Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Tissue integration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Deep Tissue Integration is a system that addresses the long-term patterns of resistance in the connective tissues of the body. Deep Tissue Integration attempts to readjust the body through myofascial release. Through a series of eight to ten sessions, the therapist will assess postural...
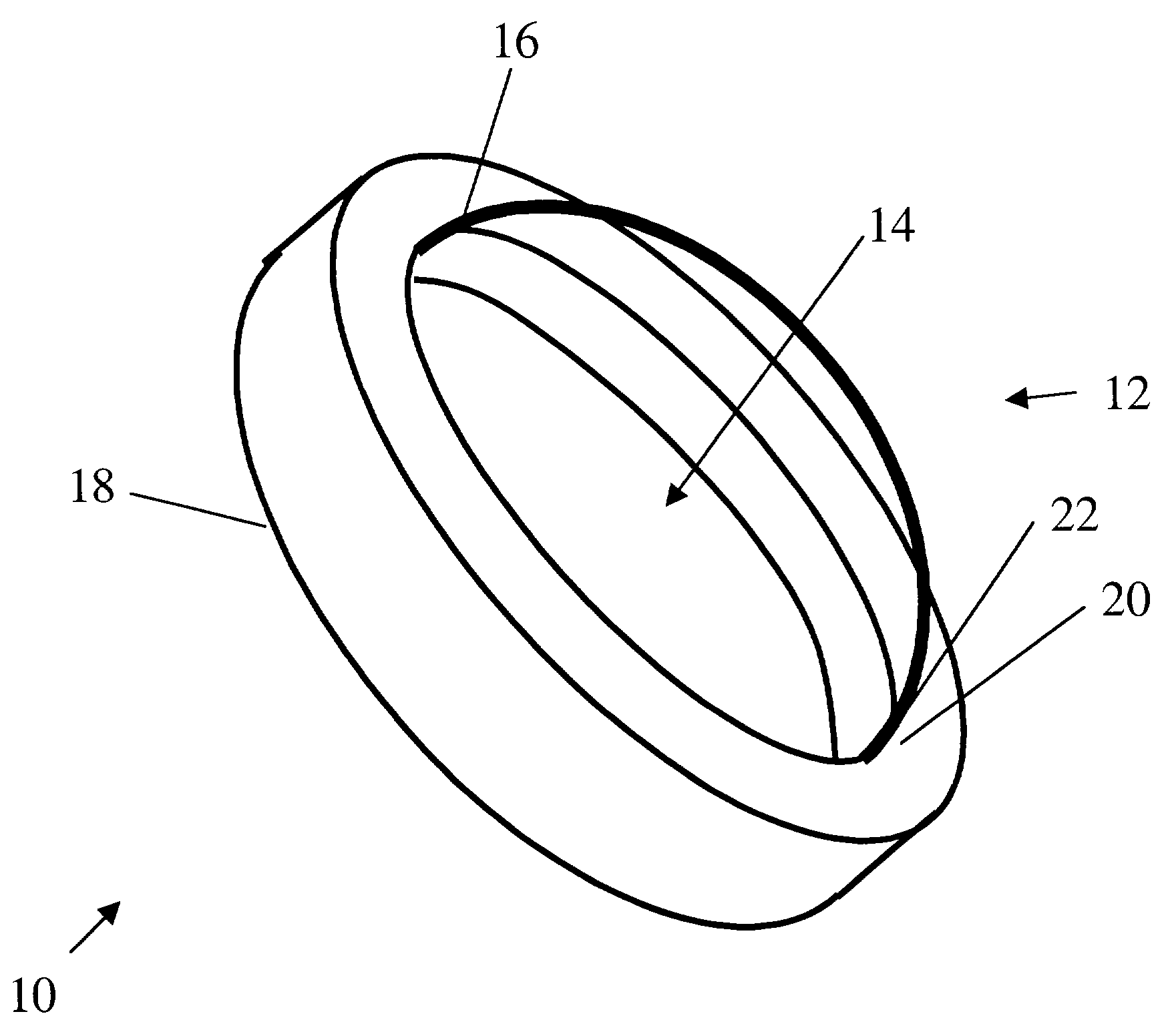
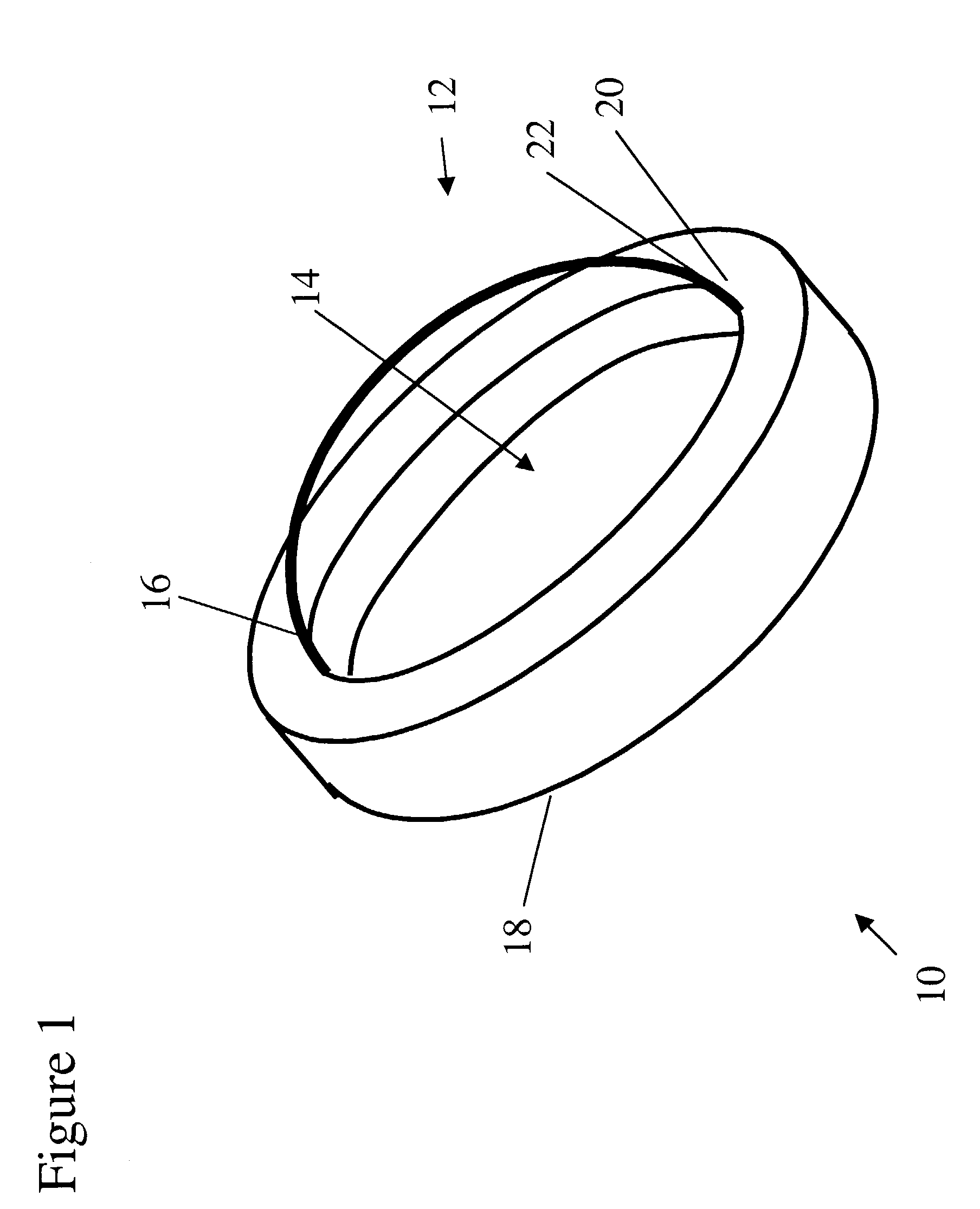
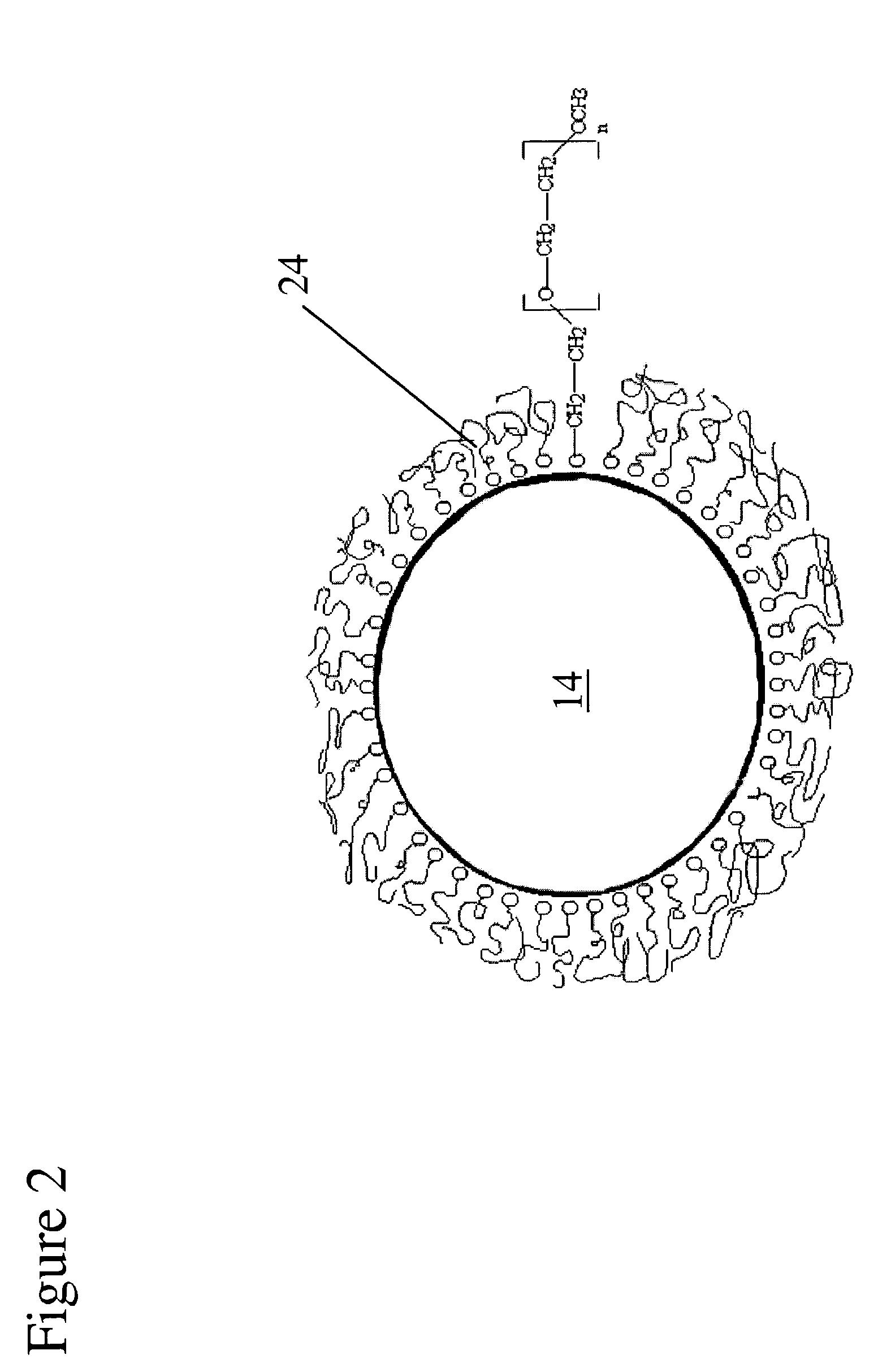
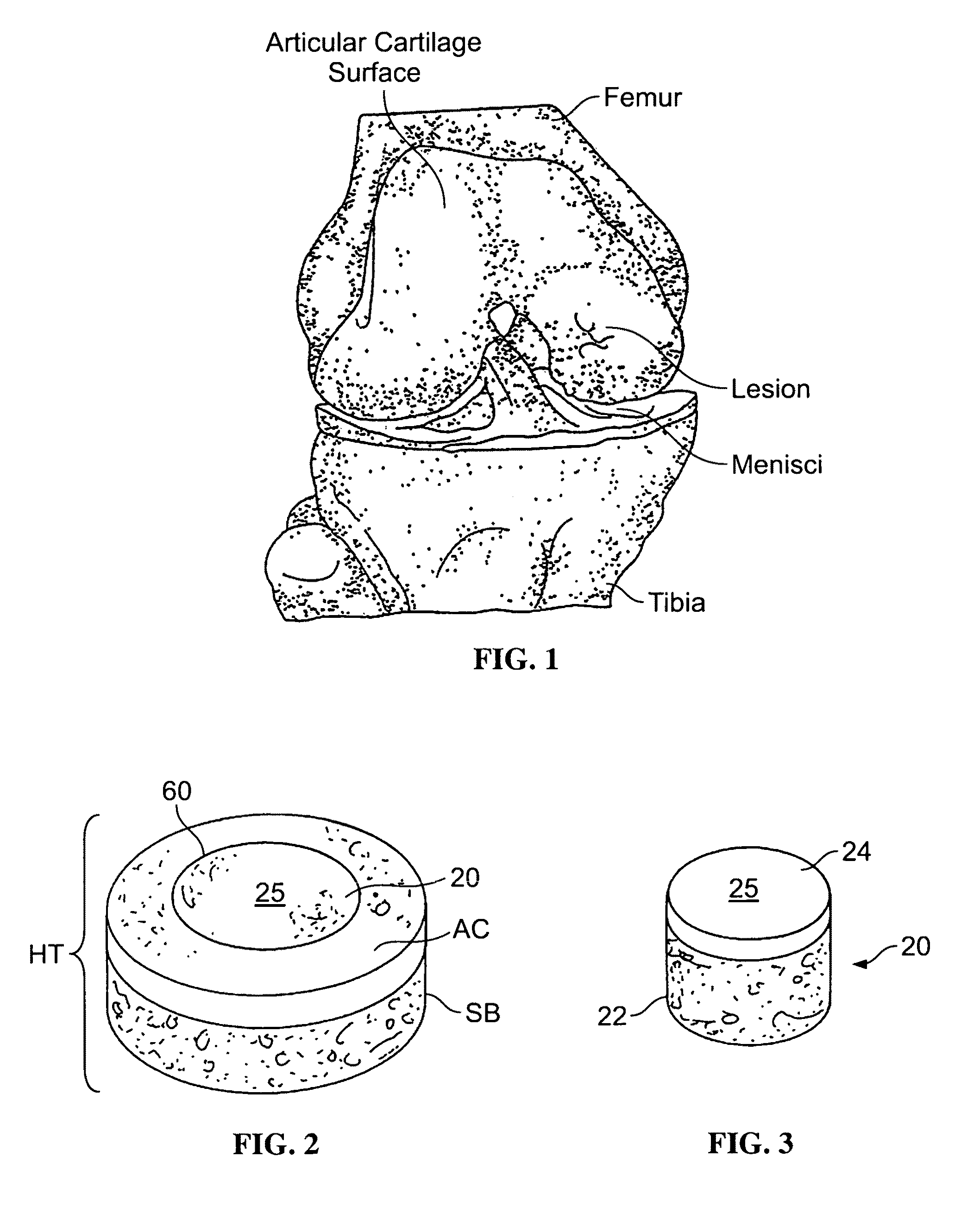
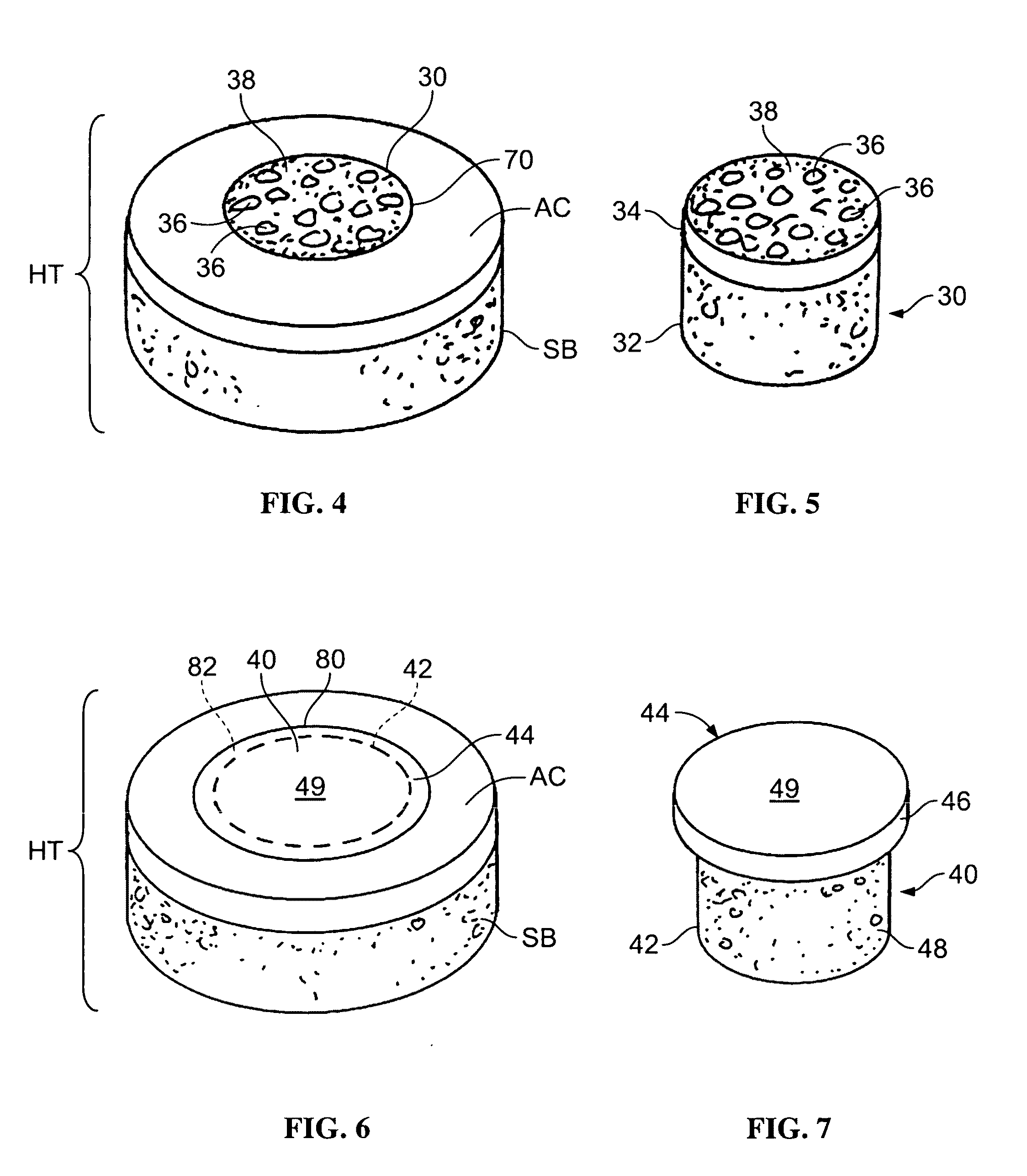
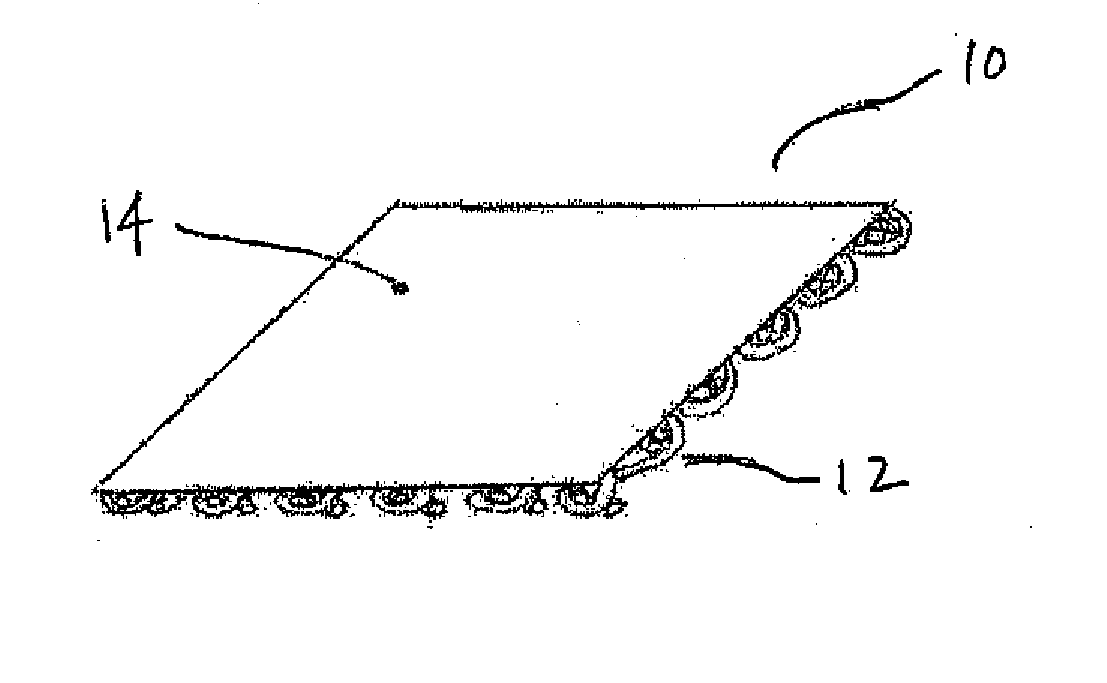
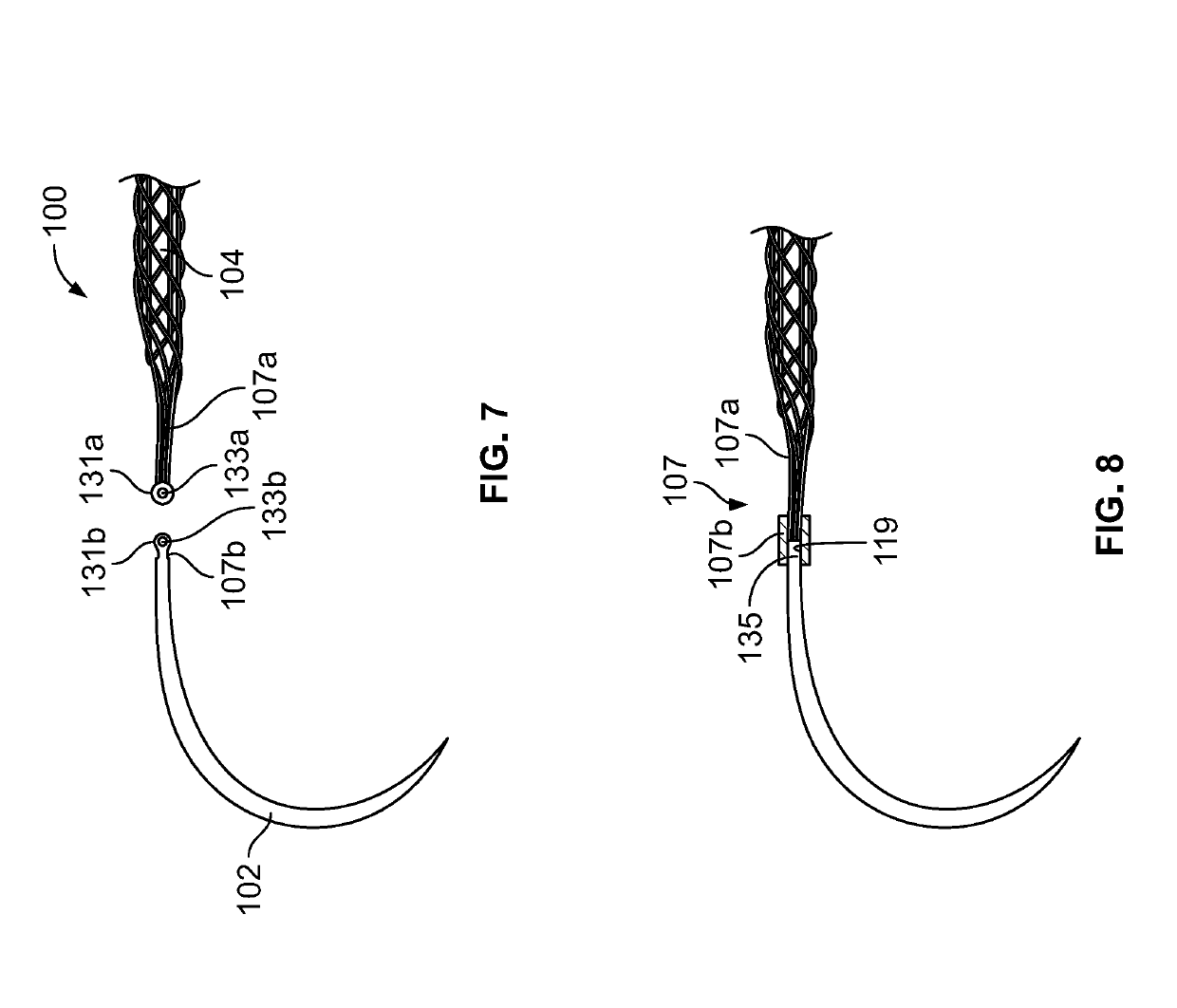
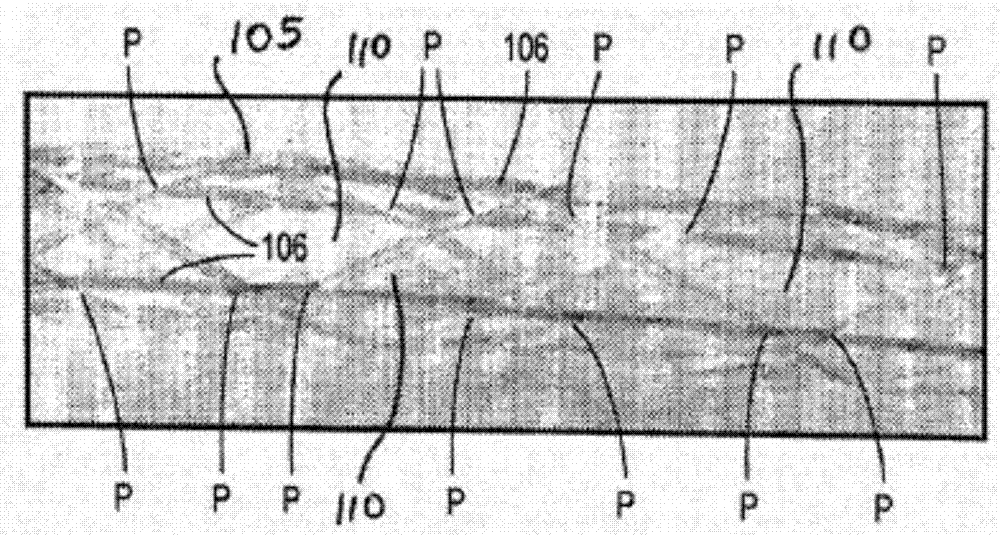
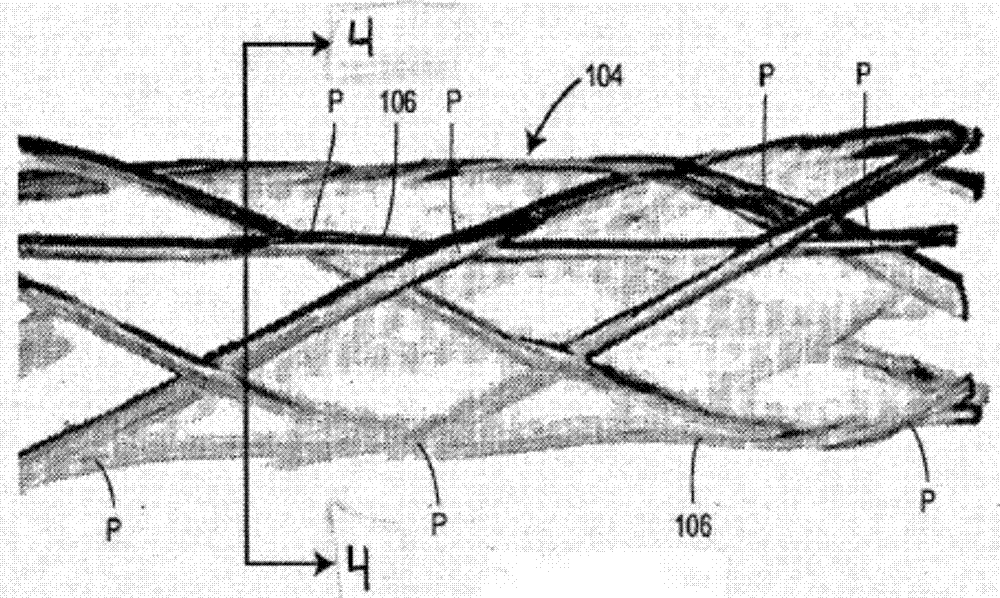
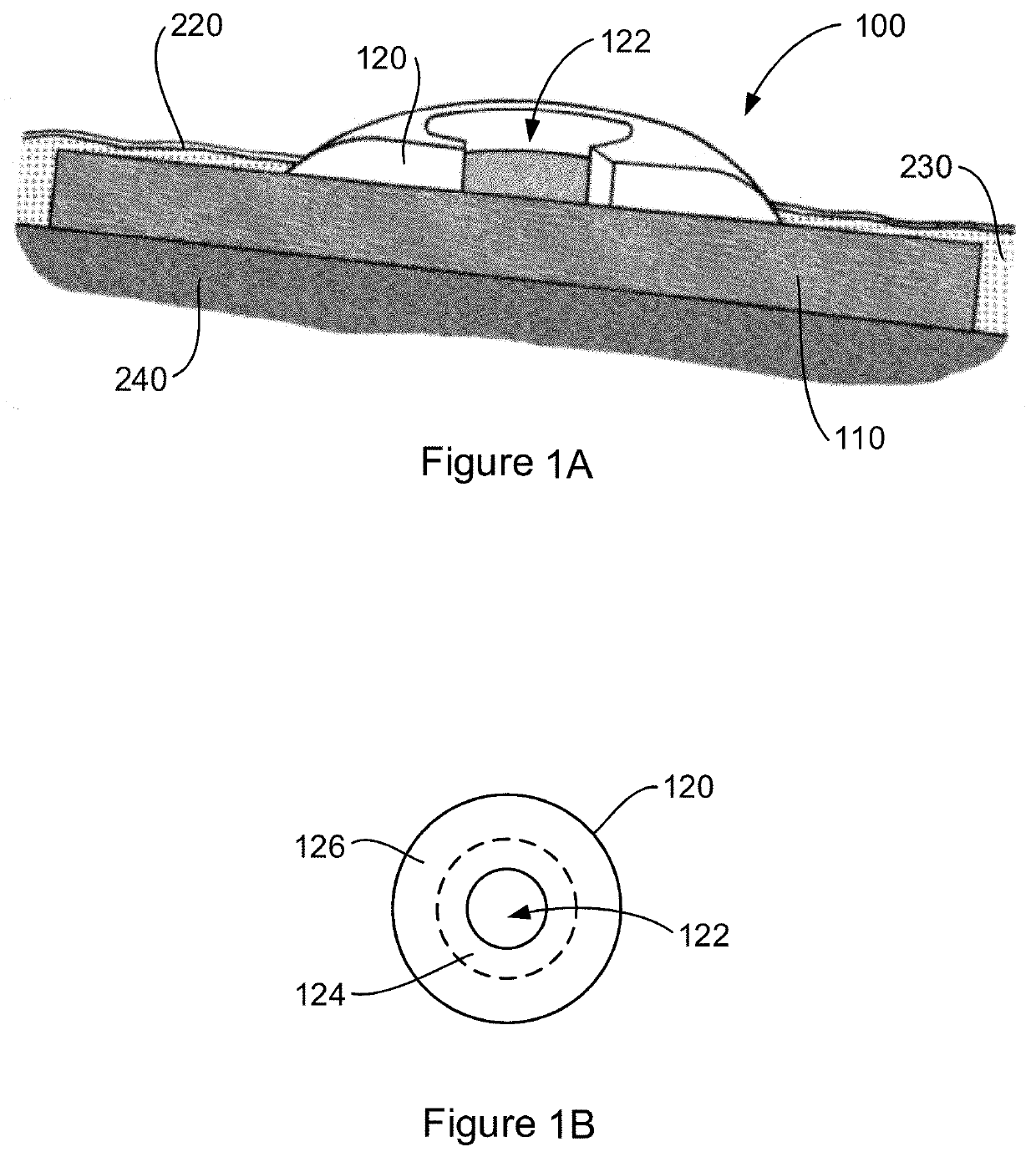
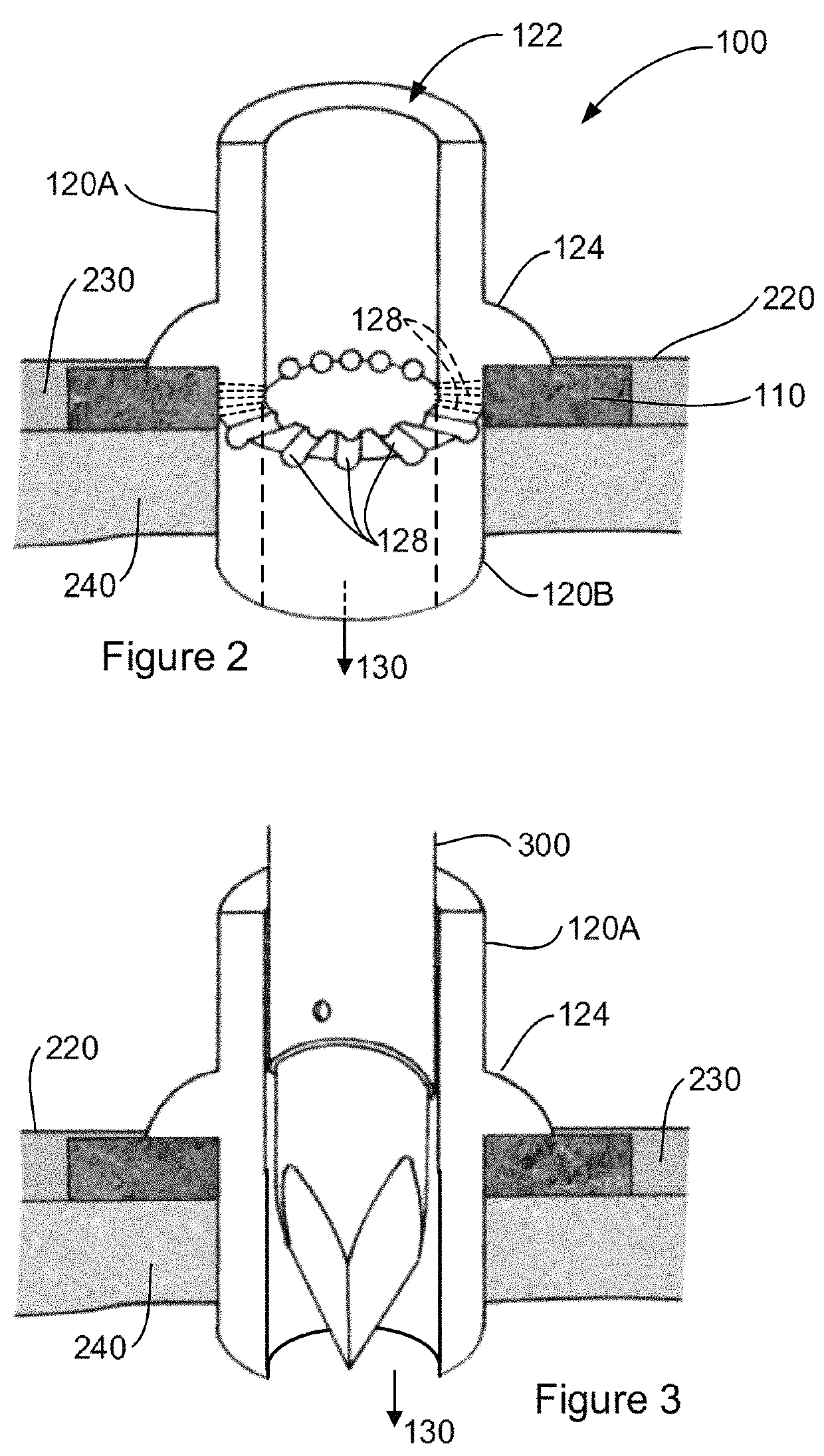
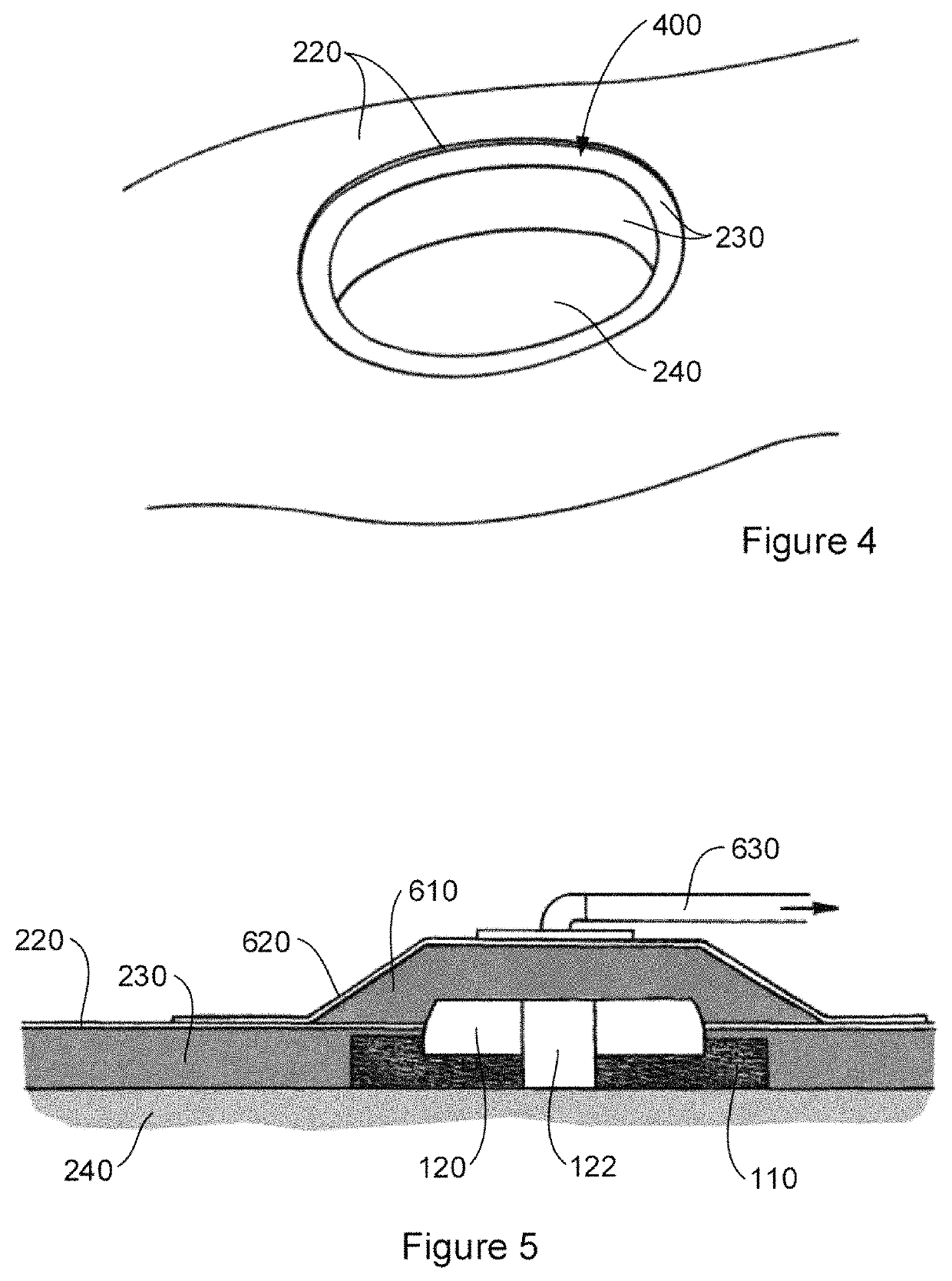
Tissue integration design for seamless implant fixation
The present invention relates to orthopaedic implants having a fenestrated hollow shell and a biologic core. These design features provide an improved interface between the implant and the surrounding tissue, aiding fixation, and provide a vehicle for applying new bone healing and enhancing modalities, such as gene therapy, tissue engineering, and growth factors.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
Stent graft with external scaffolding and method
ActiveUS20170231749A1Promote tissue ingrowthEasy to integrateStentsBlood vesselsTissue integrationStent grafting
A scaffolded stent-graft includes a graft material comprising an inner surface and an outer surface. The inner surface defines a lumen within the graft material. The scaffolded stent-graft further includes a scaffold comprising a mesh coupled to the graft material at the outer surface. The scaffold is configured to promote tissue ingrowth therein. In this manner, the scaffold enhances tissue integration into the scaffolded stent-graft. The tissue integration enhances biological fixation of the scaffolded stent-graft in vessels minimizing the possibility of endoleaks and migration.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Artificial cornea
InactiveUS6976997B2Improve mechanical propertiesEasy to suture onto recipient bedMaterial nanotechnologyCoatingsDiseasePostoperative inflammation
The invention provides implants suitable for use as an artificial cornea, and methods for making and using such implants. Artificial corneas having features of the invention may be two-phase artificial corneas, or may be three phase artificial corneas. These artificial corneas have a flexible, optically clear central core and a hydrophilic, porous skirt, both of which are biocompatible and allow for tissue integration. A three-phase artificial cornea will further have an interface region between the core and skirt. The artificial corneas have a high degree of ocular tolerance, and allow for tissue integration into the skirt and for epithelial cell growth over the surface of the prosthesis. The use of biocompatible material avoids the risk of disease transmission inherent with corneal transplants, and acts to minimize post-operative inflammation and so to reduce the chance or severity of tissue necrosis following implantation of the synthetic cornea onto a host eye.