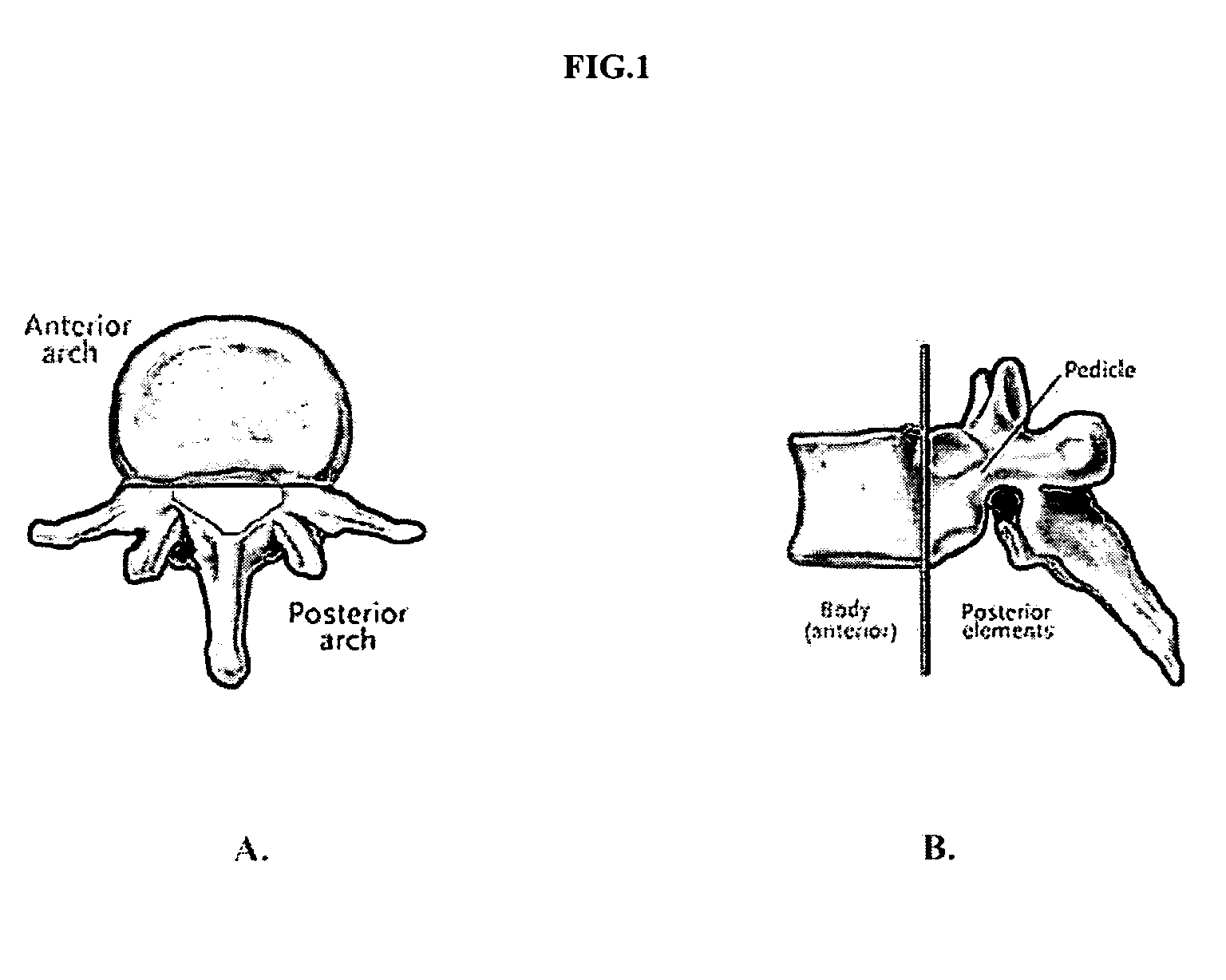
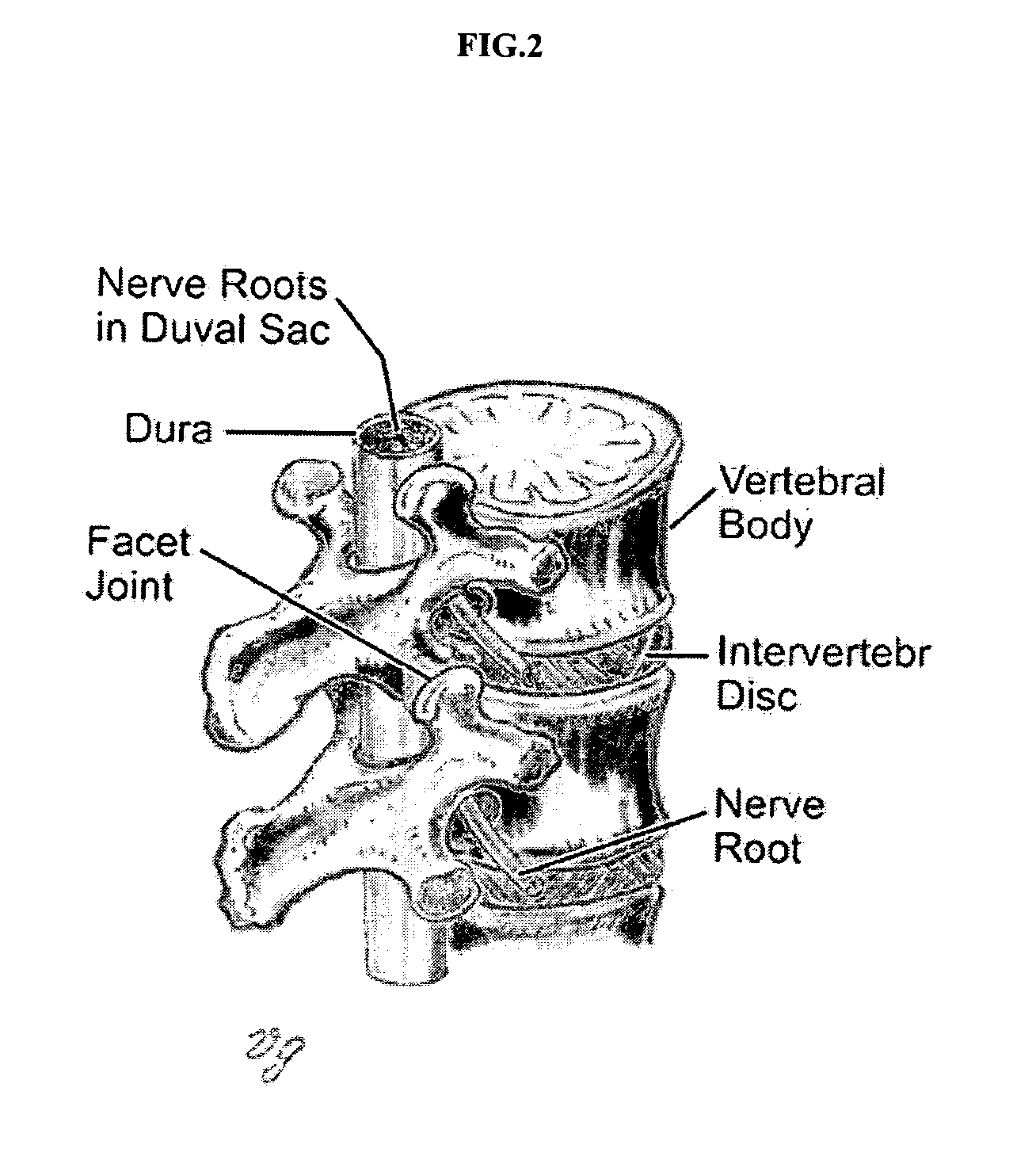
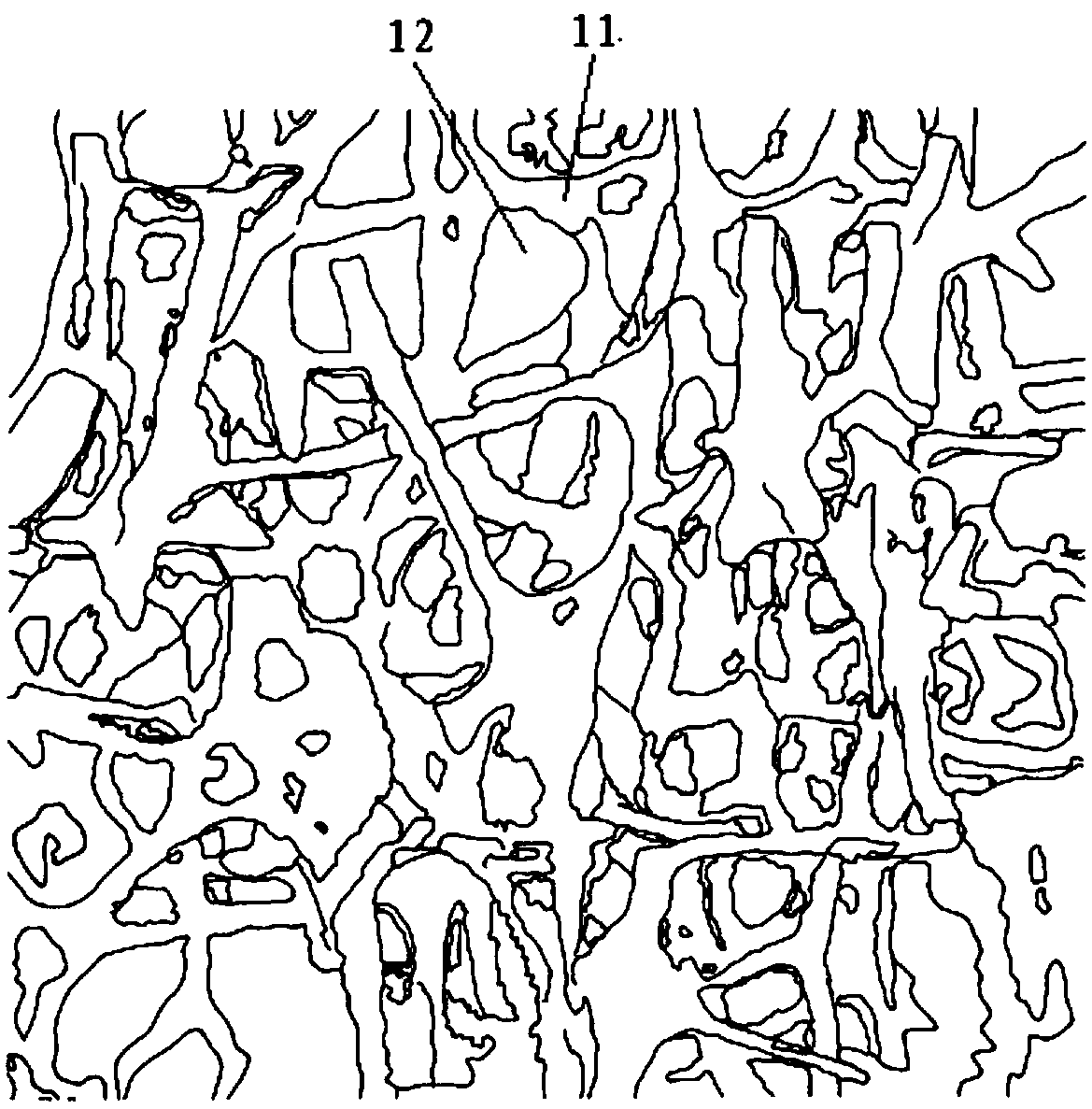Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
94 results about "Trabecular bone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
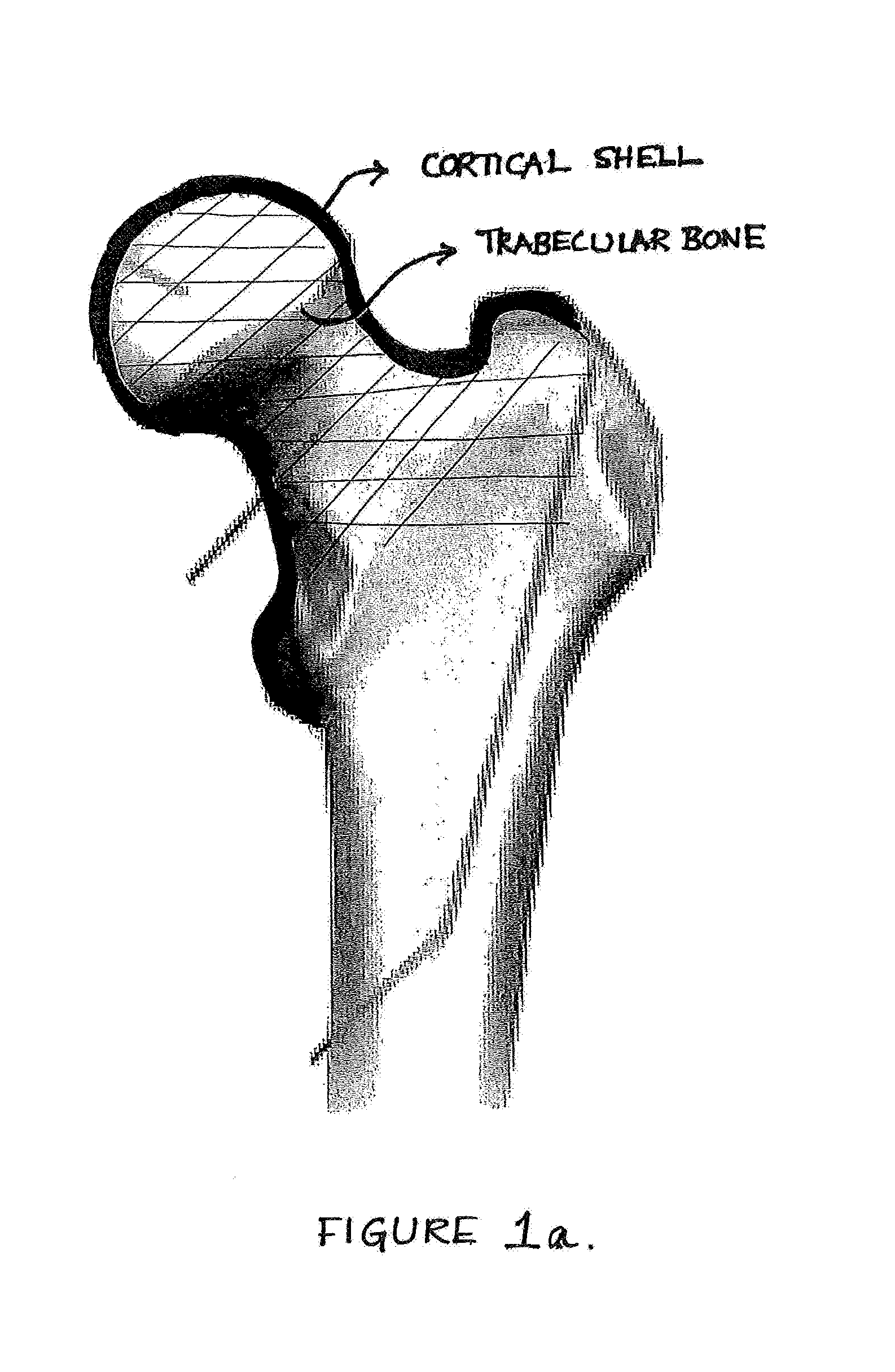
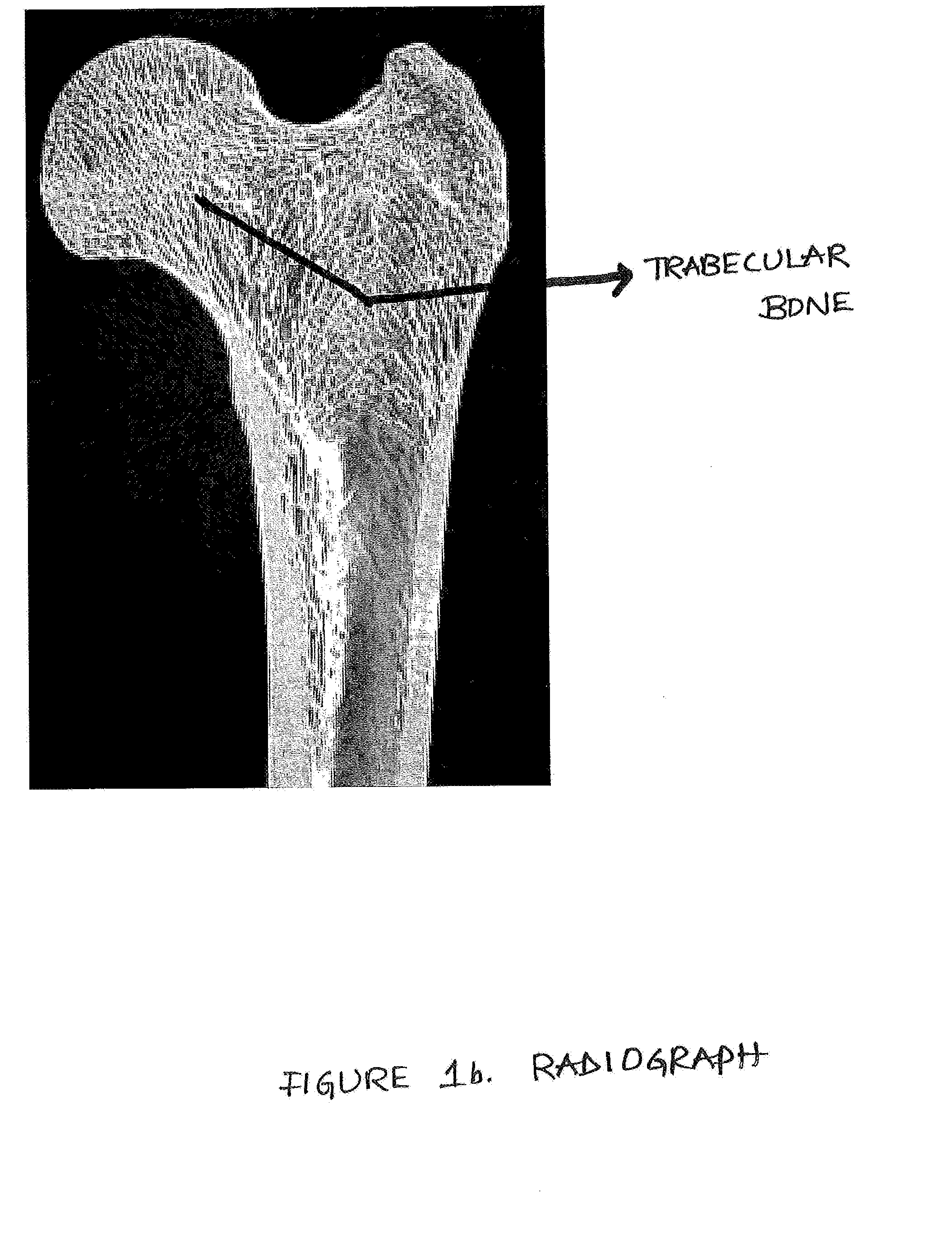
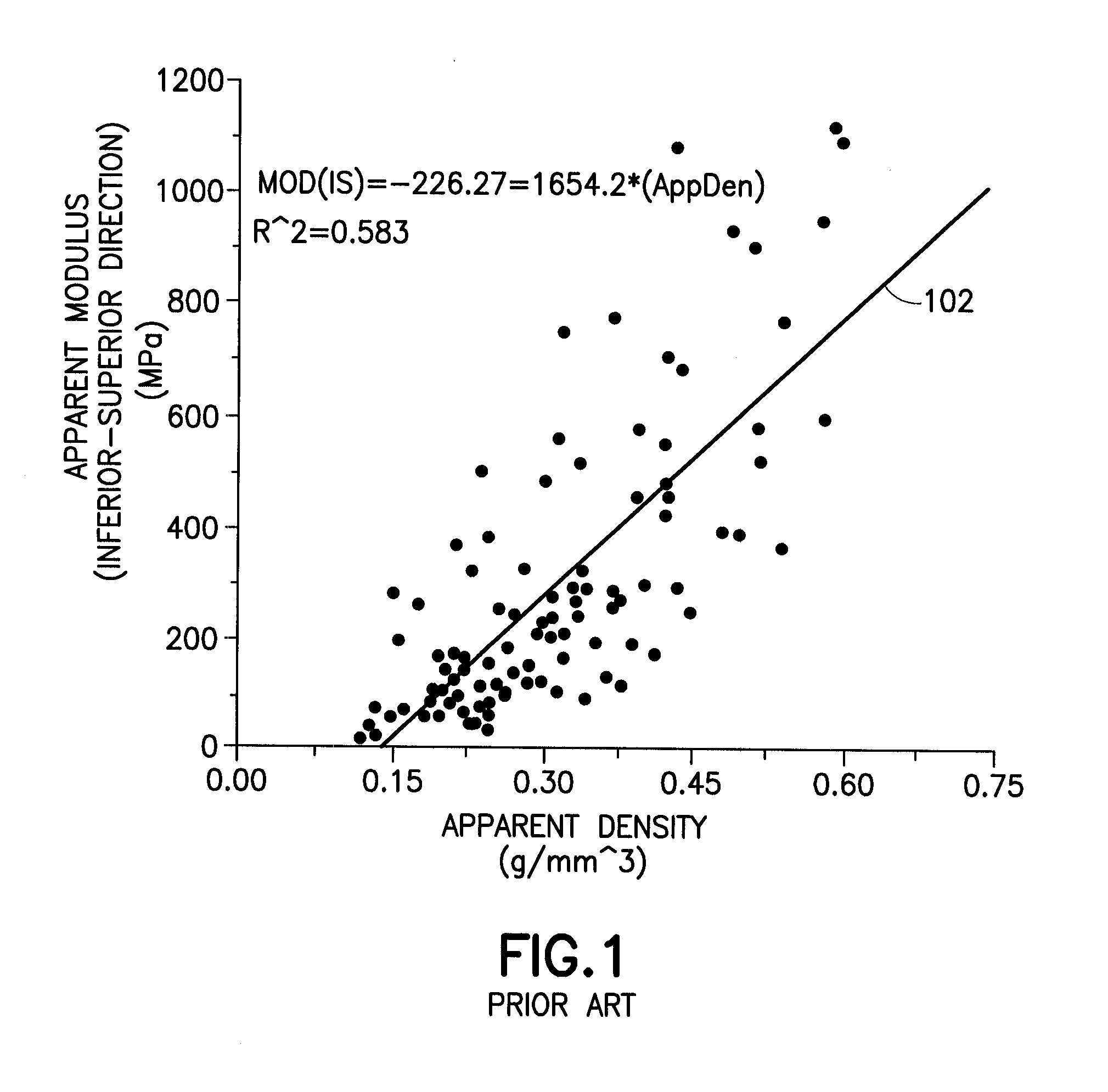
Trabecular bone is bone tissue arranged in a meshwork of thin plates or beams that is commonly found at the center of long bones and that constitutes a large part of the hip and vertebrae. Also called cancellous bone or spongy bone.
