Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1376results about "Emergency protection arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
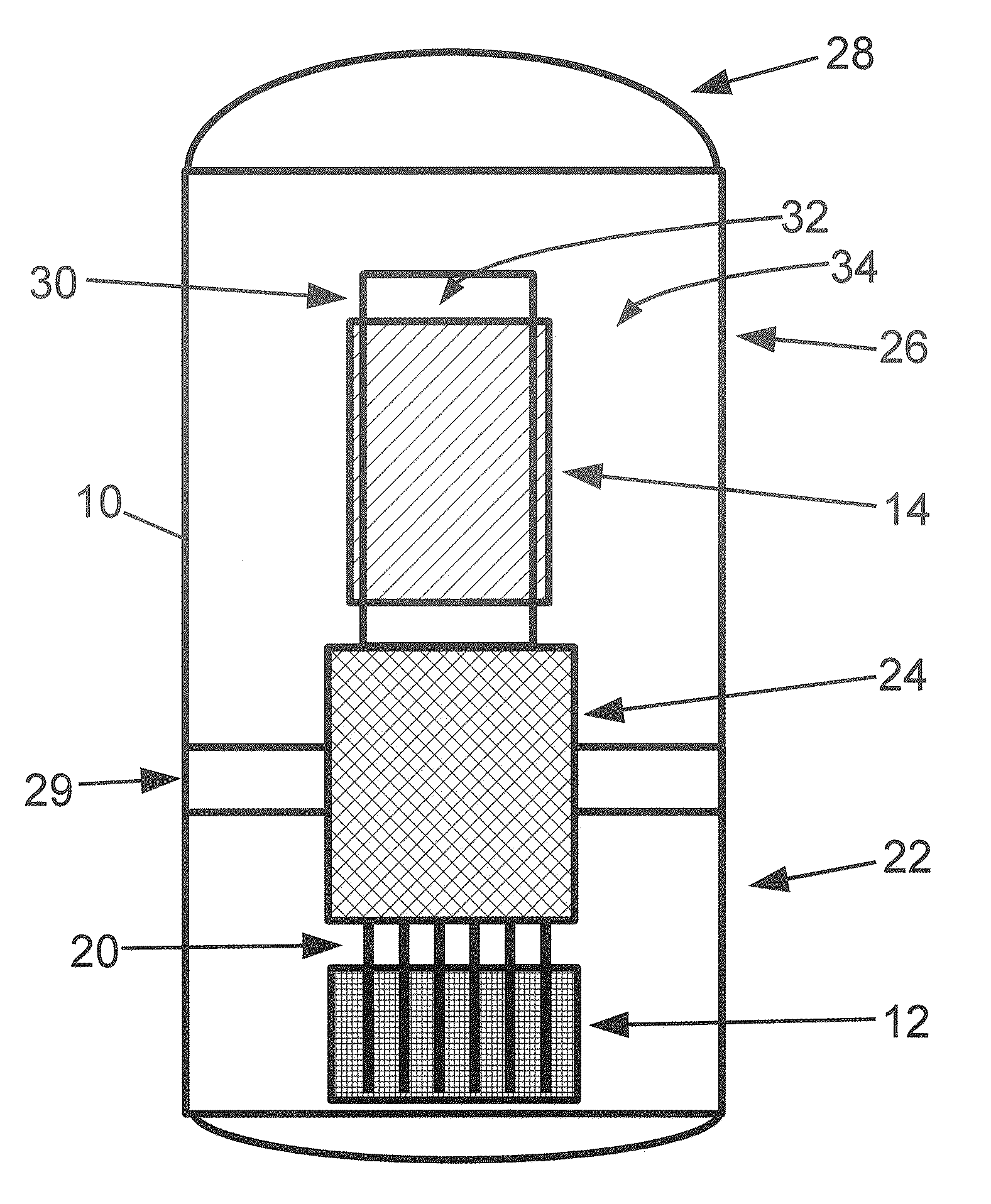
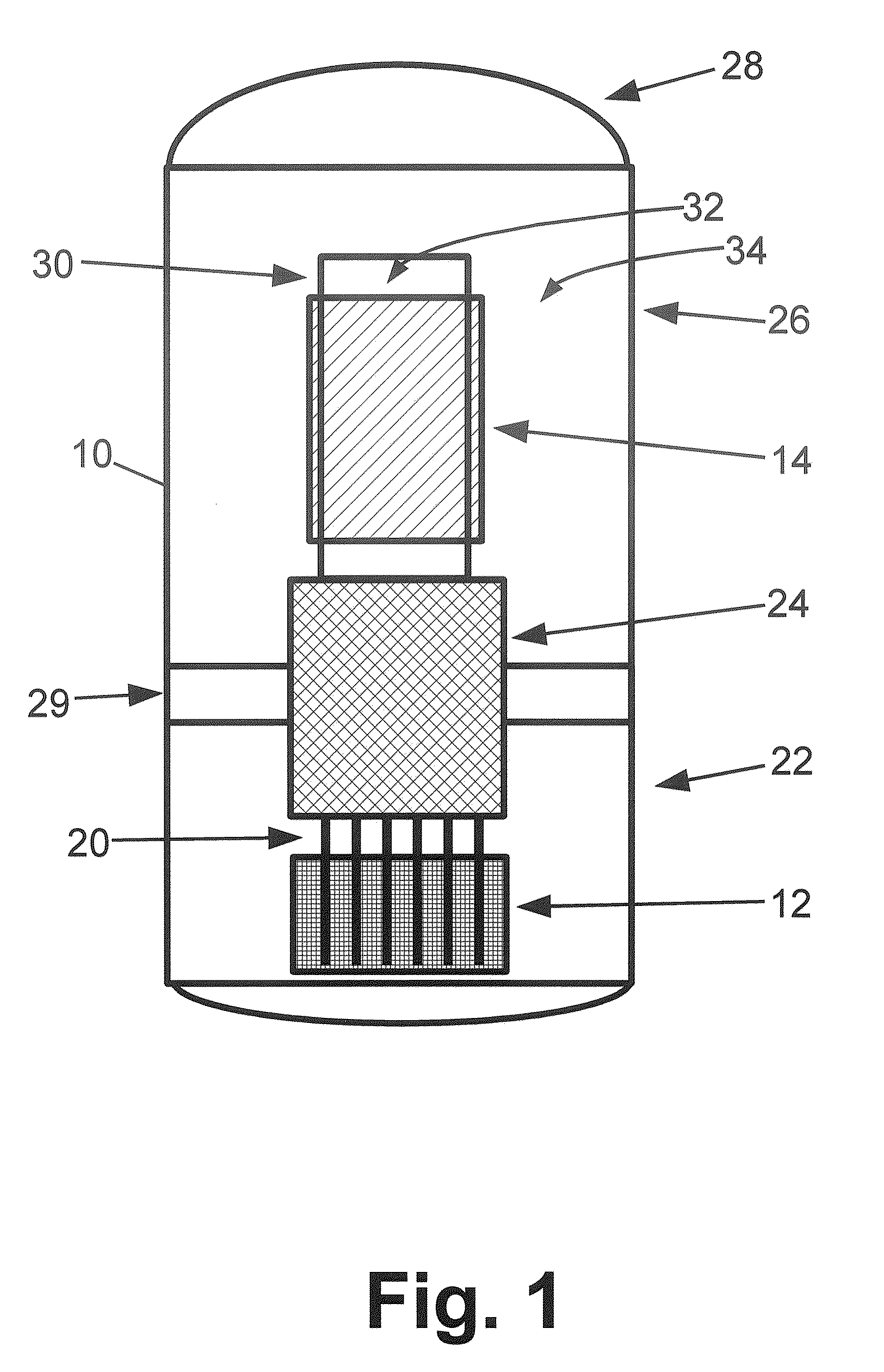
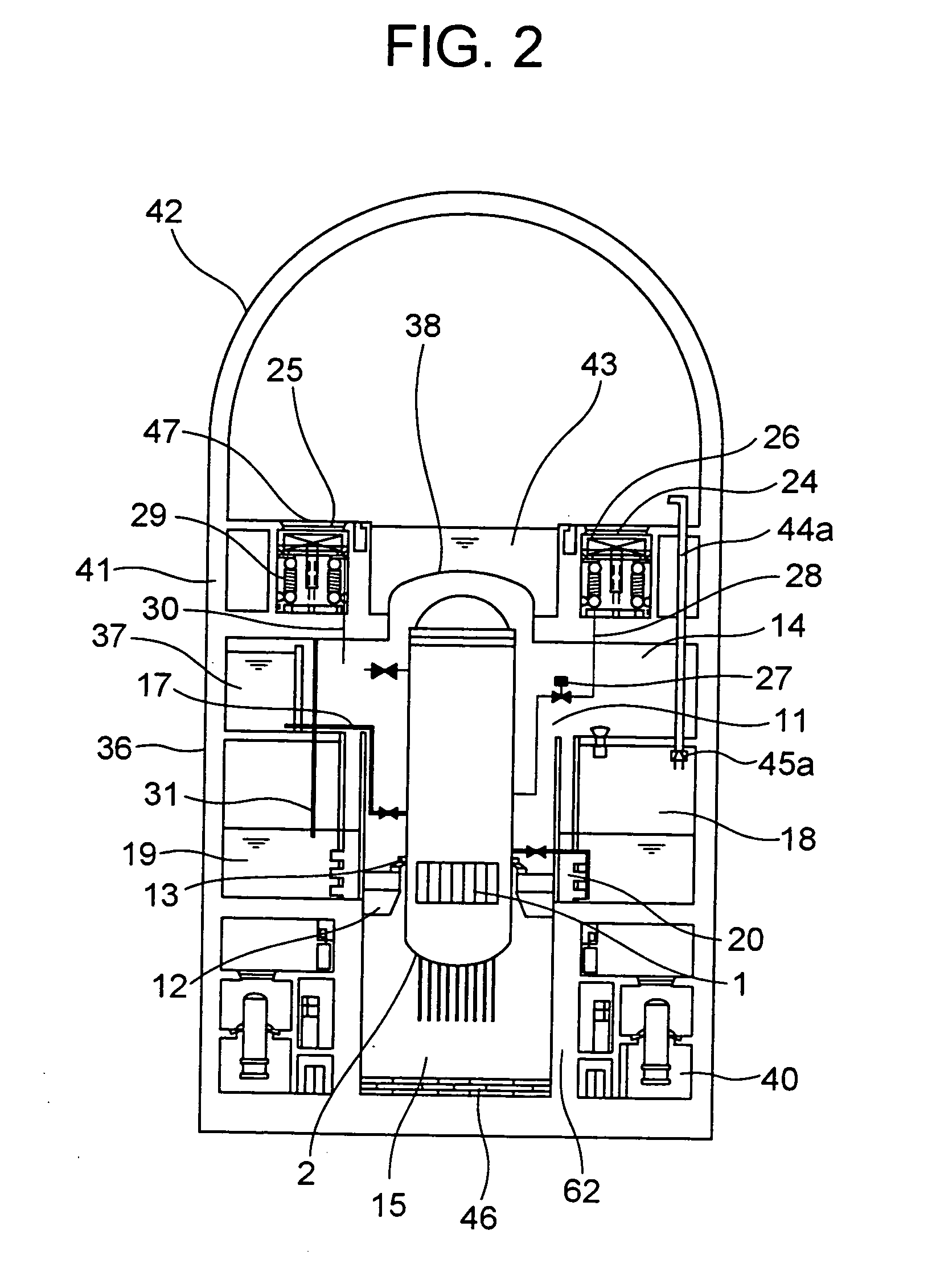
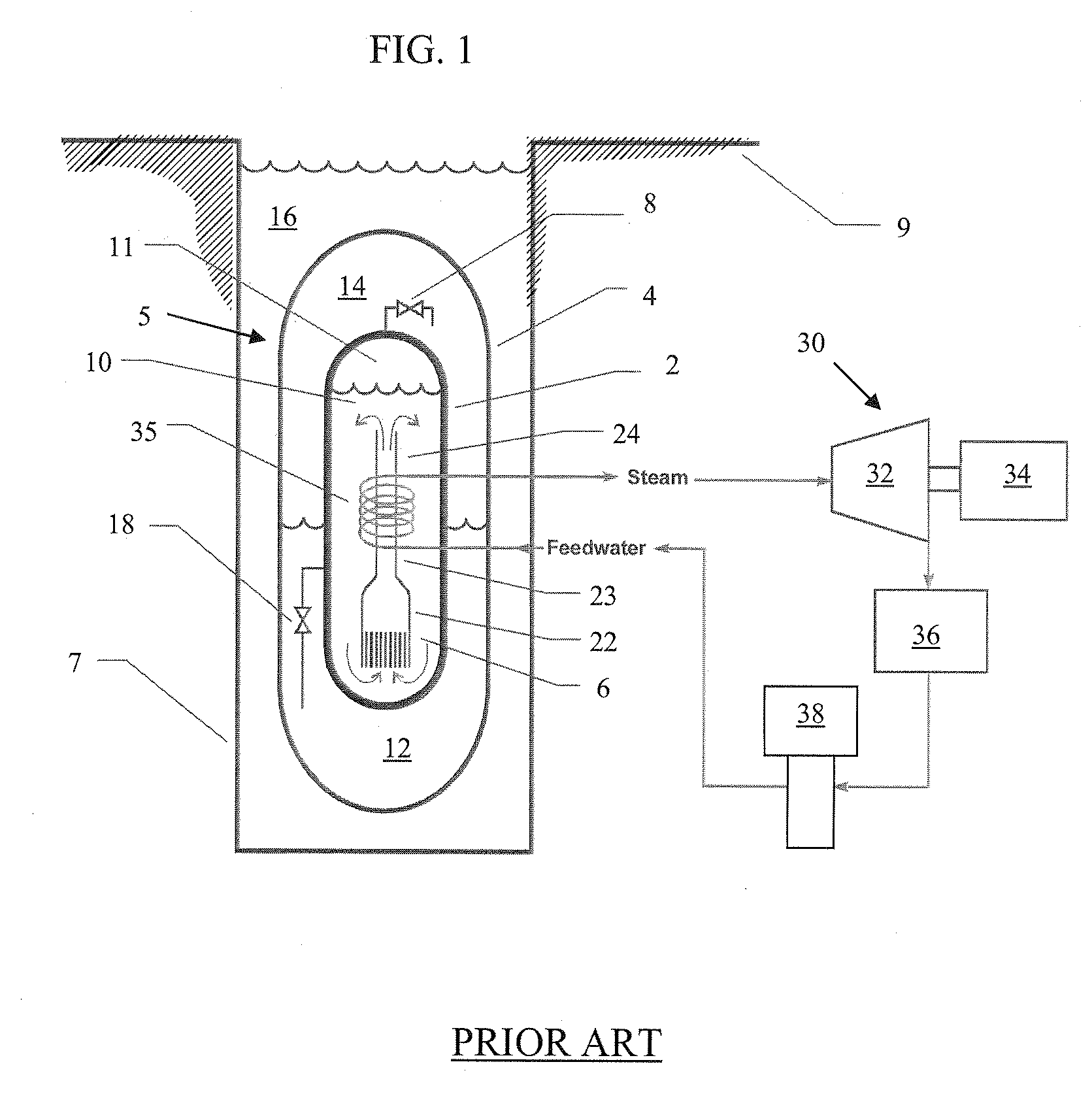
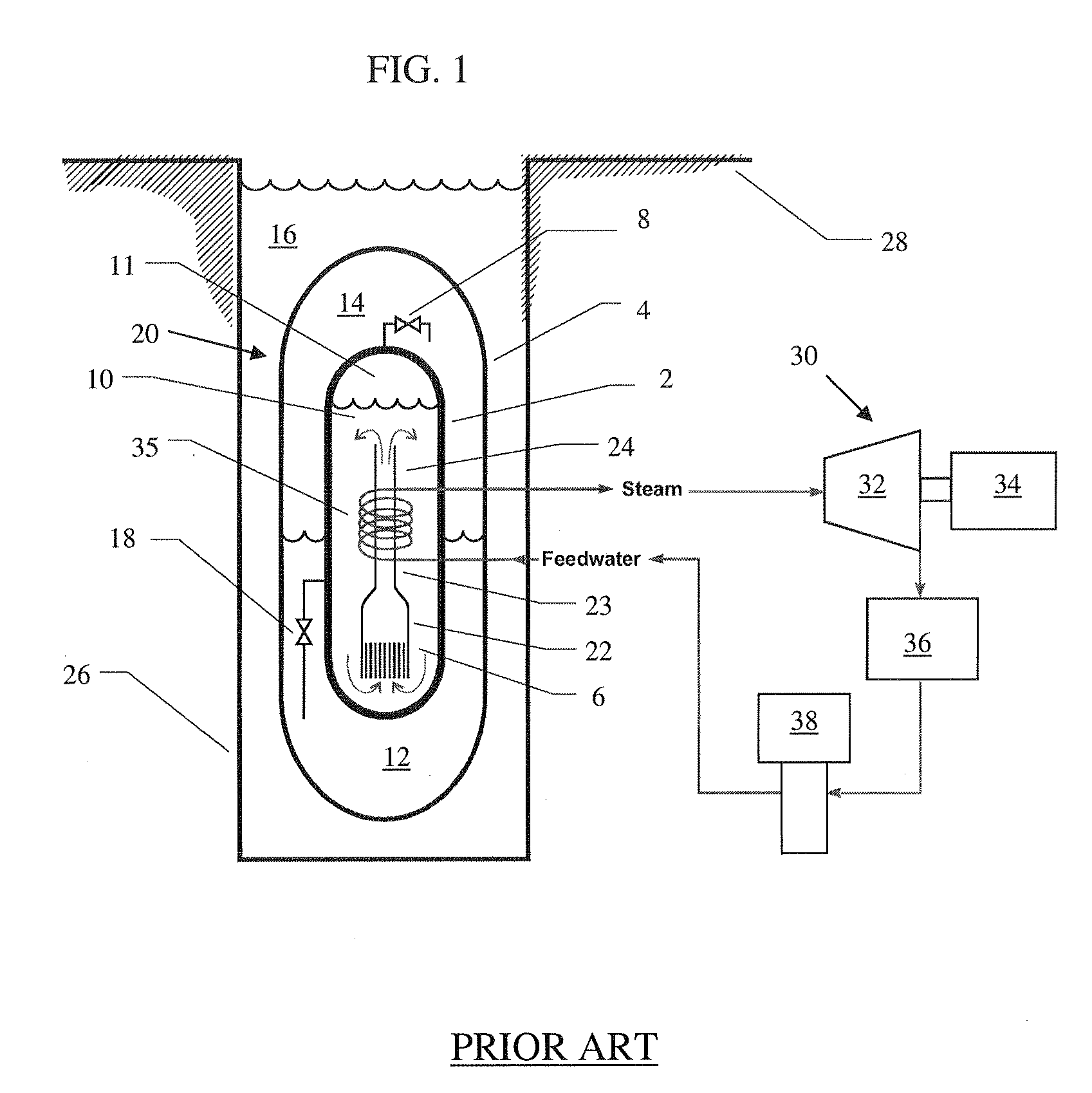
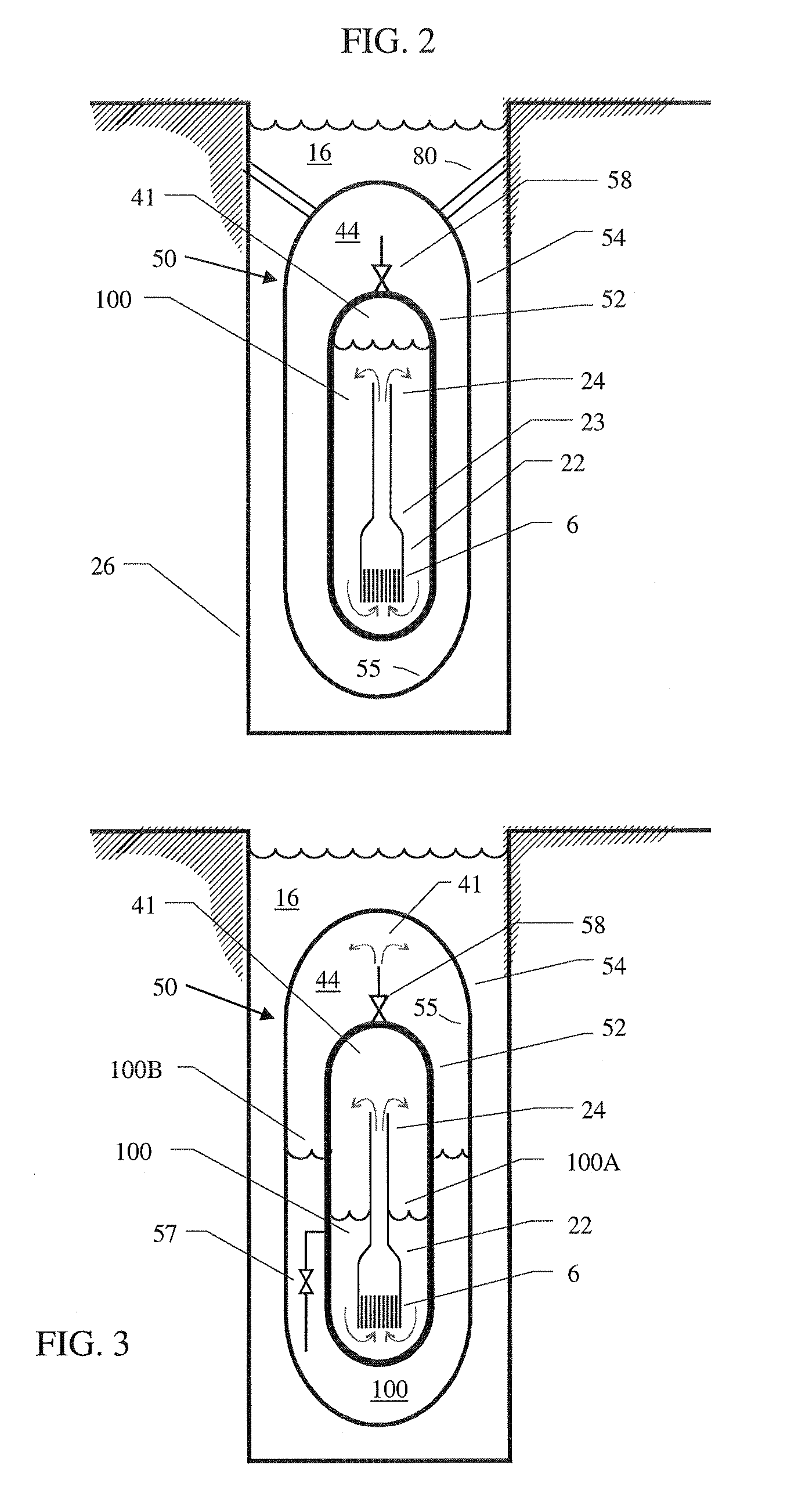
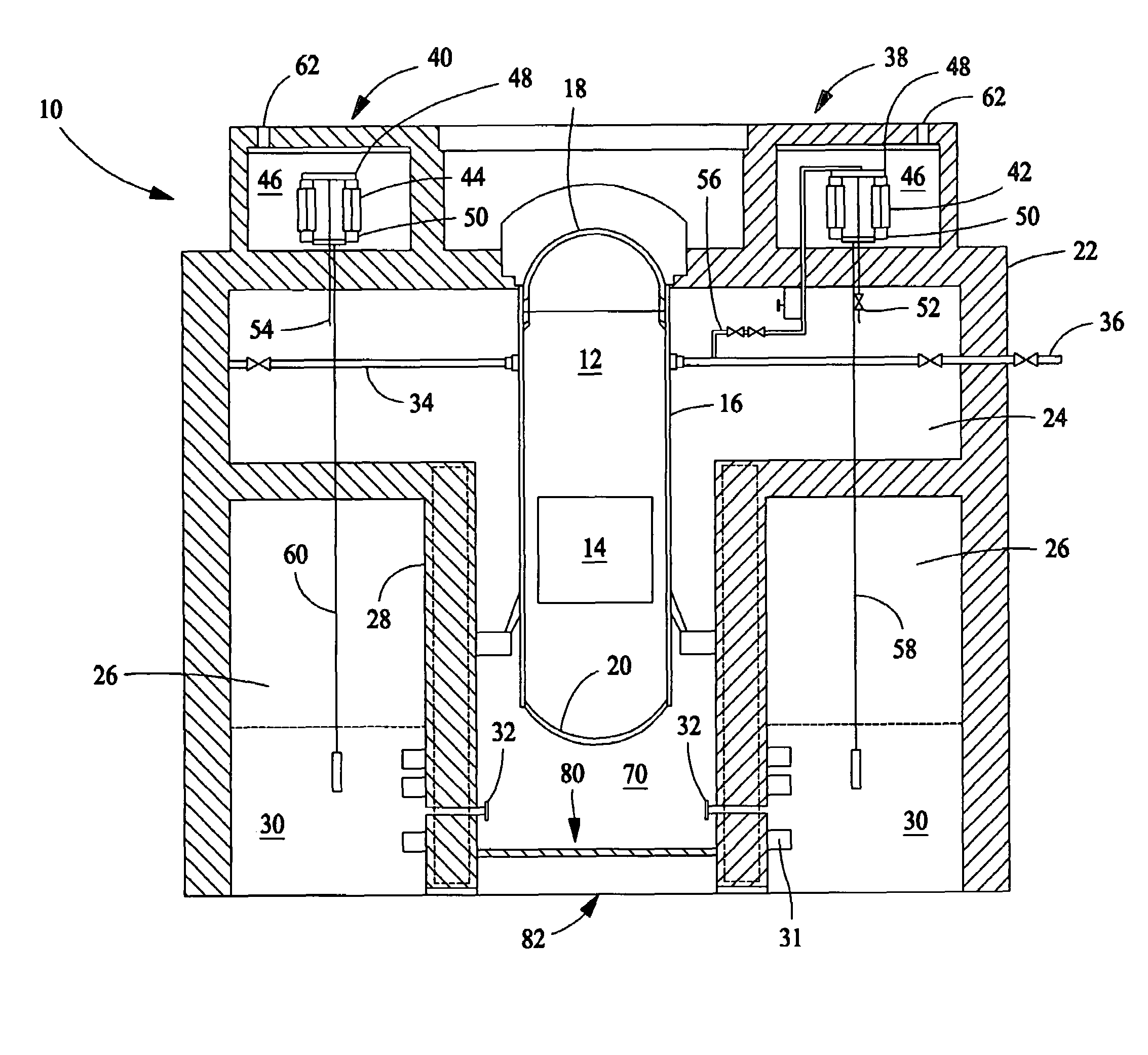
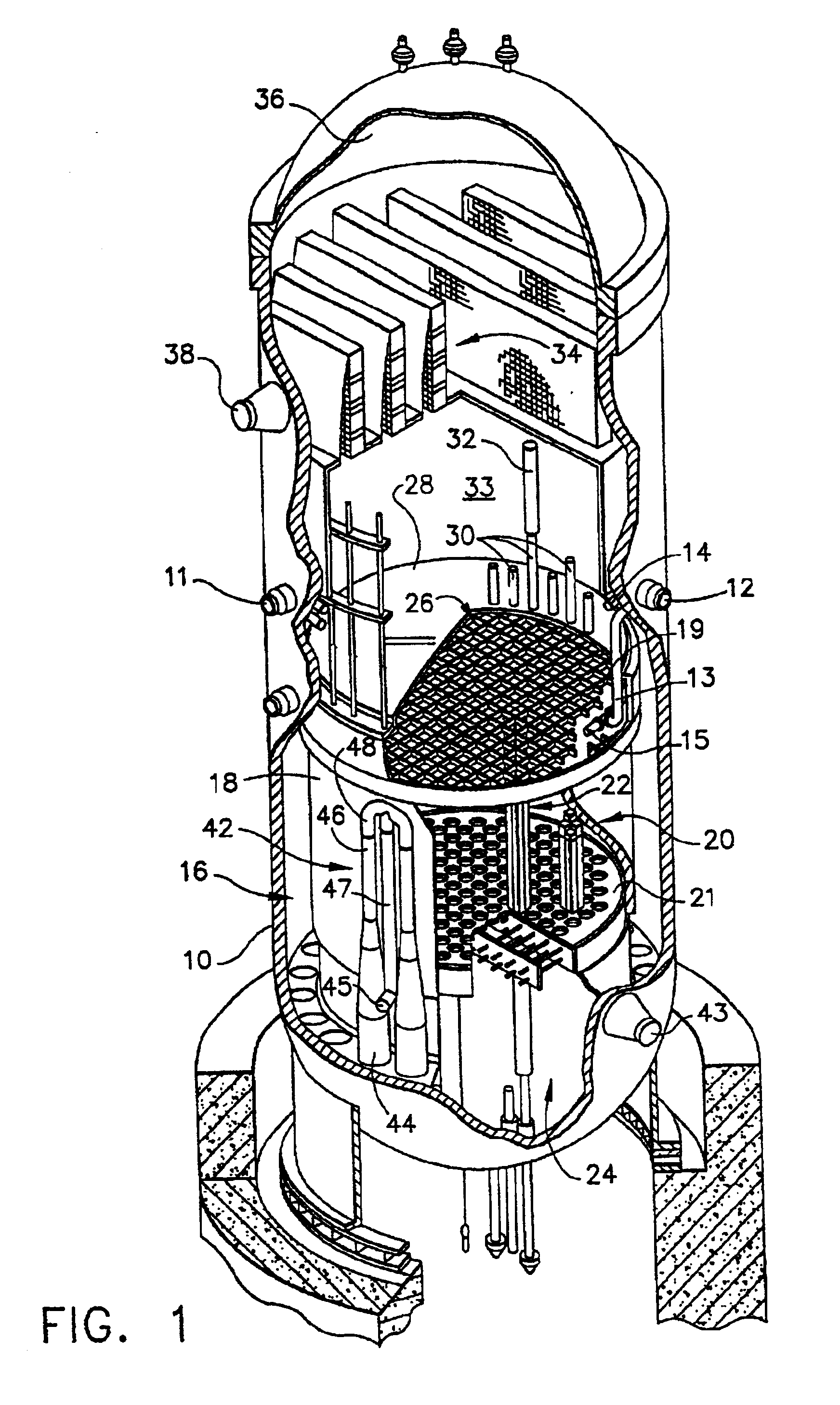
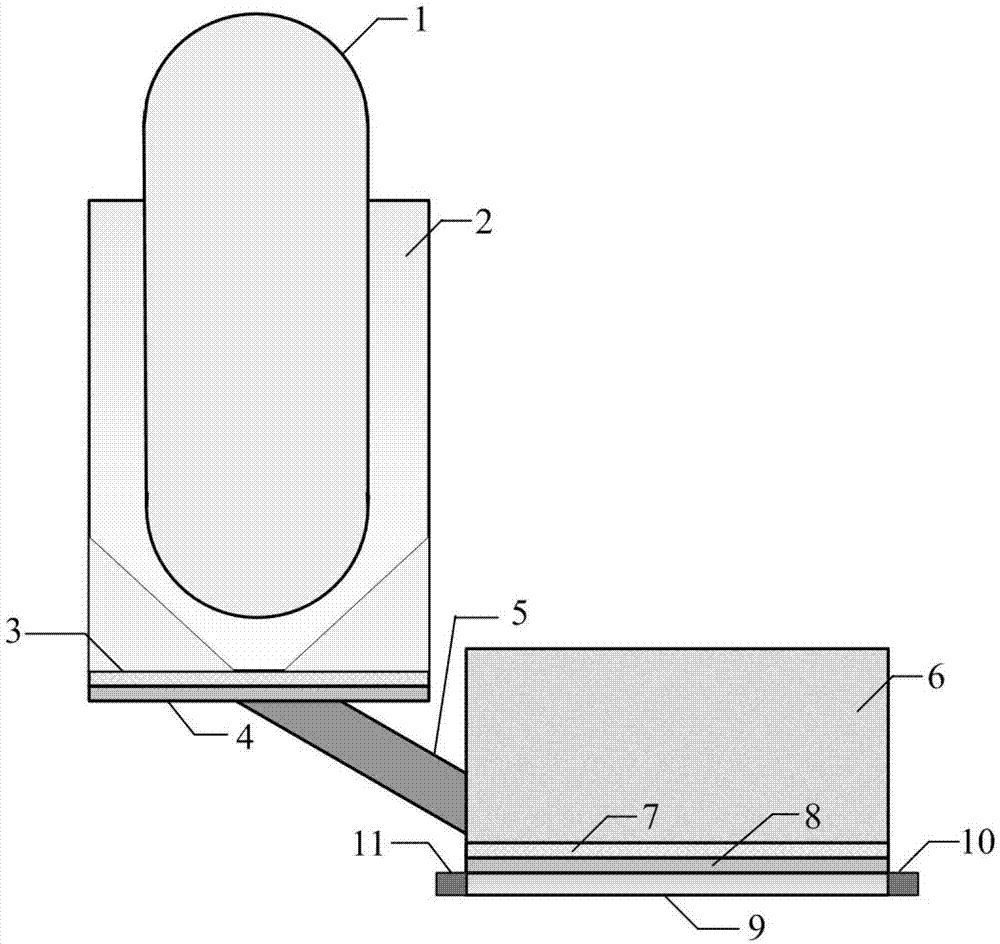
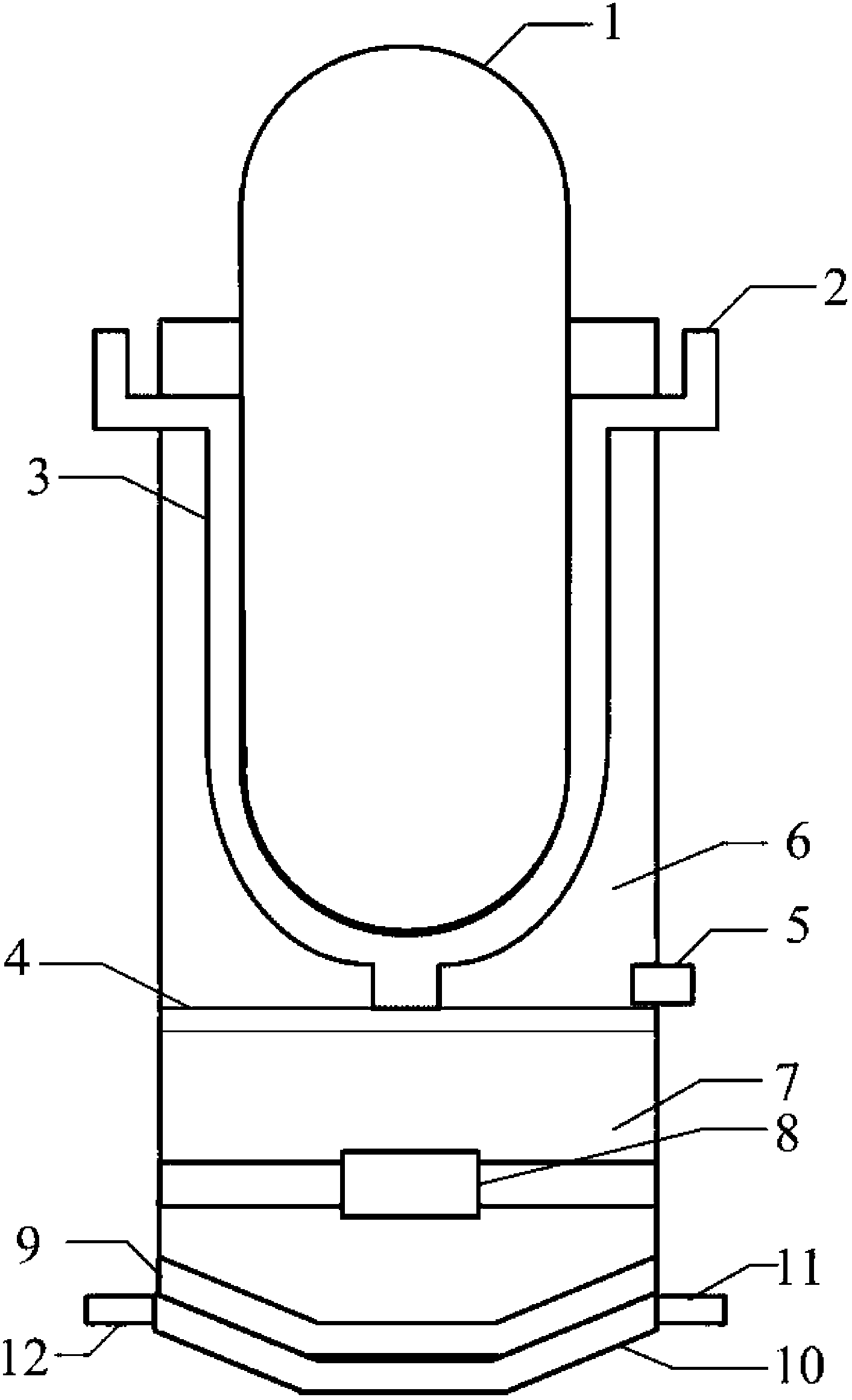
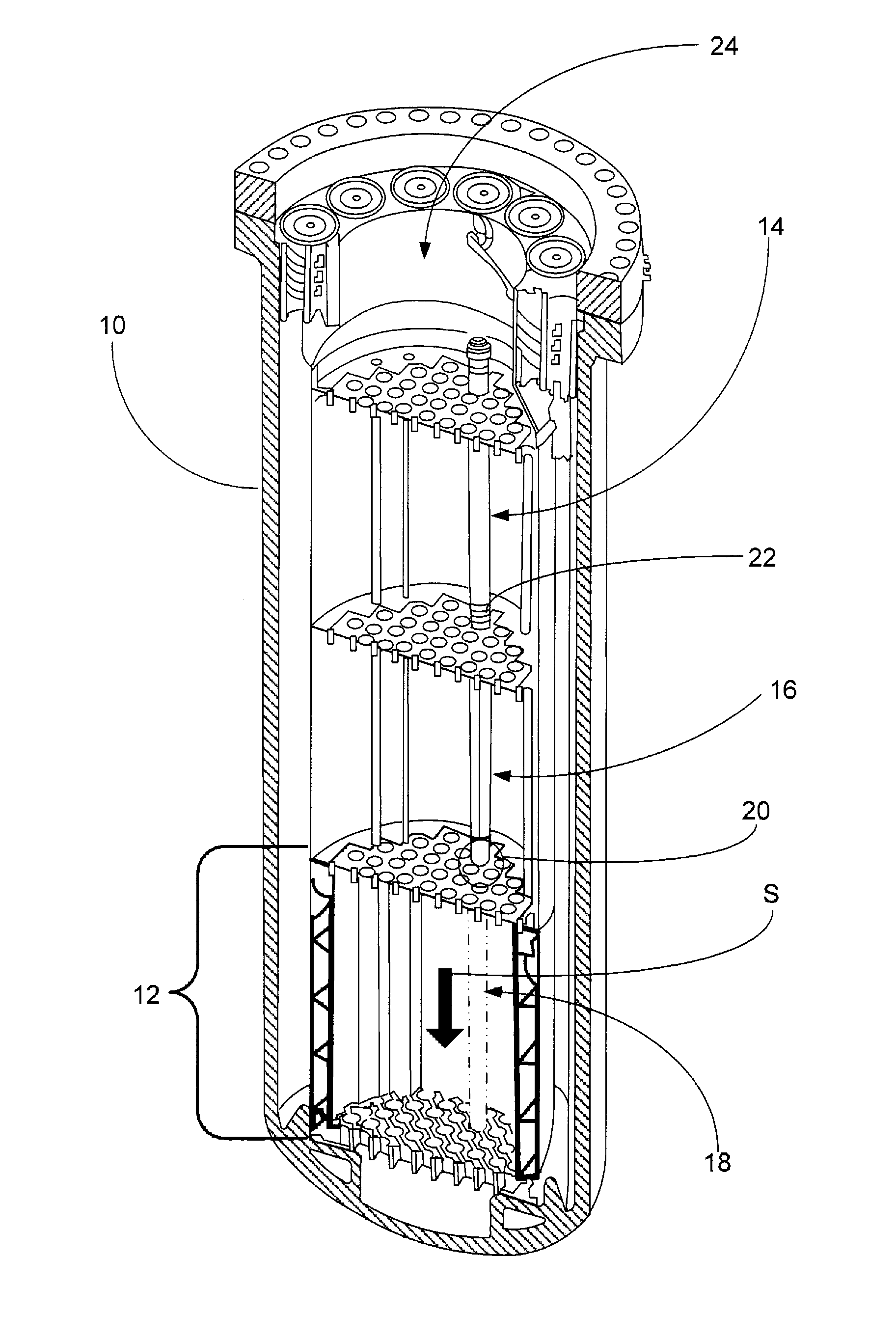
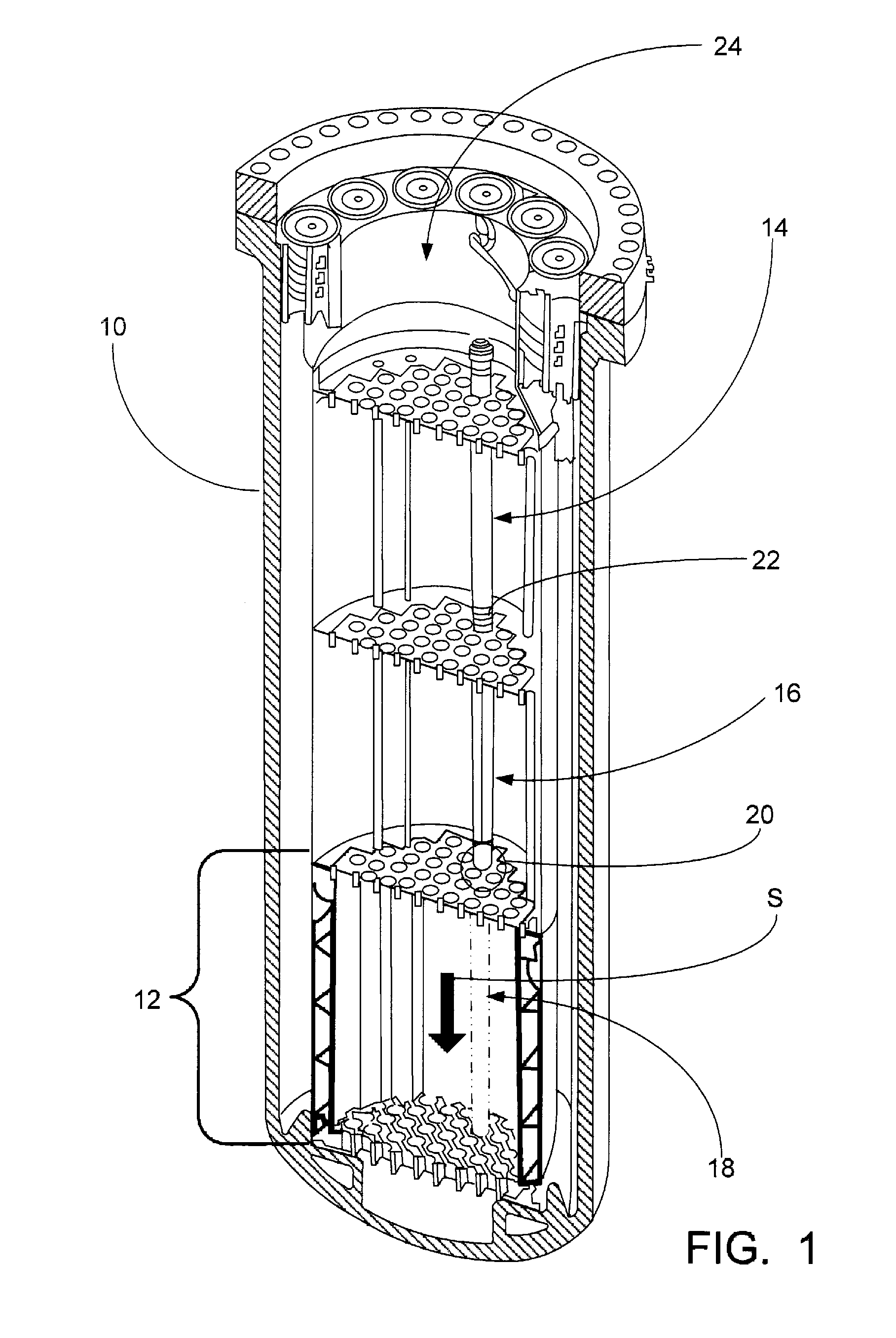
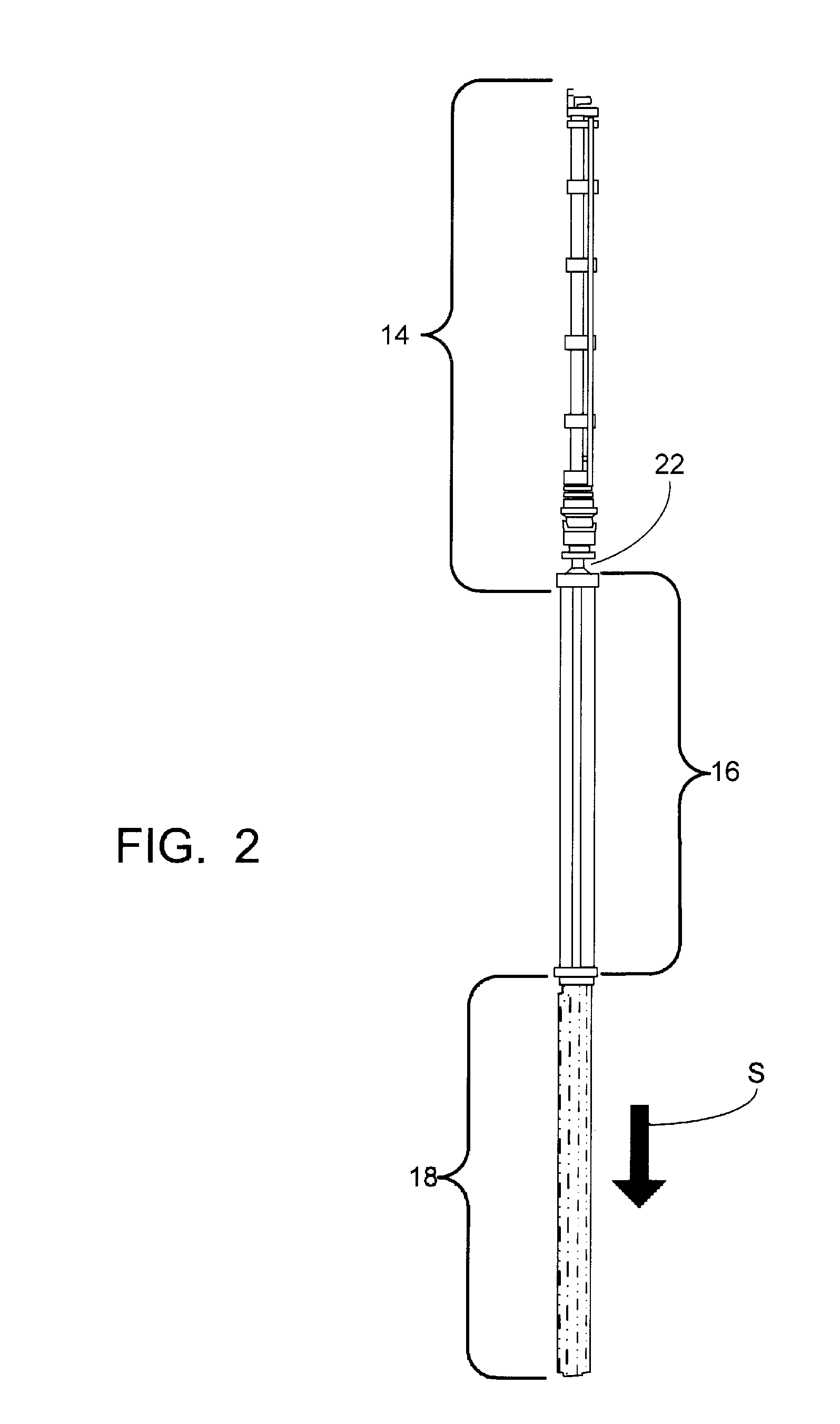
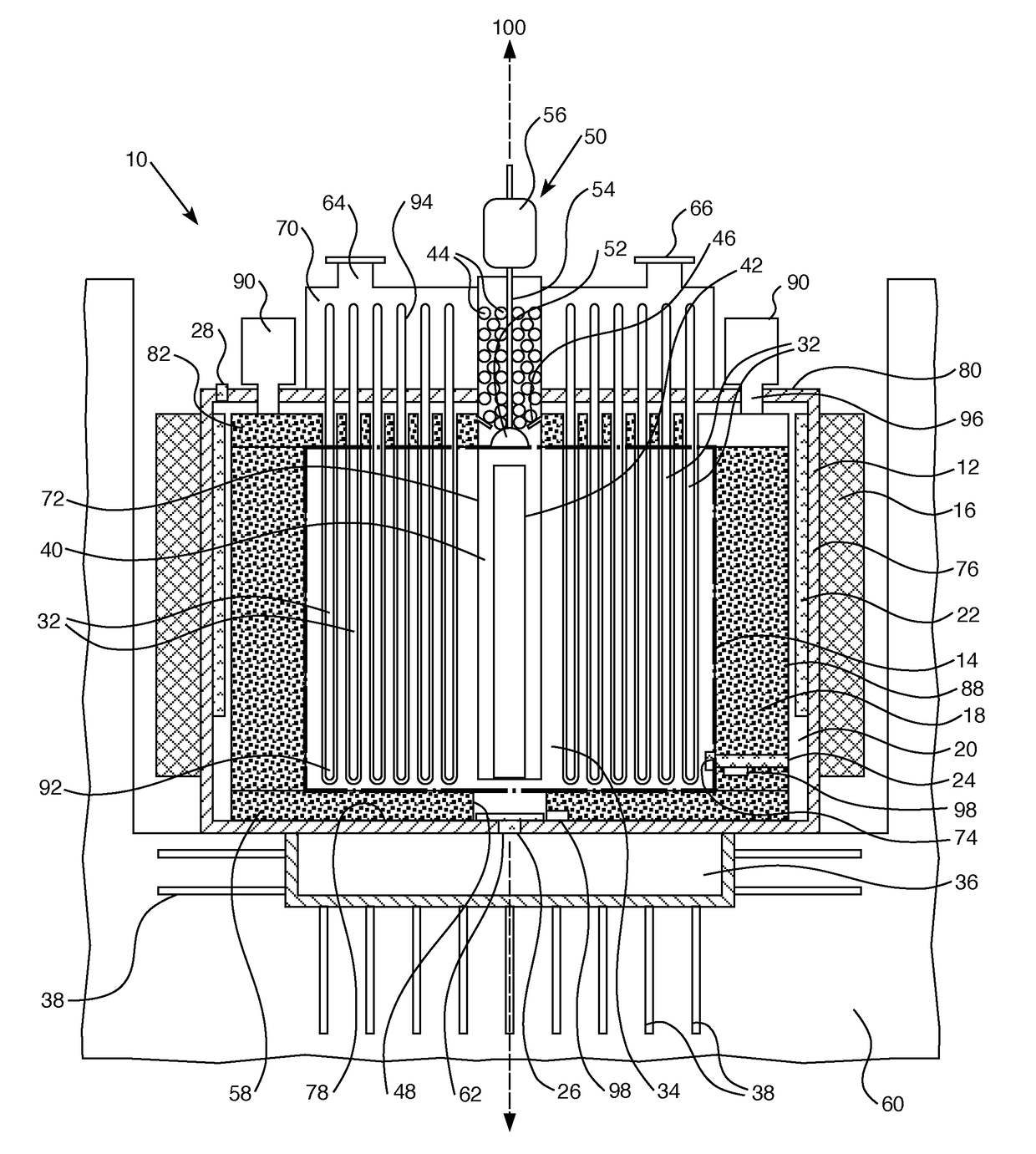
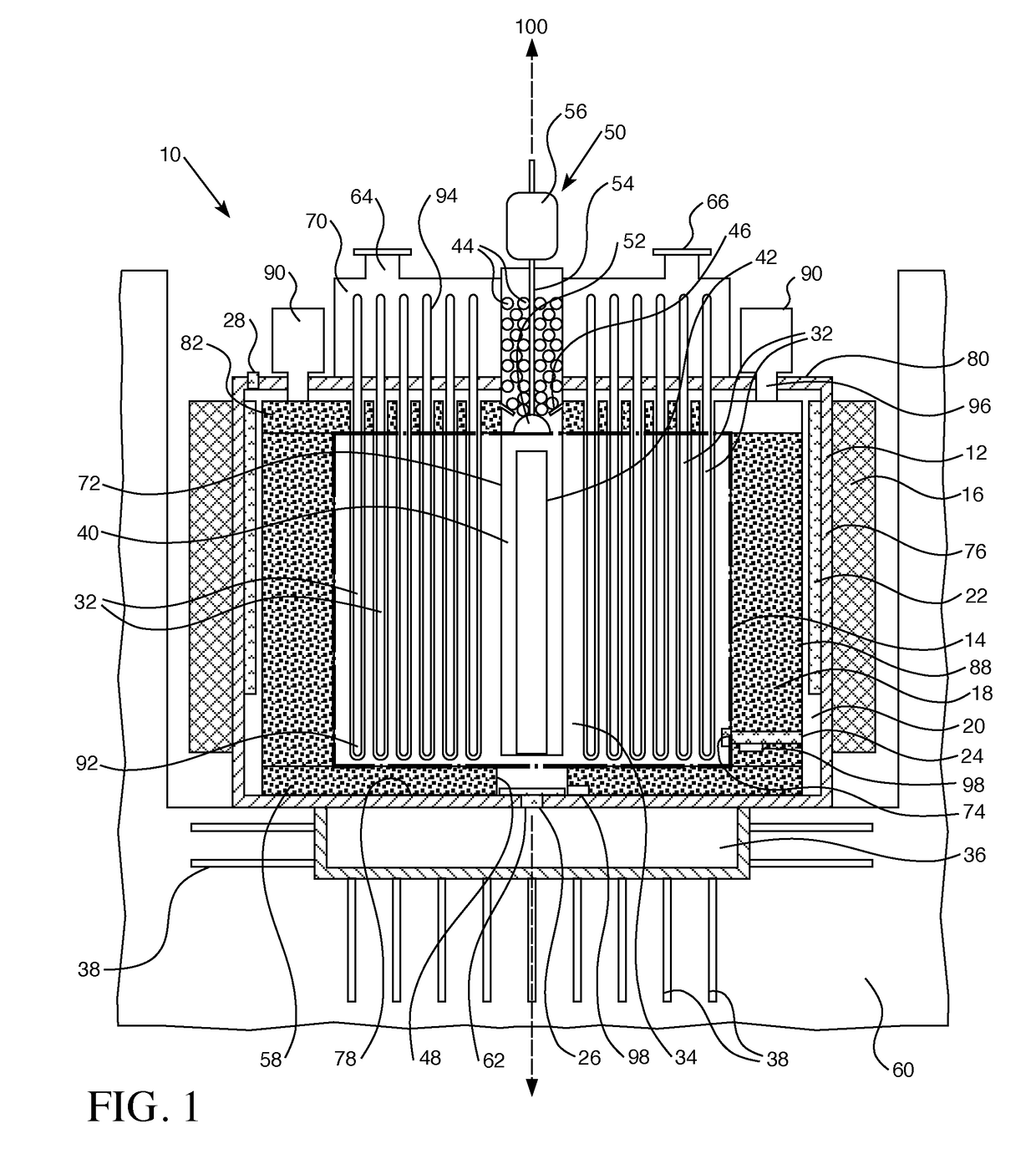
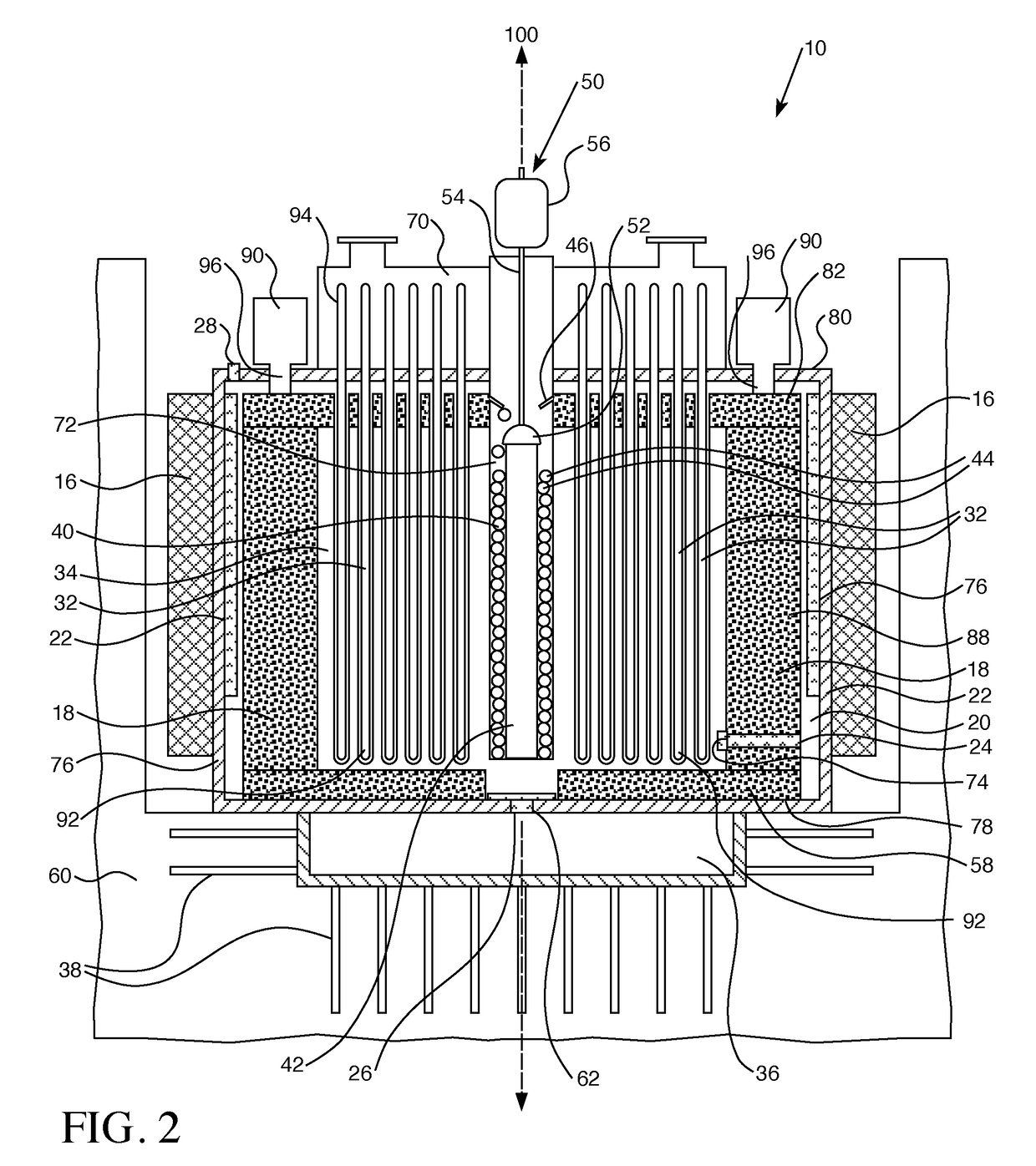
Control rod drive mechanism for nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20100316177A1Nuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A control rod drive mechanism (CRDM) for use in a nuclear reactor, the CRDM comprising: a connecting rod connected with at least one control rod; a lead screw; a drive mechanism configured to linearly translate the lead screw; an electromagnet coil assembly; and a latching assembly that latches the connecting rod to the lead screw responsive to energizing the electromagnet coil assembly and unlatches the connecting rod from the lead screw responsive to deenergizing the electromagnet coil assembly. The latching assembly is secured with and linearly translates with the lead screw, while the electromagnet coil assembly does not move with the lead screw. The electromagnet coil assembly is at least coextensive with a linear translation stroke over which the drive mechanism is configured to linearly translate the lead screw.
