Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
130 results about "Inverse fft" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
IFFT (Inverse FFT) converts a signal from the frequency domain to the time domain. The FFT of a non-periodic signal will cause the resulting frequency spectrum to suffer from leakage.
Efficient space-time adaptive processing (STAP) filter for global positioning system (GPS) receivers
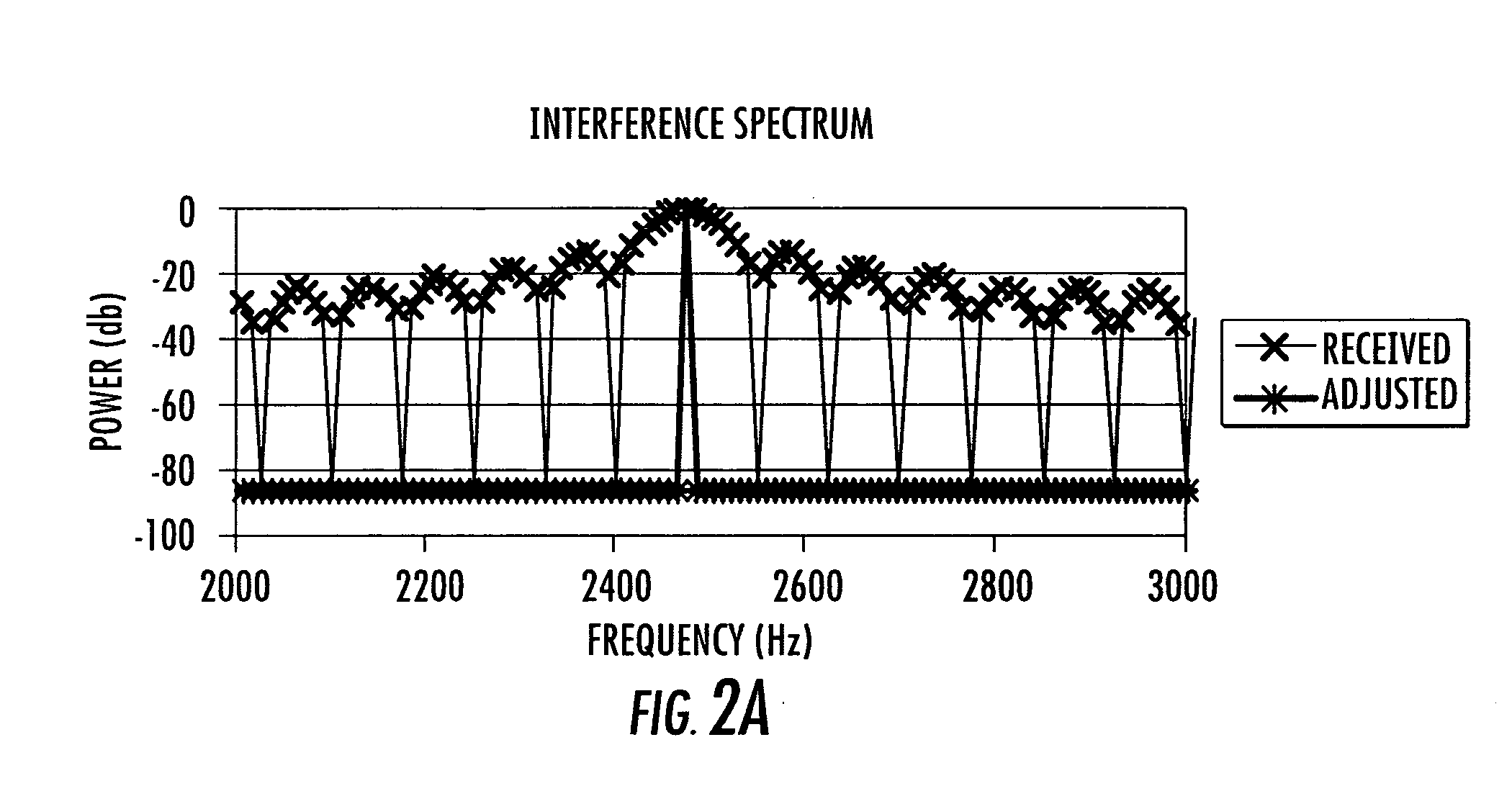
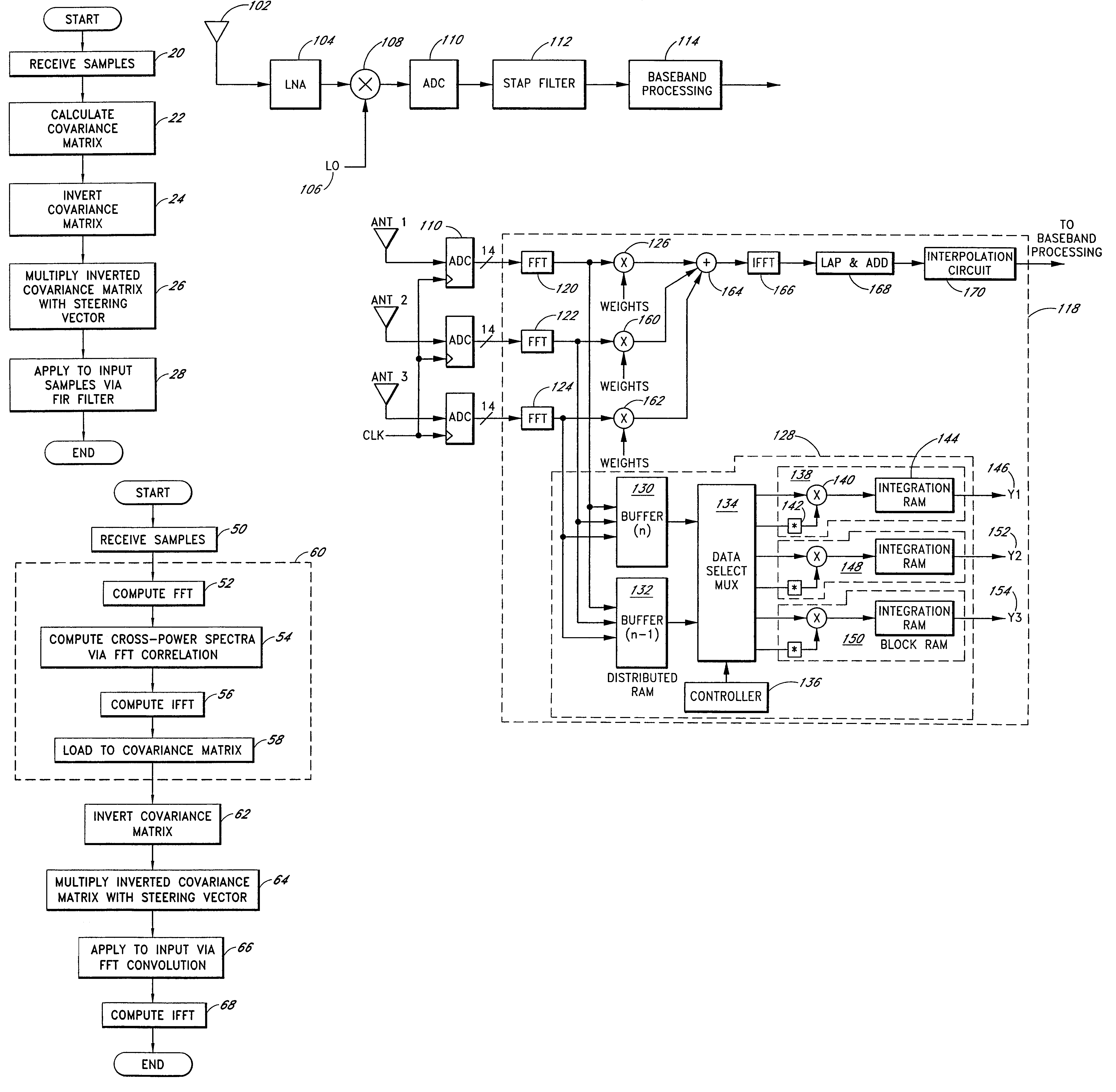
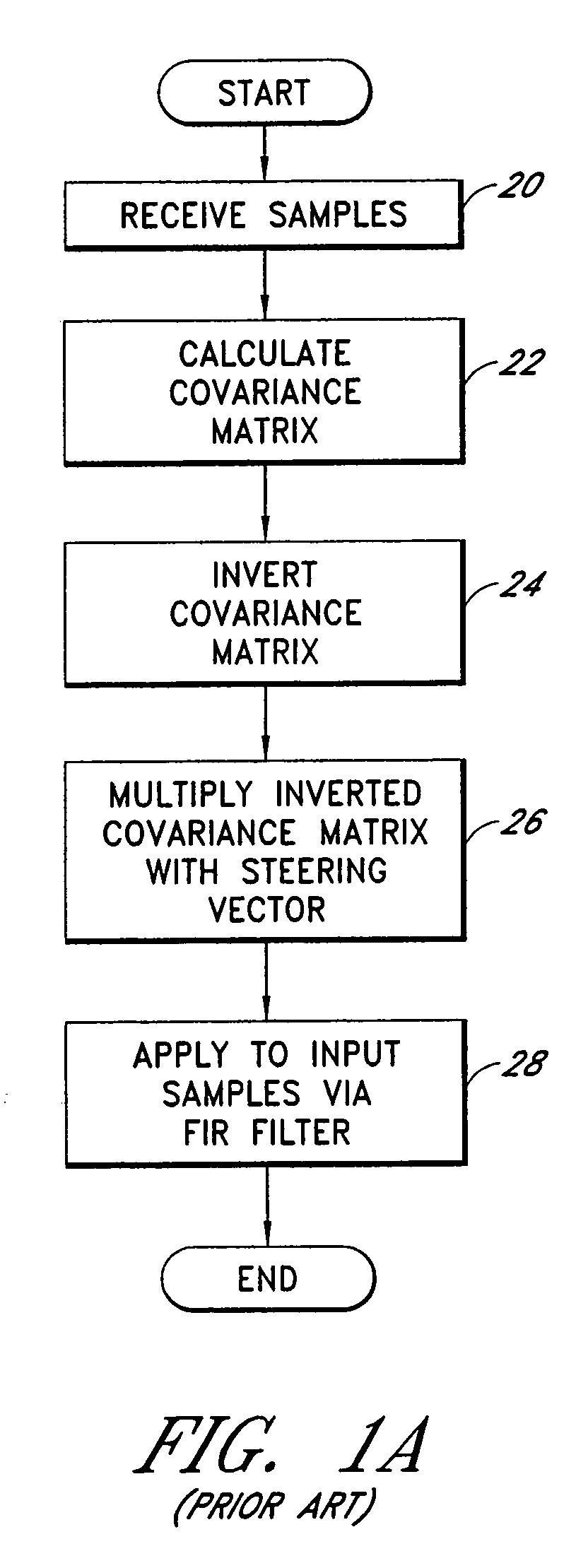
InactiveUS6952460B1Easy to trackEfficiently null a relatively large number of jammersBeacon systems using radio wavesCommunication jammingComputation complexityFourier transform on finite groups
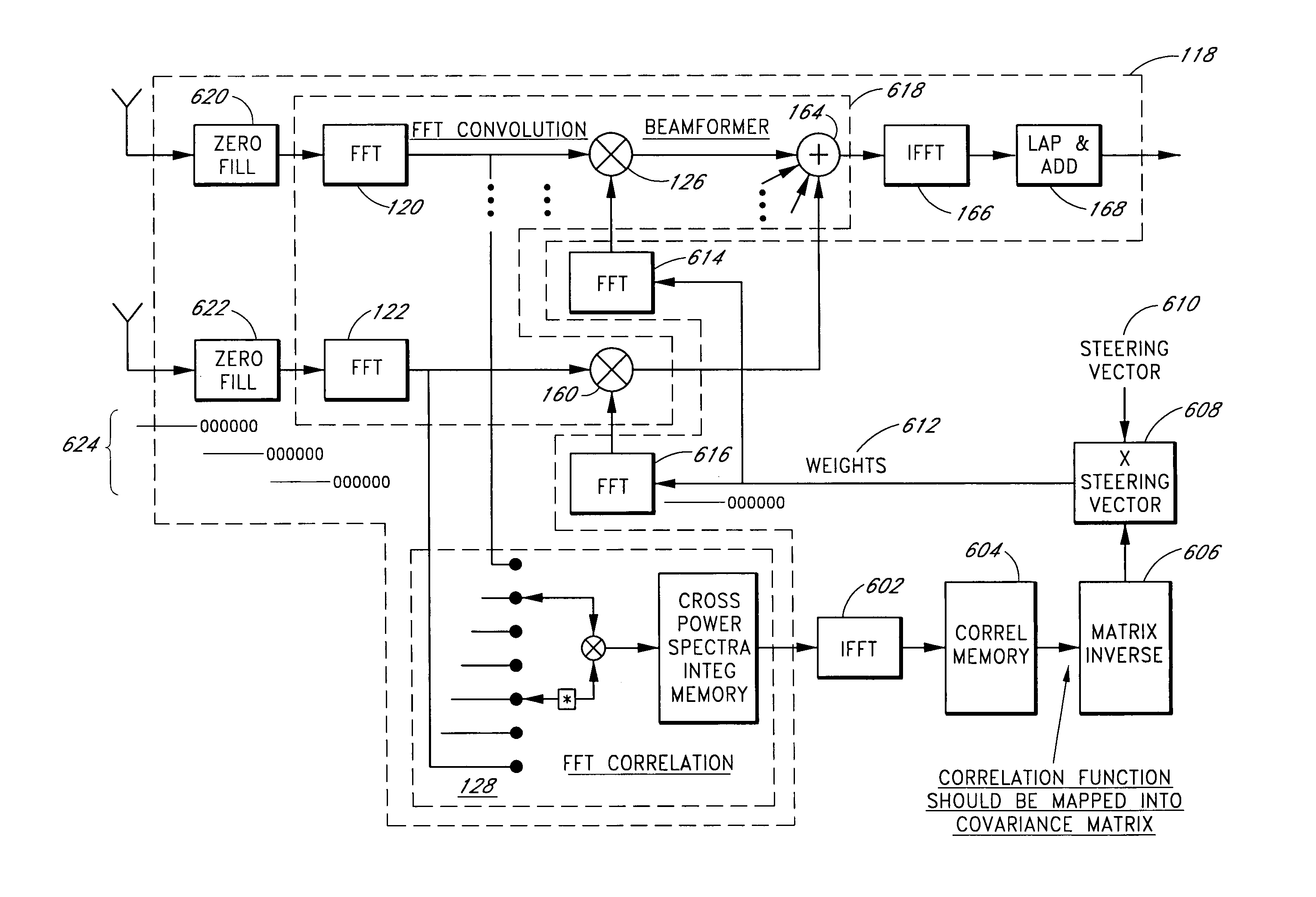
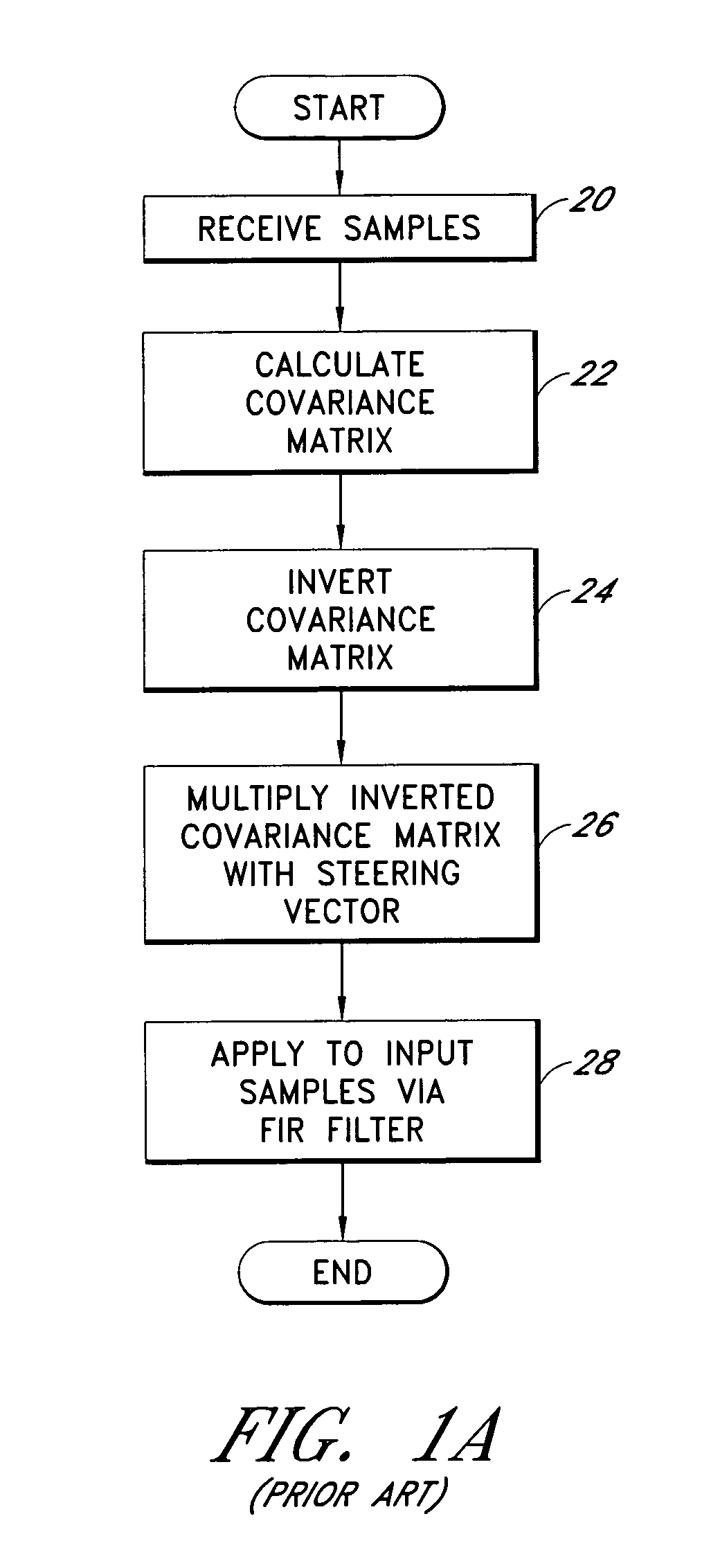
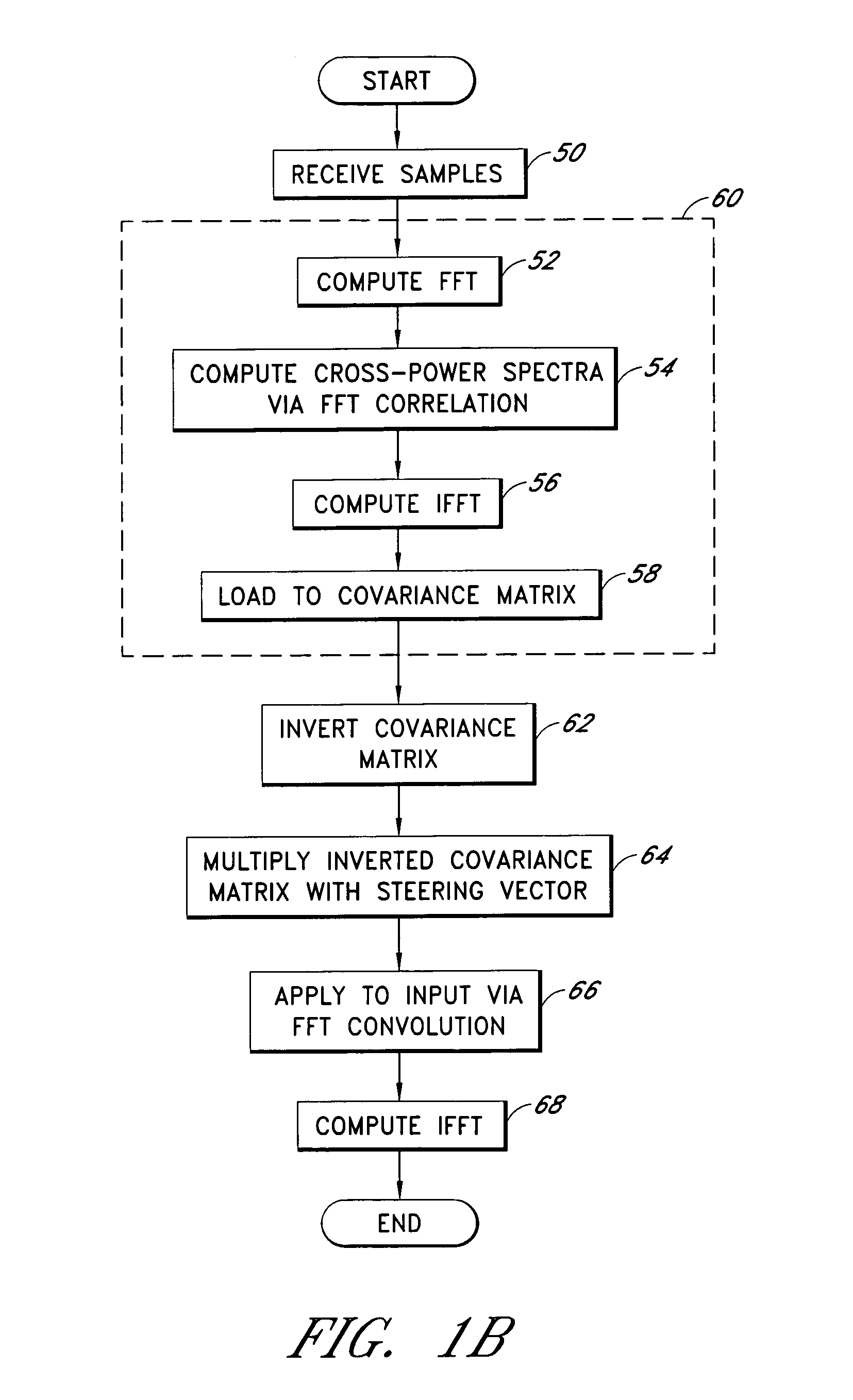
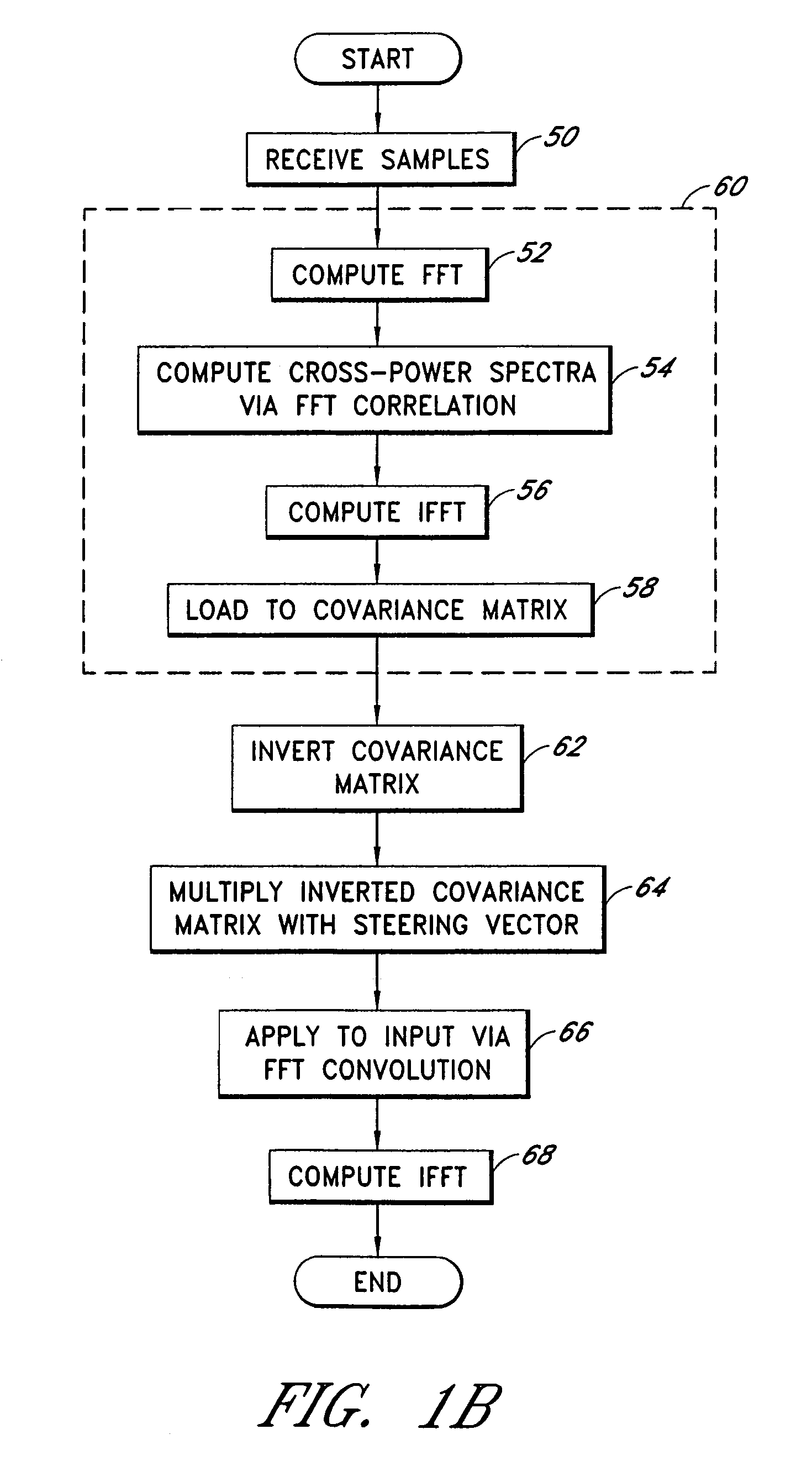
A system for efficiently filtering interfering signals in a front end of a GPS receiver is disclosed. Such interfering signals can emanate from friendly, as well as unfriendly, sources. One embodiment includes a GPS receiver with a space-time adaptive processing (STAP) filter. At least a portion of the interfering signals are removed by applying weights to the inputs. One embodiment adaptively calculates and applies the weights by Fourier Transform convolution and Fourier Transform correlation. The Fourier Transform can be computed via a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). This approach advantageously reduces computational complexity to practical levels. Another embodiment utilizes redundancy in the covariance matrix to further reduce computational complexity. In another embodiment, an improved FFT and an improved Inverse FFT further reduce computational complexity and improve speed. Advantageously, embodiments can efficiently null a relatively large number of jammers at a relatively low cost and with relatively low operating power.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
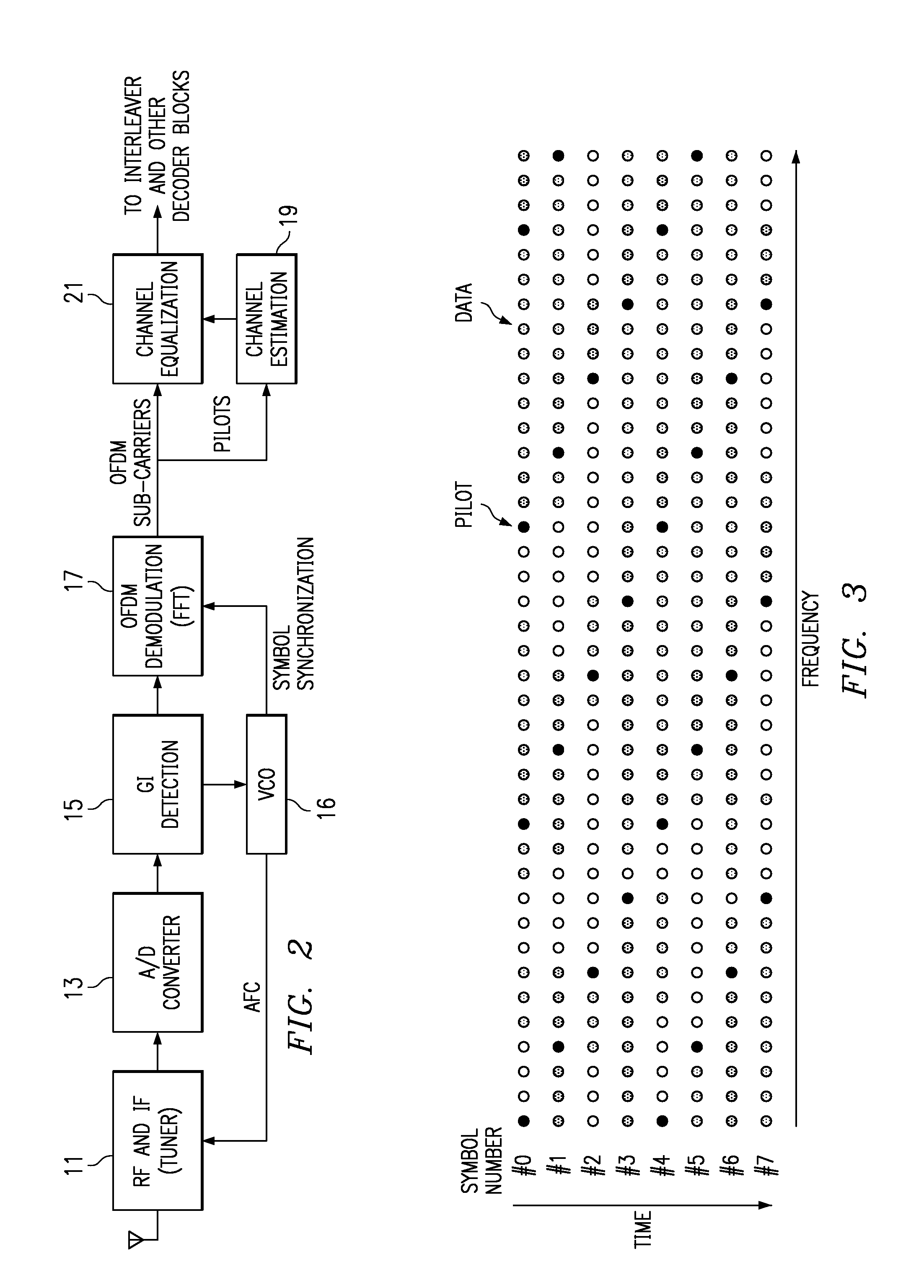
Multi-path equalization for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication system
ActiveUS7099270B2Transmission control/equalisingAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFourier transform on finite groupsEqualization
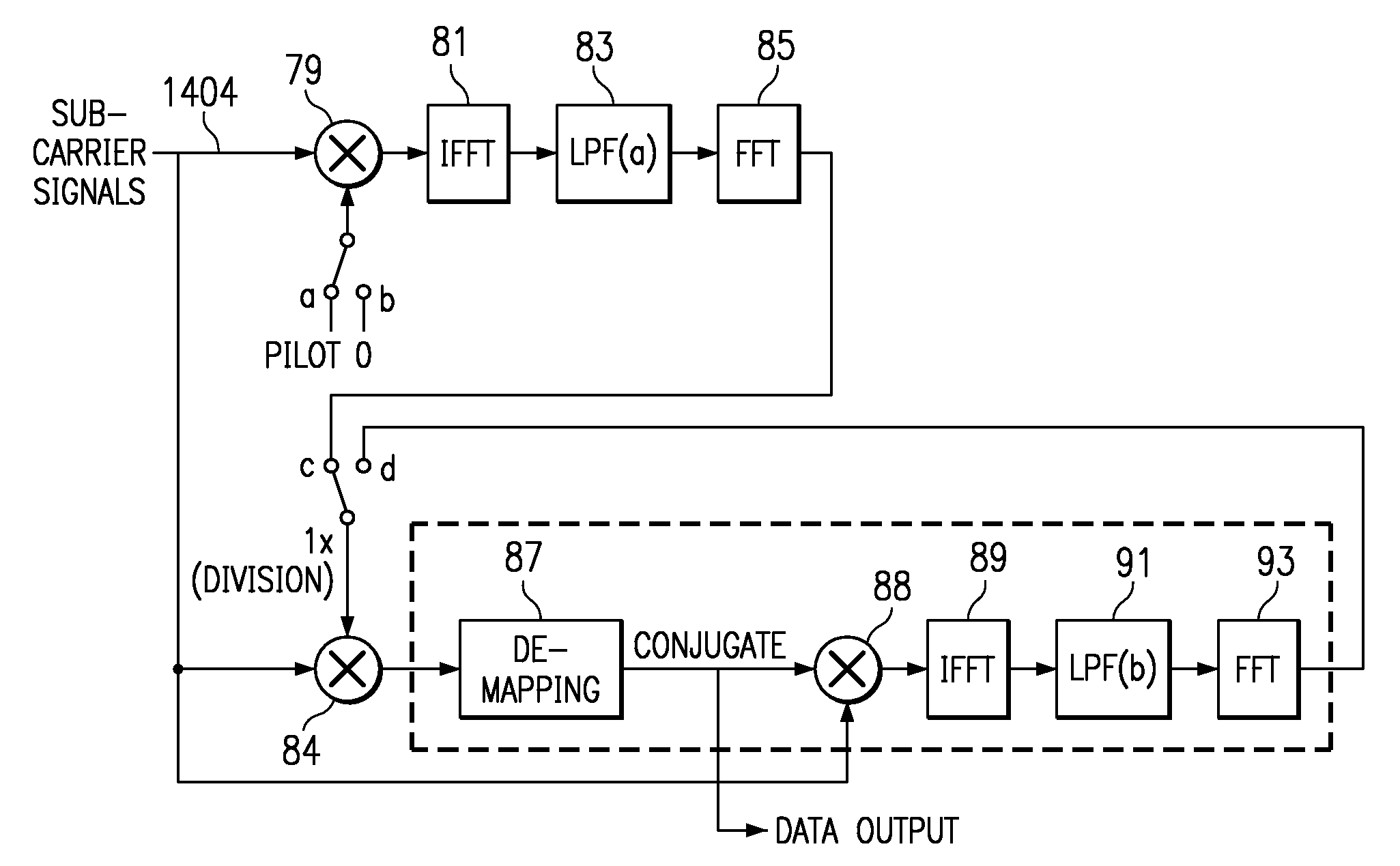
A multi-path equalization system for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication (OFDM) system includes a first estimator for estimating the channel characteristic using pilot signal. A divider is coupled to the estimator for dividing each sub-carrier with the channel characteristic to get the equalization to the data signal. A de-mapper uses the phase and amplitude correction of the channel estimate to recover the data signals. An improved channel estimation is provided by a repeat channel estimation feedback loop that includes the de-mapper a multiplier, an inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT), a low pass filter and a fast Fourier transform (FFT). The improved channel estimation is obtained by multiplying at the multiplier the conjugate of the de-mapped data to the input sub-carriers and applying inverse FFT, low pass filtering and FFT to get the new channel estimate. Each