Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "Prevent Image Artifacts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
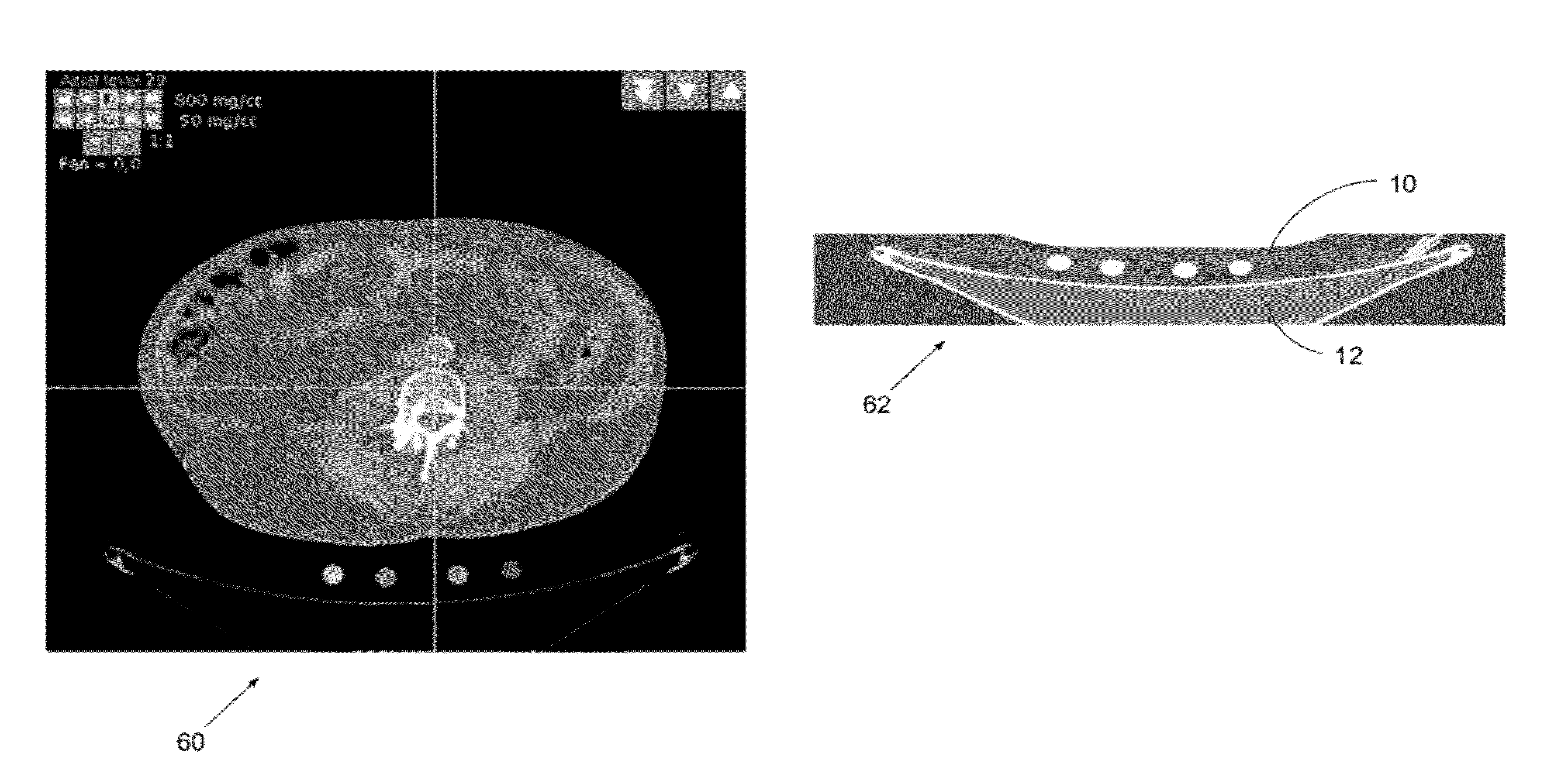
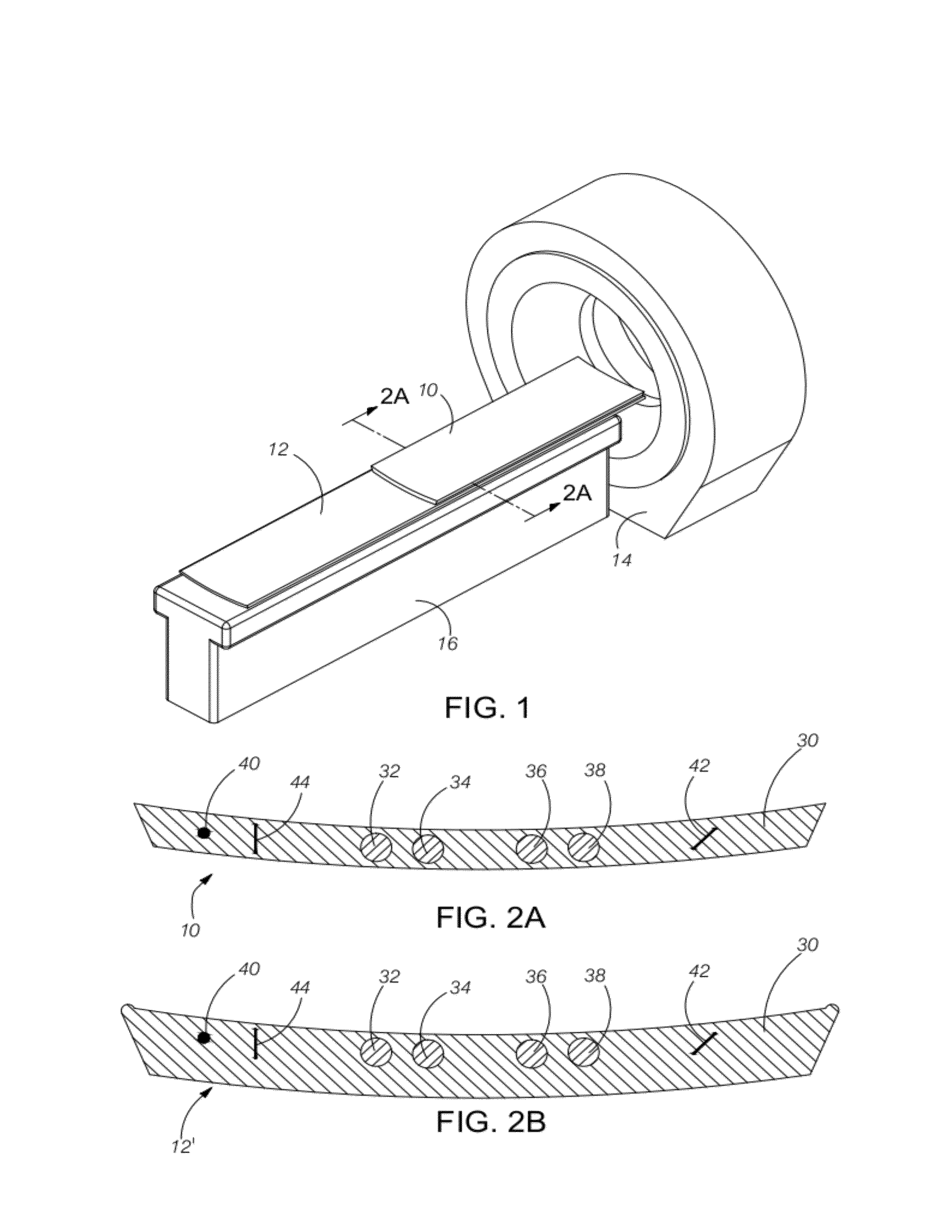
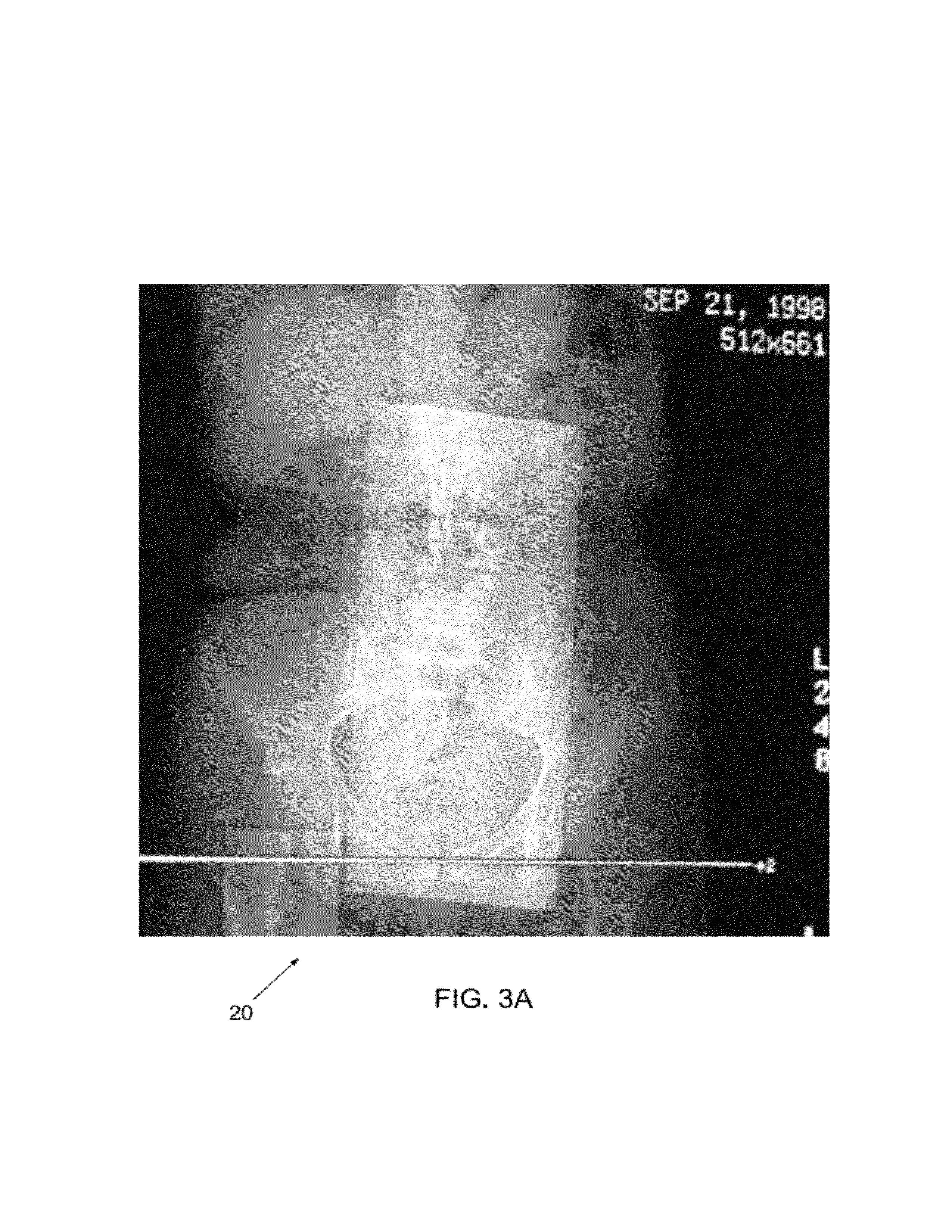
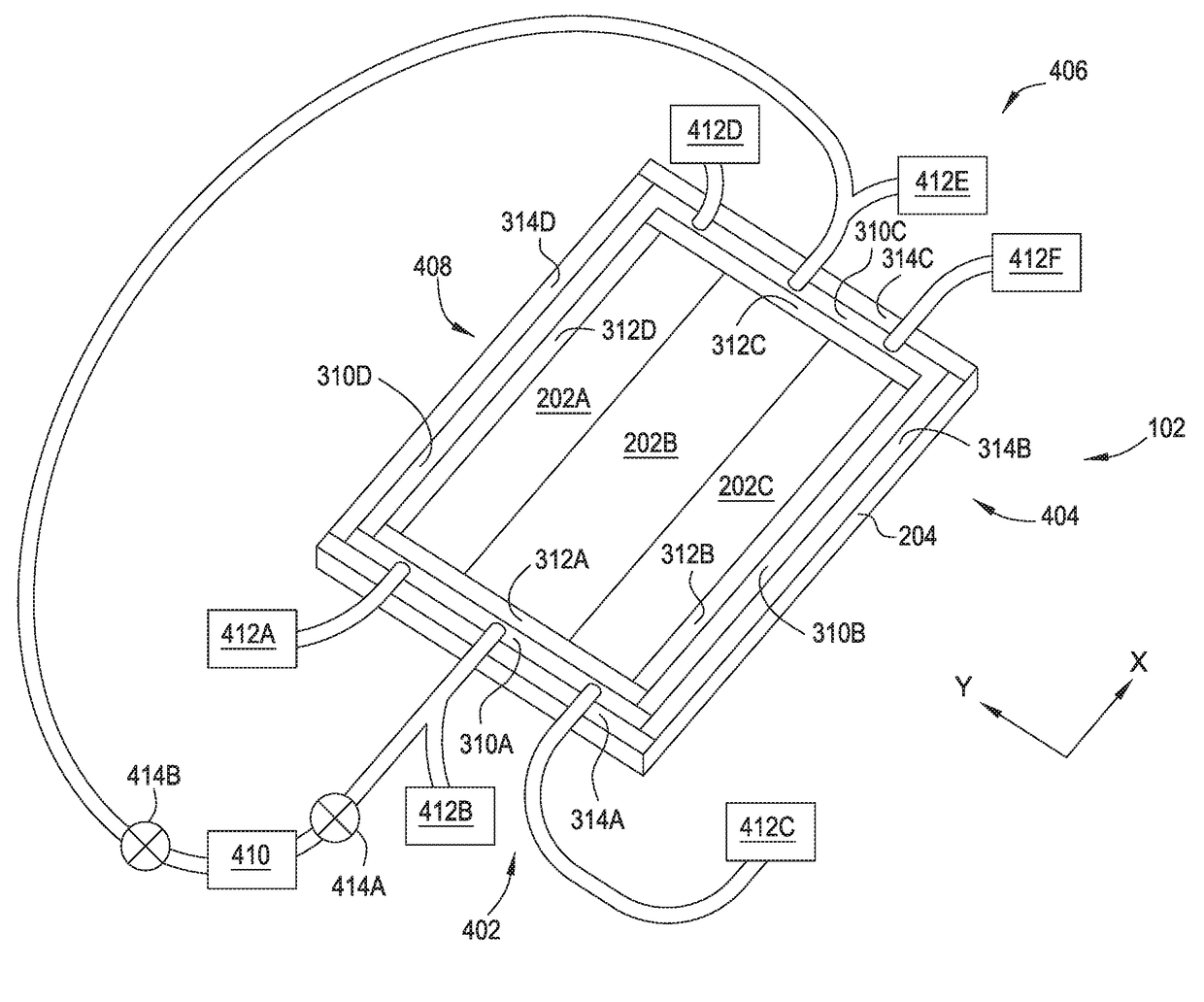
Extended and fixed INTable simultaneously imaged calibration and correction methods and references for 3-D imaging devices
ActiveUS8186880B1Small cross-sectional sizeMinimizes patient movementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingReference sampleImage calibration
Calibration and reference samples with reduced cross-sectional areas encased within imaging tables or couch pads have low attenuation properties and provide patient comfort. The samples are stable and provide reproducible images without artifacts. The torso-length samples avoid positioning errors and misalignment. Sample density or mass calibration materials include calcium compounds representative of bone and calcifications, iodine compounds for contrast angiography, gadolinium compounds for MRI, and fat and tissue equivalent materials. Density corrections for variable patient scatter and imperfect image reconstructions improve quantitative measurement. Automated computer methods detect the samples and record readings on all images over the extent of the scans without operator interaction. Spatial references function as location references and enable spatial correction of device imperfections such as point spread function (PSF) or motion for improved images. Comparative analysis of backward and forward projections corrects images based on simultaneous imaging of the references of known properties.
Owner:ARNOLD BEN A
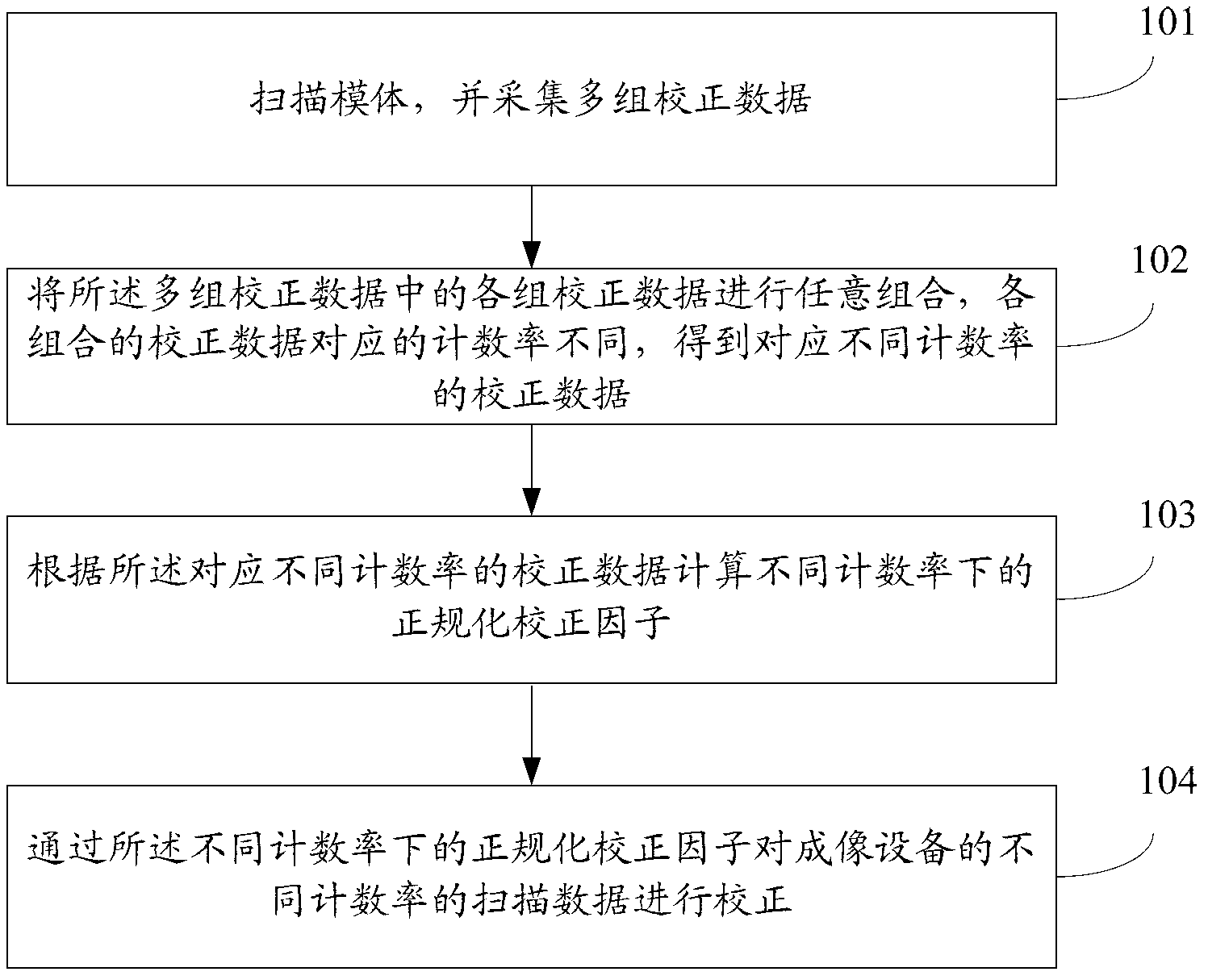
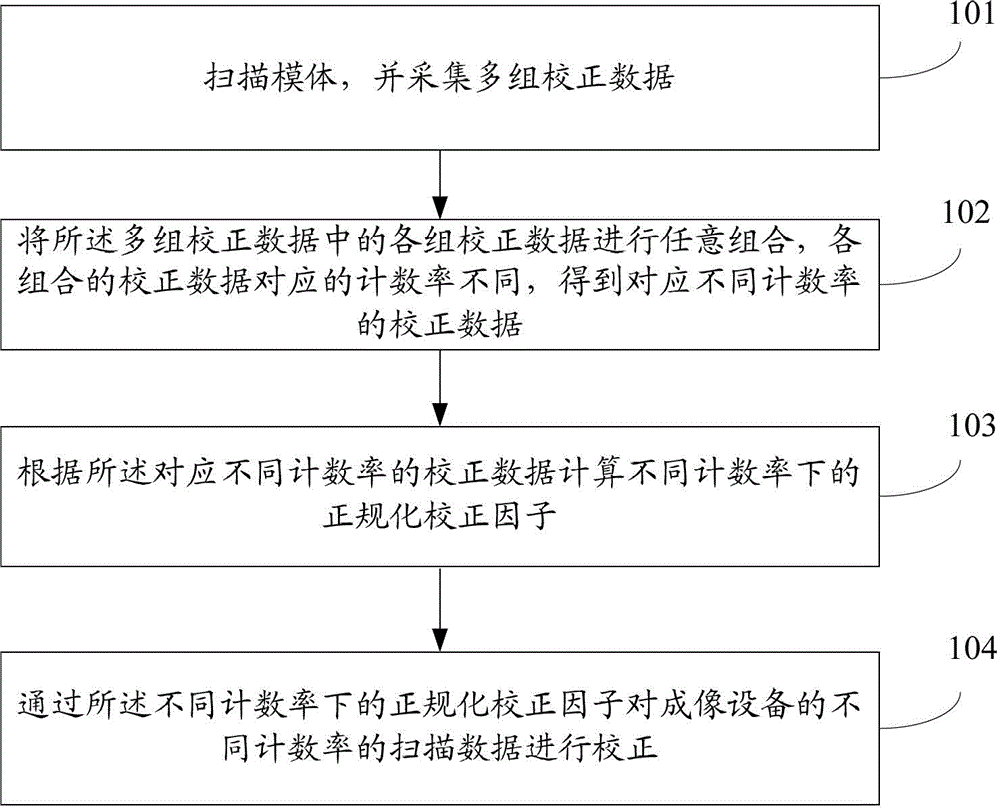
Method and device for normal correction of scanning data in imaging equipment
ActiveCN103315763APrevent Image ArtifactsReduce acquisition timeComputerised tomographsTomographyCounting rateAcquisition time
An embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for normal correction of scanning data in imaging equipment. The method includes scanning a model and acquiring a plurality of groups of correction data; optionally combining the groups of correction data to obtain correction data combinations corresponding to different counting rates, thus obtaining correction data corresponding to the different counting rates; calculating normal correction factors under the different counting rates according to the correction data corresponding to the different counting rates; and correcting scanning data different in counting rate in the imaging equipment through the normal correction factors under the different counting rates. The method and the device according to the embodiment have the advantages that acquisition time of correction data can be shortened and the problem of image artifacts caused by mismatch of the counting rates is also avoided.
