Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
348results about How to "Lower insertion force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
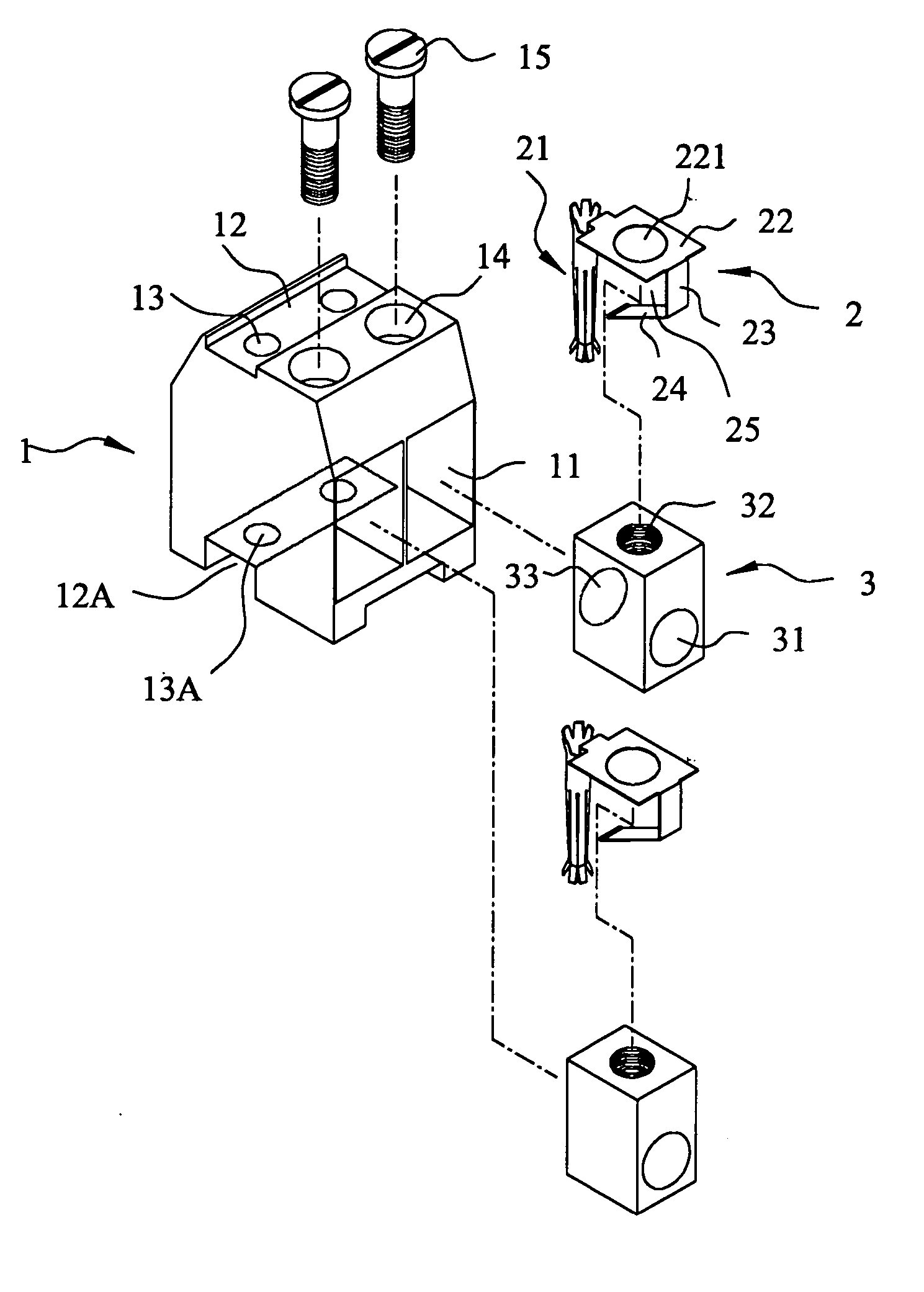
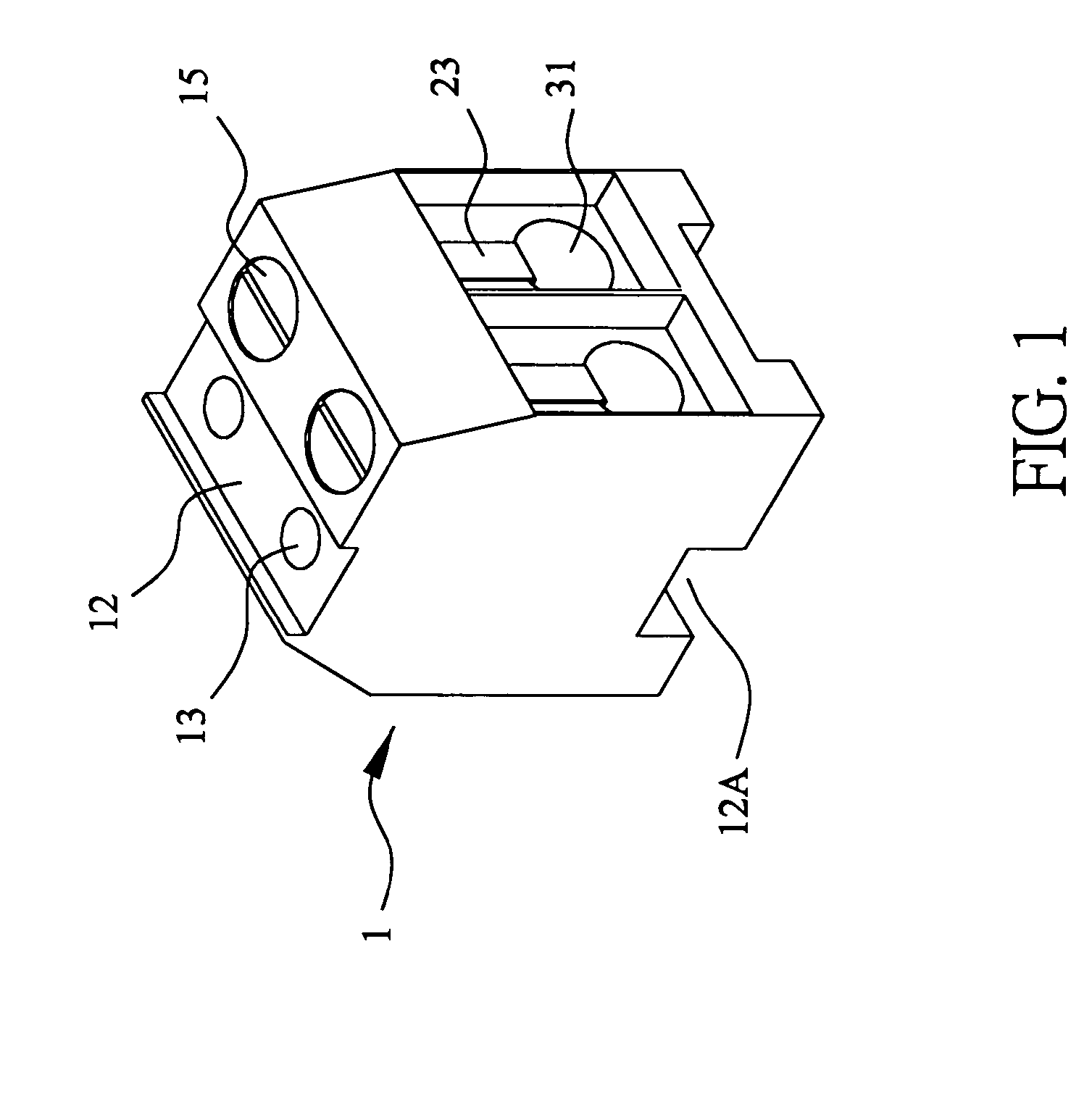
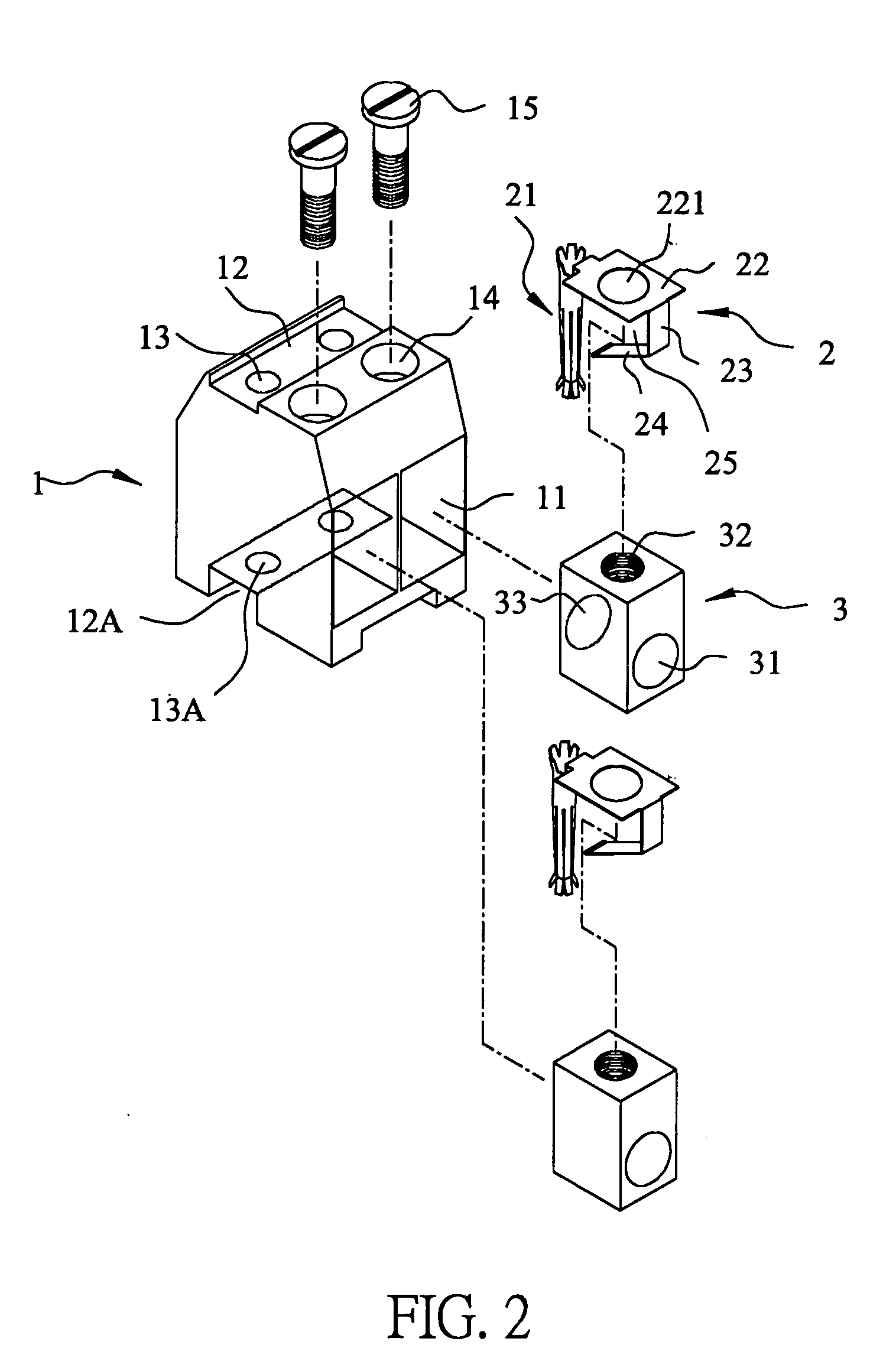
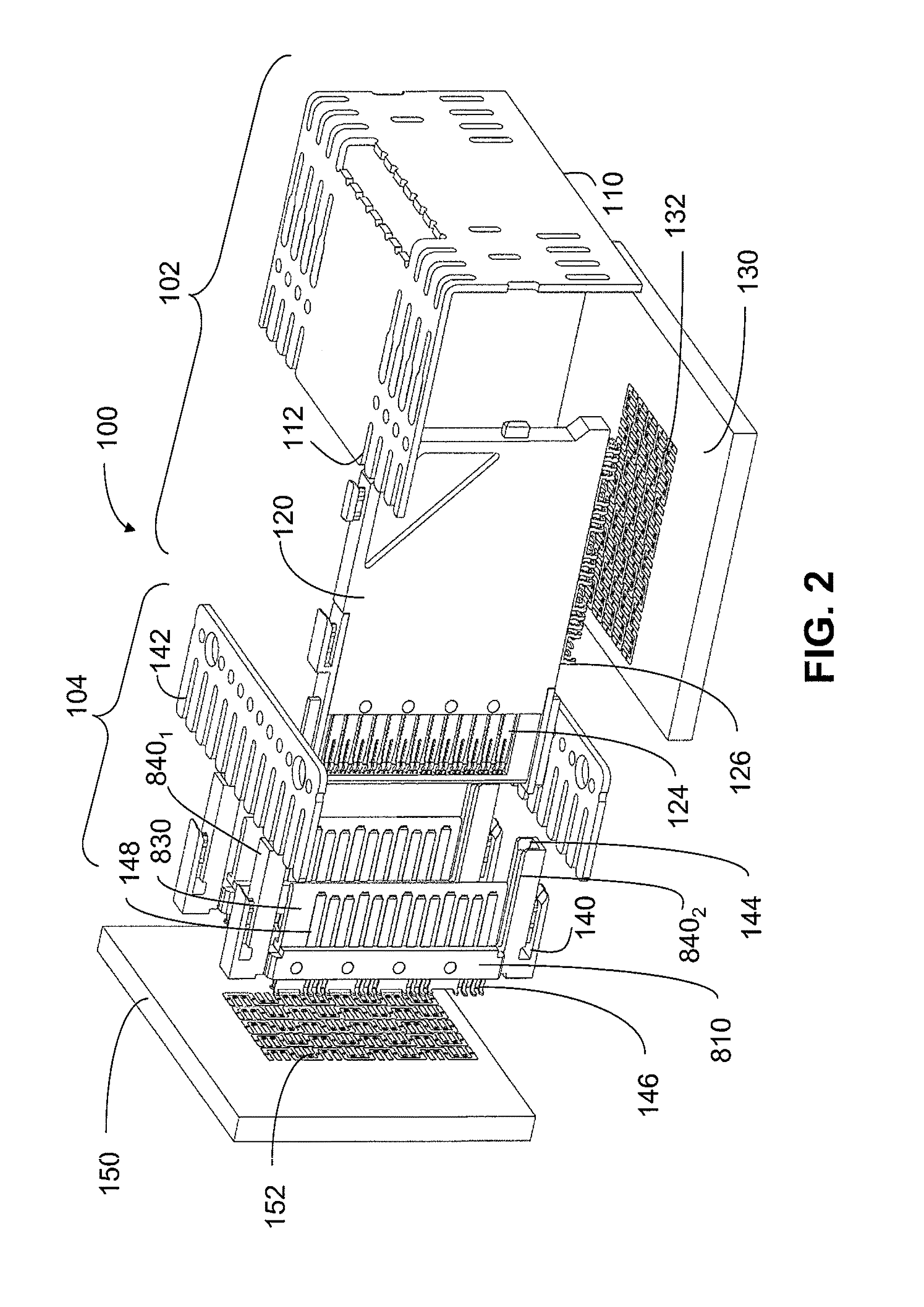
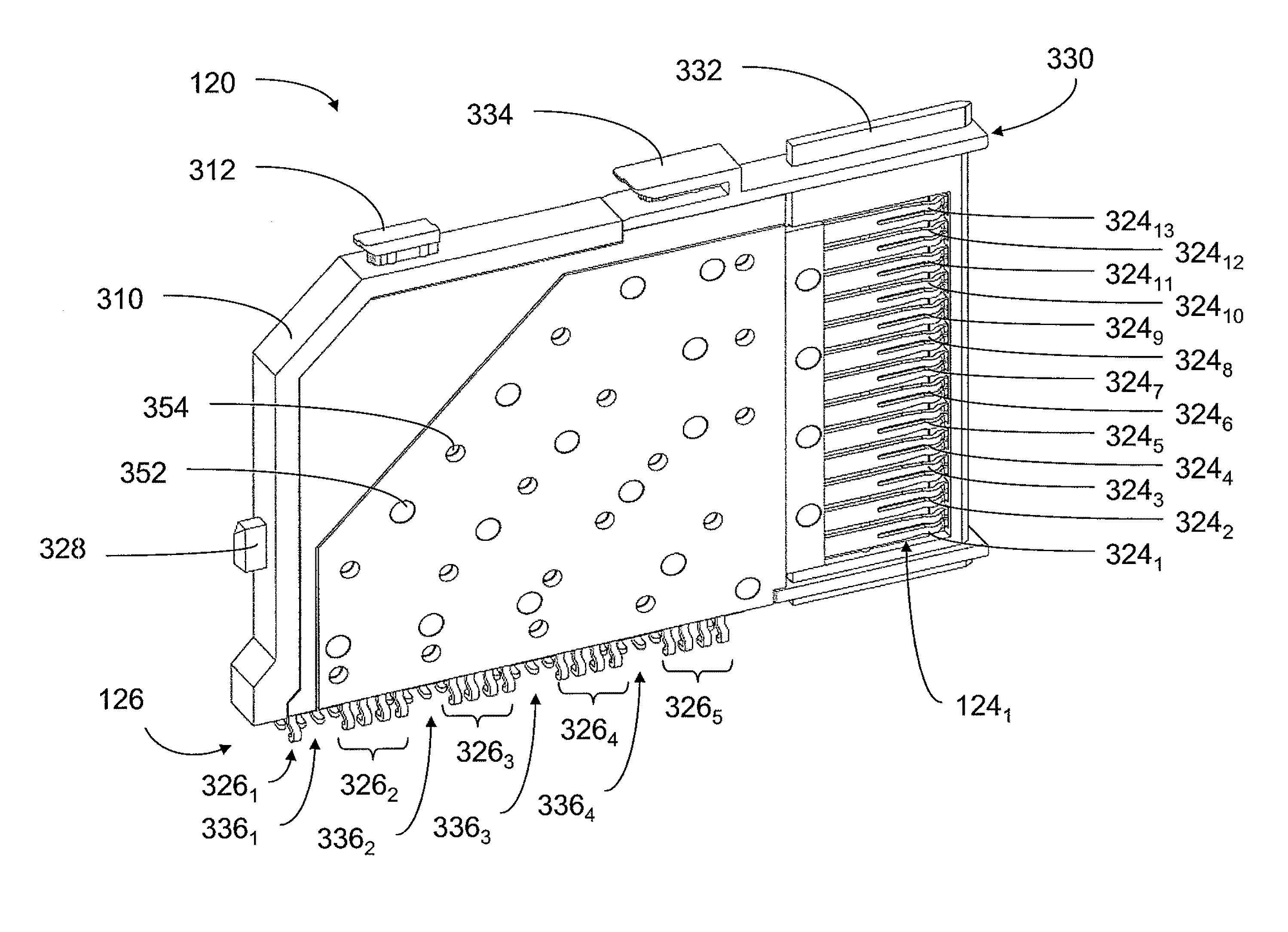
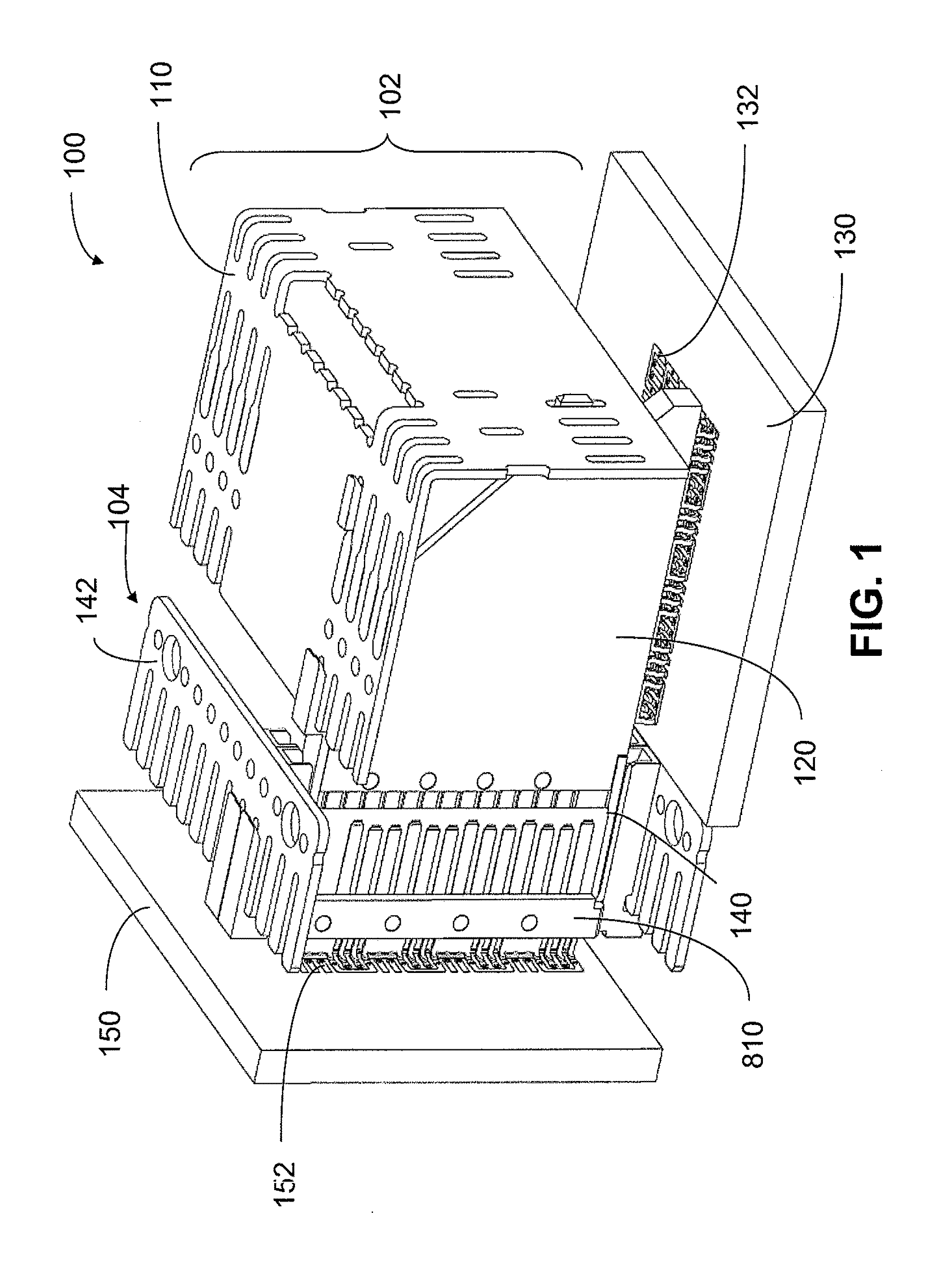
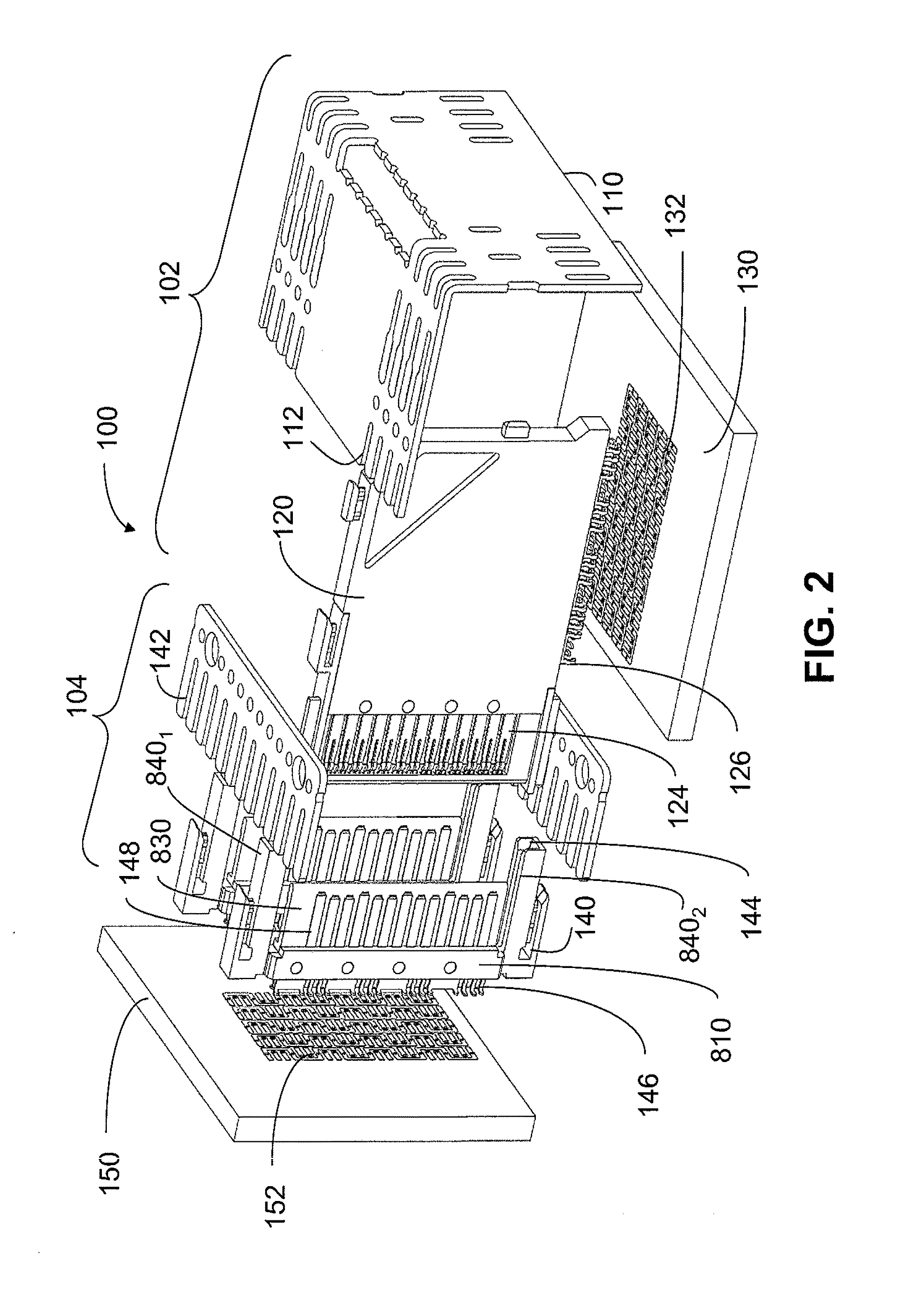
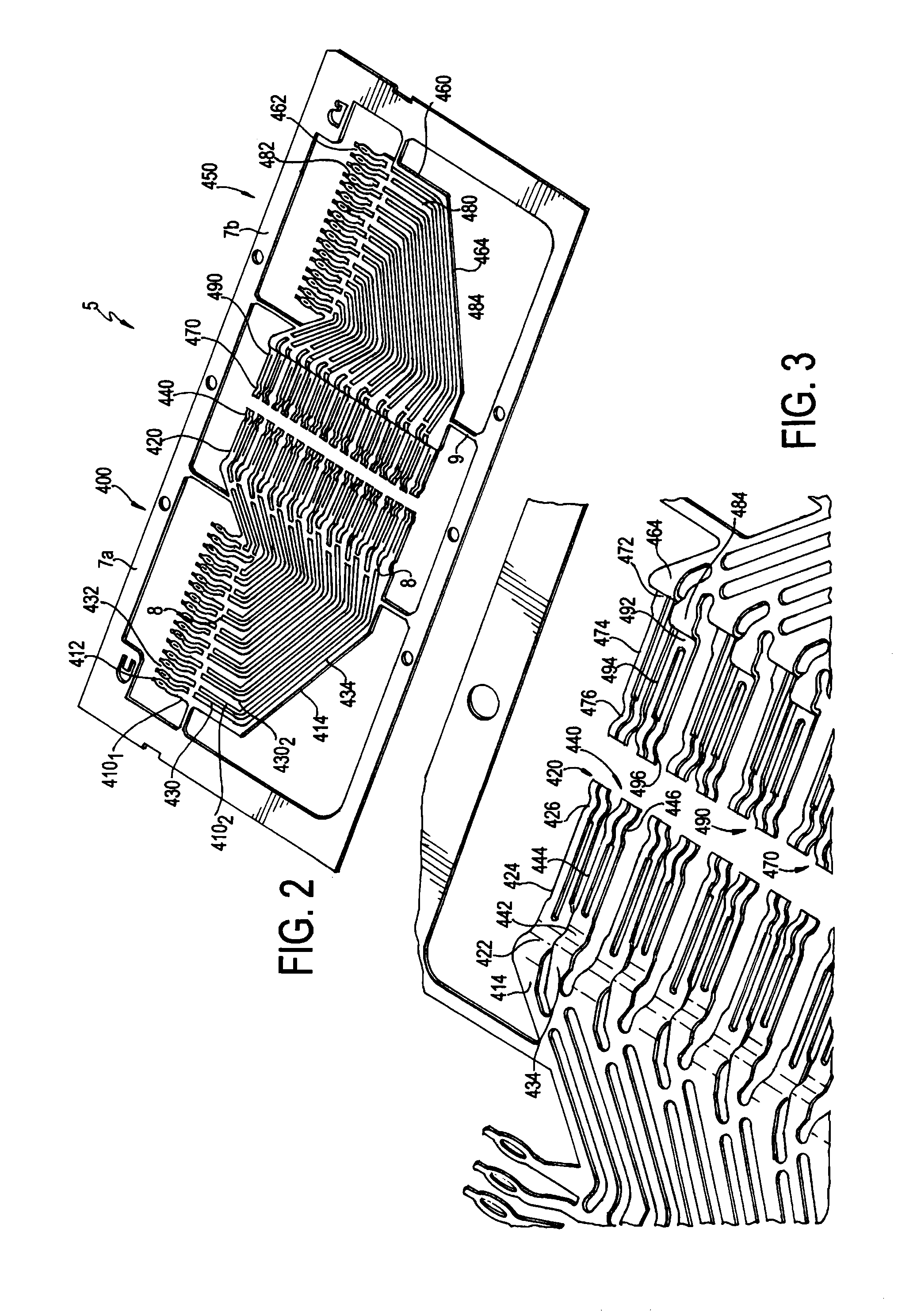
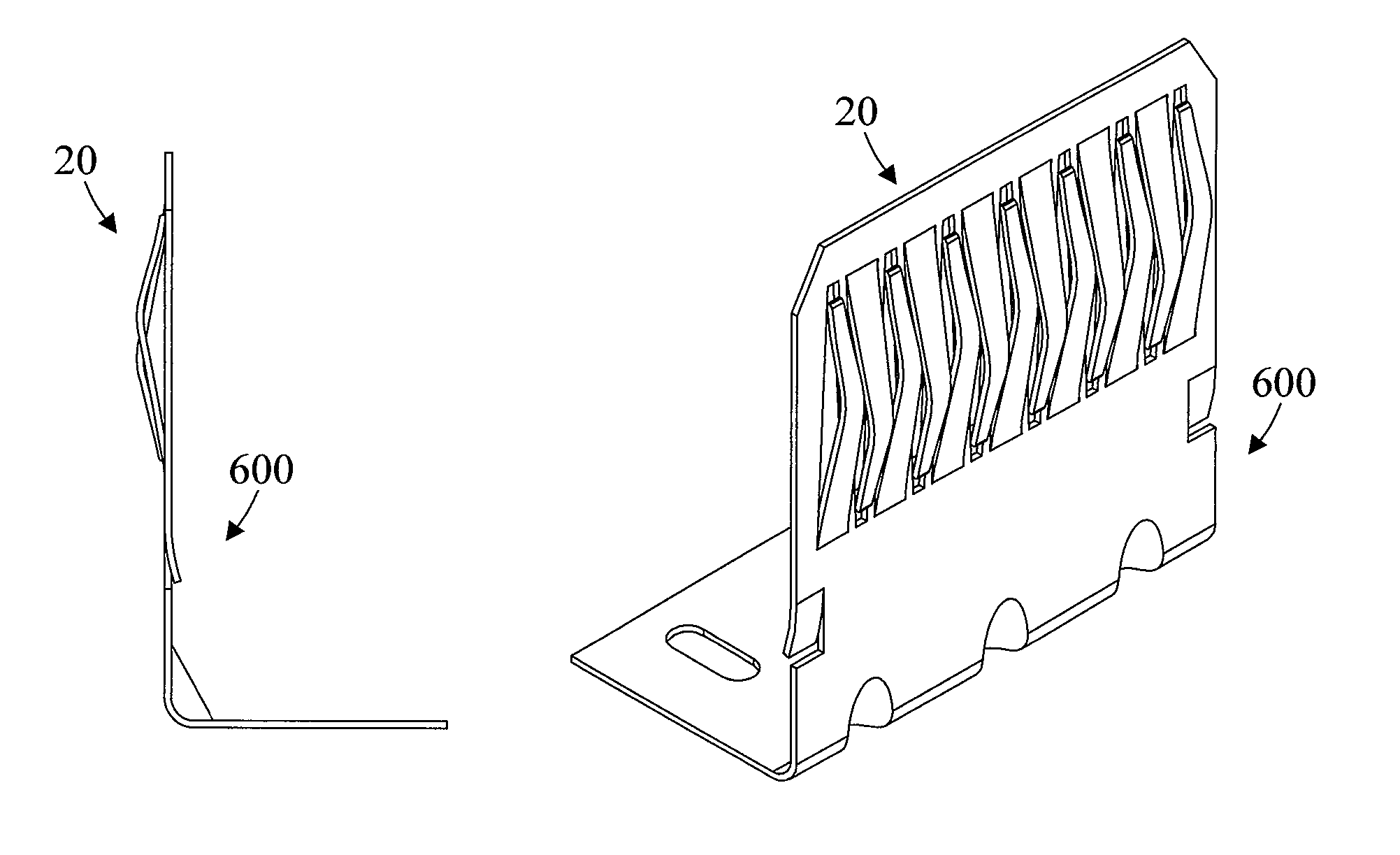
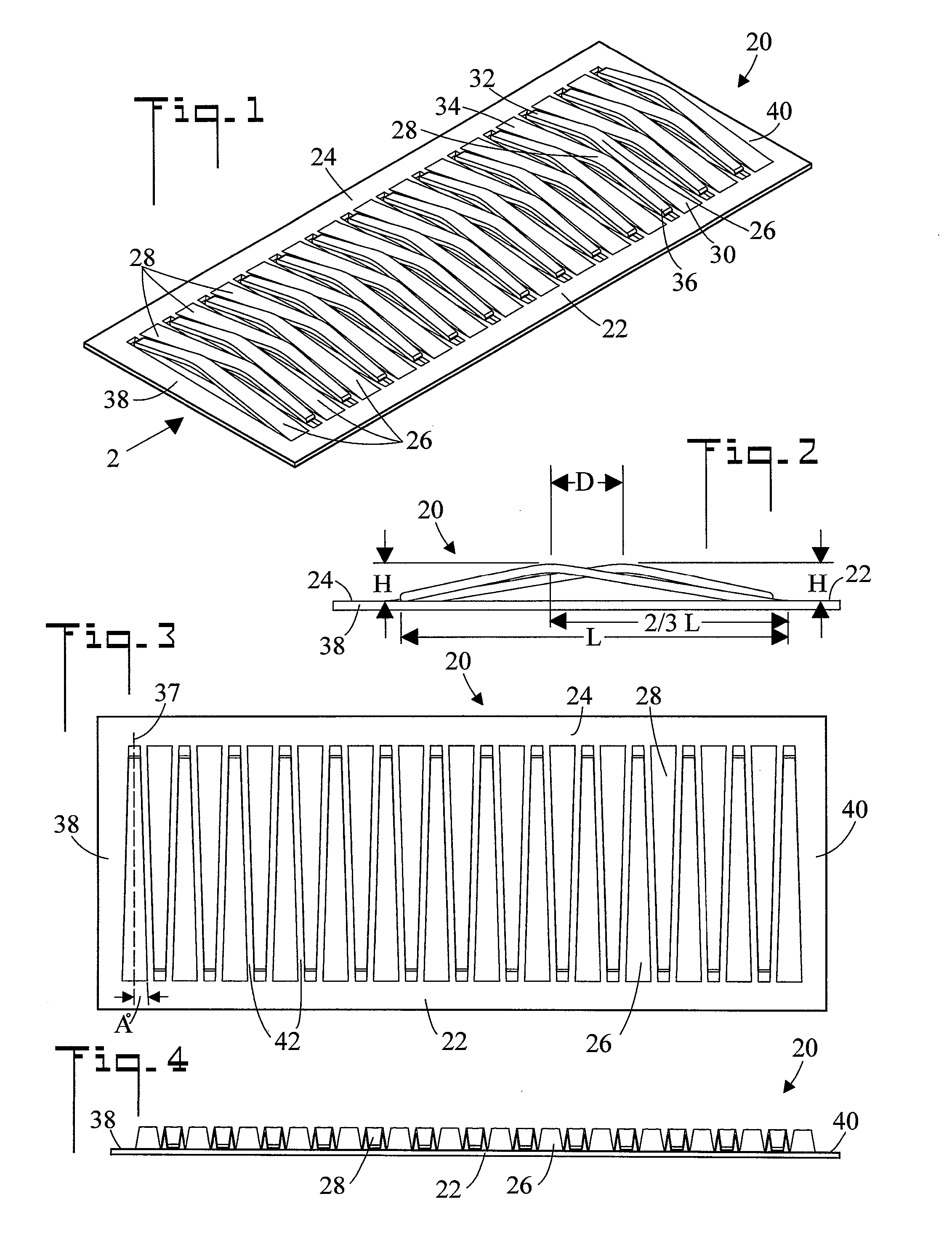
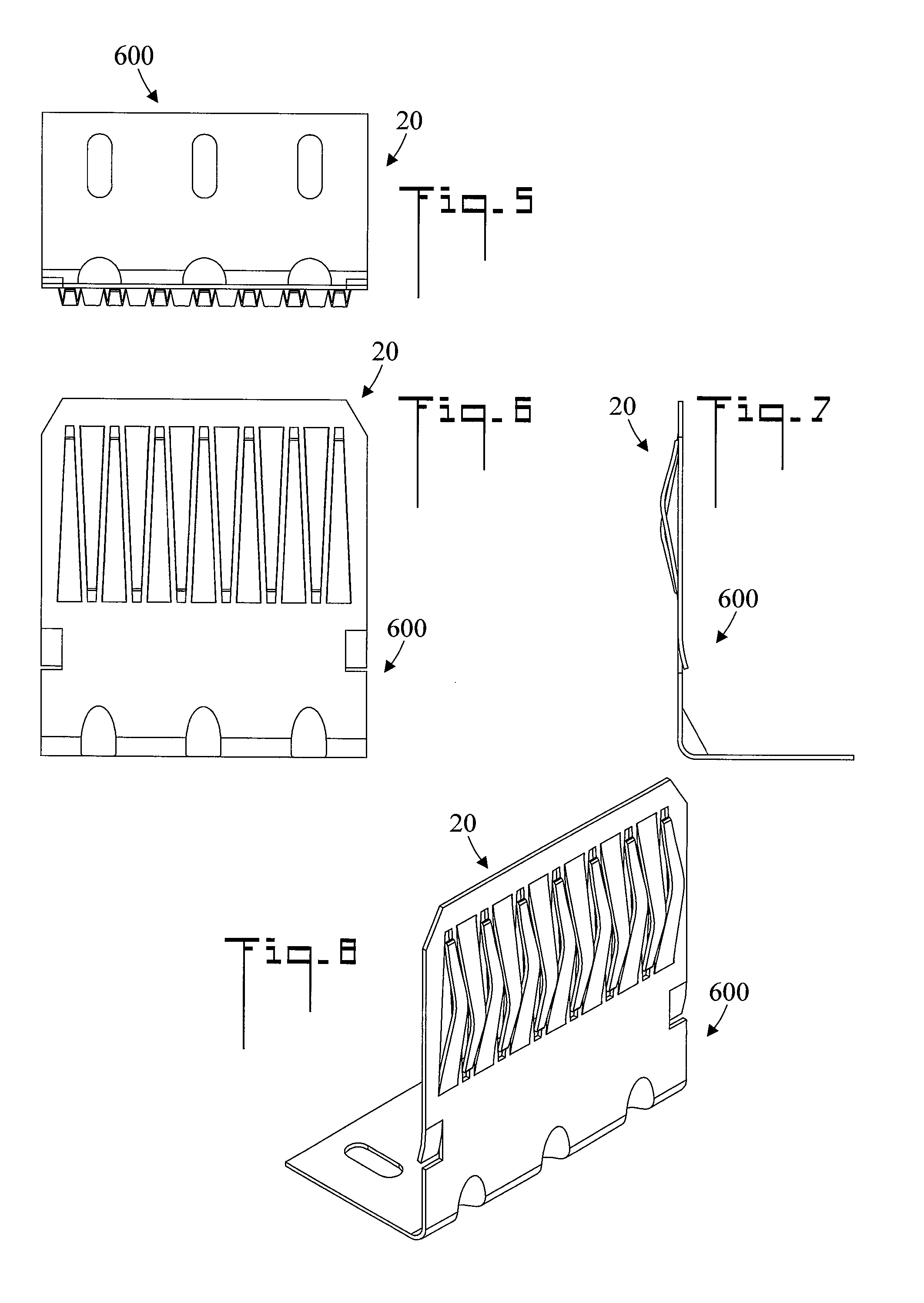
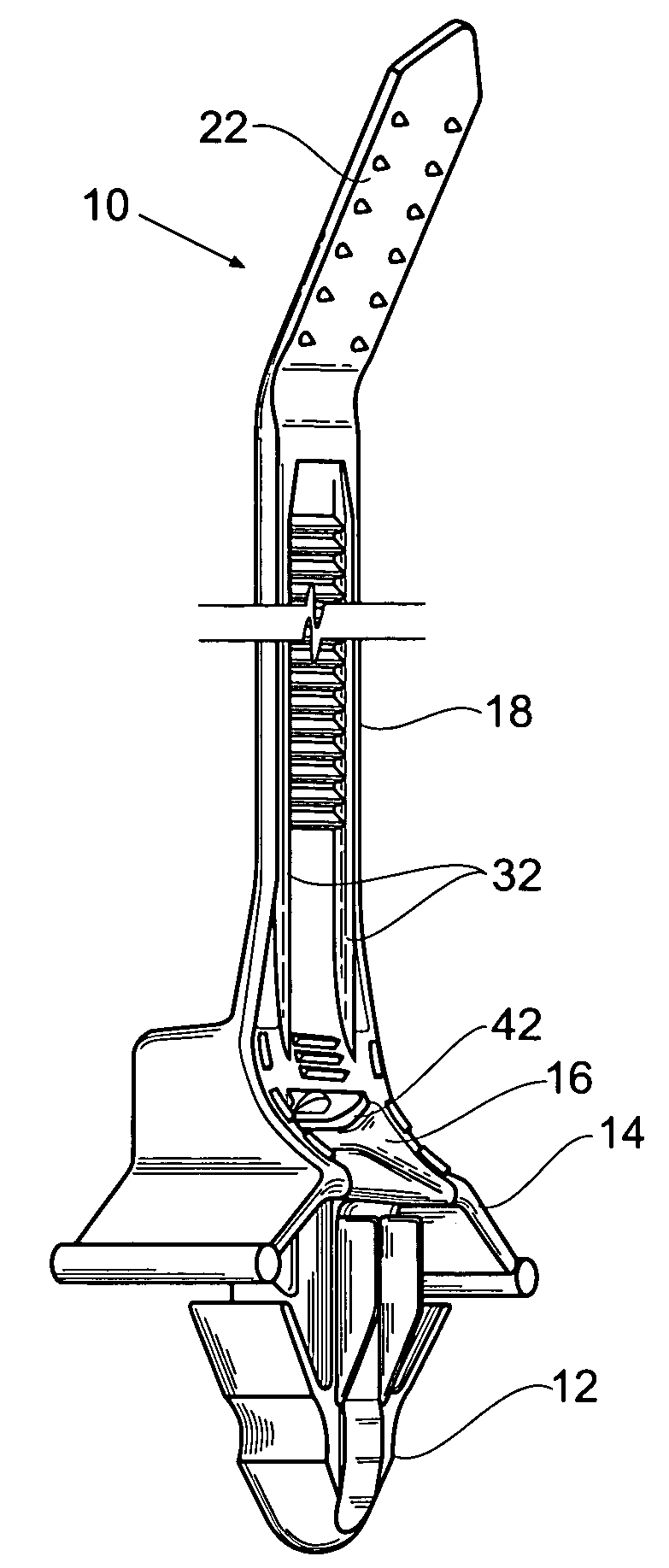
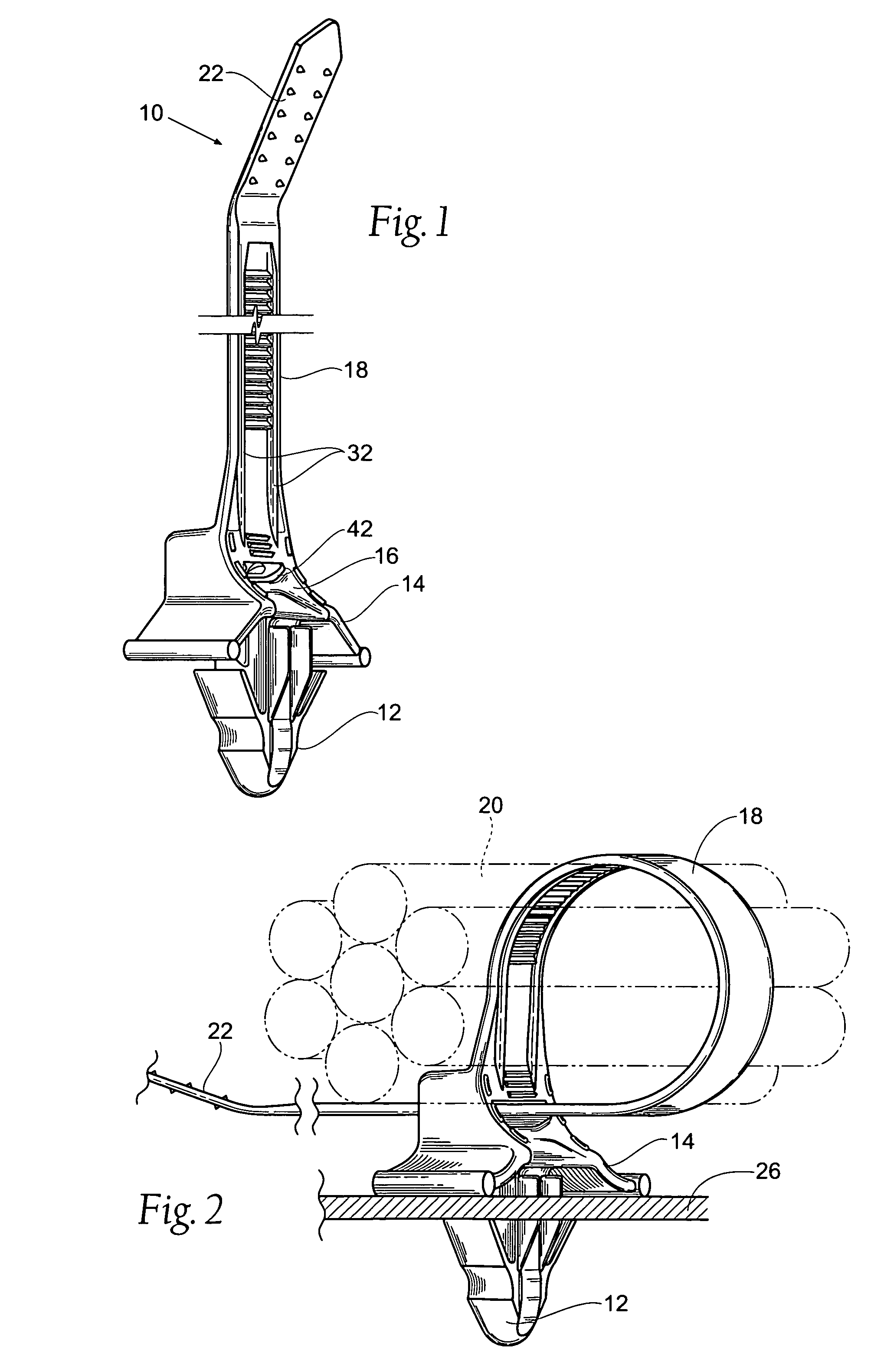
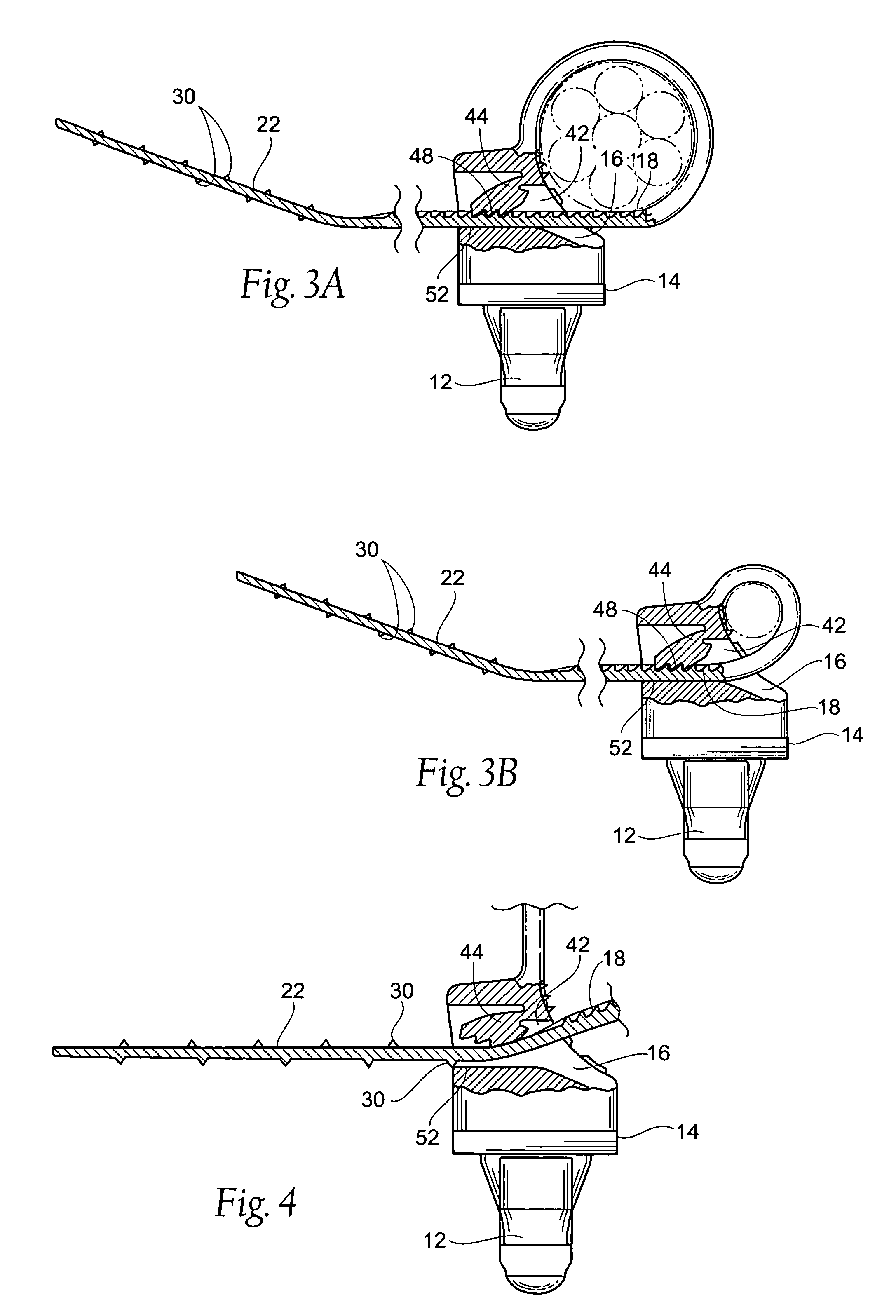
Structure of connector
InactiveUS20050130508A1Low insertion forceLarge contact areaClamped/spring connectionsLower faceHeat generation
A connector includes a housing forming at least one receptacle and a terminal received in each receptacle. The housing has upper and lower faces in which opposite slots are defined. Through holes are defined in the slots and extending to the receptacle. The terminal has an engagement section, a retention section extending from the engagement section, an extension section extending from the retention section and opposite to the engagement section and a wire engaging section projecting from the extension section. The engagement section includes a plurality of circumferentially spaced resilient leaves forming a cylinder axially aligned with the holes defined in the upper and lower faces of the housing. Thus, when a pin of a mating connector is fit into the cylinder of the engagement section through either one of the holes of the housing, the pin is completely surrounded by the leaves and a large contact area is formed between the pin and the engagement section. Due to the resiliency of the leaves, only a low insertion force is needed in completing insertion of the pin into the engagement section. Firm engagement, low impedance and low noise, as well as reduced heat generation, can be realized between the pin and the engagement section.
