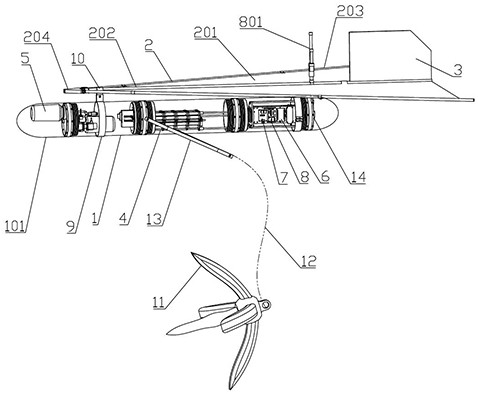
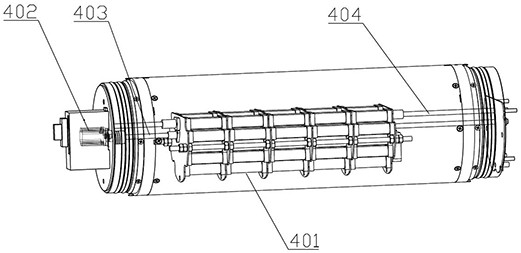
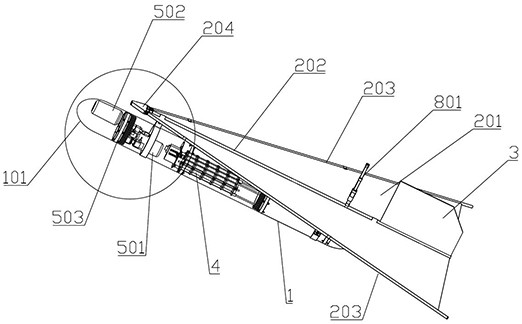
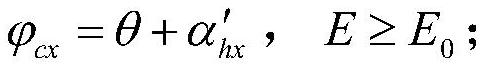Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Glider" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The glider is a pattern that travels across the board in Conway's Game of Life. It was first discovered by Richard K. Guy in 1970, while John Conway's group was attempting to track the evolution of the R-pentomino. Gliders are the smallest spaceships, and they travel diagonally at a speed of one cell every four generations, or c/4. The glider is often produced from randomly generated starting configurations.
Virtual anchoring navigation control algorithm for wave glider
InactiveCN111142541AEliminate precision errorsPosition/course control in two dimensionsGliderControl theory
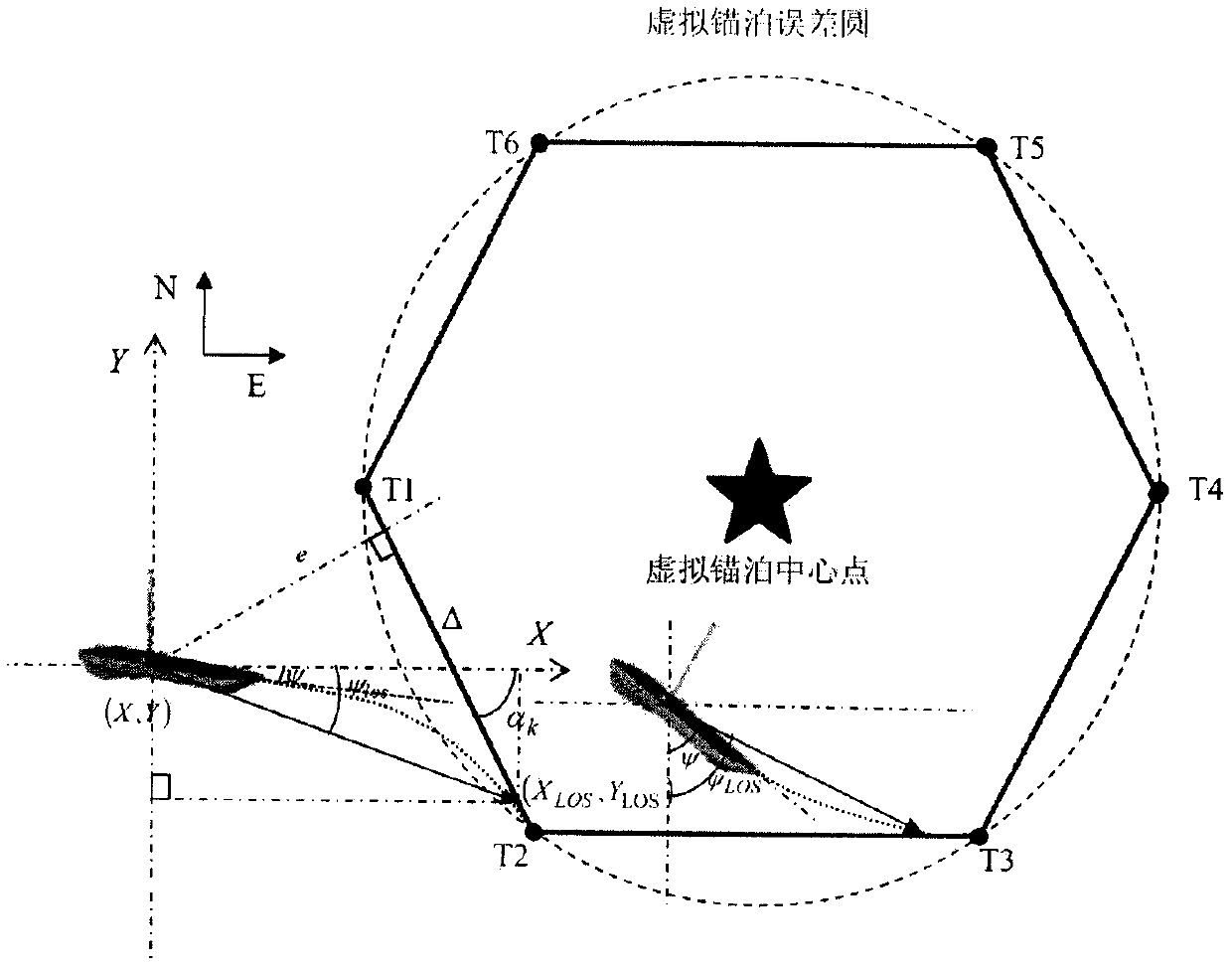
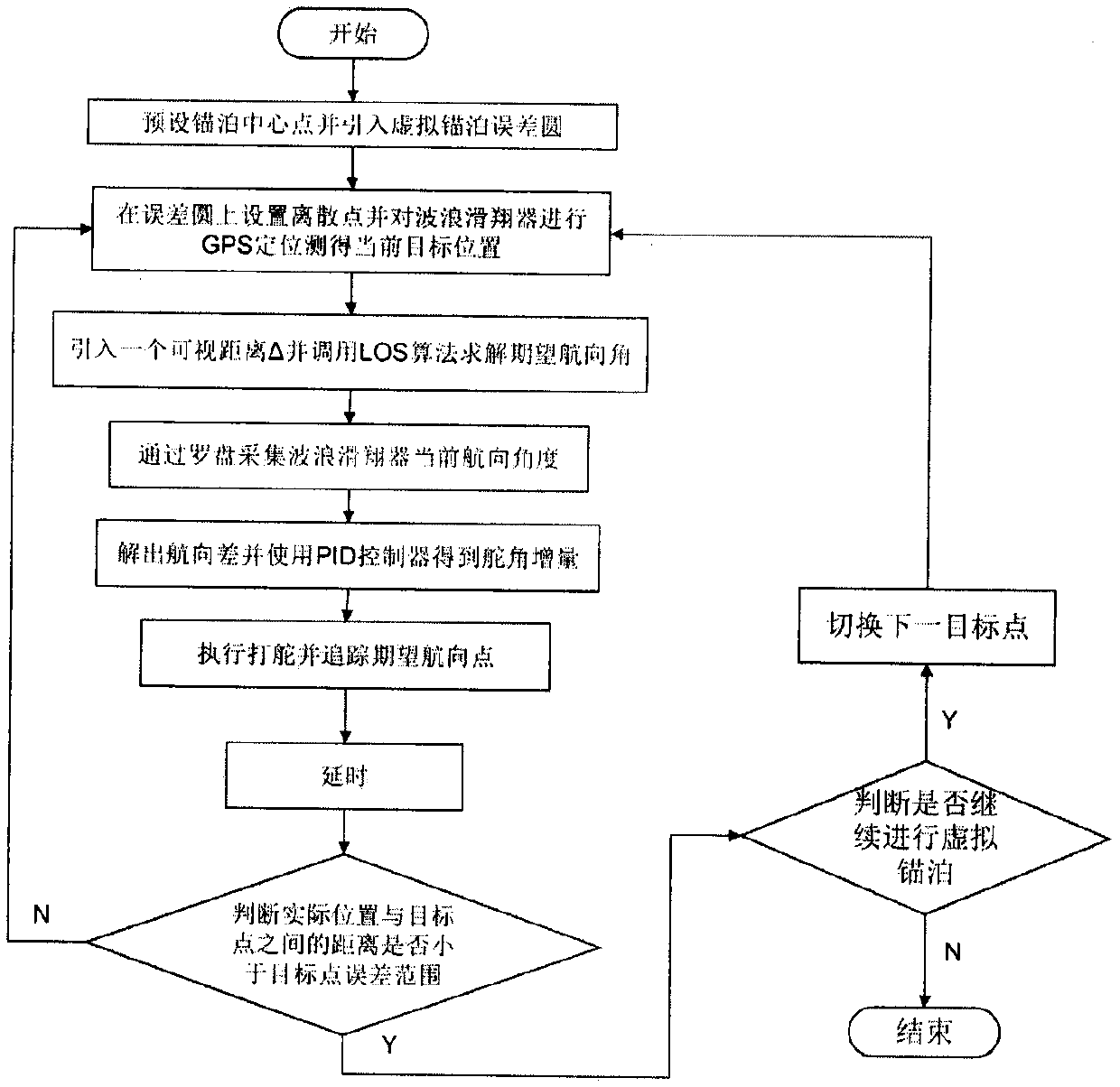
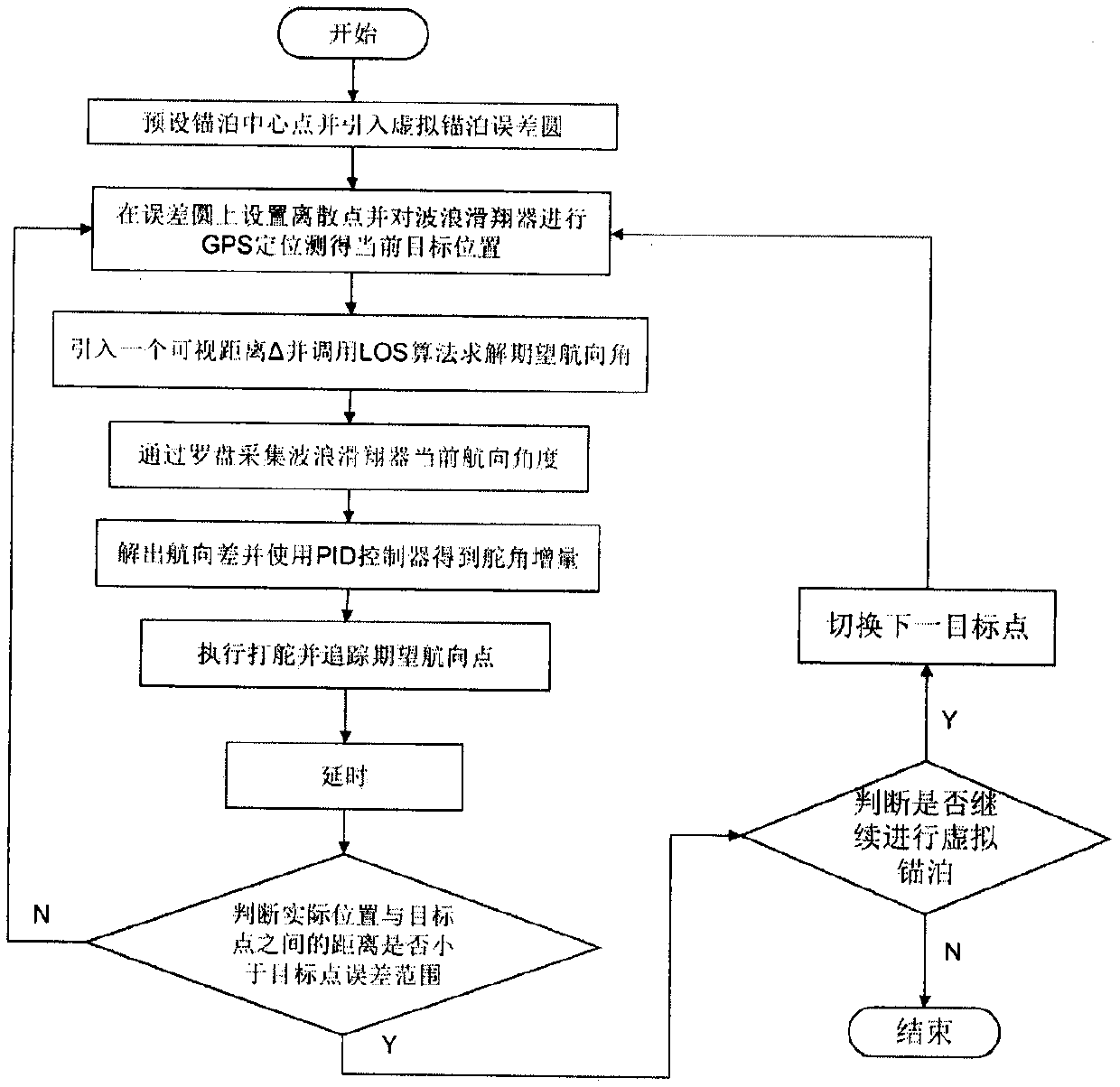
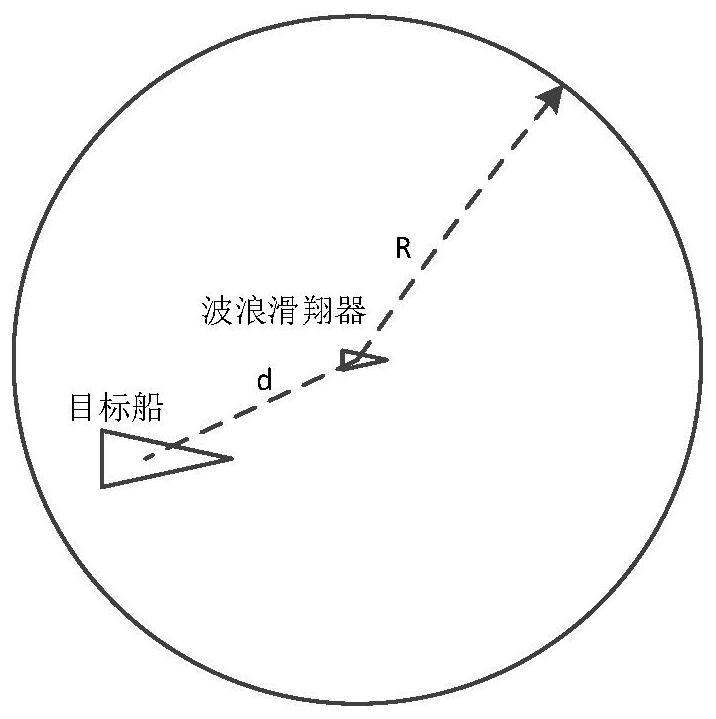
The virtual anchoring navigation control means that a wave glider performs virtual anchoring control within a certain range of an anchoring point, marine data can be conveniently obtained for a long time, and a marine environment can be conveniently detected. An algorithm comprises the steps of setting a virtual anchoring center point, introducing a virtual mooring error circle, and giving an error circle radius R; carrying out curve discretization on the virtual mooring error circle, which means converting circular curve trajectory tracking into linear path tracking for tracking a plurality of target points, allowing a compass to collect a current course angle psi, allowing a GPS module to perform positioning on the wave glider in real time, calculating an expected course angle psi los byan LOS algorithm, inputting a course difference between an actual course angle and an expected course angle into a PID controller, solving a current expected rudder angle delta and executing steering; and after the wave glider enters the error range of the target point, switching to a next target point, and performing continuous target heading point tracking. According to the invention, a virtualanchoring navigation control algorithm is designed to eliminate precision errors caused by an external environment during anchoring, and through the continuous tracking of a target heading point, thereentry into the anchoring state can be achieved when deviating from the anchoring state.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV +1
Global path planning method for wave glider
PendingCN111189468AShort calculation timeSmall amount of calculationInstruments for road network navigationGliderSimulation
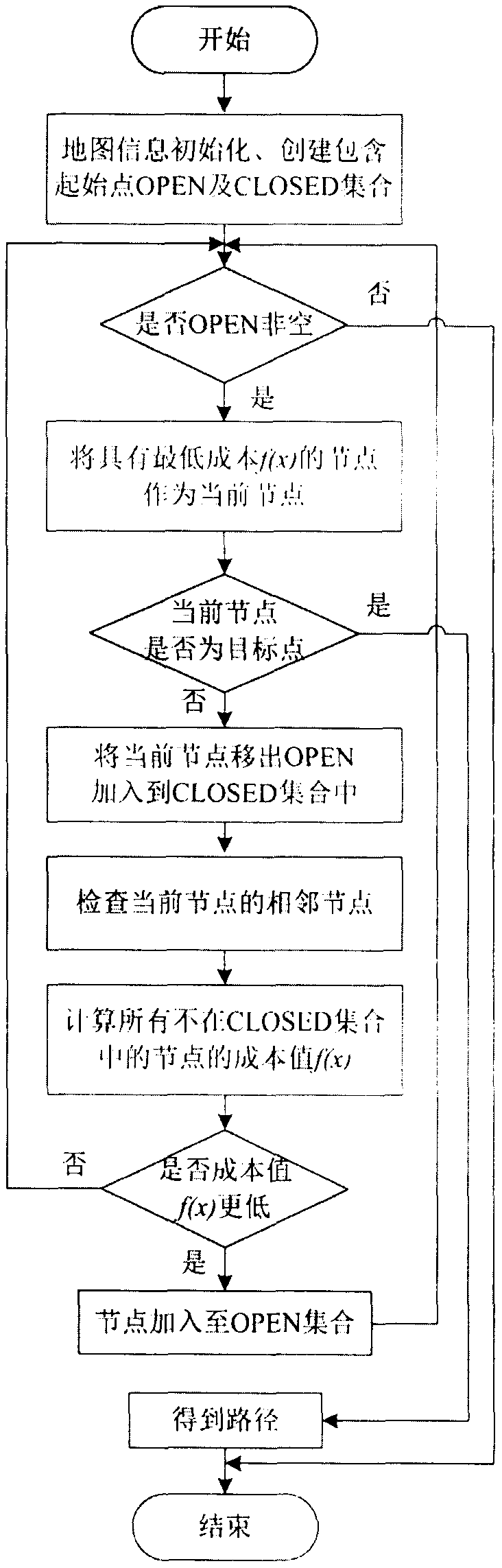
The invention discloses a global path planning method for a wave glider, and particularly relates to the field of autonomous navigation observation of the wave glider, and the wave glider is an unmanned autonomous vehicle which converts wave fluctuation into forward power by utilizing a special double-body structure of the wave glider. Aiming at a sailing observation task executed by the wave glider, an improved A * algorithm is utilized to obtain a shortest-distance global optimal path, and the method has the advantages of short calculation time, small calculation amount and improvement of task execution efficiency.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV +1
Method and system for path planning of wave glider
ActiveUS20210286361A1Navigational aids with satellite radio beacon positioningNavigational calculation instrumentsReal time navigationReal-time data
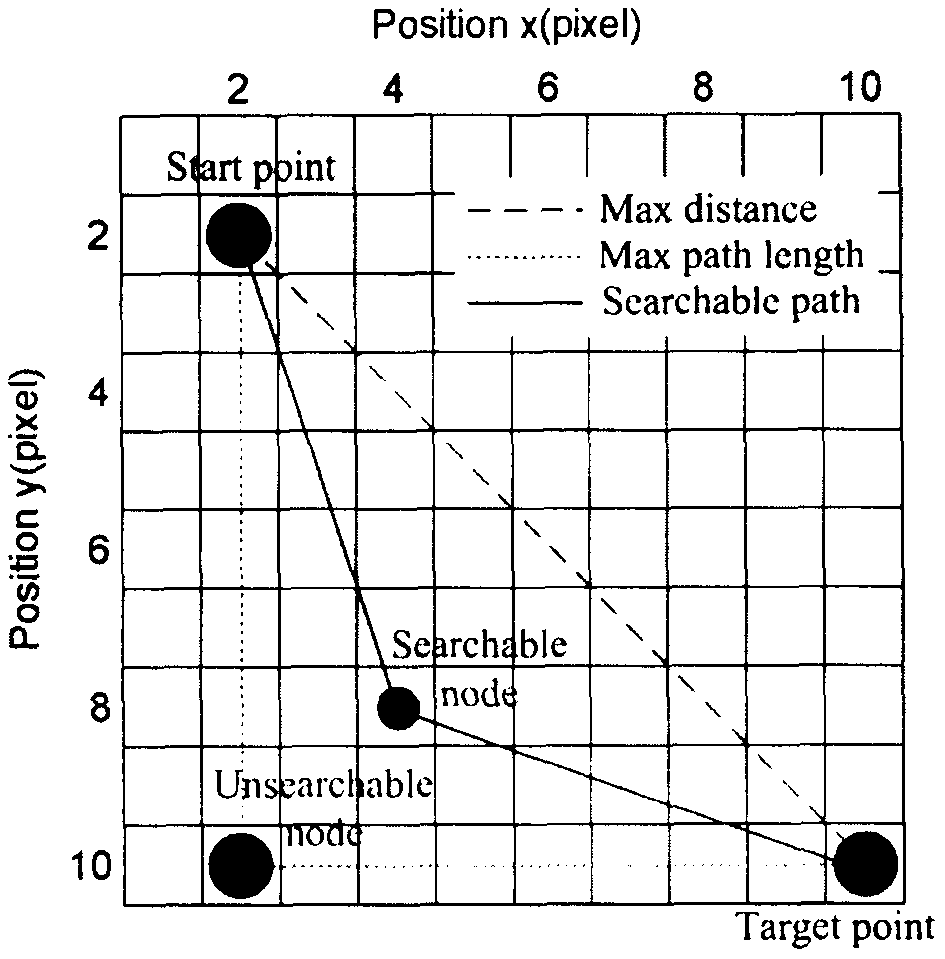
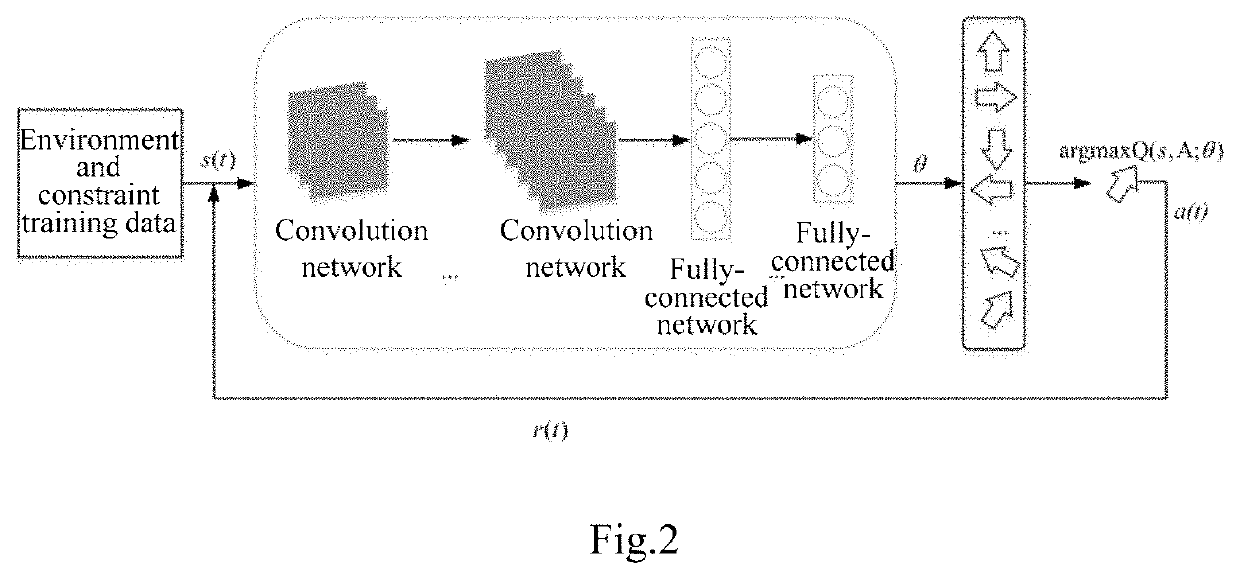
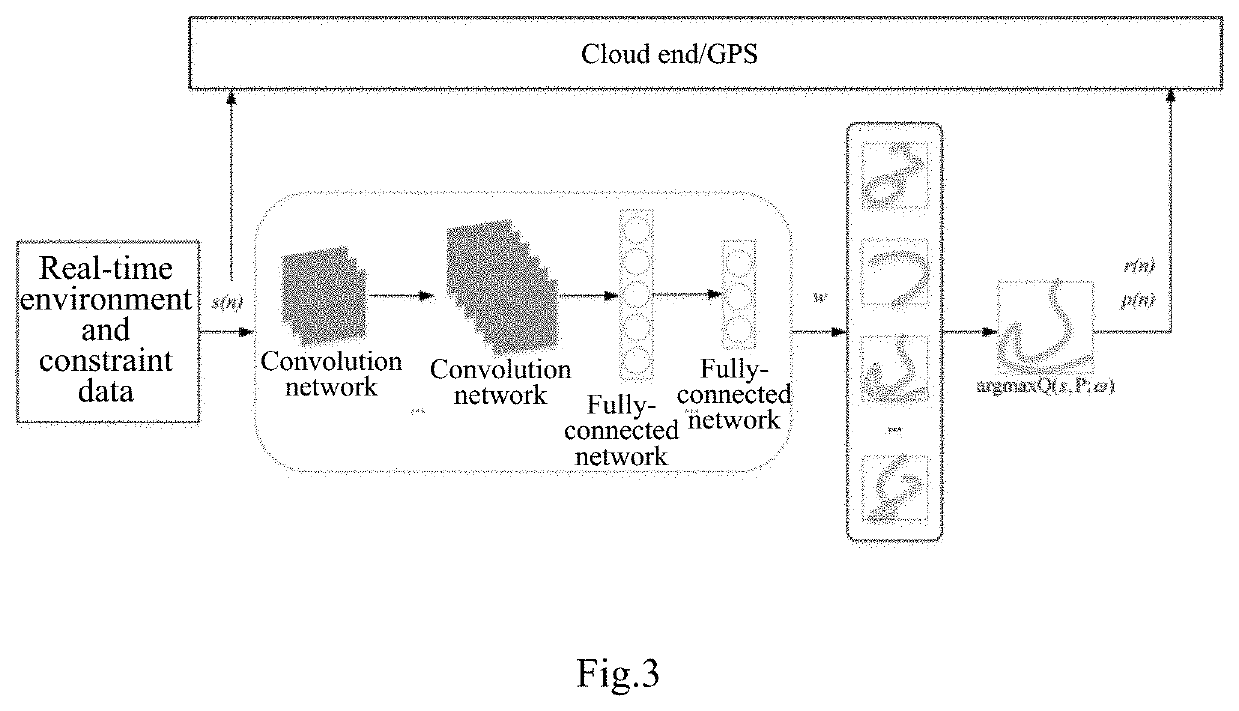
The invention relates to a method and system for path planning of a wave glider, comprising acquiring historical navigation data of the glider and an underwater vehicle via a shore-based monitoring center; fitting historical navigation data nonlinearly by a deep learning neural network to obtain a trained network; acquiring real-time navigation data of the glider at an off-line end, real-time navigation data and predetermined shipping track data of the vehicle; obtaining the set of off-line optimized path planning schemes of the glider by the above data and the trained network; and determining an optimal path planning scheme of the glider by the deep learning neural network according to real-time data and constraint data of the glider at the on-line end. The invention can reasonably plan the path of the glider and ensure continuous and reliable information interaction between the glider and the vehicle.
