Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
230results about How to "Good mechanical integrity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
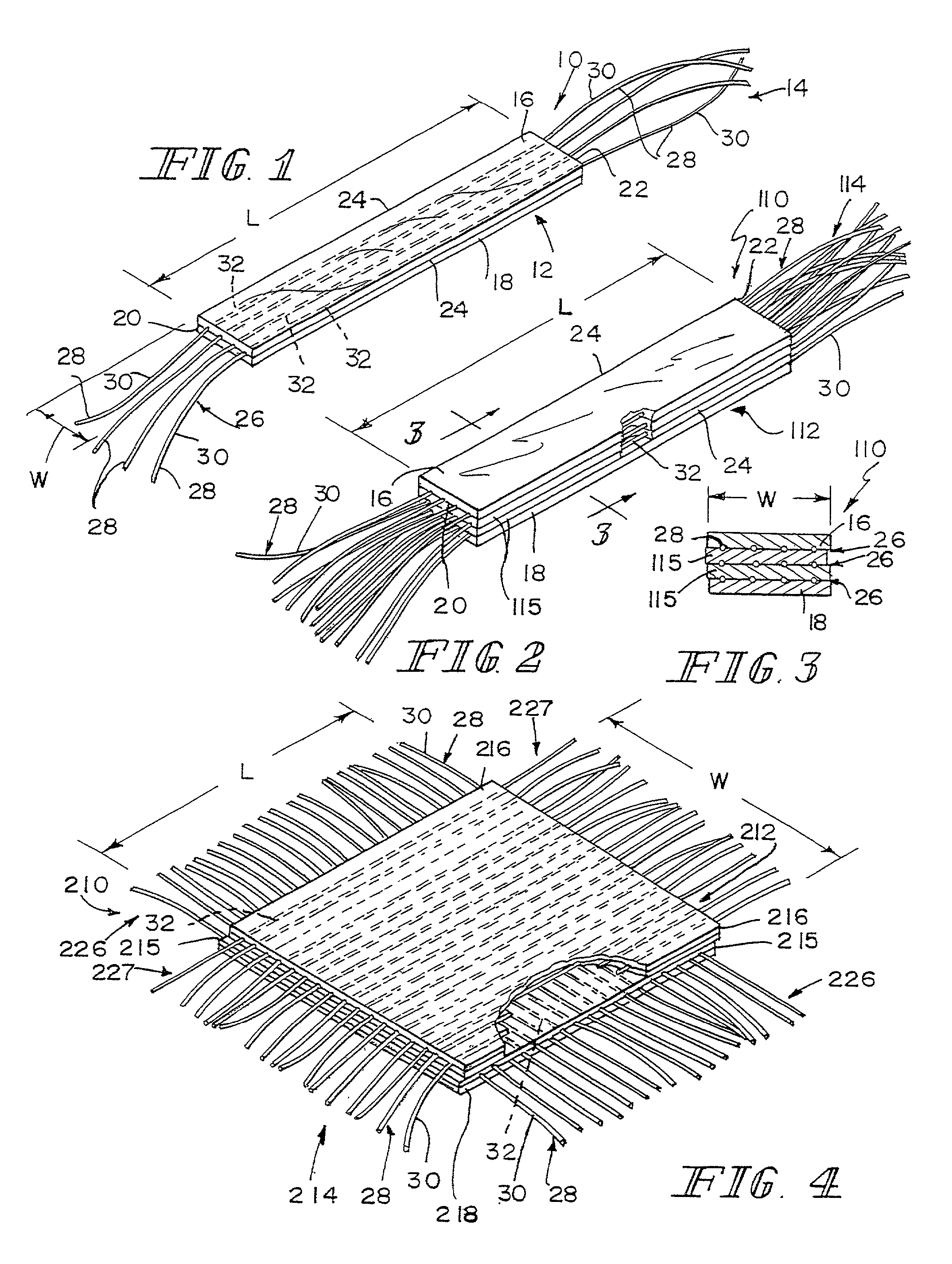
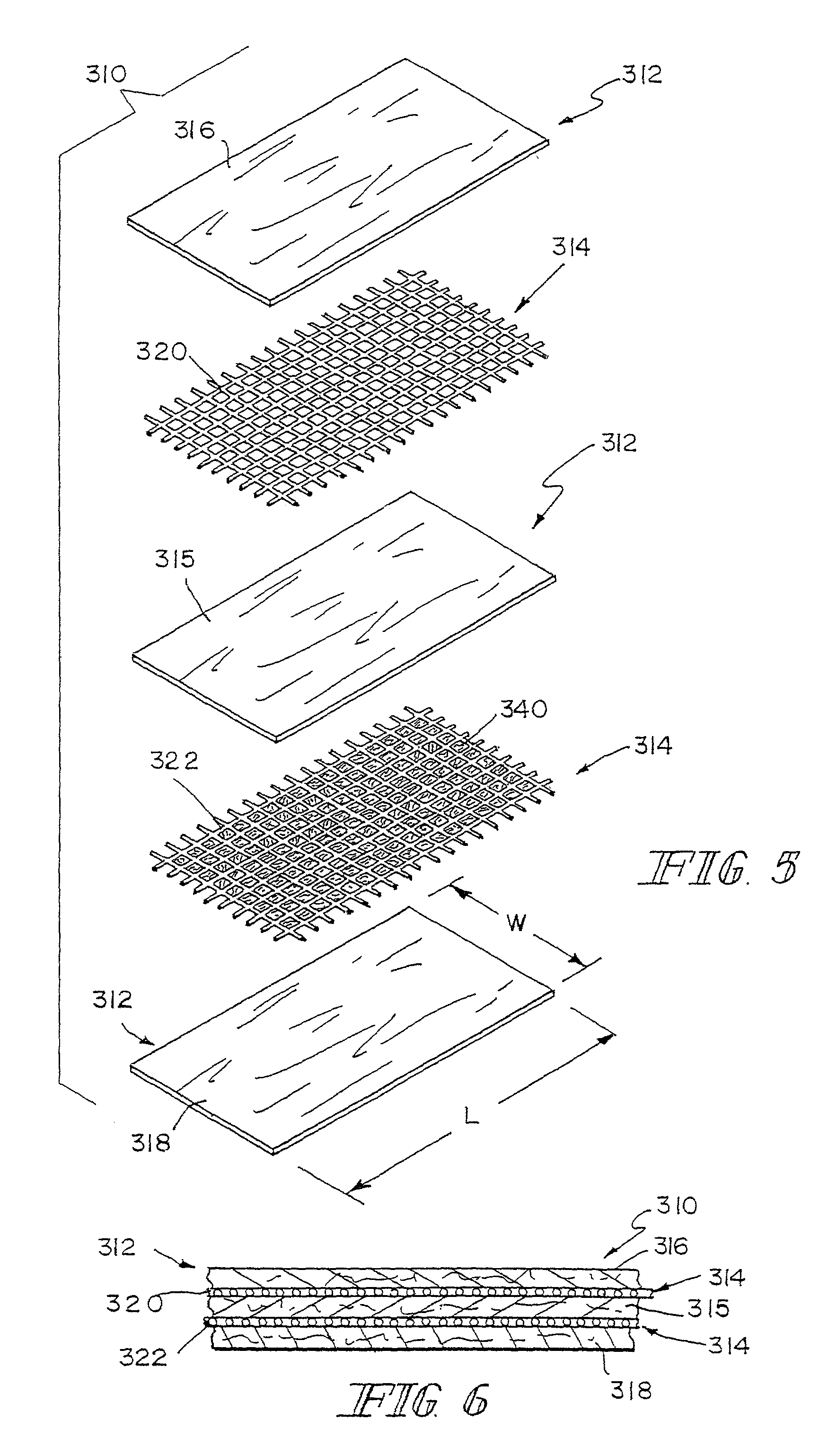
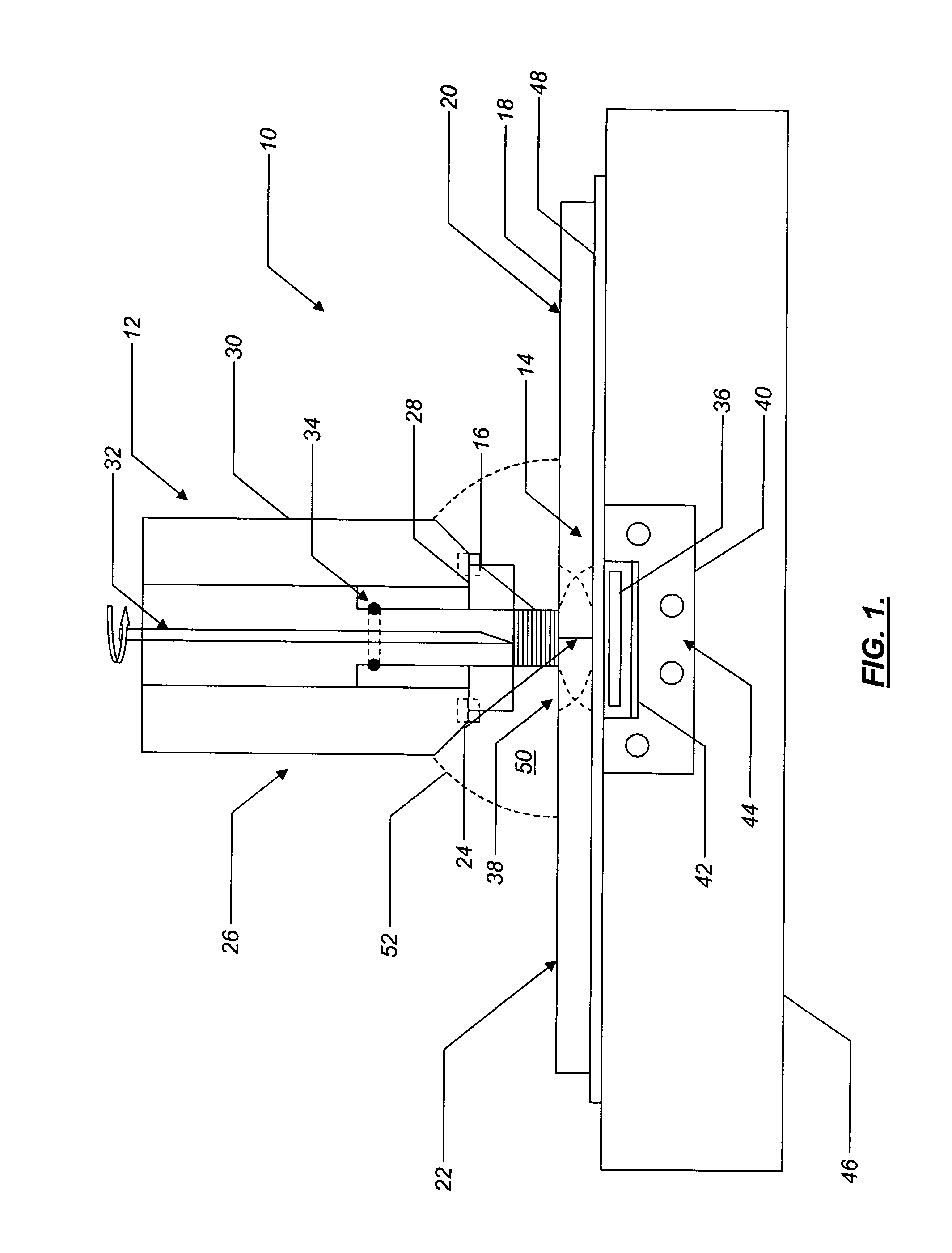
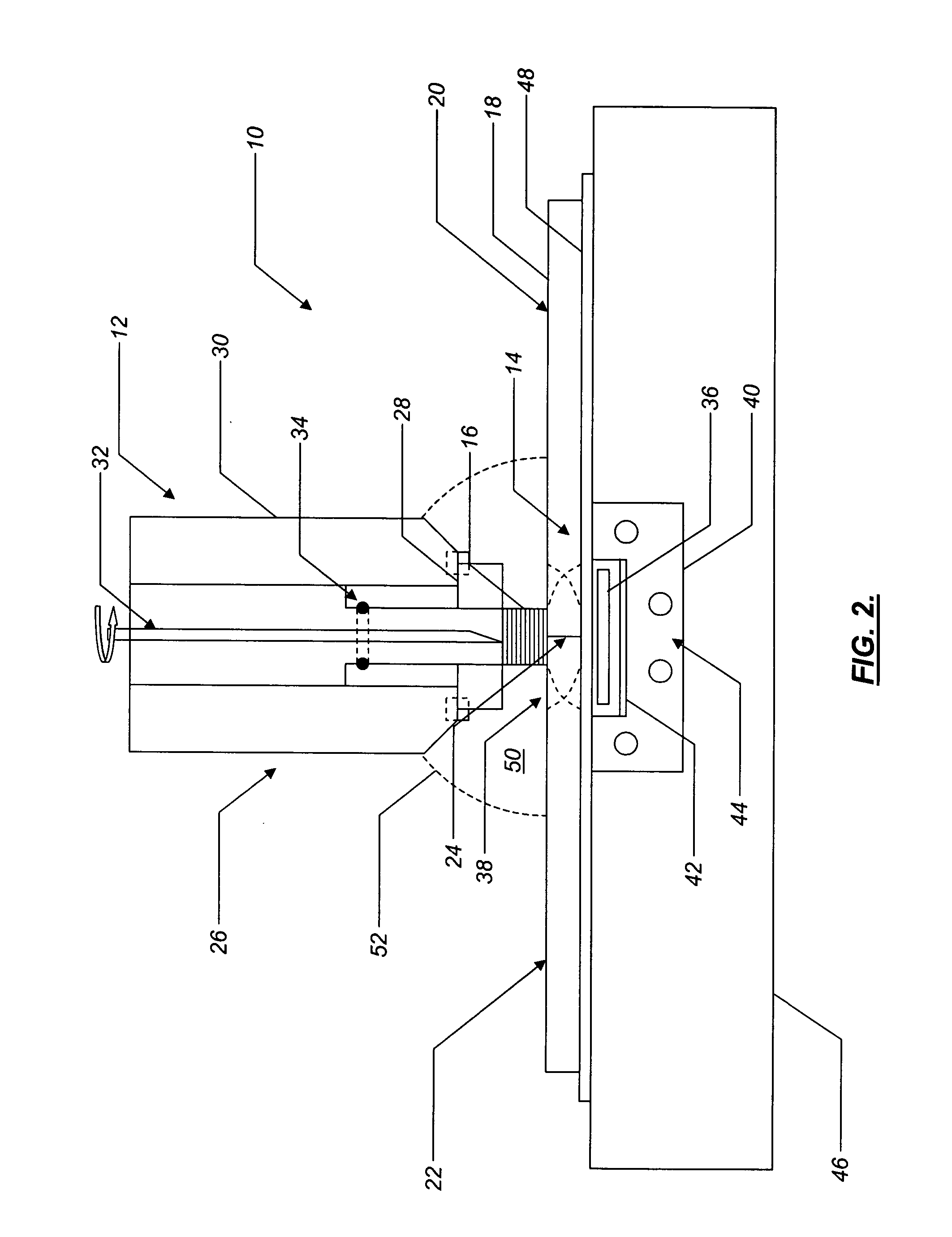
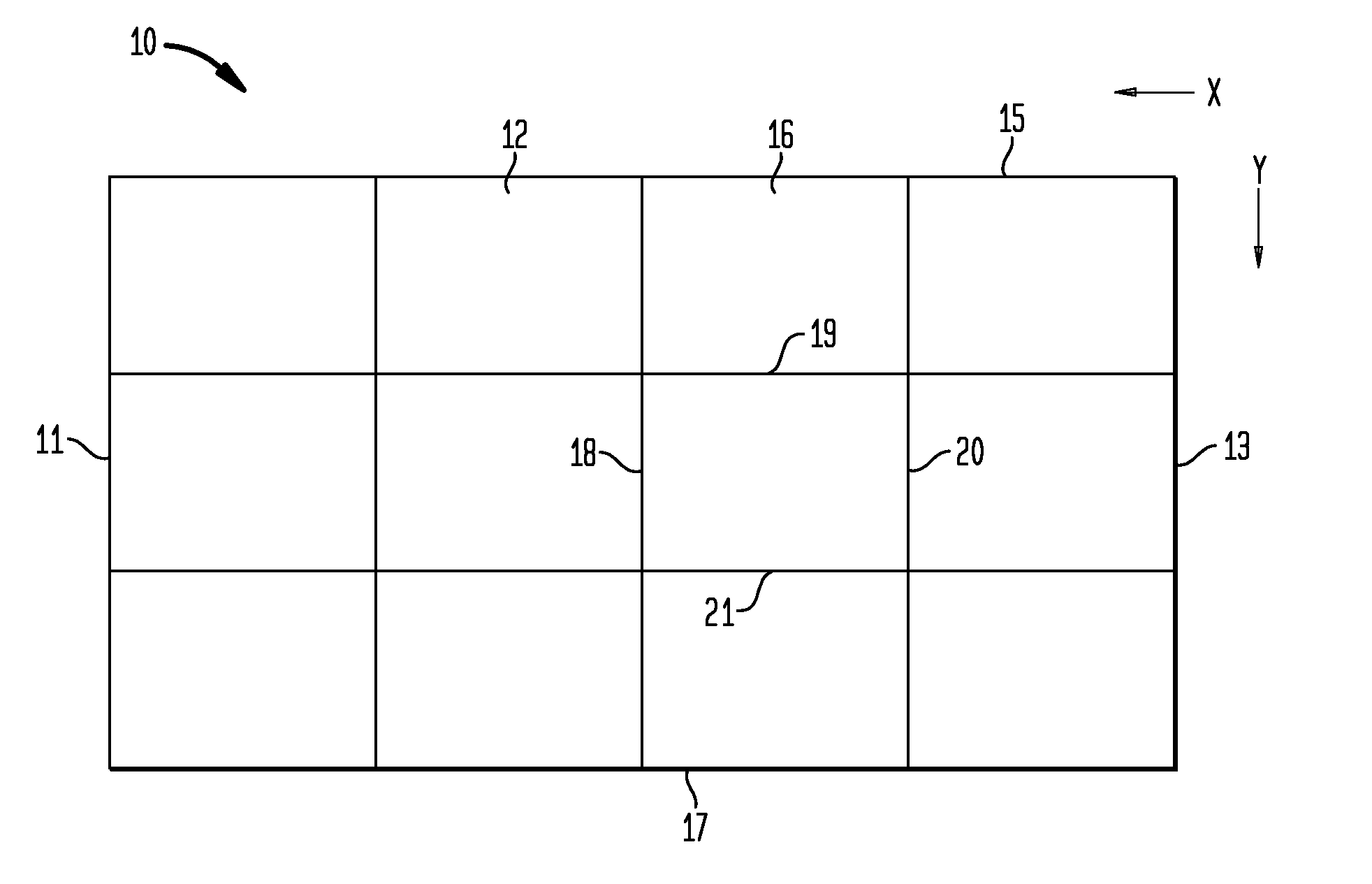
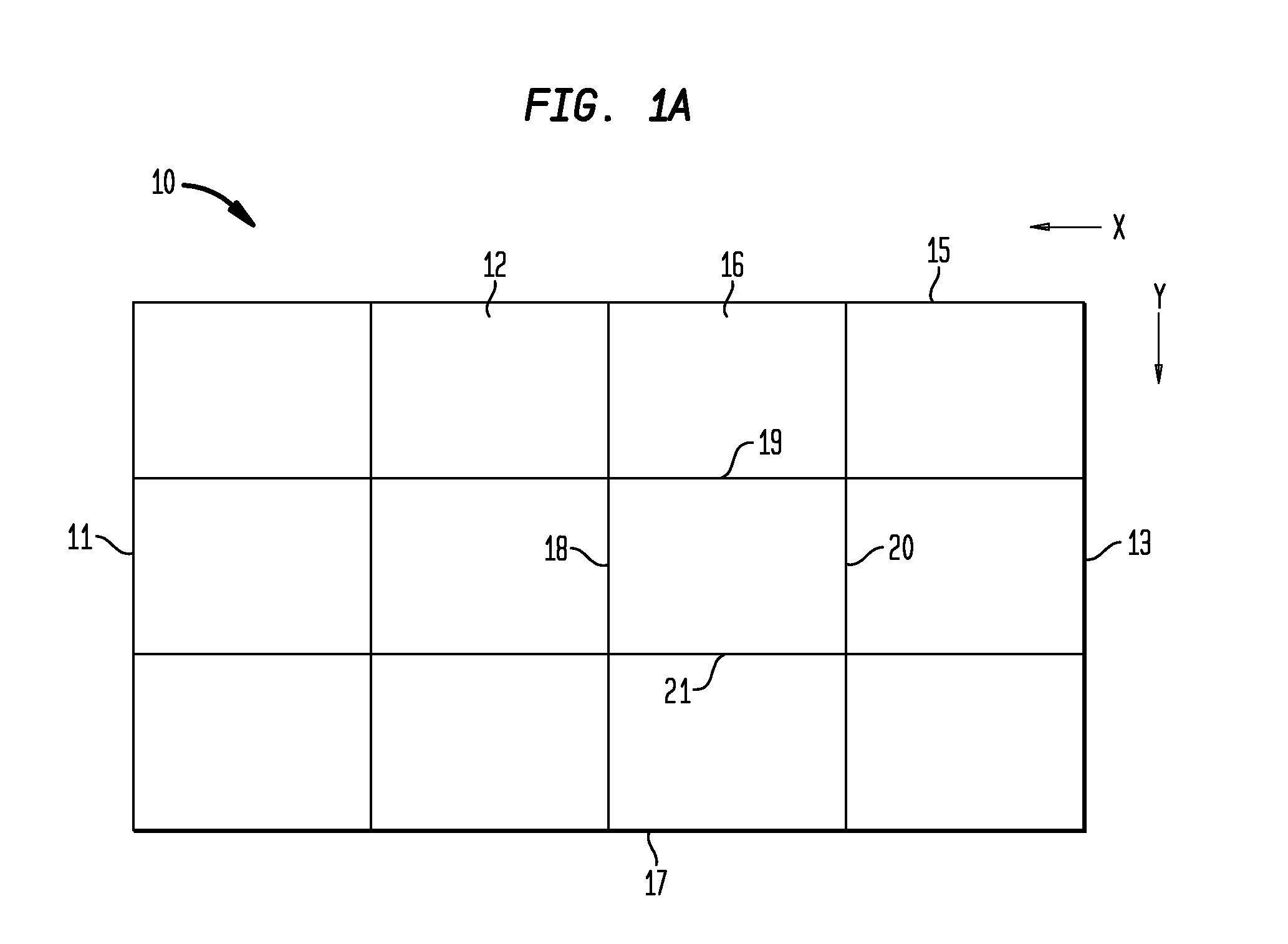
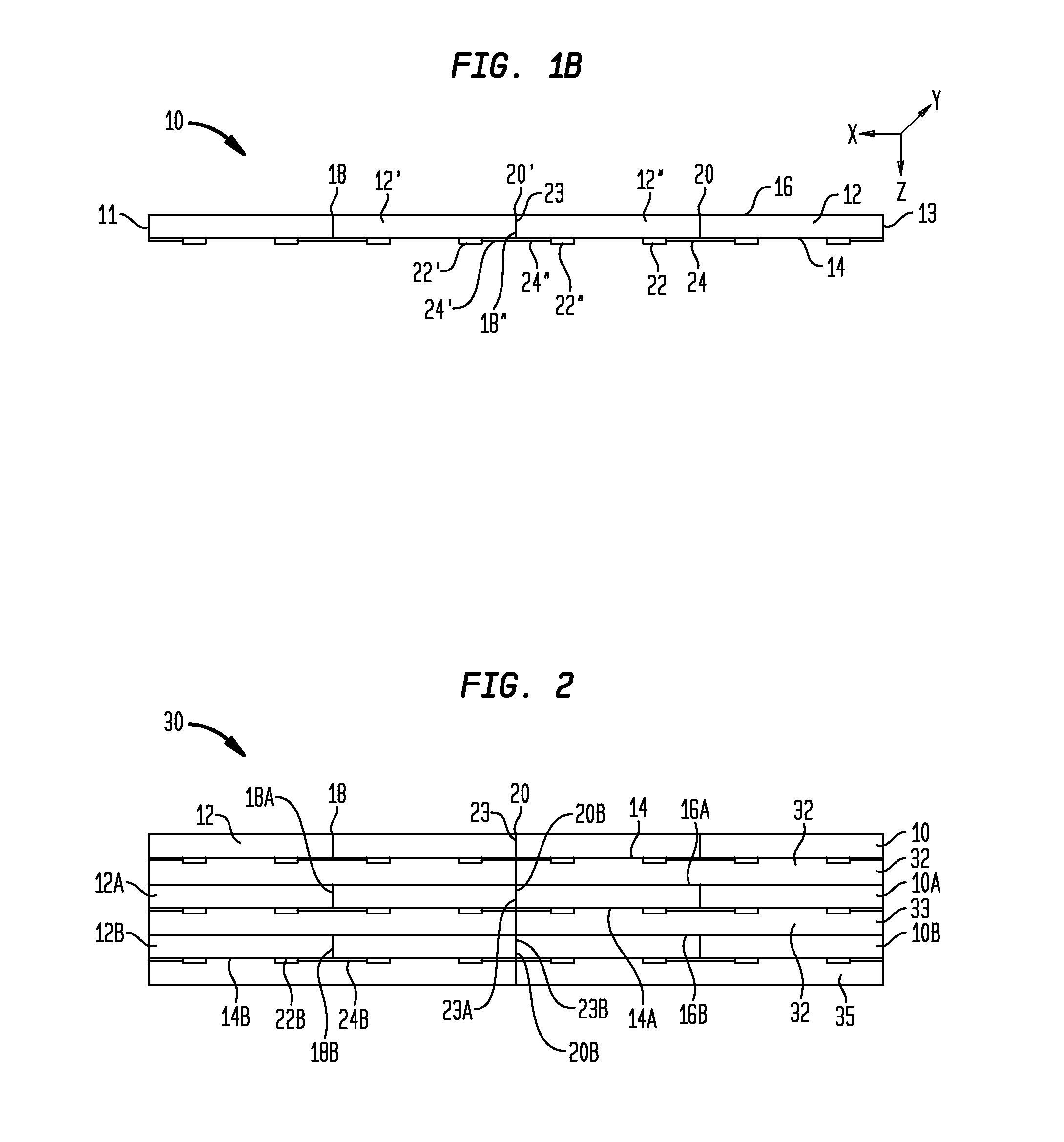
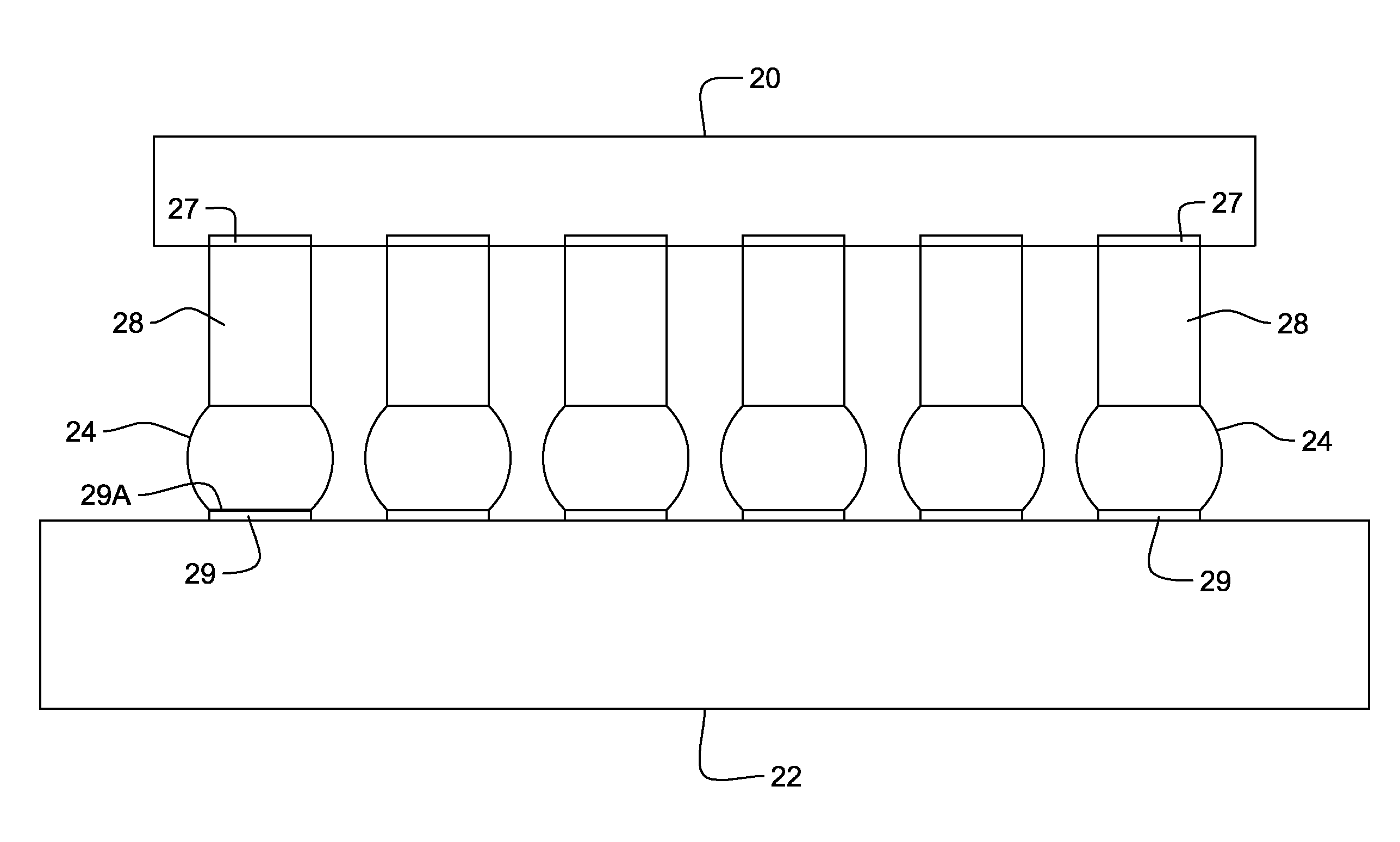
Hybrid biologic-synthetic bioabsorbable scaffolds
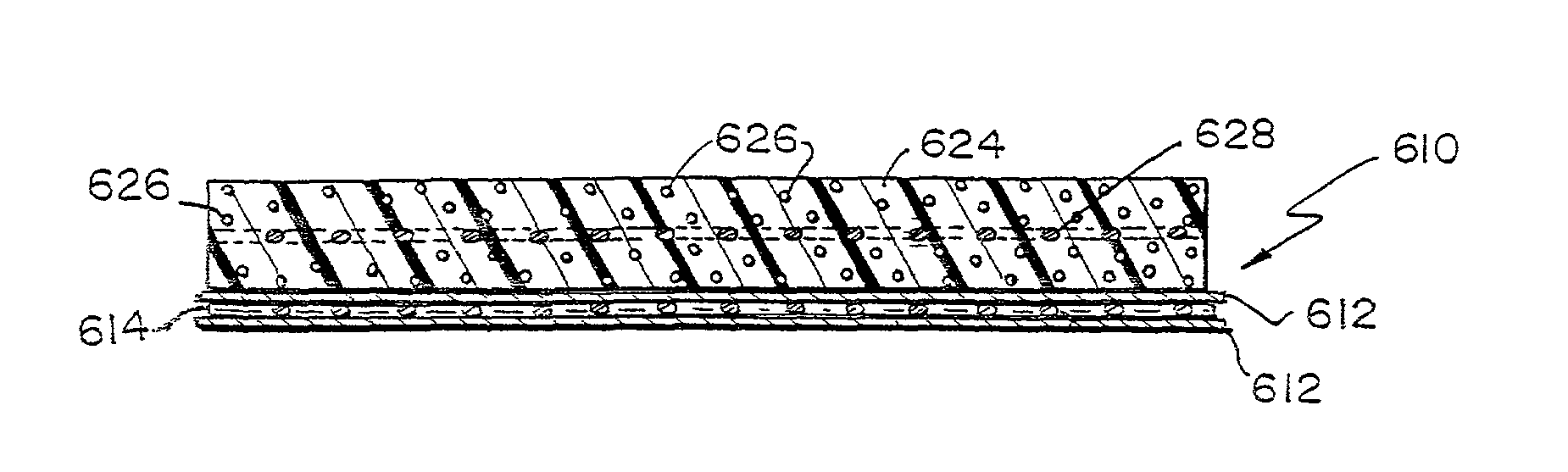
ActiveUS8366787B2Increase surface areaGood mechanical integritySuture equipmentsBone implantBioabsorbable scaffoldCell-Extracellular Matrix
A bioprosthetic device is provided for soft tissue attachment, reinforcement, and or reconstruction. The device comprises a naturally occurring extracellular matrix portion and a three-dimensional synthetic portion. In illustrated embodiments, the naturally occurring extracellular matrix portion comprises layers of small intestine submucosa, and the three-dimensional synthetic portion comprises a foam or a three-dimensional mesh, textile, or felt.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Microstructure device including a metallization structure with self-aligned air gaps between closely spaced metal lines
InactiveUS20090294898A1Low dielectric constantAvoiding cost-intensive sophisticated lithography processSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLithographic artistImage resolution
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Plated terminations
InactiveUS7177137B2Improved termination featureEliminate or greatly simplify thick-film stripesFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricHigh densityEngineering
A multilayer electronic component includes a plurality of dielectric layers interleaved with a plurality of internal electrode elements and a plurality of internal anchor tabs. Portions of the internal electrode elements and anchor tabs are exposed along the periphery of the electronic component in one or more aligned columns. Each exposed portion is within a predetermined distance from other exposed portions in a given column such that bridged terminations may be formed by depositing one or more plated termination materials over selected of the respectively aligned columns. Internal anchor tabs may be provided and exposed in prearranged relationships with other exposed conductive portions to help nucleate metallized plating material along the periphery of a device. External anchor tabs or lands may be provided to form terminations that extend to top and / or bottom surfaces of the device. Selected of the conductive elements may be formed by a finite volume percentage of ceramic material for enhanced durability, and external lands may be thicker than internal conductive elements and / or may also be embedded in top and / or bottom component surfaces. A variety of potential internal electrode configurations are possible including ones configured for orientation-insensitive component mounting and for high density peripheral termination interdigitated capacitors.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
System and method of plating ball grid array and isolation features for electronic components
