Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
442results about "Forehearths" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
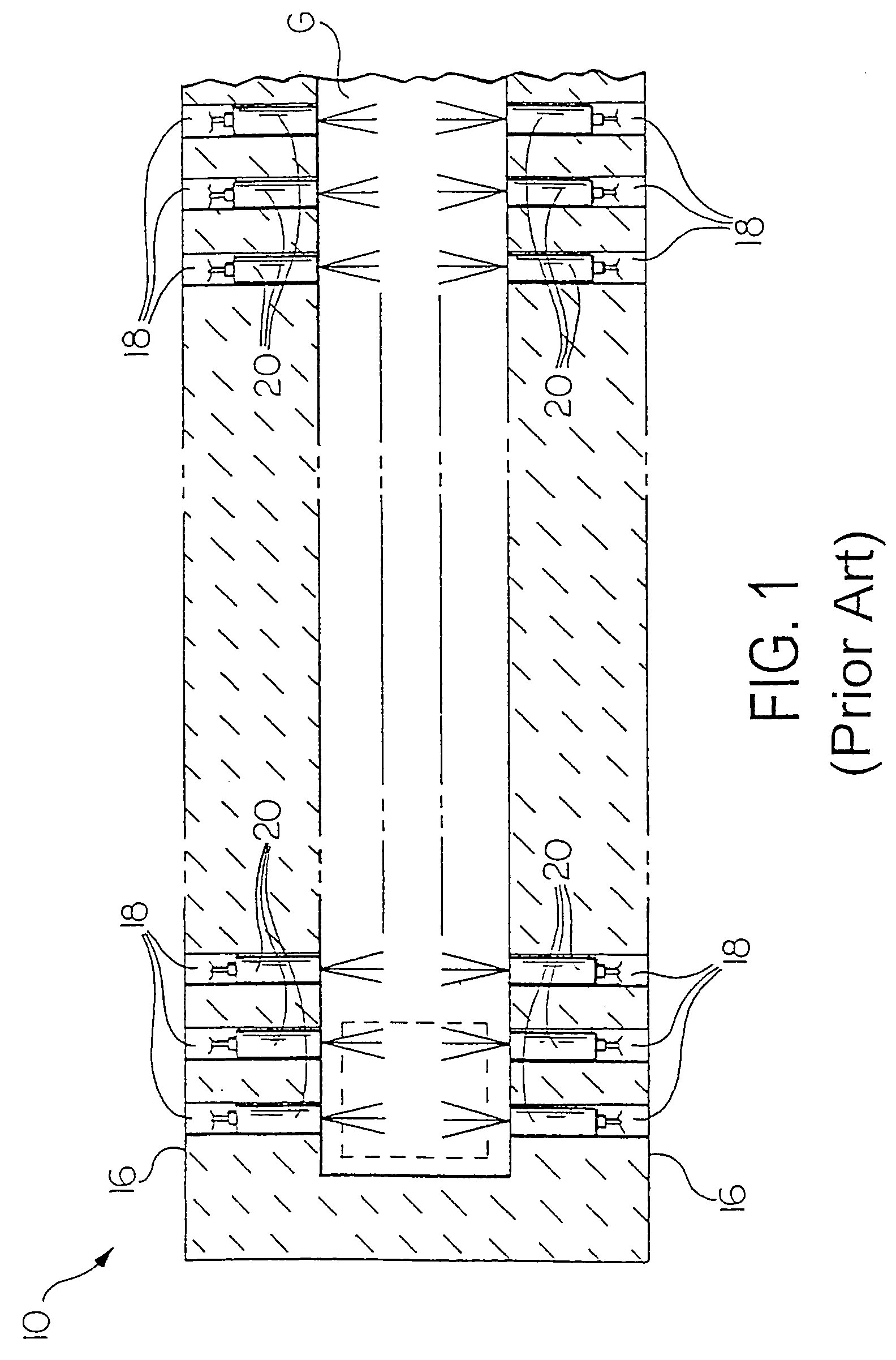
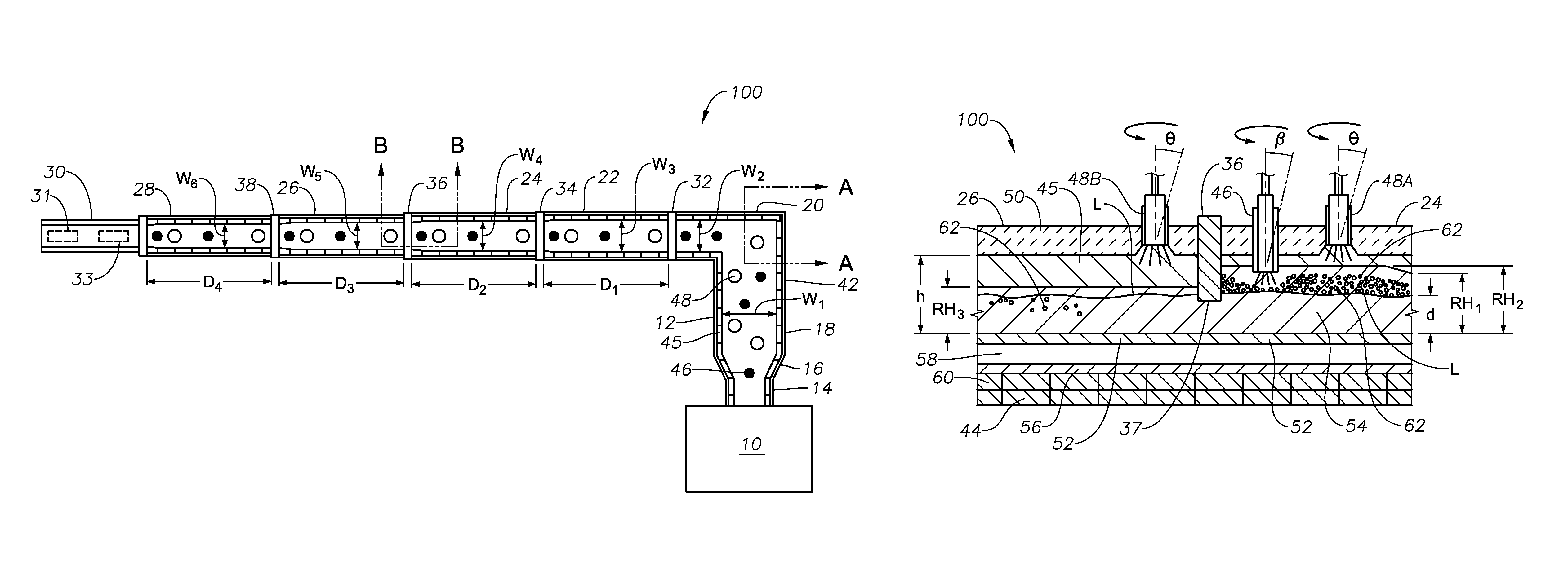
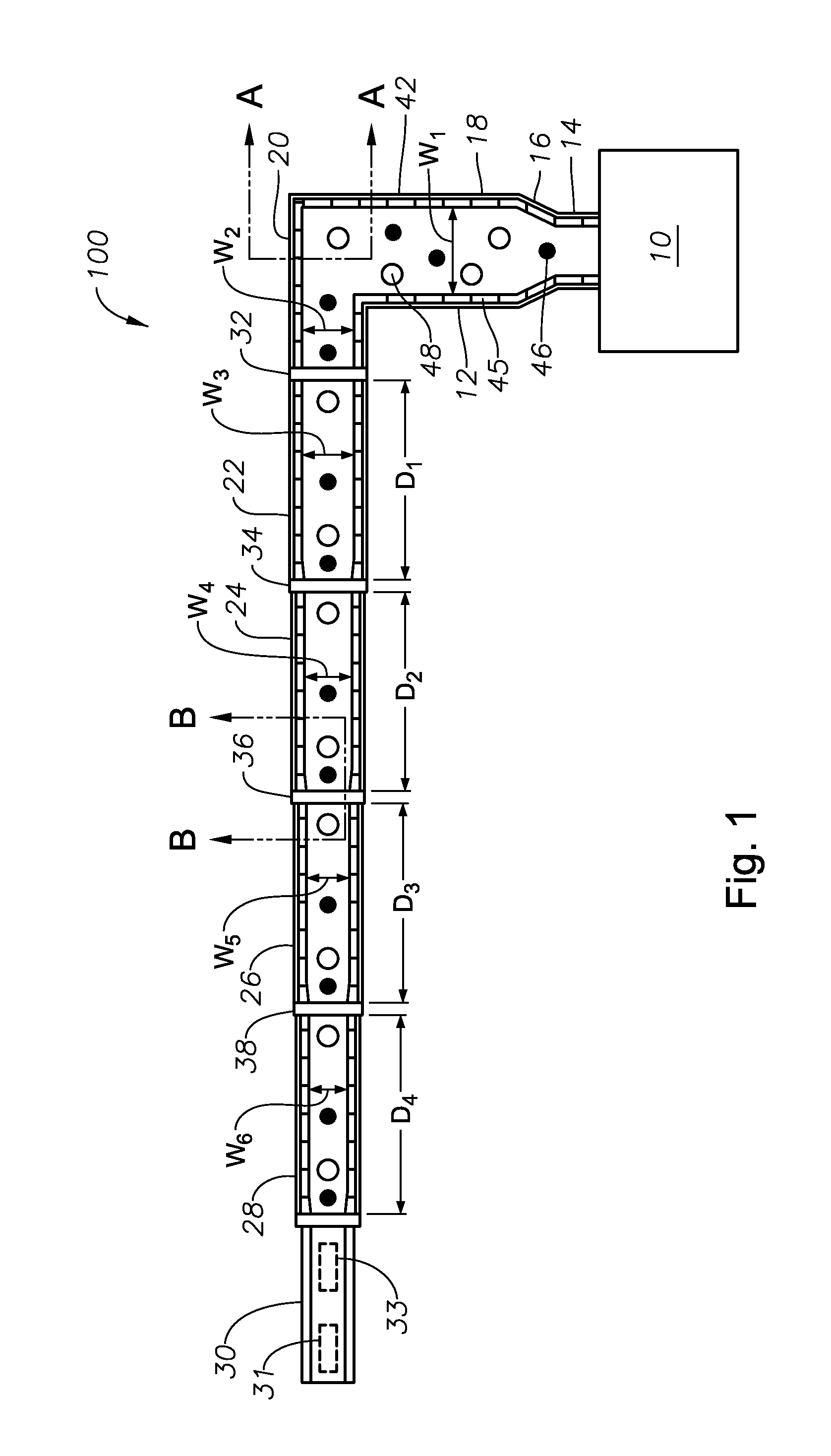
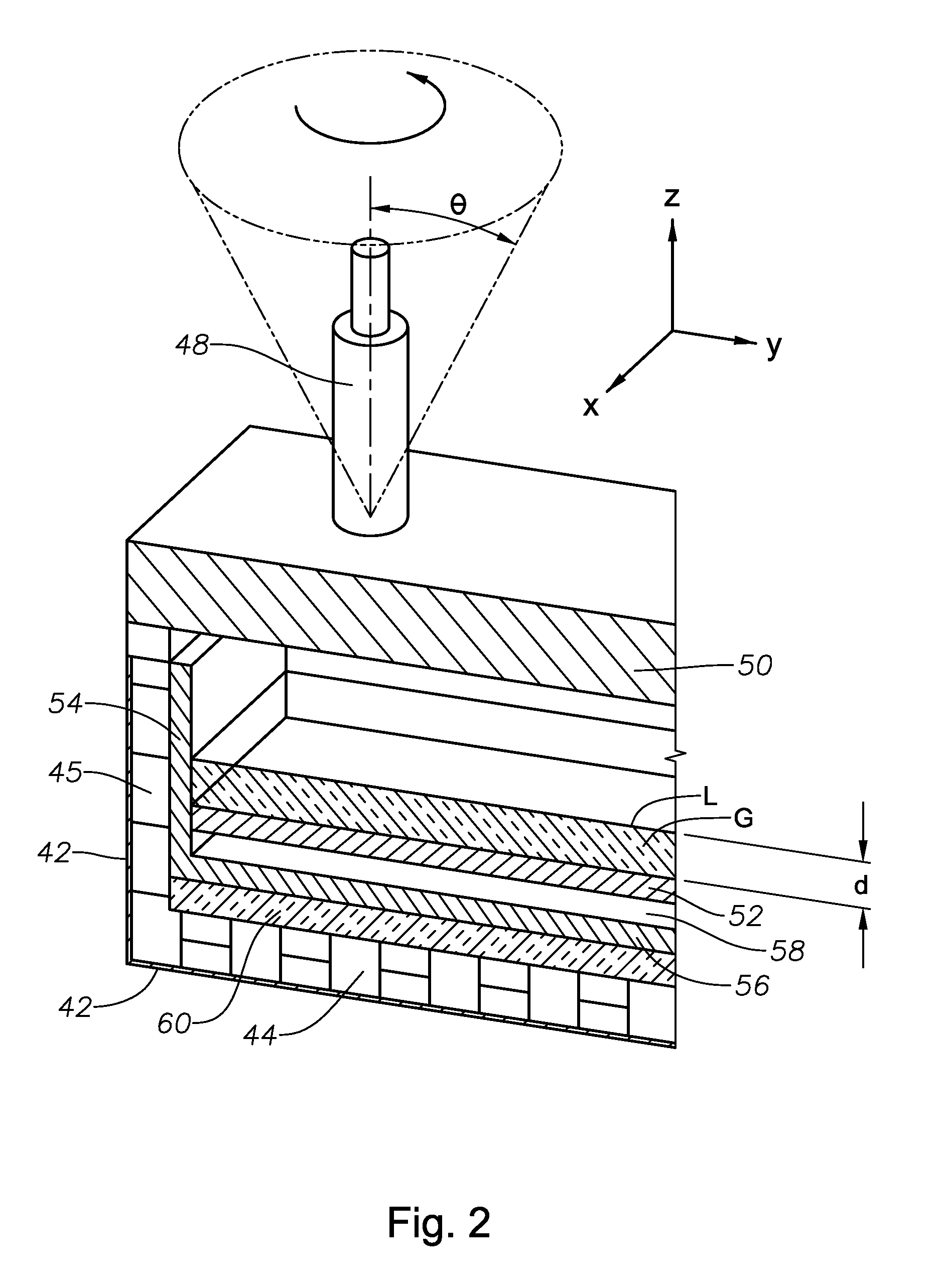
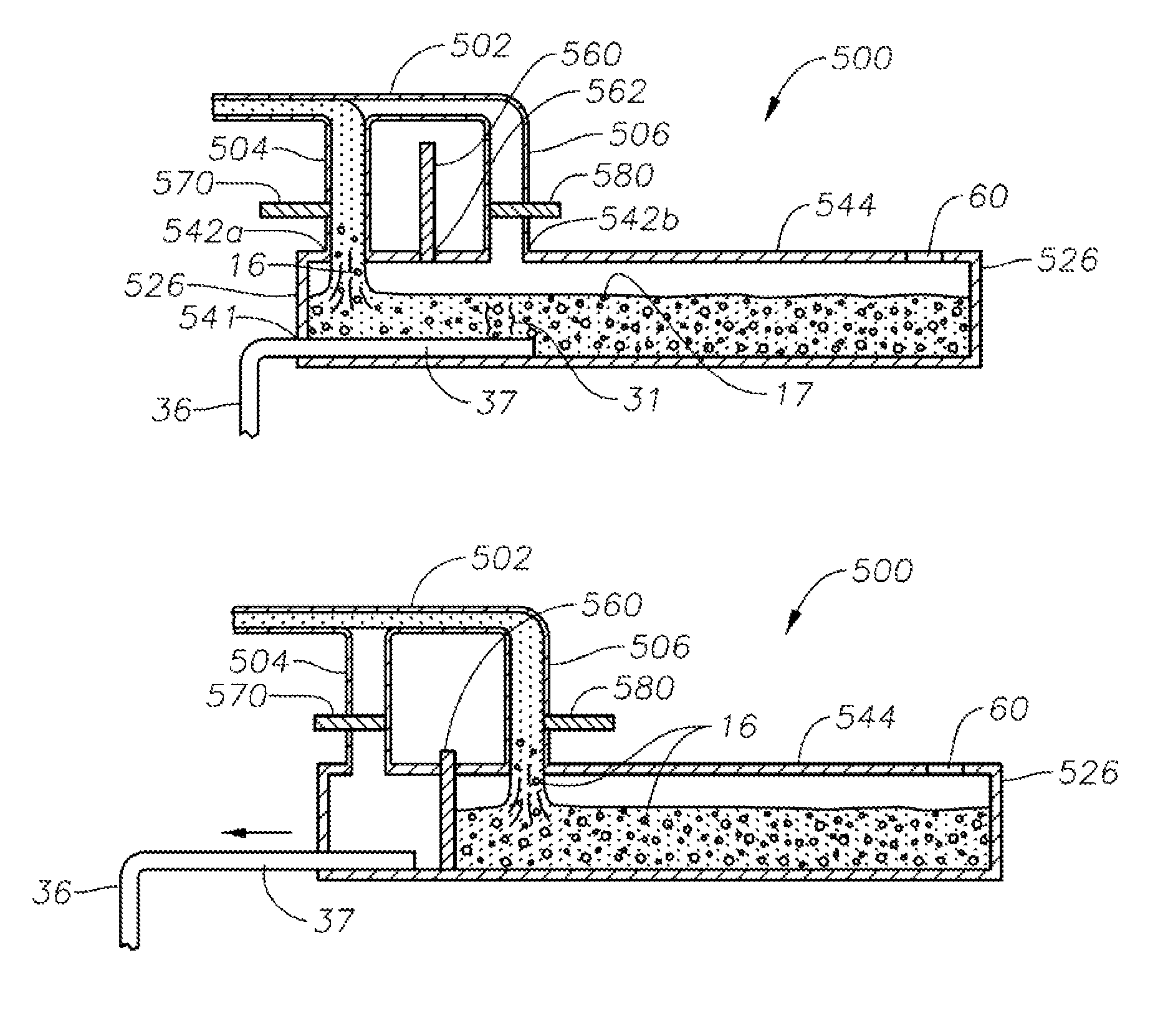
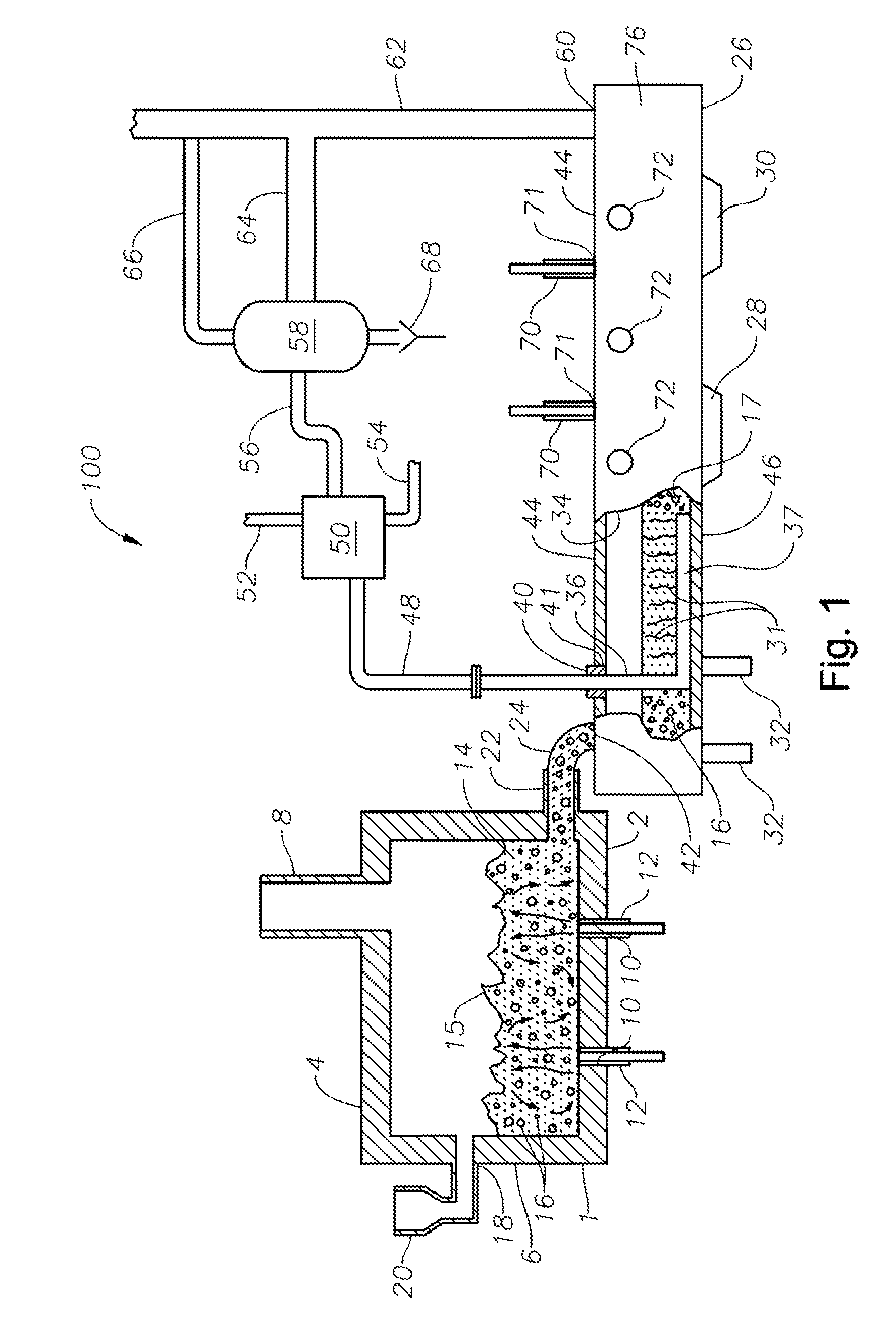
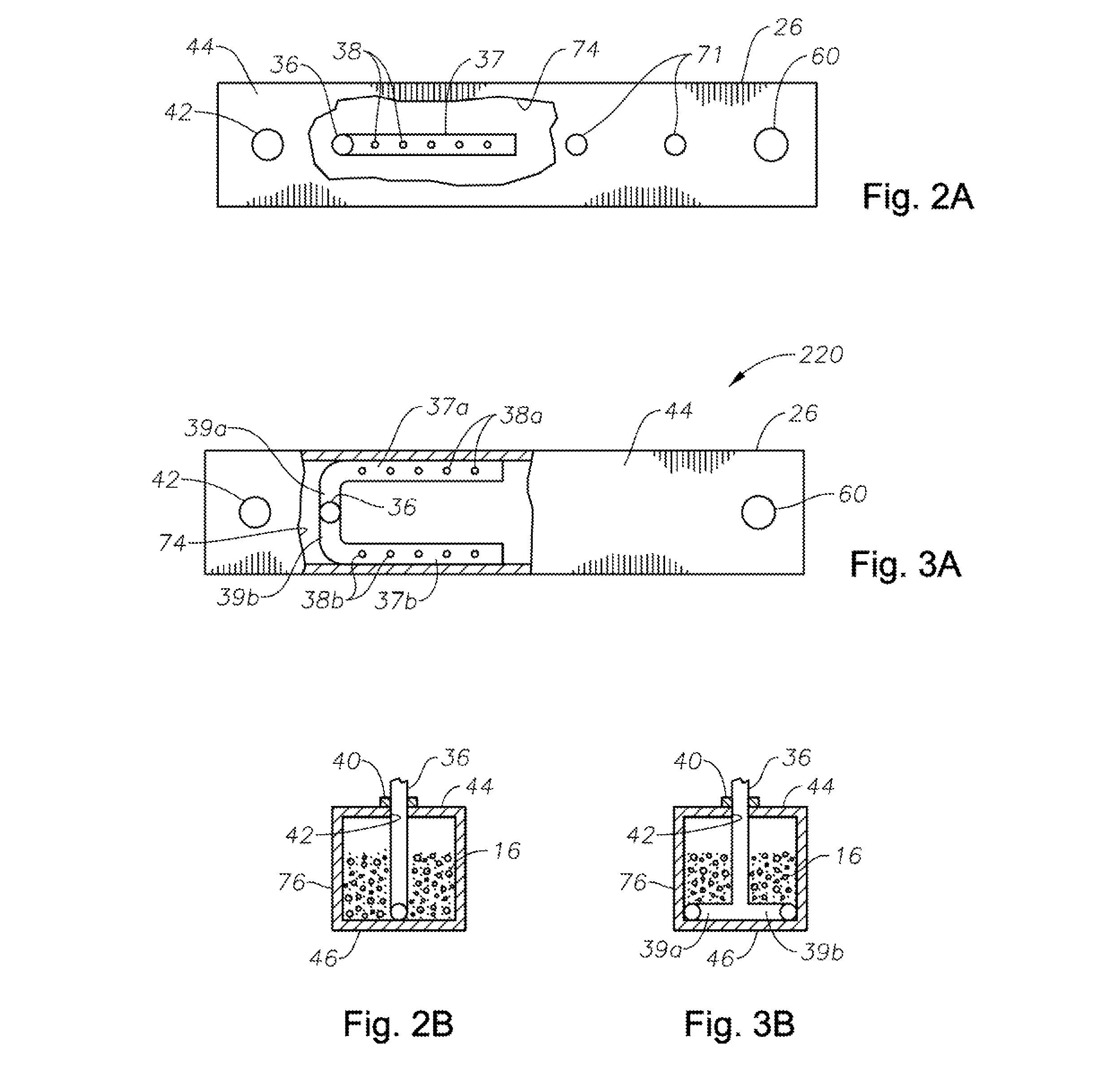
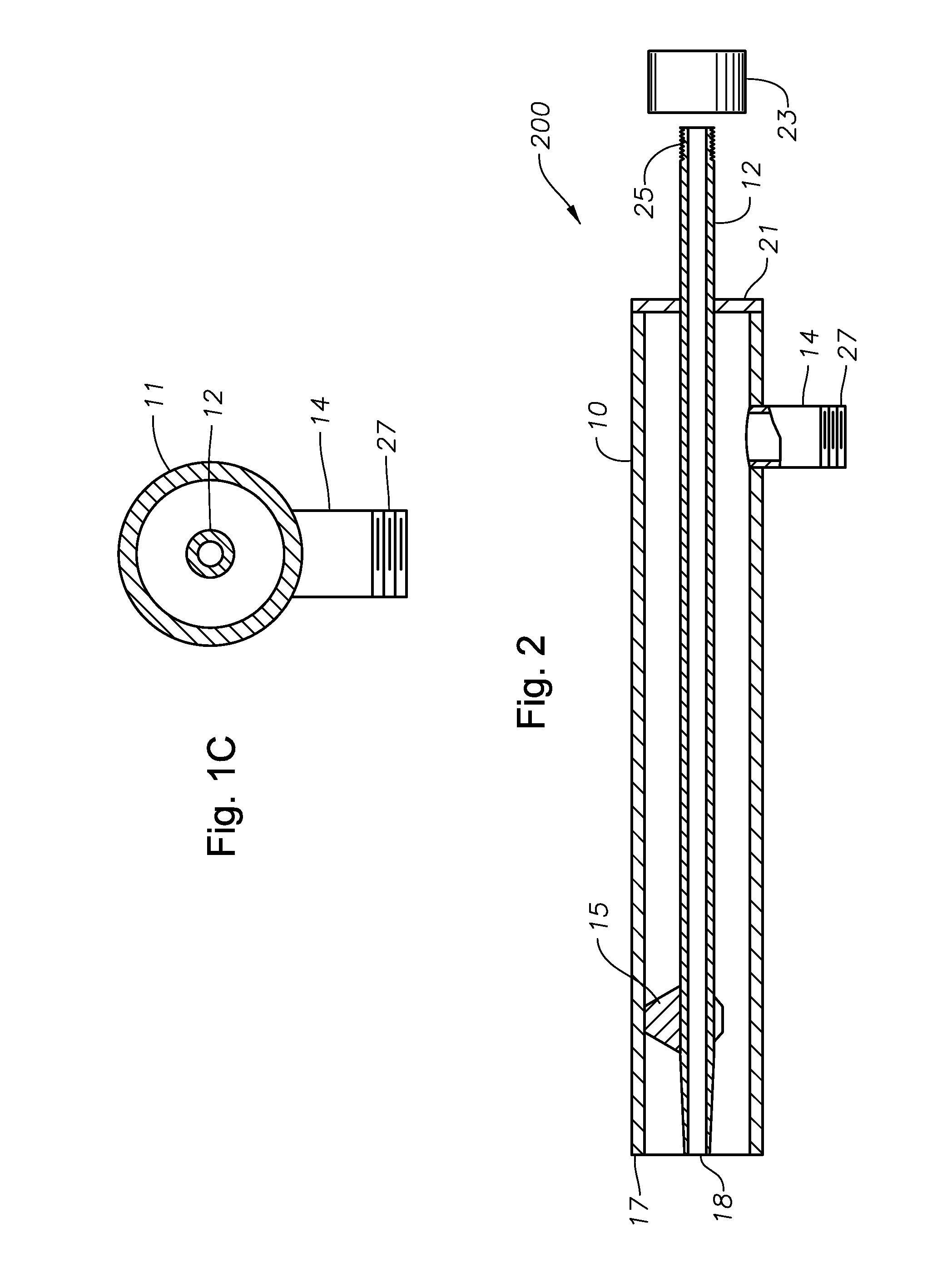
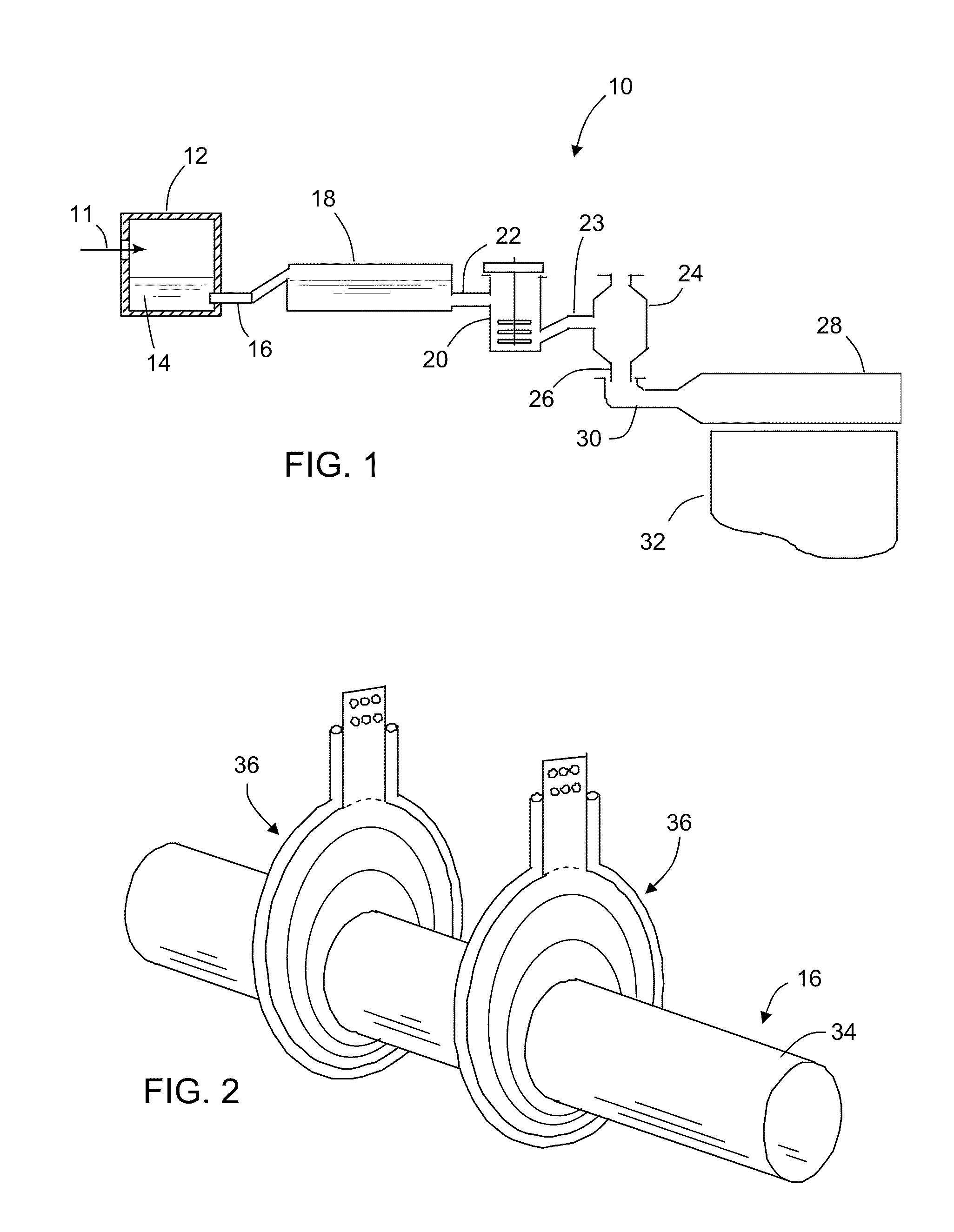
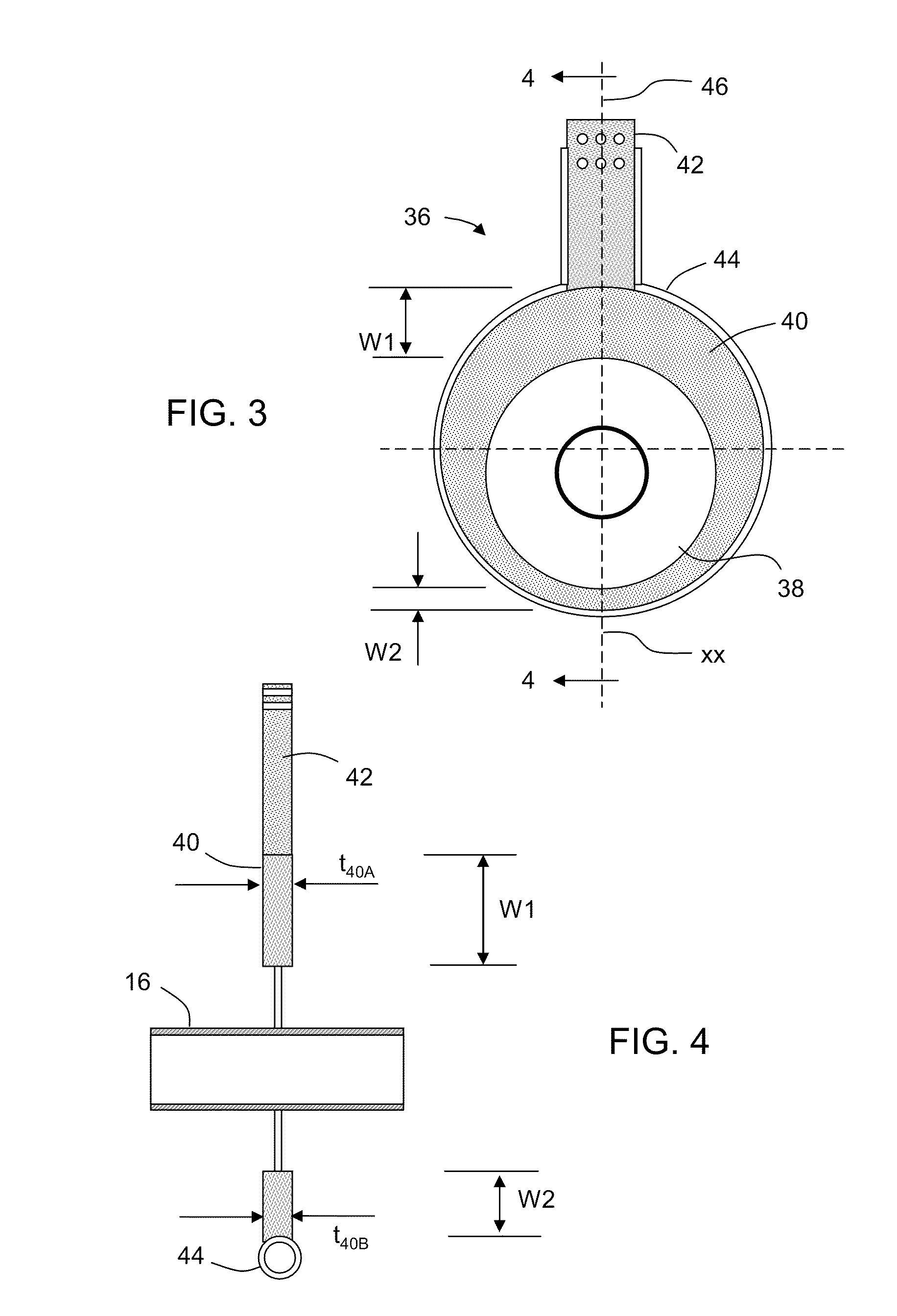
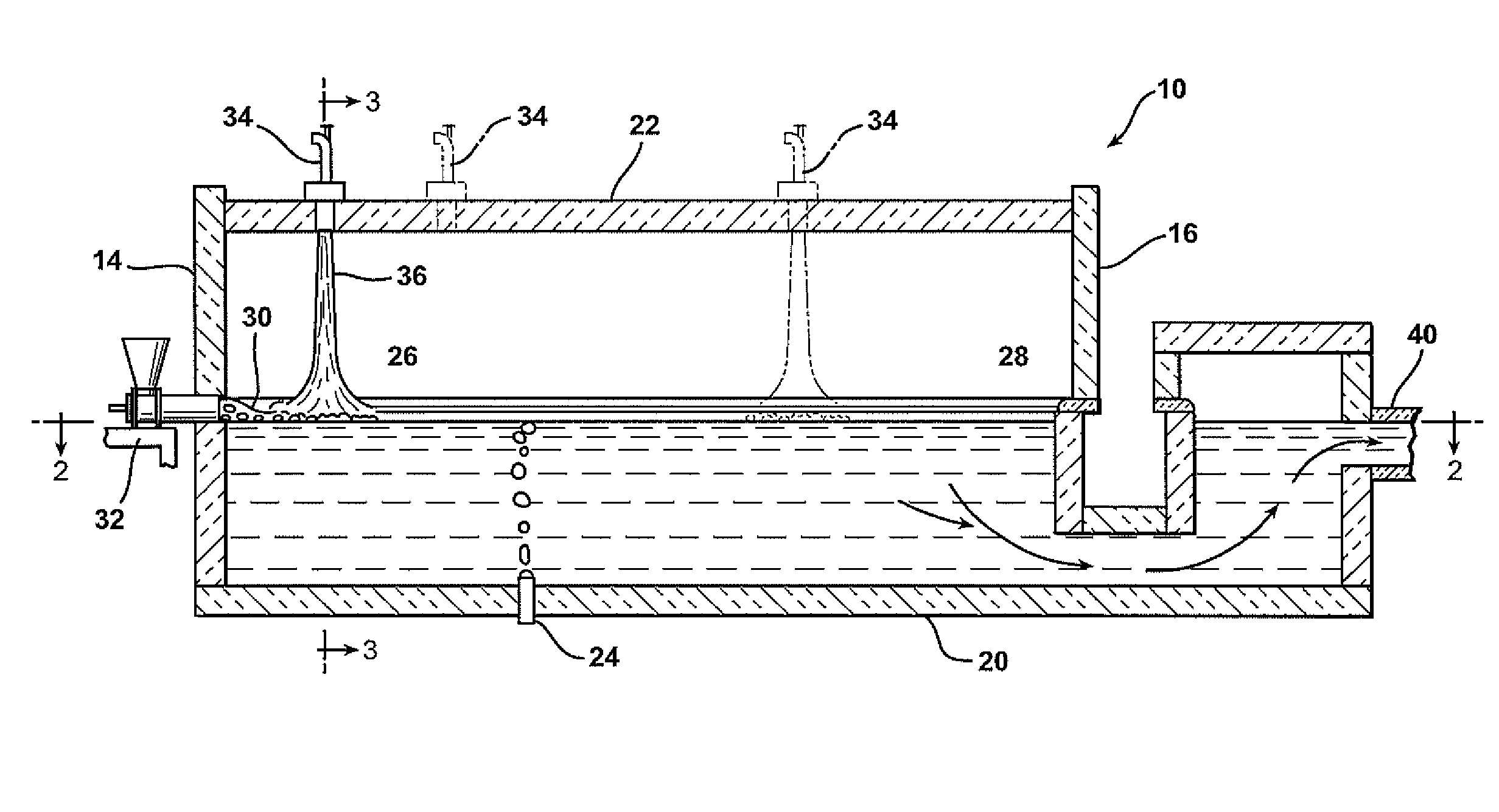
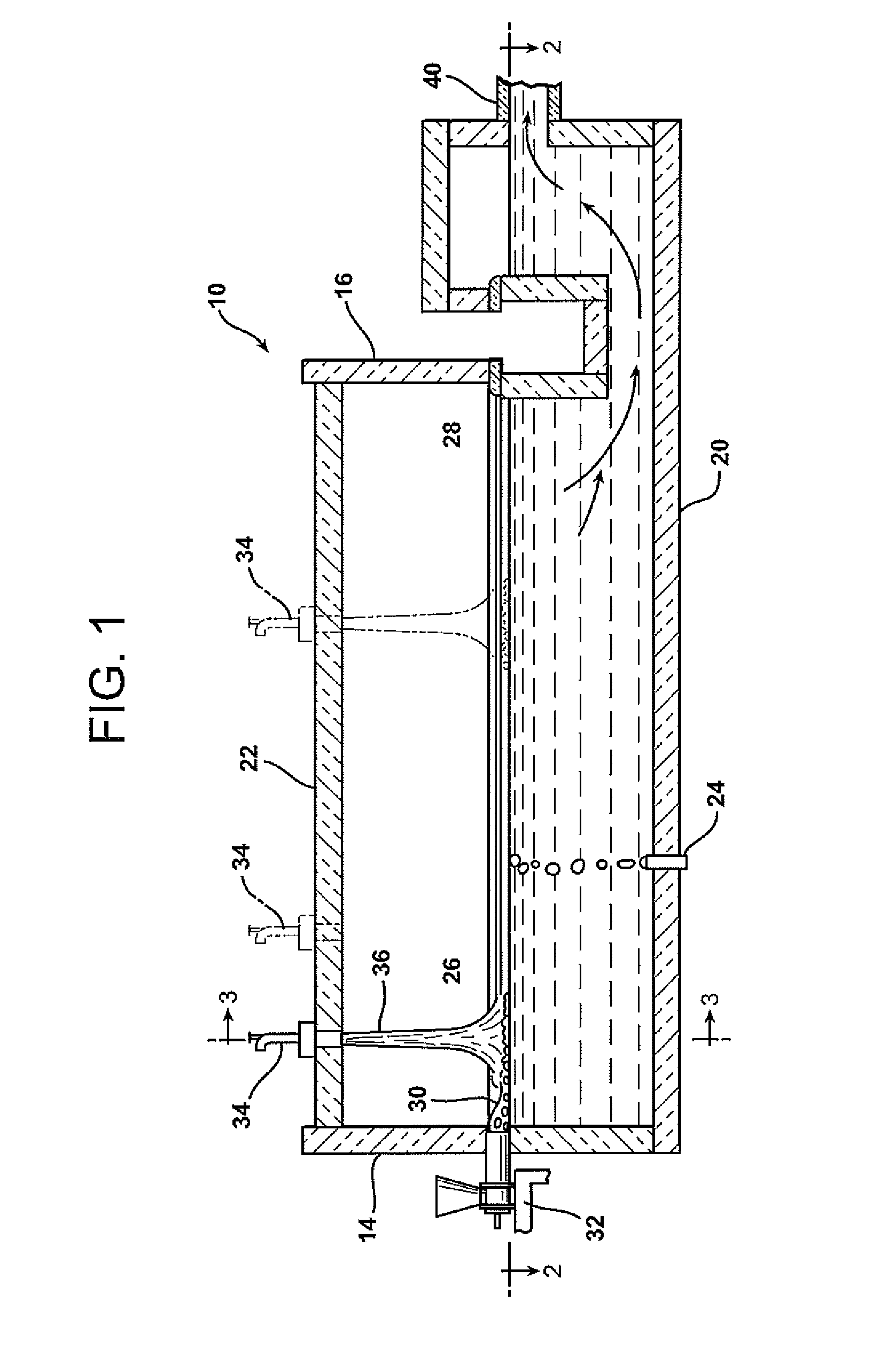
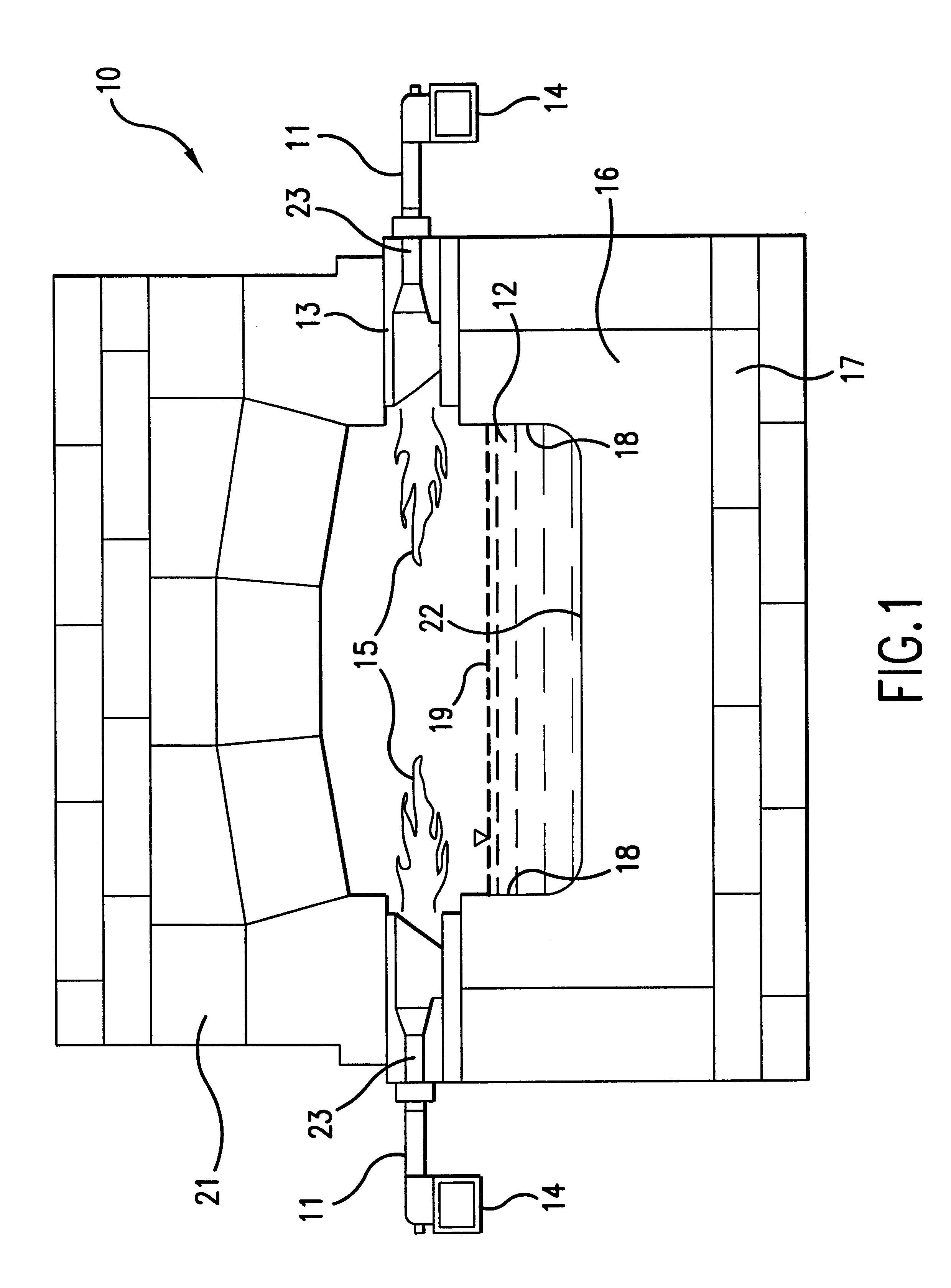
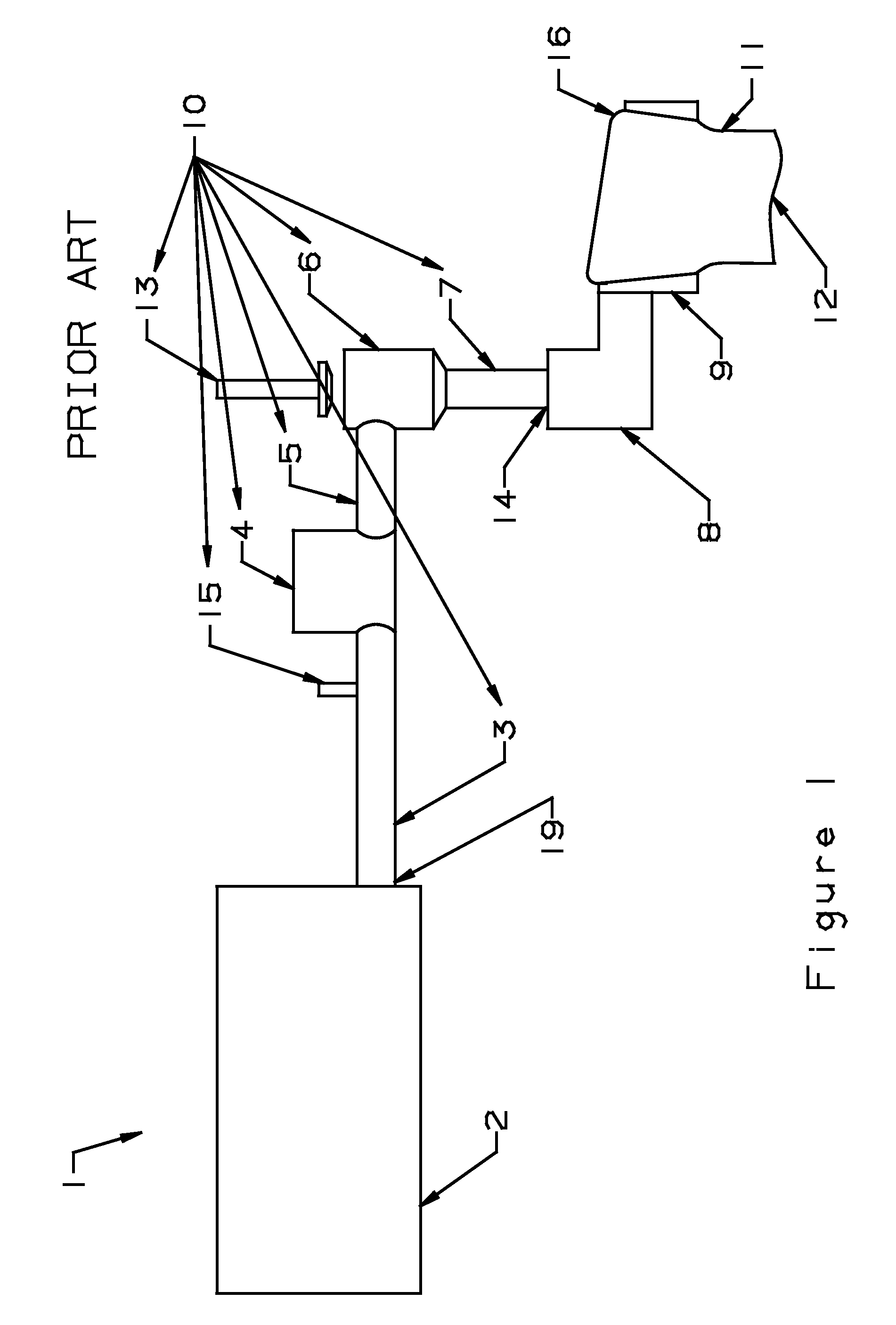
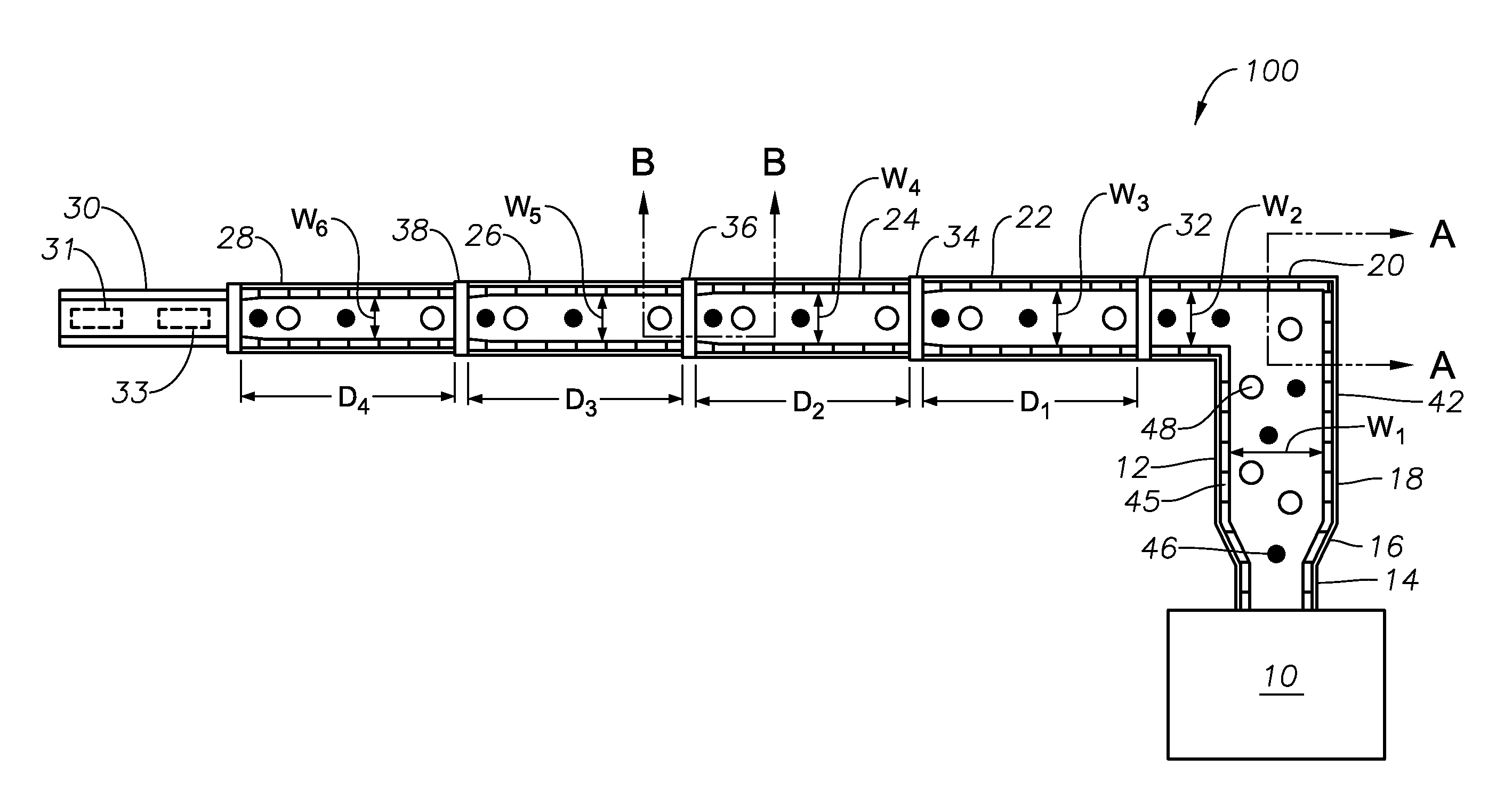
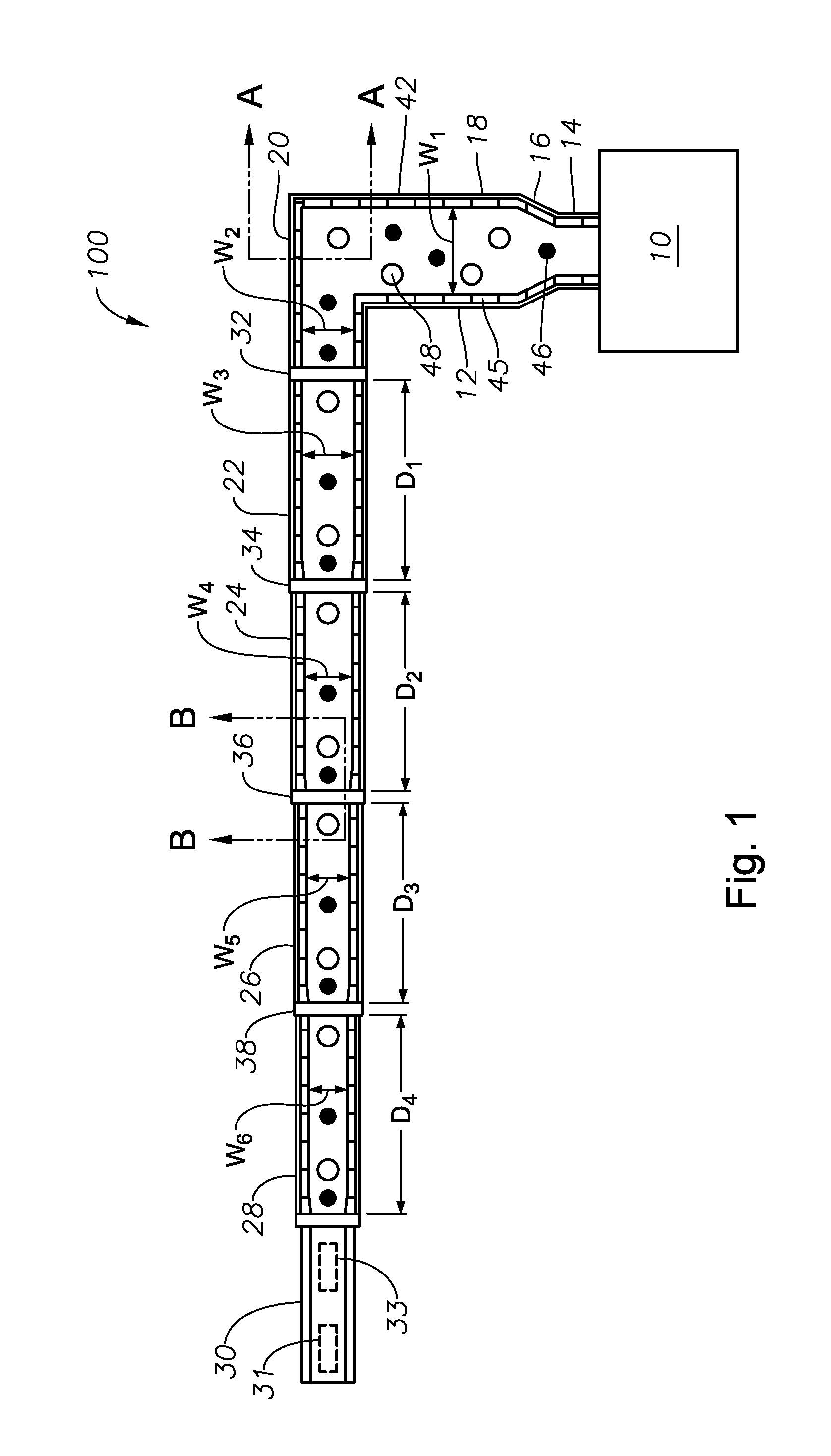
Oxygen-fired front end for glass forming operation
