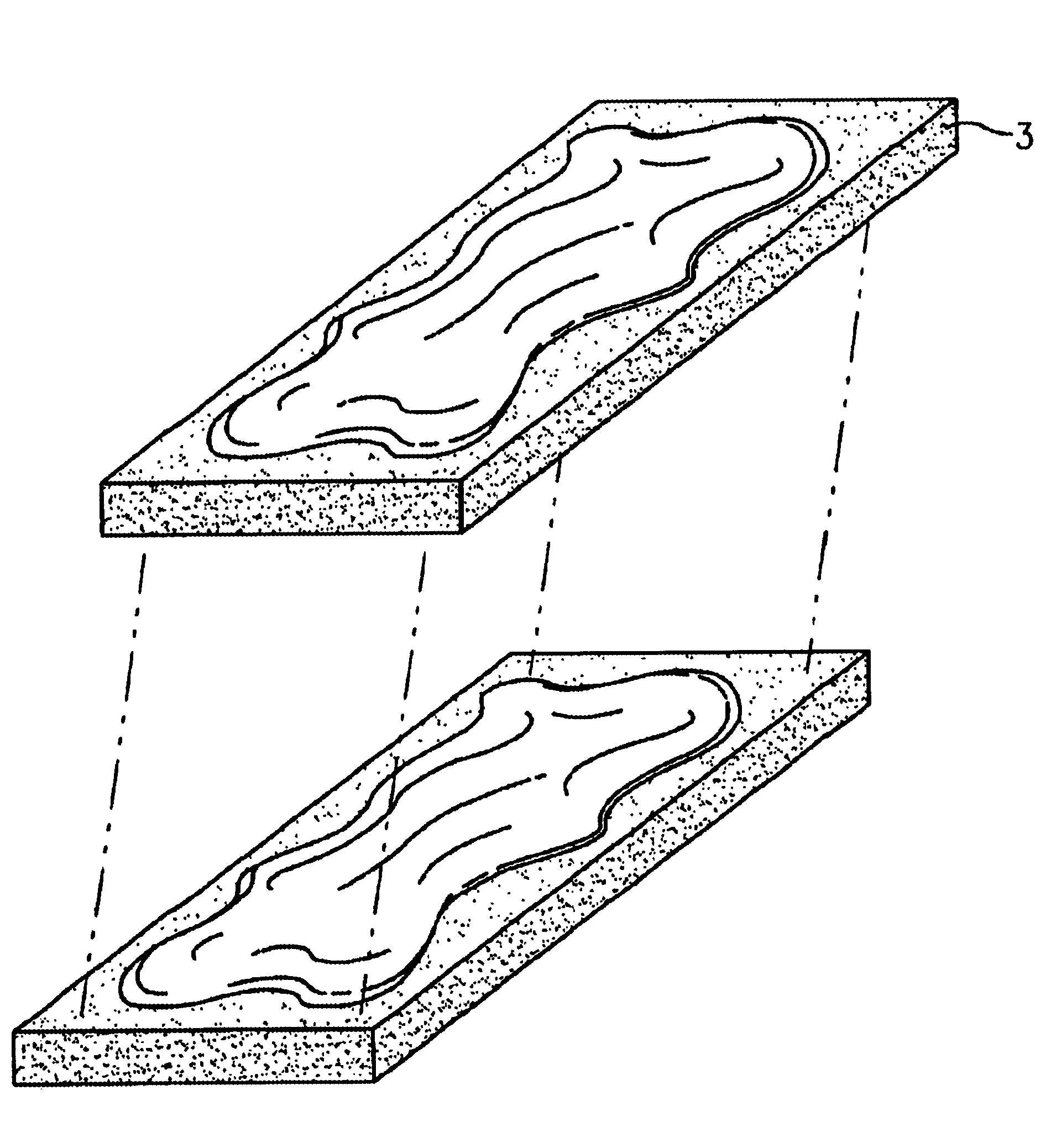
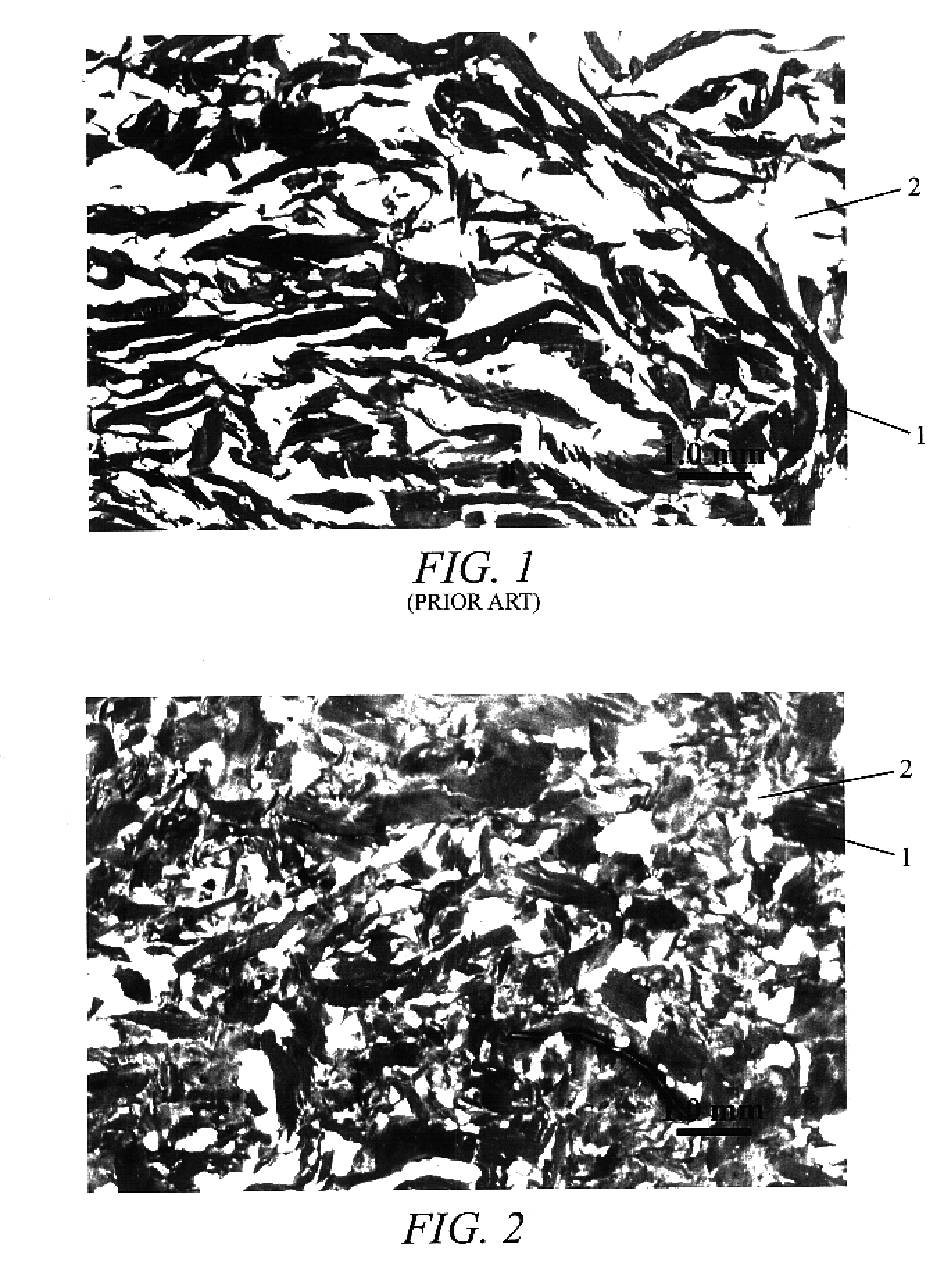
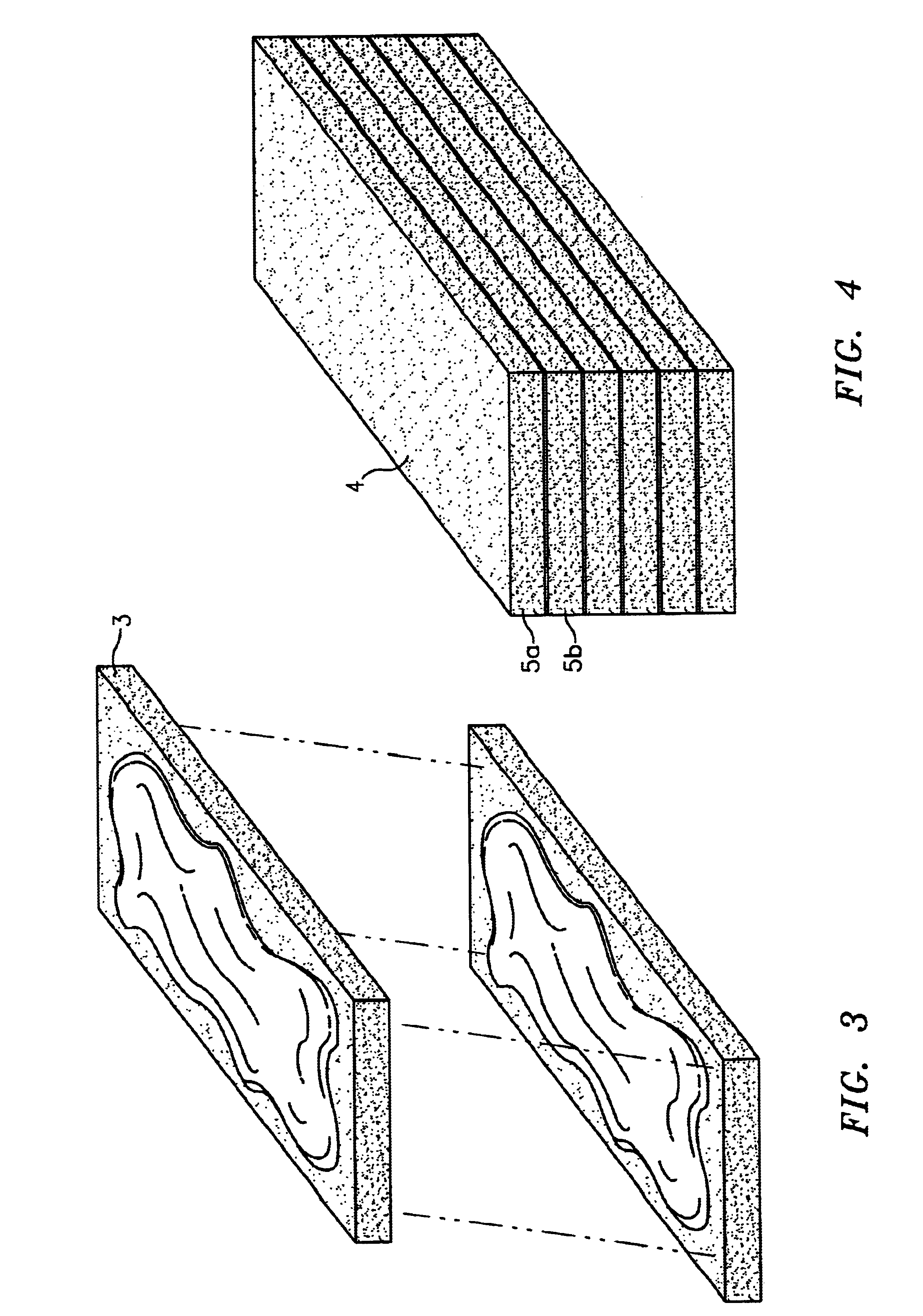
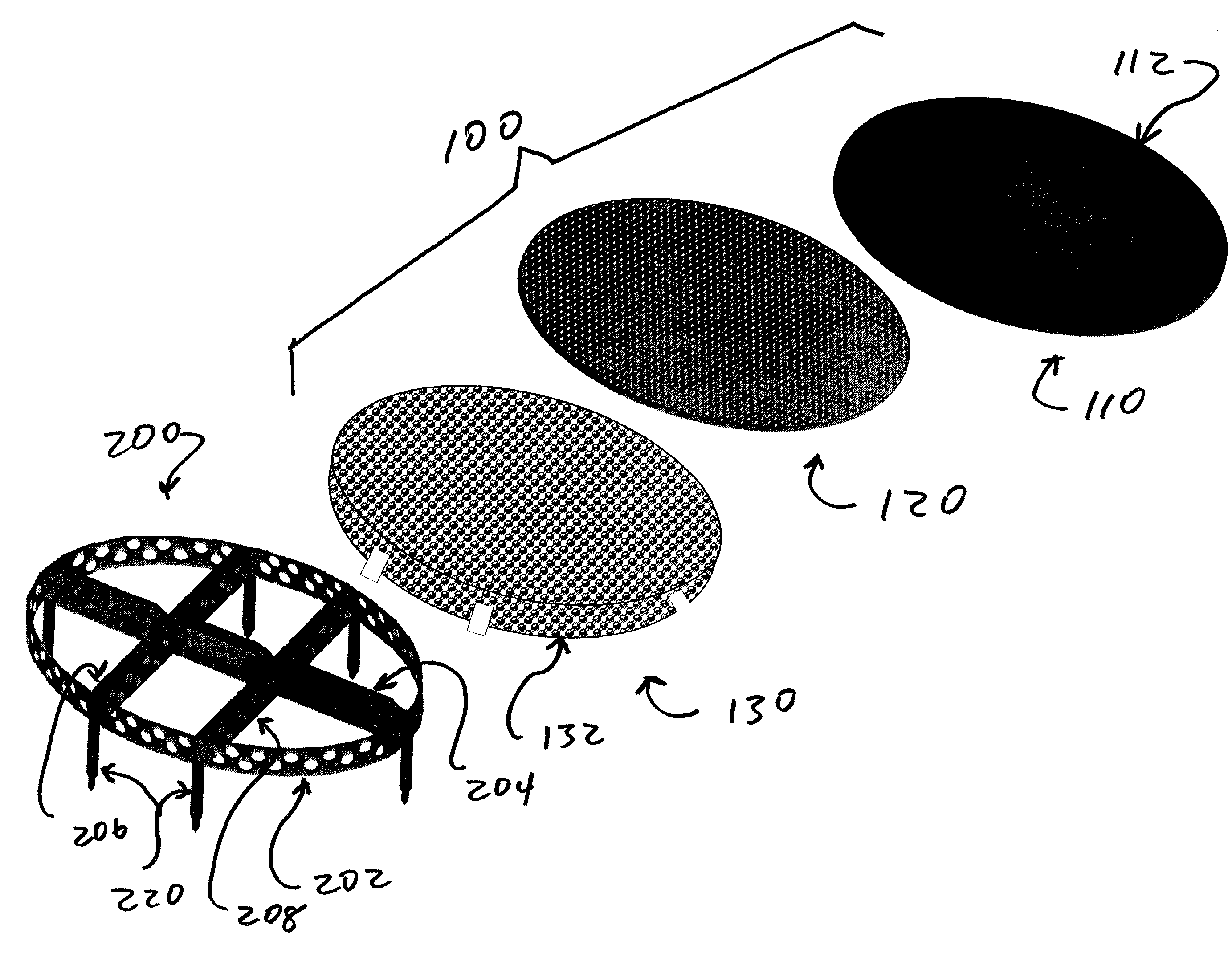
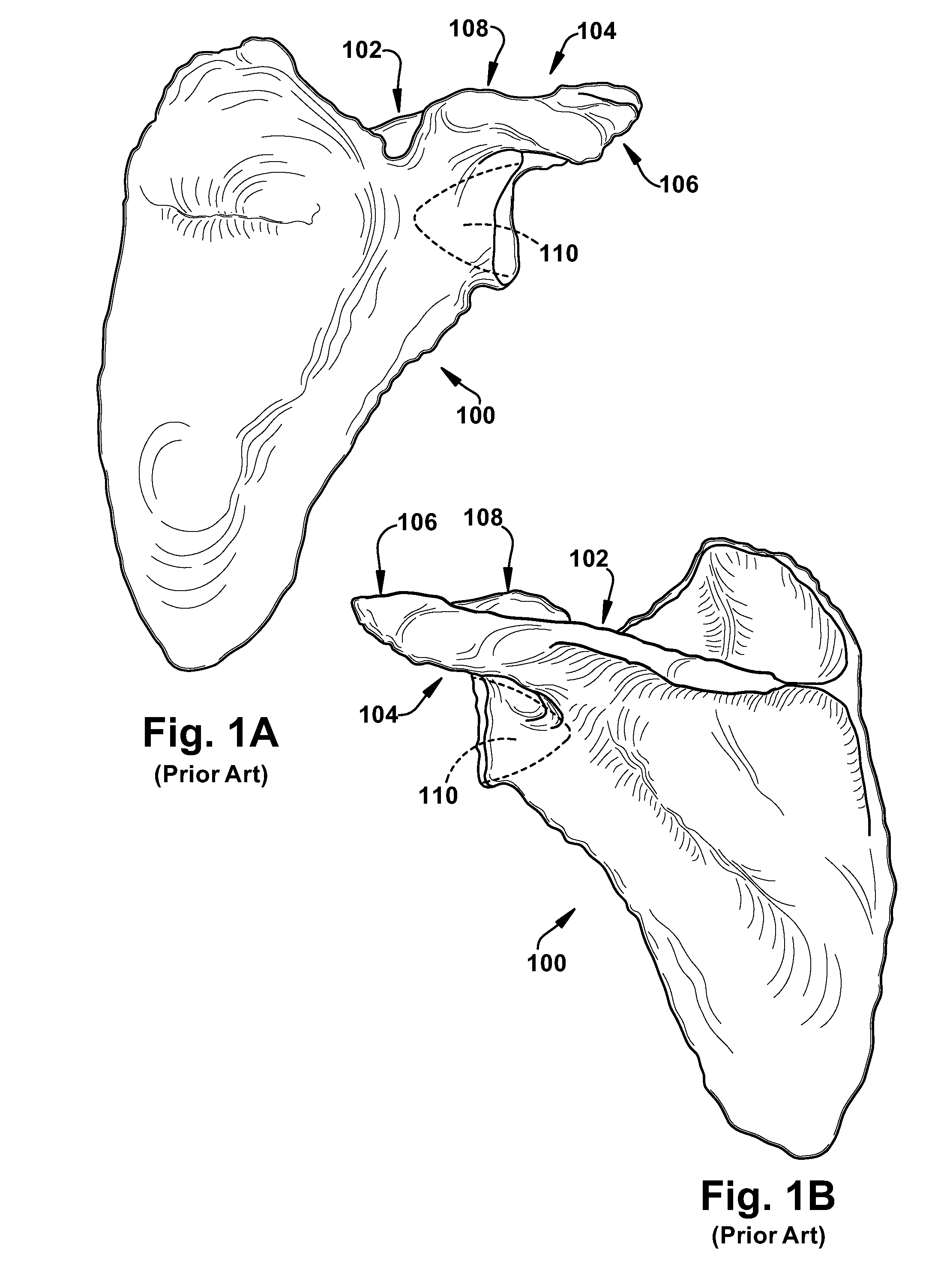
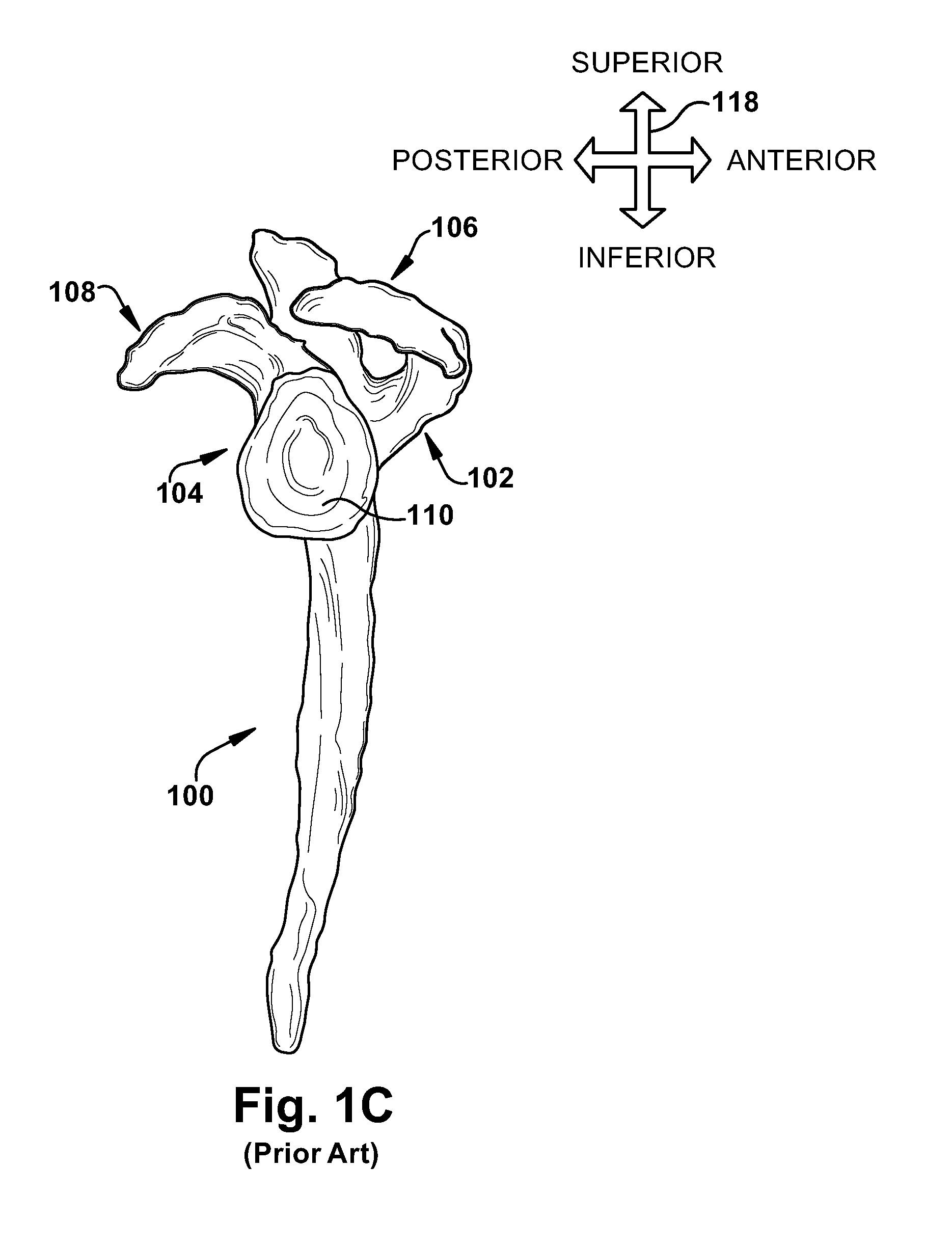
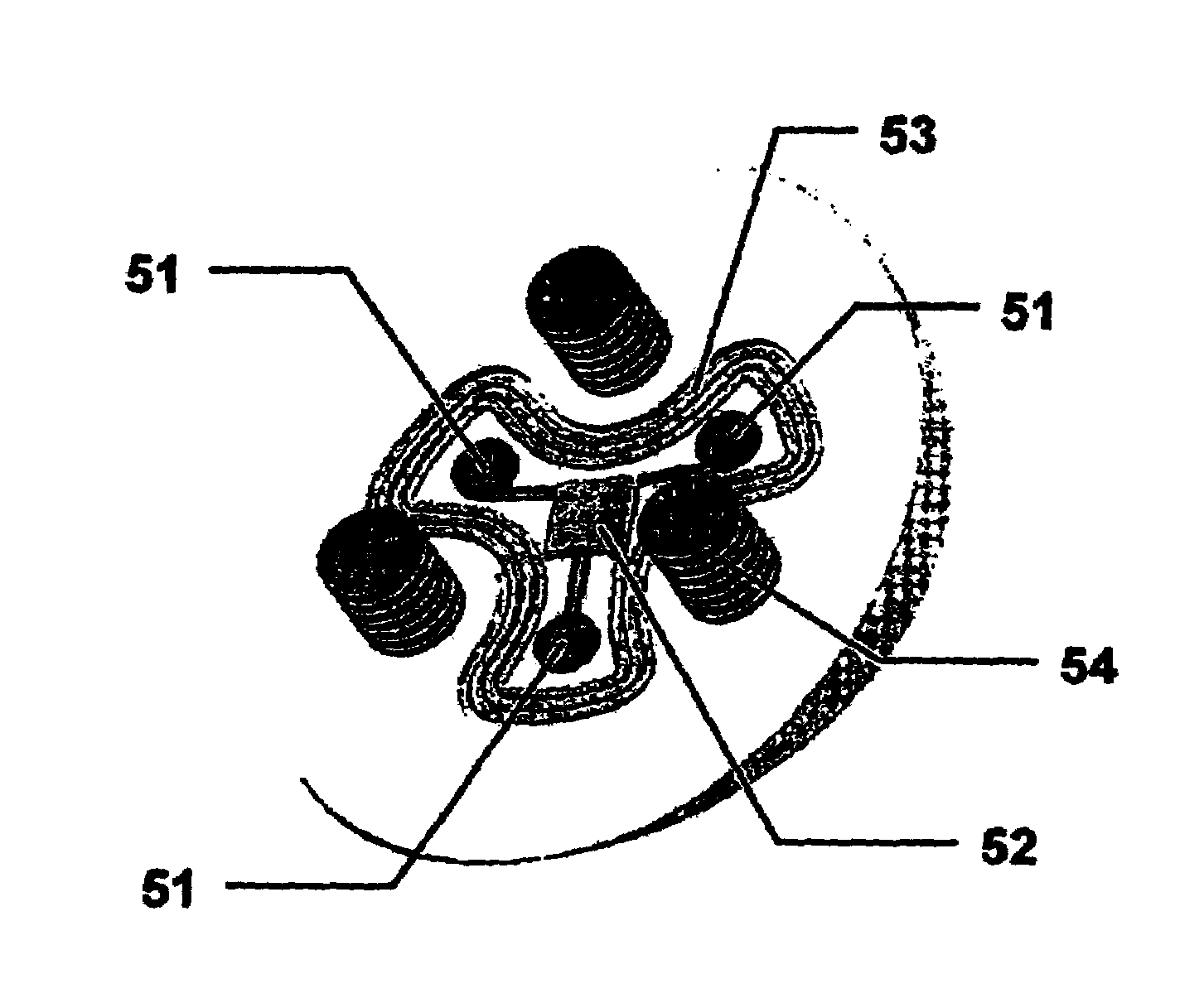
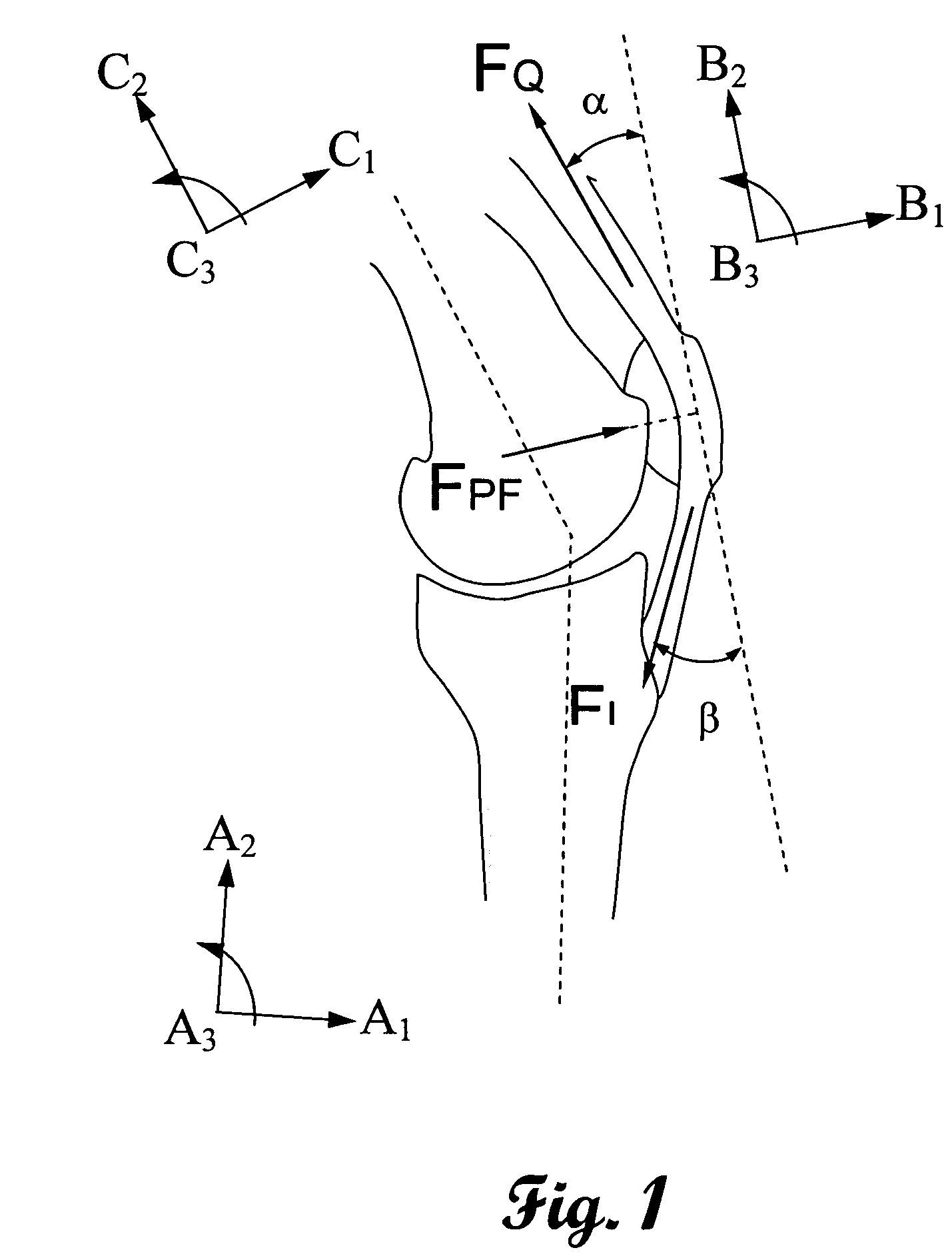
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1217results about "Shoulder joints" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
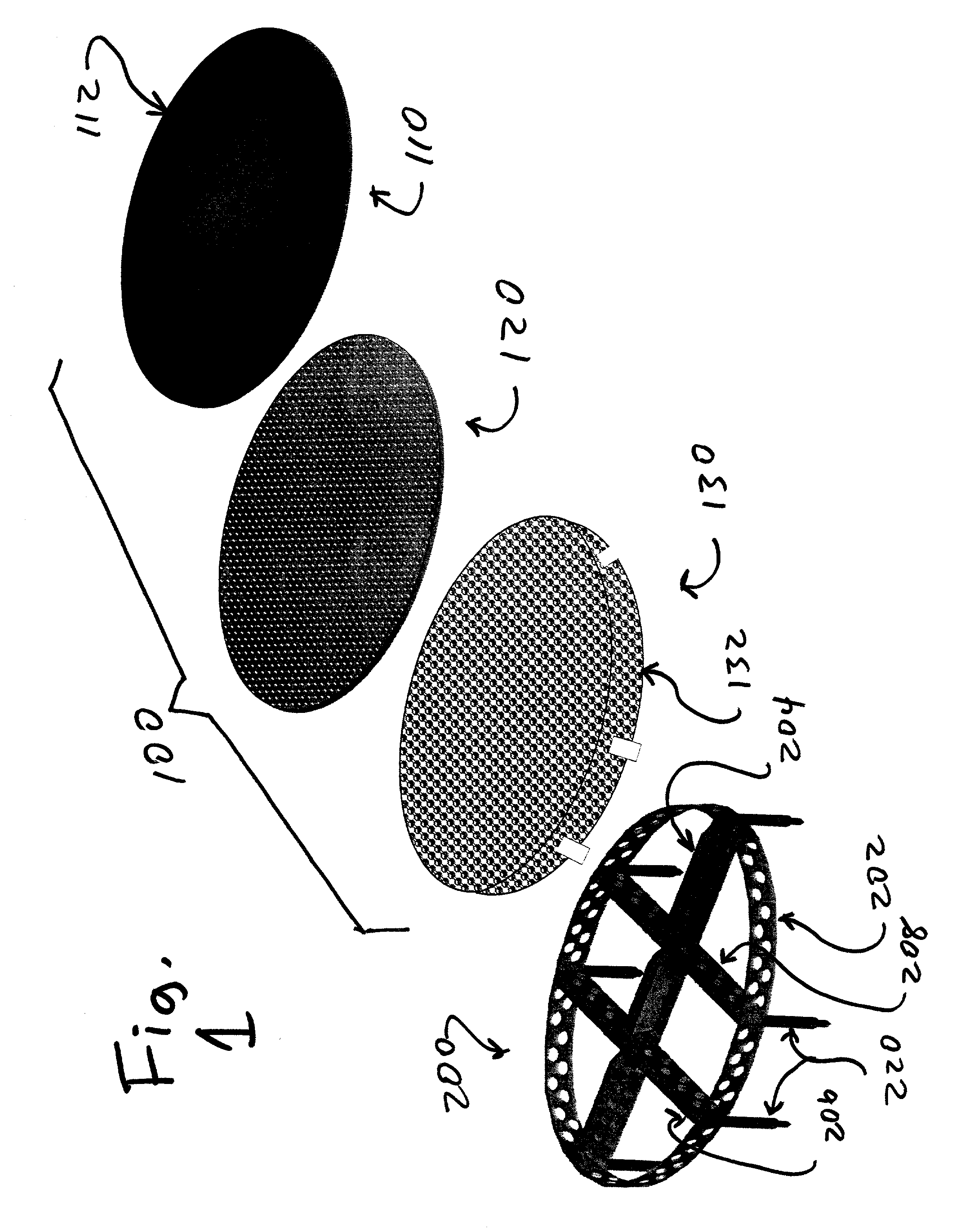
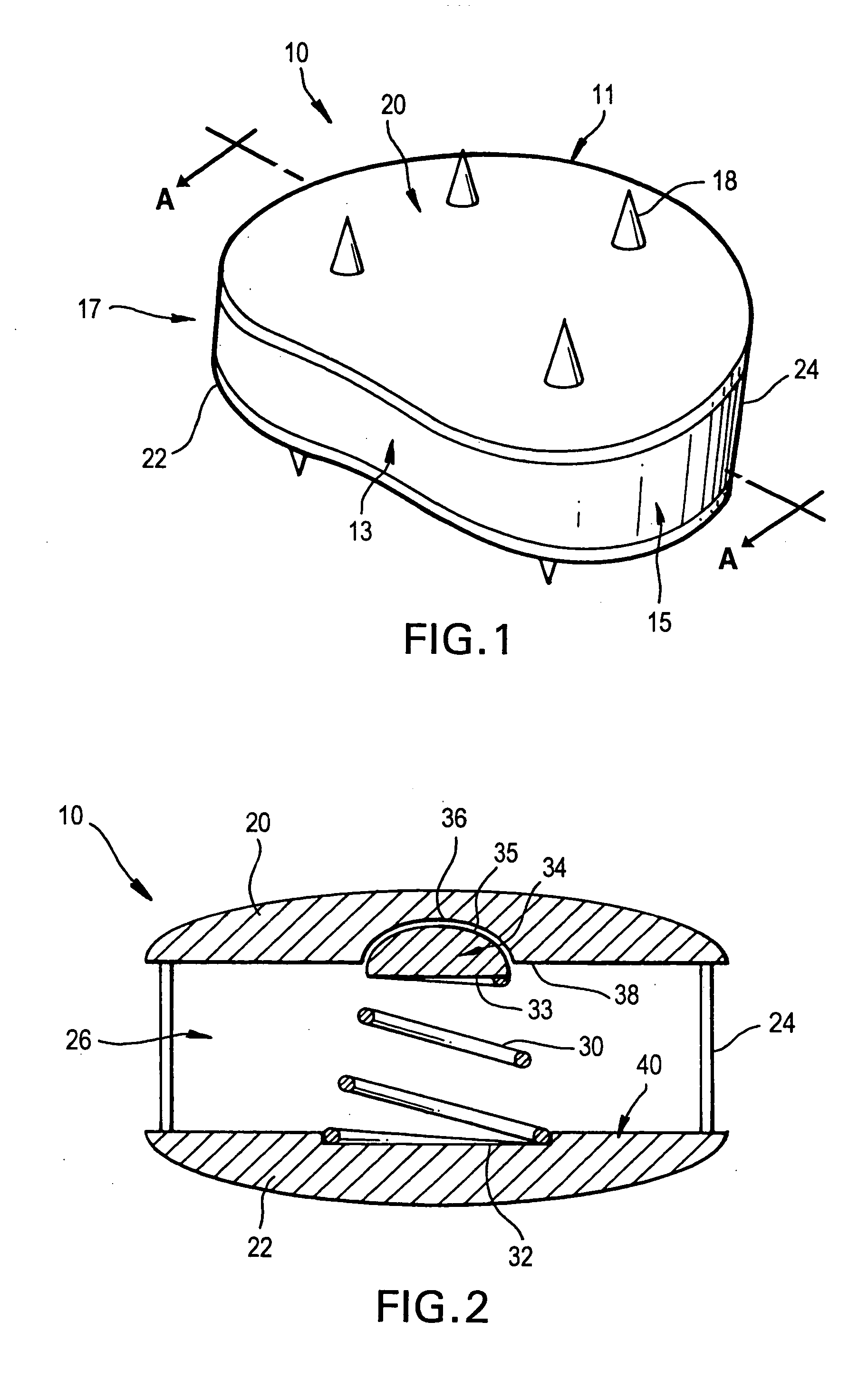
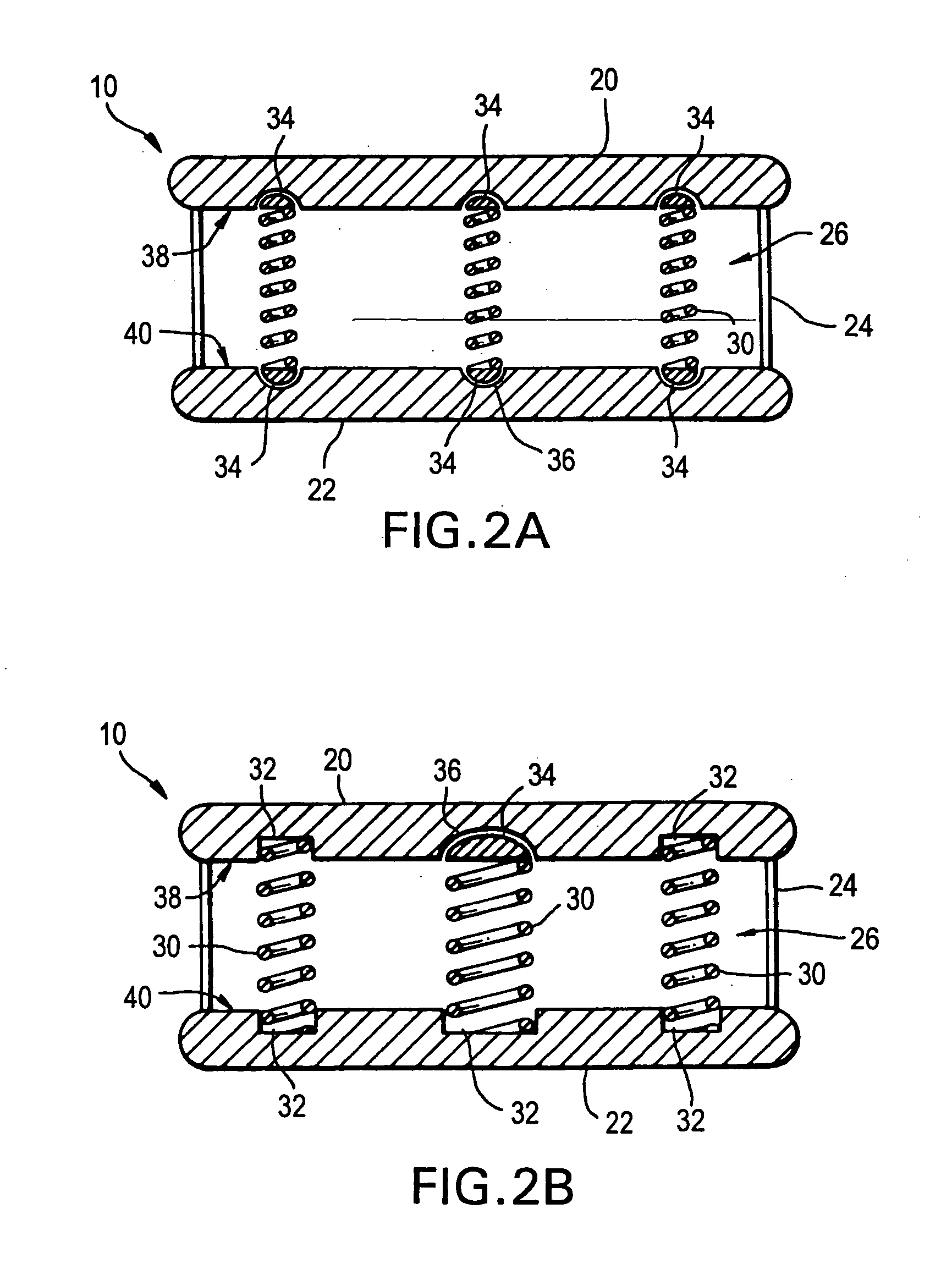
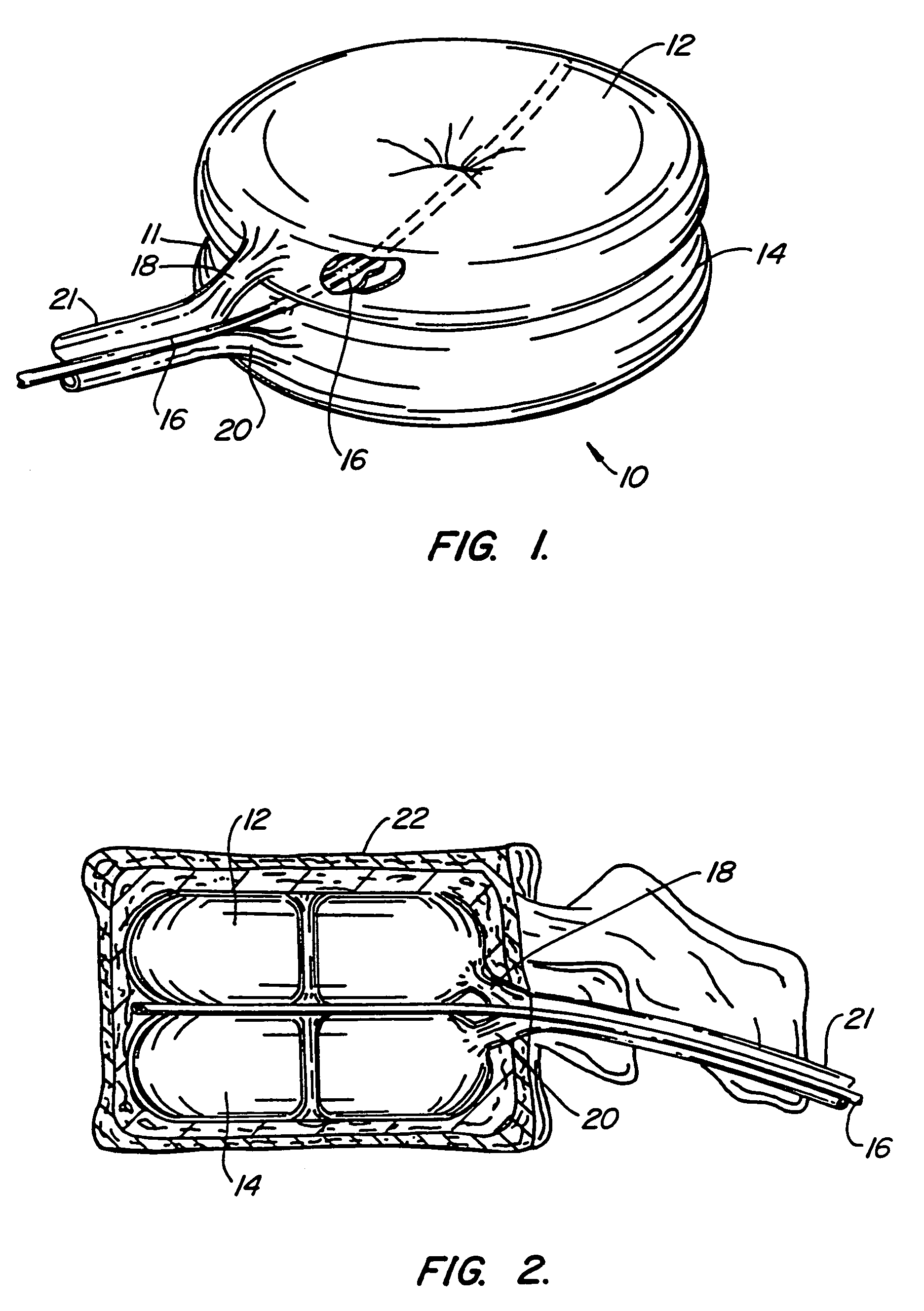
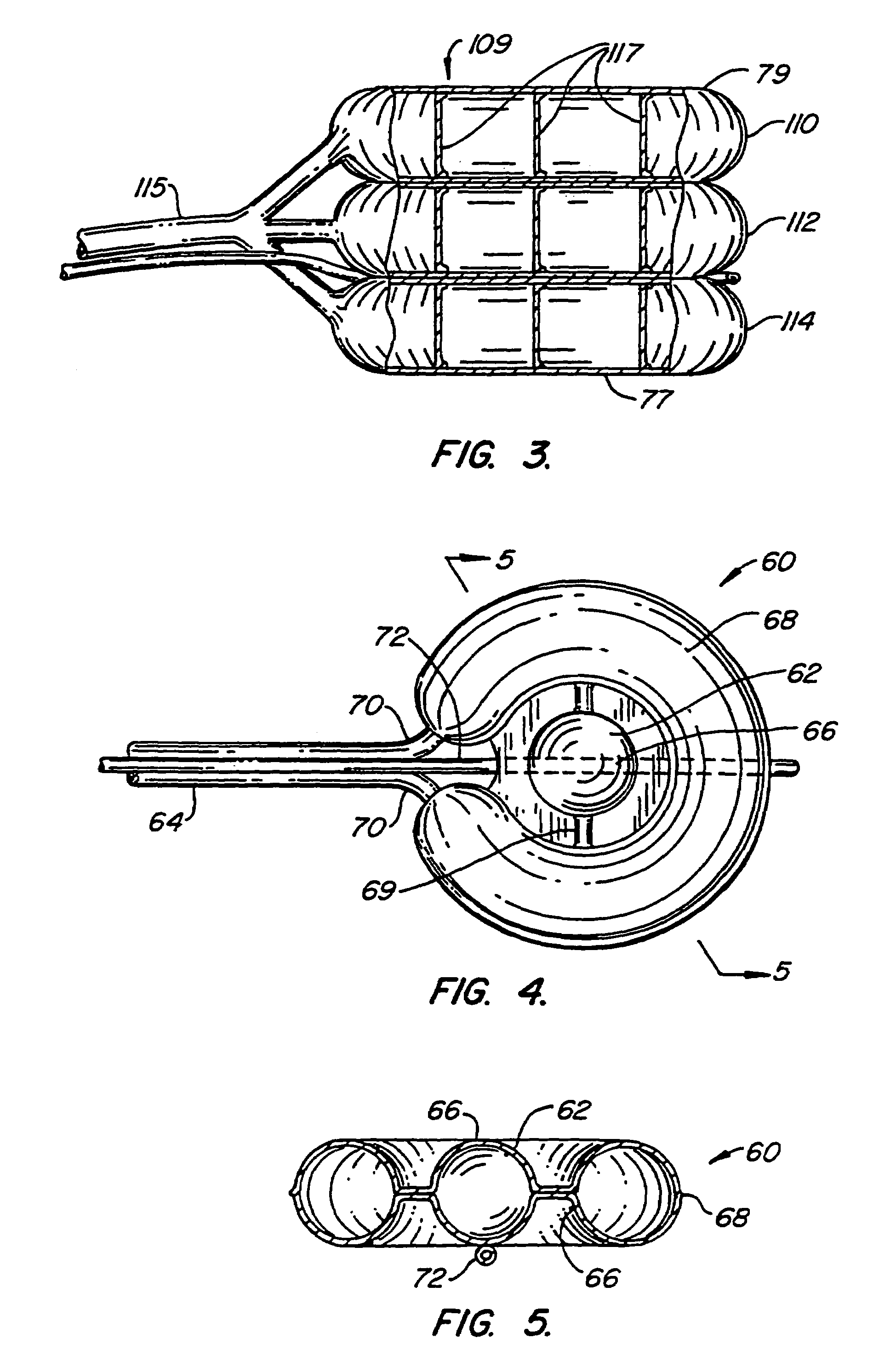
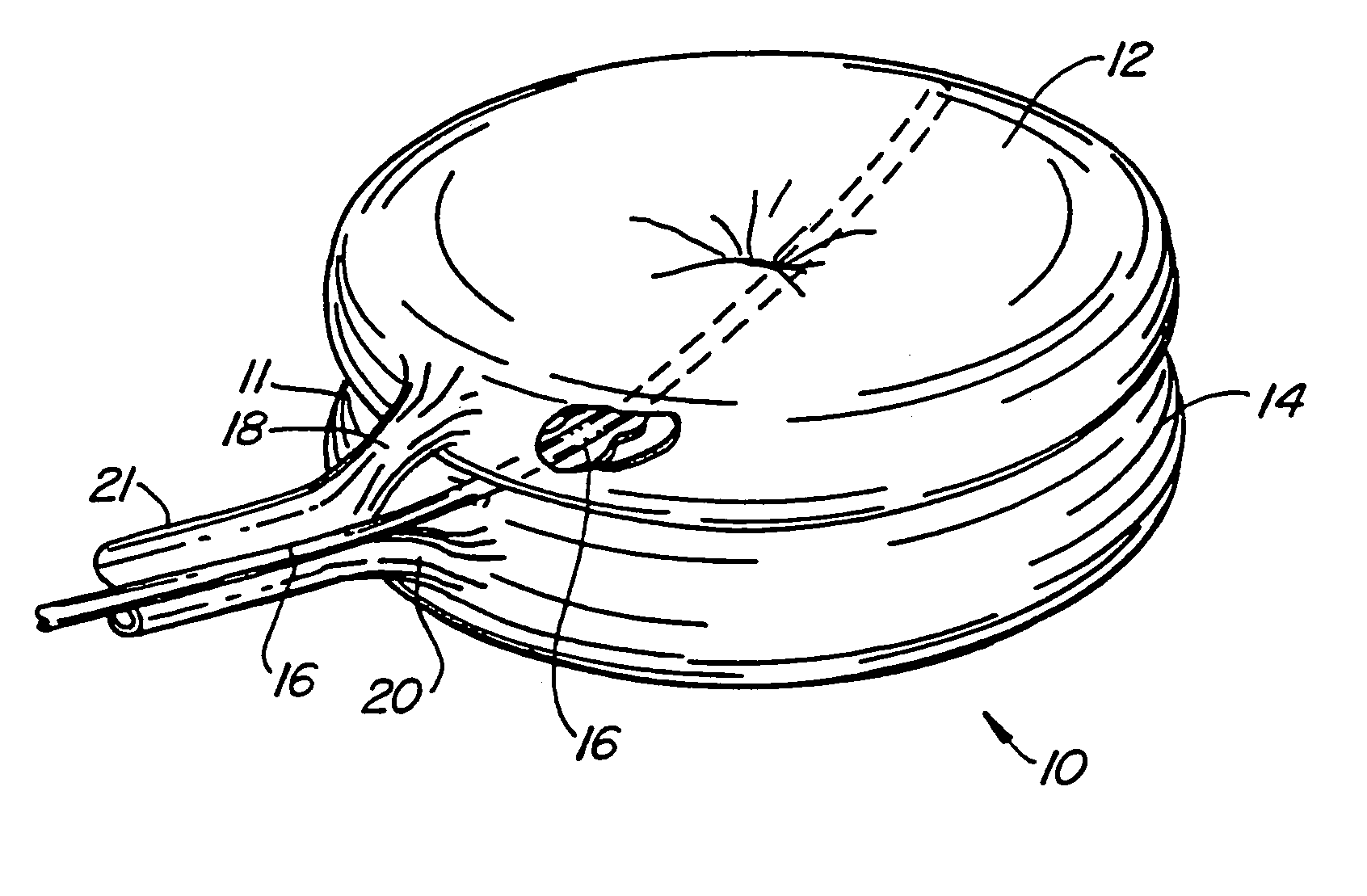
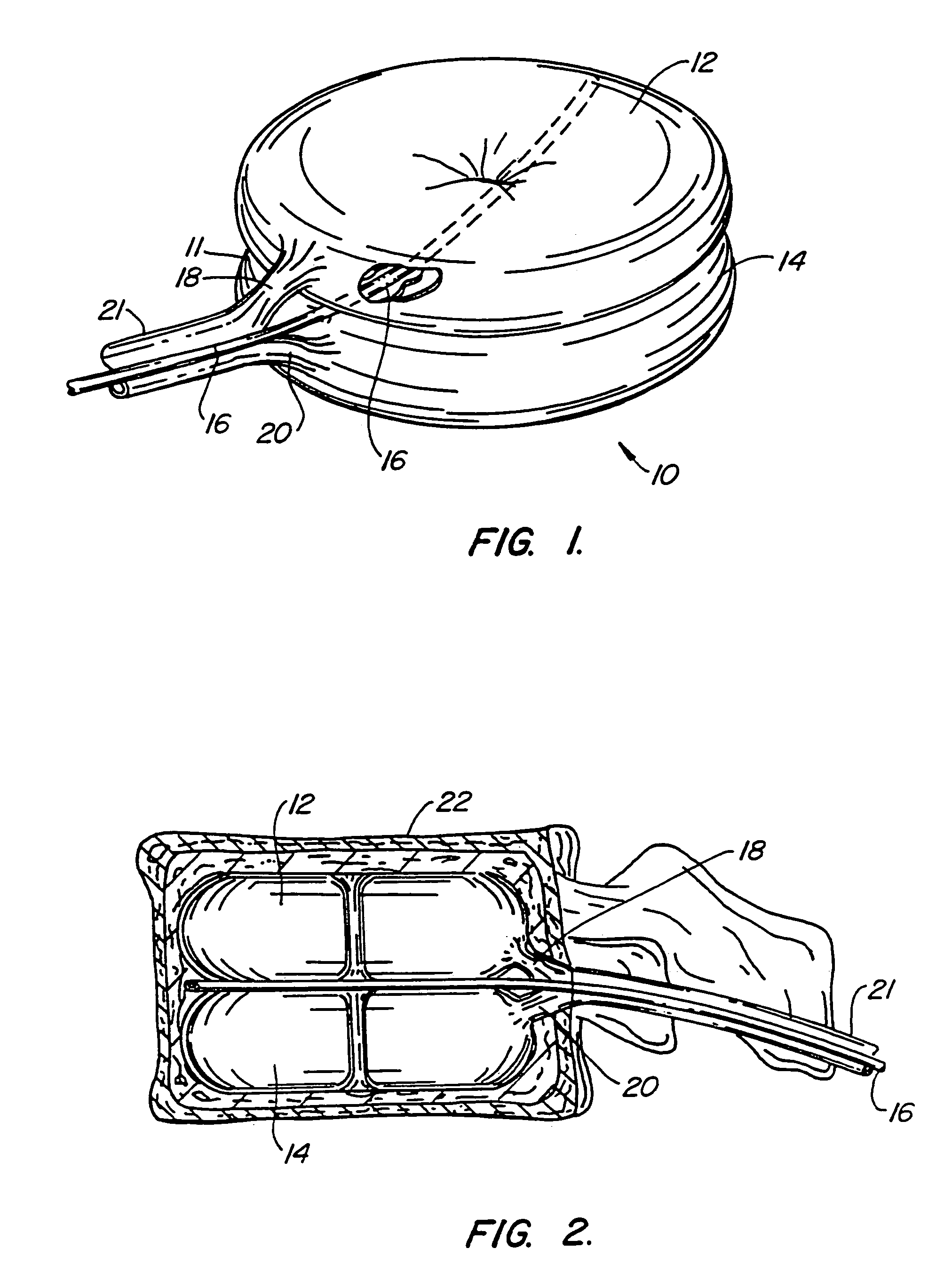
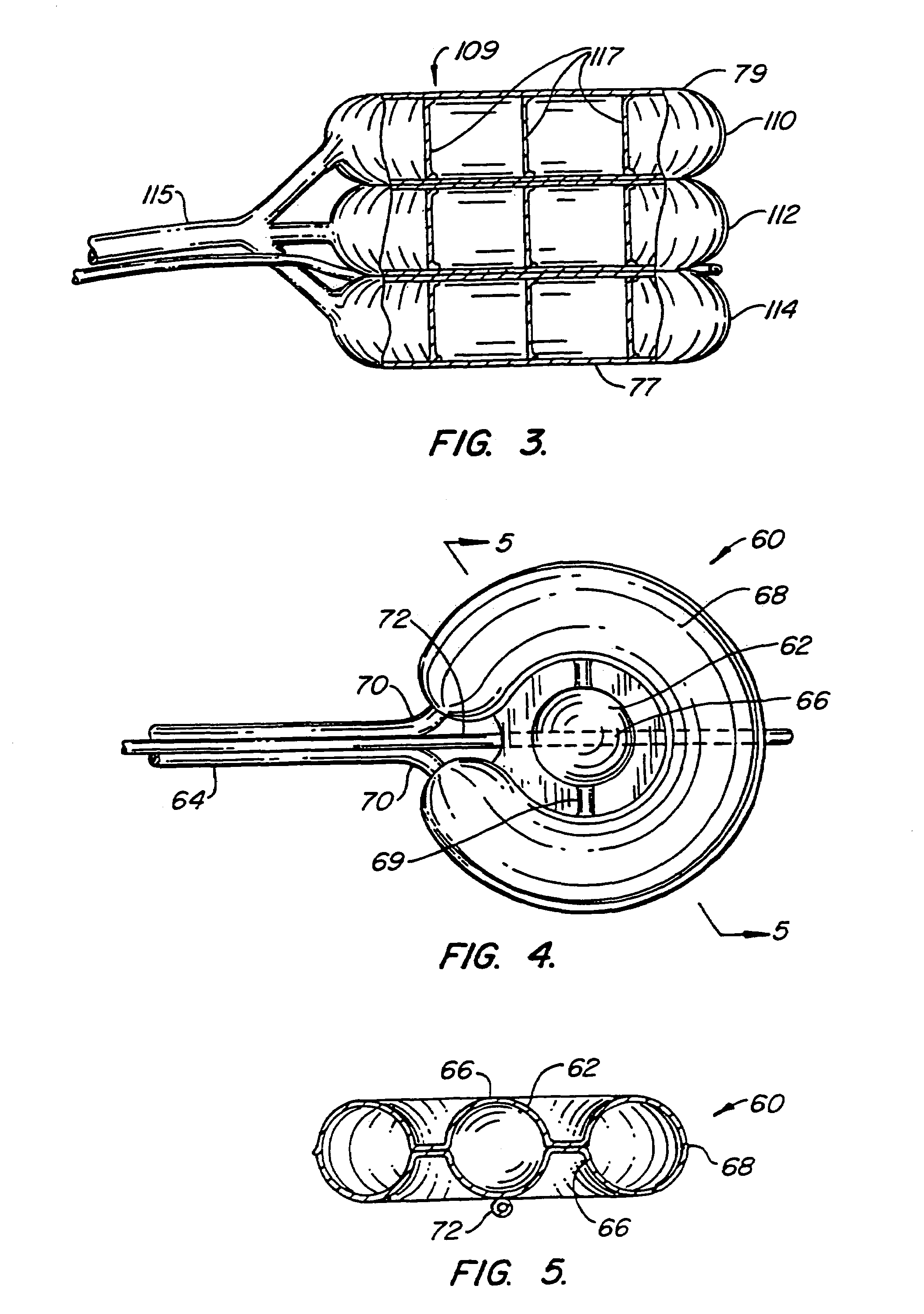
Osteogenic implants derived from bone
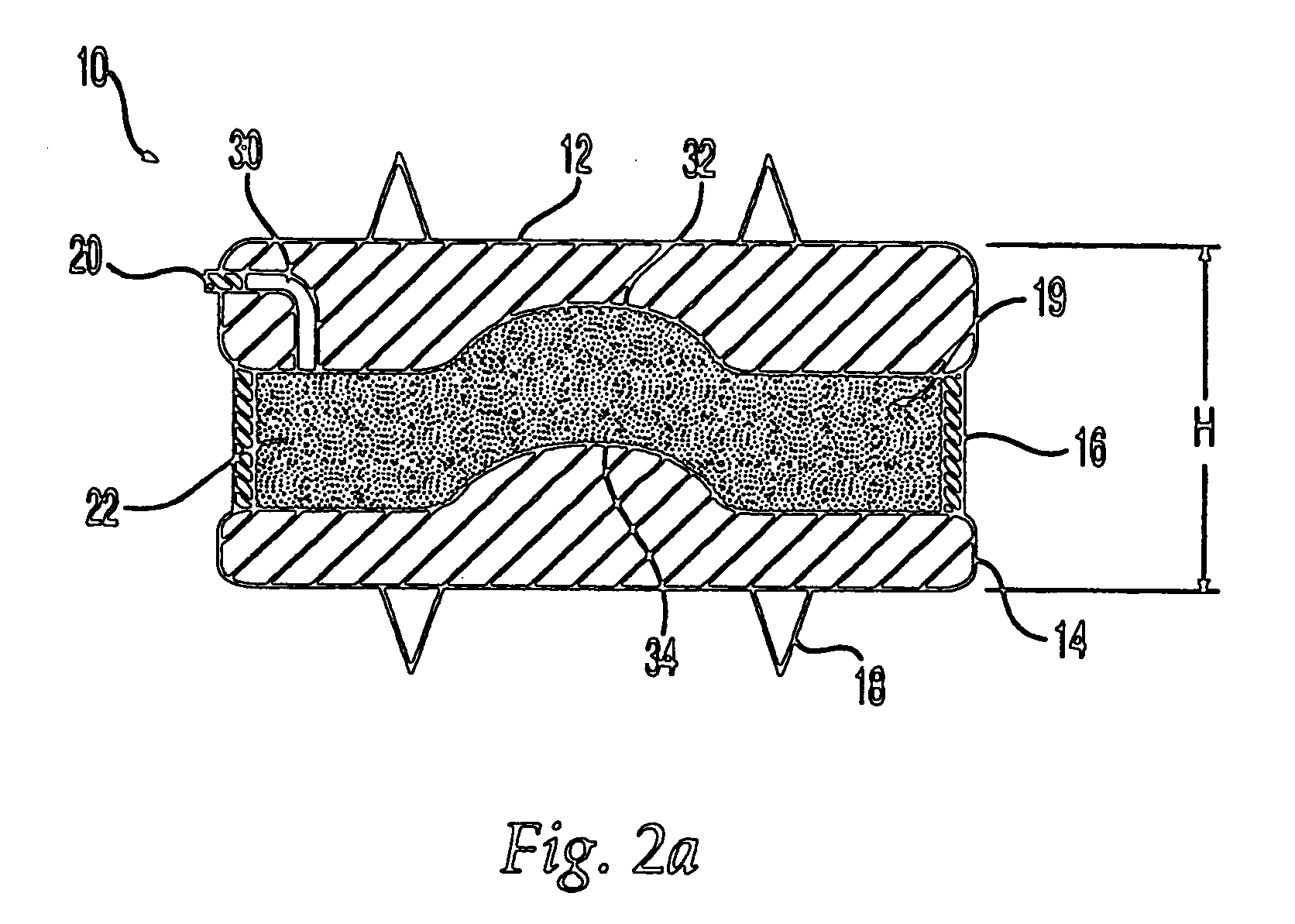
An osteogenic osteoimplant in the form of a flexible sheet comprising a coherent mass of bone-derived particles, the osteoimplant having a void volume not greater than about 32% and a method of making an osteogenic osteoimplant having not greater than about 32% void volume, the method comprising: providing a coherent mass of bone-derived particles; and, mechanically shaping the coherent mass of bone-derived particles to form an osteogenic osteoimplant in the form of a flexible sheet.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Cartilage repair implant with soft bearing surface and flexible anchoring device
InactiveUS9050192B2Strong and more permanent fixationSoft and bendableJoint implantsHip jointsCartilage repairSurgical implant
A surgical implant for replacing hyaline cartilage in a knee or other articulating synovial joint has an anchoring side on one side of the implant adapted for fixing the implant to one of the bones in the joint, and a bearing surface on the opposite side of the implant for lubricious rubbing and sliding contact with another bone in the joint. The anchoring side can be configured with an irregular surface for tissue ingrowth. The bearing side can include hydrogel. The implant can be rolled up from an original shape and surgically inserted by arthroscopic means, and opens into its original shape when released inside the joint.
