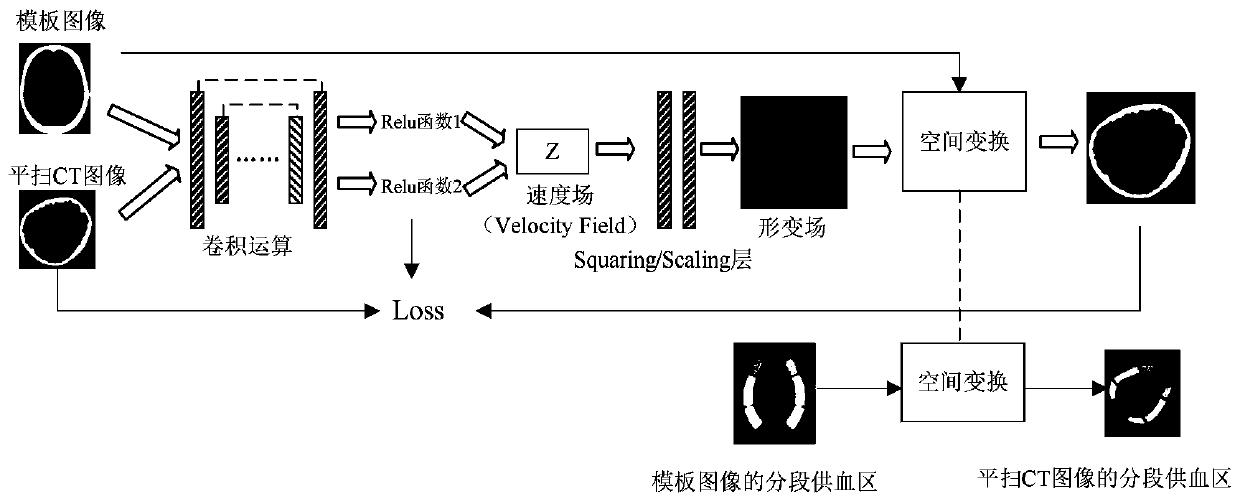
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
773results about "Radiation diagnostic image/data processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
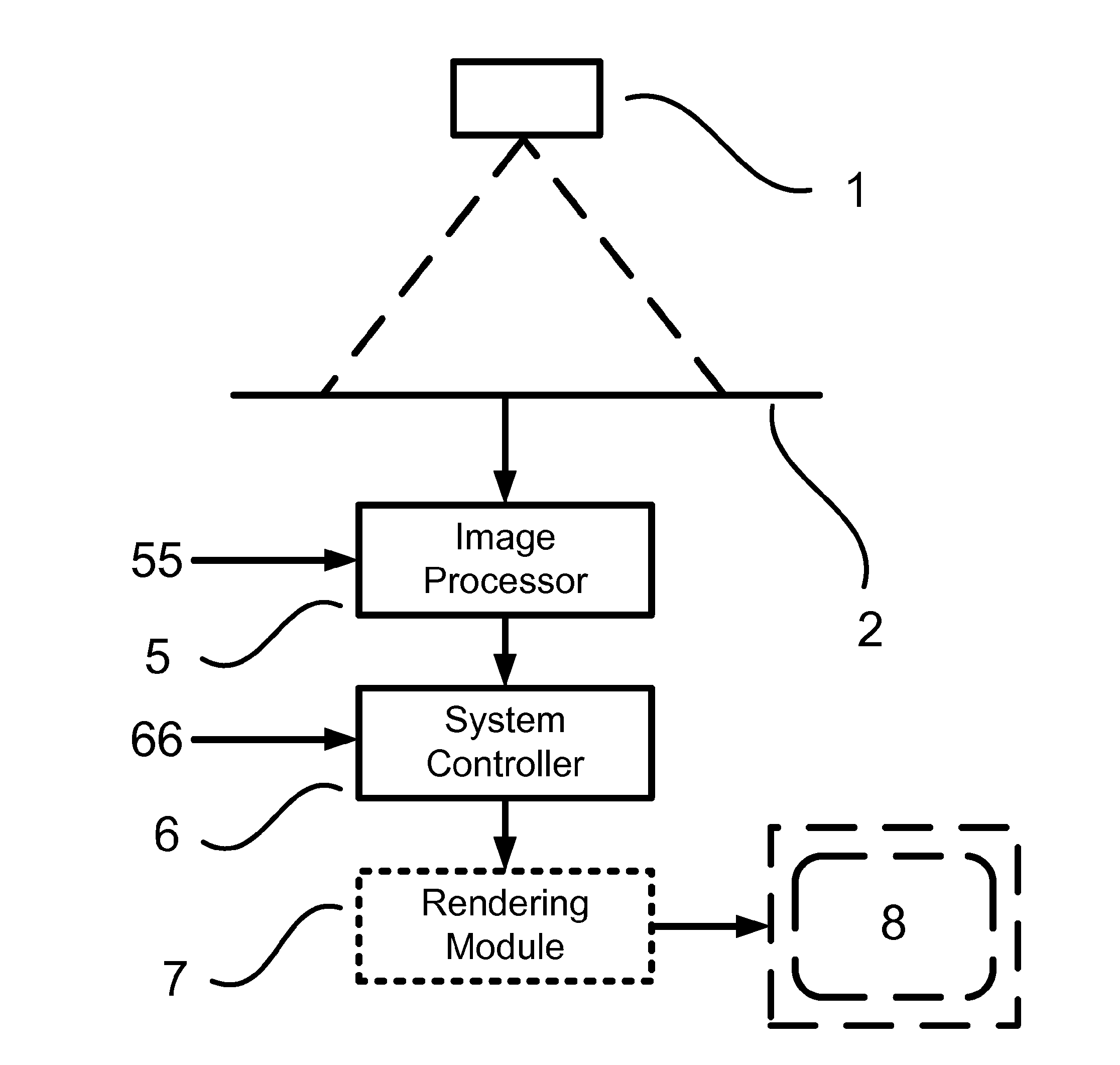
Methods, Devices, Systems, Circuits and Associated Computer Executable Code for Detecting and Predicting the Position, Orientation and Trajectory of Surgical Tools
The present invention includes methods, devices, systems, circuits and associated computer executable code for detecting and predicting the position and trajectory of surgical tools. According to some embodiments of the present invention, images of a surgical tool within or in proximity to a patient may be captured by a radiographic imaging system. The images may be processed by associated processing circuitry to determine and predict position, orientation and trajectory of the tool based on 3D models of the tool, geometric calculations and mathematical models describing the movement and deformation of surgical tools within a patient body.
Owner:ORTHOPEDIC NAVIGATION
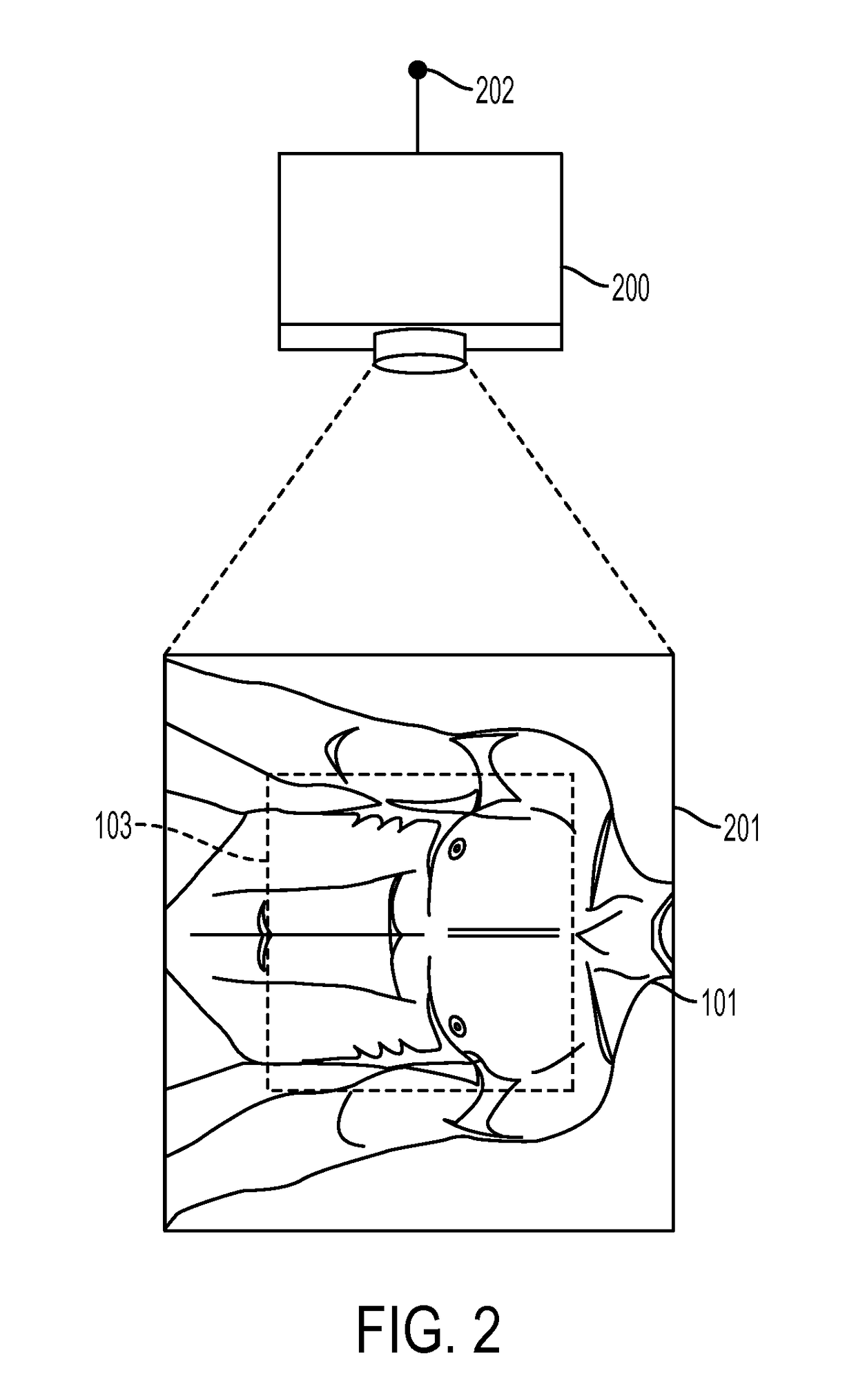
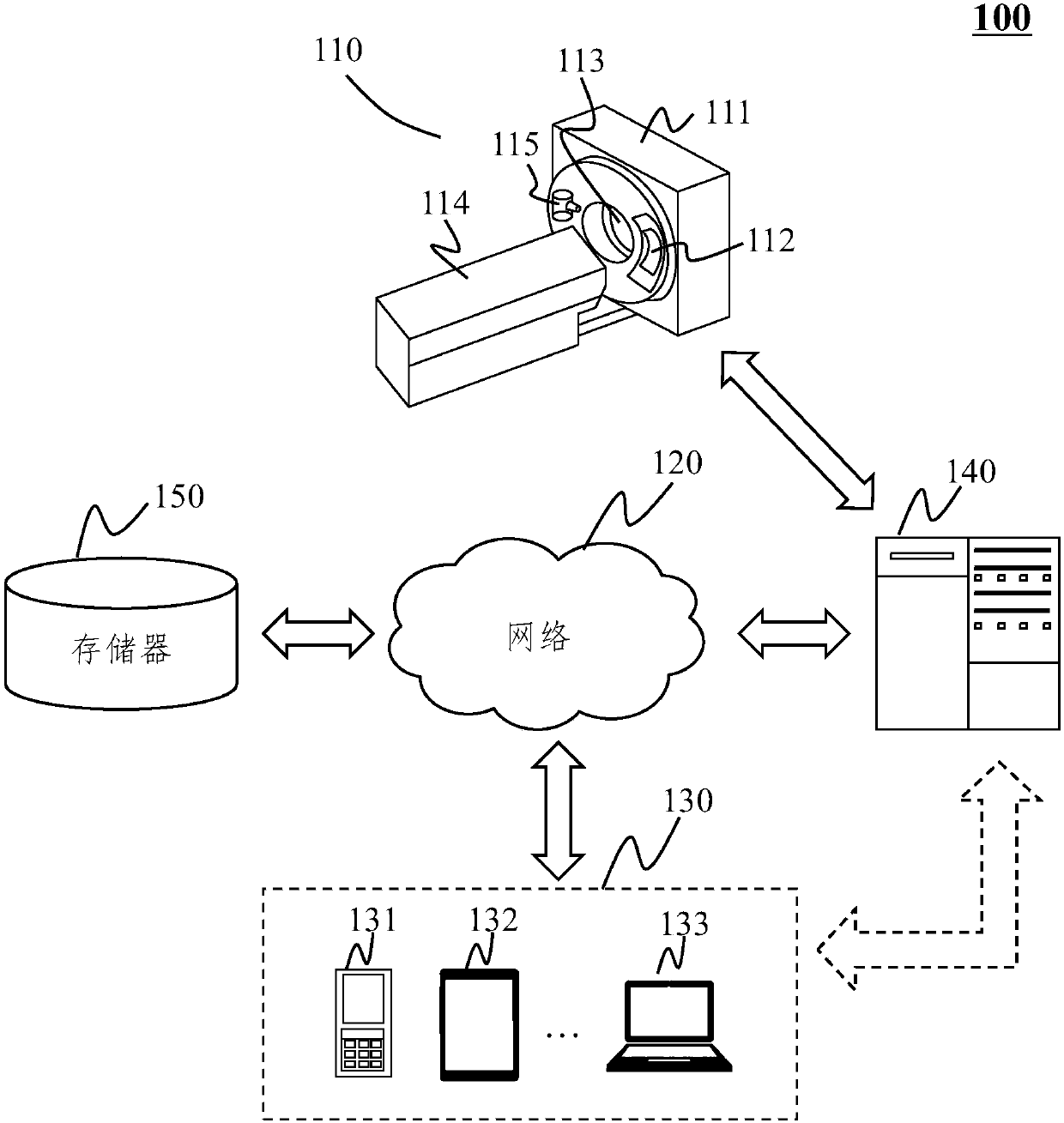
Assisted Guidance and Navigation Method in Intraoral Surgery
InactiveUS20140234804A1Shorten the construction periodGood curative effectRadiation diagnostic image/data processingTeeth fillingVisual positioningSurgical department
An assisted guidance and navigation method in intraoral surgeries is a method using computerized tomography (CT) photography and an optical positioning system to track medical appliances, the method including: first providing an optical positioning treatment instrument and an optical positioning device; then obtaining image data of the intraoral tissue receiving treatment through CT photography, precisely displaying actions of the treatment instrument in the image data, and real-time checking an image and guidance and navigation. Therefore, during the surgery, the existing use habits of the physicians are not affected and accurate and convenient auxiliary information is provided, and attention is paid to using the treatment instrument in physical environments such as a patient's tooth or dental model.
Owner:HUANG JERRY T +1
System and method of predicting future fractures
Methods of predicting fracture risk of a patient include: obtaining an image of a bone of the patient; determining one or more bone structure parameters; predicting a fracture line with the bone structure parameter; predicting a fracture load at which a fracture will happen; estimating body habitus of the patient; calculating a peak impact force on the bone when the patient falls; and predicting a fracture risk by calculating the ratio between the peak impact force and the fracture load. Inventive methods also includes determining the effect of a candidate agent on any subject's risk of fracture.
Owner:IMATX
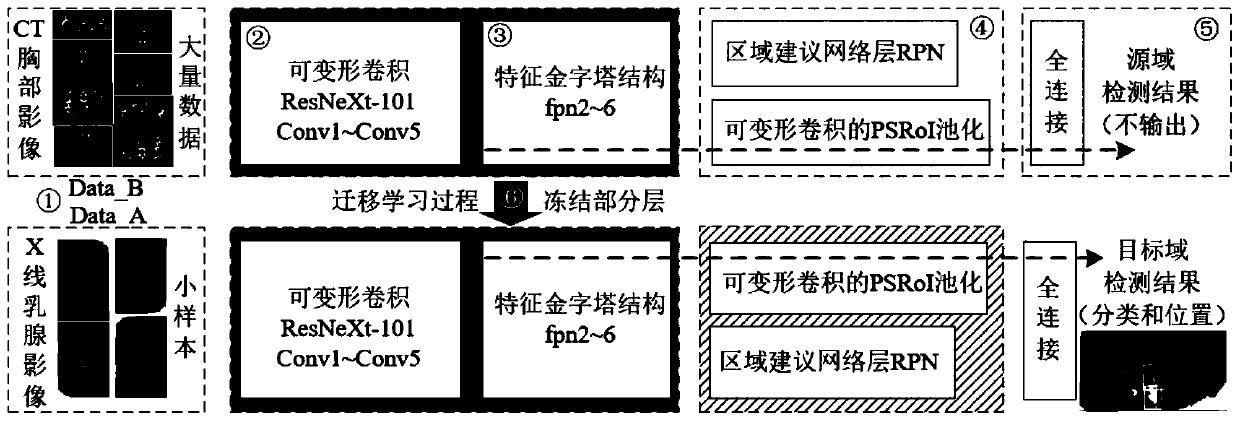
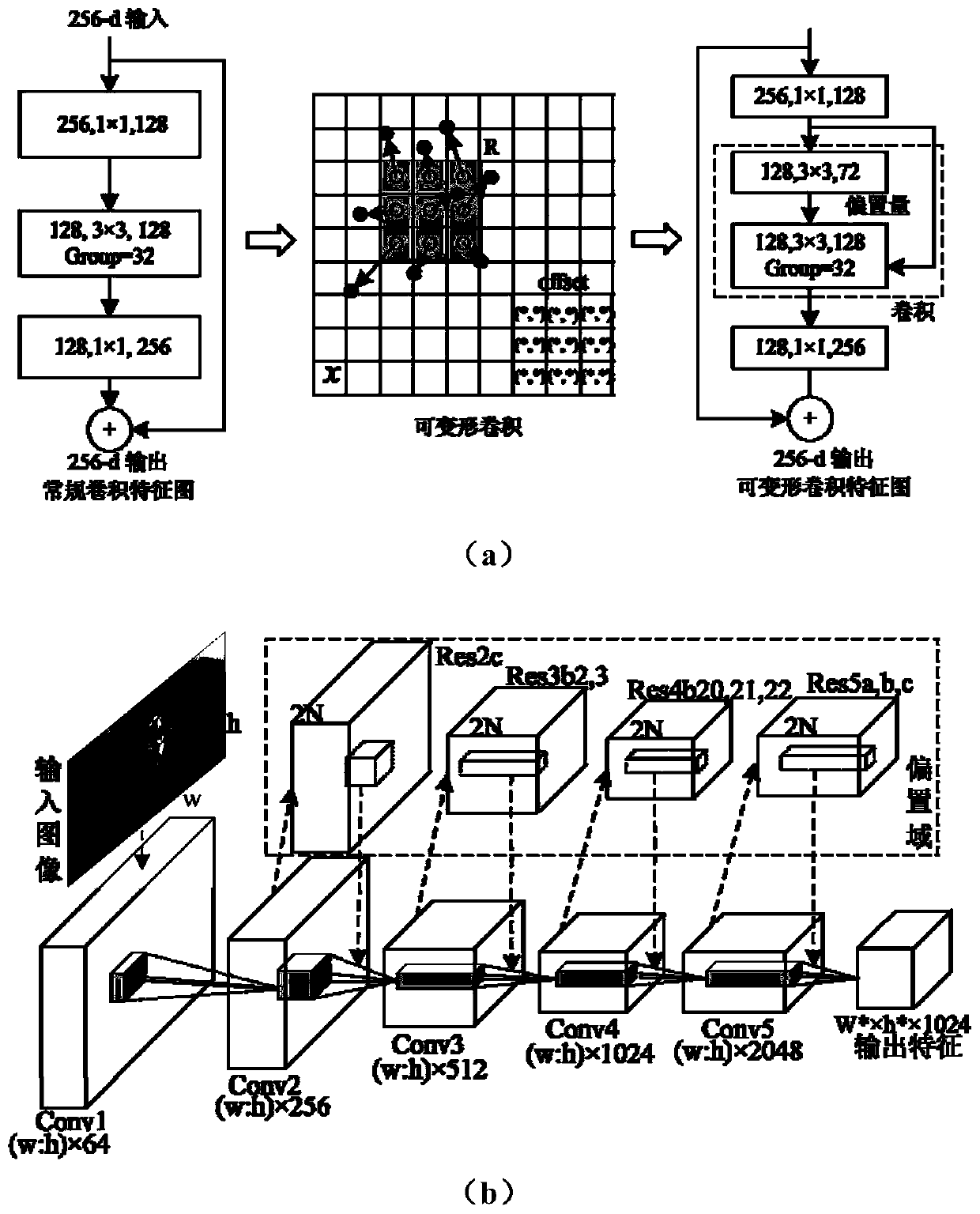
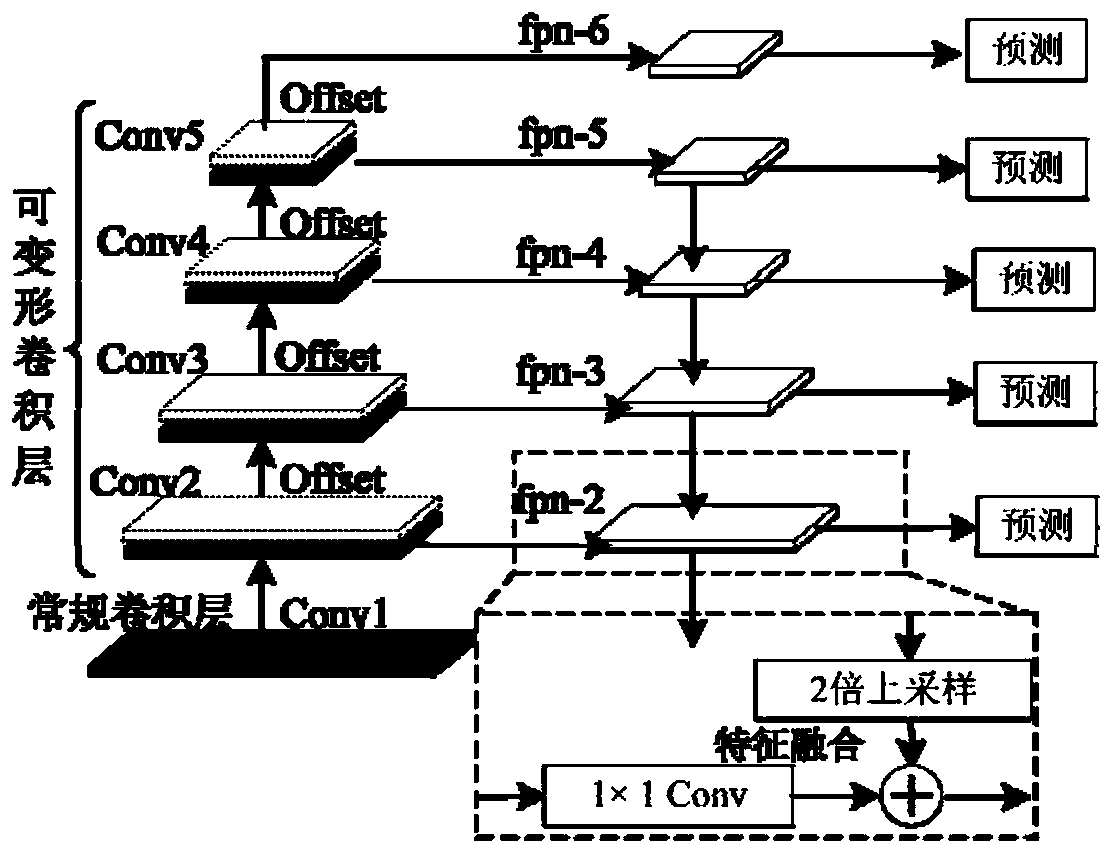
Method for detecting X-ray mammary gland lesion image based on feature pyramid network under transfer learning
ActiveCN110674866AImprove robustnessImprove the extraction effectImage enhancementImage analysisData setImage detection
The invention provides a method for detecting an X-ray mammary gland lesion image based on feature pyramid network under transfer learning. The method comprises the steps: 1, establishing a source domain data set and a target domain data set; 2, establishing a deformable convolution residual network layer by a deformable convolution and extended residual network module; 3, establishing a multi-scale feature extraction sub-network based on a feature pyramid structure through a feature map up-sampling and feature fusion method in combination with a deformable convolution residual network layer;4, establishing a deformable pooling sub-network sensitive to the focus position; 5, establishing a post-processing network layer to optimize a prediction result and a loss function; and 6, migratingthe training model to a small sample molybdenum target X-ray mammary gland focus detection task so as to improve the detection precision of the network model on the focus in the small sample image. According to the method, a transfer learning strategy is combined to realize focus image processing in a small sample medical image.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