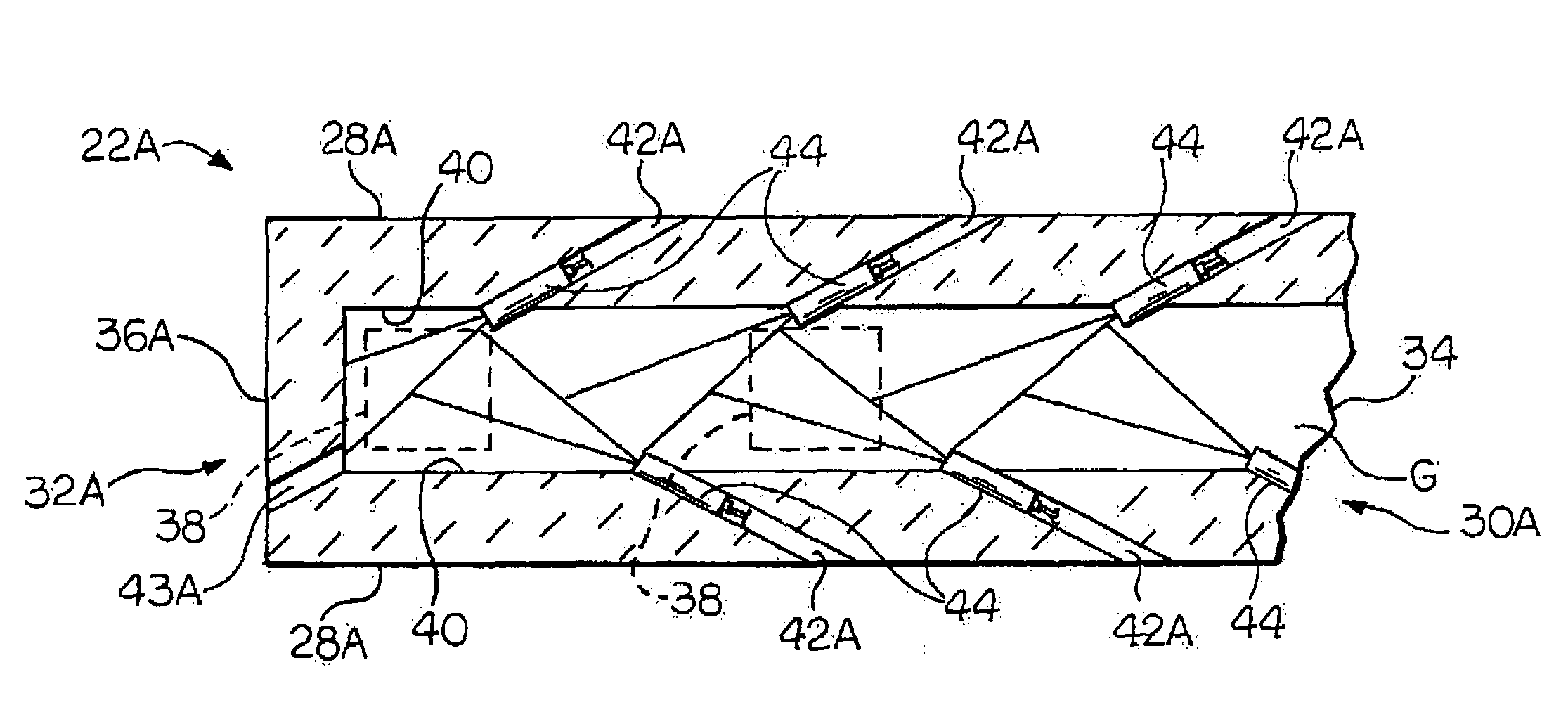
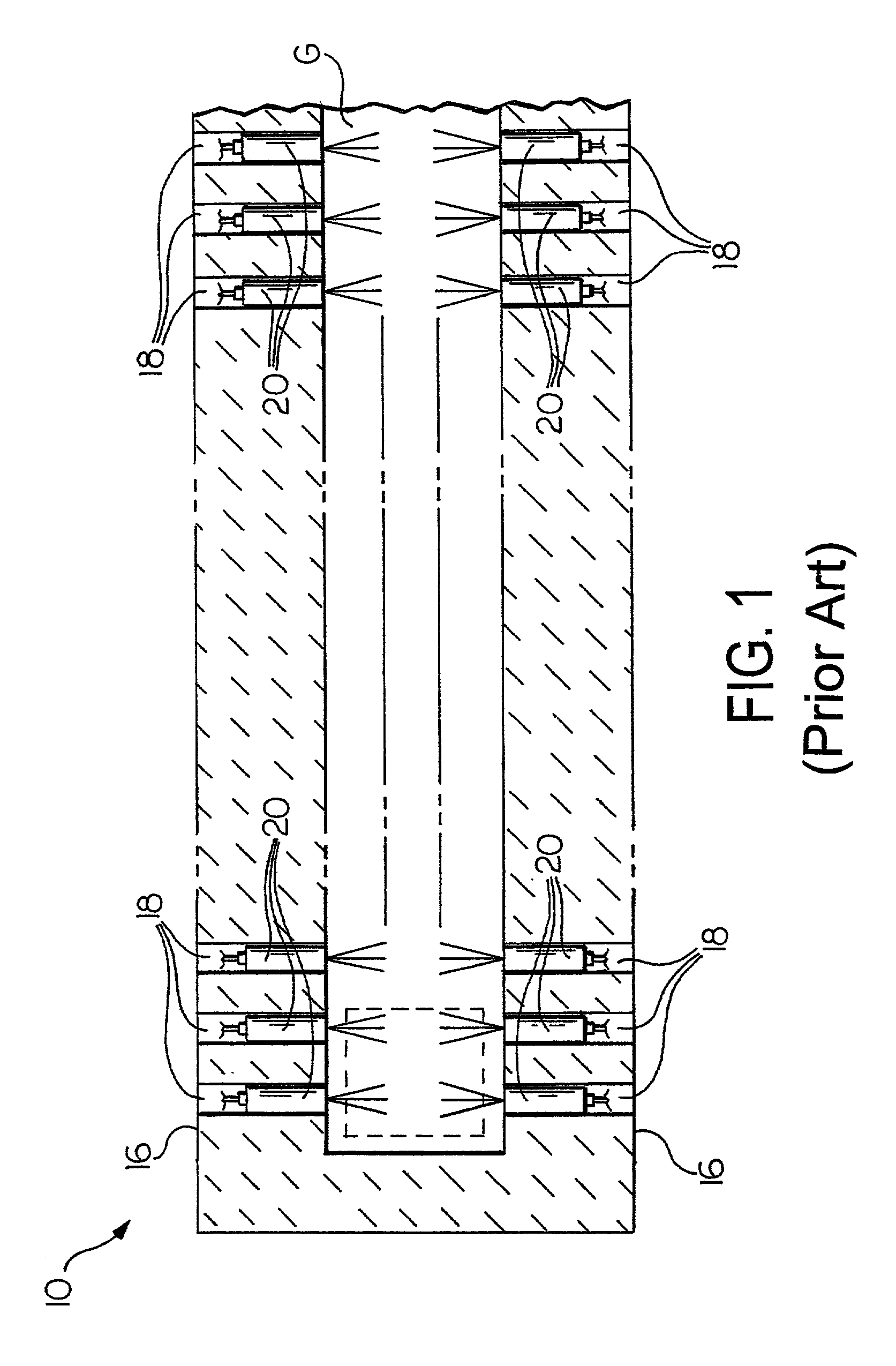
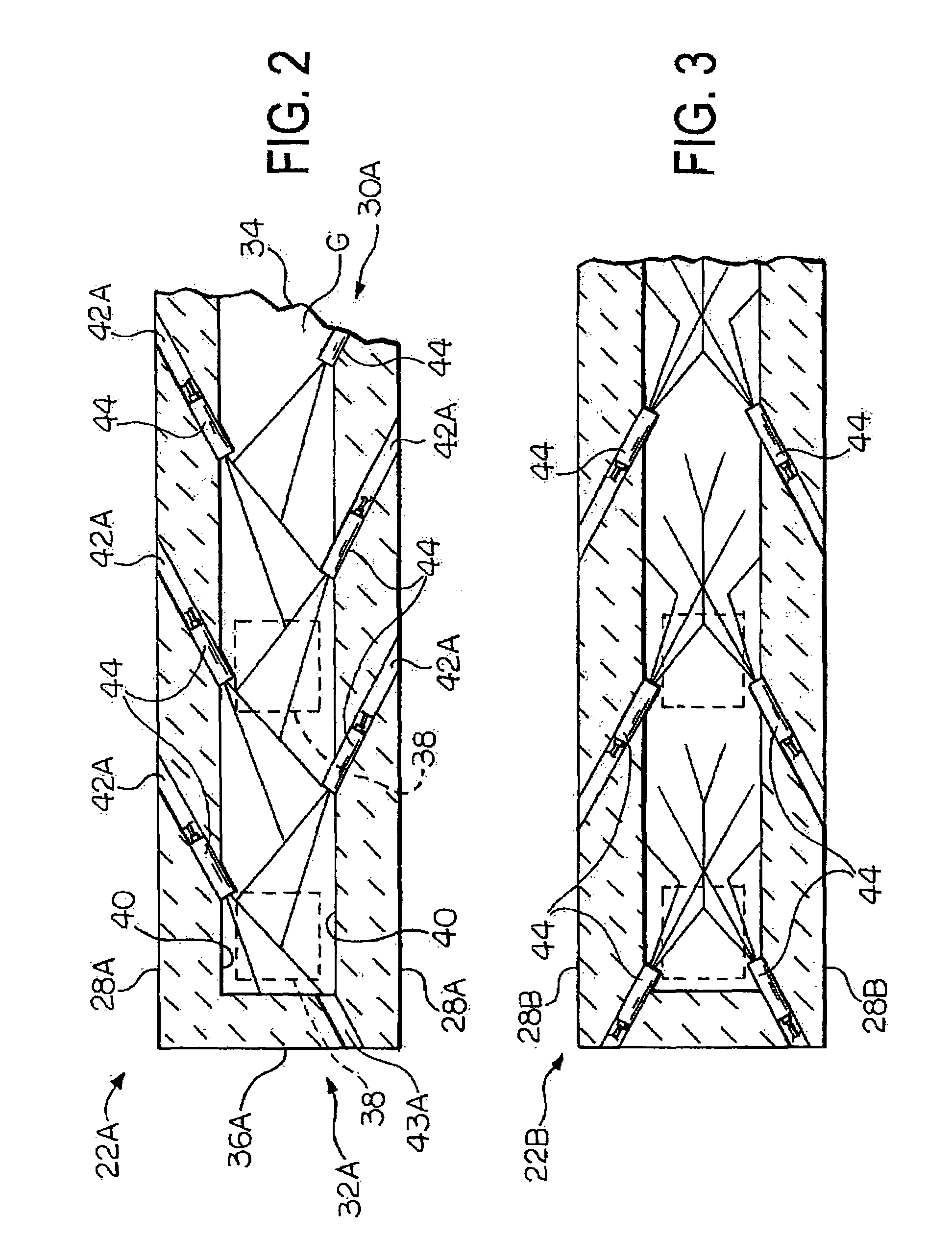
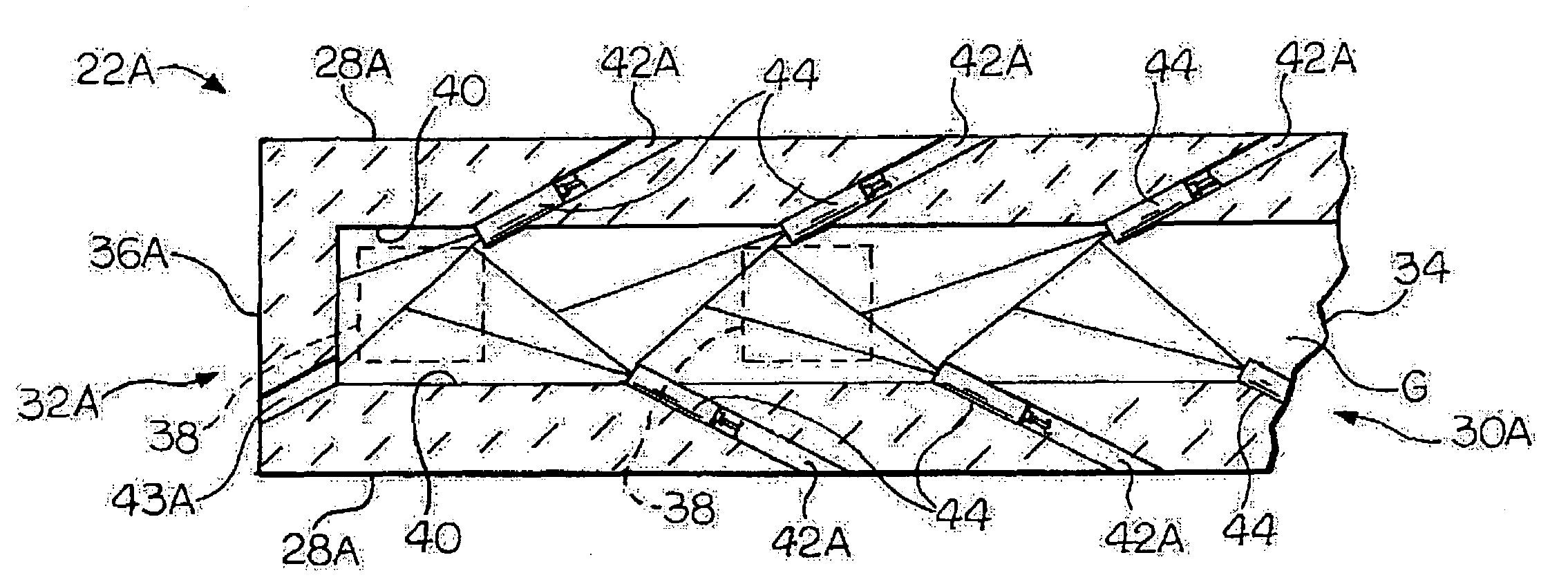
A front end for a glass forming operation comprises an open channel and at least one burner. The channel has at least one surface. The surface has at least one hole therein. The burner is oriented in the hole at an acute angle relative to the surface. In another embodiment of the invention, the channel has a top and a pair of sidewalls each having a surface. At least one hole is in at least one of the surfaces. The hole is at an acute angle relative to at least one surface. The burner is an oxygen-fired burner. In yet another embodiment of the invention, the top and sidewalls each have a super structure surface constructed of refractory material. The channel has an upstream end and a downstream