InactiveUS7463474B2Improved termination featureEliminate or greatly simplify thick-film stripesFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsEngineeringElectronic component
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Lock and Key Through-Via Method for Wafer Level 3 D Integration and Structures Produced
InactiveUS20100078770A1High yieldFirmly connectedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThinningActive devices
A three dimensional device stack structure comprises two or more active device and interconnect layers further connected together using through substrate vias. Methods of forming the three dimensional device stack structure comprise alignment, bonding by lamination, thinning and post thinning processing. The via features enable the retention of alignment through the lamination process and any subsequent process steps thus achieving a mechanically more robust stack structure compared to the prior art.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Plated terminations
InactiveUS6960366B2Improved termination featureEliminate and greatly simplifyResistor terminals/electrodesFinal product manufactureTermination problemEngineering
Improved termination features for multilayer electronic components are disclosed. Monolithic components are provided with plated terminations whereby the need for typical thick-film termination stripes is eliminated or greatly simplified. Such termination technology eliminates many typical termination problems and enables a higher number of terminations with finer pitch, which may be especially beneficial on smaller electronic components. The subject plated terminations are guided and anchored by exposed internal electrode tabs and additional anchor tab portions which may optionally extend to the cover layers of a multilayer component. Such anchor tabs may be positioned internally or externally relative to a chip structure to nucleate additional metallized plating material. External anchor tabs positioned on one or both of top and bottom surfaces of a monolithic structure can facilitate the formation of selective wrap-around plated terminations. The disclosed technology may be utilized with a plurality of monolithic multilayer components, including interdigitated capacitors, multilayer capacitor arrays, and integrated passive components. A variety of different plating techniques and termination materials may be employed in the formation of the subject self-determining plated terminations.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Lock and Key Through-Via Method for Wafer Level 3D Integration and Structures Produced Thereby
ActiveUS20110111560A1High yieldFirmly connectedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringThinning
A three dimensional device stack structure comprises two or more active device and interconnect layers further connected together using through substrate vias. Methods of forming the three dimensional device stack structure comprise alignment, bonding by lamination, thinning and post thinning processing. The via features enable the retention of alignment through the lamination process and any subsequent process steps thus achieving a mechanically more robust stack structure compared to the prior art.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Plated terminations and method of forming using electrolytic plating
InactiveUS20070014075A1Improved termination featureEliminate and greatly simplifyElectrolytic capacitorsResistor terminals/electrodesCombined useEngineering