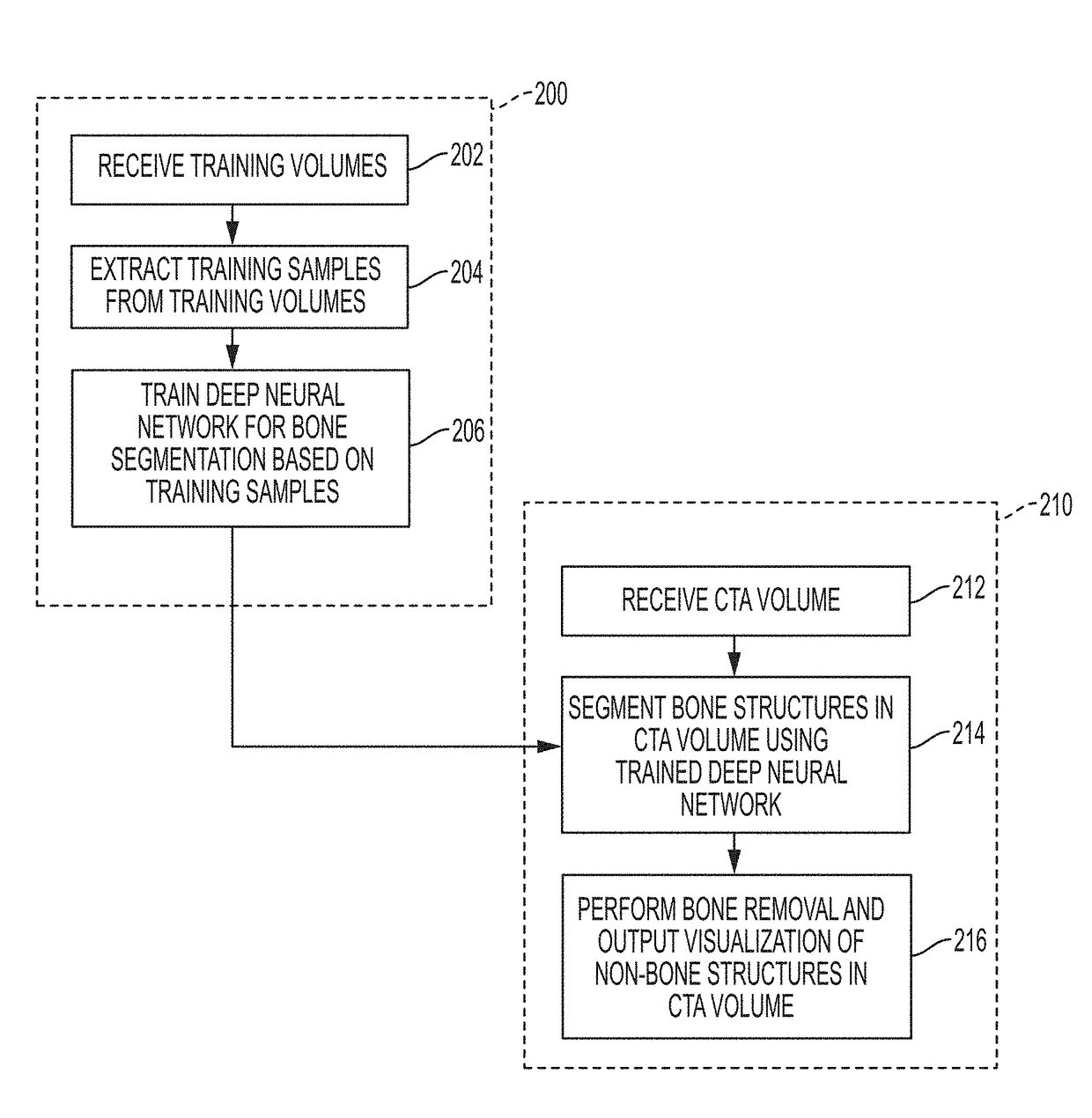
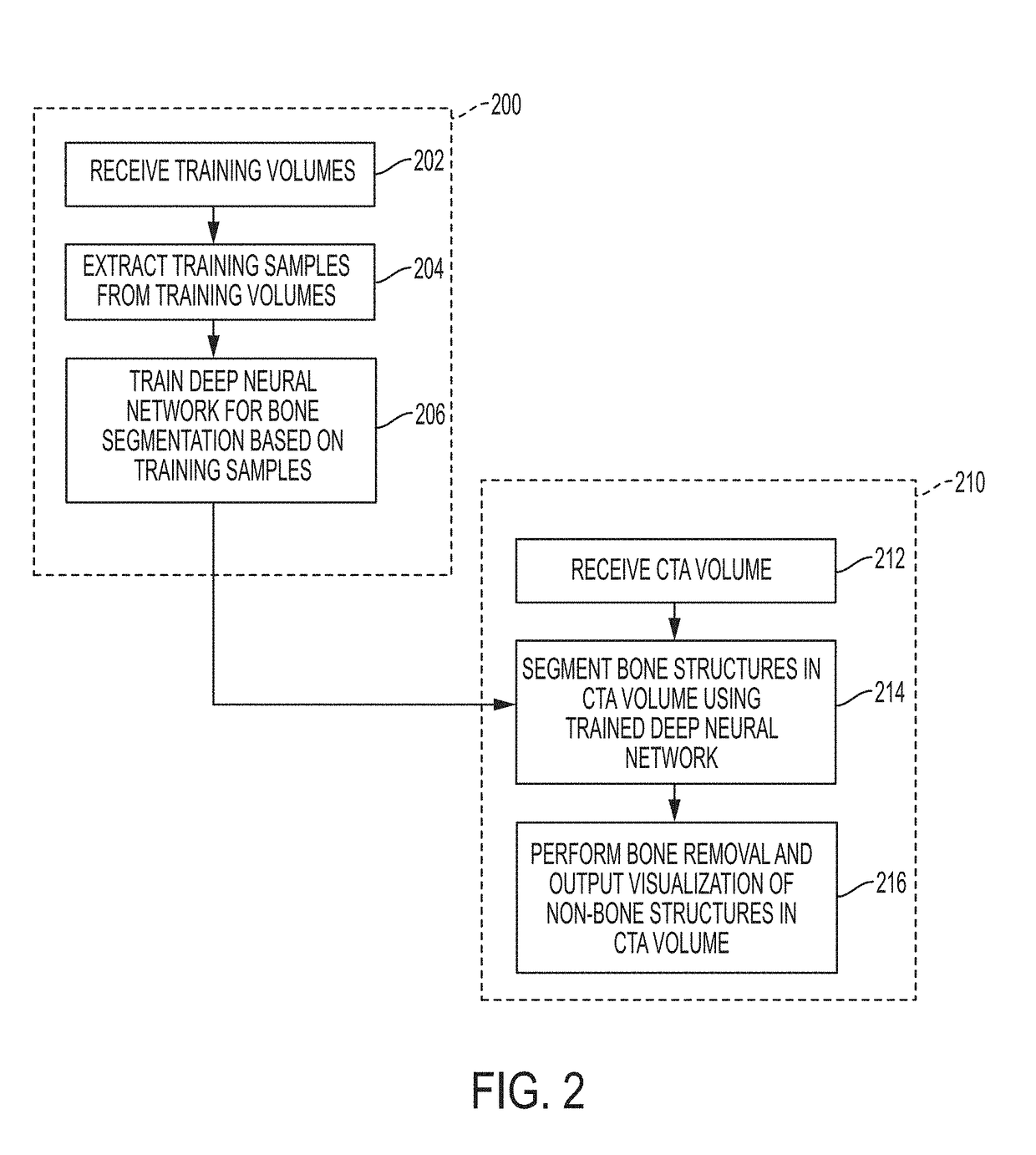
Deep Learning Based Bone Removal in Computed Tomography Angiography
A method and apparatus for deep learning based automatic bone removal in medical images, such as computed tomography angiography (CTA) volumes, is disclosed. Bone structures are segmented in a 3D medical image of a patient by classifying voxels of the 3D medical image as bone or non-bone voxels using a deep neural network trained for bone segmentation. A 3D visualization of non-bone structures in the 3D medical image is generated by removing voxels classified as bone voxels from a 3D visualization of the 3D medical image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
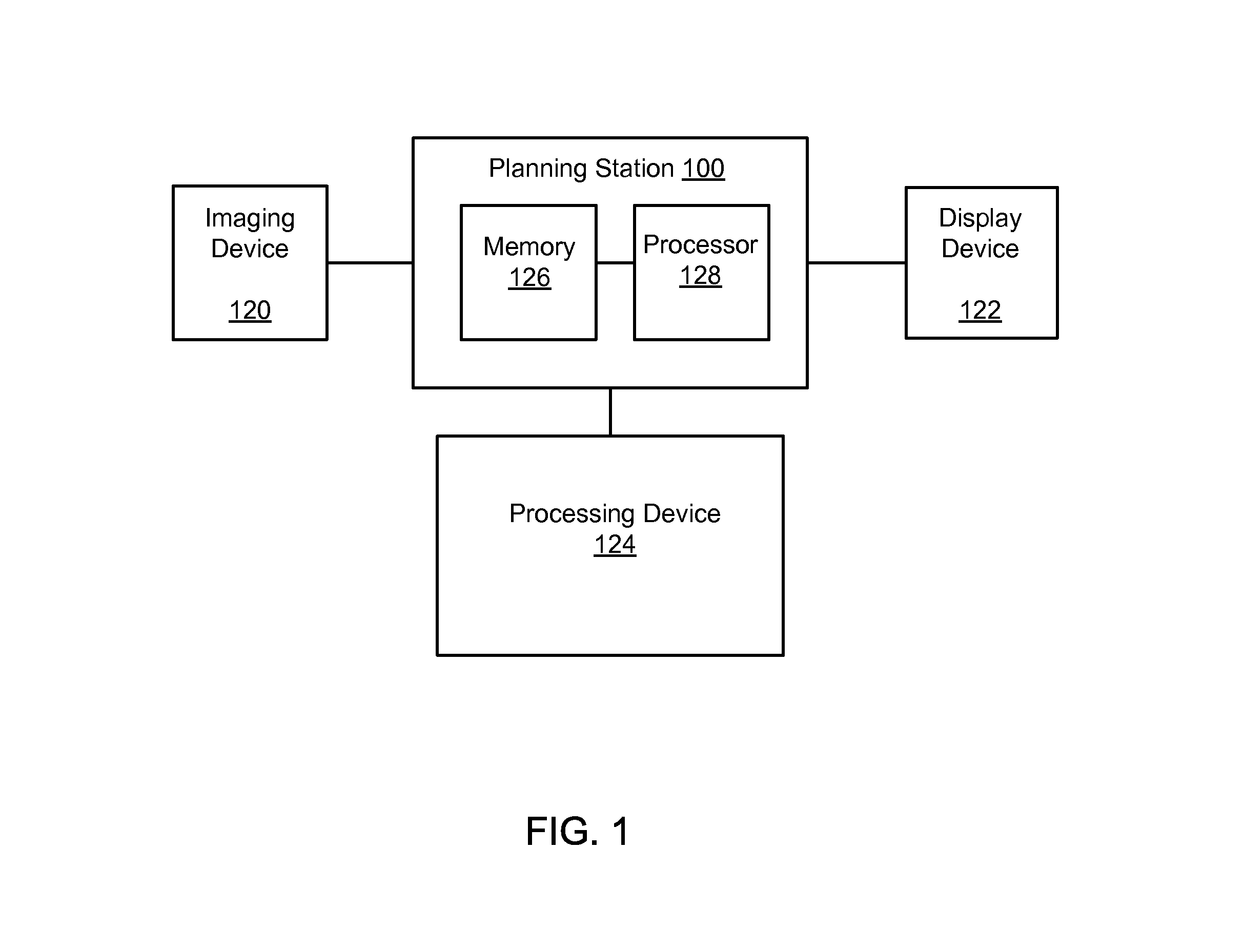
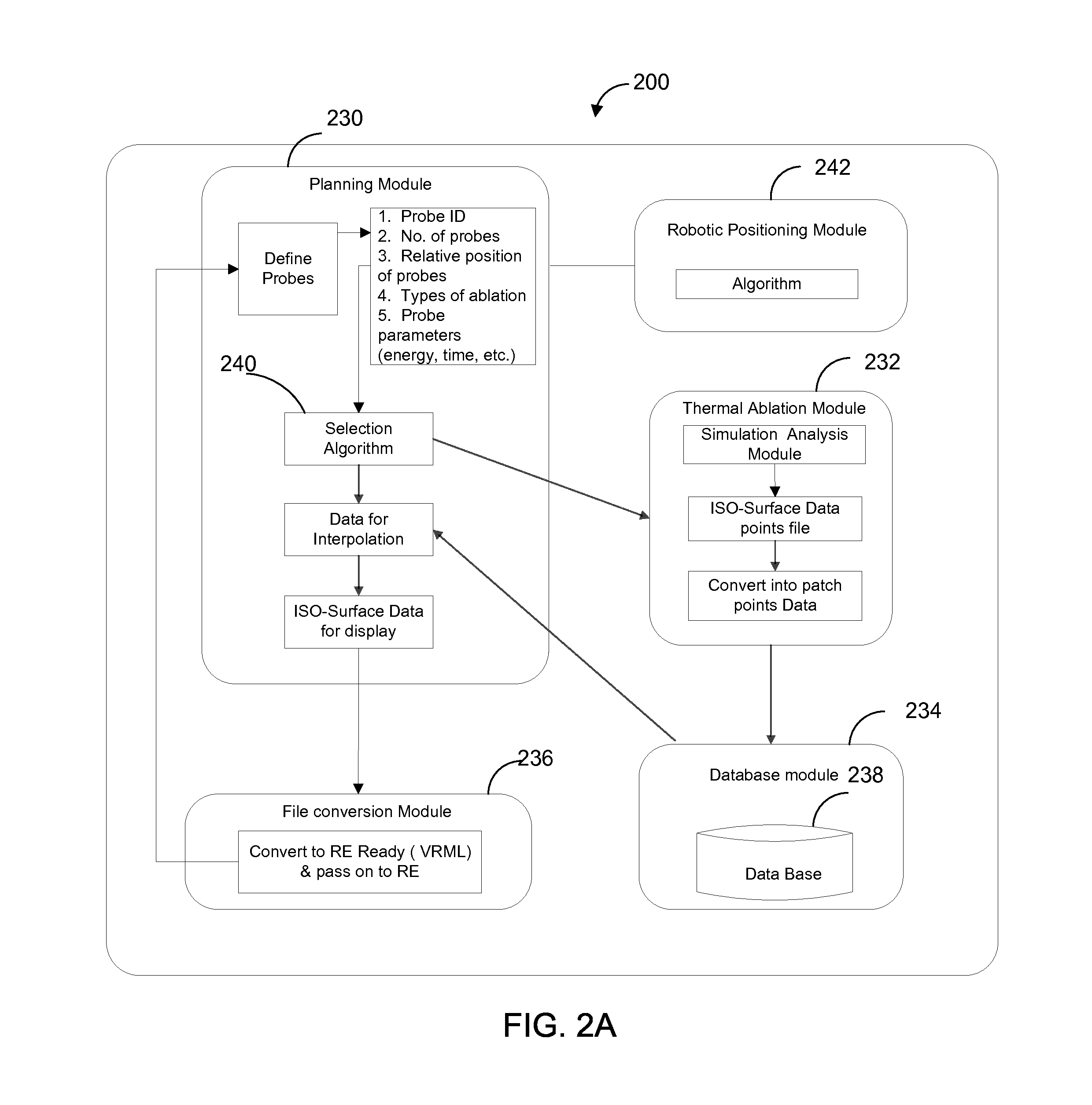
Systems and methods for planning image-guided interventional procedures
InactiveUS20130072784A1Radiation diagnostic image/data processingSurgical needlesThermal energyDisplay device
In some embodiments, a planning station can receive image data associated with an image(s) of an area of interest within a body of a patient and display the image(s) on a display device. A user can make a selection of a first interventional tool and a second interventional tool about which information is stored in a memory of the planning station. The planning station can execute a simulation viewable on the display device of a treatment plan for disposing the first and second interventional tools in the body of the patient and applying thermal energy from the first and second interventional tools to the body of the patient. The planning station can generate a thermal model of the thermal effect collectively produced on tissue of the patient by the first interventional tool and the second interventional tools and display the thermal model on the display device.
Owner:PERFINT HEALTHCARE PVT
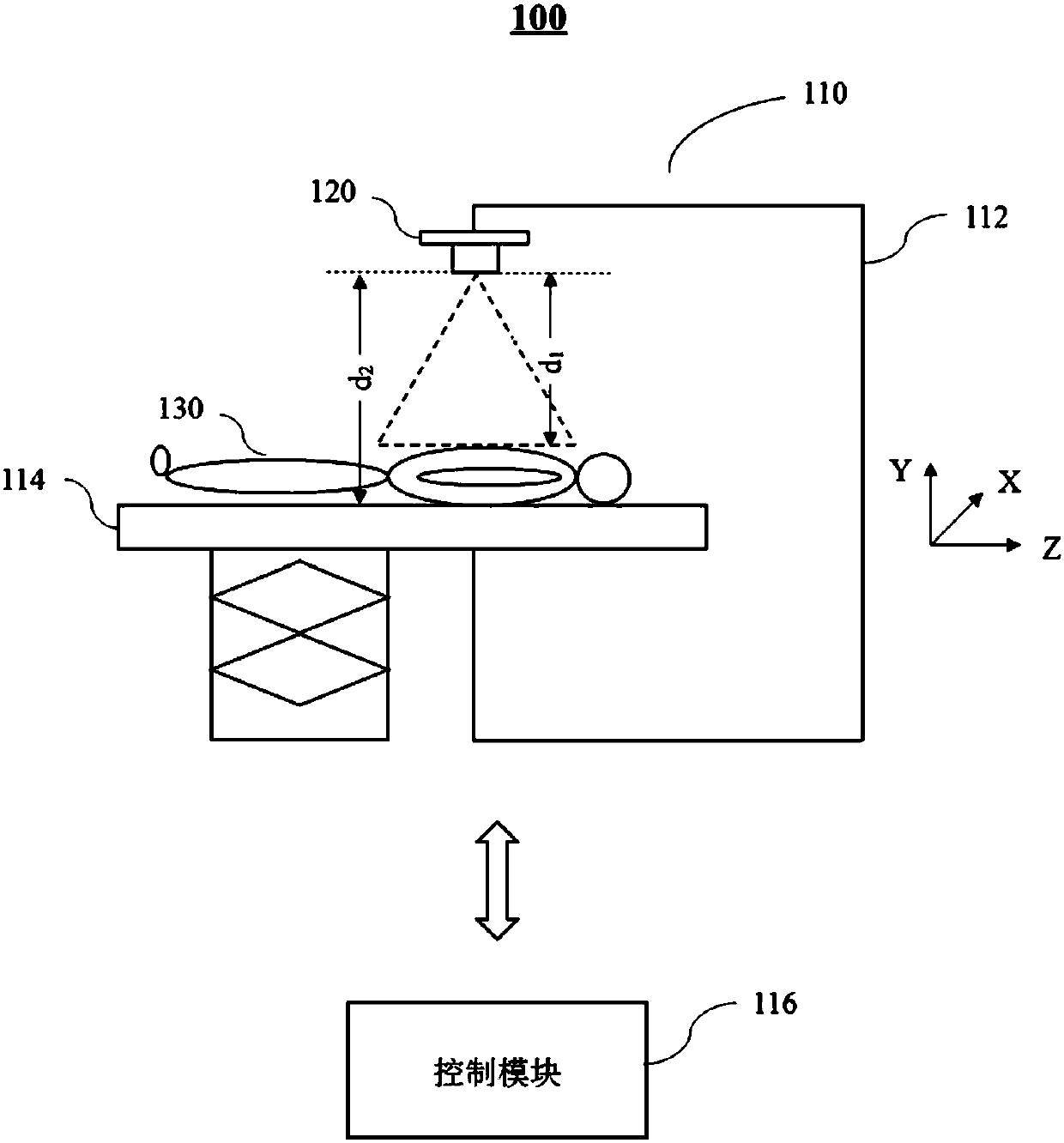
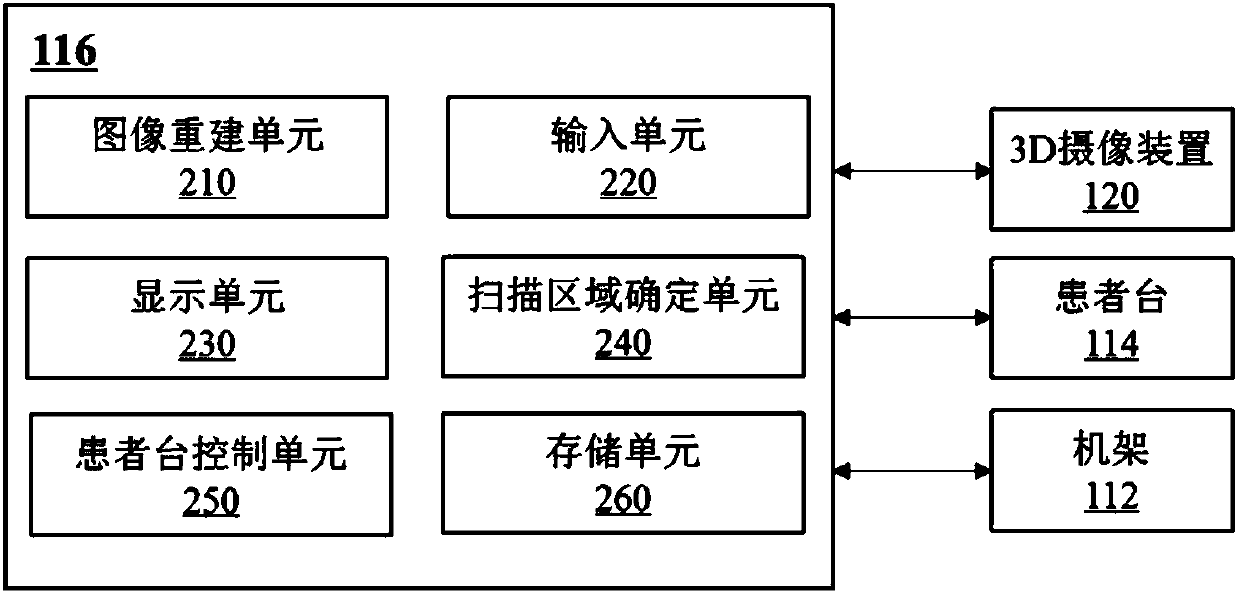
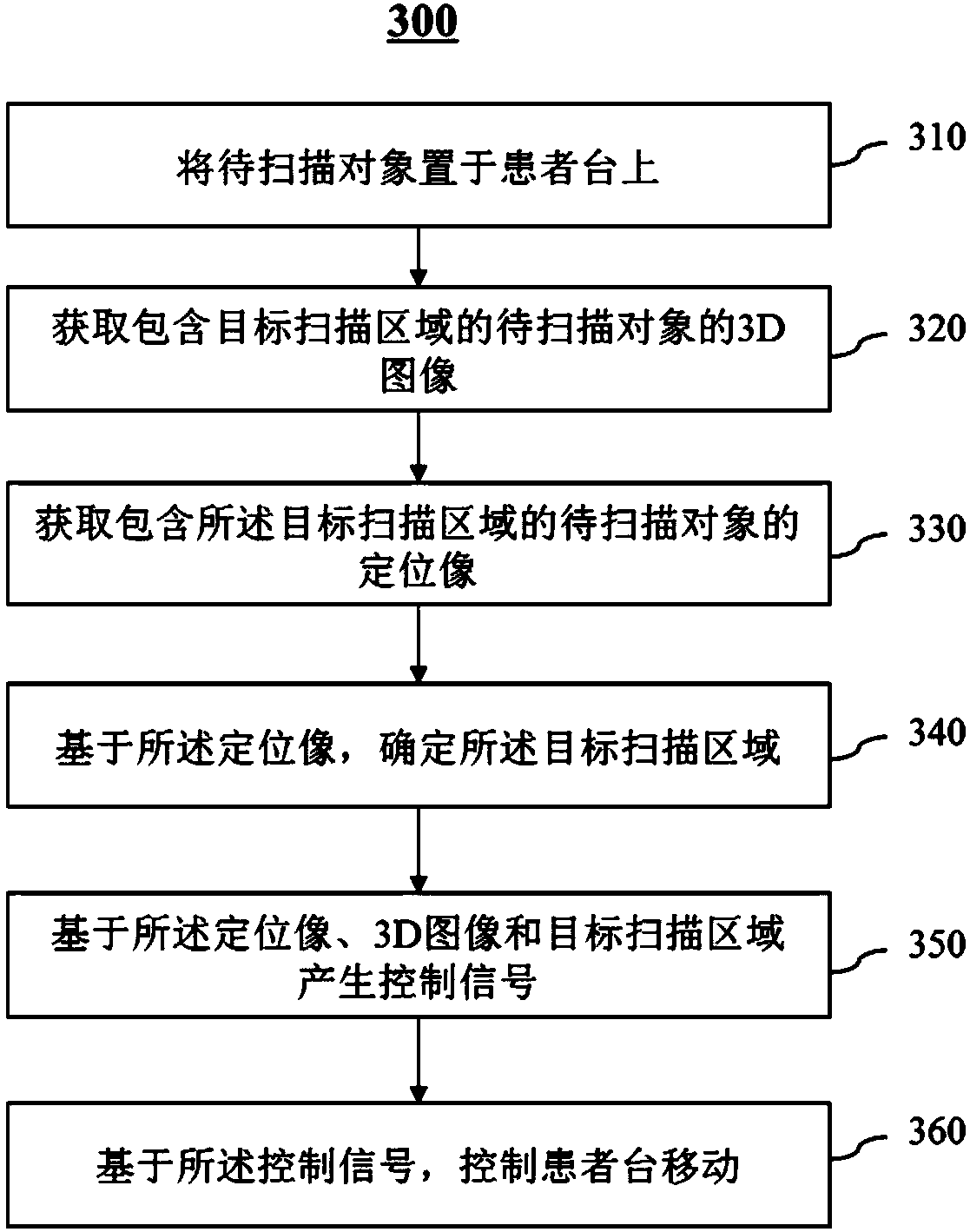
Positioning method and system for imaging scanning
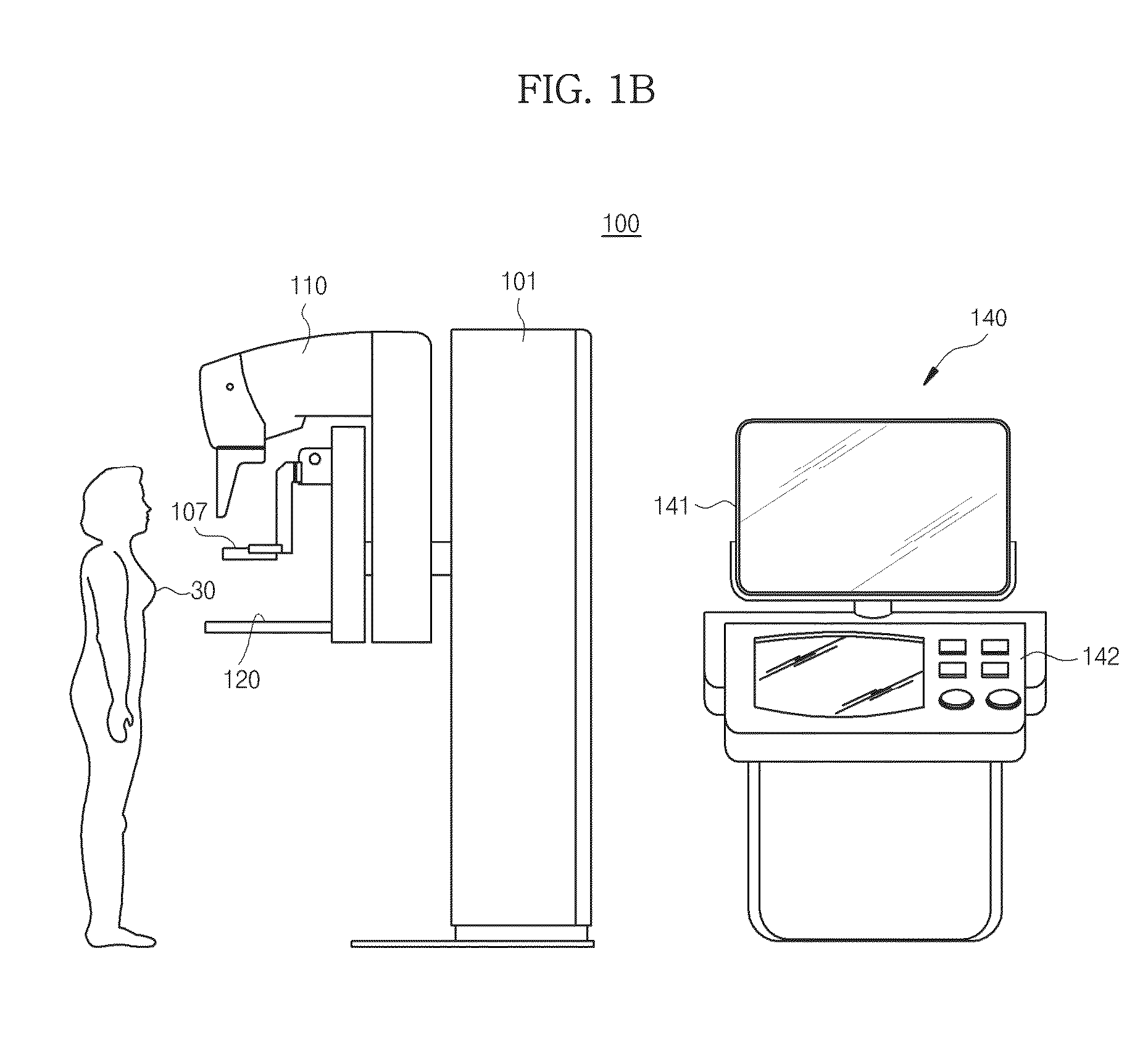
ActiveCN107789001AImprove scanning efficiencyImprove accuracyRadiation diagnostic image/data processingRadiation diagnostic device control3d image3d camera
The invention discloses a positioning method and system for imaging scanning. The method includes the steps of putting a to-be-scanned object on a patient table; obtaining a 3D image including a target scanning area of the to-be-scanned object through a 3D camera shooting device, wherein the 3D image includes depth information of the to-be-scanned object; obtaining a positioning image including the target scanning area of the to-be-scanned object through a scanning device; determining the target scanning area based on the positioning image; moving the patient table in at least one direction based on the positioning image, the 3D image and the target scanning area. By means of the positioning system, a user does not need to position a patient manually before scanning, positioning can be directly and automatically conducted after scanning of a positioning piece is completed, scanning efficiency is improved, and the positioning accuracy can be improved by means of a 3D field depth camerashooting technology.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
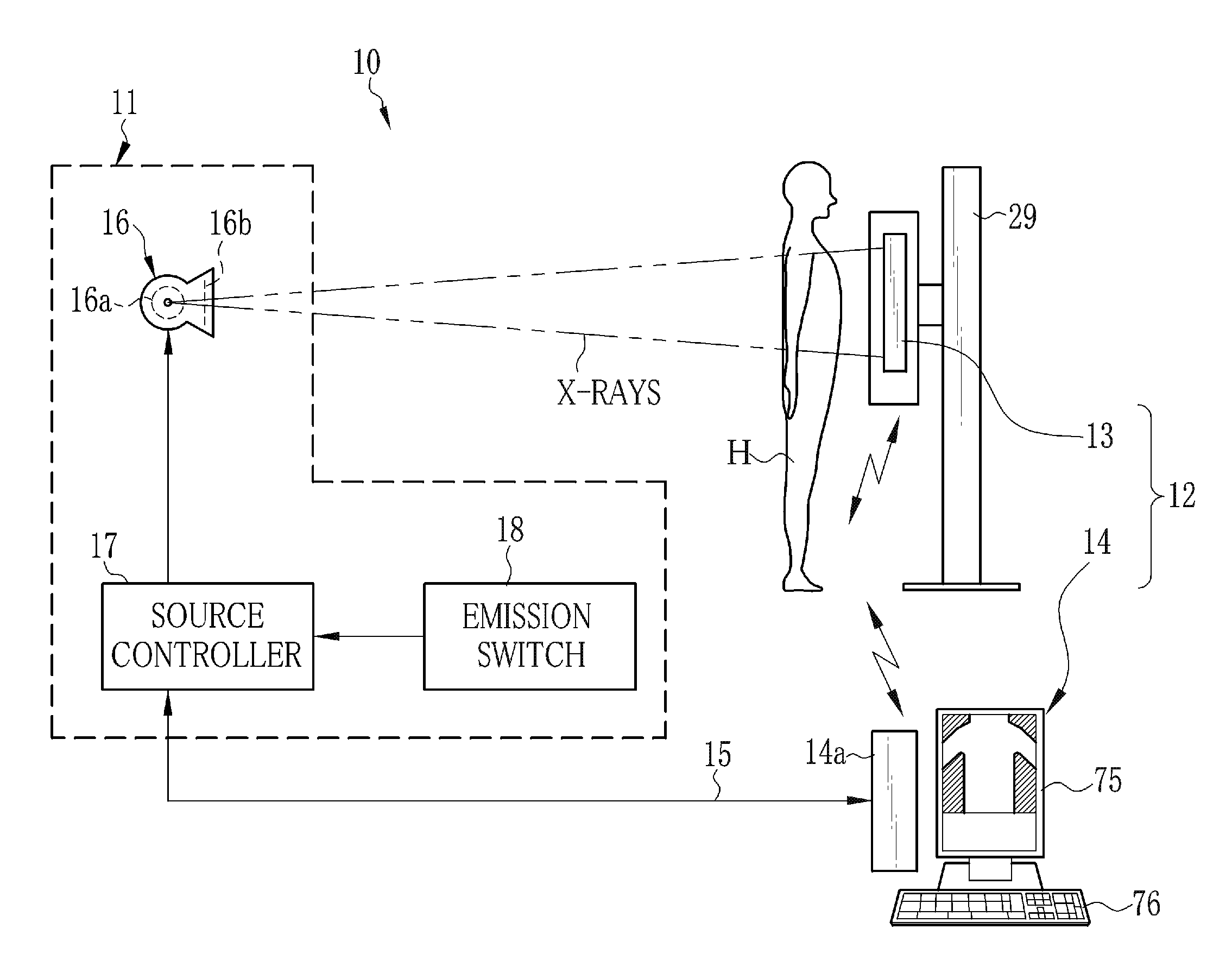
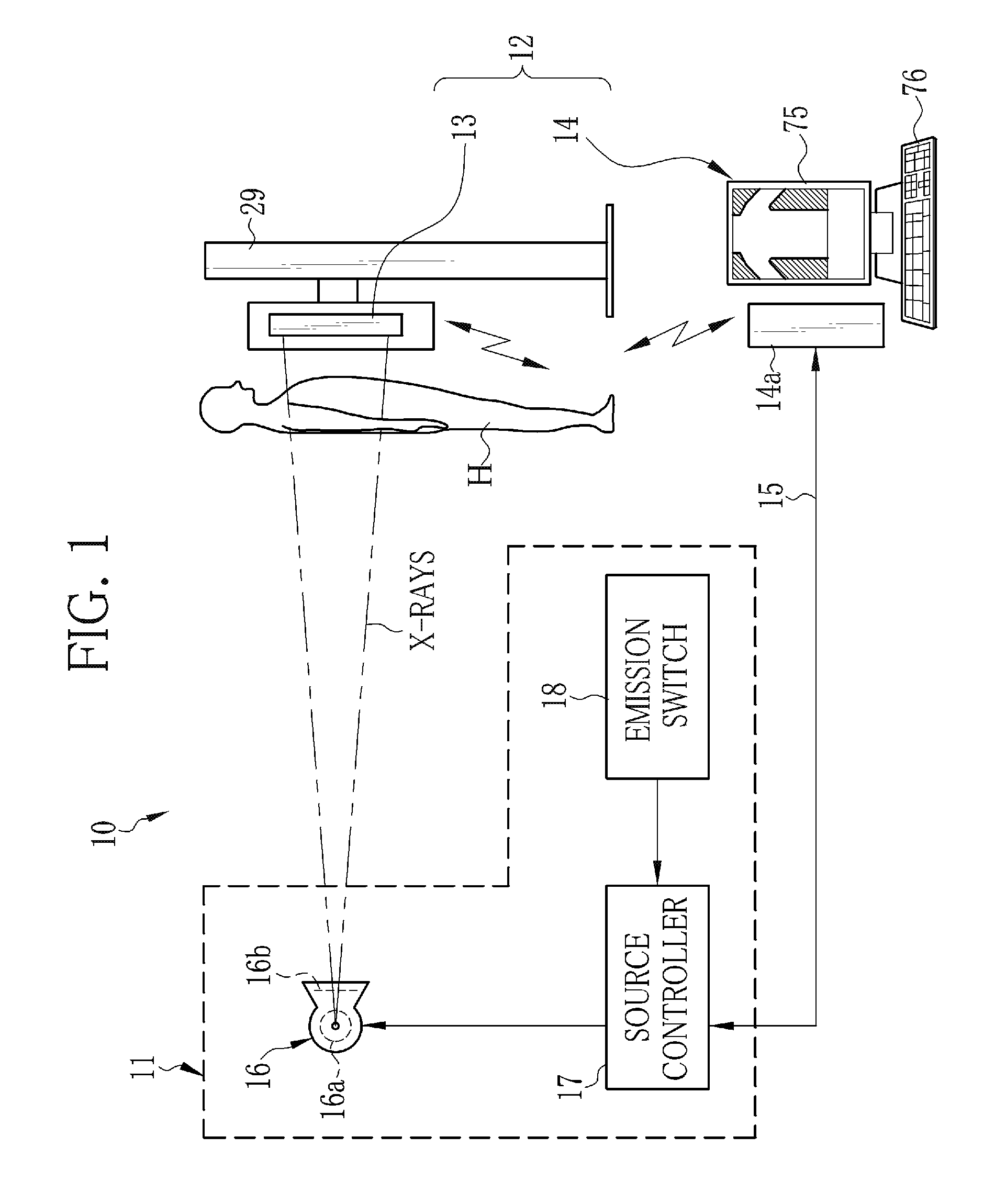
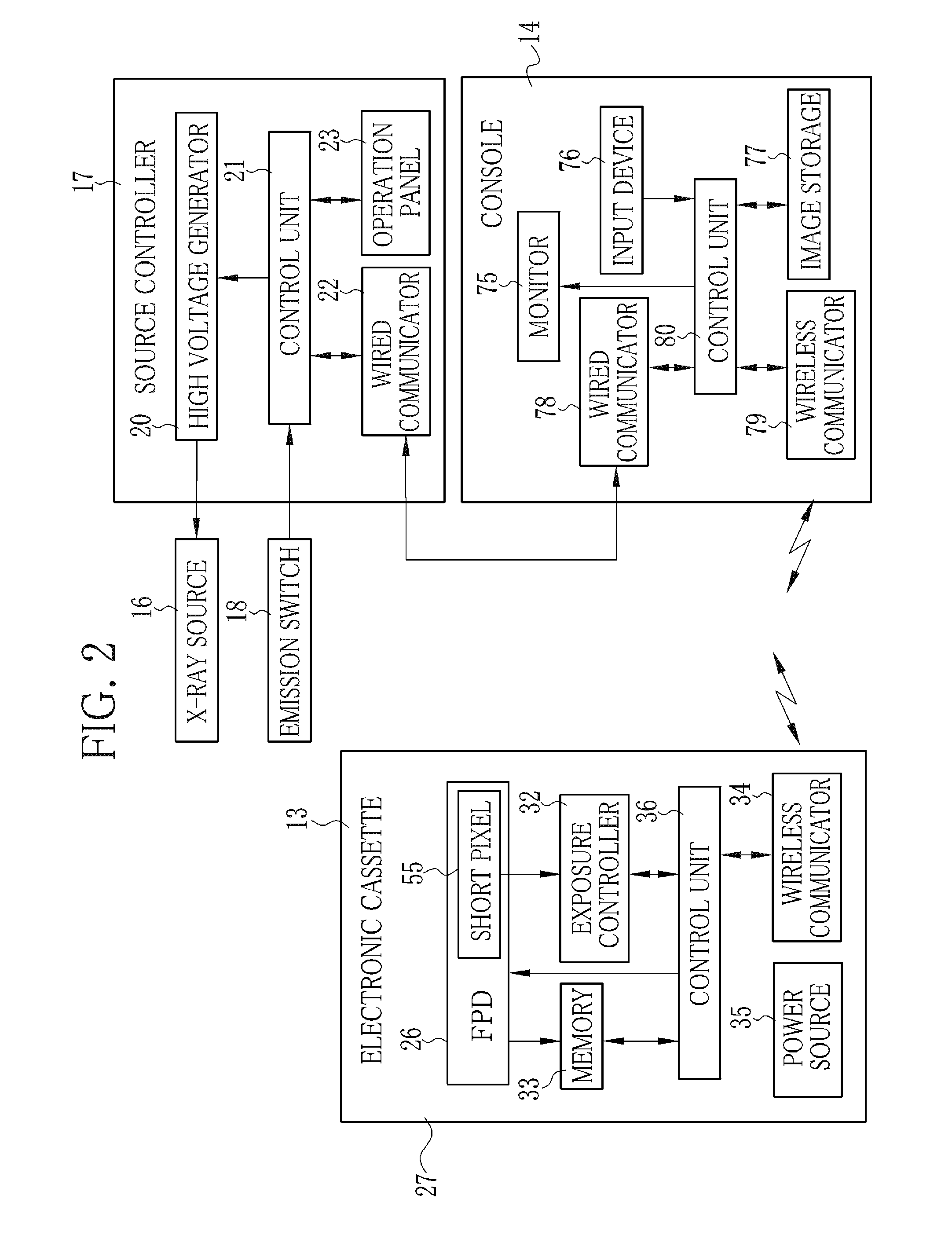
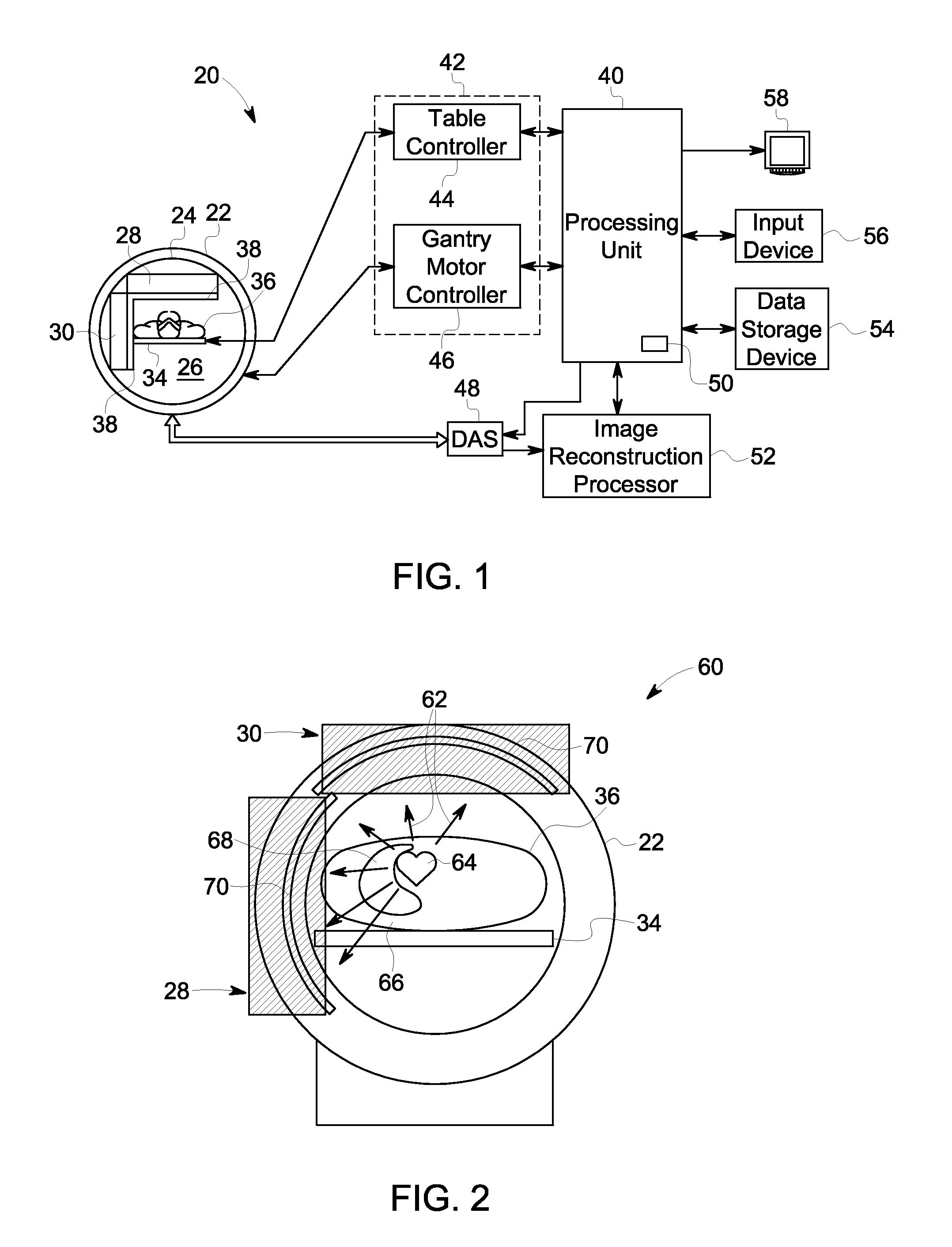
Radiation imaging apparatus and control method thereof, and radiation imaging system