end. At least one of the surfaces has a plurality of holes therein. The burners extend at an acute angle relative to at least one surface and in a plane extending between the upstream end and the downstream end and perpendicular to at least one surface. Oxygen-fired burners extend axially through corresponding holes.
Owner:OCV INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
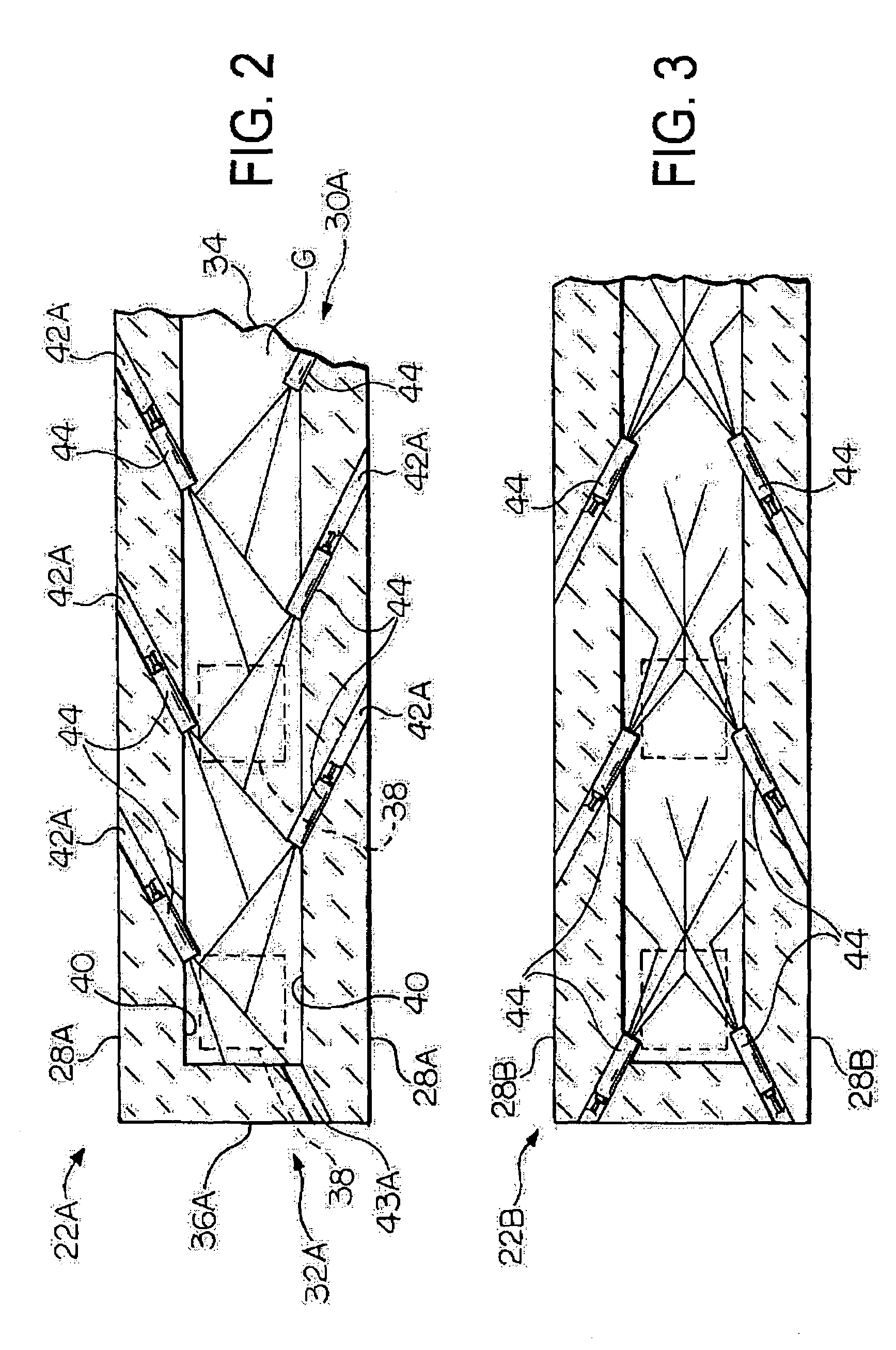
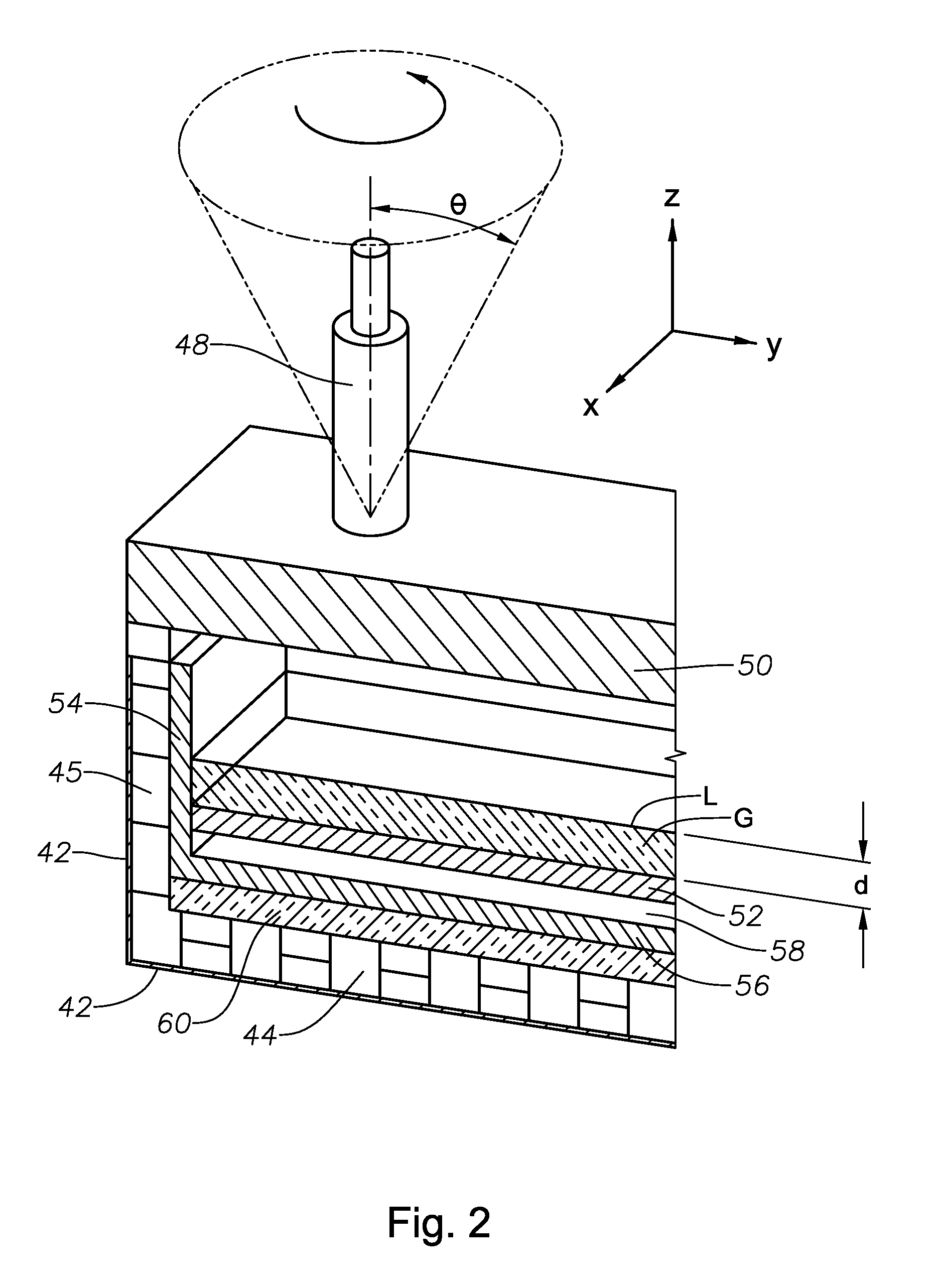
Low heat capacity gas oxy fired burner
A front end for a glass forming operation including an open channel and at least one burner. The channel surface has at least one burner port and a burner oriented in the burner port at an acute angle relative to the channel surface. The surface may be a top, side or end wall and the burner port is at an acute angle relative to the surface of the wall.