Owner:FORMAE
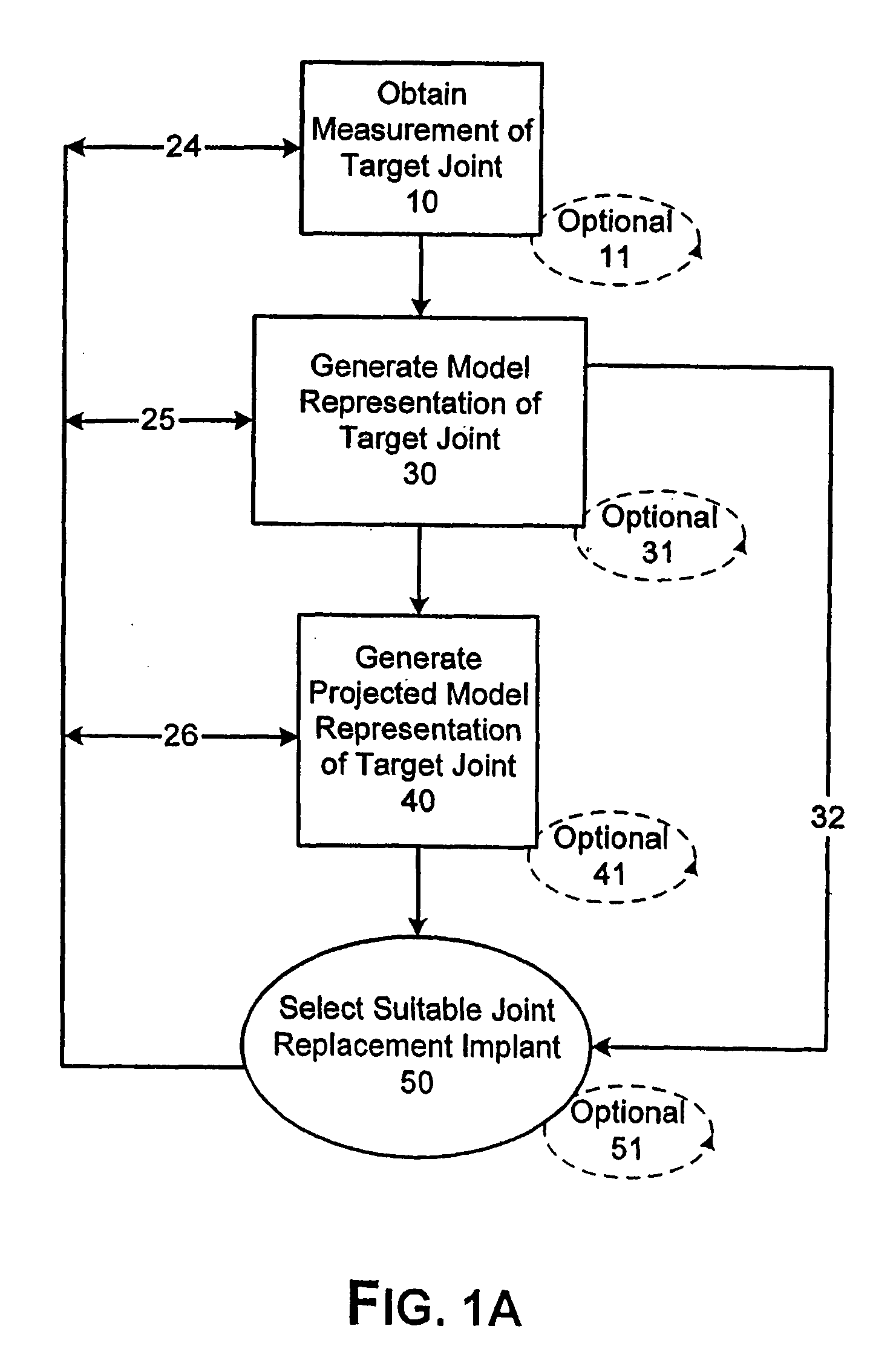
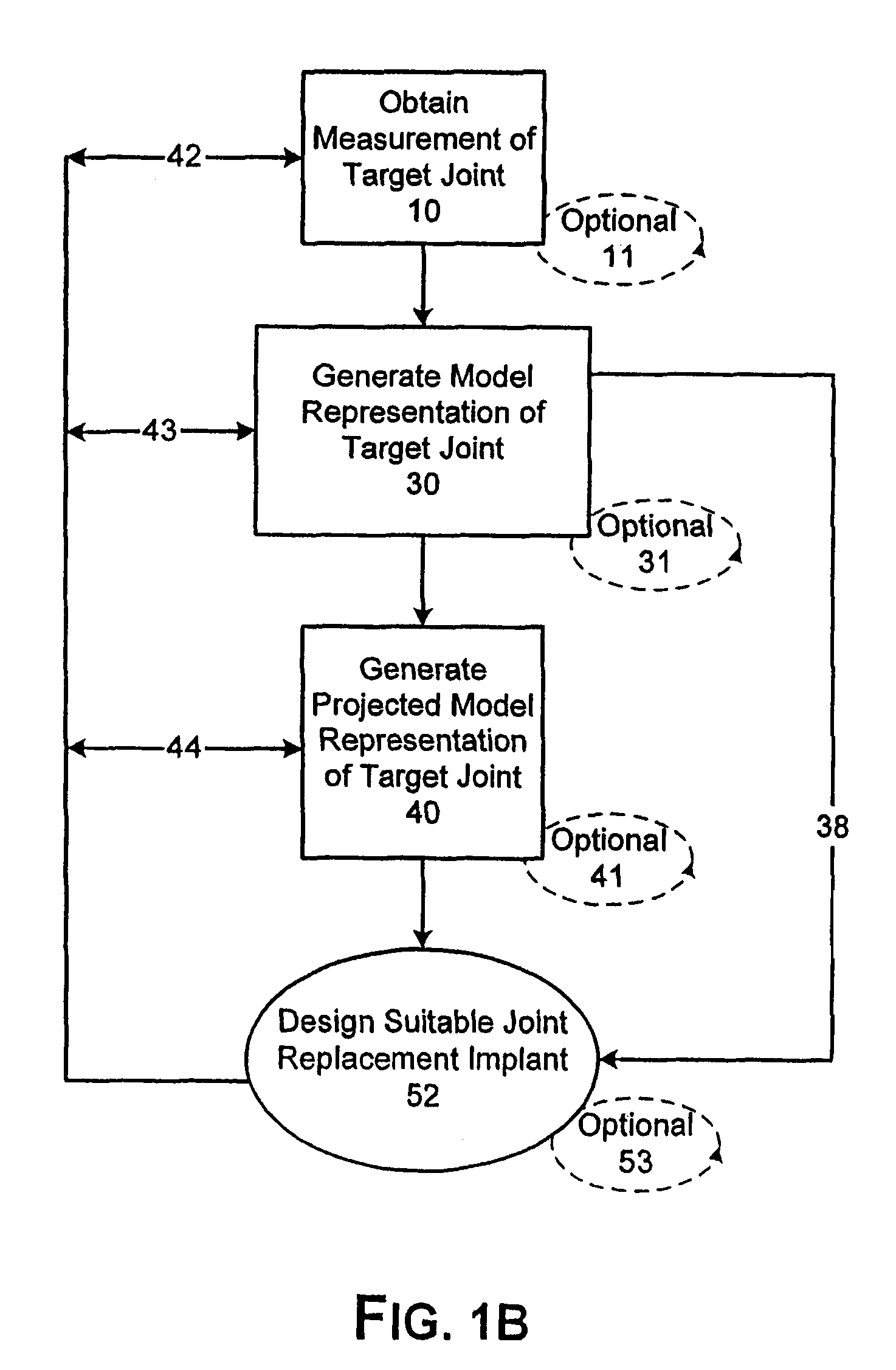
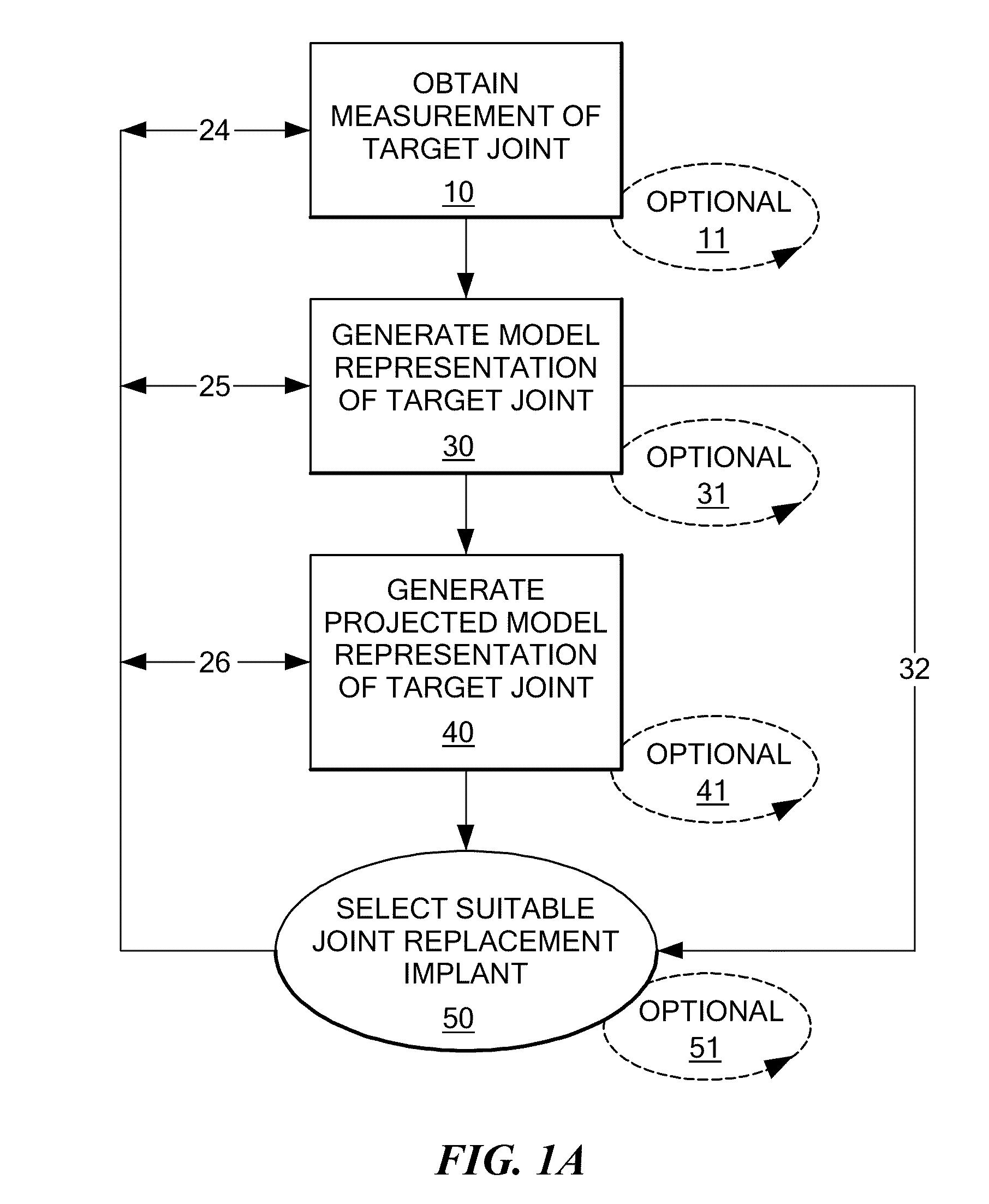
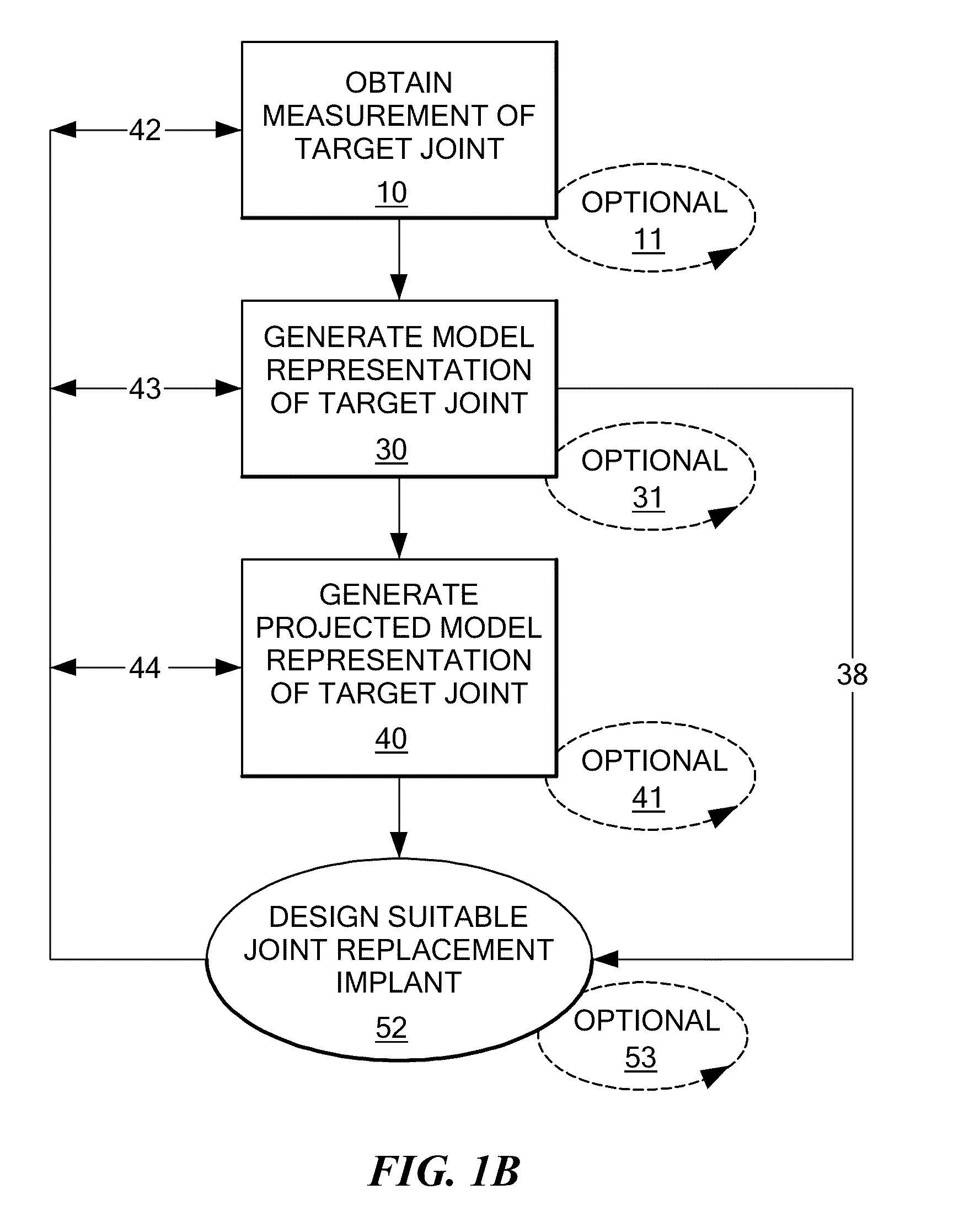
System and method of designing and manufacturing customized instrumentation for accurate implantation of prosthesis by utilizing computed tomography data
ActiveUS20050148843A1Quickly and accurately attachesPrecise positioningPerson identificationJoint implantsMedicineControl data
A method and system may be used to design and control the manufacture of a surgical guide for implanting a prosthetic component. The system includes a bone surface image generator, a surgical guide image generator, and a surgical guide image converter. The bone surface image generator receives three dimensional bone anatomical data for a patient's bone and generates a bone surface image. The surgical guide image generator generates a surgical guide image from the bone surface image and an image of a prosthesis imposed on the bone surface image. The supporting structure of the generated surgical guide image conforms to the surface features of the three dimensional bone surface image. The surgical guide image is converted by surgical guide image converter into control data for operating a machine to form a surgical guide that corresponds to the surgical guide image.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Implants for replacing cartilage, with negatively-charged hydrogel surfaces and flexible matrix reinforcement
ActiveUS9314339B2Strong and durableStrong and secure anchoringFinger jointsWrist jointsFiberChemical agent
A permanent non-resorbable implant allows surgical replacement of cartilage in articulating joints, using a hydrogel material (such as a synthetic polyacrylonitrile polymer) reinforced by a flexible fibrous matrix. Articulating hydrogel surface(s) are chemically treated to provide a negative electrical charge that emulates the negative charge of natural cartilage, and also can be treated with halogenating, cross-linking, or other chemical agents for greater strength. For meniscal-type implants, the reinforcing matrix can extend out from the peripheral rim of the hydrogel, to allow secure anchoring to soft tissue such as a joint capsule. For bone-anchored implants, a porous anchoring layer enables tissue ingrowth, and a non-planer perforated layer can provide a supportive interface between the hard anchoring material and the softer hydrogel material.
Owner:FORMAE
Intervertebral disc prosthesis
InactiveUS7001431B2Improved polymer cureImproved implant characteristicInternal osteosythesisAnkle jointsIntervertebral discPolymer
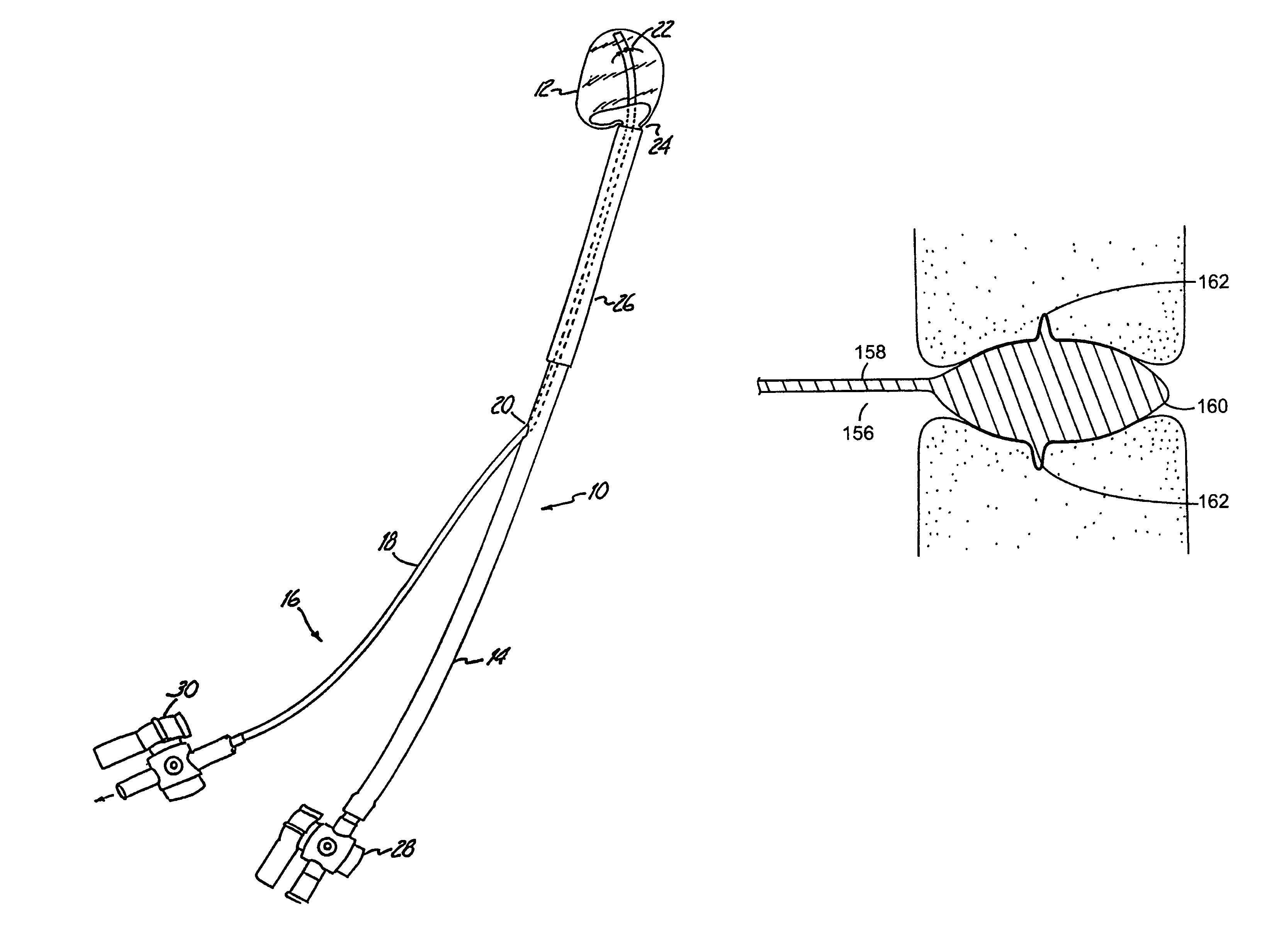
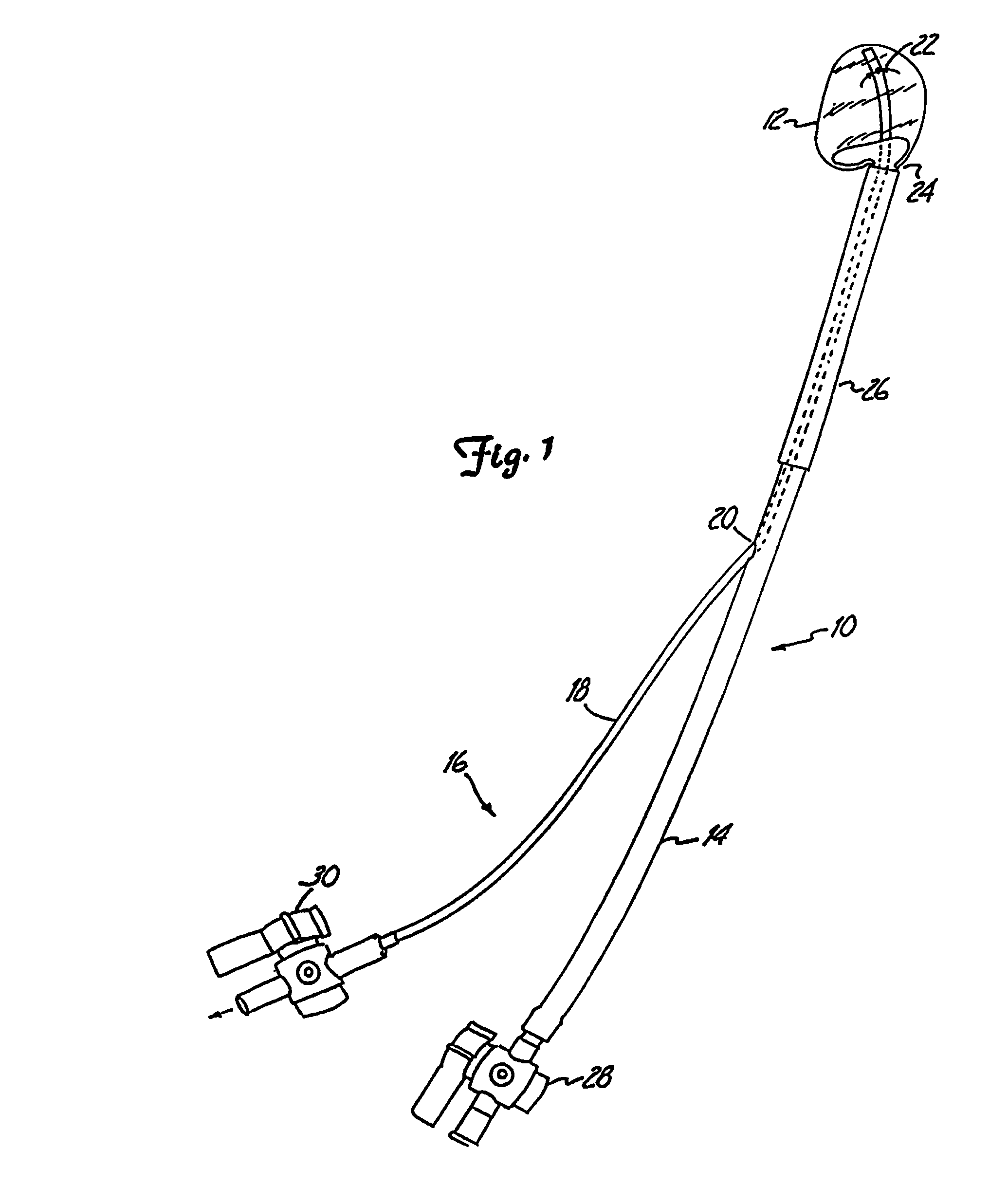
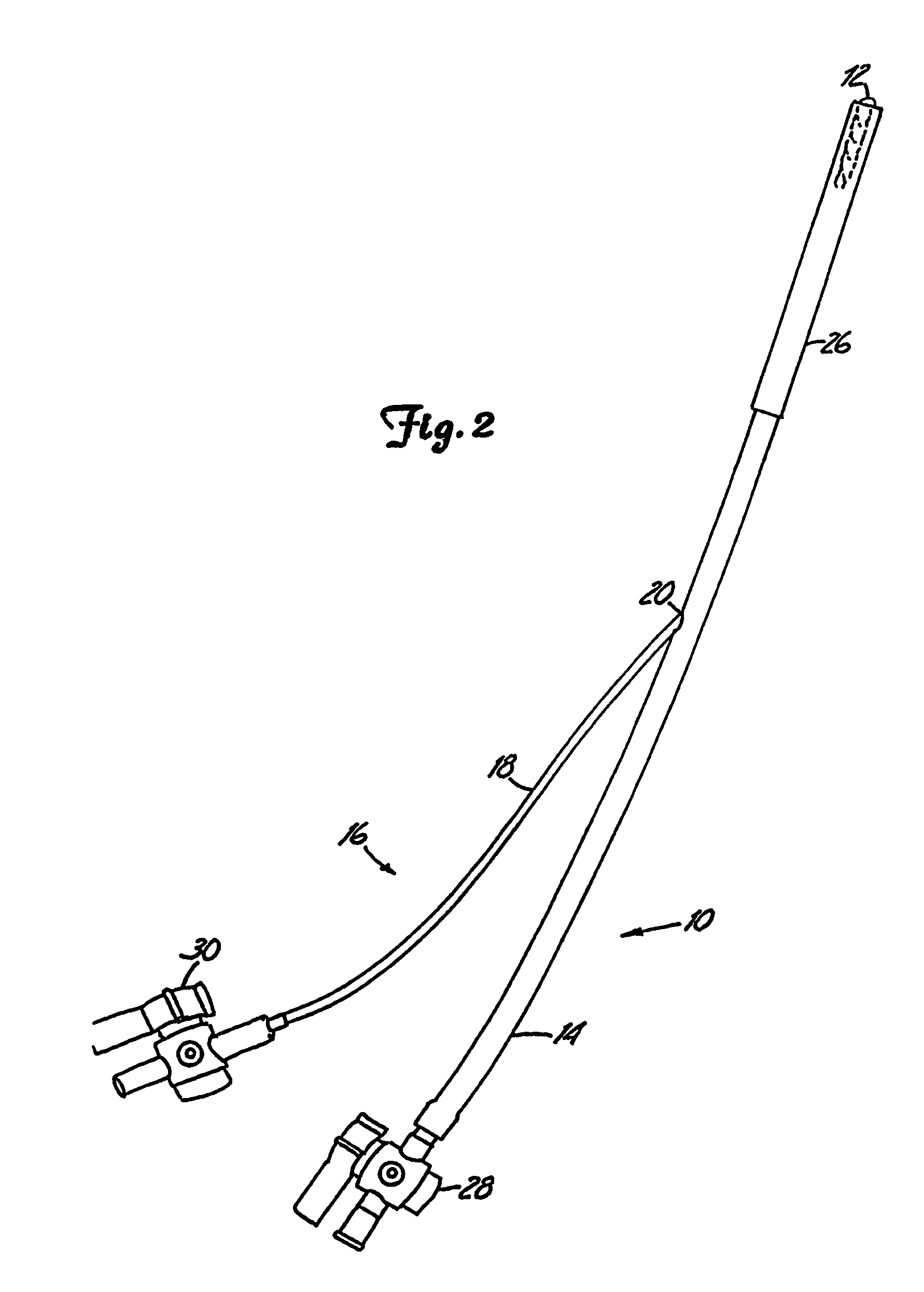
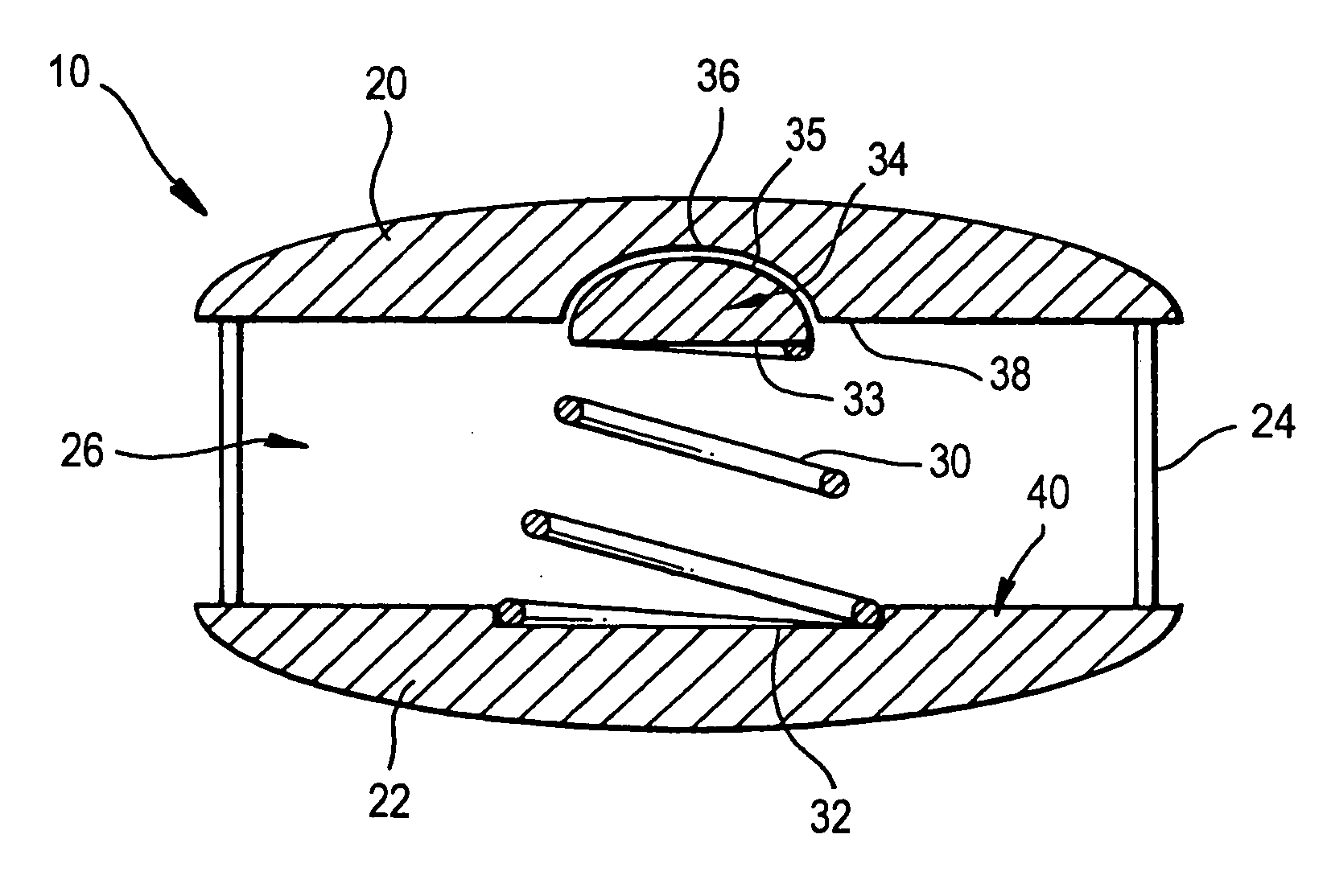
A system for repairing an intervertebral disc by delivering and curing a biomaterial in situ within the disc. The system includes both a device, having an insertable balloon and related lumen, controls and adapters, as well as an in situ curable biomaterial (and related biomaterial delivery means). The system can allow the doctor to determine a suitable endpoint for biomaterial delivery, by controlling distraction and / or biomaterial delivery pressure, and in turn, to deliver a desired quantity of biomaterial to the balloon in order to achieve improved polymer cure and implant characteristics. Also provided is a related method for repairing an intervertebral disc by using such a system to deliver and cure the biomaterial in situ. The system can be used to implant a prosthetic total disc, or a prosthetic disc nucleus in a manner that leaves the surrounding disc tissue substantially intact.