Owner:BWXT NUCLEAR OPERATIONS GRP
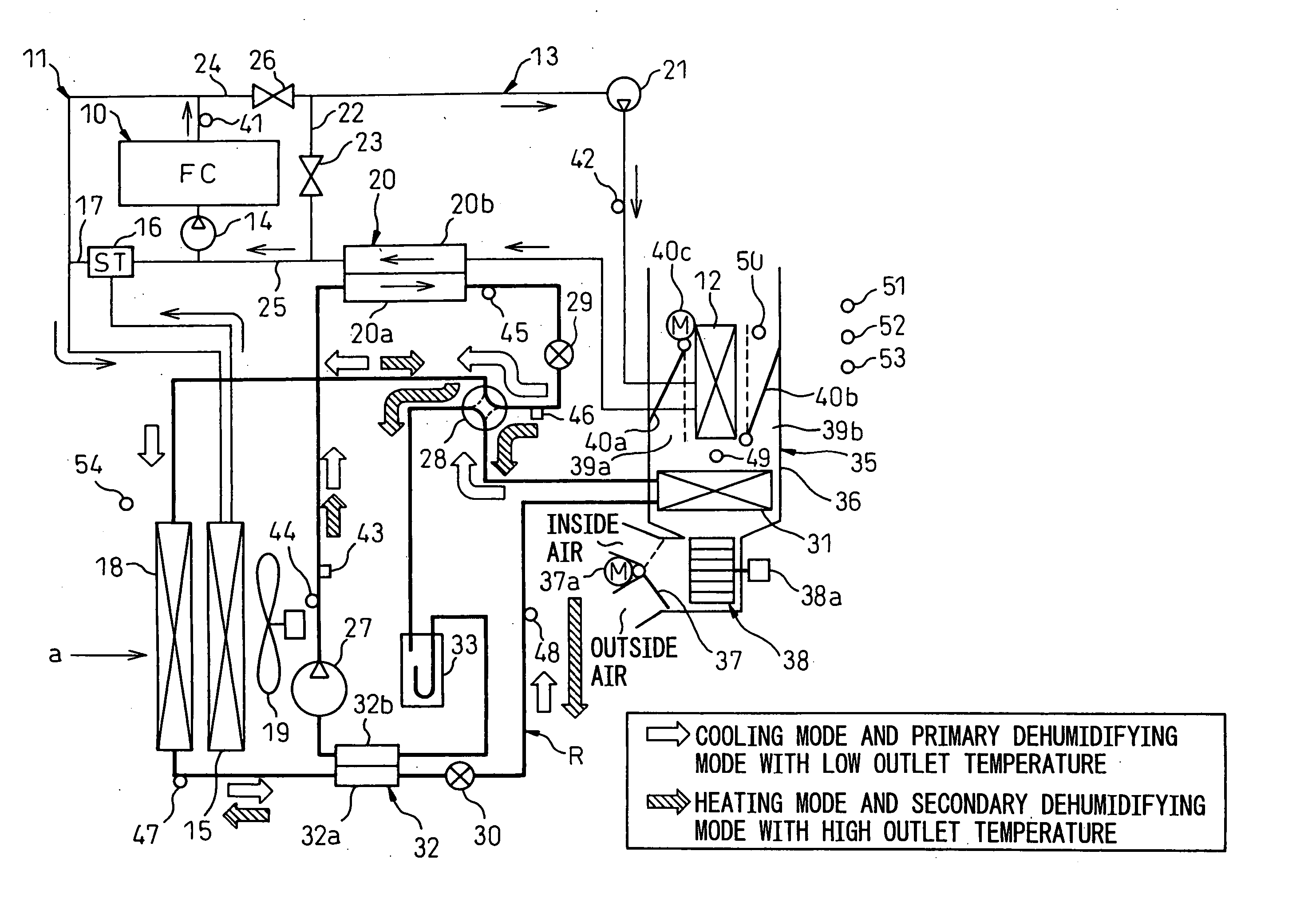
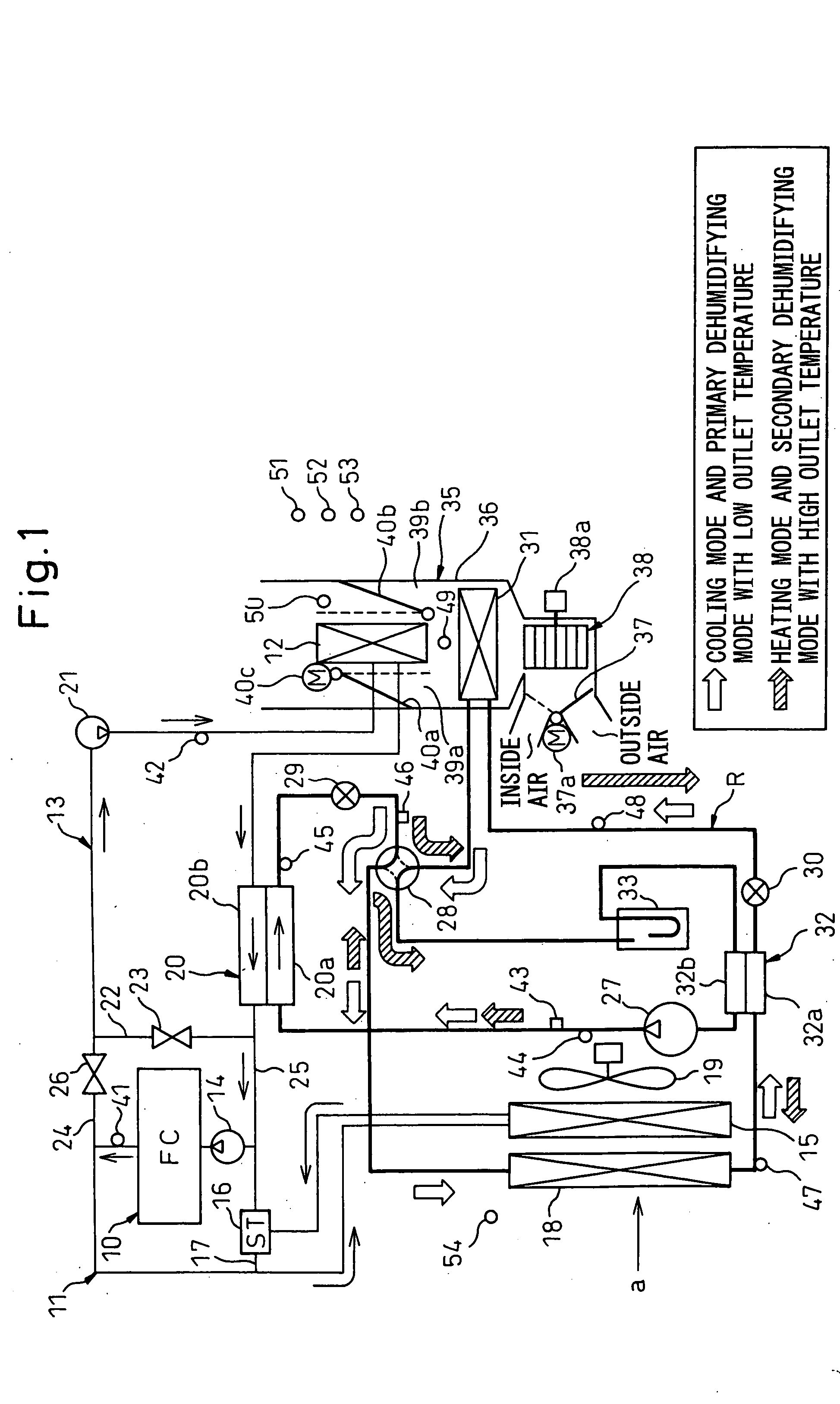
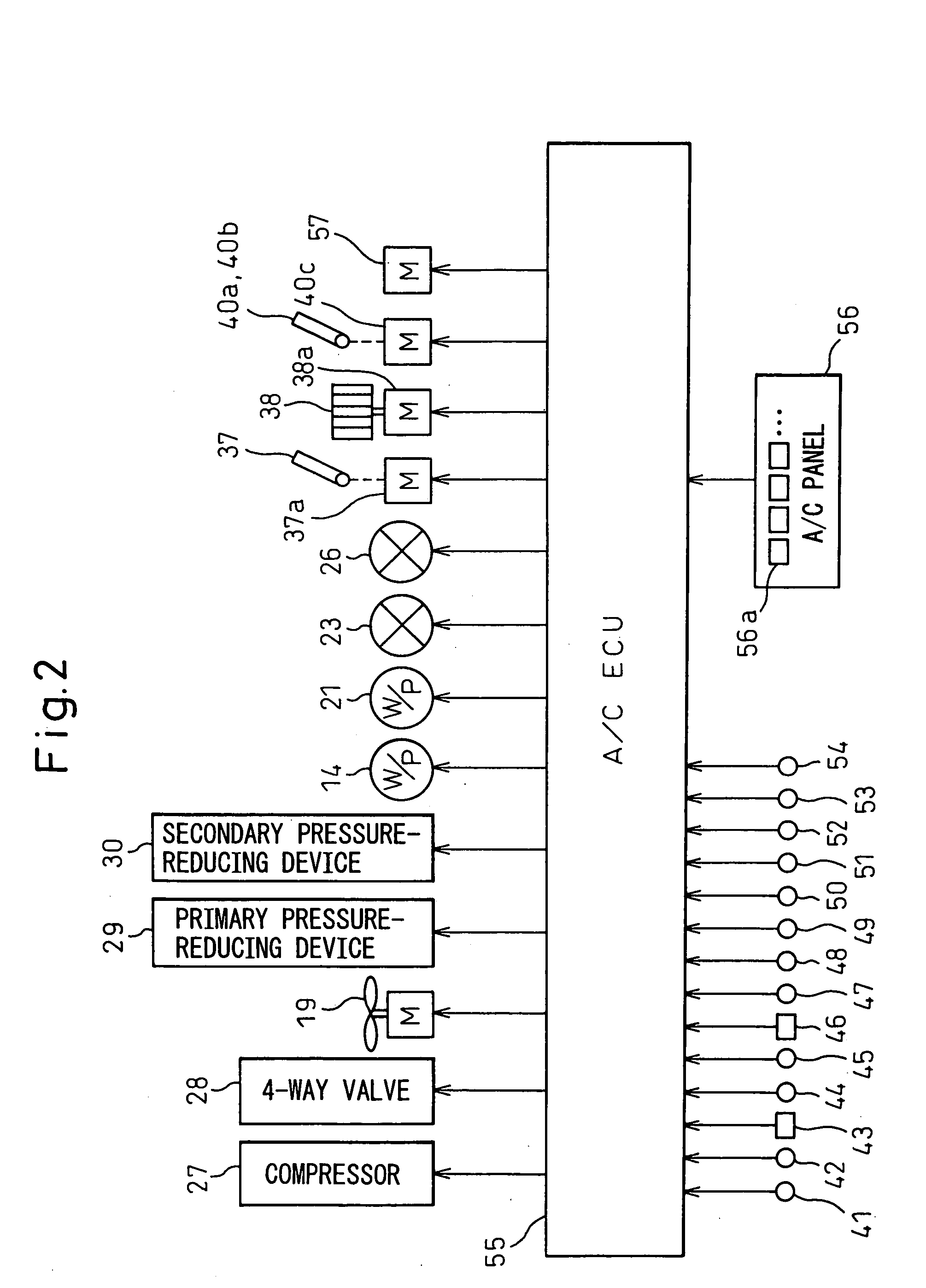
Automotive air conditioning system
InactiveUS20050178523A1Increase immediate effect of heating performanceImprove immediacyPower to auxillary motorsEmergency protection arrangementsEngineeringCoolant temperature
An automotive air conditioning system has a primary hot water circuit 11 located on a side where a vehicle installed heat generator 10 is located and a secondary hot water circuit 13 which includes a hot water type heater core 12 for heating passenger compartment outlet air, whereby when in a heating mode, in the event that a coolant temperature TW1 of the primary hot water circuit is lower than a coolant temperature TW2 of the secondary hot water circuit 13, an opening and closing valve 26 is closed, whereas an opening and closing valve 23 is opened, so that a state is created in which the hot water circuits 11, 13 are separated from each other. On the other hand, in the event that the coolant temperature TW1 of the primary hot water circuit becomes higher than the coolant temperature TW2 of the secondary hot water circuit 13, the opening and closing valve 26 is opened, whereas the opening and closing valve 23 is closed, so that a state is created in which the hot water circuits 11, 13 are connected to each other.
Owner:DENSO CORP
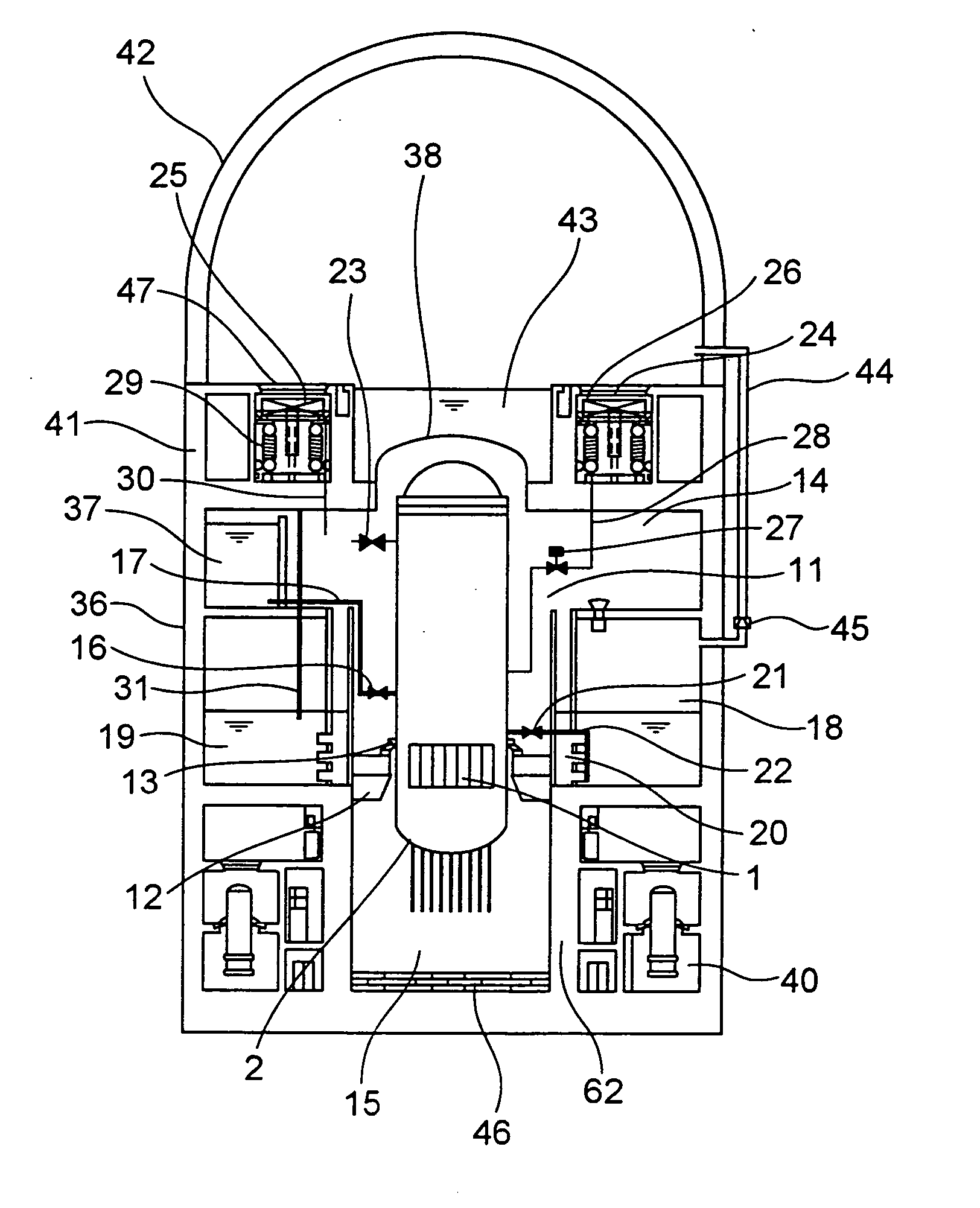
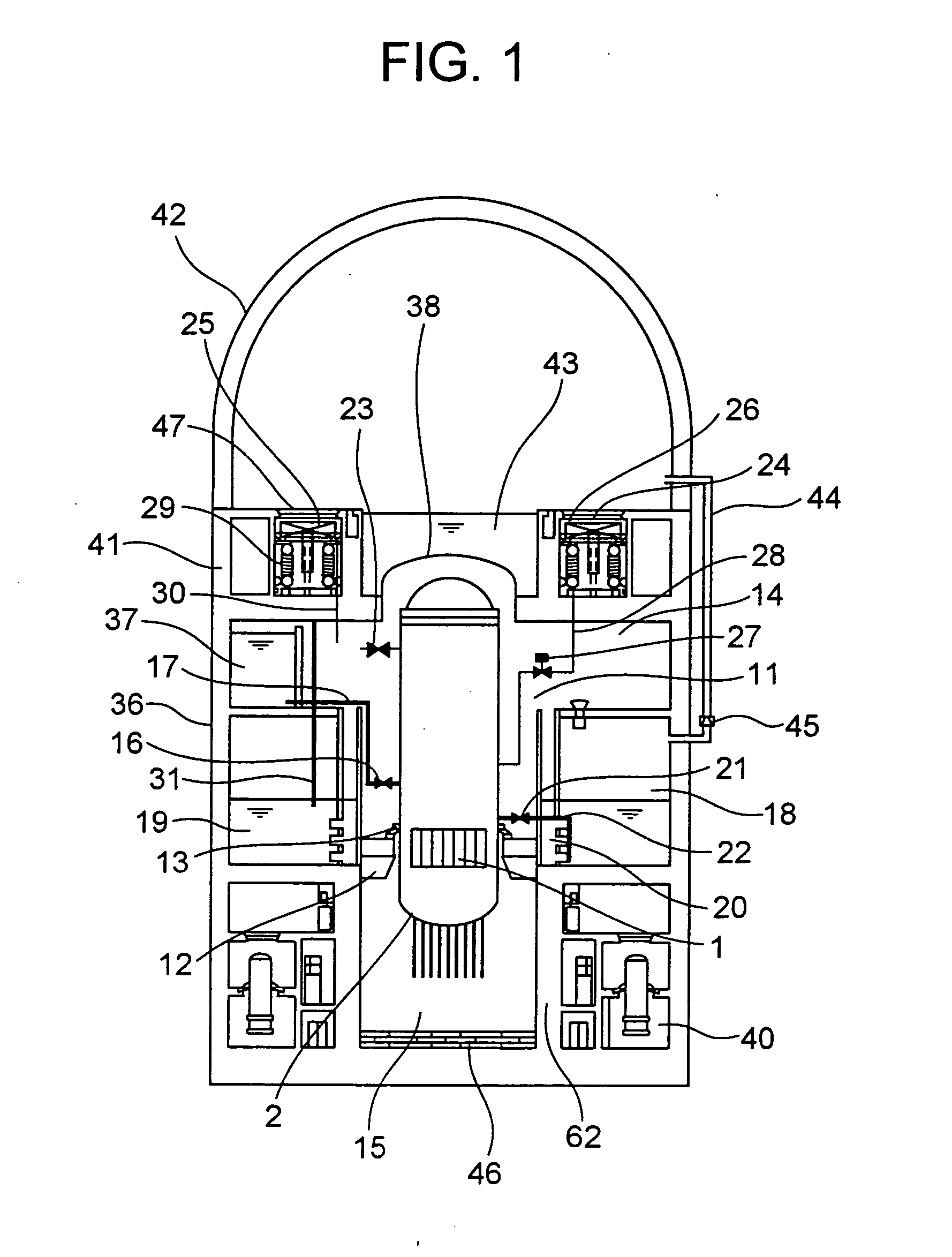
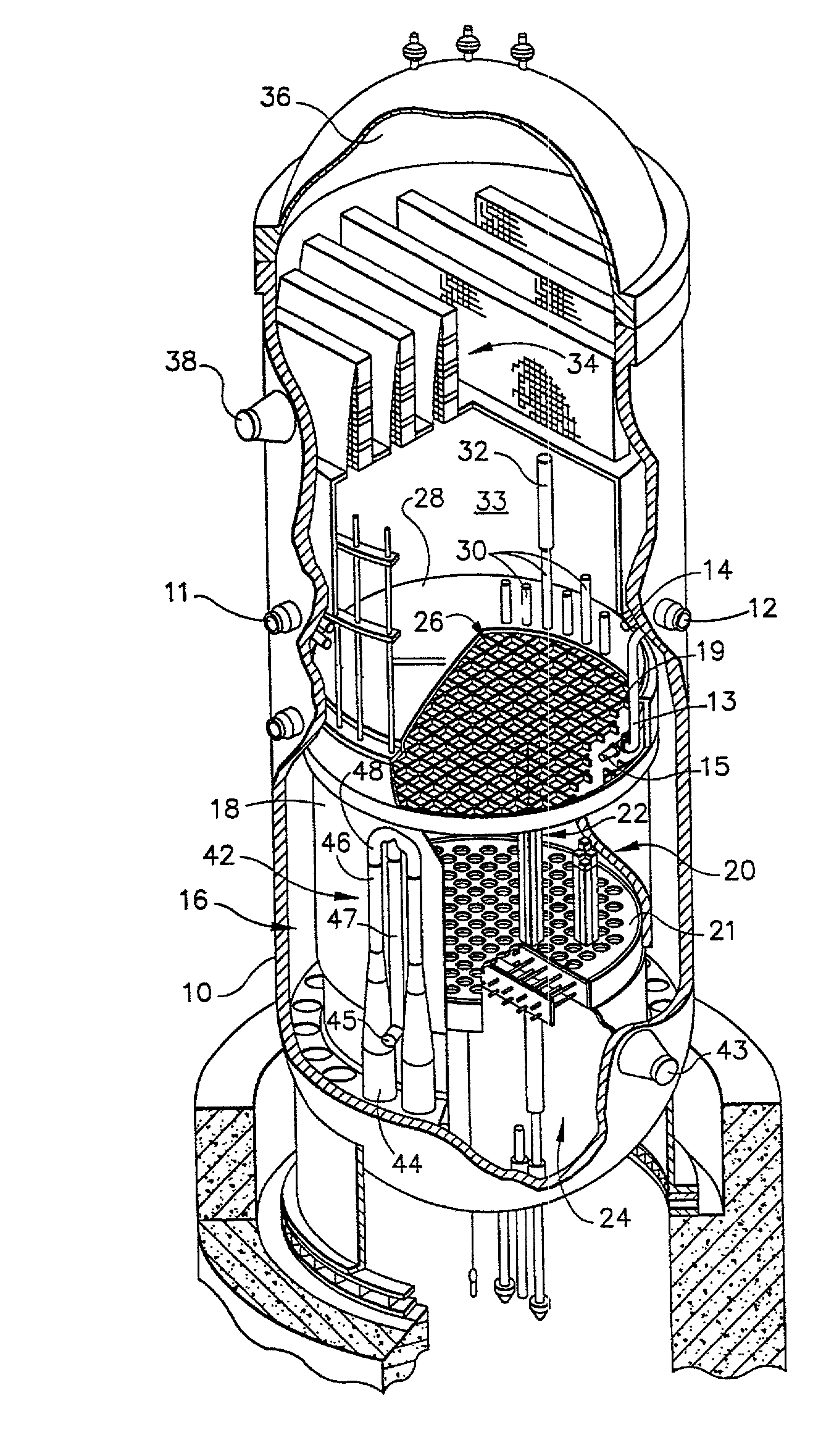
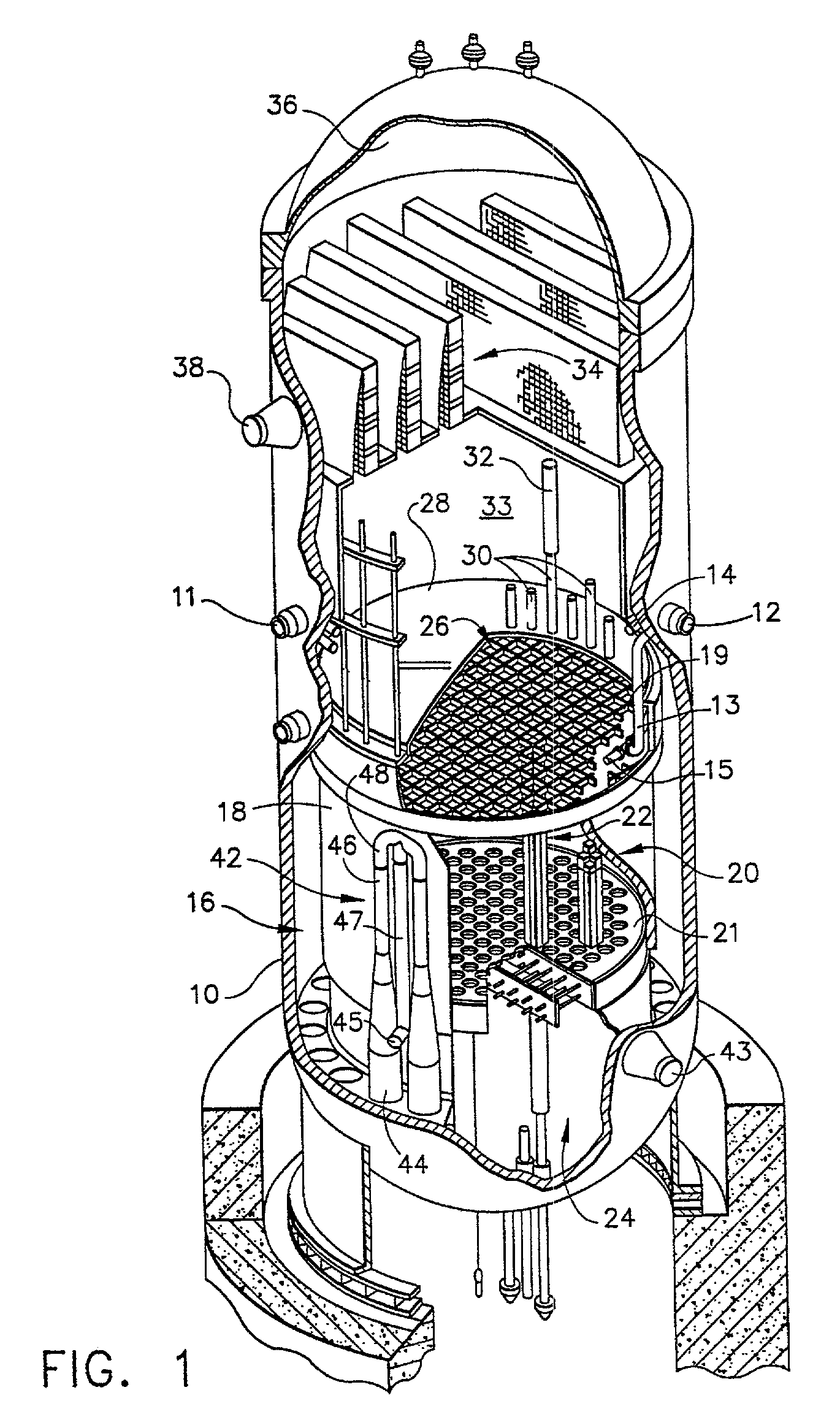
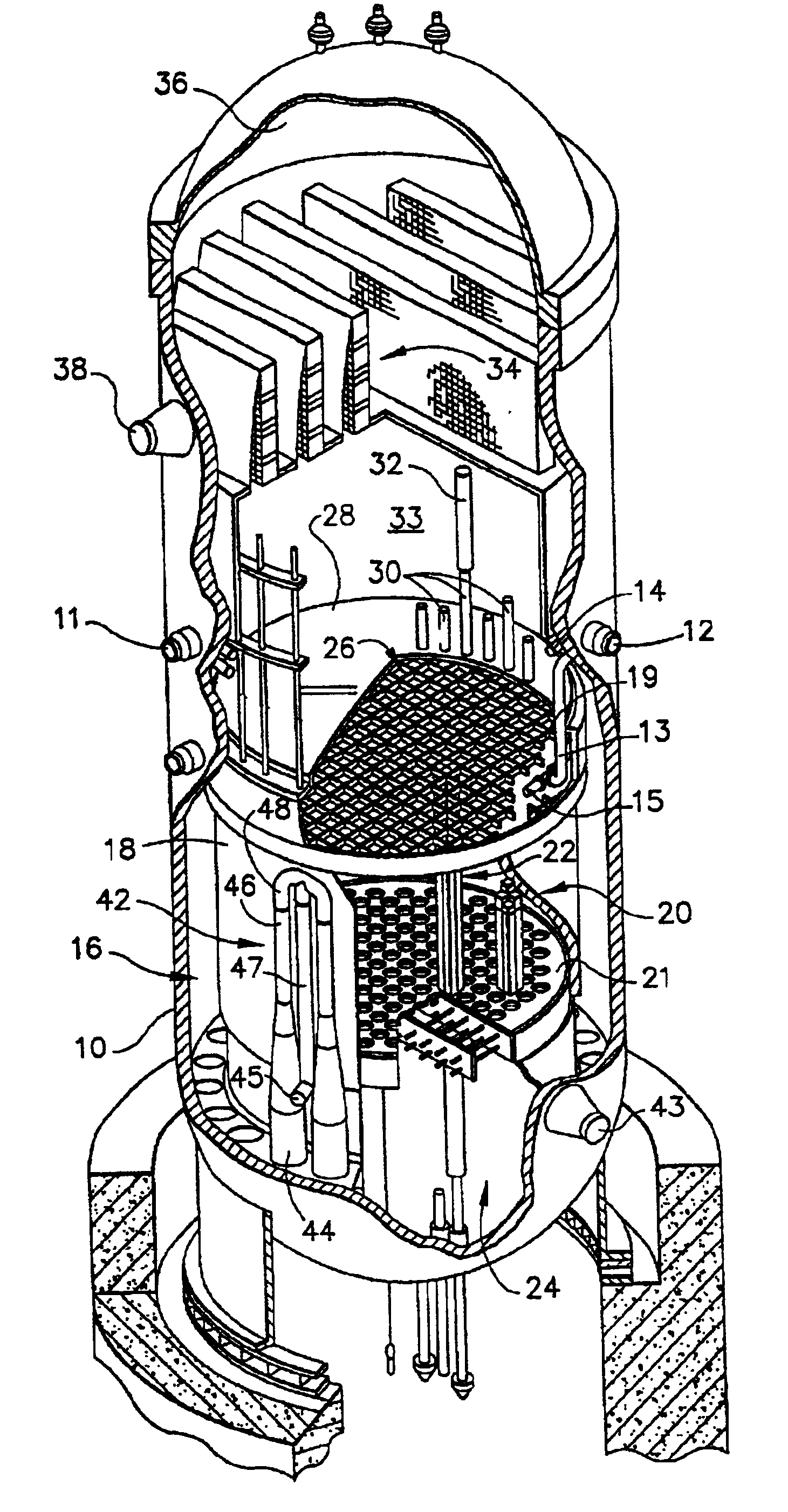
Reactor containment vessel and boiling water reactor power plant
ActiveUS20070092053A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsPower stationReactor pressure vessel
A containment vessel includes a primary containment vessel containing a reactor pressure vessel, an upper secondary containment vessel arranged above the primary containment vessel, and a gas-phase vent pipe linking the primary containment vessel and the upper secondary containment vessel by way of an isolation and connection switching system. The gas-phase vent pipe may be arranged either inside or outside the primary containment vessel and the upper secondary containment vessel. Alternatively, it may be embedded in the wall. An igniter may be arranged in the upper secondary containment vessel. The air in the upper secondary containment vessel may be replaced by nitrogen. A gravity-driven flooding system pool may be arranged in the upper secondary containment vessel and cooling water may be led from the inside of the pool to the inside of the primary containment vessel.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
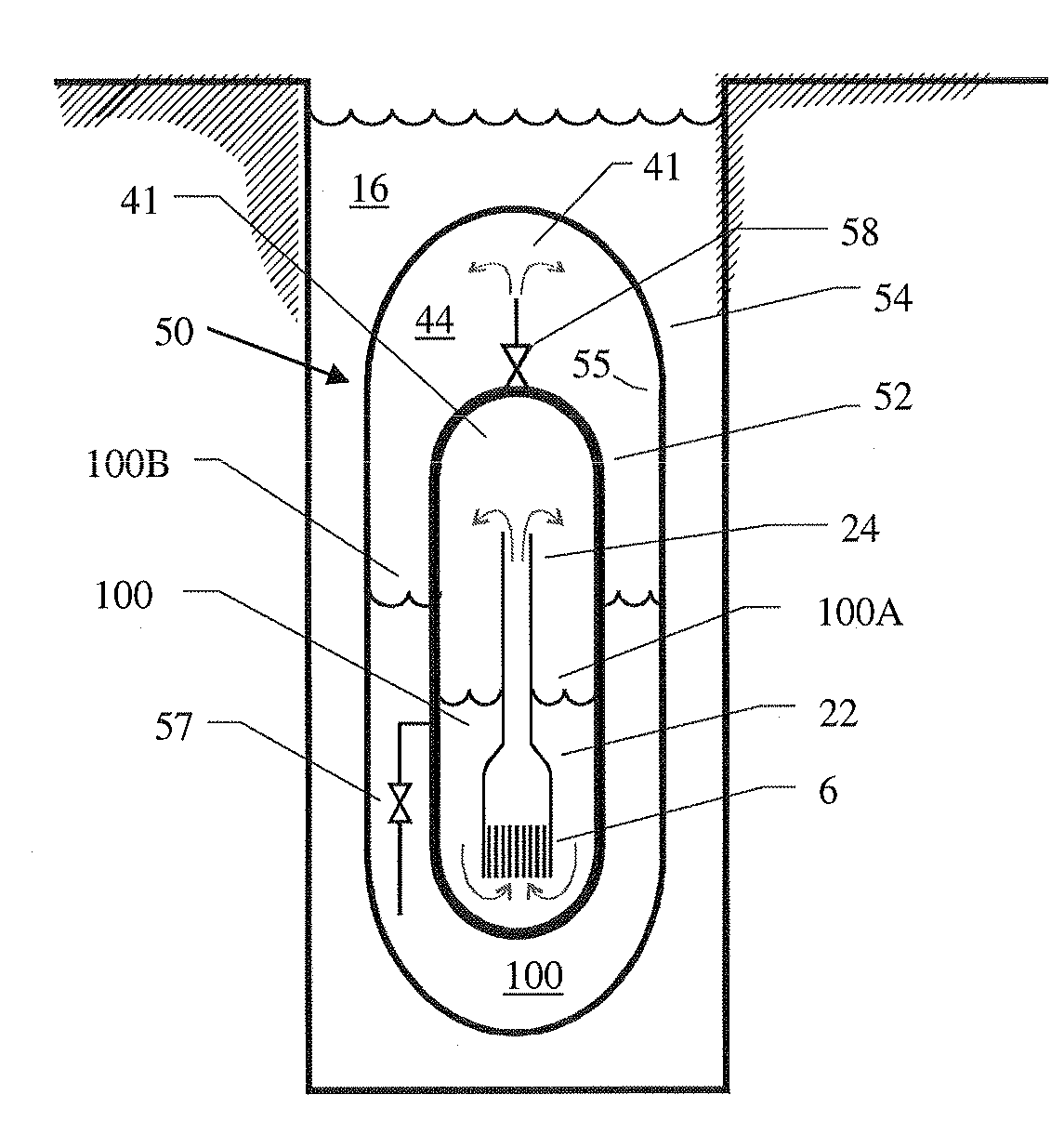
Submerged containment vessel for a nuclear reactor
A power module assembly includes a reactor core immersed in a coolant and a reactor vessel housing the coolant and the reactor core. An internal dry containment vessel submerged in liquid substantially surrounds the reactor vessel in a gaseous environment. During an over-pressurization event the reactor vessel is configured to release the coolant into the containment vessel and remove a decay heat of the reactor core through condensation of the coolant on an inner surface of the containment vessel.
Owner:NUSCALE
Passive emergency feedwater system
A power module assembly includes a reactor vessel containing a reactor core surrounded by a primary coolant. A containment vessel is adapted to be submerged in a containment cooling pool and to prohibit a release of the primary coolant outside of the containment vessel. A secondary cooling system is configured to remove heat generated by the reactor core. The heat is removed by circulating liquid from the containment cooling pool through the primary coolant.