Owner:OCV INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
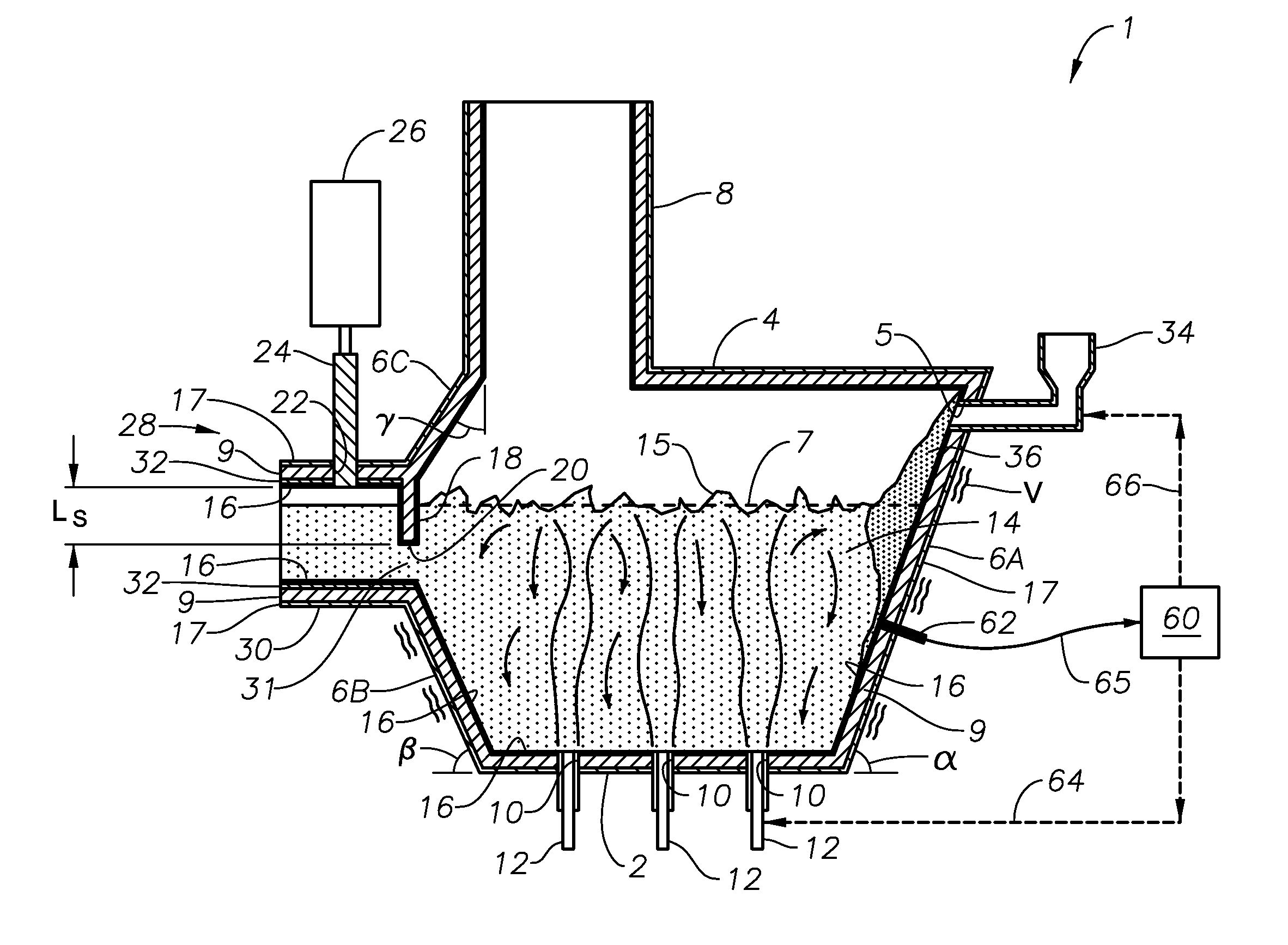
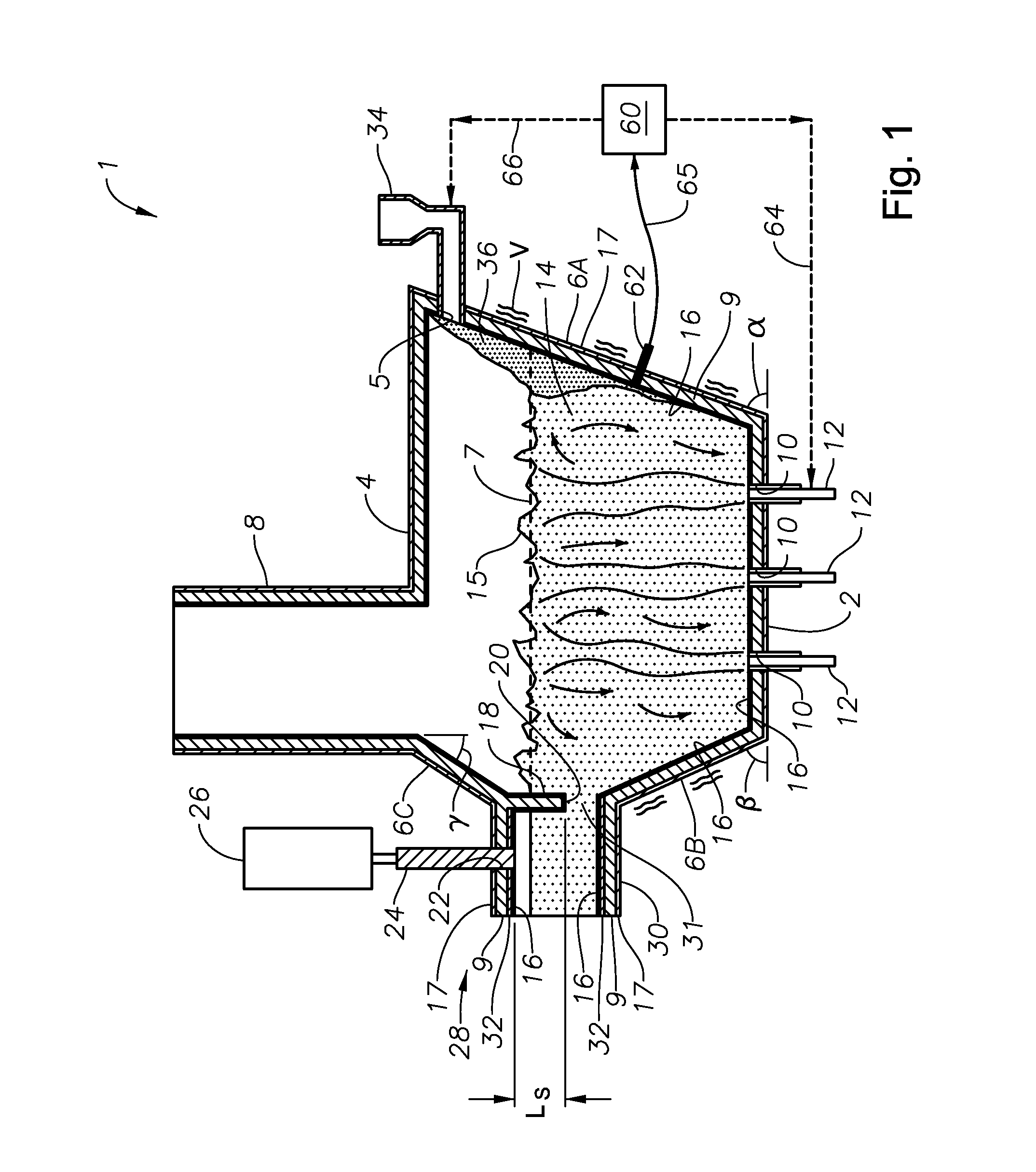
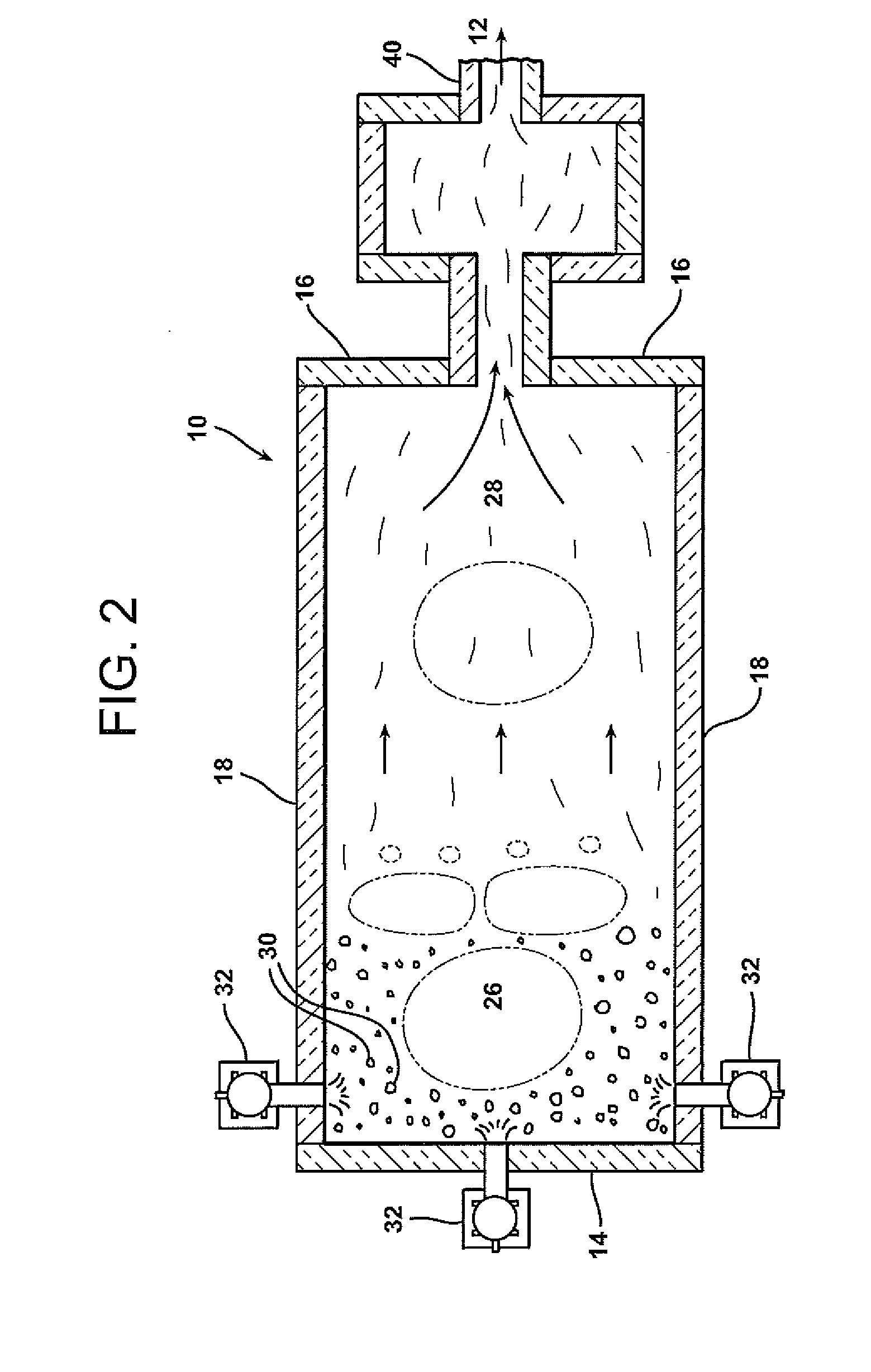
Submerged combustion melting processes for producing glass and similar materials, and systems for carrying out such processes
Processes of controlling submerged combustion melters, and systems for carrying out the methods. One process includes feeding vitrifiable material into a melter vessel, the melter vessel including a fluid-cooled refractory panel in its floor, ceiling, and / or sidewall, and heating the vitrifiable material with a burner directing combustion products into the melting zone under a level of the molten material in the zone. Burners impart turbulence to the molten material in the melting zone. The fluid-cooled refractory panel is cooled, forming a modified panel having a frozen or highly viscous material layer on a surface of the panel facing the molten material, and a sensor senses temperature of the modified panel using a protected thermocouple positioned in the modified panel shielded from direct contact with turbulent molten material. Processes include controlling the melter using the temperature of the modified panel. Other processes and systems are presented.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Submerged combustion melting processes for producing glass and similar materials, and systems for carrying out such processes
Processes of controlling submerged combustion melters, and systems for carrying out the methods. One process includes feeding vitrifiable material into a melter vessel, the melter vessel including a fluid-cooled refractory panel in its floor, ceiling, and / or sidewall, and heating the vitrifiable material with a burner directing combustion products into the melting zone under a level of the molten material in the zone. Burners impart turbulence to the molten material in the melting zone. The fluid-cooled refractory panel is cooled, forming a modified panel having a frozen or highly viscous material layer on a surface of the panel facing the molten material, and a sensor senses temperature of the modified panel using a protected thermocouple positioned in the modified panel shielded from direct contact with turbulent molten material. Processes include controlling the melter using the temperature of the modified panel. Other processes and systems are presented.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
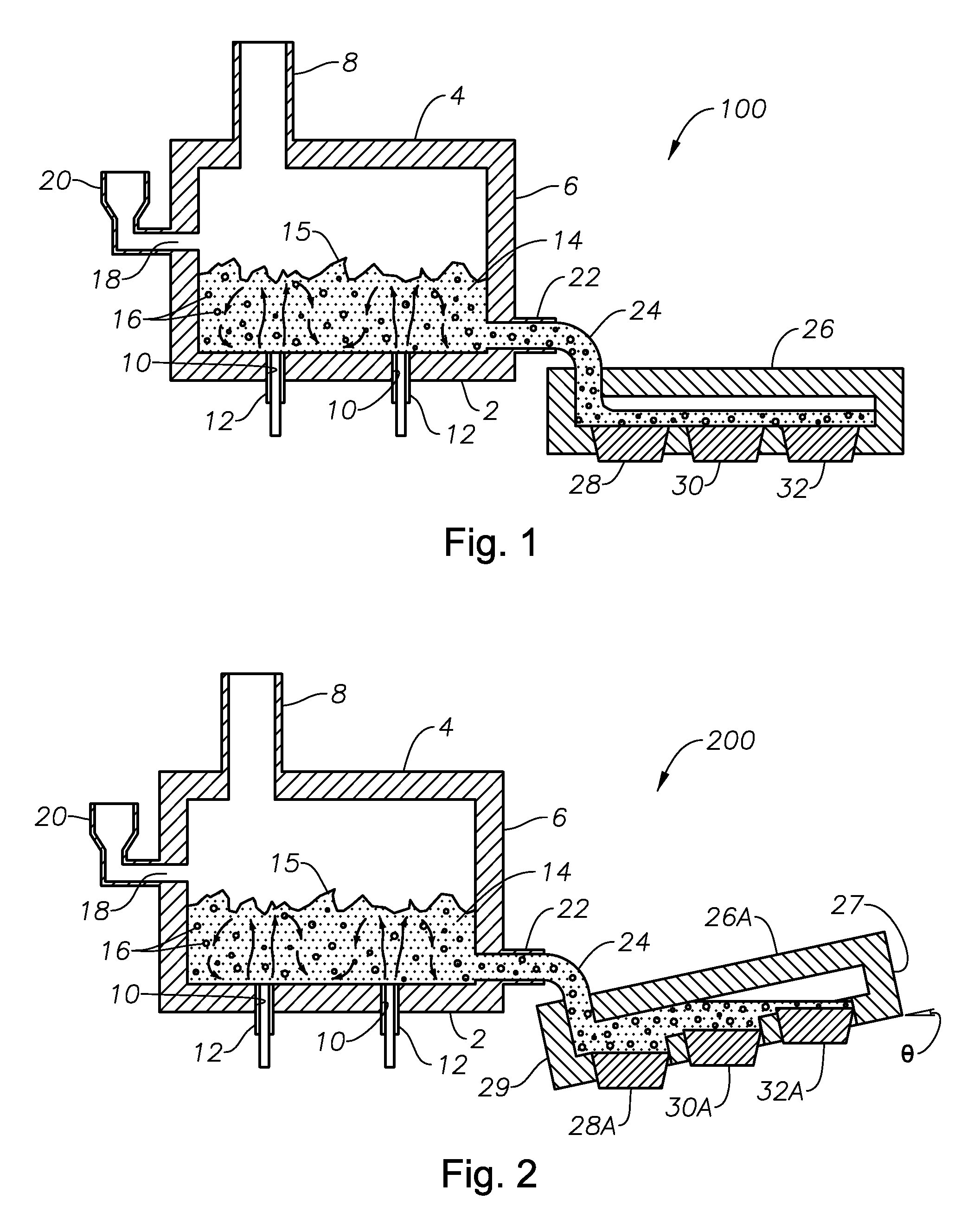
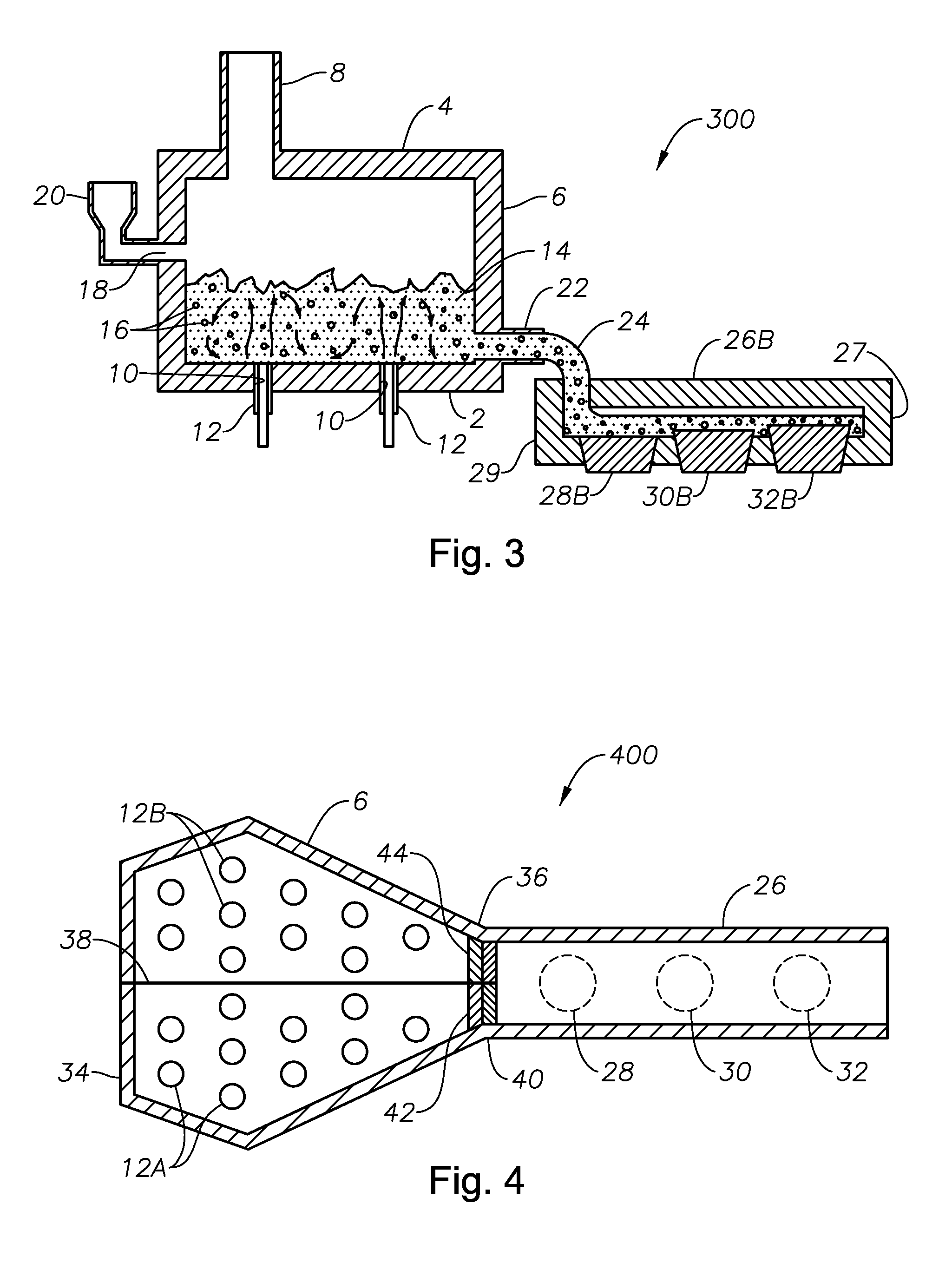
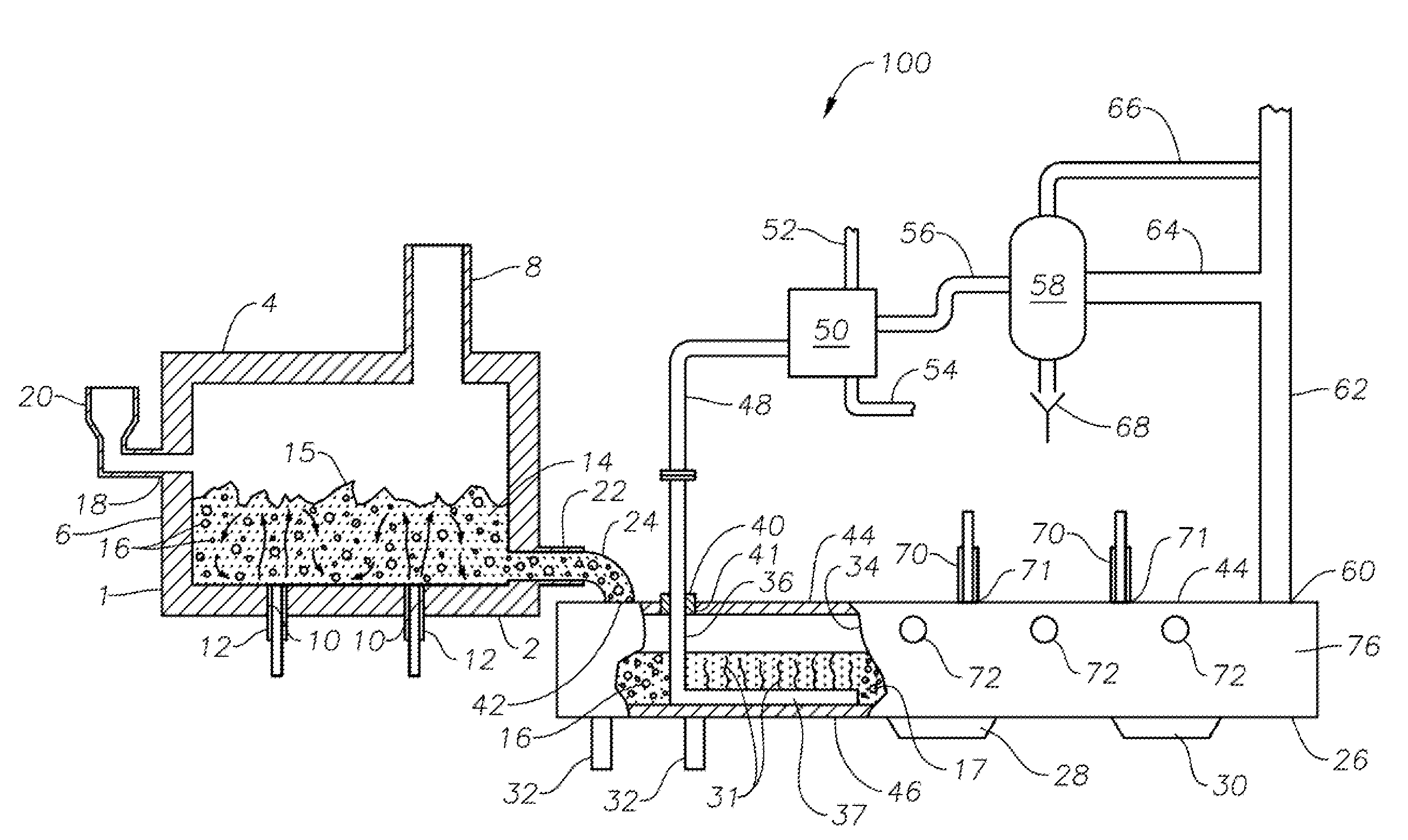
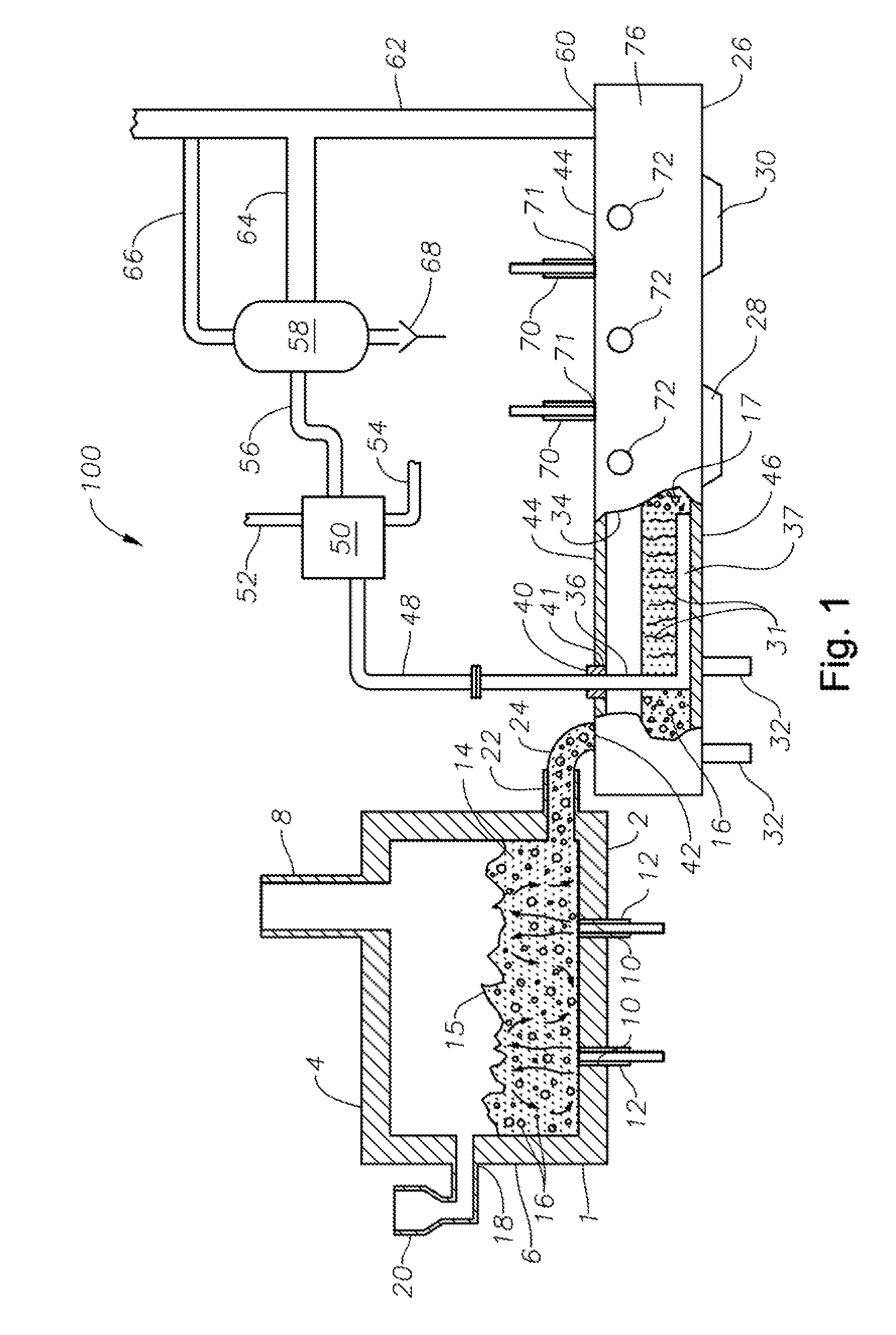
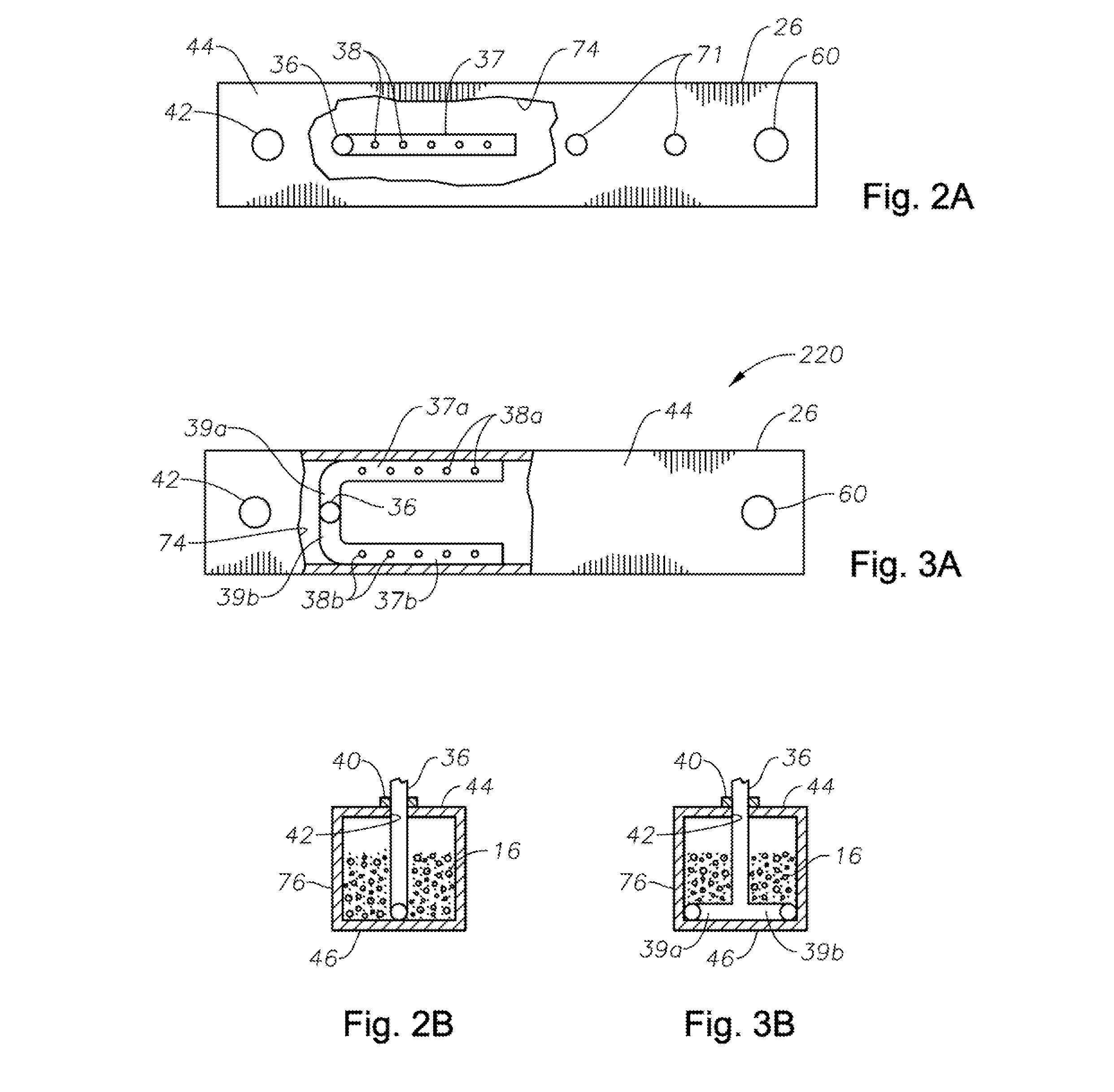
Apparatus, systems and methods for conditioning molten glass
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
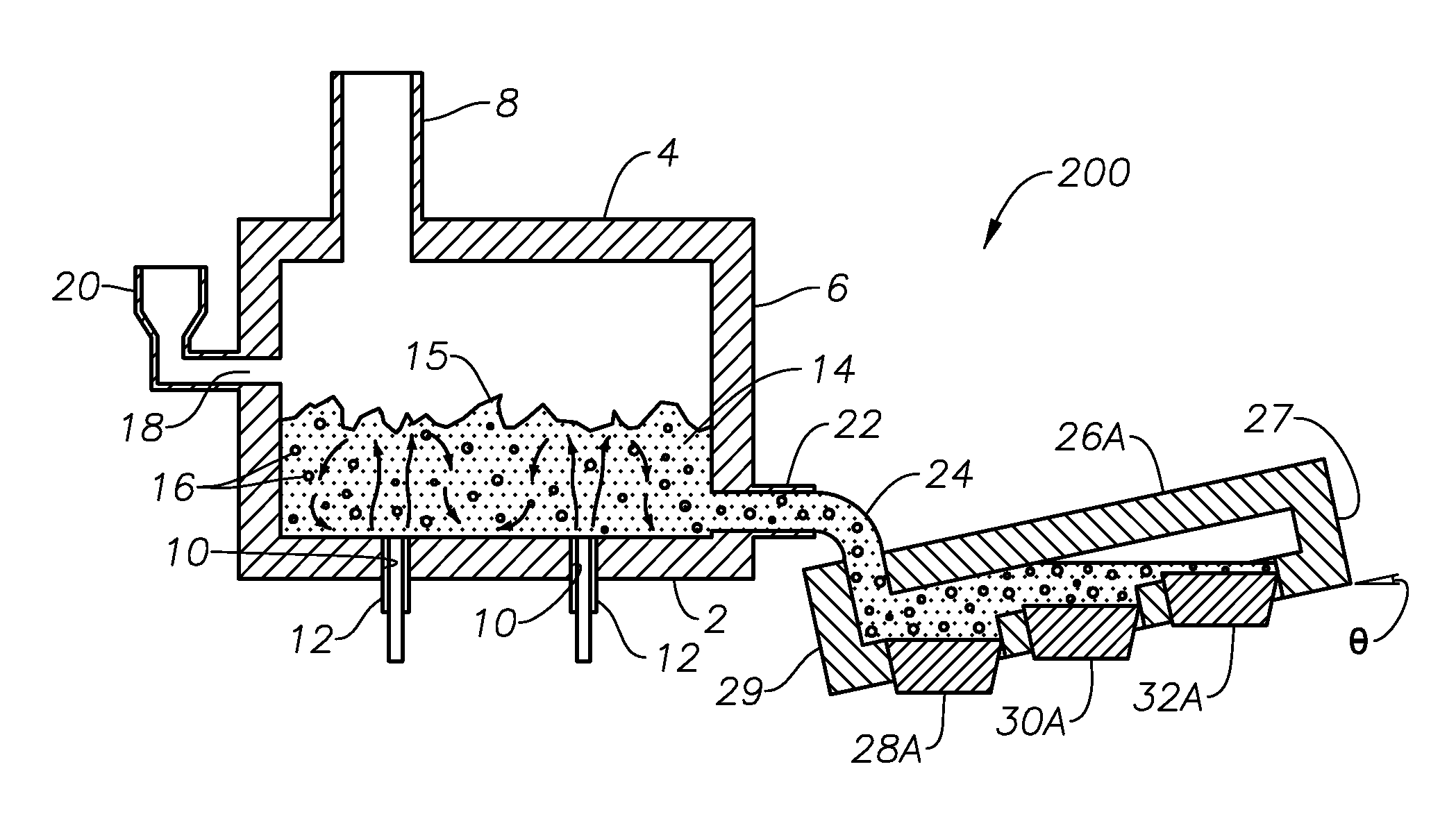
Apparatus, systems and methods for reducing foaming downstream of a submerged combustion melter producing molten glass
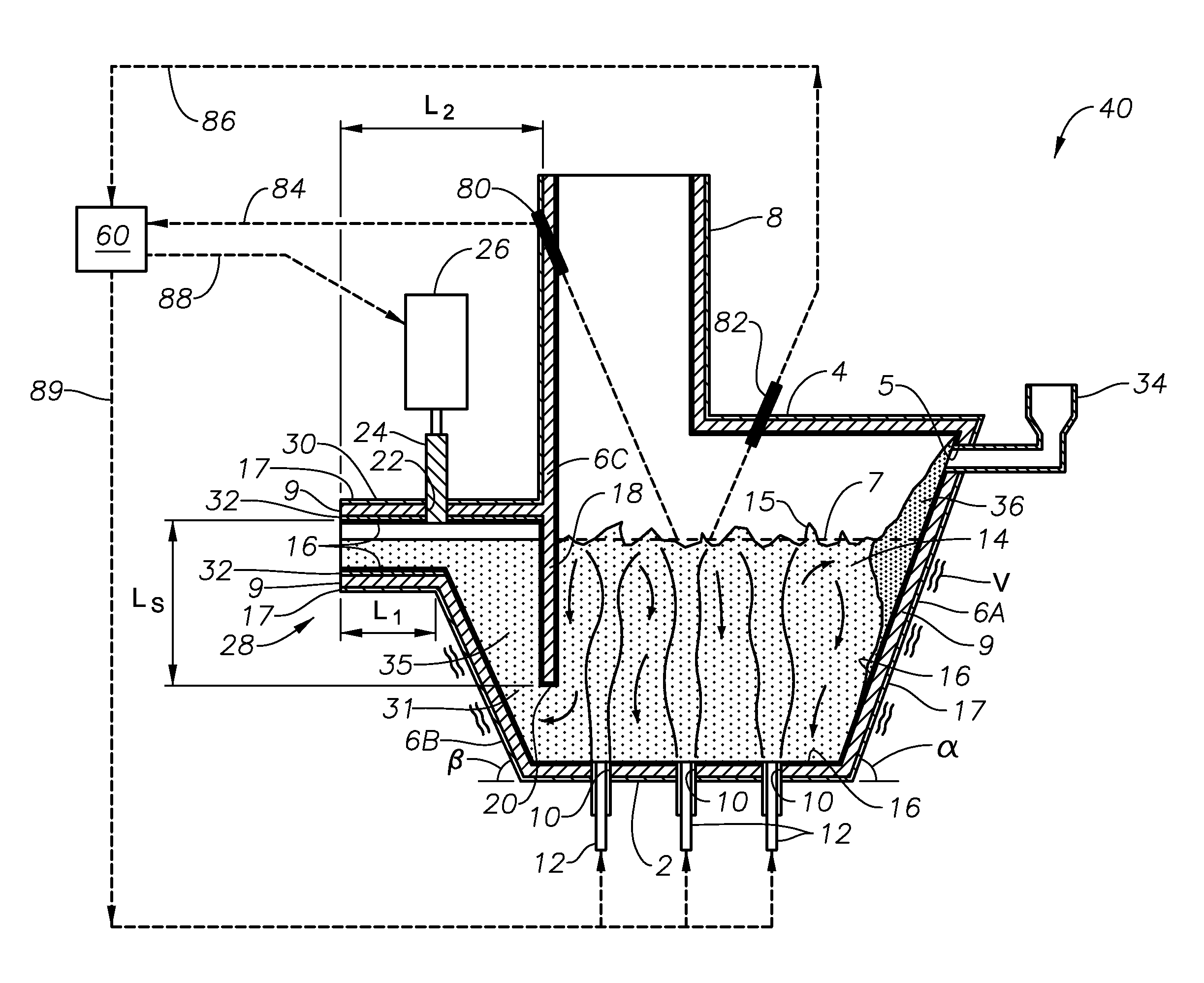
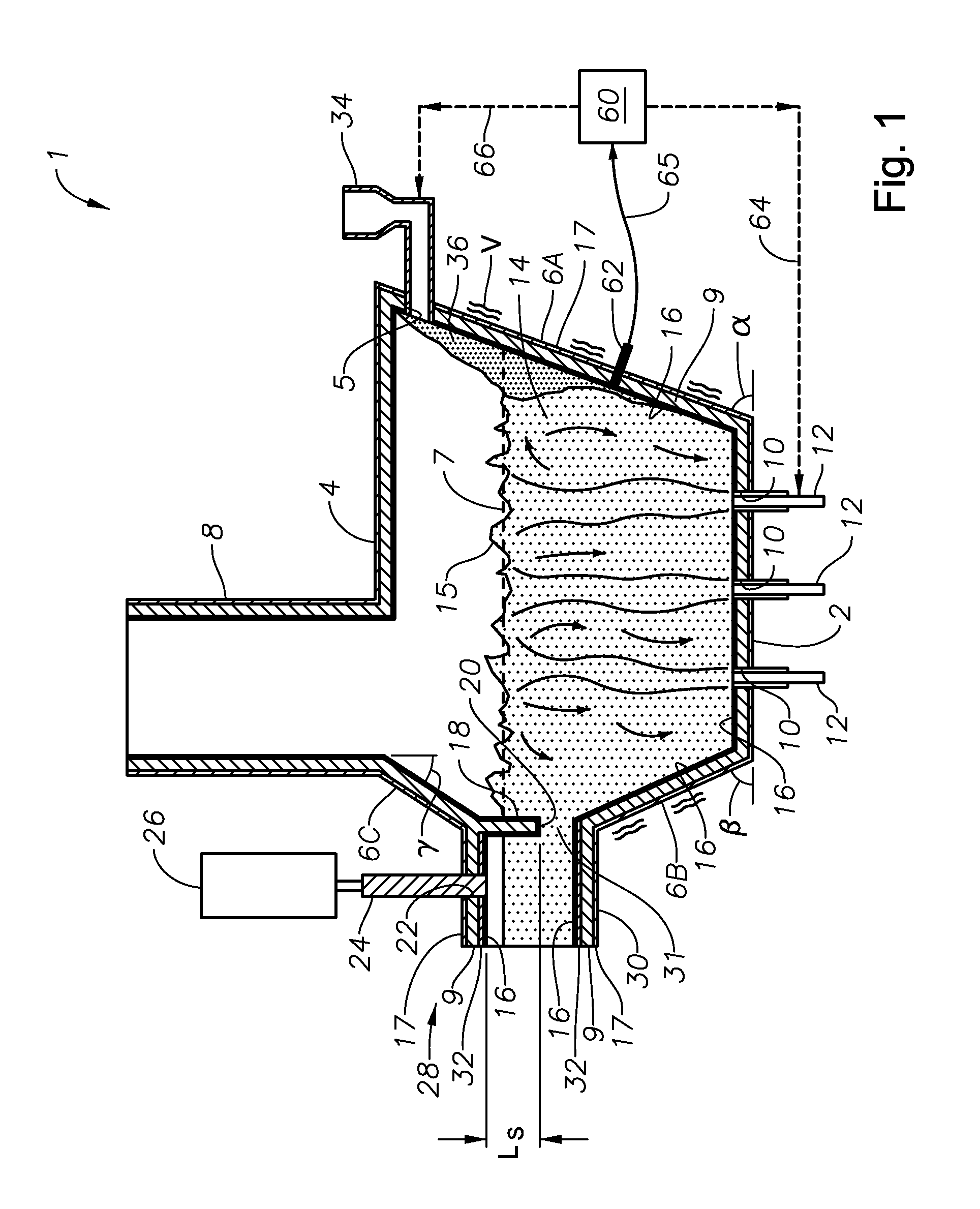