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Allograft osteochondral plug combined with cartilage particle mixture
InactiveUS20090291112A1Promoting cartilage cell migration intoPromoting proliferationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInterference fitSubchondral bone
An allograft osteochondral plug is combined with a mixture that includes freeze-milled cartilage particles, and such combination is used to repair defects in articular cartilage. The plug includes an subchondral bone portion and an integral overlying cartilage cap which is treated to remove cellular debris and proteoglycans. At least a portion of the plug has a lateral dimension selected to form an interference fit against a tissue layer exposed as a result of a bore formed in a defect area in articular cartilage of a host. The cartilage particle mixture is placed adjacent at least a portion of the plug for promoting cartilage cell migration into (i.e., from the adjacent host cartilage) and proliferation in the bore, and for enhancing tissue integration between the plug and patient (i.e., host) tissue when the plug is inserted into the bore. Methods for surgical implantation of the plug into a patient are also disclosed.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Tissue integration implant
The present invention relates to a tissue defect repair implant including a porous material, wherein the material is expandable or compressible. The implant may be a scaffold, and may also be formed of a material such as, for example, collagen or demineralized bone matrix. Another aspect of the invention may be a method for the repair of a tissue defect in a patient in need thereof, including implanting an implant between two adjacent tissues, wherein the implant may include a porous material which is expandable or compressible. The two tissues may be soft tissue and hard tissue, and alternatively, the two tissues may be soft tissue, and may further be the same or different soft tissues.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
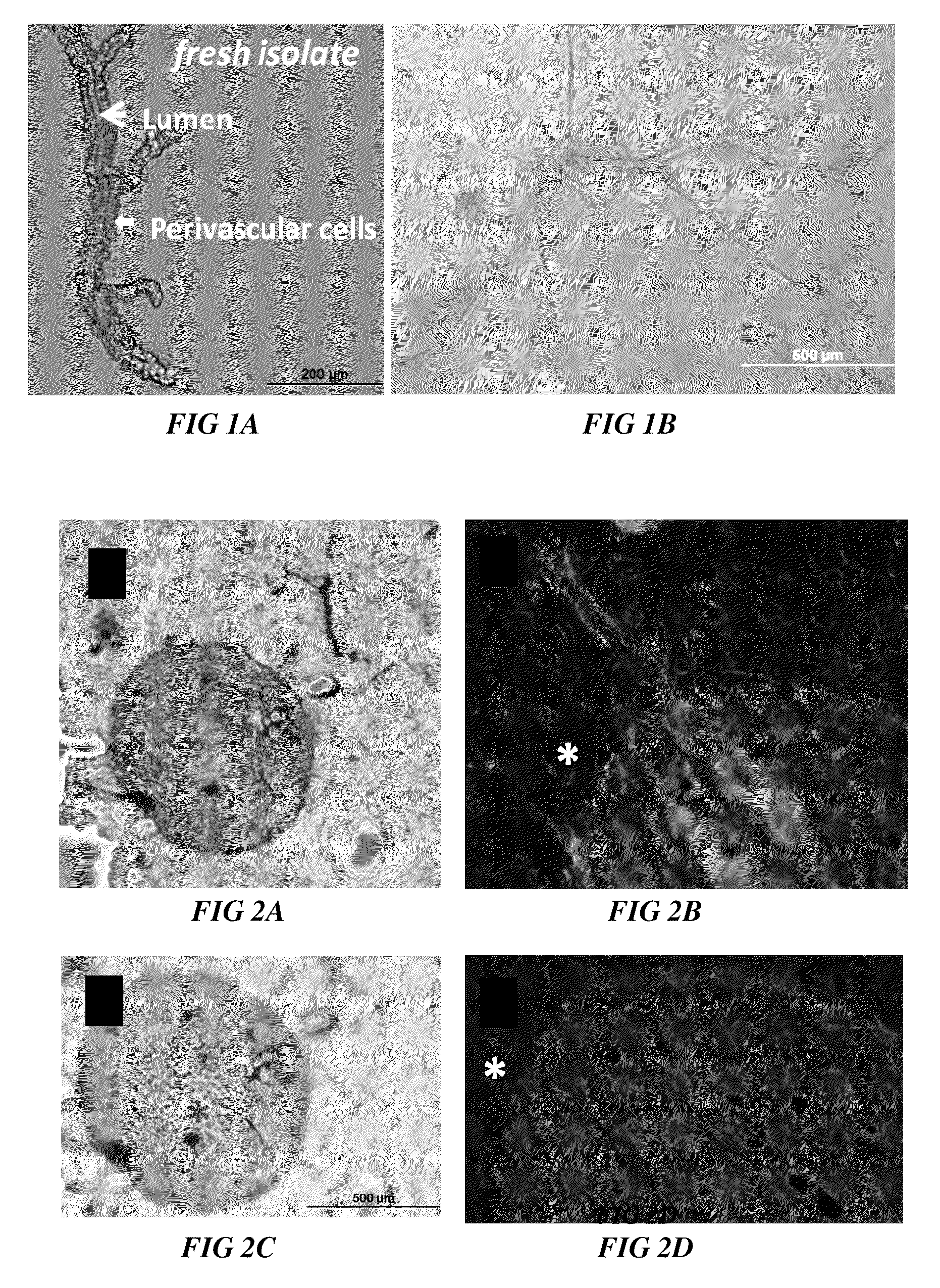
Methods and compositions to support tissue integration and inosculation of transplanted tissue and transplanted engineered penile tissue with adipose stromal cells
ActiveUS20110218396A1Improve efficiencyEasy to integrateNon-surgical orthopedic devicesPenis implantsSexual impotenceTissue integration
