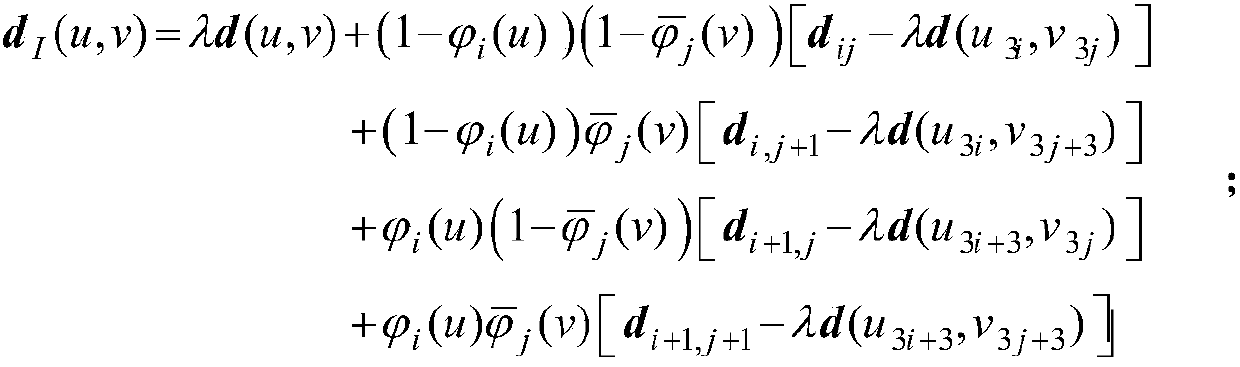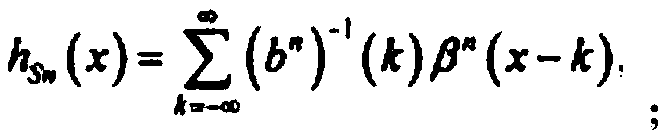Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Anatomical atlas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
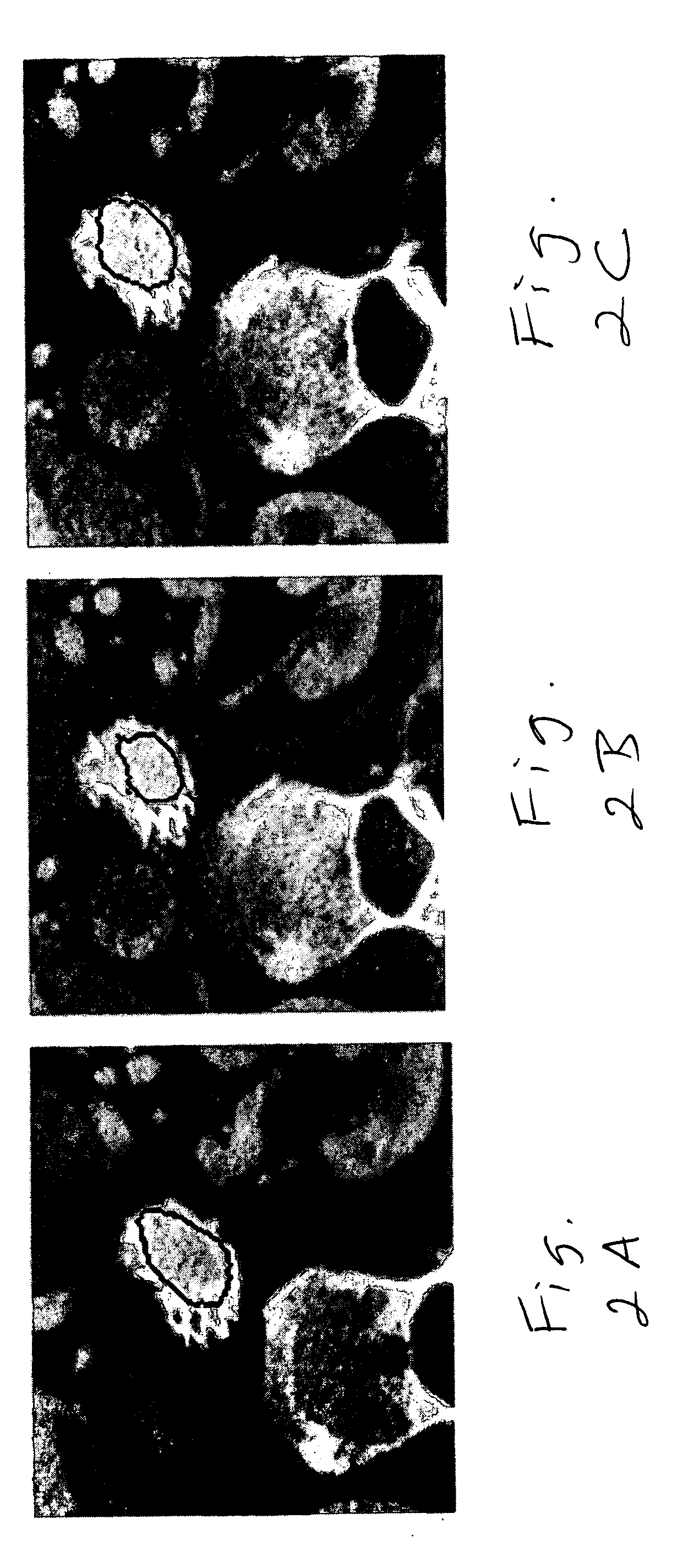
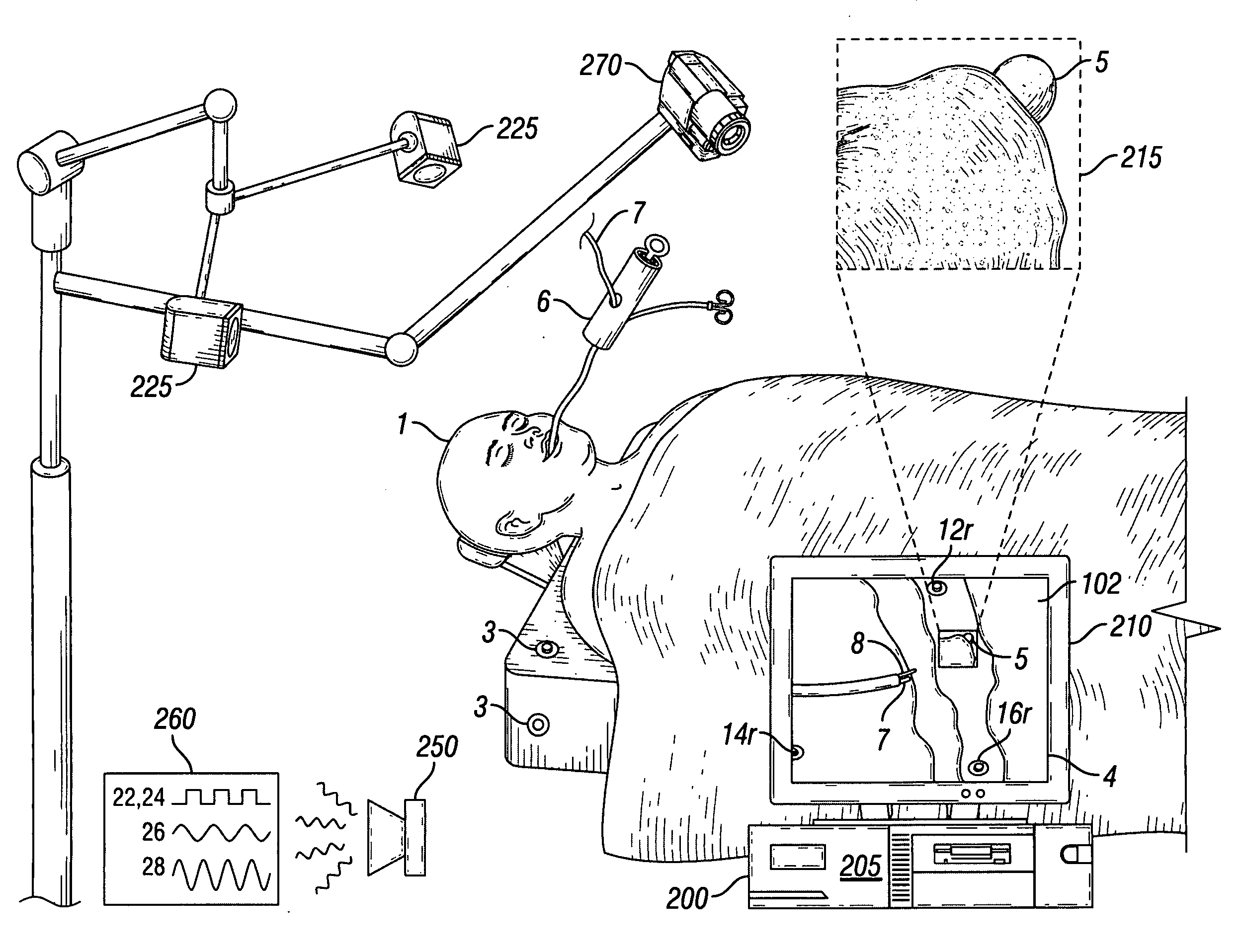
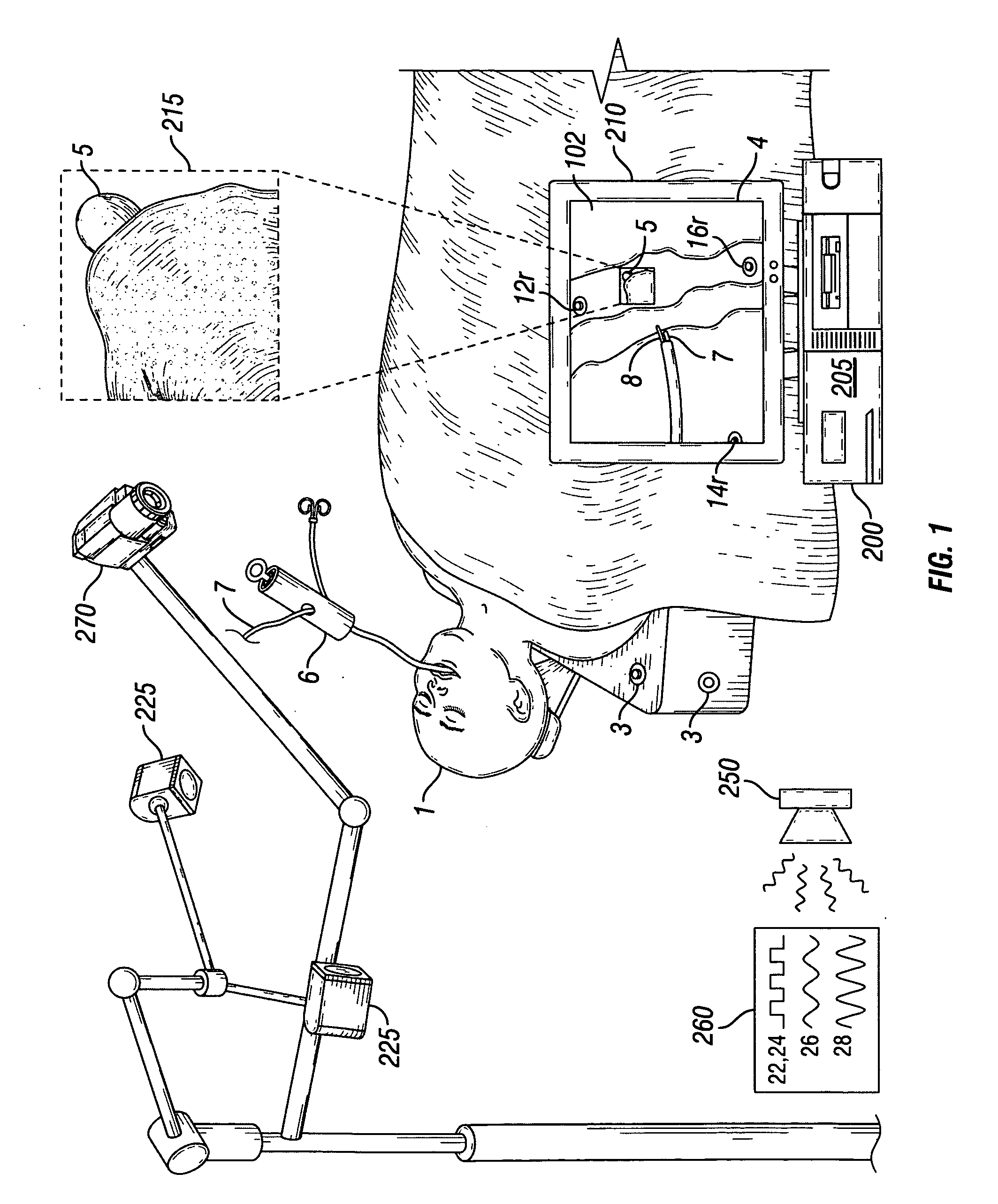
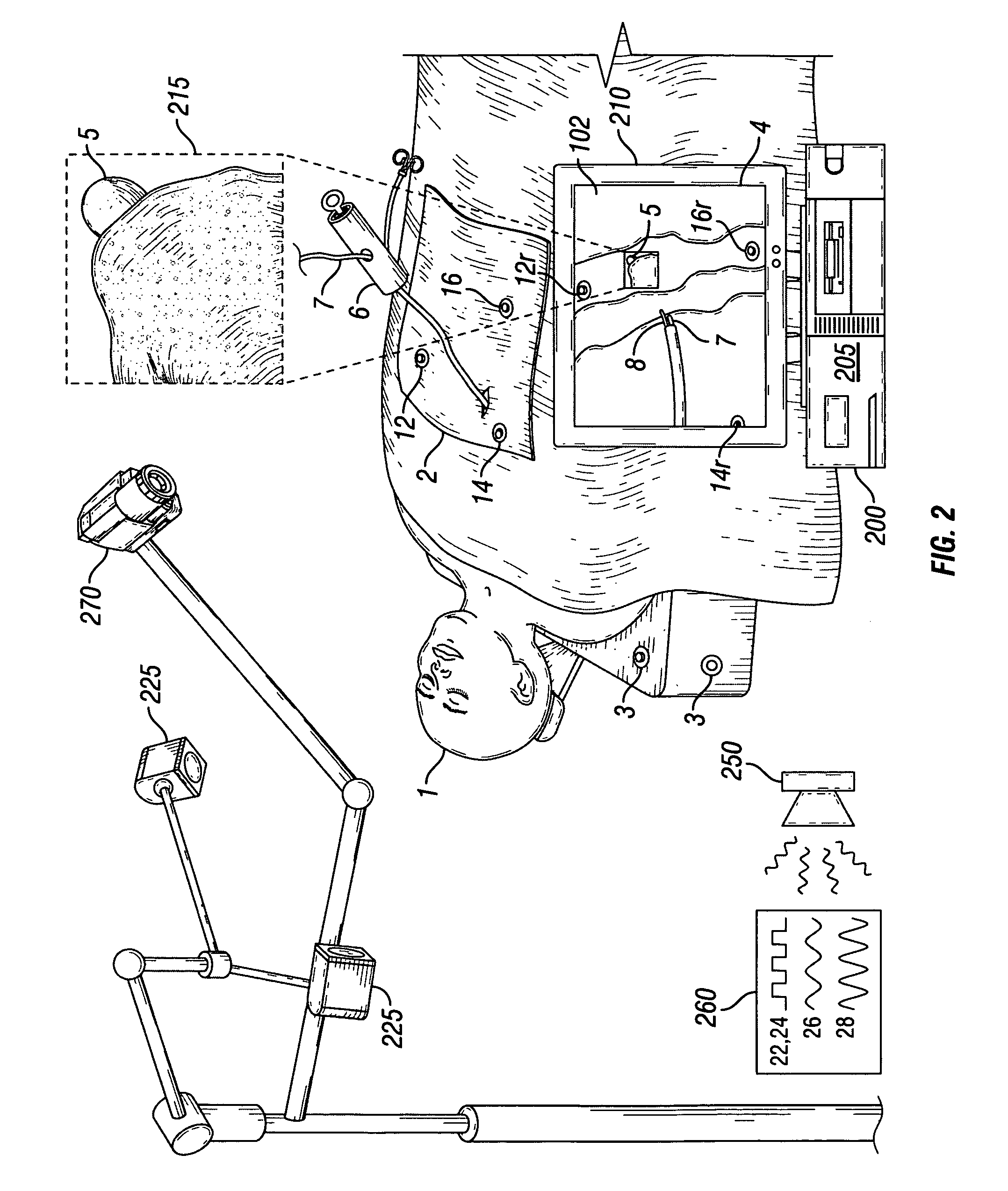
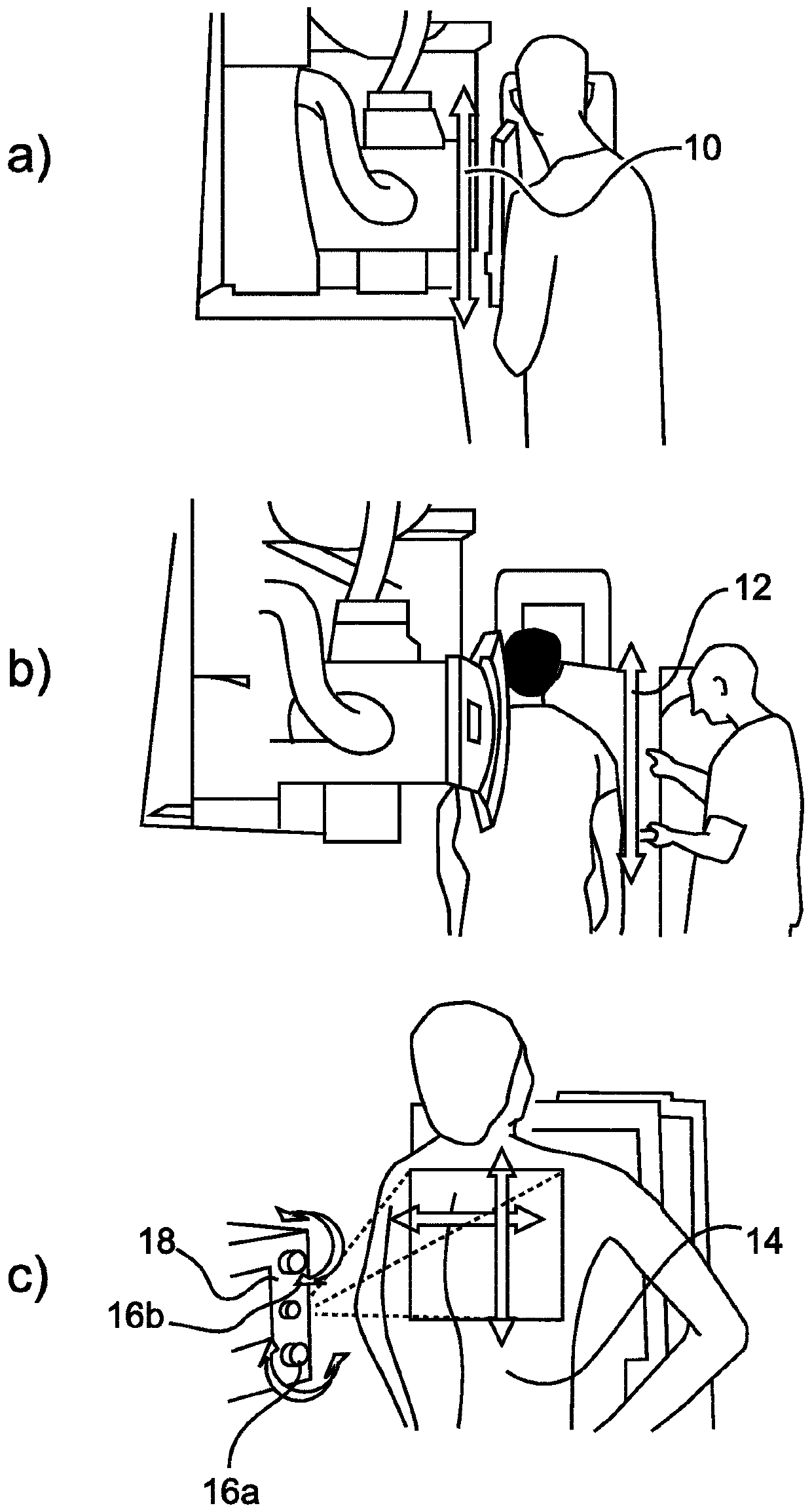
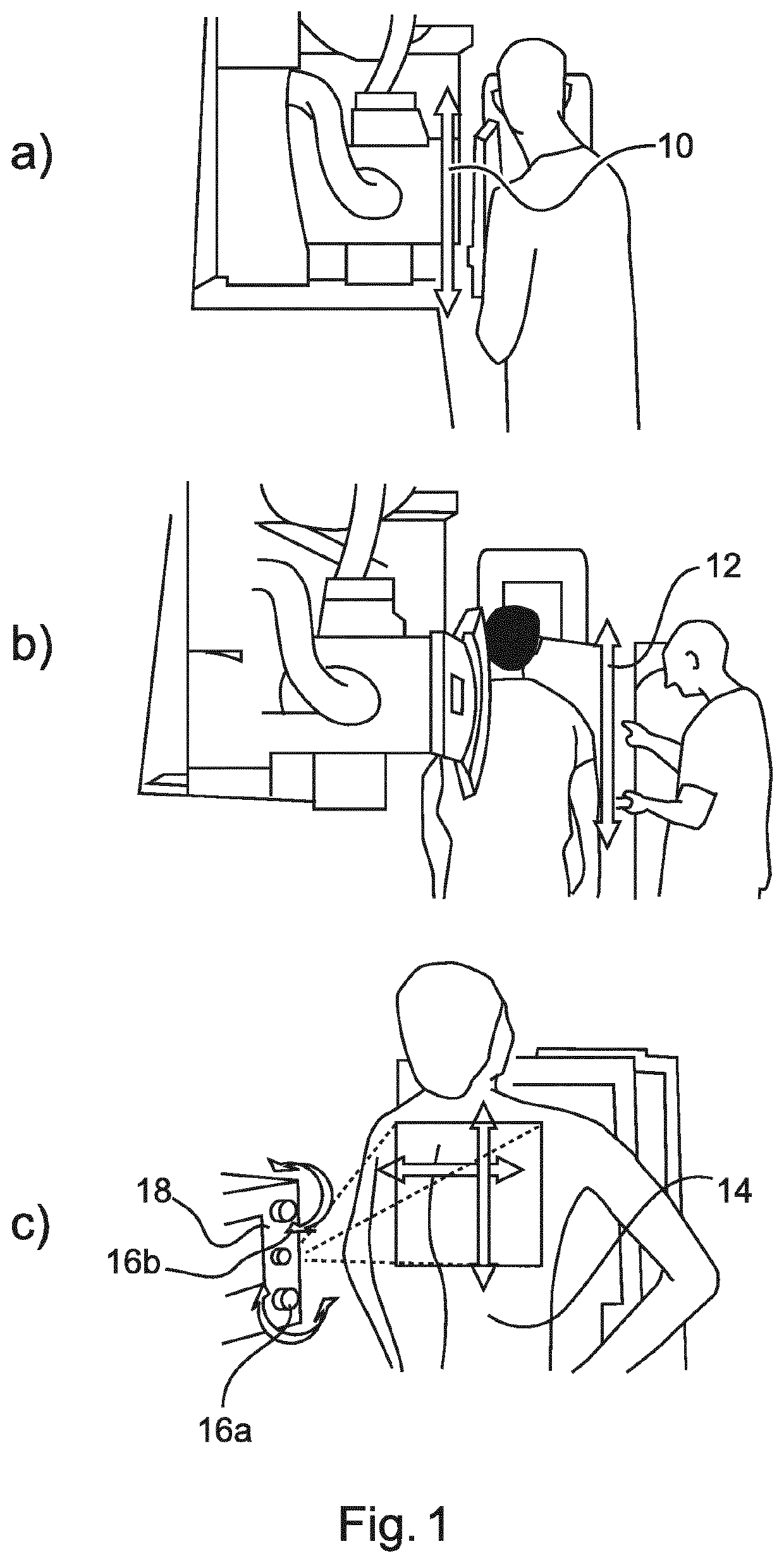
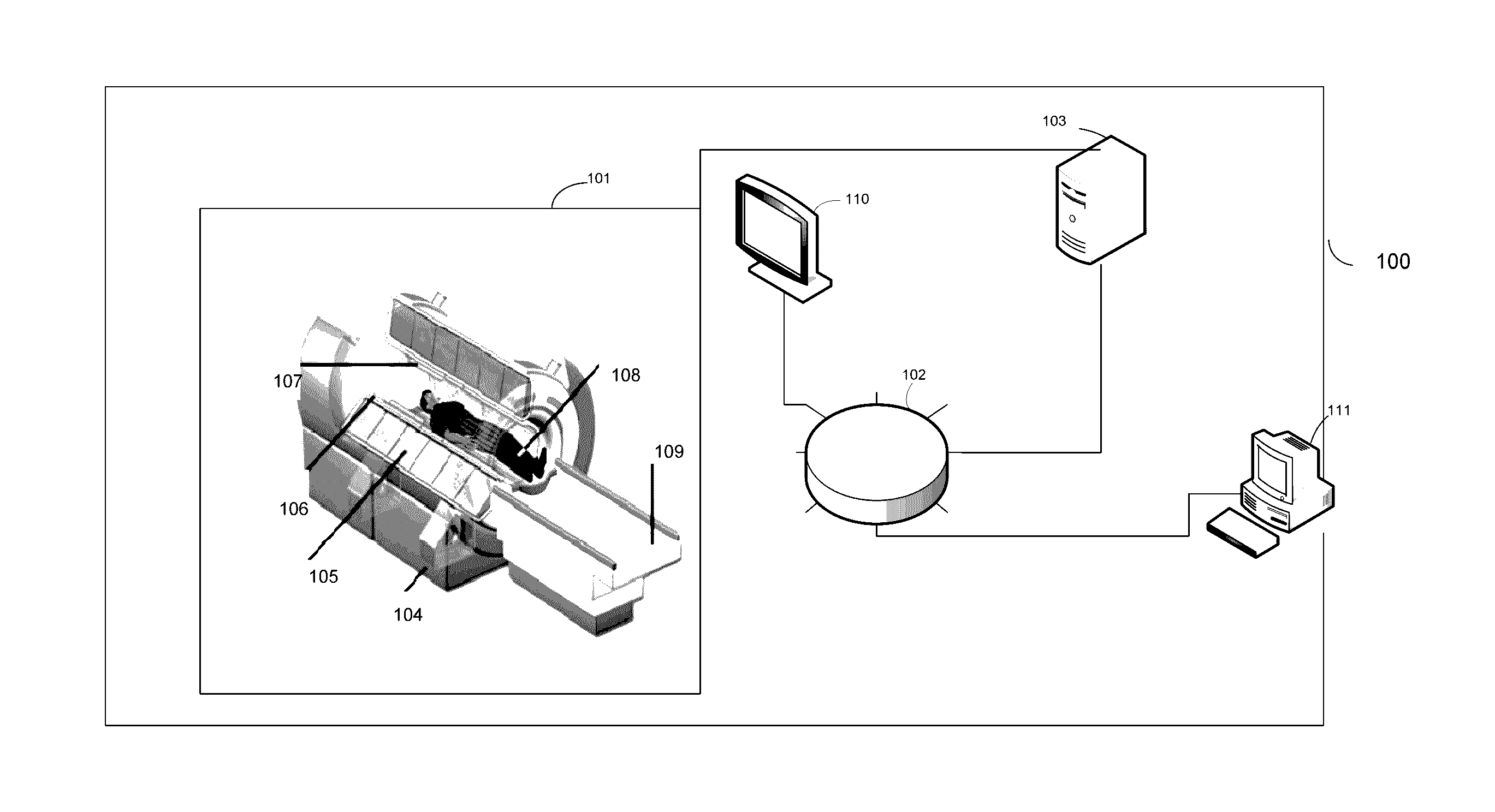
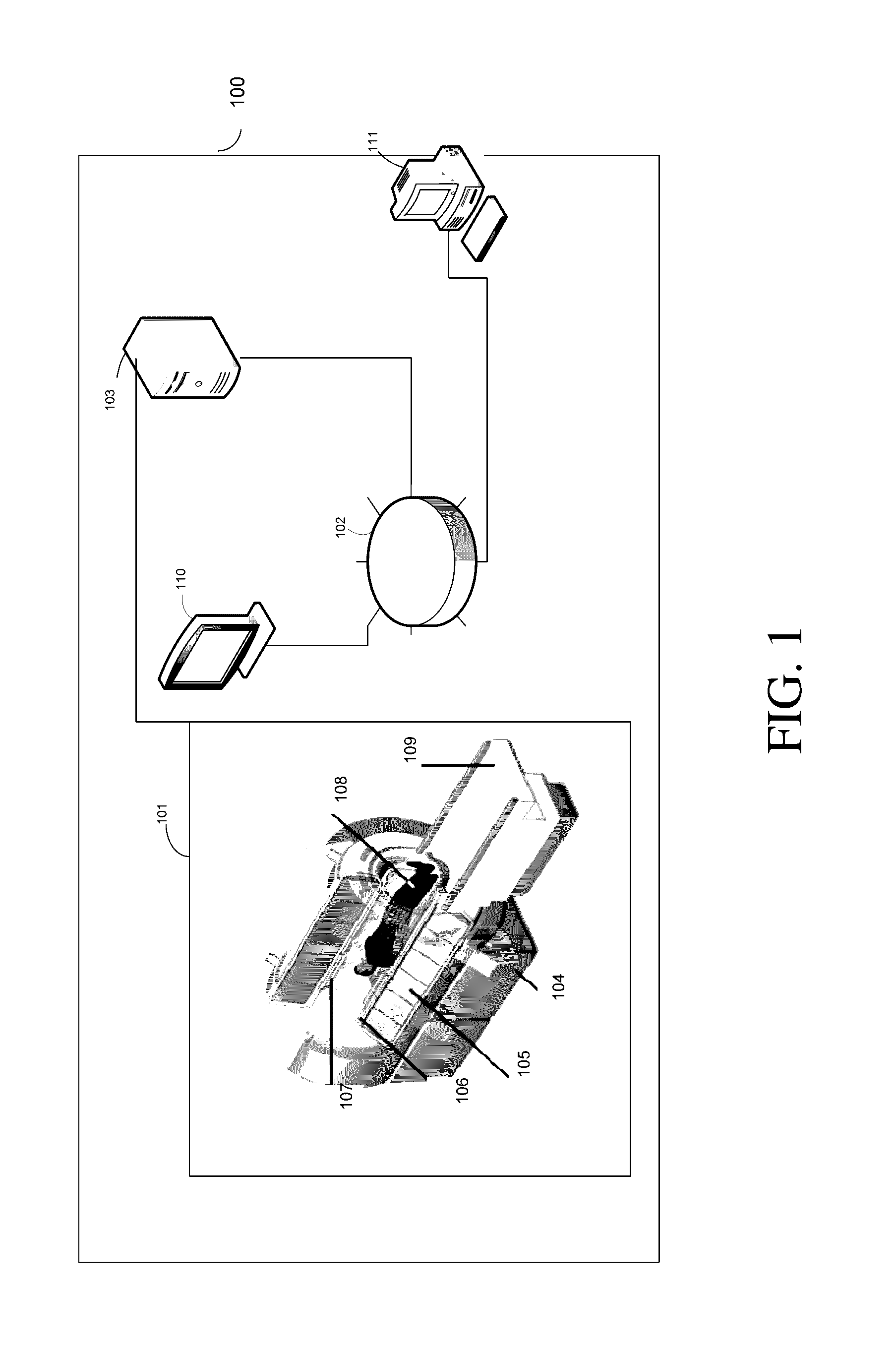
Videotactic and audiotactic assisted surgical methods and procedures
InactiveUS20080243142A1Medical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesAnatomical structuresSurgical operation
The present invention provides video and audio assisted surgical techniques and methods. Novel features of the techniques and methods provided by the present invention include presenting a surgeon with a video compilation that displays an endoscopic-camera derived image, a reconstructed view of the surgical field (including fiducial markers indicative of anatomical locations on or in the patient), and / or a real-time video image of the patient. The real-time image can be obtained either with the video camera that is part of the image localized endoscope or with an image localized video camera without an endoscope, or both. In certain other embodiments, the methods of the present invention include the use of anatomical atlases related to pre-operative generated images derived from three-dimensional reconstructed CT, MRI, x-ray, or fluoroscopy. Images can furthermore be obtained from pre-operative imaging and spacial shifting of anatomical structures may be identified by intraoperative imaging and appropriate correction performed.
