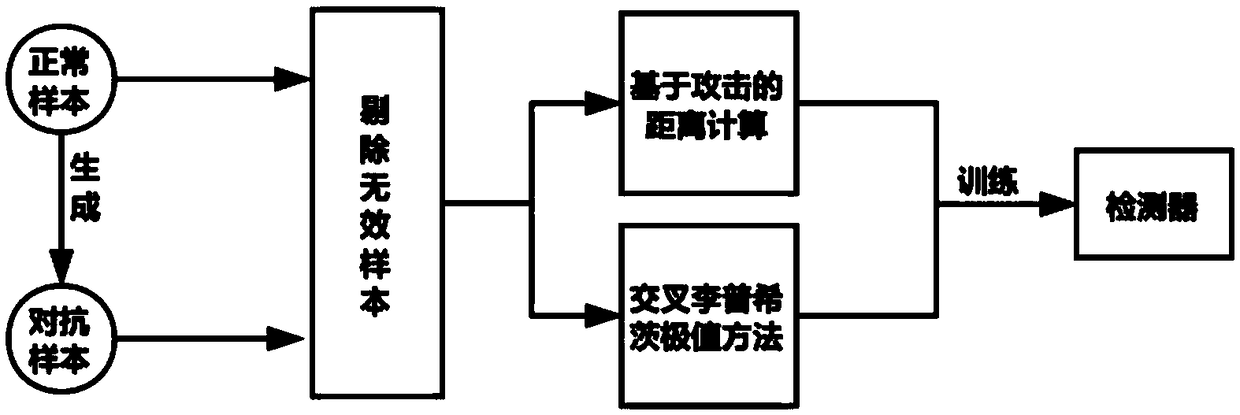
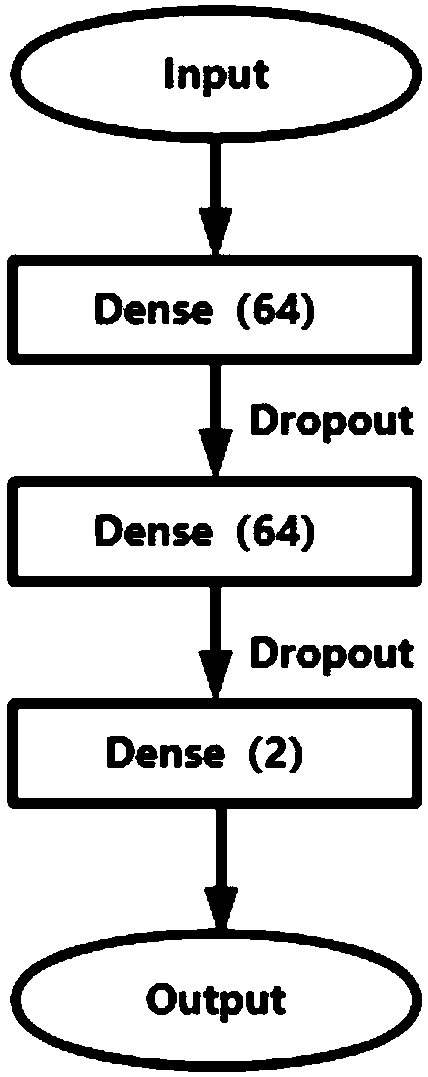
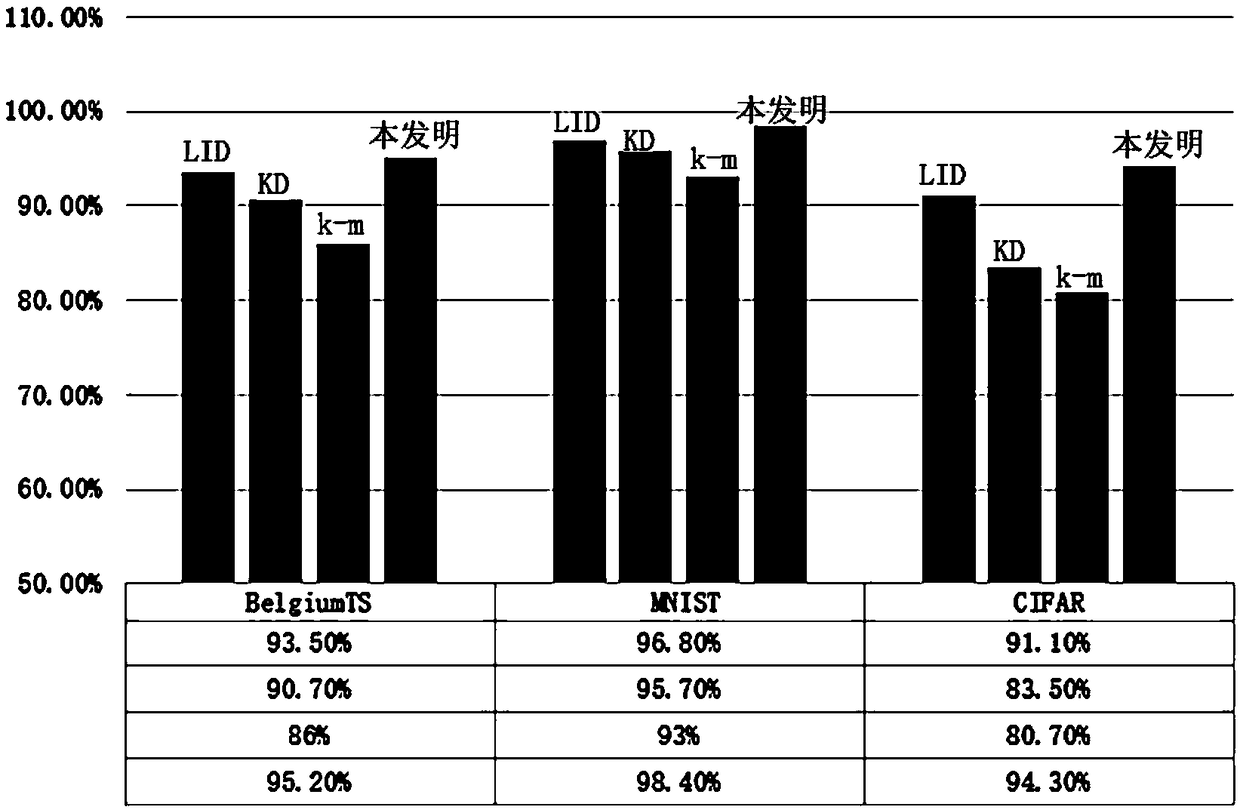
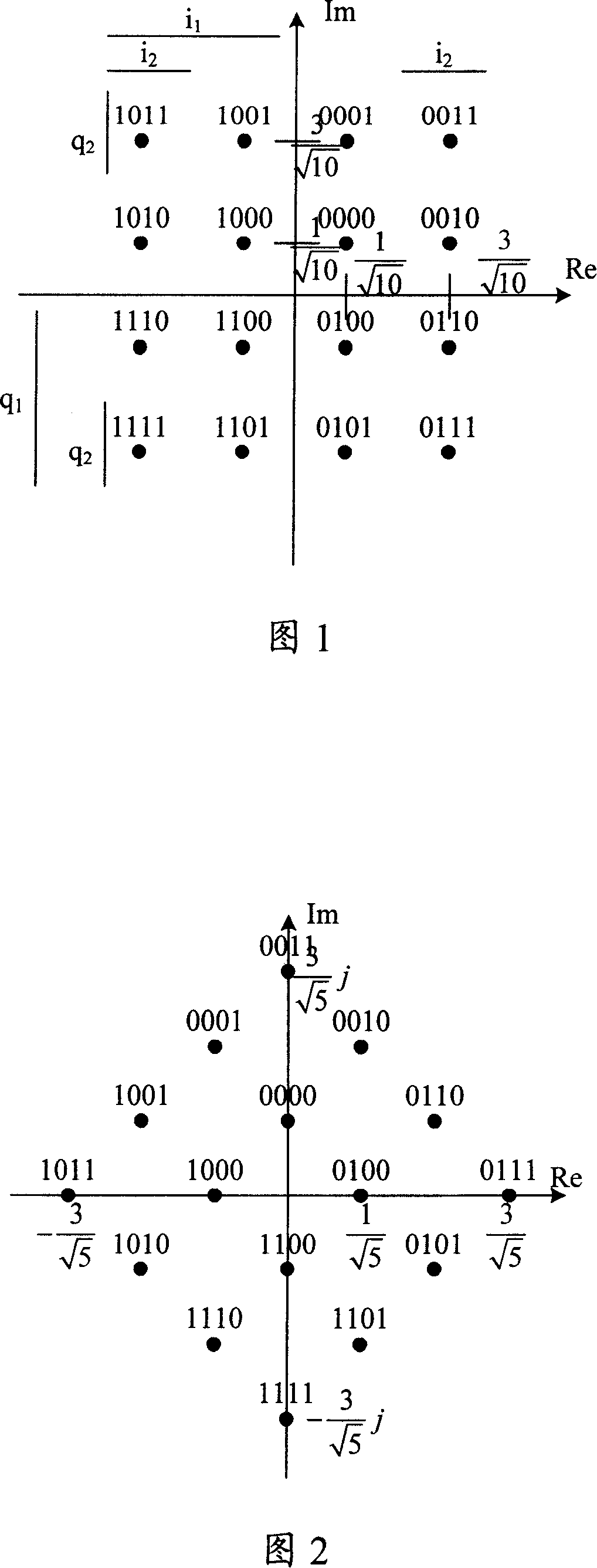
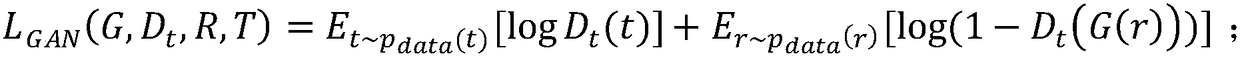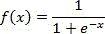Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
168 results about "Decision boundary" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
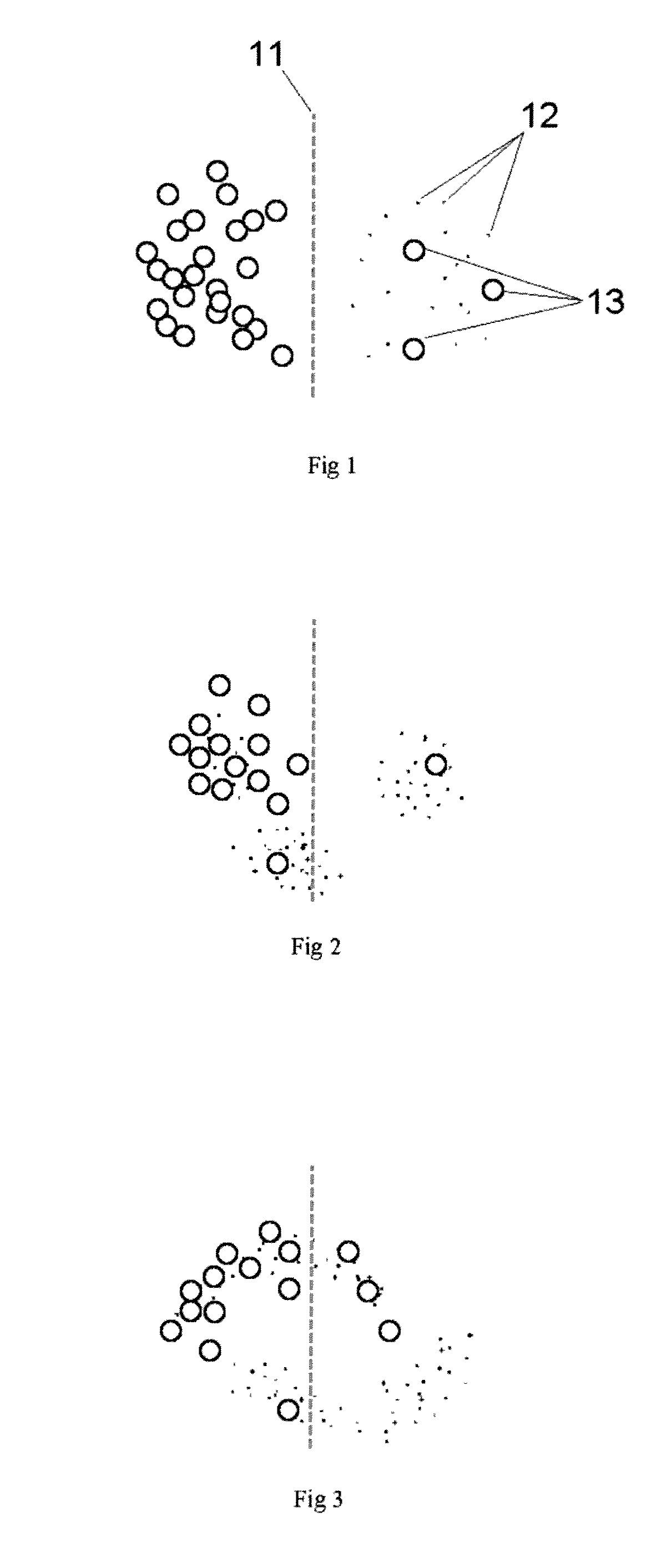
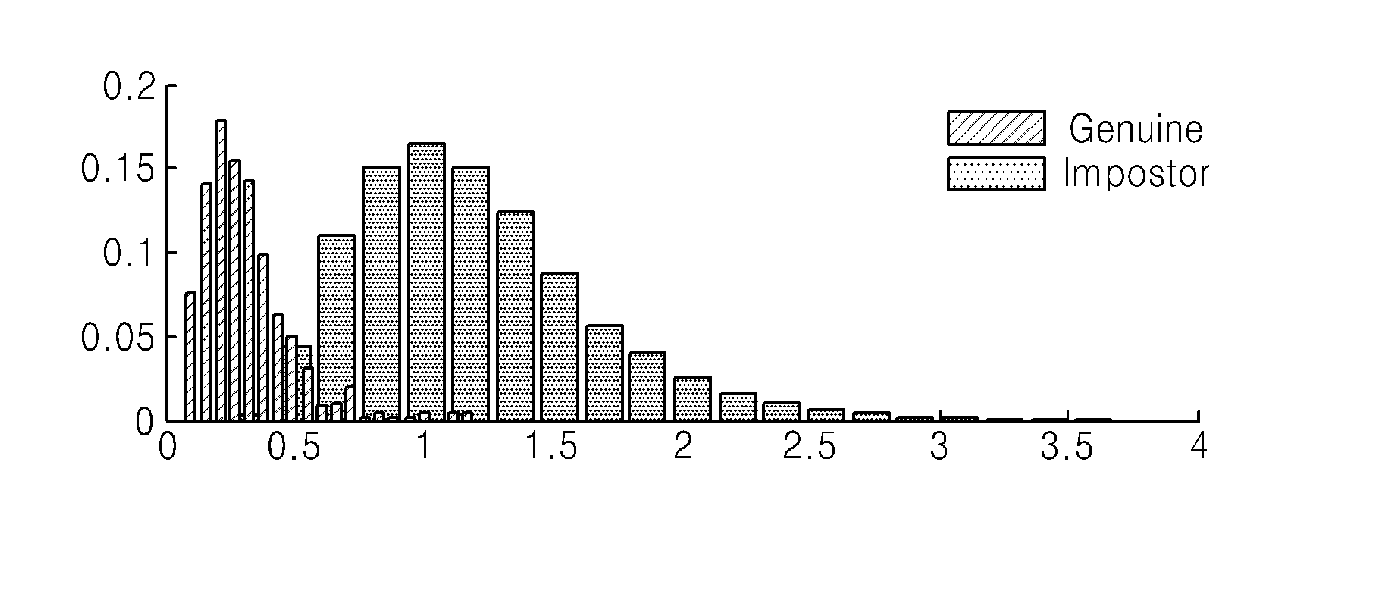
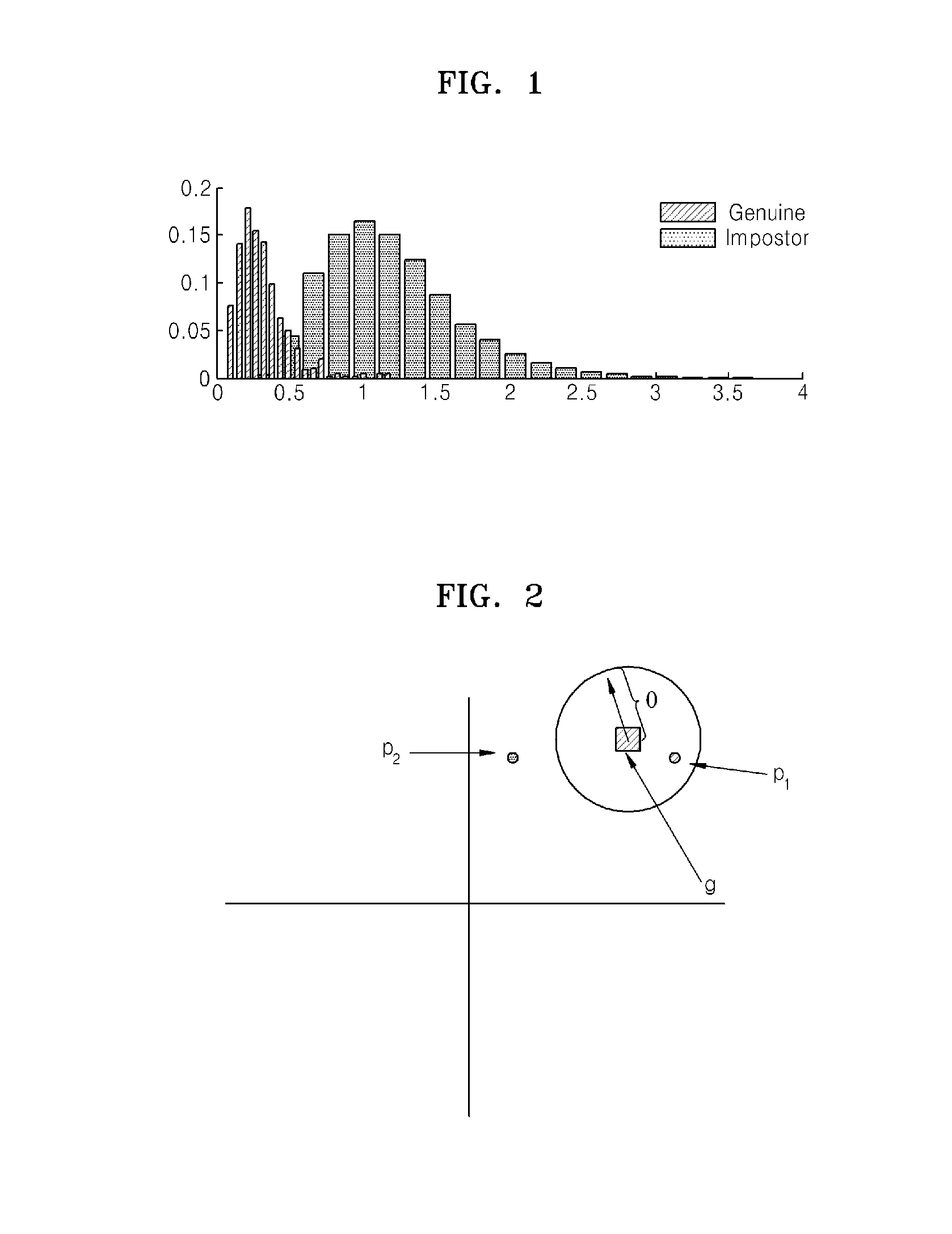
In a statistical-classification problem with two classes, a decision boundary or decision surface is a hypersurface that partitions the underlying vector space into two sets, one for each class. The classifier will classify all the points on one side of the decision boundary as belonging to one class and all those on the other side as belonging to the other class.
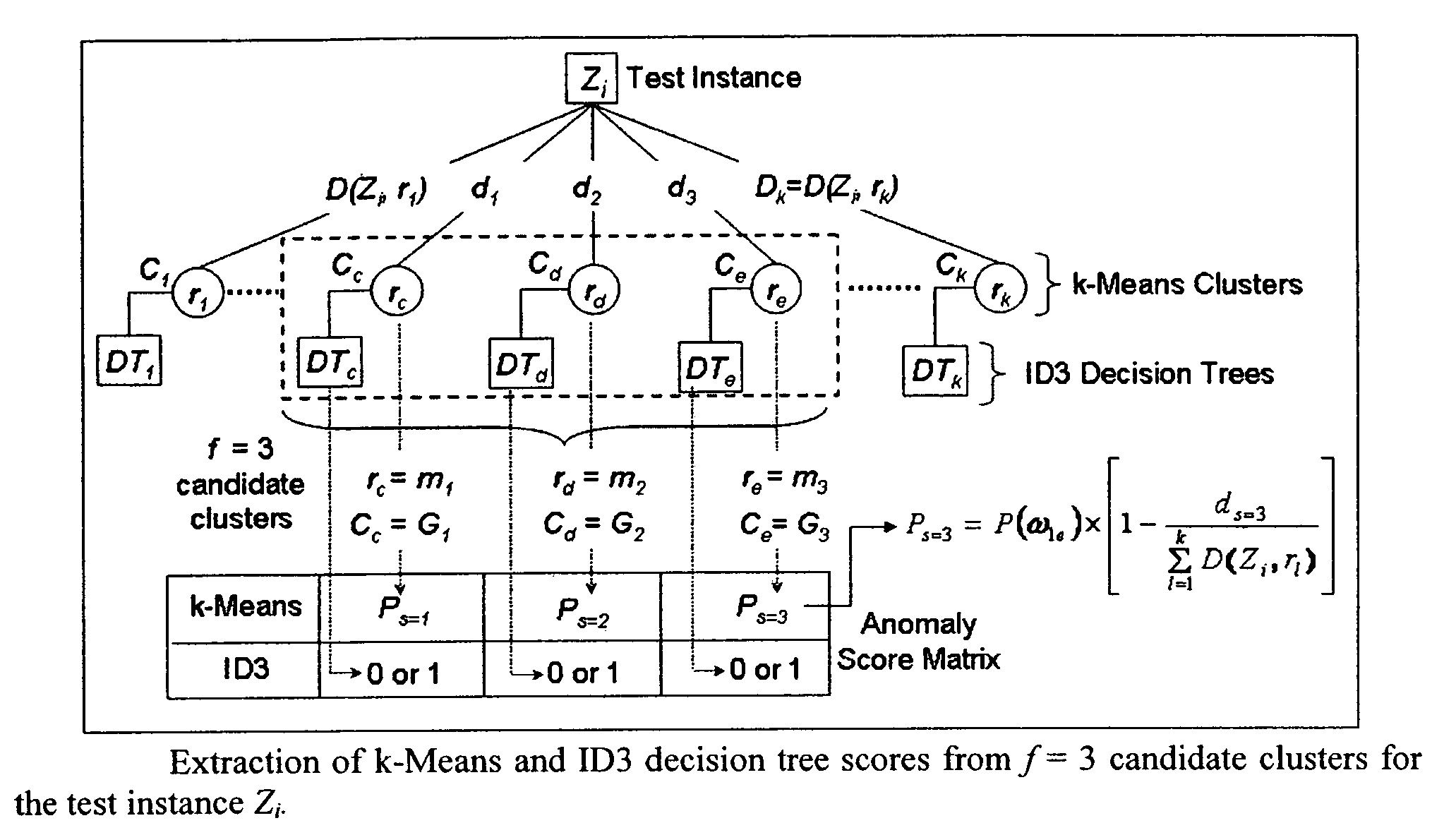
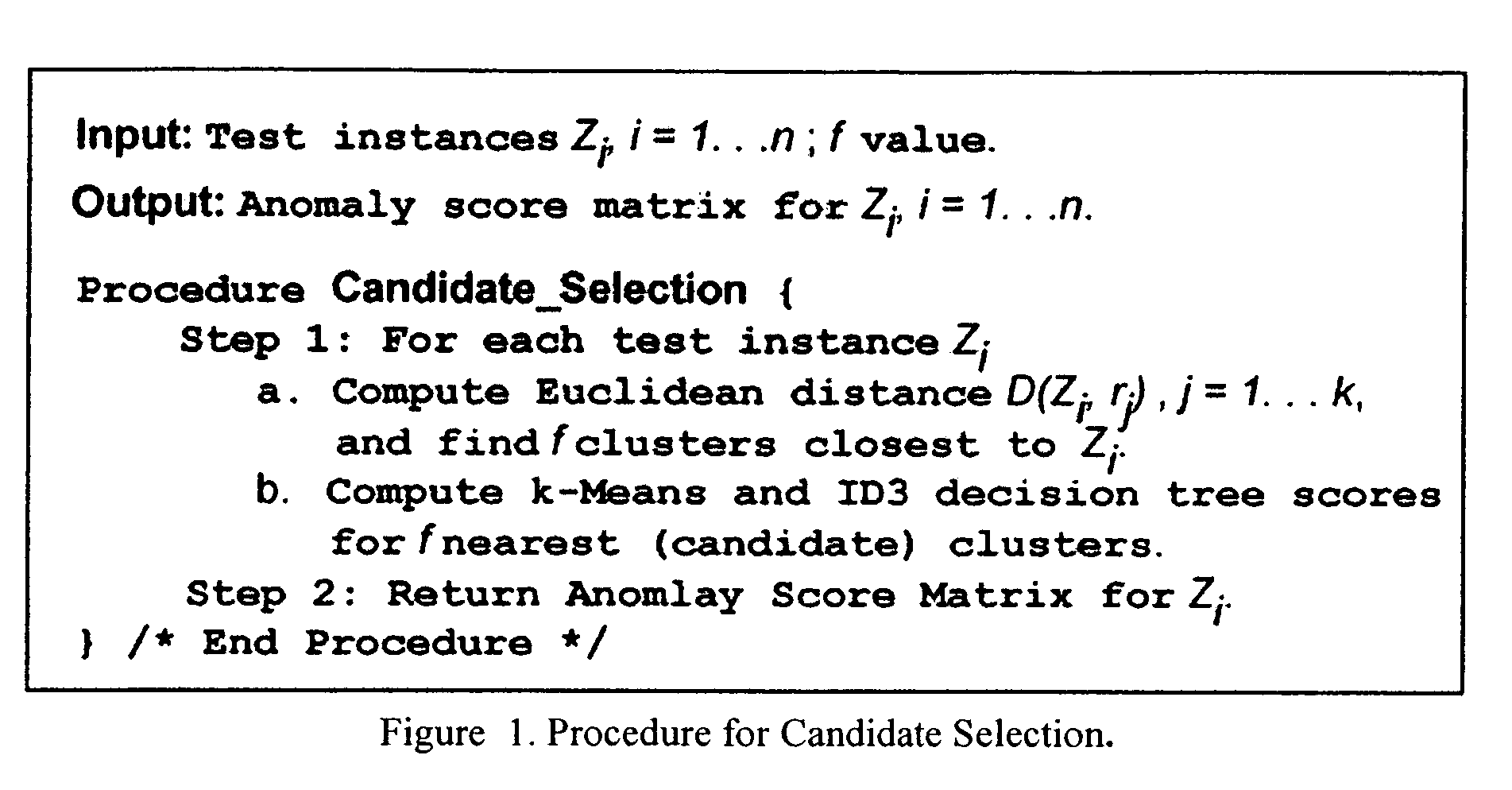
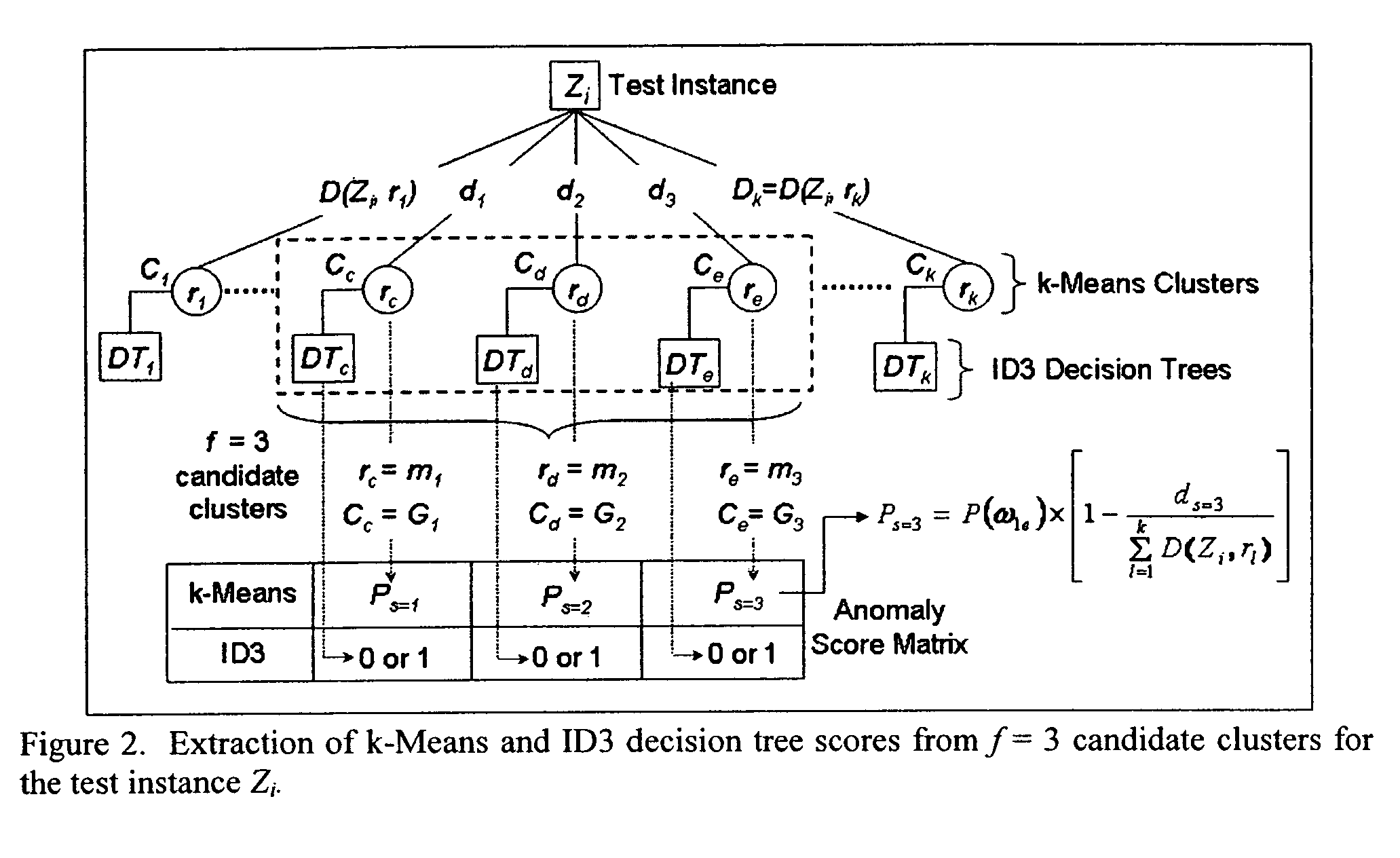
Method to indentify anomalous data using cascaded K-Means clustering and an ID3 decision tree
The invention is a computer implemented technique for id entifying anomalous data in a data set. The method uses cascaded k-Means clustering and the ID3 decision tree learning methods to characterize a training data set having data points with known characterization. The k-Means clustering method first partitions the training instances into k clusters using Euclidean distance similarity. On each training cluster, representing a density region of normal or anomaly instances, the invention builds an ID3 decision tree. The decision tree on each cluster refines the decision boundaries by learning the sub-groups within the cluster. A test data point is then subjected to the clustering and decision trees constructed form the training instances. To obtain a final decision on classification, the decisions of the k-Means and ID3 methods are combined using rules: (1) the Nearest-neighbor rule, and (2) the Nearest-consensus rule.