Owner:SHENYANG INTELLIGENT NEUCLEAR MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
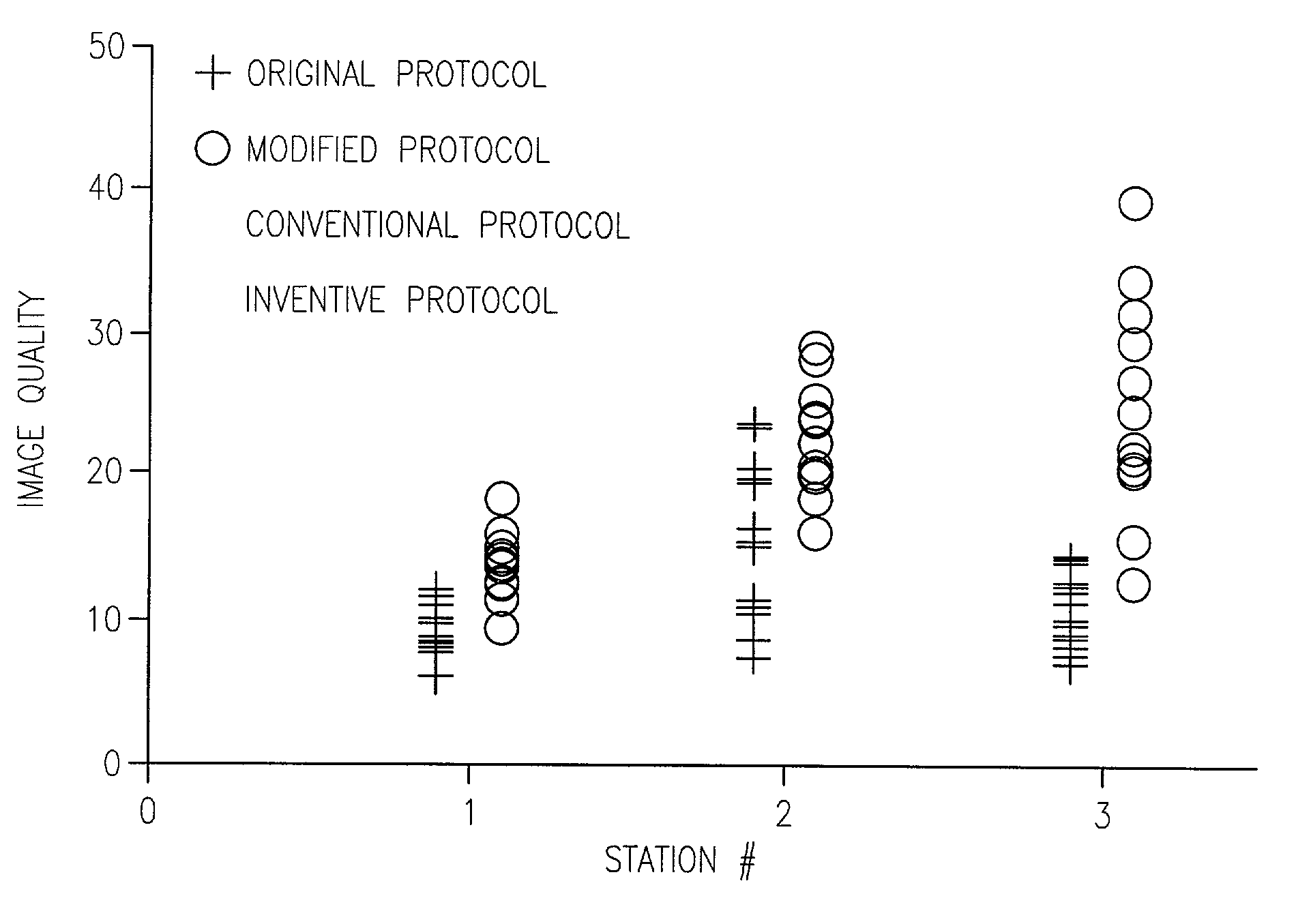
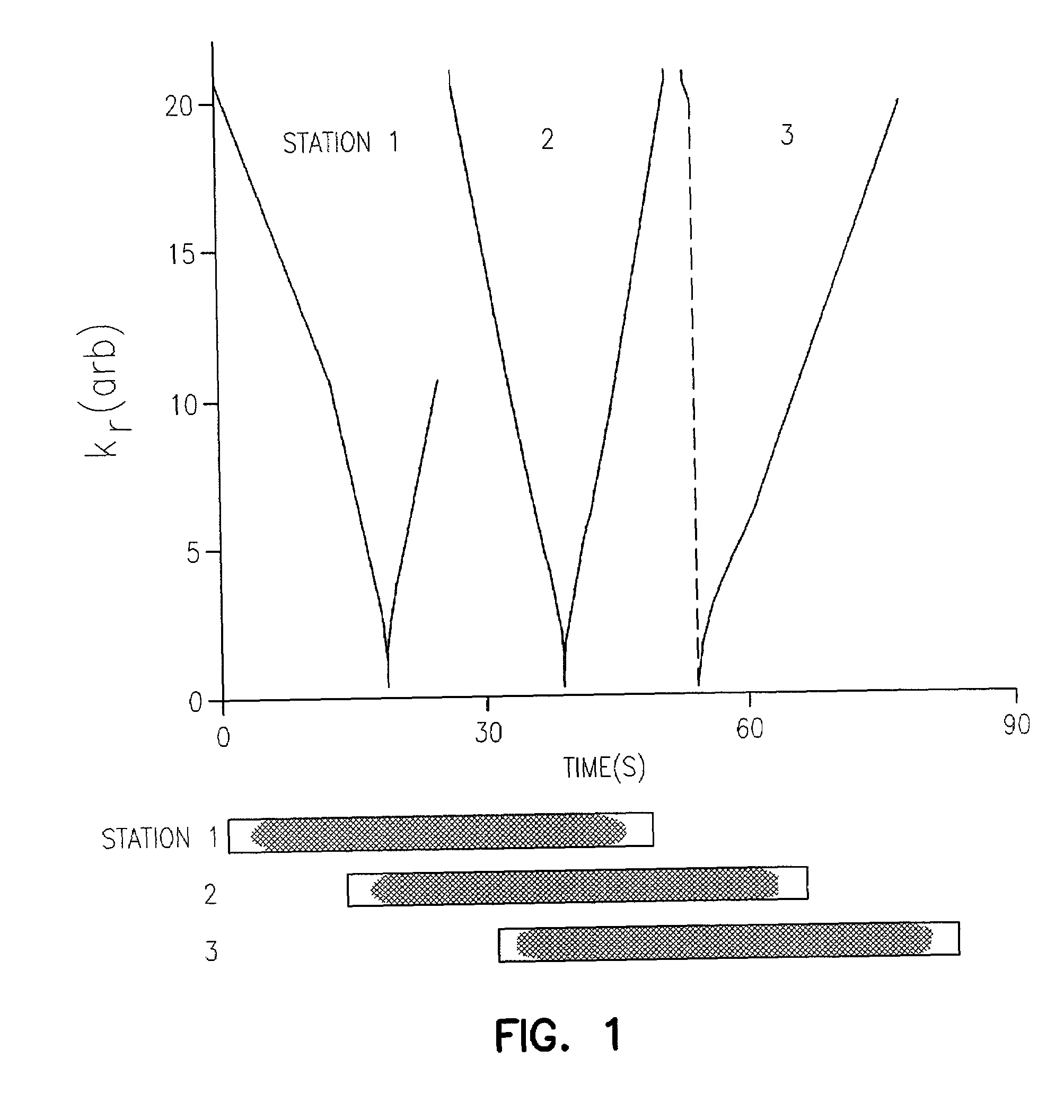
Method and apparatus for anatomically tailored k-space sampling and recessed elliptical view ordering for bolus-enhanced 3D MR angiography
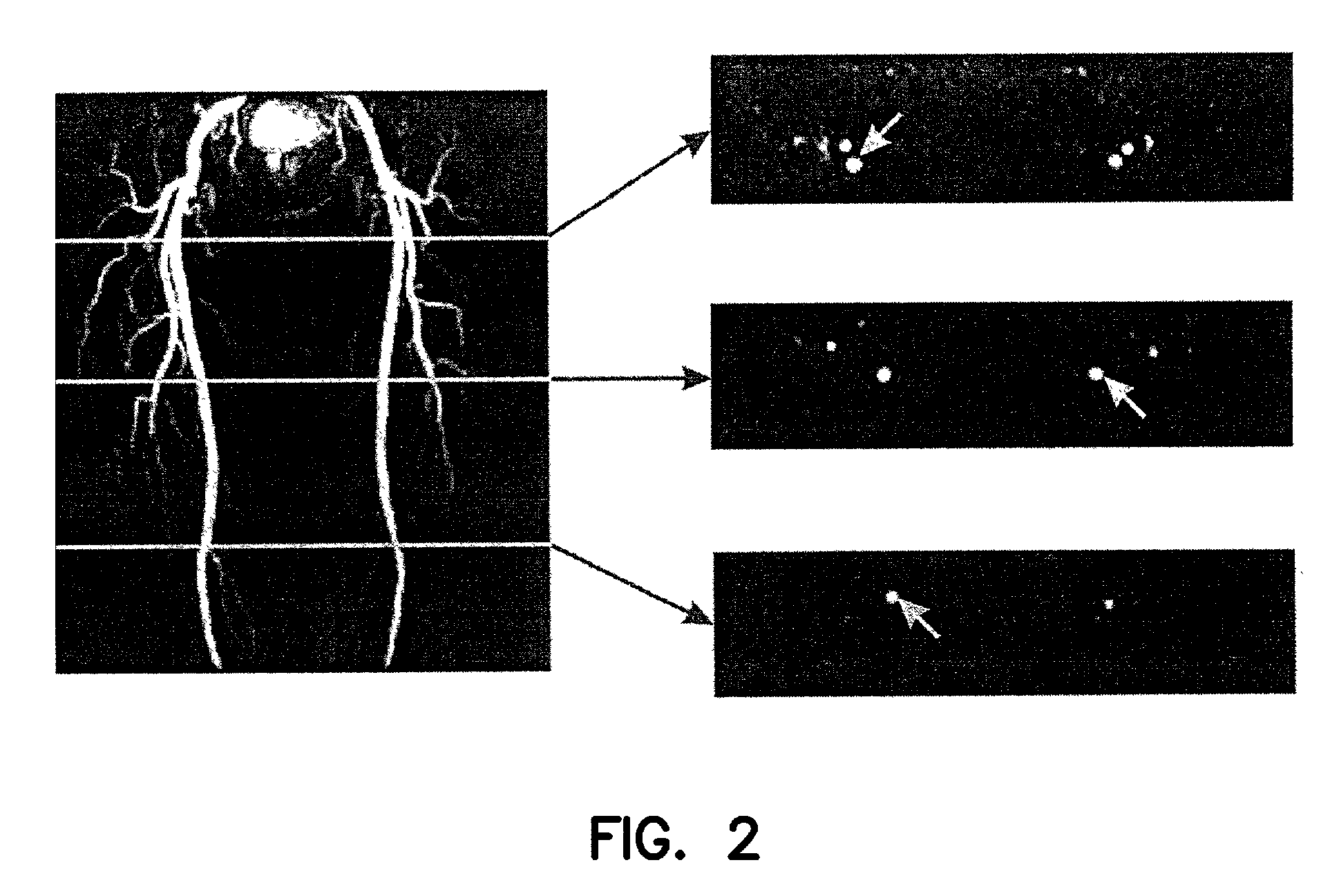
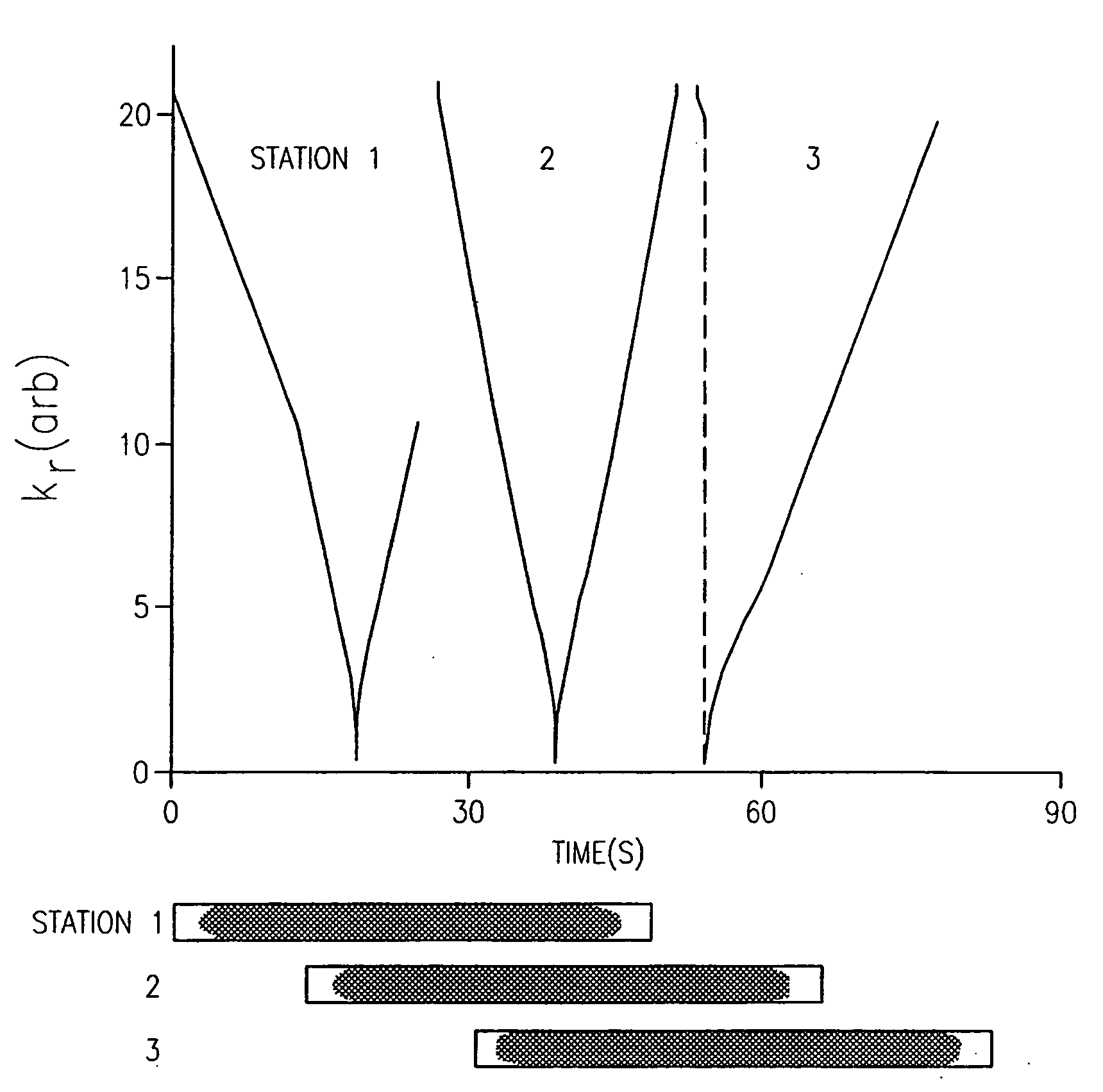
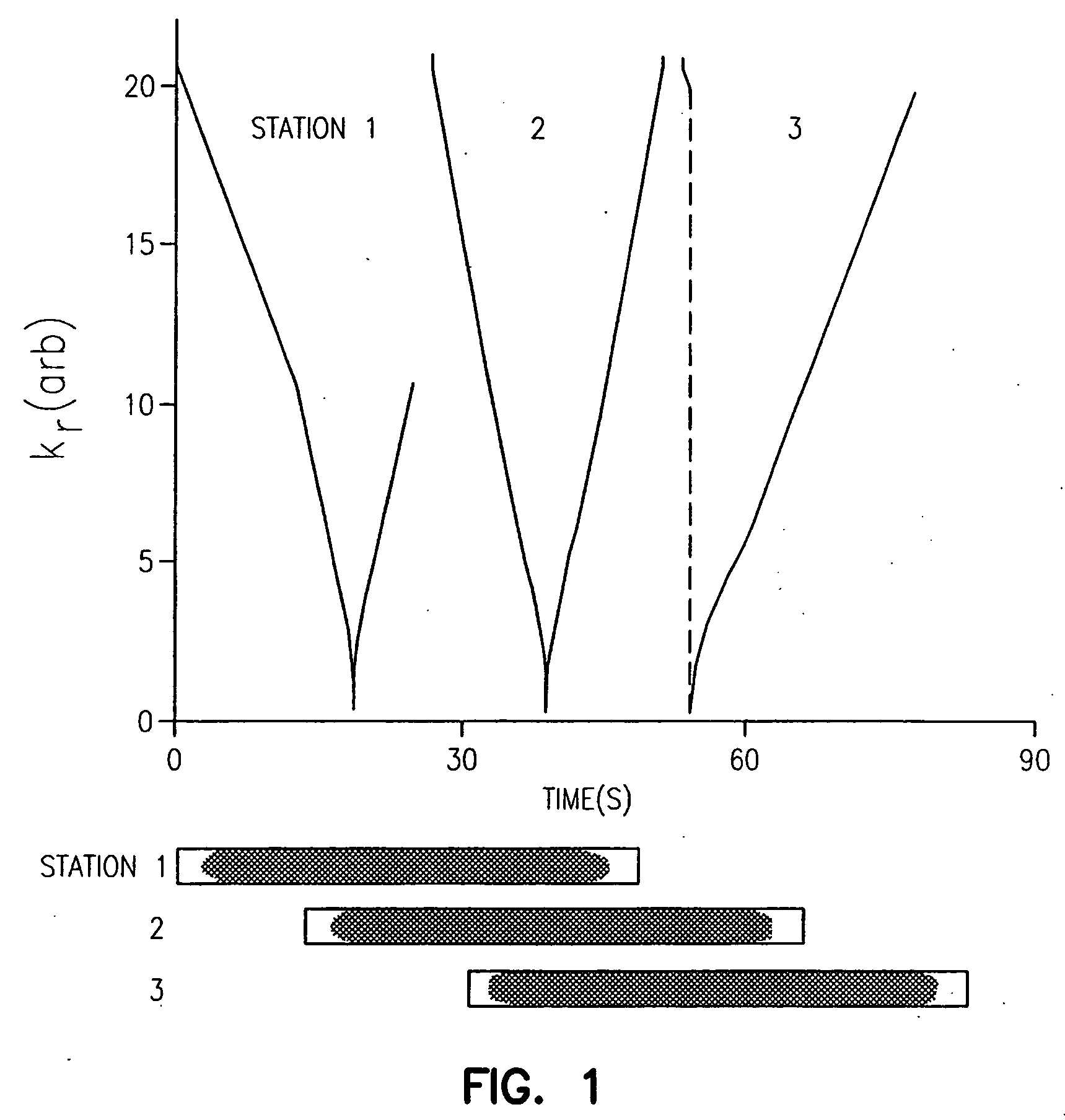
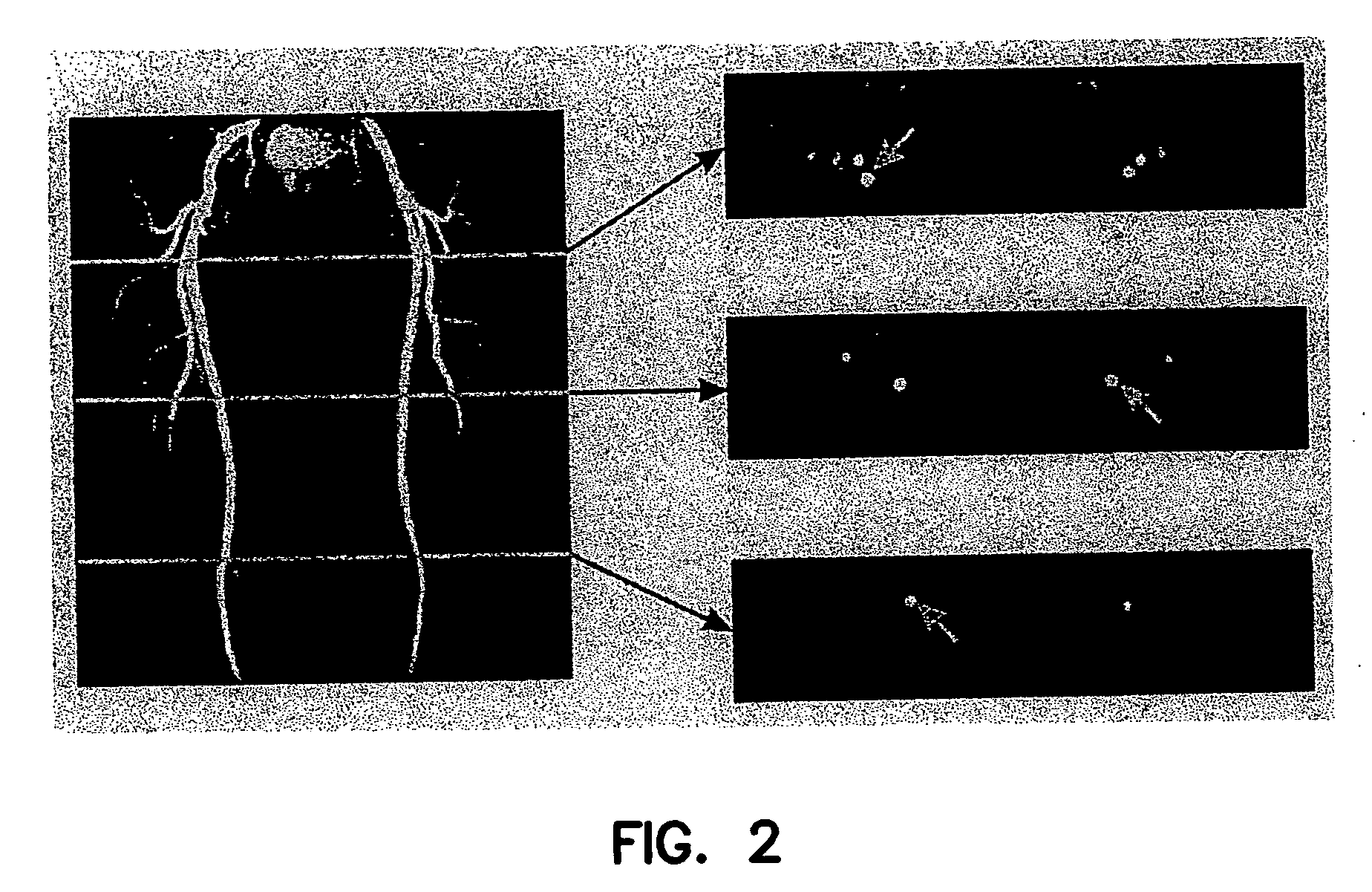
InactiveUS7003343B2Increasing dose sharingMinimize timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging qualityBlood vessel
Current bolus chase magnetic resonance angiography is limited by the imaging time for each station. Tailoring the density of k-space sampling along the anterior-posterior direction of the coronal station allows a substantial decrease in scan time that leads to greater contrast bolus sharing among stations and consequently a significant improvement in image quality. Fast arterial-venous transit in the carotid arteries requires accurate, reliable timing of the acquisition to the bolus transit to maximize arterial signal and minimize venous artifacts. The rising edge of the bolus is not utilized in conventional elliptical-centric view ordering because the critical k-space center must be acquired with full arterial enhancement. The invention provides a recessed elliptical-centric view ordering scheme is introduced in which the k-space center is acquired a few seconds following scan initiation. The recessed view ordering is shown to be more robust to timing errors in a patient studies.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Method and apparatus for anatomically tailored k-space sampling and recessed elliptical view ordering for bolus-enhanced 3D MR angiography
InactiveUS20050203377A1Increasing dose sharingMinimize timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging qualityImage quality
Current bolus chase magnetic resonance angiography is limited by the imaging time for each station. Tailoring the density of k-space sampling along the anterior-posterior direction of the coronal station allows a substantial decrease in scan time that leads to greater contrast bolus sharing among stations and consequently a significant improvement in image quality. Fast arterial-venous transit in the carotid arteries requires accurate, reliable timing of the acquisition to the bolus transit to maximize arterial signal and minimize venous artifacts. The rising edge of the bolus is not utilized in conventional elliptical-centric view ordering because the critical k-space center must be acquired with full arterial enhancement. The invention provides a recessed elliptical-centric view ordering scheme is introduced in which the k-space center is acquired a few seconds following scan initiation. The recessed view ordering is shown to be more robust to timing errors in a patient studies.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
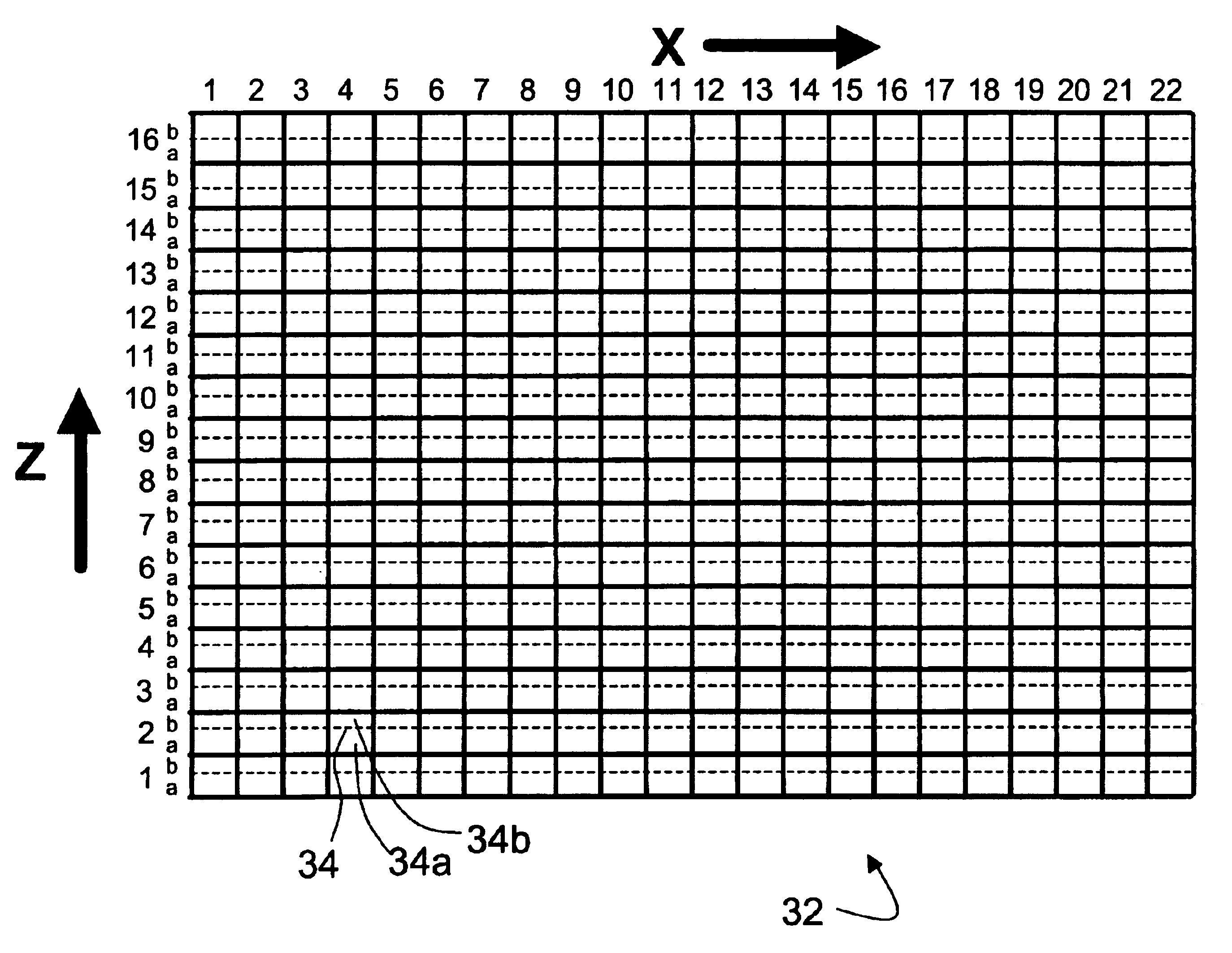
Dynamic detector interlacing for computed tomography
InactiveUS6963631B2Increase sampleAvoid aliasingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersData acquisition
A data acquisition system (DAS) (30) for a computed tomography (CT) scanner (12) includes a two-dimensional array (32) of detectors (34) which is arranged to detect x-rays produced by the CT scanner (12). Each detector (34) is divided into two sub-detectors (34a, 34b) along an axial direction (z). A high-speed switching circuit (40) combines selected adjacent sub-detector outputs (34a, 34b), e.g. combining a sub-detector n alternately with sub-detectors (n−1) and (n+1). The high-speed switching circuit (40) switches its configuration between DAS measurements to produce interlaced DAS output signals along the axial direction (z).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
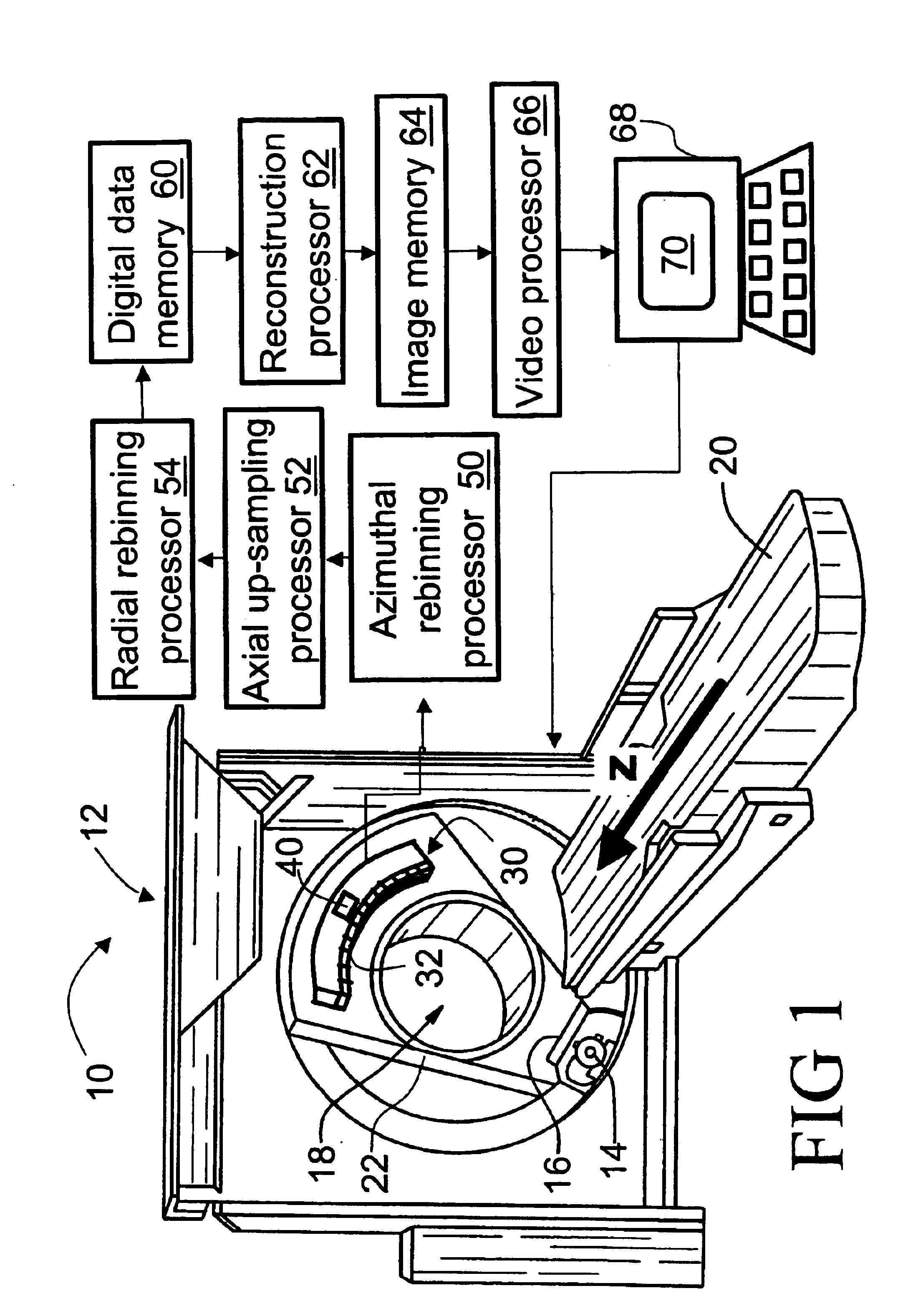
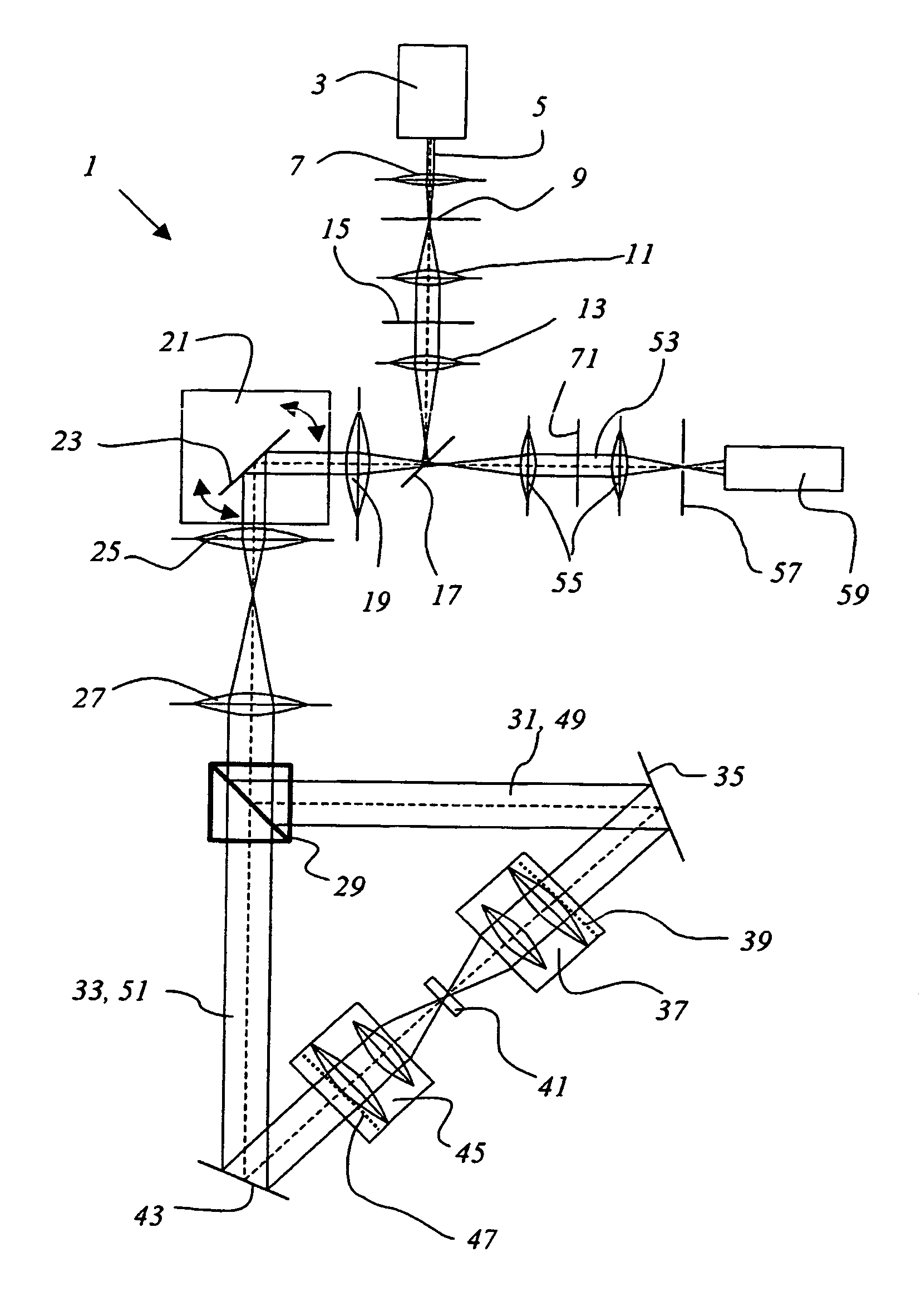
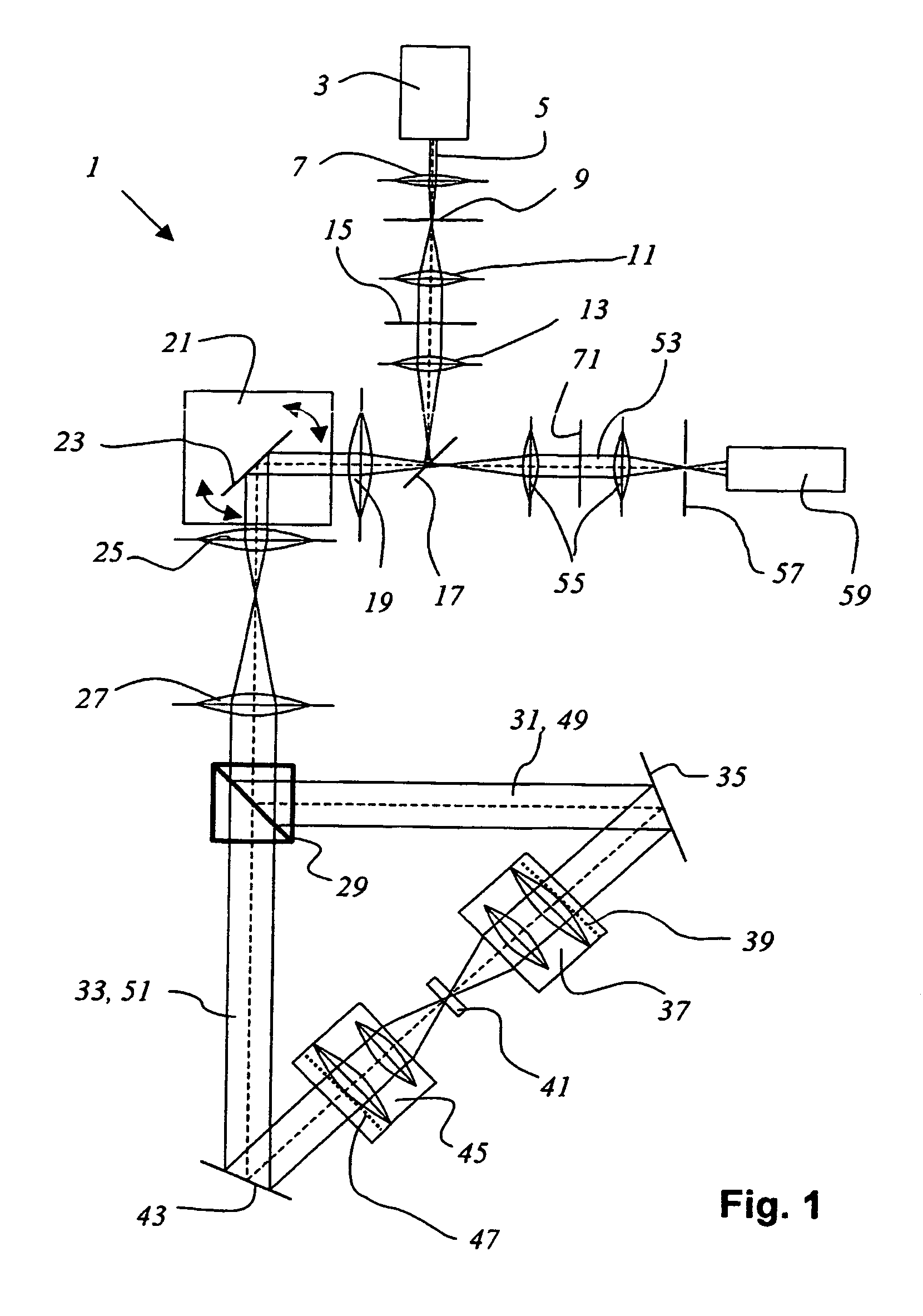
Propeller MRI with phase correction
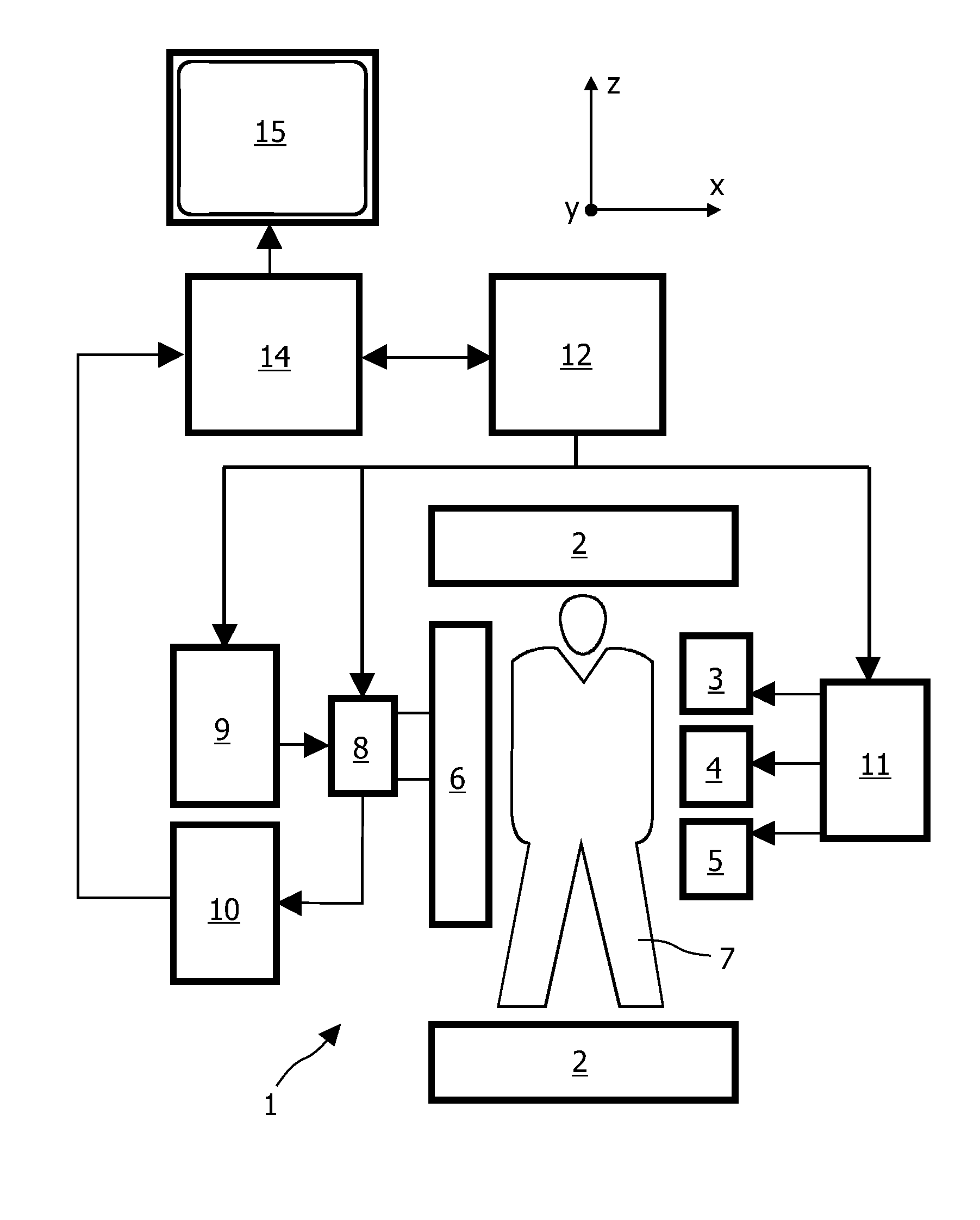
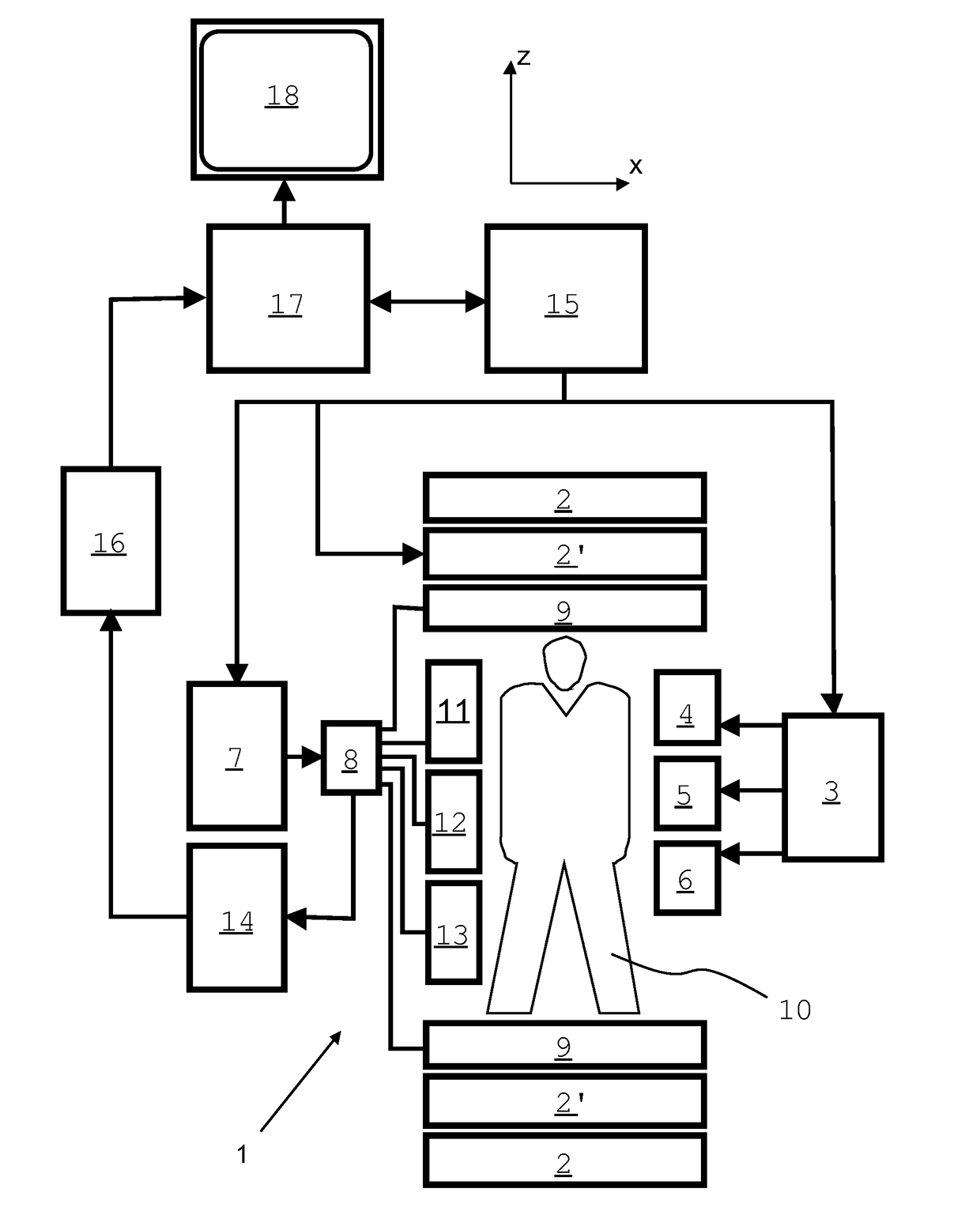
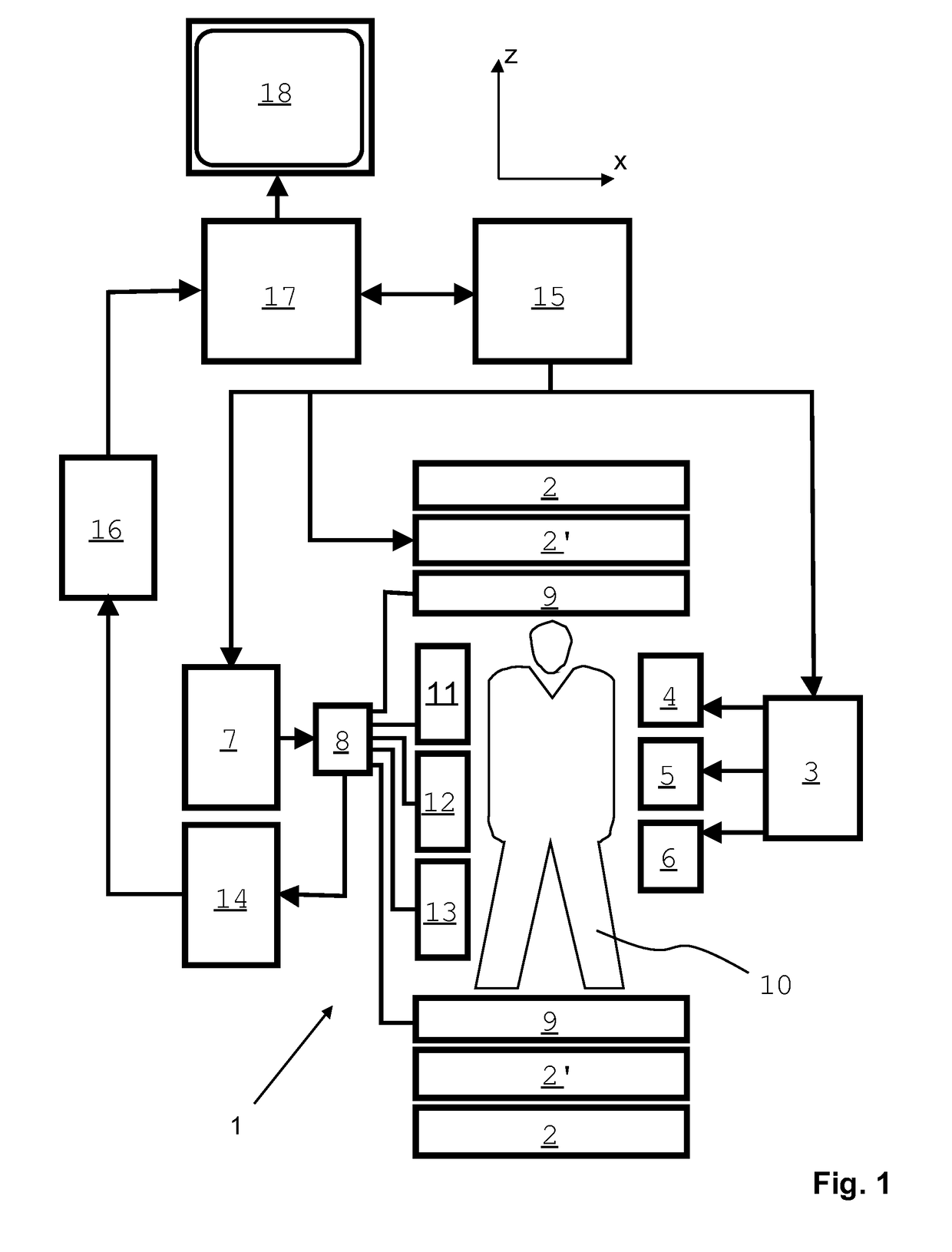
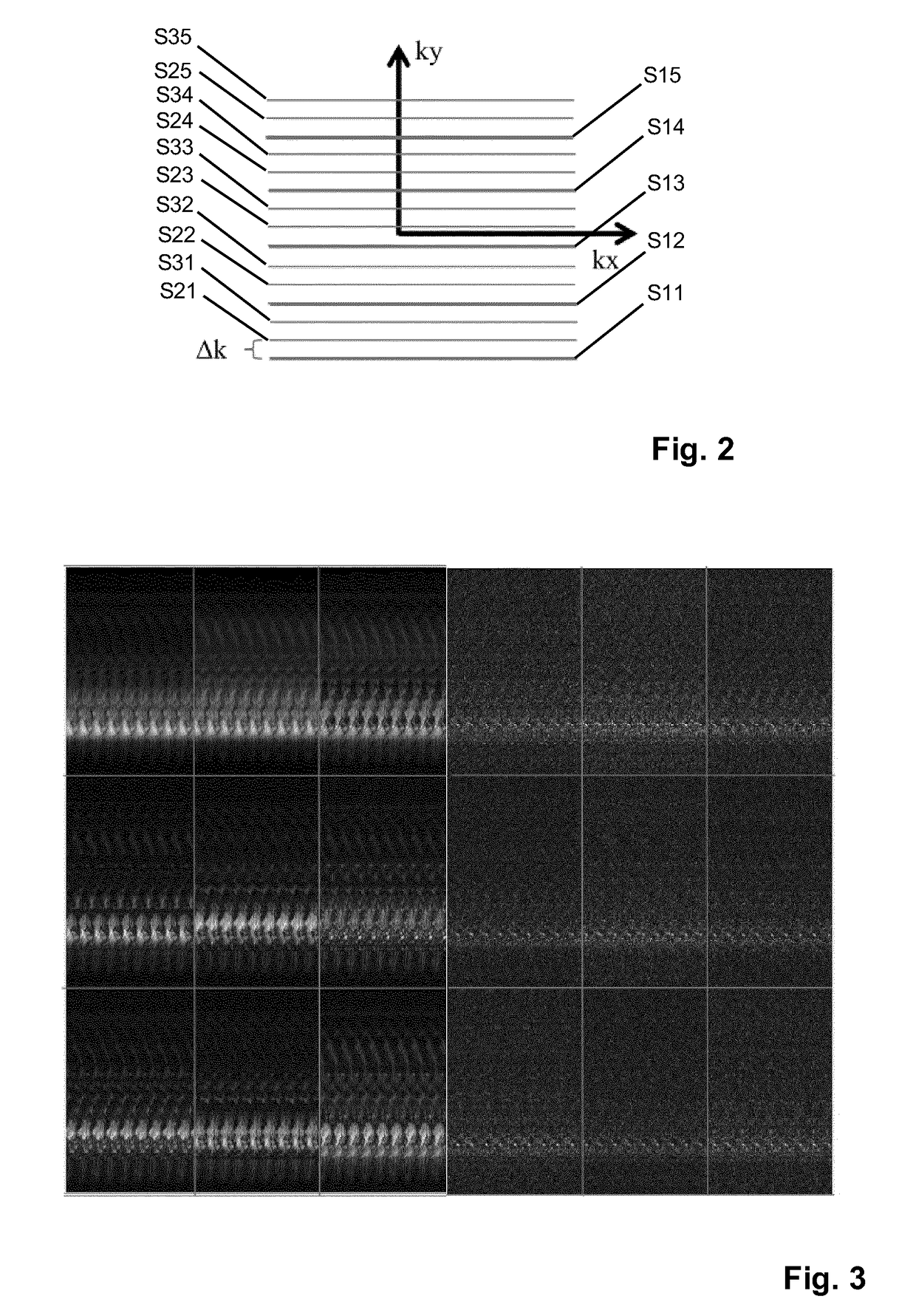
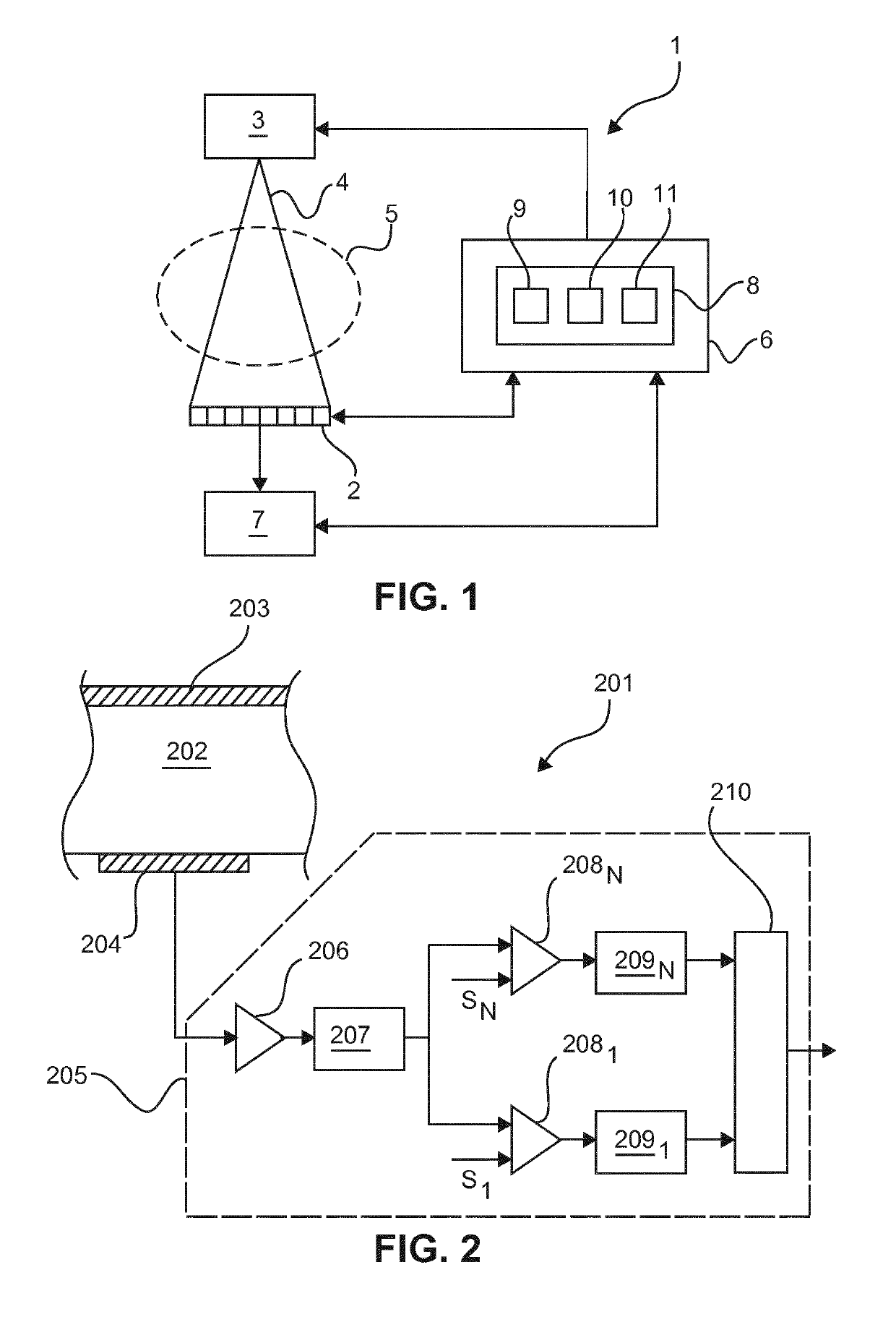
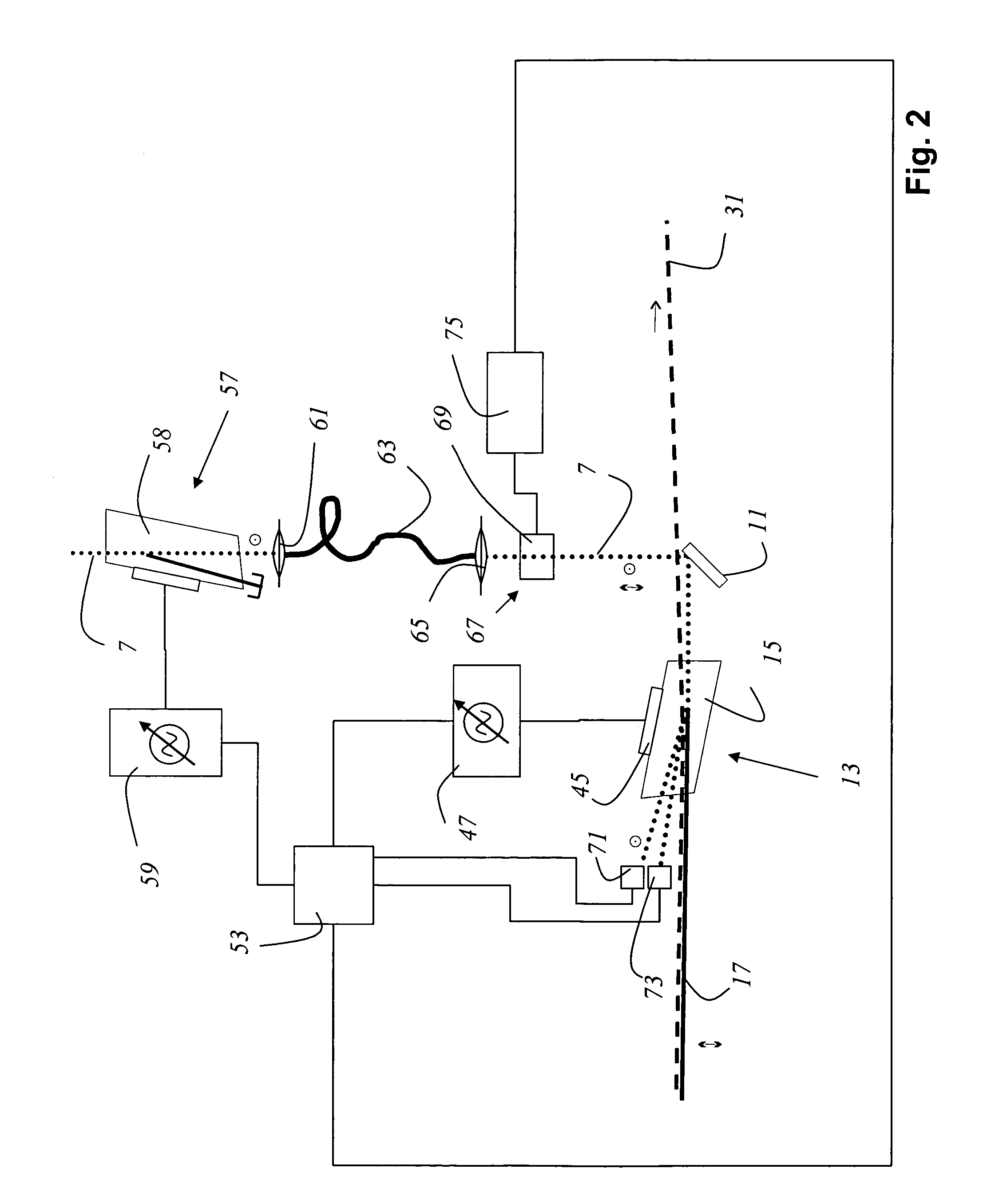
ActiveUS20100117645A1Prevent Image ArtifactsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase correctionMagnetic field gradient
