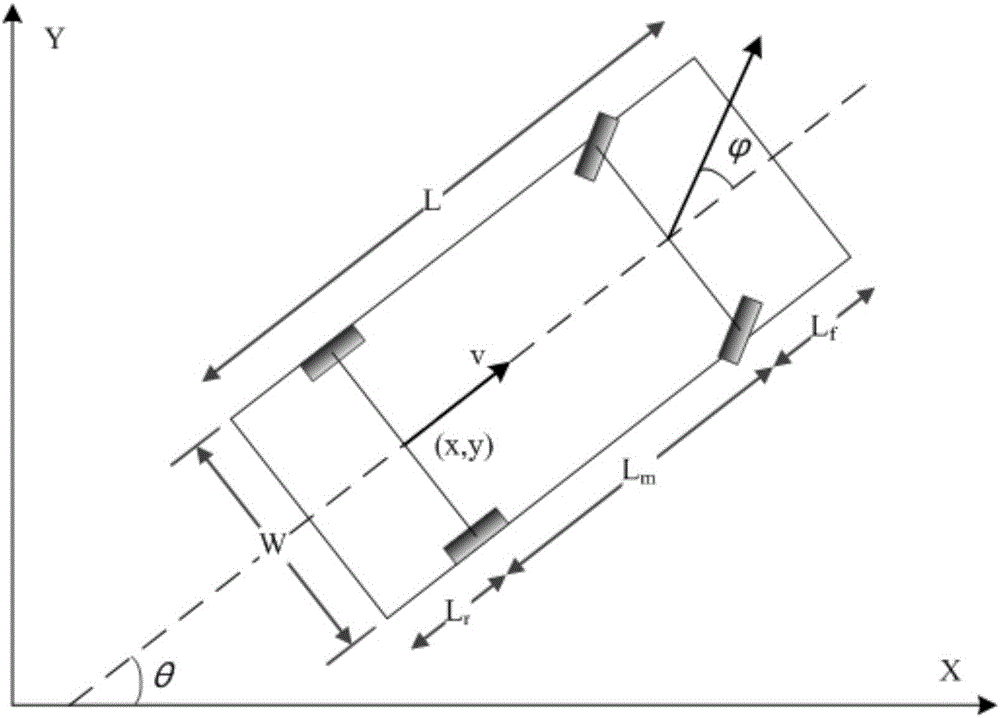
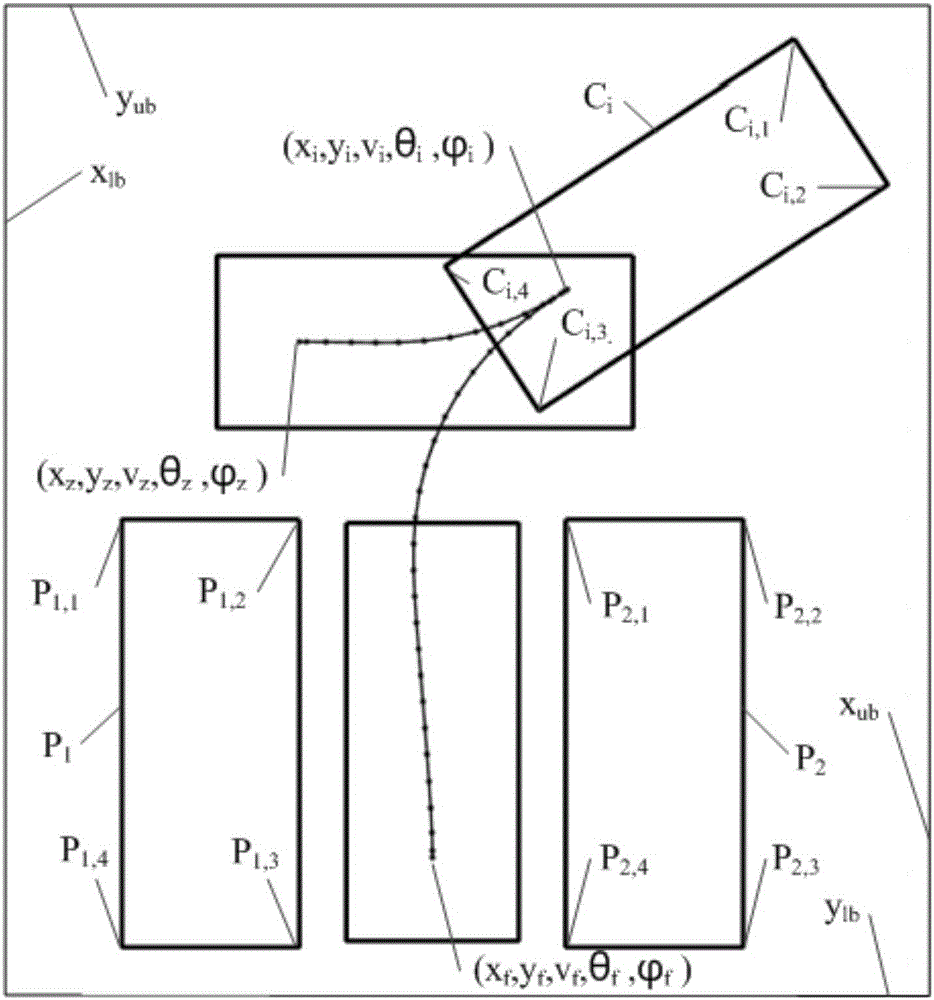
Vehicle autonomous parking path programming method used for multiple parking scenes
ActiveCN105857306APlanning results are safe and feasibleEasy to trackControl devicesRange of motionParking guidance and information
The invention provides a vehicle autonomous parking path programming method used for multiple parking scenes. The method is used for automatically parking a vehicle in a parking space through an autonomous parking system when the autonomous parking system detects the available parking space. The method includes the steps that target parking space information is detected, and a parking scene is determined; the initial state and target state of the to-be-parked vehicle are determined; a vehicle kinematics differential equation is established; state variables and control variables of the vehicle are segmented, equidistance sampling is performed on each segment according to certain time step, and to-be-optimized variables are obtained; an equality constraint, boundary constraints and inequality constraints of the to-be-optimized variables are formed; motion range constraints of the to-be-parked vehicle are formed according to the motion range limit in the parking process of the vehicle; an optimization objective is determined, and an objective function is established; and by means of a nonlinear programming solver, an optimal solution of a parking path is obtained. The vehicle autonomous parking path programming method is suitable for the multiple parking scenes, the design is reasonable, abundant information can be provided so as to control autonomous parking of the vehicle, and the security coefficient is high.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiple video cameras synchronous quick calibration method in three-dimensional scanning system
A synchronous quick calibration method of a plurality of video cameras in a three-dimensional scanning system, which includes: (1) setting a regular truncated rectangular pyramid calibration object, setting eight calibration balls at the vertexes of the truncated rectangular pyramid, and respectively setting two reference calibration balls at the upper and lower planes; (2) using the video cameras to pick-up the calibration object, adopting the two-threshold segmentation method to respectively obtain the corresponding circles of the upper and lower planes, extracting centers of the circles, obtaining three groups of corresponding relationships between circle center points in the image and the centres of calibration ball in the space, solving the homography matrix to obtain the internal parameter matrix and external parameter matrix and obtaining the distortion coefficient, taking the solved video camera parameter as the initial values, and then using a non-linear optimization method to obtain the optimum solution of a single video camera parameter; (3) obtaining in sequence the external parameter matrix between a plurality of video cameras and a certain video camera in the space, using the polar curve geometric constraint relationship of the binocular stereo vision to establish an optimizing object function, and then adopting a non-linear optimization method to solve to get the optimum solution of the external parameter matrix between two video cameras.
