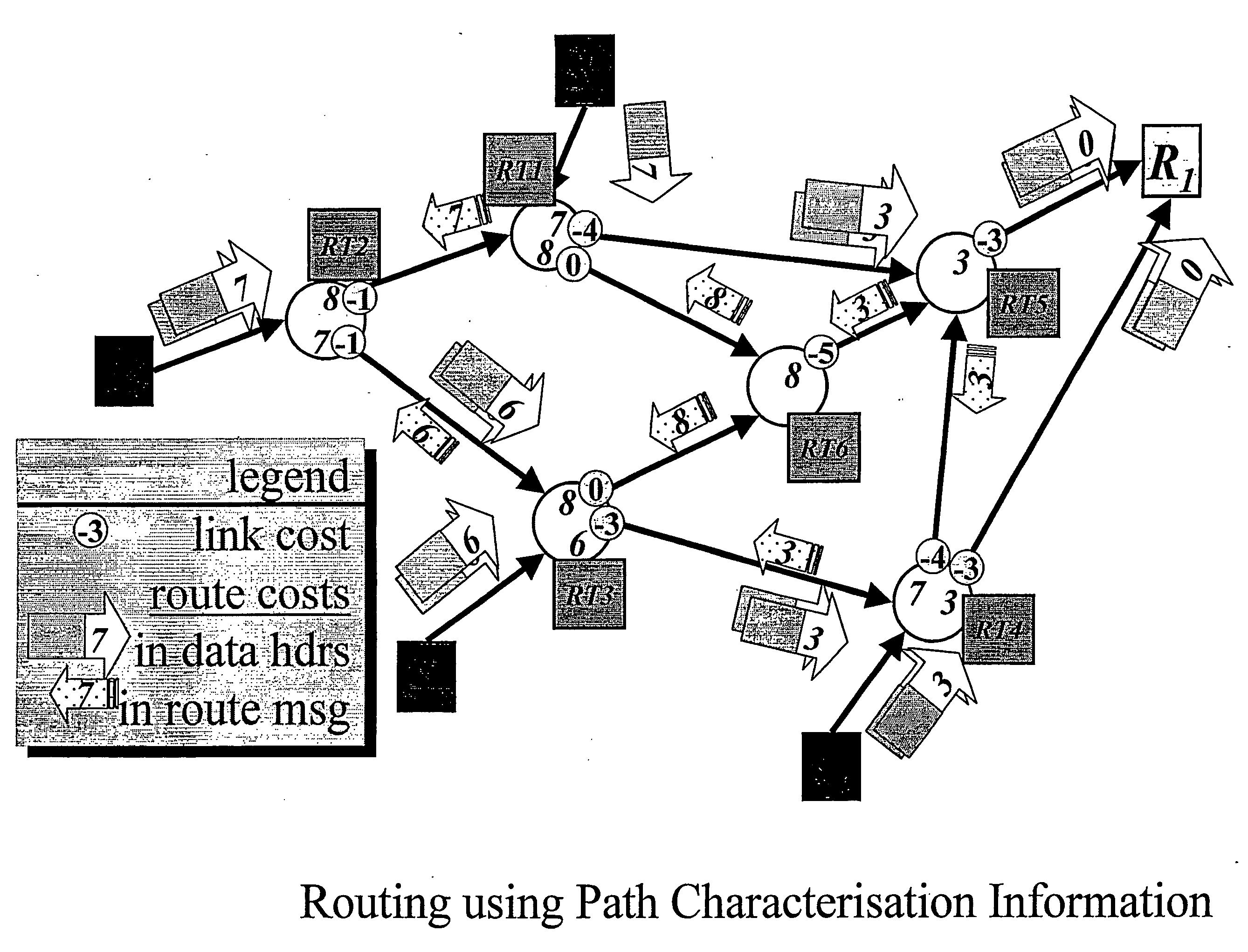
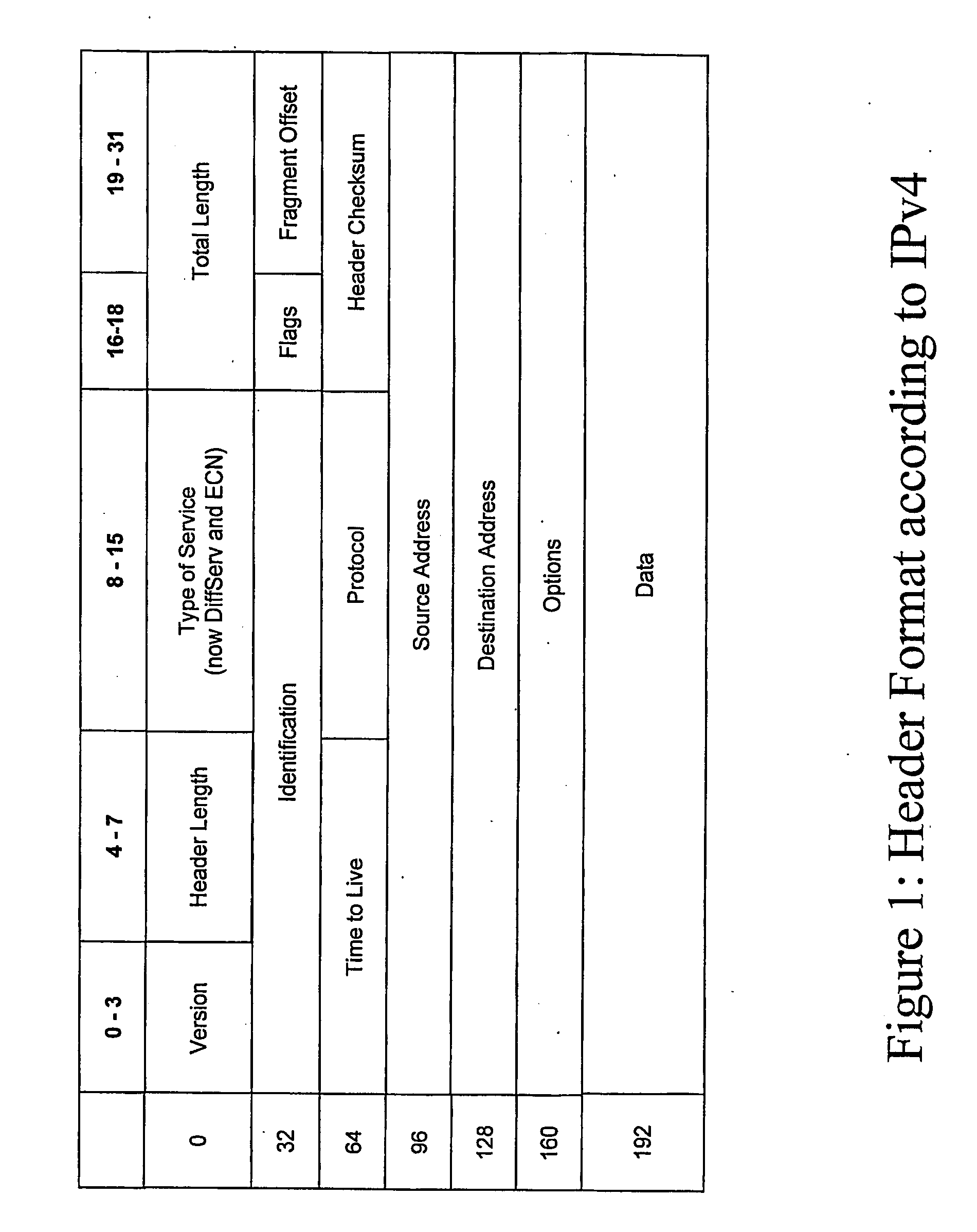
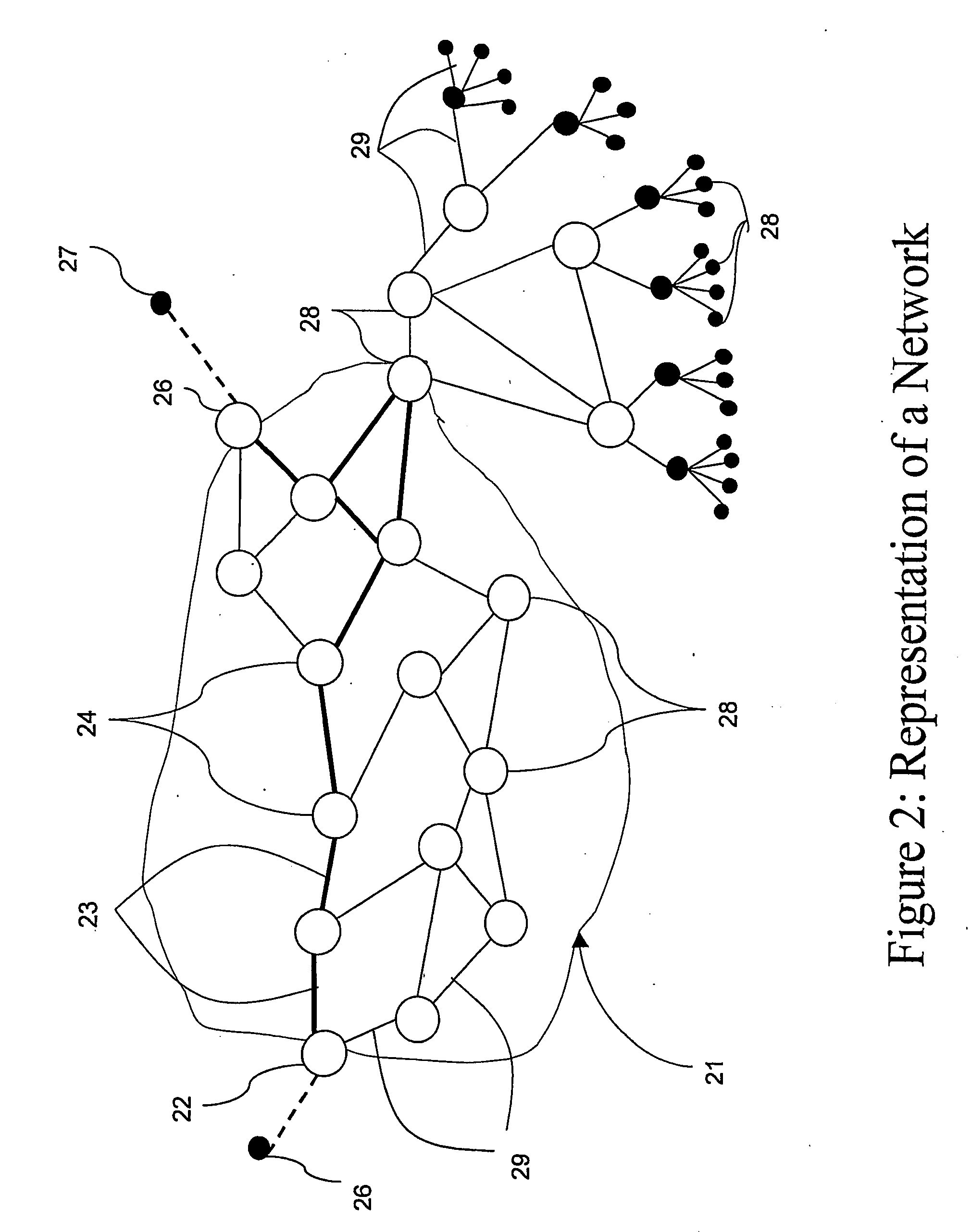
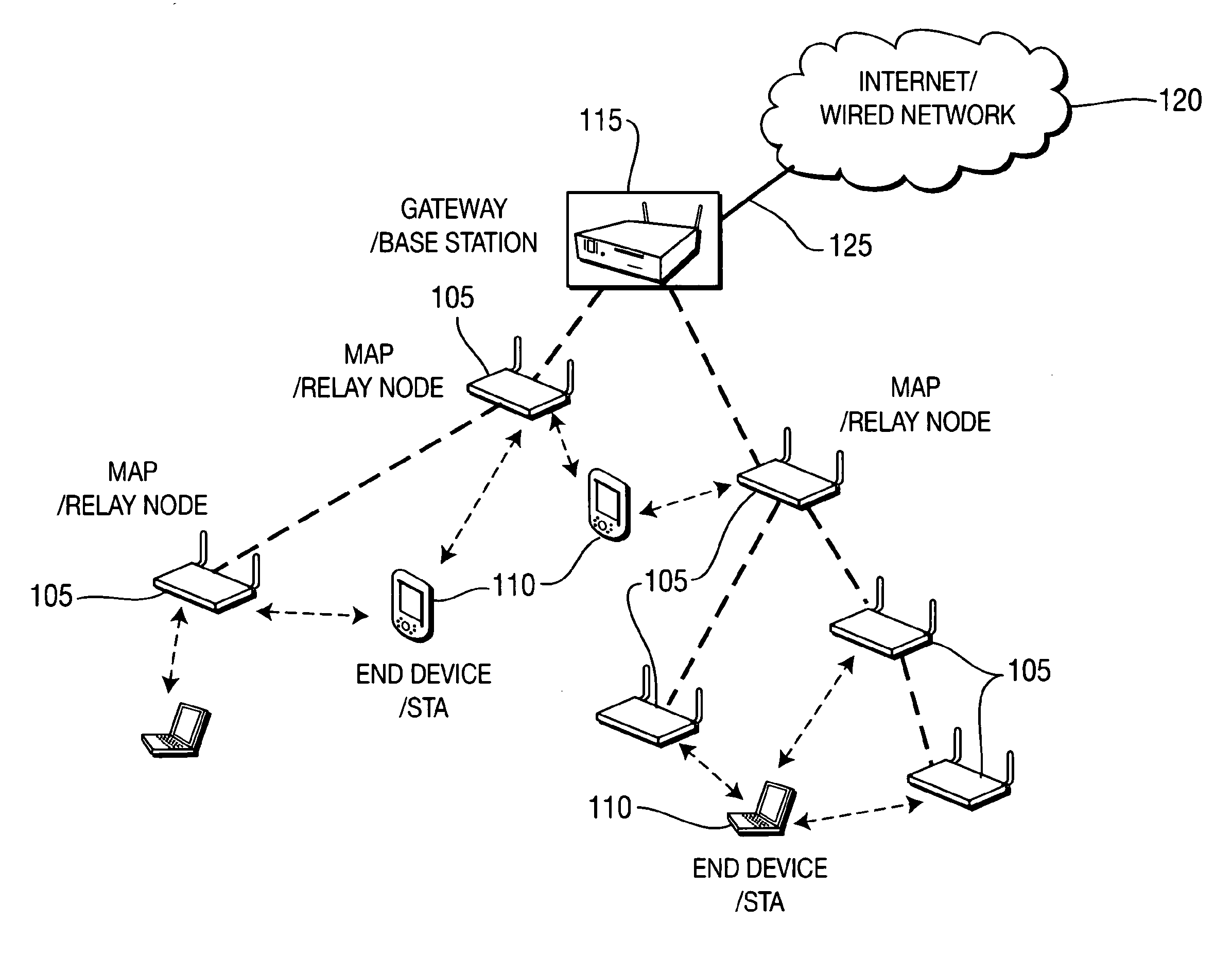
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
364 results about "Routing decision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Decision Routing uses the discipline of Decisis to incorporate math, statistics, logic and economics to seek understanding of all relevant factors before deciding. Armed with the whole truth analysis and decision-making the “final judgment” can be surprisingly simple (or as Einstein put it – as simple as possible, but not simpler!)
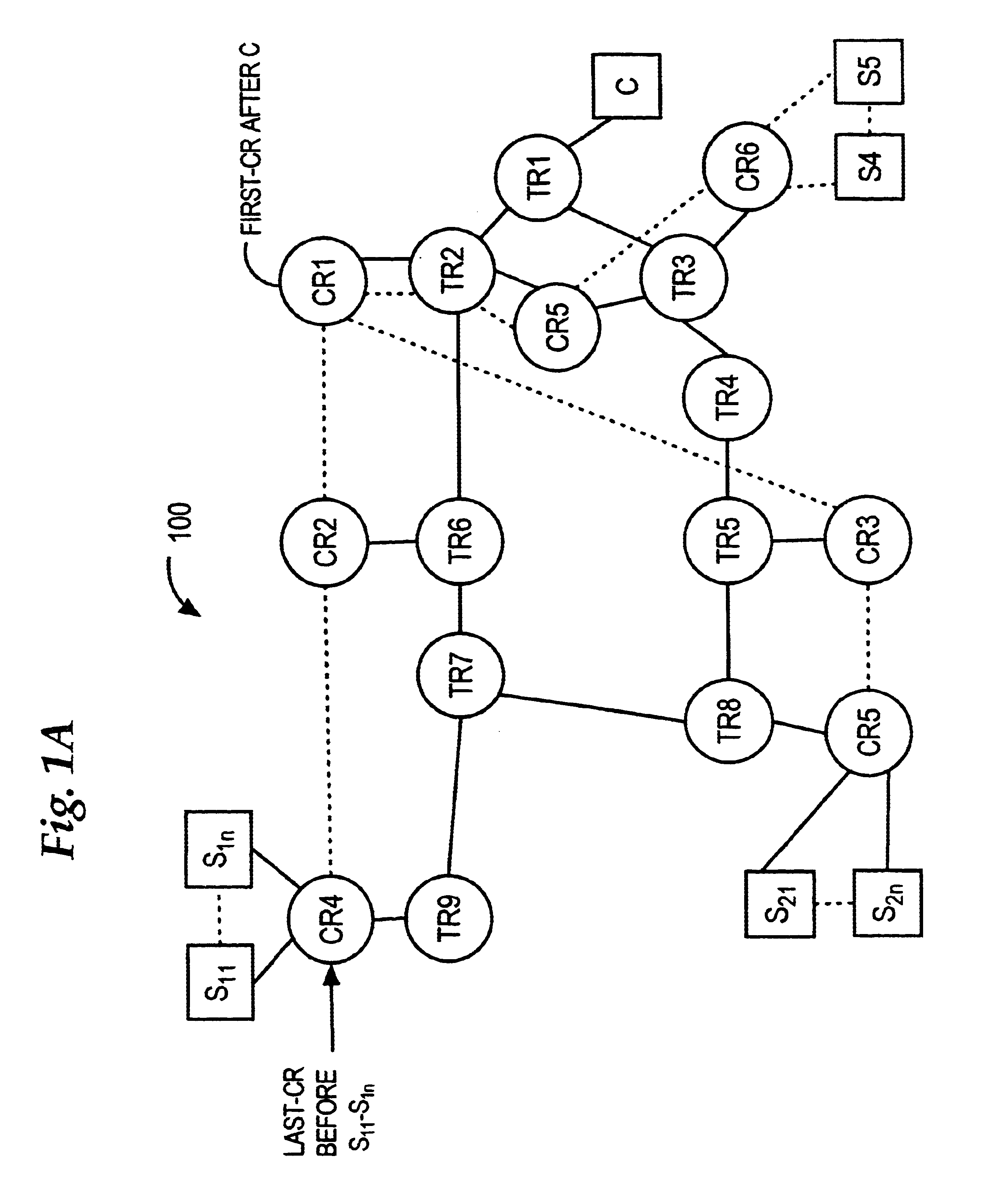
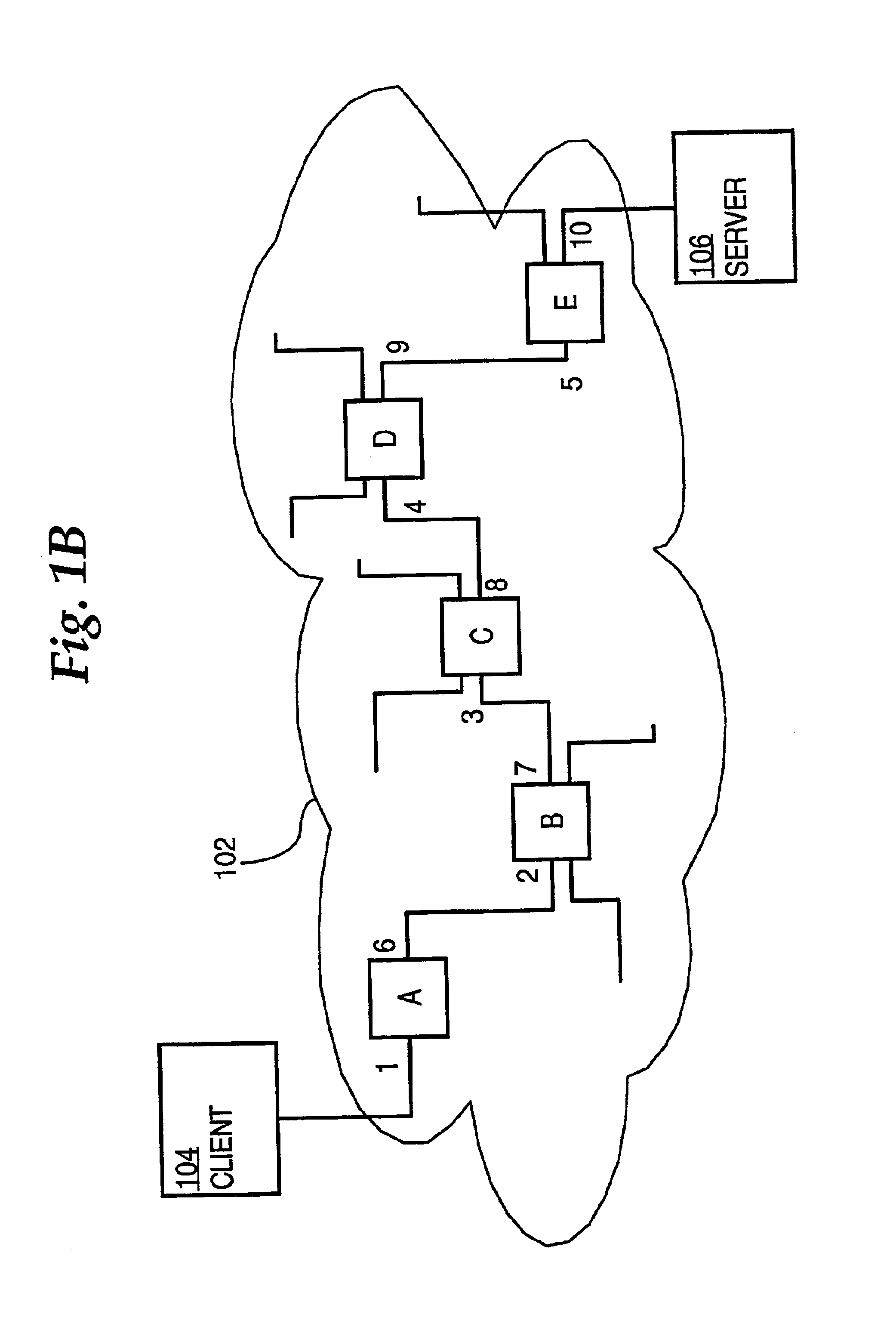
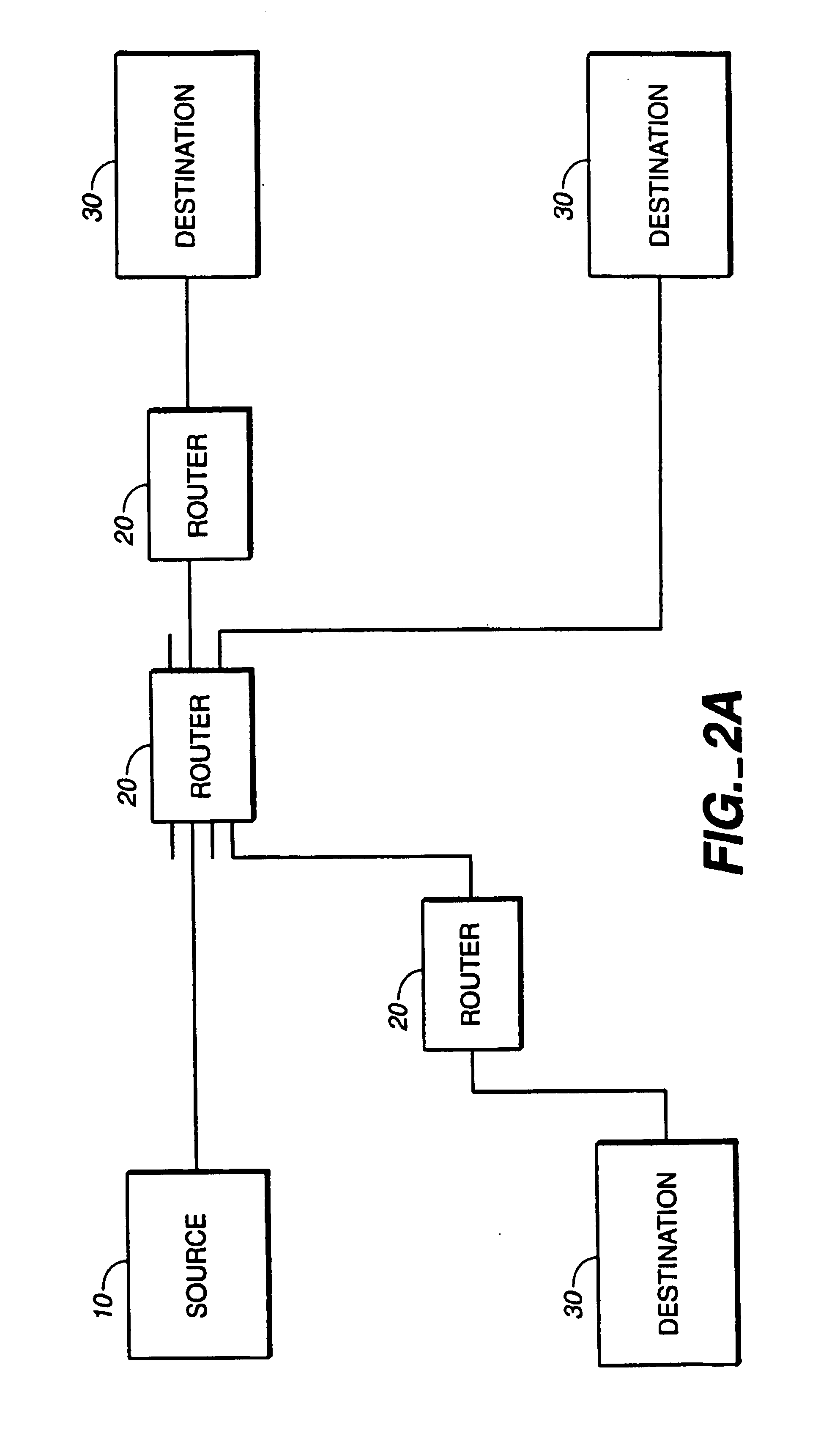
Server load balancing using IP option field approach to identify route to selected server
InactiveUS20060233155A1Improve efficiencyData switching by path configurationRouting decisionField methods
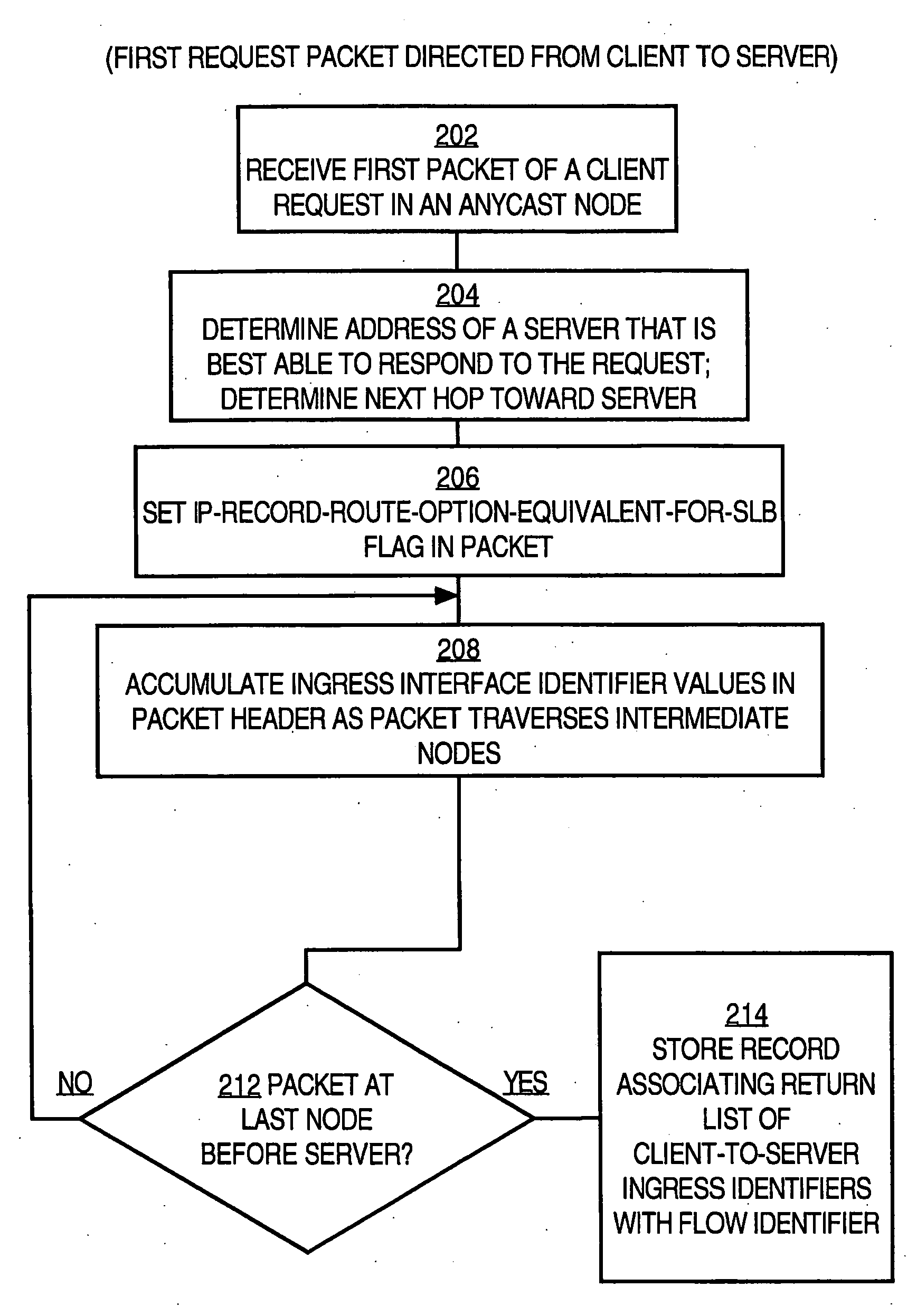
A router for routing data from a client through load-balancing nodes to a selected load-balanced server among a plurality of servers in a network involves: receiving, at a last load balancing node associated with a selected server among the plurality of servers, a first packet of a server reply to a request from the client; storing identifiers of ingress interfaces on which the packet arrives, in a send path list for server load balancing, as the first packet of the server reply is routed from the last load balancing node to the client using hop-by-hop decisions; receiving subsequent packets of the client request; and forwarding the subsequent packets to the selected server only on a route that is defined by the send path list and without hop-by-hop routing decisions. Packet flows are routed from the same client to the same server without hop-by-hop routing decisions or repeated load-balancing decisions.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
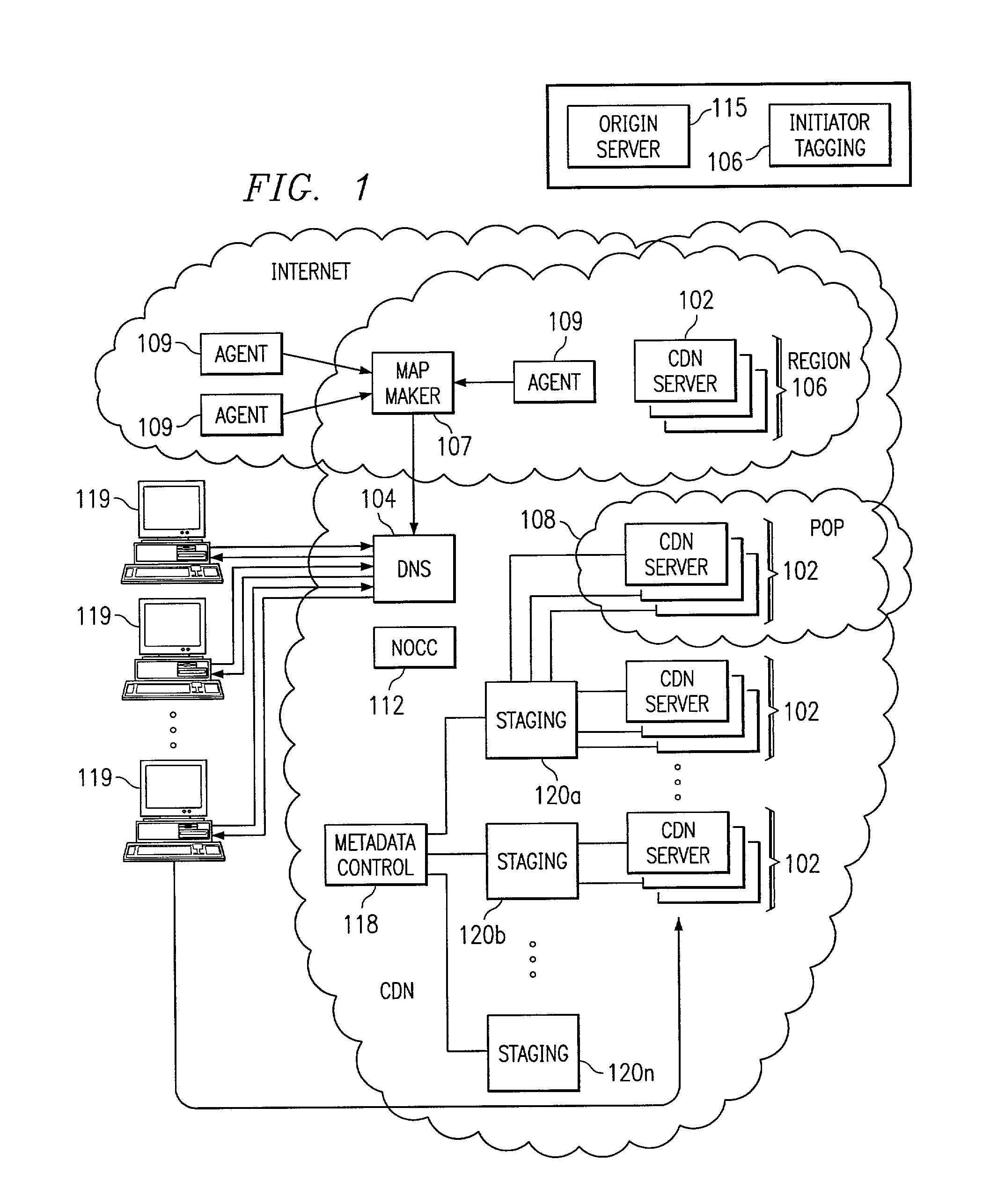
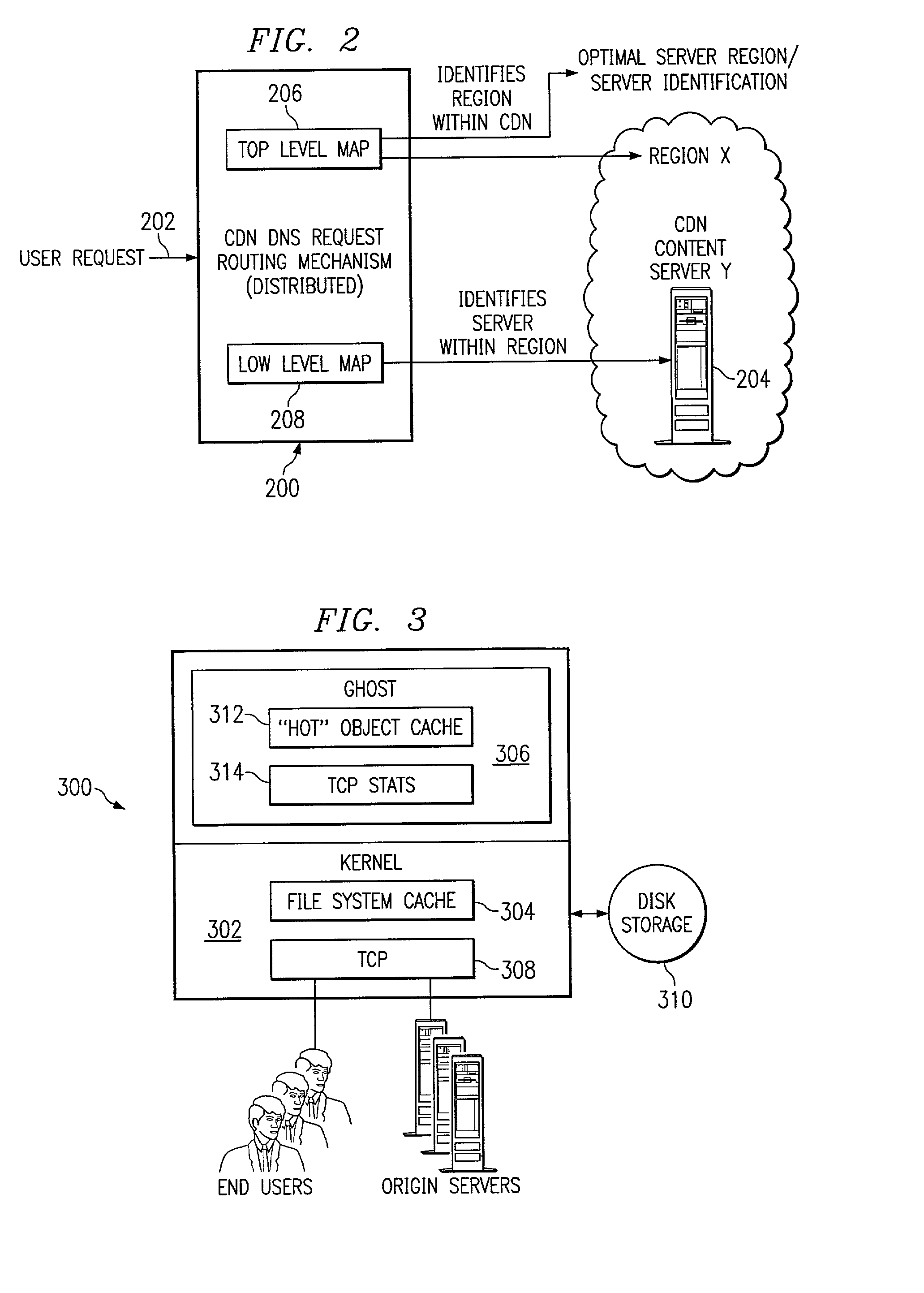
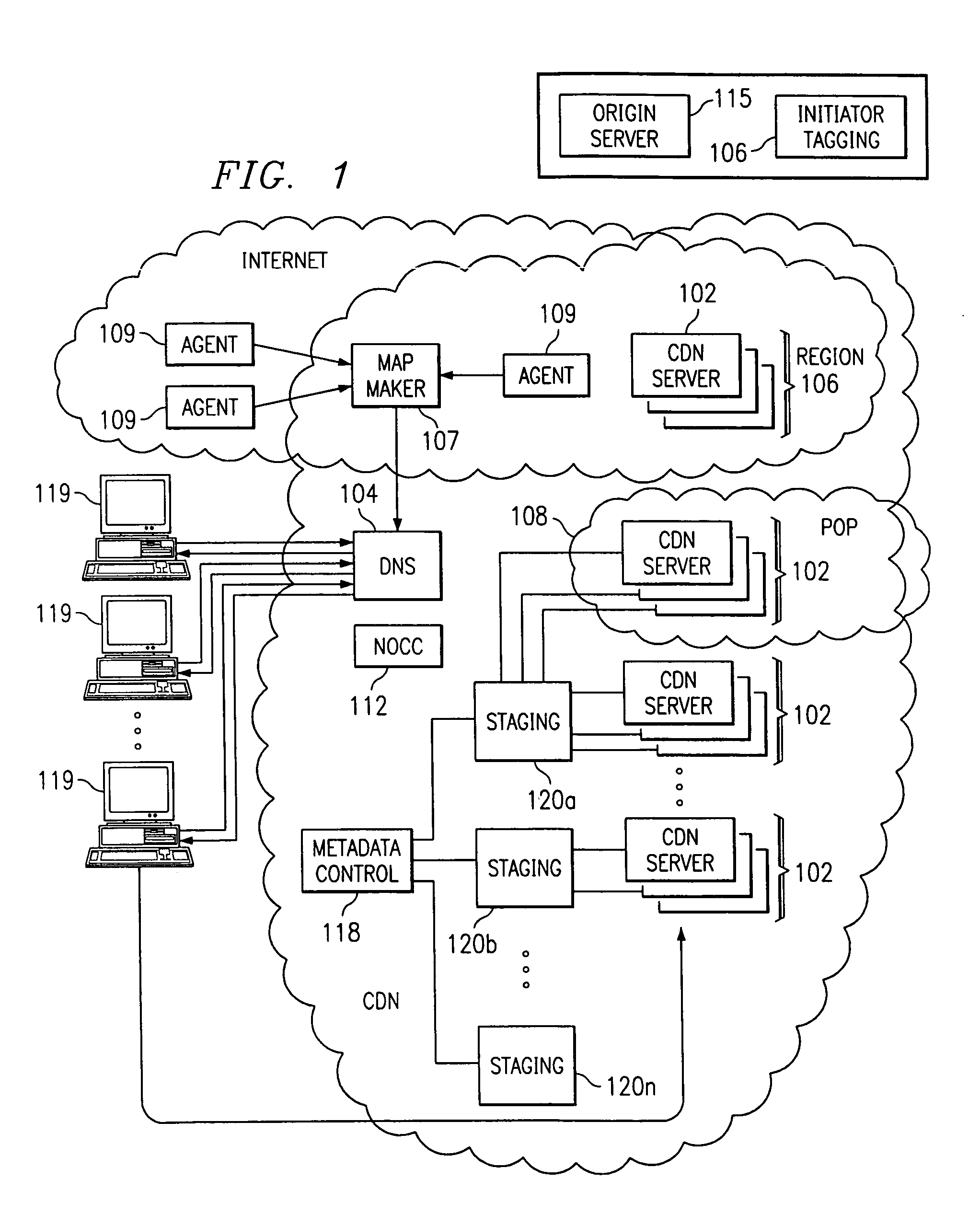
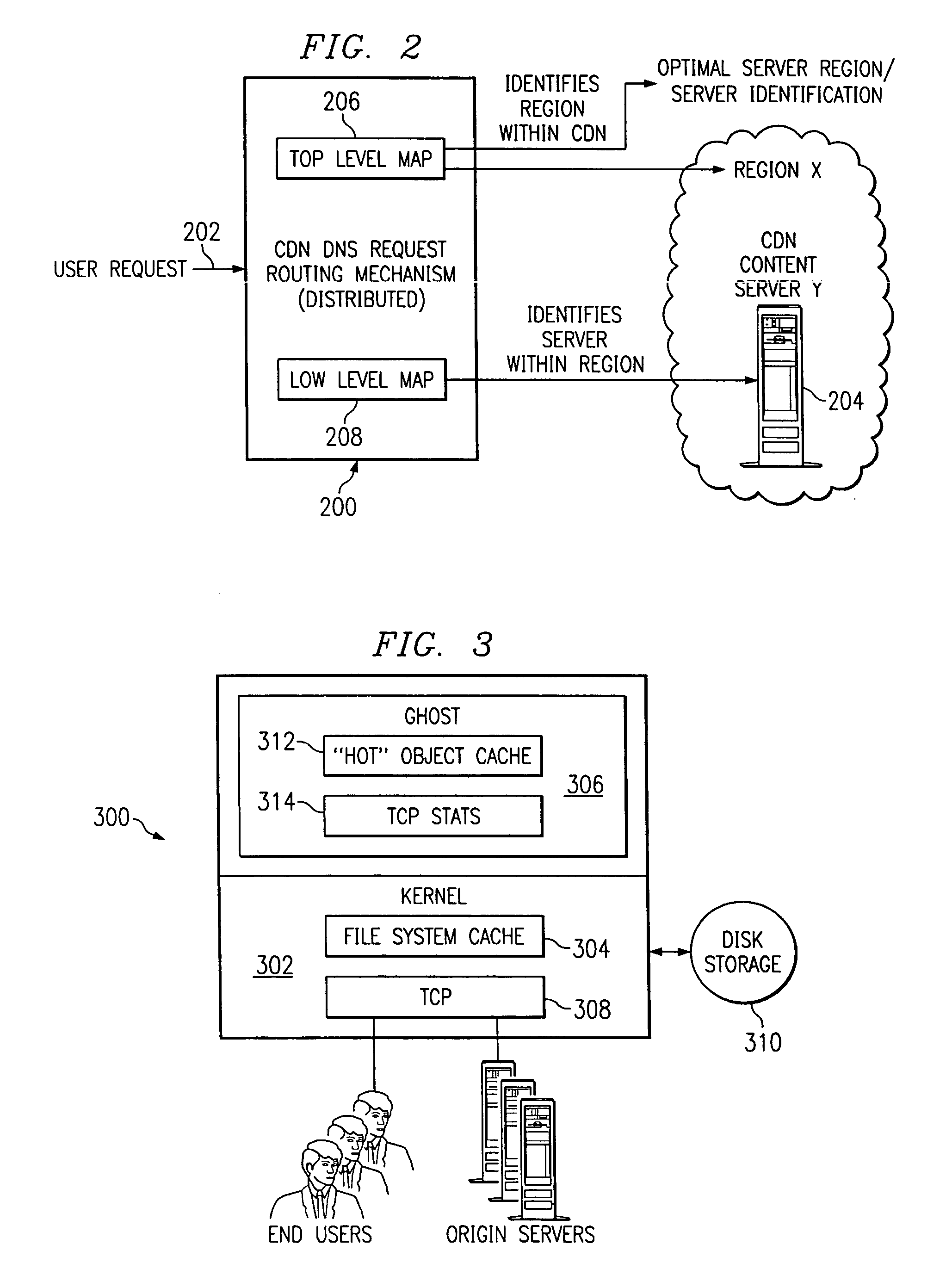
Content delivery network map generation using passive measurement data
ActiveUS7007089B2Easy mappingImprove subsequent routingDigital computer detailsData switching networksGeneration processRouting decision
A routing method operative in a content delivery network (CDN) where the CDN includes a request routing mechanism for routing clients to subsets of edge servers within the CDN. According to the routing method, TCP connection data statistics are collected are edge servers located within a CDN region. The TCP connection data statistics are collected as connections are established between requesting clients and the CDN region and requests are serviced by those edge servers. Periodically, e.g., daily, the connection data statistics are provdied from the edge servers in a region back to the request routing mechanism. The TCP connection data statistics are then used by the request routing mechanism in subsequent routing decisions and, in particular, in the map generation processes. Thus, for example, the TCP connection data may be used to determine whether a given quality of service is being obtained by routing requesting clients to the CDN region. If not, the request routing mechanism generates a map that directs requesting clients away from the CDN region for a given time period or until the quality of service improves.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Content delivery network map generation using passive measurement data
InactiveUS20060143293A1Improve subsequent routingDigital computer detailsData switching networksGeneration processRouting decision
