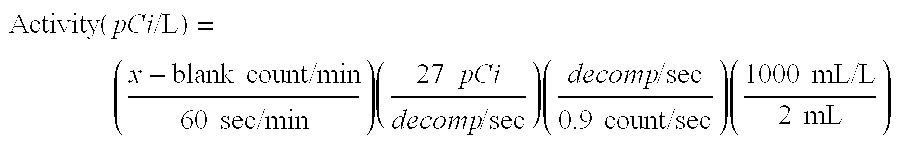Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
874results about "Radioactive contaminants" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
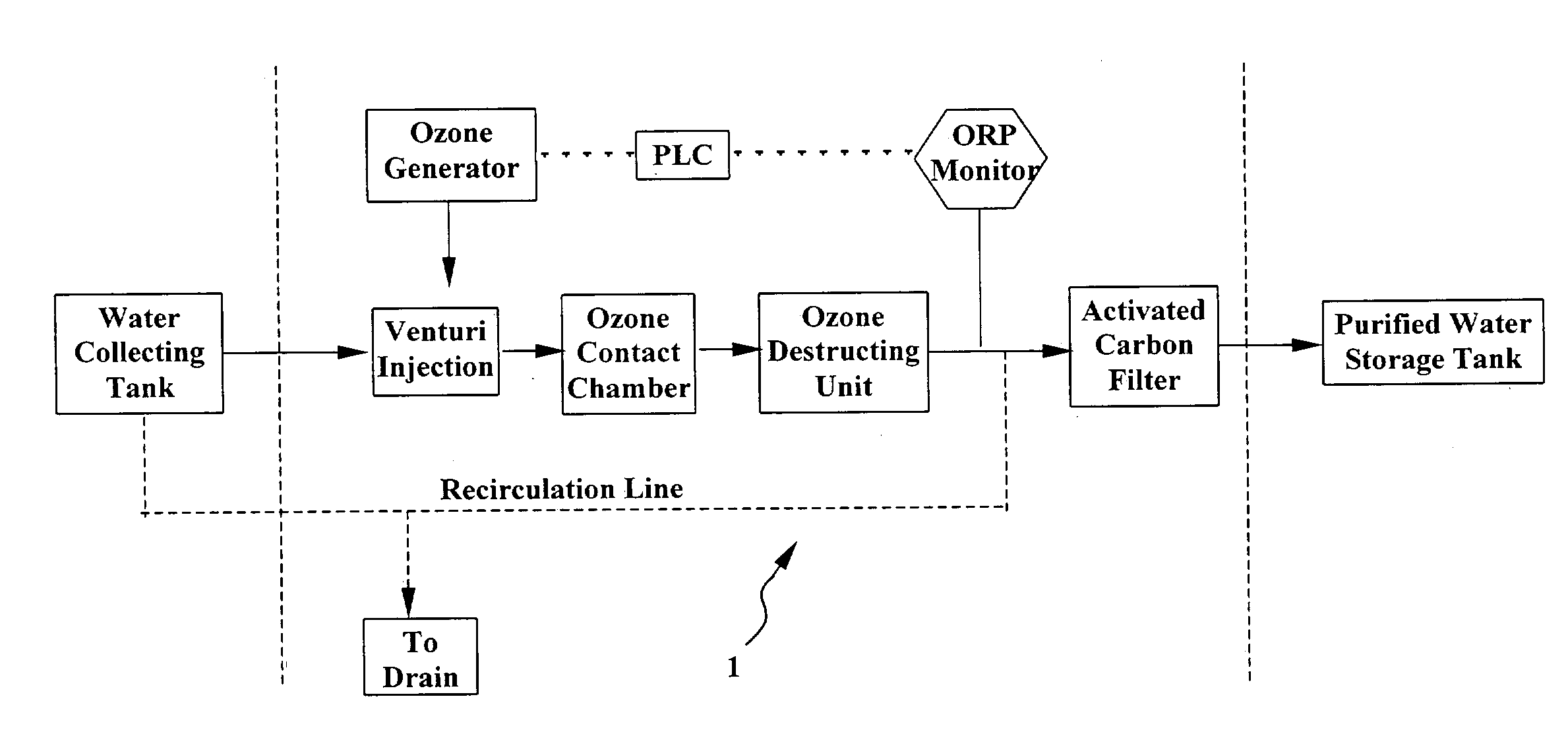
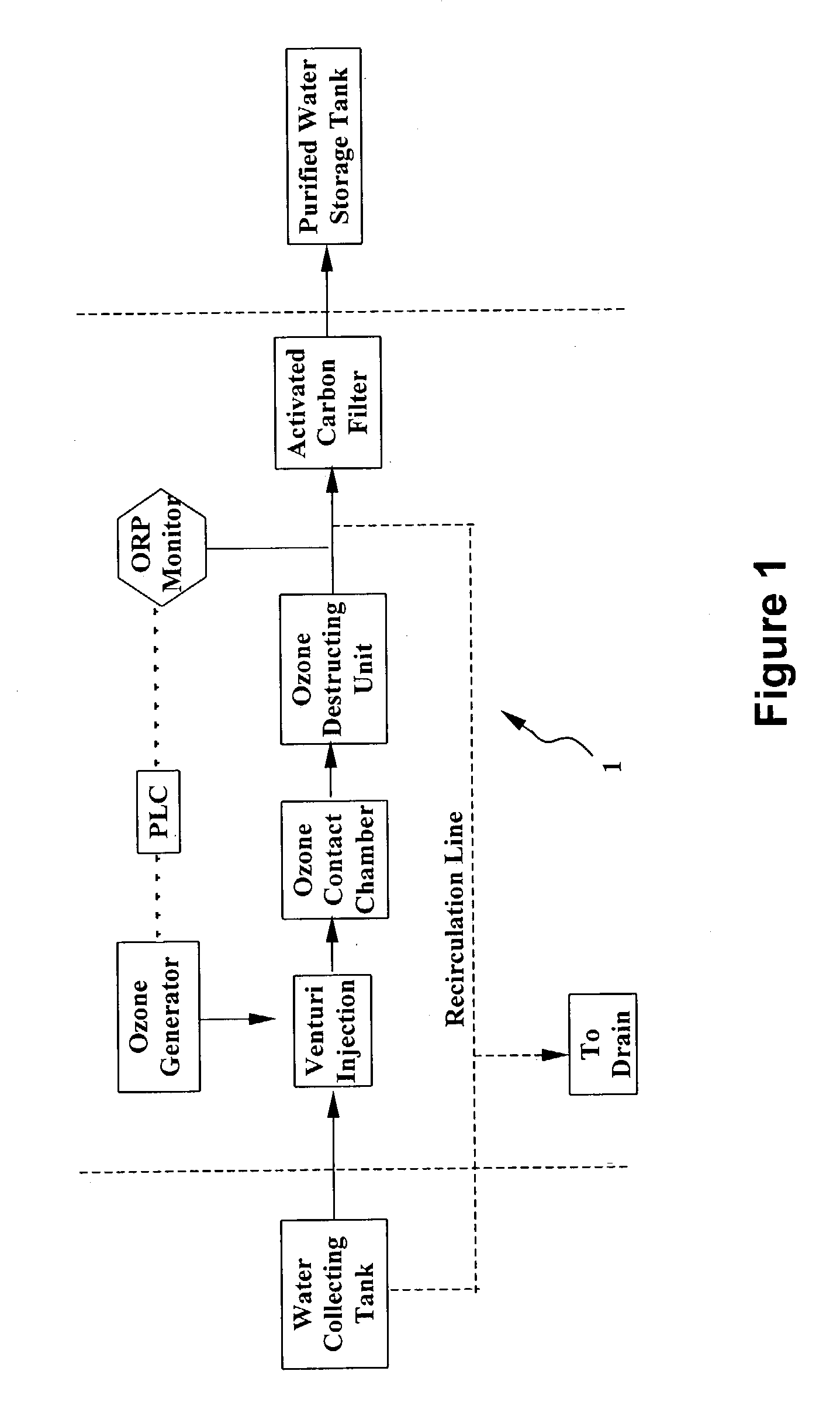
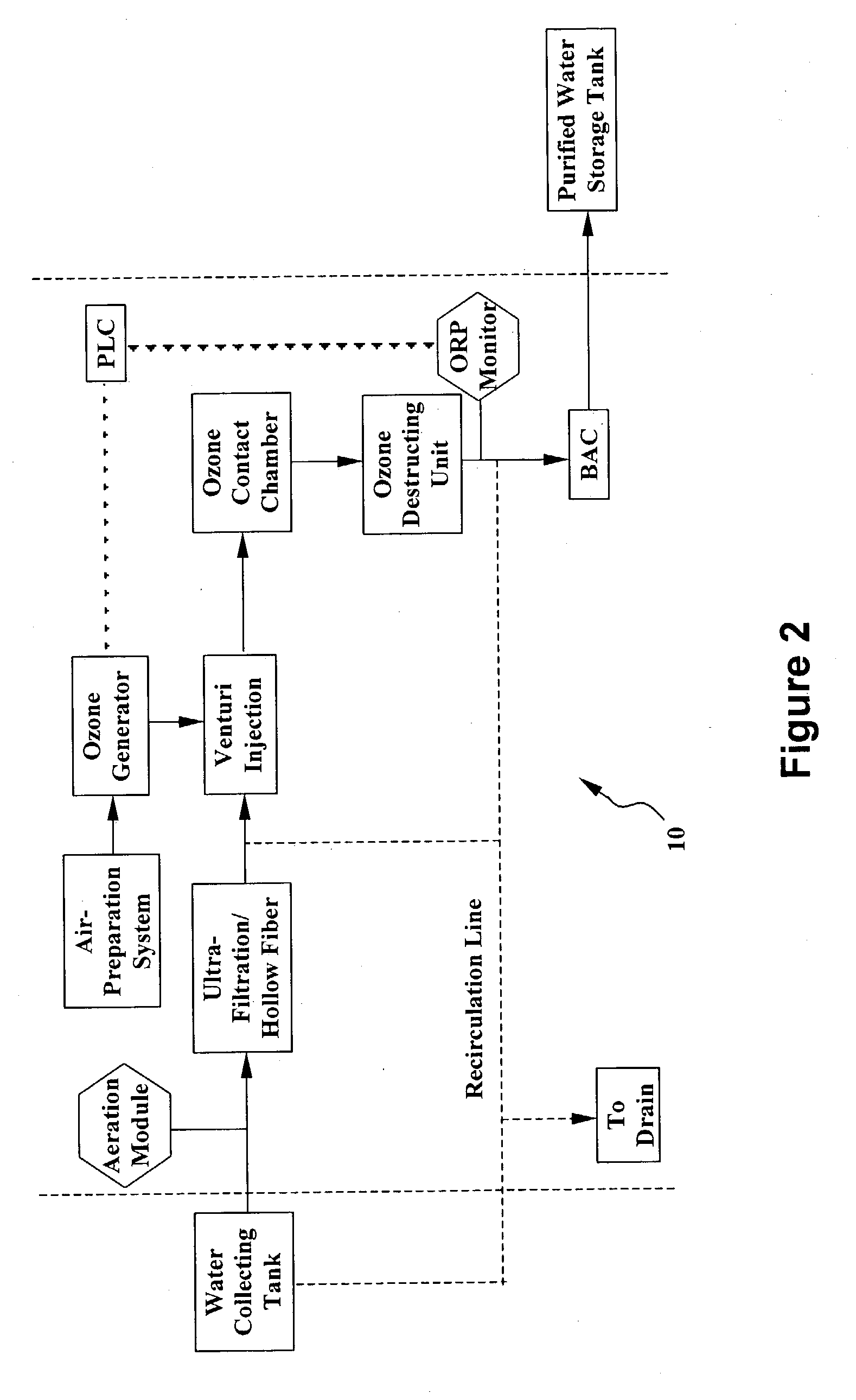
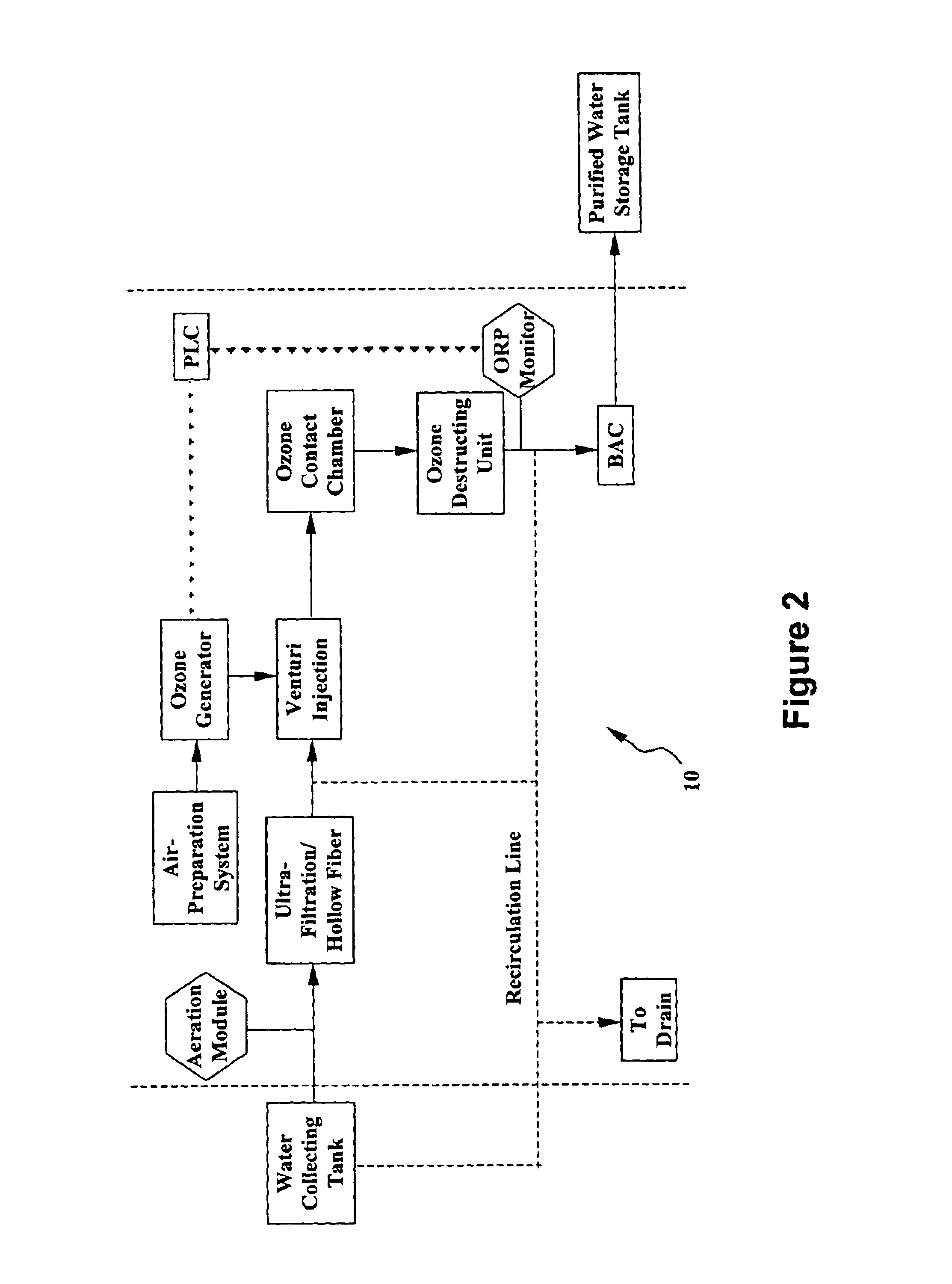
System and method for water purification
InactiveUS20040168989A1Treatment using aerobic processesSedimentation separationBiological activated carbonActivated carbon filtration
A self-contained, portable water purification system, including (a) an ozone supply, (b) an ozone contact chamber for mixing a contaminated or potentially contaminated water stream with ozone generated by such ozone supply, (c) an ozone destruction unit for destructing ozone contained in the water stream and converting said water stream into an oxygen-rich and ozone-depleted water stream, and (d) a downstream biologically active carbon filter, for receiving such oxygen-rich and ozone-depleted water stream and biologically destructing at least a portion of contaminants contained therein.