Owner:YEH SHENG HSING
Electrical connector having improved terminal configuration
ActiveUS7549897B2Small sizeImproving impedanceElectric discharge tubesSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersElectrical performanceEngineering
An electrical terminal of the type to be inserted into an aperture of an electrical panel member is provided. The electrical terminal may include a base, an insertion portion extending from the base to a first end, a slit formed through the insertion portion and defining a compliant portion having a first leg and a second leg. Midpoints of each or both legs may be offset from the midpoint of the slit to achieve improved mechanical and electrical performance within a connector. Also provided is an electrical terminal having a tip that facilitates alignment with a panel member aperture and provides tactile feedback to a user, as well as an electrical terminal having a mounting end that is substantially smaller than its mating end, and connectors containing such terminals. Methods of routing electrical traces between adjacent electrical terminals are also provided.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS LOGISTICS AG (CH)
High density electrical connector with variable insertion and retention force
ActiveUS8182289B2Lower insertion forceImprove retentionTwo-part coupling devicesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsElectricityHigh density
An interconnection system that includes a daughter card and backplane electrical connectors mounted to printed circuit boards at connector footprints. The spring rate of beam-shaped contacts in the daughter card connector increases while mating with the backplane connector so that the retention force may be greater than the insertion force. Such a change in spring rate may be achieved by positioning the beam-shaped contacts adjacent a surface of a connector housing. That surface may include a projection that aligns with the beam-shaped contact. When the connectors are unmated, the beam-shaped contact may be spaced from the projection. As the connectors begin to mate, a central portion of the beam-shaped contact may be pressed against the projection, which has the effect of shortening the beam length and increasing its stiffness.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
High density electrical connector with variable insertion and retention force
ActiveUS20110212649A1High retention forceHigh spring rateTwo-part coupling devicesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsElectricityBackplane
An interconnection system that includes a daughter card and backplane electrical connectors mounted to printed circuit boards at connector footprints. The spring rate of beam-shaped contacts in the daughter card connector increases while mating with the backplane connector so that the retention force may be greater than the insertion force. Such a change in spring rate may be achieved by positioning the beam-shaped contacts adjacent a surface of a connector housing. That surface may include a projection that aligns with the beam-shaped contact. When the connectors are unmated, the beam-shaped contact may be spaced from the projection. As the connectors begin to mate, a central portion of the beam-shaped contact may be pressed against the projection, which has the effect of shortening the beam length and increasing its stiffness.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
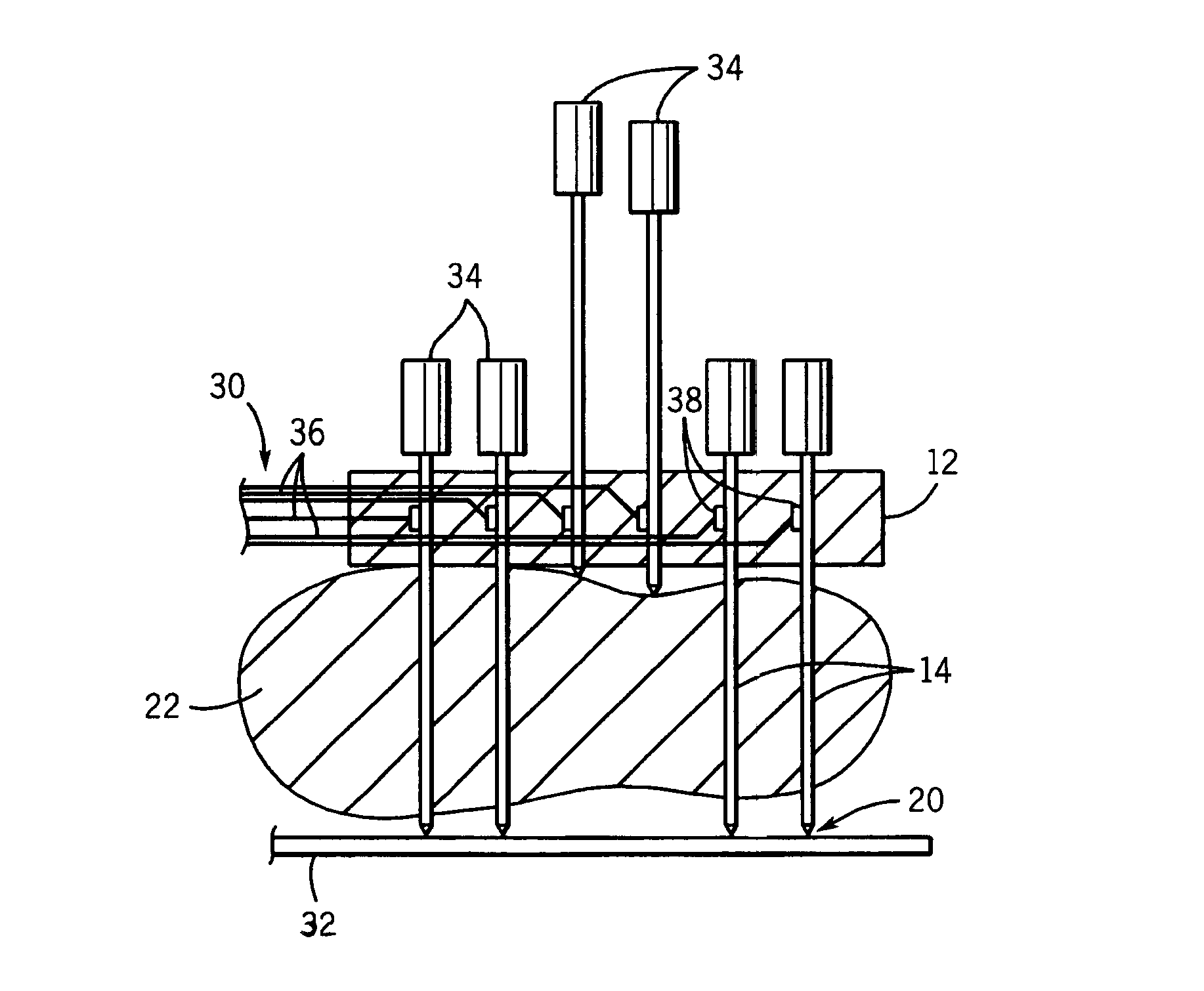
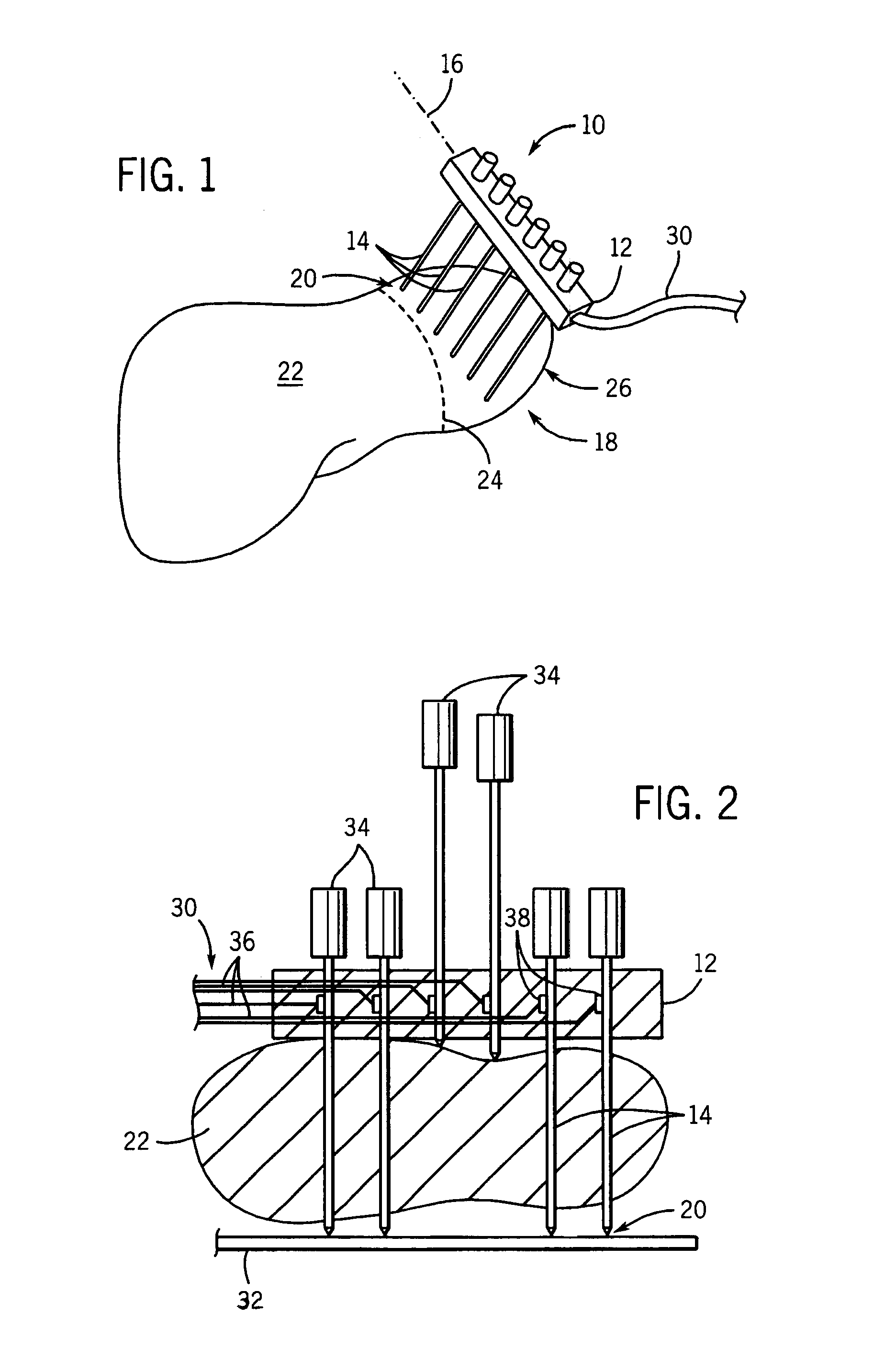
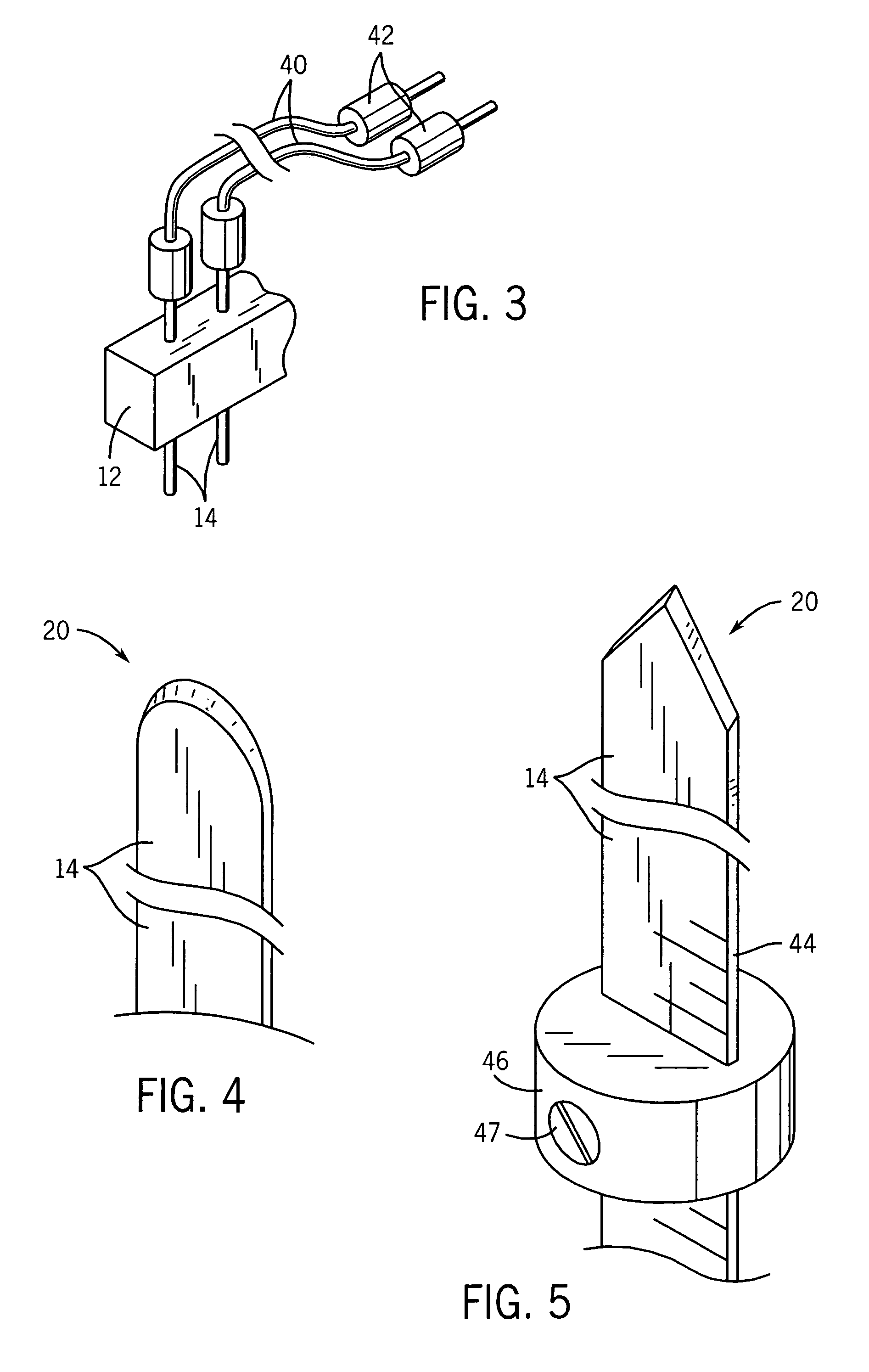
Electrode array for tissue ablation
ActiveUS7367974B2Fast ablationFlow of bloodDiagnosticsSurgical needlesElectrode arrayTissue ablation
An electrode array allows for rapid ablation of a strip of tissue in an organ providing a barrier to blood loss during resection operations.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
High density electrical connector and PCB footprint
ActiveUS8272877B2Reduces instanceImprove signal integrityTwo-part coupling devicesElectrical connection printed elementsHigh densityElectrical conductor
An interconnection system that includes a daughter card and backplane electrical connectors, each mounted to a printed circuit board at a connector footprint. The backplane connector has conductive elements with transition regions that allow the mating contact portions to be positioned on a uniform pitch while contact tail portions can be shaped to improve signal integrity or to provide a more compact and / or mechanically robust footprint. The conductive elements in both connectors are configured such that the contact tails of the ground conductors align from column to column, but the planar portions of the ground conductors in one column align with a pair of signal conductors in the other column, which improves mechanical and signal integrity. Mechanical integrity may be improved by forming the connector footprints with pads for the ground conductors that span multiple columns.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
