Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
278 results about "Core cooling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Porous media cold plate
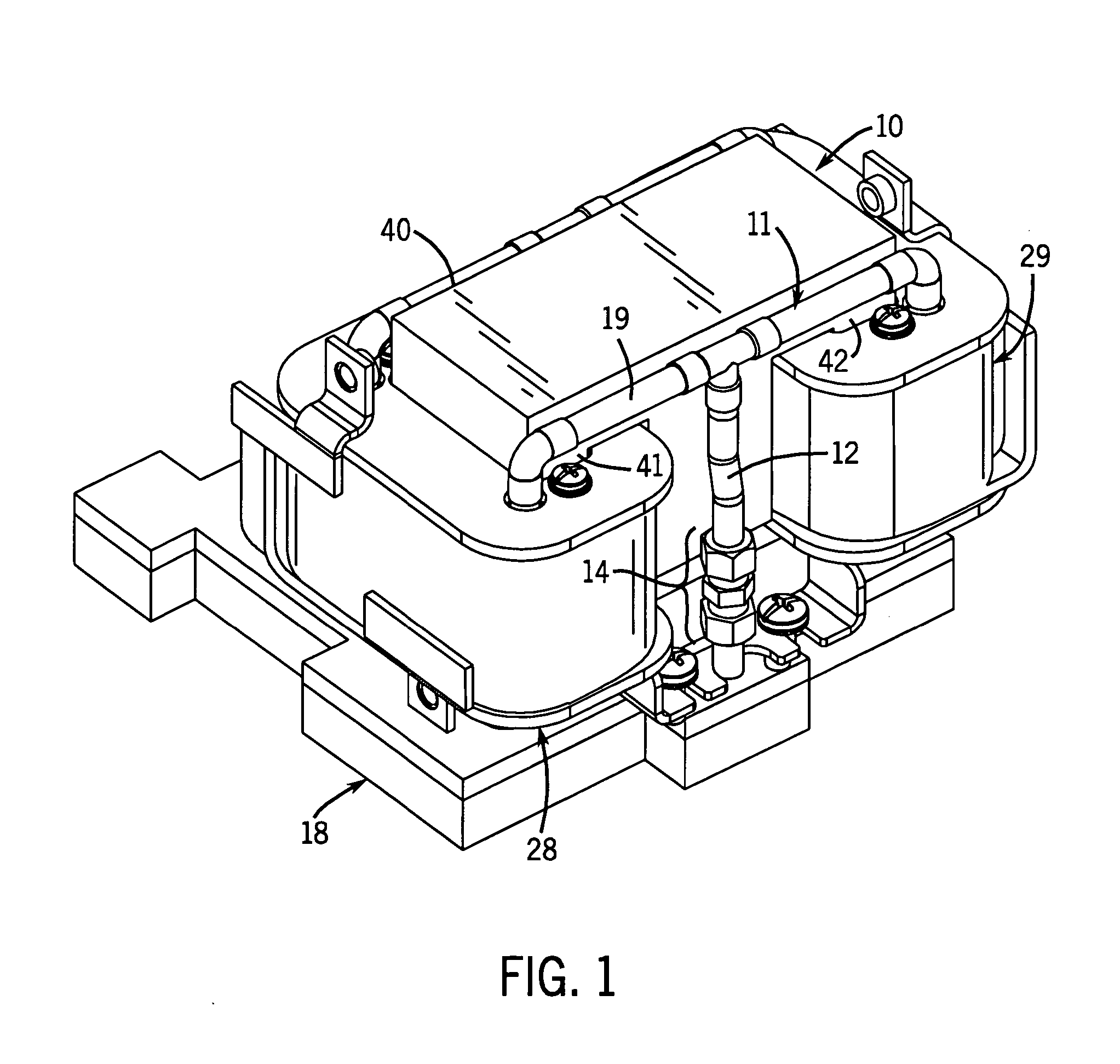
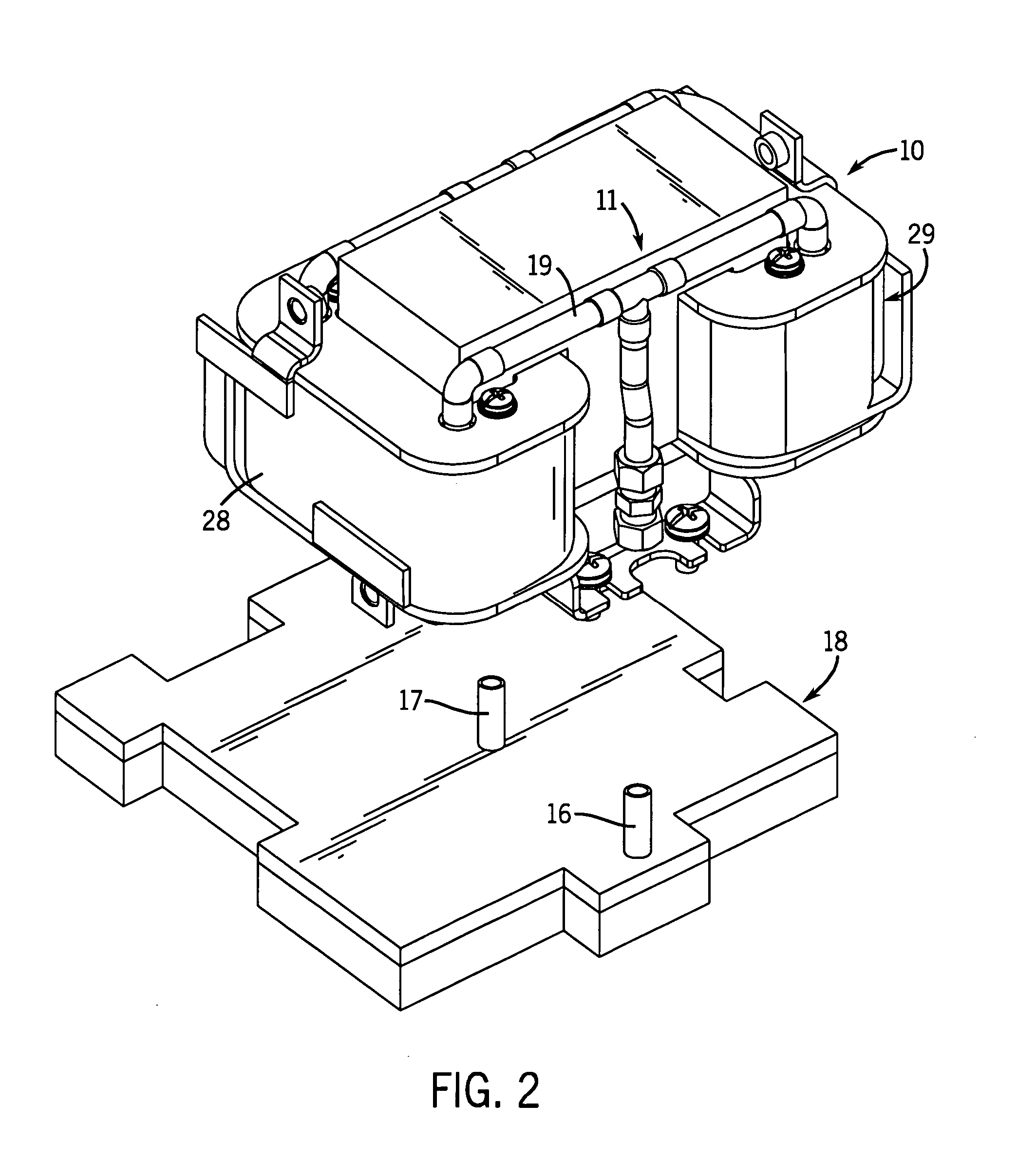
ActiveUS20050082037A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPorous mediumCold plate
A heat exchanger for cooling a heat generating device including a base having a recess with a base coolant inlet opening and a base coolant outlet opening. A porous core is positioned within the recess of the base, and has a core coolant inlet opening and a core coolant outlet opening that are arranged in corresponding relation with base coolant inlet opening and a base coolant outlet opening so as to be in fluid communication. A porous gasket is pinched between the porous core and the base.
Owner:THERMAL
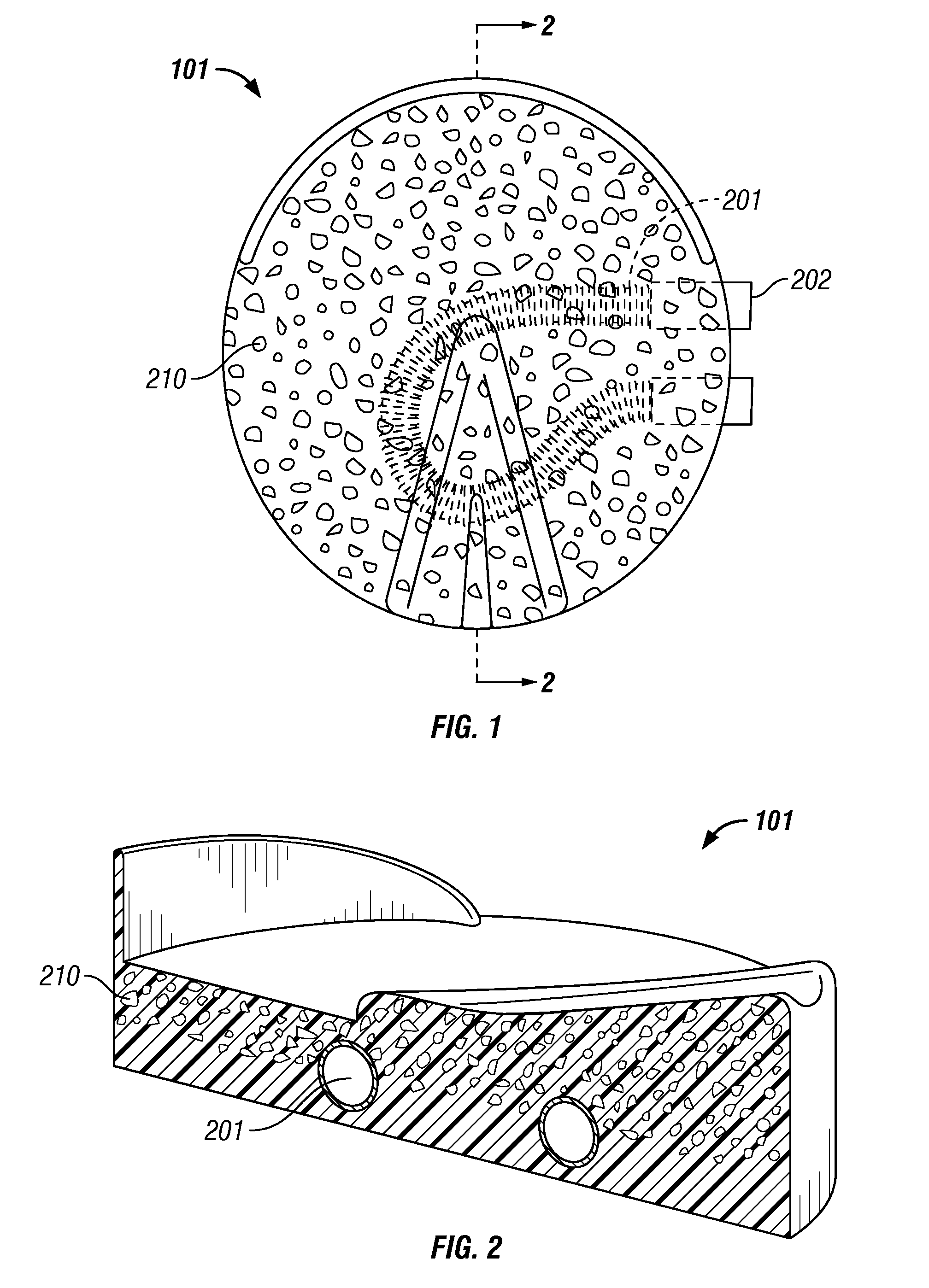
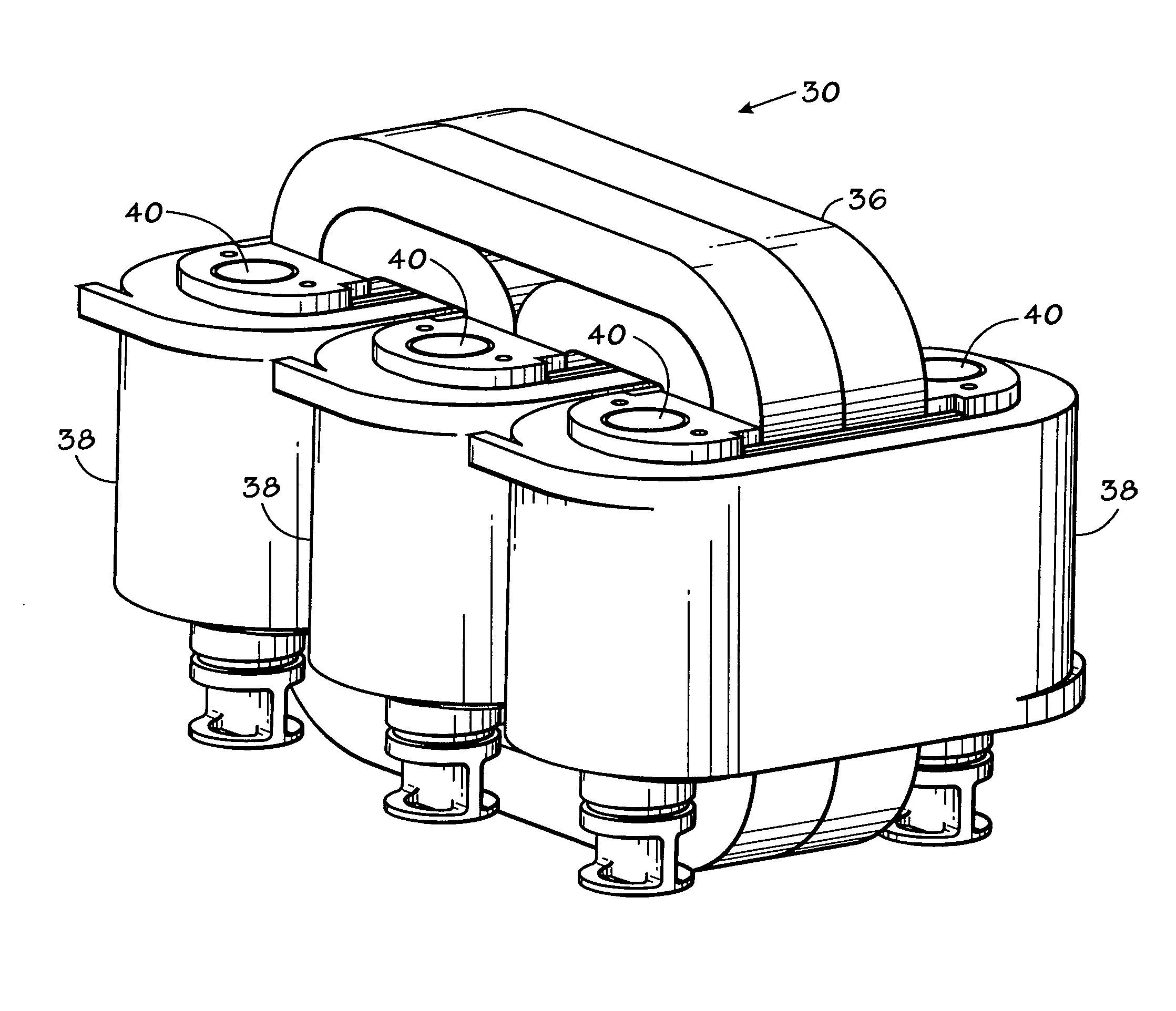
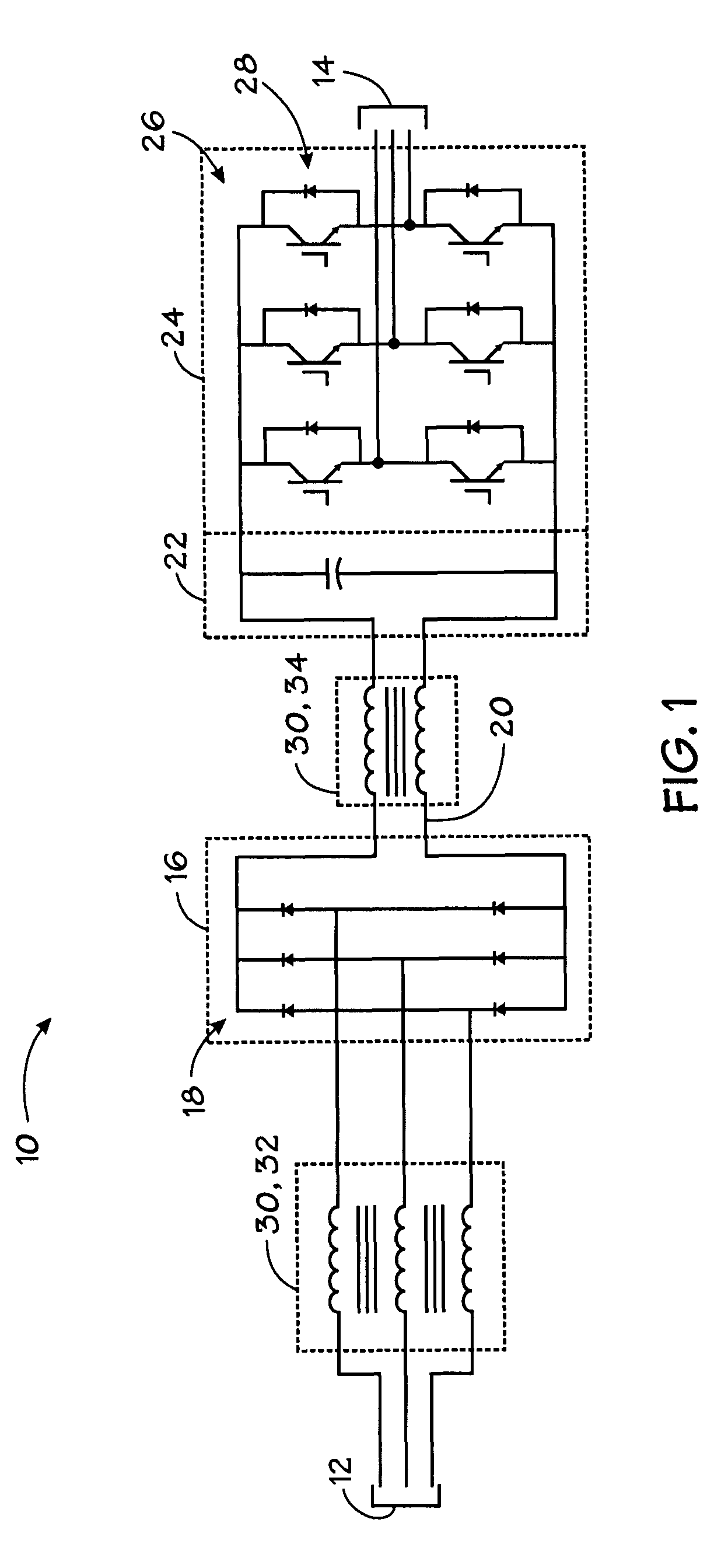
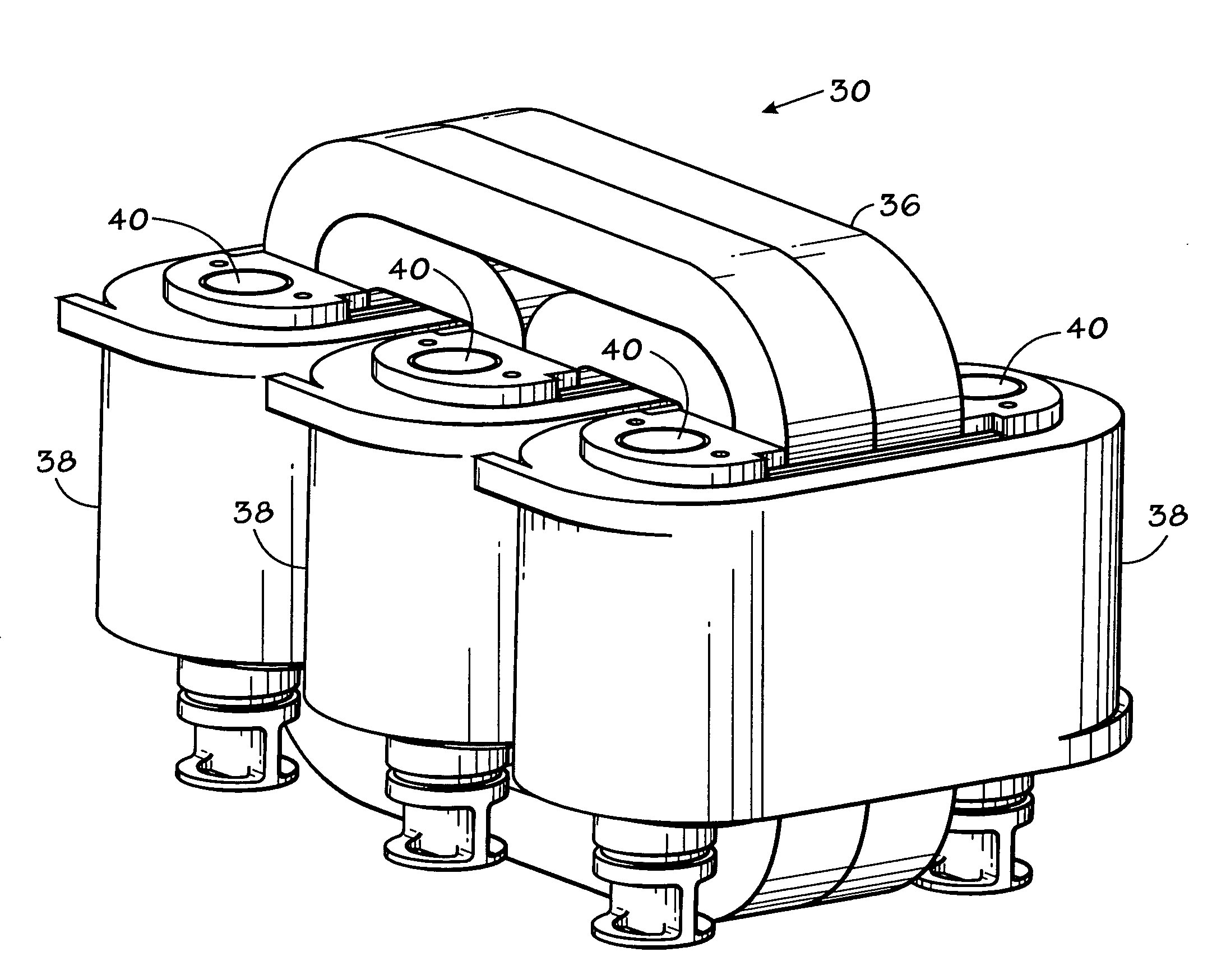
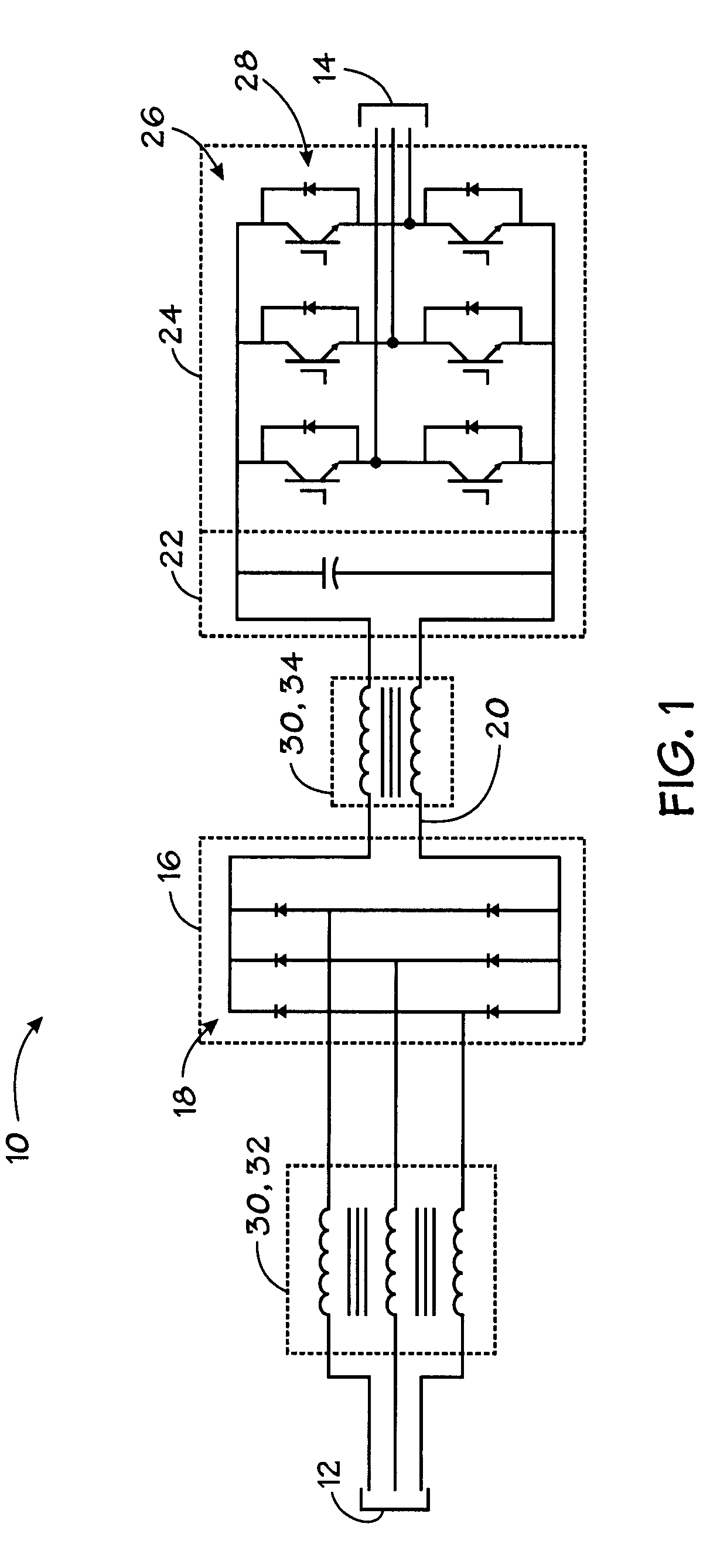
Core cooling for electrical components
InactiveUS20060044103A1Minimize the numberAvoid possibilityTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionTransformers/inductances coolingElectrical conductorBobbin
A cooling system is provided for electrical components in which cooling assemblies (11, 45) are inserted in non-magnetic cores of the electrical components, and in which tubes provide both inflow and outflow of a cooling medium. The non-magnetic cores may be bobbins (30) for an inductor assembly or the core of a capacitor (40). The tubes may form a loop (11) in more than one plane to prevent inducing current in a single turn, or they may be split-flow closed-end tubes (45) inserted from one end of the electrical component. The bobbin cores (31) are also constructed with a non-conductive portion to prevent inducing a current in a single turn of a conductor.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