sub-carrier is divided with new channel characteristic to get new equalization to the data signal. The channel estimation is repeated until there is convergence. The output is provided after the de-mapper. In the case of channel decoding to improve performance a Viterbi decoder and convolutional encoder is coupled in loop between the de-mapper and the multiplier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multi-path equalization for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication system
ActiveUS20030227866A1Evenly goodTransmission control/equalisingAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsViterbi decoderCommunications system
A multi-path equalization system for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication (OFDM) system includes a first estimator for estimating the channel characteristic using pilot signal. A divider is coupled to the estimator for dividing each sub-carrier with the channel characteristic to get the equalization to the data signal. A de-mapper uses the phase and amplitude correction of the channel estimate to recover the data signals. An improved channel estimation is provided by a repeat channel estimation feedback loop that includes the de-mapper a multiplier, an inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT), a low pass filter and a fast Fourier transform (FFT). The improved channel estimation is obtained by multiplying at the multiplier the conjugate of the de-mapped data to the input sub-carriers and applying inverse FFT, low pass filtering and FFT to get the new channel estimate. Each sub-carrier is divided with new channel characteristic to get new equalization to the data signal. The channel estimation is repeated until there is convergence. The output is provided after the de-mapper. In the case of channel decoding to improve performance a Viterbi decoder and convolutional encoder is coupled in loop between the de-mapper and the multiplier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
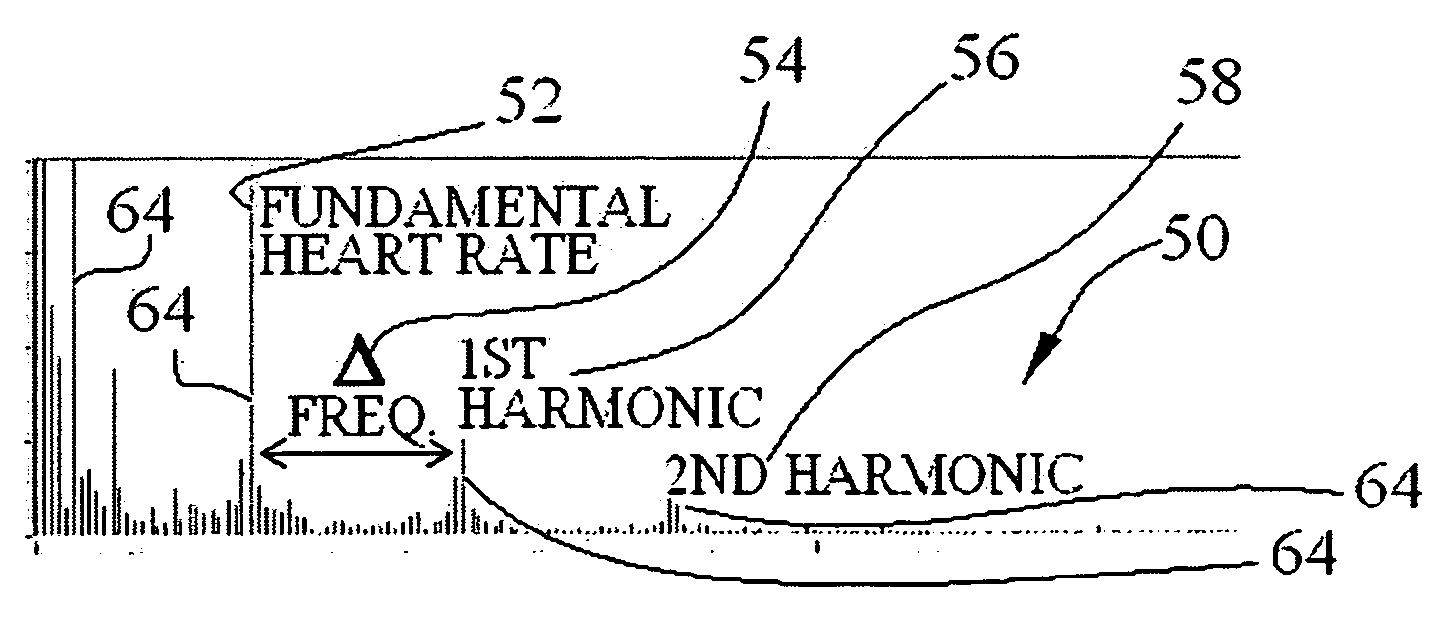
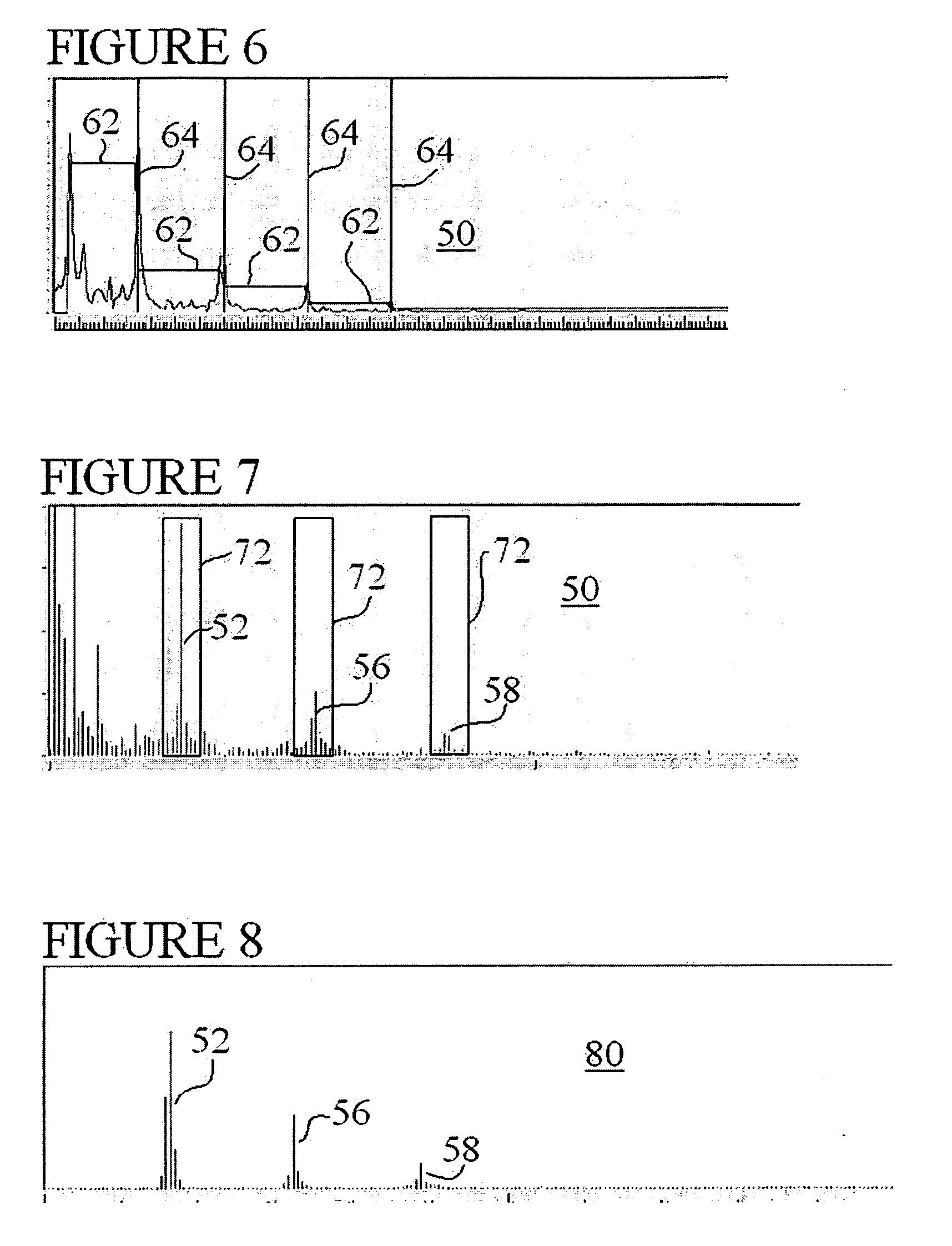
Techniques for accurately deriving physiologic parameters of a subject from photoplethysmographic measurements
ActiveUS20080167564A1Good for scrollingUndesirable frequency content eliminated and reducedCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationData setPulse oximeters
Several techniques are disclosed for isolating either heart or breath rate data from a photoplethysmograph, which is a time domain signal such as from a pulse oximeter. The techniques involve the use of filtering in the frequency domain, after a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) has been conducted on a given photoplethysmograph also references as a given set of discrete time-domain data. The filtering may be applied to an identified fundamental frequency and one or more harmonics for heart related parameters. The filter may be truncated to the frequency data set and further applied multiple times to improve roll off. After filtering, an Inverse FFT (IFFT) is used to reconstruct the time-domain signal, except with undesirable frequency content eliminated or reduced. Calculation or measurement of parameters is then conducted on this reconstructed time-domain signal.