Owner:TEMPEST ENVIRONMENTAL SYST
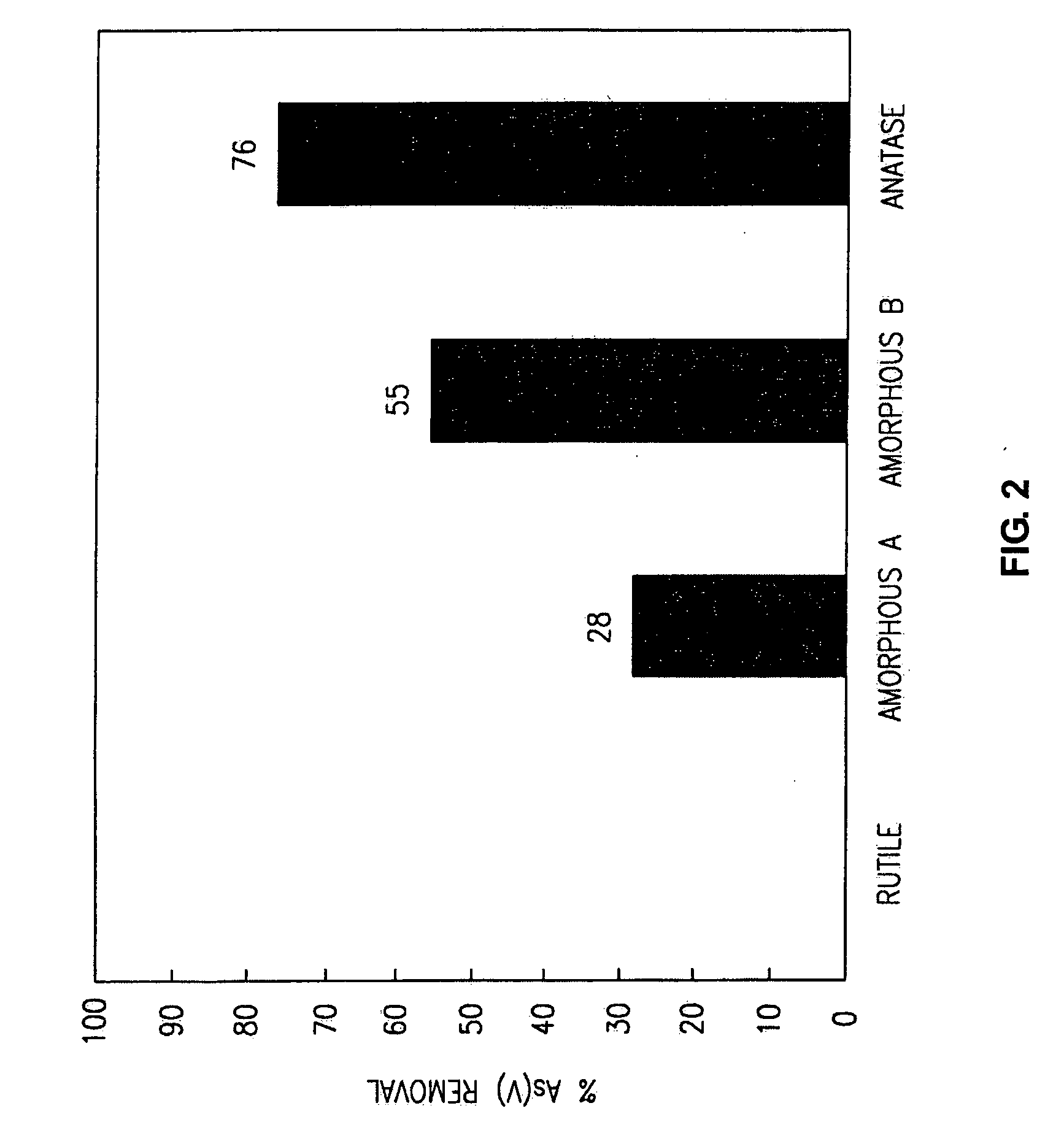
Methods of preparing a surface-activated titanium oxide product and of using same in water treatment processes
InactiveUS6919029B2Inhibit dissolution and migrationMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesHigh rateTitanium
A method for producing a surface-activated crystalline titanium oxide product having a high adsorptive capacity and a high rate of adsorption with respect to dissolved contaminants includes the steps of preparing a titanium oxide precipitate from a mixture comprising a hydrolysable titanium compound and heating the precipitate at a temperature of less than 300° C., without calcining the precipitate. Preferably, the titanium oxide product includes crystalline anatase having primary crystallite diameters in the range of 1-30 nm. The surface-activated crystalline titanium oxide product is used in methods to remove dissolved inorganic contaminants from dilute aqueous streams by suspending the product in an aqueous stream or by filtering an aqueous stream through a bed of the product. In another method, a hydrolysable titanium compound is added to an aqueous stream so that titanium oxides form as a co-precipitate with dissolved contaminants within a bed of particulate material.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for treating radioactive wastewater
ActiveCN103177784AImprove processing precisionReduce competitionGeneral water supply conservationRadioactive contaminantsStrong acidsIon exchange
The invention discloses a method for treating radioactive wastewater. The method for treating the radioactive wastewater comprises the steps of firstly carrying out reverse osmosis treatment on the radioactive wastewater, then enabling the radioactive wastewater to enter a continuous electrodeionization unit to be treated, and further removing radionuclide so as to enable treated wastewater to reach discharge requirements; and respectively filling different mixed ion exchange resin in a plain water chamber and a thick water chamber in a continuous electrodeionization membrane stack of the continuous electrodeionization unit, wherein mixed ion exchange resin filled in the plain water chamber comprises, by volume ratio, 30%-60% of strong-acid cation exchange resin, 40%-60% of strong-base anion exchange resin, and 0%-30% of weak-base anion exchange resin, mixed ion exchange resin filled in the thick water chamber comprises, by volume ratio, 20%-50% of strong-acid cation exchange resin, and the balance strong-base anion exchange resin. A weak dissociation polymer portion is used for improving selectivity of continuous electrodeionization membrane stack to trace amount radionuclide, radionuclide with extremely concentration can be effectively removed, and the method for treating the radioactive wastewater ensures that the final discharged water satisfies the discharge requirements.
Owner:BEIJING QINGHE CHAOHUA TECH CO LTD
Oxidative Treatment Method
InactiveUS20100320156A1Quickly and efficiently decomposeEffective treatmentWater/sewage treatment by irradiationDecorative surface effectsElectrolysisWaste stream
The present invention provides a method for oxidizing a substance (e.g., in a waste stream, drinking water, a paper pulp slurry, or on a surface), which uses free radicals and reactive species generated from multiple oxidants. The method comprises combining peroxynitrite or peroxynitrous acid and at least one additional oxidizing agent for a period of time sufficient to oxidize the substance of interest. The peroxynitrite or peroxynitrous acid preferably is formed by irradiation of nitrate ion and / or nitric acid (e.g., with UV or gamma rays). The yield of free radicals and reactive species, which are the intermediate species that perform the oxidation may be increased by addition of a catalysts, electromagnetic radiation, sonic waves, and / or electrolysis.
Owner:TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
Water purification method
InactiveUS20140175015A1Conveniently and efficiently purifyingInexpensivelyWaste water treatment from quariesWaste water treatment from ceramic industriesPurification methodsSorbent
A water purification method comprising adding a purification agent to water having a contaminant concentration of 1 μg / L to 10 g / L, the purification agent containing an adsorbent having an average particle size of 100 nm to 500 μm, an iron-based flocculant, and an alkaline substance; causing the adsorbent to adsorb at least a part of the contaminants in water; settling the adsorbent with the adsorbed contaminants by the iron-based flocculant; and removing the sediment from water, wherein the purification agent is added in an amount of 0.01 g to 20 g per liter of water, can purify contaminated water conveniently and efficiently.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method and system for treating radioactive waste water