A multilayer electronic component includes a plurality of dielectric layers interleaved with a plurality of internal electrodes. Internal and / or external anchor tabs may also be selectively interleaved with the dielectric layers. Portions of the internal electrodes and anchor tabs are exposed along the periphery of the electronic component in respective groups. Each exposed portion is within a predetermined distance from other exposed portions in a given group such that termination structures may be formed by deposition and controlled bridging of a thin-film plated material among selected of the exposed internal conductive elements. Electrolytic plating may be employed in conjunction with optional cleaning and annealing steps to form directly plated portions of copper, nickel or other conductive material. Once an initial thin-film metal is directly plated to a component periphery, additional portions of different materials may be plated thereon.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Method for forming plated terminations
InactiveUS7152291B2Improved termination featureEliminate or greatly simplify thick-film stripesElectrolytic capacitorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTermination problemEngineering
Improved method steps for terminating multilayer electronic components are disclosed. Monolithic components are formed with plated terminations whereby the need for typical thick-film termination stripes is eliminated or greatly simplified. Such termination technology eliminates many typical termination problems and enables a higher number of terminations with finer pitch, which may be especially beneficial on smaller electronic components. Electrode and dielectric layers are provided in an interleaved arrangement and selected portions of the electrode layers are exposed. Electrically isolated anchor tabs may optionally be provided and exposed in some embodiments. Termination material is then plated to the exposed portions of the electrode layers until exposed portions of selected such portions thereof are connected. A variety of different plating techniques and termination materials may be employed in the formation of the subject self-determining plated terminations.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Edge connect wafer level stacking
ActiveUS20080083976A1Low costSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectronic component
A method of making a stacked microelectronic package by forming a microelectronic assembly by stacking a first subassembly including a plurality of microelectronic elements onto a second subassembly including a plurality of microelectronic elements, at least some of the plurality of microelectronic elements of said first subassembly and said second subassembly having traces that extend to respective edges of the microelectronic elements, then forming notches in the microelectronic assembly so as to expose the traces of at least some of the plurality of microelectronic elements, then forming leads at the side walls of the notches, the leads being in electrical communication with at least some of the traces and dicing the assembly into packages. Additional embodiments include methods for creating stacked packages using substrates and having additional traces that extend to both the top and bottom of the package.