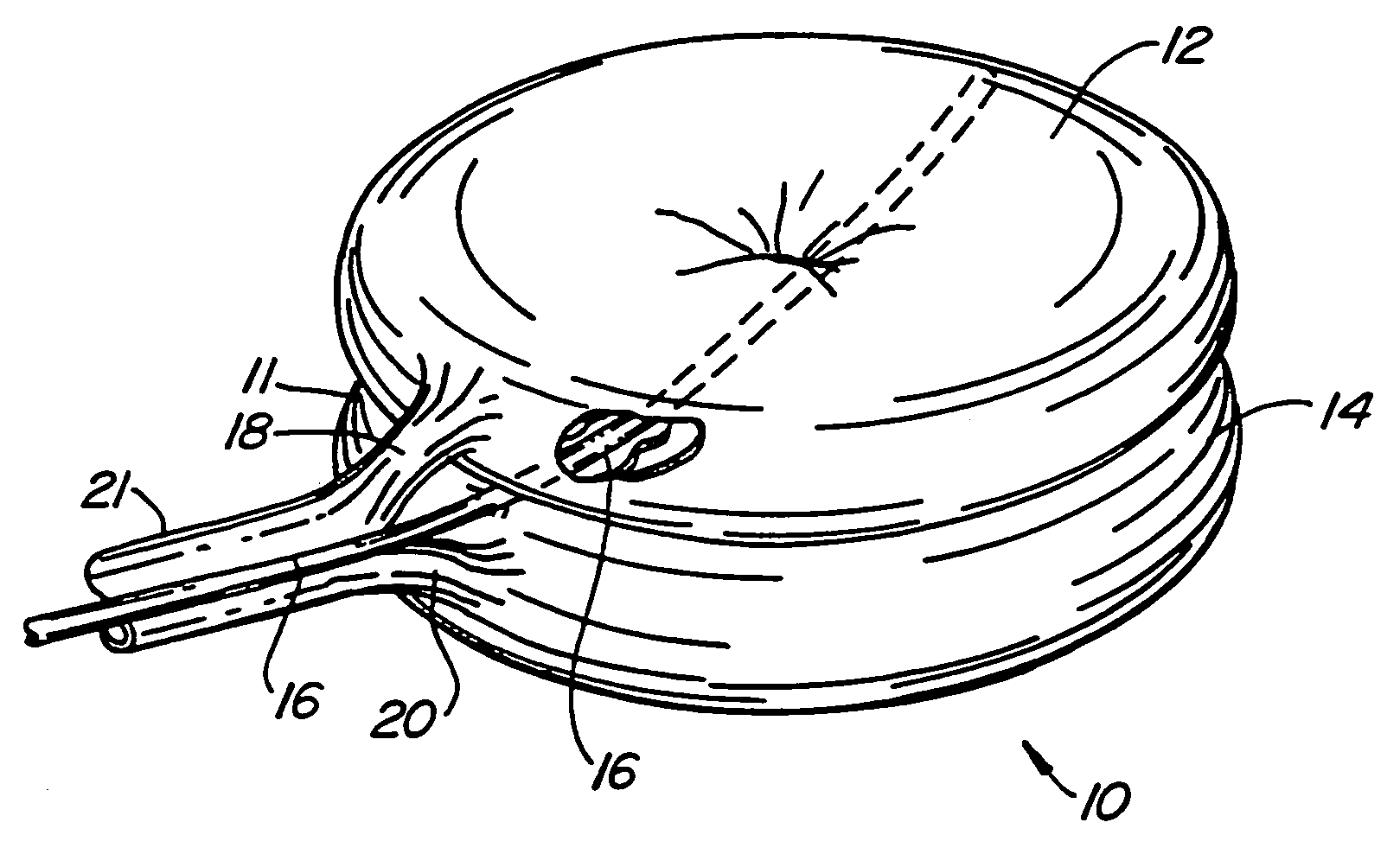
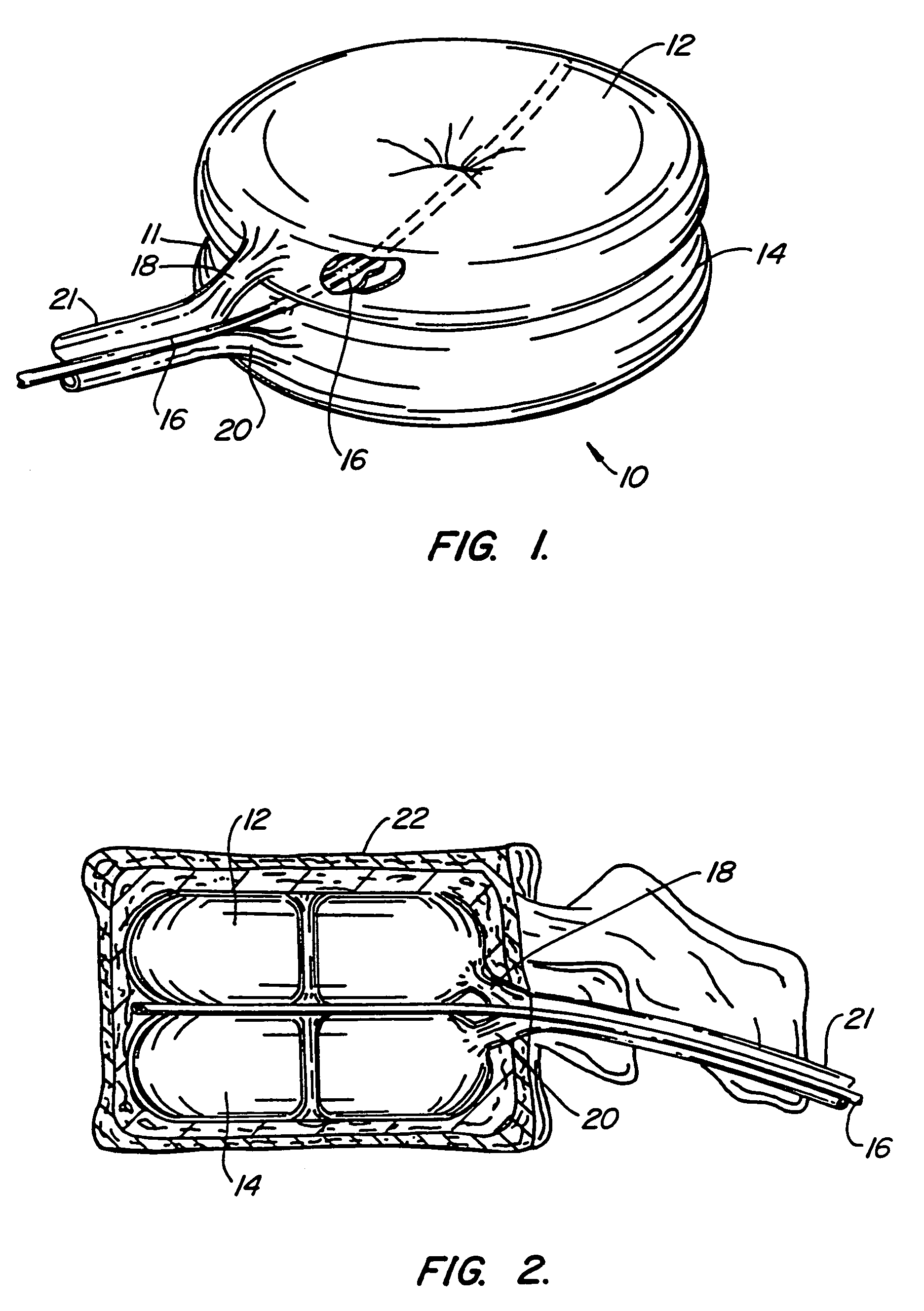
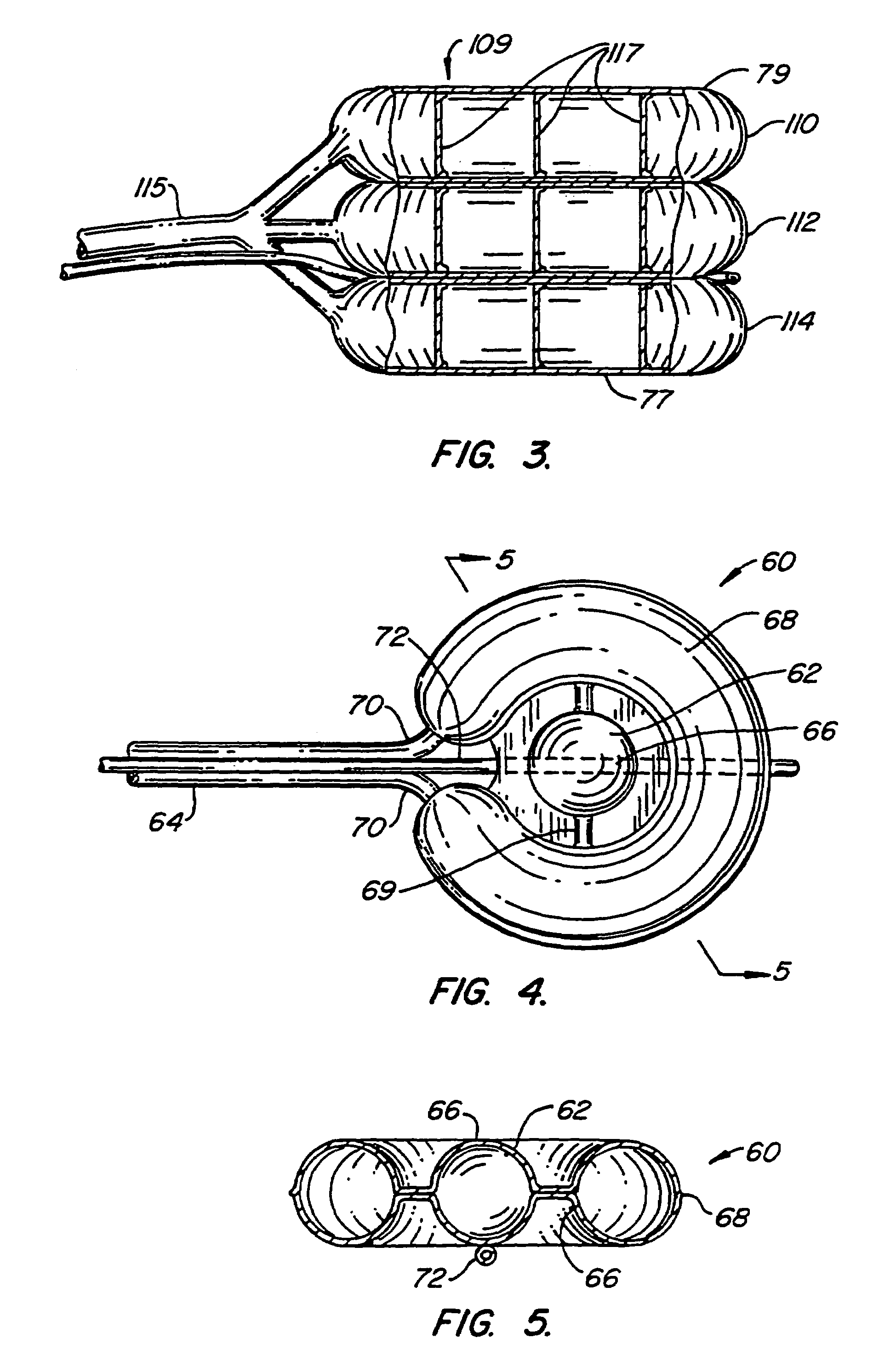
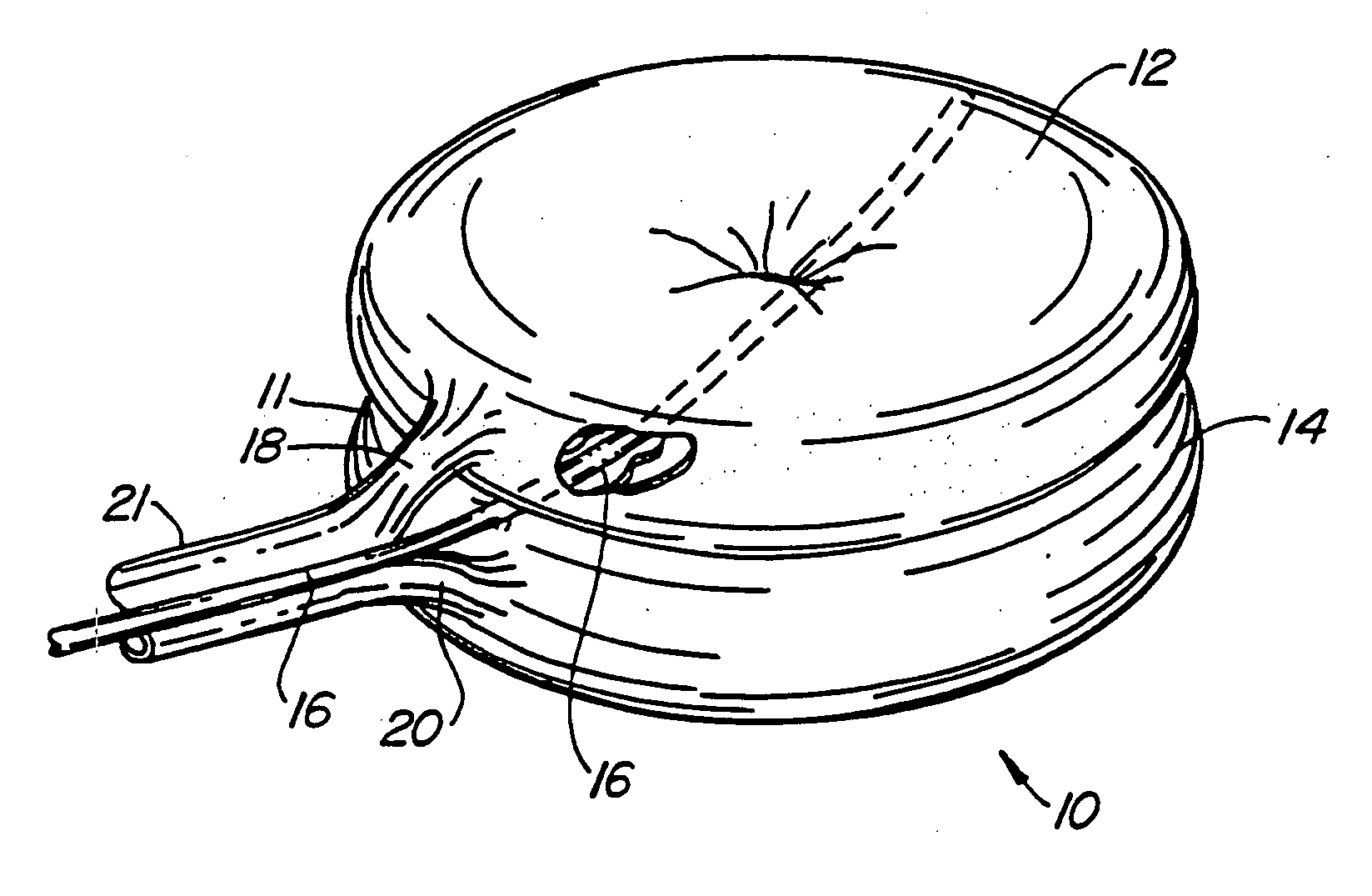
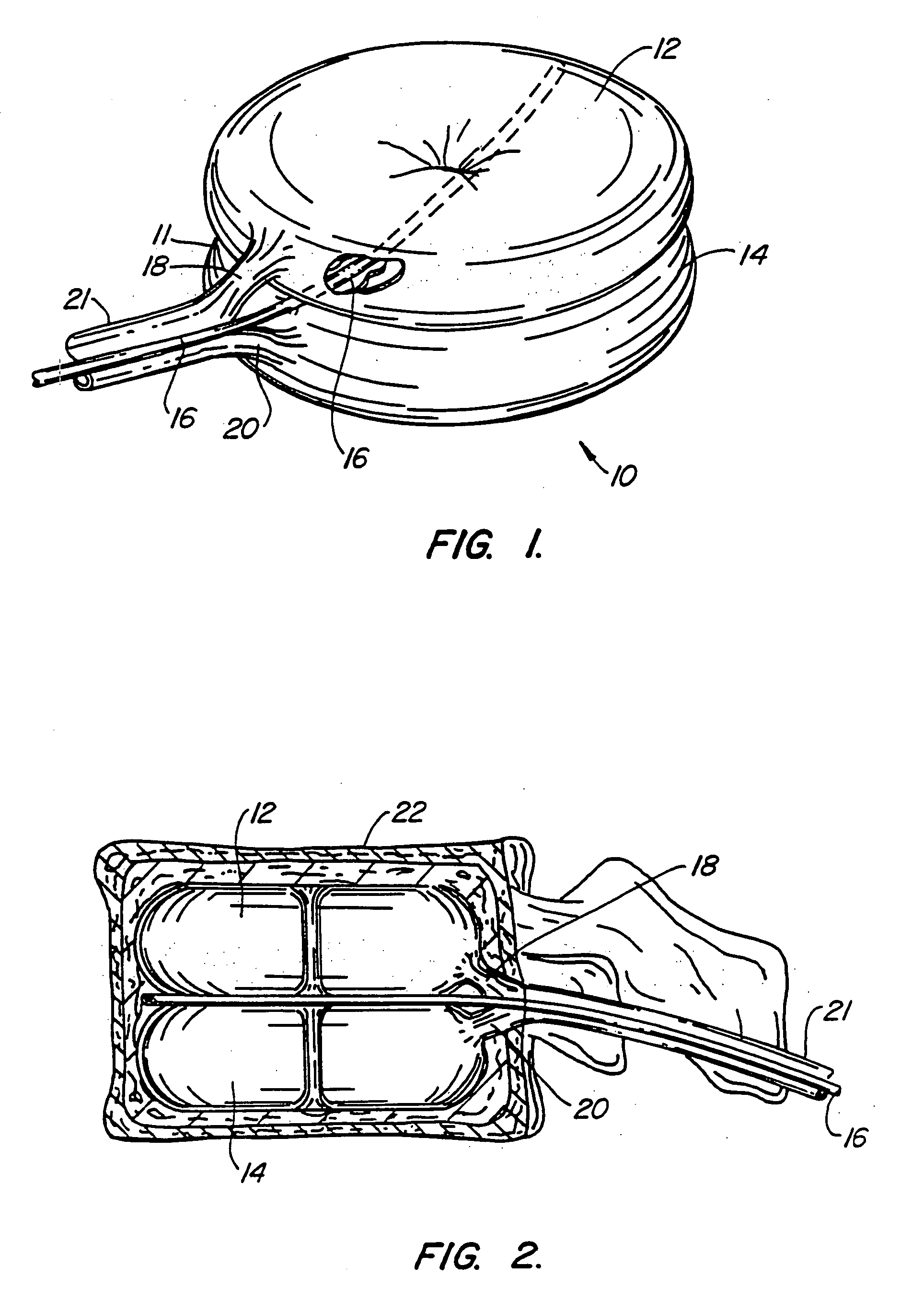
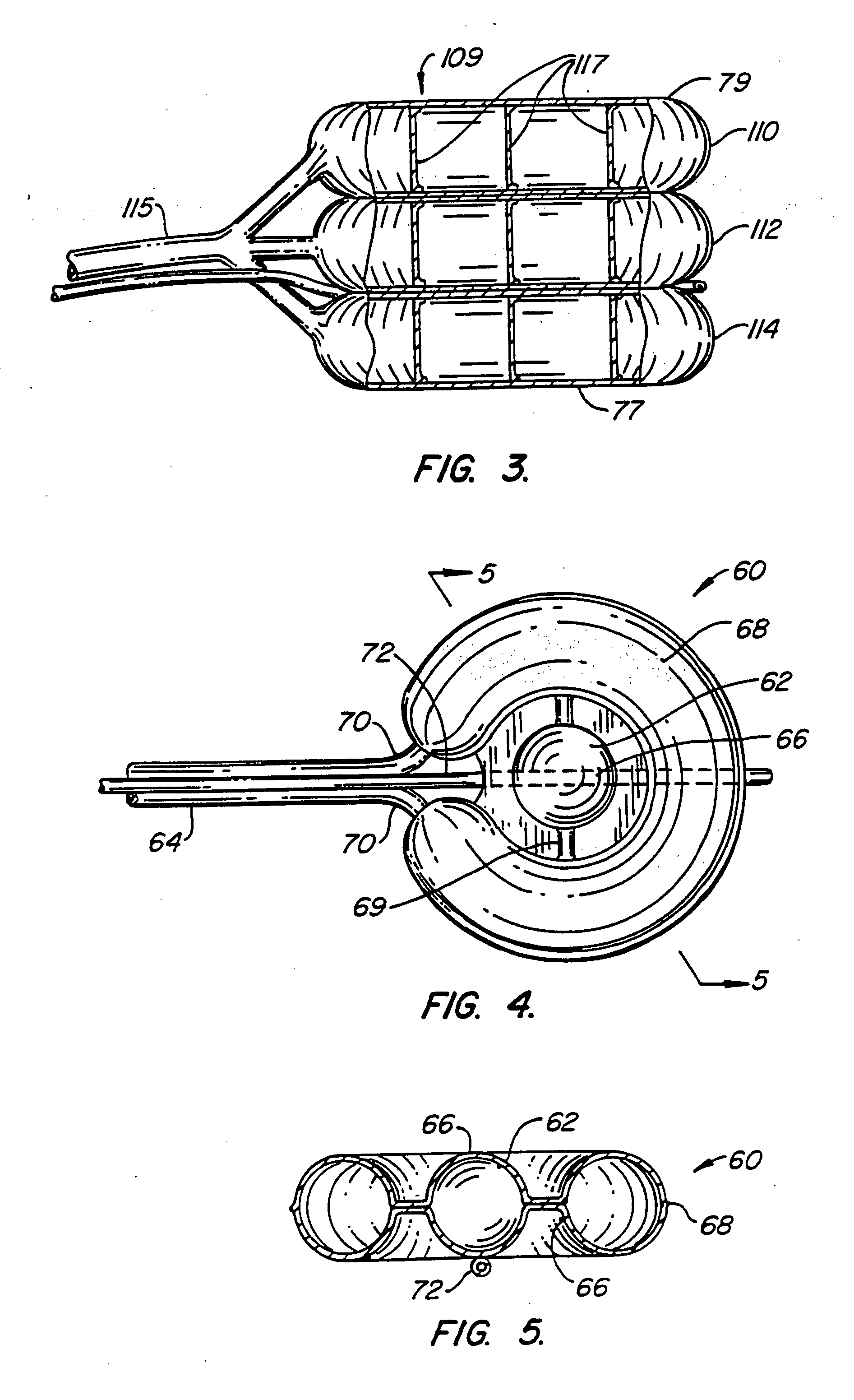
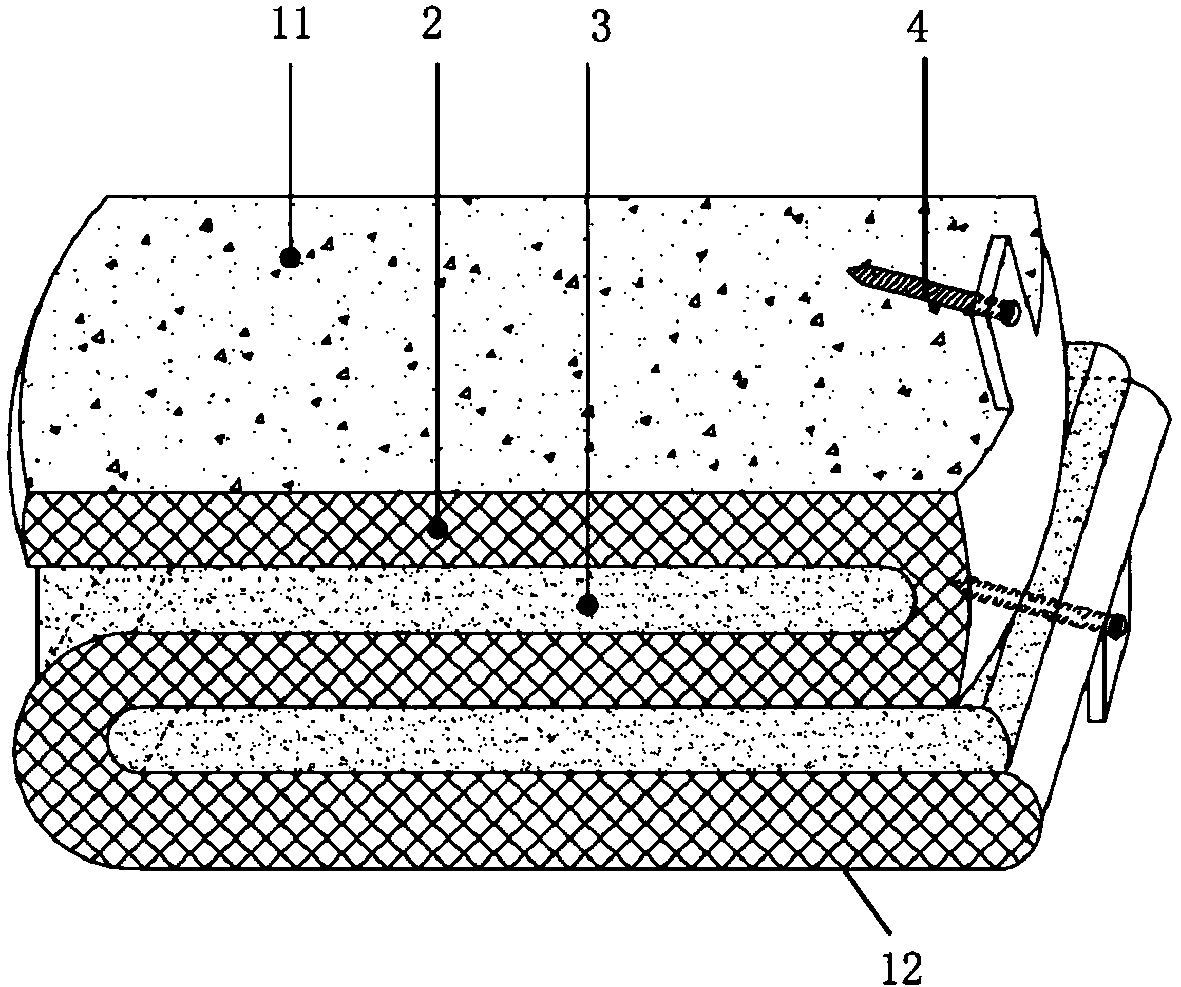
Inflatable device for use in surgical protocol relating to fixation of bone
InactiveUS7261720B2Easy to compressEasy to foldSurgical furnitureInternal osteosythesisBone CortexTrabecular bone
A balloon for use in compressing cancellous bone and marrow (also known as medullary bone or trabecular bone). The balloon comprises an inflatable balloon body for insertion into said bone. The body has a shape and size to compress at least a portion of the cancellous bone to form a cavity in the cancellous bone and / or to restore the original position of the outer cortical bone, if fractured or collapsed. The balloon desirably incorporates restraints which inhibit the balloon from applying excessive pressure to various regions of the cortical bone. The wall or walls of the balloon are such that proper inflation of the balloon body is achieved to provide for optimum compression of the bone marrow. The balloon can be inserted quickly into a bone. The balloon can be made to have a suction catheter. The balloon can be used to form and / or enlarge a cavity or passage in a bone, especially in, but not limited to, vertebral bodies. Various additional embodiments facilitate directionally biasing the inflation of the balloon.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
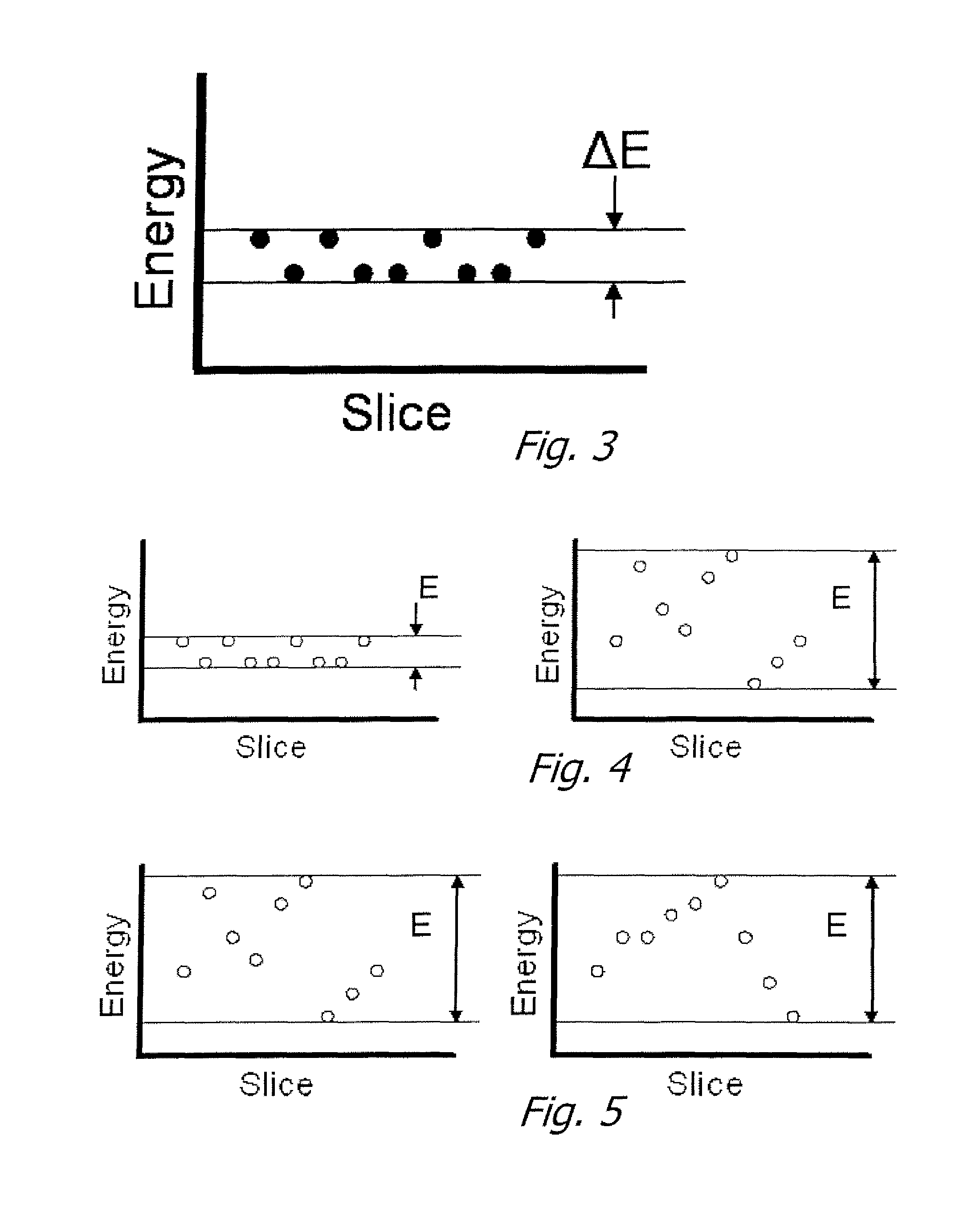
Digital topological analysis of trabecular bone MR images and prediction of osteoporosis fractures
The invention provides method, system and device for determining trabecular bone structure and strength by digital topological analysis, and offers, for the first time, a demonstration of superior associations between vertebral deformity and a number of architectural indices measured in the distal radius, thus permitting reliable and noninvasive detection and determination of the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. A preferred embodiment provides imaging in three dimension of a region of trabecular bone, after which the 3D image is converted into a skeletonized surface representation. Digital topological analysis is applied to the converted image, and each image voxel is identified and classified as a curve, a surface, or a junction; and then associated with microarchitectural indices of trabecular bone to quantitatively characterize the trabecular bone network. The invention is applicable in vivo, particularly on human subjects, or ex vivo.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