High speed, high density electrical connector
ActiveUS20120214344A1Smooth connectionLower insertion forceElectric discharge tubesCoupling contact membersPath lengthHigh density
A broadside coupled connector assembly has two sets of conductors, each separate planes. By providing the same path lengths, there is no skew between the conductors of the differential pair and the impedance of those conductors is identical. The conductor sets are formed by embedding the first set of conductors in an insulated housing having a top surface with channels. The second set of conductors is placed within the channels so that no air gaps form between the two sets of conductors. A second insulated housing is filled over the second set of conductors and into the channels to form a completed wafer. The ends of the first and second sets of conductors and the blades are jogged in both an x- and y-coordinate to reduce crosstalk and improve electrical performance.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
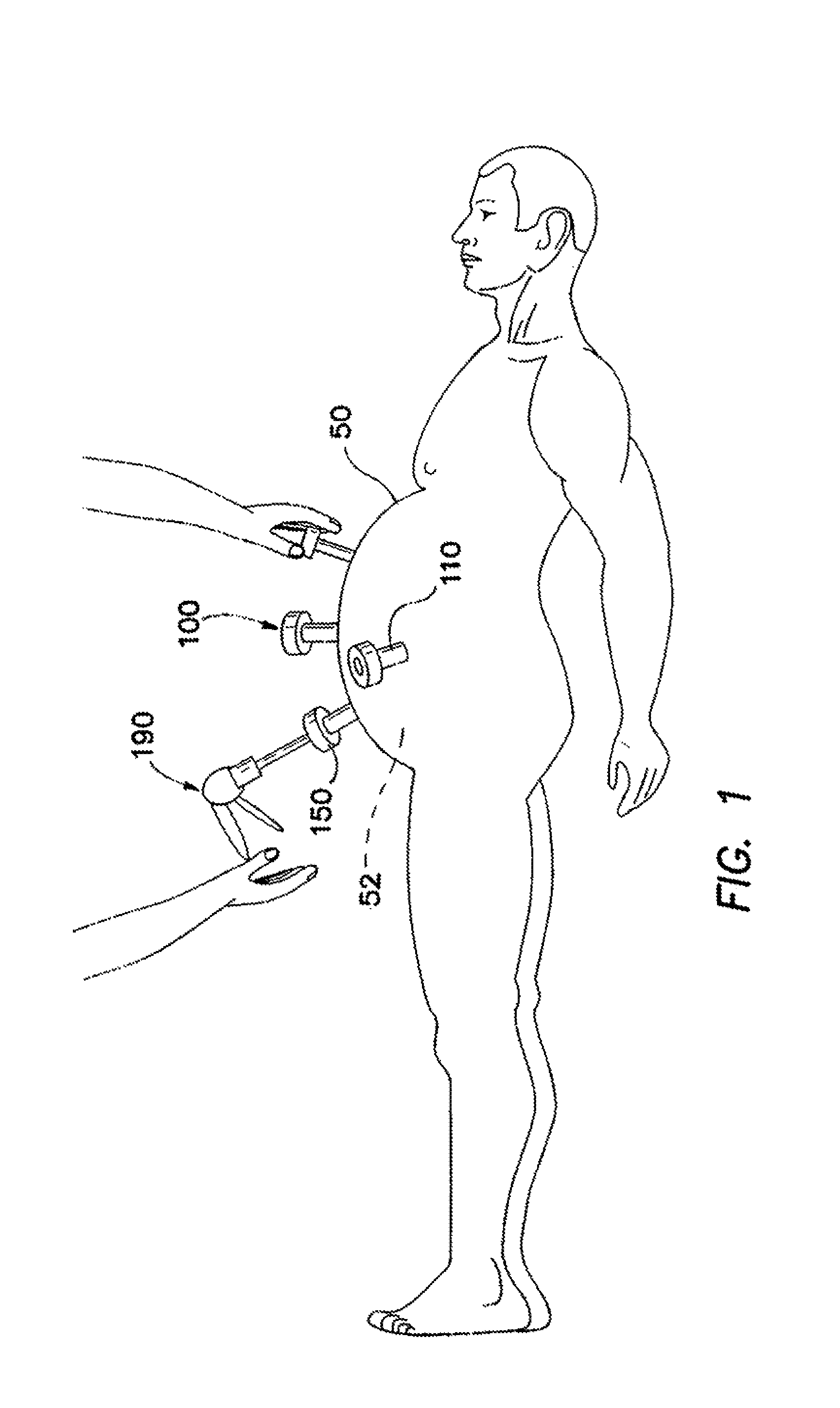
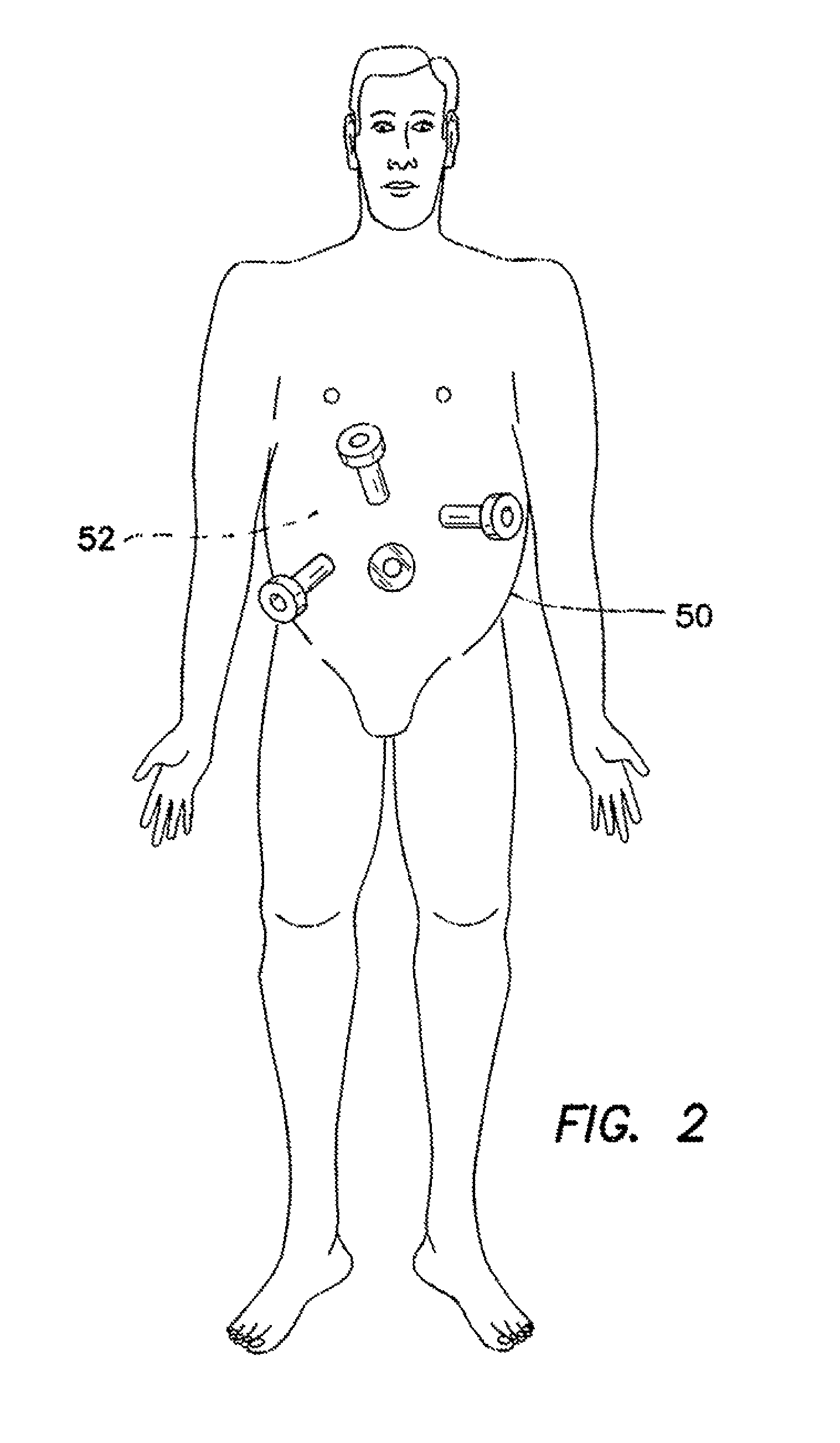
Rotating needle driver and apparatuses and methods related thereto
ActiveUS20100234856A1Reduce insertion forceReduce deformationVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsAbdominal trocarBiomedical engineering
Featured is a medical instrument driver, a robotic apparatus embodying such a medical instrument driver and methods related thereto for inserting a medical instrument into tissue of a mammal (e.g., human). Such medical instruments include medical needles, biopsy needles, trocars, cutters and introducers. Such a medical instrument driver according to the present invention is configured and arranged so that medical instrument is rotated as it is being moved longitudinally for insertion into the tissue such that the medical instrument is spiraling as it pierces and traverses the tissue to the target area.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
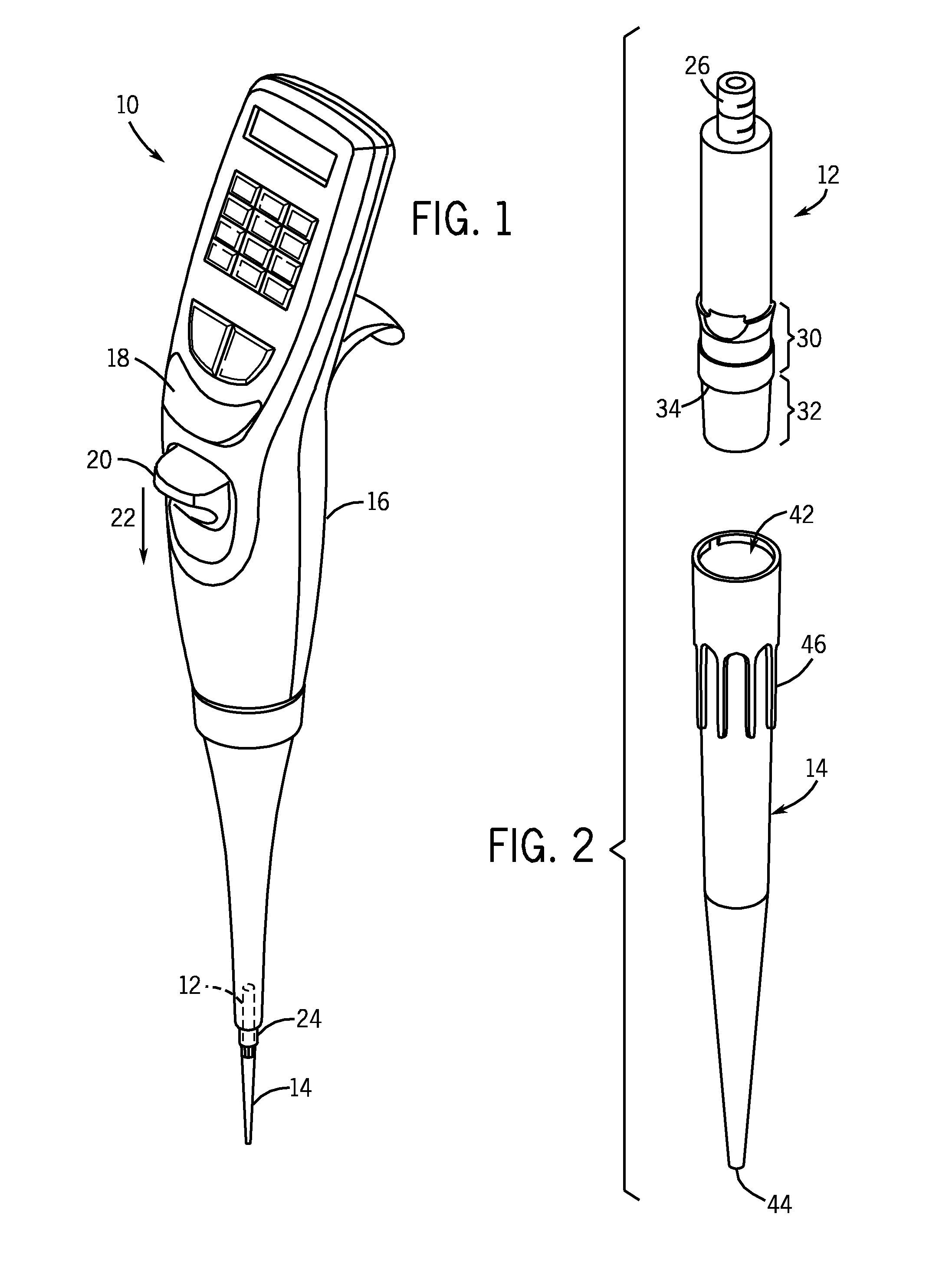
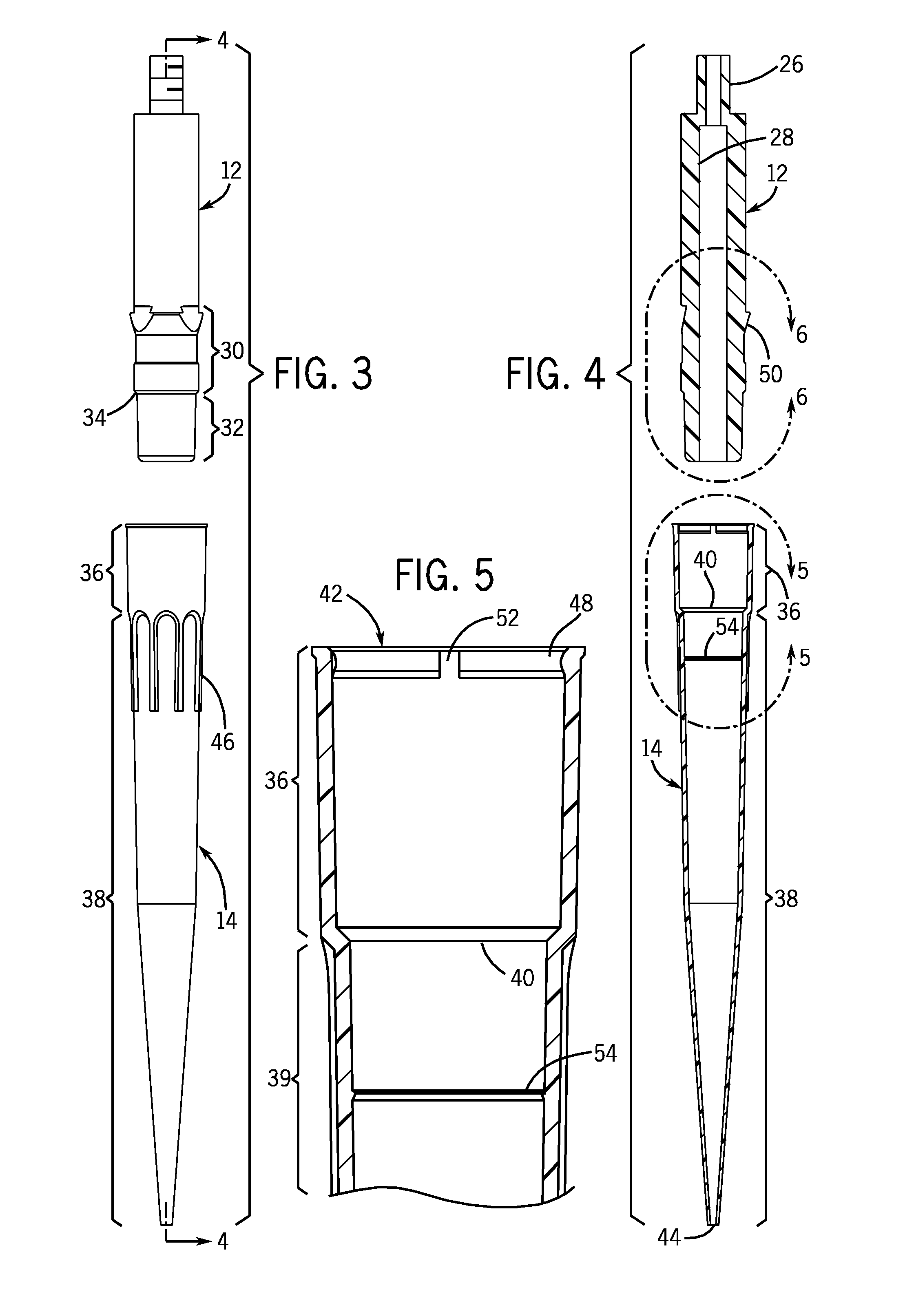
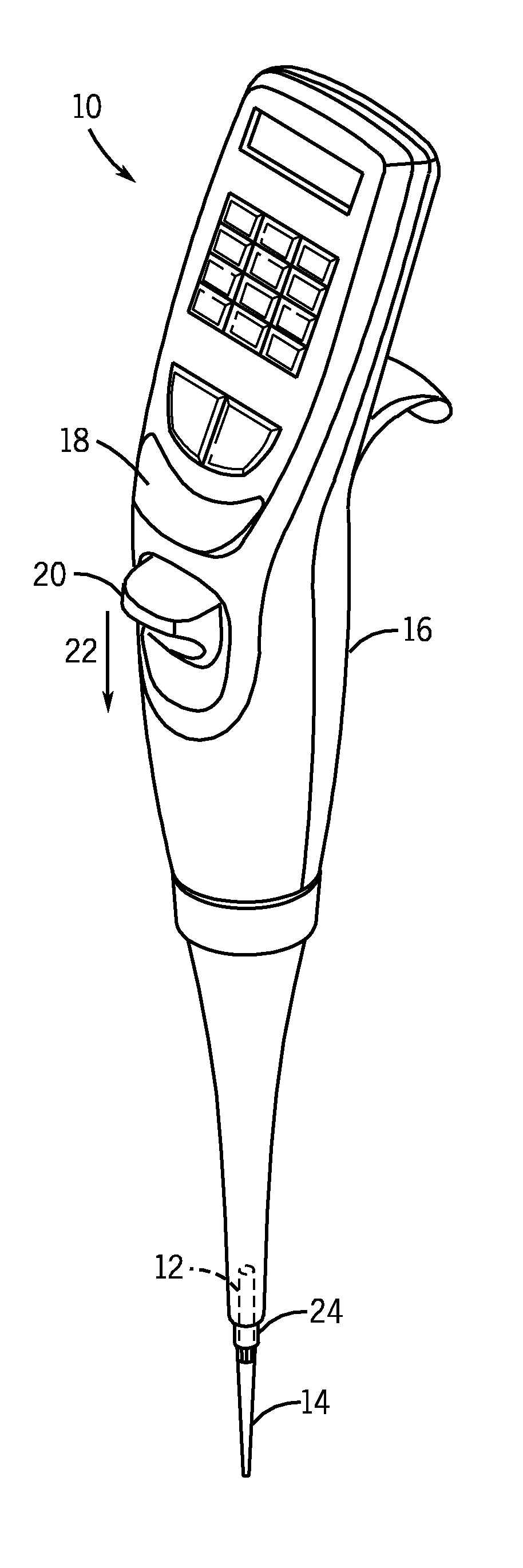
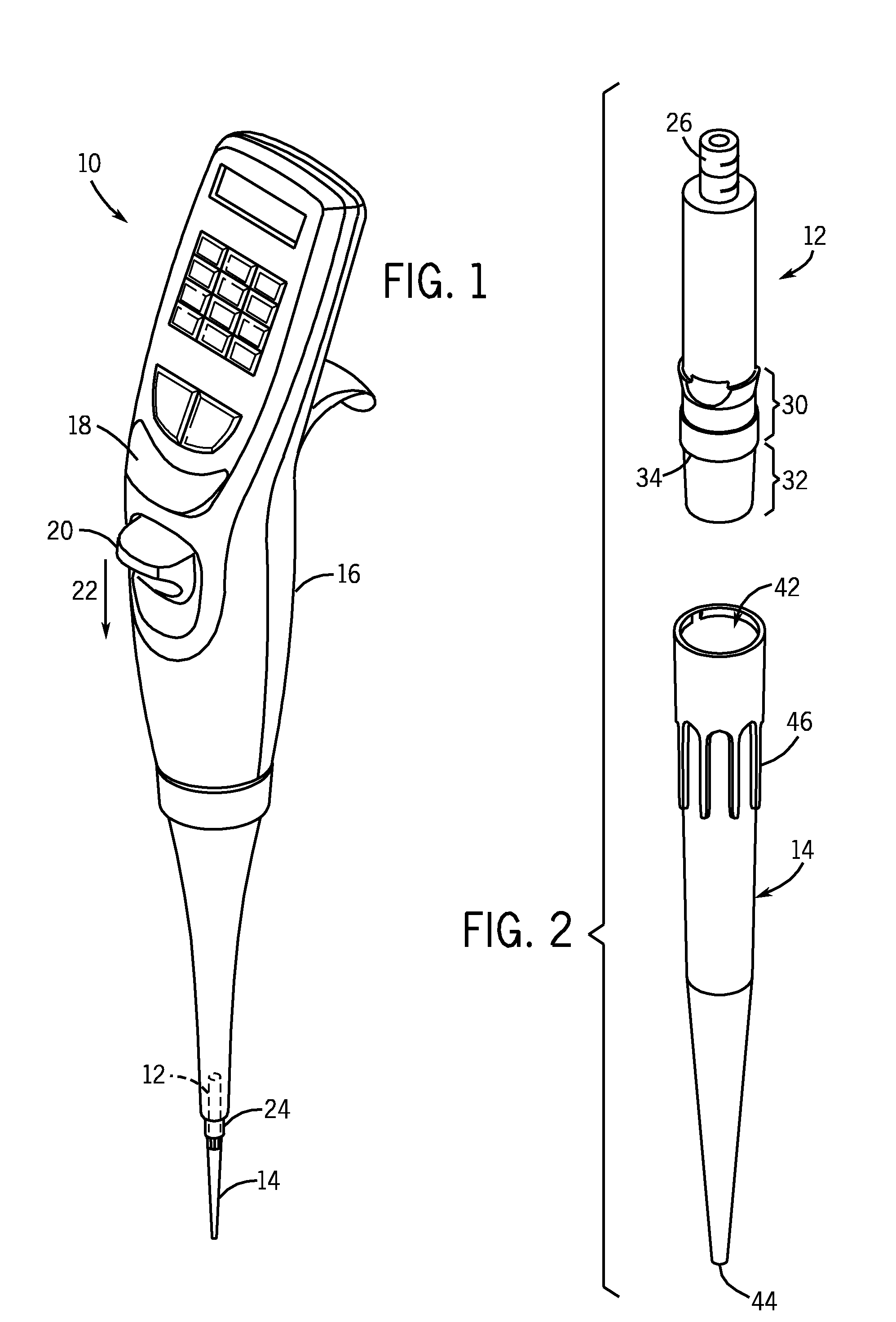
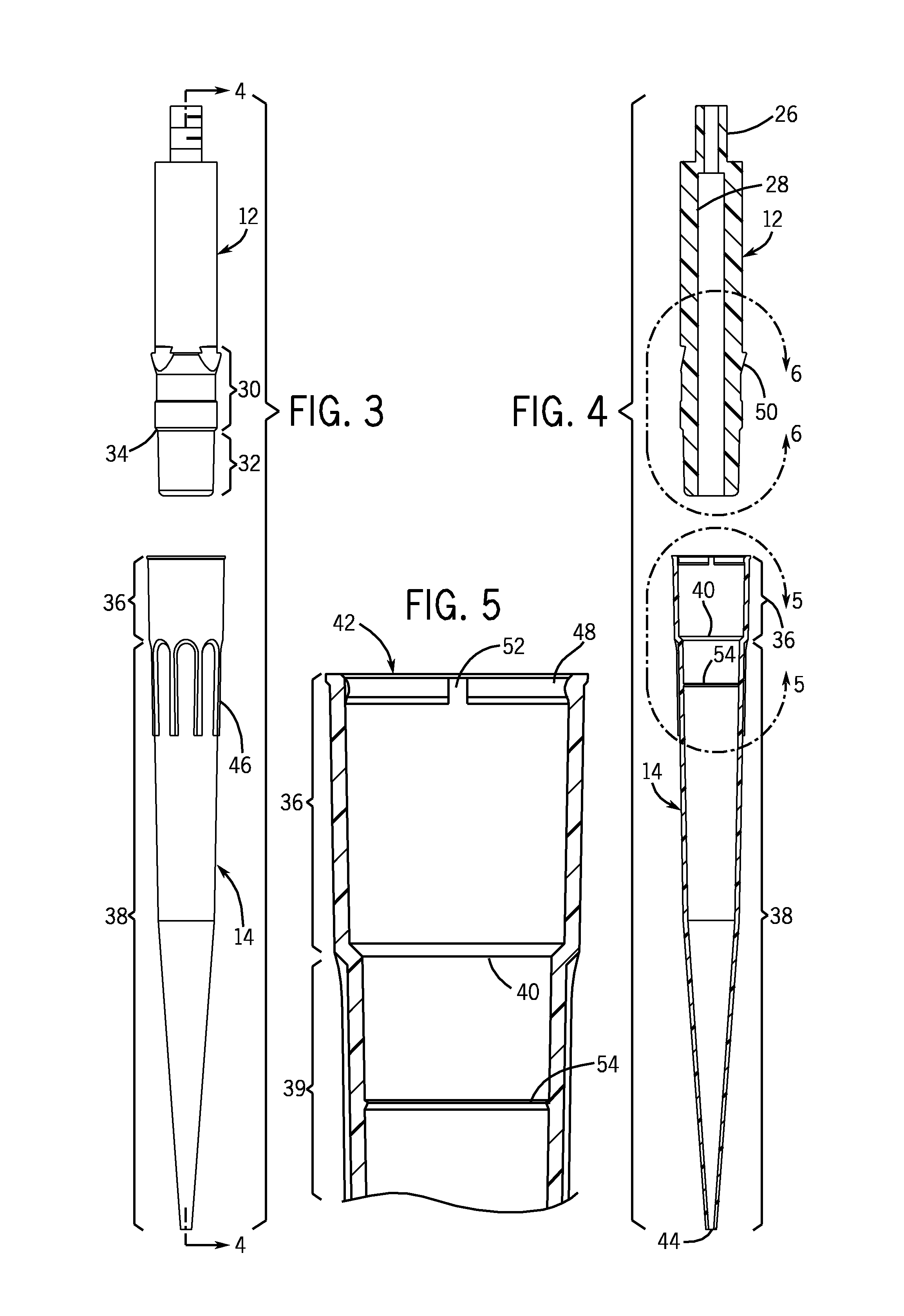
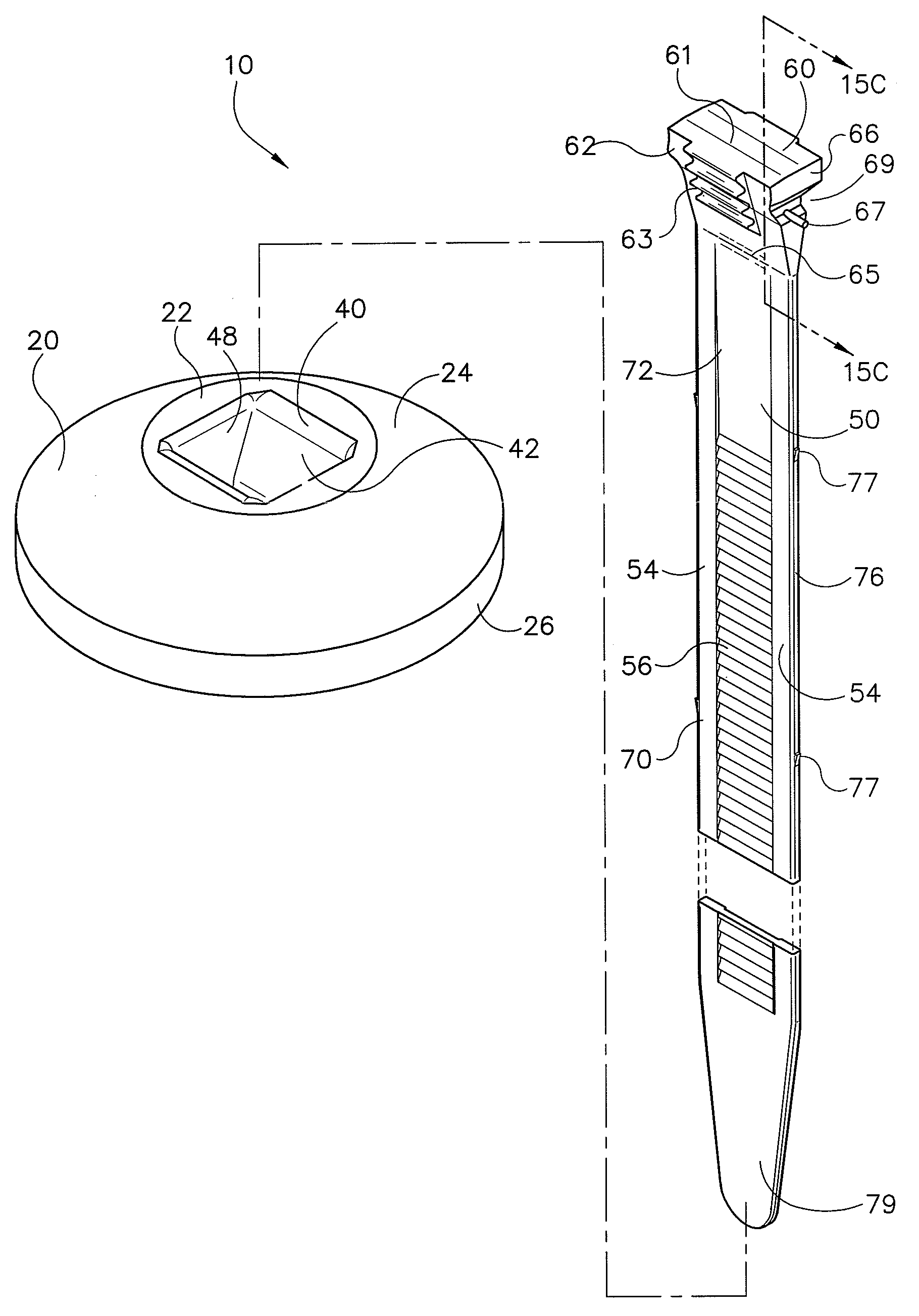
Locking pipette tip and mounting shaft
ActiveUS7662343B2Maintain roundnessFacilitate reliable engagementWithdrawing sample devicesBurettes/pipettesPipetteEngineering
The invention relates to a pipette tip mounting shaft configuration and a disposable pipette tip having a matching configuration. The mounting shaft includes a locking section located above a lower sealing section. The locking section has outwardly extending locking lobes circumferentially spaced around the mounting shaft and located above a stop member that separates the lower sealing section from the upper locking section. When the mounting shaft is fully inserted into the collar of the mating disposable pipette tip, the tip locks onto the mounting shaft. The bore of the pipette tip includes a circumferential shelf separating its upper collar from the tip sealing area which is located below the circumferential shelf. The locking lobes gently flexes and distorts the pipette tip collar out of round as the mounting shaft is inserted in the pipette tip, rather than stretching the tip collar. The circumferential shelf on the pipette tip between the tip collar and the barrel isolates the sealing area at the upper end of the barrel from distortion, thus facilitating reliable sealing engagement.
Owner:INTEGRA BIOSCI CORP
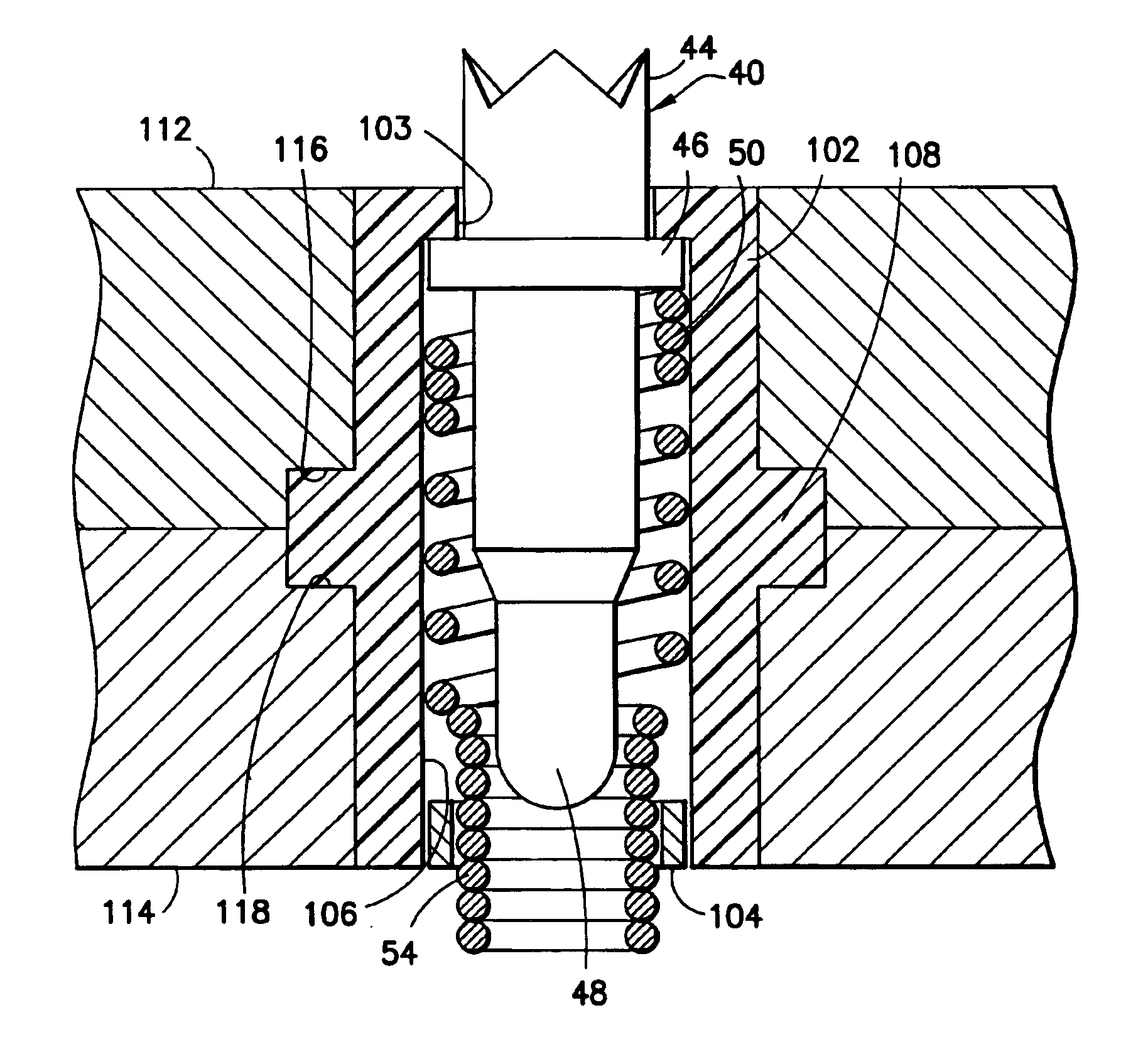
Shielded integrated circuit probe
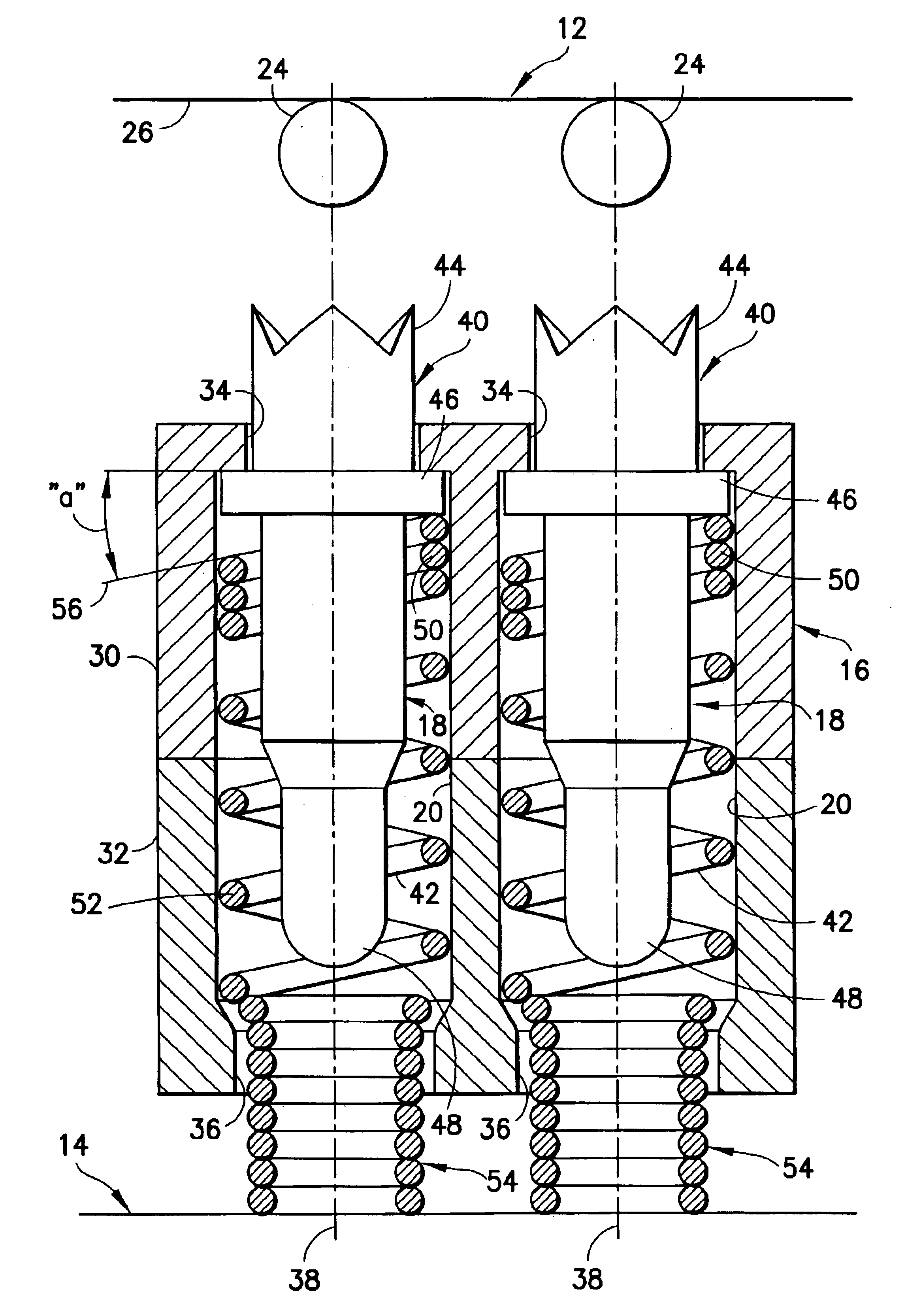
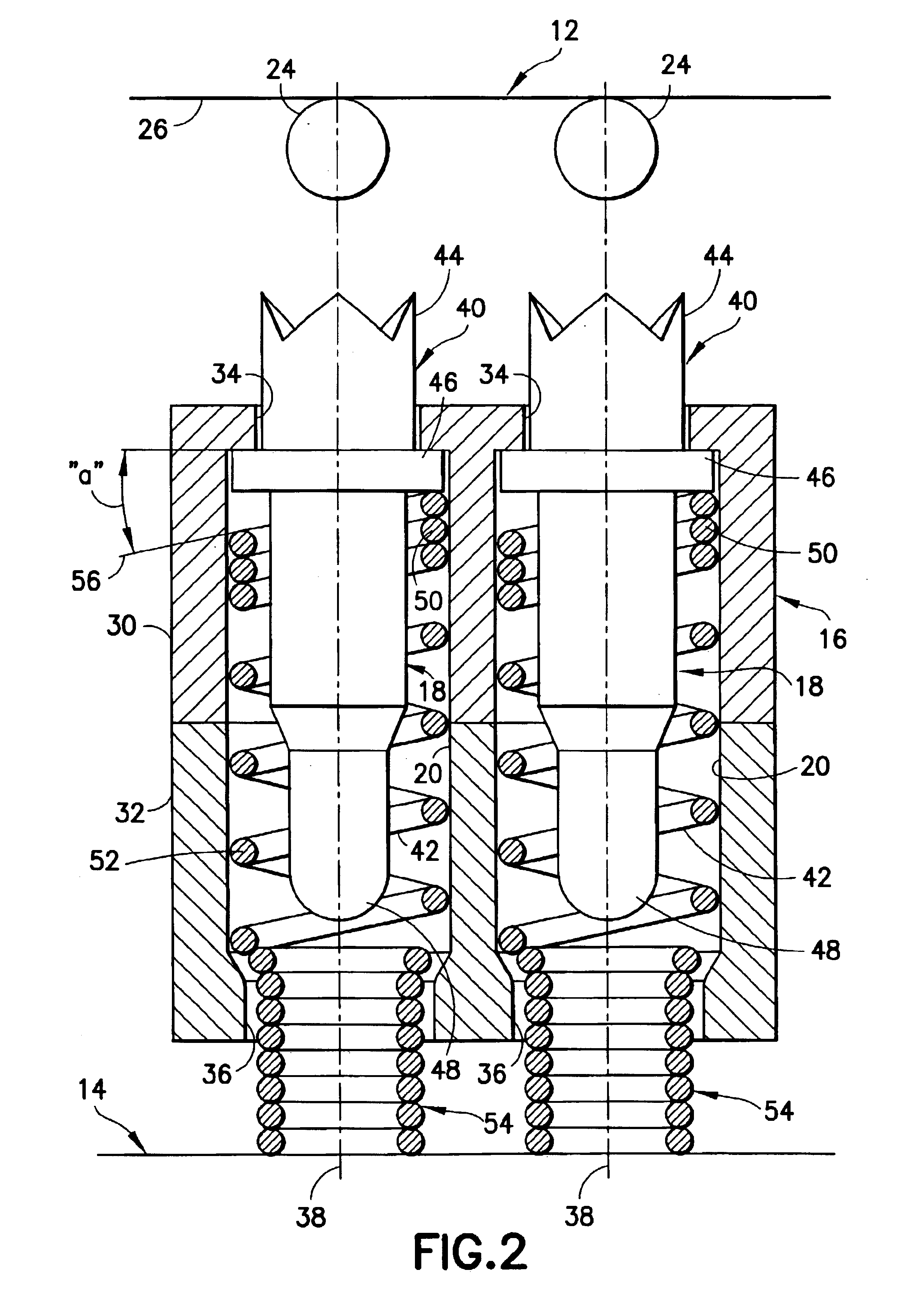
InactiveUS6937045B2Reliable electrical connectionLow insertion force parameterCoupling contact membersMeasurement instrument housingElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A test probe consists of an elongated screw machine contact biased by a helical spring and mounted in a through hole of a non-conductive substrate. One end of the contact includes a crown for engaging a solder ball lead of an IC package, and the contact includes an intermediate collar which maintains the contact within the through hole. The helical spring is disposed about the contact, with one end thereof engaging the lower end of the collar. The other end of the helical spring has contiguous coils and is of a reduced diameter so as to extend beyond the lower end of the non-conductive substrate to make electrical contact with a printed circuit board. When the test probe is compressed between the IC package and the printed circuit board, the inherent twisting of the helical spring causes the contact to tilt and make electrical contact with the contiguous coils, thereby establishing a direct electrical path between the IC package and the printed circuit board, with minimum resistance and minimum inductance. In an alternate embodiment, each probe is disposed within a dielectric housing which, in turn, is disposed in a through hole in a conductive substrate to effectively shield the probe from electrical interference.