ActiveUS20130202086A1Improve image qualitySimple structureRadiation diagnostic image/data processingDosimetersRadiation imagingExposure control
An FPD detects an X-ray image of an object. The FPD includes a plurality of pixels arranged in its image capturing field. Each pixel receives X-rays emitted from an X-ray source, and outputs a pixel value in accordance with an X-ray dose applied thereto. A pixel determiner determines a minimum-value pixel out of the pixels based on the pixel values of the pixels. The minimum-value pixel is a pixel whose pixel value is the lowest. The pixel determiner sets the minimum-value pixel as an exposure control pixel. A comparator compares a first integrated value, which is an integrated value of the pixel values of the minimum-value pixel, with a predetermined first threshold value. The comparator performs X-ray emission control such that, when the first integrated value has reached the first threshold value, the X-ray source stops emitting the X-rays.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Imaging system
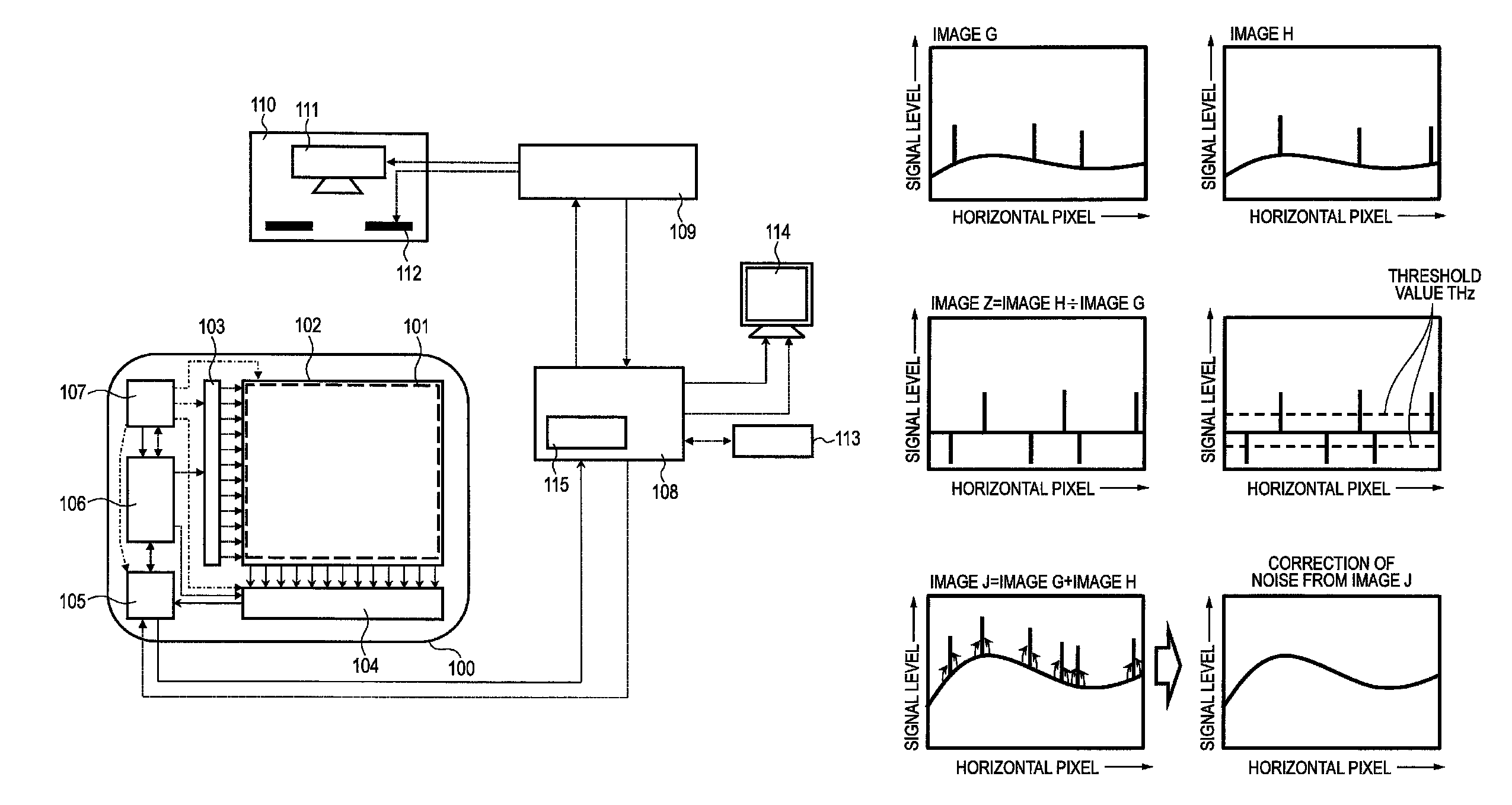
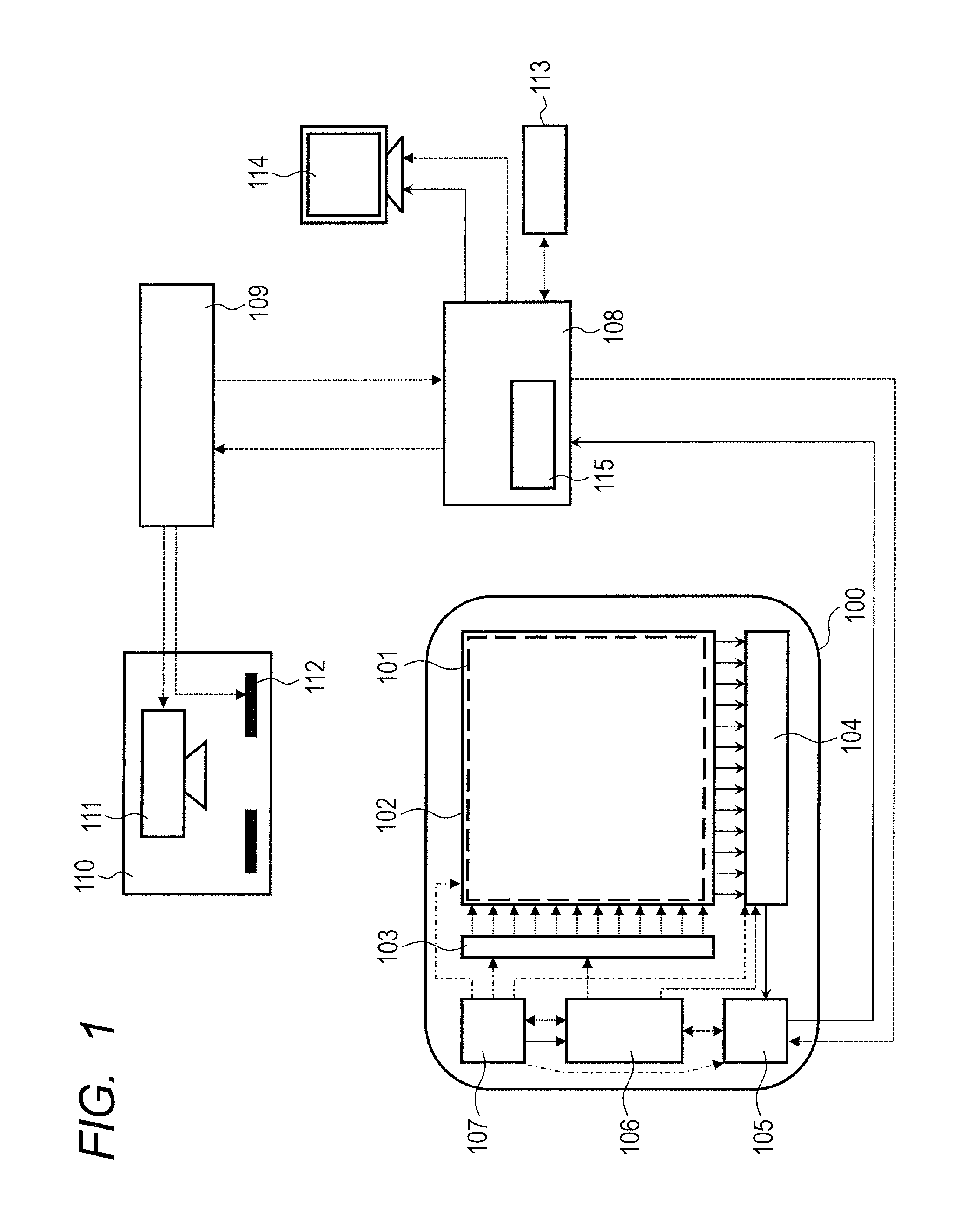
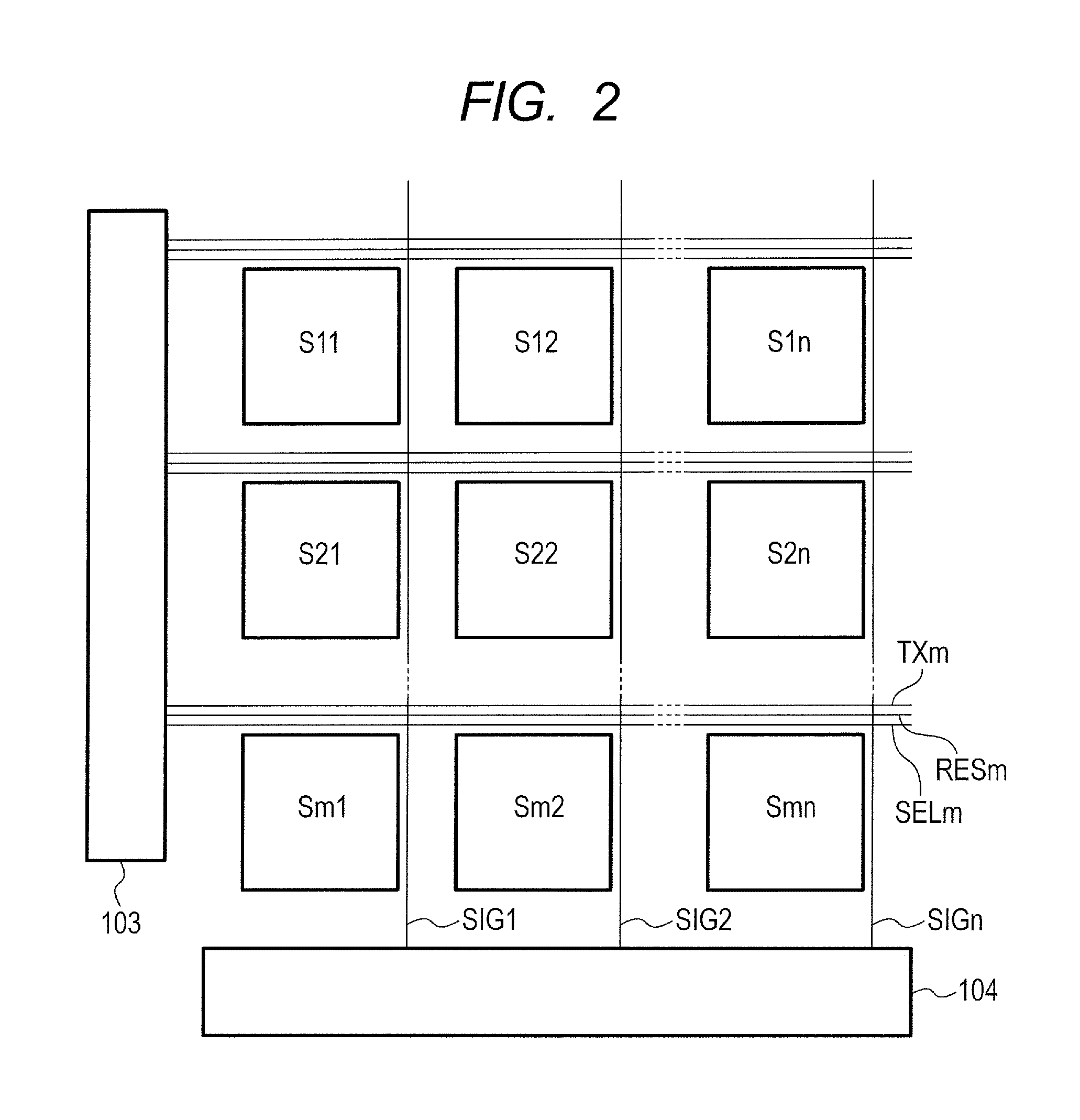
ActiveUS9468414B2Simple processCancel noiseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage systemPhysics
An imaging system comprises: a plurality of pixels each for converting light, converted from radiation by a conversion unit, into an electrical signal; an extracting unit that extracts, based on an image formed based on output signals from the pixels, a pixel with noise generated by the radiation that has transmitted through the conversion unit to arrive at the pixels; and a correcting unit that performs correction to remove the noise with respect to an output signal from the extracted pixel, wherein the extracting unit extracts the pixel with the noise by performing division between first and second images, the first image being formed based on the output signals from the pixels in accordance with the radiation to the conversion unit during a first period, the second image being formed based on these output signals in accordance with that radiation during a second period after the first period.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and apparatus for adjusting a field of view for exposure of an x-ray system, and an x-ray system
InactiveUS20130077745A1Fulfil requirementsRadiation diagnostic image/data processingTomographySoft x rayDisplay device
A method for adjusting a field of view for exposure of an X-ray system is provided. The method comprises: capturing an image of a patient on an examining table of the system by an image sensor, wherein the image sensor is placed at a predetermined position in the system; displaying the captured image on a display for selection of a region of interest or a point of interest by a user on the image; automatically determining a target position of an X-ray source in response to the selection of the region of interest or the point of interest on the image, wherein a desired field of view for exposure covering the region of interest or the point of interest is obtained when the X-ray source is located at the target position; and automatically locating the X-ray source at the target position in response to the determination of the target position.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC +1
Medical image display system
InactiveUS20140010344A1Improve diagnostic accuracyEasy to useImaging devicesRadiation diagnostic image/data processingGratingImaging processing
A medical image display system is shown. The medical image display system includes, a fringe scanning type capturing apparatus or a Fourier transformation type capturing apparatus; an image processing section; a display section; and a control section. The capturing apparatus includes, an X-ray source; a first grating and a second grating; a subject table; and an X-ray detector. The image processing section generates a plurality of reconstructed images for diagnosis based on an image signal of a subject captured with the capturing apparatus. The display section displays at least two of the plurality of reconstructed images. The control section detects an abnormal candidate on each of the plurality of reconstructed images and controls display order of the plurality of reconstructed images displayed on the display section based on a result of detecting.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