A routing method operative in a content delivery network (CDN) where the CDN includes a request routing mechanism for routing clients to subsets of edge servers within the CDN. According to the routing method, TCP connection data statistics are collected are edge servers located within a CDN region. The TCP connection data statistics are collected as connections are established between requesting clients and the CDN region and requests are serviced by those edge servers. Periodically, e.g., daily, the connection data statistics are provdied from the edge servers in a region back to the request routing mechanism. The TCP connection data statistics are then used by the request routing mechanism in subsequent routing decisions and, in particular, in the map generation processes. Thus, for example, the TCP connection data may be used to determine whether a given quality of service is being obtained by routing requesting clients to the CDN region. If not, the request routing mechanism generates a map that directs requesting clients away from the CDN region for a given time period or until the quality of service improves.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
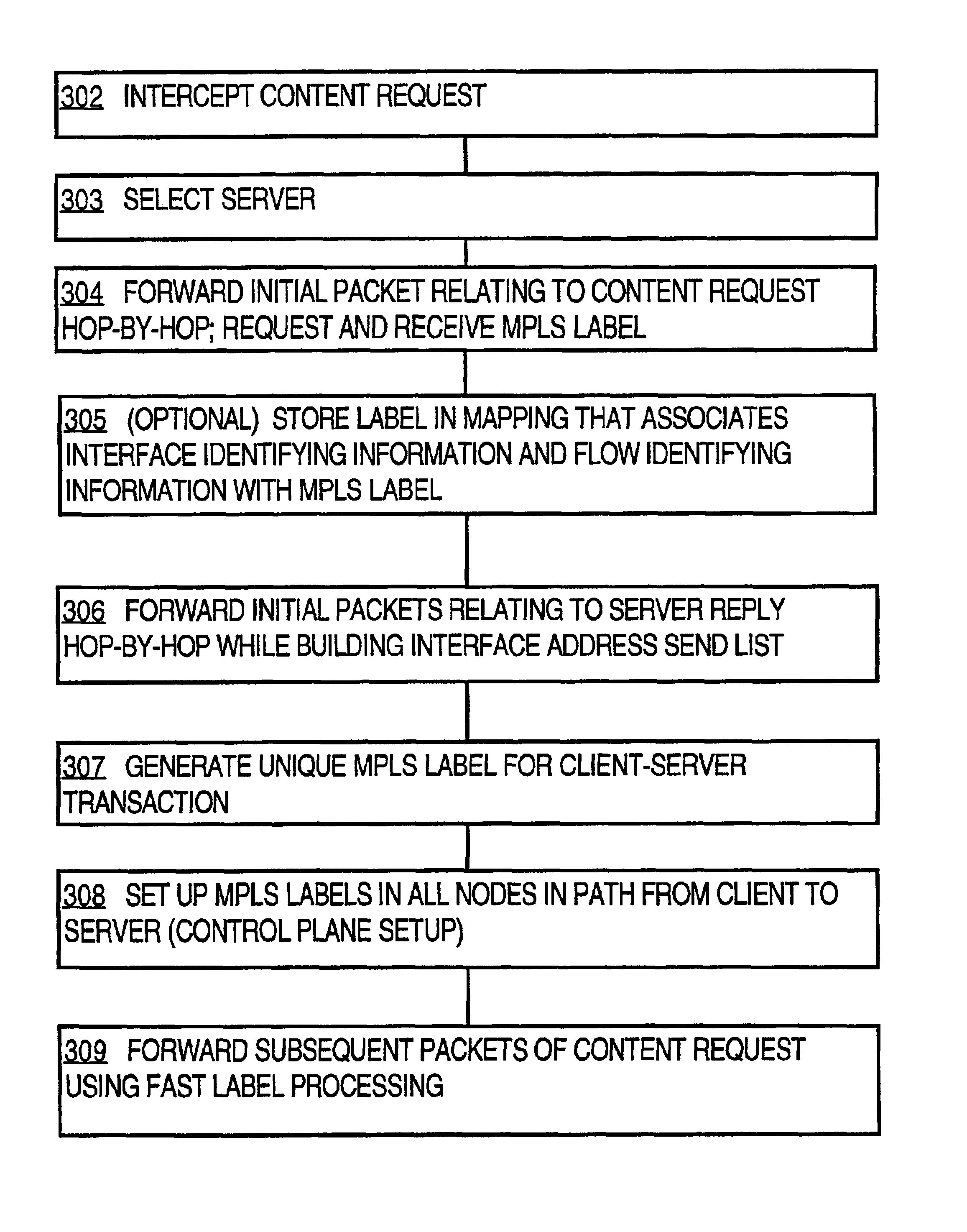
Method and apparatus for routing data to a load balanced server using MPLS packet labels
InactiveUS6856991B1Improve efficiencyDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsRouting decisionNetwork packet
A method of routing data to a load-balanced server through a network having one or more load-balancing nodes is disclosed. The first packet of a client request is received at one of the load-balancing nodes, which stores information identifying a flow associated with the packet and an incoming interface identifier. The node then makes a server load-balancing decision and stores an outgoing interface identifier. When the packet reaches the last load-balancing node before the selected server, that last node also requests an MPLS label to uniquely identify the flow, connection and route. The label is stored in a mapping at the last node that associates the label with the flow and interface identifying information. The packet is routed to the selected server. The first server response packet is switched hop-by-hop and the MPLS label is stored at each node traversed by the response packets, in association with a flow identifier and incoming and outgoing interface identifiers. For all other packets in the request and response, nodes fast-switch the packets based on the label mappings. As a result, packet flows are rapidly routed from the same client to the same server without time-consuming hop-by-hop routing decisions or repeated load-balancing decisions.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
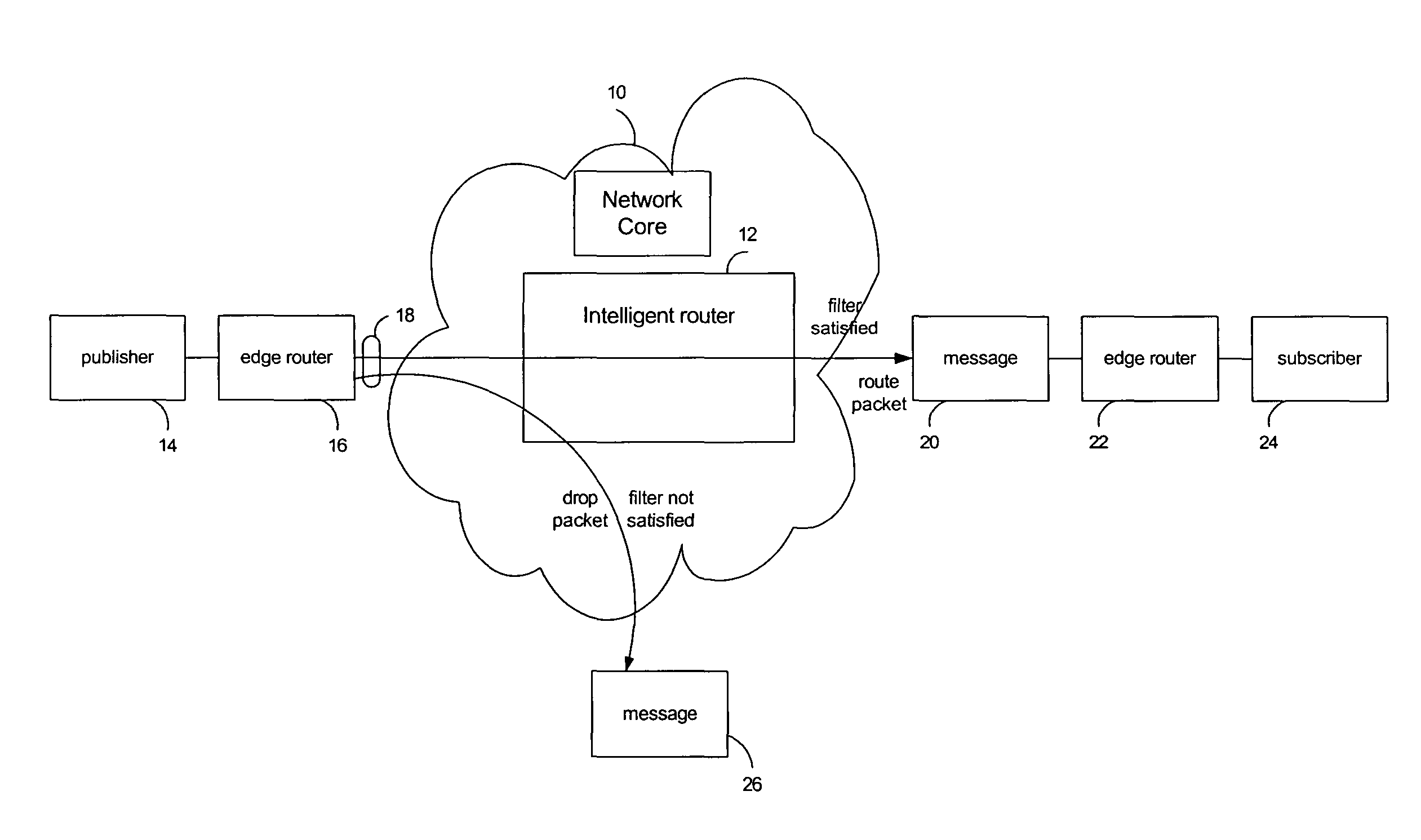
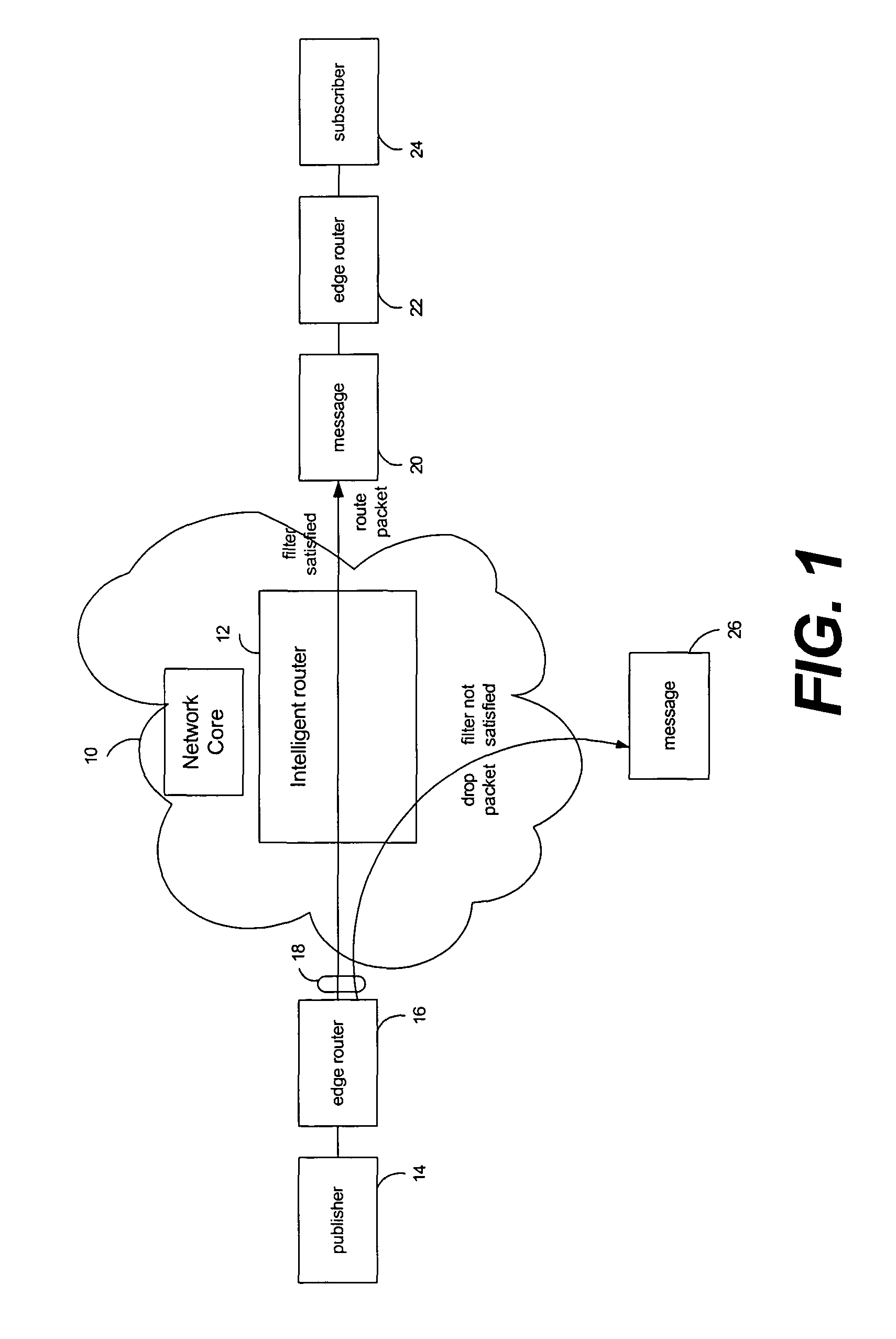
Caching with selective multicasting in a publish-subscribe network
ActiveUS7672275B2Efficient routingOvercome disadvantagesData switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesRouting decisionEncapsulated data
Packet routing via payload inspection at routers in a core of a distributed network. Packets include subjects and attributes in addition to routing information. The subjects correspond with particular types of content for subscriptions, and the attributes encapsulate the data or content. The routers store filters corresponding with subscriptions to content. Upon receiving a packet, a router inspects the payload section of the packet containing the attributes in order to retrieve the attributes and apply them to the filters for the subscriptions. If an attribute satisfies a filter, the packet is routed to the next link. If the attributes do not satisfy the filters, the router discards the packet. These routing decisions are distributed among routers in the network core. The router locally caches the data in the network core.
Owner:PRECACHE
Systems, methods, and devices for managing routing
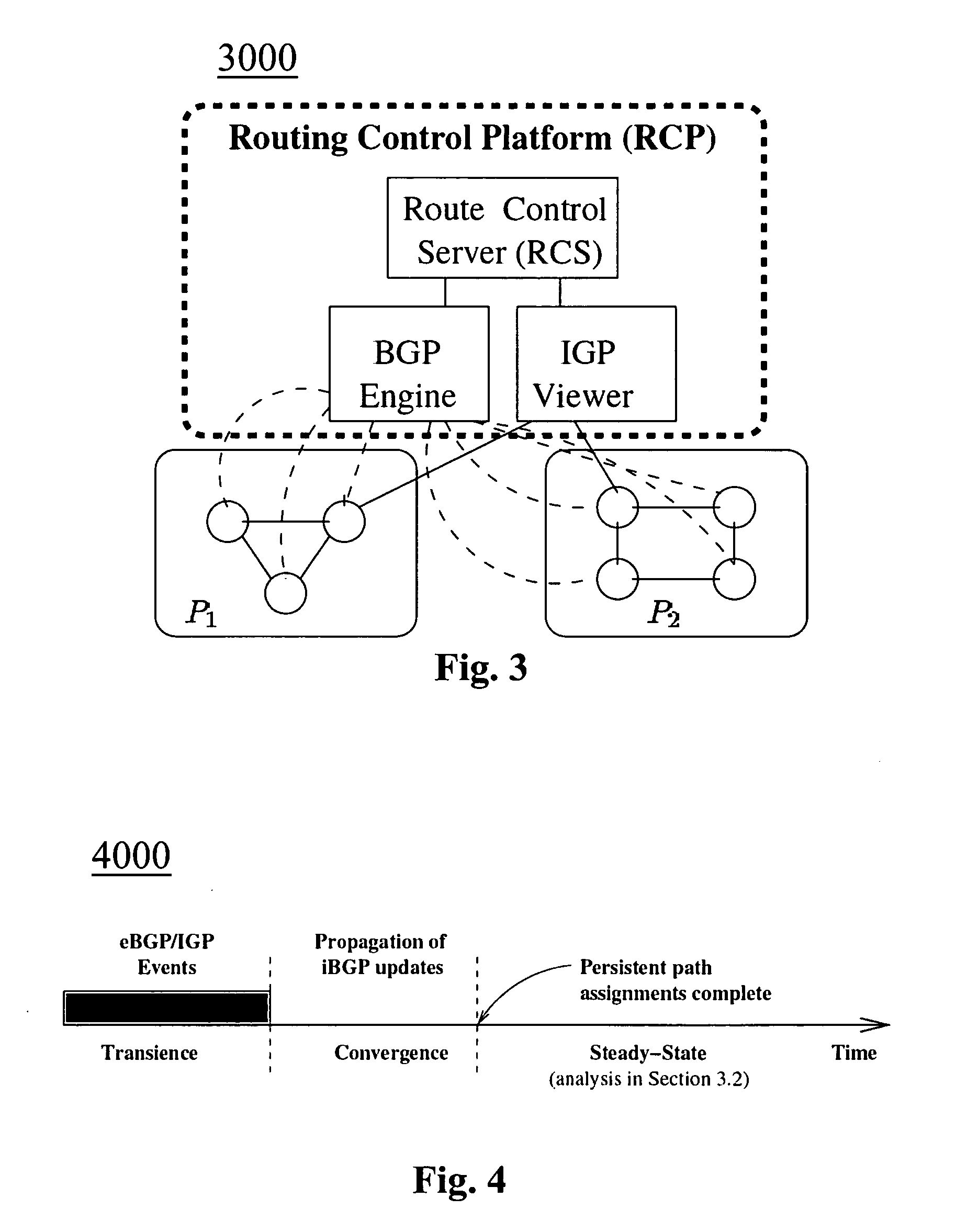
Certain exemplary embodiments comprise a method comprising a plurality of activities, comprising: for each of the plurality of routing entities in an AS: obtaining IGP topology information; learning available BGP routes associated with the routing entity; utilizing the available BGP routes and the IGP topology information for all routing entities in the AS, assigning the routing entity a customized routing decision comprising a BGP route; and sending the customized routing decision to the routing entity.