Owner:ARIES ELECTRONICS
High speed, high density electrical connector
ActiveUS8814595B2Smooth connectionEnhanced couplingElectric discharge tubesCoupling contact membersElectricityPath length
A broadside coupled connector assembly has two sets of conductors, each separate planes. By providing the same path lengths, there is no skew between the conductors of the differential pair and the impedance of those conductors is identical. The conductor sets are formed by embedding the first set of conductors in an insulated housing having a top surface with channels. The second set of conductors is placed within the channels so that no air gaps form between the two sets of conductors. A second insulated housing is filled over the second set of conductors and into the channels to form a completed wafer. The ends of the first and second sets of conductors and the blades are jogged in both an x- and y-coordinate to reduce crosstalk and improve electrical performance.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
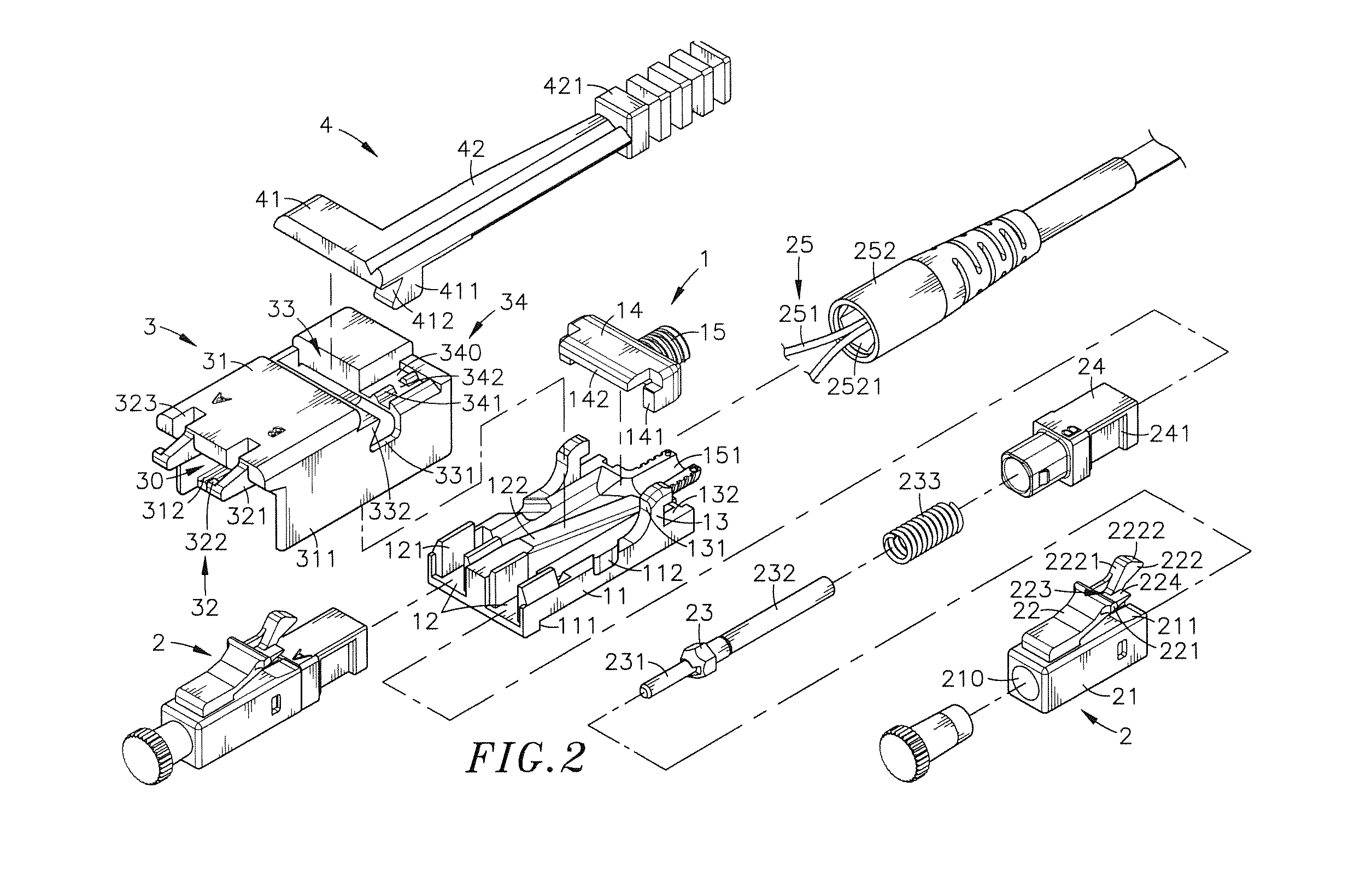
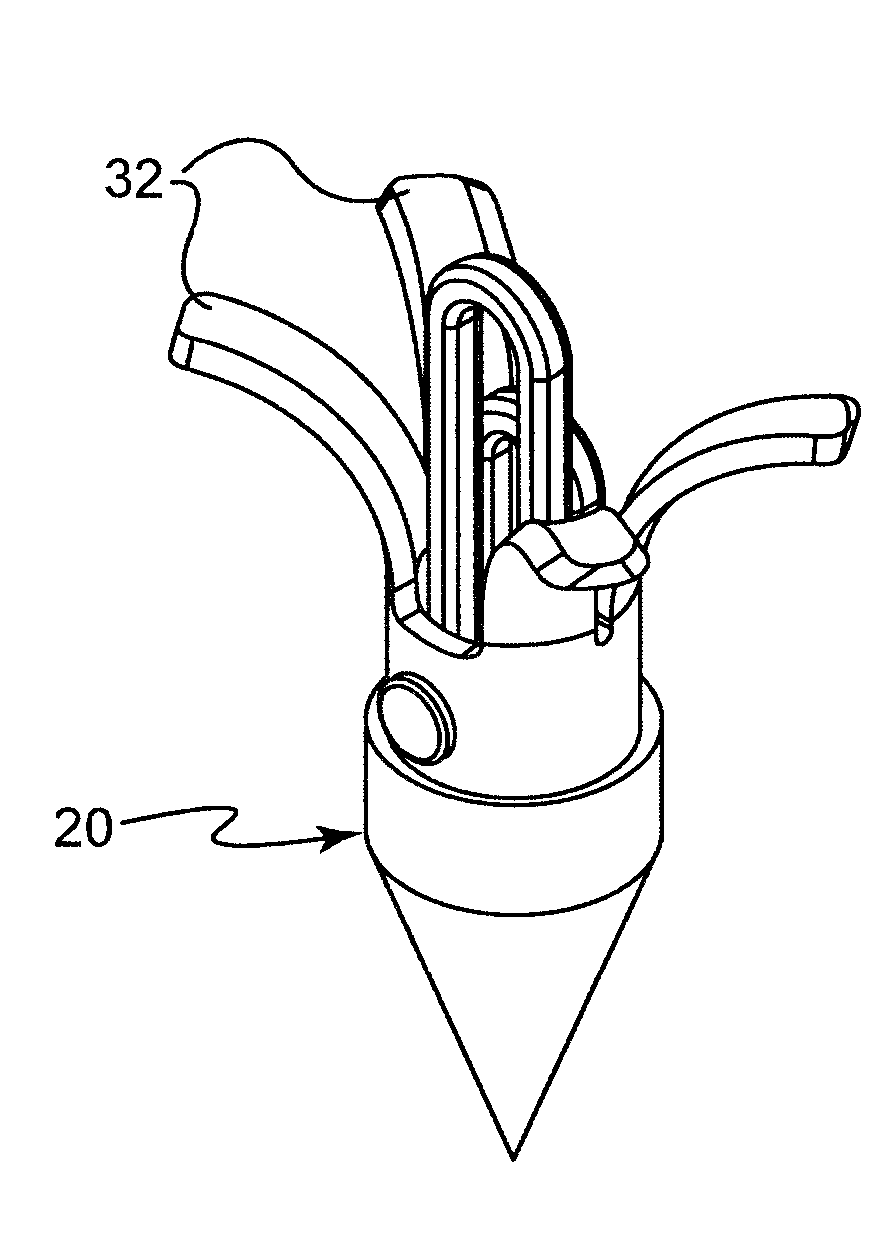
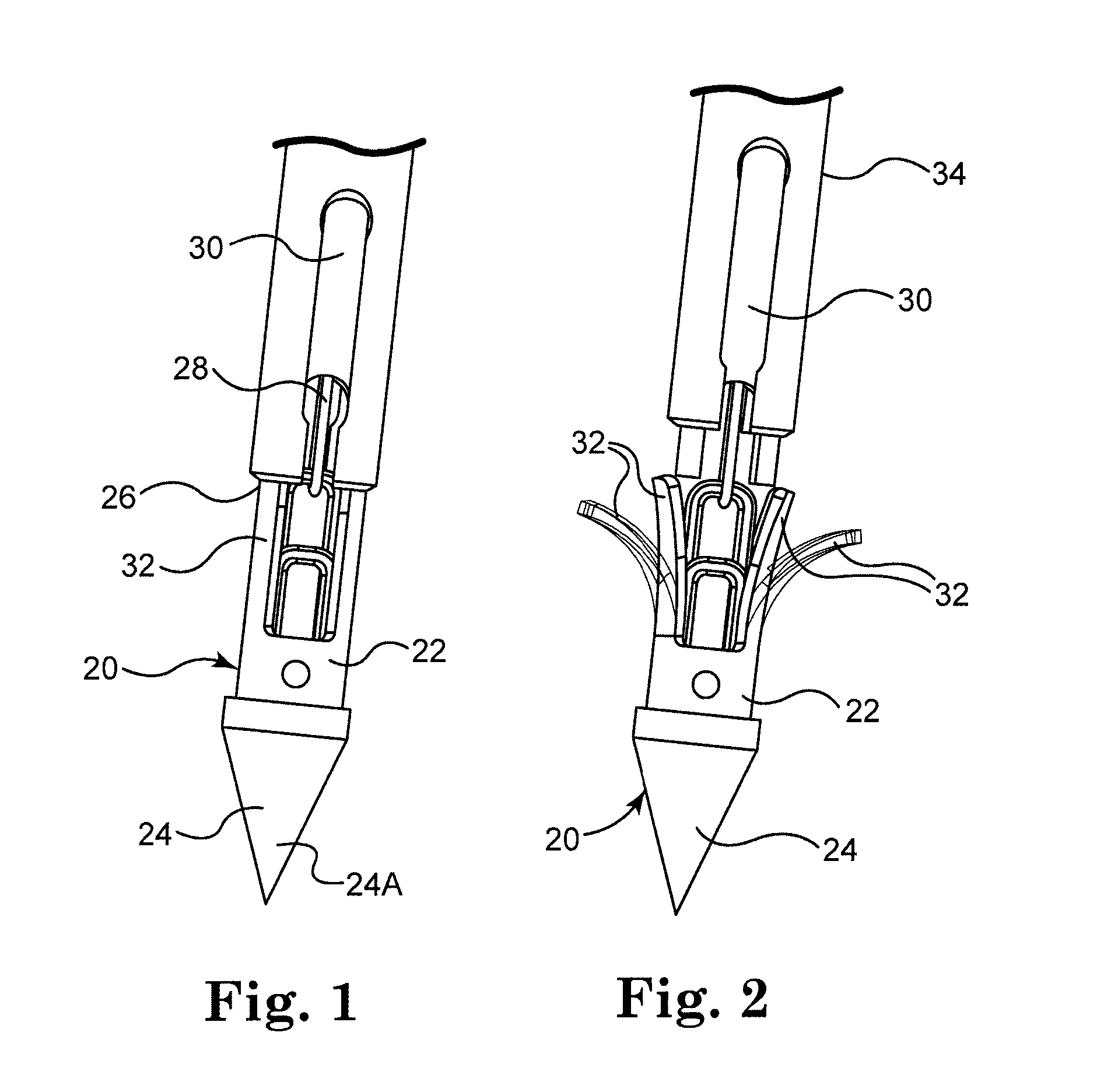
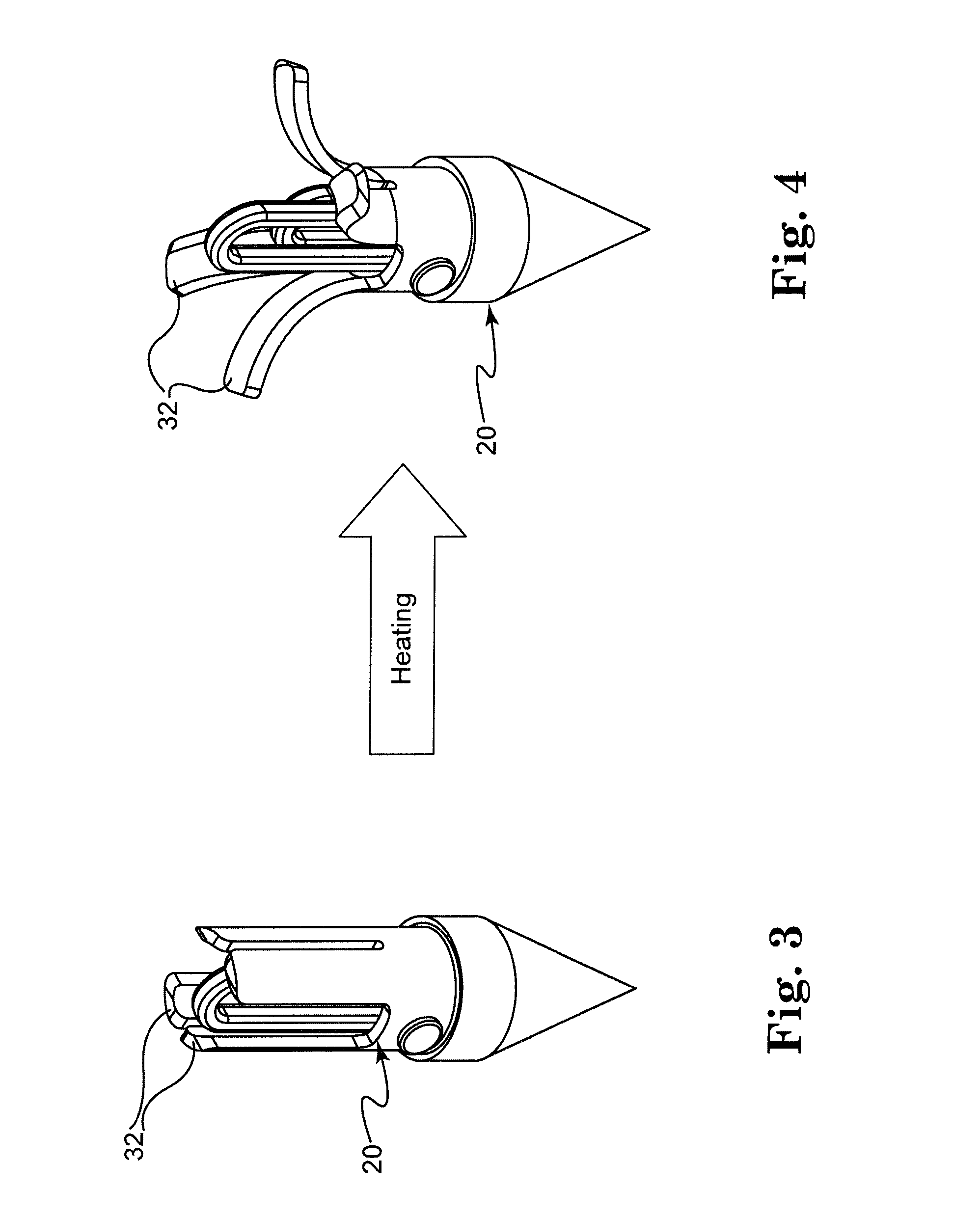
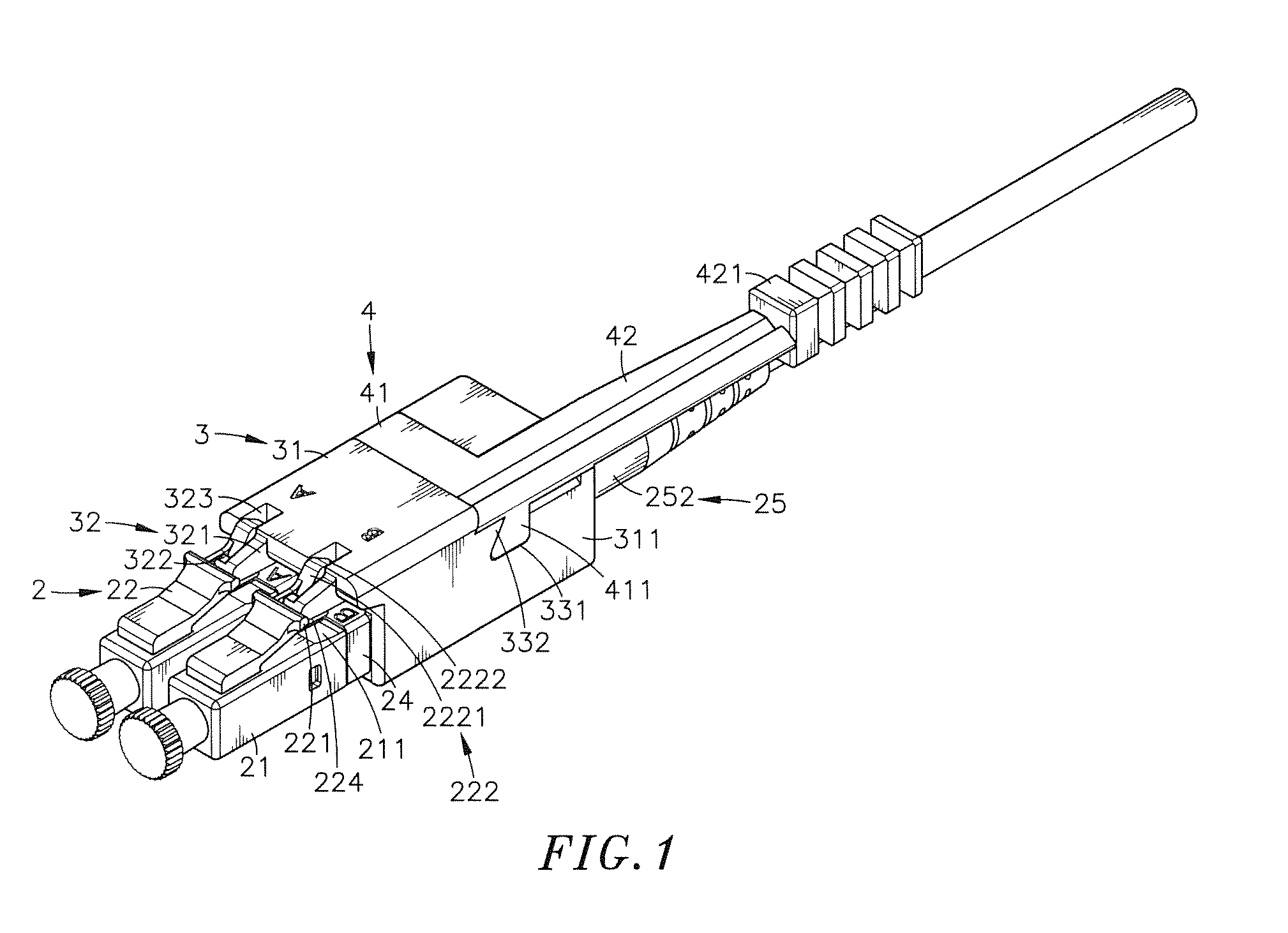
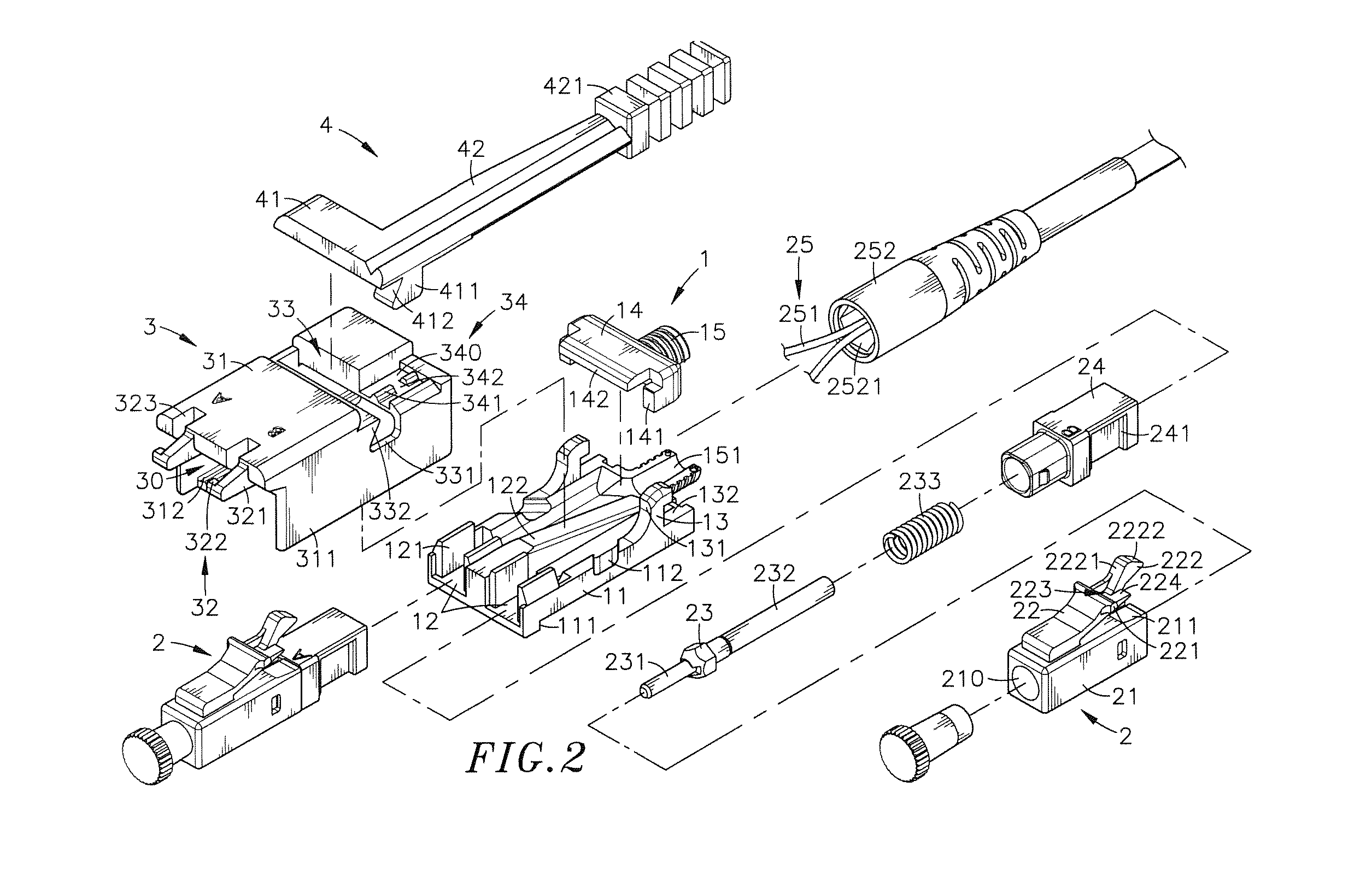
Optical fiber connector assembly
ActiveUS20150177463A1Conveniently mountedLower insertion forceCoupling light guidesEngineeringOptical fiber connector
An optical fiber connector assembly includes a receptacle, two connectors accommodated in respective accommodation grooves in the receptacle and having a respective clip located at a top side thereof for engagement with a respective retaining groove in a mating optical fiber adapter, an optical fiber cable having two optical fibers respectively mounted in the connectors, and a sliding cover covered on the receptacle and movable relative to the receptacle to elastically deform the clips and to further disengage the clips from the respective retaining grooves of the optical fiber adapter for allowing removal of the optical fiber connector assembly out of the optical fiber adapter with less effort.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Fluid connector latches with profile lead-ins
ActiveUS20110204621A1Little strengthReduce insertion force requirementPipe elementsCouplingsEngineeringMetallic Lead
A female receiving connector for connecting sections of tubing is provided. The female receiving connector includes a housing having a top housing portion and a bottom housing portion coupled to the top housing portion. The female receiving connector also includes a button moveably coupled within the housing. A locking plate is coupled to the button and configured to move with the button. The locking plate has a profile lead-in having an interfacing surface located at a proximal side of the profile lead-in for interfacing a male connector. The interfacing surface extends along at least a portion of at least three sides of an aperture of the locking plate and is tapered along one or more of the at least three sides. Additionally, the profile lead-in includes a locking surface located at a distal side of the profile lead-in for securing the male connector within the housing of the female receiving connector. A substantially flat surface is located between the interfacing surface and the locking surface.