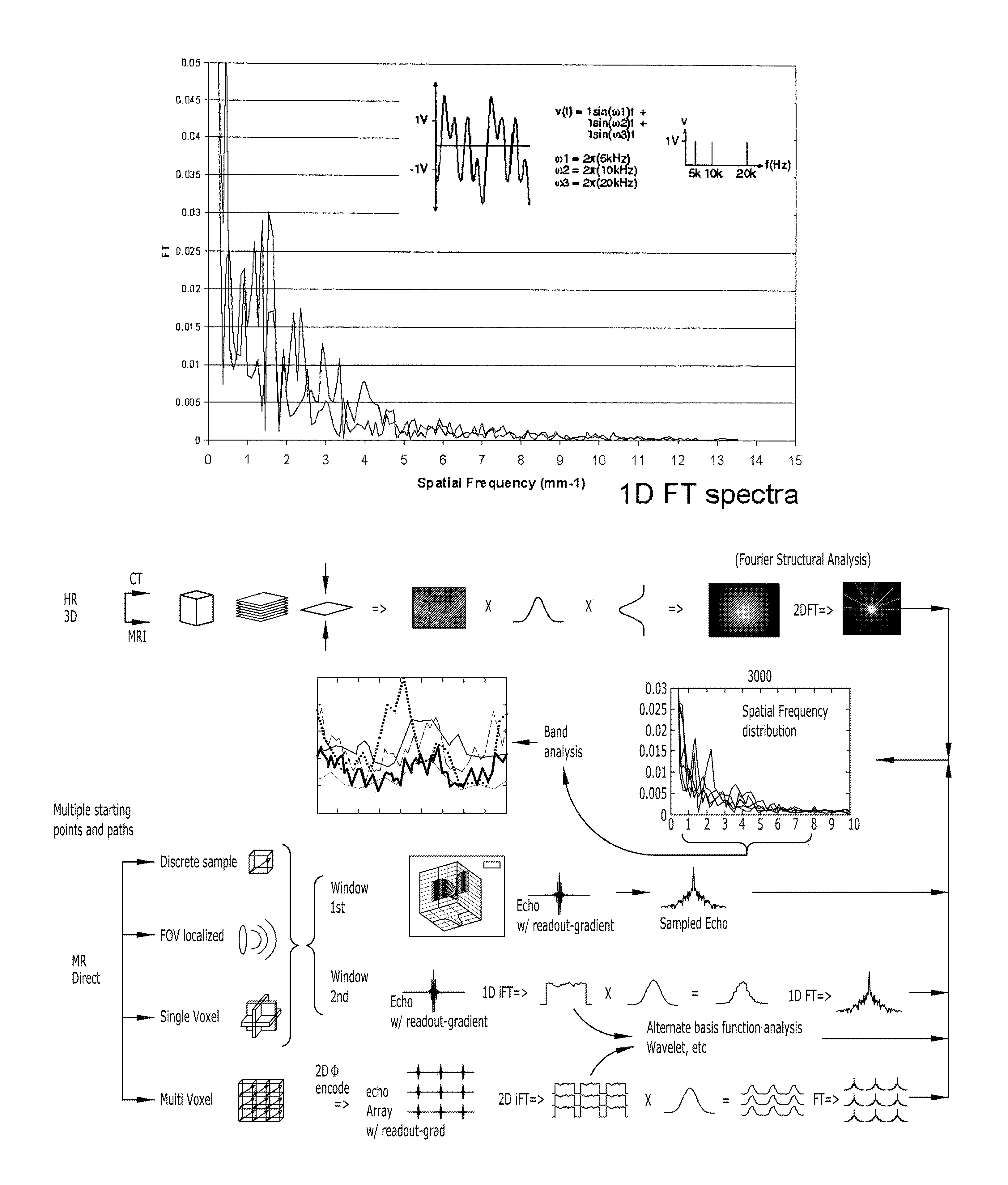
Structure assessment using spatial-frequency analysis
InactiveUS20070167717A1Measurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringFrequency spectrumSpectroscopy
The disclosed innovation is a method for acquiring spatial frequency spectra from specific locations in a 3D sample using modifications of the current MRI techniques for localized NMR spectroscopy. The innovation in its simplest abstraction is to add the use of a read out gradient to the current NMR spectroscopy pulse sequences and record the resultant echo. These techniques generate spectra from a selected region or generate an image of the results over a region of the sample. These methods can be applied to analyzing the structure of trabecular bone as well as for analyzing or diagnosing disease in cases where there is a difference in the spatial frequency power spectrum due to physiologic or disease processes. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:OSTEOTRONIX MEDICAL PTE LTD
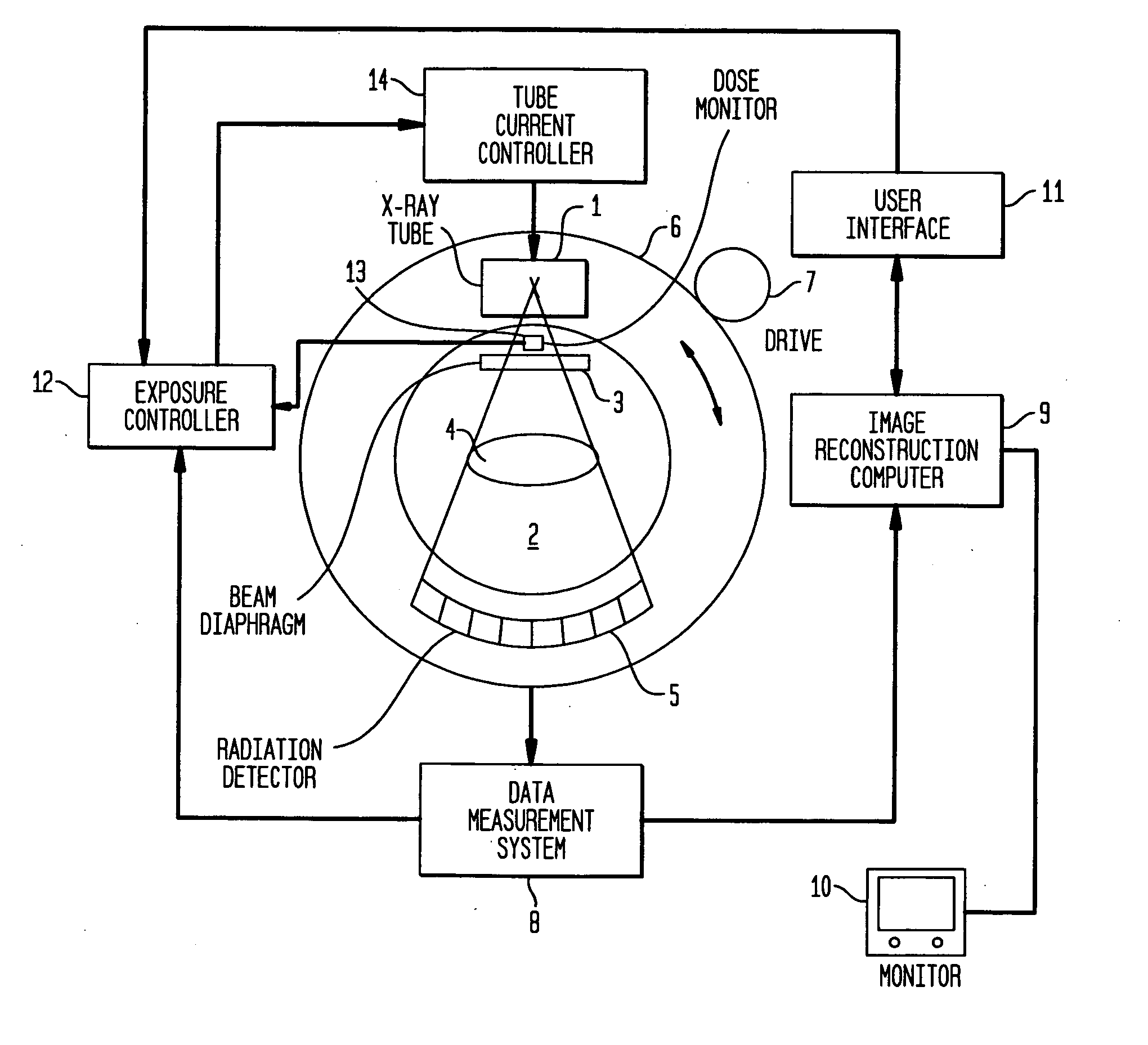
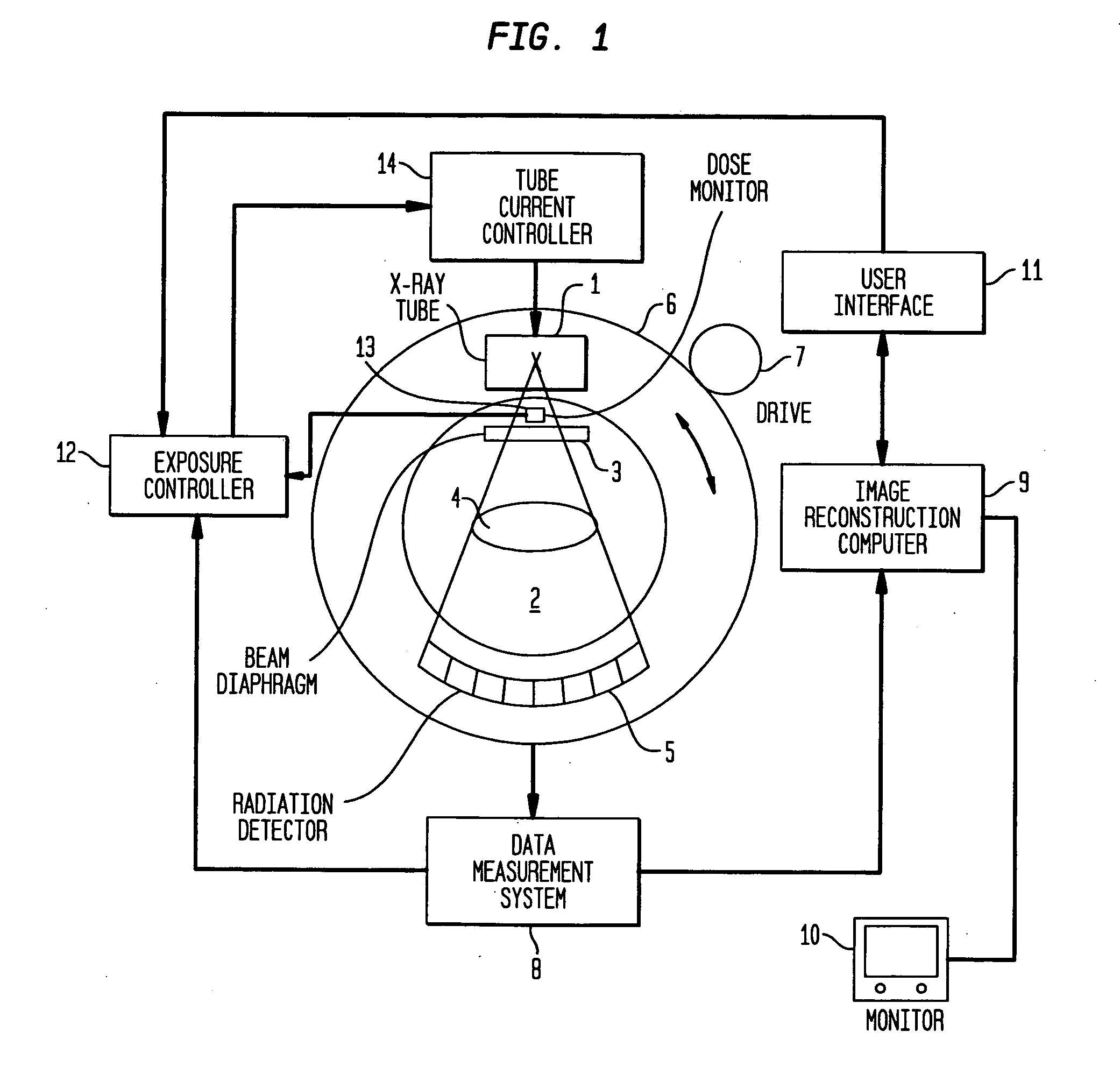
X-ray image analyzing system and program
An X-ray image analyzing system, including:an X-ray source for radiating an X-ray; an X-ray detector for detecting an X-ray image radiated onto an x-ray image detection surface, wherein phase contrast X-ray simple imaging is capable of being performed determining a trabecular bone index computing region, computing a trabecular bone index indicating a state of a trabecula from image data in the trabecular bone index computing region, determining a bone-flesh boundary index computing region by a second region determination method different from the first region determination method, and computing a bone-flesh boundary index indicating smoothness of a bone-flesh boundary from image data in the bone-flesh boundary index computing region.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
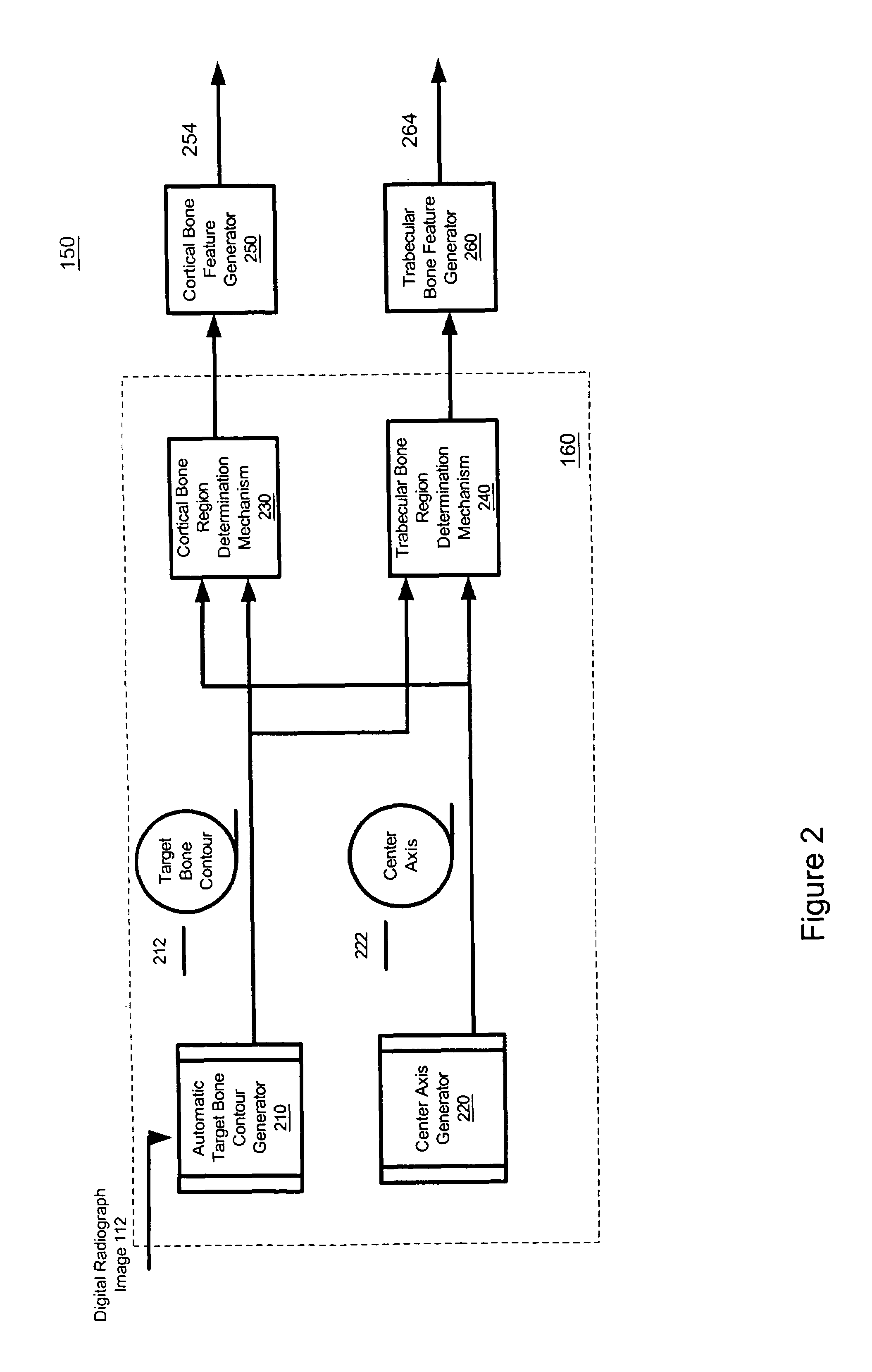
Method and system for automatically identifying regions of trabecular bone tissue and cortical bone tissue of a target bone from a digital radiograph image
InactiveUS7539332B1Image enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMedicineBone tissue
System and method for automatically extracting at least one region of a first type of bone tissue from a target bone. A digital radiograph image with the target bone is received. Based on the digital radiograph image, at least one region of a first type of bone tissue is automatically identified or extracted. This region can then be utilized for different purposes, such as assessment, qualitative assessment, quantitative assessment, analysis, spatial domain analysis, frequency domain analysis, and calculation of one or more target bone features.