High-speed precise electric spindle cooling system
InactiveCN102120266AGuaranteed temperature stabilityControl temperature riseCooling/ventillation arrangementSupports/enclosures/casingsElectricityThermal energy
The invention relates to the technical field of an electric spindle, in particular to a high-speed precise electric spindle cooling system which comprises an electric spindle shell cooling part, an electric spindle core cooling part and a bearing spindle core lubricating / cooling part, wherein when the electric spindle works, the temperature rise change can be controlled within + / -1 DEG C. The concrete scheme is as follows: a ring sleeve type heat pipe cooling mode is arranged at the electric spindle shell part, and the heat of the shell is taken away quickly by increasing the cooling contact surface; the spindle core cooling part is provided with symmetrical bar-type heat pipes which are uniformly distributed on the spindle core, and the spindle core is cooled by use of the high-speed conductivity and homoiothermy of the heat pipes; and a spindle core liquid lubricating / cooling mode is adopted at the bearing lubricating / cooling part, and makes full use of the high rotation speed of the high-speed electric spindle to generate centrifugal force so that the lubricating / cooling liquid is uniformly distributed on the bearing roller. The temperature stability of the electric spindle can be ensured, the processing precision error caused by thermal expansion of the electric spindle is minimized, and the service life of the spindle and the spindle bearing can be prolonged at the same time.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH
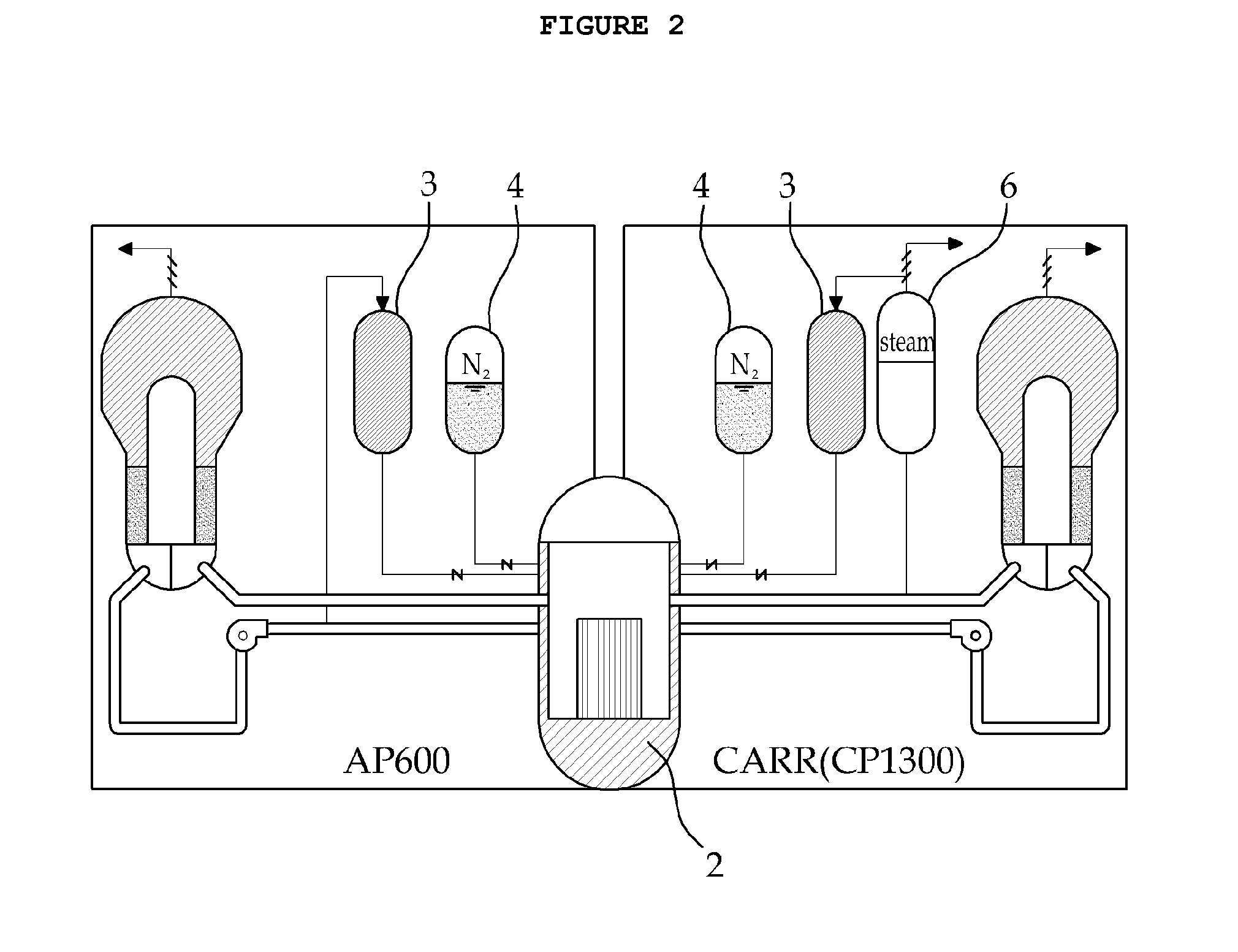
Device combining in-core and out-of-core dwelling of molten material of large-scale passive nuclear power plant