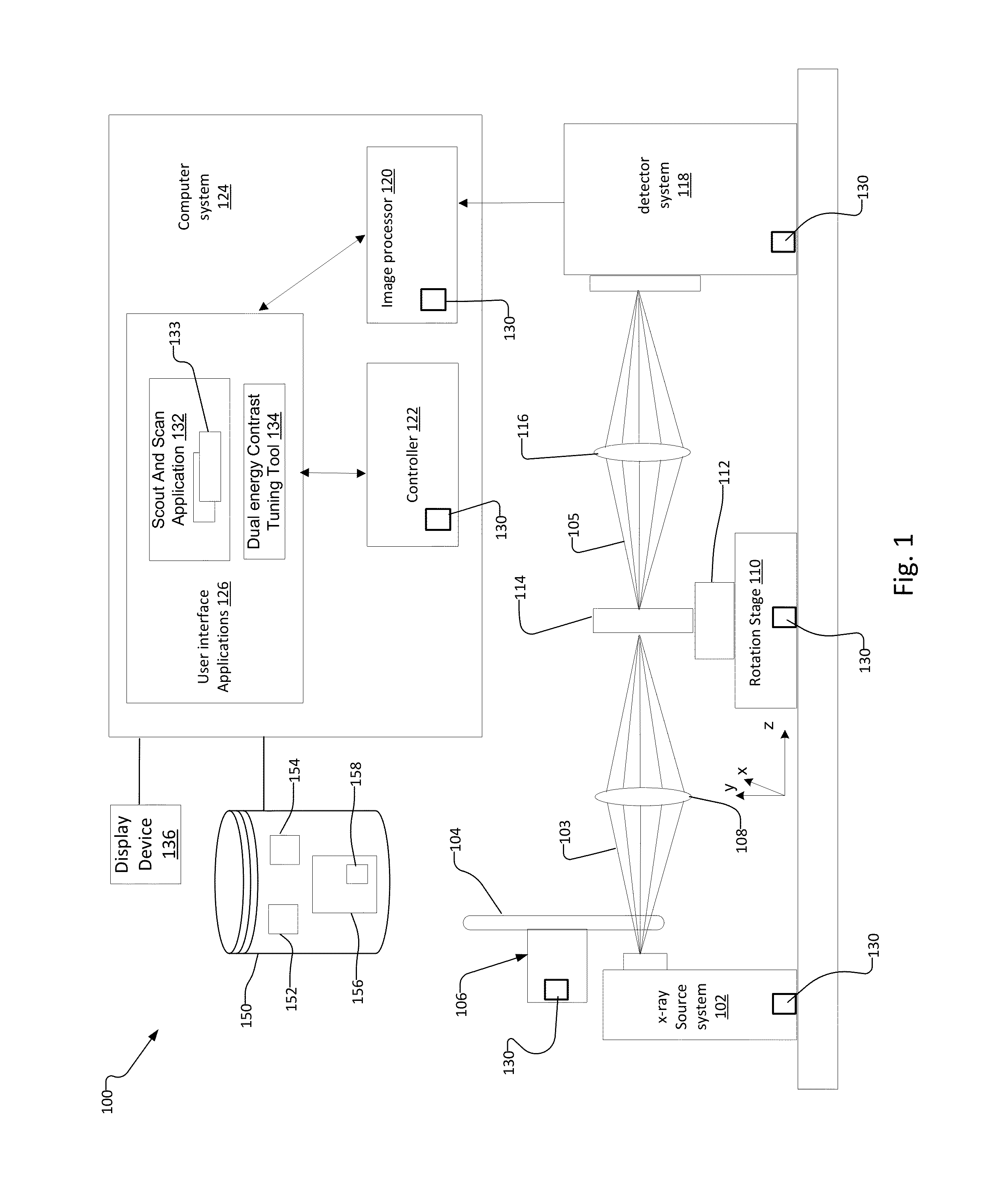
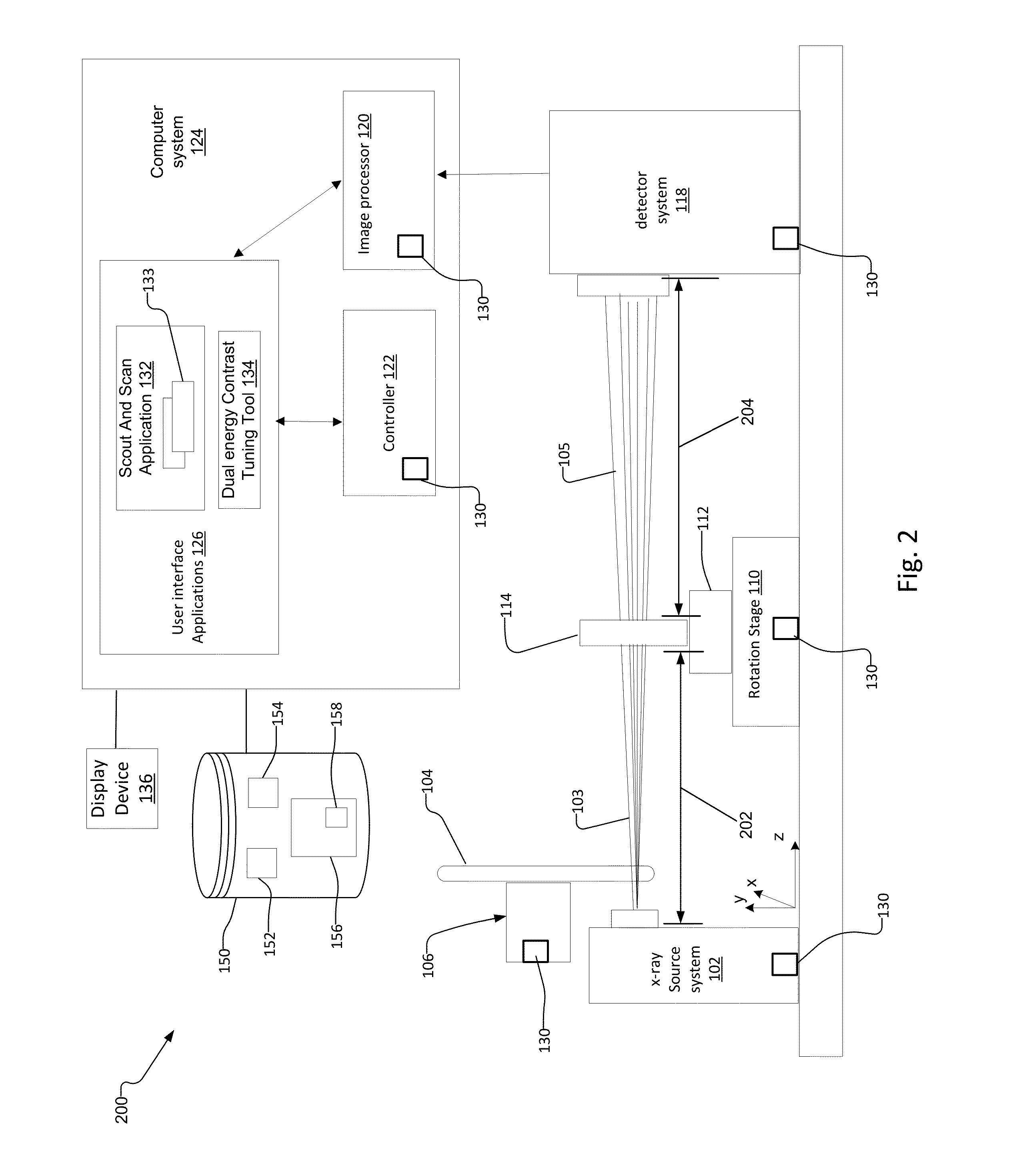
Multi Energy X-Ray Microscope Data Acquisition and Image Reconstruction System and Method
ActiveUS20140233692A1Increase contrastImprove image qualityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setHigh energy
A multi energy, such as dual-energy (“DE”), x-ray imaging system data acquisition and image reconstruction system and method enables optimizing the image contrast of a sample. Using the DE x-ray imaging system and its associated user interface applications, an operator performs a low energy (“LE”) and high energy (“HE”) x-ray scan of the same volume of interest of the sample. The system creates a low-energy reconstructed tomographic volume data set from the set of low-energy projections and a high-energy tomographic volume data set from the set of high-energy projections. This enables the operator to control the image contrast of selected slices, and apply the information associated with optimizing the contrast of the selected slice to all slices in the low-energy and high-energy tomographic data sets. This creates a combined volume data set from the LE and HE volume data sets with optimized image contrast throughout.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
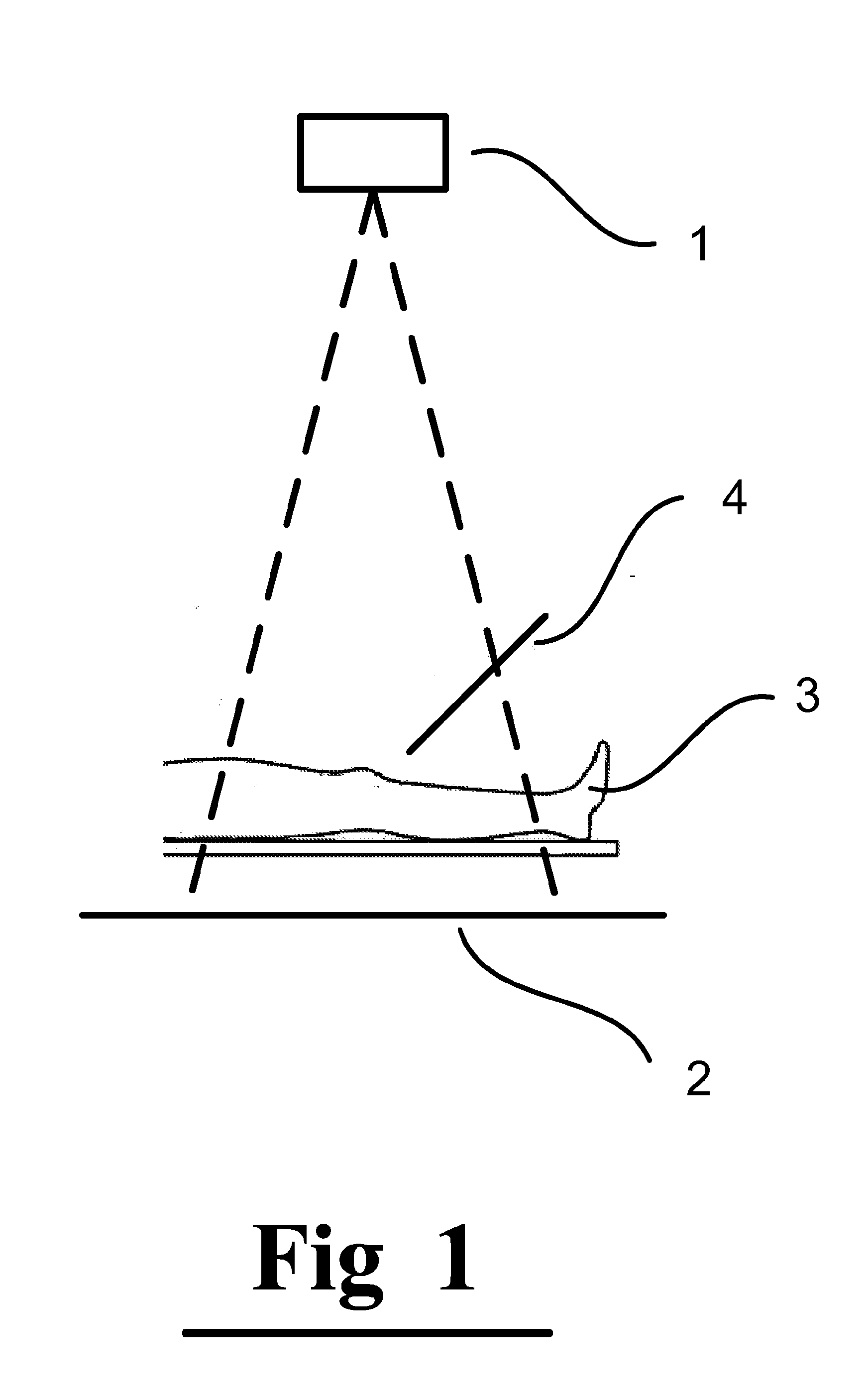
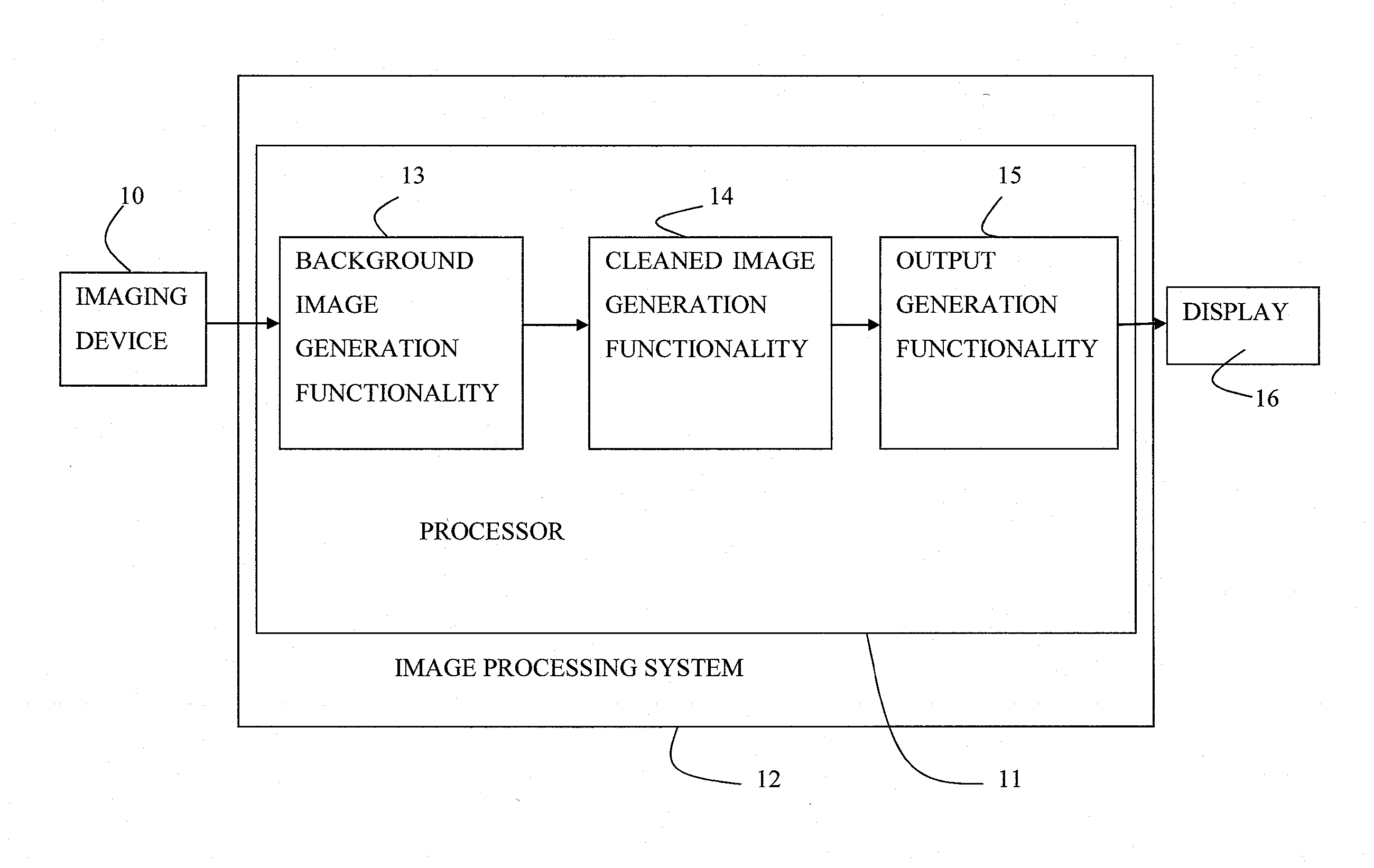
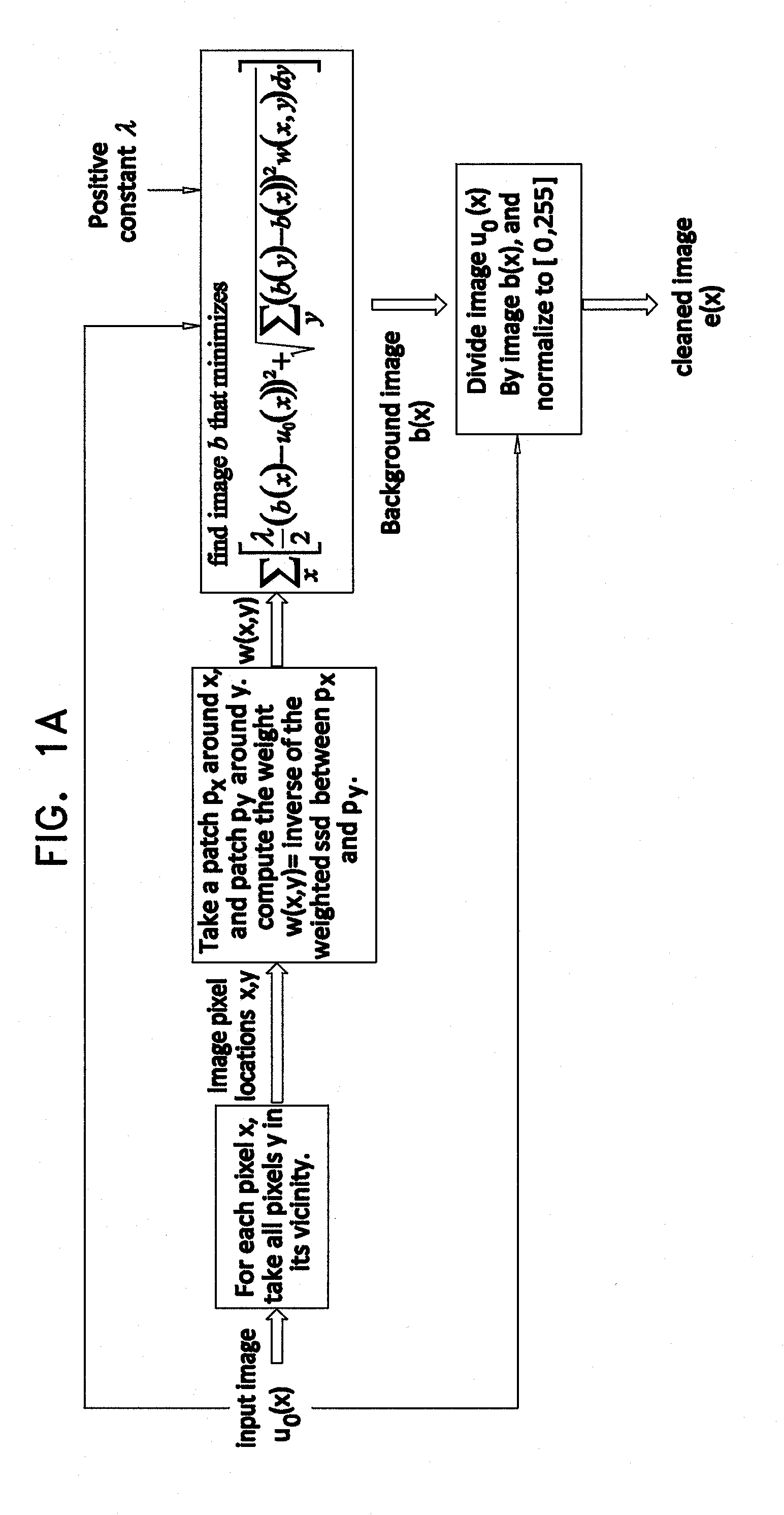
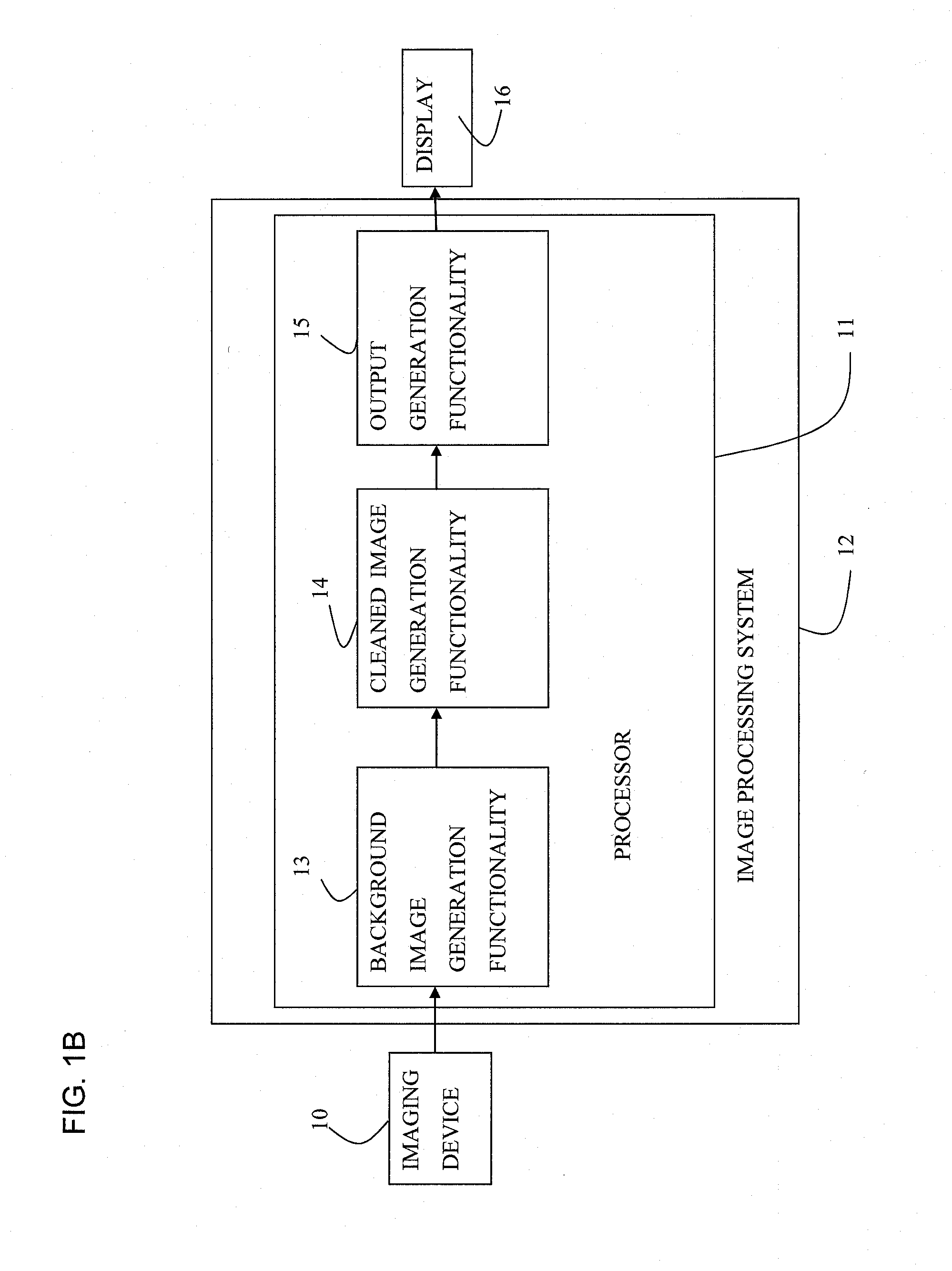
Luminal background cleaning
ActiveUS20140140597A1Improve visualizationImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Display device
Apparatus and methods are described for use with an input angiogram image of a device inserted inside a portion of subject's body, the angiogram image being acquired in the presence of contrast agent. At least one processor (11) includes background-image-generation functionality (13) configured to generate a background image in which a relative value is assigned to a first pixel with respect to a second pixel, at least partially based upon relative values of surroundings of the first pixel and the surroundings of the second pixel in the input image. Cleaned-image-generation functionality (14) generates a cleaned image in which visibility of the radiopaque portions of the device is increased relative to the input image, by dividing the input image by the background image. Output-generation functionality (15) drives a display (16) to display an output based upon the cleaned image. Other applications are also described.
Owner:SYNC RX
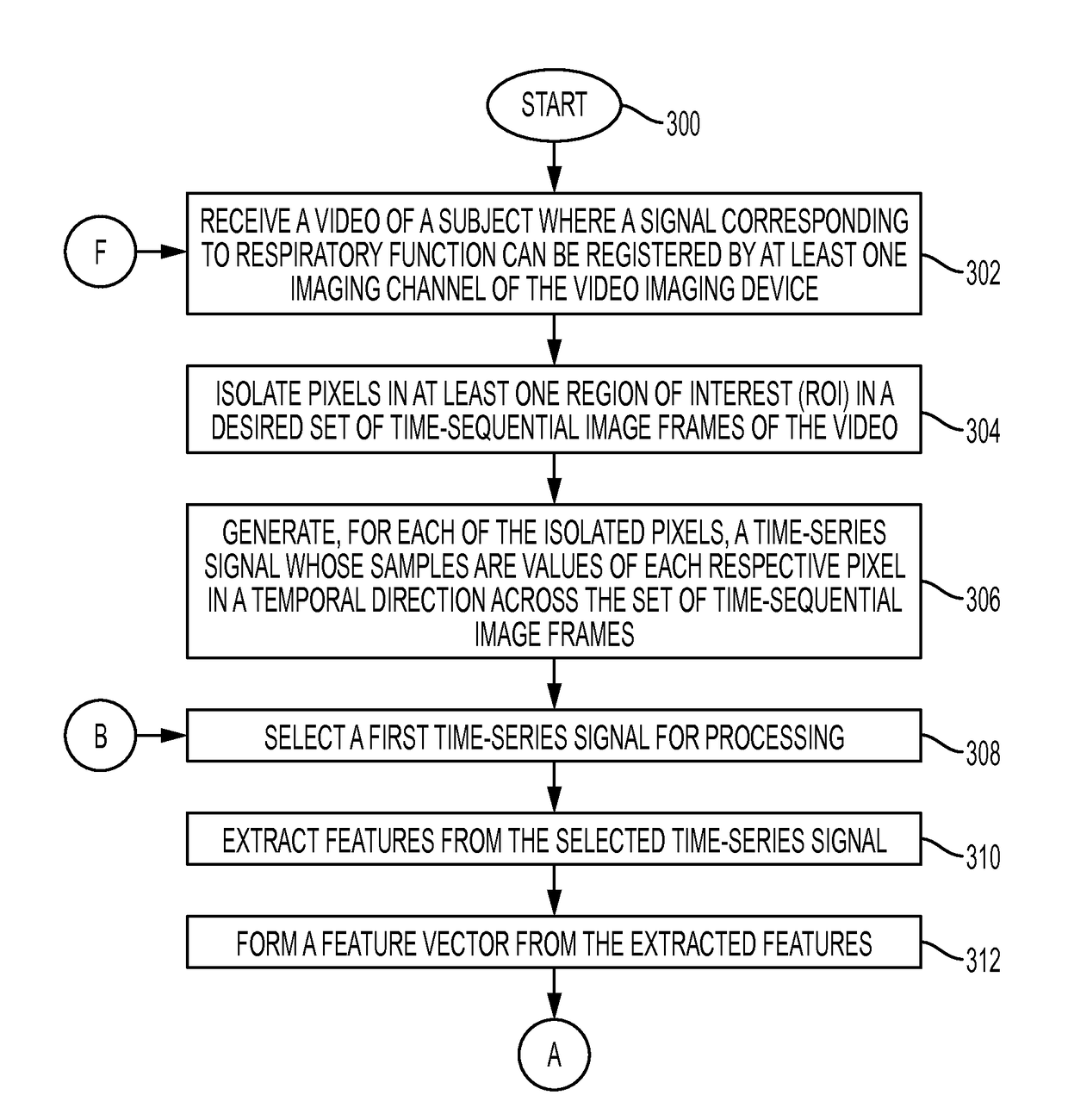
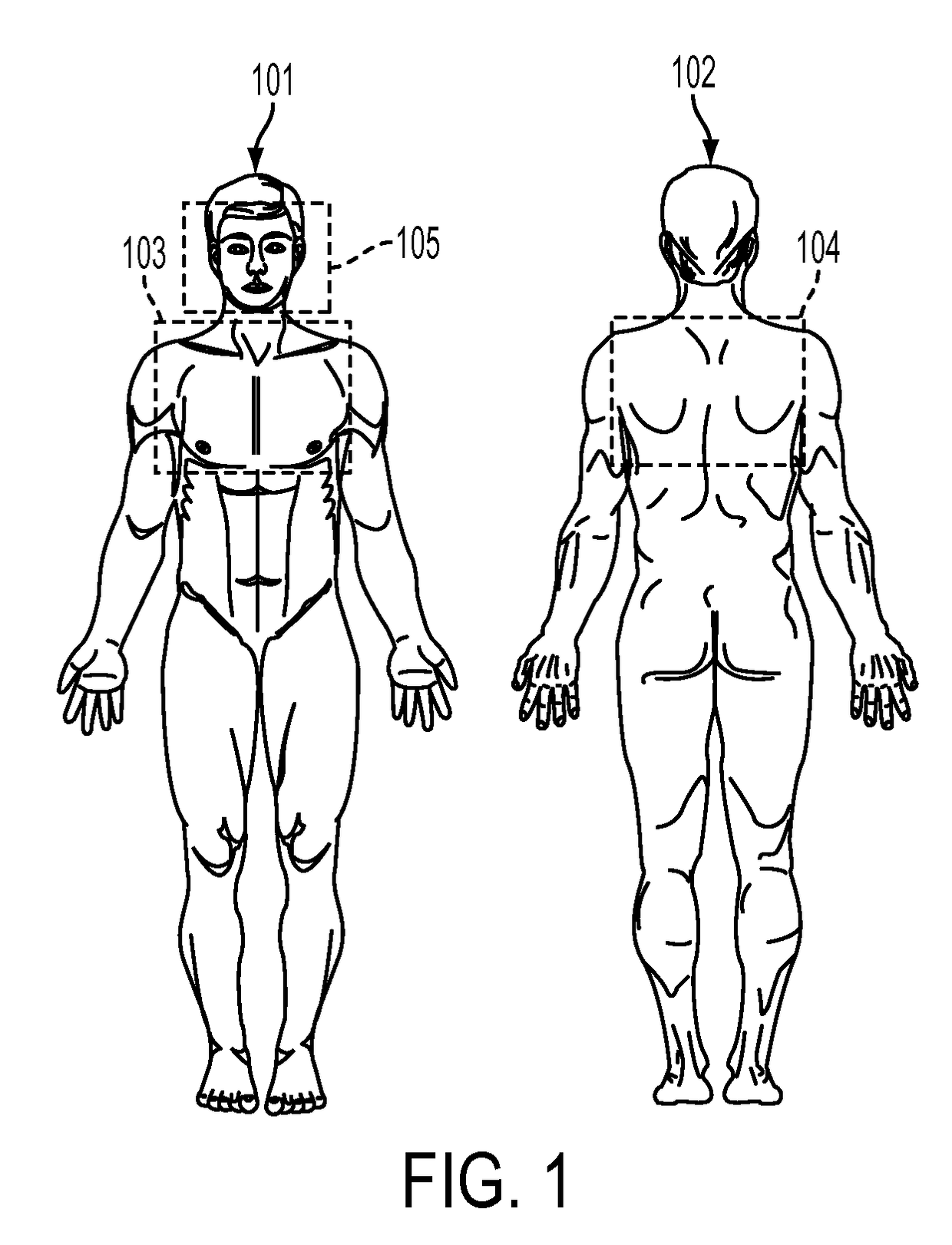
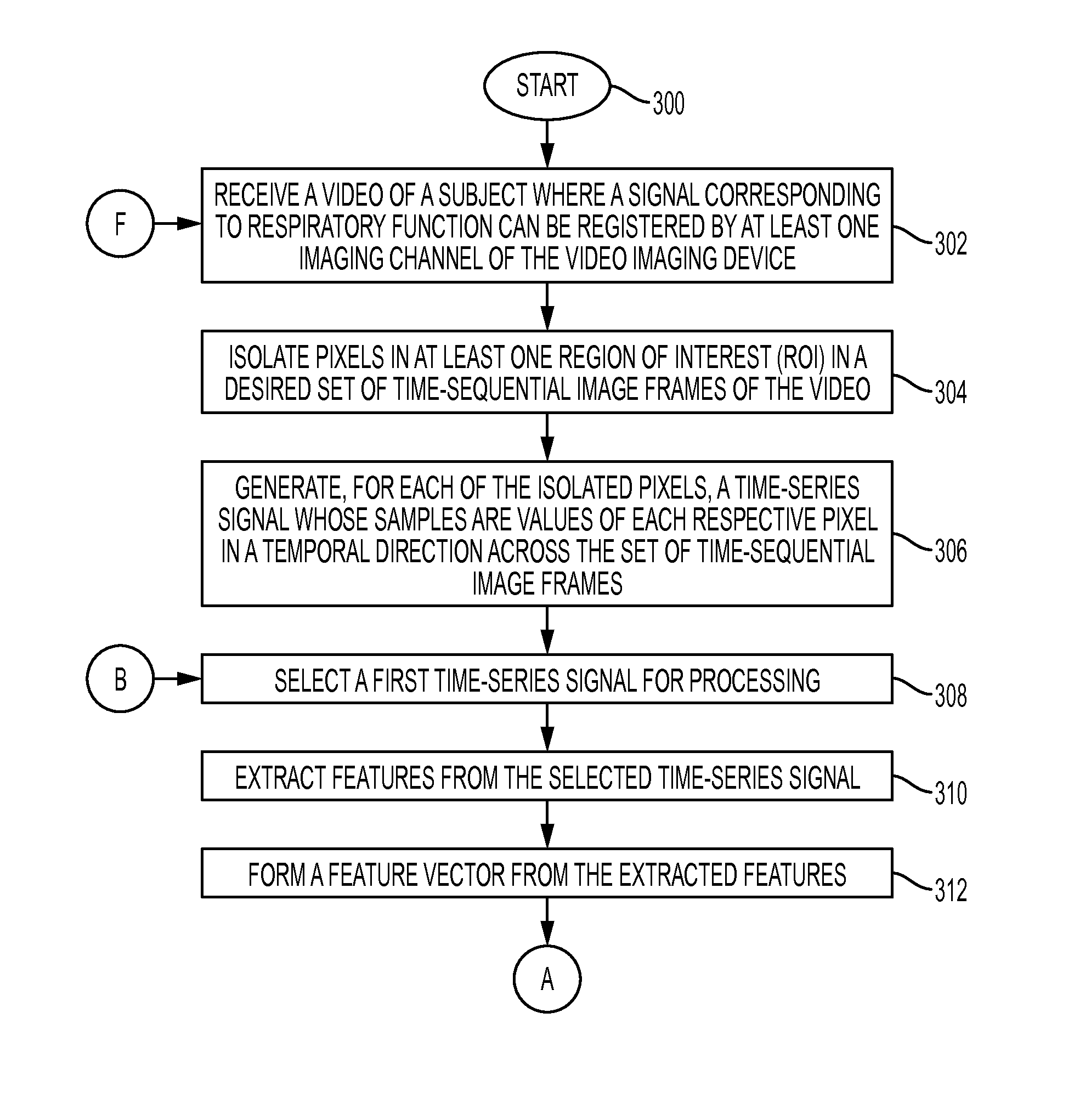
Determining a respiratory pattern from a video of a subject
What is disclosed is a system and method for determining a subject's respiratory pattern from a video of that subject. One embodiment involves receiving a video comprising N≧2 time-sequential image frames of a region of interest (ROI) of a subject where a signal corresponding to the subject's respiratory function can be registered by at least one imaging channel of a video imaging device. The ROI comprises P pixels. Time-series signals of duration N are generated from pixels isolated in the ROI. Features are extracted from the time-series signals and formed into P-number of M-dimensional vectors. The feature vectors are clustered into K clusters. The time-series signals corresponding to pixels represented by the feature vectors in each cluster are averaged along a temporal direction to obtain a representative signal for each cluster. One of the clusters is selected. A respiratory pattern is determined for the subject based on the representative signal.