The invention relates to a device for MRI of a body (7) placed in an examination volume. The device (1) comprises means (2) for establishing a substantially homogeneous main magnetic field in the examination volume, means (3, 4, 5) for generating switched magnetic field gradients superimposed upon the main magnetic field, means (6) for radiating RF pulses towards the body (7), control means (12) for controlling the generation of the magnetic field gradients and the RF pulses, means (10) for receiving and sampling MR signals, and reconstruction means (14) for forming MR images from the signal samples. According to the invention, the device (1) is arranged to generate a series of MR signals by subjecting at least a portion of the body (7) to an MRI sequence, to acquire the MR signals as a plurality of k-space blades according to the PROPELLER scheme, to compute phase errors from the phase differences of pairs of k-space blades having different rotation angles, to perform a phase correction of the acquired k-space blades on the basis of the computed phase errors, and to reconstruct an MR image from the acquired and phase-corrected MR data set.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Texture morphing process provided by the preferred embodiment of the present invention
InactiveUS6906732B1Simplify and reduce computationFast and efficientCathode-ray tube indicatorsAnimationMorphingComputational science
A fast, texture morphing algorithm for real-time computer simulation and video games dynamically generates objects “on the fly” by simplifying and reducing the computational load required for a texture morphing / blending process. Incremental interpolation techniques compute a morph parameter based on previous value and morph change rate. Precomputed initial and incremental morph parameter values for each texel component are applied during real-time morphing procedures using integer arithmetic. Approximation errors are reduced by incrementing / decrementing by an extra integer value when the number of morph iterations is a multiple of a frame counter. The frame counter avoids over-runs, and the morphing procedure is “snapped” the texel value to the precise texture target value to prevent under-runs and corresponding artifacts. Interlacing (applying interpolation to a subset of the texels each frame) significantly reduces computational load without introducing significant image artifacts. The morph texture buffer data structure is initially decomposed off-line to reduce the number of real-time calculations required to manipulate texel component data.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Cylindrical beam large visual field X-ray computed tomography (CT) imaging system
InactiveCN104597062AHigh resolutionNo stitching requiredUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationData acquisitionX-ray
The invention relates to a cylindrical beam large visual field X-ray computed tomography (CT) imaging system. The system consists of a radiation source system, a capillary modulation system, a sample platform system and a detector system which are sequentially and coaxially connected in an optical way, wherein a capillary device which is used for forming a modulation radiation source so as to enable a cylindrical beam X-ray to be formed by the modulation radiation source is arranged between imaging target samples of the radiation source system and the sample platform system; an X-ray source of the radiation source system is connected with a capillary tube of the capillary modulation system, so that a cylindrical parallel beam is obtained; the detector system is used for acquiring data by adopting a multi-channel signal processor. According to the imaging system, the radiation source system and the detector system are fixed, a rotary table can rotate, the radiation source is capable of emitting the cylindrical beam X-ray after being modulated by the capillary modulation system, and the conventional scanning can be completed for once only by rotating the sample platform at 180 degrees, so that the acquired data is complete; parallel beam is used for reconstruction, and the reconstruction belongs to accurate reconstruction; compared with the conventional system, the cylindrical beam large visual field X-ray CT imaging system is capable of shortening half of the scanning time.
