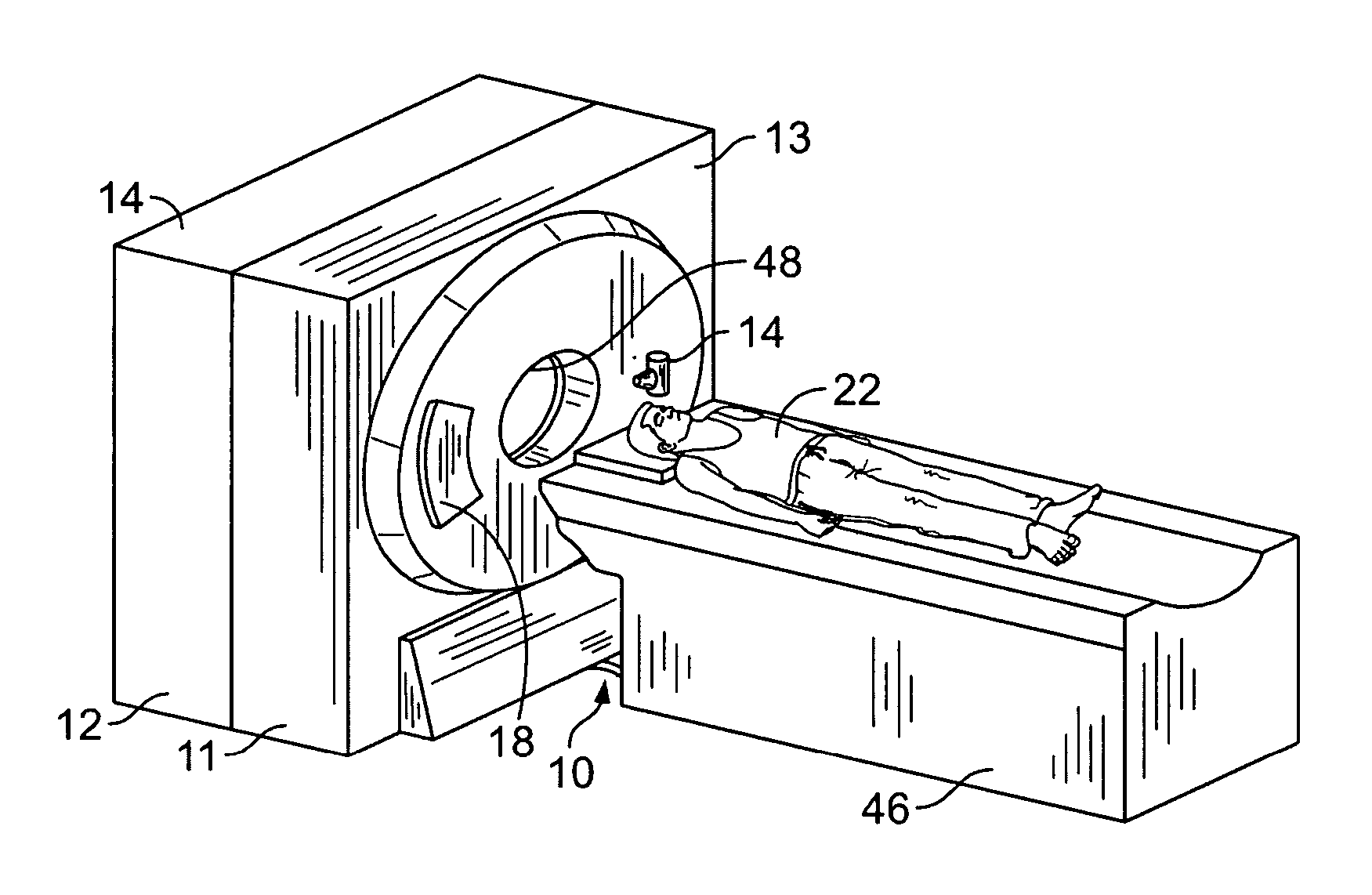
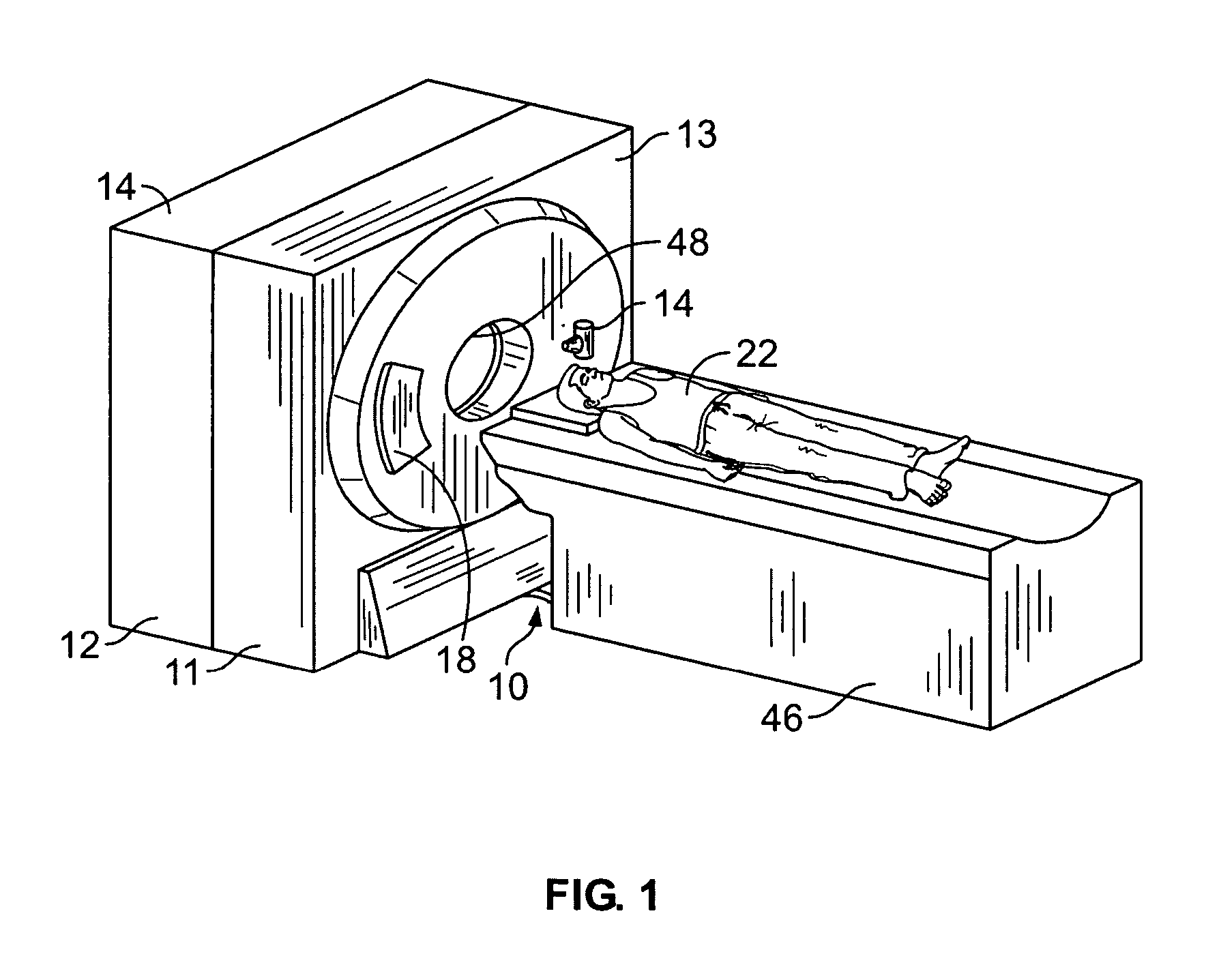
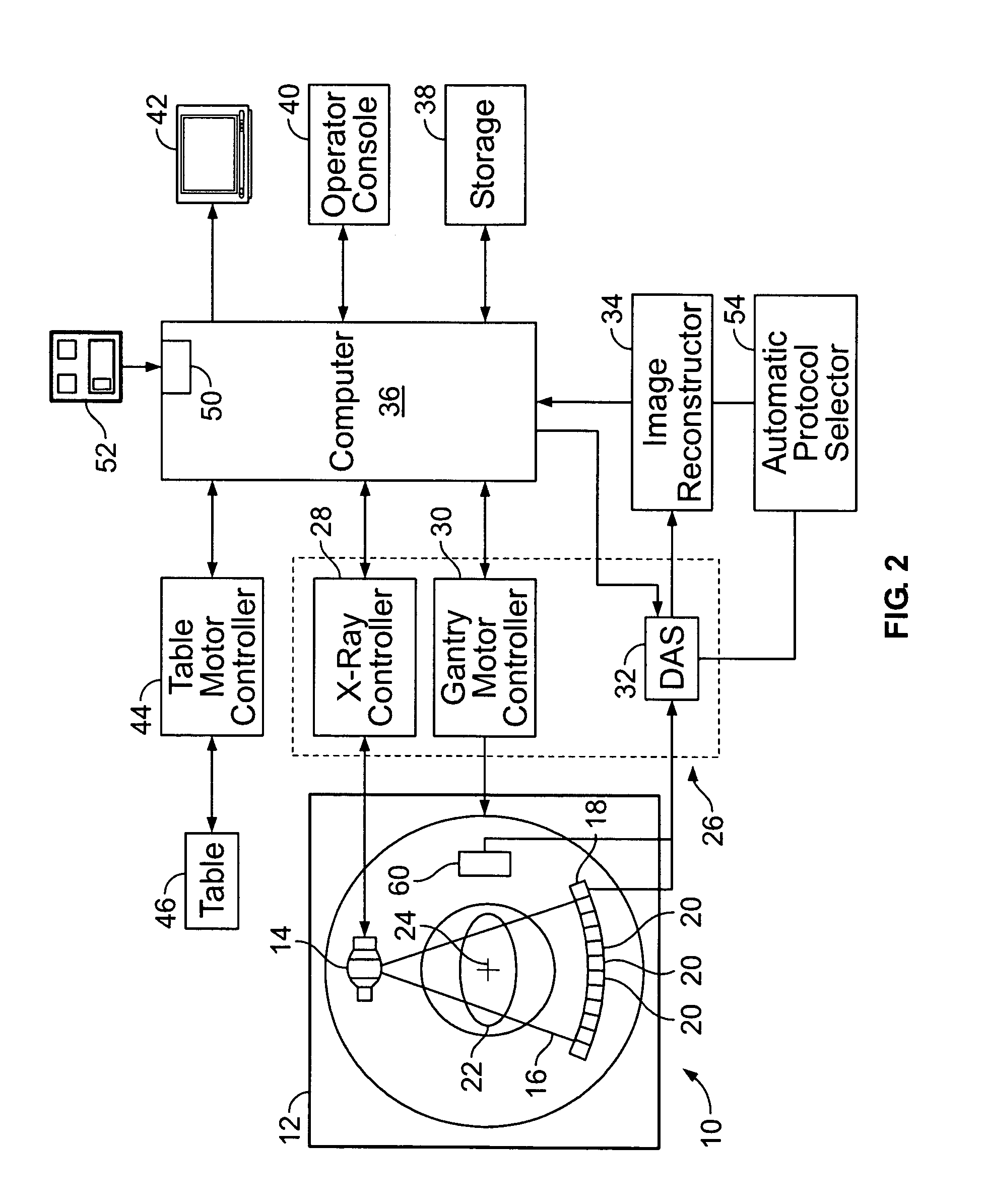
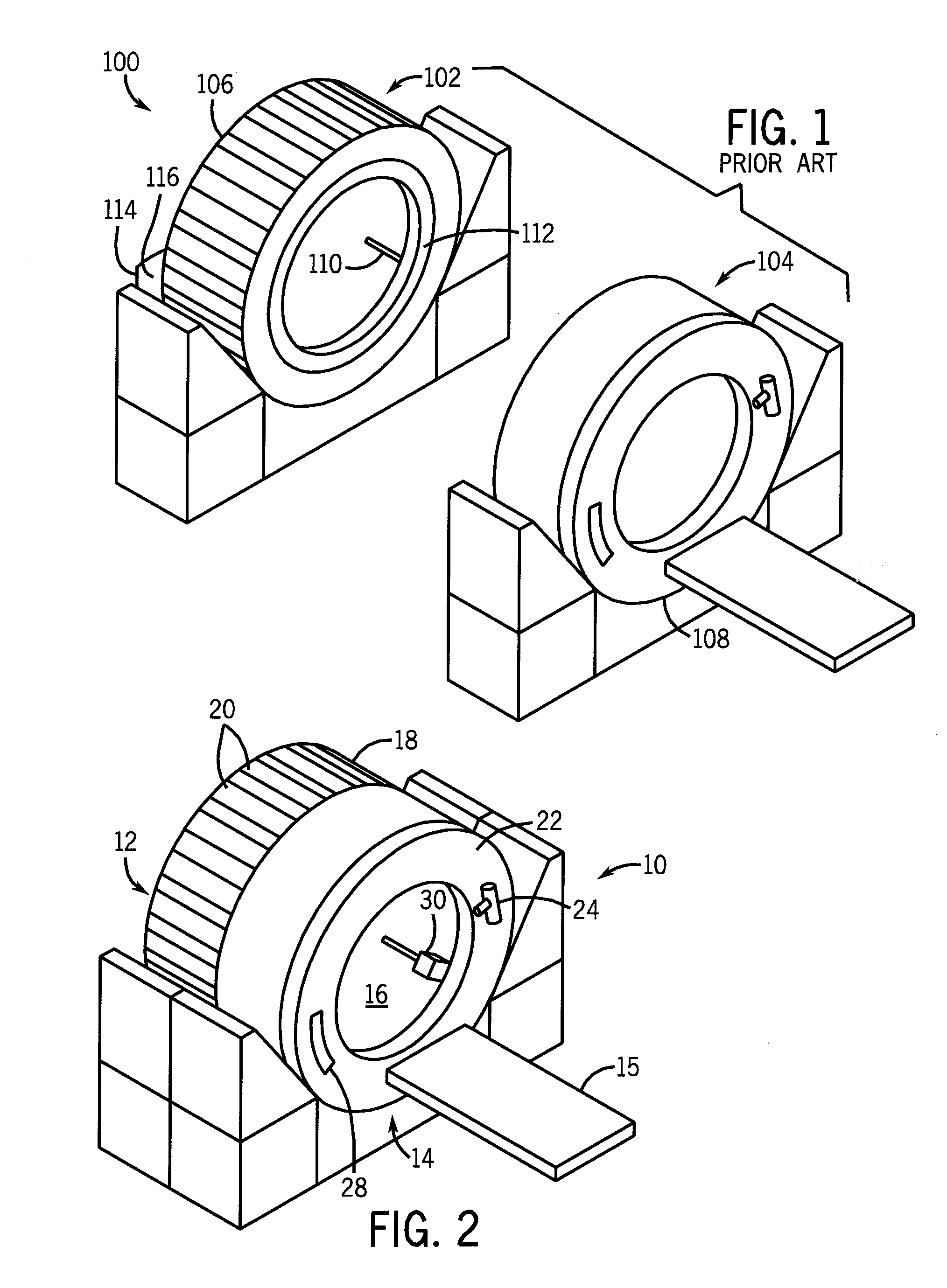
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
625 results about "Positron emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Positron emission or beta plus decay (β⁺ decay) is a subtype of radioactive decay called beta decay, in which a proton inside a radionuclide nucleus is converted into a neutron while releasing a positron and an electron neutrino (νₑ). Positron emission is mediated by the weak force. The positron is a type of beta particle (β⁺), the other beta particle being the electron (β⁻) emitted from the β⁻ decay of a nucleus.