InactiveCN103578580AImplementation of off-stack coolingImplement in-heap retentionNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsCore catcherPressurized water reactor
The invention provides a device combining in-core and out-of-core dwelling of a molten material of a large-scale passive nuclear power plant. The device comprises a concrete sacrificial layer (4), a core catcher chamber (7), a core catcher refractory layer (8), a cooling channel inlet (9), a cooling channel outlet (10) and a core catcher bottom cooling channel (11). The invention provides a set of device organically combining molten material out-of-core cooling with an IVR (interactive voice response) system, when IVR succeeds, in-core dwelling of the molten material can be realized; and after the IVR fails, out-of-core dwelling of the molten material is realized by passive cooling of the core catcher bottom cooling channel, and the capability of mitigating severe accidents of the large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant is further enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Nuclear power plant using nanoparticles in emergency systems and related method
InactiveUS20080212733A1Improve heat transfer performanceNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsNuclear plantMotor drive
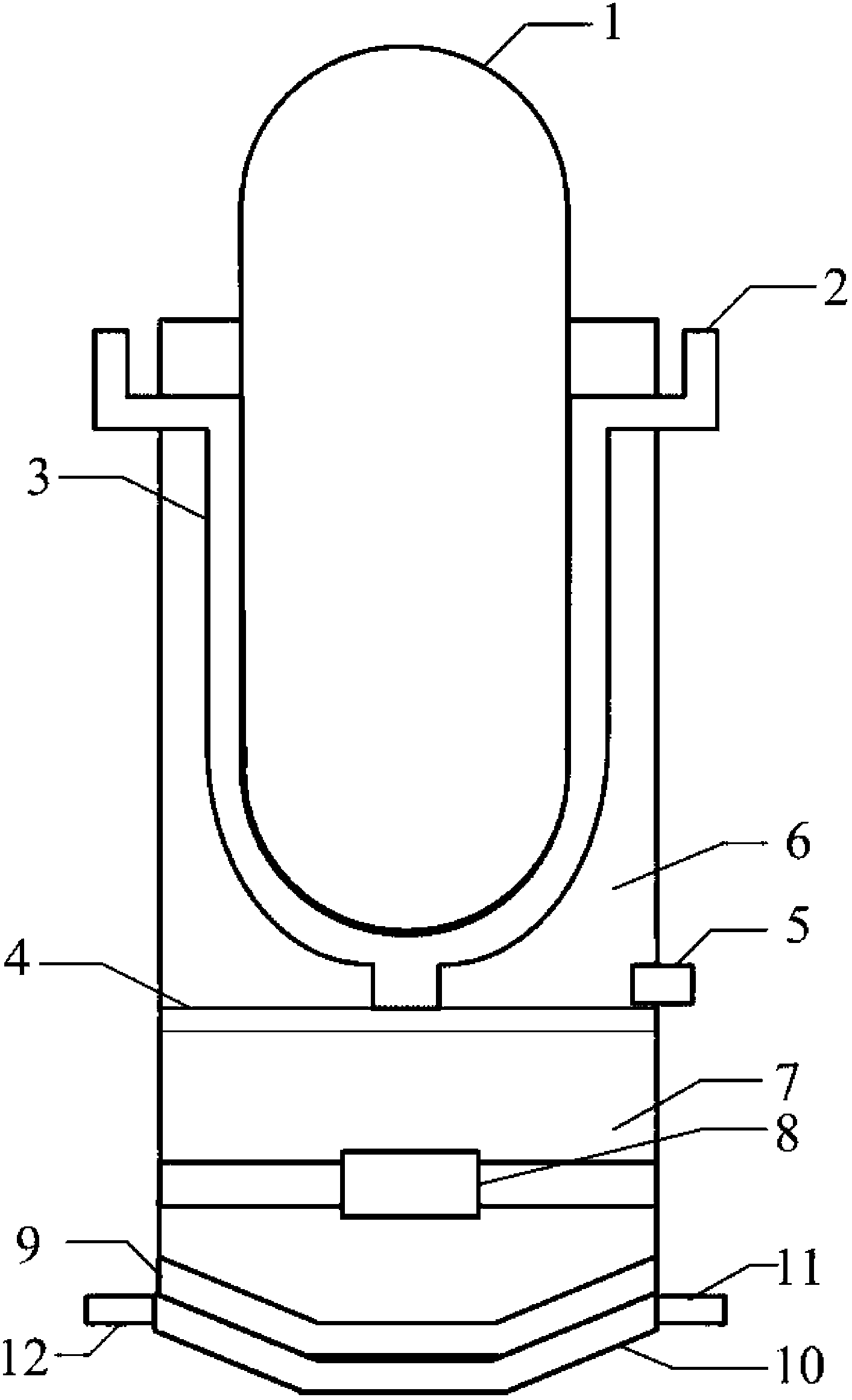
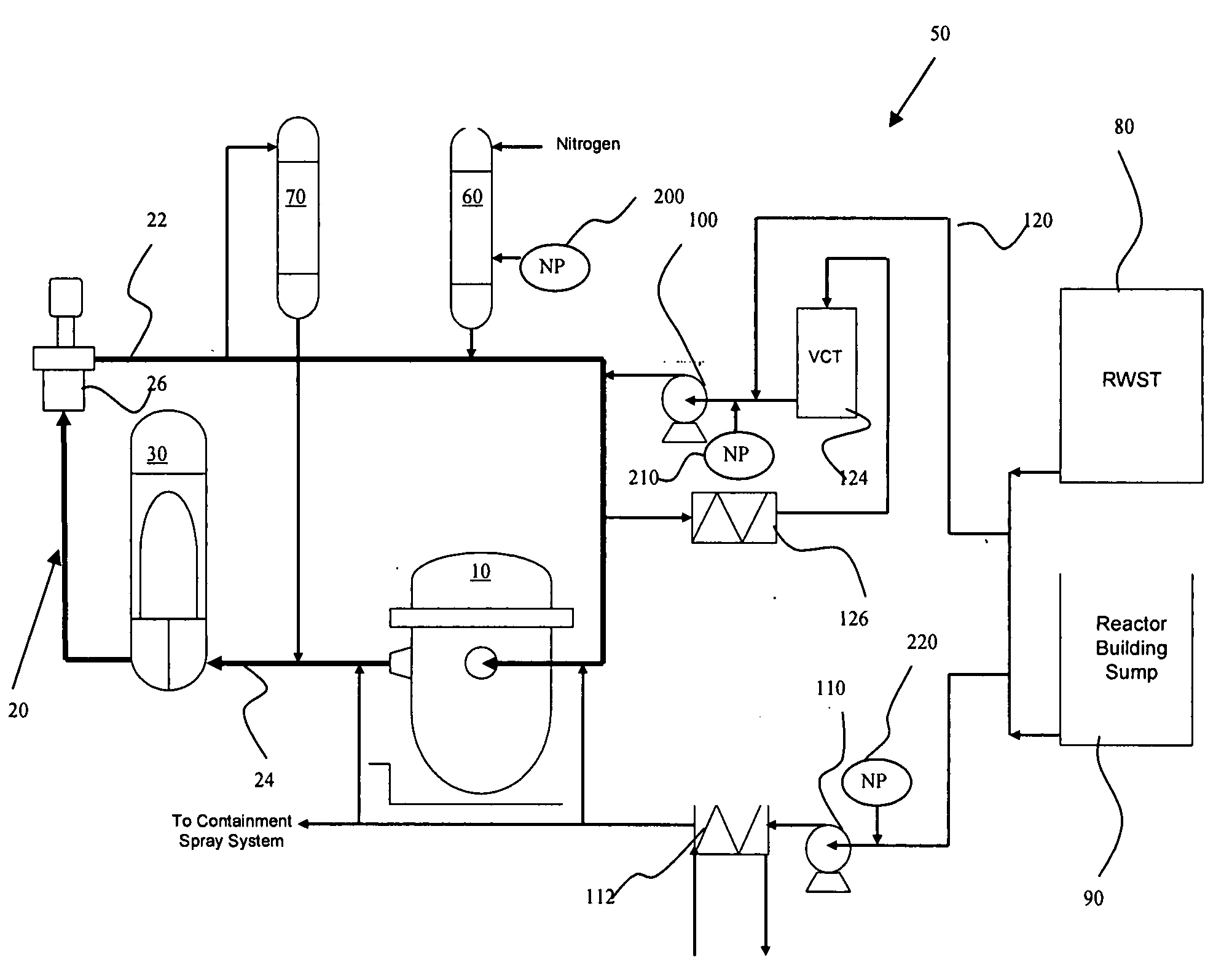
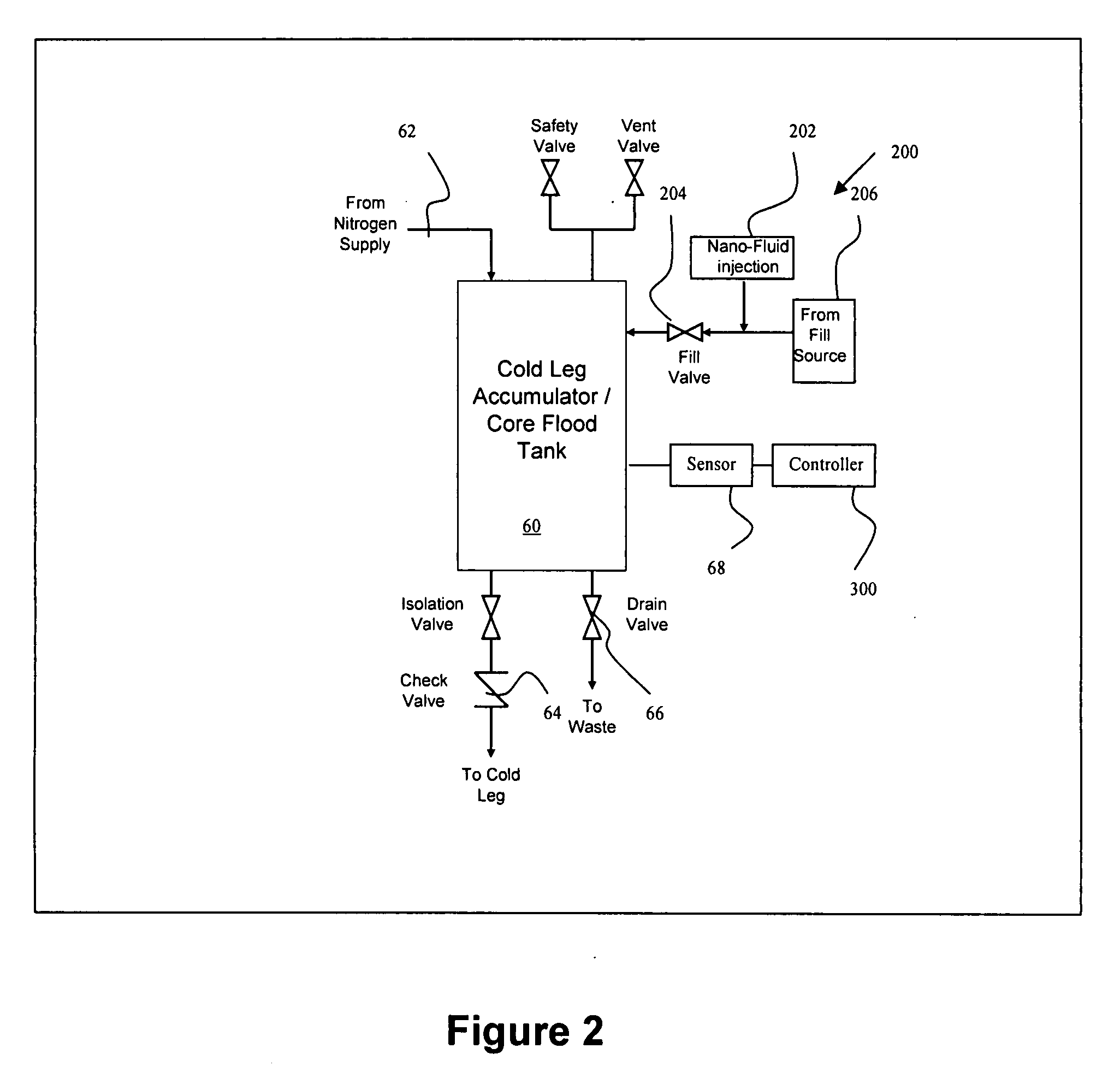
A nuclear power plant with an improved cooling system using nanoparticles in solid or fluid form is provided. The nanoparticles are delivered in locations such as the cold leg accumulator and high and low pressure pumps of an emergency core cooling system. Motor driven valves and pressurization can aid in the delivery. Methods for providing the nanoparticles are also provided.
Owner:AREVA NP SAS
Core cooling for electrical components