Owner:COMPUMED
Device, Composition and Method for Prevention of Bone Fracture and Pain
InactiveUS20140194887A1Low viscosityStrong bonesDiagnosticsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCross-linkBone structure
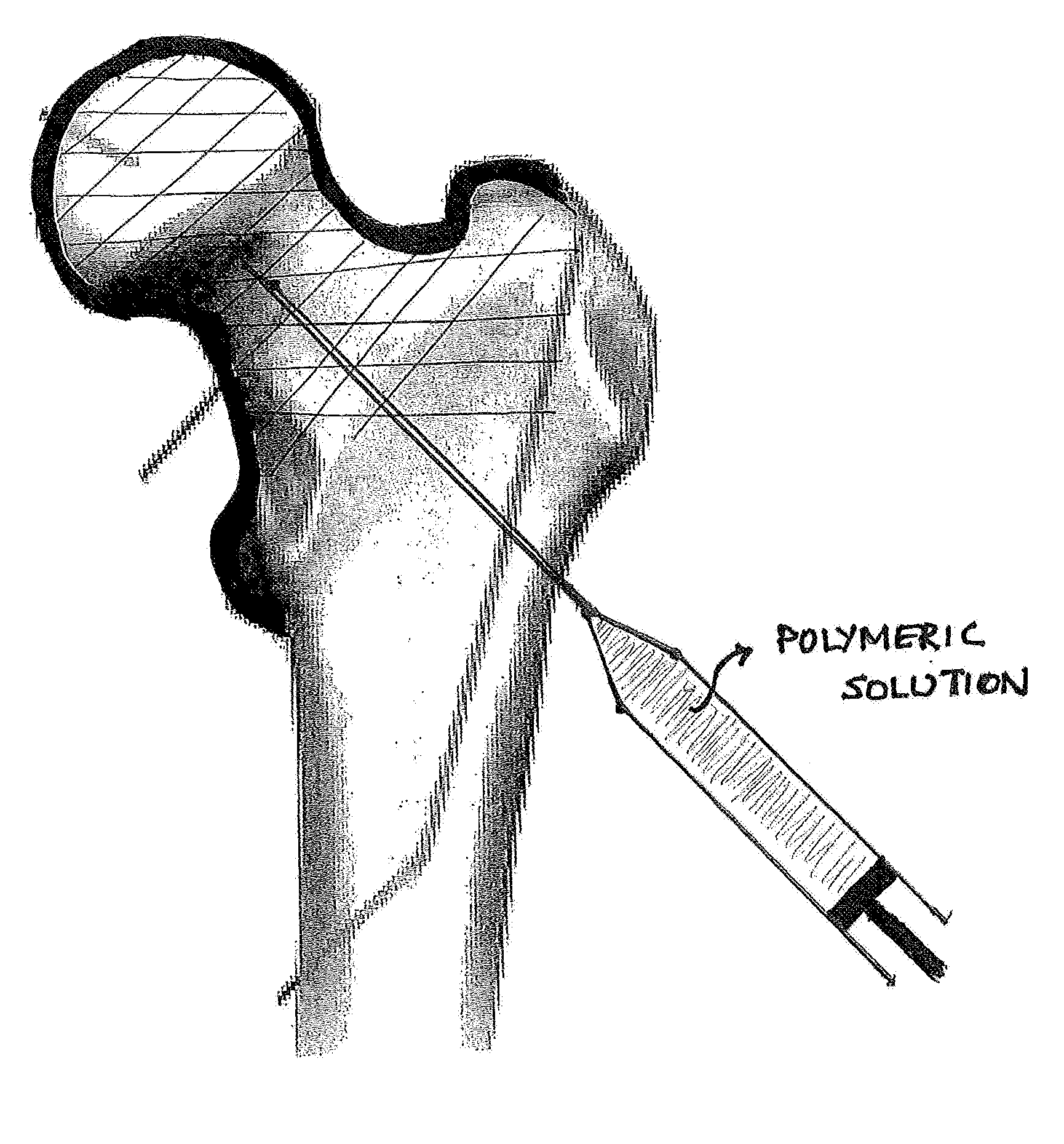
Methods, apparatus, compositions for reinforcing bone structures are disclosed as well as a reinforced bone structure itself. By injecting a low viscosity polymeric solution into a trabecular bone region at least partly surrounded by cortical bone allowing it to cross-link in-situ, a non-degradable gel can effectively reinforce the region by retaining fluid in the constrained space within the cortical shell. Due to the low viscosity of the pre-cross-linked aqueous polymeric solution, the entire site could be filled effectively and consistently. Additionally, by injecting a low viscosity pre-cursor, the solution fills the natural intra-trabecular spaces without substantial alteration of the trabecular structure at the site.
Owner:SHENOY VIVEK
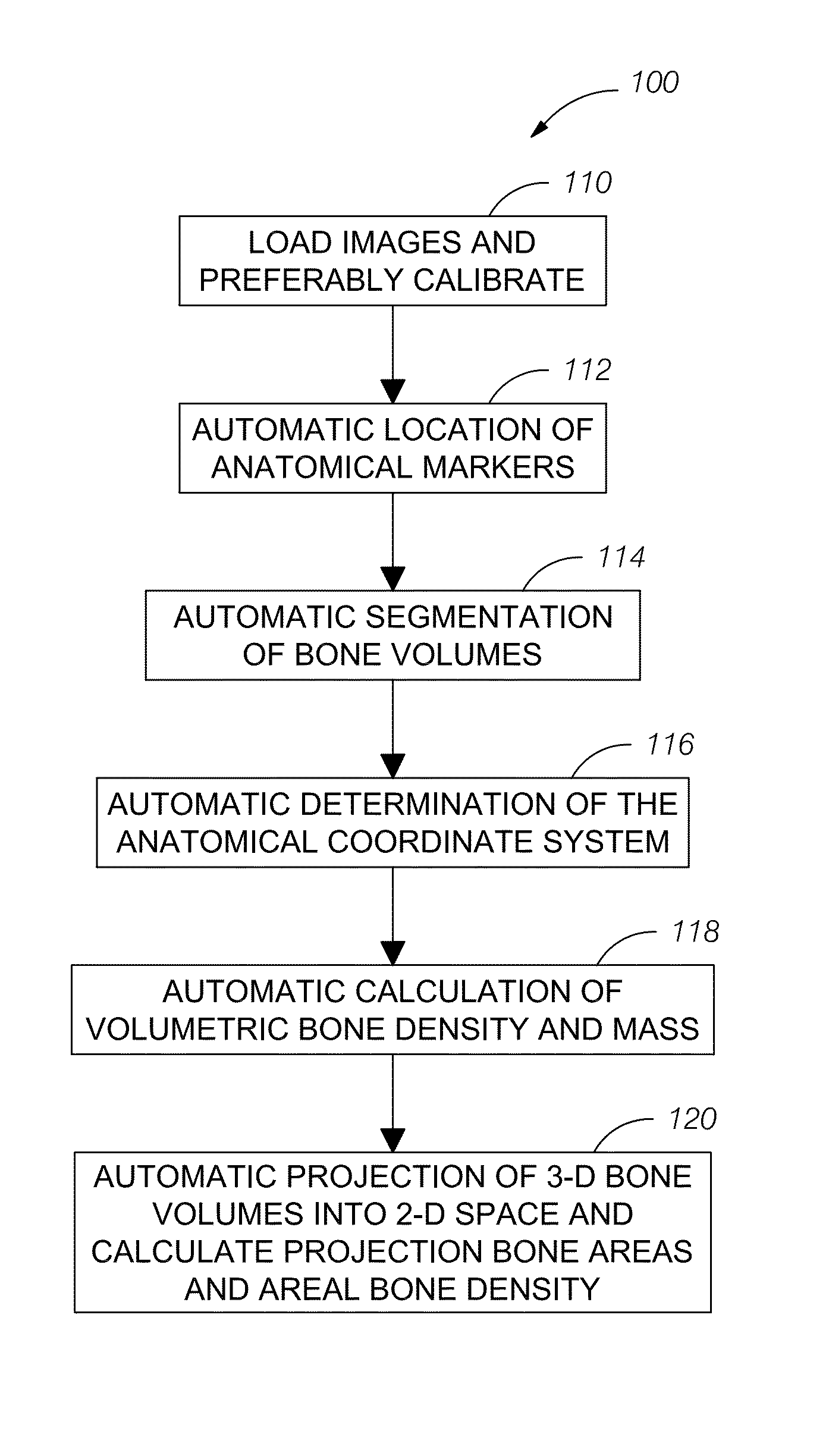
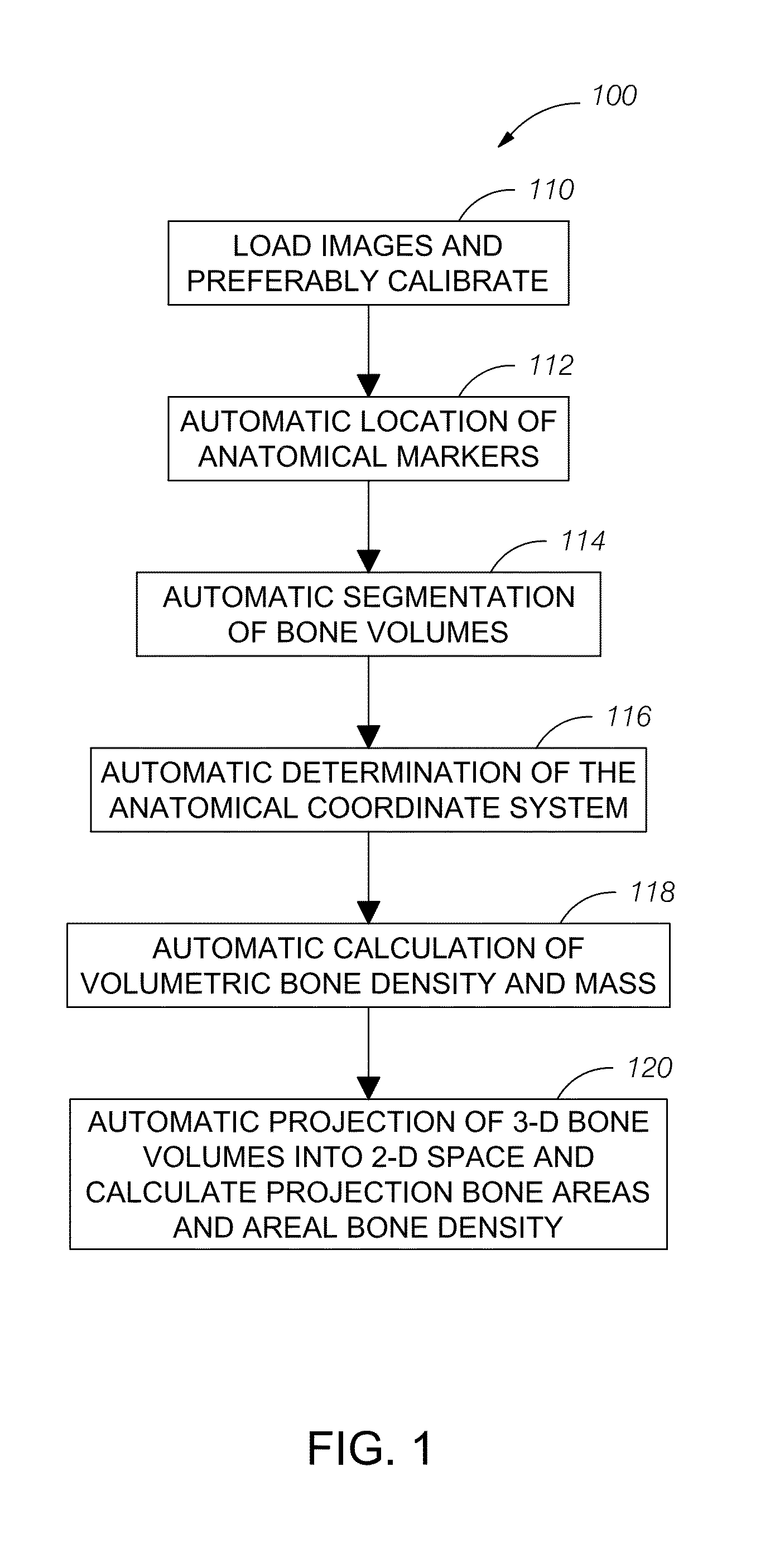
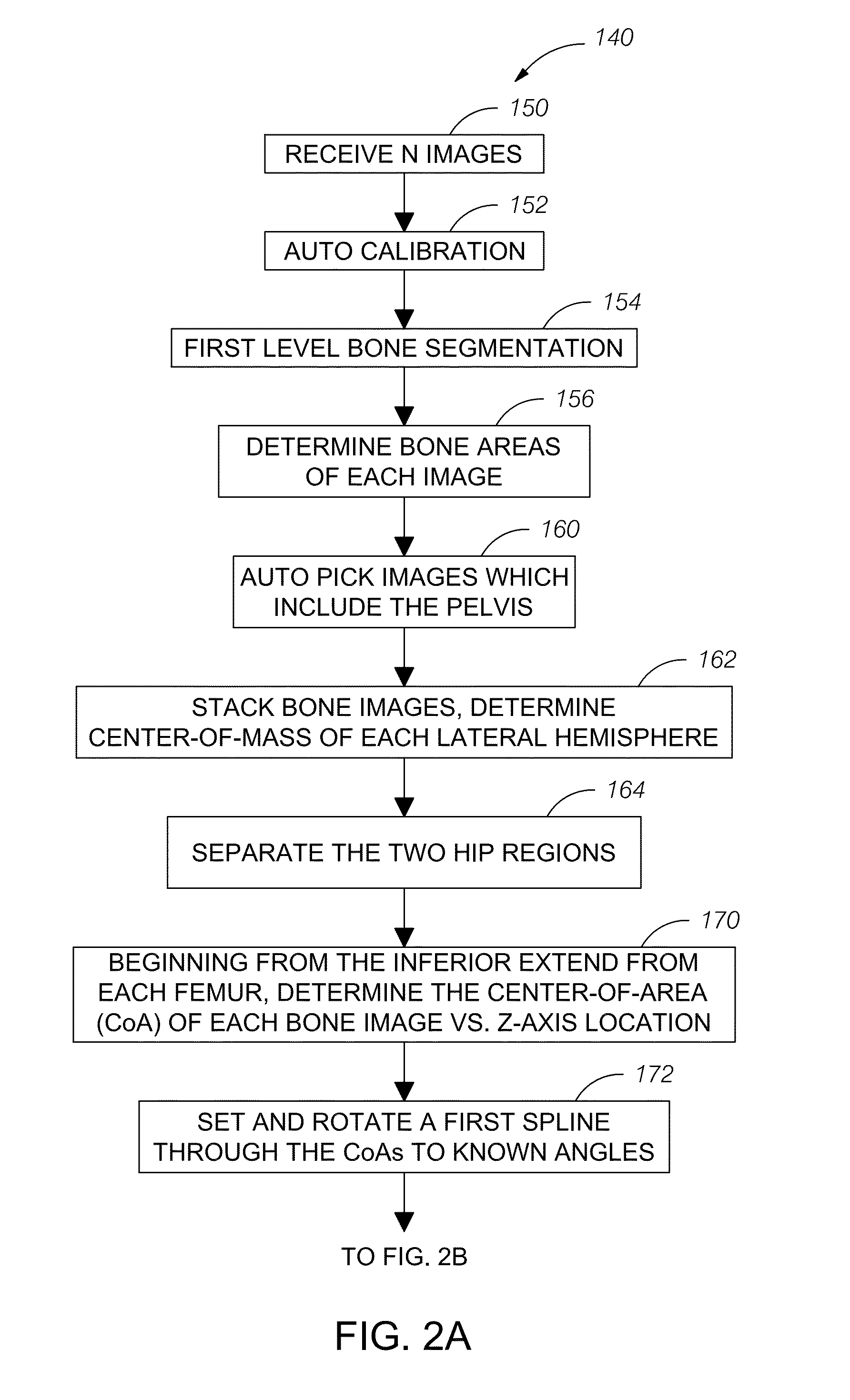
Automatic method and system for measurements of bone density and structure of the hip from 3-D X-ray imaging devices
ActiveUS8649577B1Reduce effortShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresVoxel
A method uses a computer and software to measure bone density and structure of the proximal femur of the hip from a volumetric set of images containing pixels representing x-ray attenuation of the subject which are acquired with three-dimensional X-ray imaging devices. The method automatically locates anatomical markers of the hip without operator interaction, automatically positions regions of interest (ROIs) for measurement, automatically determines bone density measures of the ROIs, and automatically reports the results for individual subjects. Bone density measurements of ROIs include the integral bone of the total hip and neck as well as trabecular bone. The method automatically identifies a three-dimensional region-of-interest (ROI) volume which includes the hip, determines a three-dimensional coordinate system referenced to the anatomy of the subject, analyzes the ROI volume to identify voxels in the volume which satisfy defined criteria, and determines a measure of bone structure.