Owner:STARR LIFE SCI
Optical Transmitter and Optical OFDM Communication System
InactiveUS20110249978A1Reduce signalingReduce impactModulated-carrier systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOriginal dataCarrier signal
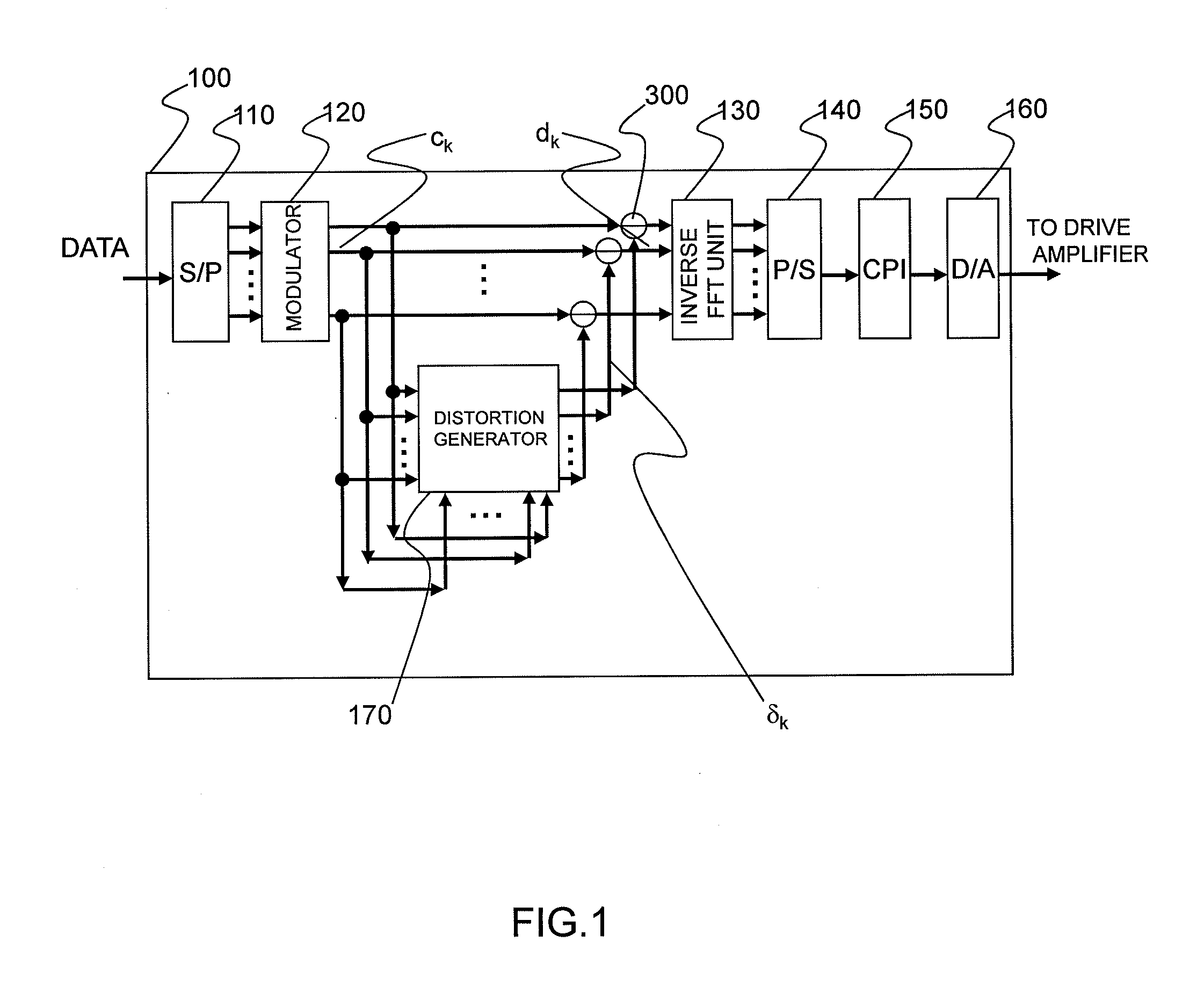
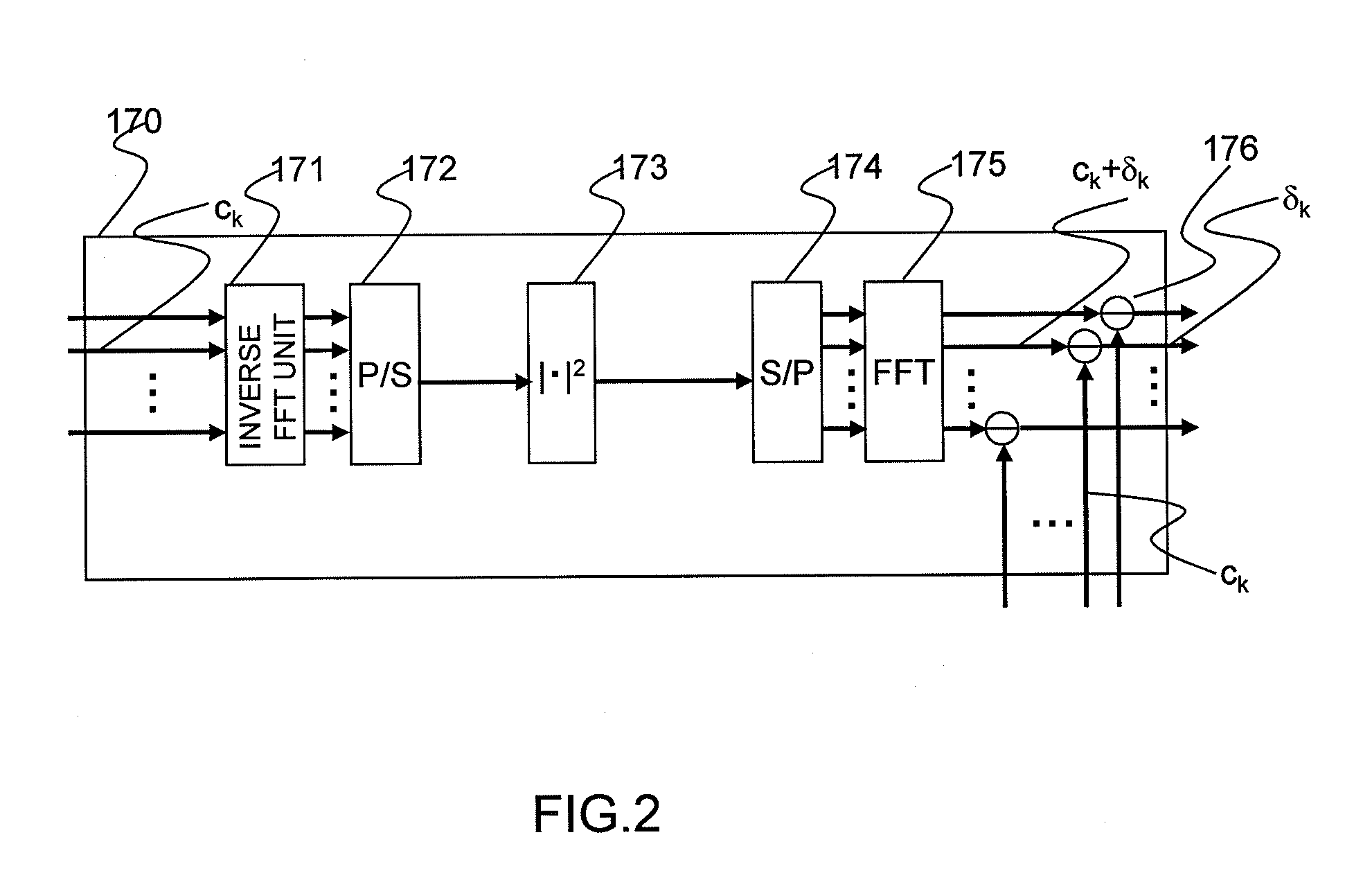
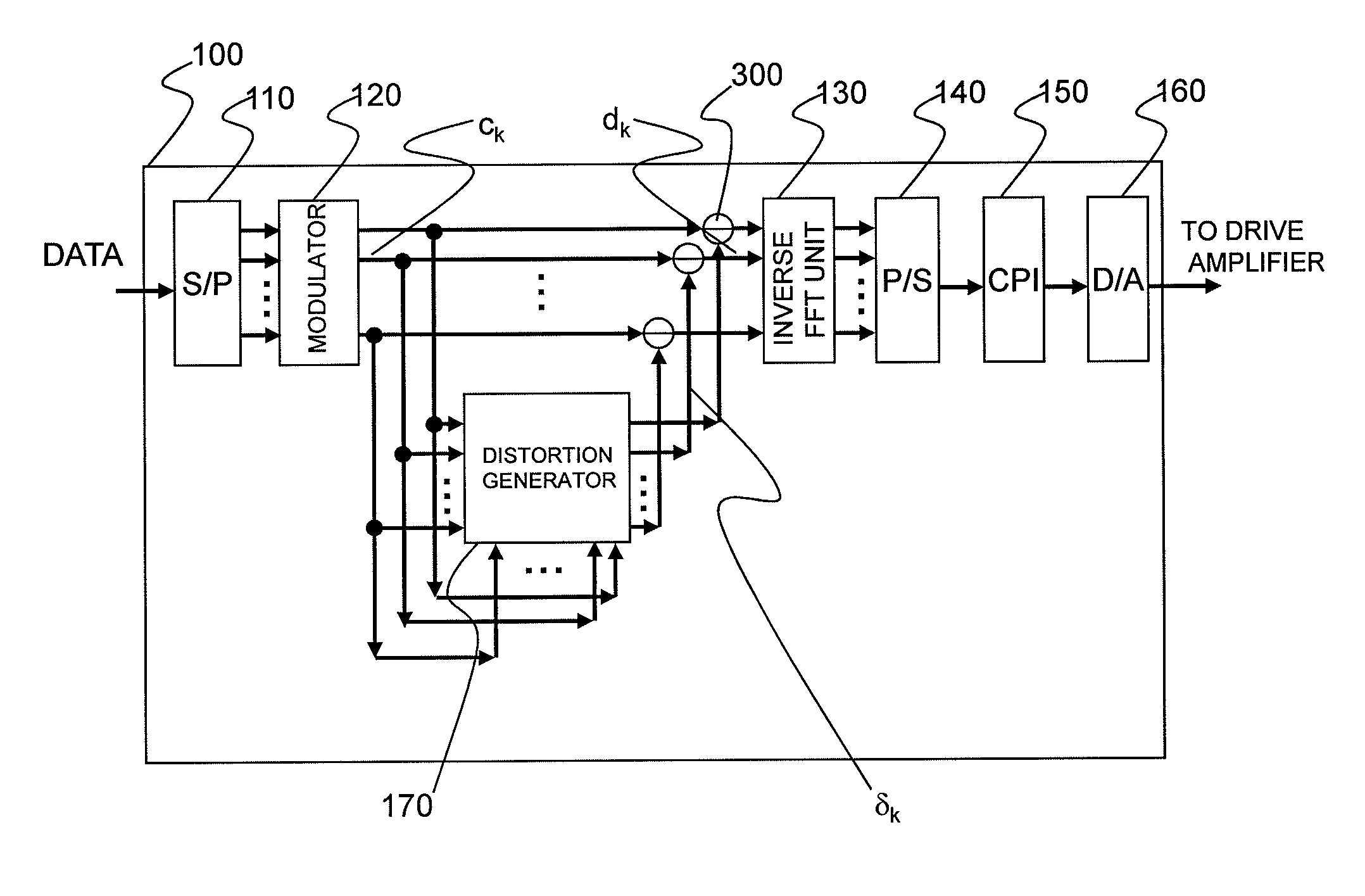
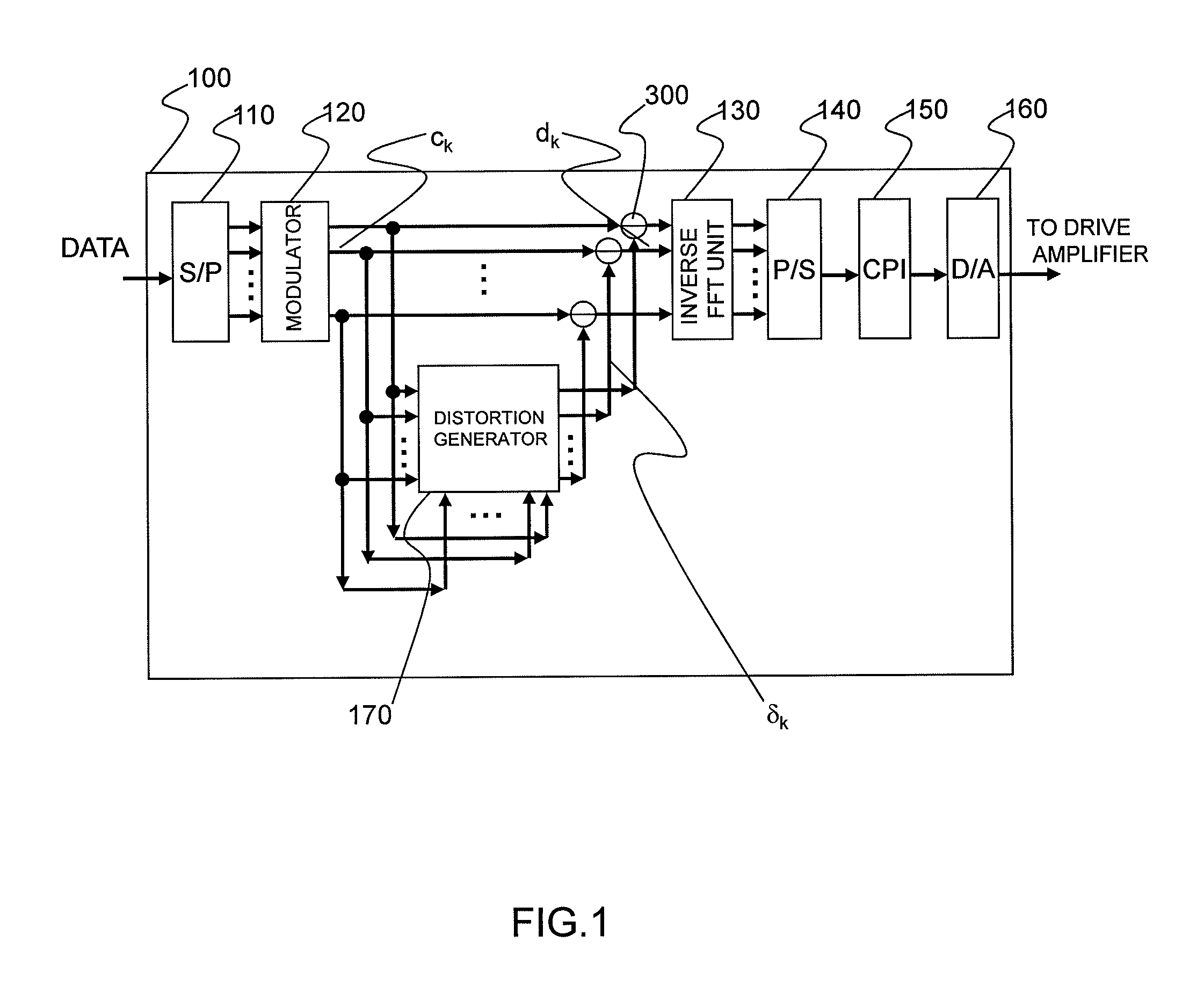
Distortion of a reception signal which is attributable to interference between subcarriers during photoelectric conversion is reduced in an optical OFDM communication system without broadening the signal band. A transmission signal processing unit (100) in a transmitter is provided with a distortion generating circuit (distortion generating unit) (170). A subcarrier signal is utilized as an input signal for the circuit. The distortion generating circuit (170) generates a baseband OFDM signal by means of inverse FFT calculation using the input signal, computes the square of the absolute value of the signal, and restores the subcarrier signal by mean of FFT calculation. Because interference between subcarriers is also included in the signal, the distortion element generated by the interference between the subcarriers can be extracted when the difference from the input signal is found. The signal obtained by subtracting the distortion element from the subcarrier signal, which has been modulated using the original data to be communicated, is used as the transmission signal. The transmission signal is photoelectrically converted with a receiver. The interference between subcarriers generated at this time is smaller than when the aforementioned processing is not performed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Methods and apparatus for encoding information in a signal by spectral notch modulation
ActiveUS20070025456A1Increasing signal bandwidth and transmit power and data rateEasy to useCombined modulated pulse demodulationAngle modulationTime domainFrequency spectrum
A spectral notch modulation technique for encoding information in a signal involves transforming the signal into the frequency domain via a fast Fourier transform (FFT) of length N, such that the signal is represented by N frequency bins, selectively nulling M of the N frequency bins, where nulled combinations of M frequency bins respectively correspond to encoded information bits, transforming the selectively nulled signal to the time domain via an inverse FFT, and transmitting the selectively nulled signal. At the receiving end, the signal is demodulated to recover the encoded information by transforming the signal into the frequency domain via a fast Fourier transform (FFT) of length N, identifying the set of M nulled frequency bins among the N frequency bins, and converting the set of M nulled frequency bins to corresponding information bits.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMM INC
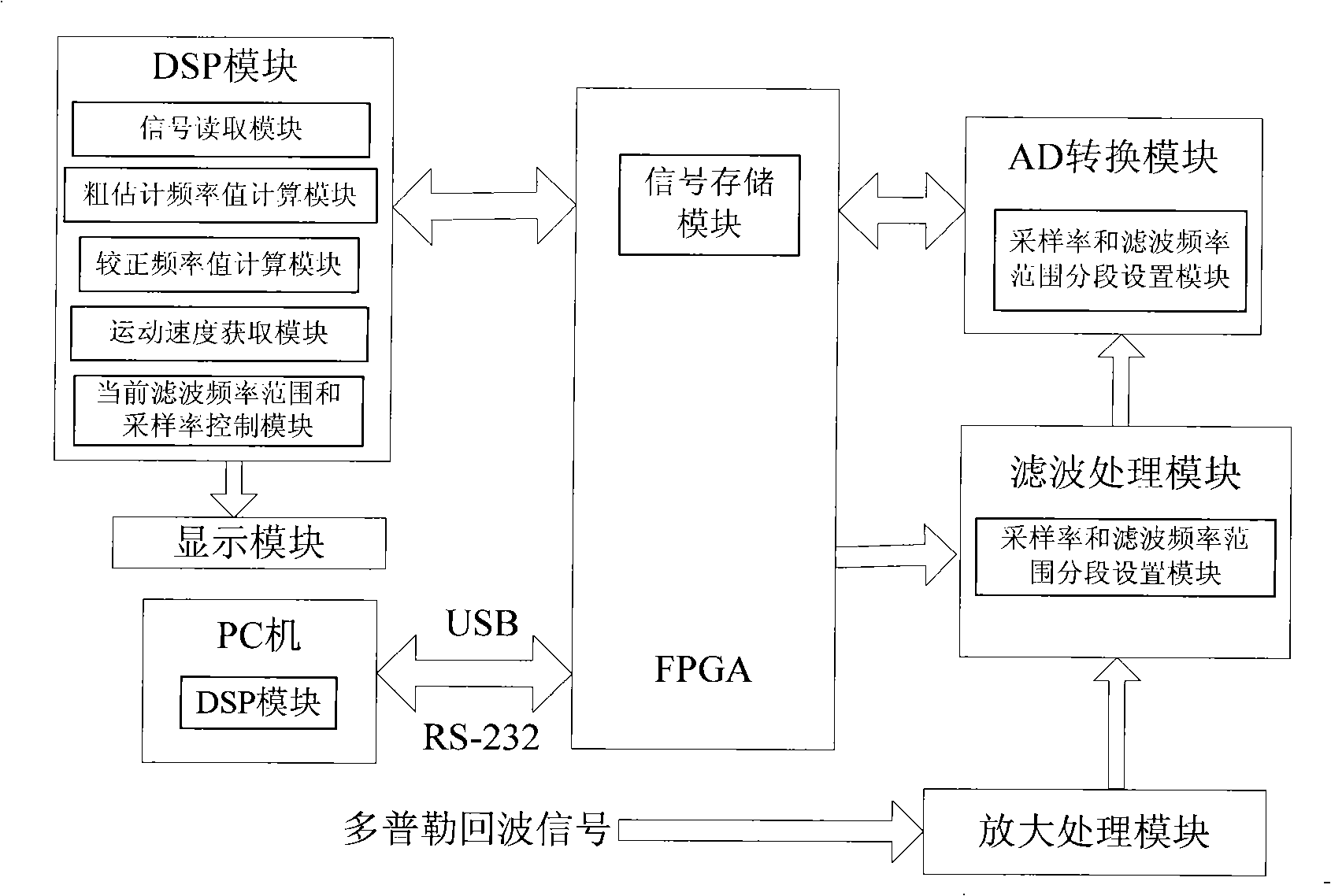
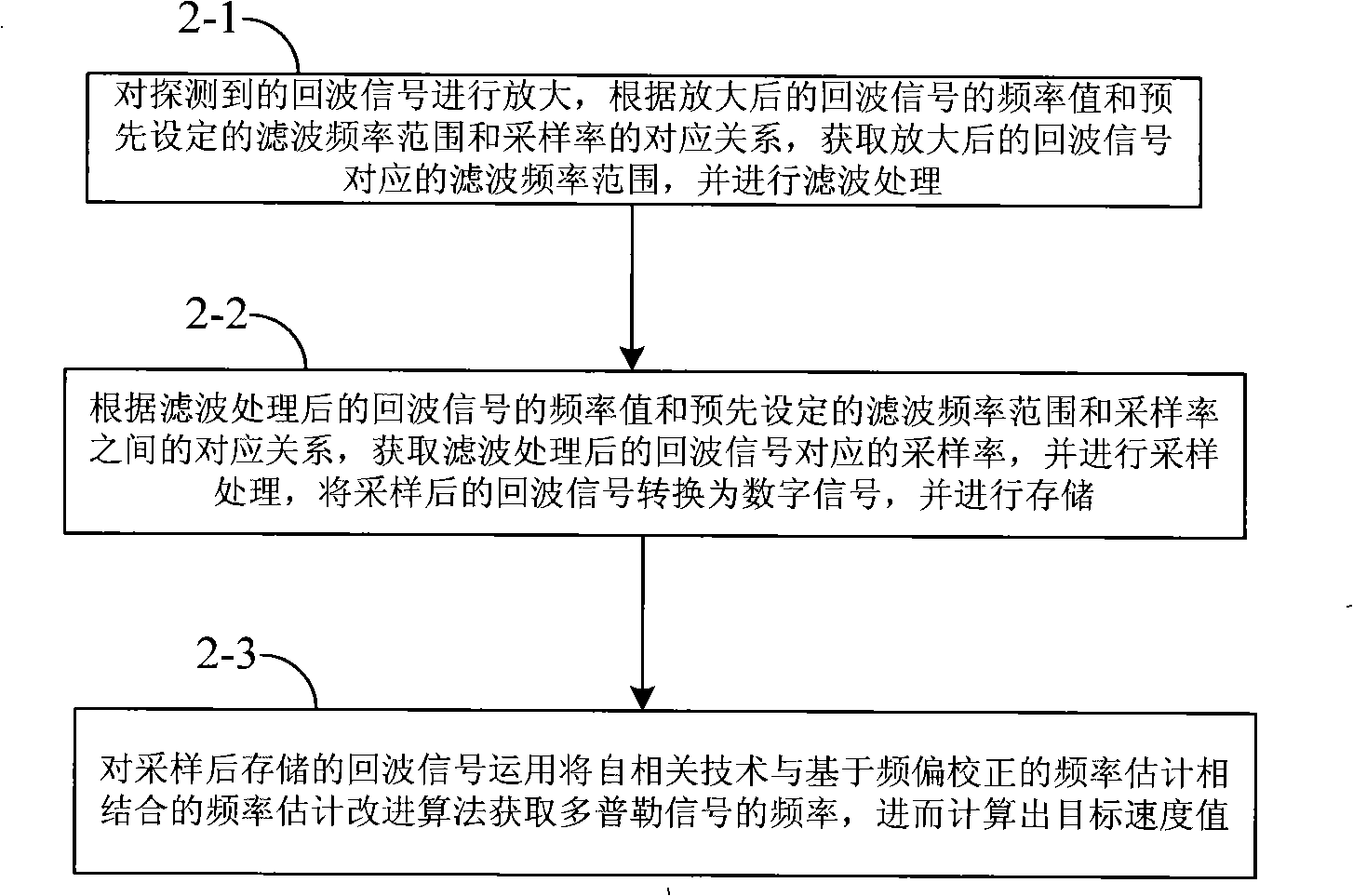
Echo signal processing equipment and method of Doppler speed measuring laser radar
InactiveCN101320086ASmall amount of calculationGuaranteed accuracyElectromagnetic wave reradiationDoppler velocityRadar
The invention provides a Doppler velocity metering laser radar echoed signal processing unit and a method. The processing unit mainly comprises a signal storage module and a DSP module; wherein, the signal storage module is used for storing the echoed signals of a tested object; the echoed signals are digital signals which are converted by A / D; the DSP module is used for reading the echoed signals in the signal storage module and carrying out the FFT to obtain the power spectrum of the signals, and then the rough estimated frequency value is obtained according to the power spectrum; the power spectrum is carried out the inverse FFT and then the self correlation functions of the echoed signals are obtained, the correction frequency value is obtained according to the self correlation functions, the rough estimated frequency value and the correction frequency value are added to obtain the Doppler frequency of the echoed signals, and the movement velocity of the tested object is calculated according to the Doppler frequency. The device and the method combine the self correlation technology with the frequency deviation estimation improvement algorithm which is based on the frequency deviation correction, and the velocity of the test object can be effectively worked out.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
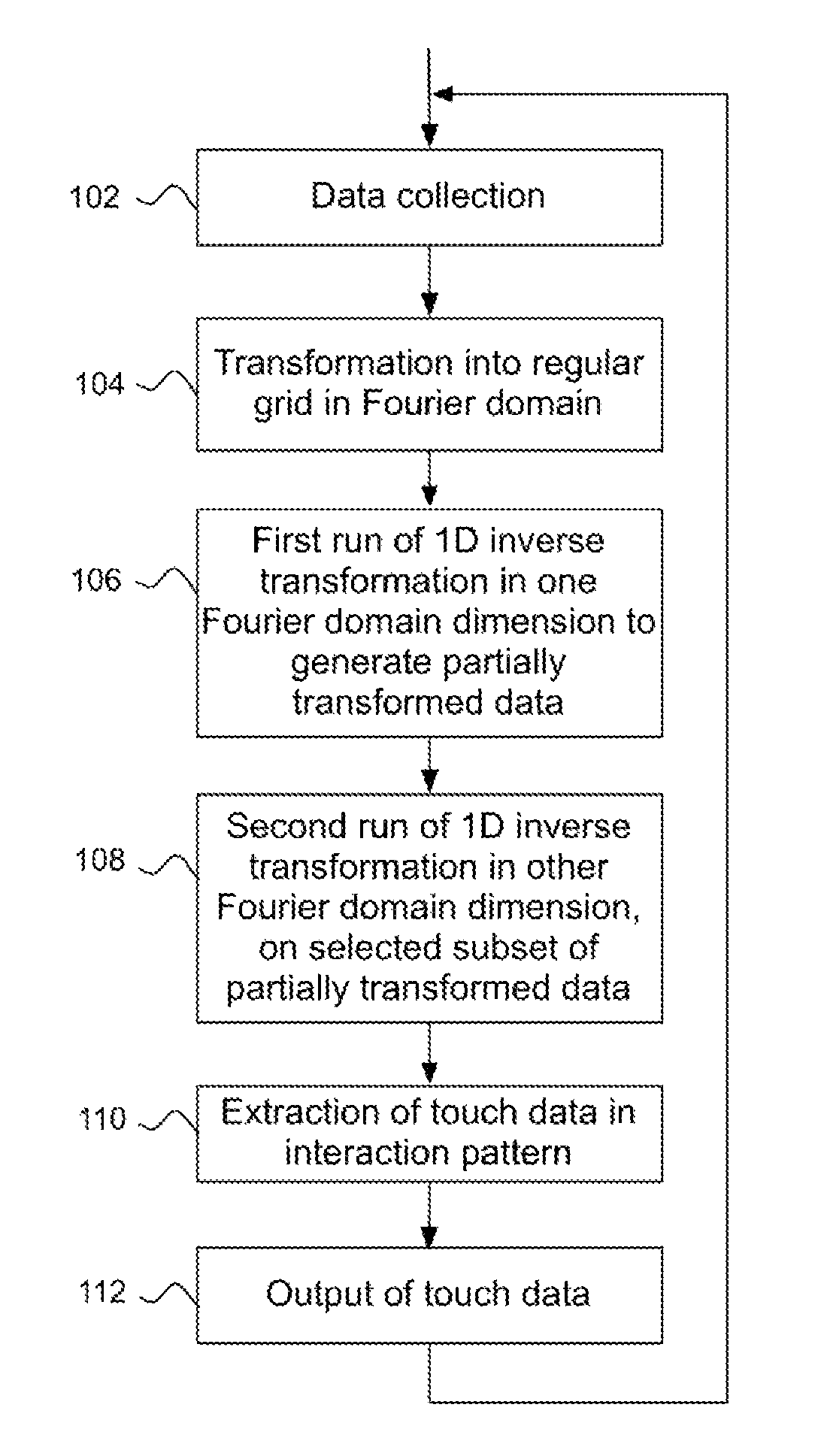
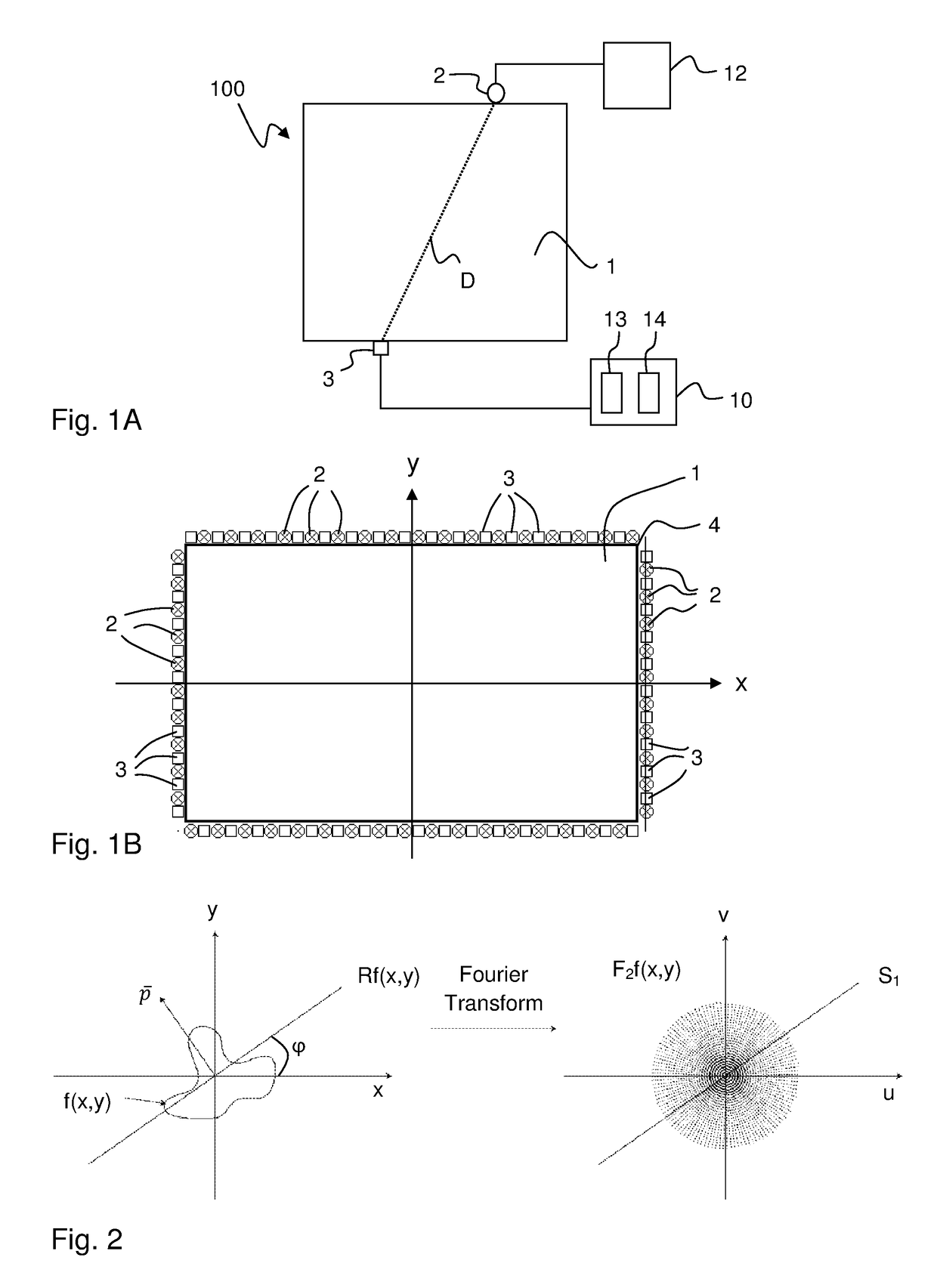
Efficient tomographic processing for touch determination
InactiveUS9684414B2Reduce needImprove processing speedSubstation equipmentInput/output processes for data processingRegular gridTomography