InactiveUS7129808B2Minimize the numberAvoid possibilityTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionTransformers/inductances coolingElectrical conductorBobbin
A cooling system is provided for electrical components in which cooling assemblies (11, 45) are inserted in non-magnetic cores of the electrical components, and in which tubes provide both inflow and outflow of a cooling medium. The non-magnetic cores may be bobbins (30) for an inductor assembly or the core of a capacitor (40). The tubes may form a loop (11) in more than one plane to prevent inducing current in a single turn, or they may be split-flow closed-end tubes (45) inserted from one end of the electrical component. The bobbin cores (31) are also constructed with a non-conductive portion to prevent inducing a current in a single turn of a conductor.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
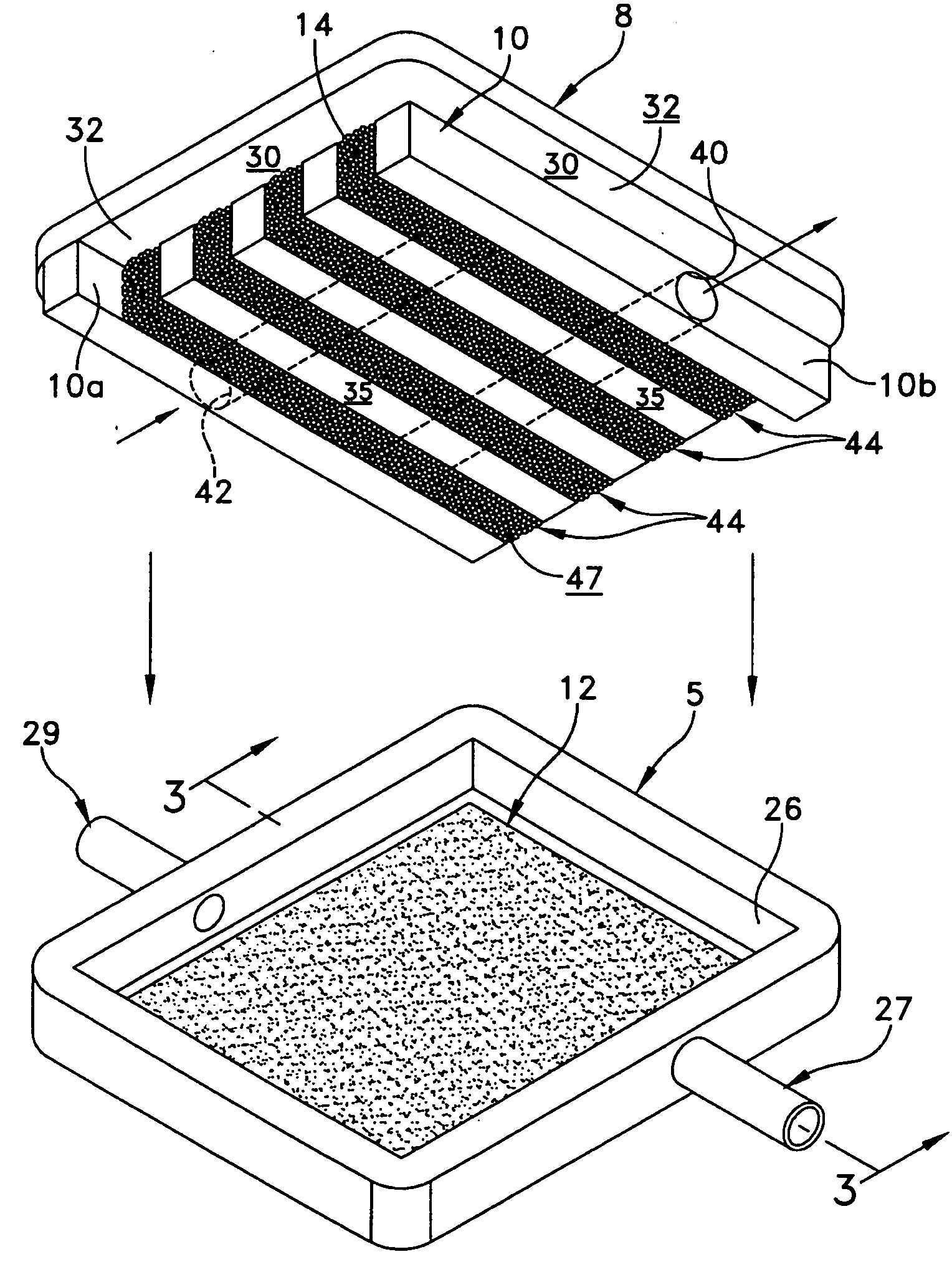
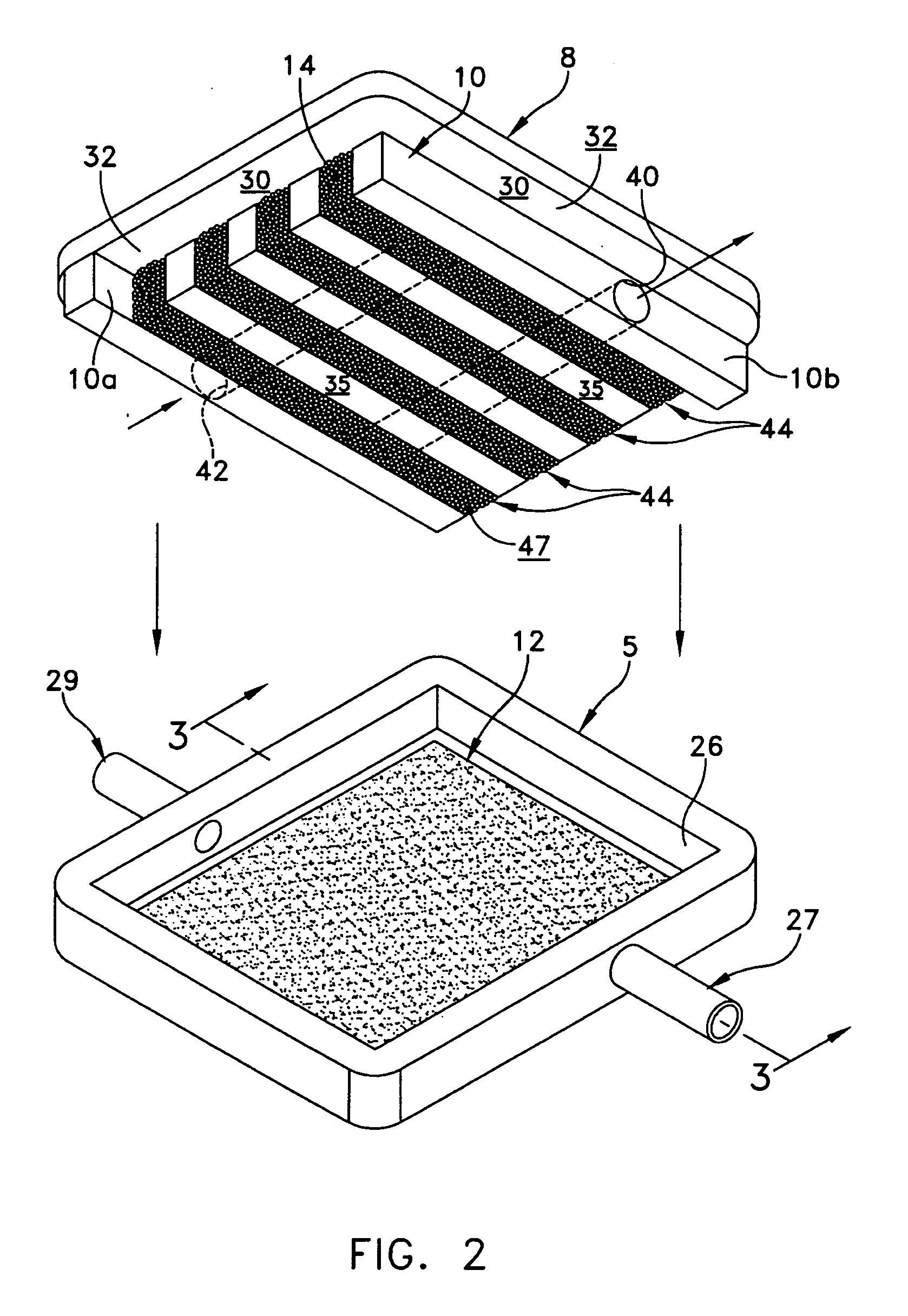
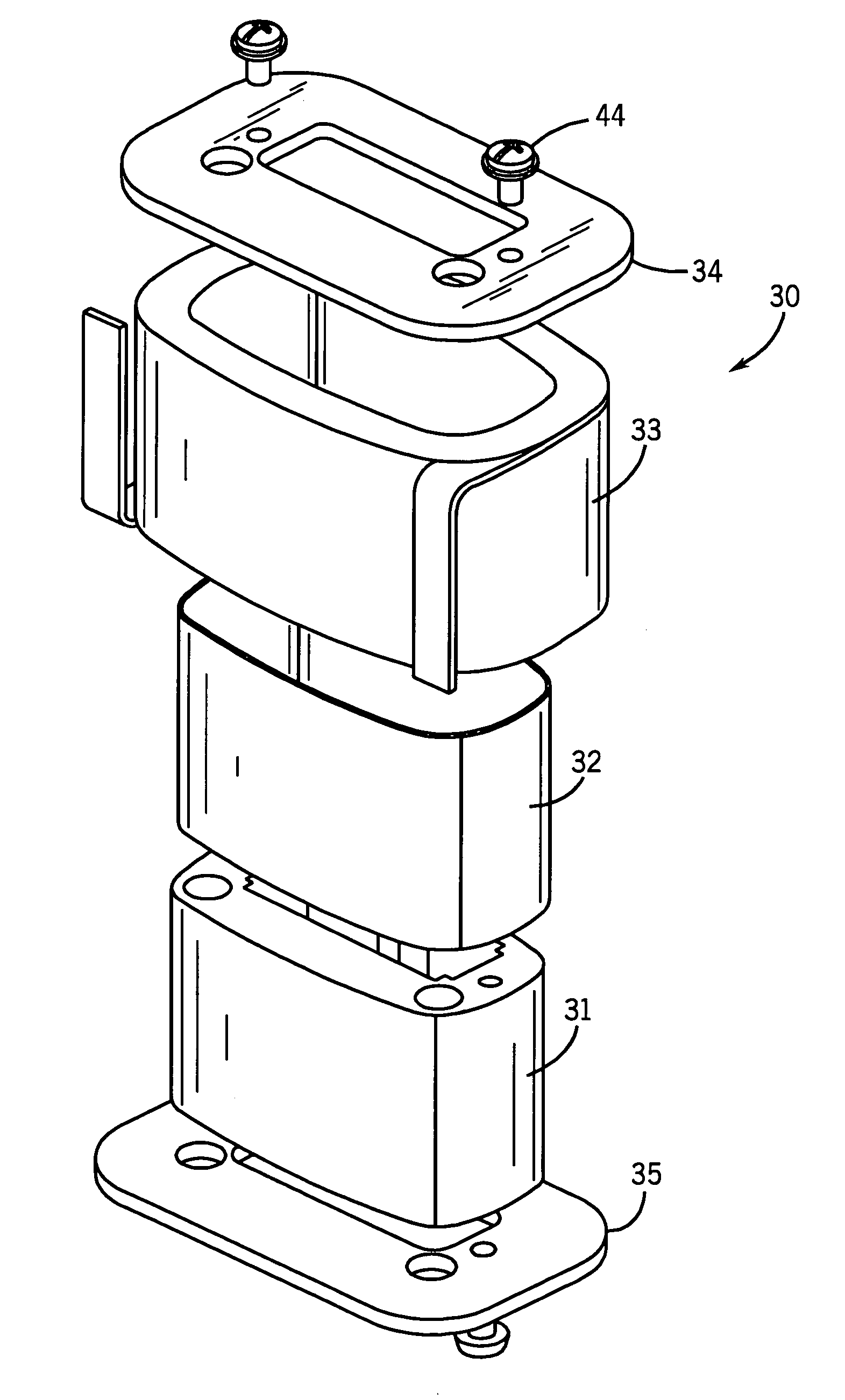
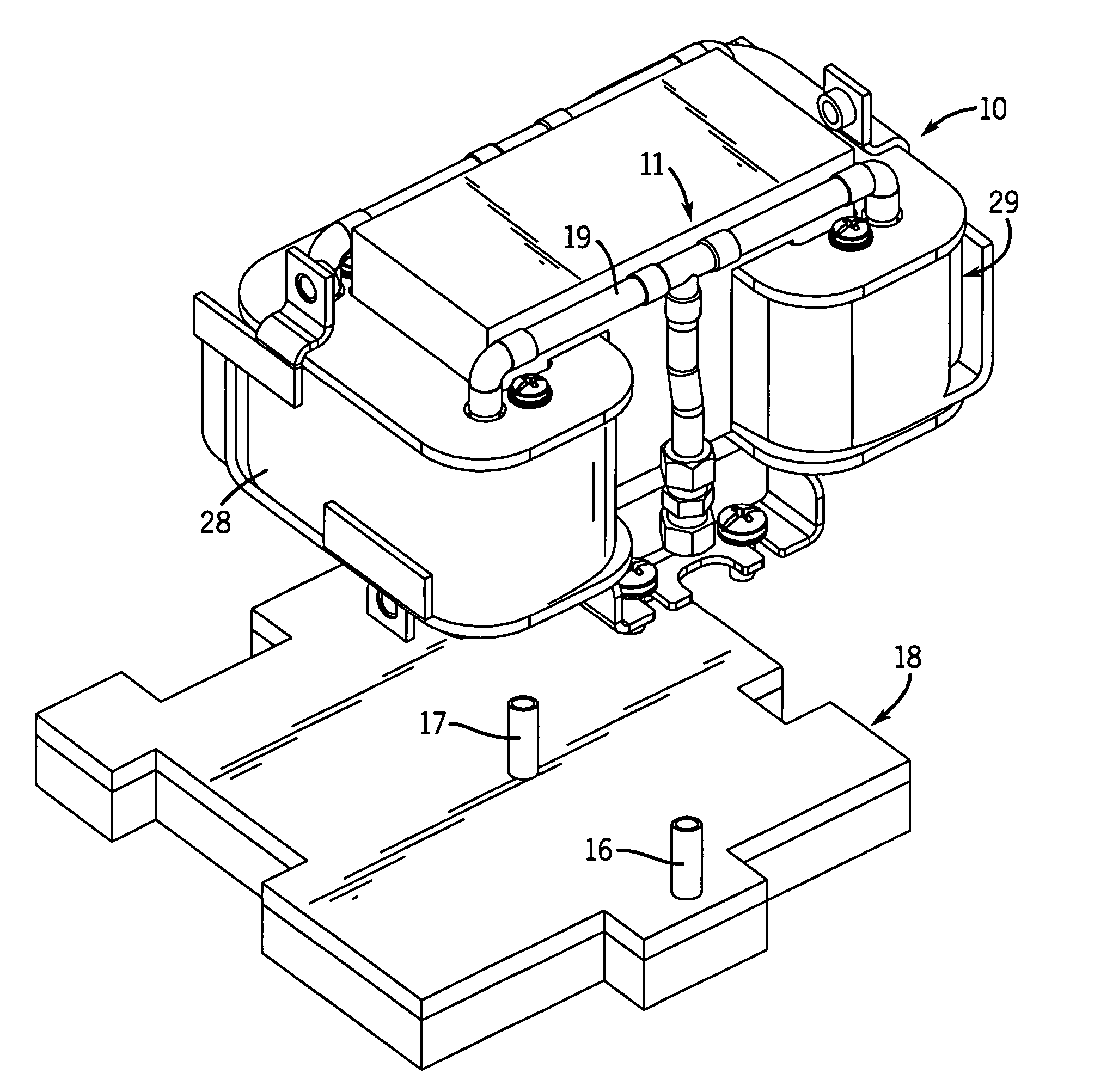
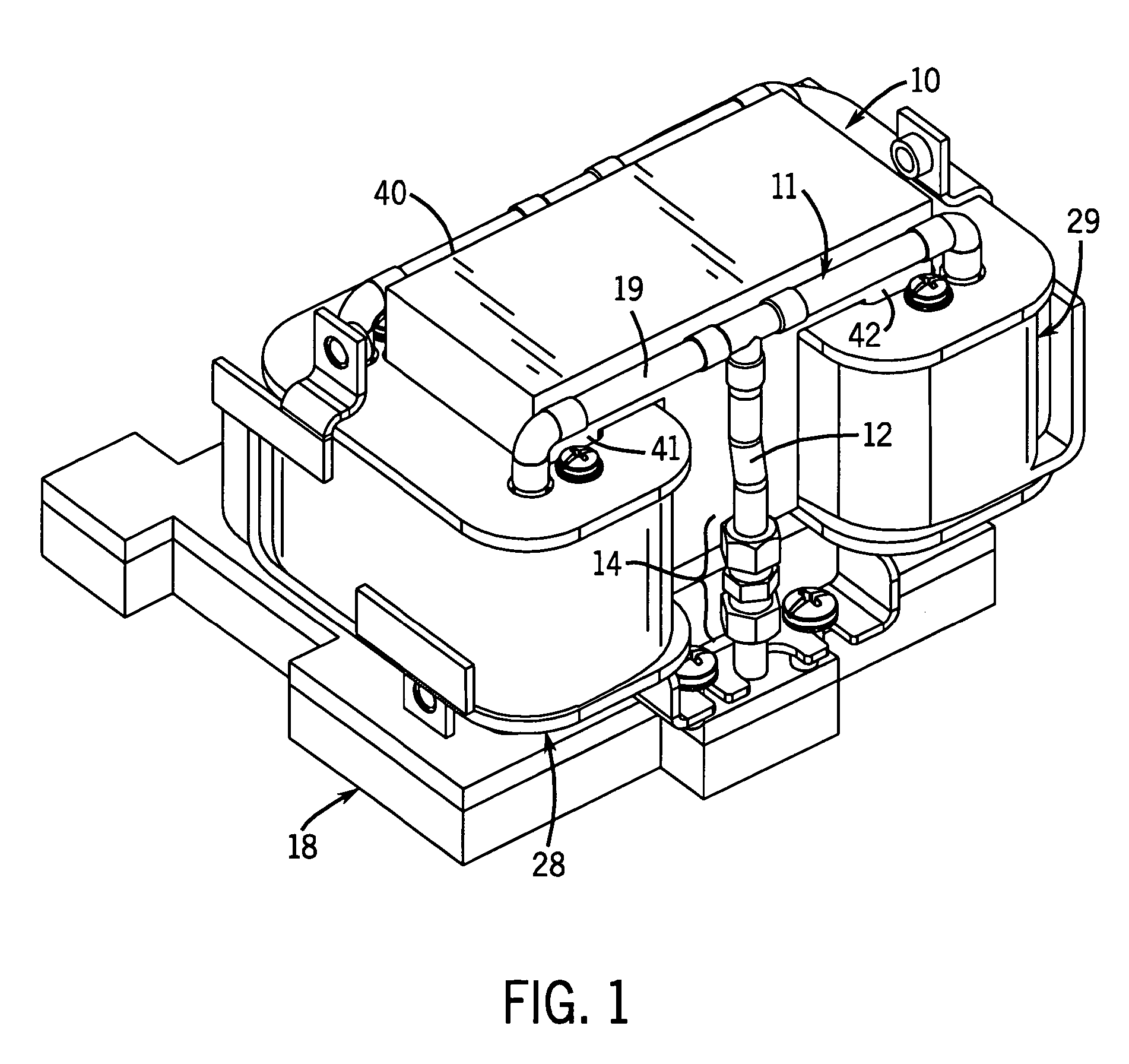
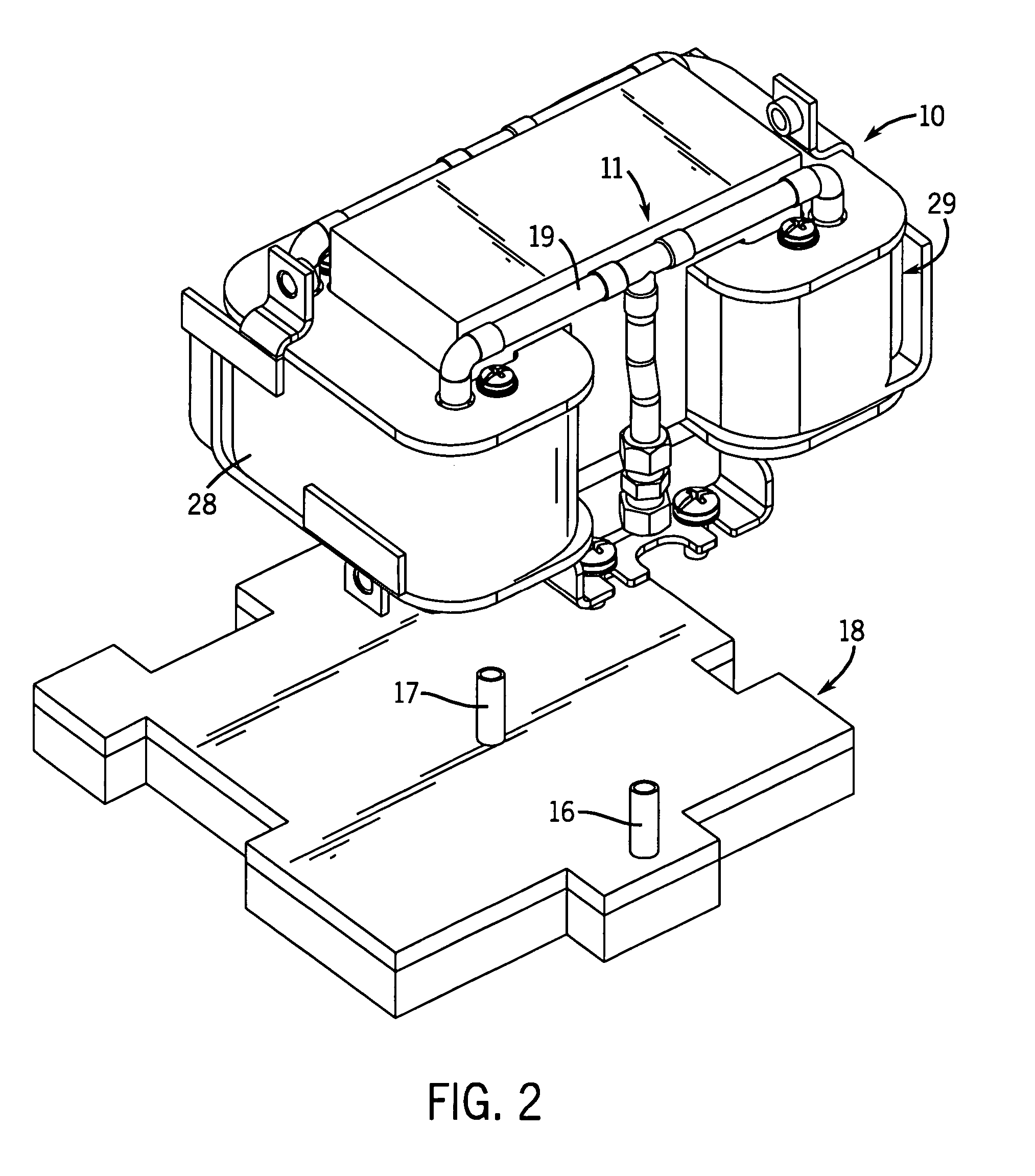
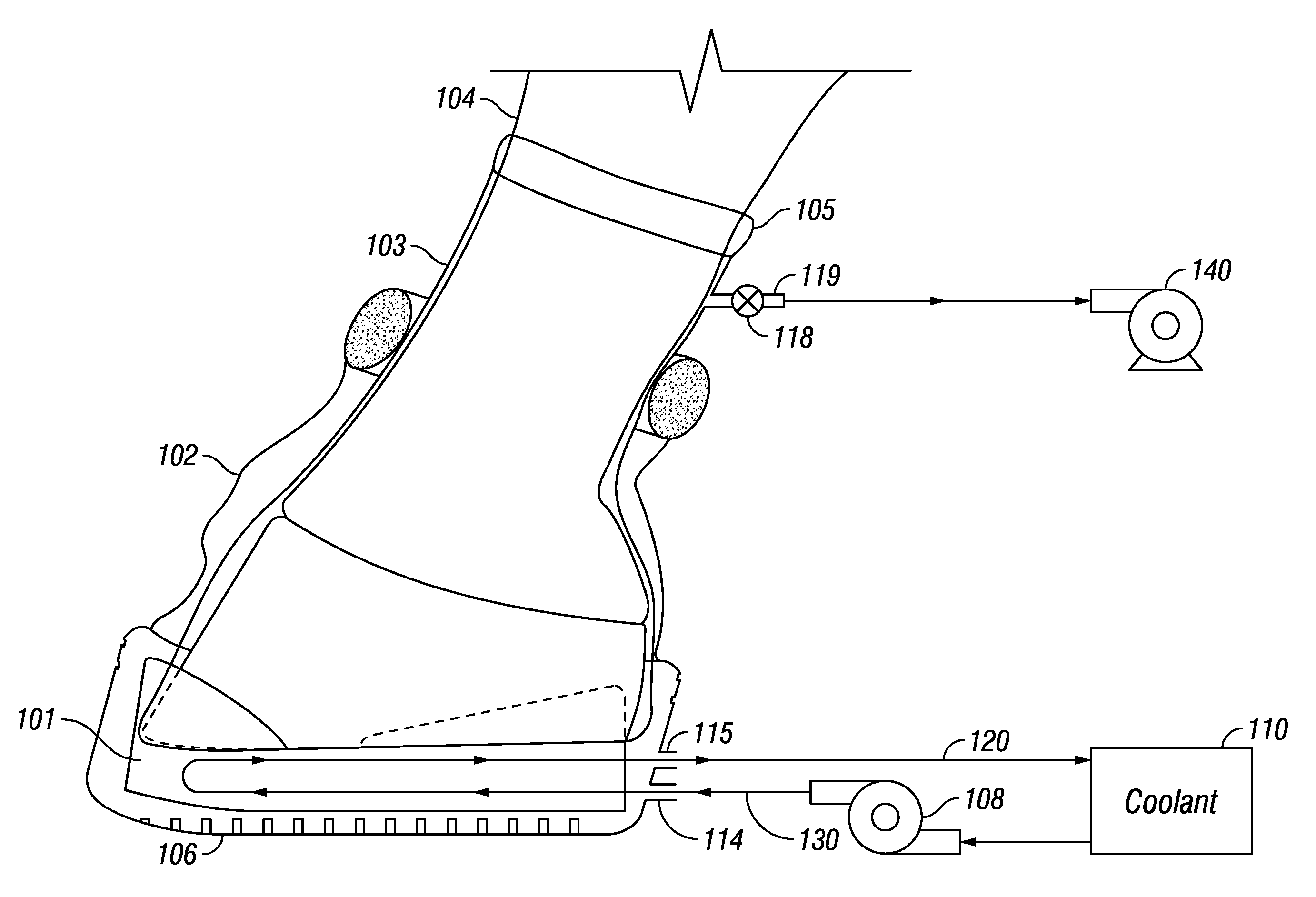
Equine Cold Therapy Apparatus and Method
ActiveUS20100095641A1Heating fastImprove performanceProtection coversVeterinary bandagesEquine SpeciesEngineering
Apparatus for and methods of core cooling the blood of an equine animal. The apparatus is a flexible boot having disposed in it an orthotic pad that has means for circulating coolant so the bottom hoof area of an equine can be cooled. Optionally the pad is designed to allow cooling under vacuum. In some aspects the apparatus also provides means for cooling the lower leg of the equine in a way designed to allow coolant circulated through the boot pad to also be circulated through the leg cooling means while maintaining a controlled temperature against the leg surface. The invention is also a method of core cooling an animal utilizing the apparatus described.