Owner:DISC DYNAMICS
Controlled artificial intervertebral disc implant
ActiveUS20050251260A1Reduce the amount requiredProlong lifeBone implantJoint implantsMedicineAxial compression
The invention relates to an artificial intervertebral disc for placement between adjacent vertebrae. The artificial intervertebral disc is preferably designed to restore disc height and natural disc curvature, allow for a natural range of motion, absorb shock and provide resistance to motion and axial compression. Furthermore, the intervertebral disc may be used in the cervical, the thoracic, or the lumbar regions of the spine. The artificial intervertebral disc may include either singularly or in combination: an interior including at least one spring member preferably incorporating a arcuate surface member, a flexible core, the flexible core preferably being a slotted core, a ring spring, a winged leaf spring, or a leaf spring, or The articulating member preferably being attached to one of the endplate by an intermediate shock absorbing element.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
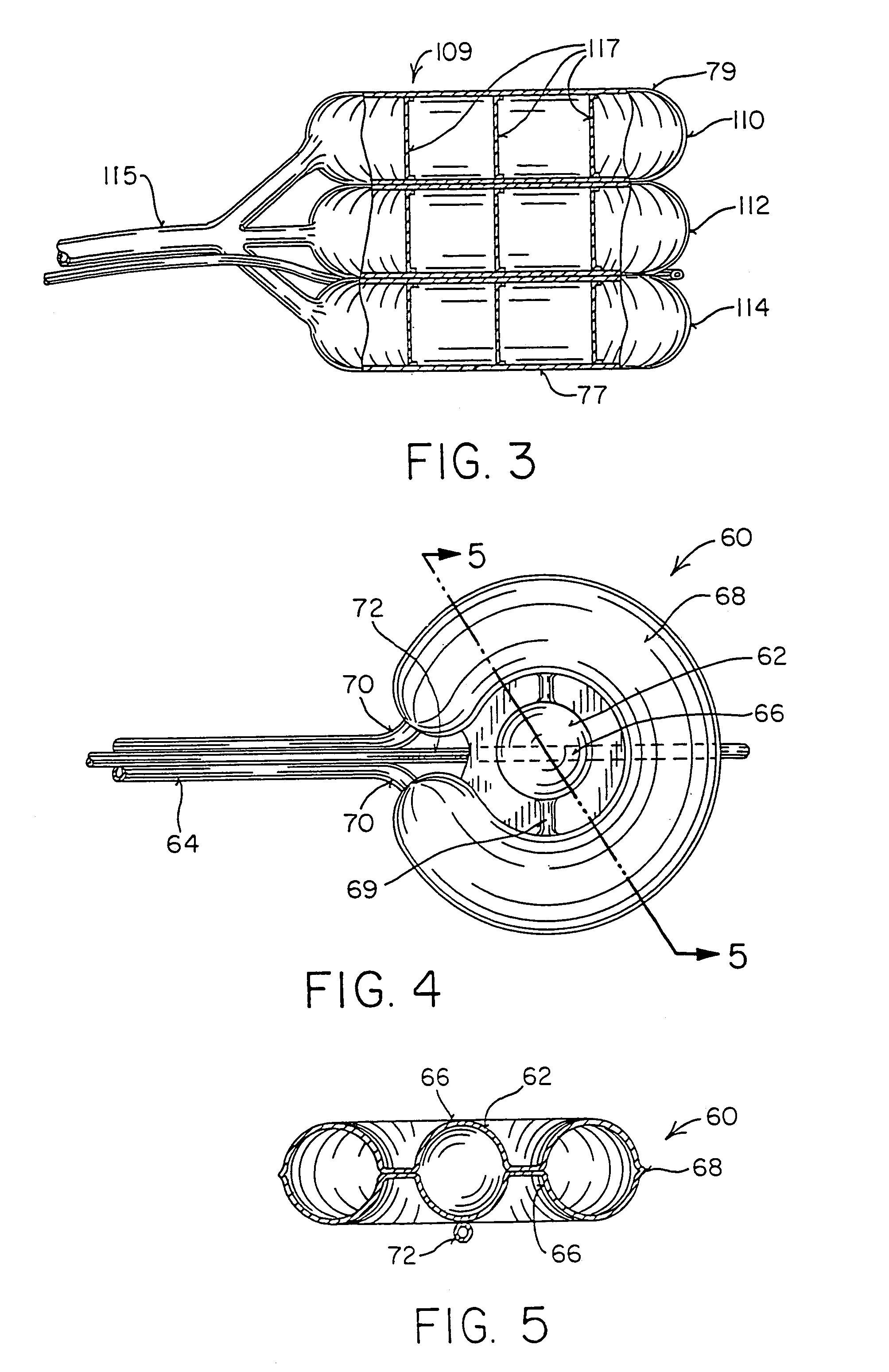
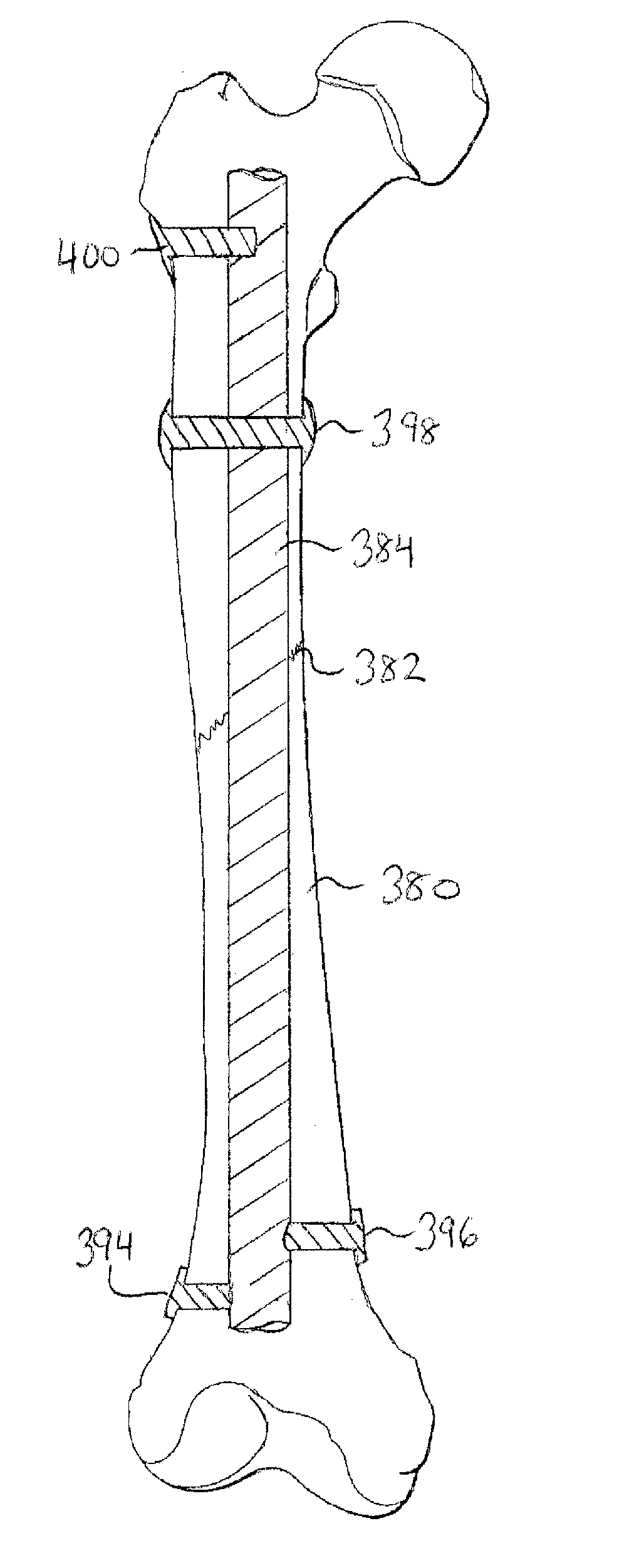
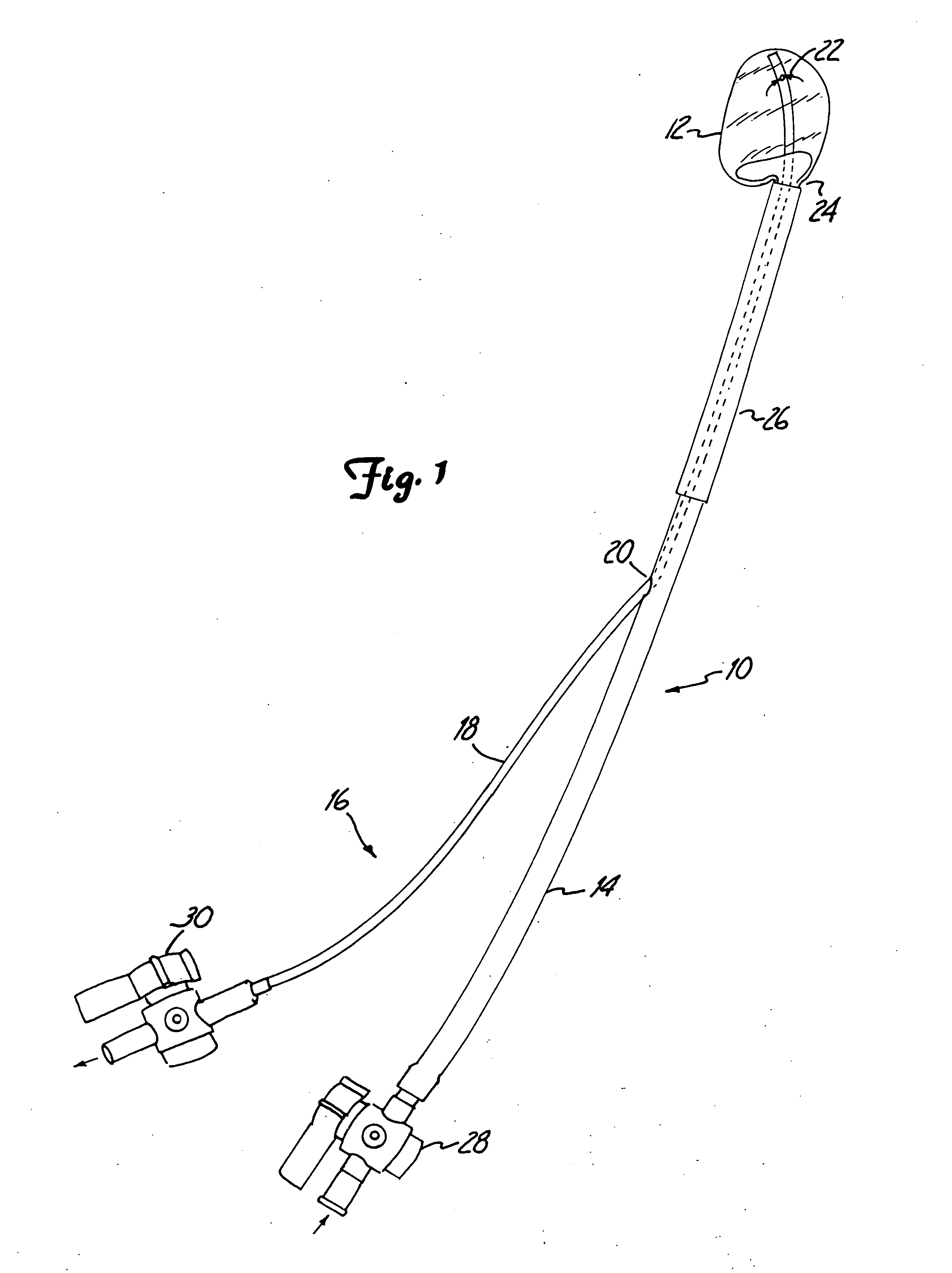
Inflatable device for use in surgical protocol relating to fixation of bone
InactiveUS6981981B2Improve clinical outcomesWorsen conditionSurgical furnitureInternal osteosythesisFilling materialsCancellous bone
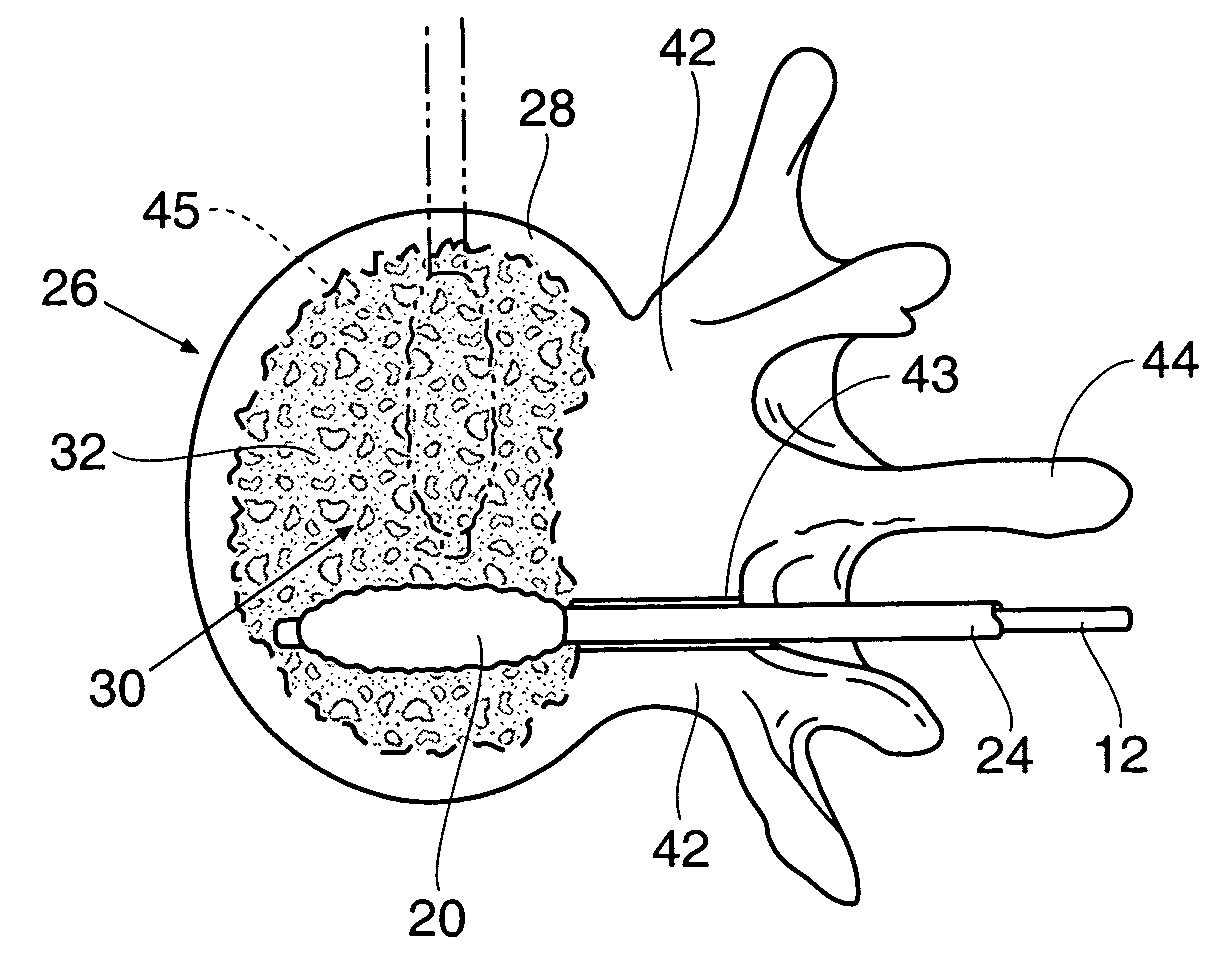
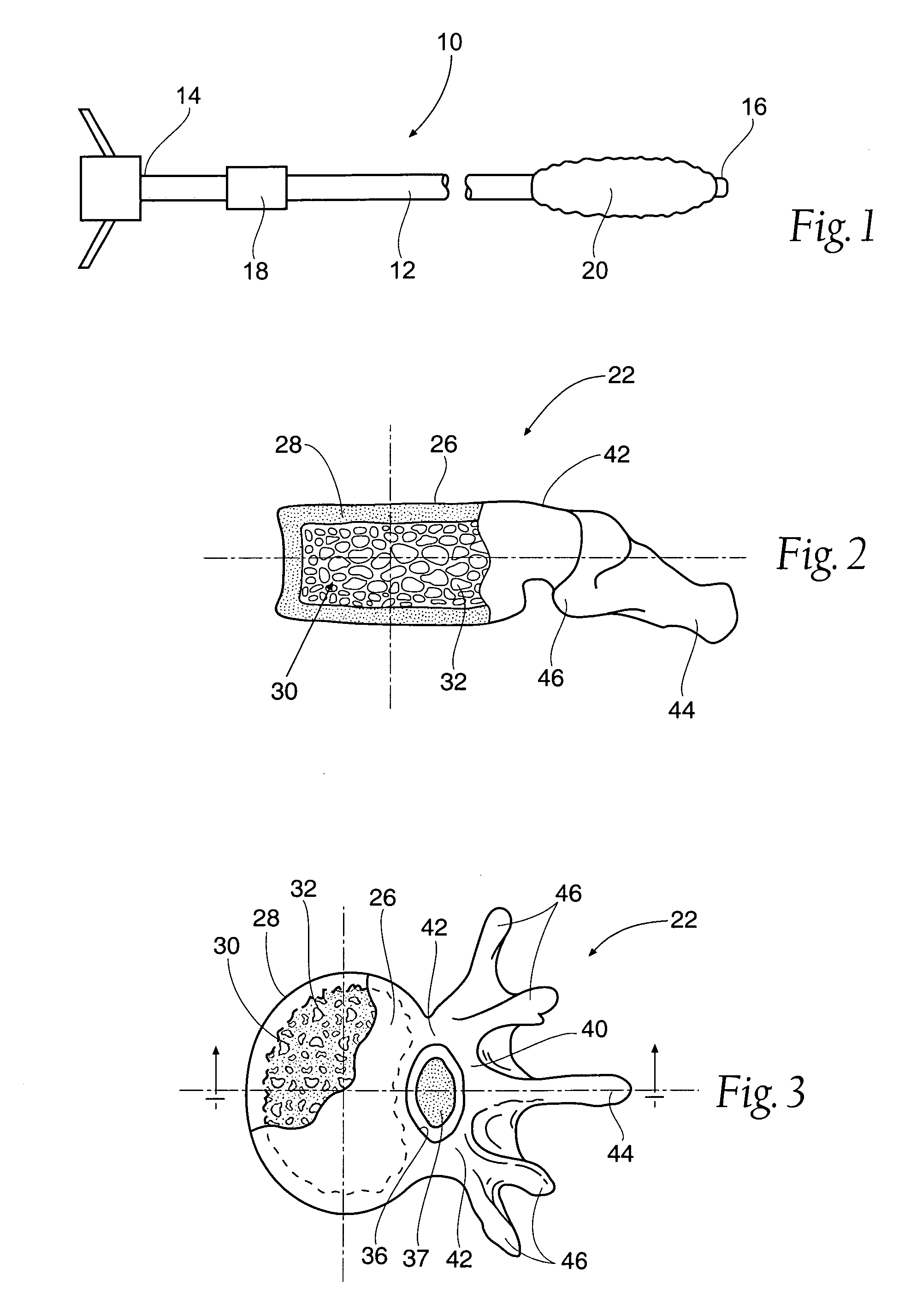
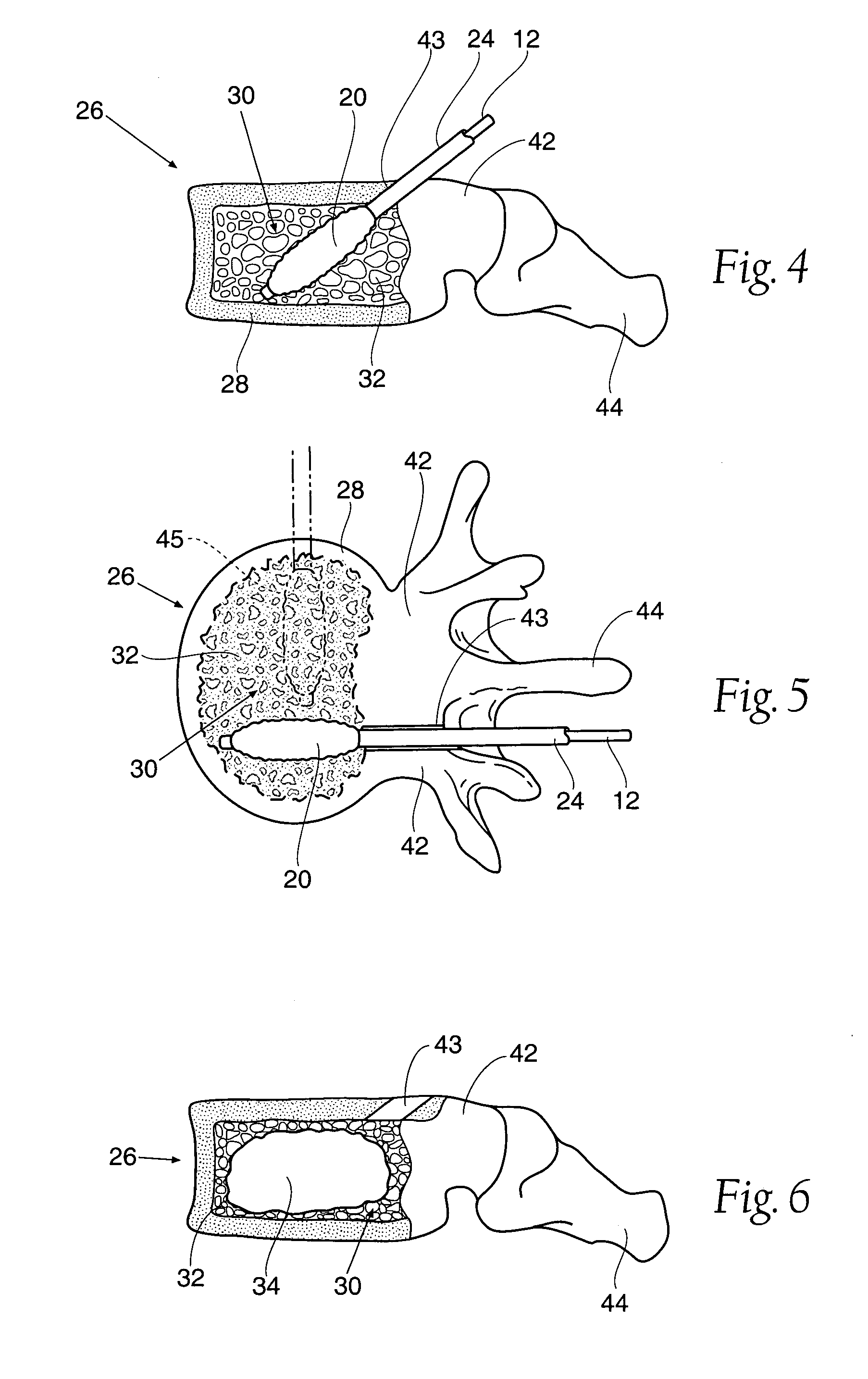
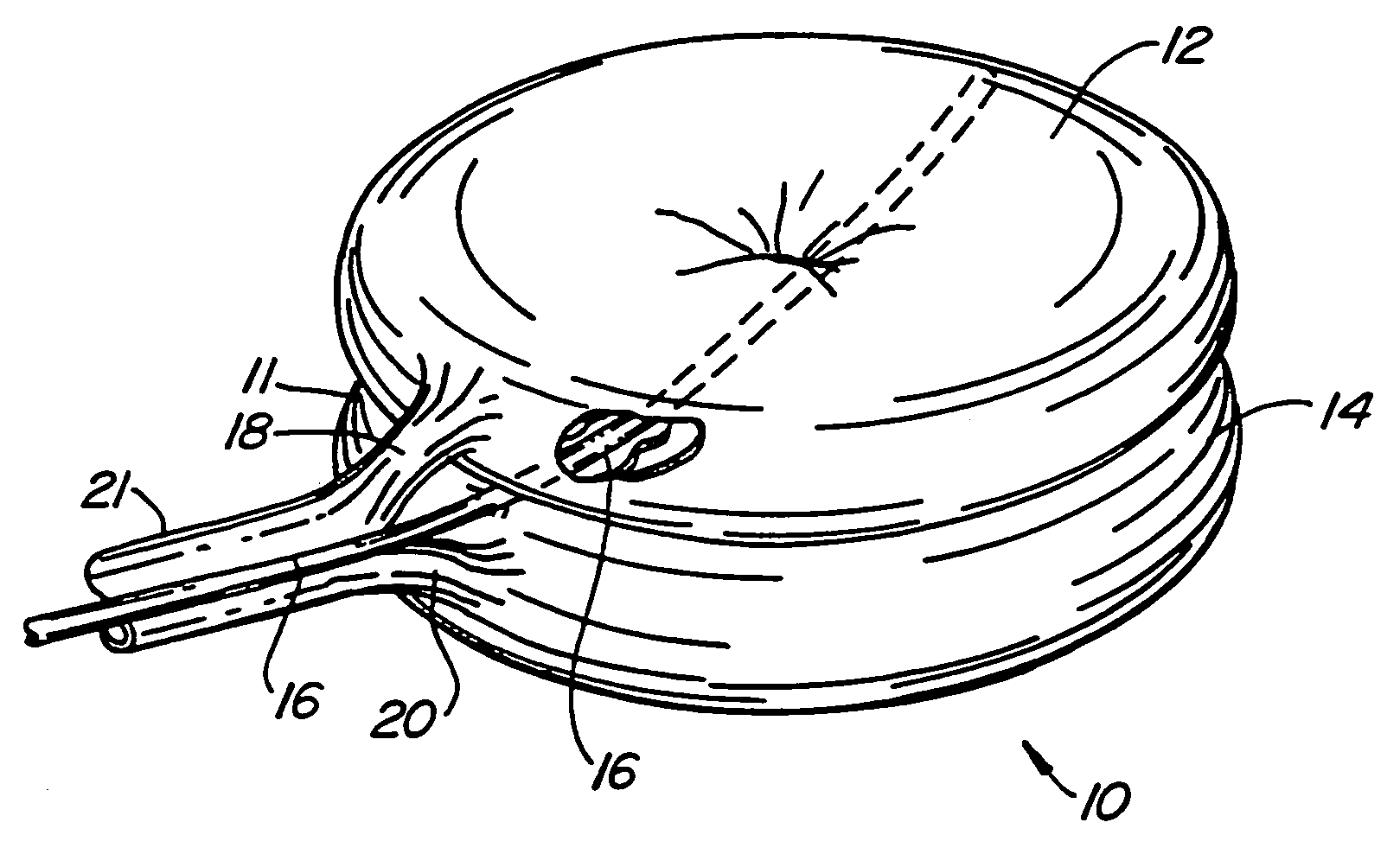
Systems for treating a bone, e.g. a vertebral body, having an interior volume occupied, at least in part, by cancellous bone provide a first tool, a second tool, and a third tool. The first tool establishes a percutaneous access path to bone. The second tool is sized and configured to be introduced through the percutaneous access path to form a void that occupies less than the interior volume. The third tool places within the void through the percutaneous access path a volume of filling material. Related methods for treating a bone, e.g. a vertebral body, having an interior volume occupied, at least in part, by cancellous bone provide establishing a percutaneous access path to bone. A tool is introduced through the percutaneous access path and manipulated to form a void that occupies less than the interior volume. A volume of filling material is then placed within the void through the percutaneous access path.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
Systems and methods for treating fractured or diseased bone using expandable bodies
Systems and methods treat fractured or diseased bone by deploying more than a single therapeutic tool into the bone. In one arrangement, the systems and methods deploy an expandable body in association with a bone cement nozzle into the bone, such that both occupy the bone interior at the same time. In another arrangement, the systems and methods deploy multiple expandable bodies, which occupy the bone interior volume simultaneously. Expansion of the bodies form cavity or cavities in cancellous bone in the interior bone volume.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
Implant Device and Method for Manufacture
A knee implant includes a femoral component having first and second femoral component surfaces. The first femoral component surface is for securing to a surgically prepared compartment of a distal end of a femur. The second femoral component surface is configured to replicate the femoral condyle. The knee implant further includes a tibial component having first and second tibial component surfaces. The first tibial component surface is for contacting a proximal surface of the tibia that is substantially uncut subchondral bone. At least a portion of the first tibial component surface is a mirror image of the proximal tibial surface. The second tibial component surface articulates with the second femoral component surface.