Owner:NAT DEEP SEA CENT +1
Local path planning method for wave glider
PendingCN111522334AImprove navigation efficiencyPosition/course control in two dimensionsGliderClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a local path planning method for a wave glider and particularly relates to the field of autonomous navigation observation of the wave glider. The wave glider is an unmanned autonomous vehicle which converts wave fluctuation into forward power by utilizing a special double-body structure of the wave glider. The wave glider is advantaged in that aiming at a wave glider to execute a sailing observation task, a local path is obtained by utilizing an artificial potential energy field algorithm, and the wave glider is smooth and continuous, a local optimal point is avoided, and task execution efficiency is improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA +1
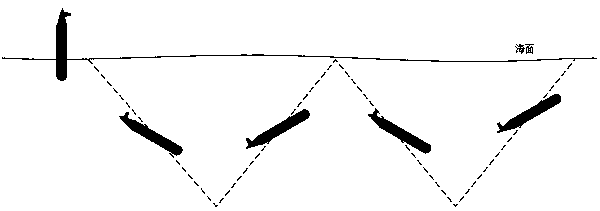
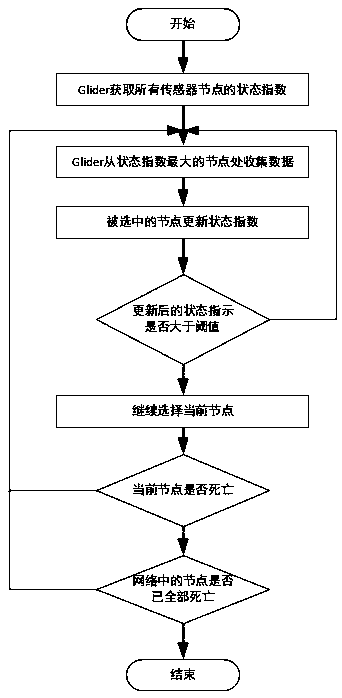
Underwater sensor network data collection method based on glider
ActiveCN111542016ALow costImprove data qualitySonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionParticular environment based servicesComputation complexityDynamic planning
The invention relates to an underwater sensor network data collection method based on a glider, and the method comprises the stepsthat a proper sensor node is selected to collect data in a communication range in a process that the glider operates along a sawtooth-shaped track; in the data collection process, the glider carries out dynamic planning on the sensor nodes, and sensor node scheduling isoptimized; an off-line calculation and on-line scheduling mode is adopted, so that the calculation load is reduced; the Poynting exponential algorithm is improved, a threshold is set, the broadcasting frequency and the energy consumption caused by broadcasting are reduced, the communication load is reduced, and the service life of the underwater sensor network is prolonged. According to the underwater data collection method, a glider is used as a data collection platform, so that a large-range and long-time data collection task can be realized; by adopting an exponential algorithm with a threshold value, the calculation complexity of solving dynamic programming is reduced, the communication consumption is reduced on the basis of ensuring the data collection quality, the sensor schedulingis optimized, and the service life of the underwater sensor network is maximized.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Current-driven anchoring type long-endurance glider
InactiveCN110683025AImprove securityImprove privacyUnderwater vesselsMooring equipmentBuoyancy regulationGlider
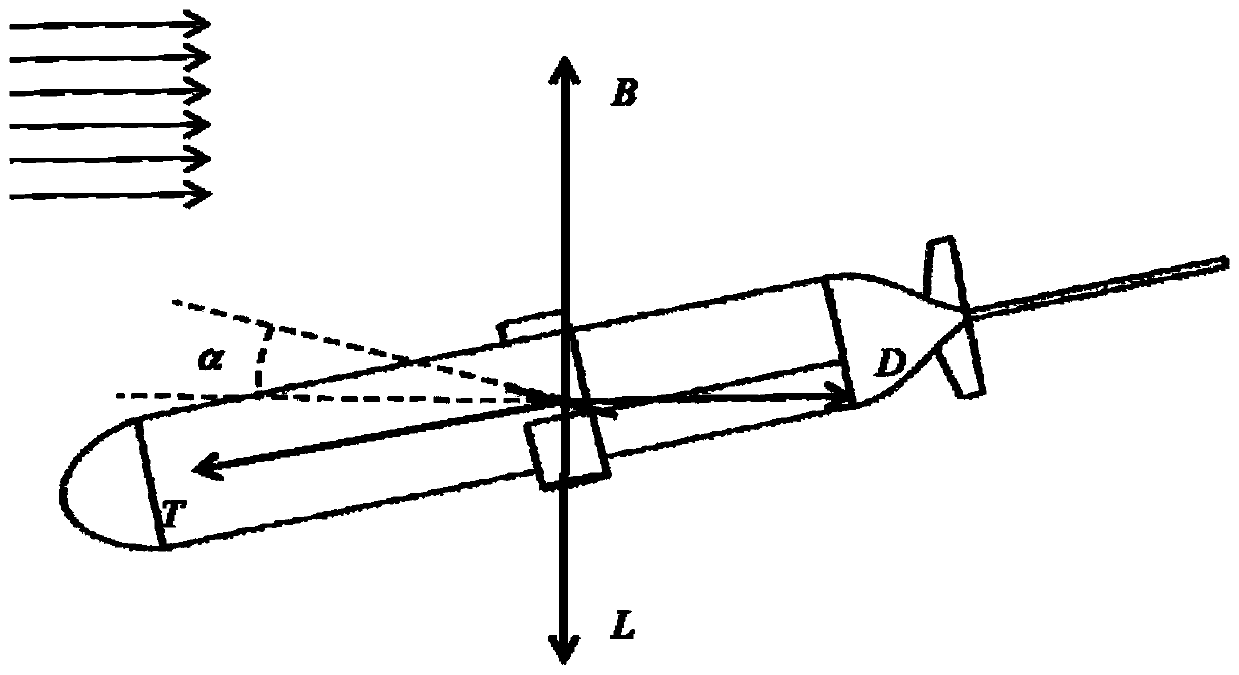
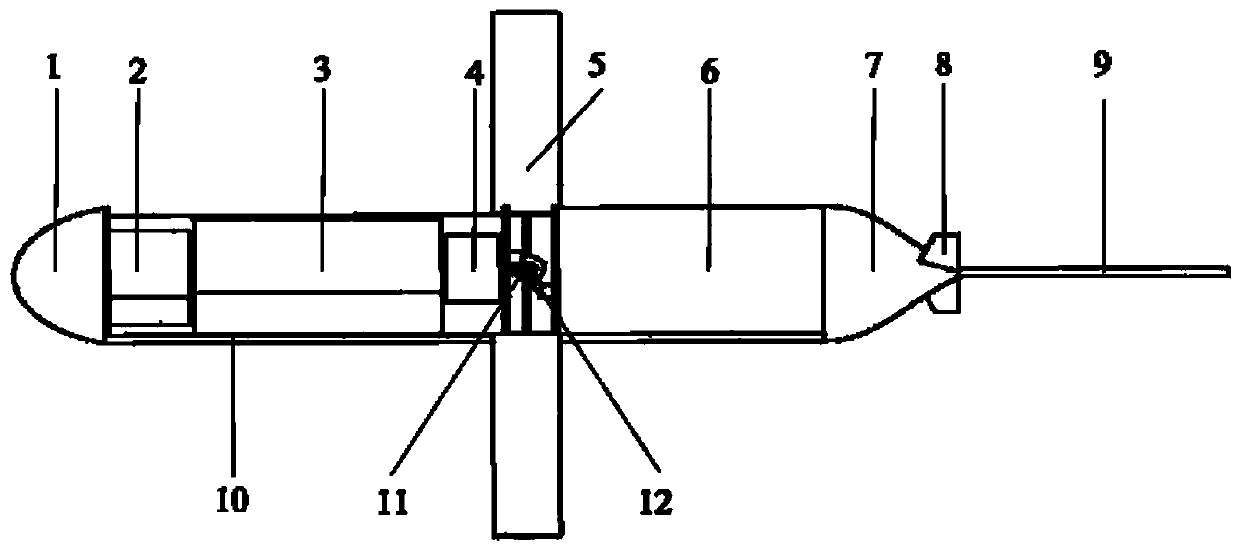
The invention belongs to the technical field of gliding type submersibles, and particularly relates to a current-driven anchoring type long-endurance glider. The ocean flow field widely existing is effectively used, through adjusting the attack angle between an adjusting type transverse hydrofoil and the incoming flow, different kinds of lift and resistance are generated, the glider is driven to float upwards and dive, and a glider does not need to rely on a buoyancy adjusting device. The glider can float out of the water surface at regular intervals, an antenna rod on the tail is used for communication and data transmission, and the glider is fixed in a certain area through an anchoring system and cannot go with the stream. Meanwhile, the glider has the capacity of monitoring the profilemarine environment, energy consumption is low, long-time uninterrupted operation is achieved, under the condition that a regional current exists, the glider has the high safety and tacitness, energy consumption is low, long endurance is achieved, control is reliable, and the glider is suitable for area ocean environment monitoring.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Deep sea seabed observation base station data quasi-real-time acquisition method