Owner:RUETENIK MONTY L
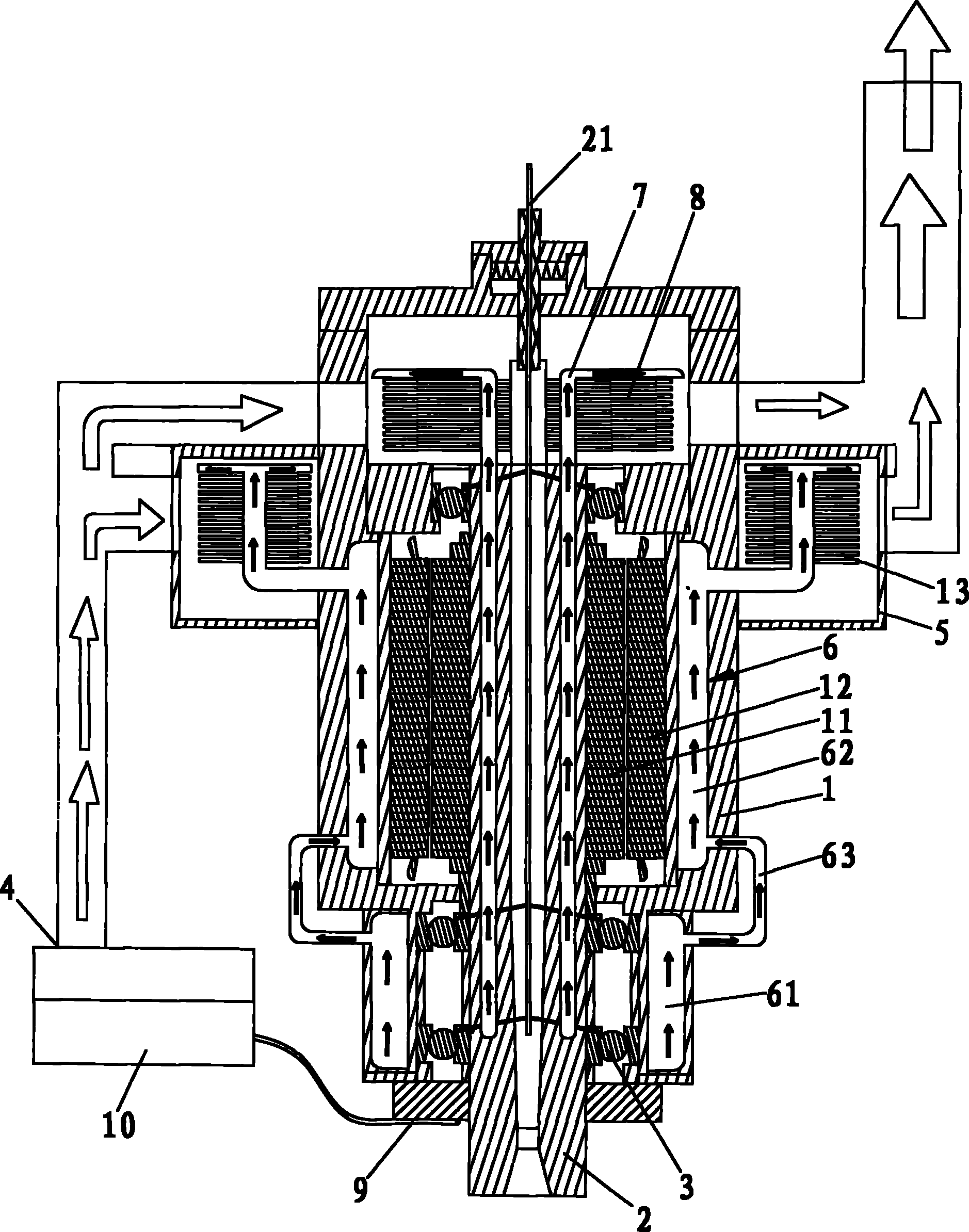
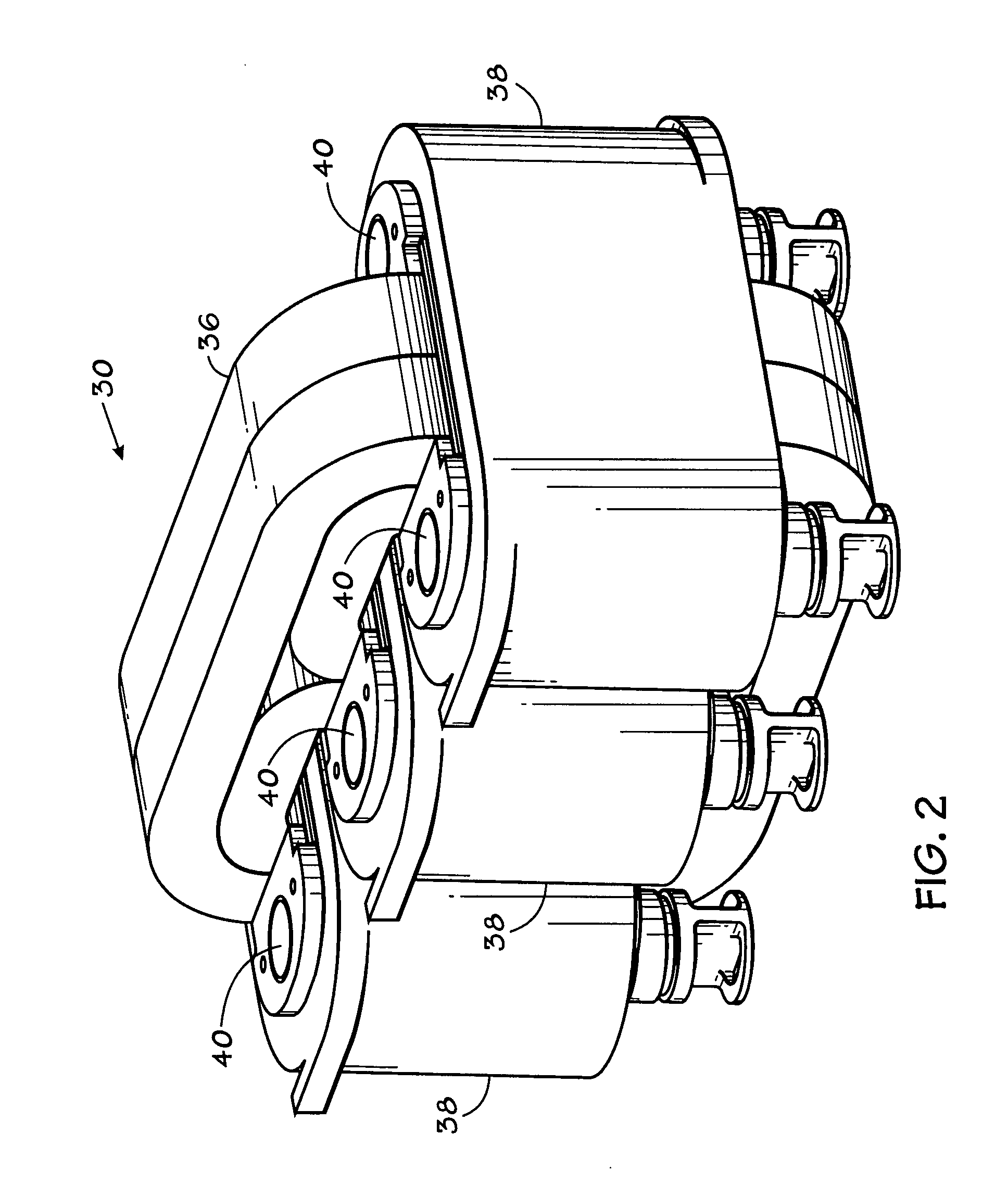
Electric coil and core cooling method and apparatus
InactiveUS7893804B2Improve heat transfer performanceReduce thermal resistanceTransformers/inductances coolingFixed inductancesCooling fluidCore cooling
Provided is an electrical apparatus comprising a magnetic core, a conductive coil wound around at least a part of the core, a cooling element configured to receive a cooling fluid to cool the core and the coil during operation, and at least one biasing element operatively associated with the core to urge the core and the coil into engagement with the cooling element despite differential expansion or contraction of the core and the coil and manufacturing tolerances. Further provided is a method for making an electrical apparatus comprising disposing a conductive coil wound around at least a part of a magnetic core, disposing a cooling element between the core and the coil, the cooling element configured to receive a cooling fluid to cool the core and the coil during operation, and urging the core and the coil into engagement with the cooling element despite differential expansion or contraction of the core and the coil and manufacturing tolerances.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
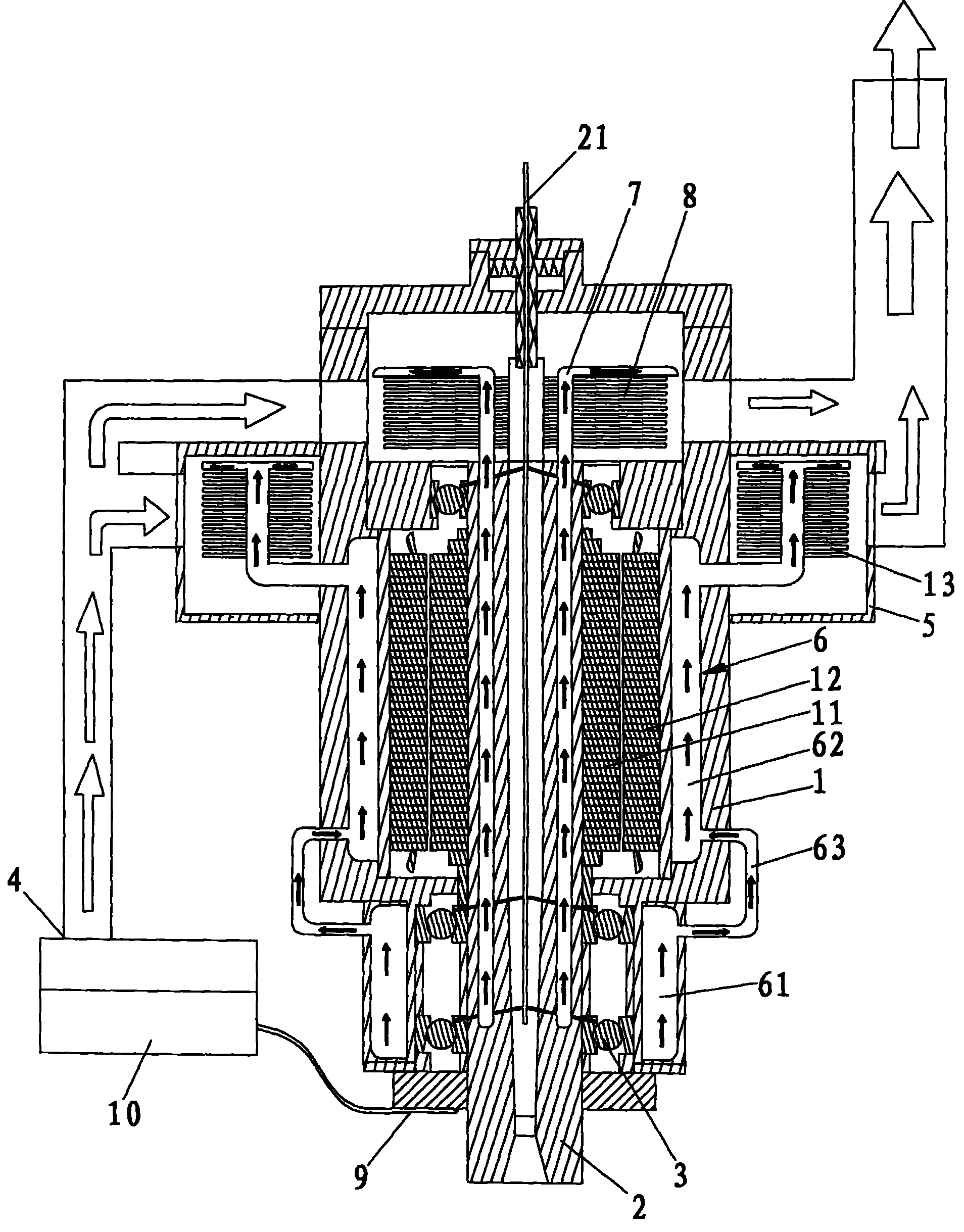
Electric coil and core cooling method and apparatus
InactiveUS20090002110A1Improve cooling effectImprove heat distributionTransformers/inductances coolingInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureCooling fluidCore cooling
Provided is an electrical apparatus comprising a magnetic core, a conductive coil wound around at least a part of the core, a cooling element configured to receive a cooling fluid to cool the core and the coil during operation, and at least one biasing element operatively associated with the core to urge the core and the coil into engagement with the cooling element despite differential expansion or contraction of the core and the coil and manufacturing tolerances. Further provided is a method for making an electrical apparatus comprising disposing a conductive coil wound around at least a part of a magnetic core, disposing a cooling element between the core and the coil, the cooling element configured to receive a cooling fluid to cool the core and the coil during operation, and urging the core and the coil into engagement with the cooling element despite differential expansion or contraction of the core and the coil and manufacturing tolerances.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
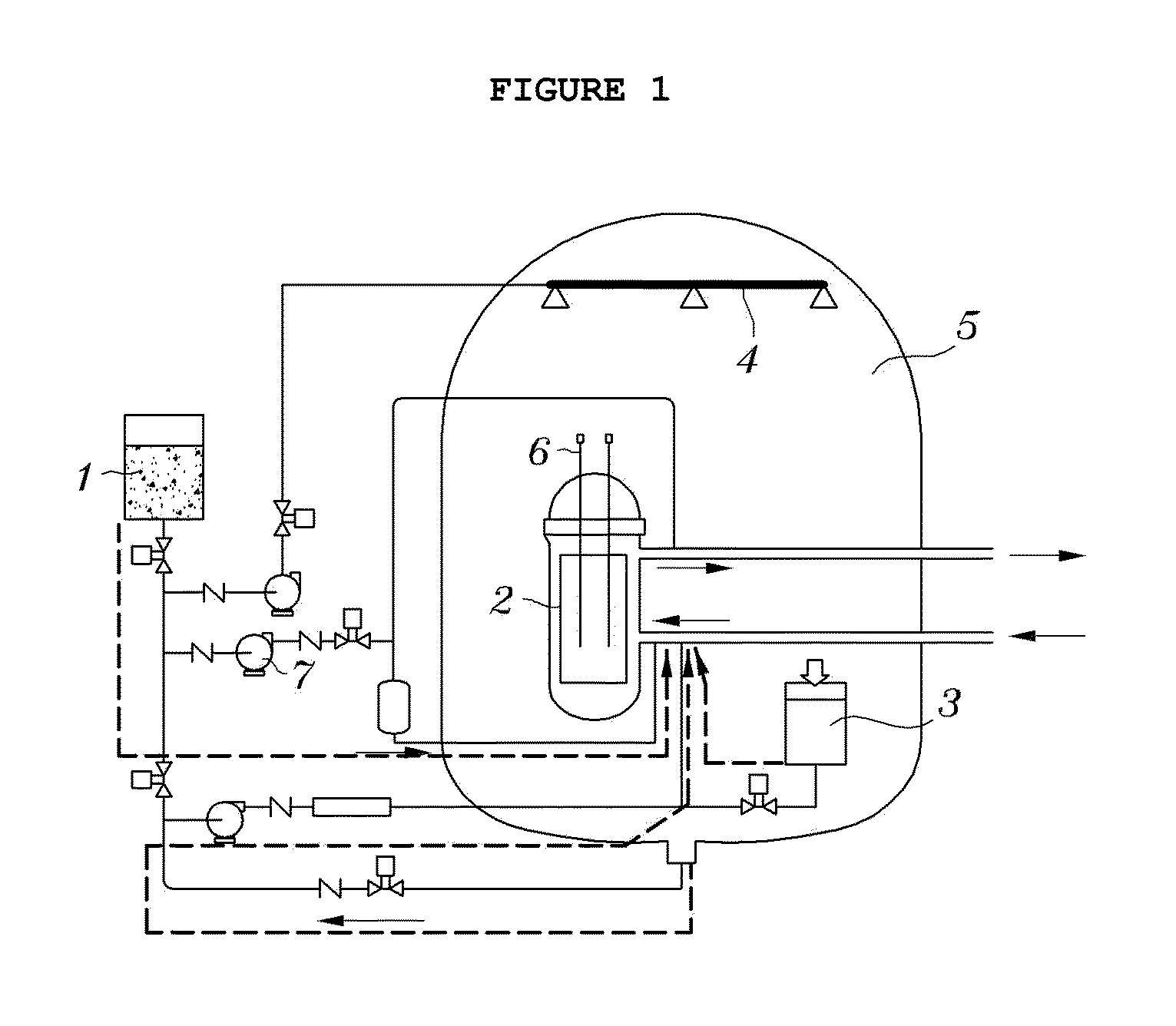
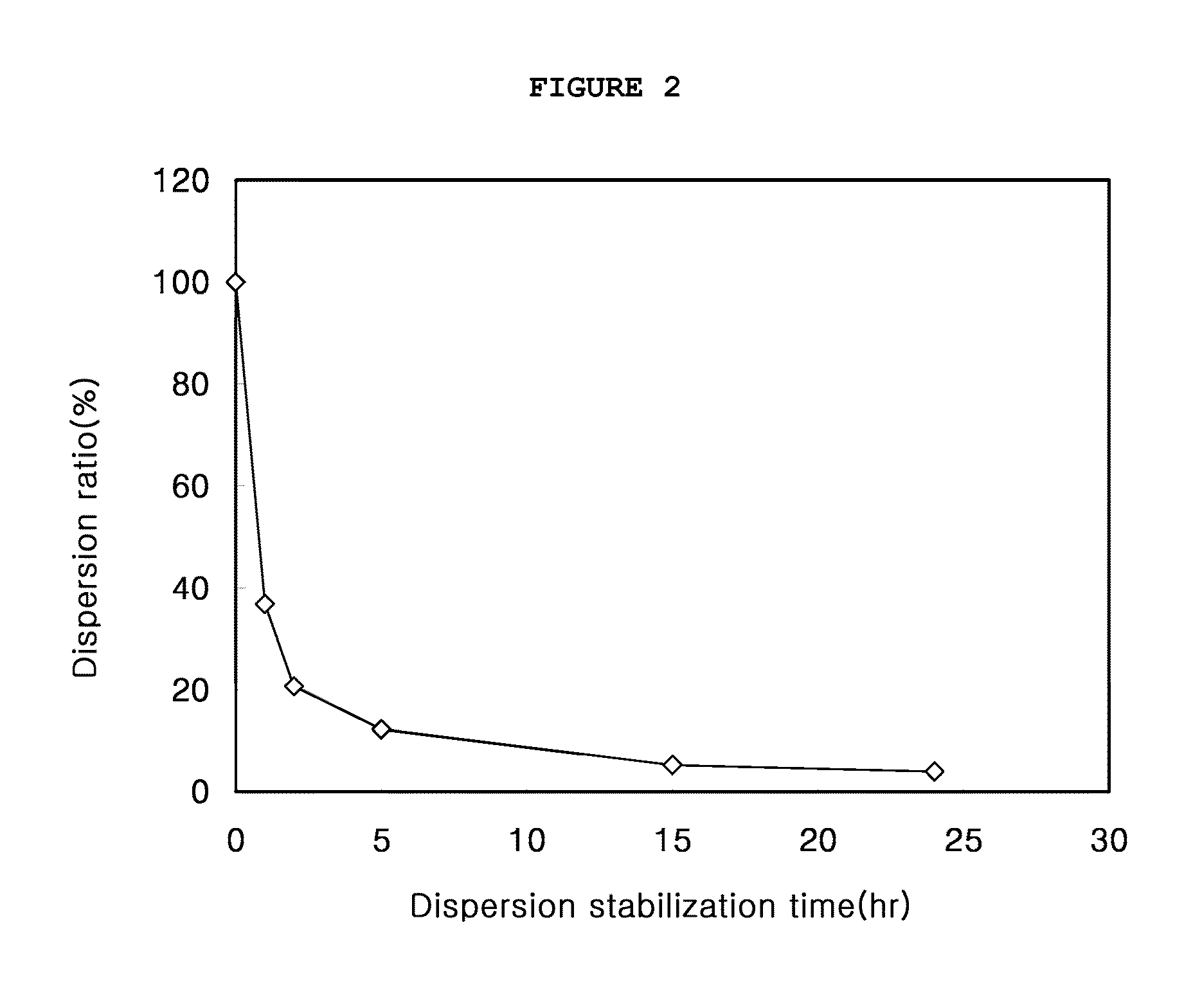
Coolant with dispersed neutron poison micro-particles, used in scwr emergency core cooling system
InactiveUS20100239062A1Nuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
Disclosed is a coolant with dispersed neutron poison micro-particles, used in a supercritical water-cooled reactor (SCWR) emergency core cooling system. Since the neutron poison micro-particles are uniformly dispersed in the coolant of the emergency core cooling system for a long period time, their fluidity is not lowered even though the polarity of water is changed in a supercritical state. Therefore, the neutron poison micro-particles absorb neutrons produced from nuclear fission in a nuclear reactor core. Accordingly, the neutron poison micro-particles can be appropriately used as a means for controlling neutrons and stopping a nuclear reactor in the SCWR emergency core cooling system.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Refractory metal core cooling technologies for curved leading edge slots
A turbine engine component has an airfoil portion with a leading edge portion. The leading edge portion includes a plurality of staggered holes for causing fluid to flow over a surface of the airfoil portion. A method for forming the leading edge portion using refractory metal core technology is described.