Owner:LOUISIANA TECH RES CORP
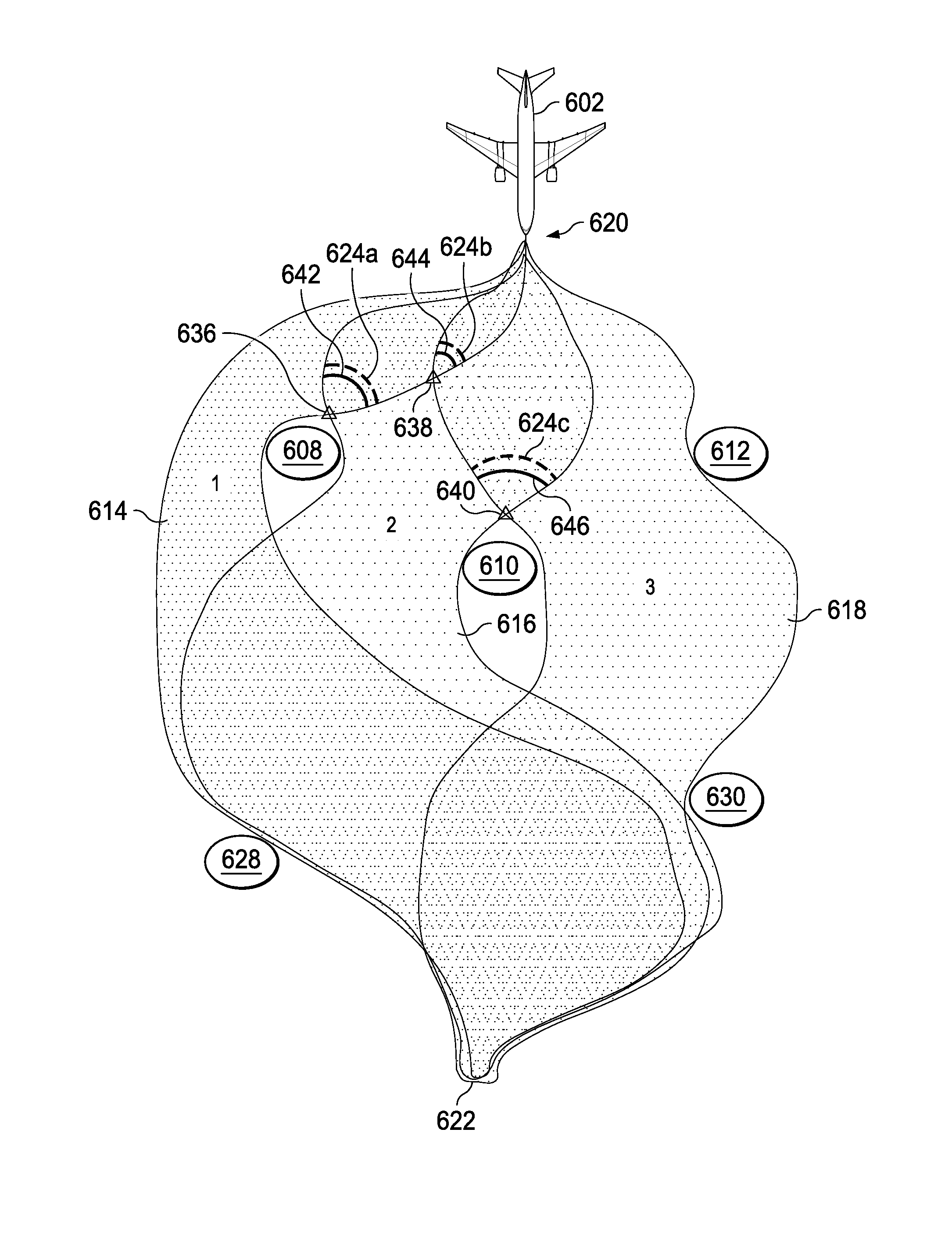
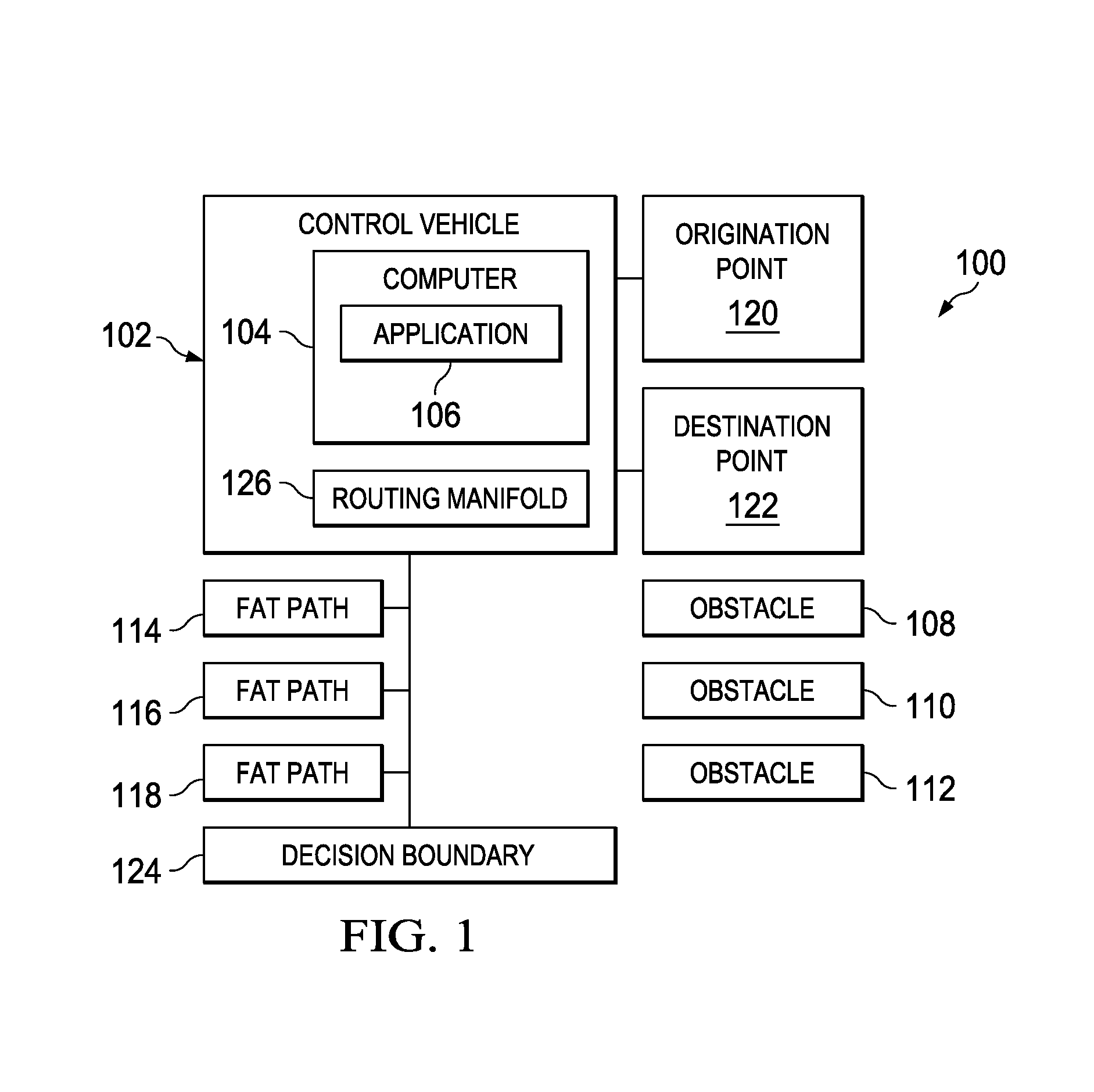
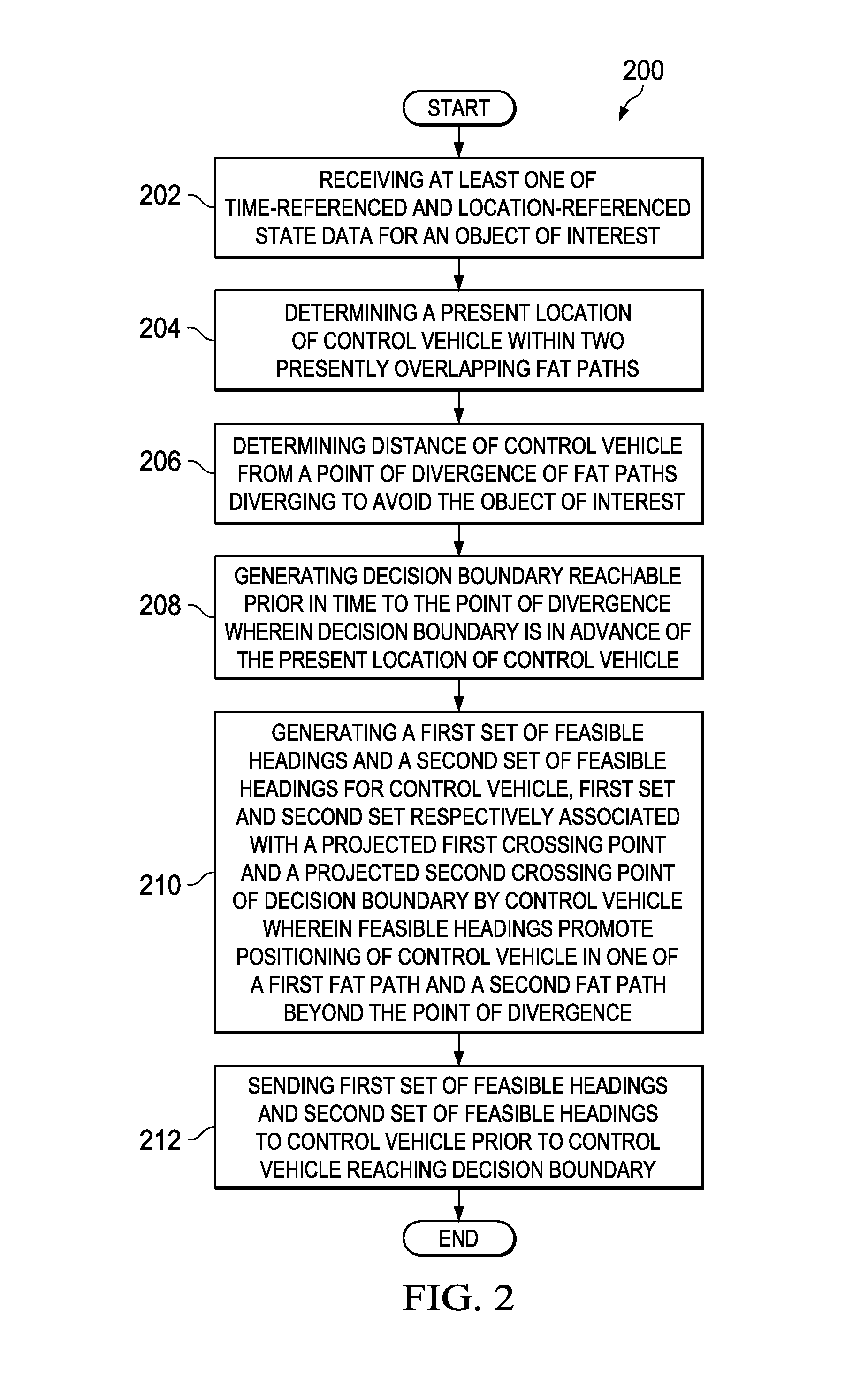
System and method for routing decisions in a separation management system
InactiveUS8868328B1Avoid rangeAnti-collision systemsNavigation instrumentsRouting decisionDecision boundary
A method comprising computer receiving at least one of time and location-referenced state data for an object of interest, determining present location of a vehicle within two presently overlapping fat paths, fat paths comprising homotopically distinct regions of travel, determining distance of vehicle from a point of divergence of fat paths, fat paths diverging to avoid object, the computer generating a decision boundary reachable prior in time to point of divergence wherein decision boundary is in advance of the present location of vehicle, computer generating a first second set of feasible headings for the vehicle, the first and second set respectively associated with a projected first and second crossing points of the decision boundary by vehicle wherein feasible headings promote positioning of vehicle in one of fat paths beyond point of divergence, and computer sending first and second sets of feasible headings to vehicle prior to vehicle reaching decision boundary.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
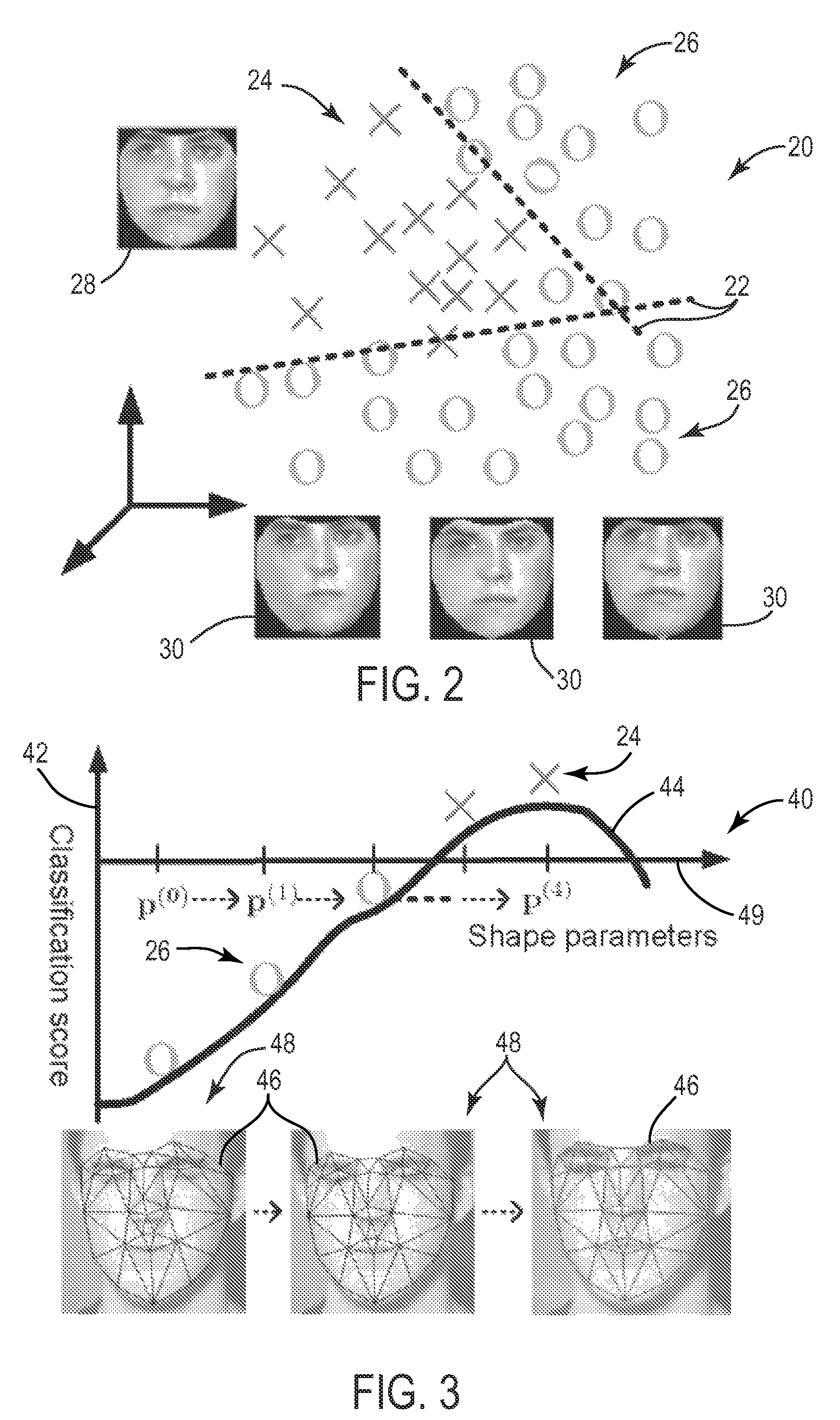
Generic face alignment via boosting
ActiveUS20080310759A1Maximizing a strong classifier scoreMaximizing a strong classifierCharacter and pattern recognitionGround truthPattern recognition
There is provided a discriminative framework for image alignment. Image alignment is generally the process of moving and deforming a template to minimize the distance between the template and an image. There are essentially three elements to image alignment, namely template representation, distance metric, and optimization method. For template representation, given a face dataset with ground truth landmarks, a boosting-based classifier is trained that is able to learn the decision boundary between two classes-the warped images from ground truth landmarks (e.g., positive class) and those from perturbed landmarks (e.g., negative class). A set of trained weak classifiers based on Haar-like rectangular features determines a boosted appearance model. A distance metric is a score from the strong classifier, and image alignment is the process of optimizing (e.g., maximizing) the classification score. On the generic face alignment problem, the proposed framework greatly improves the robustness, accuracy, and efficiency of alignment.
Owner:UTC FIRE & SECURITY AMERICAS CORPORATION INC
Method and system for improving pattern recognition system performance
InactiveUS6847731B1Improve robustnessMore system robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionDiscriminantDecision boundary
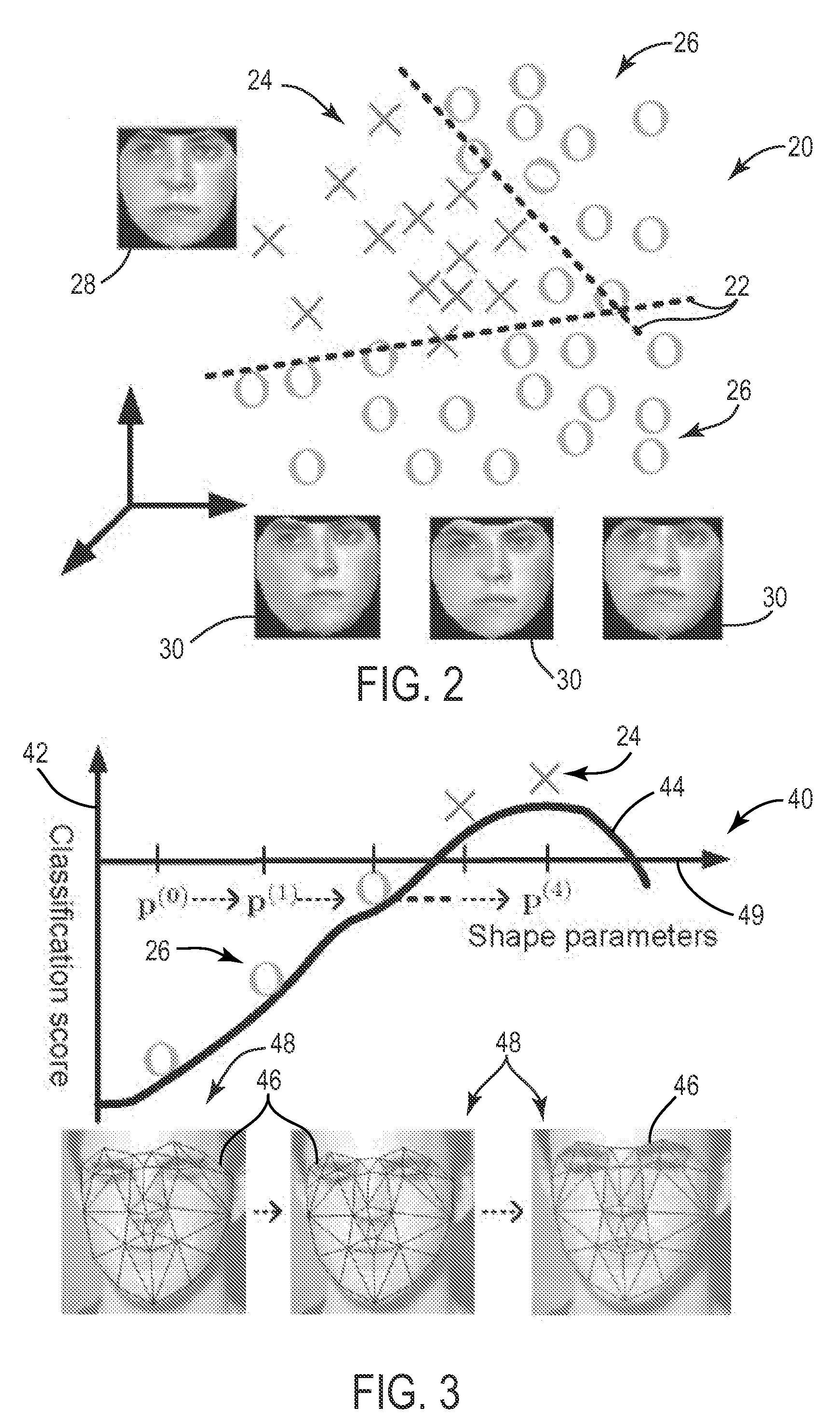
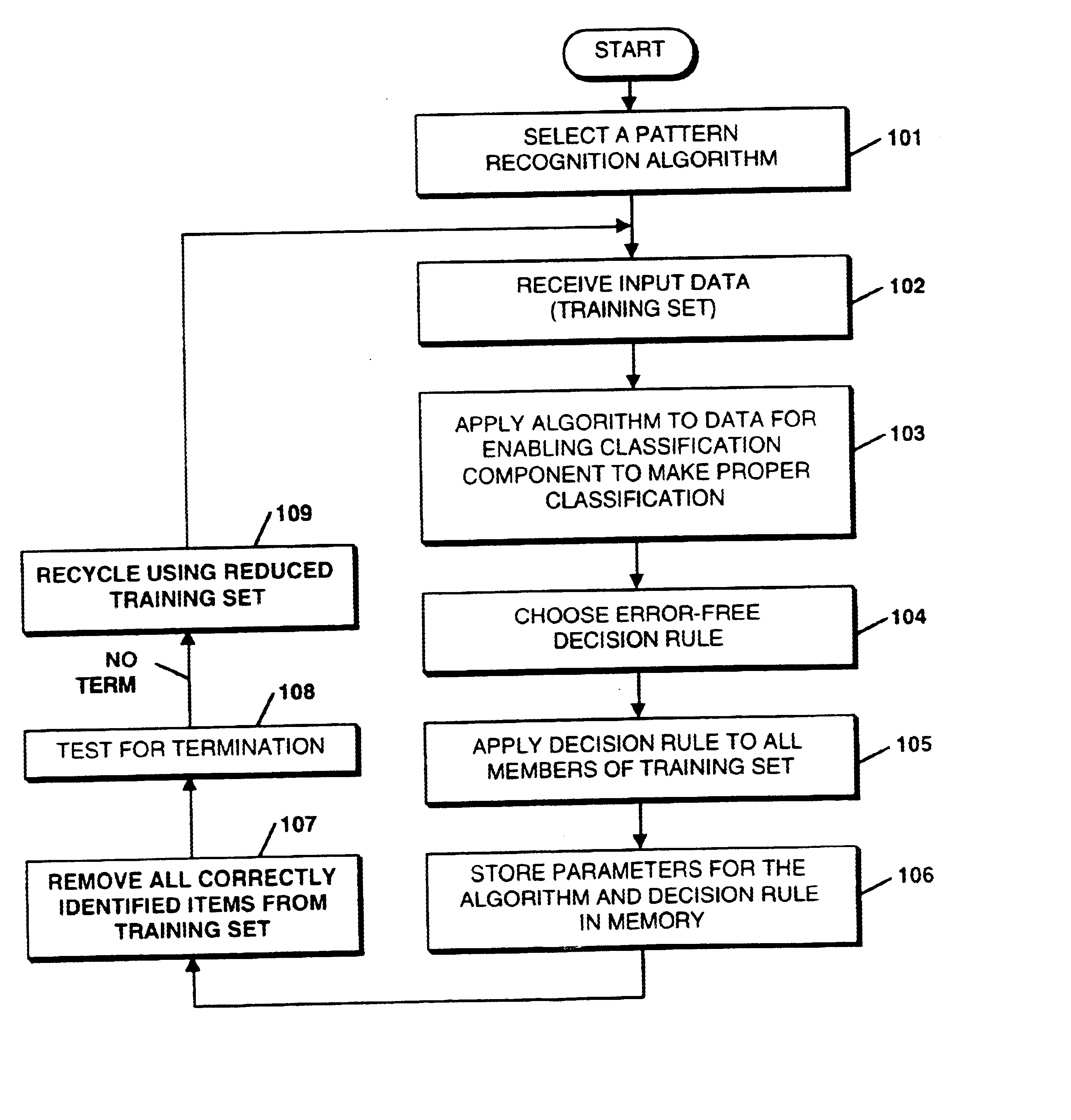
Stand-alone or assistive pattern recognition system and process enabling error free classification of all objects in a training set and application to unclassified objects. Parameters and / or features of the data objects in a training set are selected and measured, from which discriminants are computed. The measured data is plotted in discriminant space and decision boundaries or thresholds determined, preferably such that at least one object from one class is isolated from the remaining objects, removed from the training set, and the process repeated until an acceptable number of unclassified objects remain. The system can be applied sequentially to classify all the members of the training set belonging to one class and then applied to objects in other classes. Fuzzy quantifiable determinations of an object's likelihood of class membership can be made. Objects' positions and classifications are obtainable in an optical system using Fourier techniques without limitation to linearly discriminable problems.