The present invention generally relates to methods, compositions and uses thereof for enhancing vascularization of a tissue or cell transplant for transplantation into a subject. In particular, one aspect of the present invention provides methods and compositions comprising the use of a population of stromal vascular fraction (SVF) cells to encapsulate or surround a tissue or cell transplant to enhance vascularization of the tissue or cell transplant. Another aspect of the present invention provides methods and compositions for enhancing vascularization of a tissue or cell transplant by combining a population of SVF cells with a tissue or cell transplant to form a transplant mixed with SVF cells. Another aspect provides a composition comprising an engineered corpus cavernosum tissue comprising SVF cells and corpus cavernosum cells, wherein the SVF cells can be mixed with or encasing the corpus cavernosum cells, and methods of uses thereof, for example in method for the treatment of impotence and erectile dysfunction and / or enhance or construct a penis. In some embodiments, the SVF cells can be generically engineered to secrete therapeutic proteins or pro-angiogenic factors.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC +1
Implants with absorbalbe and non-absorbable features for the treatment of female pelvic conditions
ActiveUS20130197300A1Improves tissue integrationReduce the likelihood of infectionAnti-incontinence devicesSurgeryDiseaseTissue integration
Described are methods, devices, and systems related to implants for the treatment of a female pelvic condition. The implants include absorbable and non-absorbable materials and can be introduced into the pelvic area transvaginally. Meshes of the invention provide benefits relating to improved tissue integration into the mesh, reduced infection likelihood, improved patient comfort following implantation, or combinations of thereof.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Biosynthetic functional cellulose (BC) fibers as surgical sutures and reinforcement of implants and growing tissue
Embodiments of the invention are based on the fermentation of bacteria to produce nano-cellulose in oxygen permeable tubular bioreactors. The resulting hydrogel non-hollow fiber can be stretched and dewatered to form strong, stiff yet flexible fiber. The fiber can be dehydrated by freeze drying or solvent exchange to form macroporous material and then optionally soaked with a solution of growth factors, anti-inflammatory drugs, and / or anitibacterial agents to provide a slow release drug delivery device in fiber form. The surface of the fiber is composed of nano-structured cellulose which promotes cell migration, tissue integration, and the healing process. BC fibers are not degraded in the human body and thus are well suited as reinforcement of implants and growing tissue. Uses for the BC fibers include surgical sutures, and reinforcing and promoting regeneration of damaged tissue or implants.
Owner:BC GENESIS
Device for tissue reinforcement having microporous and macroporous structures