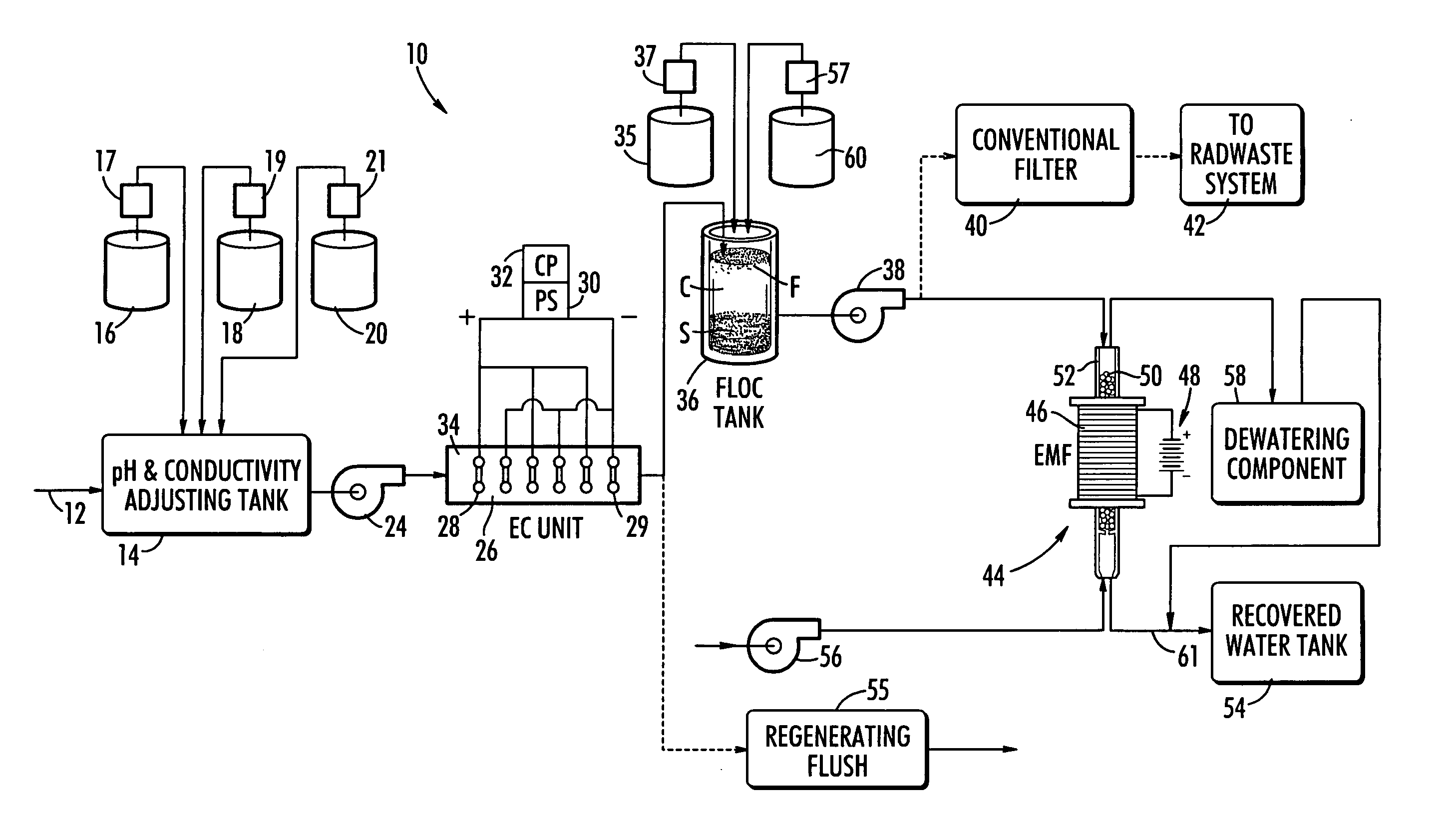
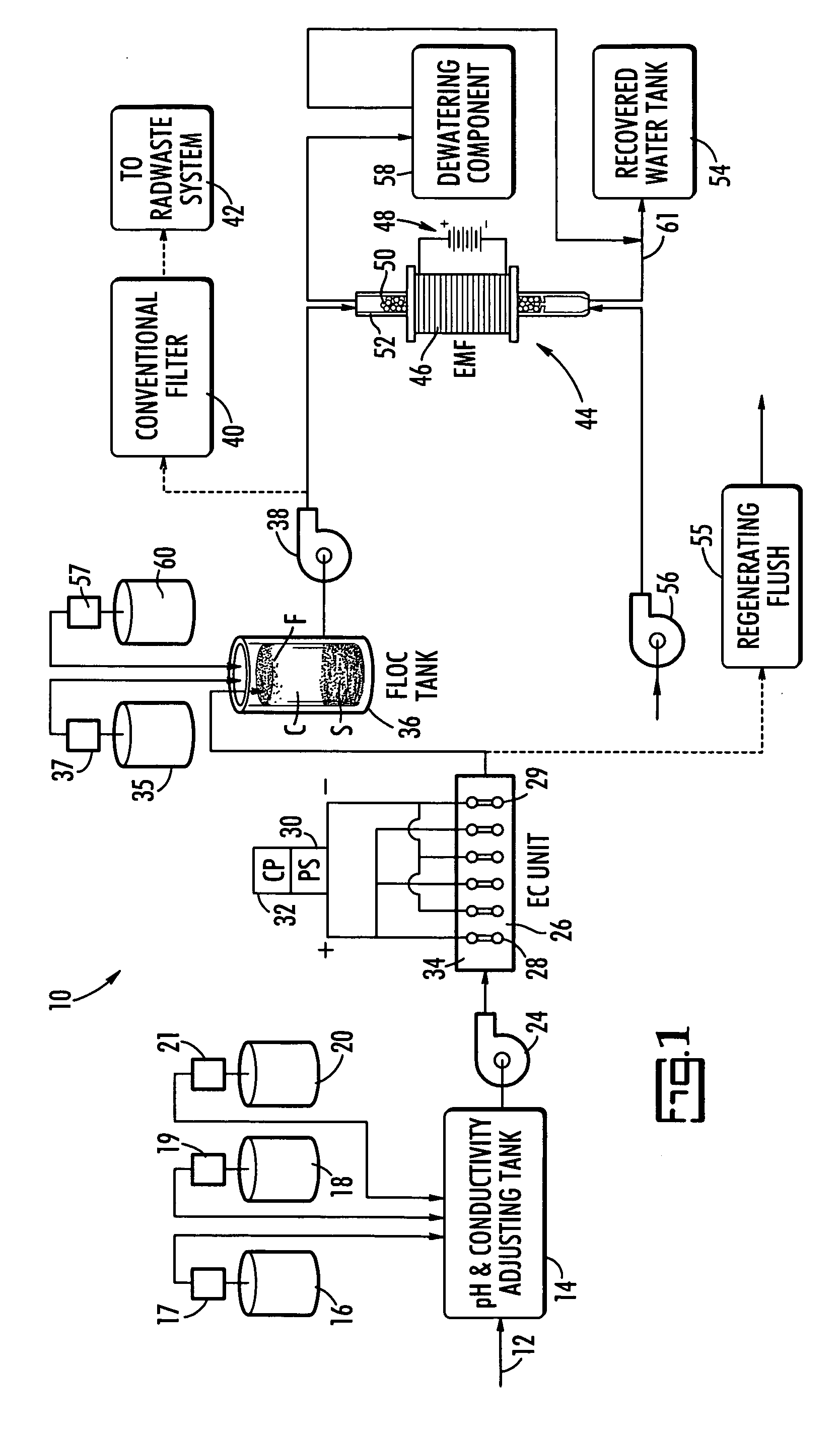
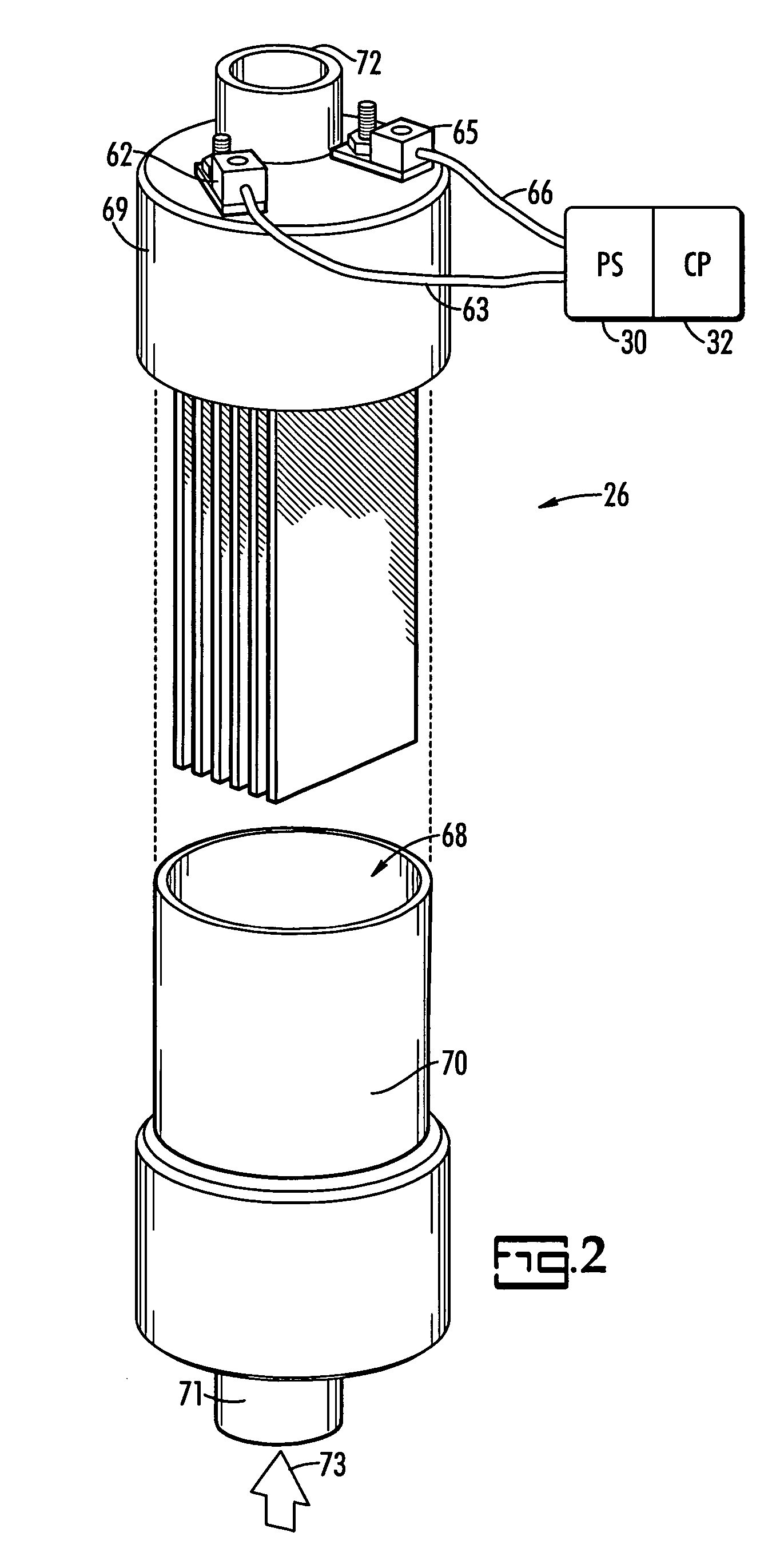
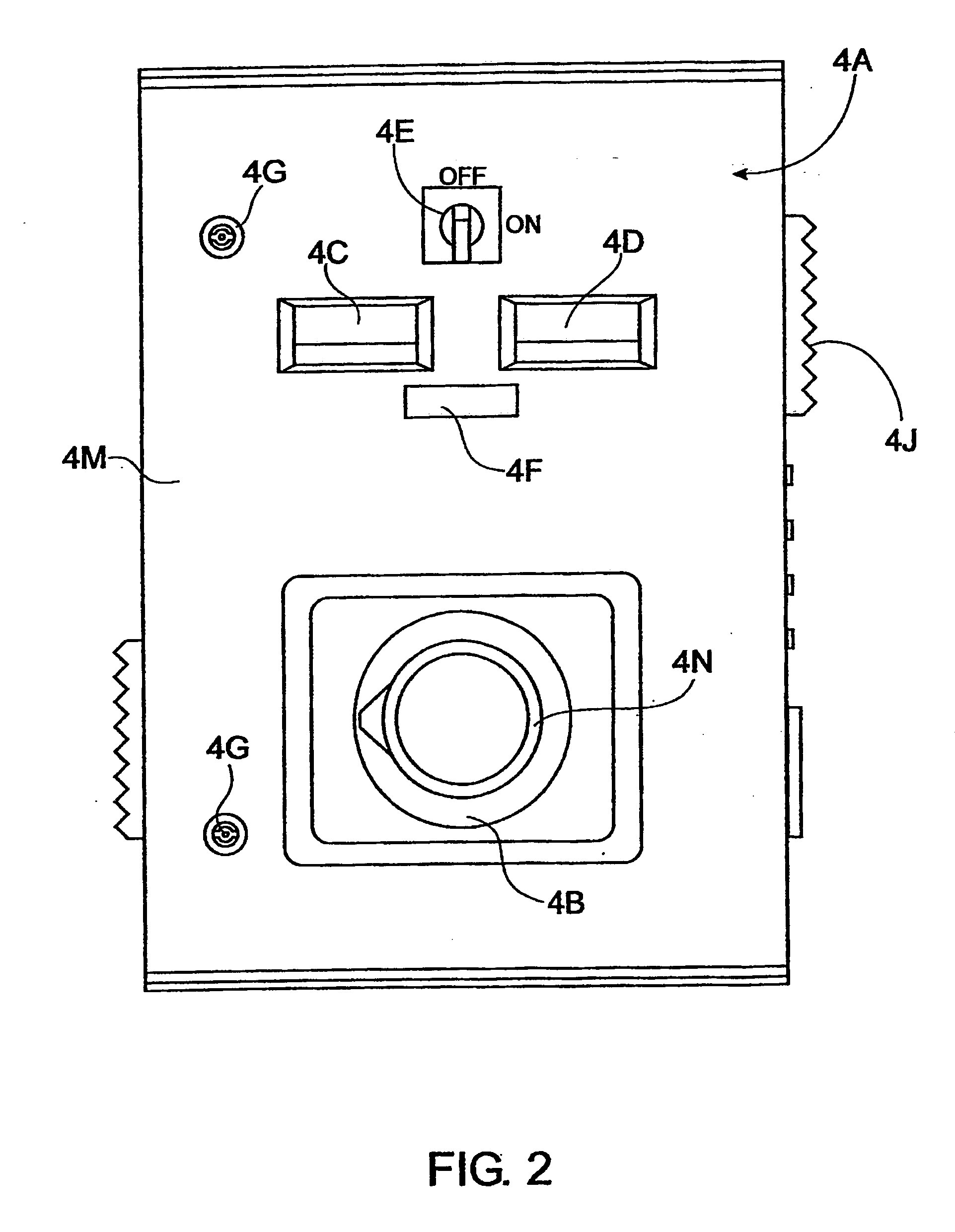
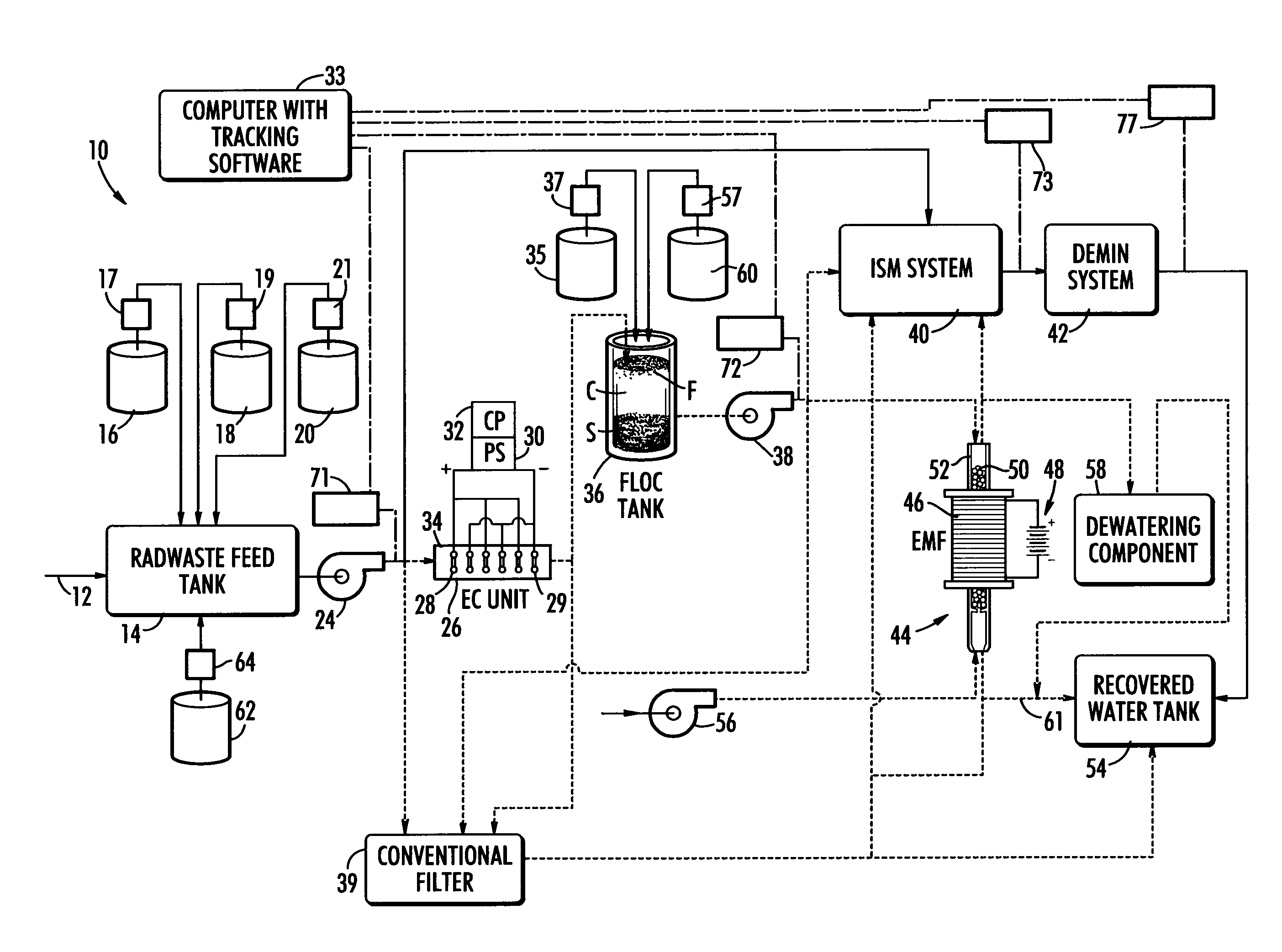
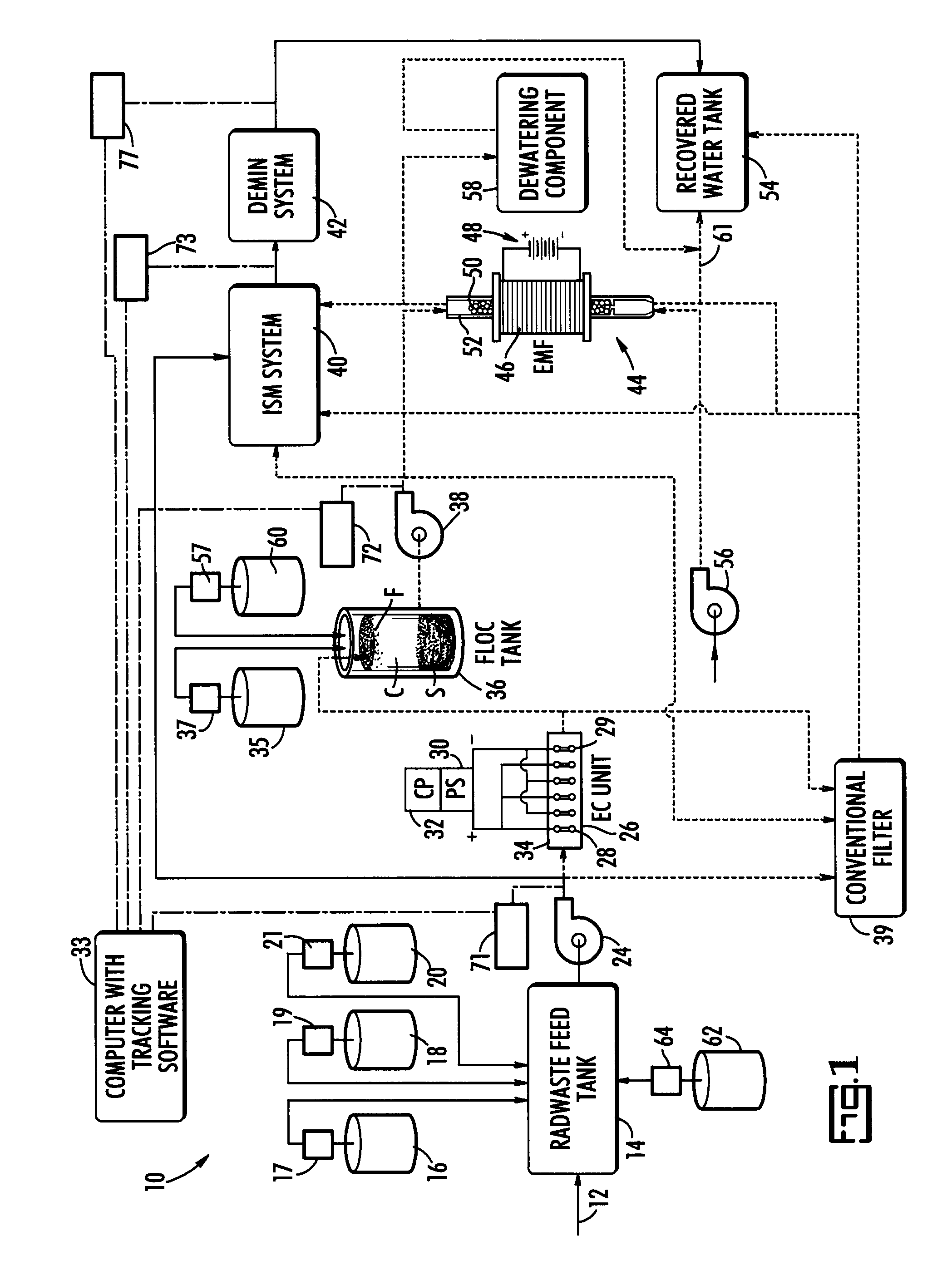
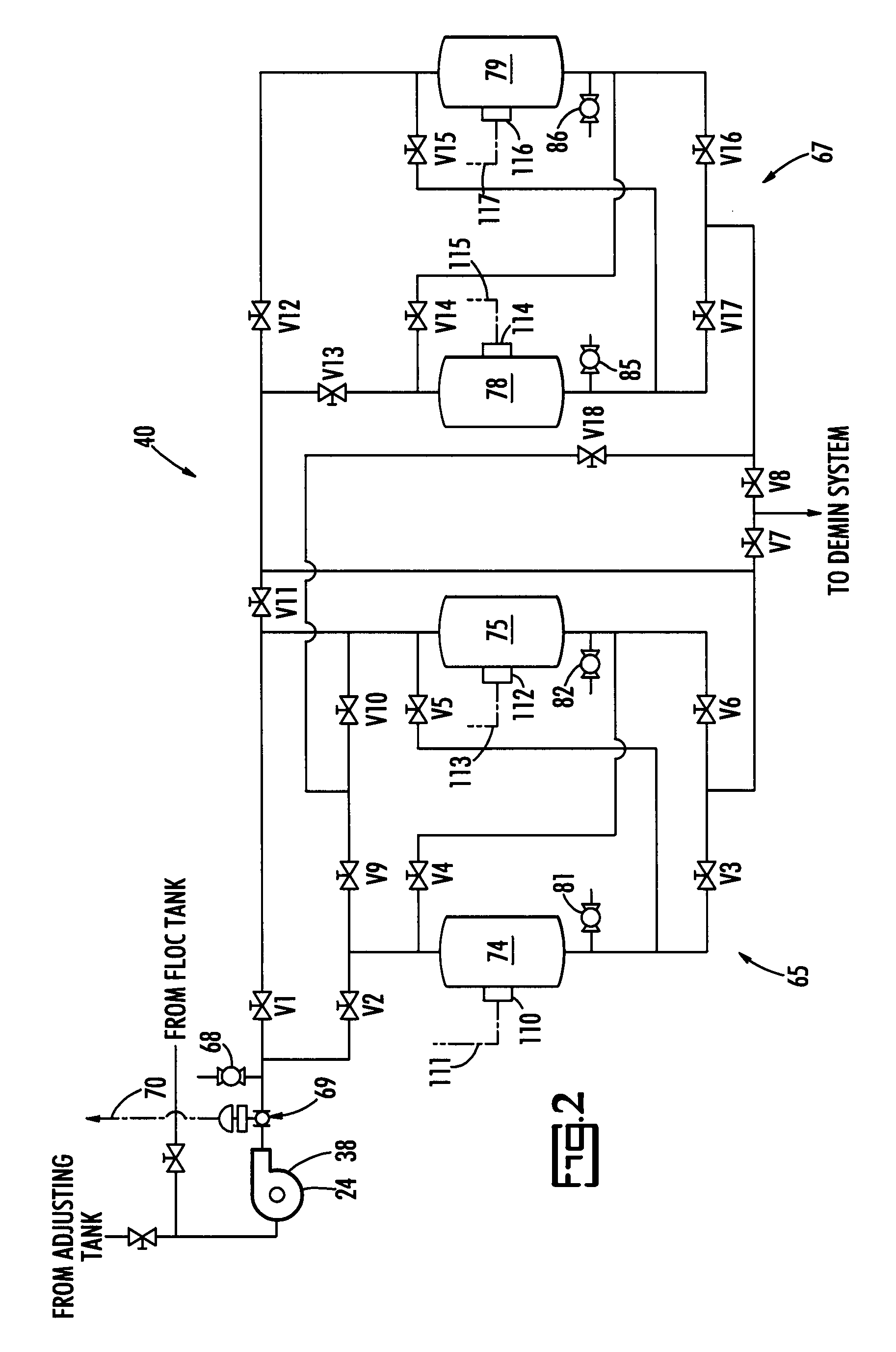
ActiveUS20070131621A1Easy to useLoss in efficiencyElectrolysis componentsLiquid separation by electricityFiltrationElectro coagulation
A method and apparatus for treating radioactive waste water containing contaminating ions, colloids and suspended solids having like (usually negative) charges preventing their precipitation. An electric current is passed through the waste water in an EC assembly to cause electro-coagulation of the contaminants and anodes of this assembly are made of a metal that dissolves to provide cations for neutralizing the negative charges and forming precipitates containing neutralized contaminants. Precipitates are then separated from waste water by an electro-magnetic or other filtering unit. The water pH and conductivity may be adjusted before the EC assembly and additives may be introduced into its effluent for enlargement of precipitate particles, improvement of filtration, improvement of dewaterability, and / or enhancement of magnetism.
Owner:ENERGYSOLUTIONS LLC
System and method for water purification
InactiveUS6824695B2Treatment using aerobic processesSedimentation separationBiological activated carbonActivated carbon filtration
A self-contained, portable water purification system, including (a) an ozone supply, (b) an ozone contact chamber mixing a contaminated or potentially contaminated water stream with ozone generated by such ozone supply, (c) an ozone destruction unit for destructing ozone contained in the water stream and converting said water stream into an oxygen-rich and ozone-depleted water stream, and (d) a downstream biologically active carbon filter, for receiving such oxygen-rich and ozone-depleted water stream and biologically destructing at least a portion of contaminants contained therein.
Owner:TEMPEST ENVIRONMENTAL SYST
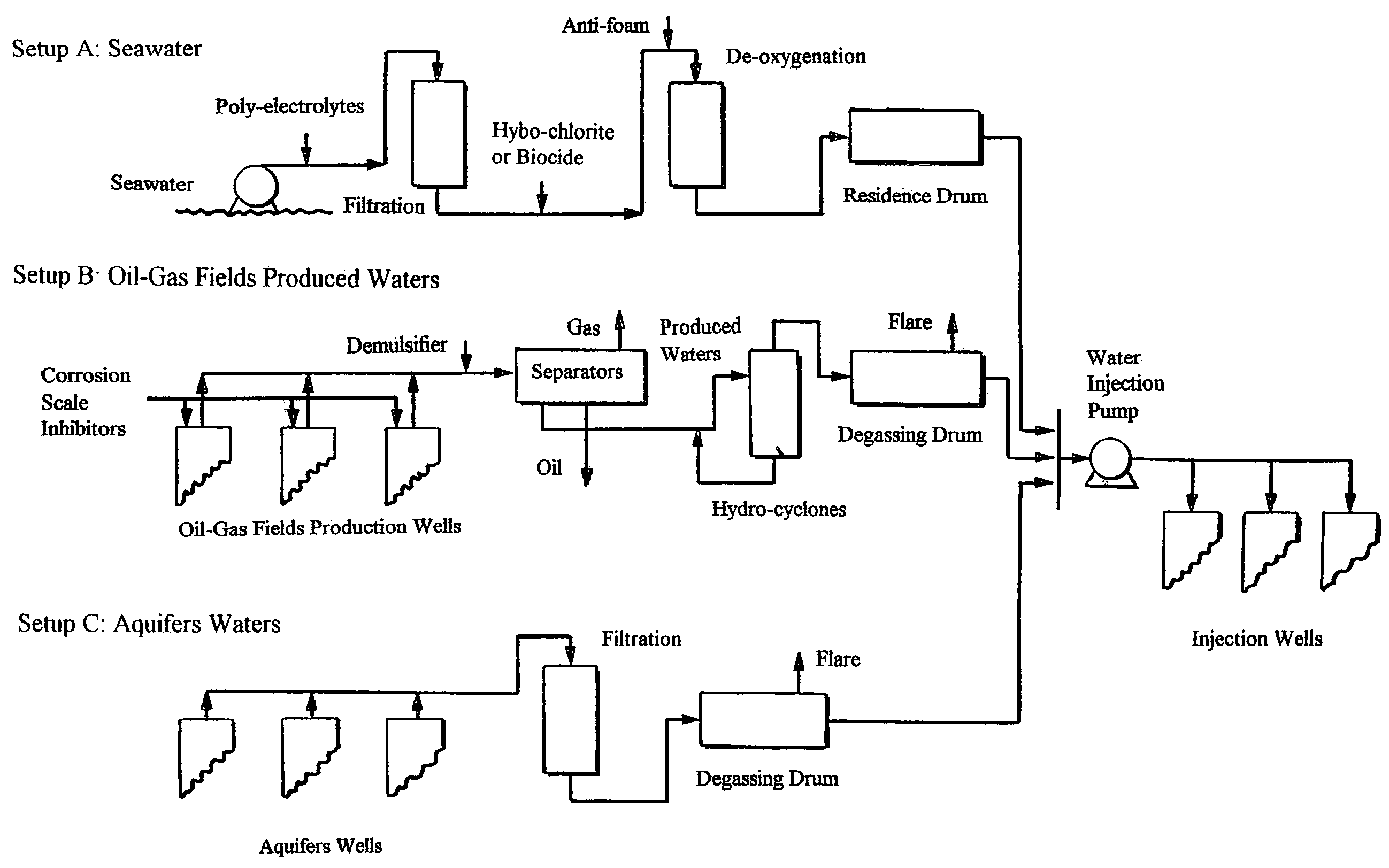
Methods to solve alkaline-sulfate scales and related-gases problems
InactiveUS7093663B1Sufficient absorption capacityLimited aqueous solubilitySeparation devicesFluid removalRadonProduced water
Methods for the removal of alkaline and sulfate scales from aqueous saline streams such as seawater, oil-gas fields produced waters, formation waters, and the like. Such processing methods can also be extended for the simultaneous removal of hydrogen sulfide, and / or sulfur dioxide, and / or oxides of nitrogen, and / or carbon dioxide from gaseous streams. The same processing concept with modified methods can further be employed for the removal of gases such as radon, hydrogen sulfide, sulfur dioxide, oxides of nitrogen, and carbon dioxide from gaseous streams.
Owner:BADER MANSOUR S
Graphene oxide-based composite membrane for treating radioactive wastewater
InactiveCN105664738AHigh retention rateAchieve enrichmentSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisFiltrationIon
The invention relates to a graphene oxide-based composite membrane for treating radioactive wastewater and a preparation method thereof.According to the membrane, a porous carrier is pre-modified through a silane coupling agent, and the graphene oxide-based composite membrane is prepared from a polydopamine and graphene oxide compound by adopting a vacuum filtration method.The method is characterized in that a polydopamine bionic self-assembly technology and a graphene oxide sheet are compounded, the size dimension of a membrane nanochannel is accurately adjusted, the selectivity or the rejection rate of the membrane on radionuclide ions is increased, and concentration and removal of radionuclide are achieved.According to the graphene oxide-based composite membrane for treating the radioactive wastewater and the preparation method thereof, the preparation process is simple and easy to operate, good repeatability is achieved, the water flux and ion rejection rate of the composite membrane are significantly increased, the separating property of a long-time operating membrane is stable, and a wide application prospect in the fields such as membrane-method radioactive wastewater treatment and heavy metal wastewater treatment is achieved.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Formulations and methods for removing heavy metals from waste solutions containing chelating agents
ActiveUS20140124447A1Waste water treatment from quariesSolid sorbent liquid separationHeavy metalsChemistry
Described are chemical formulations that remove heavy metals from waste solutions containing a chelating agent. Also disclosed are methods for removing heavy metals from waste solutions utilizing such chemical formulations.