Owner:XEROX CORP
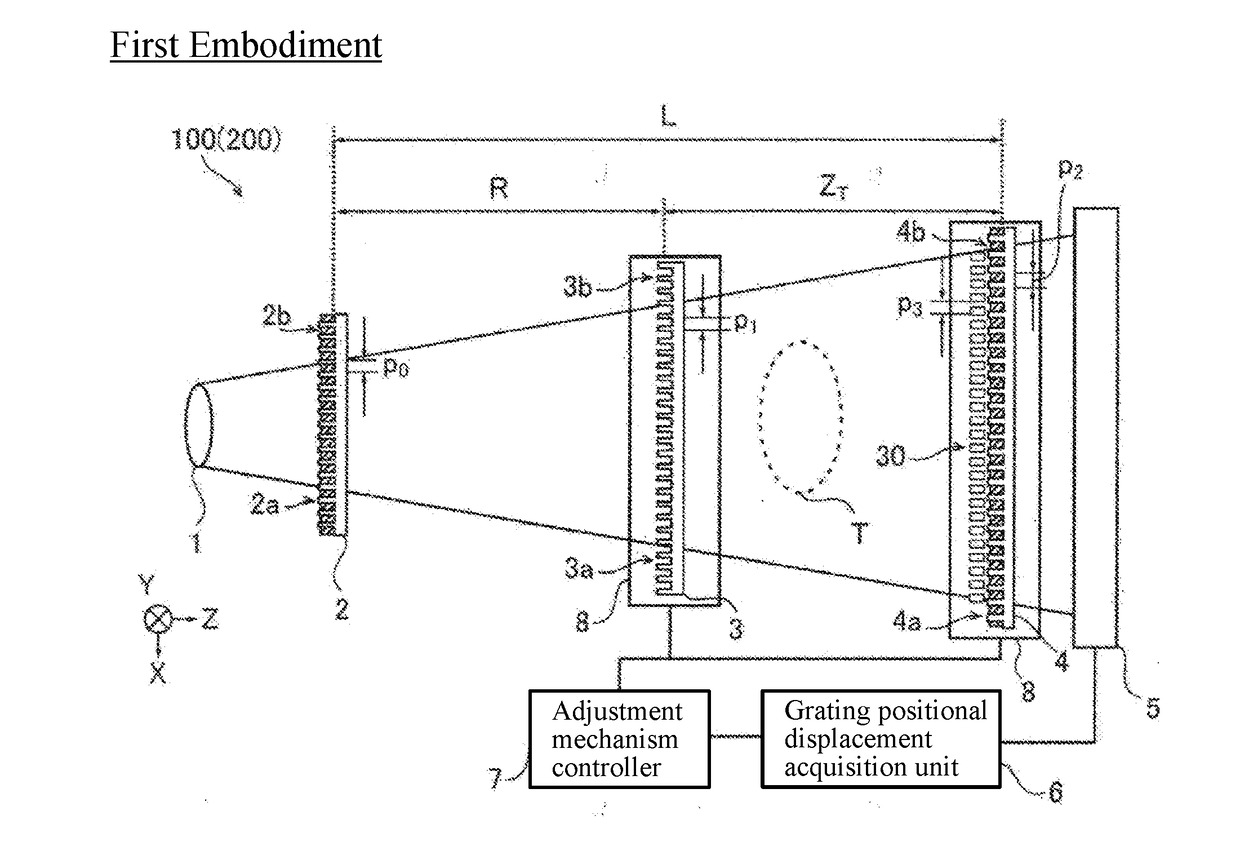
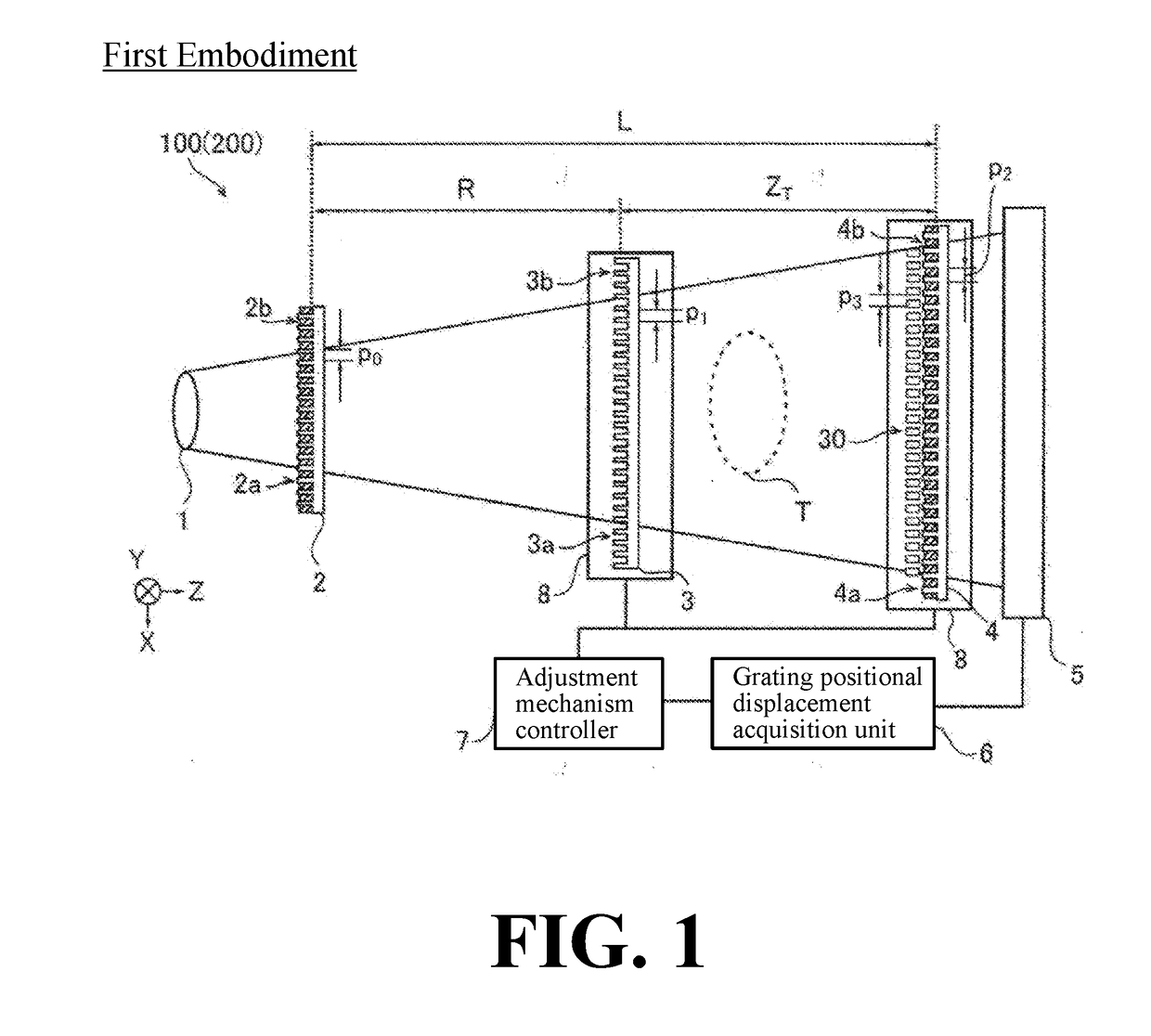
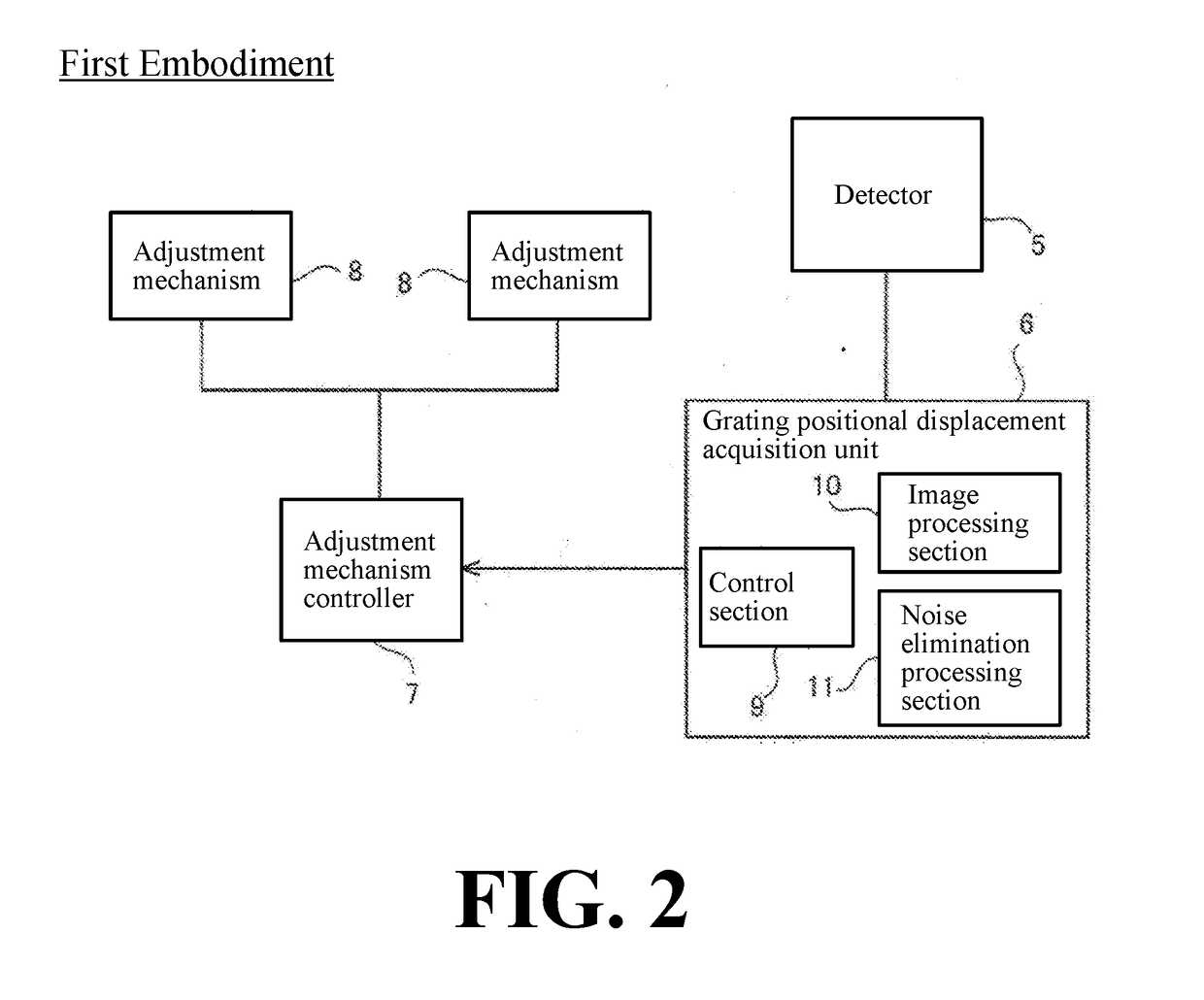
X-ray phase contrast imaging system
ActiveUS20180306734A1Shorten adjustment timeCancel noiseImage enhancementImaging devicesGratingX-Ray Phase-Contrast Imaging
An X-ray phase contrast imaging system includes an X-ray source, a detector, a plurality of gratings including a first grating and a second grating, and a grating positional displacement acquisition section configured to obtain a positional displacement of the grating based on a Fourier transform image obtained by Fourier transforming an interference fringe image detected by the detector.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
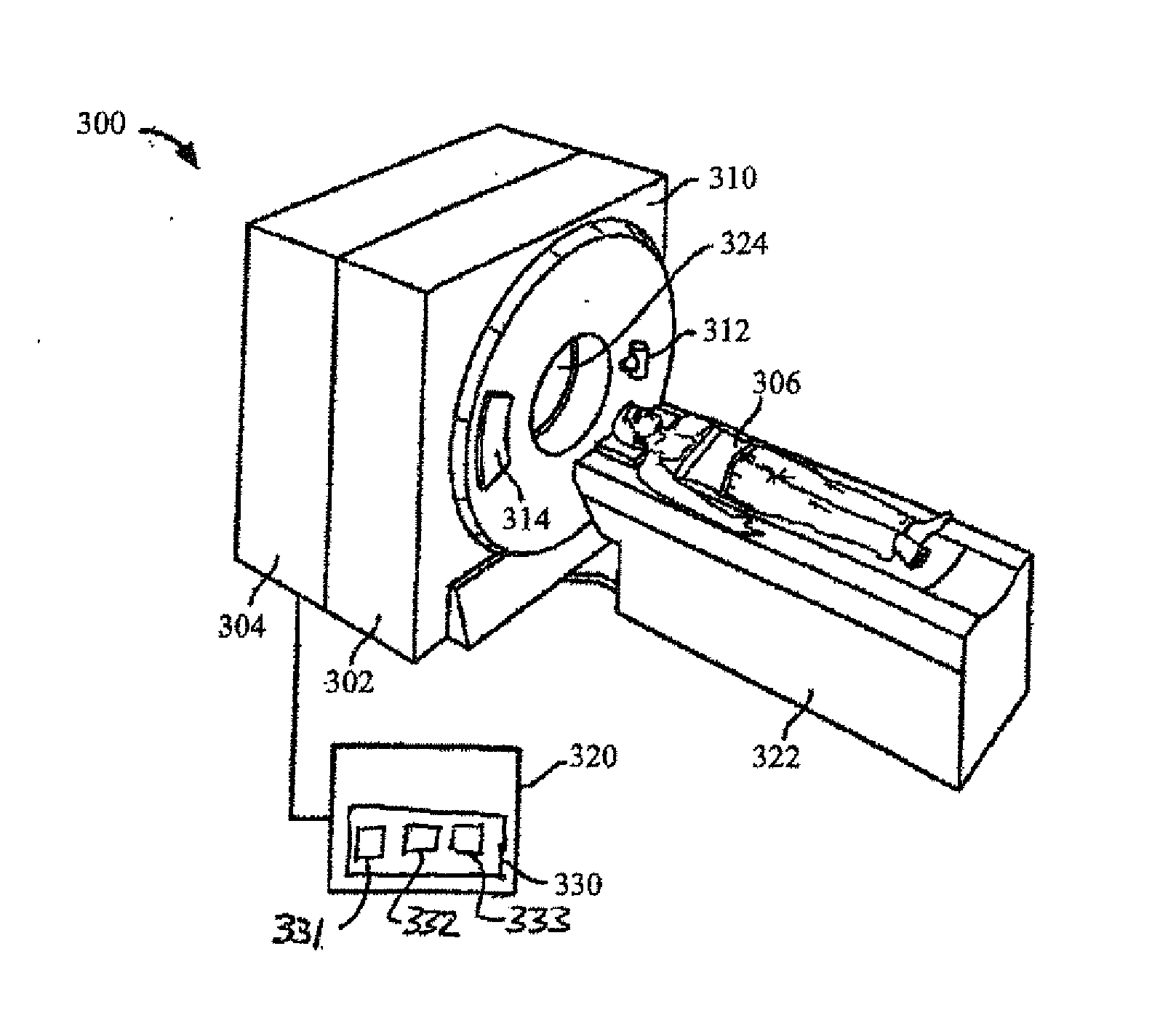
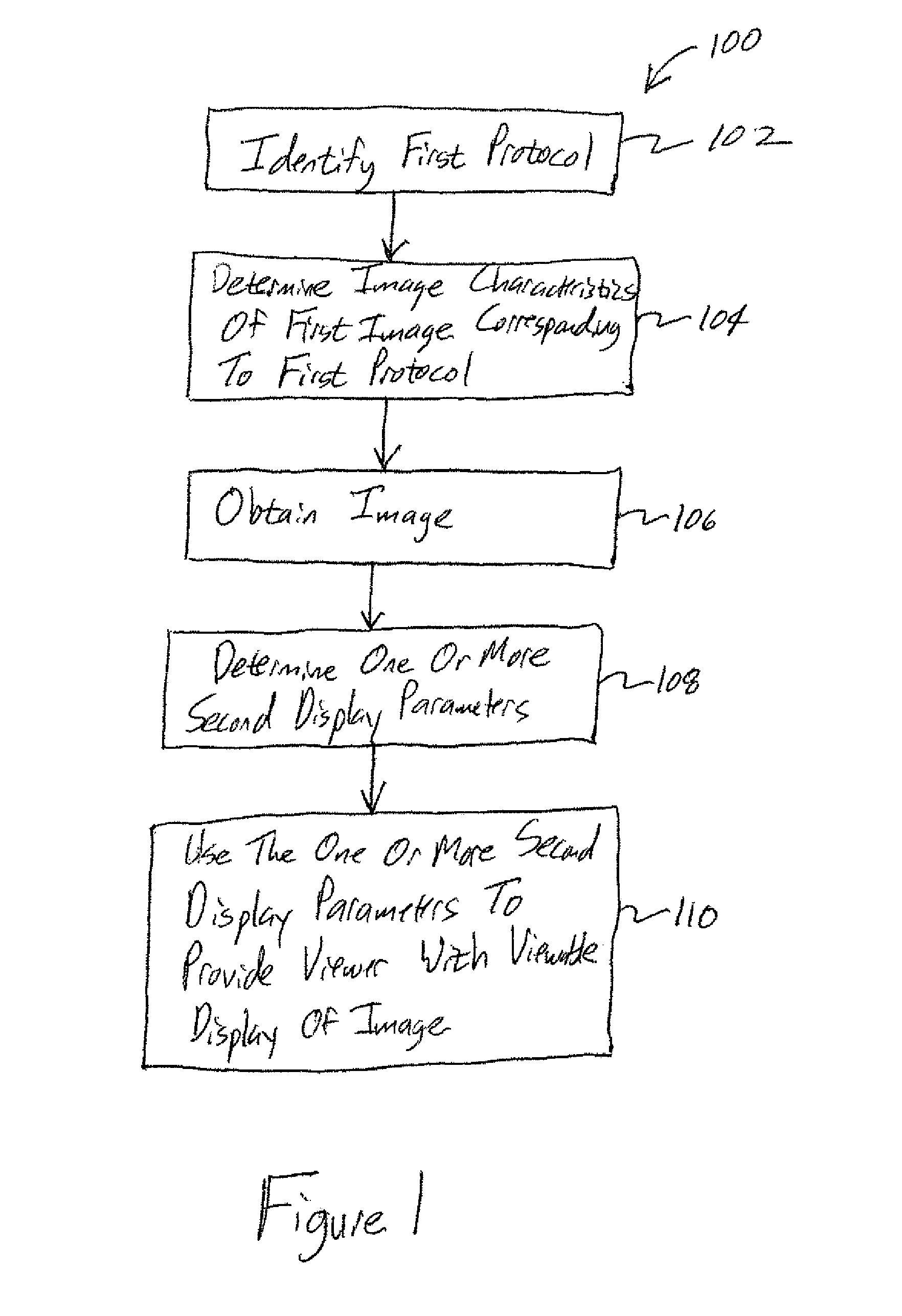
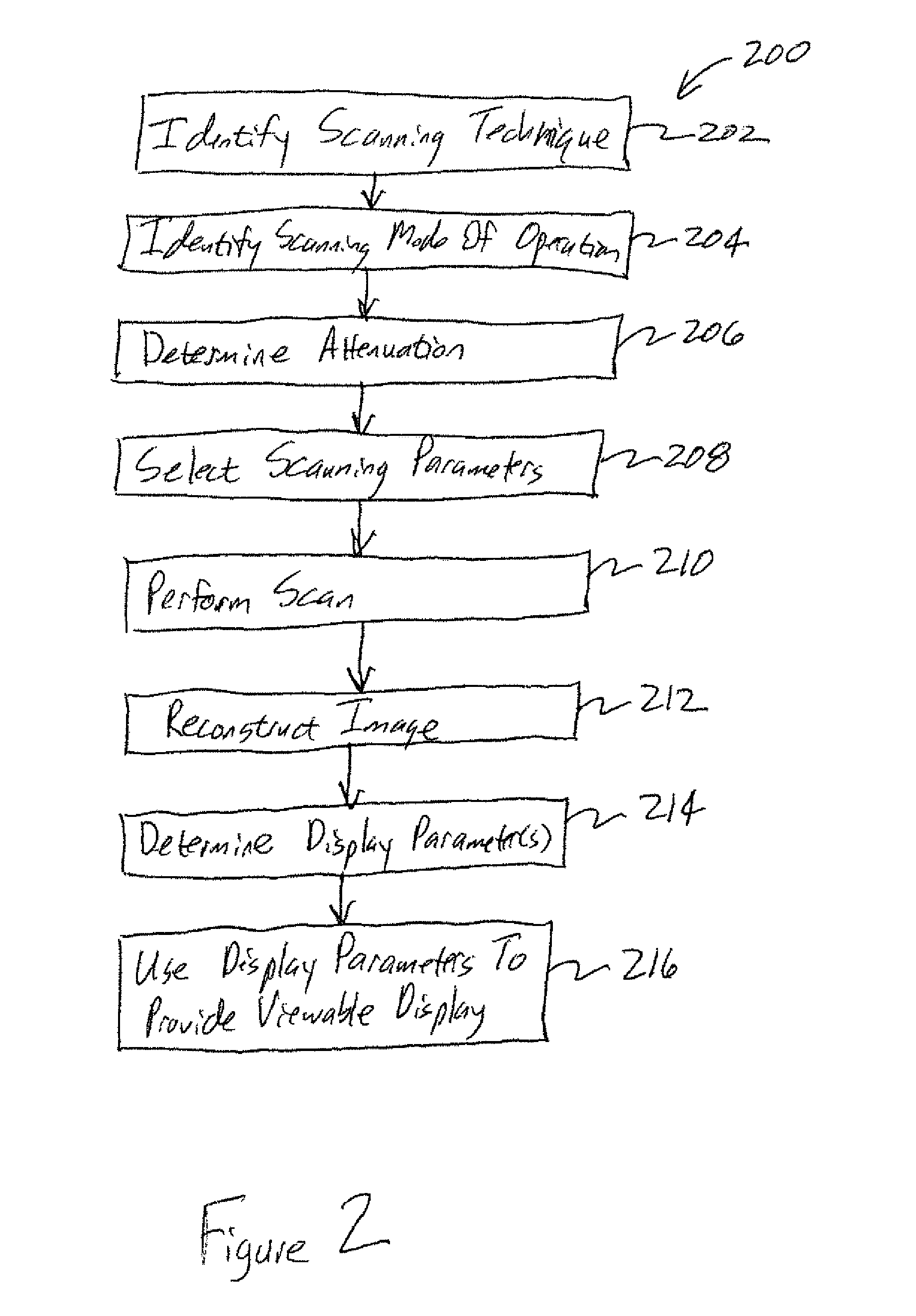
Systems and methods for selecting image display parameters
An imaging system includes an identification module, a determination module, and a display module. The identification module is configured to identify one or more first scanning parameters and one or more first display parameters corresponding to a first image, and to identify one or more second scanning parameters corresponding to scanning information acquired during a second scan. The determination module is configured to determine, based on the one or more first scanning parameters and the one or more second scanning parameters, one or more second display parameters so that the scanning information acquired during the second scan may be used to provide a second image appearing more similar to the first image. The display module is configured to use the one or more second display parameters to provide the second image configured to be displayed to a viewer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
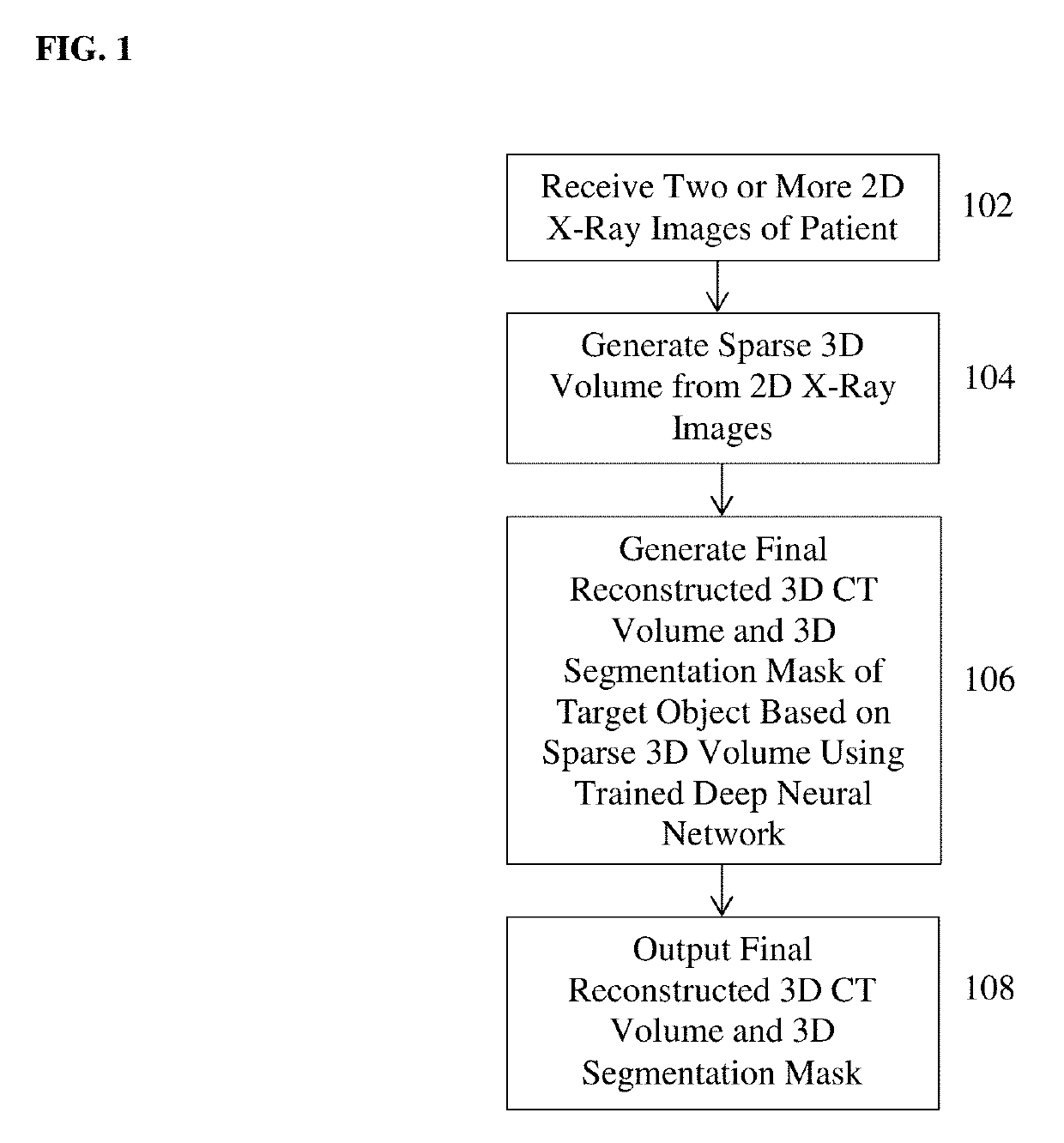
Method and System for 3D Reconstruction of X-ray CT Volume and Segmentation Mask from a Few X-ray Radiographs
A method and apparatus for automated reconstruction of a 3D computed tomography (CT) volume from a small number of X-ray images is disclosed. A sparse 3D volume is generated from a small number of x-ray images using a tomographic reconstruction algorithm. A final reconstructed 3D CT volume is generated from the sparse 3D volume using a trained deep neural network. A 3D segmentation mask can also be generated from the sparse 3D volume using the trained deep neural network.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
X-ray imaging apparatus and X-ray image generating method
ActiveUS9014455B2Improve discriminationRadiation diagnostic image/data processingCharacter and pattern recognitionSingle imageX ray image
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
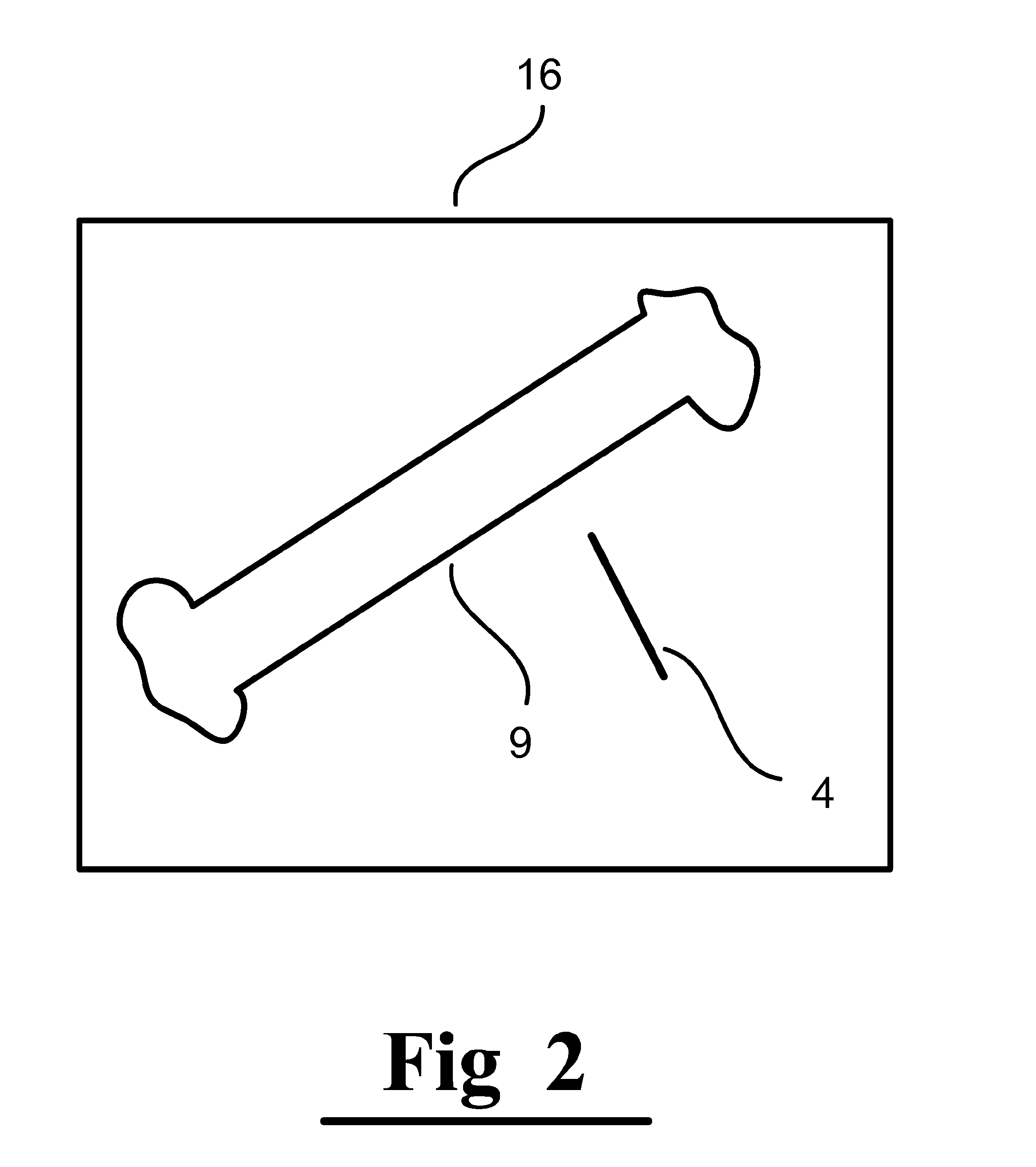
Simulated bone or tissue manipulation
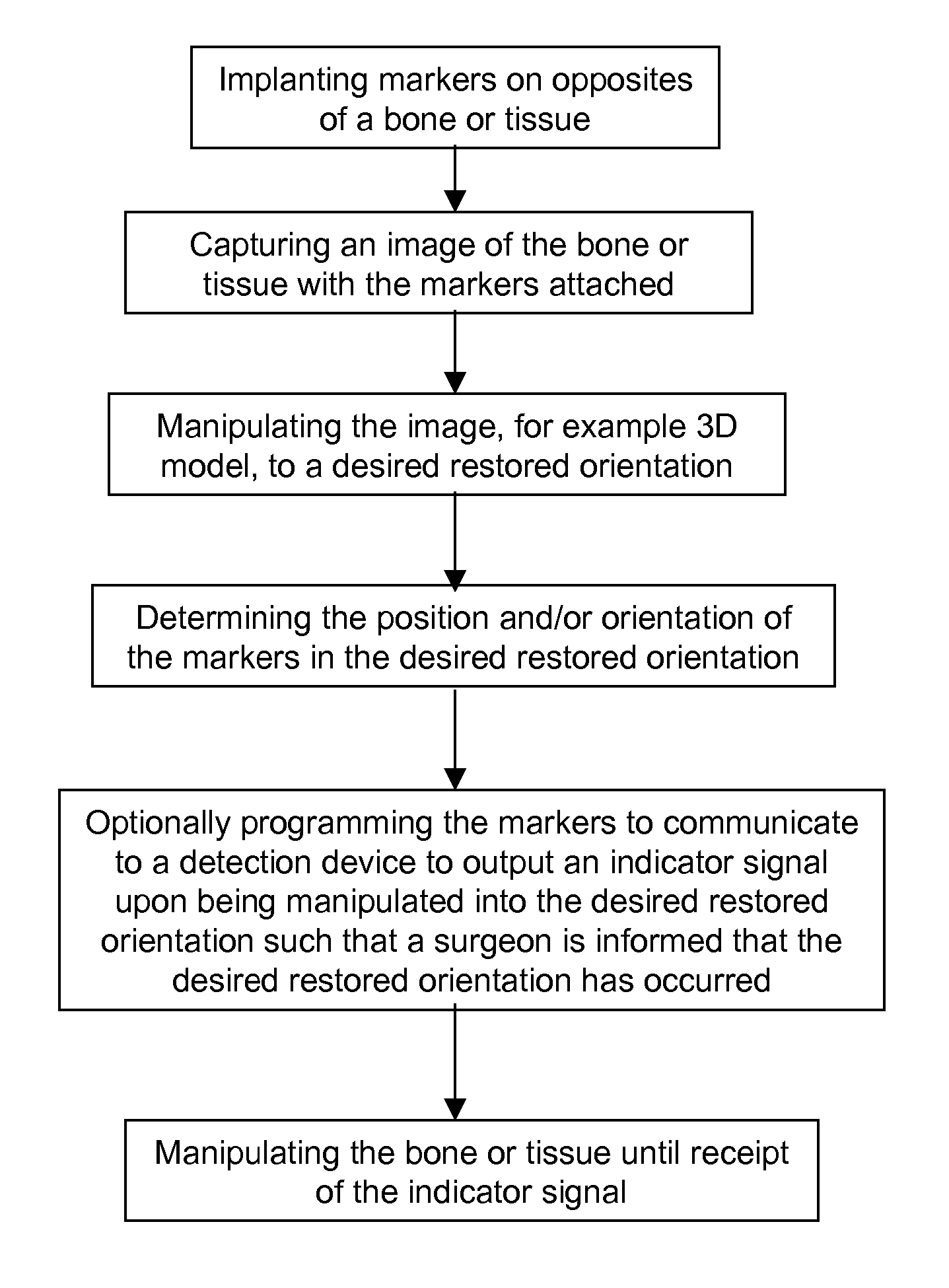
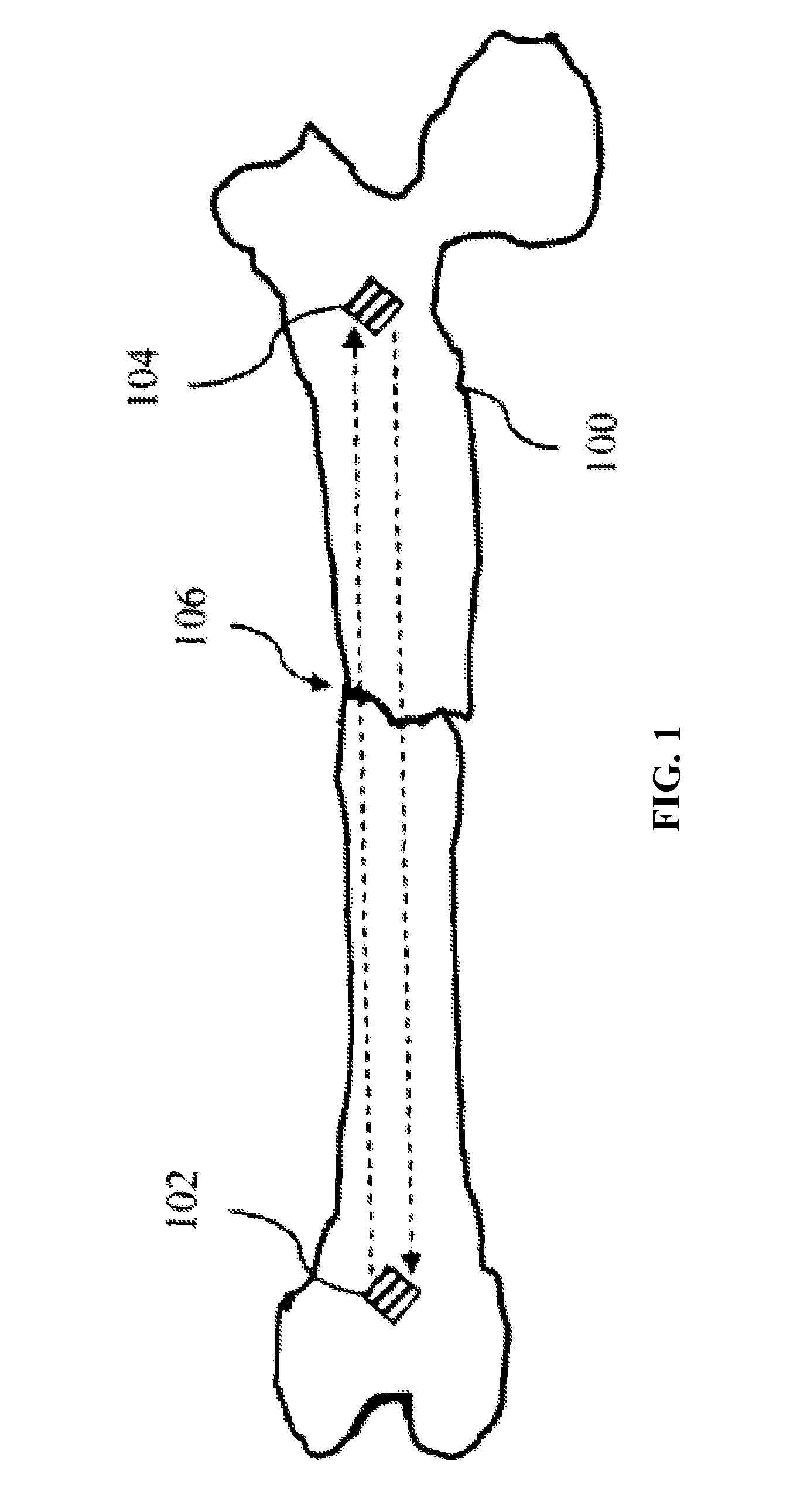
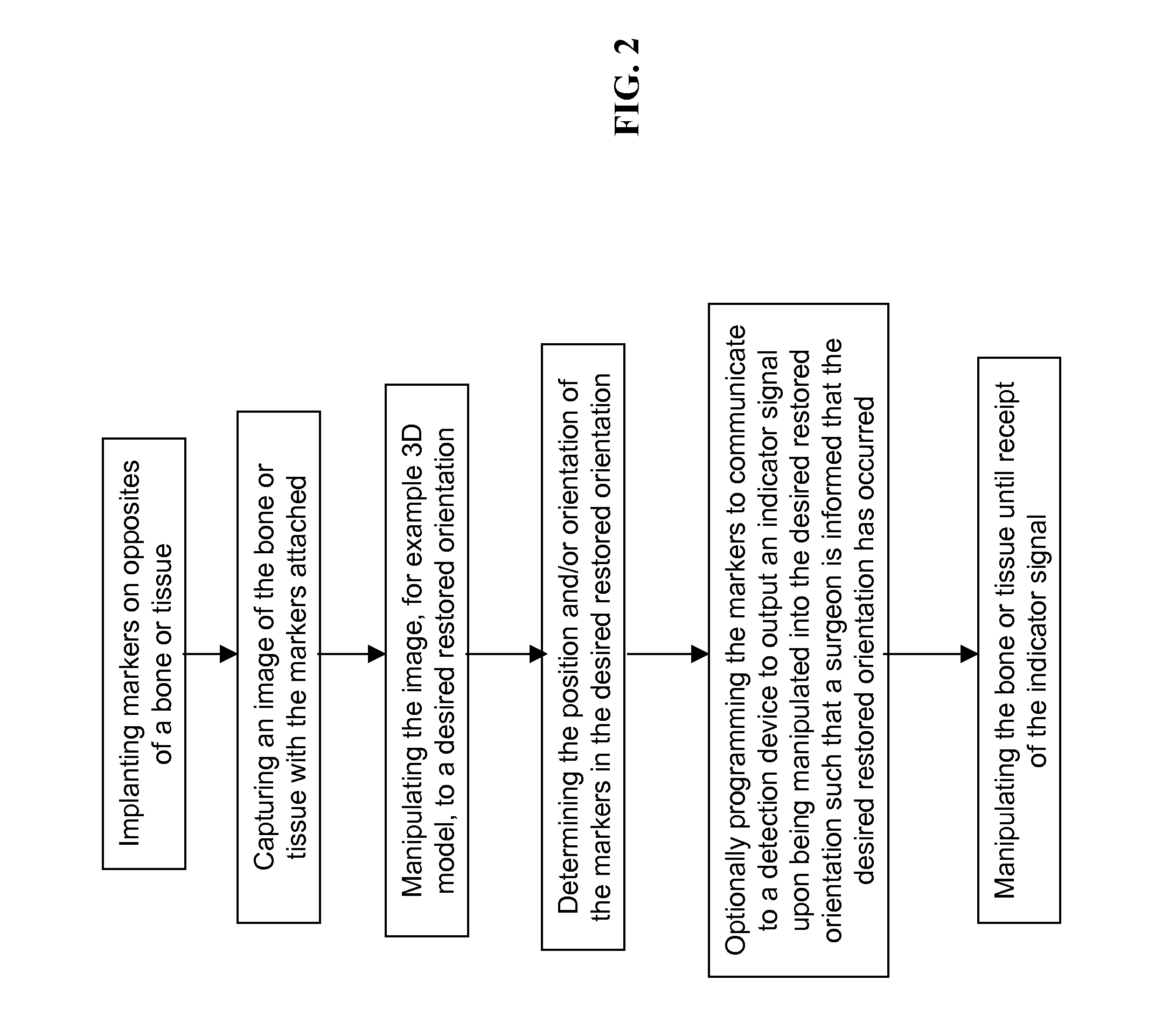
ActiveUS8565853B2Improve accuracyMagnetic measurementsRadiation diagnostic image/data processingBone tissueFractured bone
The present invention is directed to a system and method for performing tissue, preferably bone tissue manipulation. The system and method may include implanting markers on opposite sides of a bone, fractured bone or tissue to facilitate bone or tissue manipulation, preferably in-situ closed fracture reduction. The markers are preferably configured to be detected by one or more devices, such as, for example, a detection device so that the detection device can determine the relative relationship of the markers. The markers may also be capable of transmitting and receiving signals. An image may be captured of the bone or tissue and the attached markers. From the captured image, the orientation of each marker relative to the bone fragment may be determined. Next, the captured image may be manipulated in a virtual or simulated environment until a desired restored orientation has been achieved. The orientation of the markers in the desired restored orientation may then be determined. The desired relationship between markers may then be programmed into, for example, the detection device. Next, actual physical reduction and / or manipulation of the bone may begin. During the manipulation procedure, the orientation of the markers may be continuously monitored and when the markers substantially align with the virtual or simulated orientation of the markers in the desired restored orientation, an indicator signal is transmitted.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Systems and methods for attenuation compensation in nuclear medicine imaging based on emission data