Owner:IMAGE ANALYSIS
Magnetic field gradient structure characteristic assessment using one dimensional (1D) spatial-frequency distribution analysis
InactiveUS7932720B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientFrequency spectrum
The disclosed innovation is a method for acquiring spatial frequency spectra from specific locations in a 3D sample using modifications of the current MRI techniques for localized NMR spectroscopy. The innovation in its simplest abstraction is to add the use of a read out gradient to the current NMR spectroscopy pulse sequences and record the resultant echo. These techniques generate spectra from a selected region or generate an image of the results over a region of the sample. These methods can be applied to analyzing the structure of trabecular bone as well as for analyzing or diagnosing disease in cases where there is a difference in the spatial frequency power spectrum due to physiologic or disease processes. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:OSTEOTRONIX MEDICAL PTE LTD
System and method for automatically segmenting bones in computed tomography angiography data
A system and method for automatically segmenting bone regions from Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) volume data is disclosed. A locally operated bone detector distinguishes between bone regions and contrast agent filled vessels. A filtering operator removes small noise from the detected bone regions. A dilator expands the filtered detected bone regions to adjacent trabecular bones. A processor applies the dilated detected bone regions to the CTA volume data. A display shows the applied CTA volume data.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
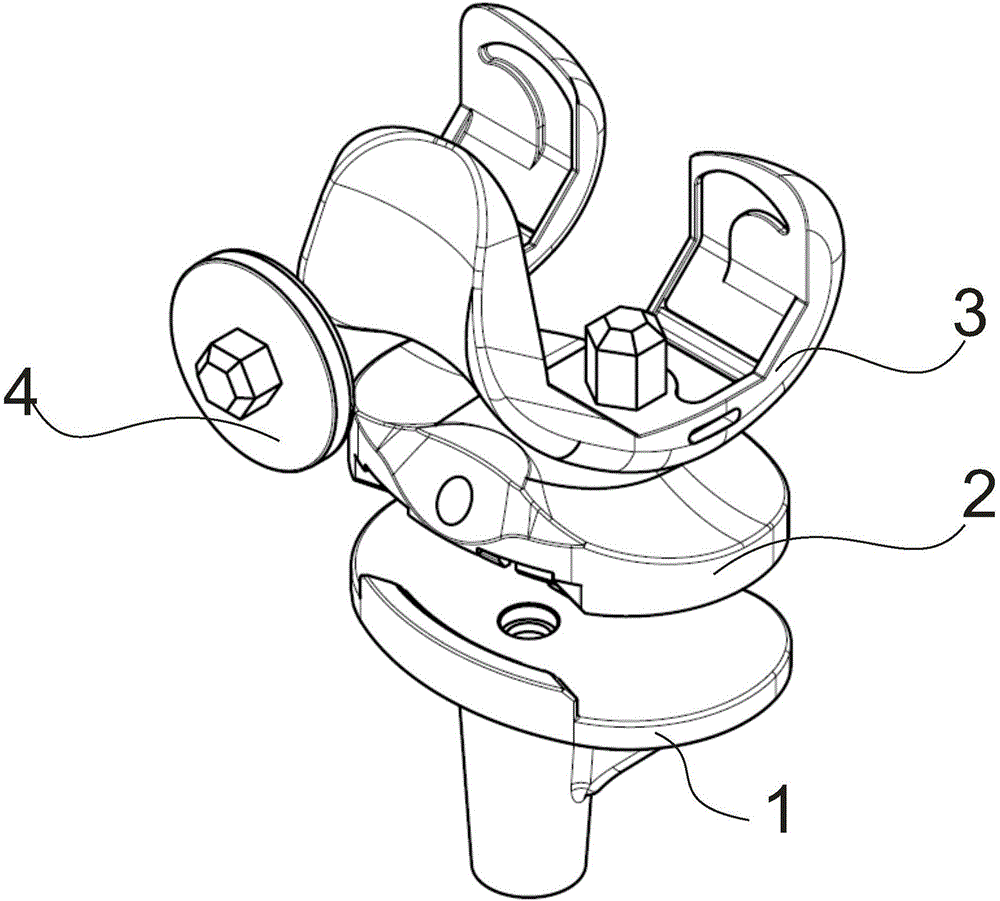
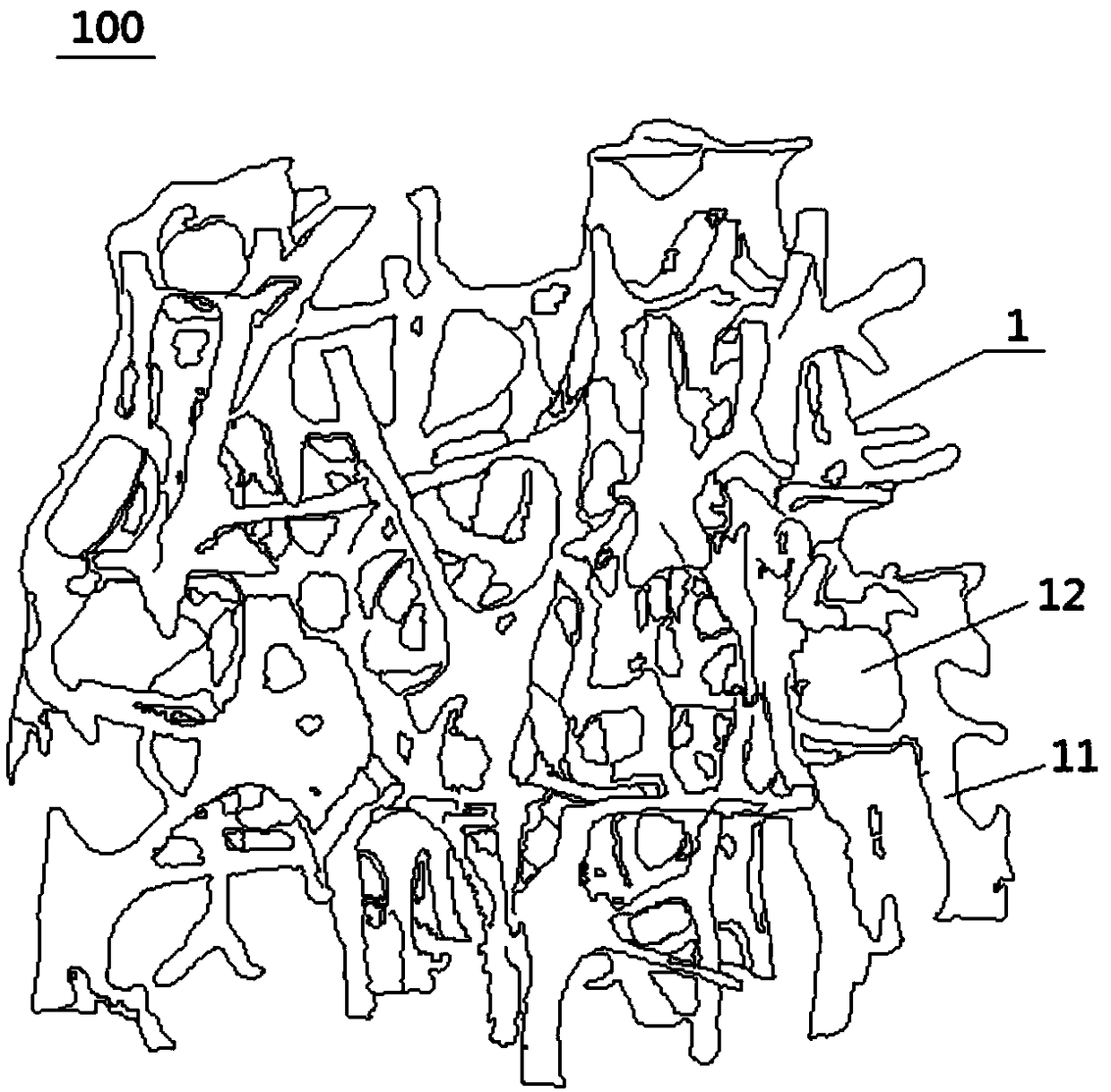
Bone induction differentiated metal bone trabecula knee joint prosthesis and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of medical apparatus, and particularly relates to a bone induction differentiated metal bone trabecula knee joint prosthesis and a preparation method thereof under the precision control using incremental manufacturing technology. The prosthesis comprises a femoral condyle prosthesis, a tibial plateau prosthesis, a tibial plateau pad prosthesis and a patellar prosthesis. Osseointegration interfaces of the femoral condyle prosthesis, tibial plateau prosthesis and patellar prosthesis is in the structure of the bone induction differentiated metal bone trabecula. The preparation method comprises the steps of determining the gradient structure of stress and strain in knee prosthesis, determining the parameters of the porous structure of trabecular bone, establishing a three-dimensional model of the porous structure, conducting slicing and stratification treatment of the three-dimensional model, and conducting electron beam incremental manufacturing of the knee joint prosthesis metal bone trabecula, cooling to obtain the final finished product. The bone induction differentiated metal bone trabecula knee joint prosthesis and the preparation method thereof for the first time achieve the balance between the stress and bone induction performance for stress regions of different osseointegration interfaces of bone in knee joint, satisfy the differentiation requirement of bone induction, provide a preparation method of mass production, and effectively reduces manufacturing cost.
Owner:JIASITE HUAJIAN MEDICAL EQUIP (TIANJIN) CO LTD
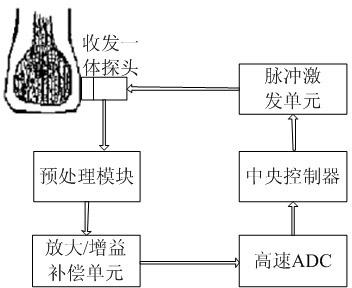
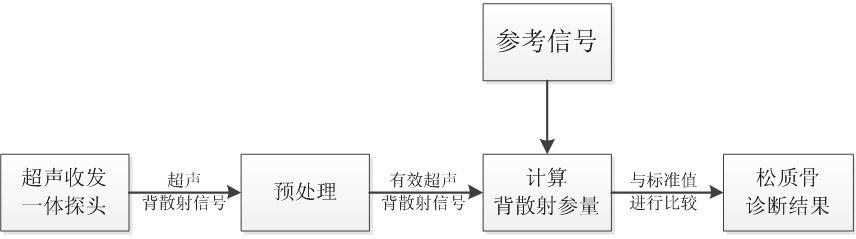
Cancellous bone diagnosis system based on ultrasound backscattering signal parameters
InactiveCN102198009AOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesCalcaneusSonification
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical ultrasonography, and particularly relates to a cancellous bone diagnosis system based on ultrasound backscattering signal parameters. The system comprises an ultrasound backscattering signal acquisition module, a pretreatment module, a backscattering parameter calculation module and a cancellous bone state evaluation module. In the invention, an ultrasound transceiver probe is used to acquire ultrasound backscattering signals from the calcaneus of a human body; effective cancellous bone ultrasound backscattering signals are extracted; the calculation module is used to calculate four parameters, i.e. backscattering coefficient, apparent integration backscattering coefficient, spectral centroid shift and mean trabecular bone spacing; and finally, the health state of the cancellous bone is analyzed by comparing the four parameters with standard values stored in an internal standard database in the system. Compared with the traditional ultrasound transmission diagnosis system based on broadband ultrasound attenuation and ultrasound propagation velocity, the diagnosis system provided by the invention can obtain the complete information of the cancellous bone structure, thereby better detecting the health state of the cancellous bone of a human body.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Inflatable device for use in surgical protocol relating to fixation of bone
InactiveUS20070299455A1Easy to compressEasy to foldInternal osteosythesisSurgical furnitureBone CortexTrabecular bone
A balloon for use in compressing cancellous bone and marrow (also known as medullary bone or trabecular bone). The balloon comprises an inflatable balloon body for insertion into said bone. The body has a shape and size to compress at least a portion of the cancellous bone to form a cavity in the cancellous bone and / or to restore the original position of the outer cortical bone, if fractured or collapsed. The balloon desirably incorporates restraints which inhibit the balloon from applying excessive pressure to various regions of the cortical bone. The wall or walls of the balloon are such that proper inflation of the balloon body is achieved to provide for optimum compression of the bone marrow. The balloon can be inserted quickly into a bone. The balloon can be made to have a suction catheter. The balloon can be used to form and / or enlarge a cavity or passage in a bone, especially in, but not limited to, vertebral bodies. Various additional embodiments facilitate directionally biasing the inflation of the balloon.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
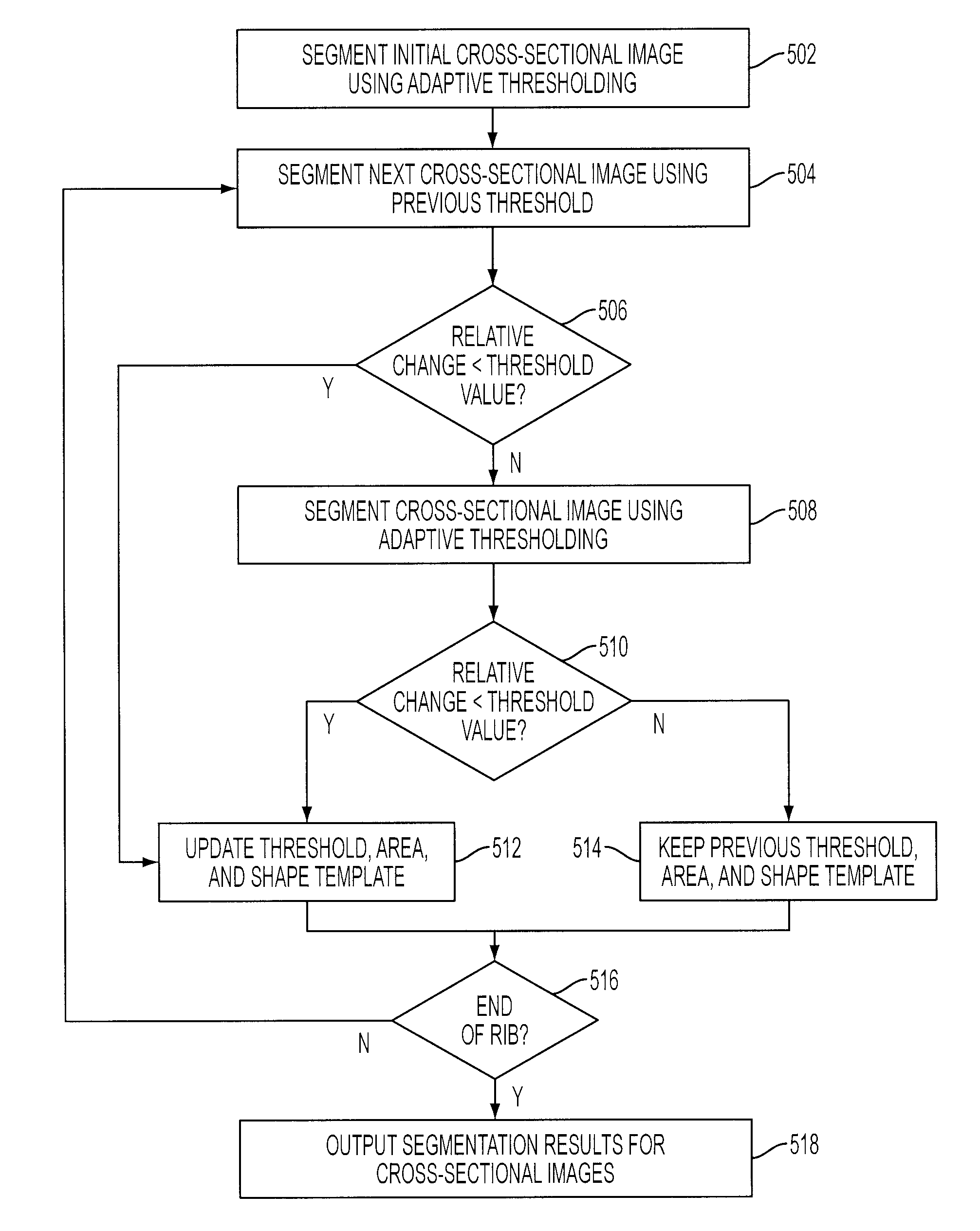
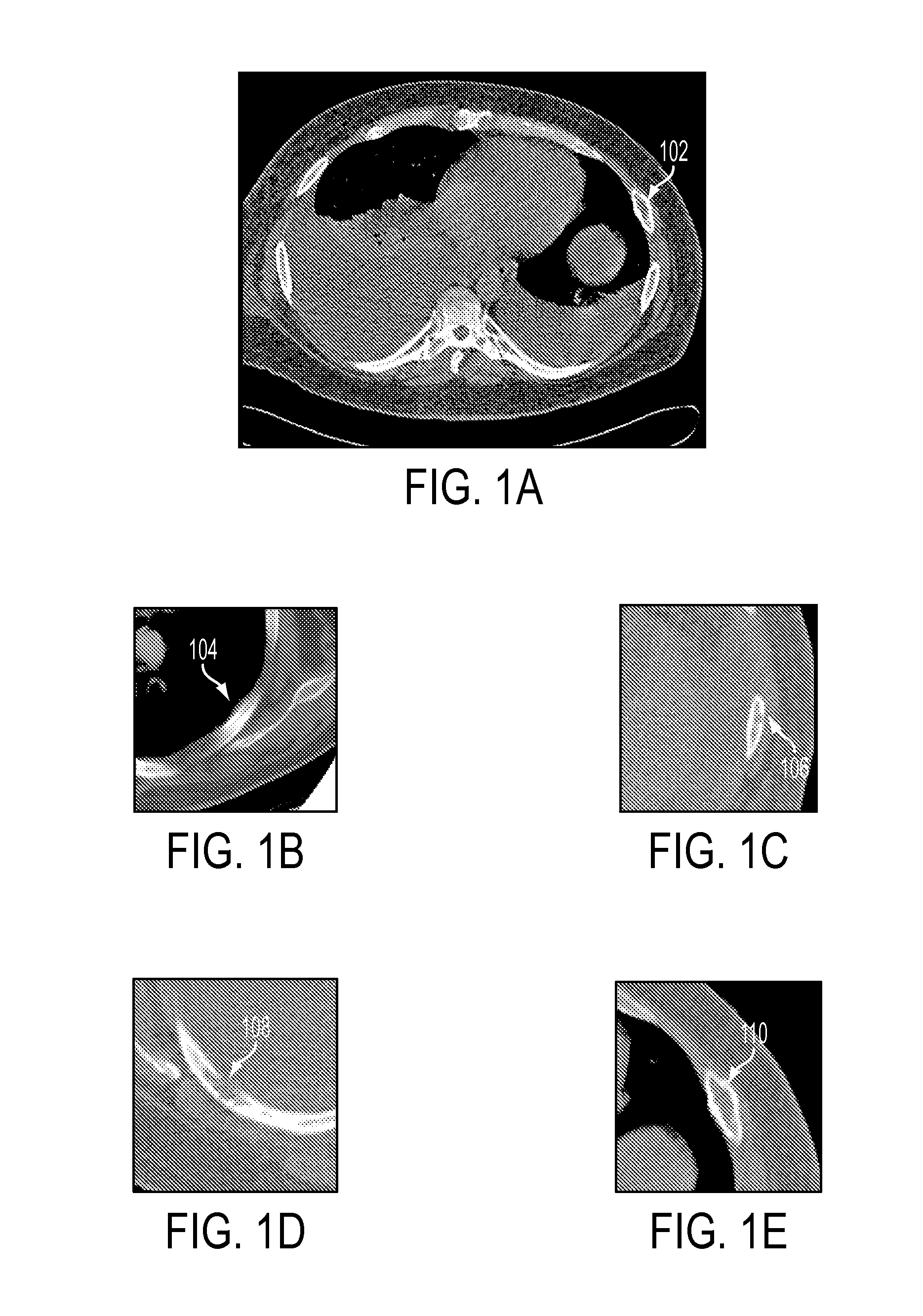
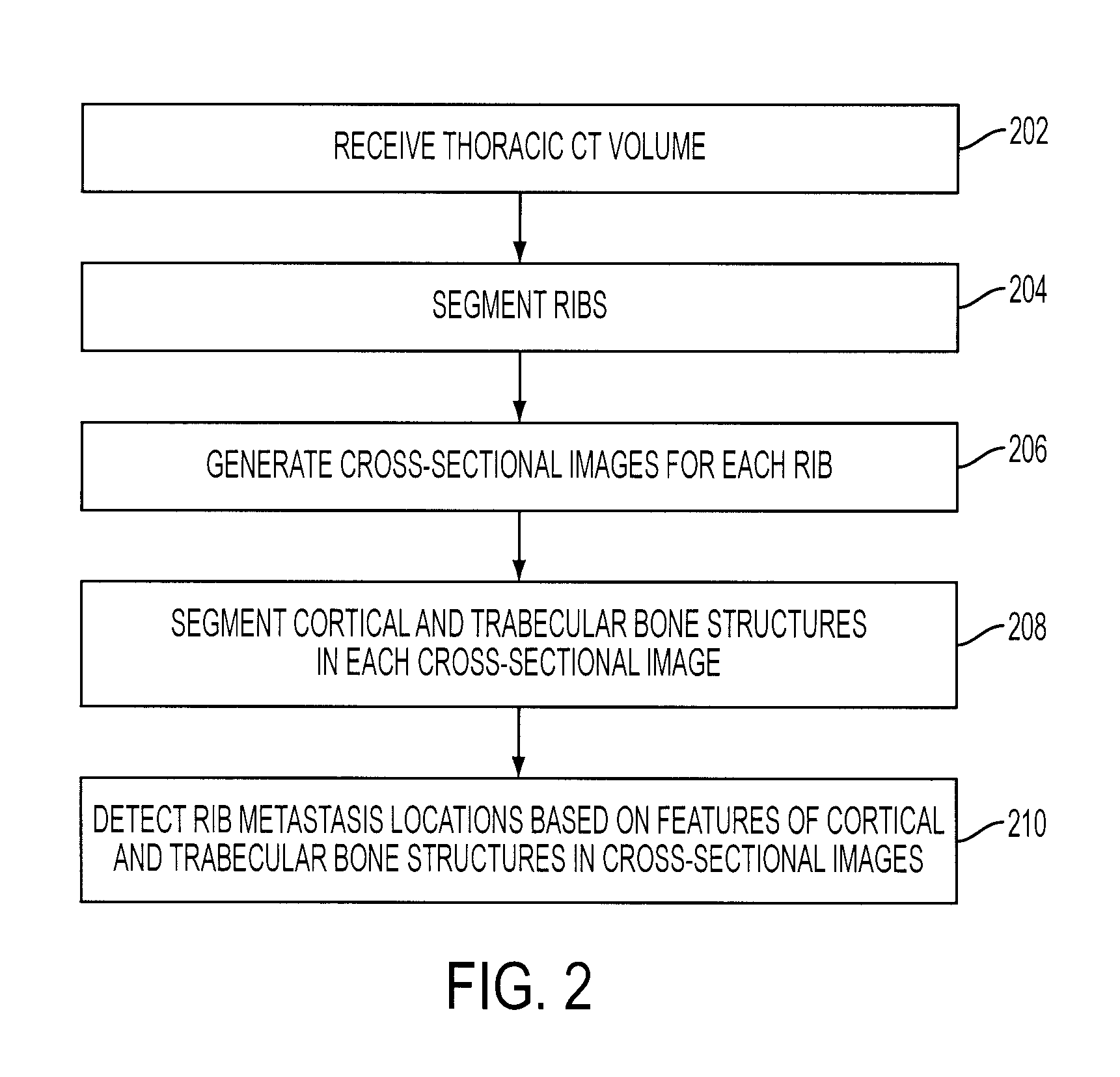