InactiveUS20080082177A1Enhancing tissue repairPromote tissue regenerationAnti-incontinence devicesSurgeryTissue integrationBiomedical engineering
A device for tissue reinforcement. The device has a macroporous structure. At least a section of the macroporous structure is coated with a microporous coating. The microporous and macroporous morphologies allow both cell in-growth and tissue integration.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Implants with absorbalble and non-absorbable features for the treatment of female pelvic conditions
ActiveUS20170035542A1Easy to integrateReduce the likelihood of infectionAnti-incontinence devicesSurgeryDiseaseTissue integration
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
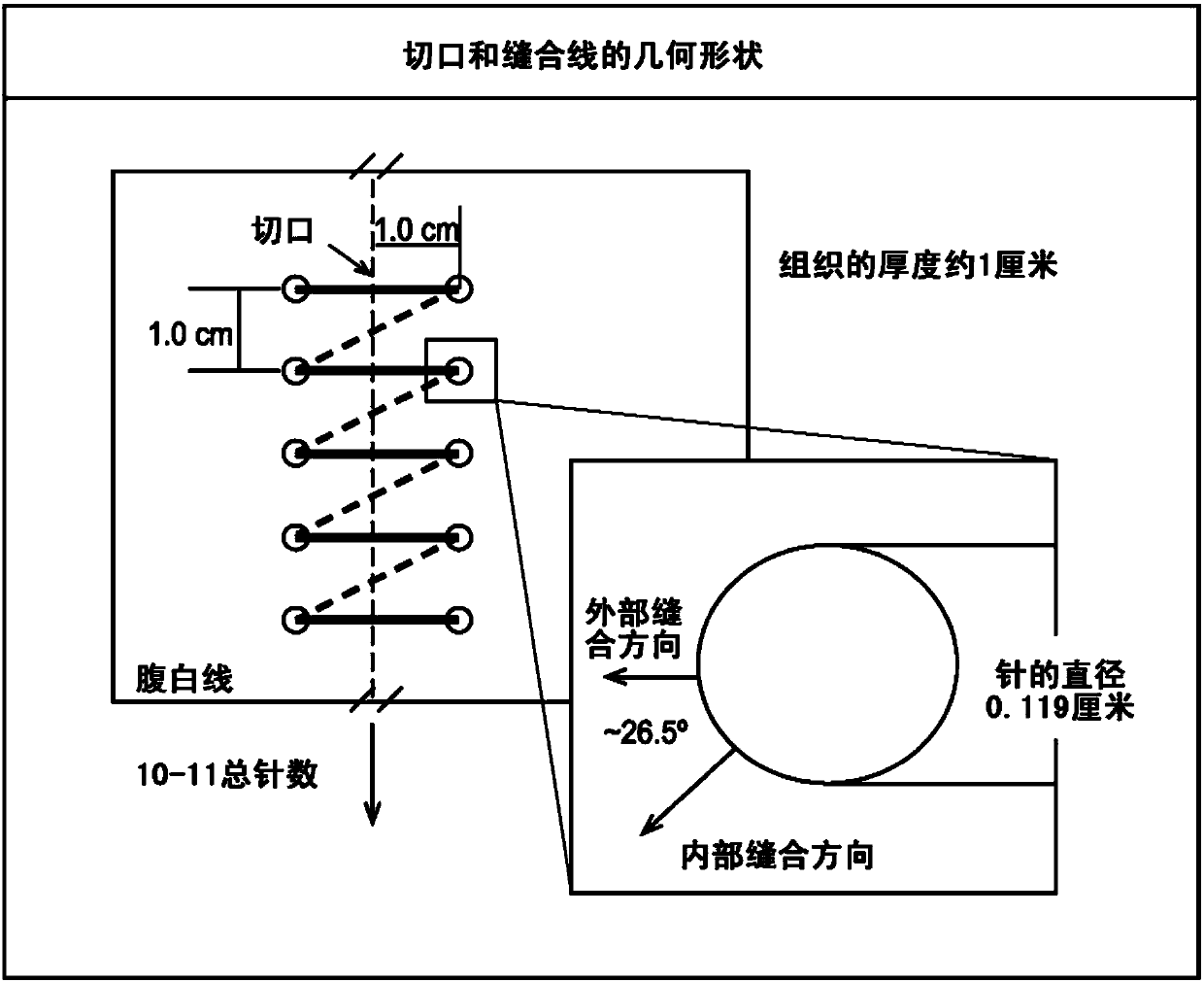
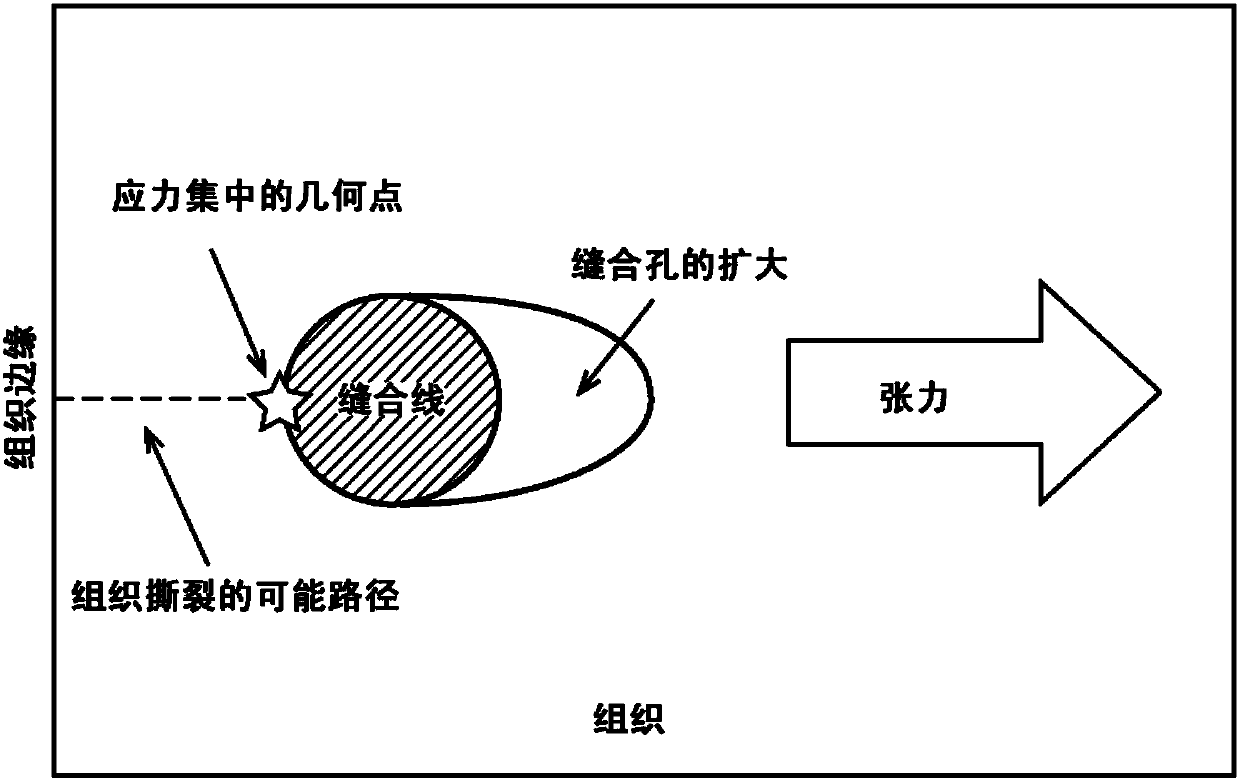
Improved suture
A medical device includes a surgical needle attached to a hollow tubular suture. The suture is constructed of macroporous hollow tubular wall that facilitates and allows tissue integration into the suture core subsequent to introduction to the body, thereby preventing suture pull-through and improving biocompatibility.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Tissue integration design for seamless implant fixation
The present invention relates to orthopaedic implants having a fenestrated hollow shell and a biologic core. These design features provide an improved interface between the implant and the surrounding tissue, aiding fixation, and provide a vehicle for applying new bone healing and enhancing modalities, such as gene therapy, tissue engineering, and growth factors.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
Indirect attachment of a needle to a mesh suture
A medical device includes a surgical needle, an elongated suture, and an intervening segment. The elongated suture has a first end proximate to the needle and a second end located away from the needle. The elongated suture also includes a plurality of fibers defining a mesh wall between the first and second ends. A plurality of pores extend through the mesh wall, at least some which are in the macroporous size range of greater than 200 microns for facilitating tissue integration when introduced into a body. The intervening segment is disposed between and connected to either or both ends of the elongated suture and the needle. The intervening segment includes one or more fibers of the plurality of fibers and has a cross-sectional dimension smaller than a cross-sectional dimension of the mesh wall such that the intervening segment facilitates indirect attachment of the elongated macroporous mesh suture to the needle.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Methods and compositions to support tissue integration and inosculation of transplanted tissue and transplanted engineered penile tissue with adipose stromal cells
