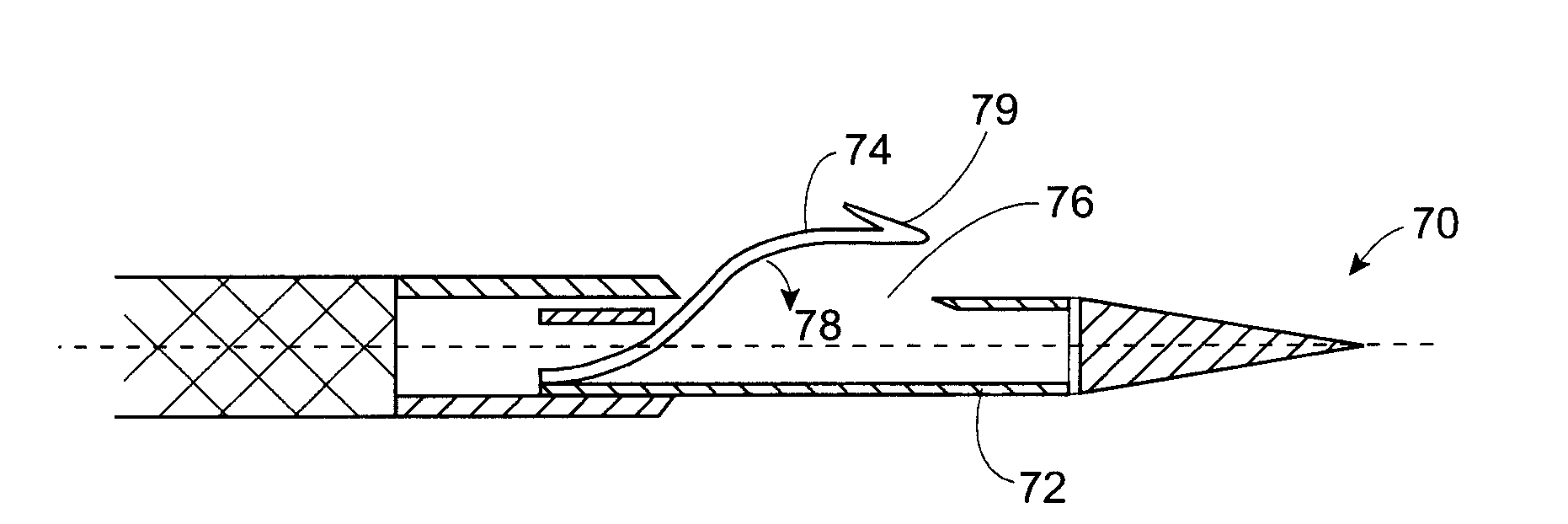
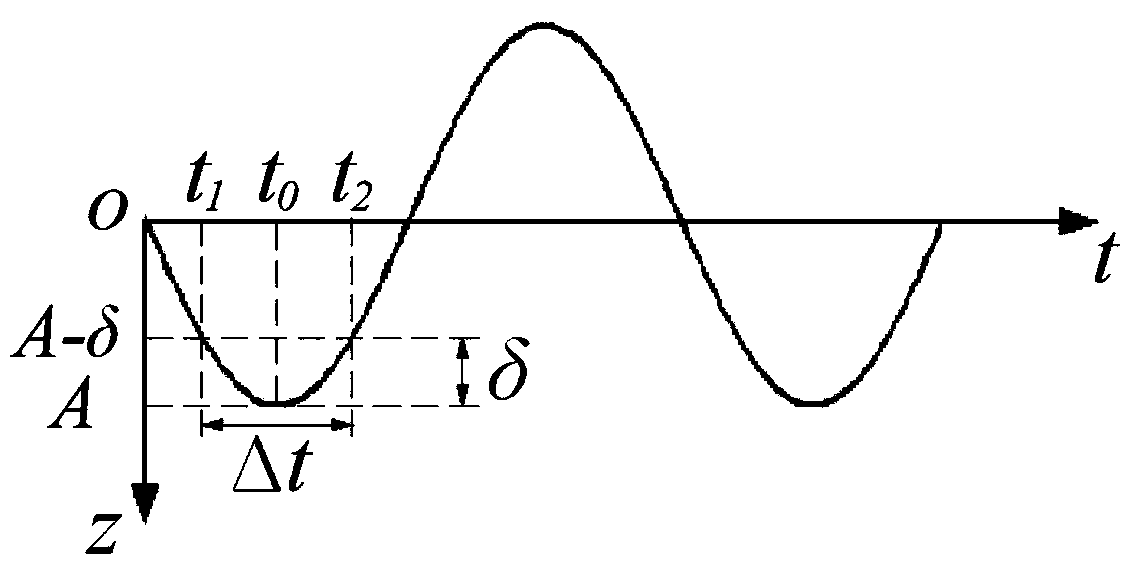Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2789 results about "Cutting force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cutting force is a fundamental physics concept that describes the amount of force used in a specific amount of area. This "force per area" relationship is used to derive the amount of stress applied to an object that is being cut. When the stress overcomes the strength of the material it is being applied to,...