Owner:RTX CORP
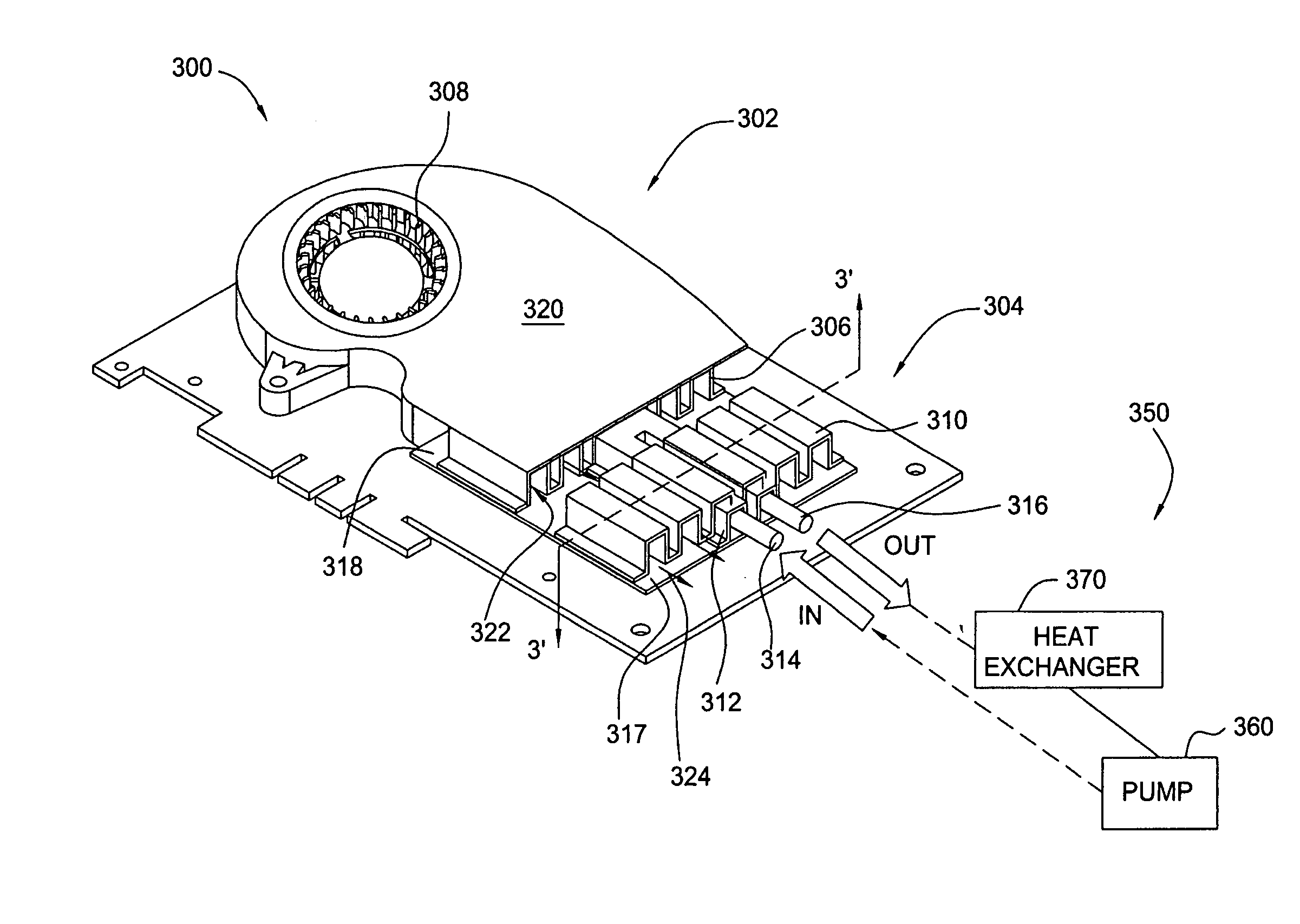
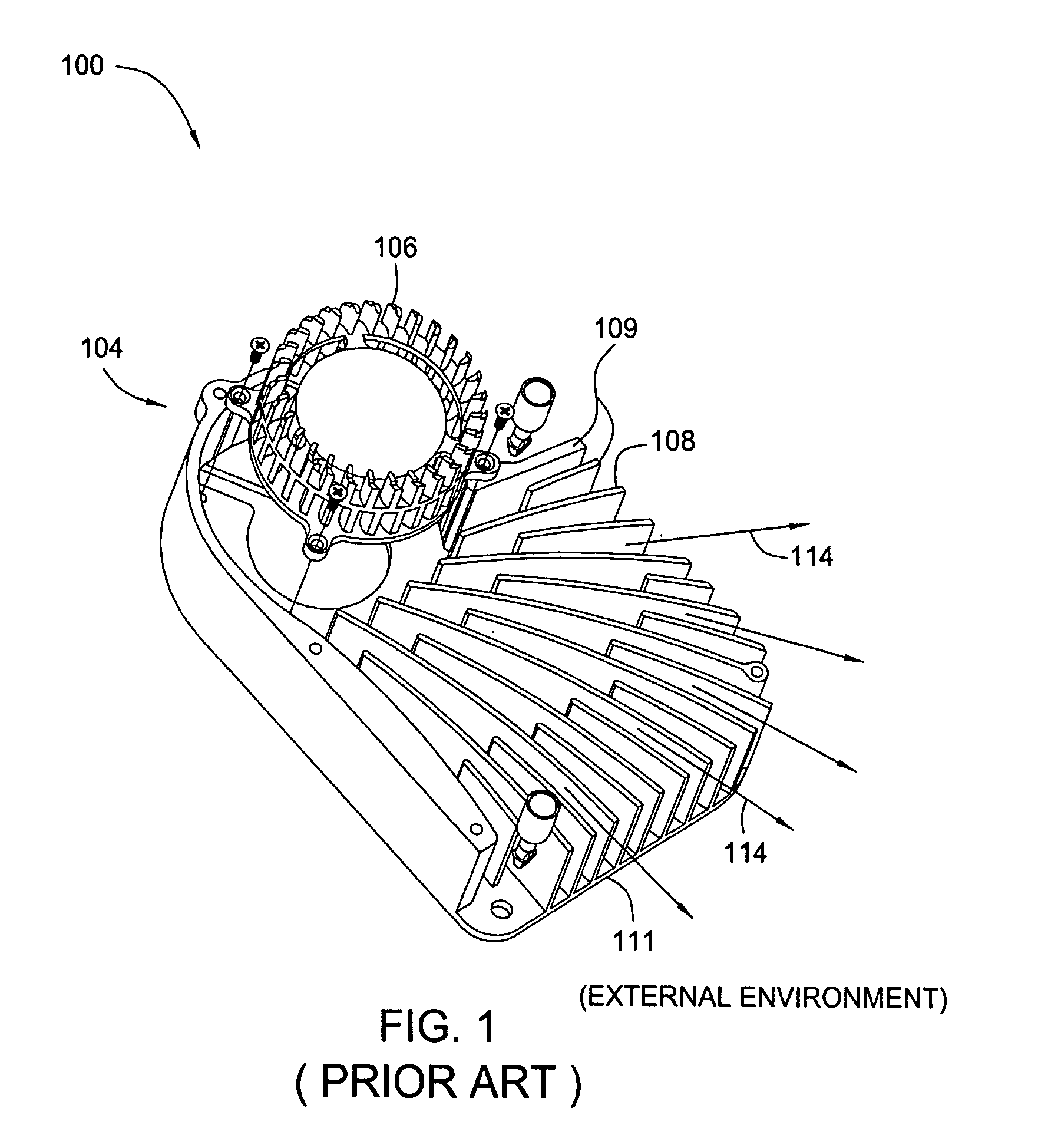
Modular, scalable thermal solution
ActiveUS7151667B2Digital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsComputer moduleModularity
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Module type pressurized water reactor
ActiveCN103489488ABig free spaceOptimize layoutNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementPressurized water reactorProcess engineering
The invention provides a module type pressurized water reactor. A reactor module is composed of a reactor body, a cooling agent system, and a safety system, the reactor body, the cooling agent system, and the safety system are all enclosed in a steel safety shell, and the whole reactor module is immersed in a reactor safety water pool, taking the pool water as the final hot trap for heat discharging of accidents. Emergency core cooling and emergency excess heat discharging are achieved by adopting a complete passive way, and the pressure inhibition and long-term heat discharging of the safety shell are achieved through repressing the water in the water pool and the reactor safety water pool; and during the processes of reloading and maintenance of reactor, through arranging a reloading water jacket between the safety shell reloading channel flange and the reactor container flange, direct-moving underwater fuel lifting operation is achieved between the safety shell and the spent fuel pool. A reactor factory can be provided with a plurality of reactor modules, all reactor modules co-use material loading equipment and other nuclear auxiliary systems, and the safety and economy of the reactor are improved through modularized combination arrangement. The module type pressurized water reactor is suitable for being applied to the fields of nuclear electricity generation, gas application, heat application, sea water desalination, and the like.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
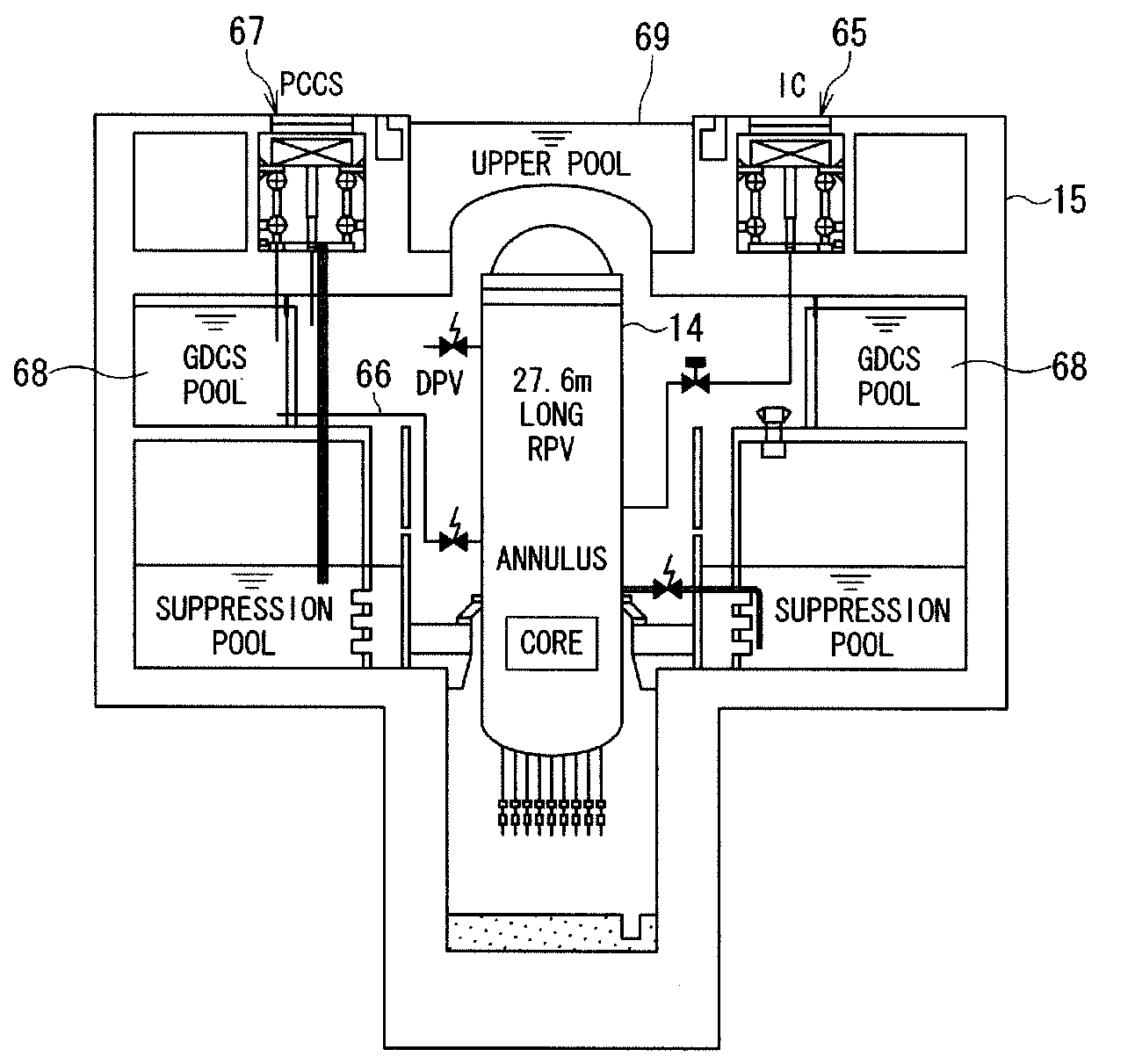
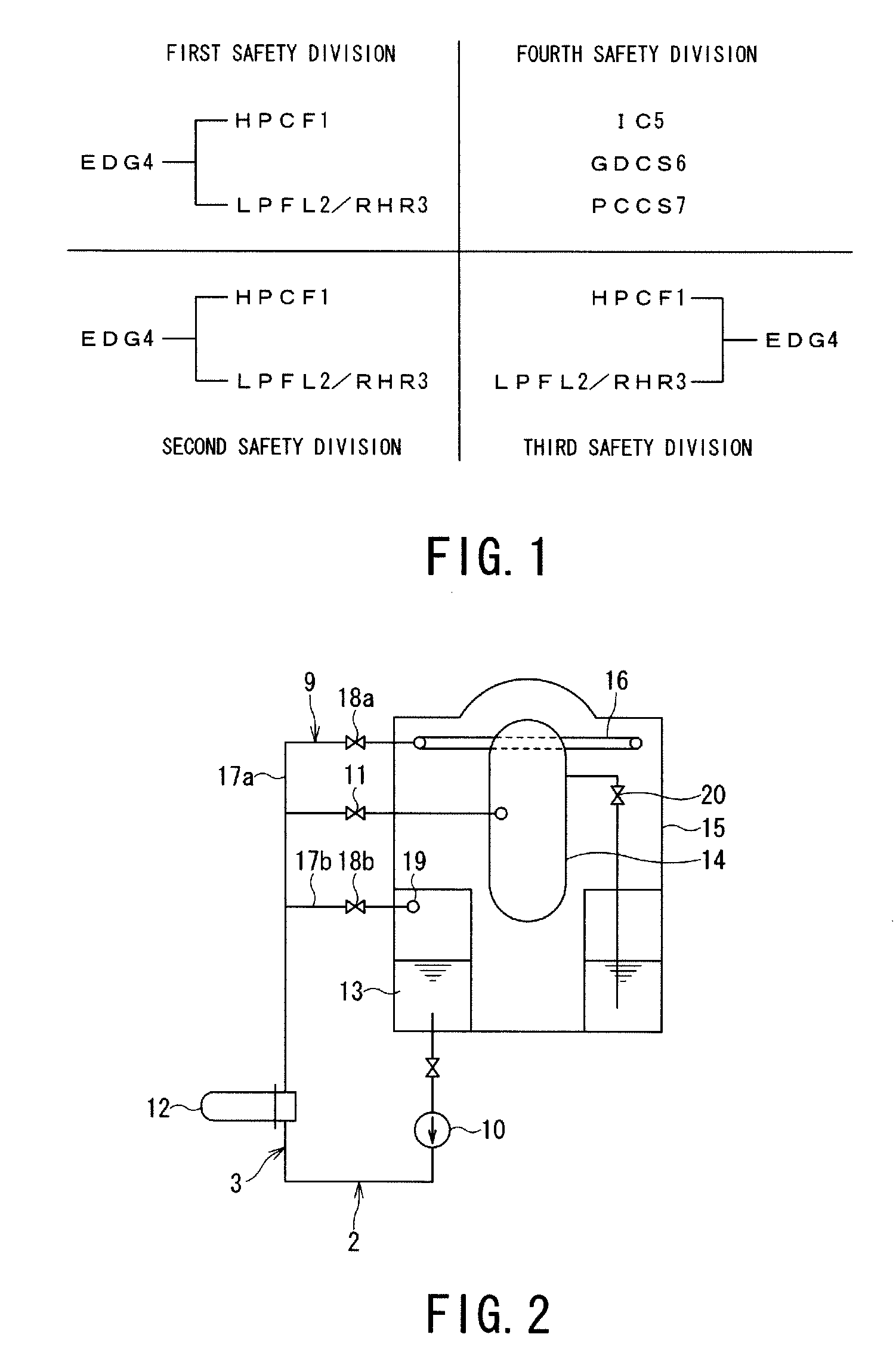
Emergency core cooling system
InactiveUS20080317193A1Improve securityPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationHigh pressureDiesel generator
An emergency core cooling system is provided with a hybrid safety system composed of an active safety system and a static safety system for ensuring the safety against a severe natural phenomenon such as a giant earthquake and a mega hurricane. An emergency core cooling system for a boiling water reactor includes four safety divisions in total: three safety divisions for an active safety system having a high pressure reactor core cooling system, a low pressure reactor core cooling system, a residual heat removal system, and an emergency diesel generator; and one safety division for a static safety system having an isolation condenser, a gravity drop reactor core cooling system, and a static containment vessel cooling system.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Temperature-triggered passive accident residual heat removal system for pool type reactor
ActiveCN104269194AImprove reliabilityEfficient take awayNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementSystems designFree cooling
The invention discloses a temperature-triggered passive accident residual heat removal system for a pool type reactor. The system consists of a direct reactor core cooling system and an auxiliary reactor safety container cooling system. The system has the significant advantage that the direct reactor core cooling system and the auxiliary reactor safety container cooling system share one air cooling system, so that the system design of the reactor is greatly simplified, and the construction cost is saved. The auxiliary reactor safety container cooling system realizes natural cooling through ambient air on the outer side of a safety container, and the process has the characteristic of passiveness. The passive accident residual heat removal system is passive, independent, high in efficiency and high in reliability and meets the safety design requirement for the pool type reactor.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Emergency core cooling system (ECCS) for nuclear reactor employing closed heat transfer pathways
InactiveUS20130156143A1Power plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A containment structure contains an interior volume, and a nuclear reactor is disposed in the interior volume. An ultimate heat sink pool is disposed outside of the containment structure. A condenser includes a plurality of closed-path heat pipes or closed-path thermosiphons having first ends and opposite second ends. The closed-path heat pipes or closed-path thermosiphons are embedded in the containment structure with the first ends protruding into the interior volume and the second ends protruding outside of the containment structure.
Owner:BWXT NUCLEAR ENERGY
Increased efficiency strainer system
ActiveUS20110084008A1Avoid flowOpen efficientlyNuclear energy generationNuclear elementsEngineeringHigh pressure
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided an increased efficiency strainer system which is particularly suited for use in the emergency core cooling system of a nuclear power plant. In certain embodiments of the present invention, the strainer system includes one or more strainer cassettes or cartridges, with each such cassette or cartridge including a plurality of strainer pockets disposed in side-by-side relation to each other. In these embodiments, multiple cassettes or cartridges may be assembled together to form a strainer module of the strainer system. The strainer pockets of the cartridge each define an inflow end. Within the cartridge, or the module including multiple cartridges, the inflow ends of one or more of the strainer pockets may be enclosed by an elastic metal membrane. When in a closed position, the membrane prevents liquid flow into the corresponding strainer pocket via the inflow end thereof. The membrane remains closed when only a low pressure load is exerted thereon, but is deflected or deformed into an open position when a high pressure load is exerted thereon. The movement of the membrane to its open position effectively opens the corresponding strainer pocket, thus allowing for the flow of liquid into the interior of the strainer pocket via the inflow end thereof.