Owner:NANTONG TONGYANG MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL MFR +1
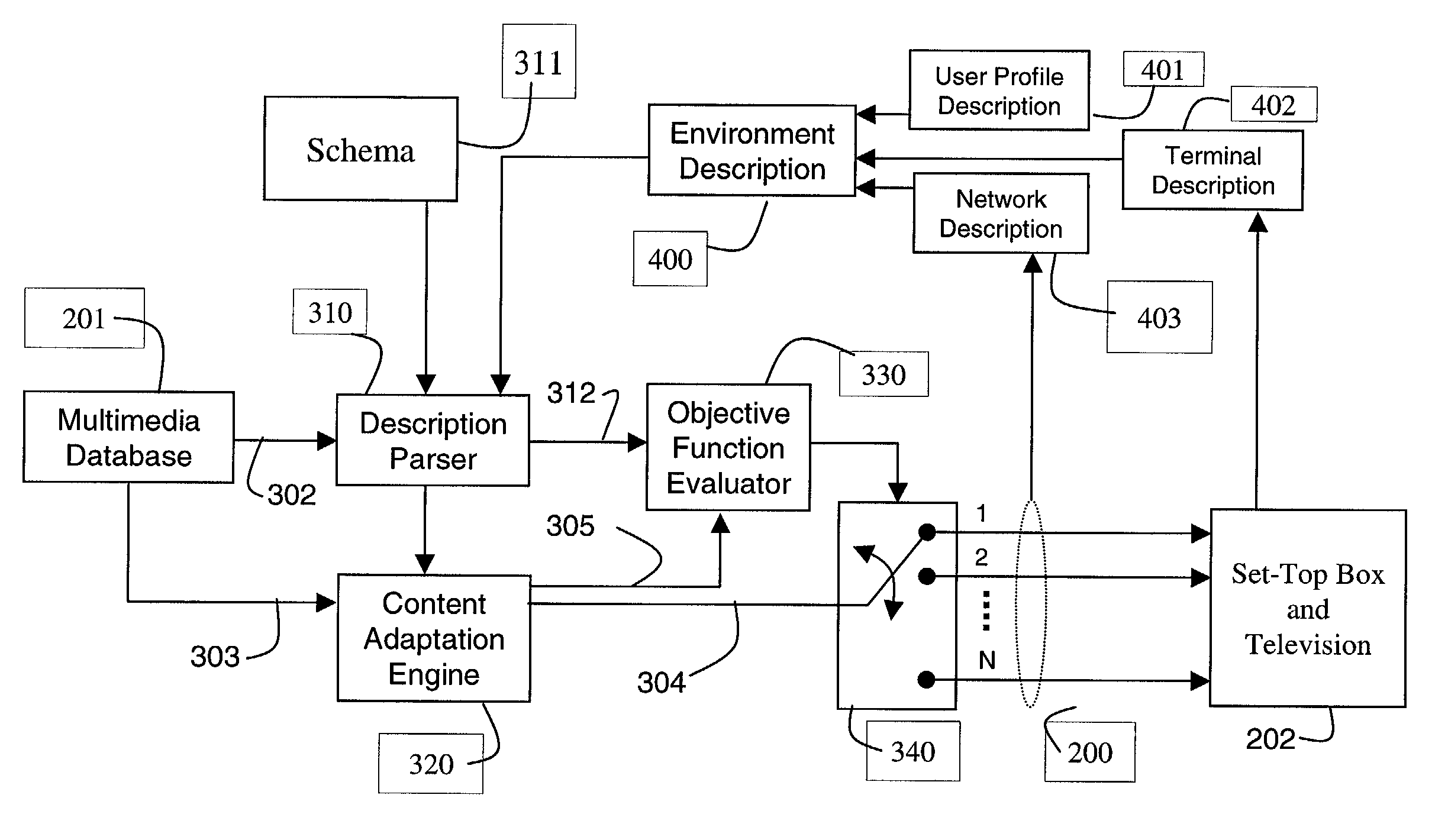
Dynamic optimal path selection in multiple communications networks
InactiveUS7099277B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsObject functionComputer science
A method and system connects a first terminal via multiple networks to a second terminal. An environment description is acquired and parsed by a description parser into cost parameters using a set of rules. An objective function evaluates the cost parameters to determine an optimal path to connect the first terminal to the second terminal through the multiple networks using a switch. The selection of the optimal path can be done periodically during a particular application session.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
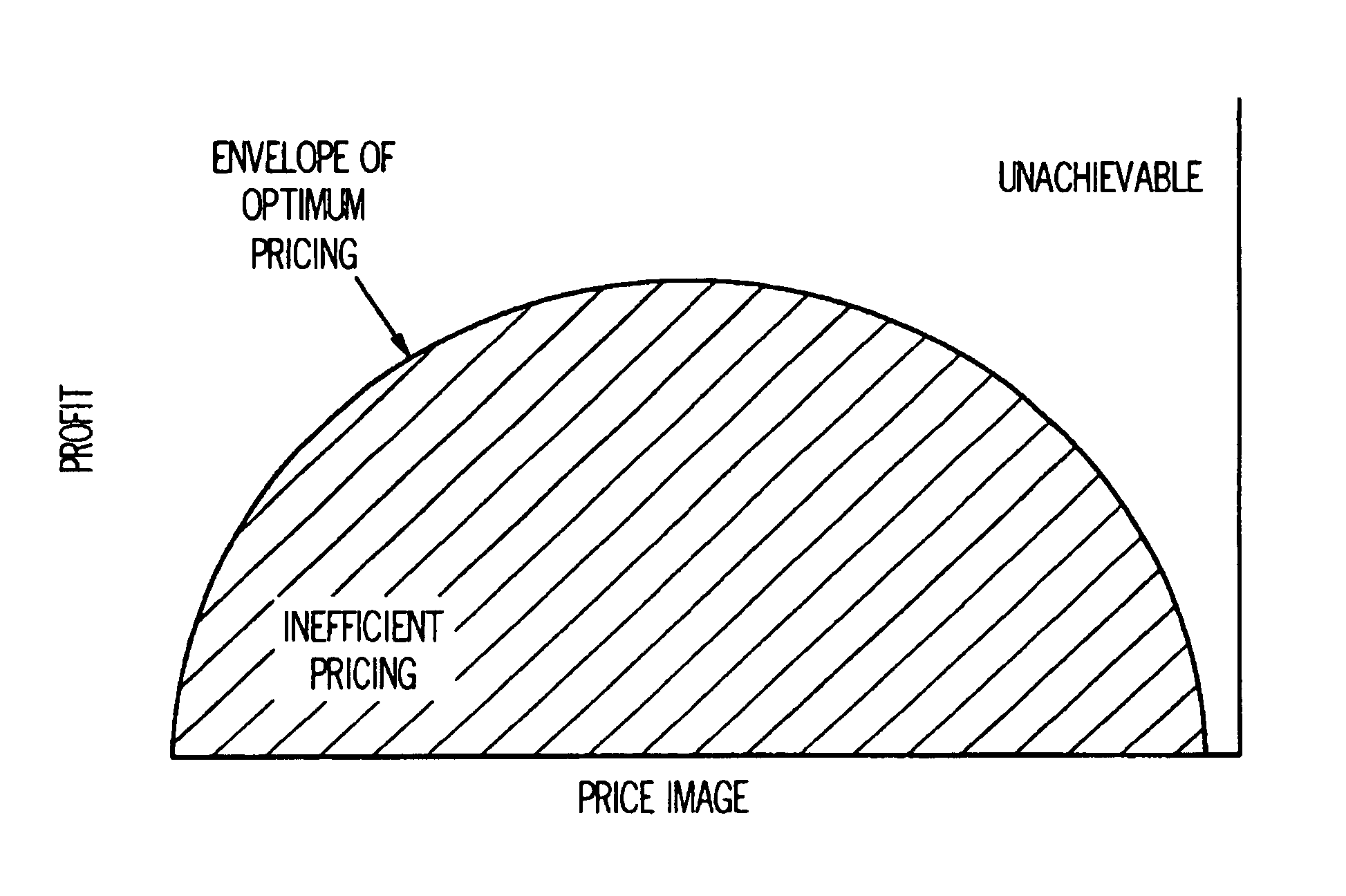