Owner:天津三英精密仪器股份有限公司
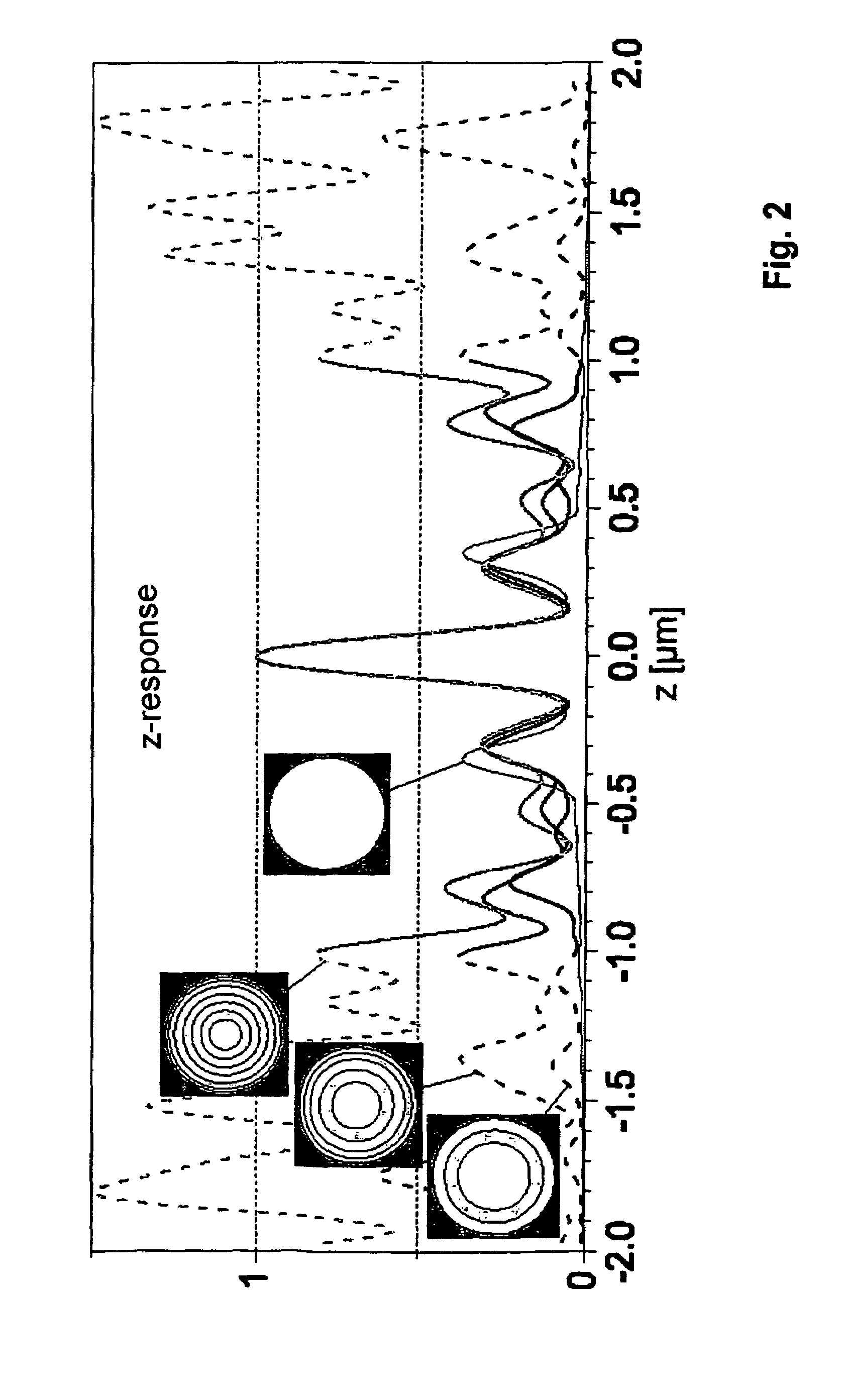
Confocal 4-pi microscope and method for confocal 4-pi microscopy
InactiveUS7333207B2Simply and efficiently avoids image artifactPrevent Image ArtifactsRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryMicroscopeMicroscopy
The invention relates to a confocal 4π microscopy method which is characterized by coherently illuminating a sample from two sides by one objective each with illumination light which has at least one illumination wavelength whereby a stationary illumination wave having a main illumination maximum and secondary illumination maxima is produced by interference of the illumination light in the sample. The detection light emitted by the sample has at least one detection wavelength and is detected through the two objectives. The detection light is made to interfere, thereby producing in the sample a detection pattern having a main detection maximum, secondary detection maxima and detection minima in such a manner that the secondary illumination maxima and the detection minima overlap at least partially.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Ct system and ct method
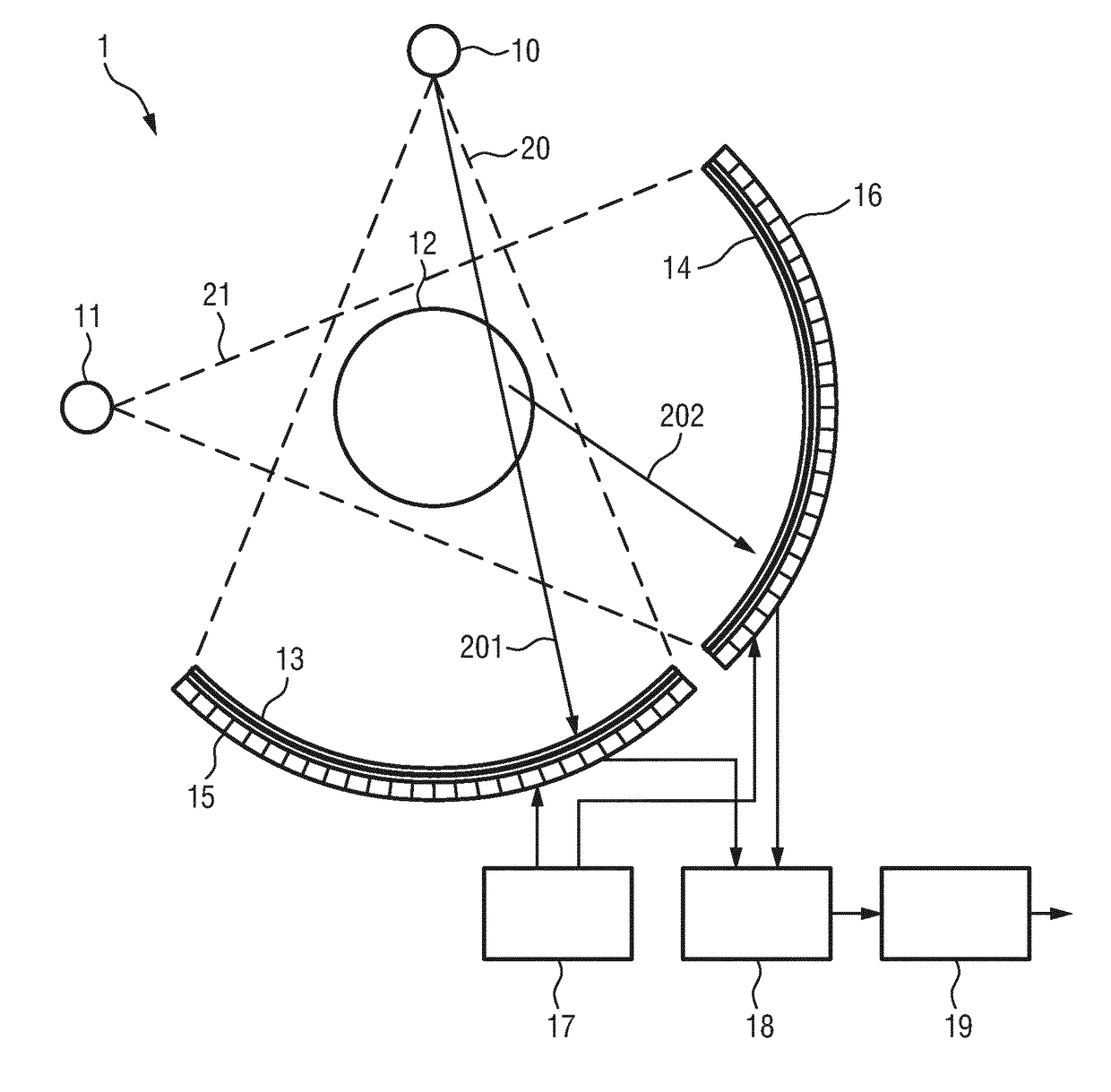
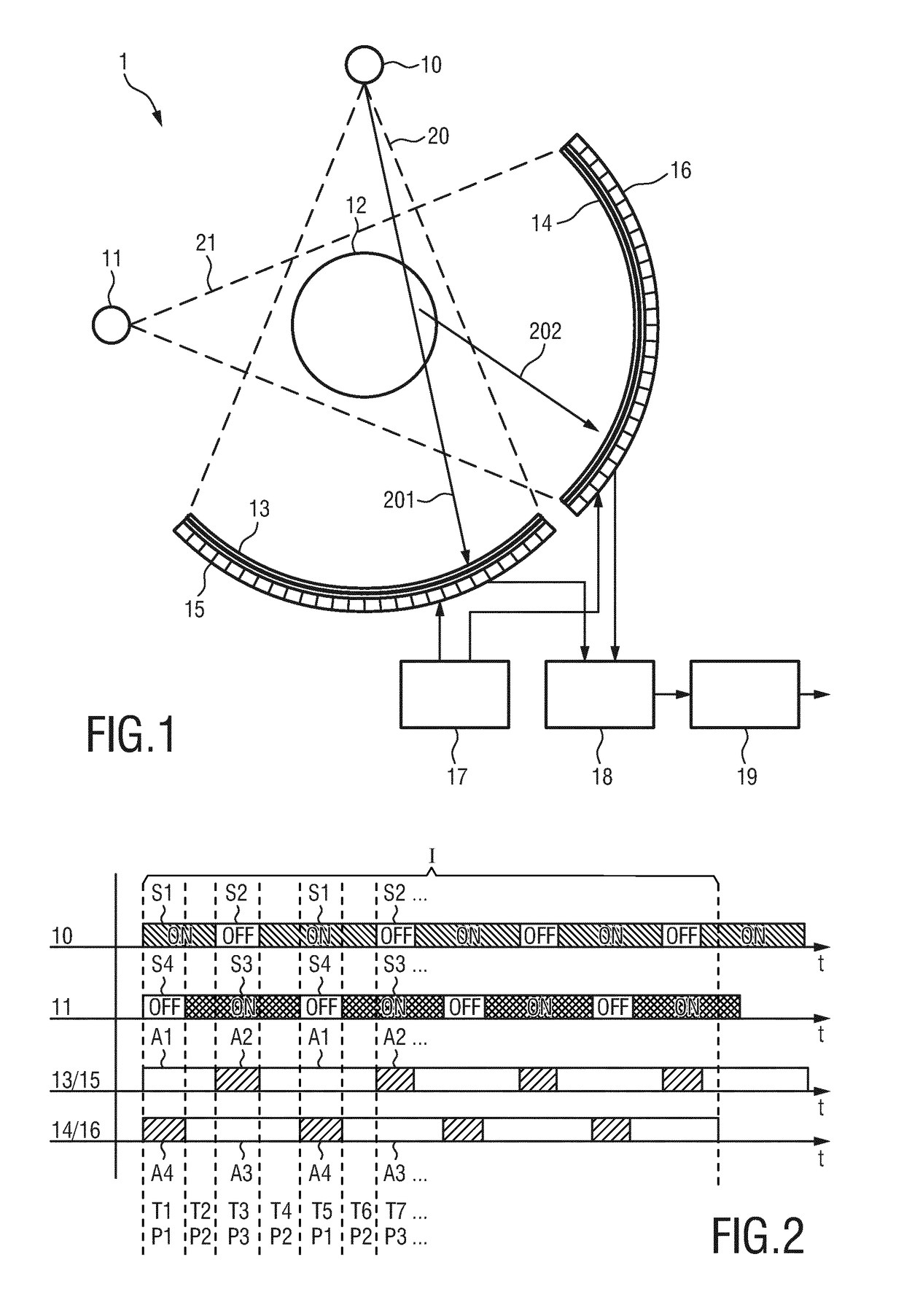
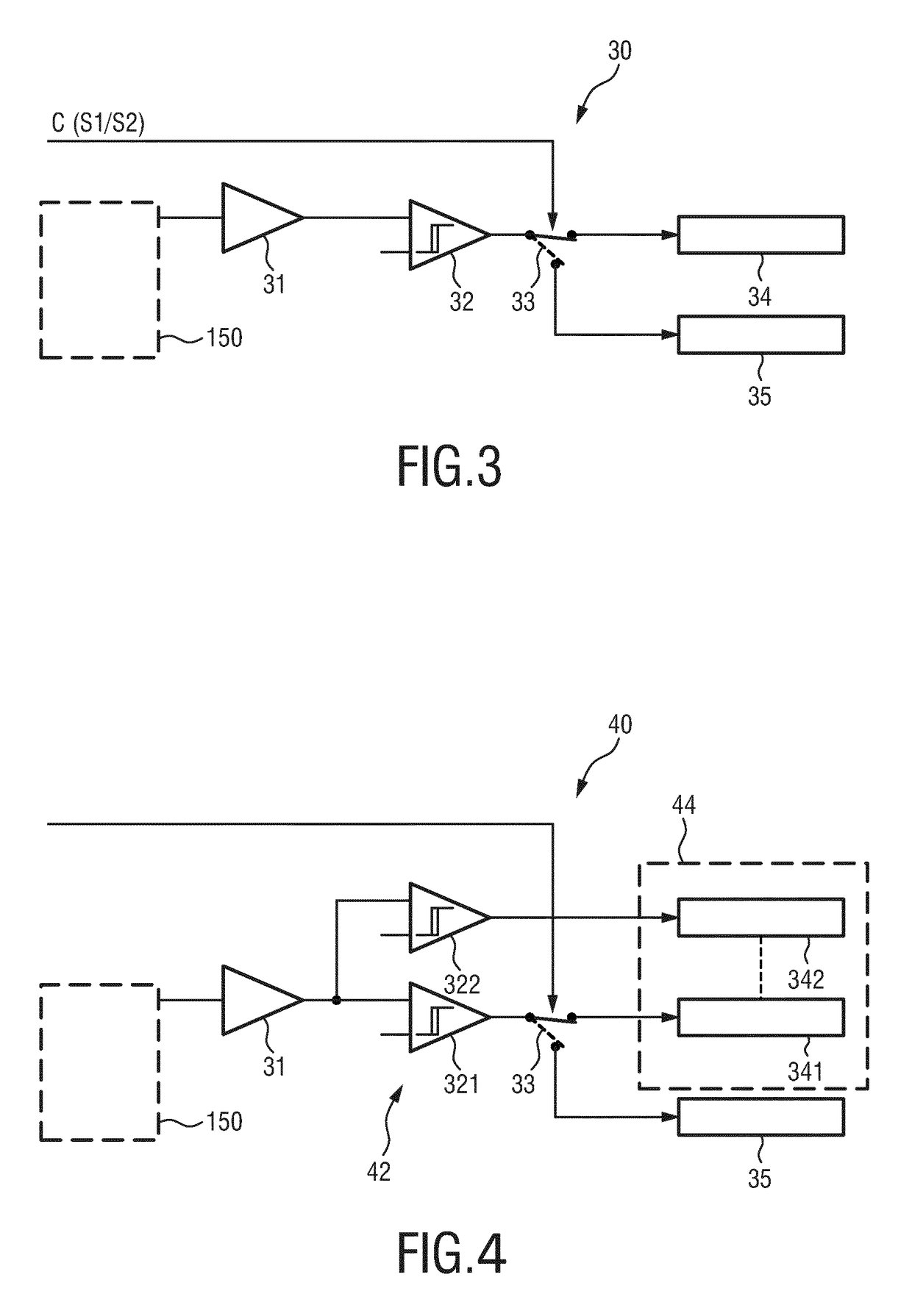
ActiveUS20180284035A1Negative effectPrevent Image ArtifactsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputerised tomographsX-rayEngineering
The present invention relates to a dual- or multi-source CT system and method. For suppressing or even completely eliminating the negative effects of cross-scatter, the proposed CT system comprises two x-ray sources (10, 11), two detectors (13, 14), two read-out units (15, 16), a control unit (17) and a reconstruction unit (19). Further, a scatter correction unit (18) is provided or the read-out units (15, 16) are configured to generate scatter-corrected read-out signals from the detected radiation, wherein a scatter-corrected read-out signal is generated from the radiation detected by a detector during a single projection interval (I) including multiple repetitions of three phases, in which the sources are alternately switched on and off and in which the read-out units alternately register primary radiation or cross-scatter radiation.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
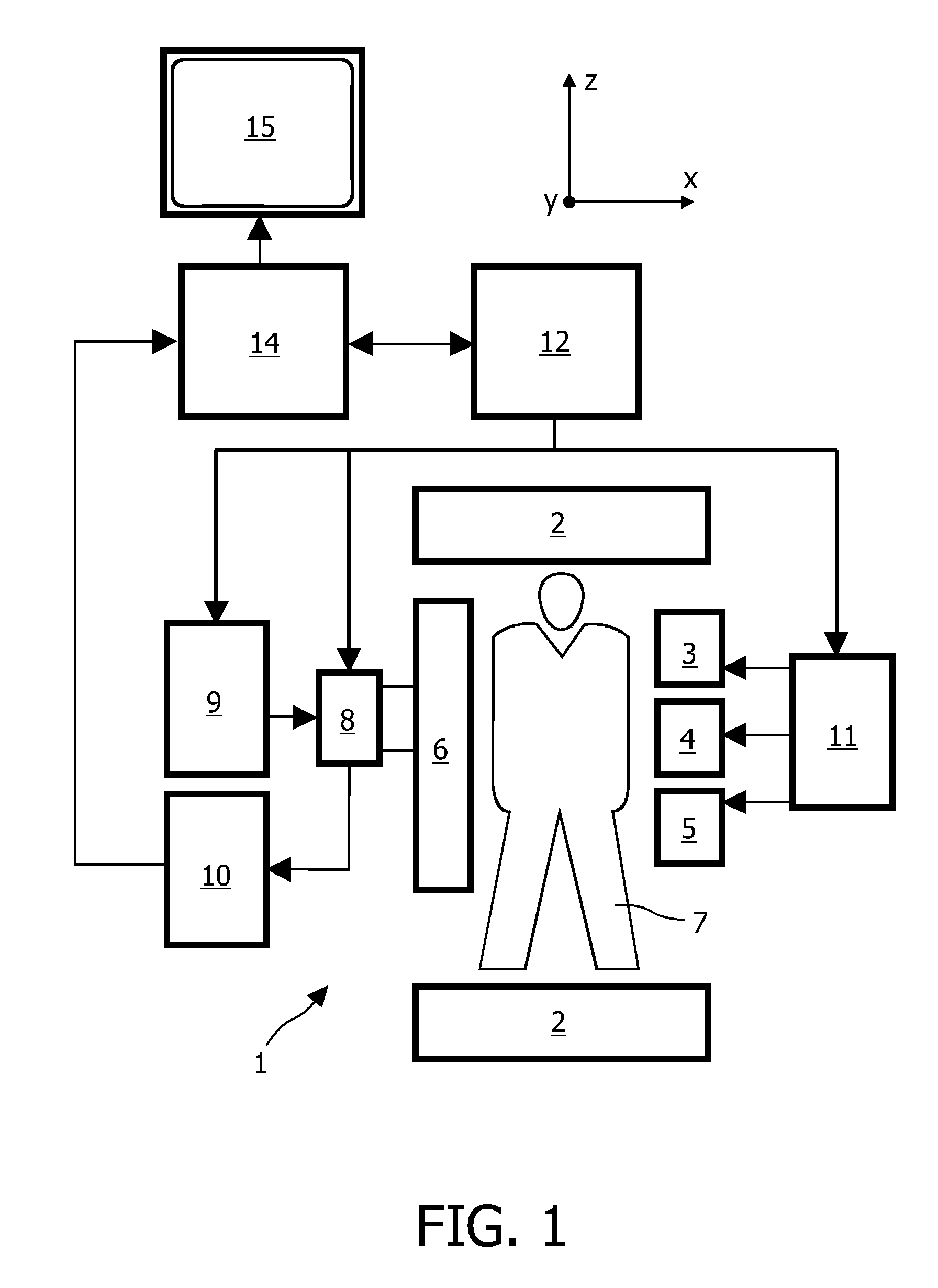
PROPELLER MRI with phase correction
ActiveUS8314614B2Prevent Image ArtifactsMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase correctionMagnetic field gradient
A device for MRI of a body (7) placed in an examination volume includes a main magnet (2) for establishing a substantially homogeneous main magnetic field in the examination volume. Gradient coils (3, 4, 5) generate switched magnetic field gradients superimposed upon the main magnetic field. An RF antenna (6) radiates RF pulses towards the body (7). A control system (12) controls the generation of the magnetic field gradients and the RF pulses. A demodulator (10) receives and samples MR signals. A computer (14) forms MR images from the signal samples. The computer (1) is arranged to generate a series of MR signals by subjecting at least a portion of the body (7) to an MRI sequence, to acquire the MR signals as a plurality of k-space blades according to the PROPELLER scheme, to compute phase errors from the phase differences of pairs of k-space blades having different rotation angles, to perform a phase correction of the acquired k-space blades on the basis of the computed phase errors, and to reconstruct an MR image from the acquired and phase-corrected MR data set.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
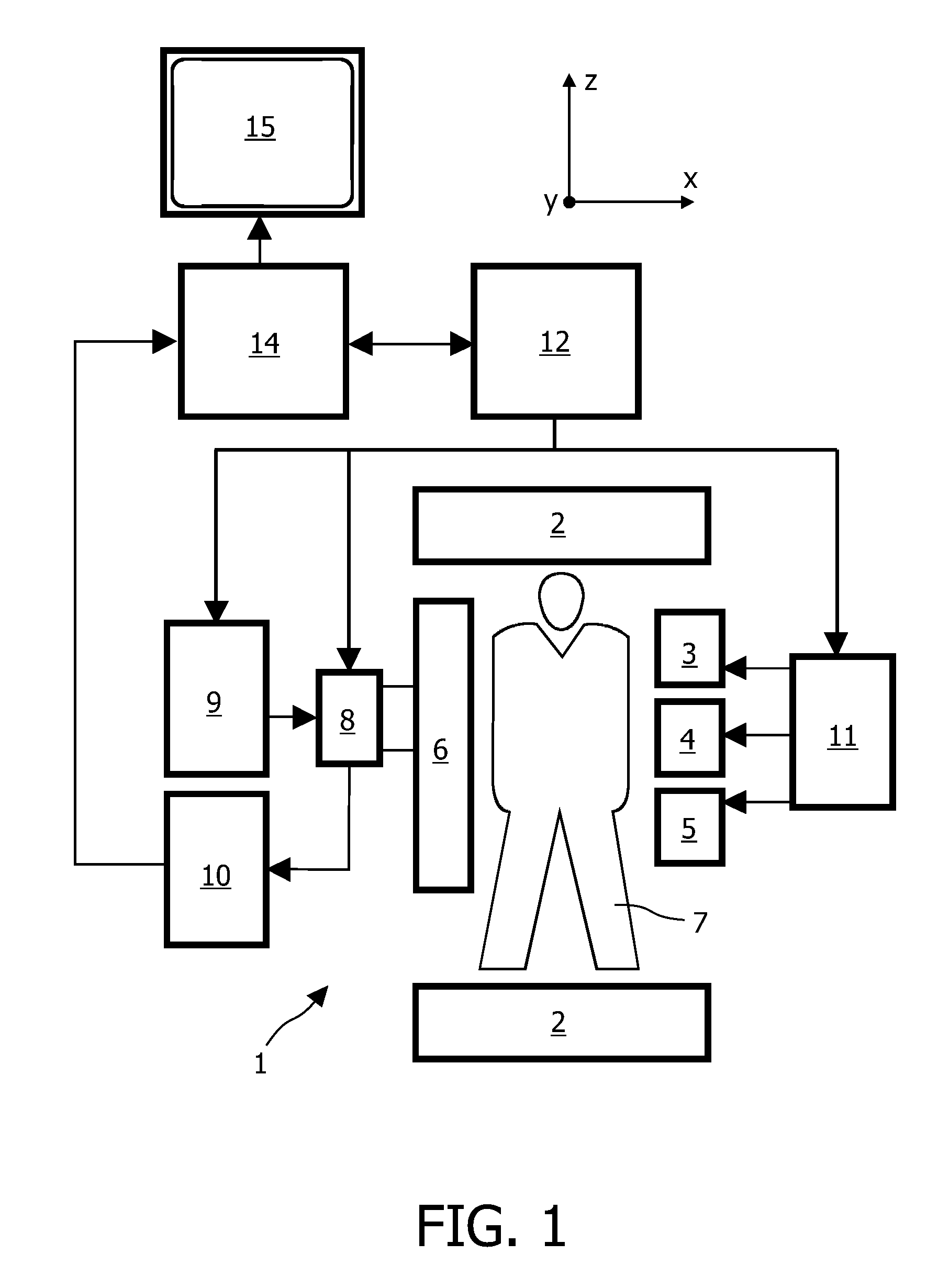
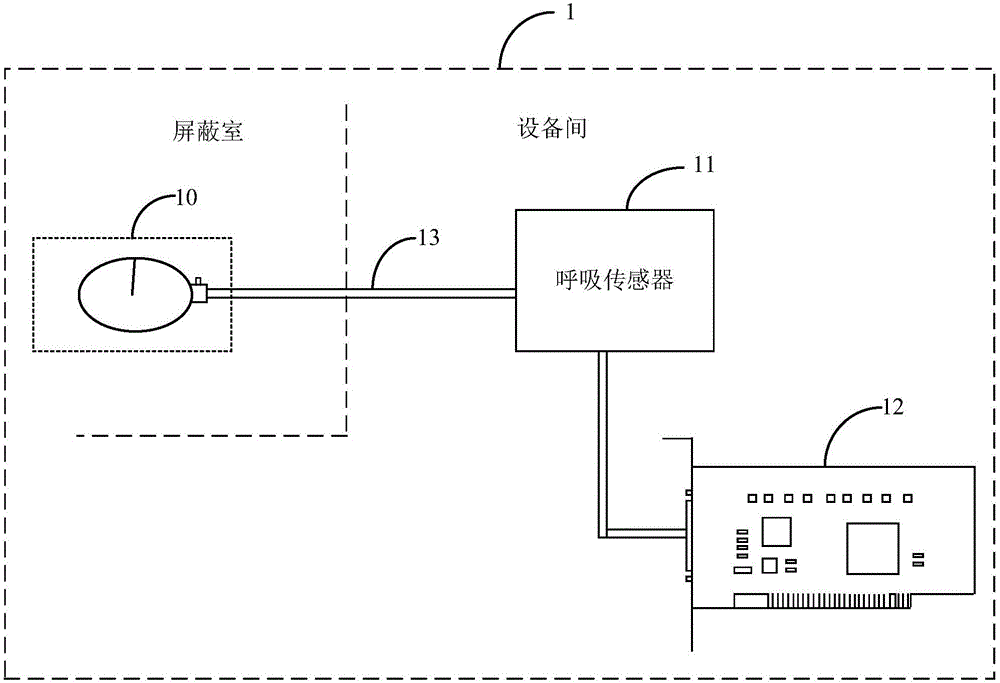
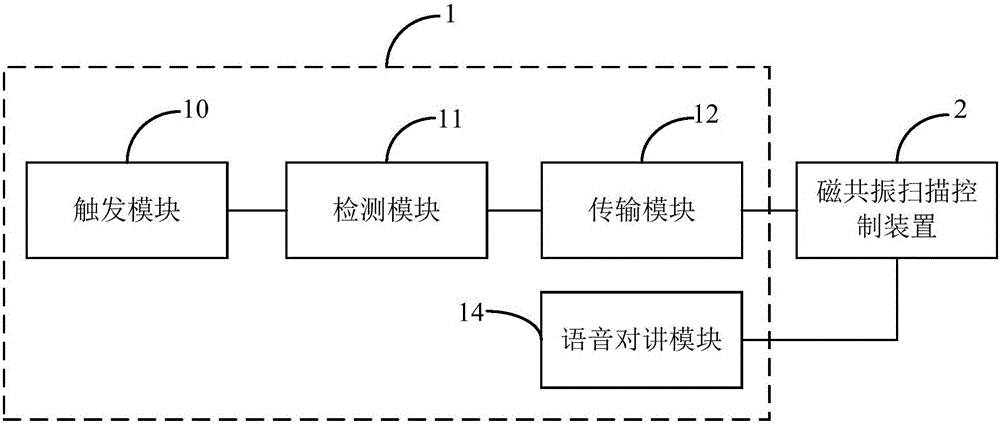
Magnetic resonance scanning trigger device and system and method for magnetic resonance scanning control
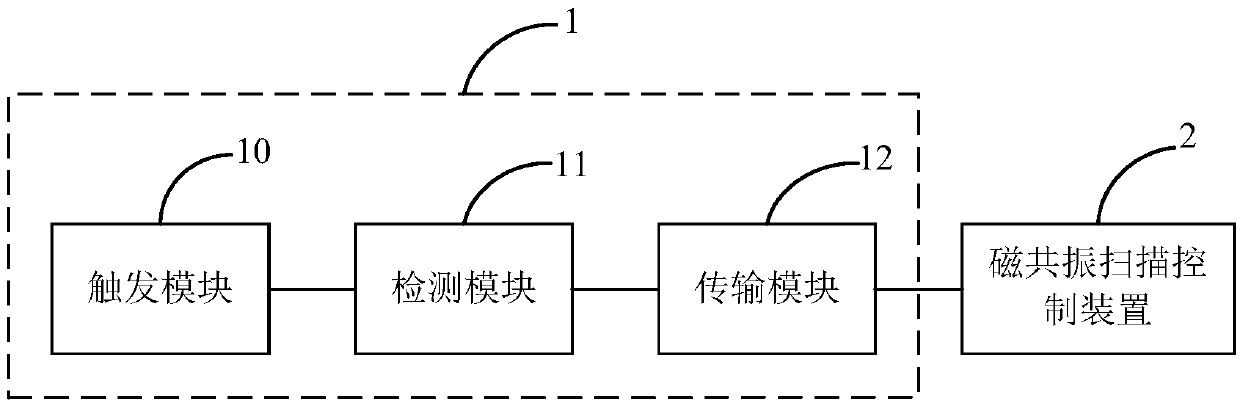
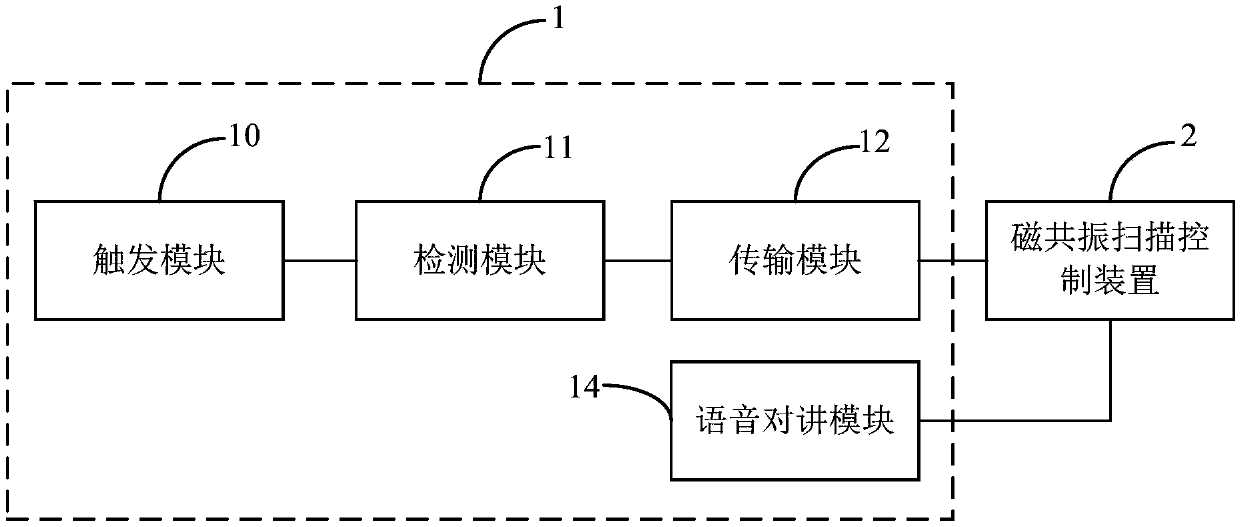
ActiveCN106419918ASolve problems prone to image artifactsPrevent Image ArtifactsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceControl system