Apparatus including a flow channel defined by a floor, roof, and sidewall structure connecting the floor and roof. One or more combustion burners is positioned in either the roof, the sidewall structure, or both, and transfer heat to a molten mass of glass containing bubbles having a bubble atmosphere flowing through the flow channel. The burners contribute to formation of a channel atmosphere above the molten glass. Apparatus includes a device, at least a portion of which is positionable under a level of the molten glass in the flow channel, configured to emit a composition into the molten glass under the level to intimately contact the composition with the molten glass and bubbles therein. The composition diffuses into the bubbles to form modified atmosphere bubbles sufficiently different from the channel atmosphere to increase diffusion of a species in the channel atmosphere into the modified atmosphere bubbles.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Systems and methods for glass manufacturing
Submerged combustion systems and methods of use to produce glass. One system includes a submerged combustion melter having a roof, a floor, a wall structure connecting the roof and floor, and an outlet, the melter producing an initial foamy molten glass. One or more non-submerged auxiliary burners are positioned in the roof and / or wall structure and configured to deliver combustion products to impact at least a portion of the bubbles with sufficient force and / or heat to burst at least some of the bubbles and form a reduced foam molten glass.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Process of using a submerged combustion melter to produce hollow glass fiber or solid glass fiber having entrained bubbles, and burners and systems to make such fibers
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Apparatus and method for reducing gaseous inclusions in a glass
InactiveUS20100199721A1Lower the volumeForehearthsGlass furnace apparatusFlat panel displayGlass manufacturing
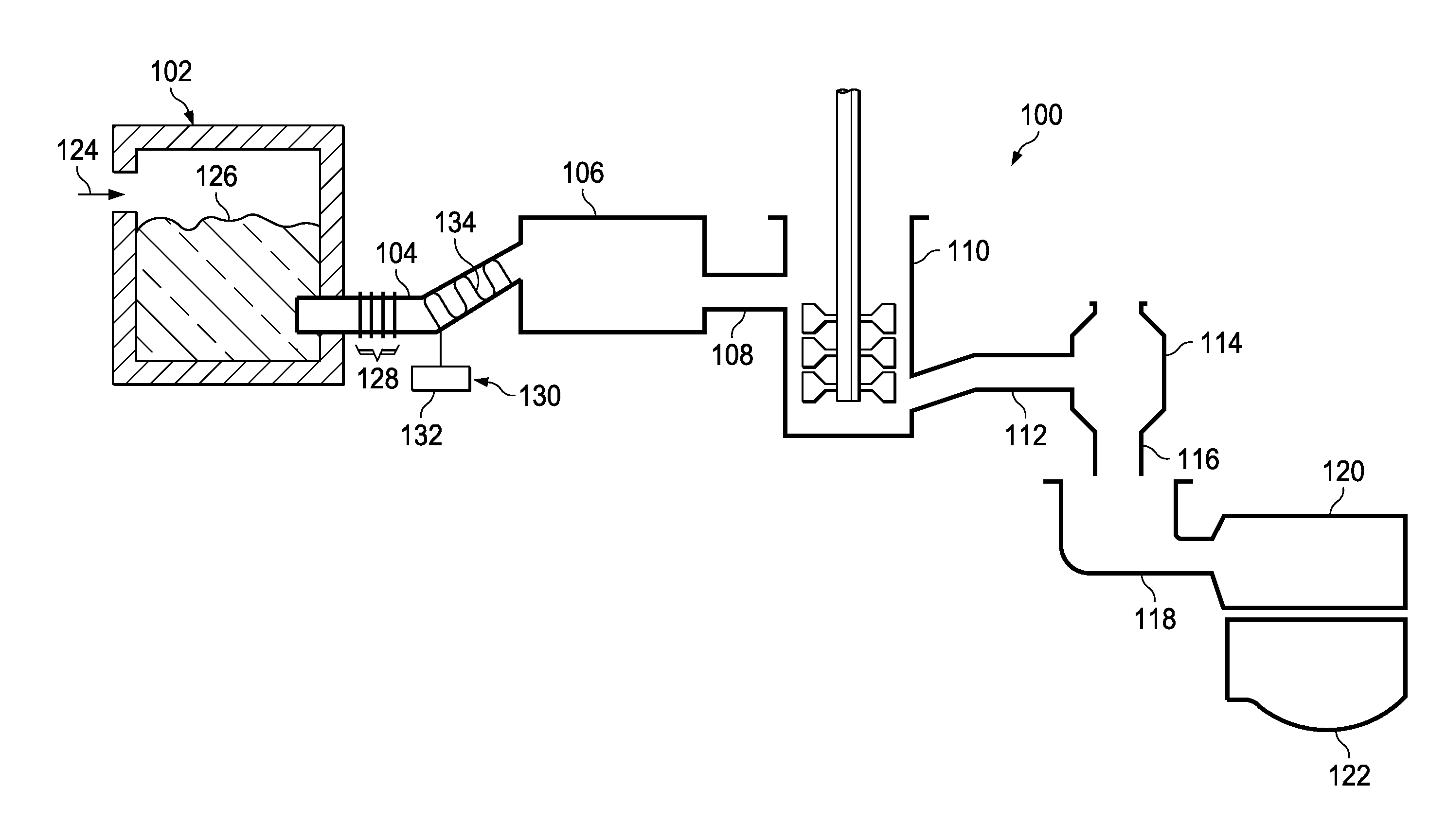
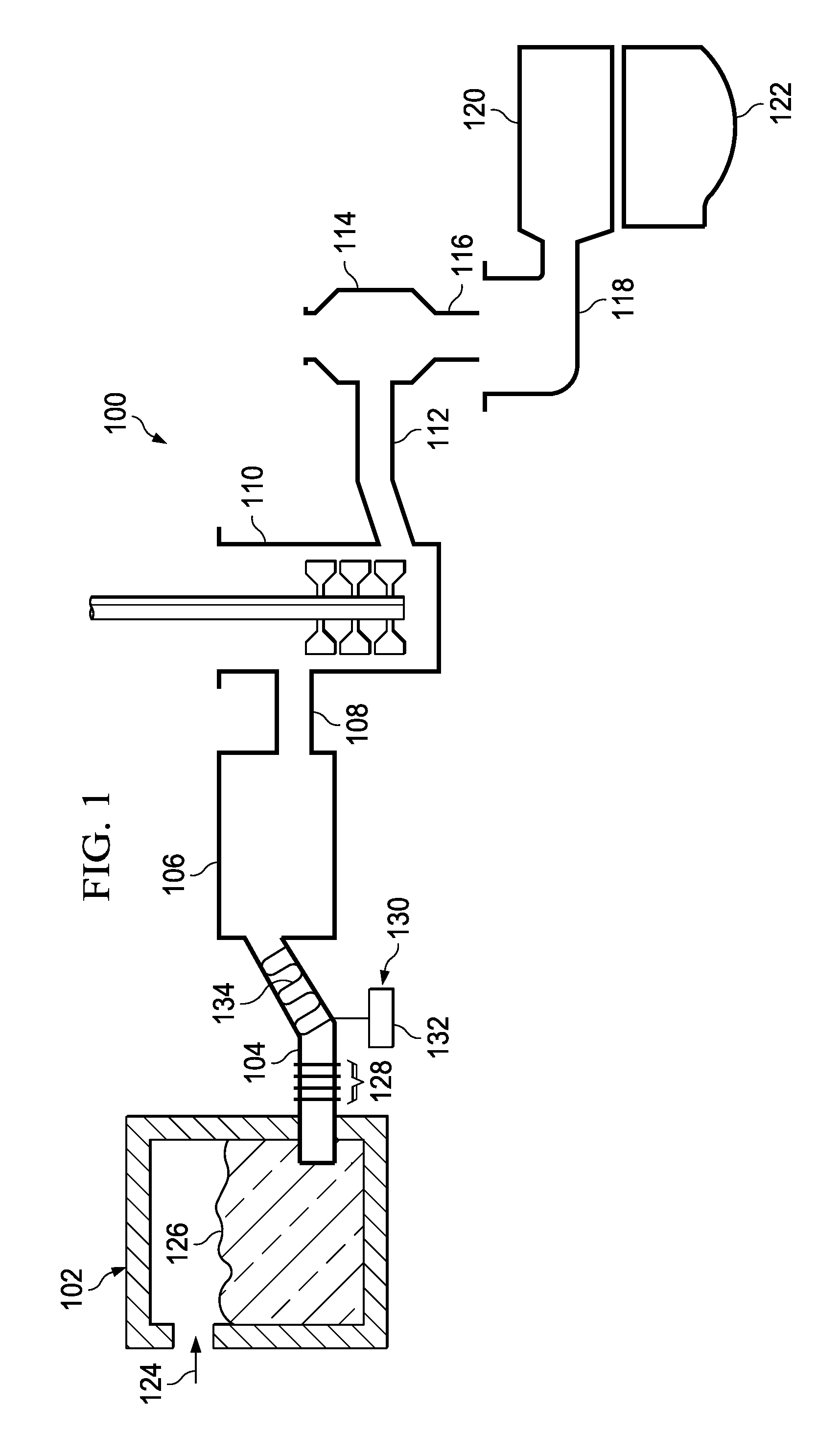
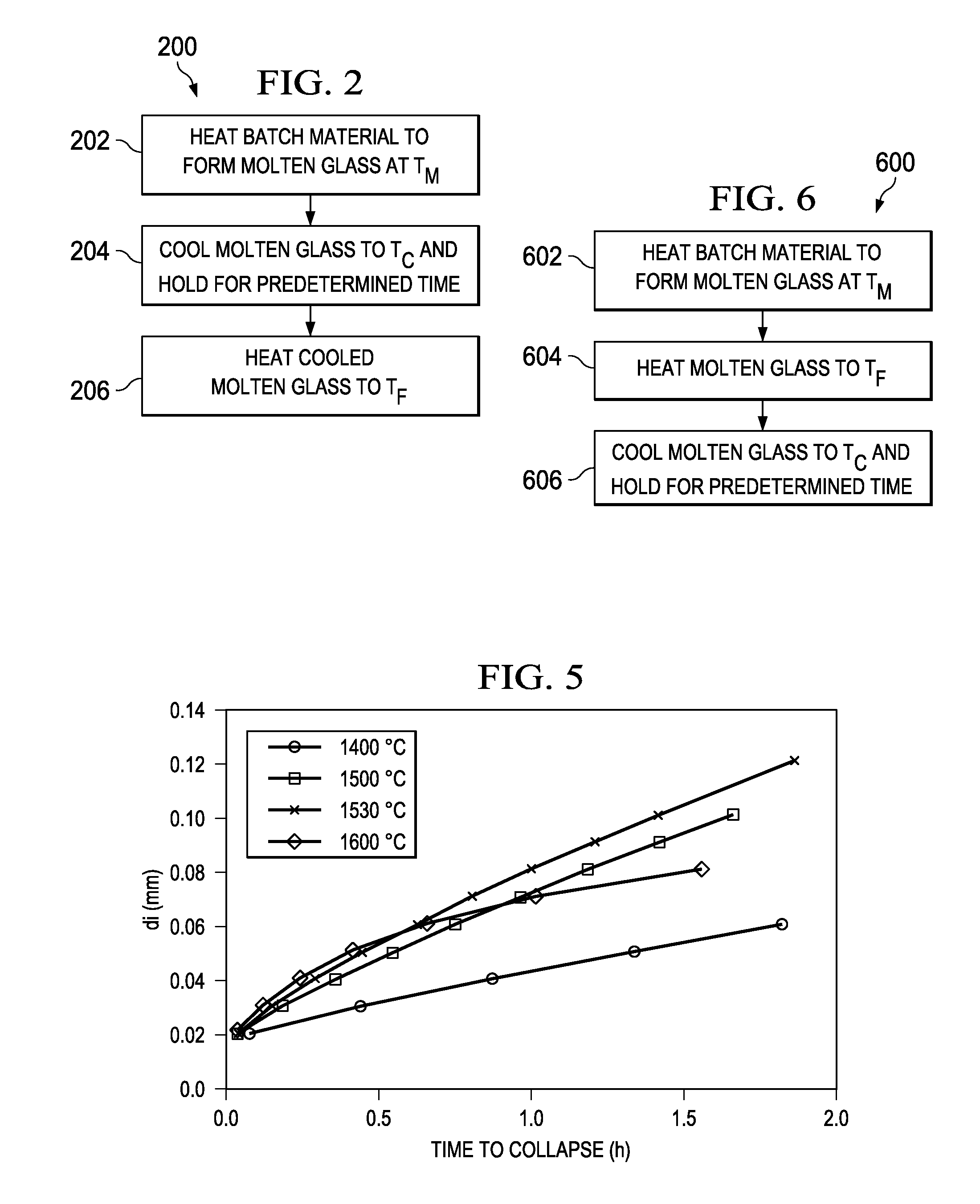
A glass manufacturing system and a method are described herein for reducing gaseous inclusions in high melting temperature or high strain point glasses, such as those that are used as glass substrates in flat panel display devices. In one embodiment, the method including the steps of: (a) heating a batch material within a melting vessel to form molten glass at a melting temperature TM, the molten glass comprising a multivalent oxide material; (b) heating the molten glass within a fining vessel to a fining temperature TF≧TM; and (c) cooling the molten glass within a refractory tube after the first heating step or after the second heating step to a cooling temperature TC less than TM, where the molten glass remains within the refractory tube for a predetermined resident time to reduce a volume of the gaseous inclusions in the molten glass and cause gas species to migrate out of the gaseous inclusions into the molten glass such that at least a portion of the gaseous inclusions collapse into the molten glass.