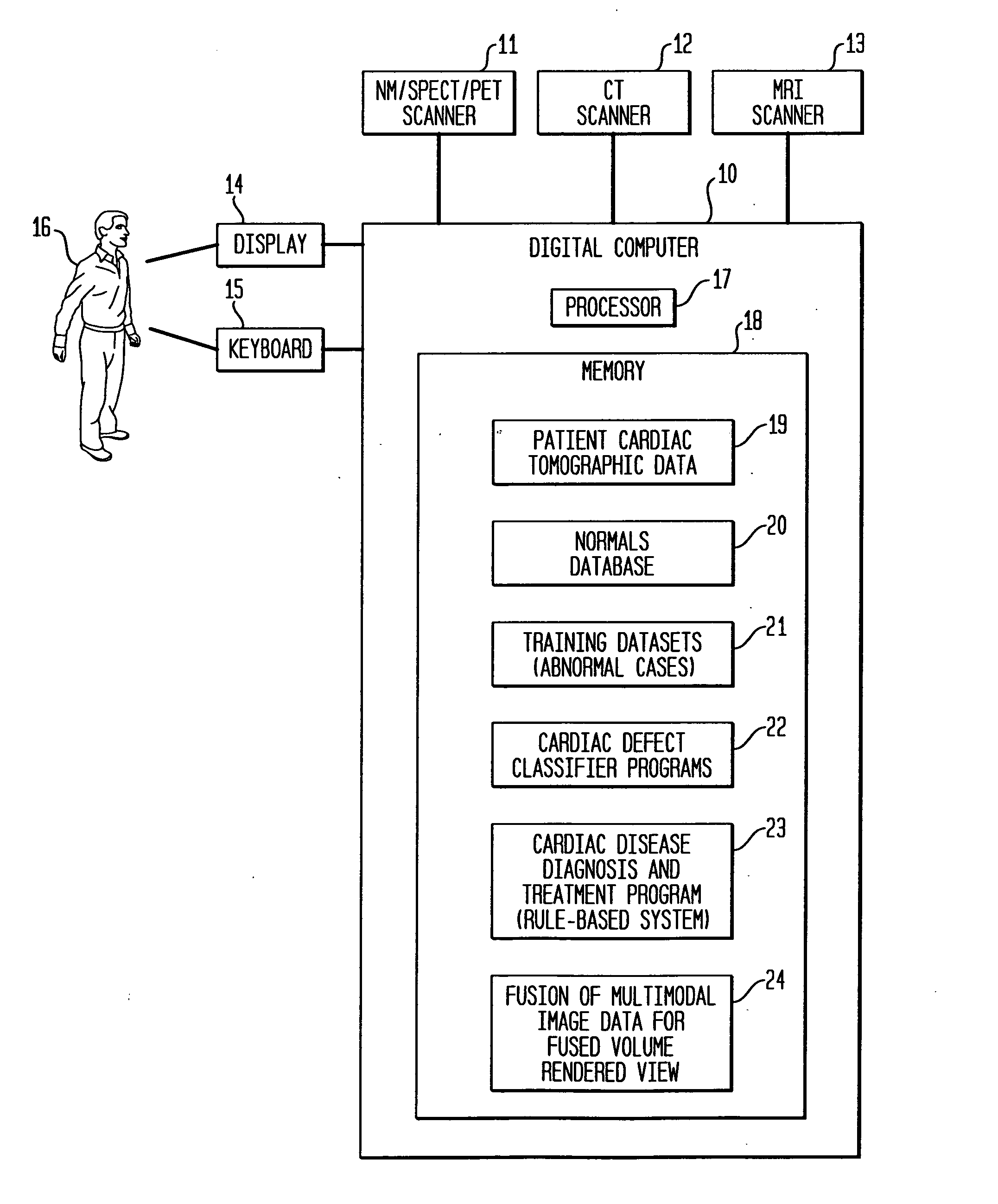
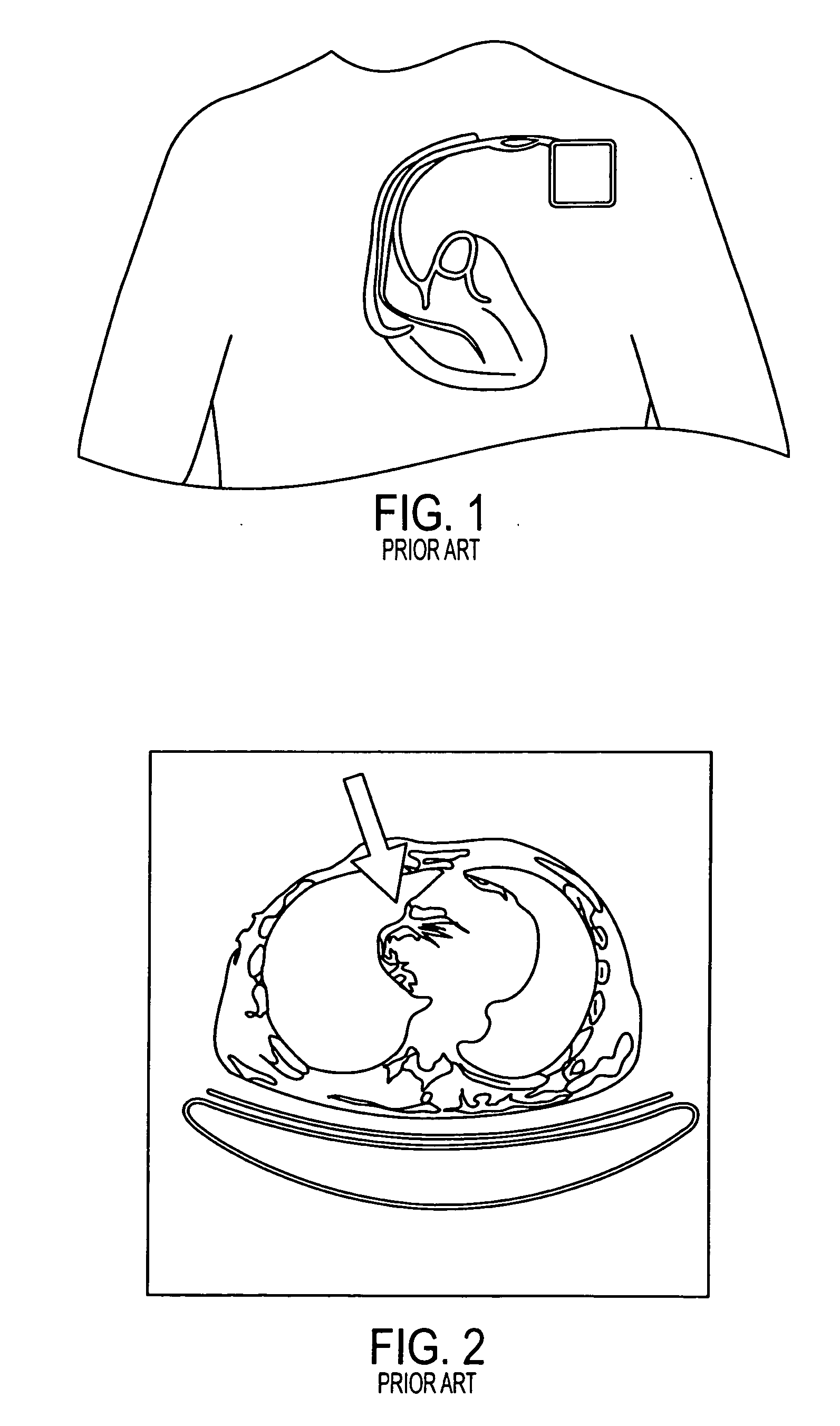
Dedicated display for processing and analyzing multi-modality cardiac data
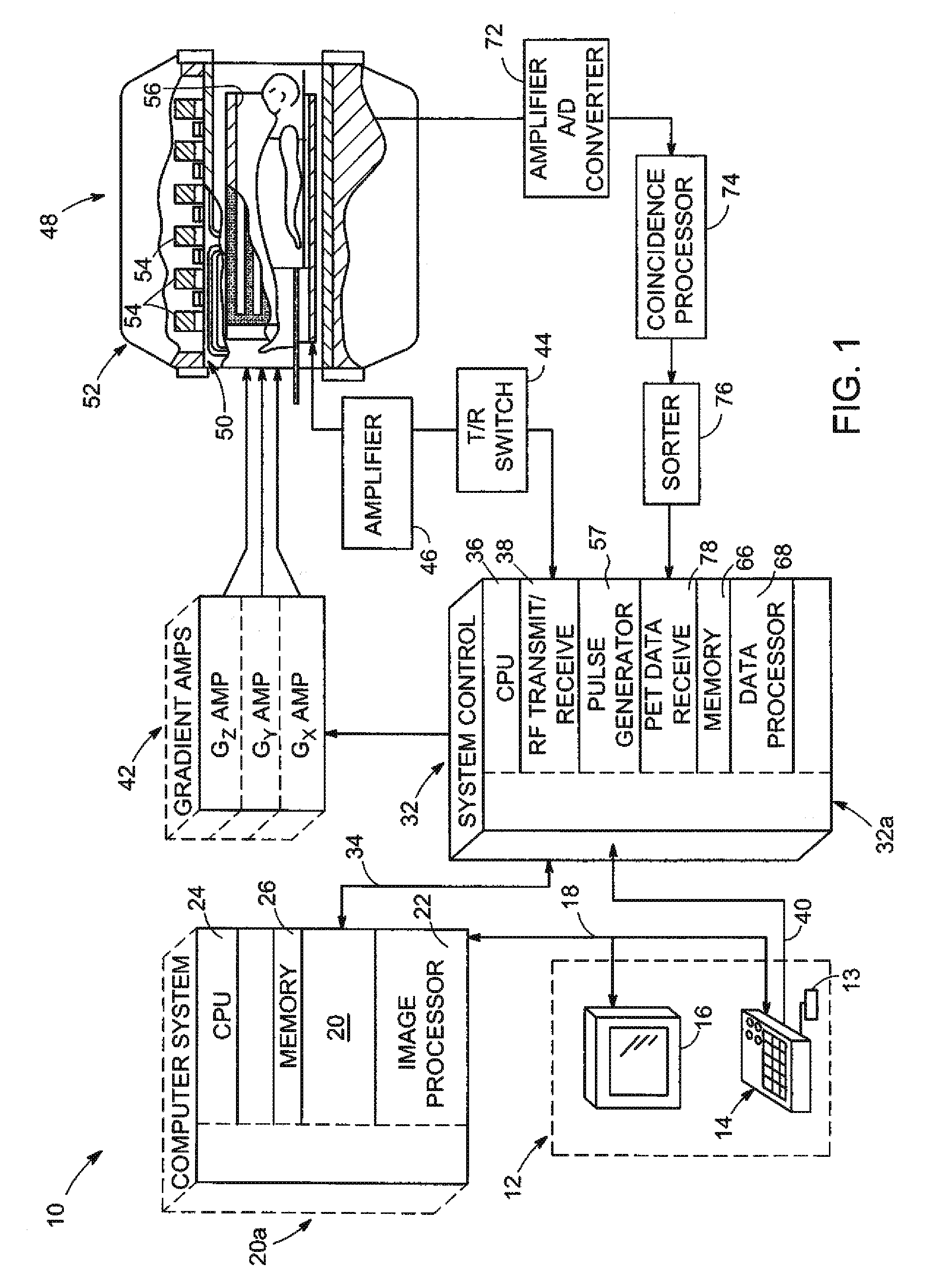
For diagnosis and treatment of cardiac disease, images of the heart muscle and coronary vessels are captured using different medical imaging modalities; e.g., single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), positron emission tomography (PET), electron-beam X-ray computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or ultrasound (US). For visualizing the multi-modal image data, the data is presented using a technique of volume rendering, which allows users to visually analyze both functional and anatomical cardiac data simultaneously. The display is also capable of showing additional information related to the heart muscle, such as coronary vessels. Users can interactively control the viewing angle based on the spatial distribution of the quantified cardiac phenomena or atherosclerotic lesions.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
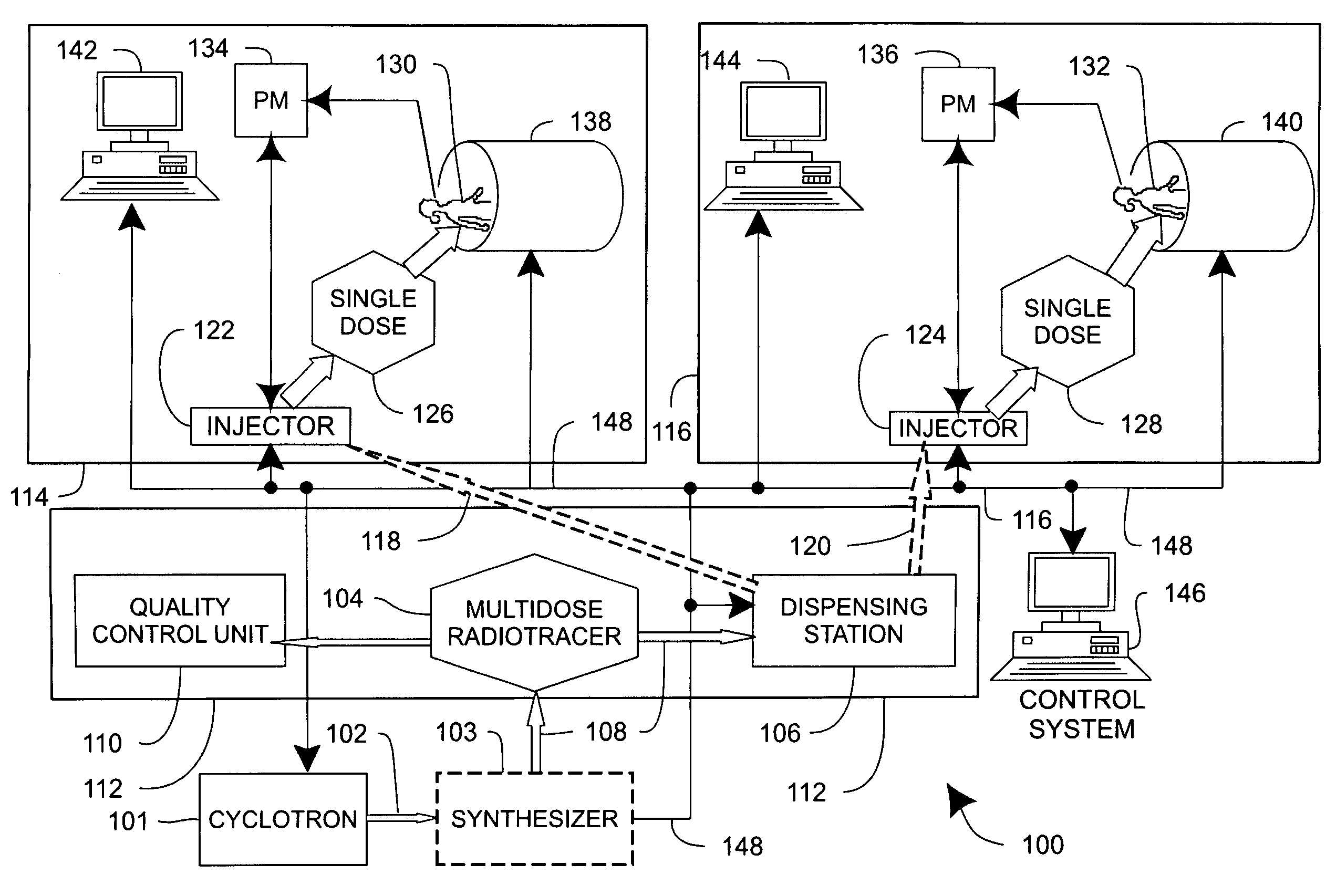
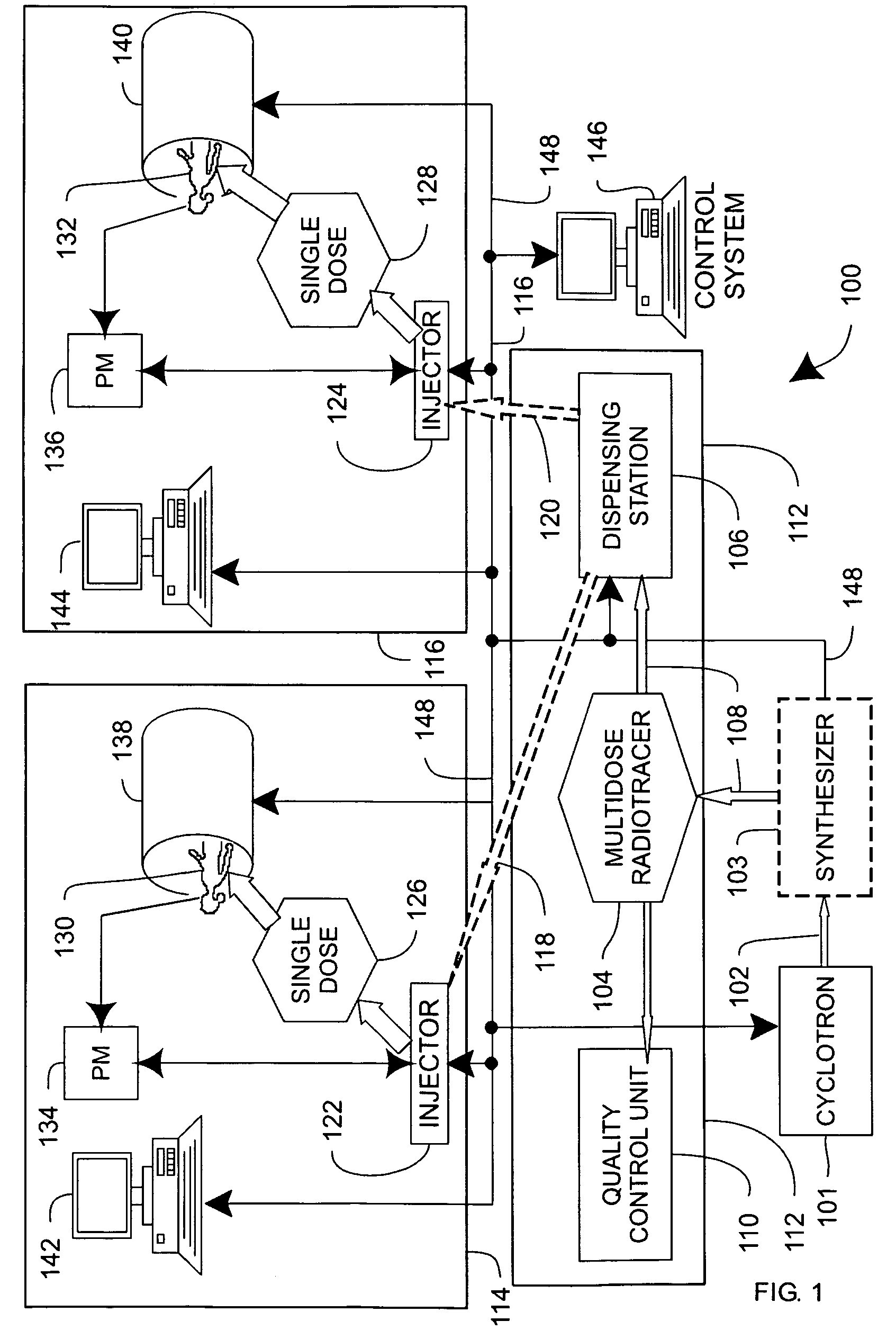
Systems, methods and apparatus for preparation, delivery and monitoring of radioisotopes in positron emission tomography
ActiveUS7734331B2Economy of scaleImprove distributionMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDrug and medicationsRadioactive tracerQuality control
In one aspect, systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which a dispensing station dispenses a large quantity of a radiotracer to one or more positron emission tomography imaging stations. In some aspects a quality control unit verifies the quality of the radiotracer. In some embodiments, components of the system are coupled by a local area network. In some aspects, each positron emission tomography imaging station includes an injector system, a physiological monitoring device, and a positron emission tomography scanner. All of the devices can be controlled by a computer system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
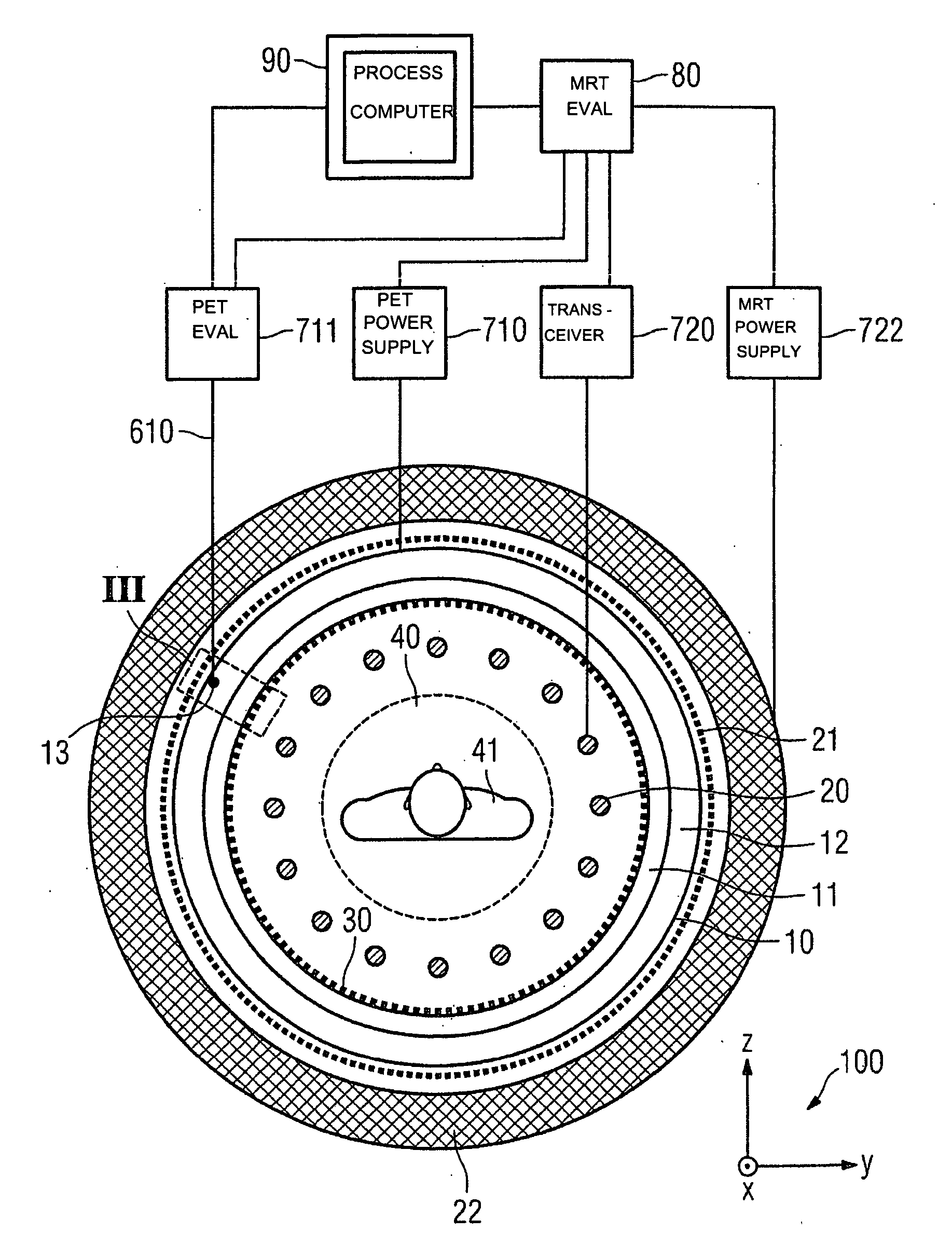
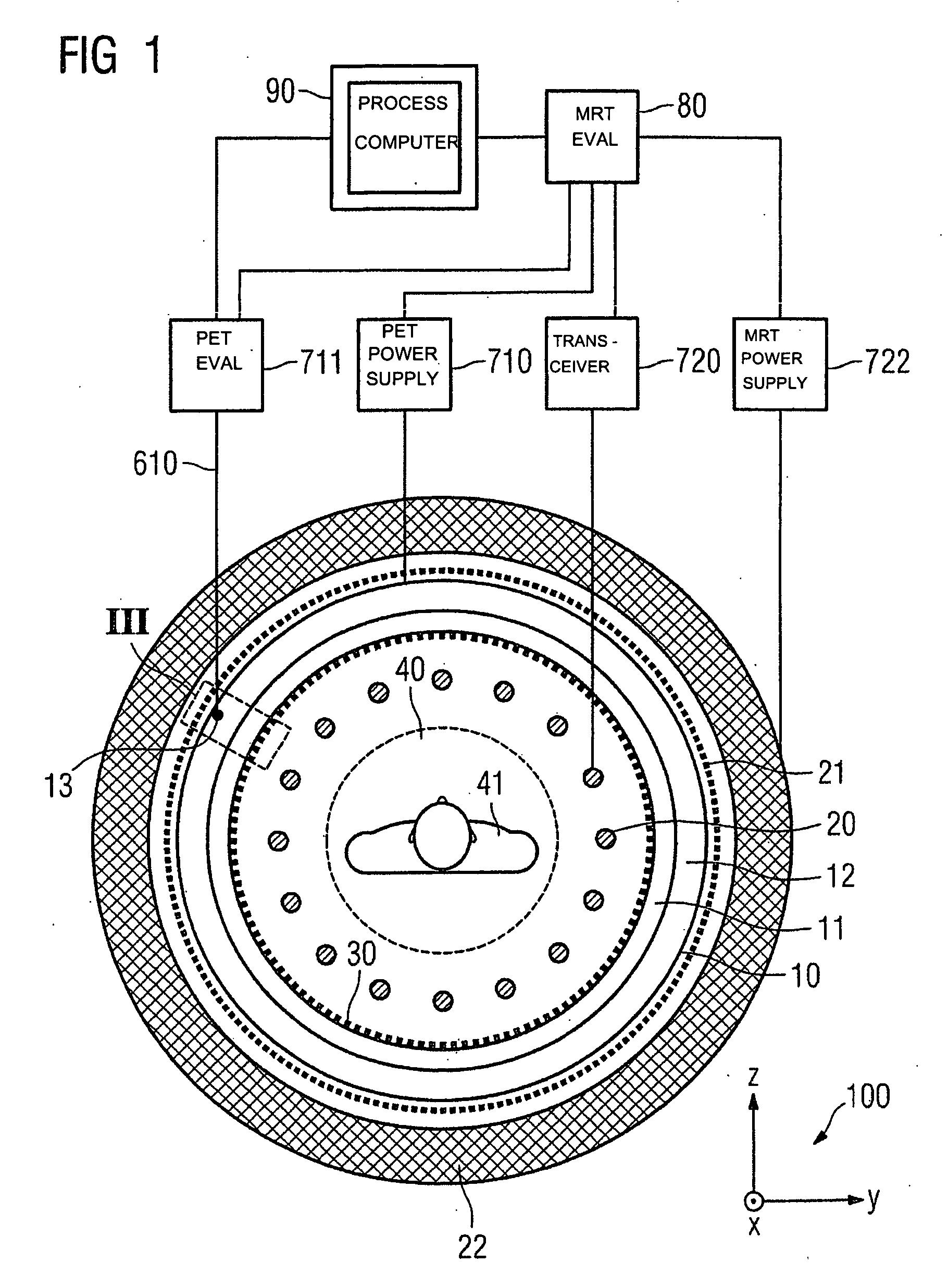
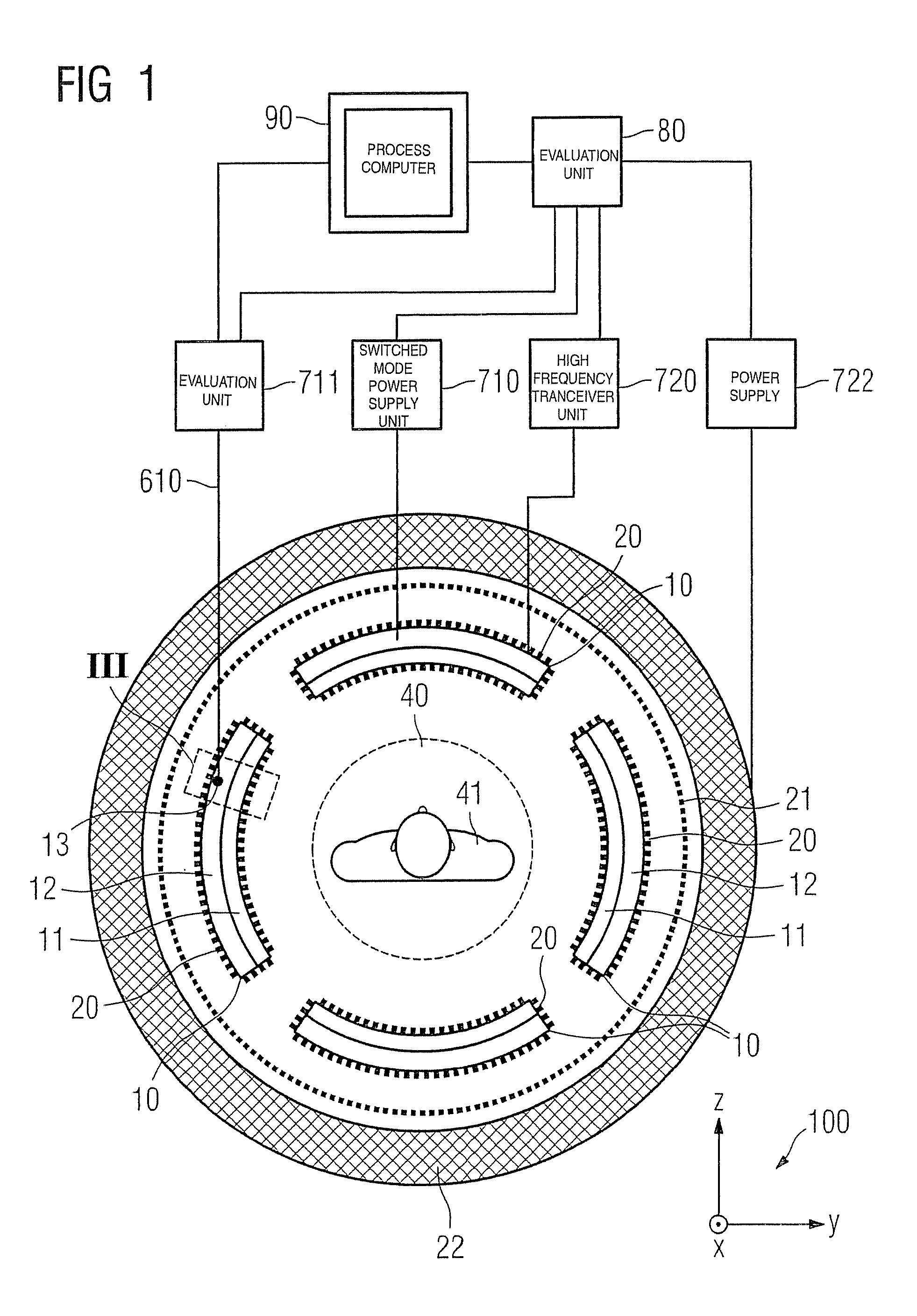
Combined positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance tomography unit
InactiveUS20060251312A1Save spaceShorten the timeMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionPositron emission tomography unitElectron
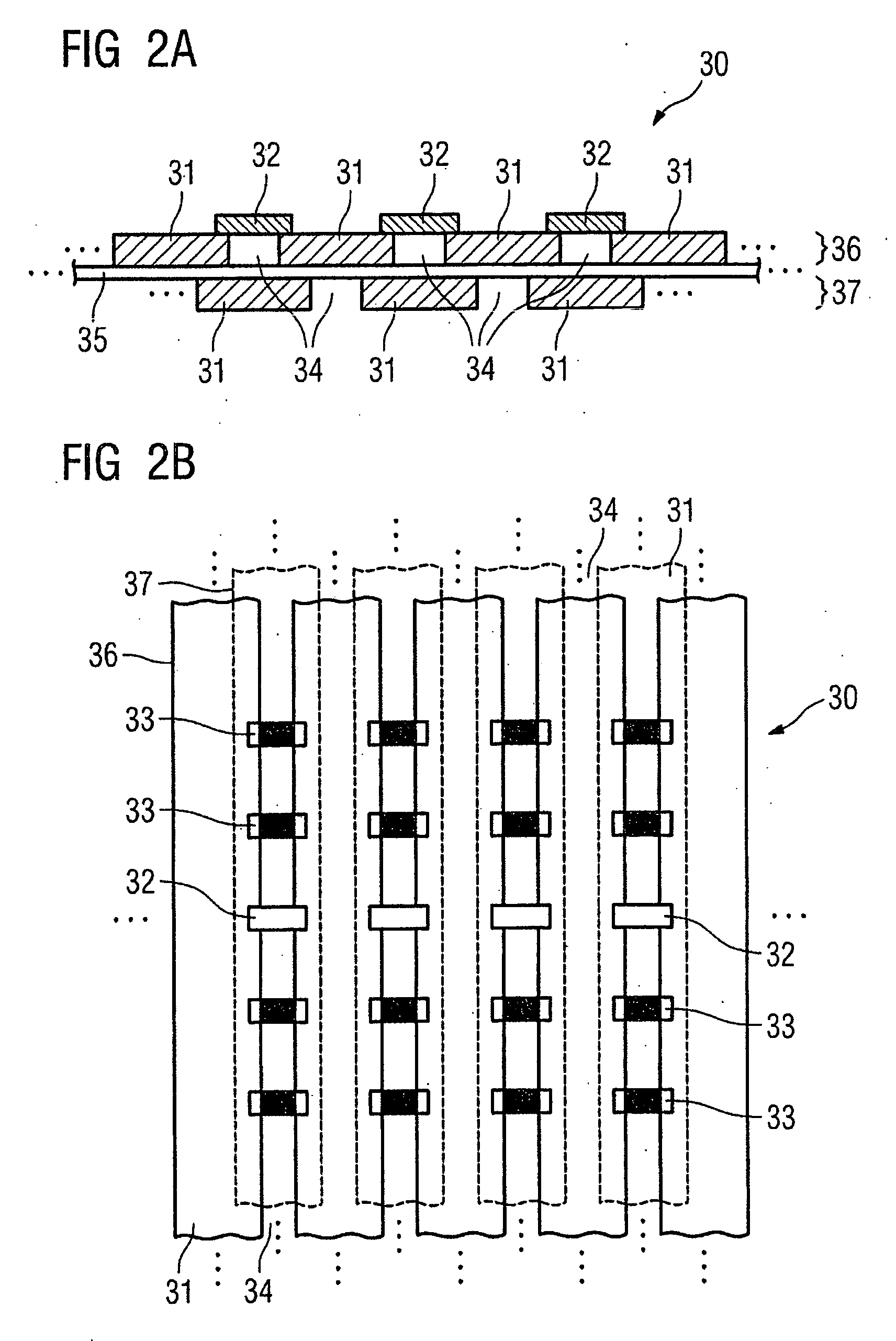
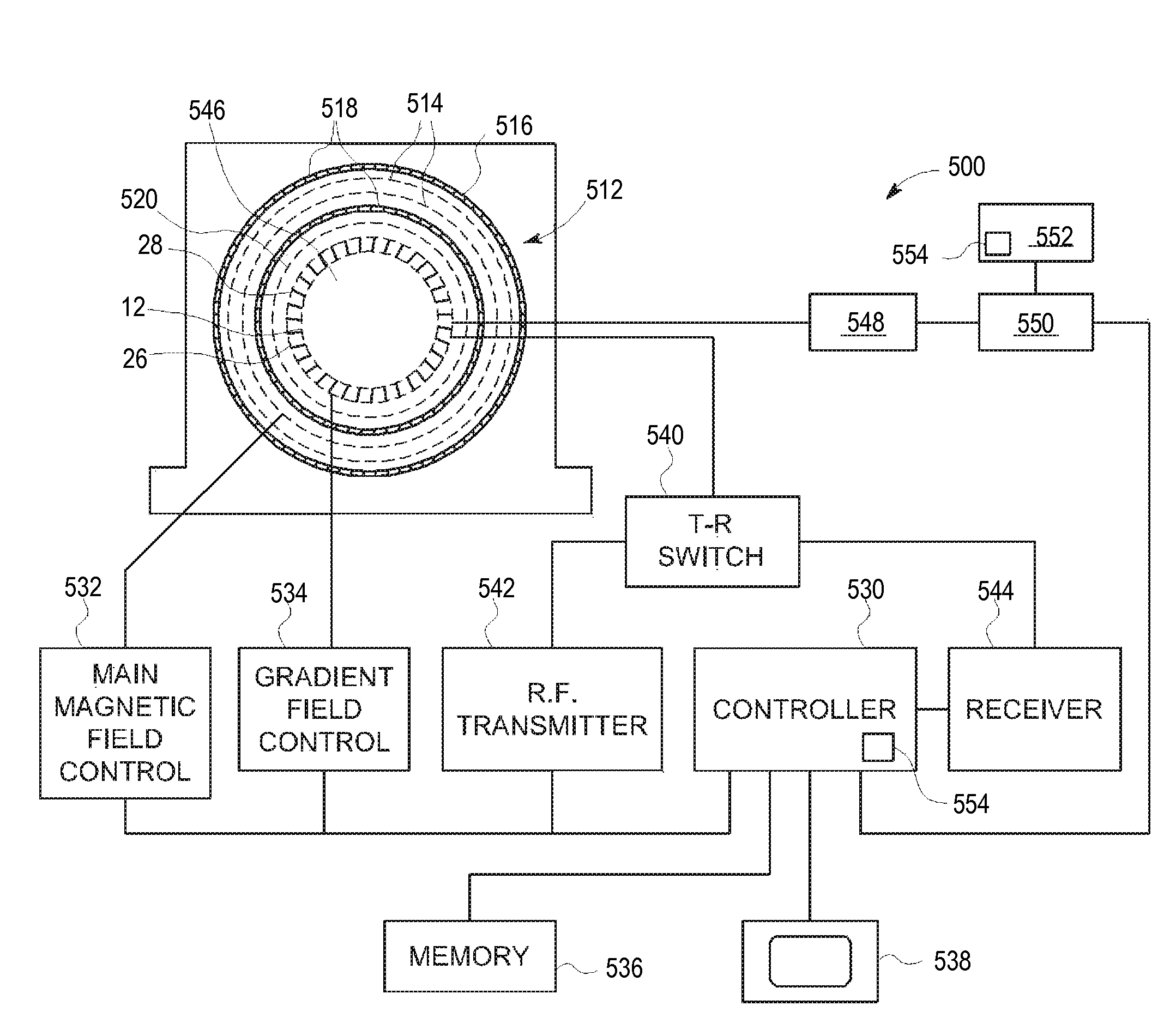
Combined positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance tomography unit for imaging an examination object in an examination space, comprising a positron emission tomography unit that has a unit part assigned to the examination space, and a first evaluation unit for evaluating the electric signals for a positron emission tomography image of the examination object. The unit part in this case comprises a gamma ray detector with an assigned electronics unit. Furthermore, the combined unit comprises a magnetic resonance tomography unit and a second evaluation unit for evaluating the magnetic resonance signals for a magnetic resonance image of the examination object. The magnetic resonance unit in this case has a high frequency antenna device as well as a gradient coil system, the high frequency antenna device being arranged nearer to the examination space than the gradient coil system, as well as a high frequency shield arranged between the gradient coil system and the high frequency antenna device. The positron emission tomography unit part is arranged in this case between the high frequency shield and the high frequency antenna device, and is provided, at least on the side facing the high frequency antenna device, with a shielding cover that is caused by the high frequency antenna device and is opaque to high frequency radiation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