Owner:CONFORMIS
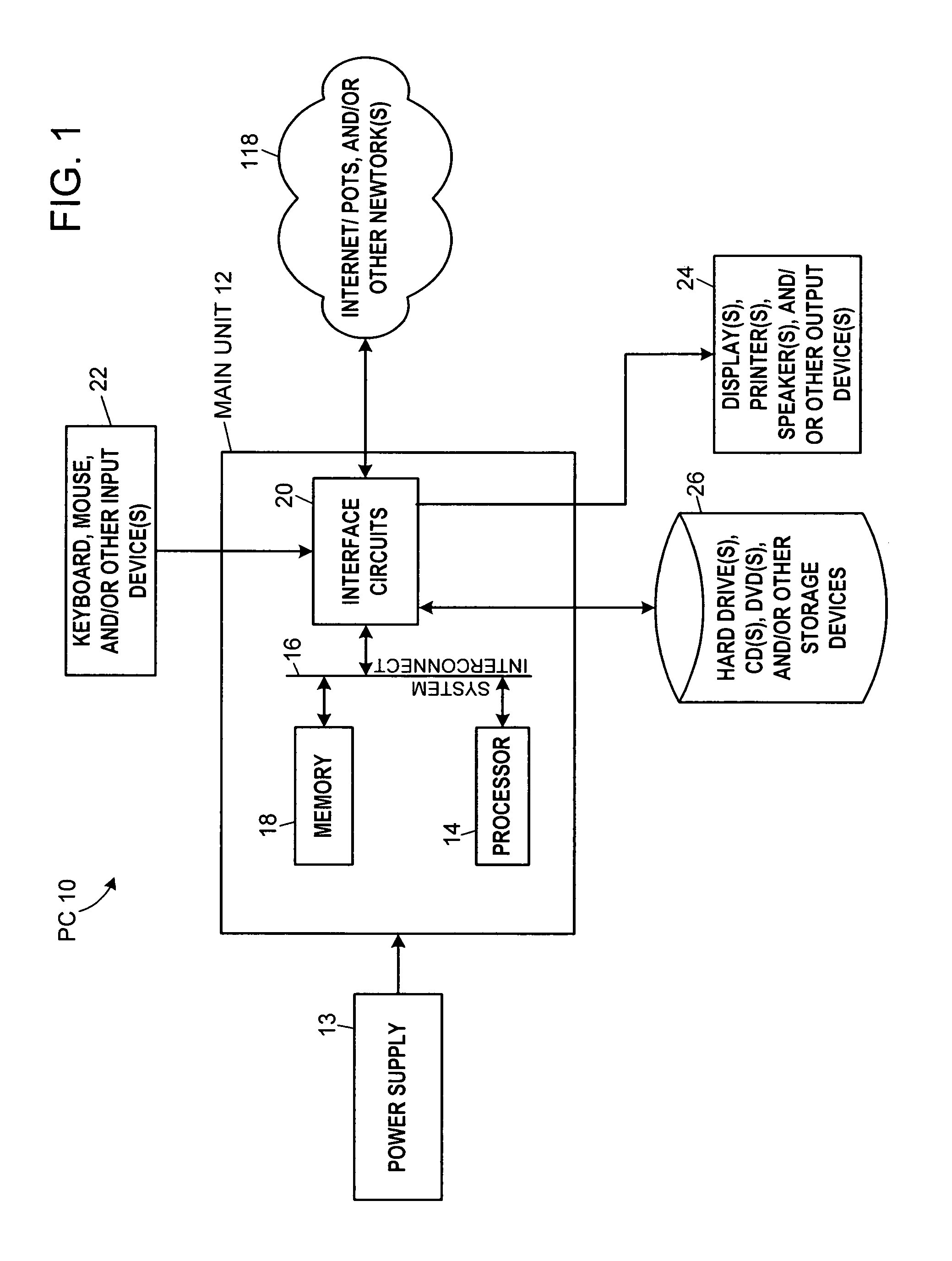
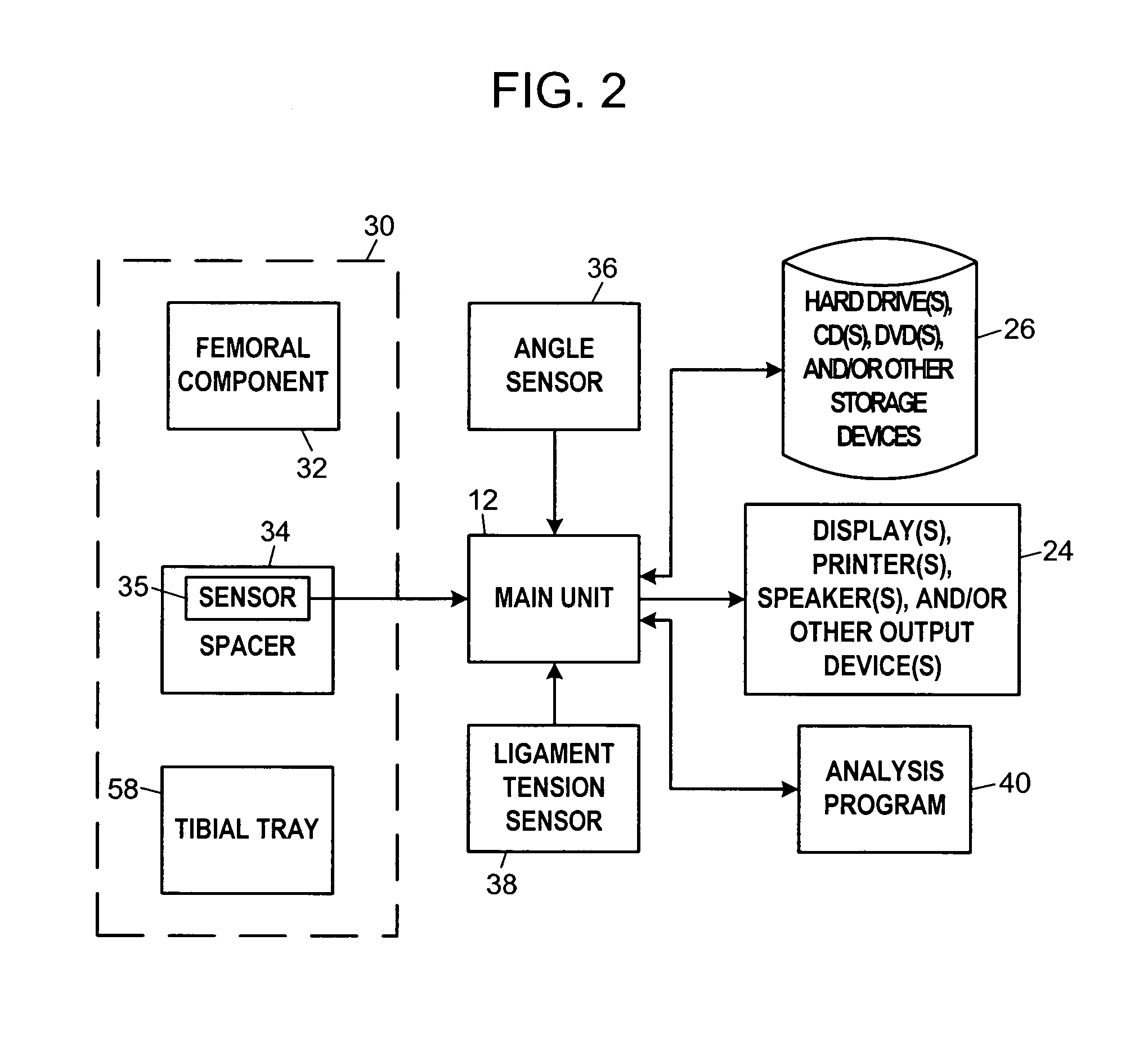
System and method for prosthetic fitting and balancing in joints
InactiveUS7575602B2Physical therapies and activitiesFinger jointsProsthesis fittingArtificial joints
A system and method for prosthesis fitting in joints comprising an artificial condyle and a spacer which cooperates with the condyle to form an artificial joint. The spacer embedded with at least one sensor which is responsive to a force generated between the condyle and the spacer. The artificial joint is adapted to move between a flexed position and an extended position defining a range of motion. The sensor is responsive to the force and generates an output representative of that force. The output is transmitted, either wirelessly or other, to a processor which utilizes an analysis program to display a representation of the forces applied. A practitioner utilizing the displayed analysis may intraoperatively determine the adjustments and balancing required within the artificial joint. The system may also utilize a ligament tension sensor which generates data representative of tension on a ligament of the artificial joint, and a joint angle sensor responsive to the range of motion of the artificial joint. The processor may be adapted to store the outputted sensor data to provide the practitioner with statistically relevant historical data.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Intervertebral disc implant
ActiveUS20050197702A1Reduce the amount requiredProlong lifeBone implantLigamentsCircular discAxial compression
The invention relates to an artificial intervertebral disc for placement between adjacent vertebrae. The artificial intervertebral disc is preferably designed to restore disc height and lordosis, allow for a natural range of motion, absorb shock and provide resistance to motion and axial compression. Furthermore, the intervertebral disc may be used in the cervical, the thoracic, or the lumber regions of the spine. The artificial intervertebral disc may include either singularly or in combination: an interior at least partially filled with a fluid; a valve for injecting fluid into the interior of the disk; a central region having a stiffness that is preferably greater than the stiffness of the outer regions thus enabling the disc to pivot about the central region. The central pivot may be formed by a center opening, a central chamber, an inner core or a central cable.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
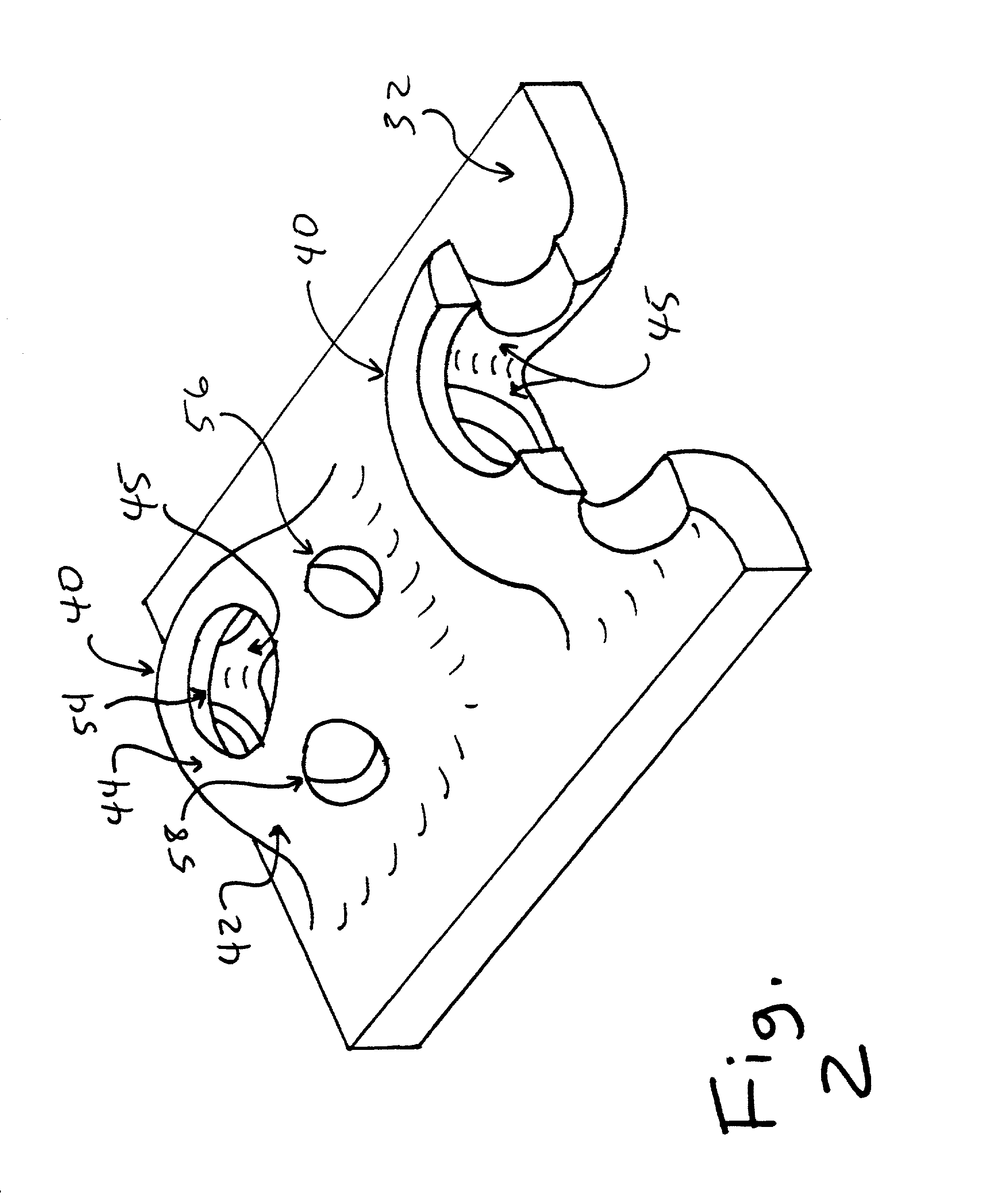
Prosthetic hip joint having sintered polycrystalline diamond compact articulation surfaces
InactiveUS6290726B1Improve wear resistanceReduce coefficient of frictionFinger jointsWrist jointsArticular surfacesProsthesis
Prosthetic joints, components for prosthetic joints, superhard bearing and articulation surfaces, diamond bearing and articulation surfaces, substrate surface topographical features, materials for making joints, bearing and articulation surfaces, and methods for manufacturing and finishing the same, and related information are disclosed, including a prosthetic hip joint having sintered polycrystalline diamond articulation.
Owner:DIAMICRON
Method for treating a vertebral body
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
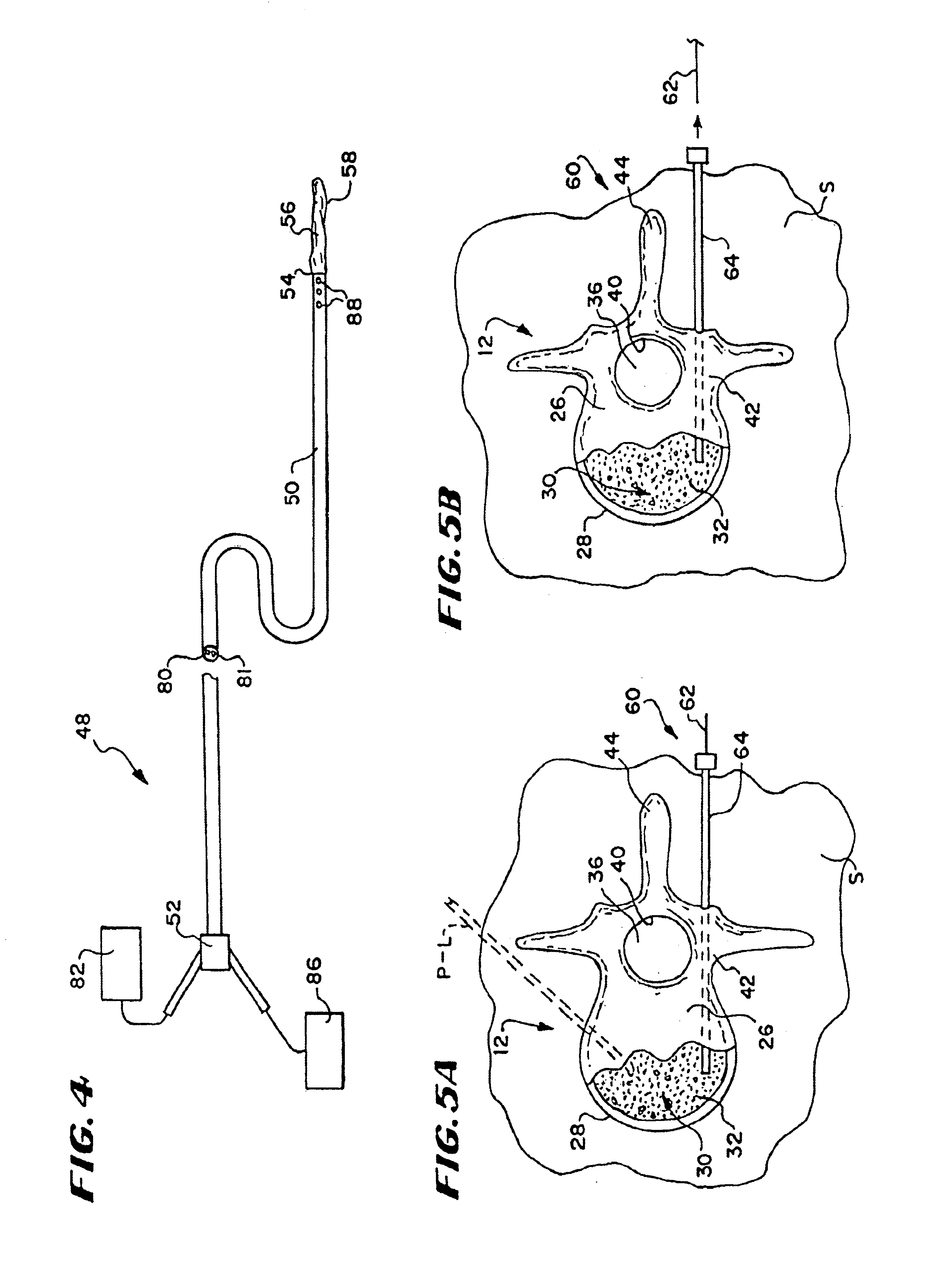
Inflatable device for use in surgical protocol relating to fixation of bone
InactiveUS7261720B2Easy to compressEasy to foldSurgical furnitureInternal osteosythesisBone CortexTrabecular bone
A balloon for use in compressing cancellous bone and marrow (also known as medullary bone or trabecular bone). The balloon comprises an inflatable balloon body for insertion into said bone. The body has a shape and size to compress at least a portion of the cancellous bone to form a cavity in the cancellous bone and / or to restore the original position of the outer cortical bone, if fractured or collapsed. The balloon desirably incorporates restraints which inhibit the balloon from applying excessive pressure to various regions of the cortical bone. The wall or walls of the balloon are such that proper inflation of the balloon body is achieved to provide for optimum compression of the bone marrow. The balloon can be inserted quickly into a bone. The balloon can be made to have a suction catheter. The balloon can be used to form and / or enlarge a cavity or passage in a bone, especially in, but not limited to, vertebral bodies. Various additional embodiments facilitate directionally biasing the inflation of the balloon.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
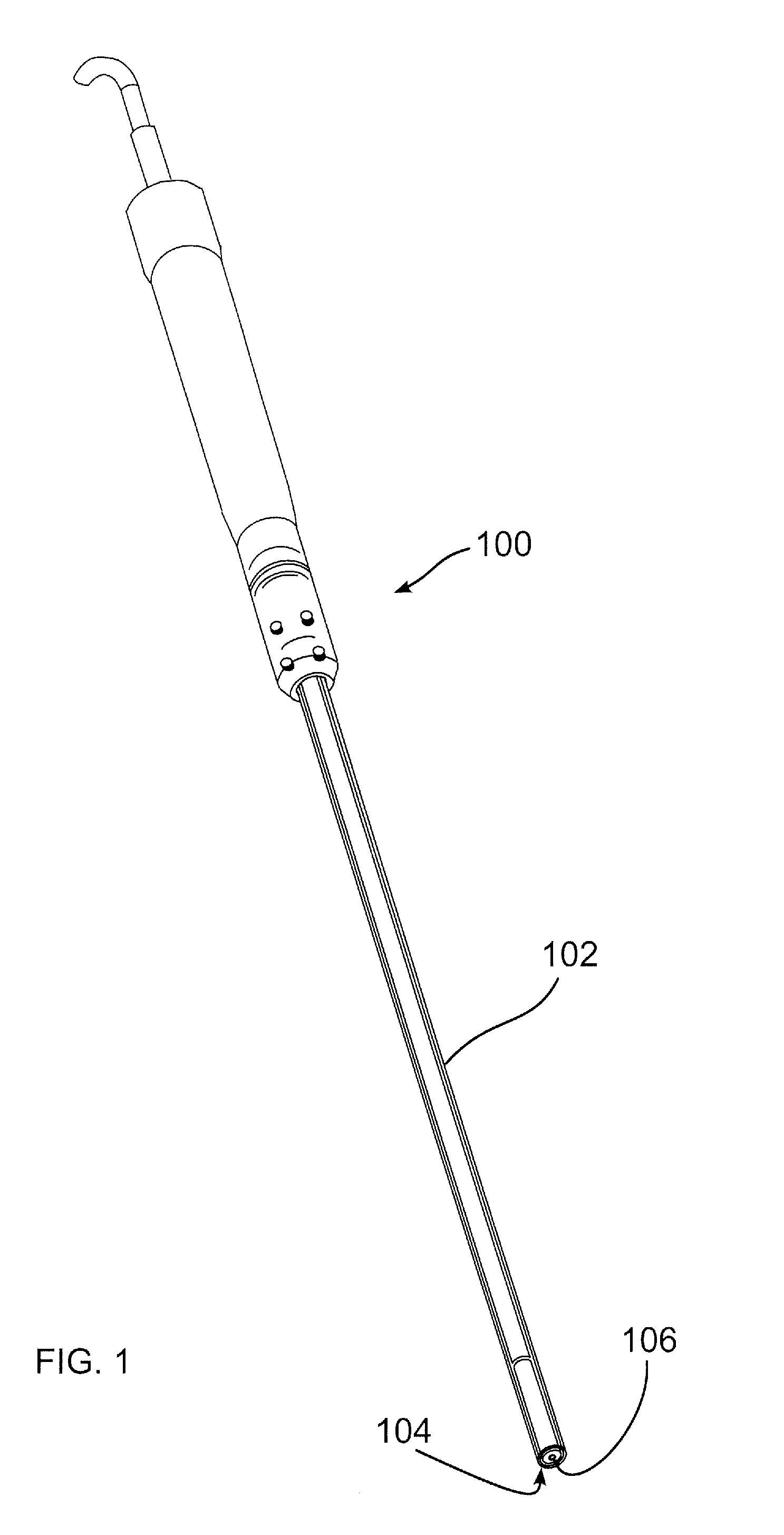
Methods and devices for intracorporeal bonding of implants with thermal energy
The present invention provides a method for stabilizing a fractured bone. The method includes positioning an elongate rod in the medullary canal of the fractured bone and forming a passageway through the cortex of the bone. The passageway extends from the exterior surface of the bone to the medullary canal of the bone. The method also includes creating a bonding region on the elongate rod. The bonding region is generally aligned with the passageway of the cortex. Furthermore, the method includes positioning a fastener in the passageway of the cortex and on the bonding region of the elongate rod and thermally bonding the fastener to the bonding region of the elongate rod while the fastener is positioned in the passageway of the cortex.
Owner:P TECH
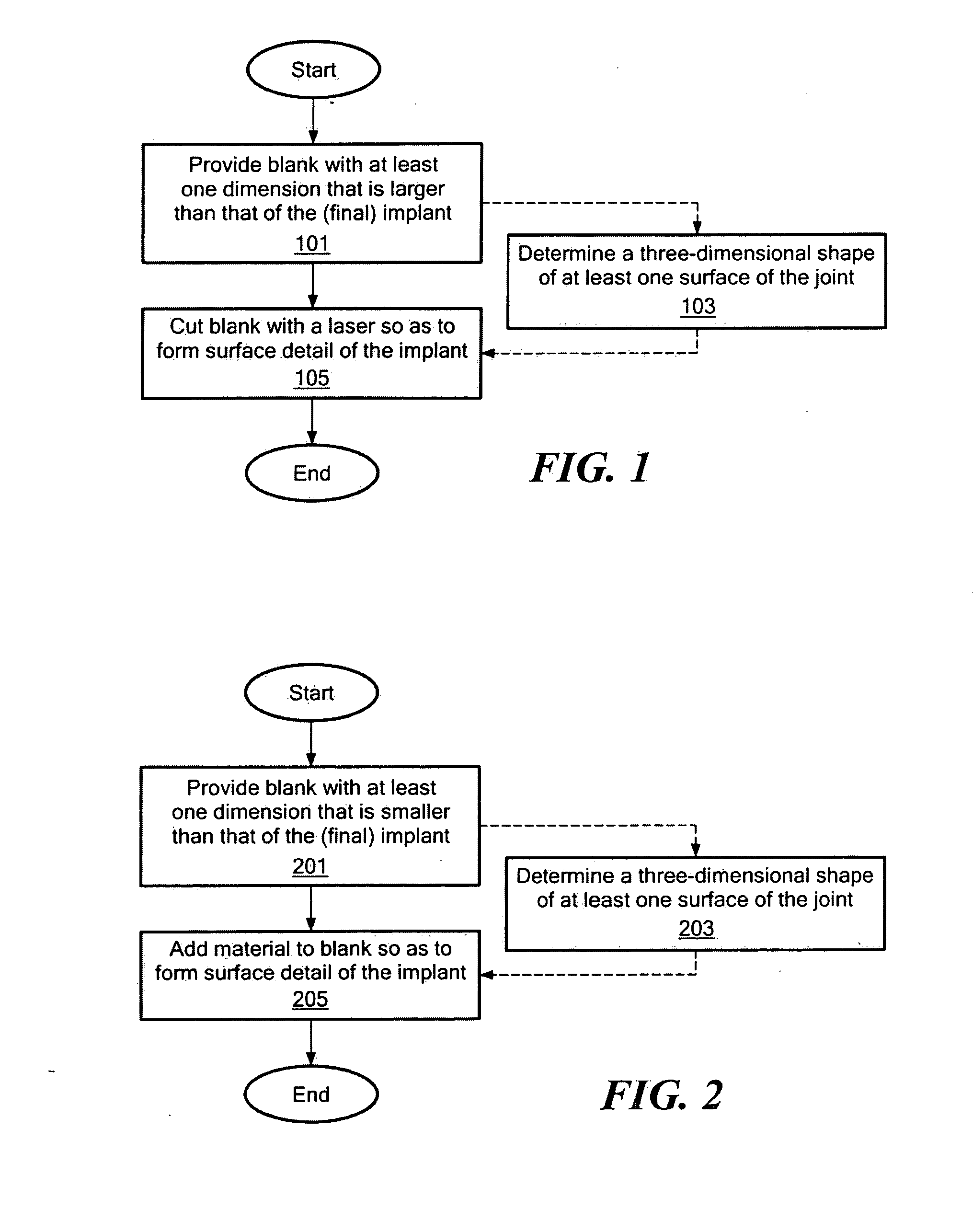
Minimally invasive joint implant with 3-dimensional geometry matching the articular surfaces
ActiveUS7799077B2Increase successFacilitating the integration of a wide variety of cartilageFinger jointsWrist jointsArticular surfacesArticular surface
This invention is directed to orthopedic implants and systems. The invention also relates to methods of implant design, manufacture, modeling and implantation as well as to surgical tools and kits used therewith. The implants are designed by analyzing the articular surface to be corrected and creating a device with an anatomic or near anatomic fit; or selecting a pre-designed implant having characteristics that give the implant the best fit to the existing defect.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Minimally Invasive Joint Implant with 3-Dimensional Geometry Matching the Articular Surfaces
InactiveUS20110066245A1Facilitating the integration of a wide variety of cartilageIncrease successFinger jointsWrist jointsArticular surfacesArticular surface
This invention is directed to orthopedic implants and systems. The invention also relates to methods of implant design, manufacture, modeling and implantation as well as to surgical tools and kits used therewith. The implants are designed by analyzing the articular surface to be corrected and creating a device with an anatomic or near anatomic fit; or selecting a pre-designed implant having characteristics that give the implant the best fit to the existing defect.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Diamond-surfaced cup for use in a prosthetic joint
InactiveUS6488715B1Improve wear resistanceReduce coefficient of frictionFinger jointsWrist jointsArticular surfacesSacroiliac joint
Prosthetic joints, components for prosthetic joints, superhard bearing and articulation surfaces, diamond bearing and articulation surfaces, substrate surface topographical features, materials for making joints, bearing and articulation surfaces, and methods for manufacturing and finishing the same, and related information are disclosed, including a diamond-surfaced cup for use in a prosthetic joint.
Owner:DIAMICRON
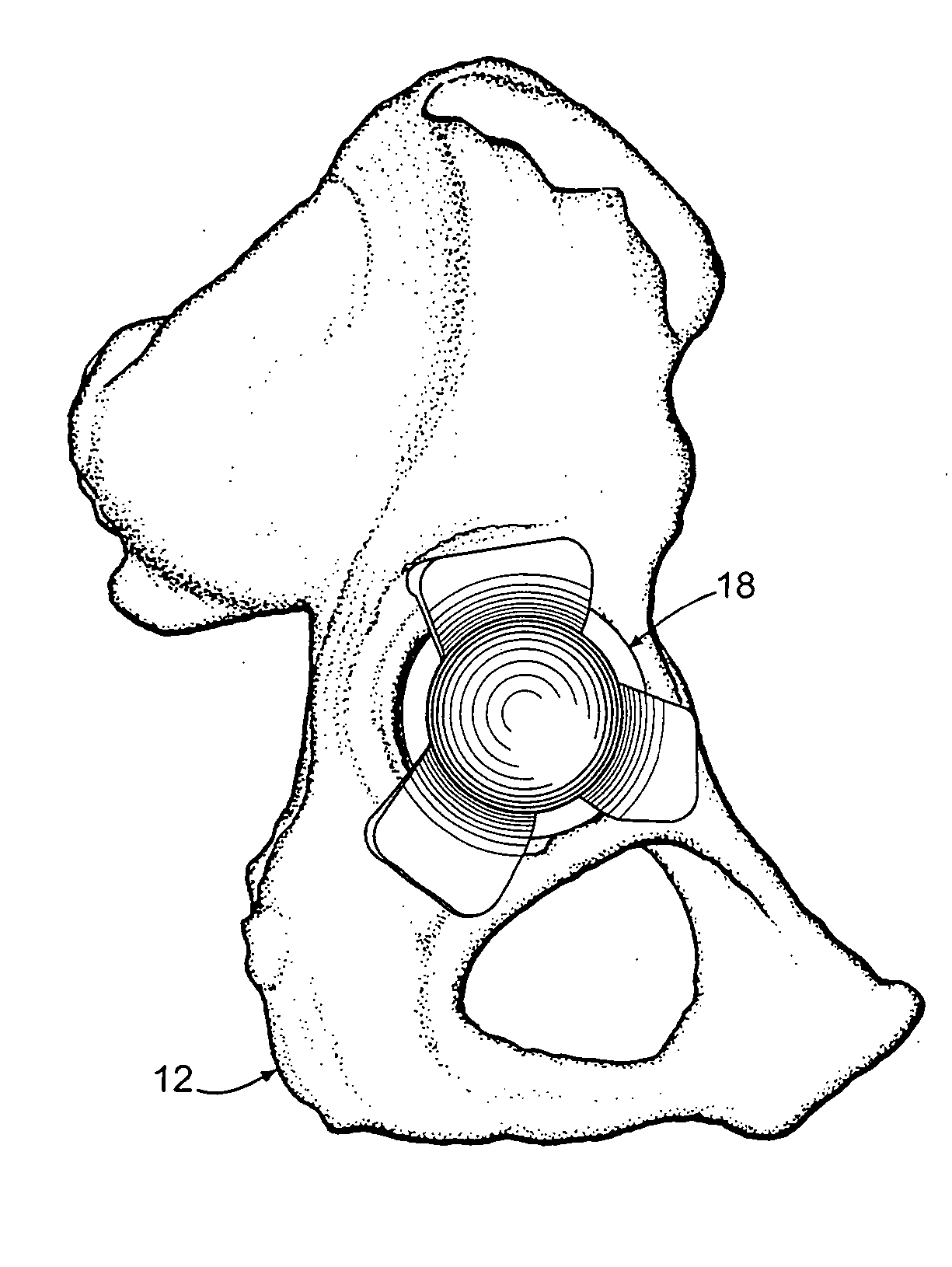
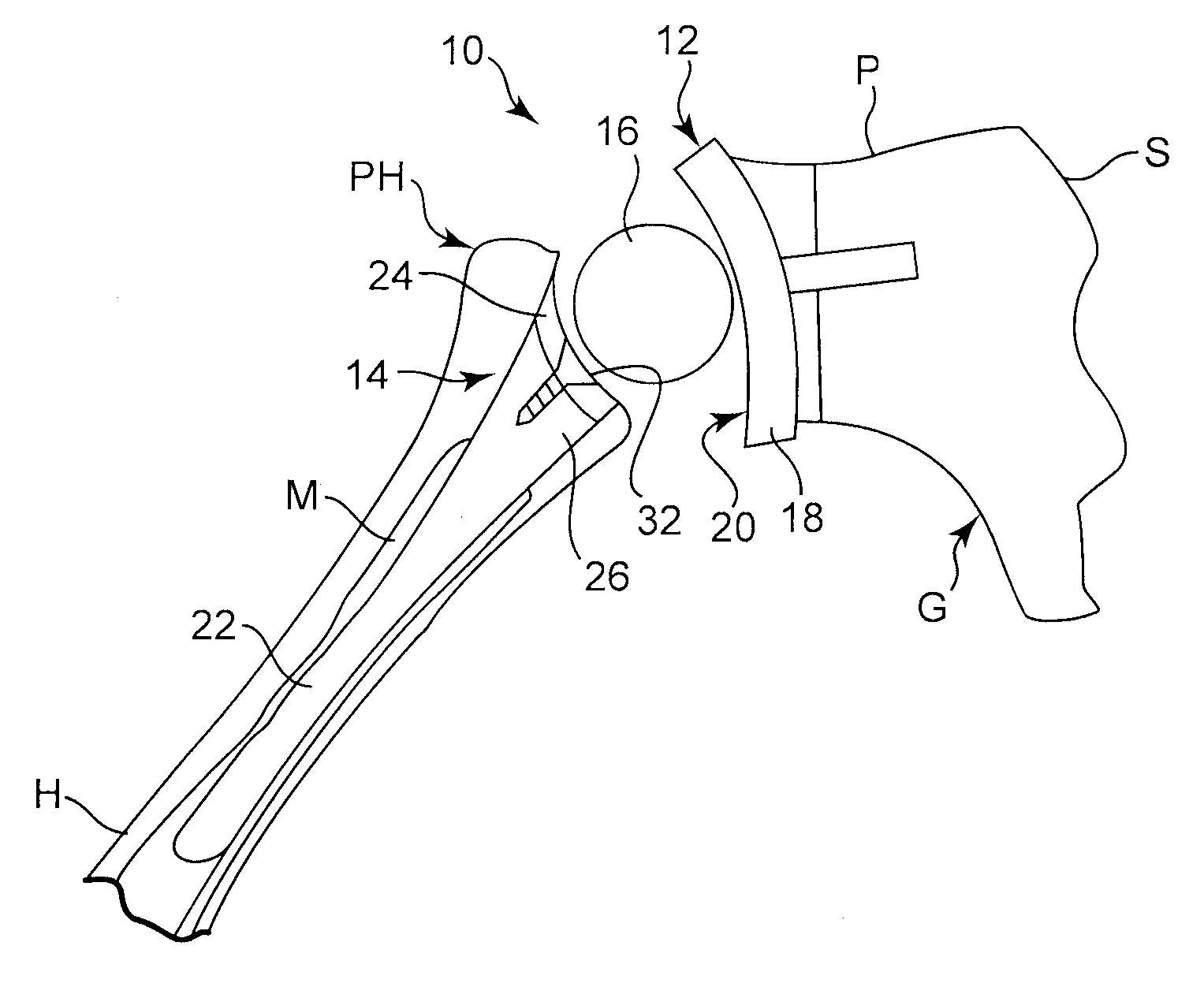
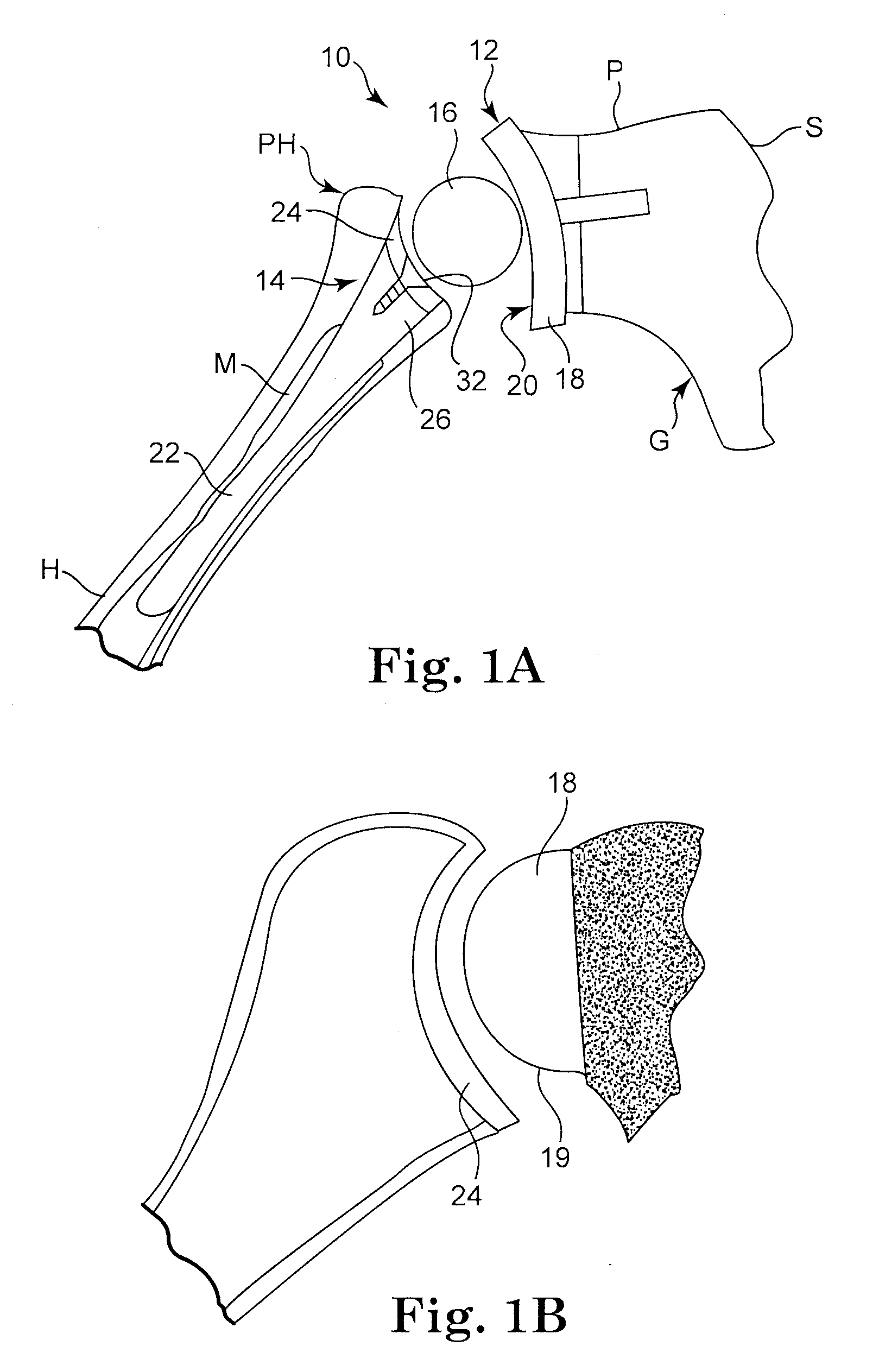
Intra-articular joint replacement
A method for implanting an intra-articular shoulder prosthesis is provided. The method includes removing a proximal portion of a humerus. The proximal portion of the humerus preferably forms a resected portion. The resected portion has a convex outer surface and an inner surface. The method further includes engaging the convex outer surface of the resected portion with a cut surface of the proximal portion of the humerus. The cut surface of the proximal portion of the humerus and / or the inner surface of the resected portion are optionally processed to form a generally concave surface, such as by impacting. In one embodiment, the inner surface of the resected portion is impacted into engagement with the cut surface of the proximal portion of the humerus. The generally concave inner surface of the resected portion forms a concave articular surface to receive an interpositional implant.