Owner:CORNING INC
Apparatus for use in direct resistance heating of platinum-containing vessels
InactiveUS20110204039A1Improve uniformityEqually distributedForehearthsTank furnacesPlatinumElectrical resistance and conductance
An apparatus for use in direct resistance heating of a molten glass-carrying vessel, such as a finer or connecting pipe, is provided. The apparatus comprises a flange comprises a plurality of electrically-conductive rings that include an inner ring joined to the vessel's exterior wall during use of the flange and an outer ring that receives electric current during use of the flange. The innermost ring comprises a high-temperature resistant metal preferably comprising at least 80% platinum, and the outermost ring preferably comprising at least 99.0% nickel. This combination of materials both increases the reliability of the flange and reduces its cost. Either one or both of the width or thickness of one or both of the inner or outer rings varies as a function of angular position relative to the vessel. The width and / or thickness of the inner and the outer rings with relation to each other produces a uniform current distribution in the flange and the vessel.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method Of Manufacturing S-Glass Fibers In A Direct Melt Operation And Products Formed There From
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Apparatus, systems and methods for reducing foaming downstream of a submerged combustion melter producing molten glass
Apparatus including a flow channel defined by a floor, roof, and sidewall structure connecting the floor and roof. One or more combustion burners is positioned in either the roof, the sidewall structure, or both, and transfer heat to a molten mass of glass containing bubbles having a bubble atmosphere flowing through the flow channel. The burners contribute to formation of a channel atmosphere above the molten glass. Apparatus includes a device, at least a portion of which is positionable under a level of the molten glass in the flow channel, configured to emit a composition into the molten glass under the level to intimately contact the composition with the molten glass and bubbles therein. The composition diffuses into the bubbles to form modified atmosphere bubbles sufficiently different from the channel atmosphere to increase diffusion of a species in the channel atmosphere into the modified atmosphere bubbles.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
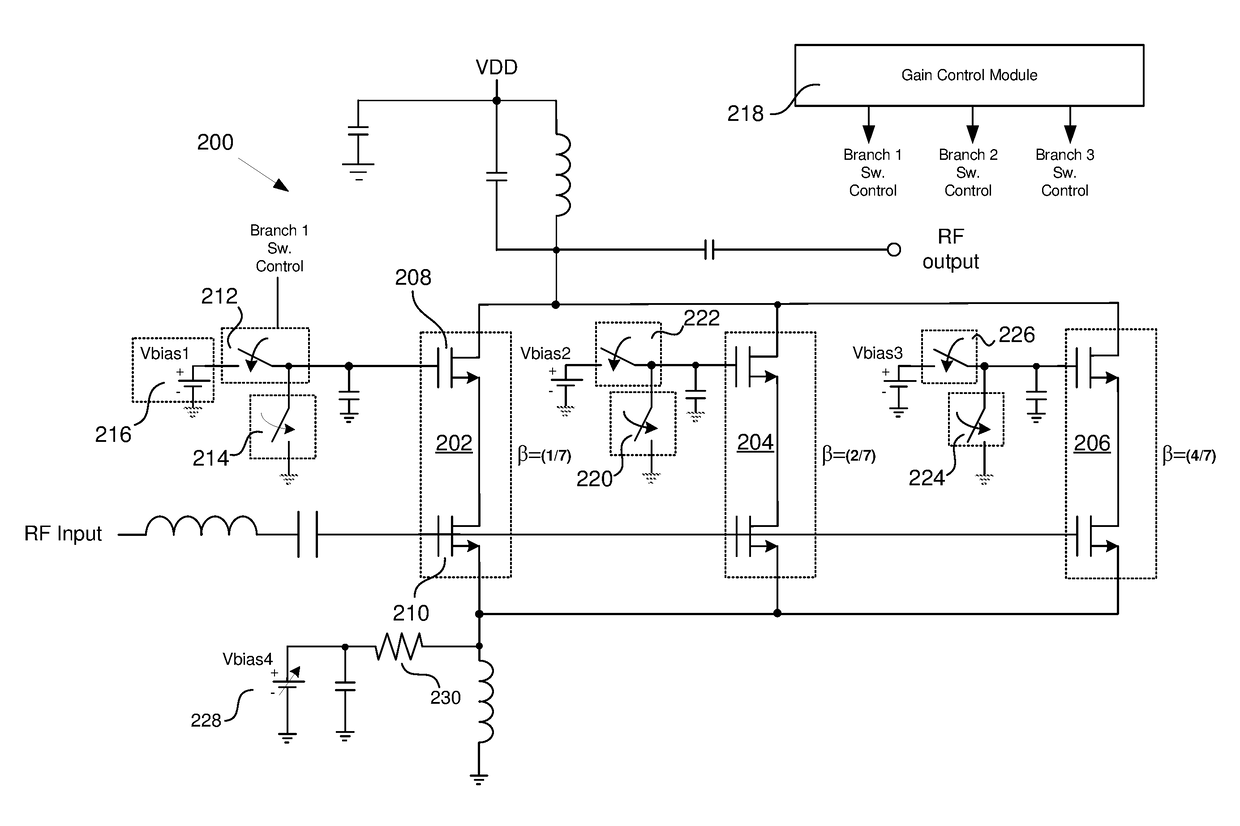
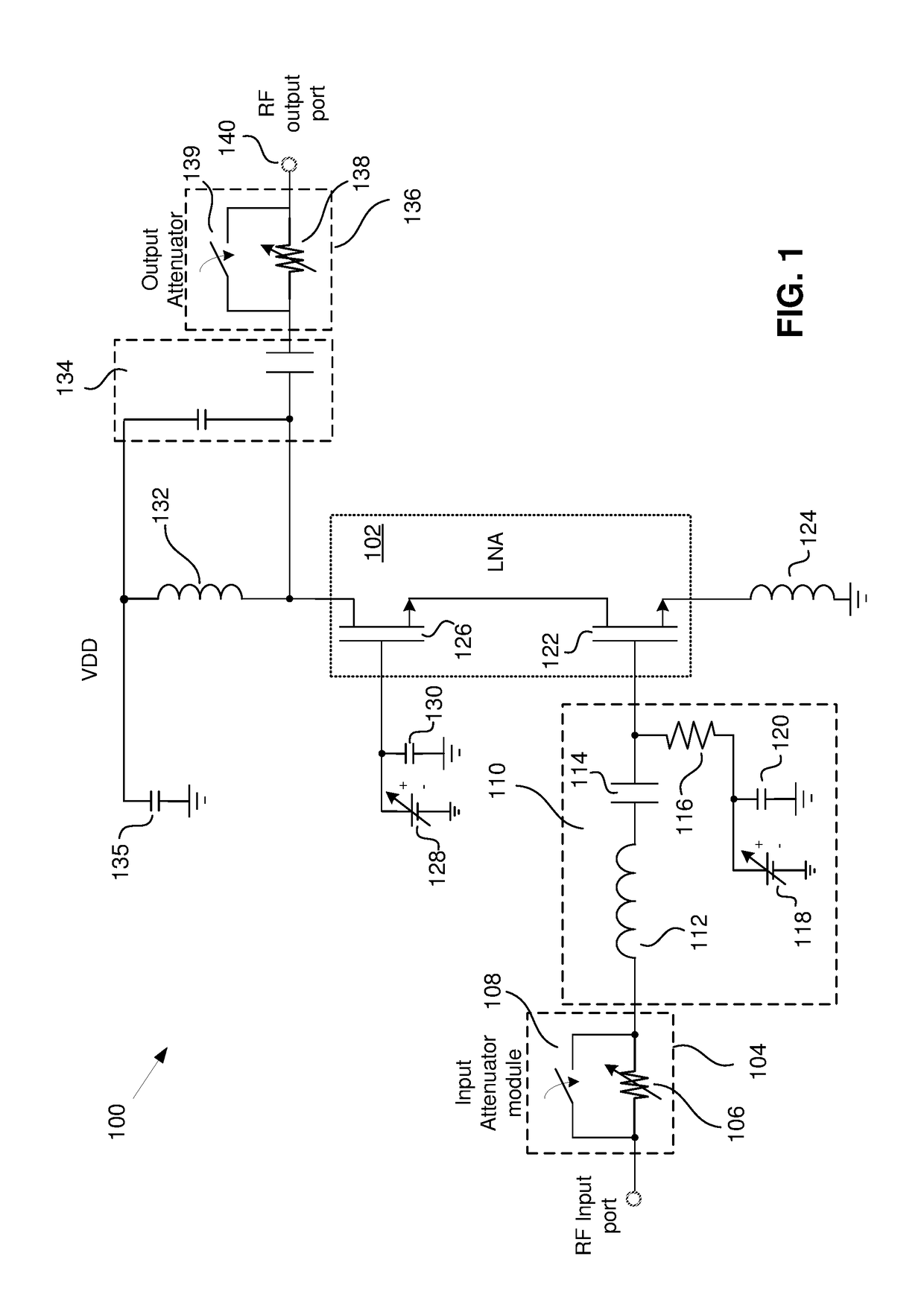
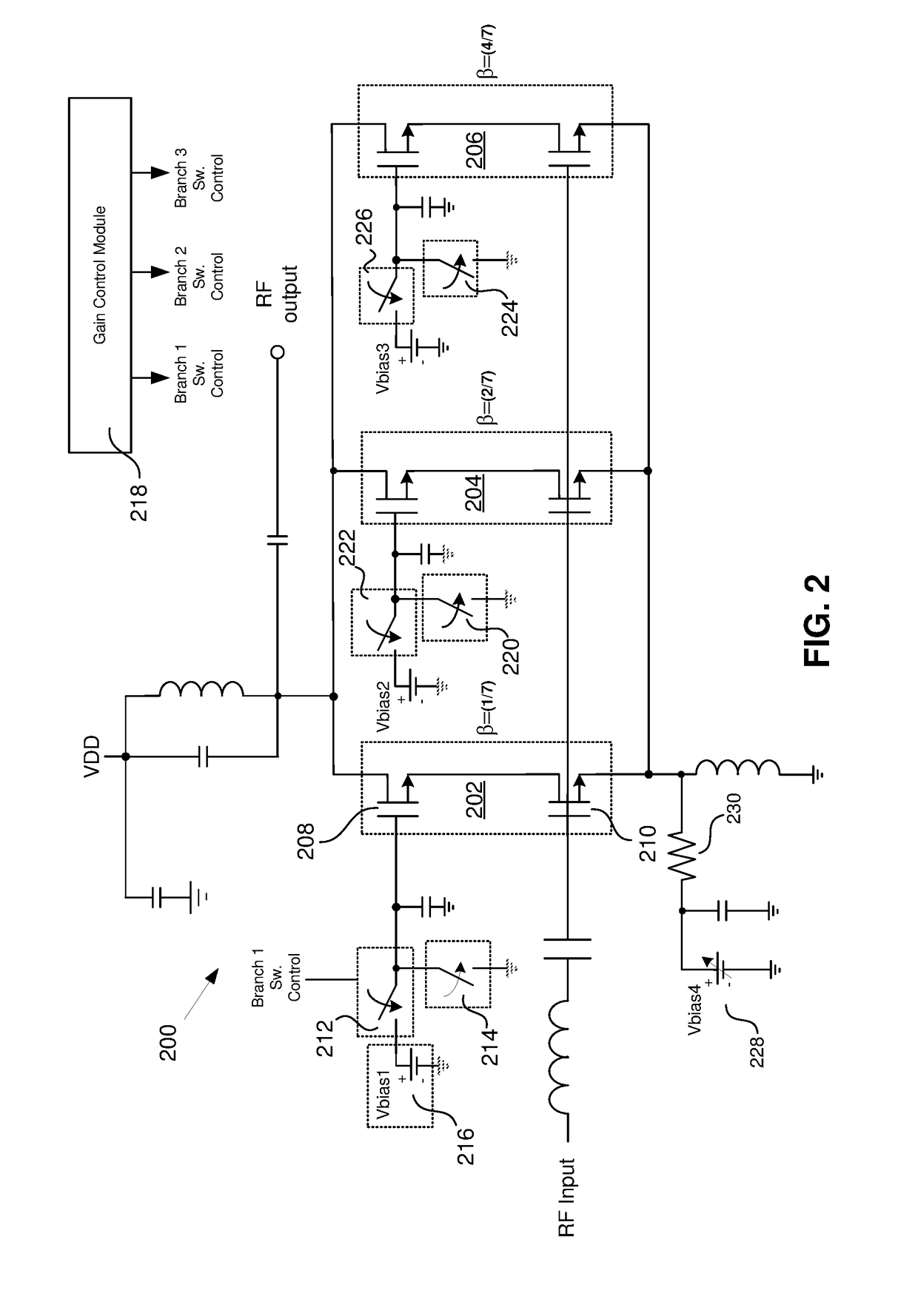
LNA with Programmable Linearity
A receiver front end capable of receiving and processing intraband non-contiguous carrier aggregate (CA) signals using multiple low noise amplifiers (LNAs) is disclosed herein. A cascode having a “common source” input stage and a “common gate” output stage can be turned on or off using the gate of the output stage. A first switch is provided that allows a connection to be either established or broken between the source terminal of the input stage of each cascode. Further switches used for switching degeneration inductors, gate / sources caps and gate to ground caps for each legs can be used to further improve the matching performance of the invention.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
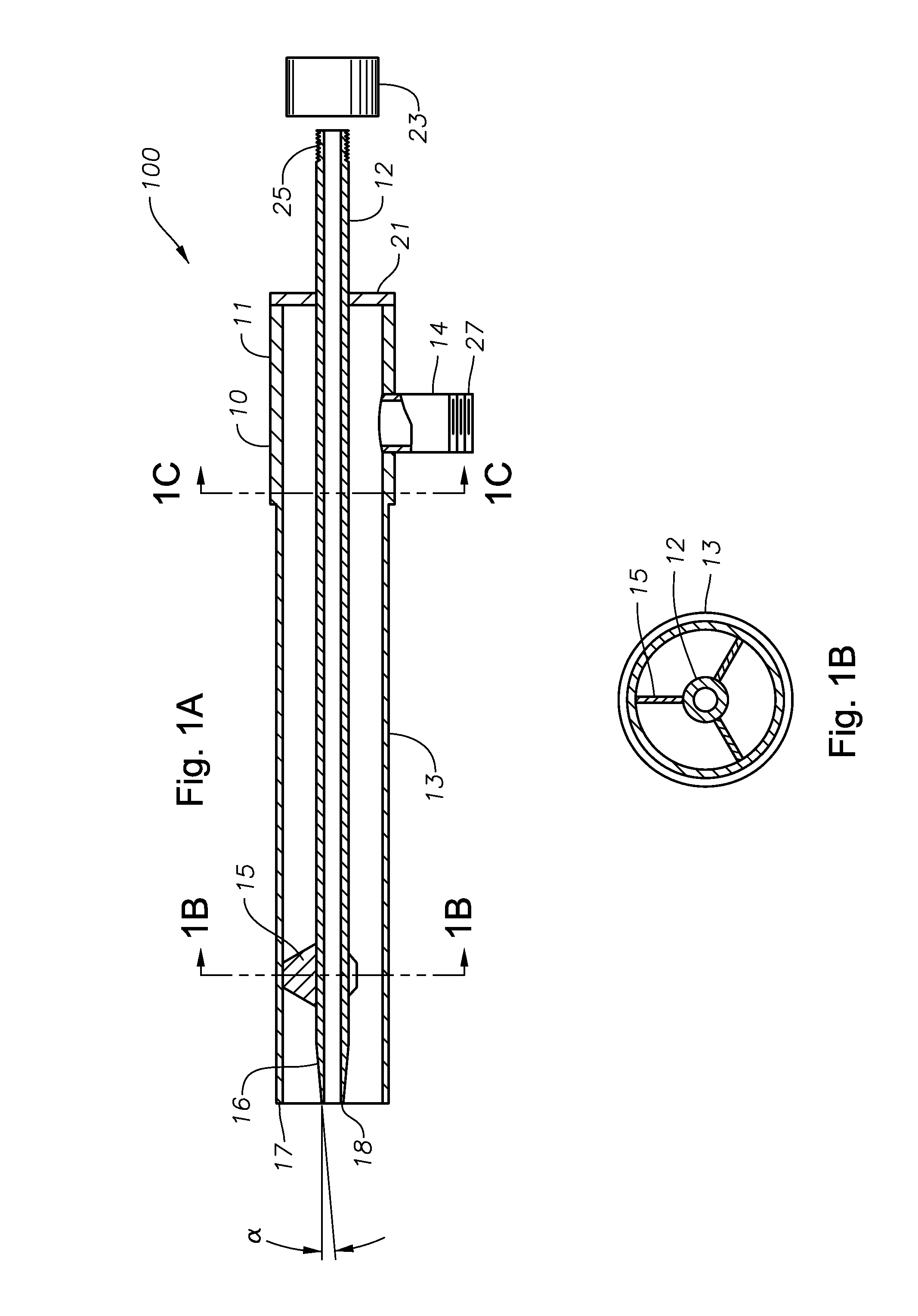
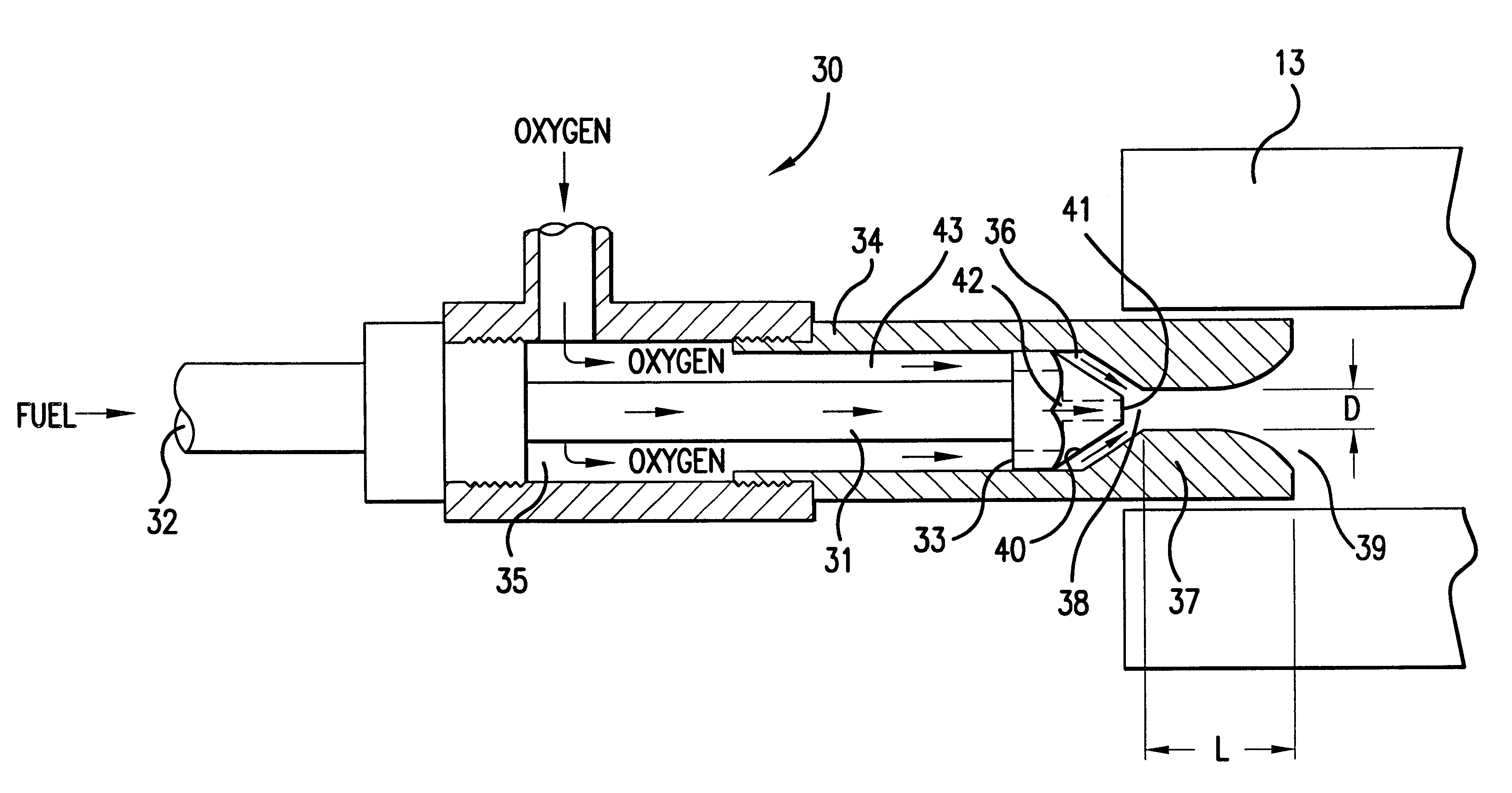
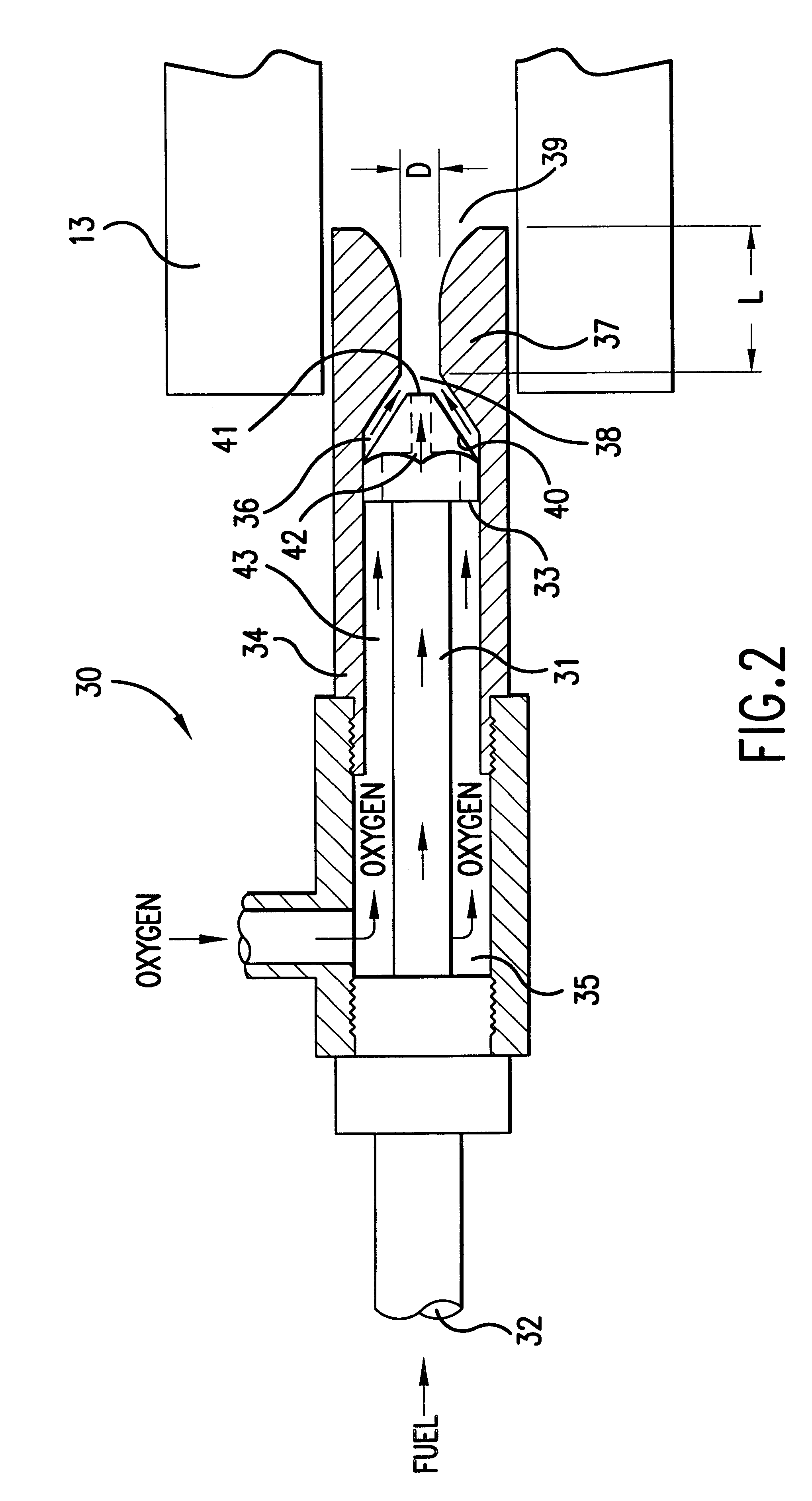
Oxygen-gaseous forehearth burner for air-fuel and oxy-fuel forehearth burner block geometries
InactiveUS6233974B1Fuel efficiencyEasy temperature controlForehearthsGlass furnace apparatusNuclear engineeringOxygen
An oxy-gaseous fuel burner for a forehearth system having an oxygen conduit, a fuel conduit disposed concentrically within the oxygen conduit and forming an annulus between the fuel conduit and the oxygen conduit, a precombustor conduit disposed at the oxygen outlet end of the oxygen conduit, and a fuel tip disposed at the fuel outlet end of the fuel conduit. The outlet of the fuel tip is disposed at or upstream of the inlet to the precombustor conduit.