Owner:NORTHEAST PHOTOSCI
Class-imbalance problem classification method based on expansion training data set
InactiveCN108470187AImprove classification accuracyGood lifting effectCharacter and pattern recognitionData setDecision boundary
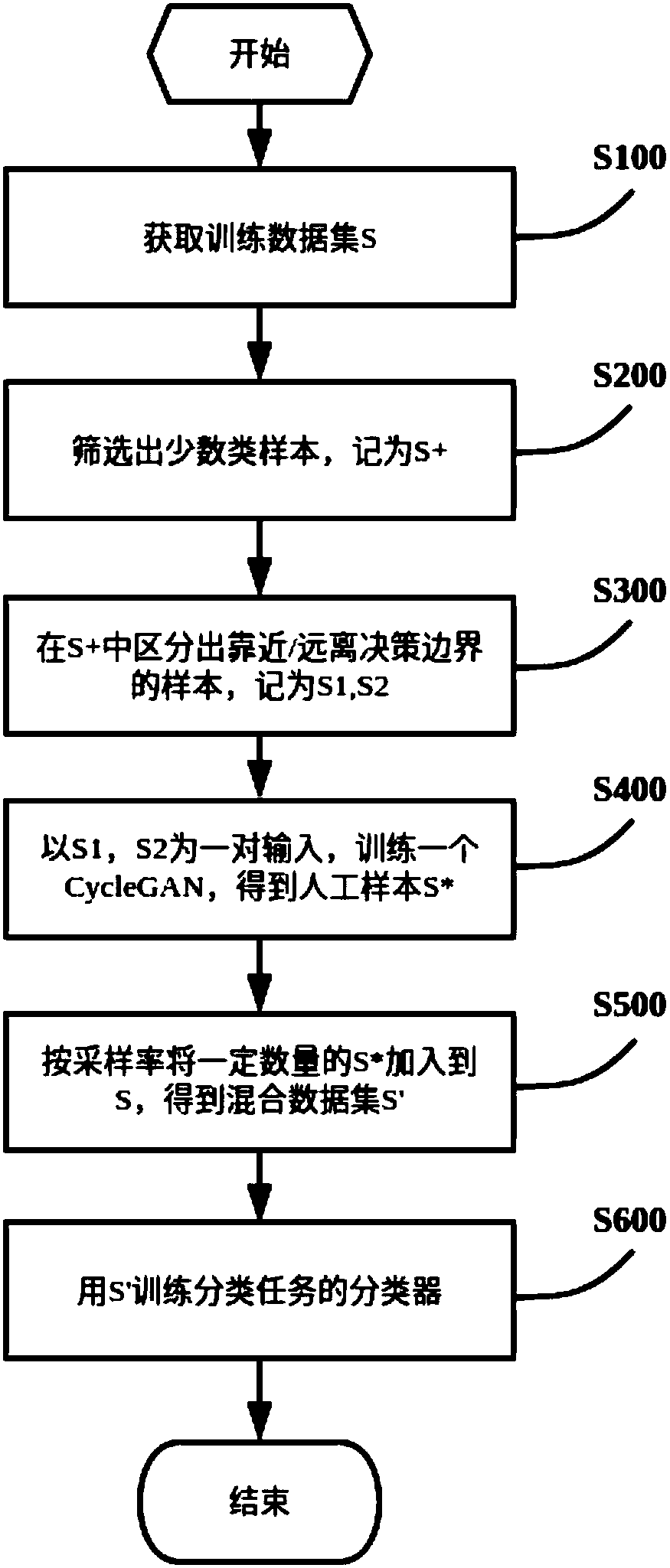
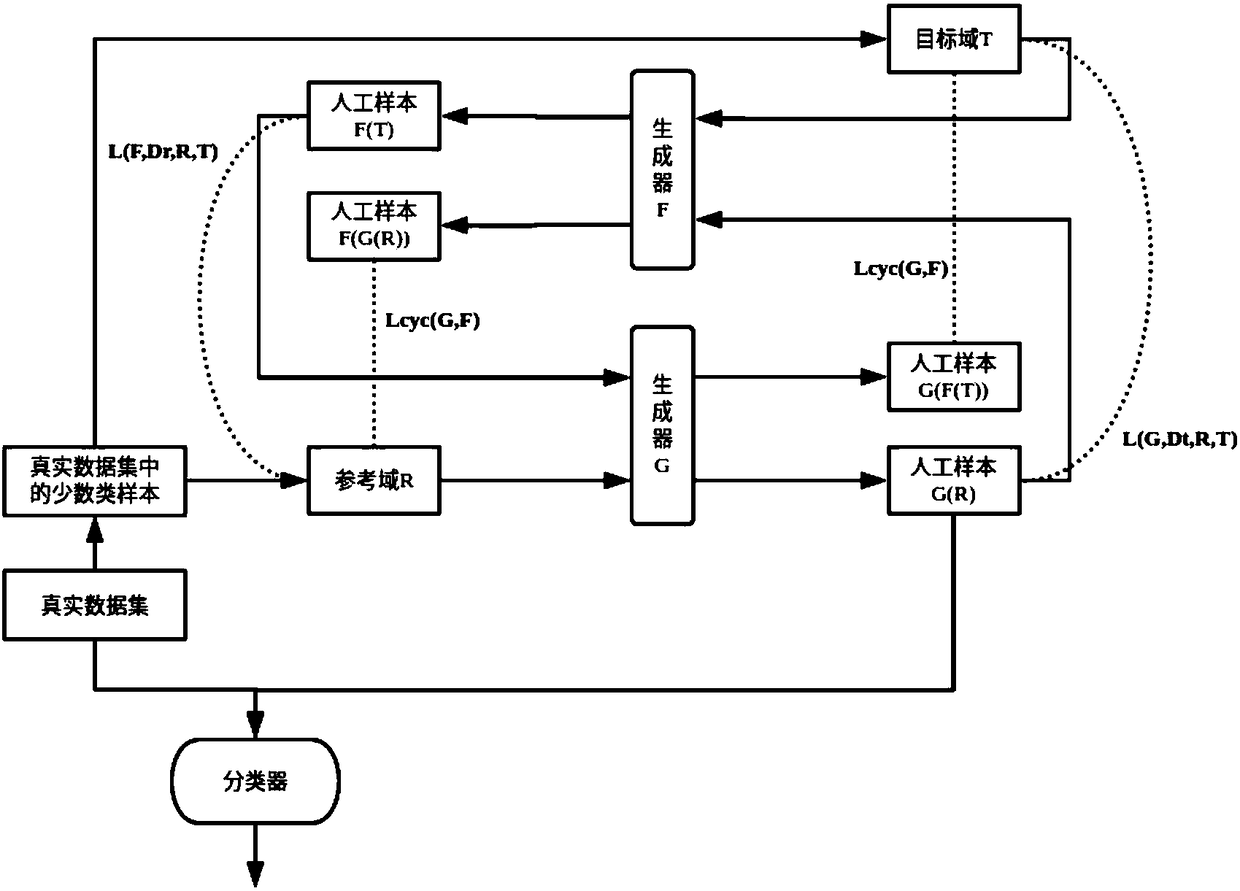
The invention discloses a class-imbalance problem classification method based on expansion training data set; the method comprises the following steps: obtaining a true data set needed by a classification task; screening a few class samples from the true data set, and distinguishing samples that are close to and far away from the decision boundary; inputting said samples, running a productive confrontation network, thus obtaining artificial samples similar to the true data; adding certain amount of artificial samples into the true data set, thus obtaining a mixed data set; inputting the mixeddata set, and using a classifier to classify. The method combines a CycleGAN model with the boundary information of an original data set, thus effectively simulating distribution features of the truedata. The method samples small sample data so as to improve the classifier precision, and effectively preventing the class-imbalance problem from affecting the classification task.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
System and Method for Joint Classification Using Feature Space Cluster Labels
InactiveUS20090092299A1Improving CAD classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionDecision boundaryCharacteristic space
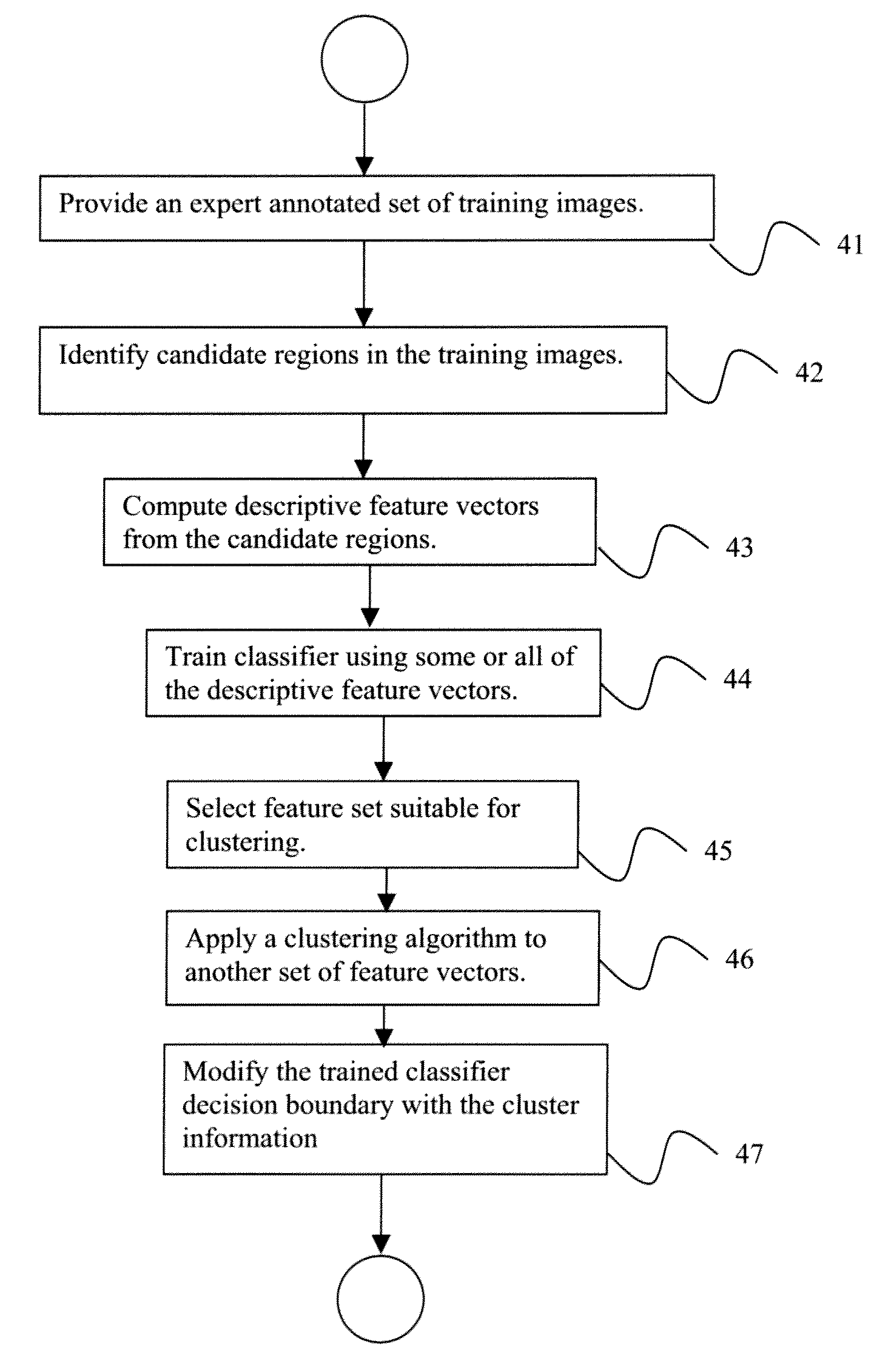
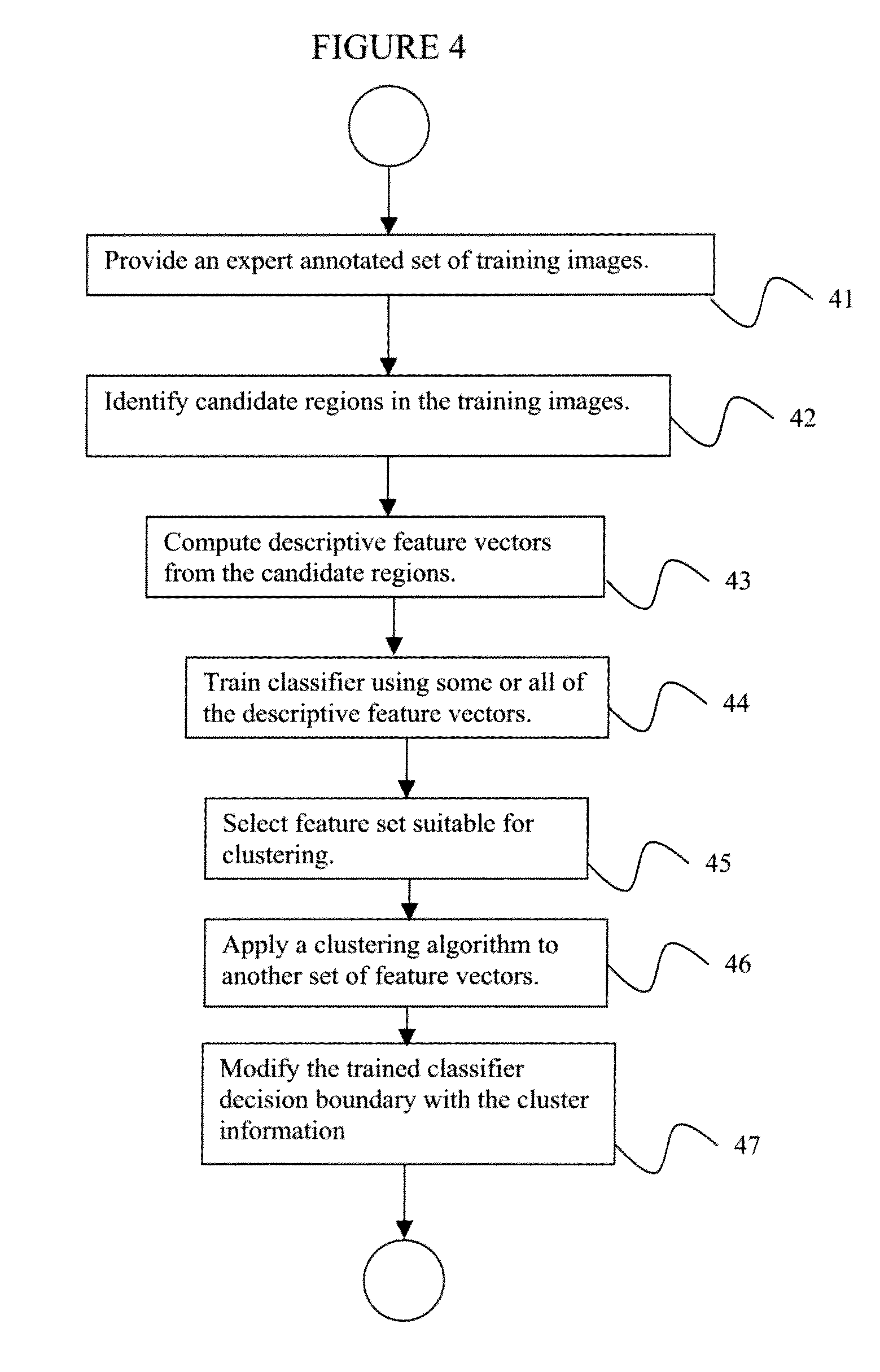
A method for training a classifier for use in a computer aided detection system includes providing a training set of images acquired from a plurality of patients, each said image including one or more candidate regions that have been identified as suspicious by a candidate generation step of a computer aided detection system, and wherein each said image has been manually annotated to identify lesions, using said training set to train a classifier adapted for identifying a candidate region as a lesion or non-lesion, clustering candidate regions having similar features for each patient individually, and modifying said trained classifier decision boundary with an additional classification step incorporating said individual candidate region clustering.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
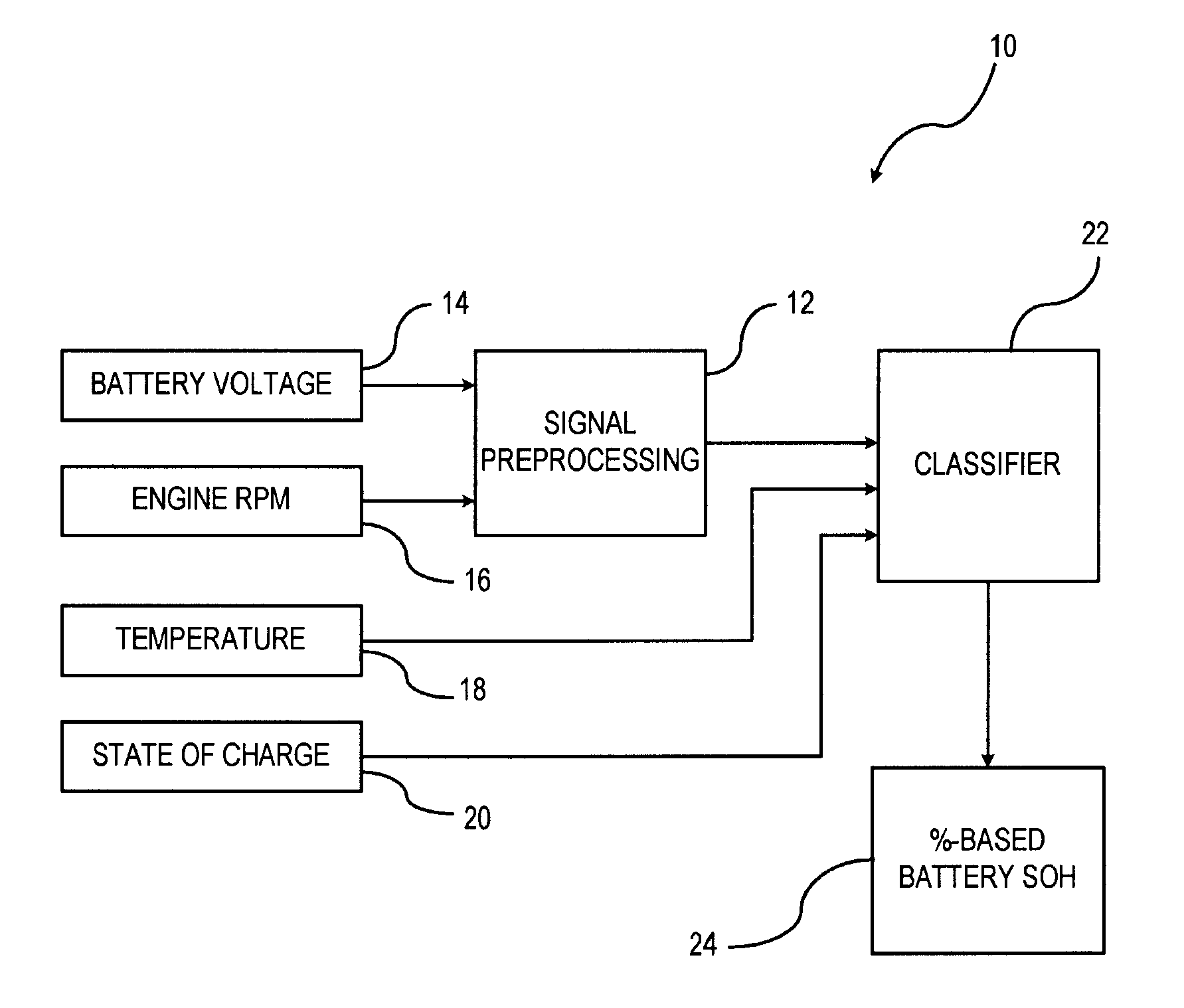
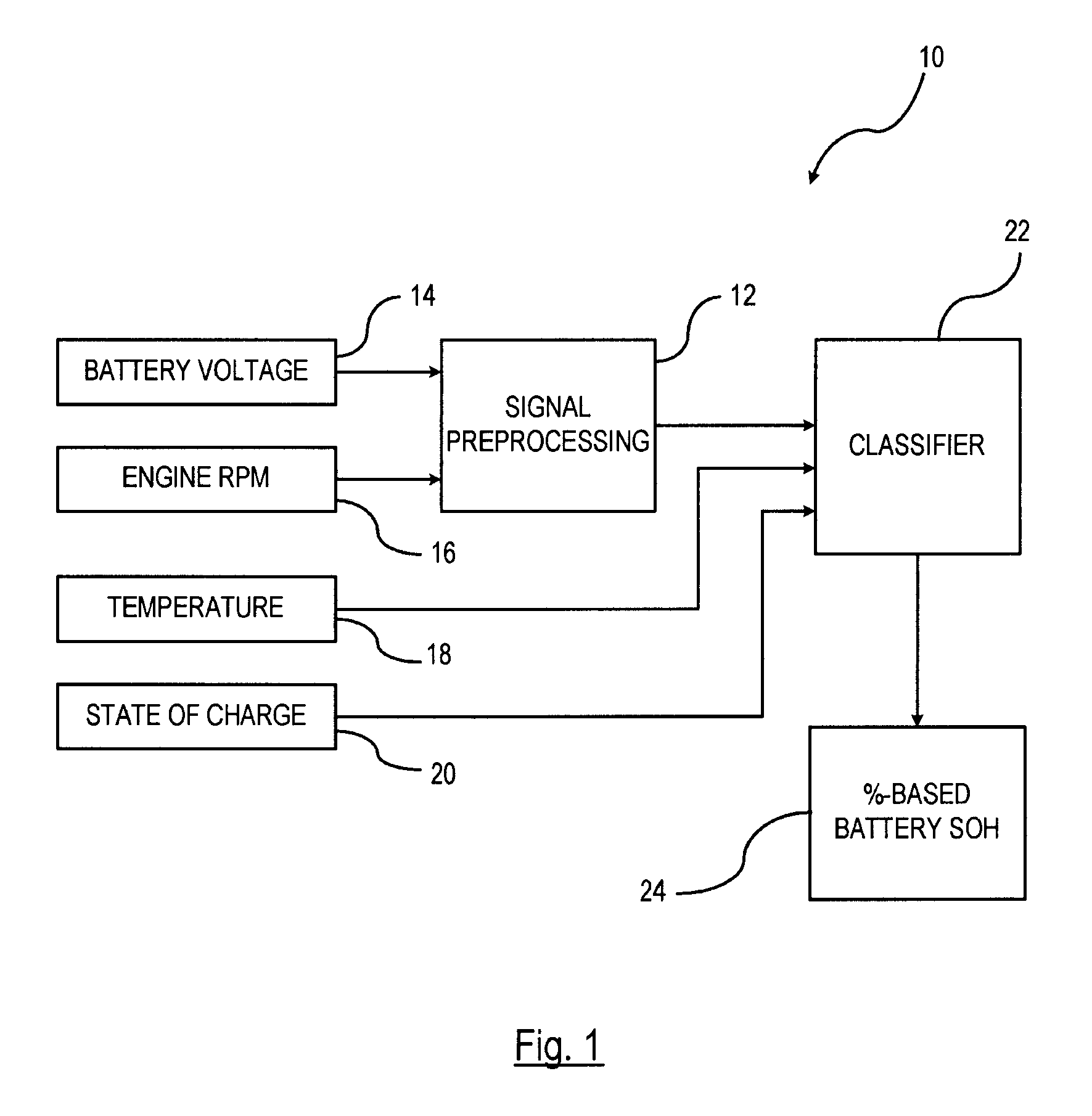
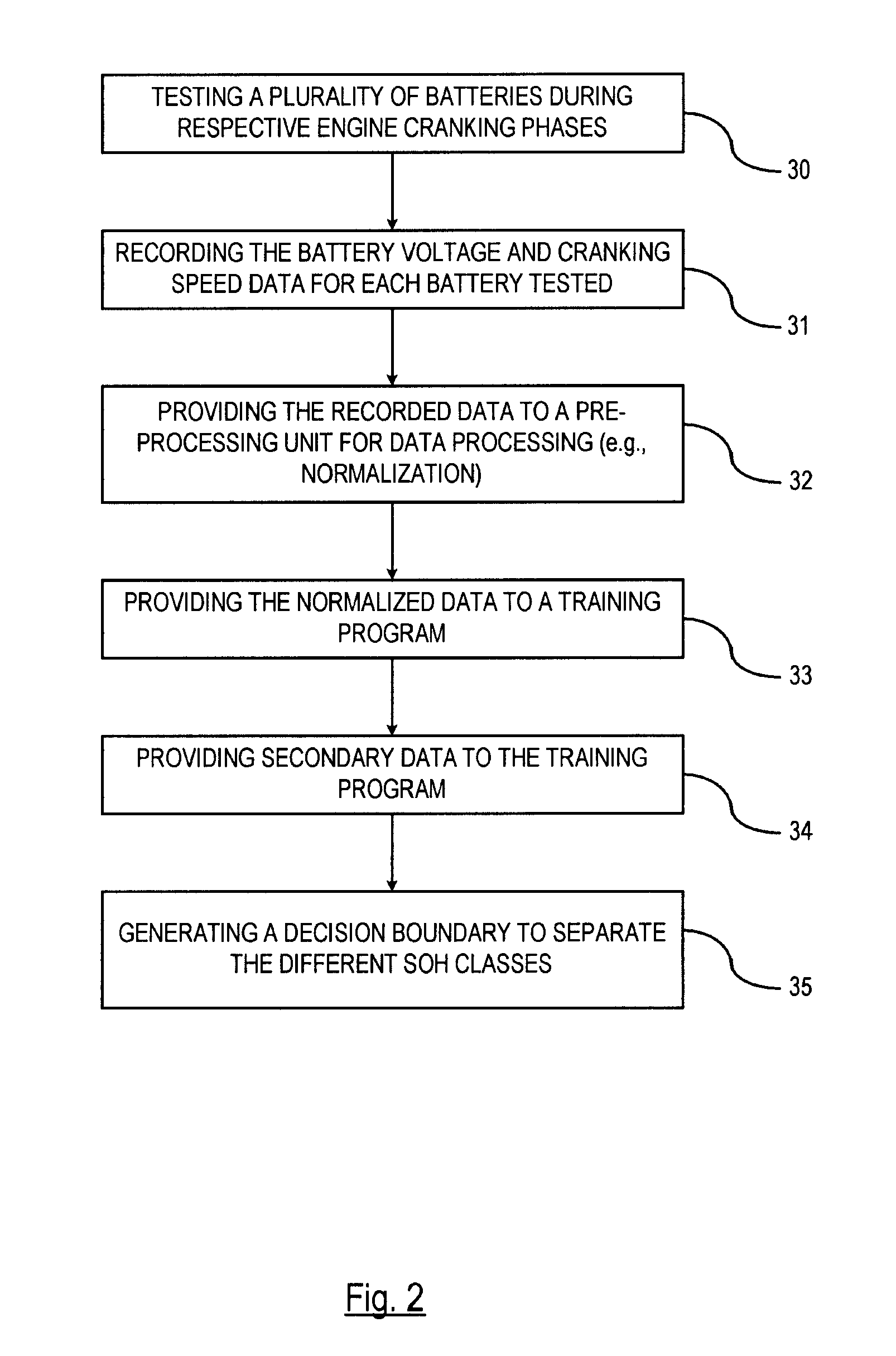
Pattern recognition approach to battery diagnosis and prognosis
ActiveUS20090326841A1Eliminate useElectrical testingDigital computer detailsDecision boundaryState of health
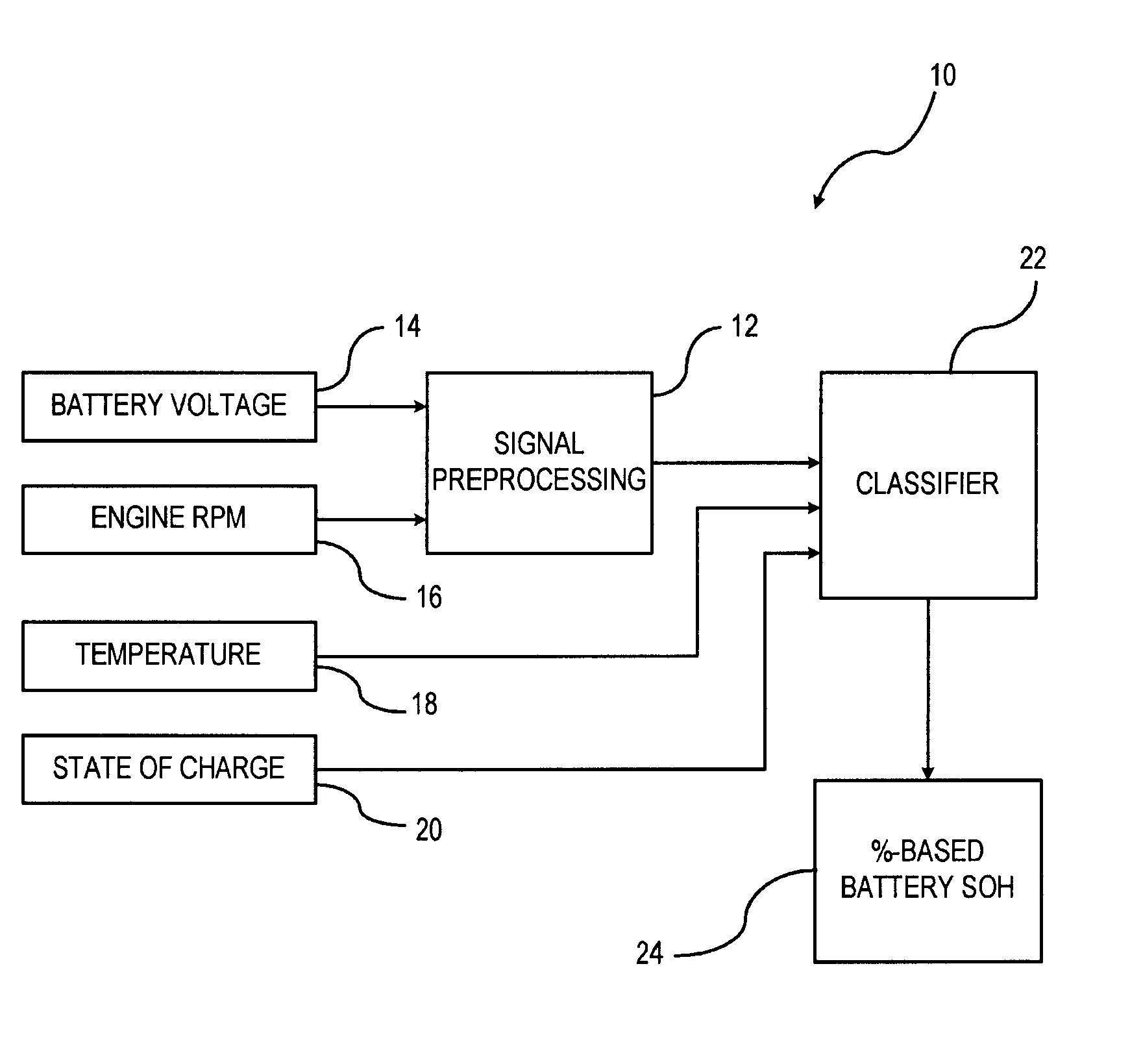
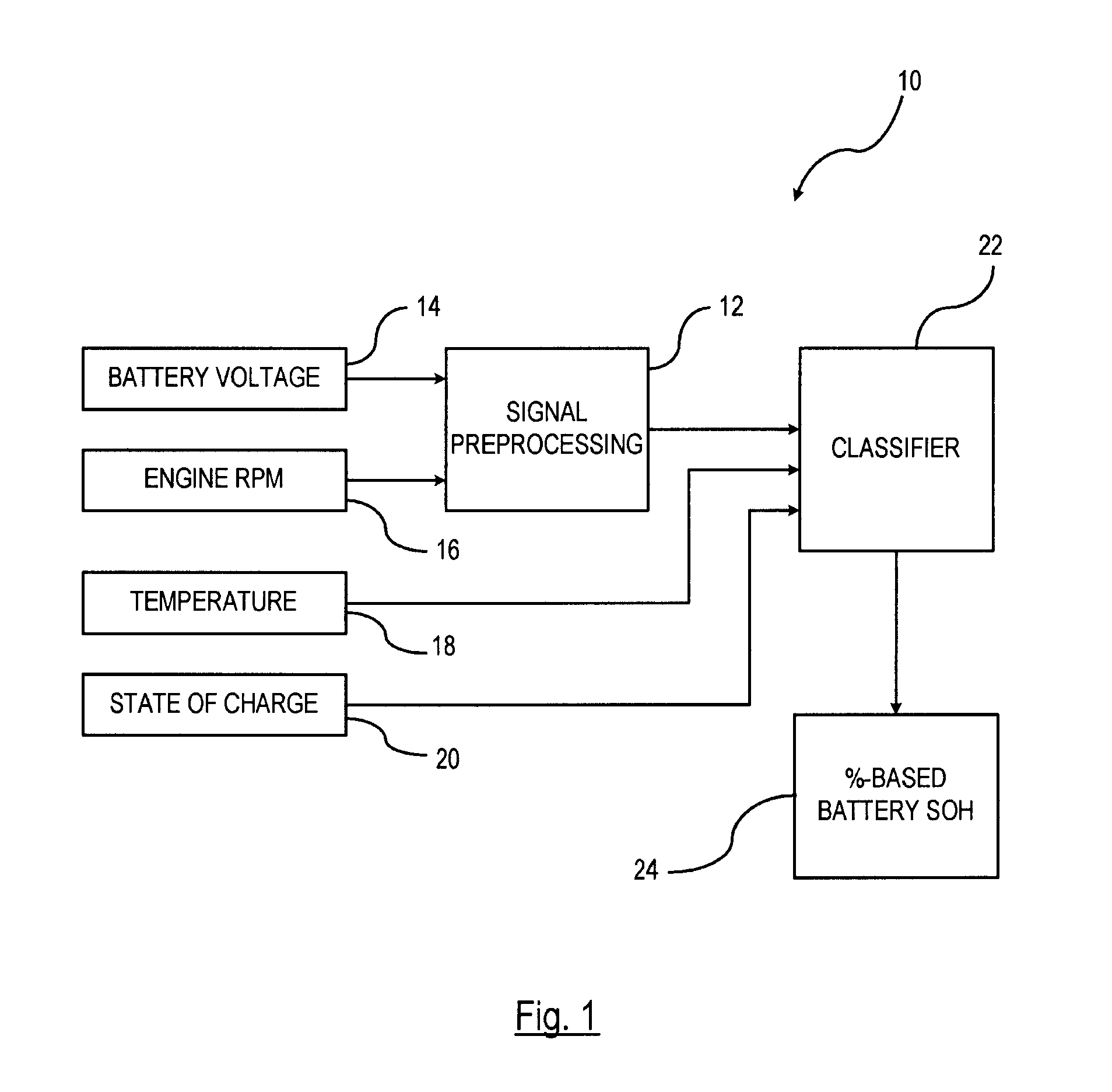
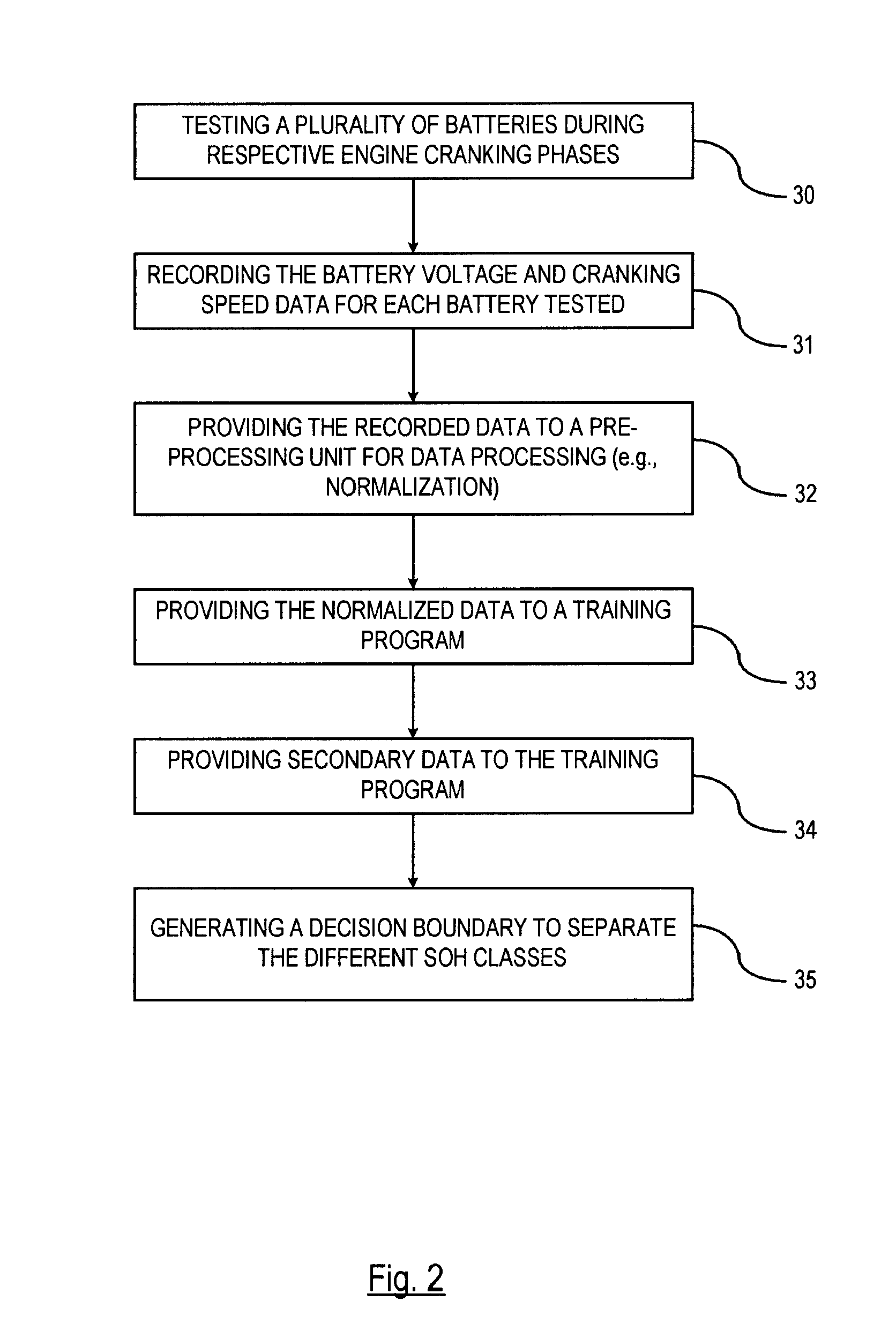
A method is provided for determining a state-of-health of a battery in a vehicle-during an engine cranking phase. An engine cranking phase is initiated. Characteristic data is recorded that includes battery voltage data and engine cranking speed data during the engine cranking phase. The characteristic data is provided to a pre-processing unit. The pre-processing unit normalizes the characteristic data for processing within a classifier. The normalized data is input o the classifier for determining the vehicle battery state-of-health. The classifier has a trained state-of-health decision boundary resulting from a plurality of trials in which predetermined characterization data is collected with known classes. The battery state-of-health is classified based on the trained state-of-health decision boundary.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
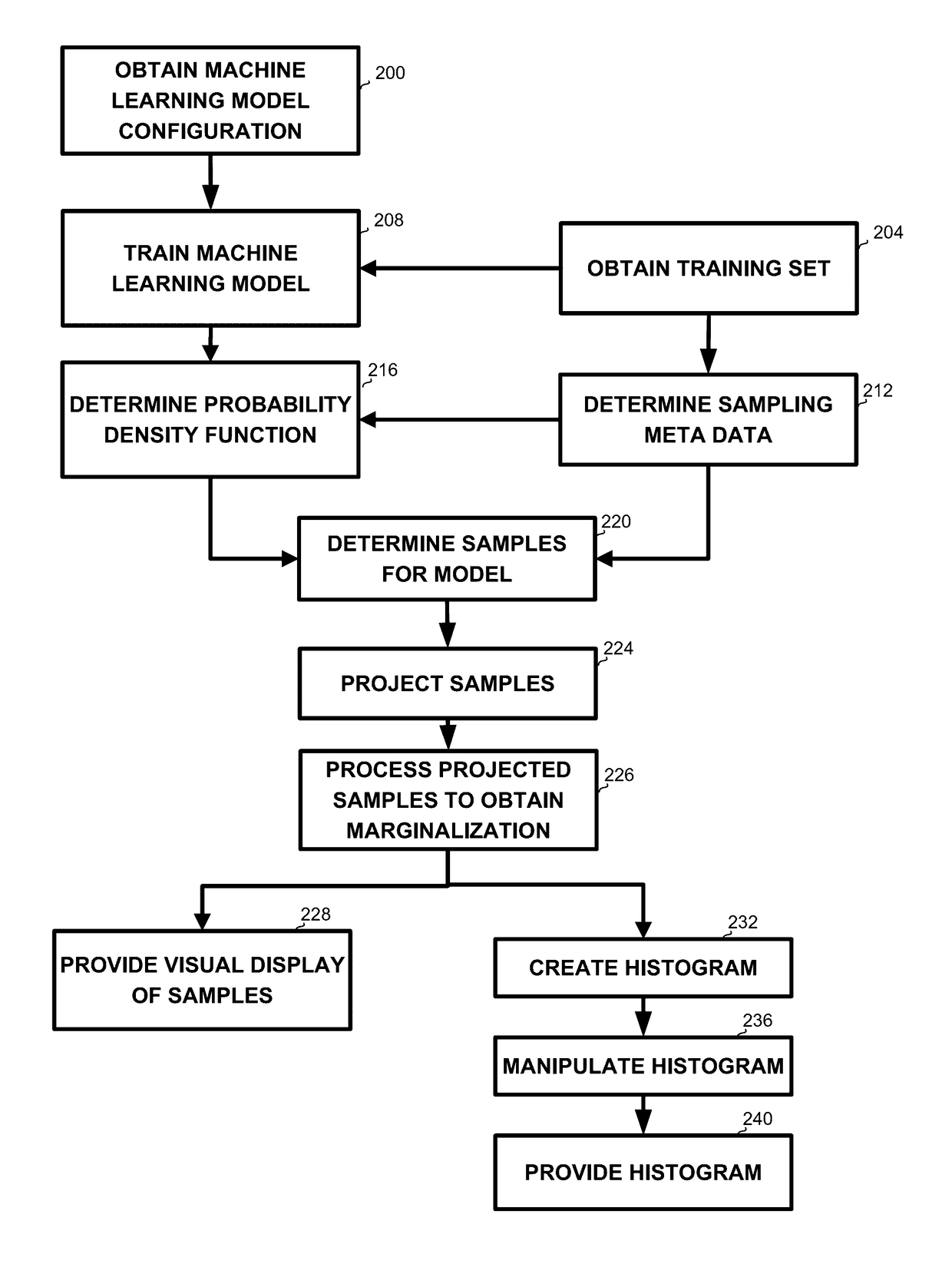
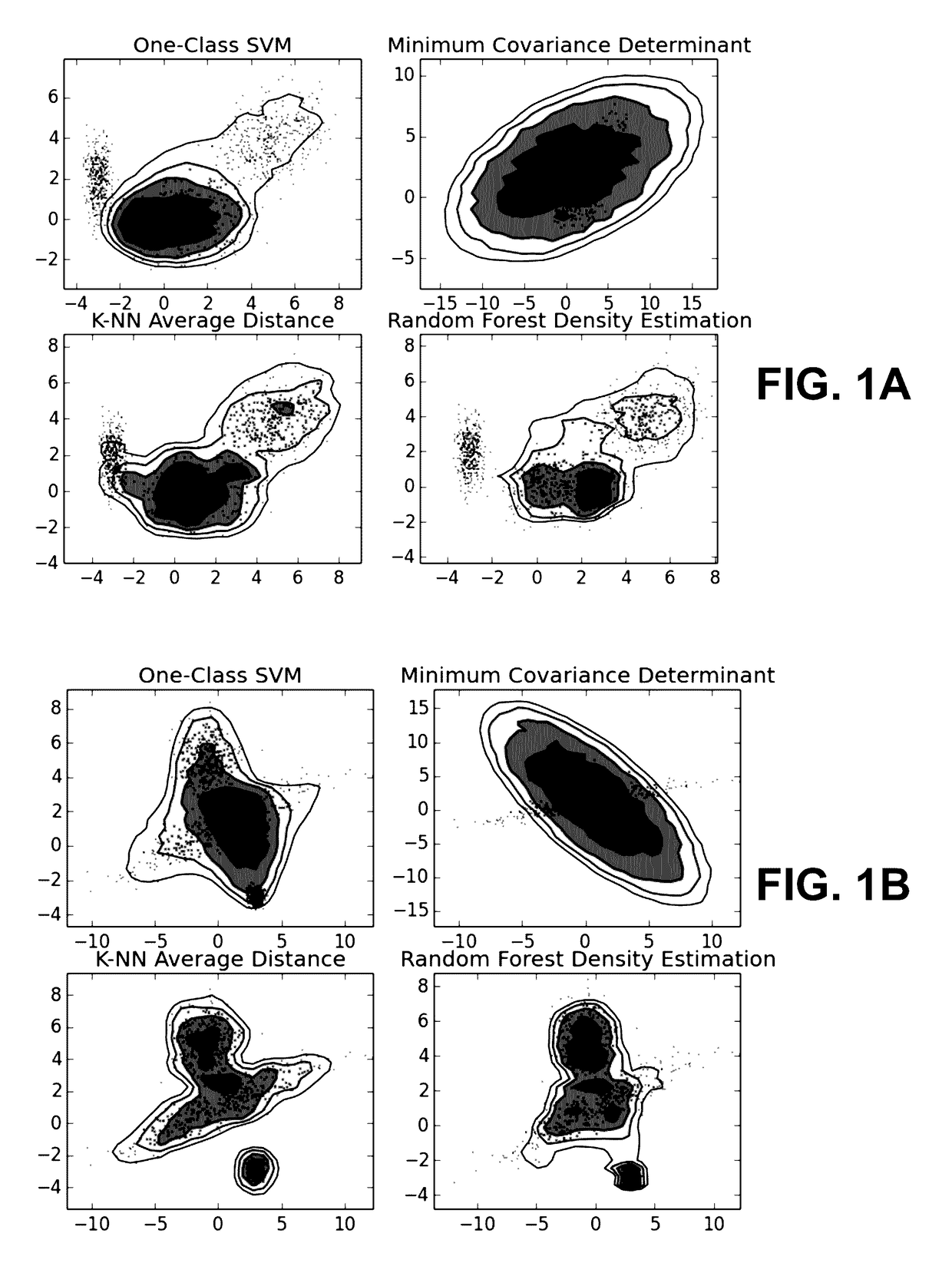
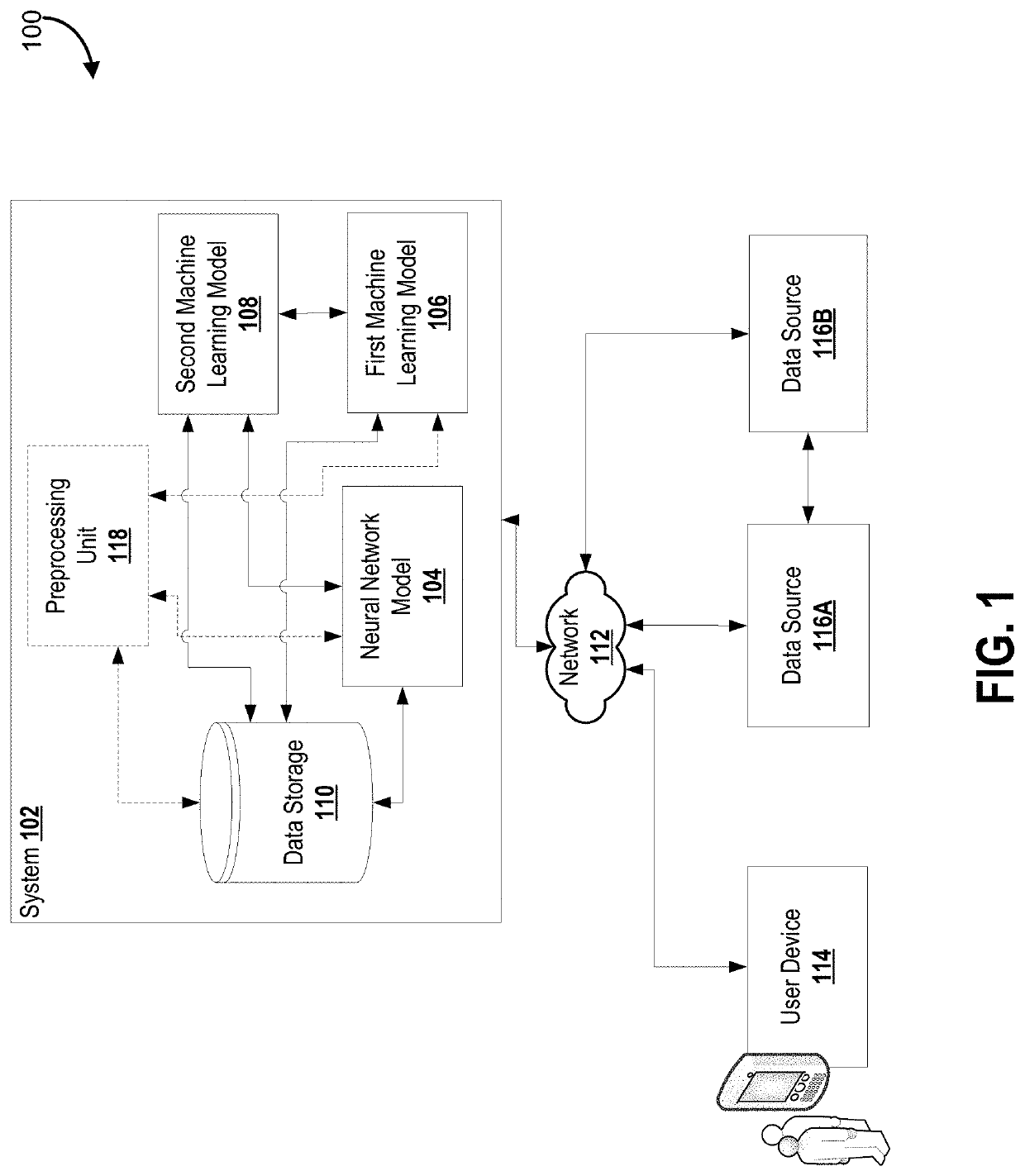
Subspace projection of multi-dimensional unsupervised machine learning models
A computer-implemented method, apparatus and computer program product for projecting a machine learning model, the method comprising: obtaining a computerized multi-dimensional unsupervised anomaly detection model; obtaining a probability density function of the anomaly detection model; determining samples of the anomaly detection model, based on the probability density function; projecting the samples over at least one dimension set to obtain projected samples; processing the projected samples to obtain decision boundaries of the anomaly detection model over the at least one dimension set; and providing a visual display of the decision boundaries on a display device.