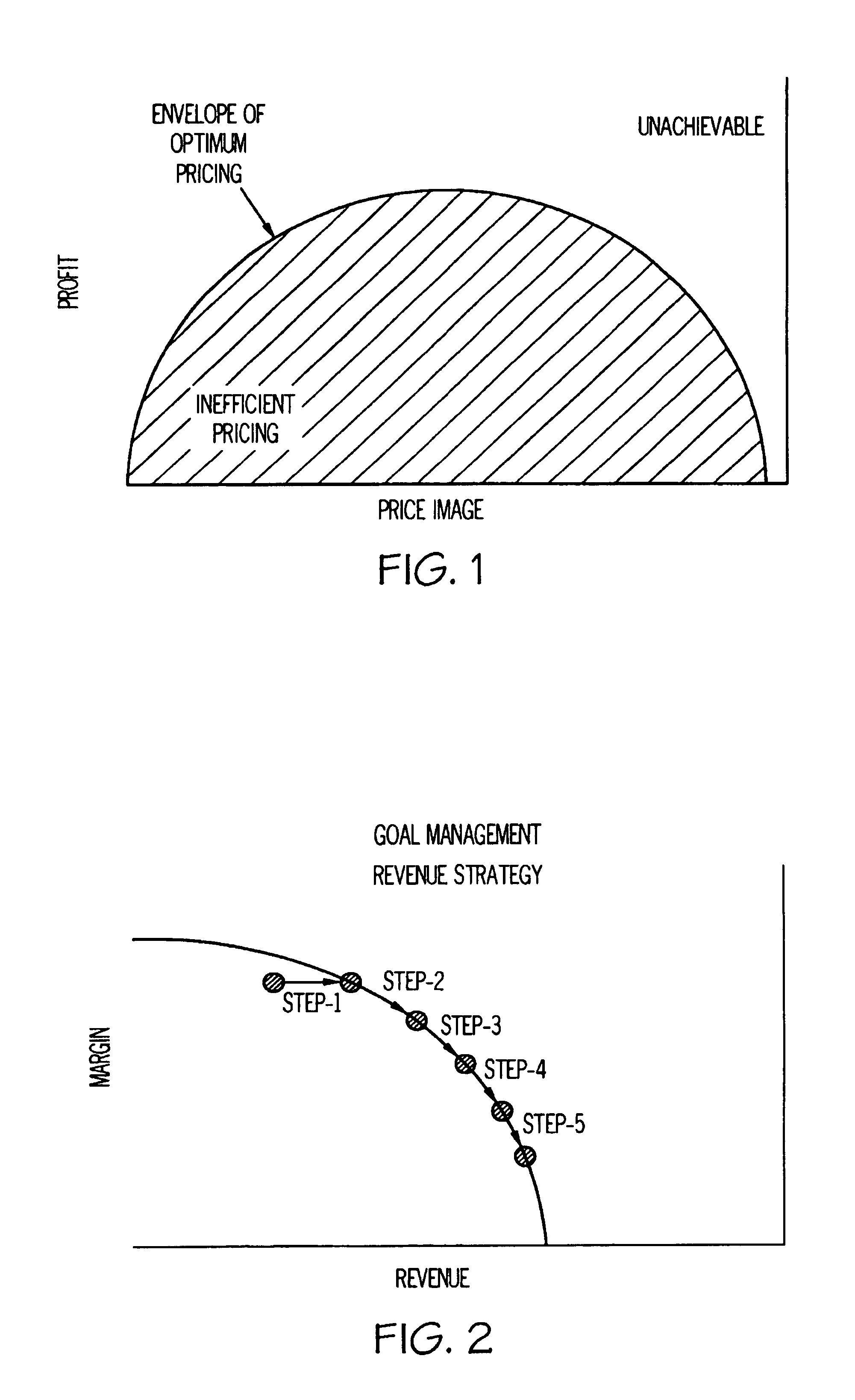
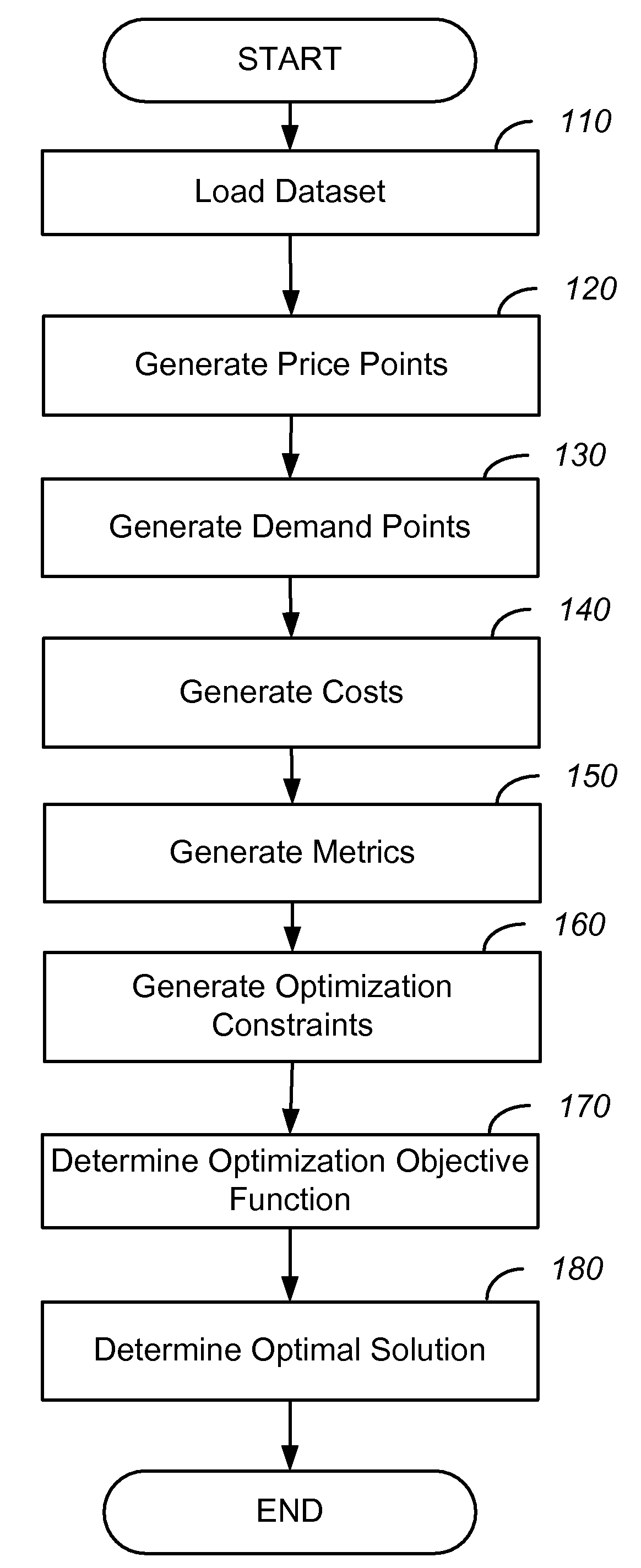
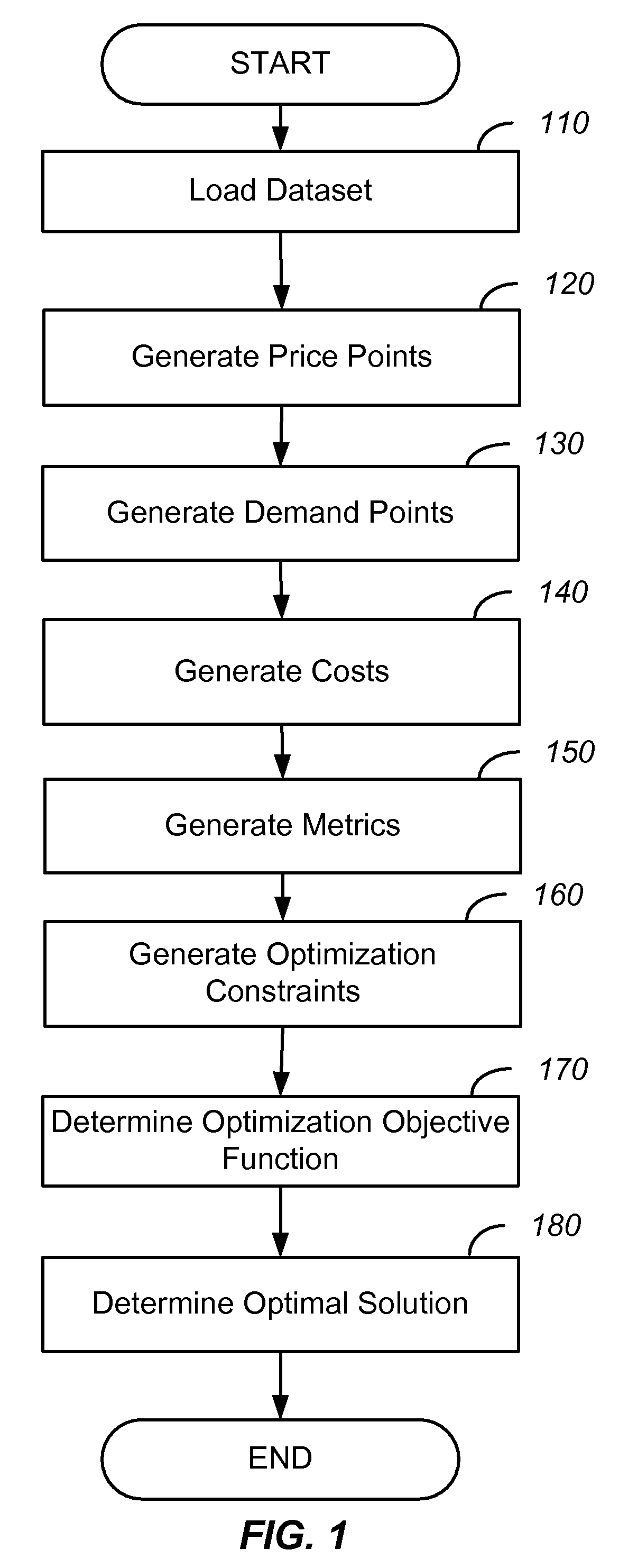
System And Method For Simultaneous Price Optimization And Asset Allocation To Maximize Manufacturing Profits
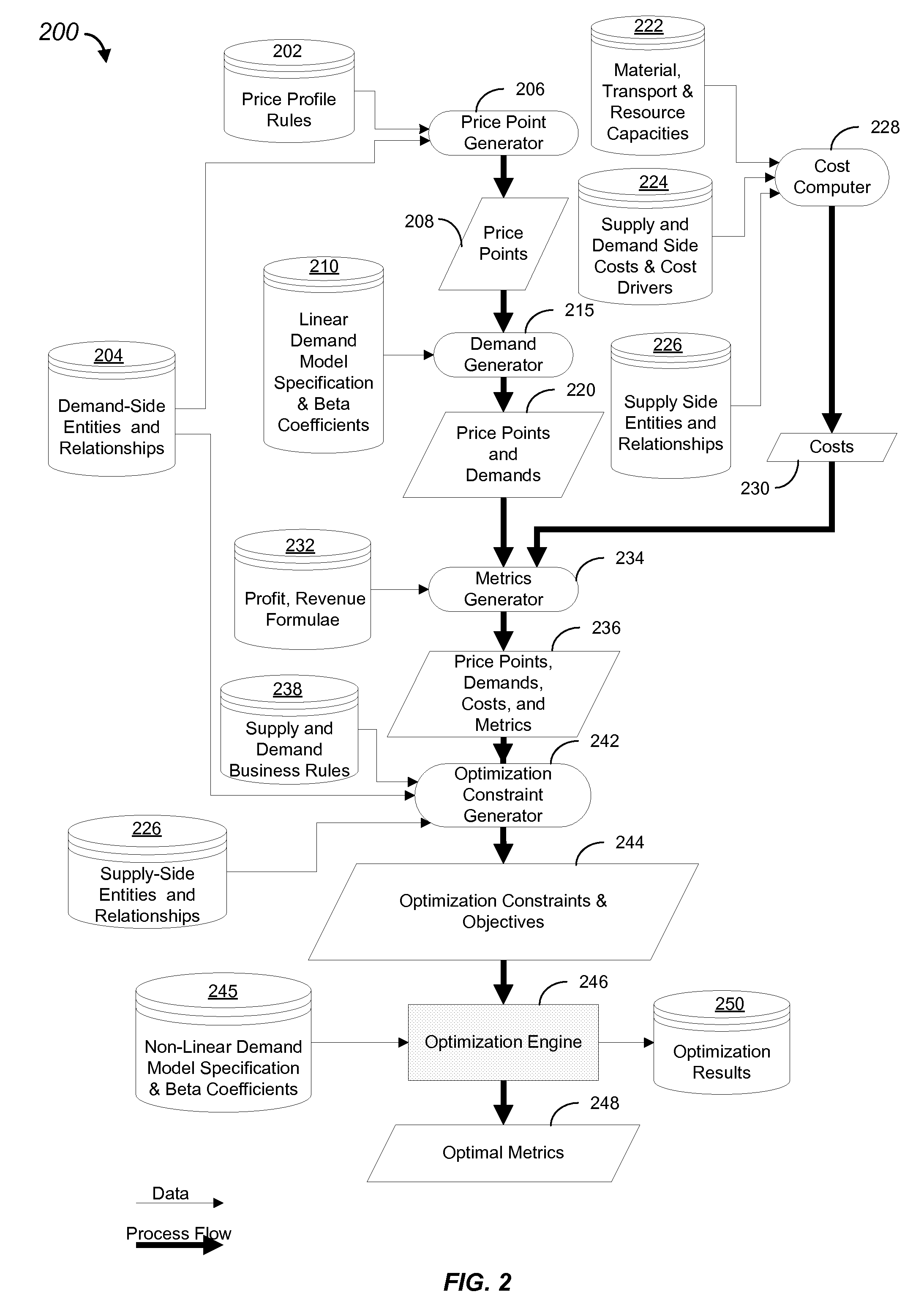
Systems and methods in accordance with various embodiments of the present invention provide for a system and method for simultaneous price optimization and asset allocation to maximize manufacturing profits. In one embodiment, a set of price points for the item and a set of expected demand values for each price point are determined. A supply-side constraint which models inventory, replenishment, and capacities associated with replenishment and a joining constraint, which requires that the set of expected demand values be equal to a planned supply of the item, are determined. A demand-side constraint is determined. Further, an