Touch sensitivity is enabled using a touch system that comprises a panel configured to conduct signals, e.g. by TIR, along detection lines across a rectangular touch surface with first and second spatial dimensions. A signal processor operates to transform energy values for the detection lines into Fourier coefficients arranged as data points on a regular grid defined by first and second frequency dimensions. To generate an interaction pattern for the touch surface, the signal processor operates a first 1D inverse FFT on the data points with respect to the second frequency dimension, so as to generate first values transformed into the second spatial dimension, and operates a second 1D inverse FFT on a selected subset of the first values with respect to the first frequency dimension to generate second values that represent the interaction pattern. The selected subset is defined by the data points that fall within an extent of the touch surface in the second spatial dimension, thereby reducing the total number of inverse FFT operations.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
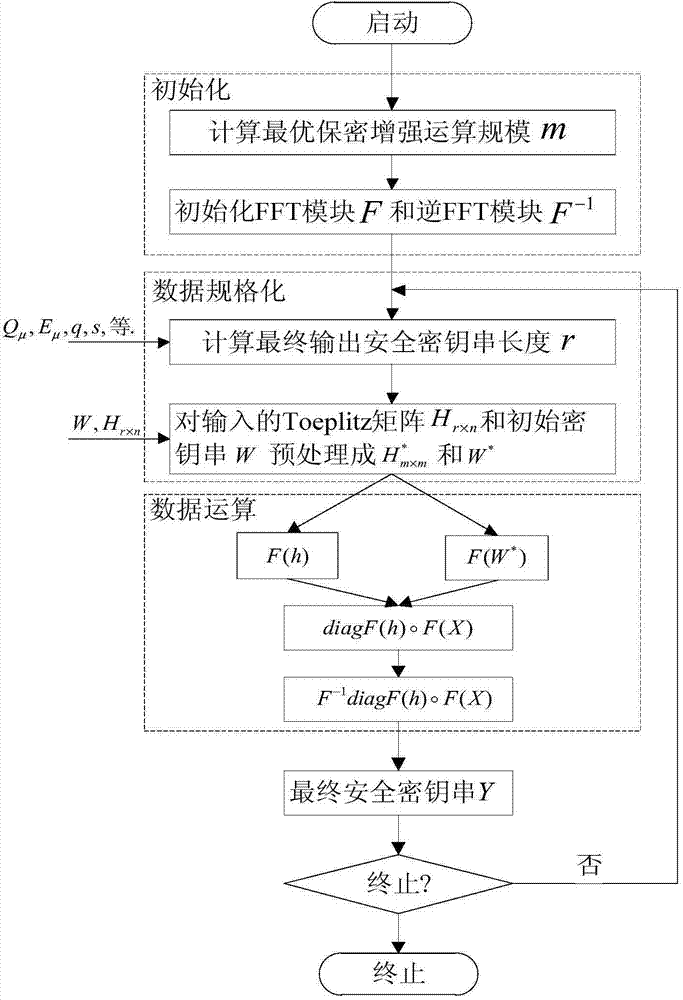
Quantum secret key distribution privacy amplification method supporting large-scale dynamic changes
ActiveCN104506313AIncrease flexibilityEasy to handleKey distribution for secure communicationCounting rateData operations
The invention discloses a quantum secret key distribution privacy amplification method supporting large-scale dynamic changes. The method includes the steps of firstly, conducting initialization, wherein the optimal operation scale m of an FFT module is calculated according to the actual running parameters of a quantum secret key distribution system when the privacy amplification method is started, and the initialization scale is an FFT operation and inverse FFT operation module of m; secondly, normalizing data, wherein the final security secret key length r is calculated according to the detector counting rate Q mu of the quantum secret key distribution system, the quantum bit error rate E mu, the corrected weak security secret key length n and the security parameter s of the quantum secret key distribution system, and normalizing an initial secret key string and a Toeplitz matrix according to the parameter m, the parameter n and the parameter r; thirdly, conducting data operation, wherein the operation process of the Toeplitz matrix and the initial secret key string is operated through the FFT technology, the first r items of the calculation result are taken to form a result vector, namely, the final security secrete key. The method has the advantages of being high in flexibility, better in processing performance, and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and device for removing accompaniment from song
ActiveCN103943113AImprove purityAmplitude Spectrum EnhancementSpeech analysisAudio frequencyInverse fft
The invention provides a method for removing an accompaniment from a song. The method comprises the steps that an accompaniment audio signal and a song audio signal are obtained; FFT is carried out on the song audio signal and the accompaniment audio signal to obtain a song audio signal amplitude spectrum, an accompaniment audio signal amplitude spectrum and the phase of the song audio signal; the accompaniment audio signal amplitude spectrum is enhanced; the enhanced accompaniment audio signal amplitude spectrum is subtracted from the song audio signal amplitude spectrum to obtain a result, inverse FFT is carried out with the combination of the phase and the result, and therefore an audio signal without the accompaniment is obtained. The invention further provides a device for removing the accompaniment from the song. According to the method and device for removing the accompaniment from the song, the degree of purity of the song obtained after separation is accomplished can be improved, separation execution efficiency is high, and an algorithm is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:FUJIAN STAR NET EVIDEO INFORMATION SYST CO LTD
Method and system for receiving a multi-carrier signal
InactiveUS20050220001A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission systemsTime domainPrior information
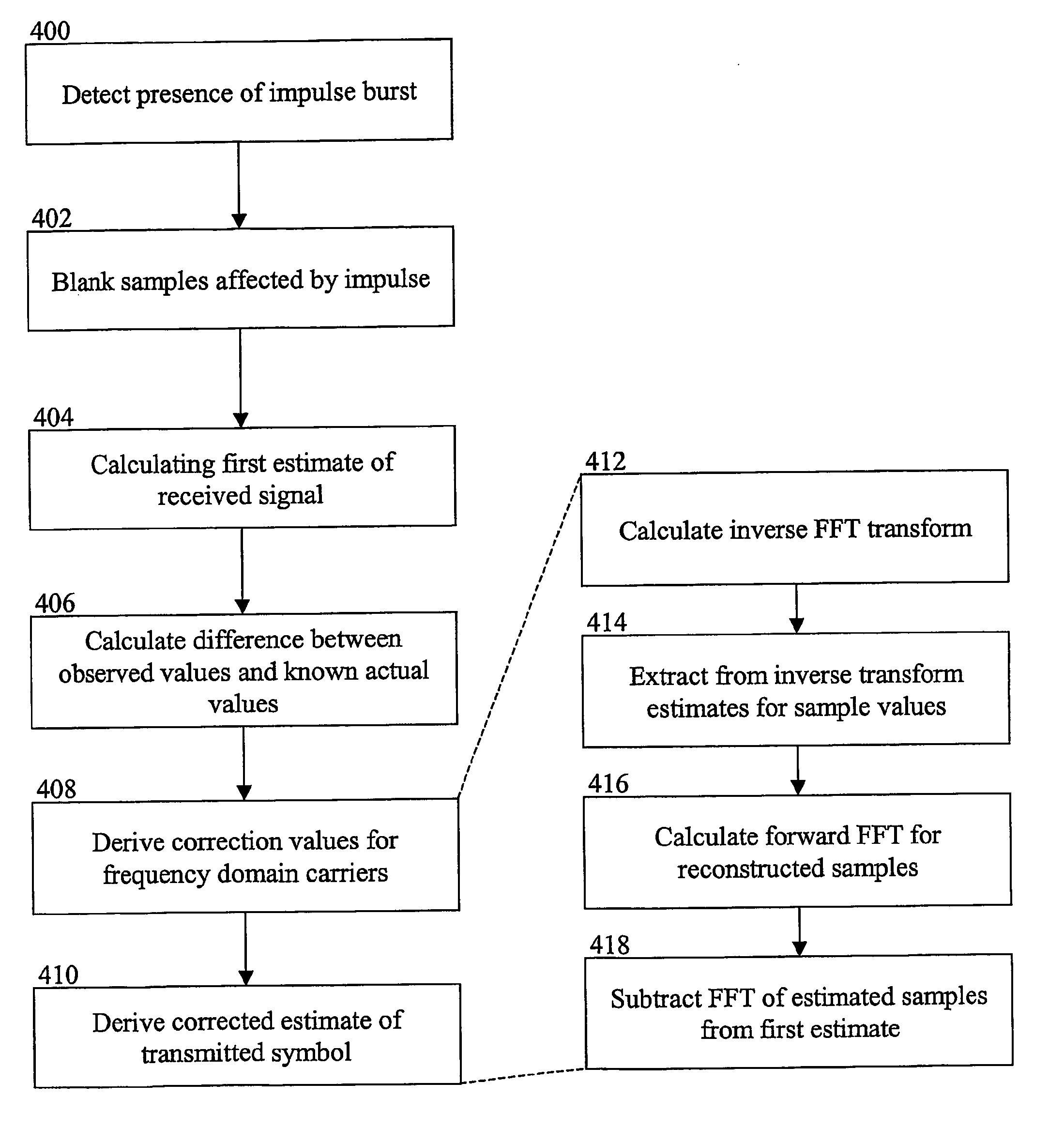
Method and system for tolerating impulsive burst noise in pilot based OFDM systems, especially using DVB-T standard. The method contains following steps: 1) recognition of the impulse position and possibly length in the time domain symbol, 2) blanking of those samples of the symbol where significant amount of impulse noise is present, 3) calculating the first estimate of the received signal from the blanked symbol, 4) using a prior information (guard band carriers, pilot carriers) an estimate of the blanked symbol is calculated using inverse FFT on the differences of the observed carrier values from the known values in the frequency domain, 5) correction values for the frequency domain carriers are derived taking the FFT of the restored time domain samples, 6) finally the corrected estimate of the received symbol is derived by summing the correction values of step 5 to the first estimate of carriers derived in step 3. The method allows correction of relatively long bursts of impulse noise with minor degradation. The method provides considerably reliable data reception in broadcast systems.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