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical magnetic resonance scanning control and provides a magnetic resonance scanning trigger device, and a system and method for magnetic resonance scanning control. According to the invention, the magnetic resonance scanning trigger device composed of a trigger module, a detection module and a transmission module is adopted, so that when a user gets ready for holding breath, the trigger module will start a corresponding state change according to the user's trigger operation; the detection module detects a state of the trigger module and generates corresponding instruction information when the trigger module starts the state change; information amplifying processing is conducted to the instruction information; and the transmission module receives the instruction information treated by the amplifying processing, converts the amplified instruction information into a corresponding digital signal and sends the signal to a magnetic resonance scanning control device. In this way, the magnetic resonance scanning control device can control the magnetic resonance scanning device to start scanning the user according to the digital signal. The user can autonomously select the time for scanning start, so that image artifacts caused when the user is not well-prepared can be avoided.
Owner:SHENZHEN BASDA MEDICAL APP
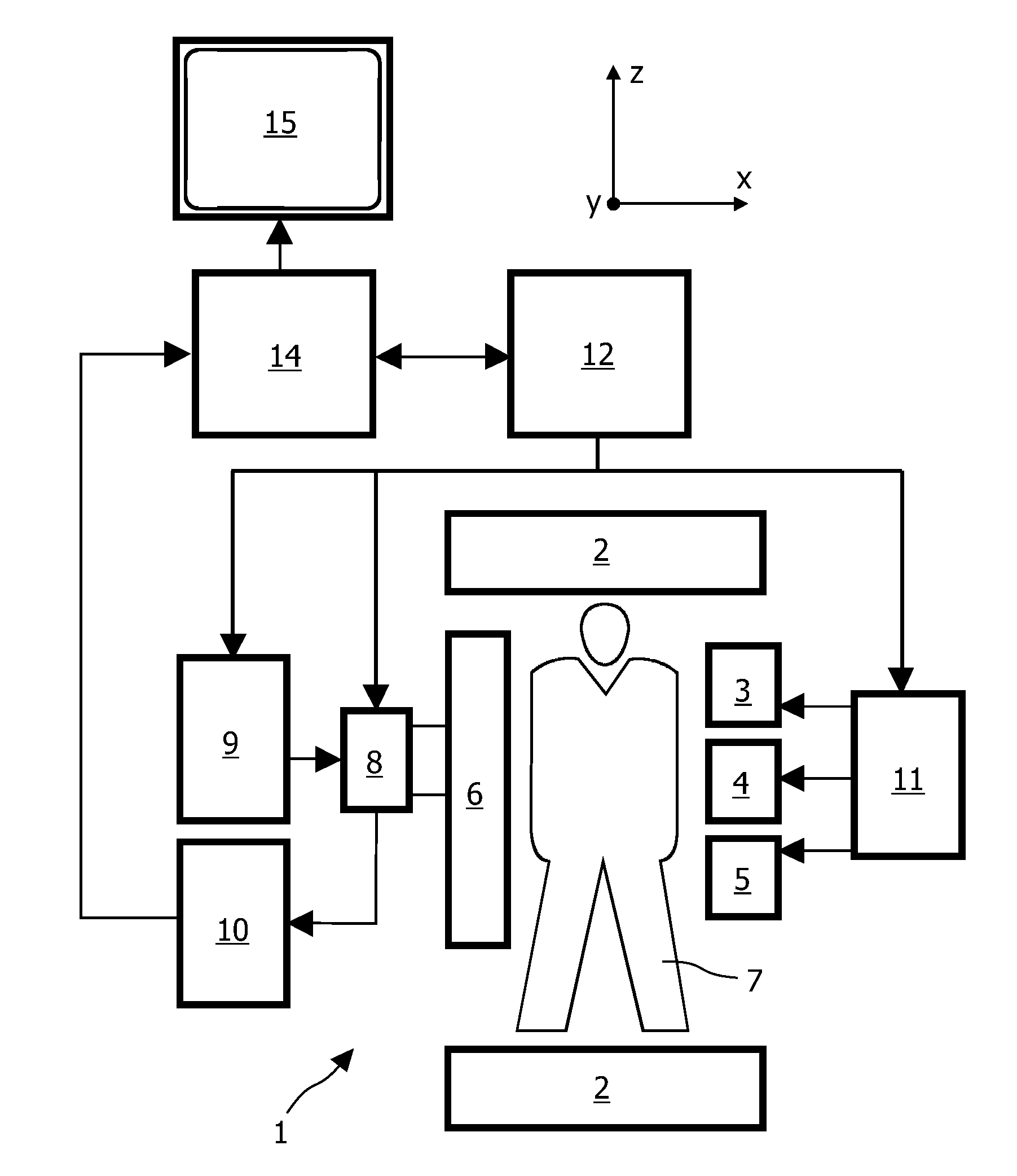
Mr imaging with motion detection
ActiveUS20180210058A1Prevent Image ArtifactsReduce weightMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientMotion correction
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of an object (10) placed in the examination volume of a MR device (1). It is an object of the invention to provide a method that enables efficient motion-compensation and / or motion-correction and that is compatible with Cartesian sampling of k-space. The method of the invention comprises: —generating MR signals by subjecting the object (10) to a MR imaging sequence of at least one RF pulse and switched magnetic field gradients; —acquiring the MR signals as a plurality of temporally successive subsets, each subset comprising a number of k-space profiles with sub-sampling of k-space, wherein the subsets complement each other to form a fully sampled set of k-space profiles; —reconstructing a single-subset MR image from each subset; —computing a gradient MR image from each single-subset MR image; and —detecting motion by comparing the gradient MR images with each other. Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device (1) and to a computer program for a MR device (1).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Dead-time calibration for a radiation detector
ActiveUS20190146098A1Reduce Image ArtifactsEffective compensationRadiation intensity measurementDead timePhysics
The invention relates to a correction device (8) for a radiation detector (2) including detector elements each for detecting incident photons. The correction device (8) is configured to read detection signals representative of an incident photon flux detected by the detector elements for different incident photon fluxes, and an evaluation unit (11) configured to determine for each detector element a dead time of the detector element and a parameter representative of an effective area of the detector element on the basis of a collective evaluation of the detection signals of the respective detector element. Further, the correction device (8) is configured to determine for each detector element correction parameters to compensate for differences in the effective areas and in the dead times of the detector elements on the basis of the determined parameters representative of the effective area and the determined dead times of the detector elements.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Integrated electronic RF shielding apparatus for an MRI magnet
InactiveCN1611186ALow costReduce installation costsMagnetic/electric field screeningMagnetic property measurementsElectronic systemsEngineering
An integrated electronic system housing and magnet structure (12) for an imaging system (10) includes a housing (40) and a radio frequency shield (46). The housing (40) is coupled to the magnet structure (13) and contains imaging system support electronics (42). The radio frequency shield (46) is coupled to the housing (40) and prevents radio frequency interference of a radio frequency receiver coil (30) from the imaging system support electronics (42).