Owner:CALDWELL DONALD +3
Server load balancing using IP option field approach to identify route to selected server
ActiveUS7088718B1Improve efficiencyData switching by path configurationRouting decisionNetwork packet
A method of routing data from a client through one or more load-balancing nodes to a selected load-balanced server among a plurality of servers in a network involves: receiving, at a last load balancing node associated with a selected server among the plurality of servers, a first packet of a server reply to a request from the client; setting a first flag value in the first packet of the server reply; storing one or more identifiers of ingress interfaces on which the packet arrives, in a send path list for server load balancing, as the first packet of the server reply is routed from the last load balancing node to the client using hop-by-hop decisions; receiving one or more subsequent packets of the client request; setting a second flag value in each of the subsequent packets; and forwarding the subsequent packets to the selected server only on a route that is defined by the send path list and without hop-by-hop routing decisions. As a result, packet flows are rapidly routed from the same client to the same server without time-consuming hop-by-hop routing decisions or repeated load-balancing decisions.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
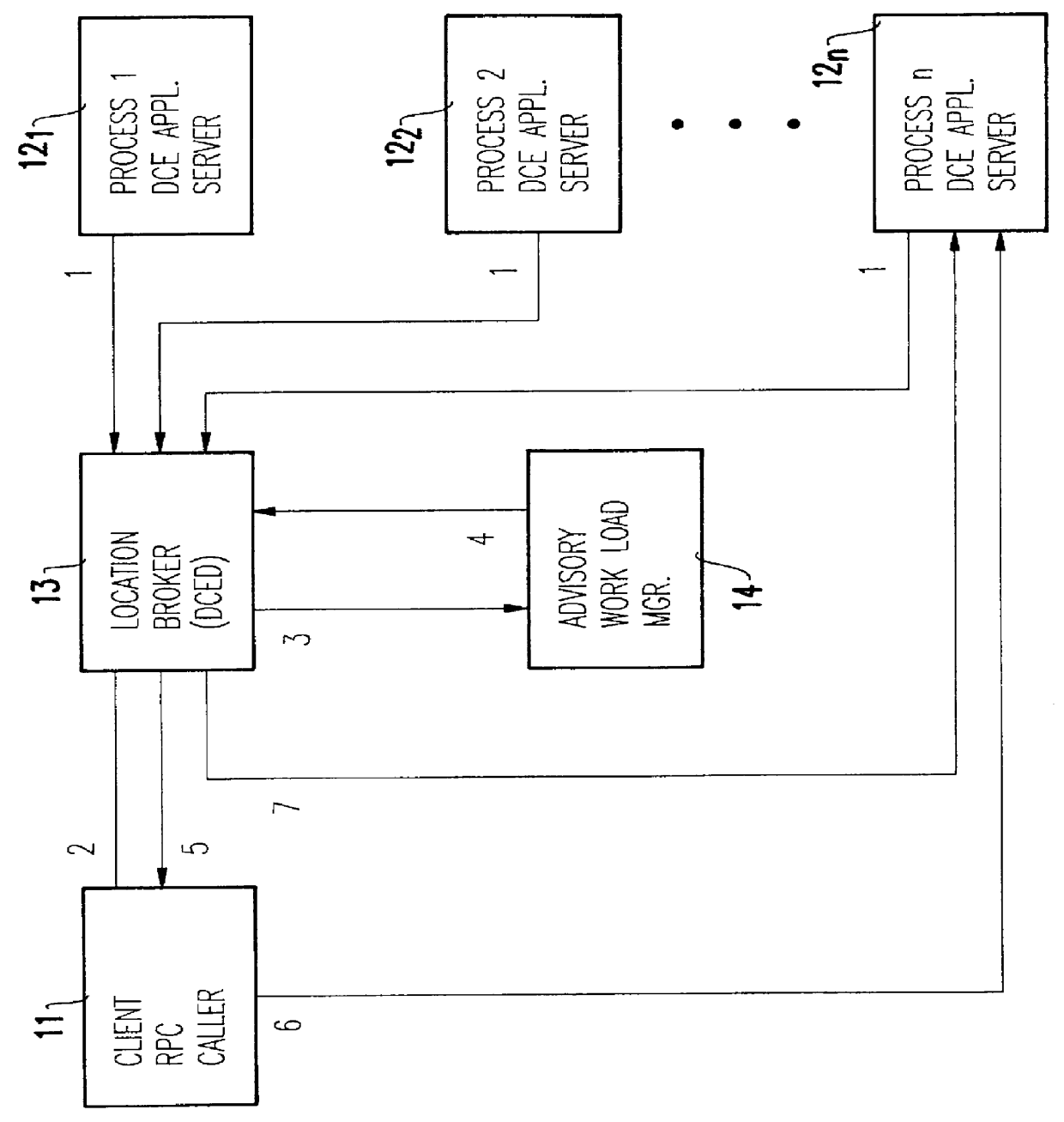
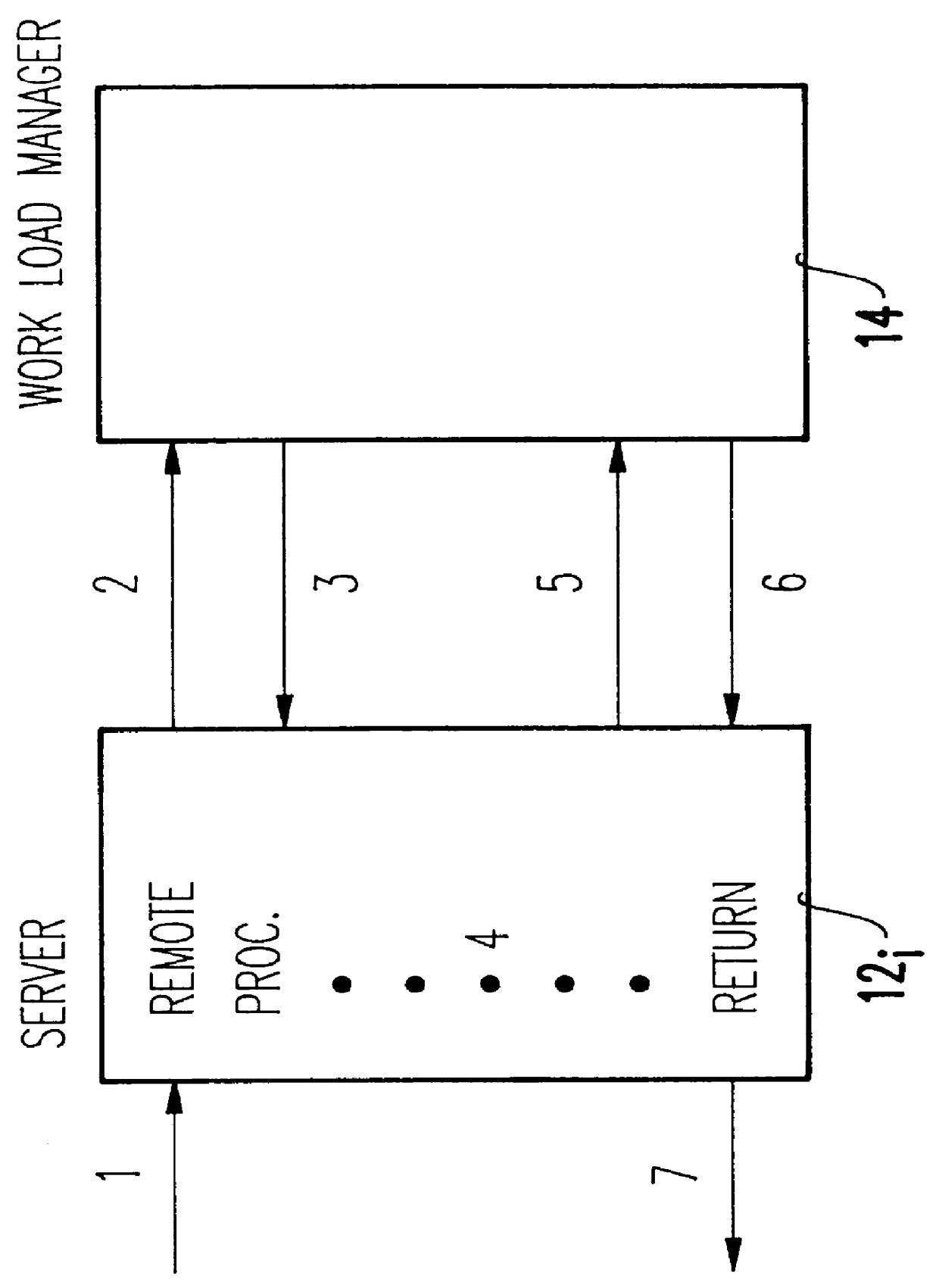
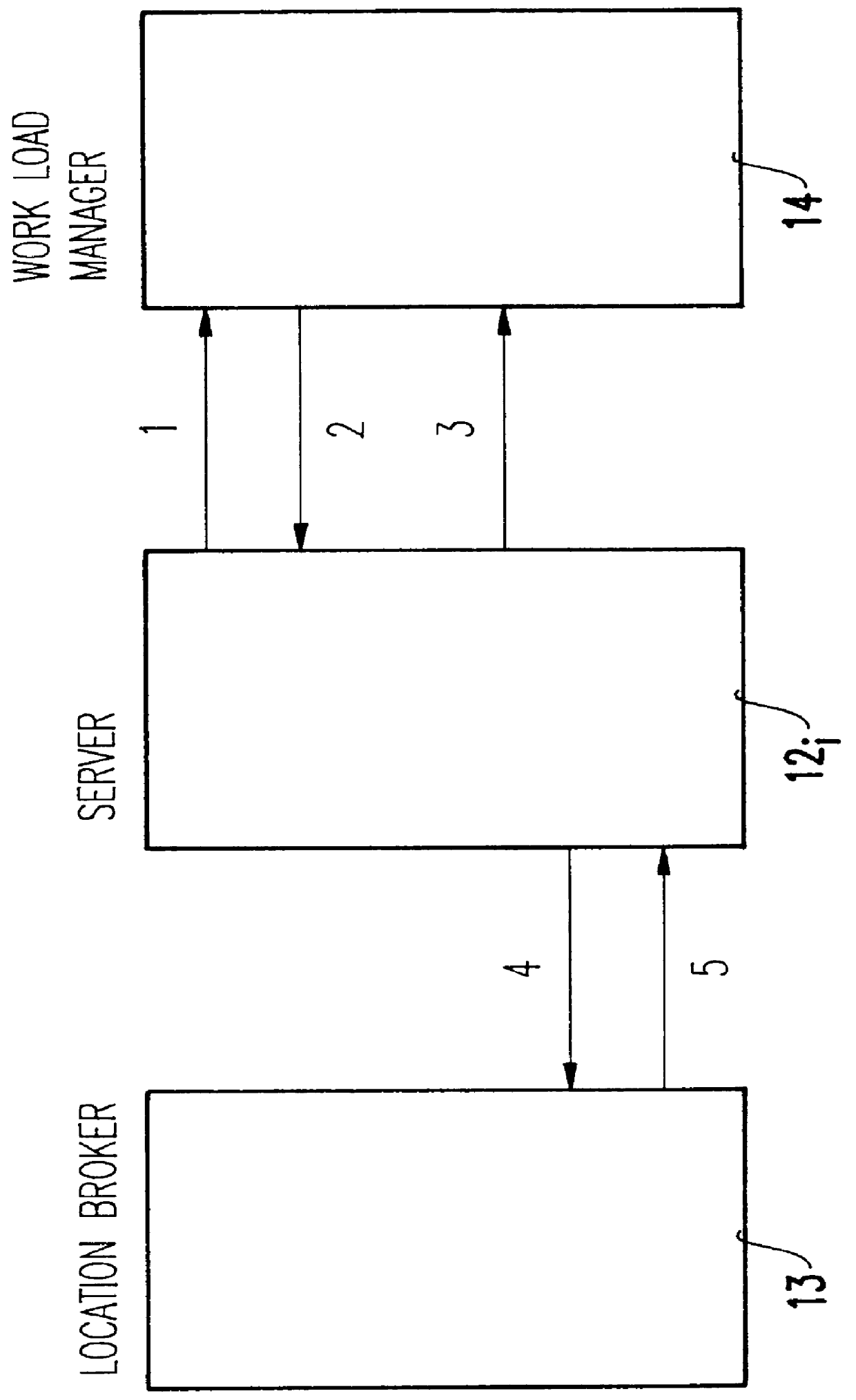
Integrating distributed computing environment remote procedure calls with an advisory work load manager
InactiveUS6067580AResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsAmbulatory systemDistributed Computing Environment
Distributed computing environment (DCE) remote procedure calls (RPCs) are integrated with an advisory work load manager (WLM) to provide a way to intelligently dispatch RPC requests among the available application server processes. The routing decisions are made dynamically (for each RPC) based on interactions between the location broker and an advisory work load manager. Furthermore, when the system contains multiple coupled processors (tightly coupled within a single frame, or loosely coupled within a computing complex, a local area network (LAN) configuration, a distributed computing environment (DCE) cell, etc.), the invention extends to balance the processing of RPC requests and the associated client sessions across the coupled systems. Once a session is assigned to a given process, the invention also supports performance monitoring and reporting, dynamic system resource allocation for the RPC requests, and potentially any other benefits that may be available through the specific work load manager (WLM).
Owner:IBM CORP
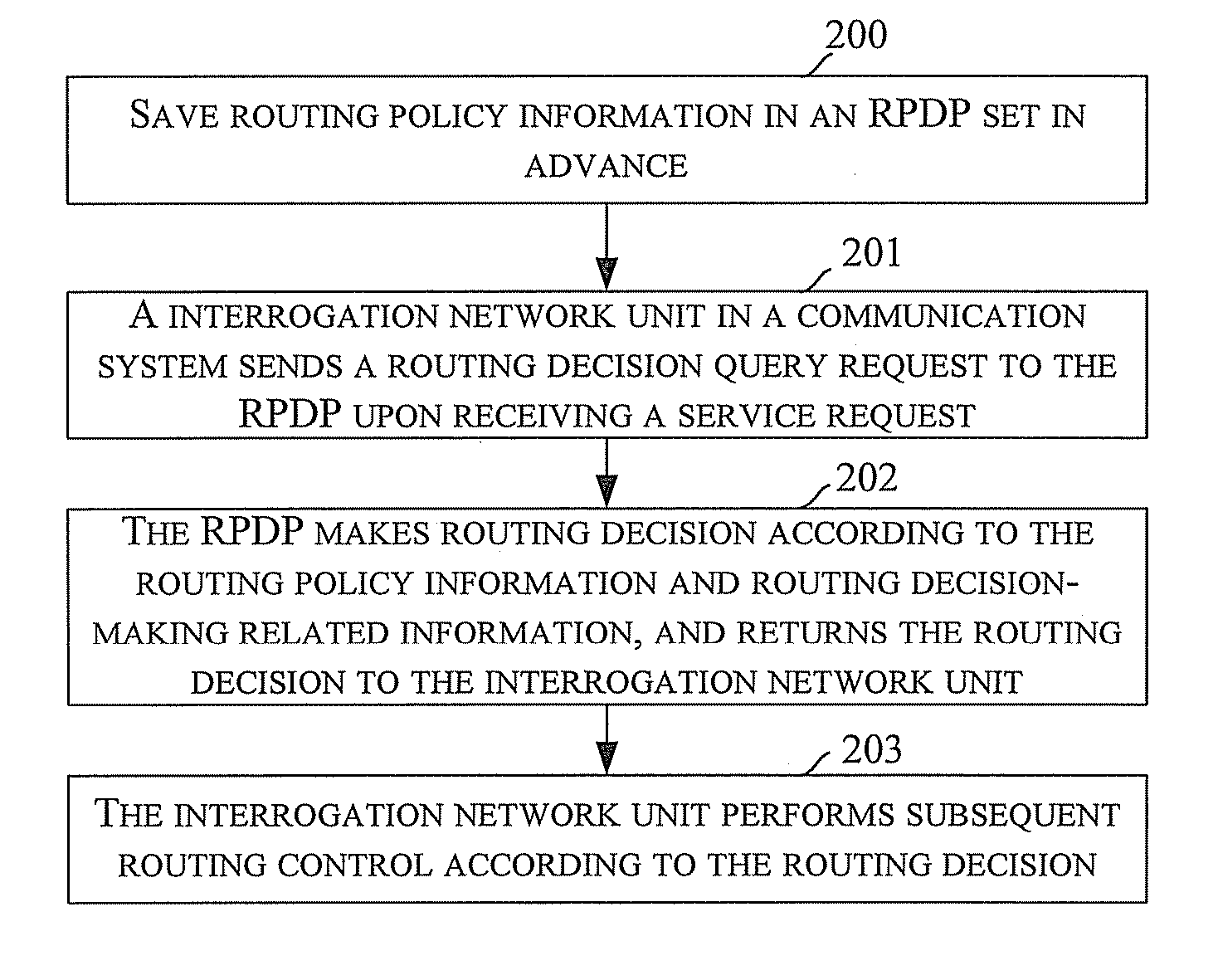
Method and system for routing control
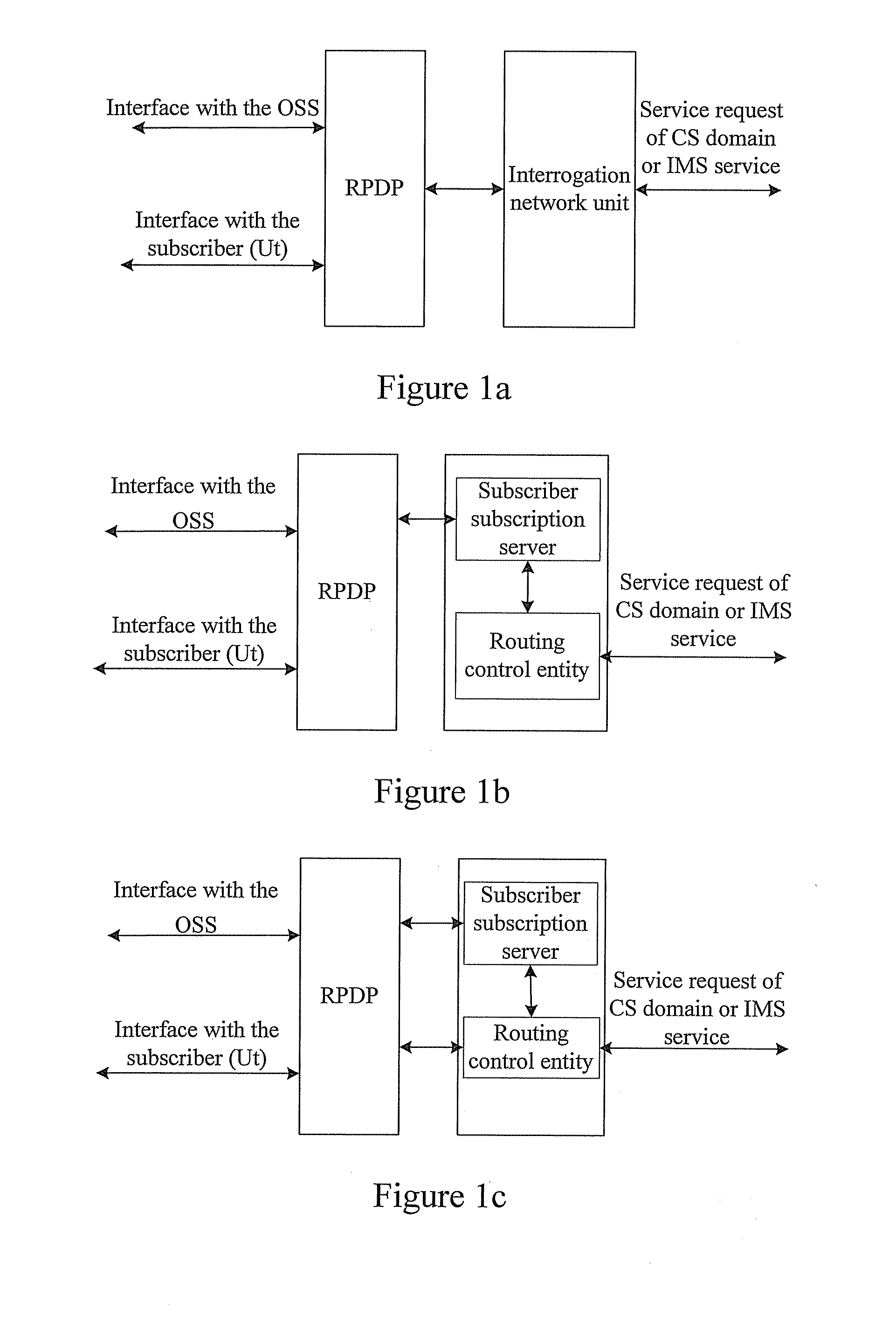
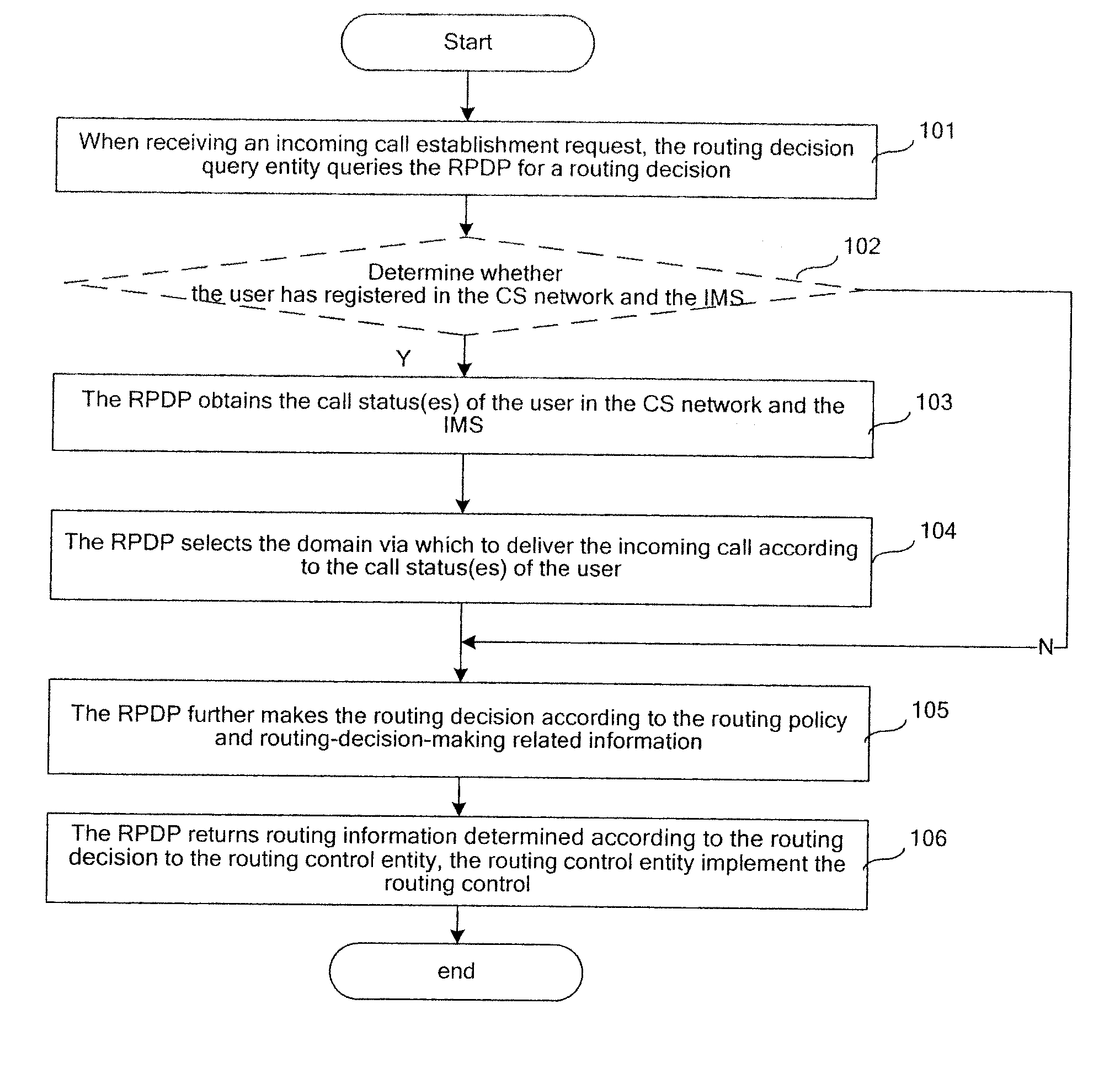
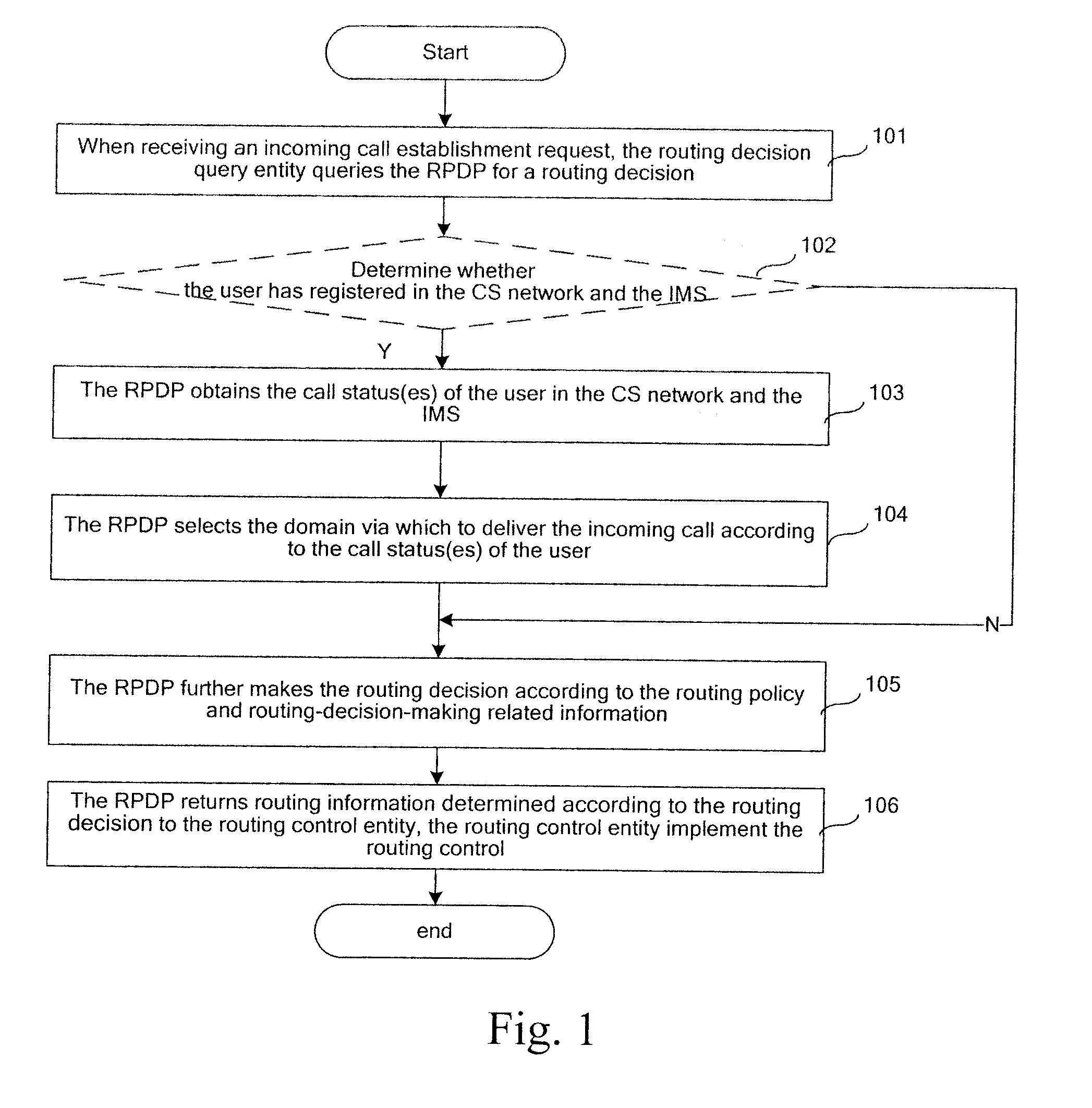
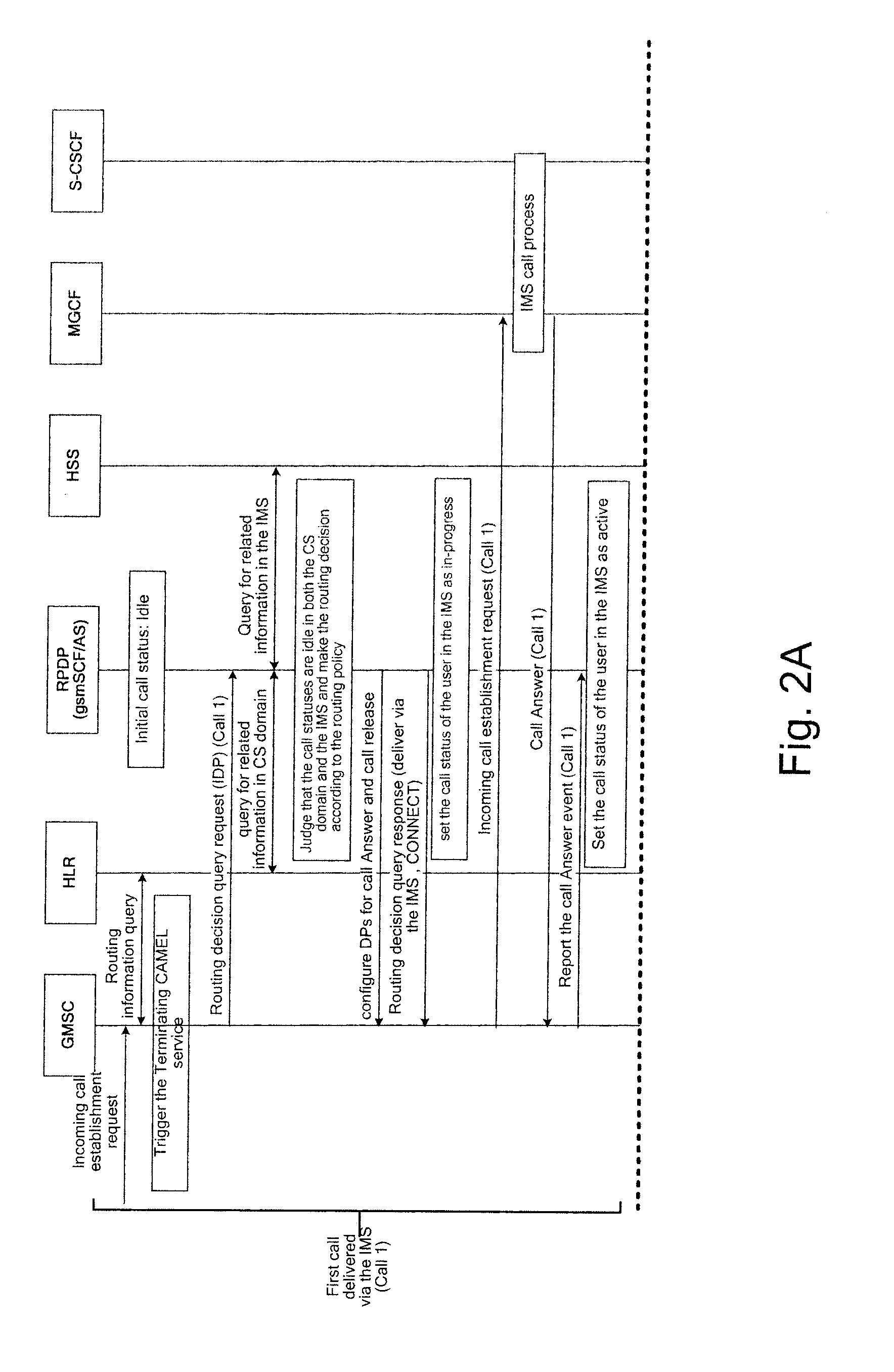
InactiveUS20080039104A1Routing decisionImprove user experienceWireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRouting decisionPolicy decision
Embodiments of the present invention disclose a method for routing control applied to a communication system including a CS domain and an IMS and in which a Routing Policy Decision-making Point (RPDP) is set; and the method includes: initiating a routing query to the RPDP by an interrogation network unit in the communication system upon receiving a service request; making a routing decision by the RPDP according to routing decision-making related information and the routing policy information, returning the routing decision to the interrogation networking unit by the RPDP; and performing subsequent routing control by the interrogation network unit according to the routing decision. Embodiments of the present invention also disclose a system for routing control. In accordance with the embodiments of the present invention, across-domain routing control is thus realized in different network application environments according to different demands.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for routing data to a load balanced server using MPLS packet labels
InactiveUS20050149531A1Improve efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLoad SheddingRouting decision