System and Method for Automatic Detection of Rib Metastasis in Computed Tomography Volume
ActiveUS20080137932A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionLymphatic SpreadComputing tomography
A method and system for automatically detecting rib metastasis in a thoracic CT volume is disclosed. The ribs are segmented in said CT volume by recursive tracing. A series of cross-sectional images are then generated along a centerline of each rib. Cortical and trabecular bone structures are segmented in each of the cross-sectional images for each rib. Features are calculated for each cross-sectional image based on characteristics of the cortical and trabecular bone structures, and alterations are detected in the cross-sectional images based on the features. Rib metastasis is detected in a rib when an alteration is detected in a number of consecutive cross-sectional images along the centerline of the rib.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Tissue engineering cartilage construction method using bone matrix gelatin
A tissue engineering cartilage construction method using bone matrix gelatin which comprises, using cartilage cell for isolated culture or base material stem cell for isolated culture to evoke cartilage cell i.e. seed cell, fetching New Zealand rabbit or human embryon os longum and metaphysic trabecular bone to construct bone matrix gel BMG, inoculating the seed cells harvested through isolated culture onto cortex bone or cancellous bone BMG for extracorporal culture.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Artificial bone nanocomposite and method of manufacture
A composition suitable for bone replacement is provided. The composition is a nanocomposite matrix, resembling both the structure and the properties of natural bone, including morphology, composition and mechanical characteristics. The nanocomposite is preferably porous and comprises: (1) micro or nano scale cellulose crystals or fibres; (2) hydroxyapatite nanoparticles; (3) Poly L-Lactide Acid or poly glycolic acid; and (4) a coupling agent, for example a surfactant, preferably an anionic surfactant such as sodium dodecyl sulfate. The composition is useful as an artificial bone replacement or bone graft, is preferably biomimetic, and can be suitable for use, for example, in trabecular bone substitution and osteoanagenesis applications. A method of fabrication of the nanocomposite is also provided.
Owner:EFTEKHARI SAMIN
Virtual bone biopsy
ActiveUS20050031179A1Reduce noise imagingReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisResonanceMri image
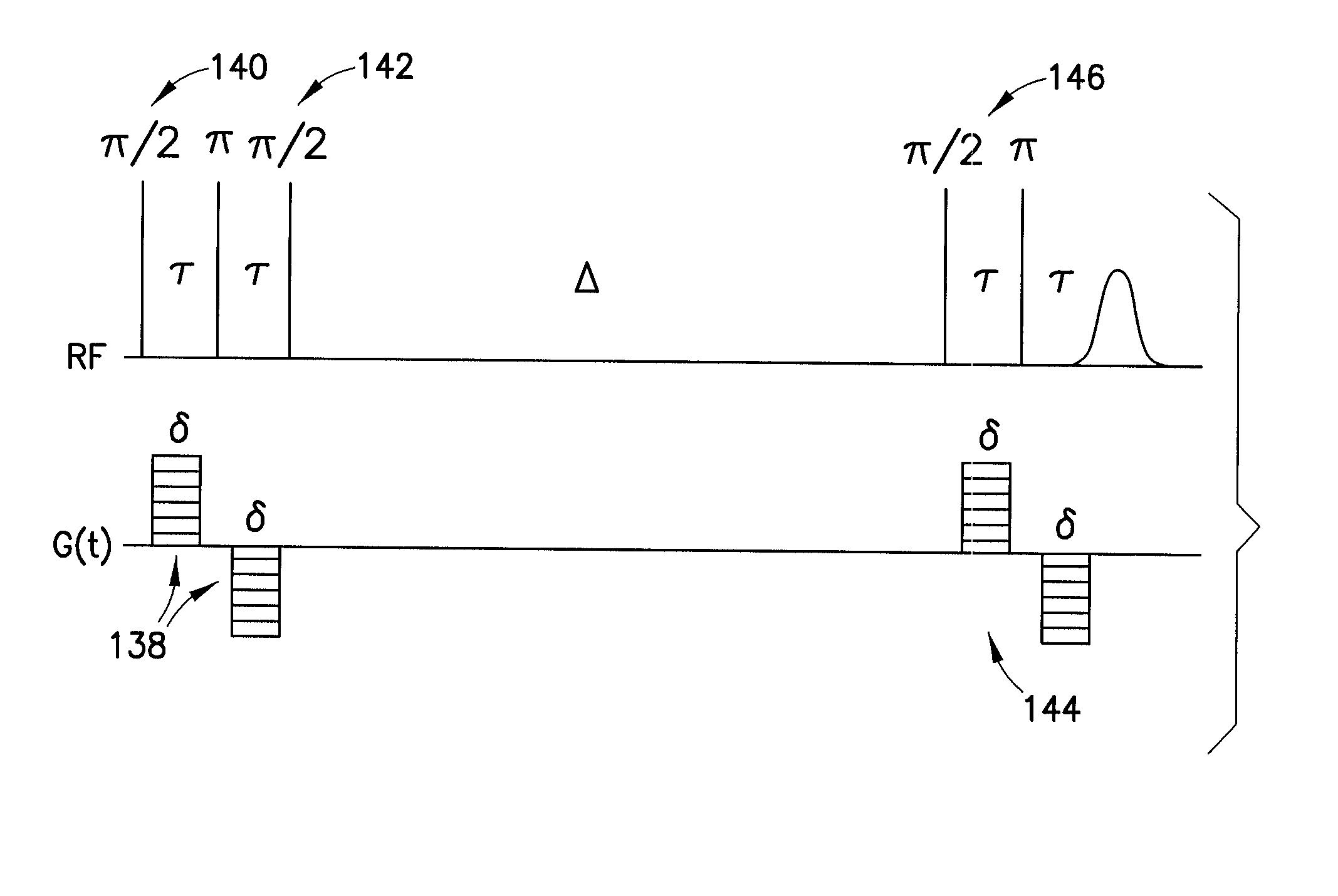
The present indention comprises a system and method for analyzing trabecular bone structure. A means for scanning the trabecular bone using a magnetic resonance image (MRI) scanner generates bone image data, which is then processed including correcting, deshadi4 and reducing noise in the image data.
Owner:PENNSYLVANIA THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF
Digital topological analysis of trabecular bone MR images and prediction of osteoporosis fractures
The invention provides method, system and device for determining trabecular bone structure and strength by digital topological analysis, and offers, for the first time, a demonstration of superior associations between vertebral deformity and a number of architectural indices measured in the distal radius, thus permitting reliable and noninvasive detection and determination of the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. A preferred embodiment provides imaging in three dimension of a region of trabecular bone, after which the 3D image is converted into a skeletonized surface representation. Digital topological analysis is applied to the converted image, and each image voxel is identified and classified as a curve, a surface, or a junction; and then associated with microarchitectural indices of trabecular bone to quantitatively characterize the trabecular bone network. The invention is applicable in vivo, particularly on human subjects, or ex vivo.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method and composition for treating osteonecrosis and/or avascular necrosis
InactiveUS20070287988A1Improve methodFilling void and defectStentsOrganic active ingredientsBiological bodySubchondral bone
By providing an elastic form stable material which is capable of being delivered directly to a specific desired location within a living creature and provides increased strength and rigidity to the injected location, disorders of the trabecular bone or subchondral tissue of a living creature are able to be effectively treated. Treatment of necrosis of the bone beneath the cartilage in skeletal joints and other defects in bony or cartilaginous structures is achieved with a variation of the subject material specific to each application. In the preferred method, the elastic form stable material is injected directly into the affected area, thereby achieving the desired result.
Owner:BONWRX INC
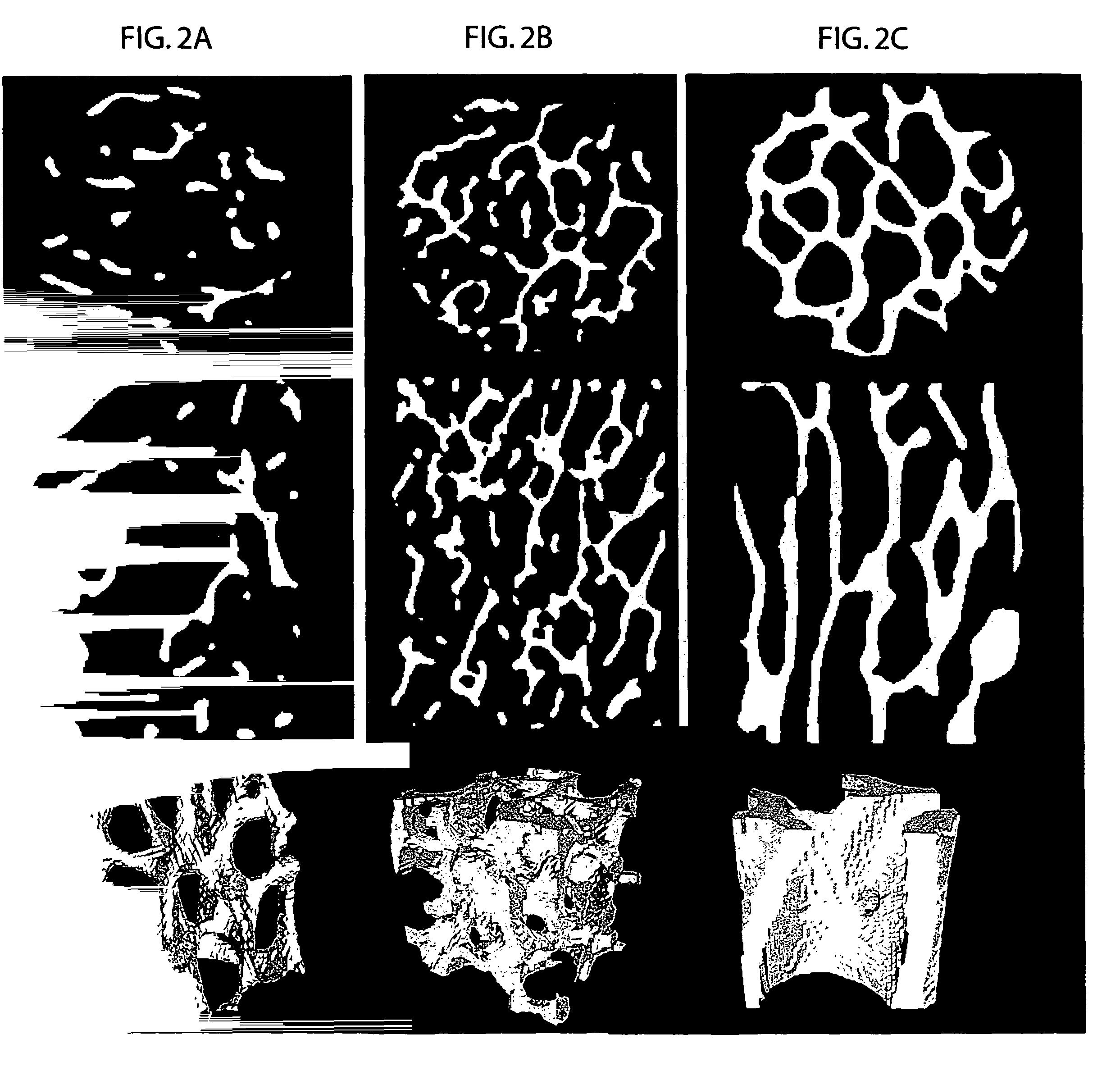
Gradient and porous magnesium alloy material used for bone defect repair
The invention discloses a gradient and porous magnesium alloy material used for bone defect repair. The preparation method of the gradient and porous magnesium alloy material comprises the steps of preparing a prefabrication body from magnesium alloy powder and an additive under a gradient pressure and sintering the prefabrication body by adopting a vacuum sintering process; the gradient and porous magnesium alloy material is characterized in that a plurality of pores communicating with each other are formed in each of the interior and the surface of the gradient and porous magnesium alloy material; the pores are in gradient distribution; the porosity size is in reverse proportion to the density of bone tissues around an implantation space in a specific direction, that is, a part with a higher cortical bone mineral density corresponds to a magnesium alloy part with a smaller porosity while a part with a lower trabecular bone mineral density corresponds to a magnesium alloy part with a higher porosity; an area with a higher porosity has a higher degradation velocity; an area with a lower porosity is conductive to strength increase thereof; the contact area between the body fluid and porous magnesium alloy is reduced; and the degradation velocity is more slowly; therefore the degradation velocity of magnesium alloy can be well matched with the bone tissue healing velocity as far as possible.