Owner:TESSERA INC
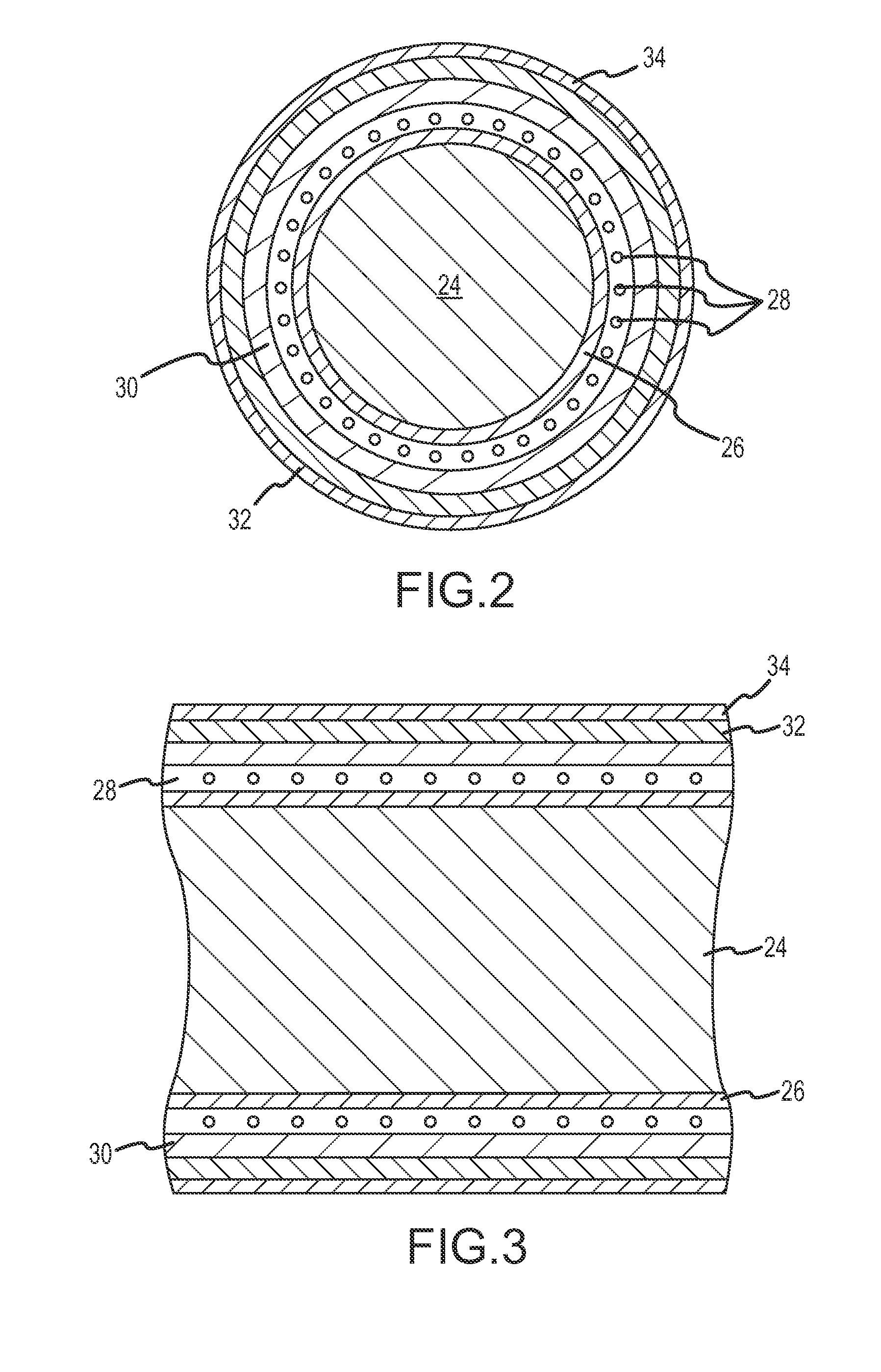
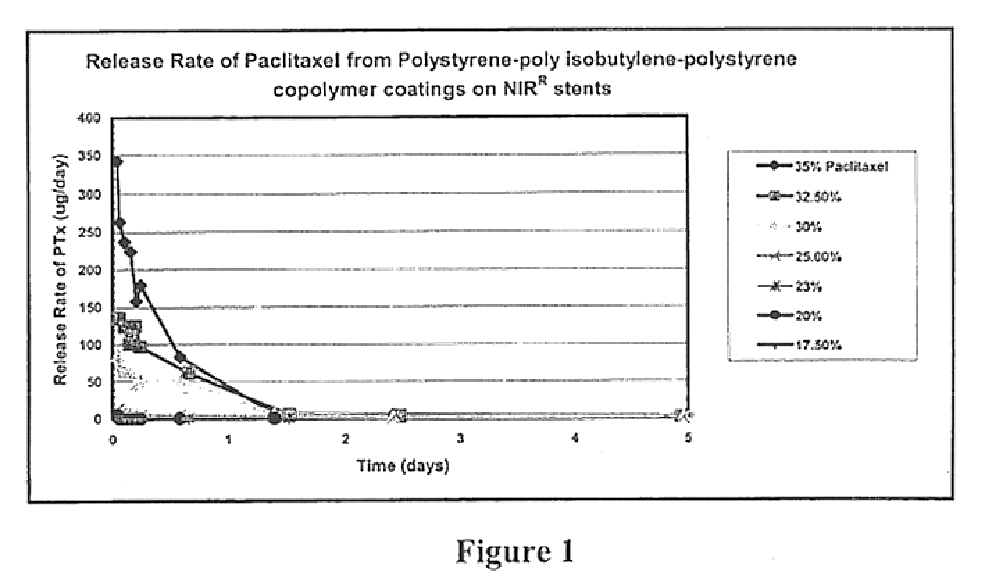
Catheter Shaft and Method of its Manufacture
ActiveUS20090166913A1Increase flexibilityIncrease resistanceMedical devicesLaminationHardnessCo extrusion
A method of manufacturing a catheter shaft includes the steps of forming an inner layer of a first polymeric material, forming a plait matrix layer including a second polymeric material about the inner layer, and forming an outer layer of a third polymeric material about the plait matrix layer. The plait matrix layer includes a braided wire mesh partially or fully embedded within the second polymeric material, which is different from at least one of the first polymeric material forming the inner layer and the third polymeric material forming the outer layer. The second polymeric material has a higher yield strain and / or a lower hardness than at least the first polymeric material, and preferably both the first and the third polymeric materials. The first polymeric material and the third polymeric material may be different or the same. The catheter shaft may be formed by stepwise extrusion, co-extrusion, and / or reflow processes.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
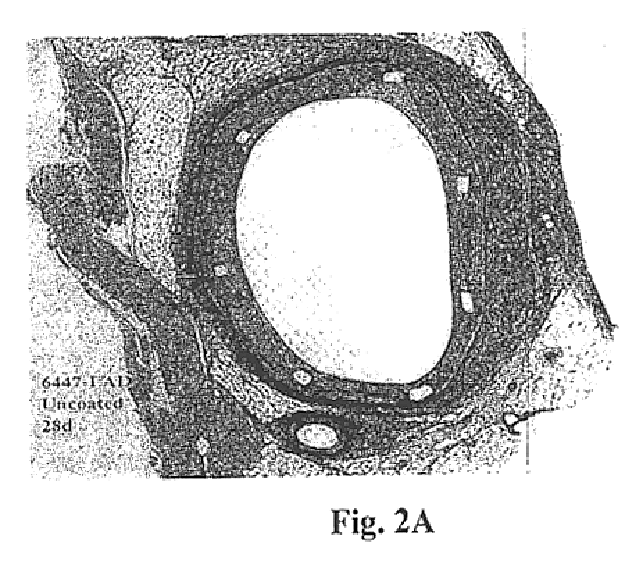
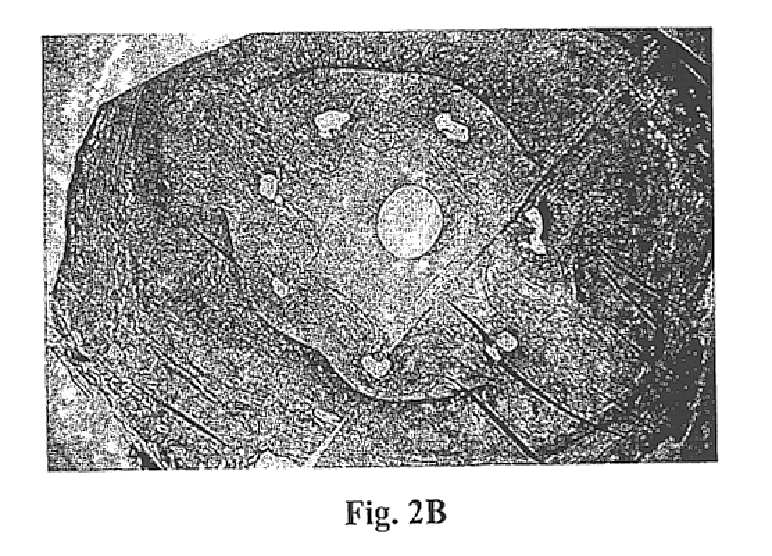
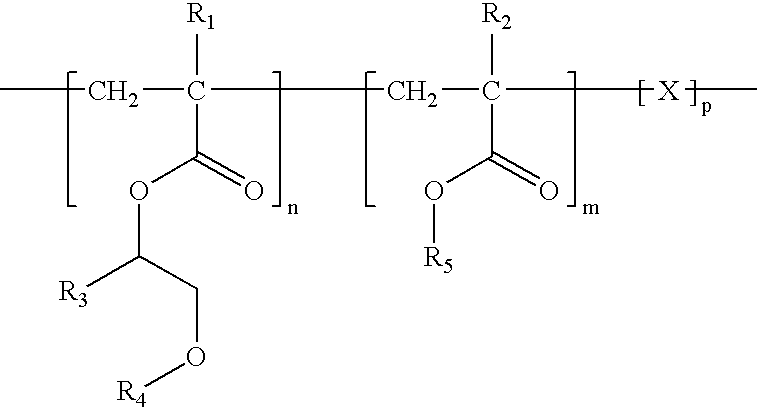
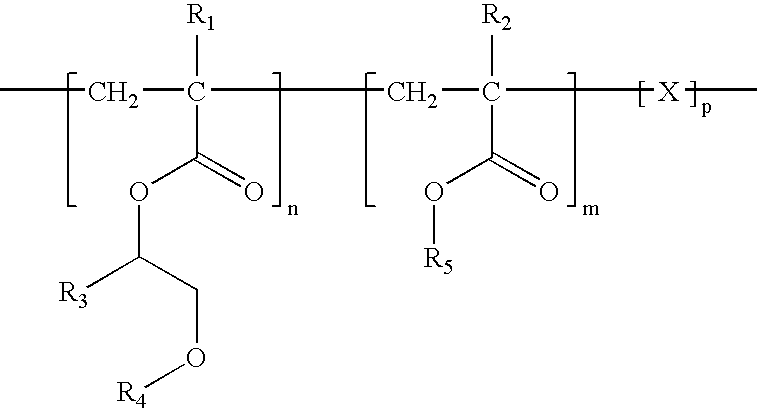
Drug delivery compositions and medical devices containing block copolymer
InactiveUS6855770B2Good mechanical integrityGood biocompatibilityOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsThermoplasticMethacrylate
A composition for delivery of a therapeutic agent is provided. The composition comprises: (a) a biocompatible block copolymer comprising one or more elastomeric blocks and one or more thermoplastic blocks and (b) a therapeutic agent, wherein the block copolymer is loaded with the therapeutic agent. The block copolymer is preferably of the formula X—(AB)n, where A is an elastomeric block, B is a thermoplastic block, n is a positive whole number and X is a seed molecule. The elastomeric blocks are preferably polyolefin blocks, and the thermoplastic blocks are preferably selected from vinyl aromatic blocks and methacrylate blocks. According to another aspect of the invention, a medical device is provided, at least a portion of which is insertable or implantable into the body of a patient. The medical device comprises (a) the above biocompatible block copolymer and (b) a therapeutic agent, wherein the block copolymer is loaded with the therapeutic agent. According to another aspect of the present invention, a method of treatment is provided in which the above device is implanted or inserted into a patient, resulting in the release of therapeutic agent in the patient over an extended period. According to yet another aspect of the invention, a coated medical device is provided which comprises: (a) an intravascular or intervascular medical device and (b) a coating over at least a portion of the intravascular or intervascular a medical device, wherein the coating comprises the above biocompatible block copolymer.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Plated terminations
InactiveUS20050046536A1Improved termination featureEliminate and greatly simplifyWave amplification devicesResistor terminals/electrodesTermination problemEngineering
Improved termination features for multilayer electronic components are disclosed. Monolithic components are provided with plated terminations whereby the need for typical thick-film termination stripes is eliminated or greatly simplified. Such termination technology eliminates many typical termination problems and enables a higher number of terminations with finer pitch, which may be especially beneficial on smaller electronic components. The subject plated terminations are guided and anchored by exposed internal electrode tabs and additional anchor tab portions which may optionally extend to the cover layers of a multilayer component. Such anchor tabs may be positioned internally or externally relative to a chip structure to nucleate additional metallized plating material. External anchor tabs positioned on top and bottom sides of a monolithic structure can facilitate the formation of wrap-around plated terminations. The disclosed technology may be utilized with a plurality of monolithic multilayer components, including interdigitated capacitors, multilayer capacitor arrays, and integrated passive components. A variety of different plating techniques and termination materials may be employed in the formation of the subject self-determining plated terminations.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Plated terminations
InactiveUS7154374B2Improved termination featureEliminate or greatly simplify thick-film stripesResistor terminals/electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTermination problemEngineering
Improved termination features for multilayer electronic components are disclosed. Monolithic components are provided with plated terminations whereby the need for typical thick-film termination stripes is eliminated or greatly simplified. Such termination technology eliminates many typical termination problems and enables a higher number of terminations with finer pitch, which may be especially beneficial on smaller electronic components. The subject plated terminations are guided and anchored by exposed internal electrode tabs and additional anchor tab portions which may optionally extend to the cover layers of a multilayer component. Such anchor tabs may be positioned internally or externally relative to a chip structure to nucleate additional metallized plating material. External anchor tabs positioned on top and bottom sides of a monolithic structure can facilitate the formation of wrap-around plated terminations. The disclosed technology may be utilized with a plurality of monolithic multilayer components, including interdigitated capacitors, multilayer capacitor arrays, and integrated passive components. A variety of different plating techniques and termination materials may be employed in the formation of the subject self-determining plated terminations.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Plated terminations
InactiveUS6972942B2Improved termination featureEliminate or greatly simplify thick-film stripesFixed capacitor dielectricSolid-state devicesTermination problemEngineering
Improved termination features for multilayer electronic components are disclosed. Monolithic components are provided with plated terminations whereby the need for typical thick-film termination stripes is eliminated or greatly simplified. Such termination technology eliminates many typical termination problems and enables a higher number of terminations with finer pitch, which may be especially beneficial on smaller electronic components. The subject plated terminations are guided and anchored by exposed internal electrode tabs and additional anchor tab portions which may optionally extend to the cover layers of a multilayer component. Such anchor tabs may be positioned internally or externally relative to a chip structure to nucleate additional metallized plating material. External anchor tabs positioned on one or both of top and bottom surfaces of a monolithic structure can facilitate the formation of selective wrap-around plated terminations. The disclosed technology may be utilized with a plurality of monolithic multilayer components, including interdigitated capacitors, multilayer capacitor arrays, and integrated passive components. A variety of different plating techniques and termination materials may be employed in the formation of the subject self-determining plated terminations.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Edge connect wafer level stacking
ActiveUS20080083977A1Low costSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMechanical engineering
In accordance with an aspect of the invention, a stacked microelectronic package is provided which may include a plurality of subassemblies, e.g., a first subassembly and a second subassembly underlying the first subassembly. A front face of the second subassembly may confront the rear face of the first subassembly. Each of the first and second subassemblies may include a plurality of front contacts exposed at the front face, at least one edge and a plurality of front traces extending about the respective at least one edge. The second subassembly may have a plurality of rear contacts exposed at the rear face. The second subassembly may also have a plurality of rear traces extending from the rear contacts about the at least one edge. The rear traces may extend to at least some of the plurality of front contacts of at least one of the first or second subassemblies.