Owner:NORDSON CORP
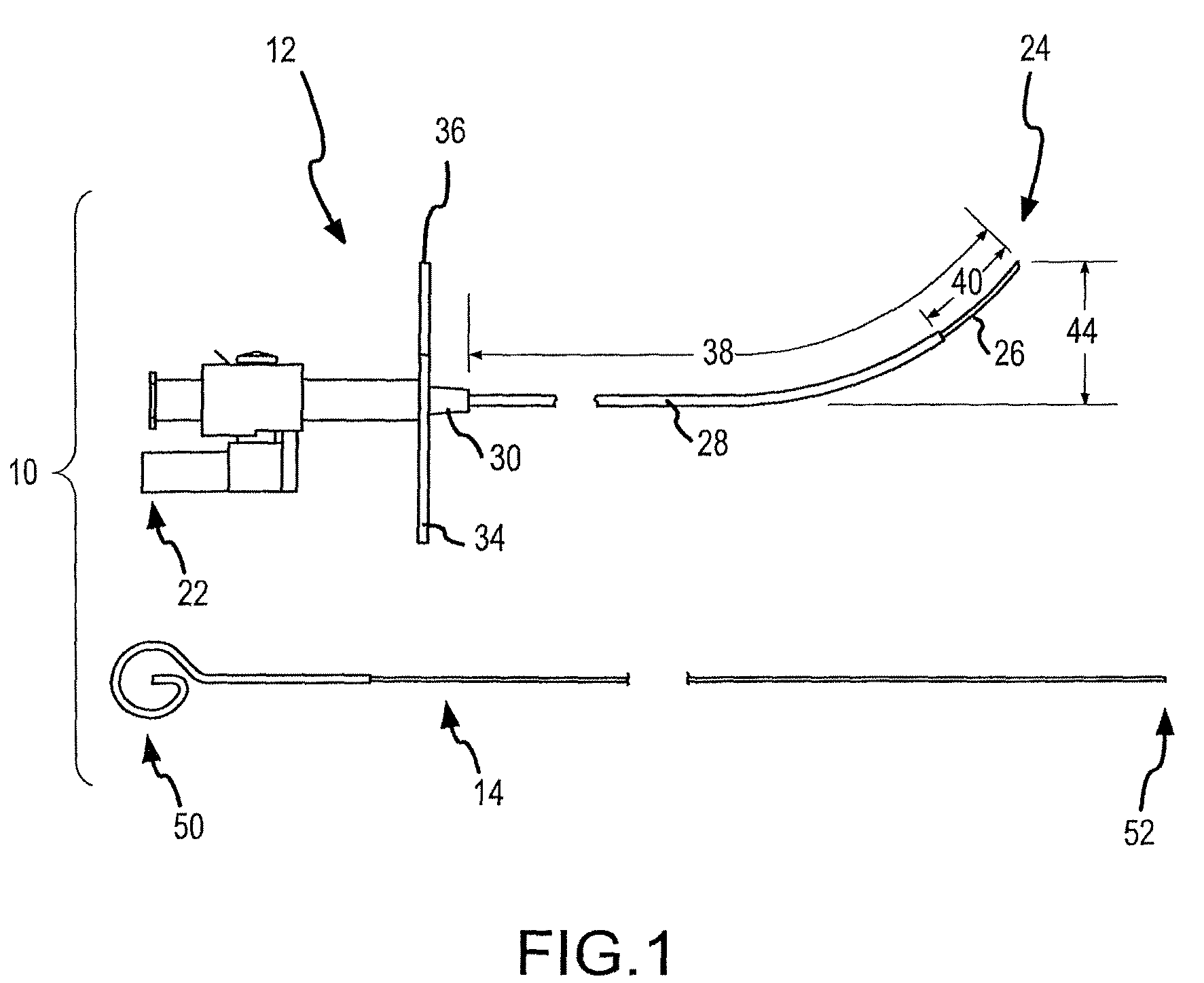
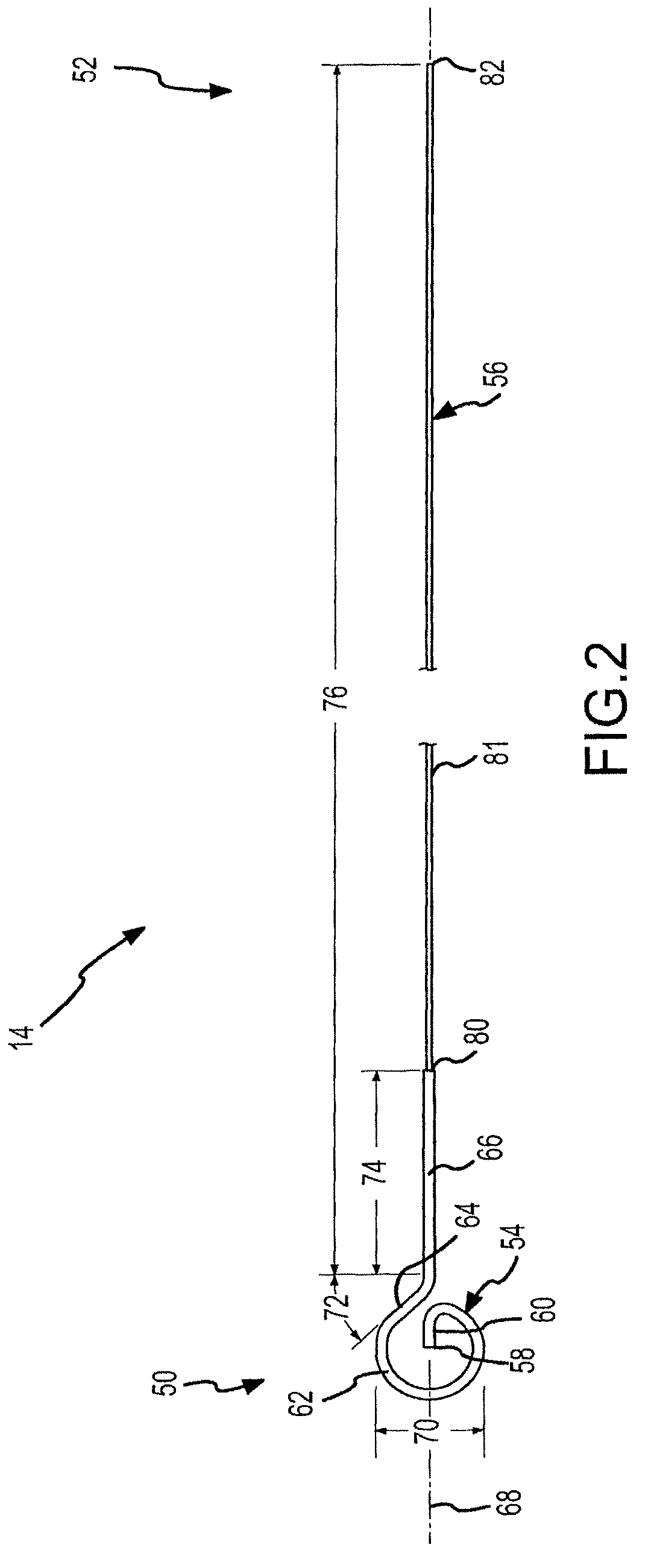
Transseptal puncture needle and needle assemblies
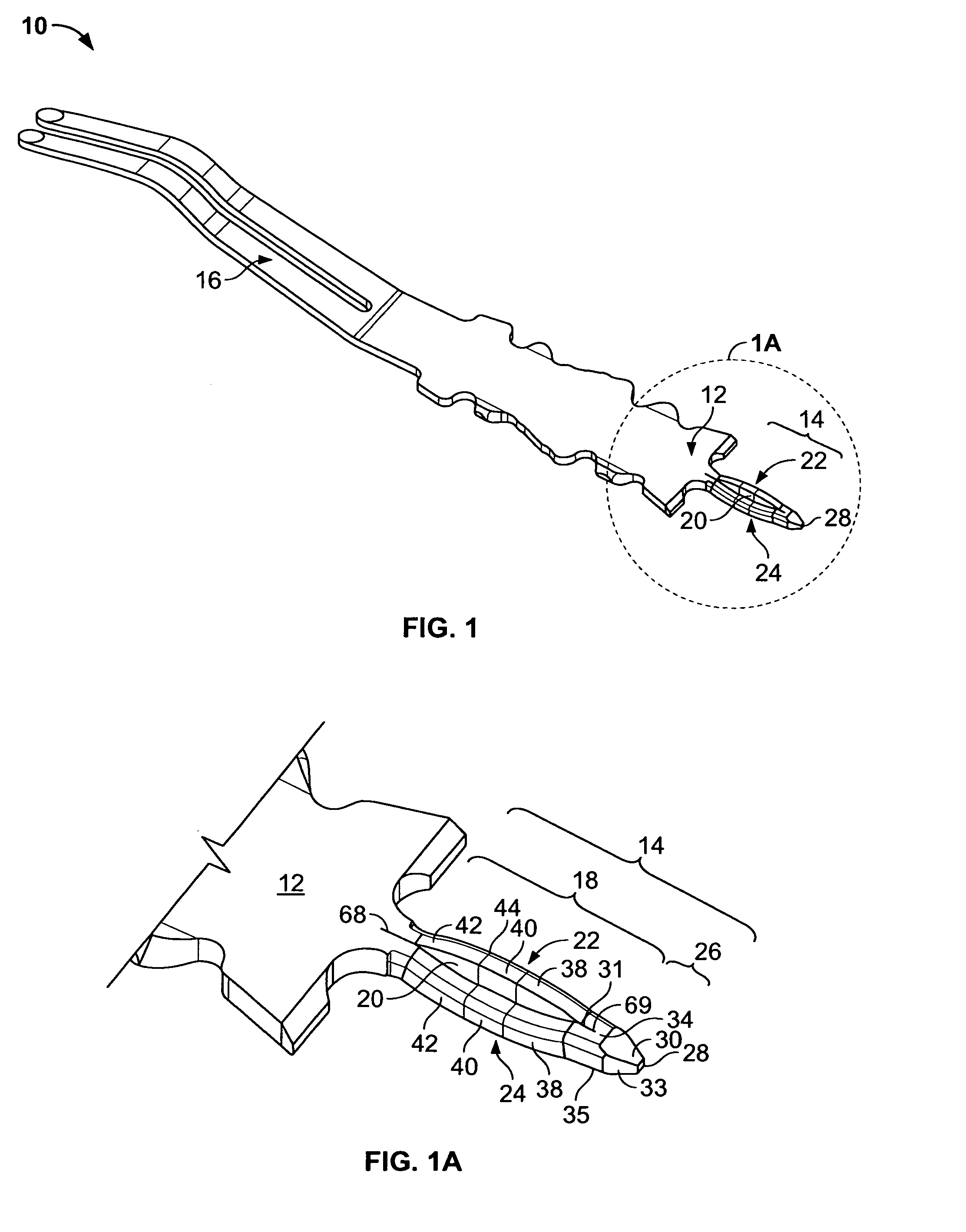
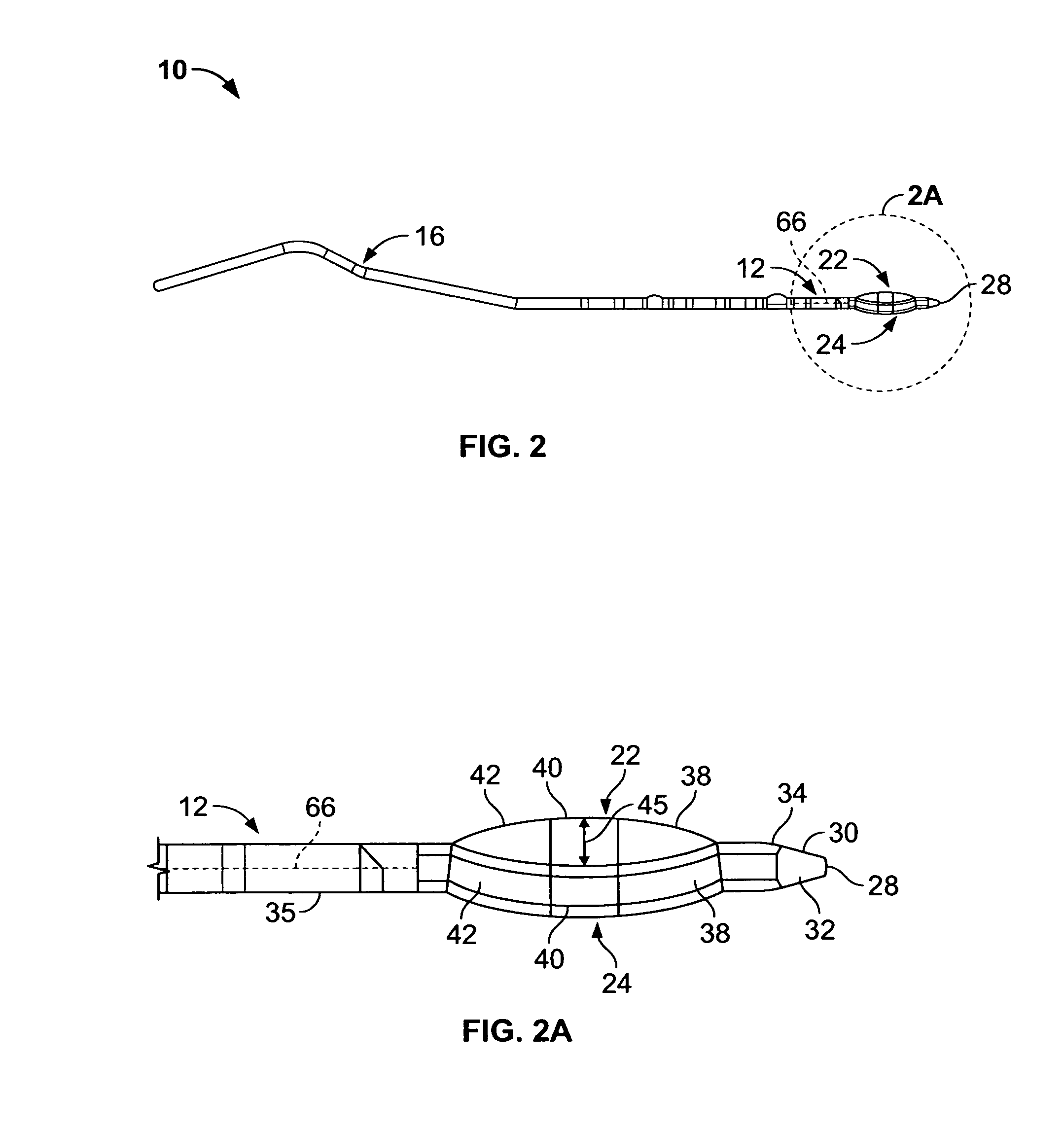
ActiveUS8114110B2Risk minimizationLower insertion forceGuide needlesDiagnosticsMedicineDistal segment
A transseptal needle includes an elongate needle body having a distal end and a proximal end and a cannular needle tip located proximate the distal end of the needle body. The needle tip has a distal segment, a proximal segment, and a longitudinal axis. An inner surface of the needle tip defines a passageway spanning at least a portion of the needle tip, and an outer surface of the needle tip defines a wall with the inner surface. The distal segment of the needle tip also includes a wedge surface and a dome-shaped region. The wedge surface forms a wedge angle of other than 90 degrees relative to the longitudinal axis. The dome-shaped region, which intersects the wedge surface, includes at least two bevels that intersect the wedge surface and that intersect each other at one or more points on the needle tip.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
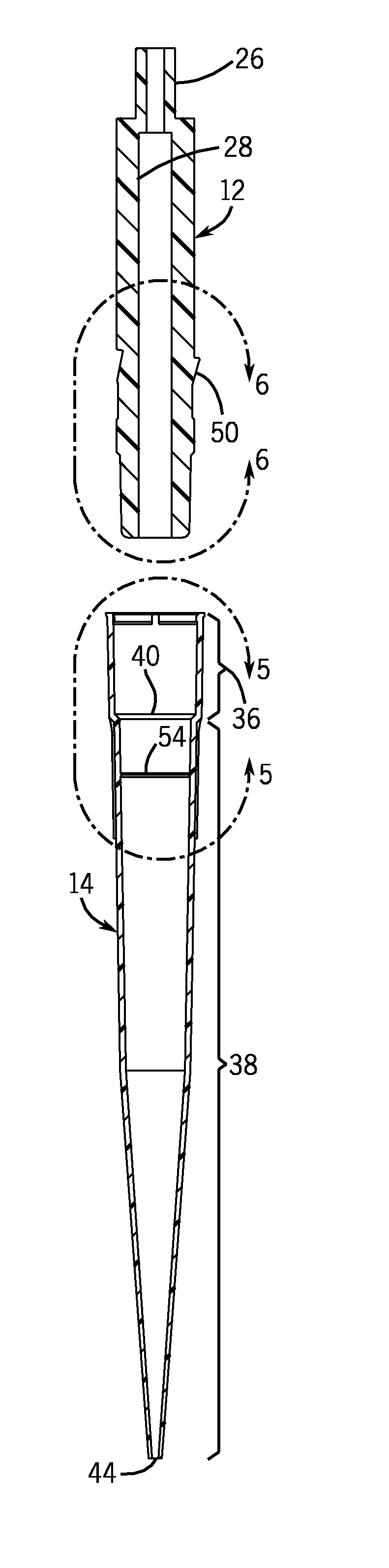
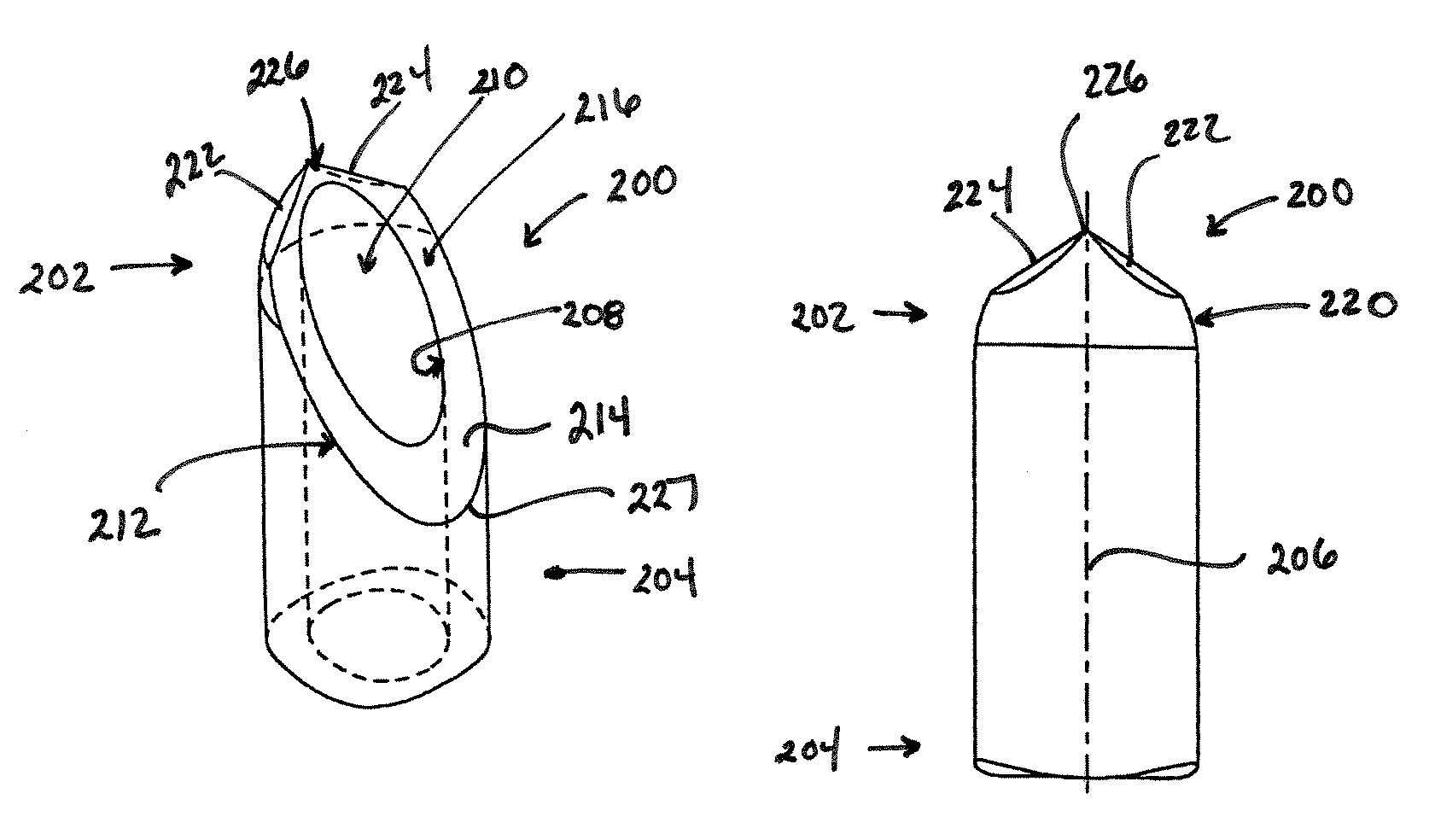
Disposable Pipette Tip
ActiveUS20100034706A1Maintain roundnessFacilitate reliable engagementAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionPipetteHand held
In one aspect, the invention relates to a pipette tip mounting shaft configuration and a disposable pipette tip having a matching configuration. The mounting shaft includes a locking section located above a lower sealing section. The locking section has outwardly extending locking lobes located above a stop member and a lower sealing section located below the stop member. In certain embodiments, the diameter of the mounting shaft below the stop member is reduced in order to lessen insertion and ejection forces, which is particularly helpful for hand-held multi-channel pipettors. In these embodiments, the lower sealing section contains either a frustoconical sealing section, or an annular groove and a sealing ring, such as a flouroelastomeric O-ring seal. When the mounting shaft is fully inserted into the collar of the mating disposable pipette tip, the tip locks onto the mounting shaft. The bore of the pipette tip includes a circumferential shelf or shoulder separating its upper collar from the tip sealing area which is located below the circumferential shelf. The tip collar preferably includes a locking ring located at or near the upper opening for the mounting shaft. The dimensions of the collar, and in particular the distance between its circumferential shelf and the locking ring, are selected to match the dimensions of the mounting shaft between the stop member and the upper end of the locking lobes, thus locking the pipette tip in a secure, reliable position and orientation while using ergonomic insertion and ejection forces. The locking lobes preferably include a ramp portion that gently flexes and distorts the pipette tip collar out of round as the mounting shaft is inserted in the pipette tip, rather than stretching the tip collar. The circumferential shelf on the pipette tip between the tip collar and the barrel isolates the sealing area at the upper end of the barrel from distortion, thus facilitating reliable sealing engagement between the lower sealing section of the mounting shaft and the sealing ring in the upper end of the barrel of the pipette tip.
Owner:INTEGRA BIOSCI CORP
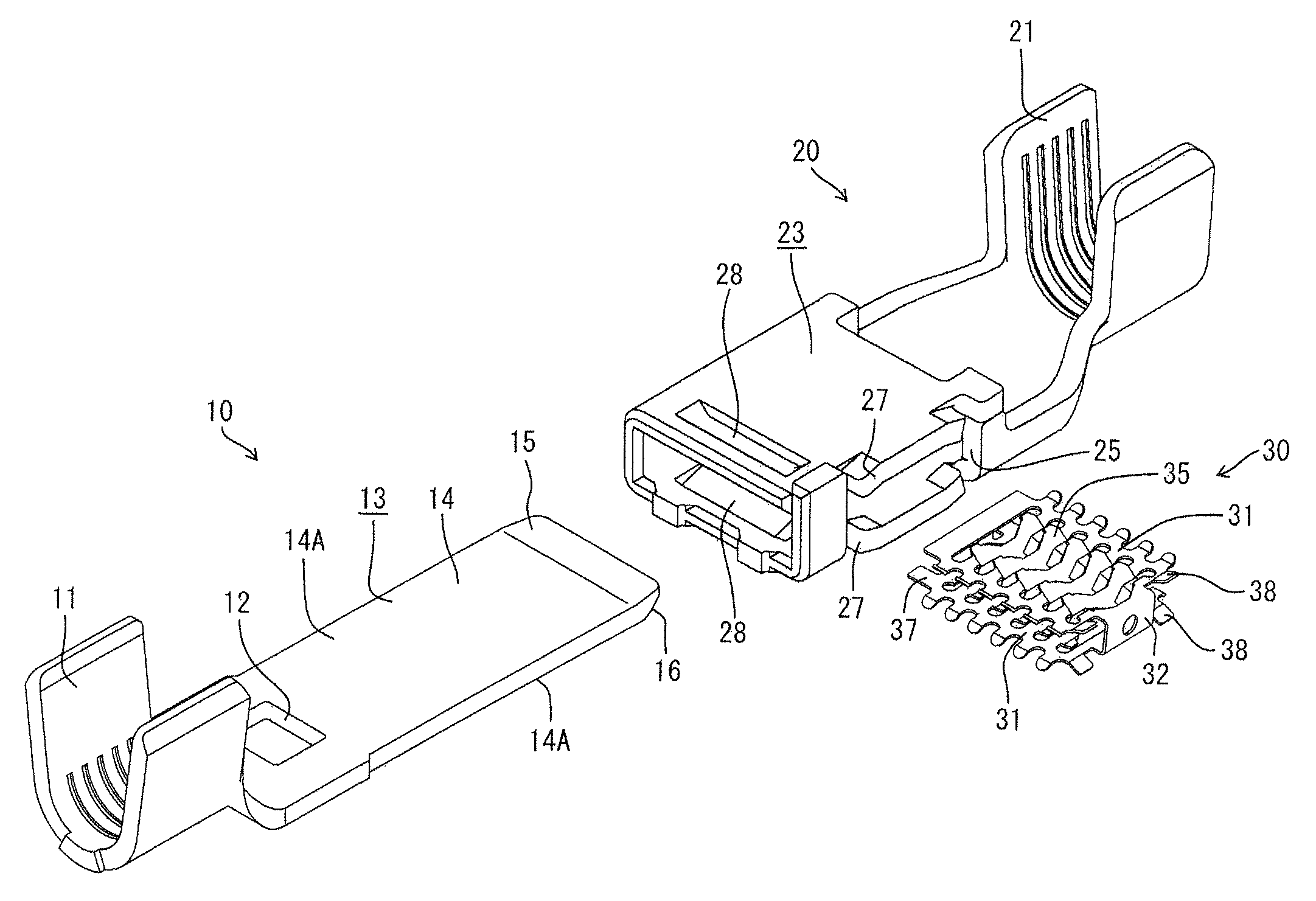
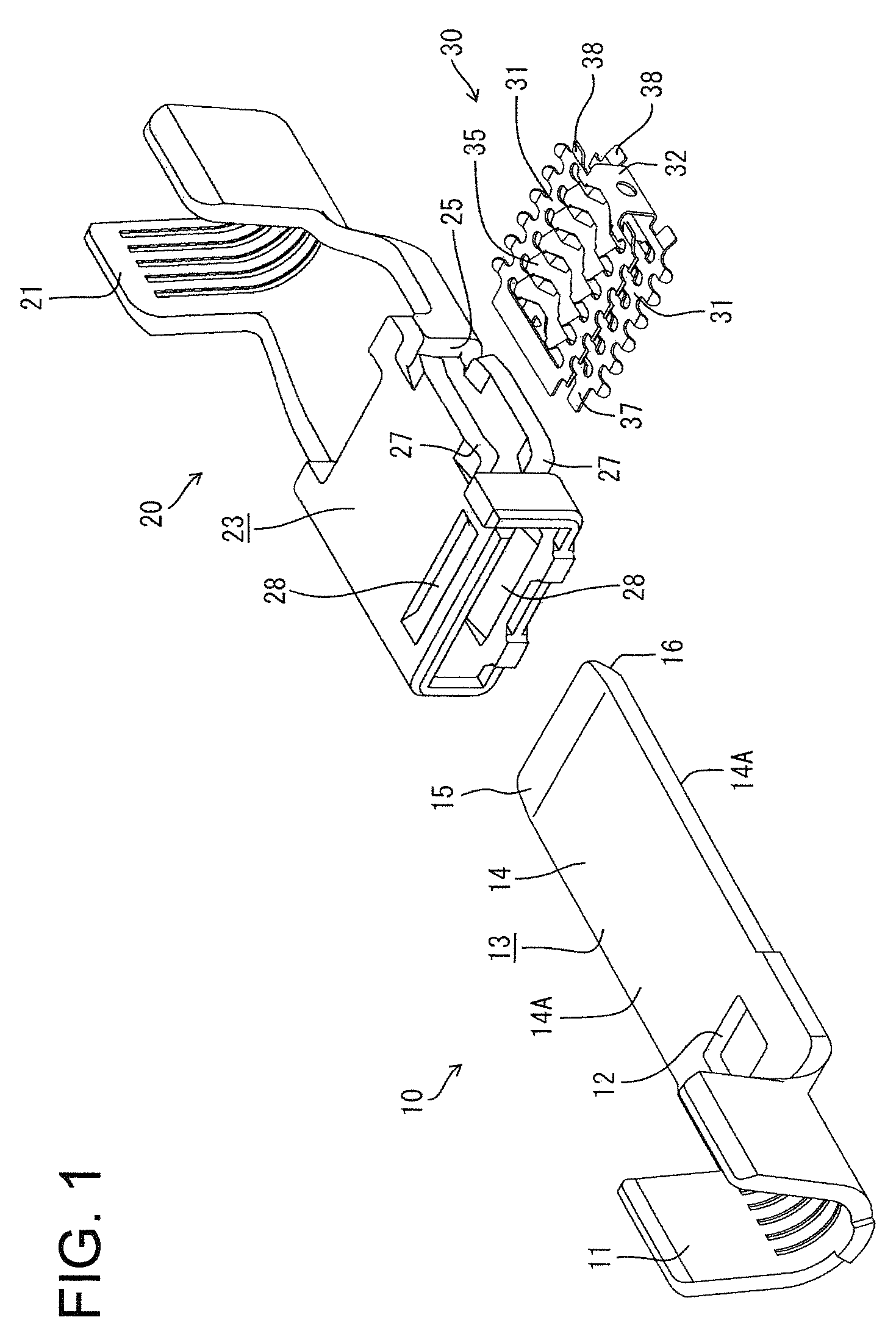
Terminal fitting connecting structure
InactiveUS8128441B2Lower insertion forcePreventing shaking and twisting movementElectrically conductive connectionsElectric discharge tubesEngineeringLouver
A connecting structure has a male terminal (10) including a tab (13) and a female terminal (20) including a rectangular connecting tube (23) that receives the tab (13). A louver spring (30) is housed in the connecting tube (23) and has two spaced apart contact piece rows (31) each including juxtaposed resilient contact pieces (35) with contact portions (36) facing each other. The tab (13) resiliently contacts the contact portions (36) by being inserted between the contact portions (36) while resiliently displacing the contact piece rows (31) at the opposite sides. Inclined surfaces (15, 16) are formed adjacent a tip of the tab (13) of the male terminal (10) to gradually thin the tab (13) toward the tip. The inclined surfaces (15, 16) are formed so that the positions of base end edges (15A, 16A) connected to flat surfaces 14A differ in forward and backward directions.
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
Conductive Material For Connecting Part And Method For Manufacturing The Conductive Material
ActiveUS20080090096A1Excellent propertyLow coefficient of frictionHot-dipping/immersion processesElectrically conductive connectionsConductive materialsAlloy
There is provided a conductive material comprising a base material made up of a Cu strip, a Cu—Sn alloy covering layer formed over a surface of the base material, containing Cu in a range of 20 to 70 at.%, and having an average thickness in a range of 0.1 to 3.0 μm, and an Sn covering layer formed over the Cu—Sn alloy covering layer having an average thickness in a range of 0.2 to 5.0 μm, disposed in that order, such that portions of the Cu—Sn alloy covering layer are exposed the surface of the Sn covering layer, and a ratio of an exposed area of the Cu—Sn alloy covering layer to the surface of the Sn covering layer is in a range of 3 to 75%. The surface of the conductive material is subjected to a reflow process and preferably, an arithmetic mean roughness Ra of the surface of the material in at least one direction, is not less than 0.15 μm while the arithmetic mean roughness Ra thereof, in all directions, is not more than 3.0 μm and the average thickness of the Cu—Sn alloy covering layer is preferably not less than 0.2 μm. The conductive material is fabricated by a method whereby the surface of the base material is subjected to roughening treatment, an Ni plating layer, a Cu plating layer and an Sn plating layer are formed, as necessary, over the surface of the base material, and subsequently, a reflow process is applied.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Electrical contact having multiple cantilevered beams
ActiveUS8821170B1Small insertion forceHigh currentElectrically conductive connectionsCoupling device detailsCantilevered beamEngineering
An electrical contact includes a first set of spaced apart cantilevered beams connected to a first rail, and a second set of cantilevered beams connected to a second rail. The first set of cantilevered beams project toward the second rail, and the second set of cantilevered beams project toward the first rail, wherein the first and second sets of cantilevered beams reside in alternating relationship. Each cantilevered beam is bowed and is outwardly tapered from its connected proximal to its unconnected distal end.