A method of routing data to a load-balanced server through a network having one or more load-balancing nodes is disclosed, comprising receiving a label value; storing the label value in a load balancing mapping at a load-balancing node in a network, wherein the load balancing mapping associates the label with a packet flow and with interface identifying information; and forwarding subsequent packets of the flow to a selected load-balancing server. The forwarding route is defined by the load-balancing mapping and without hop-by-hop routing decisions. The first server response packet is switched hop-by-hop and the label is stored at each node traversed by the response packets, with a flow identifier and interface identifiers. For other request and response packets, nodes fast-switch the packets based on the label mappings; thus, packet flows are rapidly routed from the client to the same server without time-consuming hop-by-hop routing or repeated load-balancing decisions.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for delivering packet data over a multiplicity of communication links
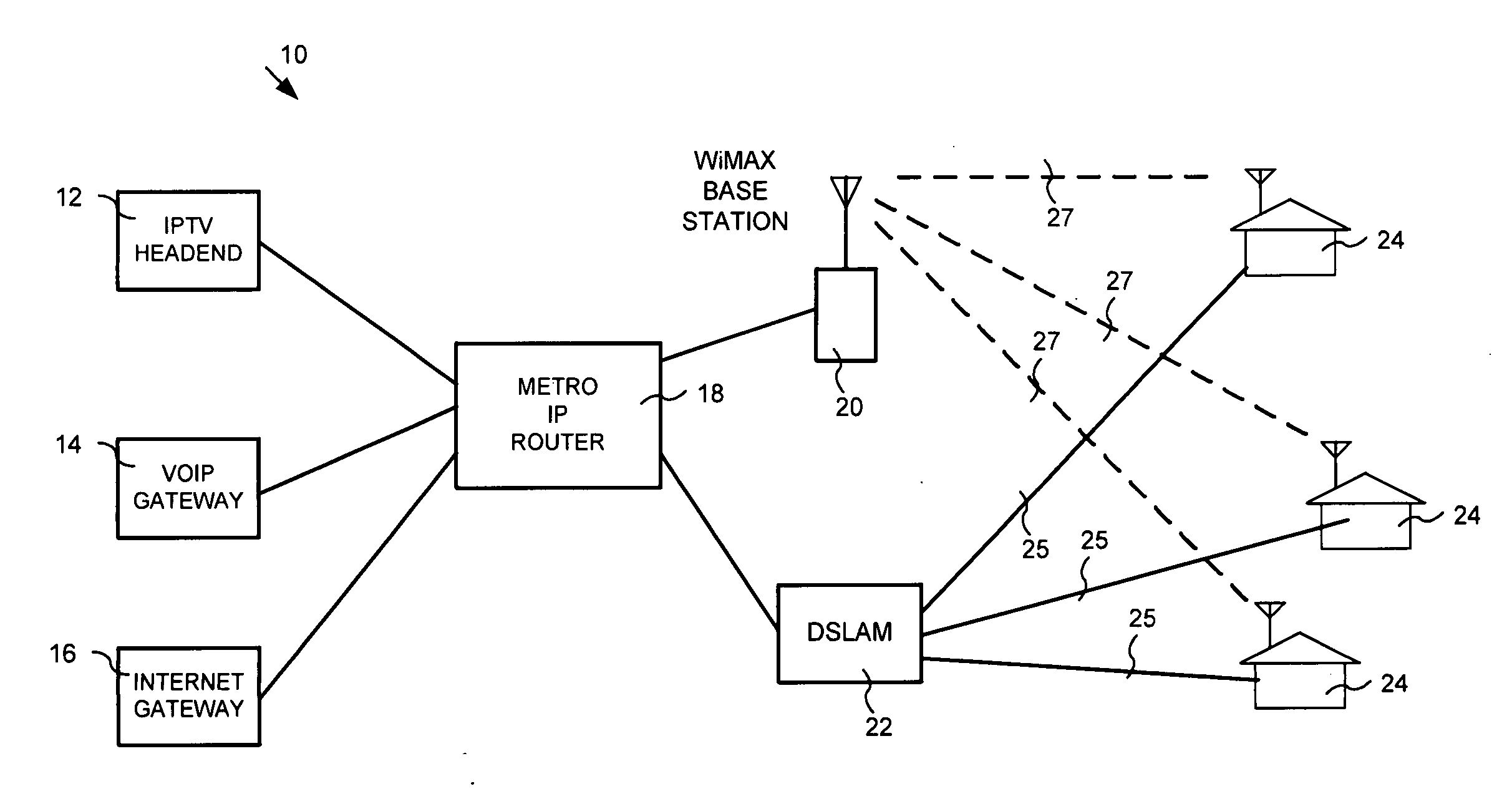
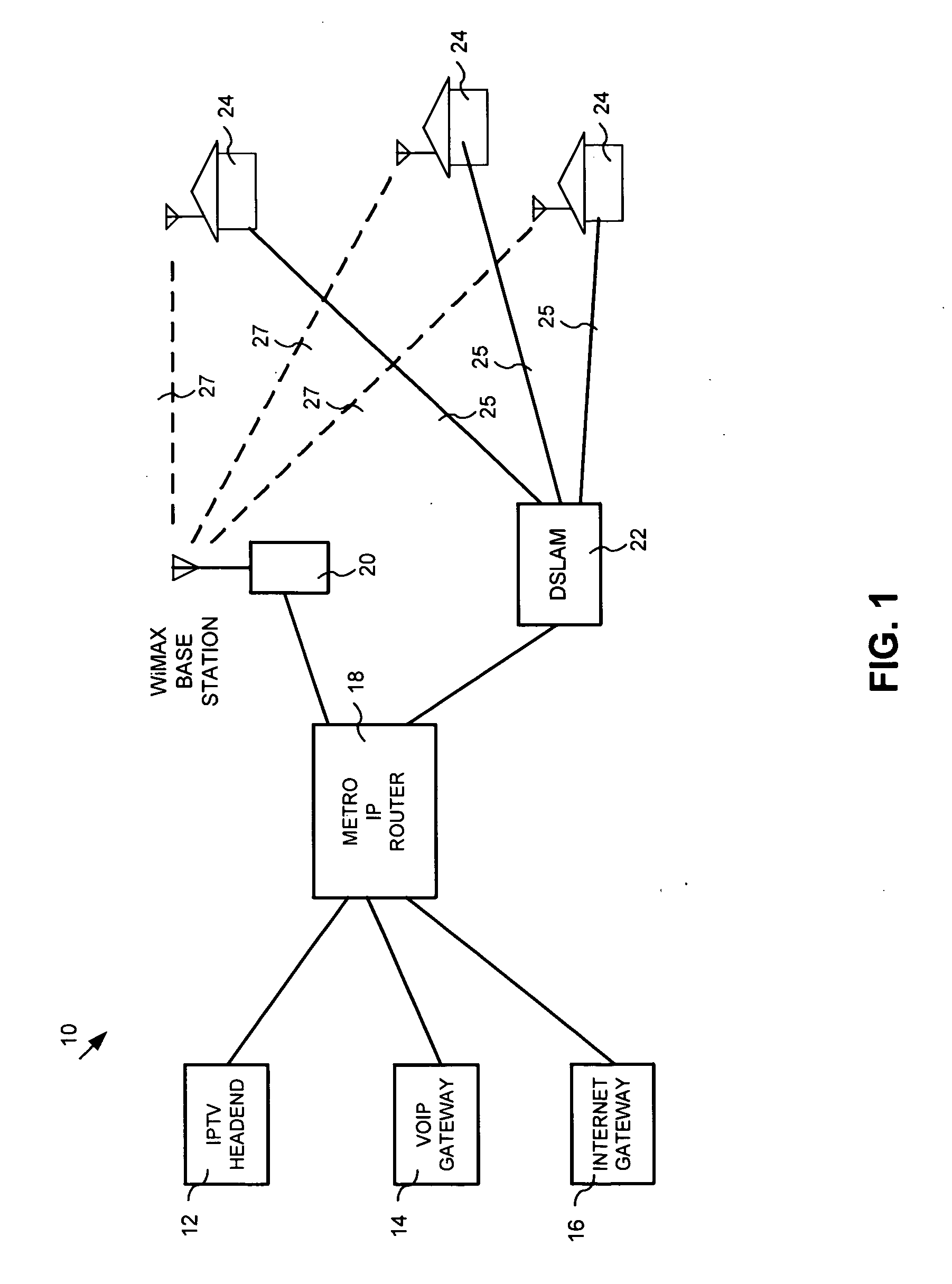
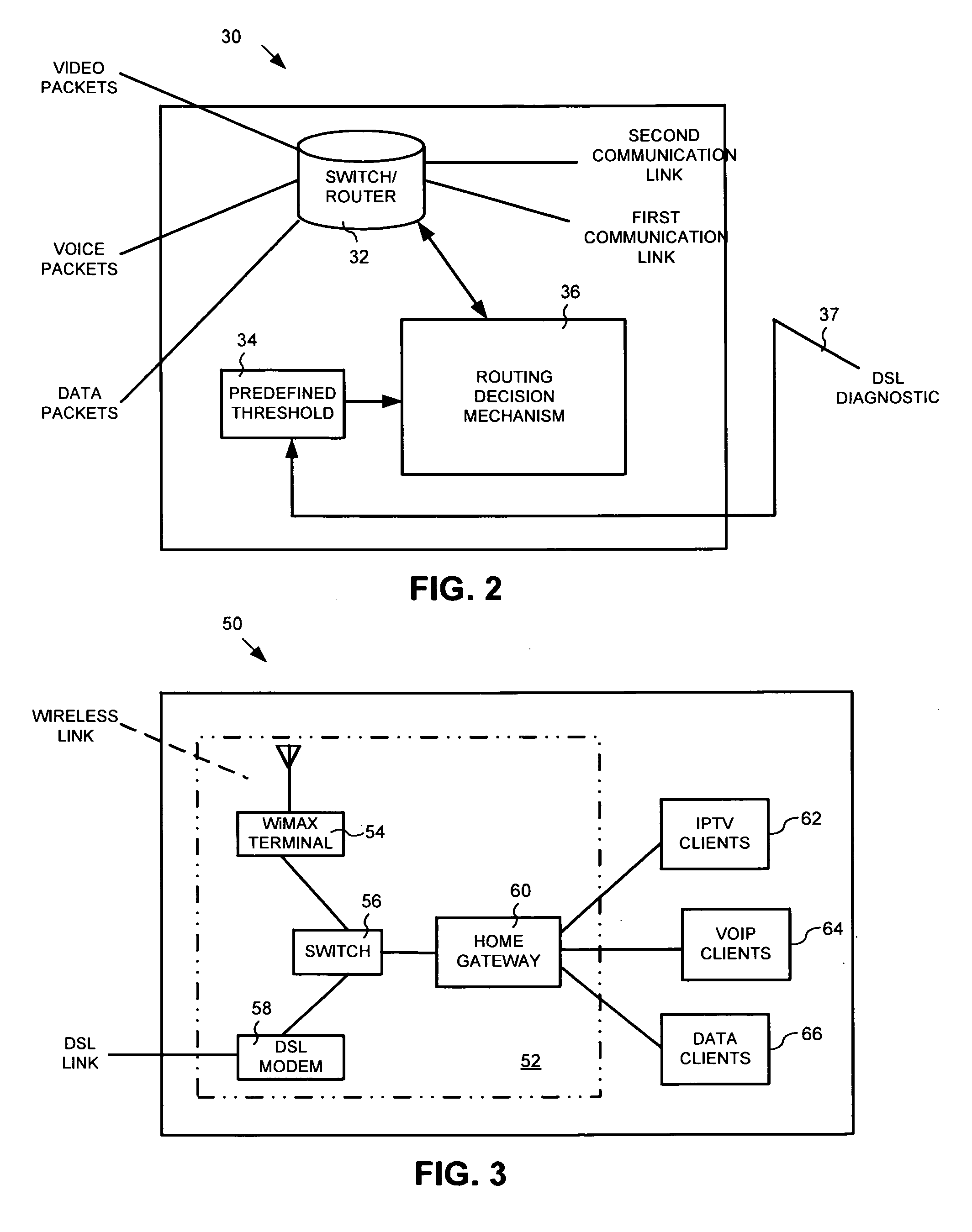
InactiveUS20100061244A1Significant additional infrastructure costManaging congestionError preventionTransmission systemsRouting decisionTelecommunications link
This invention provides a system, method and apparatus for managing congestion on heterogeneous network communication links, the first communication link and second communication link being heterogeneous with respect to each other. The system, method and apparatus including a routing decision module, the routing decision module evaluating a queue of information packets scheduled for transmission across the first communication link to determine whether to generate a command signal to route a portion of information packets over the second communication link. The system, method and apparatus may further include a communication link threshold module, the communication link threshold module storing threshold limit values corresponding to a first communication link technology of the first communication link.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
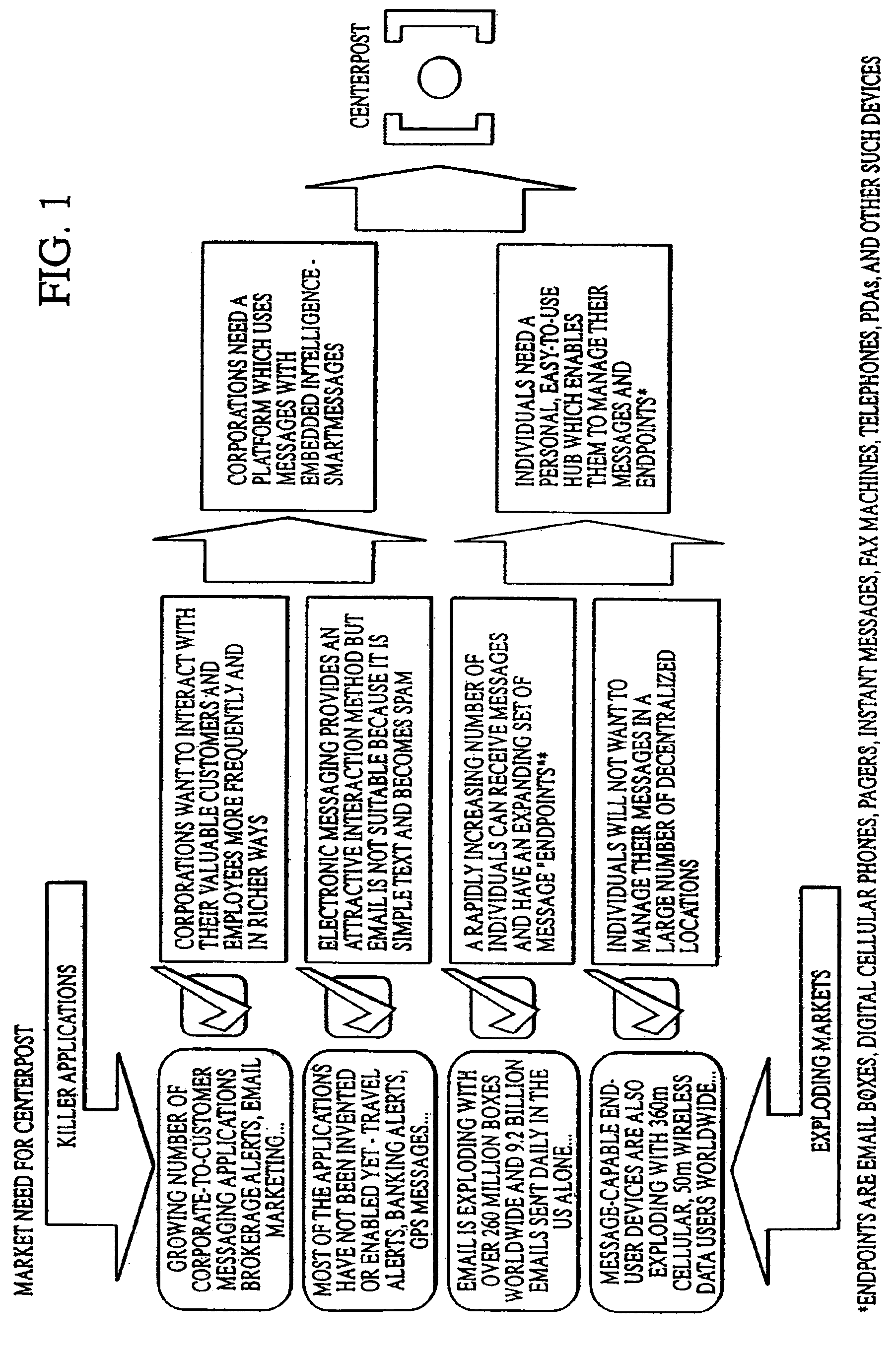
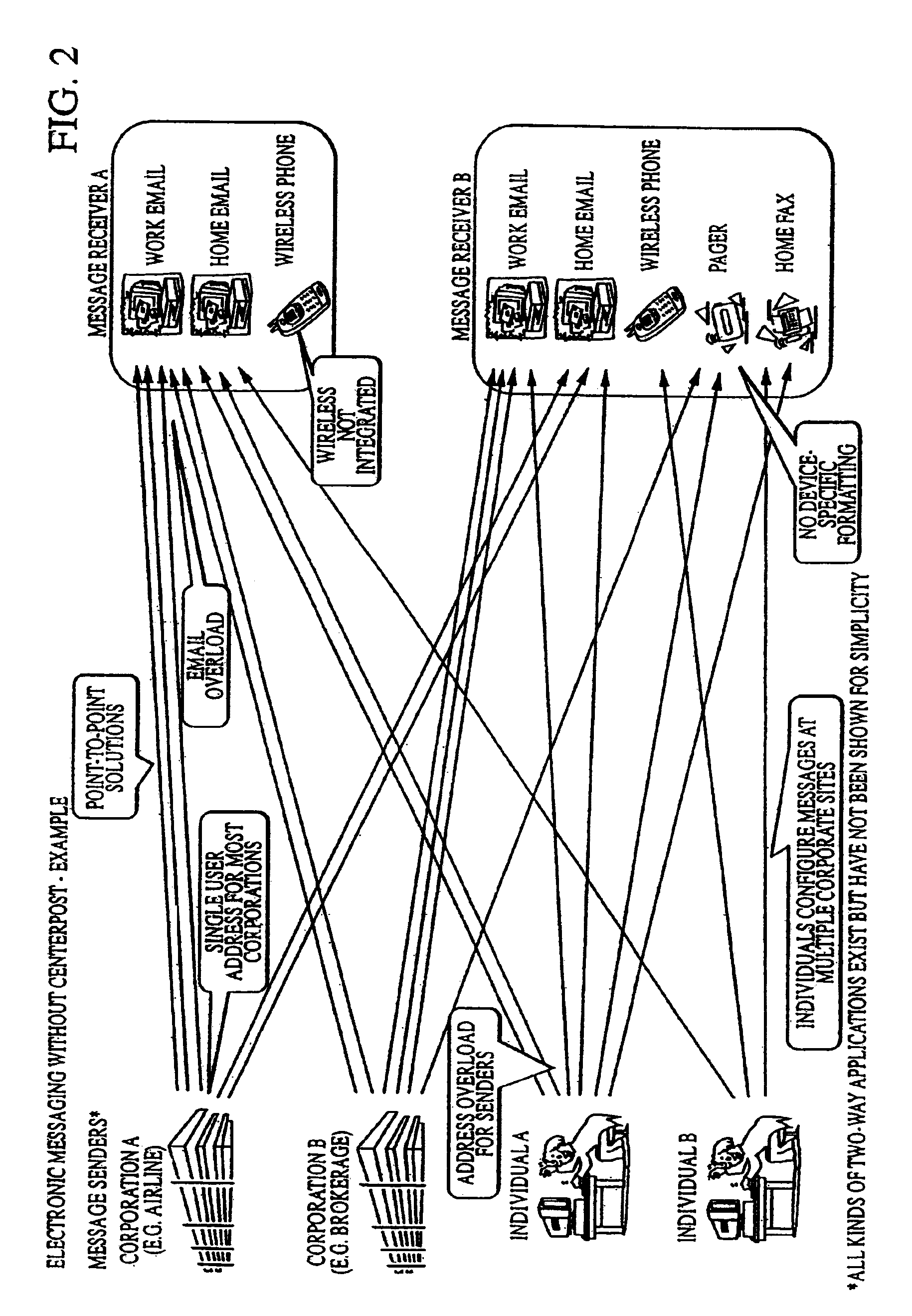
Method and system for content driven electronic messaging
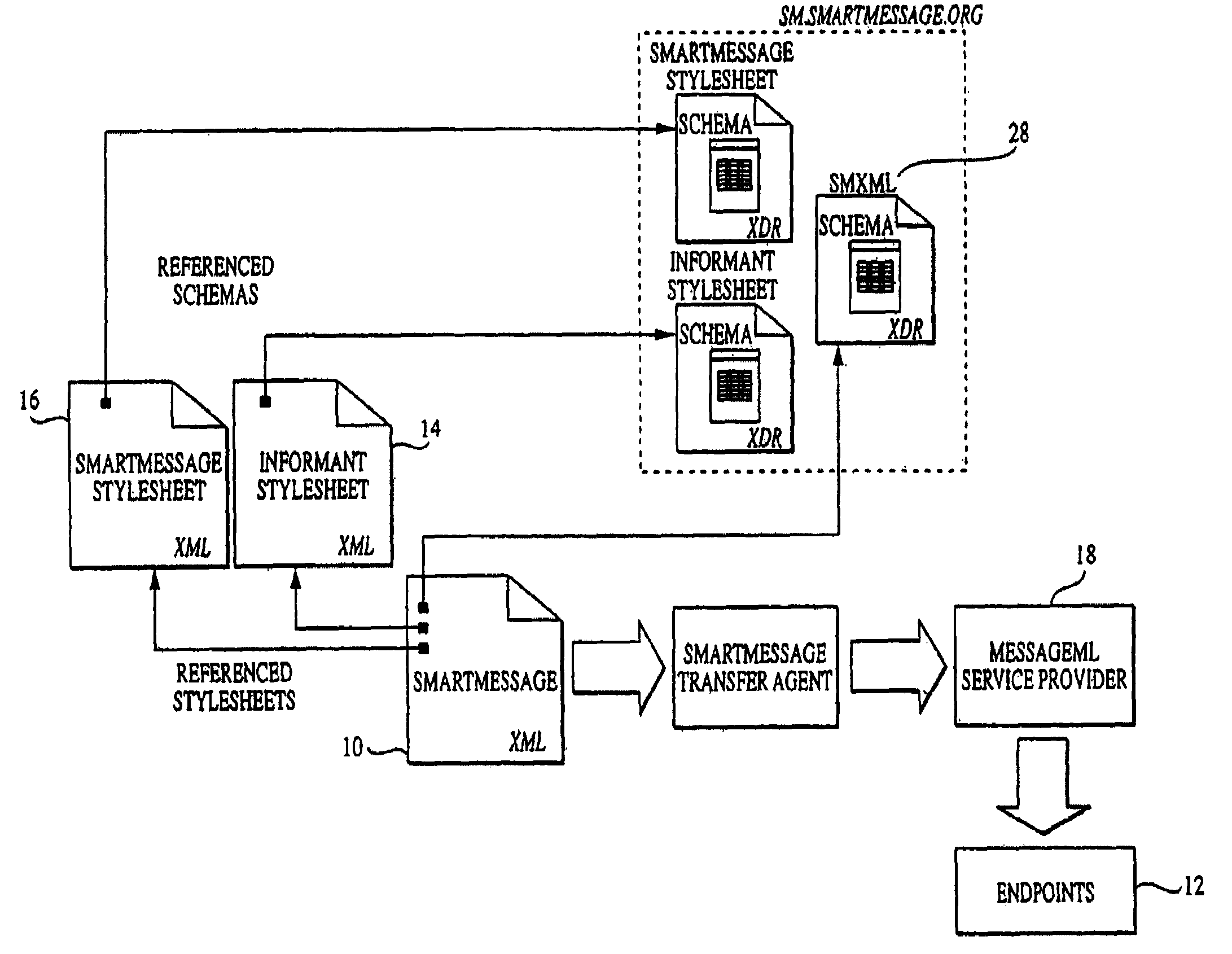
InactiveUS7177909B2Improve abilitiesReduce complexityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationRouting decisionApplication software
A method and system of electronic messaging is disclosed in which the electronic messaging system is configured such that the message content contains information which will drive the routing decision process. The message itself can be prioritized and routed to a pre-defined communications device or application, even before the recipient of the message has read the message. The sender focuses on the content and MessageML provides the constructs to tag the content and properly transform it into a viewable format for delivery to the target communications device. A method is disclosed for providing content driven electronic messaging that enables individuals to receive XML electronic messages using an electronic messaging system. Once an Informant Stylesheet and SmartMessage Stylesheet are created, a SmartMessage can be sent to a MessageML Service Provider, who will receive the SmartMessage, process it, and deliver the SmartMessage to a user's defined endpoint.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS +1
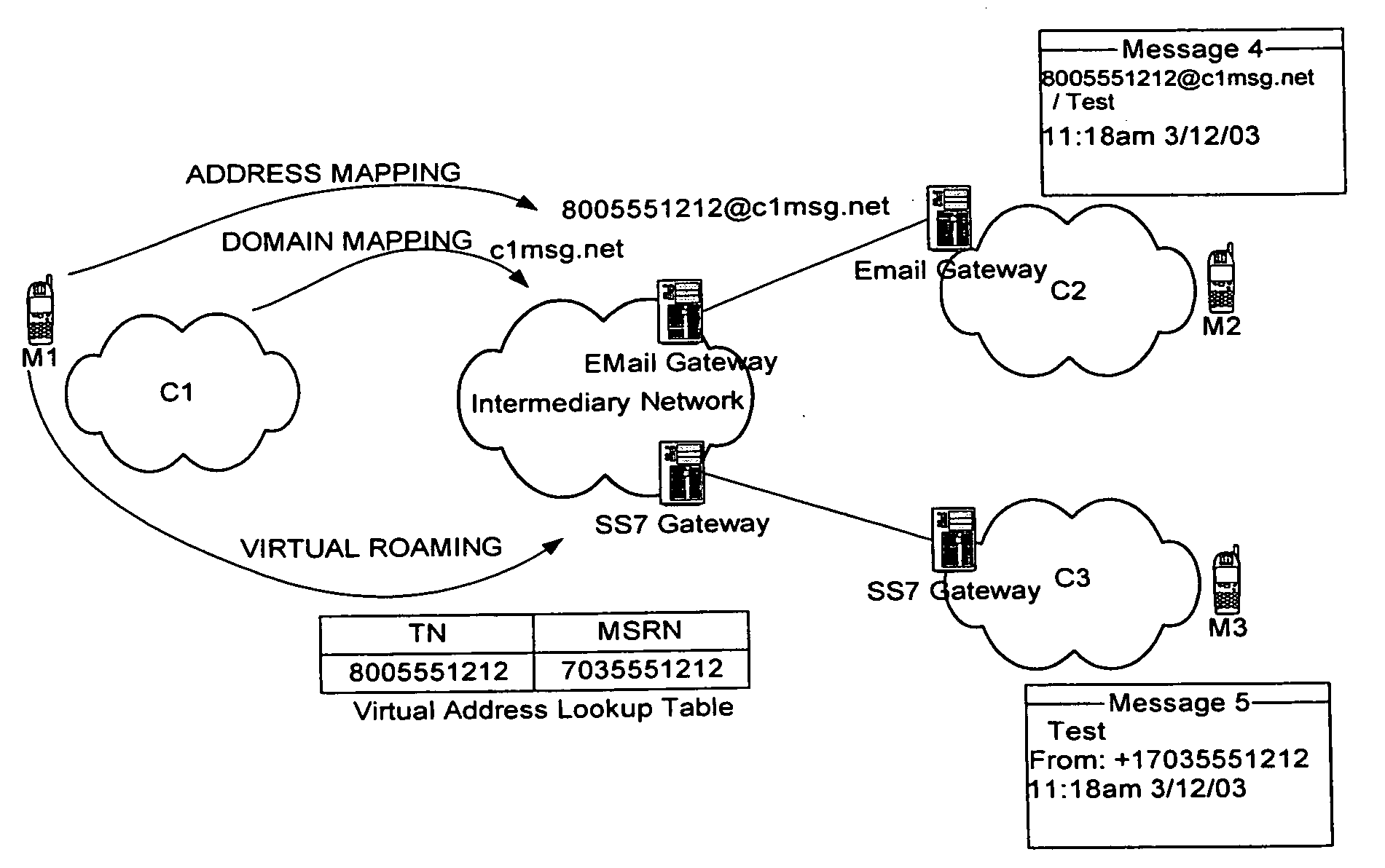
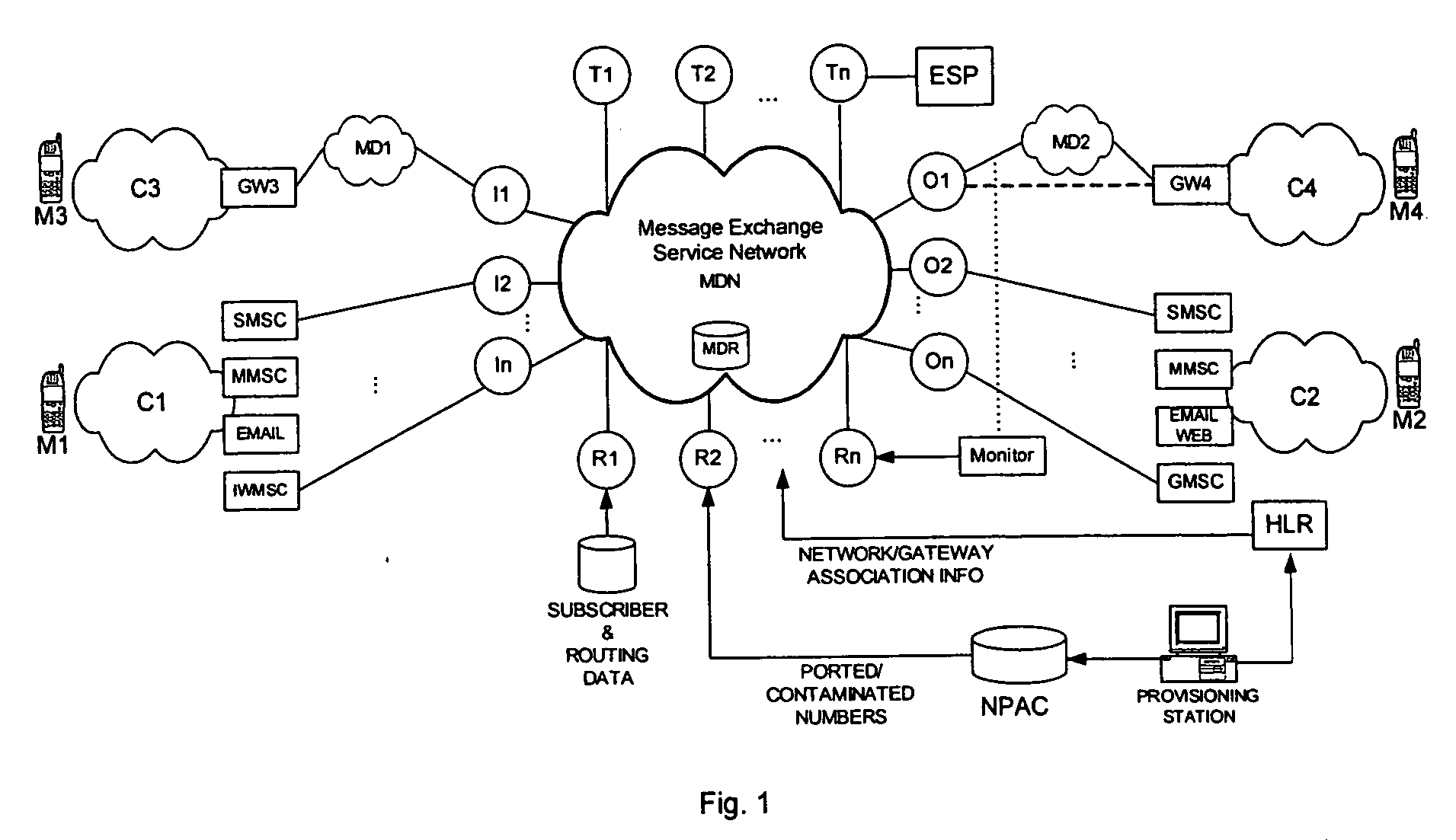
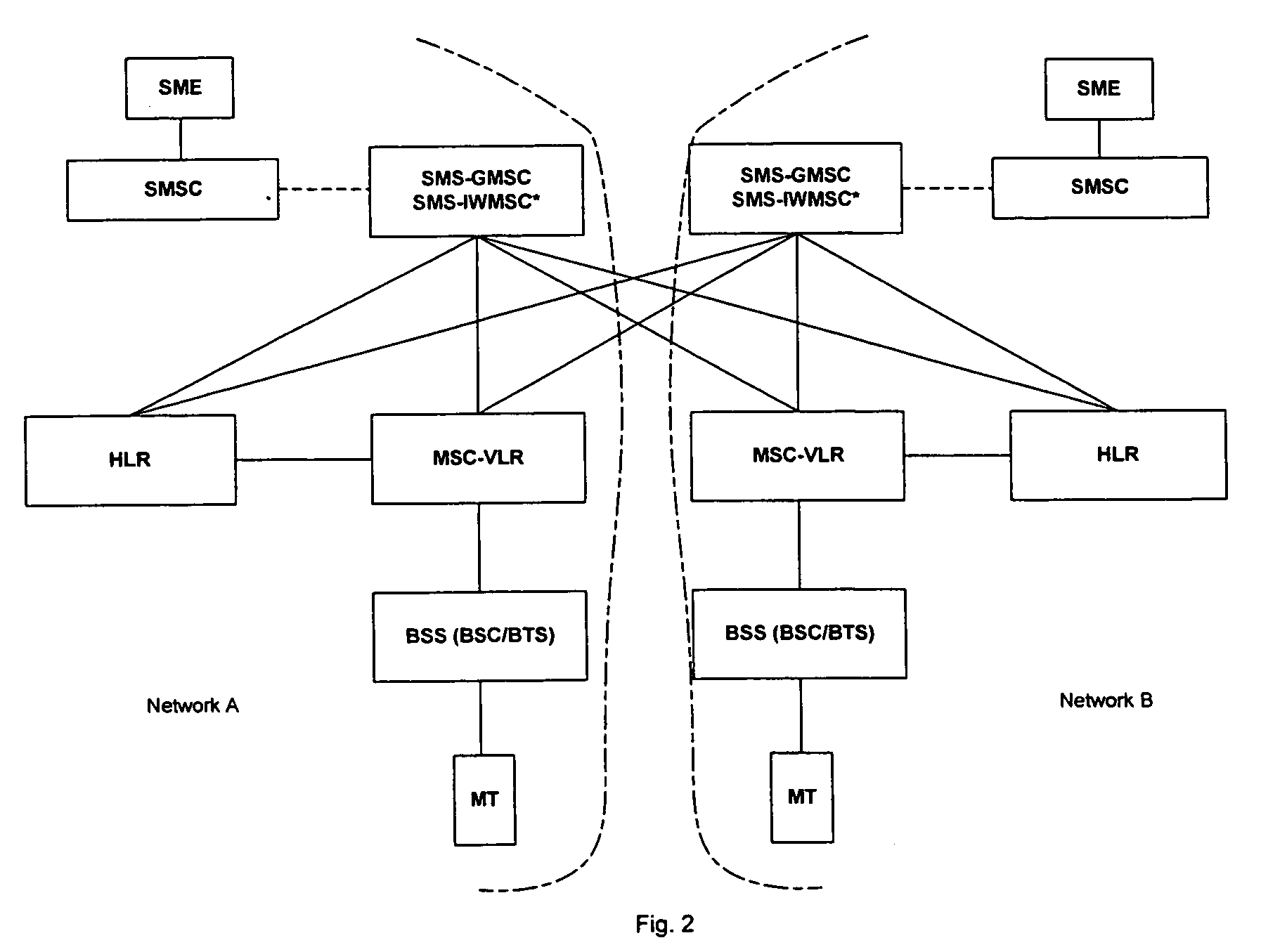
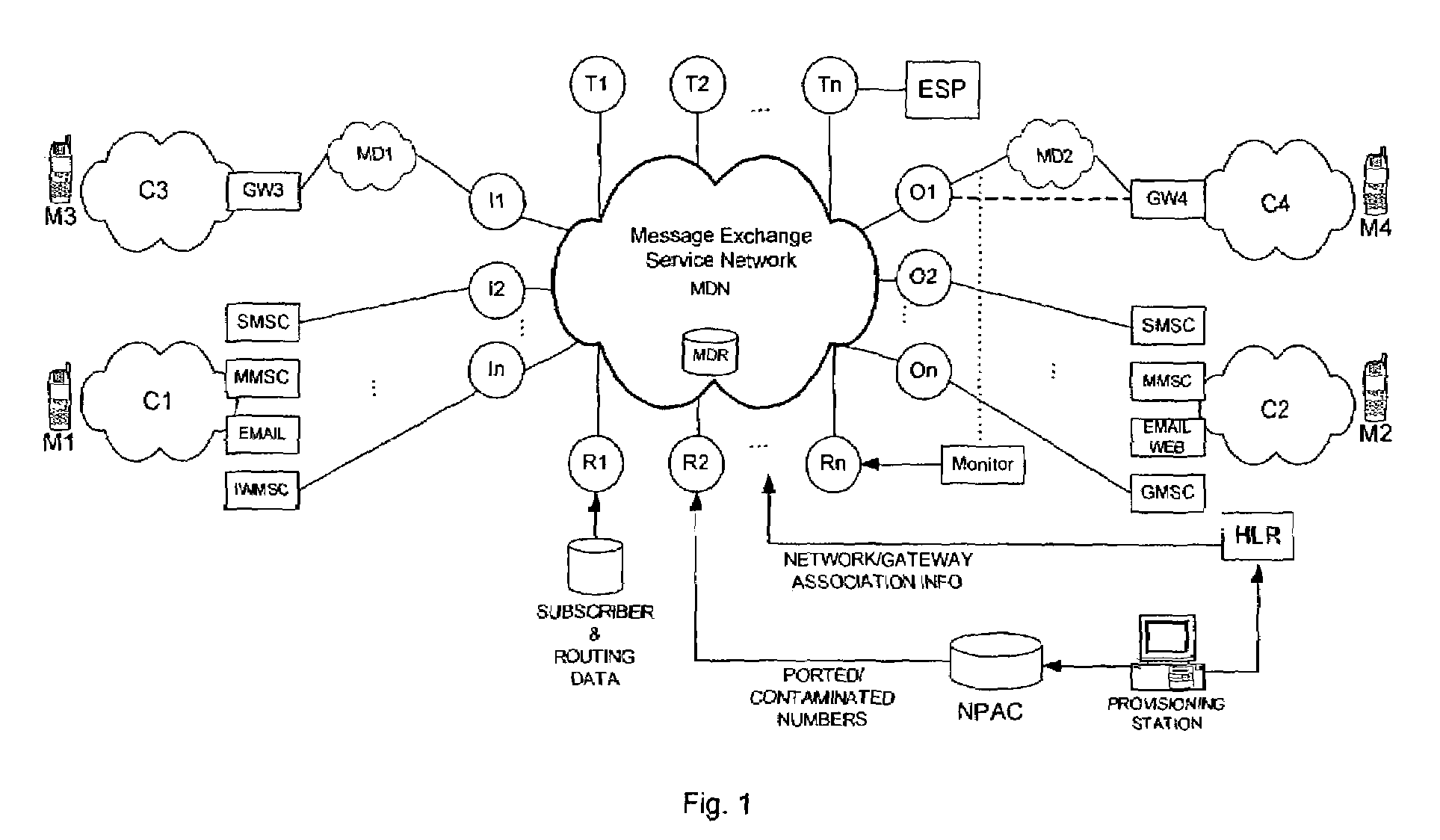
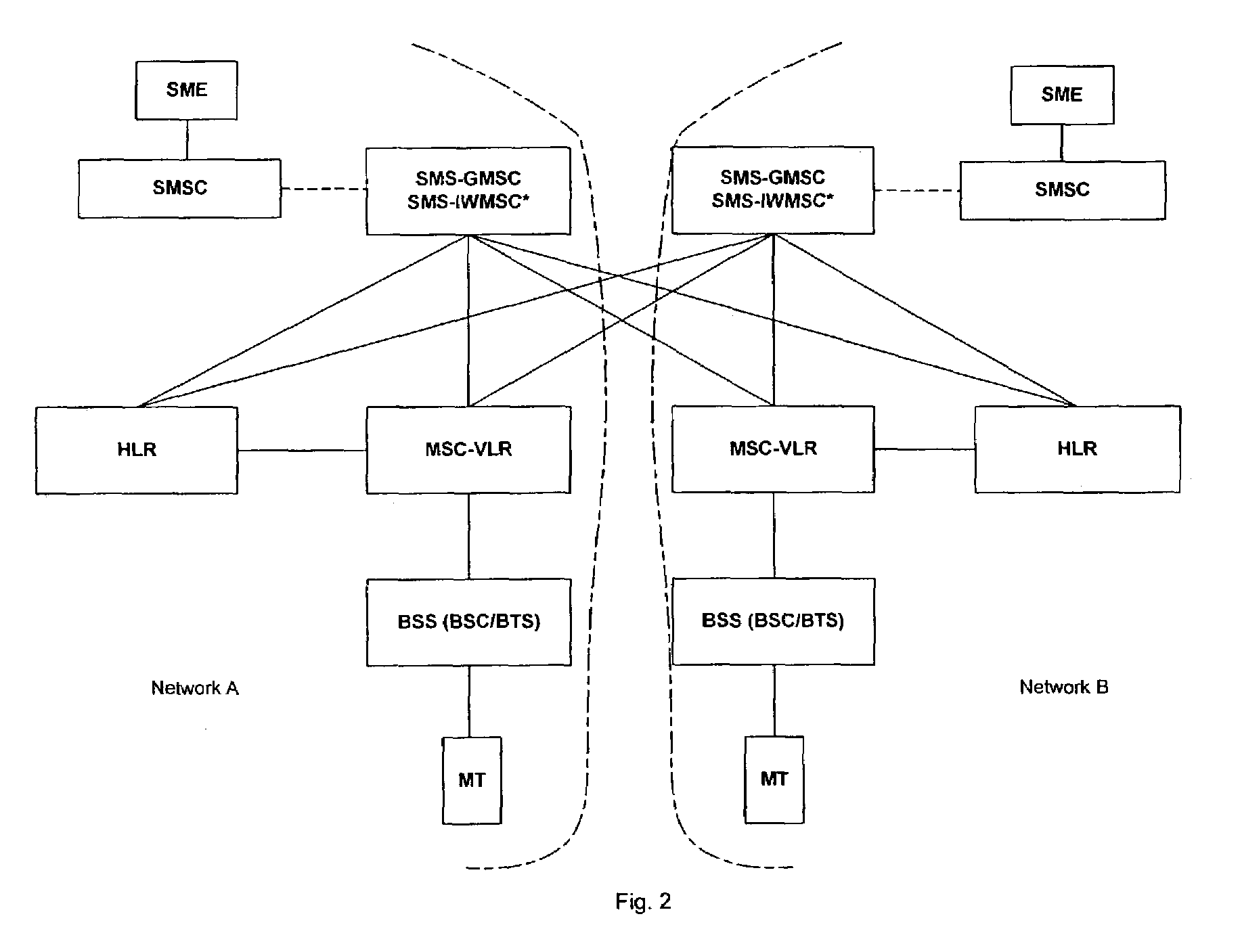
Intermediary network system and method for facilitating message exchange between wireless networks
ActiveUS20050215250A1Raise the possibilityInformation formatData switching by path configurationRouting decisionPublic land mobile network
Network System and Method for facilitating message exchange between mobile subscribers belonging to the same or different public land mobile networks, possibly incorporating different standards. Message exchange between two subscribers of the same or different networks may involve one or more lookups on subscription data, zero or more message transformations, one or more routing decisions including application of costing functions, and, storage and propagation of the message in one or more Core or Intermediary networks. The messages may be of type, among others, SMS (Short Message Service), MMS (Multimedia Message Service), or EMAIL.
Owner:SYBASE 365 INC
Intermediary network system and method for facilitating message exchange between wireless networks