Owner:THATCHER CO INC
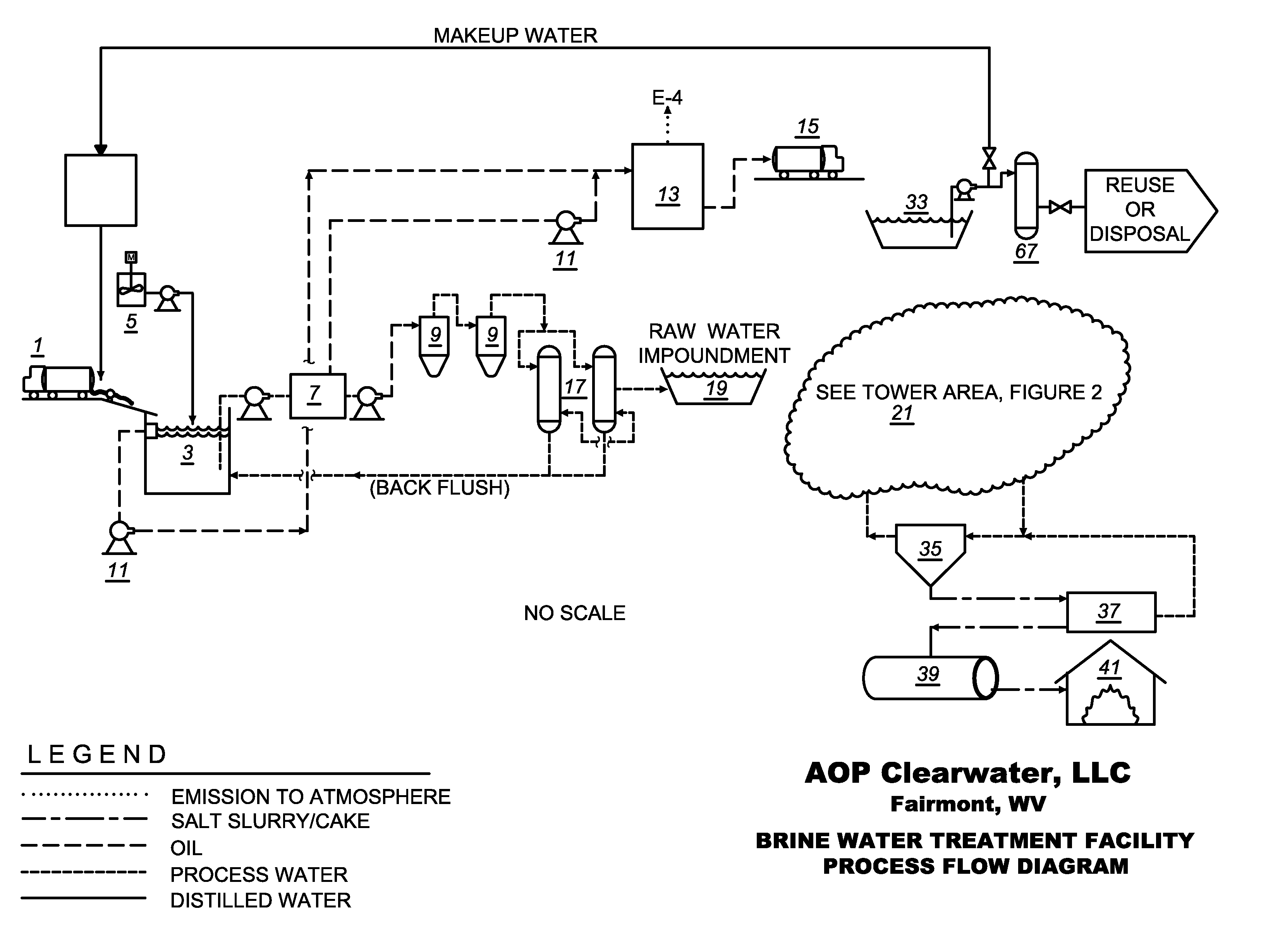
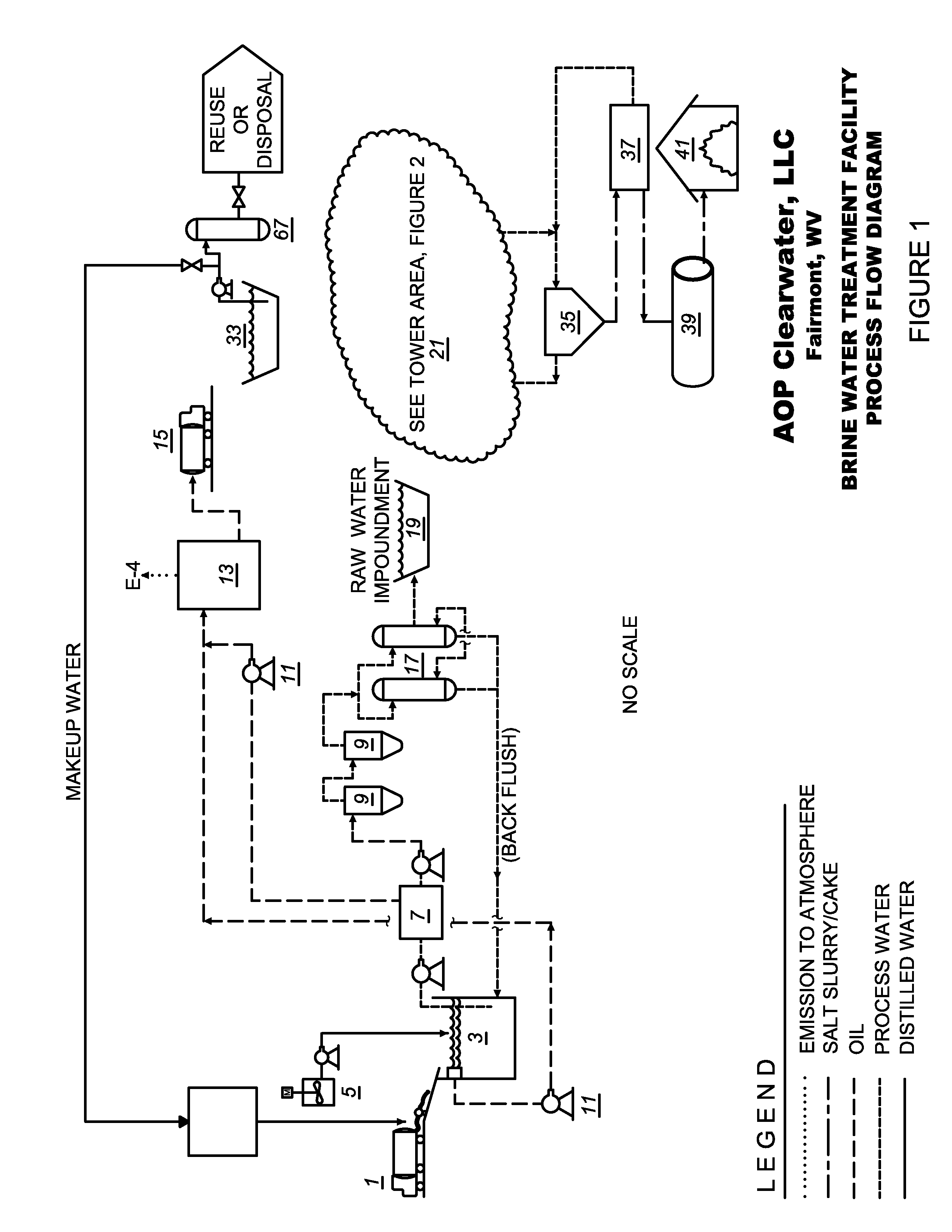
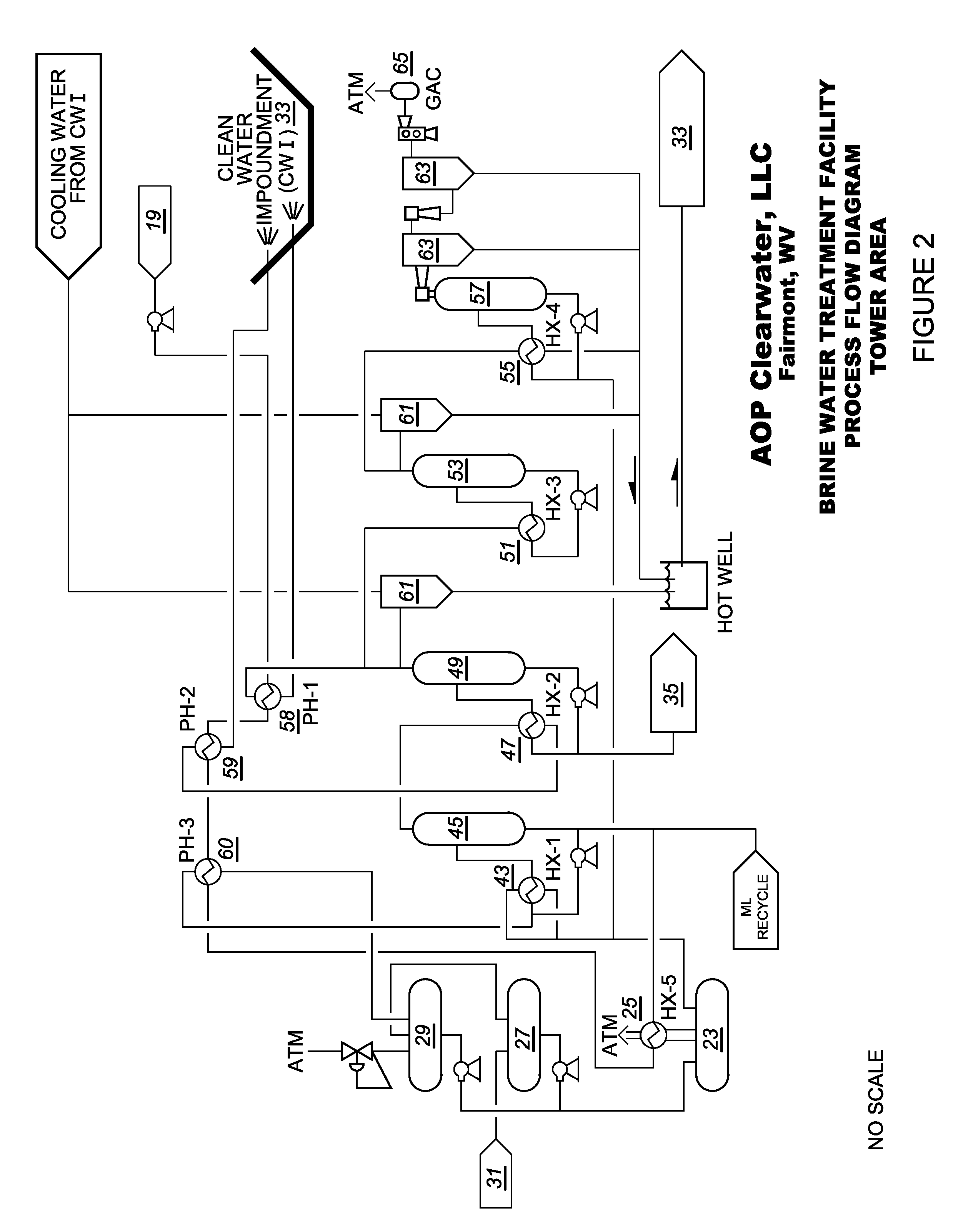
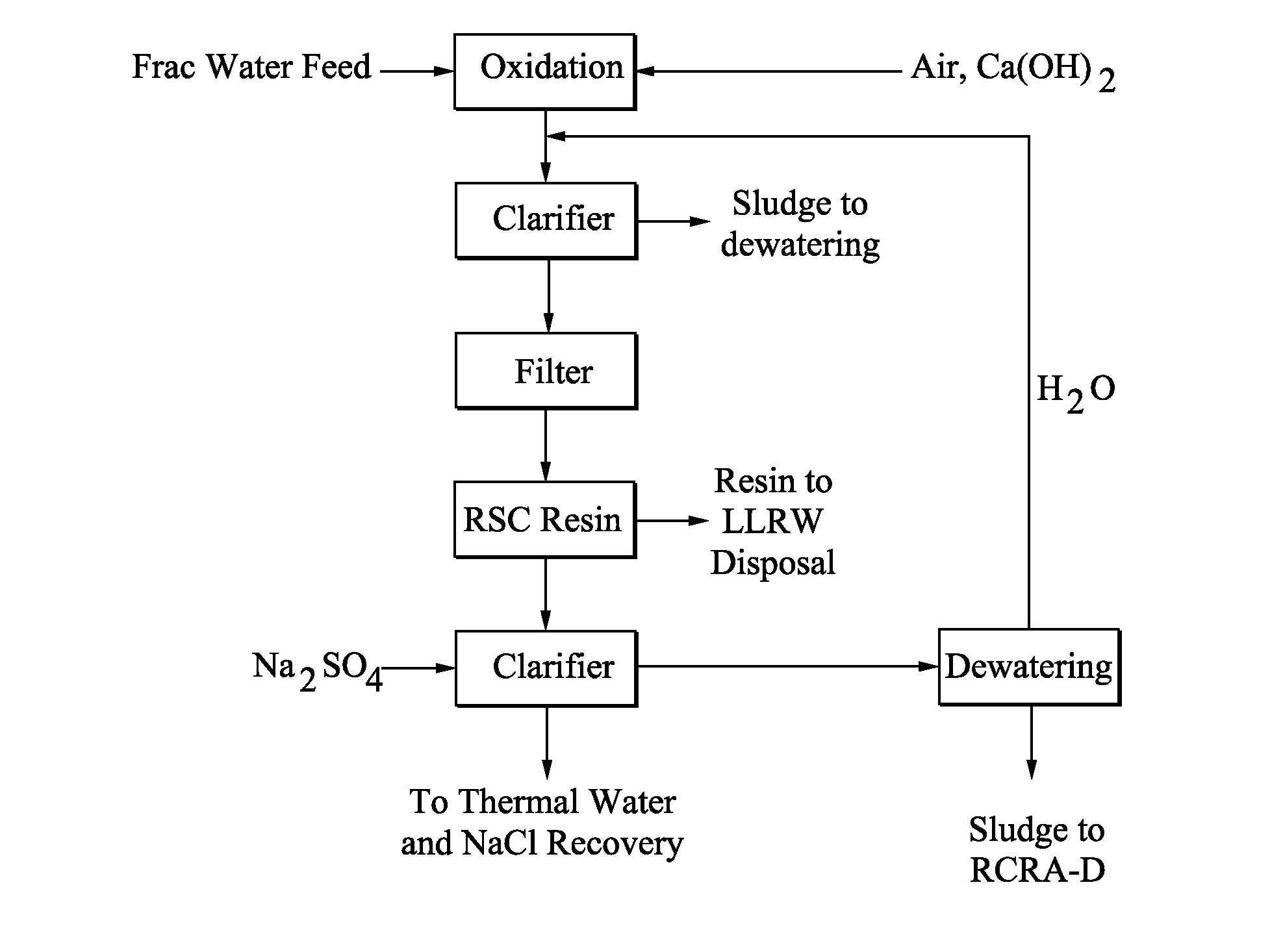
Brine water recycle process
Embodiments provided herein include methods and apparatuses for purification and recycling of hydrofracture water used in natural gas drilling and production. Embodiments include removal of dissolved solids by precipitation with sodium sulfate and by evaporation using, for example, a multiple effect evaporator.
Owner:FAIRMONT BRINE PROCESSING
Process using rare earths to remove oxyanions from aqueous streams
ActiveUS7338603B1Efficiently and effectively removedReduce the concentration of pollutantsWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeRadioactive contaminantsCation-exchange capacityParticulates
Oxyanions of various contaminant elements, such as chromium, antimony, molybdenum, tungsten, vanadium and uranium, are removed from water and other aqueous feeds by treating the feed with (1) a sorbent comprising one or more rare earth compounds, usually mixed or supported on particulate solids having a cation exchange capacity less than 20 milliequivalents per 100 grams or (2) an aqueous solution of one or more soluble rare earth compounds.