Owner:TESSERA INC
Coating on a balloon comprising a polymer and a drug
ActiveUS20100063570A1Rapid drug releaseGood mechanical integrityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineMedical device
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
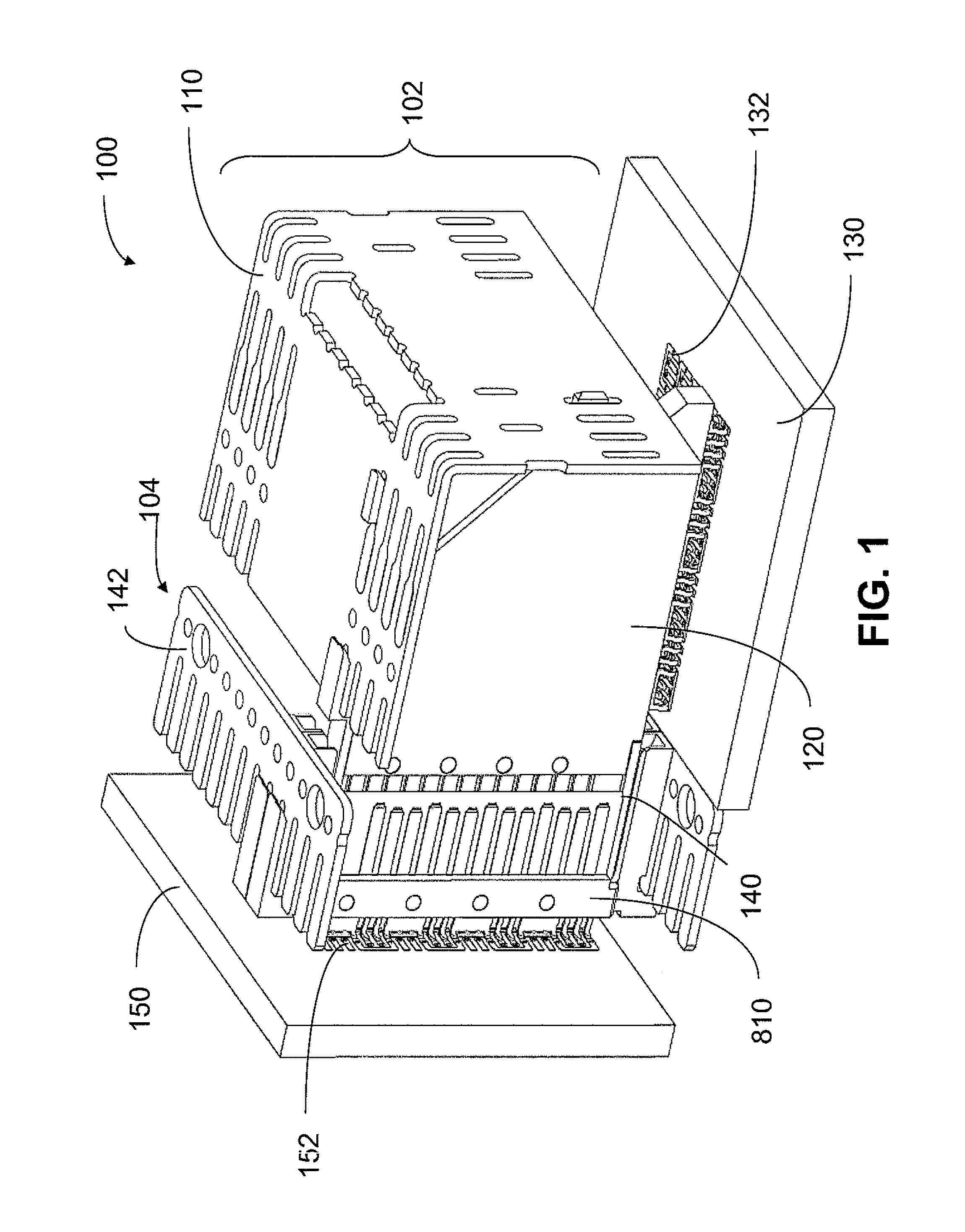
High density electrical connector with variable insertion and retention force
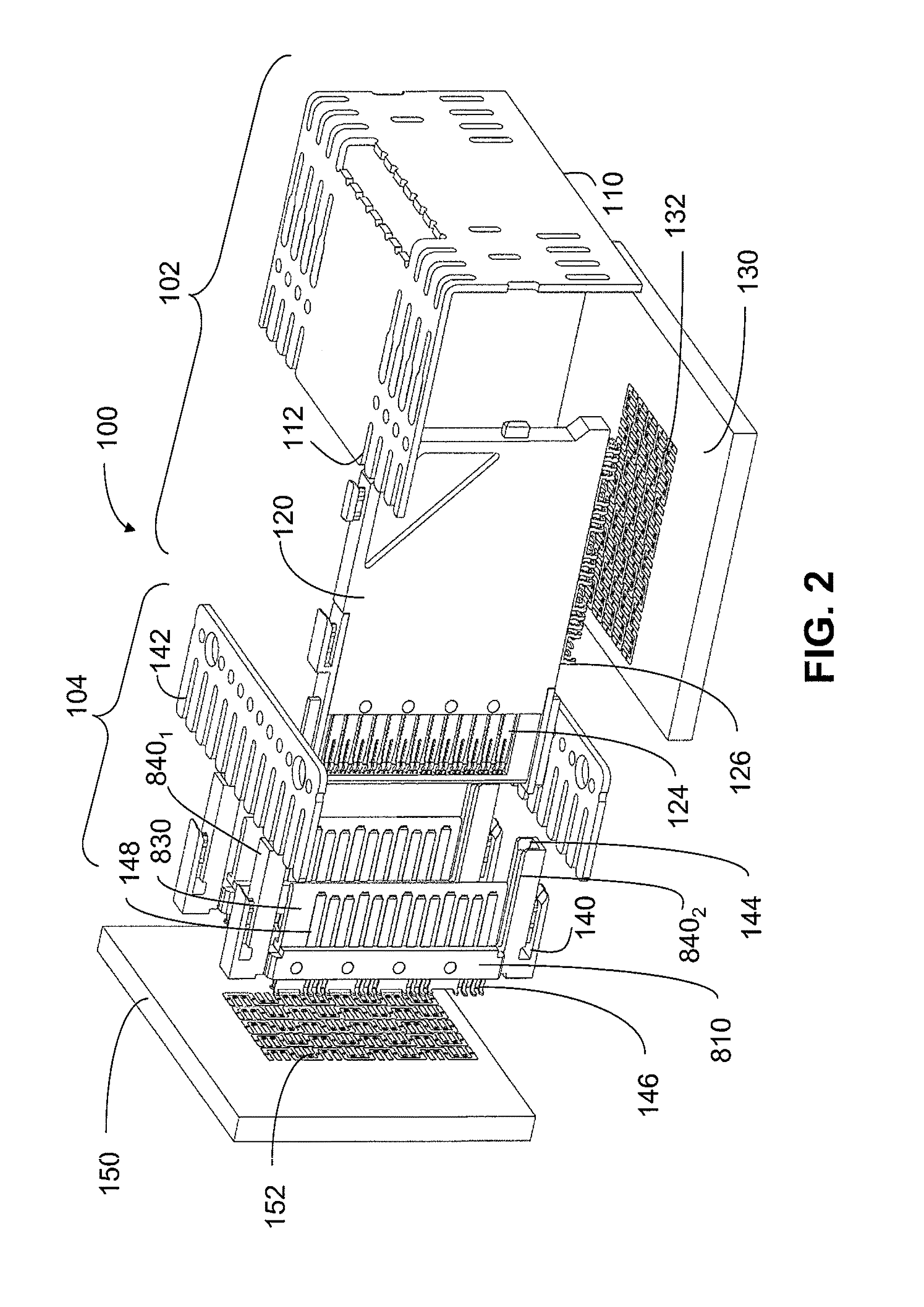
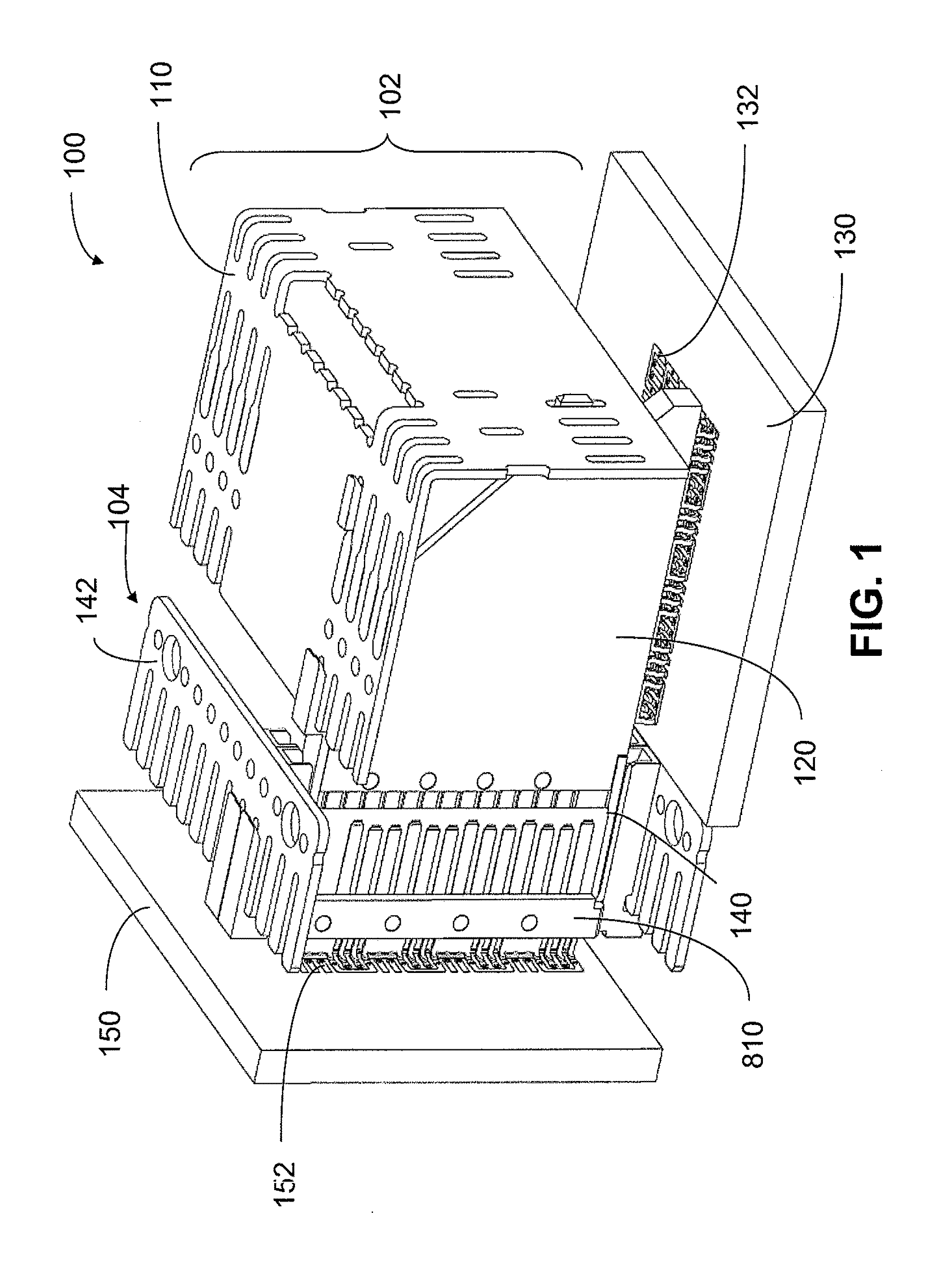
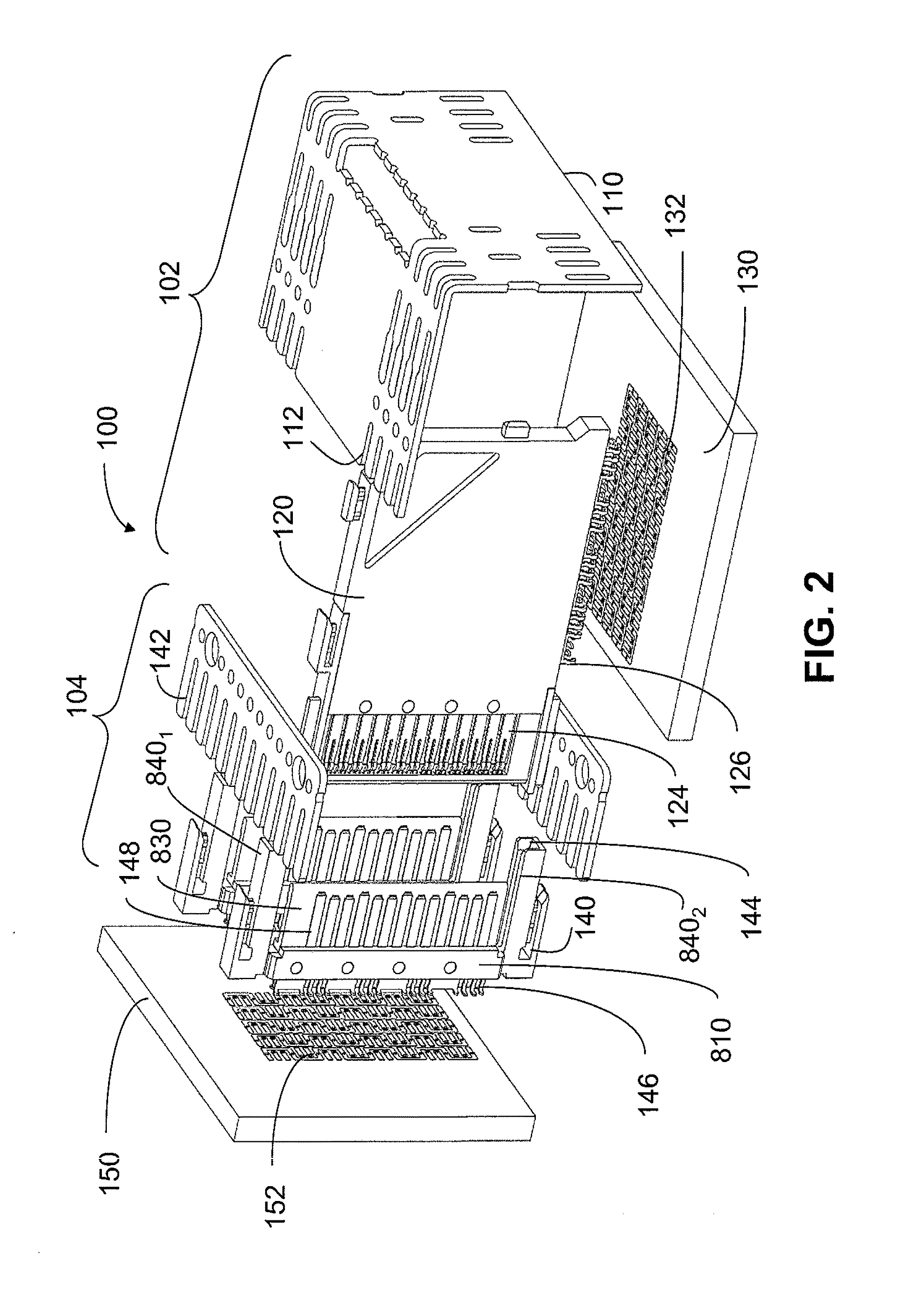
ActiveUS8182289B2Lower insertion forceImprove retentionTwo-part coupling devicesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsElectricityHigh density
An interconnection system that includes a daughter card and backplane electrical connectors mounted to printed circuit boards at connector footprints. The spring rate of beam-shaped contacts in the daughter card connector increases while mating with the backplane connector so that the retention force may be greater than the insertion force. Such a change in spring rate may be achieved by positioning the beam-shaped contacts adjacent a surface of a connector housing. That surface may include a projection that aligns with the beam-shaped contact. When the connectors are unmated, the beam-shaped contact may be spaced from the projection. As the connectors begin to mate, a central portion of the beam-shaped contact may be pressed against the projection, which has the effect of shortening the beam length and increasing its stiffness.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
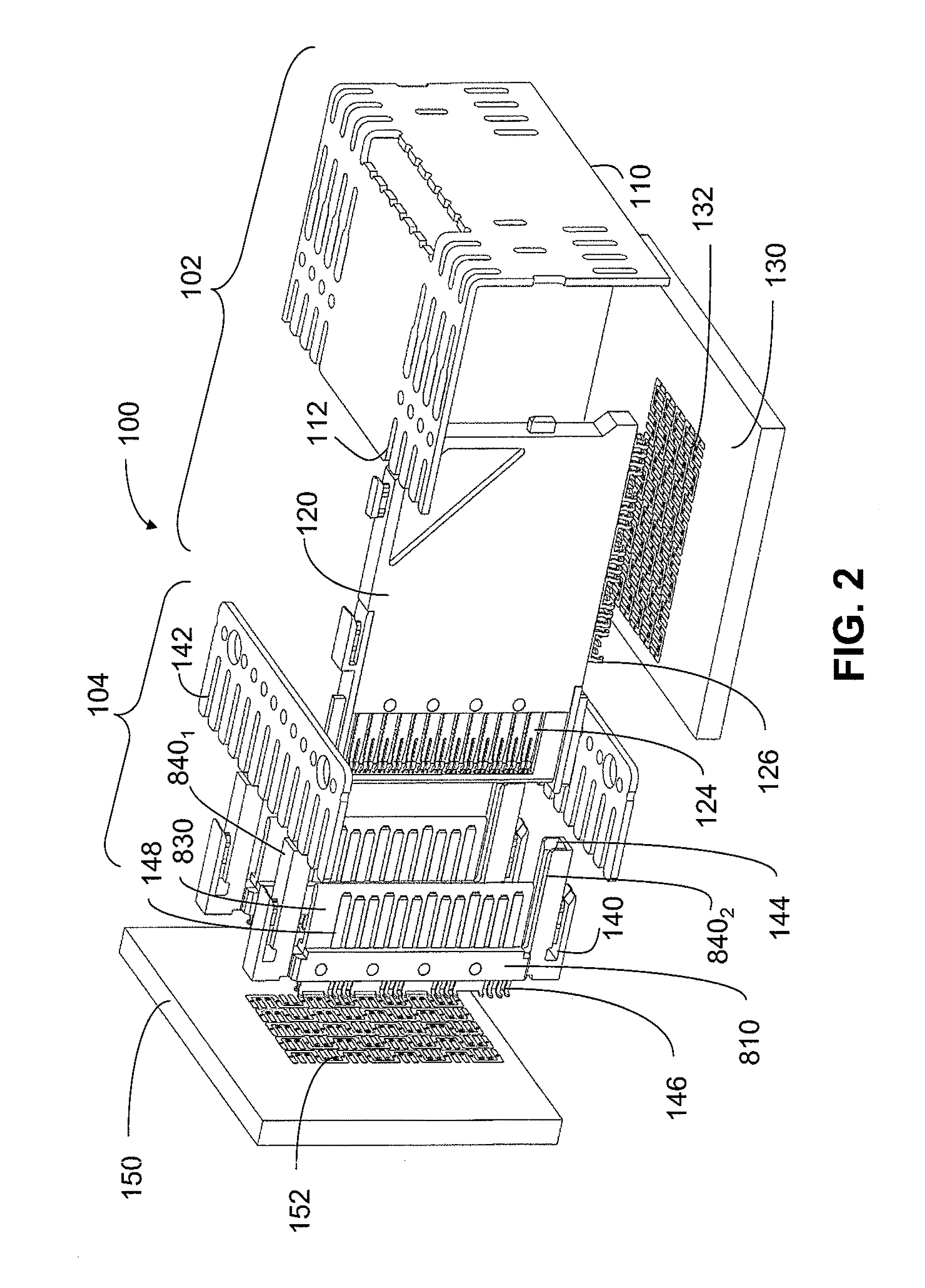
High density electrical connector with variable insertion and retention force
ActiveUS20110212649A1High retention forceHigh spring rateTwo-part coupling devicesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsElectricityBackplane
An interconnection system that includes a daughter card and backplane electrical connectors mounted to printed circuit boards at connector footprints. The spring rate of beam-shaped contacts in the daughter card connector increases while mating with the backplane connector so that the retention force may be greater than the insertion force. Such a change in spring rate may be achieved by positioning the beam-shaped contacts adjacent a surface of a connector housing. That surface may include a projection that aligns with the beam-shaped contact. When the connectors are unmated, the beam-shaped contact may be spaced from the projection. As the connectors begin to mate, a central portion of the beam-shaped contact may be pressed against the projection, which has the effect of shortening the beam length and increasing its stiffness.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