InactiveUS7154901B2Raise the possibilityInformation formatData switching by path configurationRouting decisionWireless mesh network
Network System and Method for facilitating message exchange between mobile subscribers belonging to the same or different public land mobile networks, possibly incorporating different standards. Message exchange between two subscribers of the same or different networks may involve one or more lookups on subscription data, zero or more message transformations, one or more routing decisions including application of costing functions, and, storage and propagation of the message in one or more Core or Intermediary networks. The messages may be of type, among others, SMS (Short Message Service), MMS (Multimedia Message Service), or EMAIL.
Owner:SYBASE 365 INC
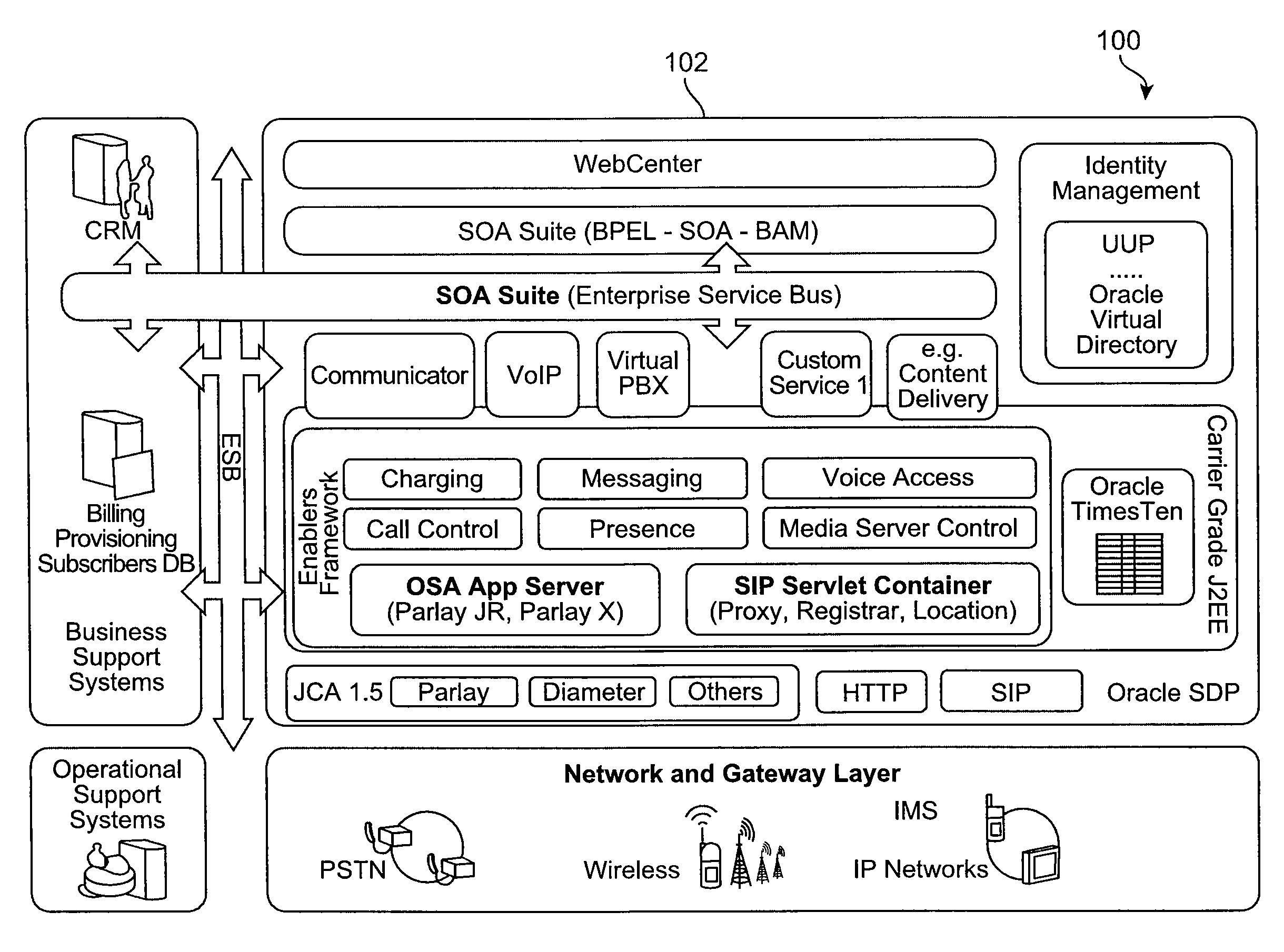
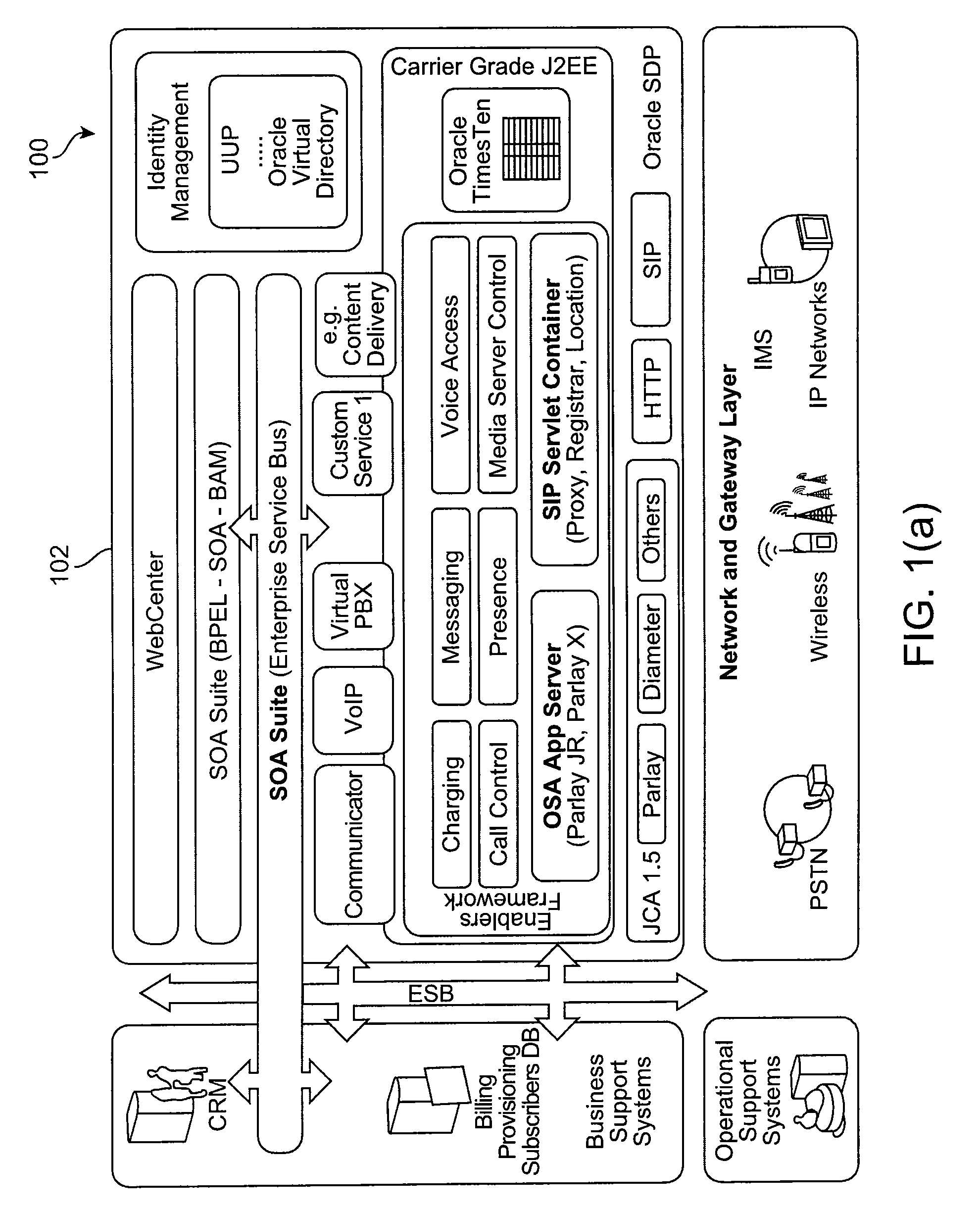
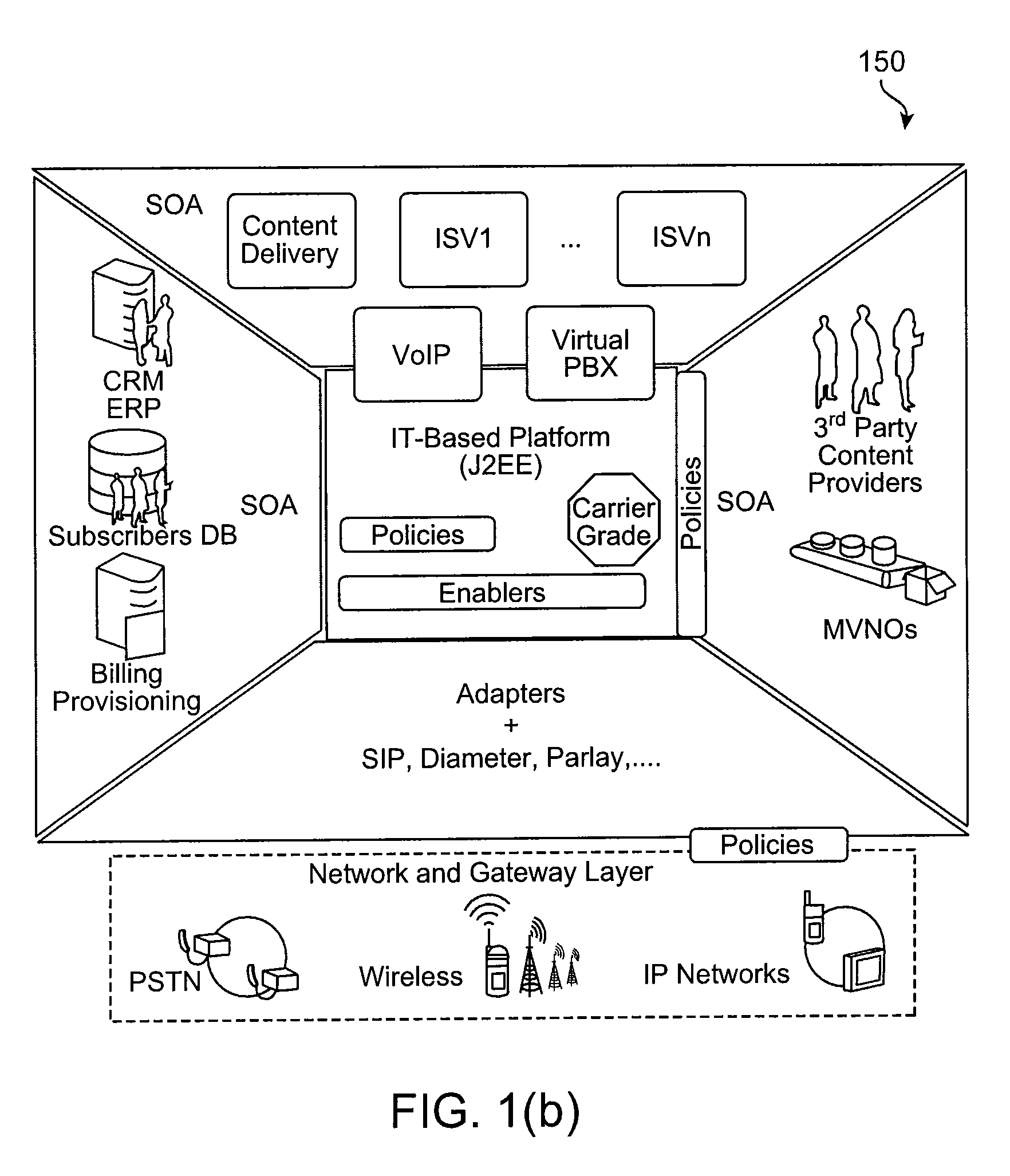
Service oriented architecture-based scim platform
ActiveUS20090187919A1Overcome deficienciesInterprogram communicationTransmissionRouting decisionRouting table
Service Capability Interaction Manager (SCIM)-type functionality is provided at a horizontal service layer in an Service Oriented Architecture (SOA)-based approach. SCIM composition is provided at multiple levels, including the level of composition where servlets have full access to the context information of the service layer. SCIM composition also occurs at the level of an application dispatching messages to multiple applications / services for processing the messages. The functionality at the service layer also can be programmed using policies, such that routing decisions can be made dynamically as the result of processing conditions and actions. An incoming message can result in a Web service being triggered that in turn triggers a BPEL or SOA workflow, the workflow calling multiple operations to process the message as a result of a routing table or header, environmental and contextual information at the service level, and other information such as user preference or presence information.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
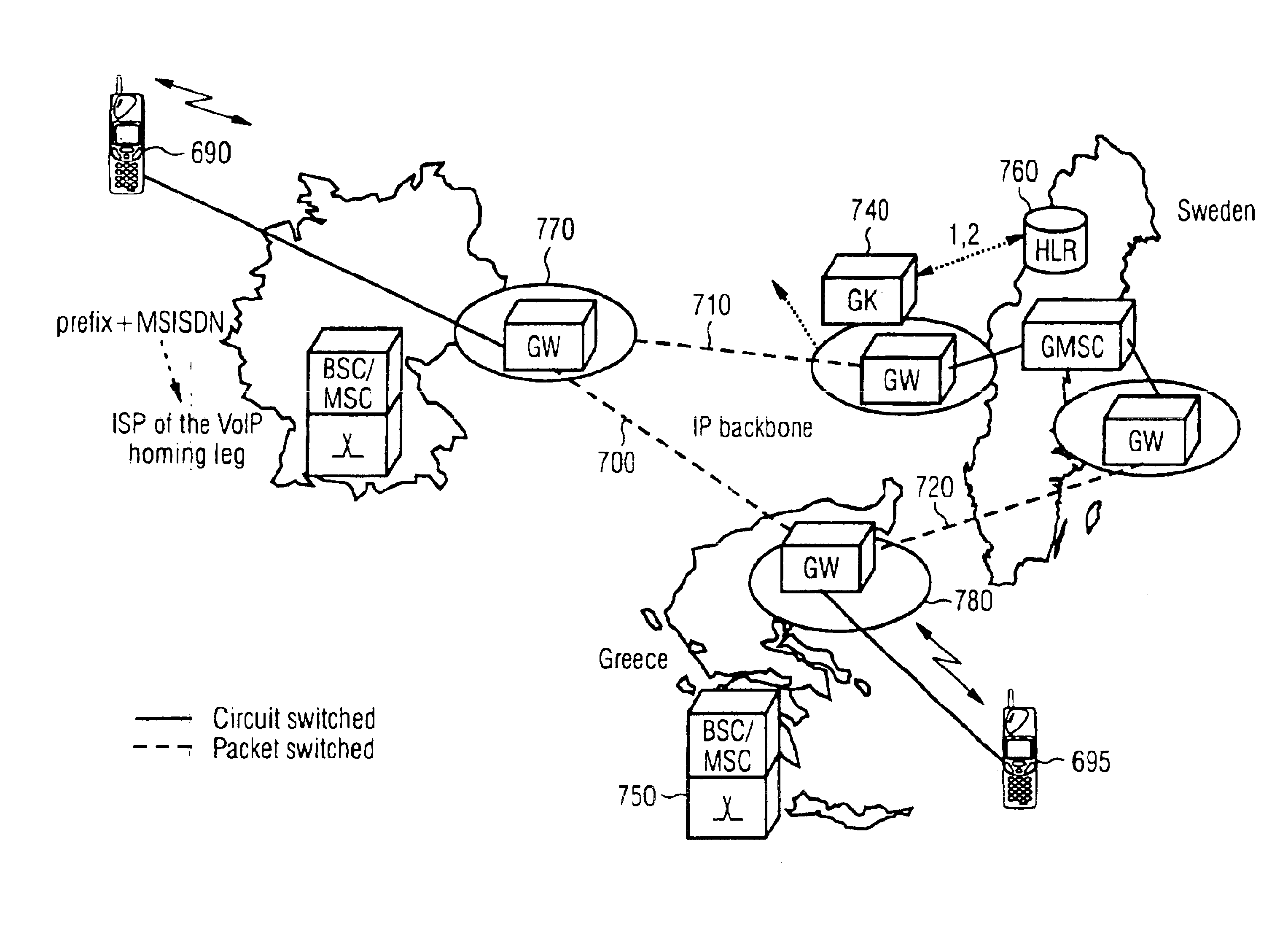
Methods and systems for call routing and codec negotiation in hybrid voice/data/internet/wireless systems
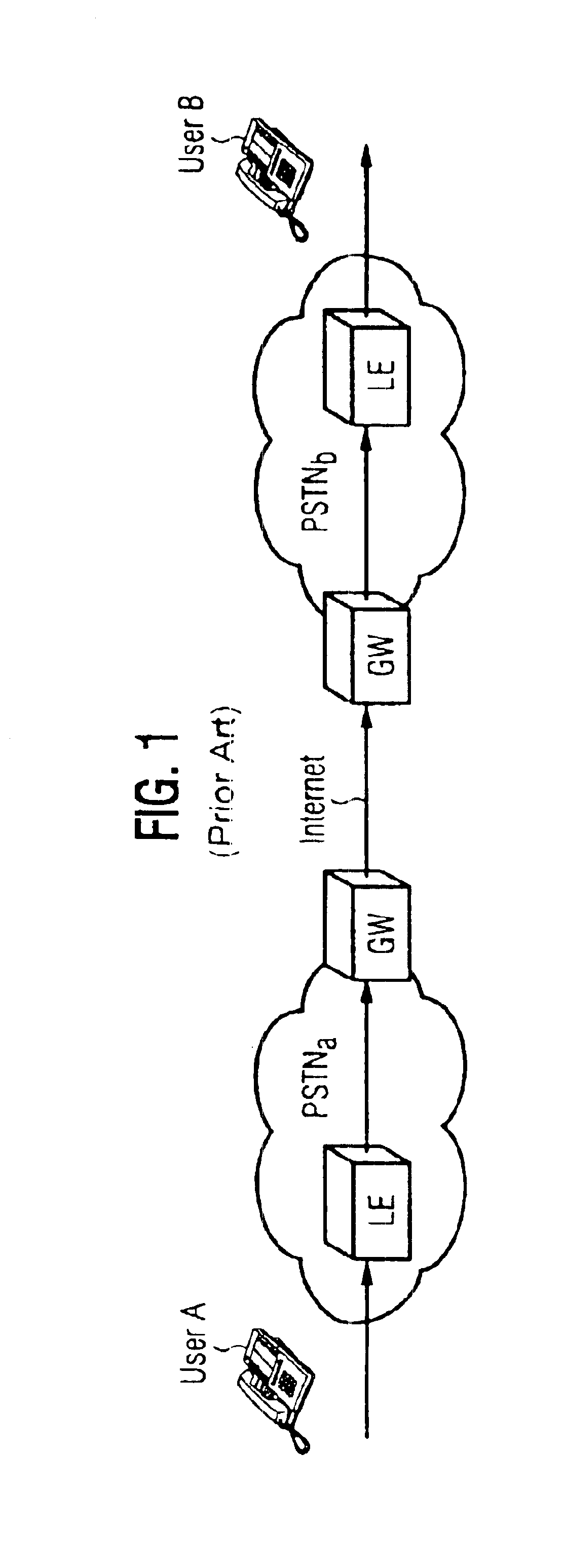
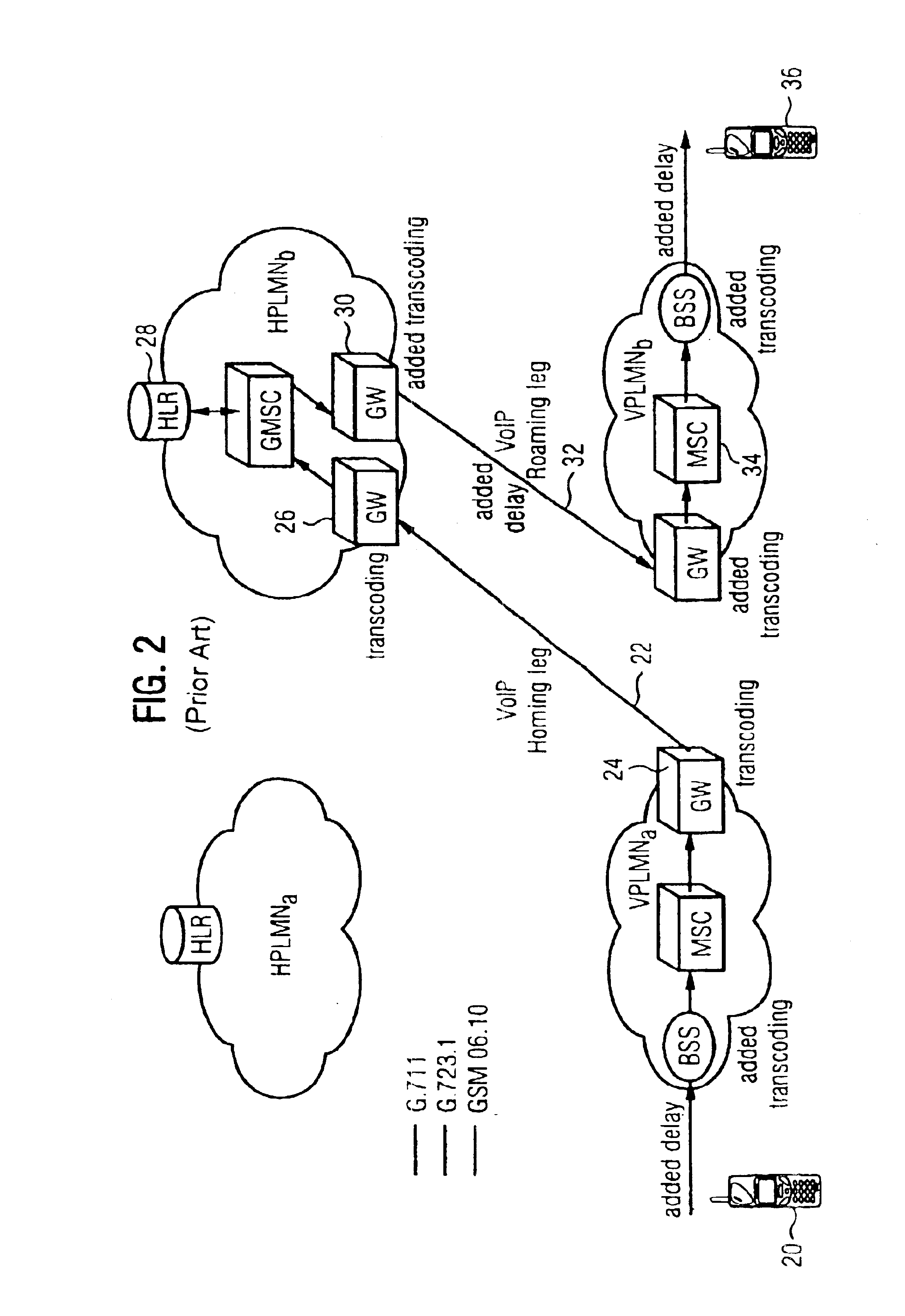
InactiveUS6856612B1Minimize delayMinimize the numberInterconnection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsThe InternetTranscoding
A method and system for communicating information includes evaluation regarding routing of calls performed at a call control point in an ITSP and / or wireless network. A PIC identity associated with another party's preferences is acquired and sent to the call control point. The PIC identity identifies the type of the carrier network (e.g., circuit switched or VoIP) and is used to make further routing decisions. If a circuit-switched carrier is identified, the IP homing leg is terminated at the voice gateway in the recipient's HPLMN and information is sent over to the GMSC where normal, circuit-switched routing procedures. If a VoIP carrier is identified then the called user's roaming number is retrieved from the HLR, and the call is further routed directly over the IP domain towards a voice gateway at the visited network minimizing the number of transcodings. Additional transcoding steps can be avoided if a single encoding is agreed upon according to “tandem free operation” (TFO). Combining inband signaling through the telephony exchanges and out-of-band signaling in the IP network it is possible to achieve, for a mobile subscriber, one encoding and one decoding of a voice.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
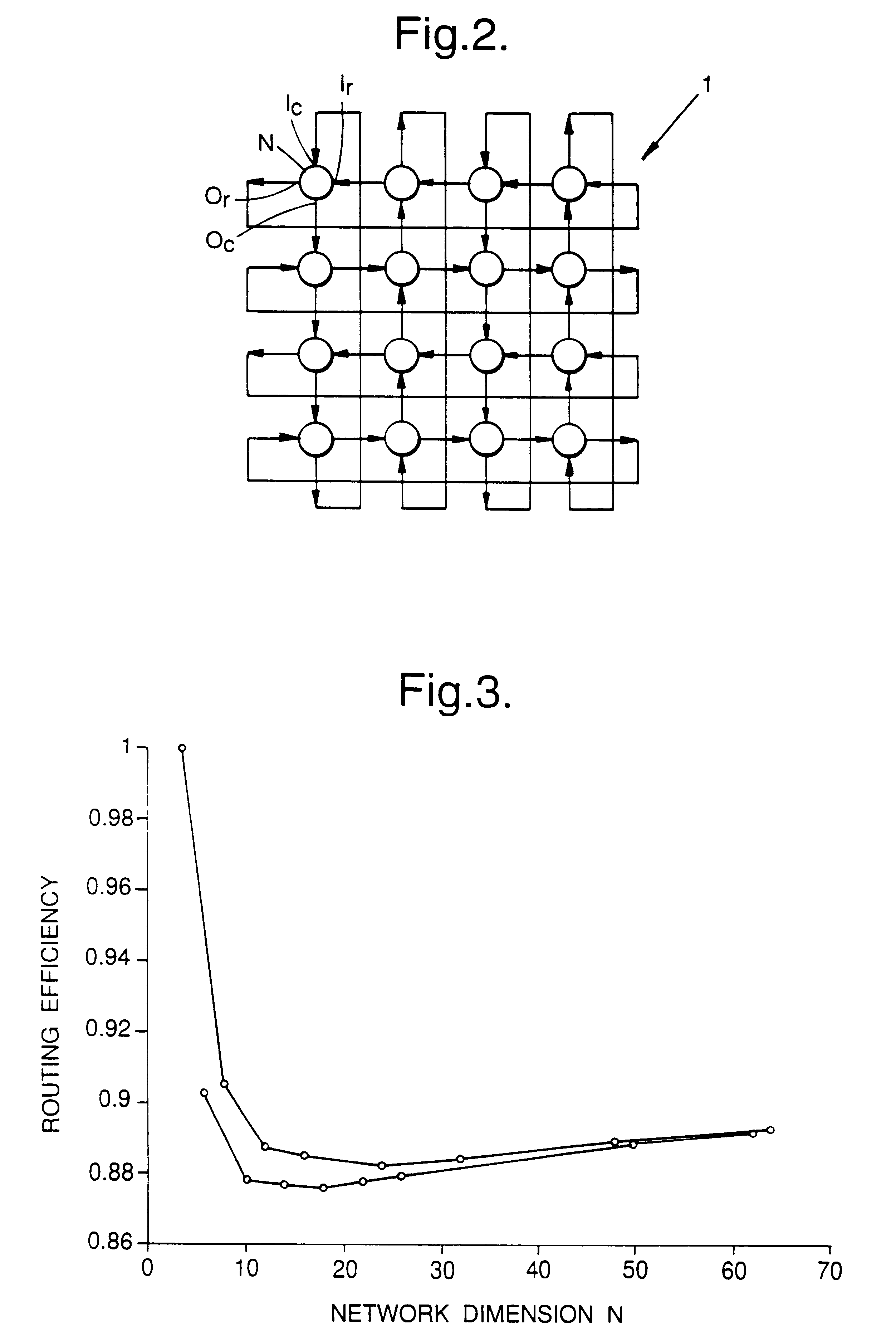
Dead reckoning routing of packet data within a network of nodes having generally regular topology
InactiveUS6272548B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsDigital computer detailsRouting decisionComputer science
A packet is routed by "dead reckoning" on a network having a generally regular topology. The packet is received at a node where a local routing decision is made. The packet is output in a direction selected according to the routing decision. The packet carries in addition to a destination address a directional flag indicating explicitly the preferred direction of onward travel and the routing decision is made using this flag. Several flags may be used, corresponding to different dimensions of the network.