Owner:BELLWETHER ELECTRONIC CORP
Button head tie
ActiveUS20100306967A1Lower insertion forceFeature is removedSnap fastenersPipe supportsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A button head tie has a button head and a tie strap. The button head is a generally flat member having an aperture for receiving the tie strap. The aperture includes lead-in ramps to facilitate tie strap insertion and is configured to prevent angled tie strap insertion. The tie strap is a flat elongate member having a wedge that is captured within the aperture. The remainder of the strap passes through the aperture. The wedge and strap have teeth and serrations on both sides, respectively, the teeth and serrations being engageable. In use, the strap is looped around a bundle and inserted into the aperture to either side of the wedge. Strap insertion force is reduced by standoff tabs which elevate the wedge out of aperture, temporarily, during installation. When loop tension is applied to the bundle, the wedge is pulled into the aperture, compressively locking the strap.
Owner:HELLERMANNTYTON CORP
Integrated circuit test probe
InactiveUS6844749B2Reliable electrical connectionLow insertion force parameterElectric discharge tubesCoupling contact membersCoil springSolder ball
A test probe consists of an elongated screw machine contact biased by a helical spring and mounted in a through hole of a non-conductive substrate. One end of the contact includes a crown for engaging a solder ball lead of an IC package, and the contact includes an intermediate collar which maintains the contact within the through hole. The helical spring is disposed about the contact, with one end thereof engaging the lower end of the collar. The other end of the helical spring has contiguous coils and is of a reduced diameter so as to extend beyond the lower end of the non-conductive substrate to make electrical contact with a printed circuit board. When the test probe is compressed between the IC package and the printed circuit board, the inherent twisting of the helical spring causes the contact to tilt and make electrical contact with the contiguous coils, thereby establishing a direct electrical path between the IC package and the printed circuit board, with minimum resistance and minimum inductance.
Owner:ARIES ELECTRONICS
Bone anchor comprising a shape memory element and utilizing temperature transition to secure the bone anchor in bone
A bone anchor that uses temperature transition of a shape memory material to expand the anchor within a bone. Thermal transformation of the metallic crystal state (and hence the stress / strain properties) of shape memory alloy (e.g., Nitinol, NiTi) expands engagement elements within the bone to fix the bone anchor in place. Various self-locking assemblies for attached suture material to the bone anchor are also disclosed.
Owner:TORNIER INC
Harness clamp tie
InactiveUS20070023586A1Reduced installation tensionIncreased fastener stabilityPipe supportsElectrical apparatusEngineeringFrenulum
A harness clamp tie includes a locking head and a flexible strap extending outwardly from the locking head. The strap is insertable through the locking head to form a loop that can be used at least one item. A pawl in the locking head secures the strap. Nonslip rails formed along the outer edge of the strap face and clamping rails formed on the locking head aid in securing small items. Conic friction points are formed on both sides of the strap surface to provide a mechanical grip for pulling the strap through the locking head. A mounting fastener extends from the locking head in the opposite direction. The fastener secures the tie to a mounting structure such as an aperture in a panel. The fastener includes a pair of flexible winged springs which help to stabilize the tie and hold the tie perpendicular to the panel.
Owner:HELLERMANNTYTON CORP
Optical fiber connector assembly
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
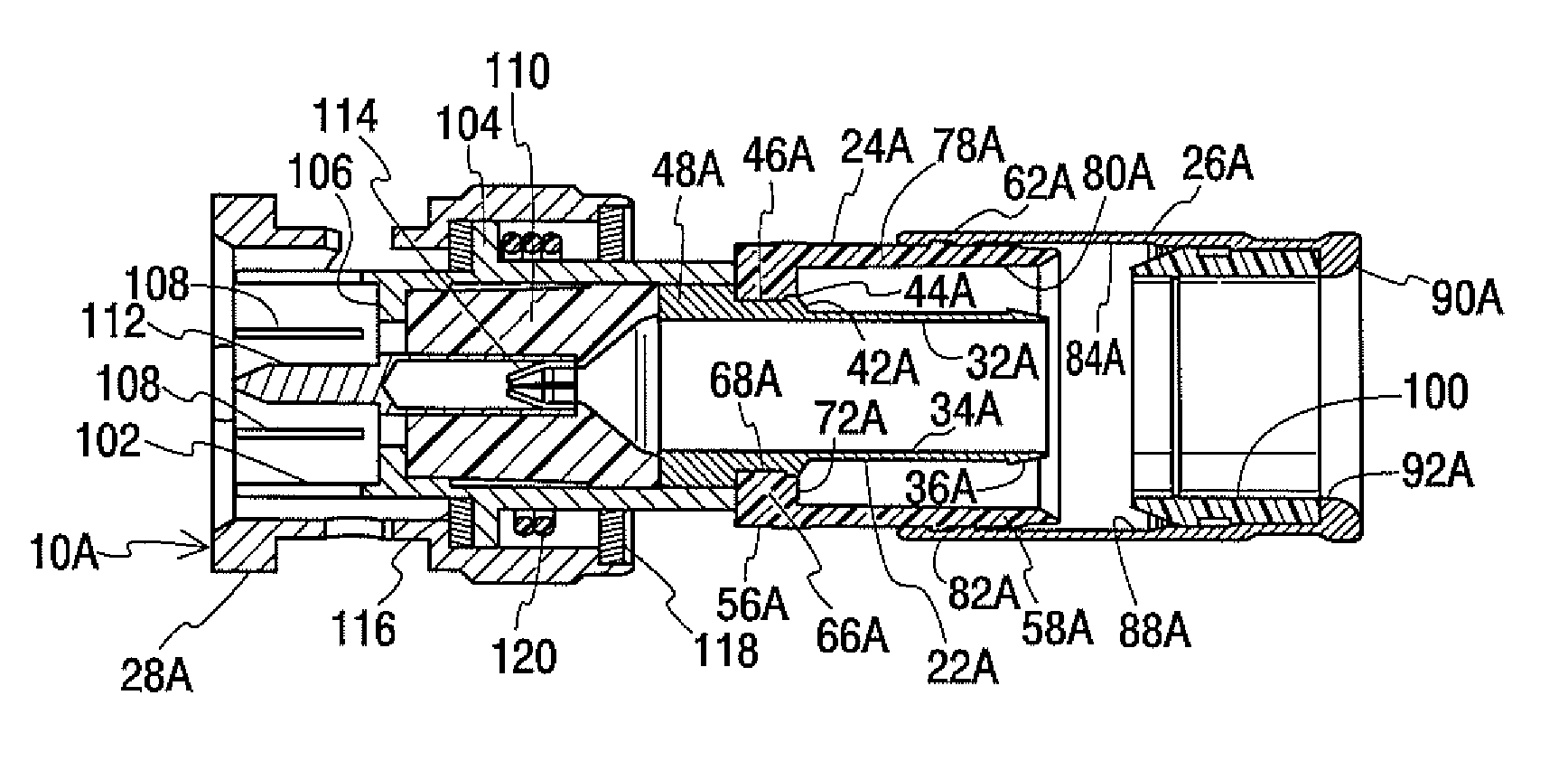
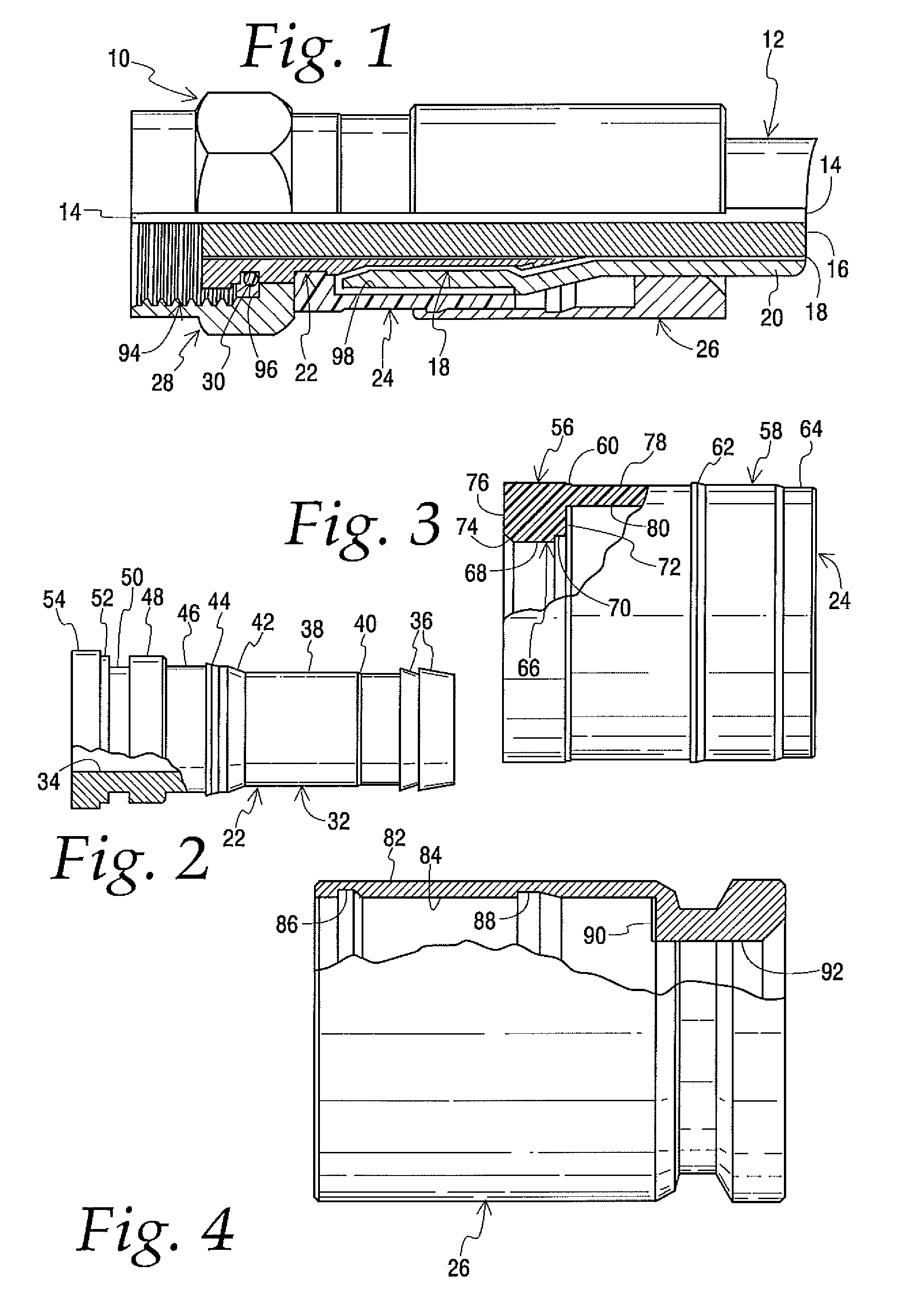
Coaxial cable connector
ActiveUS7914326B2Lower insertion forceSimple processElectrically conductive connectionsVisual observationCoaxial cable
Owner:IDEAL IND INC +1
Transseptal Puncture Needle and Needle Assemblies
ActiveUS20090171276A1Lower insertion forceRisk minimizationGuide needlesDiagnosticsWedge angleProximate
A transseptal needle includes an elongate needle body having a distal end and a proximal end and a cannular needle tip located proximate the distal end of the needle body. The needle tip has a distal segment, a proximal segment, and a longitudinal axis. An inner surface of the needle tip defines a passageway spanning at least a portion of the needle tip, and an outer surface of the needle tip defines a wall with the inner surface. The distal segment of the needle tip also includes a wedge surface and a dome-shaped region. The wedge surface forms a wedge angle of other than 90 degrees relative to the longitudinal axis. The dome-shaped region, which intersects the wedge surface, includes at least two bevels that intersect the wedge surface and that intersect each other at one or more points on the needle tip.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
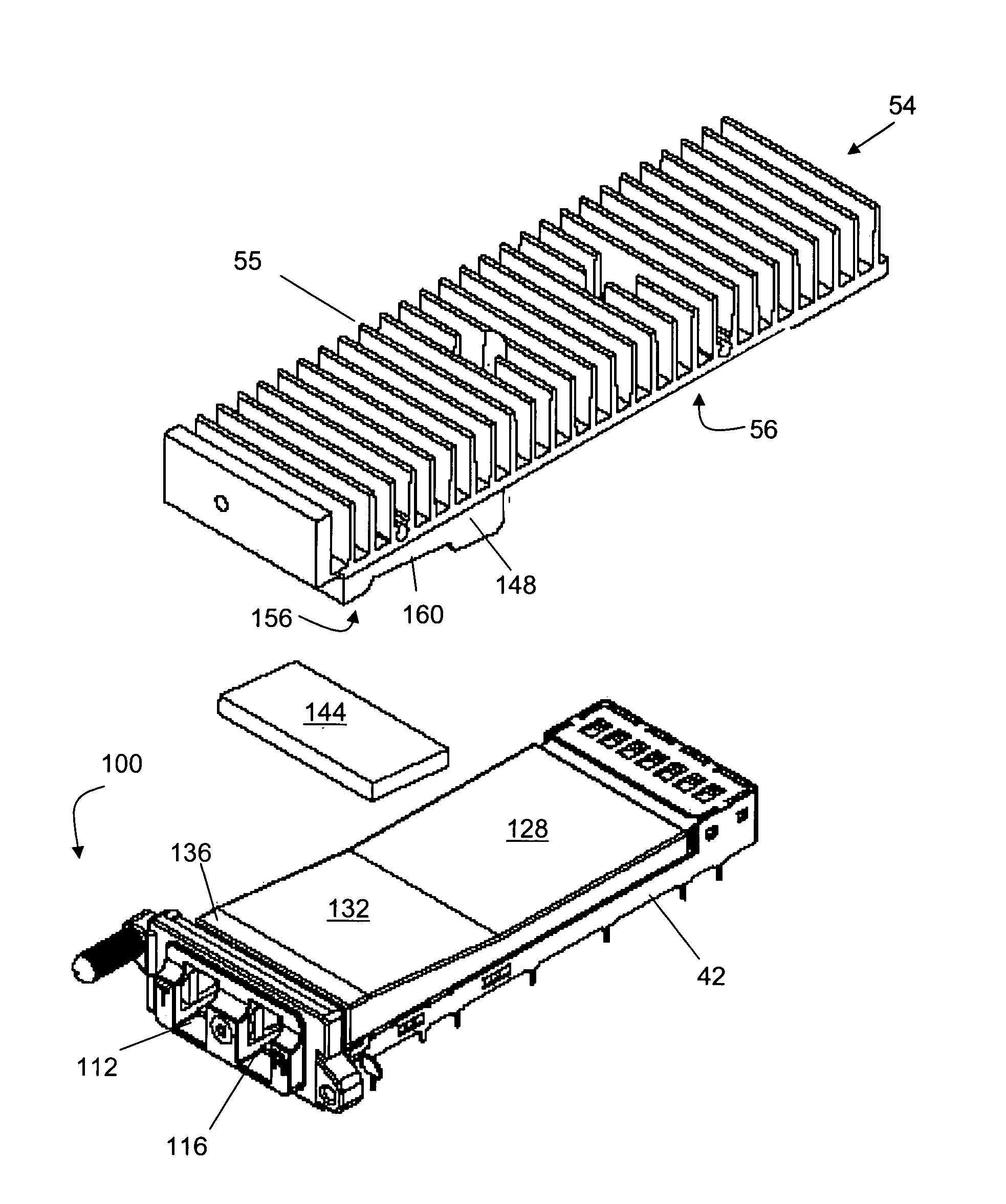
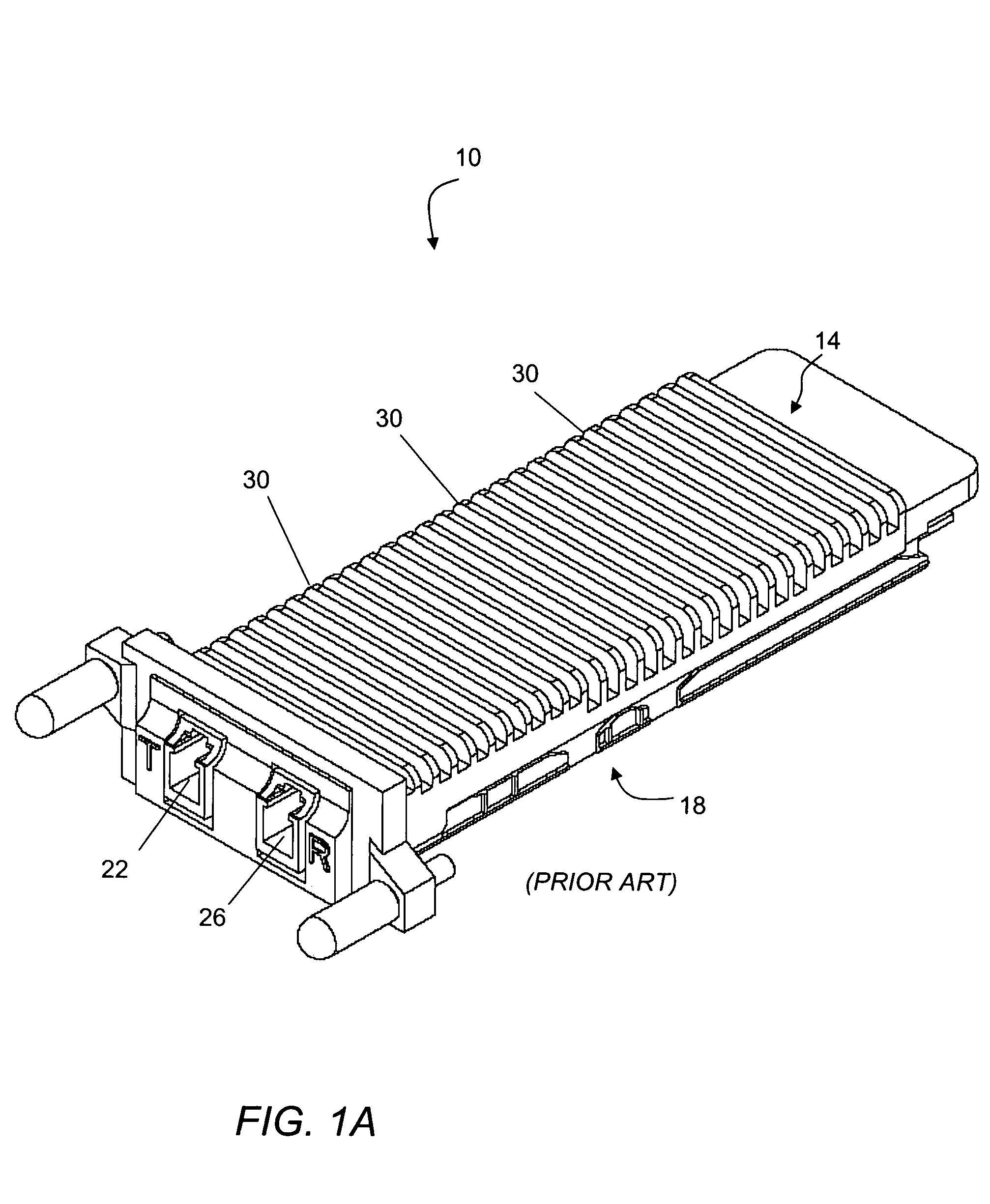
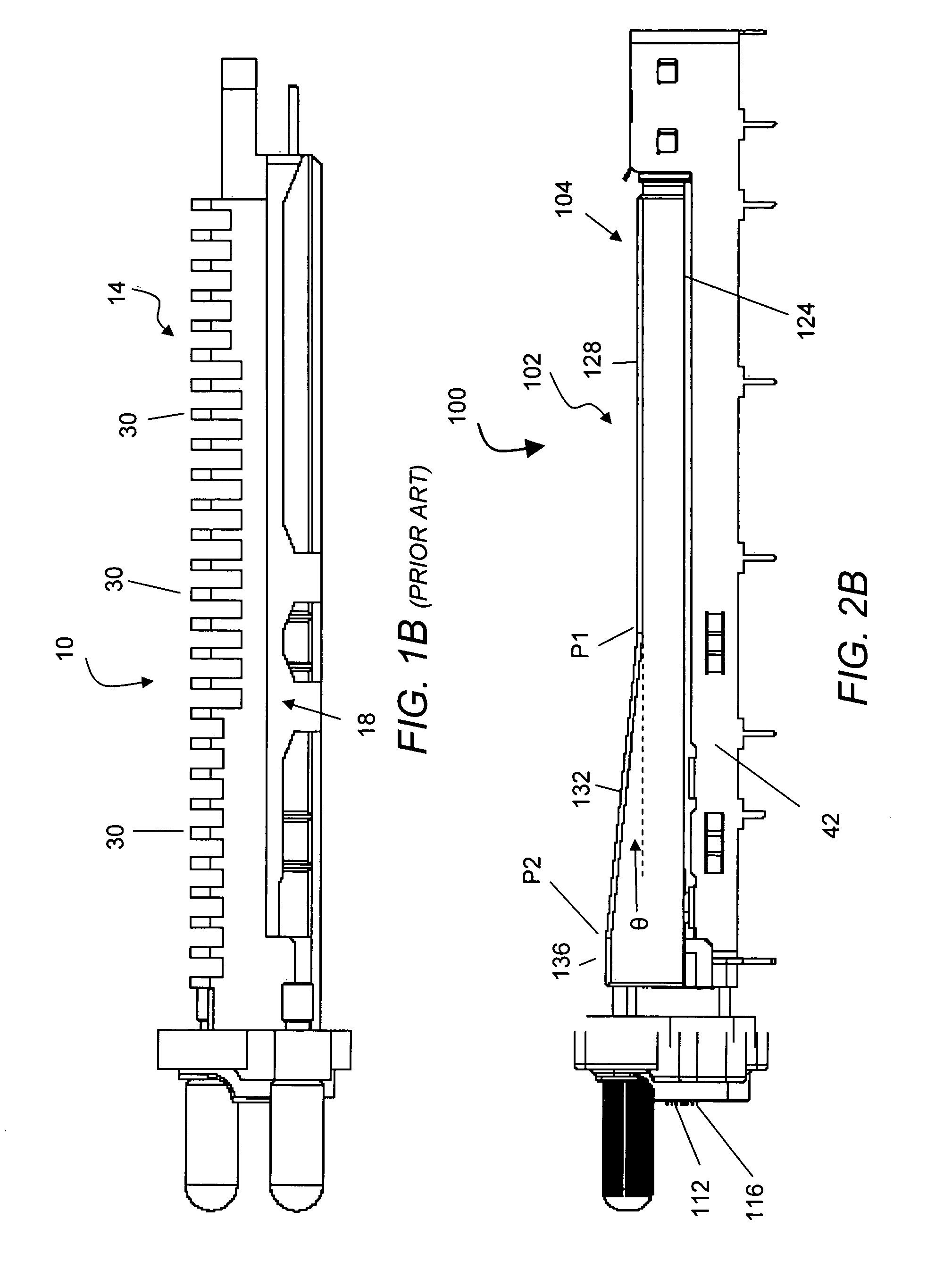
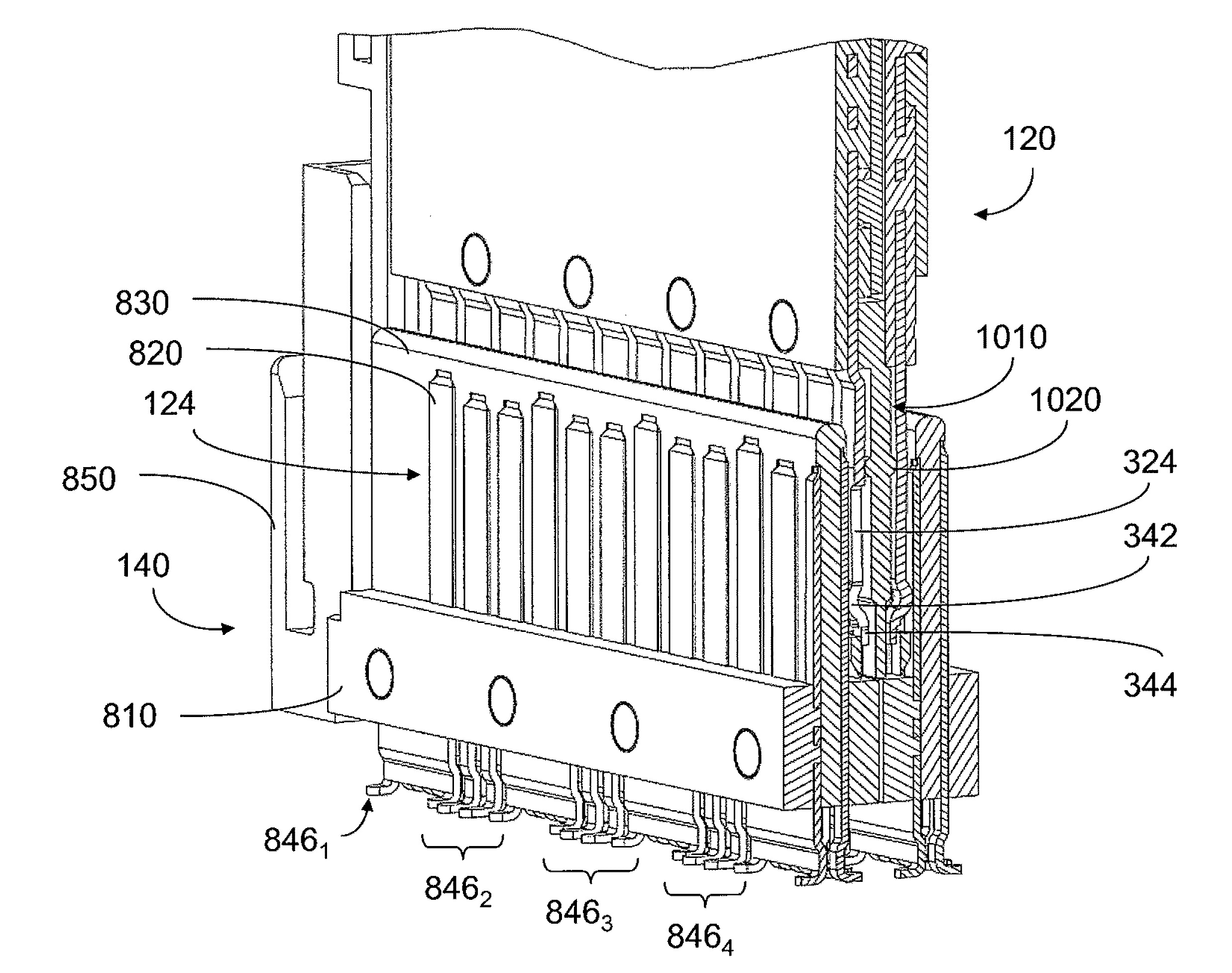
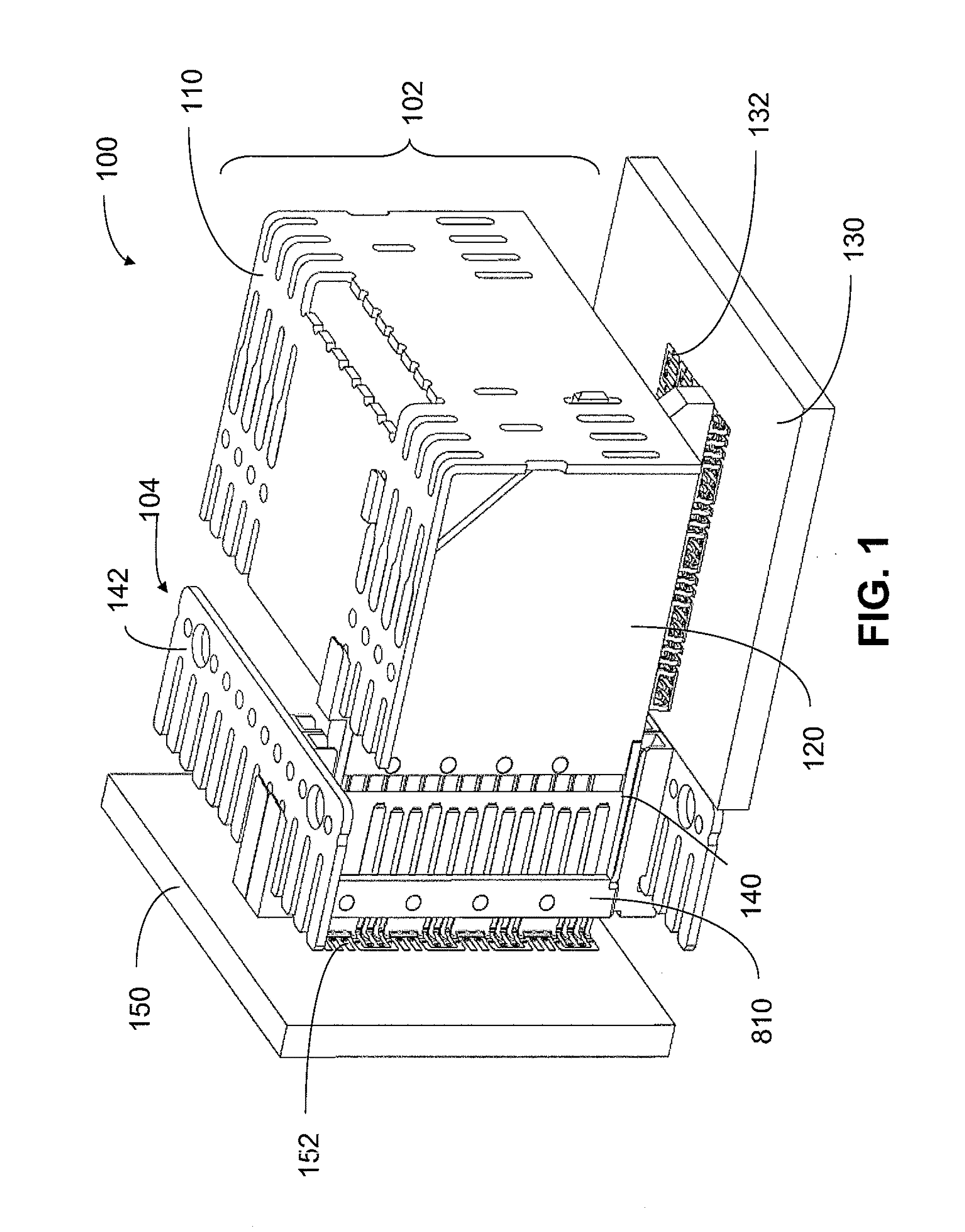
Pluggable electronic module
ActiveUS7145773B2Lower insertion forceSlidable card holdersCard stiffenersEngineeringElectronic component
A pluggable electronic module is provided that has an electronic component and a module body enclosing the electronic component. The module body has a first surface and a second surface. The first surface has a first area substantially parallel to the second surface and a second area that defines a non-zero angle with respect to the first area. The second area contacts a thermal sink to dissipate heat generated by the electronic component. The pluggable electronic module has a reduced insertion force in comparison with conventional pluggable electronic modules.