Owner:AGT INTERNATIONAL INC
Pattern recognition approach to battery diagnosis and prognosis
ActiveUS8972213B2Eliminate useResistance/reactance/impedenceDigital computer detailsDecision boundaryState of health
A method is provided for determining a state-of-health of a battery in a vehicle-during an engine cranking phase. An engine cranking phase is initiated. Characteristic data is recorded that includes battery voltage data and engine cranking speed data during the engine cranking phase. The characteristic data is provided to a pre-processing unit. The pre-processing unit normalizes the characteristic data for processing within a classifier. The normalized data is input o the classifier for determining the vehicle battery state-of-health. The classifier has a trained state-of-health decision boundary resulting from a plurality of trials in which predetermined characterization data is collected with known classes. The battery state-of-health is classified based on the trained state-of-health decision boundary.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
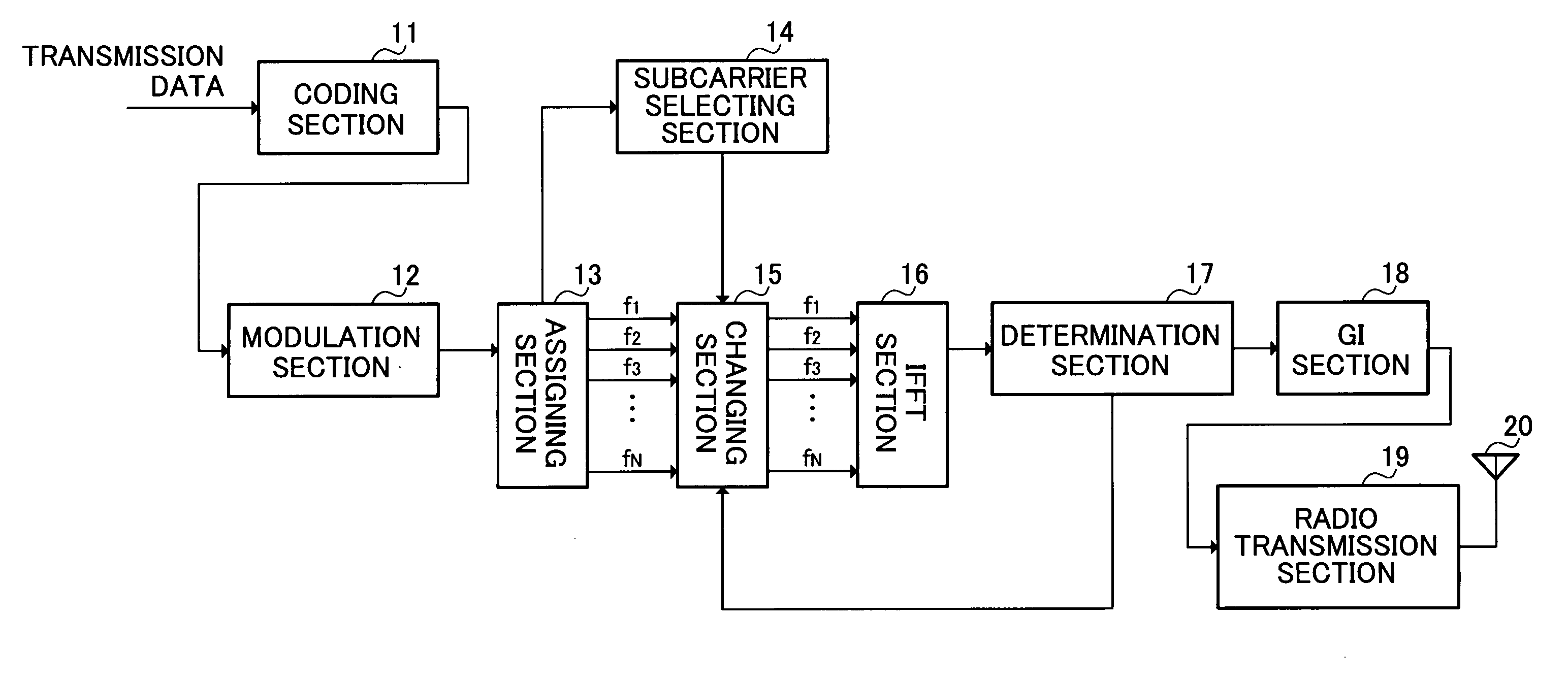
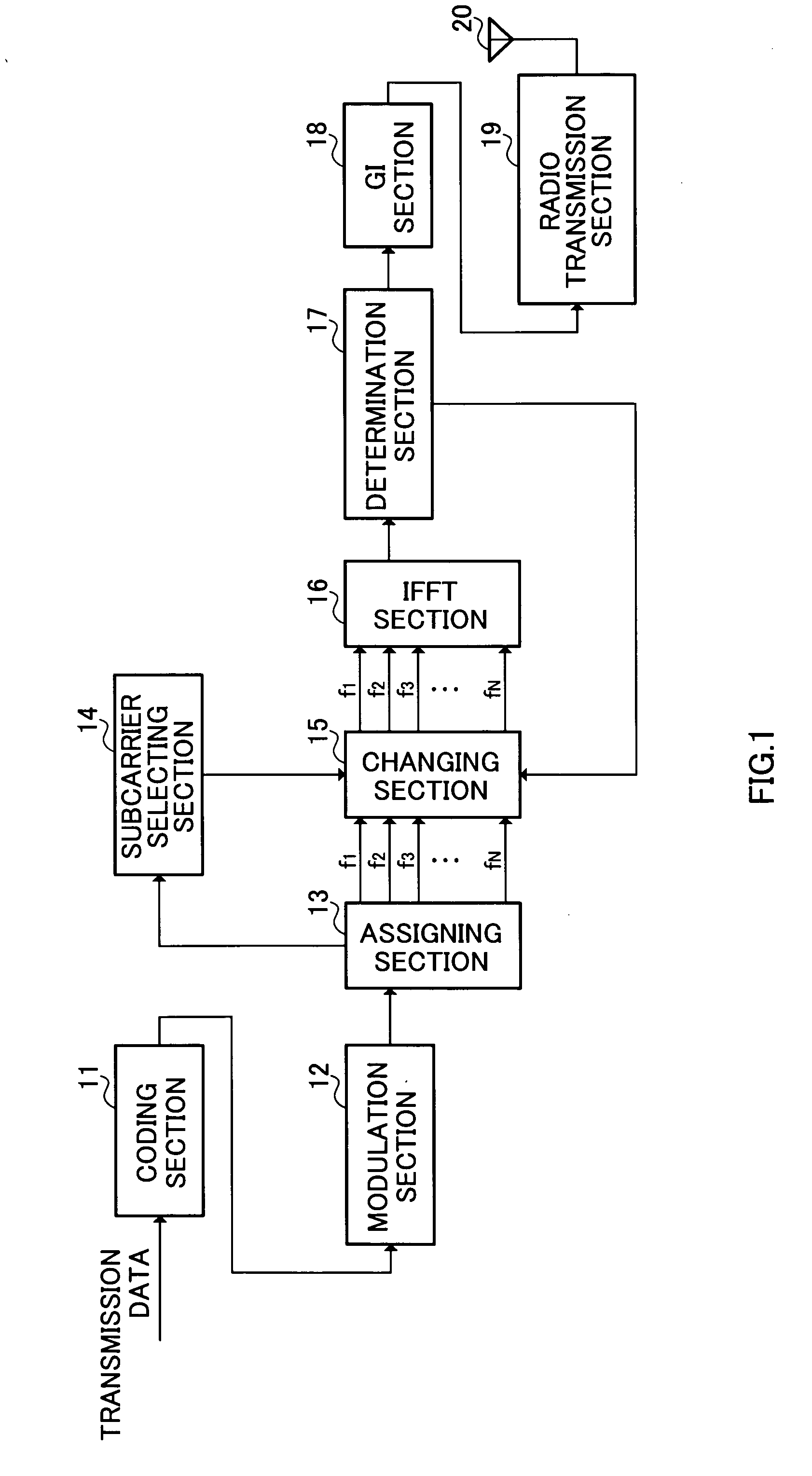
Radio transmission apparatus and peak power suppression method in multicarrier communication
InactiveUS20070047431A1Deterioration in degradationDeterioration in throughputFrequency-division multiplexMulti-frequency code systemsFast Fourier transformDecision boundary
A radio transmission apparatus capable of suppressing peak power without causing deterioration in throughput and degradation in transmission efficiency in multicarrier communication. In this apparatus, a coding section (11) codes transmission data, a modulation section (12) modulates the coded data to generate a symbol, an assigning section (13) assigns the symbol to one of a plurality of subcarriers constituting a multicarrier signal, a changing section (15) change the phase of each of the plurality of subcarriers within a range that does not cross a decision boundary for signal points on an IQ plane, and an IFFT section (16) generates a multicarrier signal by inverse fast Fourier transform.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Generic face alignment via boosting
ActiveUS8155399B2Maximizing a strong classifier scoreMaximizing a strong classifierCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionGround truth
Owner:UTC FIRE & SECURITY AMERICAS CORPORATION INC
Supervised fault learning using rule-generated samples for machine condition monitoring
InactiveUS20120304008A1Error detection/correctionTesting/monitoring control systemsFeature vectorDecision boundary
A machine fault diagnosis system is provided. The system combines a rule-based predictive maintenance strategy with a machine learning system. A simple set of rules defined manually by human experts is used to generate artificial training feature vectors to portray machine fault conditions for which only a few real data points are available. Those artificial training feature vectors are combined with real training feature vectors and the combined set is used to train a supervised pattern recognition algorithm such as support vector machines. The resulting decision boundary closely approximates the underlying real separation boundary between the fault and normal conditions.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
System and method for machine learning architecture for enterprise capitalization
ActiveUS20210049700A1Reduce ambiguityTechnical challenge to overcomeMathematical modelsFinanceData setDecision boundary
Systems and methods are described in relation to specific technical improvements adapted for machine learning architectures that conduct classification on numerical and / or unstructured data. In an embodiment, two neural networks are utilized in concert to generate output data sets representative of predicted future states of an entity. A second learning architecture is trained to cluster prior entities based on characteristics converted into the form of features and event occurrence such that a boundary function can be established between the clusters to form a decision boundary between decision regions. These outputs are mapped to a space defined by the boundary function, such that the mapping can be used to determine whether a future state event is likely to occur at a particular time in the future.