Owner:TORNIER SA SAINT ISMIER
Methods and devices for utilizing thermal energy to bond, stake and/or remove implants
ActiveUS20090024161A1Short cycleSuture equipmentsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsThermal energyBody tissue
A fastener including material meltable at a temperature not likely to produce substantial tissue necrosis of neighboring body tissue, or “bondable material”, is caused to soften or melt by the application of vibratory energy, advantageously including ultrasonic vibratory energy. Vibratory energy is applied using a horn applied to the fastener, and tuned to generate vibratory motion proximate the horn, or at a point distal to the horn, for example at a point along the fastener body, or at the end of the fastener. Melted or softened material of the fastener bonds to a contacting surface, which may be body tissue or another implant. The contacting surface may also include bondable material, softenable or meltable through vibratory energy derived from contact with the fastener. To improve a bond, particularly where dissimilar materials are to be bonded, one or more contacting surfaces is provided with a roughened or porous surface, or a surface including one or more cavities or projections into or onto which softened or melted bondable material may form, bonding once the bondable material has cooled.
Owner:P TECH
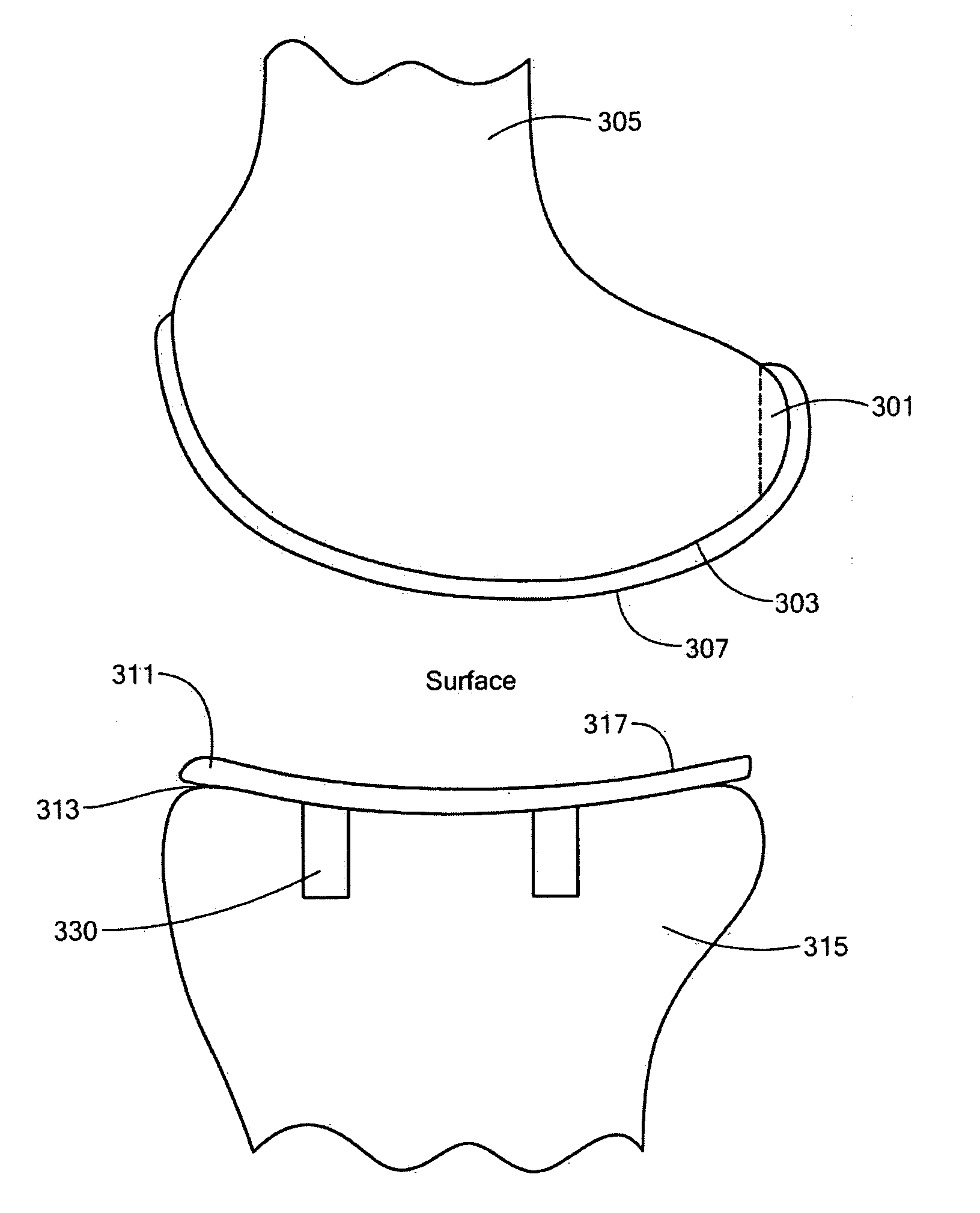
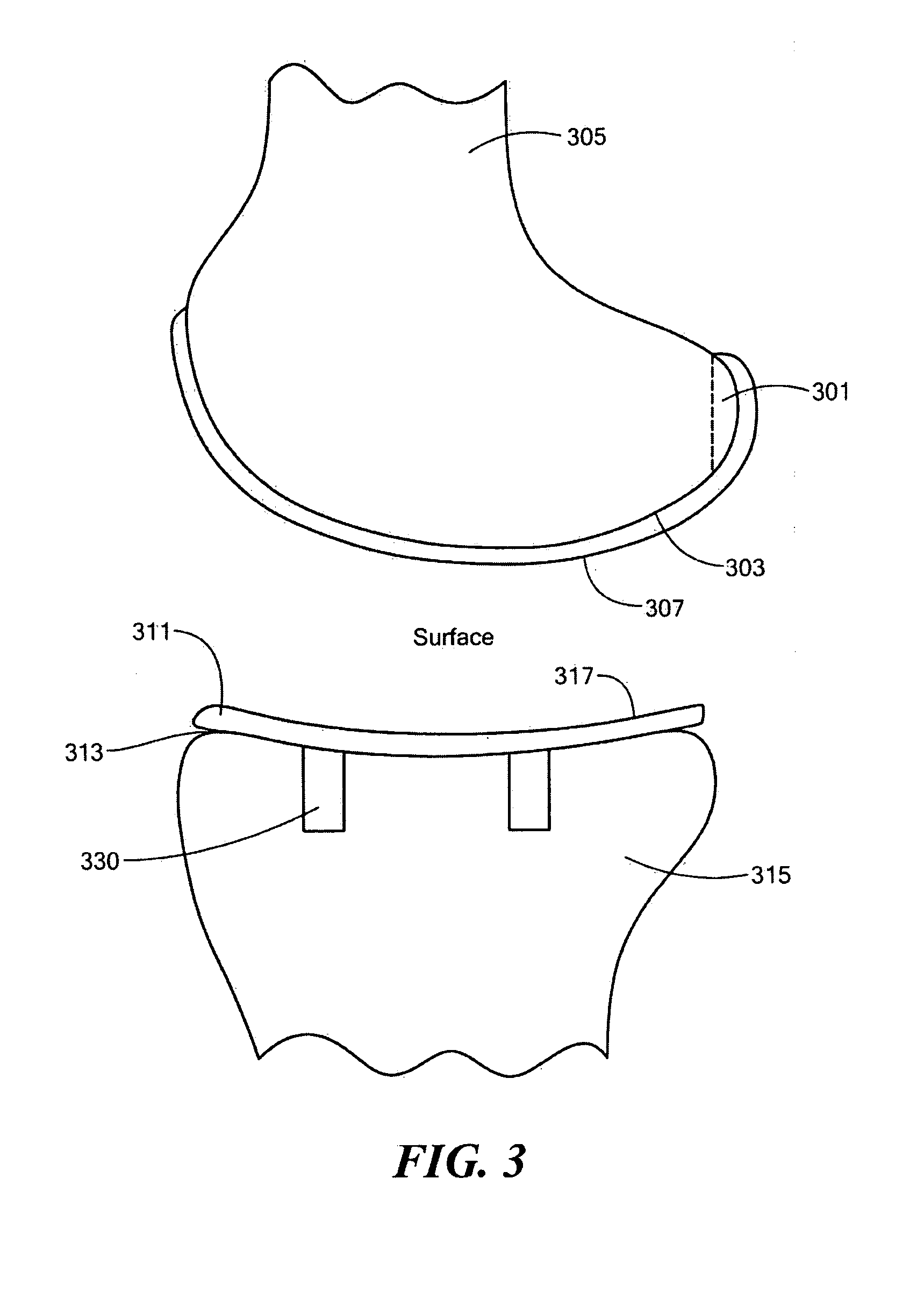
System of preoperative planning and provision of patient-specific surgical aids
A method for assisting a user with surgical implementation of a preoperative plan includes generating a physical native tissue model of a native patient tissue. The physical native tissue model includes at least one primary patient tissue area including a surface of interest, at least one secondary patient tissue area including no surfaces of interest, and a base surface for engaging a supporting structure. The physical native tissue model, as generated, includes at least one information feature providing clinically useful information to the user. The information feature is substantially separated from the surface of interest. An apparatus for assisting a user with surgical implementation of a preoperative plan is also provided.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
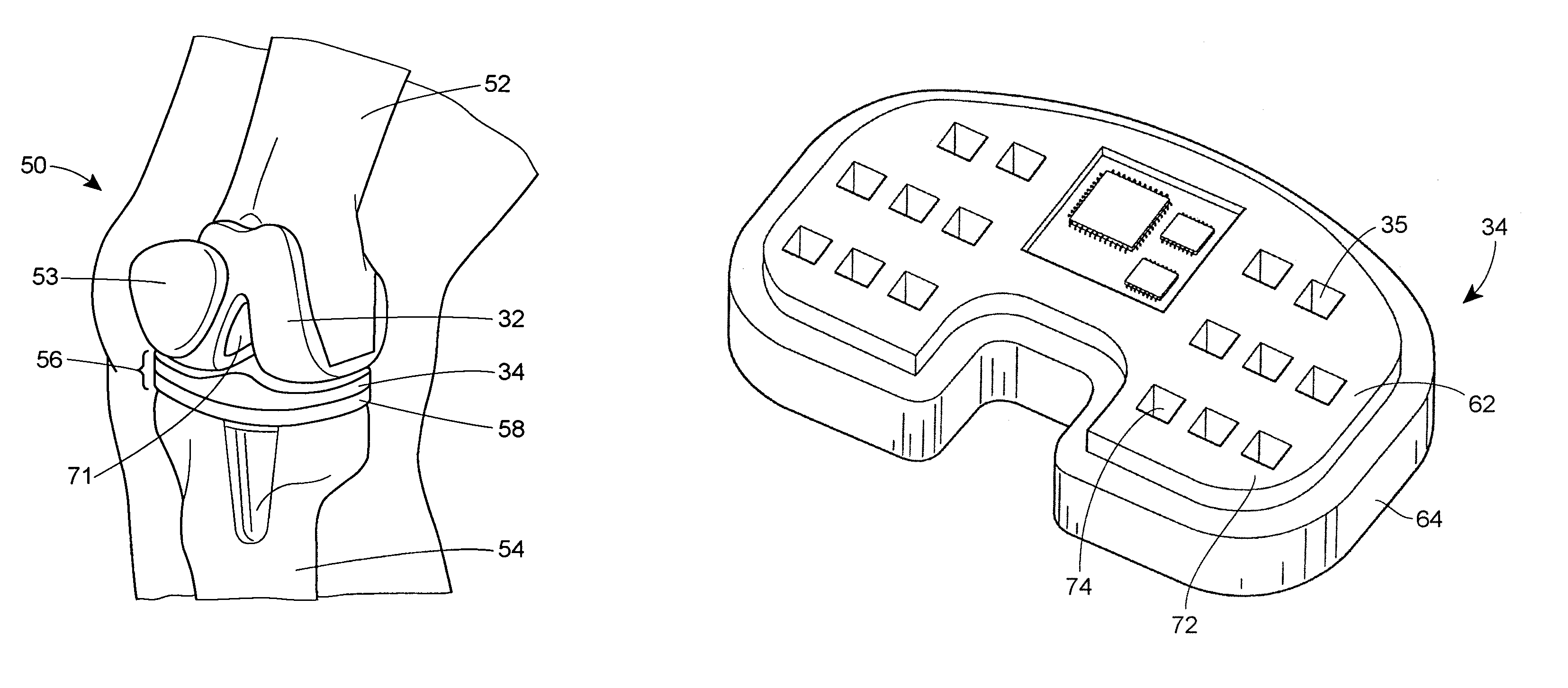
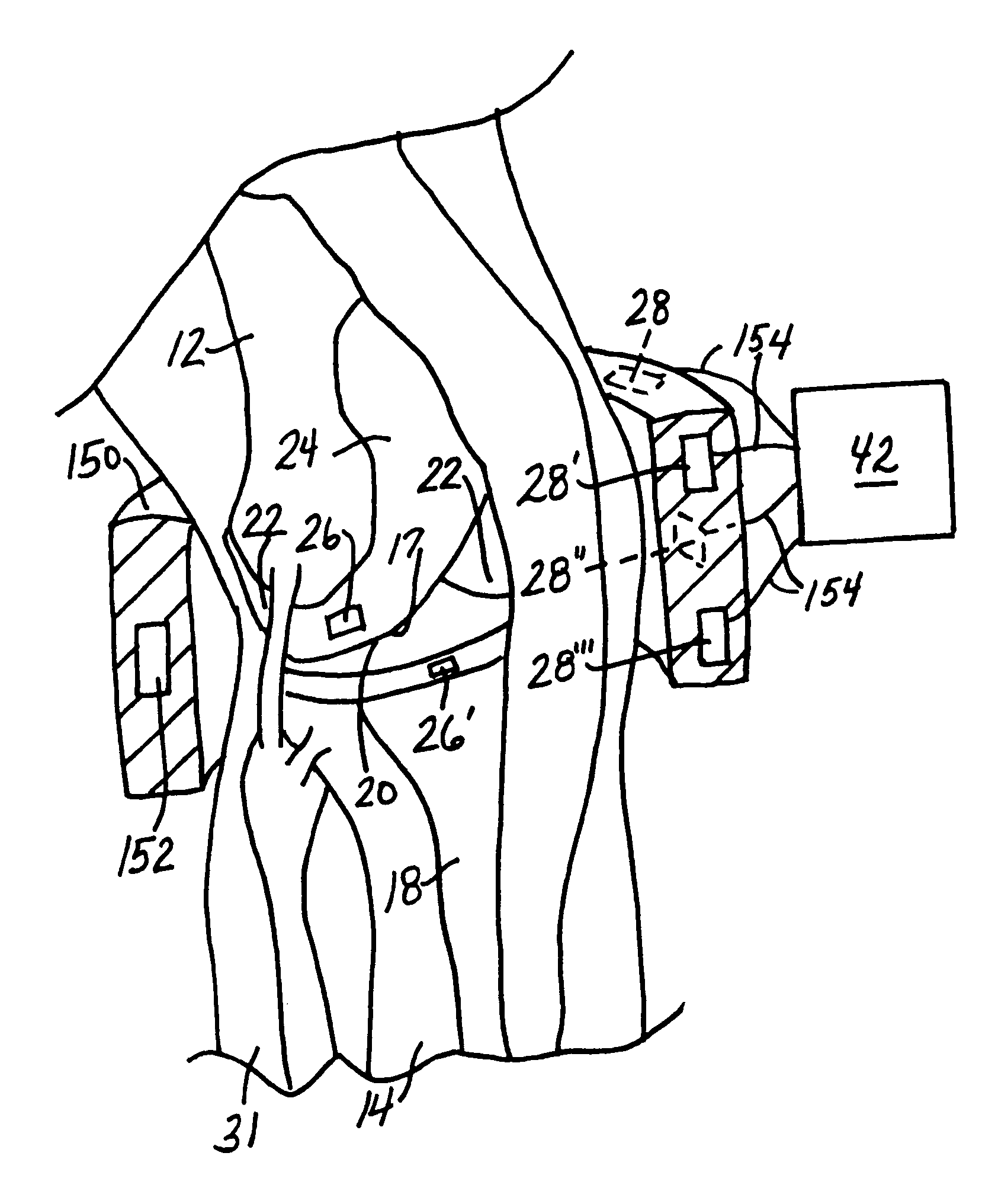
In-vivo orthopedic implant diagnostic device for sensing load, wear, and infection
InactiveUS7097662B2Understand kinematics of jointReliable implantEndoradiosondesCatheterEngineeringIn vivo
A device for providing in vivo diagnostics of loads, wear, and infection in orthopedic implants having at least one load sensor associated with the implant, at least one temperature sensor associated with the implant, at least one vibration sensor associated with the implant, and at least one signal processing device operatively coupled with the sensors. The signal processing device is operable to receive the output signal from the sensors and transmit a signal corresponding with the output signal.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
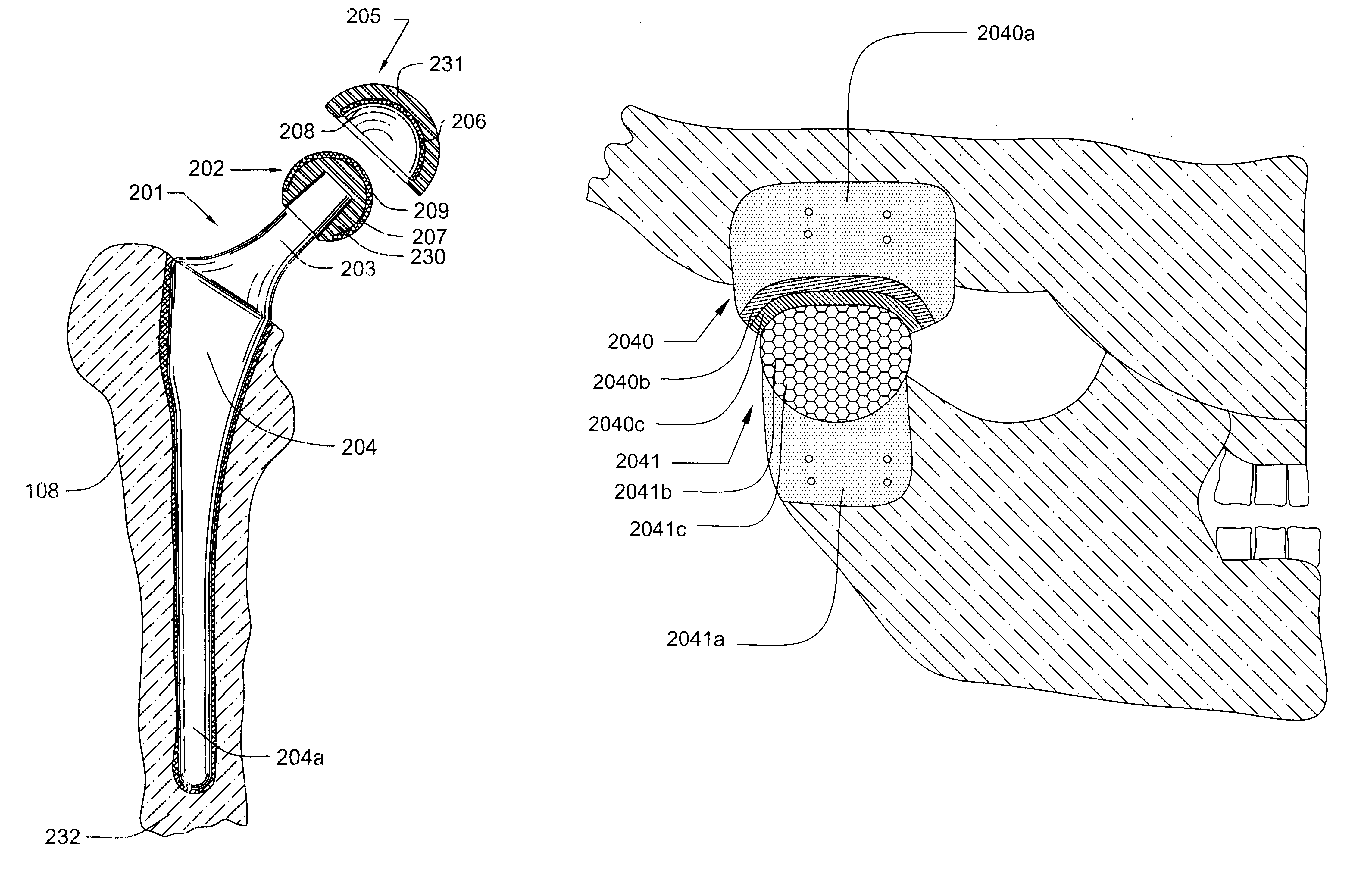
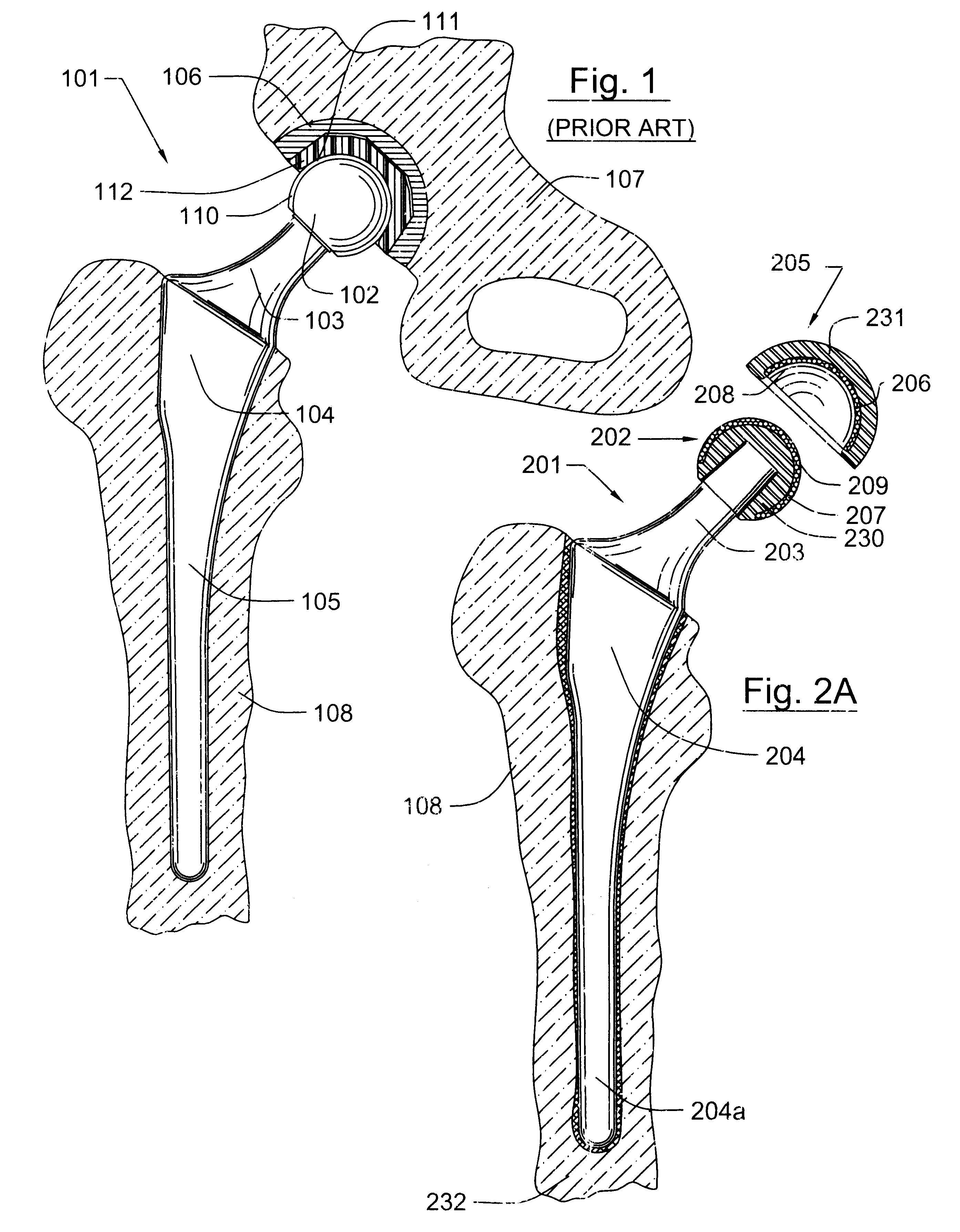
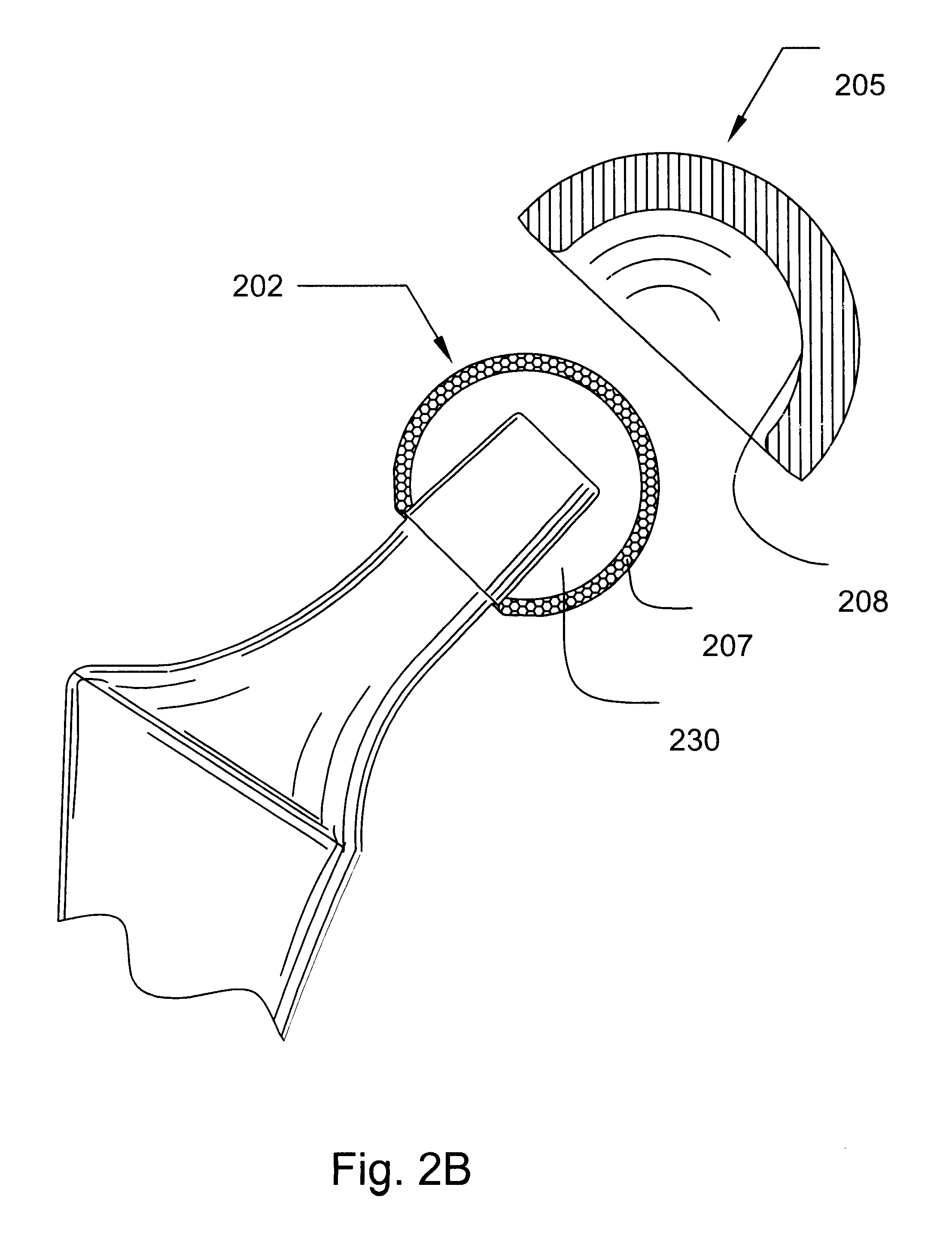
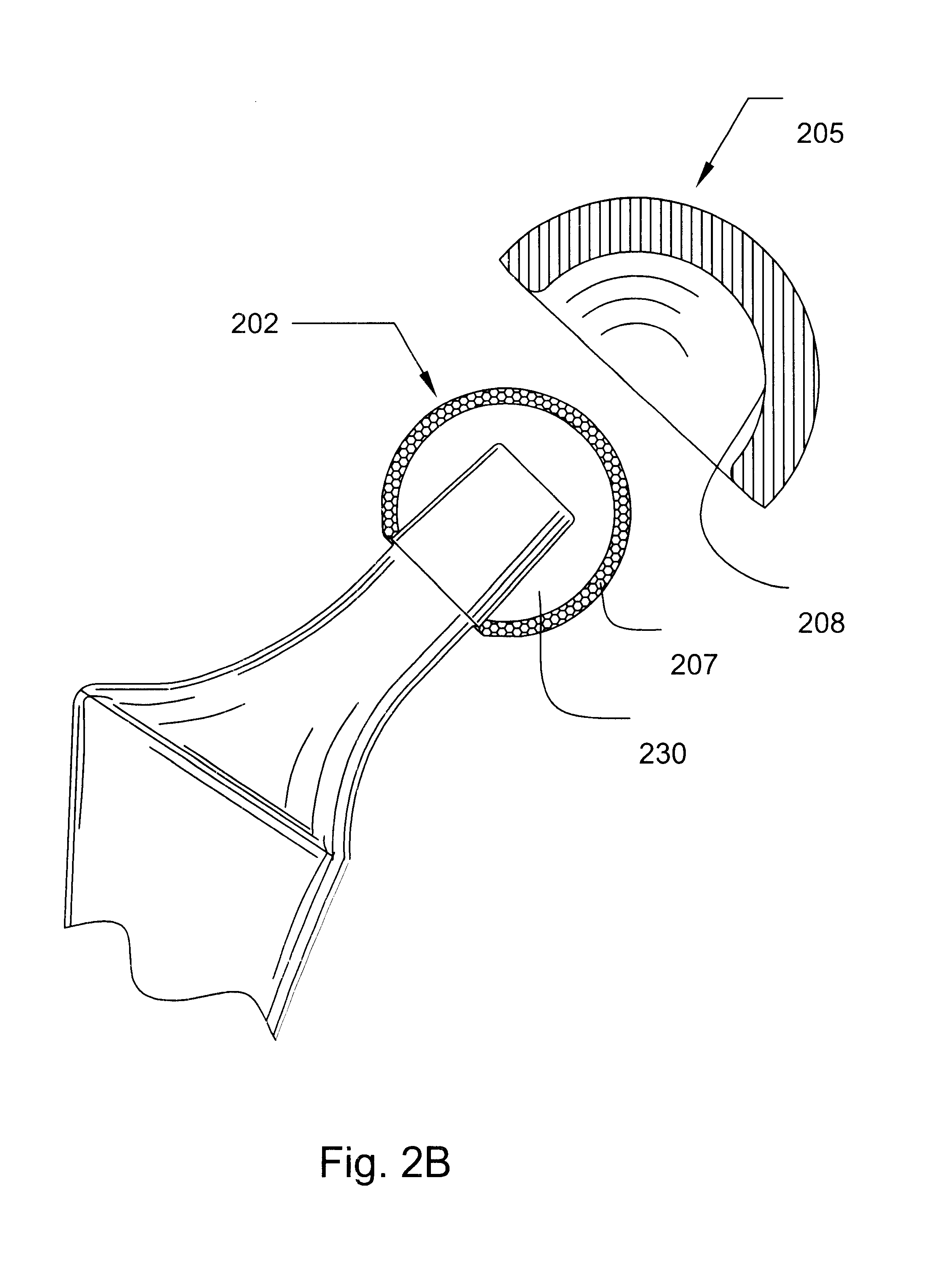