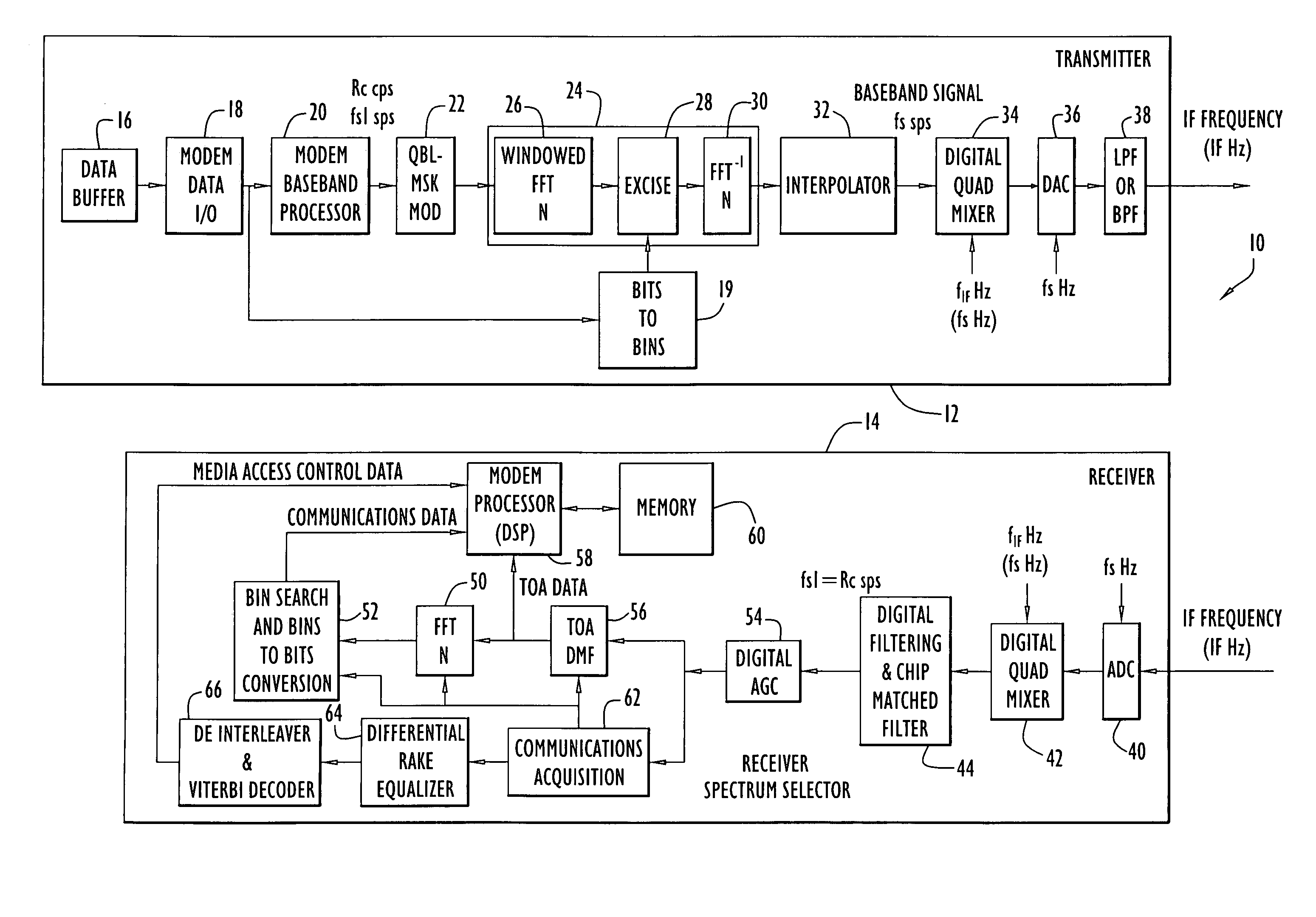
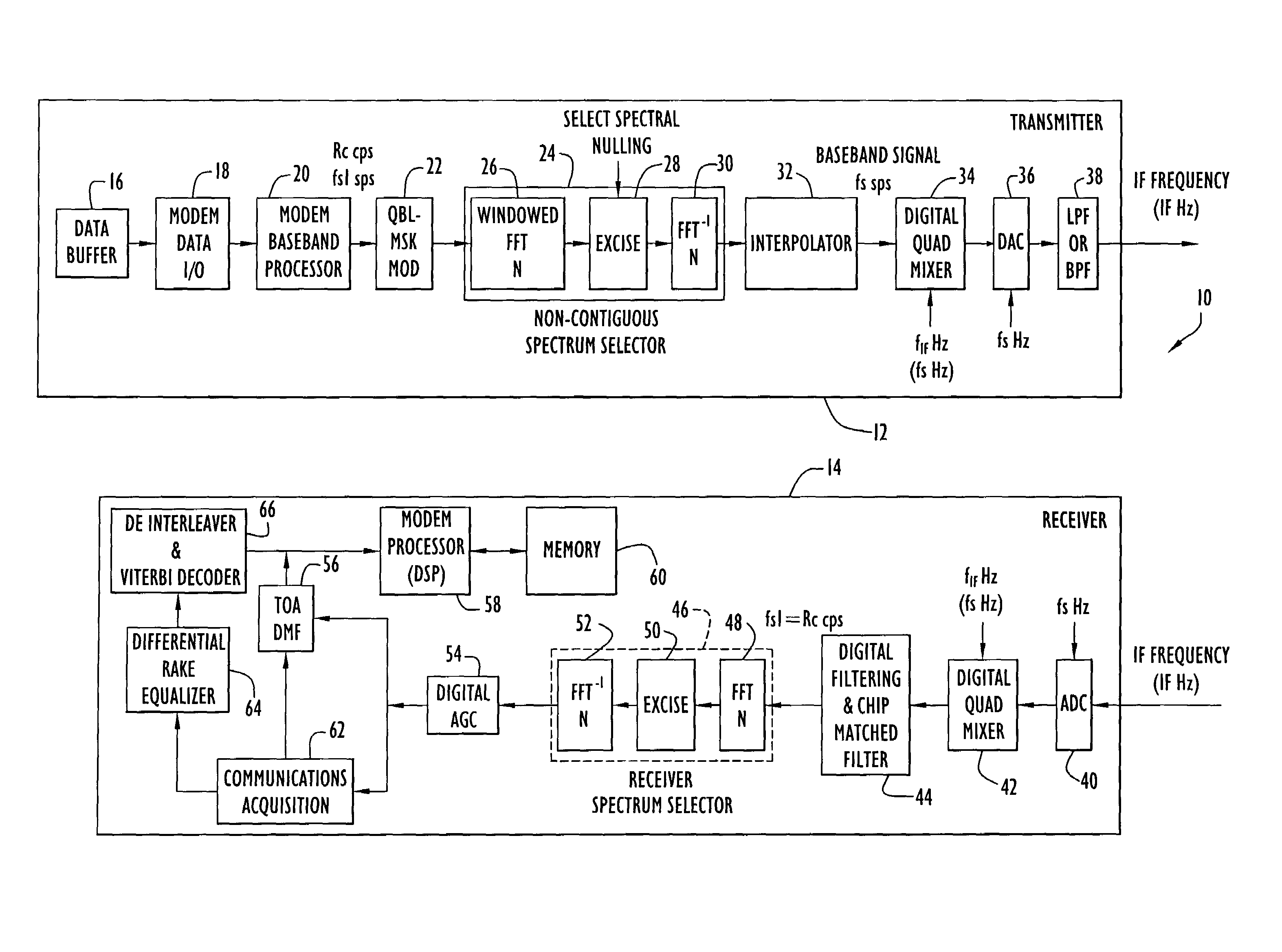
Methods and apparatus for transmitting non-contiguous spread spectrum signals for communications and navigation
ActiveUS7366243B1Eliminate distractionsWithout reducing signal energyMultiplex system selection arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsTime domainFrequency spectrum
A technique for transmitting a spread spectrum signal using plural non-contiguous frequency bands separated by segments of frequency spectrum excluded from use involves: generating a digital time-domain spread spectrum signal; converting the time-domain signal to a frequency-domain signal via an FFT; excising a portion of the frequency-domain signal by selectively removing frequency bins of the frequency-domain signal to cause spectral nulling of the transmit signal at the frequencies of the excluded segments; and converting the excised frequency-domain signal to an excised time-domain signal via an inverse FFT, which is then converted to an analog signal for transmission. The non-contiguous spectrum selection technique is implemented in a transmitter that transmits data communication signals or navigation signals, and permits use of plural, non-contiguous frequency bands to transmit a wide bandwidth signals that cannot be transmitted in a continuous frequency band due to constrains in the allocated frequency spectrum available for transmission.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMMUNICATIONS INC
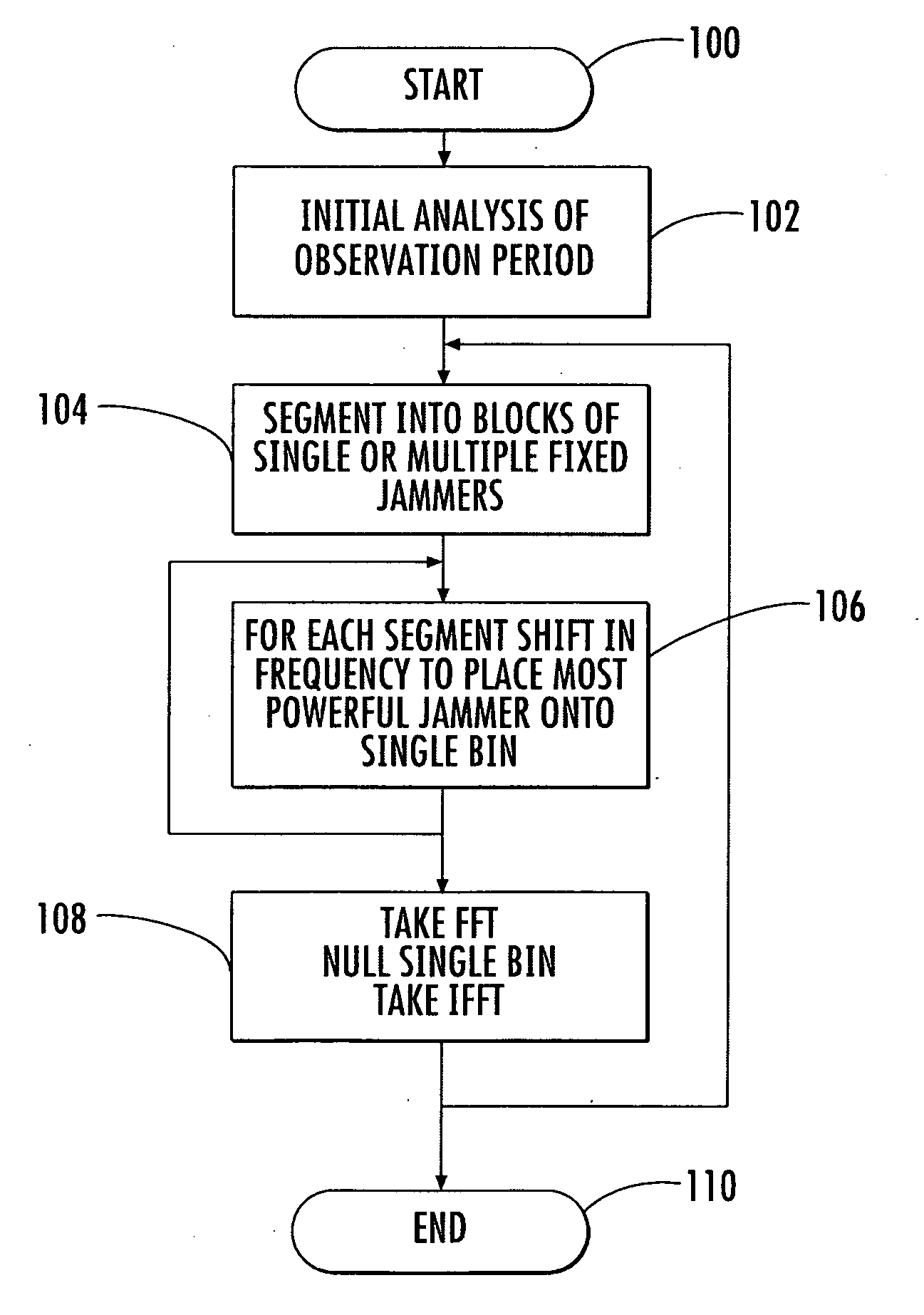
System and method for removing interfering narrowband signals from wide bandwidth receive signal
ActiveUS20060176965A1Removing narrowband interferenceOvercomes drawbackError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTime domainBroadband
In accordance with the present invention, the system and method removes interfering signals from a communications signal and includes a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) circuit for taking the FFT of a received signal and segmenting the signal into segments. A frequency shifting circuit can shift each segment in frequency to place an interfering signal within a single FFT band to be later substantially nulled. An inverse FFT circuit can place the segments of signals back within the time domain.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMM INC
Method for quickly simulating airborne phased array pulse Doppler (PD) radar clutter
ActiveCN103207387AReduce in quantityImprove Simulation EfficiencyWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsSynthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a method for quickly simulating airborne phased array pulse Doppler (PD) radar clutter. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image; dividing the whole clutter scene into rectangular scattering units, and regarding each scattering unit as a point scattering body distributed in the center of the unit; acquiring the initial backscattering coefficient of each scattering unit; dividing the clutter scene into equidistant rings; upsampling a transmitted signal of a PD radar, and performing fast Fourier transform (FFT) on an upsampling result to obtain U(omega); calculating the amplitude A of each scattering unit; calculating the radar backscattering coefficient of each equidistant ring; acquiring an impulse response function of a system, and performing FFT on the function to obtain H(omega); and multiplying U(omega) by H(omega), and performing inverse FFT on a multiplication result to obtain a clutter signal received in a period corresponding to a transmitted pulse. By the method, natural scene clutter is quickly simulated in the airborne PD radar system under the condition of high resolution.
Owner:北京理工雷科电子信息技术有限公司
Techniques for accurately deriving physiologic parameters of a subject from photoplethysmographic measurements
InactiveUS20130085354A1Good for scrollingUndesirable frequency content eliminated and reducedCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationData setPulse oximeters
Several techniques are disclosed for isolating either heart or breath rate data from a photoplethysmograph, which is a time domain signal such as from a pulse oximeter. The techniques involve the use of filtering in the frequency domain, after a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) has been conducted on a given photoplethysmograph also references as a given set of discrete time-domain data. The filtering may be applied to an identified fundamental frequency and one or more harmonics for heart related parameters. The filter may be truncated to the frequency data set and further applied multiple times to improve roll off. After filtering, an Inverse FFT (IFFT) is used to reconstruct the time-domain signal, except with undesirable frequency content eliminated or reduced. Calculation or measurement of parameters is then conducted on this reconstructed time-domain signal.