Owner:ROYAL BANK OF CANADA
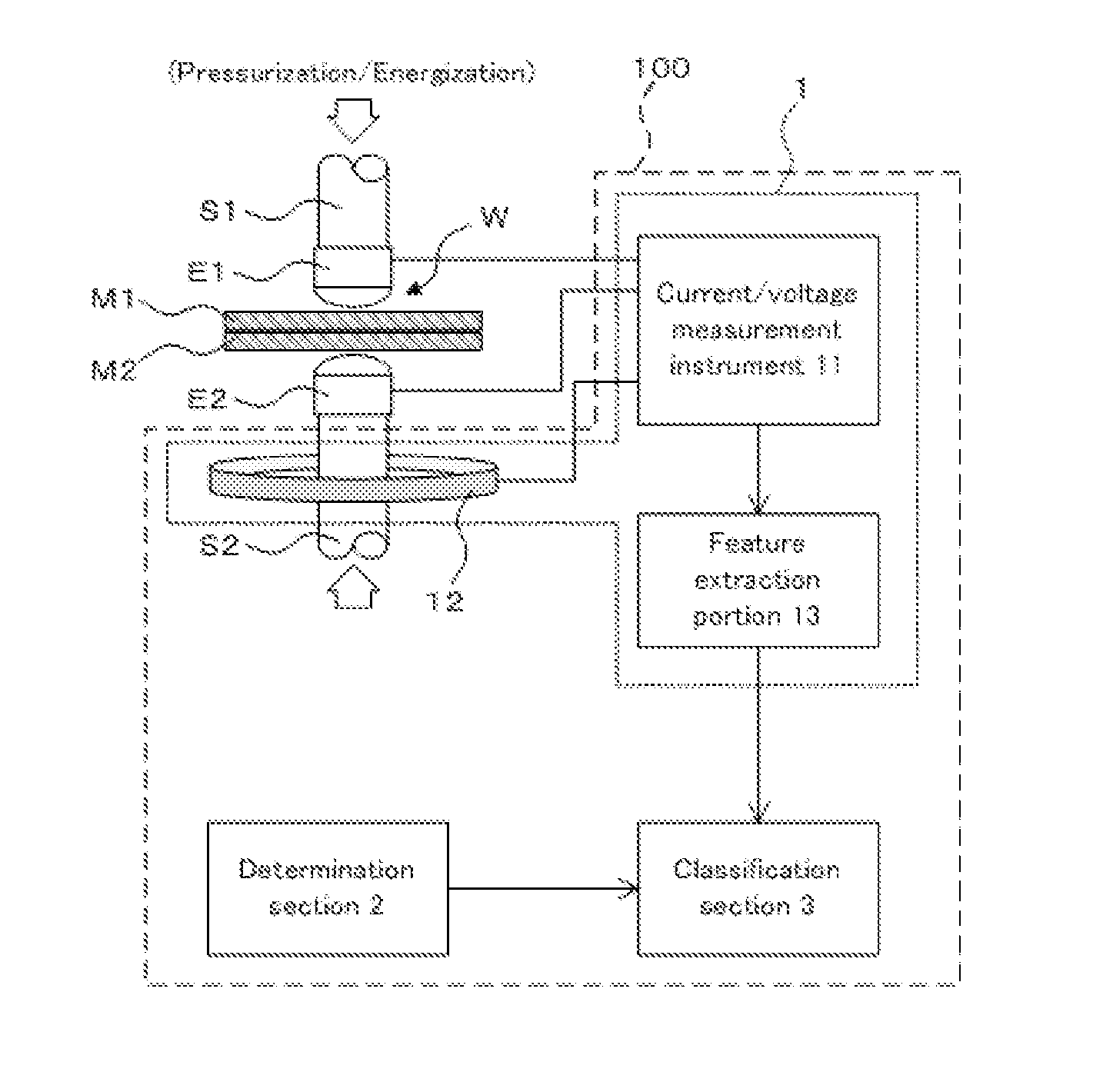
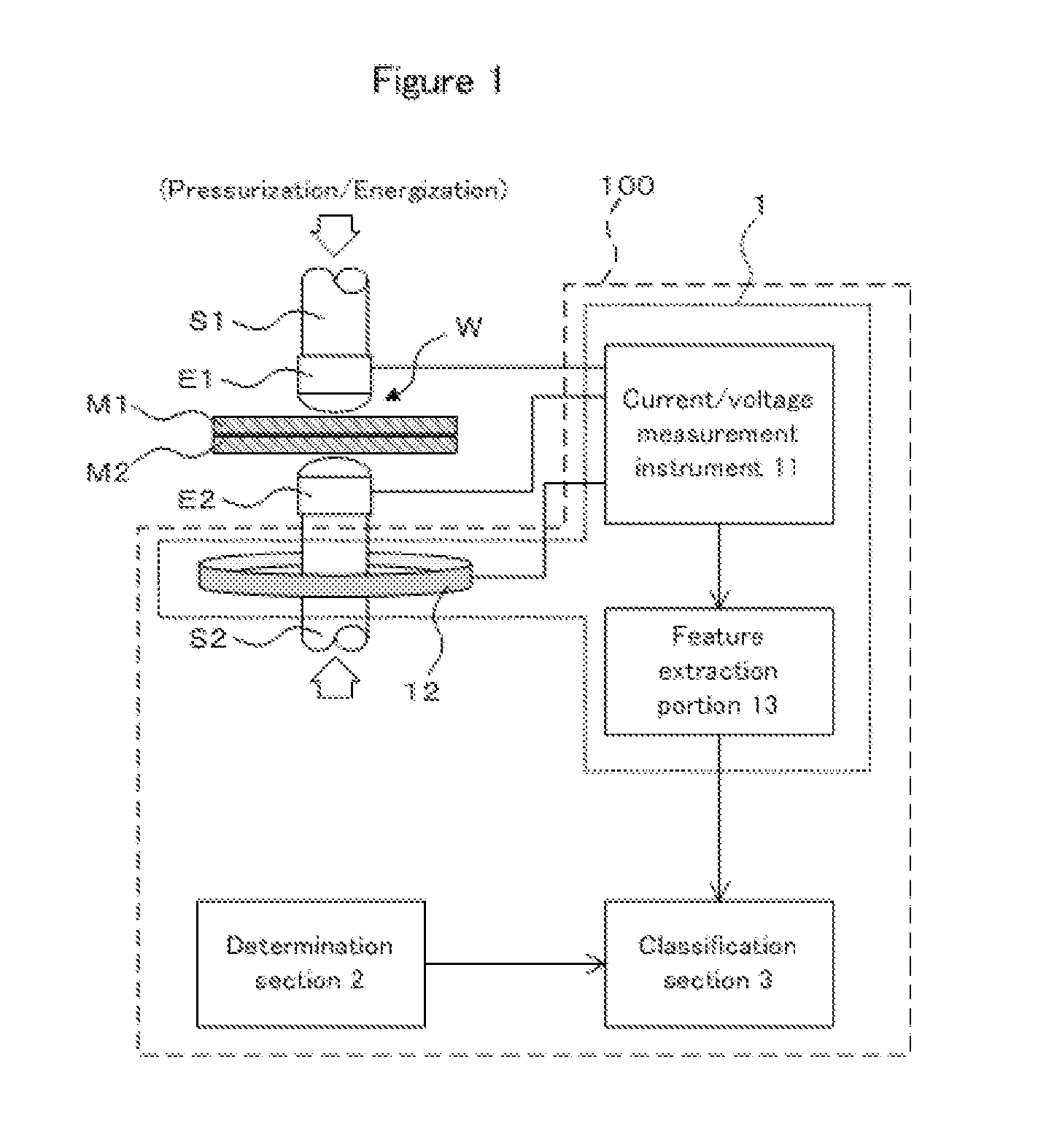
Welding quality classification apparatus
InactiveUS20130248505A1Avoid welding qualityImprove accuracyArc welding apparatusResistance welding apparatusDecision boundaryData set
The welding quality classification apparatus relating to the present invention is an apparatus, wherein a data point indicating feature information of a welded joint to be classified whose welding quality is unknown is mapped to a point in a mapping space which has a dimensional number higher than the number of the features constituting the feature information, and the welding quality of a welded joint to be classified is classified based on which of regions of two welding qualities, which are formed by separating the mapping space with a decision boundary, contains the mapped point, and wherein a discriminant function is determined by adopting a weight which minimizes the sum of the classification error corresponding to classification accuracy of a training dataset and a regularization term having a positive correlation with the dimensional number of the discriminant function as weight for each feature constituting the discriminant function indicating the decision boundary.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL & SUMITOMO METAL CORP
Selective up-sampling combined method for weighted ensemble classification prediction of unbalanced data flows
InactiveCN107341497AImprove recognition rateImprove classification performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmMinority class
The invention relates to the technical field of data mining, and discloses a selective up-sampling combined method for weighted ensemble classification prediction of unbalanced data flows. The method comprises the following steps of: screening minority class samples of history data blocks according to a similarity, and selecting samples closest to the current training data block in the aspect of concept; synthesizing the selected samples into new samples in a decision boundary area so as to selectively implement up-sampling; and carrying out weighted ensemble classification on the new sample by adoption of a probability distribution relevancy-based weight distribution strategy. According to the method, the minority class sample information is effectively increased through selecting history data with high similarities and synthesizing new data at the boundary area, so that the decision domain of the minority class is enlarged; and meanwhile, in order to adapt the dynamic data with concept drift and use an ensemble classification thought, the probability distribution relevancy-based weight distribution strategy is designed, so that the overall classification precision is enhanced. Experiment results show that the method is capable of effectively improving the minority class identification rate and the overall classification performance, and has the advantage of better processing the unbalanced data flows.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
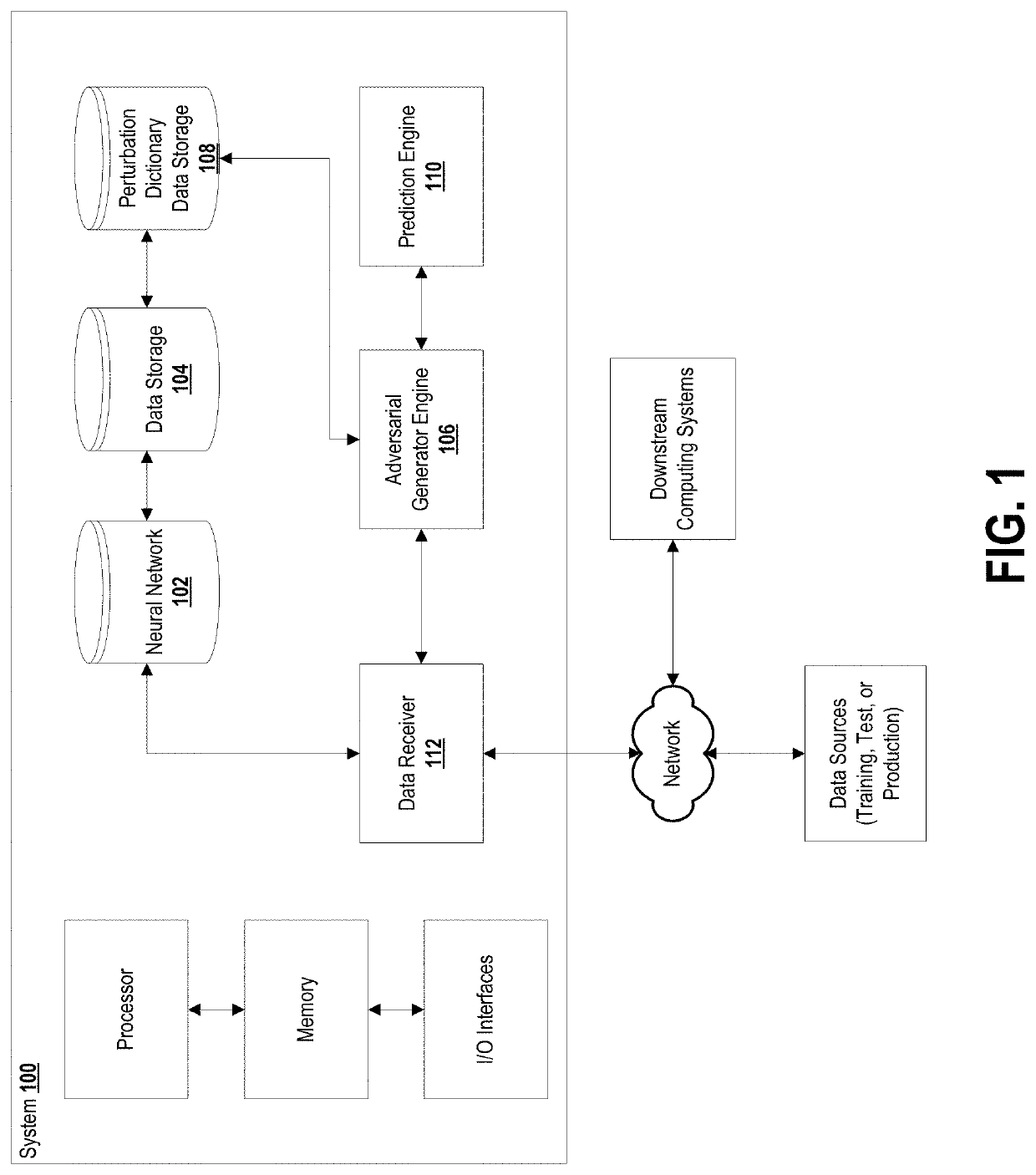
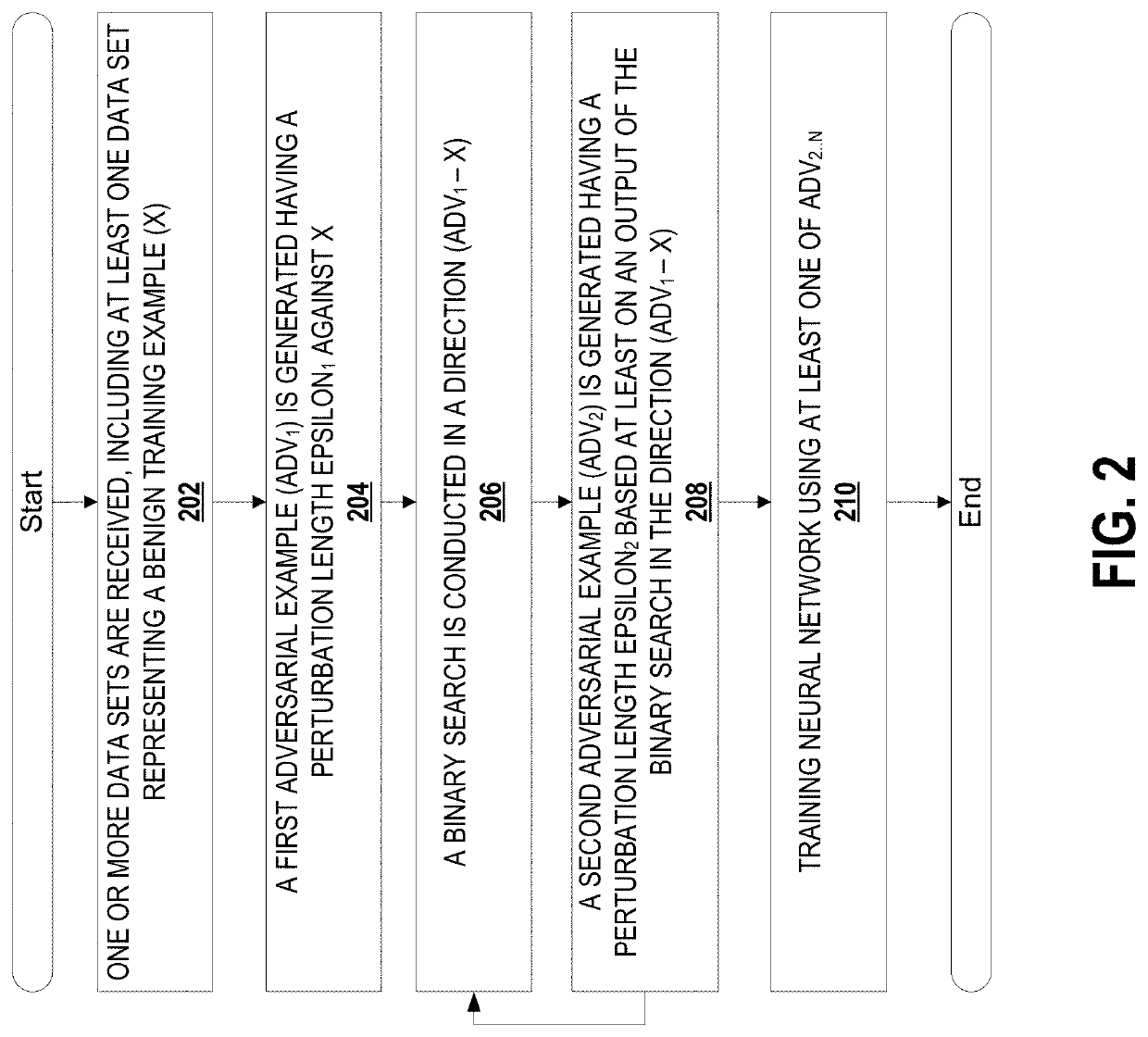
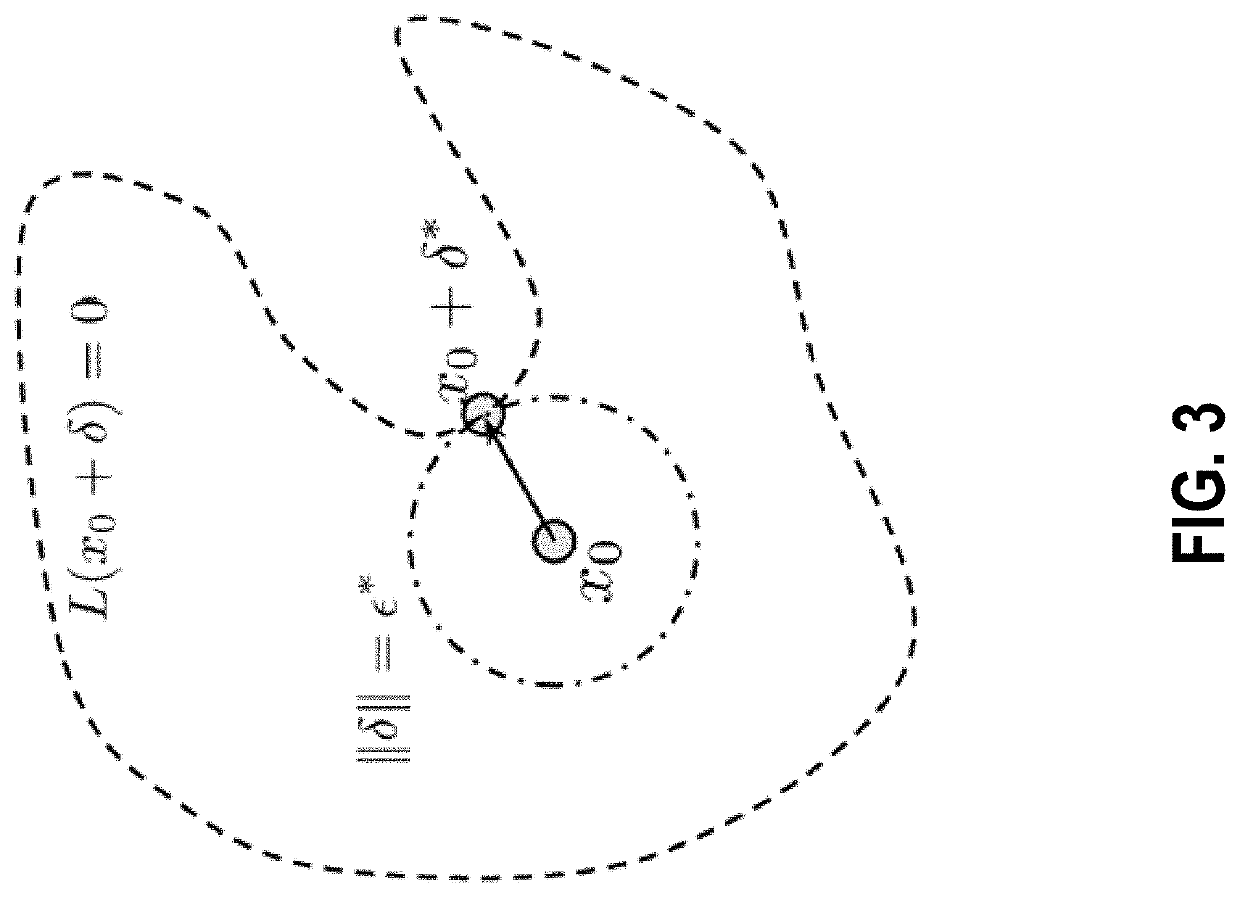
System and method for max-margin adversarial training
ActiveUS20200134468A1High strengthDegrades accuracy of predictionEnsemble learningKernel methodsData setDecision boundary
A system for generating an adversarial example in respect of a neural network, the adversarial example generated to improve a margin defined as a distance from a data example to a neural network decision boundary. The system includes a data receiver configured to receive one or more data sets including at least one data set representing a benign training example (x); an adversarial generator engine configured to: generate, using the neural network, a first adversarial example (Adv1) having a perturbation length epsilon1 against x; conduct a search in a direction (Adv1-x) using the neural network; and to generate, using the neural network, a second adversarial example (Adv2) having a perturbation length epsilon2 based at least on an output of a search in the direction (Adv1-x).