ActiveUS8727965B2Promote formationIncreased vascularizationNon-surgical orthopedic devicesPenis implantsTissue integrationCavernous tissue
The present invention generally relates to methods, compositions and uses thereof for enhancing vascularization of a tissue or cell transplant for transplantation into a subject. In particular, one aspect of the present invention provides methods and compositions comprising the use of a population of stromal vascular fraction (SVF) cells to encapsulate or surround a tissue or cell transplant to enhance vascularization of the tissue or cell transplant. Another aspect of the present invention provides methods and compositions for enhancing vascularization of a tissue or cell transplant by combining a population of SVF cells with a tissue or cell transplant to form a transplant mixed with SVF cells. Another aspect provides a composition comprising an engineered corpus cavernosum tissue comprising SVF cells and corpus cavernosum cells, wherein the SVF cells can be mixed with or encasing the corpus cavernosum cells, and methods of uses thereof, for example in method for the treatment of impotence and erectile dysfunction and / or enhance or construct a penis. In some embodiments, the SVF cells can be generically engineered to secrete therapeutic proteins or pro-angiogenic factors.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC +1
Conductive and degradable implant for pelvic tissue treatment
ActiveUS20150238300A1Promote healthy tissue growthPromote healingAnti-incontinence devicesCoatingsTissue integrationPelvic diaphragm muscle
Described is a pelvic implant comprising a biodegradable conductive mesh. The mesh can include biodegradable and electrically conductive polymer, and can be stimulated with a current to generate an electric field to promote an improved tissue response following placement of the implant. The invention also describes methods and systems including the pelvic implant comprising a biodegradable conductive mesh for the treatment of pelvic floor conditions. Implants of the invention provide benefits relating to improved tissue integration into the mesh, resulting in pelvic tissue reconstruction. Tissue reconstruction and elimination of the mesh materials can lead to a better clinical outcome for the patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Fish skin-derived medical collagen membrane with compact outer layer and loose inner layer and preparation method of medical collagen membrane
PendingCN113372436AEasy to integratePromote proliferationConnective tissue peptidesSurgeryHydrolysatePepsin