Owner:SECURE NATURAL RESOURCES LLC
Methods of preparing a surface-activated titanium oxide product and of using same in water treatment processes
A method for producing a surface-activated crystalline titanium oxide product having a high adsorptive capacity and a high rate of adsorption with respect to dissolved contaminants includes the steps of preparing a titanium oxide precipitate from a mixture comprising a hydrolysable titanium compound and heating the precipitate at a temperature of less than 300° C., without calcining the precipitate. Preferably, the titanium oxide product includes crystalline anatase having primary crystallite diameters in the range of 1-30 nm. The surface-activated crystalline titanium oxide product is used in methods to remove dissolved inorganic contaminants from dilute aqueous streams by suspending the product in an aqueous stream or by filtering an aqueous stream through a bed of the product. In another method, a hydrolysable titanium compound is added to an aqueous stream so that titanium oxides form as a co-precipitate with dissolved contaminants within a bed of particulate material.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Electrocoagulation system
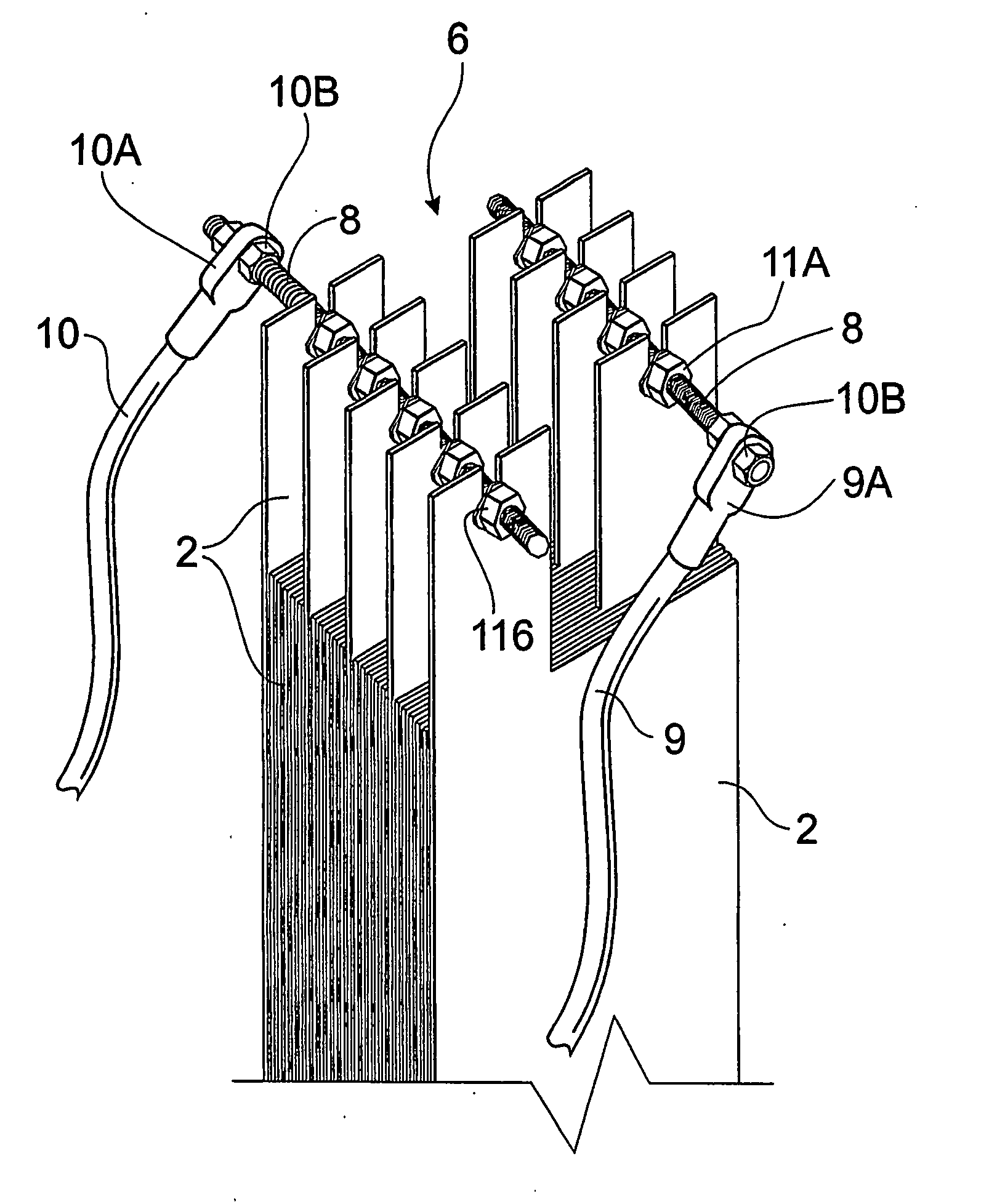
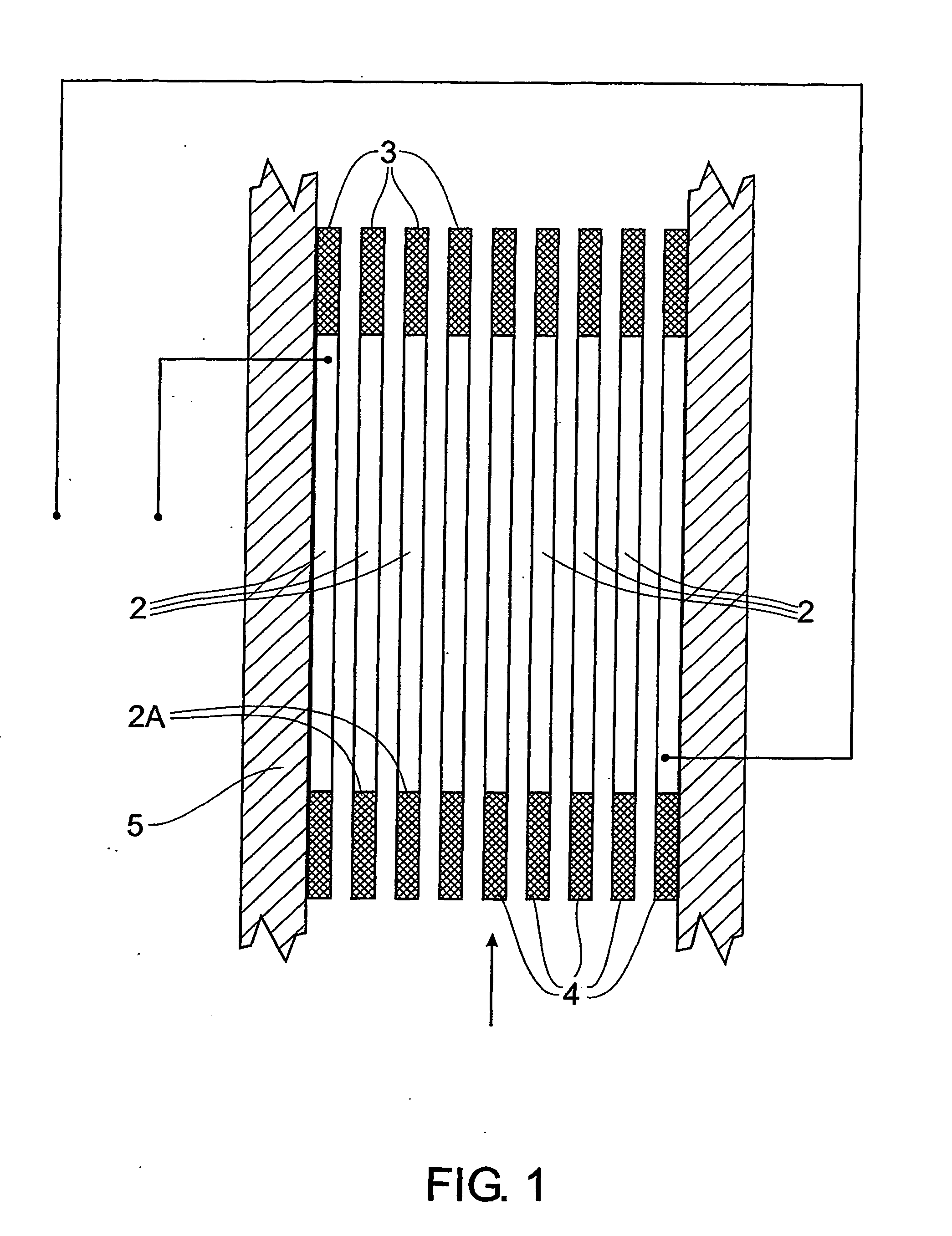
InactiveUS20060096853A1Convenient treatmentLimitations is associated with assembliesWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationCellsElectrocoagulationPower flow
A control assembly for an electrocoagulation cell (1) comprising a plurality of electrodes, a releasable connection means (6) between at least a selection of the electrodes and electrical connection means (9, 10, 9A, 10A) attached to the releasable connection means (6) which in use is connectable to a power supply (12). An electrocoagulation system comprising a plurality of electrodes (2), an electrolytic cell (1) having an internal chamber which contains the plurality of electrodes (2), and a power supply (12) connectable to a power source and also connectable to the electrodes said power supply having control means (14, 24) for providing a selected constant output current or selected constant output voltage whereby the electrolytic cell may process samples of varying characteristics.
Owner:AQUENOX
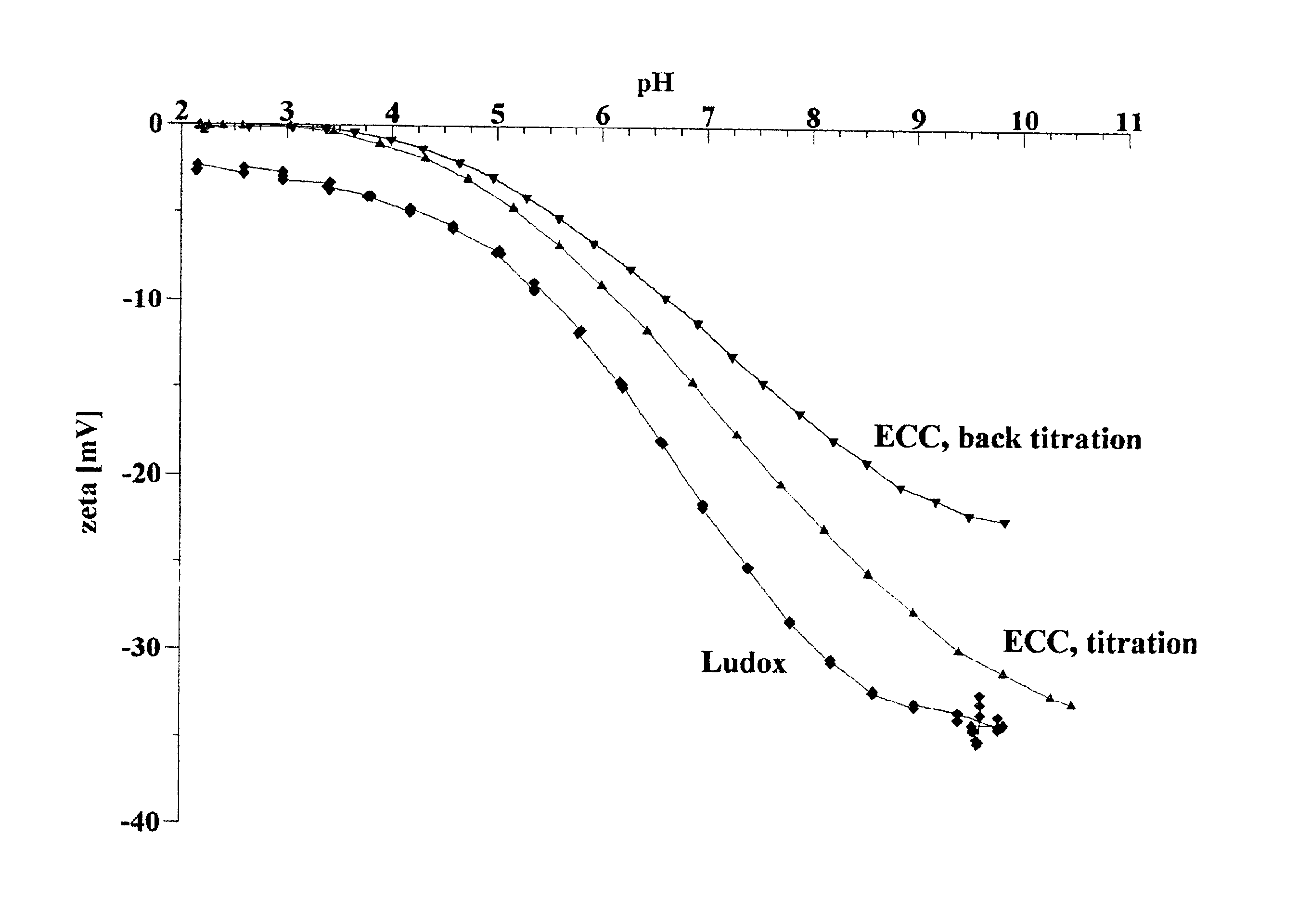
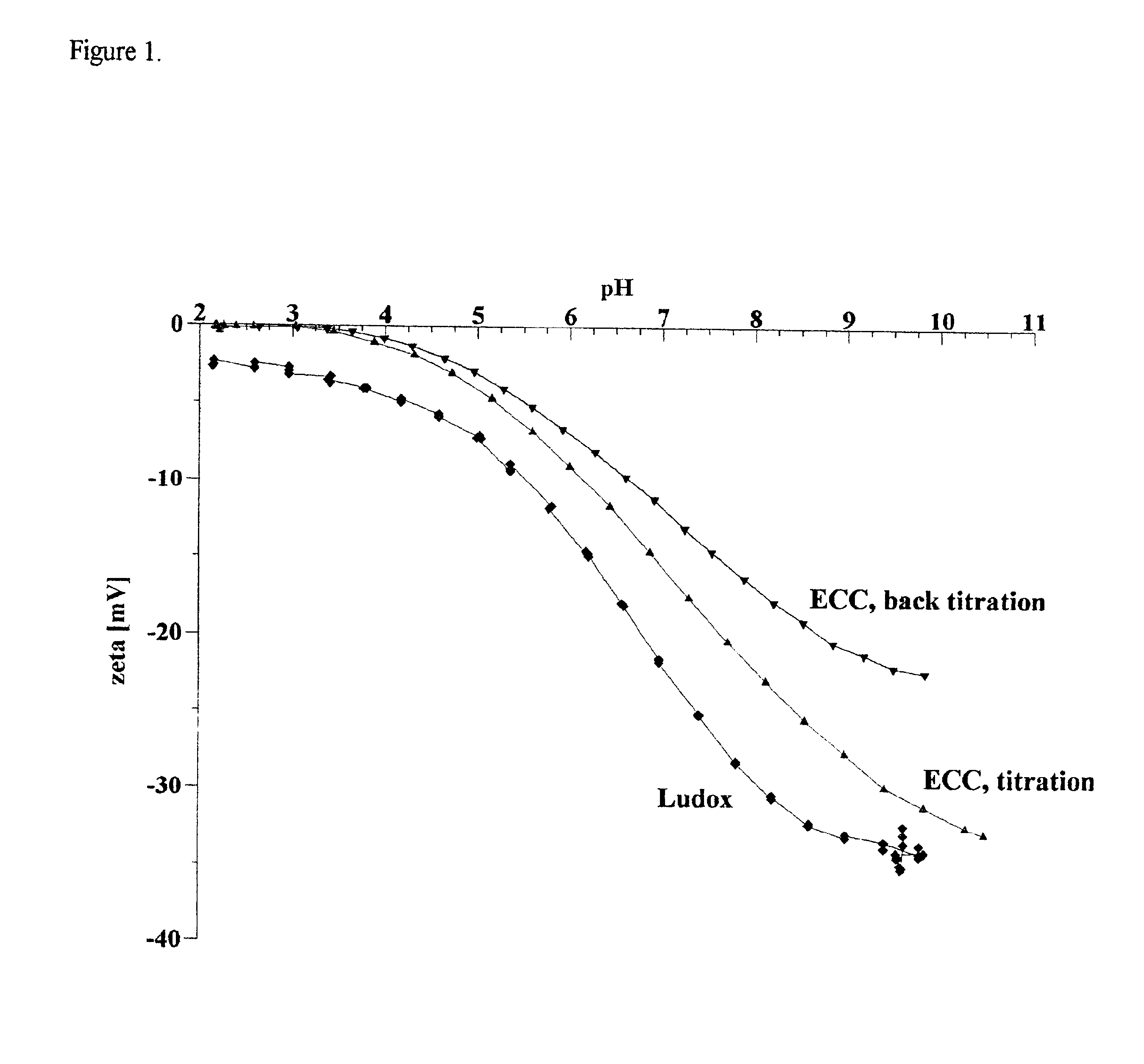
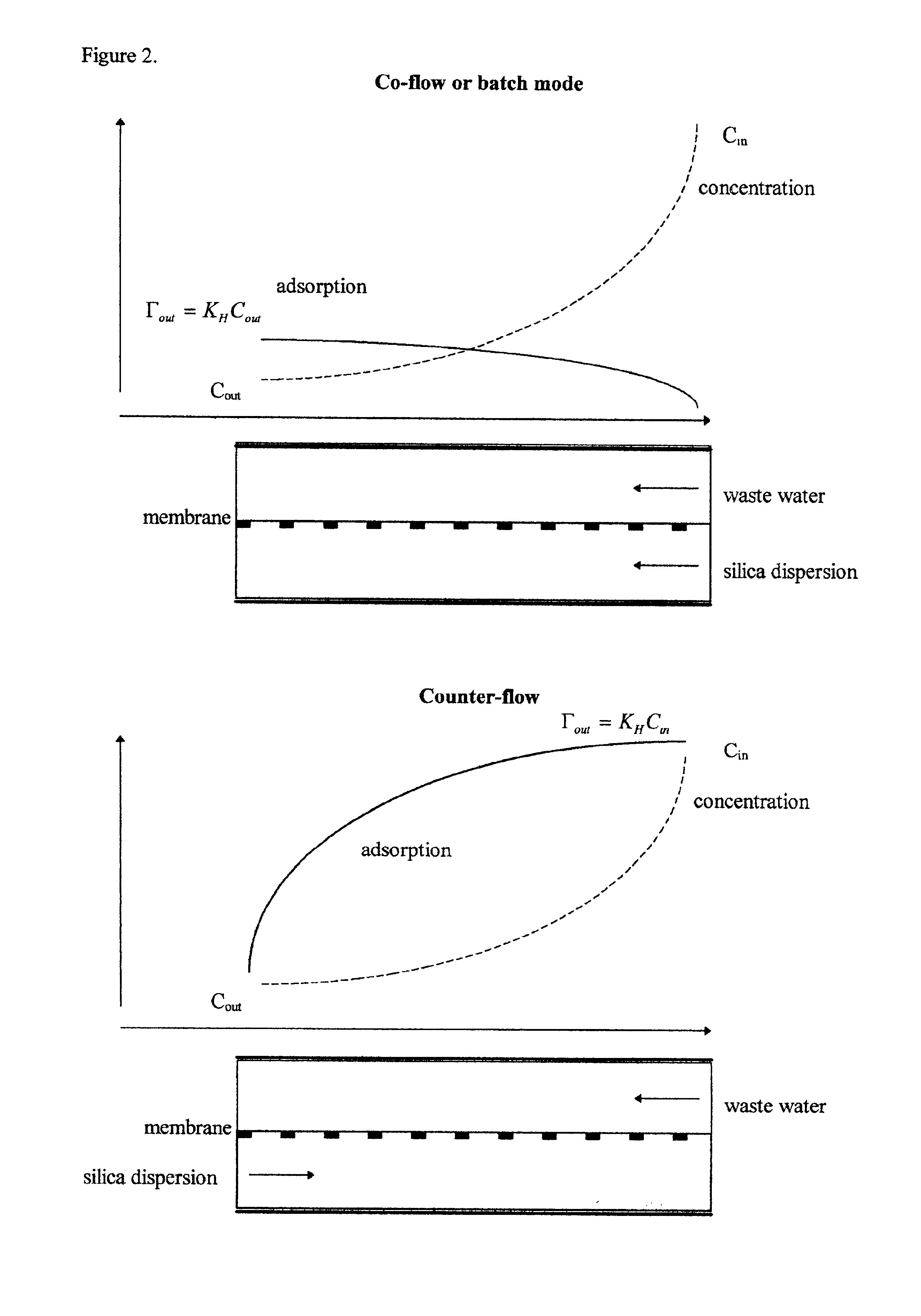