ActiveUS20130248719A1Reconstruction from projectionMedical imagingUltrasound attenuationEnergy window
Systems and methods for attenuation compensation in nuclear medicine imaging based on emission data are provided. One method includes acquiring emission data at a plurality of energy windows for a person having administered thereto a radiopharmaceutical comprising at least one radioactive isotope. The method also includes performing a preliminary reconstruction of the acquired emission data to create one or more preliminary images of a peak energy window and a scatter energy window and determining a body outline of the person from at least one of the reconstructed preliminary image of the peak energy window or of the scatter energy window. The method further includes identifying a heart contour and segmenting at least the left lung. The method additionally includes defining an attenuation map based on the body outline and segmented left lung and reconstructing an image of a region of interest of the person using an iterative joint estimation reconstruction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
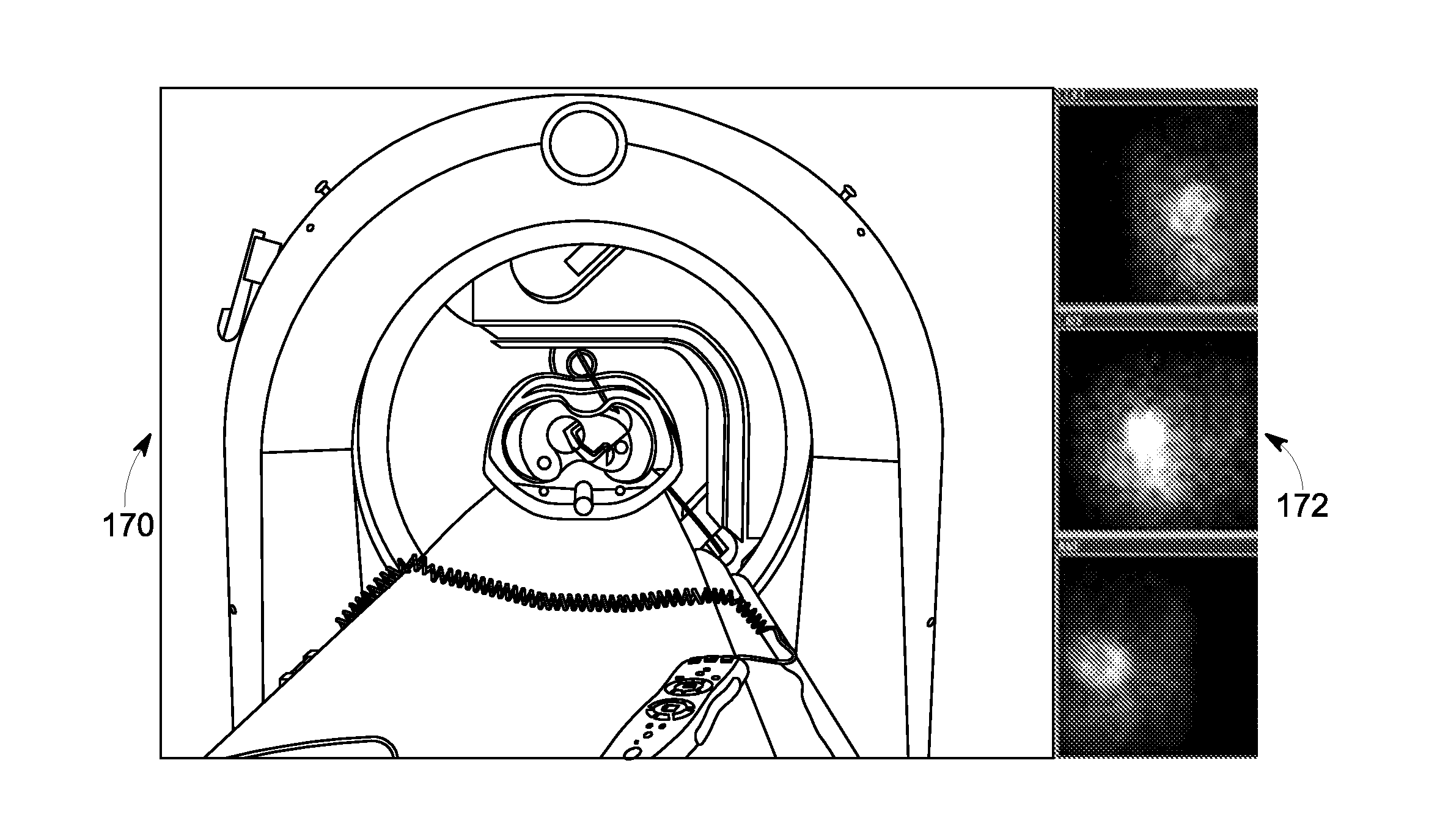
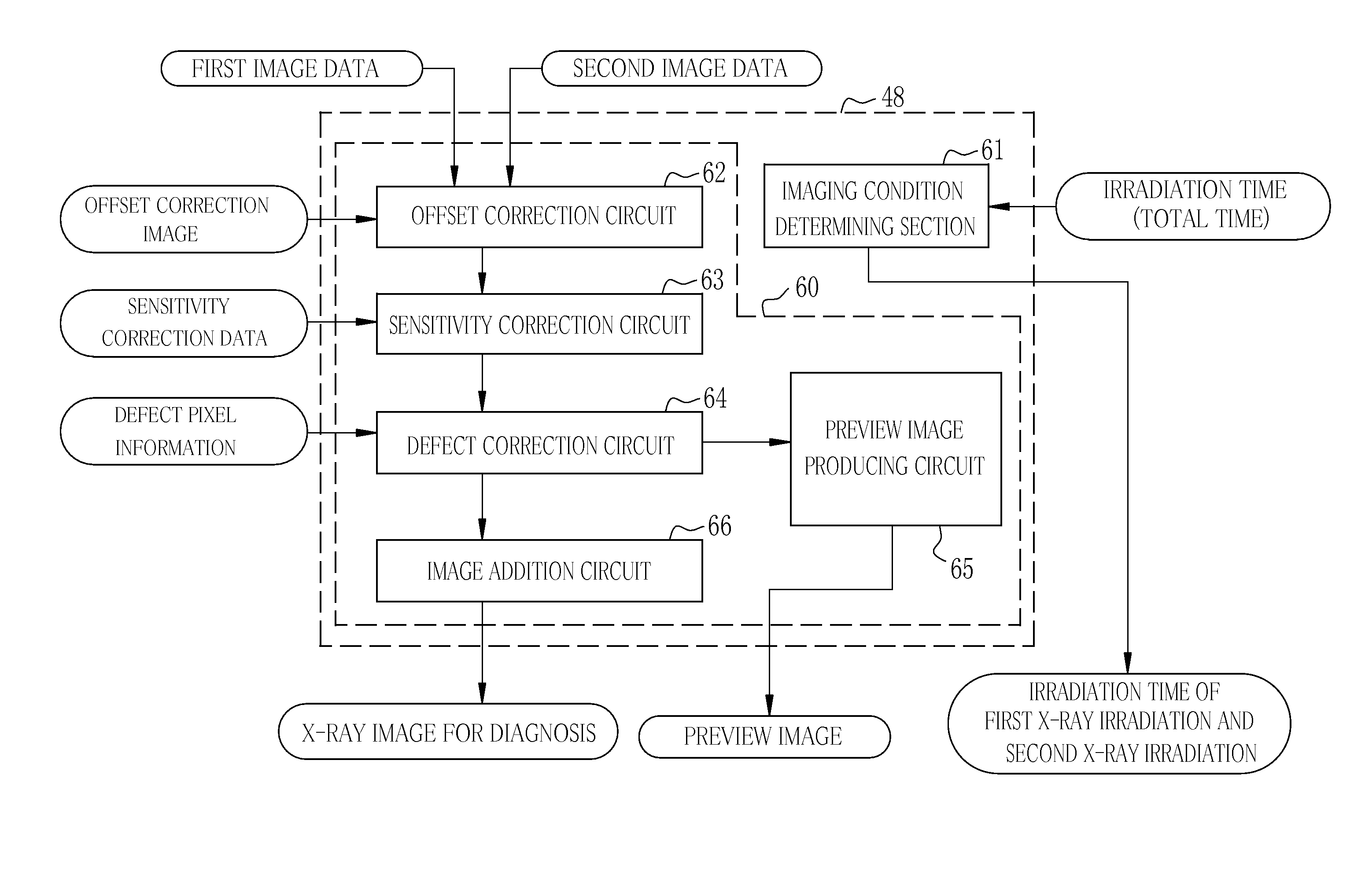
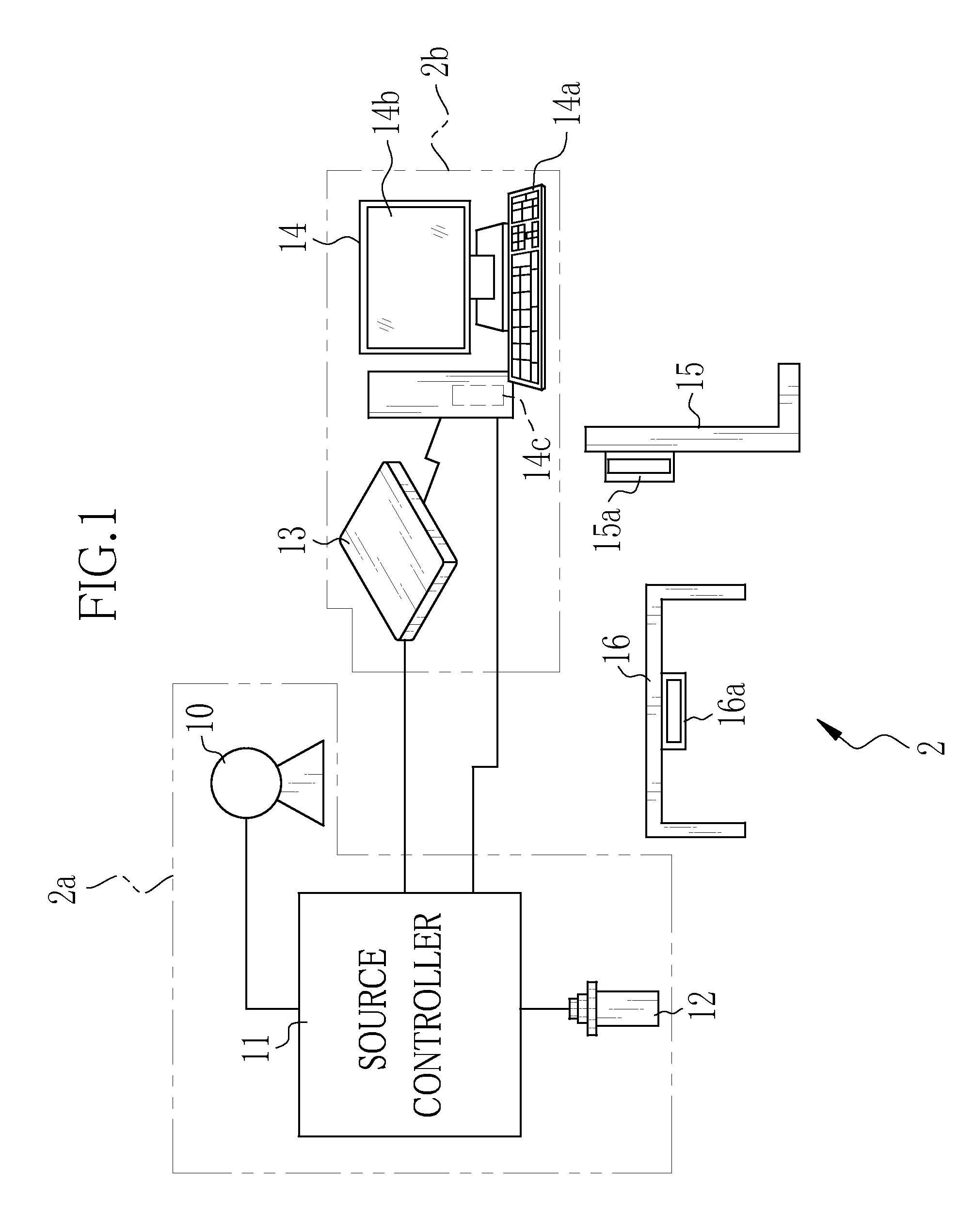
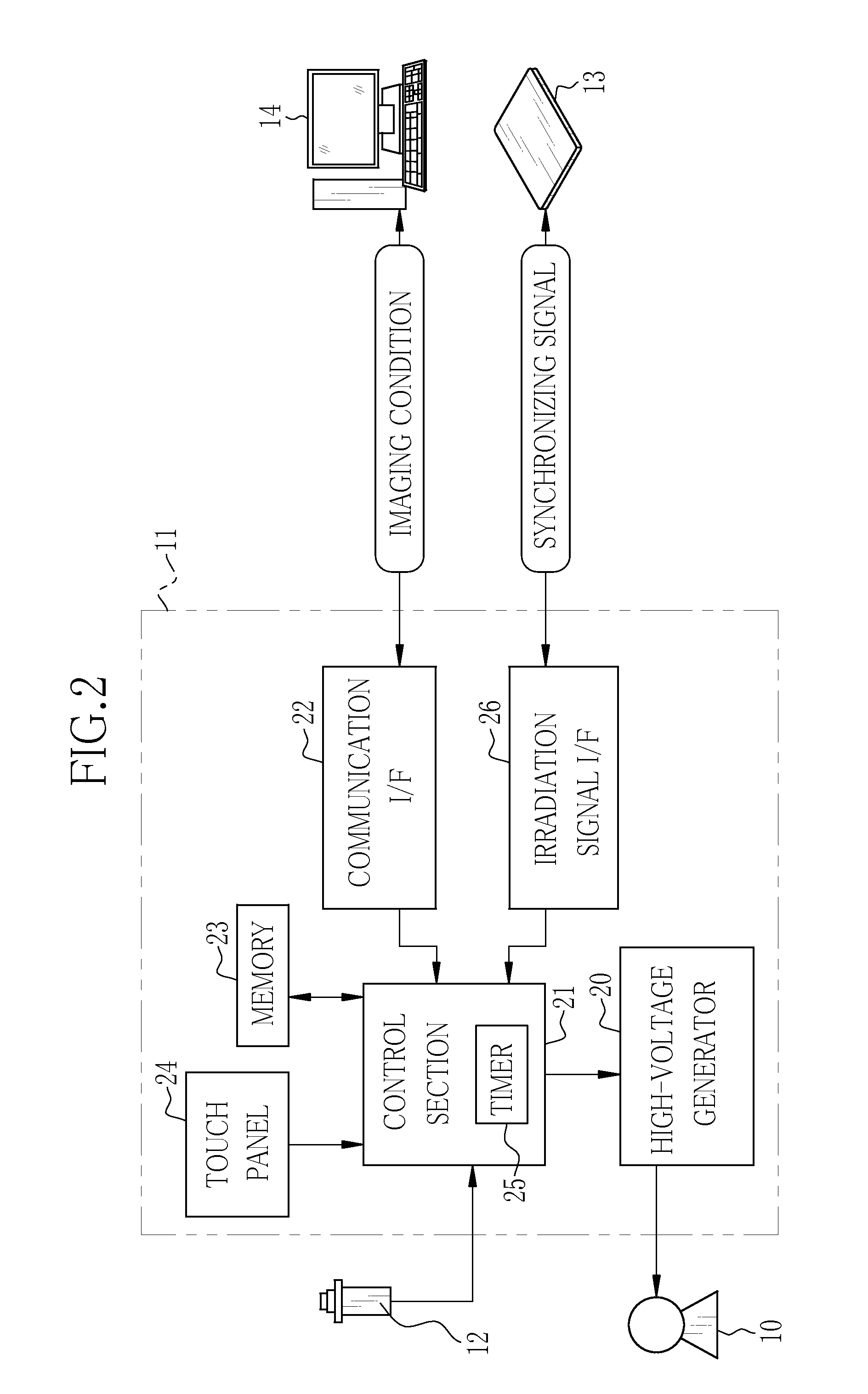
Radiation imaging system and operation method thereof, and radiation image detecting device and storage medium storing operation program therefor
ActiveUS20150189194A1Shorten the timeTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryX-rayRadiation imaging
In an X-ray imaging system, first X-ray irradiation and second X-ray irradiation are performed in performing X-ray imaging once. A preview producing circuit subjects first image data outputted from a sensor panel after the first X-ray irradiation is finished to binning processing or thinning processing to produce a preview image. The produced image is transmitted through a communication I / F to a console while the sensor panel performs an accumulation operation in the second X-ray irradiation. The preview image is displayed on a monitor of the console in the second X-ray irradiation.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
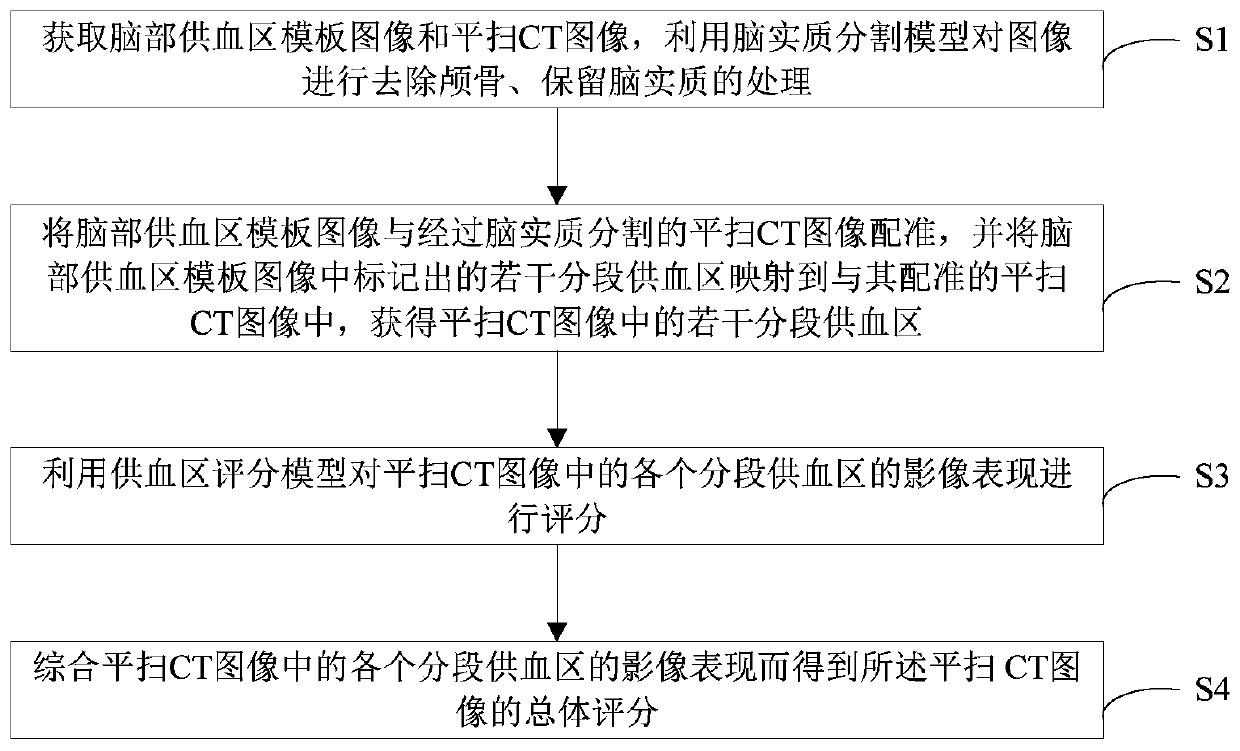
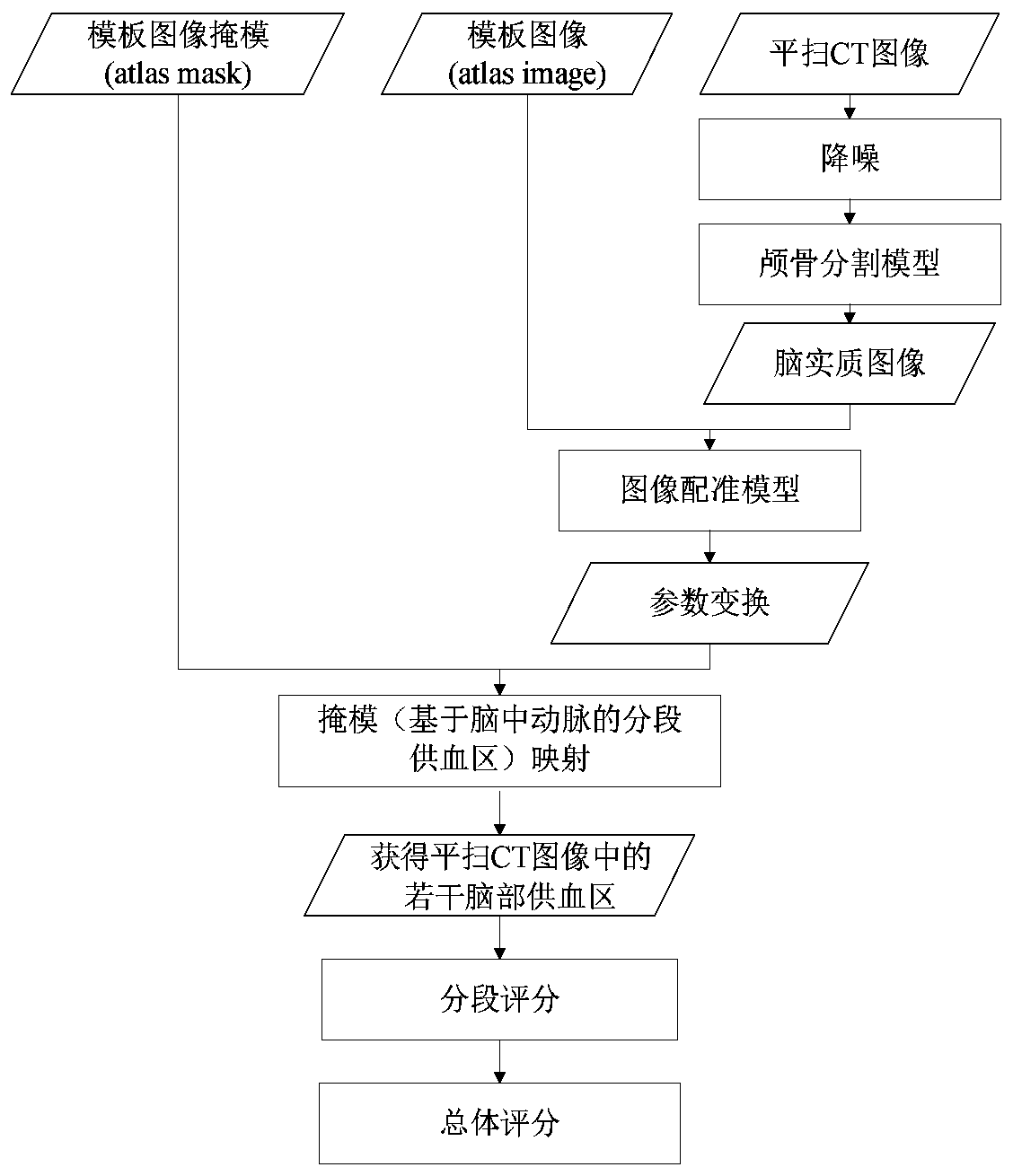
Evaluation system and evaluation method for early noncontrast CT image of stroke, and readable storage medium
ActiveCN110934606AReduce subjective differencesImprove diagnostic efficiencyImage enhancementMedical imagingImage evaluationSkull bone
The invention provides an evaluation system and evaluation method for an early noncontrast computed tomography (CT) image of stroke, and a readable storage medium. The evaluation system includes a preprocessing module, a brain blood supply area segmentation module, a segmentation scoring module and a comprehensive scoring module; a brain parenchyma segmentation unit can realize the processing of removing a skull and retaining a brain parenchyma of the noncontrast CT image; the brain blood supply area segmentation module is used to register a brain blood supply area template image to the noncontrast CT image, and map a plurality of segmented blood supply areas marked in the brain blood supply area template image to the noncontrast CT image registered with the areas to obtain a plurality ofsegmented blood supply areas in the noncontrast CT image; and the comprehensive scoring module is used to score the image performance of each segmented blood supply area in the noncontrast CT image toobtain an overall score of the noncontrast CT image. The evaluation system can assist doctors for diagnose in the early diagnosis and treatment of the stroke, reduce the subjective difference of thedoctors, and help improve the diagnosis efficiency and accuracy; and the evaluation method and the readable storage medium have the same advantages.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINGMAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
System and method of predicting future fractures
Methods of predicting fracture risk of a patient include: obtaining an image of a bone of the patient; determining one or more bone structure parameters; predicting a fracture line with the bone structure parameter; predicting a fracture load at which a fracture will happen; estimating body habitus of the patient; calculating a peak impact force on the bone when the patient falls; and predicting a fracture risk by calculating the ratio between the peak impact force and the fracture load. Inventive methods also includes determining the effect of a candidate agent on any subject's risk of fracture.