Owner:ROYAL BANK OF CANADA
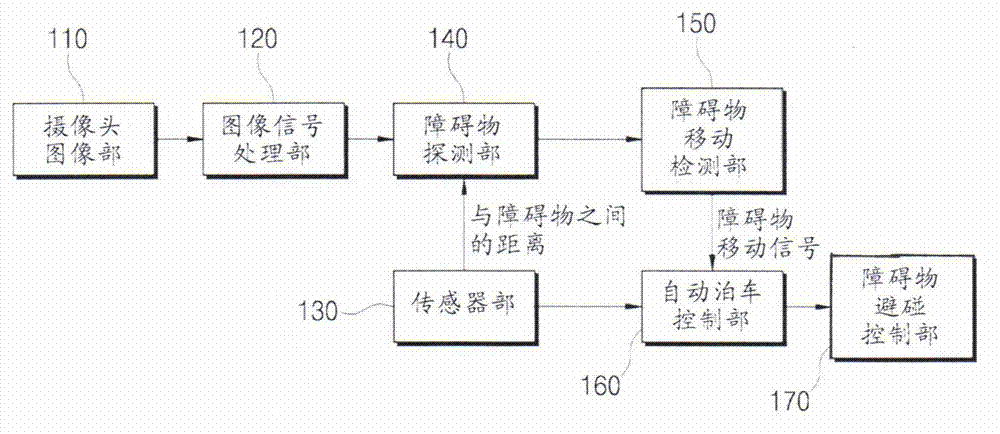
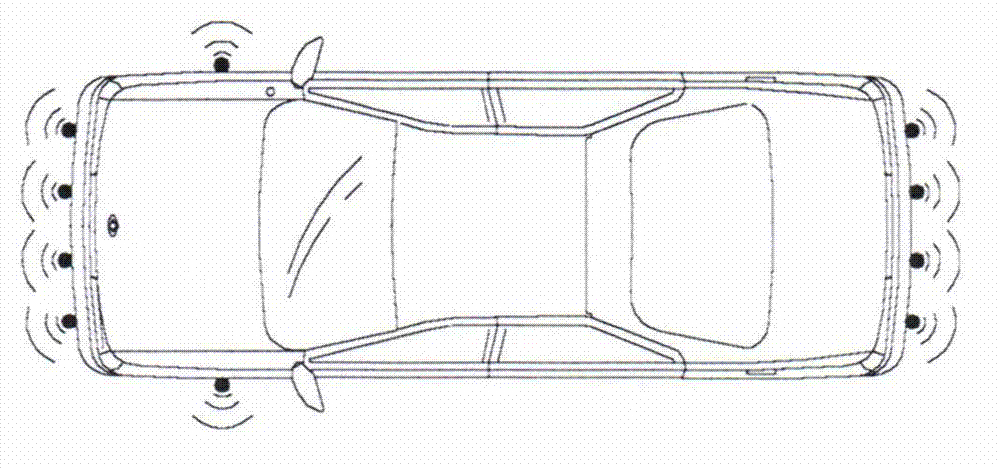
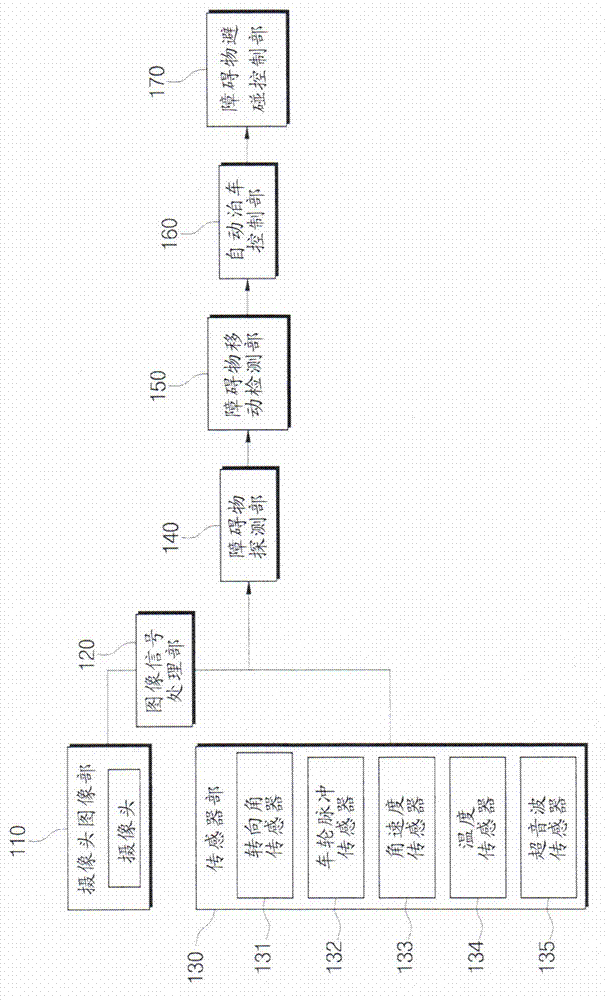
Apparatus and method avoiding collision with obstacles in automatic parking assistance system
The invention relates to an apparatus and method avoiding collision with obstacles in automatic parking assistance system. According to the invention, a plurality of sensors are arranged in the front part, the rear part, and the side parts of a vehicle, so that the moving detection area of the obstacles is enlarged, an obstacle area in the prior art which detects the obstacles in all of the images and only detects the images having brightness changes is replaced, the movement of the obstacles is detected by means of a main component analyzing method and an obstacle image characteristic valve, and a support vector machine is employed to indicate the decision boundaries by means of some of support vectors. According to the support vector machine, the detection performance is improved because the movement of the obstacles is detected by the main component analyzing method and the obstacle image characteristic value; the obstacle detection and the movement can be automatically detected without the need for drivers' operation, thereby being convenient; and the minimal change of a device in prior art can be realized by adding the functions of obstacle movement detection and collision avoidance.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD
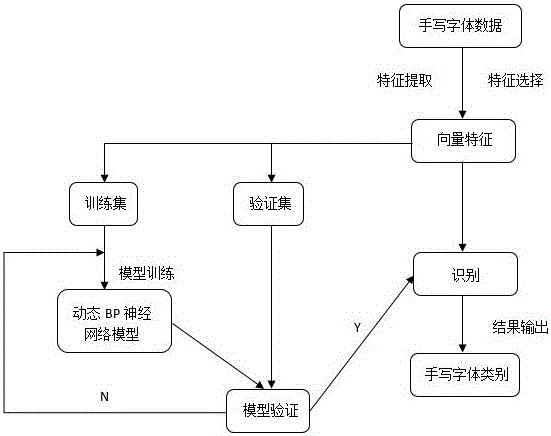
Handwritten form identification system of BP neural network based on dynamic sample selection strategy
InactiveCN106022273ARealize dynamic samplingShort training timeCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsData setDecision boundary
The invention provides a handwritten form identification system of BP neural network based on a dynamic sample selection strategy. Weights of different layers of network neurons are initialized randomly; a gradient descent method is used to optimize the network weight, in first round of iteration, all samples are used to calculate the total gradient, the total gradient is used to update the weights of different layers, and whether a sample serves as a training sample in next round of iteration is determined according to whether the sample is far from a decision boundary, and the training samples selected in the last round are used to calculate the total gradient, update the weights of different layers and select samples for next round of iteration repeatedly till the minimal stop error or the maximal interaction frequency is reached; and the obtained neural network is used to identify an unknown hand-written font sample. Compared with a traditional classification technology, According to sample selection strategy of the invention, the samples are selected dynamically according to the distances to the decision boundary, the amount of training sample is decreased step by step, and an algorithm can effectively solve the problem that training time of the BP network is too long in a big data set.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
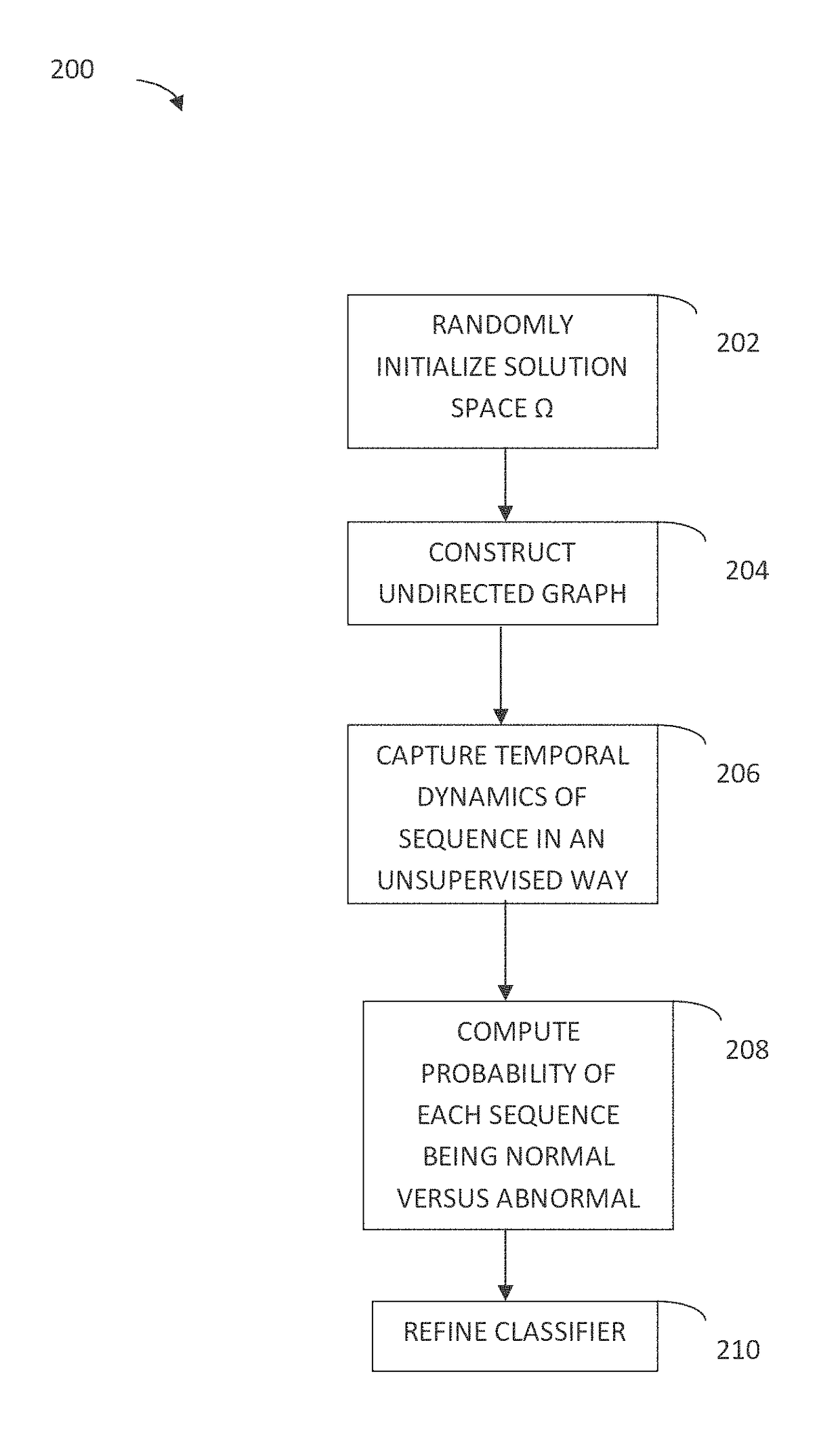
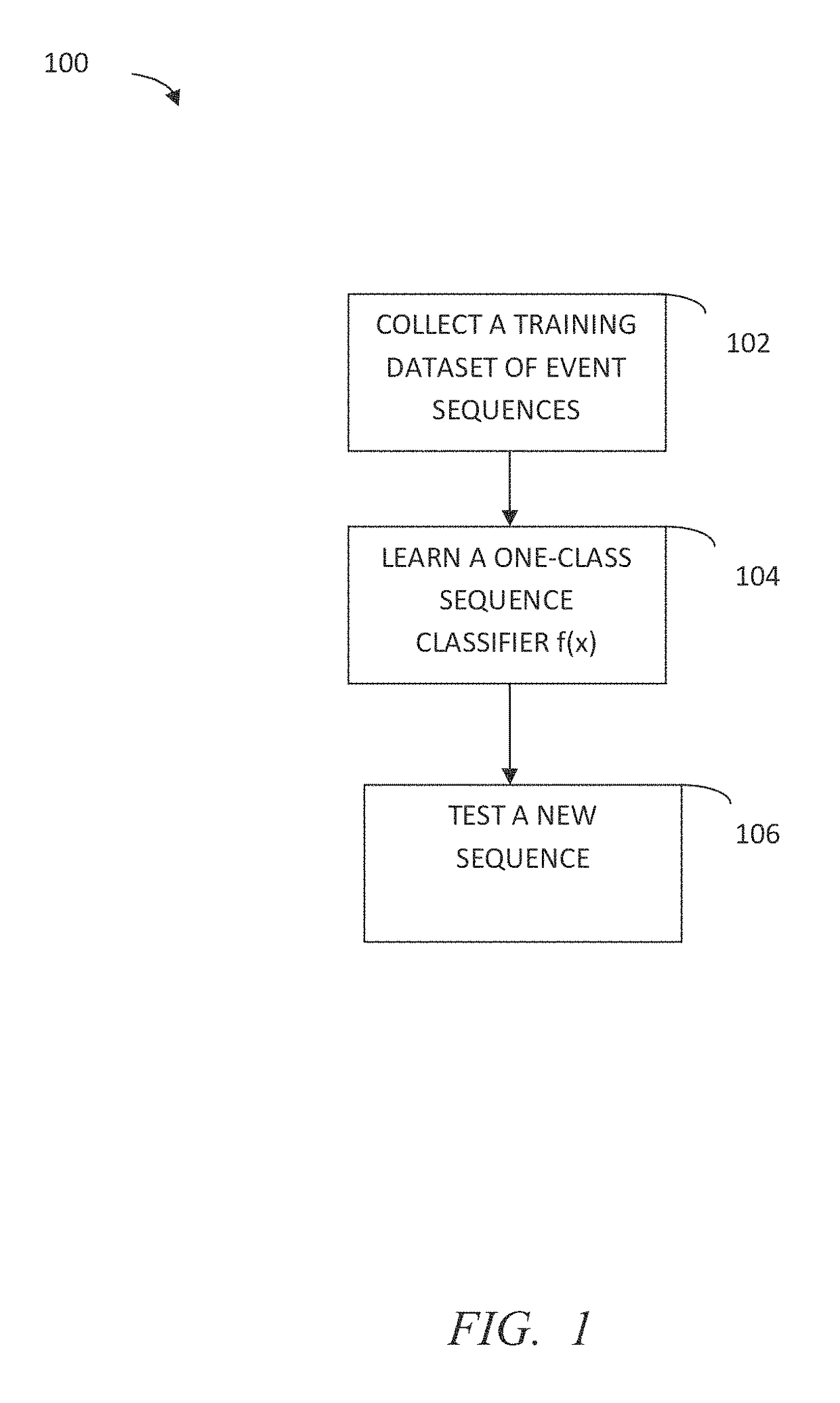
Sequential anomaly detection
A dataset including at least one temporal event sequence is collected. A one-class sequence classifier f(x) that obtains a decision boundary is statistically learned. At least one new temporal event sequence is evaluated, wherein the at least one new temporal event sequence is outside of the dataset. It is determined whether the at least one new temporal event sequence is one of a normal sequence or an abnormal sequence based on the evaluation. Numerous additional aspects are disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
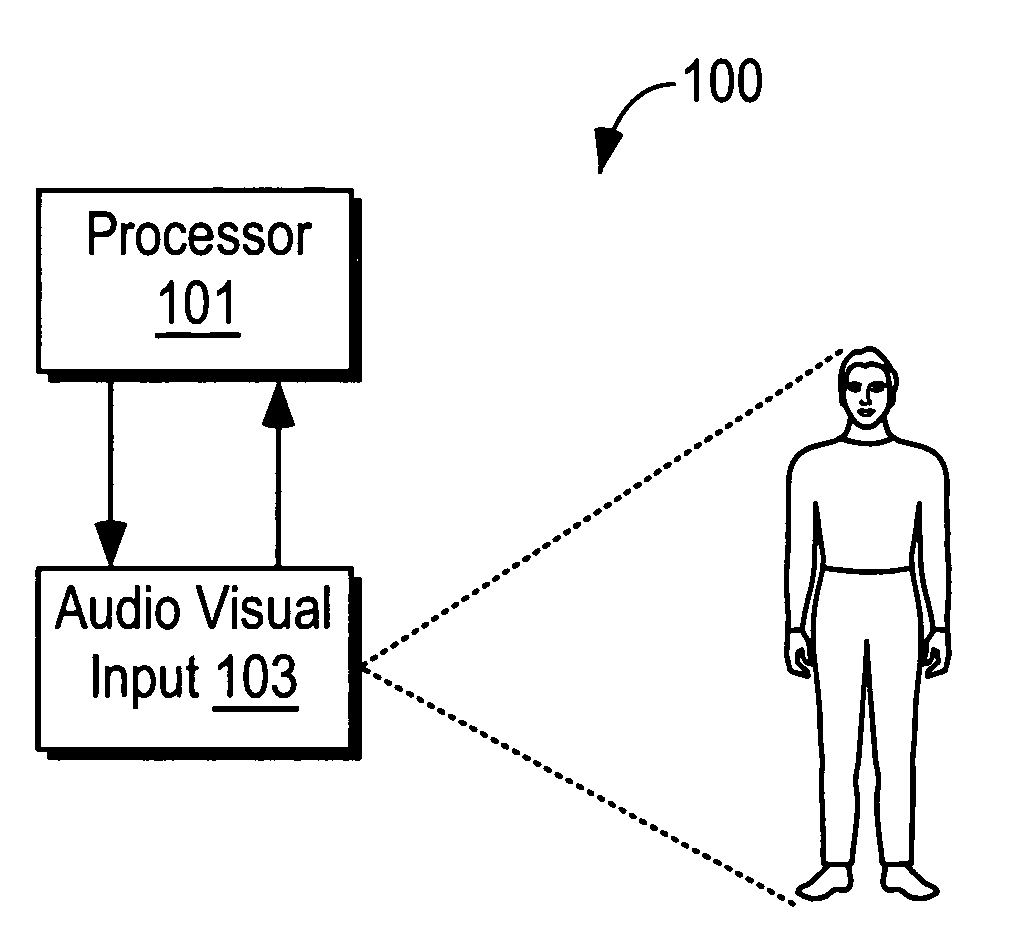
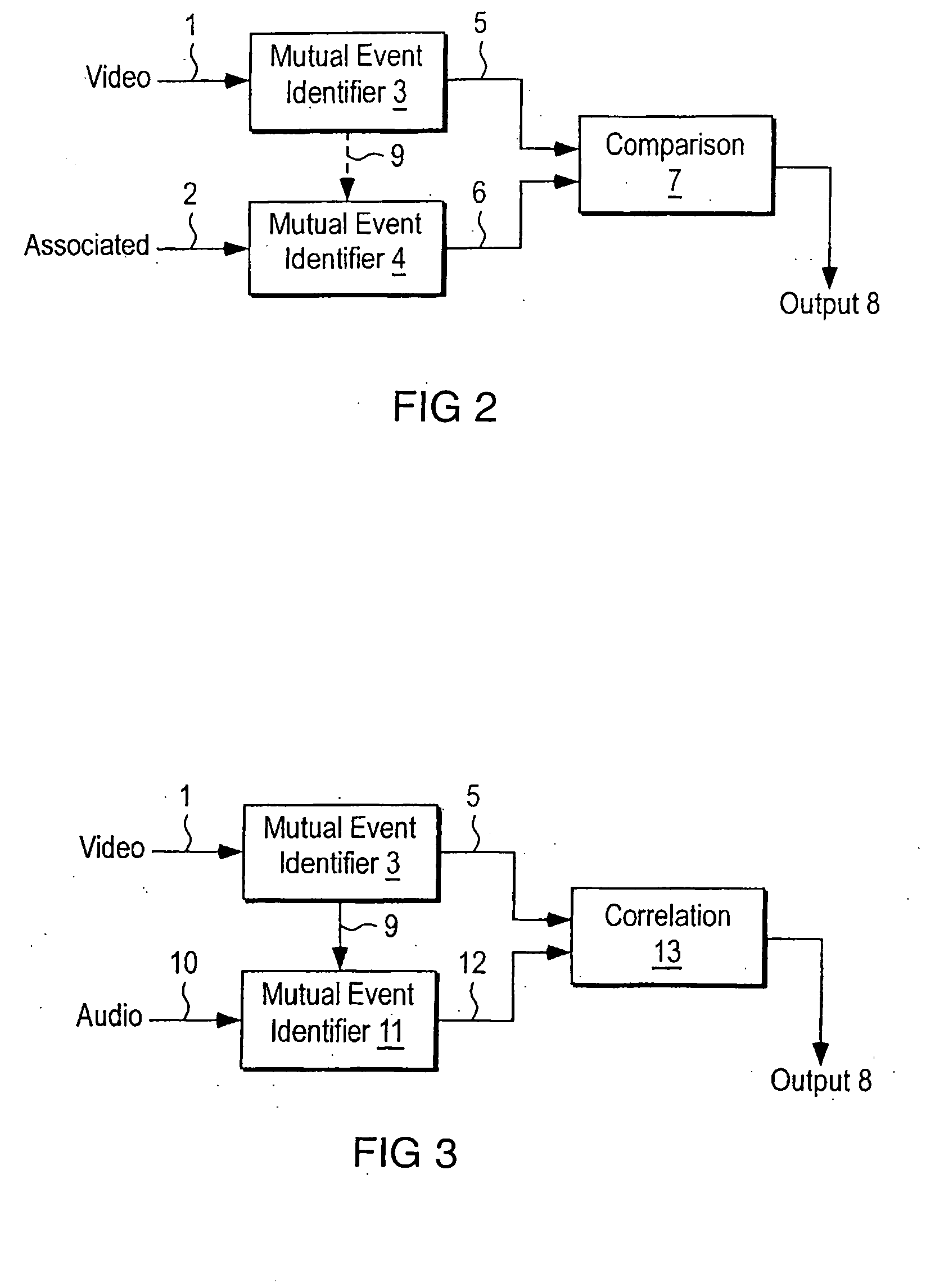
Method, system, and program product for measuring audio video synchronization independent of speaker characteristics
InactiveUS20080111887A1Eliminate the effects ofReduce the impactTelevision system detailsCarrier indexing/addressing/timing/synchronisingDecision boundaryPhase filter
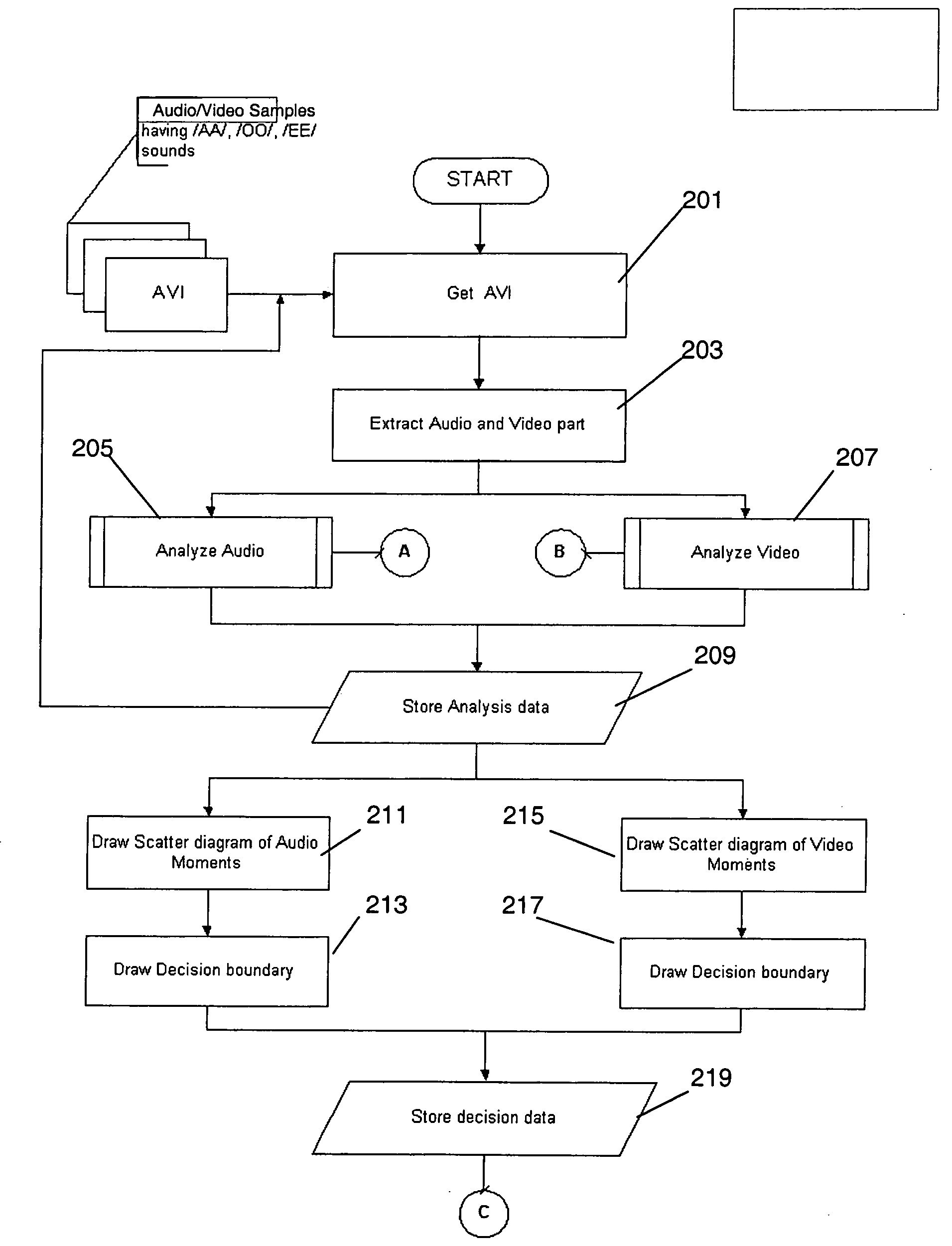
Method, system, and program product for measuring audio video synchronization. This is done by first acquiring audio video information into an audio video synchronization system. The step of data acquisition is followed by analyzing the audio information, and analyzing the video information. Next, the audio information is analyzed to locate the presence of sounds therein related to a speaker's personal voice characteristics. The audio information is then filtered by removing data related to a speakers personal voice characteristics to produce a filtered audio information. In this phase filtered audio information and video information is analyzed, decision boundaries for Audio and Video MuEv-s are determined, and related Audio and Video MuEv-s are correlated. In Analysis Phase Audio and Video MuEv-s are calculated from the audio and video information, and the audio and video information is classified into vowel sounds including AA, EE, OO, silence, and unclassified phonemes. This information is used to determine and associate a dominant audio class in a video frame. Matching locations are determined, and the offset of video and audio is determined.