Owner:STARR LIFE SCI
Inverse fast fourier transform (IFFT) with overlap and add
InactiveUS7197095B1Efficiently null a relatively large number of jammersReduced to practiceBeacon systems using radio wavesDigital computer detailsComputation complexitySpace-time adaptive processing
A system for efficiently filtering interfering signals in a front end of a GPS receiver is disclosed. Such interfering signals can emanate from friendly, as well as unfriendly, sources. One embodiment includes a GPS receiver with a space-time adaptive processing (STAP) filter. At least a portion of the interfering signals are removed by applying weights to the inputs. One embodiment adaptively calculates and applies the weights by Fourier Transform convolution and Fourier Transform correlation. The Fourier Transform can be computed via a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). This approach advantageously reduces computational complexity to practical levels. Another embodiment utilizes redundancy in the covariance matrix to further reduce computational complexity. In another embodiment, an improved FFT and an improved Inverse FFT further reduce computational complexity and improve speed. Advantageously, embodiments can efficiently null a relatively large number of jammers at a relatively low cost and with relatively low operating power.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Receiving method for bandwidth expansion of 1553B communication bus
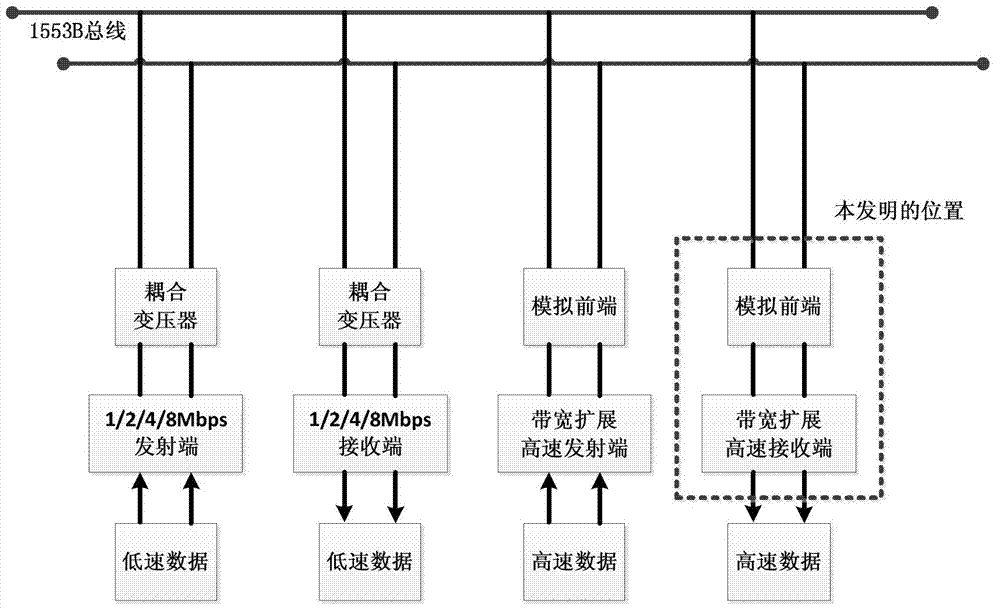
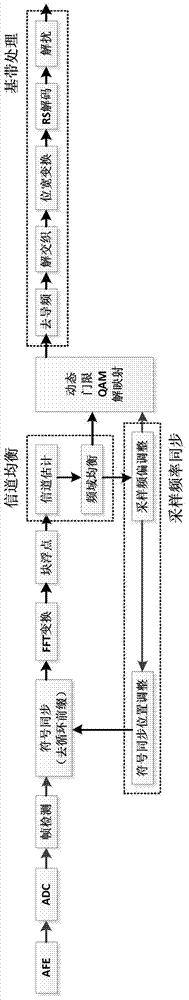
InactiveCN102821080AImprove frequency band utilizationIncrease data transfer rateTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMultiple carrier systemsCommunication deviceFrequency offset
The invention relates to a 1553B digital communication device. In order to expand the communication capacity, expand the data-transfer capacity and enhance the communication properties such as property in resisting interference and the like in a 1553B bus, the invention provides the technical scheme: a receiving method for bandwidth expansion of a 1553B communication bus. The following method sub-modules: an analog front end (AFE), a frame detecting module, a symbol synchronizing module, an inverse FFT (fast Fourier transformation) module, a block floating point module, a channel balancing module, a frequency offset synchronizing module, a QAM (quadrature amplitude modulation) de-mapping module of a dynamic threshold and a base-band processing module are provided in the receiving method, wherein the AFE is used for performing signal amplification and AD (analog-to-digital) conversion, sampling an analog signal into a digital signal and transmitting; the frame detecting module is used for detecting the access situation of a frame; the IFFT module is used for processing a base-band signal. The method provided by the invention is mainly used for 1553B digital communication.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for detecting water depth of offshore sea by X-band radar
InactiveCN103293521AHigh resolutionCalculation method is simpleOpen water surveyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSea wavesSurface gravity
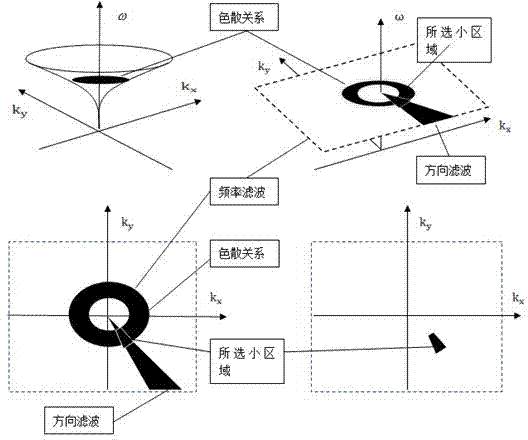
The invention relates to a method for detecting the water depth of an offshore sea by an X-band radar. The method includes the steps: acquiring sea surface echograms of a detection zone by the aid of the X-band radar, and performing three-dimensional FFT (fast Fourier transformation) for the acquired N echo image sequences to obtain transformed image spectra; filtering the image spectra by the aid of corresponding filter technique and separating a signal from noise; transforming the filtered image spectra into two-dimensional wave number spectra under a wave number coordinate (kx, ky) at a fixed frequency; transforming the two-dimensional wave number spectra into sea wave spectra of a frequency area by the aid of two-dimensional inverse FFT and an MTF (modulation transfer function); calculating a wave number corresponding to a single component spectrogram at the fixed frequency; and extracting a water depth information graph from three-dimensional spectra by inverting the water depth according to a sea surface gravity wave dispersion relation. A new method for detecting the water depth is provided, water depth measuring resolution ratio is high, water depth sea graphs of all seas in an area detected by the X-band radar can be formed, and results are straightforward.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Apparatus and method for active vibration control of hybrid vehicle
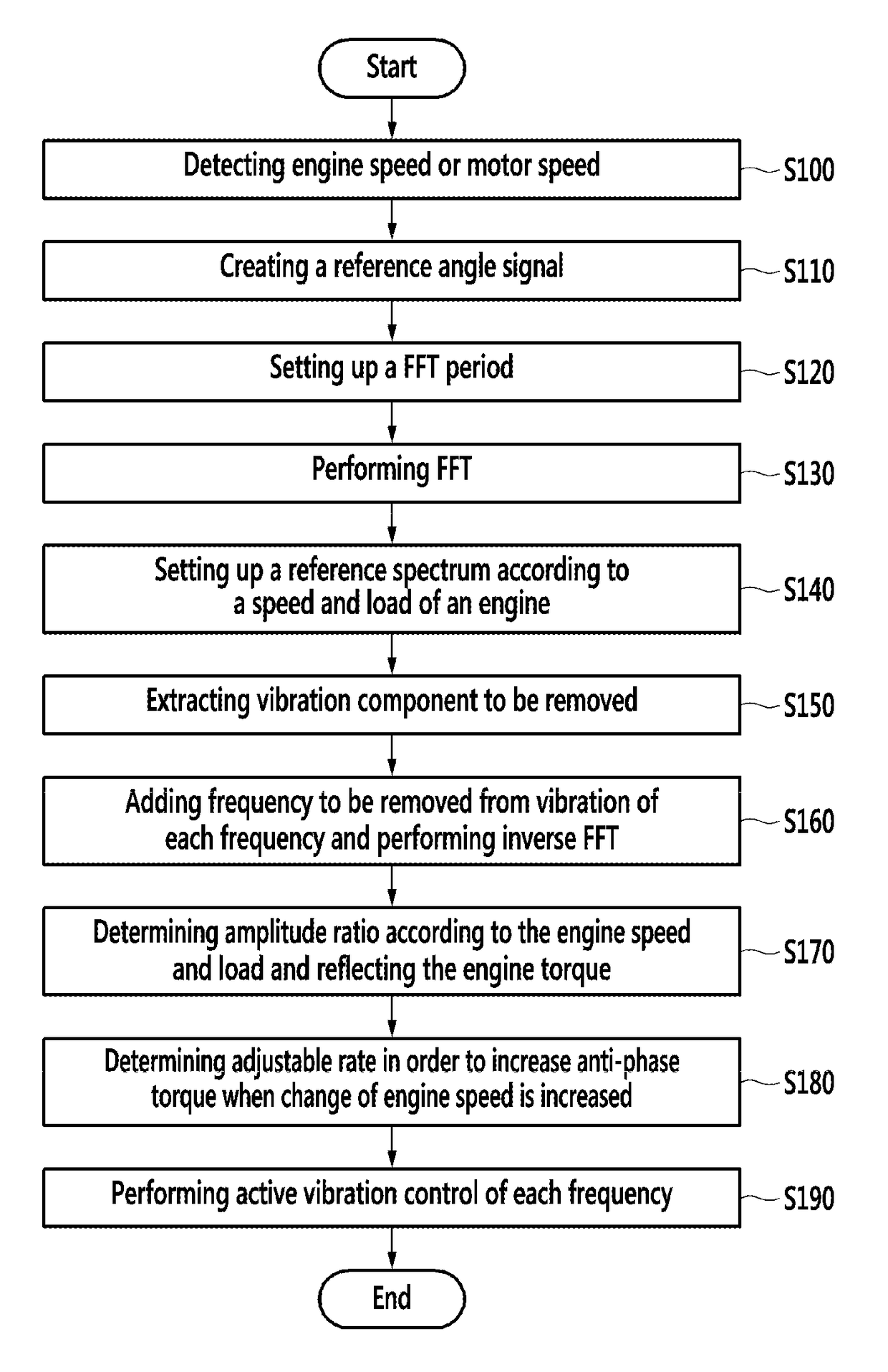
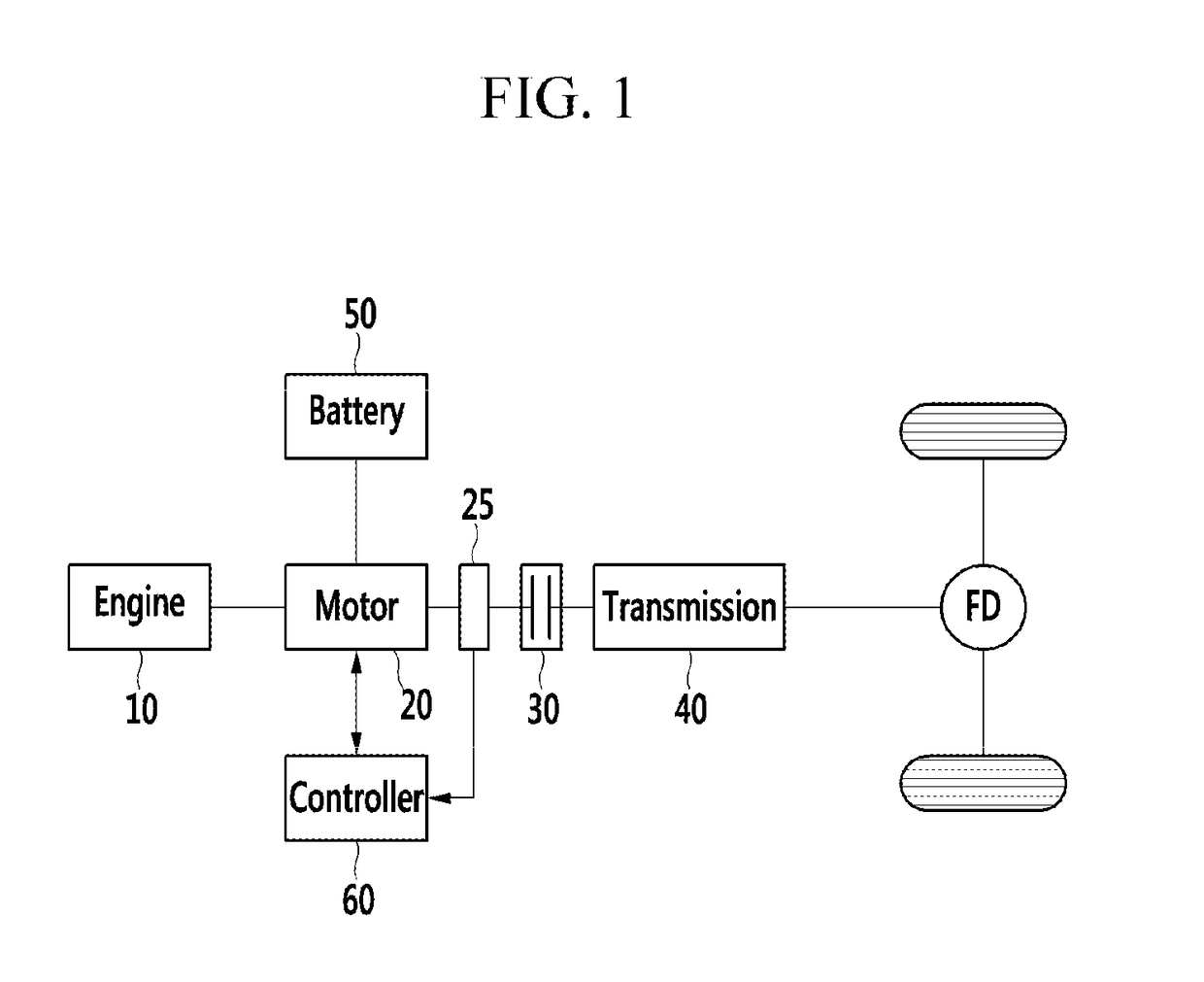
ActiveUS9981652B2Control is complicatedEliminate useProgramme controlDigital data processing detailsMotor speedEngineering
The present disclosure relates to an apparatus and a method for active vibration control of a hybrid electric vehicle. Exemplary forms provide a method for active vibration control of a hybrid electric vehicle that may include detecting an engine speed or a motor speed; selecting a reference angle signal based on position information of a motor or an engine; establishing a period of fast Fourier transform (FFT) and performing FFT of the engine speed or the motor speed corresponding to the period of the FFT from the reference angle signal; establishing a reference spectrum according to an engine speed and an engine load; extracting a vibration components to be removed based on information of the reference spectrum; summing vibration components to be removed according to the frequencies and performing inverse FFT; determining an amplitude ratio according to the engine speed and the engine load; determining an adjustable rate such that a speed change amount of the engine is increased as an anti-phase torque is increased; and performing active vibration control of each frequency based on the information of the basic amplitude ratio, the adjustable rate, and the engine torque.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
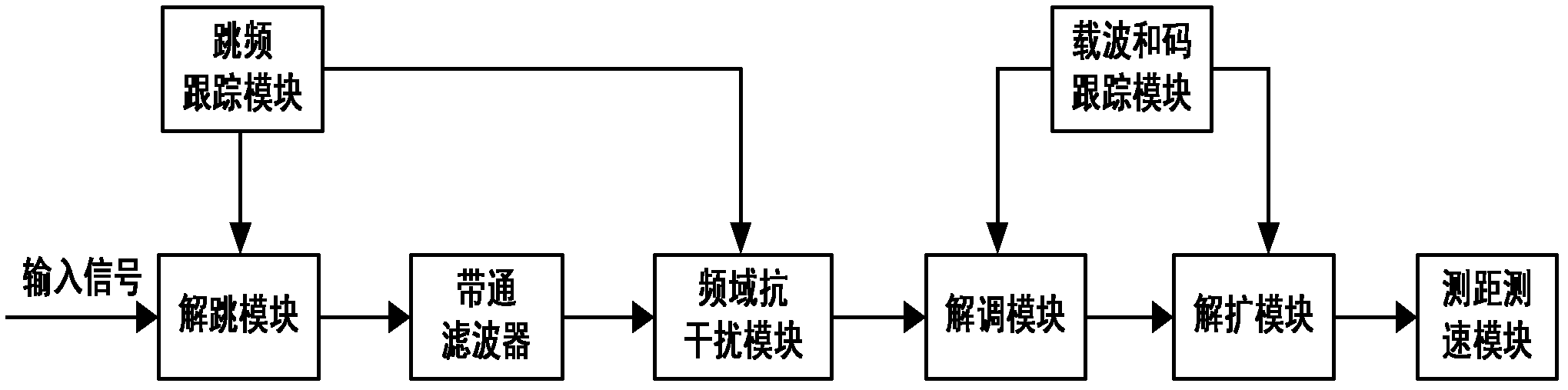
Method for improving frequency domain anti-interference performance of direct-spread/frequency-hopping mixed spread frequency system
InactiveCN102437865ASolve the problem of deteriorating anti-jamming performanceNarrowband Interference Signal SuppressionTransmissionCarrier signalBand-pass filter
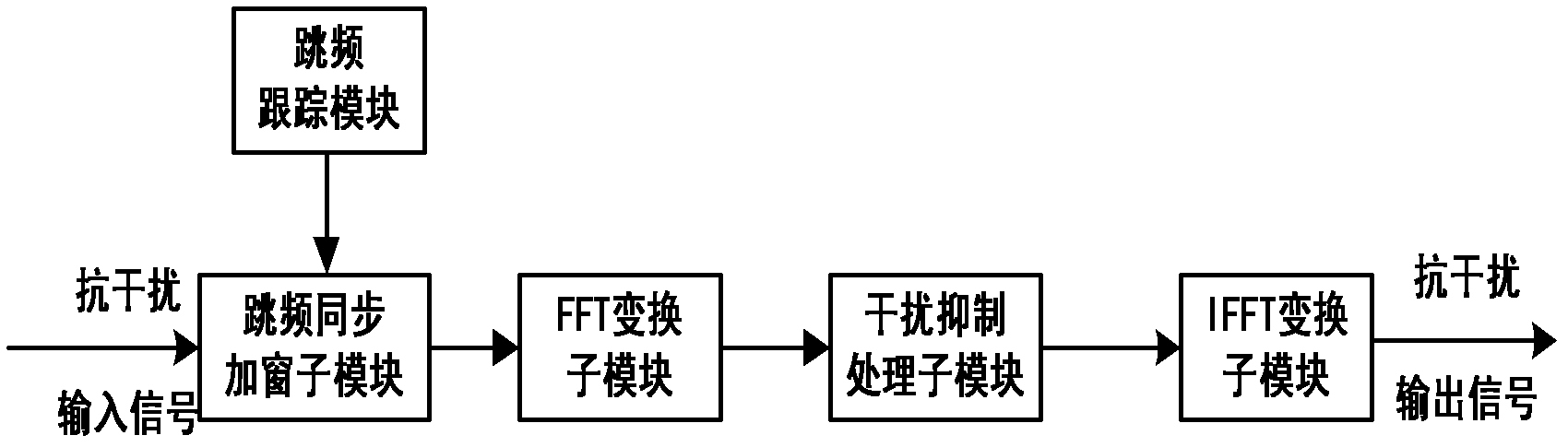