objective function to maximize profits is determined, based on the set of price points, the set of expected demand values, and subject to the supply-side, joining, and demand-side constraints. Based on the objective function, an optimal price profile for the item is provided.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Topology optimization method using equivalent static loads
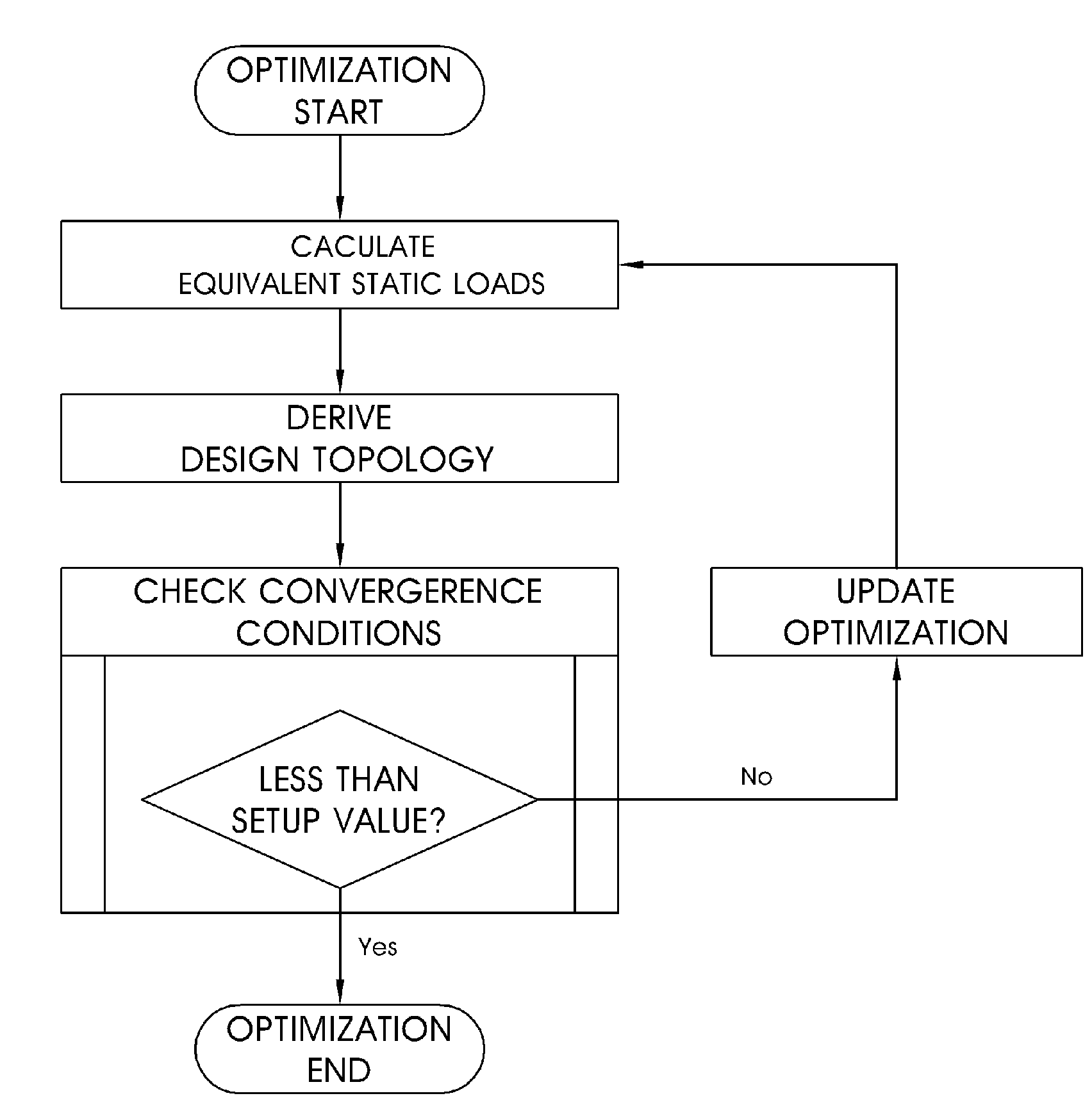
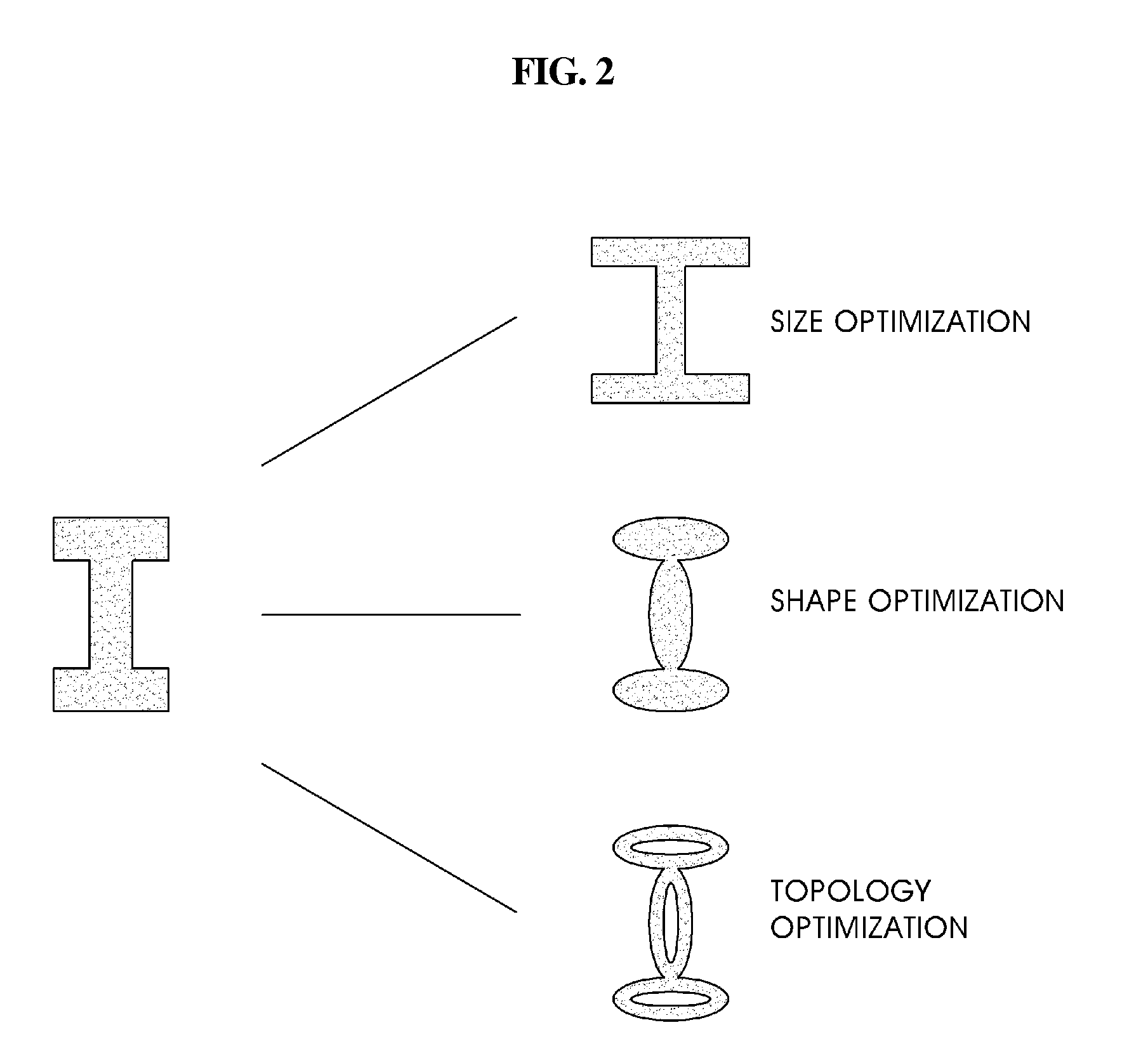
InactiveUS20100058257A1Accurate solutionReduce in quantityMulti-objective optimisationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTopology optimizationEngineering
A topology optimization method. Characteristics of a structure to be designed are differentiated to calculate equivalent static loads. A relative fraction of material is adopted as a design variable. It is determined whether or not an element