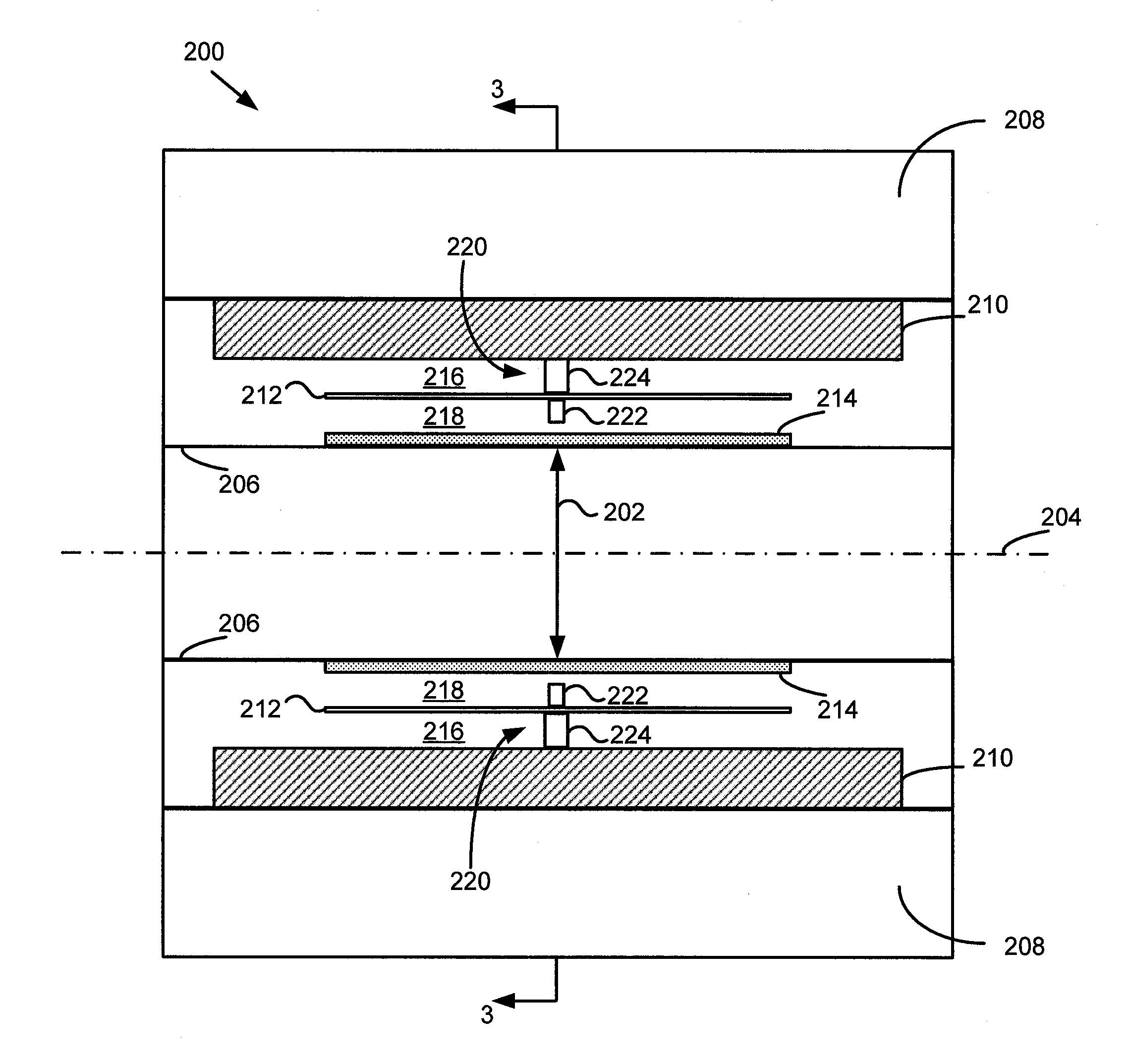
System and apparatus for detecting gamma rays in a pet/mri scanner
ActiveUS20080265887A1Material analysis by optical meansElectric/magnetic detectionPhotodetectorRadio frequency
A gamma ray detector ring for a combined positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system is integrated into a radio frequency (RF) coil assembly such that the detector ring is integrated with a RF shield. Each gamma ray detector in the detector ring includes a scintillator component that emits light when a gamma ray is detected and a photodetector component designed to be sensitive to the frequency of light produced by the scintillator. A RF shield may be integrated into a detector ring such that the RF shield is positioned between the scintillator and photodetector components of each detector, thereby saving valuable radial space within the imaging system. Multiple such detector rings may be located adjacent to one another to increase axial coverage and enable three-dimensional PET imaging techniques.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Labeling targeting agents with gallium-68 and gallium-67
InactiveUS7011816B2Safe and fastAccurate detectionOrganic active ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersElutionPositron emission tomographic
A method and compositions are described for labeling a targeting agent with Ga-68, in which eluate from an acid-eluted Ge-68 / Ga-68 generator is combined with a macrocycle-containing targetable agent. The labeling method and compositions disclosed ensure that a simple elution of gallium-68, taken directly from a generator, can be used without further manipulation to quantitatively label a macrocycle-containing targetable agent. The Ga-68 labeled targeting agent so produced is useful with specific targeting agents, and is most especially useful in a pretargeting method for positron emission tomographic detection.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Nuclear imaging using three-dimensional gamma particle interaction detection
InactiveUS20050023474A1High resolutionReduce uncertaintySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDetector arrayPerformed Imaging
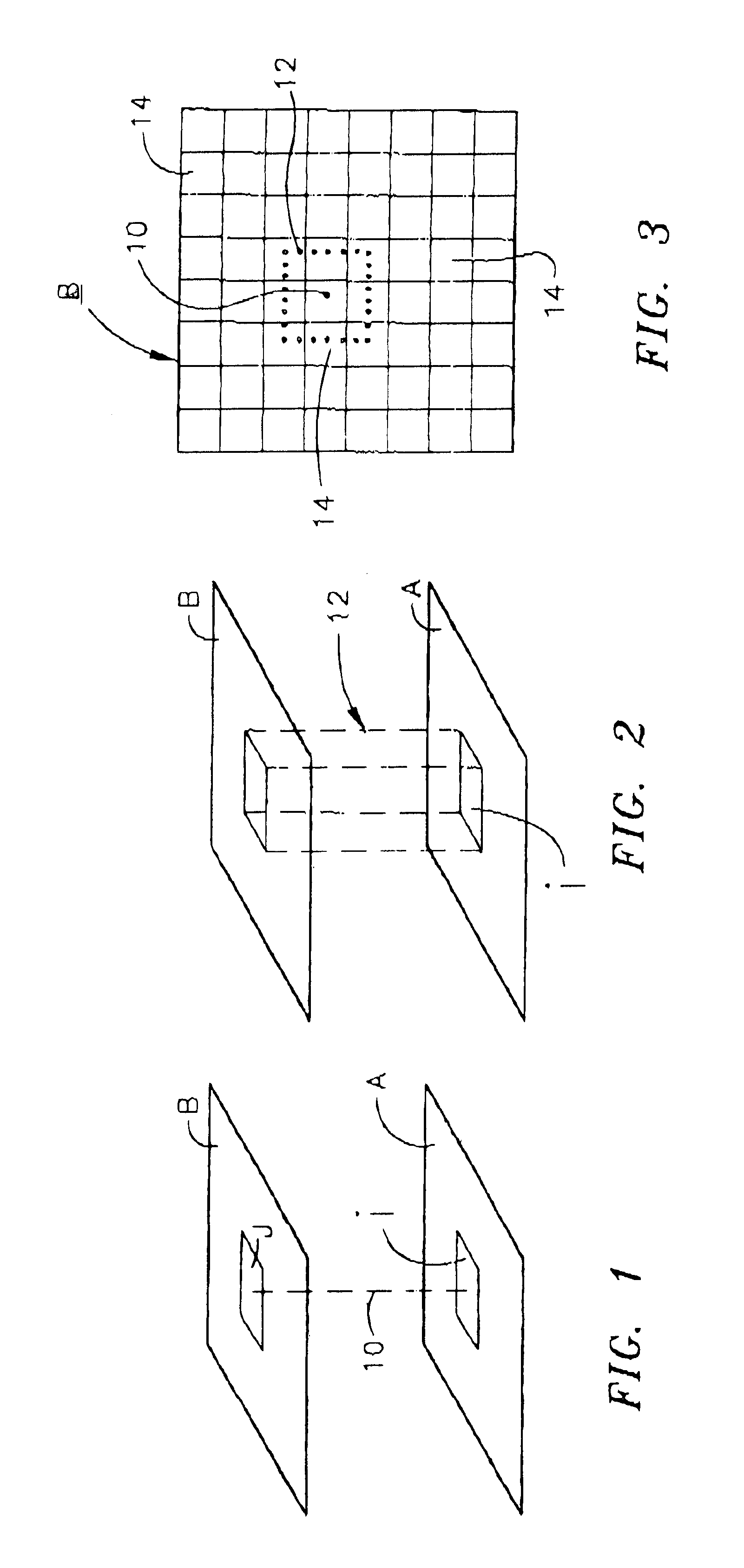
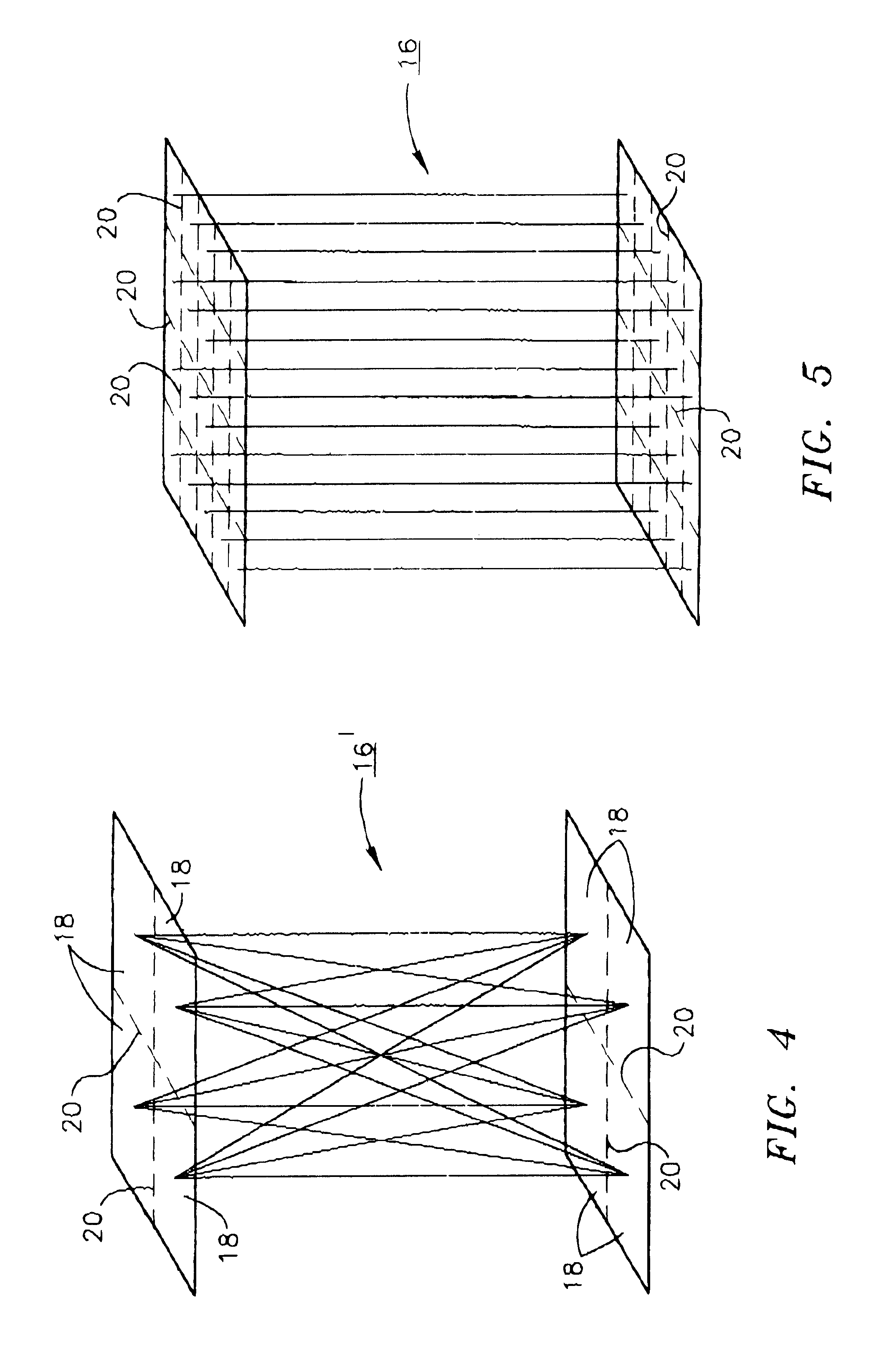
An improved method of, and apparatus for, nuclear imaging takes advantage of the ability to determine the depth of gamma ray / electron interaction within a semiconducting gamma ray detector to determine the (most highly probable) location of the first gamma ray / electron interaction within the detector. Lines of interaction constructed between opposing detector arrays, extending between the location of the first gamma ray / electron interaction in each detector associated with the coincident detection of gamma radiation, permits a positron-emitting object of interest to be imaged according to protocols known in the art, but with better spatial resolution than previously believed to have been known.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
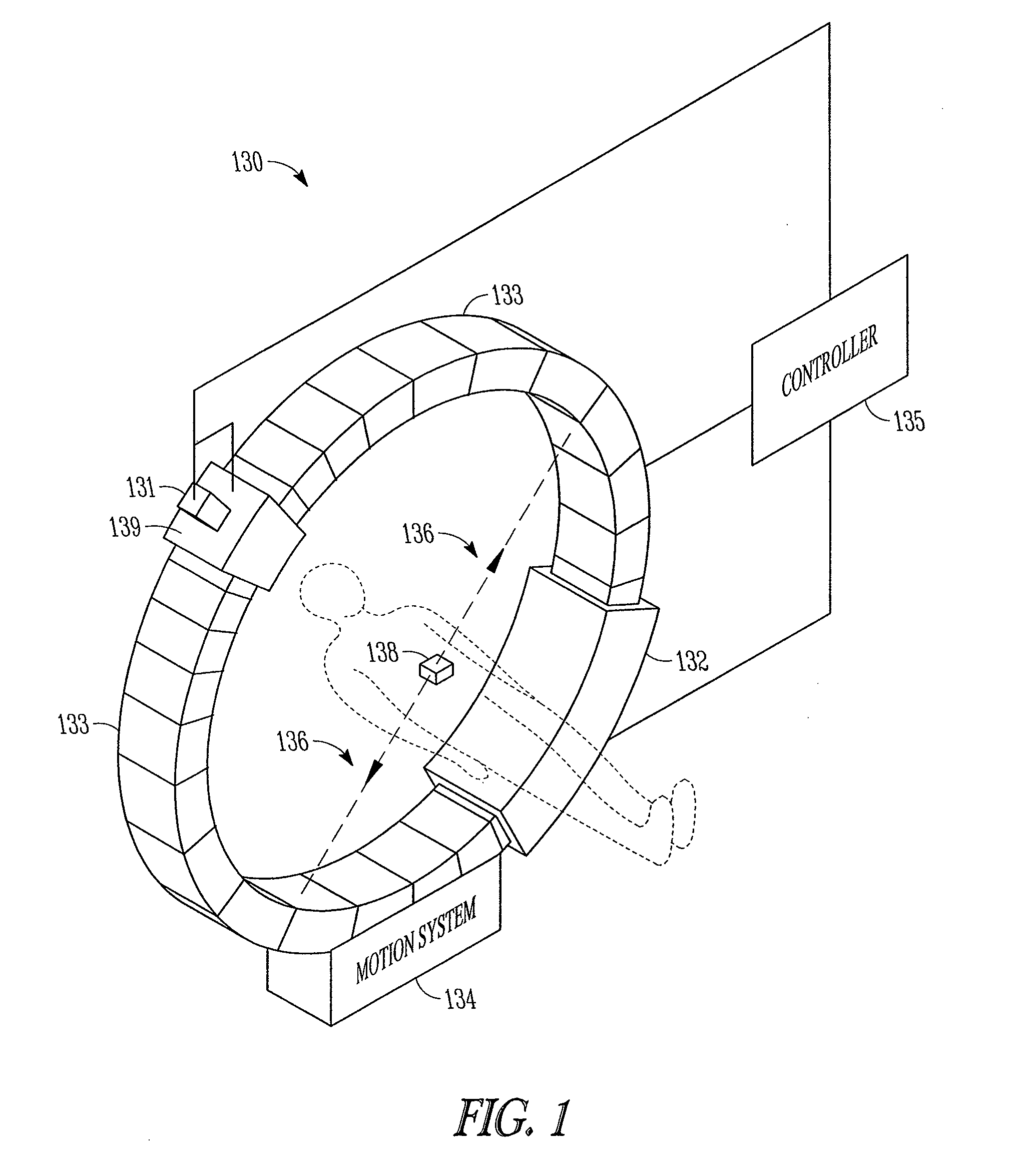
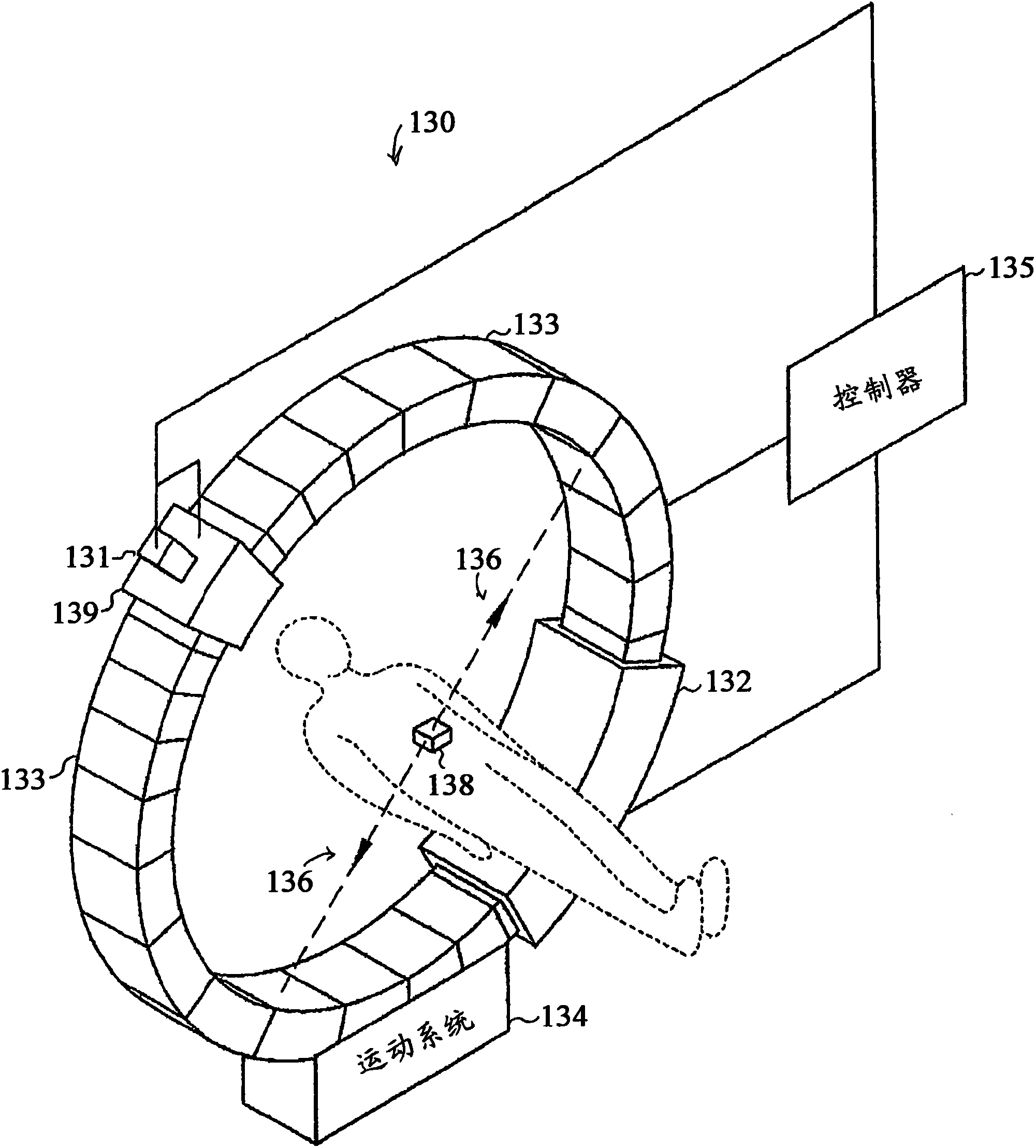
Method and apparatus for real-time tumor tracking