Owner:GILDENBERG PHILIP L
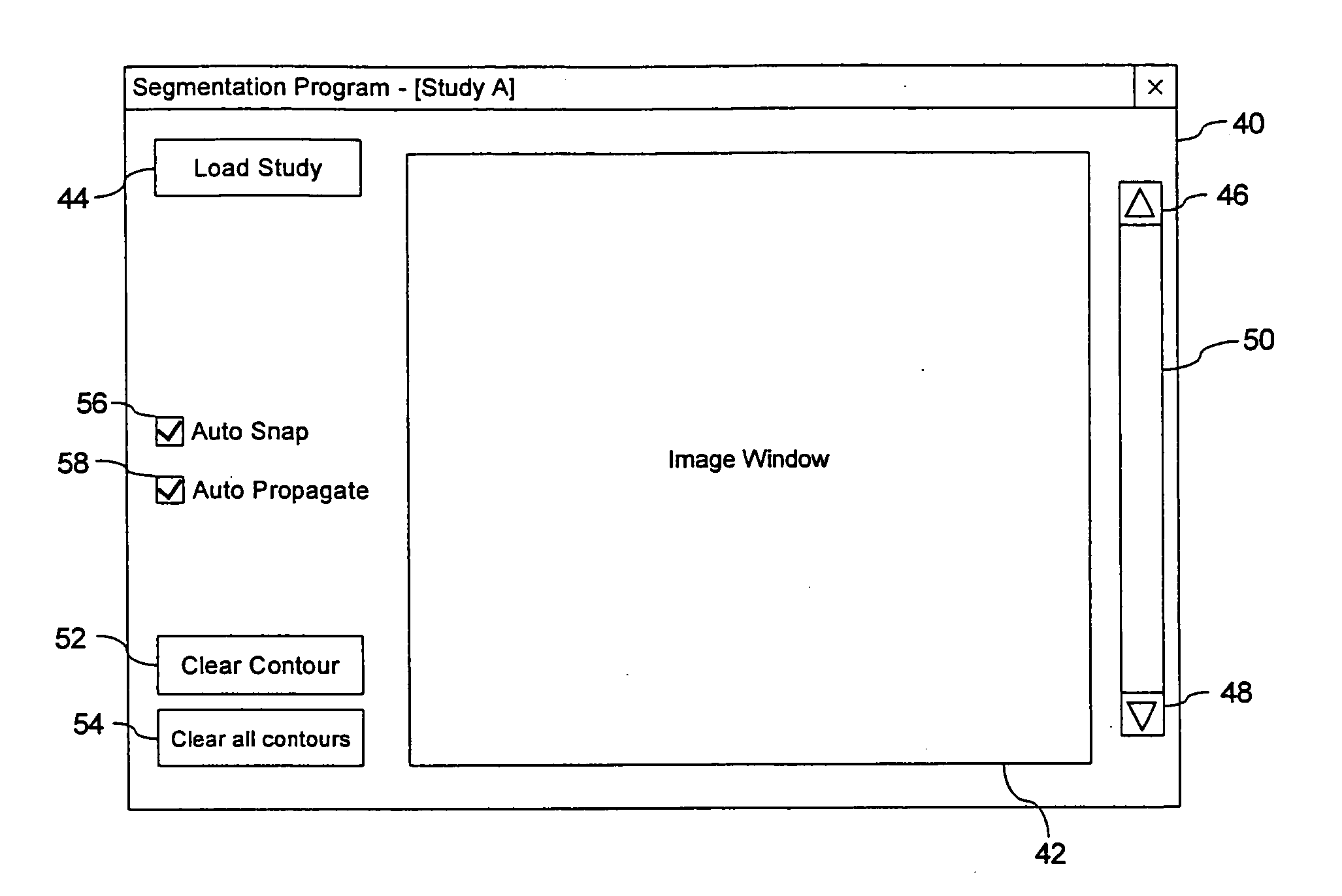
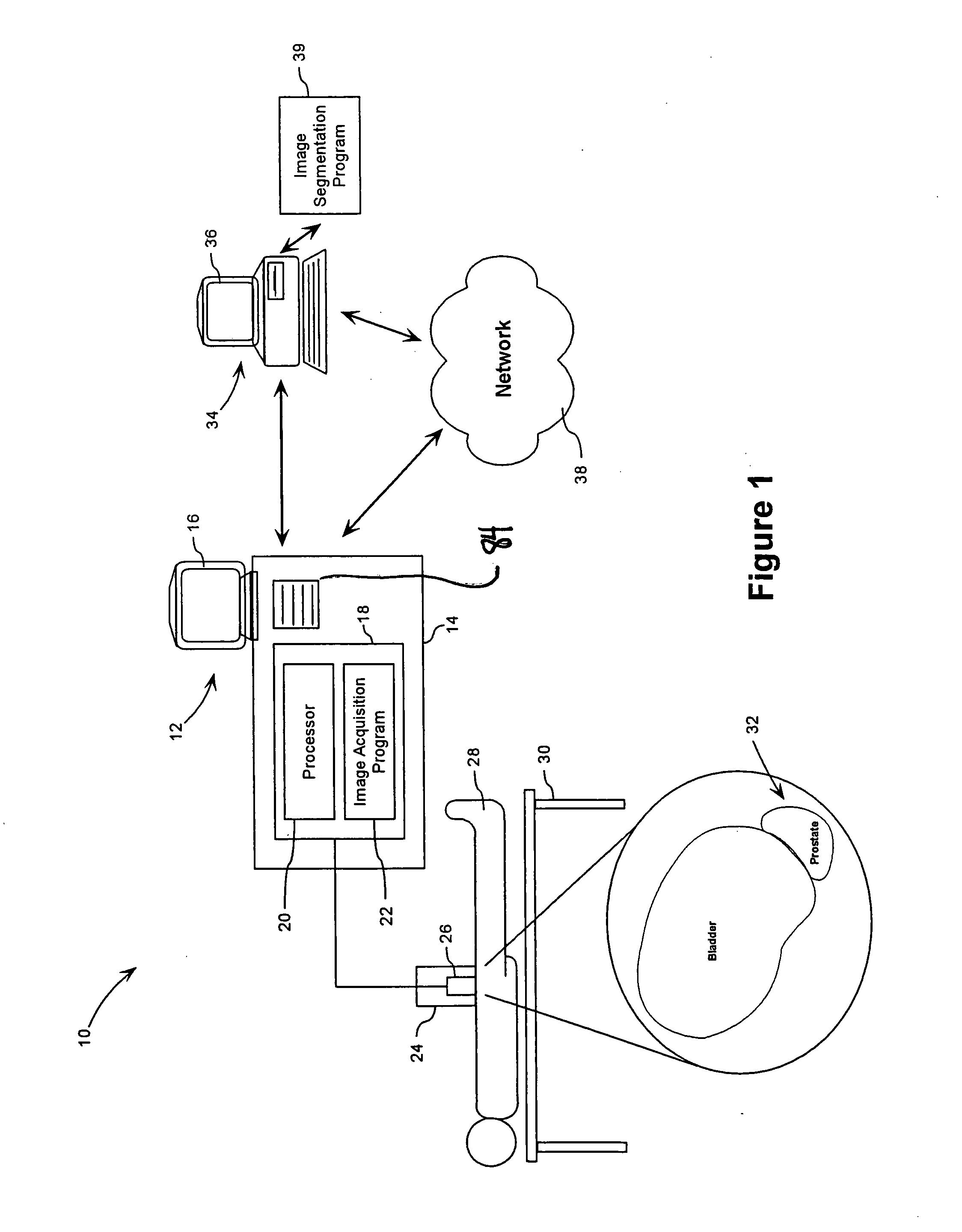
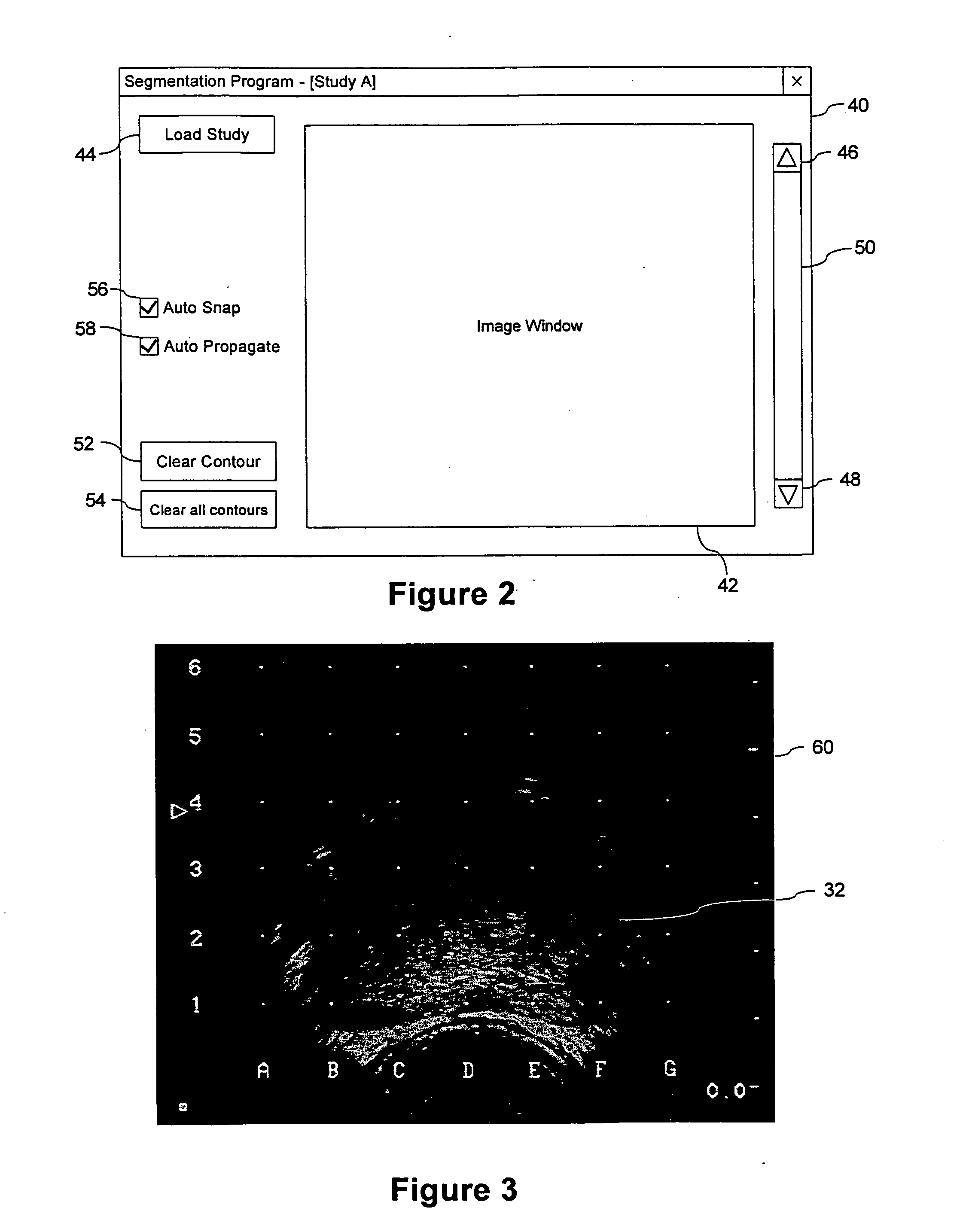
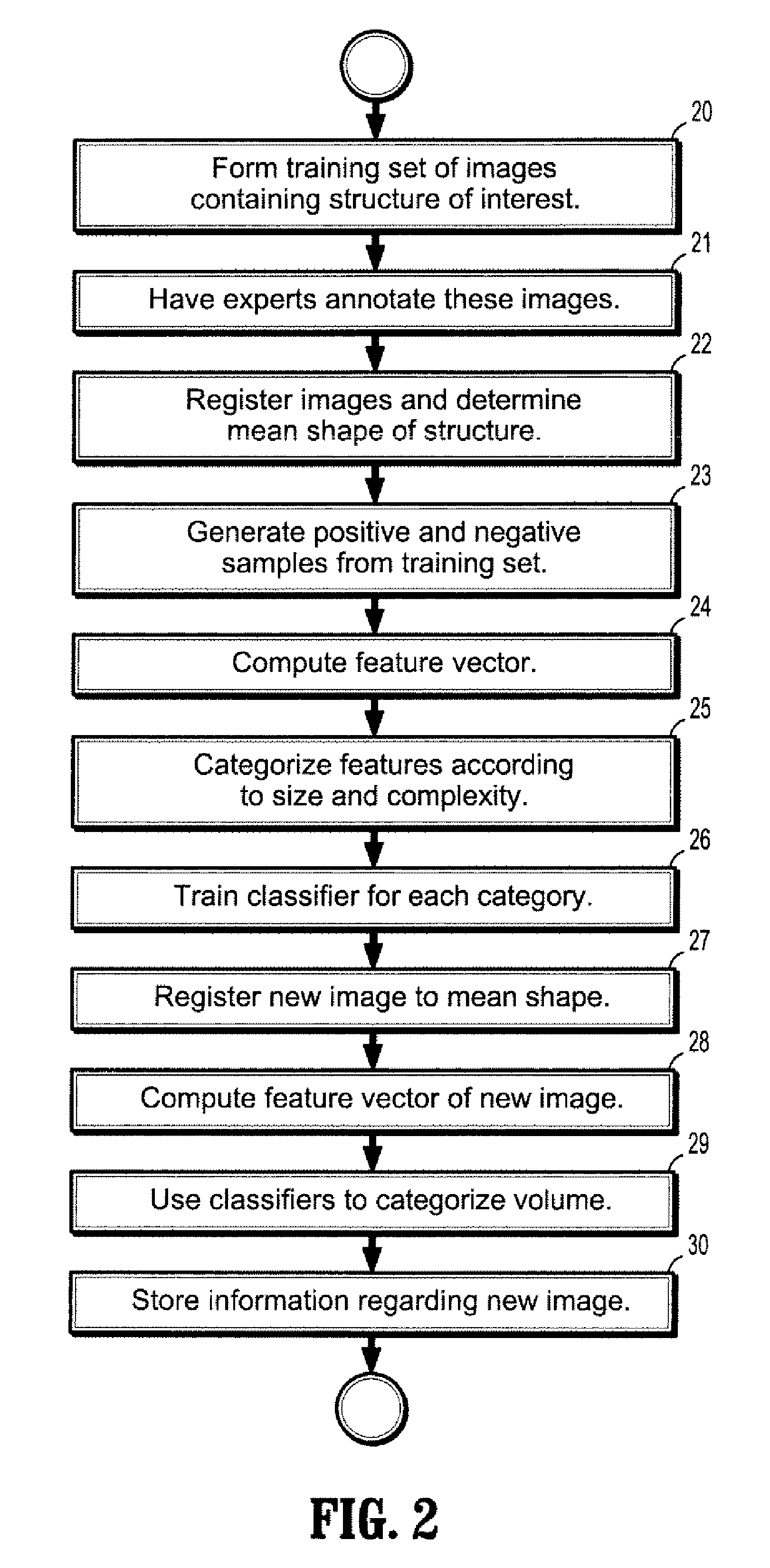
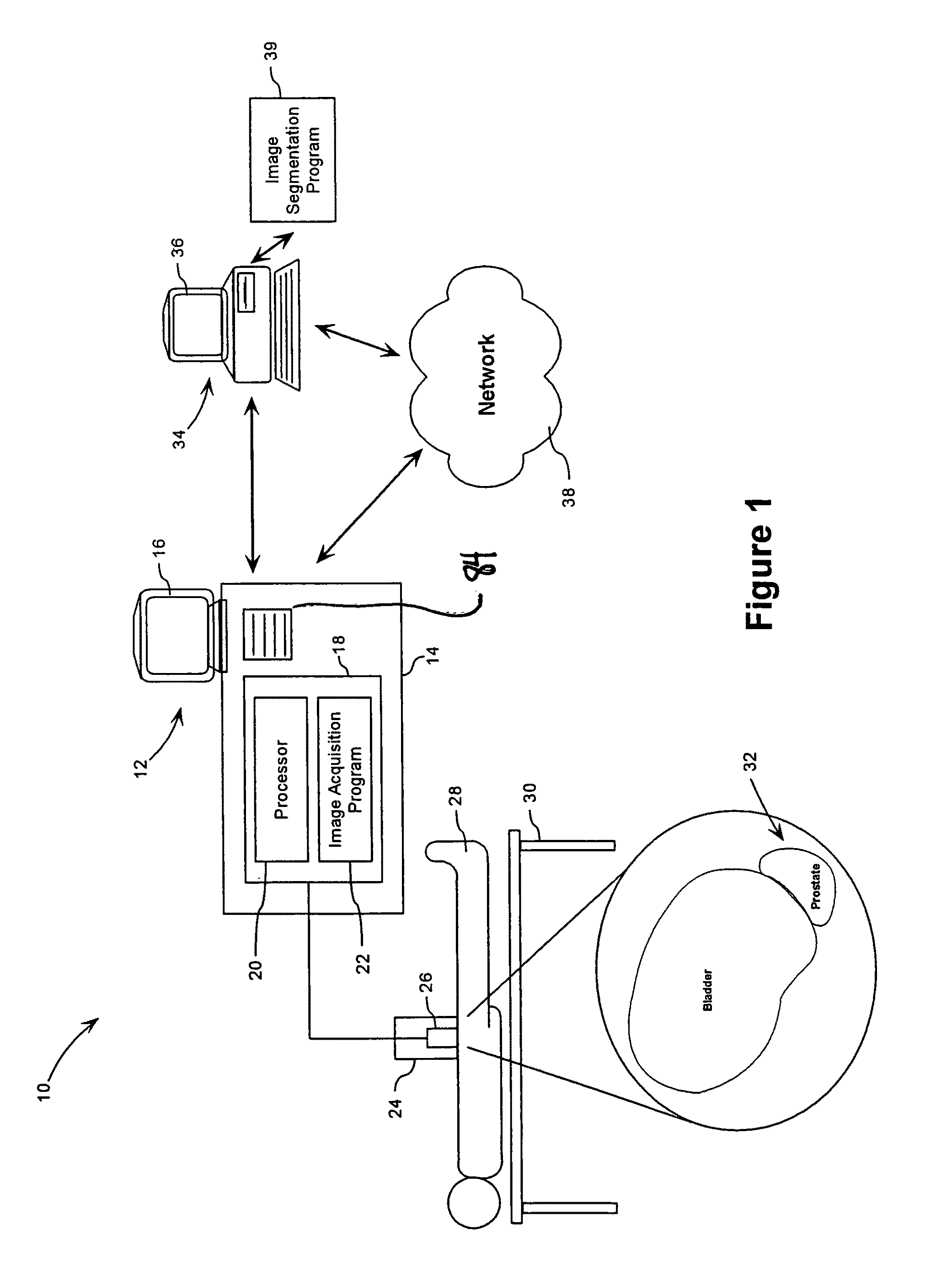
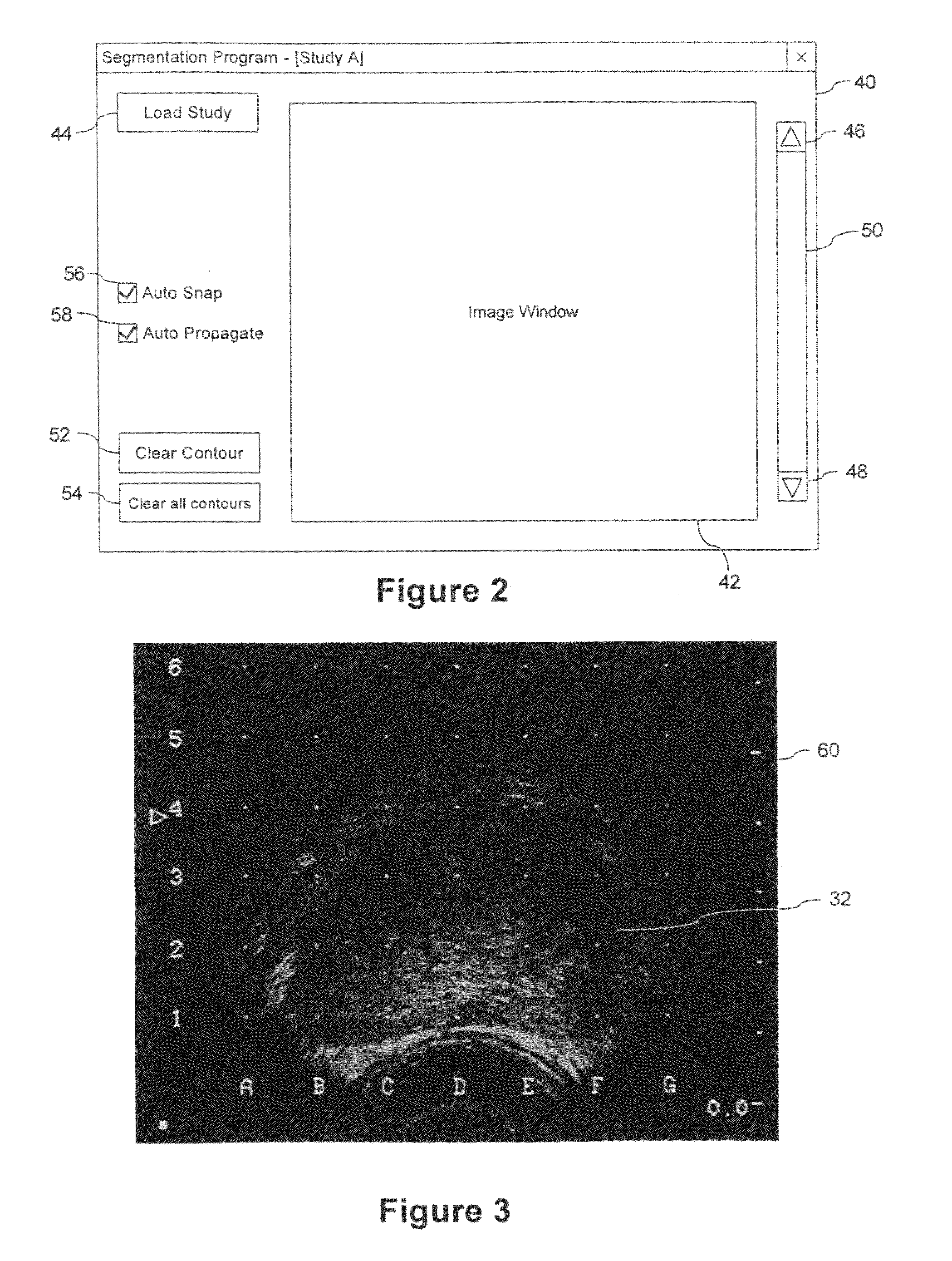
System and Method for Segmenting a Region in a Medical Image
ActiveUS20080267468A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationShape change
A method and computer program are provided for segmenting a prostate from a medical image such as an ultrasound image. Each slice in a study is analysed and uses a manual initialization to obtain an initial contour, in which a user selects initial points that are automatically rendered on the image. An automatic refinement stage then snaps the contour to the prostate boundary in the image based on a pre-stored anatomical atlas and edge information obtained from the image. A manual adjustment stage may then be performed and if selected, the contour is automatically propagated to the next image slice to avoid the manual initialization. An auxiliary image slice may be referred to, which indicates how the prostate shape changes from slice to slices e.g. by providing a perpendicular profile.