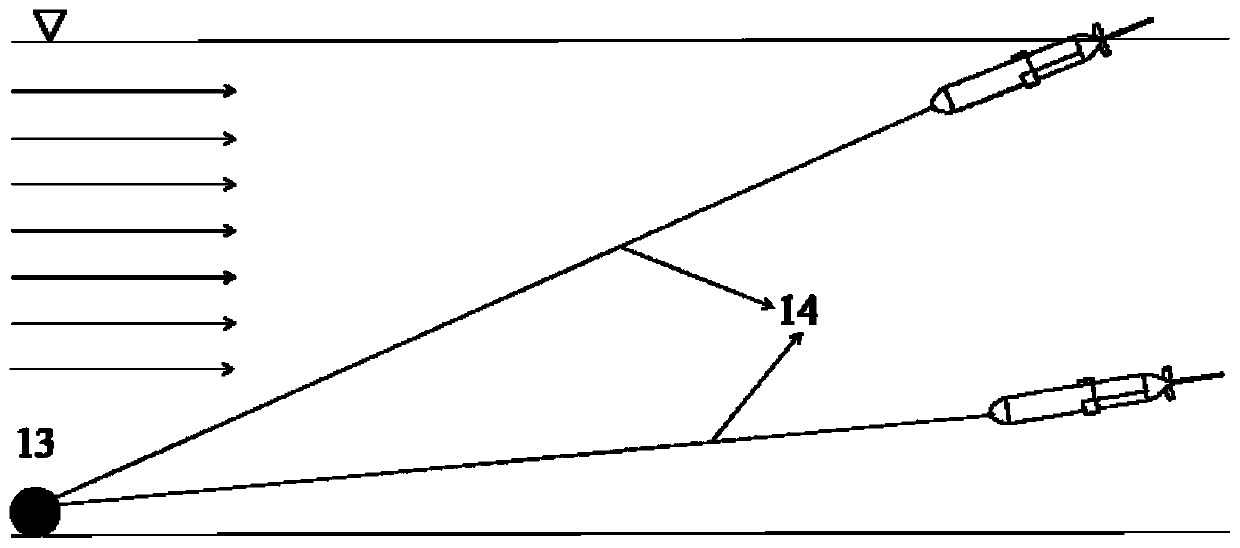
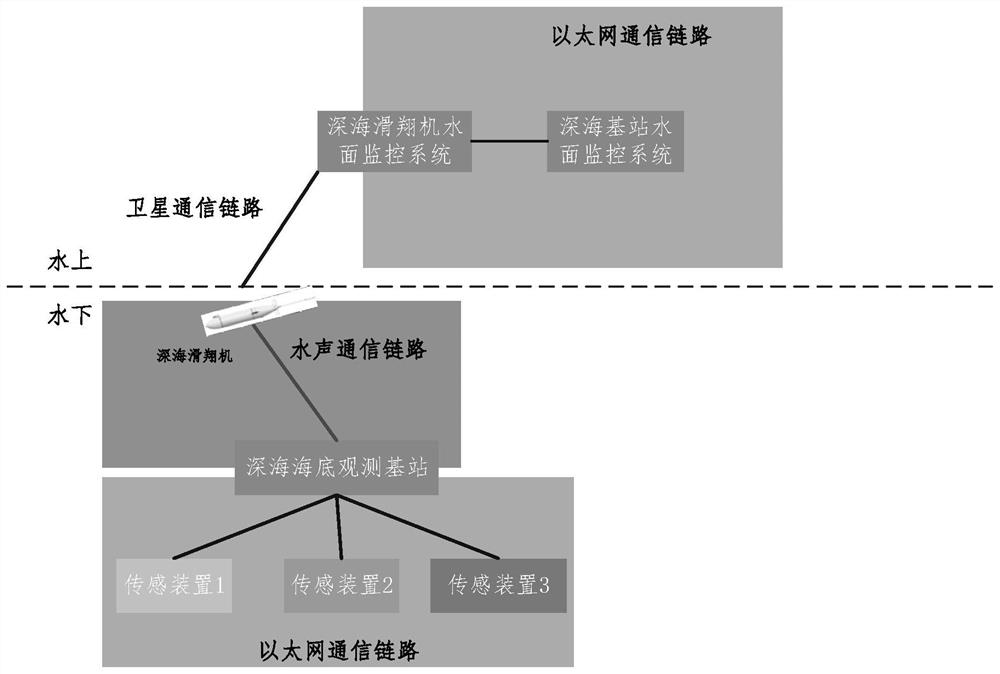
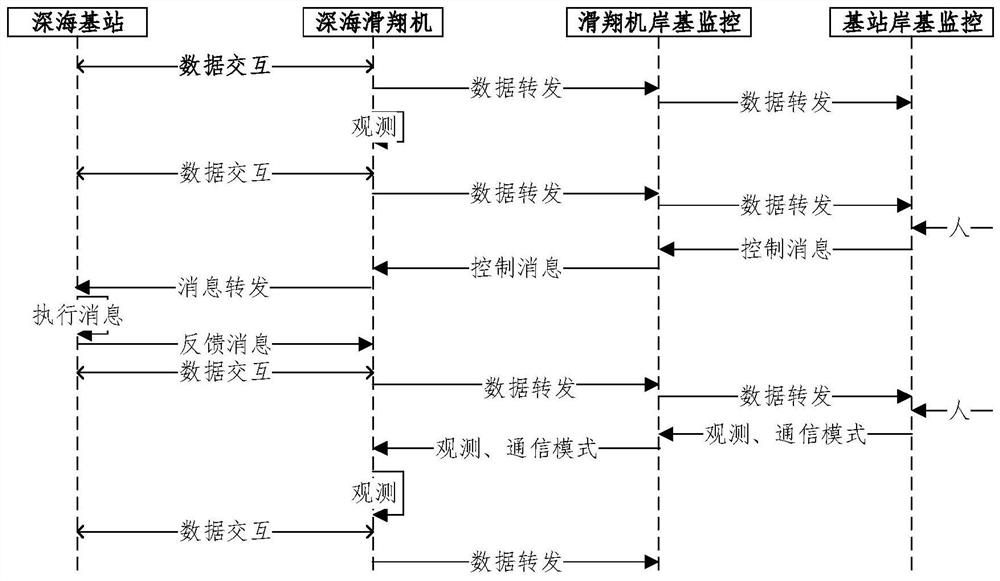
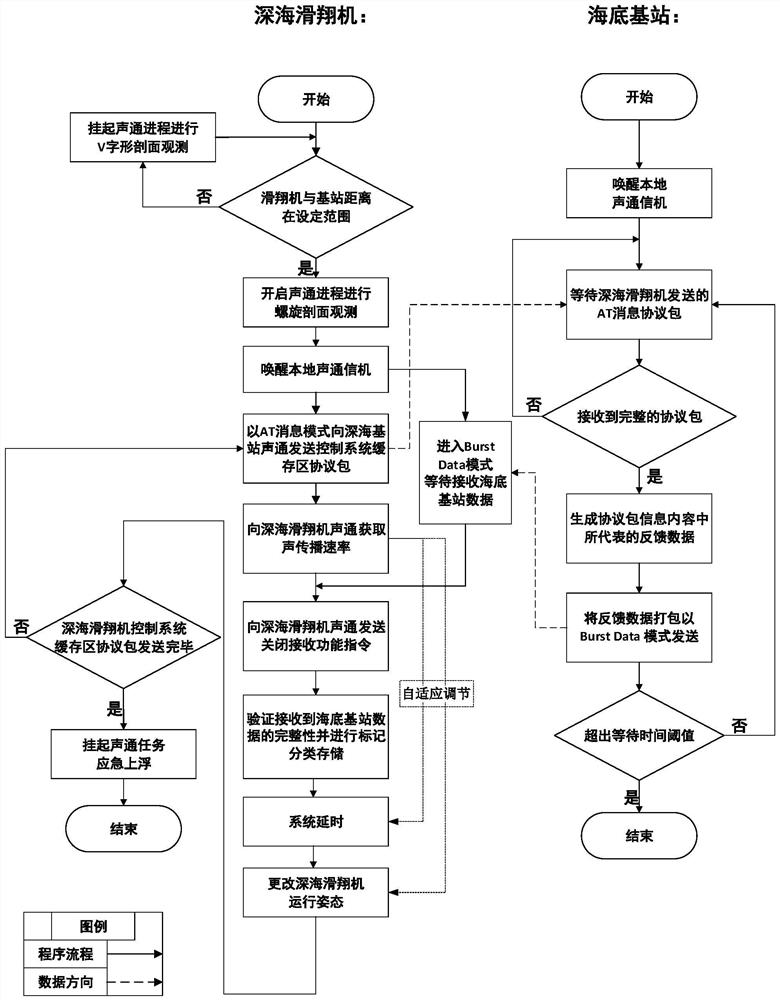
PendingCN114666727ARealize communication backup requirementsNetwork traffic/resource managementParticular environment based servicesChannel dataGlider
The invention relates to a deep sea seabed observation base station data quasi-real-time acquisition method, which uses a deep sea glider as a communication relay, and the deep sea glider and a seabed observation base station are integrated with an Evologic18 / 34OEM version underwater acoustic communication set to carry out acoustic channel data interaction. In the water surface communication stage, a shore-based monitoring center configuration instruction is firstly received and stored in a glider control system cache region, and in the task observation stage, operation and configuration parameters of a base station and a sensing device carried by the base station are issued by means of an underwater acoustic communication link, and key information data or specified scientific data on the base station are acquired; and after the glider floats up to the water surface, observation data of the glider, data of the base station and the sensor device carried by the base station and configuration parameter return results are returned to a shore-based monitoring center in real time through an iridium link, so that shore-based monitoring personnel can monitor the seabed observation base station system in an office and issue an operation instruction.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Energy-saving glider capable of increasing advancing speed of ship
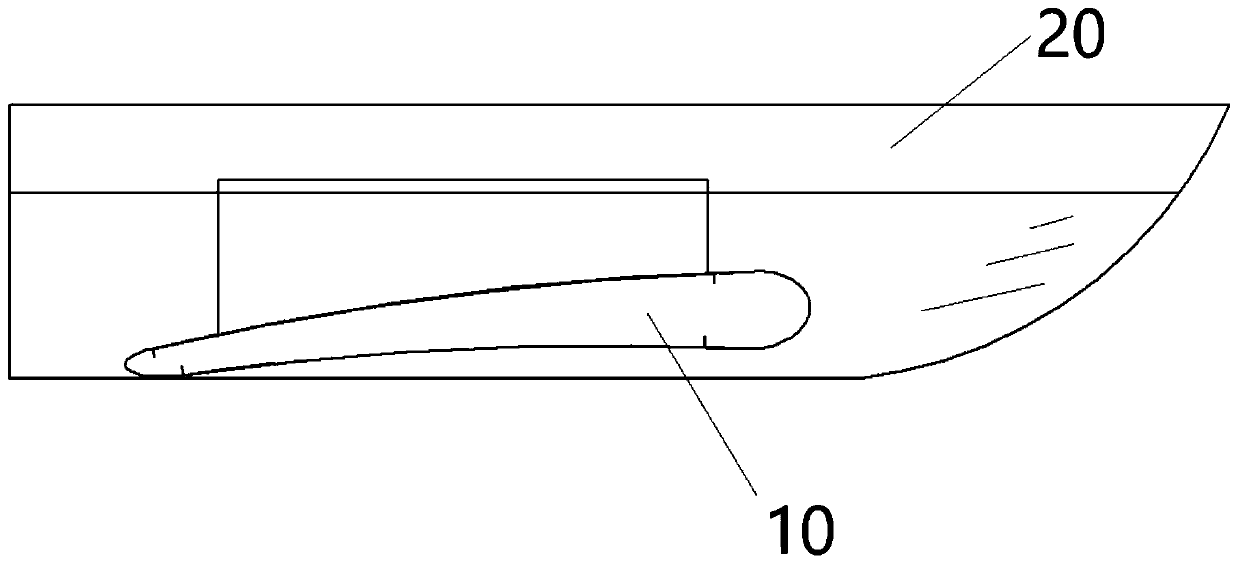
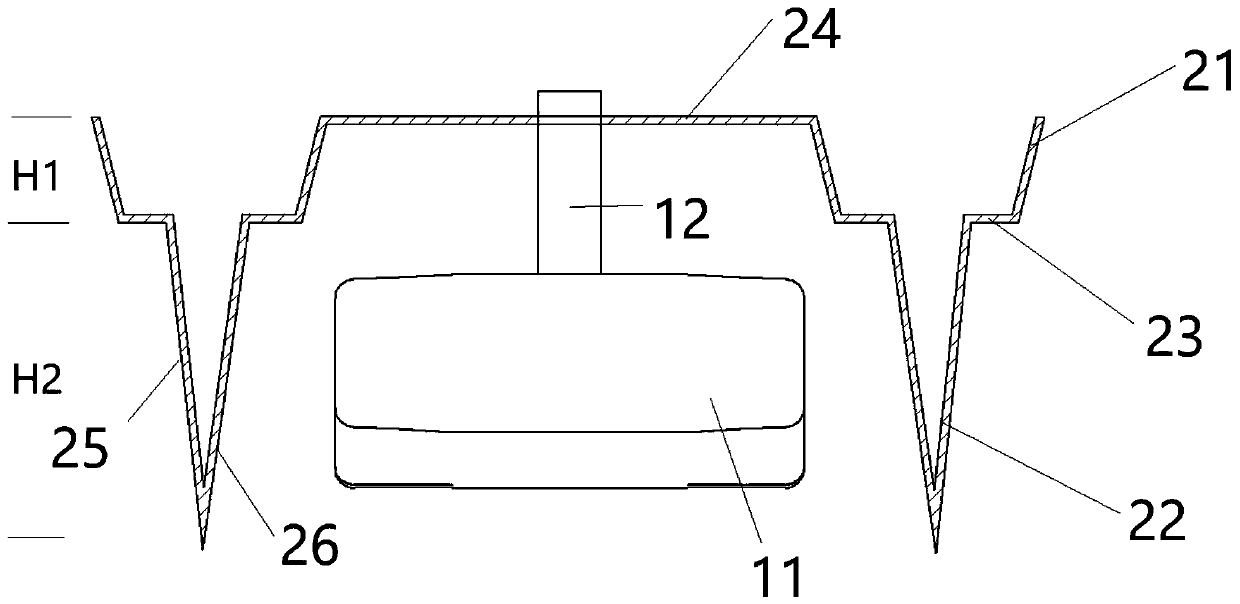
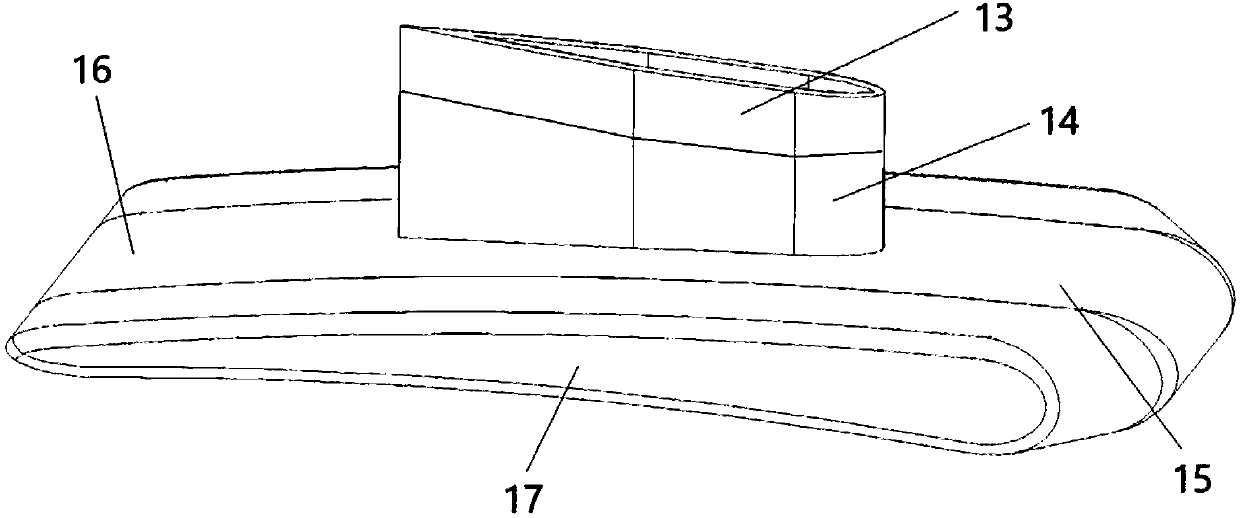
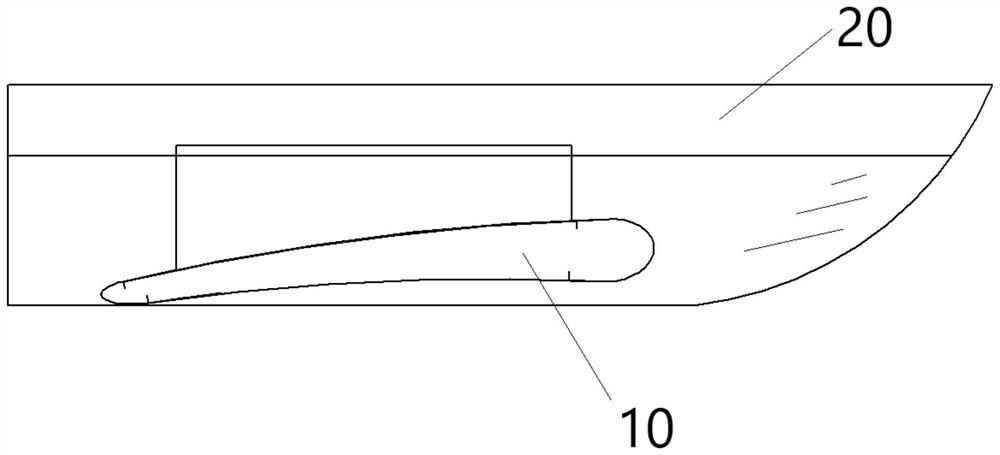
InactiveCN111469977AIncrease profitWatercraft hull designHydrodynamic/hydrostatic featuresGliderMechanical engineering
The invention discloses an energy-saving glider capable of increasing the advancing speed of a ship, which is applied to a ship body 20, wherein the ship body 20 at least comprises a pair of catamaranship bodies which are connected with each other through a connecting deck 24, an aircraft 10 is installed at the bottom of the ship body 20, and the lowermost part of the aircraft 10 is not lower than the bottom of the ship body 20; an aircraft 10 is arranged at the lower part of the connecting deck 24, the aircraft 10 comprises an aircraft wing part 11 and a connecting part 12, the aircraft 10 is connected to a connecting deck 14 through the connecting part 12, the aircraft wing part 11 is provided with an attack angle, the connecting part 12 is of a hollow structure, and the aircraft wing part 11 is communicated with the hollow structure of the connecting part 12 through an opening; and the aircraft wing part 11 of the aircraft 10 is provided with an inner cavity of a hollow structure,a plurality of air outlet holes 40 are formed in the surface of the aircraft wing part 11, the aircraft 10 is used for supporting the ship body 20 towards the water surface in the navigation process,and supercavitation is formed around the aircraft 10, so that the driving resistance is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Device for testing wave power conversion efficiency of wave glider
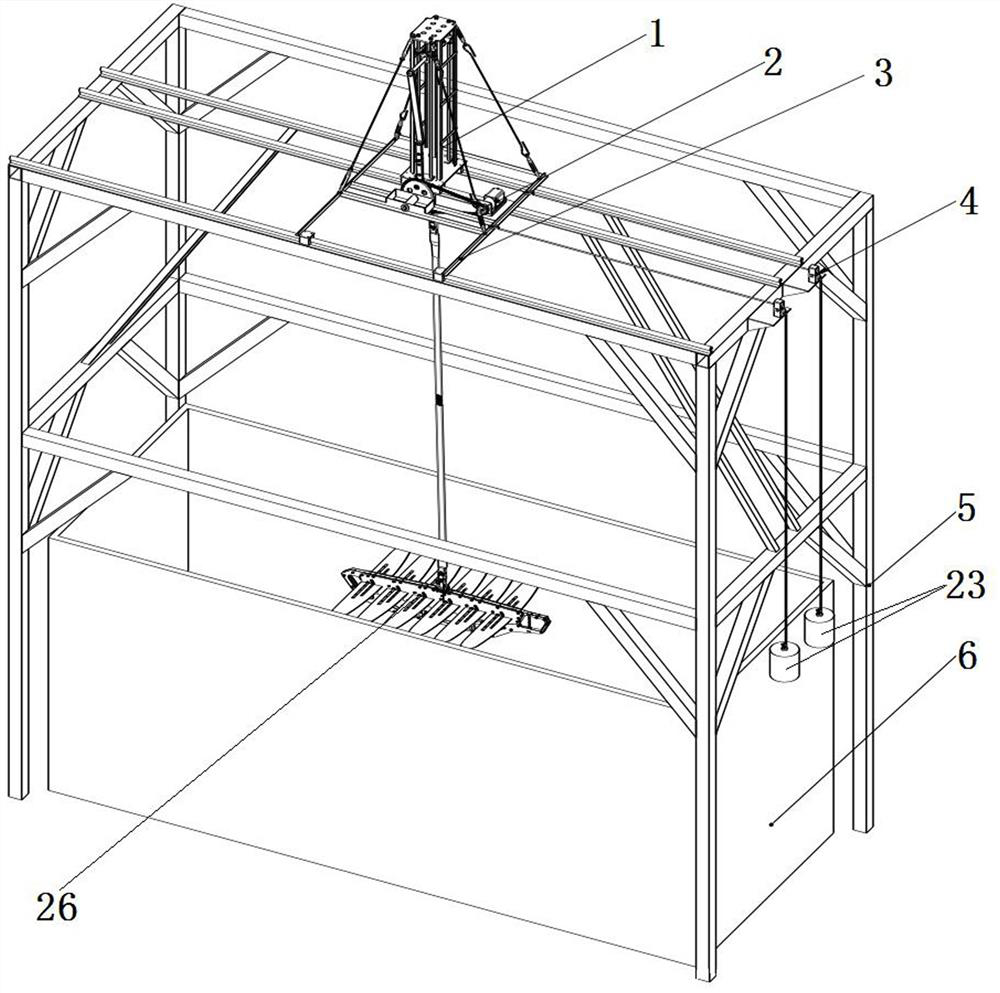
ActiveCN114235011AIncreased drag simulation structureCompact structureOpen water surveySea energy generationGliderSmall footprint
The invention discloses a wave power conversion efficiency testing device for a wave glider, and relates to the technical field of wave glider research, the wave power conversion efficiency testing device comprises a rack, a driving mechanism, a lifting mechanism, a resistance simulation mechanism and a water tank, the driving mechanism is connected with the lifting mechanism, the lifting mechanism is slidably arranged above the rack, and the water tank is arranged below the rack; the lower end of the lifting mechanism is connected with the wave glider, the wave glider is located in the water tank containing liquid, one end of the lifting mechanism is provided with the resistance simulation mechanism, and the resistance generated by the resistance simulation mechanism is opposite to the sliding direction of the lifting mechanism. According to the invention, the resistance simulation structure is added, and an adjustable resistance simulation structure is provided, so that different resistances can be simulated; the structure is compact, the adjustment is convenient, and the experiment can be carried out in a space with a small occupied area.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA +2