The invention provides a method for improving the frequency domain anti-interference performance of a direct-spread / frequency-hopping mixed spread frequency system and aims to solve the problems of influence on the anti-interference performance caused by discontinuous phase and poor suppression performance of a fast time-varying interference signal. The method is implemented by adopting the technical scheme that: a distance measurement and speed measurement receiver having a frequency domain anti-interference function consists of a de-hopping module, a band-pass filter, a frequency domain anti-interference module, a demodulation module, a de-spreading module and a distance measurement and speed measurement module, which are sequentially connected on the same line in series, a frequency-hopping tracking module which is bridged on the de-hopping module and the frequency domain anti-interference module in parallel, and a carrier and code tracking module which is bridged on the demodulation module and the de-spreading module in parallel; and the frequency domain anti-interference module is divided into a windowing sub-module which is in frequency-hopping synchronization with the frequency-hopping tracking module, a fast Fourier transformation (FFT) sub-module, an interference suppression processing sub-module and an inverse FFT (IFFT) sub-module. The method is applicable to suppression of a narrow-band interference signal.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
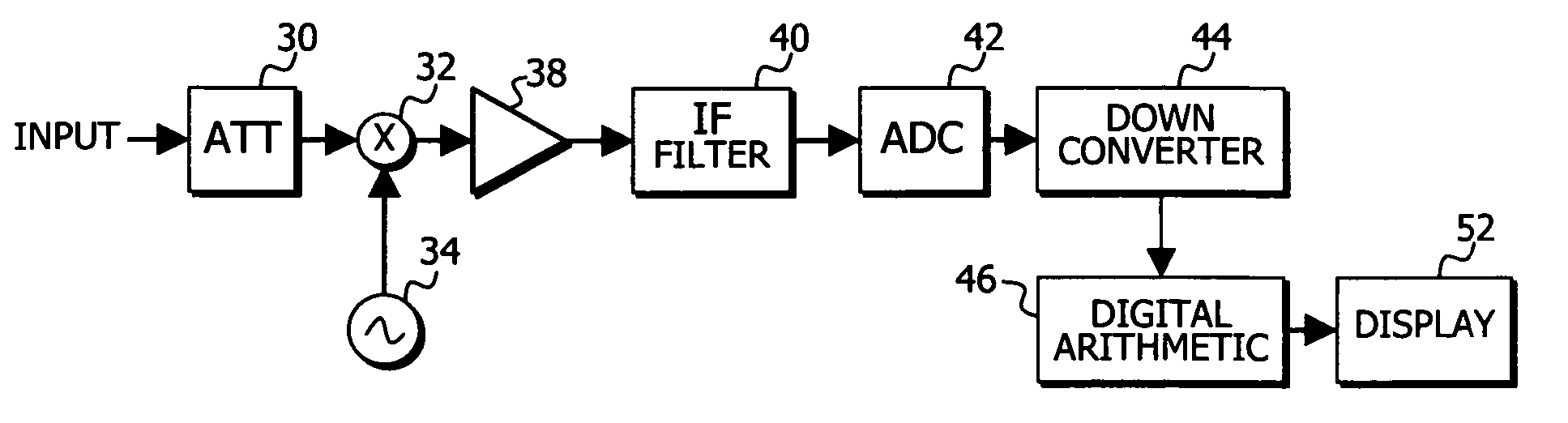
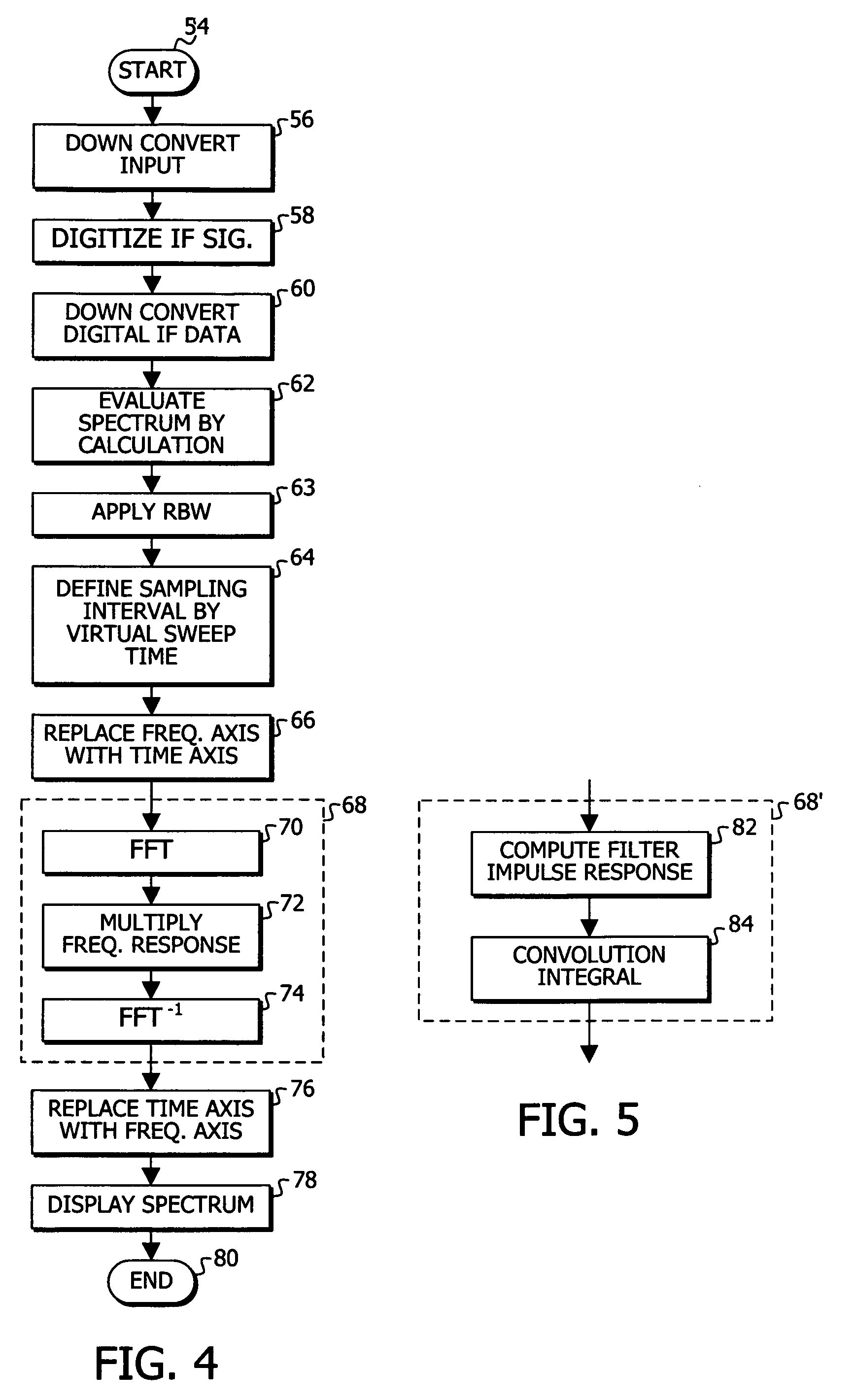
Data processing method for spectrum analyzer
ActiveUS20060291631A1Maintain compatibilitySpectral/fourier analysisAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingFrequency spectrumFrequency response
A data processing method is provided to enable a calculation based signal analyzer, such as an FFT based spectrum analyzer, to produce results corresponding to a swept spectrum analyzer employing a video bandwidth (VBW) filter. Once a spectrum is produced the frequency axis is replace by a corresponding time axis, so that a time domain filter, such as a video bandwidth (VBW) filter can be applied. In a first example, the filter characteristics are applied by performing an FFT on display spectrum data, which has had its frequency axis replaced by a corresponding time axis, produce frequency domain data, multiplying by the frequency response to produce a filtered version, performing an inverse FFT and replacing the time axis with the original frequency axis to produce a filtered version of the display spectrum data. In another example, a filter impulse response is computed based upon the desired filter characteristics, a convolution integral of the display spectrum data, which has had its frequency axis replaced by a corresponding time axis, and the filter impulse response is conducted, and the time axis is replace by the original frequency axis to produce filtered display spectrum data.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
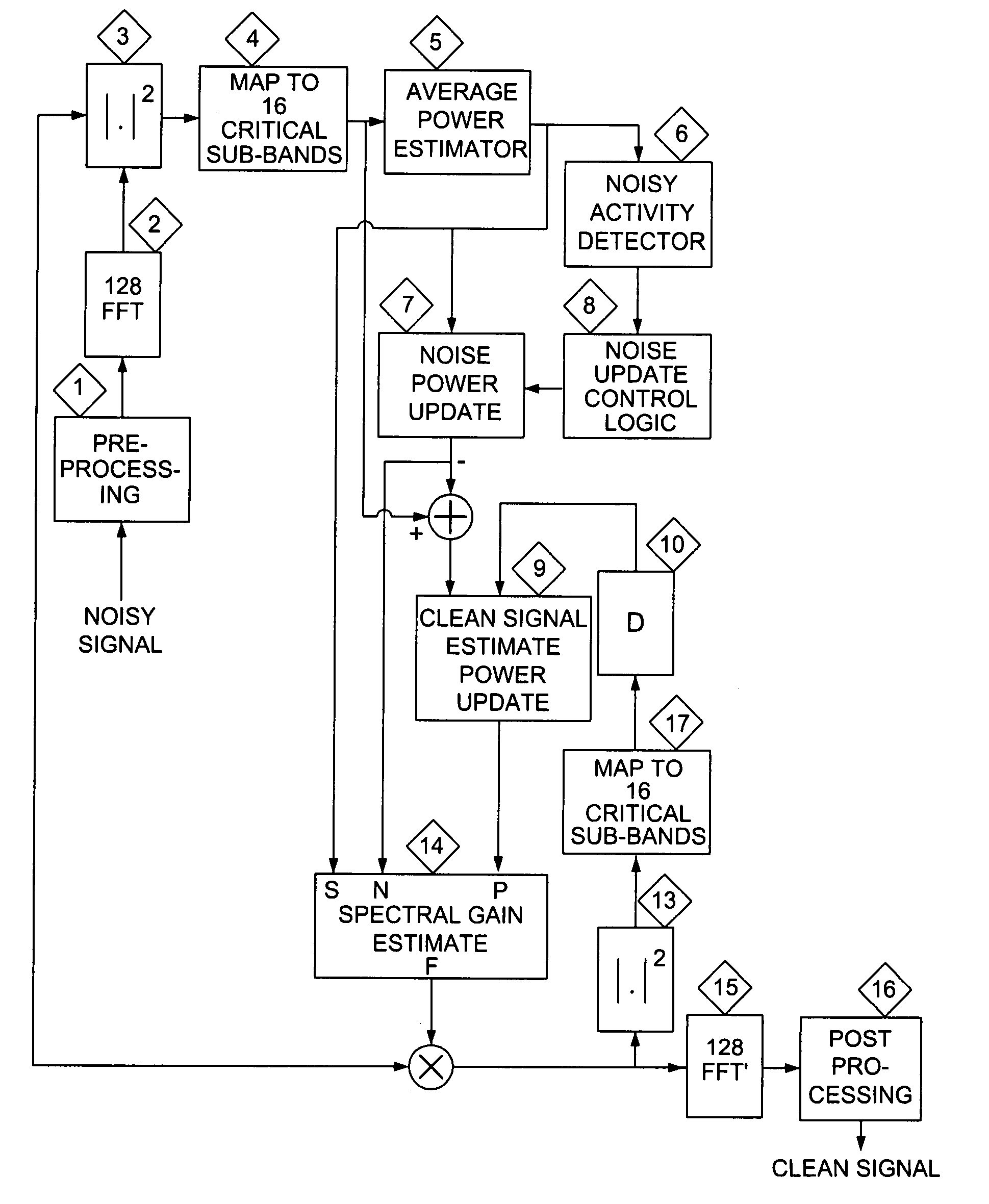
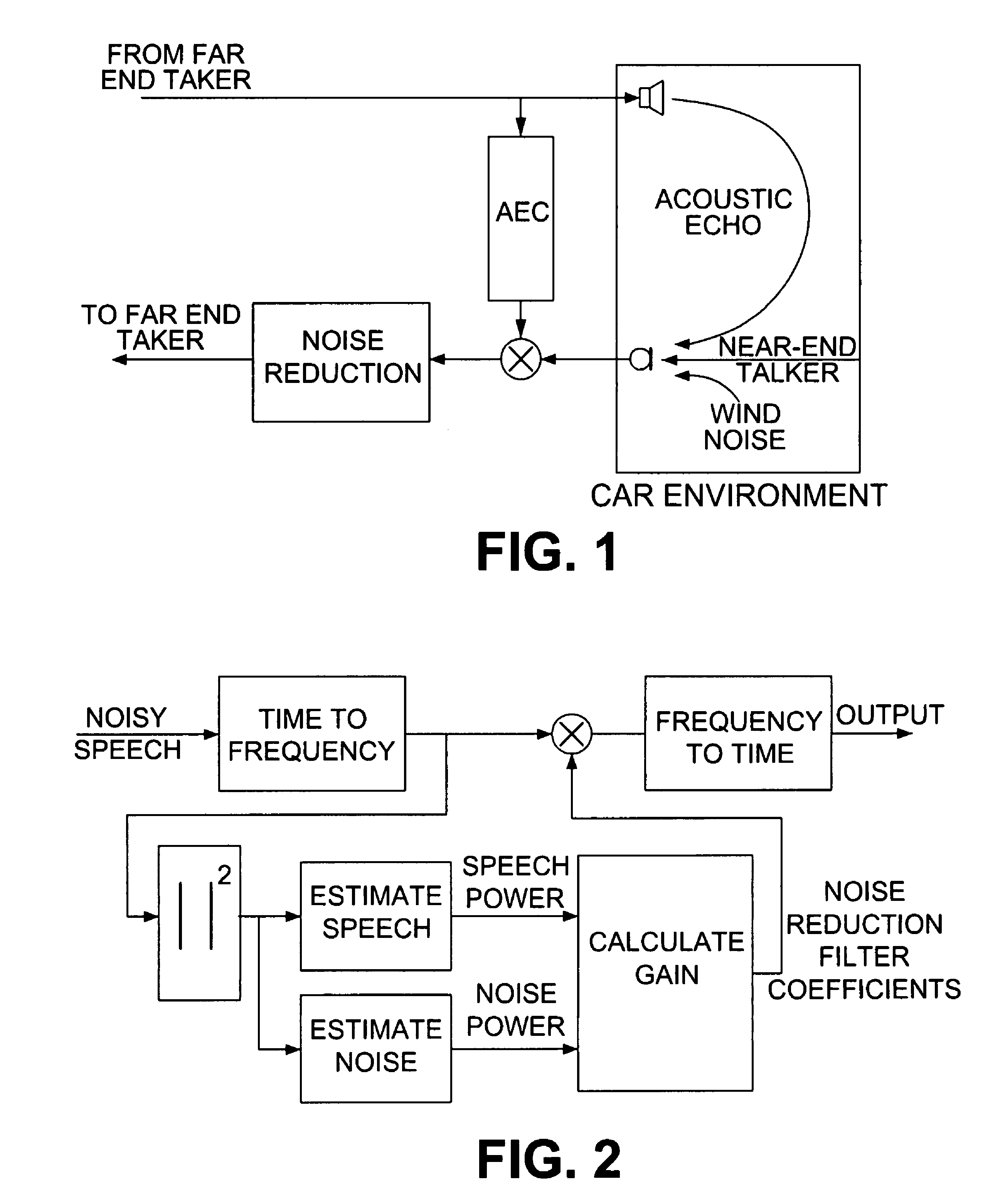
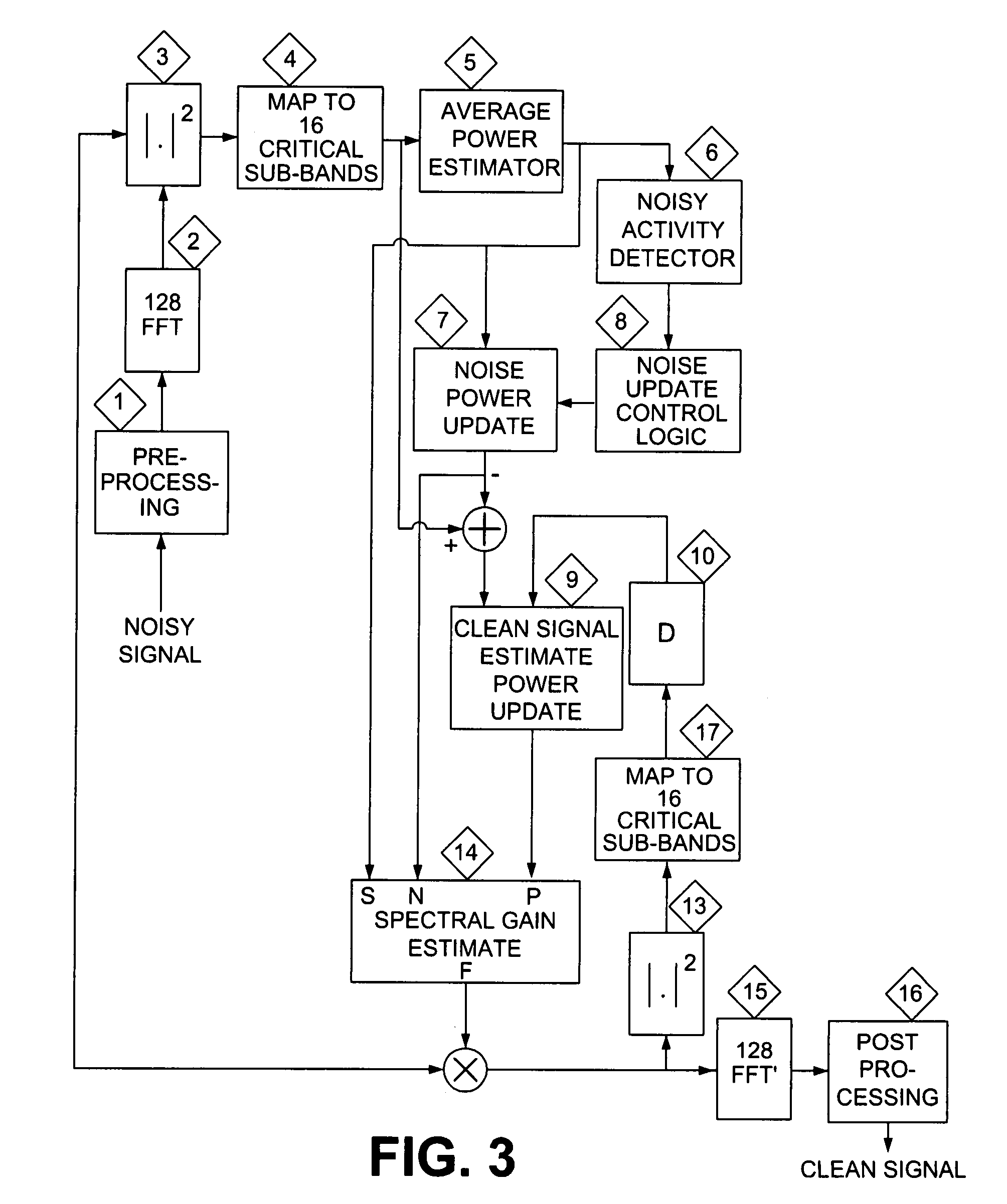
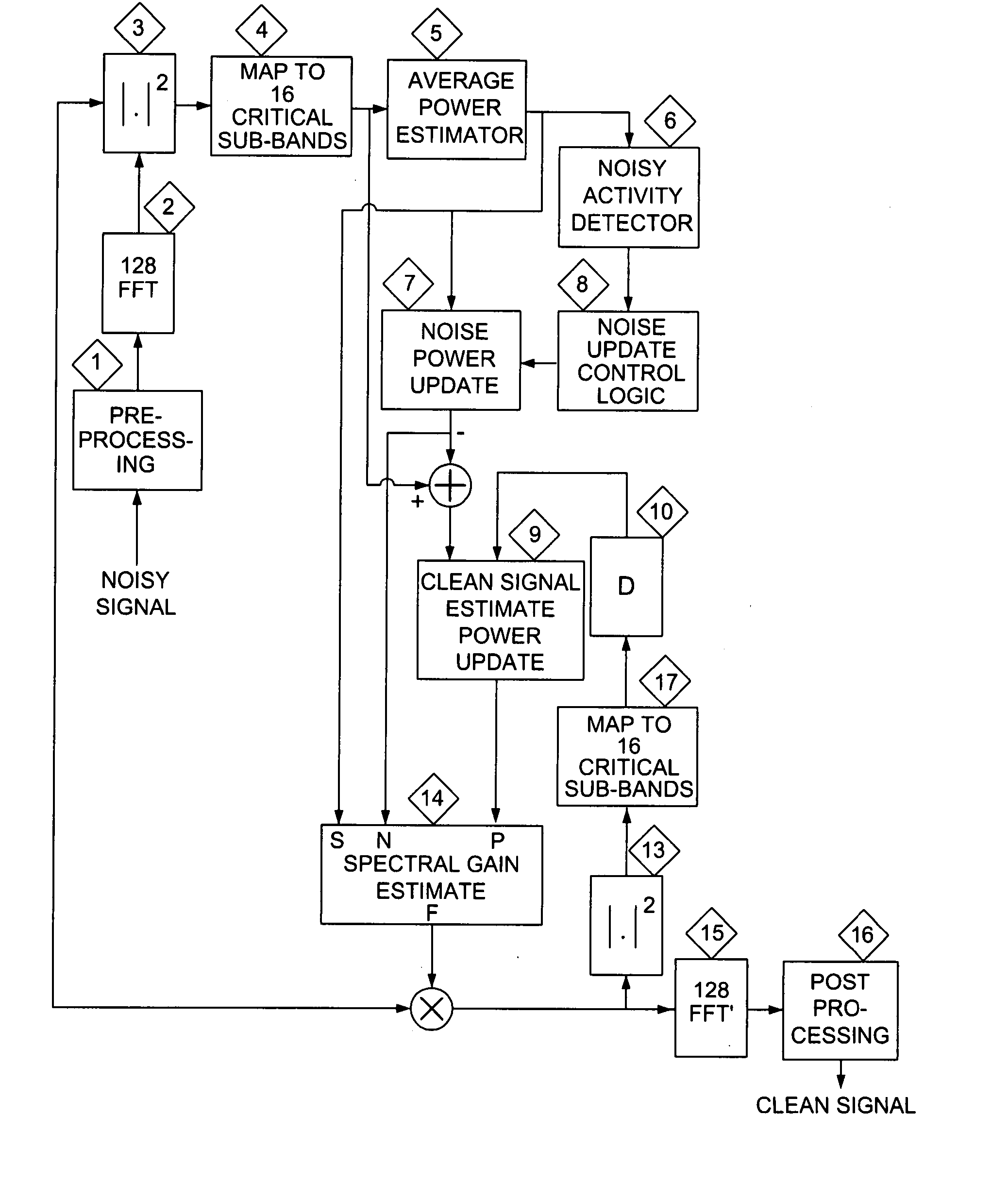
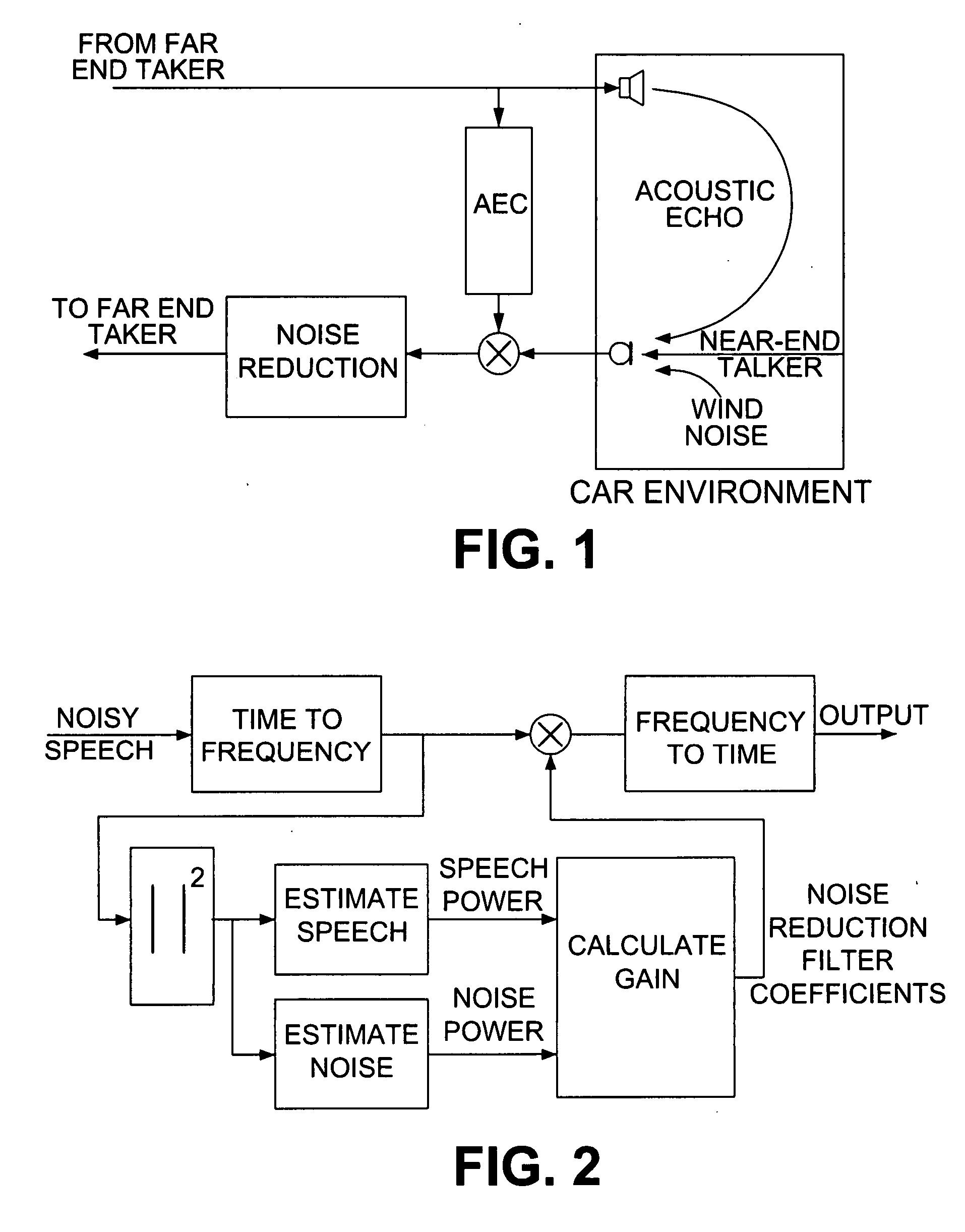
Low complexity noise reduction method
ActiveUS8010355B2Low computing complexityImprove performanceSpeech recognitionTransmissionTime domainFourier transform on finite groups
A method of reducing noise in a speech signal involves converting the speech signal to the frequency domain using a fast fourier transform (FFT), creating a subset of selected spectral subbands, determining the appropriate gain for each subband, and interpolating the gains to match the number of FFT points. The converted speech signal is then filtered using the interpolated gains as filter coefficients, and an inverse FFT performed on the processed signal to recover the time domain output signal.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
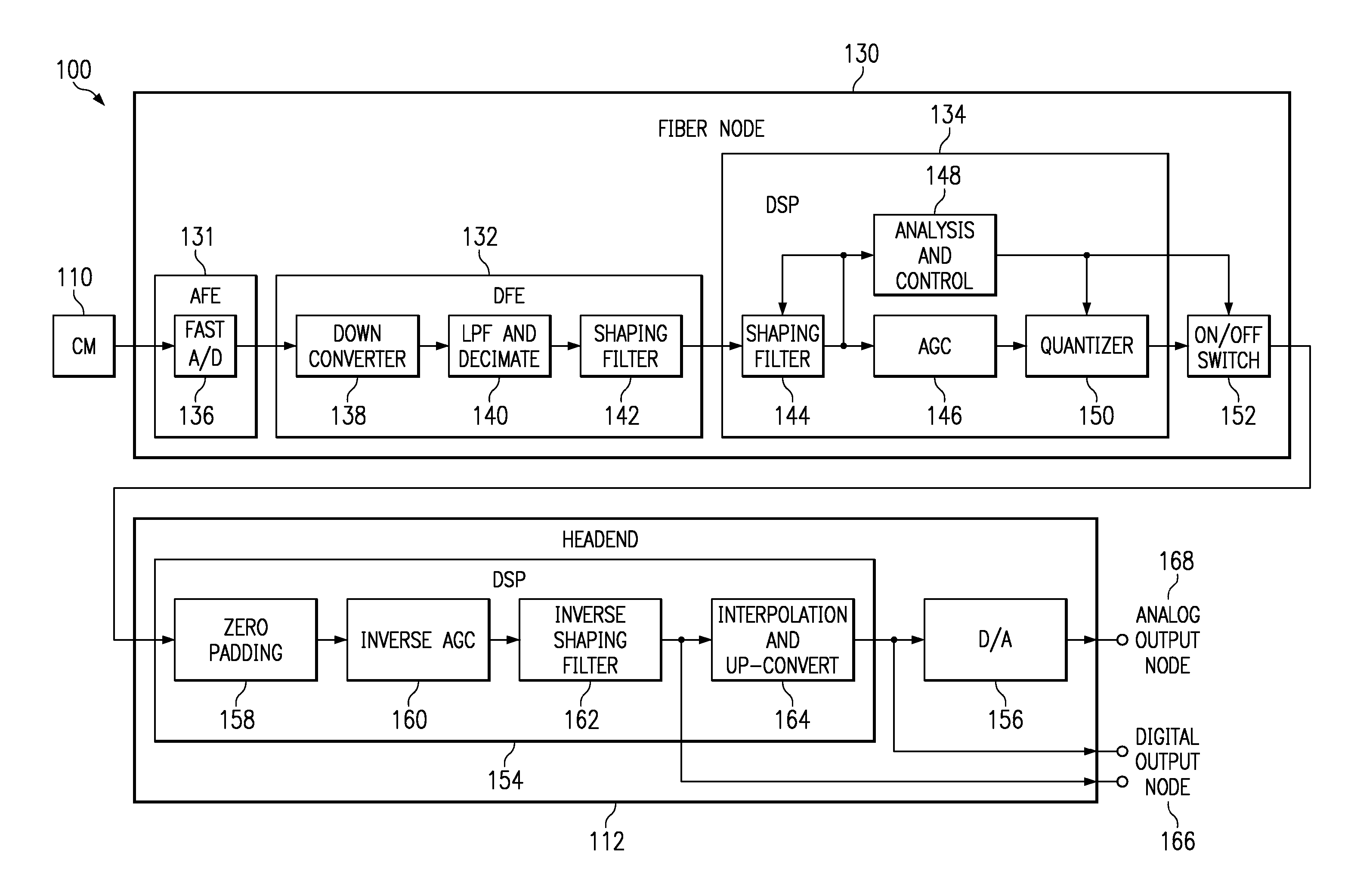
Signal Compression for Fiber Node
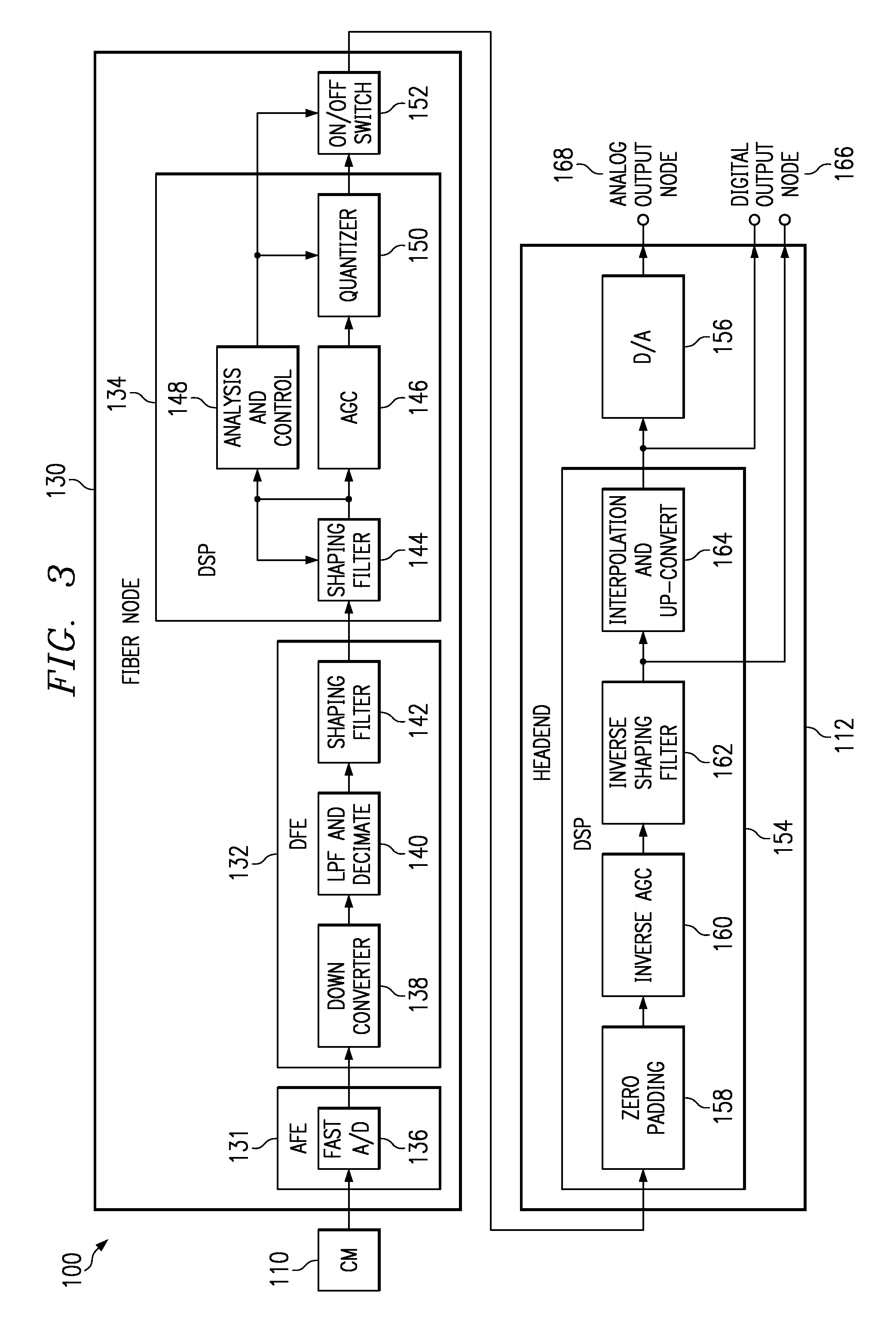
ActiveUS20070288977A1Effectively use frequencyCapacityTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionFiberModem device
A method, device and network for compressing cable modem data signals and conserving bandwidth within the network. Cable modems transmit upstream data signals to a fiber node which compresses the data signals and transmits the compressed signals upstream to a headend which decompresses the data signals. The fiber node compression may be by a shaping filter or a fast Fourier transform (FFT) function. The headend decompression may be by an inverse shaping filter or an inverse FFT function.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
FPGA-based InSAR channel amplitude and phase error estimation method
InactiveCN104931968AImprove coherenceReduce the effects of spurious noiseRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumRadar systems
The invention discloses an FPGA-based inter-channel amplitude and phase error characteristic frequency domain windowing estimation method. The problem of reduced inter-channel coherence, which is caused by inconsistent amplitude and phase characteristics of multiple channels of the existing radar system, is solved. The method comprises the steps that (1) channel data are input; (2) time-frequency conversion is carried out on channel signals; (3) spectrum alignment is carried out on the spectrums of the channel signals; (4) FFT conversion is carried out on a spectrum alignment result; (5) windowing is carried out on the FFT conversion result of spectrum alignment; (6) and inverse FFT operation is carried out the windowed data to acquire inter-channel amplitude and phase error characteristic estimation. According to the invention, fast and efficient functions of FFT time-frequency conversion and time sequence logic control of FPGA are fully used; a high-quality amplitude and phase error characteristic estimation result can be acquired under the condition of large spurious noise; the influence of spurious noise on the estimation result is reduced; and the method can be applied to a two-channel and / or multi-channel radar real-time signal processing system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Original echo generation method for airborne Interference synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN1808172AShorten the timeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSpace constantInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
The invention relates to a method for generating a machine carried interference synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) original echo wave. The method comprises: step 1: implementing position method of Fourier transformation (FFT) on equivalent back scattering coefficientª†1ú¼2(xú¼ª†), and then multiplying a phase function with defocus item and reducing and enlarging factor P1ú¢exp{j(ªš2 / alphaª†0ú®ª†ú½j[ª©1,2(ªš) / 4B]ª†2}; stp2: implementing distance FFT on the result form step 1, then multiplying a phase function with reducing and enlarging factor P2ú¢exp{j(1-ª©1,2(ªš)) / ª©1,2(ªš)BªÃ}; step 3: implementing distance inverse FFT on the result from the step 2, then multiplying a phase function with reducing and enlarging factor P3ú¢exp{-Jú¿1 / 4Bú®ª†2}; step 4: implementing distance inverse FFT on the result from the step 3, then multiplying a phase function with space constant exciting response function, distance horizontal shift factor and the reducing and enlarging factor P4ú¢Gú¿ªšú¼ªÃú¼ª†0ú®exp{-jªÃª†s1,2ú½j[ª©1,2(ªš)-1]BªÃ2}; step 5: implementing two dimensional inverse FFT on the result from step 4 and getting the needed original echo wave data h1ú¼2(xíõú¼ríõ).