The invention provides a medical collagen membrane with a compact outer layer and a loose inner layer in structure. Fish skin pepsin-solubilized collagen is dissolved in an acid solution to prepare collagen solutions with different concentrations, then laying is performed according to the concentrations from high to low, and pressing is performed to prepare a collagen membrane, wherein the fish skin pepsin-solubilized collagen is prepared by treating fish skin with alkali liquor, and then carrying out enzymolysis with pepsin under a weak acid condition; an enzymatic hydrolysate is centrifuged, a supernate is collected, and the supernate is salted out; precipitates are collected, the precipitates are redissolved with a weak acid solution, and then dialysis treatment is performed; and a dialysate is freeze-dried to prepare the fish skin pepsin-solubilized collagen. The collagen membrane prepared in the invention has three layers of different structures, the aperture of the inner layer is relatively large to promote the growth of osteoblasts, the small aperture of the outer layer can prevent soft tissue cells from entering and allow stem cells and nutrient substances to pass through, and a certain transition layer exists between the inner layer structure and the outer layer structure to facilitate tissue integration.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Implants with absorbable and non-absorbable features for the treatment of female pelvic conditions
ActiveUS9468512B2Easy to integrateReduce the likelihood of infectionAnti-incontinence devicesSurgeryDiseaseTissue integration
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Mesh suture with anti-roping characteristics
InactiveCN107405145APrevents lateral loads from flatteningPrevent pull throughSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesTissue integrationBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides a medical device that includes a surgical needle attached to a mesh suture having anti-roping elements. The suture is constructed of a macroporous mesh wall that facilitates and allows tissue integration subsequent to introduction to the body, thereby preventing suture pull-through and improving biocompatibility. Advantageously, the anti-roping elements serve to maintain the desired construct of the mesh wall when undergoing axial tensile loads by resisting elongation and loss of outer mesh wall macroporosity, while still permitting a flattening of the suture with lateral loading.
Owner:高级缝合有限公司
Improved suture
Owner:ADVANCED SUTURES LTD
Implantable interface device
ActiveUS10918847B2Easy to integrateMaintain capacityMedical devicesCatheterTissue integrationSurgery
An interface device for implantation in a subject includes a tissue integration layer and a crowning element. The tissue integration layer has a porous structure adapted for ingress of tissue to anchor the device when implanted. The crowning element is adapted for epidermal attachment when the device is implanted and is configured such that once implanted, part of the crowning element extends through the epidermis and is accessible from outside the subject's body. The porous structure of the tissue integration layer is interconnected for tissue ingress during implantation.