Method and apparatus for real-time tracking of a target in a human body. In one embodiment of the invention, positron emission marker may be implanted into a target, the positron emission marker having a low activity positron isotope. In one embodiment, annihilation gamma rays associated with the low activity positron isotope may be detected using a plurality of position-sensitive detectors. In another embodiment, the target may be tracked in real-time based on a position of the positron emission marker.
Owner:XU TONG +2
Registration of thoracic and abdominal imaging modalities
InactiveUS7397934B2Precise positioningMinimal computationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementImaging modalitiesX-ray
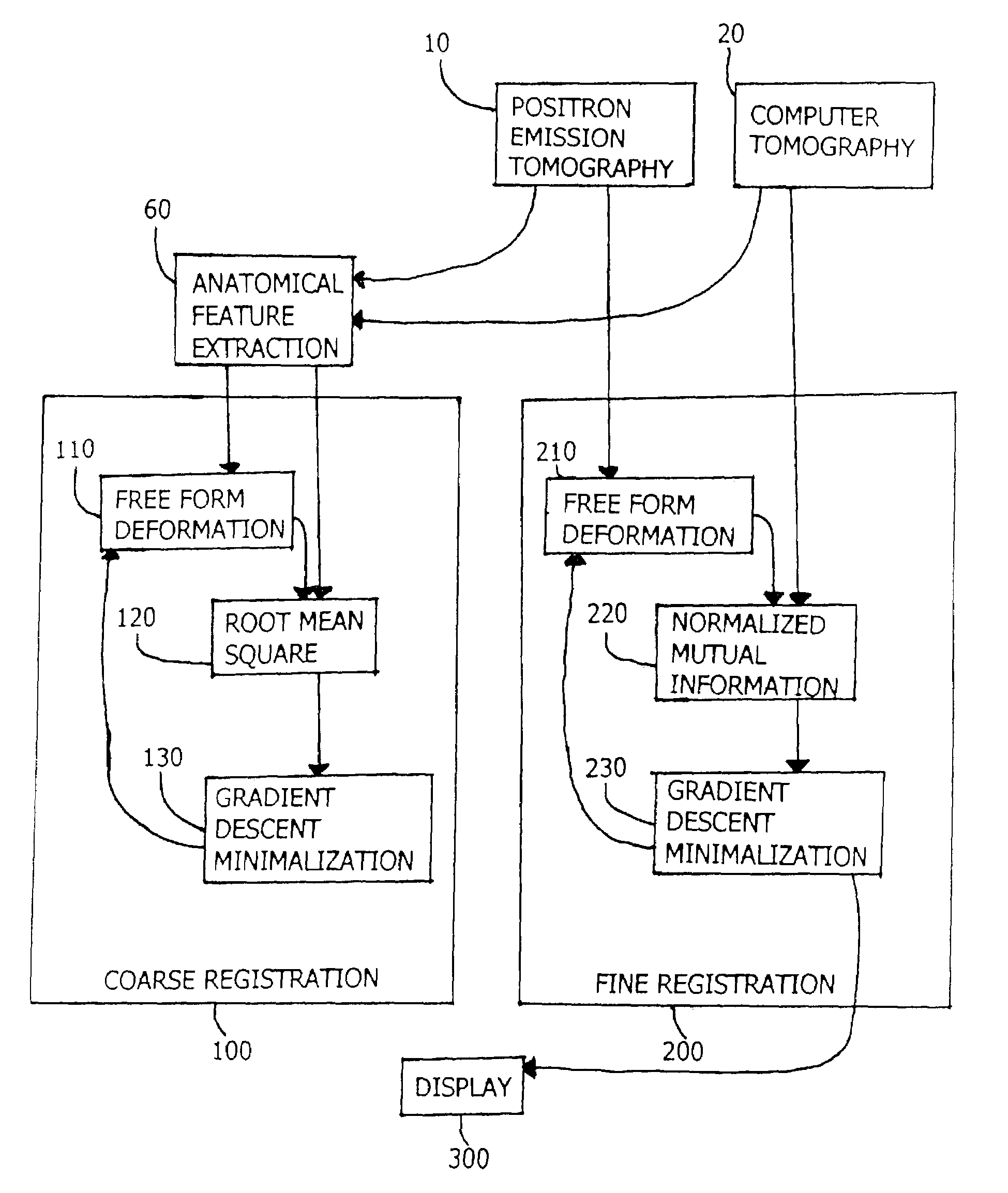
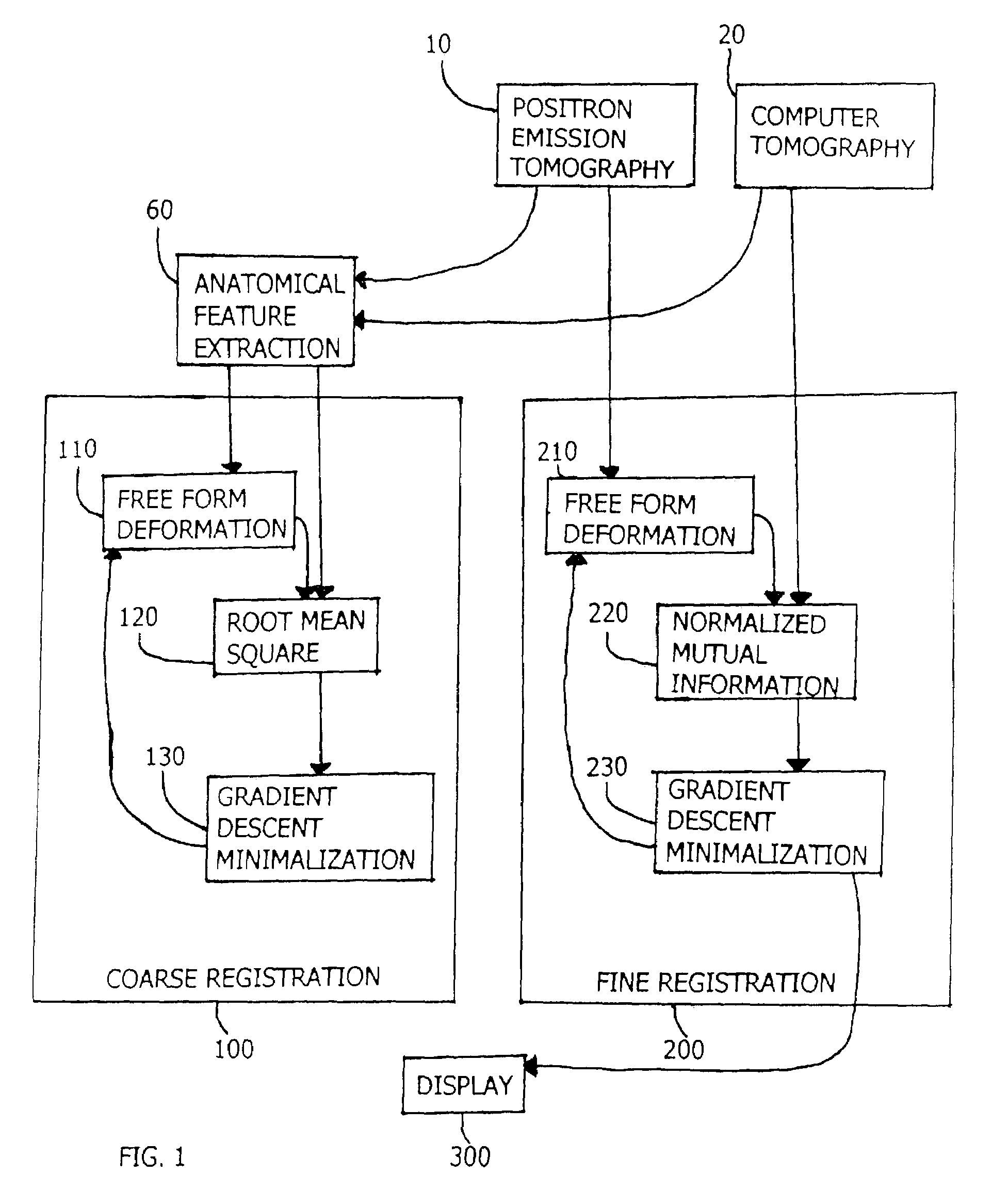
This disclosure presents an improved method for registering anatomical medical images and functional medical images. The example deals with the registration of x-ray computer tomography images with positron emission tomography images. The process is characterized by clinically useful registration with minimal computer calculations and minimal delay for computation. A nonrigid B-Spline free form deformation is used in both a preliminary coarse registration and the finished fine registration. Additional steps are used to insure accurate and complete registrations.
Owner:SEGAMI R L
System and apparatus for detecting gamma rays in a PET/MRI scanner
ActiveUS7667457B2X/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentElectric/magnetic detectionPhotodetectorRadio frequency
A gamma ray detector ring for a combined positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system is integrated into a radio frequency (RF) coil assembly such that the detector ring is integrated with a RF shield. Each gamma ray detector in the detector ring includes a scintillator component that emits light when a gamma ray is detected and a photodetector component designed to be sensitive to the frequency of light produced by the scintillator. A RF shield may be integrated into a detector ring such that the RF shield is positioned between the scintillator and photodetector components of each detector, thereby saving valuable radial space within the imaging system. Multiple such detector rings may be located adjacent to one another to increase axial coverage and enable three-dimensional PET imaging techniques.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for emission guided radiation therapy
ActiveUS8017915B2Radiation applicationsRadiation diagnostic device controlRadiation therapyPositron annihilation
An apparatus comprising a radiation source, coincident positron emission detectors configured to detect coincident positron annihilation emissions originating within a coordinate system, and a controller coupled to the radiation source and the coincident positron emission detectors, the controller configured to identify coincident positron annihilation emission paths intersecting one or more volumes in the coordinate system and align the radiation source along an identified coincident positron annihilation emission path.
Owner:REFLEXION MEDICAL INC
Method and apparatus for emission guided radiation therapy
ActiveCN101970043AElectrotherapyRadiation diagnostic device controlRadiation therapyPositron annihilation
An apparatus comprising a radiation source, coincident positron emission detectors configured to detect coincident positron annihilation emissions originating within a coordinate system, and a controller coupled to the radiation source and the coincident positron emission detectors, the controller configured to identify coincident positron annihilation emission paths intersecting one or more volumes in the coordinate system and align the radiation source along an identified coincident positron annihilation emission path.