Owner:MERATIVE US LP
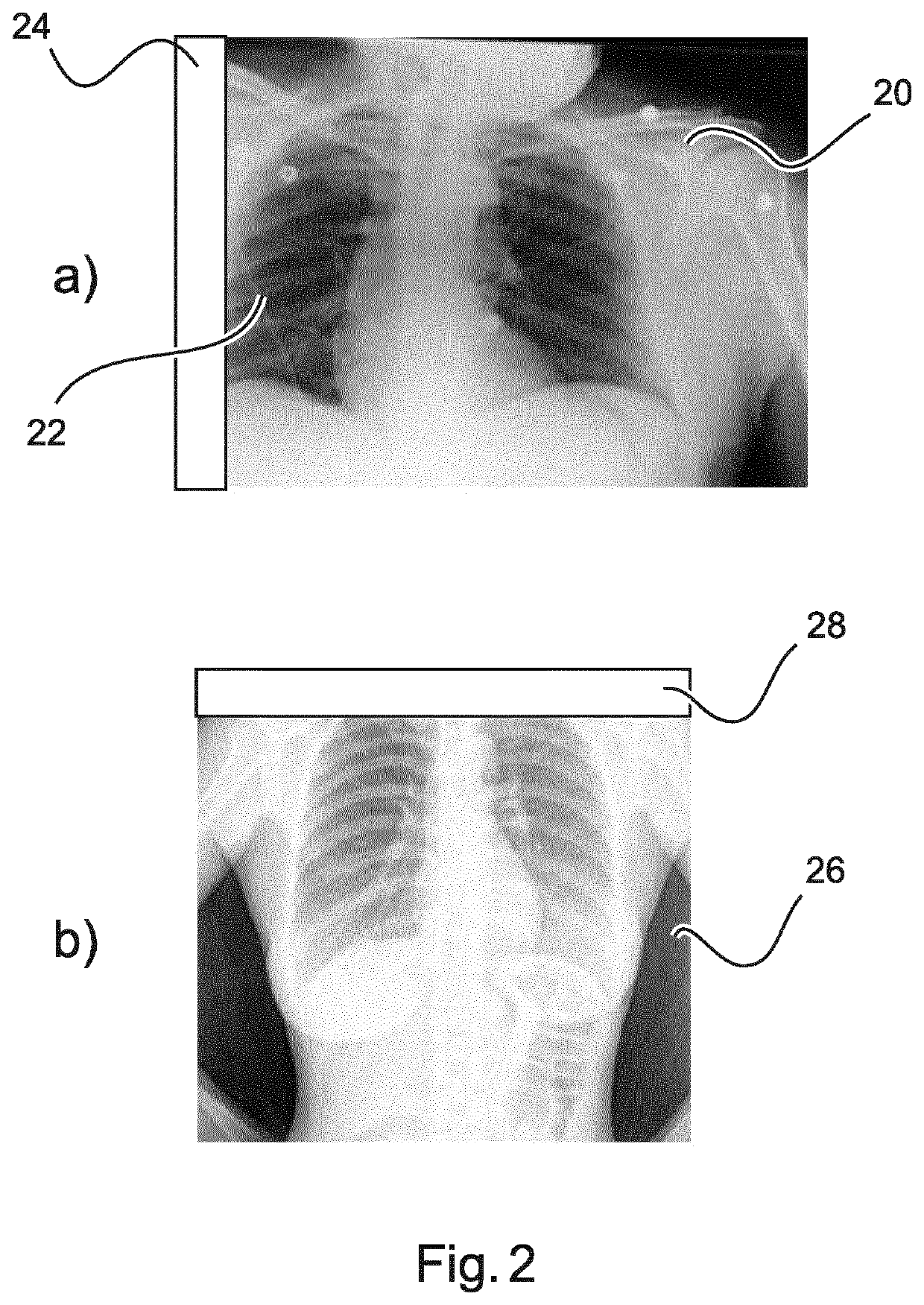
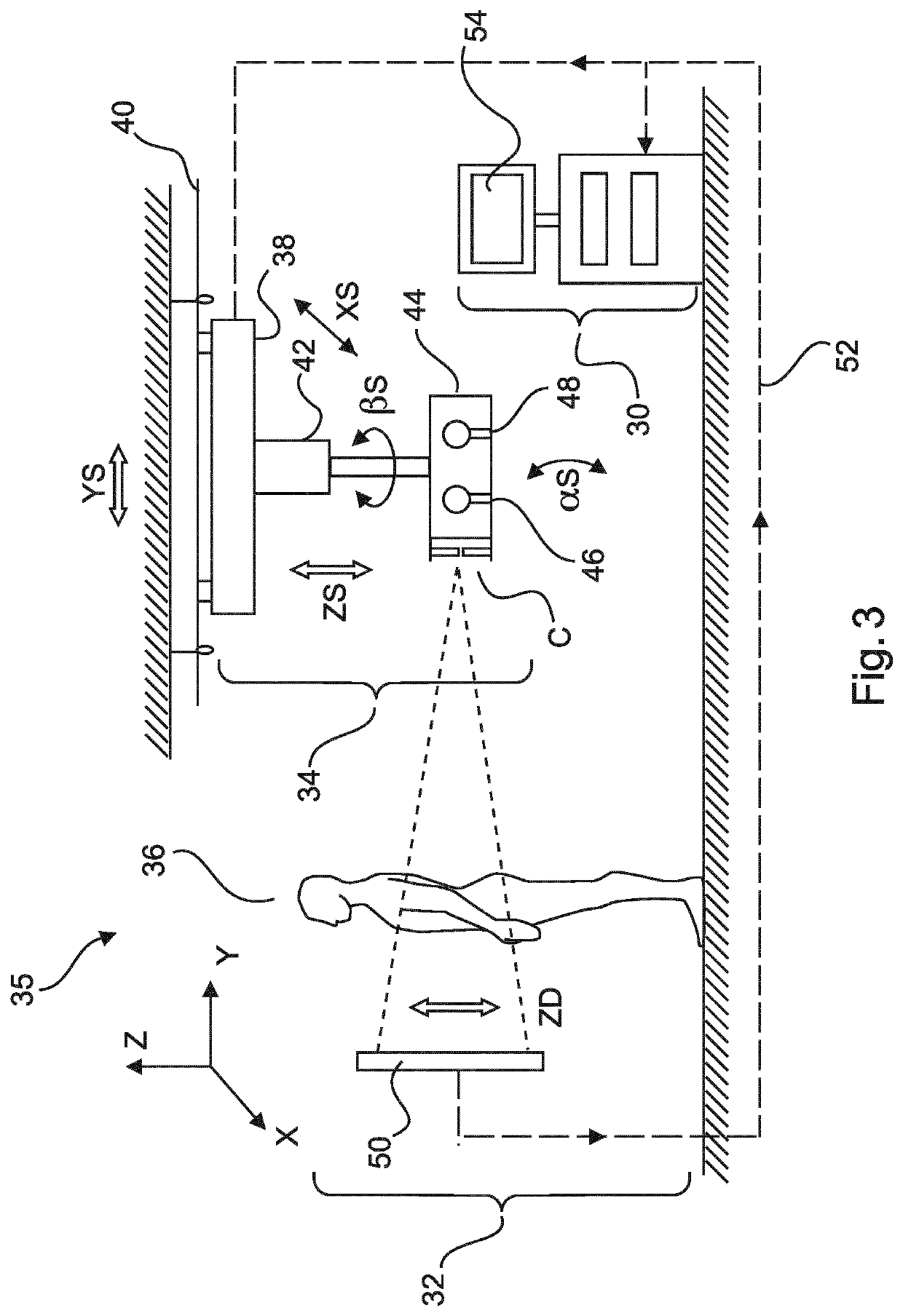
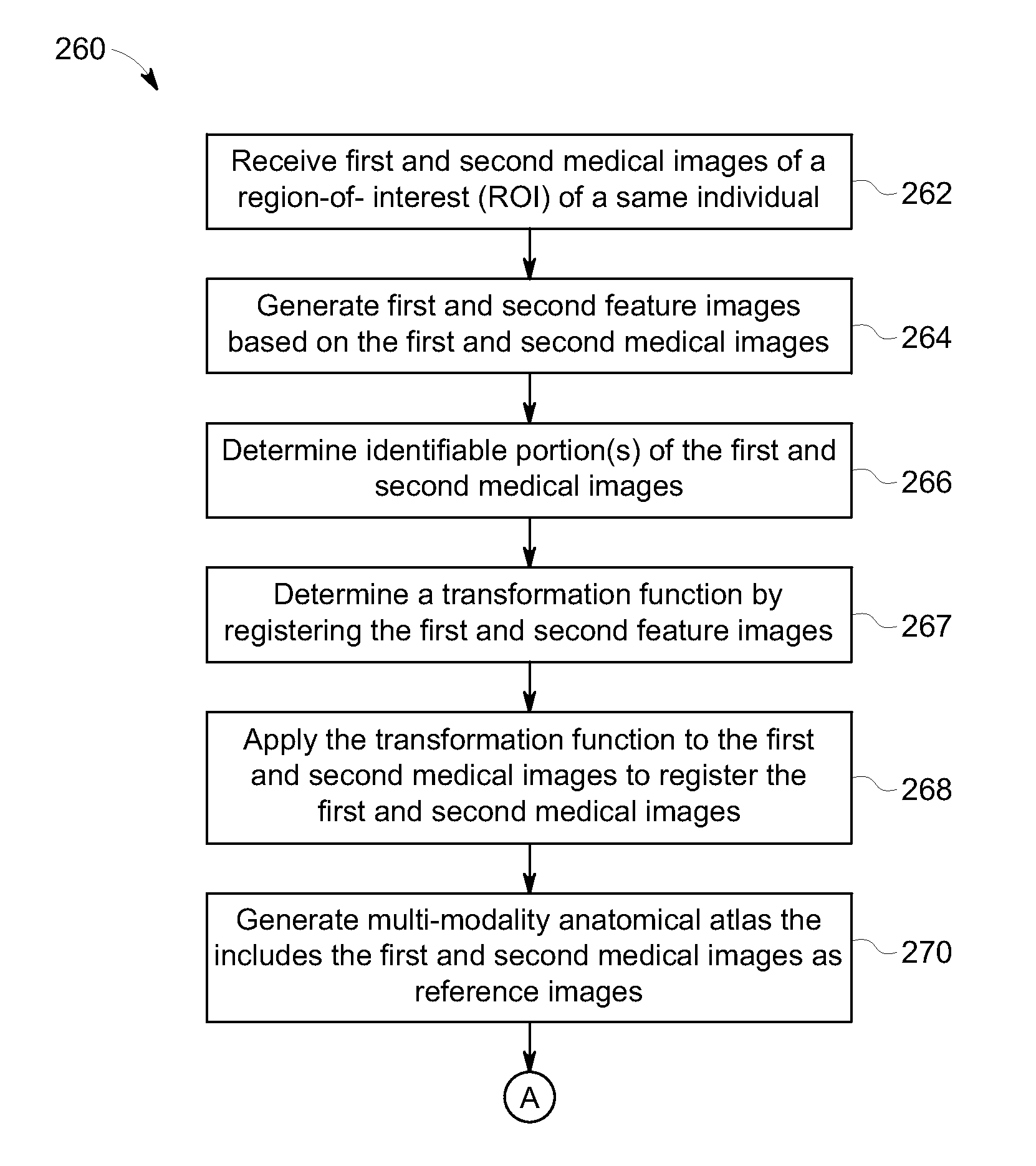
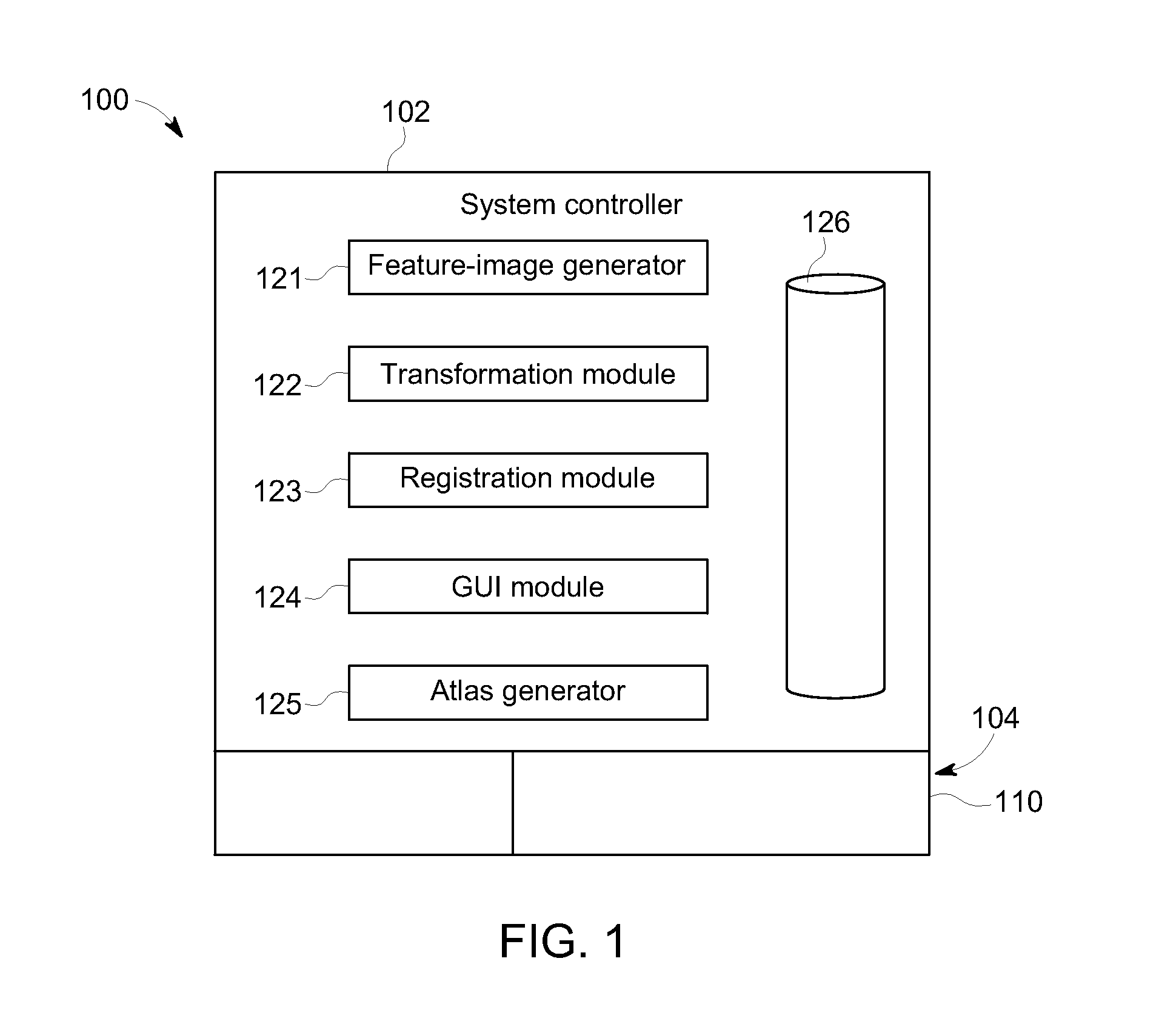
Methods and systems for determining a transformation function to automatically register different modality medical images
ActiveUS20140029812A1Image enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPattern recognition
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system for improved image segmentation
A system and method of identifying anatomical structures in a patient. The method includes the acts of acquiring an image of the patient, the image including a set of image elements; segmenting the image to categorize each image elements according to its substance; computing the probability that the categorization of each image element is correct; resegmenting the image starting with image elements that have a high probability and progressing to image elements with lower probabilities; aligning at least one of the image elements with an anatomical atlas; and fitting the anatomical atlas to the segmented image.
Owner:TOMOTHERAPY INC
Methods and apparatus for registration of medical images
InactiveUS20110019885A1Robust registrationImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical featureRegister based
In methods and an apparatus for registering two medical images of a subject, a first image is compared with a first anatomical atlas and a second image with a second anatomical atlas, to generate labels for anatomical features in each image. The first anatomical atlas has at least two anatomical features in common with the second, and each label includes a suggested location of the anatomical feature to which it relates. A number of labels are identified for each image, and a value of a similarity function between labels of the respective images is calculated. The two images are registered based on the value of the similarity function.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
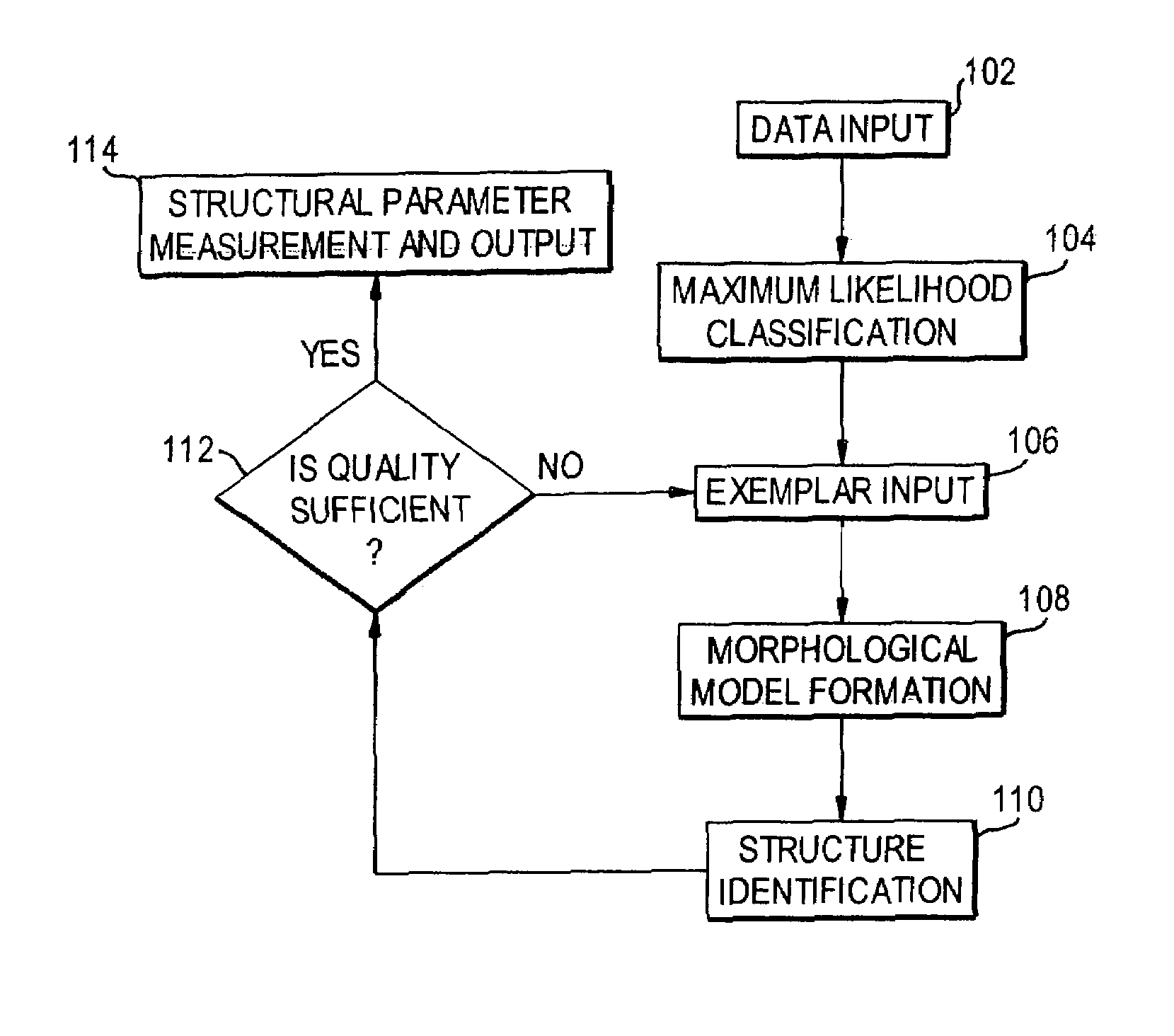
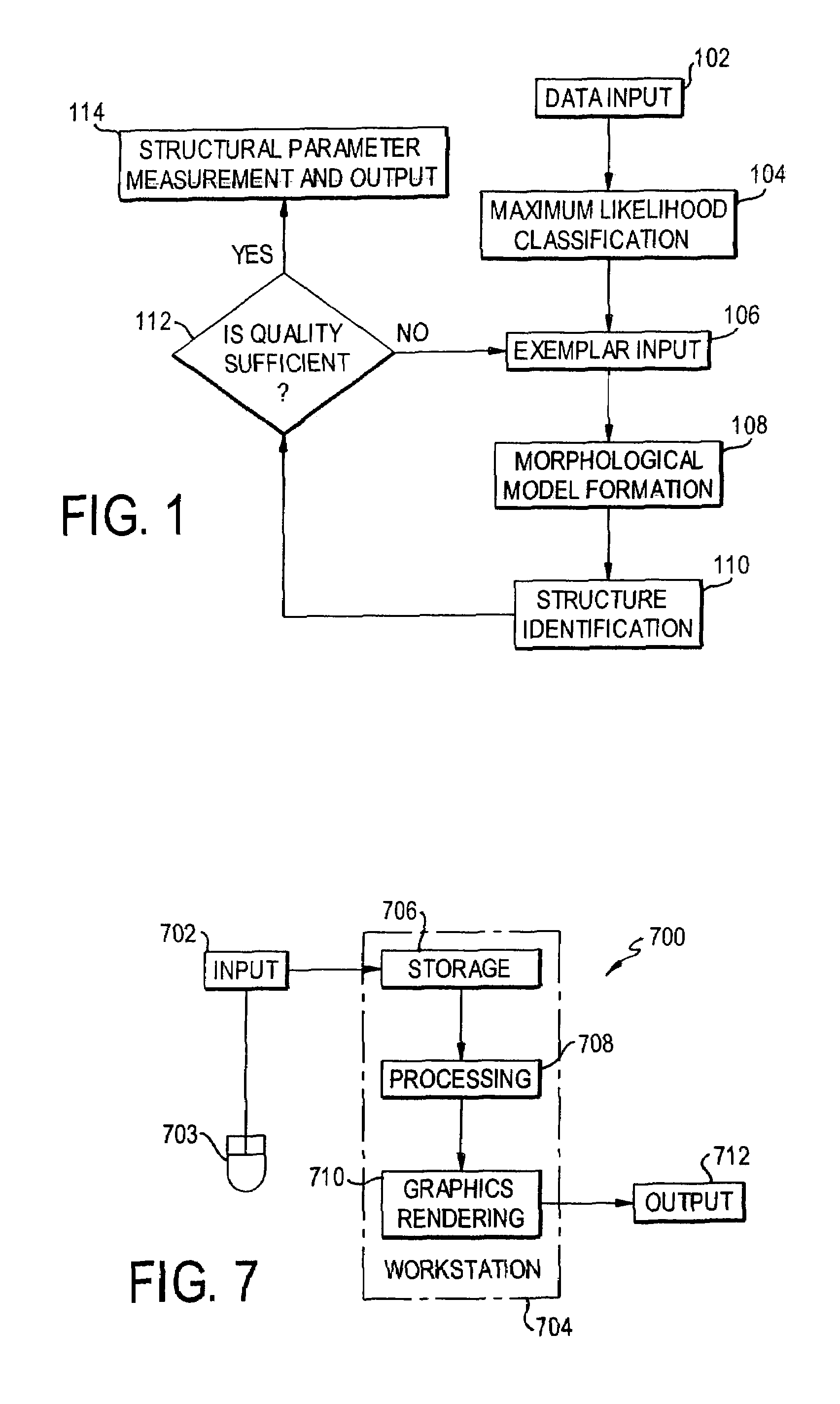
Semi-automated measurement of anatomical structures using statistical and morphological priors
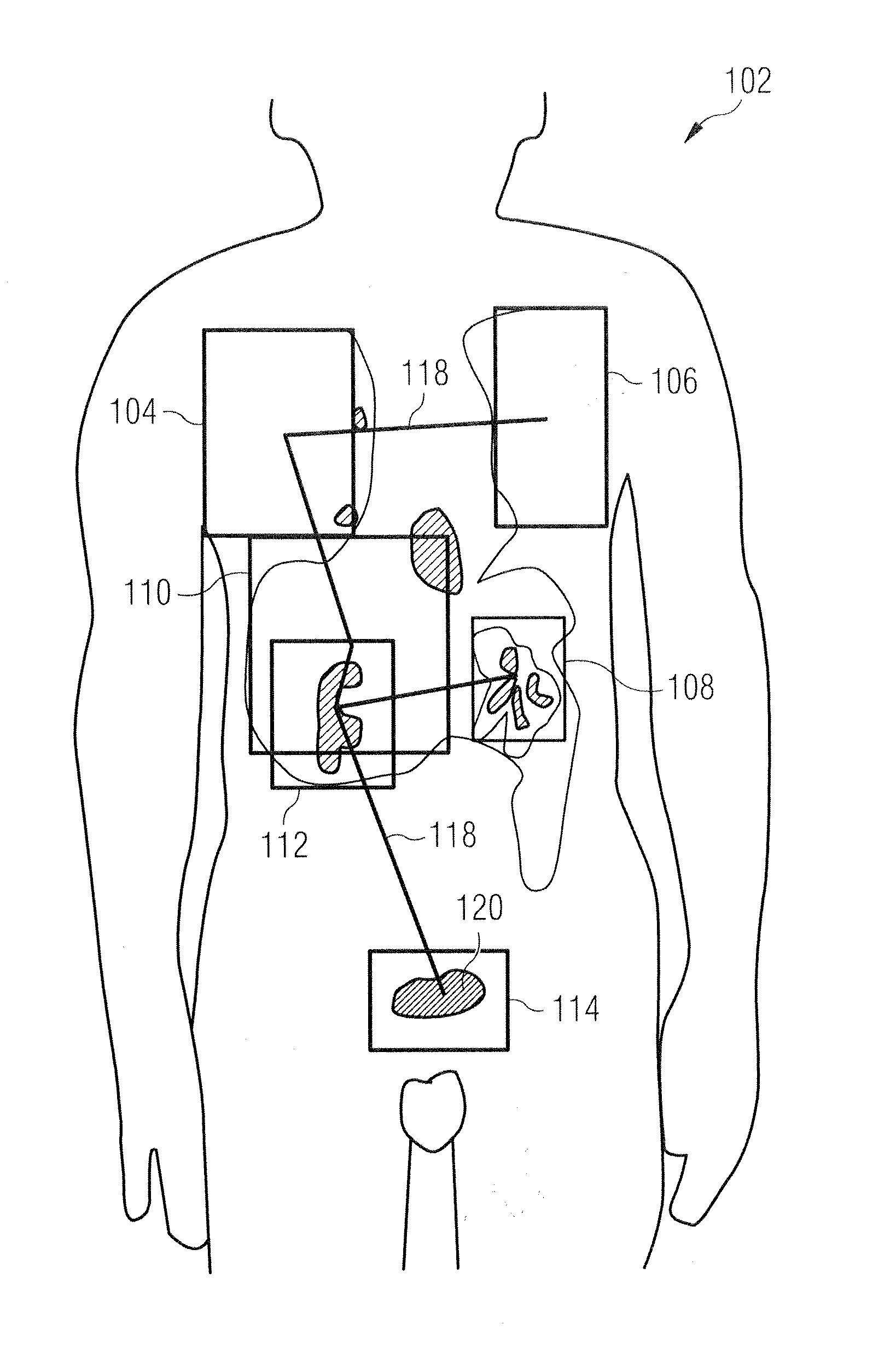
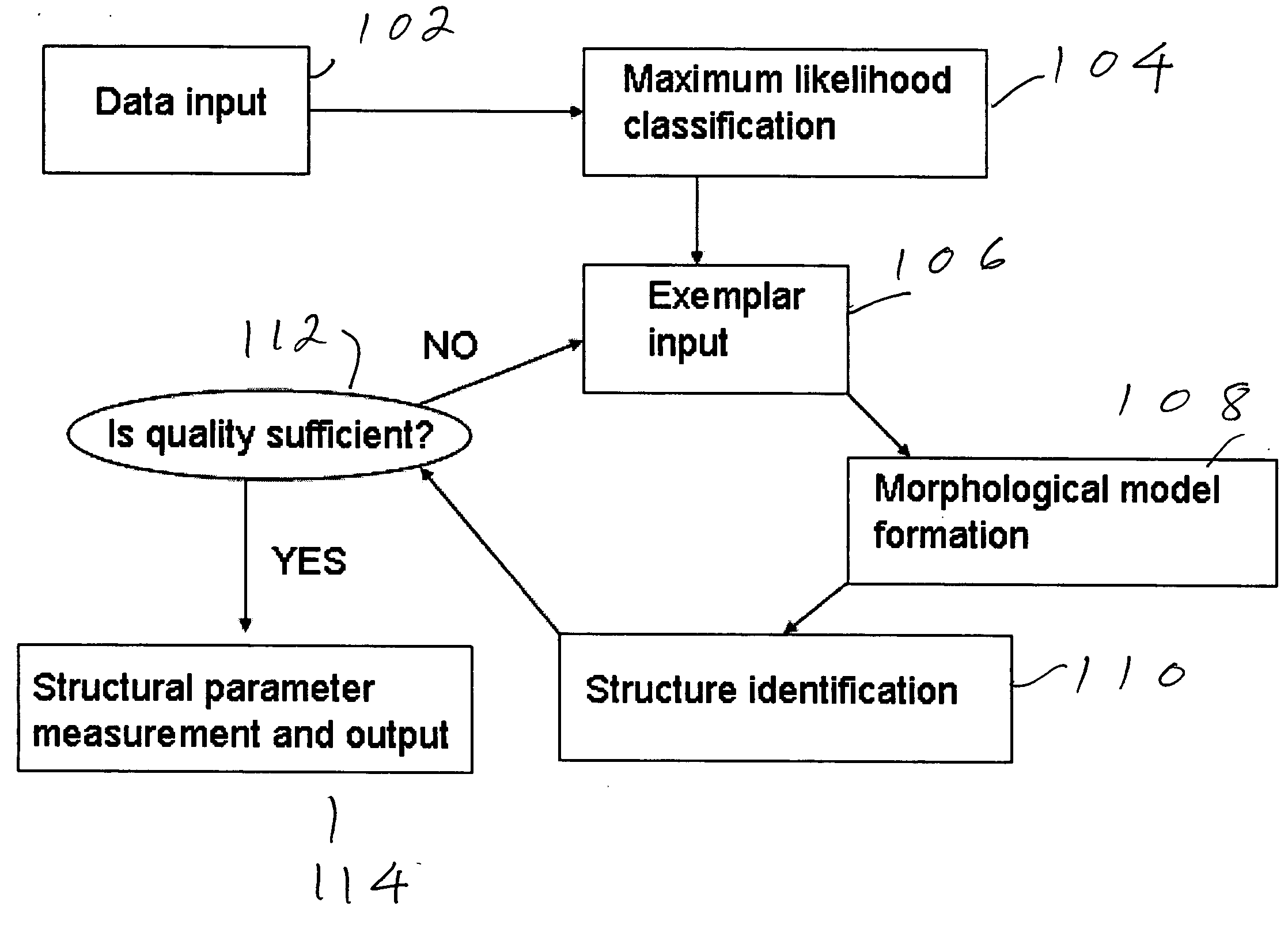
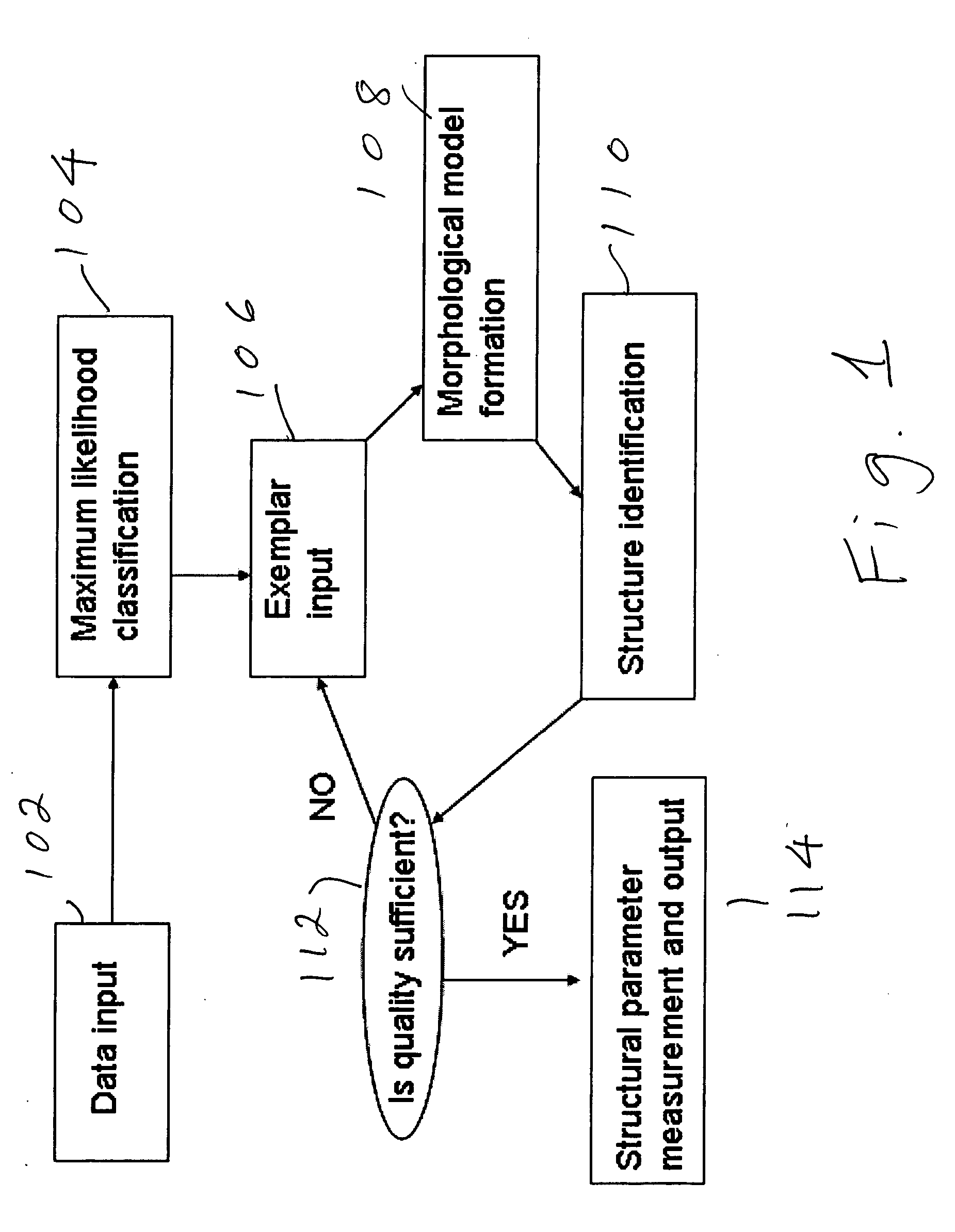
ActiveUS20050069183A1Operate rapidly and accuratelyMinimize changesImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresUser input
Structures are delineated in medical or other images. First, various tissue types present in the image are statistically described using a maximum likelihood classifier. Second, the tissue of interest is described using an exemplar, which is derived either from an anatomical atlas or from user input. Third, the structure of interest is morphologically described. The process can be iterated until a desired level of accuracy is achieved.