Typhoon observation-oriented ocean glider control method
ActiveCN112965529AIncrease flexibilityReduced time to target locationPosition/course control in three dimensionsGliderTyphoon
The invention discloses a typhoon observation-oriented ocean glider control method. According to the method, an intelligent component library of an ocean glider is established, the intelligent component library comprises sensor data of the ocean glider and an ocean glider control algorithm, and intelligent components are stored in three types including a path planning component, a sensor processing component and a navigation component. Different assemblies can be selected according to needs for path planning, and typhoon observation is carried out. The problems that an ocean glider is poor in flexibility in the control process and is greatly influenced by the ocean environment can be solved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
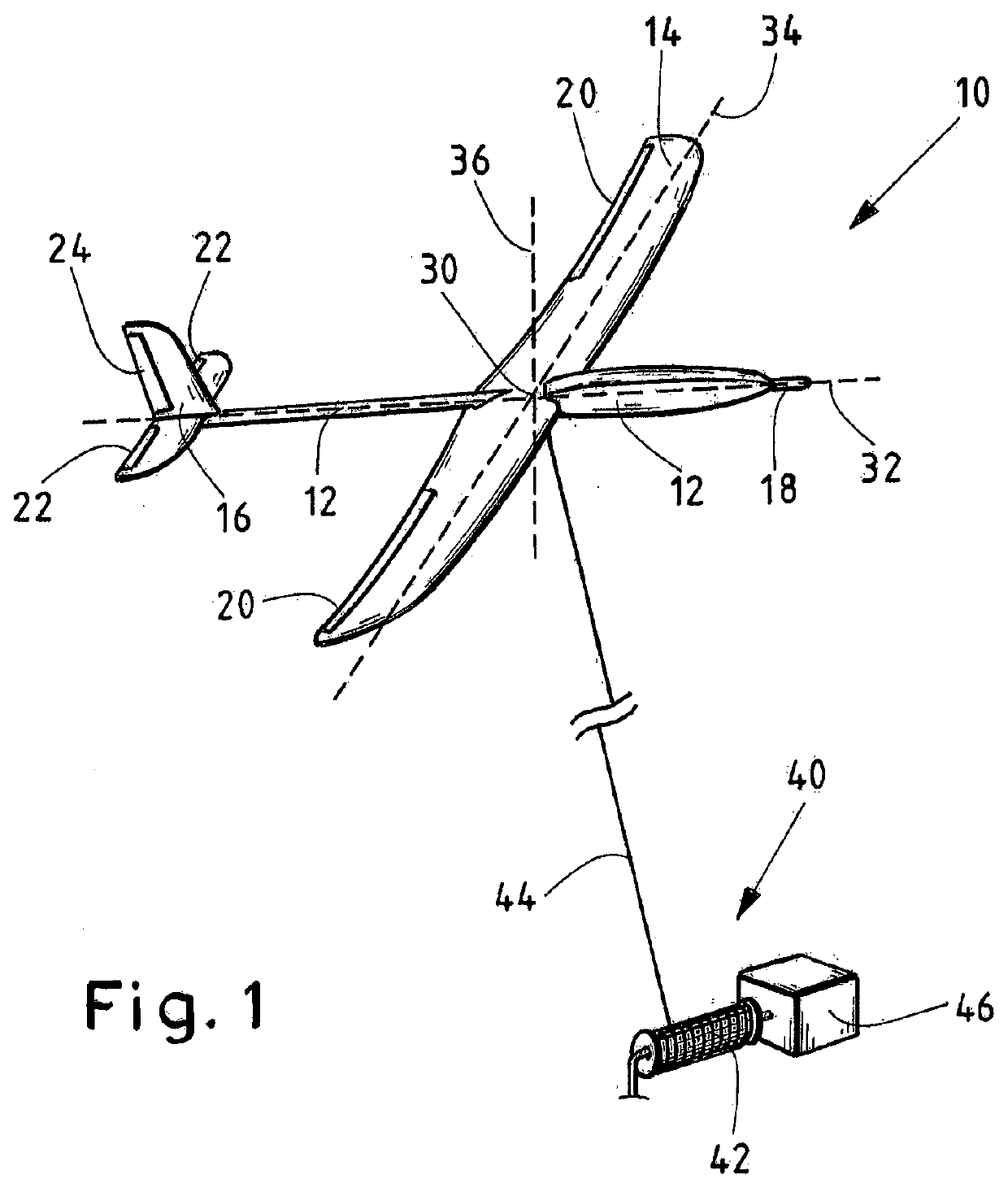
Flying apparatus
Owner:HOWARD DAVID
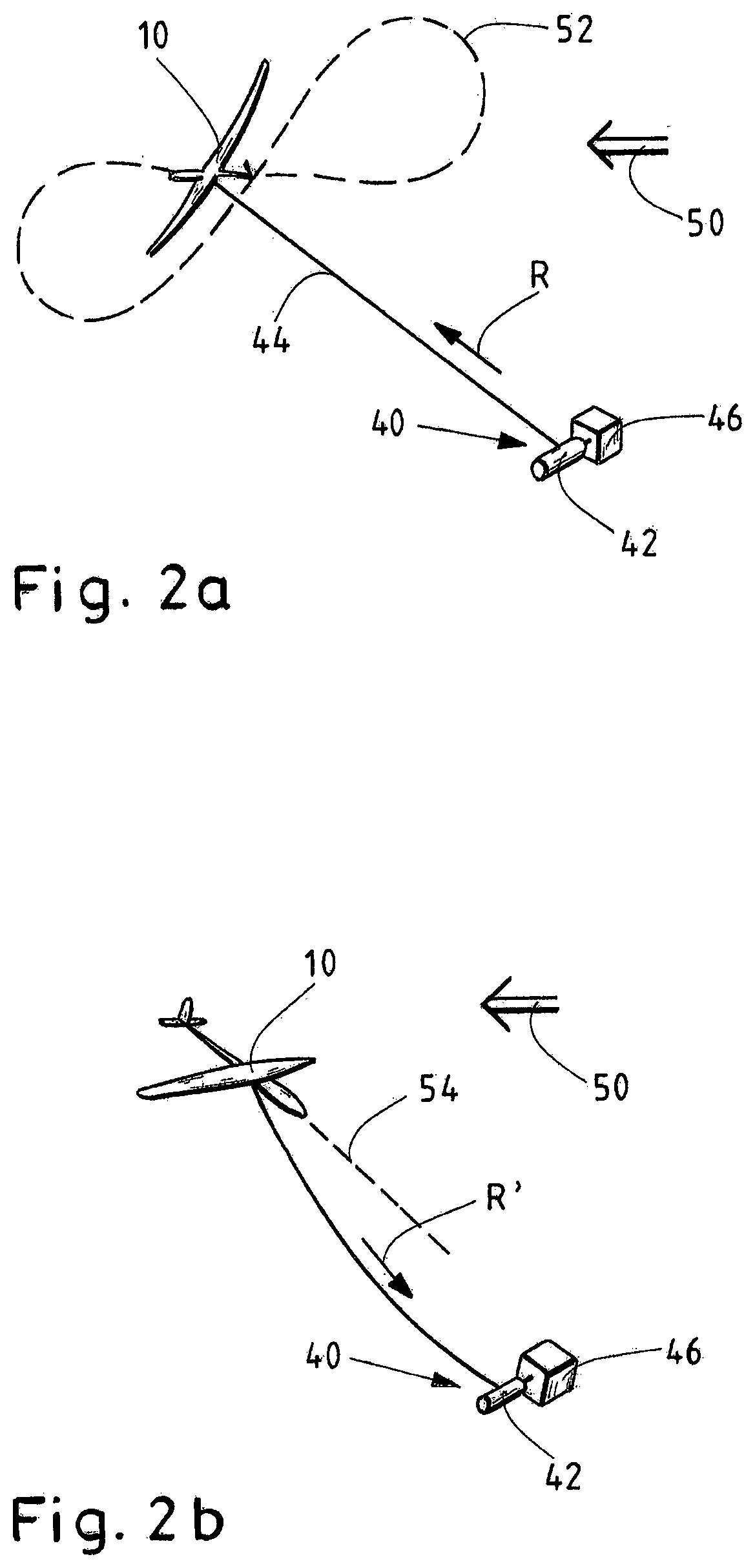
System and method for airborne wind energy production
ActiveUS20210047033A1Low aerodynamic resistance and dragHigh aerodynamic liftTethered aircraftGlidersGliderElectric machine
A system for electric power production from wind includes a glider having an airfoil, an on-board steering unit, a flight controller for controlling the steering unit, and a connection unit for a tether. The system further includes a ground station including a reel for the tether, a rotating electrical machine connected to the reel, and a ground station controller for controlling the reel and the rotating electrical machine. A master controller operates the system in at least first and second operation modes. In the first operation mode electric power is produced with the rotating electrical machine from rotation of the reel caused by reeling out the tether using a lift force generated upon exposure of the airfoil of the airborne glider to wind. In the second operation mode, the reel is driven by the rotating electrical machine, thereby reeling in the tether onto the reel.
Owner:AMPYX POWER
Ballistic design method for downstroke section with terminal angle and velocity constraints
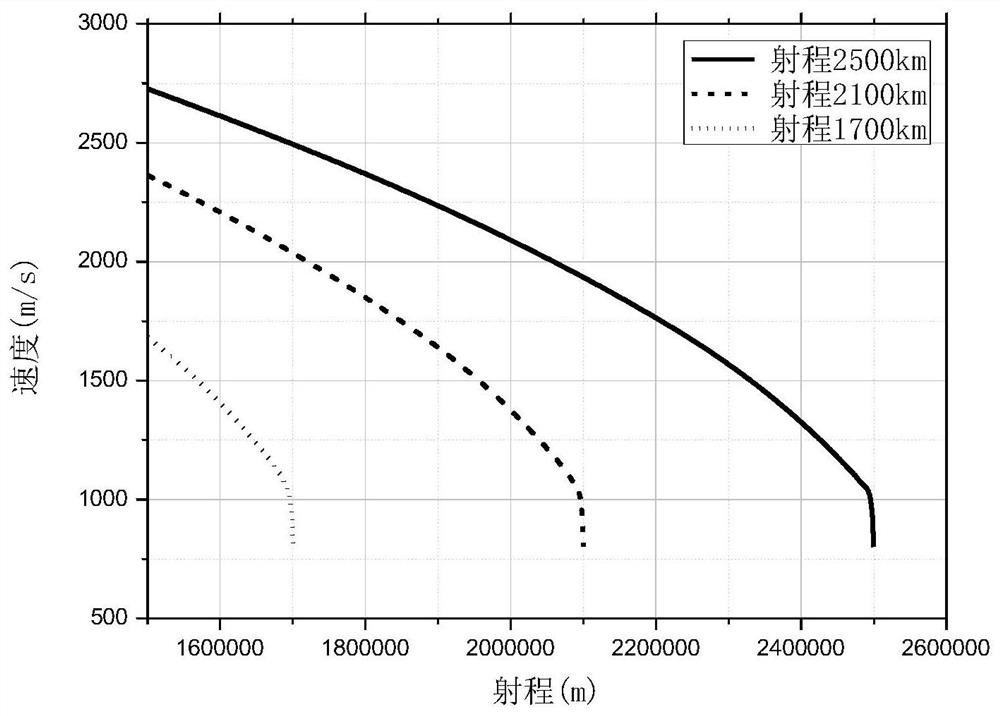
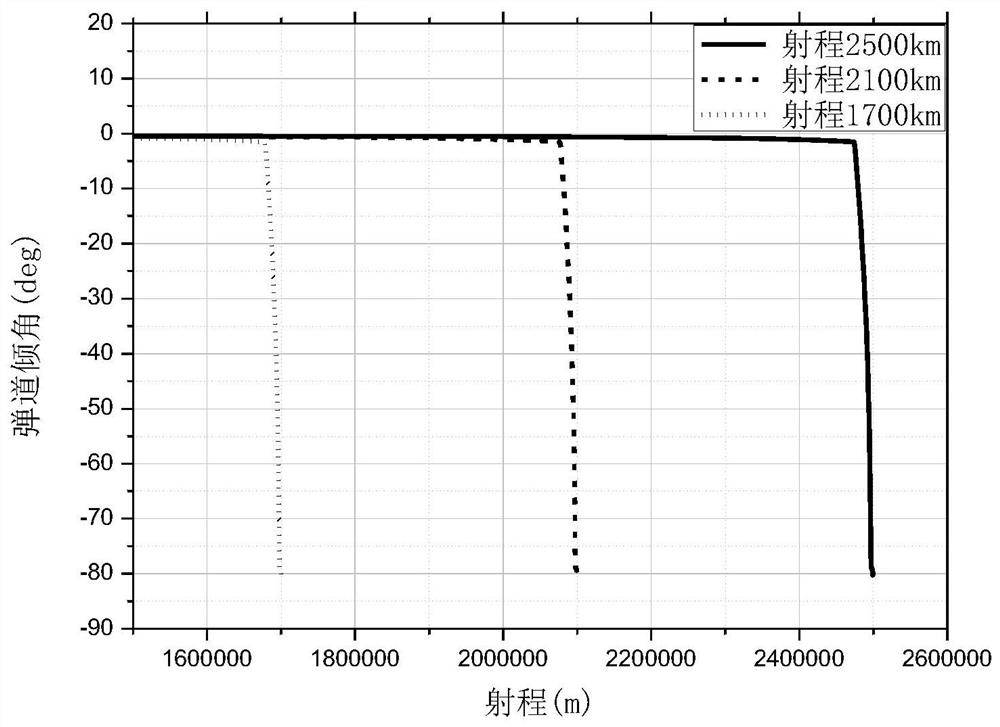
ActiveCN107341295BGenerate fastMeet the precision requirementsGeometric CADConstraint-based CADGliderMechanical energy
The invention particularly relates to a design method for a down-press section trajectory with terminal angle and speed constraints. The method comprises the steps of determining a down-press starting point; designing a down-press section attack angle; and calculating a trajectory. Firstly a reference gliding trajectory is designed, mechanical energy of a gliding maneuvering warhead corresponding to a starting moment of the down-press point is determined on the trajectory and defined as mechanical base energy E0, the mechanical energy of the down-press starting point of each trajectory is controlled to be near the mechanical base energy E0, and the starting point of the down-press point is determined; secondly the down-press section attack angle is designed by adopting an adaptive design method meeting the terminal angle constraint; thirdly, the down-press section trajectory is designed; and finally the trajectory is calculated, and all results can meet precision requirements. The method is simple and novel, is high in trajectory generation speed, and is very suitable for engineering application.
Owner:THE GENERAL DESIGNING INST OF HUBEI SPACE TECH ACAD
An energy-saving gliding device that can increase the speed of the hull
InactiveCN111469977BIncrease profitWatercraft hull designHydrodynamic/hydrostatic featuresGliderMechanical engineering