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
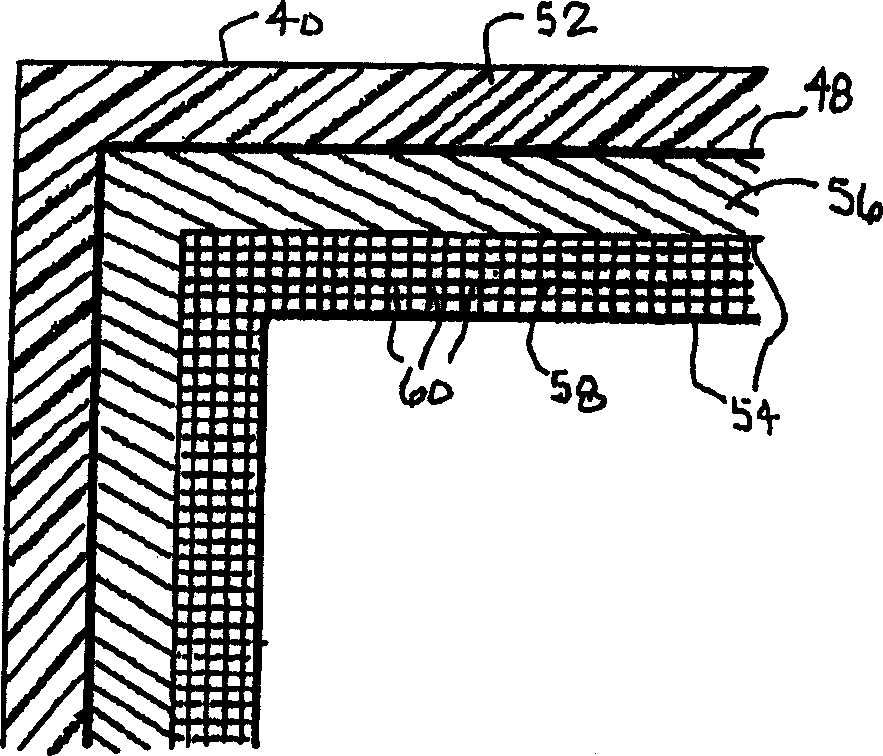
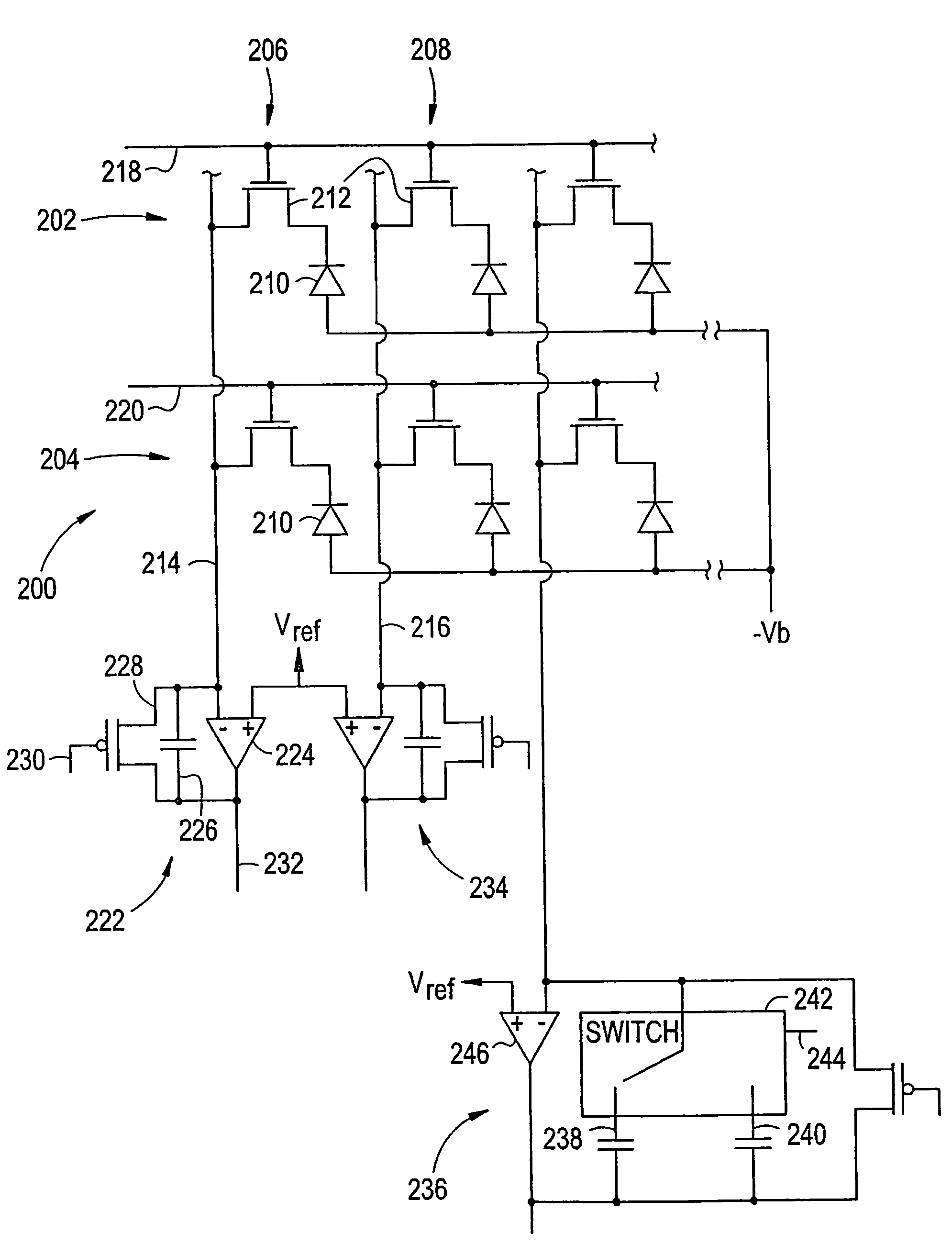
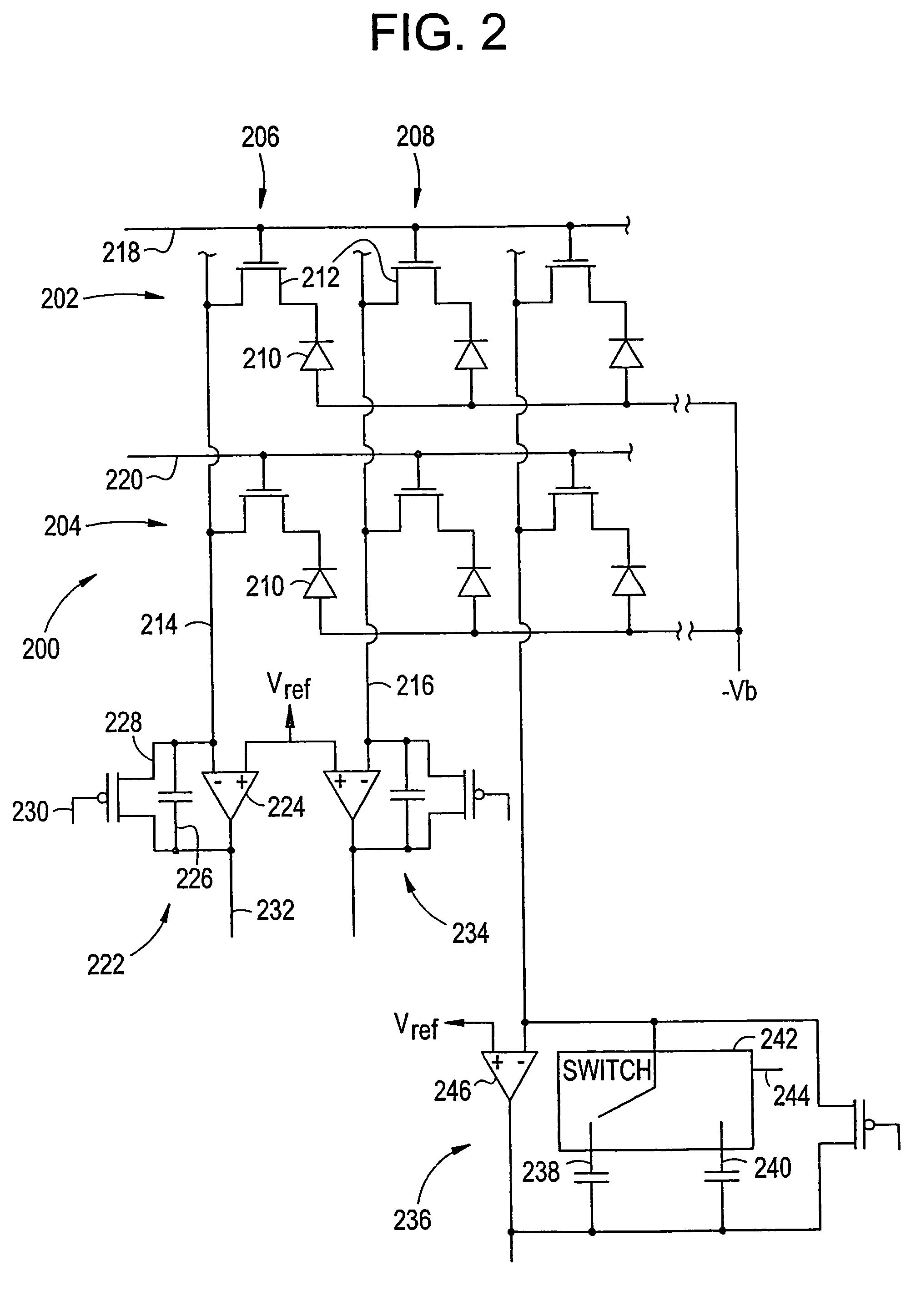
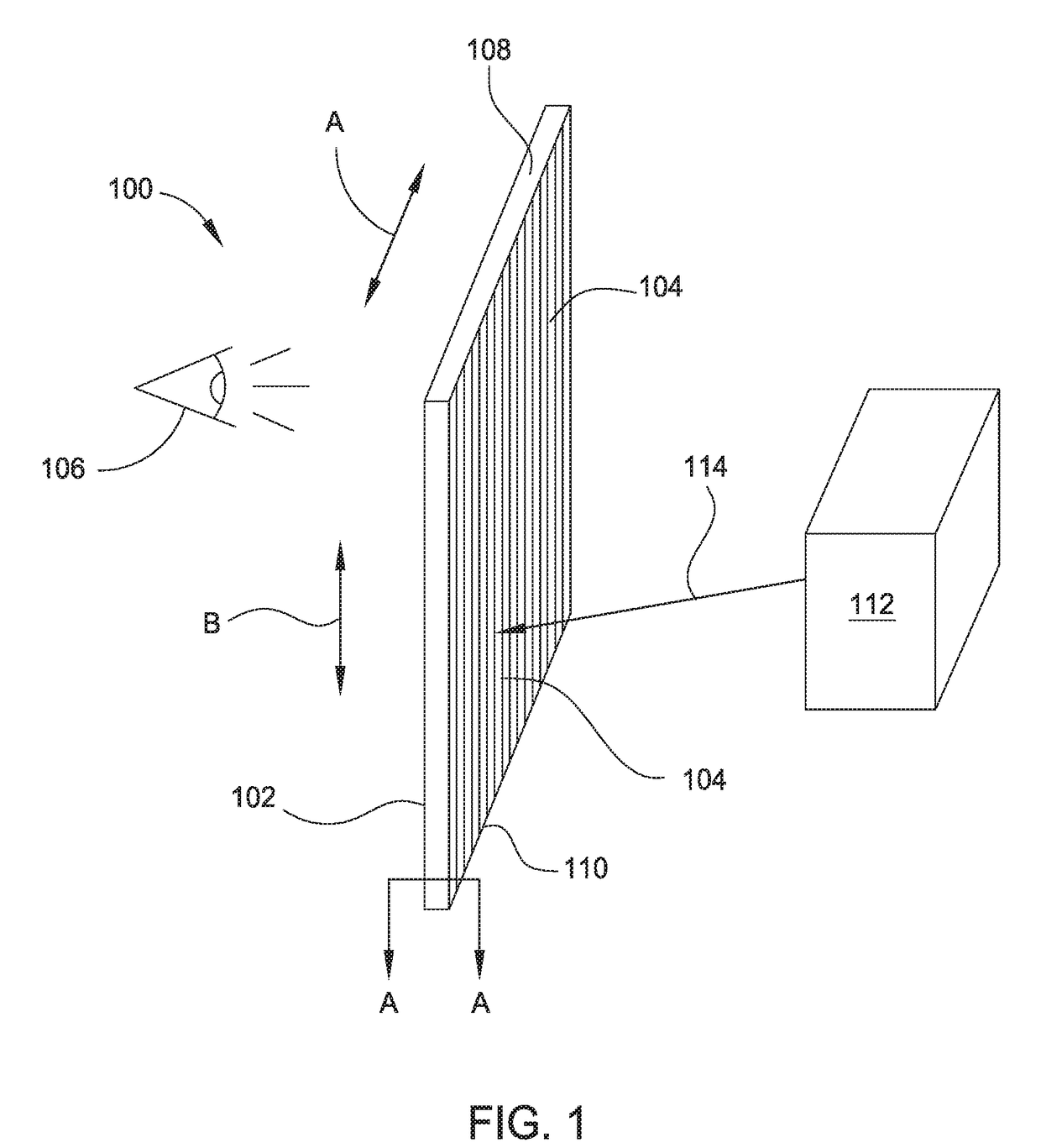
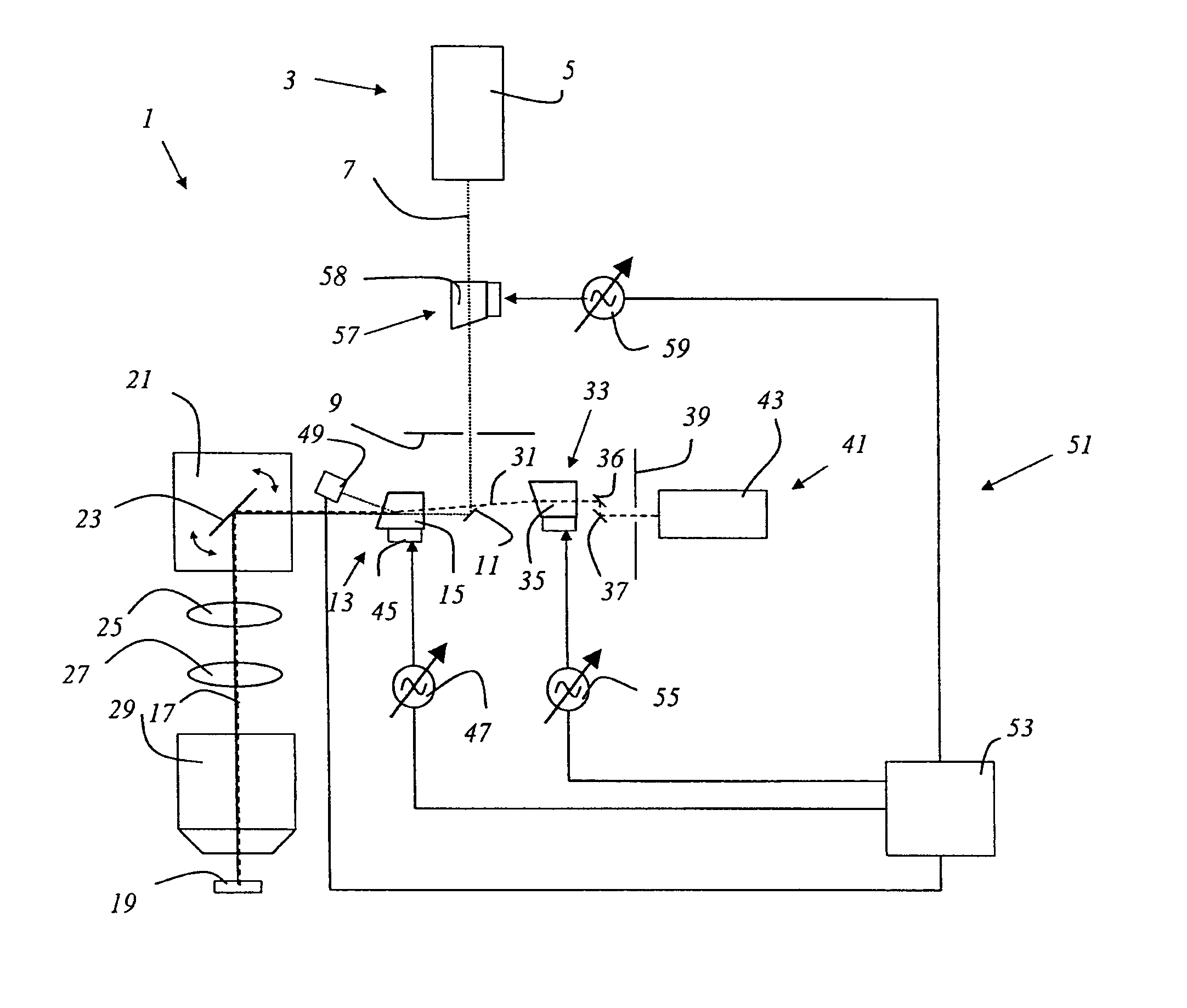
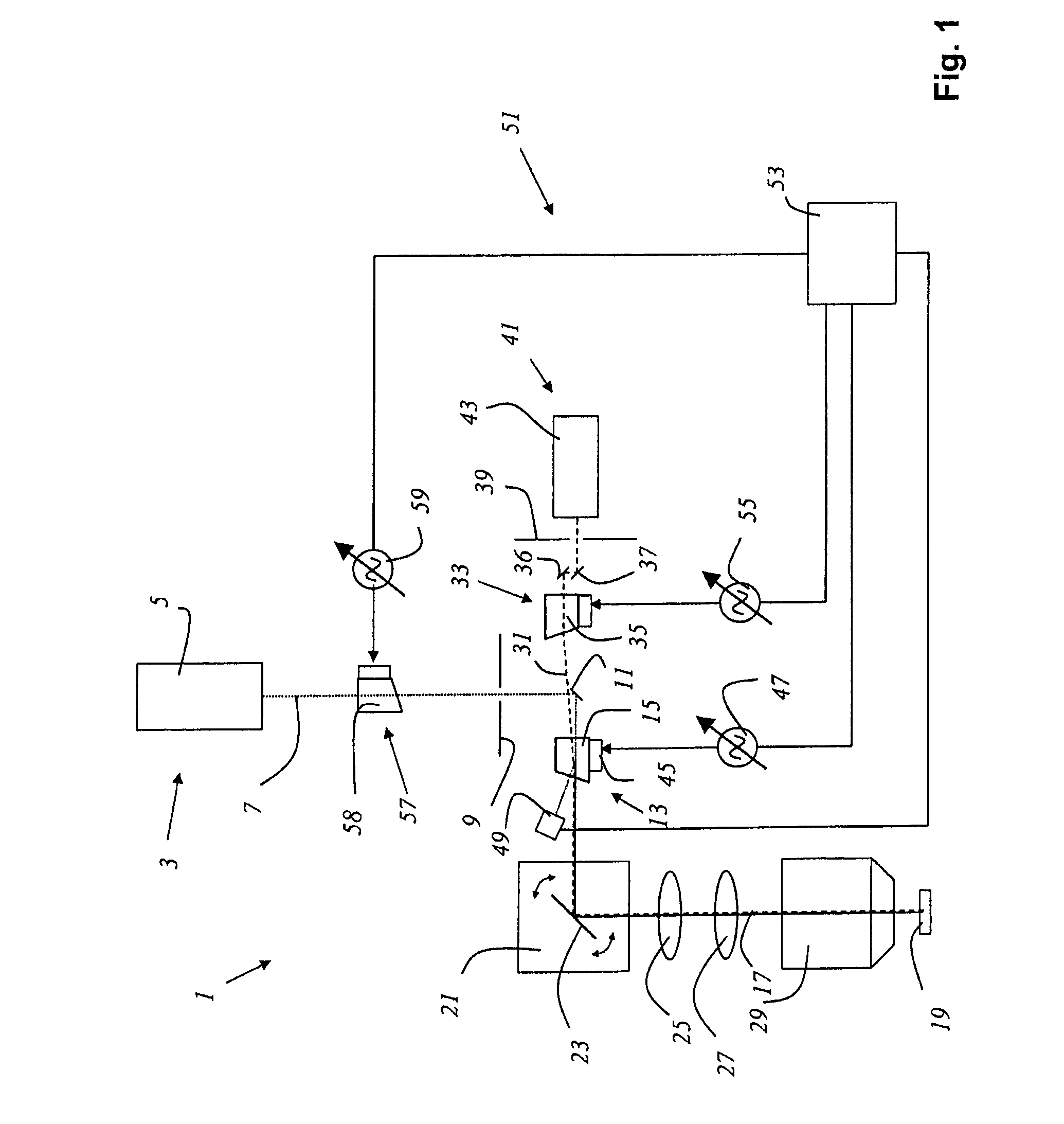
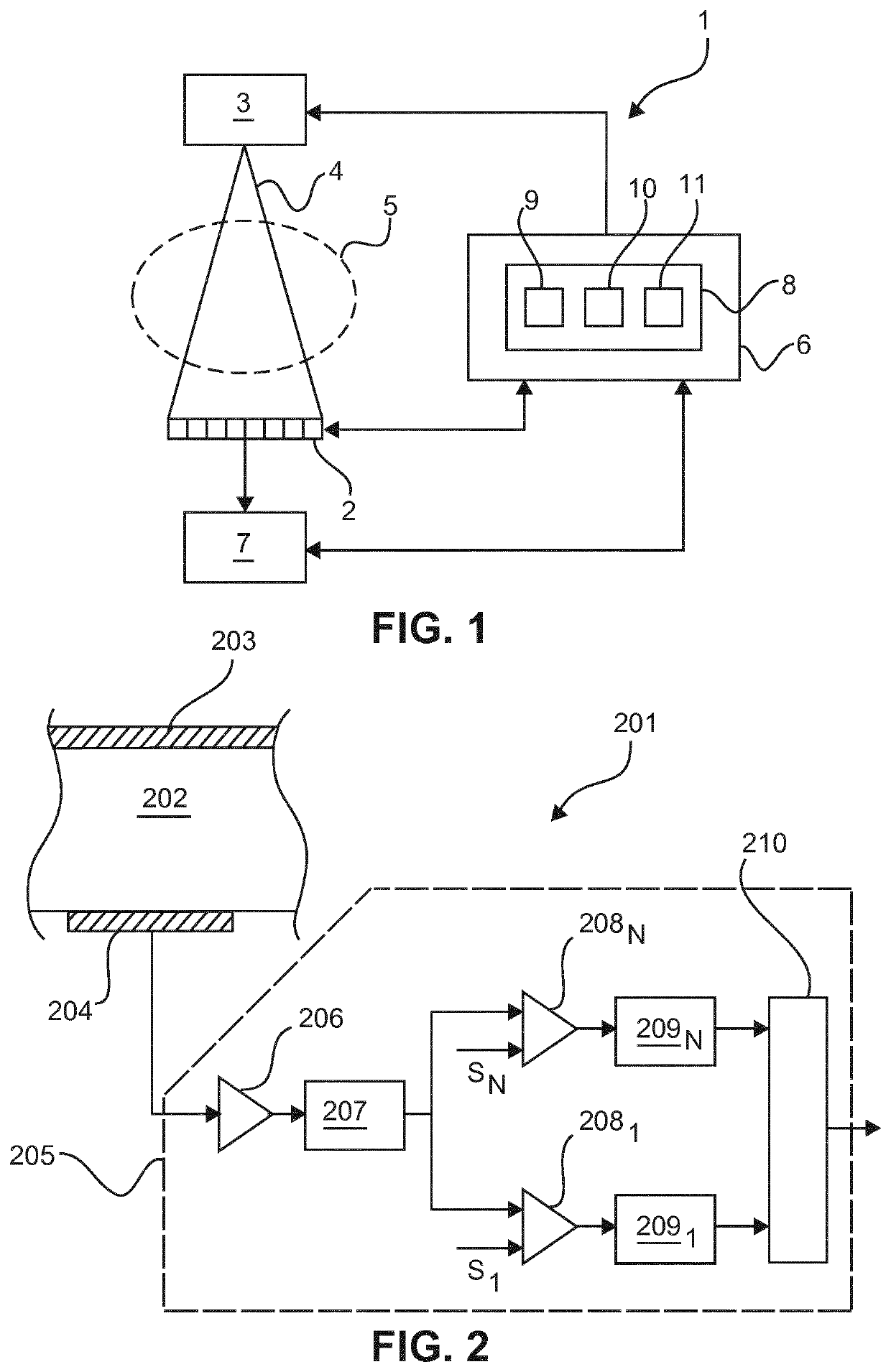
Method and apparatus for preventing image artifacts
InactiveUS7561196B2Prevent Image ArtifactsAvoid saturationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsStart timeFrame time
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
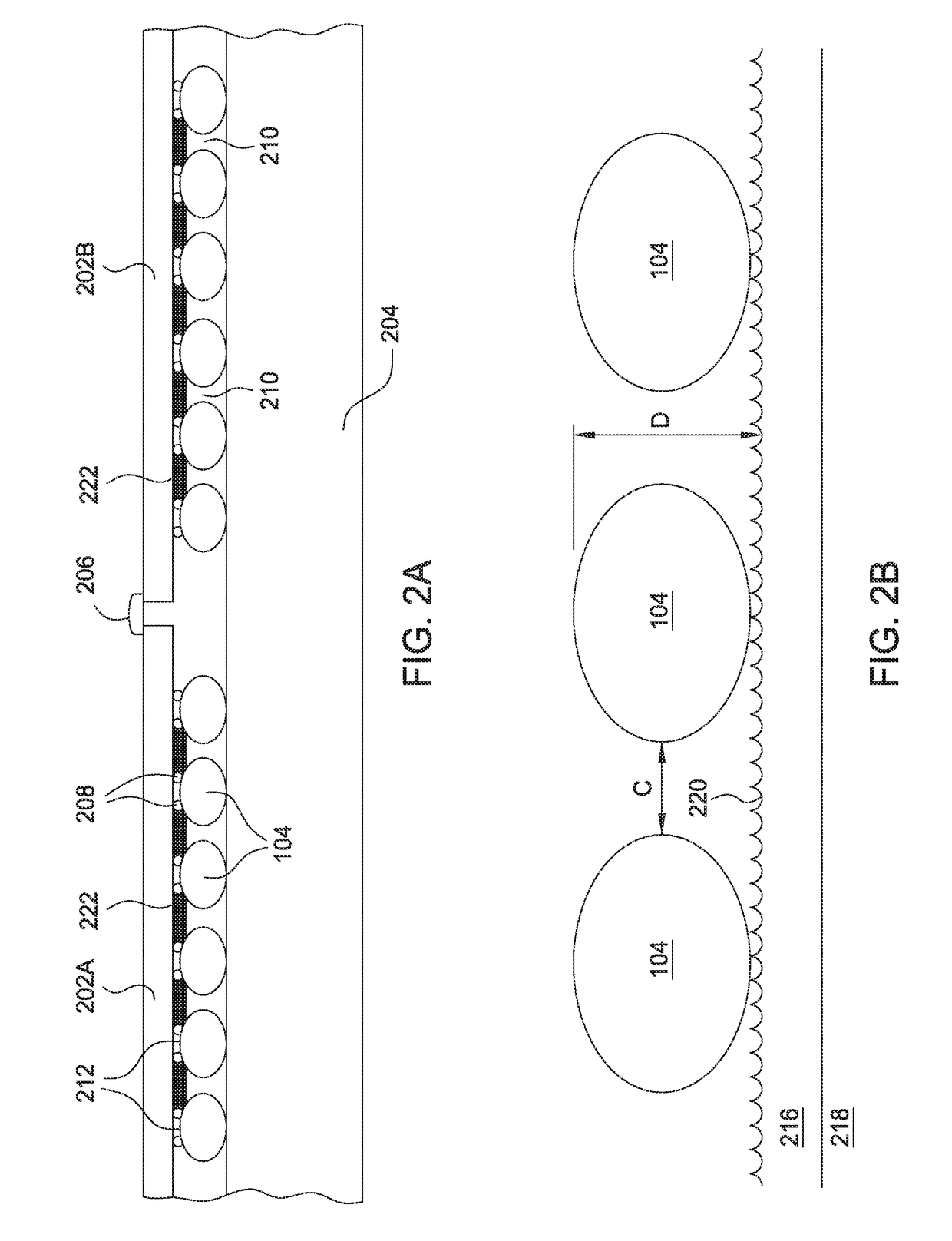
Vacuum hold-down of seamless image panel to polycarbonate protective frontplane
ActiveUS20180157349A1Prevent Image ArtifactsReduce exerciseDigital data processing detailsCasings with display/control unitsImage ArtifactEngineering
The disclosure described herein generally relates to an image panel and a method of compressing the image panel. A breather assembly is coupled to at least one edge of the image panel and a vacuum is drawn through the breather assembly to pull the image panel portion and the front panel into intimate contact with phosphors sandwiched therebetween. The breather assembly draws the vacuum from the air pockets between adjacent phosphors to pull the image panel flat and thus prevent image artifacts from forming while also permitting the image panel portion and the front plane panel to move independently.
Owner:PRYSM SYST INC
Device and Method for Fusing Image Data from a Multi-Camera System for a Motor Vehicle
InactiveUS20190392567A1Facilitate data fusionEasy to integrateTelevision system detailsImage enhancementPixel densityImage analysis
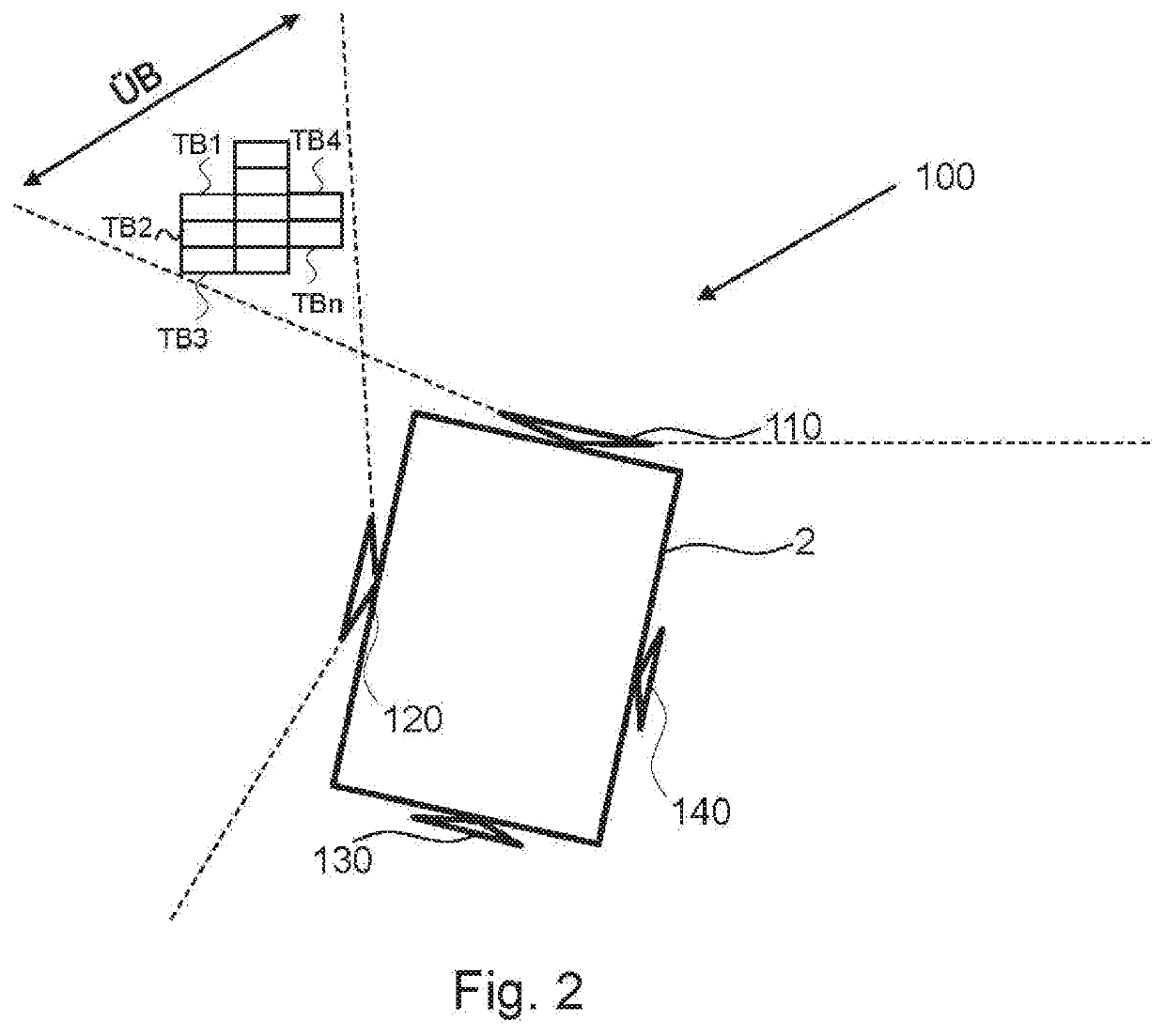
A device (1) for fusing image data from a multi-camera system (100) for a motor vehicle includes: an image analysis device (10) configured to define subregions (TB1, TB2, . . . , TBn) of an overlap region (ÜB) of at least two cameras (110, 120) of the multi-camera system; an acquisition device (20) configured to acquire pixel densities of the subregions (TB1, TB2, . . . , TBn) of the overlap region; and a computing device (30) configured to determine pixel density deviations and to select adjacent subregions (TB1, TB2, . . . , TBn) with deviations below a threshold value for a total image overlay.