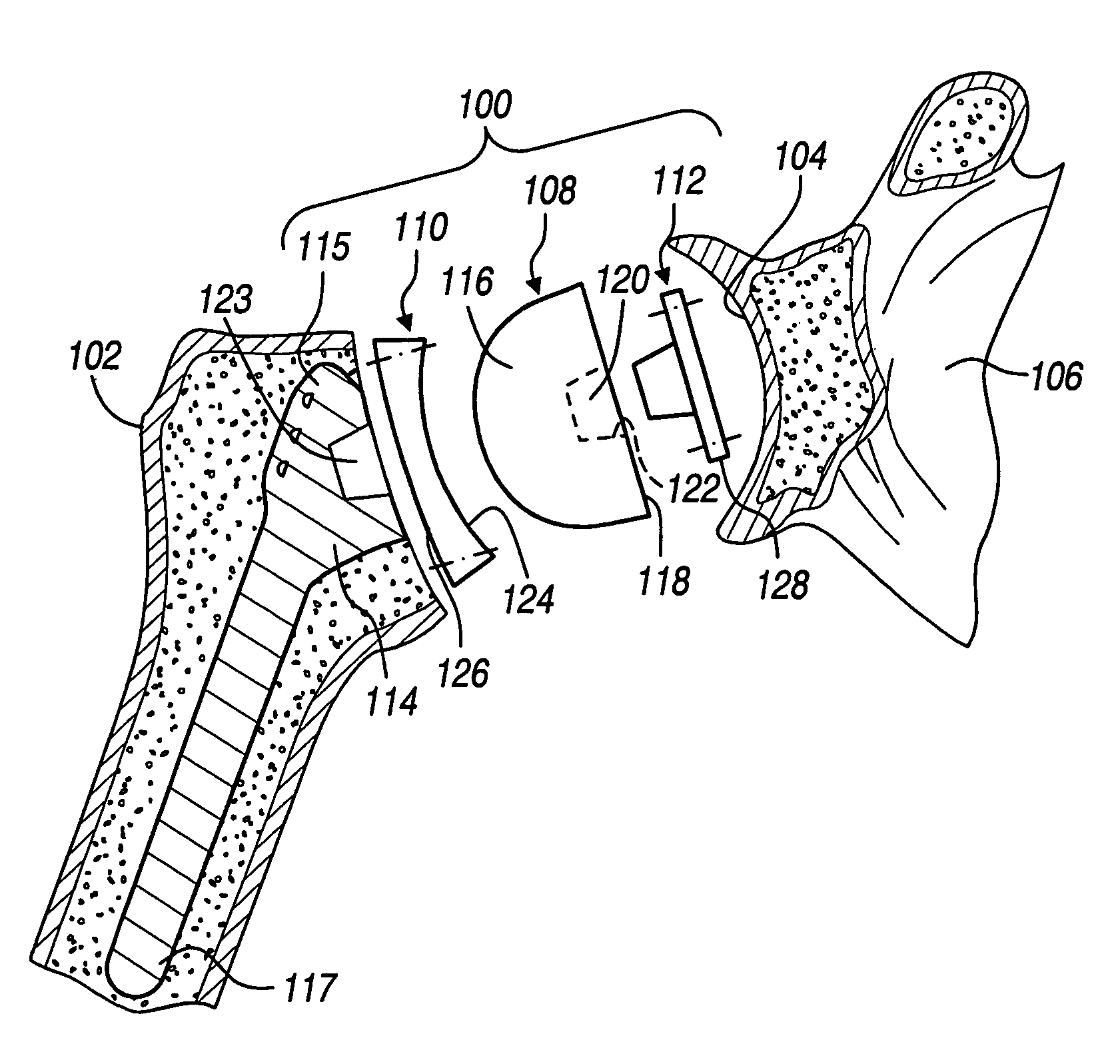
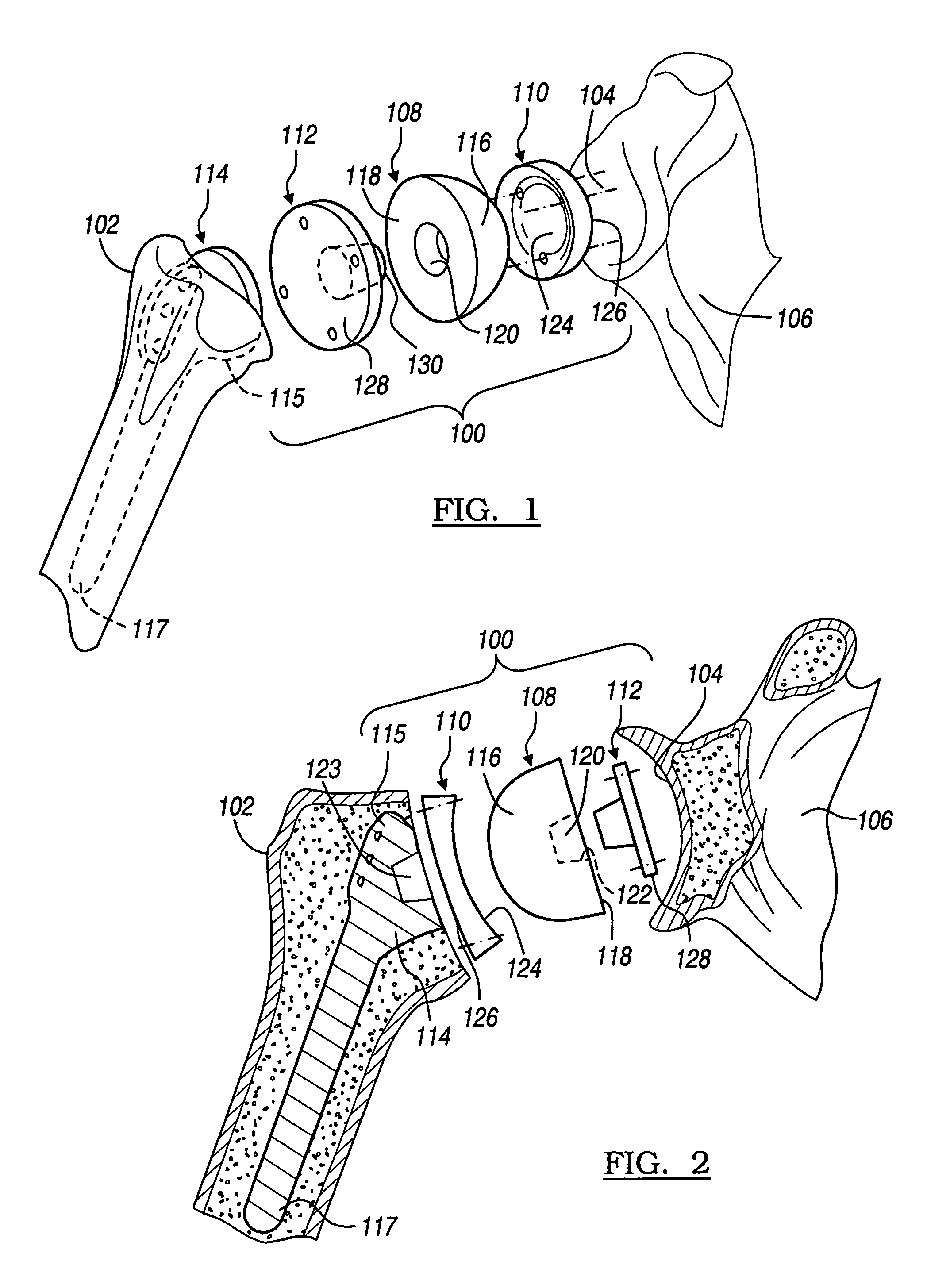
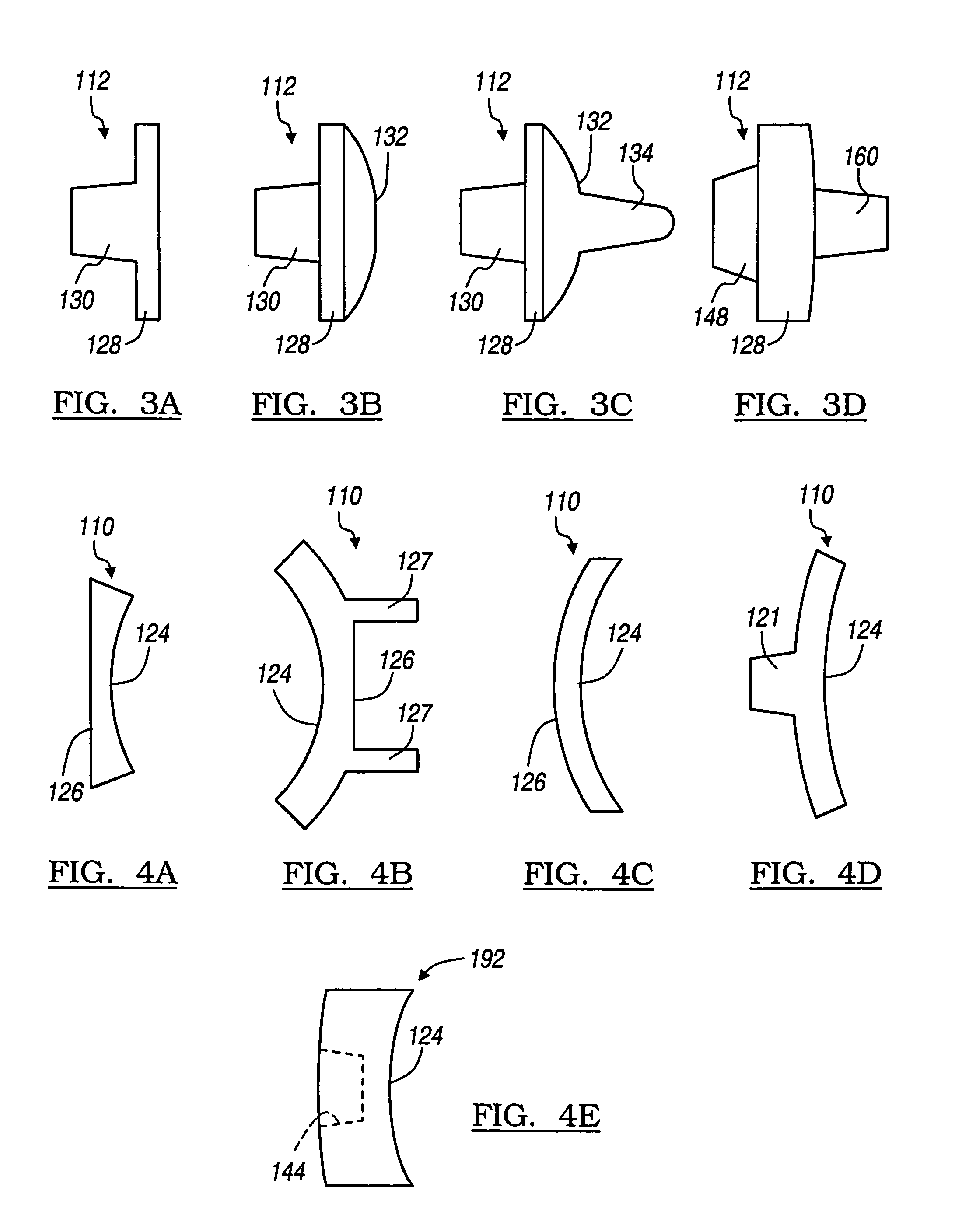
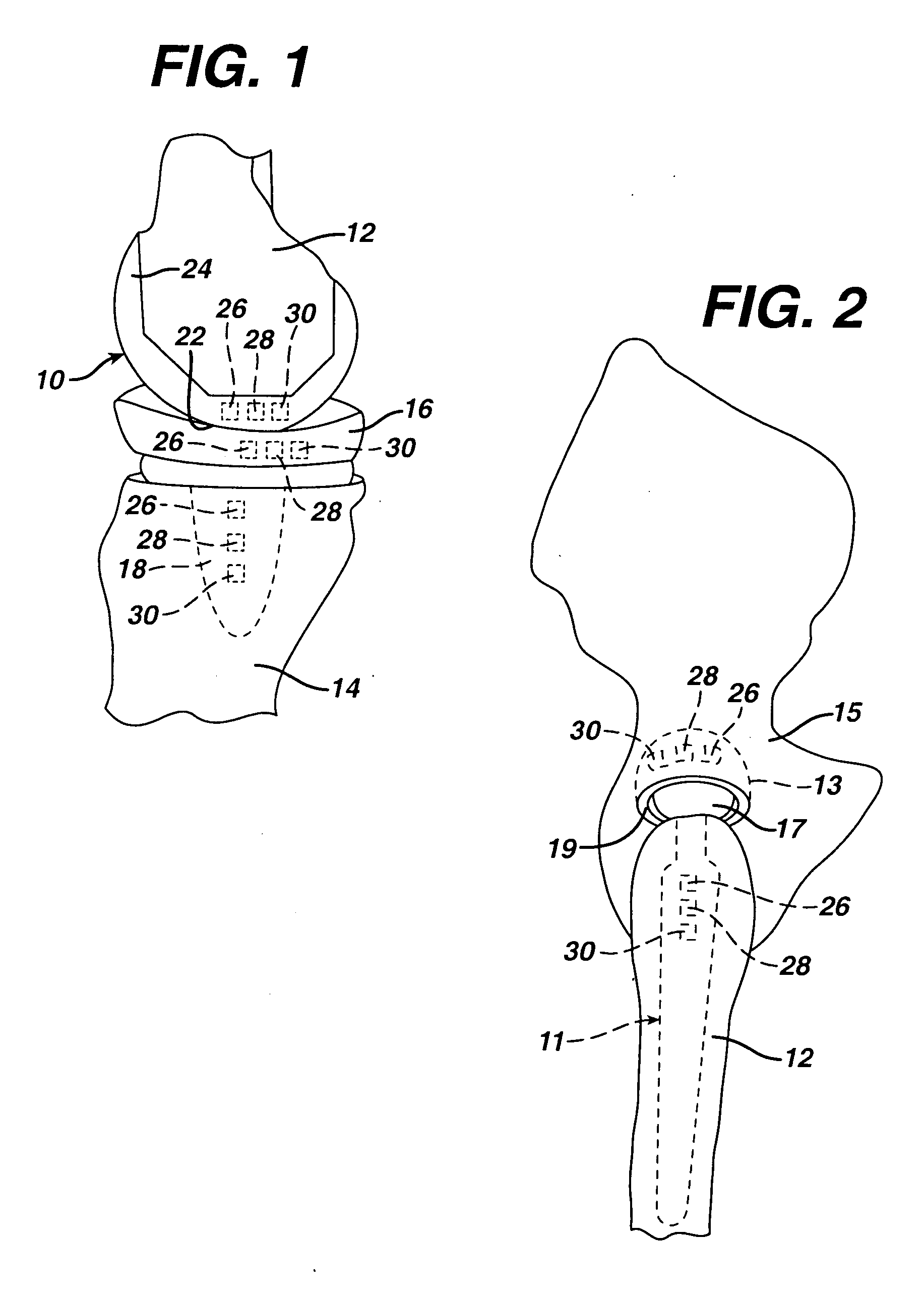
Shoulder implant assembly
An implant assembly and associated method for selectively performing reverse and traditional arthroplasty for a shoulder joint that includes a humerus and a glenoid. The implant assembly may include a head, a cup, a humeral stem and an adapter. The method includes inserting the humeral stem to the humerus and connecting a male taper of the adapter to a female taper of the head. For reverse arthroplasty, the method includes attaching the adapter to the glenoid and the cup to the stem. For traditional arthroplasty, the method includes attaching the adapter to the humeral stem and the cup to the glenoid. The method also includes articulating the head with the cup.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Devices and methods using an expandable body with internal restraint for compressing cancellous bone
Devices and methods compress cancellous bone. In one arrangement, the devices and methods make use of an expandable body that includes an internal restraint coupled to the body. The internal restraint directs expansion of the body. In one arrangement, a method for treating bone inserts the device having the internal restraint inside bone and causes directed expansion of the body in cancellous bone. Cancellous bone is compacted by the directed expansion.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
Orthopedic and dental implant devices providing controlled drug delivery
Implantable prosthetic devices are provided for controlled drug delivery, for orthopedic and dental applications. The device may include a prosthetic device body having at least one outer surface area; two or more discrete reservoirs located in spaced apart positions across at least a portion of the outer surface area, the reservoirs formed with an opening at the surface of the device body and extending into the device body; and a release system disposed in the reservoirs which comprises at least one therapeutic or prophylactic agent, wherein following implantation into a patient the therapeutic or prophylactic agent is released in a controlled manner from the reservoirs. The prosthetic device body preferably is a joint prosthesis or part thereof, such as a hip prosthesis, a knee prosthesis, a vertebral or spinal disc prosthesis, or part thereof. Optional reservoir caps may further control release kinetics.
Owner:MICROCHIPS INC
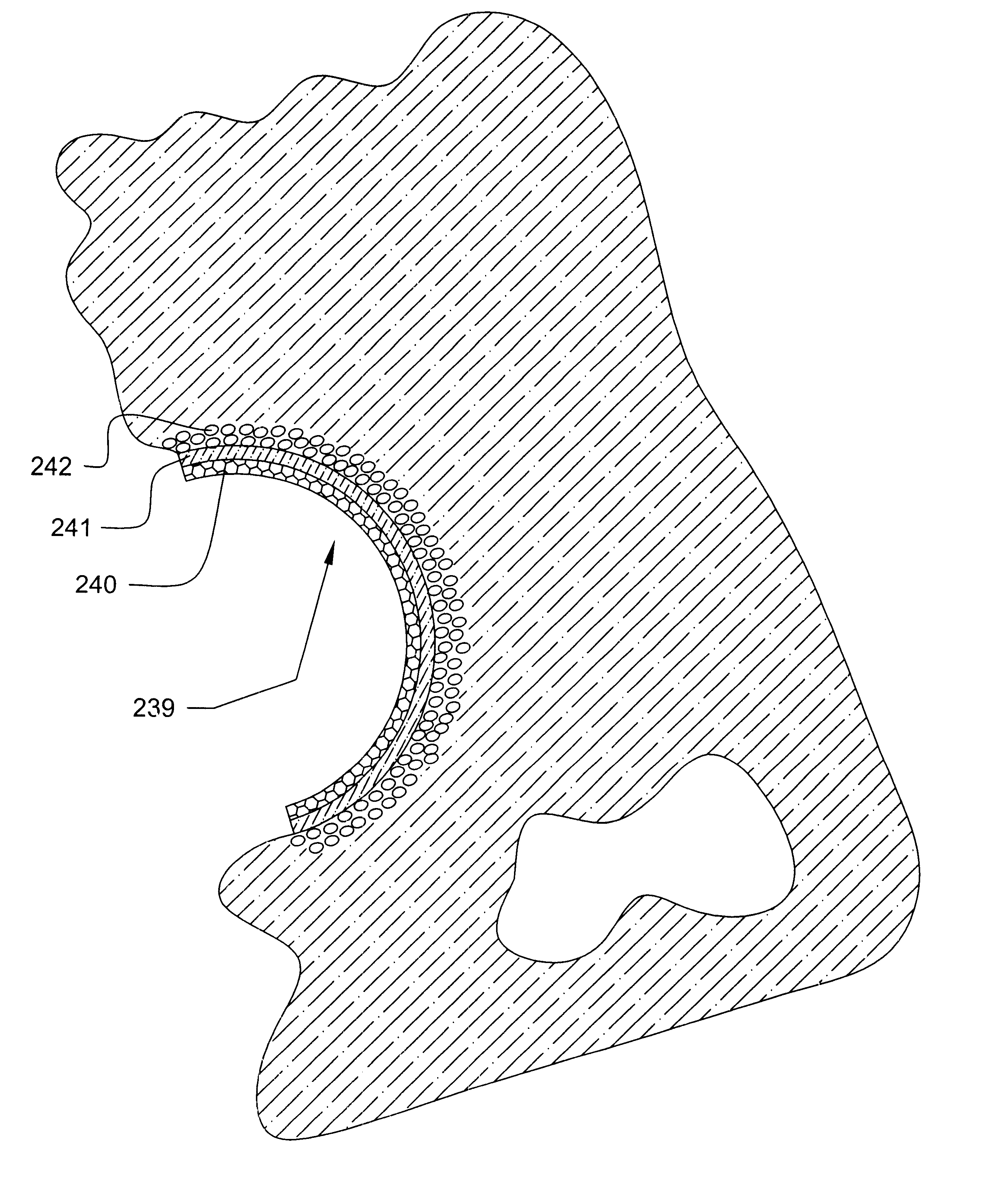
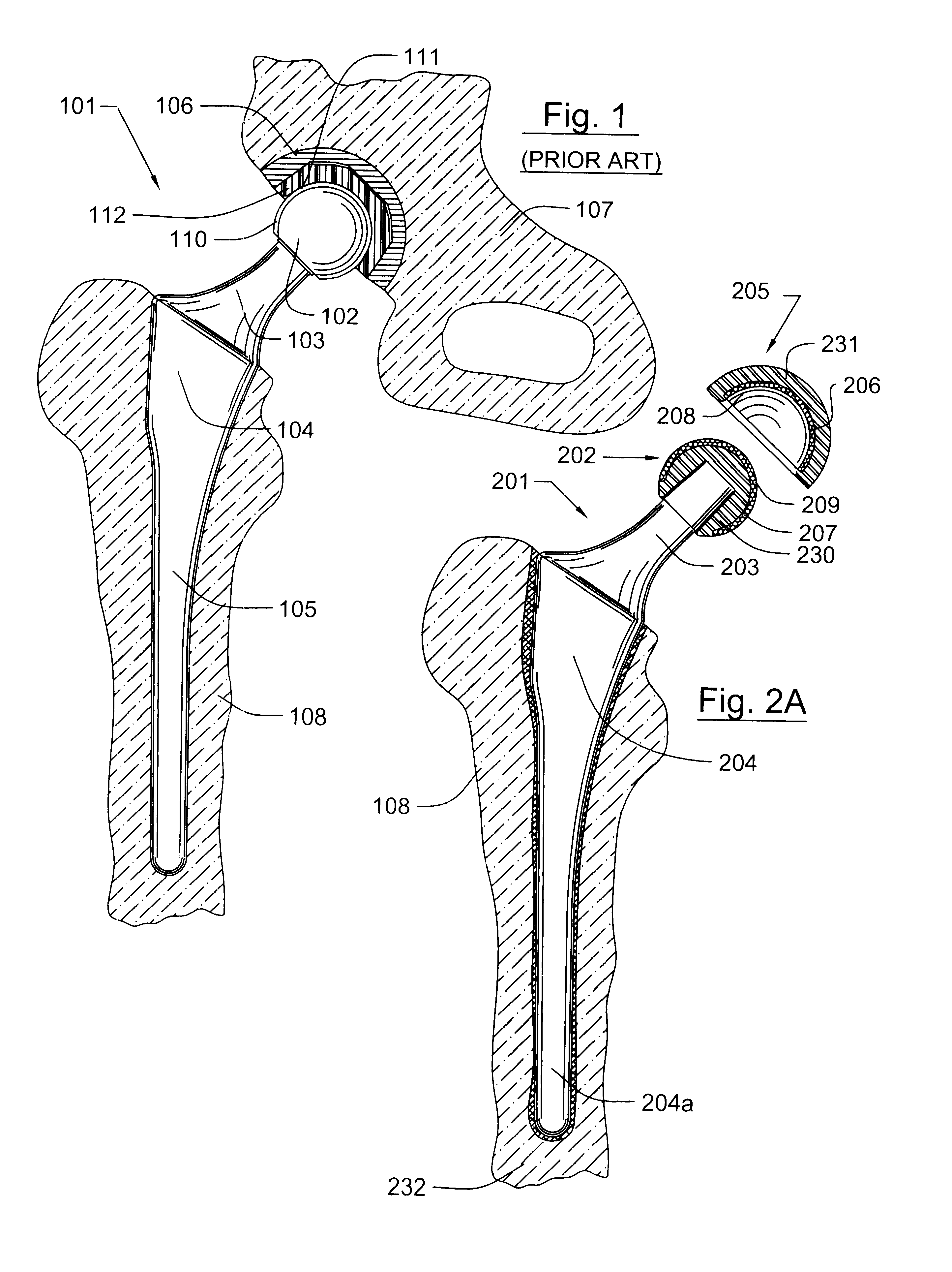
Tissue integration design for seamless implant fixation
The present invention relates to orthopaedic implants having a fenestrated hollow shell and a biologic core. These design features provide an improved interface between the implant and the surrounding tissue, aiding fixation, and provide a vehicle for applying new bone healing and enhancing modalities, such as gene therapy, tissue engineering, and growth factors.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
Orthopaedic element with self-contained data storage