The invention discloses an energy-saving glider capable of increasing the advancing speed of a ship, which is applied to a ship body 20, wherein the ship body 20 at least comprises a pair of catamaranship bodies which are connected with each other through a connecting deck 24, an aircraft 10 is installed at the bottom of the ship body 20, and the lowermost part of the aircraft 10 is not lower than the bottom of the ship body 20; an aircraft 10 is arranged at the lower part of the connecting deck 24, the aircraft 10 comprises an aircraft wing part 11 and a connecting part 12, the aircraft 10 is connected to a connecting deck 14 through the connecting part 12, the aircraft wing part 11 is provided with an attack angle, the connecting part 12 is of a hollow structure, and the aircraft wing part 11 is communicated with the hollow structure of the connecting part 12 through an opening; and the aircraft wing part 11 of the aircraft 10 is provided with an inner cavity of a hollow structure,a plurality of air outlet holes 40 are formed in the surface of the aircraft wing part 11, the aircraft 10 is used for supporting the ship body 20 towards the water surface in the navigation process,and supercavitation is formed around the aircraft 10, so that the driving resistance is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
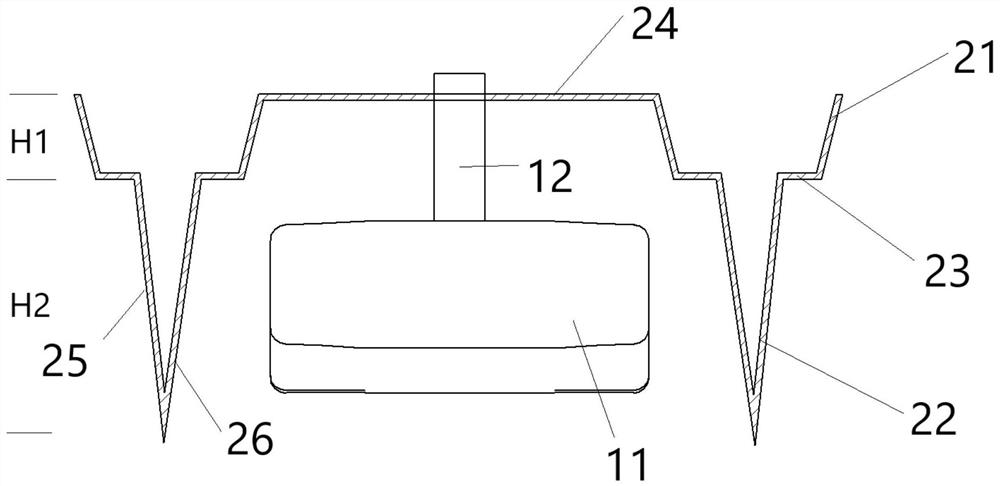
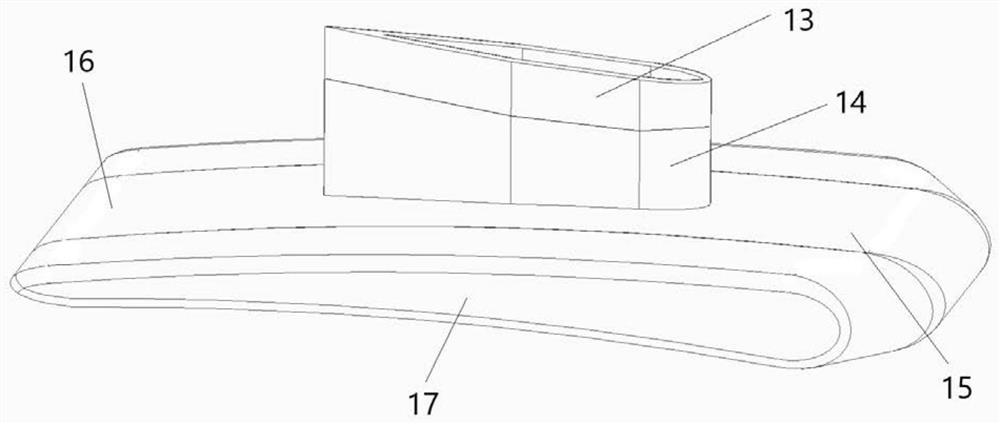
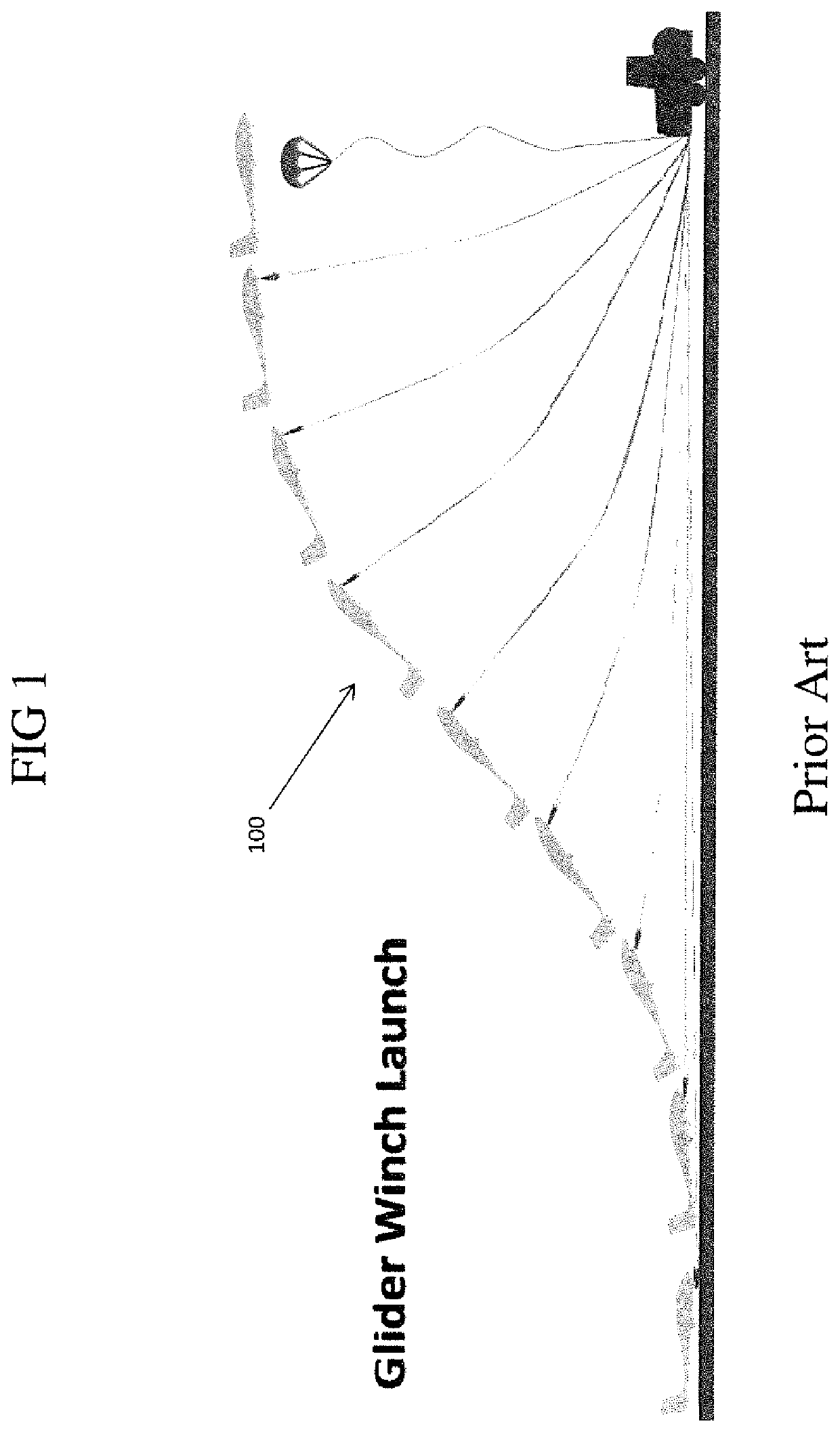
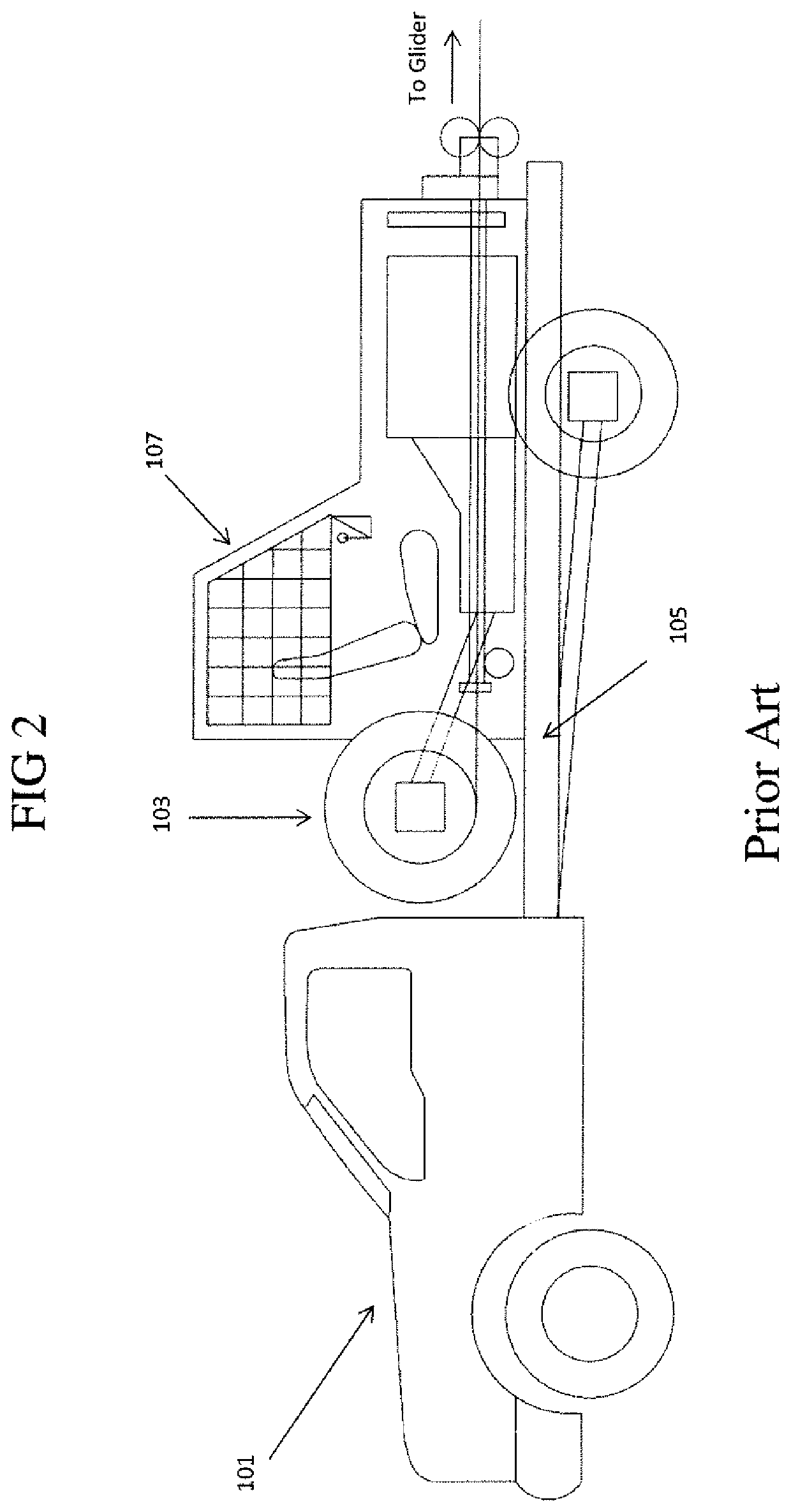
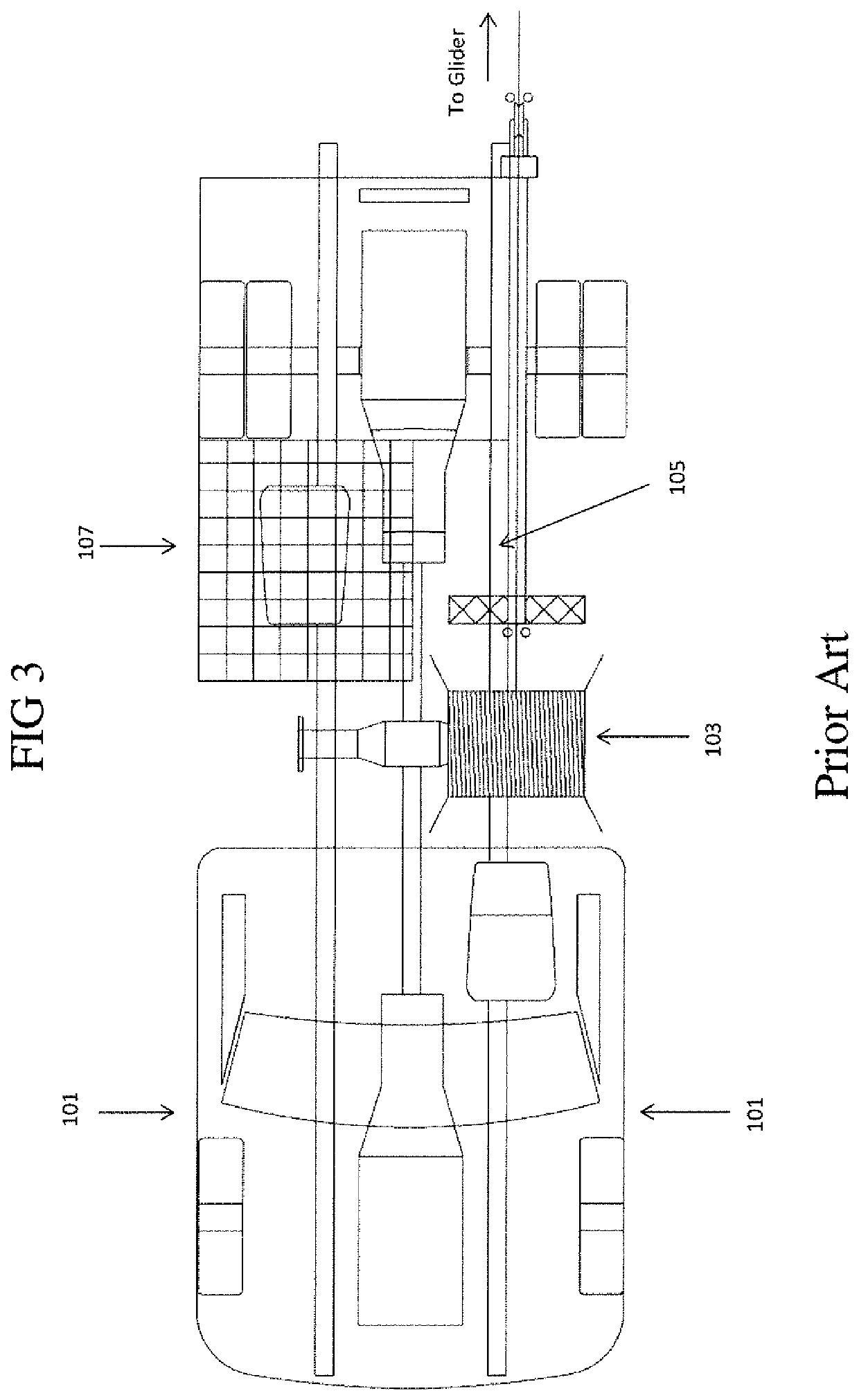
Glider winch/truck combination and method of use
Owner:MECKLENBURG GREGORY BRUCE
Flying wing glider airfoil resistance coefficient grey estimation method
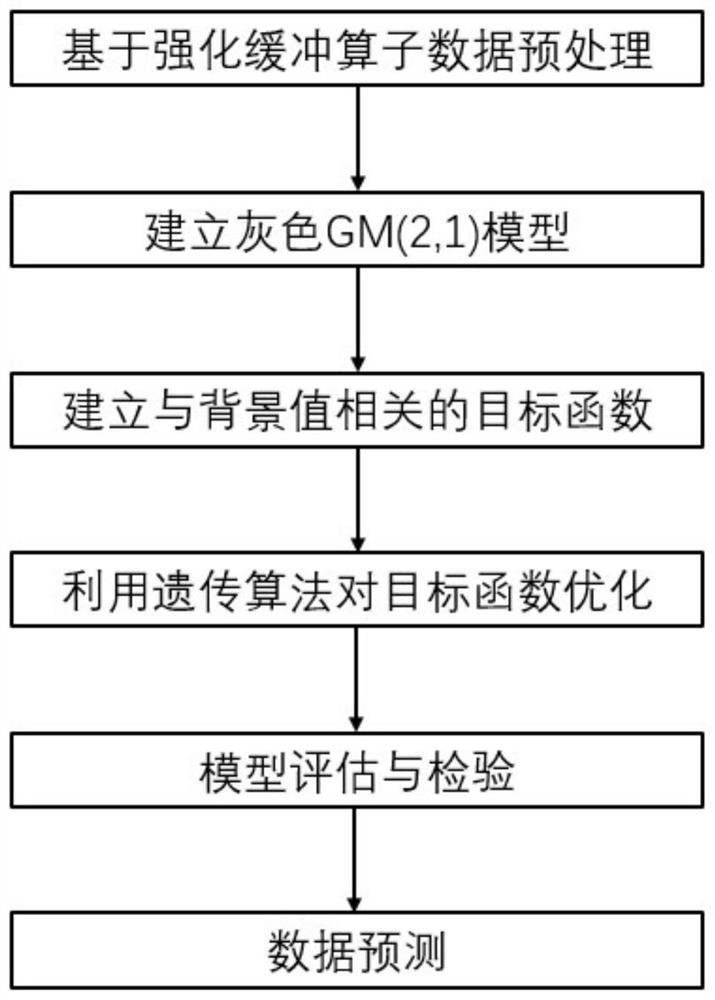
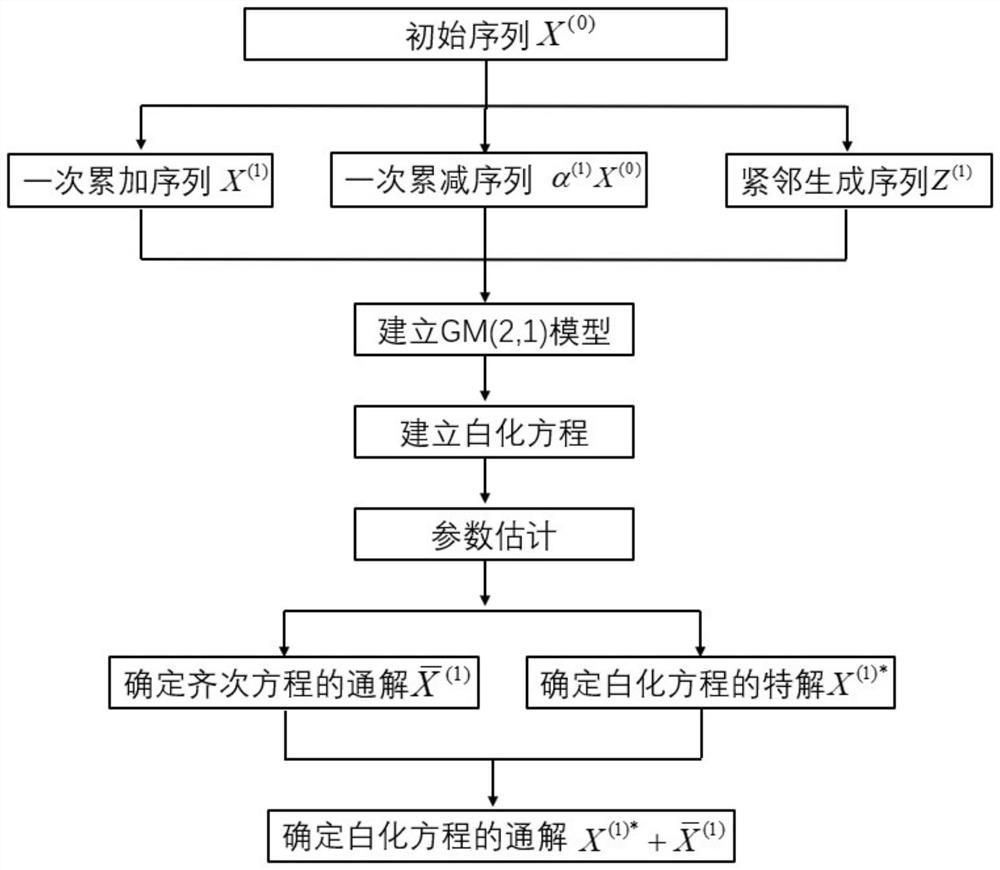
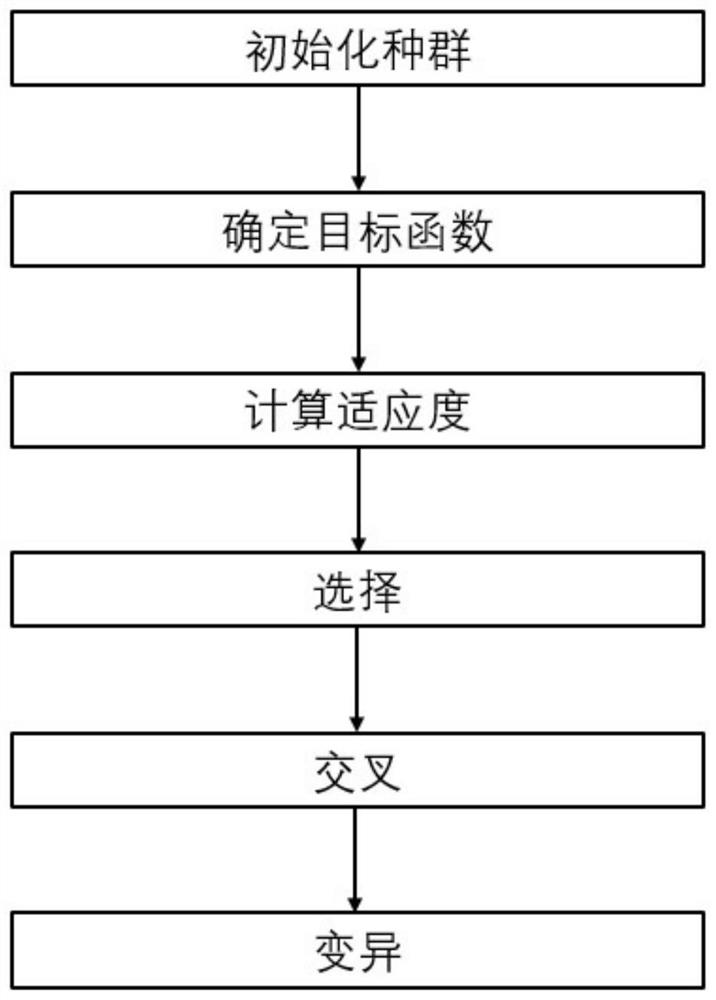
PendingCN114386177AImprove forecast accuracyImprove fitting accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationGliderMathematical model
The invention relates to a flying wing glider airfoil resistance coefficient grey estimation method, and belongs to the technical field of underwater vehicle research. The method aims at solving the problem that a large amount of solving time needs to be consumed in an existing underwater vehicle fluid simulation link, and reference is provided for accurate prediction of unsolved parameters through a mathematical model. The method takes a gray GM (2, 1) model as a core, and comprises the following steps of: firstly, preprocessing a known data sequence by utilizing an enhanced buffer operator; then, establishing an objective function related to a gray model background value, and performing optimization in combination with a genetic algorithm; and finally, predicting an unsolved resistance coefficient. A calculation result shows that the designed model has very high fitting precision, and the prediction precision of the resistance coefficient is remarkably improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Heading control method of adaptive floating body for wave glider
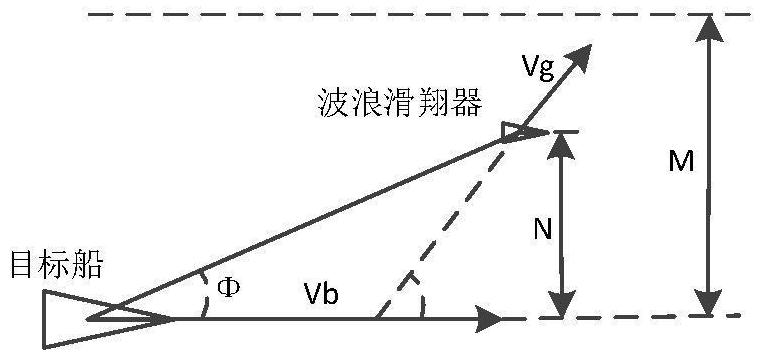
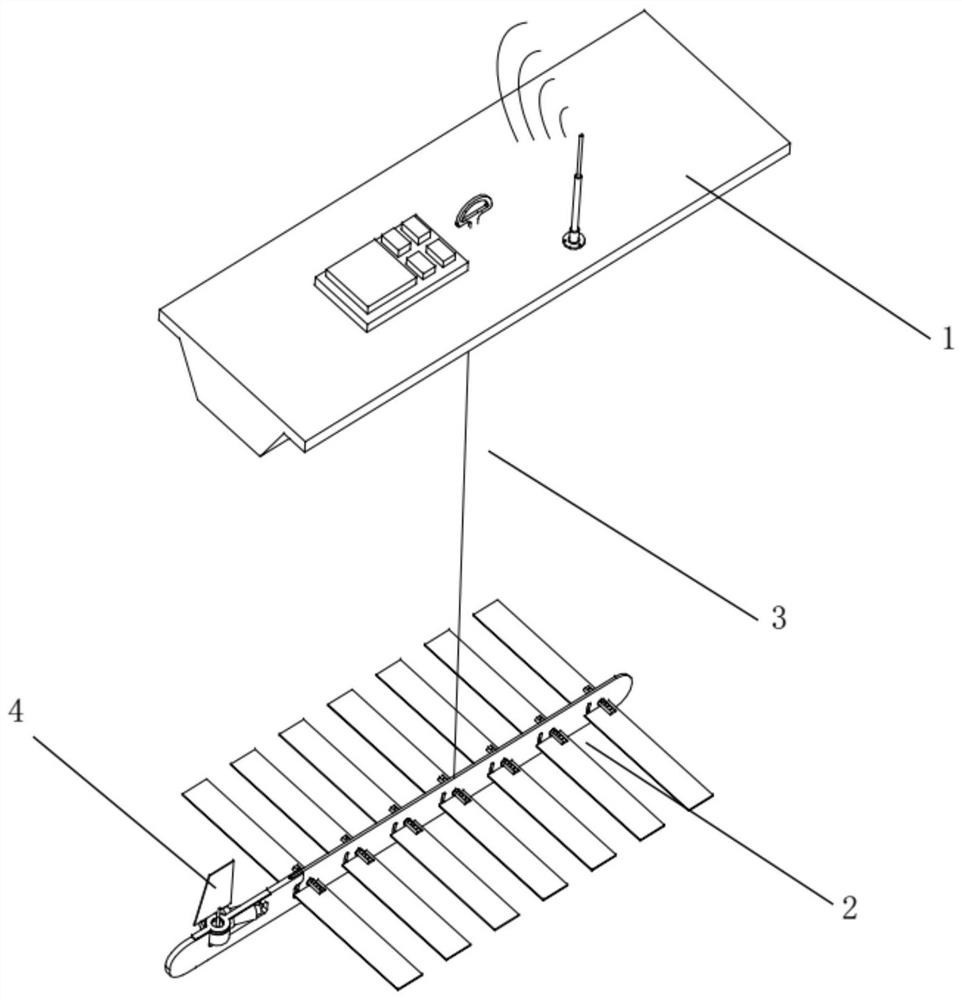
ActiveCN109062236BImproved heading control capabilityOvercoming the problem of unstable control systemAttitude controlGliderControl system
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
A low-cost wave glider maritime navigation collision avoidance method
ActiveCN113012473BLow costReduce power consumptionMarine craft traffic controlRadio transmissionMaritime navigationGlider
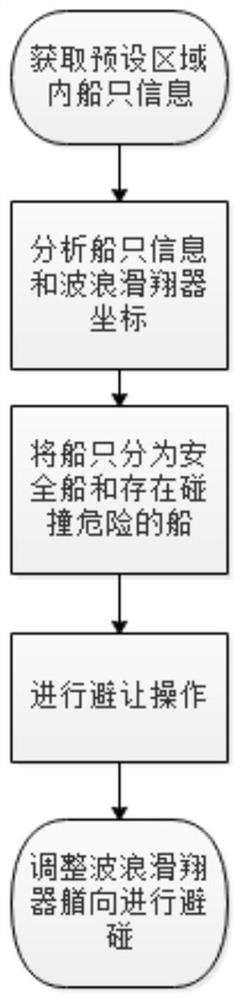
The present invention relates to the technical field of wave glider collision avoidance, in particular to a low-cost wave glider maritime collision avoidance method. The wave glider communicates with the ground station through satellites, and the ground station receives the information returned by the wave glider. S1: Acquisition AIS information sent to the Internet by ships in the preset area; S2: According to the ship information and wave glider coordinates, classify the ships into safe ships and ships with collision risk; S3: According to the AIS information of ships with collision risk, Carry out collision avoidance according to the preset avoidance operation. The method does not need to install collision avoidance equipment on the glider, reduces the power consumption of the glider, and the wave glider can avoid collision of ships at a long distance.