Owner:NUSCALE
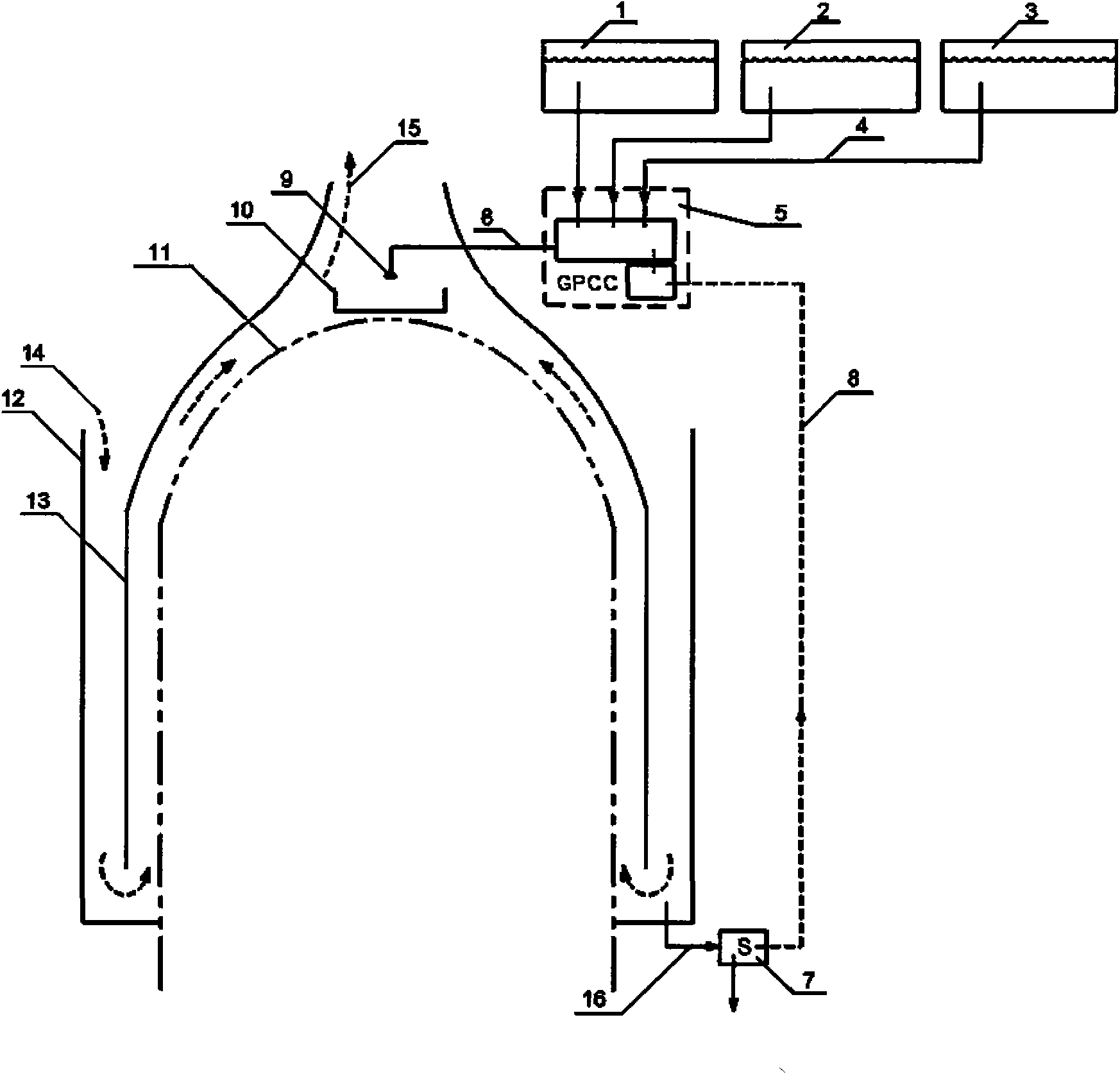
High-capacity and fully passive containment cooling system
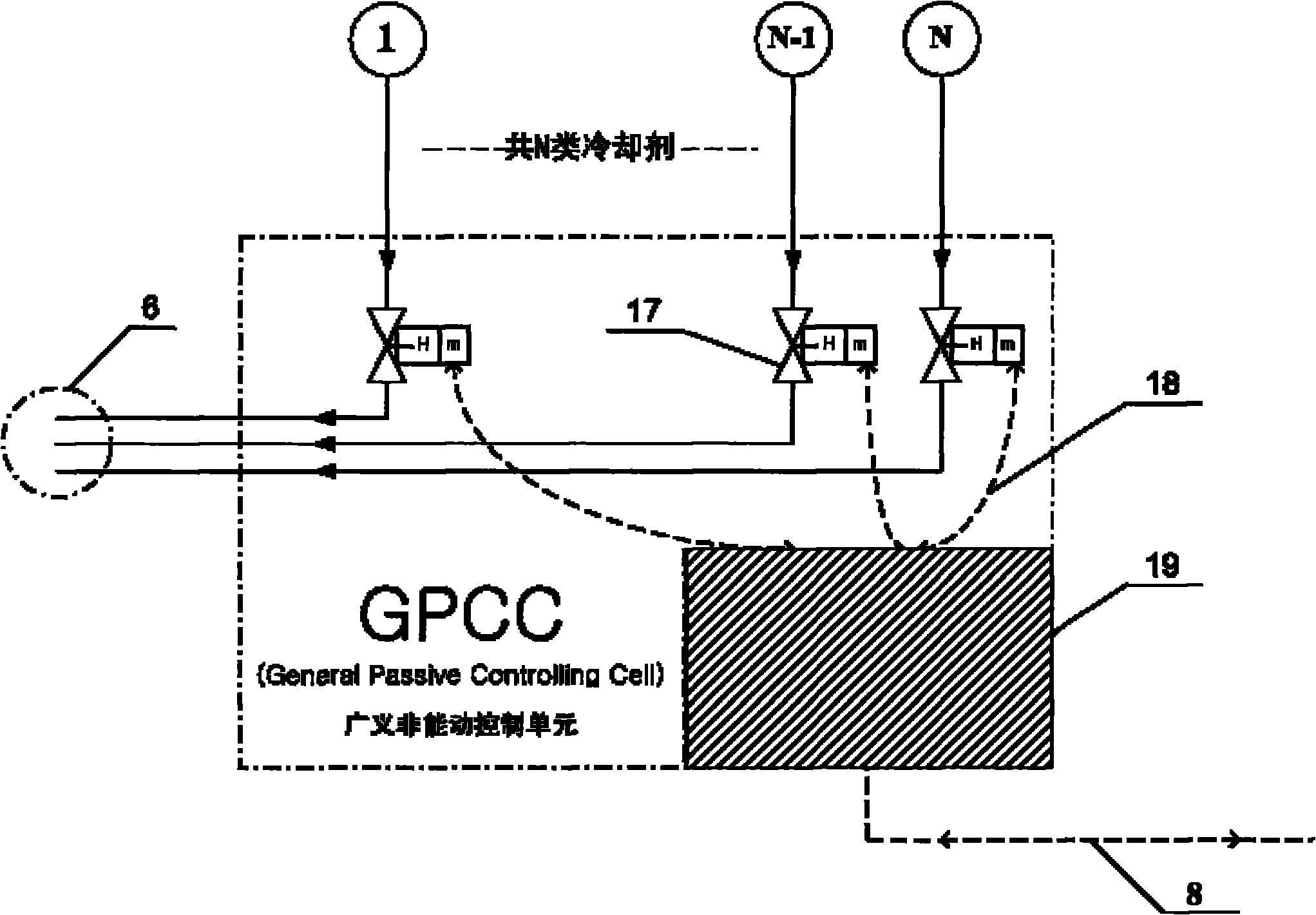
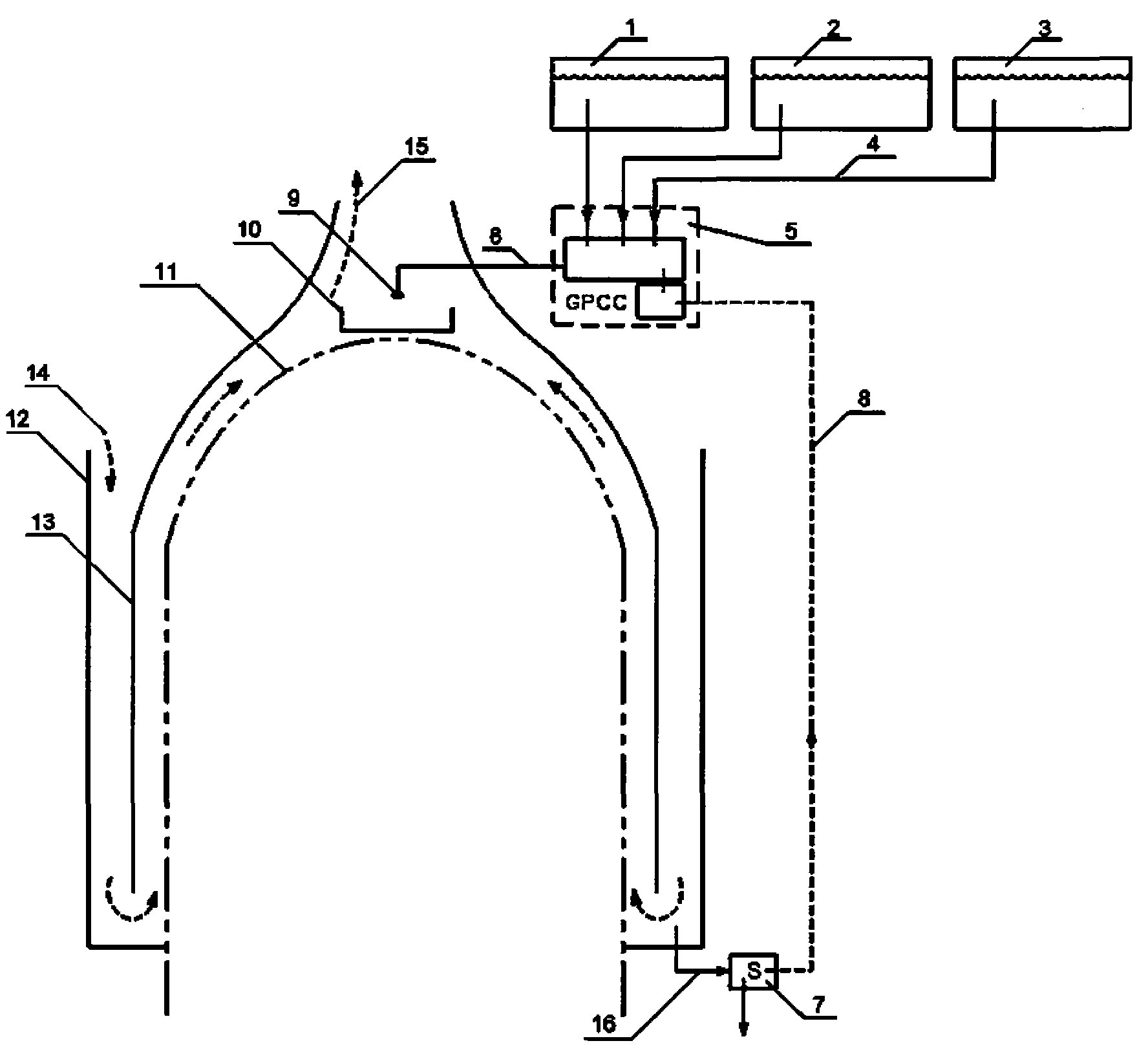
ActiveCN102081976AImprove efficiencyImprove heat transfer efficiencyNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear engineeringCooling power
The invention belongs to a containment cooling system, in particular, to a high-capacity and fully passive containment cooling system. The containment cooling system is used for collecting thermotechnical parameters related to the containment by using a sensor and tracking a cooling process; a plurality of storage boxes for storing different coolants is arranged above the containment; the dynamic control of containment cooling power can be realized by choosing the types of the coolants and adjusting the flows of the coolants; and by using a generalized passive control unit, the start-up and the whole running process of the containment cooling system can be completely independent on external power supply, thus the containment cooling system has a characteristic of fully passiveness.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
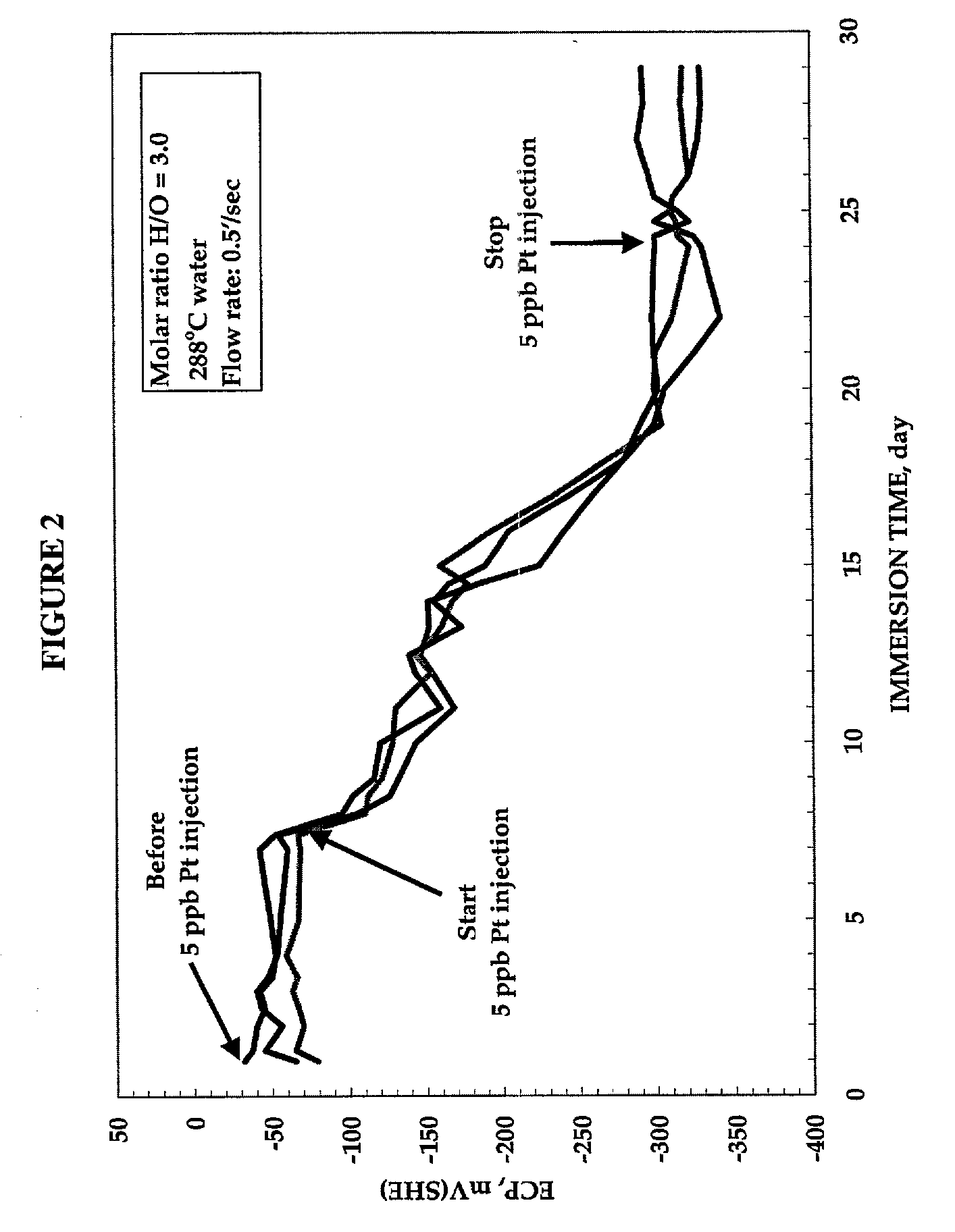
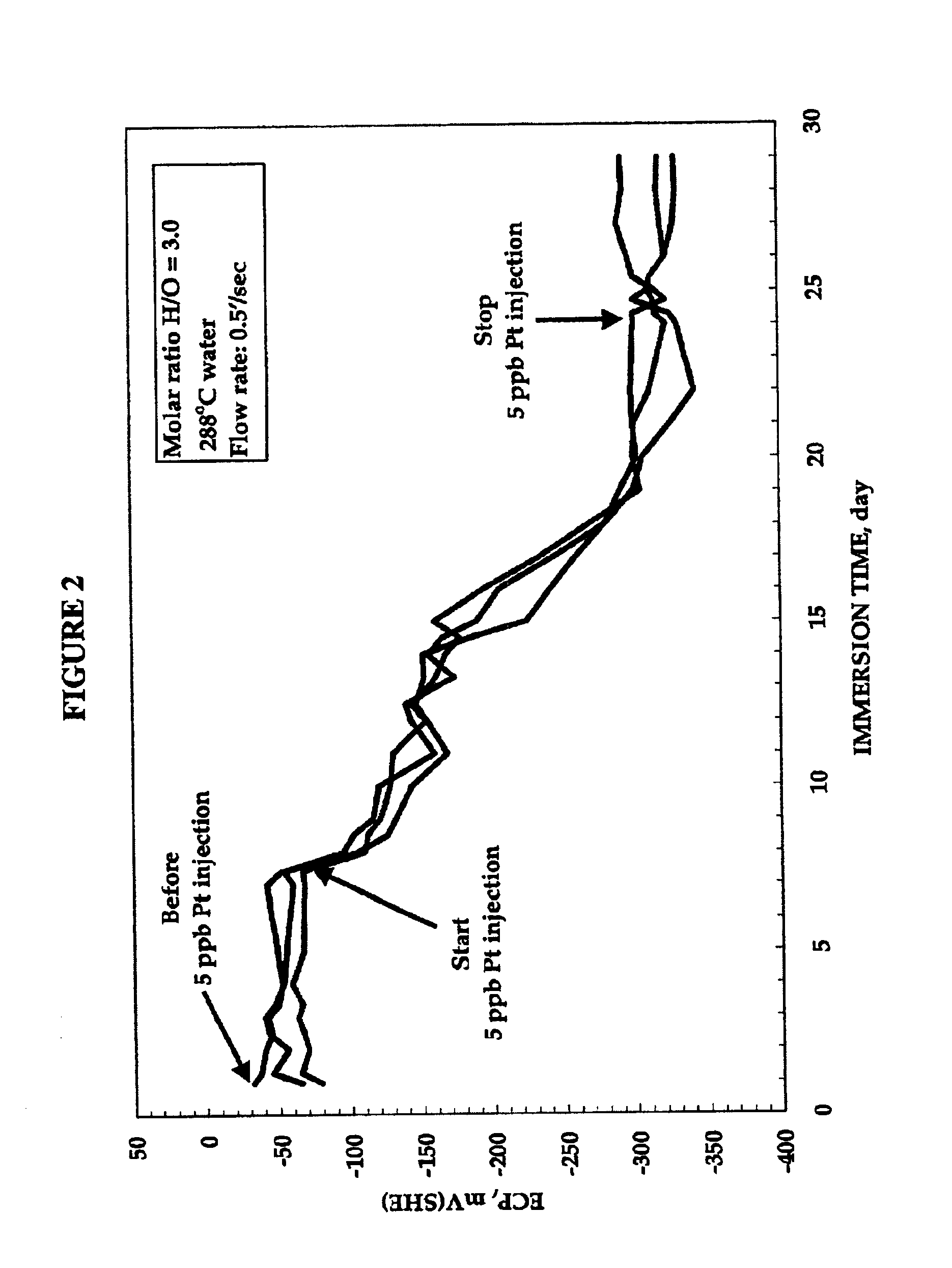
Process to mitigate stress corrosion cracking of structural materials in high temperature water
InactiveUS6724854B1Reduce crackingReducing the electrochemical corrosion potentialPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNanoparticleStress corrosion cracking
A method for mitigating stress corrosion cracking in high temperature water includes introducing catalytic nanoparticles and dielectric nanoparticles to the high temperature water in an amount effective to reduce a electrochemical corrosion potential of the high temperature water.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
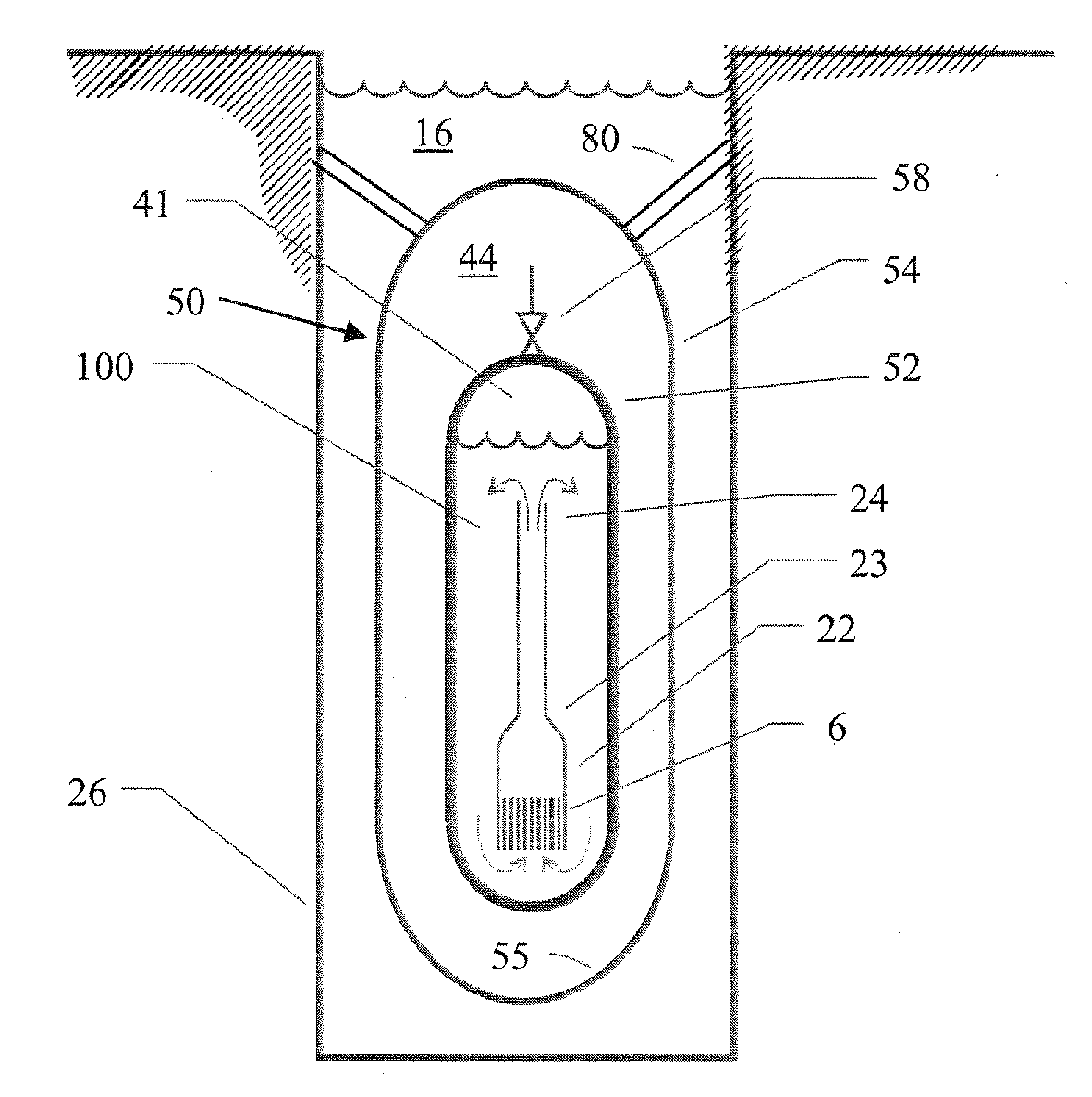
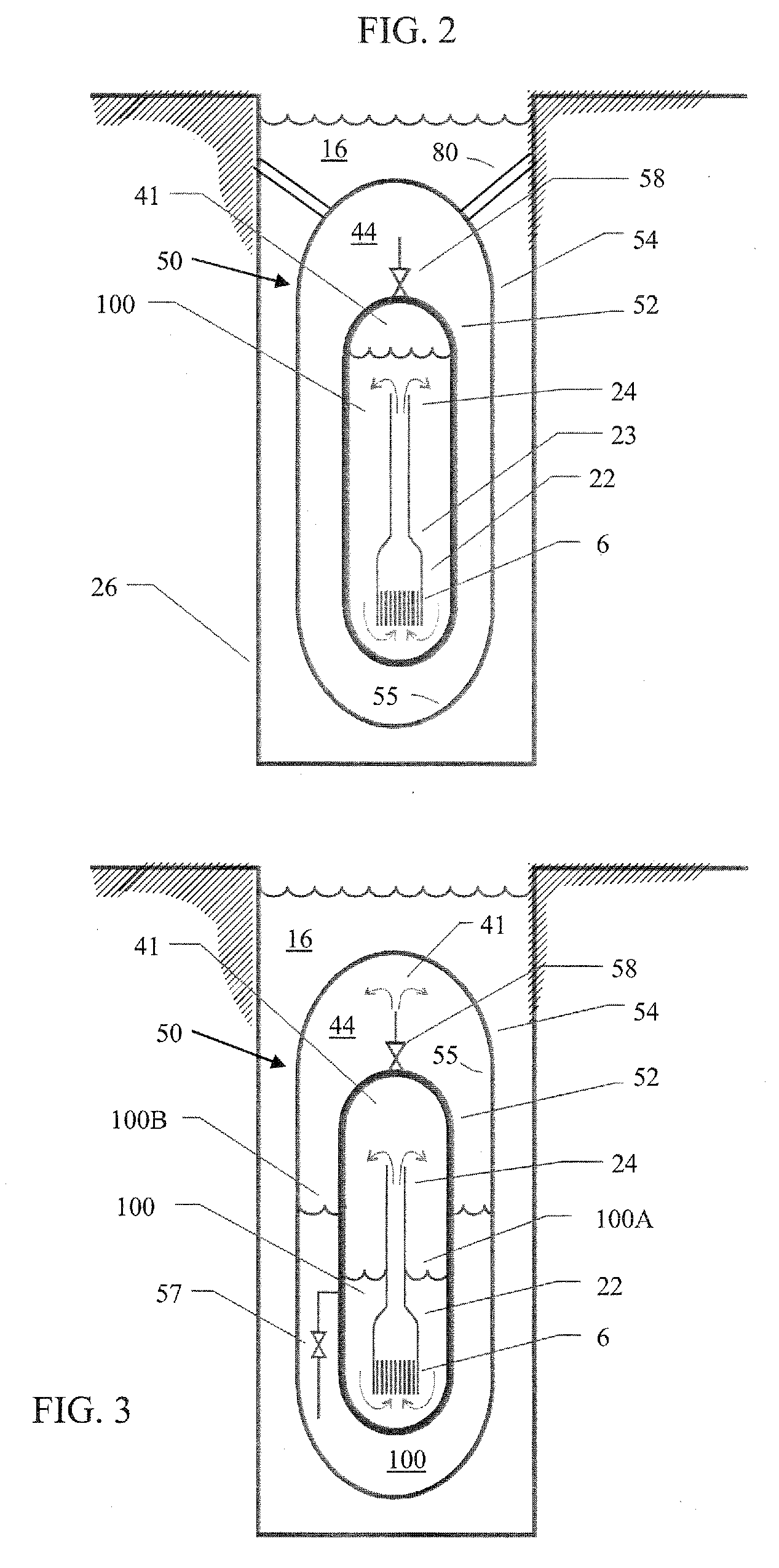
Evacuated containment vessel for a nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20090161812A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsNuclear reactorEngineering
A system includes a containment vessel configured to prohibit a release of a coolant, and a reactor vessel mounted inside the containment vessel. An outer surface of the reactor vessel is exposed to below atmospheric pressure, wherein substantially all gases are evacuated from within the containment vessel.