Owner:CONTI TEMIC MICROELECTRONIC GMBH
Scanning microscope having an acoustooptical component
ActiveUS7087891B2Illuminating light power level fluctuations,Prevent Image ArtifactsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansOptoelectronicsAcousto-optics
A scanning microscope having an acoustooptical component that splits out illuminating light for illumination of a sample from the output light of at least one light source, and conveys detected light proceeding from the sample to a detector, comprises, in the beam path of the output light from which the illuminating light is split out, at least one monitoring detector which is the measuring element of a control circuit. The scanning microscope is characterized in that fluctuations over time in the illuminating light power level are largely eliminated.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Magnetic resonance scanning trigger device and magnetic resonance scanning control system and method
ActiveCN106419918BSolve problems prone to image artifactsPrevent Image ArtifactsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceControl system
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical magnetic resonance scanning control and provides a magnetic resonance scanning trigger device, and a system and method for magnetic resonance scanning control. According to the invention, the magnetic resonance scanning trigger device composed of a trigger module, a detection module and a transmission module is adopted, so that when a user gets ready for holding breath, the trigger module will start a corresponding state change according to the user's trigger operation; the detection module detects a state of the trigger module and generates corresponding instruction information when the trigger module starts the state change; information amplifying processing is conducted to the instruction information; and the transmission module receives the instruction information treated by the amplifying processing, converts the amplified instruction information into a corresponding digital signal and sends the signal to a magnetic resonance scanning control device. In this way, the magnetic resonance scanning control device can control the magnetic resonance scanning device to start scanning the user according to the digital signal. The user can autonomously select the time for scanning start, so that image artifacts caused when the user is not well-prepared can be avoided.
Owner:SHENZHEN BASDA MEDICAL APP
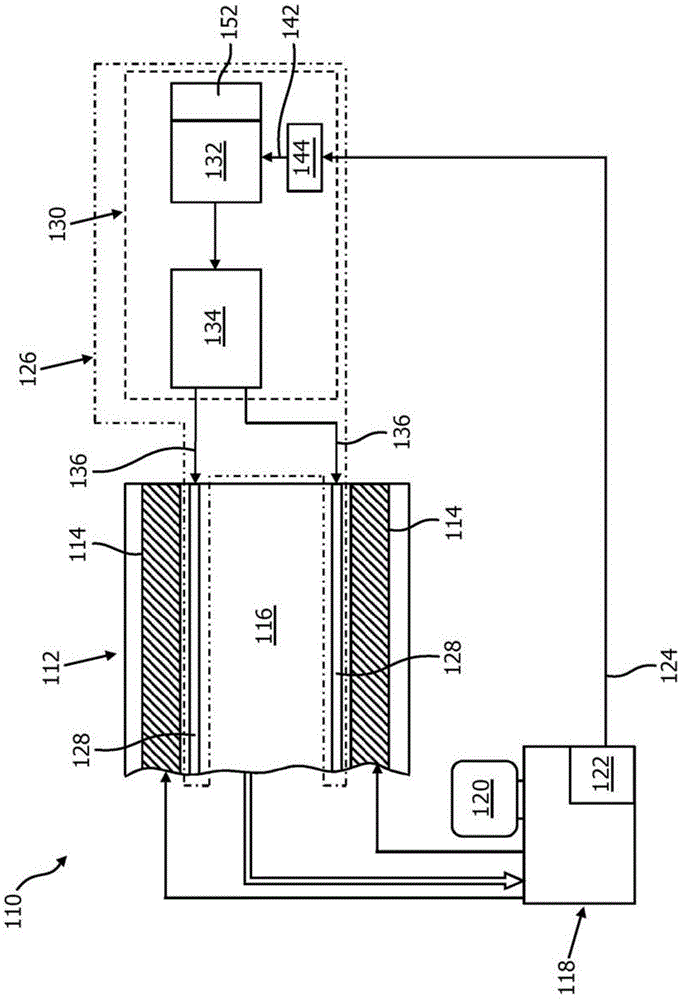
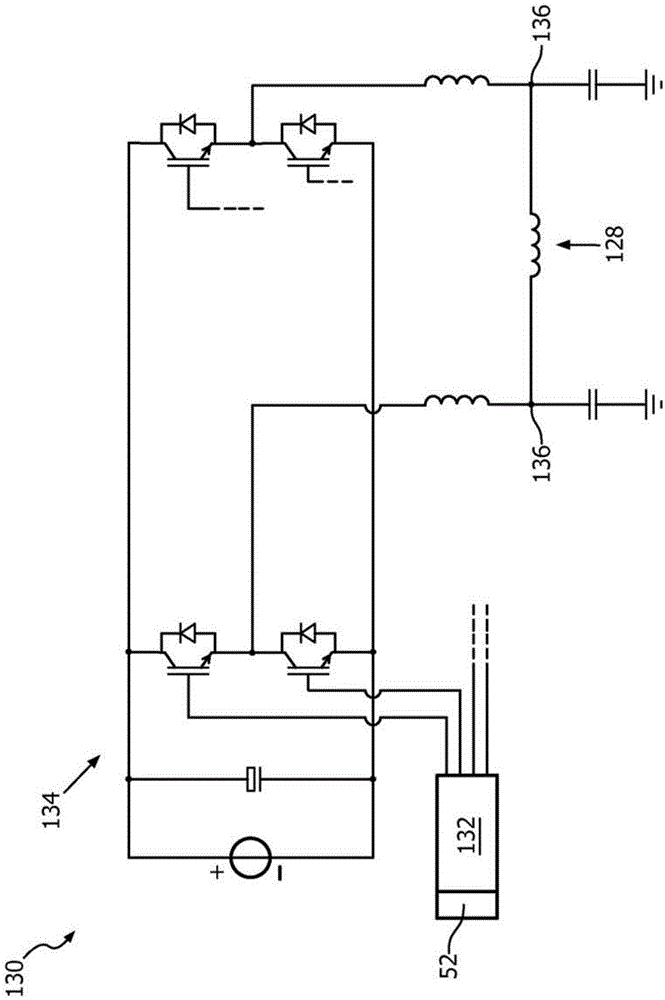
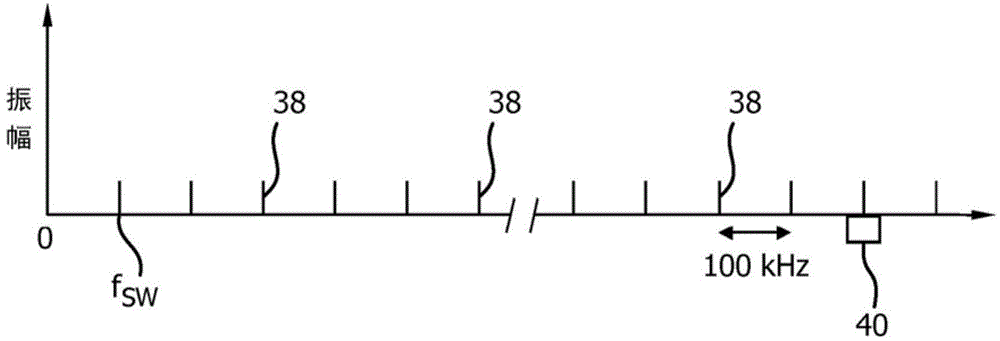
Switching -frequency -controlled switch -mode power supply unit for powering magnetic resonance system gradient coils
InactiveCN104380131AAvoid the aforementioned interferenceContinuous control of interference levelsMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyPulse controlResonance
A power supply unit (130) for powering at least one gradient coil (128) of a magnetic resonance (MR) examination system (110) with a main magnet (114) having, in at least one state of operation, a substantially static magnetic field strength, and with an MR measurement signal bandwidth, the power supply unit (130) comprising: a switched-mode power converter (134) for powering the at least one gradient coil (128), comprising at least one switching member provided to switch between a conducting state configuration and an essentially non-conducting state configuration at a first fundamental switching frequency (fSW); a pulse control unit (132) designed to provide switching pulses at the first fundamental switching frequency (fSW) for controlling the switching of the at least one switching member; wherein, upon triggering by a trigger signal (142), the pulse control unit (132) is provided to change the first fundamental switching frequency (fSW) to at least a second fundamental switching frequency (fSW).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
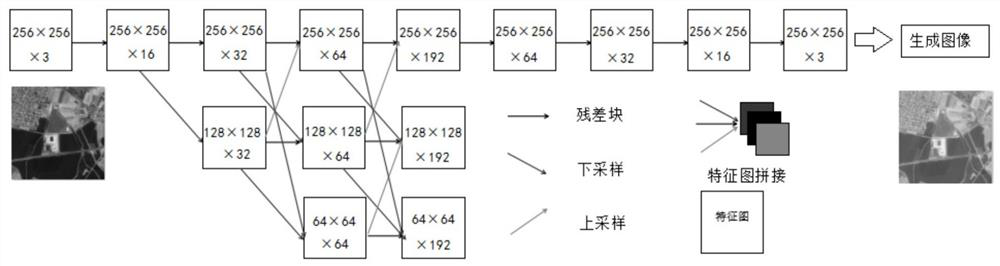
Method and device for creating remote sensing image style migration model
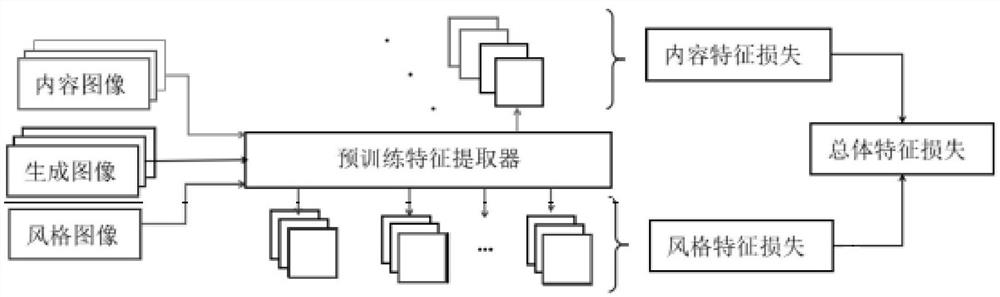
ActiveCN114022352AMaintain propertiesAvoid Style ImbalanceGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringThresholding
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for creating a remote sensing image style migration model, and the method comprises the steps: employing an iteration mode to execute the following steps until the obtained overall feature loss reaches a preset threshold value: inputting an original image into an initial learning algorithm model, and obtaining a generated image; inputting the original image, the generated image and the style image into a pre-training model to obtain overall feature loss; adjusting parameters of the initial learning algorithm model, weights of a plurality of different pieces of feature information in the pre-training model and a mixing ratio between the weight of the content feature information and the weight of the style feature information according to the overall feature loss; and taking the initial learning algorithm model adjusted according to the overall feature loss conforming to a preset threshold as a remote sensing image style migration model. Through the scheme of the embodiment, the style imbalance of the strong style image is avoided, the texture feature and the color feature of the original image are maintained, and the obvious real style effect is achieved.
Owner:成都国星宇航科技股份有限公司
Vacuum hold-down of seamless image panel to polycarbonate protective frontplane
ActiveUS10296041B2Prevent Image ArtifactsReduce exerciseDigital data processing detailsSolid-state devicesPhosphorEngineering
