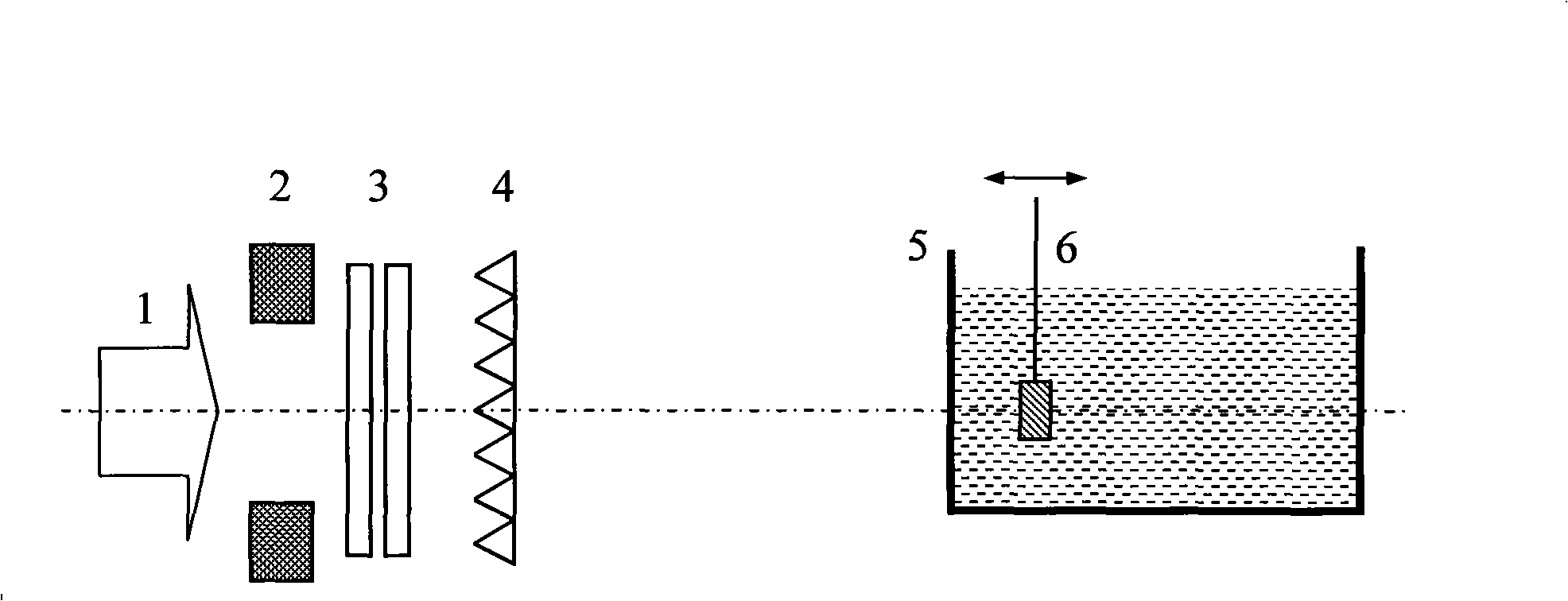
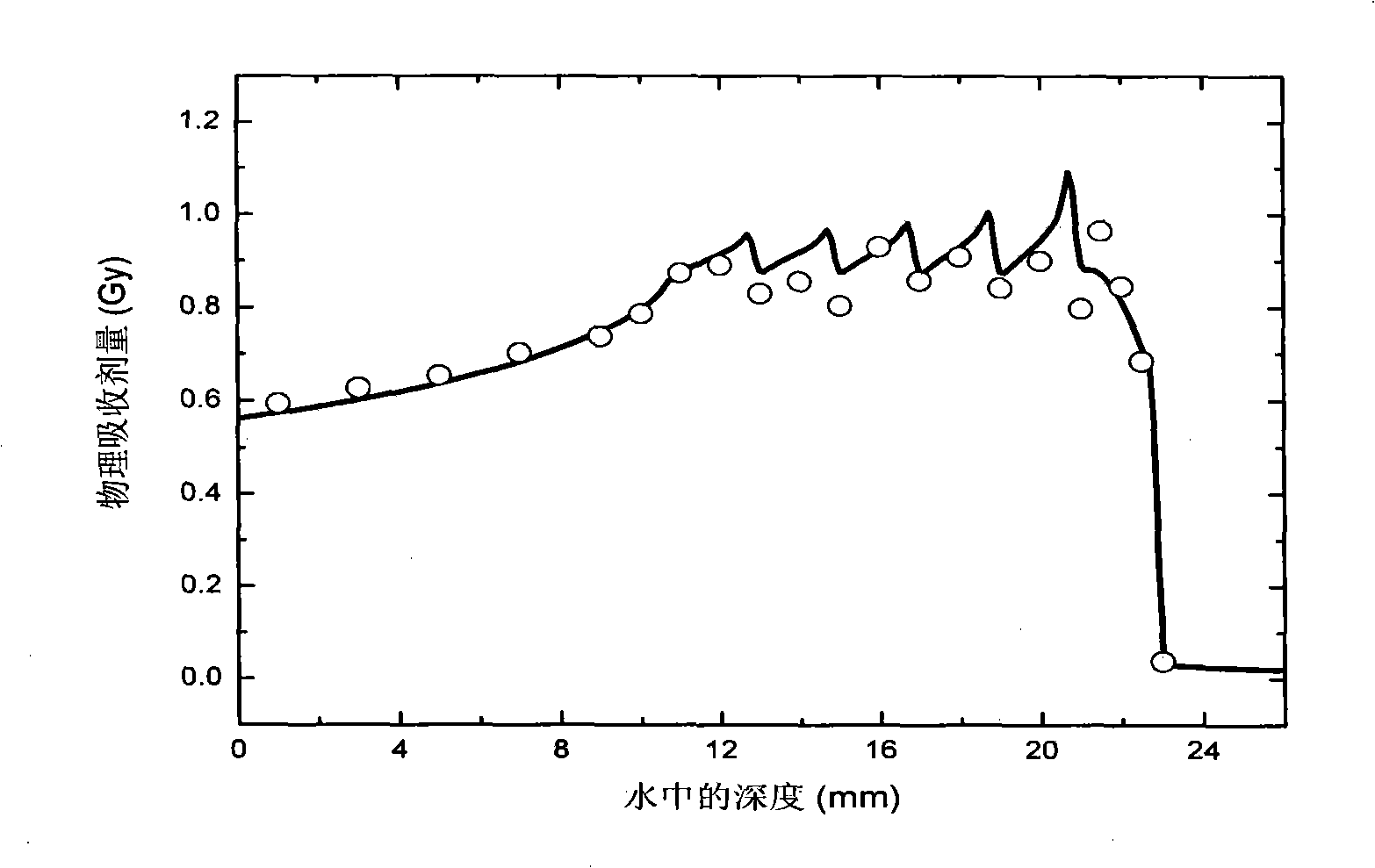
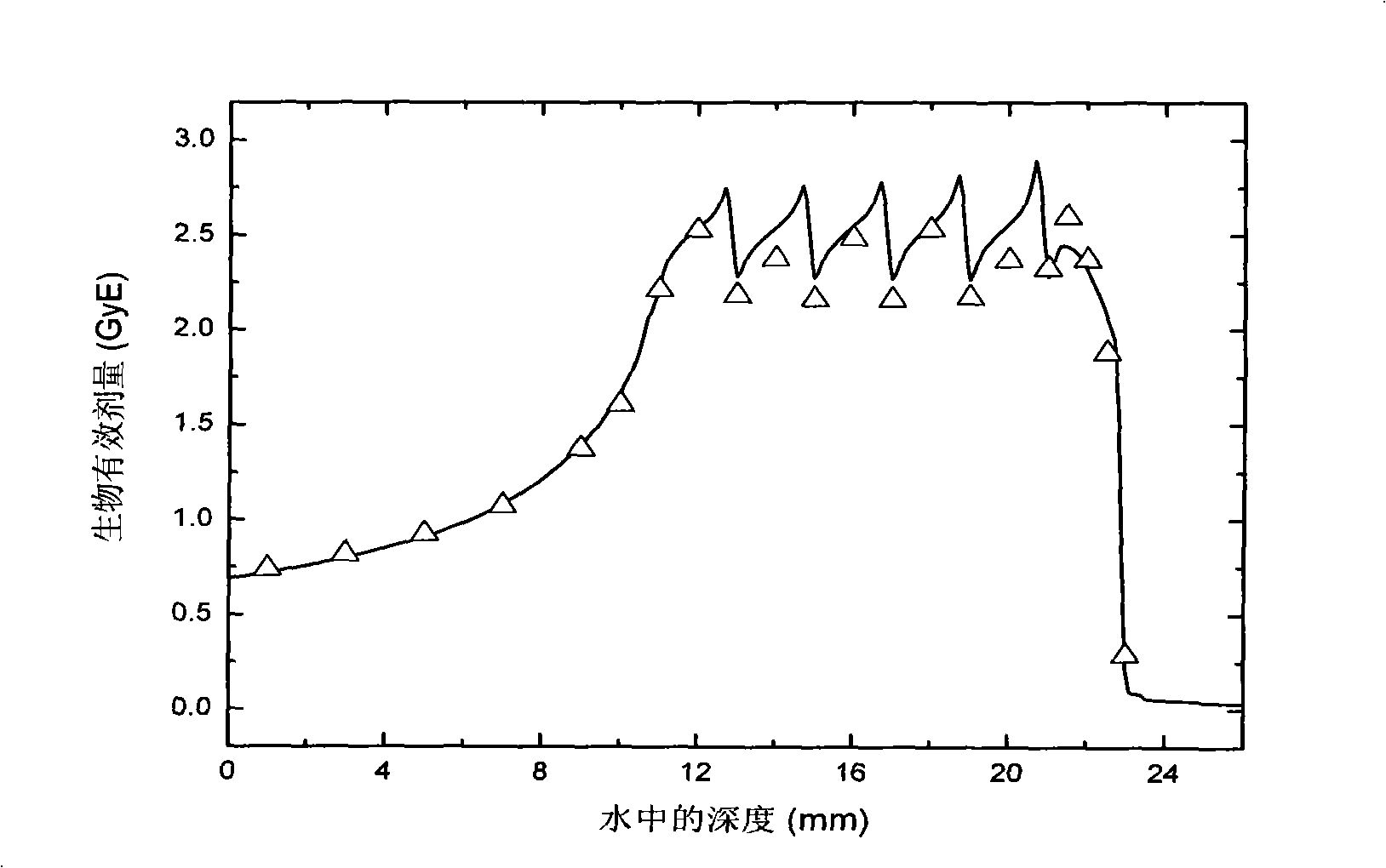
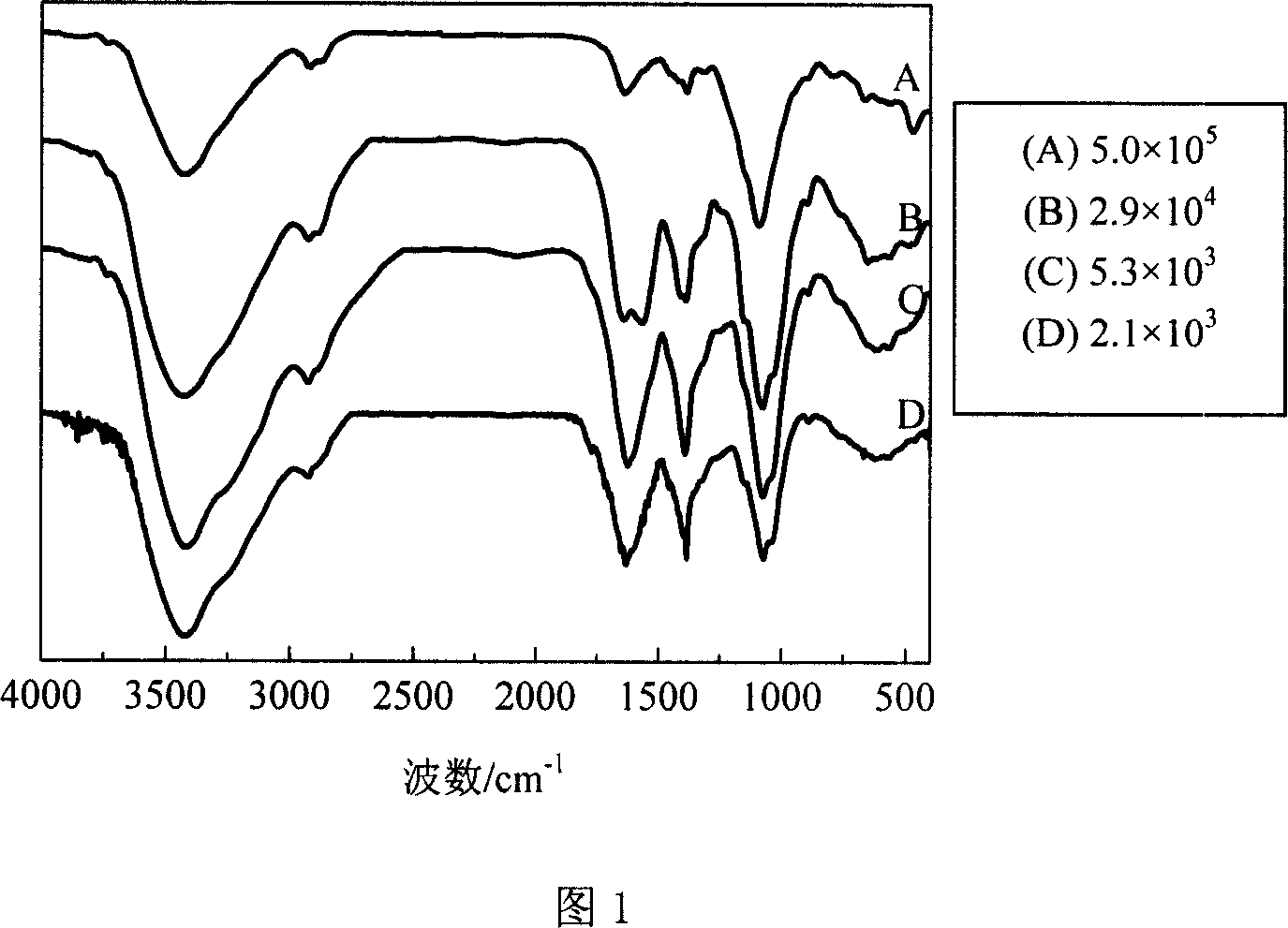
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
299 results about "Absorbed dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Absorbed dose is a dose quantity which is the measure of the energy deposited in matter by ionizing radiation per unit mass. Absorbed dose is used in the calculation of dose uptake in living tissue in both radiation protection (reduction of harmful effects), and radiology (potential beneficial effects for example in cancer treatment). It is also used to directly compare the effect of radiation on inanimate matter such as in radiation hardening.