Owner:PIXEL INSTR CORP
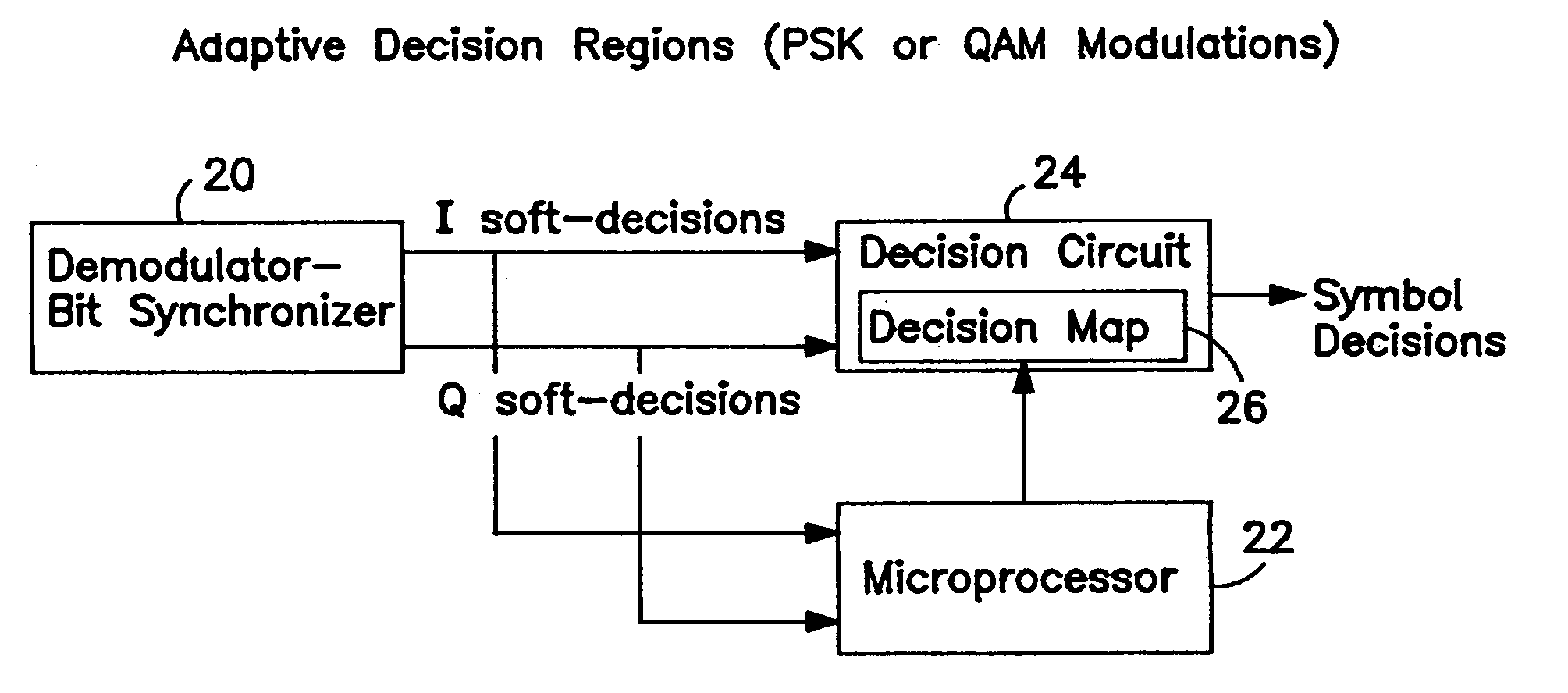
Adaptive decision regions and metrics
InactiveUS7197090B1Reduce complexityReduce weightDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationDecision boundaryPhase shifted
An improved decoding technique useful for hard decision decoding, such as quadrature phase shift keying (PSK) and quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), as well as soft-decision techniques, such as Viterbi decoding and trellis decoding. The system in accordance with the present invention provides adaptive decision regions for hard-decision decoding techniques and adaptive metrics for soft-decision detection techniques in which the decision boundaries and reference constellations, respectively are optimized in order to minimize the bit error rate (BER). In particular, the decision boundaries and metrics are optimized based on the locations of the received constellation points. By adaptively adjusting the decision boundaries and metrics, the BER can be greatly improved with the need for nonlinear predistortion at the transmitter thus reducing the hardware complexity and weight of the transmitter which provides additional benefits in applications, such as satellite communication systems, where the transmitter is located on the satellite.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method and device for decoding a signal of multiple input/multiple output system
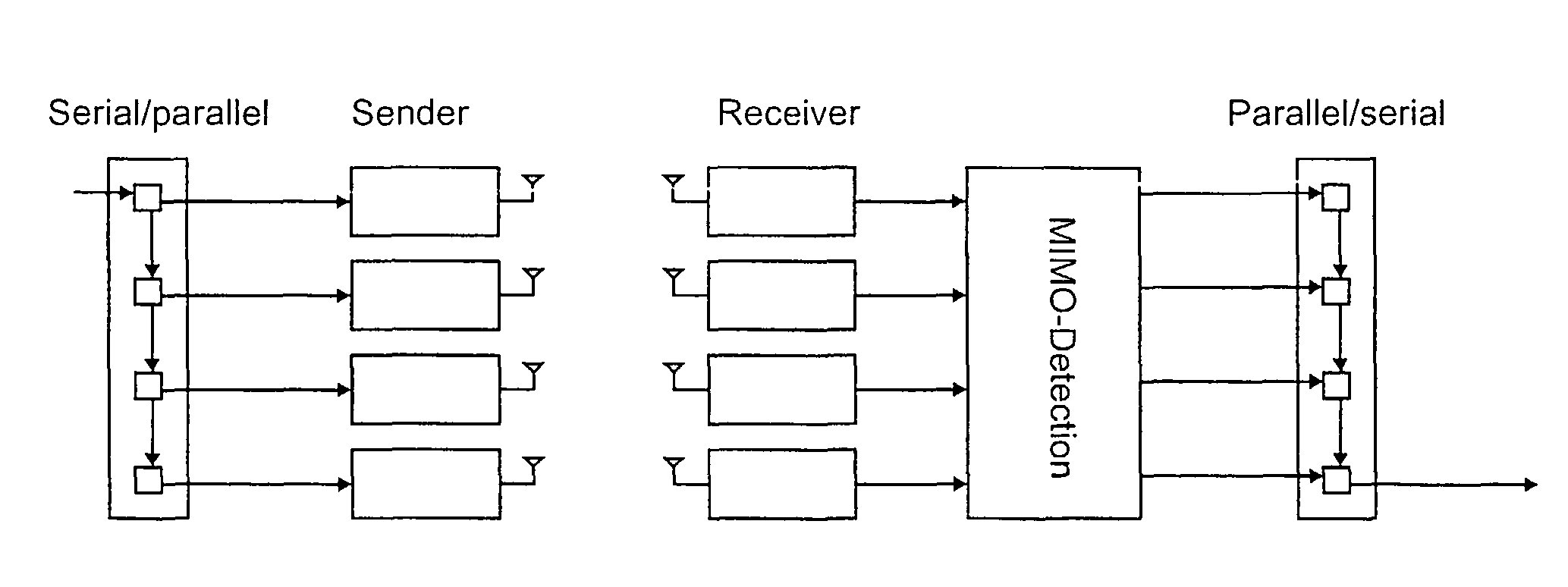
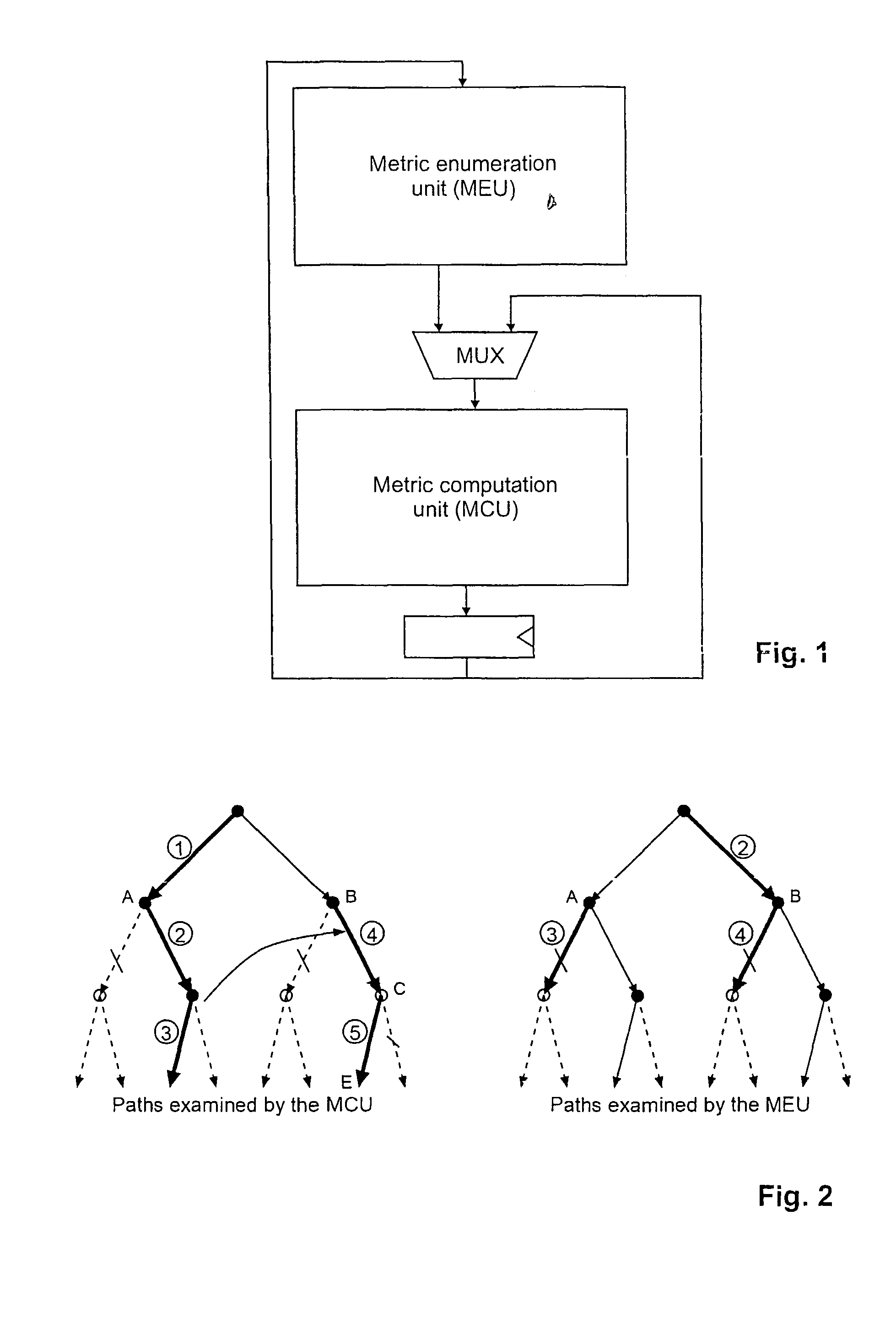
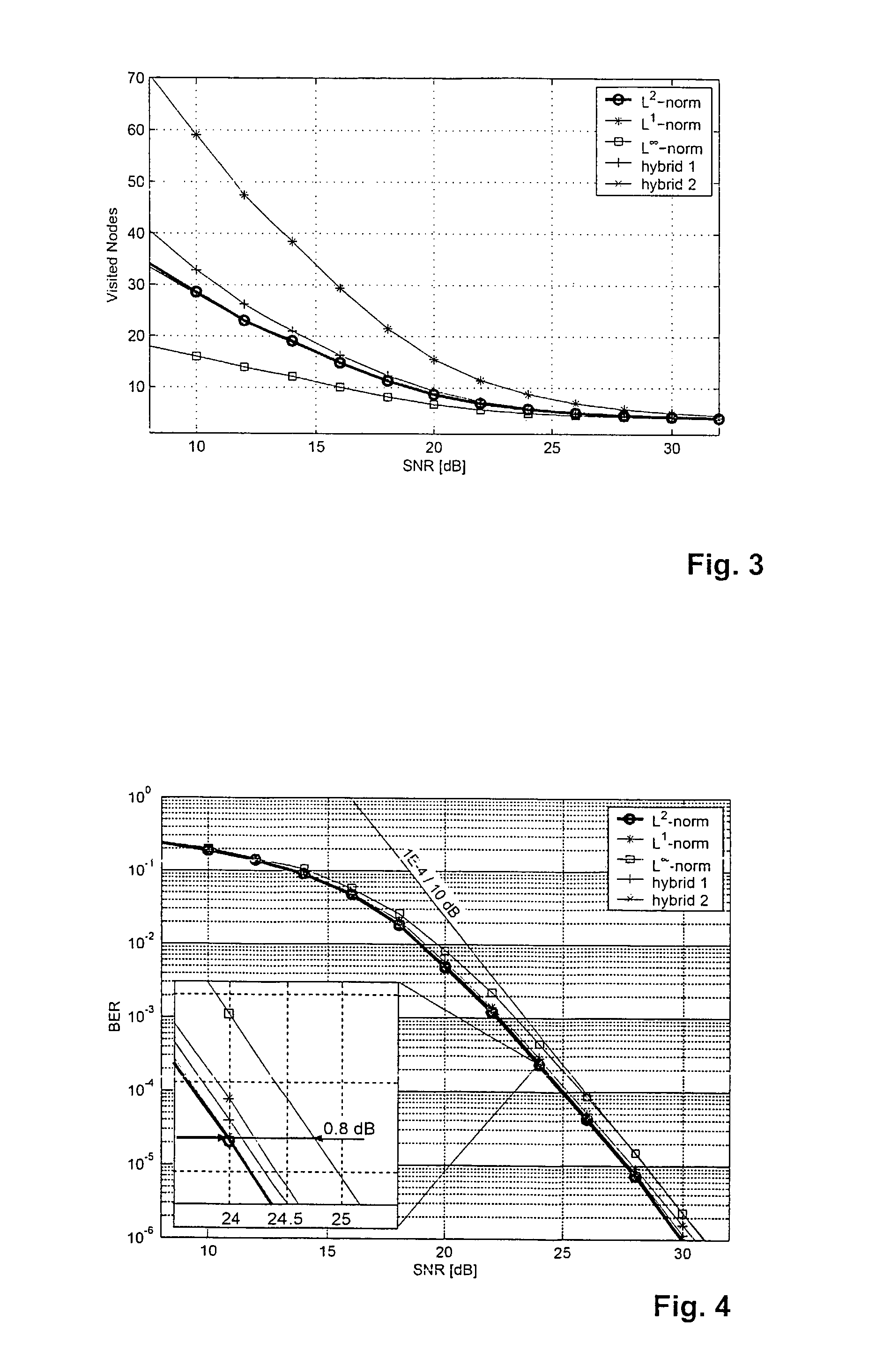
InactiveUS7782971B2Efficient implementationReduce error rateDiversity/multi-antenna systemsBaseband systemsQR decompositionDecision boundary
The method for decoding a received signal in a multiple input / multiple output system uses QR-decomposition of the linear channel matrix, but then applies a non-Euclidean norm during tree traversal. Two separate hardware units, namely an MCU and a MEU, art provided for concurrent operation. The MCU determines a next child node, while the MEU determines next best parent nodes on the previously processed tree levels, which makes it possible to retrace the path to a next starting node without investing dedicated processing steps (e.g., cycles). On each tree level, the possible coordinates are grouped into several circular sets in the complex plane, and a series of decision boundaries is calculated for each set that allows a quick evaluation of the optimum coordinate in each set.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
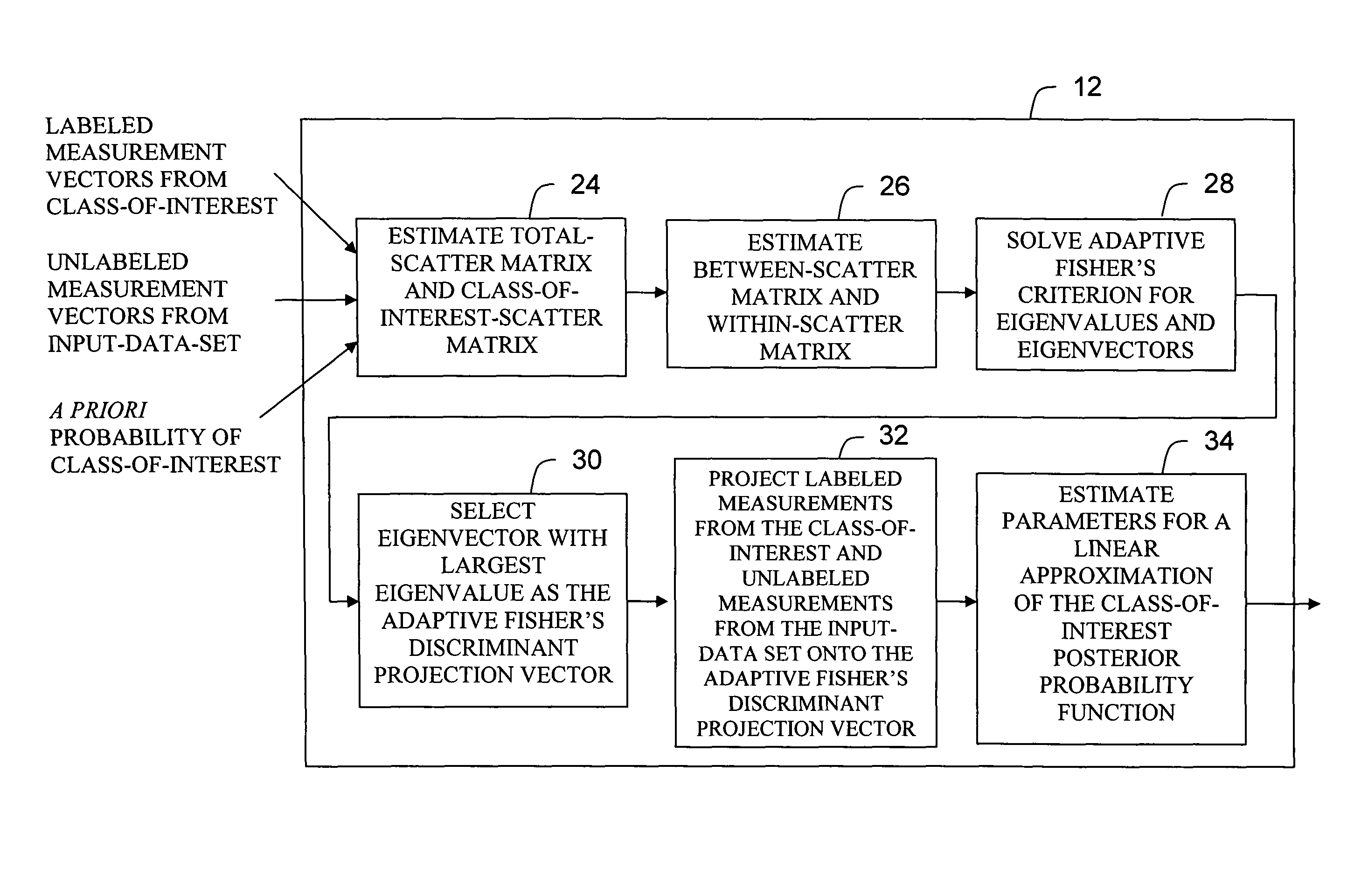
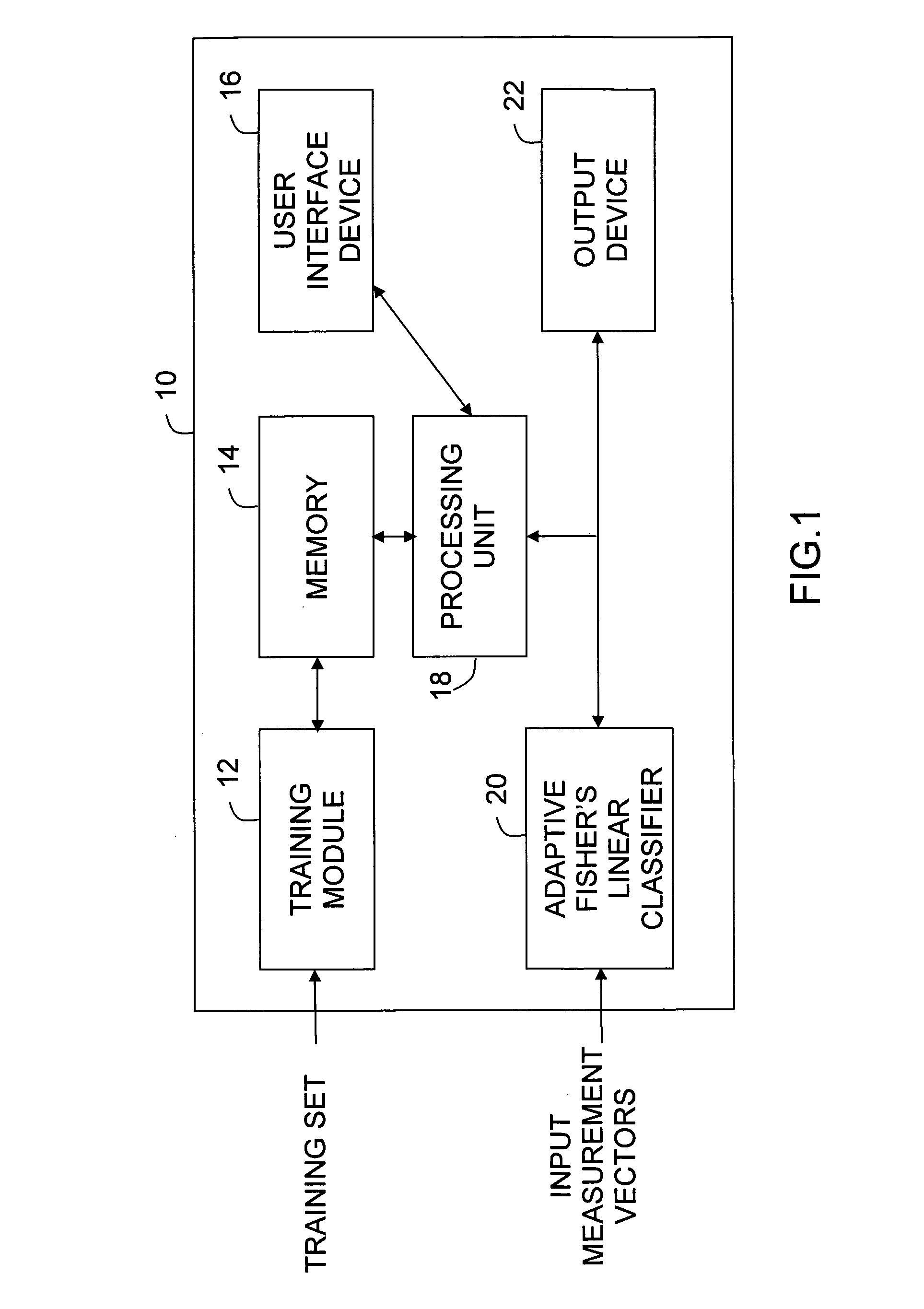
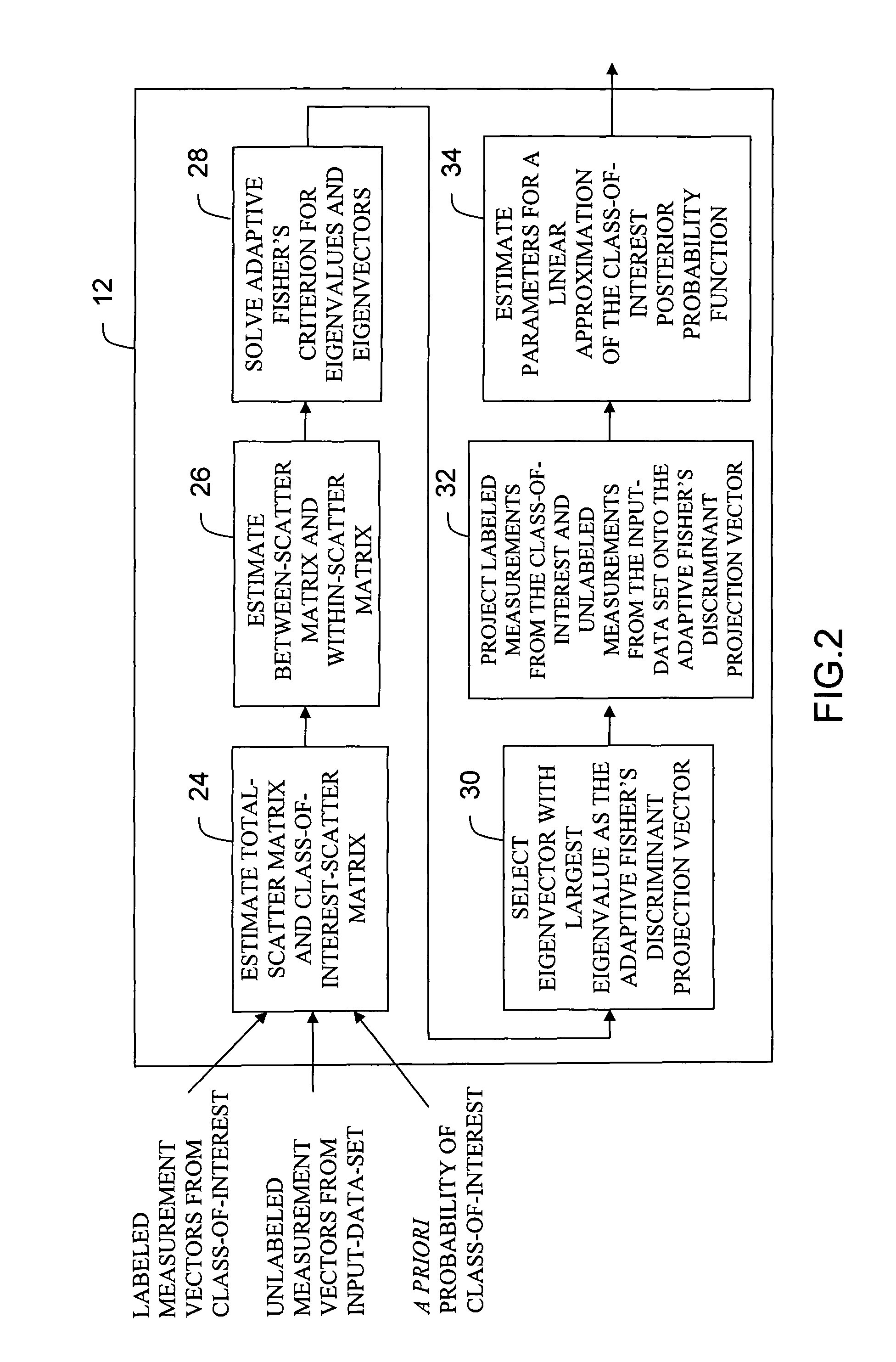
Adaptive fisher's linear discriminant
InactiveUS7961956B1Good decisionEliminate requirementsDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionDiscriminantData set
This invention relates generally to a system and method for classifying input patterns into two classes, a class-of-interest or a class-other, utilizing an Adaptive Fisher's Linear Discriminant method capable of estimating an optimal Fisher's linear decision boundary for discriminating between the two classes, when training samples are provided a priori only for the class-of-interest. The system and method eliminates the requirement for any a priori knowledge of the other classes in the data set to be classified. The system and method is capable of extracting statistical information corresponding to the “other classes” from the data set to be classified, without recourse to the a priori knowledge normally provided by training samples from the other classes. The system and method can re-optimize (adapt) the decision boundary to provide optimal Fisher's linear discrimination between the two classes in a new data set, using only unlabeled samples from the new data set.
Owner:MINTER THOMAS CECIL
Pattern recognition method and apparatus for data protection
InactiveUS20090080778A1Program control using stored programsUser identity/authority verificationPattern recognitionDecision boundary
Provided a secure pattern recognition method. The method includes: receiving data and generating a probe by converting the received data into a template for pattern recognition; accessing a gallery that is a template registered and stored in advance; determining a region to which the probe belongs and obtaining the center point of the region; obtaining a hash value of the center point and coordinate of the probe; and determining whether or not the hash value of the center point and a hash value stored in the gallery are equal and determining whether or not the probe and the gallery are classified into the same class by calculating whether or not the coordinate of the probe is inside a decision boundary configured with thresholds on the basis of the coordinates of the center point.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
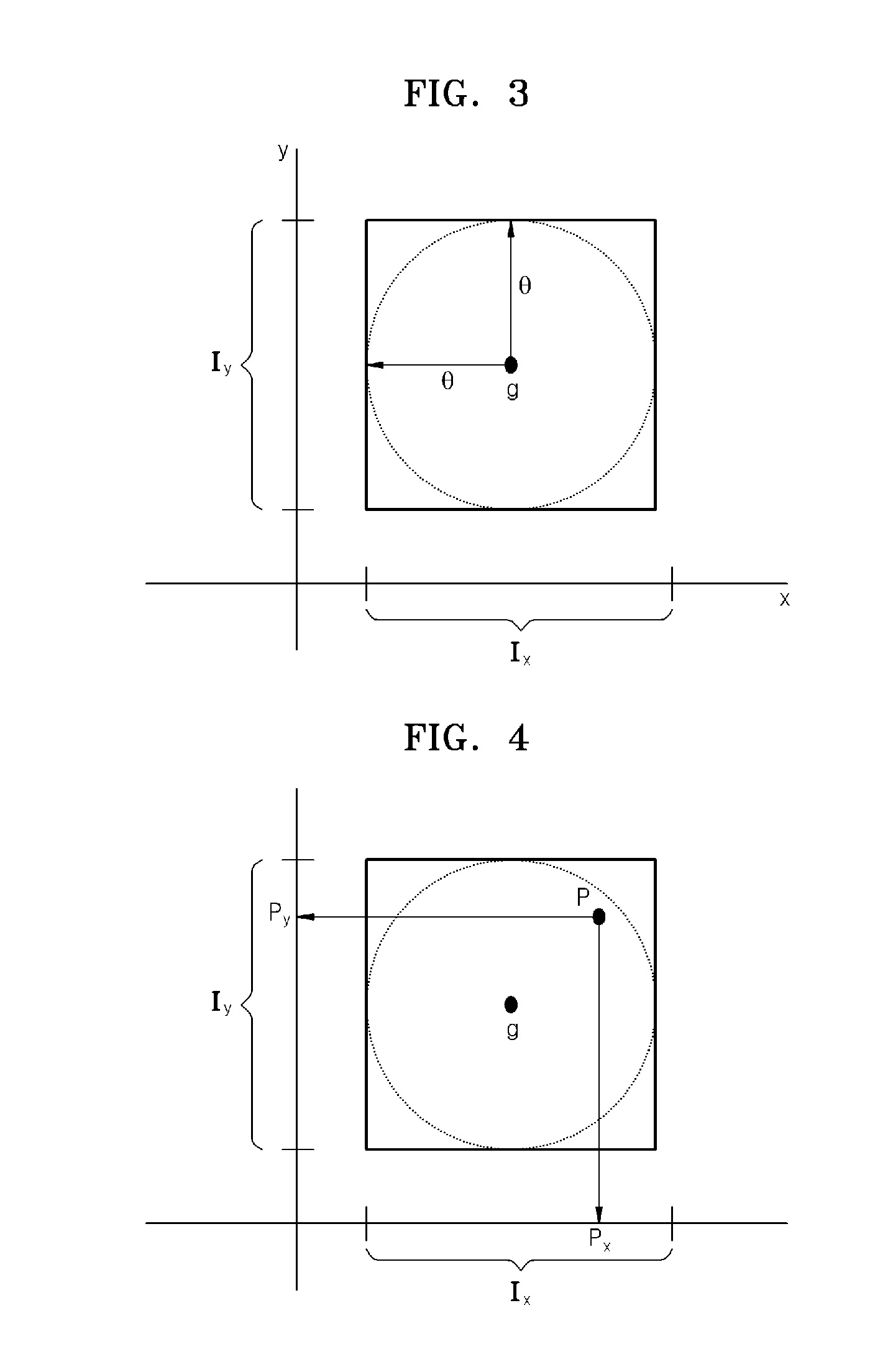
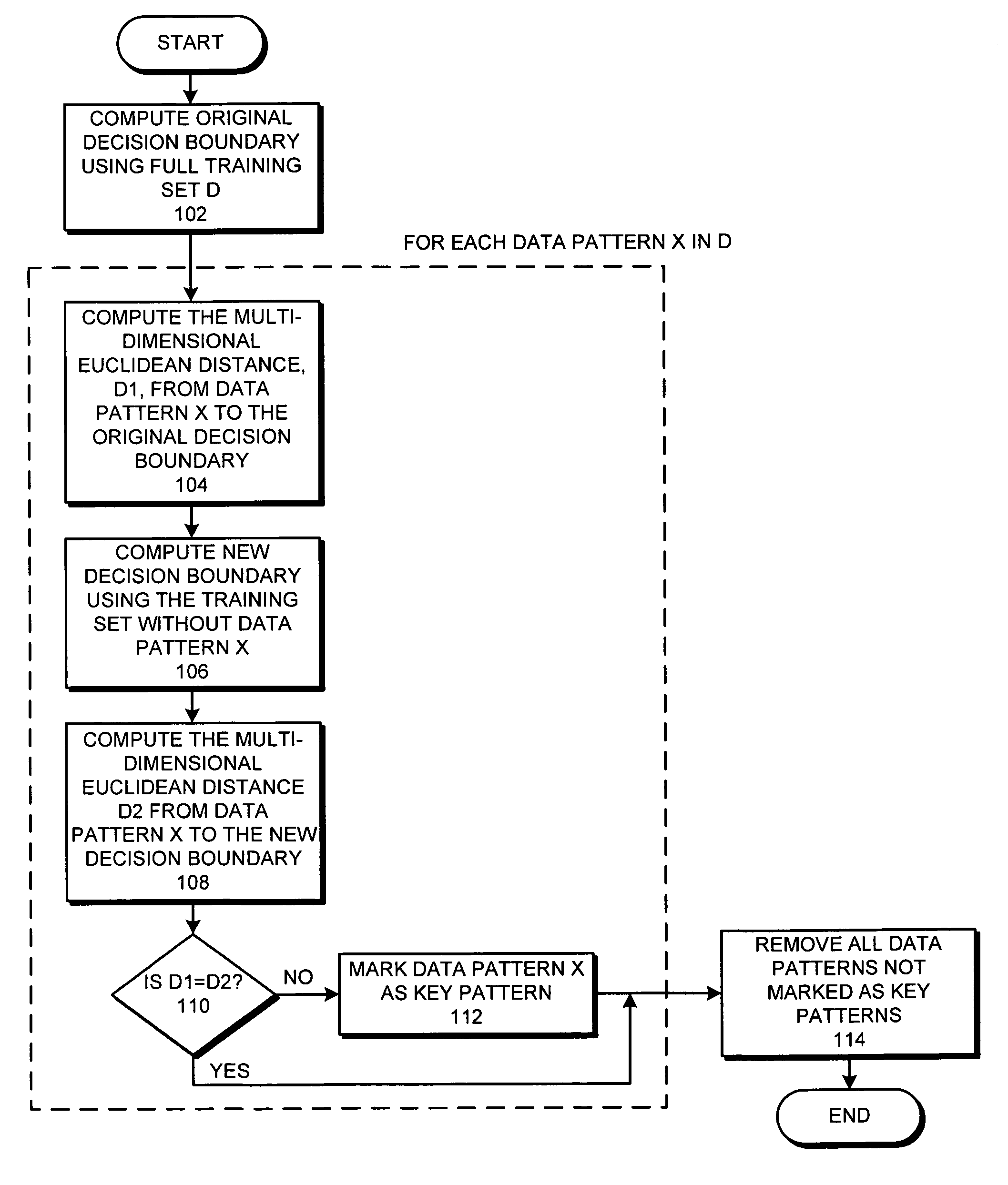
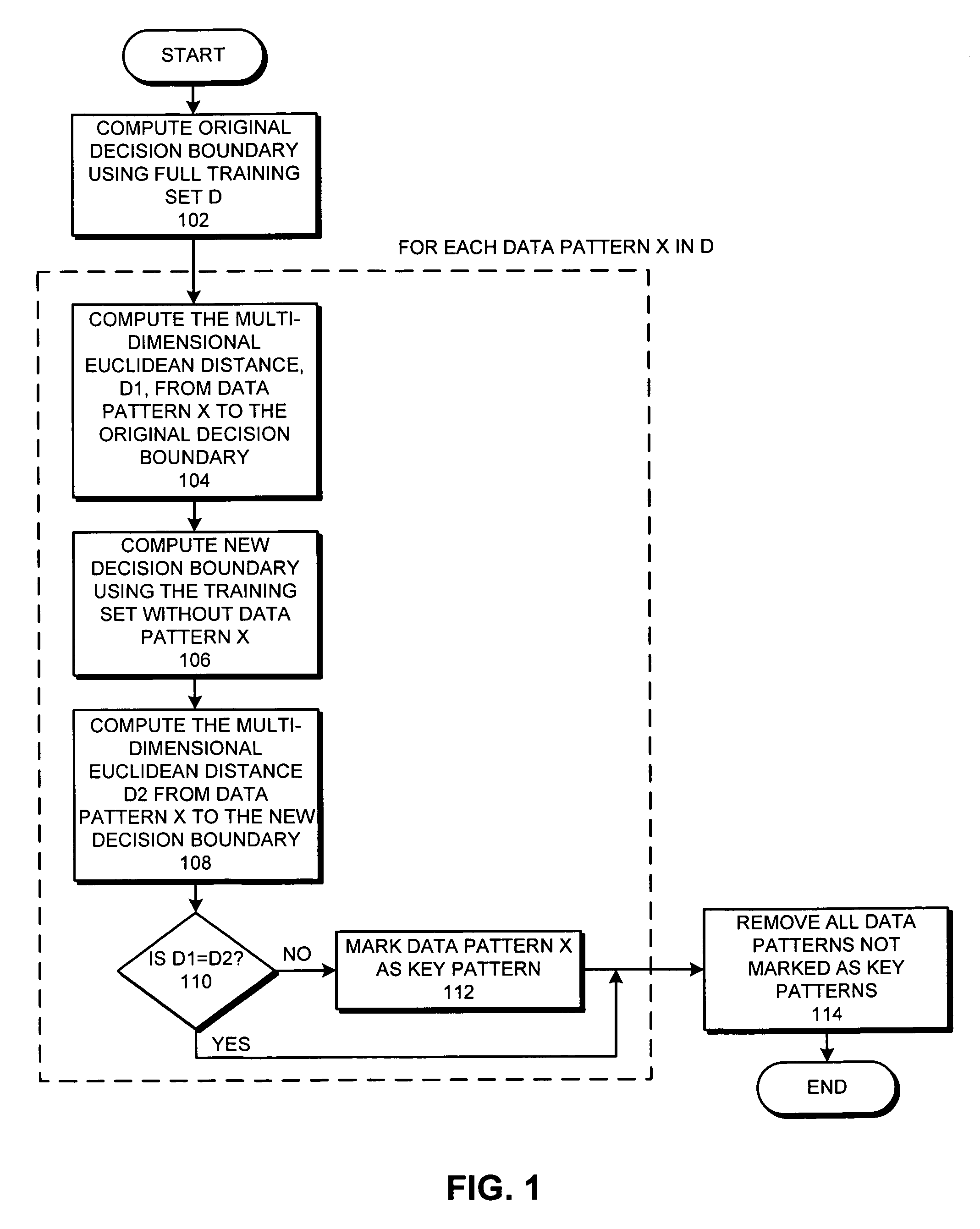
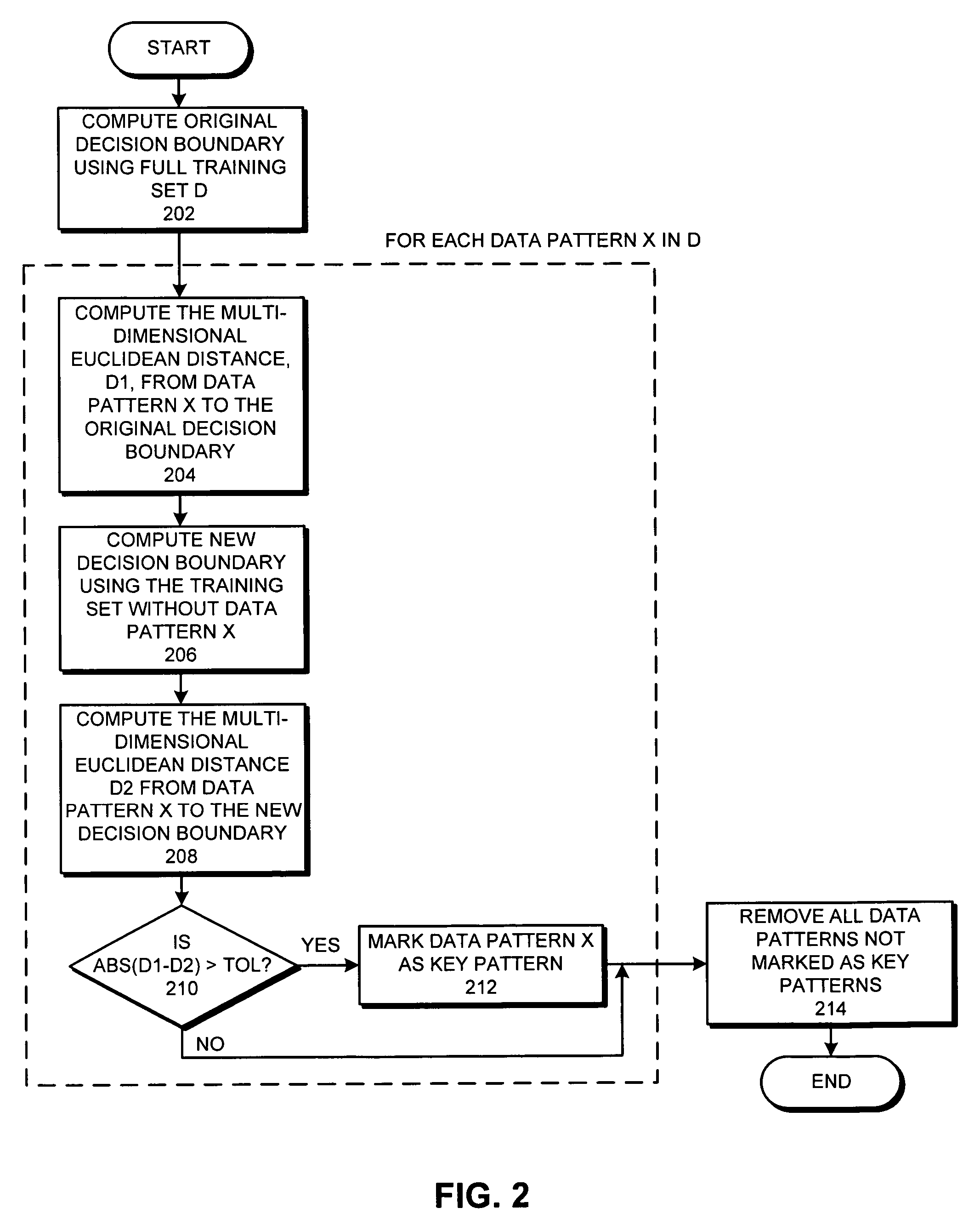
Reducing the size of a training set for classification
ActiveUS7478075B2Reduce design sizeDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setDecision boundary
A system that reduces the size of a design data set. During this design data set reduction operation, the system computes a decision boundary which separates a first group of data patterns in a training data set from a second group of data patterns in the training data set. For each data pattern in the training data set, the system determines if removing the data pattern from the training data set substantially affects the resulting decision boundary. If so, the system marks the data pattern as a key pattern. The system then removes all data patterns that are not marked as key patterns to produce a reduced training data set which represents the decision boundary.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method, system, and program product for measuring audio video synchronization
InactiveUS20070153125A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionDecision boundaryInformation gain
Method, system, and program product for measuring audio video synchronization. This is done by first acquiring audio video information into an audio video synchronization system. The step of data acquisition is followed by analyzing the audio information, and analyzing the video information. In this phase audio and video information is analyzed, decision boundaries for Audio and Video MuEv-s are determined, and related Audio and Video MuEv-s are correlated. In Analysis Phase Audio and Video MuEv-s are calculated from the audio and video information, and the audio and video information is classified into vowel sounds including AA, EE, OO, silence, and unclassified phonemes This information is used to determine and associate a dominant audio class in a video frame. Matching locations are determined, and the offset of video and audio is determined.