Owner:VIRTUALSCOPICS
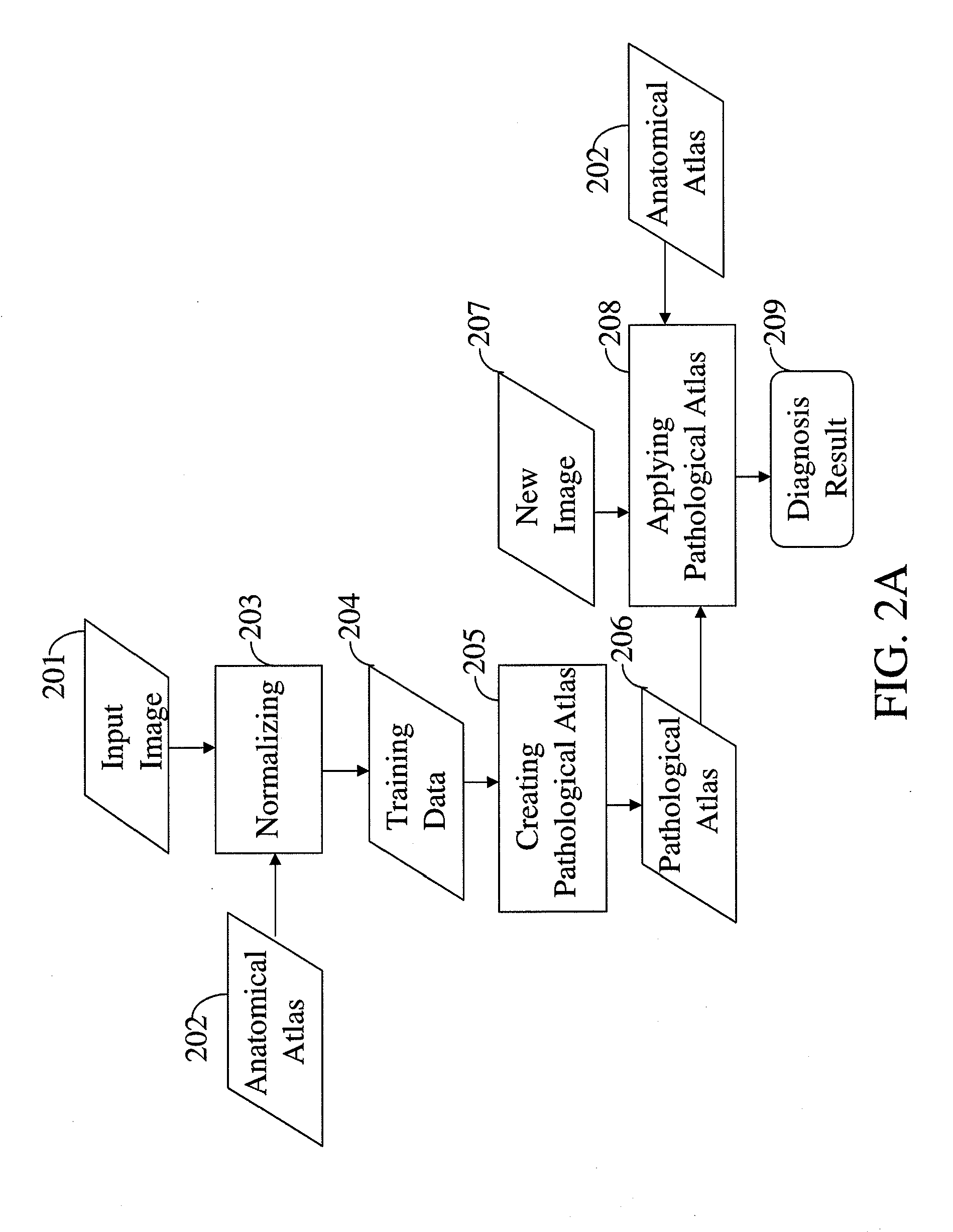
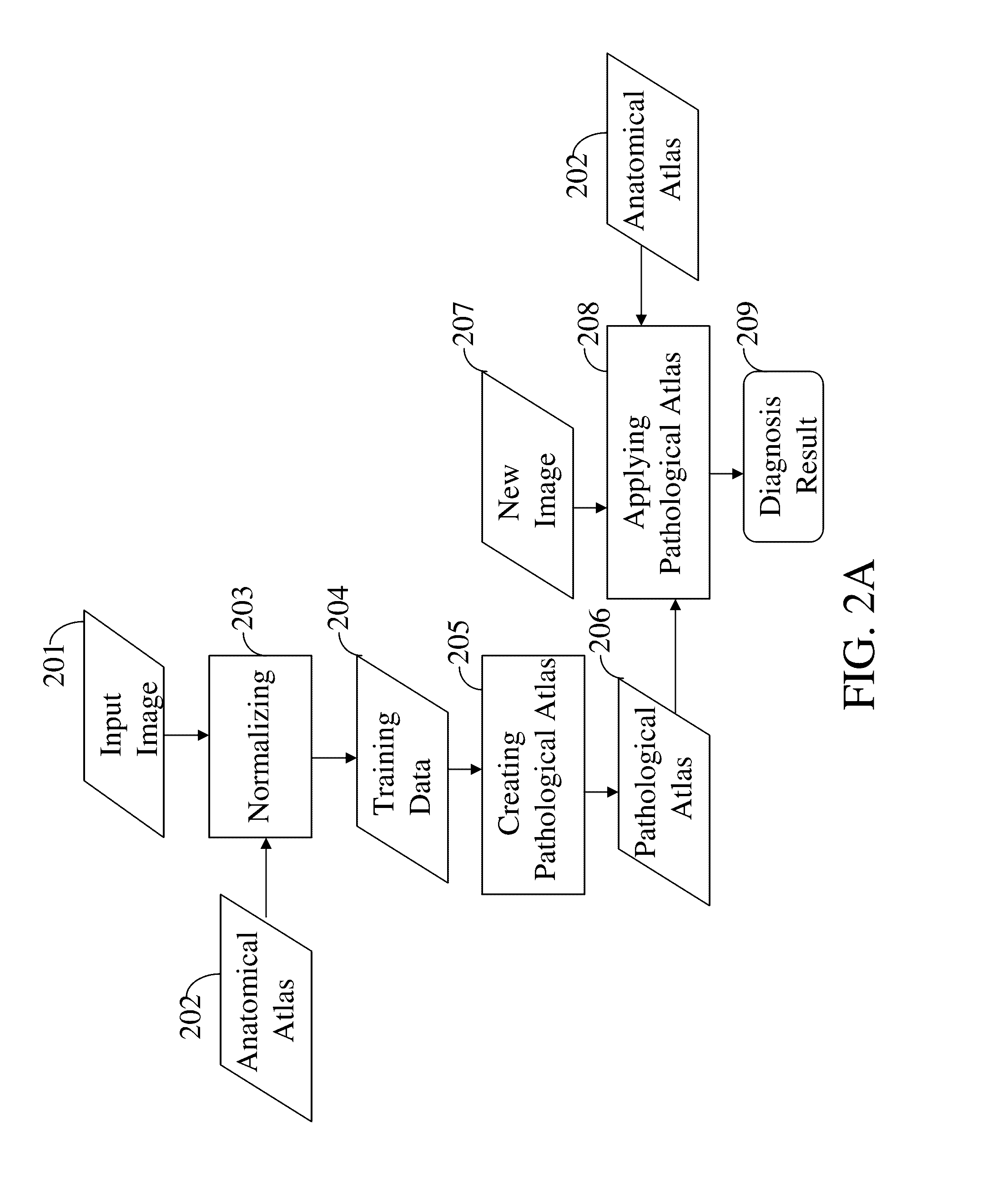
Intelligent Atlas for Automatic Image Analysis of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
A non-invasive imaging system, including an imaging scanner suitable to generate an imaging signal from a tissue region of a subject under observation, the tissue region having at least one substructure; a signal processing system in communication with the imaging scanner to receive the imaging signal from the imaging scanner; and a data storage unit in communication with the signal processing system, wherein the data storage unit stores an anatomical atlas comprising data encoding spatial information of the at least one substructure in the tissue region, and a pathological atlas corresponding to an abnormality of the tissue region, wherein the signal processing system is adapted to automatically identify, using the imaging signal, the anatomical atlas, and the pathological atlas, a presence of the abnormality or a precursor abnormality in the subject under observation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
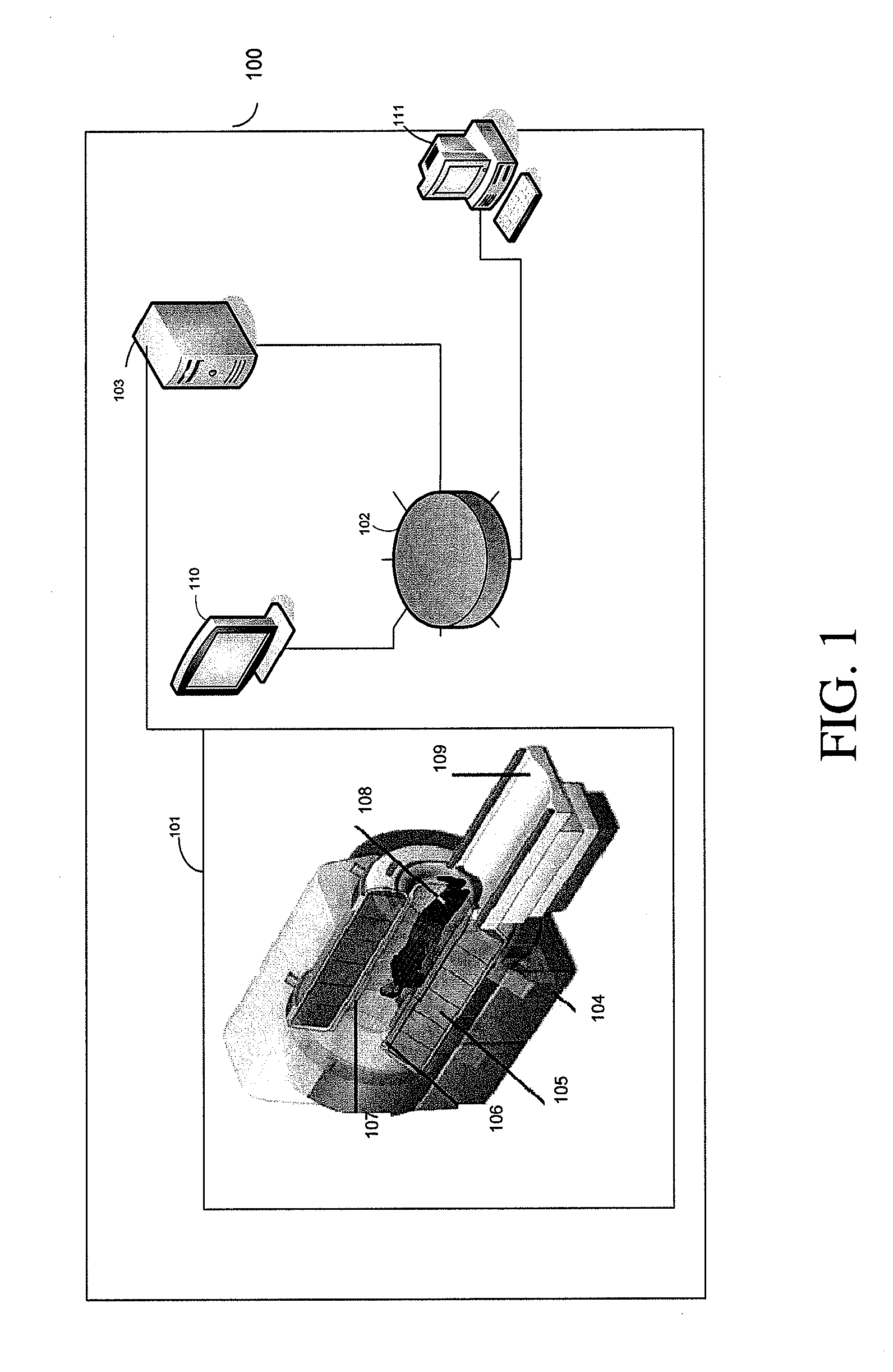
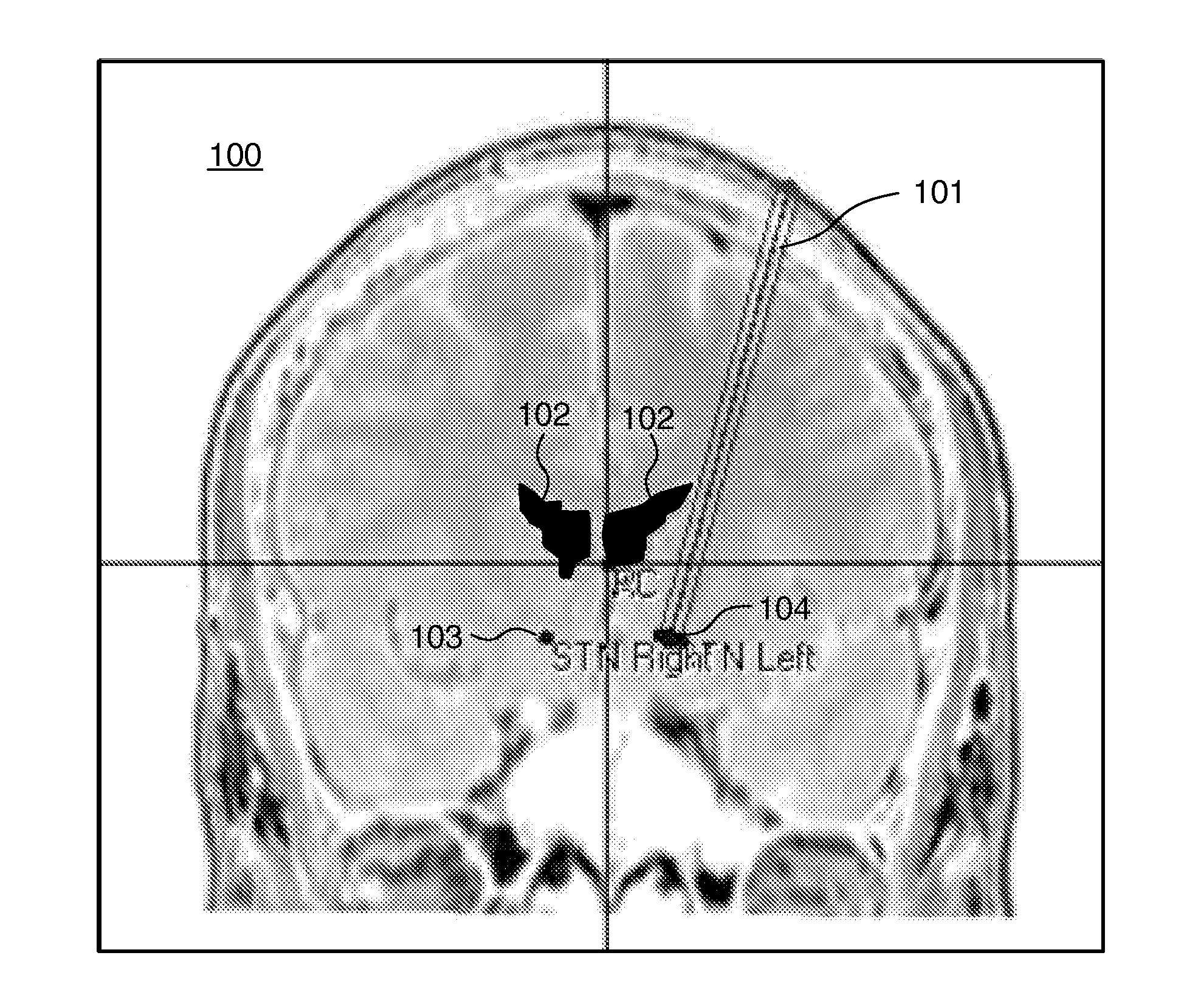
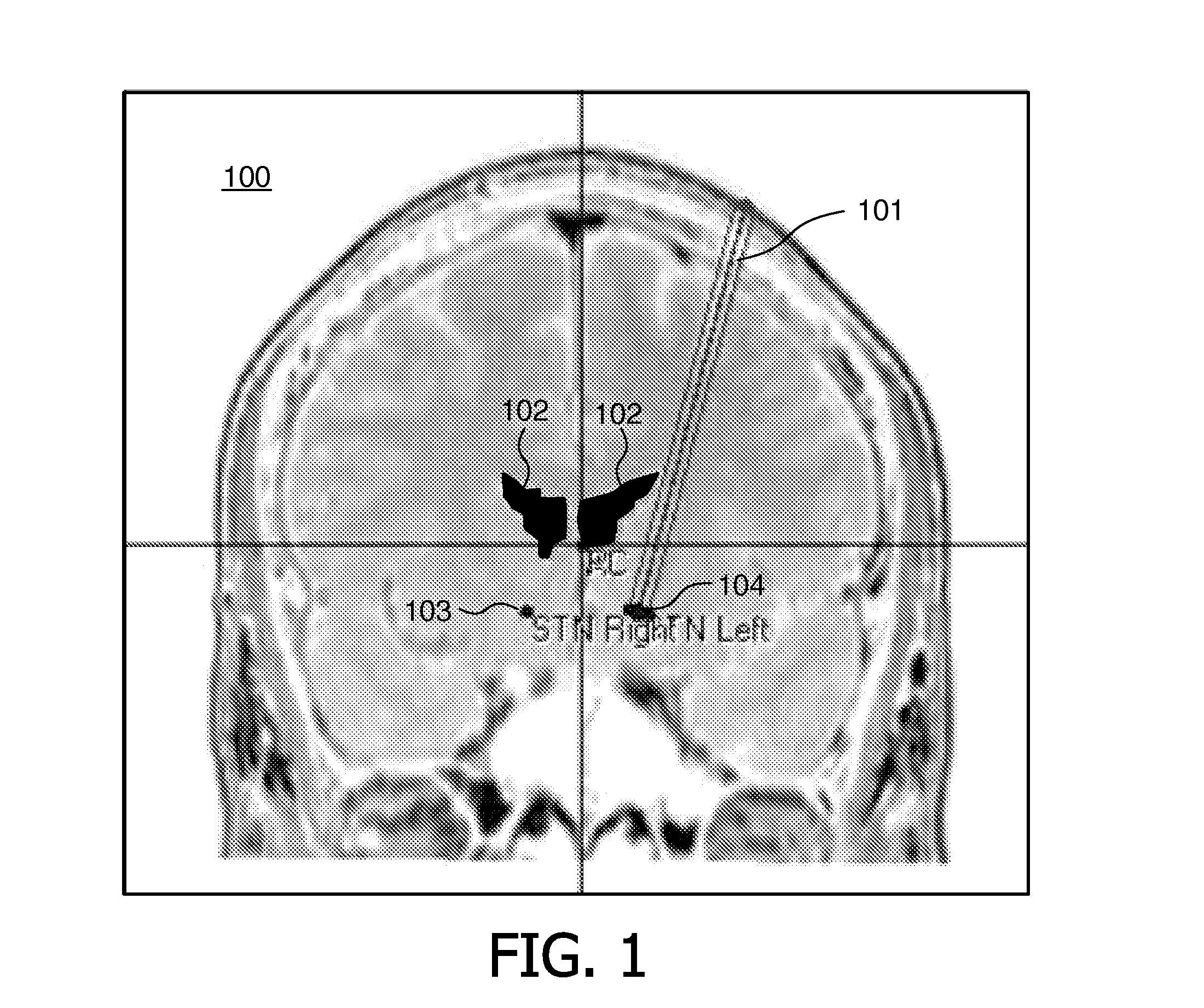
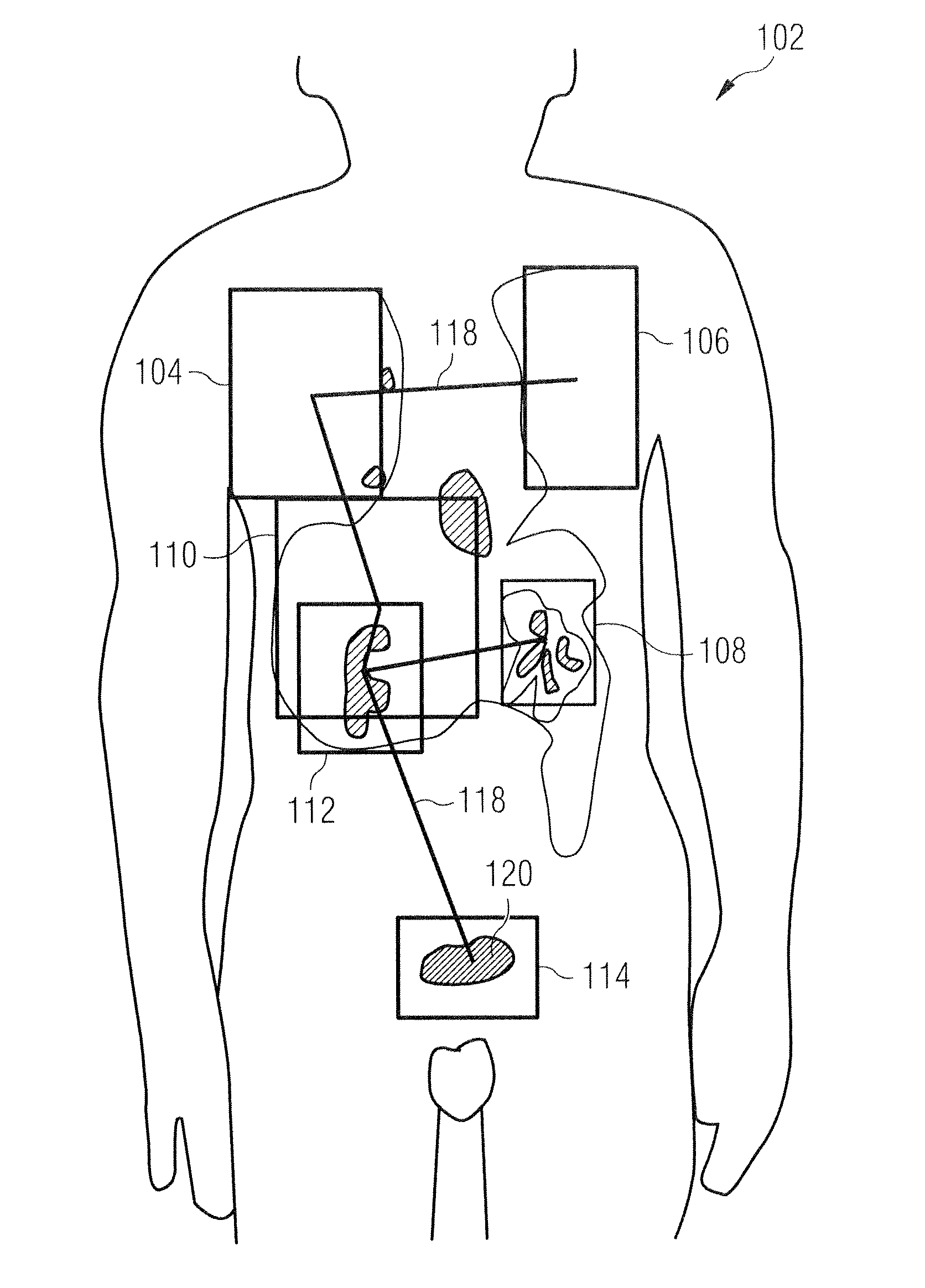
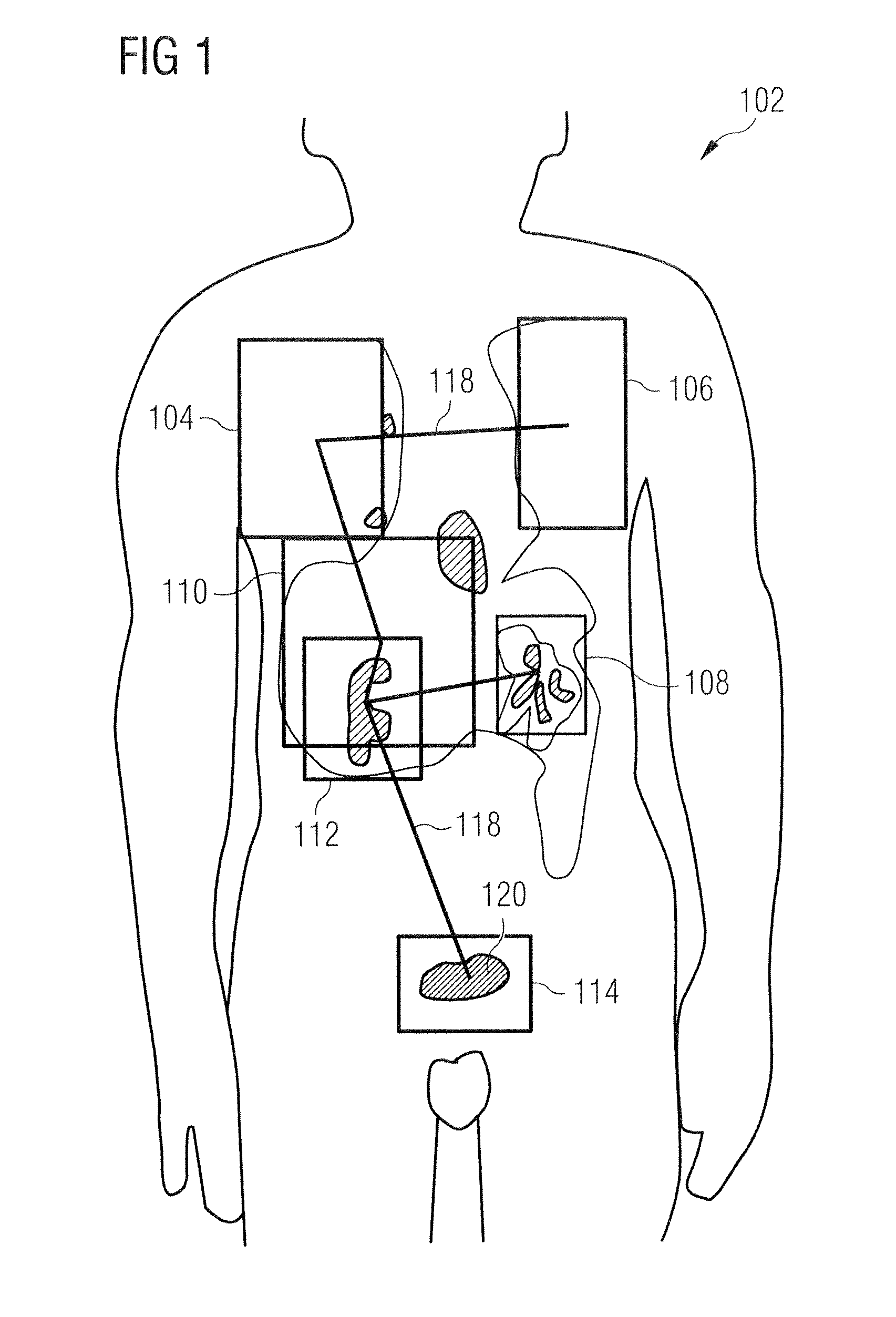
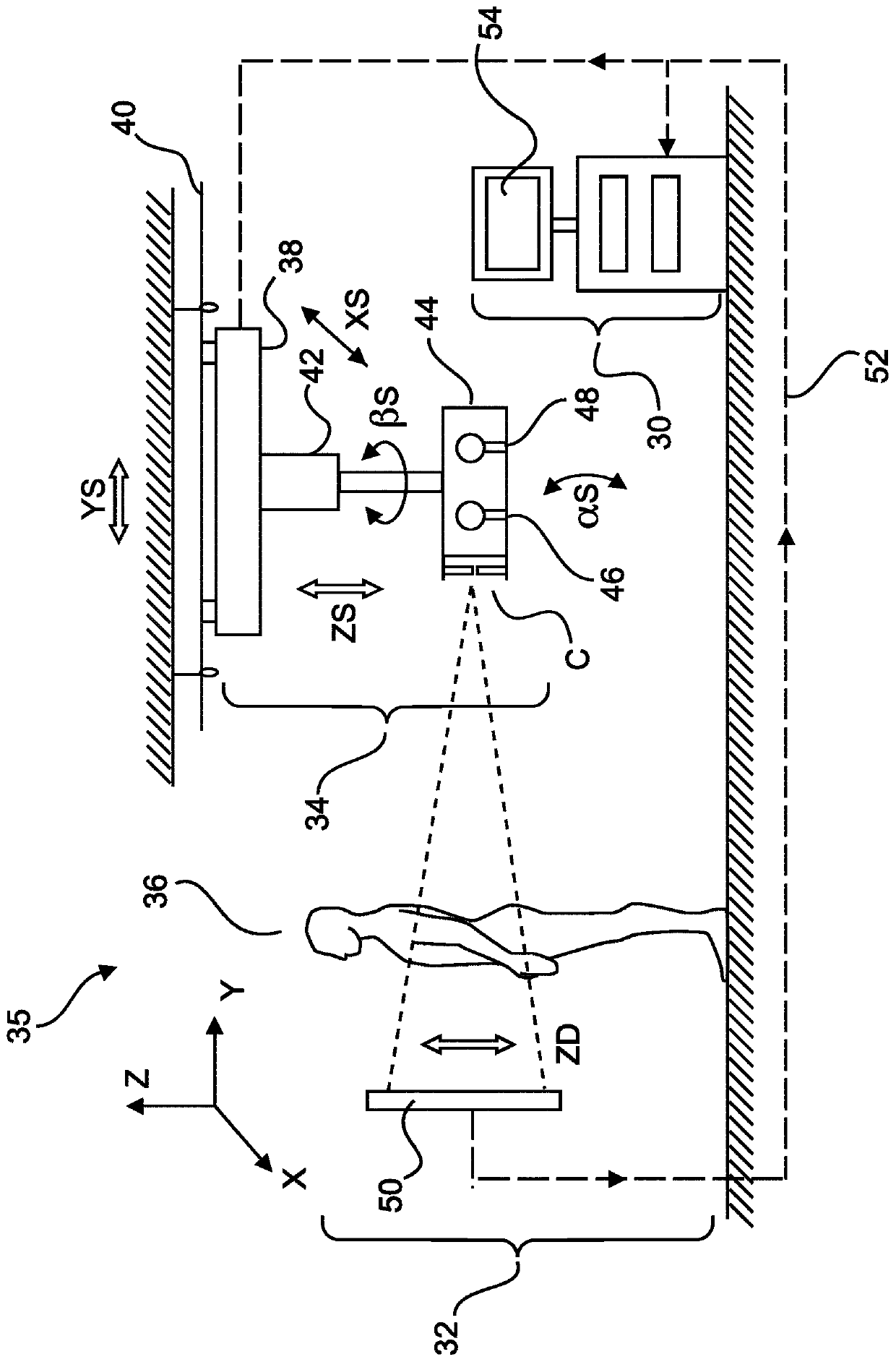
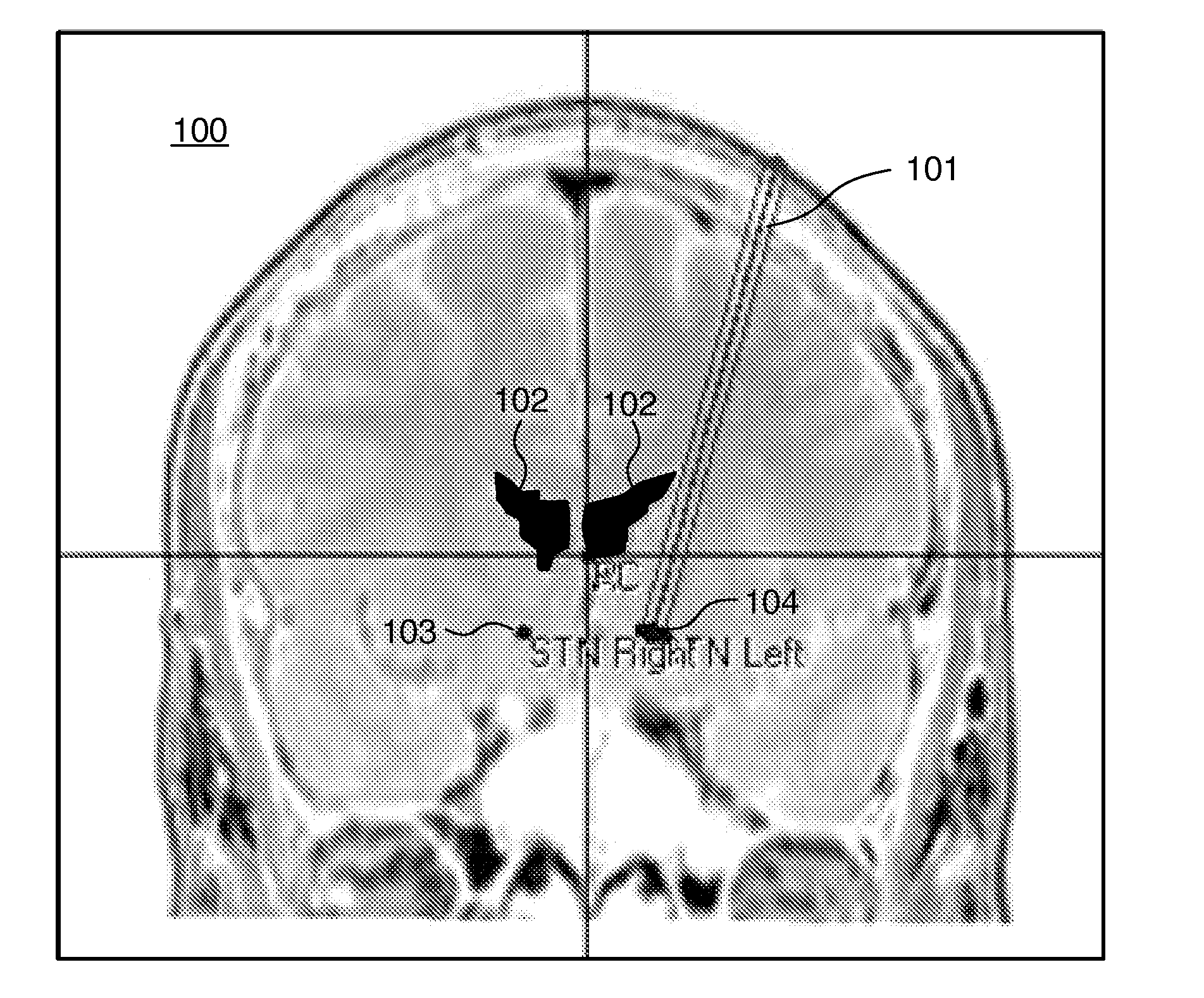
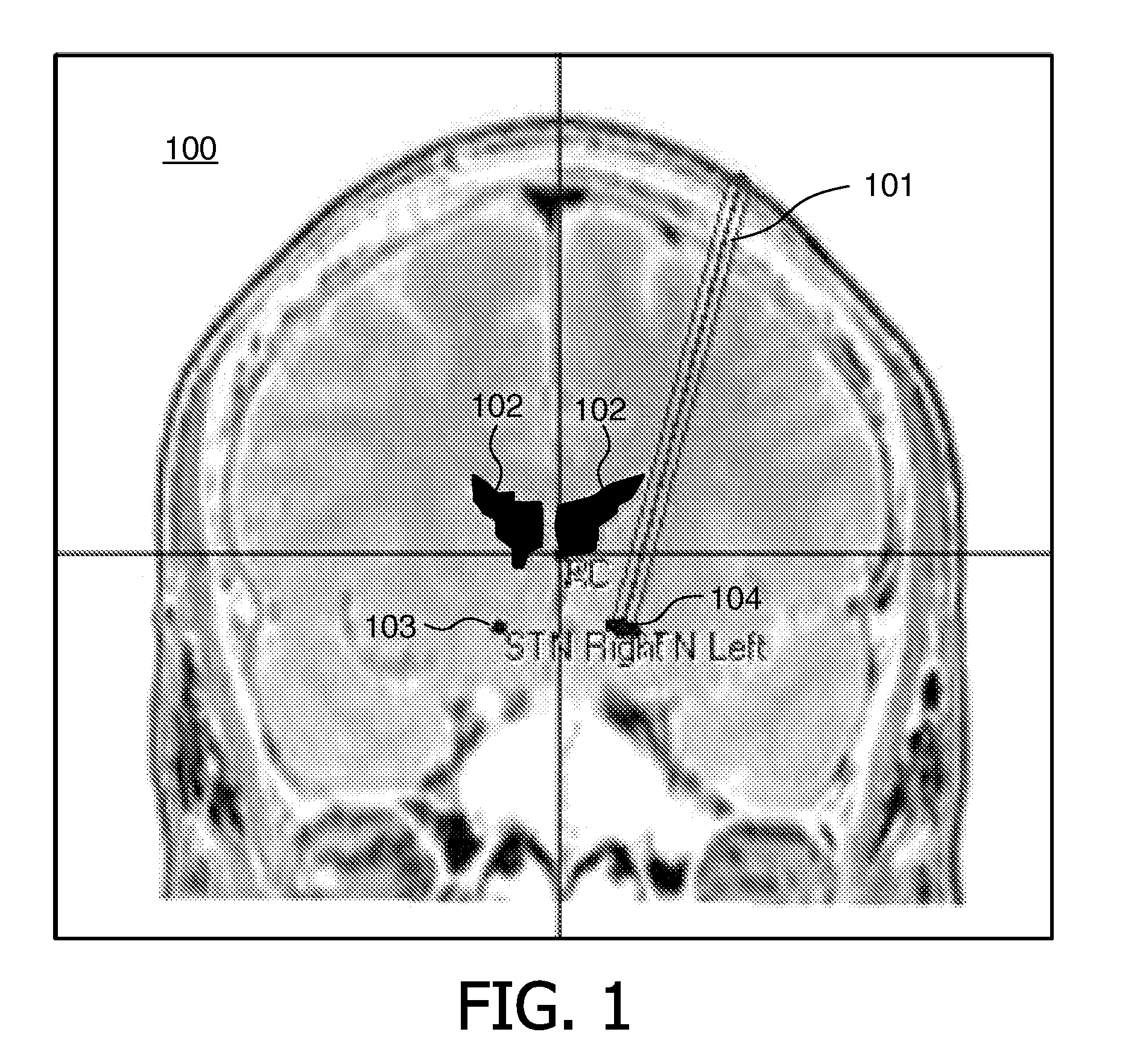
Visualizing surgical trajectories
ActiveUS20120099770A1Display clearSimple structureSurgical navigation systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionAnatomical structures3d image
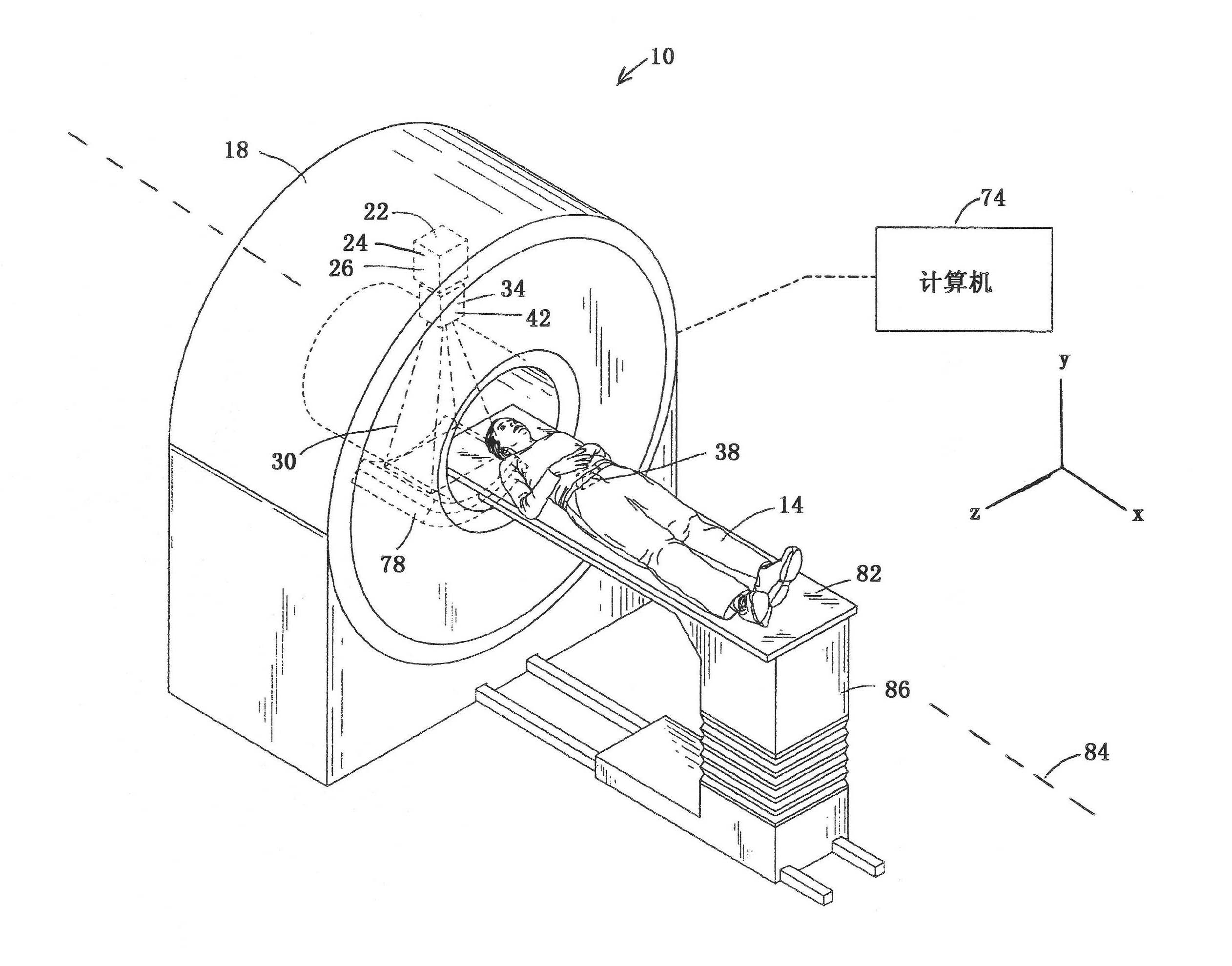
A method is provided for visualizing a surgical trajectory (32, 101, 42, 46, 47). The method comprises steps of receiving (71) 3D imaging information (31) of a region to undergo surgery and combining (72) the received 3D imaging information (31) with data from a digitized anatomical atlas. As a result, a combined map of the region to undergo surgery is obtained. The combined map comprises expected positions of anatomical structures (102, 103, 104) in the region to undergo surgery. The method further comprises steps of receiving (73) the surgical trajectory (32, 101, 42, 46, 47) for the surgery, determining (74) positions of intersections (43, 44) of the surgical trajectory (32, 101, 42, 46, 47) with the anatomical structures (102, 103, 104) and providing (75) the positions of the intersections (43, 44) in a coordinate system aligned with the surgical trajectory (32, 101, 42, 46, 47).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Physical specimen 3D printing method
ActiveCN110992804AEasy to observeEasy to learnAdditive manufacturing apparatusEducational modelsComputer printing3d printer
The invention relates to a physical specimen 3D printing method which comprises the following steps: (1) preservative treatment: carrying out preservative treatment on a selected physical specimen; (2) anatomy and manufacturing: manufacturing a required specimen according to an anatomical atlas; (3) bleaching and swashing: carrying out bleaching treatment on the specimen, and then swashing with tap water; (4) trimming: trimming and cleaning the anatomical specimen; (5) scanning: scanning the specimen by using a 3D scanning tool; (6) processing of a specimen image: trimming and synthesizing thescanned image by using a computer; and (7) printing: printing the specimen by using a 3D printer. The real biological specimen is used as a raw material to print the specimen, the shape structure iscomplete and unchanged, the sense of reality is strong, the process is simple, and the time is short; massive different materials can be used for preparation, and inconvenience brought to experiment teaching due to shortage of physical specimens is solved.