An orthopaedic element has an information storage portion. A transmitter portion and an internal power source portion may be associated with the body of the orthopaedic element. Information, such as data related to the orthopaedic element, patient or caregiver can be stored in the information storage portion. The transmitter portion is coupled to the information storage portion and the internal power source portion. The stored information is selectively transmitted to an external receiver and data interpretation device.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
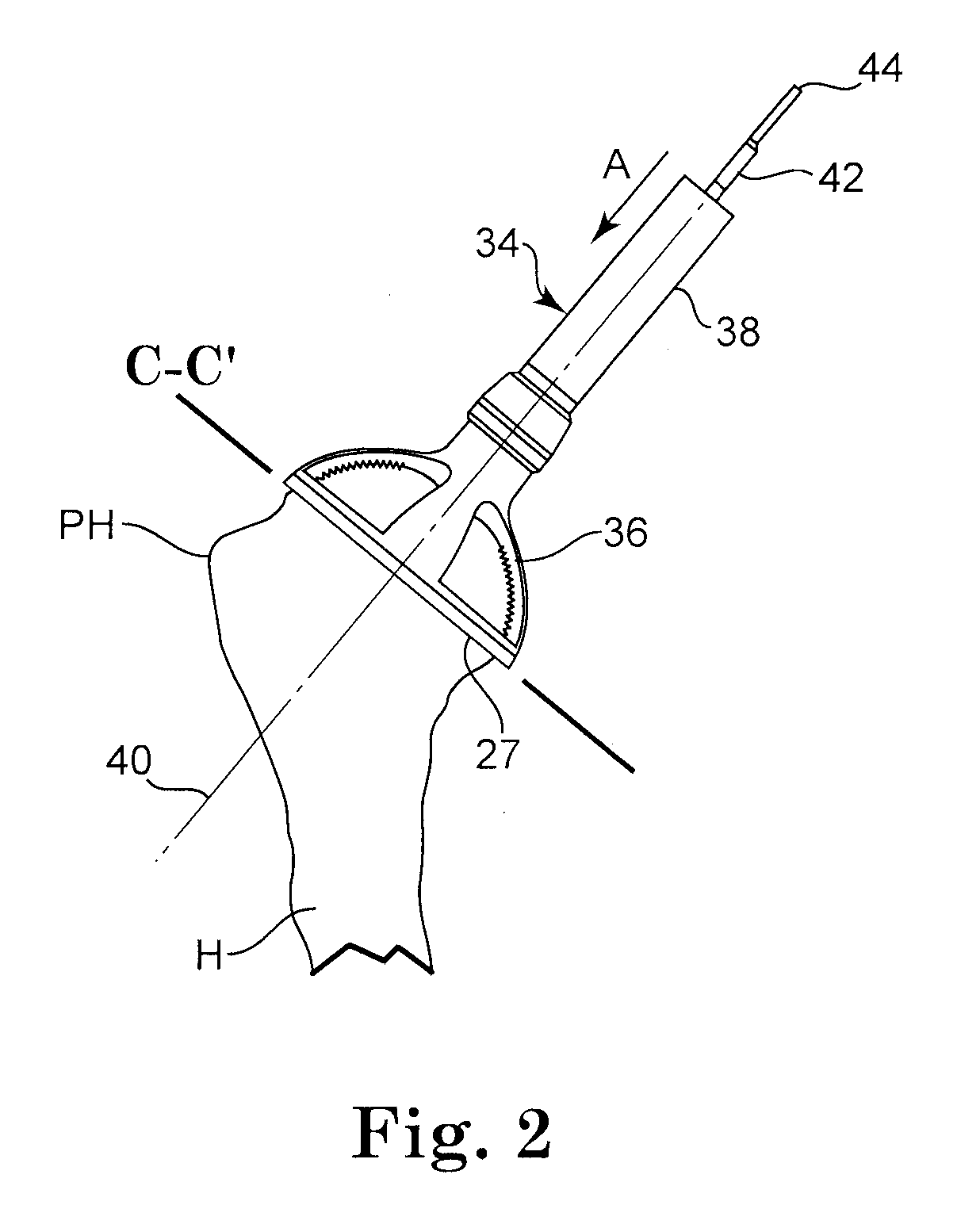
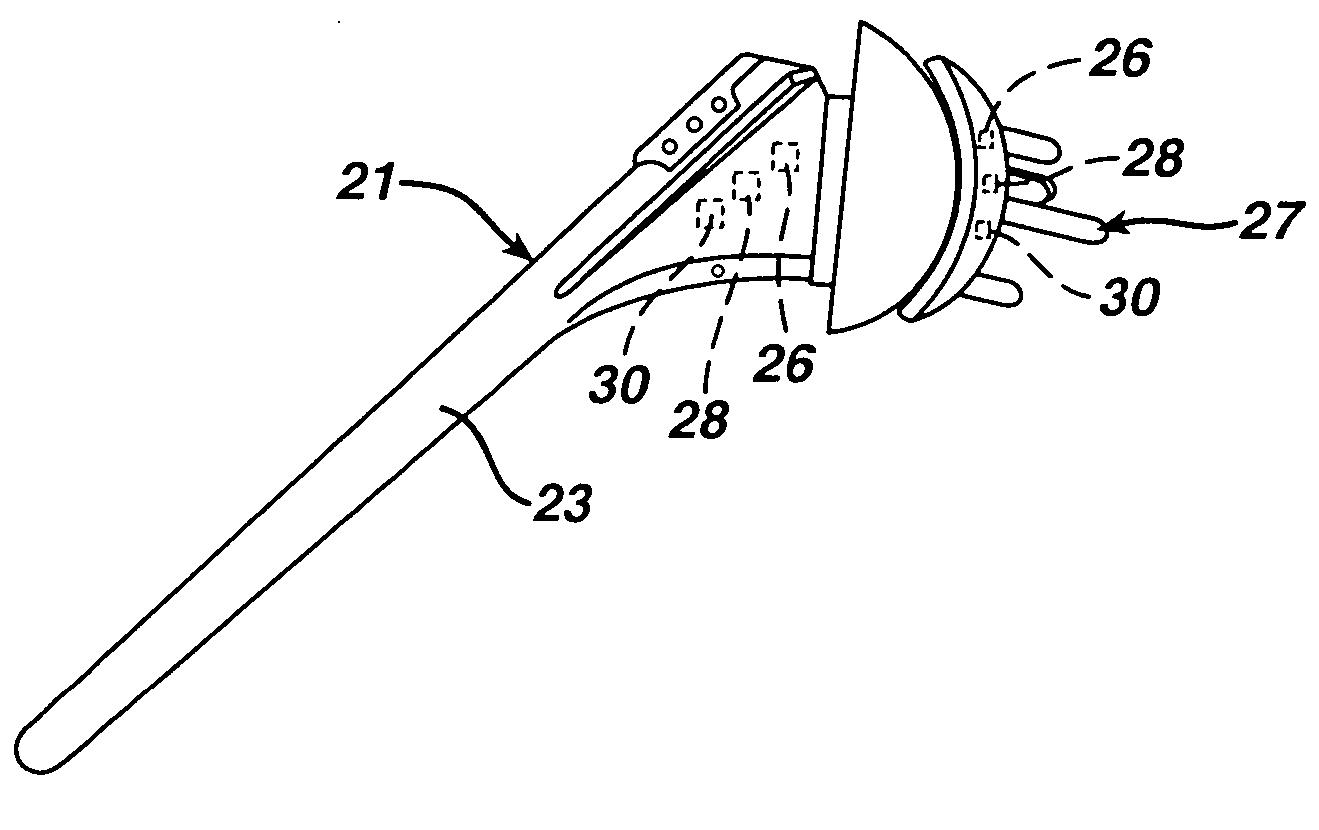
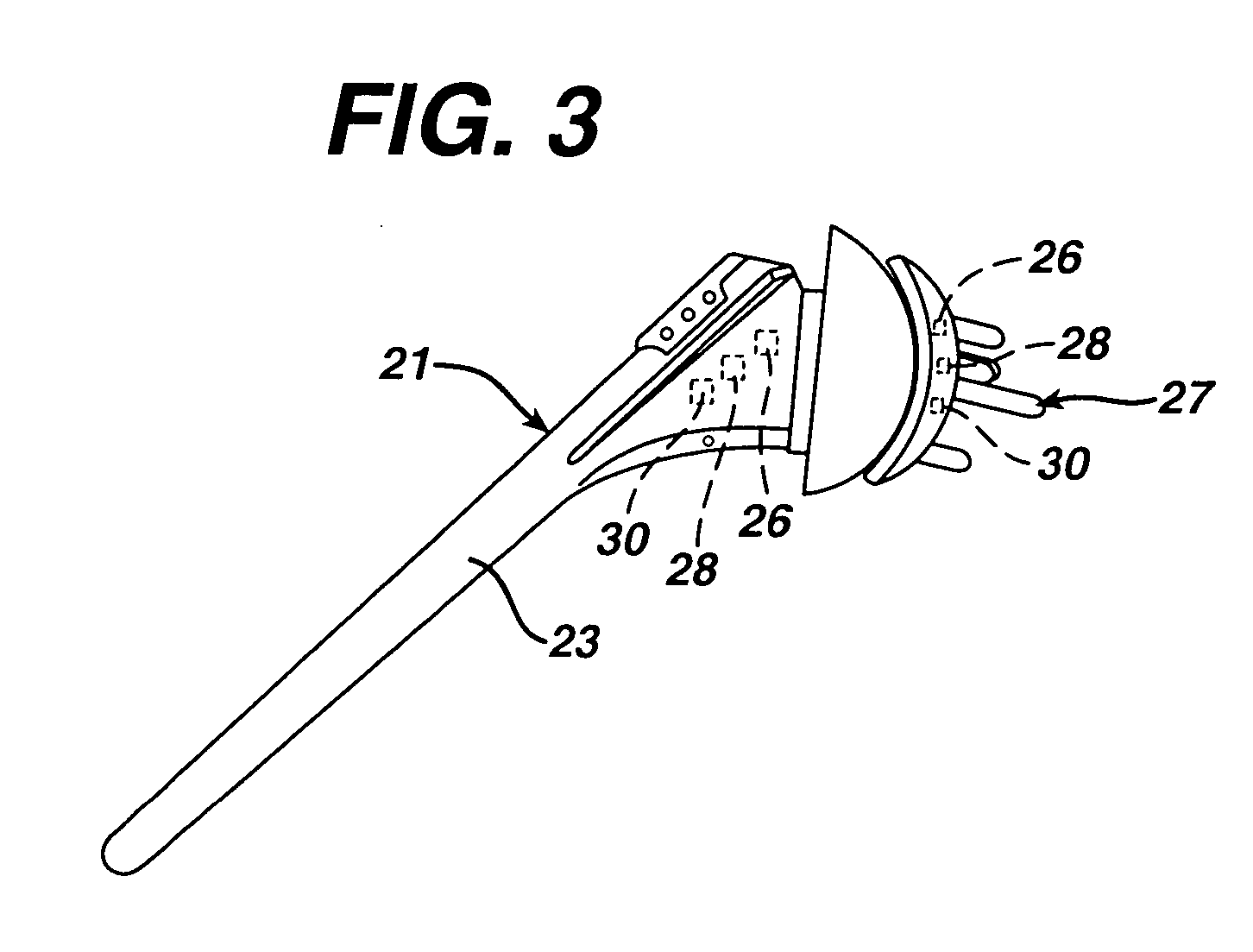
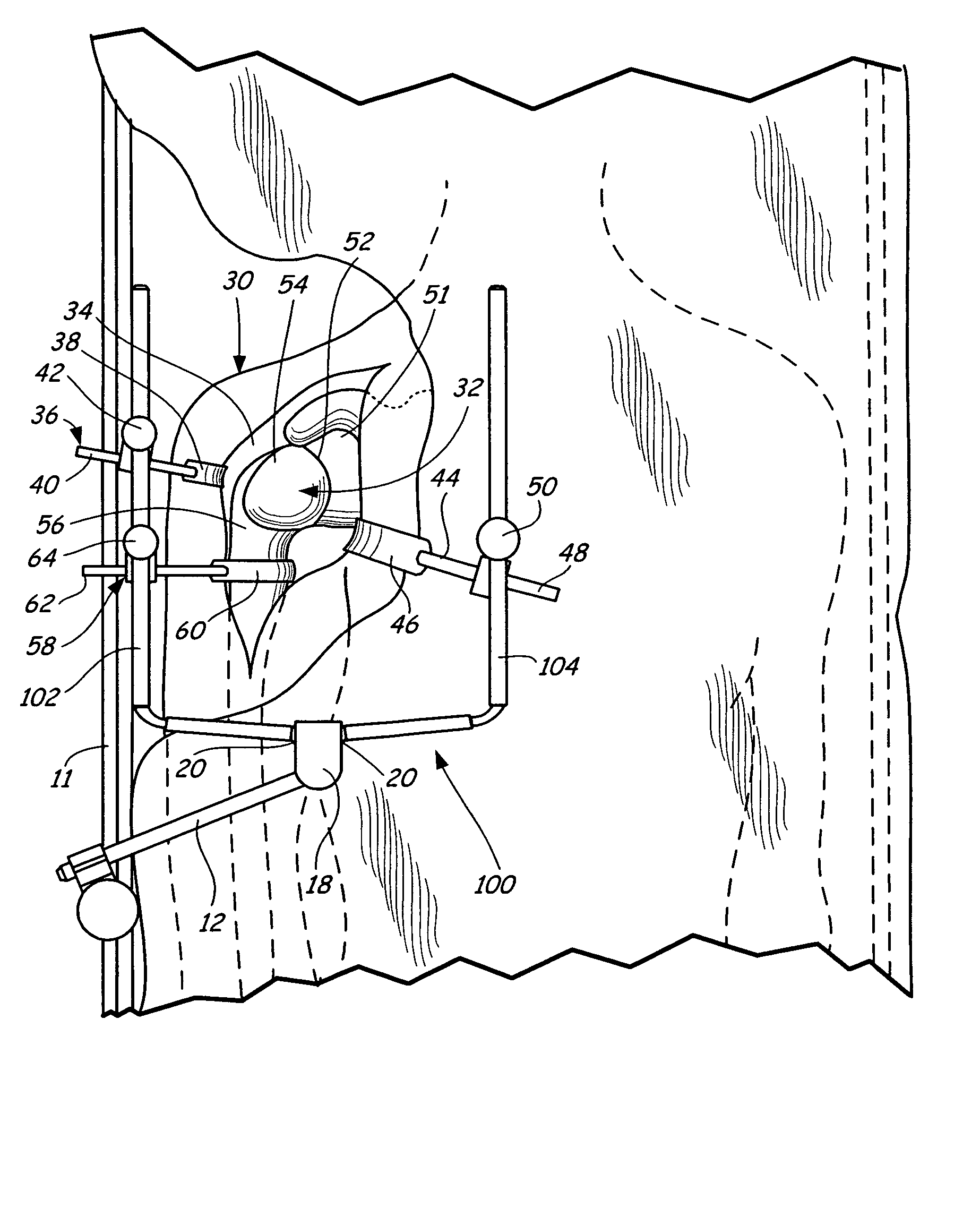
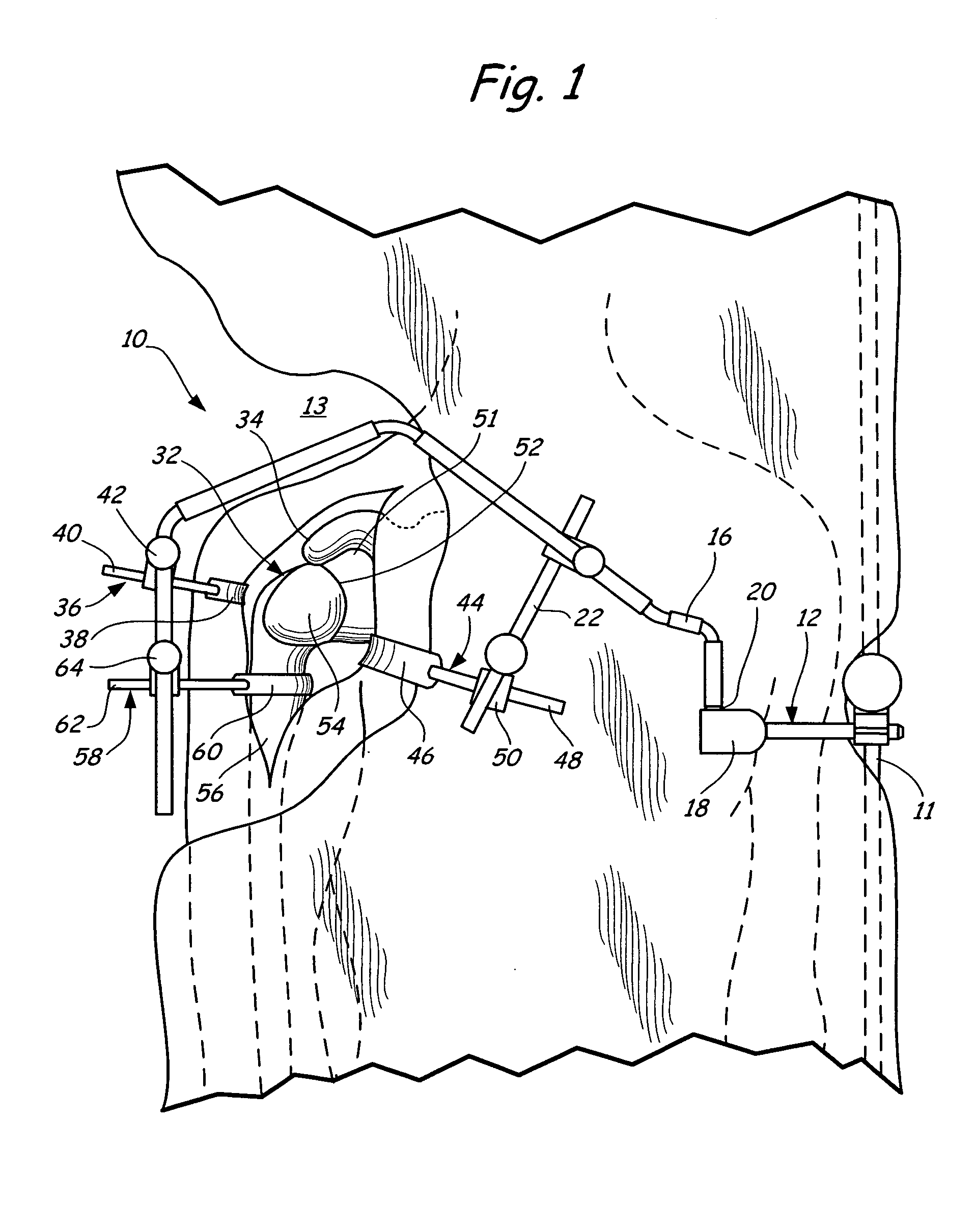
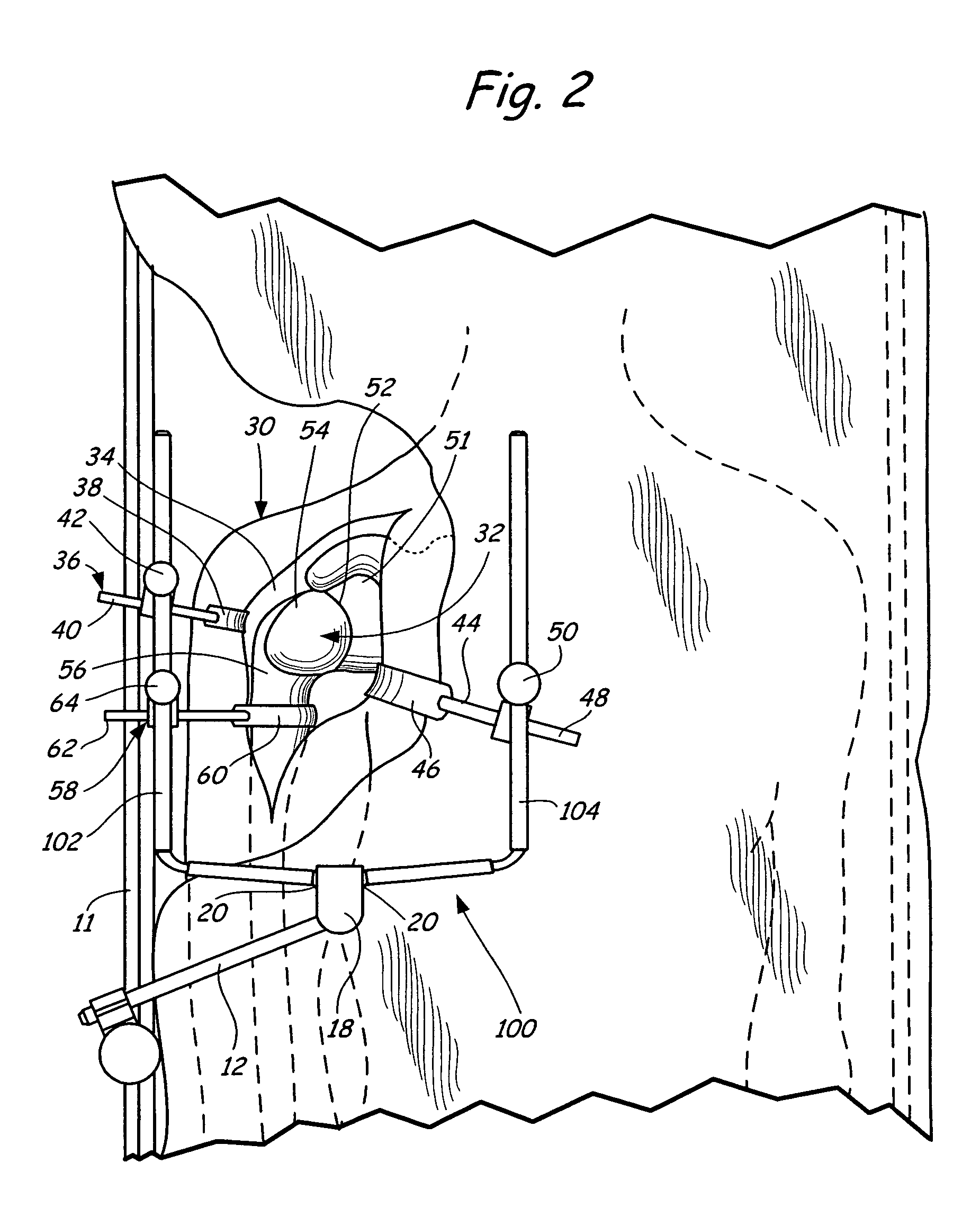
Method of performing shoulder surgery
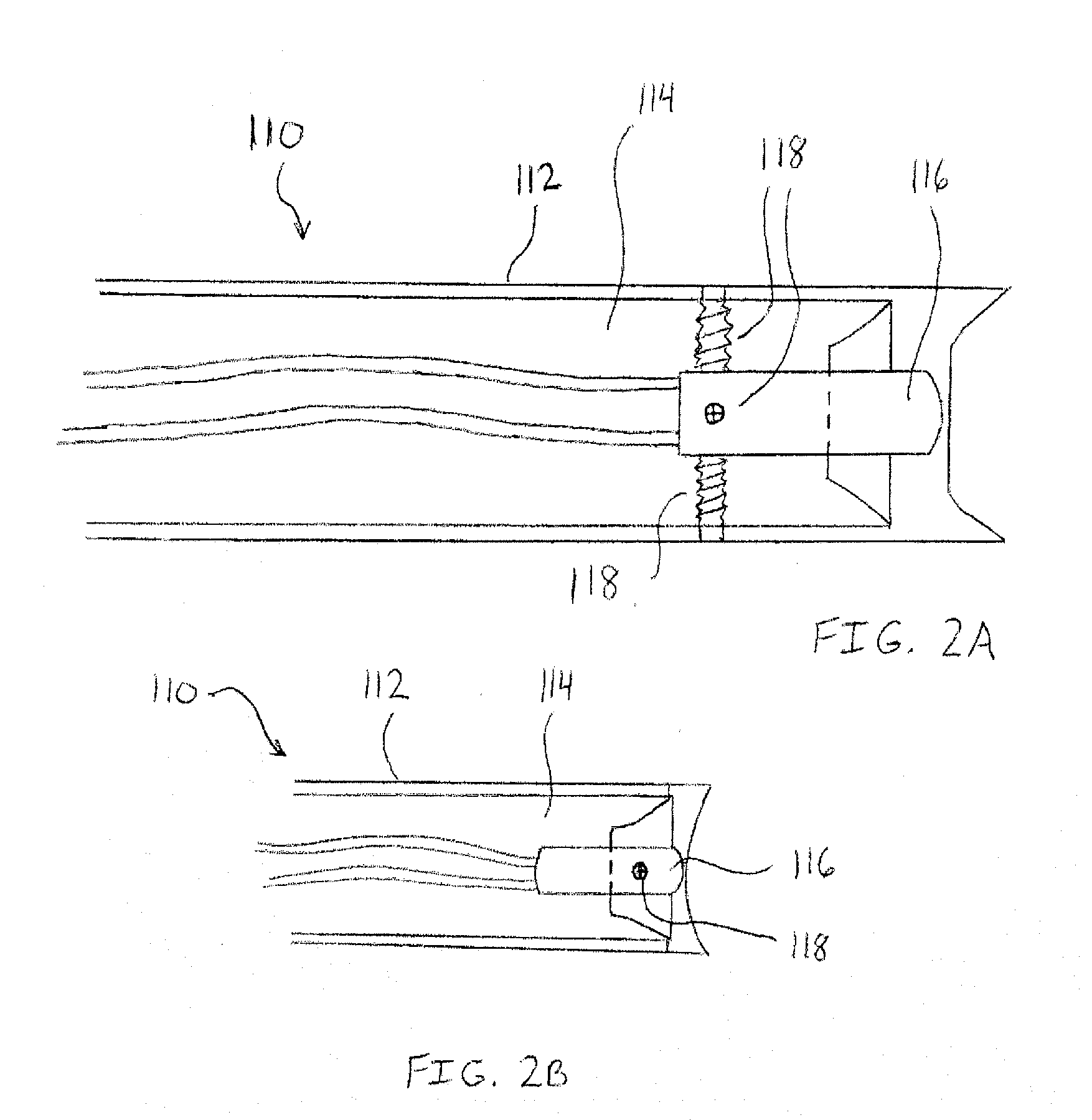
A method of performing a shoulder joint surgery involving a scapula having a glenoid cavity, a humerus and a humeral ball on a surgical table includes mounting a retractor support to the surgical table and positioning the retractor support about the shoulder joint. The skin and flesh layers proximate the shoulder joint are incised and the skin and flesh layers are manually retracted with a retractor. The retractor is secured in a selected position by attaching the retractor to the retractor support.
Owner:MINNESOTA SCI
Knee joint prosthesis
InactiveUS20050043808A1Eliminate the effects ofImprove propertiesImpression capsAnkle jointsTissue repairProsthesis
A method, and related composition and apparatus for repairing a tissue site. The method involves the use of a curable polyurethane biomaterial composition having a plurality of parts adapted to be mixed at the time of use in order to provide a flowable composition and to initiate cure. The flowable composition can be delivered using minimally invasive means to a tissue site and there fully cured provide a permanent and biocompatible prosthesis for repair of the tissue site. Further provided are a mold apparatus, e.g., in the form of a balloon or tubular cavity, for receiving a biomaterial composition, and a method for delivering and filling the mold apparatus with a curable composition in situ to provide a prosthesis for tissue repair.
Owner:ADVANCED BIO SURFACE
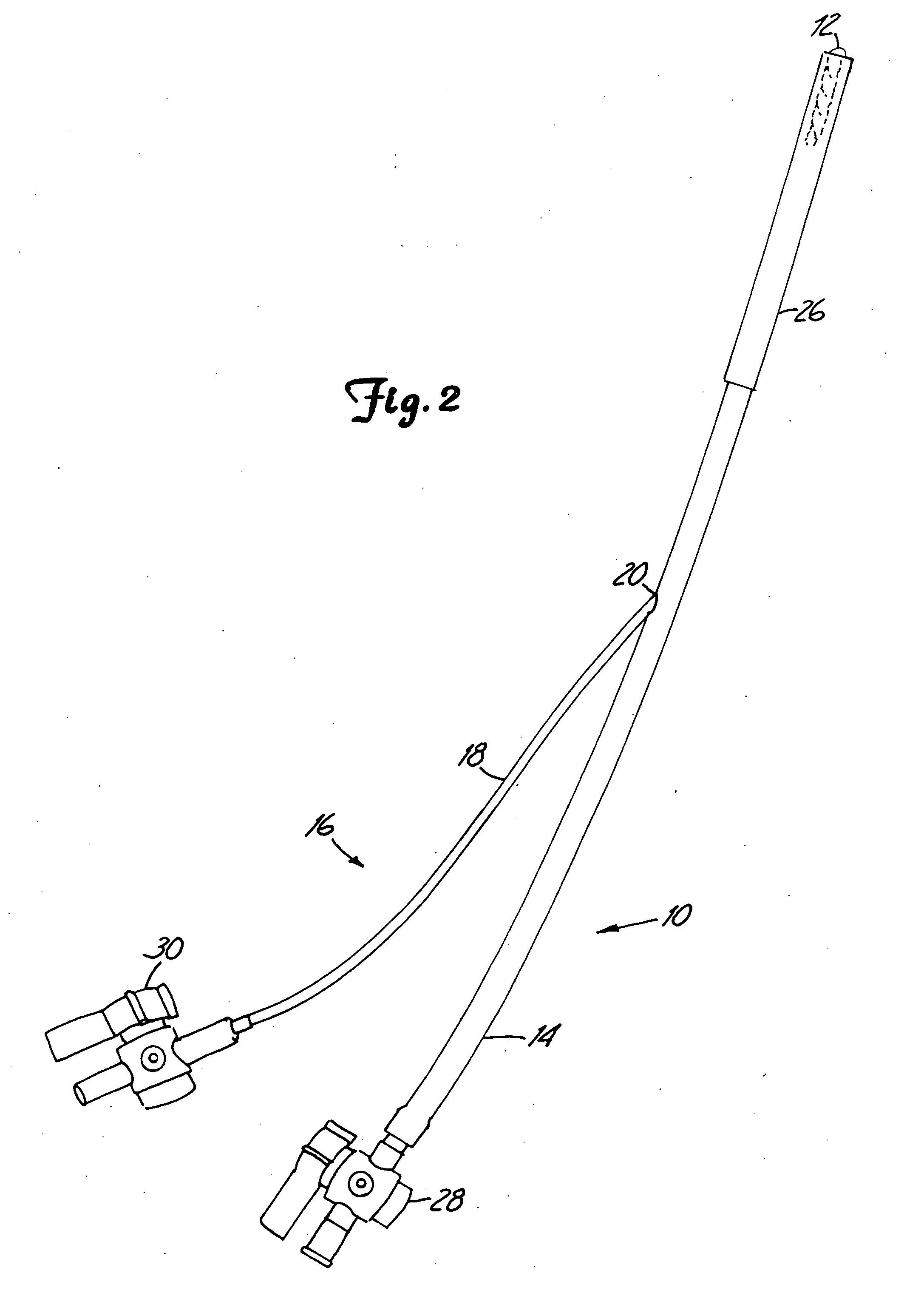
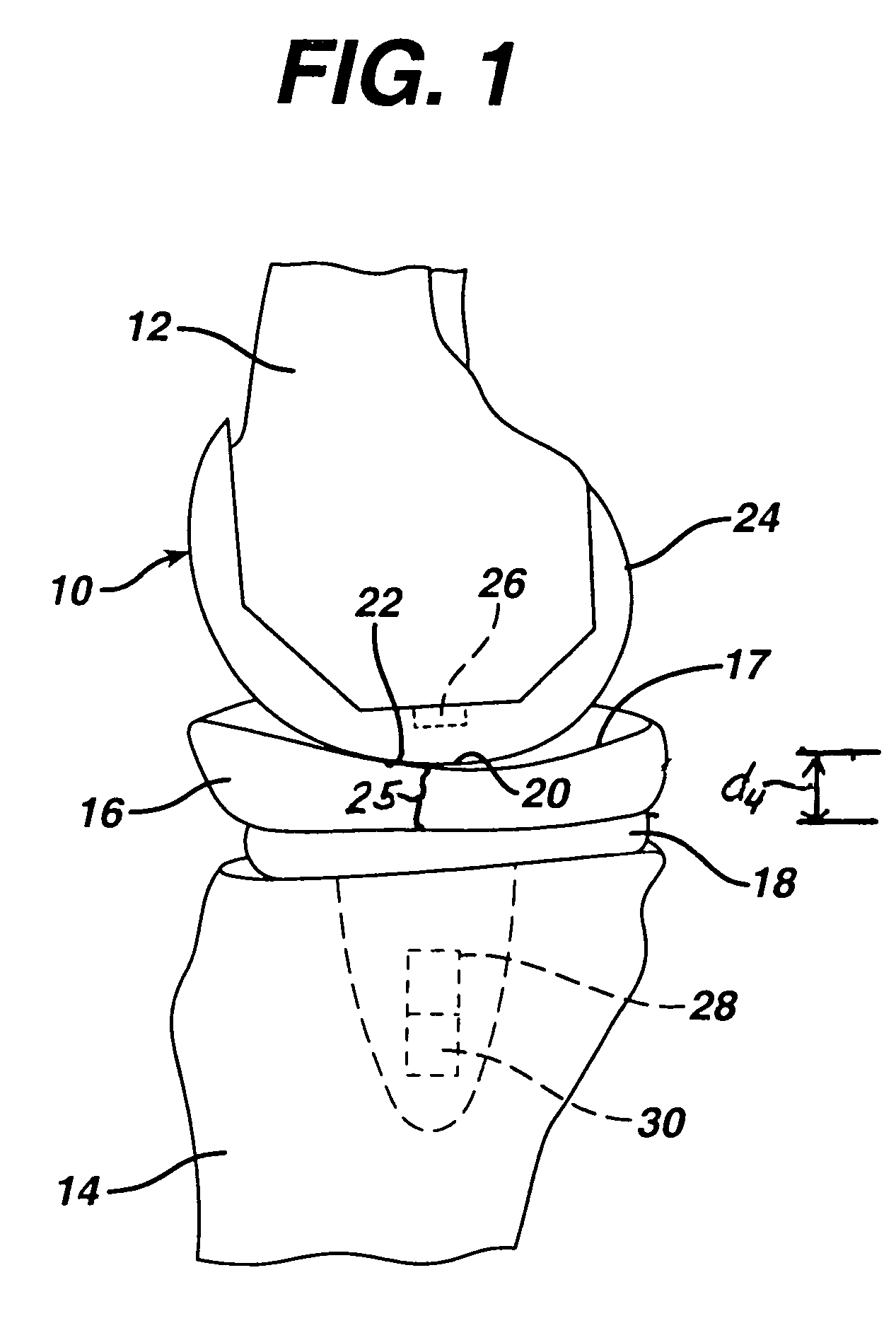
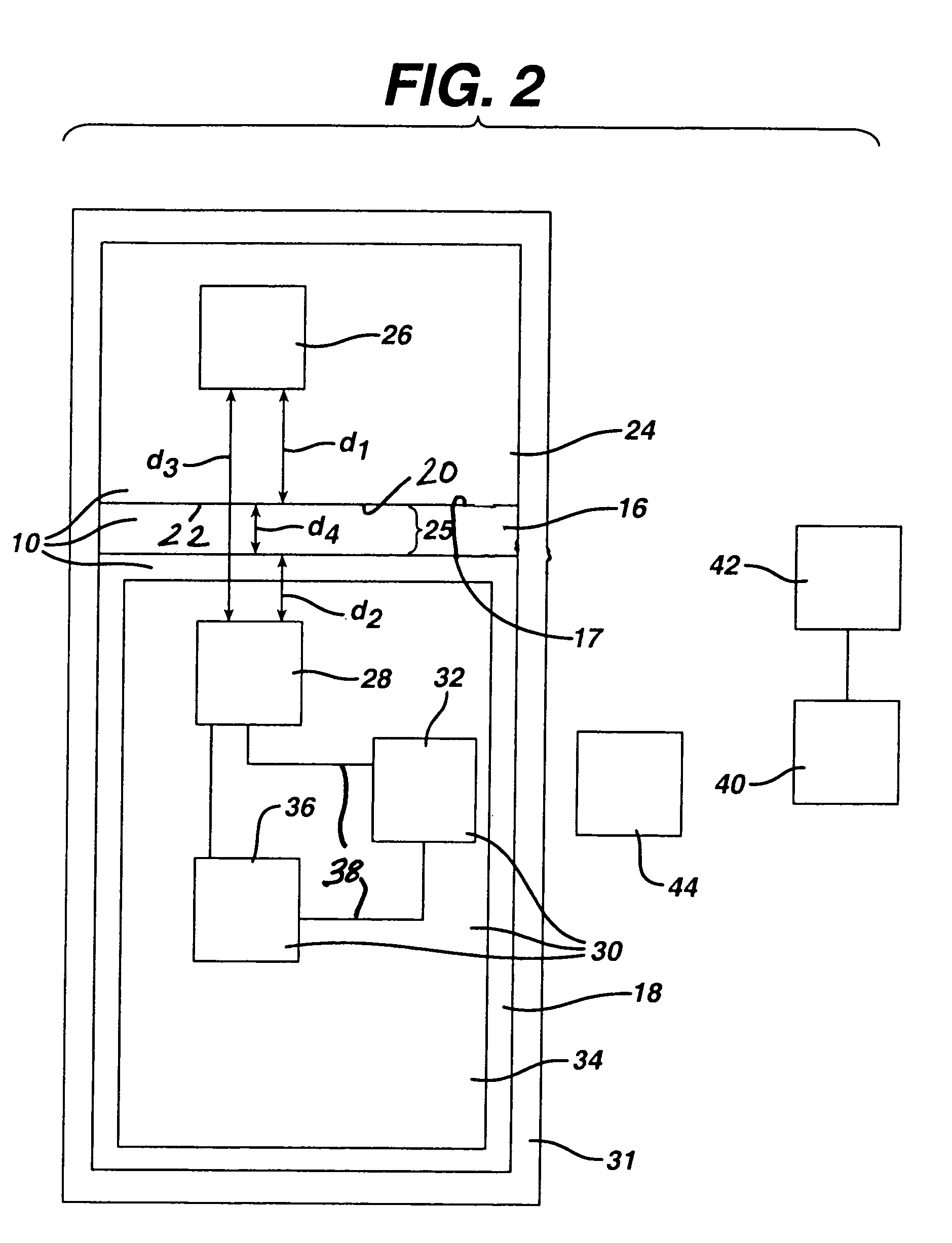
In vivo joint space measurement device and method
A joint endoprosthesis system has first and second prosthetic components. The second prosthetic component has a bearing surface. The interface of the bearing surface and the first prosthetic component defines the joint articulation. A signal source and sensor are affixed on opposite sides of the joint articulation. The signal source generates a first signal that is received by the sensor. The sensor generates a second signal that has a characteristic that varies depending on the distance between the sensor and the signal source. A transmitter transmits a signal. The signal has a characteristic that varies depending on the characteristic of the second signal. This system can be used to measure a dimension of the joint space and to determine whether a dimension of the joint space has changed over time. The system may alternatively use magnets and magnetic sensors.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com