Owner:PATENTPORTFOLIO 2 S A R L
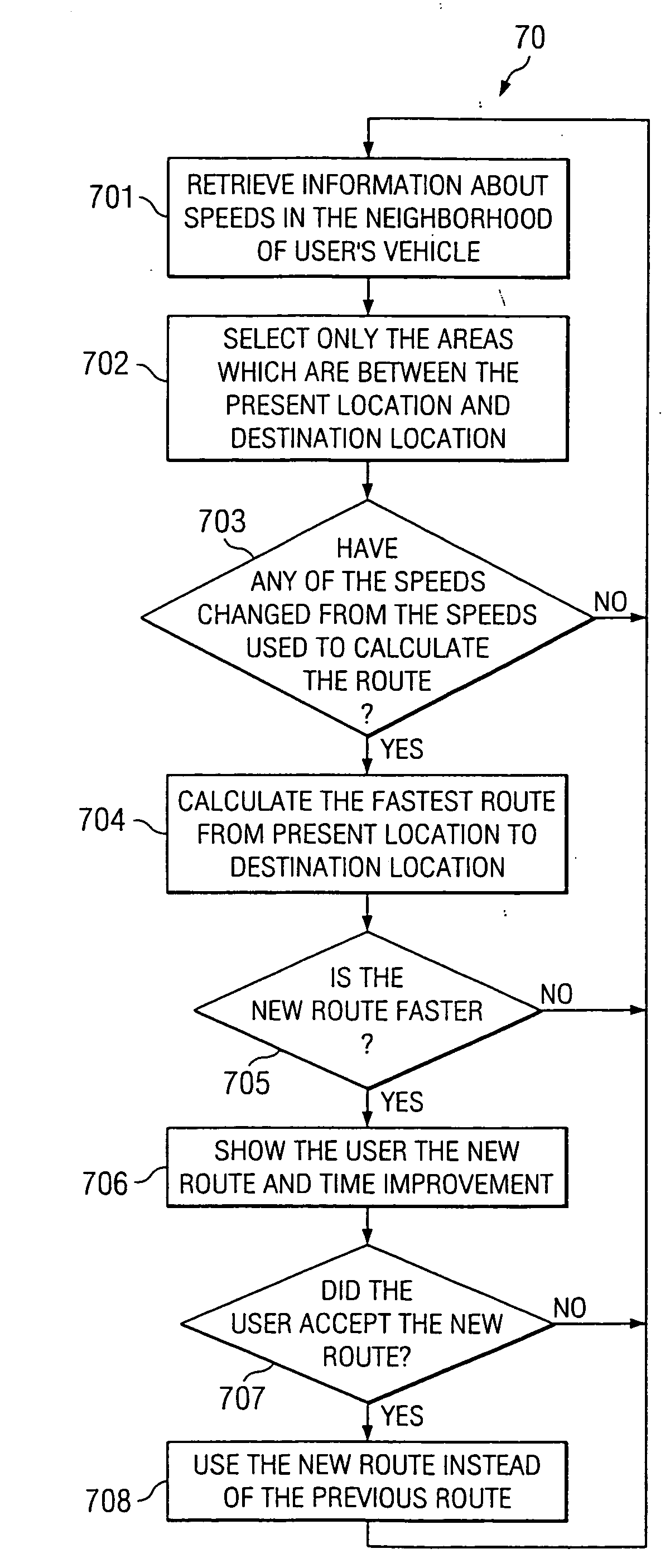
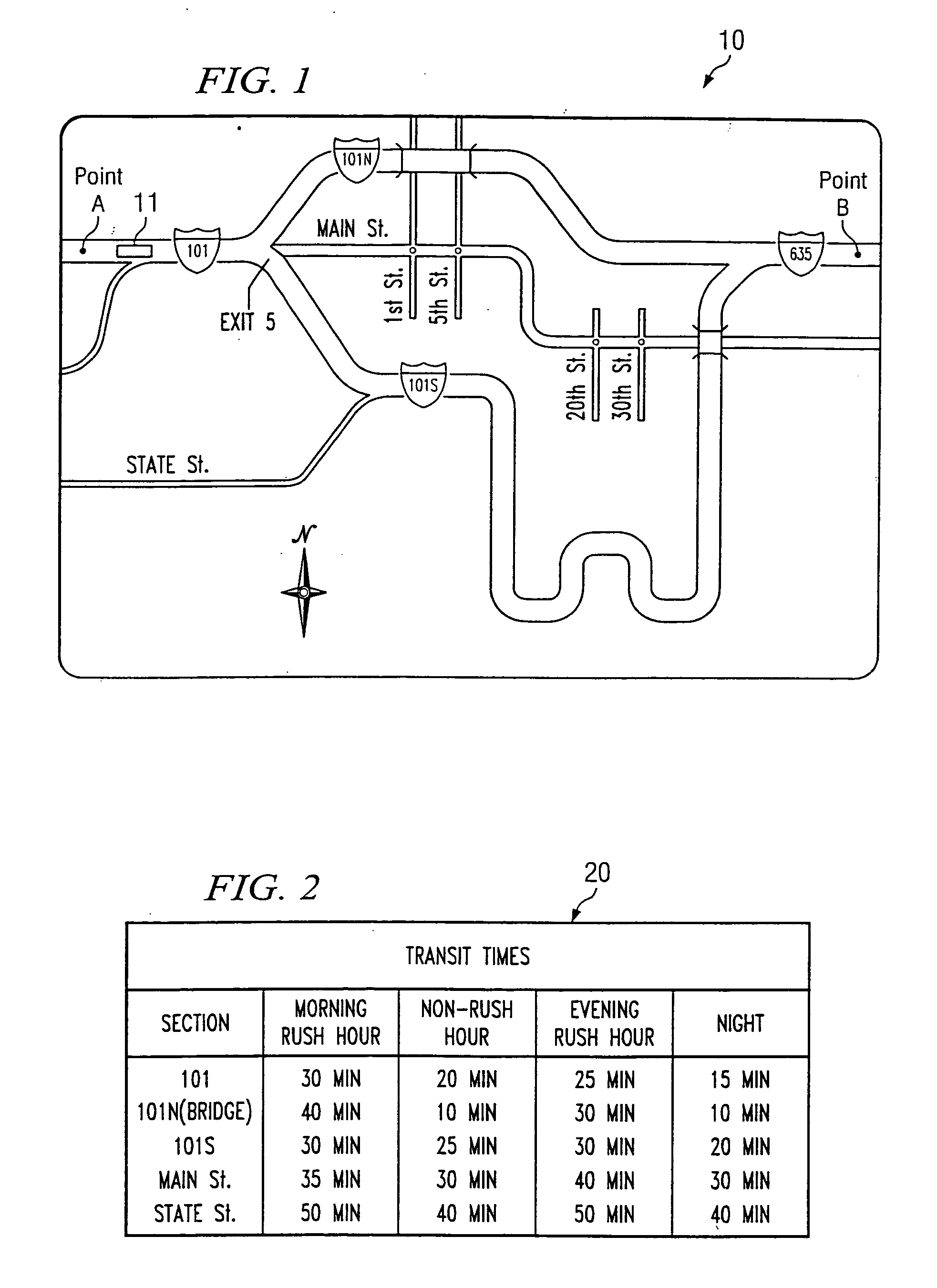
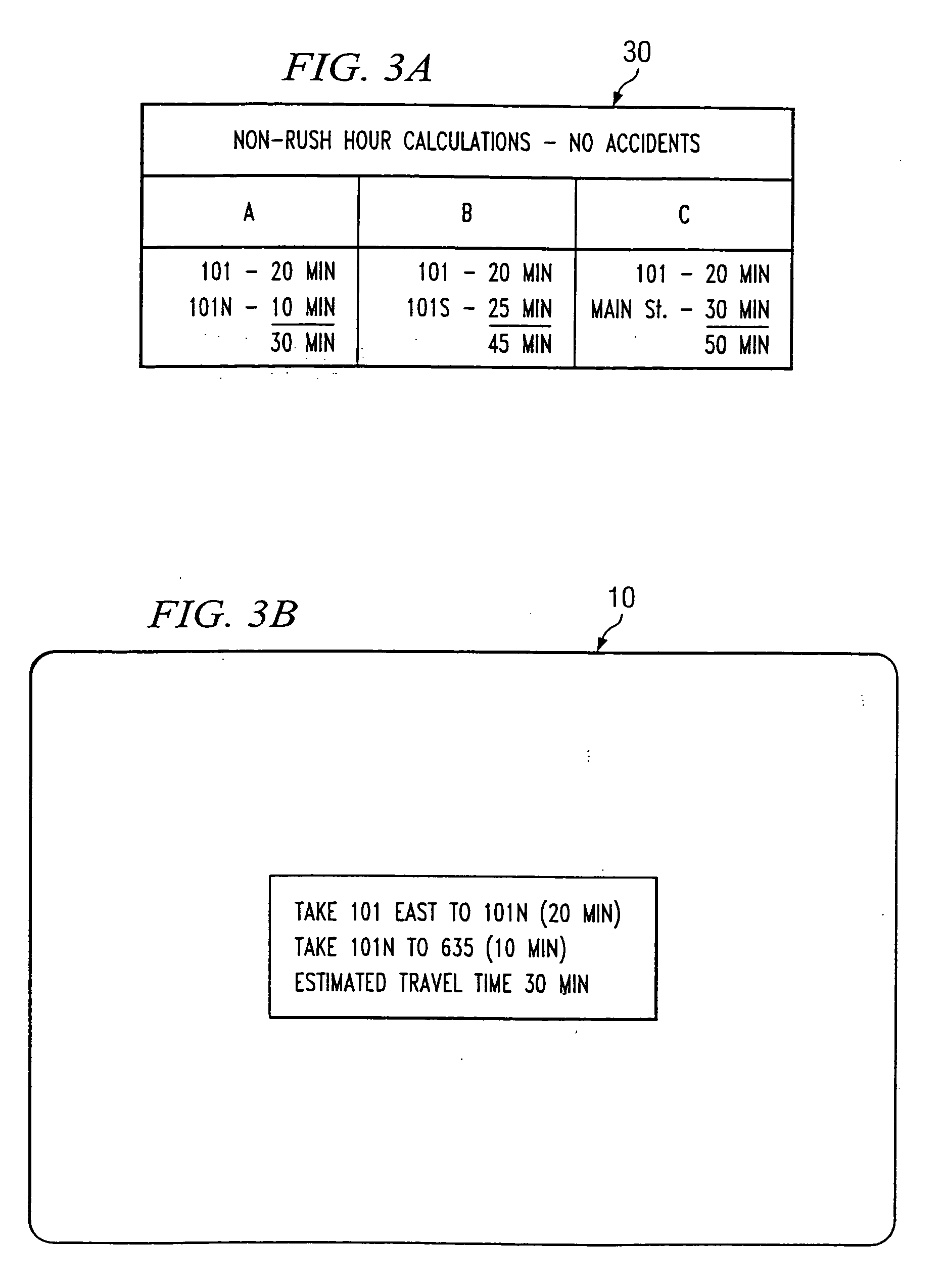
System and method for dynamic navigational route selection
InactiveUS20050273250A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlRouting decisionTraffic delay
A navigation system and method factors into its routing decisions information pertaining to transient delays encountered from time to time, one example of such a transient delay is accident information obtained from currently available broadcast traffic flow sources. The system can also factor in historically available traffic delay data based on time of day or other parameters. The navigation system keeps track of the routes traveled by the vehicle (or user) and the times of transit of such routes. When a user requests a route based upon given end-points, the navigation system can use its own stored historical data, as well as currently available traffic delay data, to calculate and announce a given route.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
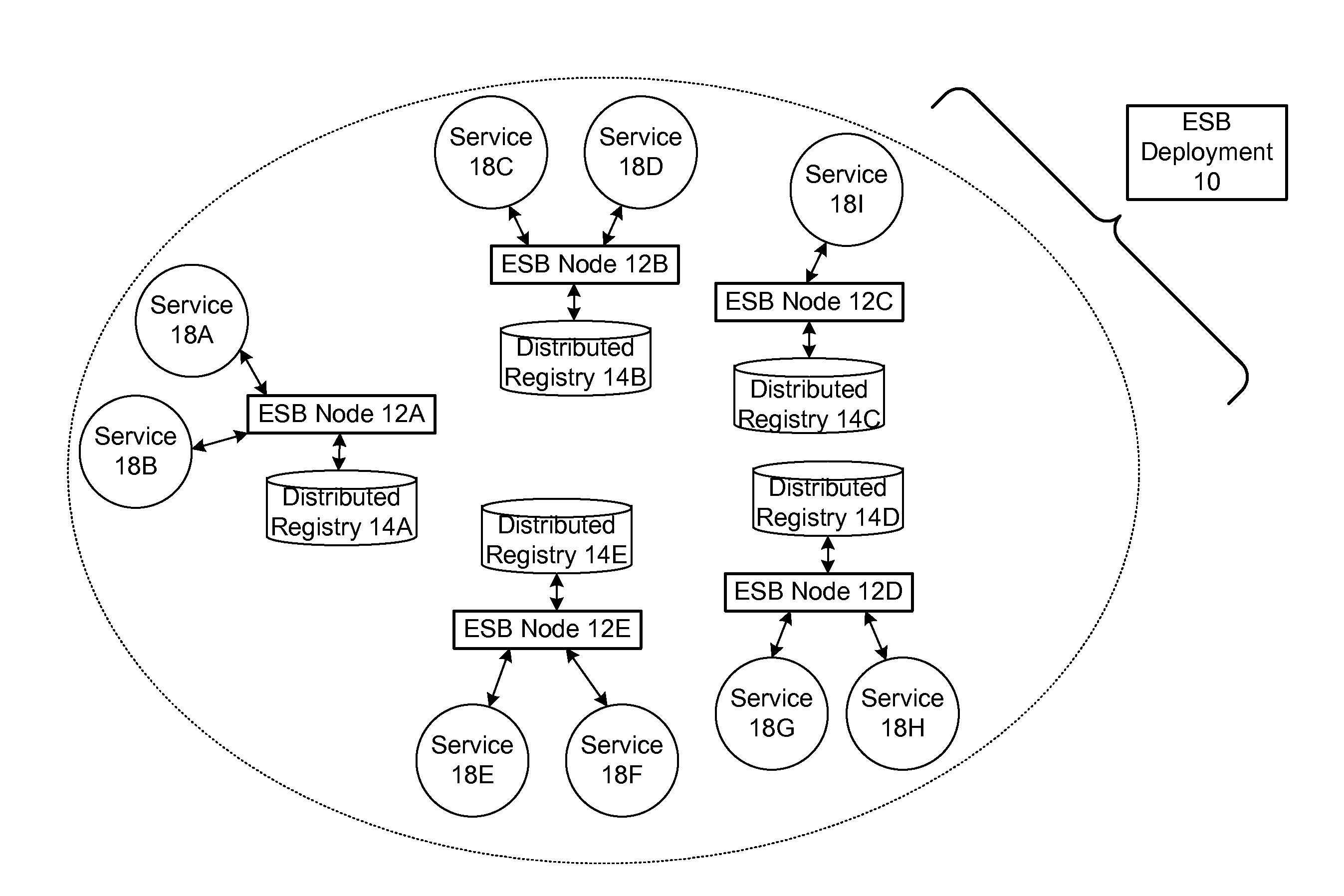
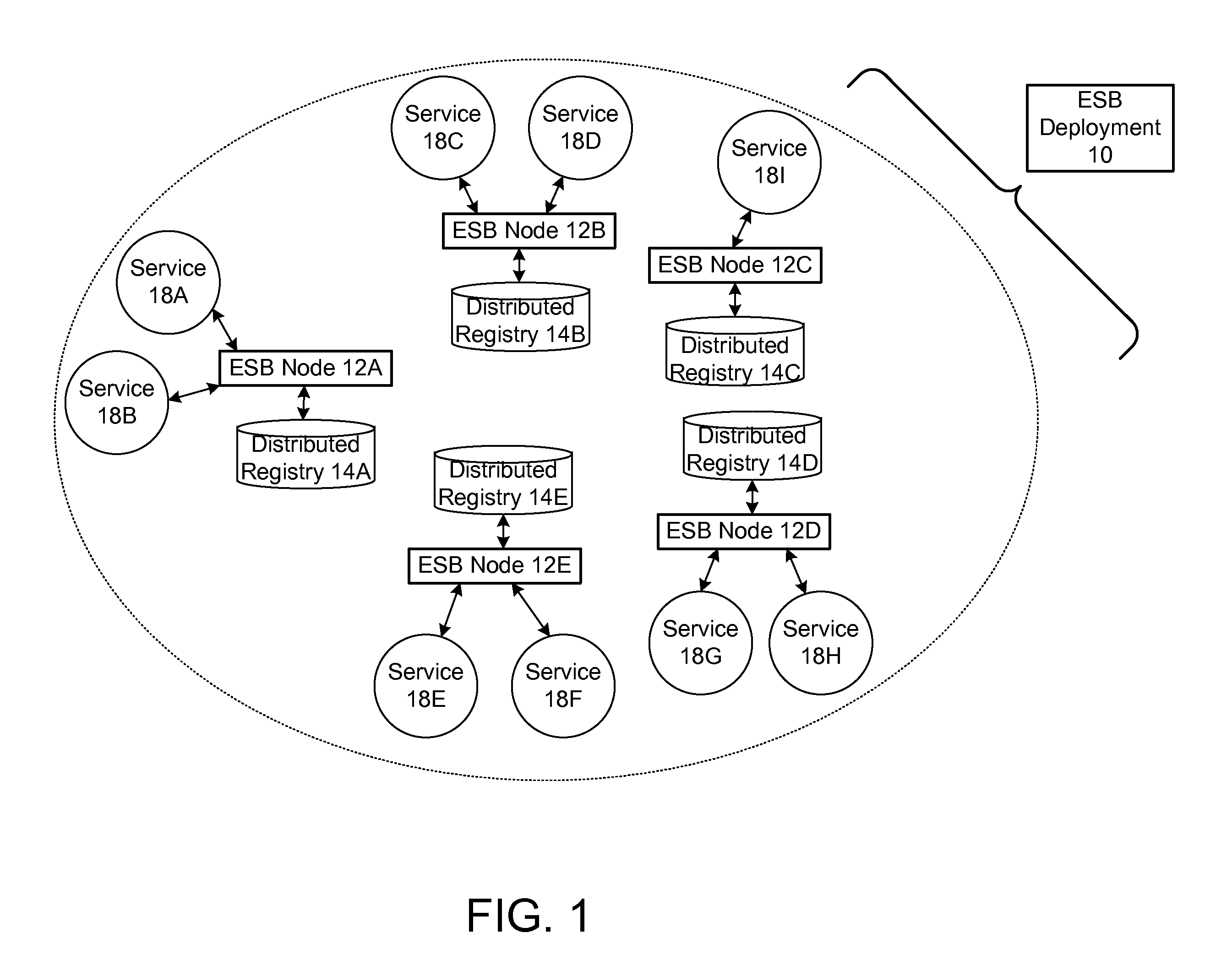
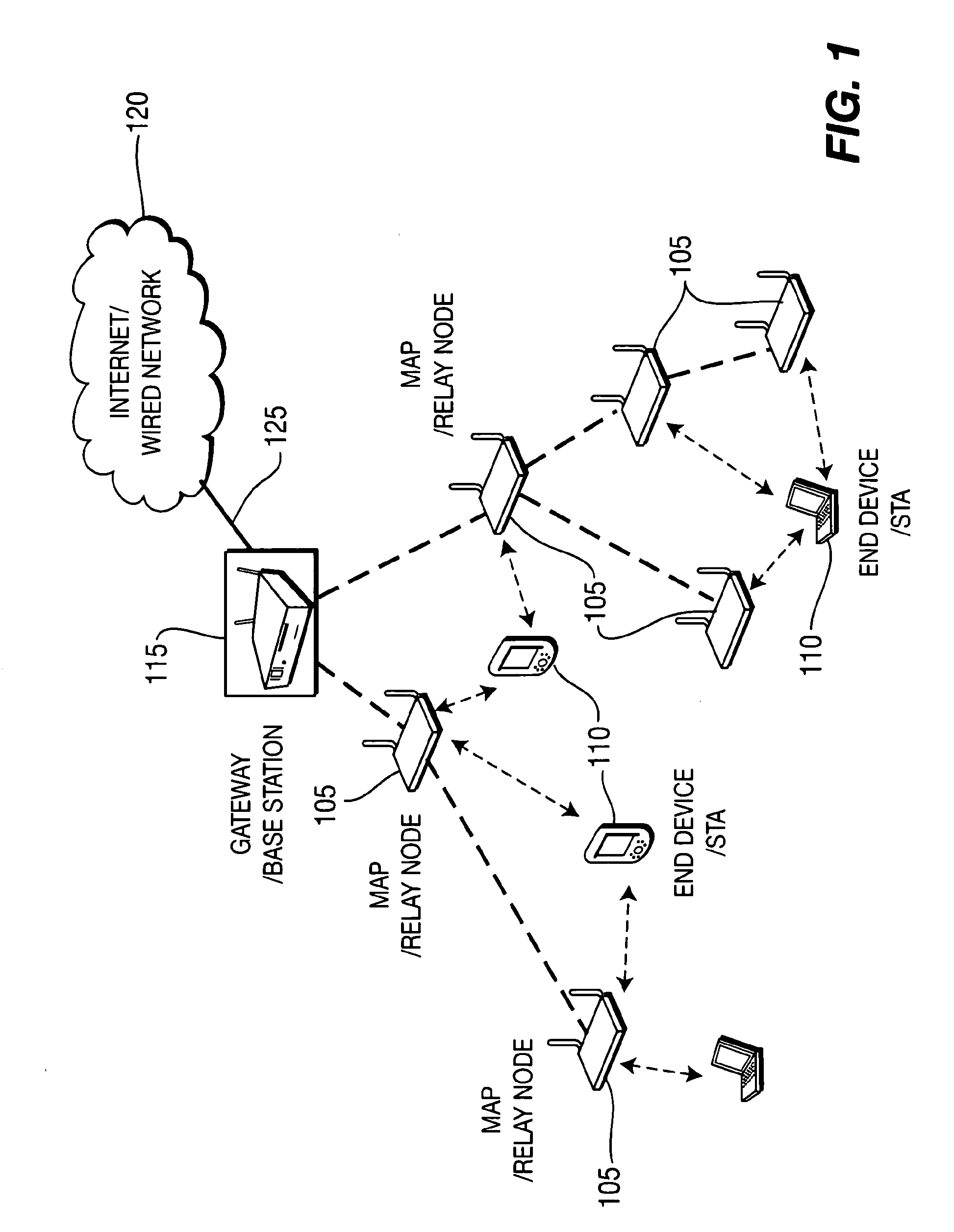
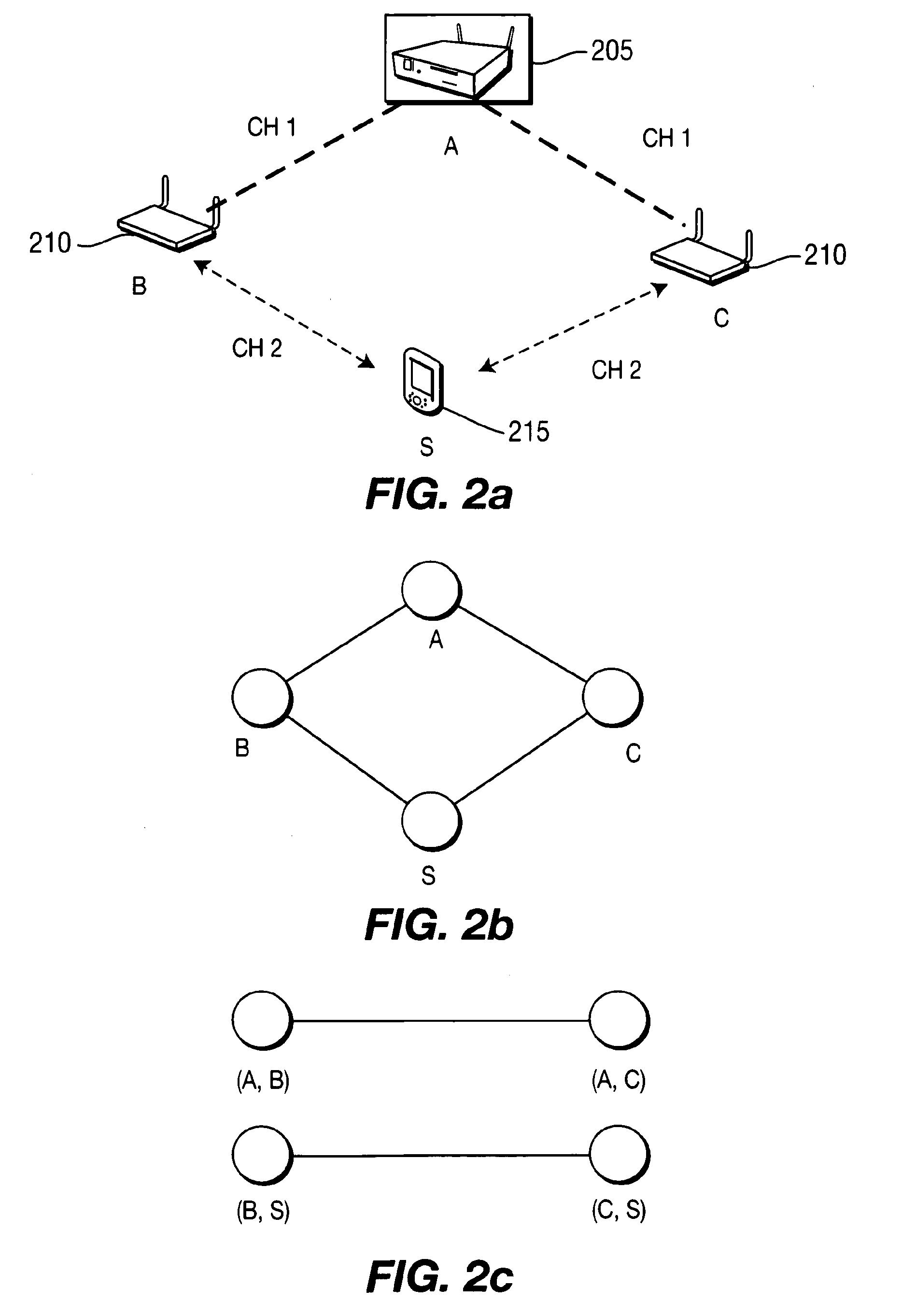
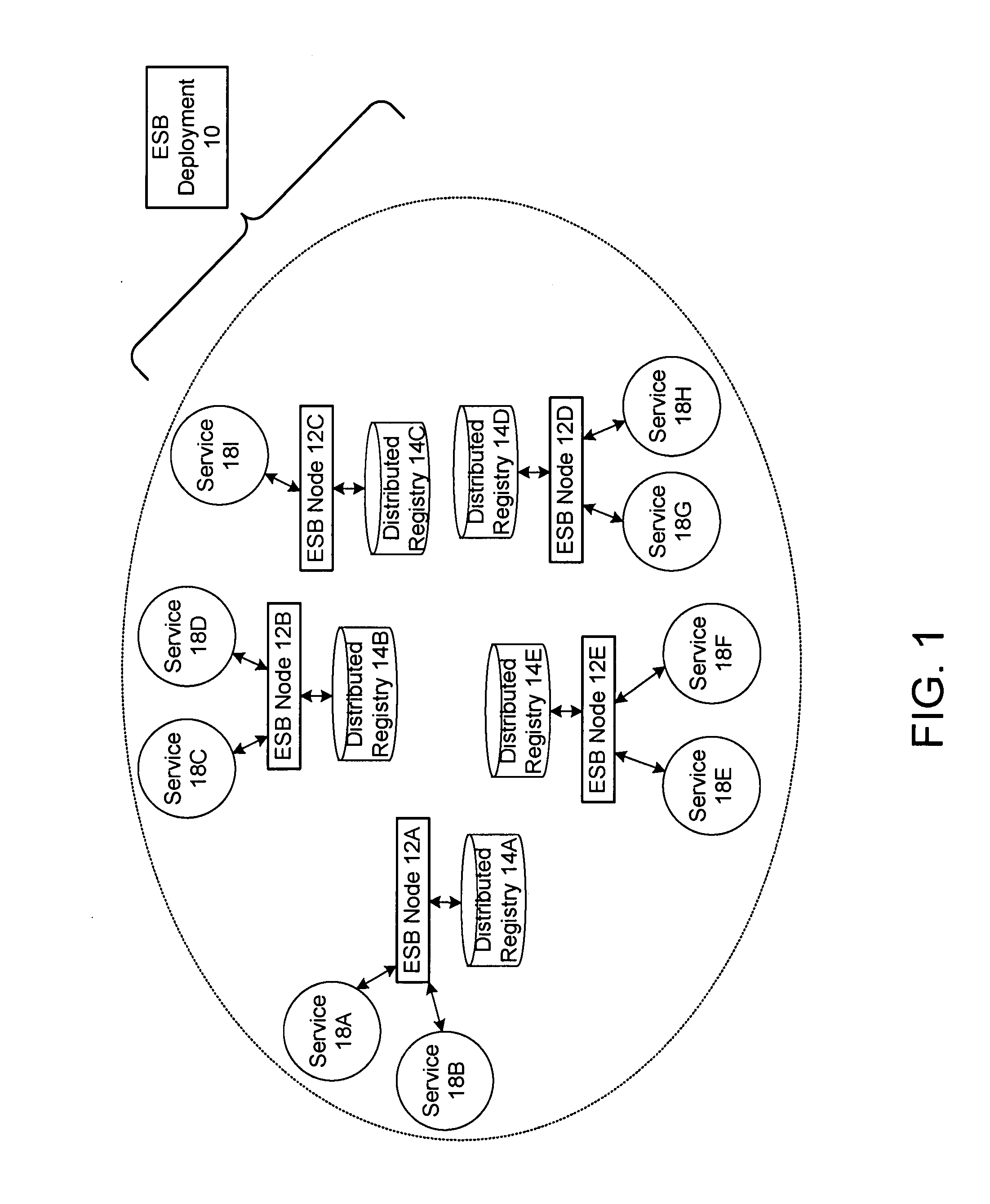
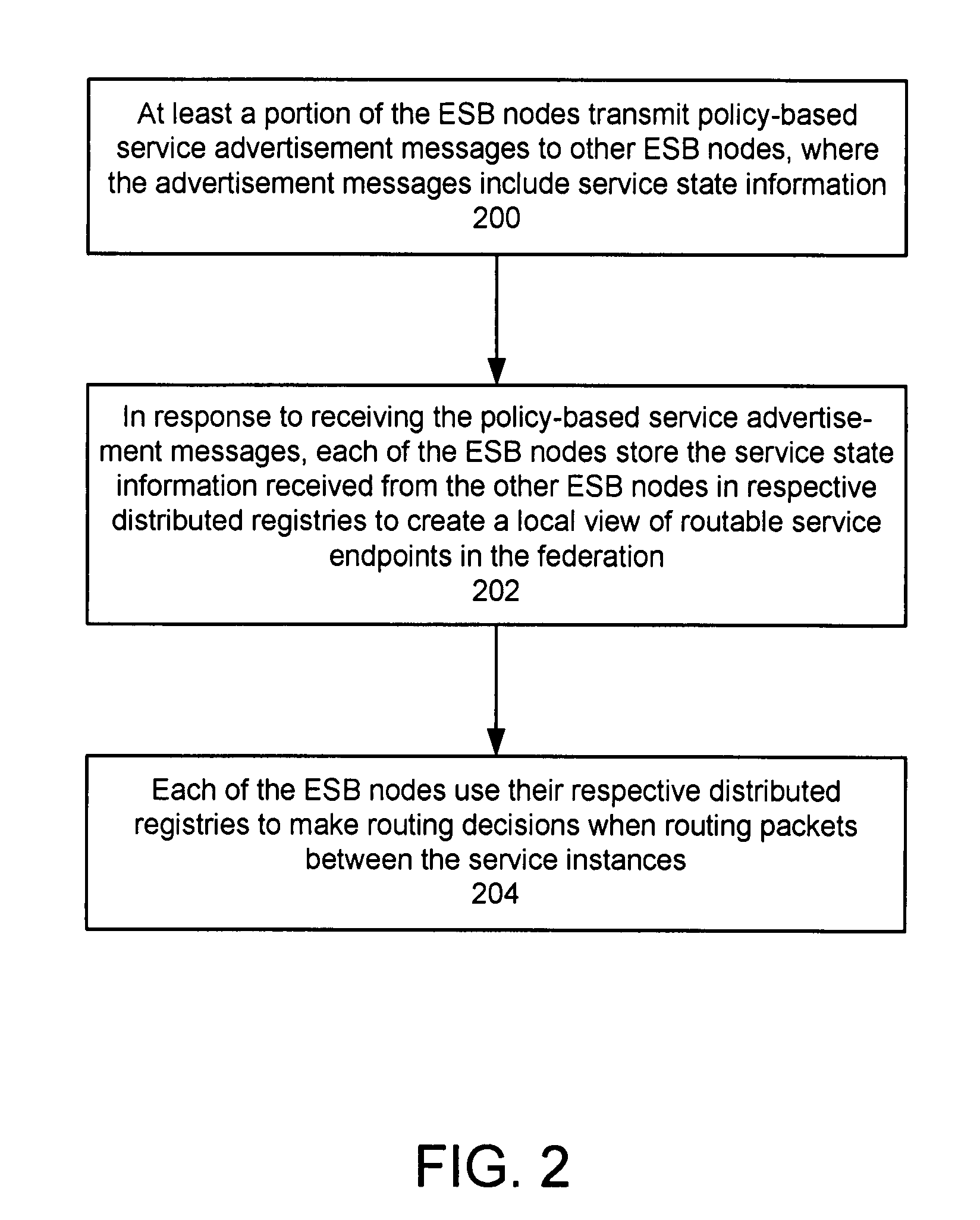
Protocol for enabling dynamic and scalable federation of enterprise service buses
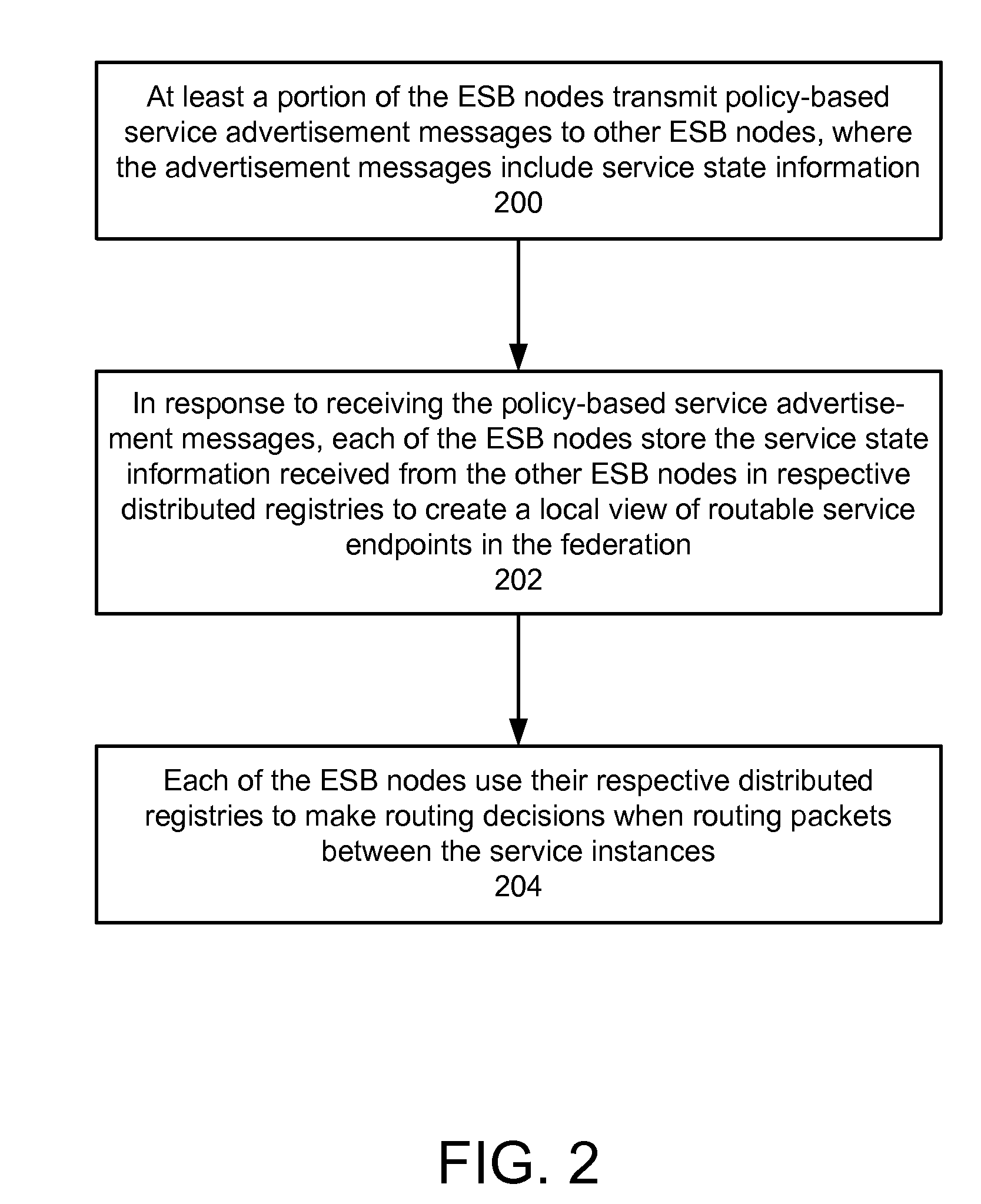
ActiveUS20090070456A1Multiple digital computer combinationsMarketingRouting decisionEnterprise services
In a method and system for creating a federation of a plurality of enterprise service buses (ESBs), a plurality of ESB nodes provide connectivity to one or more services. According to a protocol, at least a portion of the ESB nodes transmit policy-based service advertisement messages to other ESB nodes, wherein the policy-based service advertisement messages include service state information. In response to receiving the policy-based service advertisement messages, each of the ESB nodes stores the service state information received from other ESB nodes in respective distributed registries to create a local view of routable service endpoints in the federation. Each of the ESB nodes then uses its respective distributed registry to make routing decisions when routing service requests.
Owner:SERVICENOW INC
Method providing server affinity and client stickiness in a server load balancing device without TCP termination and without keeping flow states
InactiveUS20060130064A1Faster routingImprove efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRouting decisionNetwork packet
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method of routing in an AD HOC network
InactiveUS20060002312A1Improve spectral efficiencyOptimize resource consumptionData switching by path configurationWireless communicationGraphicsRouting decision
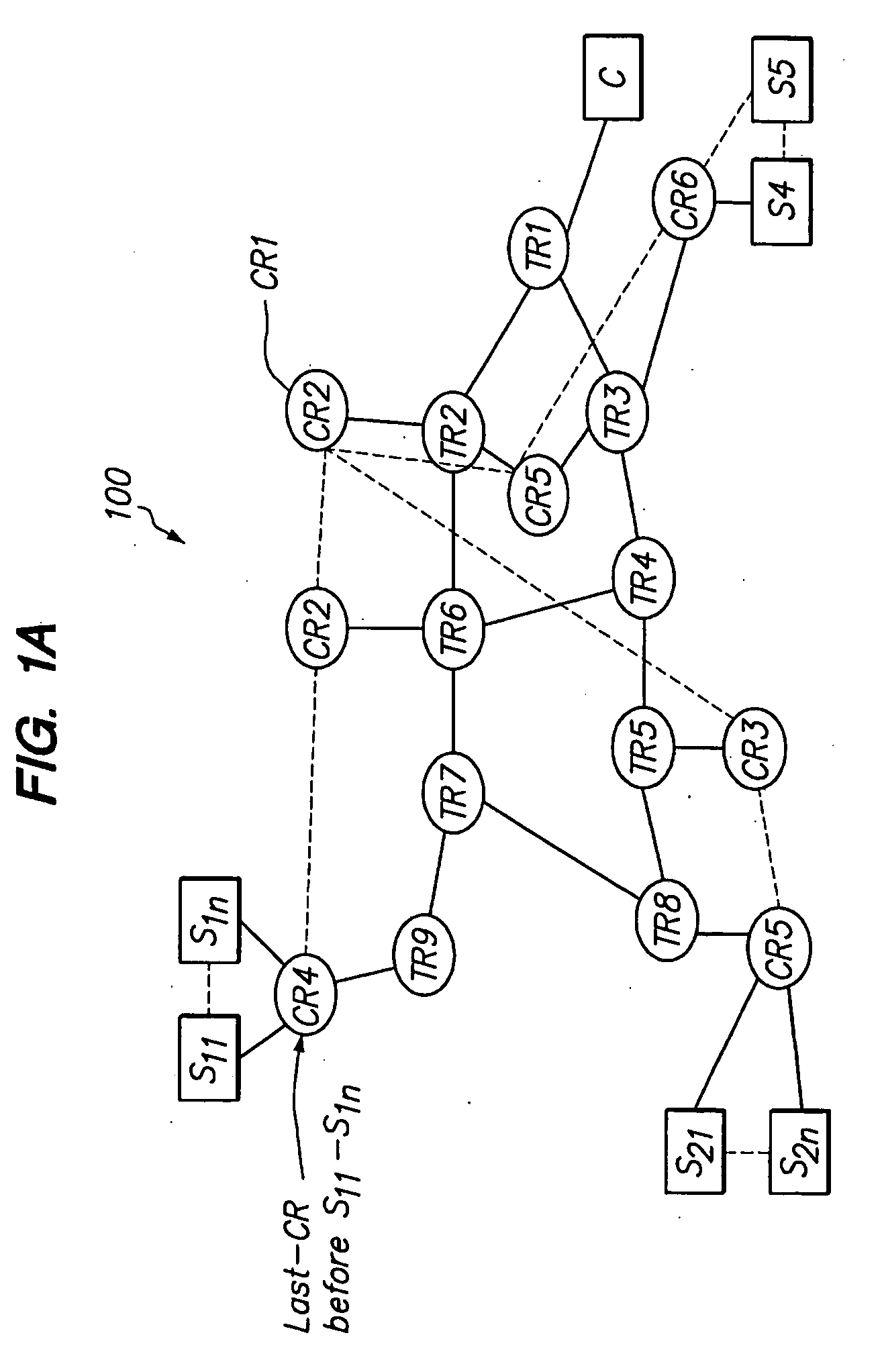
A method for the routing of information in a network comprises several communication nodes that may be mobile, the routing being done by a route between a source node and a destination node through a set of wireless communication links between the nodes of the network, the entire set forming a graph wherein the method comprises at least one step in which the graph of the network is structured as a unicast two-way link in order to obtain the relationships existing between two nodes and form, during routing decisions, sub-graphs comprising arcs that connect two nodes, the arcs sharing one and the same set of properties.
Owner:THALES SA
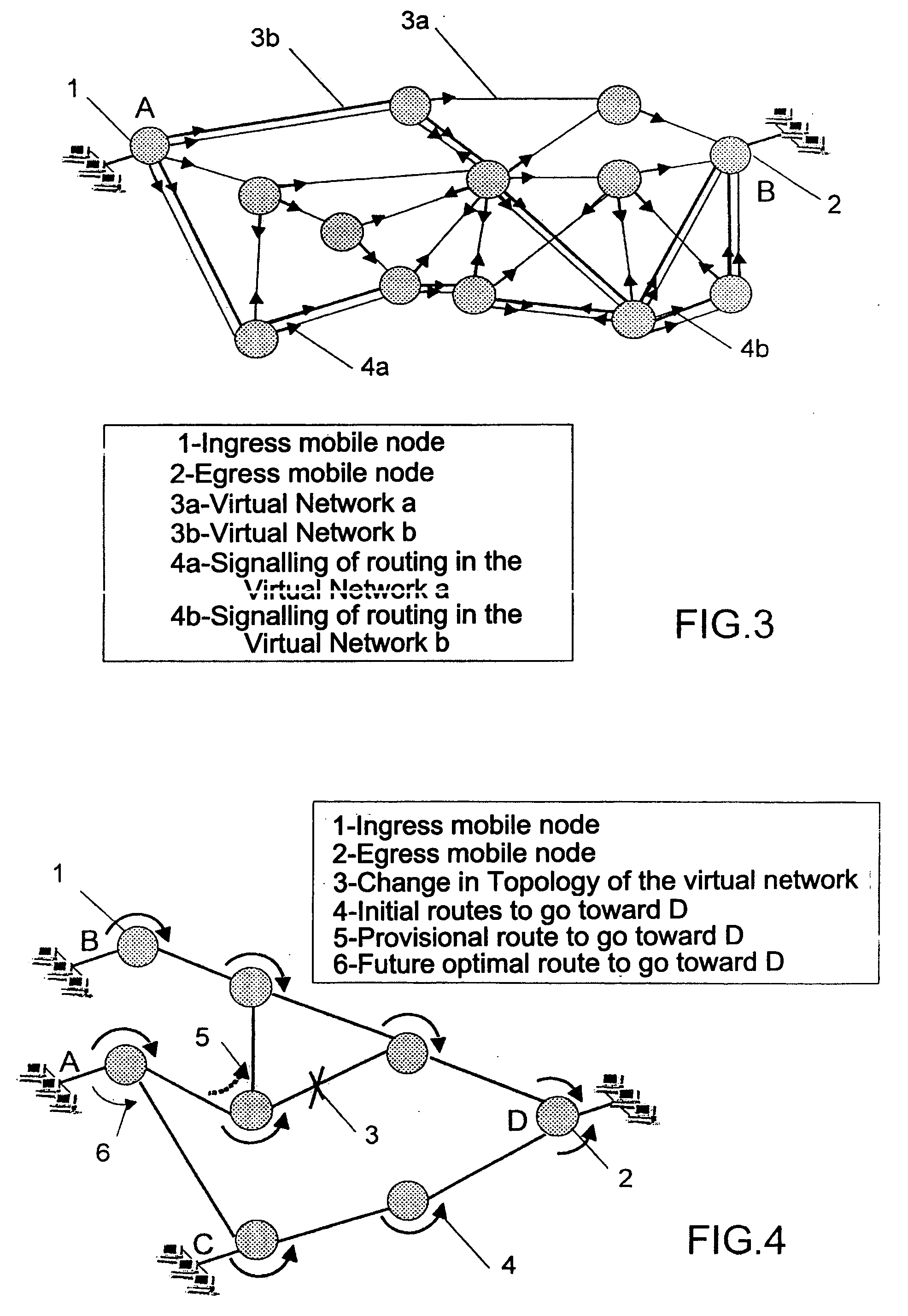
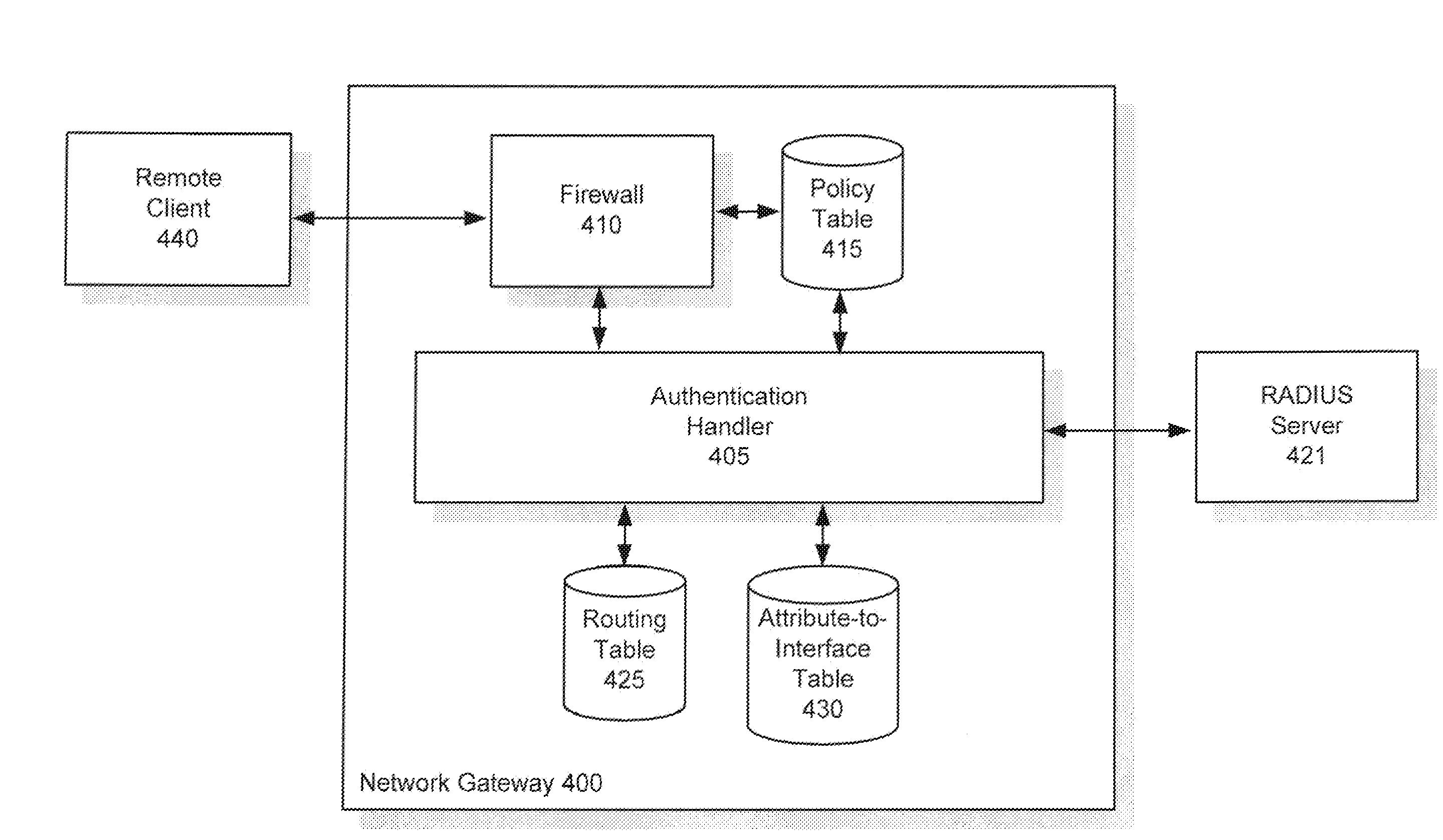
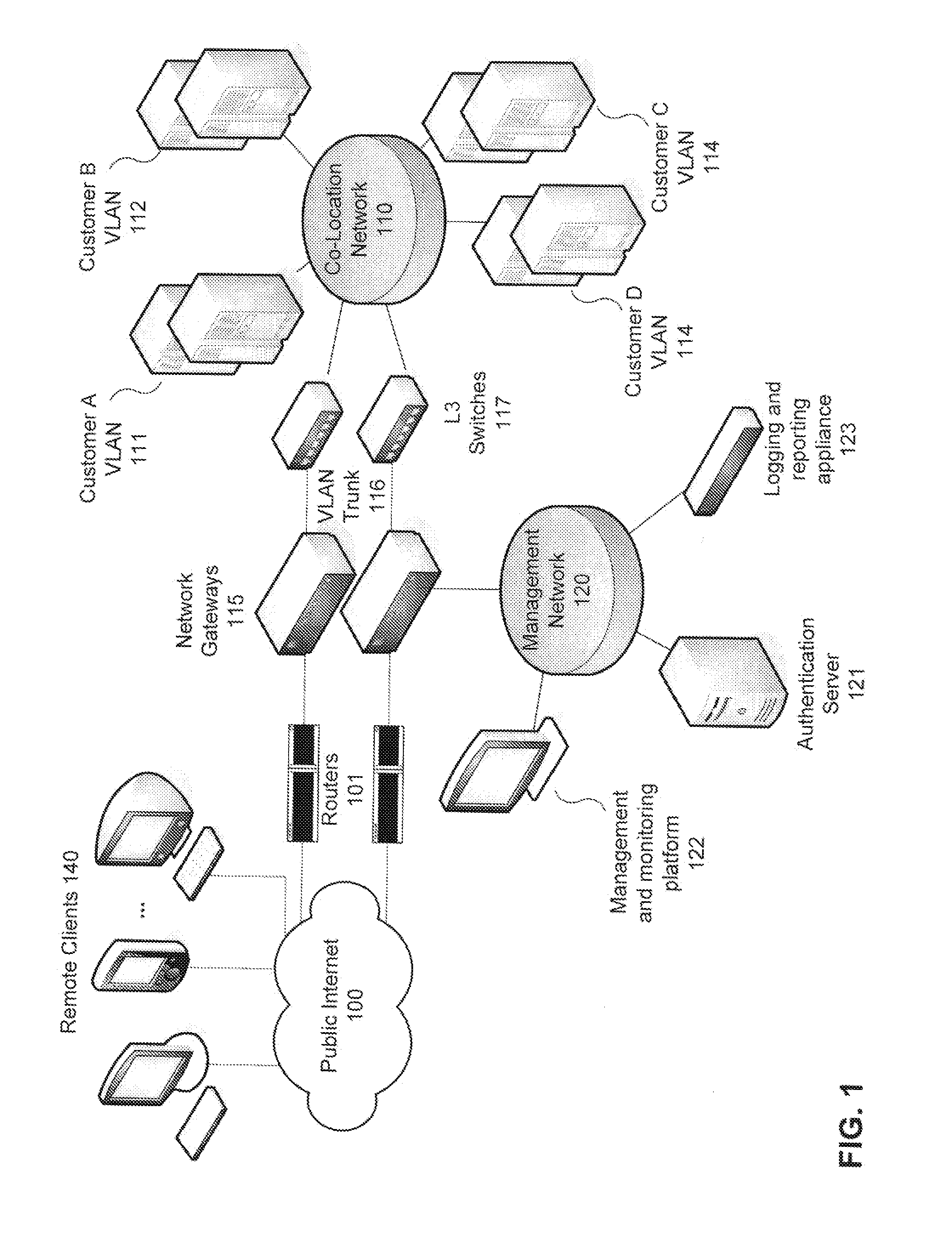
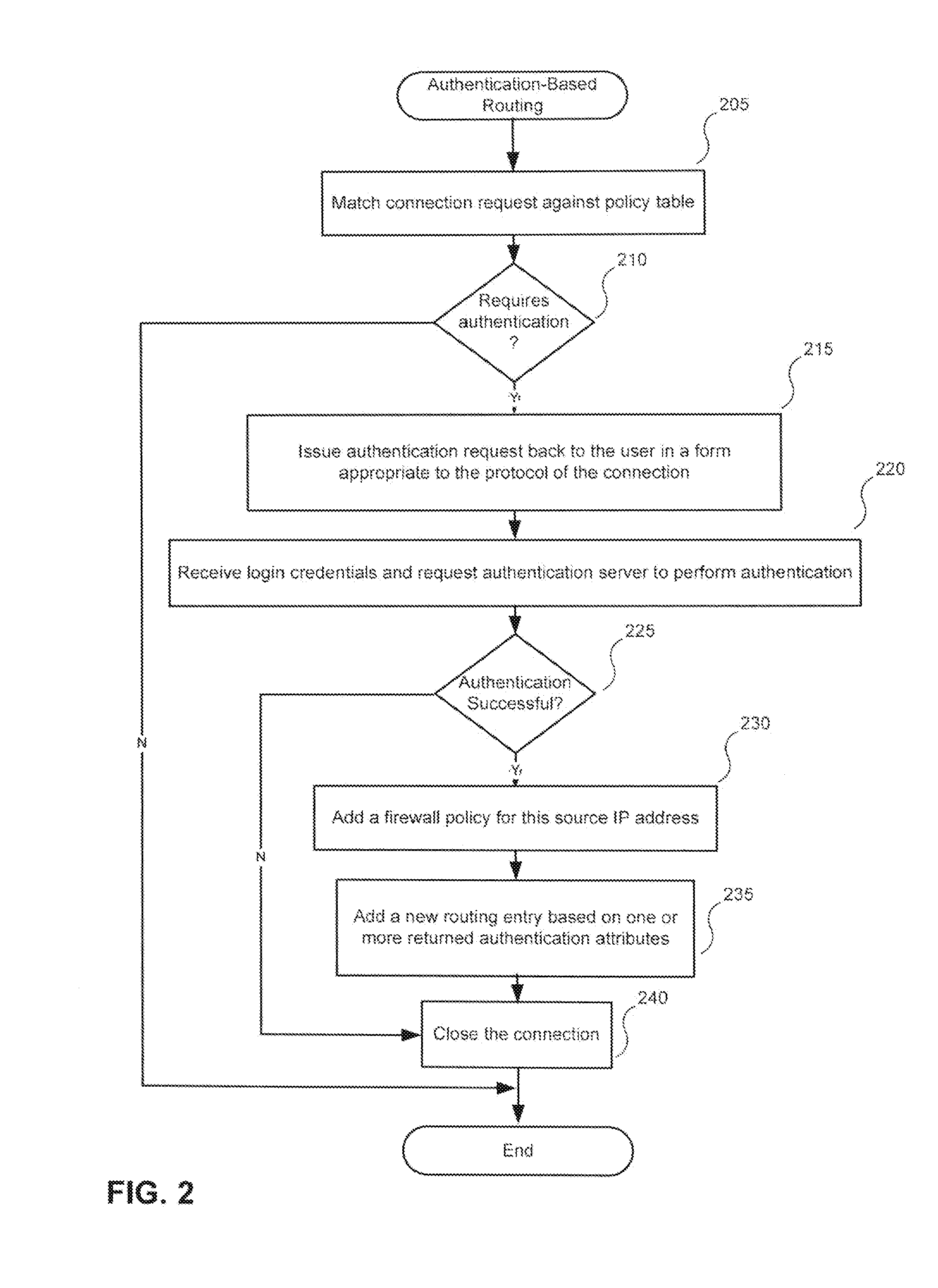
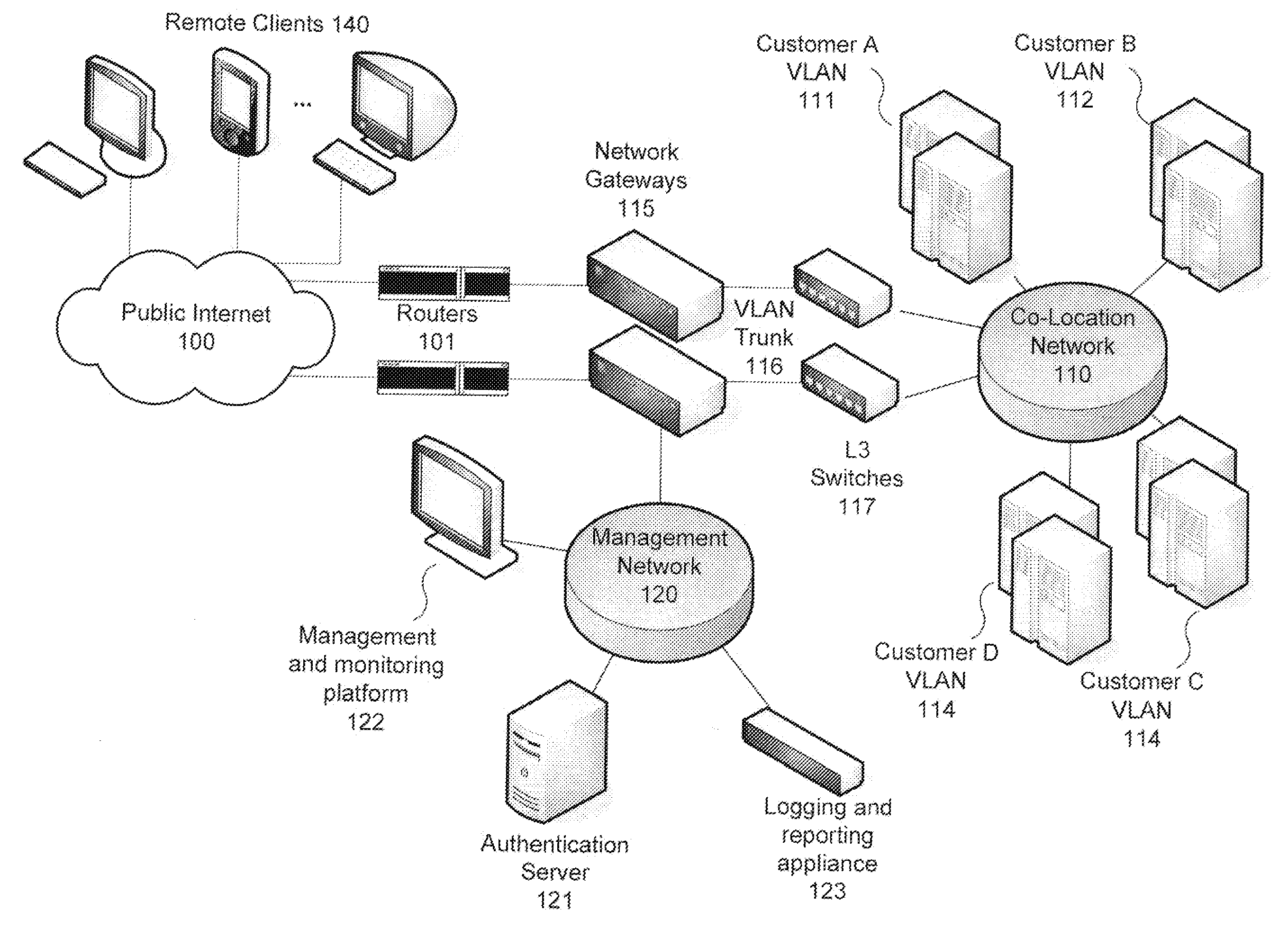
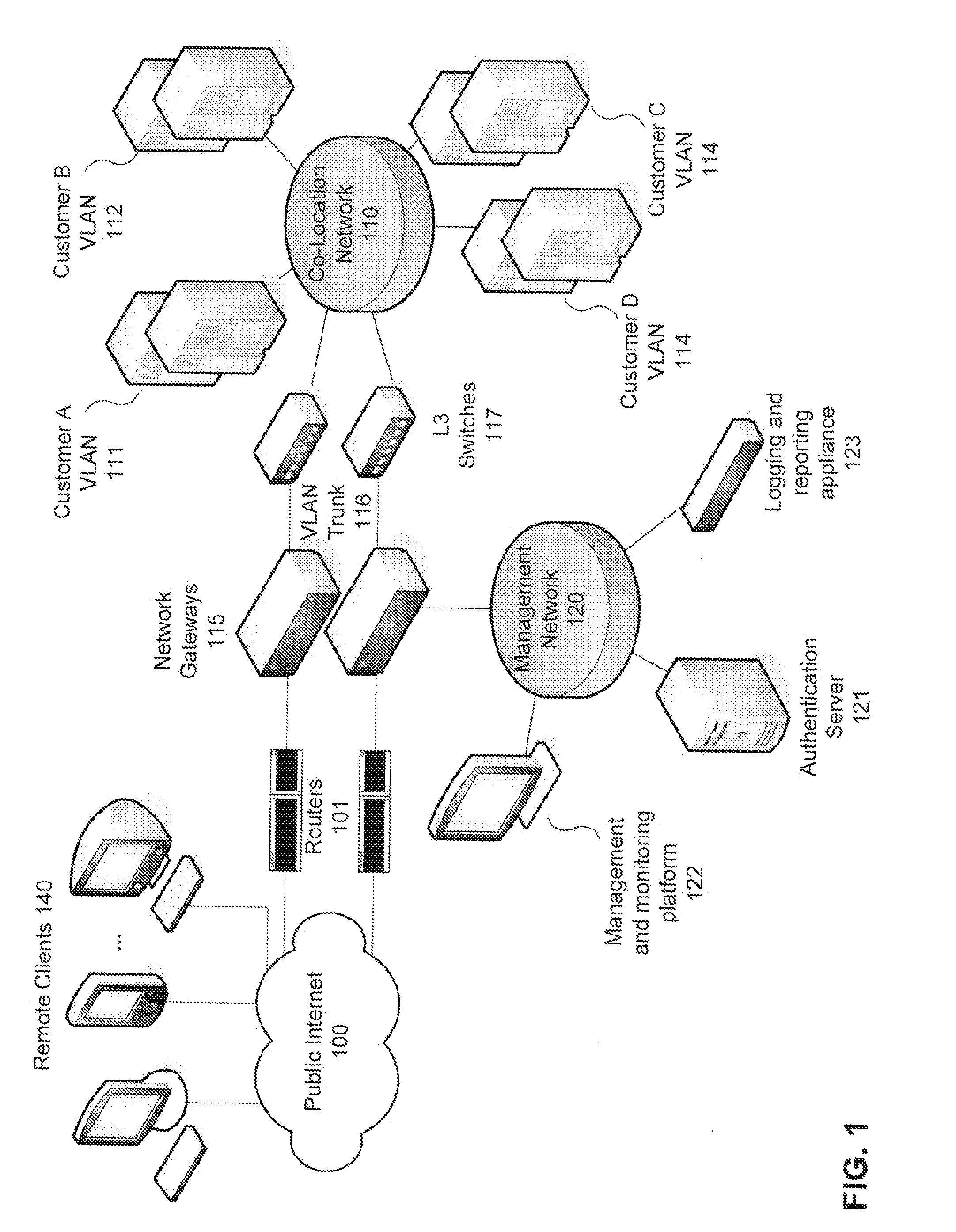
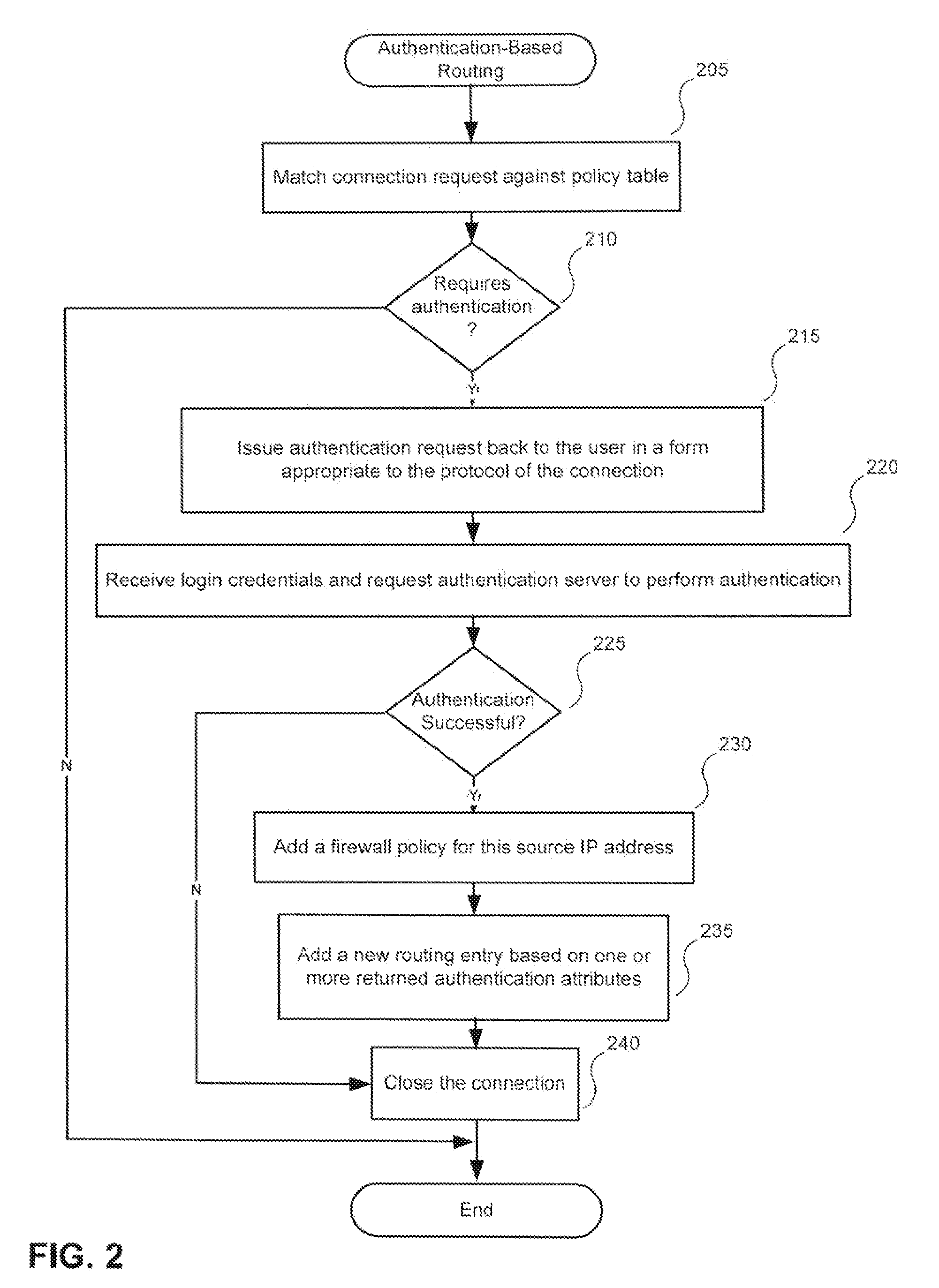
Use of authentication information to make routing decisions
InactiveUS20080028445A1Easy to transportDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationRouting decisionTraffic flow
Methods and systems for utilizing authentication attributes to determine how to direct traffic flows are provided. In one embodiment, an augmented authentication database is provided, which includes routing information for multiple users. The routing information is intended to be used to facilitate routing of traffic flows to appropriate virtual networks of a network. A request on behalf of one of the users is received at an authentication interface of the network for access to a service provided by a first virtual network. Responsive to the request, login credentials of the user are authenticated against the augmented authentication database. Responsive to successful authentication, the authentication interface receives from the augmented authentication database routing information associated with the user and causes the user to be granted access to the service by causing traffic flow associated with the user to be routed to the first virtual network based on the routing information returned.