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Techniques for accurately deriving physiologic parameters of a subject from photoplethysmographic measurements
Several techniques are disclosed for isolating either heart or breath rate data from a photoplethysmograph, which is a time domain signal such as from a pulse oximeter. The techniques involve the use of filtering in the frequency domain, after a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) has been conducted on a given photoplethysmograph also references as a given set of discrete time-domain data. The filtering may be applied to an identified fundamental frequency and one or more harmonics for heart related parameters. The filter may be truncated to the frequency data set and further applied multiple times to improve roll off. After filtering, an Inverse FFT (IFFT) is used to reconstruct the time-domain signal, except with undesirable frequency content eliminated or reduced. Calculation or measurement of parameters is then conducted on this reconstructed time-domain signal.
Owner:STARR LIFE SCI
Arrival direction estimation method based on minimum mutual entropy spectrum analysis
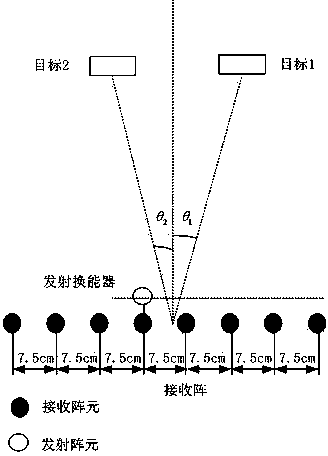
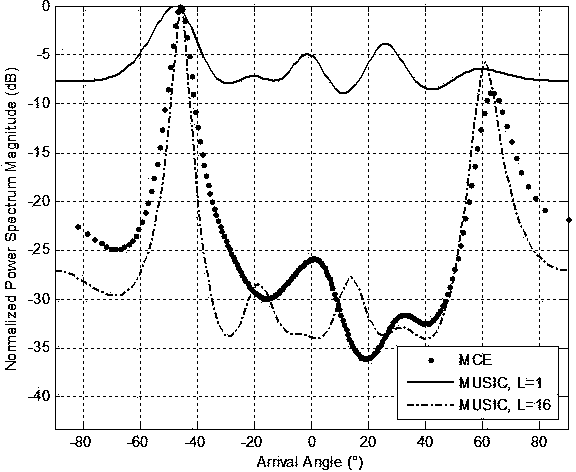
ActiveCN103713276APower Spectral Density AccurateHigh spatial spectral resolutionDirection/deviation determination systemsSpace powerPeak value
The invention discloses an arrival direction estimation method based on minimum mutual entropy spectrum analysis. The method comprises steps that: a signal is emitted by an emission energy transducer; echo of an emitted sound signal is received by a reception hydrophone array; modeling of a plane wave model is carried out for the received echo signal, and processing is carried out by utilizing the minimum mutual entropy spectrum estimation method to acquired a space power spectrum estimation value; analysis on the space power spectrum estimation value is carried out, and a corresponding abscissa of the peak value is an estimation angle of the object. According to the arrival direction estimation method, through one-time data sampling employing the array with relatively a few array elements, a spectrum analysis result with high resolution can be acquired. A cepstrum method is further employed, a convergence speed of a minimum mutual entropy spectrum analysis algorithm can be improved through reverse FFT transformation. Compared with a routine space spectrum estimation method, the arrival direction estimation method provided by the invention has advantages of higher resolution and smaller operand, and real-time processing on the array signal can be carried out. The algorithm is independent of the pre-estimated source number, and relatively good tolerance, relatively high resolution and an extremely low sidelobe level are realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Voice noise reduction method and device based on signal autocorrelation
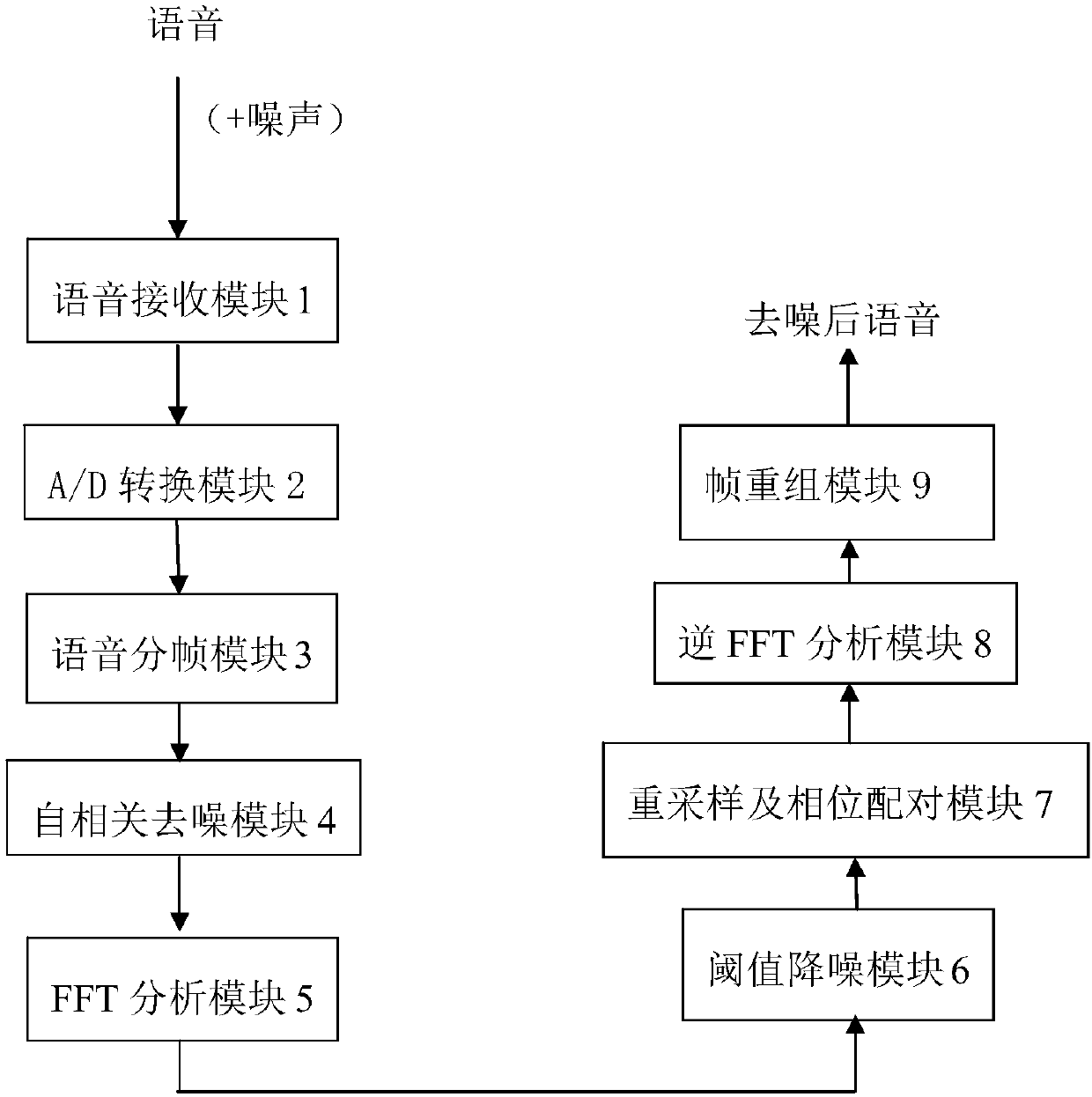
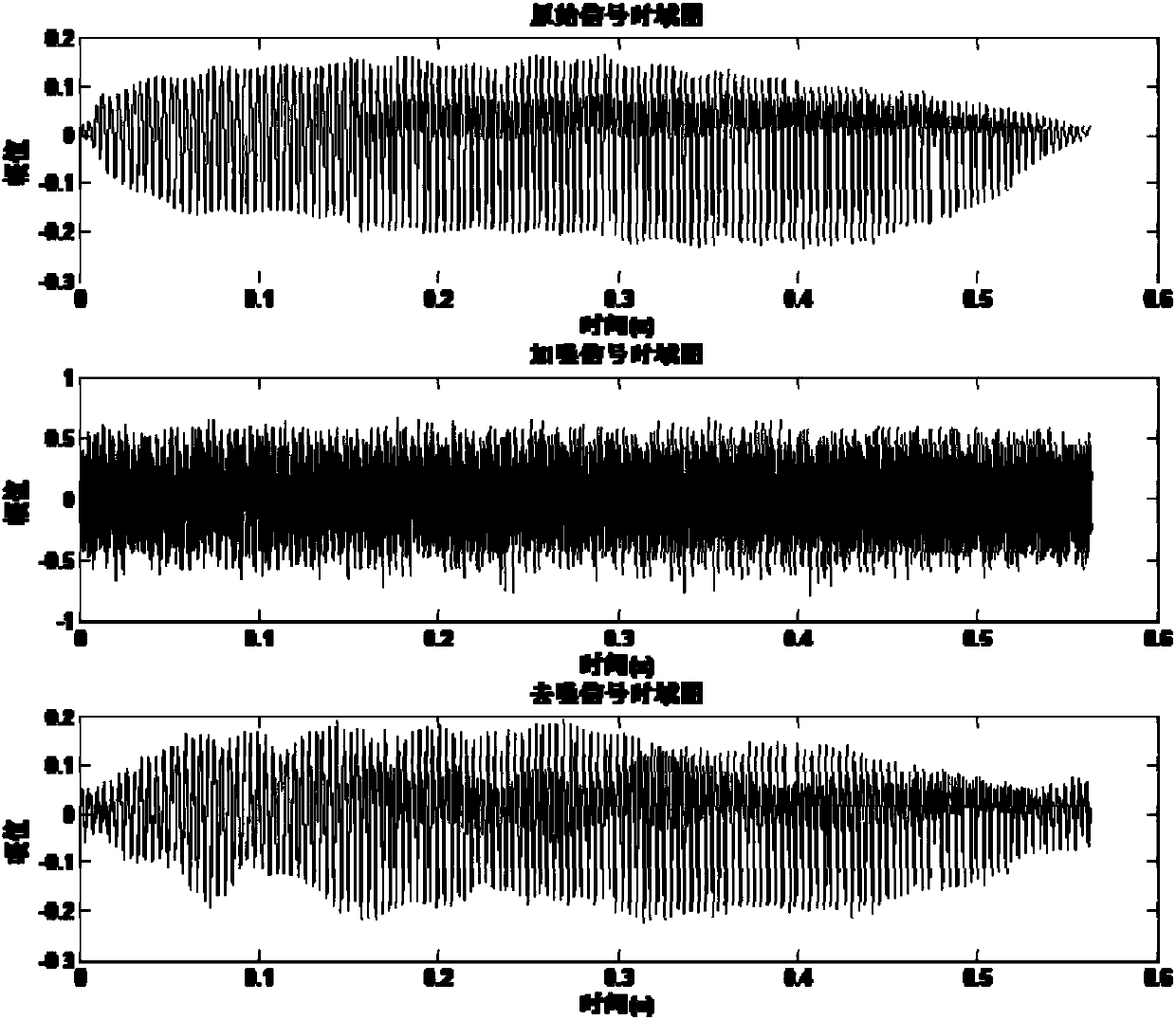
ActiveCN107785028AHigh degree of automationGood speech recognitionSpeech analysisTime delaysNoise reduction
The invention relates to a voice noise reduction method and device based on signal autocorrelation. The method comprises steps that 1), a noise-containing simulation voice signal is acquired through avoice reception module; 2), the simulation signal is converted by an A / D conversion module into a digital signal; 3), the digital signal is enframed through a voice enframing module; 4), autocorrelation operation of the signals after enframing is carried out through an autocorrelation de-noising module; 5), FFT analysis on an autocorrelation function of each noise-containing signal in a time-delay domain is carried out through an FFT analysis module; 6), threshold de-noising processing for FFT transformation is carried out through a threshold noise reduction module; 7), re-sampling of a frequency domain autocorrelation signal is carried out through a re-sampling and phase matching module, and phase matching of the frequency domain autocorrelation signal and the noise-containing signals iscarried out; 8), inverse FFT transformation is carried out by an inverse FFT transformation module through utilizing a frequency domain amplitude after processing and the phase, and the signals are returned to the time domain; and 9), recombination of each signal after de-noising is carried out through a frame recombination module to acquire voice signals after de-noising. The method is advantaged in that language sharpness can be substantially improved under the -20dB signal to noise ratio strong noise environment.
Owner:SHANGHAI YINGBO ACOUSTICS ENG TECH
Optical transmitter and optical OFDM communication system
InactiveUS8467687B2Reduce signalingReduce impactModulated-carrier systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOriginal dataCarrier signal
Distortion of a reception signal which is attributable to interference between subcarriers during photoelectric conversion is reduced in an optical OFDM communication system without broadening the signal band. A transmission signal processing unit (100) in a transmitter is provided with a distortion generating circuit (distortion generating unit) (170). A subcarrier signal is utilized as an input signal for the circuit. The distortion generating circuit (170) generates a baseband OFDM signal by means of inverse FFT calculation using the input signal, computes the square of the absolute value of the signal, and restores the subcarrier signal by mean of FFT calculation. Because interference between subcarriers is also included in the signal, the distortion element generated by the interference between the subcarriers can be extracted when the difference from the input signal is found. The signal obtained by subtracting the distortion element from the subcarrier signal, which has been modulated using the original data to be communicated, is used as the transmission signal. The transmission signal is photoelectrically converted with a receiver. The interference between subcarriers generated at this time is smaller than when the aforementioned processing is not performed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Low complexity noise reduction method
ActiveUS20070255560A1Minimizing speech distortionReduce computational complexitySpeech recognitionSpeech synthesisTime domainFrequency spectrum
A method of reducing noise in a speech signal involves converting the speech signal to the frequency domain using a fast fourier transform (FFT), creating a subset of selected spectral subbands, determining the appropriate gain for each subband, and interpolating the gains to match the number of FFT points. The converted speech signal is then filtered using the interpolated gains as filter coefficients, and an inverse FFT performed on the processed signal to recover the time domain output signal.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com