exists based on an objective function and constraints. Design topology is derived through a linear static analysis that processes the equivalent static loads as multiple loading conditions. Topology of the structure to be designed is compared with the design topology, and thereby the progress of optimization is determined. The topology optimization processes are terminated when a difference of the compared result is less than a setup value, and are returned to an initial step when the difference is greater than the setup value, and the equivalent static loads are calculated using the design topology as a new structure to be designed.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUNDATION HANYANG UNIV)
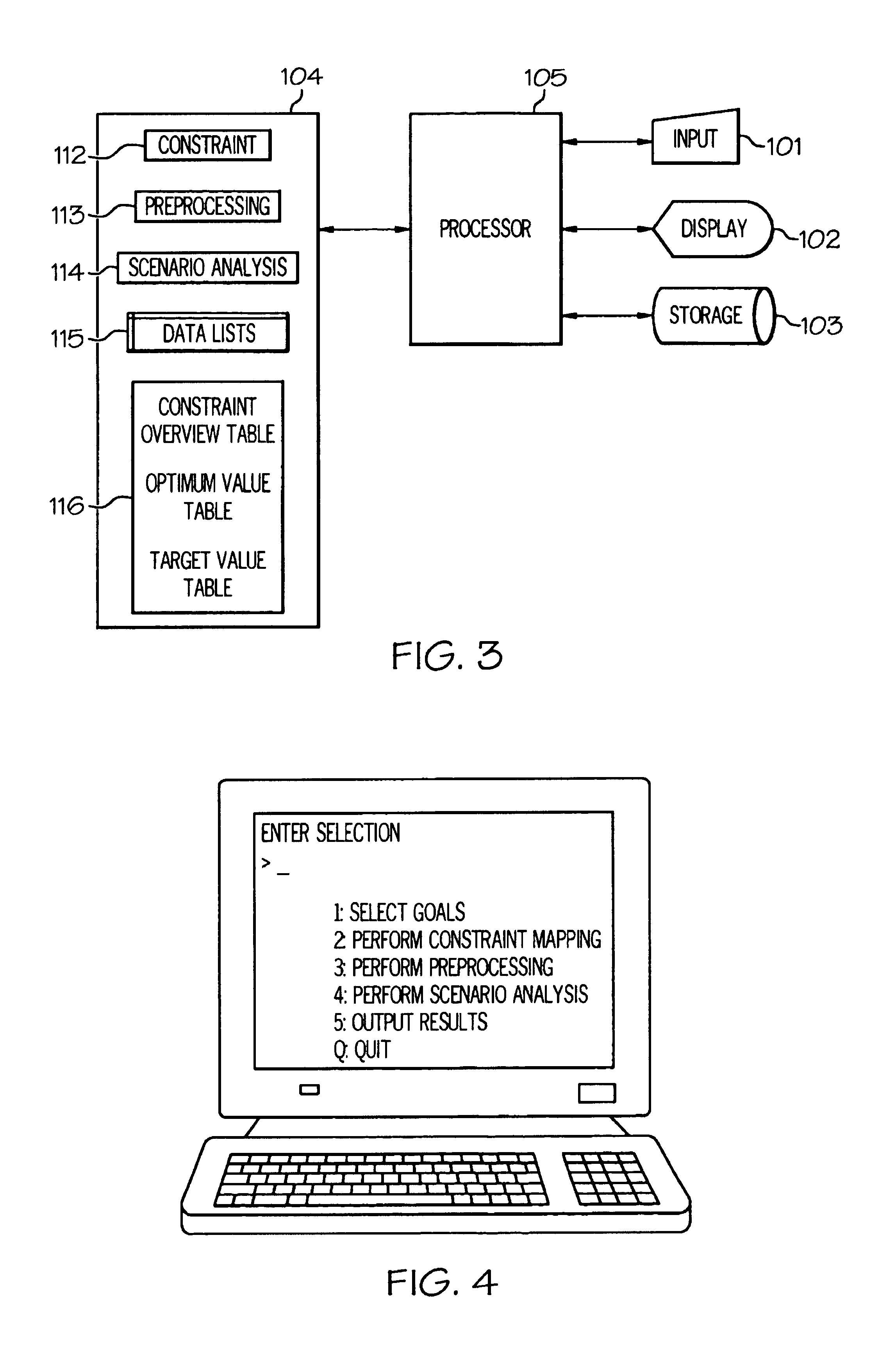
System, Method and Apparatus for Allocating Resources by Constraint Selection
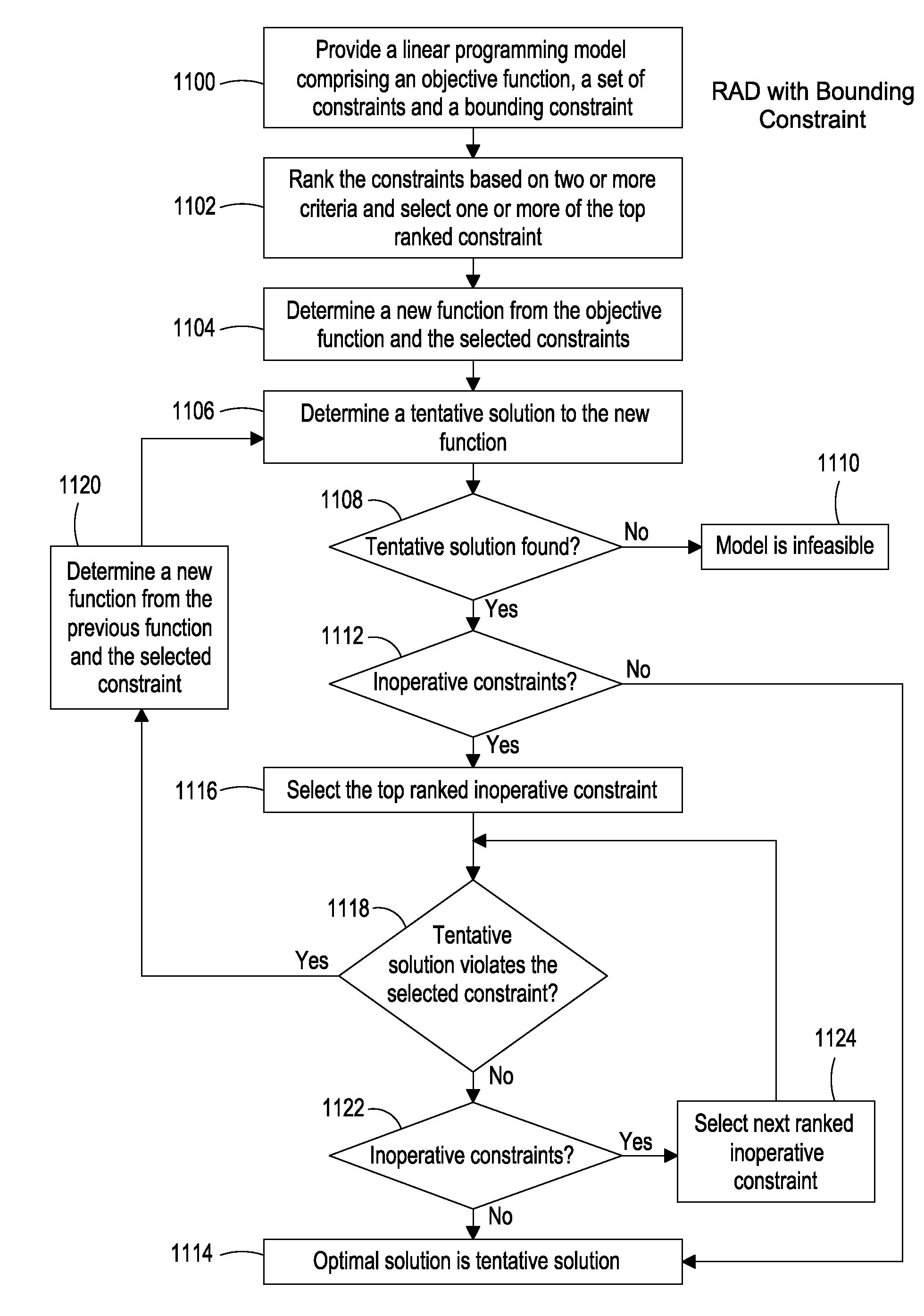