Owner:REFLEXION MEDICAL INC
Combined positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance tomography unit
InactiveUS7323874B2Save spaceShorten the timeMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionElectrical conductorDevice form
Owner:SIEMENS AG
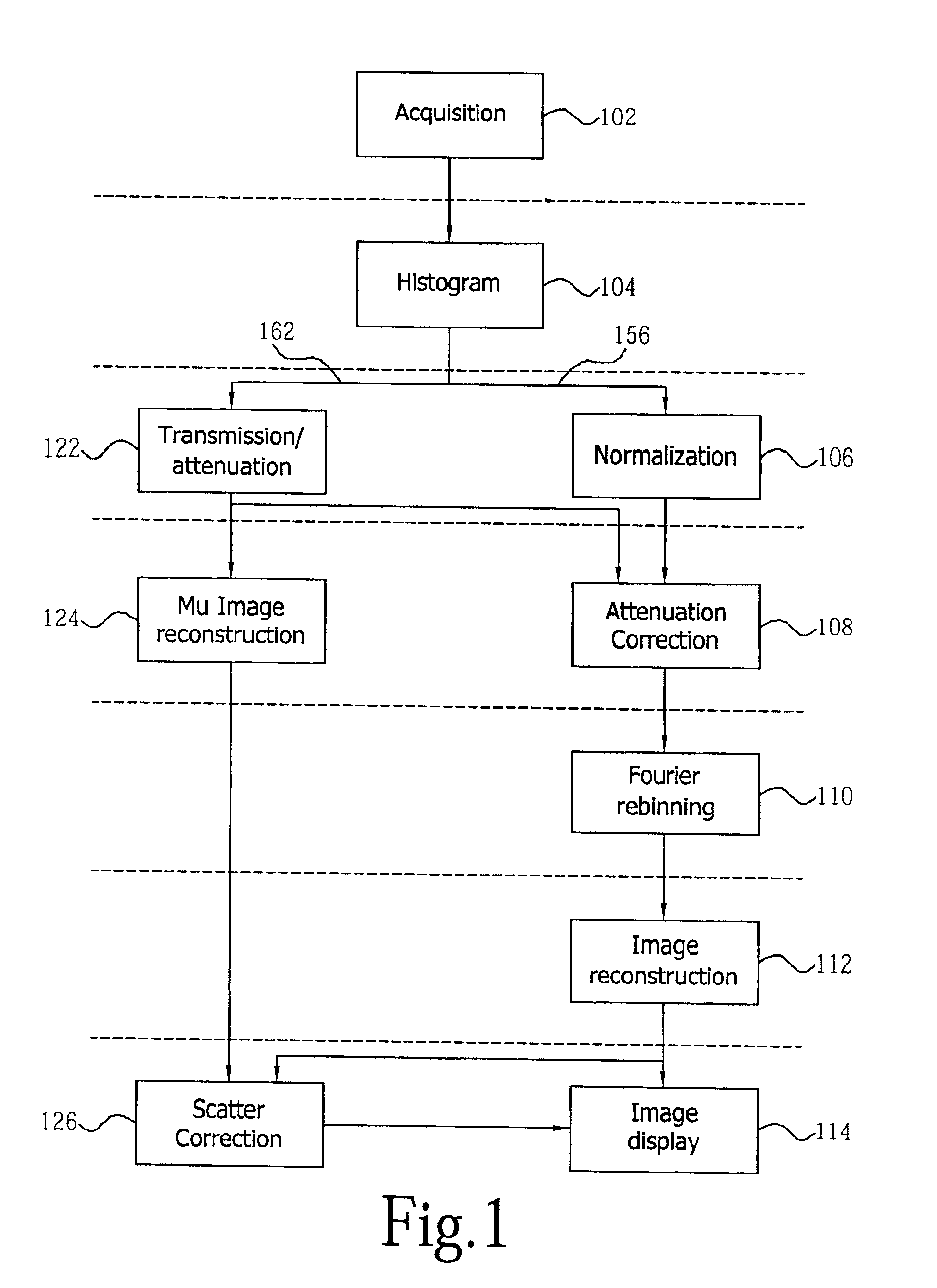
Continuous tomography bed motion data processing apparatus and method
InactiveUS6915004B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData synchronizationUltrasound attenuation
Apparatus and methods for three dimensional image reconstruction from data acquired in a positron emission tomograph (PET). This invention uses a parallel / pipelined architecture for processing the acquired data as it is acquired from the scanner. The asynchronously acquired data is synchronously stepped through the stages performing histogramming, normalization, transmission / attenuation, Mu image reconstruction, attenuation correction, rebinning, image reconstruction, scatter correction, and image display.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
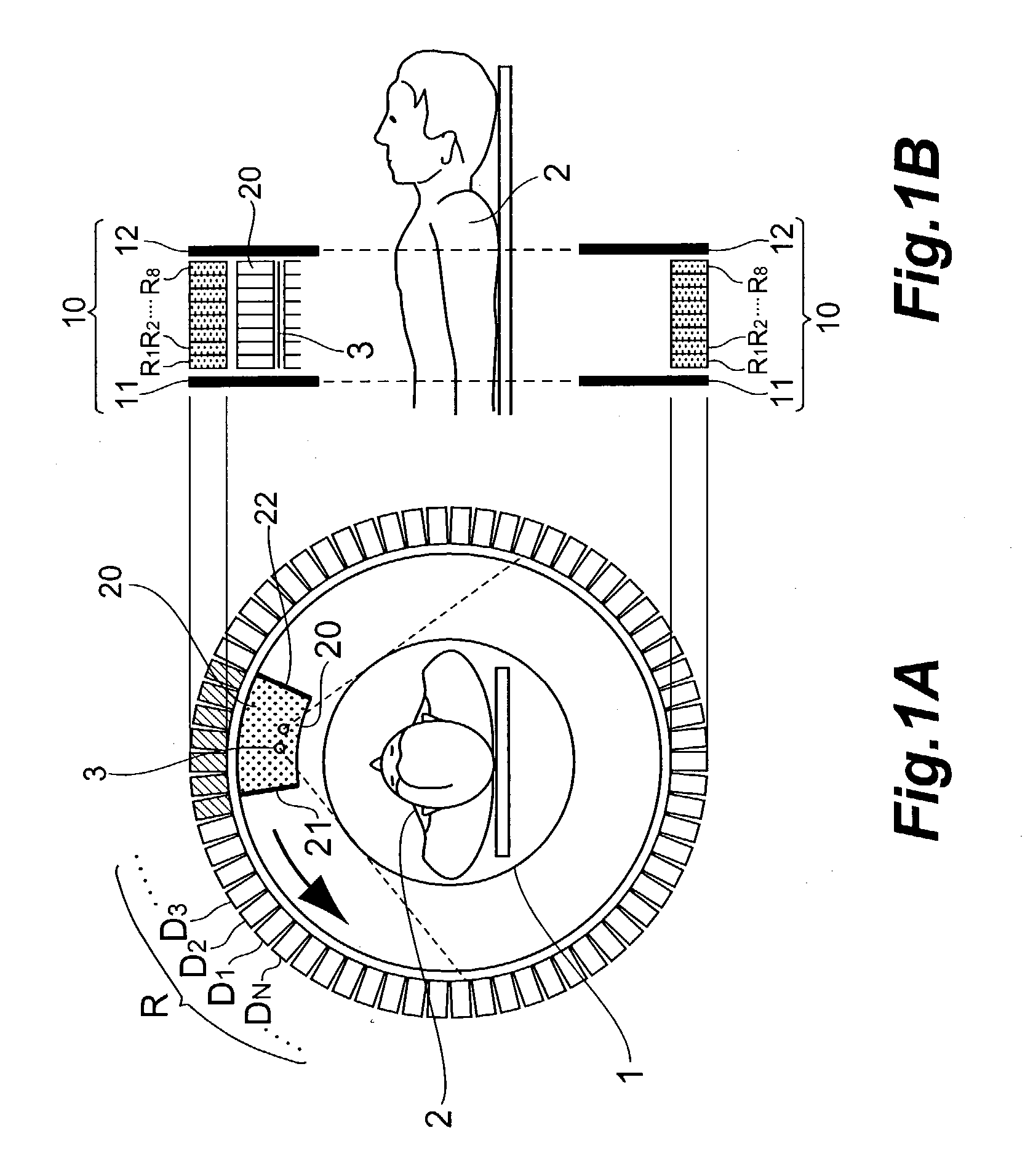
Pet device
InactiveUS20030189174A1Short timeImprove accuracyHandling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansCompanion animalField of view
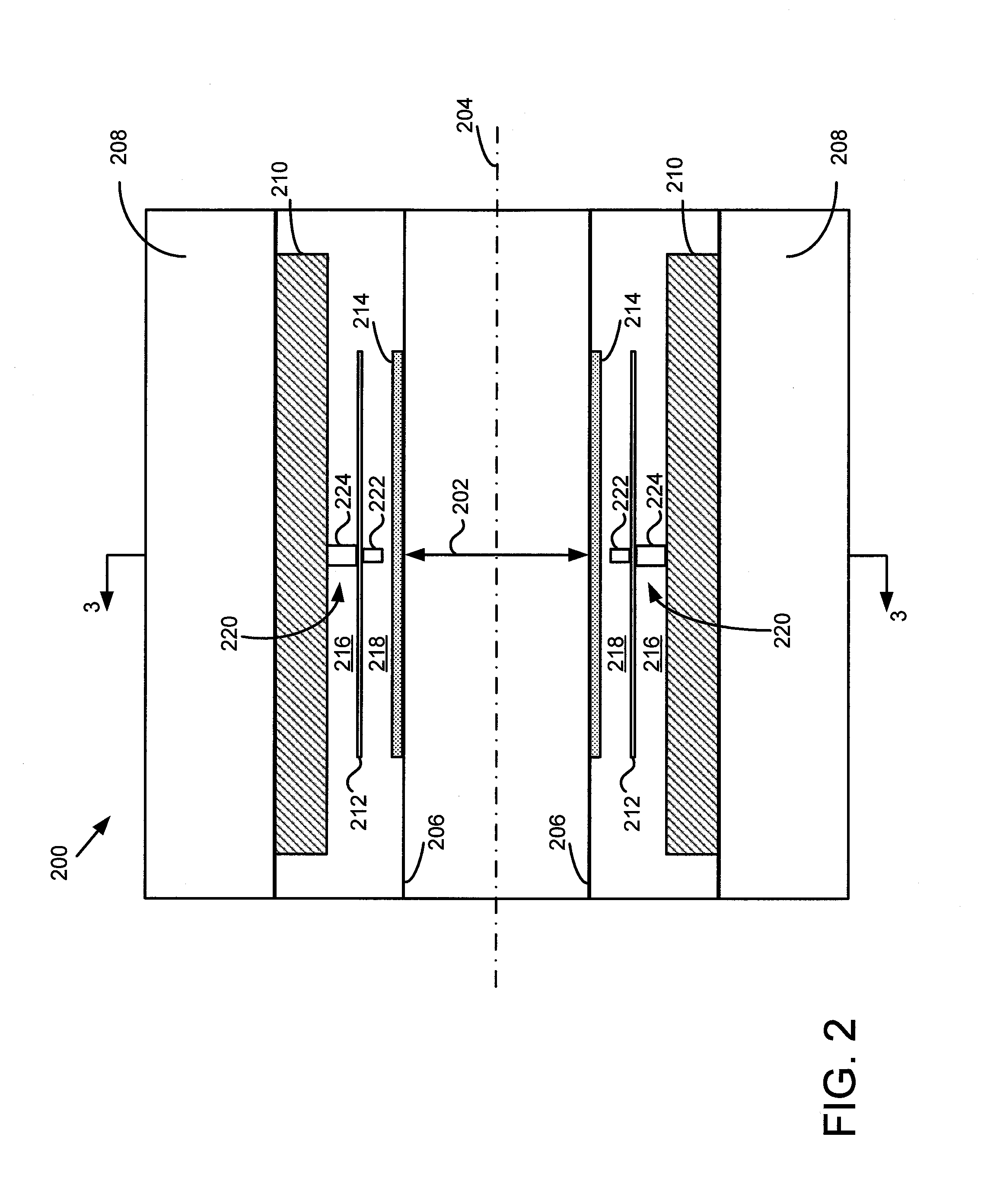
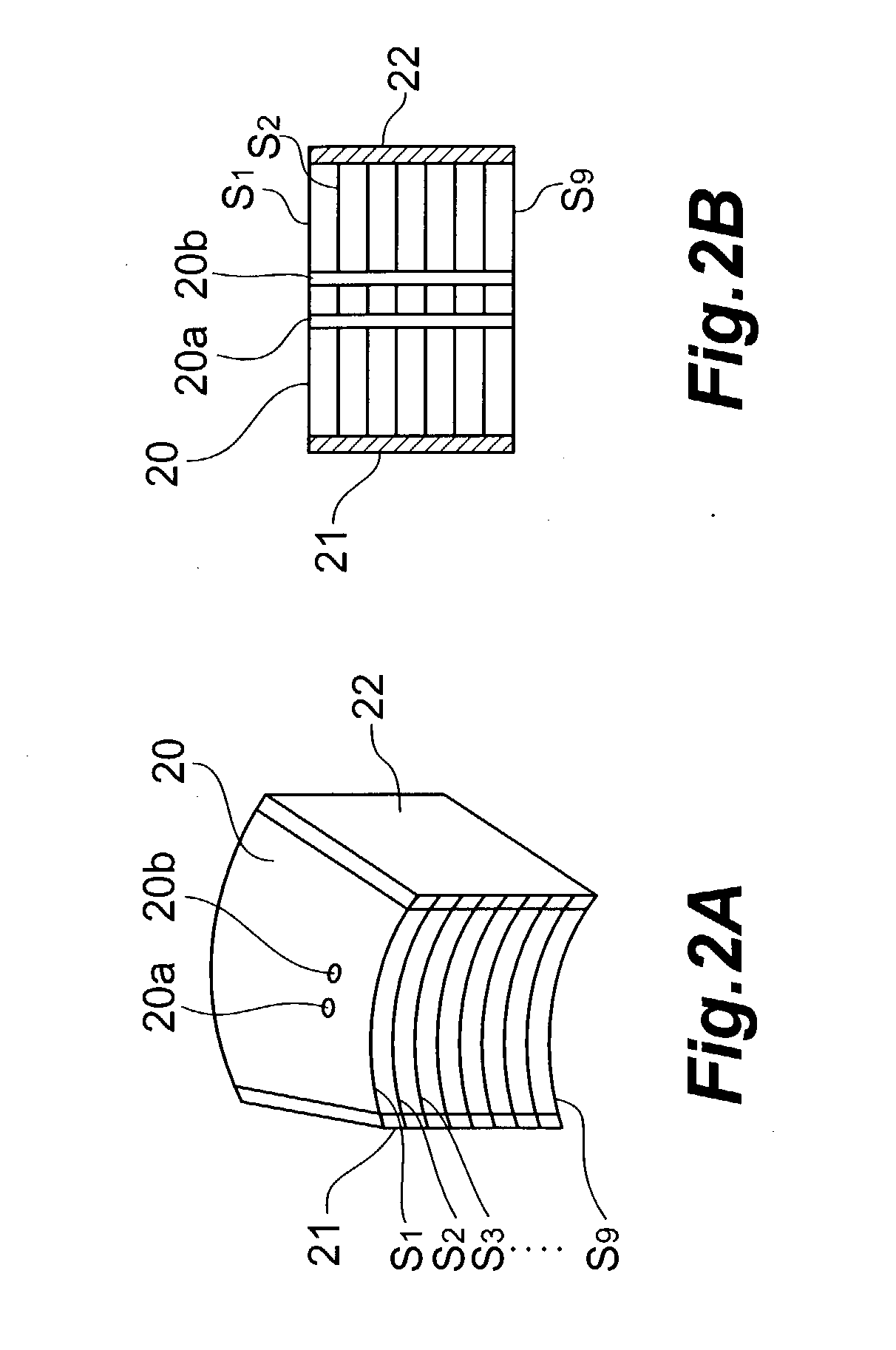
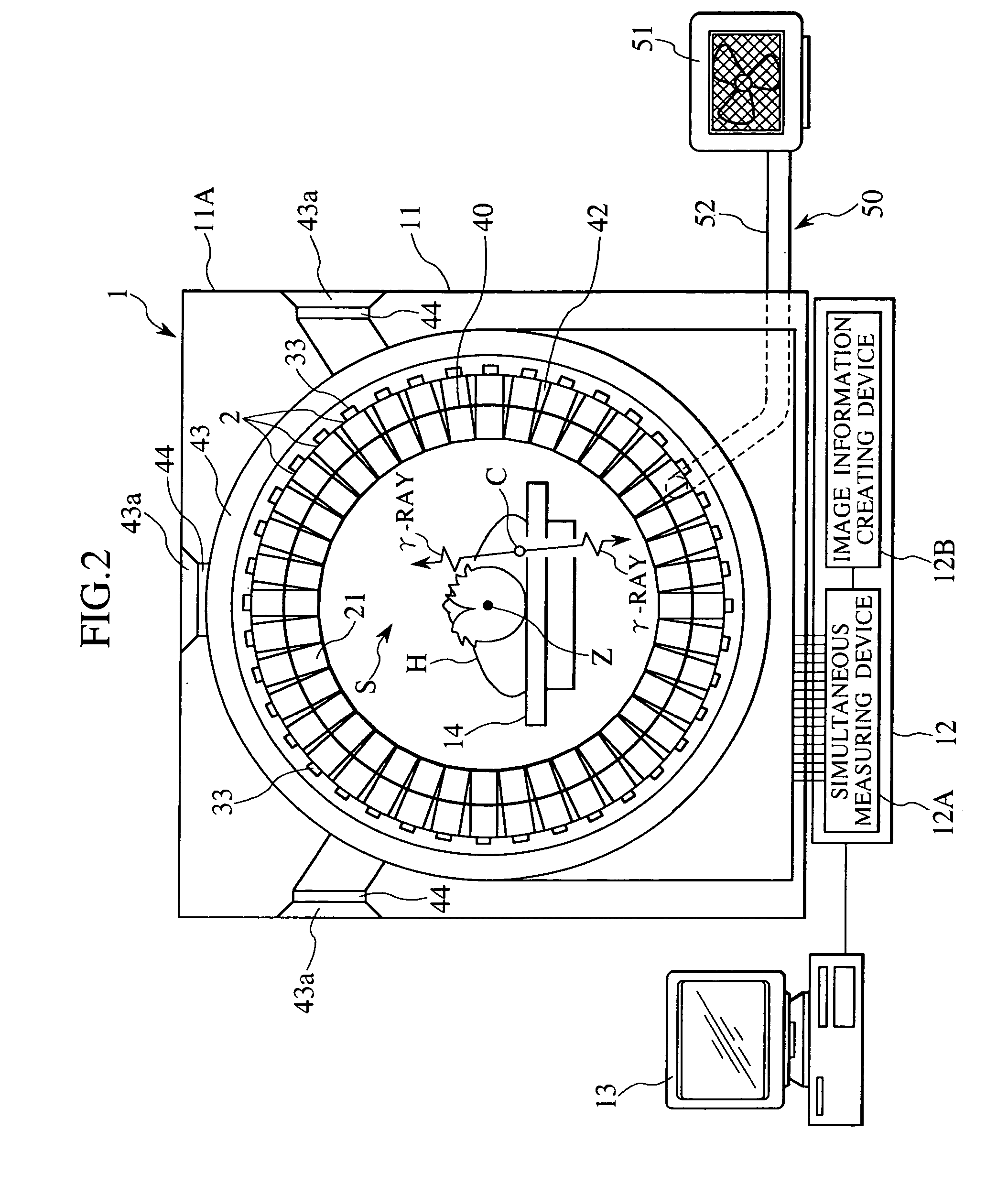
A rotating ceptor 20 provided inside a detector portion 10 includes nine shield plates S1 to S9 disposed in parallel to each other in between adjacent detector rings R, acts as a collimator, and allows only those photon pairs that have traveled approximately parallel to a slice plane to be made incident upon photon detectors D located behind the rotating ceptor 20. Each of the shield plates S is not formed annularly, and provided near the measurement field of view 1 of part of N photon detectors D that constitute each of the detector rings R. The rotating ceptor 20 is rotatable about its center axis. Each of the shield plates S is provided with bar-shaped radiation source insertion holes 20a and 20b for allowing a bar-shaped positron emission radiation source 3 to be inserted therein and supported thereby.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
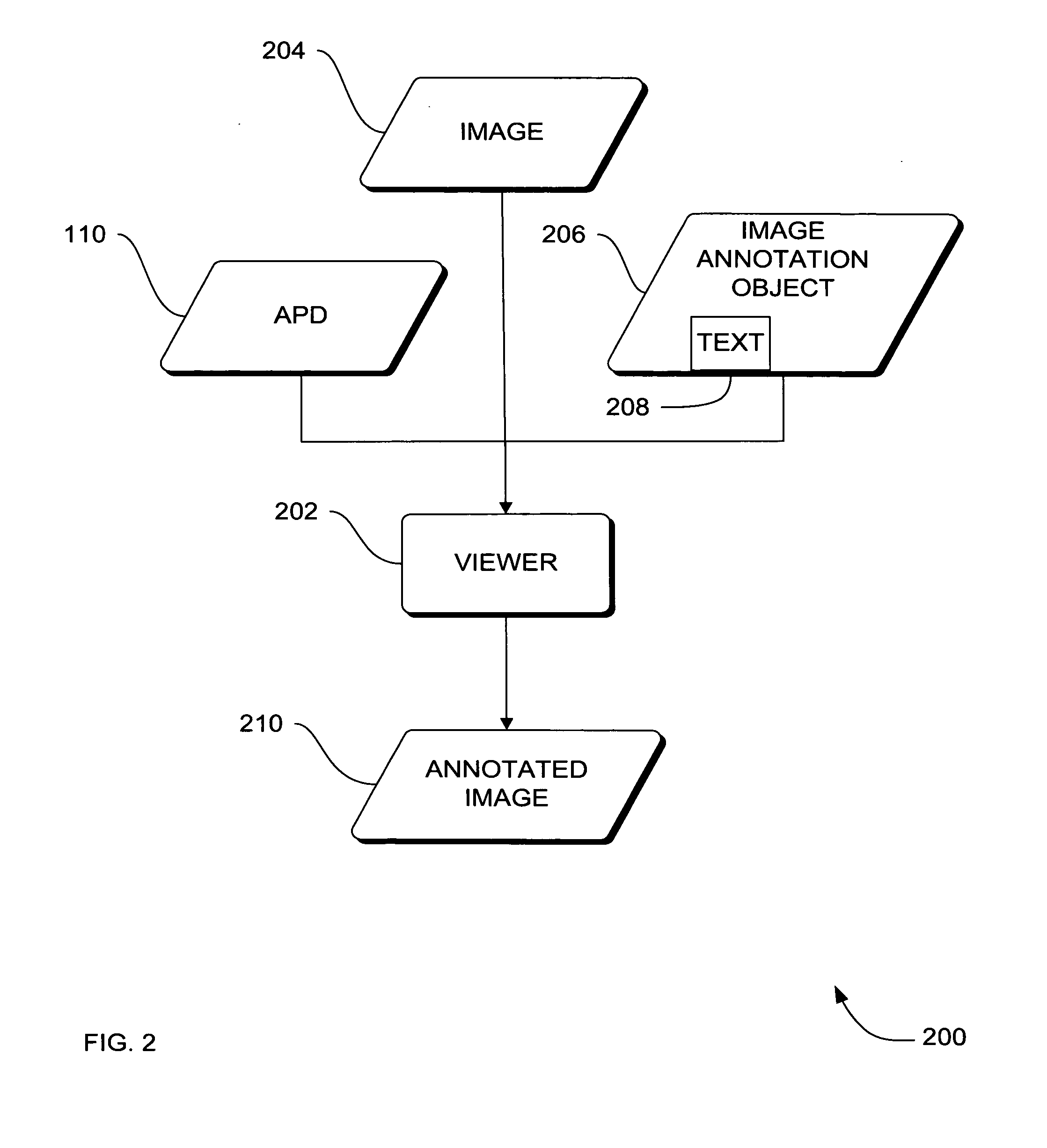
Systems, methods and apparatus for image annotation
InactiveUS20050235272A1Convenient packaging of the annotation instruction more readily and convenientlyReduce needSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsSonificationResonance
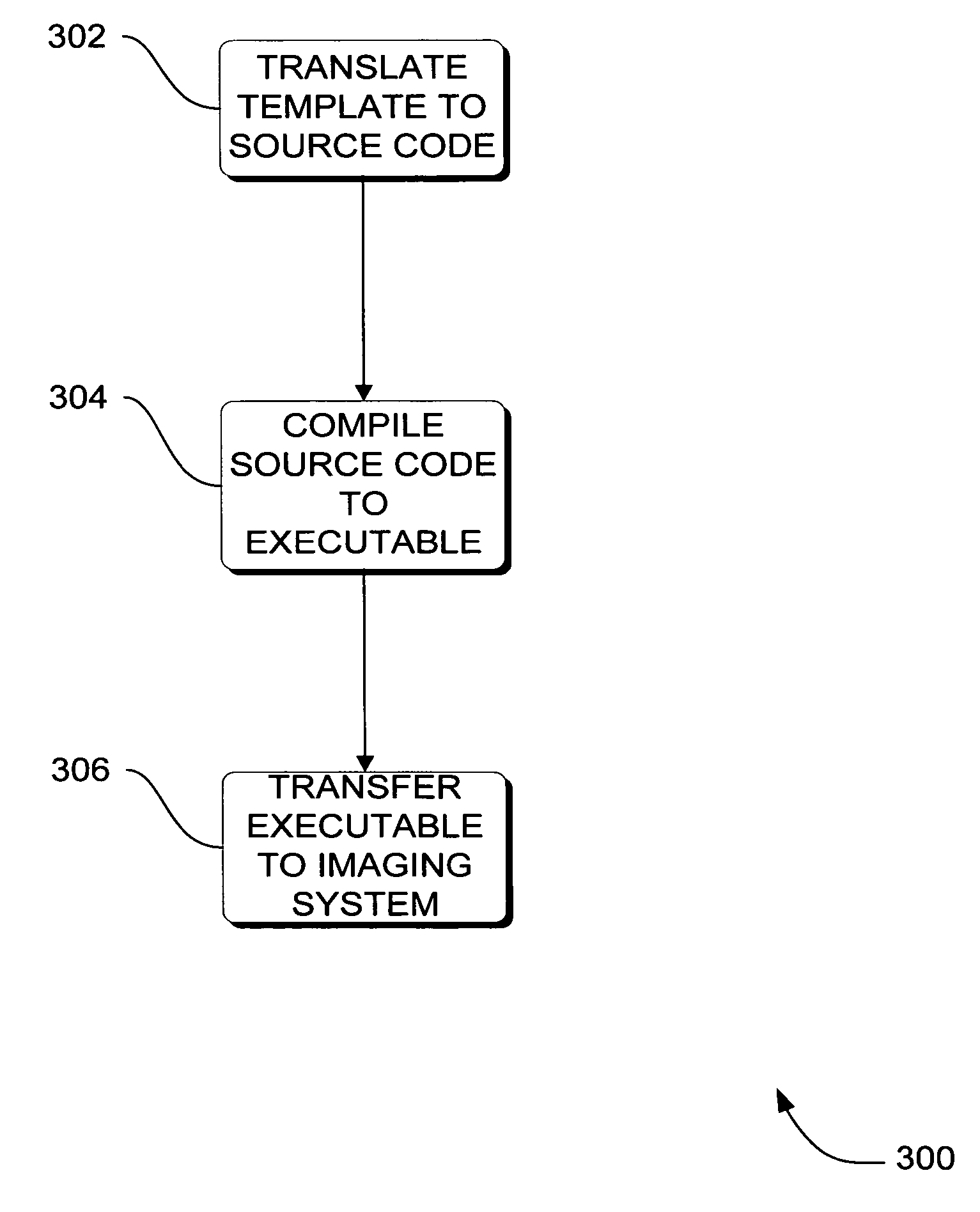
Systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which a non-procedural image annotation template is translated into source code, and compiled into an image annotation executable that has native computer instructions for an imaging system. In some embodiments, an image viewer on the imaging system accesses the native instructions and invokes the native instructions to annotate an image with text information. In some embodiments, the imaging system is a magnetic resonance, computer tomography, X-ray, ultrasound, or positron emission tomography imaging system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