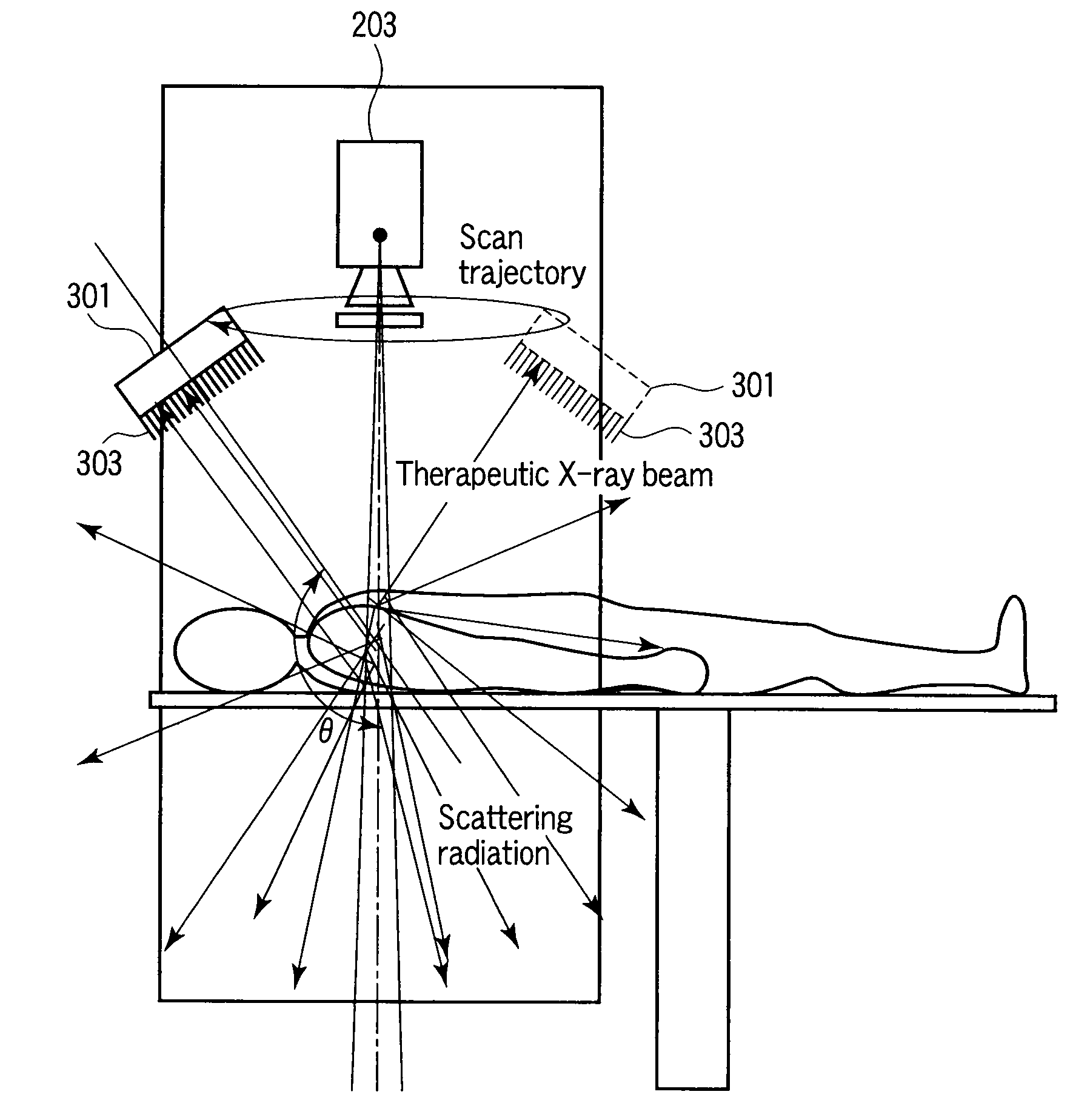
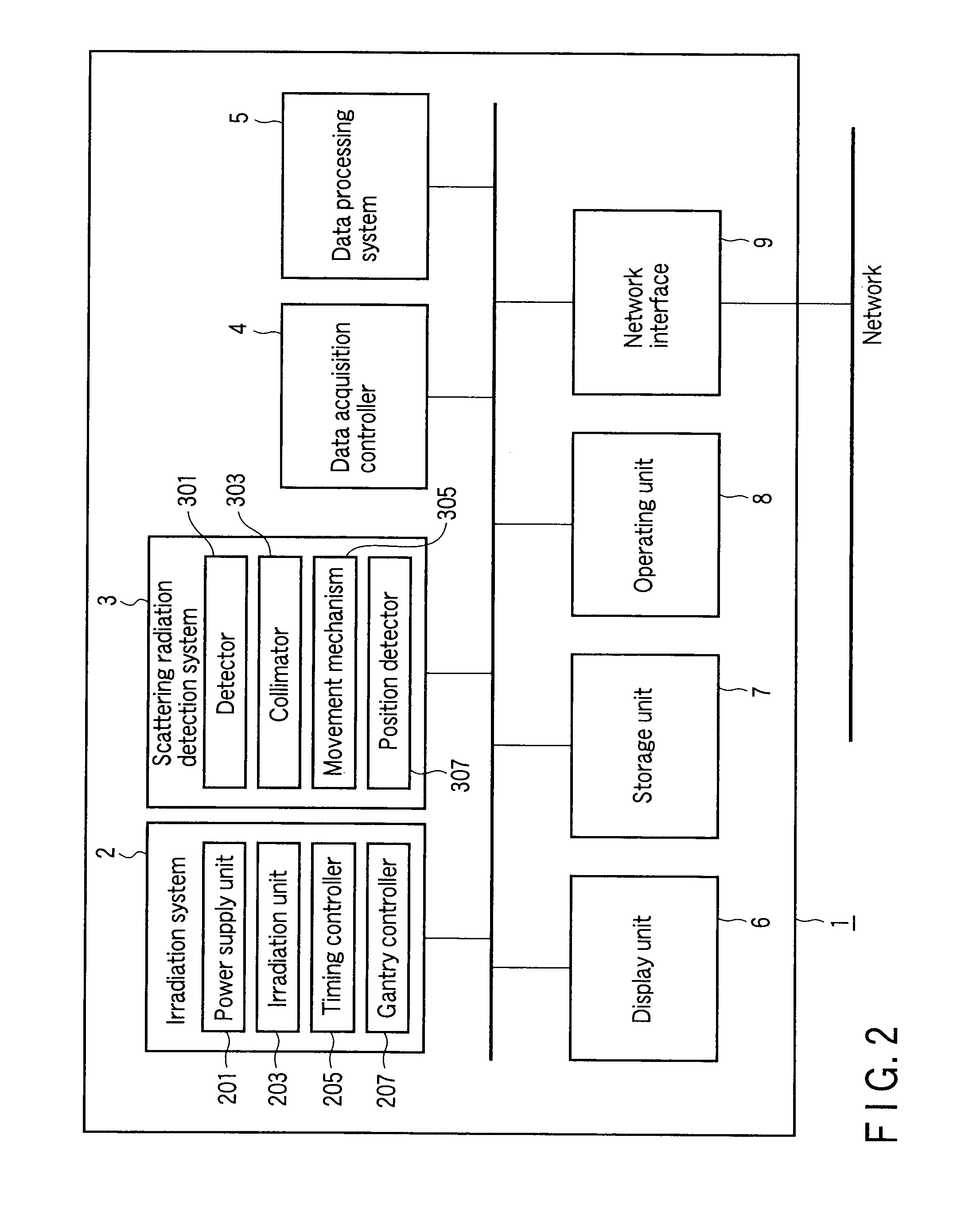
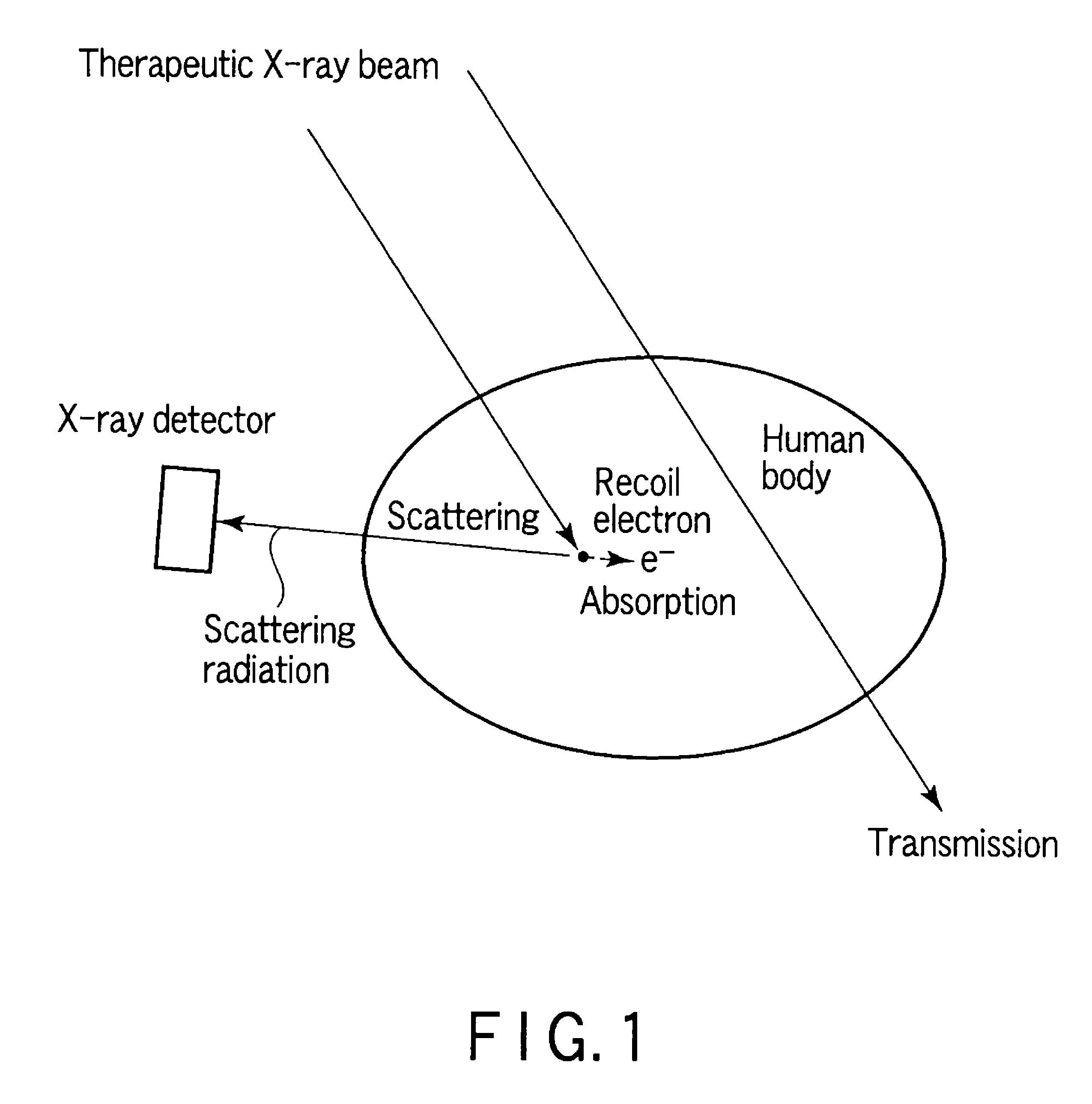
Radiotherapy support apparatus
ActiveUS20090175418A1Performed accurately and safelyExcessive irradiationX-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyVolumetric dataComputer science
A radiotherapy treatment support apparatus includes a storage unit which stores absorption dose volume data expressing a spatial distribution of absorption dose in a subject, a generation unit which generates fusion data associated with morphology volume data of the subject and the absorption dose volume data so as to be associated with a plurality of segments, and a display unit which displays an image which has the distribution of absorption dose superimposed on the two-dimensional morphology image of the subject using the fusion data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method and system for radiographic imaging with organ-based radiation profile prescription
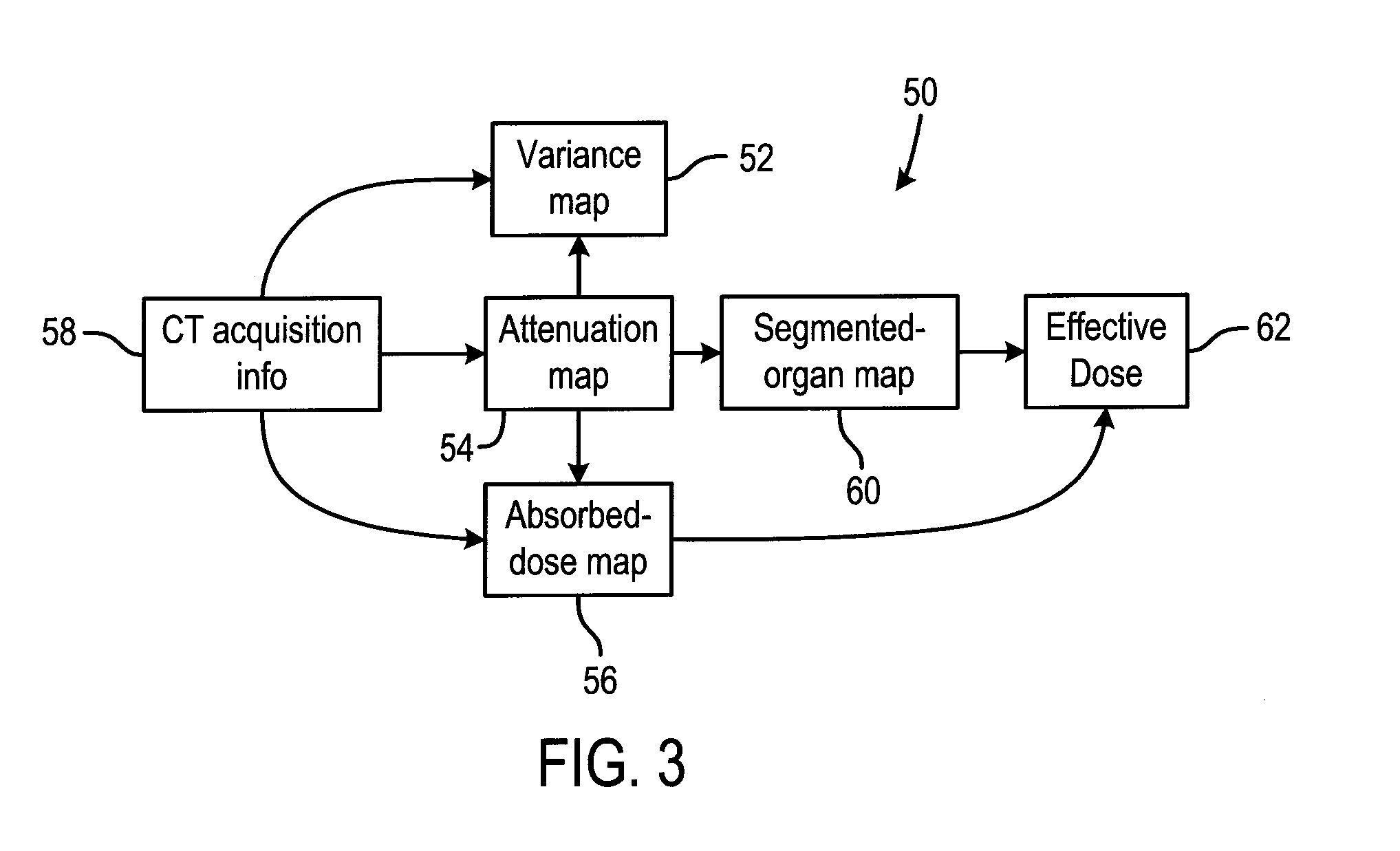
InactiveUS20070147579A1Minimizes effective doseMaximizing image qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingFiltrationX-ray
A method and system is disclosed that minimizes the effective dose to an object by determining a segmented component map for the object, parametrizing tube current / energy level / x-ray filtration / x-ray pulse width as a function of time, determining a corresponding absorbed dose map and variance map, and determining an energy level / tube current profile or curve that results in a desirable effective dose to the object and a desirable noise variance throughout the image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ground equivalent fluence calculating method for electronic component charged particle irradiation effect
InactiveCN103116176ASolve the technical problem of large error in simulation testThe calculations are realisticDosimetersProtection layerElectron
The invention relates to a simulating test method of an electronic component and discloses a ground equivalent fluence calculating method for an electronic component charged particle irradiation effect. The ground equivalent fluence calculating method for the electronic component charged particle irradiation effect aims to solve the technical problem that a ground simulation test of the irradiation effect of the existing electronic component is large in experimental error. The ground equivalent fluence calculating method for the electronic component charged particle irradiation effect comprises the following steps: measuring the energy spectrum of orbit charged particles received by the electronic component; utilizing the method of Monte-Carlo or the program of GEANT4 to calculate the in-orbit lonization and the displacement absorbed dose D1 which pass through a protection layer and reach the surface of the electronic component; determining the thickness of a sensitive area of the electronic component; determining the types and energy of particles under the selected condition of the test, calculating the lonization and the displacement absorbed dose D2 of the sensitive area under the condition of the test through the method of Monte-Carlo or the program of GEANT4; and calculating the equivalent fluence phi and the irradiation time t under the condition of a laboratory according to D1=D2. The ground equivalent fluence calculating method for the electronic component charged particle irradiation effect is used for a simulation test of the electronic component.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Serotonin for capturing carbon dioxide gas and serotonin absorbent