Owner:FORTINET
Treatment of Data in Networks
ActiveUS20080240115A1Available capacityRemoving the overhead of routing informationMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsData switching by path configurationRouting decisionIntelligent decision
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Joint association, routing and rate allocation in wireless multi-hop mesh networks
InactiveUS20100322141A1Maximize network throughputImprove fairnessNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsRouting decisionMesh networking
A method and apparatus are described including collecting network information, determining an association, bandwidth allocation and routing scheme based on the collected network information, notifying a mesh access point of the association, the bandwidth allocation and the routing scheme and notifying a client node of its association information. Also described are a method and apparatus including measuring link quality and channel conditions, reporting results of the measuring act to a controller, receiving a routing decision and data forwarding instructions from the controller and forwarding the routing decision and the data forwarding instructions to a client node. Further described are a method and apparatus including measuring link quality and channel conditions, reporting results of the measuring act to a controller, receiving association instructions from the centralized controller and updating previously stored association instructions with the received association instructions.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
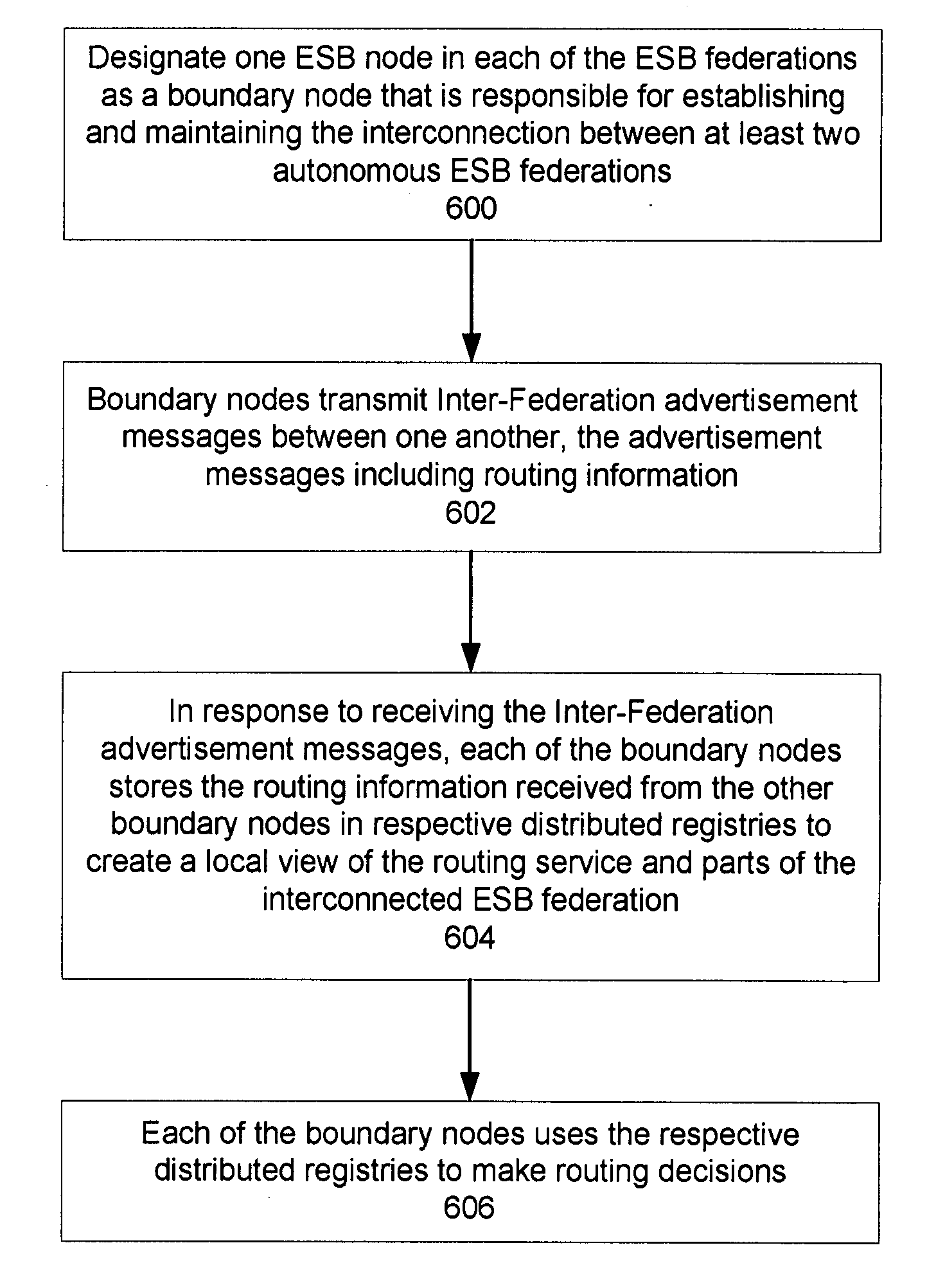
Protocol for enabling dynamic and hierarchical interconnection of autonomous federations of enterprise service buses
InactiveUS20090077251A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionRouting decisionInterconnection
In a method and system for creating an interconnection between autonomous enterprise service buses (ESB) federations, each one of the ESB federations comprise at least one ESB deployment, which further include a plurality of ESB nodes that provide connectivity to one or more services. According to a protocol, a first ESB node is designated in each of the ESB federations as a boundary node that is responsible for establishing and maintaining an interconnection between at least two of the ESB federations. Advertisement messages are transmitted between the boundary nodes that include routing information. In response to receiving the advertisement messages, each of the boundary nodes store the routing information received from other boundary nodes in respective distributed registries to create a local view of routable service endpoints in the federation. Each of the boundary nodes then use the respective distributed registries to make routing decisions when routing service requests.
Owner:IBM CORP
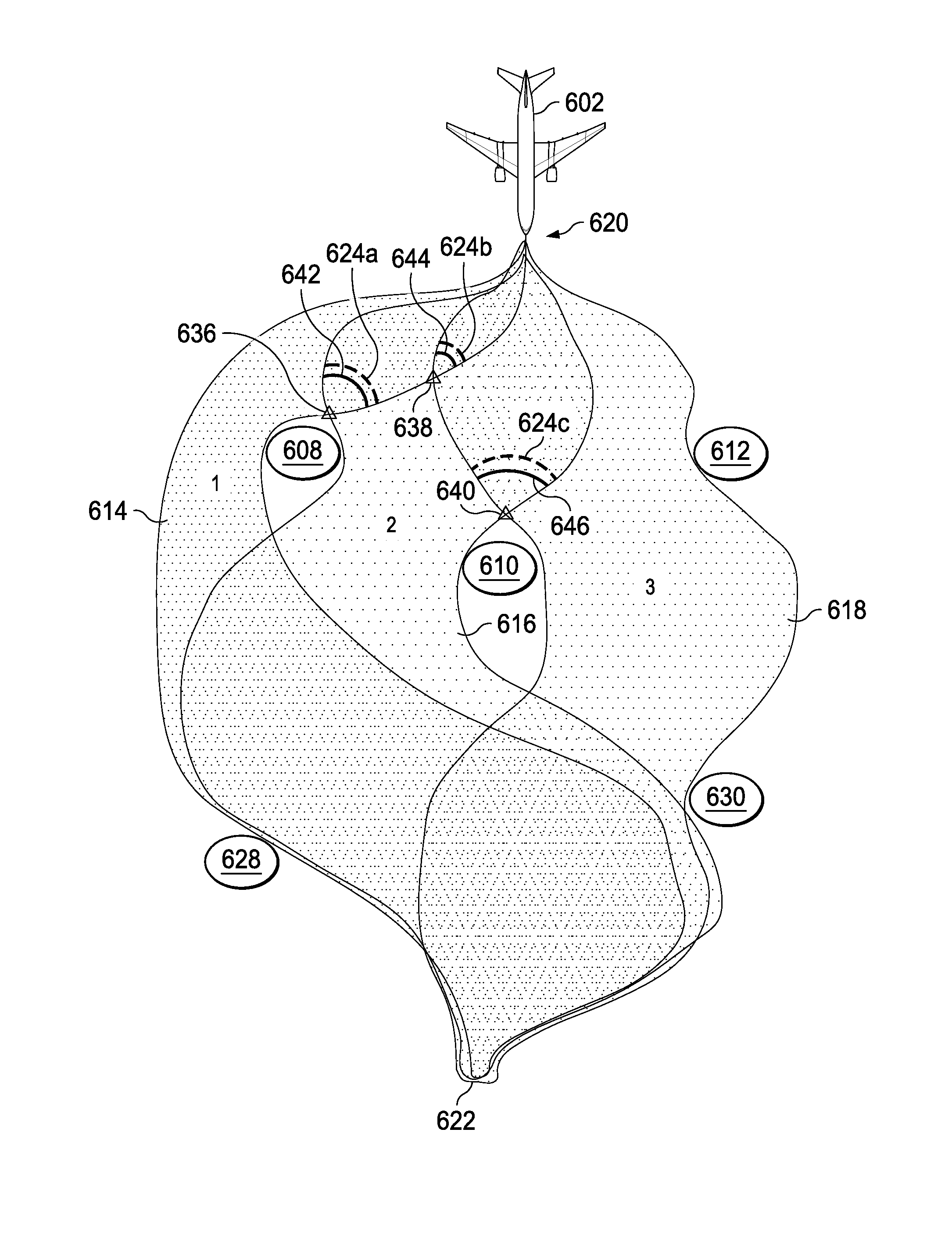
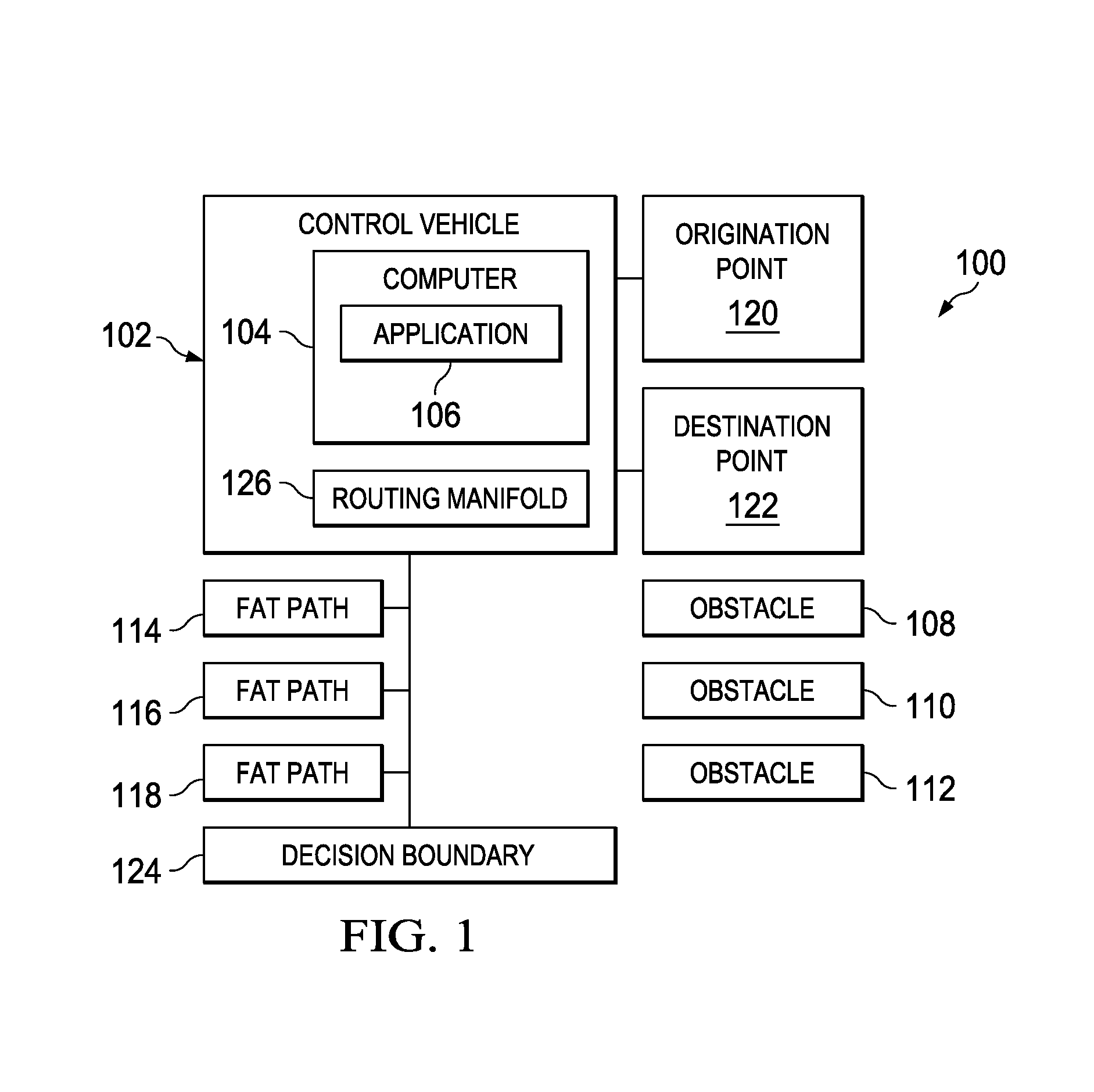
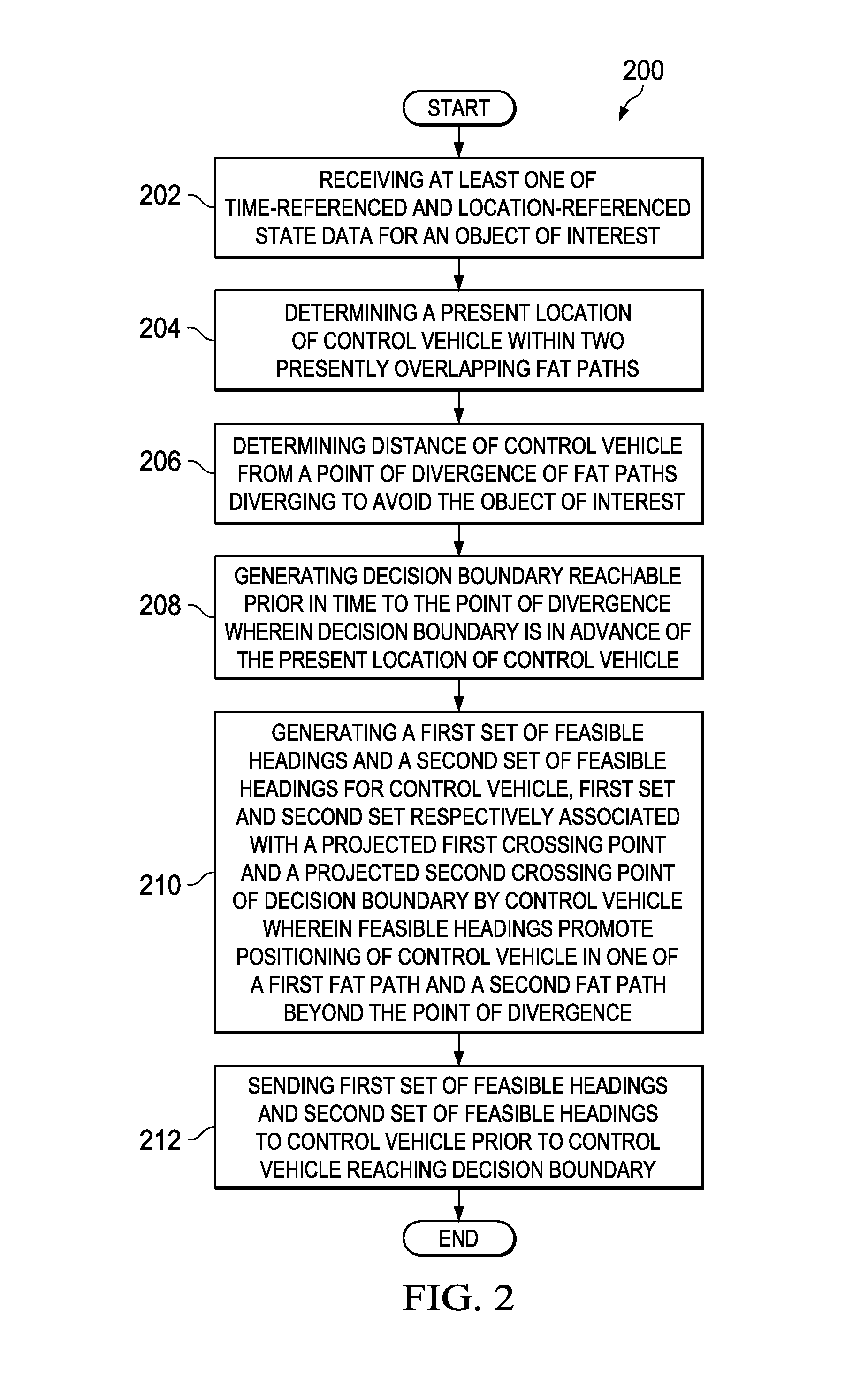
System and method for routing decisions in a separation management system
InactiveUS8868328B1Avoid rangeAnti-collision systemsNavigation instrumentsRouting decisionDecision boundary
A method comprising computer receiving at least one of time and location-referenced state data for an object of interest, determining present location of a vehicle within two presently overlapping fat paths, fat paths comprising homotopically distinct regions of travel, determining distance of vehicle from a point of divergence of fat paths, fat paths diverging to avoid object, the computer generating a decision boundary reachable prior in time to point of divergence wherein decision boundary is in advance of the present location of vehicle, computer generating a first second set of feasible headings for the vehicle, the first and second set respectively associated with a projected first and second crossing points of the decision boundary by vehicle wherein feasible headings promote positioning of vehicle in one of fat paths beyond point of divergence, and computer sending first and second sets of feasible headings to vehicle prior to vehicle reaching decision boundary.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Use of authentication information to make routing decisions