Owner:IMATX INC
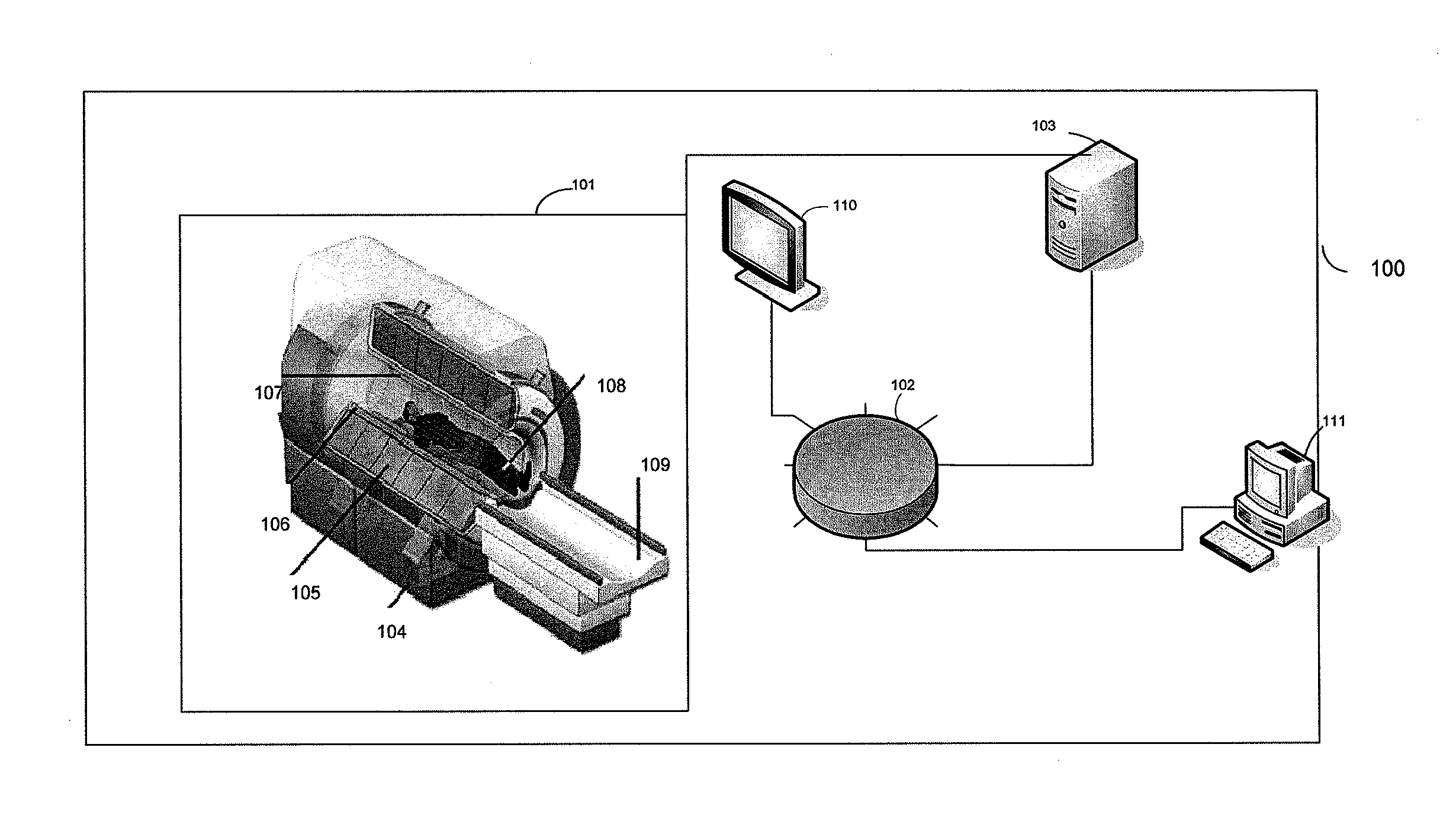
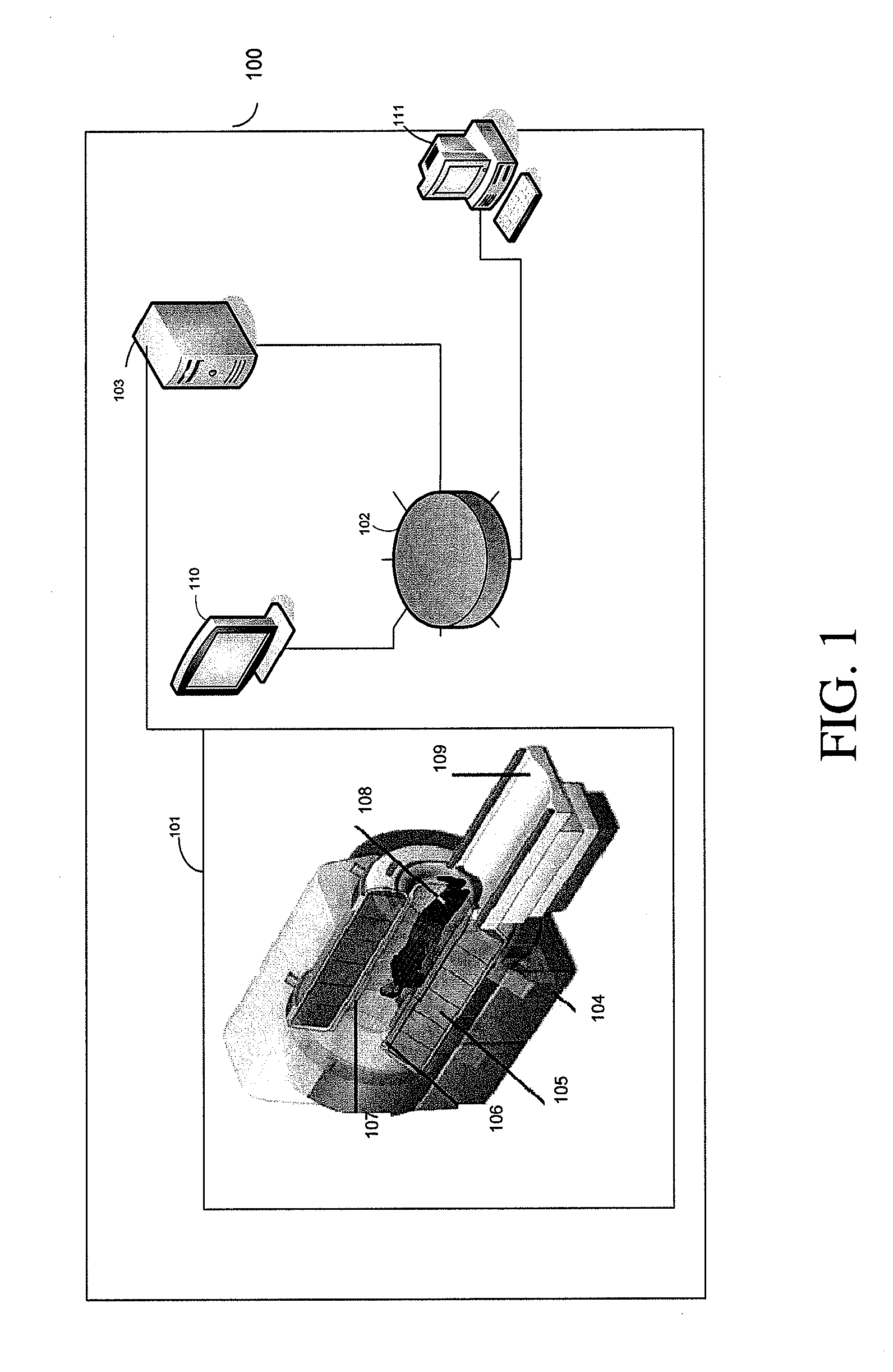
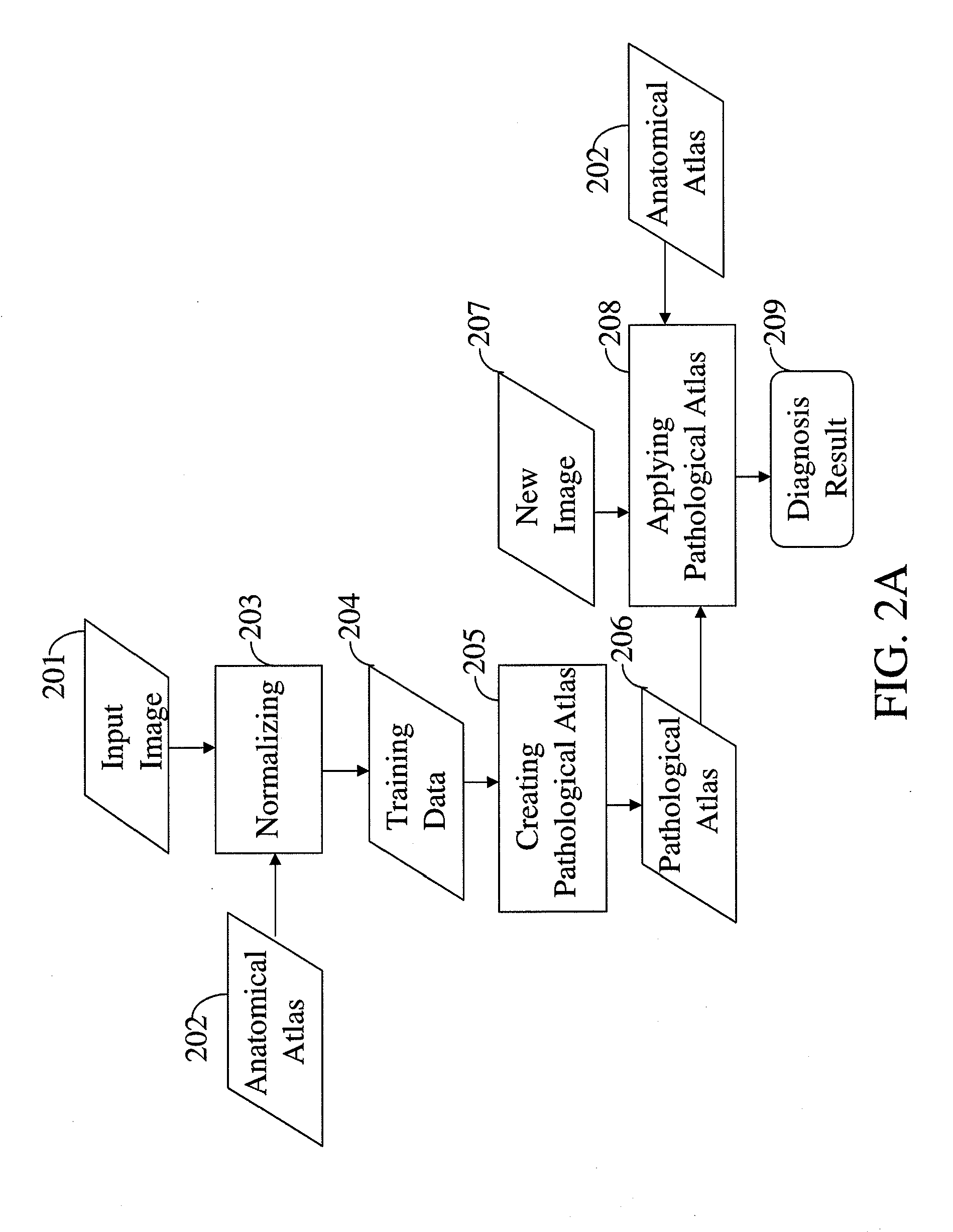
Intelligent Atlas for Automatic Image Analysis of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
A non-invasive imaging system, including an imaging scanner suitable to generate an imaging signal from a tissue region of a subject under observation, the tissue region having at least one substructure; a signal processing system in communication with the imaging scanner to receive the imaging signal from the imaging scanner; and a data storage unit in communication with the signal processing system, wherein the data storage unit stores an anatomical atlas comprising data encoding spatial information of the at least one substructure in the tissue region, and a pathological atlas corresponding to an abnormality of the tissue region, wherein the signal processing system is adapted to automatically identify, using the imaging signal, the anatomical atlas, and the pathological atlas, a presence of the abnormality or a precursor abnormality in the subject under observation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Image segmentation system, method and apparatus, and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN107798682AImprove robustnessAccurate segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage segmentation
The present application provides an image segmentation system, method and apparatus, and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises: obtaining image data, wherein the image data comprises at least one rib; determining a rib region, wherein the rib region comprises at least a portion of ribs; randomly selecting a rib in the ribs as a target rib; processing the target rib by using a classifier trained through a machine learning method, and obtaining a rib probability map; determining a starting point of the target rib; carrying out model tracking on the target rib based on the ribprobability map and the starting point; and based on a model tracking result, segmenting the target rib to obtain segmented ribs. According to the technical scheme of the present application, model tracking is carried out based on the machine learning method, so that the robustness of the model tracking algorithm is improved and that the ribs can be successfully segmented in the image is ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
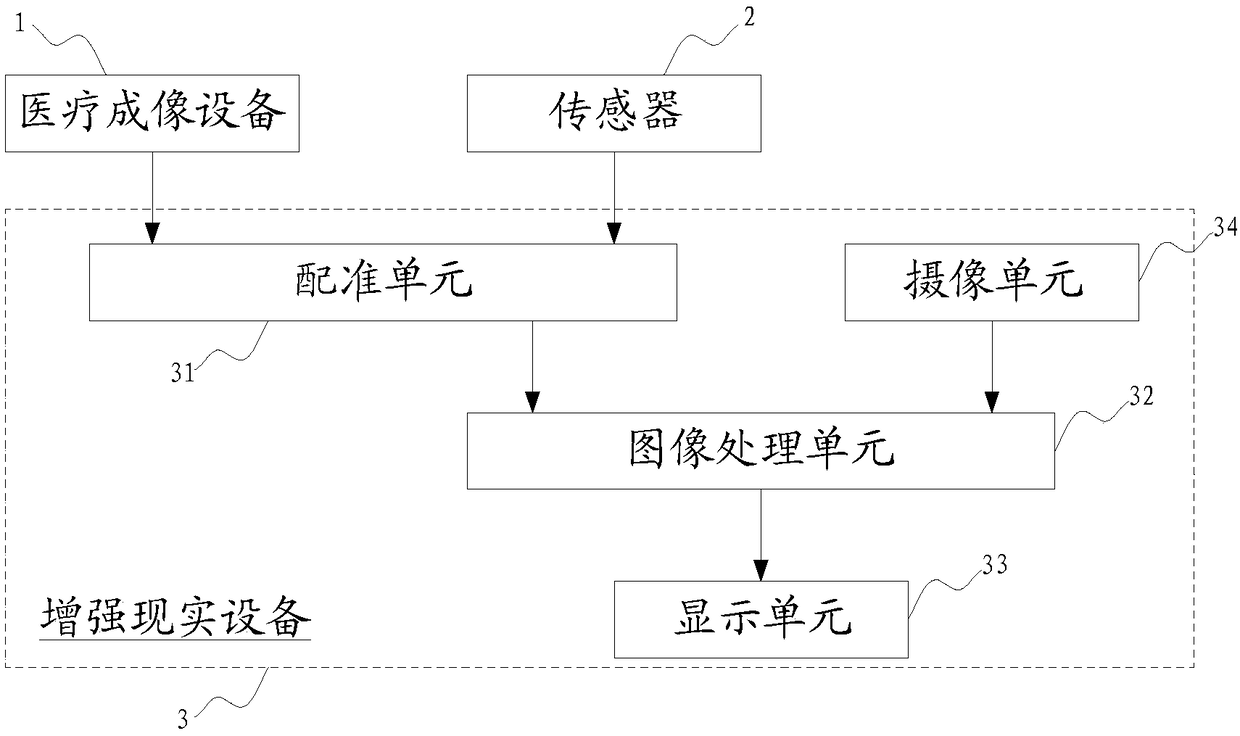
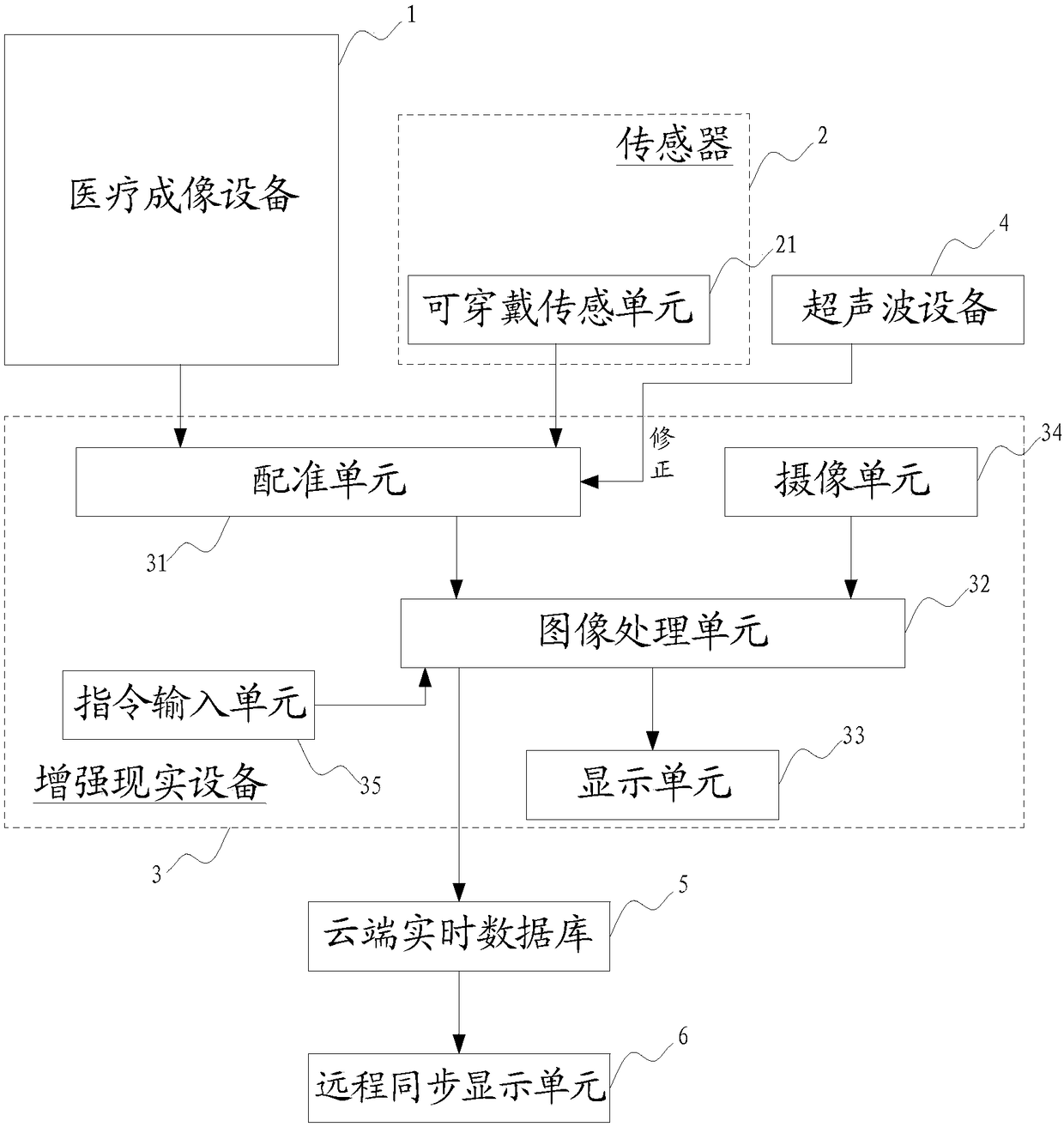
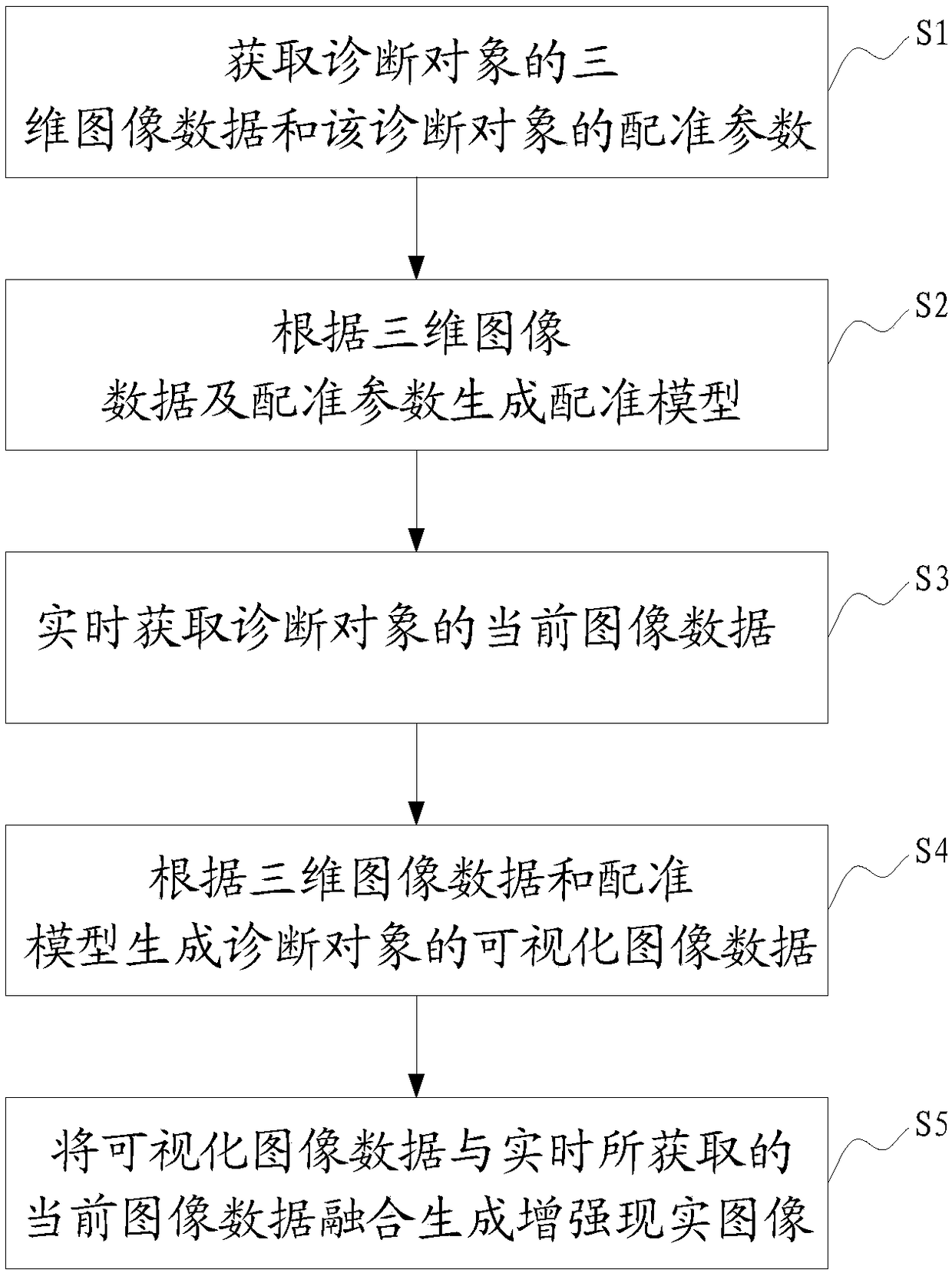
Medical diagnosis auxiliary system and method
ActiveCN108324246AImprove accuracyGood treatment effectDiagnostic signal processingRadiation diagnostic image/data processingMedical equipmentTreatment effect
The invention relates to the technical field of medical equipment, in particular to a medical diagnosis auxiliary system. The medical diagnosis auxiliary system can comprise medical imaging equipment,a sensor and augmented reality equipment, wherein the medical imaging equipment is used for acquiring three-dimensional image data of a diagnosed object; the sensor is used for acquiring registrationparameters of the diagnosed object; the augmented reality equipment comprises a registration unit, a camera shooting unit and an image processing unit; the registration unit is used for generating aregistration model according to the three-dimensional image data and the registration parameters; the camera shooting unit is used for acquiring current image data of the diagnosed object in real time; the image processing unit is used for generating visual image data of the diagnosed object according to the three-dimensional image data and the registration model; and the image processing unit canfuse the visual image data with the current image data to generate augmented reality images. By the system, three-dimensional images corresponding to organs in the body of a patient can be provided in real time on the basis of the perspective of an observer, thus, the observer can clearly position the positional relation of the internal organs and the body surface, and therefore, the diagnosis accuracy of the patient and the treatment effect are improved effectively.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Determining a respiratory pattern from a video of a subject