The invention belongs to the technical fields of resource environment and chemical engineering, and relates to a serotonin absorbent for capturing carbon dioxide gas, which particularly consists of mono etobaccool amine solution and an activating agent; the activating agent is polyamine the molecule of which comprises two or more than two amino-groups / imino groups; and the molar ratio of the mono etobaccool amine liquid and the activating agent is 4-1 to 1. The serotonin absorbent for capturing carbon dioxide gas is mixed with water to obtain the serotonin absorbent, and can be directly used for capturing carbon dioxide. As cheaper MEA (Mono Etobaccool Amine) is adopted as the main body of the absorbent, the serotonin absorbent for capturing carbon dioxide gas has the characteristics of low cost, large absorbed dose and high desorption quantity; moreover, the causticity of the serotonin absorbent is lower; the serotonin absorbent for capturing carbon dioxide gas is suitable for removing the carbon dioxide in a plurality of chemical engineering reaction tail gases, burning flue-gases and natural mixed gases, and can also be used for removing the carbon dioxide in urban coal gases and natural gases, etc. Moreover, the serotonin absorbent for capturing carbon dioxide gas is beneficial for industrial application.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Mentoring method and device for measuring effective dose on real time
ActiveCN104749605AReal-time measurementEnhanced Radiation ProtectionX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNon real timeTissue Model
The invention belongs to the radiation dose monitoring technology, and specifically relates to a monitoring method and device for measuring effective dose on real time. The method comprises the steps of manufacturing a simulated human organ or tissue model; performing monte carlo simulation calculation through a computer to obtain absorbing dose of a plurality of points in the organ or tissue model so as to obtain an average value; finding out the points in which the absorbing dose is the same as the calculated average value in the organ or tissue model; arranging a detector on the points corresponding to the organ or tissue model, wherein the measurement result represents the average absorbing dose DT, R of the organ or tissue; calculating the effective dose for a human body by the calculation formula of the effective dose E according to the weight factor wT of the organ or tissue and the selected value of the radiation weight factor wR. With the adoption of the method and the device, the effective dose for workers can be directly measured, and thus the radiation protection can be conveniently optimized.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Method for non-destructive measuring of radiation dose
InactiveUS7098470B2Accurate acquisitionMaterial analysis by optical meansBy pulling from meltDosimetry radiationFluorescence
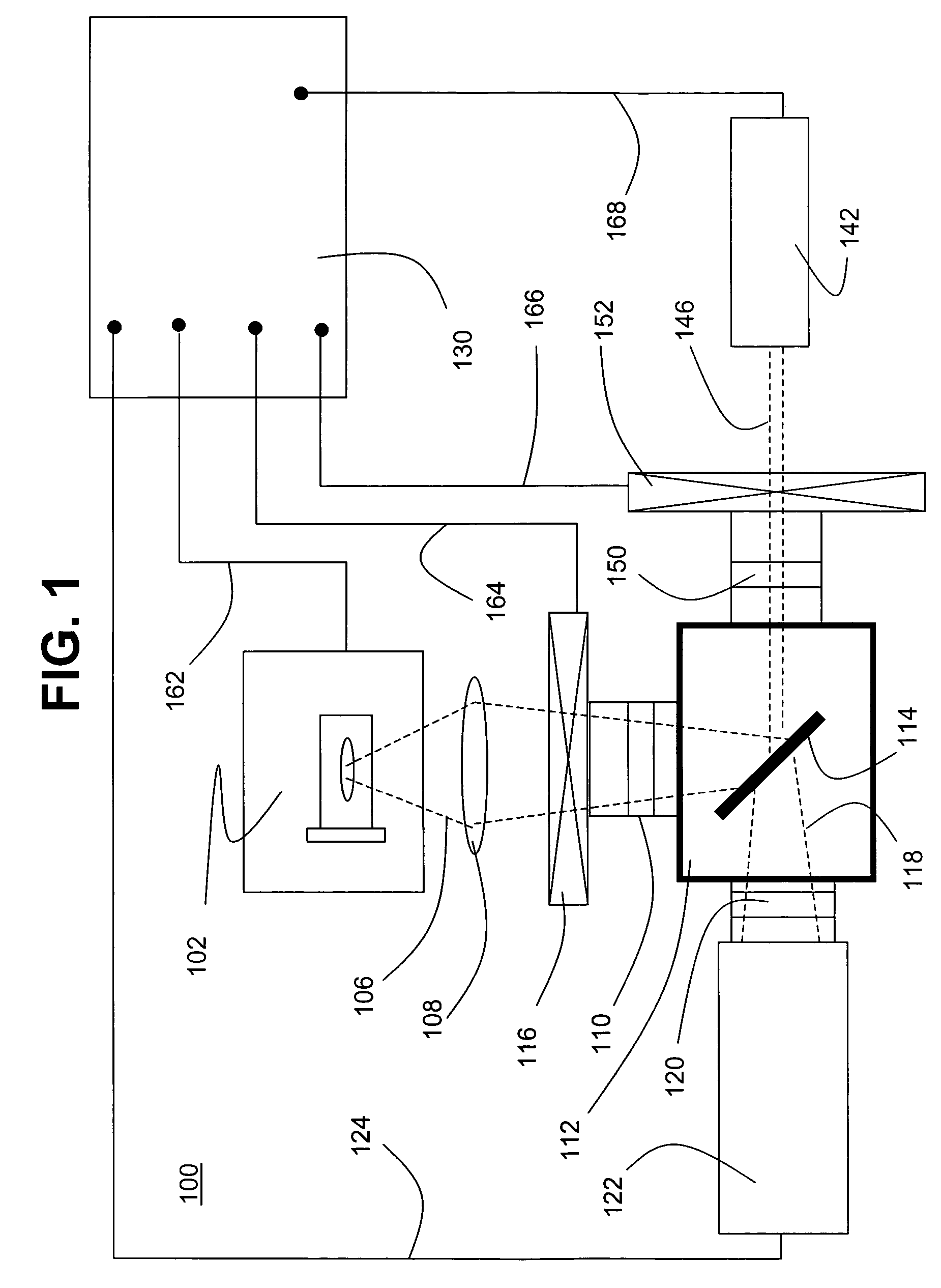
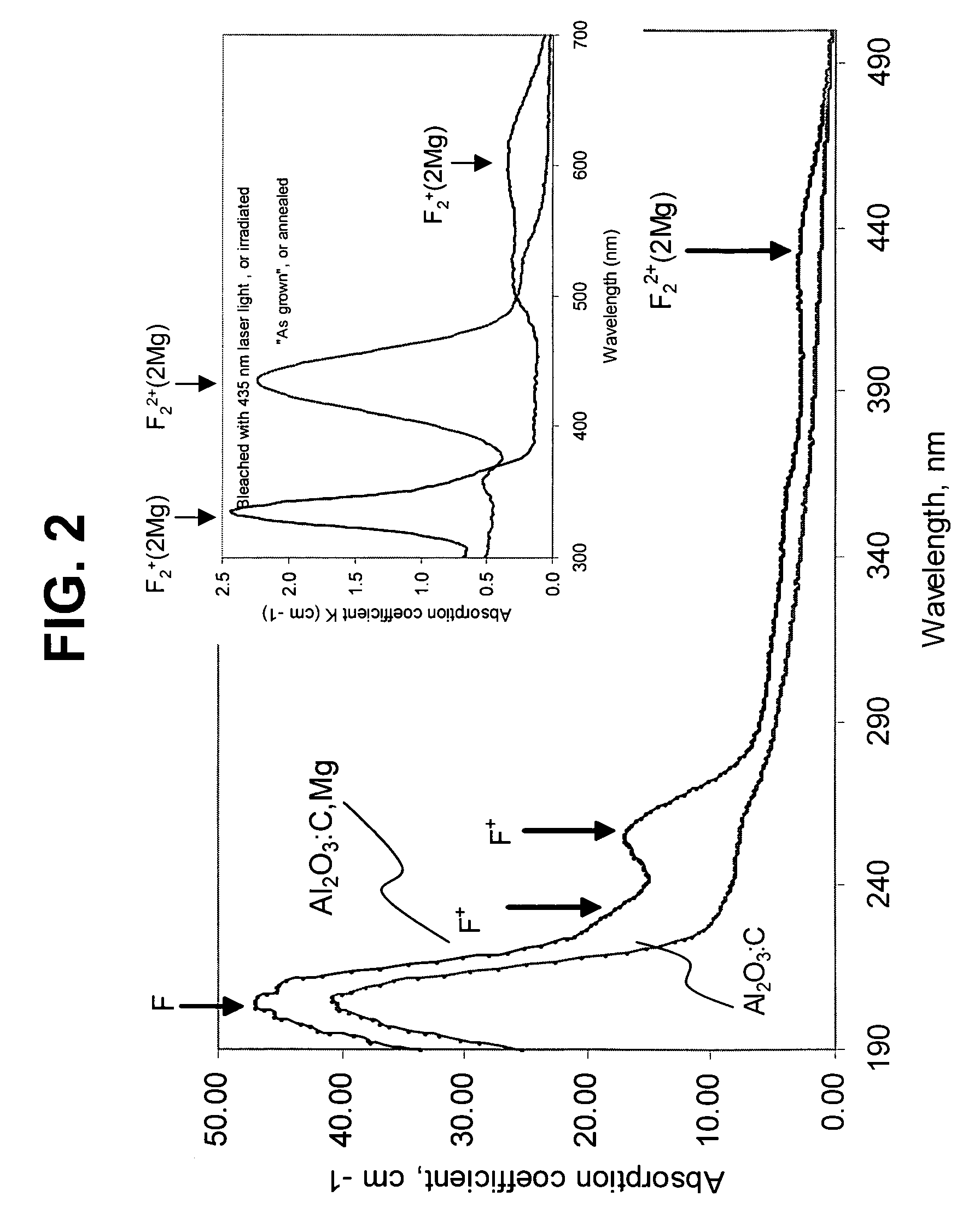
The invention presents a method of radiation dosimetry and radiation field imaging. It utilizes luminescent material based on aluminum oxide doped with carbon and magnesium (Al2O3:C,Mg) and containing aggregate oxygen vacancy defects. Storage of dosimetric information is based on ionization of the crystal matrix, generation of free electrons and capture of electrons and holes by traps and color centers. An absorbed dose is determined by non-destructive readout of fluorescence from color centers induced by radiation. The preferred mode of measurements is to illuminate the Al2O3:C,Mg phosphor with a red laser (at 635 or 650 nm) and to measure the intensity of 750 nm fluorescence. Method allows for high temperature and environmental stability of dose information. The detector material is insensitive to room light before and after the irradiation and provides a fast data rate during scanning for imaging of radiation fields.