Method for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by means of silica as an adsorbent in counter-flow selective dialysis
Owner:DISPERSION TECHNOLOGY
Methods of preparing a surface-activated titanium oxide product and of using same in water treatment processes
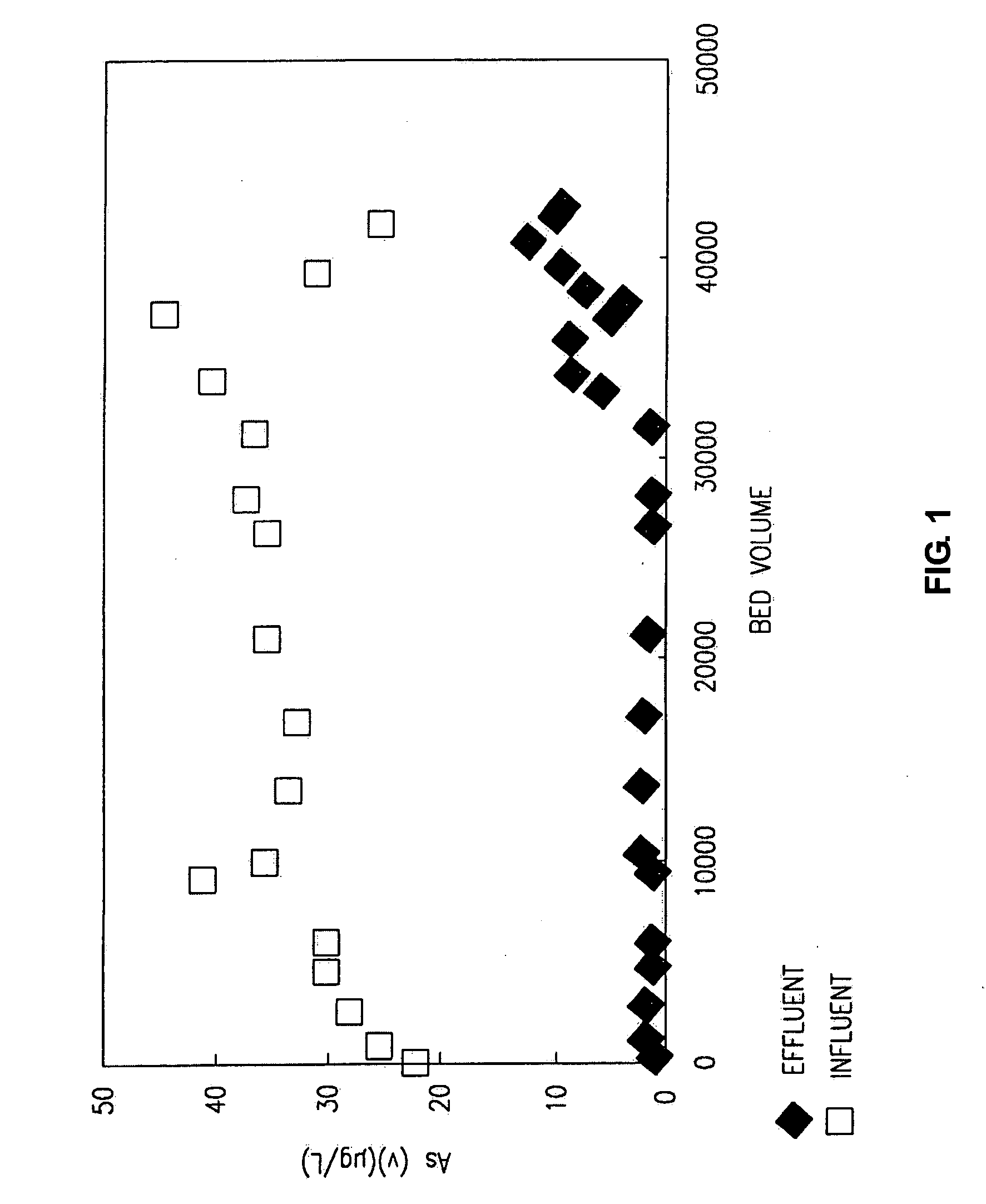
InactiveUS20060091079A1Rate of removalMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesArsenateHigh rate
A method for removing dissolved contaminants from solution using a surface-activated crystalline titanium oxide product having a high adsorptive capacity and a high rate of adsorption with respect to dissolved contaminants, in particular, arsenate and arsenite. Preferably, the titanium oxide product includes crystalline anatase having primary crystallite diameters in the range of 1-30 nm. The surface-activated titanium oxide is combined with other filter media to further improve the removal of dissolved contaminants.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
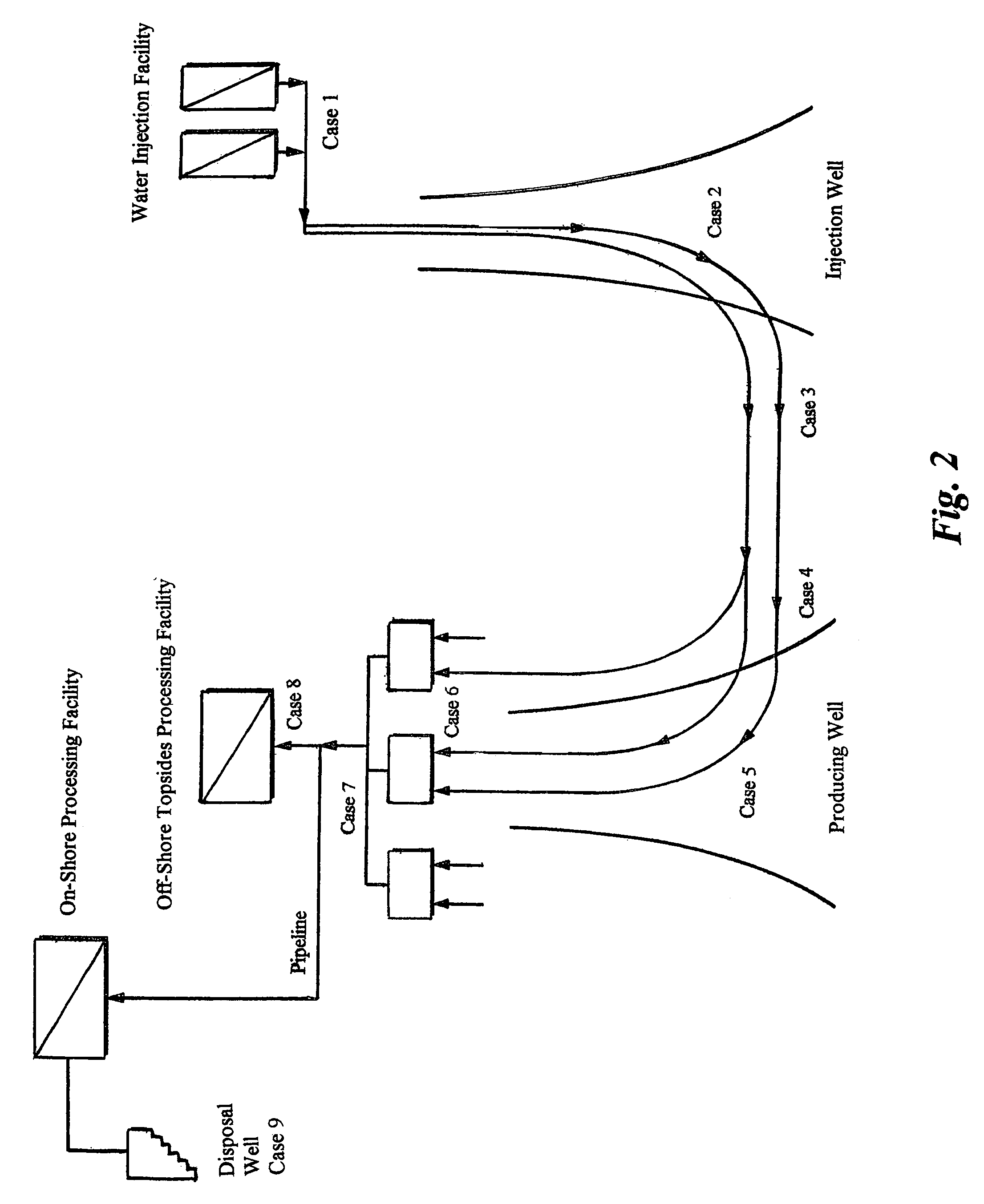
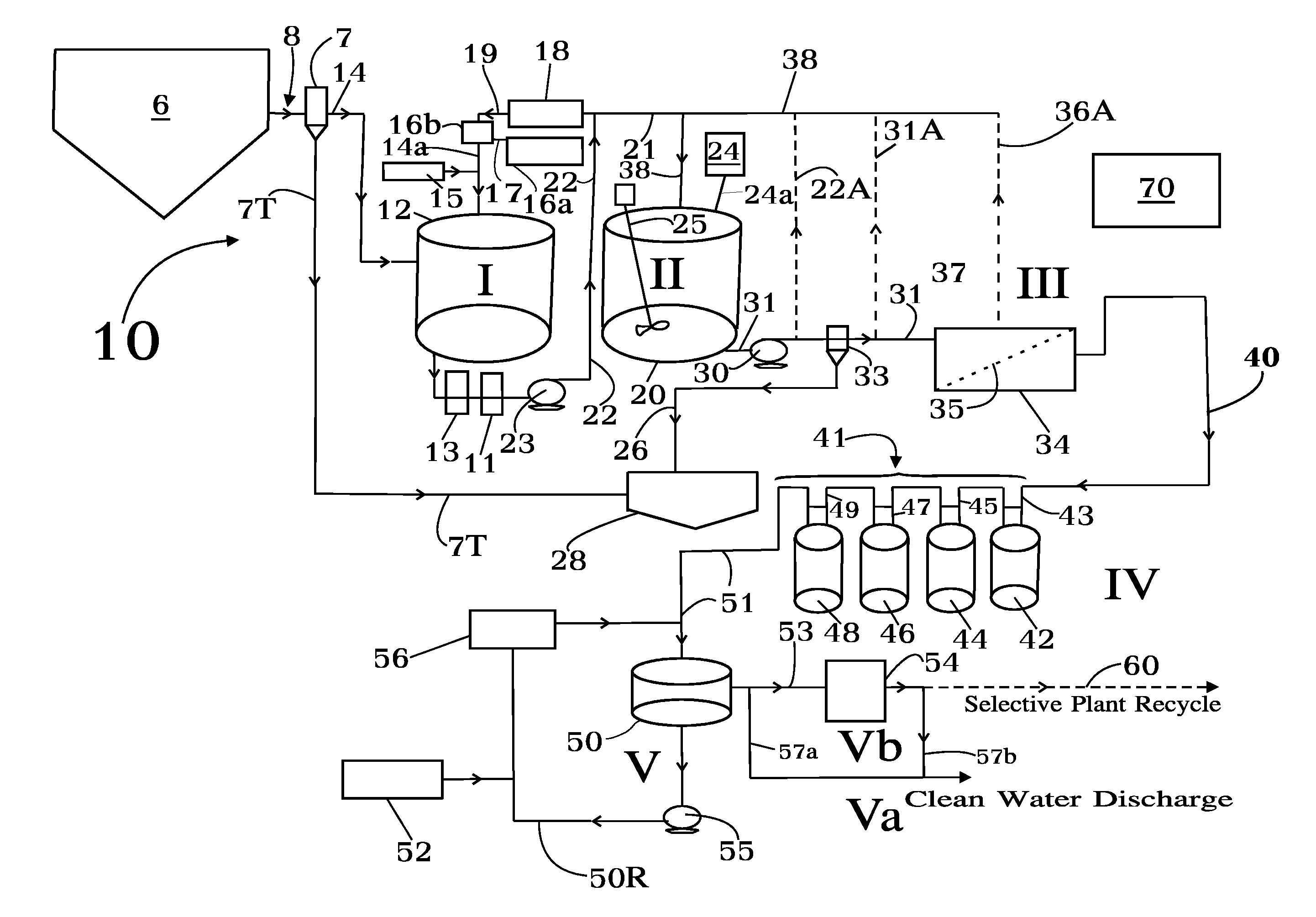
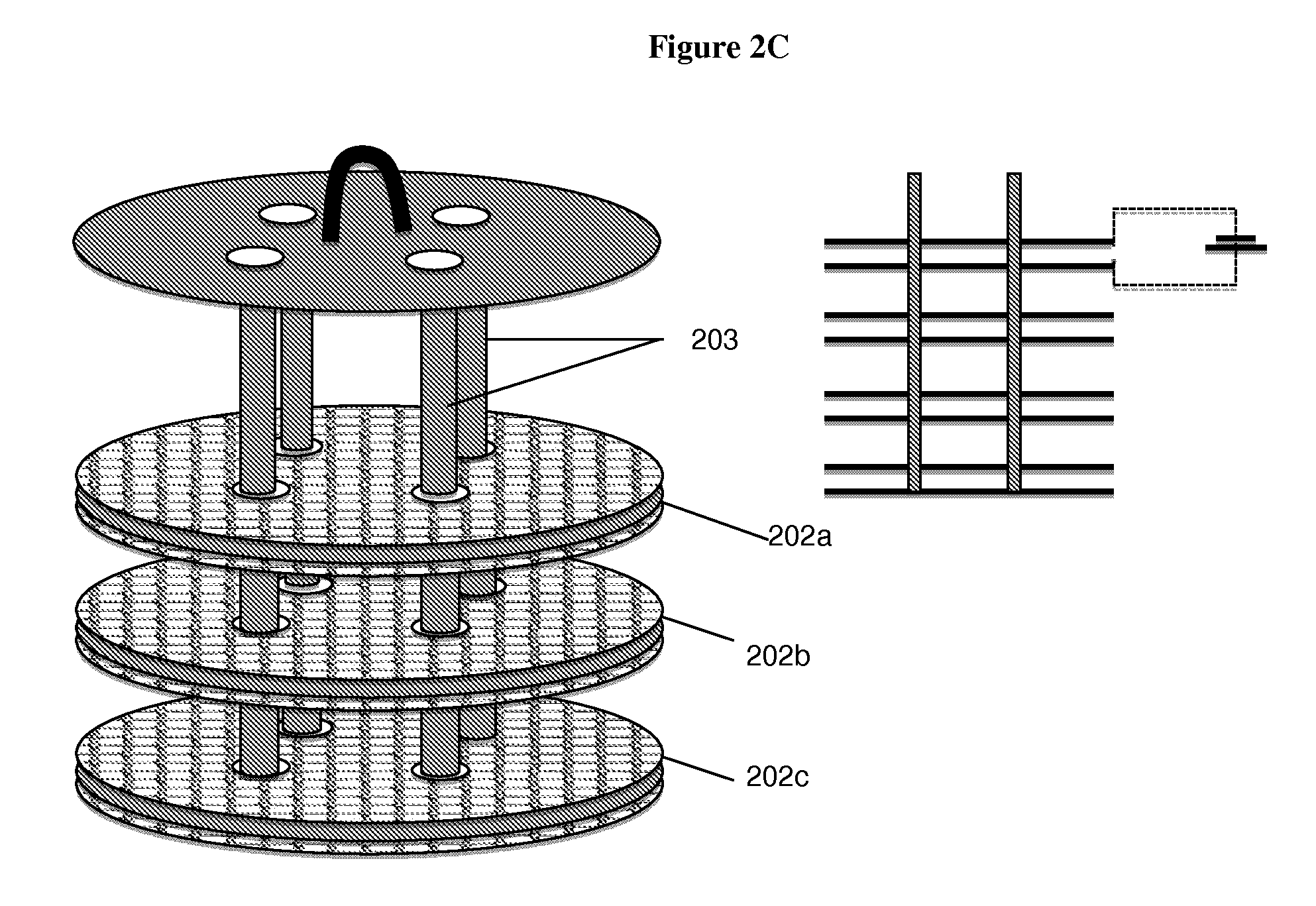
Concentrate treatment system
In one aspect the invention provides a system for treating a wastestream, particularly a radwaste, for safe disposal and, in final processing converting it into one or both forms including an aqueous form for safe discharge to the environment and a solidified form for safe disposal. In another aspect the invention provides the capacity to employ a step where a specific target element strategy can be set up synchronizing sorbent substance choices and multiple recycle options to remove target substances from wastestream as a part of its Sorption or Powder Sorbent Isotopic Reduction step (II). Other steps cooperate with Sorption step (II) including Oxidation (I), Solid-Liquid separation (III), and Selective Ion Exchange (IV) to deliver the wastestream to final processing.
Owner:AVANTECH LLC
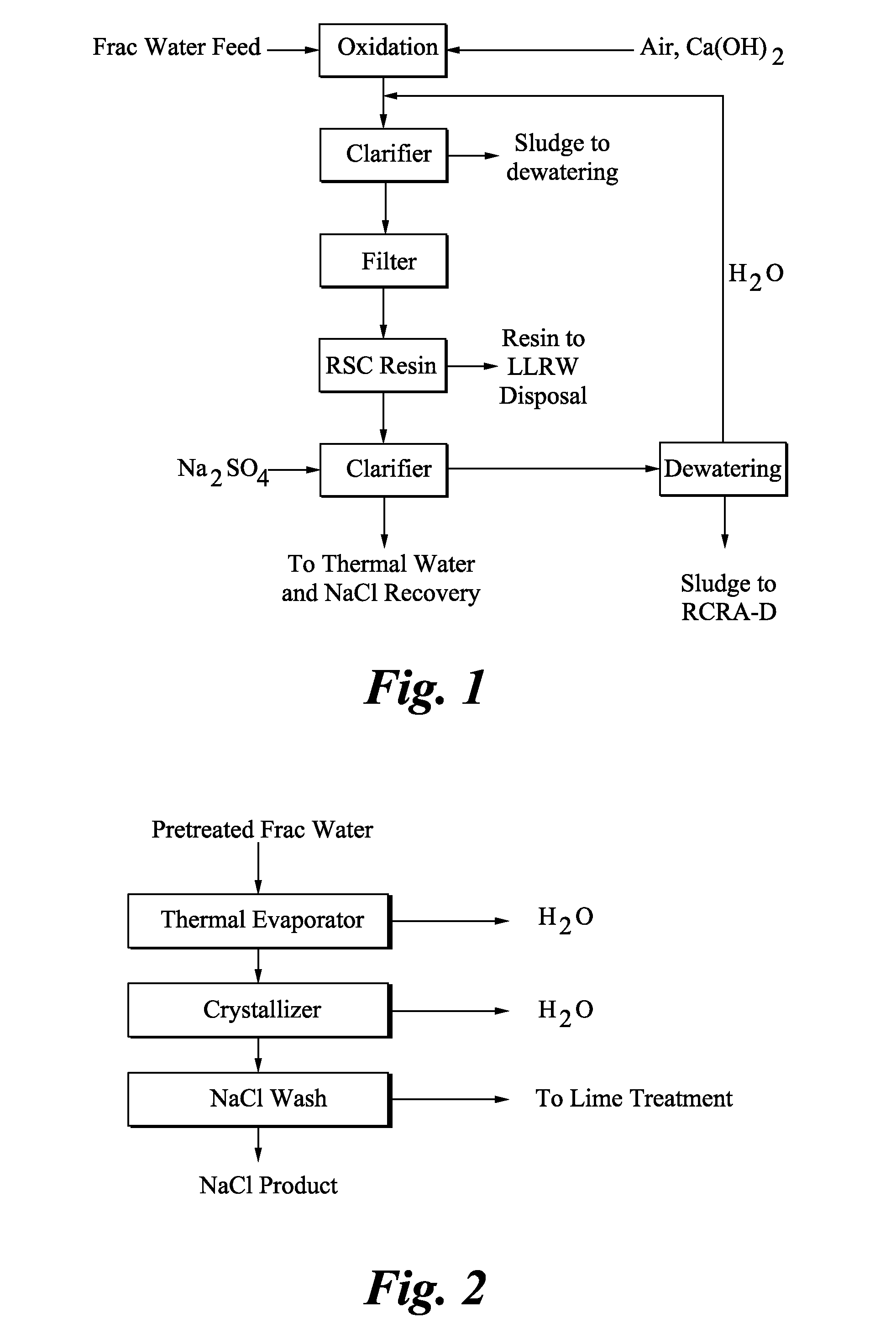
Norm removal from frac water
ActiveUS20120097614A1Solid sorbent liquid separationWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationSaline waterWater flow
A method for treating low barium frac water includes contacting a frac water stream with a radium selective complexing resin to produce a low radium stream, passing the low radium stream through a thermal brine concentrator to produce a concentrated brine; and passing the concentrated brine through a thermal crystallizer to yield road salt.