Owner:河南中博科技有限公司
System for interpretation of image patterns in terms of anatomical or curated patterns
ActiveUS20170220850A1Reduce chanceIncrease speedImage enhancementImage analysisData setIon distribution
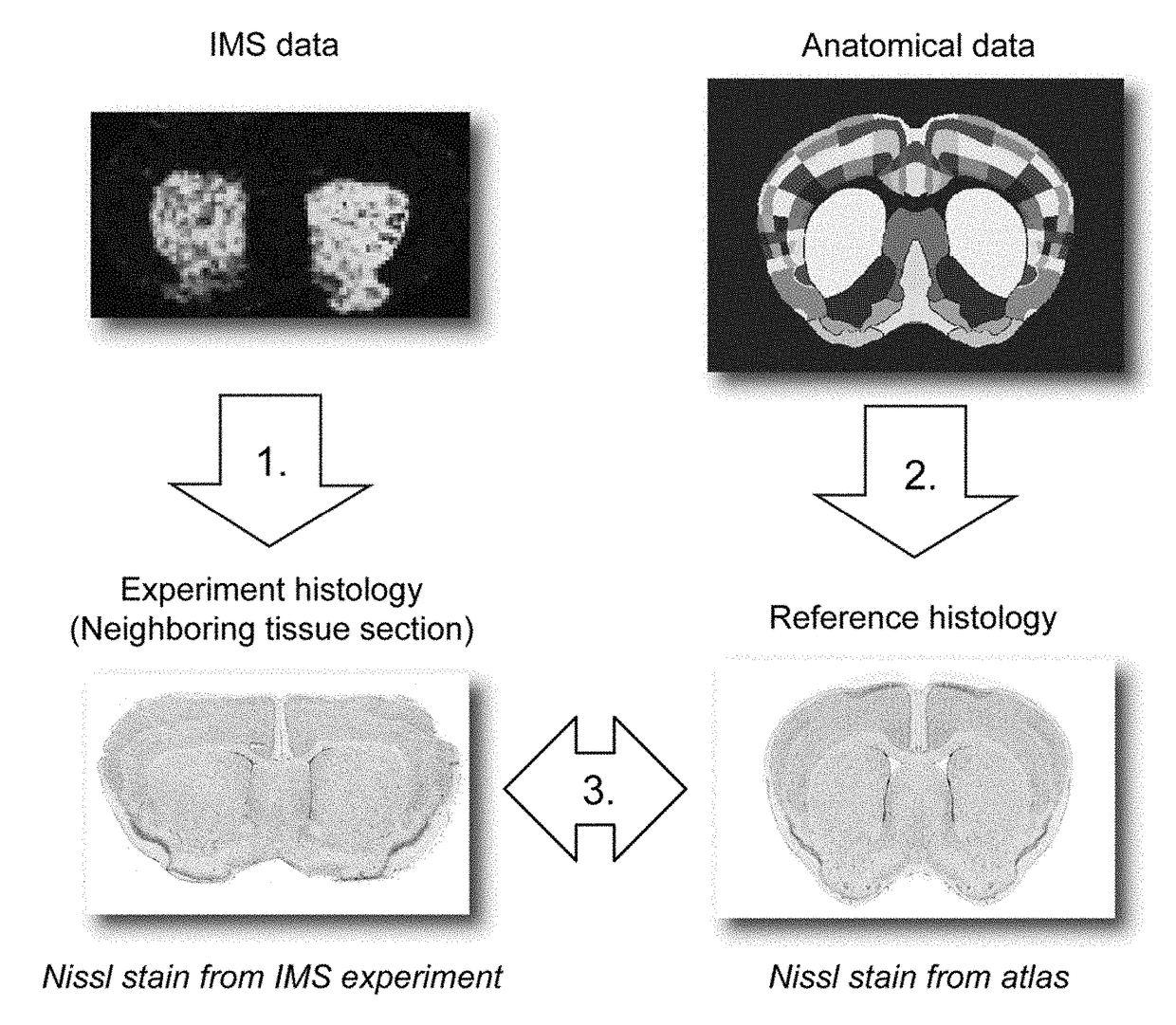
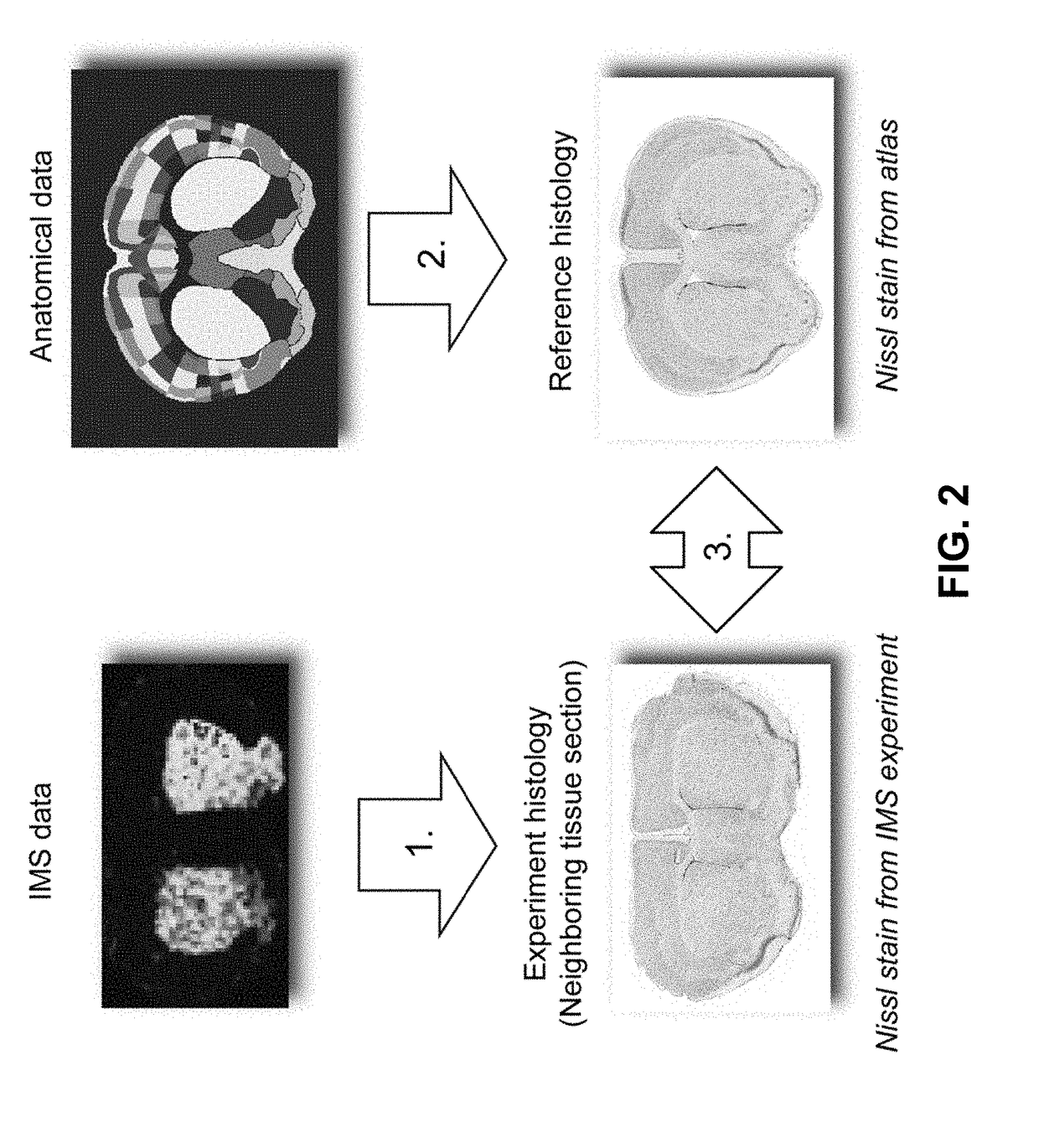
Imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) has become a prime tool for studying the distribution of biomolecules in tissue. Although IMS data sets can become very large, computational methods have made it practically feasible to search these experiments for relevant findings. However, these methods lack access to an important source of information that many human interpretations rely upon: anatomical insight. In this work, this need is addressed by (1) integrating a curated anatomical data source with an empirically acquired IMS data source, establishing an algorithm-accessible link between them; and (2) demonstrating the potential of such an IMS-anatomical atlas link by applying it toward automated anatomical interpretation of ion distributions in tissue.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN +1
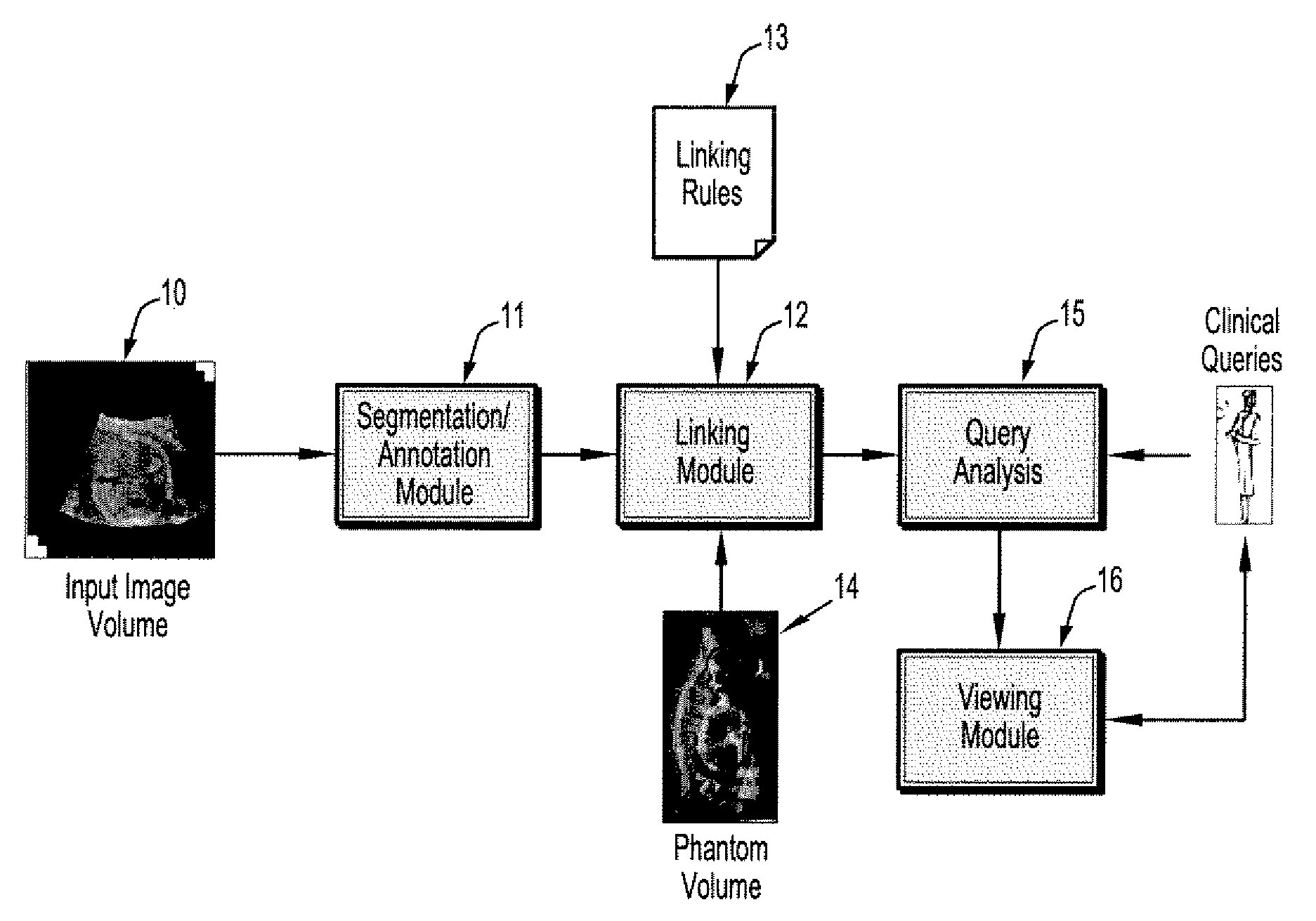
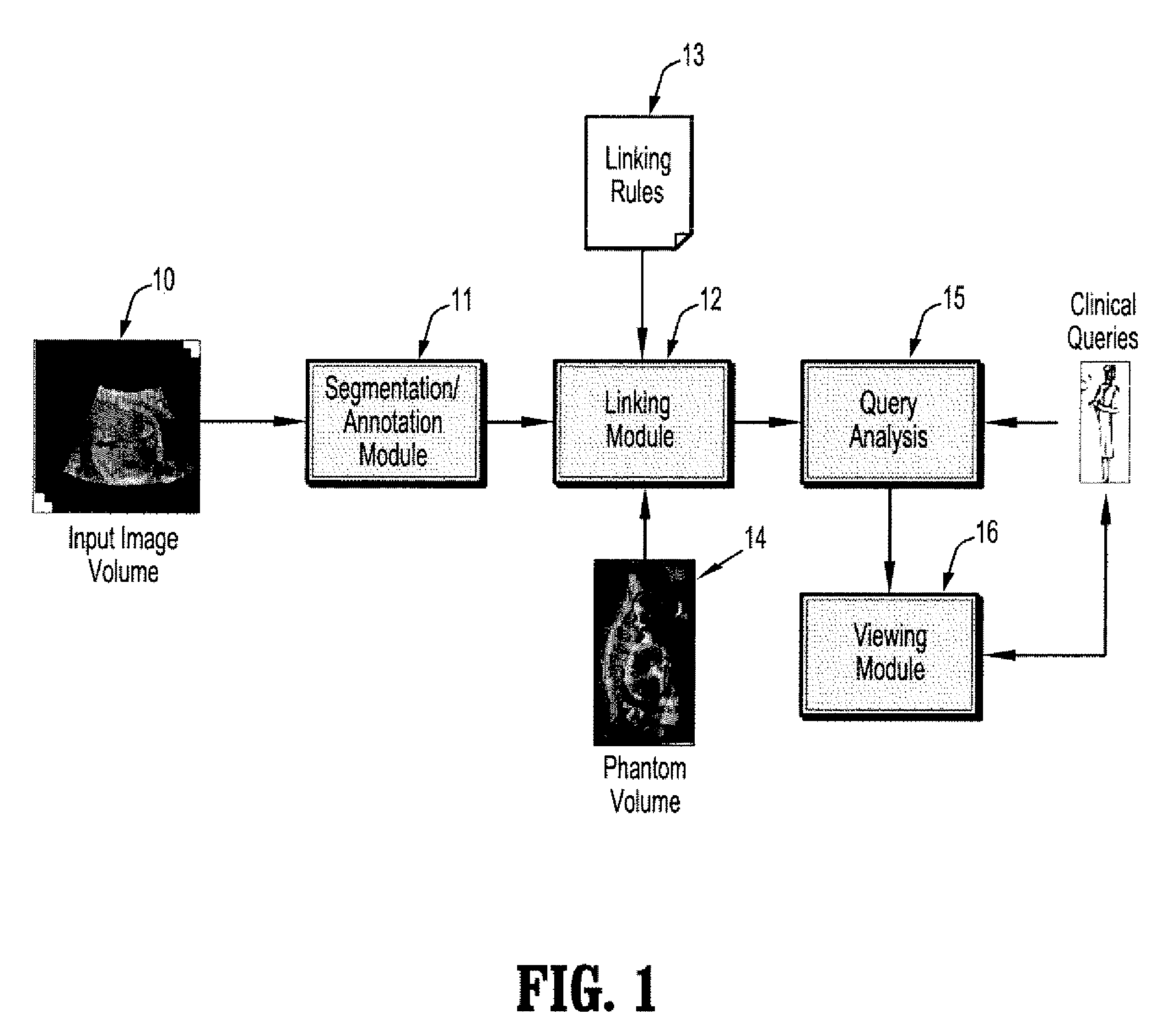
System and method for semantic indexing and navigation of volumetric images
ActiveUS7889898B2Quick navigationEasy to browseCharacter and pattern recognitionMedical imagesNoun phraseComputer science
A method for navigating digital medical images includes providing a digitized patient medical image of a structure of interest in a patient, using a pre-trained classifier to segment the structure of interest from the image, creating links from the structure of interest to a corresponding structure in an anatomical atlas, receiving a query to view the structure of interest, parsing the query to identify one or more keywords from noun phrases in the query, mapping a keyword to a corresponding structure in the anatomical atlas, wherein the anatomical atlas structure is associated with a link to the corresponding structure in the patient image, and following the link to display said patient structure of interest.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
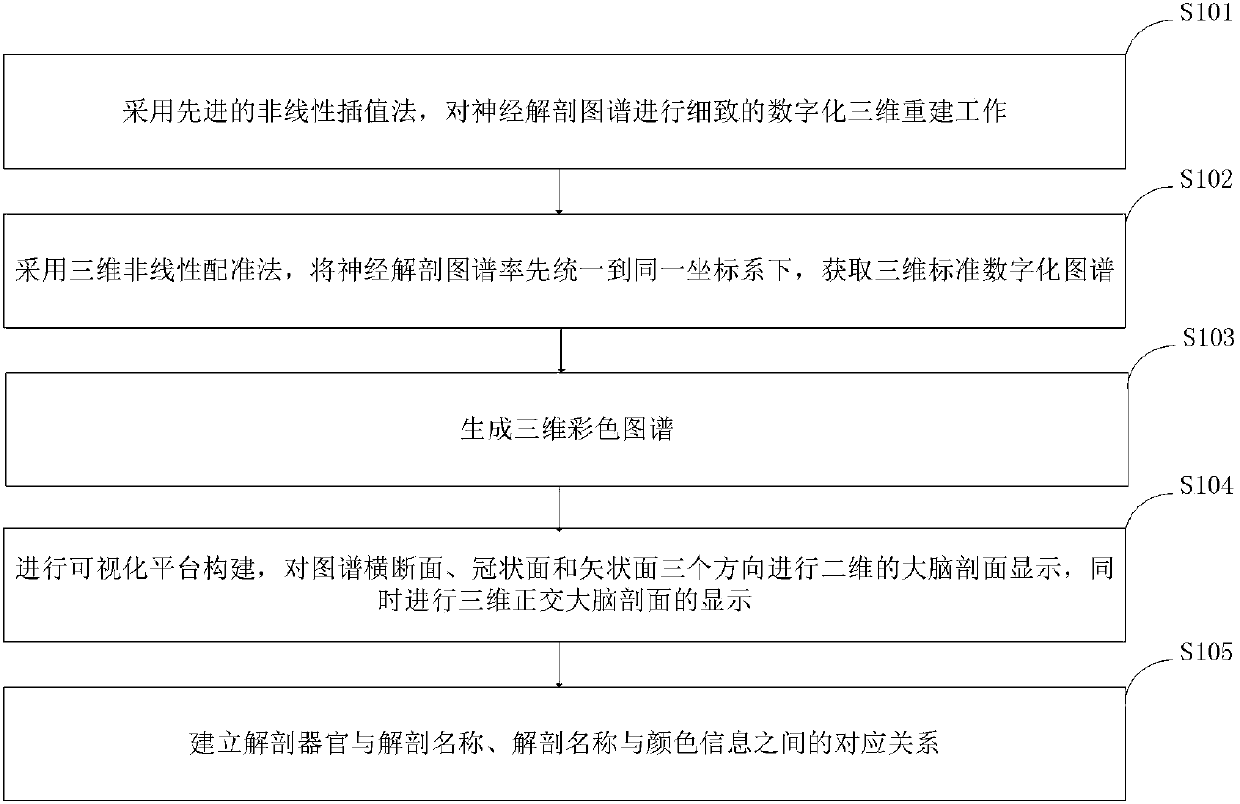
Three dimensional visualization application method of anatomical atlas in neurosurgery operation navigation system
InactiveCN107590856AHigh data accuracyClear outlineImage analysisSurgical navigation systemsAnatomical structuresCoronal plane
The present invention belongs to the medical field, and discloses a three dimensional visualization application method of anatomical atlas in a neurosurgery operation navigation system. The three dimensional visualization application method comprises the steps of adopting an advanced non-linear interpolation method to carry out the careful digital three-dimensional reconstruction work on the anatomical atlas; adopting a three-dimensional non-linear registration method to unify the neuroanatomical atlas to a same coordinate system firstly, and obtaining the three-dimensional standard digital atlas; generating the three-dimensional color atlas; constructing a visualization platform, displaying a two-dimensional brain section from the three directions of an atlas cross-section, a coronal plane and a sagittal plane, at the same time, displaying a three-dimensional orthogonal brain section; establishing the correspondence relationships between the anatomical organs and the anatomical names,and between the anatomical names and the color information. The method of the present invention displays the two-dimensional sections of the anatomical atlas, also displays the three-dimensional orthogonal sections of the atlas, enables the contours of the anatomical structures to be clearer relatively and the subordination relationship to be clearer, is very suitable for the teaching of the neuroanatomy, and is convenient for the neurologists to learn.