Owner:NUSCALE
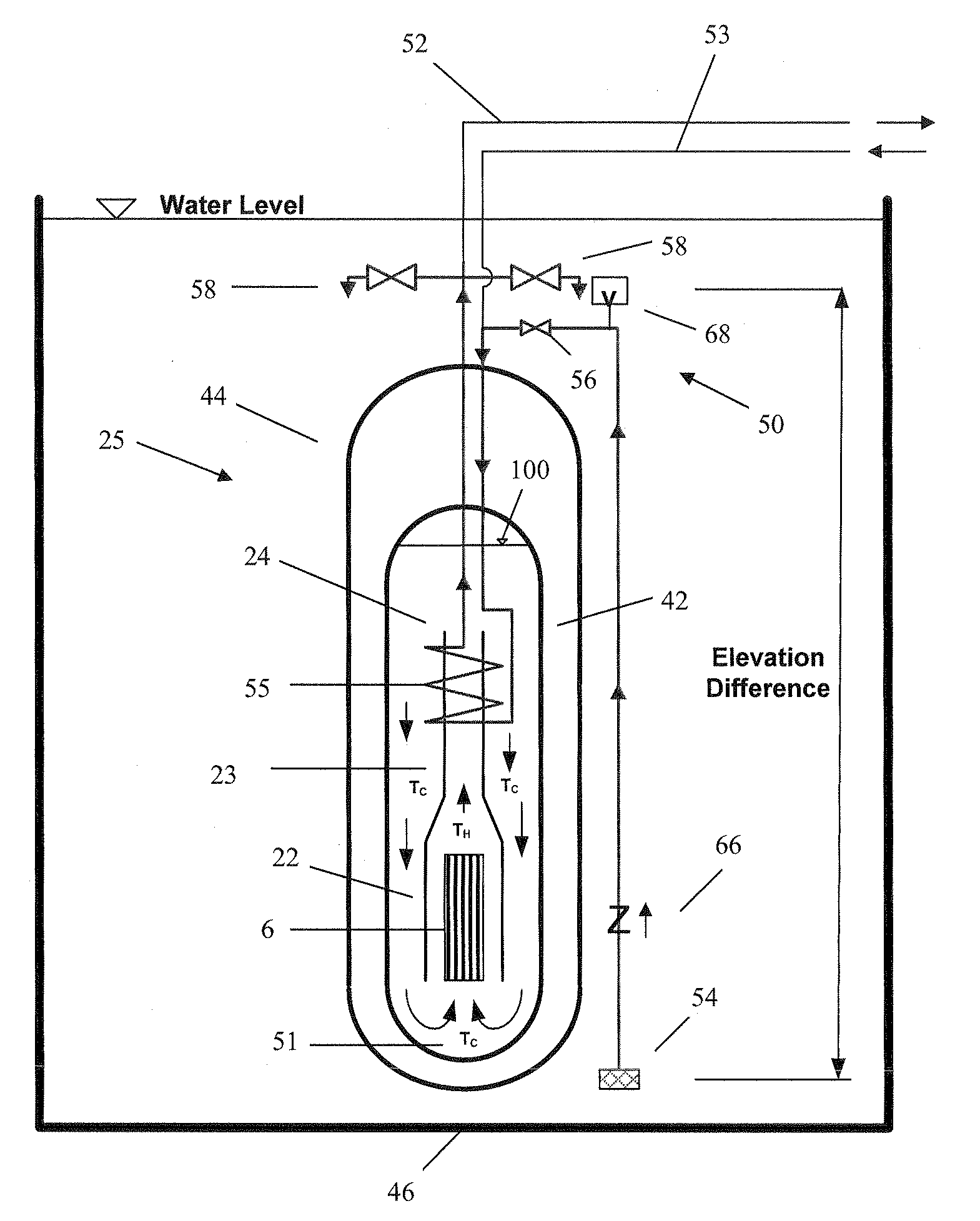
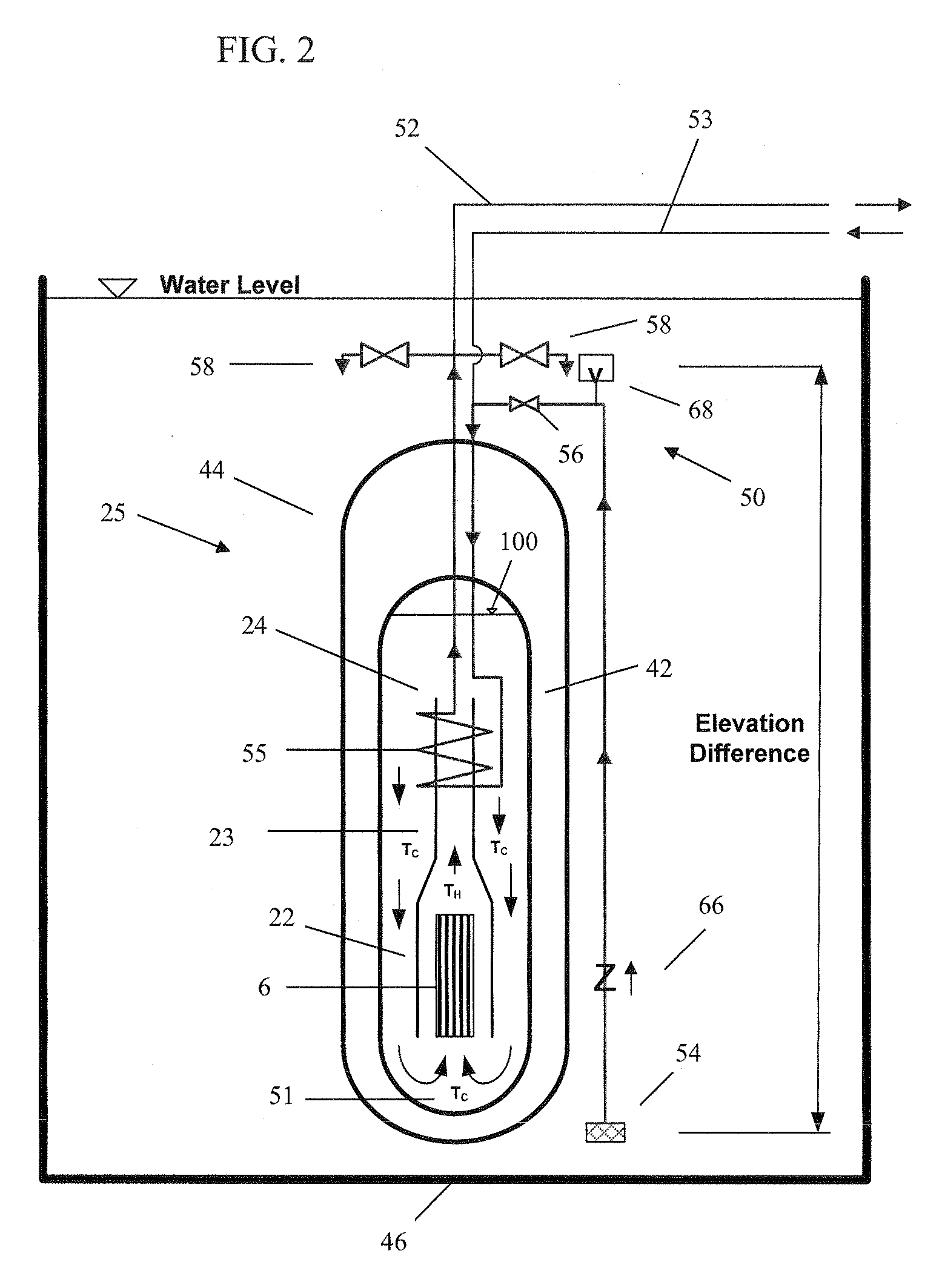
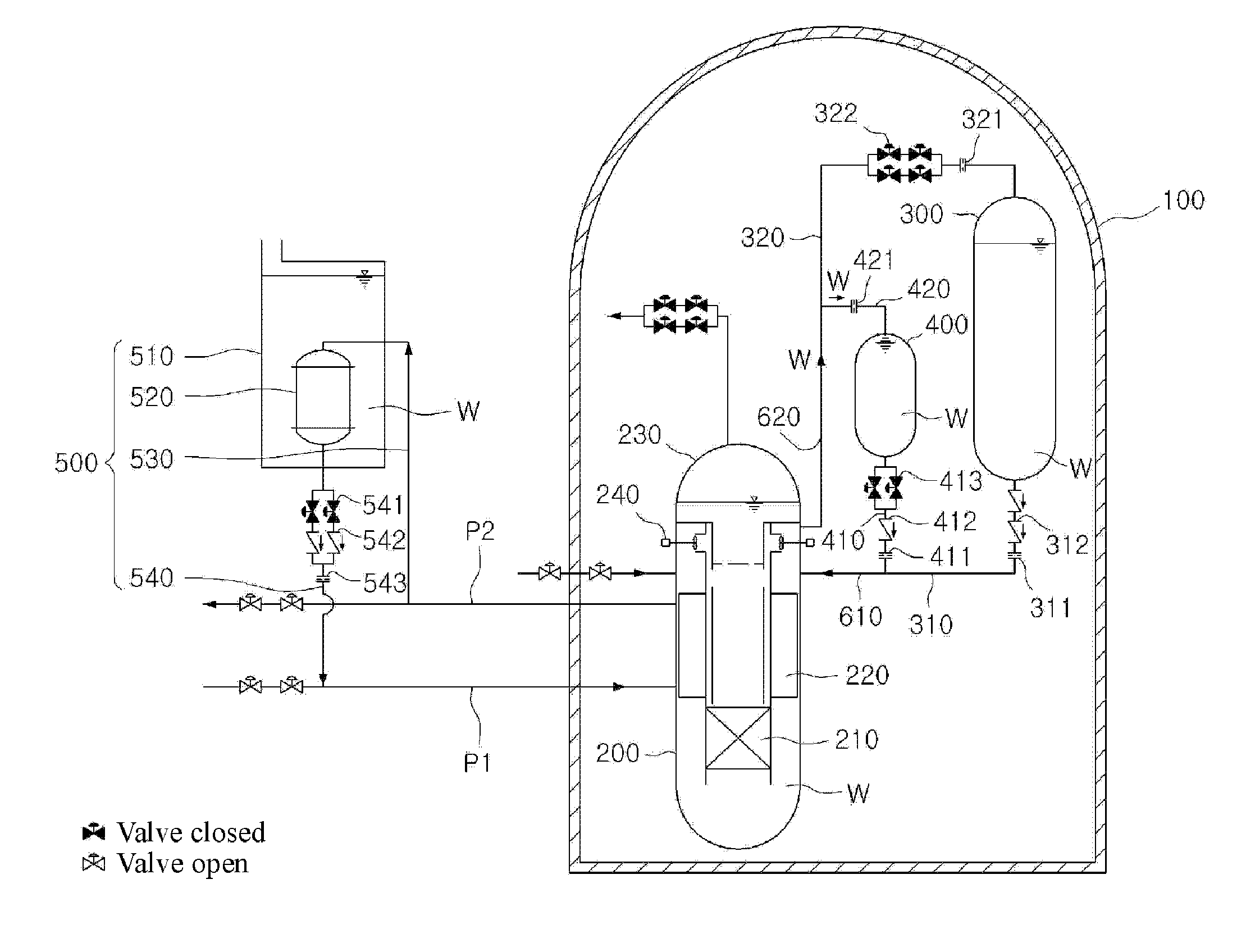
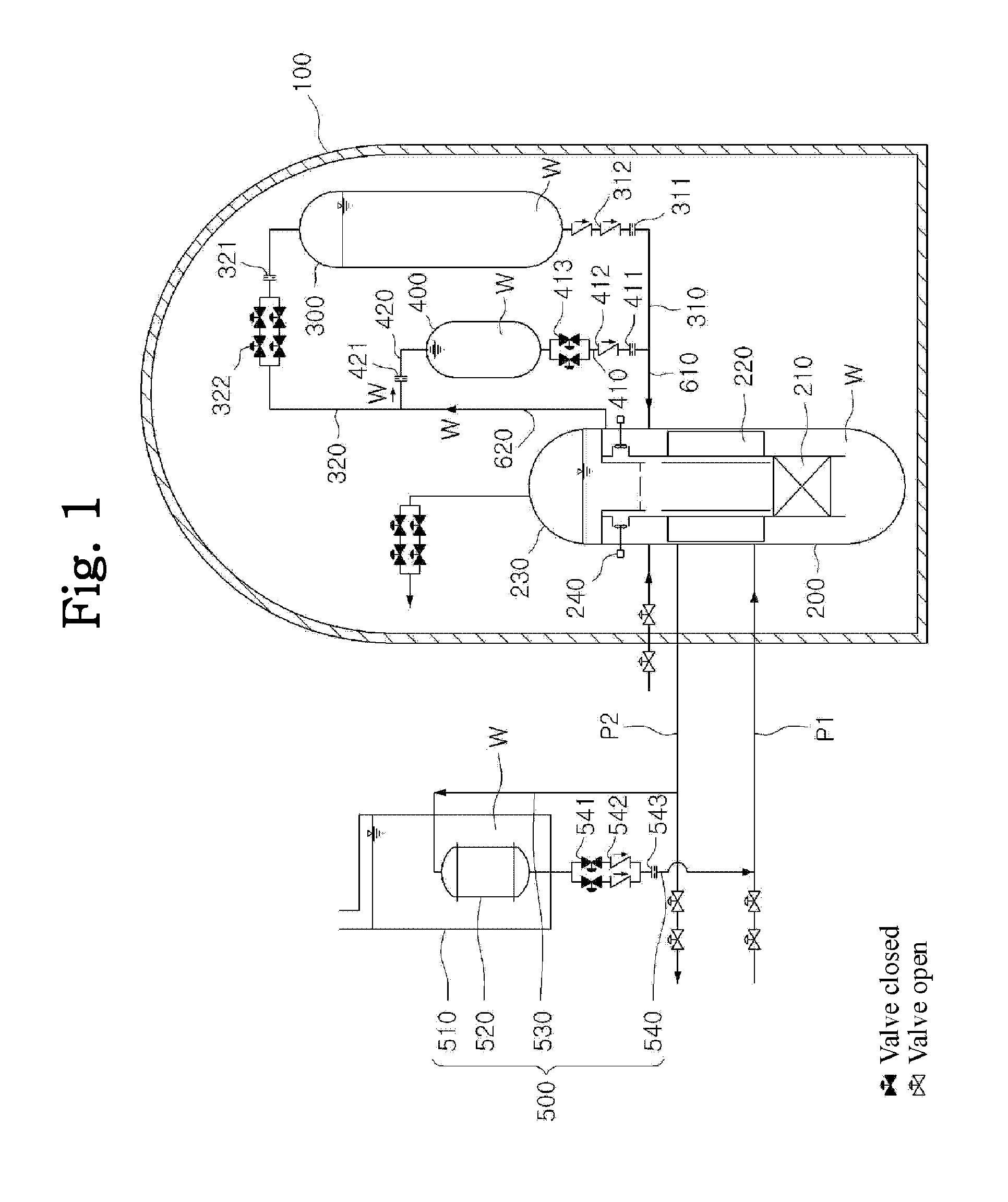
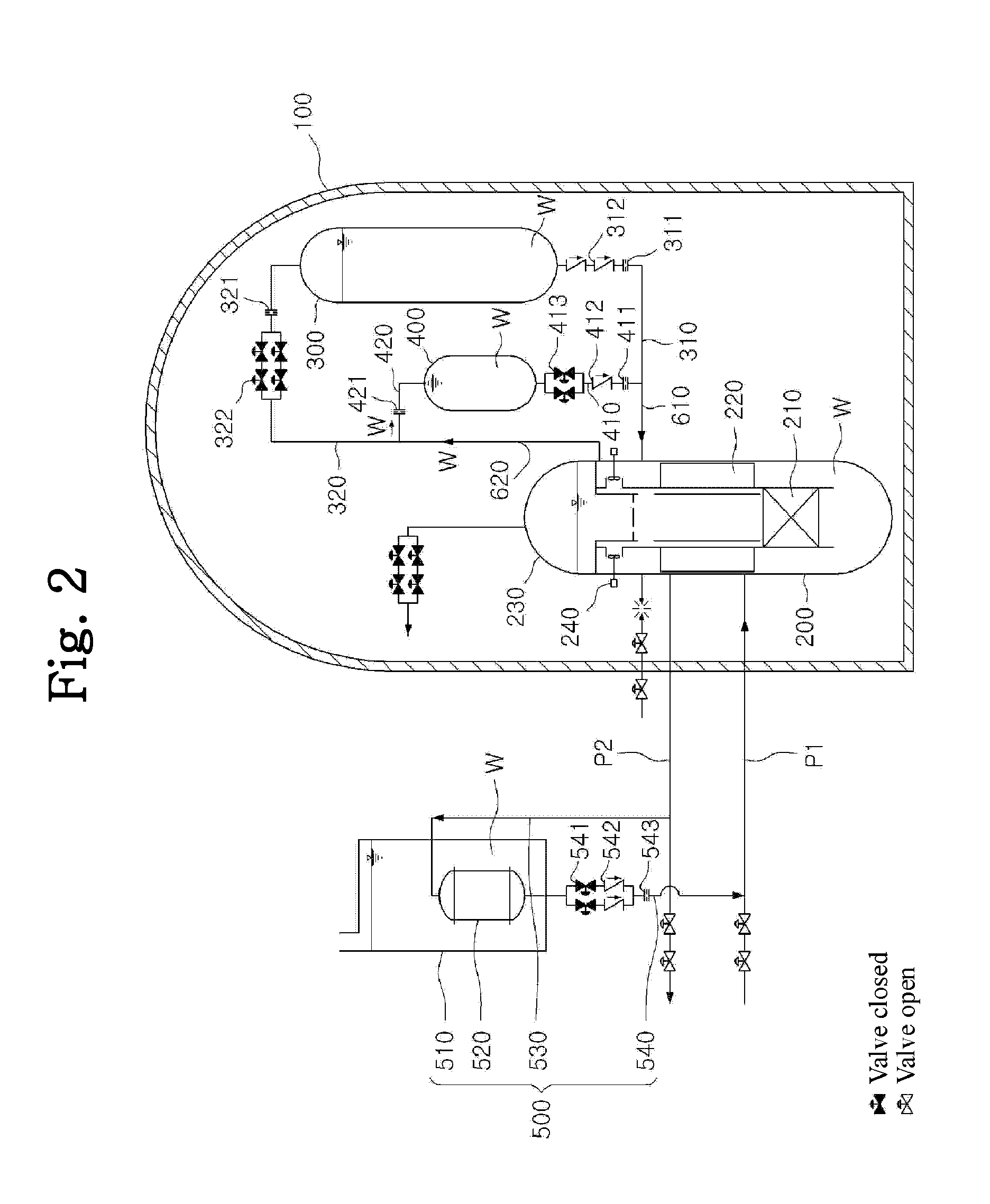
Passive safety system of integral reactor
ActiveUS20140016734A1Maintain water levelSimple facilitiesPower plant safety arrangementIntegral reactorsNuclear engineeringNitrogen gas
A passive safety system includes a containment, a reactor in the containment, a plurality of safety injection tanks connected with the reactor and having water and nitrogen gas to supply water thereof into the reactor through a safety injection line communicating to the first safety injection line upon a loss of coolant accident, a plurality of core makeup tanks connected with the reactor to supply water thereof into the reactor through a second safety injection line communicating to a safety injection line upon the loss of coolant accident, and a plurality of passive residual heat removal systems to remove residual heat from the reactor upon the loss of coolant accident or a non-loss of coolant accident. The water in each of the safety injection tank is stably supplied to the reactor for many hours by a differential head resulting from gravity or gas pressure.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
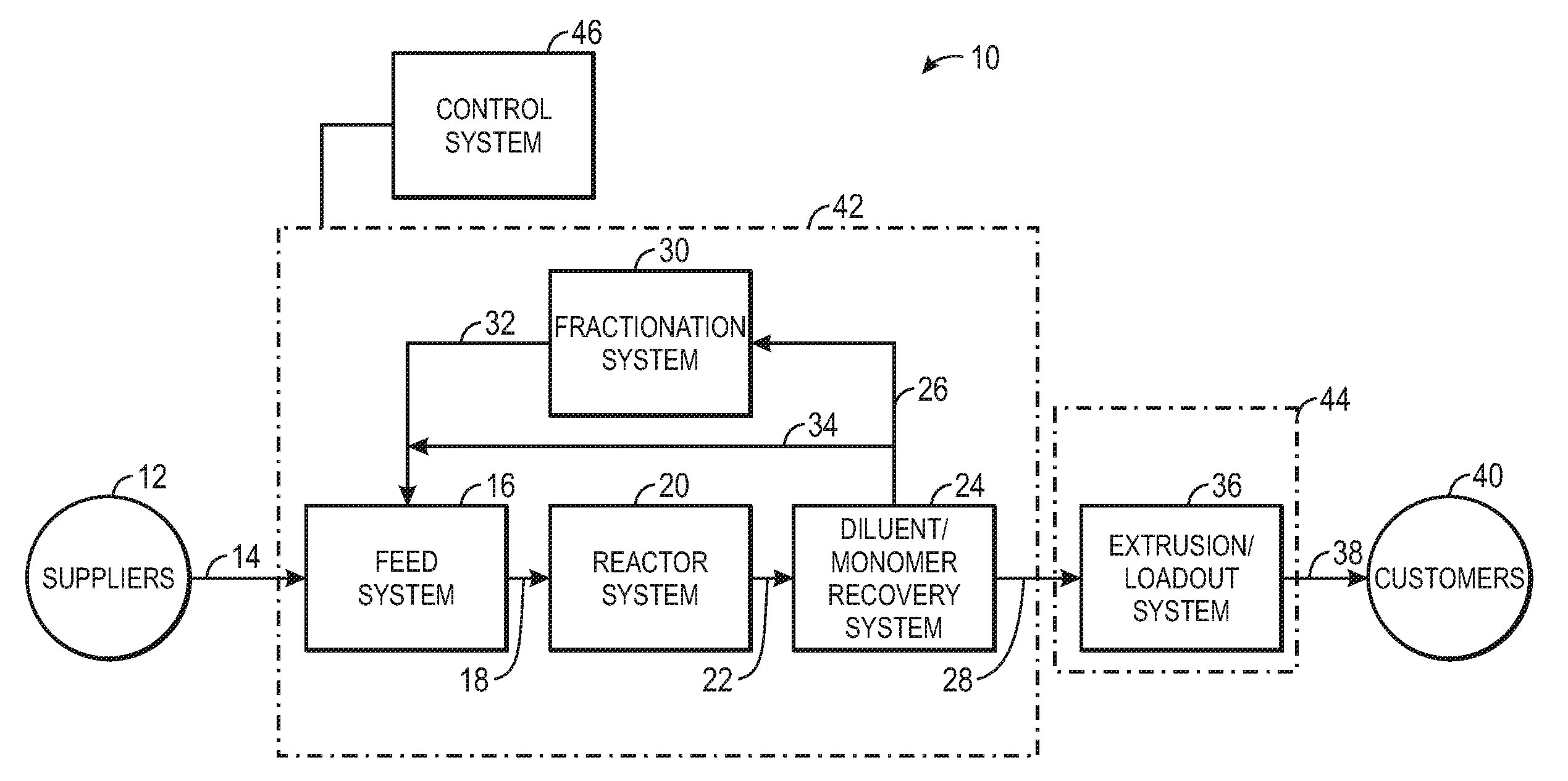
System and method for closed relief of a polyolefin loop reactor system
ActiveUS20110311014A1Process control/regulationEmergency protection arrangementsPolyolefinReactor system
A reactor system including an enclosed pressure relief system and / or a control system. The enclosed pressure relief system including a slurry separation system communicatively coupled with a pressure relief valve coupled to a loop reactor such that activation of the pressure relief valve results in discharge of a slurry from the loop reactor to the slurry separation system, wherein the slurry separation system is capable of separating solid and liquid components from gas components of the slurry and transmitting the gas components to a flare via a flare header.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
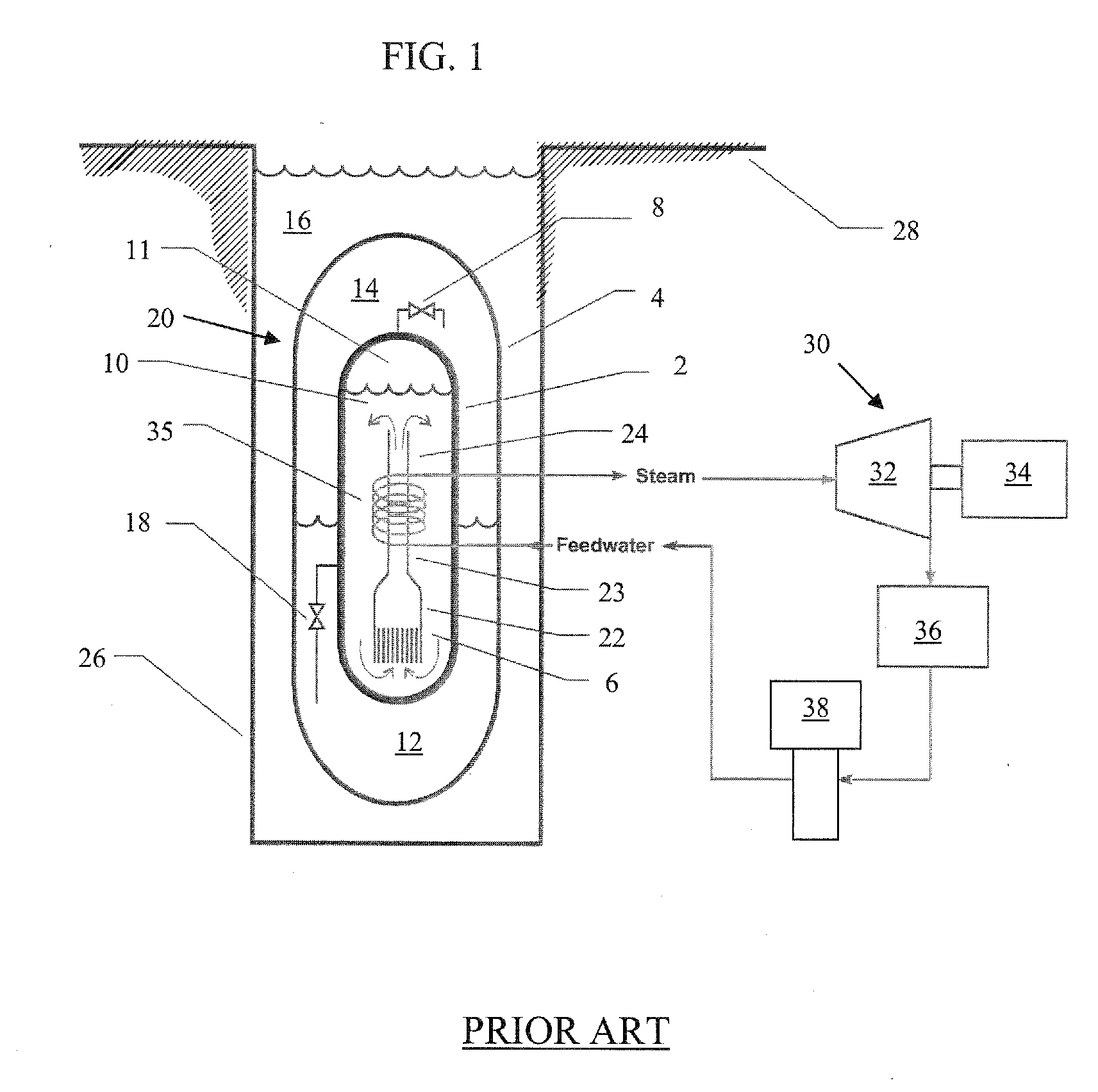
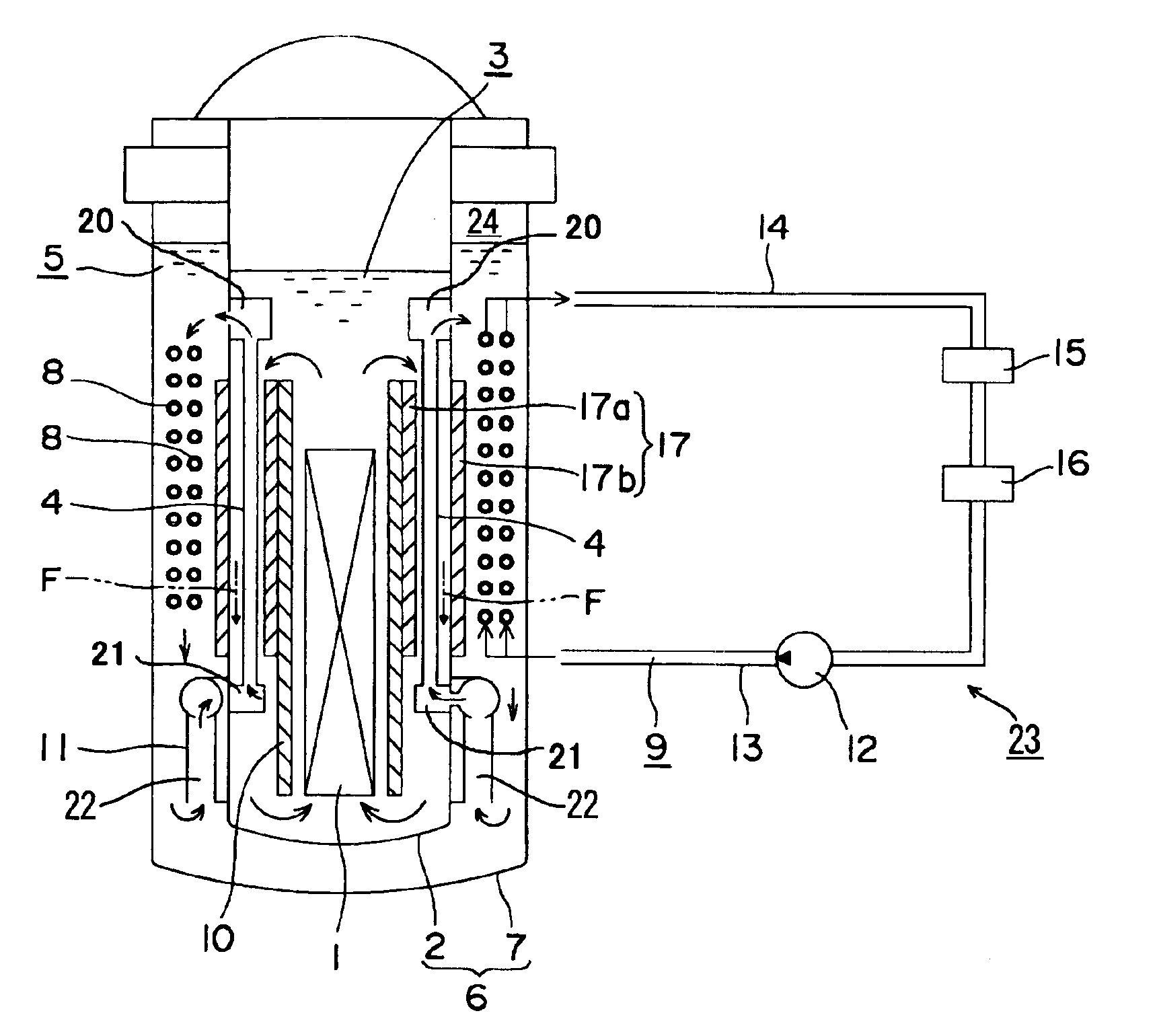
Nuclear reactor
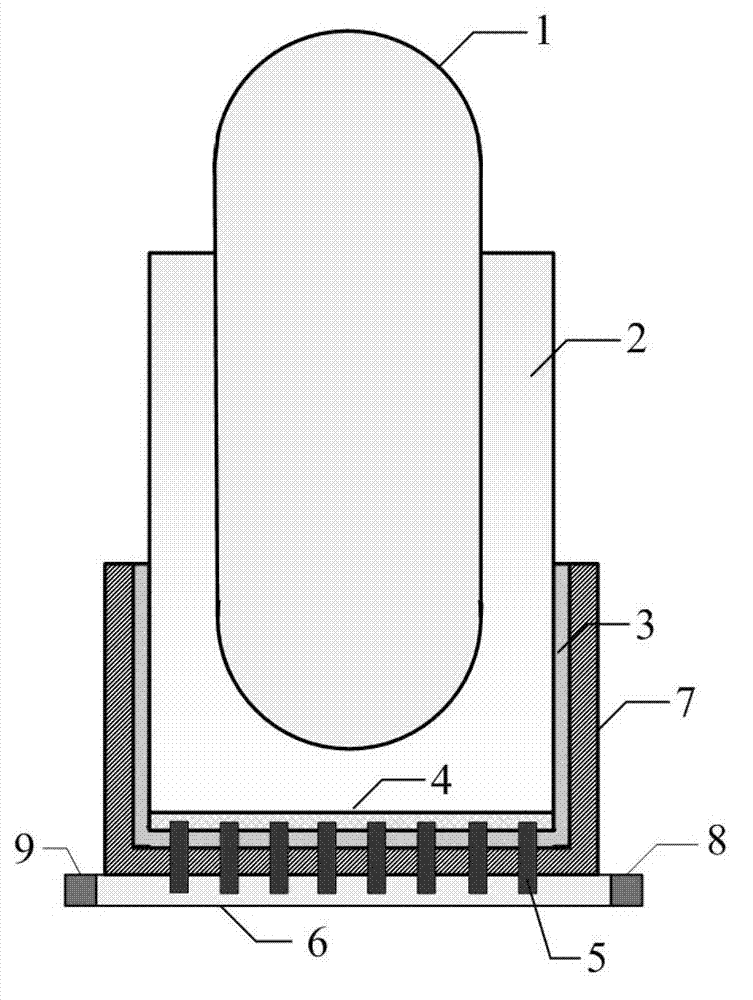
InactiveUS6944255B2Small sizeReduce manufacturing costIntegral reactorsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactorHeat transfer tube
A nuclear reactor in which a secondary or tertiary coolant system of a nuclear steam supply system is simplified, comprising: a reactor vessel (2) which integrates a reactor core (1); a first coolant (3) which is stored in the reactor vessel (2) and heated by the reactor core (1) to convect; a first heat transfer tube (4) which is arranged in the reactor vessel (2) and comes into contact with the first coolant (3); and a second coolant (5) which is supplied from the outside of the reactor vessel (2) to the first heat transfer tube (4), cools the first coolant (3) and led to the outside of the reactor vessel (2).