Owner:OZLOBSTERS PTY LTD
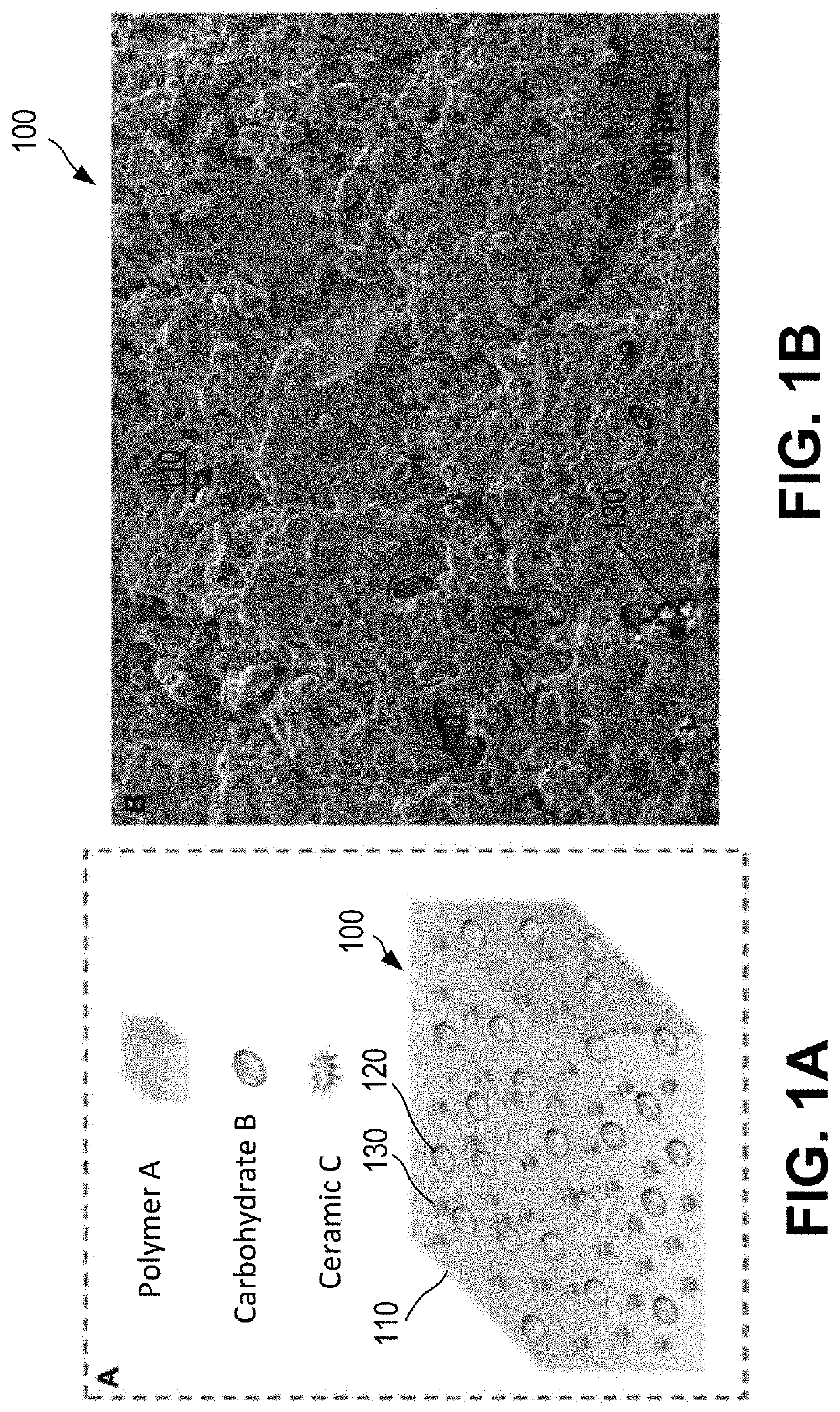
Bioresorbable implant with inside-out resorption for enhanced bone ingrowth and tissue integration and method of manufacturing thereof
PendingUS20210236693A1Easy to integratePromote osseointegrationTissue regenerationProsthesisOsteoblastBone ingrowth
Disclosed is a bioresorbable implant with enhanced bone ingrowth and tissue integration utilizing an inside-out resorption mechanism and a method to manufacture a bioresorbable implants for use in osteotomies and bone-soft tissue reconstruction surgeries. The bioresorbable implant includes a polymer A (e.g., an aliphatic polymer matrix) and / or poly(propylene fumarate)), a carbohydrate B (e.g., a bioresorbable natural carbohydrate filler) and a ceramic C. The implant may be a porous scaffold structures with suitable porosity, pore size, pore interconnectivity, and mechanical properties for enhanced osteoblast penetration and bone formation to fabricate tissue integrating bioresorbable implants. The implant may be shaped as wedges, bone void fillers, and soft tissue fixation implant like screws, rods and / or anchors. In some embodiments, the implant may be a putty.
Owner:SDIP INNOVATIONS PTY LTD
Graft material having selectively advanced permeability structure and method
ActiveUS20190159881A1Improve breathabilityAccurate placementStentsSurgeryTissue integrationProsthesis
A laser is used to form openings within a graft material to selectively enhance permeability of a prosthesis for tissue integration therein. A feature of utilizing a laser to create the openings for tissue integration builds from its tunability. More particularly, the laser precisely places openings in any pattern and location, and on any textile that forms the graft material. Further, the power and focus of the laser is precisely adjusted to control the diameter and shape of the openings. All parameters of the openings can be controlled at will, allowing for the opportunity to selectively enhance and optimize the permeability of the graft material in a vessel.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
MRI and ct contrast-enabled composite implants for image-guided tissue regeneration and therapy
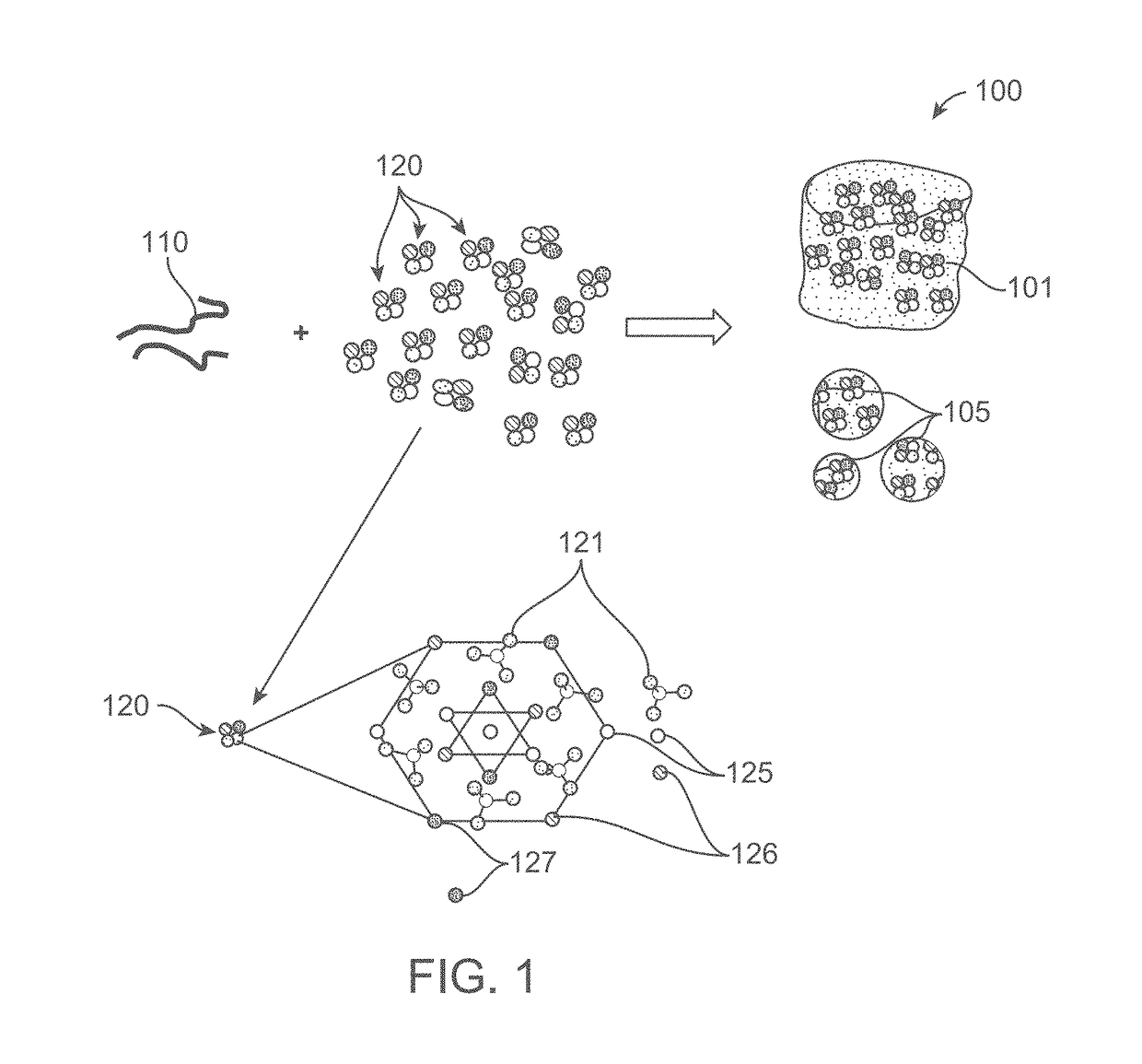
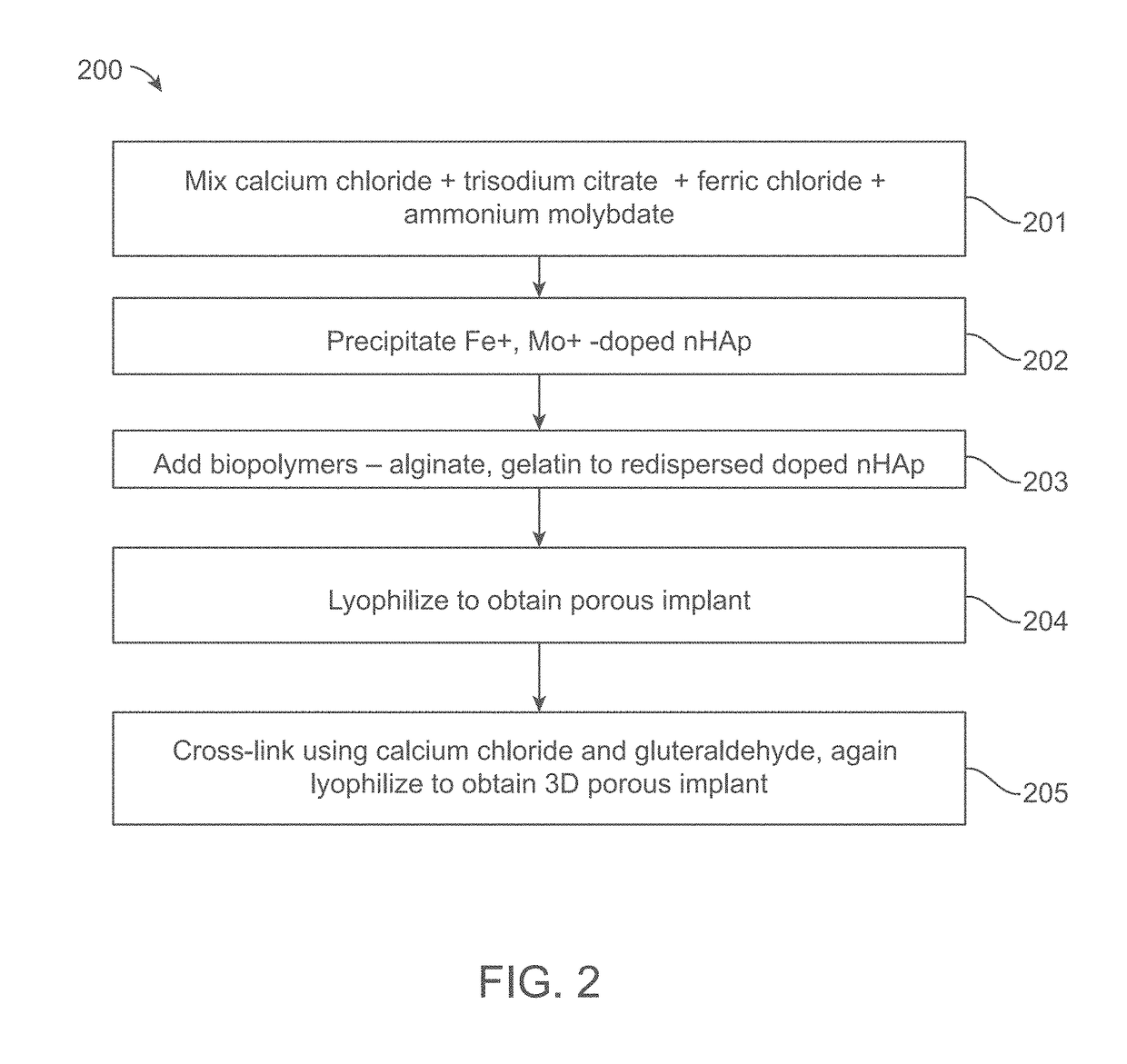
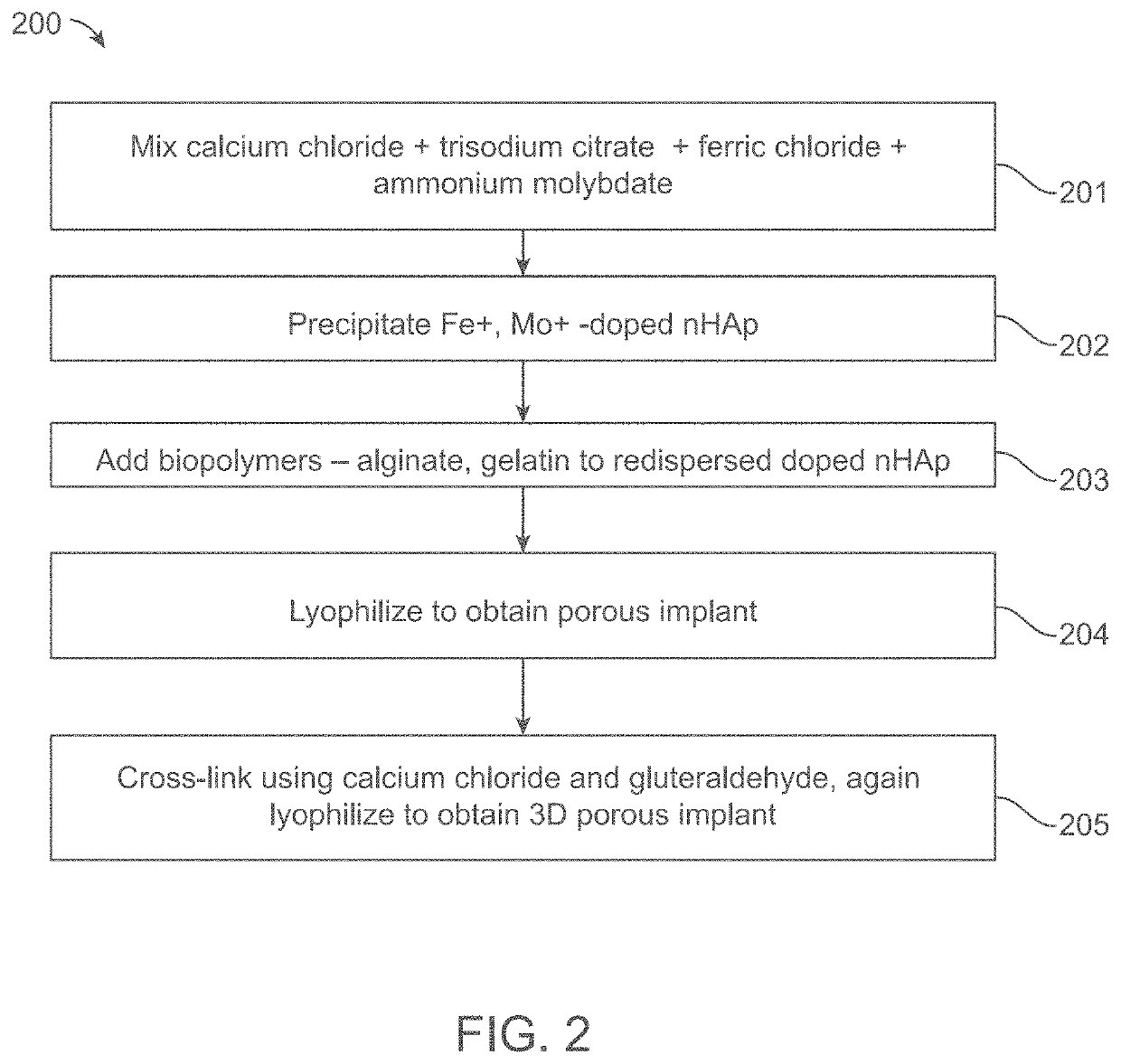
A composite implant for providing simultaneous magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomographic (CT) imaging contrast is disclosed. The composite implant is formed of a calcium compound in the form of nano or microparticles doped with a first dopant configured to provide MRI contrast and a second dopant configured to provide CT contrast. The calcium compound is loaded onto a polymer gel matrix and lyophilized to form a mass with 3-dimensionally interconnected porosity, configured to provide tissue integration and proliferation sites. Methods of forming the composite implant are also disclosed. The implant could be a scaffold or bead structured to enable treatment of human or animal patient for bone / cartilage injury or defect by implantation, with MRI and CT monitoring.
Owner:AMRITA VISHWA VIDYAPEETHAM
Modified metal materials, surface modifications to improve cell interactions and antimicrobial properties, and methods for modifying metal surface properties
The present disclosure is directed to modified metal materials for implantation and / or bone replacement, and to methods for modifying surface properties of metal substrates for enhancing cellular adhesion (tissue integration) and providing antimicrobial properties. Some embodiments comprise surface coatings for metal implants, such as titanium-based materials, using (1) electrochemical processing and / or oxidation methods, and / or (2) laser processing, in order to enhance bone cell-materials interactions and achieve improved antimicrobial properties. One embodiment comprises the modification of a metal surface by growth of in situ nanotubes via anodization, followed by electrodeposition of silver on the nanotubes. Other embodiments include the use of LENS™ processing to coat a metal surface with calcium-based bioceramic composition layers. These surface treatment methods can be applied as a post-processing operation to metallic implants such as hip, knee and spinal devices as well as screws, pins and plates.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
Implantable interface device
ActiveUS20160263366A1Minimise fibroblast deathEasy to integrateMedical devicesCatheterTissue integrationCuticle