Owner:刘立军
System and method for segmenting a region in a medical image
A method and computer program are provided for segmenting a prostate from a medical image such as an ultrasound image. Each slice in a study is analysed and uses a manual initialization to obtain an initial contour, in which a user selects initial points that are automatically rendered on the image. An automatic refinement stage then snaps the contour to the prostate boundary in the image based on a pre-stored anatomical atlas and edge information obtained from the image. A manual adjustment stage may then be performed and if selected, the contour is automatically propagated to the next image slice to avoid the manual initialization. An auxiliary image slice may be referred to, which indicates how the prostate shape changes from slice to slice, e.g. by providing a perpendicular profile.
Owner:MERATIVE US LP
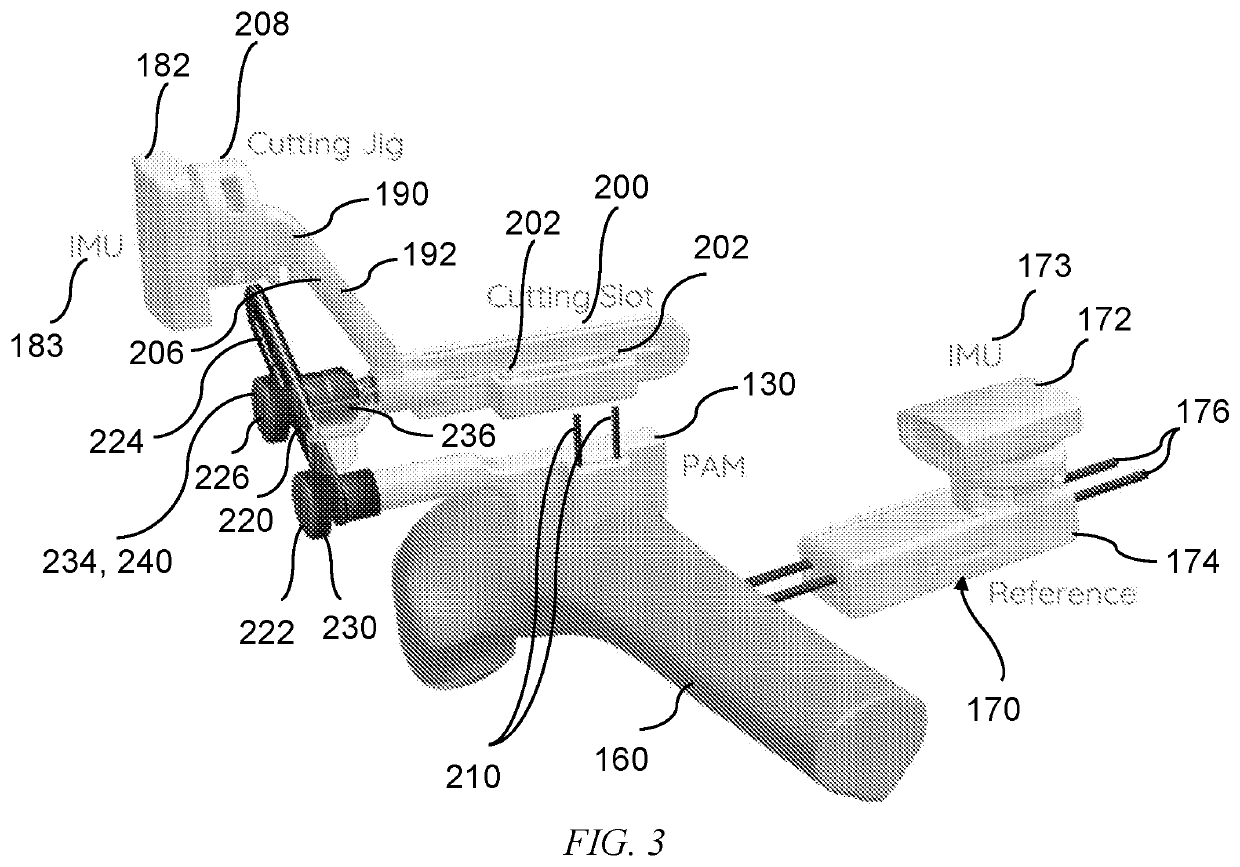
Methods and devices for knee surgery with inertial sensors
ActiveUS20210000612A1High precisionReduce in quantityStrain gaugeSurgical navigation systemsHuman bodyKnee Joint
A method of navigating a cutting instrument, via a computer system, the method comprising: (a) mounting a patient-specific anatomical mapper (PAM) to a human in a single known location and orientation, where the PAM includes a surface precisely and correctly mating with a human surface correctly in only a single location and orientation; (b) mounting a reference inertial measurement unit (IMU) to the human; (c) operatively coupling a guide to the PAM, where the guide includes an instrument inertial measurement unit (IMU) and at least one of a cutting slot and a pin orifice; (d) outputting data from the reference IMU and the instrument IMU indicative of changes in position and orientation of the guide with respect to the human; (e) repositioning the guide with respect to the human to a position and an orientation consistent with a plan for carrying out at least one of a cut and pin placement; and, (f) visually displaying feedback concerning the position and orientation of the guide with respect to the human using data output from the reference IMU and the instrument IMU, which data is processed by a computer program and the computer program directs the visually displayed feedback.
Owner:TECHMAH MEDICAL LLC
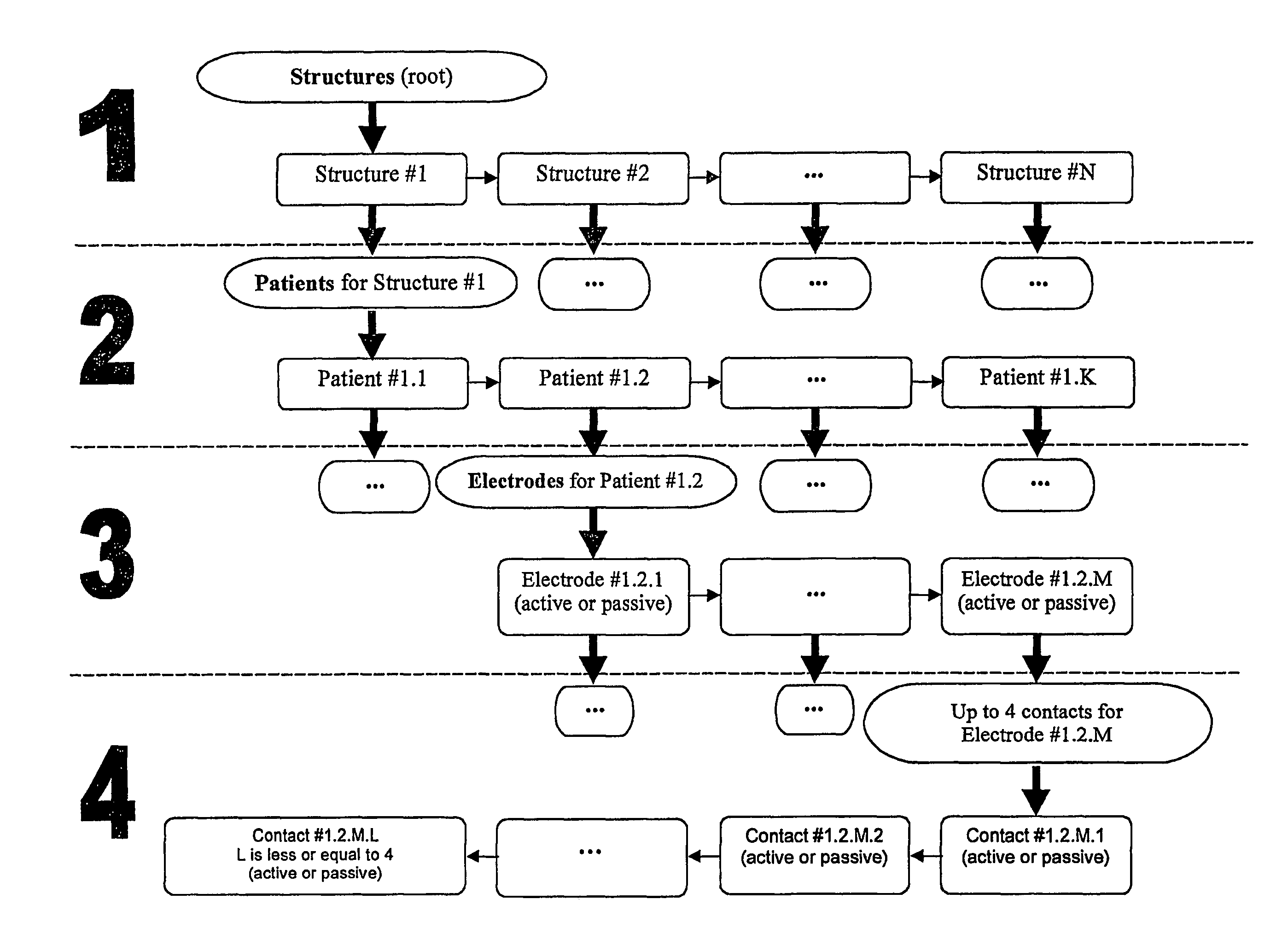
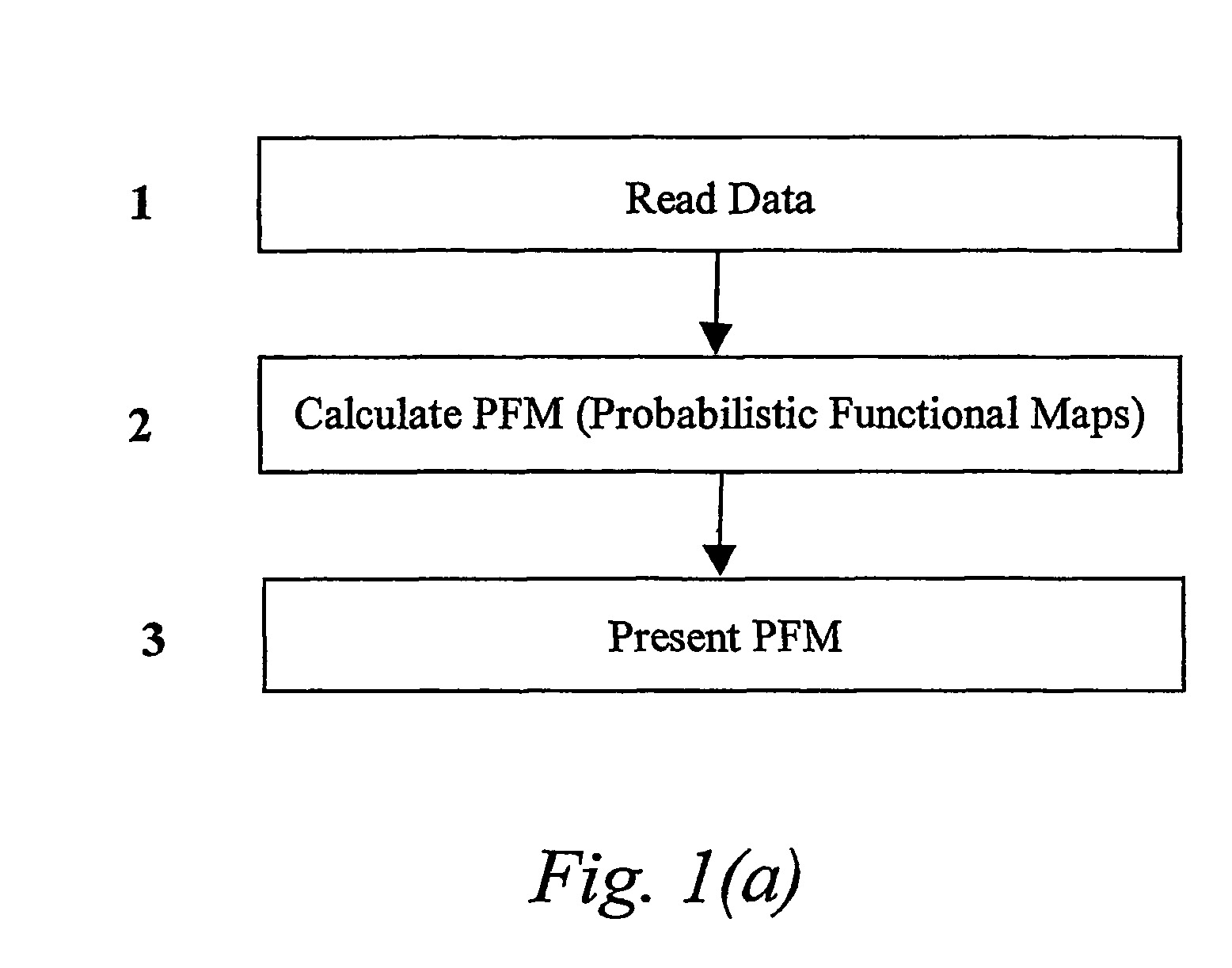
Methods and apparatus for calculating and presenting the probabilistic functional maps of the human brain
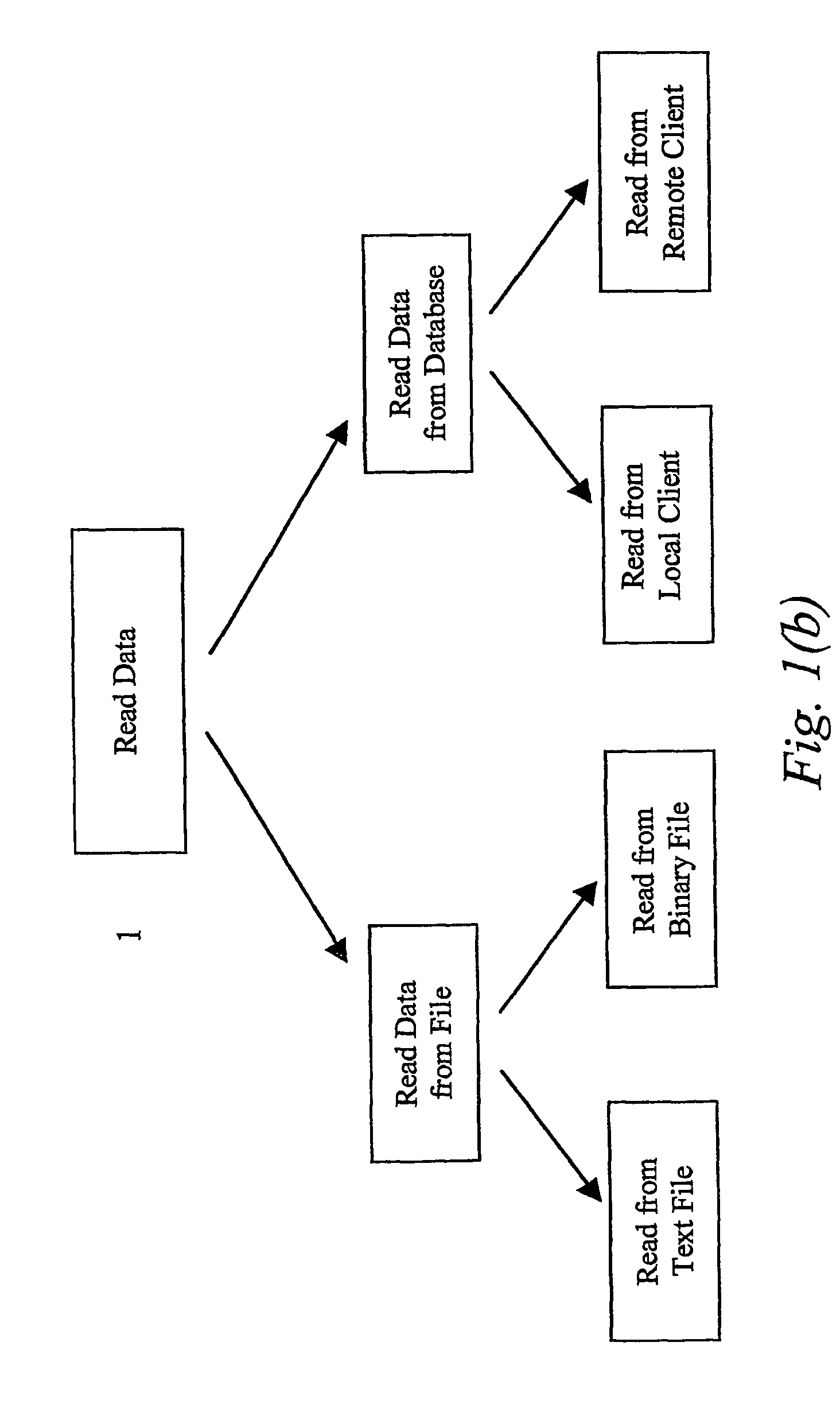
The present invention proposes a method for calculating, presenting, and combining probabilistic functional maps (PFMs) of the human brain representing the probability of structures existing. The method comprises three major steps: reading of data containing the coordinates of contacts, calculating the PFMs, and presenting the PFMs. The data can be read from a file in text or binary format or from a database as local or remote client. The PFM calculation comprises the following steps: forming 3D models of contacts, normalizing the contact models, voxelizing the contact models, calculating an atlas function, and calculating the PFM. The PFM can be presented alone or along with anatomical atlases. Both 3D and 2D interfaces can be used for presentation. The proposed method also includes different ways of combining the contact data and / or existing PFMs from multiple sources. This mechanism is the basis of an internet portal for stereotactic and functional neurosurgery.