Owner:BL TECH INC
Contaminant removal apparatus and installation method
InactiveUS20050247571A1High cost-effectiveImprove efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationWater treatment parameter controlElectrocoagulationElectrical battery
This invention relates to a method of installation of an electrocoagulation (EC) system to remove contaminants from wastewater which includes the steps of: (i) measuring conductivity of the wastewater; (ii) from the result obtained in step (i) determining the number of electrically connected electrodes or unipolar electrodes required in the EC system for efficient removal of the contaminants, and (iii) from step (ii) assessing a range of current and / or voltage to be applied to an EC cell included in the EC system.
Owner:AQUENOX
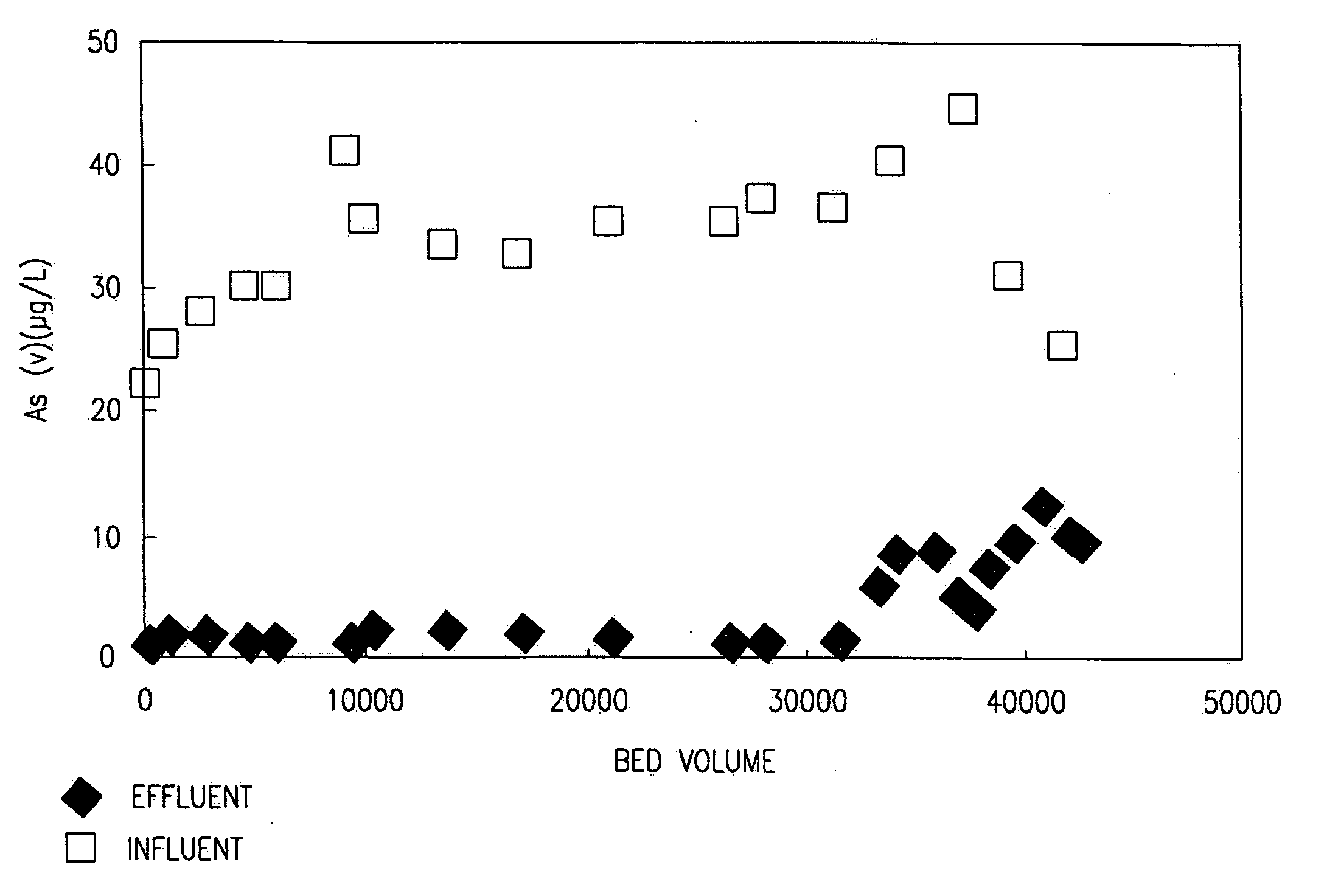
Process and System for Treating Radioactive Waste Water to Prevent Overloading Demineralizer Systems
ActiveUS20090038961A1Easily backflushedAvoid disposition problemsTreatment involving filtrationSolid sorbent liquid separationWastewaterRadioactive waste
A process and system for treating waste water containing contaminants to prevent excessive accumulation on demineralizer media of a driver contaminate capable of such accumulation before another contaminant can reach a predetermined level of accumulation. The waste water is treated upstream of the demineralizer media with removal means for specifically removing the driver contaminant while leaving the other contaminant for subsequent removal by the demineralizer media. The amount of accumulation on the demineralizer media of the other contaminant is monitored, and the supplying of treated waste water to the demineralizer media is terminated when its accumulation reaches the predetermined level.
Owner:ENERGYSOLUTIONS LLC
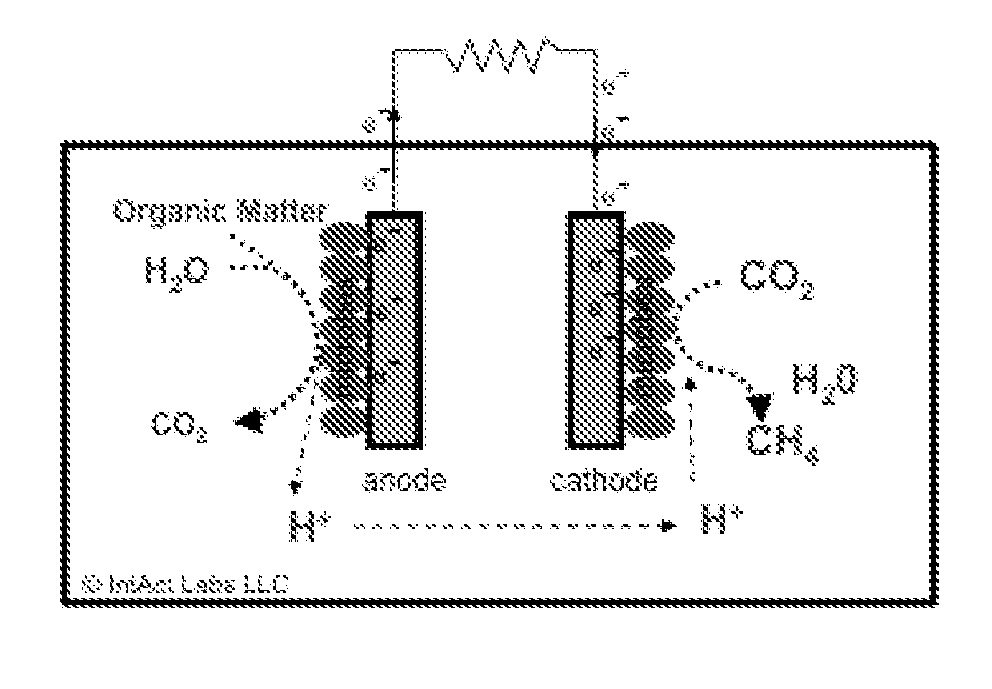
Bio-electrochemical system for treating wastewater
ActiveUS20130299400A1Simple and robust systemIncreasing wastewater treatment rateTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesSpecific water treatment objectivesWastewaterBioelectrochemistry
The invention relates to bio-electrochemical systems for treating wastewater, and sour gas produced by anaerobic digestion of organic material. The invention further relates to novel anode / cathode pairing schemes, and electric and hydraulic architectures for use in bio-electrochemical systems.
Owner:CAMBRIAN INNOVATION
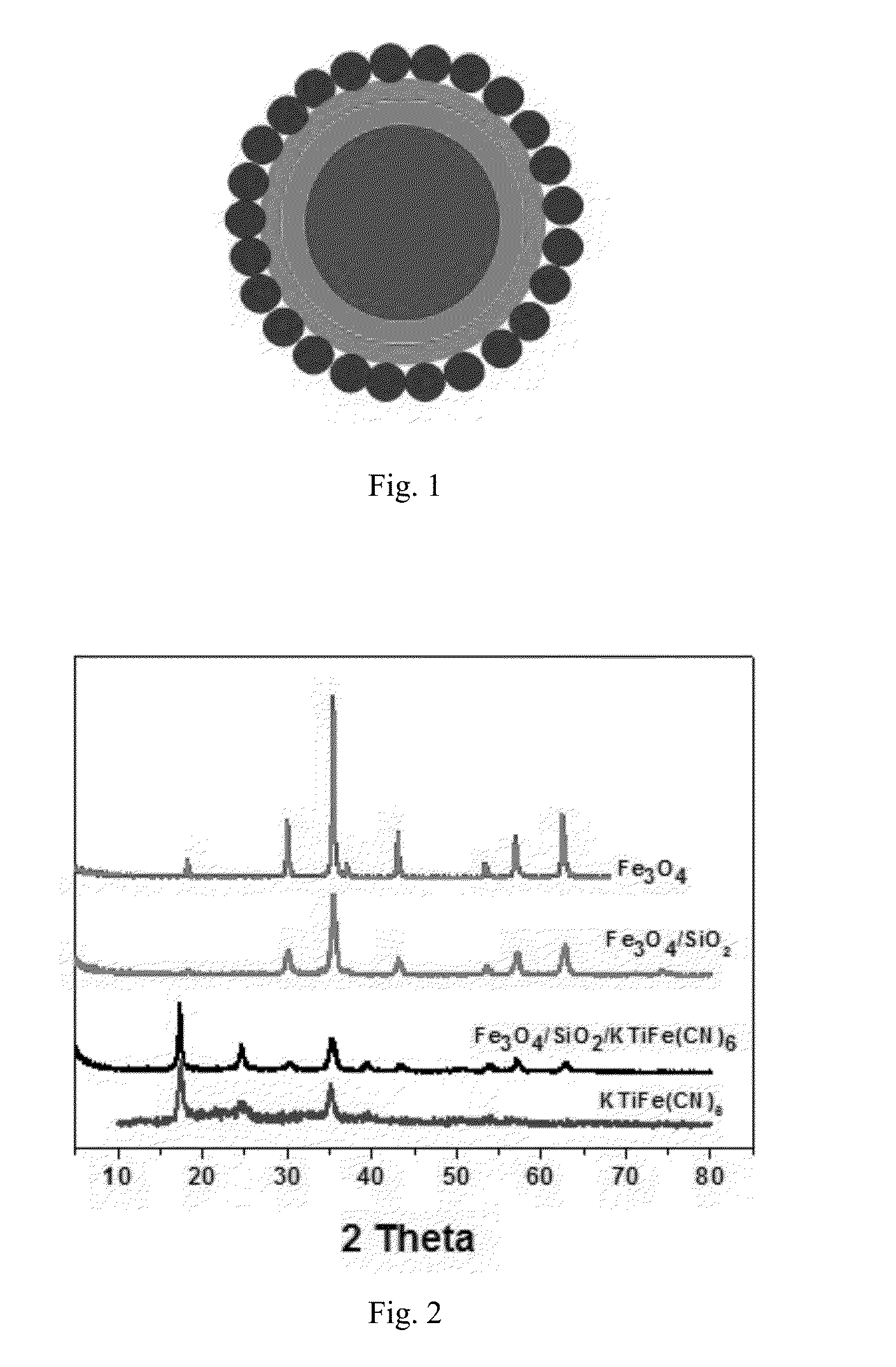
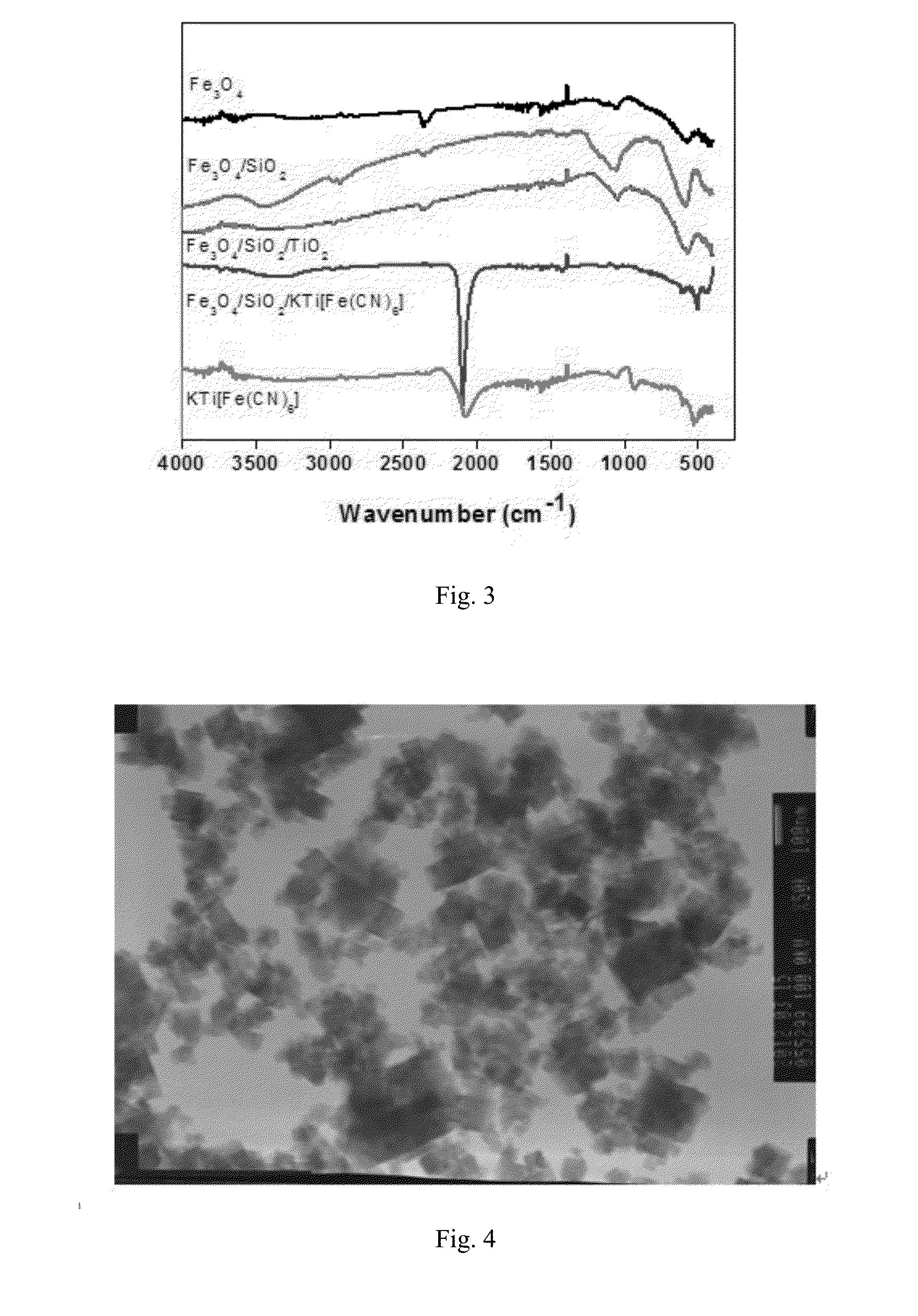
MAGNETIC CORE COATED INORGANIC ION ADSORBENT FOR REMOVING Cs IONS IN RADIOACTIVE WASTEWATER AND PREPARATION METHOD THEREOF
ActiveUS20150231598A1Good alkali resistanceInhibiting oxidation of the magnetic core materialOther chemical processesRadioactive contaminantsHydration reactionSorbent
The invention discloses a micron-grade magnetic core coated ferrocyanide adsorbent for removing Cs ions in radioactive wastewater and a preparation method thereof. The adsorbent takes magnetic Fe3O4 as a core, the surface is coated with a dense SiO2 single layer serving as a protective layer, and an active component is metal ion stabilized potassium ferrocyanide coated on the outer layer, wherein stabilized metal ions comprise Ti, Zn, Cu, Ni, Co, and Zr. The particle size of the adsorbent is 0.2-5 μm, the adsorbent in the outermost layer is conductive to improving the adsorption efficiency for Cs+ ions, and an external magnetic field is adopted for realizing solid-liquid phase separation. The preparation method comprises the following steps: coating a hydrated metal oxide of Ti, Zr or Co, Ni, Cu or Zn on the surface of Fe3O4SiO2 to form a composite magnetic material, wherein the hydrated oxide performs hydroxyl polymerization reaction with the surface of SiO2 to produce M—O—Si bonds to improve the bonding strength between M and the surface of SiO2; and finally reacting the composite magnetic material with a potassium ferrocyanide solution to form the required composite adsorbent, wherein the metal ions M achieve the effects of stabilizing the ferrocyanide and also achieve a bridge effect for bonding the ferrocyanide and the composite magnetic material together.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Extraction of Sulfate from Water
InactiveUS20120031850A1Reduce metal contentLess soluble in waterSedimentation separationRadioactive contaminantsAluminium chlorideAluminite
Sulfate anions and divalent metal ions, such as magnesium, strontium and barium, in water are removed by treating the water with polyaluminum chloride, usually together with lime, to form ettringite and similar crystalline species which are readily removable by settling, filtration and the like. Iron is also removed by oxidation in a variation of the process. The process is particularly useful for treating aqueous solutions used in well treatment, where flowback fluids can provide some of the divalent metal ions necessary to form the ettringite-like materials, thus reducing the amount of lime otherwise necessary and further facilitating recycling of the fluid.