Owner:ECLIPSE
Heating equipment and process for noble metal stock path
InactiveCN101357819ATemperature process optimizationElectric heating closed-loop control mediation function is powerfulForehearthsGlass productionMeasurement deviceLow voltage
The invention relates to a precious metal material channel heating device and a method which are used during the manufacturing process of flat glass and can achieve the purpose of providing the high-quality glass to a molding zone, the precious metal material channel heating device comprises a glass liquid upper extraction zone, a clarification zone, a stirring zone, a cooling zone, a material supply zone, a heating control unit for heating various zones and a measurement device for measuring the temperature of various zones, a direct electric heating device is arranged in the stirring zone, the direct electric heating device is the direct current low-voltage and high-current heating control unit which is connected on the wall of a precious metal pipe, indirect electric heating devices are arranged in the cooling zone and the material supply zone, the indirect electric heating devices wind precious metal heating wires outside the wall of the precious metal material channel pipe or adhere silicon carbide heating plates on the outside of the wall of the precious metal material channel, the precious metal heating wires or the silicon carbide heating plates are connected with the heating control unit, mixed electric heating devices are arranged in the upper extraction zone and the classification zone, and the precious metal material channel heating device has the advantages of reducing pollution, saving energy, improving production efficiency and having high glass quality.
Owner:HENAN GUOKONG YUFEI ELECTRONICS GLASS
Method for electrically energizing and heating platinum composite tube structure
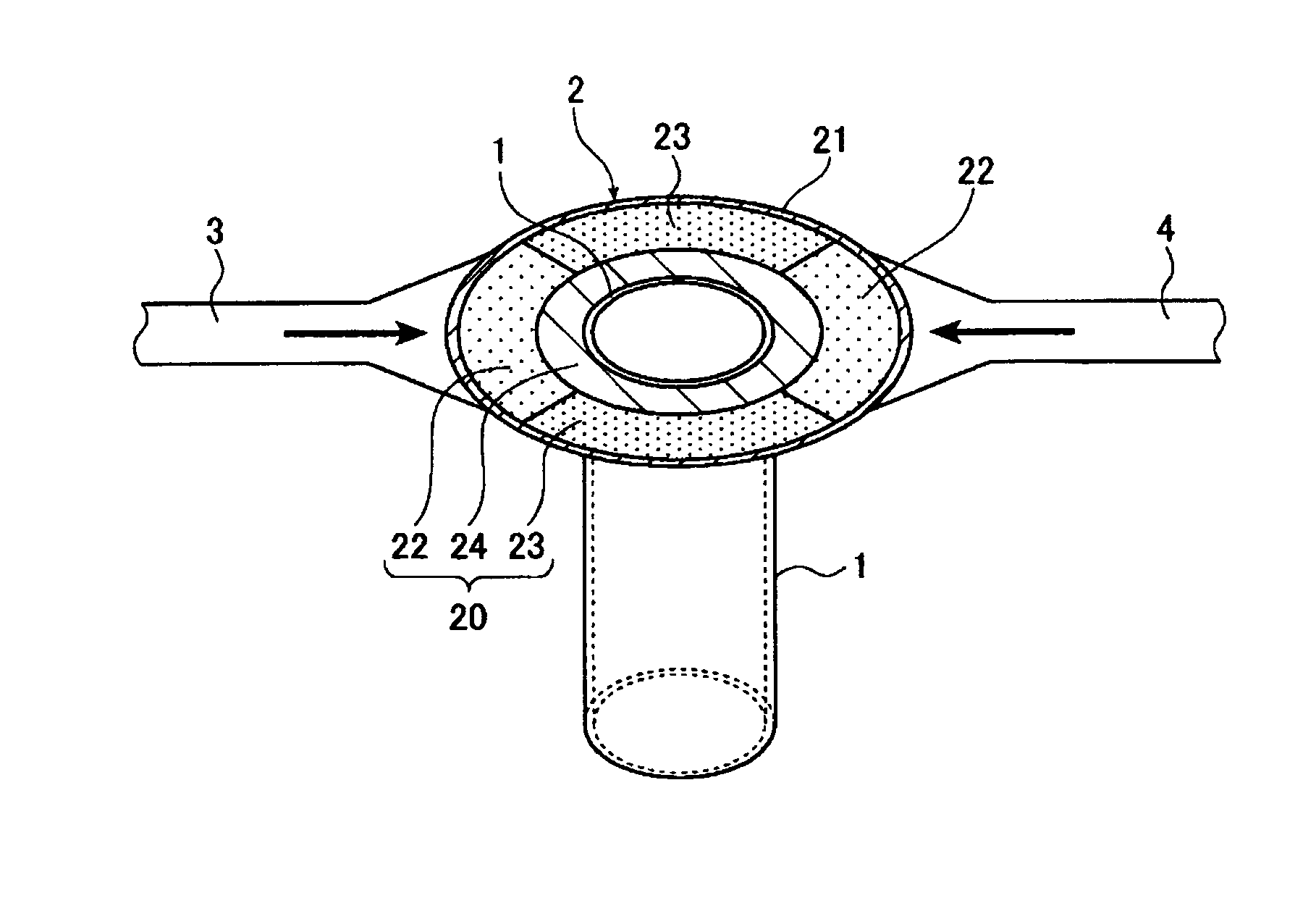
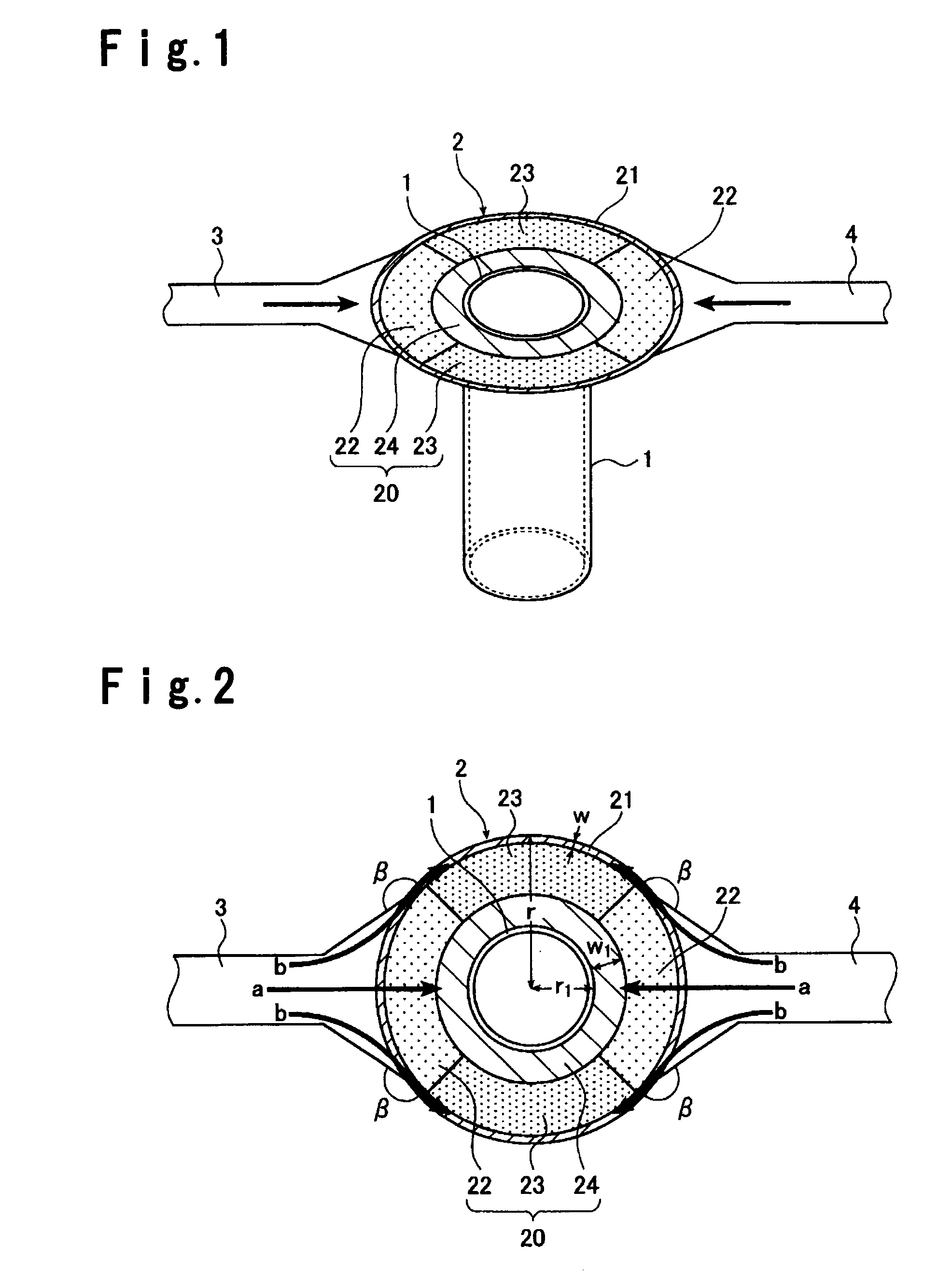
ActiveUS20080083250A1Eliminate mixingQuality improvementGlass drawing apparatusGlass transportation apparatusElectricityPlatinum
There is provided a method for electrically energizing and heating a platinum or platinum-alloy composite tube structure having a structure including a first main tube, a second main tube, and a branch tube connecting the first main tube and the second main tube, which prevents a local part of the branch tube from being electrically energized and heated in an excessive or insufficient manner. There is provided a method for electrically energizing and heating a platinum or platinum-alloy composite tube structure having a structure including a first main tube, a second main tube, and a branch tube connecting the first main tube and the second main tube, the method comprising dividing an energizing path for the branch tube into a first energizing path from the first main tube to the branch tube and a second energizing path from the branch tube to the second main tube; and performing energization control for the first energizing path and energization control for the second energizing path independently of each other.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Glass manufacturing apparatus and a structural member thereof
ActiveUS20080087046A1Avoid conductionGlass drawing apparatusGlass transportation apparatusPlatinumMetallic materials
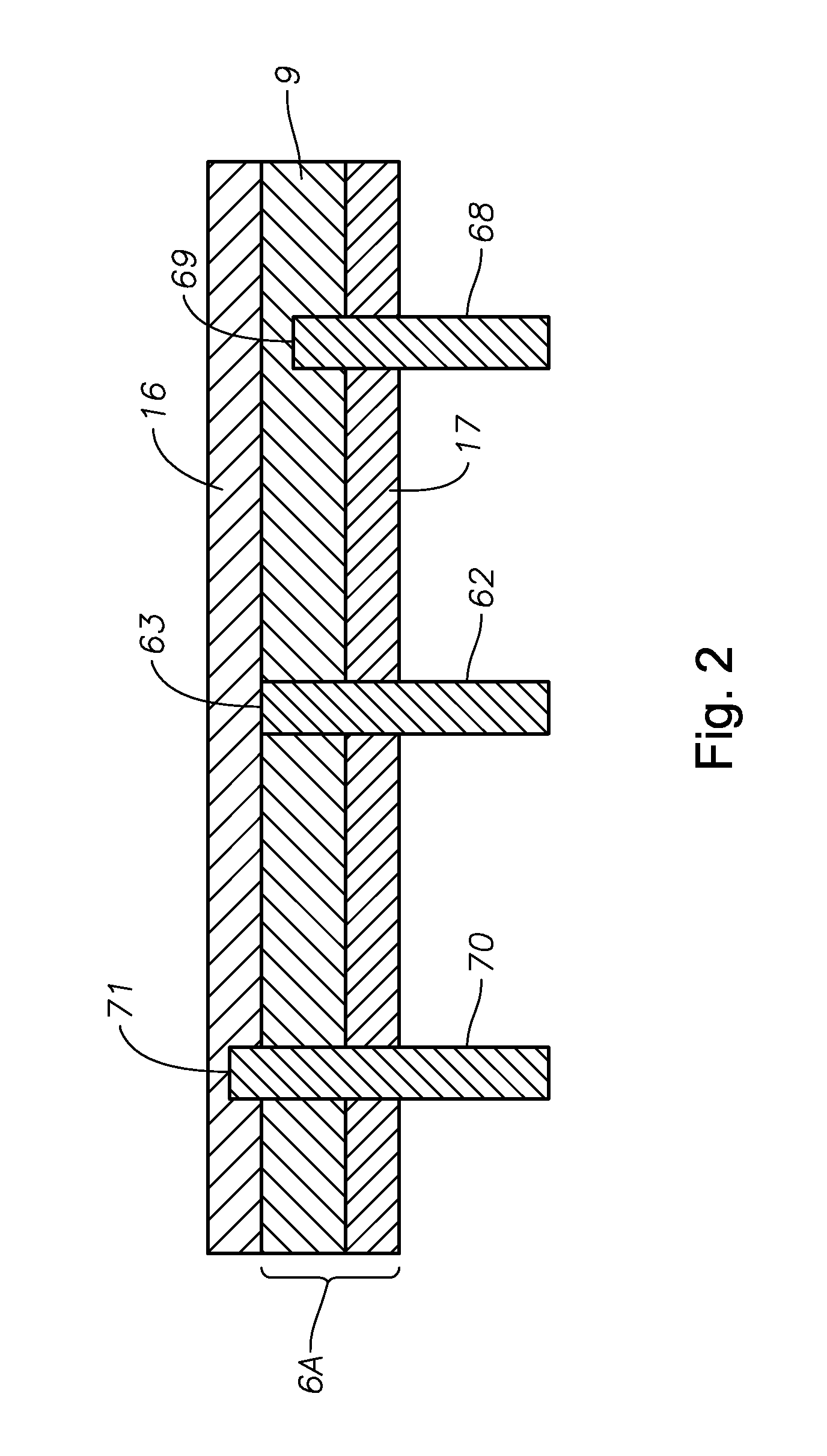
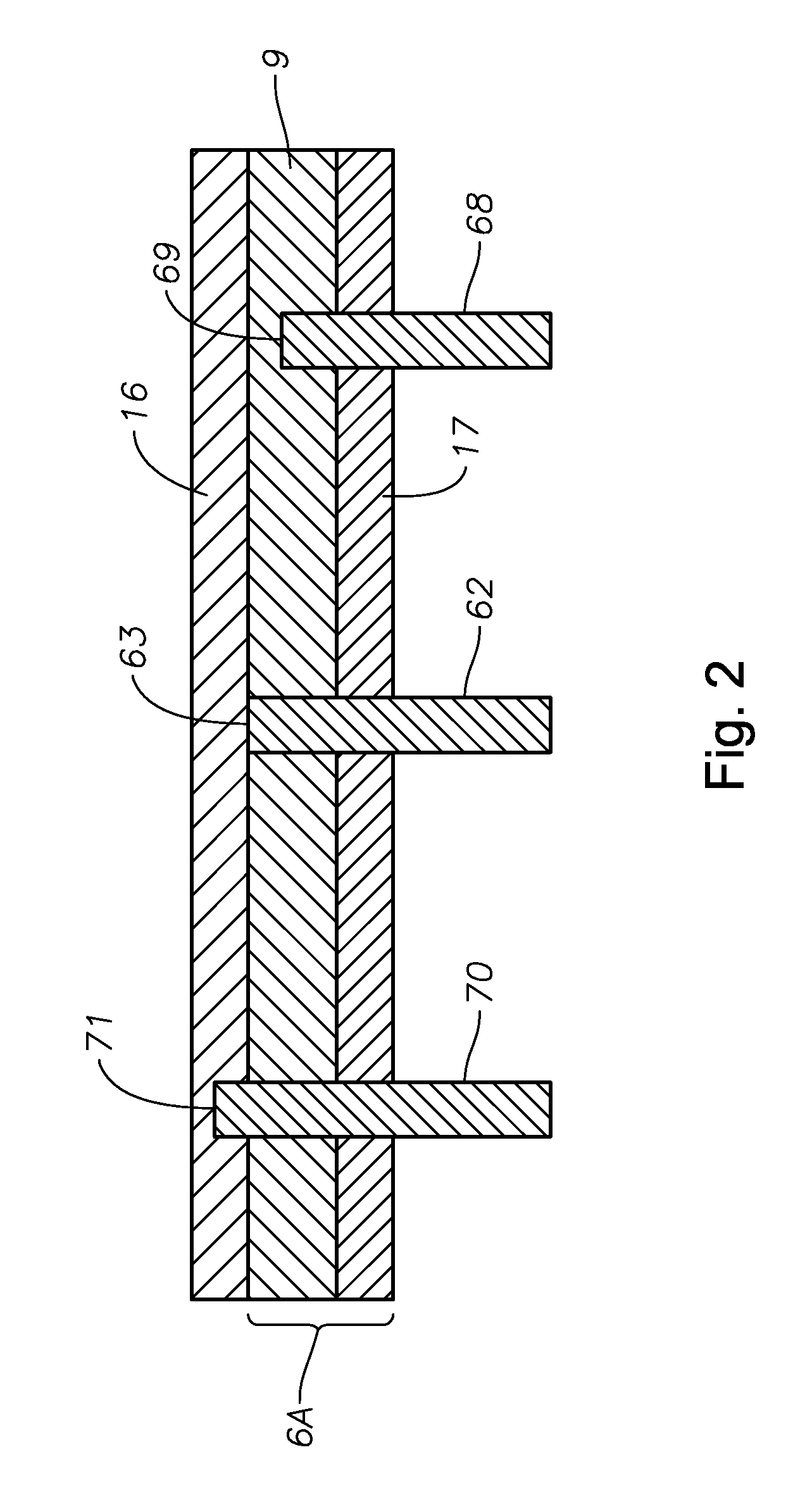
A hollow tubular body for molten glass by which local-overheating in the electrode for conduction heating is prevented. A hollow tubular body having a platinum or platinum alloy hollow tube, used for conduction heating is characterized in that a ring electrode is joined to the outer circumference of the hollow tube, at least one lead-out electrode is joined to an outer edge of the ring electrode, and the ring electrode comprises a core portion of electrode of platinum or platinum alloy and a thick portion of platinum or platinum alloy or of a metallic material other than platinum or platinum alloy, provided at an outer side of the core portion of electrode.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
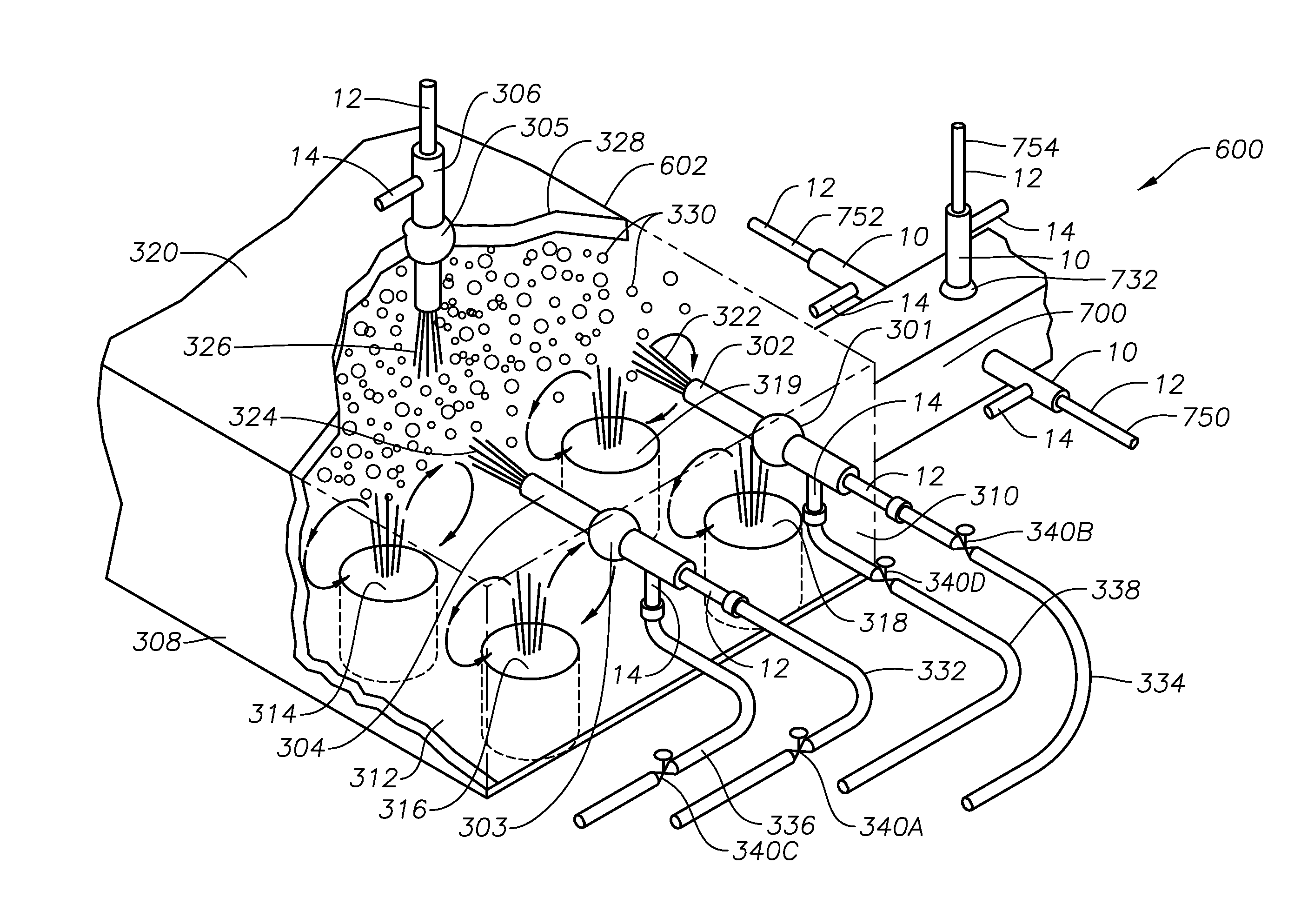
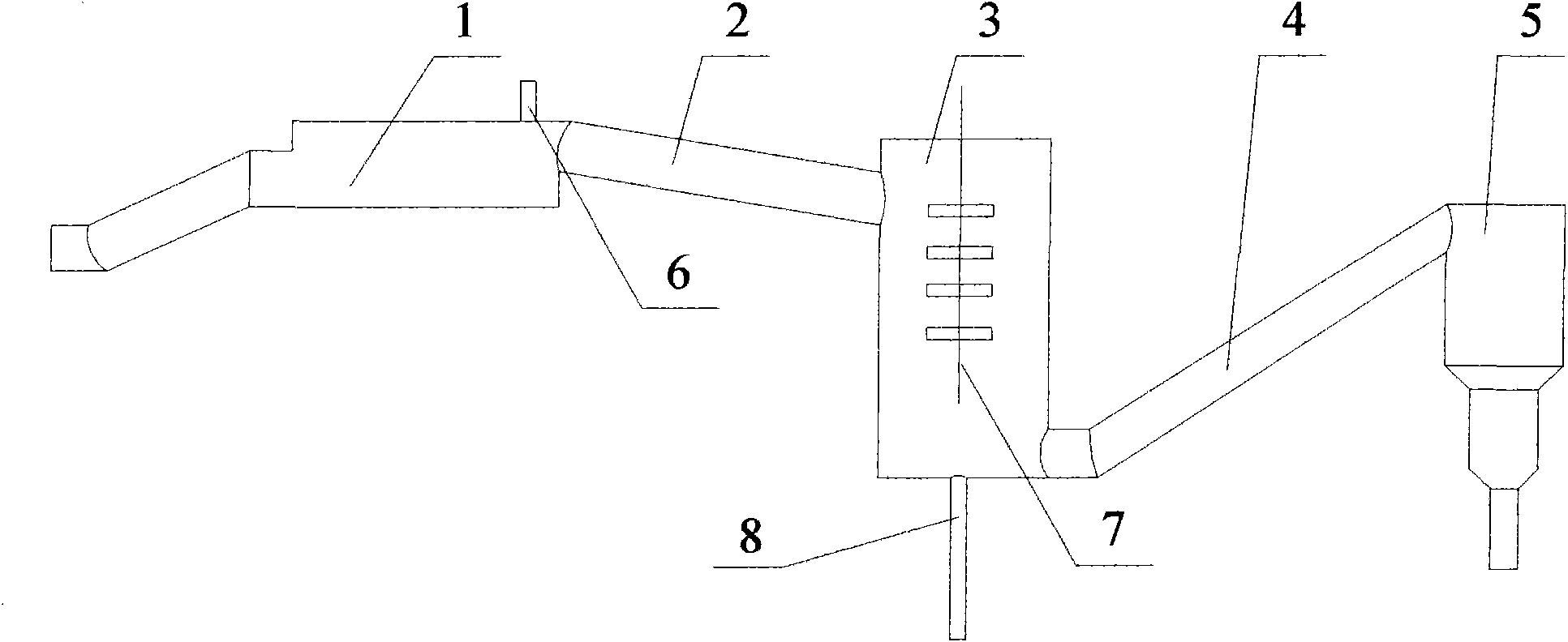
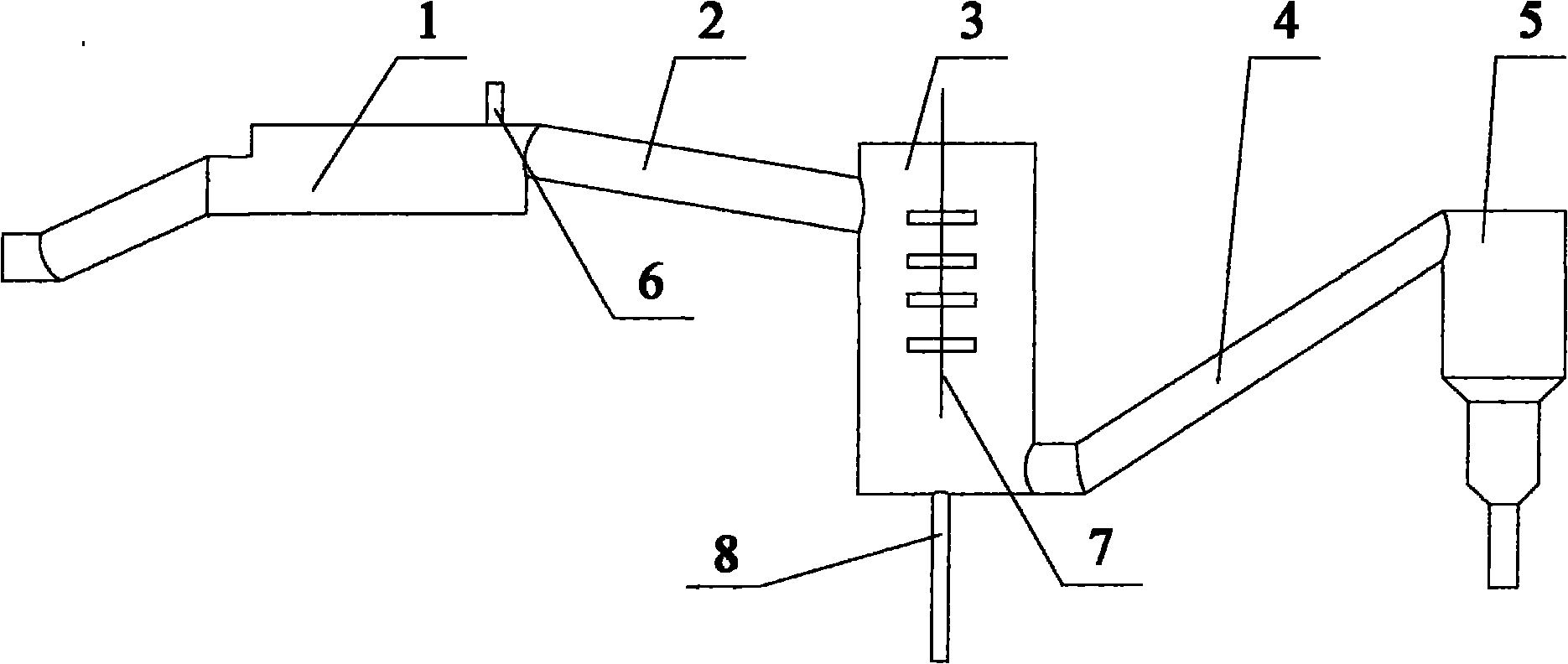
Method and apparatus for the conditioning and homogenization of glass melts
InactiveUS20070089460A1Efficient HomogenizationIncrease flexibilityForehearthsFlow mixersLongitudinal planeEngineering
A method and apparatus for the conditioning and homogenization of glass melts that are transported in flow channels with a vertical central longitudinal plane and side walls, by using the effect of alternating cross-section changes in the flow direction and stirrers with vertical stirrer shafts installed in the flow direction. The glass melt is transported through at least one flow channel, in which cross-section changes on both sides are created by several consecutive protrusions installed in the flow direction. The protrusions are directed towards the central longitudinal plane and on their upstream sides and downstream sides have wall areas that are arranged at such an angle to the central longitudinal plane, that no right-angled or acute-angled corners are created in the flow channel. The stirrers are installed between consecutive downstream sides and the upstream sides of the protrusions.