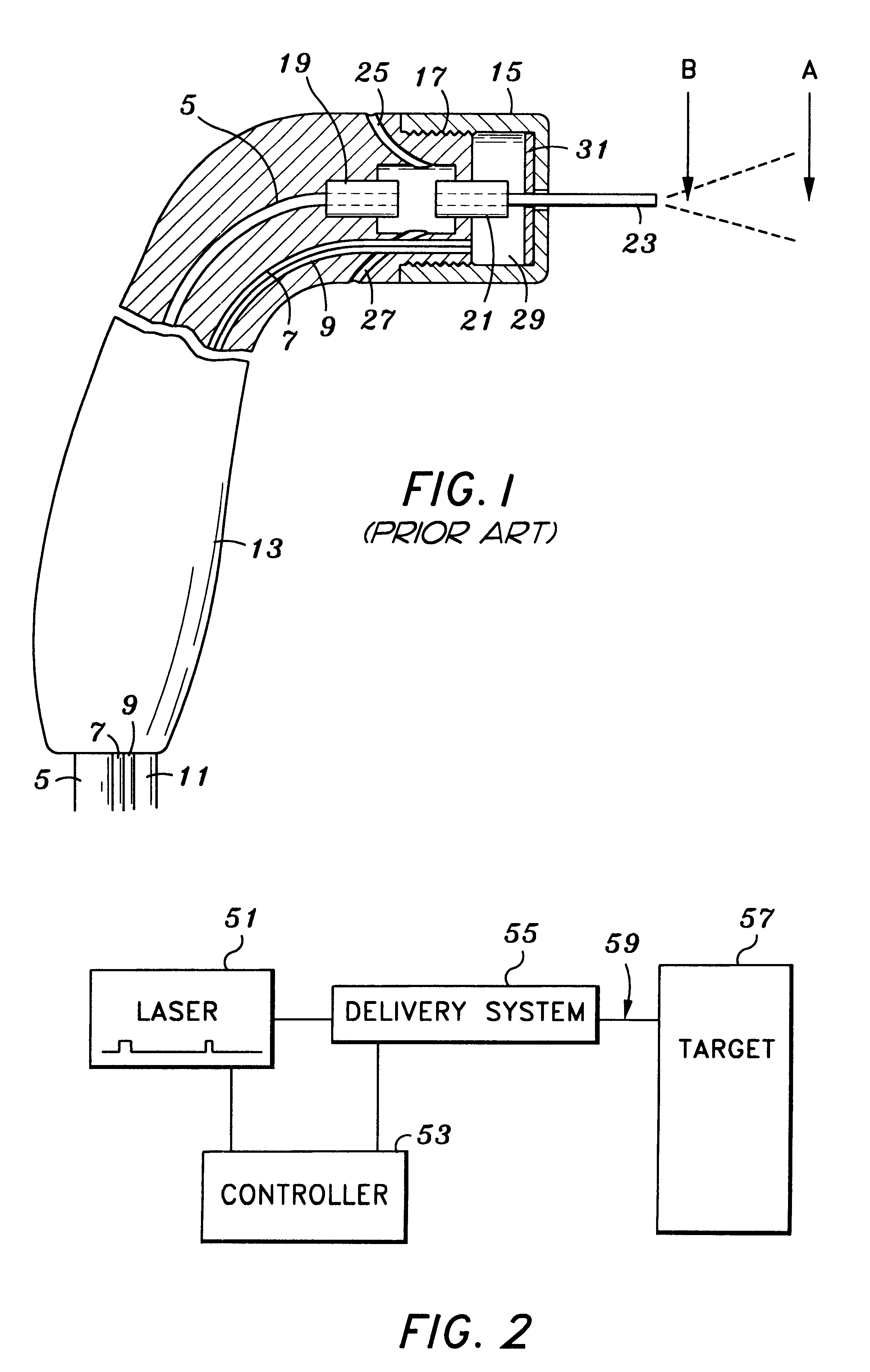
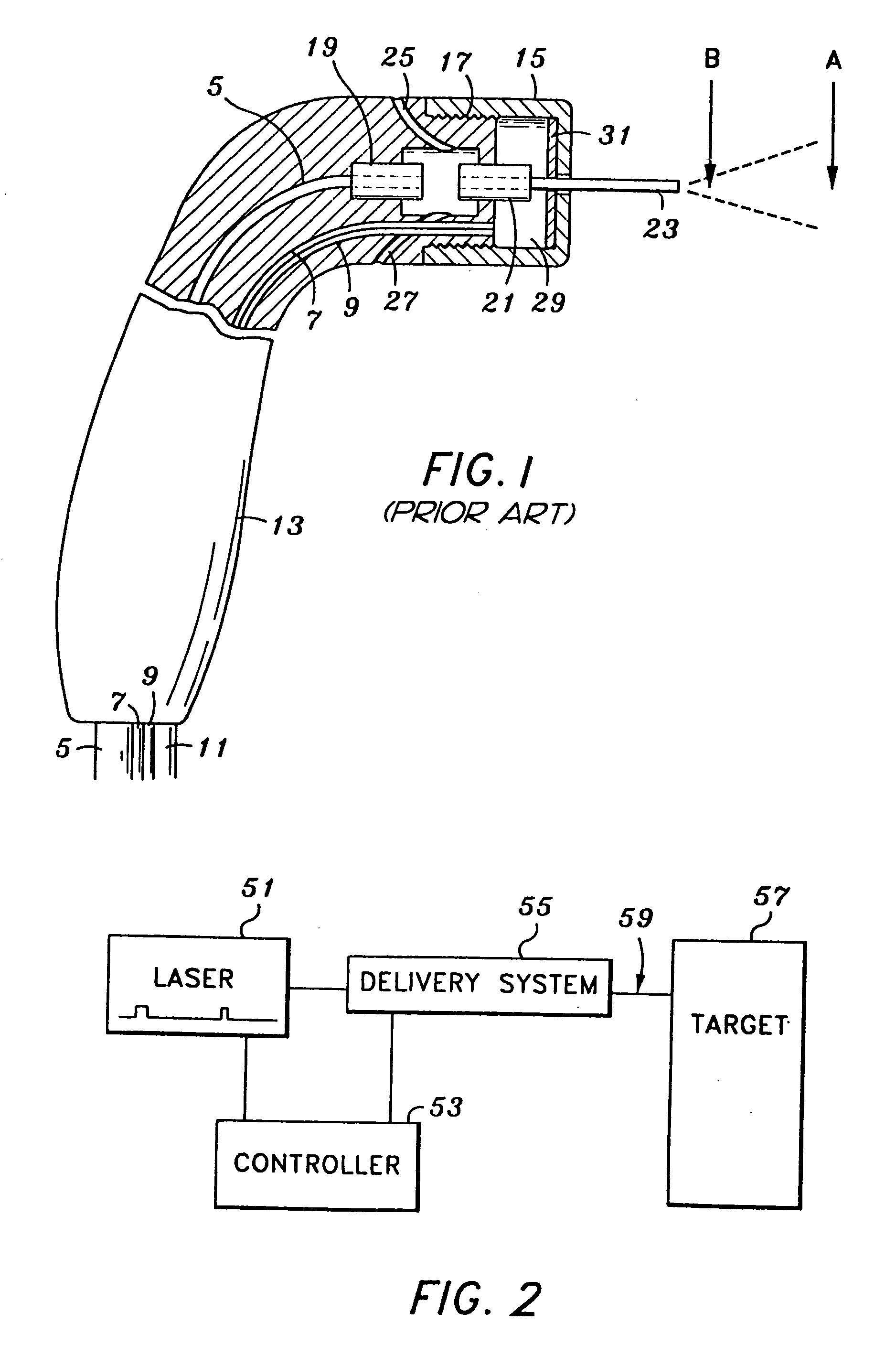
Tissue remover and method
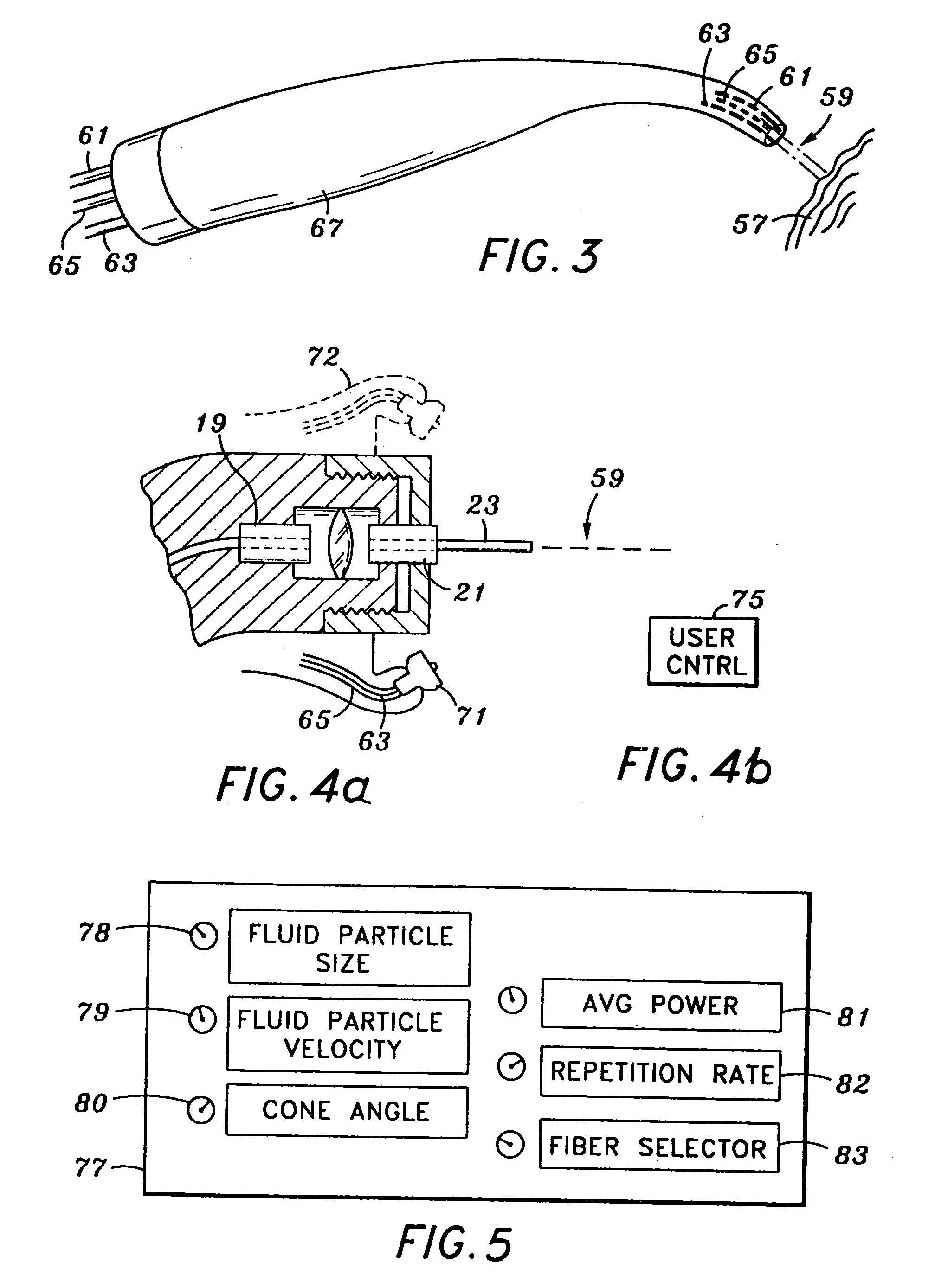
InactiveUS6669685B1Fine and smooth incisionEasy to controlMedical devicesFluid jet surgical cuttersMedicineCutting force
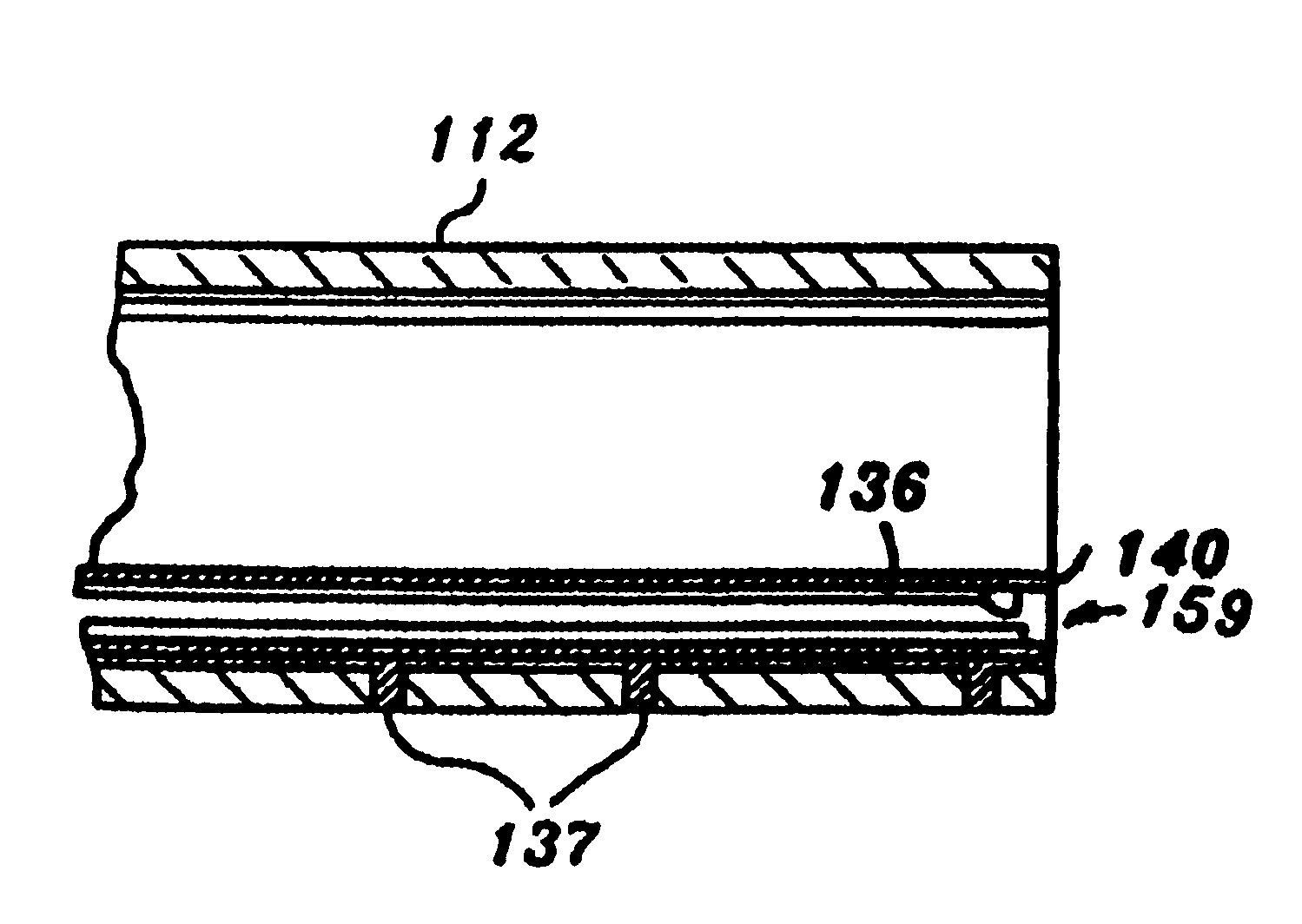
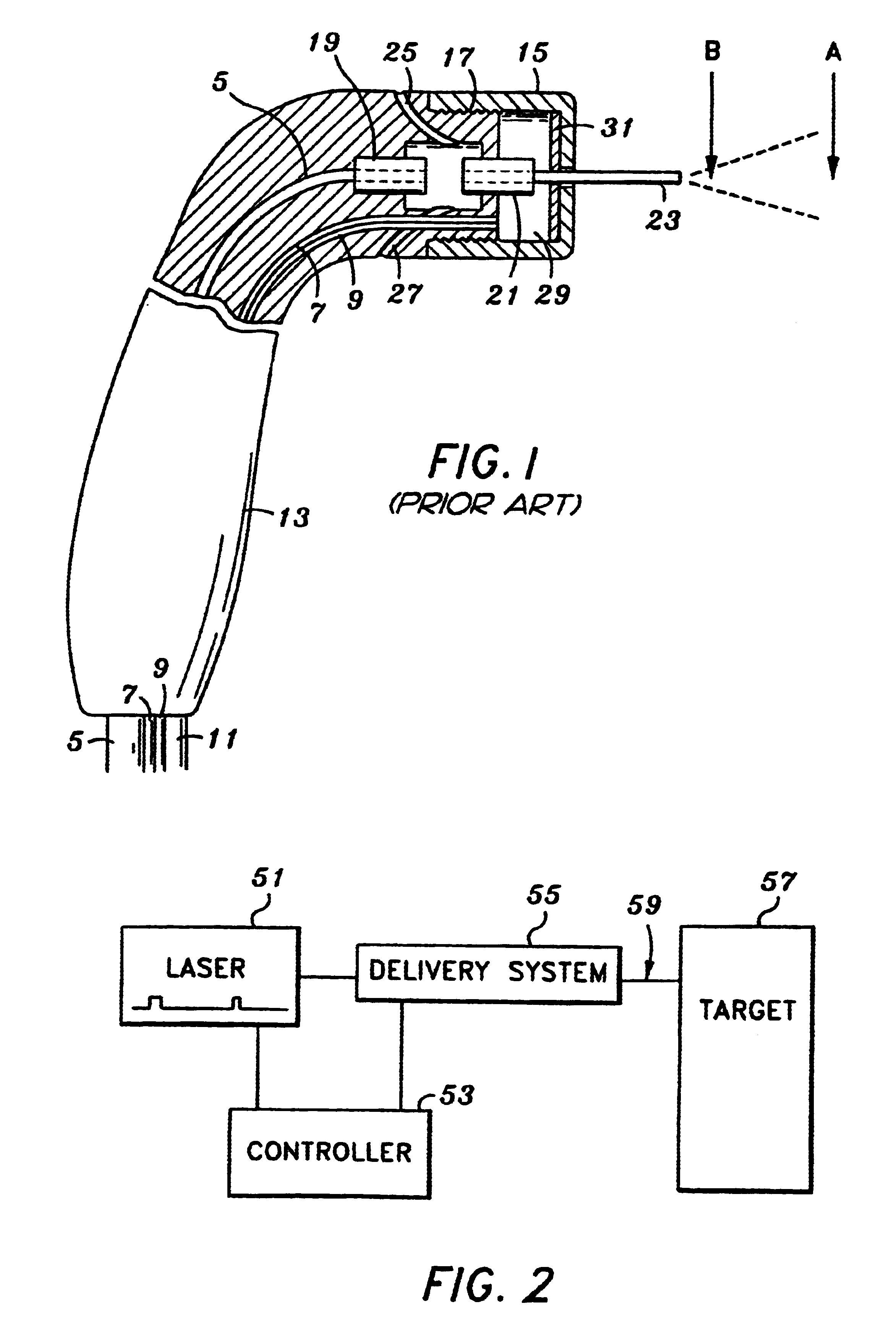
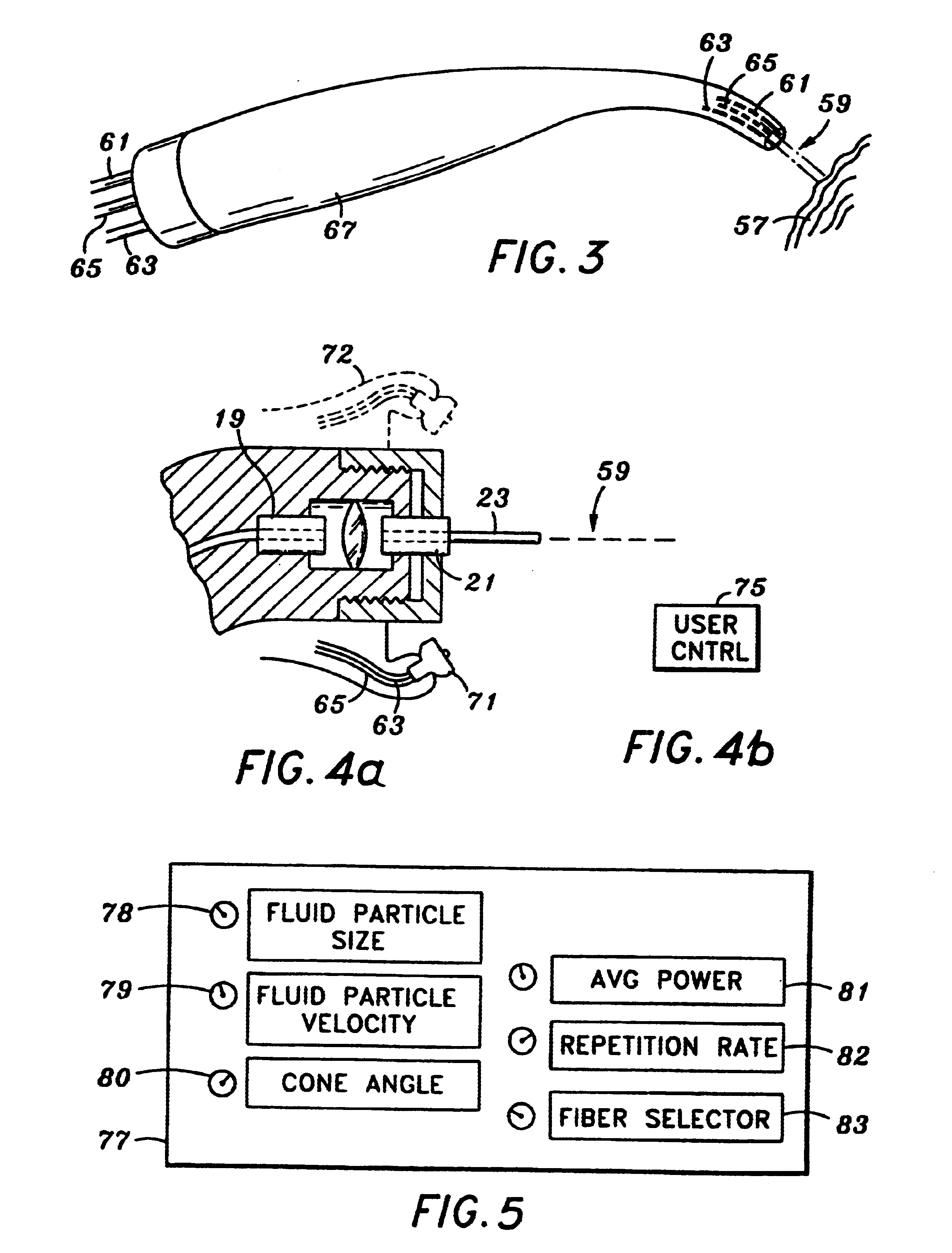
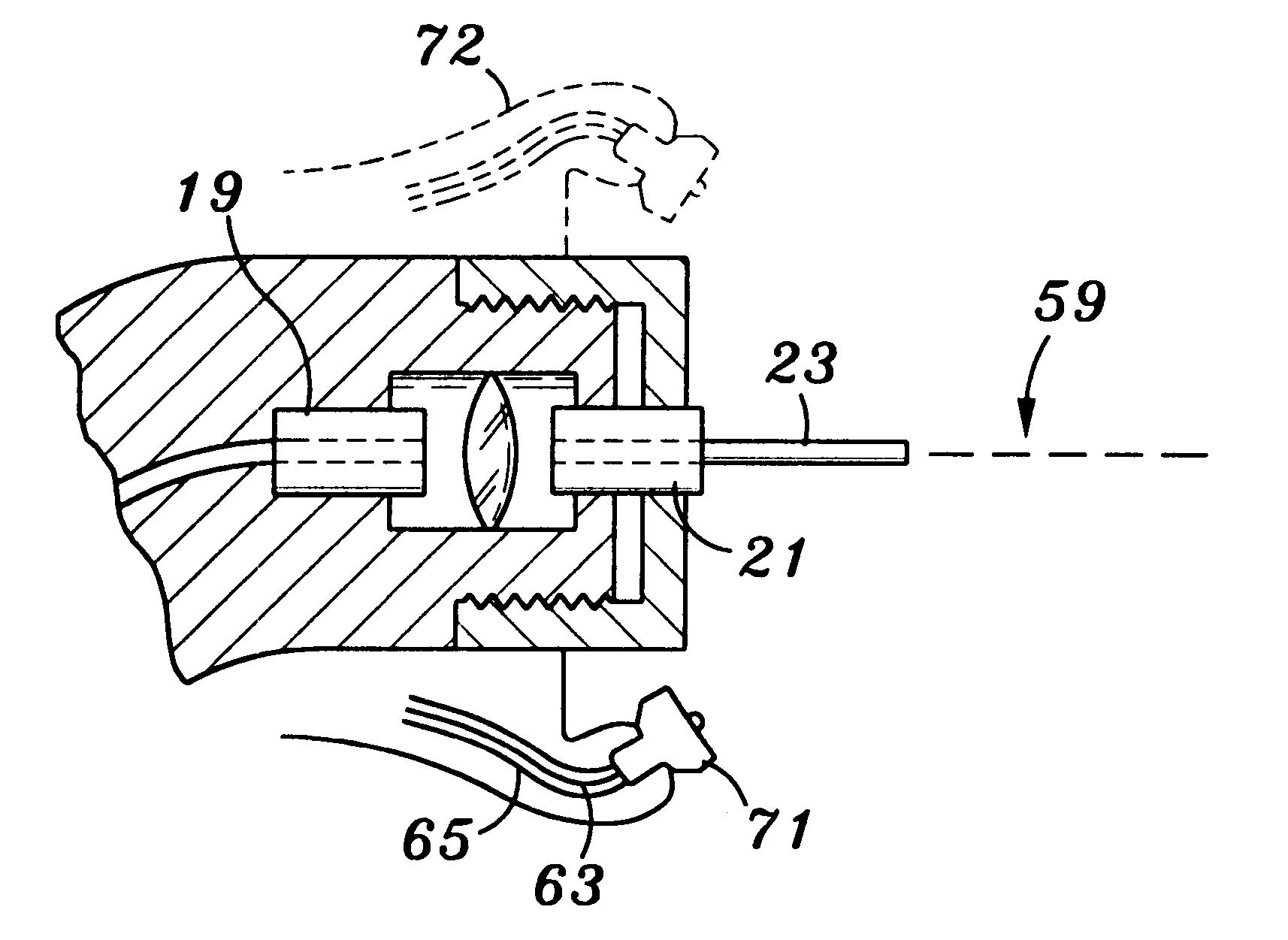
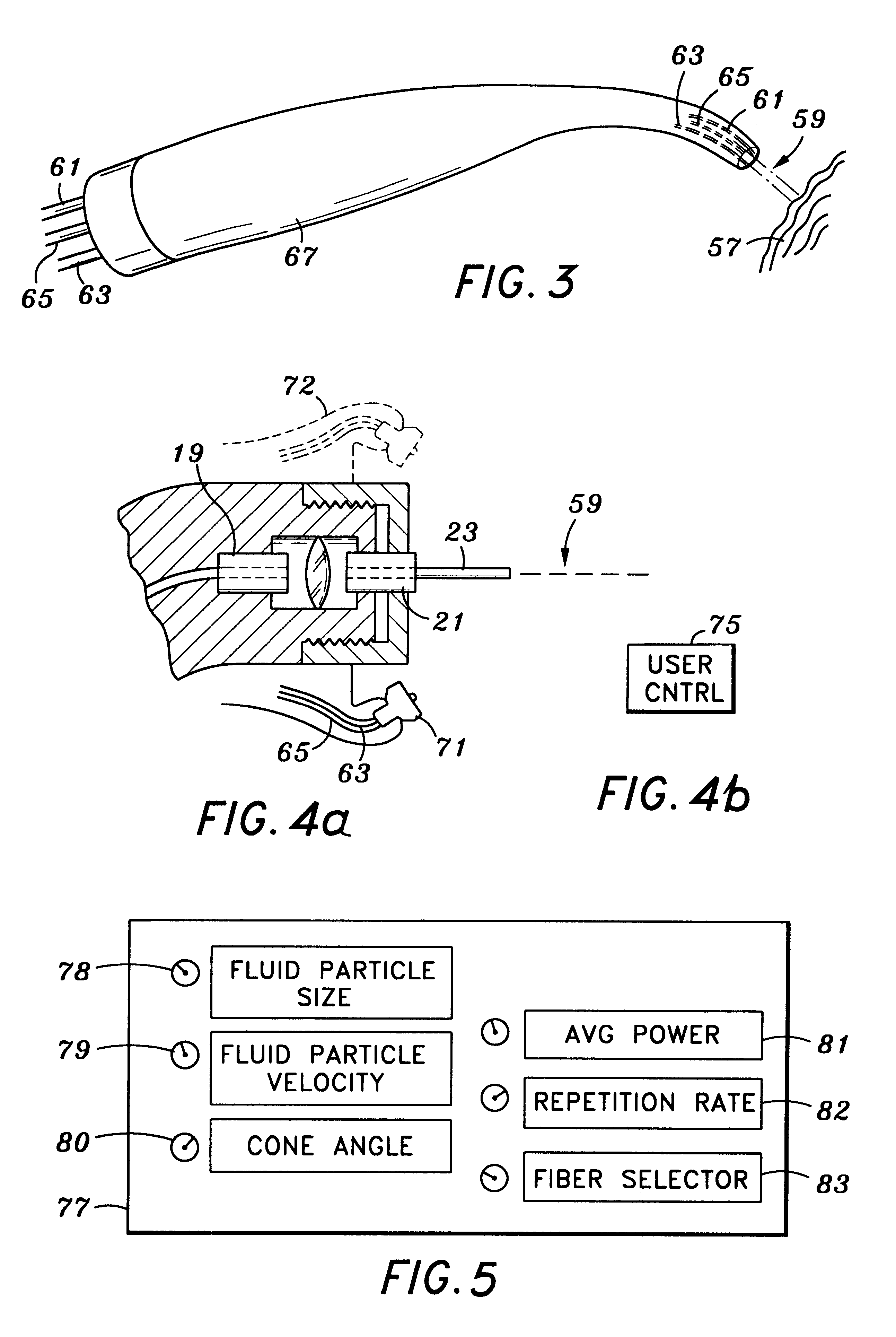
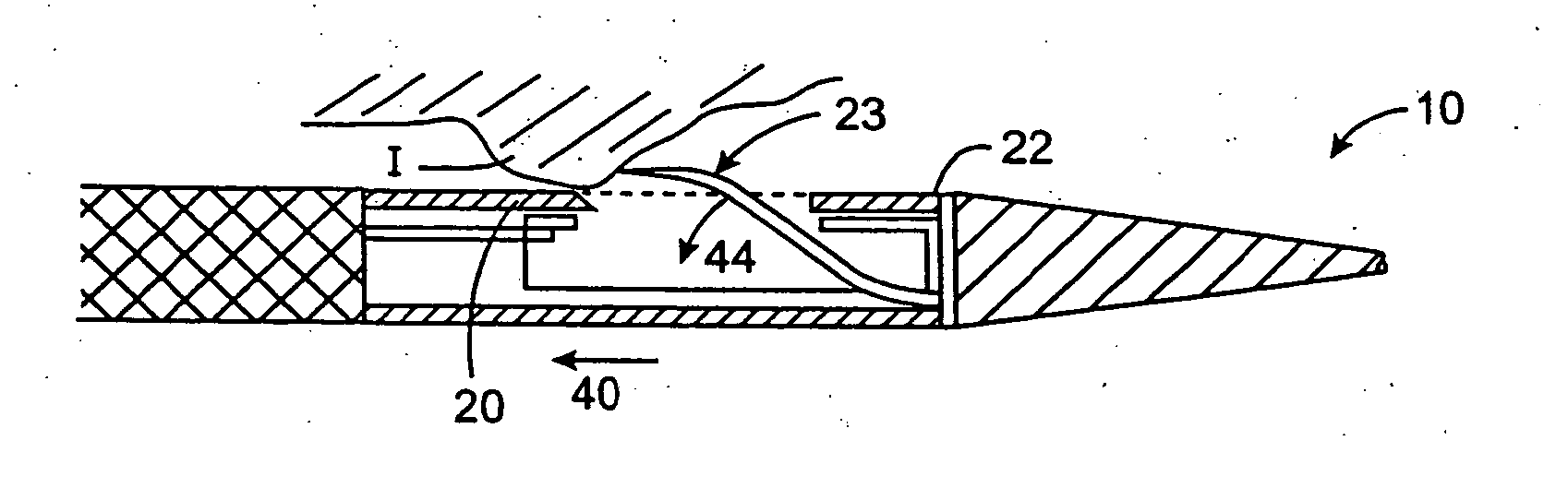