What is disclosed is a system and method for determining a subject's respiratory pattern from a video of that subject. One embodiment involves receiving a video comprising N≧2 time-sequential image frames of a region of interest (ROI) of a subject where a signal corresponding to the subject's respiratory function can be registered by at least one imaging channel of a video imaging device. The ROI comprises P pixels. Time-series signals of duration N are generated from pixels isolated in the ROI. Features are extracted from the time-series signals and formed into P-number of M-dimensional vectors. The feature vectors are clustered into K clusters. The time-series signals corresponding to pixels represented by the feature vectors in each cluster are averaged along a temporal direction to obtain a representative signal for each cluster. One of the clusters is selected. A respiratory pattern is determined for the subject based on the representative signal.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Systems and methods for dynamic scanning with multi-head camera
A nuclear medicine (NM) multi-head imaging system is provided that includes a gantry, plural detector units mounted to the gantry, and at least one processor operably coupled to at least one of the detector units. The detector units are mounted to the gantry. Each detector unit defines a detector unit position and corresponding view oriented toward a center of the bore. Each detector unit is configured to acquire imaging information over a sweep range corresponding to the corresponding view. The at least one processor is configured to, for each detector unit, determine plural angular positions along the sweep range corresponding to boundaries of the object to be imaged, generate a representation of each angular position for each detector unit position, generate a model based on the angular positions using the representation, and determine scan parameters to be used to image the object using the model.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
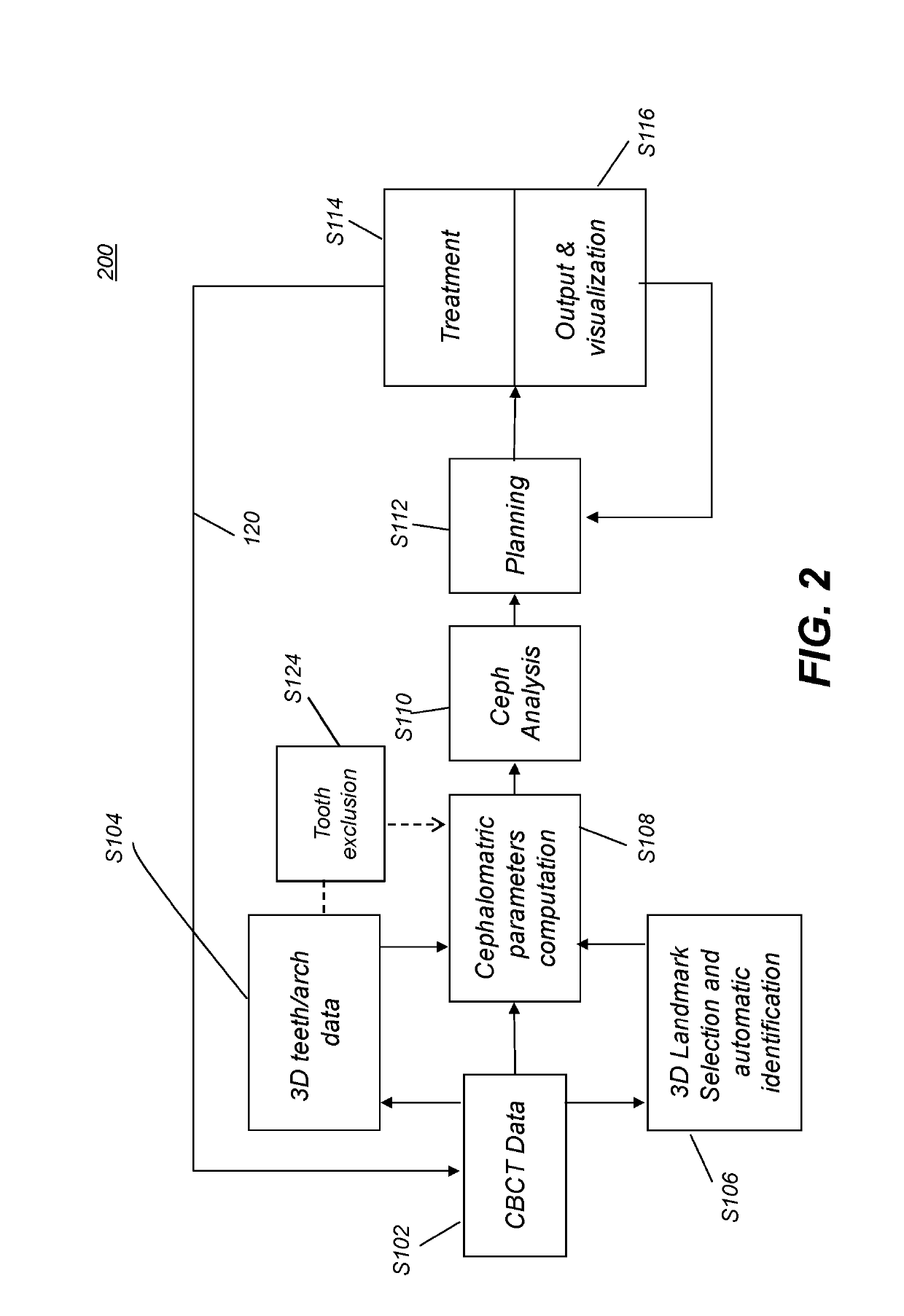
Reconstruction of a virtual computed-tomography volume to track orthodontics treatment evolution
ActiveUS20190328489A1Speed of computationCorrection capabilityMedical simulationImage enhancementCephalometric filmCephalometric analysis
Method and / or apparatus embodiments for 3-D cephalometric analysis of a patient according to the application can display reconstructed volume image data from a computed tomographic scan of a patient's head including segmented dentition elements having an initial arrangement from one or more 2D / 3D views; can compute and display a plurality of cephalometric parameters for the patient according to the reconstructed volume image data; then use the patient specific cephalometric parameters and population biometry data, to identify one or more maxillofacial / dental abnormalities; and compose patient specific treatment plans to correct selected dentition abnormalities using maxillofacial / dental structure, which can be composed in a final tooth arrangement in a final virtual CT volume. One or more aligners can be generated to incrementally move dentition from the initial arrangement to the final tooth arrangement.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
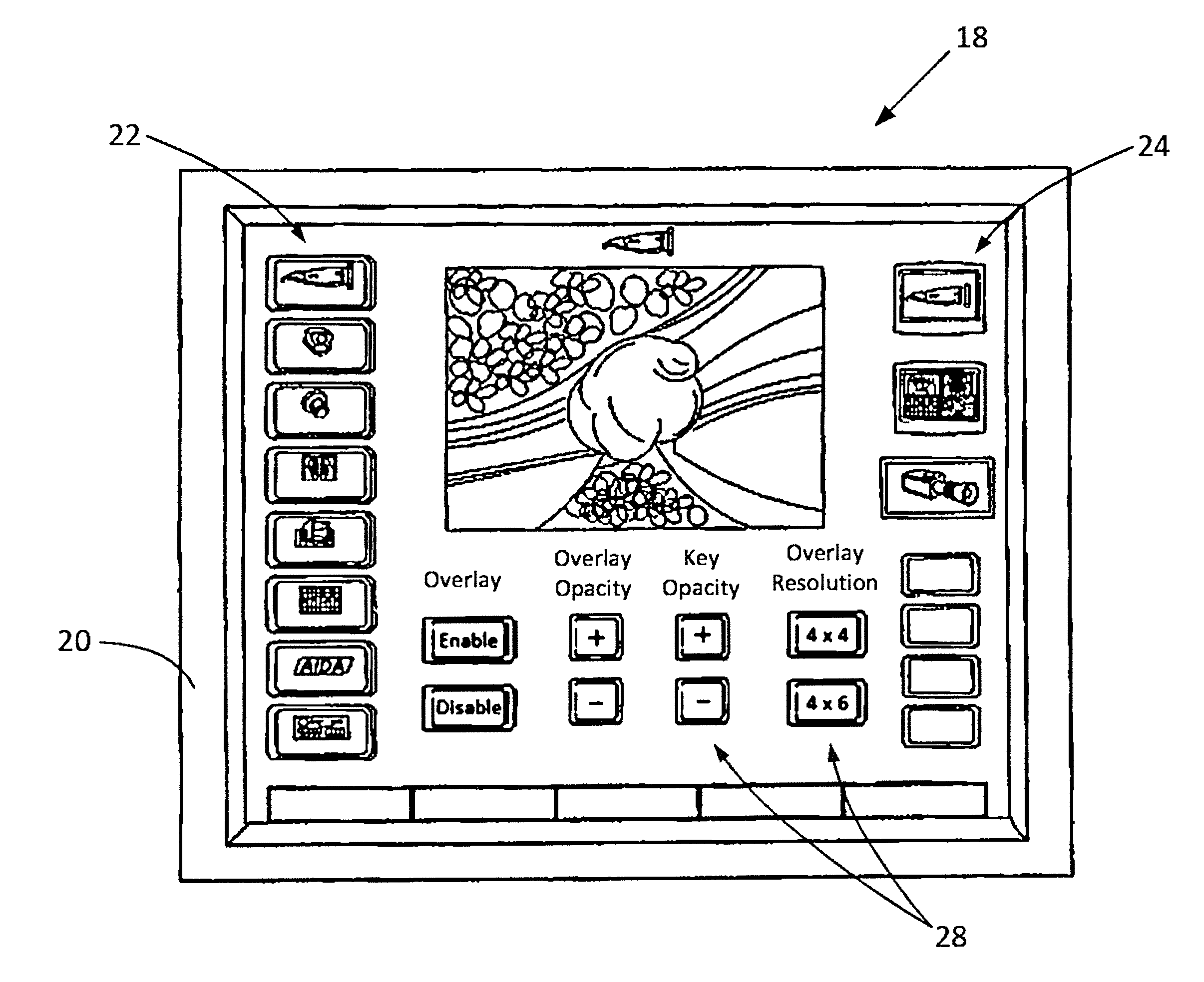
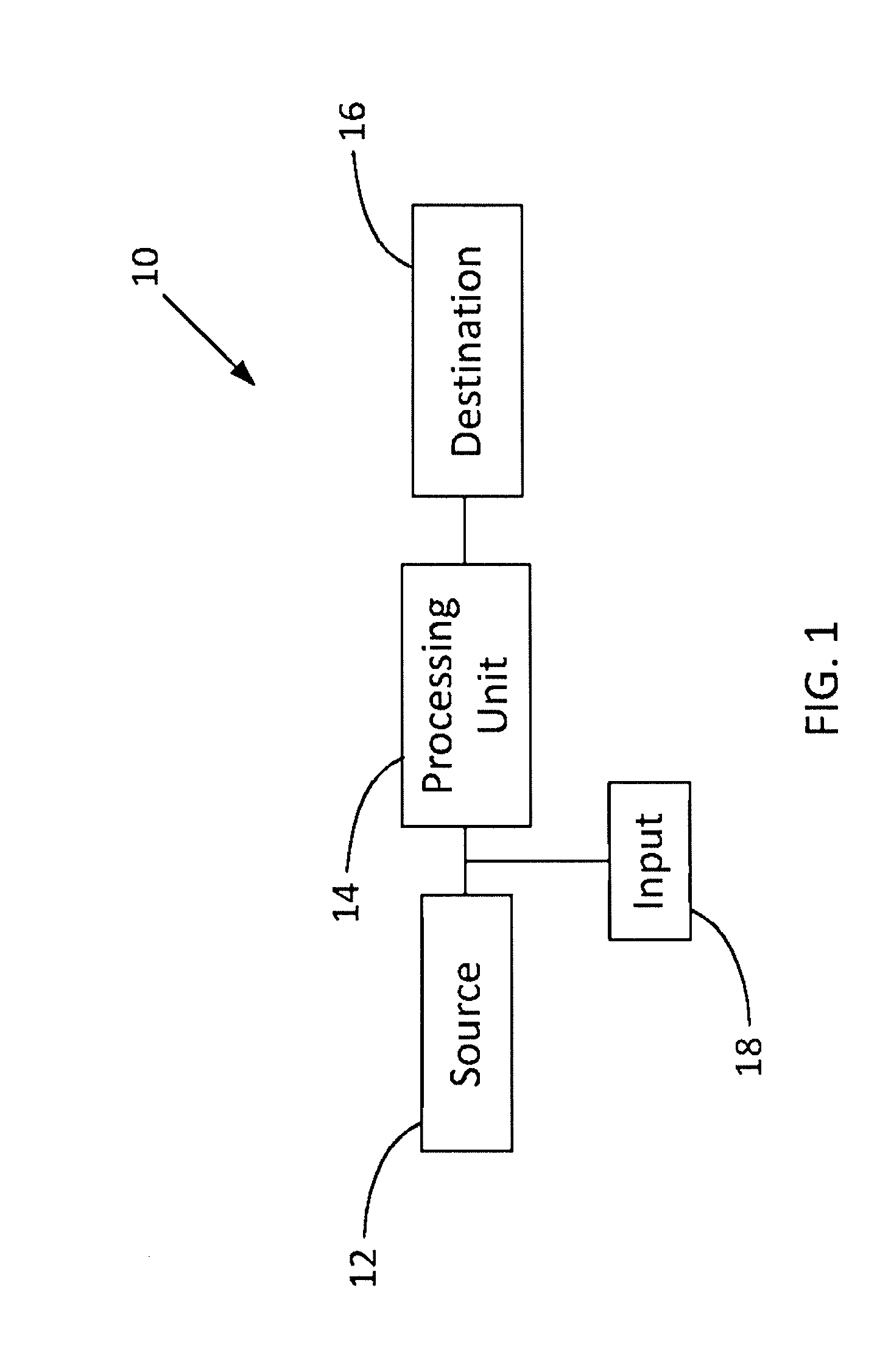
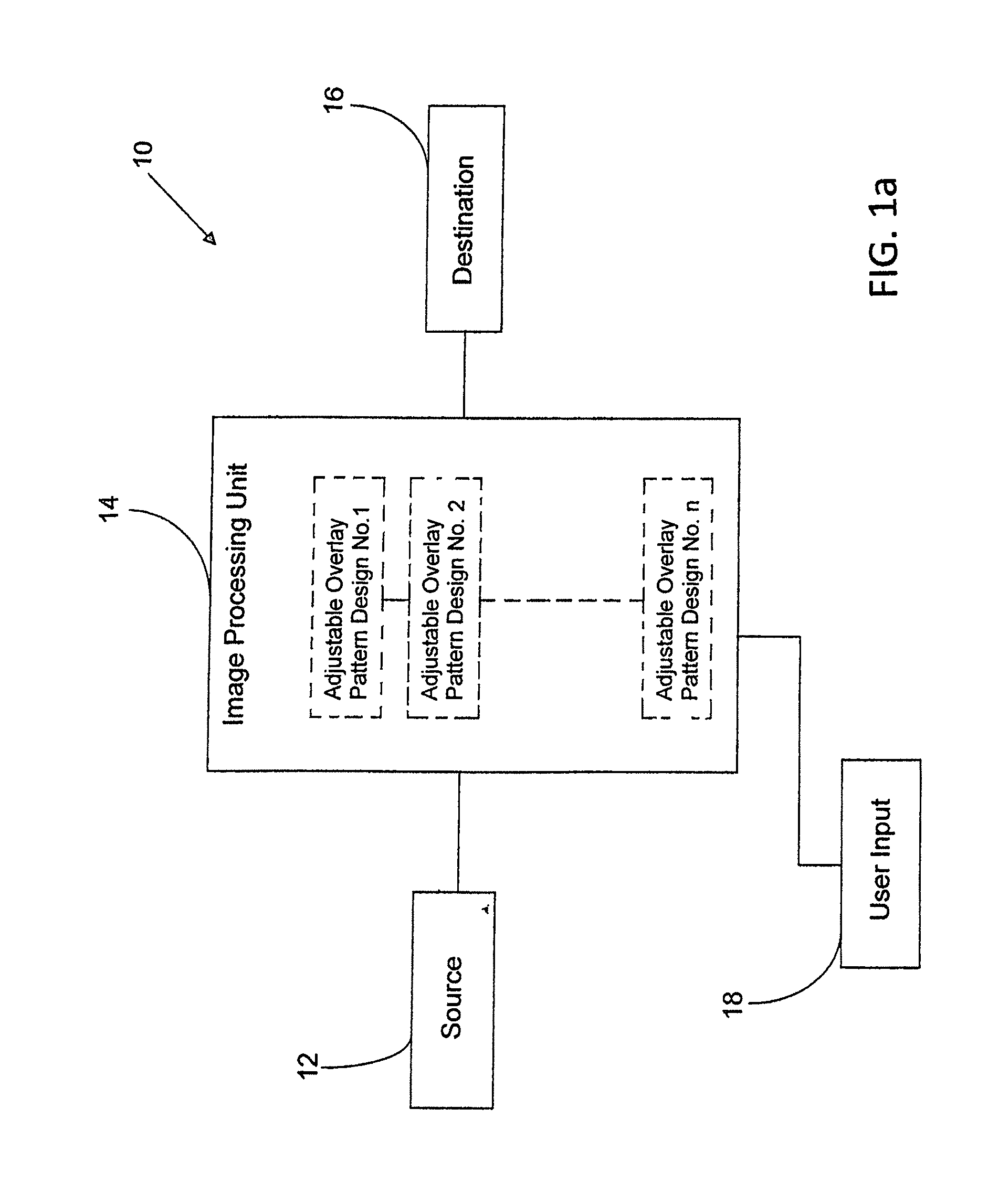
Multi-Source Medical Display
ActiveUS20140037165A1Broaden the field of applicationSimple and cost-effectiveImage analysisRadiation diagnostic image/data processingDisplay deviceX-ray
A system for indicating an area of interest on an image, including a source of image data, an image processing unit, a user interface, and a destination, which may be a display. The image data may be ultrasound, X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging, nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic resonance tomography, computed tomography or surgical image data. The image processing unit may be configured to receive the image data from the source and combine it with a desired overlay pattern selected from a plurality of overlay patterns for indicating an area of interest on the image, which is then displayed on the display. The overlay pattern may include a key with coordinates or labels. Properties of the overlay pattern and the image data may be adjusted independently or automatically.
Owner:KARL STORZ IMAGING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com