Owner:CENTRAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF ELECTRIC POWER INDUSTRY
Large-scale passive nuclear plant reactor core catcher with bottom water injection and external cooling
InactiveCN103177778AImplement off-heap retentionImprove securityNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear plantCore catcher
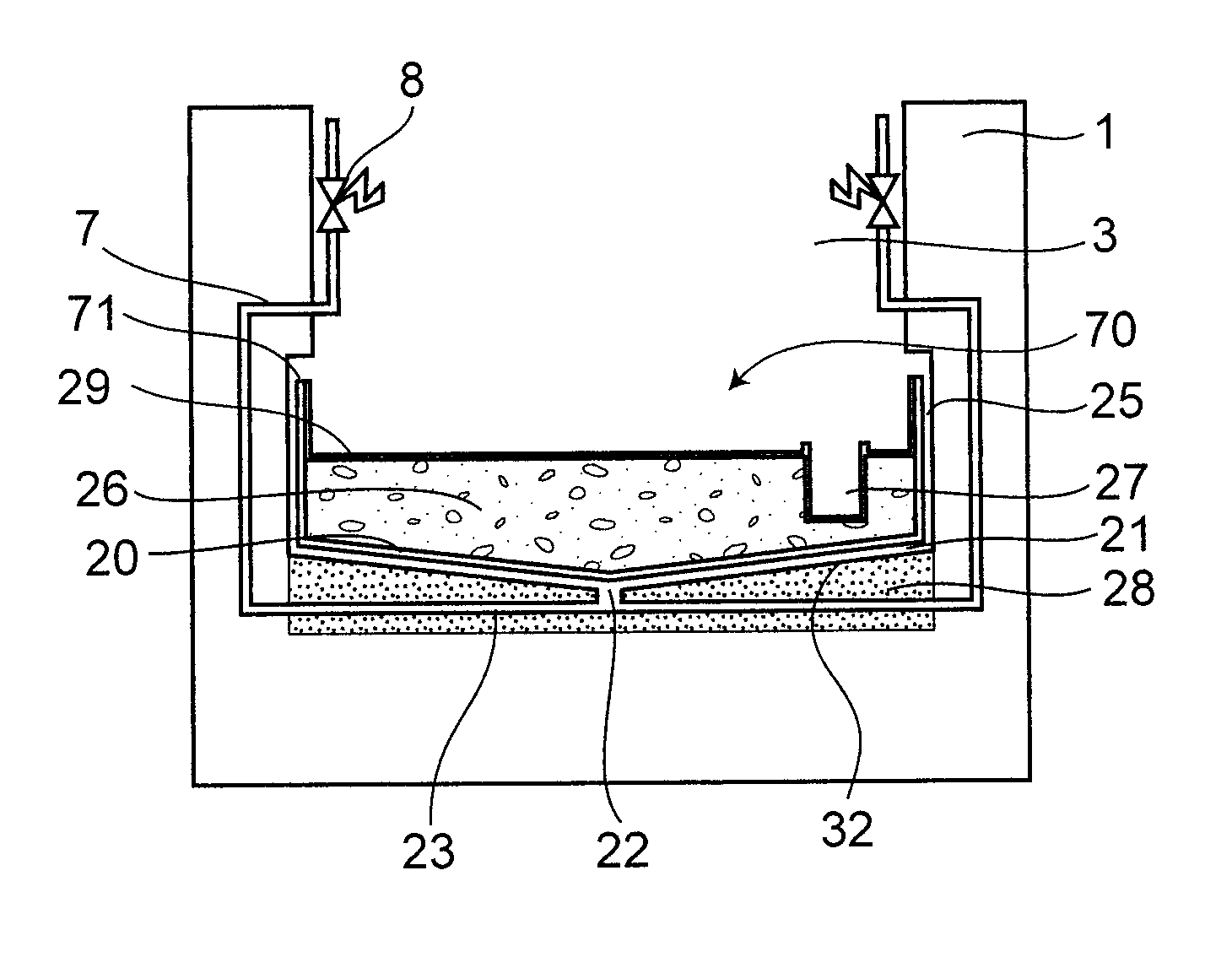
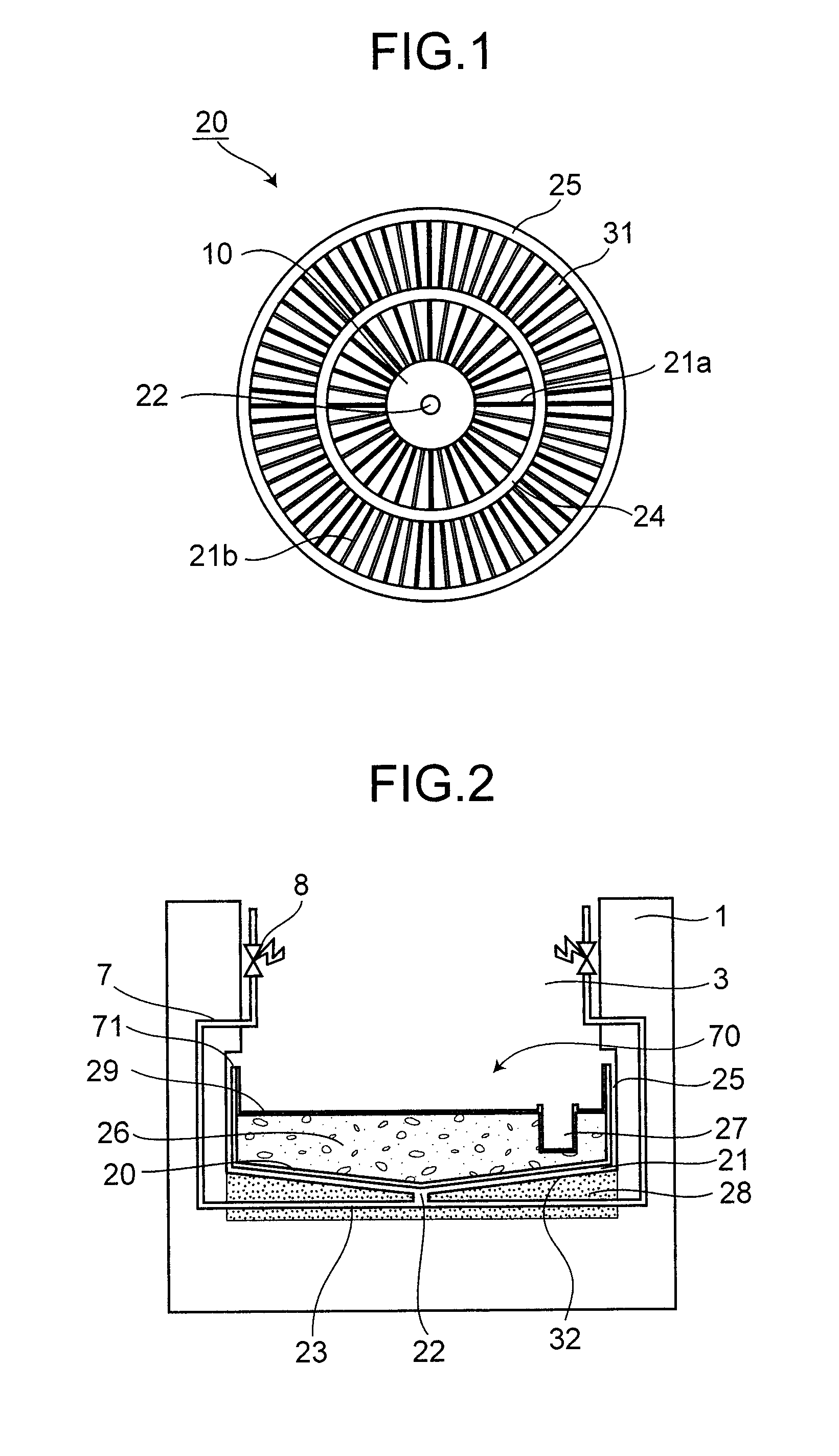
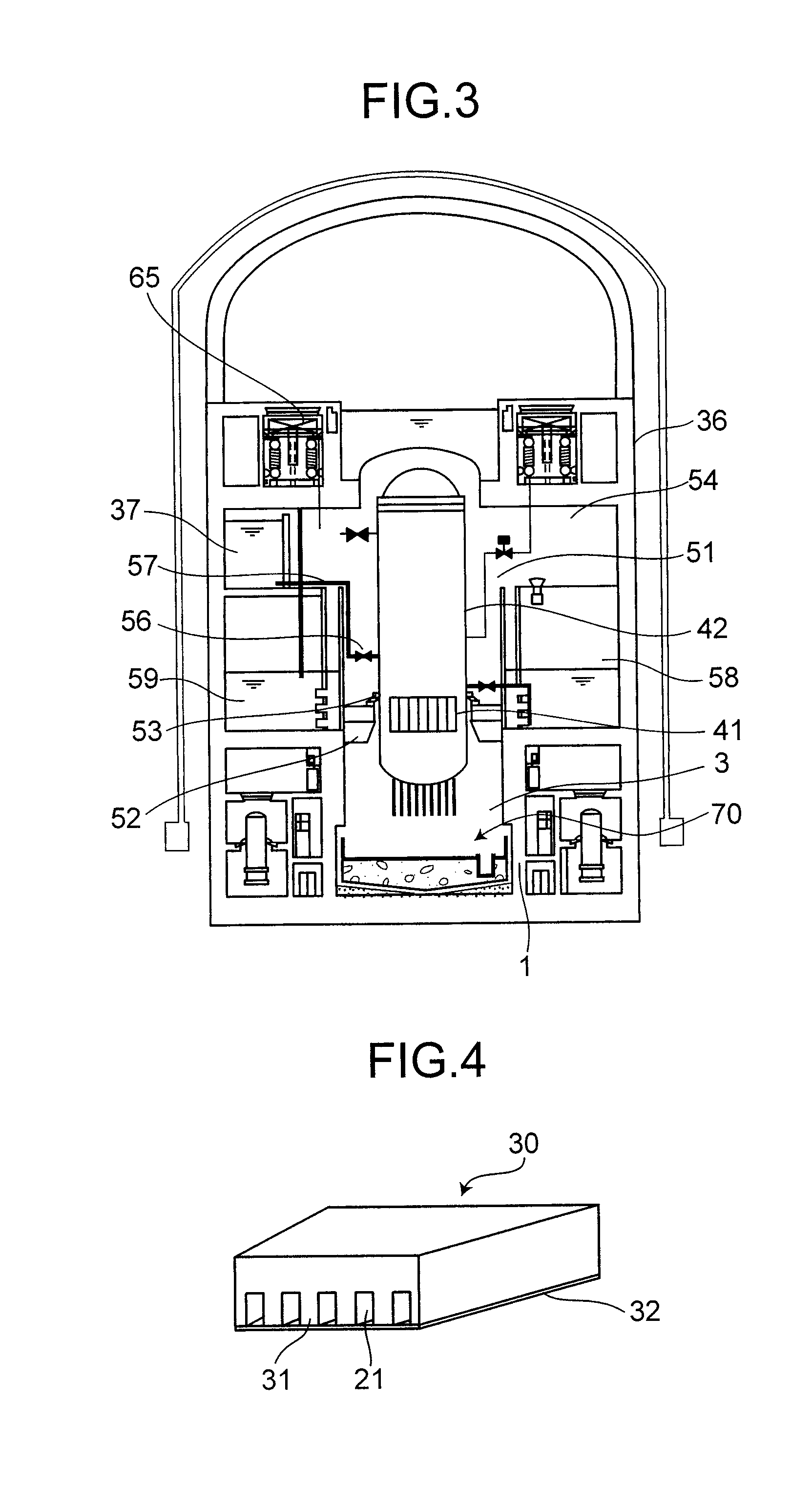
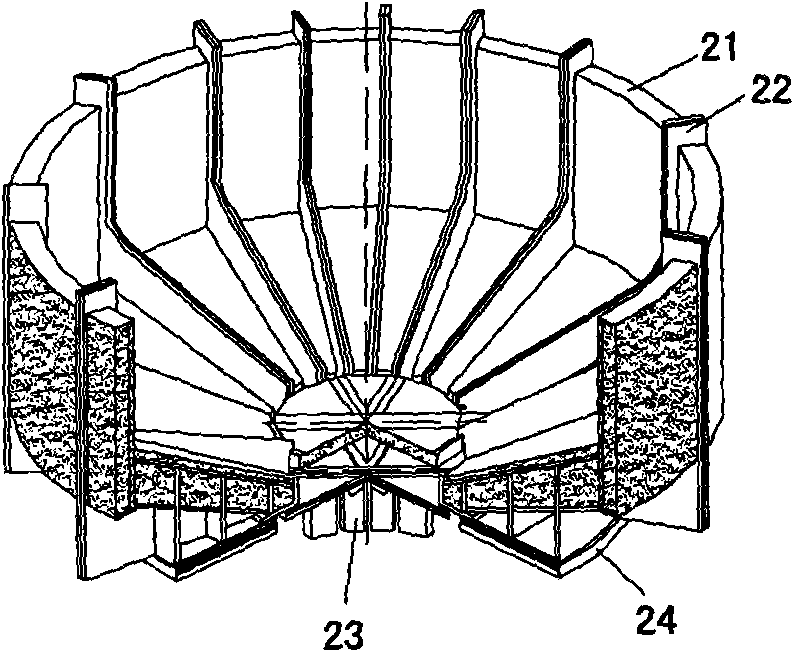
The invention provides a large-scale passive nuclear plant reactor core catcher with bottom water injection and external cooling. The catcher comprises a reactor cavity coating the lower middle part of a reactor pressure vessel, and a reactor cavity concrete soleplate is formed at the bottom of the reactor cavity; a refractory layer is formed on the side surface of the reactor cavity and the bottom of the reactor cavity concrete soleplate; a steel cylinder is sleeved outside the refractory layer; an external cooling passage is formed at the bottom of the steel cylinder, and a cooling passage inlet and a cooling passage outlet are respectively formed at the two outward-extending ends of the external cooling passage; and dozens of nozzles are fixed at the bottom of the steel cylinder, and the upper ends of the nozzles extend into the reactor cavity concrete soleplate while the lower ends of the nozzles extend into the external cooling passage. According to the invention, the dilution and the temperature reduction of a melt are implemented through the melting of concrete by adopting the reactor cavity concrete soleplate as a sacrificial material. A reactor core melt is collected in the refractory layer after the reactor cavity concrete soleplate is molten through, so that the security and the reliability of a nuclear plant are further improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Application of catalytic nanoparticles to high temperature water systems to reduce stress corrosion cracking
InactiveUS20030012686A1Reducing electrochemical corrosion potentialReduce componentsNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactorNanoparticle
A method and system for reducing stress corrosion cracking in a hot water system, such as a nuclear reactor, by reducing the electrochemical corrosion potential of components exposed to high temperature water within the structure. The method comprises the steps of: providing a reducing species to the high temperature water; and providing a plurality of noble metal nanoparticles having a mean particle size of up to about 100 nm to the high temperature water during operation of the hot water system. The catalytic nanoparticles, which may comprise at least one noble metal, form a colloidal suspension in the high temperature water and provide a catalytic surface on which a reducing species reacts with least one oxidizing species present in the high temperature water. The concentration of the oxidizing species is reduced by reaction with the reducing species on the catalytic surface, thereby reducing the electrochemical corrosion potential of the component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Isotope production system with separated shielding
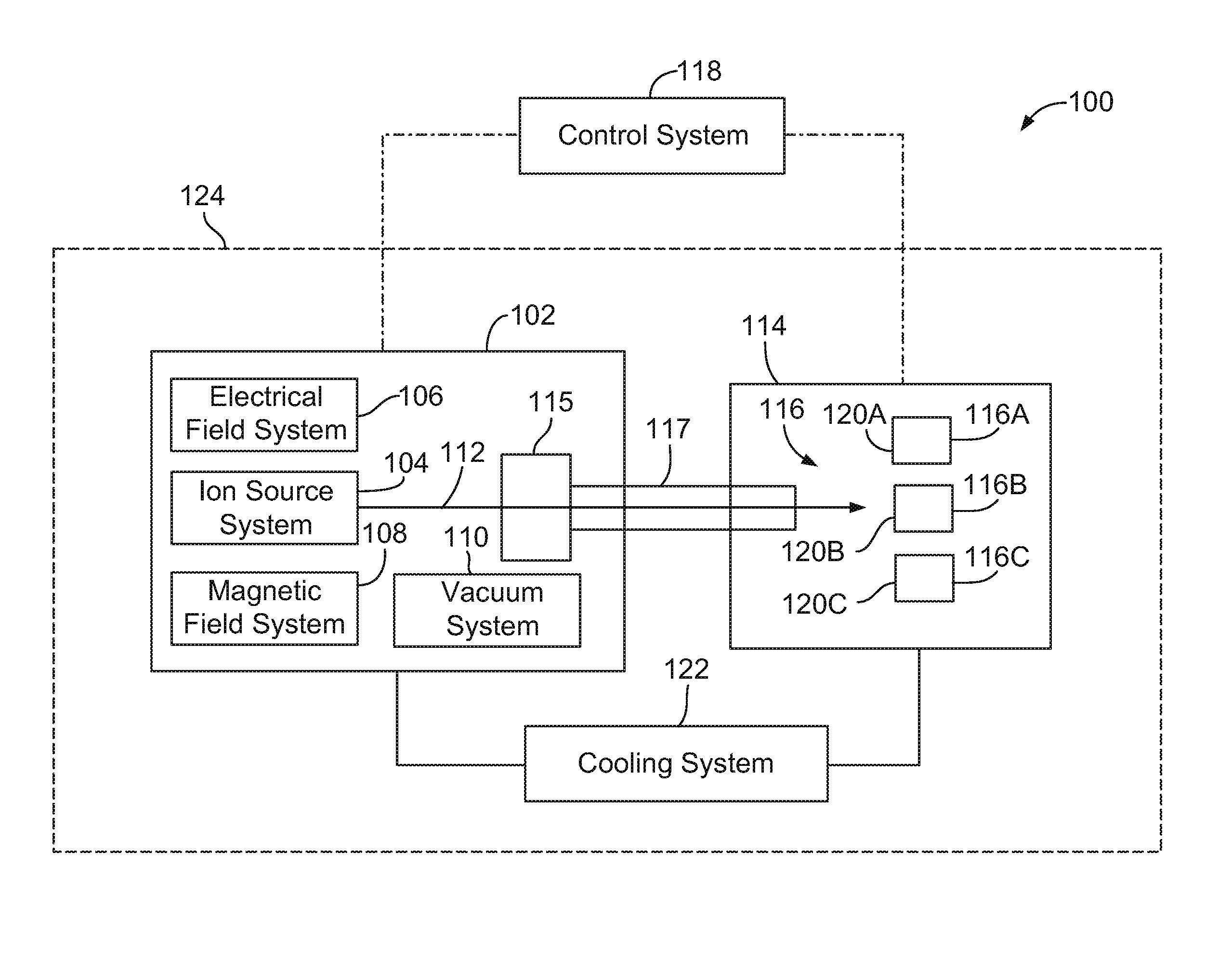
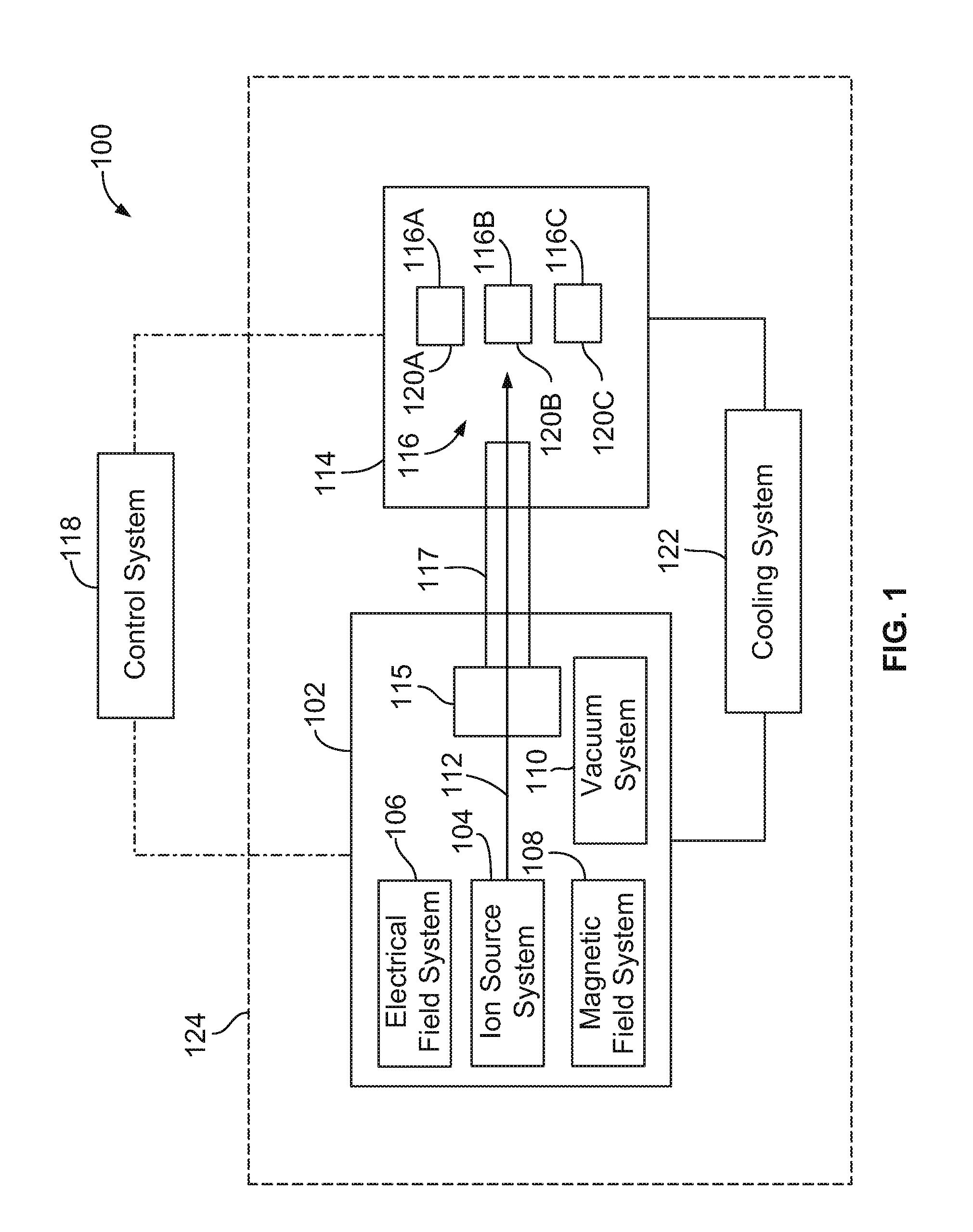
ActiveUS20100329406A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationParticle beamLight beam
An isotope production system that includes a cyclotron having a magnet yoke that surrounds an acceleration chamber. The cyclotron is configured to direct a particle beam from the acceleration chamber through the magnet yoke. The isotope production system also includes a target system that is located proximate to the magnet yoke. The target system is configured to hold a target material and includes a radiation shield that extends between the magnet yoke and the target location. The radiation shield is sized and shaped to attenuate gamma rays emitted from the target material toward the magnet yoke. The isotope production system also includes a beam passage that extends from the acceleration chamber to the target location. The beam passage is at least partially formed by the magnet yoke and the radiation shield of the target system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
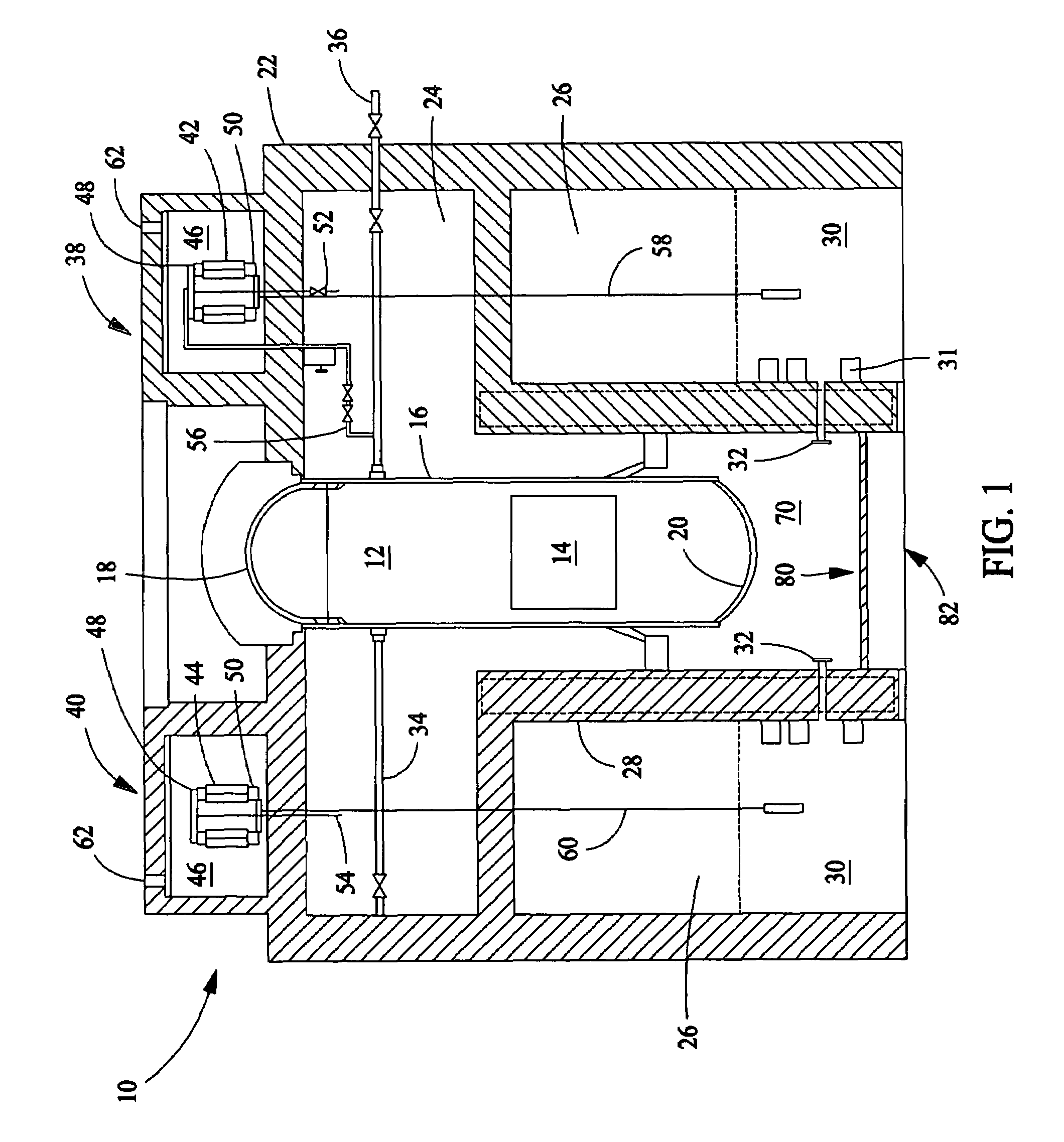
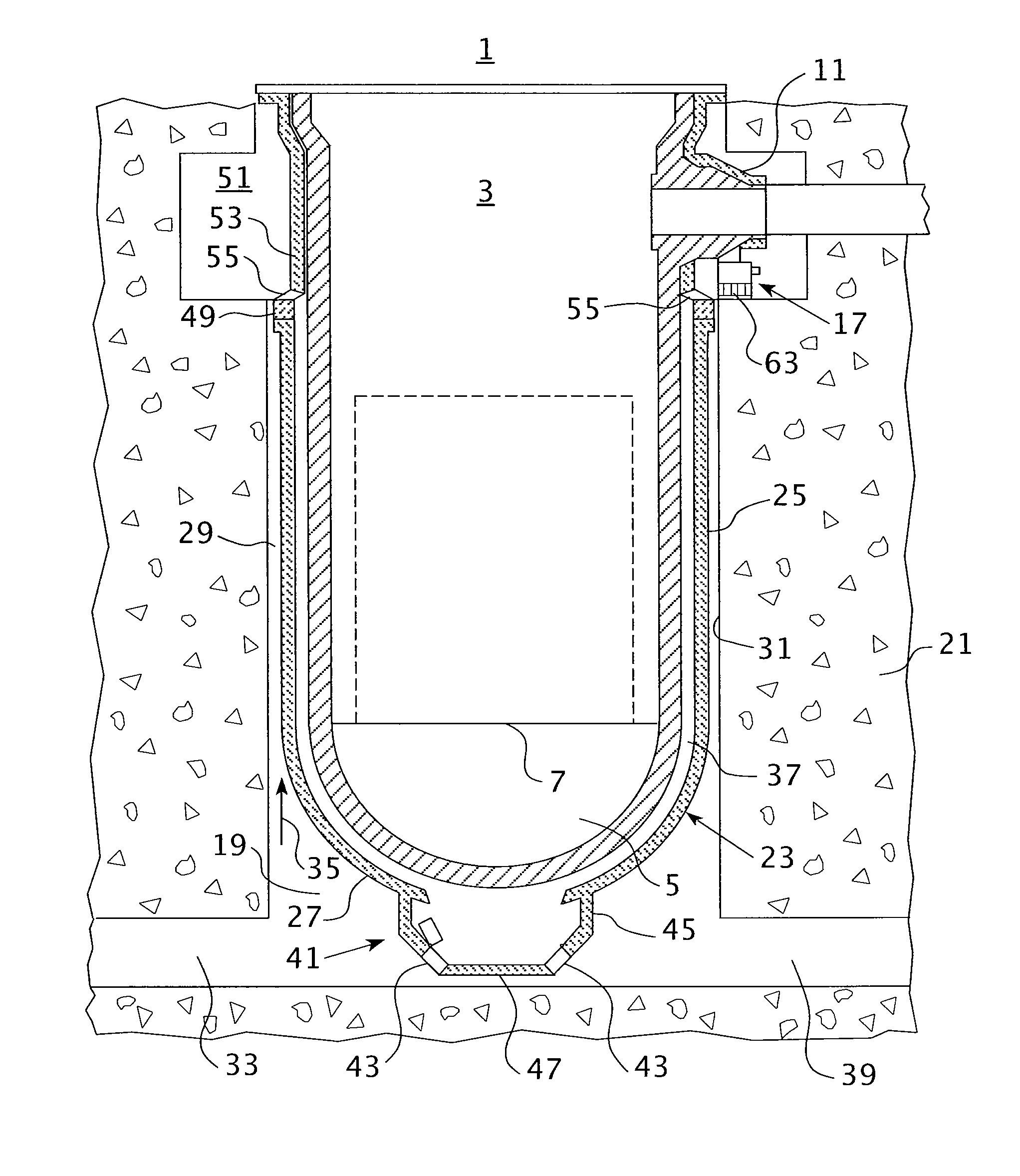
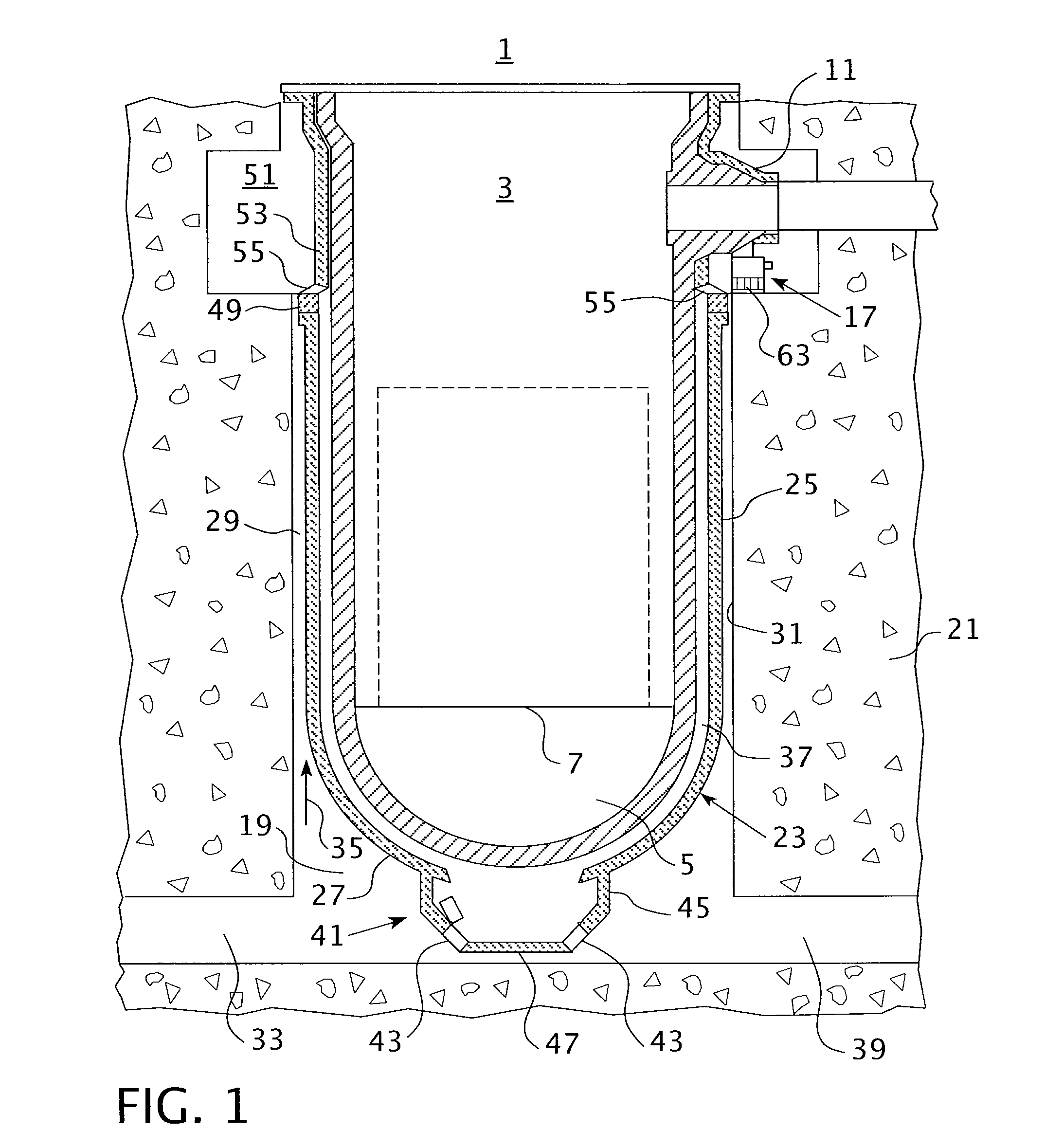
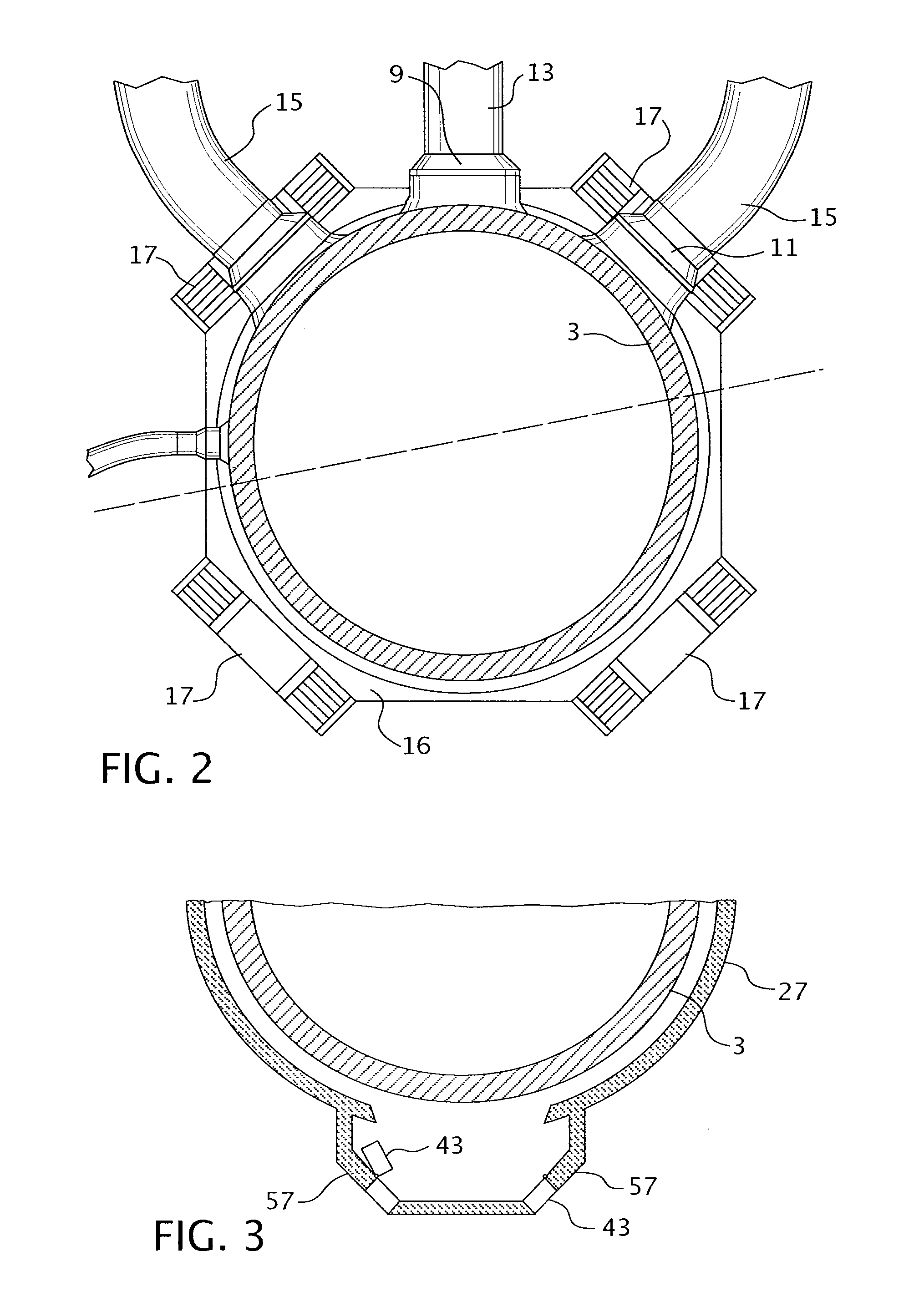
Core catcher cooling
InactiveUS7558360B1Nuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsCore catcherEngineering
An assembly includes a base grid configured to be disposed below a pressure vessel and spaced vertically above a floor of a containment vessel to define a sump therebetween. The assembly further includes an annular wall extending vertically upwards from the floor and laterally bounding the base grid and the sump. The wall separates the sump from a suppression pool, an inlet passage extending through the wall and providing flow communication between the sump and the suppression pool, and an outlet passage extending through the wall and providing flow communication between the sump and the suppression pool.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Application of catalytic nanoparticles to high temperature water systems to reduce stress corrosion cracking
InactiveUS6793883B2Reducing electrochemical corrosion potentialReduced dose rateNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactorNanoparticle
A method and system for reducing stress corrosion cracking in a hot water system, such as a nuclear reactor, by reducing the electrochemical corrosion potential of components exposed to high temperature water within the structure. The method includes the steps of: providing a reducing species to the high temperature water; and providing a plurality of noble metal nanoparticles having a mean particle size of up to about 100 nm to the high temperature water during operation of the hot water system. The catalytic nanoparticles, which may contain at least one noble metal, form a colloidal suspension in the high temperature water and provide a catalytic surface on which a reducing species reacts with least one oxidizing species present in the high temperature water. The concentration of the oxidizing species is reduced by reaction with the reducing species on the catalytic surface, thereby reducing the electrochemical corrosion potential of the component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
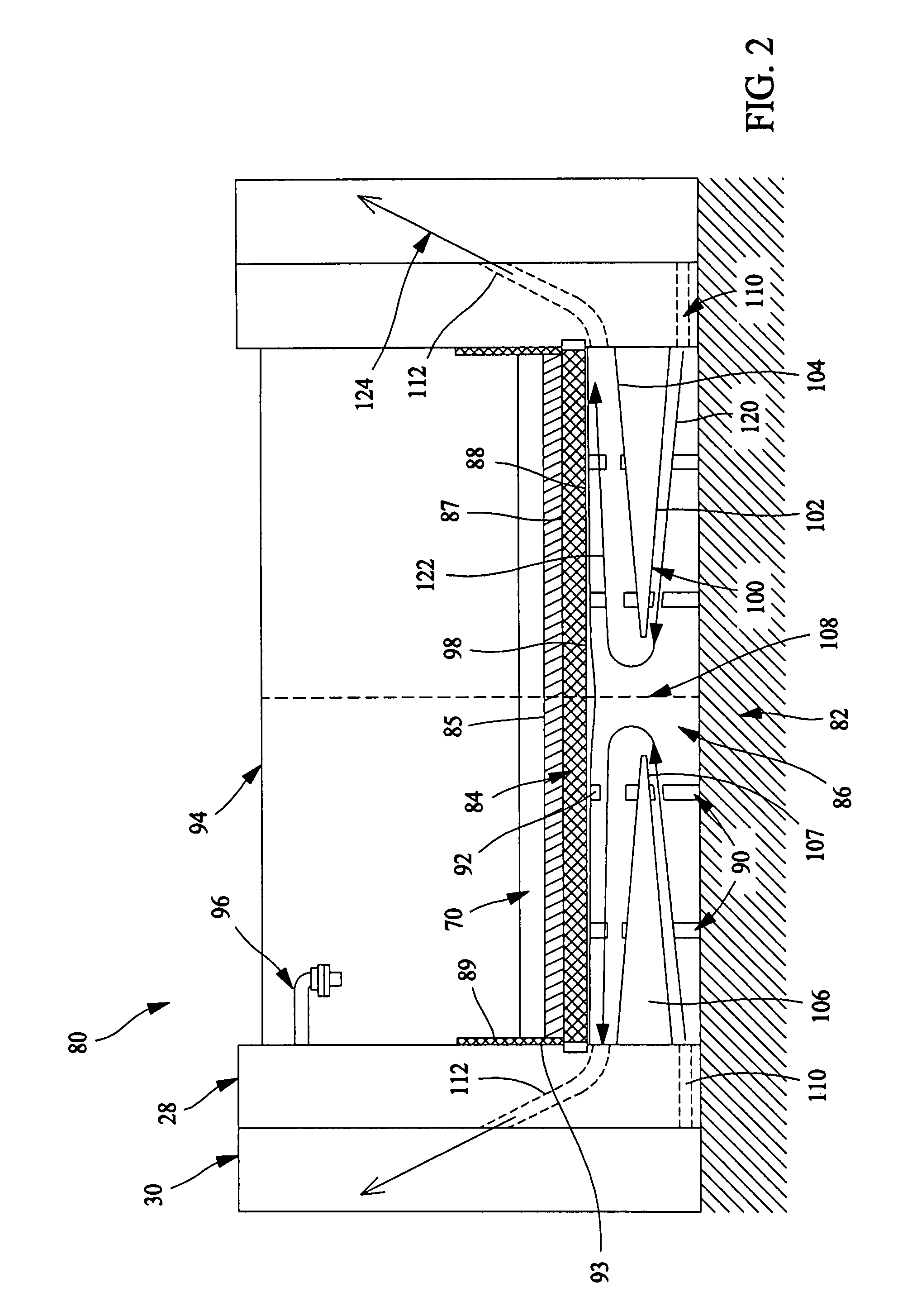
Apparatus for positioning and cooling lining layer of damaged LWR nuclear reactor
InactiveCN1585034AImprove melt fluidityImprove cooling conditionsNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsCore catcherNuclear reactor
The invention relates to apparatus for positioning and cooling melting lining layer when the melting lining layer flows out of the reactor shell during accident. The improvements of invention are described as following: the design of the cooling lining layer trap which has steel basket shell and arranged in sub-reactor, wherein sacrifice material is filled in the steel basket for diluting the component containing uranium and steel component of the lining layer; the shape (arrangement) of the sacrifice material in reactor core; the choice for optimum number of the sacrifice material; installation of guiding device used for the lining layer flowing into the reactor core trap. Especially, the thickness of bottom of the cooling jacket is larger than the thickness of the side wall thereof for no less than 30%, and the cooling jacket inclines to its center for 10 to 20 degree; the diluent and sacrifice material is made into blocks packed in steel shell.