Owner:LANDAUER INC
Composite enhanced high-flexibility microporous silicone rubber foam material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a composite enhanced high-flexibility microporous silicone rubber foam material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method is characterized in that the preparation method comprises the steps of performing mixing and forming to 100 parts of silicone rubber base material, 10-25 parts of reinforcing agent, 2-3 parts of structure controlling agent, 80-100 parts of pore-forming agent, 0-3 parts of radiation sensitizer, 1-2 parts of tackifier and 1-3 parts of functional additive, performing radiation crosslinking at gamma ray absorbed dose of 40-60kGy, performing solventing-out pore forming through warm water, and performing drying to obtain the microporous silicone rubber foam material with excellent performance. The composite enhanced high-flexibility microporous silicone rubber foam material prepared by adopting the preparation method disclosed by the invention presents black gloss, is soft in texture, is tiny in pore diameter, is proper in crosslinking density and gel content, is higher in tensile strength and elongation at break and is excellent in resilience, the process is convenient, the energy saving performance and environmental friendliness are good, the repeatability is good and the production efficiency is high.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
Variance reduction simulation system, program product, and related methods
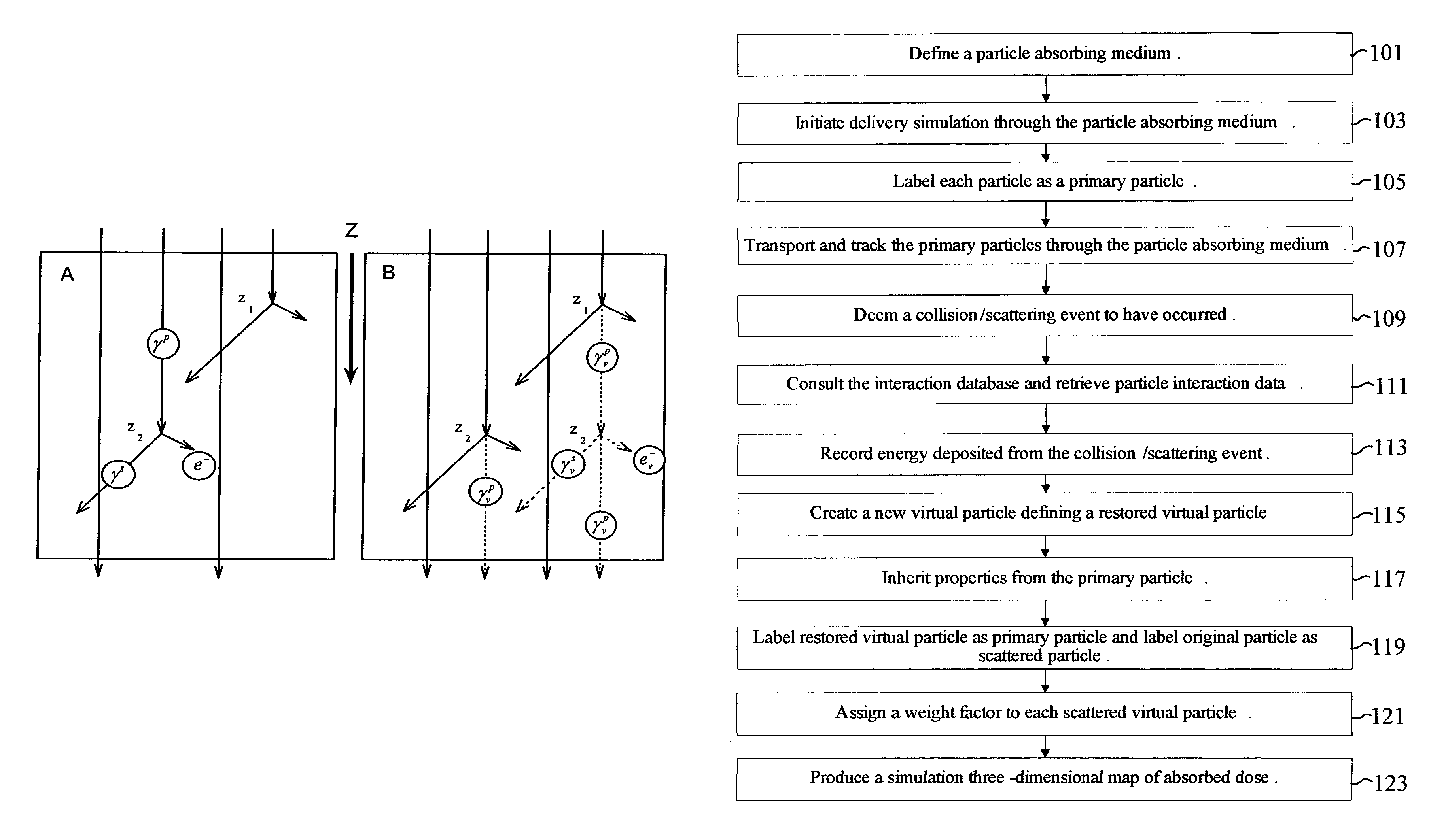
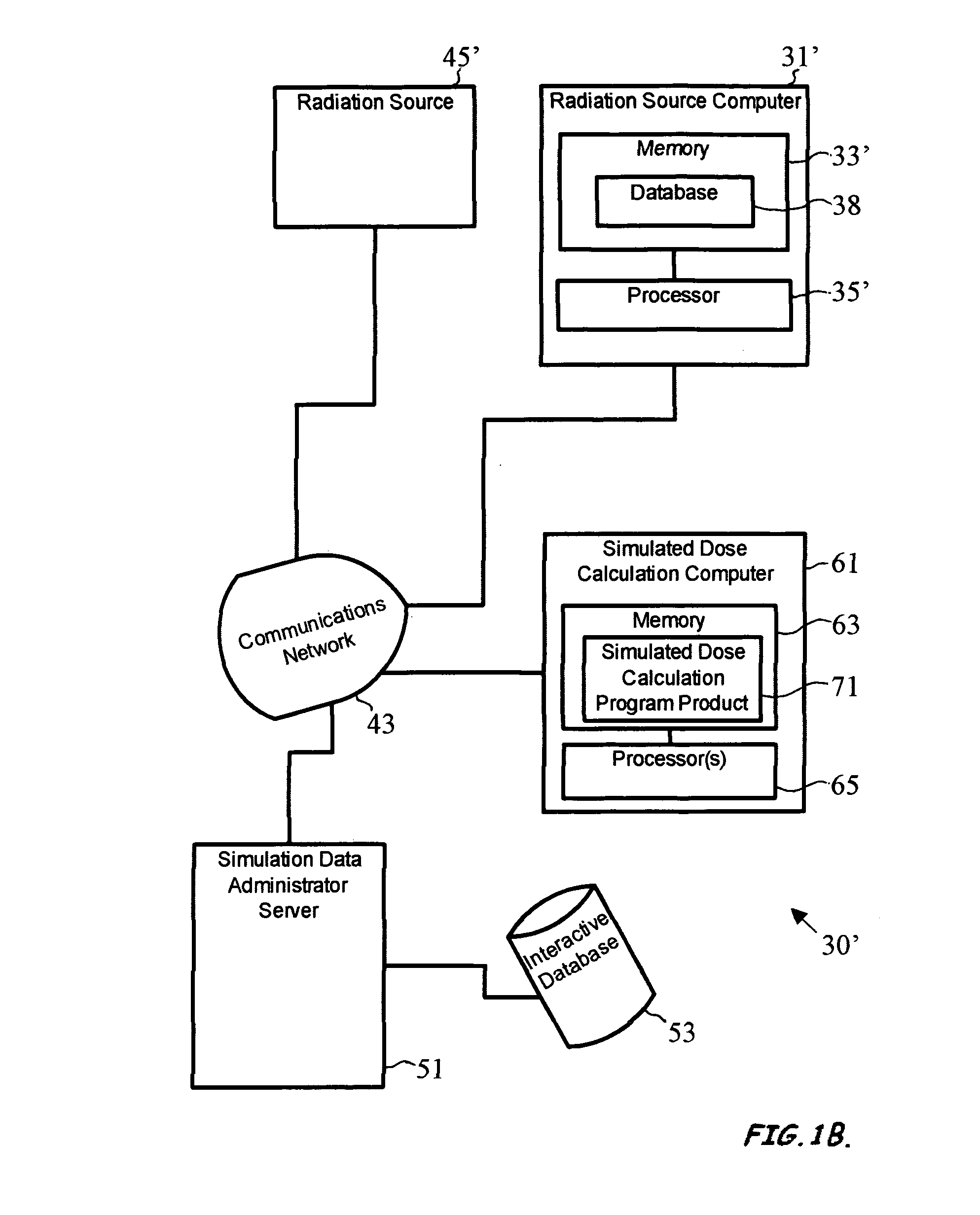
ActiveUS8125813B2Improve computing efficiencyCost efficientDigital storageProbabilistic CADParticle interactionComputer science
A system to provide enhanced computational efficiency in a simulation of particle transport through a medium, program product, and related methods are provided. The system can include a simulation data administrator server having access to an interaction database including records related to parameters describing interactions of particles in an absorbing medium to provide particle interaction parameters, and a simulated dose calculation computer in communication with the simulation data administrator server through a communications network. The system can also included simulated dose calculation program product stored in memory of the simulated dose calculation computer and including instructions that when executed by a processor causes the processor to perform for each of a plurality of particles deliverable from a particle source the operations of providing parameters for a medium to perform a Monte Carlo simulation to develop a map of simulated absorbed dose in the medium, and artificially adjusting simulation particle fluxes to achieve a substantially constant variance throughout a depth of the medium.
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
Irradiation system having cybernetic parameter acquisition system
InactiveUS20050077472A1Easily and safely treatMaterial analysis by optical meansMachines/enginesContinuous measurementElectron