Owner:CETC NINGBO MARINE ELECTRONICS RES INST
A wave glider waypoint tracking method based on fusion of upper and lower body heading information
ActiveCN106990787BAvoid flexible chain entanglementImproved heading control performancePosition/course control in two dimensionsGliderClassical mechanics
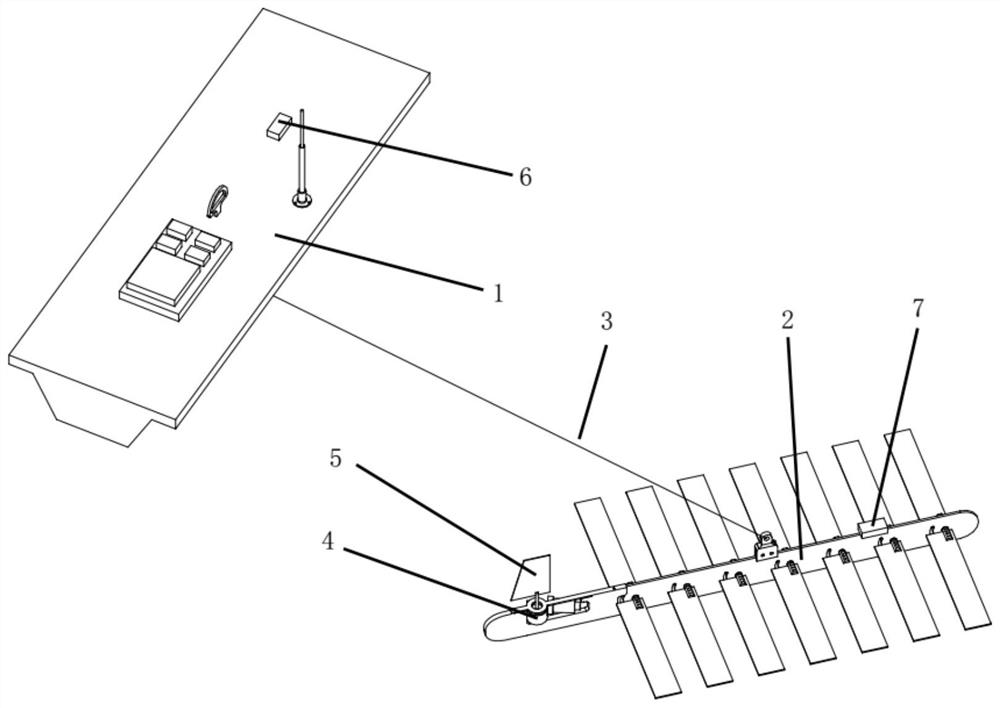
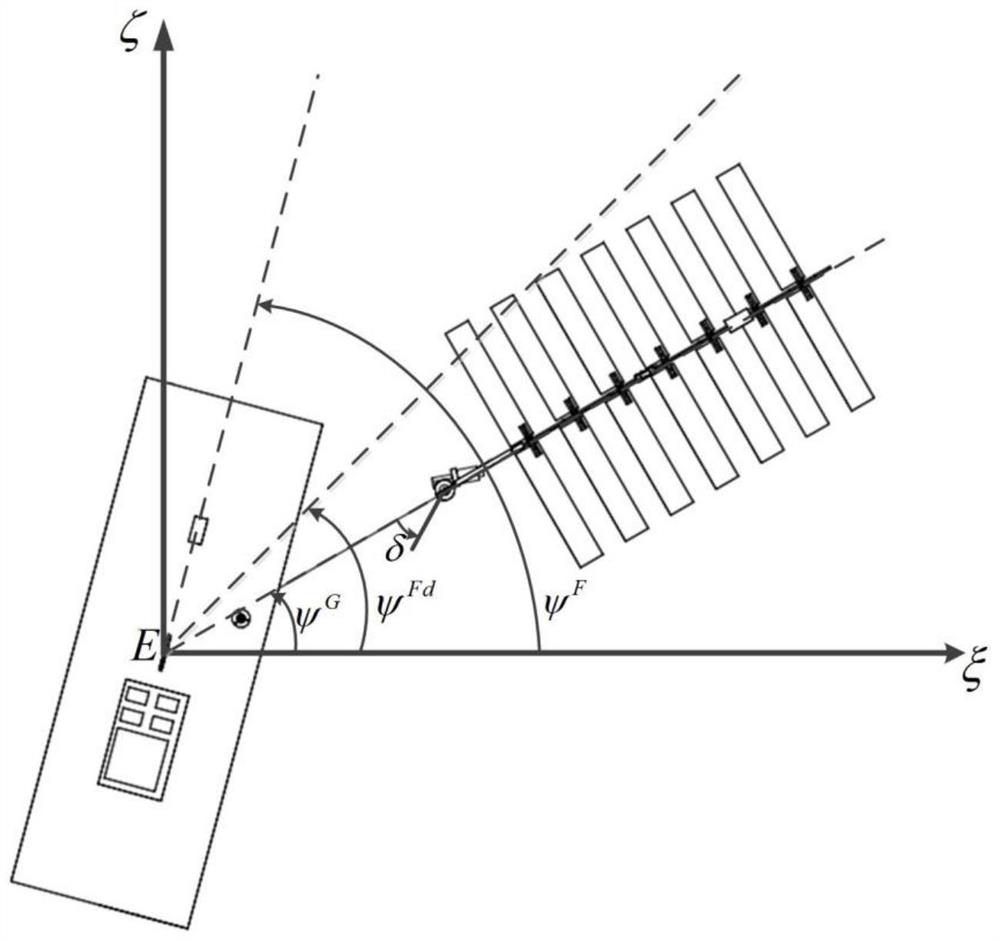
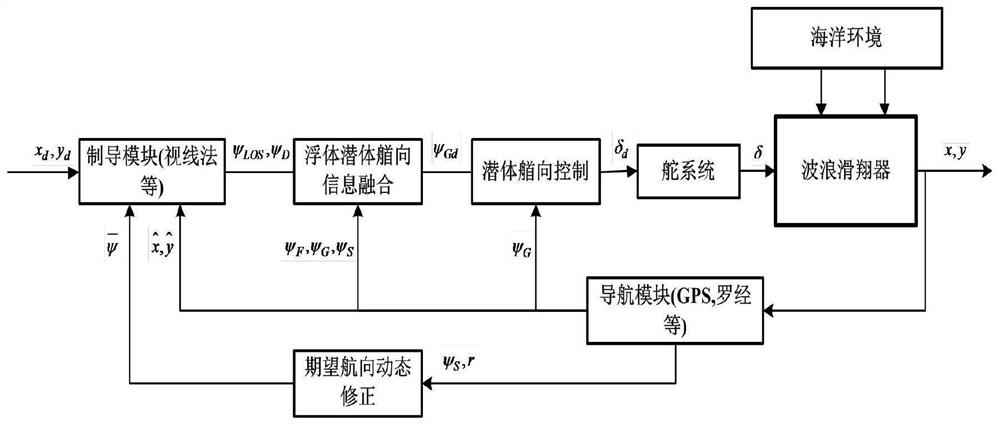
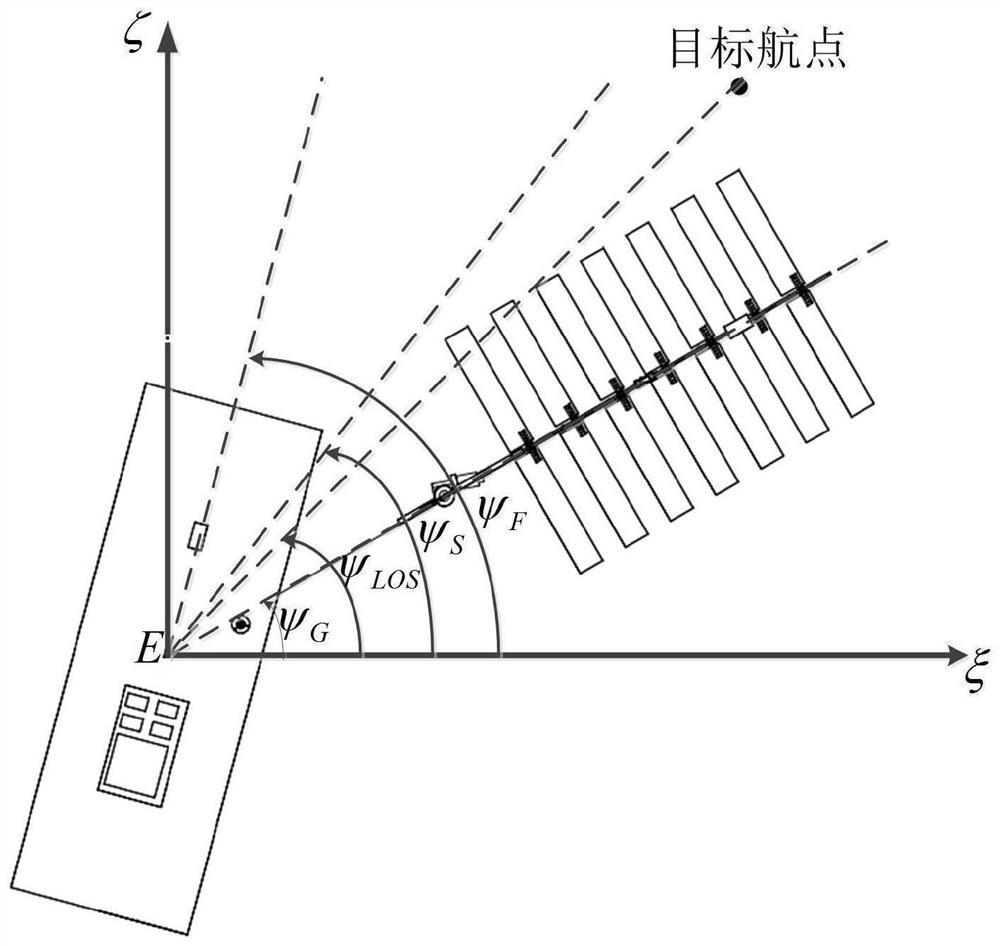
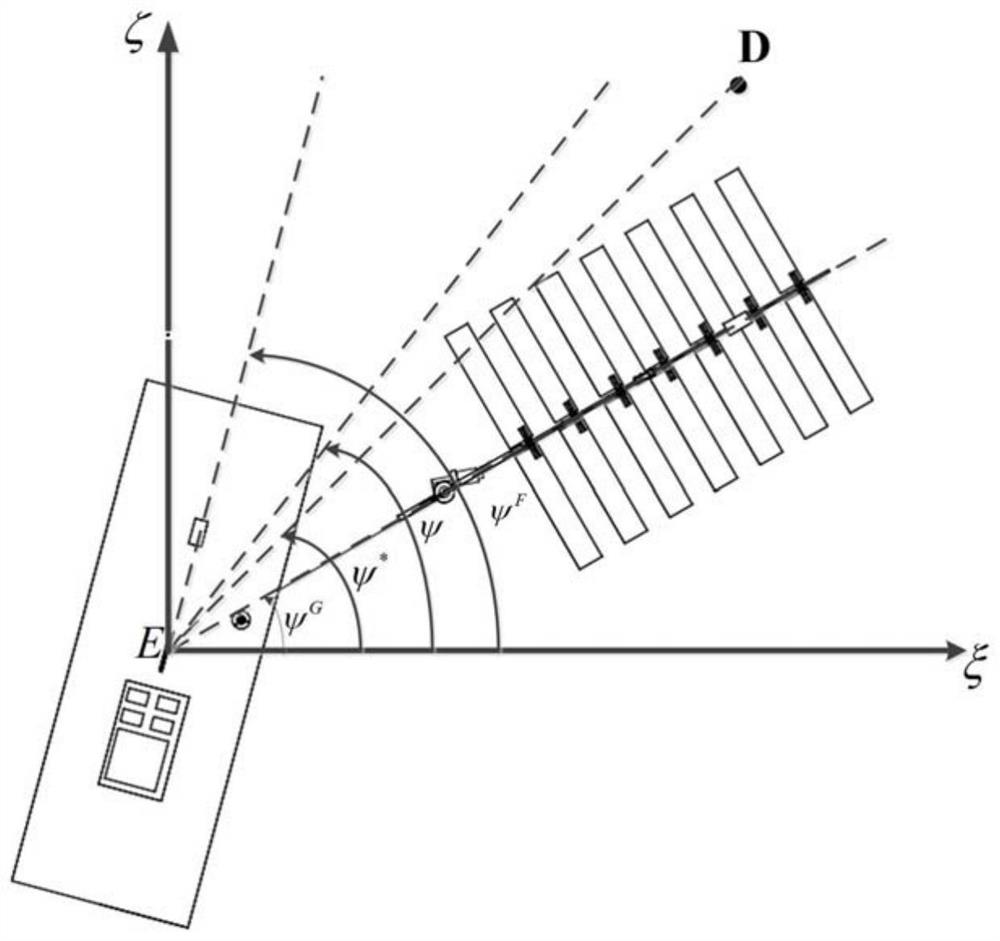
The invention provides a wave glider waypoint tracking method based upper and lower body heading information fusion. A steering engine of a wave glider is installed in a submerged body. The steering engine is controlled by a main computer for directly controlling the steering of the submerged body. The steering of a floating body can be supported by the drag force of the submerged body. The floating body and the submerged body are provided with a heading sensor respectively for measuring the floating body heading [psi]F and the submerged body heading [psi]G to sent to the main computer. The main computer completes fusion of heading information of the floating body and the submerged body of the wave glider, and corrects the expected course angle combined with the dynamic characteristics in the navigation process so as to complete the waypoint tracking task. The method can effectively avoid the soft chain winding phenomenon which is unique to the structure of the hard-soft multi-system structure of the wave glider and improve the course control performance of the wave glider and the waypoint tracking ability under the external disturbance force such as wind and flow.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
An underwater fatigue-resistant shock-absorbing device suitable for wave energy glider
InactiveCN109591986BCompact structureEasy to installUnderwater vesselsUnderwater equipmentGliderFatigue fractures
Owner:CSIC NO 710 RES & DEV INST
A low-power self-heave submersible buoy based on hang glider and its working method
ActiveCN114104199BAccelerate the process of ascending and descendingReduce power consumptionWaterborne vesselsBuoysGliderHydraulic pump
The invention discloses a low power consumption self-heave submersible buoy based on a gliding wing, which belongs to the field of underwater fixed-point observation platforms. The submersible mark includes a submerged mark body, and an unpowered glider is set above the submerged mark body; the unpowered glider includes a delta wing, the axis of the delta wing is parallel to the axis of the submerged mark body, and the tip of the delta wing is at the bow of the submerged mark body Right above the upper part, the tail center of the delta wing is rigidly fixed with an empennage; a battery pack and a drive mechanism for driving the battery pack to move back and forth along the axis of the submersible body are arranged inside the submersible body; A water depth control module is provided, and the water depth control module includes an inner oil bag, an outer oil bag, an oil circuit and a hydraulic pump. In the present invention, a large-area triangular gliding wing is installed above the submersible body, and then the movable battery pack and the water depth control module are used to adjust the pitching attitude of the submersible body, so that the fluid generates a heave force on the glider, and accelerates the up and down of the submersible latent process, reducing the overall power consumption.