ActiveUS20080134193A1Efficient memory usageGood decisionProgram synchronisationDigital computer detailsObject functionResource allocation
The present invention provides a system, method and apparatus for allocating resources with a linear programming model comprising an objective function and a set of constraints describing feasible allocations of the resources. The method ranks constraints based on a numerical measure derived from criteria selected from at least a first and second group and selects one or more of the top-ranked constraints. A new problem is determined from the model's objective function, the previously selected constraints, and the newly selected constraints, and a tentative resource allocation is determined based on the new problem. Whenever the tentative resource allocation violates a model constraint not in the current problem, one or more of the top-ranked such violated constraints are selected, and the new problem determination and tentative resource allocation steps are repeated. The resources are allocated according to the tentative resource allocation when it does not violate any model constraints.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
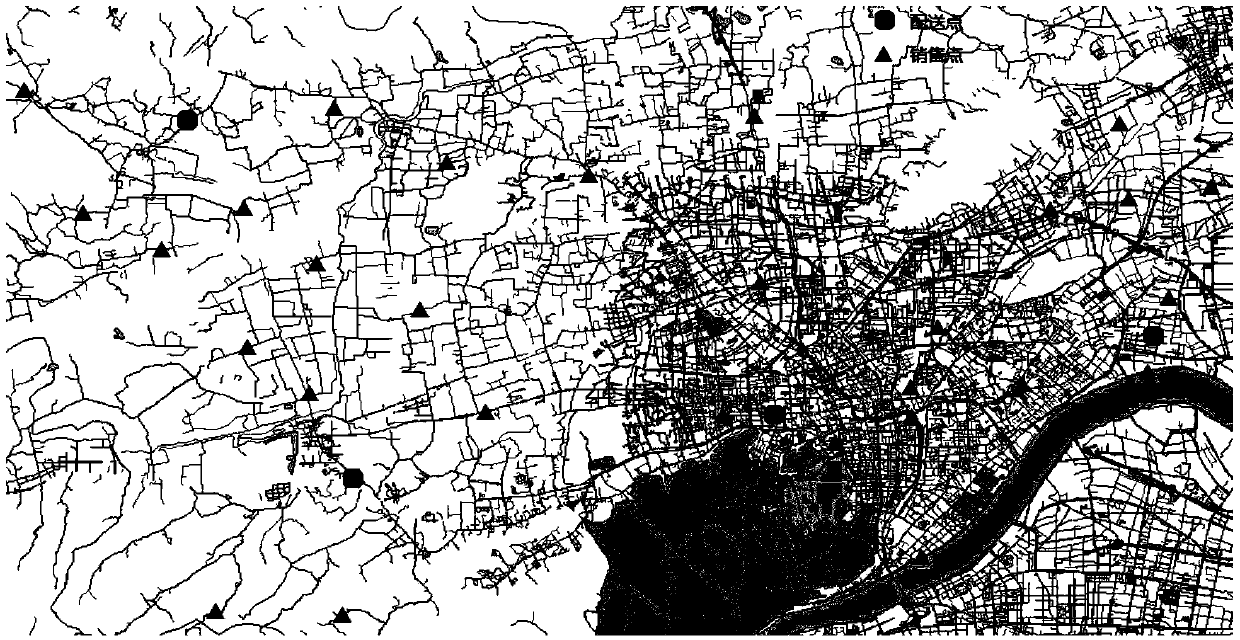
Logistics distribution control method with soft time windows
A logistics distribution control method with soft time windows includes the following steps: (A1) a network model is built, cost resistances are assigned to roads to which network data are concentrated, and taking road nodes into consideration, toll weights are assigned to road traffic light intersections and toll stations; (A2) an optimized vehicle routing model with soft time windows (VRPTW) is built, a target function is established with lowest transportation costs, and the transportation costs are respectively composed of fixed distribution vehicle cost, transportation cost, vehicle waiting cost and delay cost; (A3) a fuzzy clustering analysis algorithm is designed, and a method based on the integration of quantitative analysis and qualitative analysis is adopted for clustering; (A4) a heuristic optimized vehicle routing algorithm is designed, the optimized vehicle routing algorithm is adopted for distribution target nodes in each class, and thereby a distribution result can be obtained. The logistics distribution control method with soft time windows adopts the distances of actual delivery road network routes between distribution nodes as a calculation basis and also takes the actual traffic capacities of roads, large network node number and transportation time needed by distribution nodes into consideration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com