Owner:V·B·哈本斯基 +17
Large passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant crucible-type reactor core catcher
InactiveCN103177779AImprove securityImprove reliabilityNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear plantCore catcher
The invention discloses a large passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant crucible-type reactor core catcher which comprises a reactor cavity concrete bottom plate (4), a crucible cooling system water filling nozzle (6), a crucible cooling system water vapor outlet (7), a crucible component (8), a crucible cooling system cavity (9) and a melt collector (10). The reactor core catcher is organically combined with an interactive voice response (IVR) system, the safety of the nuclear power plant can be further improved, and the reliability of the system is higher due to the crucible design.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant reactor core catcher with melt expansion room
InactiveCN103165198AIncrease heat transfer areaImprove cooling effectNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsCore catcherPressurized water reactor
The invention provides a large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant reactor core catcher with a melt expansion room. The large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant reactor core catcher with the melt expansion room comprises a reactor cavity which coats the middle lower portion of a reactor pressure vessel, a reactor cavity concrete base plate is arranged on the lower portion of the reactor cavity, and a reactor cavity refractory layer is arranged on the lower portion of the reactor cavity concrete base plate. The upper end of a melt release passage is communicated with the reactor cavity refractory layer, and the lower end of the melt release passage is communicated with the melt expansion room. The inner wall of the melt release passage surrounds the refractory layer. An expansion room concrete base plate is arranged on the lower portion of the melt expansion room, an expansion room refractory layer is arranged on the lower portion of the expansion room concrete base plate, and an expansion room outside cooling passage is arranged on the lower portion of the expansion room refractory layer. Two ends of the expansion room outside cooling passage extend outwards and are respectively an outside cooling passage entrance and an outside cooling passage exit. The large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant reactor core catcher with the melt expansion room is used for successively implementing expansion, retention and cooling of the melt when the a pressure container loses efficacy and can strengthen capacity of relieving severe accidents of the large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Device combining in-core and out-of-core dwelling of molten material of large-scale passive nuclear power plant
InactiveCN103578580AImplementation of off-stack coolingImplement in-heap retentionNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsCore catcherPressurized water reactor
The invention provides a device combining in-core and out-of-core dwelling of a molten material of a large-scale passive nuclear power plant. The device comprises a concrete sacrificial layer (4), a core catcher chamber (7), a core catcher refractory layer (8), a cooling channel inlet (9), a cooling channel outlet (10) and a core catcher bottom cooling channel (11). The invention provides a set of device organically combining molten material out-of-core cooling with an IVR (interactive voice response) system, when IVR succeeds, in-core dwelling of the molten material can be realized; and after the IVR fails, out-of-core dwelling of the molten material is realized by passive cooling of the core catcher bottom cooling channel, and the capability of mitigating severe accidents of the large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant is further enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
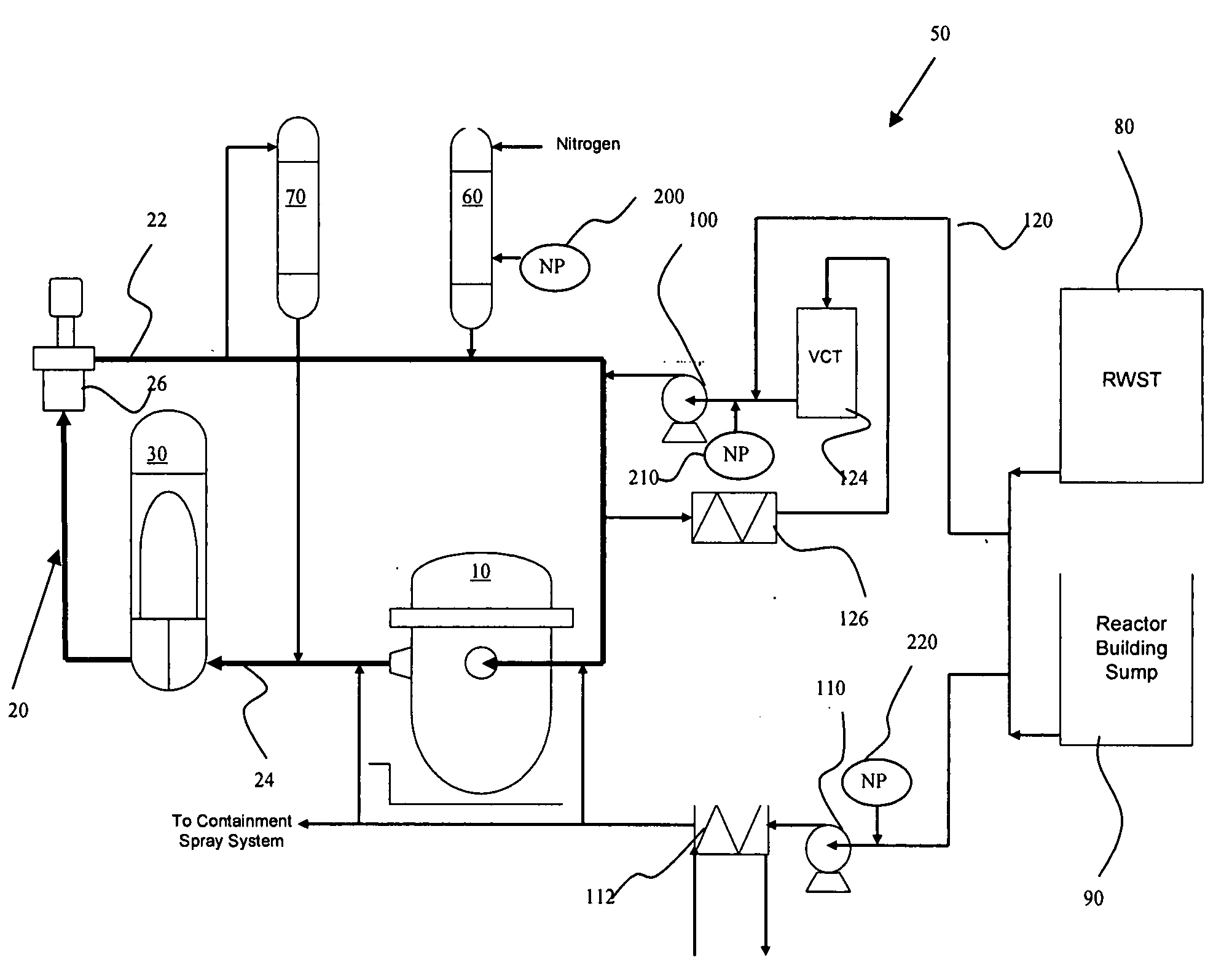
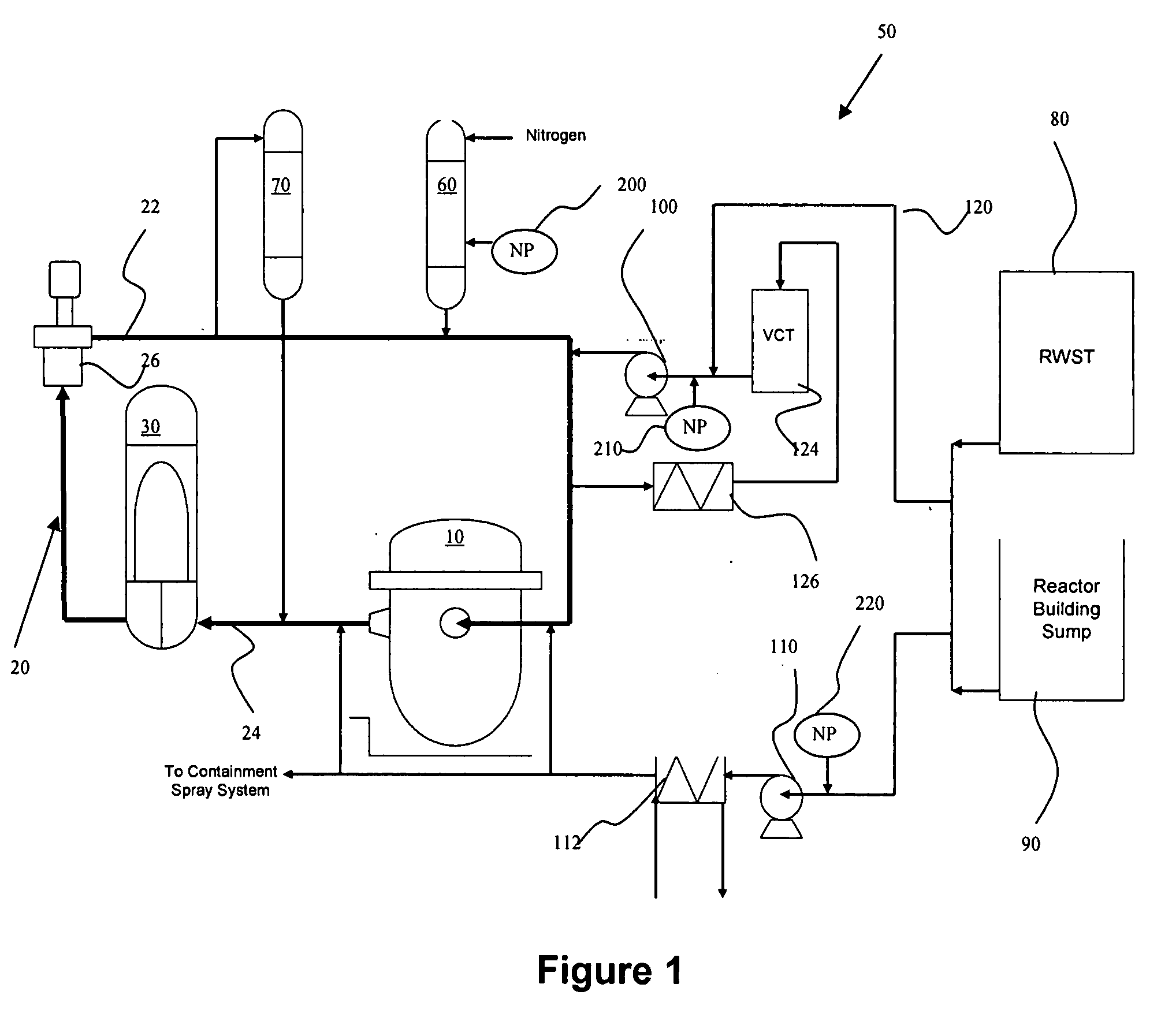
Nuclear power plant using nanoparticles in emergency systems and related method
InactiveUS20080212733A1Improve heat transfer performanceNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsNuclear plantMotor drive
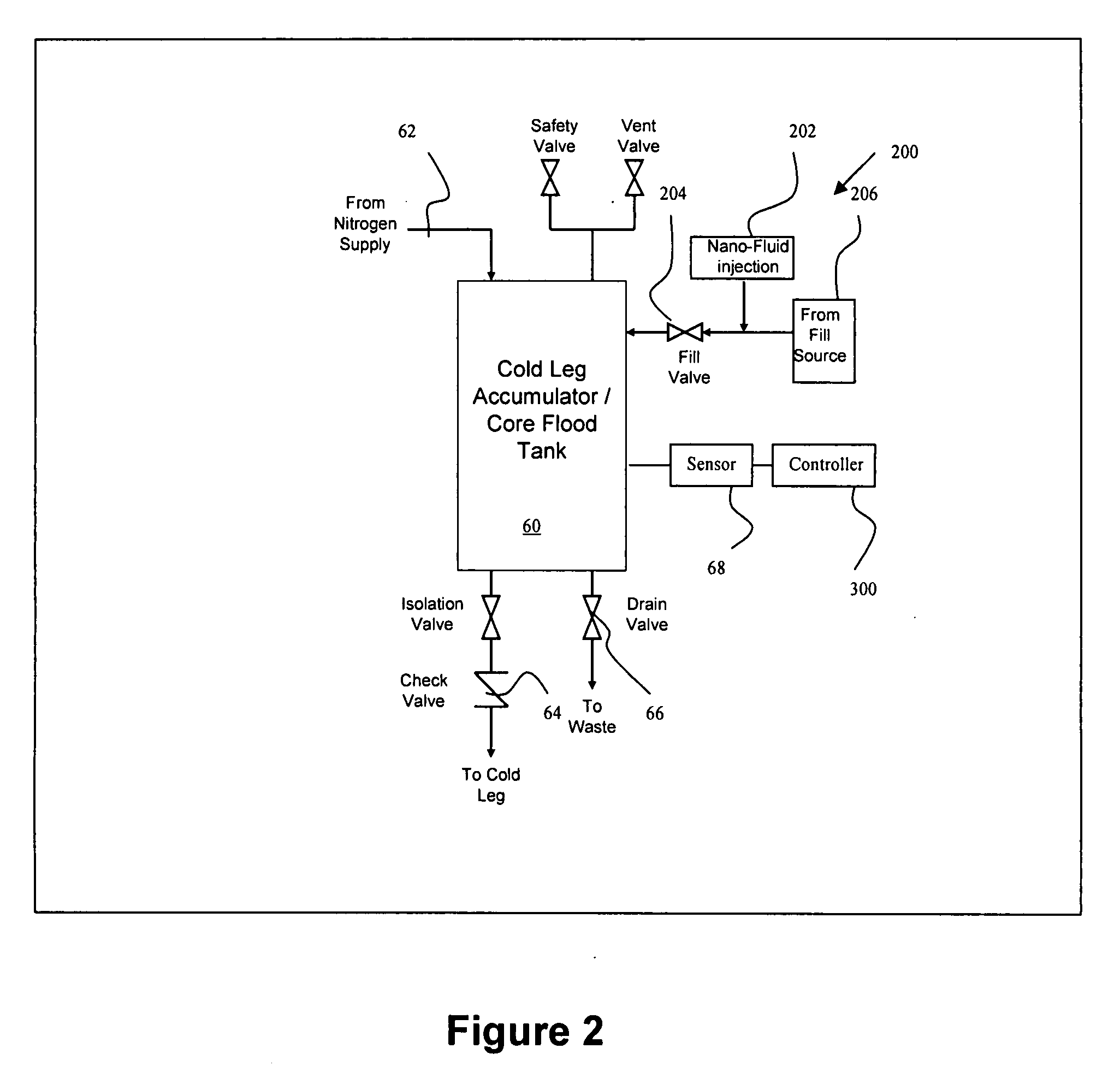
A nuclear power plant with an improved cooling system using nanoparticles in solid or fluid form is provided. The nanoparticles are delivered in locations such as the cold leg accumulator and high and low pressure pumps of an emergency core cooling system. Motor driven valves and pressurization can aid in the delivery. Methods for providing the nanoparticles are also provided.
Owner:AREVA NP SAS
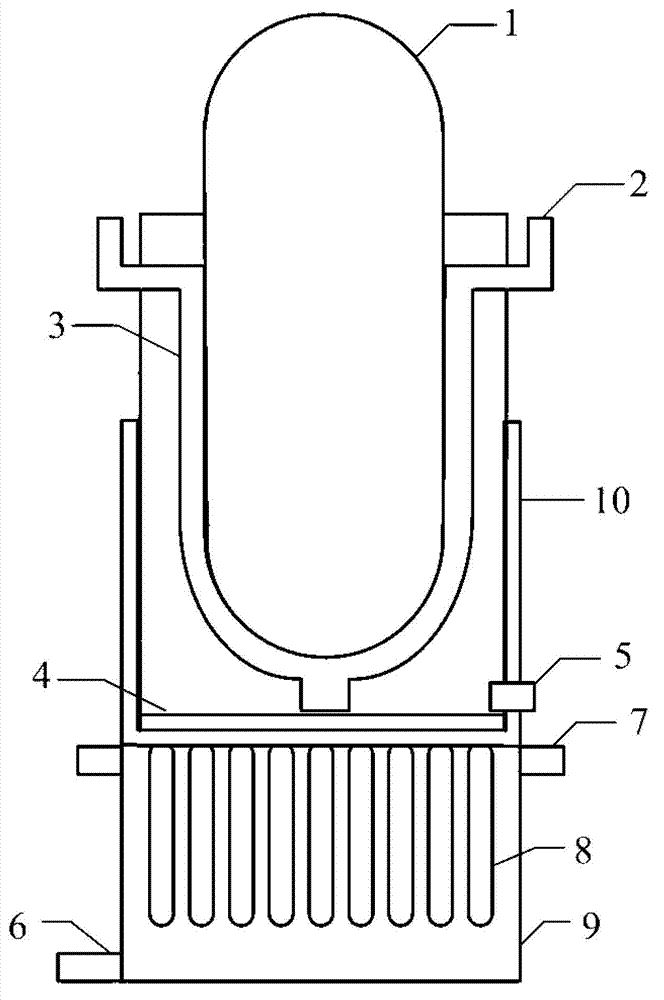
Core catcher, manufacturing method thereof, reactor containment vessel and manufacturing method thereof
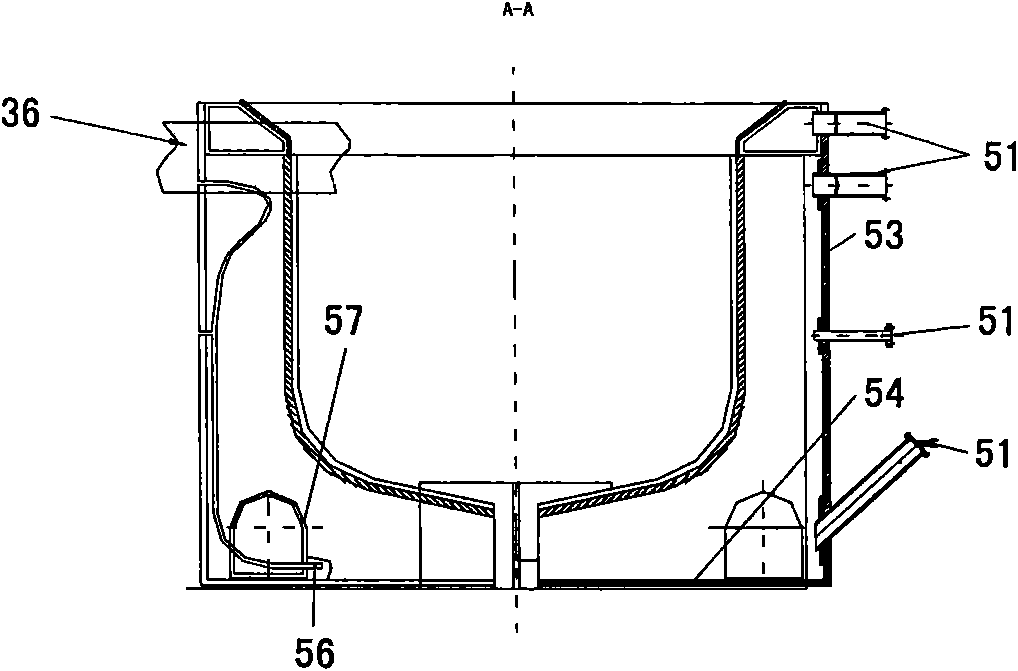
Core debris generated during a molten reactor core in a reactor containment vessel penetrating the reactor containment vessel is configured to be caught by a core catcher located beneath the reactor containment vessel which has a main body having first stage cooling water channels and second stage surrounded by cooling fins extending radially. The number of the second stage cooling channels is larger than that of the first stage cooling channels. Cooling water is supplied from a cooling water injection opening and distributed to the first cooling water channels at a distributor. An intermediate header is formed between the first and the second cooling water channels, and the cooling water is distributed to the second cooling water channels uniformly.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Nuclear power station non-active engineering safety system
InactiveCN102163469AReduce the risk of secondary side radioactive leakage in accidents such as rupture (SGTR)Prevent and Mitigate MeltthroughNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsActive safetySteam condensation
The invention belongs to a nuclear power station safety system, and in particular relates to a nuclear power station non-active engineering safety system. The system comprises a secondary non-active residual heat removal exchanger, a steam condensation water tank, a non-active reactor cavity water injection system, a non-active high pressure reactor core water supplementing tank and related valves and pipelines. When a nuclear power station is in a design basis accident or a hyper design basis accident, a series of non-active and active safety devices are invested in steps, and a reactor primary circuit and a reactor core are timely, rapidly and effectively cooled, thus a nuclear power station smoothly enters into a safe cold shut-down amplifier state, a reactor disaster consequence is inhibited or alleviated, incident harm is reduced, and the safety of the nuclear power station is improved.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
Containment filtering and discharging system
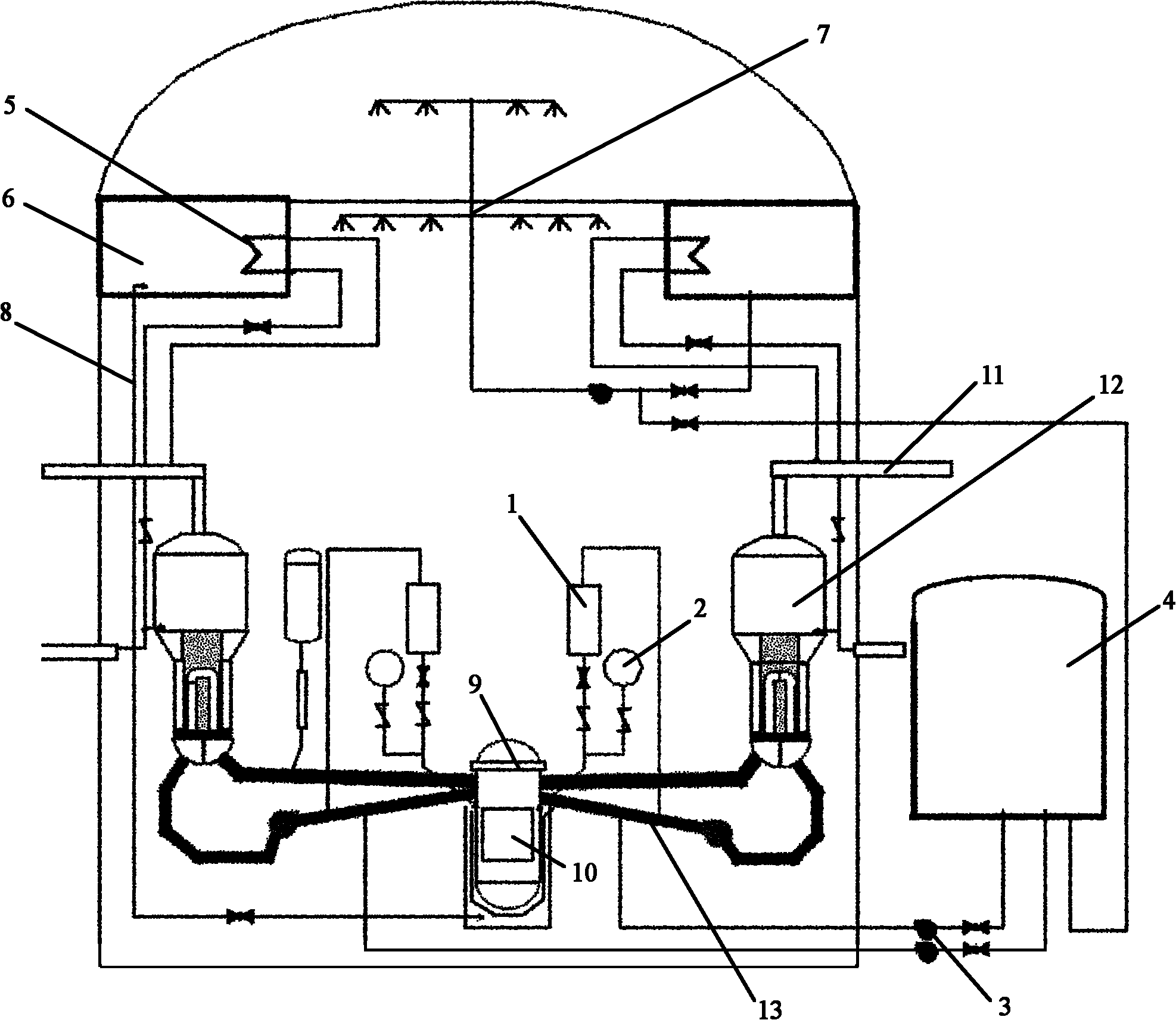
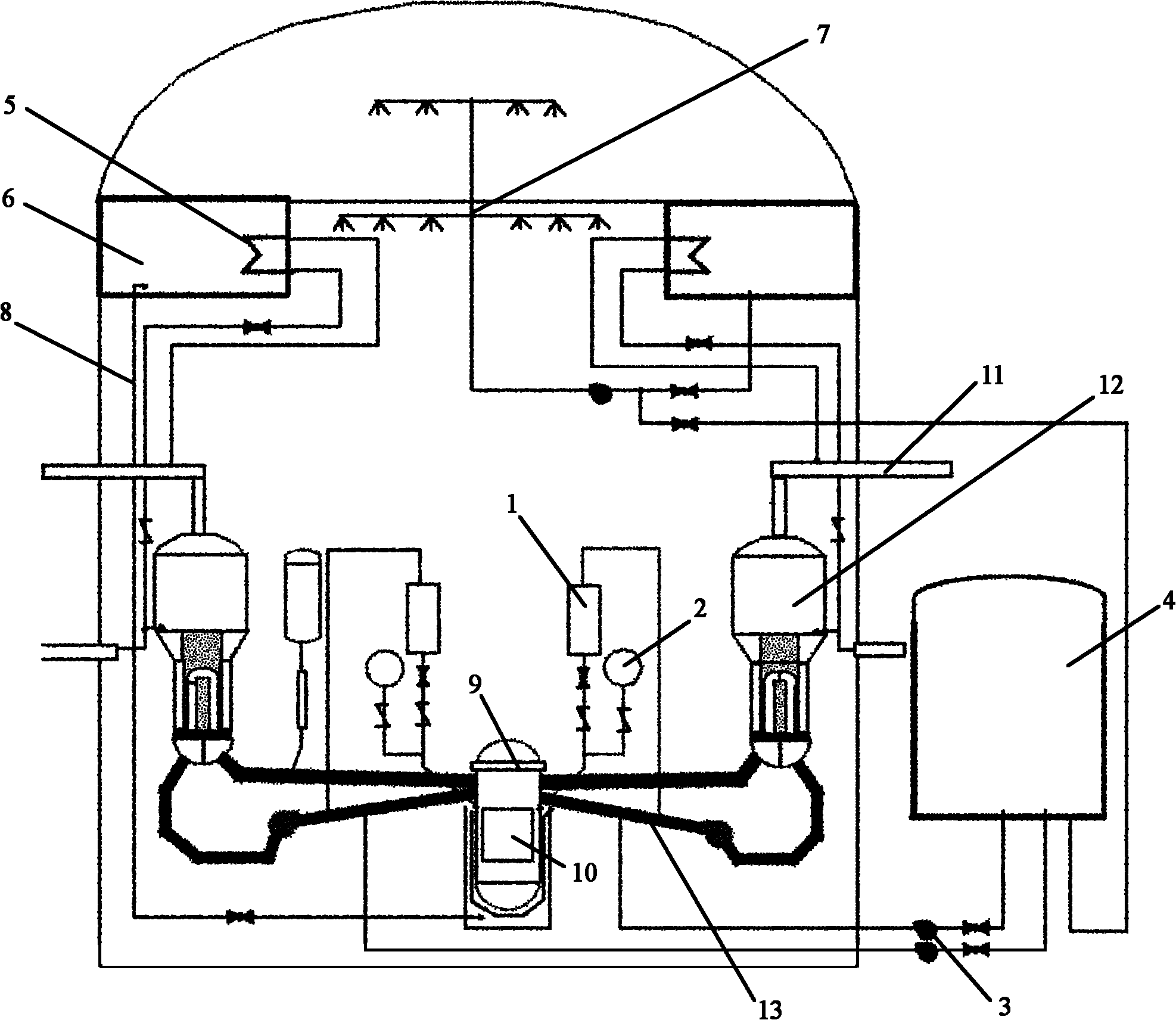
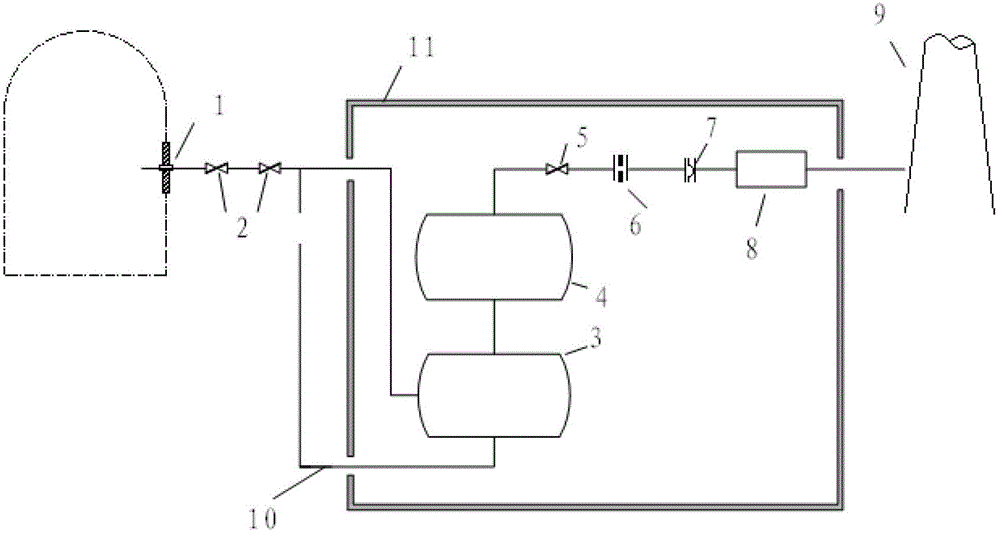
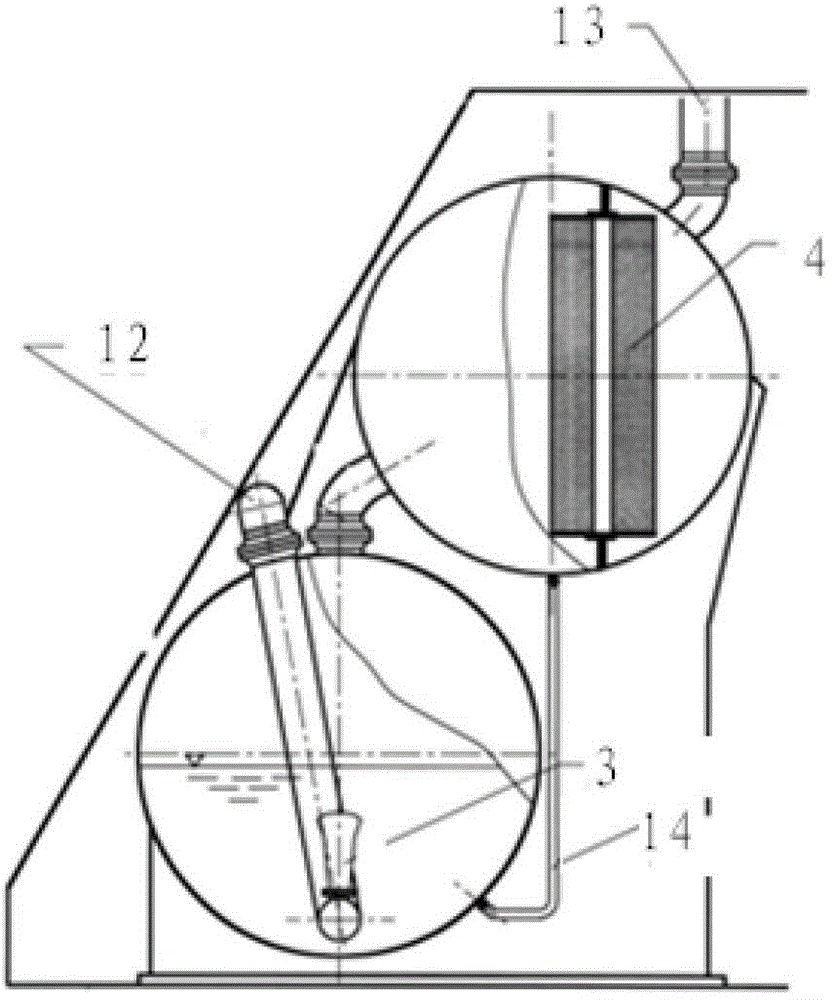
InactiveCN102723114AImprove filtering effectAccumulated radioactivityNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsLiquid wasteRadioactive agent