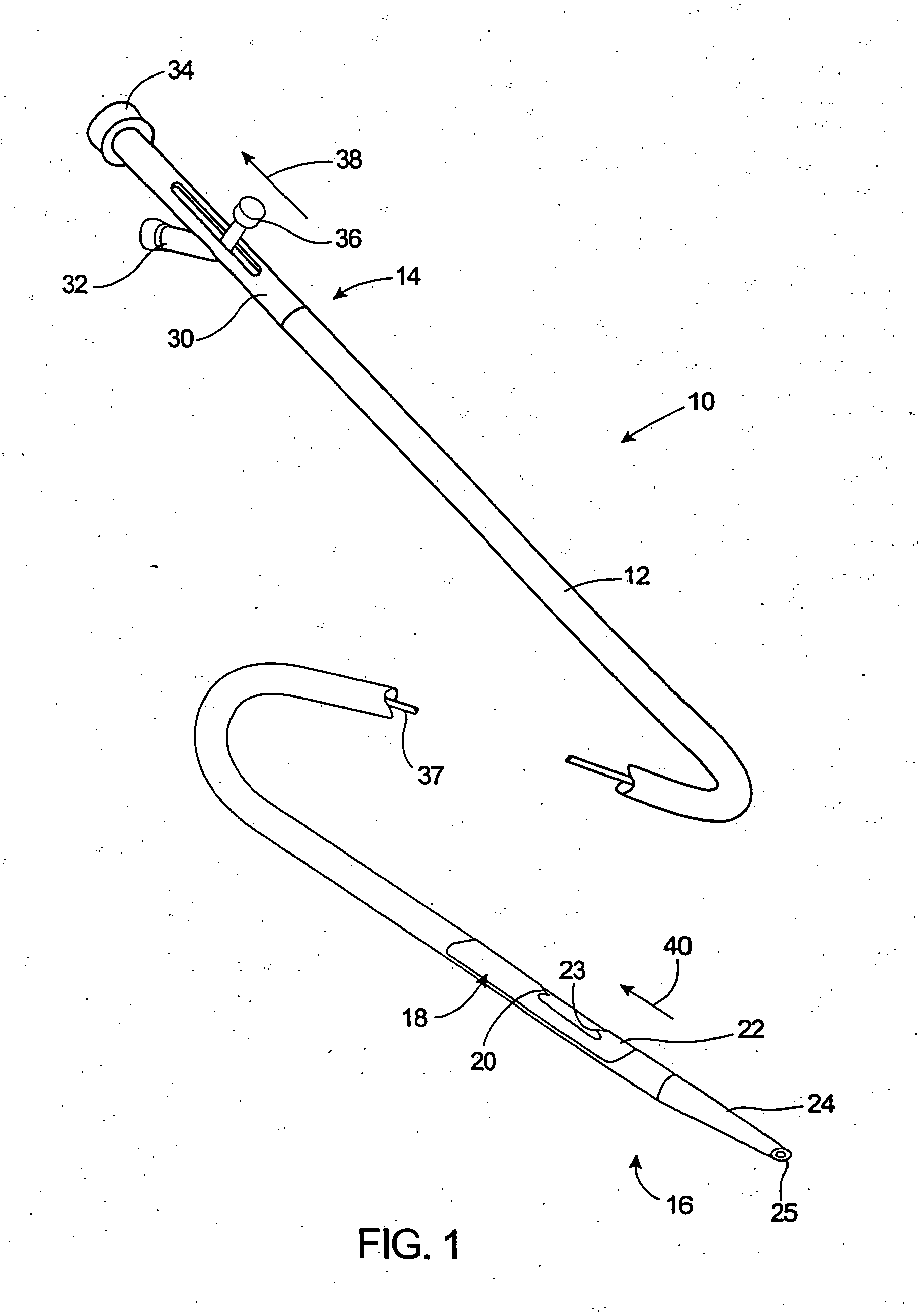
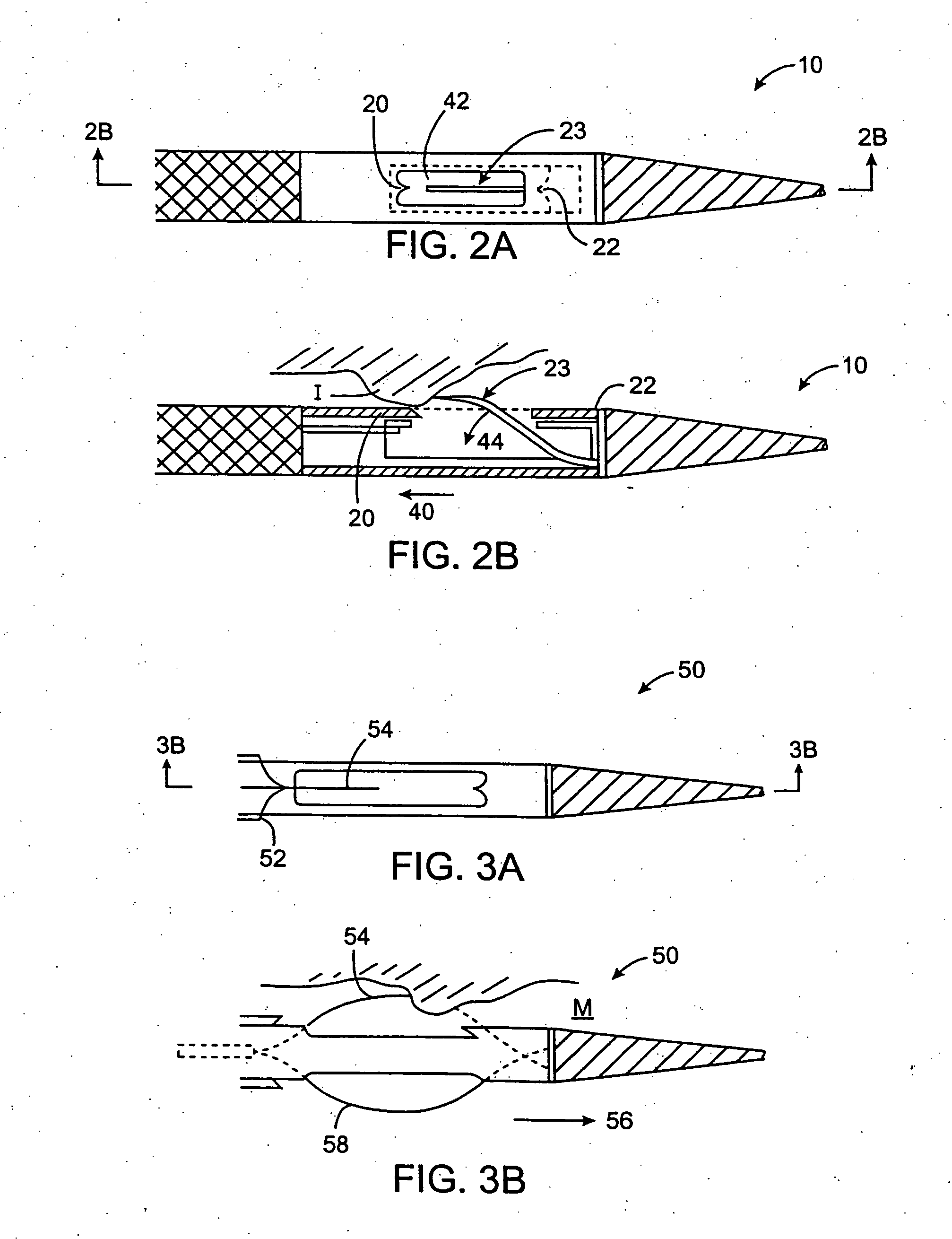
An electromagnetically induced cutting mechanism provides accurate cutting operations on soft tissues. The electromagnetically induced cutter is adapted to interact with atomized fluid particles. A tissue remover comprises an aspiration cannula housing a fluid and energy guide for conducting electromagnetically induced cutting forces to the site within a patient's body for aspiration of soft tissue. The cannula is provided with a cannula distal end. The proximal end of the cannula is provided with fluid flow connection to an aspiration source. Separated soft tissue and fluid are aspirated through the cannula distal end and the cannula by an aspiration source at the proximal end of the cannula.
Owner:BIOLASE TECH INC
Tissue remover and method
An electromagnetically induced cutting mechanism provides accurate cutting operations on soft tissues. The electromagnetically induced cutter is adapted to interact with atomized fluid particles. A non-thermal tissue remover comprises an aspiration cannula housing a fluid and energy guide for conducting electromagnetically induced mechanical cutting forces to the site within a patient's body for aspiration of soft tissue. The cannula is provided with an aspiration inlet port adjacent the cannula distal end. The proximal end of the cannula is provided with fluid flow connection to an aspiration source. Separated soft tissue and fluid are aspirated through the aspiration inlet port and the cannula by an aspiration source at the proximal end of the cannula.