High density electrical connector and PCB footprint
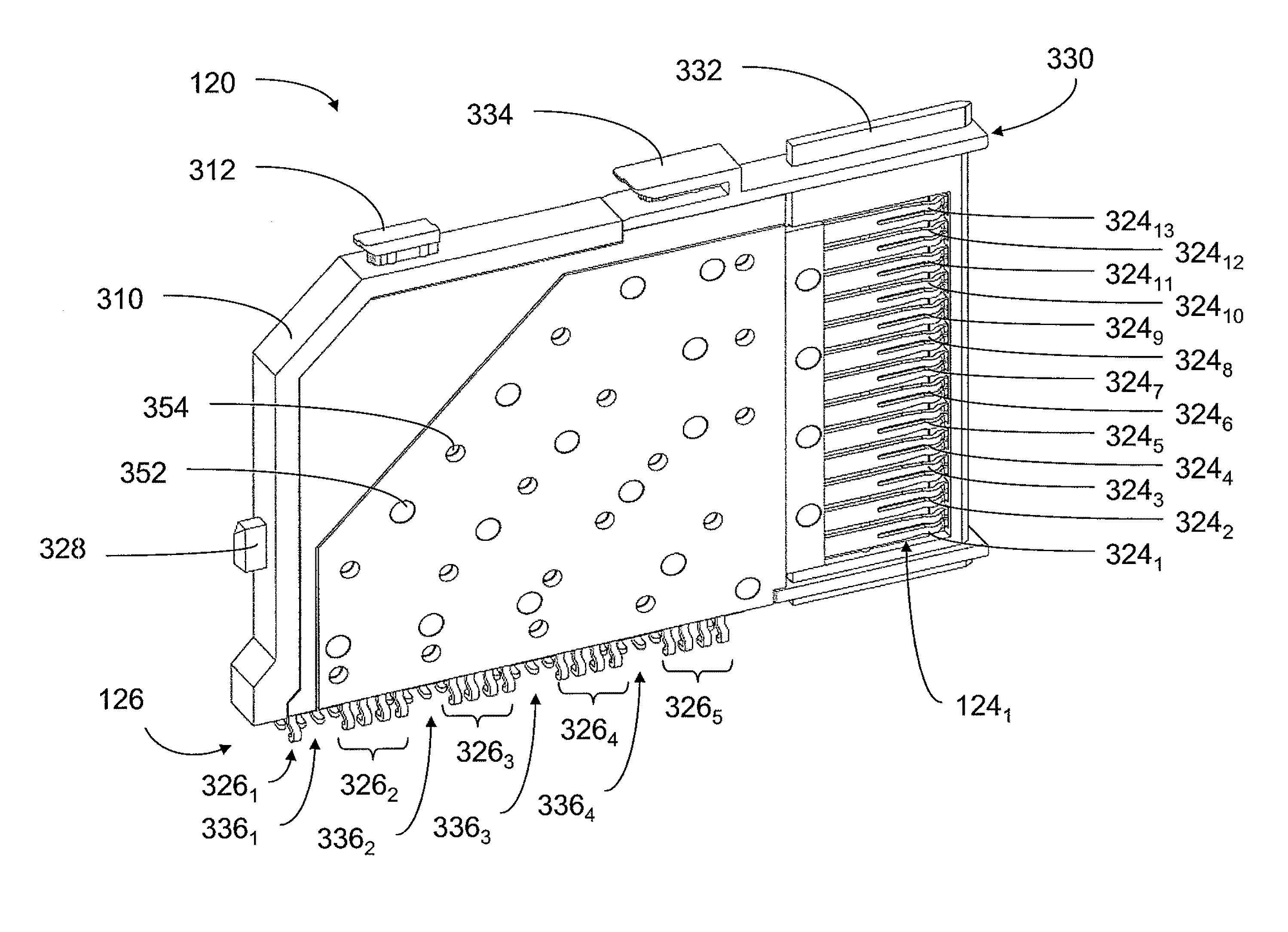
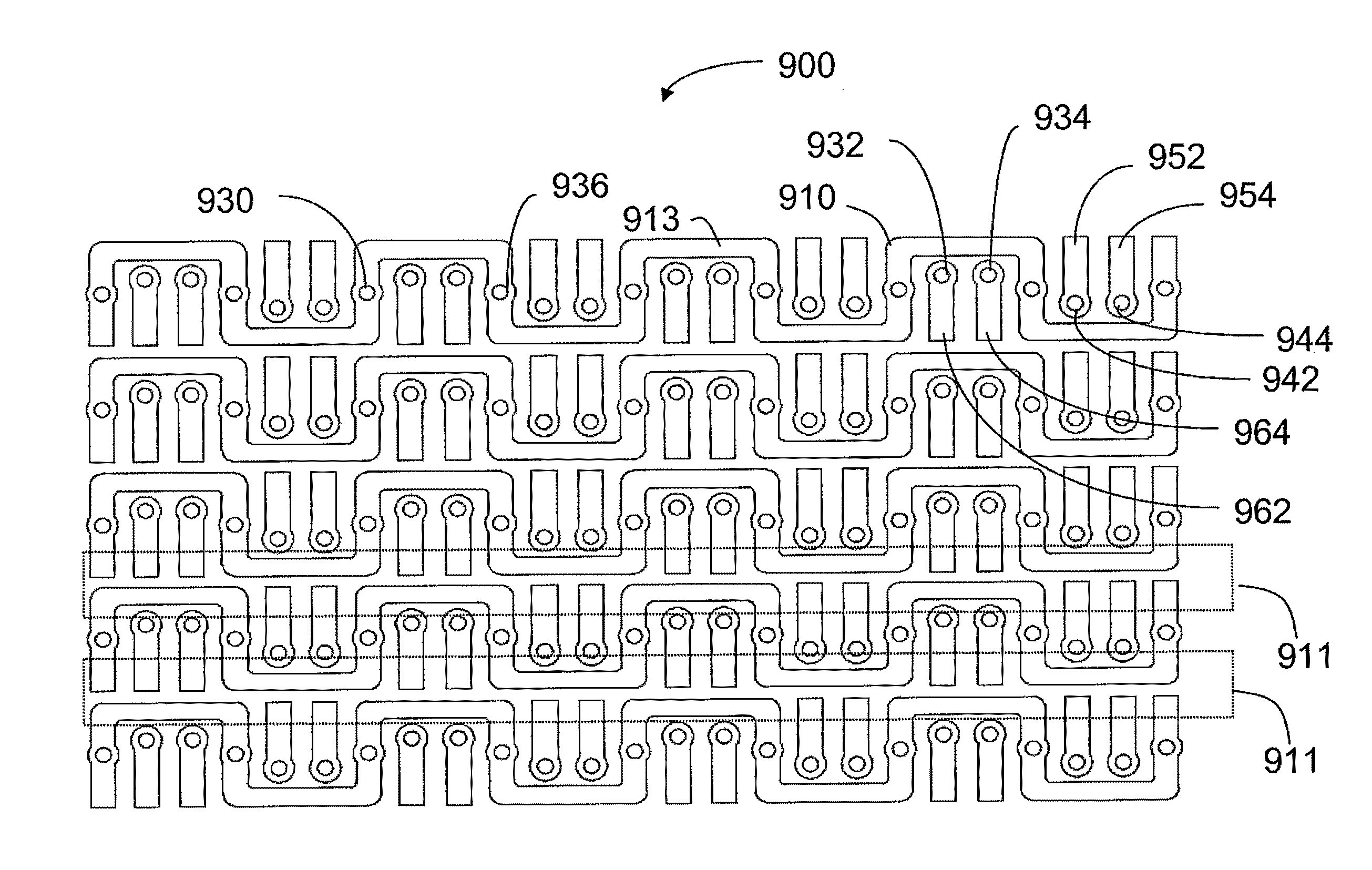
ActiveUS8272877B2Reduces instanceImprove signal integrityTwo-part coupling devicesElectrical connection printed elementsHigh densityElectrical conductor
An interconnection system that includes a daughter card and backplane electrical connectors, each mounted to a printed circuit board at a connector footprint. The backplane connector has conductive elements with transition regions that allow the mating contact portions to be positioned on a uniform pitch while contact tail portions can be shaped to improve signal integrity or to provide a more compact and / or mechanically robust footprint. The conductive elements in both connectors are configured such that the contact tails of the ground conductors align from column to column, but the planar portions of the ground conductors in one column align with a pair of signal conductors in the other column, which improves mechanical and signal integrity. Mechanical integrity may be improved by forming the connector footprints with pads for the ground conductors that span multiple columns.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
Wound dressing and method for controlling severe, life-threatening bleeding
InactiveUS20050038369A1Stanching flowAvoid bleedingBiocideNon-adhesive dressingsWound dressingClot formation
This invention is directed to advanced hemorrhage control wound dressings, and methods of using a producing same. The subject wound dressing is constructed from a non-mammalian material for control of severe bleeding. The wound dressing is formed of a biomaterial comprising chitosan for controlling severe bleeding. The kind of severe, life-threatening bleeding contemplated by this invention is typically of the type not capable of being stanched when a conventional gauze wound dressing is applied with conventional pressure to the subject wound. The wound dressing being capable of substantially stanching the flow of the severe life-threatening bleeding from the wound by adhering to the wound site, to seal the wound, to accelerate blood clot formation at the wound site, to reinforce clot information at the wound site and prevent bleed out from the wound site, and to substantially prohibit the flow of blood out of the wound site.