Irradiation system including a cybernetic parameter acquisition system, for acquiring parameter data associated with an object to be irradiated. The system includes apparatus for measuring doses of electron beams that are absorbed by an object subjected to irradiation. The absorbed dose can be continuously measured during an irradiation process, and adjustment can be made to operating parameters of the irradiation system in accordance with the measured absorbed dose.
Owner:STERIS CORP
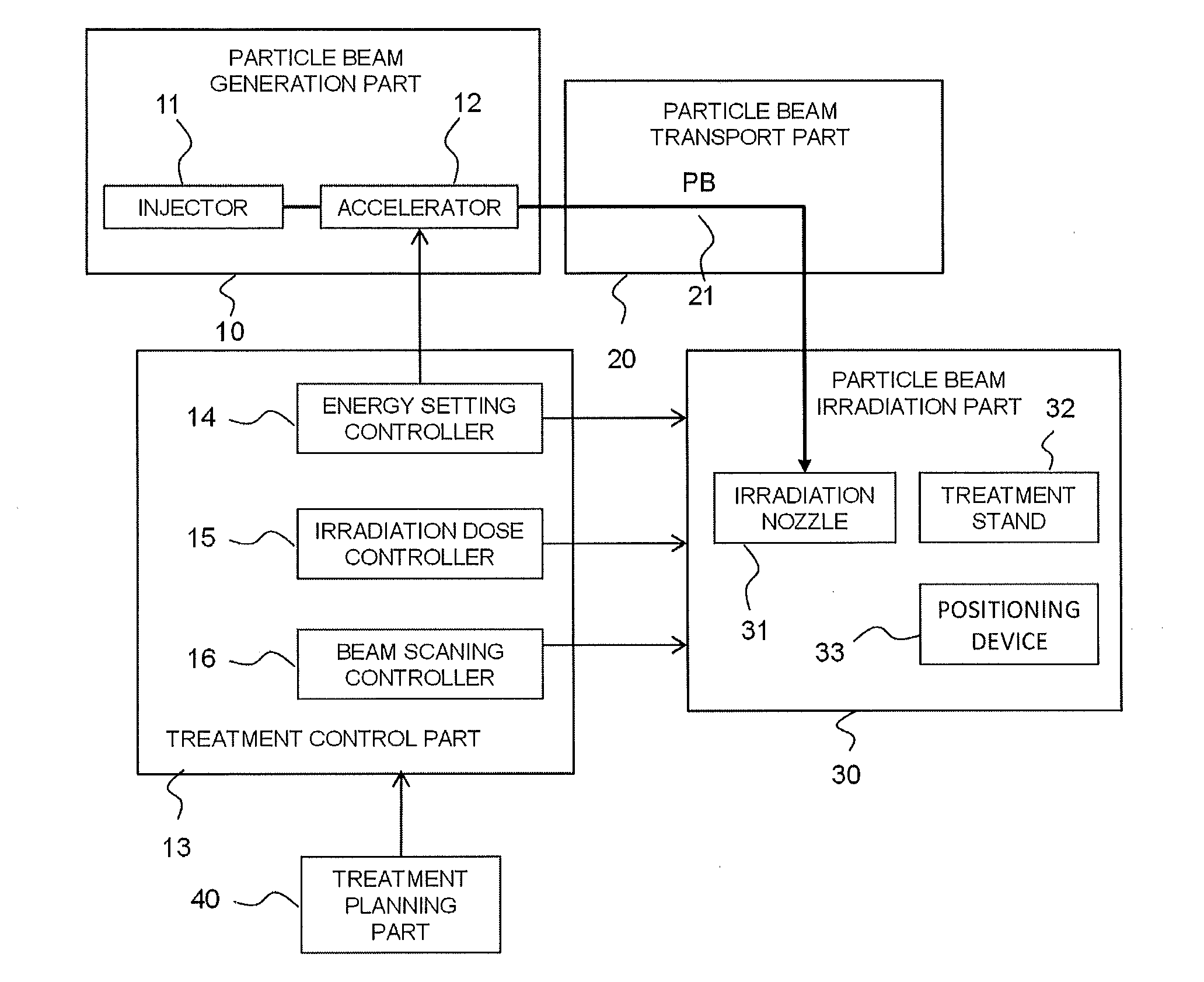
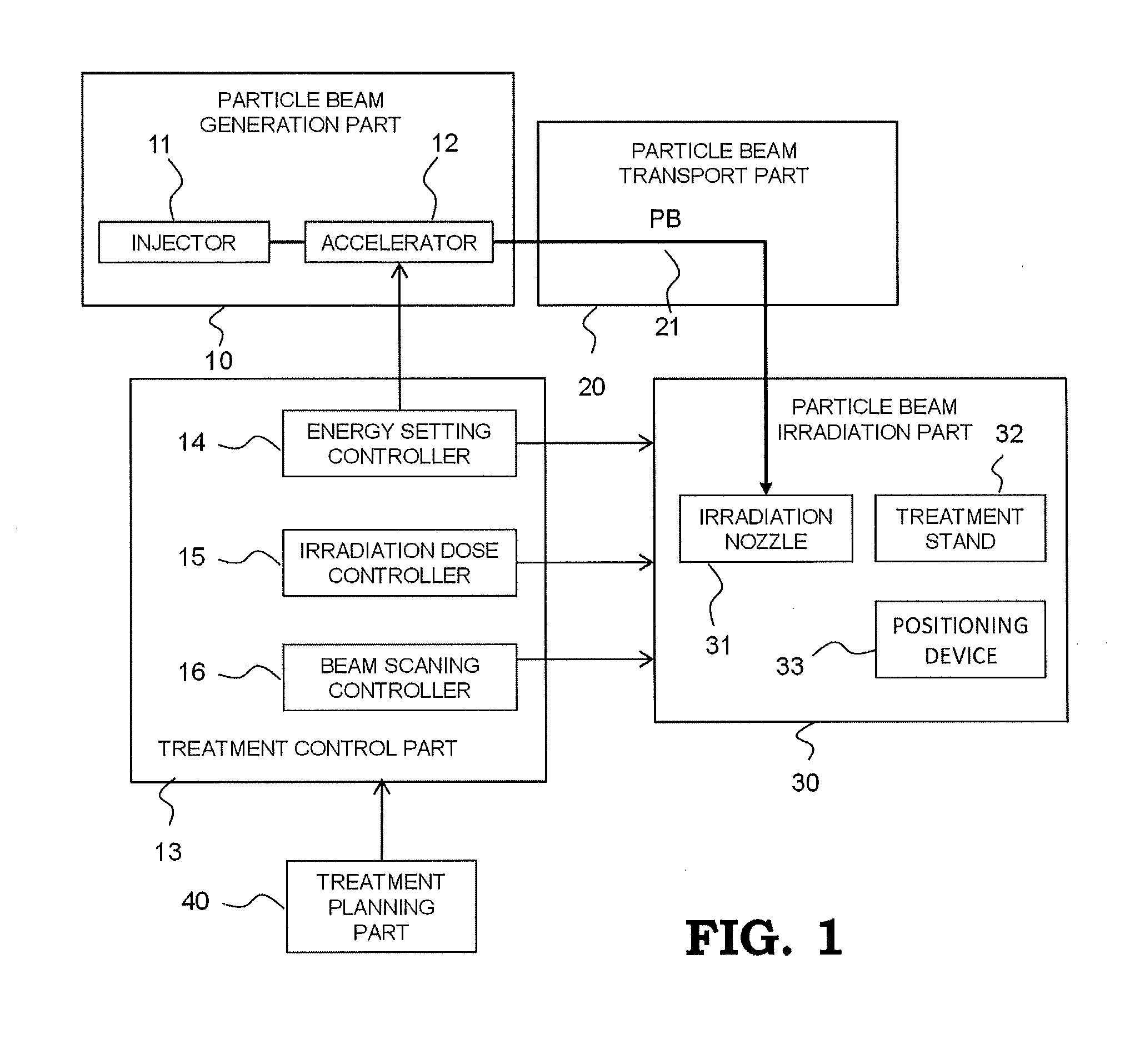
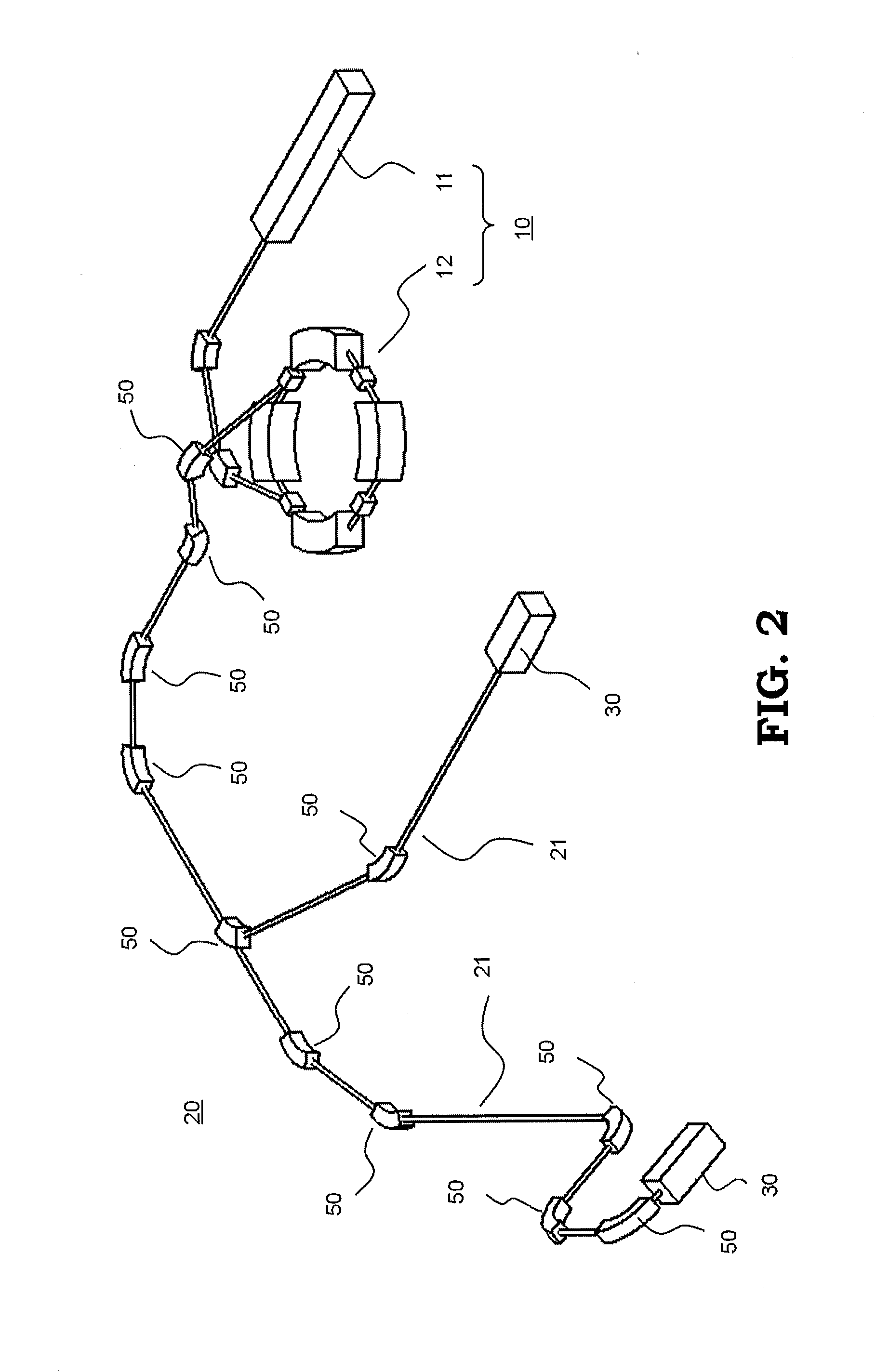
Particle beam treatment device and irradiation dose setting method of the particle beam treatment device
ActiveUS20120313002A1Avoid excessive changesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsBragg peakDose profile
A particle beam treatment device includes an irradiation nozzle which moves a particle beam in a direction which is perpendicular to an advancing direction; a dose monitor which measures the dose of the particle beam; a planning part which sets the irradiation dose applied to a target volume; and a controlling part which controls the irradiation dose applied to a target volume based on irradiation dose set value which is set by a value measured by the dose monitor and the planning part, wherein the planning part stores the absorbed dose distribution data in the depth direction which is prepared in advance using the absorbed dose at the reference depth which is a predetermined position nearer to an incident side of the particle beam than the position of Bragg peak as the reference and calculates the irradiation dose set value using the absorbed dose at the reference depth.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Silicone rubber microporous foam material adopting mixed cellular structure and preparation method of silicone rubber microporous foam material
The invention discloses a silicone rubber microporous foam material adopting a mixed cellular structure and a preparation method of the silicone rubber microporous foam material. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: mixing 100 parts of a silicone rubber base material, 15-45 parts of a reinforcing agent, 2-3 parts of a structure controlling agent, 60-125 parts of a pore-forming agent and 3-5 parts of a radiosensitizer, forming, radiating through gamma rays so as to enable the formed product to be crosslinked, wherein the radiation absorbed dose is 30-70 kGy, performing solventing-out section by section to form holes, and drying, so as to obtain the silicone rubber microporous foam material with excellent performance. According to the invention, the method that radiation crosslinking cooperates with solventing-out hole forming is adopted, so that crosslinking is uniform, control is convenient, energy conservation and environment friendliness are realized, the process is simple, reproducibility is good, and production efficiency is high; the prepared silicone rubber microporous foam material adopts the mixed cellular structure, and is excellent in comprehensive performance, small in hole, pure white in color, soft in texture, proper in crosslinking density and gel content, high in tensile strength and elongation at break and low in permanent tensile deformation and compression deformation.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
Dose monitoring detector calibration device and method in heavy ion beam treating carcinoma
ActiveCN101285887A3D Conformal Radiation Therapy ControlImprove treatment efficiencyDosimetersBragg peakTumor target