Owner:BIOLASE INC
Tissue remover and method
InactiveUS20040068256A1Fine and smooth incisionEasy to controlFluid jet surgical cuttersSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesCutting forceBiomedical engineering
An electromagnetically induced cutting mechanism provides accurate cutting operations on soft tissues. The electromagnetically induced cutter is adapted to interact with atomized fluid particles. A tissue remover comprises an aspiration cannula housing a fluid and energy guide for conducting electromagnetically induced cutting forces to the site within a patient's body for aspiration of soft tissue. The cannula is provided with a cannula distal end. The proximal end of the cannula is provided with fluid flow connection to an aspiration source. Separated soft tissue and fluid are aspirated through the cannula distal end and the cannula by an aspiration source at the proximal end of the cannula.
Owner:BIOLASE INC
Apparatus and methods for material capture and removal
InactiveUS20060235334A1Reduce amountEasy to cutSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCutting forceArtery organ
Catheters, kits, and methods are provided for removing material from a body lumen. The catheters and methods may be used in a variety of body lumens, including but not limited to coronary and other arteries. In general, the catheter has a cutting element that cuts material while the material is engaged by a material capture device on the catheter body. Preferably, the material capture device tensions the material during cutting, which reduces the amount of cutting force required. The material capture device typically follows a path that draws material into the catheter body. Preferably, but not necessarily, the material capture device may be arranged on the catheter body to advance along a path outwardly from the catheter body into the material and then inwardly towards the catheter body to tension the material. The cutting element on the catheter body moves between a first position and a second position to cut the material while in tension.
Owner:CORVI TIM +5
Apparatus and methods for material capture and removal
InactiveUS20090187203A1Reduce amountReduce the amount requiredCannulasSurgical needlesCutting forceArtery organ
Catheters, kits, and methods are provided for removing material from a body lumen. The catheters and methods may be used in a variety of body lumens, including but not limited to coronary and other arteries. In general, the catheter has a cutting element that cuts material while the material is engaged by a material capture device on the catheter body. Preferably, the material capture device tensions the material during cutting, which reduces the amount of cutting force required. The material capture