Owner:青岛国数信息科技有限公司
An online identification method of yaw response parameters based on integral method
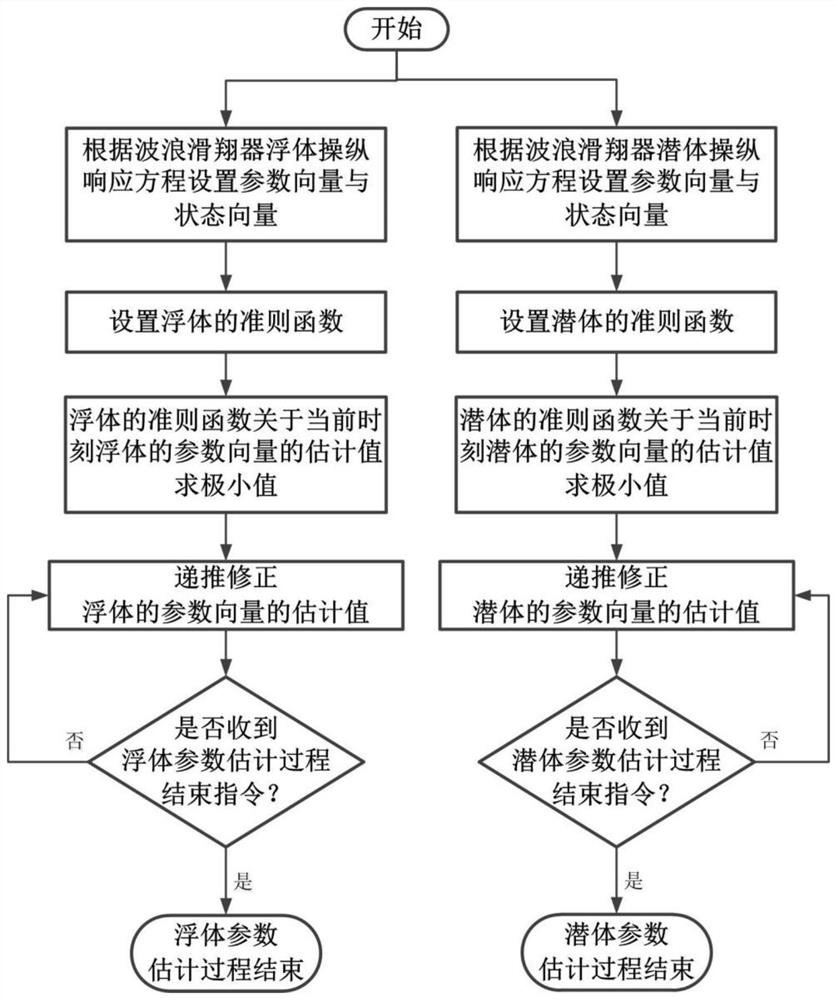
ActiveCN109782774BAvoid difficultiesPosition/course control in two dimensionsGliderControl engineering
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
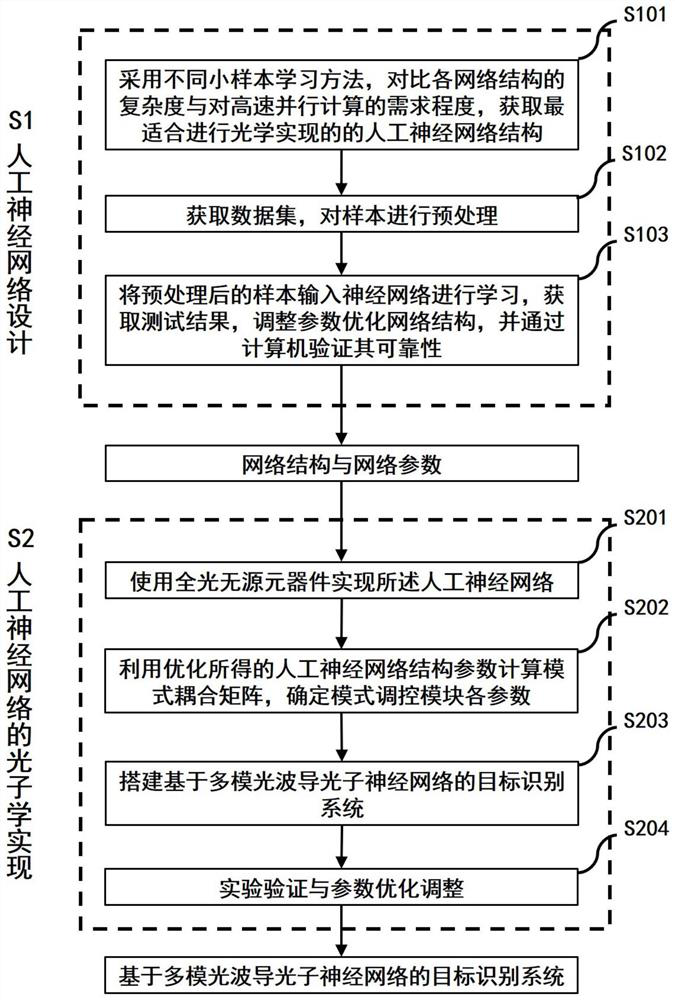
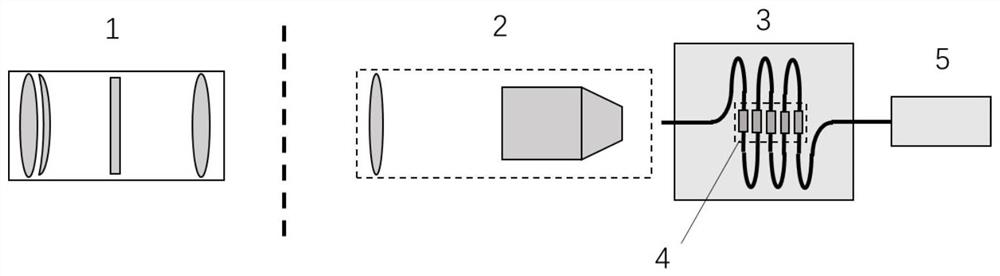
Flying target recognition system based on photon neural network and construction method
PendingCN114758193ARealize identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesPhotonicsEngineering
The invention discloses a flight target recognition system based on a photon neural network and a building method, and aims at high-speed motion aircrafts, including but not limited to aircrafts such as aircrafts, unmanned aerial vehicles, helicopters, gliders and delta wings, missiles and the like, and an ultrafast flight target recognition system of the photon neural network is built. The invention provides a flight target recognition system based on a photon neural network. The flight target recognition system based on the photon neural network comprises an imaging and filtering module, a light field scaling and coupling module, a photon neural network module, a mode regulation and control module and an output light field coupling module. The invention discloses a building method of a flight target recognition system. The building method comprises the steps of artificial neural network design and artificial neural network photonics implementation. According to the invention, a photon neural network transmission and regulation model based on all-optical passive components is designed, training is carried out for small sample learning of a high-speed flight target, a static and dynamic target identification system is established, and identification of a high-speed flight moving target is realized.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
An Approximate Dynamic Programming Optimization Control Method for Attitude Adjustment of Underwater Thermal Glider
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
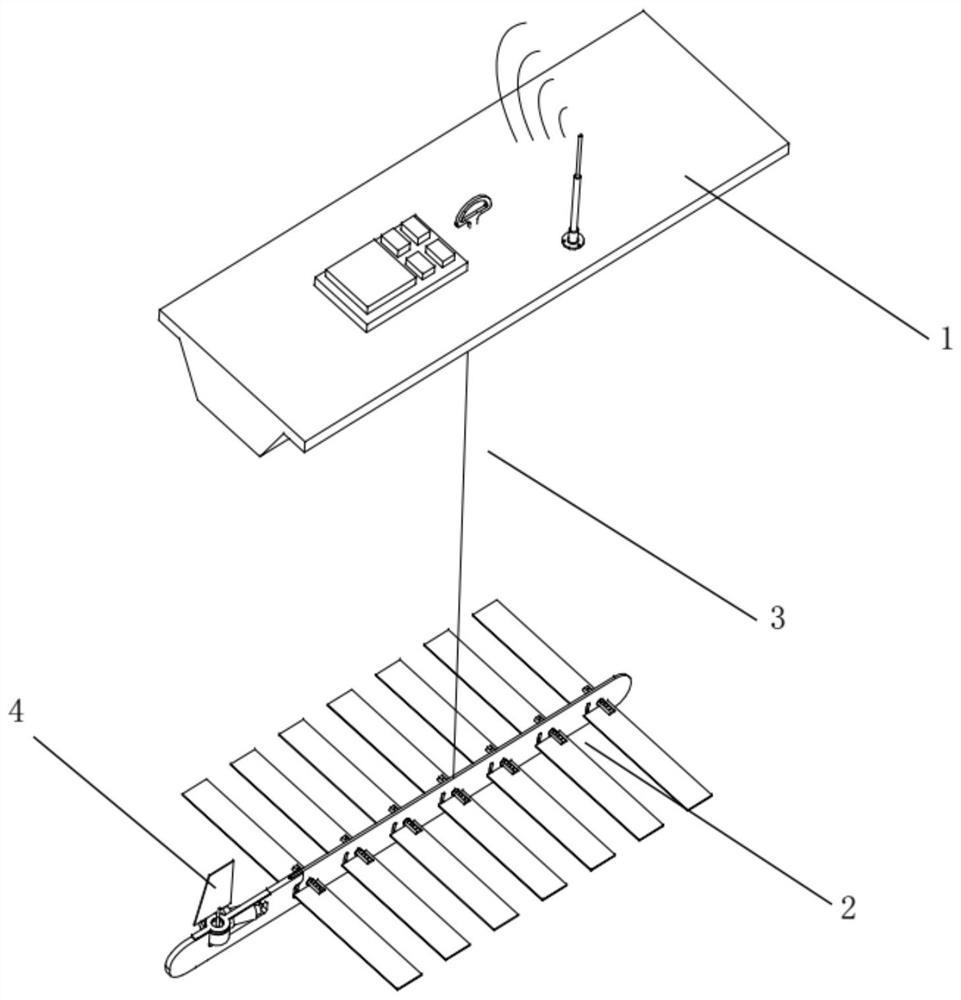
Distributed layout wave glider control system
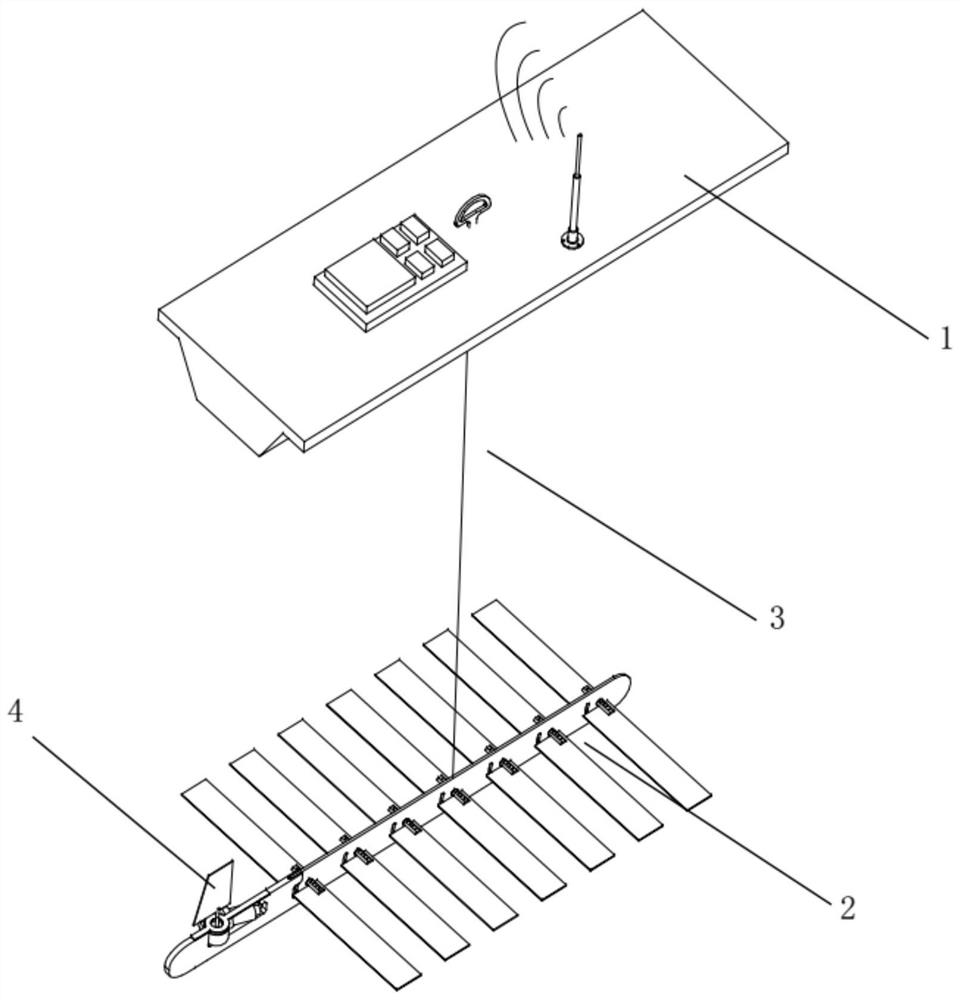
ActiveCN114828510AReduce usageBeautiful layoutCircuit arrangements on support structuresSupport structure mountingGliderControl system
The invention relates to a distributed layout wave glider control system, in particular to the technical field of wave glider motion control. The distributed wave glider control system provided by the invention comprises a cabin body, a cabin body cover plate, a bottom plate adapter plate, a child node bottom plate and a plurality of child node circuit boards, a watertight connector is arranged on the cabin body cover plate; a closed space is formed by the cabin body cover plate and the cabin body; the bottom plate adapter plate, the child node bottom plate and the child node circuit boards are all arranged in the closed space, the child node circuit boards are all arranged on the child node bottom plate, the child node bottom plate is arranged on the bottom plate adapter plate, and the child node circuit boards are arranged on the child node bottom plate. And the bottom plate adapter plate is arranged on the cabin body cover plate, is connected with the watertight connector, and is connected with a sensor outside the sealed space through the watertight connector. According to the invention, fault diagnosis of the circuit board is facilitated.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA +2
Near space glider state estimation method, storage medium and computing device
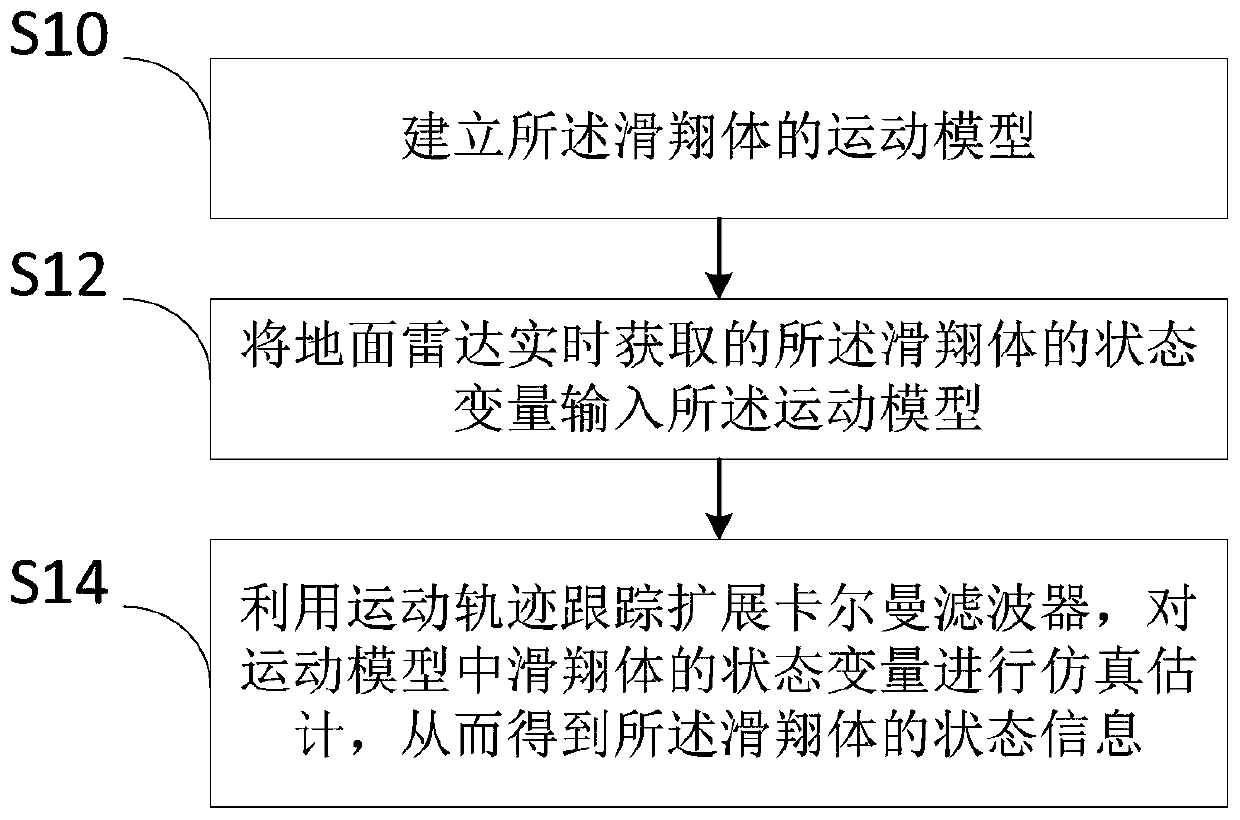
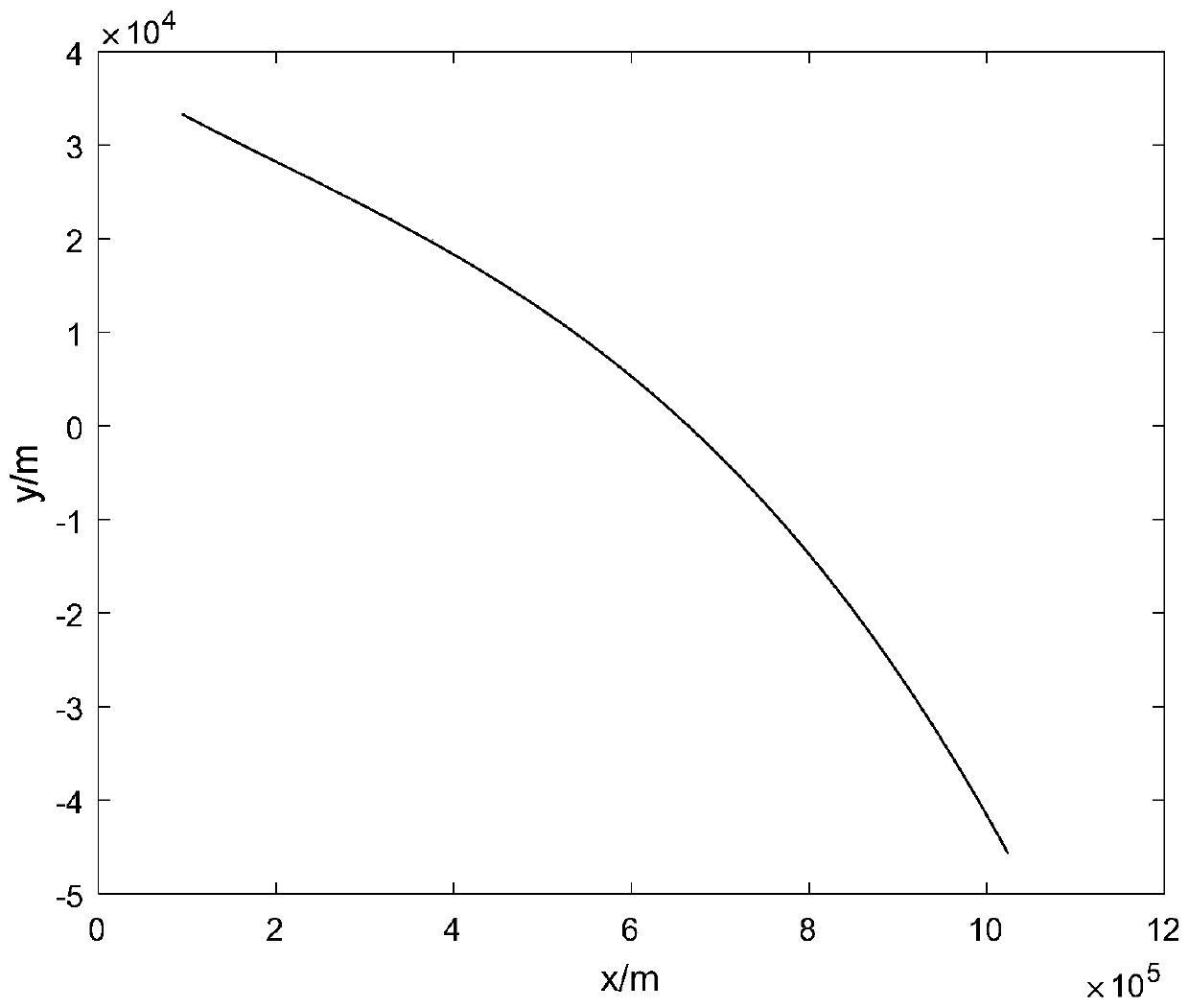
PendingCN111428343ASmall velocity estimation errorSmall Acceleration Estimation ErrorDesign optimisation/simulationGround based radarGlider
The invention discloses a near space hypersonic gliding body state estimation method. The method comprises the following steps: S10, establishing a motion model of a gliding body; S12, inputting the state variable of the gliding body, which is acquired by a ground radar in real time, into the motion model; S14, tracking an extended Kalman filter by utilizing a motion trail; performing simulation estimation on the state variables of the gliding body in the motion model, so that the state information of the gliding body is obtained. In the invention, a new maneuvering model of the near-space hypersonic gliding body is provided, wherein by means of the extended Kalman filtering, the state estimation method for the gliding body is provided.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ELECTRONICS SYST ENG
A motion prediction method for wave glider with flexible connections
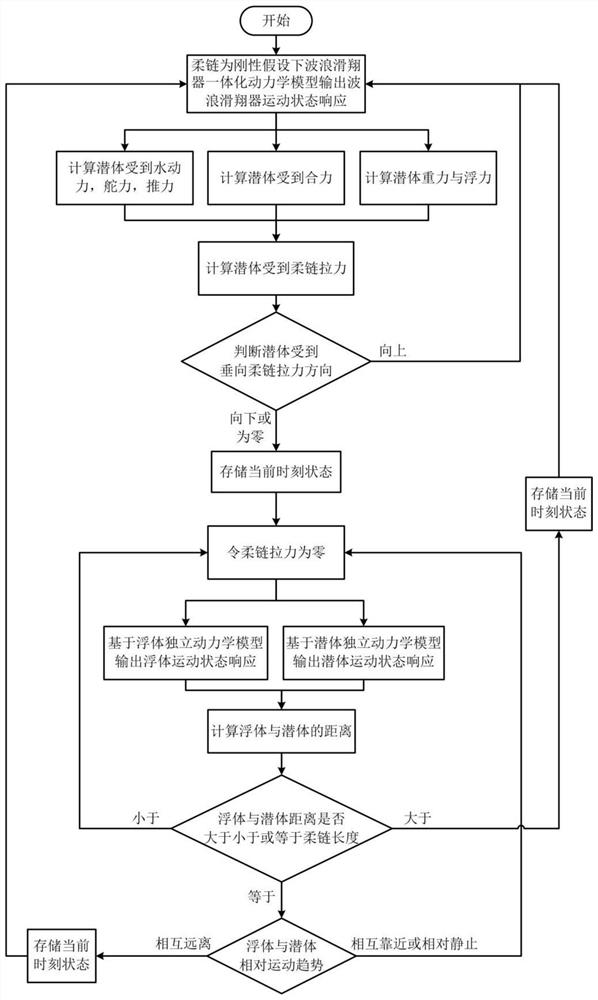
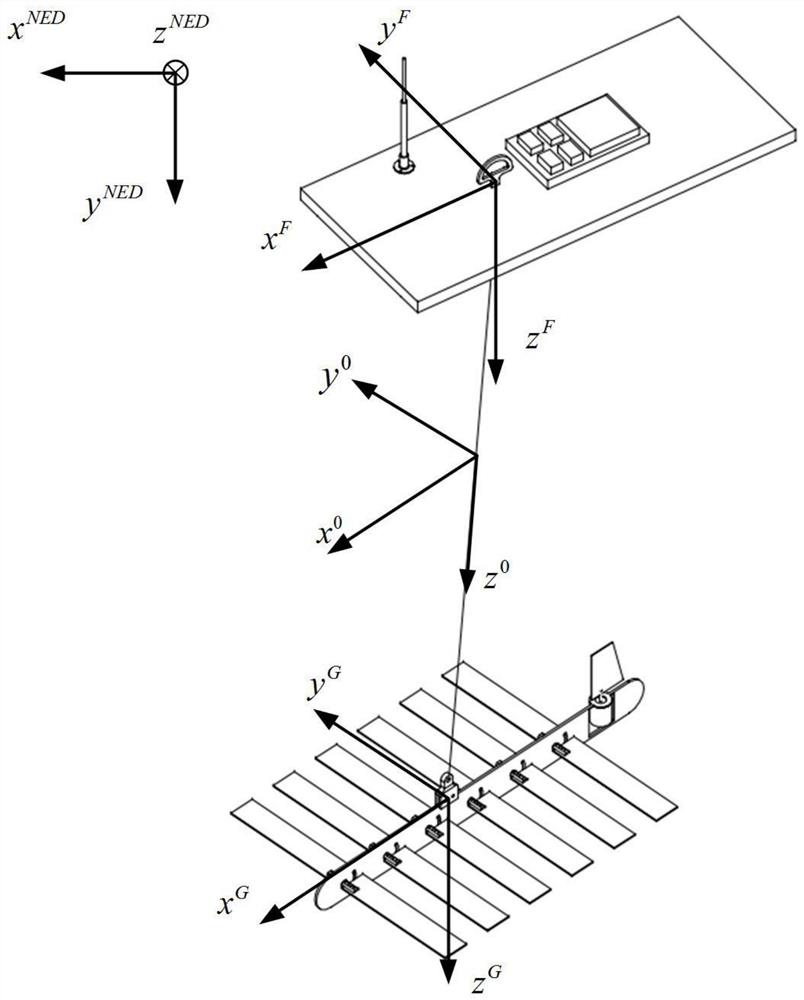
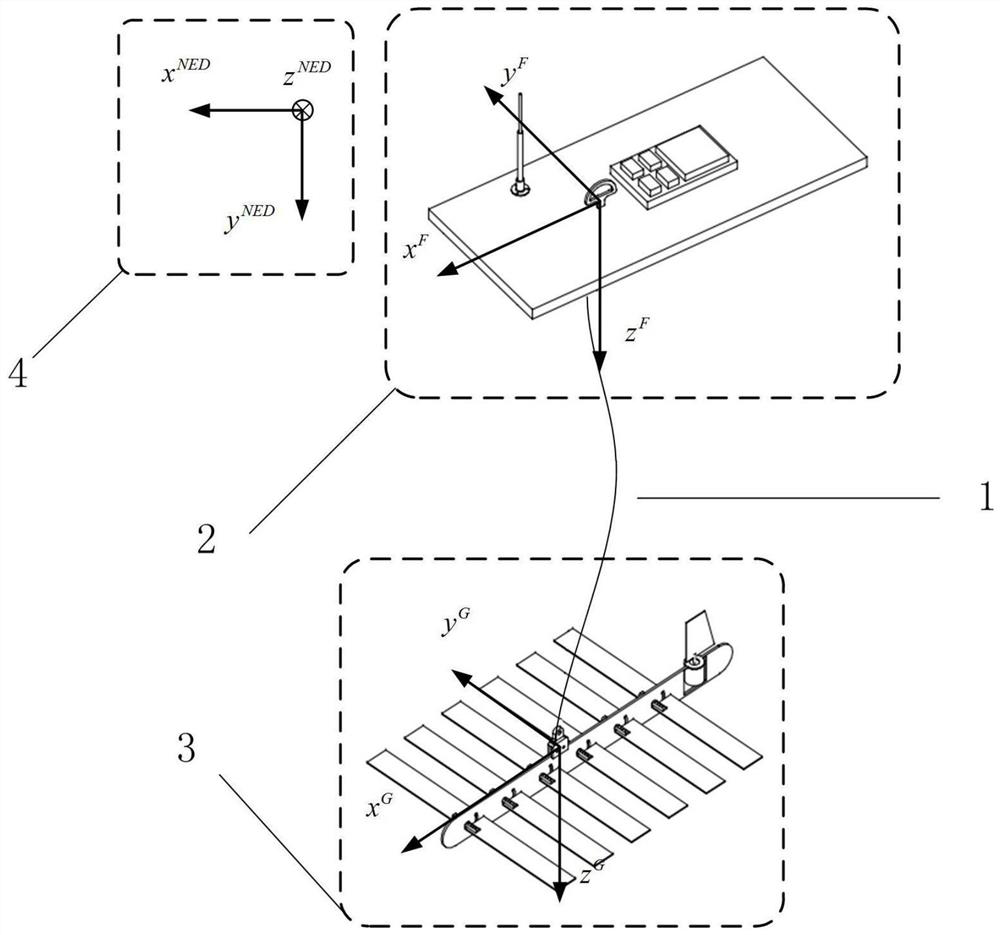
ActiveCN108520089BTrue Prediction of Motor ResponseRealistic description of dynamic characteristicsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationGliderPull force
The motion prediction method of the wave glider with flexible connection, the specific steps are as follows: (1) Obtain the rudder angle information (2) Calculate the force on the submerged body (3) Calculate the flexible chain pull force on the submerged body; (4) Judge the submerged body If the direction of the vertical flexible chain pulling force is vertically upward, then return to (2), if it is vertically downward or zero, then store the current moment state information as (5) initial state, enter (5); (6 ) to calculate the distance between the floating body and the submerged body, if the distance is less than the length of the flexible chain, then return to (5); if the distance is greater than the length of the flexible chain, then store the current state information as the initial state of (1), and return to (1); if the distance is equal to length of the flexible chain, then enter (7); (7) judge the relative movement trend of the floating body and the submerged body, if they are close to each other or relatively static in the direction of the connection between the two, then return to (5); if they are far away from each other, then store the current Time state information is used as 1) initial state, and returns (1).