Owner:PRYSM SYST INC
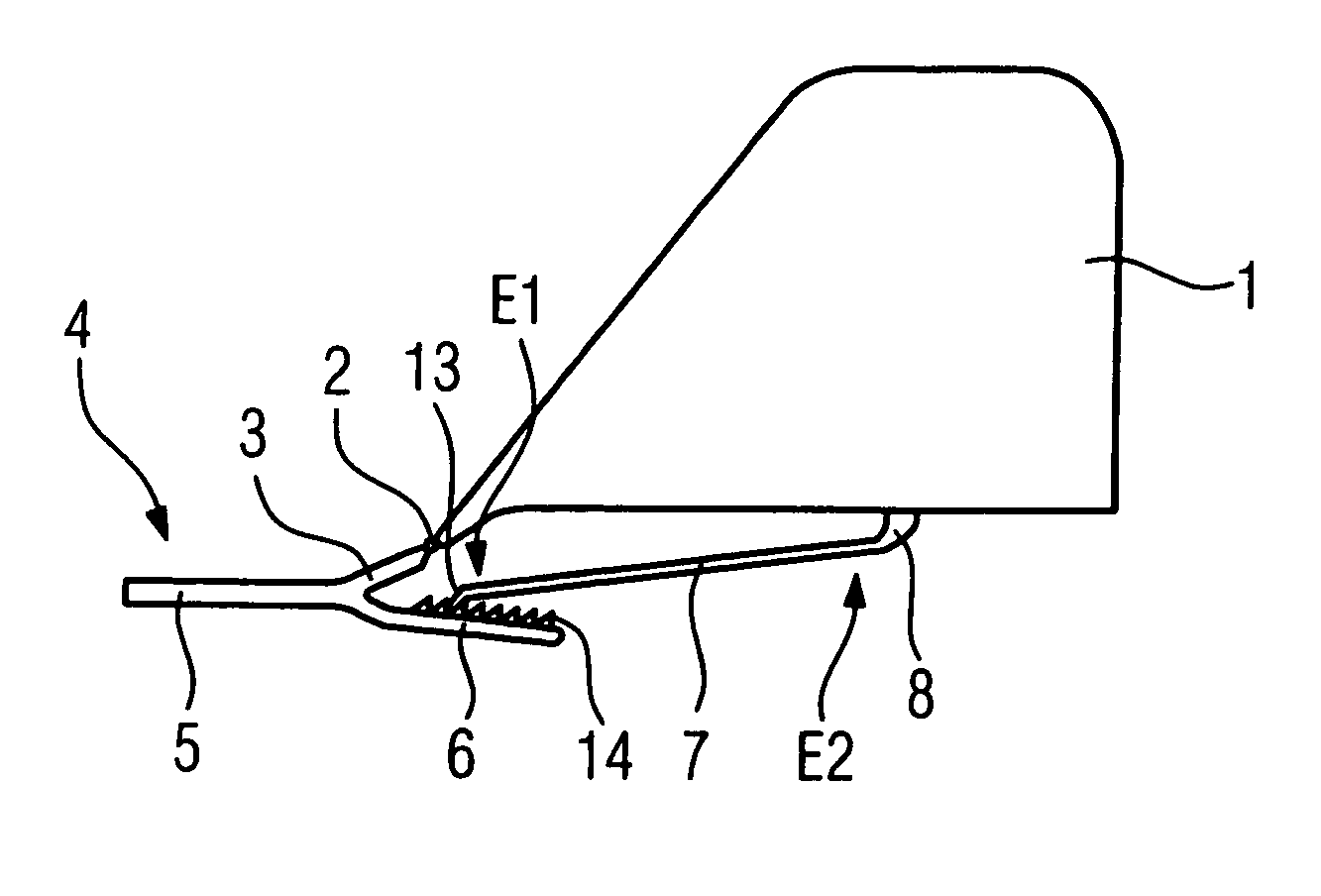
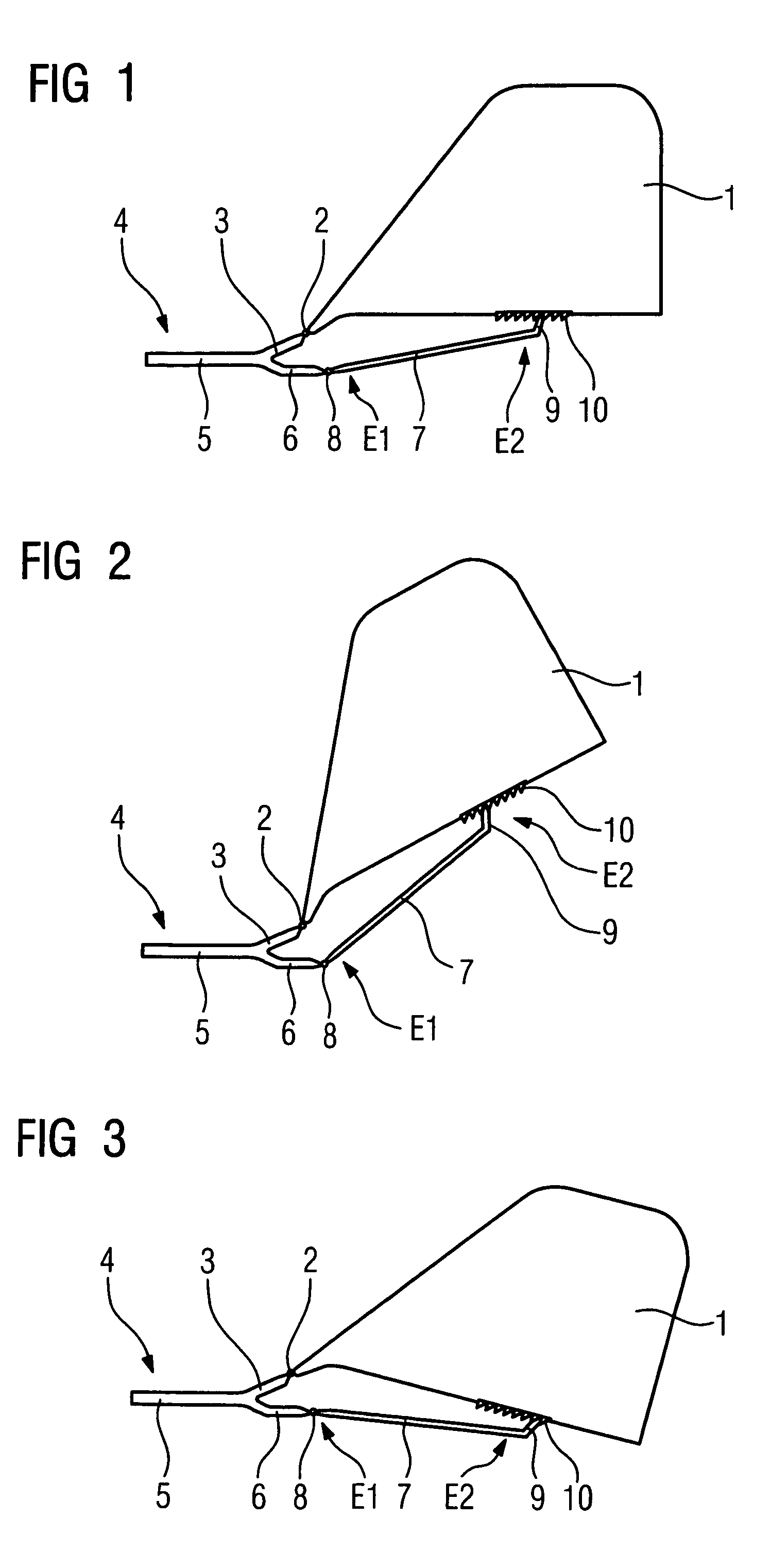
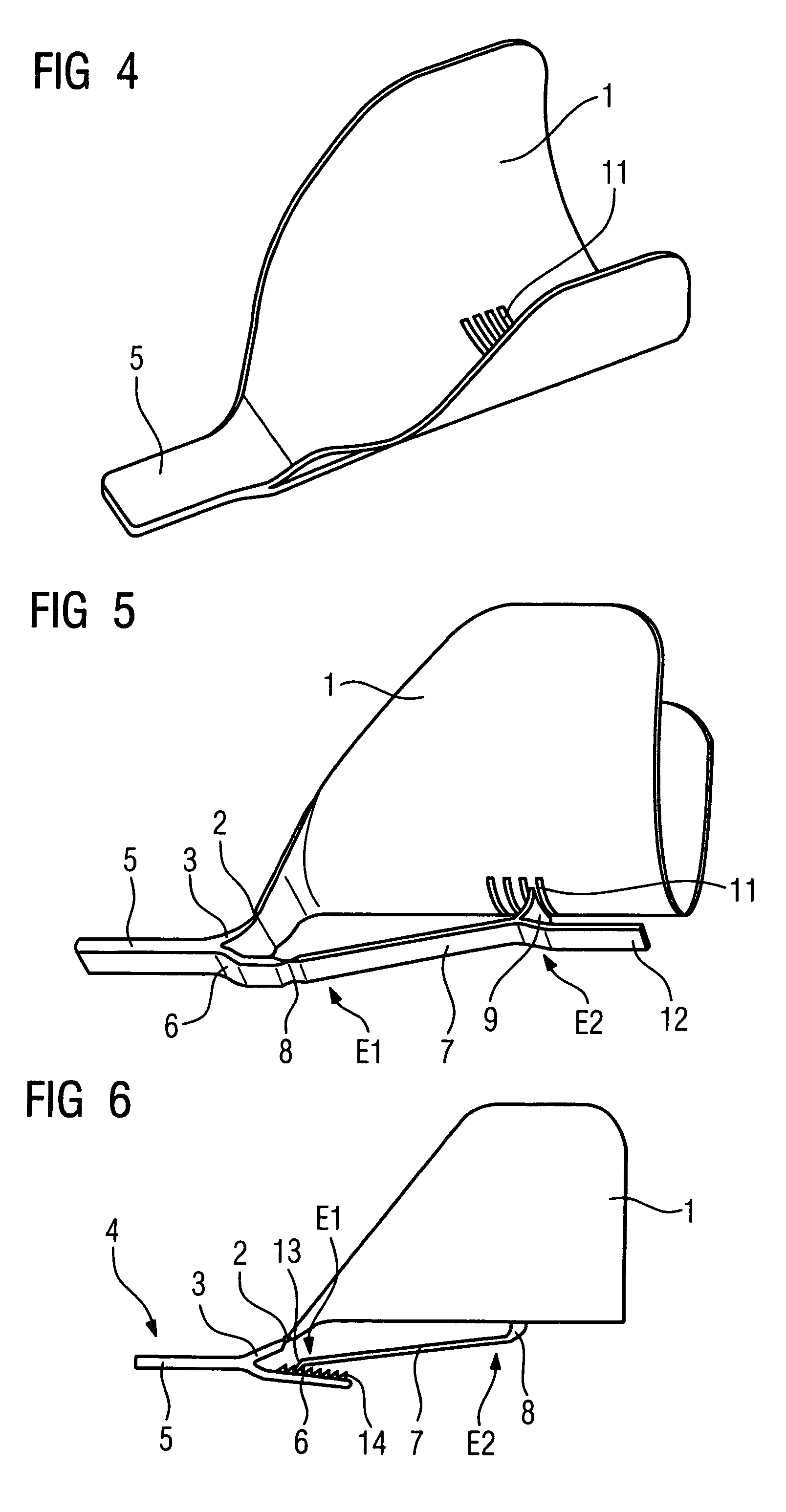
Device for support of the head
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
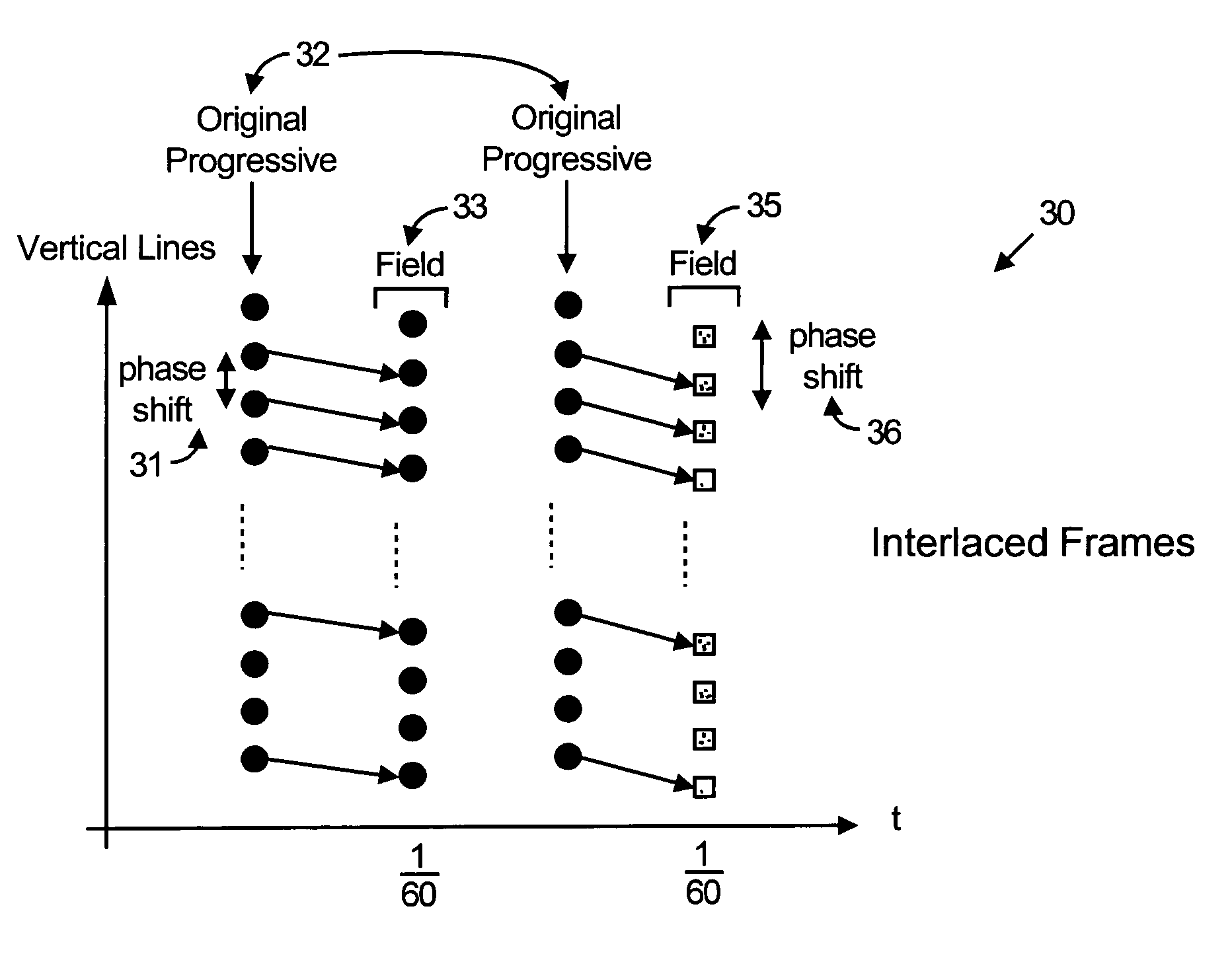
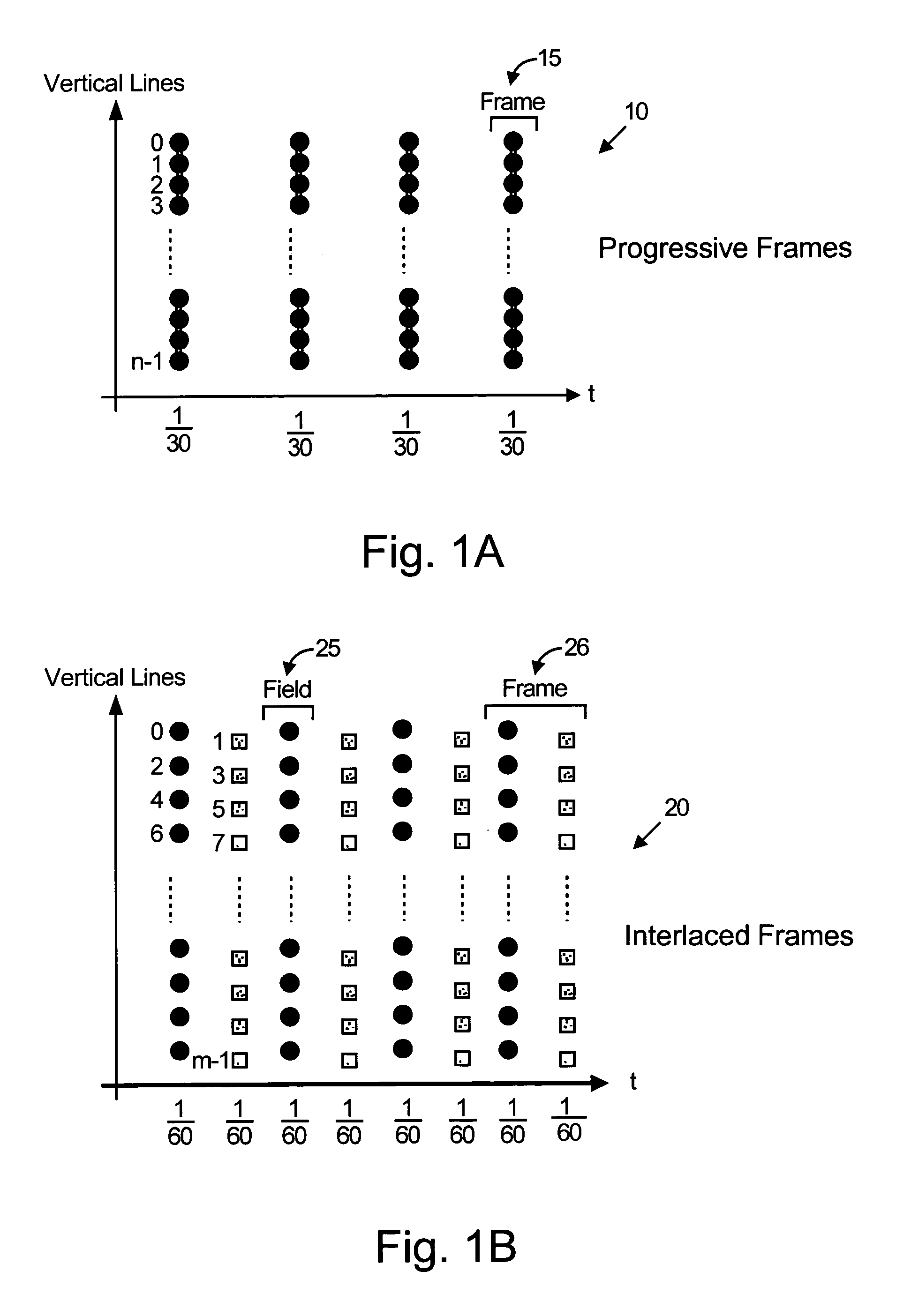
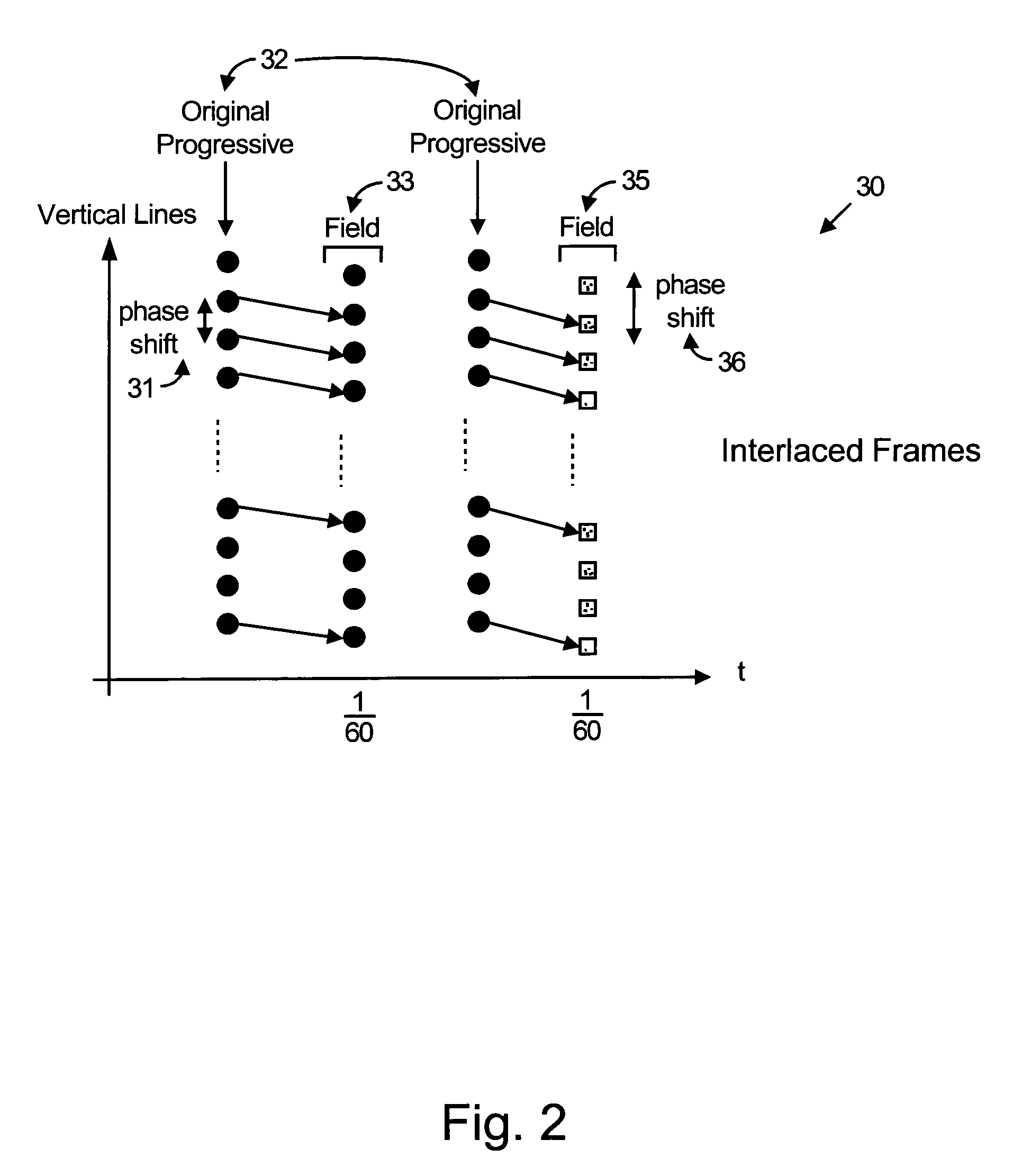
Method and apparatus for interlaced display of progressive video content
InactiveUS7440030B2High quality video displayLess complexTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer graphics (images)Display device
A method is provided for displaying progressive video content on an interlaced display device. The method comprises vertically phase shifting video lines of the progressive video content to correctly position the video lines with respect to a video field of the interlaced display device. The method further comprises scaling the video lines of progressive video content to match a vertical size of a video field of the interlaced display device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
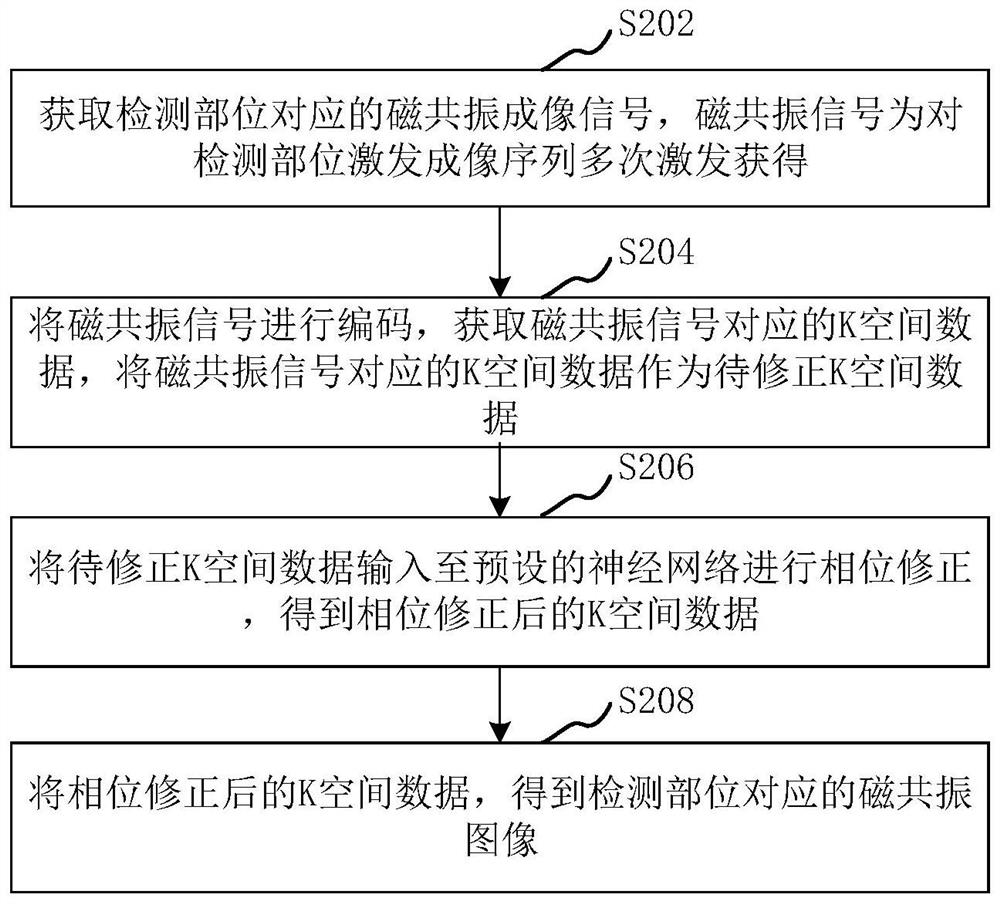
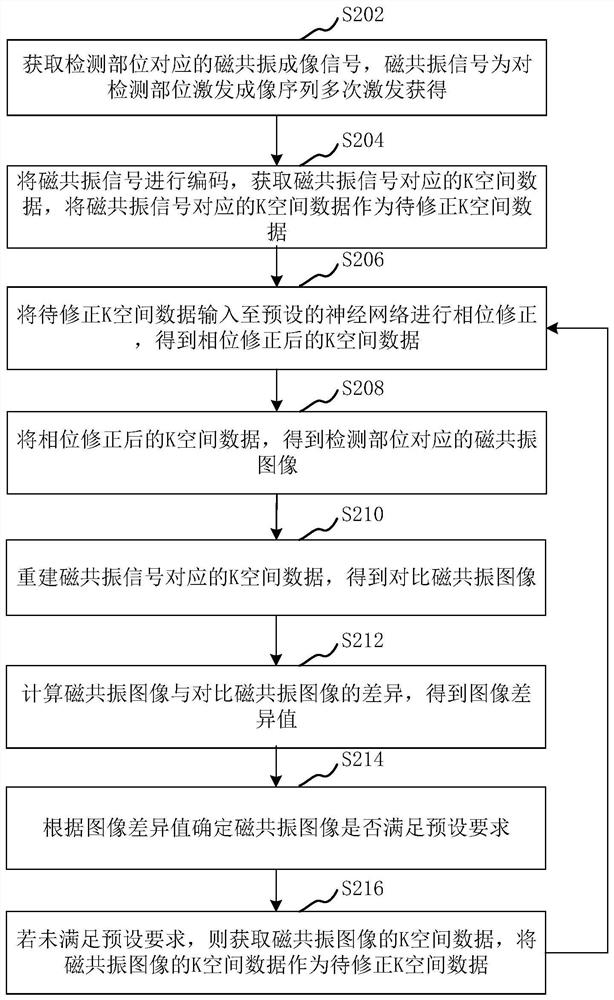
Magnetic resonance imaging method, device, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN110244246BNo need to improve the designPrevent Image ArtifactsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase correctionMri image
The present application relates to a magnetic resonance imaging method, device, computer equipment and storage medium. The method includes: acquiring a magnetic resonance imaging signal corresponding to the detection site, the magnetic resonance signal is obtained by multiple excitations of the detection site excitation imaging sequence; encoding the magnetic resonance signal, obtaining K-space data corresponding to the magnetic resonance signal, and converting the magnetic resonance signal to The K-space data corresponding to the signal is used as the K-space data to be corrected; the K-space data to be corrected is input to the preset neural network for phase correction, and the phase-corrected K-space data is obtained; the phase-corrected K-space data is reconstructed to obtain the detection The corresponding magnetic resonance images. The imaging efficiency can be improved by adopting the method.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
CT system and CT method
ActiveUS10557806B2Negative effectPrevent Image ArtifactsComputerised tomographsTomographyControl cellRadiology
The present invention relates to a dual- or multi-source CT system and method. For suppressing or even completely eliminating the negative effects of cross-scatter, the proposed CT system comprises two x-ray sources (10, 11), two detectors (13, 14), two read-out units (15, 16), a control unit (17) and a reconstruction unit (19). Further, a scatter correction unit (18) is provided or the read-out units (15, 16) are configured to generate scatter-corrected read-out signals from the detected radiation, wherein a scatter-corrected read-out signal is generated from the radiation detected by a detector during a single projection interval (I) including multiple repetitions of three phases, in which the sources are alternately switched on and off and in which the read-out units alternately register primary radiation or cross-scatter radiation.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
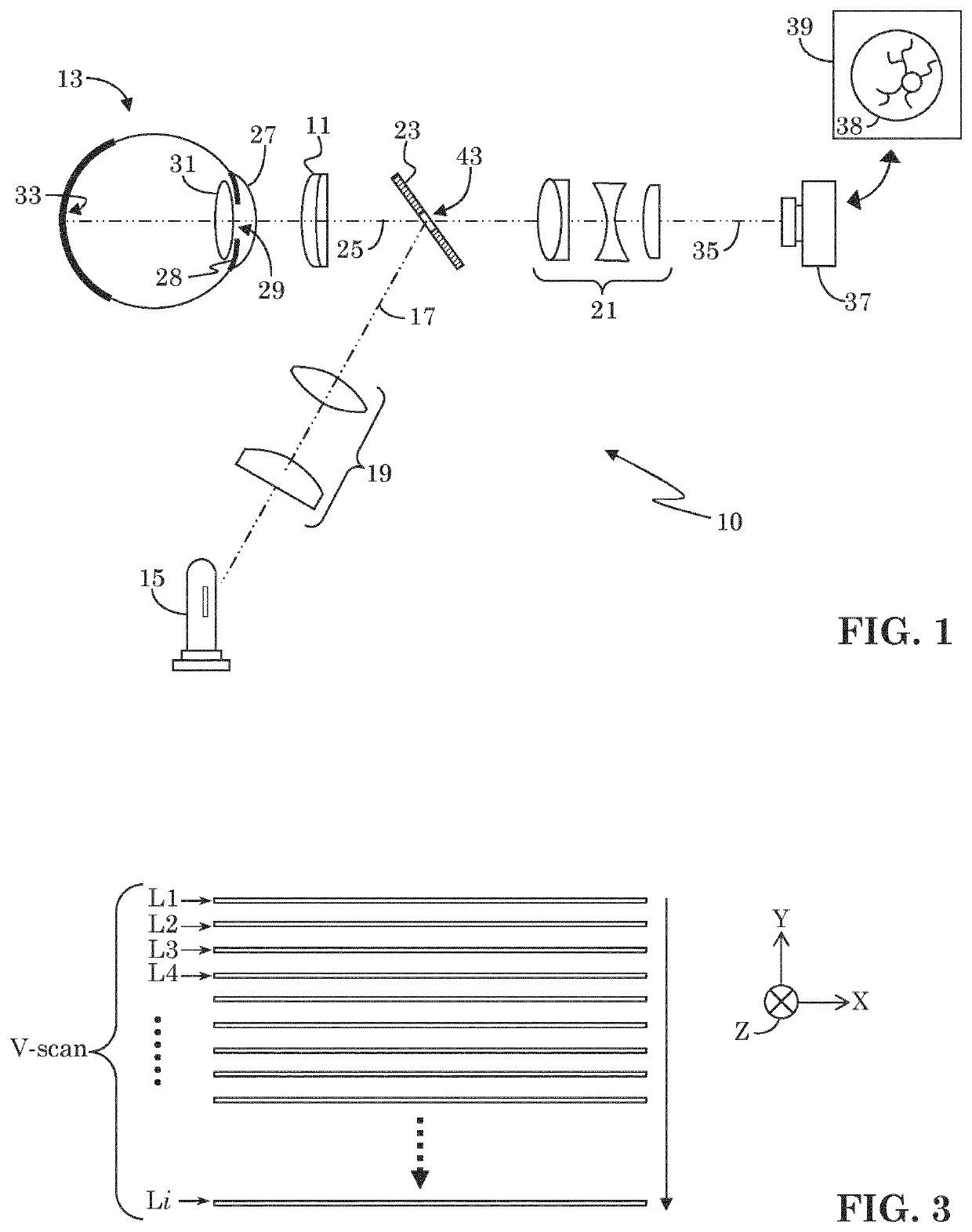
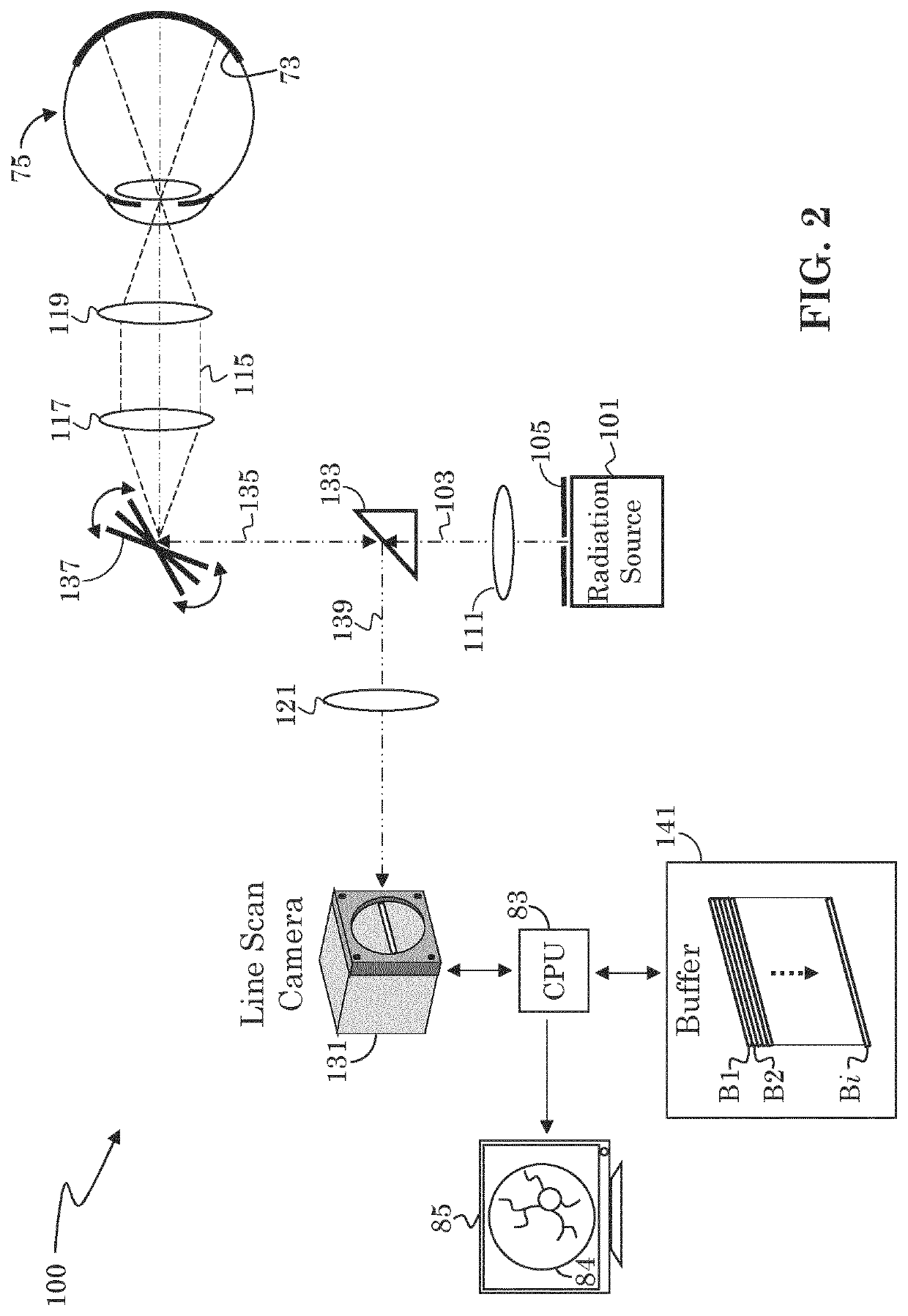
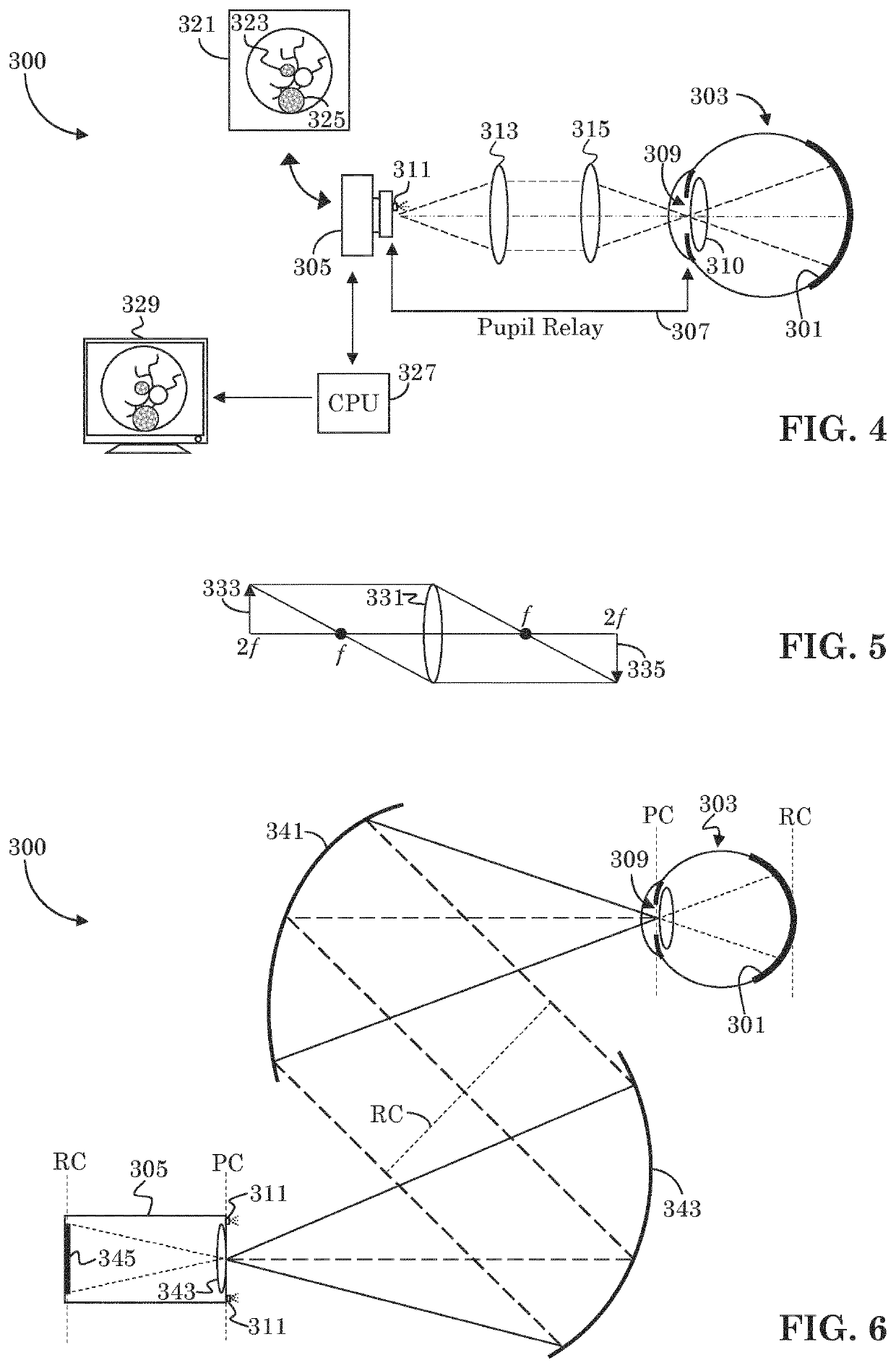
Low cost fundus imager with integrated pupil camera for alignment aid
A low cost fundus camera uses LED light sources placed adjacent the camera's imaging stop, and thereby eliminates the need for optics for introducing the light source to the camera's optical path. Lens reflex in the pupil relay is avoided by using only reflective optics in the pupil relay. Reflex from the LEDs is mitigated by actuating each LED separately, one at a time, and capturing a separate image with each actuated LED. Reflex-free regions of each captured image are extracted and combined to create a composite, reflex-free image.
Owner:CARL ZIESS MEDITEC INC +1
Method and device for normal correction of scanning data in imaging equipment
ActiveCN103315763BPrevent Image ArtifactsReduce acquisition timeComputerised tomographsTomographyCounting rateAcquisition time
An embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for normal correction of scanning data in imaging equipment. The method includes scanning a model and acquiring a plurality of groups of correction data; optionally combining the groups of correction data to obtain correction data combinations corresponding to different counting rates, thus obtaining correction data corresponding to the different counting rates; calculating normal correction factors under the different counting rates according to the correction data corresponding to the different counting rates; and correcting scanning data different in counting rate in the imaging equipment through the normal correction factors under the different counting rates. The method and the device according to the embodiment have the advantages that acquisition time of correction data can be shortened and the problem of image artifacts caused by mismatch of the counting rates is also avoided.
Owner:SHENYANG INTELLIGENT NEUCLEAR MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Dead-time calibration for a radiation detector
ActiveUS10627532B2Reduce Image ArtifactsEffective compensationMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation intensity measurementEngineeringRadiation
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com