device typically follows a path that draws material into the catheter body. Preferably, but not necessarily, the material capture device may be arranged on the catheter body to advance along a path outwardly from the catheter body into the material and then inwardly towards the catheter body to tension the material. The cutting element on the catheter body moves between a first position and a second position to cut the material while in tension.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
High-speed milling process parameter optimizing method based on dynamic model
ActiveCN102873381AImprove accuracyHigh removal rateMilling machinesSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic modelsSystem dynamics model
The invention relates to a high-speed milling process parameter optimizing method based on a dynamic model. The optimizing method includes 1) inputting structure parameter and initial cutting condition of a spindle-cutter system; 2) building a dynamic model of the spindle-cutter system, calculating a frequency response function of the cutter nose position according to the model and determining cutting force coefficient; 3) building a high speed spindle-cutter dynamic characteristic and milling interaction process model to obtain the characteristic equation of a closed loop dynamic milling system; 4) calculating a high-speed milling machining shimmy stability leaf picture; 5) selecting lathe spindle rotating speed and cutting depth to achieve high-speed milling parameter optimization with the lower bound curve of the high-speed milling machining shimmy stability leaf picture as the constraint condition and with maximum material removing rate as the optimization target. The method considers centrifugal force and gyroscopic couple effect of the cutter-cutter system in the high-speed rotating state, approaches actual work condition, improves accuracy of stability prediction, and provides effective technology for optimization of high-speed milling process parameter optimization.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Shaving implement having a moving blade
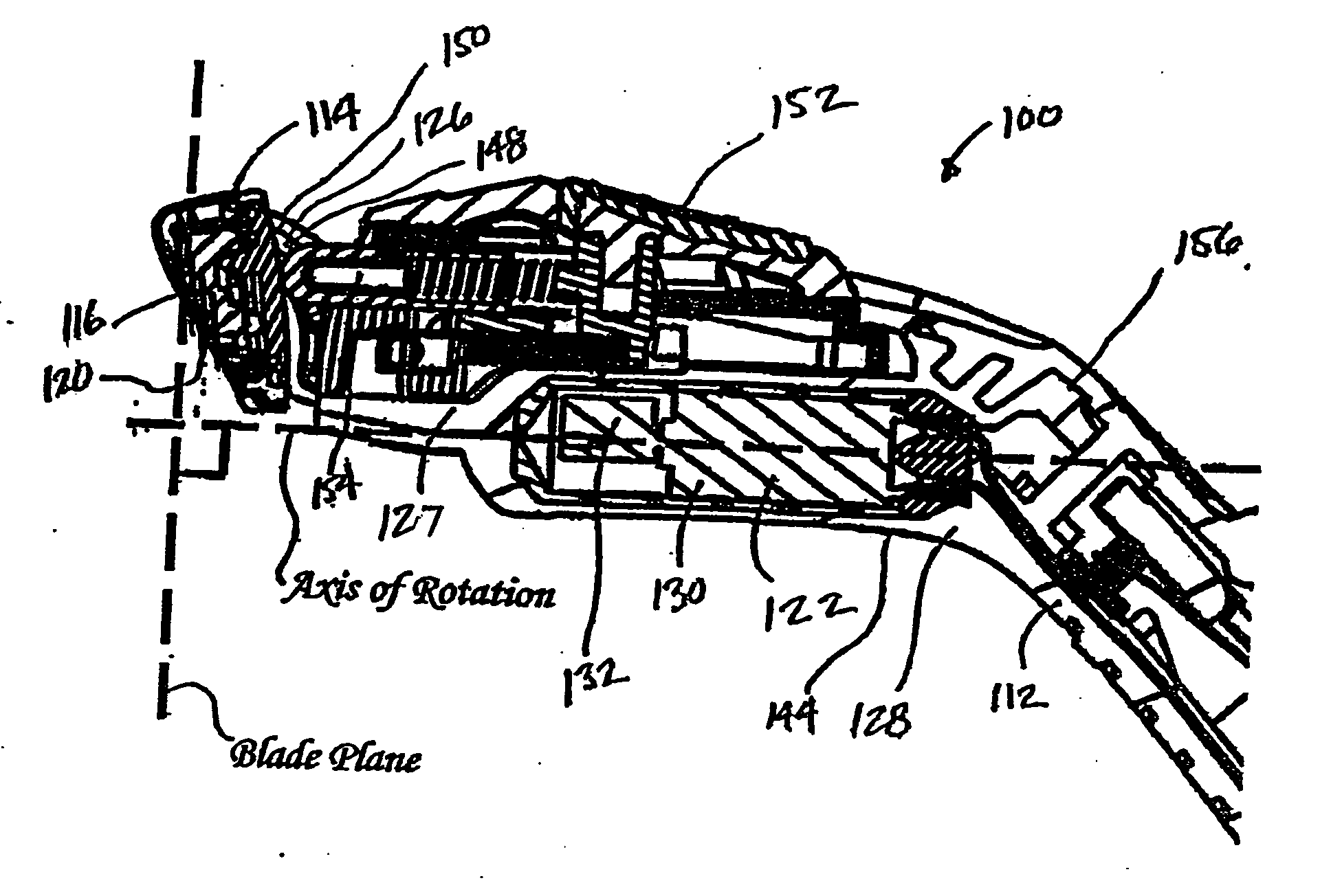
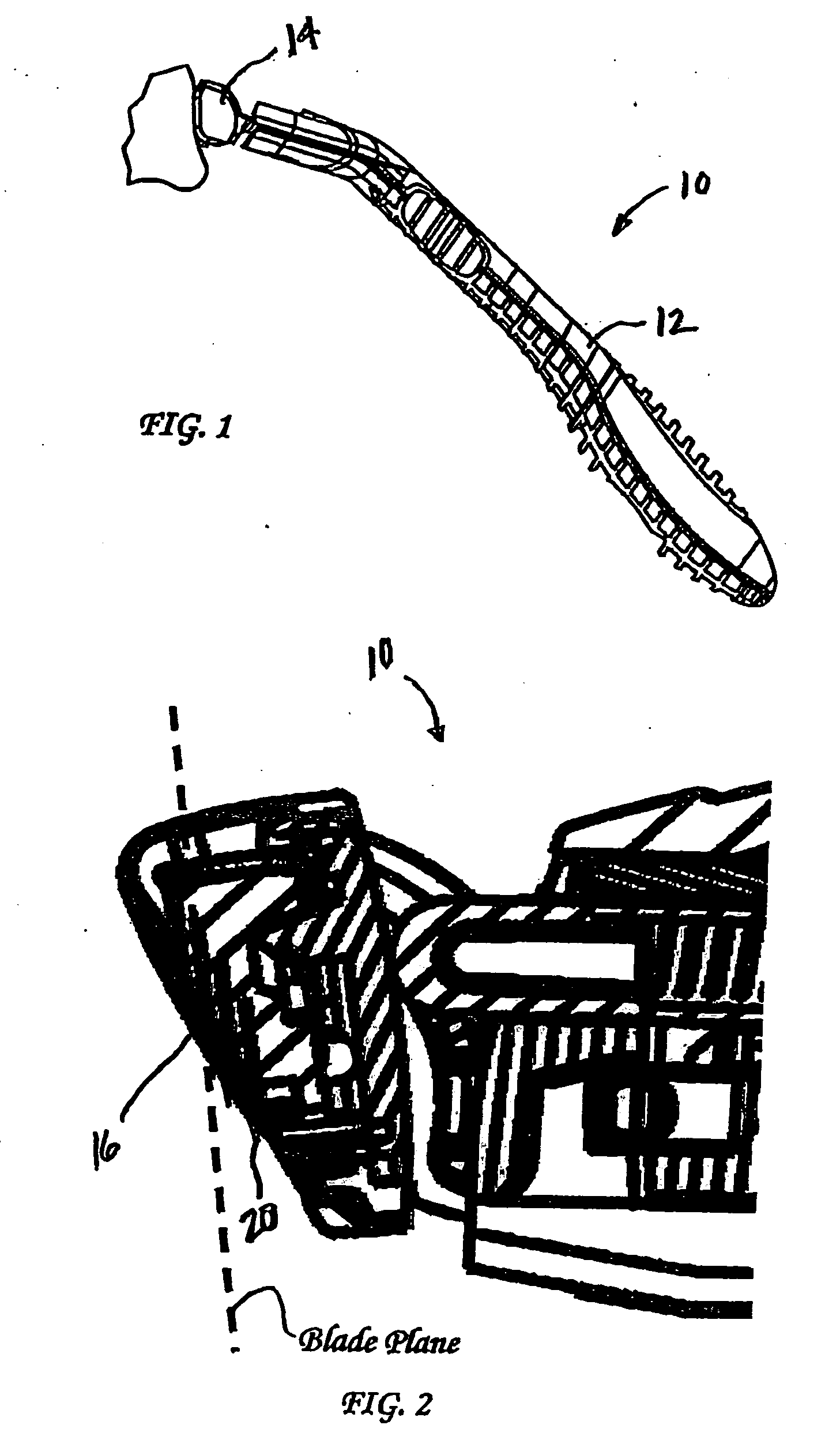
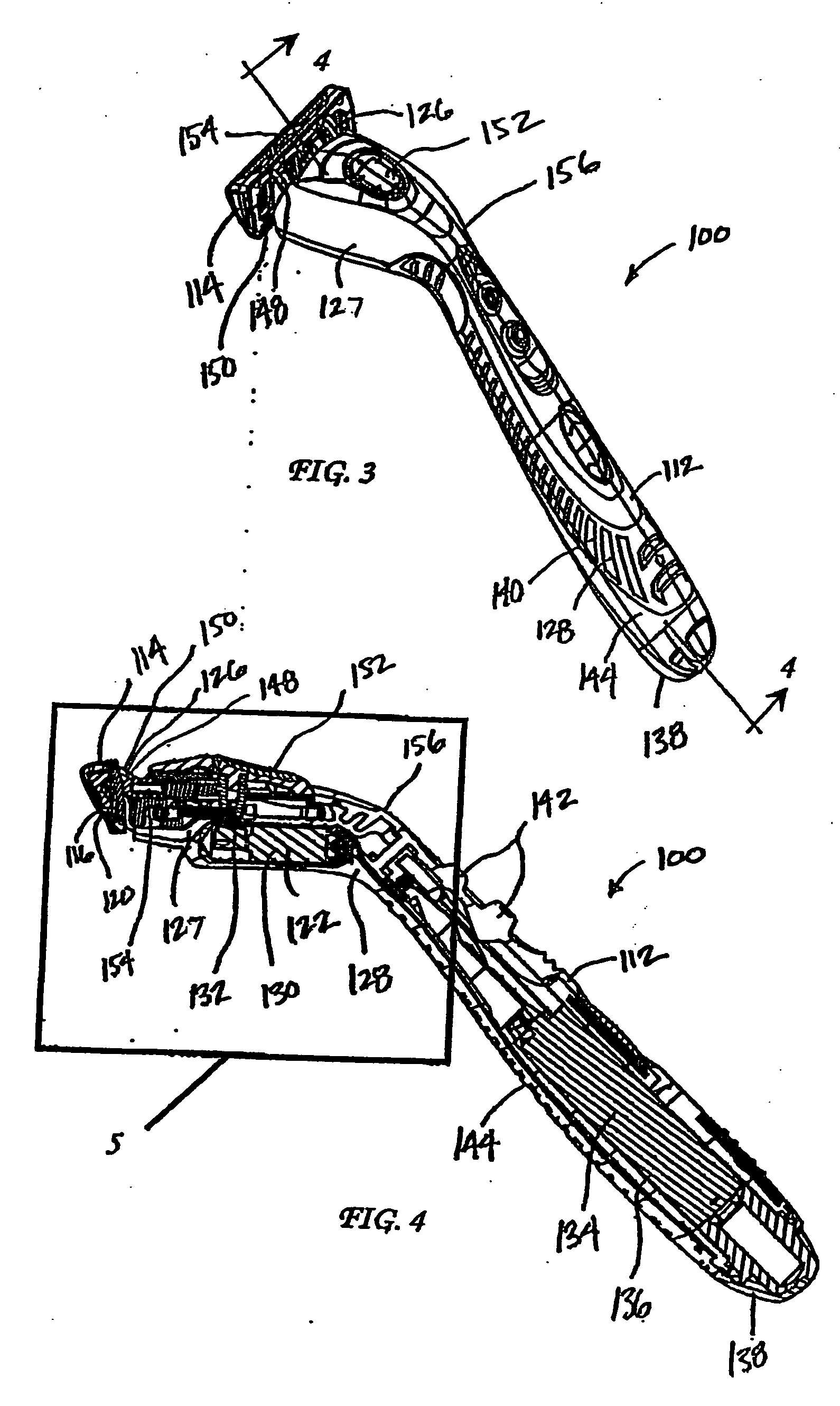
InactiveUS20060218804A1Reduce cutting forceBottle/container closurePower operated devicesEngineeringCutting force
The present invention is related to a shaving implement that includes at least a razor cartridge and a mechanism. The razor cartridge includes at least one blade that has a sharpened cutting edge and defines a blade plane. The mechanism is disposed in the shaving plane and moves the blade in the blade plane during shaving. The mechanism may be either a vibration mechanism (i.e., a motorized spinning eccentric weight), or a dithering mechanism (i.e., a piezoelectric element). The cut force required to shave, when the blades are moving in the blade plane, is significantly reduced.