Owner:PROVIDENCE HEALTH SYST OREGON +1
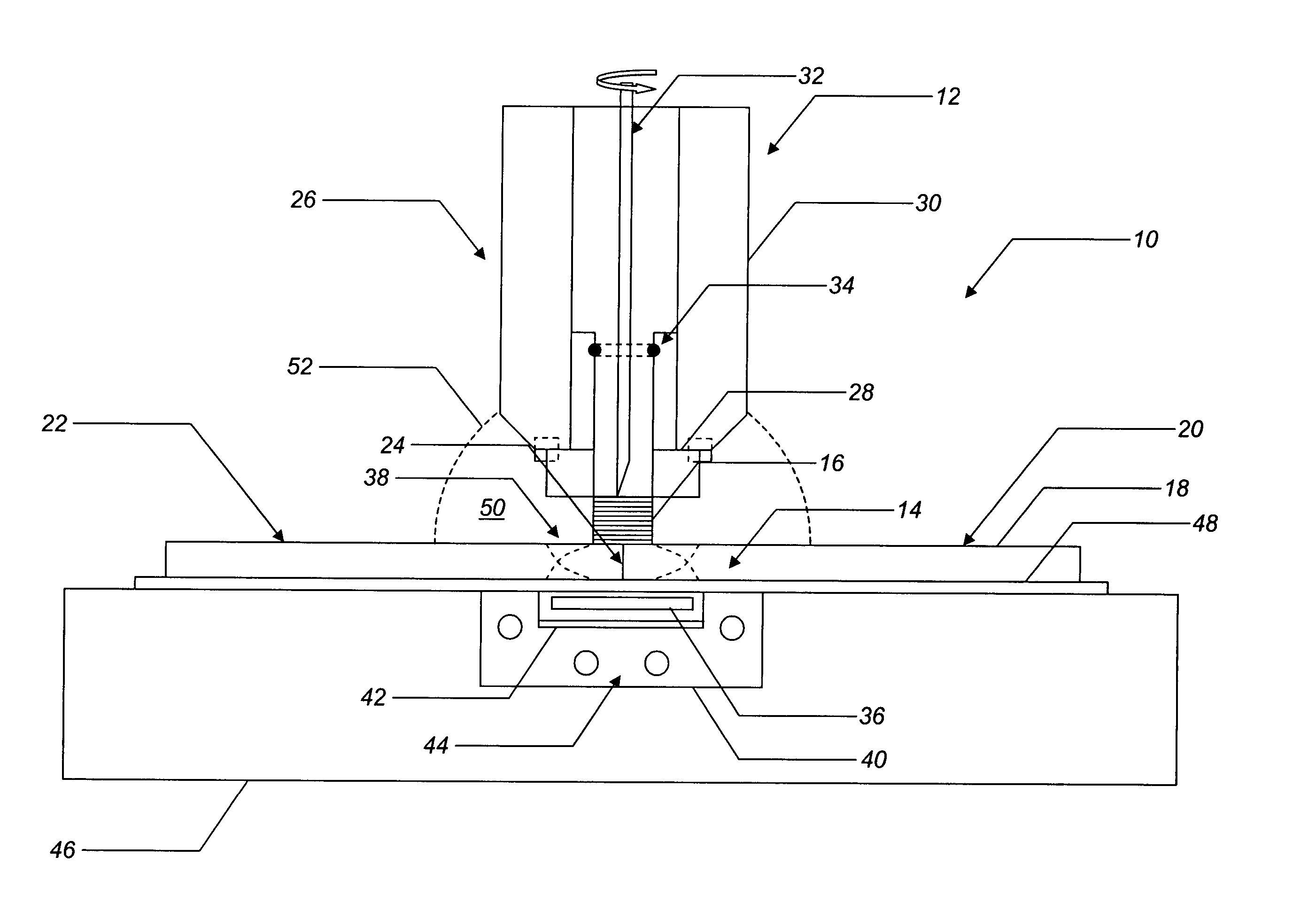
Friction stir welding apparatus and associated thermal management systems and methods
ActiveUS20050045694A1Good mechanical integrityQuality improvementWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesEngineeringThermal management system
The present invention provides a friction stir welding apparatus and associated thermal management systems and methods for joining one or more similar or dissimilar materials forming a workpiece along a joint to be welded. The friction stir welding apparatus includes a pin tool apparatus selectively disposed adjacent to and in direct contact with a first surface of the workpiece along the joint to be welded and a heating member disposed adjacent to a second surface of the workpiece along the joint to be welded, the heating member operable for controllably heating at least a portion of the workpiece adjacent to the joint to be welded. The friction stir welding apparatus also includes an annular spindle having an interior portion and an axis, the interior portion of the annular spindle at least partially defining one or more cooling channels, the one or more cooling channels operable for containing a cooling fluid. The friction stir welding apparatus further includes a shoulder disposed adjacent to the annular spindle and substantially aligned with the axis of the annular spindle and a pin tool disposed adjacent to the shoulder and substantially aligned with the axis of the annular spindle. The cooling fluid is operable for cooling at least one of the shoulder and the pin tool.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
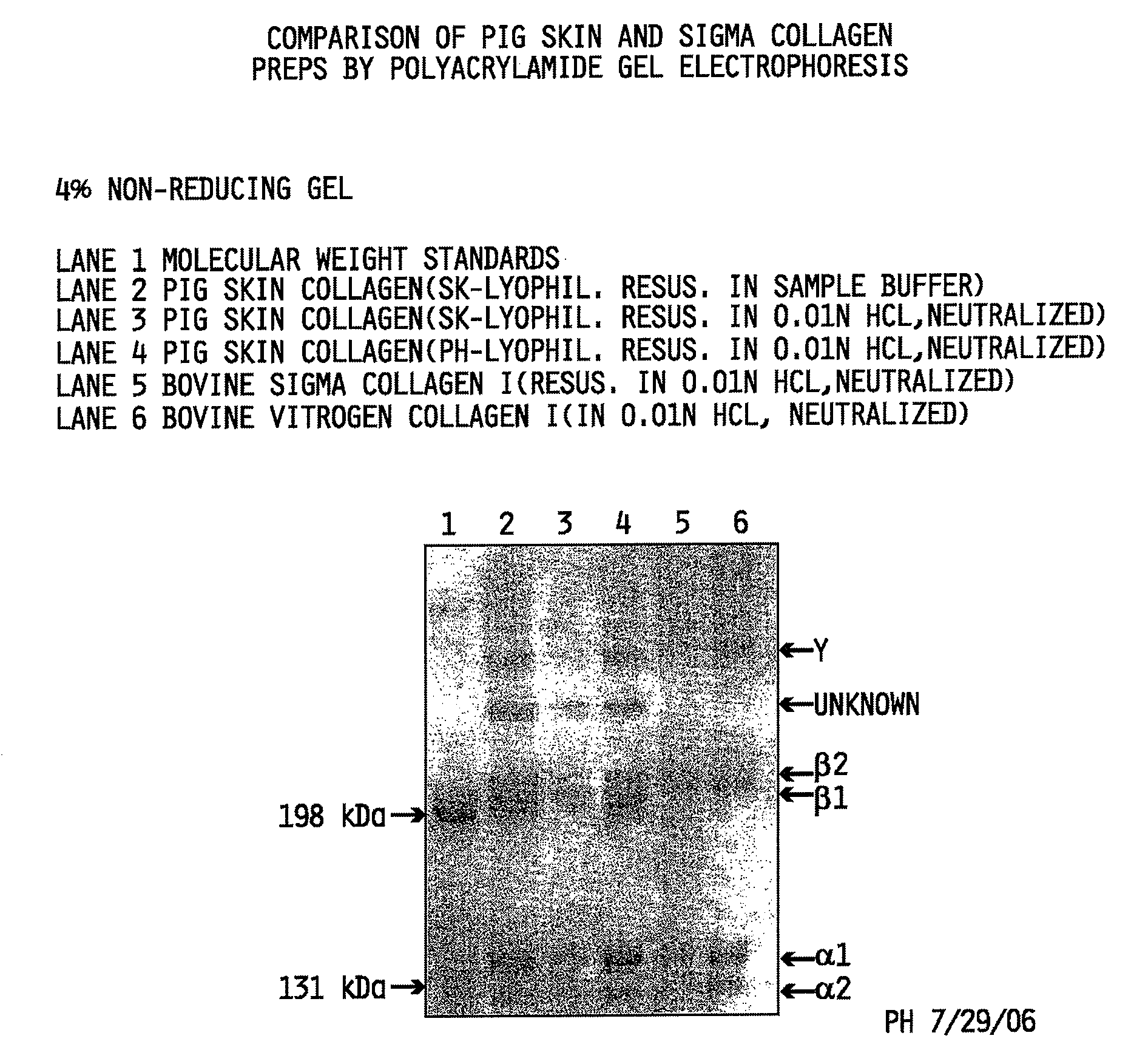
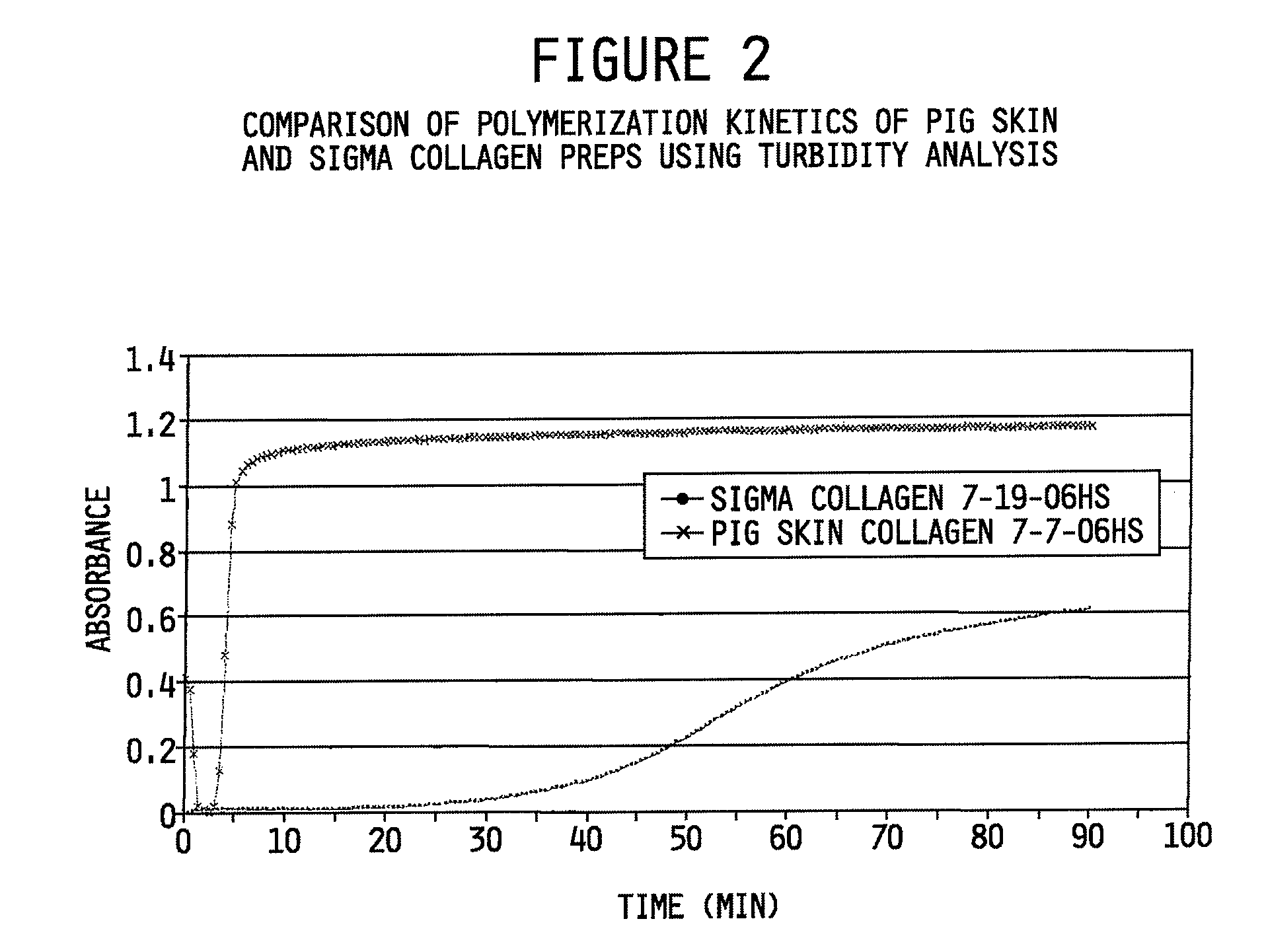
Collagen preparation and method of isolation
ActiveUS20080268052A1Facilitate hierarchical assemblyImprove mechanical propertiesPowder deliveryConnective tissue peptidesCollagen VIMechanical property
Collagen compositions, methods for preparing those collagen compositions, and graft compositions formed from those collagen compositions are provided. In particular, methods of isolating collagen that exhibits an enhanced rate of polymerization and enhanced microstructural and mechanical properties upon polymerization, such collagen compositions, and graft compositions formed from such collagen compositions are provided.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Edge connect wafer level stacking
ActiveUS20110033979A1Low costSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A method of making a stacked microelectronic package by forming a microelectronic assembly by stacking a first subassembly including a plurality of microelectronic elements onto a second subassembly including a plurality of microelectronic elements, at least some of the plurality of microelectronic elements of said first subassembly and said second subassembly having traces that extend to respective edges of the microelectronic elements, then forming notches in the microelectronic assembly so as to expose the traces of at least some of the plurality of microelectronic elements, then forming leads at the side walls of the notches, the leads being in electrical communication with at least some of the traces and dicing the assembly into packages. Additional embodiments include methods for creating stacked packages using substrates and having additional traces that extend to both the top and bottom of the package.