Owner:CIENA
Trocar cannula assembly and method of manufacture
ActiveUS8888692B1Minimize interferenceReduce contactSurgical needlesDomestic articlesInterference fitSurgery
A cannula assembly having a retention member and a method of manufacture of the cannula assembly is provided. The cannula assembly includes a cannula and a sleeve disposed around the cannula from a proximal end to a distal end. The sleeve can be pre-formed by a stretch blow molding process then advanced over the cannula. The sleeve includes an inflatable balloon and an annular ring distal the inflatable balloon. The cannula includes an annular recess. The annular ring is sized to have an interference fit with the annular recess.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
High density electrical connector and PCB footprint
ActiveUS20110212632A1Good signal integrityMechanically robustTwo-part coupling devicesElectrical connection printed elementsMechanical integrityPrinted circuit board
An interconnection system that includes a daughter card and backplane electrical connectors, each mounted to a printed circuit board at a connector footprint. The backplane connector has conductive elements with transition regions that allow the mating contact portions to be positioned on a uniform pitch while contact tail portions can be shaped to improve signal integrity or to provide a more compact and / or mechanically robust footprint. The conductive elements in both connectors are configured such that the contact tails of the ground conductors align from column to column, but the planar portions of the ground conductors in one column align with a pair of signal conductors in the other column, which improves mechanical and signal integrity. Mechanical integrity may be improved by forming the connector footprints with pads for the ground conductors that span multiple columns.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
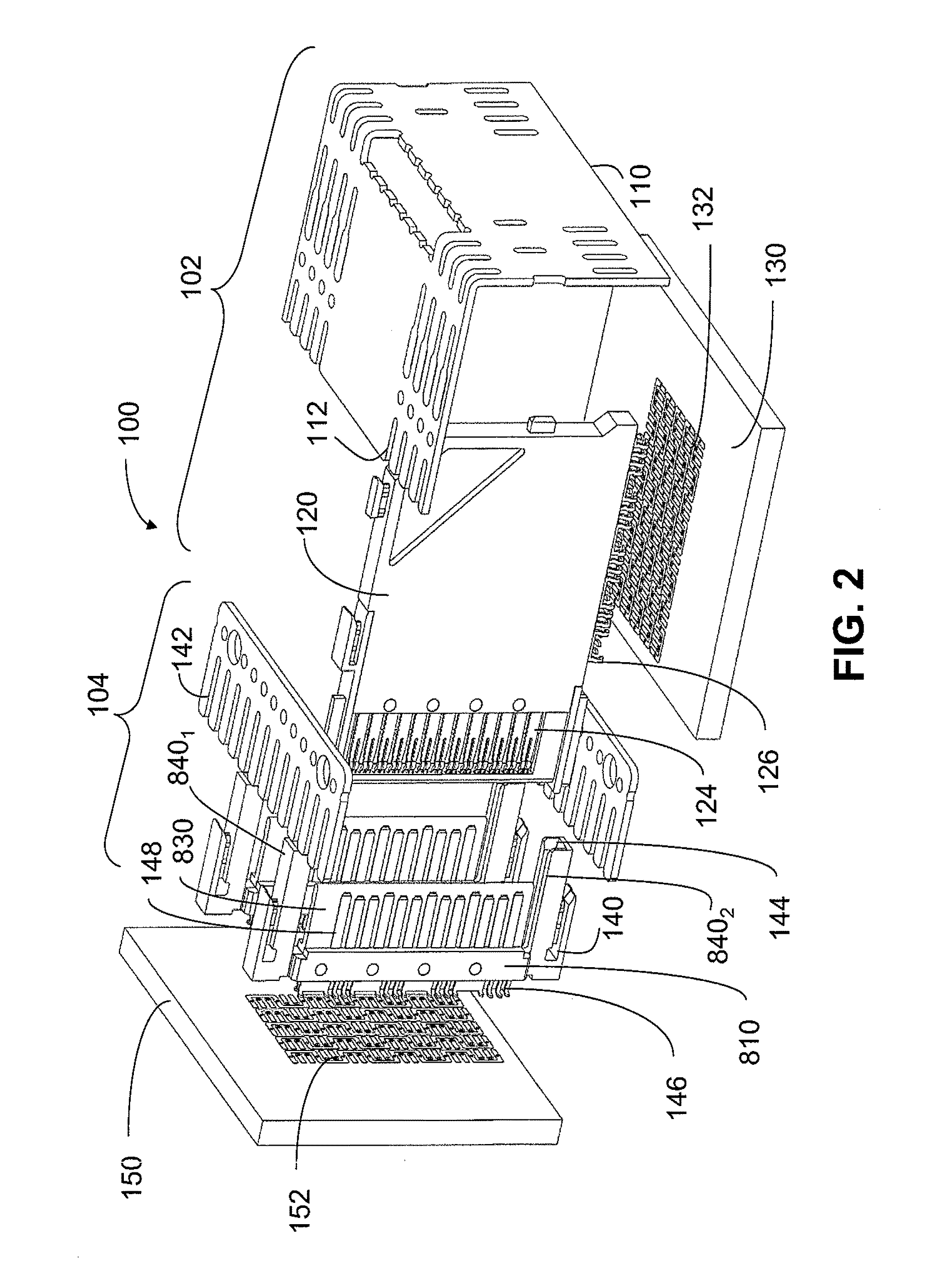
Card edge connector
A card edge connector for receiving a module and includes an insulative housing having a mounting face, a pair of side walls with a central slot formed therebetween, a tower portion extending upwardly from the side wall; a number of contacts mounted to the housing and each defining a retaining portion to fix with the housing, a deflectable contacting arm extending upwardly from the retaining portion and a soldering portion extending downwardly from the retaining portion and projecting beyond the mounting face; and an ejector rotatably mounted on the tower portion of the housing. The ejector includes a base portion, an ejecting portion extending inwardly from the base portion and protruding into the central slot to eject the memory module from the central slot and a cam lobe extending inwardly from the base portion to drive the module down, the cam lobe is located above the ejecting portion.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
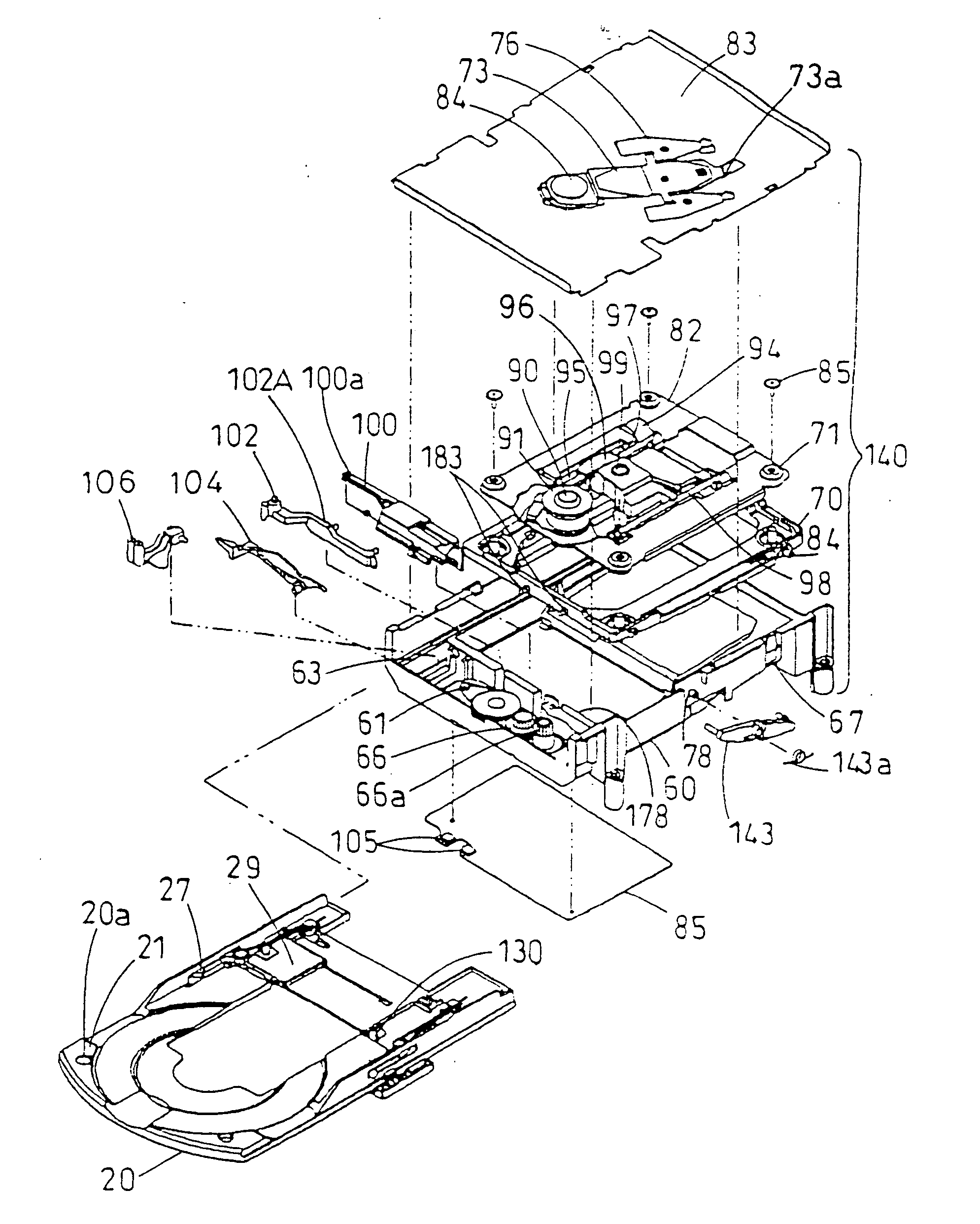
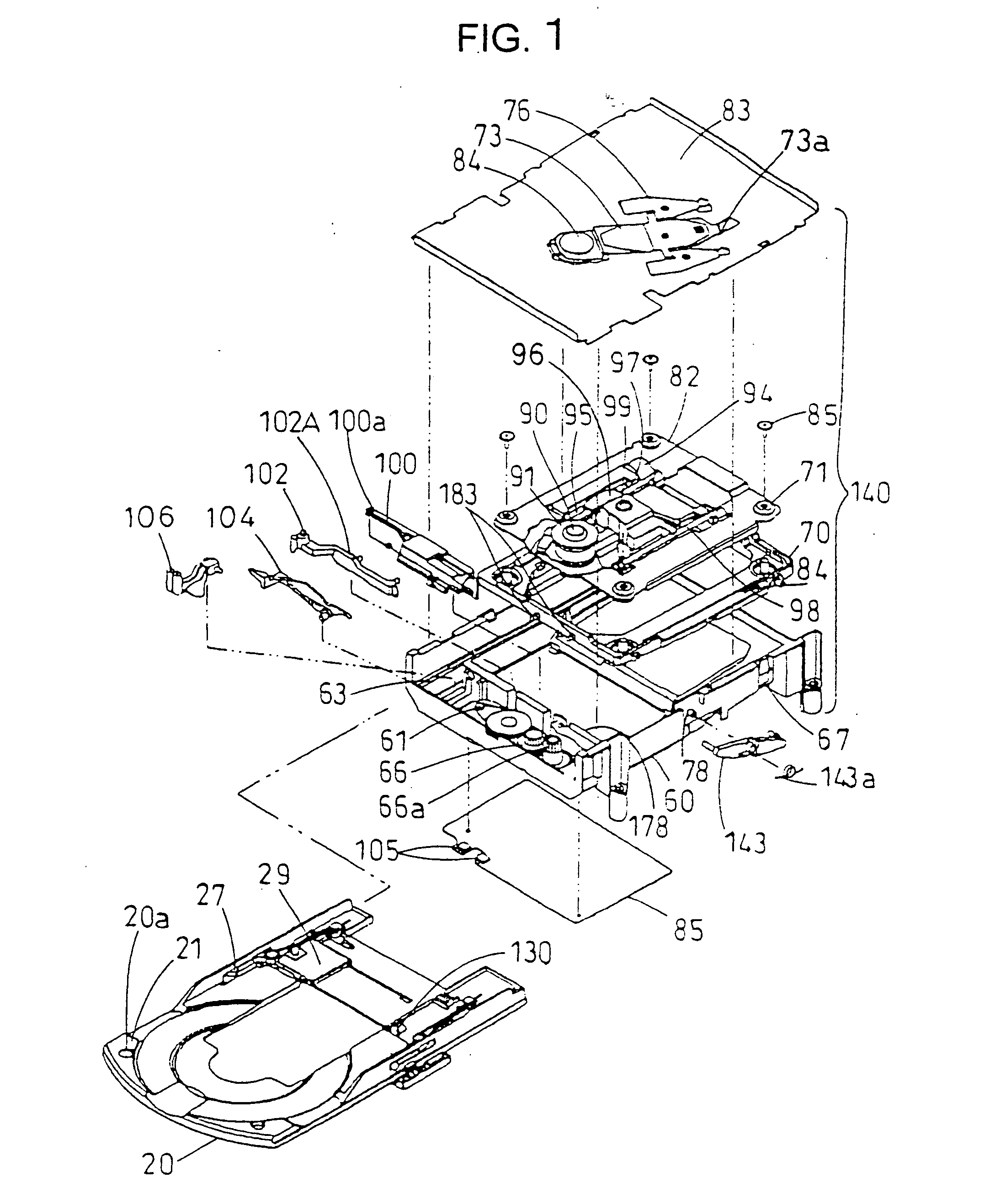
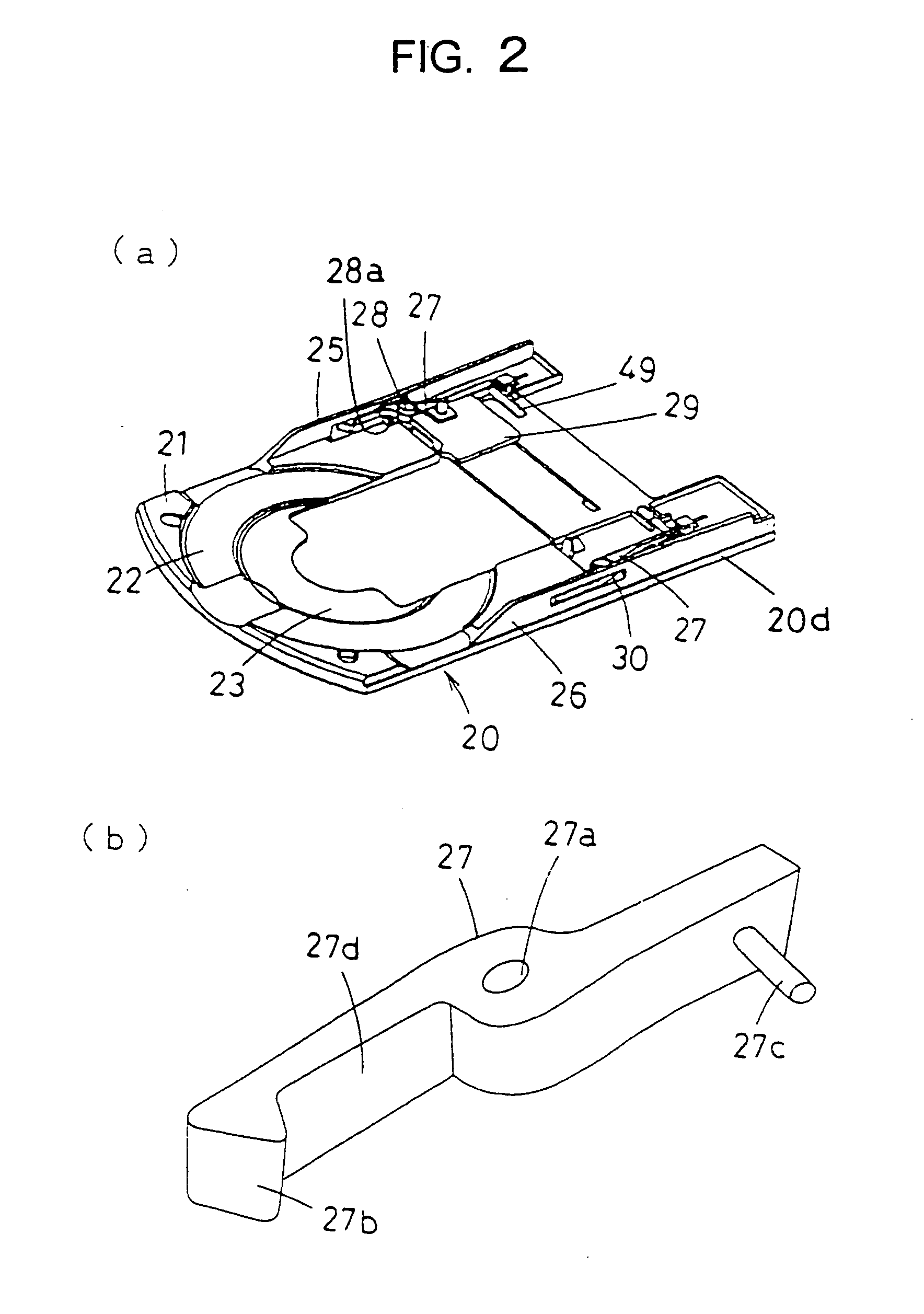
Disk apparatus
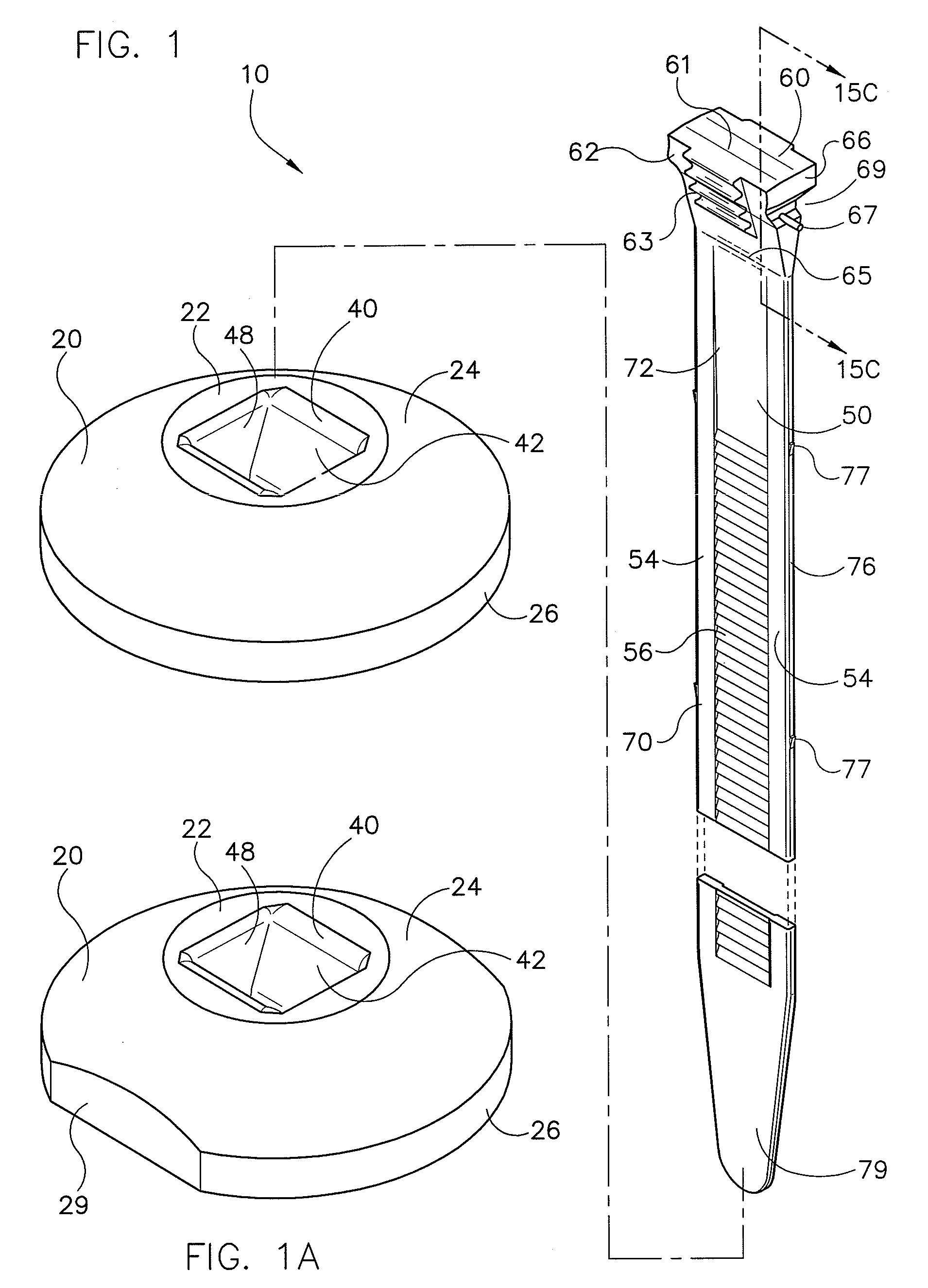
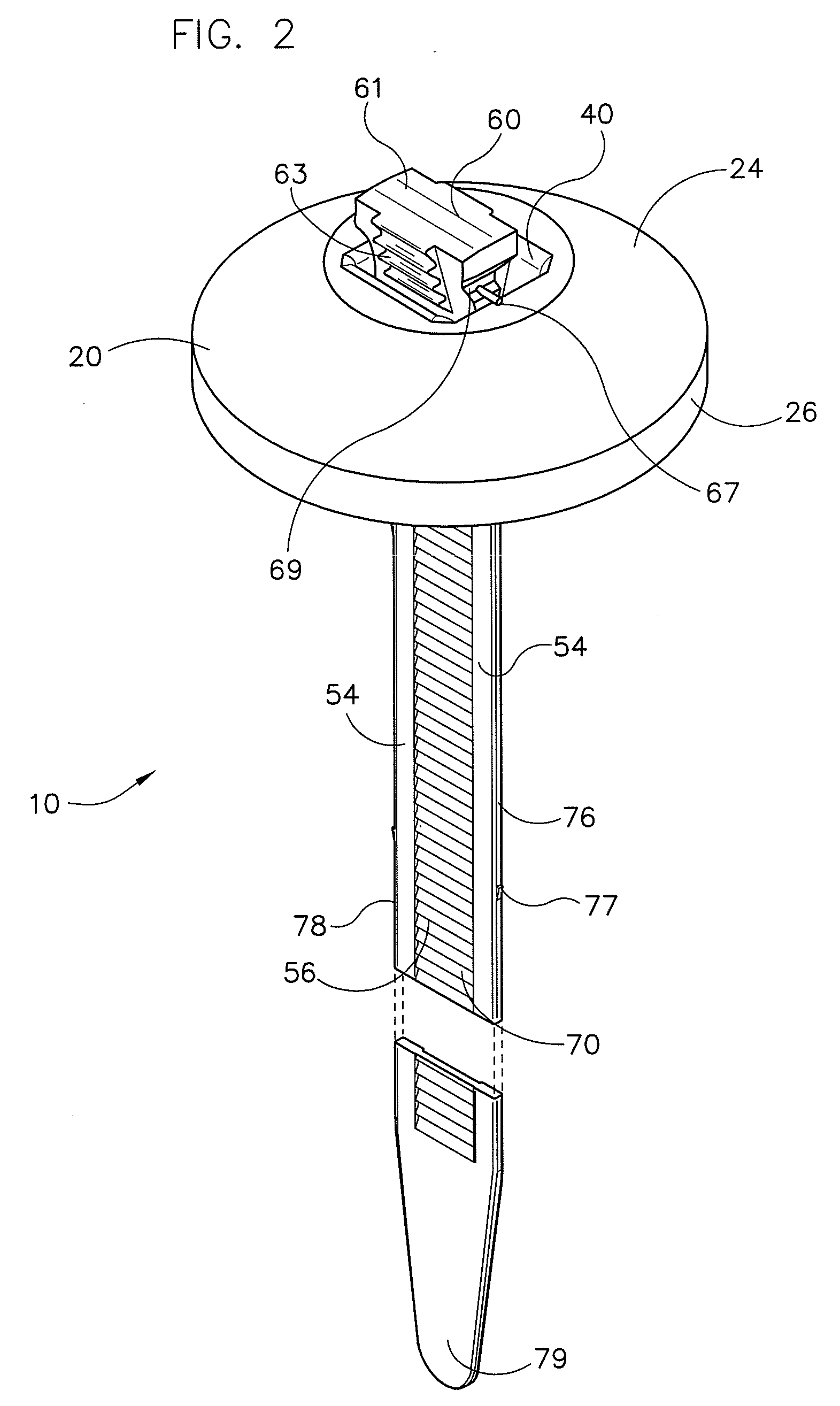
InactiveUS20050204373A1Reduce loadLower insertion forceUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionRecord information storageMechanical engineeringEngineering
A disk drive comprises a cartridge holding mechanism which has a small size and reduces a damper load. The disk drive comprises: a spindle motor 91 which mounts and rotates a disk; a traverse base 82 which holds the spindle motor 91; a rubber damper 71 which flexibly holds the traverse base 82; a mechanical chassis 60 which holds the traverse base 82 through the rubber damper 71; a tray 20 which mounts a cartridge 1 in which a disk is housed; and a loading motor 61 which moves the disk in the cartridge 1 close to the spindle motor 91 or away from the spindle motor 91. The cartridge 1 is supported by the mechanical chassis 60 through the tray 20.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com