The invention relates to a containment filtering and discharging system. As a shielding plant (11) is arranged outside a containment, a discharging and filtering sub system is arranged in the shielding plant (11), a water washing filter (3) and a metal fiber filter (4) connected with each other in sequence are arranged in the discharging and filtering sub system and the water washing filter (3) is provided with a waste liquid returning pipeline (10), gases discharged by the containment are doubly filtered by the water washing filter (3) and the metal fiber filter (4), and the waste liquid accumulated in the water washing filter (3) self-flows into the containment through the waste liquid returning pipeline (10) under the effect of gravity force. Therefore, according to the invention, serious accidents occurred in pressurized-water reactor nuclear power stations are eased, overpressure failure of the containment is prevented, radioactive substances released to the environment are reduced, safeties of the surrounding environment and personnel are protected, and the safety of the nuclear power stations are greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
Method for installing reactor core catcher of nuclear power station
ActiveCN102097137ANuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsCore catcherNuclear power
The invention provides a method for reliably installing a reactor core catcher in a narrow reactor vertical shaft, comprising the steps of: (1) installing a forging heat exchange device on a bottom plate of the reactor vertical shaft; (2) installing a hanging basket with fillers; and (3) installing a ventilation system and a lower bottom plate, wherein the step 1 for installing the forging heat exchange device further comprises the steps of: (1a) placing a plurality of forgings of a heat exchange device on the foundation of the reactor vertical shaft in advance, and confirming the actual respective positions of the forgings; (1b) installing a central fixing member and a supporting ribbed plate in the center of the vertical shaft; (1c) installing forgings on two sides of the ribbed plate according to the actual positions, and respectively fixing the forgings on the wall and the bottom plate of the vertical shaft through connecting pieces; and (1d), sequentially installing and welding the supporting ribbed plate and the forgings of the heat exchange device according to certain sequence. Accordingly, the method provided by the invention is favorable for greatly lowering the construction difficult and the construction workload at the same time of ensuring that all the parts of the reactor core capturer are safe and effective.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR IND 23 CONSTR
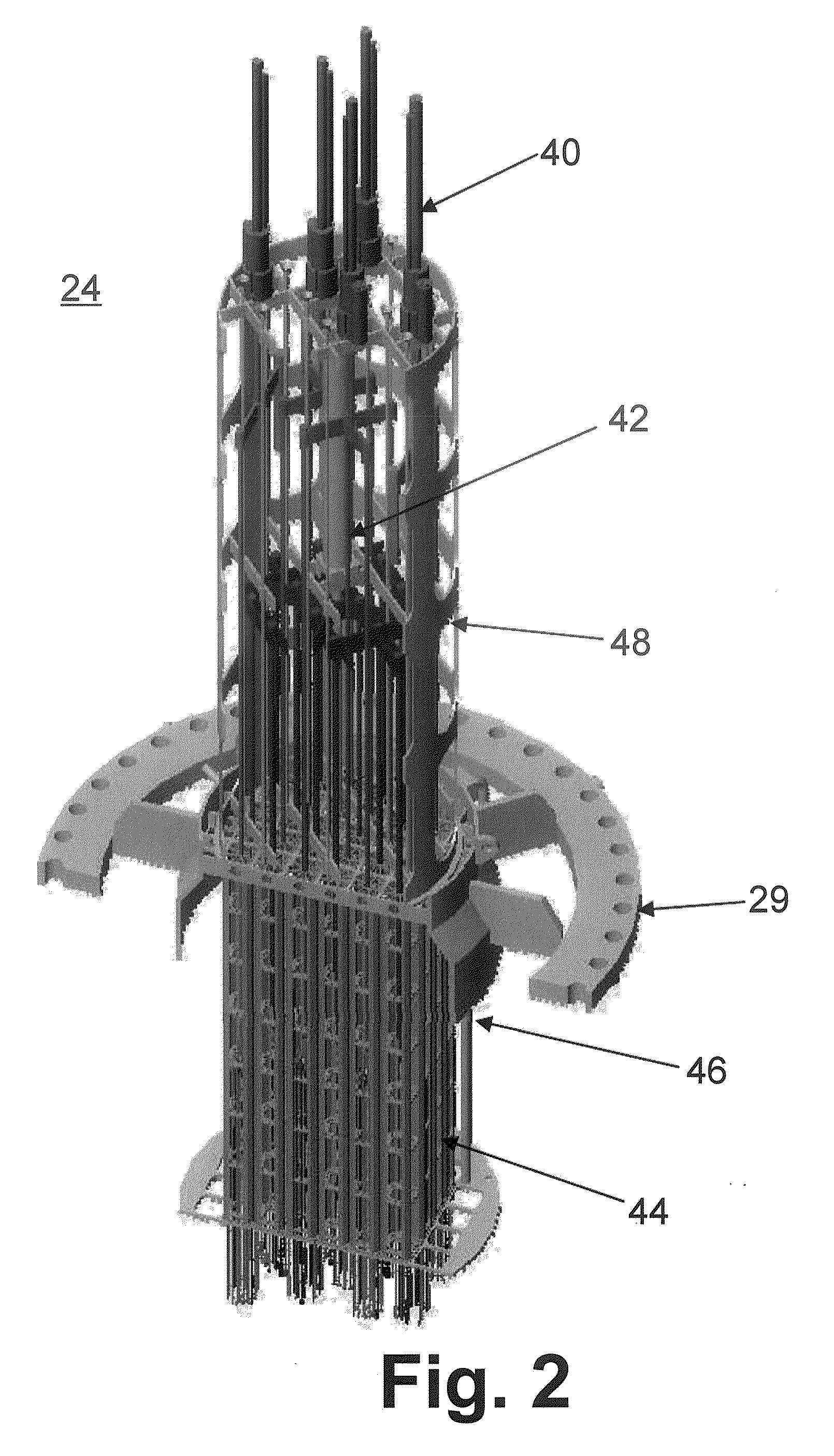
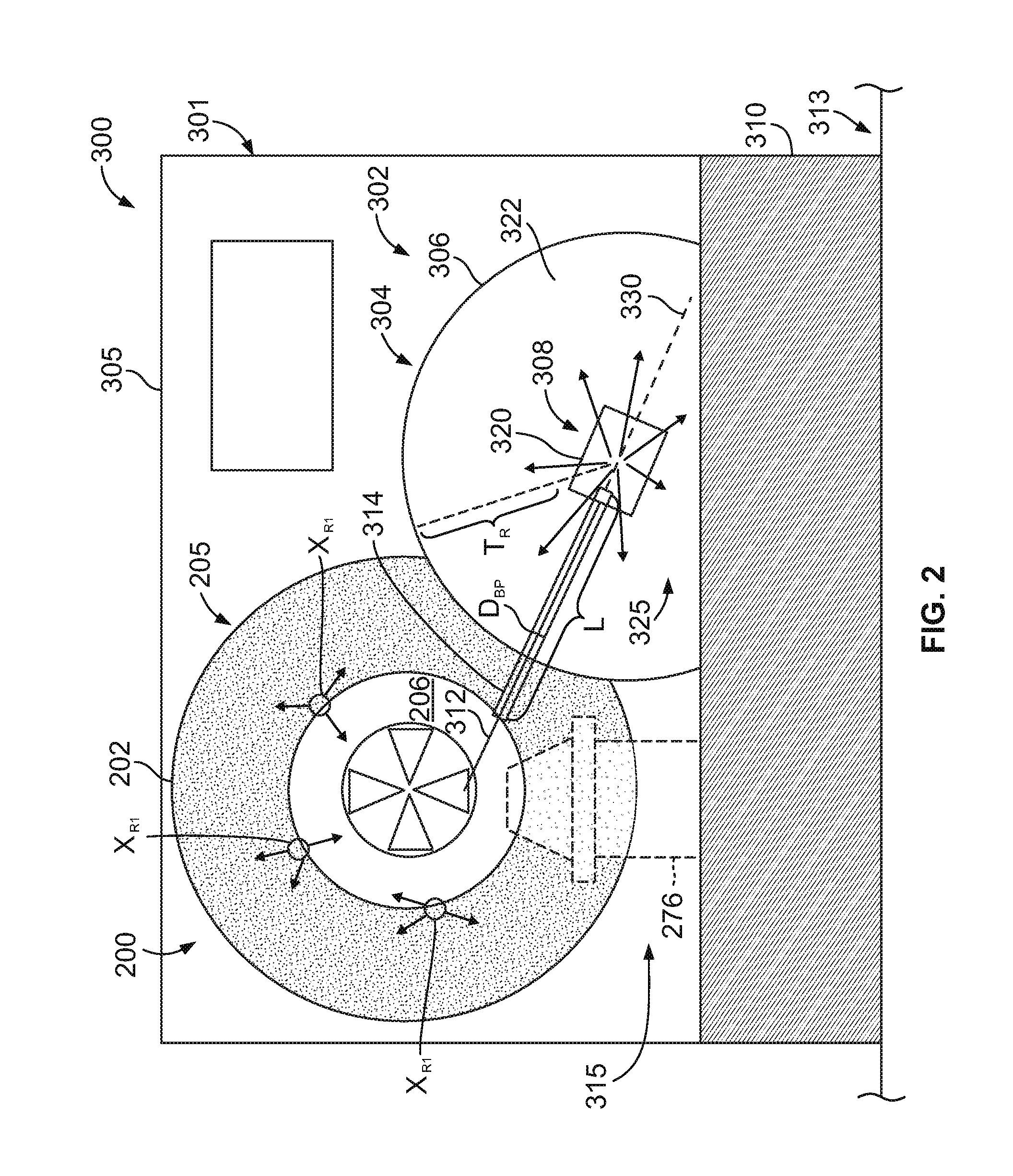
Terminal elements for coupling connecting rods and control rods in control rod assemblies for a nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20120051482A1Nuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear reactorCoupling
A nuclear reactor includes a pressure vessel, and a control rod assembly (CRA) including at least one movable control rod, a control rod drive mechanism (CRDM) for controlling movement of the at least one control rod, and a coupling operatively connecting the at least one control rod and the CRDM. The coupling includes a connecting rod engaged with the CRDM and a terminal element connected with a lower end of the connecting rod and further connected with the at least one control rod. In some embodiments the terminal element includes a first portion comprising a first material having a first density and a second portion comprising a second material having a second density that is greater than the first density. In some embodiments the terminal element has a largest dimension parallel with the connecting rod that is greater than or equal to a largest dimension transverse to the connecting rod.
Owner:BWXT MPOWER INC
Nuclear reactor vessel fuel thermal insulating barrier
ActiveUS20080198960A1Sufficient weightSmooth transitionNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsNuclear reactorInlet valve
The reactor vessel of a nuclear reactor installation which is suspended from the cold leg nozzles in a reactor cavity is provided with a lower thermal insulating barrier spaced from the reactor vessel that has a hemispherical lower section that increases in volume from the center line of the reactor to the outer extent of the diameter of tiie thermal insulating barrier and smoothly transitions up the side walls of the vessel. The space between the thermal insulating harrier and the reactor vessel forms a chamber which can be flooded with cooling water through passive valving to directly cool the reactor vessel in the event of a severe accident. The passive inlet valve for the cooling water includes a buoyant door that is normally maintained sealed under its own weight and floats open when the cavity is Hooded. Passively opening steam vents are also provided.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Heat pipe molten salt fast reactor with stagnant liquid core
A molten salt reactor is described that includes a containment vessel, a reactor core housed within the containment vessel, a neutron reflector spaced from the containment vessel and positioned between the core and the containment vessel, a liquid fuel comprised of a nuclear fission material dissolved in a molten salt enclosed within the core, a plurality of heat transfer pipes, each pipe having a first and a second end, wherein the first end is positioned within the reactor core for absorbing heat from the fuel, a heat exchanger external to the containment vessel for receiving the second end of each heat transfer pipe for transferring heat from the core to the heat exchanger, and at least one and preferably two or more reactor shut down systems, where at least one may be a passive system and at least one or both may be an active or a manually operated system. The liquid fuel in the core is kept within the core and heat pipes are used to carry only the heat from the liquid core to the heat exchanger.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
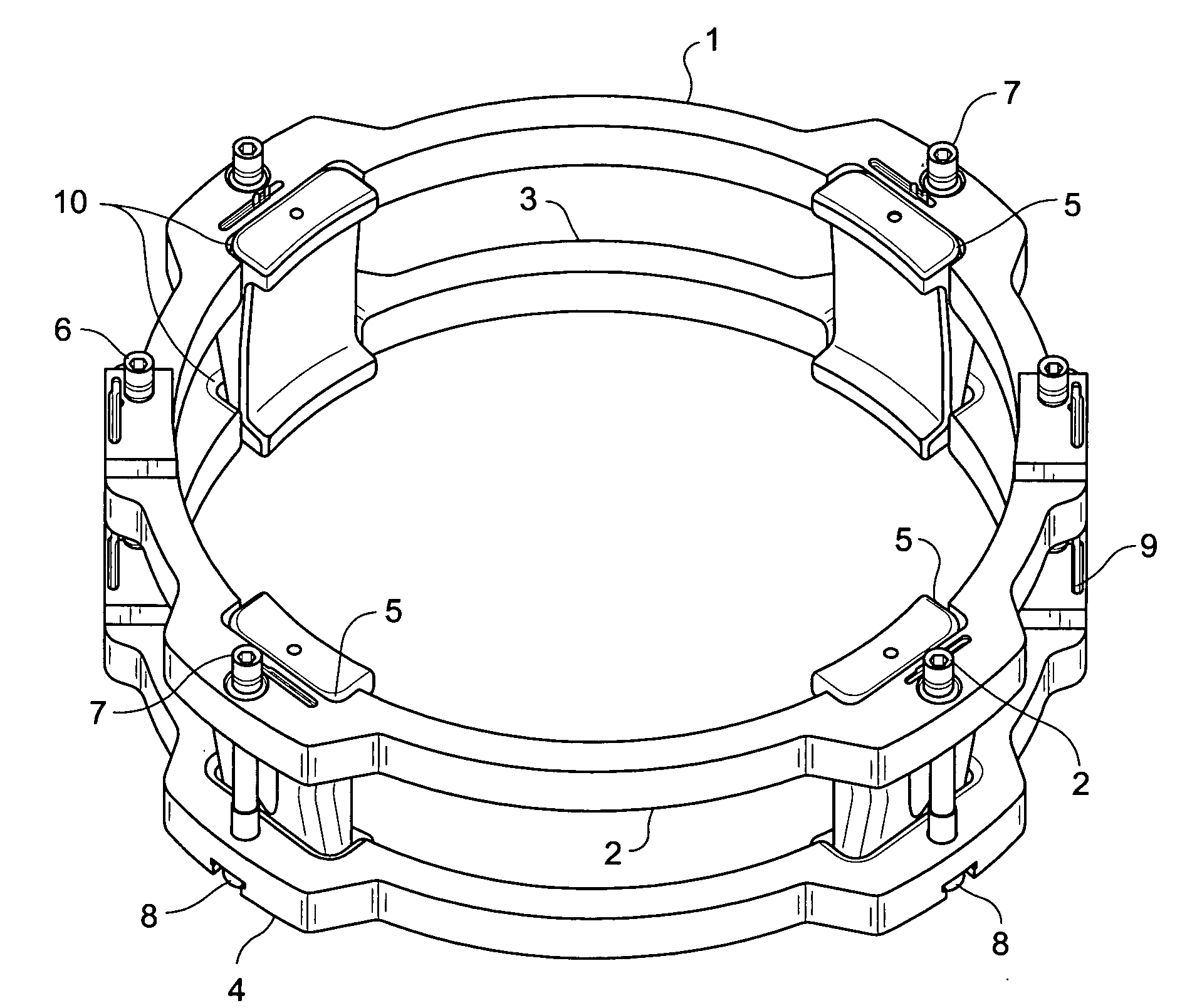
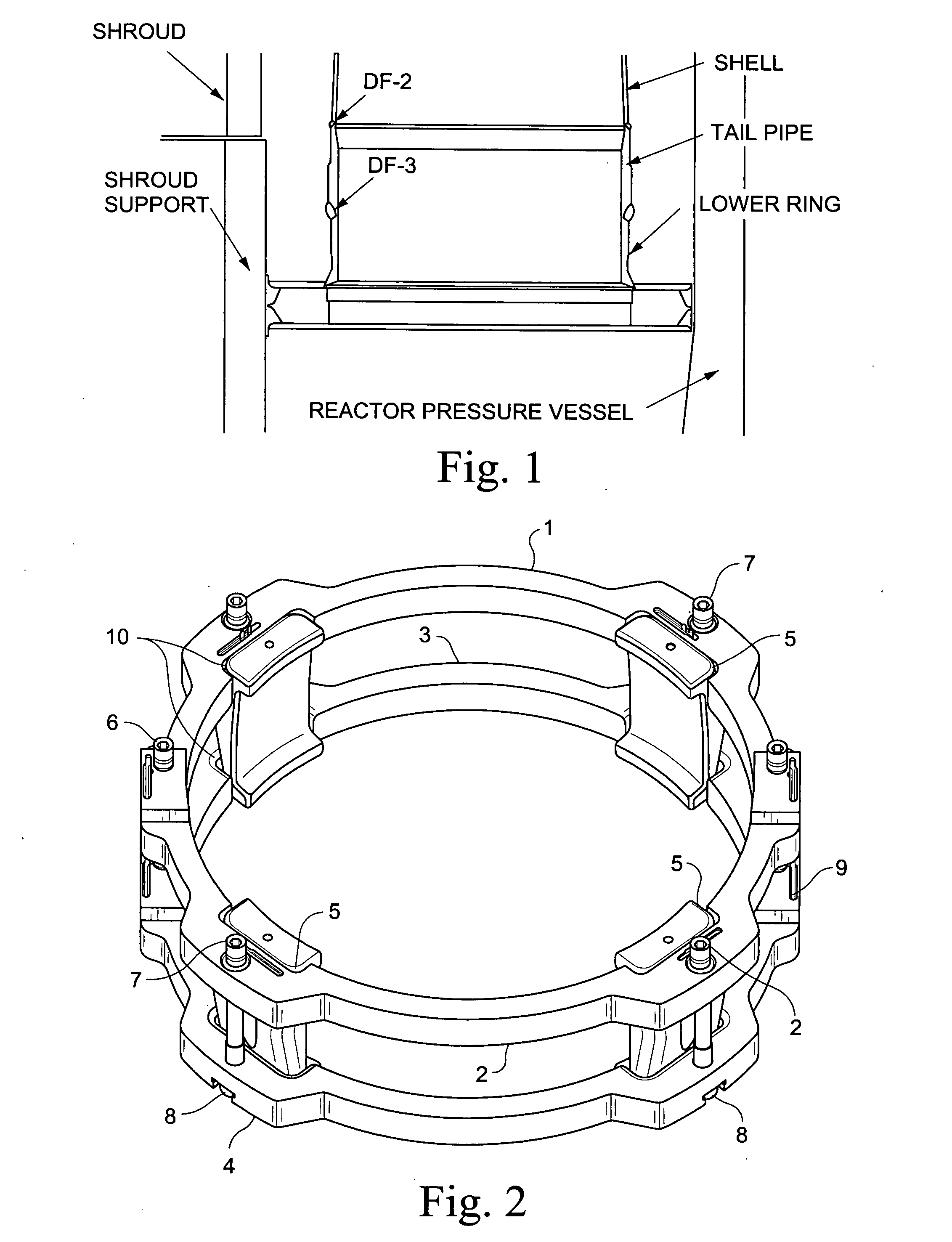
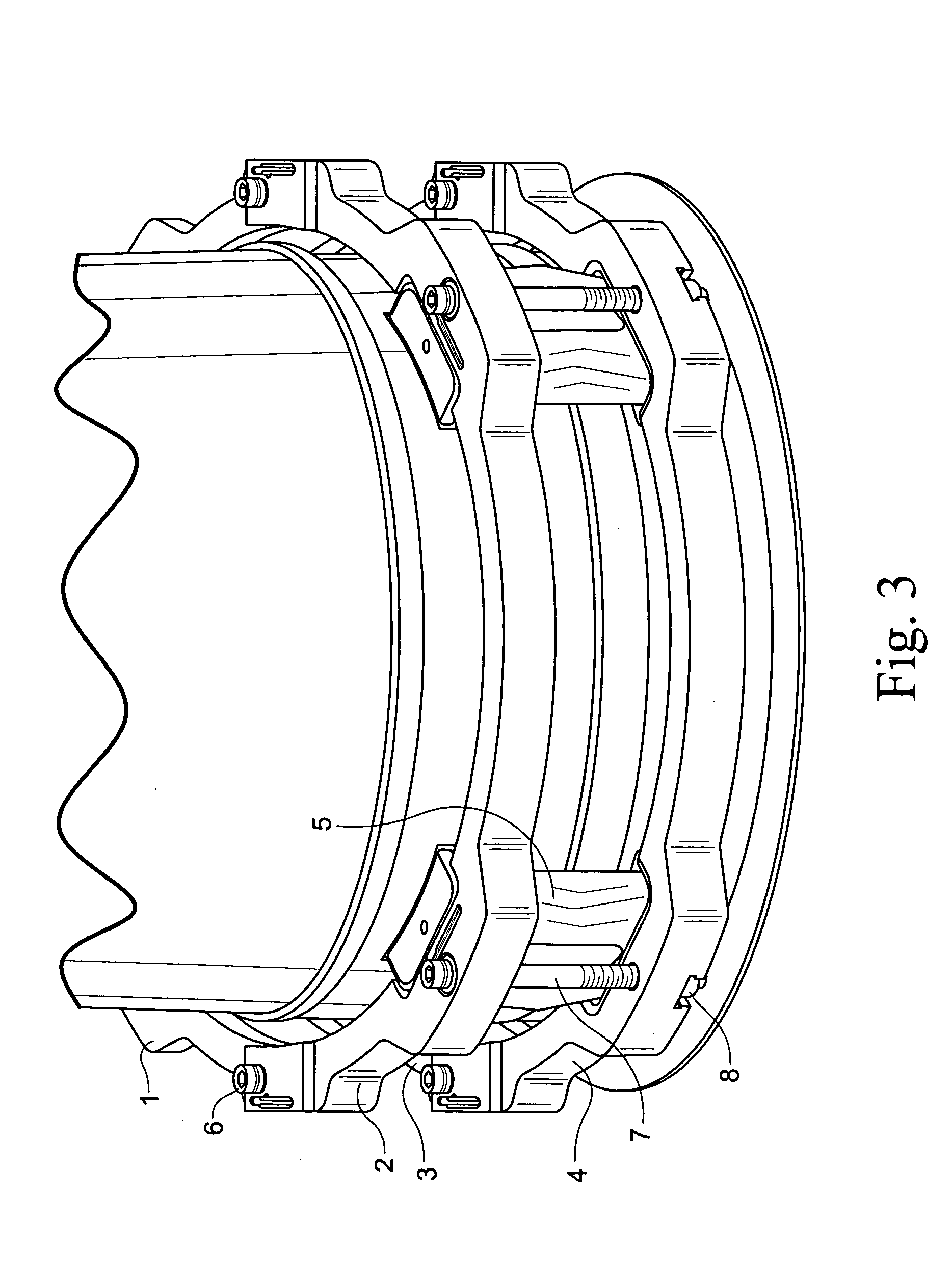
Jet pump diffuser weld repair device and method
A jet pump diffuser weld repair device includes a lower ring section and an upper ring section respectively sized to fit around a circumference of the diffuser on opposite sides of the weld to be repaired. The lower and upper ring sections are provided with a plurality of aligned gripper slots. A corresponding plurality of grippers are fit into the gripper slots, where at least one of the gripper slots and the grippers defines cam surfaces shaped to drive the grippers radially inward as lower and upper ring sections are drawn toward each other. A plurality of connector bolts are secured between the lower ring section and the upper ring section. Tightening of the connector bolts draws the lower and upper ring sections toward each other.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Self-contained emergency spent nuclear fuel pool cooling system
ActiveUS20120250813A1Nuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsSTI OutpatientCooling fluid
An auxiliary system for cooling a spent nuclear fuel pool through a submersible heat exchanger to be located within the pool. In each train or installation, a single loop or series of loops of cooling fluid (e.g., sea water or service water) is circulated. The system is modular, readily and easily installed during an emergency and can be self operating with its own power source. Multiple trains may be used in parallel in order to accomplish the required degree of spent fuel pool cooling required.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Popular searches
Nuclear reaction control Compression machines with reversible cycle Vehicular energy storage Power to electric heating circuits Heating and refrigeration combinations Control devices Air-treating devices Railway heating/cooling Propulsion using engine-driven generators Vehicle heating/cooling devices
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com