Owner:TESSERA INC
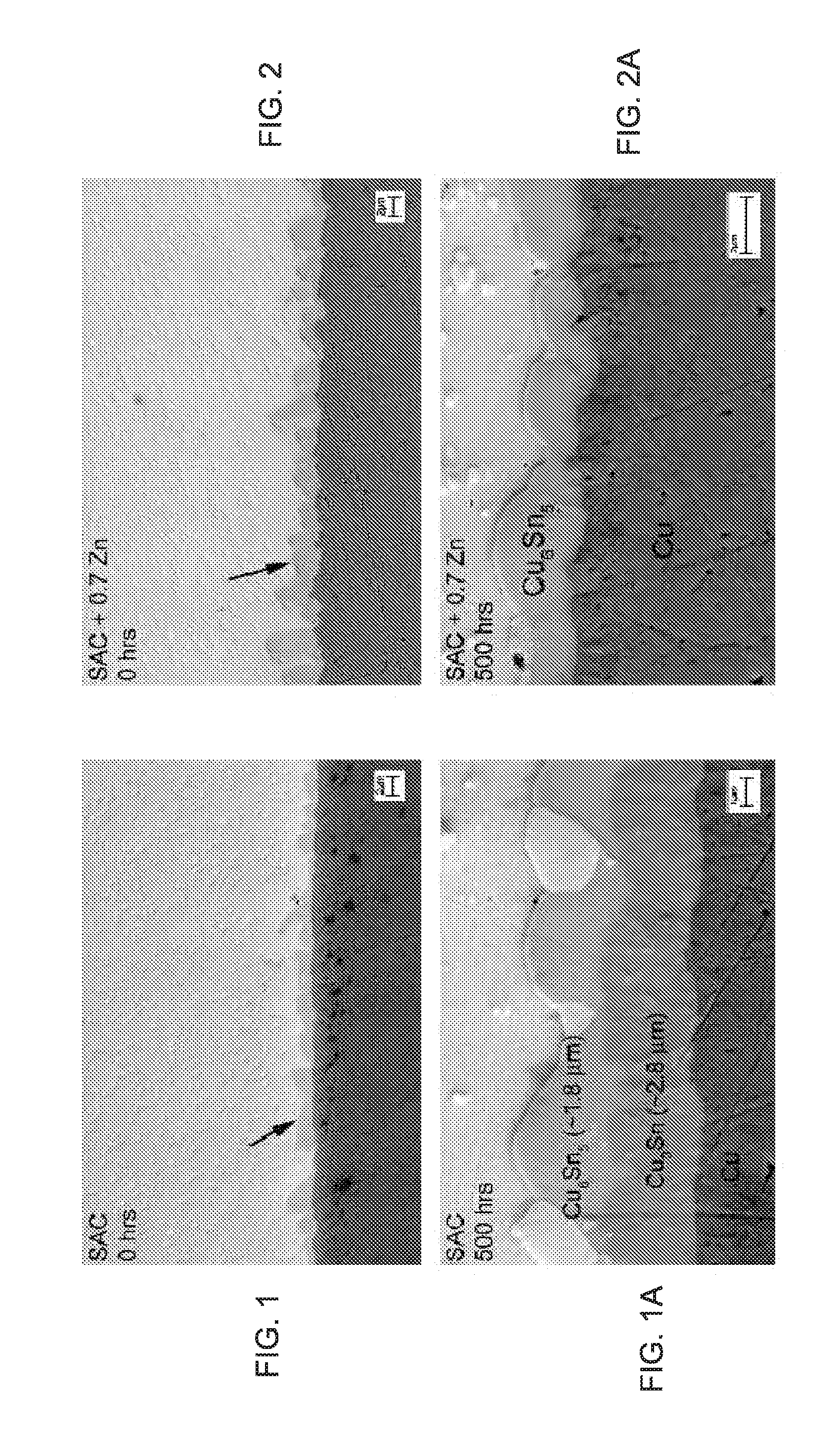
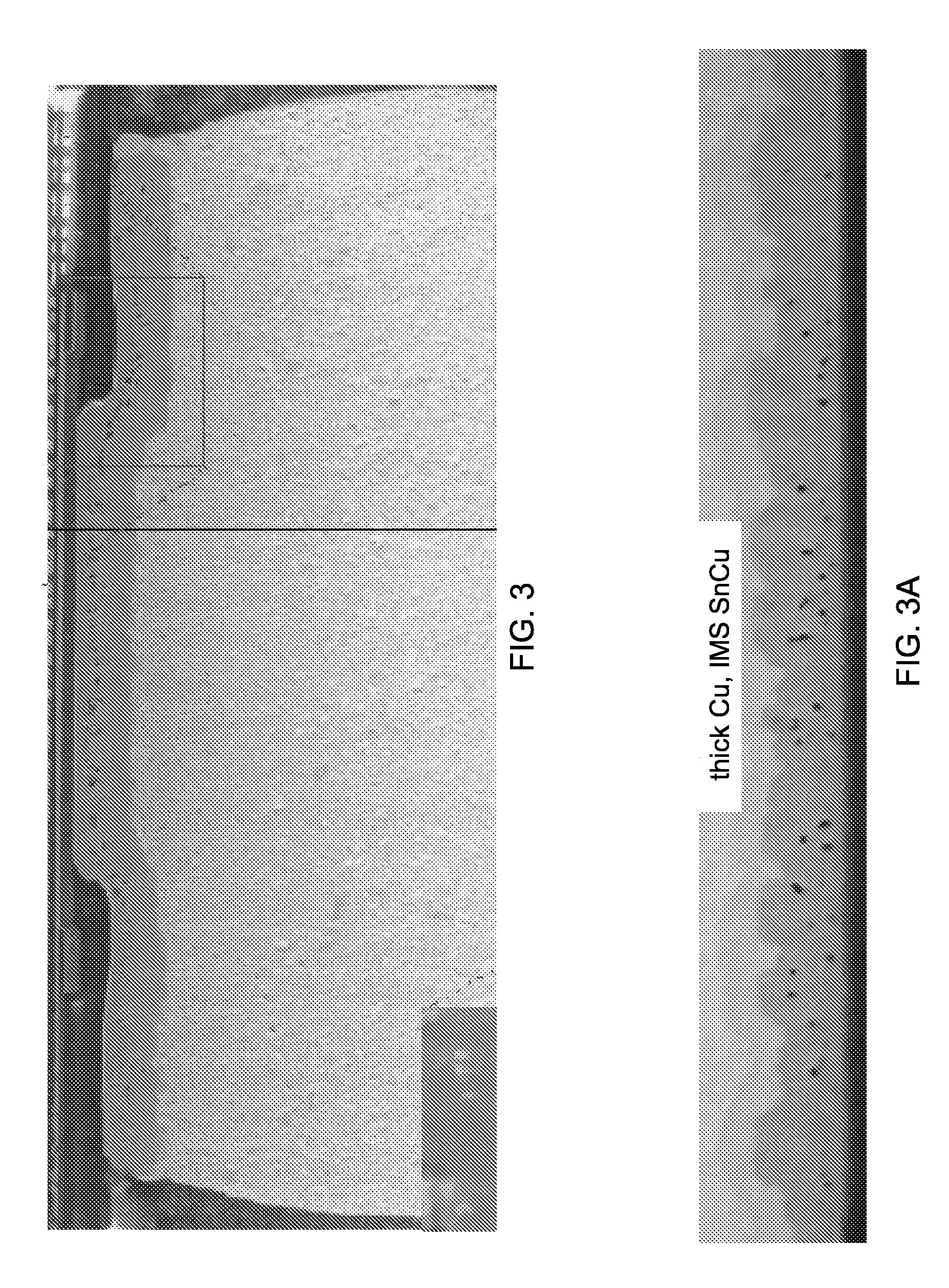
Modification of pb-free solder alloy compositions to improve interlayer dielectric delamination in silicon devices and electromigration resistance in solder joints
InactiveUS20090197114A1Good mechanical integrityImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesPrinted circuit manufactureDielectricSilicon
A solder joint comprising a solder capture pad on a substrate having a circuit; and a lead free solder selected from the group comprising Sn—Ag—Cu solder and Sn—Ag solder adhered to the solder capture pad; the solder selected from the group comprising between 0.1 to 2.0% by weight Sb or Bi, and 0.5 to 3.0% Ag. Formation of voids at an interface between the solder and the solder capture pad is suppressed, by including Zn. Interlayer dielectric delamination is suppressed, and electromigration characteristics are greatly improved. Methods for forming solder joints using the solders.
Owner:SHIH YUAN +5
Providing a surface layer or structure on a substrate
InactiveUS20050110853A1Avoid bowingGood mechanical integrityAdditive manufacturing apparatusDuplicating/marking methodsSurface layerEngineering
A method of providing a surface layer or structure on a substrate. The method comprises: a) ink jet printing spaced first segments of the surface layer or structure material on the substrate and drying or curing the first segments; and b) ink jet printing further material segments in the gaps between the first segments and drying or curing the further segments, the material and / or curing and drying conditions being different to those in step (a), all the segments, after drying or curing, forming a surface layer or structure, wherein the segment material and / or curing and drying conditions are chosen so as to control the mechanical properties of the surface layer.
Owner:FFEI LTD
Lock and Key Through-Via Method for Wafer Level 3D Integration and Structures Produced
InactiveUS20100200992A1High yieldFirmly connectedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesState of artEngineering
A three dimensional device stack structure comprises two or more active device and interconnect layers further connected together using through substrate vias. Methods of forming the three dimensional device stack structure comprise alignment, bonding by lamination, thinning and post thinning processing. The via features enable the retention of alignment through the lamination process and any subsequent process steps thus achieving a mechanically more robust stack structure compared to the prior art.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
Process for preparing a film of an oxide or a hydroxide of an element of groups IIB or IIIA of the periodic table, and the composite structures which include such a film
InactiveUS6030517AGood mechanical integrityImprove adhesionElectrolytic inorganic material coatingDuplicating/marking methodsOxidation stateElectrochemical cell
PCT No. PCT / FR96 / 00495 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 7, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 7, 1997 PCT Filed Apr. 2, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 31638 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 16, 1996Process for depositing a film of a metal oxide or of a metal hydroxide on a substrate in an electrochemical cell, wherein (i) the metal hydroxide is of formula M(OH)xAy, M representing at least one metallic species in an oxidation state i chosen from the elements in Groups II and III of the Periodic Table, A being an anion whose number of charges is n, 0<x< / =i and x+ny=i, (ii) the electrochemical cell comprises (a) an electrode comprising the substrate, (b) a counterelectrode, (c) a reference electrode and (d) an electrolyte comprising a conducting solution comprising at least one salt of the metal M, the process comprising the steps of: dissolving oxygen in the electrolyte and imposing a cathode potential of less than the oxygen reduction potential and greater than the potential for deposition of the metal M in the electrolyte in question on the electrochemical cell.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Catheter Shaft with Multiple Reinforcing Layers and Method of its Manufacture
ActiveUS20090171319A1Increase flexibility and kink resistanceEnhanced mechanical integrityGlovesPretreated surfacesHelixPolymer
A catheter shaft includes an inner layer of a first polymeric material, an intermediate layer of a second polymeric material, an outer layer of a third polymeric material, a first wire reinforcing layer encapsulated between the inner and intermediate layers, and a second wire reinforcing layer encapsulated between the outer and intermediate layers. Typically, the first wire reinforcing layer includes one or more metallic wires helically wound in one direction and the second wire reinforcing layer includes one or more metallic wires helically wound in the opposite direction. The intermediate layer is bonded to the inner and outer layers, as by extruding layers over one another or by thermal lamination or reflow bonding. Typically, the intermediate layer has a larger yield strain and / or a lower flexural modulus and / or a lower durometer than at least one of the inner layer and the outer layer.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Edge connect wafer level stacking
ActiveUS7829438B2Low costSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
In accordance with an aspect of the invention, a stacked microelectronic package is provided which may include a plurality of subassemblies, e.g., a first subassembly and a second subassembly underlying the first subassembly. A front face of the second subassembly may confront the rear face of the first subassembly. Each of the first and second subassemblies may include a plurality of front contacts exposed at the front face, at least one edge and a plurality of front traces extending about the respective at least one edge. The second subassembly may have a plurality of rear contacts exposed at the rear face. The second subassembly may also have a plurality of rear traces extending from the rear contacts about the at least one edge. The rear traces may extend to at least some of the plurality of front contacts of at least one of the first or second subassemblies.
Owner:TESSERA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com