Owner:KENT RIDGE DIGITAL LABS
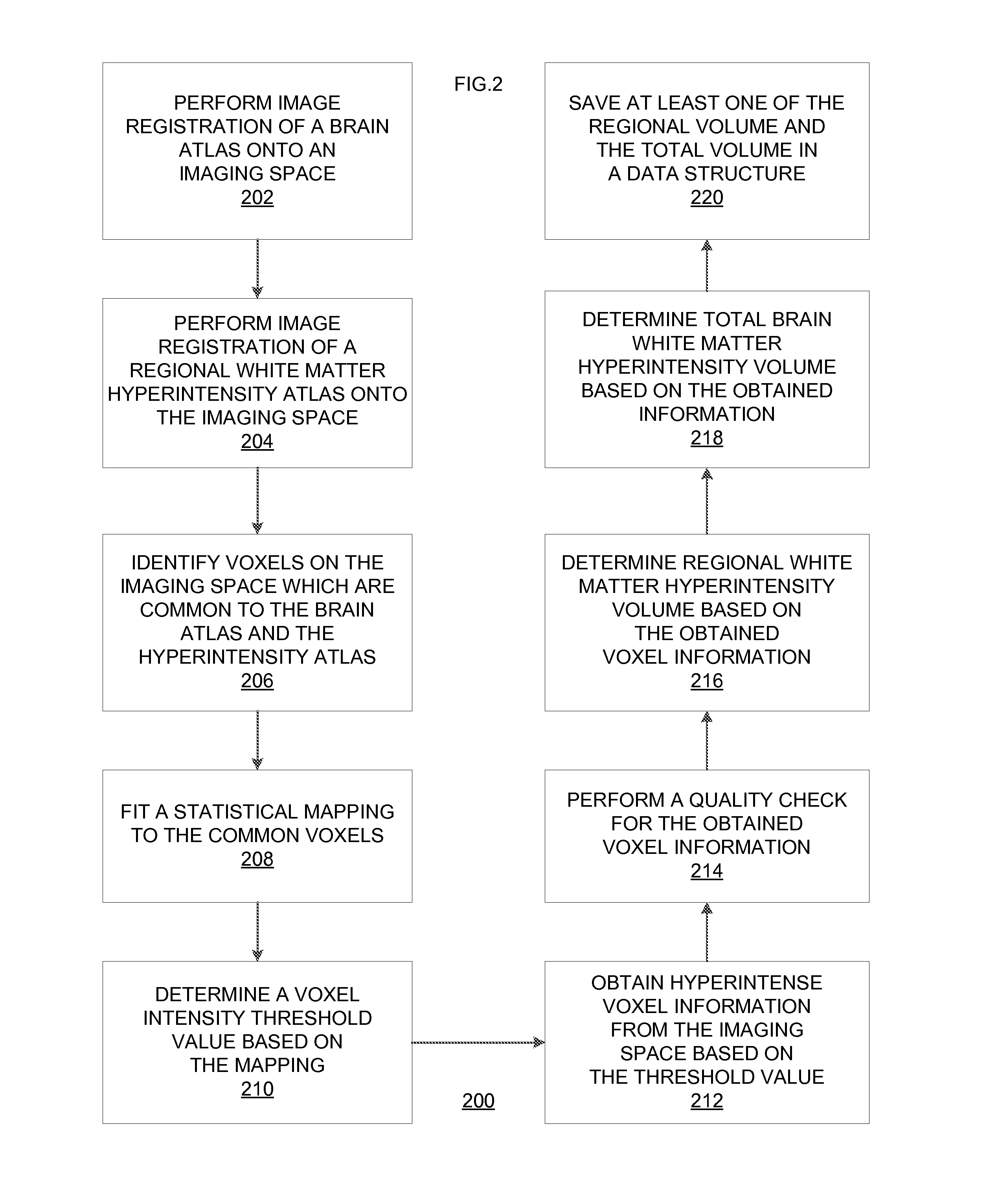
Technologies for white matter hyperintensity quantification
A method comprises selecting, via a computer, an intensity threshold value. The method also comprises defining, via the computer, a plurality of hyperintensities on imaging data based on the intensity threshold value. The method further comprises extracting, via the computer, a plurality of voxels from the imaging data based on the defining. The method additionally comprises determining, via the computer, a total volume of the voxels based on the extracting. The method also comprises determining, via the computer, a regional distribution of WMH based on an anatomical atlas and the total volume.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Semi-automated measurement of anatomical structures using statistical and morphological priors
ActiveUS7346201B2Operate rapidly and accuratelyMinimize changesImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresUser input
Structures are delineated in medical or other images. First, various tissue types present in the image are statistically described using a maximum likelihood classifier. Second, the tissue of interest is described using an exemplar, which is derived either from an anatomical atlas or from user input. Third, the structure of interest is morphologically described. The process can be iterated until a desired level of accuracy is achieved.
Owner:VIRTUALSCOPICS
Storing and recording method and classified collecting box for organ specimens and lymph node specimens in surgical operations
ActiveCN105173414AEasy to storeConvenient statisticsContainers preventing decayRigid containersSurgical operationComputer science
The invention relates to the field of medical treatment, in particular to a storing and recording method and classified collecting box for organ specimens and lymph node specimens in surgical operations. The classified collecting box for the organ specimens and the lymph node specimens in the surgical operations comprises a classification box I and a classification box II. The upper surface of the classification box I is divided into a primary lesion storing area and a distant metastasis storing area. An organ specimen storing tank is arranged in the primary lesion storing area. An anatomical atlas is arranged on the upper surface of the classification box II, and a plurality of lymph node specimen storing tanks are formed in the upper surface of the classification box II. The storing and recording method for the organ specimens and the lymph node specimens in the surgical operations comprises the steps that the classified collecting box for the organ specimens and the lymph node specimens in the surgical operations is adopted; and taken-down distant metastasis tissue is placed into distant metastasis storing tanks, then corresponding marks are pasted to the positions near the distant metastasis storing tanks, and the specific sampling positions of the distant metastasis tissue in corresponding sampling organs are marked on mark pasters. Comprehensive and detailed recording can be carried out on related information of the specimens in the surgical operations.
Owner:王洛 +1
Methods and apparatus for registration of medical images
InactiveUS8818057B2Robust registrationImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical featureRegister based
In methods and an apparatus for registering two medical images of a subject, a first image is compared with a first anatomical atlas and a second image with a second anatomical atlas, to generate labels for anatomical features in each image. The first anatomical atlas has at least two anatomical features in common with the second, and each label includes a suggested location of the anatomical feature to which it relates. A number of labels are identified for each image, and a value of a similarity function between labels of the respective images is calculated. The two images are registered based on the value of the similarity function.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
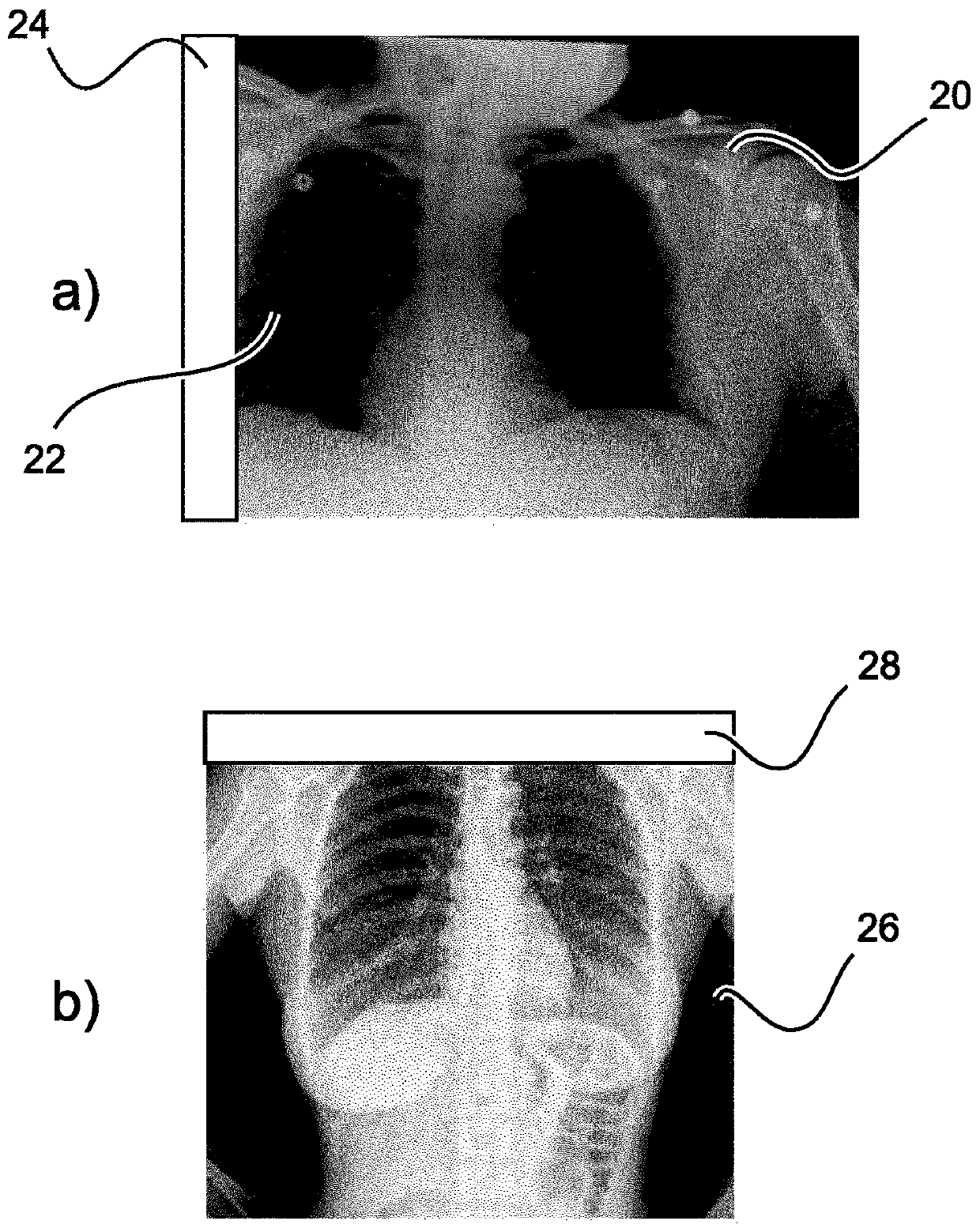
X-ray apparatus having a composite field of view
Medical radiography requires specialist control of radiography equipment to achieve good imaging results. Typical errors that can occur consist of an inappropriate field of view being accidentally applied. This results in a "cropping effect" in which portions of the region of interest of a patient which would be of clinical use are omitted from the image. Conventionally, the only solution is to re-take the entire image with a more appropriate (and inevitably larger) field of view selected. This is undesirable, because it might require recall of the patient from another location, and the patient will be subject to two exposures, thus undesirably increasing their X-ray dosage. The present application proposes to use an anatomical atlas to analyse an X-ray image output from an initial exposure, in particular to assess whether significant anatomical elements are missing from the image. If elements are missing, the field of view of the X-ray imager is recalibrated, using collimation or pan / tilt adjustments, for example. A subsequent X-ray image is obtained, and combined with the initial image, to provide an output image. Because only a small area of the region of interest may subsequently need to be exposed, a smaller additional dose results.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS NV
X-ray apparatus having a composite field of view
ActiveUS20200008768A1Reduce X-ray doseReduce doseImage enhancementImage analysisMedical radiographyExposure
Medical radiography requires specialist control of radiography equipment to achieve good imaging results. Typical errors that can occur consist of an inappropriate field of view being accidentally applied. This results in a “cropping effect” in which portions of the region of interest of a patient which would be of clinical use are omitted from the image. Conventionally, the only solution is to re-take the entire image with a more appropriate (and inevitably larger) field of view selected. This is undesirable, because it might require recall of the patient from another location, and the patient will be subject to two exposures, thus undesirably increasing their X-ray dosage. The present application proposes to use an anatomical atlas to analyse an X-ray image output from an initial exposure, in particular to assess whether significant anatomical elements are missing from the image. If elements are missing, the field of view of the X-ray imager is recalibrated, using collimation or pan / tilt adjustments, for example. A subsequent X-ray image is obtained, and combined with the initial image, to provide an output image. Because only a small area of the region of interest may subsequently need to be exposed, a smaller additional dose results.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
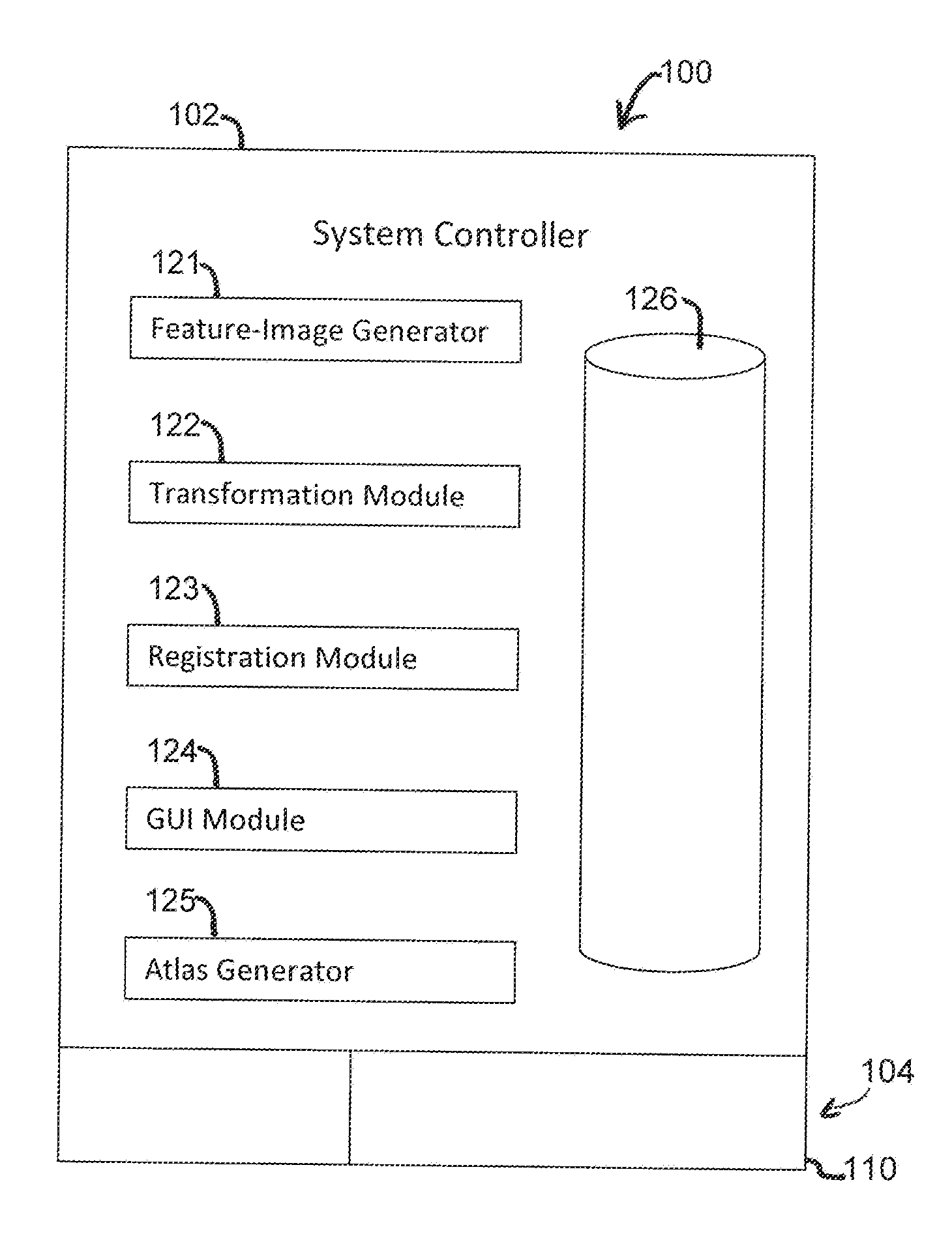
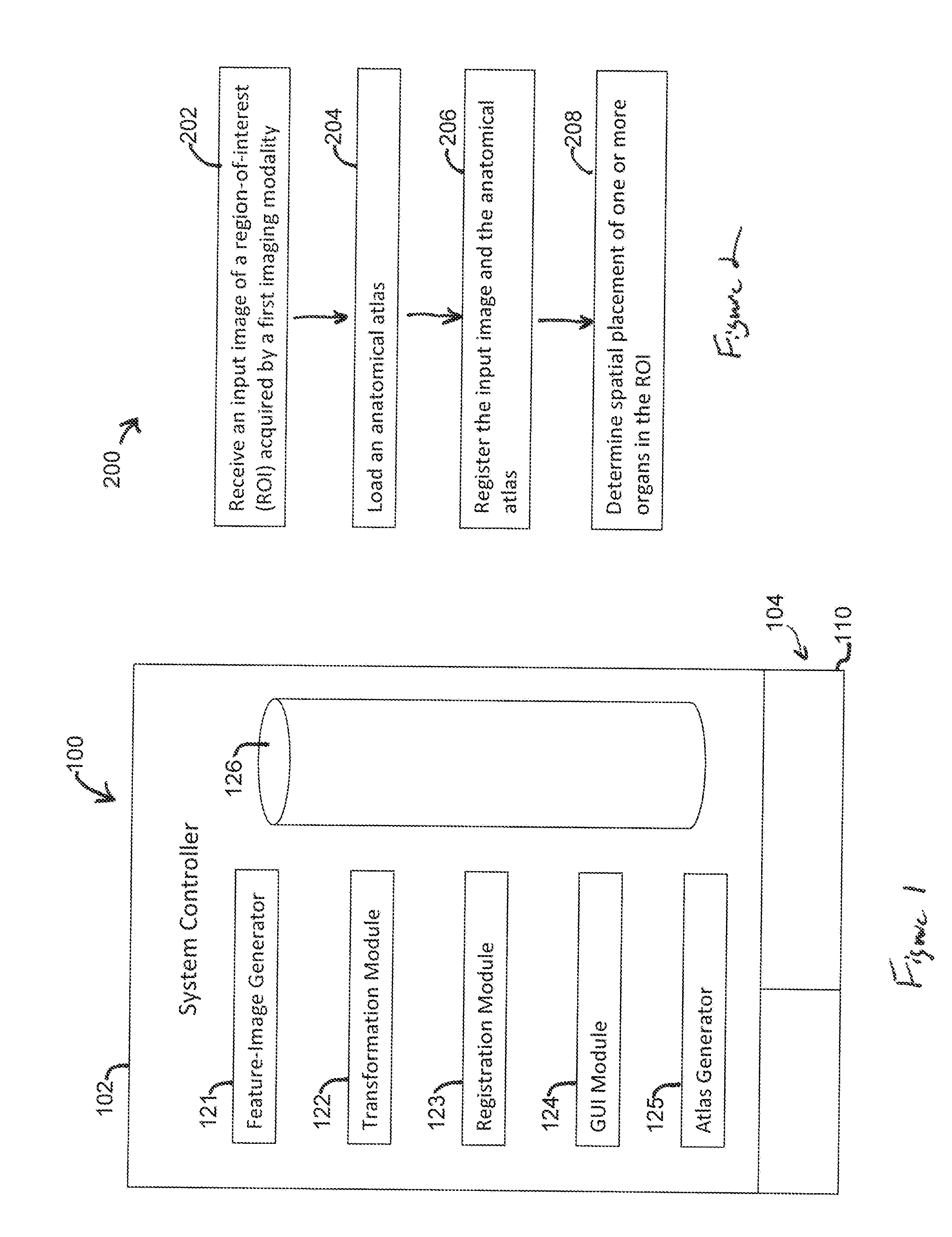
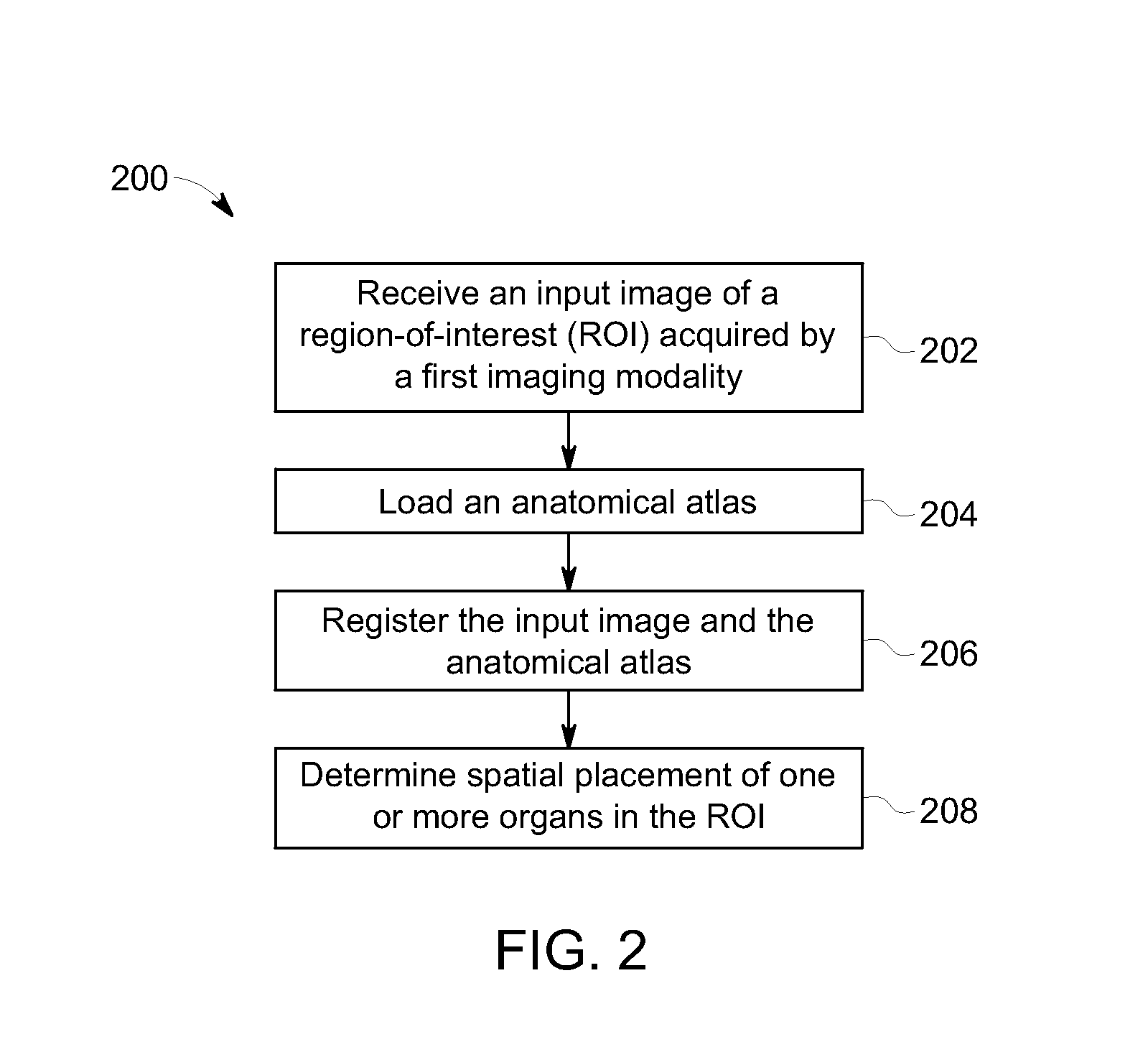
Methods and systems for determining a transformation function to automatically register different modality medical images
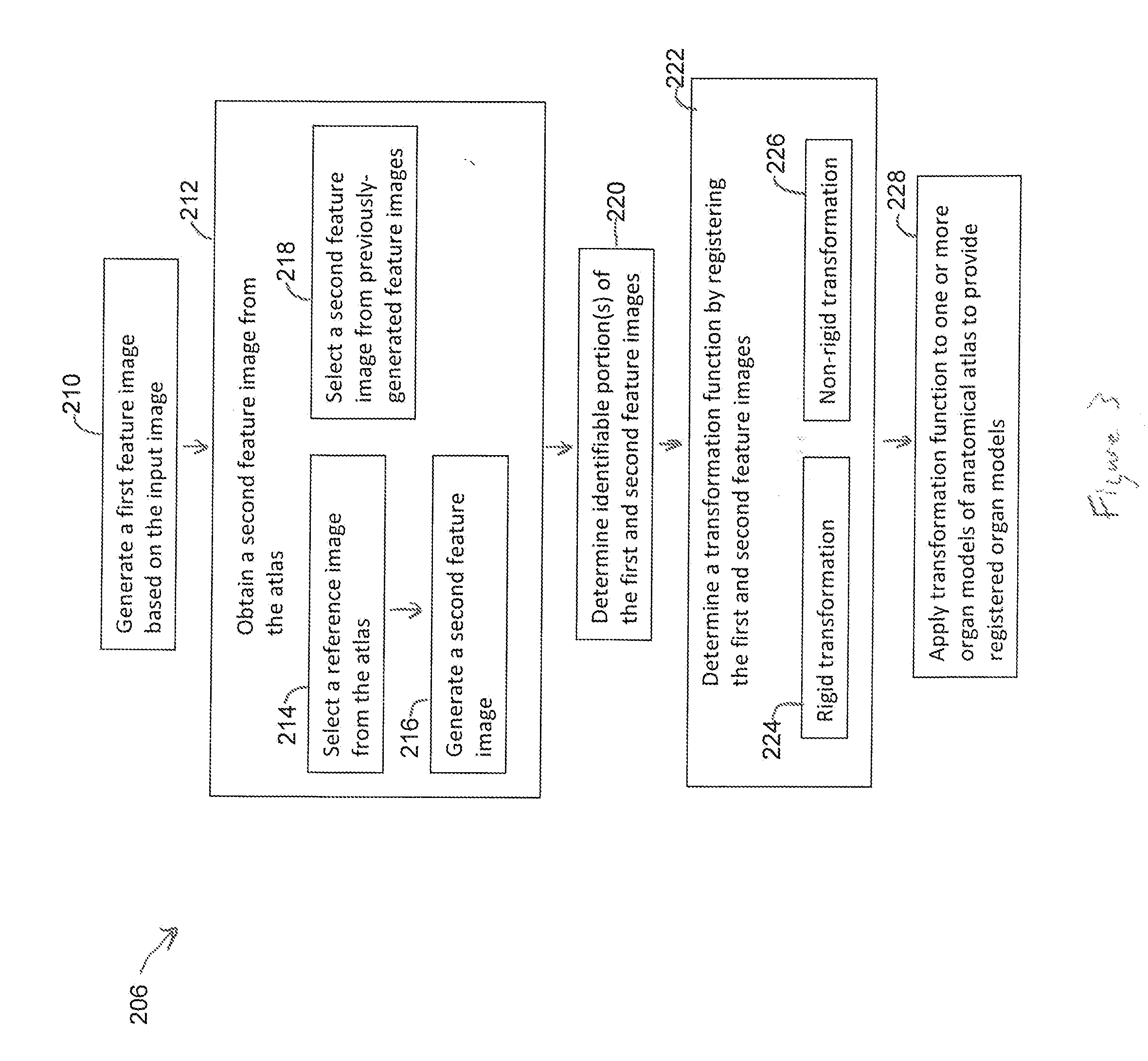
A method that includes receiving an input image of a region of interest (ROI) of an individual. The input image is a medical image acquired by a first imaging modality. The method also includes generating a first feature image based on the input image. The first feature image includes a designated anatomical feature of the ROI. The method also includes obtaining an anatomical atlas. The atlas has a reference image of the ROI of at least one other individual and an organ model. The reference image is a medical image that is acquired by a second imaging modality that is different from the first imaging modality. The method also includes determining a transformation function by registering the first feature image with a second feature image that is based on the reference image and includes the designated anatomical feature.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Intelligent atlas for automatic image analysis of magnetic resonance imaging
A non-invasive imaging system, including an imaging scanner suitable to generate an imaging signal from a tissue region of a subject under observation, the tissue region having at least one substructure; a signal processing system in communication with the imaging scanner to receive the imaging signal from the imaging scanner; and a data storage unit in communication with the signal processing system, wherein the data storage unit stores an anatomical atlas comprising data encoding spatial information of the at least one substructure in the tissue region, and a pathological atlas corresponding to an abnormality of the tissue region, wherein the signal processing system is adapted to automatically identify, using the imaging signal, the anatomical atlas, and the pathological atlas, a presence of the abnormality or a pre-cursor abnormality in the subject under observation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Visualizing surgical trajectories
ActiveUS8831307B2Simple structureSurgical navigation systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionAnatomical structures3d image
A method is provided for visualizing a surgical trajectory (32, 101, 42, 46, 47). The method comprises steps of receiving (71) 3D imaging information (31) of a region to undergo surgery and combining (72) the received 3D imaging information (31) with data from a digitized anatomical atlas. As a result, a combined map of the region to undergo surgery is obtained. The combined map comprises expected positions of anatomical structures (102, 103, 104) in the region to undergo surgery. The method further comprises steps of receiving (73) the surgical trajectory (32, 101, 42, 46, 47) for the surgery, determining (74) positions of intersections (43, 44) of the surgical trajectory (32, 101, 42, 46, 47) with the anatomical structures (102, 103, 104) and providing (75) the positions of the intersections (43, 44) in a coordinate system aligned with the surgical trajectory (32, 101, 42, 46, 47).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Surgical organ and lymph node specimen preservation record method and classification collection box
ActiveCN105173414BEasy to storeConvenient statisticsContainers preventing decayRigid containersSurgical operationLymphatic Spread
The invention relates to the medical field, in particular to a method for storing and recording surgical organs and lymph node specimens and a classification collection box. A surgical organ and lymph node specimen classification collection box includes a staging box I and a staging box II; the upper surface of the staging box I is divided into a primary tumor storage area and a distant metastasis storage area, and the primary tumor storage area is provided with an organ Specimen storage tank, the upper surface of the staging box II is provided with anatomical atlas, and the upper surface of the staging box II is also provided with a plurality of lymph node specimen storage tanks; a method for storing and recording surgical organs and lymph node specimens uses surgical organs and Lymph node specimen classification collection box; put the removed distant metastatic tissue into the distant metastatic storage tank, and then paste the corresponding label near the distant metastatic storage tank, and mark the distant metastatic tissue on the label Specific sampling locations in corresponding sampling organs. The invention can comprehensively and detailedly record the related information of the surgical specimen.