The invention relates to a device and a method for demarcating and calibrating a dose monitoring detector in heavy ion beam cancer treatment. The structure of the device is characterized in that a collimator, the dose monitoring detector, a mini ridge-shaped filter, a water tank and a standard ionization chamber are arranged on a beam flux axis in sequence. The standard ionization chamber is arranged inside the water tank. The depth position of an irradiation beam mini spread-out Bragg peak in water is obtained by measuring absorbed dose of the standard ionization chamber at different depth in aqueous medium. At the depth position, the dose monitoring detector is demarcated and calibrated by the standard ionization chamber so as to obtain demarcating and calibrating factors of the measurement of the dose monitoring detector for the mini spread-out Bragg peak cancer treatment beam with a Gauss arrangement. With the demarcating and calibrating factors, the entire process of three-dimensional conformal irradiation therapy with uniform physical absorption dose or uniform biological effective dose in a tumor target volume can be conveniently controlled, the requirements of the treatment of different clinical cases in practical clinical treatment are satisfied, and the treatment efficiency of a treatment device is improved.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for performing in vivo dosimetry
ActiveUS20050151071A1Time-efficient and accurateQuality improvementDosimetersCalibration apparatusDose deliveryRadiation beam
The present invention relates to a method enabling quantification of dose delivery in radiotherapy treatment during patient-specific treatment of the patient utilising measurements in predefined time-intervals with information means positioned in the radiation beam, between the patient and the source and converting the readings to corresponding measures in a phantom. The invention additionally covers the method to obtain the said calibration factors for the detectors. The said calibration factors are obtained for each information means, field and said definable time-interval simultaneously irradiating the information means and said phantom including detectors to measure the absorbed dose using the said patient-specific treatment without patient.
Owner:NILSSON GORGEN
Biodosimetry panels and methods
InactiveUS20140315742A1Peptide librariesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesNormal controlRadiation exposure
The present invention relates to methods and kits to assess an absorbed dose of ionizing radiation and / or the severity of tissue injury from radiation in a patient. The invention also relates to algorithms used to calculate an absorbed dose of radiation based on biomarker measurements of a plurality of biomarkers that are altered relative to a normal control in the event of radiation exposure.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC +1
Method for performing in vivo dosimetry
ActiveUS7345274B2Time-efficient and accurateQuality improvementDosimetersCalibration apparatusDose deliveryRadiotherapy treatment
The present invention relates to a method enabling quantification of dose delivery in radiotherapy treatment during patient-specific treatment of the patient utilizing measurements in predefined time-intervals with information means positioned in the radiation beam, between the patient and the source and converting the readings to corresponding measures in a phantom. The invention additionally covers the method to obtain the said calibration factors for the detectors. The said calibration factors are obtained for each information means, field and said definable time-interval simultaneously irradiating the information means and said phantom including detectors to measure the absorbed dose using the said patient-specific treatment without patient.