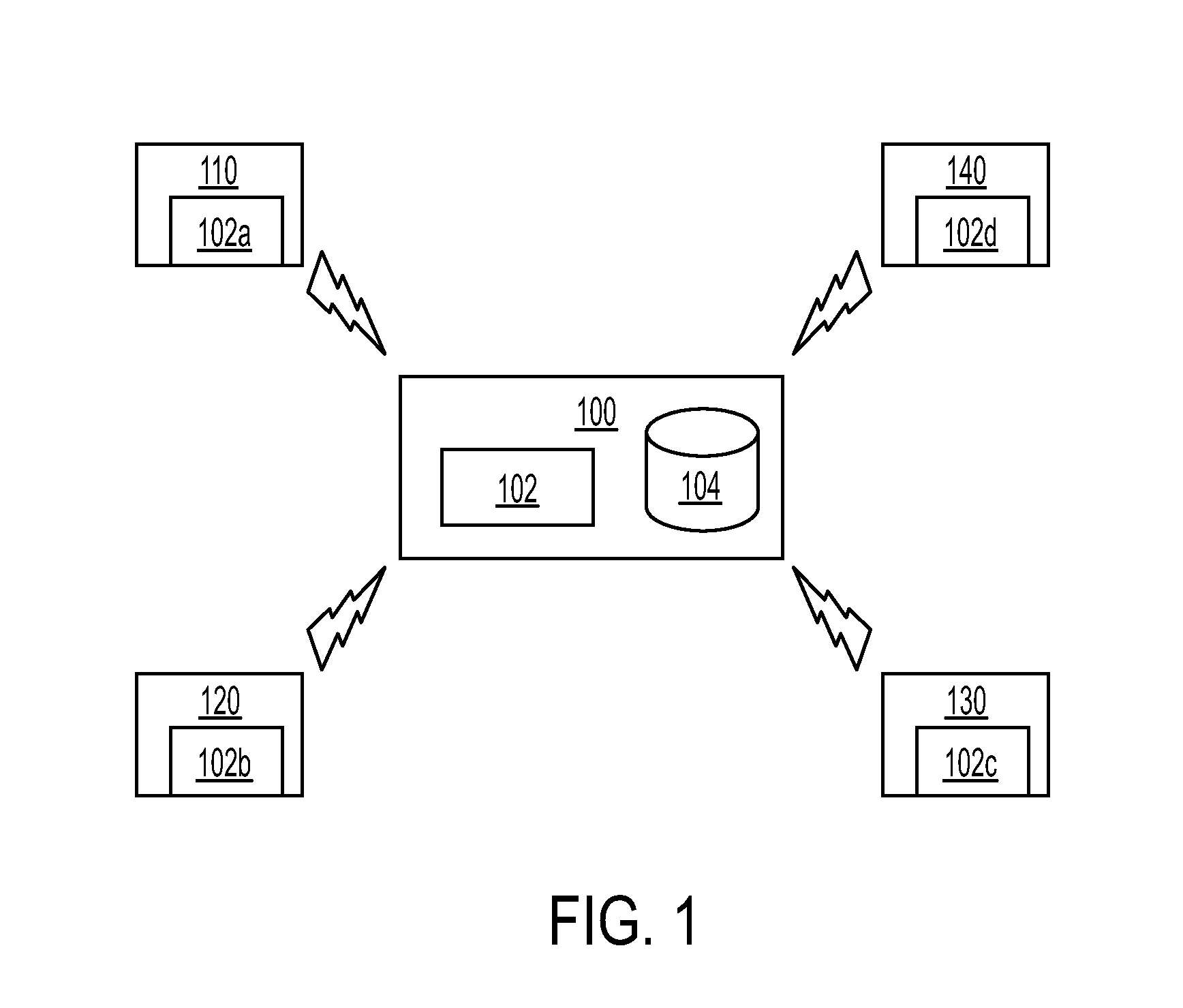
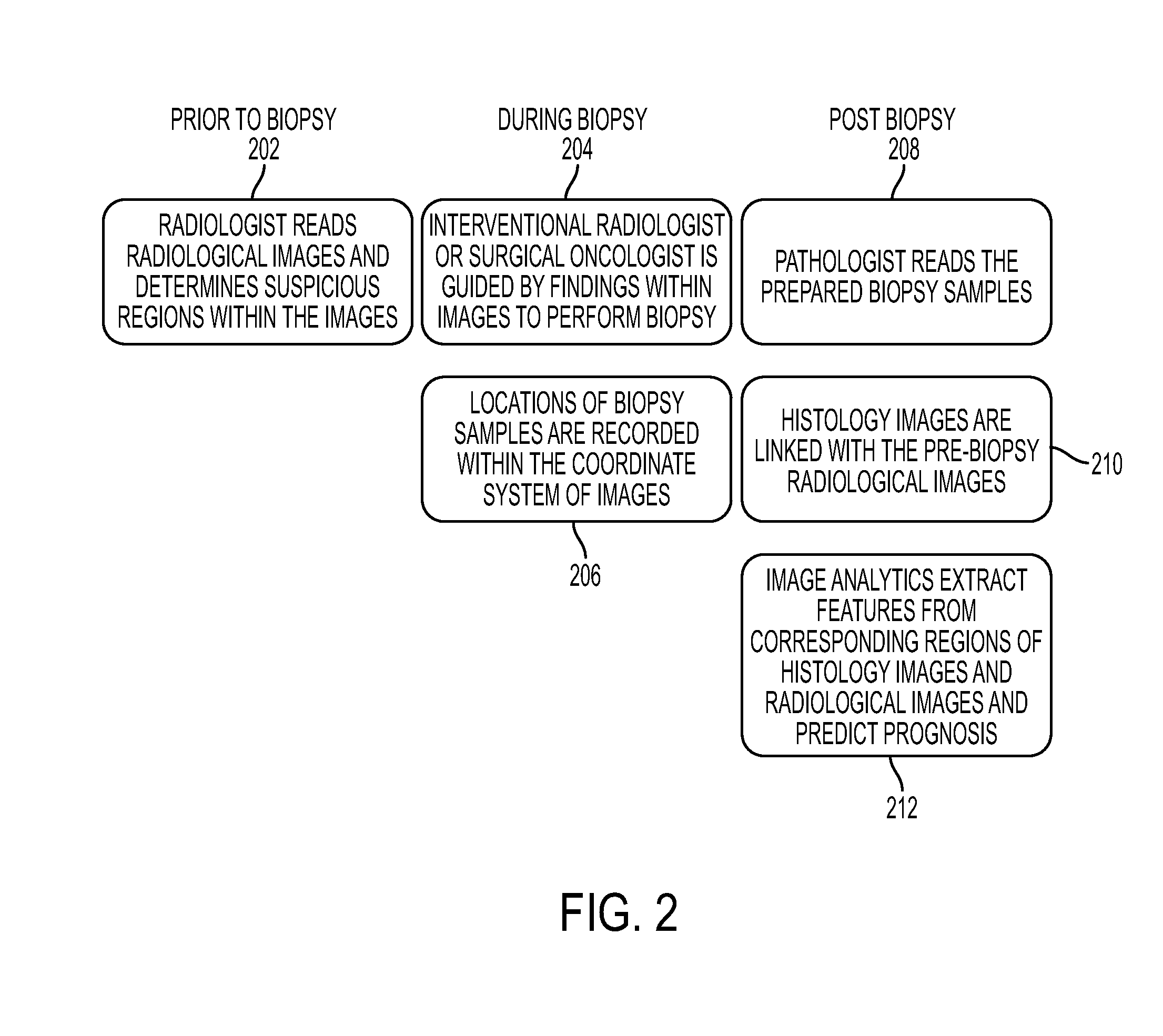
Method and system for integrated radiological and pathological information for diagnosis, therapy selection, and monitoring
ActiveUS20140314292A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationCancers diagnosis
A method and system for integrating radiological and pathological information for cancer diagnosis, therapy selection, and monitoring is disclosed. A radiological image of a patient, such as a magnetic resonance (MR), computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET), or ultrasound image, is received. A location corresponding to each of one or more biopsy samples is determined in the at least one radiological image. An integrated display is used to display a histological image corresponding to the each biopsy samples, the radiological image, and the location corresponding to each biopsy samples in the radiological image. Pathological information and radiological information are integrated by combining features extracted from the histological images and the features extracted from the corresponding locations in the radiological image for cancer grading, prognosis prediction, and therapy selection.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
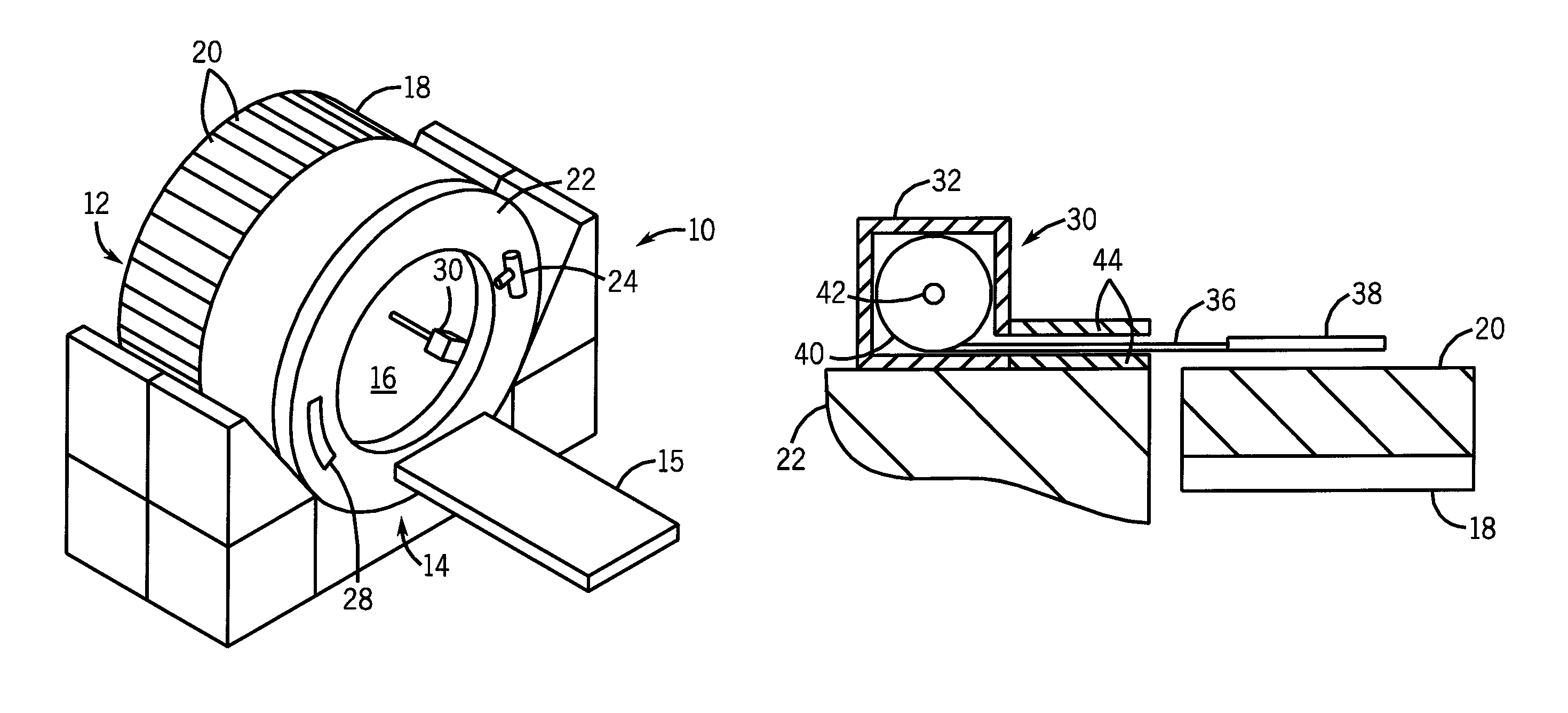
CT gantry mounted radioactive source loader for PET calibration
InactiveUS7755057B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPet imagingMedical imaging
A medical imaging system is provided including a positron emission tomography (PET) imaging apparatus and a computed tomography (CT) imaging apparatus. The CT imaging apparatus includes a rotatable gantry. A radioactive source loader is attached to the rotatable gantry to rotate therewith. The radioactive source loader further includes a radioactive source to calibrate the PET imaging apparatus.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
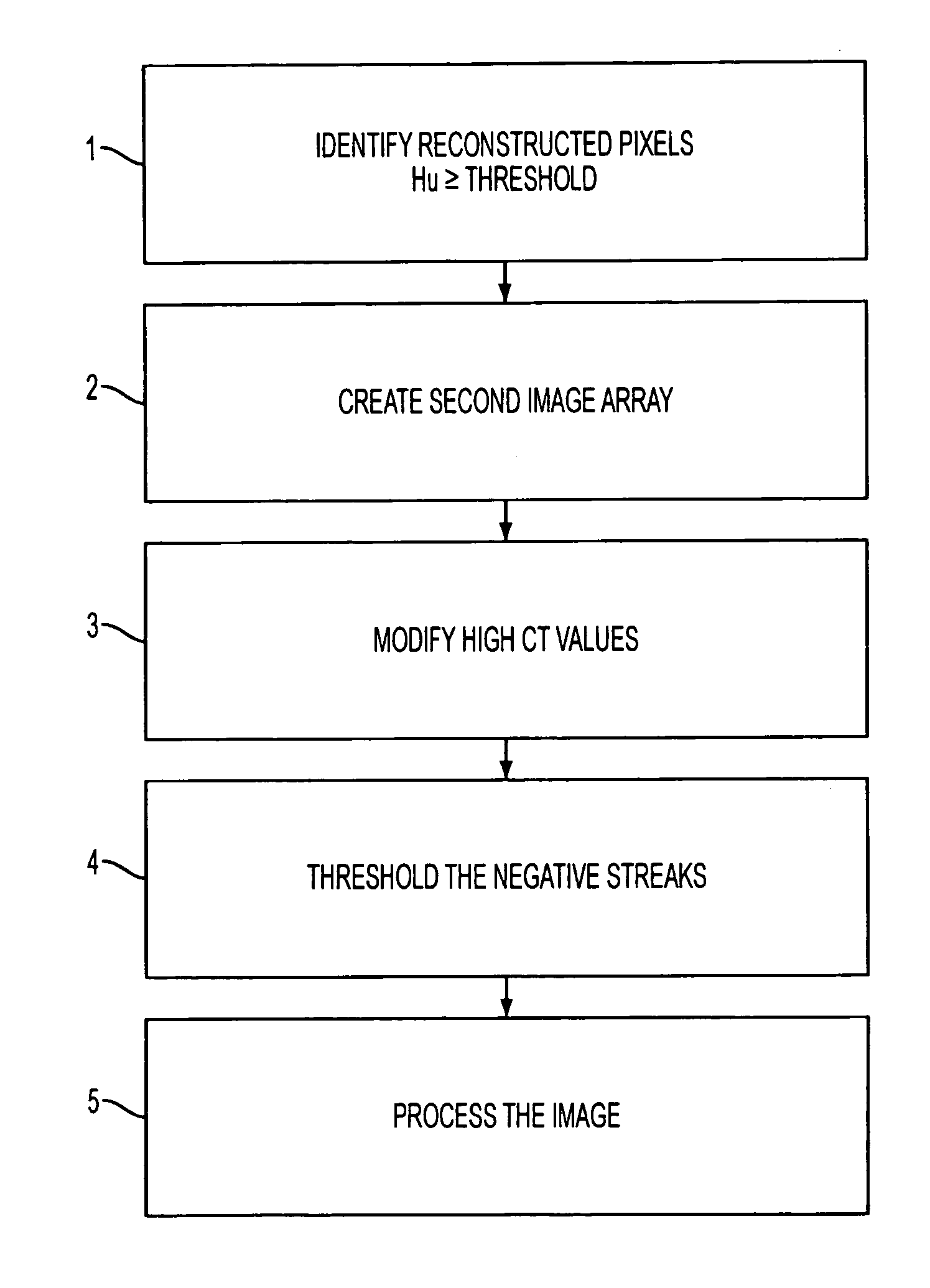
Image-based artifact reduction in PET/CT imaging
InactiveUS20060285737A1Reduce errorsSimple and robustImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionComputing tomographyCompanion animal
A method for reducing image-based artifacts in combined positron emission tomography and computed tomography (PET / CT) scans. The method includes identifying pixels in a CT image having a large HU value, identifying a region surrounding the pixels, and modifying a value of each pixel within the region.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Multi-mode little animal molecular image imaging device and imaging method
ActiveCN102764138AImage results are accurateImage results are reliableComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiagnostic Radiology ModalityData acquisition
