Hilbert transform-fundamental frequency estimation based method for estimating mean trabecular bone spacing
A trabecular and fundamental frequency technology, applied in the field of medical ultrasound, can solve problems such as large variance of estimation and excessive estimation error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] The following takes the estimation of the average trabecular spacing of a section of ultrasonic simulation signal as an example to introduce the entire estimation process, and finally compare the estimation results of the three algorithms after changing the parameters of the simulation signal to demonstrate the performance of the algorithm of the present invention.
[0042] 1. The average trabecular spacing estimation process
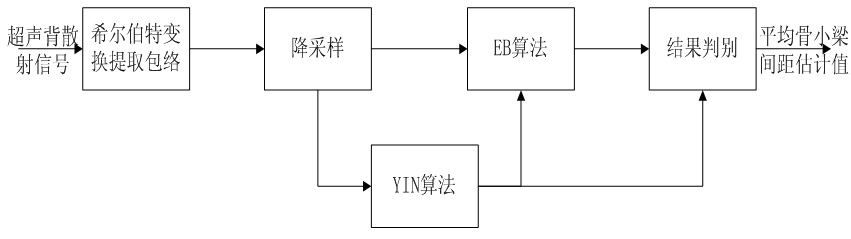
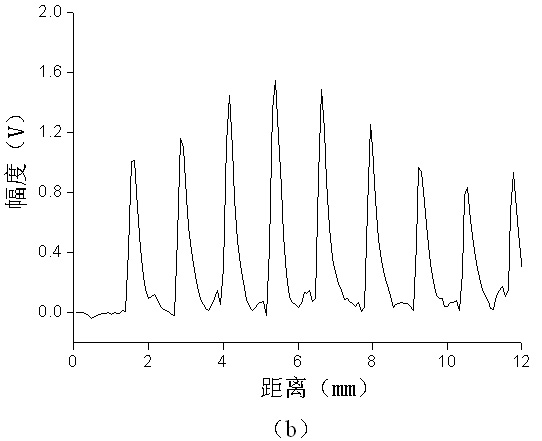
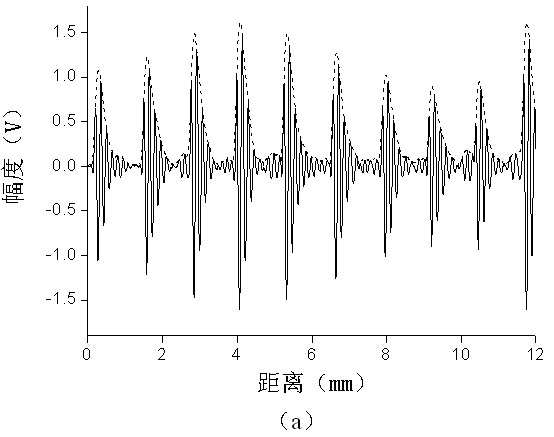
[0043] An example is given to illustrate the average trabecular spacing estimation algorithm based on Hilbert transform-fundamental frequency estimation. The block diagram of the algorithm is as figure 1 shown. After the Hilbert transform is performed on the simulated ultrasonic backscatter signal, the modulus of the obtained complex signal is the positive envelope of the ultrasonic backscatter signal. The simulated ultrasonic backscatter signal and its positive envelope are shown in Figure 2(a), where The part of the solid line is the simulatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com