Owner:BETEILIGUNGEN SORG
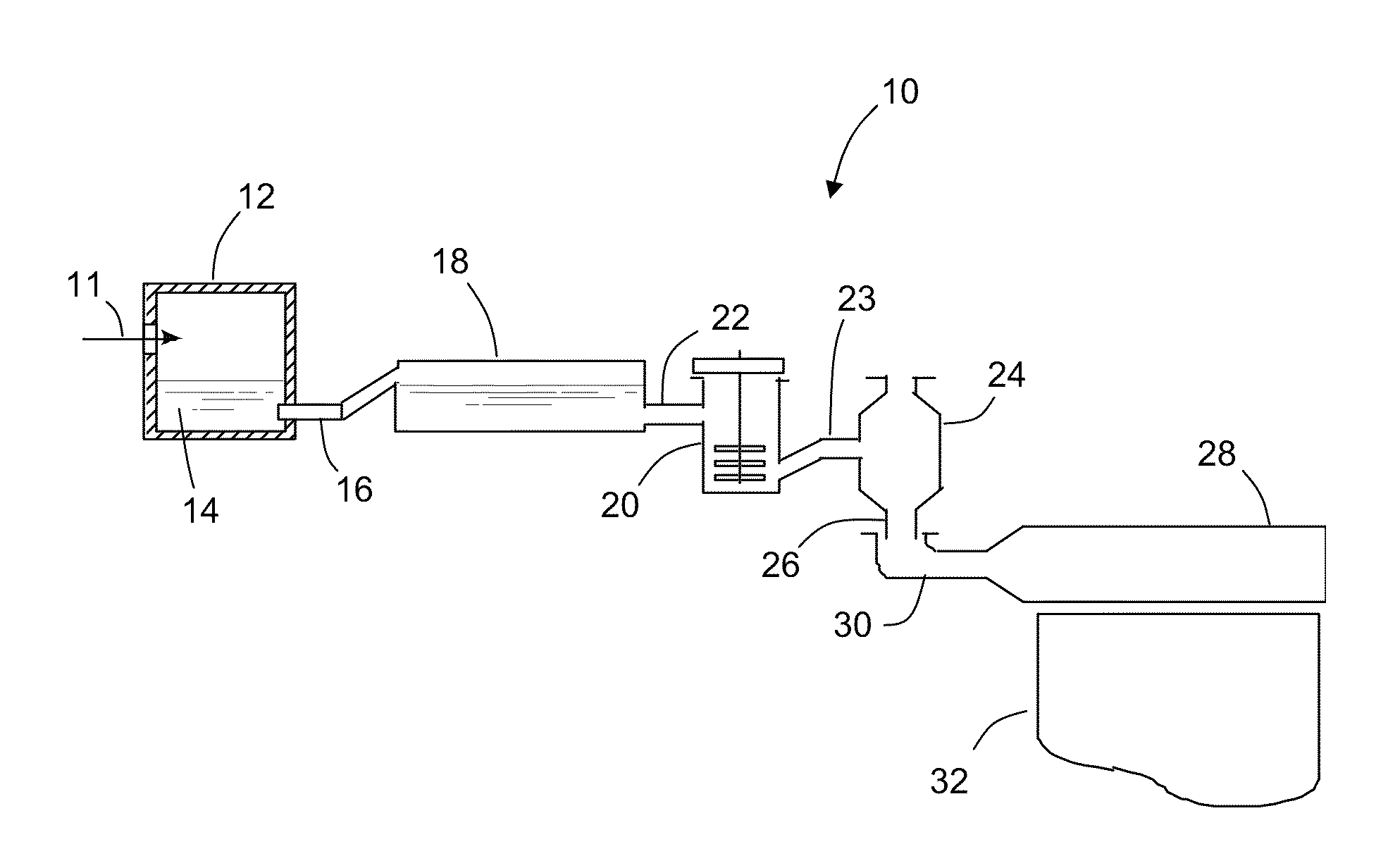
Molten glass delivery apparatus for optical quality glass
ActiveUS20090038342A1High aspect ratioImprove clarification efficiencyCharging furnaceBlowing machine gearingsEngineeringGlass sheet
A molten glass delivery system is modified to match it with the overflow downdraw process. A substantial number of defects not removed by the finer are diverted to the unusable inlet and distal edges of the sheet. In one embodiment, the stirring device is relocated from the outlet to the inlet of the finer. In another embodiment, the basic shape of the finer is preferably changed from a cylindrical shape to a Double Apex (or Gull Wing) shaped cross-section, whereby the apexes of the finer contain the glass that will form the unusable inlet end of the glass sheet. The finer vent or vents are preferably located at these apexes such that any homogeneity defects caused by the vents are diverted to the unusable inlet end of the glass sheet. The finer cross-section has a high aspect ratio for increased fining efficiency as compared to a cylindrical finer.
Owner:CORNING INC
Treatment method of glass metal in platinum channel
ActiveCN101935146AUniform compositionAchieve high temperature clarificationForehearthsGlass furnace apparatusPlatinumPollution
The invention relates to a treatment method of a glass metal in a platinum channel for reaching satisfactory clarification effect hardly reached by a common clarifying process. The treatment method of the glass metal in the platinum channel solves the problems of low quality and low efficiency of a process which requires a clarification temperature over 1600 DEG C. The invention fully integrates a clarifying process, a homogenating process, a homogenizing process and a power supply process to carry out in the platinum channel. According to different functions and conditions of different parts, the platinum thickness is 0.8-3 mm, the special stability of platinum is utilized to realize high-temperature clarification which can realize the high-quality glass metal hardly obtained by a common tank furnace, and the classified glass metal is basically in a full-closed state without external pollution or glass component volatilization so as to ensure the evenness of the glass metal components and realize the full evenness of the glass metal component by stirring in match. Fireproof insulated materials of different thicknesses are arranged at the outer side of the platinum according to different aims of different sections.
Owner:北京东旭天泽科技有限公司
Reduced size bowl for display glass melting and delivery
InactiveUS20080034798A1Eliminate stagnationReduce formationForehearthsGlass furnace apparatusFlat glassReduced size
The present invention provides an improved apparatus for forming sheet glass, wherein the apparatus includes a reservoir from which to provide molten glass, an inlet plate in fluid communication with the reservoir to receive the molten glass from the reservoir in a flow direction, the inlet pipe having a cross-sectional area orthogonal to the fluid direction, and a trough in fluid communication with the inlet pipe to receive the molten glass and that is operably coupled to a wedge-shaped sheet forming structure to form the molten glass into a glass sheet. The improvement comprises a bowl that provides fluid communication between the inlet pipe and the trough, the bowl having a cross-sectional area orthogonal to a fluid direction at the molten through the bowl that is equal to or less than the cross-sectional area of the inlet pipe, thereby preventing stagnation of the molten glass within the bowl. Another embodiment of the present invention is a method that utilizes the inventive apparatus to form glass sheet.
Owner:CORNING INC
Apparatus, systems and methods for conditioning molten glass
Channel apparatus for use with submerged combustion systems and methods of use to produce glass. One channel apparatus includes a flow channel defined by a floor, a roof, and a wall structure connecting the floor and roof, the flow channel divided into sections by a series of skimmers. Channel apparatus include both high and low momentum combustion burners, with one or more high momentum combustion burners positioned immediately upstream of each skimmer in either the roof or sidewall structure, or both, and one or more low momentum combustion burners positioned immediately downstream of each skimmer in either the roof, the sidewall structure, or both, and positioned to transfer heat to the molten mass of glass without substantial interference from foamed material. Certain embodiments include increased height of glass-contact refractory, in particular immediately upstream of the skimmers.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
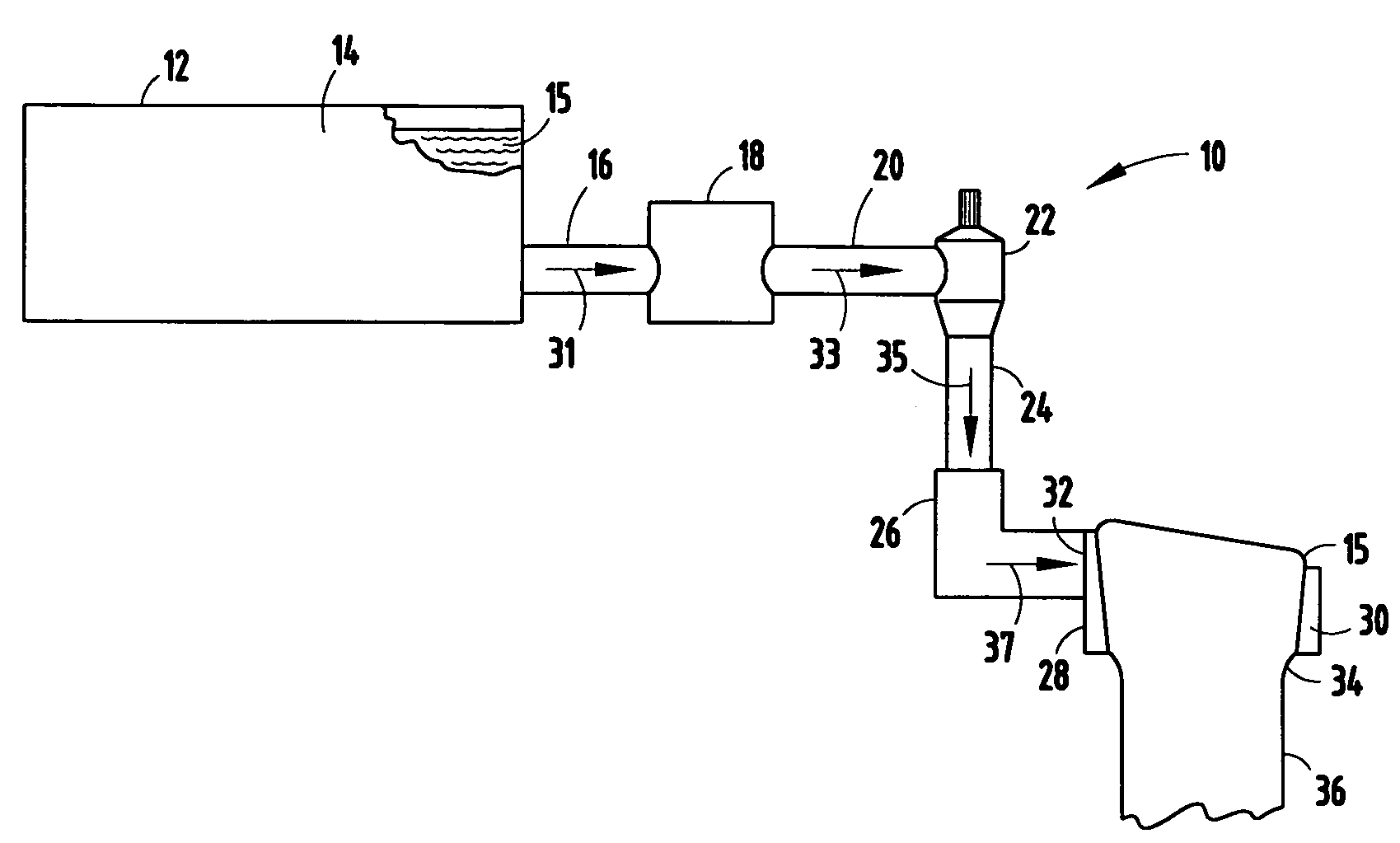
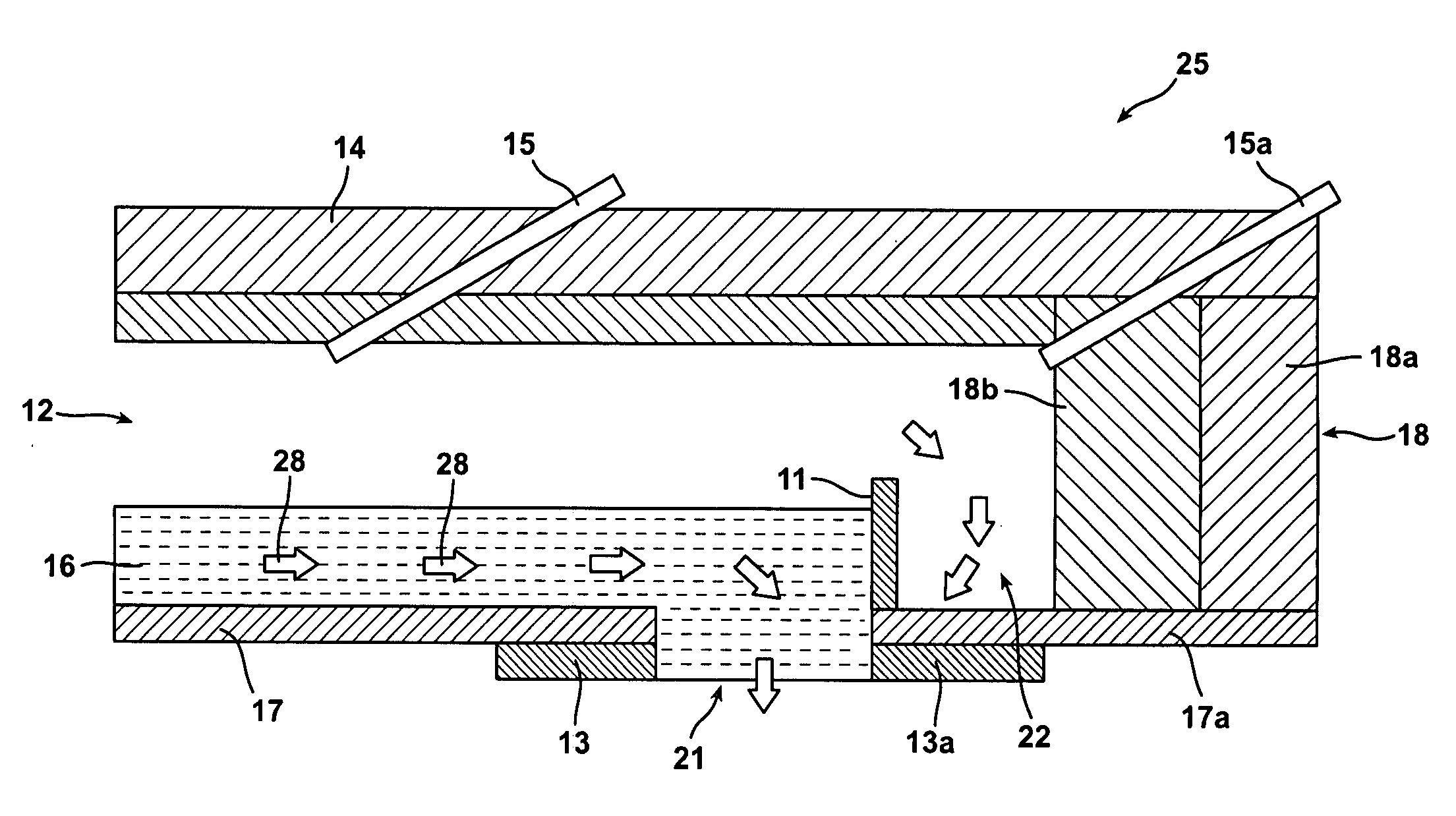
Apparatuses and methods for controlling the temperature of glass forming materials in forehearths
InactiveUS20080141721A1Decrease in shear break rateExcessive viscosityCharging furnaceForehearthsGlass fiberTemperature difference
Forehearths that create a substantially homogeneous temperature to molten glass forming materials across the end position are provided. A gas cavity, a weir, a refractory block, or a heating element in the forehearth may be utilized to reduce a temperature gradient of molten glass forming materials across the end position. Reducing the temperature difference of the molten glass forming material across the end position permits for improved chemical and physical properties of the glass fibers and the end products formed from the glass fibers. In addition, a reduction in the temperature gradient across the end position produces a more homogenous glass fiber and glass product. Further, a reduction in the shear break rate occurs when the molten glass forming material has a temperature that is substantially the same across the end position, which results in a reduction in the breakage of glass fibers and an increase in manufacturing efficiency.
Owner:OCV INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Tank furnace for producing basalt continuous fiber
ActiveCN101397182AHigh melting temperatureGuaranteed temperatureForehearthsTank furnacesMelting tankFiber
The invention relates to a tank furnace for producing basalt continuous filament and pertains to the technical field of novel inorganic non-metallic material processing equipment, the main characteristics are that the furnace body consists of a melting tank and material channels, the melting tank and the material channels are connected by non-submerged dog-holes, the melting tank is divided into a melting area and a homogenization area, a burner is arranged at the top of the furnace vertically, the burner guns of melting area and the feeding pipes are arranged in intervals, and the strong melting area of even feeding and even heating is formed. The material channels are arranged in three directions in the homogenization area of the melting tank, burner guns are arranged in the material channel in sections, the temperature of the fused mass in the material channels is guaranteed, more than 12 wiredrawing shaping areas are evenly arranged in each material channel so as to supply basalt melt mass for the wiredrawing bushing well, emptying devices are arranged at the tail part of the melting tank and the tail parts of all material channels, during the operation, the operation of discharging the meltwater can be carried out when impurities are stored in the meltwater for a long time or the varieties of raw materials are changed. The invention is in favor of improving the quality and industrialized production of the basalt continuous filament.
Owner:江苏天龙玄武岩连续纤维股份有限公司
Double platinum channel structure for ultrathin glass substrate
InactiveCN109305747AMeet the stressMeet warpForehearthsGlass furnace apparatusProduction linePlatinum
The invention belongs to the technical field of display glass production equipment and particularly relates to a double platinum channel structure for an ultrathin glass substrate. For the double platinum channel structure, by utilizing a platinum channel in the prior art, a platinum channel main body is divided into an inlet connection section, a high-temperature clarification section, a transition connection section and a stirring section which are sequentially connected with one another; by arranging two outlets at the stirring section and improving the structure on matching adaptability, on the premise without influencing the existing production capacity of the platinum channel, the flowrate requirements that matching formation can be performed, and ultrathin TFT-LCD (Thin Film Transistor-Liquid Crystal Display) liquid crystal glass is produced are met, and the problems of uncontrollable quality indexes, including stress, warping and thickness difference, of a glass product causedby large flowrate, rapidness in glass plate speed, insufficiency in formation technology time, when the ultrathin glass is produced by original equipment are solved; in addition, on the premise of realizing the production capacity of two production lines, the usage amount of platinum is greatly reduced; and as the two production lines share the platinum channel at the front end, the investments ofpersons, equipment and plants can be greatly reduced.
Owner:成都中光电科技有限公司 +1
Oxy-Fuel Burner Arrangement
InactiveUS20130071796A1Well mixedEnhanced entrainmentIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationGaseous fuel burnerEngineeringOxygen
An oxy-fuel burner arrangement having a first conduit having a nozzle aperture with an aspect ratio, D1 / D2, of greater than or equal to about 2.0. The first conduit is arranged and disposed to provide a first fluid stream, where the first fluid stream is a combustible fuel. The burner arrangement further includes at least one second conduit arranged and disposed to provide a second gas stream circumferentially around the first fluid stream, where the second gas stream includes oxygen. A precombustor is arranged and disposed to receive the first fluid stream and second gas stream where an oxy-fuel flame is produced. The geometry of the nozzle aperture and the cross-sectional geometry of the first conduit are dissimilar.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Apparatus and method for reducing gaseous inclusions in a glass
InactiveCN102307821AReduce gaseous inclusionsForehearthsGlass furnace apparatusDisplay deviceFlat panel display
A glass manufacturing system and a method are described herein for reducing gaseous inclusions in high melting temperature or high strain point glasses, such as those that are used as glass substrates in flat panel display devices. In one embodiment, the method including the steps of: (a) heating a batch material within a melting vessel to form molten glass at a melting temperature TM, the molten glass comprising a multivalent oxide material; (b) heating the molten glass within a fining vessel to a fining temperature TF = TM; and (c) cooling the molten glass within a refractory tube after the first heating step or after the second heating step to a cooling temperature TC less than TM, where the molten glass remains within the refractory tube for a predetermined resident time to reduce a volume of the gaseous inclusions in the molten glass and cause gas species to migrate out of the gaseous inclusions into the molten glass such that at least a portion of the gaseous inclusions collapse into the molten glass.
Owner:CORNING INC
Glass melting furnace, process for modifying glass melt, process for producing glass melt, process for producing glass product, and apparatus for producing glass product
InactiveUS20130239618A1Easy to installSuitable for productionCharging furnaceForehearthsHigh concentrationMolten state
Objective of the present invention is to provide a glass melting furnace, a process for modifying a glass melt and a process for producing glass melt, whereby composition-modified glass melt containing an additive component at a high concentration can be produced with an excellent quality. The glass melting furnace 10 of the present invention is a glass melting furnace 10 for adding an additive to a molten state glass to form composition-modified glass melt, discharging the composition-modified glass melt, and a forehearth 20, said forehearth comprising a feed portion to feed an additive, and a heating means to form a heating gas phase portion above the liquid surface of the glass melt to convert the additive from the feed portion into melted particles of additive below the feed portion.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Method for preventing bubbles on precious metal components
ActiveUS7628037B2RemissionOxygen partial pressure can be raised and loweredBlowing machine gearingsForehearthsProduct gasGas bubble
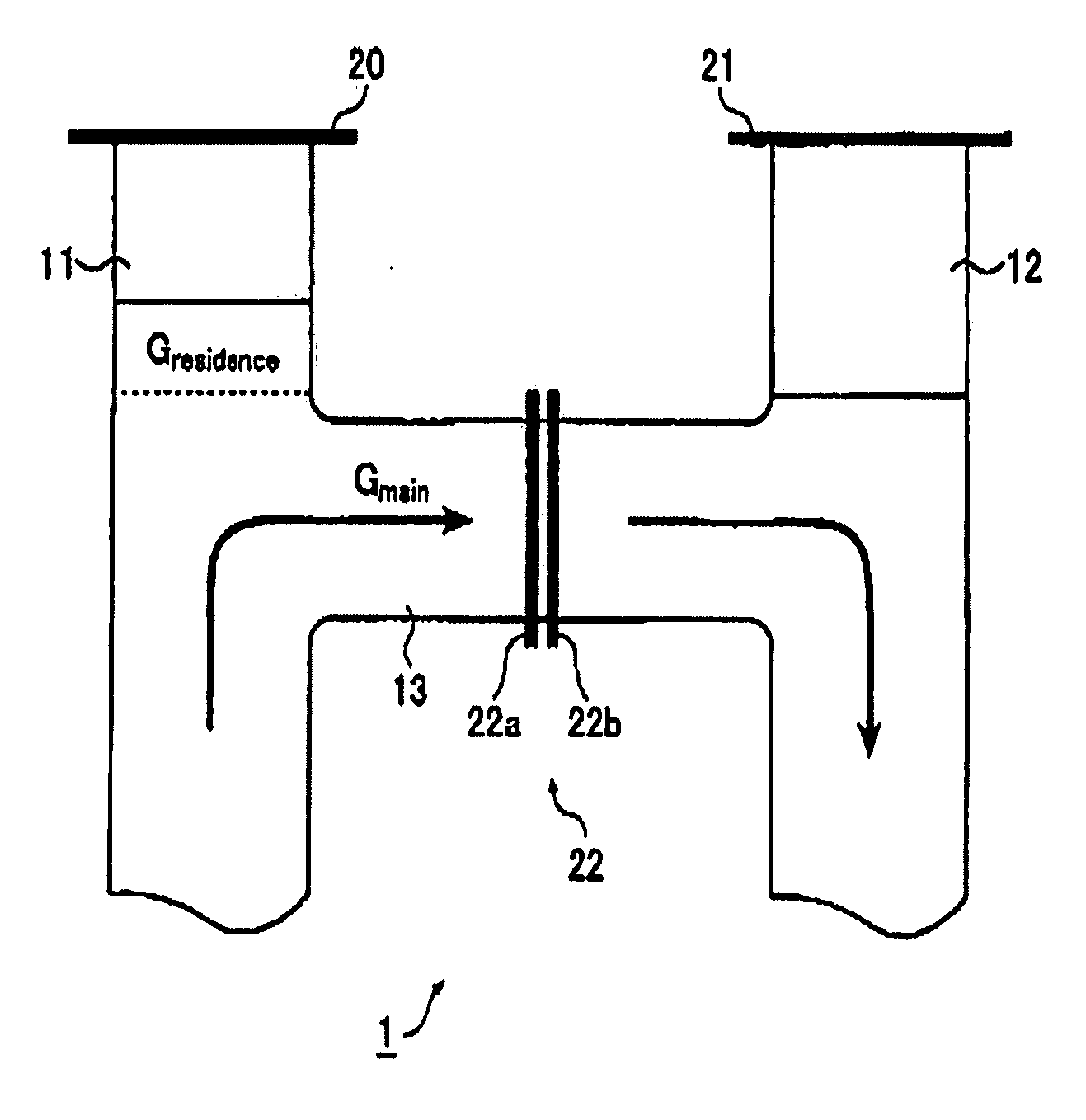
In the case of a method for manufacturing glass, with which molten glass is enclosed at least partially by precious metal walls or refractory metal walls, and with which the oxygen partial pressure of the molten glass is influenced by a treatment means to prevent disturbances, gas bubbles or other disturbances often form as a result of over-compensation. This over-compensation can be prevented by locating at least one probe (20) for determining the oxygen partial pressure at the interface—or close to the interface—of the glass melt and metal wall, and by regulating the influencing of the oxygen partial pressure in a safe range of the oxygen partial pressure with the treatment means using a regulating system (39, 45).
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Glass production device and forming process method
InactiveCN103232151AReduce qualityInhibit devitrificationForehearthsGlass furnace apparatusForming processesMaterials science
The invention discloses a glass production device and a forming process method. The glass production device comprises (1) a mixing device, (2) a melting device, (3) a cooling operating part device and (4) a forming device, wherein the mixing device is used for mixing glass raw materials; the melting device is used for melting mixed glass raw materials, and discharging air bubbles of a glass liquid; the cooling operating part device is used for homogenizing, clarifying and cooling the glass liquid, the middle lower layer of the cooling operating part device is provided with 2-100 electric heating devices and temperature measuring devices, and the distance between each electric heating device and each temperature measuring device ranges from 0.2 m to 6 m; electric heating devices and temperature measuring devices are installed in the range of 0.1 m to 1.5 m at the left corner or the right corner, close to the forming device, of the middle lower layer of the cooling operating part device; and the forming device is used for preparing the cooled glass liquid into a glass product.
Owner:杨德宁
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com