Owner:DONGGUAN REVOLUTION PROD DESIGN
Diffusion-based magnetic resonance methods for characterizing bone structure
ActiveUS7894891B2Reliable indicationIncrease heightMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringBone structureHigh resolution image
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Cortical drilling
InactiveUS20130150857A1Sharp and rapid change in resistanceImprove the immunityDental implantsSurgeryDental alveolusTrabecular bone
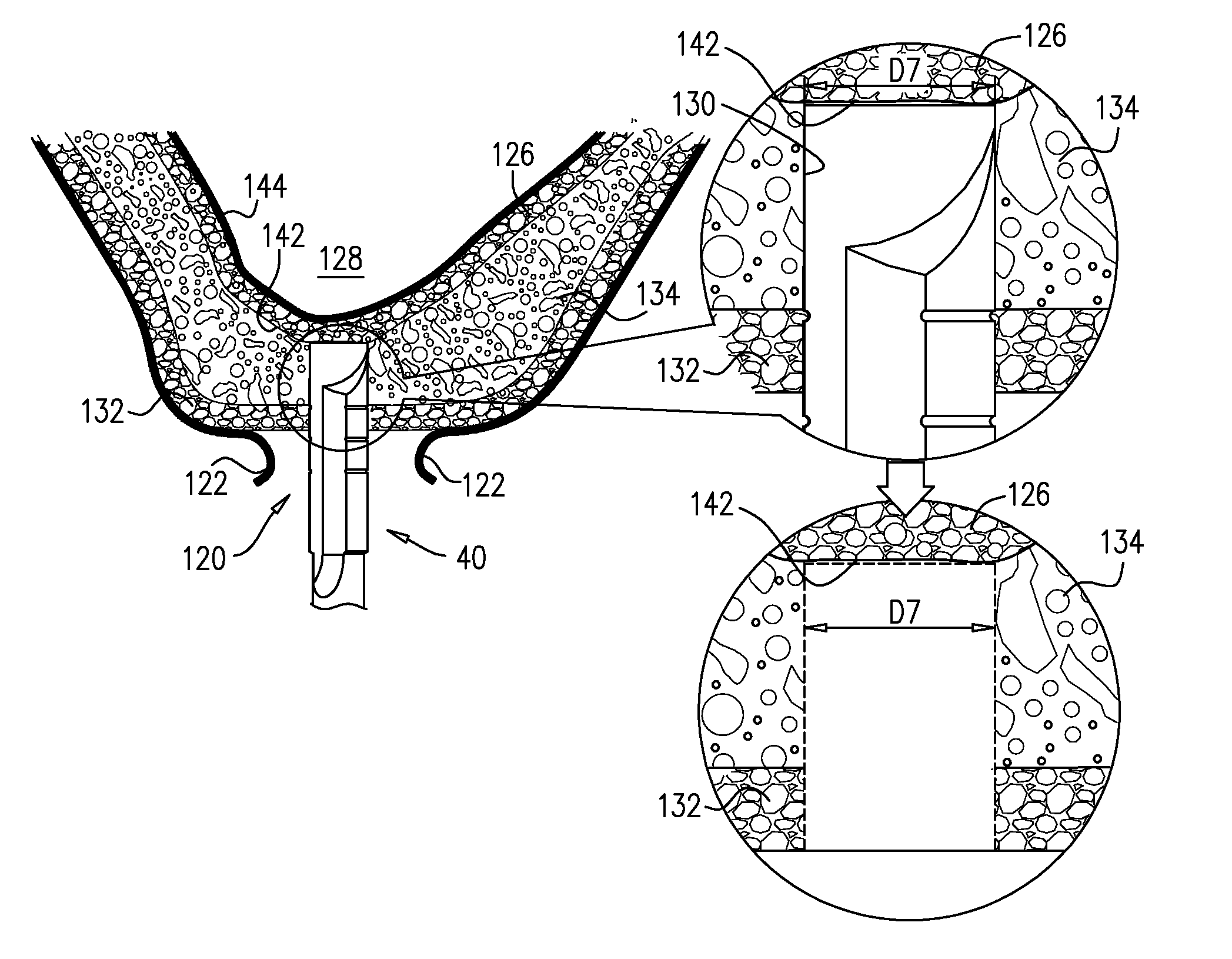
A method is provided that includes advancing a drill having a distal end through an occlusal cortex into trabecular bone of an alveolar ridge, and ceasing the advancing of the drill when the distal end of the drill reaches an occlusal surface of a superior cortex of the alveolar ridge. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MAXILLENT
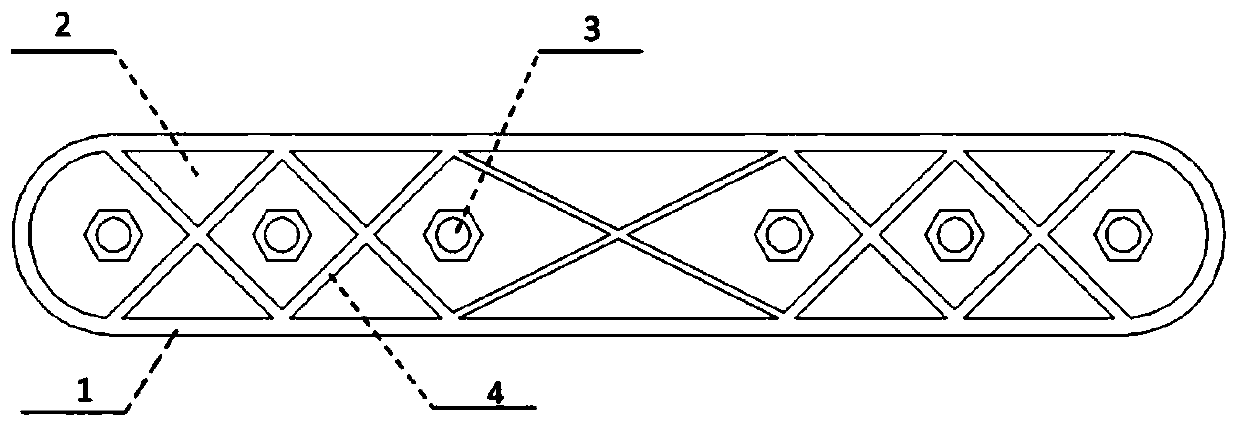
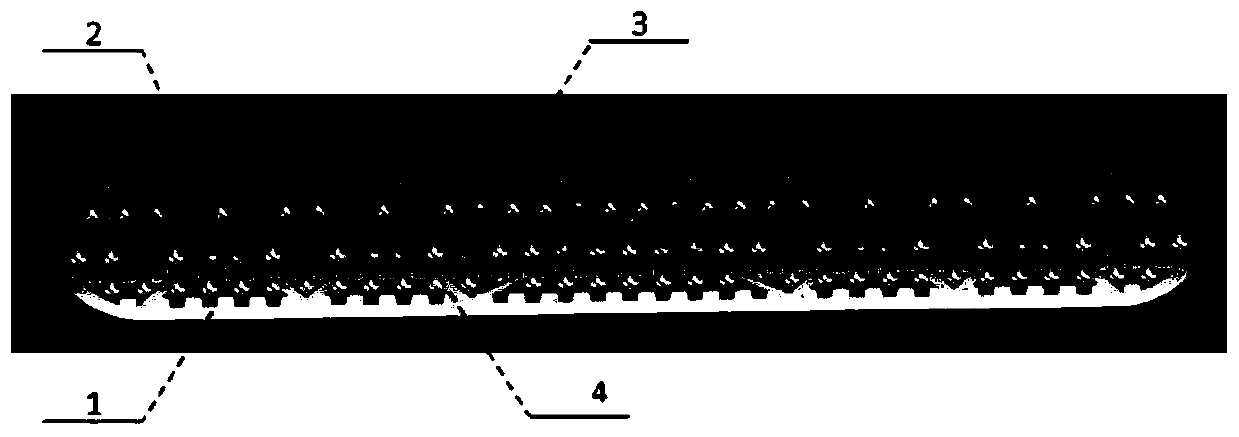
Flexible trabecular bone structure interbody fusion cage
ActiveCN104000674ALoss of activityRelieve load stress shockInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsPolyurethane elastomerDISCOGENIC DISEASE
The invention discloses a flexible trabecular bone structure interbody fusion cage, and relates to an interbody fusion cage capable of substituting intervertebral disk functions. The flexible trabecular bone structure interbody fusion cage can fuse an upper vertebral body with a lower vertebral body, and can reserve the normal gap between the fused vertebral bodies and the mobility balance between the fused vertebral bodies. The fusion cage is provided with a plate spring skeleton, the upper surface of the plate spring skeleton is provided with an upper trabecular bone structure layer, the lower surface of the plate spring skeleton is provided with a lower trabecular bone structure layer, a polycarbonate polyurethane elastomer is added to the gaps of the plate spring skeleton, the front edge or the rear edge of each of the upper trabecular bone structure layer and the lower trabecular bone structure layer is provided with a screw, and the screw is used for fixing the fusion cage on the upper and lower vertebral bodies through locking bolts. The flexible trabecular bone structure interbody fusion cage can be used for the operation treatment of cervical vertebra and lumbar discogenic diseases, and reserves the functions of the intervertebral disc as possible while fusing the adjacent vertebral bodies in order to avoid the disappear of the mobility balance between the fused vertebral bodies.
Owner:武汉光谷北宸医疗器械有限公司
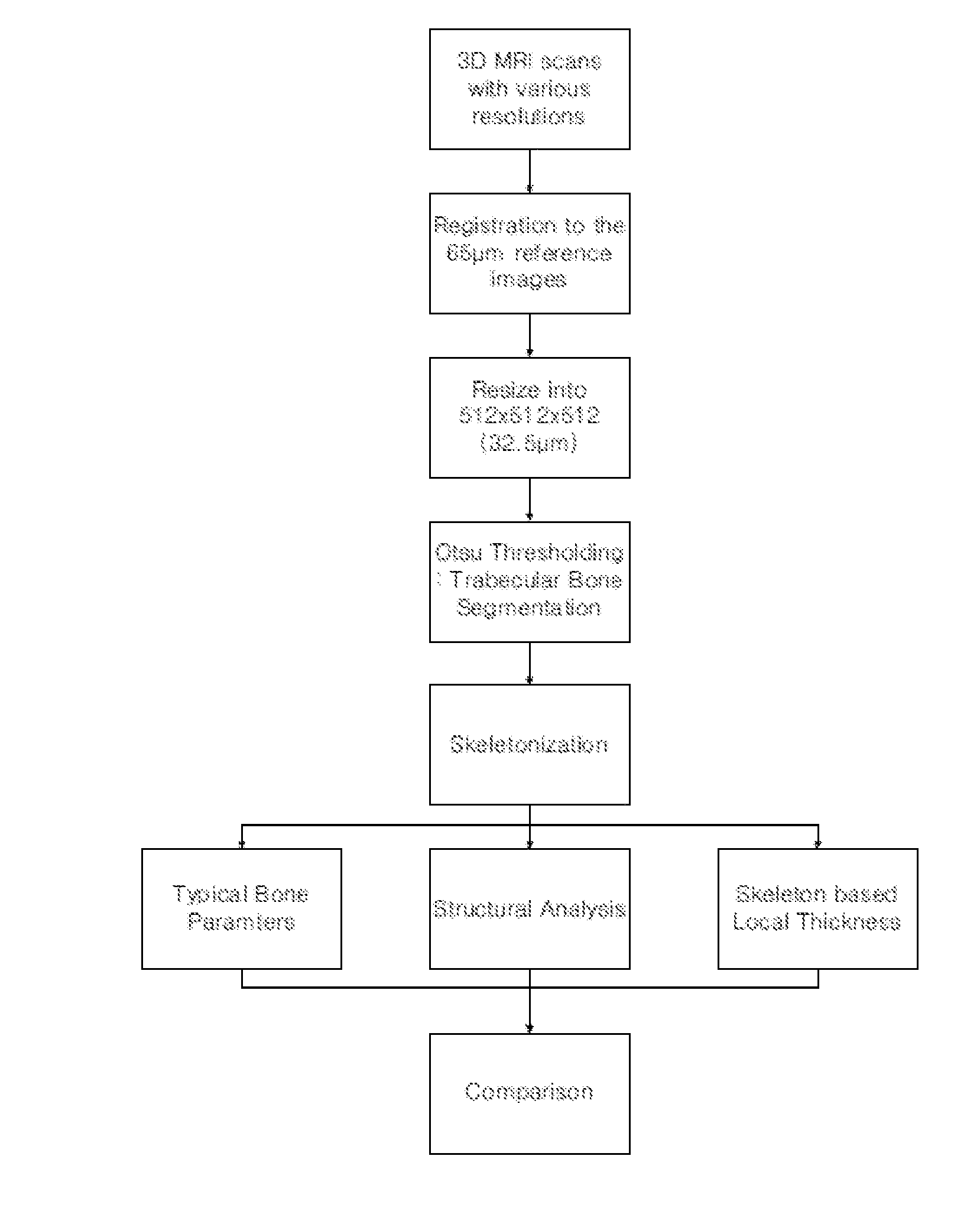
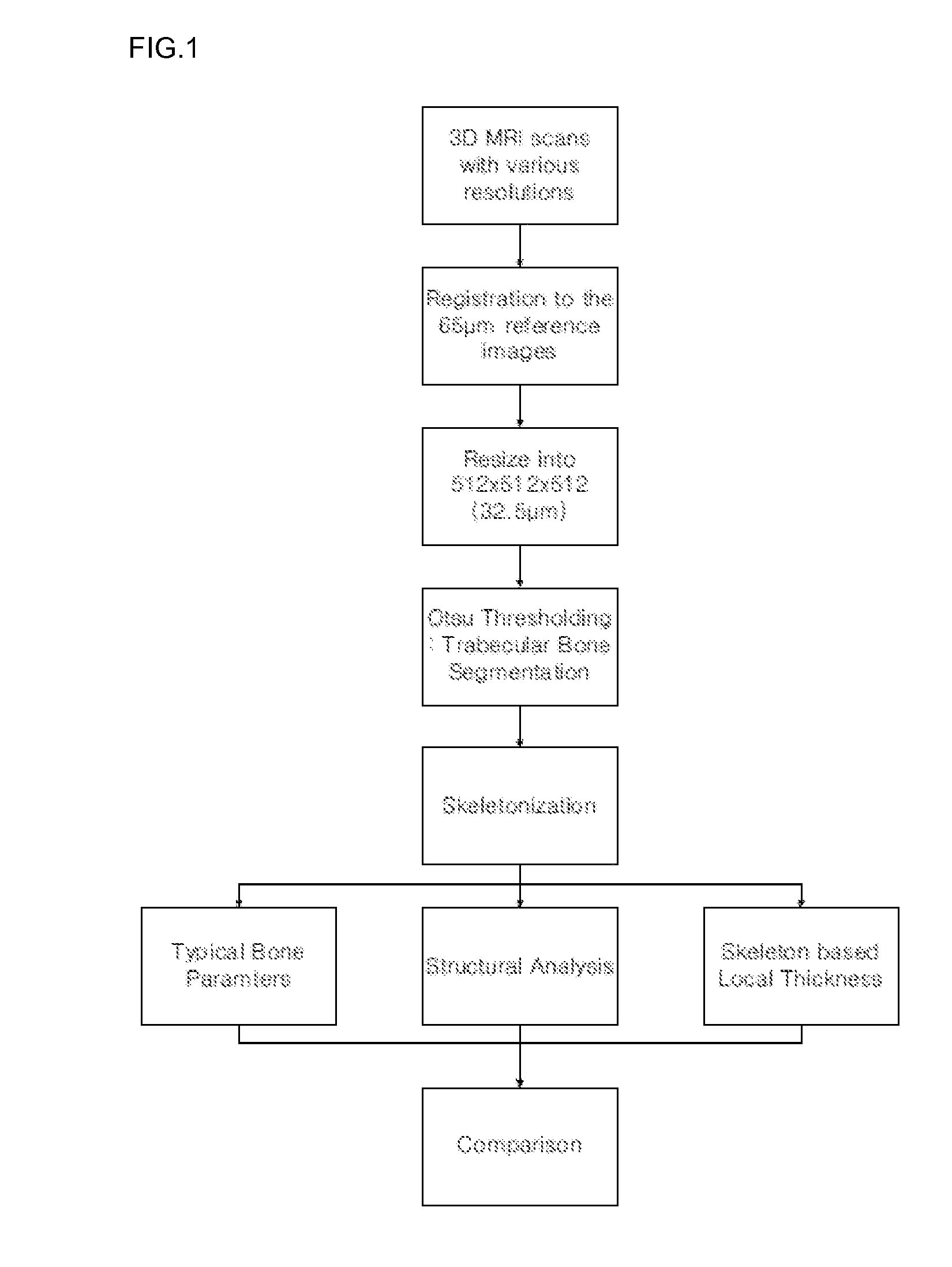
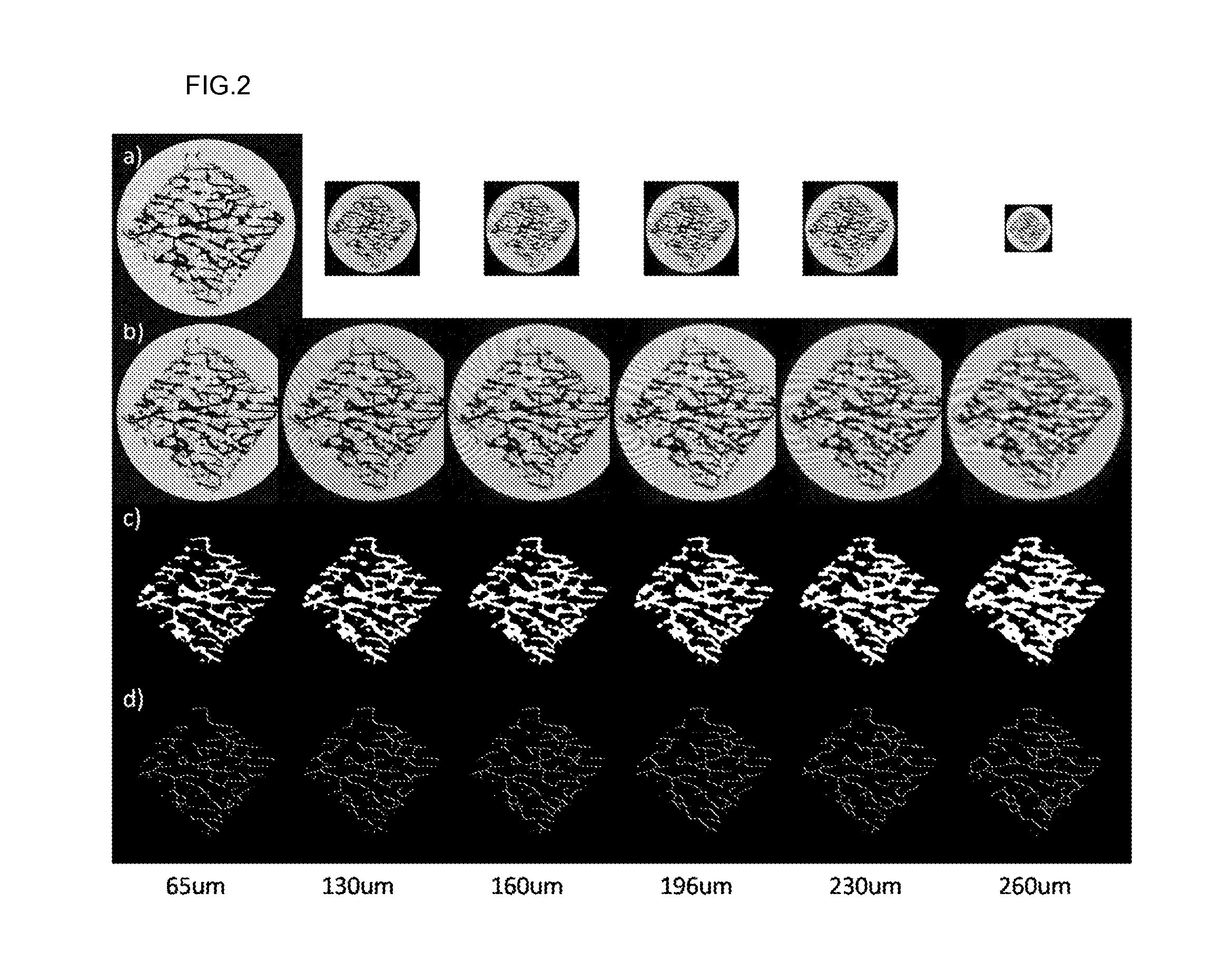
Method For Measuring Trabecular Bone Parameters From MRI Images
Disclosed is a method for measuring trabecular bone parameters from MRI images, including: scanning an experimental group with a 3D MRI scanner; segmenting the MRI images to extract bone area and perform skeletonization of the bone area; detecting end-point, joint and branch voxels in the skeleton to analyze bone structure; and measuring trabecular bone parameters based on the result of the structural analysis. The method enables diagnosing osteoporosis.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
Diffusion-based magnetic resonance methods for characterizing bone structure
ActiveUS20110105886A1Reliable indicationIncrease heightMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringBone structureHigh resolution image
A method of in vitro or in vivo nuclear magnetic resonance and / or magnetic resonance imaging, to determine bone properties by measuring the effects of molecular diffusion inside the bone specimen to derive parameters that are related to the structure of the trabecular bones. The method is a non-invasive probe that provides topological information on trabecular bone without requiring a full high-resolution image of its structure, and is compatible with clinical use.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
3D-printed porous tantalum metal bone plate
ActiveCN109793565AAids in healingAvoid stress shieldingAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone platesOsseointegrationBone growth
The invention relates to a 3D-printed porous tantalum metal bone plate. The 3D-printed porous tantalum metal bone plate is characterized in that tantalum metal powder is taken as a base material, andthe bone-imitating trabecular bone plate having bone induction property and produced by 3D printing has an interconnecting-pore structure fit for bone growth. The production method includes: under argon production, using medical grade spherical tantalum powder as a raw material to produce the porous bone plate by 3D printing; removing excess metal powder adhering to the surface of the bone plate through sandblasting; removing residual stress through heat treatment to make the surface of the bone plate smooth. By the arrangement, the porous bone plate with the bone induction property can form excellent bone integration with bone tissue so as to achieve permanent fixation in biology.