An interface device for implantation in a subject includes a tissue integration layer and a crowning element. The tissue integration layer has a porous structure adapted for ingress of tissue to anchor the device when implanted. The crowning element is adapted for epidermal attachment when the device is implanted and is configured such that once implanted, part of the crowning element extends through the epidermis and is accessible from outside the subject's body. The porous structure of the tissue integration layer is interconnected for tissue ingress during implantation.
Owner:OZLOBSTERS PTY LTD
Conductive and degradable implant for pelvic tissue treatment
ActiveUS10617505B2Promote healthy tissue growthPromote healingAnti-incontinence devicesSurgeryPelvic regionTissue integration
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Stent graft with external scaffolding and method
ActiveUS10188500B2Promote tissue ingrowthEasy to integrateStentsBlood vesselsTissue integrationStent grafting
A scaffolded stent-graft includes a graft material comprising an inner surface and an outer surface. The inner surface defines a lumen within the graft material. The scaffolded stent-graft further includes a scaffold comprising a mesh coupled to the graft material at the outer surface. The scaffold is configured to promote tissue ingrowth therein. In this manner, the scaffold enhances tissue integration into the scaffolded stent-graft. The tissue integration enhances biological fixation of the scaffolded stent-graft in vessels minimizing the possibility of endoleaks and migration.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Improved suture
A medical device includes a surgical needle attached to an elongated mesh suture. The suture is constructed of macroporous flat wall that facilitates and allows tissue integration into the suture coresubsequent to introduction to the body, thereby preventing suture pull-through and improving biocompatibility.
Owner:高级缝合有限公司
Application of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in preparing drugs for treating cerebral palsy and culture method
InactiveCN109486754AEnsure safetyGuaranteed validityCell dissociation methodsNervous disorderDiseaseCerebral paralysis
The invention relates to an application of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in preparing drugs for treating cerebral palsy and a culture method. The culture method comprises the following steps: culturing a Wharton jelly obtained from a human umbilical cord to obtain a cell clone group; then carrying out trypsin digestion on the obtained cell clone group to obtain P0 generation cells; carrying out subculture on the P0 generation cells to P4 generation; and identifying and screening surface antigens of P4 generation cells to obtain qualified human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. The human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are good in tissue integration, weak in immunogenicity and good in migrating ability, can be amplified quickly in vivo, has a multidirectional differentiative potential, can be differentiated to nerve cell directions, and can be applied to preparing drugs for treating cerebral palsy of children. The method is simple, safe, small in trauma and goodin compliance of patients, and preparation and clinical application standards and operating rules of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in preparing drugs for treating cerebral palsy of children are established, so that the culture method is safe and effective and has a good application prospect.
Owner:SHIYAN TAIHE HOSPITAL
MRI and CT contrast-enabled composite implants for image-guided tissue regeneration and therapy
ActiveUS10806805B2Powder deliveryGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsCartilage injuryComputed tomography
A composite implant for providing simultaneous magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomographic (CT) imaging contrast is disclosed. The composite implant is formed of a calcium compound in the form of nano or microparticles doped with a first dopant configured to provide MRI contrast and a second dopant configured to provide CT contrast. The calcium compound is loaded onto a polymer gel matrix and lyophilized to form a mass with 3-dimensionally interconnected porosity, configured to provide tissue integration and proliferation sites. Methods of forming the composite implant are also disclosed. The implant could be a scaffold or bead structured to enable treatment of human or animal patient for bone / cartilage injury or defect by implantation, with MRI and CT monitoring.
Owner:AMRITA VISHWA VIDYAPEETHAM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com