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Heading control method of wave glider based on adaptive heading information fusion
ActiveCN108829102BAvoid flexible chain entanglementImproved heading control performanceAttitude controlPosition/course control in two dimensionsGliderControl system
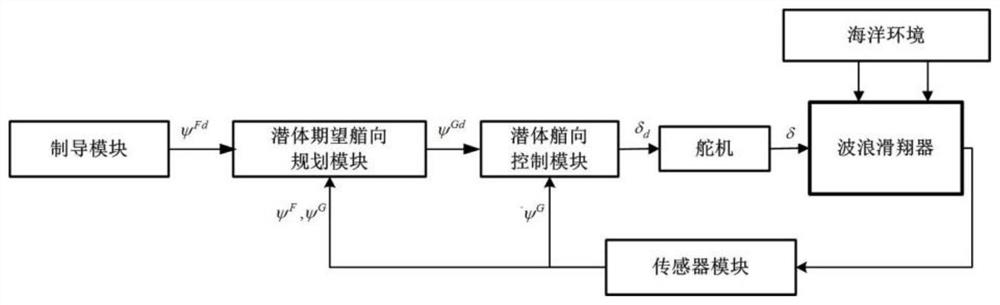
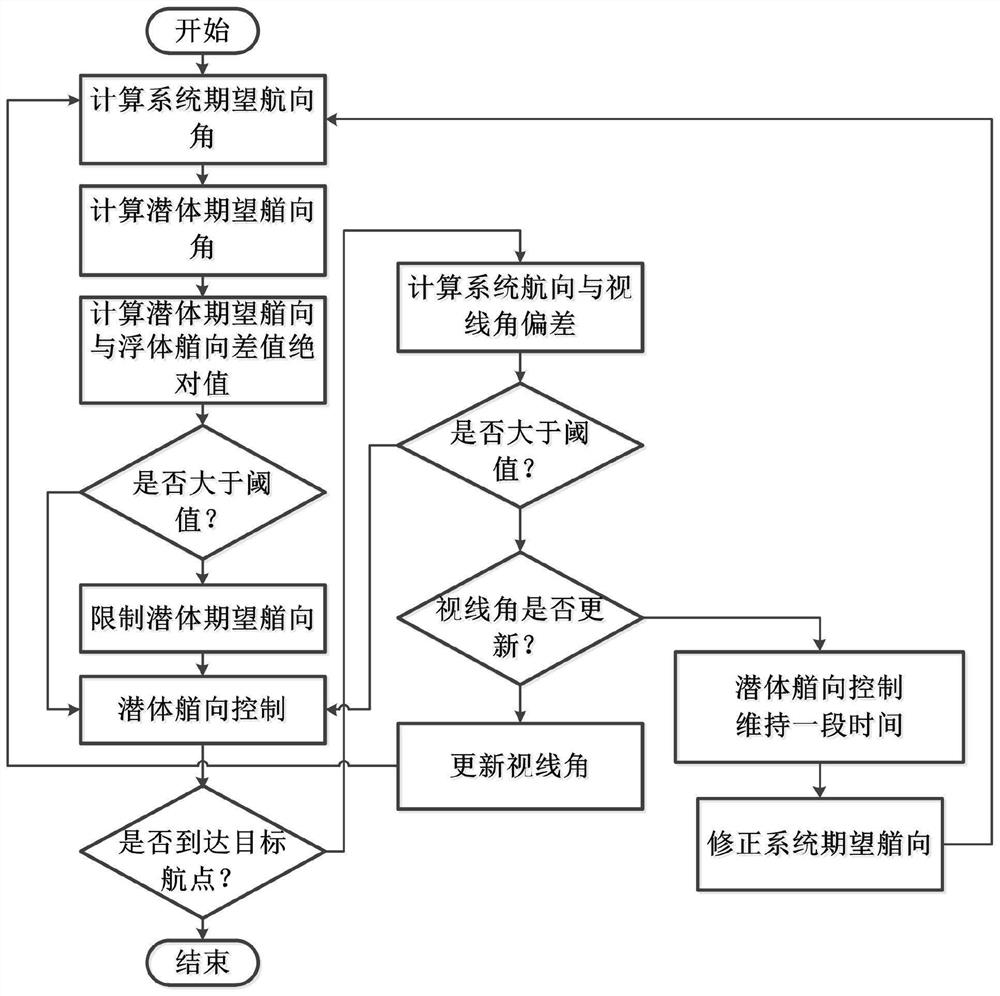
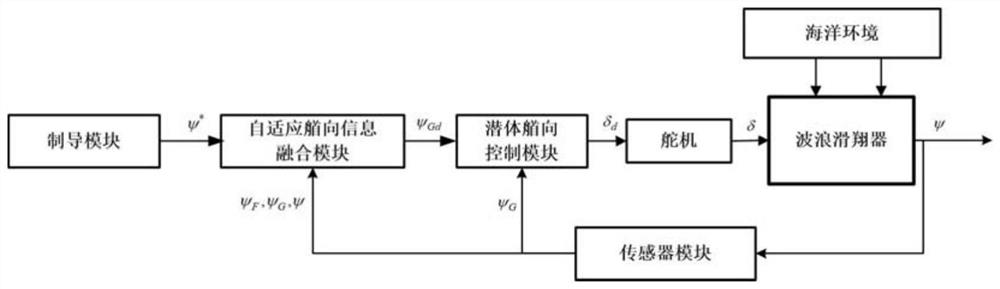
The invention provides an adaptive heading information fused course control method of a wave glider. The method comprises that (1) a guidance module provides an expected course angle; (2) an estimatedvalue of a corrected submerged floating body relative to a proportional coefficient of the system heading angle is obtained; (3) an expected heading angle of the submerged body is calculated; (4) anabsolute value of an included angle between the expected heading and the heading of the submerged body is calculated, and limited within a preset threshold; (5) the heading of the submerged body is controlled, a host computer emits a rudder angle instruction to a steering engine, and the steering engine drives a rudder plate to rotate; and (6) an absolute value of an error of the practical courseof the wave glider relative to the expected course is calculated, if the absolute value of the error is lower than a set threshold and kept for certain time, it is considered that practical output ofthe wave glider control system is converged to expected output stably, the cycle is broken out, and otherwise, the step (2) is returned to. Thus, the heading of the submerged body is controlled to indirectly control the whole course of the wave glider, the aim of course control is achieved, and the method is higher adaptive.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
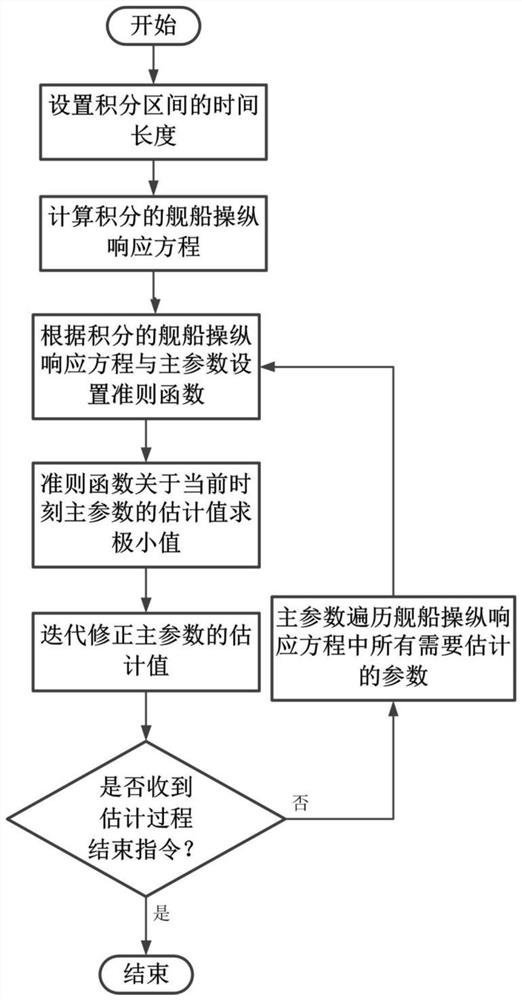
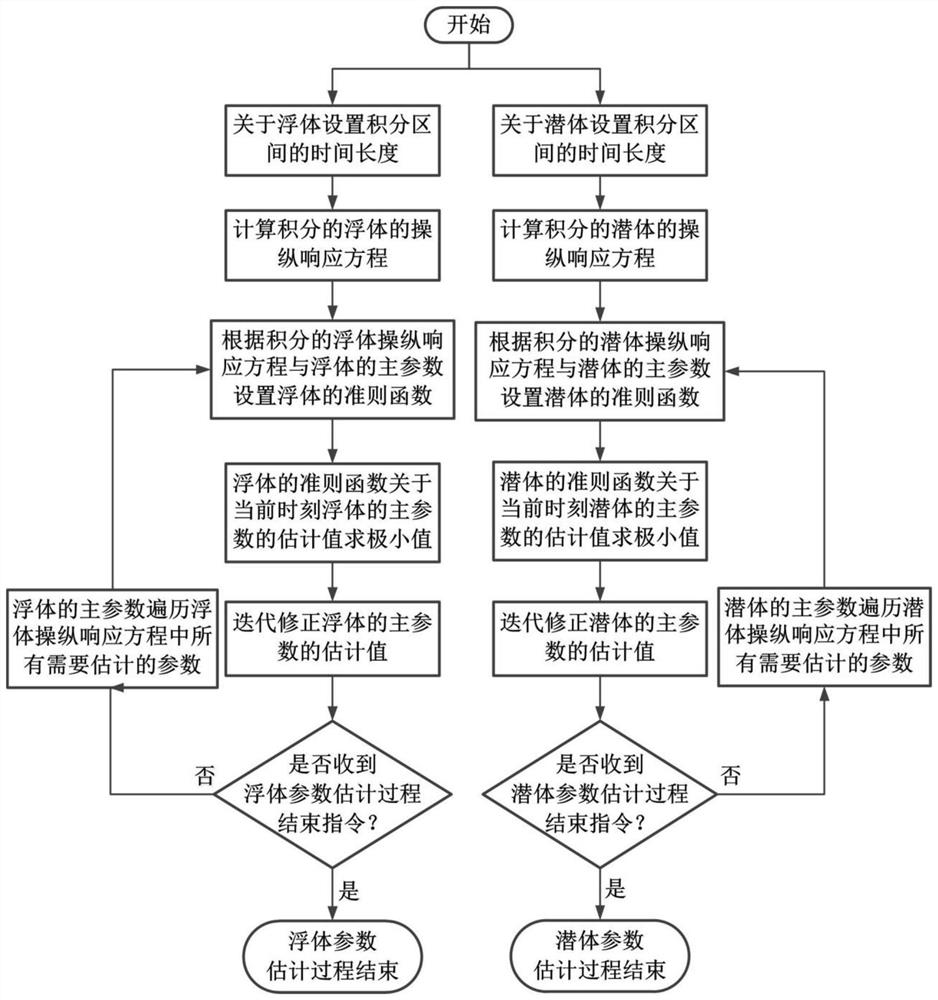
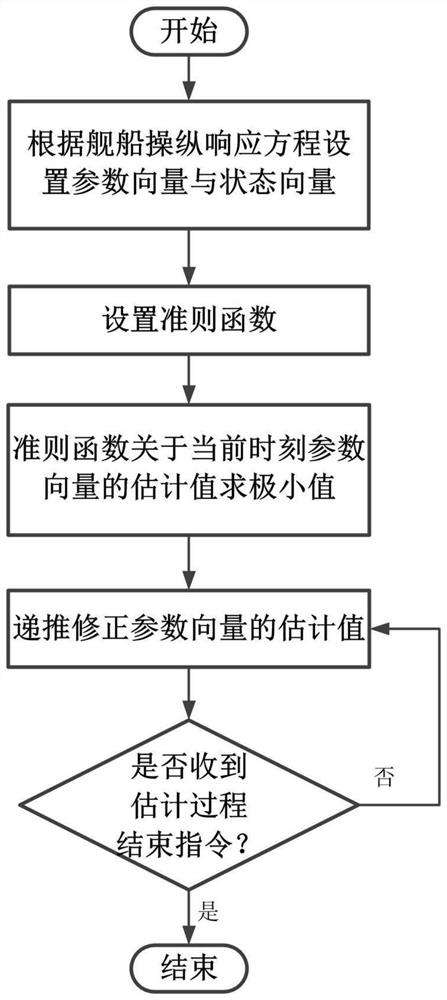
An Estimation Method of Yaw Response Parameter Vector Based on Integral Method
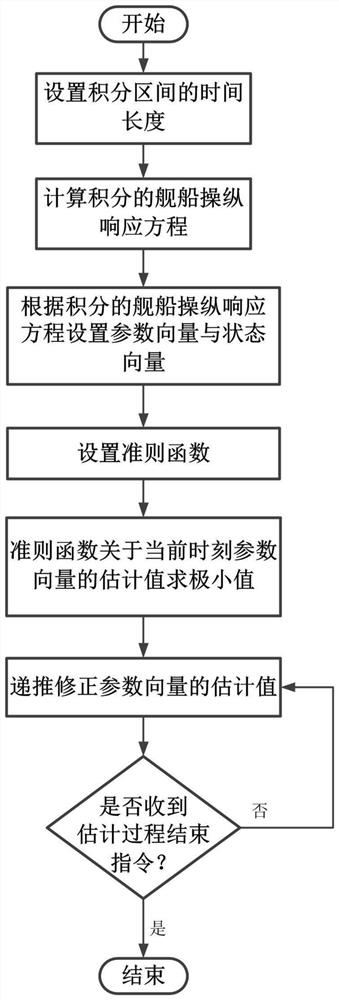
The invention provides a yaw response parameter vector estimation method based on an integration method, and belongs to the technical field of ship maneuverability modeling. The yaw response parametervector estimation method based on the integration method is suitable for ships or wave gliders. The yaw response parameter vector estimation method based on the integration method comprises the following steps that firstly, a time length L of an integration interval is set, a manipulation response equation is integrated with time to obtain an integrated manipulation response equation; then, a parameter vector and a state vector are set according to the manipulation response equation, then a criterion function is set, and the relative weight of internal parameters is adjusted by using a weightcoefficient; a minimum value of an estimated value of the criterion function with respect to a current time parameter vector is obtained, and a step factor is added to obtain an estimated value of the current time parameter vector in a recursive form; and finally, the steps are repeated until the end instruction of a estimation process is received. According to the yaw response parameter vector estimation method based on the integration method, a yaw response parameter vector can be corrected in real time in the ship sailing process, and yaw response parameters of the ships or the wave gliders which change in real time can be obtained; and compared with the prior art, the yaw response parameter vector estimation method based on the integration method has obvious advantages in the aspectsof rapidity, convenience, application range and the like.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
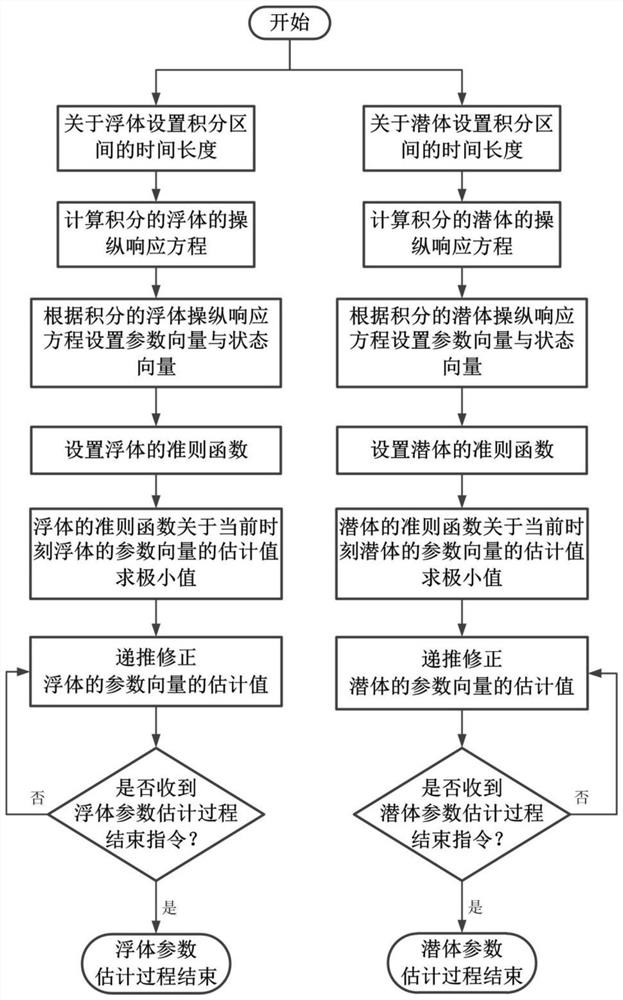
A Parallel Estimation Method of Parameter Vector of Manipulation Response Equation
The invention provides a parallel estimation method for parameter vectors of maneuvering response equations, belongs to the technical field of maneuverability model parameter estimation, and is suitable for ships or wave gliders. This method first sets the parameter vector P and the state vector Y, and satisfies P T Y=r, r is the turning angle velocity; then set the criterion function as the estimated value of P at the current moment, which is the estimated value of P at the previous moment, and μ is the weight coefficient; then add the step size to the criterion function J regarding finding the minimum value Factor λ, recursive correction λ is the step factor; finally repeat the previous step until receiving the instruction to end the estimation process. A method for parallel estimation of parameter vectors of maneuvering response equations suitable for ships and wave gliders proposed by the present invention can correct the parameter vectors in real time during the sailing process of ships, and obtain the maneuverability parameters of ships or wave gliders that change in real time Compared with the existing technology, it has significant advantages in terms of rapidity and convenience, and has a good development prospect.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com