Owner:赵德伟 +2
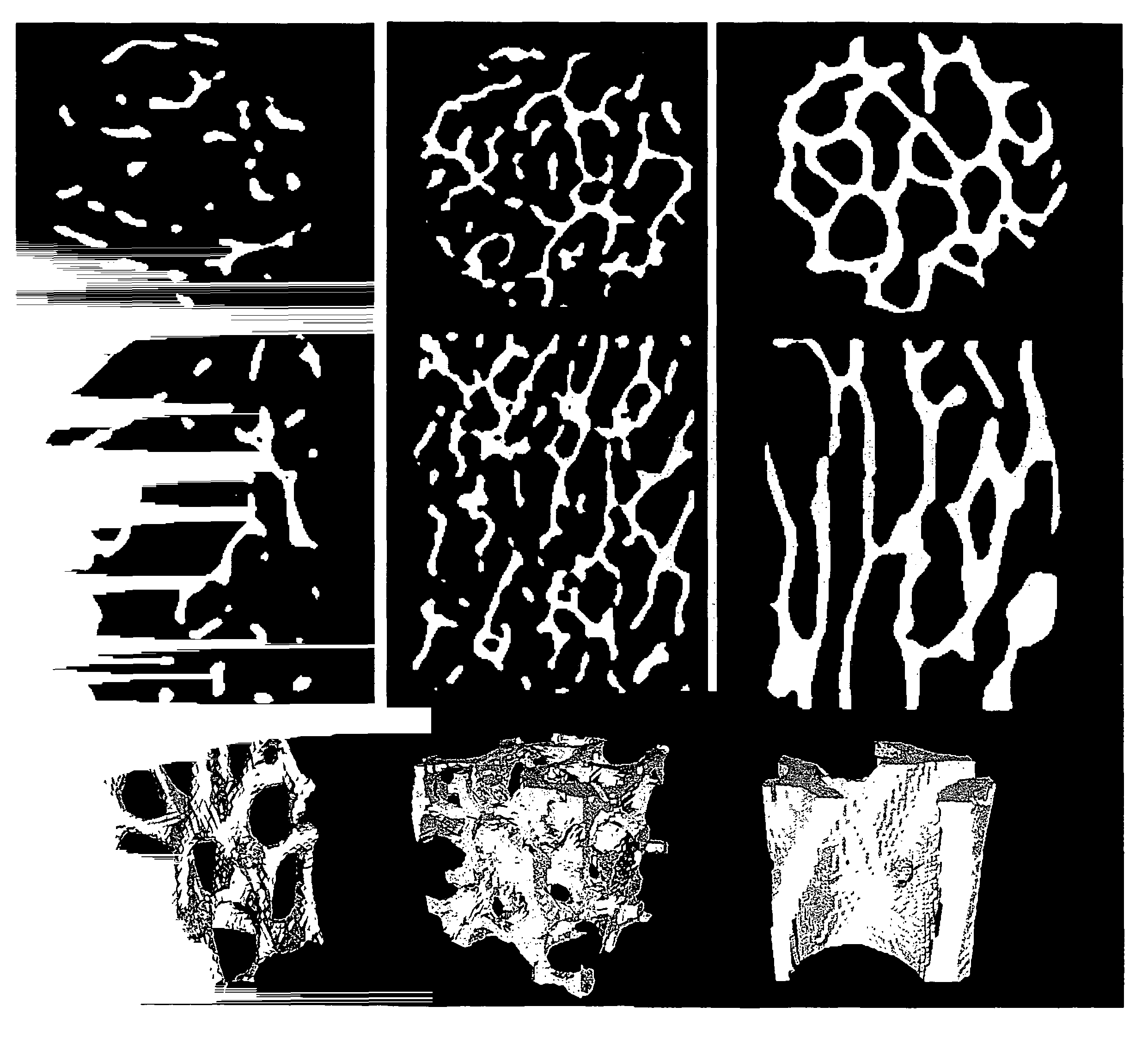
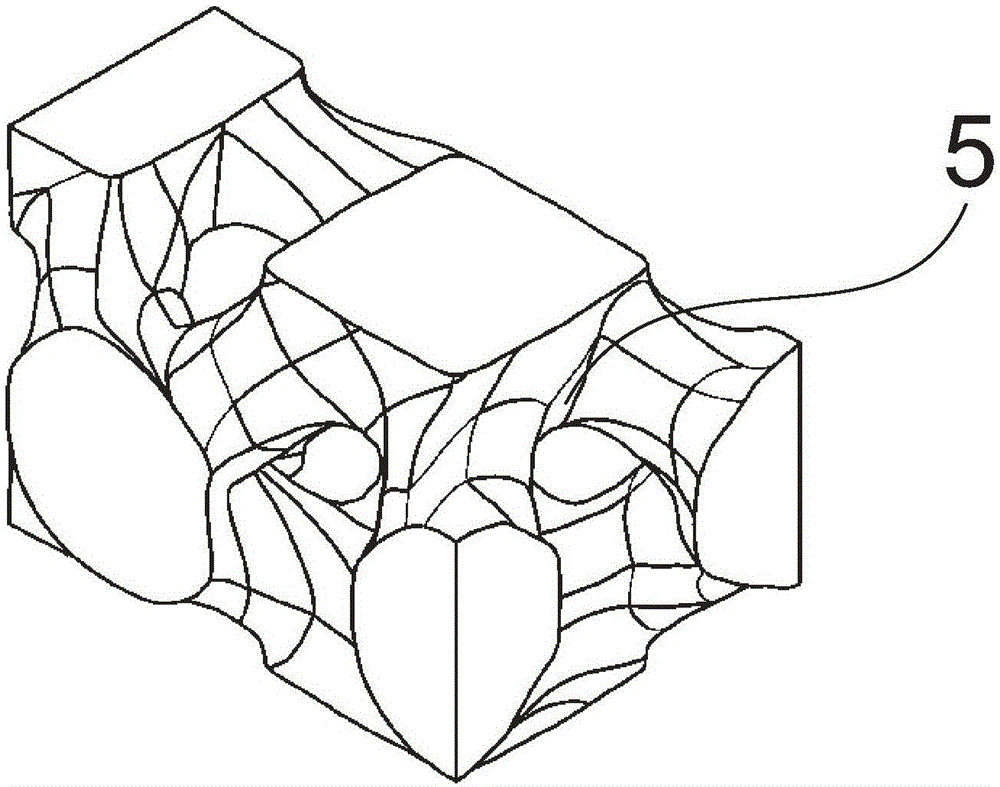
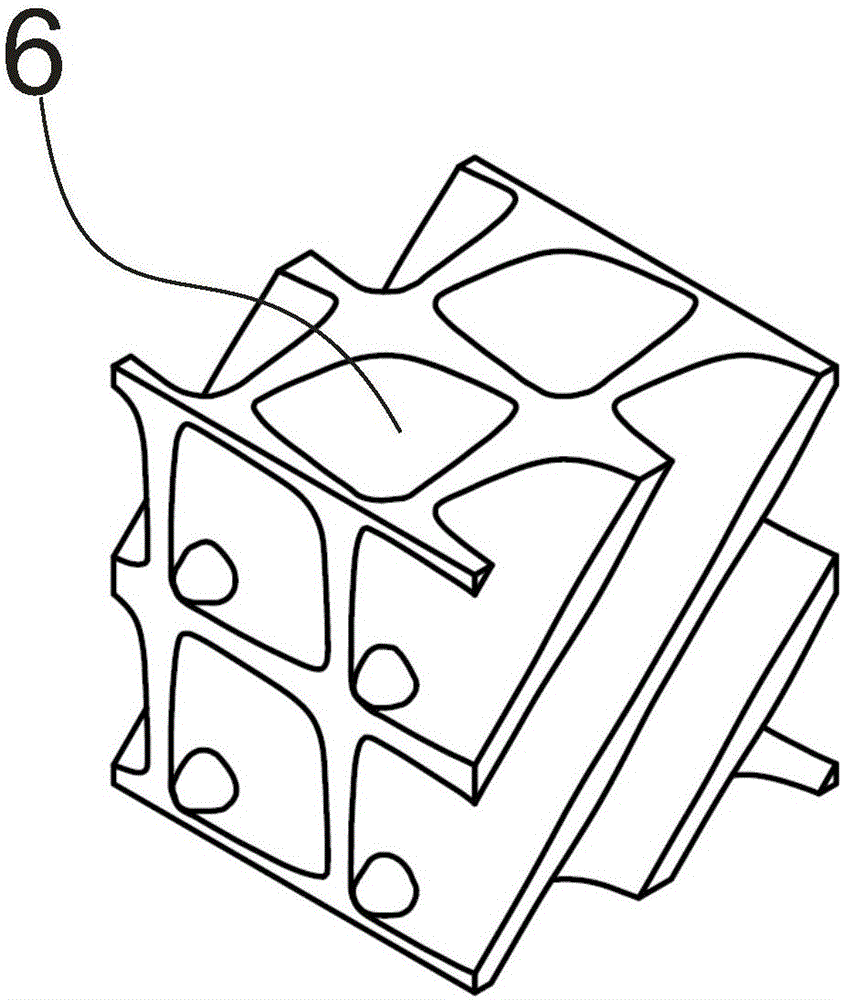
Trabecular bone structure and prosthesis using the structure
Owner:BEIJING CHUNLIZHENGDA MEDICAL INSTR
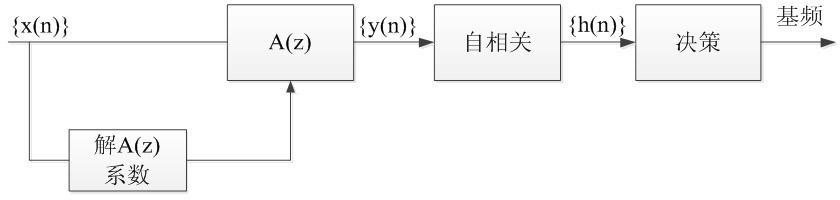
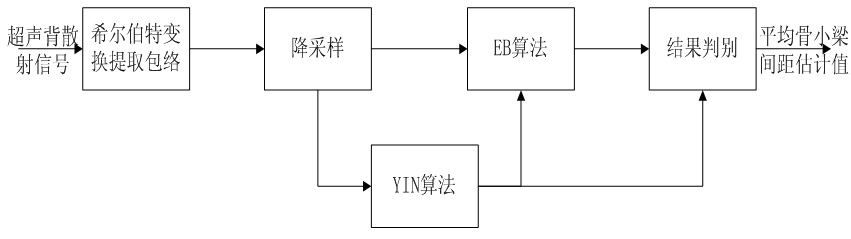
Hilbert transform-fundamental frequency estimation based method for estimating mean trabecular bone spacing
InactiveCN101889877AOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesUltrasonographyFundamental frequency
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical ultrasound, in particular to a Hilbert transform-fundamental frequency estimation based method for estimating mean trabecular bone spacing. The method comprises the following steps: first, extracting enveloping of an ultrasonic backscattered signal after analog-to-digital conversion by adopting Hilbert transform, and performing down sampling on the enveloped signal; and then, processing the enveloped signal respectively by two fundamental frequency estimation algorithms, namely instantaneous fundamental frequency estimation (EB) and Yin (YIN) based on events, finding out the fundamental frequency of the enveloped signal from a last decision module, and reckoning the mean trabecular bone spacing by the fundamental frequency and known ultrasound transmission speed. The method raises to utilize the method of Hilbert transform-fundamental frequency estimation to study the mean trabecular bone spacing for the first time, and has stronger robustness on changes of white noise, random scatter echo and regular scatter echo, and more accurate estimation on different mean trabecular bone spacing compared with the traditional method for directly estimating the mean trabecular bone spacing.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Trabecular bone analyzer
ActiveUS20150221080A1High resolutionQuantitative precisionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTrabecular boneTomographic image
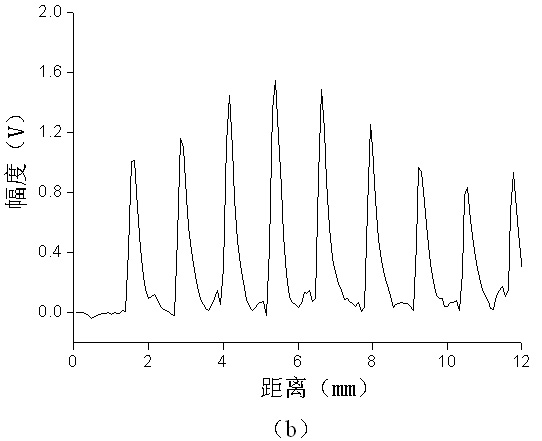
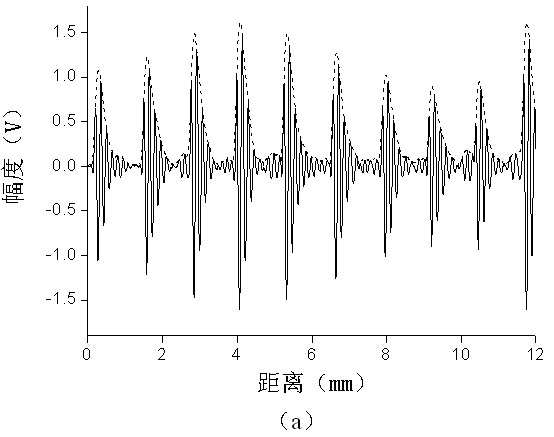
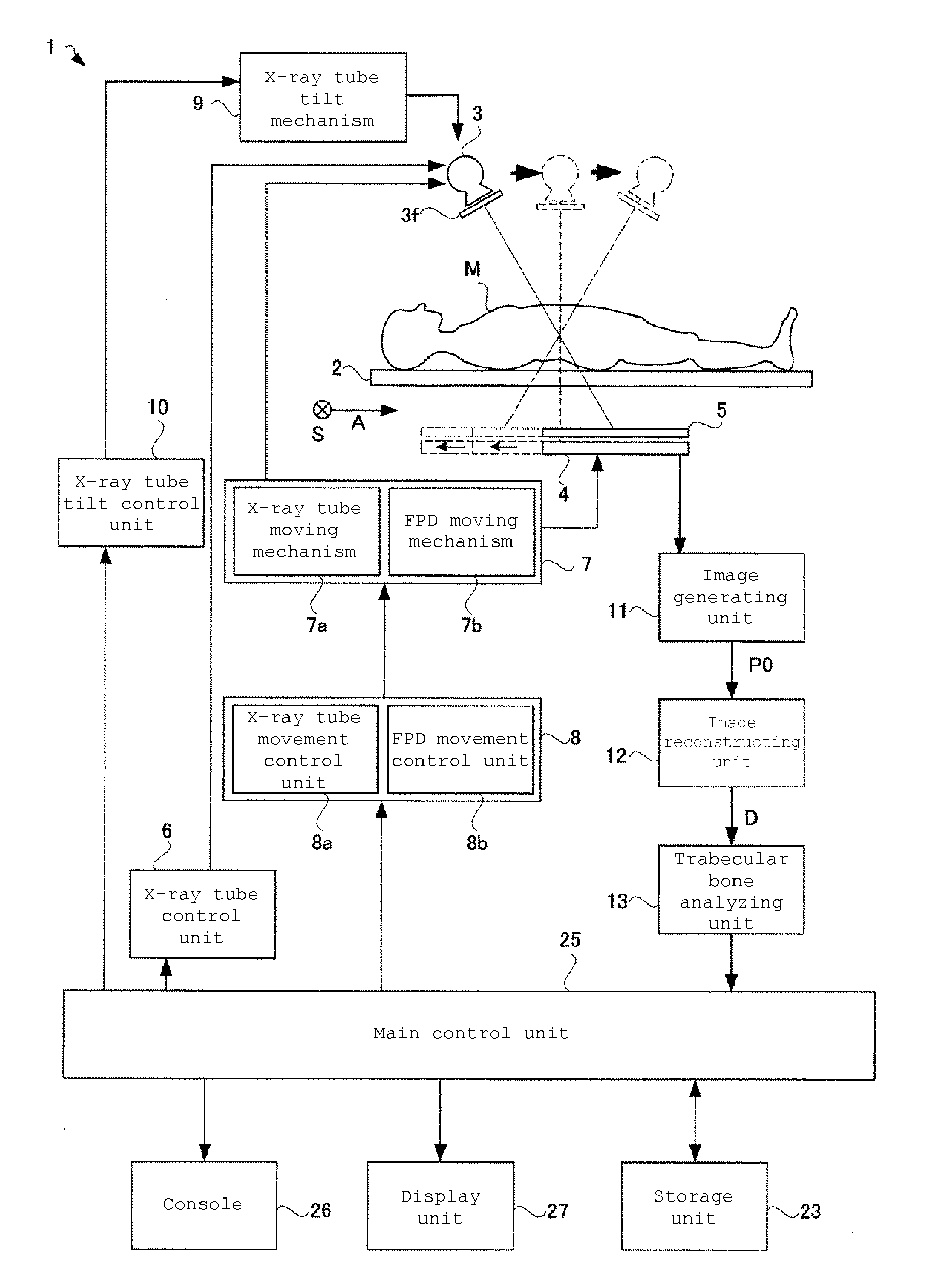
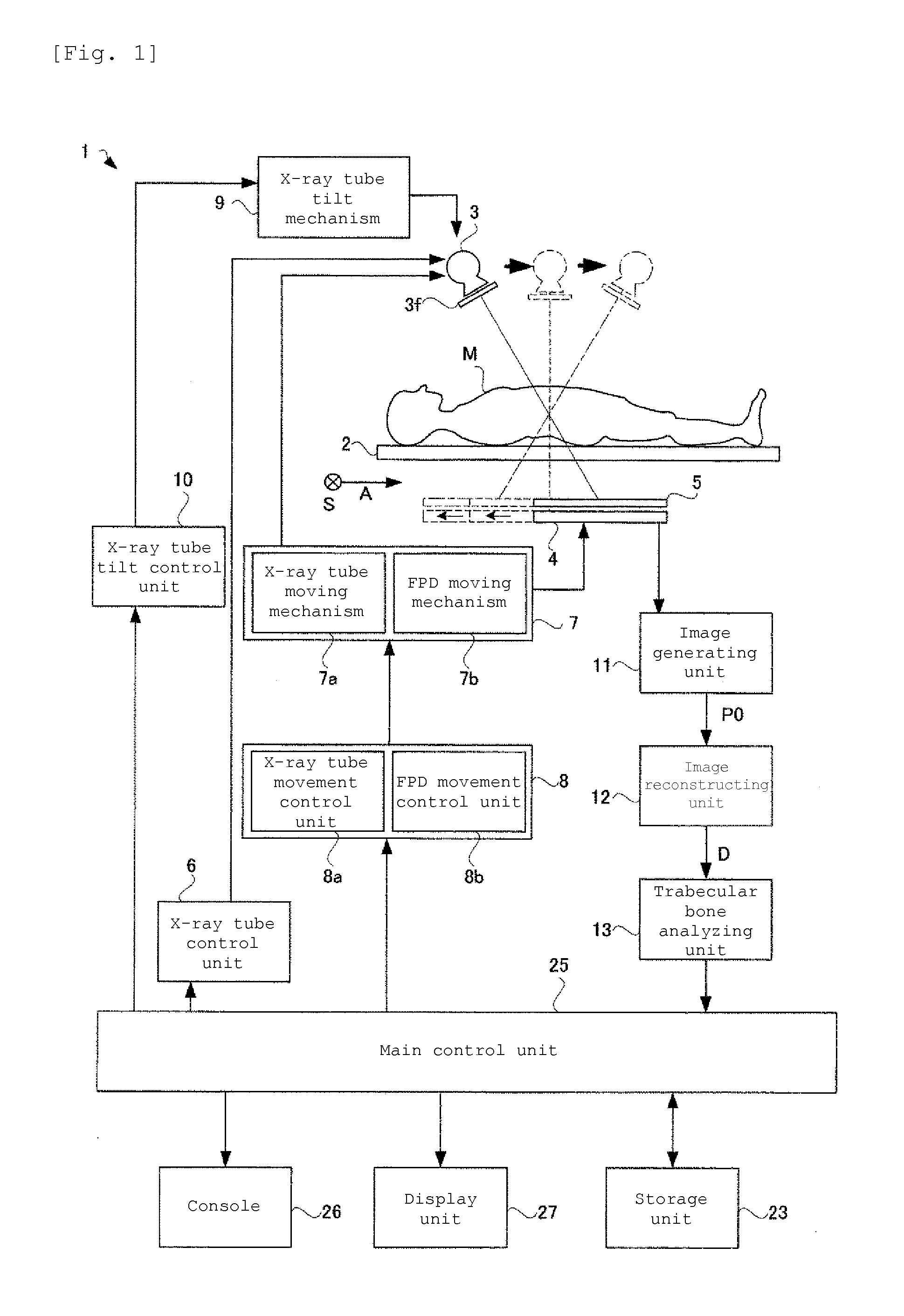
Disclosed herein is a trabecular bone analyzer that can quantitatively determine the state of trabecular bone accurately. The trabecular bone analyzer of may perform trabecular bone analysis on a tomographic image D. In the tomographic image D, trabeculae forming a network may appear without overlapping. Therefore, such trabecular bone analysis may more accurately quantify trabecular bone.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Porous Ceramic Foam Granules and Method of Producing the Same
InactiveUS20130330537A1Good mechanical integrityLayered productsCeramic shaping apparatusPrillMetallurgy
Materials and methods of producing materials for scaffolds to facilitate growth of bone tissues. Porous ceramic materials are produced by a template coating method. Polymeric foam is processed to produce treated foam. Polymer solution, ceramic powder, dispersant, and drying agent are combined, mixed, and sonicated in a multi-step process to achieve a uniform mixture. In a first coating application, treated foam and ceramic slurry are processed until visibly homogeneous and fully reticulated, then sintered to form porous ceramic materials. Through a second multi-step process, a second ceramic slurry is prepared. In a second coating application, the porous ceramic materials are coated with the second slurry, blocked pores cleared, and the material dried and sintered to form a finalized porous sintered ceramic material. The fully reticulated scaffold material provides ceramic foam scaffolds similar to trabecular bone composition and structure, providing consistent mechanical integrity and porosity for regeneration of functional bone tissues.
Owner:GENOSTEO
Methods of employing calcium phosphate cement compositions and osteoinductive proteins to effect vertebrae interbody fusion absent an interbody device
ActiveUS20080109003A1Fast stabilizationRapid strengthInternal osteosythesisBone implantMedicineBone-Inducing Protein
A minimal access method for mammalian vertebrae interbody fusion without the employment of an interbody device is described which comprises injecting a porous CaPC into an anterior portion of a disc space, and injecting an effective amount of fast-setting non-porous CaPC into an anterior portion of the disc space to rapidly produce a strong and stable interbody fusion without the employment of an interbody device. Methods are further described wherein at least one of the CaPCs comprises an effective amount of at least one osteoinductive protein. A minimal access method for vertebroplasty is described which comprises injecting an effective amount of a viscous non-porous CaPC into a vertebrae fracture channel to provide rapid stabilization and strength, and injecting a porous CaPC into trabecular bone space adjacent to the vertebrae fracture channel. Kits which relate to the methods of the present invention are described as well.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com