Owner:CONTROL COMPONENTS INC
Low Head Loss Modular Suction Strainer with Contoured Surfaces
A strainer for an emergency core cooling system (ECCS) in a nuclear power plant comprises a perforated strainer element that is immersed in a reservoir of cooling water, which is drawn through the strainer element into the emergency core cooling system. The side of the strainer element in contact with the cooling water has a contoured configuration for disrupting the formation of a flat bed of fibrous material that can trap small particulate material intended to pass through the strainer element. Incorporating this strainer element into an ECCS strainer enables the strainer to be made more compact, because the debris bed need not be spread over an unduly large area to prevent excessive head loss from the debris load in the event of a reactor loss of coolant accident. The strainer also incorporates a modular construction that uses individual strainer disc modules. Each disc module includes a perforated first disc part having a central opening and a perforated second disc part also having a central opening. The first and second disc parts fit together to form an interior space with facing perforated major surfaces and an axial opening, and connecting tubes between the discs place the axial openings in fluid communication. The entire assembly is secured together by tie rods that hold the discs together with the connecting tubes compressed between them.
Owner:CONTINUUM DYNAMICS
Temperature-controlled rolling equipment for production of metal plate in coils
ActiveCN105834214APrecise temperature controlDifferent mechanical propertiesTemperature control deviceRollsTemperature controlWork roll
The invention relates to temperature-controlled rolling equipment for production of metal thin ribbons and ultra-thin strips in coils.The temperature-controlled rolling equipment is arranged in the bilaterally symmetrical mode. The position where a working roll (15) is used for rolling strips is a rolling mill gap (20). Inlet and outlet side parts comprise measuring tension rolls (13, 17), steering rolls (12, 18), and recoiling machines (11, 19). All parts are sequentially arrayed with the rolling mill gap as the center from the inside to the outside. The equipment further comprises an uncoiling and heating device (21), a plate strip heat-compensating device (24) and a plate strip edge heating device (25) before ingress of the rolling mill gap, a roll surface heating device (26), and a roll core cooling and bearing seat cooling mechanism (3), a plate strip edge heating device (35) and the plate strip heat-compensating device (34) after egress of the rolling mill gap, a pre-coiling heating device (31), heating devices (22, 32) at positions of the steering rolls and heating devices (23, 33) at positions of the measuring tension rolls at the inlet side.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Sleeve type evaporative cooling transformer with oil-tank
InactiveCN1812014AImprove cooling effectSimple structureTransformers/inductances coolingStationary conduit assembliesTransformerFuel tank
This invention is a kind of sleeve type evaporation cooling transformer, which is consisted with mandrel, electric coil, oil tank, sleeve, air inletting tube, condenser, liquid returning tube, upper pipe, lower pipe, insulating gas, cooling medium in the bottom of the oil tank, pump and iron core cooling channel. The characteristics are that the electric coil is arranged inside of the sleeve added with cooling medium, the upper side of the sleeve can be covered or not, or setting a blowhole. The upper side of the oil tank is connected with the lower side of the air inletting tube, upper side of the air inletting tube is connected with condenser, the bottom (or the side face) of the condenser is connected with liquid returning tube, lower side of the liquid returning tube is connected with the bottom of the sleeve, cooling medium dripping in the bottom of the oil tank is connected with cooling medium in the liquid returning tube through pump. The oil tank is filled with insulating gas such as SF6 gas, mixture of SF6 gas and N2, substitute of SF6 gas, nitrogen and carbon compound gas.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low head loss modular suction strainer with contoured surfaces
A strainer for an emergency core cooling system (ECCS) in a nuclear power plant comprises a perforated strainer element that is immersed in a reservoir of cooling water, which is drawn through the strainer element into the emergency core cooling system. The side of the strainer element in contact with the cooling water has a contoured configuration for disrupting the formation of a flat bed of fibrous material that can trap small particulate material intended to pass through the strainer element. Incorporating this strainer element into an ECCS strainer enables the strainer to be made more compact, because the debris bed need not be spread over an unduly large area to prevent excessive head loss from the debris load in the event of a reactor loss of coolant accident. The strainer also incorporates a modular construction that uses individual strainer disc modules. Each disc module includes a perforated first disc part having a central opening and a perforated second disc part also having a central opening. The first and second disc parts fit together to form an interior space with facing perforated major surfaces and an axial opening, and connecting tubes between the discs place the axial openings in fluid communication. The entire assembly is secured together by tie rods that hold the discs together with the connecting tubes compressed between them.
Owner:CONTINUUM DYNAMICS
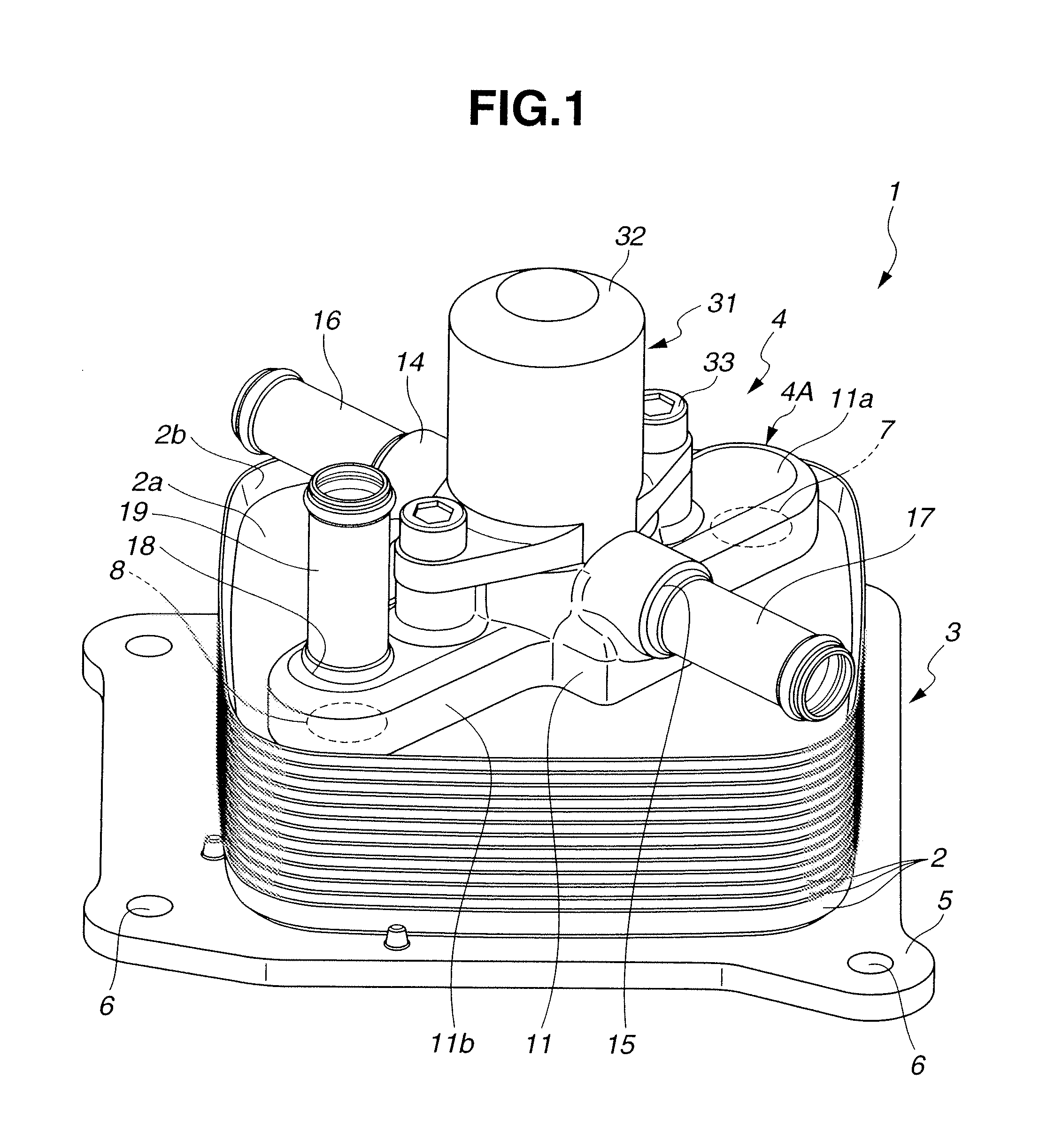
Oil cooler
InactiveUS20120061048A1Reduce frictionEasy to getExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusCoolant flowControl valves
An oil cooler includes a heat exchanger core having a plurality of plates laid one upon another to define each of an oil passage through which oil flows and a coolant passage through which coolant flows, between the plates. An uppermost plate of the plates has a core coolant inlet and a core coolant outlet. The core coolant inlet and the core coolant outlet are communicated with the coolant passage. A flow passage control valve is disposed on an uppermost part of the heat exchanger core and has a first coolant introduction opening through which coolant at a relatively high temperature is supplied and a second coolant introduction opening through which coolant at a relatively low temperature is supplied. The first coolant introduction opening and the second coolant introduction opening are changed over to be communicated with the core coolant inlet.
Owner:MAHLE FILTER SYST JAPAN CORP
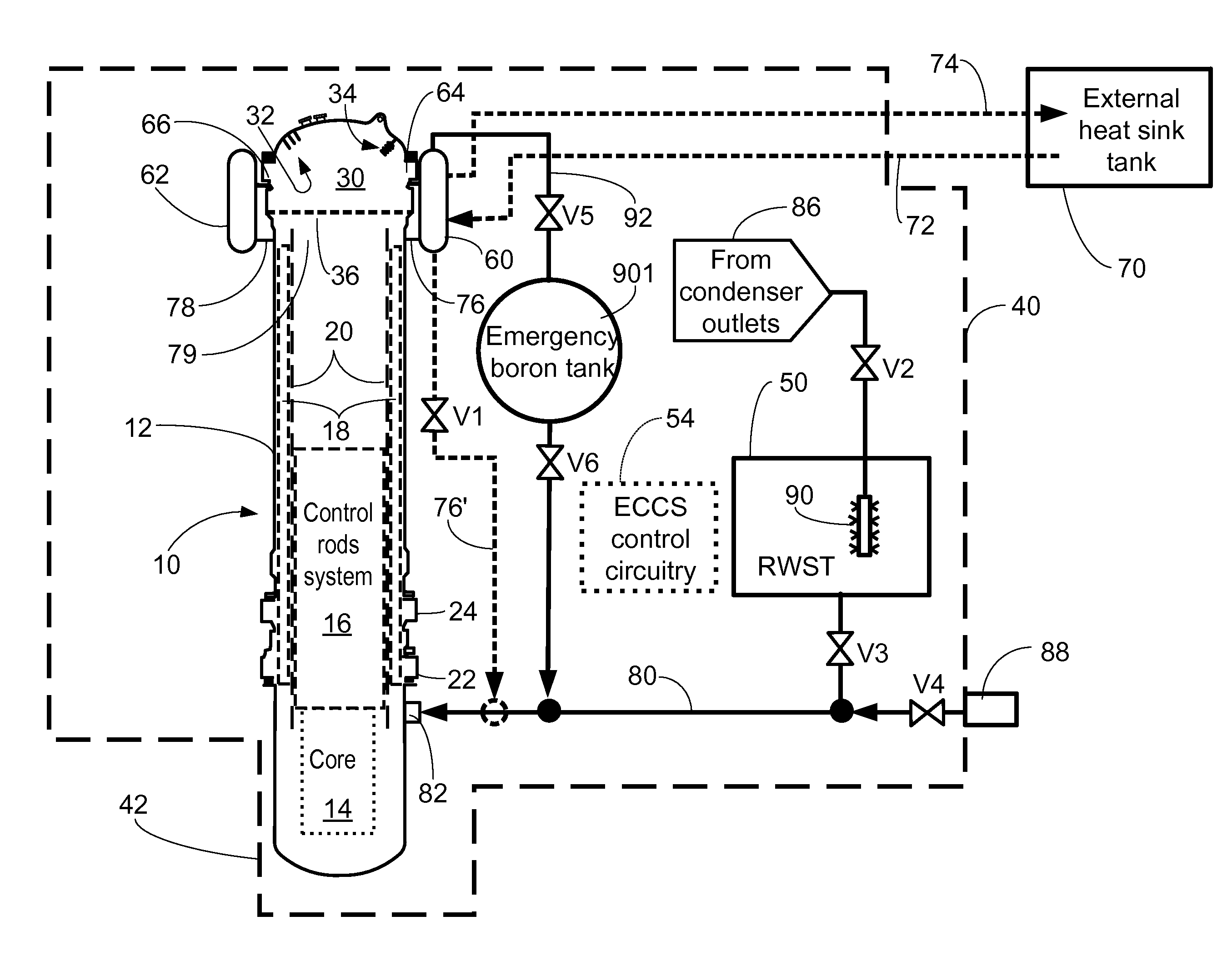
Passive high pressure safety injection tank system (HPSIT) for responding to station blackout (SBO) and loss-of-coolant accidents (LOCA)
ActiveUS20120263268A1Simplify System DesignSimplified mitigationPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationReactor systemOperation mode
A high pressure safety injection tank (HPSIT) system includes one safety injection tank (HIT) which replaces a core makeup tank (CMT) and a low pressure (approximately 4.3 Mpa or below) safety injection tank (SIT) and which can shift to and operate on a high pressure (approximately 17 Mpa) operation mode, to enable injection of emergency core coolant into a reactor system both under low pressure (approximately 4.3 Mpa or below) and high pressure (approximately 17 Mpa).
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST +1
Stator iron core, shell, motor cooling system of electric vehicle and electric vehicle
ActiveCN110365138AImprove exercise efficiencyExtended service lifeElectric propulsion mountingElectric machinesElectric vehicleChannel use
The invention provides a stator iron core, a shell, a motor cooling system of an electric vehicle and the electric vehicle. The cooling system comprises a power device, the stator iron core, an iron core cooling oil channel used for conveying cooling oil to the stator iron core, and a coil cooling oil channel. The coil cooling oil channel is provided with a first oil outlet, and the first oil outlet is located in the end of the stator iron core. The iron core cooling oil channel and the coil cooling oil channel are sequentially communicated, so that cooling oil enters the iron core cooling oilchannel firstly and then enters the coil cooling oil channel. The iron core cooling oil channel extends in the circumferential direction of the stator iron core, the coil cooling oil channel extendsin the axial direction of the stator iron core, and the power device drives cooling oil to enter the iron core cooling oil channel from the oil inlet, flow through the iron core cooling oil channel, enter the coil cooling oil channel from an oil passing opening and flow back to an oil return groove from the first oil outlet.