Owner:NILSSON GORGEN
Preparing low molecular weight chitosan by sensitizing radiation degradation method
The sensitizing and readiation degrading process of preparing low molecular weight chitosan includes the following steps: mixing refined solid chitosan with water solution of sensitizer to form semi-solid sample, regulating pH to 4 with inorganic acid or organic acid and reaching chitosan concentration of 16-25 wt% and sensitizer concentration of 15-30 wt%, gamma ray irradiation in the dosage of 1-10 kGy to degrade at room temperature, and spray drying or vacuum drying to obtain low molecular weight chitosan. Adding the sensitizer can lower the irradiation dosage greatly, and obtain chitosan product with narrow molecular weight distribution and small molecular weight. The present invention can obtain chitosan with molecular weight as low as 3000, and the process is convenient, safe, economic, practical, high in yield and environment friendly.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
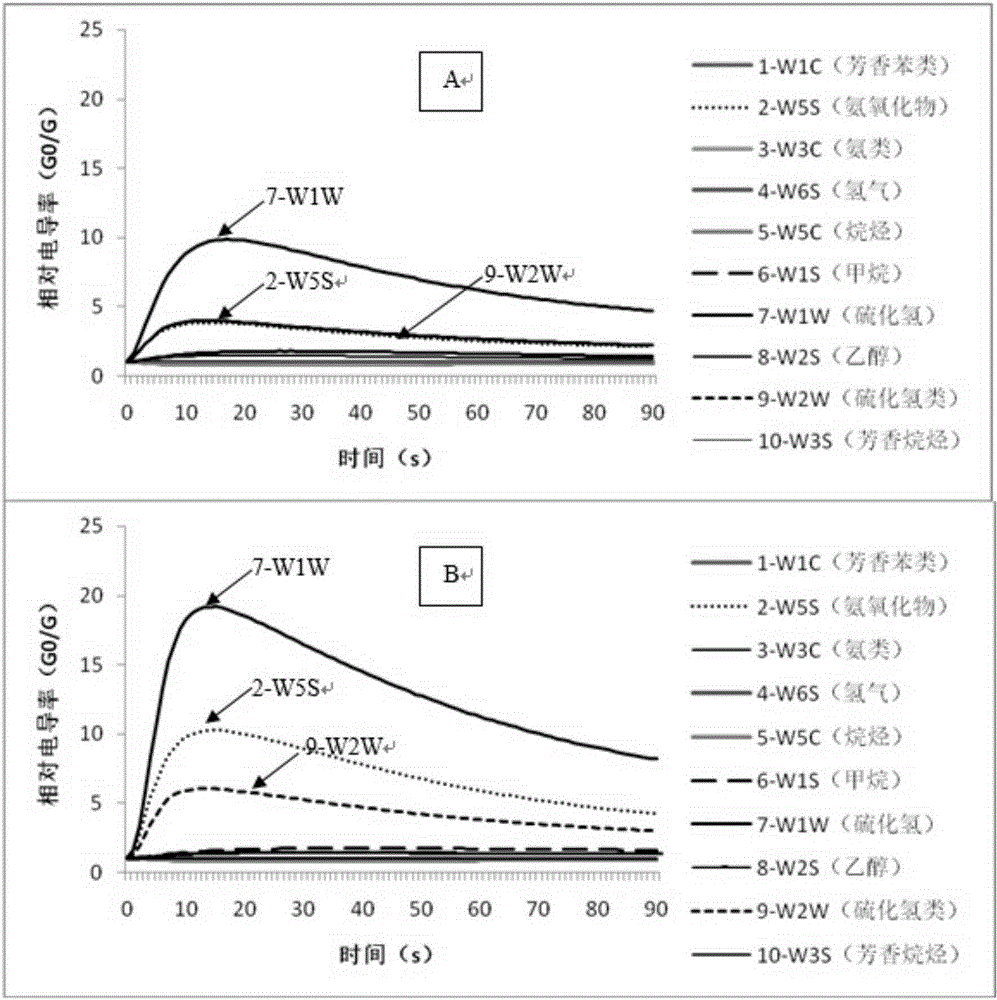
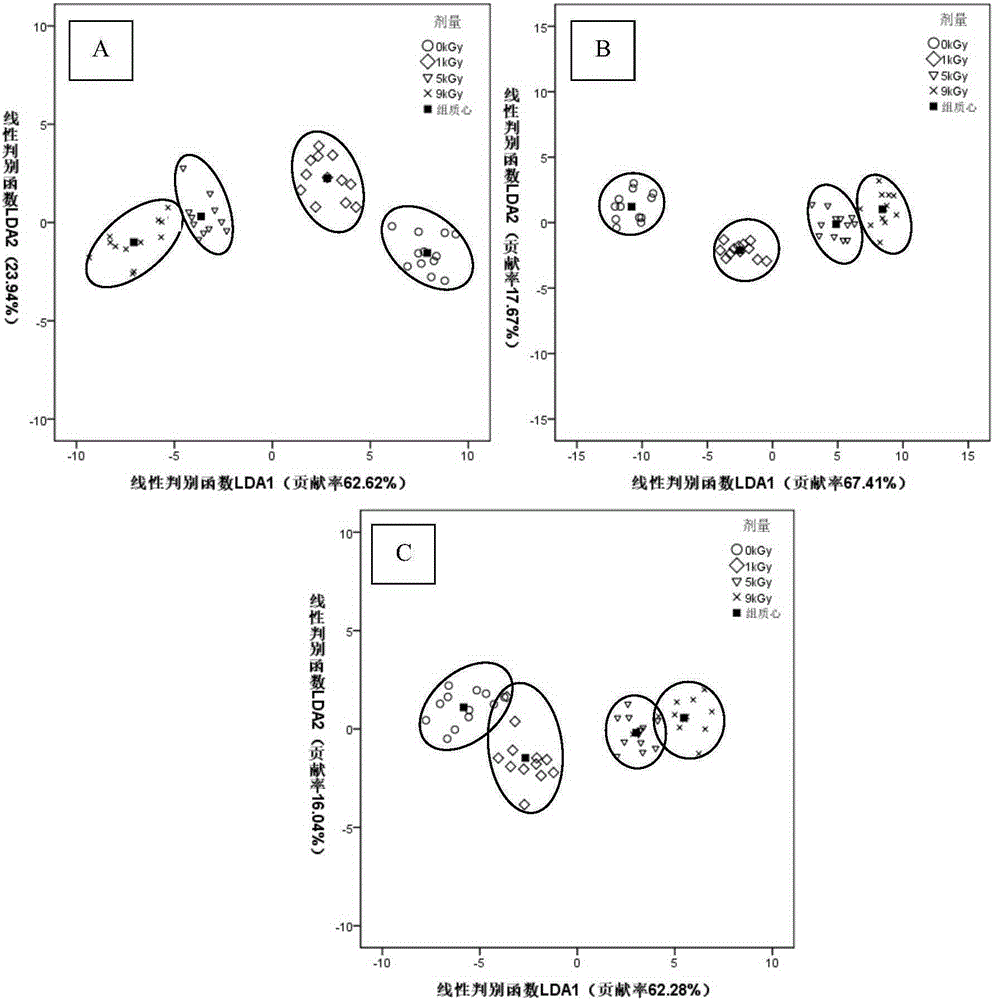
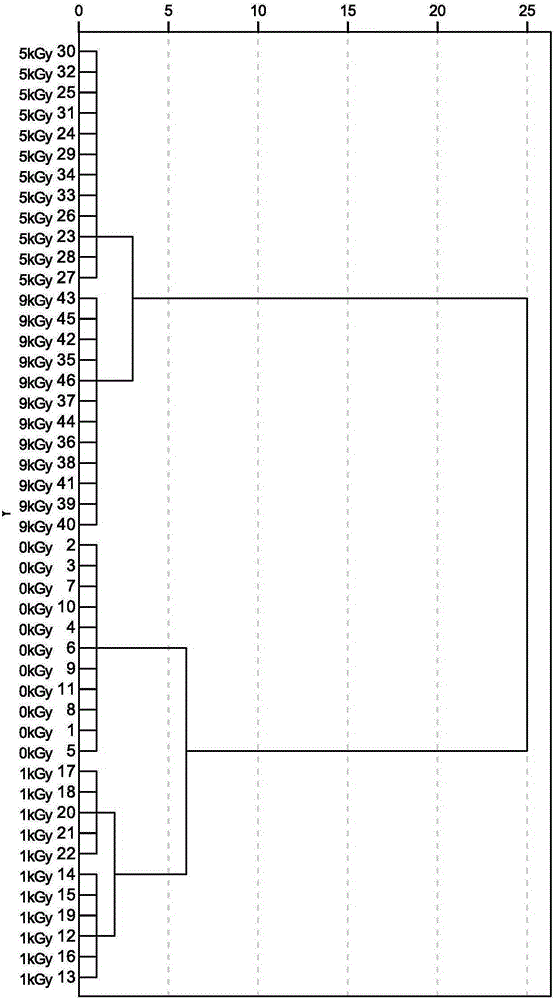
Method for rapidly identifying irradiation absorbed dose of tea by using electronic nose
The invention discloses a method for identifying whether tea is irradiated and irradiation absorbed dose and a new application of an electronic nose. The identifying method comprises: employing tea samples which are treated by irradiation of different known doses; detecting the tea samples whose irradiation absorbed doses are known by the electronic nose; drawing a response diagram of tea volatile substances detected by the electronic nose; determining an identification evaluation time; calculating the variance contribution rate of an electronic nose sensor characteristic constant of each main component and the correct rate of initial group case return discrimination, and preferably choosing an effective sensor; calculating to obtain classification function coefficients of different radiation doses, and obtaining a classification function for identifying a tea sample radiation dose; detecting an unknown tea sample by the electronic nose, calculating with the classification function, and obtaining a radiation dose of the tea. Compared with the prior art for identifying tea, the identifying method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple method, few steps, fast speed, high identification efficiency, high accuracy, etc., and the method is suitable for identifying whether the tea is irradiated or the irradiation absorbed dose.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Area exposure dosimetry and area absorbed dosimetry
The area of an irradiation region, and at least one of the area of an object region and the area of a non-object region in a radiation image obtained by radiographing an object are calculated. The effective dose of radiation from a radiation generator is acquired. An area exposure dose, the X-ray amount radiated on the object, is calculated on the basis of the area of the irradiation region, one of the area of the object region and the area of the non-object region, and an effective dose.
Owner:CANON KK
Starch hydrogel
The hydrogel forming composition contains up to 10 wt.% of the starch, up to 5 to 7.5 wt.% of polyvinylpyrrolidon, up to 5 to 10 wt.% of polyvinyl alcohol, up to 1% to 3 wt.% of water-soluble cellulose and water. The hydrogel is prepared by exposing a half-gelled material made of the composition to an electron beam or a [gamma]-ray to the extent that the total beam absorption amounts to 5 to 50 kGy.
Owner:MALAYSIAN INST FOR NUCLEAR TECH RES
Silicon carbide ceramic material and preparation method thereof
The present invention discloses a silicon carbide ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises: (1) irradiating polycarbosilane having a number average molecular weight of 300-4000 with high energy rays, wherein the absorbed dose of the polycarbosilane is 50-2000 kGy; and (2) carrying out pyrolysis on the irradiated polycarbosilane to obtain the silicon carbide ceramic material. According to the present invention, the silicon carbide ceramic material is prepared by using the in-situ irradiation method, such that only the chemical structure of the polymer is changed, and the impurity is not introduced; the irradiation process is completely controllable and the irradiation dose can be controlled according to the raw material characteristics to achieve the best effect, such that the yield of the silicon carbide ceramic material can be significantly improved, the production cost can be reduced, the production period can be shortened, and various molding processes and the production processes of the irradiated polycarbosilane cannot be affected; and the silicon carbide ceramic material prepared by using the preparation method has advantages of uniformity, further improved temperature resistance, further improved compactness, further improved tensile strength, and other properties.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Permanent magnet for particle beam accelerator and magnetic field generator
InactiveUS20050258784A1Permanent magnetsMagnetic resonance acceleratorsRare-earth elementParticle accelerator
A permanent magnet for a particle accelerator and a magnetic field generator, in which Nd—Fe—B based magnets are used but are not demagnetized so easily even when exposed to a radiation, are provided. A permanent magnet for a particle accelerator is used in an environment in which the magnet is exposed to a radiation at an absorbed dose of at least 3,000 Gy. The magnet includes R (which is at least one of the rare-earth elements), B, TM (which is at least one transition element and includes Fe) and inevitably contained impurity elements. The magnet is a sintered magnet that has been magnetized to a permeance coefficient of 0.5 or more and that has a coercivity HcJ of 1.6 MA / m or more.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Reversible electroporation device for inducing cell apoptosis
InactiveUS20120130369A1Reduce inflammationElectrotherapySurgical instrument detailsLower limitApoptosis
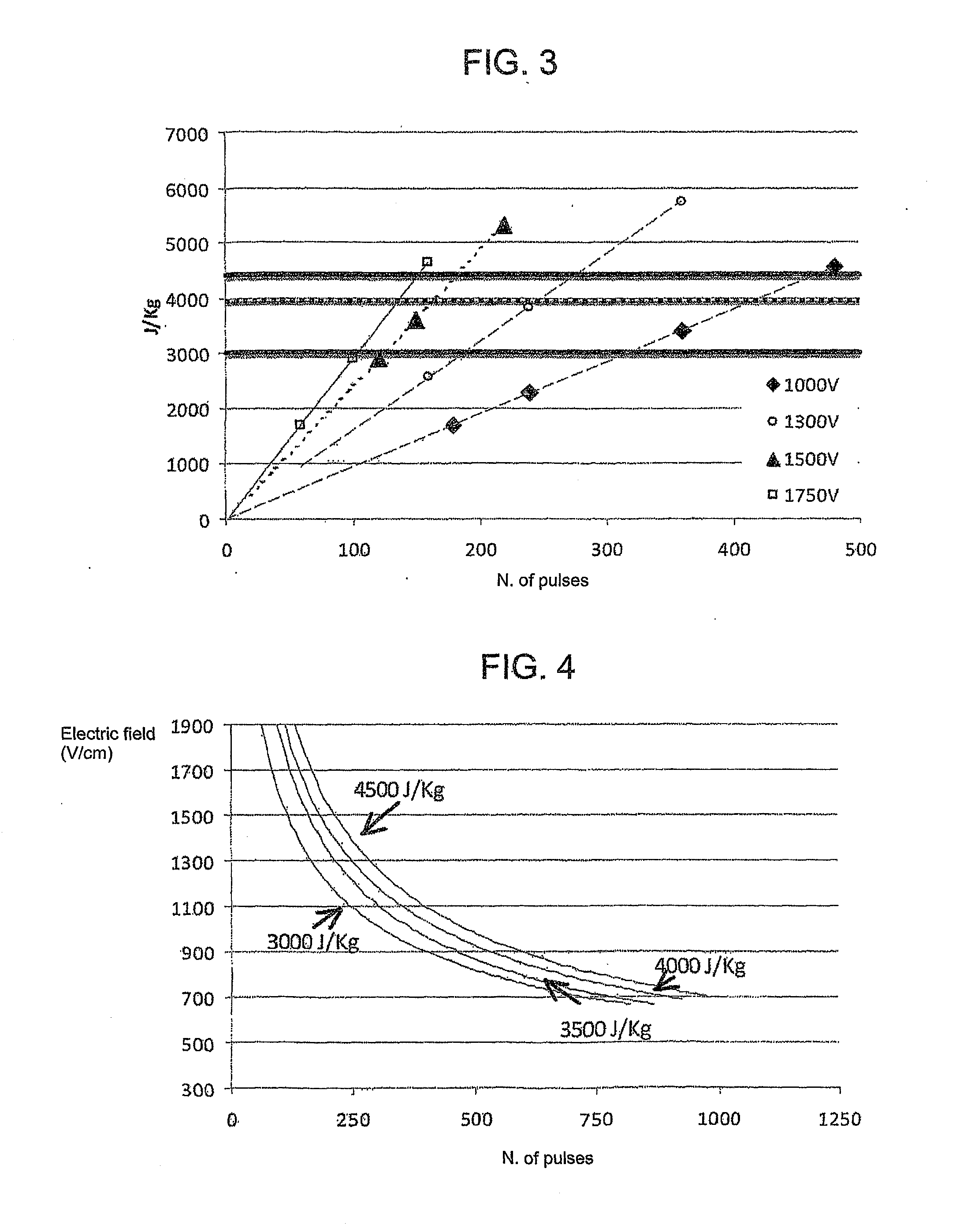
A reversible electroporation device in which an electric pulse generator generates a sequence of electric pulses delivered to electrodes coupled to a tissue in which a process of reversible electroporation that generates cell apoptosis is to be performed. The device is configured to control the amplitude of the pulses and the number of the pulses delivered to the electrodes so that the amount of energy per weight unit (absorbed dose) applied to the tissue is in a range between a first lower limit value of about 3000 J / kg and a second upper limit value of about 4500 J / kg.