The invention discloses a multi-mode little animal molecular image imaging device and an imaging method thereof. The device comprises an X-ray computer tomography (CT) system, a positron emission tomography (PET) system, a single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) system, a fluorescence molecular tomography (FMT) system, a rotating rack system, a little animal bed system, a data acquisition system and a computer, various imaging systems are sampled and stored by the data acquisition system through a data line into the computer, and various imaging systems share one little animal bed system and the same inspection shaft. According to the multi-mode little animal molecular image imaging device and the imaging method, various imaging systems share one little animal bed system and the same inspection shaft, an installing fusion molecular medicine image of four modes of X-ray CT, PET, SPECT and FMT can achieve complementary advantages of different image devices, and the obtained image result is accurate and reliable.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
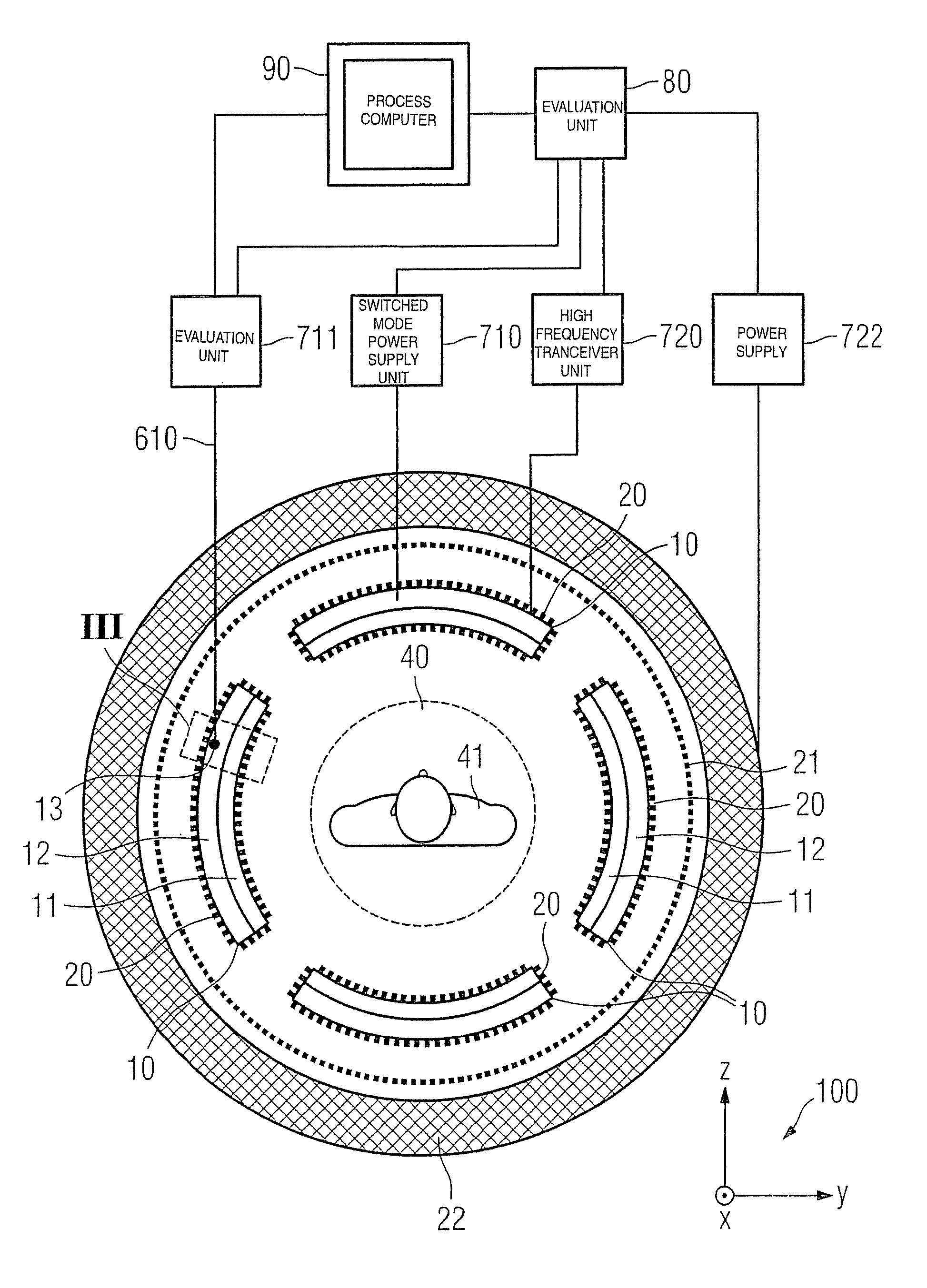
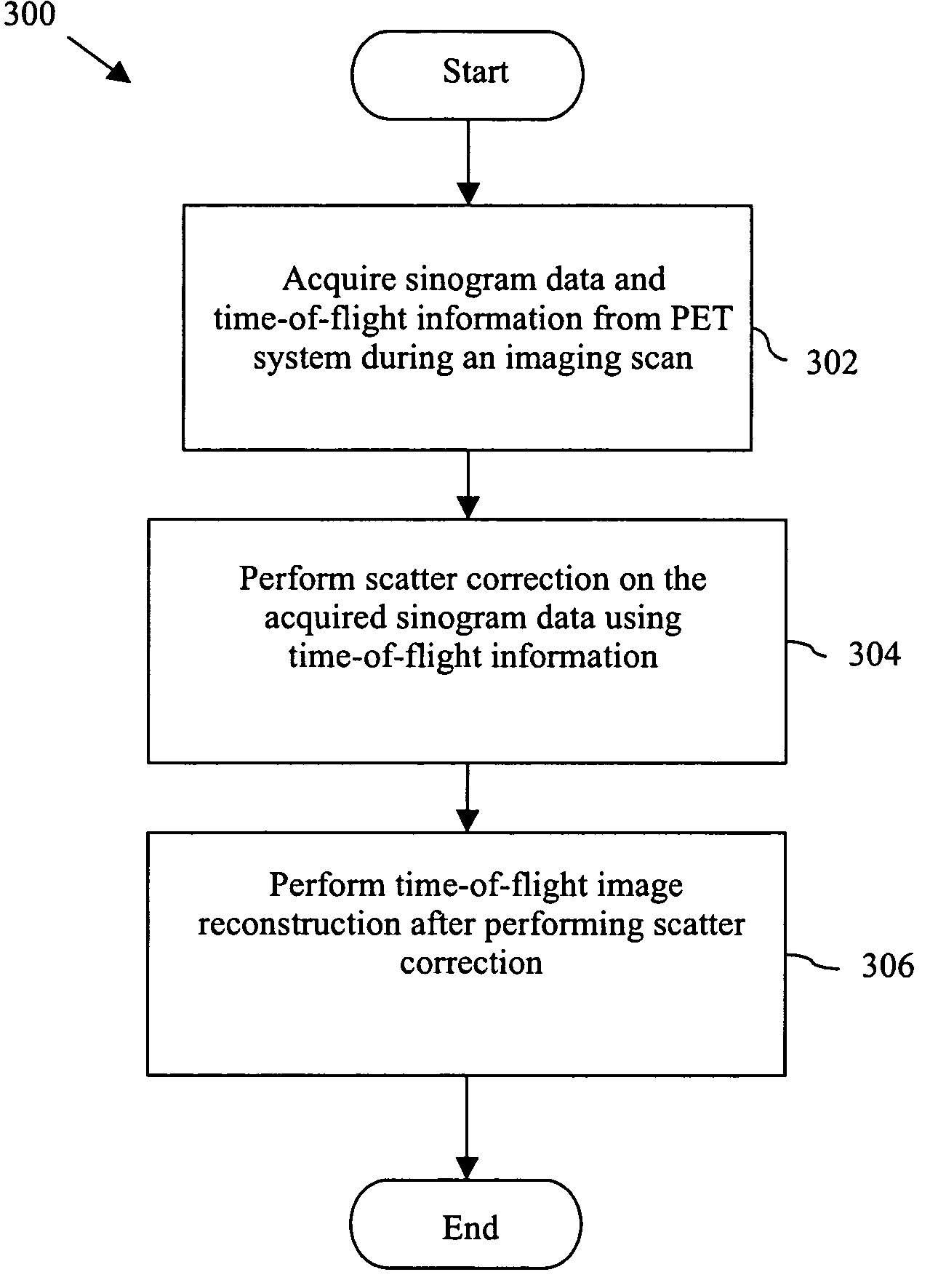
Method and system for scattered coincidence estimation in a time-of-flight positron emission tomography system
ActiveUS7129496B2Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCompanion animalComputer science
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
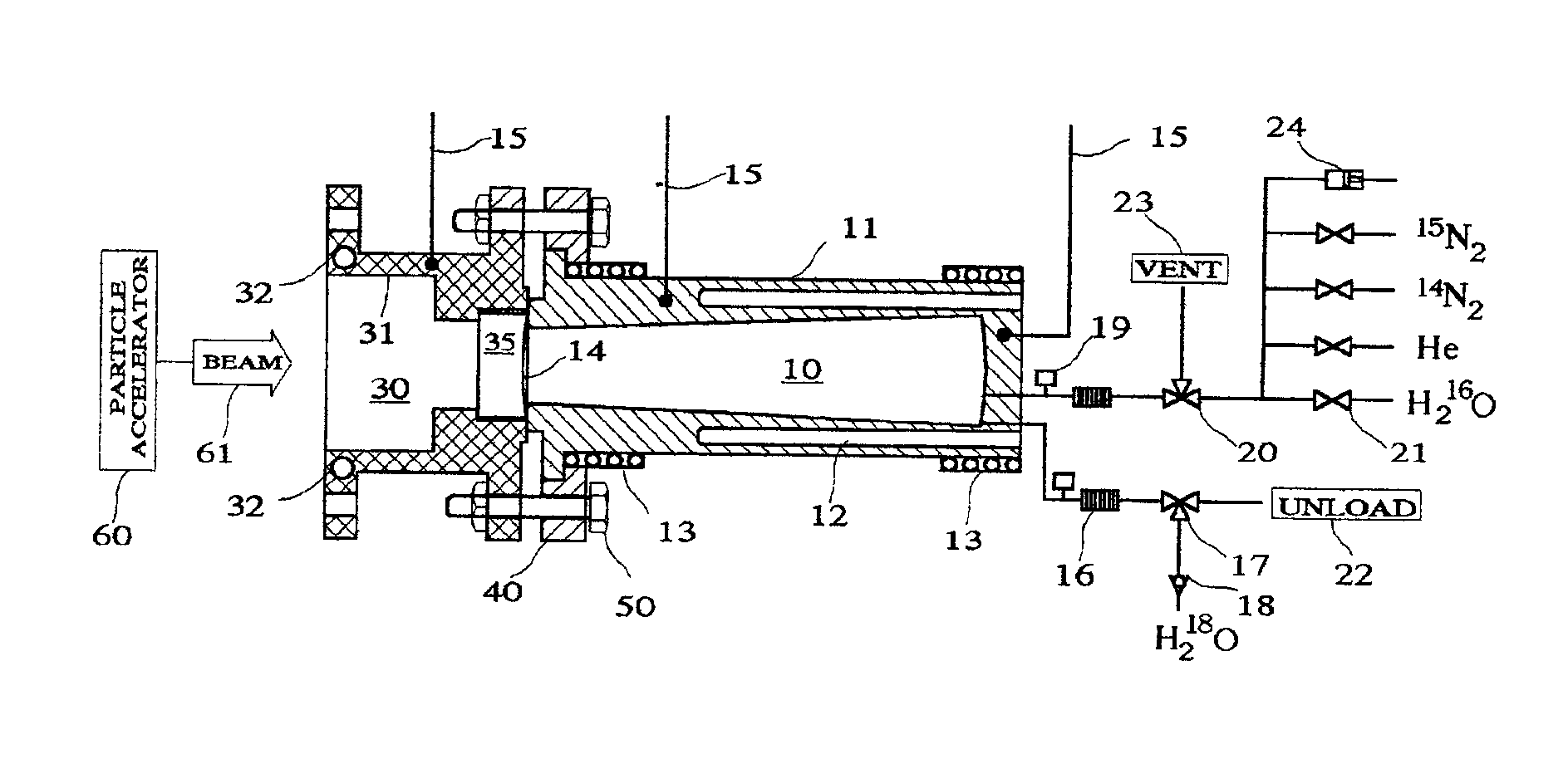
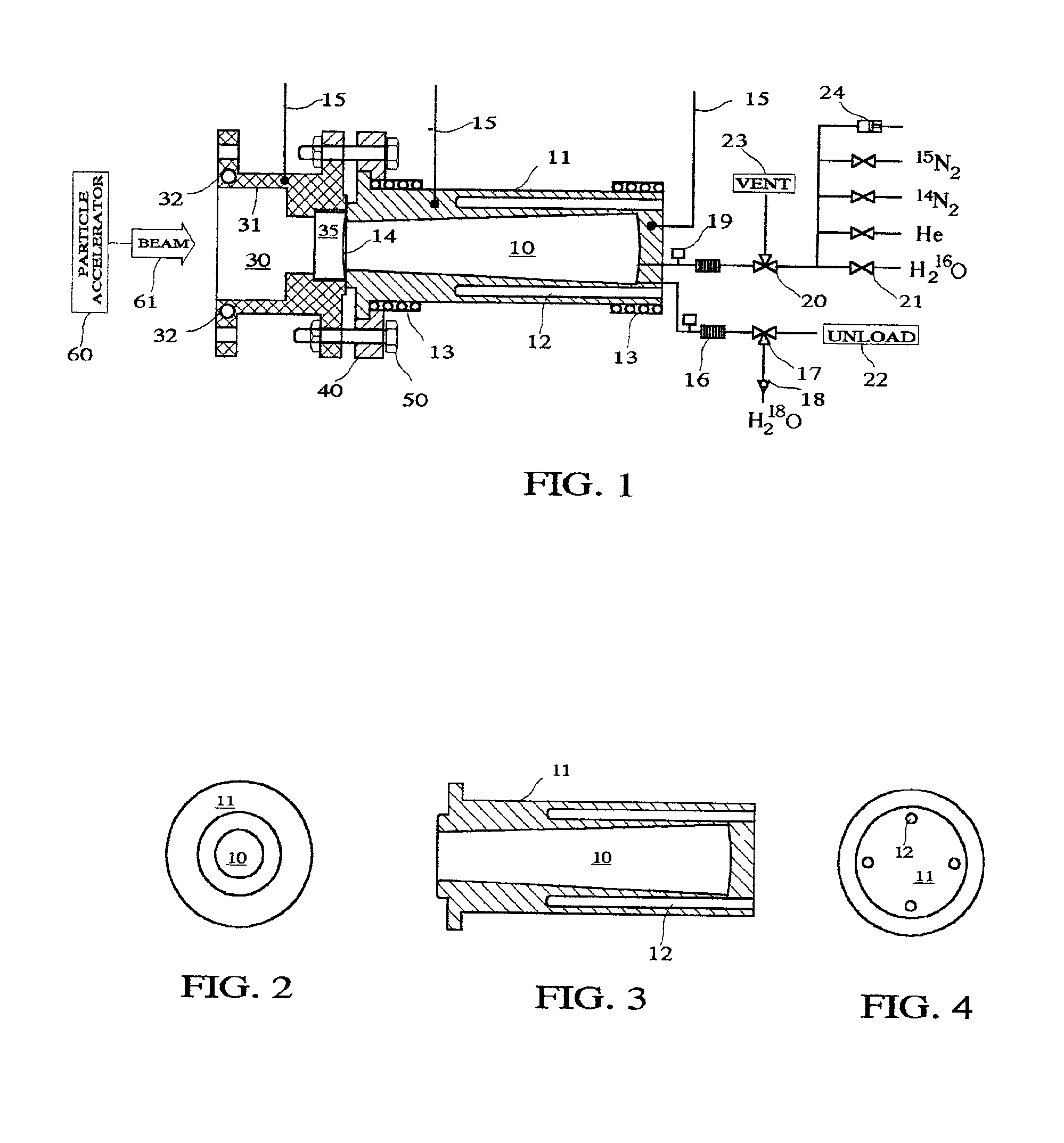
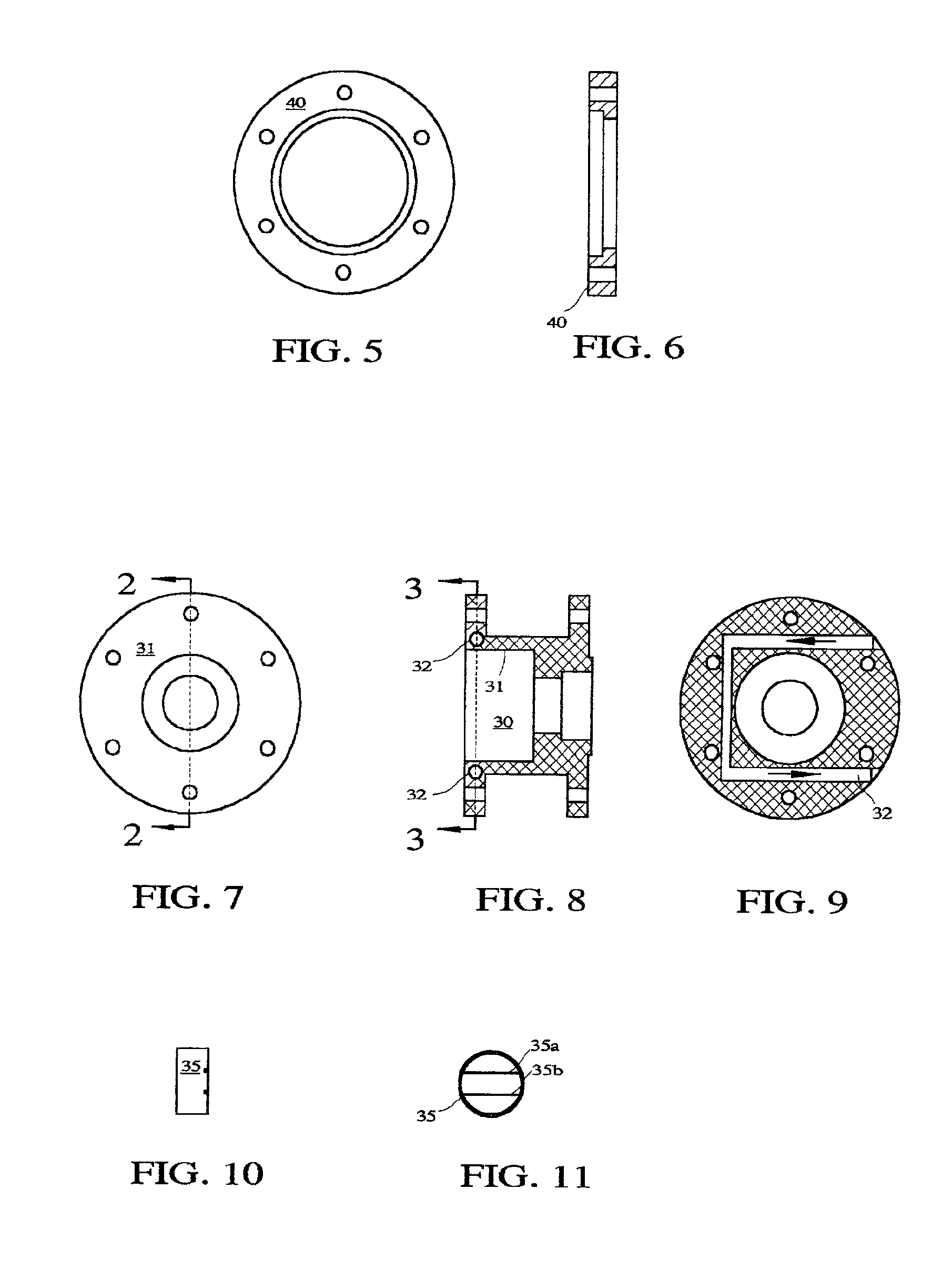
High power high yield target for production of all radioisotopes for positron emission tomography
InactiveUS6917044B2Avoid low densityConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear monitoringInstabilityAir blower
A high power high yield target for the positron emission tomography applications is introduced. For production of Curie level of Fluorine-18 isotope from a beam of proton it uses about one tenth of Oxygen-18 water compared to a conventional water target. The target is also configured to be used for production of all other radioisotopes that are used for positron emission tomography. When the target functions as a water target the material sample being oxygen-18 or oxygen-16 water is heated to steam prior to irradiation using heating elements that are housed in the target body. The material sample is kept in steam phase during the irradiation and cooled to liquid phase after irradiation. To keep the material sample in steam phase a microprocessor monitoring the target temperature manipulates the flow of coolant in the cooling section that is attached to the target and the status of the heaters and air blowers mounted adjacent to the target. When the target functions as a gas target the generated heat from the beam is removed from the target by air blowers and the cooling section. The rupture point of the target window is increased by a factor of two or higher by one thin wire or two parallel thin wires welded at the end of a small hollow tube which is held against the target window. One or two coils are used to produce a magnetic filed along the beam path for preventing the density depression along the beam path and suppression of other instabilities that can develop in a high power target.