InactiveUS20100125898A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationRouting decisionService provision
Methods and systems for utilizing authentication attributes to determine how to direct traffic flows are provided. According to one embodiment, a program storage device readable by a network device associated with a service provider is provided. The program storage device tangibly embodies a program of instructions executable by a processor of the network device to perform method steps for authenticating users and establishing appropriate service sessions. An end user from whom a connection request is received is caused to be prompted for login credentials. The received login credentials are then caused to be authenticated by an authentication server. Responsive to successful authentication, a service session is established for the end user and customer separation is maintained among the multiple customers by creating a routing entry, according to which subsequent packets associated with the service session are routed, based on authentication attributes returned by the authentication server.
Owner:FORTINET
Methods and systems for api proxy based adaptive security
ActiveUS20180337891A1Promote resultsEasy to identifyInterprogram communicationData switching networksRouting decisionSelf adaptive
The invention concerns API proxy based adaptive security. The invention implements adaptive security for API servers, while avoiding data bottlenecks and maintaining client experience. The invention provides methods and configurations for API security that may be employed at proxies for implementing routing decisions involving client messages received at said proxies. The invention also involves generating or collecting at proxies, log information that captures data corresponding to received client messages and responses from API servers—which log information correlates communications between clients, proxies and backend API servers, and includes data relevant for purposes generating API metrics and identifying anomalies and / or indicators of compromise. The invention yet further provides security server clusters configured for generating API metrics and / or identify anomalies or indicators of compromise—which may be used by proxies to terminate existing connections and block subsequent requests or messages from clients associated with the identified anomalies or indicators of compromise.
Owner:PING IDENTITY
Separation of data and control in a switching device
InactiveUS6917620B1Minimize occurrenceSize of output is increasedDigital computer detailsTime-division multiplexRouting decisionNetwork packet
A method and apparatus for switching a data packet between a source and destination in a network. The data packet includes a header portion and a data portion. The header portion includes routing information for the data packet. The method includes defining a data path in the router comprising a path through the router along which the data portion of the data packet travels and defining a control path comprising a path through the router along which routing information from the header portion travels. The method includes separating the data path and control path in the router such that the routing information can be separated from the data portion allowing for the separate processing of each in the router. The data portion can be stored in a global memory while routing decisions are made on the routing information in the control path.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method and apparatus of domain selection for routing control
ActiveUS20080102844A1Improve service experienceBroaden applicationInterconnection arrangementsAssess restrictionRouting decisionCommunications system
A method of domain selection for routing control, applied to a communication system including a Circuit Switched (CS) network and an IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) includes: obtaining call status(es) of a user in any one or both of the CS network and the IMS; selecting a domain via which an incoming call is to be delivered according to the call status(es) upon receiving a routing decision query request from a routing decision query entity, and indicating the routing decision query entity to deliver the incoming call via the CS network or the IMS selected. The method provided by embodiments of the present invention selects the domain according to the call status(es) of the user in any one or both of the CS network and the IMS. Therefore, the problem that two calls are respectively delivered via the CS network and the IMS at the same time may be avoided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com