Owner:IGEA
Lung 4D-CT image exhaling process middle phase image reconstruction method based on registration
InactiveCN104361568AReduced Radiation Dose for ImagingImage enhancementImage analysisReconstruction methodReference image
The invention discloses a lung 4D-CT image exhaling process middle phase image reconstruction method based on registration. The method includes the steps of firstly, acquiring an inhaling end phase image and an exhaling end phase image according to lung 4D-CT image data; secondly, selecting the inhaling end phase 3D-CT image as a reference image and the exhaling end phase 3D-CT image as a floating image, and registering the two phase images to obtain a motion deformation field between the two phase images; thirdly, reconstructing the lung 4D-CT image exhaling process middle phase image on the basis of the motion deformation field obtained at the second step. The method has the advantages that the 4D-CT image exhaling process middle phase image can be reconstructed by using two known special phase images, and the defect that the absorbed dose of a patient is high due to the fact that lung 4D-CT data is many in collecting phases and long in scanning time is overcome.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Carbon-based porous flexible composite wave-absorbing material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a carbon-based porous flexible composite wave-absorbing material and a preparation method thereof. The carbon-based porous flexible composite wave-absorbing material and the preparation method thereof are characterized in that pretreatment is conducted on one part of a carbon-based wave-absorbing agent, and then mixing molding is conducted on the treated carbon-based wave-absorbing agent, 0.2-0.4 part of a fluxing agent, 40-100 parts of silicone rubber, 10-30 parts of reinforcing agents, 0-5 parts of radiosensitizer and 0-3 parts of flame retardants; rubber materials molded through mixing are put into a mold, rolling is conducted on the rubber materials at 100-150 kg.cm<-2>, and a thin sheet with the thickness ranging from 0.5 mm to 5 mm is prepared; after plastic sealing is conducted on the thin sheet with the mold, the plastic-sealed thin sheet with the mold is put into a gamma-ray irradiation field or an electron beam accelerator to enable the total absorbed dose to be kept at 30-100 kGy, radiation crosslinking is conducted, after a plastic package and the mold are removed, edges are cut off, and the carbon-based porous flexible composite wave-absorbing material is obtained. According to the carbon-based porous flexible composite wave-absorbing material and the preparation method thereof, the technology is simple, complex chemical process control or professional auxiliary equipment is not needed, only simple equipment such as a double-roller mixing mill is needed, and the cost is lower; the prepared material is excellent in flexibility and wave-absorbing performance, the preparation process is easy and rapid to control, the repeatability is good, and energy conservation and environment protection are achieved.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF +1
Radiotherapy support apparatus
ActiveUS8238516B2Avoid underexposurePerformed accurately and safelyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyComputer scienceRadiotherapy treatment
A radiotherapy treatment support apparatus includes a storage unit which stores absorption dose volume data expressing a spatial distribution of absorption dose in a subject, a generation unit which generates fusion data associated with morphology volume data of the subject and the absorption dose volume data so as to be associated with a plurality of segments, and a display unit which displays an image which has the distribution of absorption dose superimposed on the two-dimensional morphology image of the subject using the fusion data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Three-dimensional dosage verification method of nuclear magnetism guidance radiation therapy based on MRI-Only
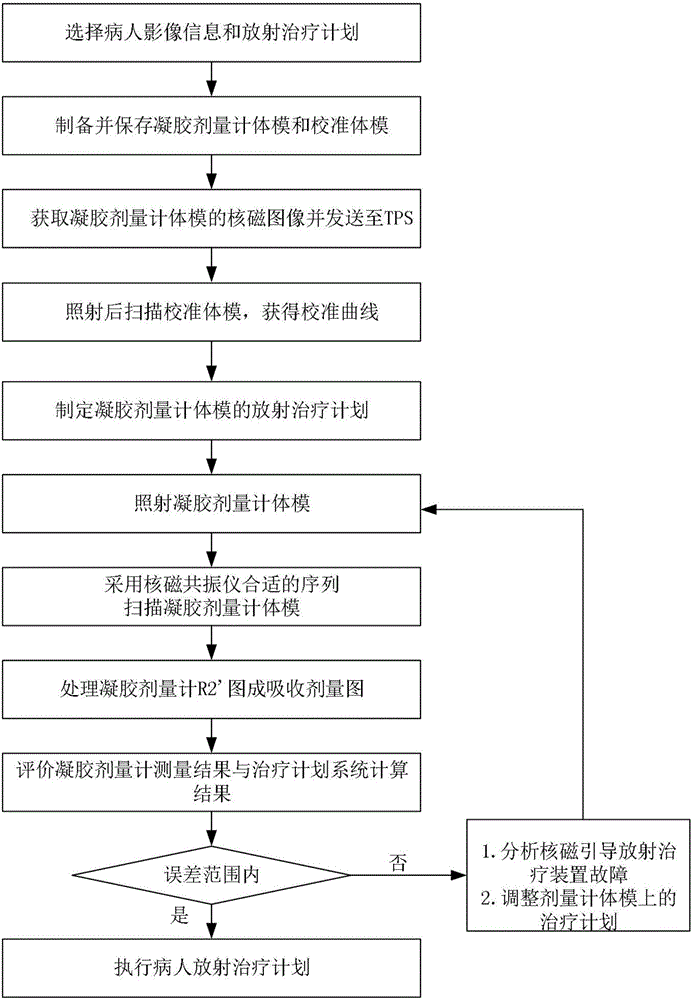
InactiveCN107519585AAccurately measure 3D dose distributionShorten the timeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDosimeterValidation methods
The present invention discloses a three-dimensional dosage verification method of nuclear magnetism guidance radiation therapy based on MRI-Only. The method comprises the following steps: selecting radiation therapy image information of a patient to be verified and a corresponding patient's radiation therapy plan, preparing and storing gel dosimeter phantom and a calibration phantom, scanning the gel dosimeter phantom to obtain the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images of a corresponding phantom, sending the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images of the corresponding phantom to a treatment plan system (TPS), irradiating and scanning the calibration phantom to obtain a calibration curve, making the radiation therapy plan of the gel dosimeter phantom, scanning the gel dosimeter phantom after irradiation, converting the images to an adsorbed dose graph, assessing results of measurement and calculation of the gel dosimeter phantom, and executing the patient's radiation therapy plan if the results of measurement and calculation of the gel dosimeter phantom accord with clinical assessment requirements. The three-dimensional dosage distribution of the nuclear magnetism guidance radiation therapy can be accurately measured and can be used for three-dimensional dosage verification to facilitate improvement of the radiation therapy effect.
Owner:徐榭
Ionizing radiation degradation method for sea cucumber polysaccharide
The invention discloses an ionizing radiation degradation method for sea cucumber polysaccharide. The method sequentially comprises the following steps of: 1) completely dissolving the sea cucumber polysaccharide into distilled water to obtain an aqueous solution of the sea cucumber polysaccharide; 2) performing ionizing radiation degradation on the aqueous solution of the sea cucumber polysaccharide at normal temperature by adopting 60 Co, wherein the absorbed dose is 2 to 200kGy; and 3) standing and settling or centrifuging the obtained product in the 2) to remove non-degradable settlement and obtain a clear solution, drying the clear solution, and thus obtaining an oligosaccharide with low molecular weight. The product obtained by adopting the method has uniform and centralized molecular weight, the molecular weight distribution index is close to 1, and the product has good uniformity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Area exposure dosimetry and area absorbed dosimetry
The area of an irradiation region, and at least one of the area of an object region and the area of a non-object region in a radiation image obtained by radiographing an object are calculated. The effective dose of radiation from a radiation generator is acquired. An area exposure dose, the X-ray amount radiated on the object, is calculated on the basis of the area of the irradiation region, one of the area of the object region and the area of the non-object region, and an effective dose.
Owner:CANON KK
CO2 packaged low-temperature low-dose irradiation refreshing method for edible mushrooms
InactiveCN102524757ARespiratory suppressionReduce negative reactionsFood preservationFood preparationMicroorganismLow dose irradiation
The invention discloses a CO2 packaged low-temperature low-dose irradiation refreshing method for edible mushrooms, comprising the following steps of: step I, deairing an edible mushroom film and charging CO2 for packaging; step II, precooling the edible mushroom packaged in the step I to be 0-4 DEG C; and step III, adopting 60Co r rays or 5-10MeV electron beam rays to perform irradiation to the edible mushroom in the step II, wherein the irradiation absorbed dose is 0.1-1.0kGy, and the inequality of irradiation dose is less than 1.25. In the invention, the comprehensive irradiation refreshing method maintaining the original color, fragrance, taste and state of the edible mushrooms is adopted, when the irradiated edible mushrooms are stored at normal temperature (10-25 DEG C), the original color, fragrance, taste and state are maintained for 4 days, and when the irradiated edible mushrooms are stored at 0-4 DEG C, the original color, fragrance, taste and state are maintained for 14 days. The packaging filled with CO2 is adopted, CO2 can effectively inhibit breathing of the edible mushrooms, irradiation is performed when the edible mushrooms are precooled to be 0-4 DEG C, at 0-4 DEG C, the breathing of the edible mushrooms can be reduced, growth reproduction of harmful microorganisms polluting the edible mushrooms is inhibited, and negative reaction of edible mushrooms, caused by irradiation, at the temperature can be reduced.
Owner:宁波超能科技股份有限公司
Device for improving efficiency of treating wastewater by irradiation of electronic accelerator
InactiveCN103319037AIncrease penetration depthLower absorbed doseMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh dosesWastewater
The invention discloses a device for improving the efficiency of treating wastewater by irradiation of an electronic accelerator. The device comprises an irradiation chamber, wherein a water treatment reactor is arranged in the irradiation chamber; a nozzle is arranged in one side of the water treatment reactor; a water discharging port is formed in the other side of the water treatment reactor; a scanning foil window is arranged above the water treatment reactor; the electronic accelerator connected with the scanning foil window is arranged outside the irradiation chamber; a contact reactor is arranged outside the irradiation chamber; a water outlet of the contact reactor is communicated with the nozzle; an air discharging hole is formed in the upper end of the irradiation chamber and is communicated with the bottom of the contact reactor. According to the device, irradiated gas which is rich in active free radicals and ozone and wastewater perform pre-oxidization reaction in the contact reactor, so that the absorption dosage of wastewater is reduced; therefore, reacted wastewater can flow into the water treatment reactor for irradiation treatment; according to the gas dissolved in the wastewater, the density of a mixer is reduced, the penetration depth of an electronic bundle is increased, a high dose-rate effect of the electronic accelerator is reduced, and the irradiation efficiency is improved.
Owner:CGN DASHENG ELECTRON ACCELERATOR TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com