Owner:王洛 +1
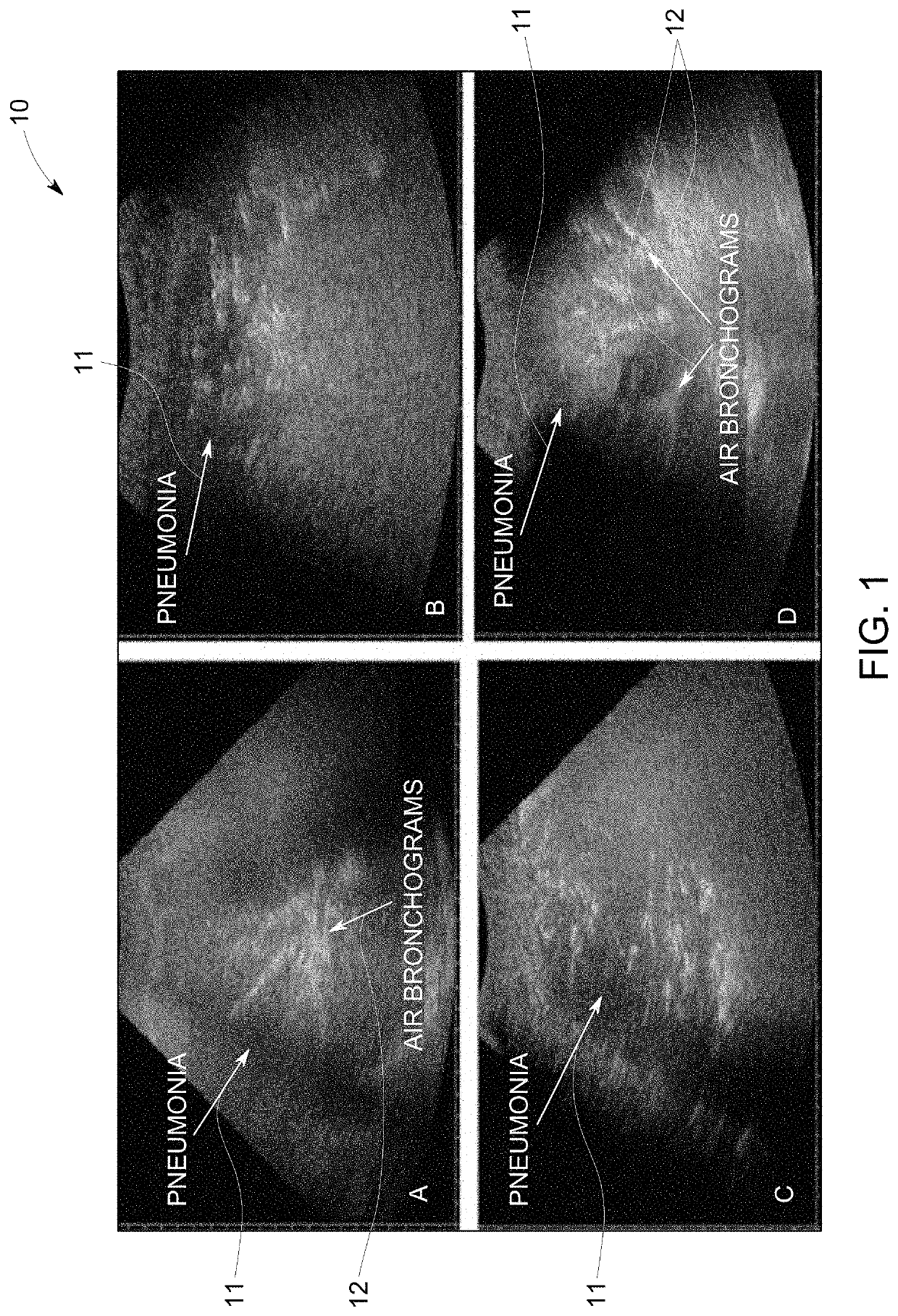
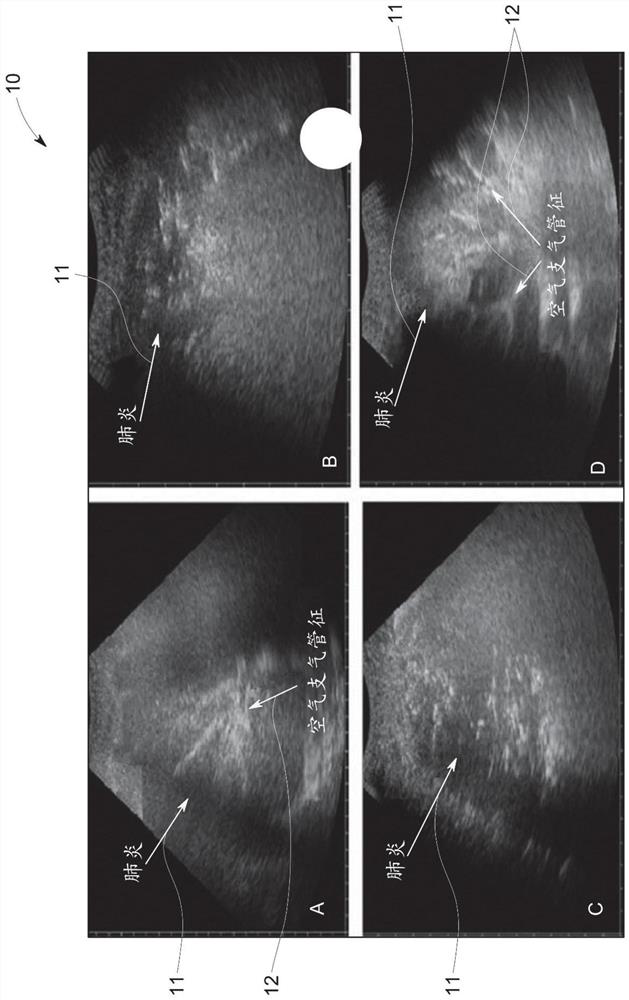
Guided lung coverage and automated detection using ultrasound devices
Systems and methods for guided lung coverage and automated detection using ultrasound devices are disclosed. The method for guided coverage and automated detection of pathologies of a subject includes positioning an ultrasound probe on a region of the subject body to be imaged. The method includes capturing a video of the subject and processing the video to generate a torso image of the subject and identify location of the ultrasound probe on the subject body. The method includes registering the video to an anatomical atlas to generate a mask of the region of the subject body comprising a plurality of sub-regions of the subject body to be imaged and superimposing the mask over the torso image. The method further includes displaying an indicator corresponding to a location of the each of the plurality of the sub-regions on the torso image. The method further includes displaying the relative position of the ultrasound probe with respect to the indicator corresponding to the location of the each of the plurality of plurality of sub-regions of the subject body to be imaged.
Owner:GE PRECISION HEALTHCARE LLC
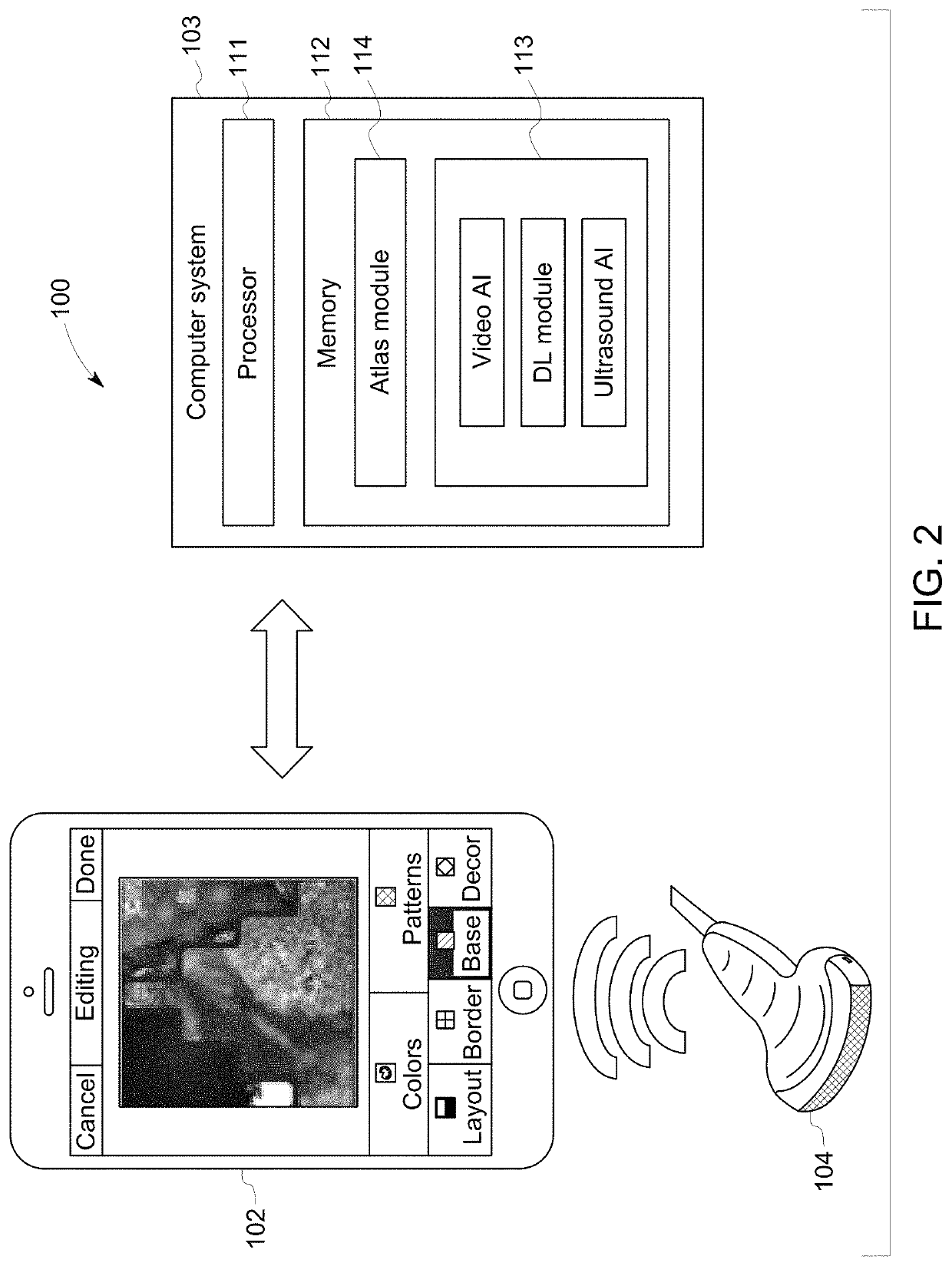
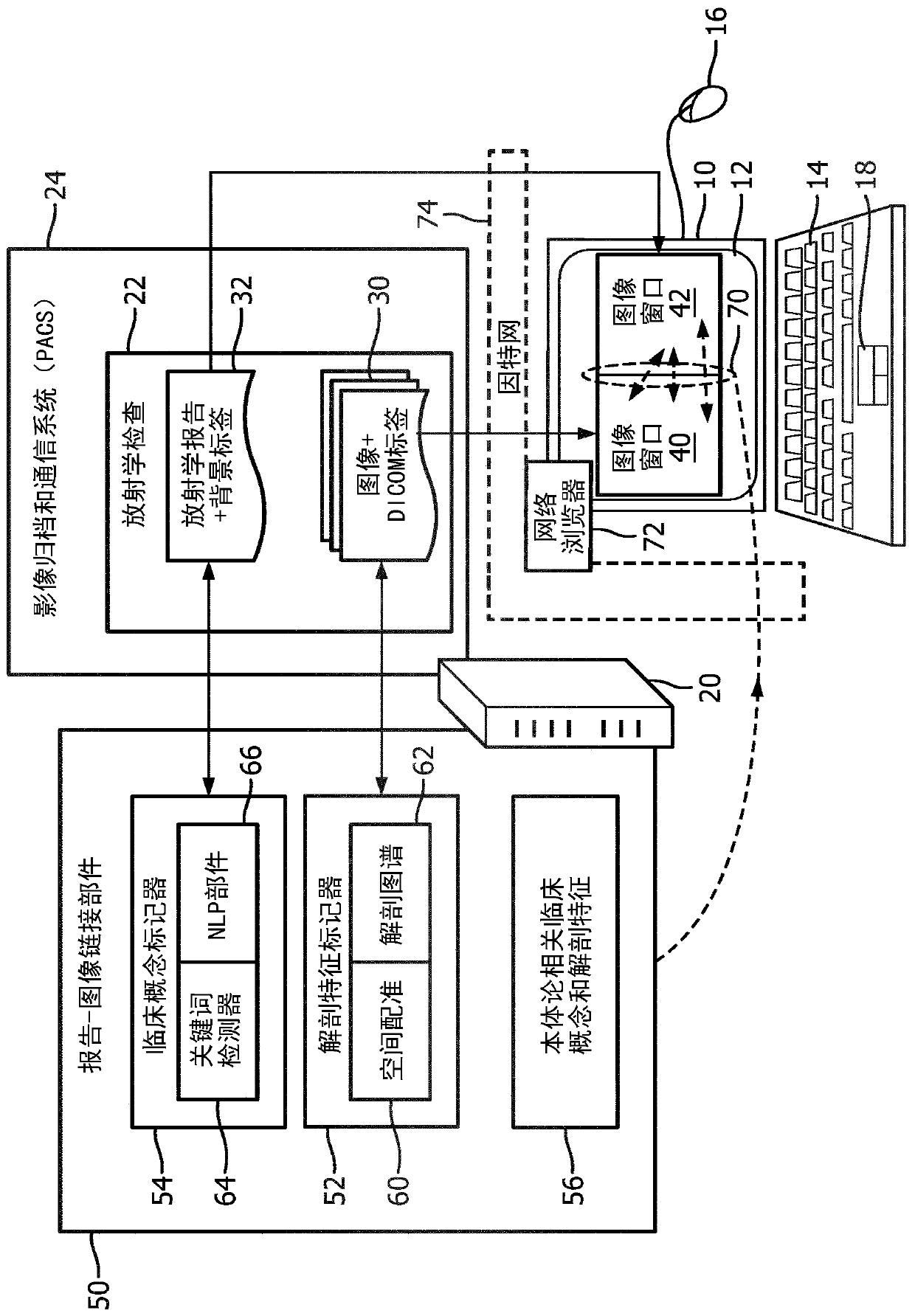
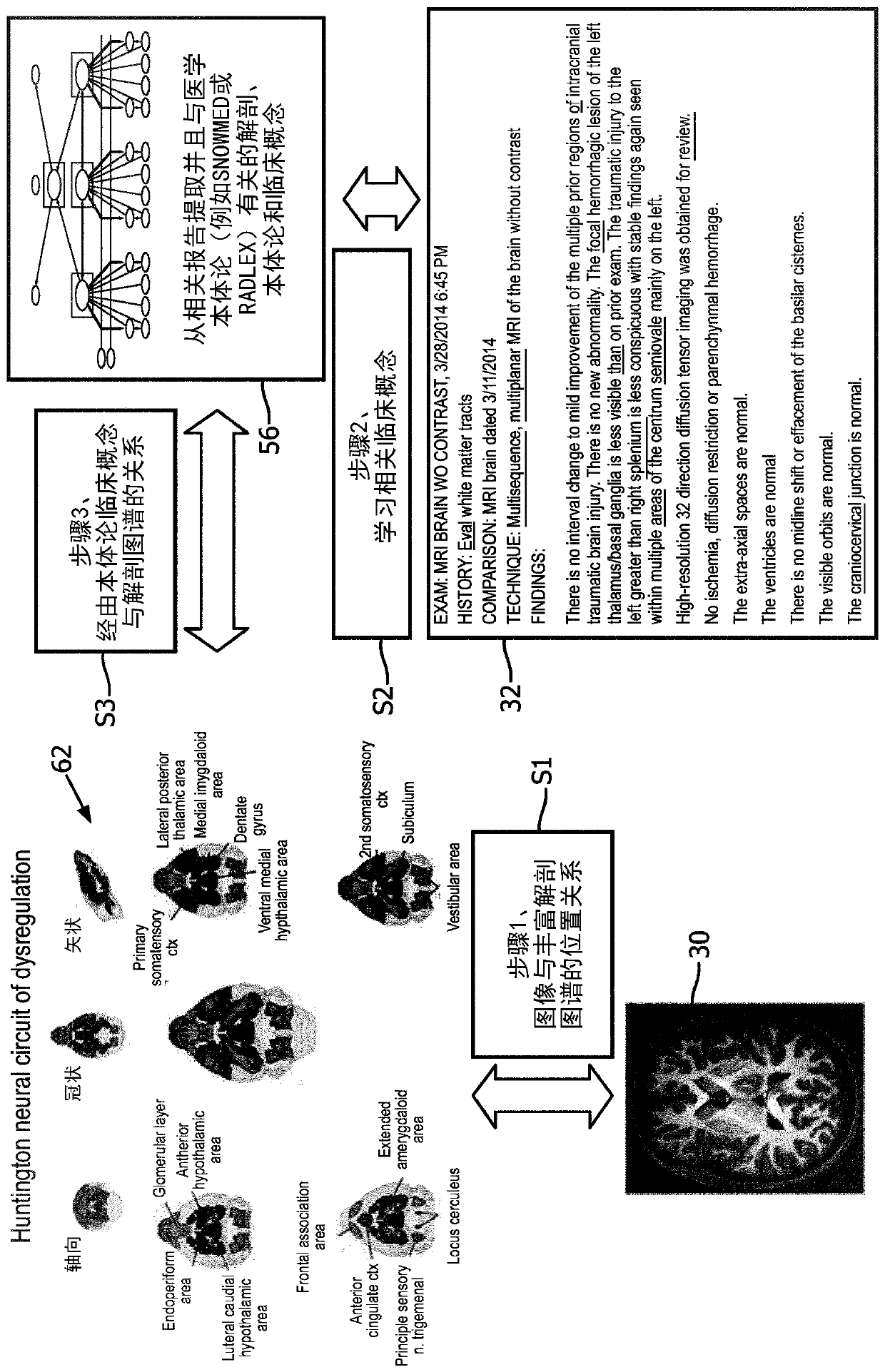
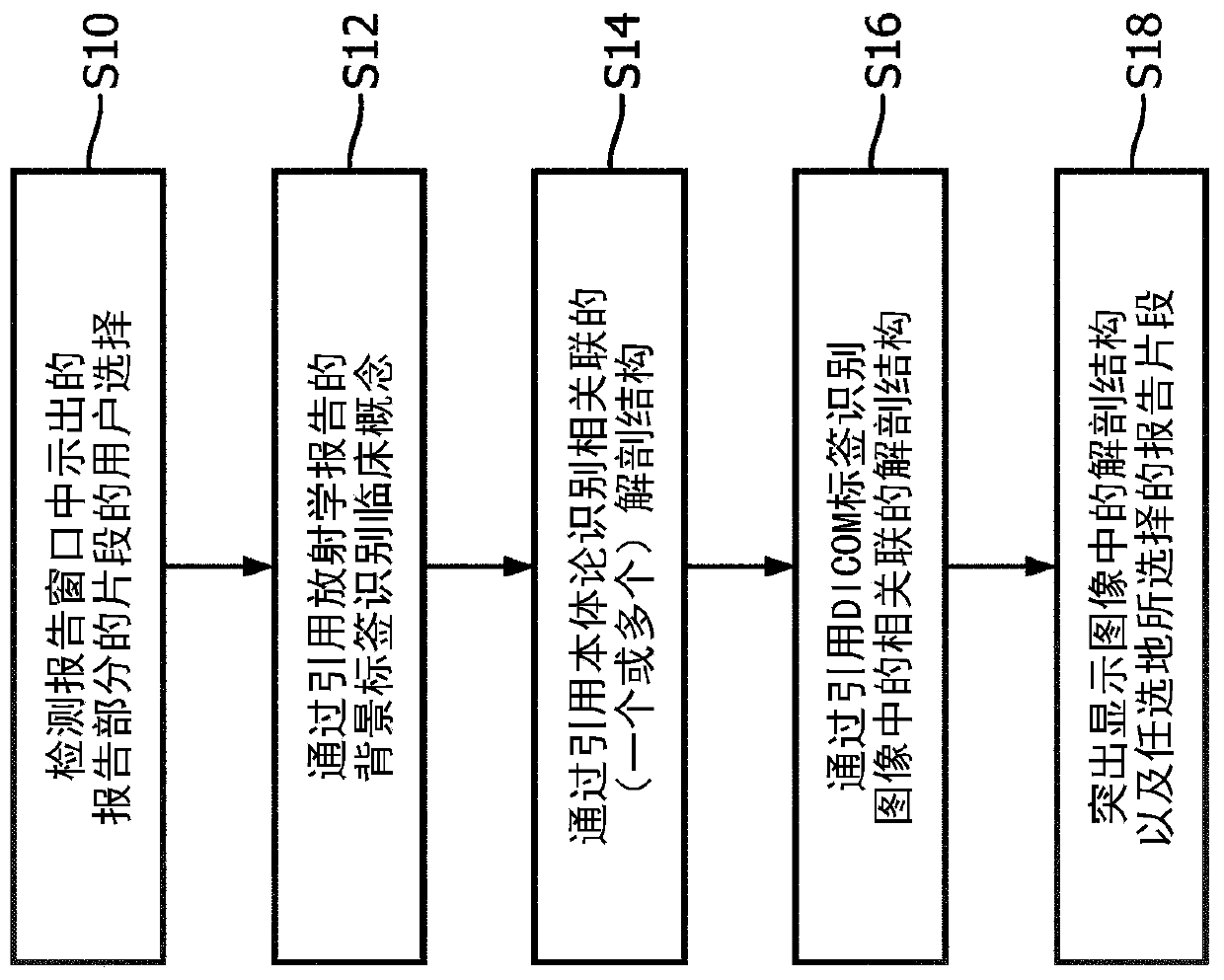
Holistic patient radiology viewer
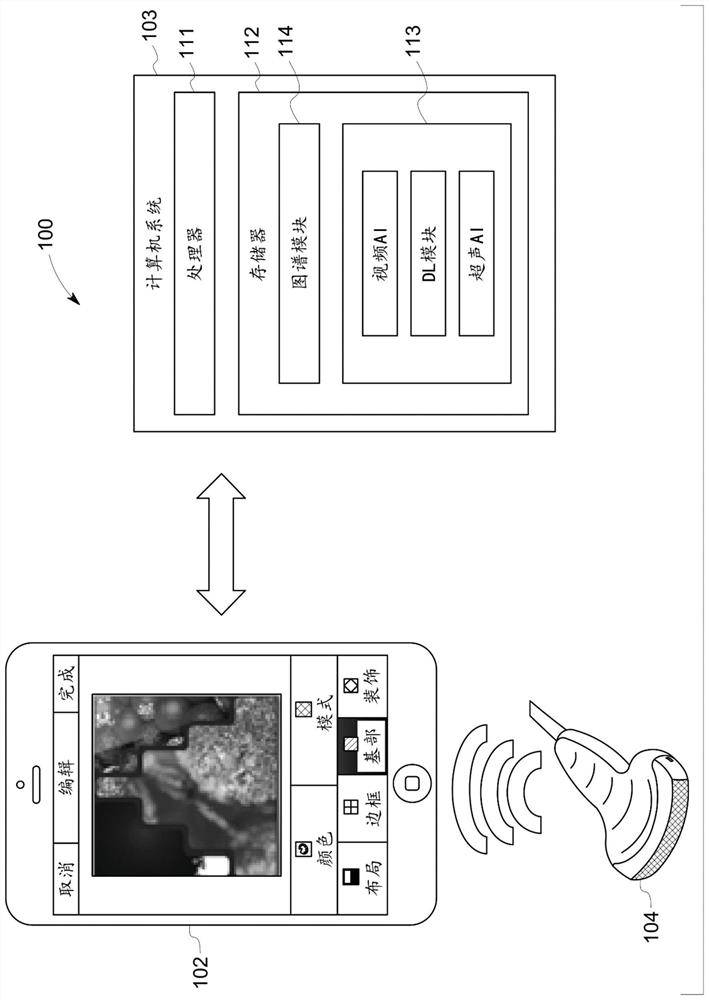
PendingCN110537227AImprove understandingMedical communicationMedical data miningNuclear medicineAnatomical atlas
A radiology viewer includes at least one electronic processor (10, 20), at least one display (12), and at least one user input device (14, 16, 18). The display shows at least a portion of a radiologyimage (30) in an image window (40), and at least a portion of a radiology report (32) in a report window (42). A selection is received of an anatomical feature shown in the image window, and a corresponding passage of the radiology report is identified and highlighted in the report window. A selection is received of a passage of the radiology report shown in the report window, and a correspondinganatomical feature of the at least one radiology image is identified and highlighted in the image window. The highlighting operations use image anatomical feature tags and report clinical concept tagsgenerated using a medical ontology (56) and an anatomical atlas (62).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
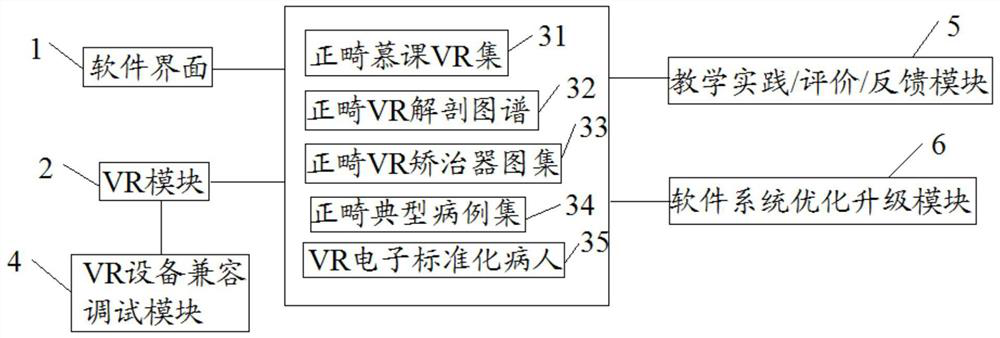
VR intelligent orthodontics teaching software
InactiveCN112258916ARealize intelligenceWork around application limitationsCosmonautic condition simulationsImage data processingHuman–computer interactionStandardize patient
The invention discloses VR intelligent orthodontics teaching software, which comprises a software interface, a VR module, a teaching software database, a VR equipment compatible debugging module, a teaching practice / evaluation / feedback module and a software system optimizing and upgrading module, wherein the teaching software database comprises an orthodontic mousse VR set, an orthodontic VR anatomical atlas, an orthodontic VR appliance atlas, an orthodontic typical case set and a VR electronic standardized patient, the software interface, the VR module, the teaching practice / evaluation / feedback module and the software system optimization and upgrading module are all connected with the teaching software database, and the VR equipment compatible debugging module is connected with the VR module. According to the invention, the application limitation of the prior art is overcome, teaching, learning, examination and evaluation integrated VR intelligent teaching software for oral cavity professional courses is provided, and a foundation is laid for realizing intellectualization and teaching resource equalization of oral cavity professional course education.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of physical specimen 3D printing method
ActiveCN110992804BEasy to observeEasy to learnAdditive manufacturing apparatusEducational modelsImaging processingComputer printing
The invention relates to a 3D printing method for physical specimens, comprising the following steps: (1) antiseptic treatment, carrying out antiseptic treatment on selected physical specimens; (2) anatomical production, producing required specimens according to the anatomical atlas; (3) bleaching and rinsing , bleach the specimen, and then rinse it with tap water; (4) trimming, trimming the anatomically prepared specimen; (5) scanning, using 3D scanning tools to scan the above specimen; (6) specimen image processing, using a computer to The scanned image is repaired and synthesized; (7) Printing, using a 3D printer to print the specimen. The invention uses real biological specimens as raw materials to print specimens, the shape and structure are intact and unchanged, the sense of reality is strong, the process is simple, and the time is short; different materials can be used for mass production, which solves the inconvenience caused by the shortage of physical specimens to experimental teaching.
Owner:河南中博科技有限公司
Guided lung coverage and automatic detection using ultrasound device
The invention discloses a system and method for guided lung coverage and automatic detection using an ultrasound device. A method for guided automatic coverage and pathology detection of a subject includes positioning an ultrasound probe on a region of a body of the subject to be imaged. The method includes capturing a video of a subject and processing the video to generate a torso image of the subject and identifying a location of an ultrasound probe on a body of the subject. The method includes registering the video with the anatomical atlas to generate a mask of a region of the subject's body to be imaged, the region including a plurality of sub-regions of the subject's body and superimposing the mask over the torso image. The method further includes displaying, on the torso image, an indicator corresponding to a location of each of the plurality of sub-regions. The method further includes displaying a relative position of the ultrasound probe relative to an indicator corresponding to a position of each of a plurality of sub-regions of the subject's body to be imaged.
Owner:GE PRECISION HEALTHCARE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com