Owner:SMART CHEM SERVICES LP
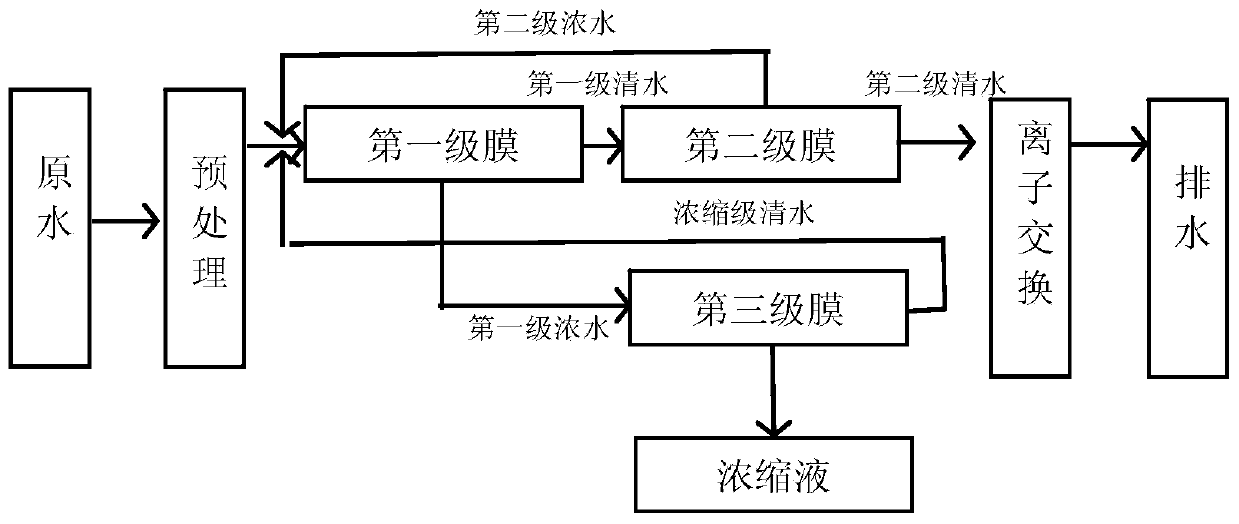
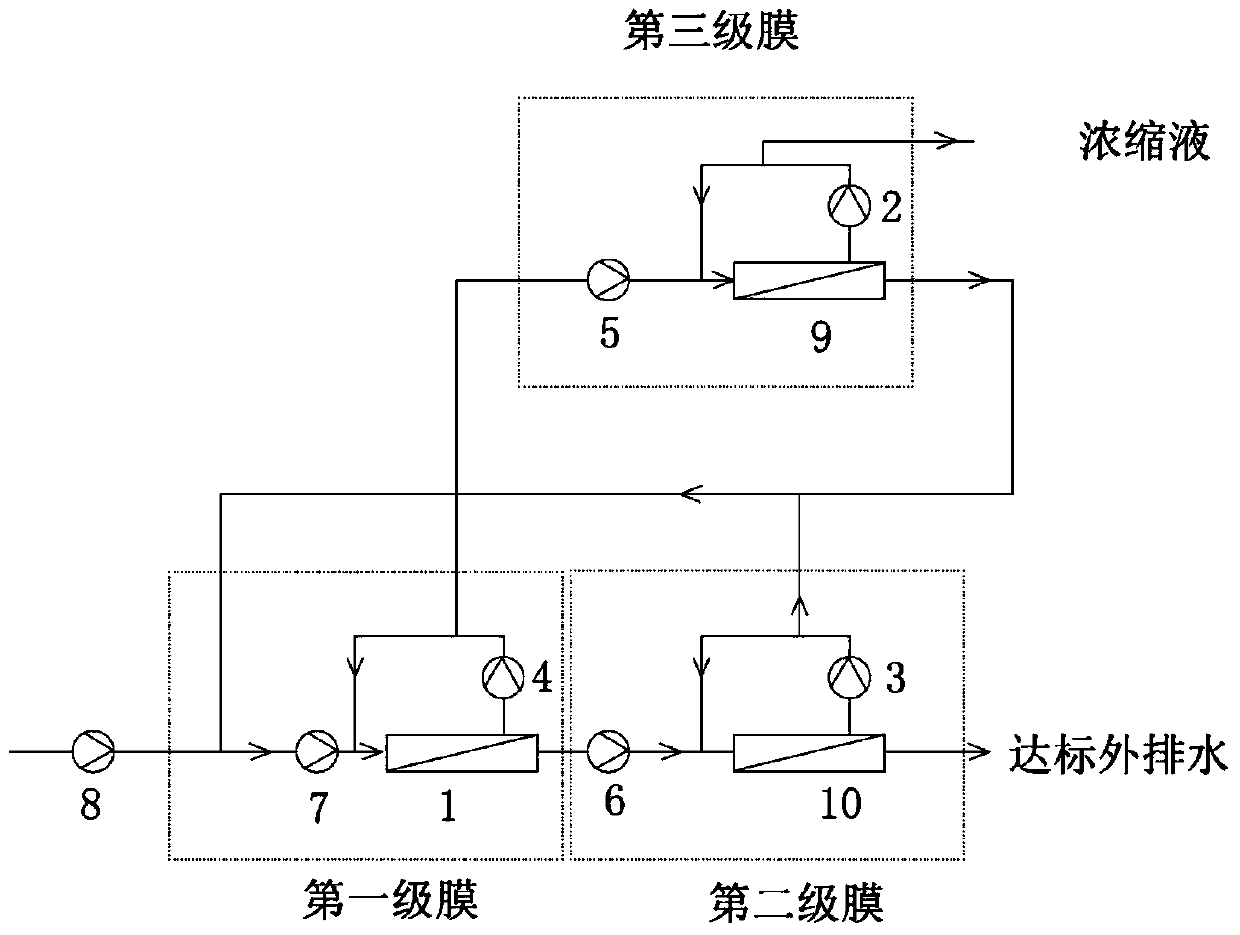
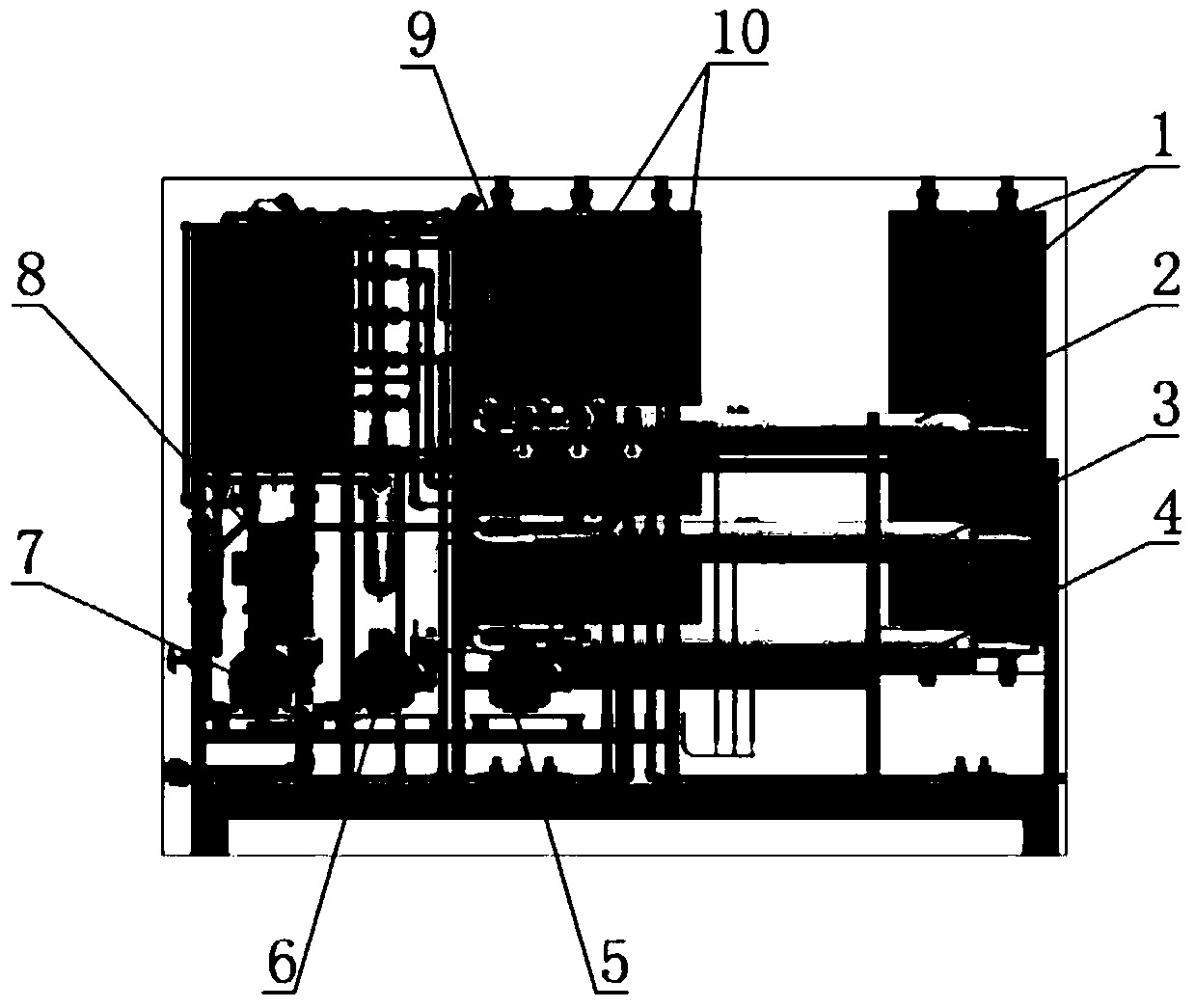
Method and device for processing radioactive wastewater
The invention provides a method and a device for processing radioactive wastewater. According to the method and the device, the radioactive wastewater is processed by a disk tubular reverse osmosis (DTRO) membrane component, so that effects of efficient decontamination factors and high cycles of concentration can be obtained at the same time. The method comprises the steps of enabling the radioactive wastewater to flow through a first-level membrane component and a second-level membrane component in sequence to obtain second-level water; and enabling first-level concentrated water out of the first-level membrane component to enter a third-level membrane component and obtain a concentrated solution.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and system for removal of contaminants from aqueous solution
A system and method for removal of uranium and other contaminants from aqueous solution, utilizing live algae, are described. The system includes a bioreactor, in which a reaction mixture of live algae, preferably photosynthetic algae, and contaminated solution are introduced; a means for introducing carbon dioxide gas in the reaction mixture; a means for exposing the reaction mixture to light; means for mixing and impelling the reaction mixture; and means for separating out algae from remediated solution.
Owner:PAN PACIFIC TEHNOLOGIES
Compositions to remove radioactive isotopes and heavy metals from wastewater
InactiveUS6855665B1Determination of the total exchange capacity of a clay or other mineral is more simple and rapidSludge treatmentOther chemical processesSludgeWastewater
The present invention provides compositions and a method to remove a plurality of radioactive isotopes and / or heavy metals simultaneously from water or wastewater. The compositions comprise lattice clays; flocculants; a neutron absorbent; catalysts; and a setter. The selected compositions is entered into a vessel and agitated with the water to produce a sludge containing the contaminants.
Owner:BLAKE ALEXANDER +1
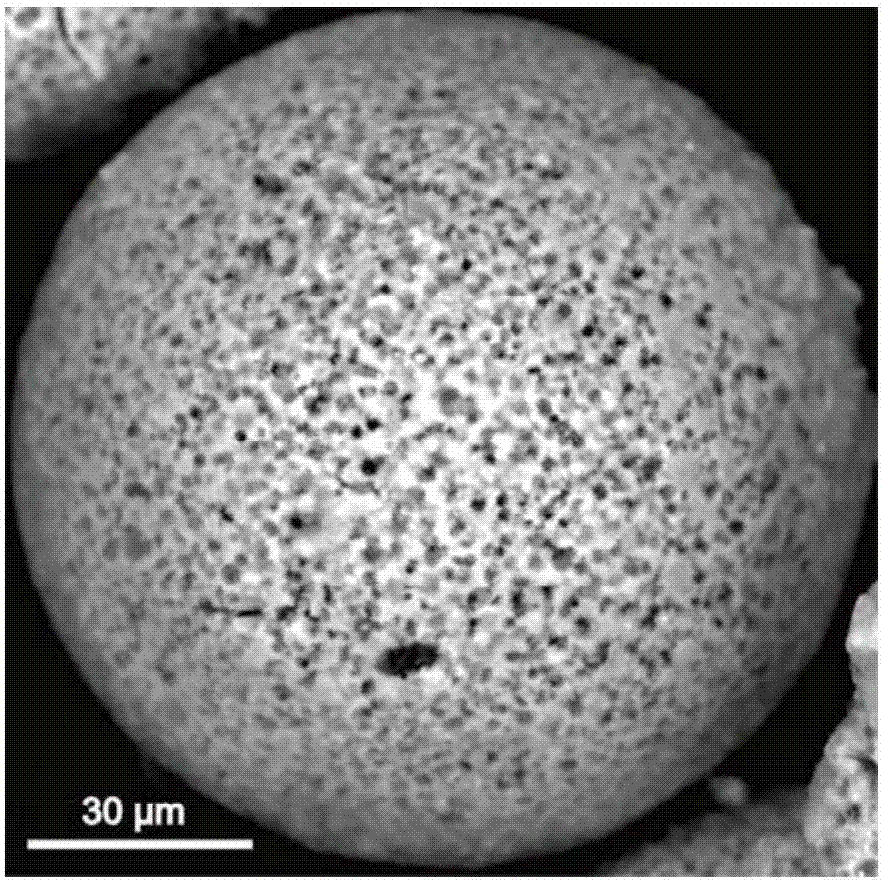
Preparation method and application of porous geological polymer microspheres
ActiveCN107973559AHigh Microsphere EfficiencyParticle size adjustableOther chemical processesRadioactive contaminantsMicrosphereSorbent
The invention discloses a preparation method of porous geological polymer microspheres. The porous geological polymer microspheres are prepared by a dispersion suspension solidification method. Compared with the prior art, low-temperature curing and one-shot molding granulation are realized without requirements of high-temperature calcination and curing and addition of other auxiliaries; and at the same time, large-scale use of solid wastes is realized, and raw materials are widely available, cost is low, process is simple, and the whole process is non-toxic and pollution-free; in addition, the preparation efficiency is high with a ball-forming degree exceeding 90%; the size of the particles can be adjusted, and the pore size distribution is uniform; the pore volume is large, and can be regulated, and a specific surface area of the microspheres reaches 110m2 / g, thus, the porous geological polymer microspheres can be directly used for packed columns for column separation. Experiments show that the porous geological polymer microspheres have a good adsorption effect on heavy metals, and can be used as adsorbents for heavy metals, and have a broad application prospect in the aspect ofremoving heavy metals and radioactive elements in water.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Sorption and separation of various materials by graphene oxides
Various aspects of the present invention pertain to methods of sorption of various materials from an environment, including radioactive elements, chlorates, perchlorates, organohalogens, and combinations thereof. Such methods generally include associating graphene oxides with the environment. This in turn leads to the sorption of the materials to the graphene oxides. In some embodiments, the methods of the present invention also include a step of separating the graphene oxides from the environment after the sorption of the materials to the graphene oxides. More specific aspects of the present invention pertain to methods of sorption of radionuclides (such as actinides) from a solution by associating graphene oxides with the solution and optionally separating the graphene oxides from the solution after the sorption.
Owner:ZONKO LLC
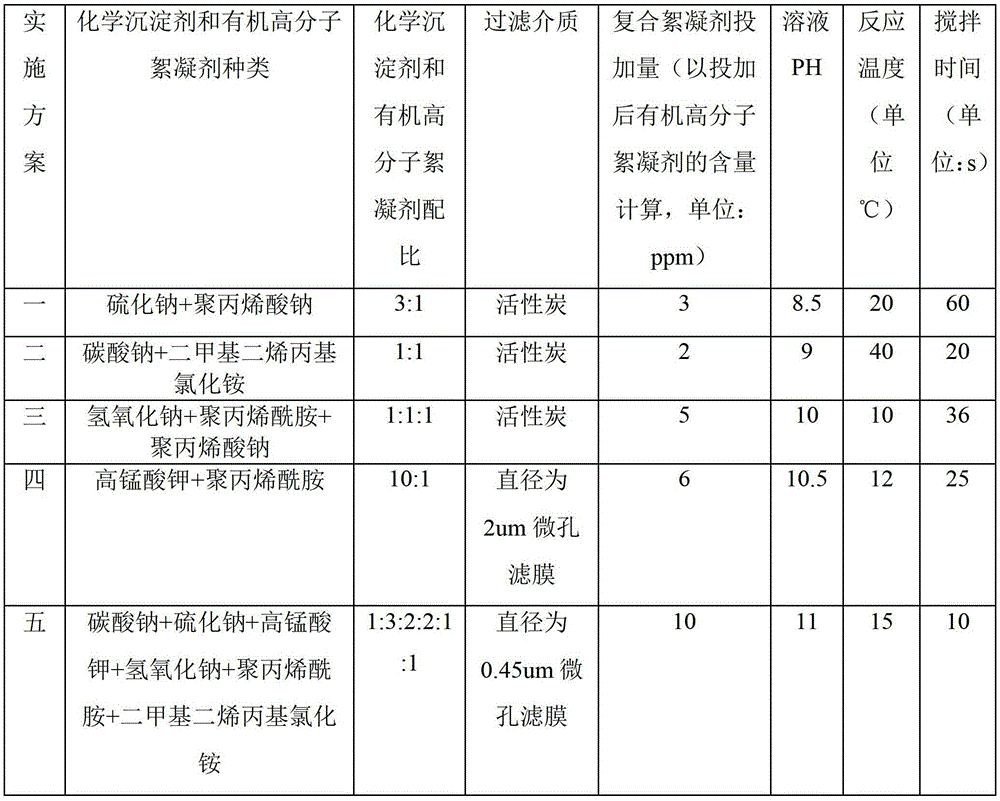
Composite flocculating agent for processing radioactive elements iron, cobalt, manganese and silver in nuclear waste water and processing method
InactiveCN103151088AGood removal effectQuick and effective removalRadioactive contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSludgeManganese
The invention discloses a composite flocculating agent for processing radioactive elements iron, cobalt, manganese and silver in nuclear waste water and a processing method, which belongs to the technical field of the nuclear waste water treatment. The composite flocculating agent consists of a chemical precipitator and an organic polymer flocculating agent, wherein the chemical precipitator is one or combination of more than one of potassium permanganate, sodium sulfide, sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide; the organic polymer flocculating agent is polyacrylamide, sodium polyacrylate and / or dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride; and the processing method comprises the following steps of configuring the composite flocculating agent, charging the composite flocculating agent, regulating a pH value of the solution, mixing, flocculating and filtering. Due to the adoption of the composite flocculating agent and the processing method, multiple radioactive element ions of ultralow trace concentration in the nuclear waste water can be efficiently removed, and advantages such as rapidness and high efficiency in reaction process, charging in one step and little dangerous chemical sludge can be realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV YIXING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION RES INST
Method for the preparation of a cesium-separating sorbent
InactiveUS6046131AImprove adsorption capacityEfficient loadingOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatmentPorosityWater insoluble
The invention provides a method for the preparation of a sorbent capable of efficiently and selectively sorbing cesium ions from an aqueous solution. The method comprises impregnating the pores of a high-porosity carrier material such as silica gel and porous adsorbent resin with water-soluble potassium or sodium hexacyanoferrate (II) and contacting the carrier material with a solution of a copper salt in a solvent in which the water-soluble hexacyanoferrate (II) is hardly soluble such as ethyl alcohol to convert the water-soluble hexacyanoferrate (II) into water-insoluble copper hexacyanoferrate (II). The cesium ions sorbed on the sorbent can be readily desorbed and the sorbent can readily be regenerated. Alternatively, the carrier material is impregnated with a water-soluble hexacyanoferrate (III) which is converted into copper hexacyanoferrate (III) followed by a reducing reaction of the same into copper hexacyanoferrate (II).
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com