Owner:HUAWEI DIGITAL POWER TECH CO LTD
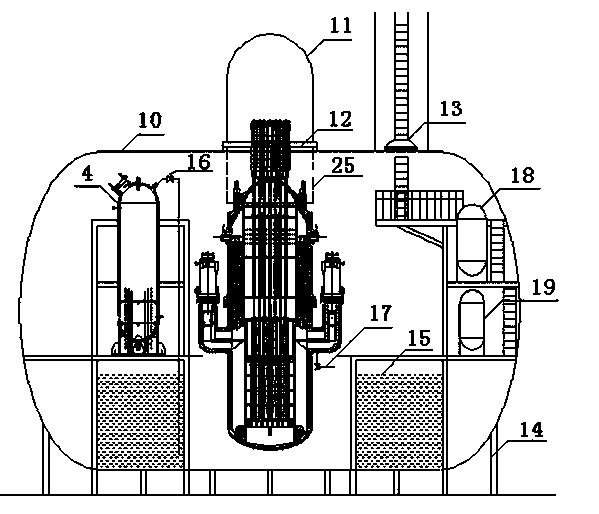
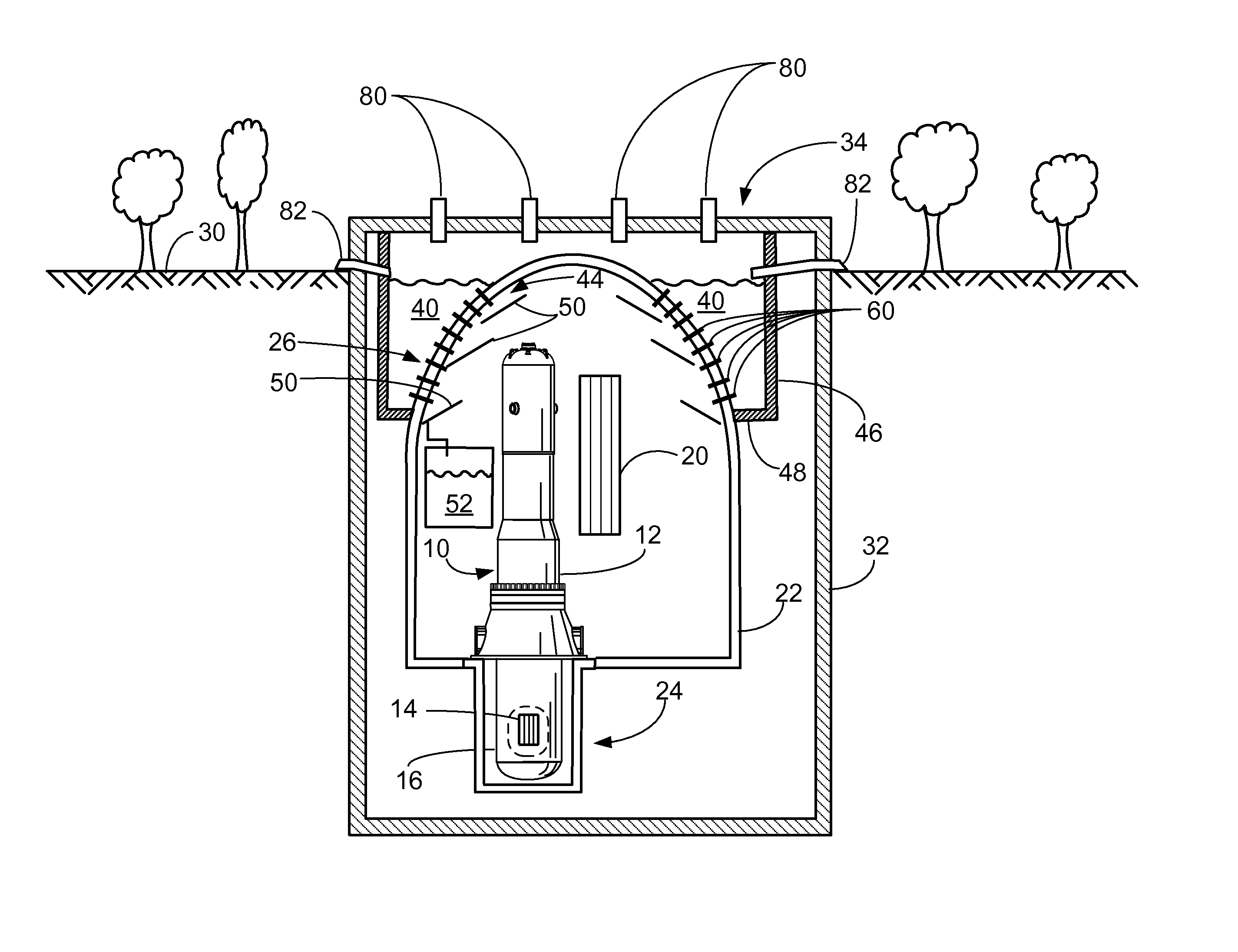
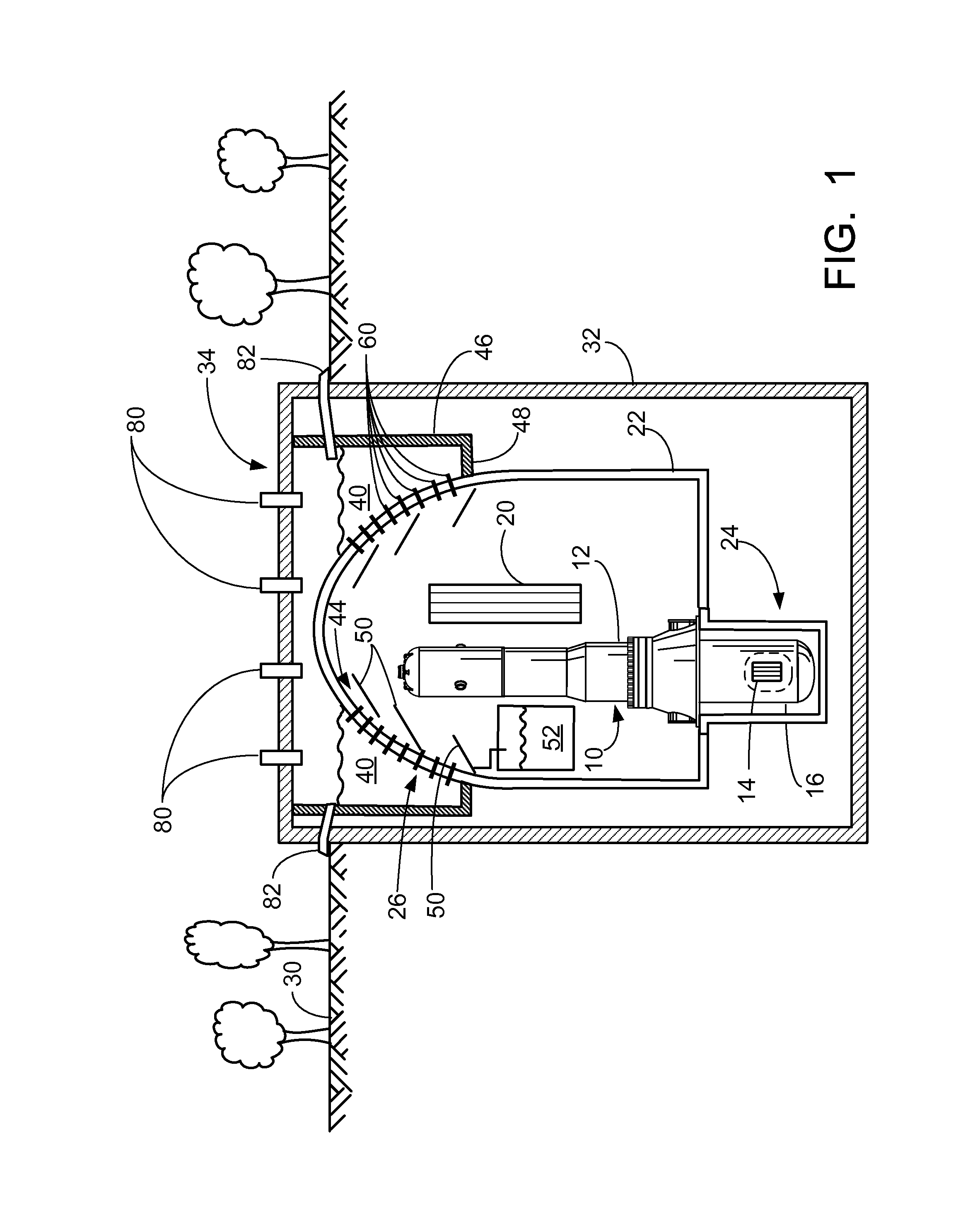
Small reactor passive core cooling system
The present invention discloses a small reactor passive core cooling system including a water replenishing tank, pipes of the water replenishing tank, a safe water injection pool, pipes of the safe water injection pool, a residual heat exchanger, pipes of the residual heat exchanger and a circle-structure shielding water pool, the circle-structure shielding water pool is arranged around a pressure vessel, the circle-structure shielding water pool is provided with a suppression pipe ad a water pipe, a pressure relief pipe is arranged between the shielding water pool and a reactor coolant, and the pressure relief pipe is used for communication of the reactor coolant and a water body in the shielding water pool, and is provided with a valve group. The small reactor passive core cooling system can be used as an important part of a passive safety system of a small containment vessel to achieve the functions of taking away reactor core decay heat and providing a safe water injection source in accidents, and can effectively suppress containment vessel peak pressure. The system equipment layout is compact, space occupation is small, arrangement is simple, and economical efficiency is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Integrated emergency core cooling system condenser for pressurized water reactor
ActiveUS20120321030A1Integral reactorsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor corePressurized water reactor
A pressurized water nuclear reactor (PWR) includes a pressure vessel having a lower portion containing a nuclear reactor core comprising a fissile material and an upper portion defining an internal pressurizer volume. A condenser is secured to, and optionally supported by, the upper portion of the pressure vessel. A condenser inlet is in fluid communication with the internal pressurizer volume. A heat sink is in fluid communication with the condenser such that the condenser operates as a passive heat exchanger to condense steam from the internal pressurizer volume into condensate while rejecting heat to the heat sink. A condenser outlet connects with the pressure vessel to return condensate to the pressure vessel. A single metal forging having a first end welded to the pressure vessel and a second end welded to the condenser inlet may provide the fluid communication between the condenser inlet and the internal pressurizer volume.
Owner:BWXT MPOWER INC
Boiling water nuclear reactor and emergency core cooling system of the same
ActiveUS20100272226A1Nuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsReactor pressure vesselNuclear reactor
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Emergency core cooling duct for emergency core cooling water injection of a nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20100278294A1Low flow resistanceImprove securityNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
The present invention relates to a longitudinally divided emergency core cooling (ECC) duct in order to efficiently inject safety water to core of a pressurized light-water nuclear reactor. The ECC duct includes side supports for preventing the flow-induced vibration in the annular downcomer, and has structural stability while thermally expanding and contracting. A longitudinally divided ECC duct for emergency core cooling water injection of a nuclear reactor is provided on the periphery of a core barrel of a nuclear reactor, includes an emergency core cooling water inlet facing a direct vessel injection nozzle, and extends in a longitudinal direction of the core barrel. The longitudinally divided ECC duct is divided into a plurality of longitudinally-divided ducts in the longitudinal direction of the longitudinally divided ECC duct.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST +1
Emergency core cooling system having core barrel injection extension ducts
InactiveUS20090232267A1Preventing level of coolingCross flow can be reducedNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsWater flowHigh pressure
An emergency core cooling system directly injects emergency core cooling water, which is supplied from a high-pressure safety injection pump or a safety injection tank for a pressurized light water reactor, into a reactor vessel downcomer. A pipe connector is completely removed from between each direct vessel injection nozzle and each injection extension duct installed on an outer surface of the core barrel, which are opposite to each other. An emergency core cooling water intake port, through which the water is injected from each direct vessel injection nozzle, is formed on the surface of each injection extension duct facing an axis of each direct vessel injection nozzle. Thereby, a structure in which a jet of the emergency core cooling water flows into the injection extension ducts is adopted in a hydraulic connection fashion.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST +1
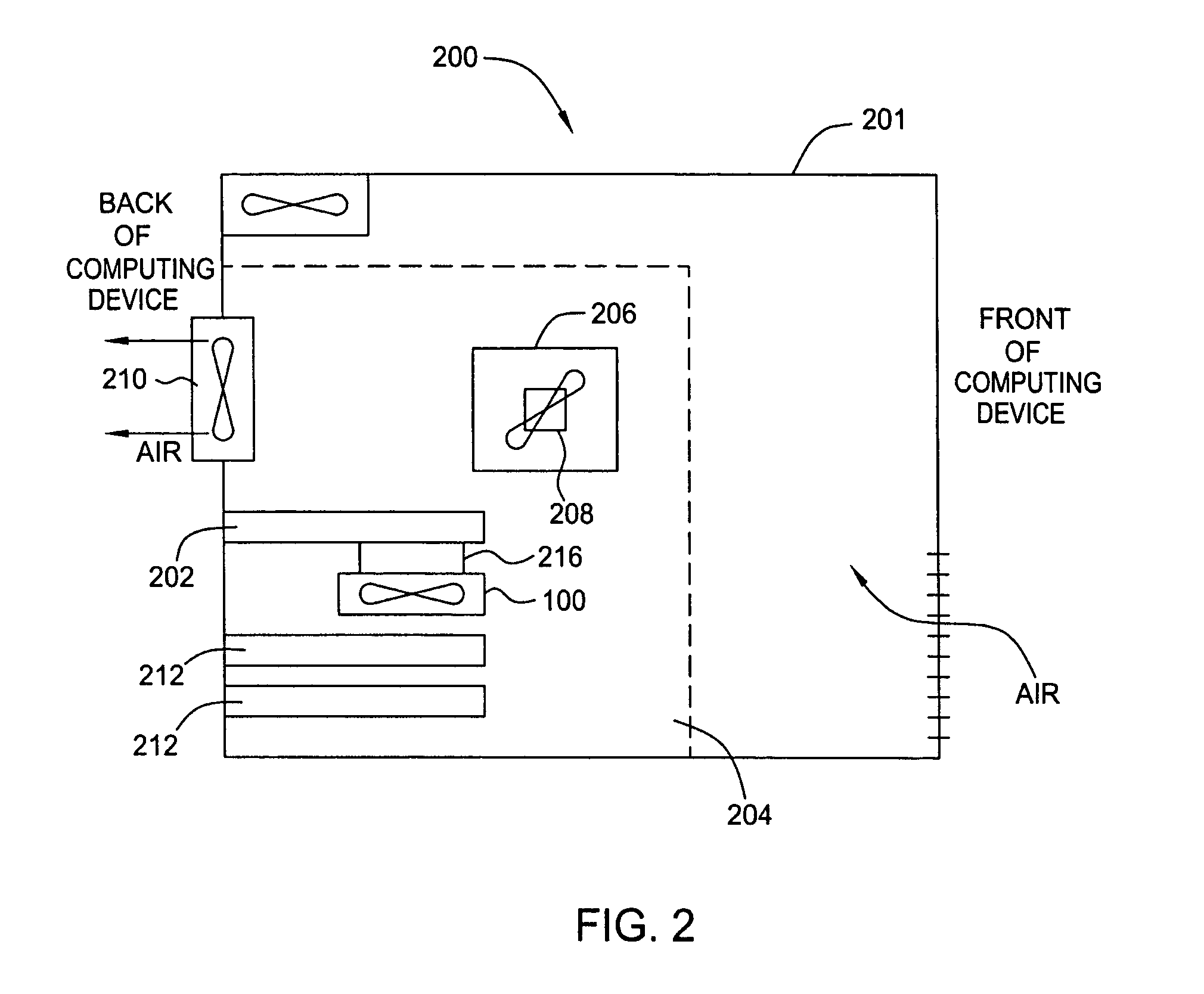
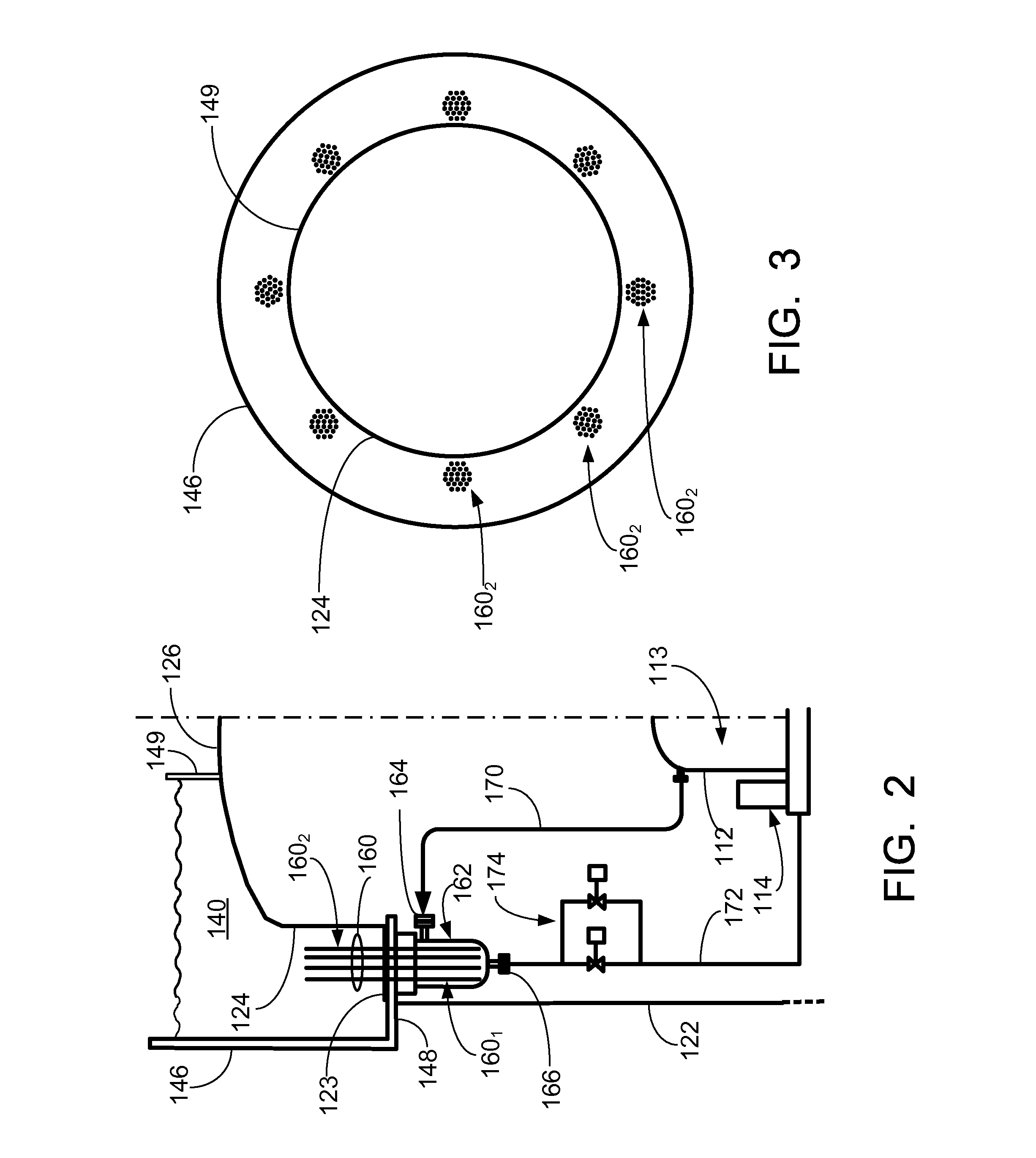
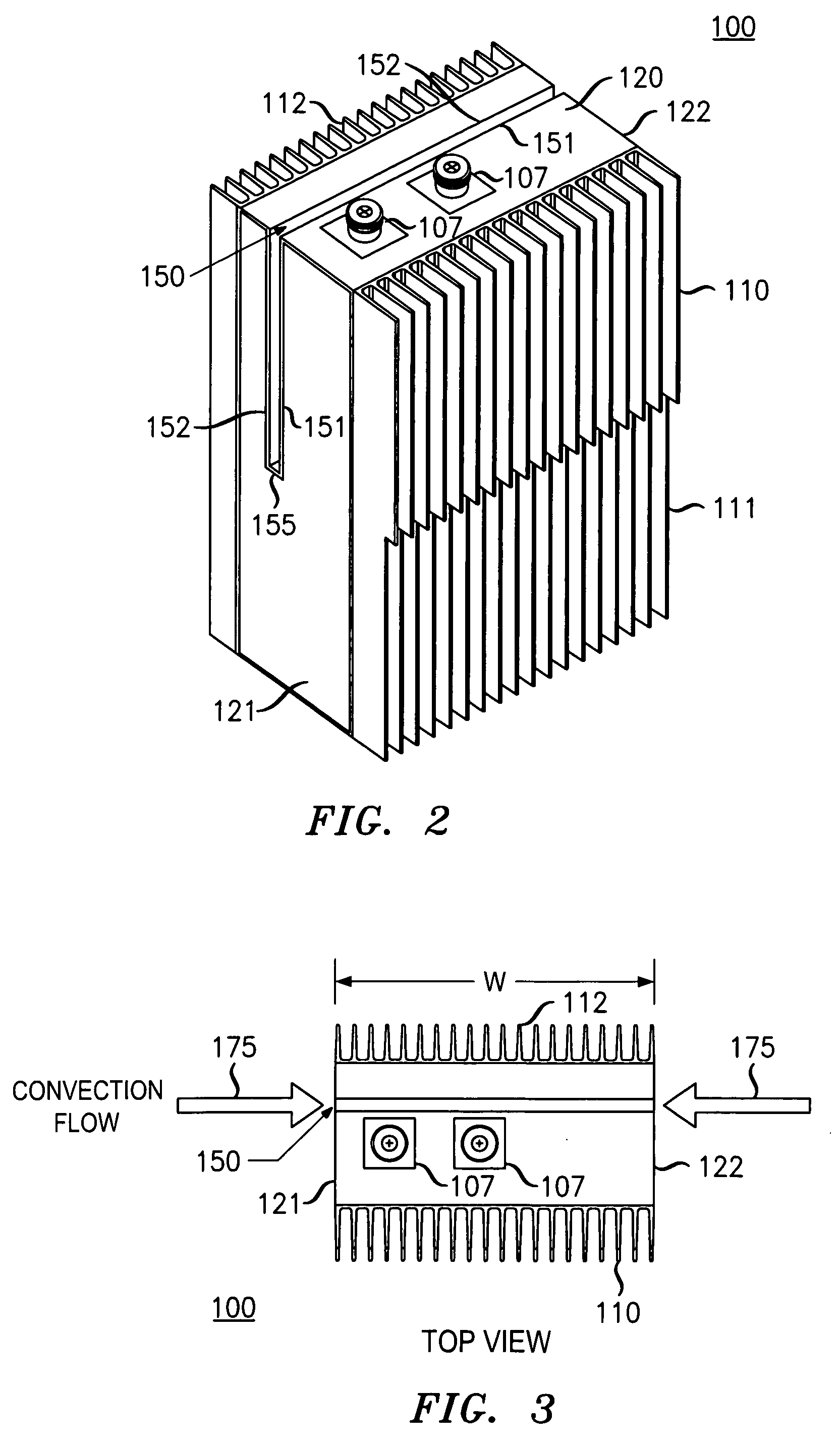
Cooling arrangement for an equipment assembly
An equipment assembly includes a core cooling slot to manage thermal effects brought about by the generation of heat from components therein. The cooling slot is positioned within the equipment assembly so that only air that is external to the equipment assembly passes through the cooling slot to provide external convection-based cooling for components in a core section inside the equipment assembly. The cooling slot also acts as a thermal barrier for redistributing heat generated by the one or more components inside the equipment assembly.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com