Owner:AMINI BEHROUZ
Combined pet/mrt unit and method for simultaneously recording pet images and mr images
A combined PET / MRT unit is disclosed that includes a PET detector which is reduced by comparison with the prior art, and that consists, for example, of a PET detector with a polygonal arrangement of the detector elements or with a PET detector ring. The PET detector is reduced in an axial direction by comparison with the detectors of the prior art, as a result of which the costs for producing the expensive PET detectors are lowered. The reduction of the PET detector is possible because the MR measurement usually lasts longer than the PET measurement, and so a reduced PET detector can be used for the temporally sequential recording of a number of PET tomograms by mechanical displacement of the PET detector. Since the MR measurement lasts substantially longer, this mechanical displacement does not lead to a lengthening of the measuring time. The invention also relates to methods for simultaneously recording MR and PET tomograms in which the PET / MRT units according to the invention are used.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Positron emission tomogrpahy detector for dual-modality imaging
InactiveUS20130284936A1Magnetic measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringConductive materials
A Positron Emission Tomography (PET) detector assembly includes a cold plate having a first side and an opposite second side, the cold plate being fabricated from a thermally conductive and electrically non-conductive material, a plurality of PET detector units coupled to the first side of the cold plate, and a readout electronics section coupled to the second side of the cold plate. A radio frequency (RF) body coil assembly and a dual-modality imaging system are also described herein.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for motion correcting medical images
A method for reducing, in an image, motion related imaging artifacts. The method includes obtaining a single image of a subject using a computed tomography (CT) imaging system, obtaining a plurality of images of the subject using a positron emission tomography (PET) imaging system, generating a plurality of consistency values, and utilizing the plurality of consistency values to register the CT image and the plurality of PET images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for positron emission mammography image reconstruction
ActiveUS6804325B1Quality improvementAccurate detectionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansLines of responseData file
An image reconstruction method comprising accepting coincidence datat from either a data file or in real time from a pair of detector heads, culling event data that is outside a desired energy range, optionally saving the desired data for each detector position or for each pair of detector pixels on the two detector heads, and then reconstructing the image either by backprojection image reconstruction or by iterative image reconstruction. In the backprojection image reconstruction mode, rays are traced between centers of lines of response (LOR's), counts are then either allocated by nearest pixel interpolation or allocated by an overlap method and then corrected for geometric effects and attenuation and the data file updated. If the iterative image reconstruction option is selected, one implementation is to compute a grid Siddon retracing, and to perform maximum likelihood expectation maiximization (MLEM) computed by either: a) tracing parallel rays between subpixels on opposite detector heads; or b) tracing rays between randomized endpoint locations on opposite detector heads.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
Nuclear medicine diagnostic apparatus, positron emission computed tomography apparatus, and detector units
InactiveUS20070080296A1Increase current leakageReduces energy resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyHigh temporal resolutionMoisture
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Kalman filtering image reconstruction method in PET imaging
ActiveCN101499173AQuality improvementRaise the bias2D-image generationComputerised tomographsFractographyImaging quality
The invention provides a method for rebuilding Kallman filtering image in PET imaging. The method includes steps as follows: obtaining a sinusoidal chart of an original projective line through PET positron emission faultage scanner, establishing a state space system, getting radioactivity activity distribution through the Kallman filtering method based on the state space and rebuilding image. The method rebuild PET image by using the Kallman filtering method based on the state space system which can increase the rebuild image quality efficiently; compared with the prior rebuild method, declination and dispersion of the rebuild result are increased greatly.
Owner:刘华锋
Multi modality imaging methods and apparatus
ActiveUS7348564B2Material analysis by optical meansCalibration apparatusUltrasound attenuationComputed tomography
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ct gantry mounted radioactive source loader for pet calibration
InactiveUS20080217541A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPet imagingMedical imaging
A medical imaging system is provided including a positron emission tomography (PET) imaging apparatus and a computed tomography (CT) imaging apparatus. The CT imaging apparatus includes a rotatable gantry. A radioactive source loader is attached to the rotatable gantry to rotate therewith. The radioactive source loader further includes a radioactive source to calibrate the PET imaging apparatus.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
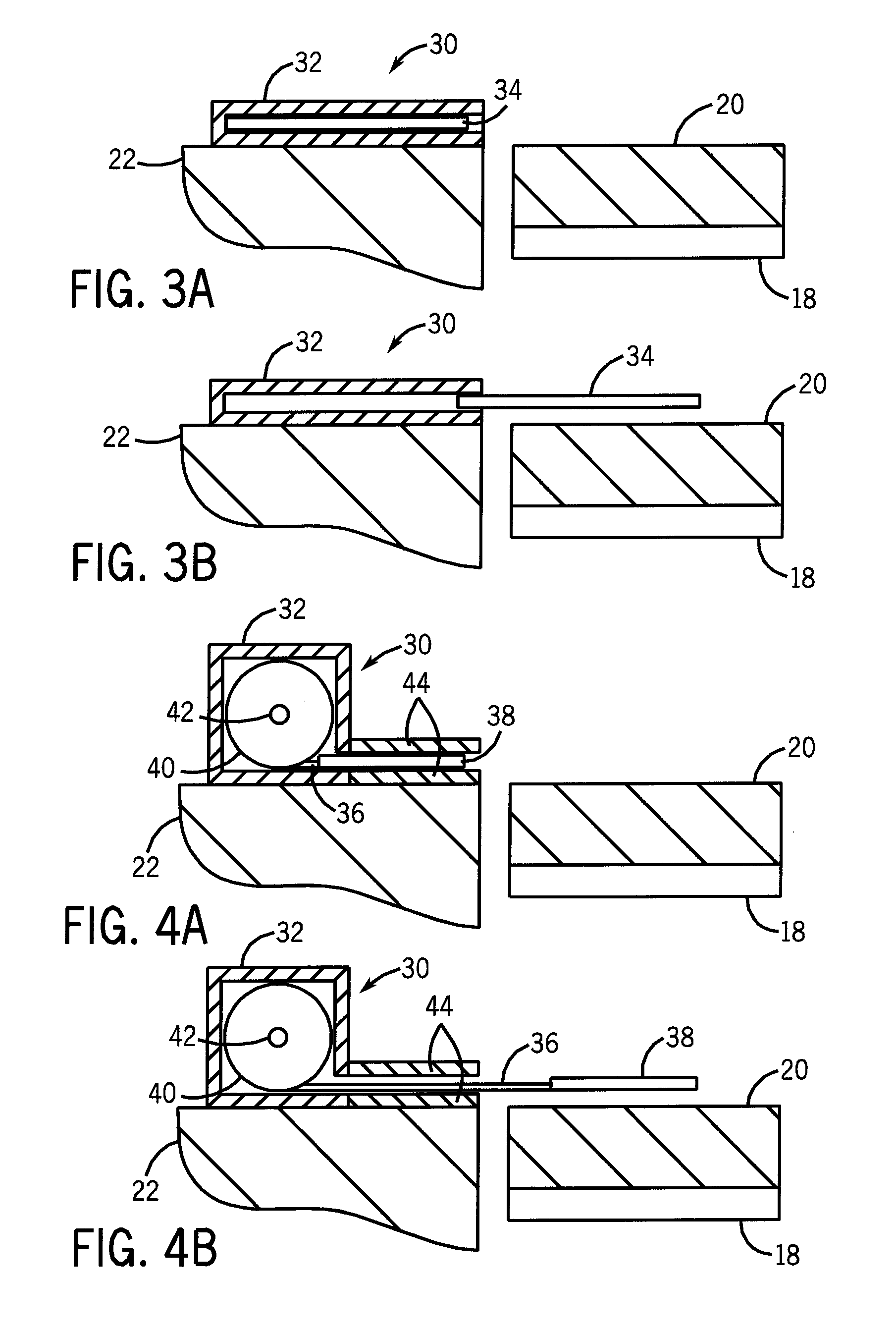
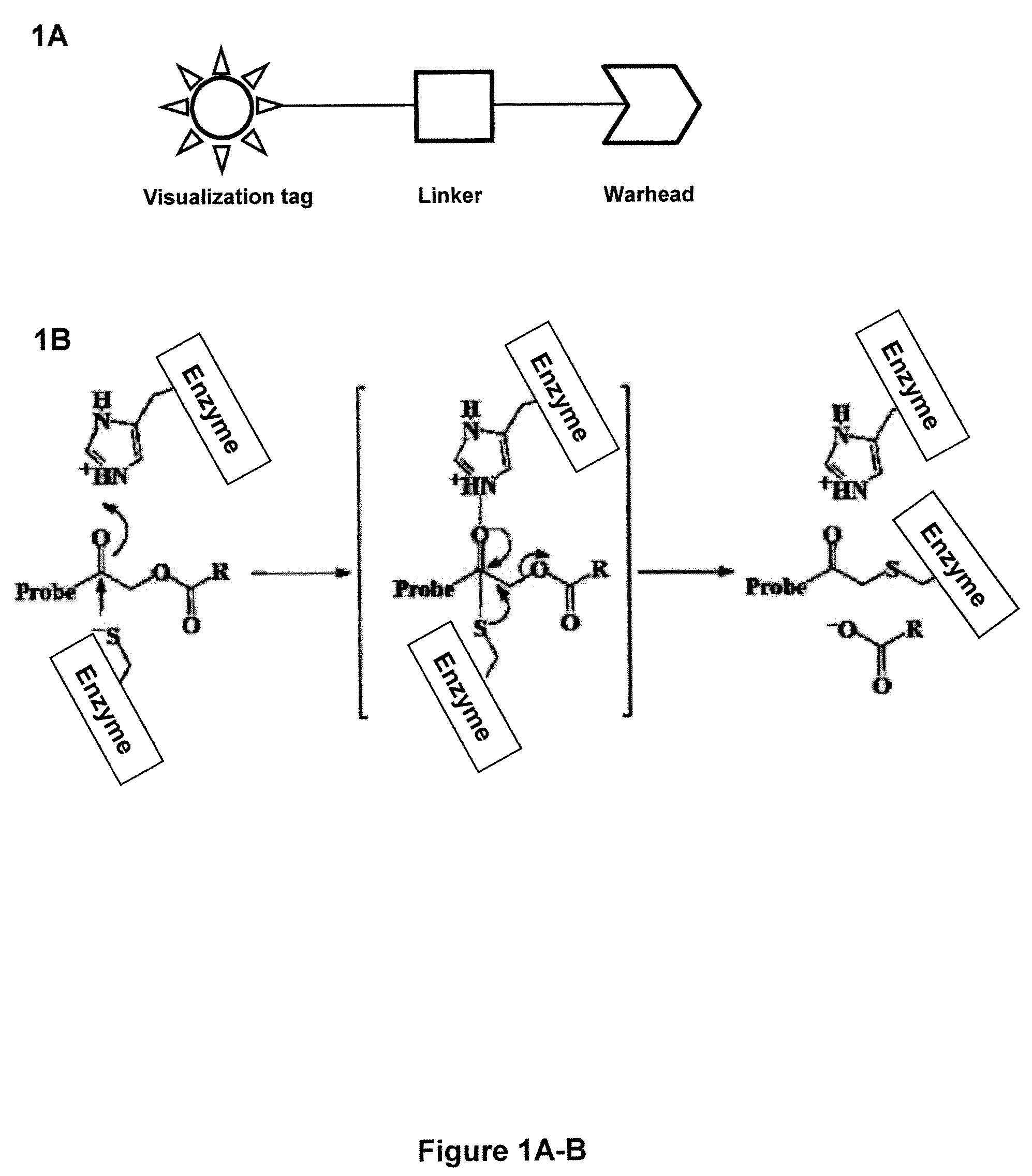
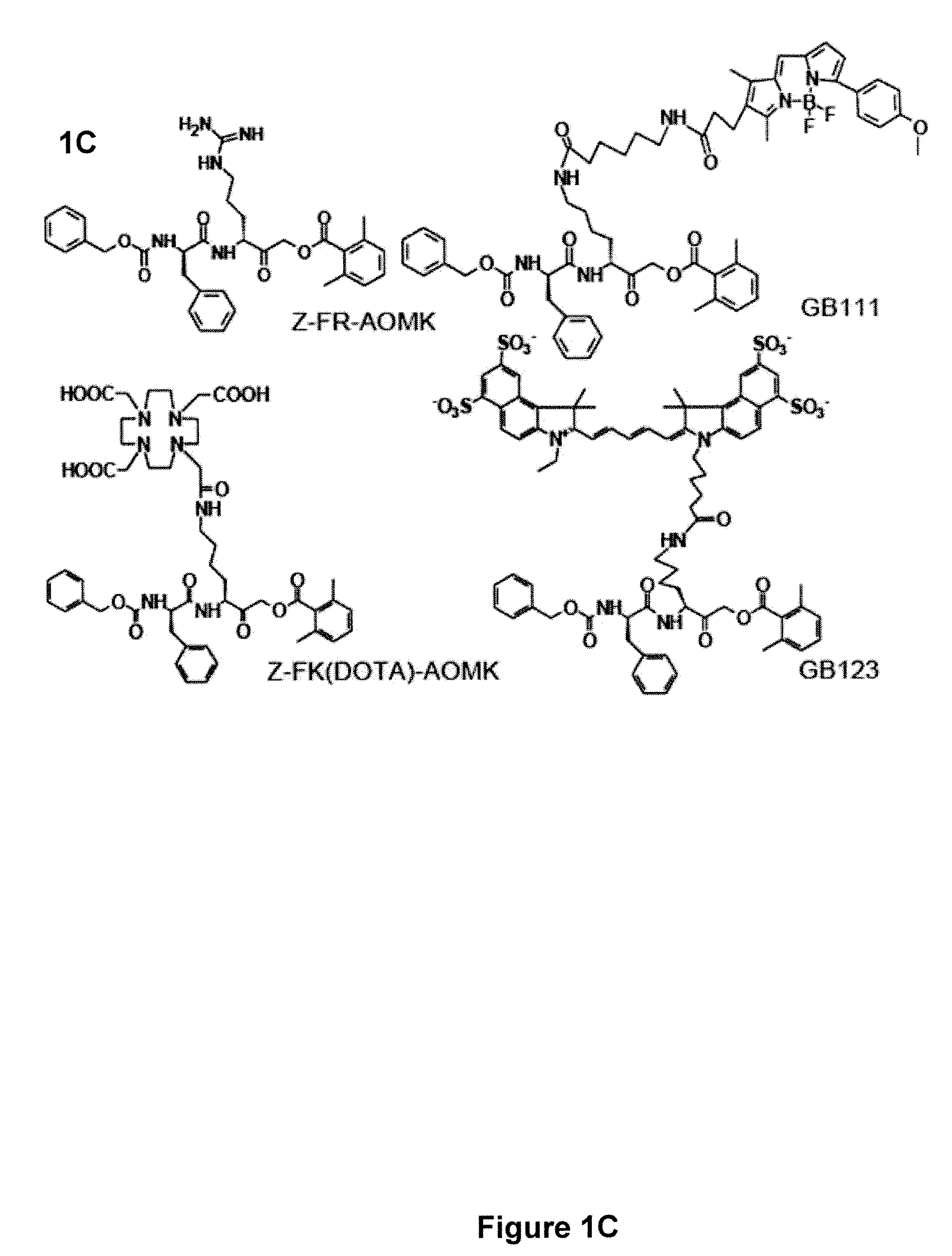
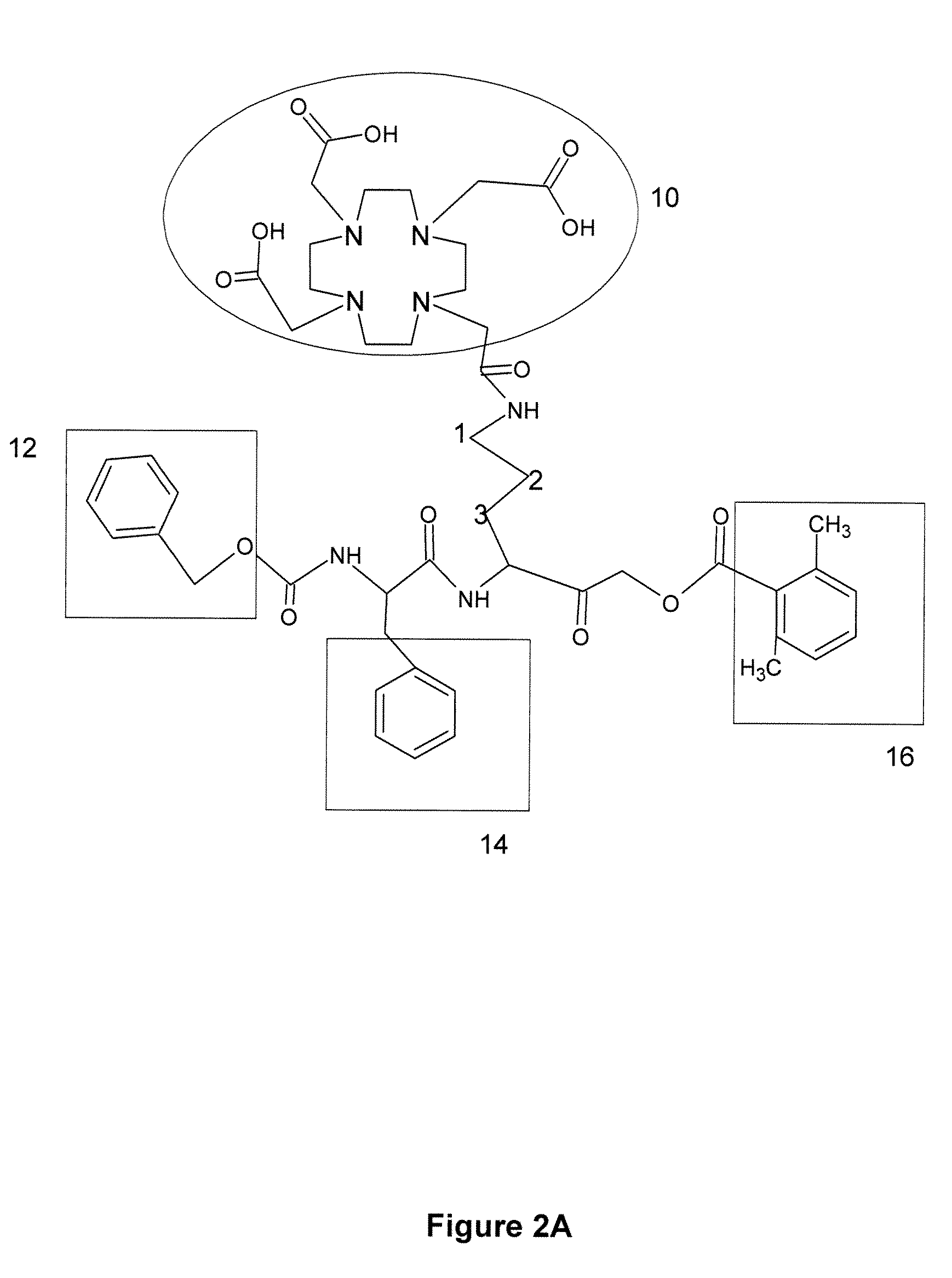
Probes for In Vivo Targeting of Active Cysteine Proteases
ActiveUS20090252677A1Stable labelingSufficient half-lifeRadioactive preparation carriersX-ray constrast preparationsActive enzymeHalf-life
Activity-based probes, which are specific for certain active cysteine proteases (caspase, cathepsin and legumain) and carry radioactive labels, are disclosed. The present probes comprise an acyloxymethyketone (AOMK) “warhead” that binds only to active enzyme. The probes further comprise peptide-like structure that targets the probe to a specific cysteine protease or protease family, and a radiolabel on the probe, which is bound to the targeted enzyme. It has been found that the present probes are stable in vivo and give specific target images distinguishable over background. The preferred probes are labeled with a positron-emitting agent such as 64Cu, 125I (SPECT) and 99mTc (PET). The probes show in vivo half-life and stability well suited for imaging.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com