Owner:PIXEL INSTR CORP
Sequential anomaly detection
A dataset including at least one temporal event sequence is collected. A one-class sequence classifier f(x) that obtains a decision boundary is statistically learned. At least one new temporal event sequence is evaluated, wherein the at least one new temporal event sequence is outside of the dataset. It is determined whether the at least one new temporal event sequence is one of a normal sequence or an abnormal sequence based on the evaluation. Numerous additional aspects are disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for receiving coded signals with the aid of channel state information
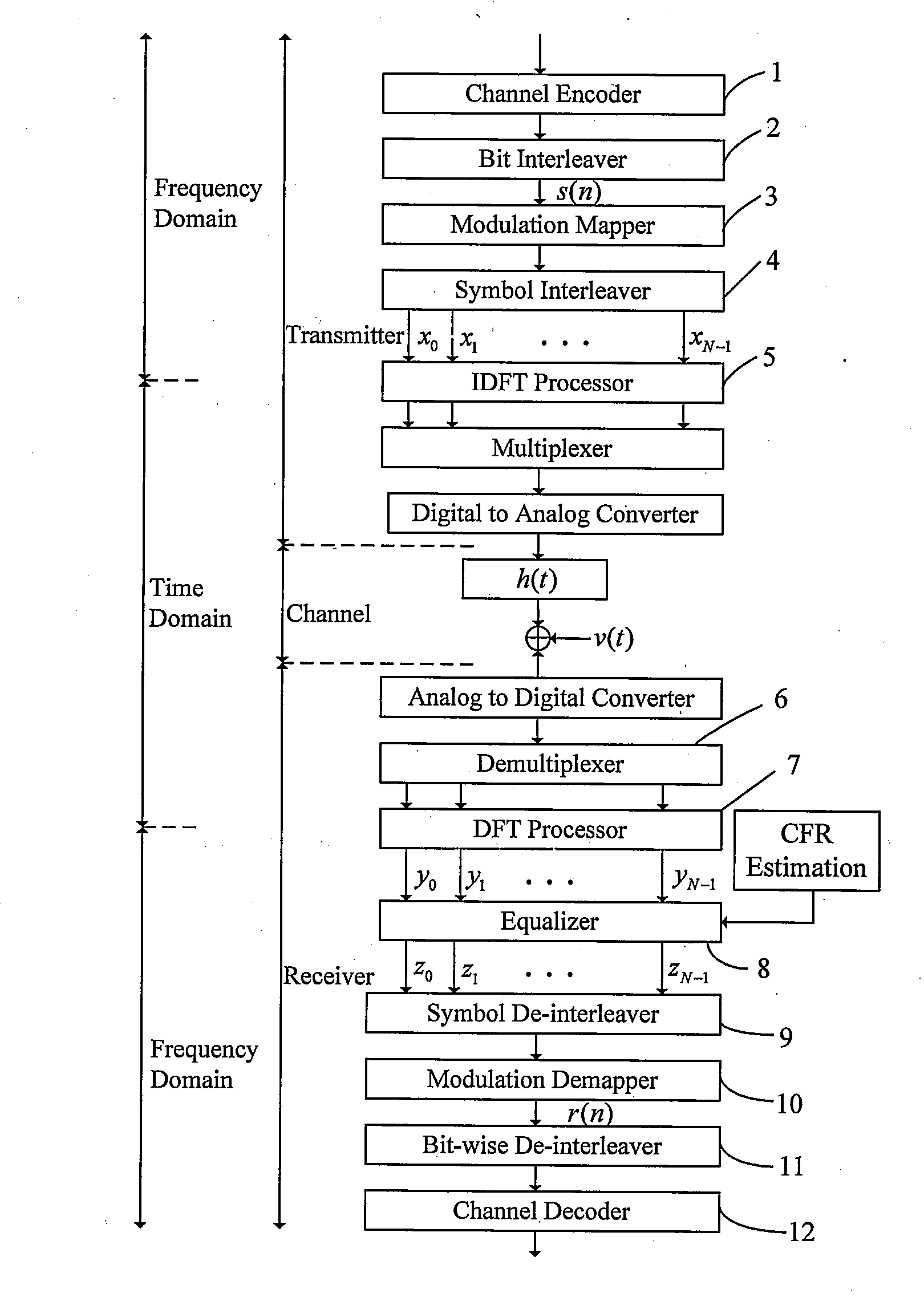
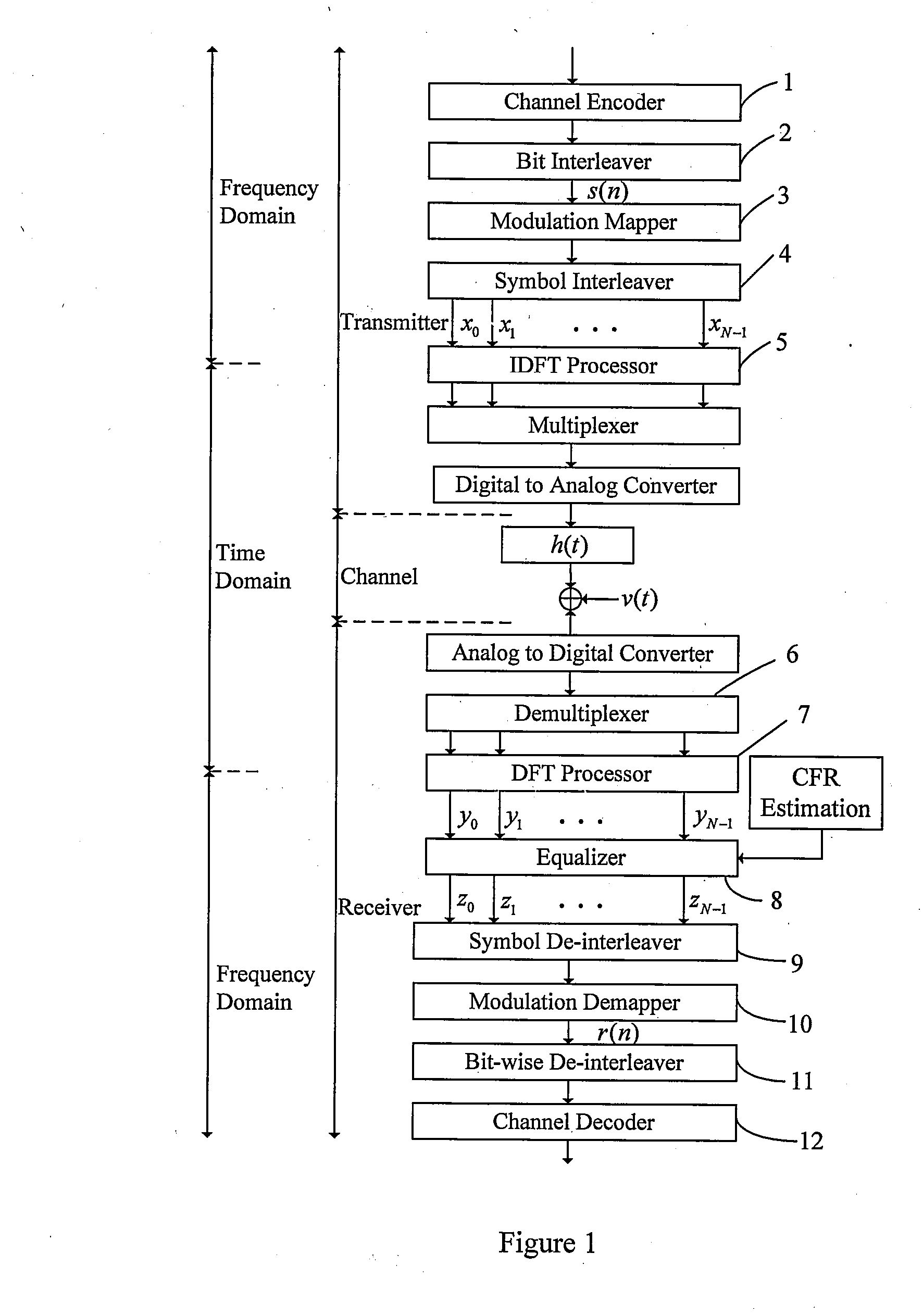
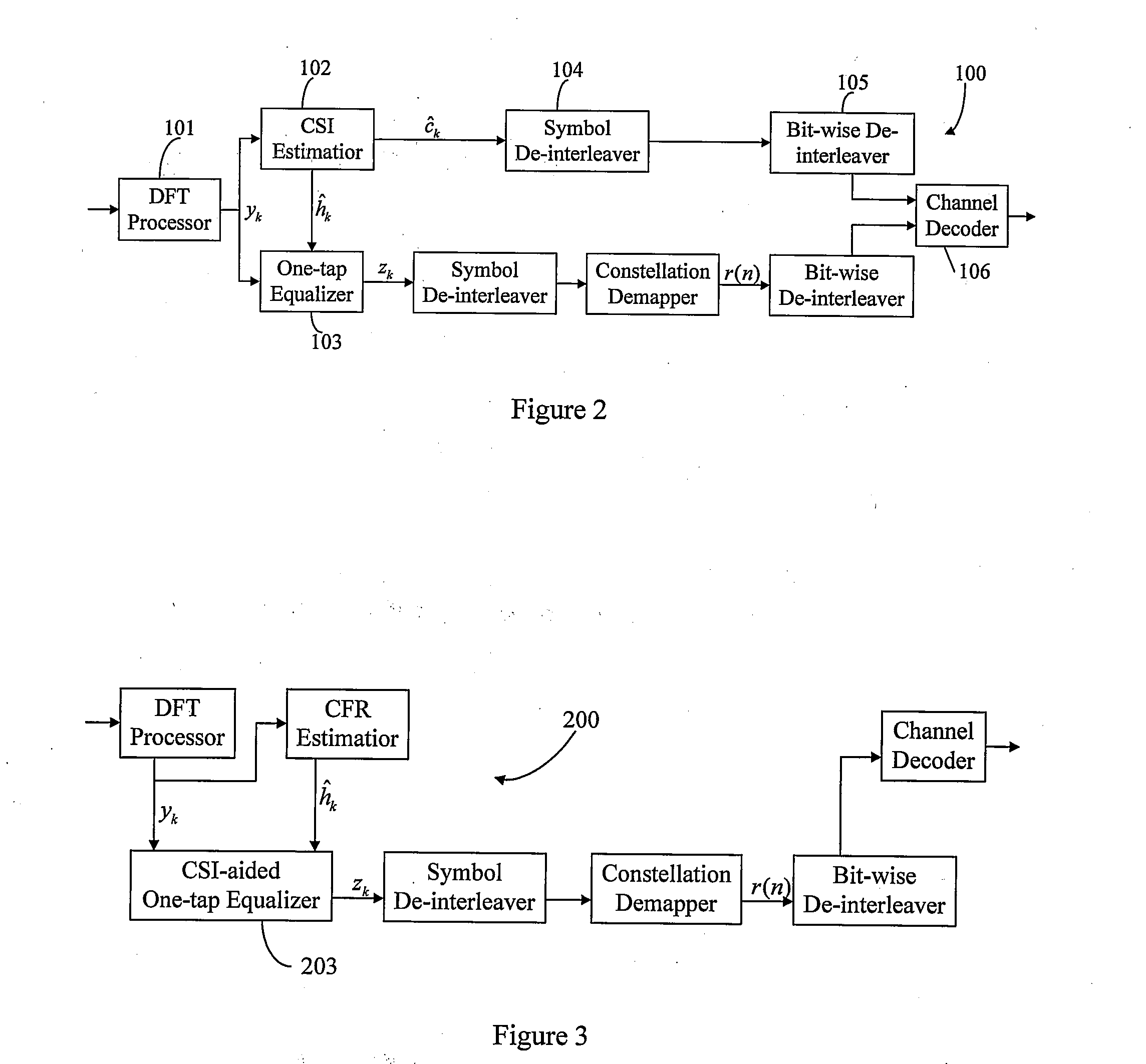
ActiveUS20090074050A1Easy to keepMultiple-port networksError preventionChannel state informationDecision boundary
Method and apparatus for receiving coded signals with the aid of CSI are provided. The method comprises: performing channel estimation to obtain a CFR estimation vector; computing a squared magnitude of the CFR estimation vector, and obtaining a normalization factor α by averaging the squared magnitudes of CFR estimations on all N subcarriers; finding a norm-shift operand m satisfying the condition that α0=2m is a power of 2 number closest to the normalization factor α; performing a CSI-aided one-tap channel equalization on an output signal vector from a DFT processor by using the norm-shift operand m; performing constellation demapping; and performing channel decoding. The method further comprises obtaining a weighting factor vector by right shifting m bits of the squared magnitude of the CFR estimation vector so that the constellation demapping can use the weighted decision boundary values in case that its input signal is sensitive to both amplitude and phase.
Owner:WIPRO LTD
An adversarial sample detection method based on the distance from a sample to a decision boundary
InactiveCN109165671AAccurate measurementEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionDecision boundaryFeature extraction
An adversarial sample detection method based on the distance from a sample to a decision boundary. Adversarial samples are generated on the basis of common samples, feature extraction is performed onall samples, that is to say, a distance estimation value from each sample to a decision boundary is calculated, the distance estimation values are taken as features of the samples to train a classifier, and the trained classifier is the detector, which is used to detect the adversarial samples. The method can be widely applied to machine learning models based on classifiers, such as speech recognition, image classification and the like, to improve the detection rate of antagonistic samples. The method can be used in an artificial intelligence API, input samples can be filtered, and the security of artificial intelligence has been significantly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Quadrature amplitude modulated soft decision method and apparatus
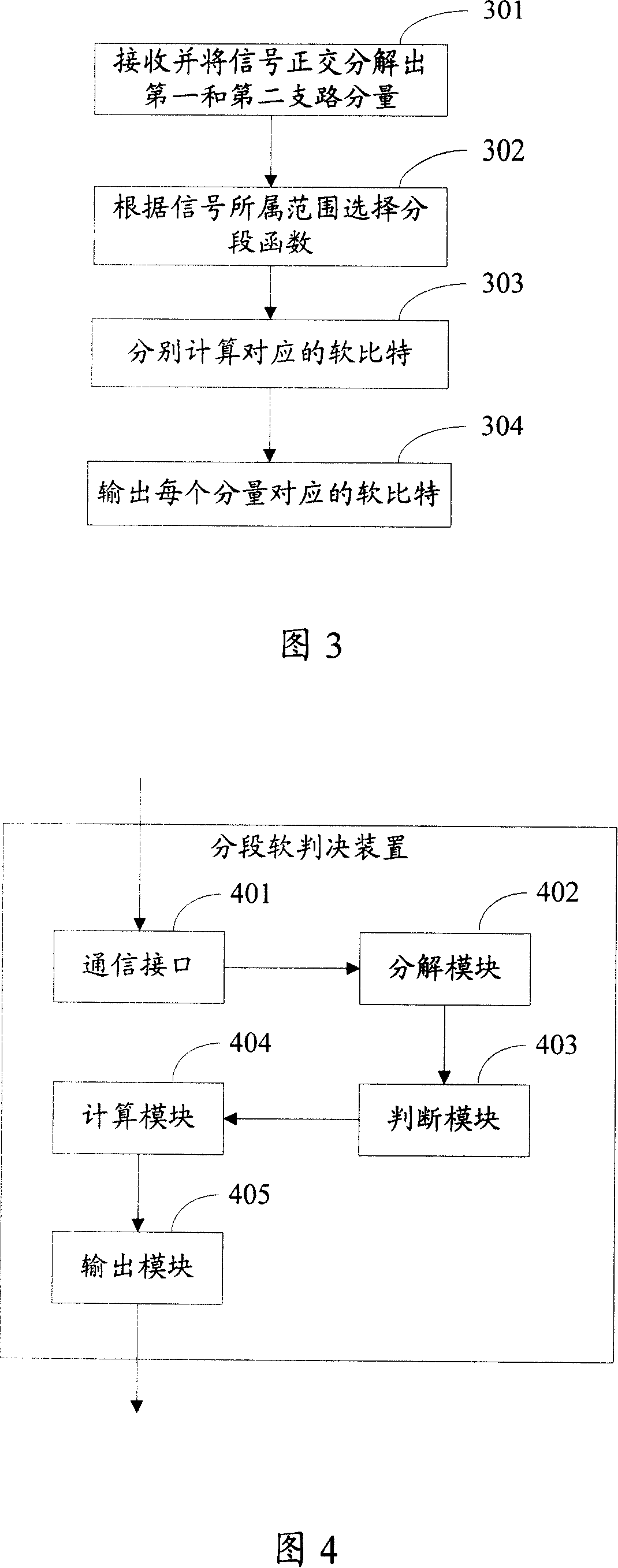
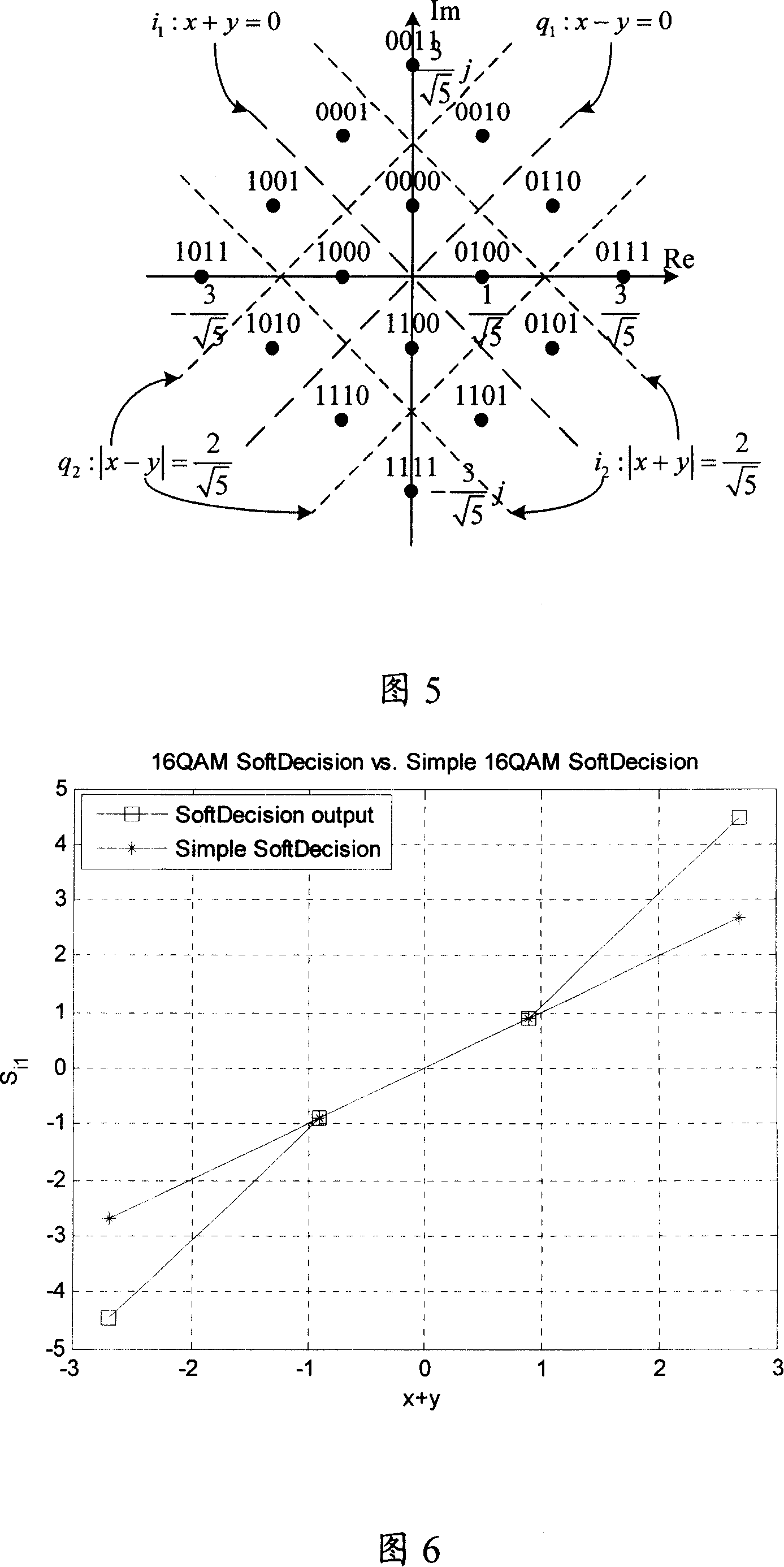
ActiveCN101136898ASimple calculationSimplify the soft decision processCode division multiplexMultiple carrier systemsCommunication interfaceDecision boundary
Being applicable to solve the issue that in current technique, demodulation procedure is too complex, the invention discloses simplified schemes for two algorithms. Scheme 1 is that using LLR algorithm and MAX-log algorithm simplifies current demodulation procedure into piecewise functions. Scheme 2 is that using minimum distance between the received signal and hard decision boundary determines amplitude of soft bits to simplify demodulation procedure further. First, the invention decomposes signal in orthogonal into first branch component, and second branch component, and then calculates their soft bits so as to accomplish soft decision-making procedure. In scheme 1, the equipment includes communication interface (CI), decomposition module (DM), judgment module (JM), computing module (CM), and output module (OM). In scheme 2, the equipment includes CI, DM, JM, CM, and OM.
Owner:LEADCORE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com