Owner:EVEREADY BATTERY CO INC
Method for optimally designing dynamic property of complete machine tool
ActiveCN102063548ASimple structureAssembly precisionSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelResonance
The invention discloses a method for optimally designing dynamic property of a complete machine tool, which comprises the following steps of: establishing a complete machine tool entity parameterized model, simplifying the structure according to the analysis requirement on the dynamics and the structure characteristic of the machine tool; and guiding the simplified entity model into a finite element analyzing software ANSYS / Workbench for grid division to obtain a complete machine finite element model. The statics analysis is carried out through the ANSYS / Workbench to obtain a complete machine prestress field, and the mode of the complete machine tool under the prestress field is obtained through the mode analysis. The complete machine tool dynamics response of a main shaft, caused by a cutting force, under different rotating speeds is obtained through resonance response analysis on the complete machine tool, and the reference is provided for the searching of the dynamics thin link and the optimization design. Finally, by using the parameterized analysis method, the rule of influencing the complete machine tool dynamic property by the structure quality and the rigidity parameter is obtained, and the dynamic rigidity thin link is obtained and optimally designed.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
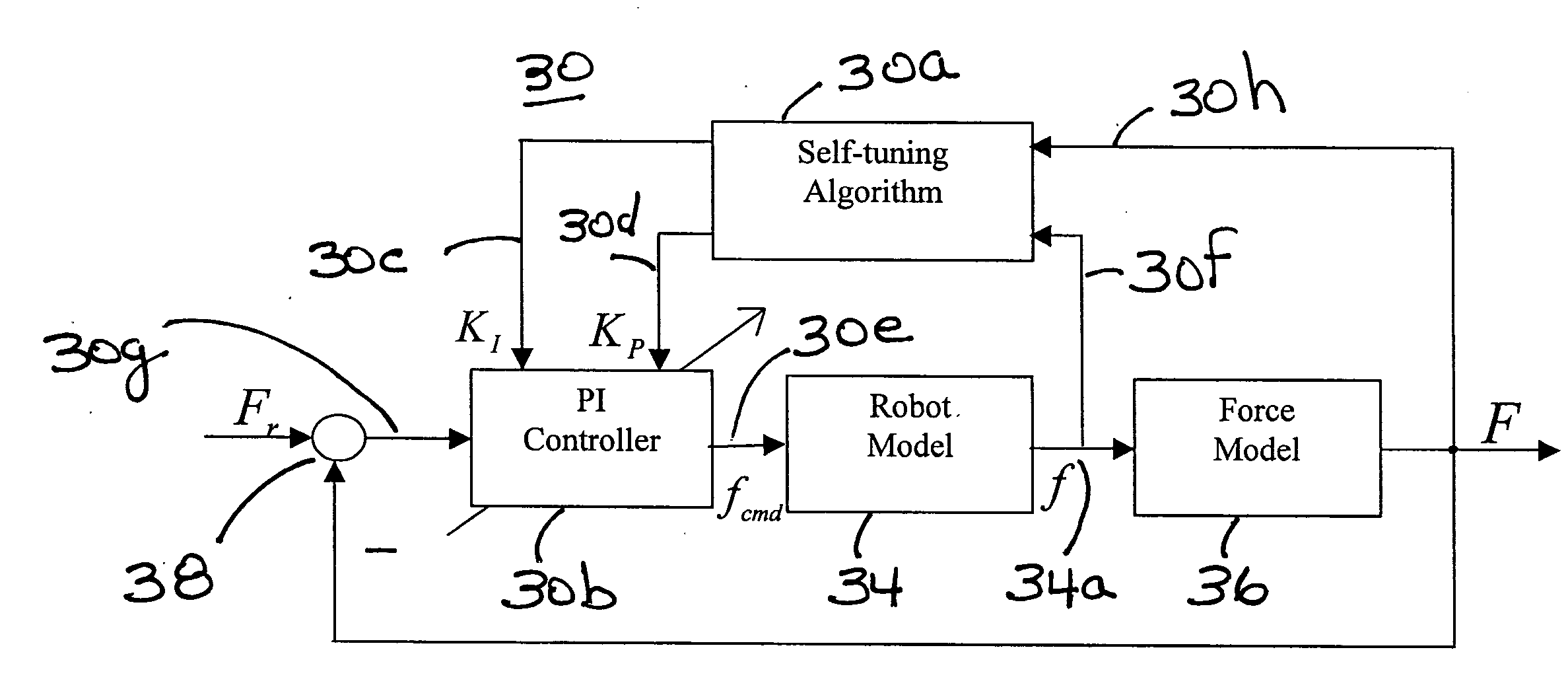
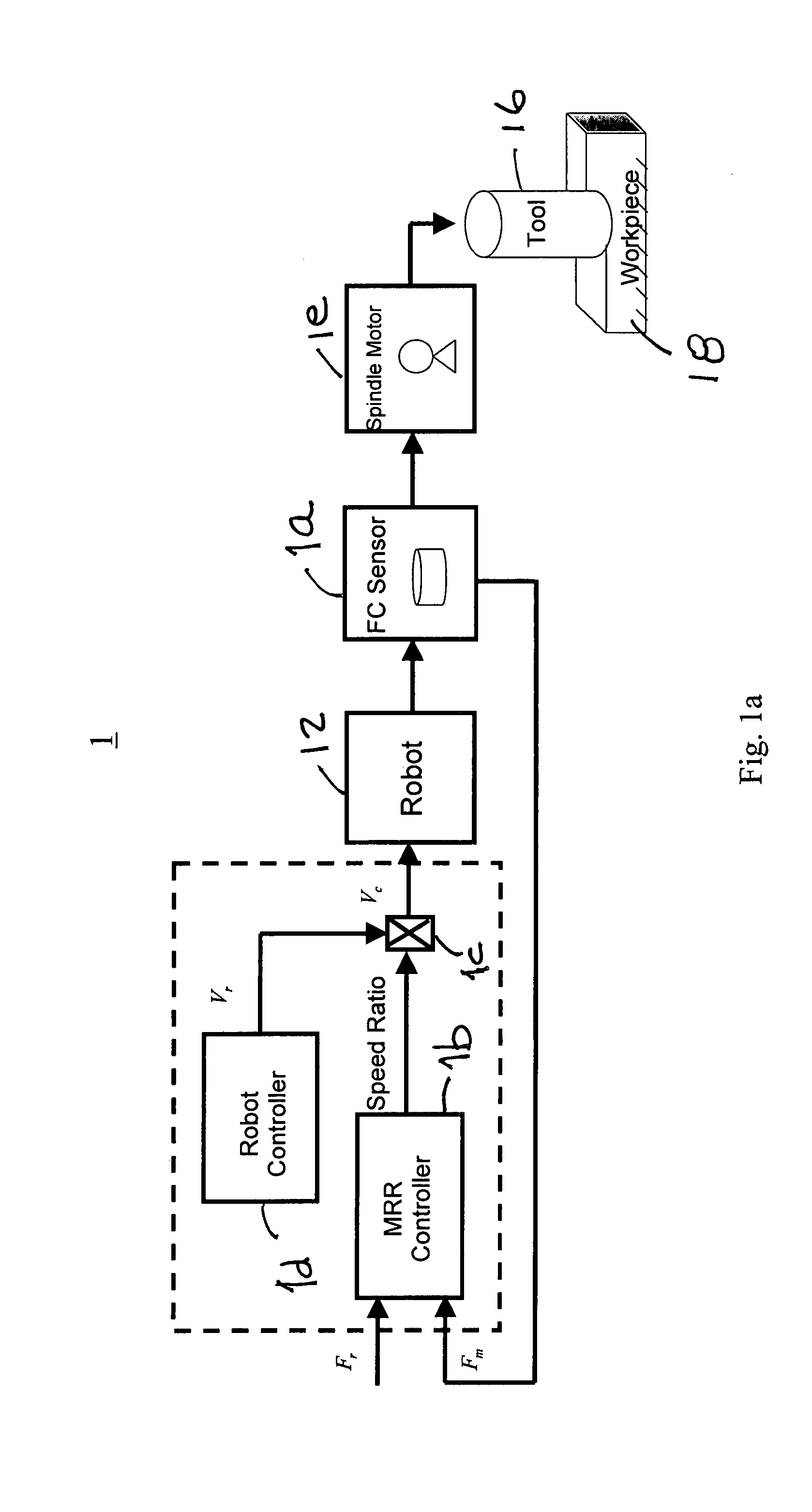
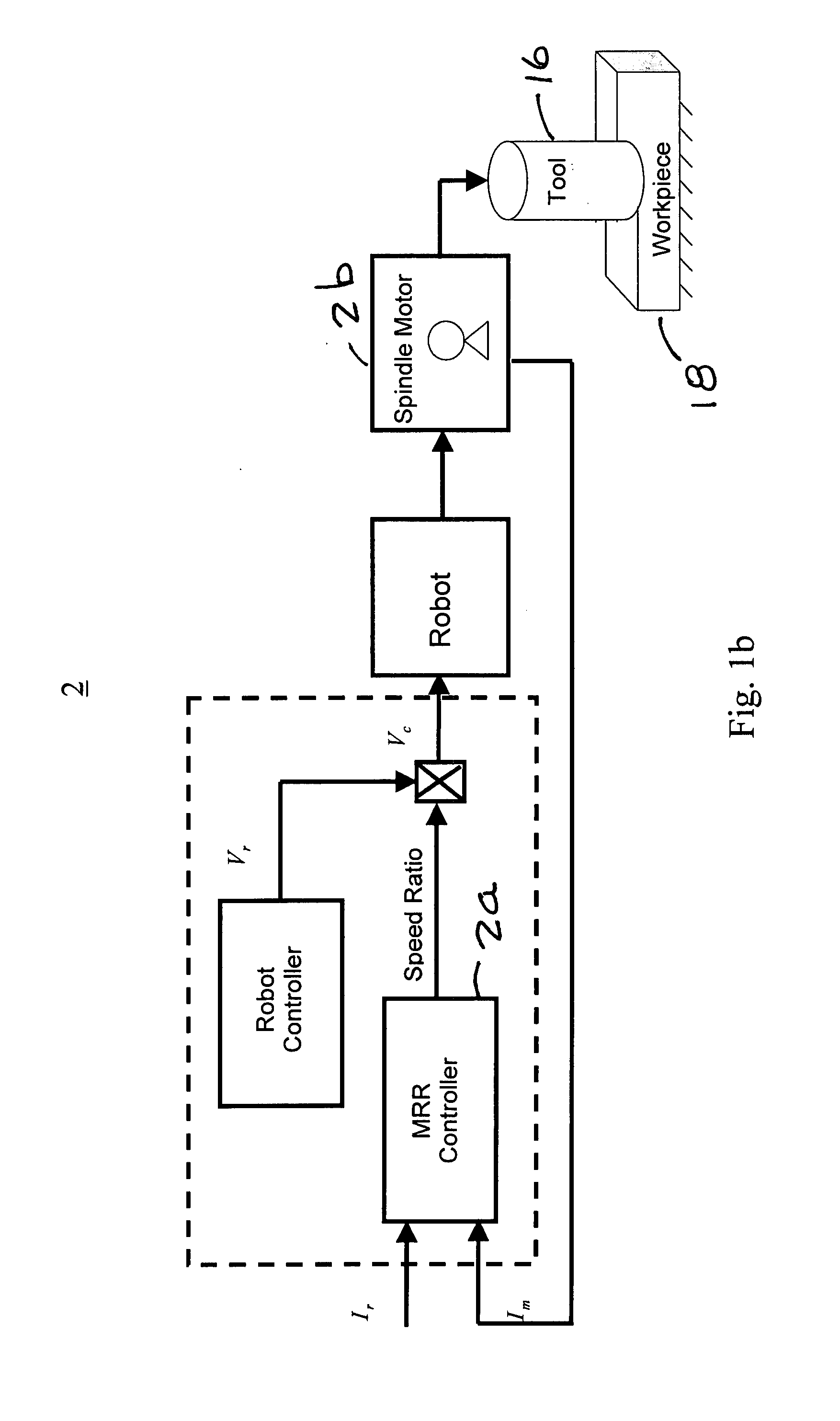
Controlled material removal rate (CMRR) and self-tuning force control in robotic machining process
InactiveUS20080065257A1Programme-controlled manipulatorMeasurement/indication equipmentsSelf-tuningMaterial removal
A method and apparatus for a robotic machining process that gives a controlled removal rate of material from a workpiece when an object, tool or workpiece, held by a robot is brought into contact with a stationary object, workpiece or tool. A signal indicative of the force applied by the held object t the stationary object is used to control the rate at which the robot moves the held object in relation to the stationary object. Associated with the robot is a controller that has tunable proportional and integral gains. The controller determines a command for the feed rate of the tool when the tool engages the workpiece. In response to that command, the proportional and integral gains are tuned to obtain a cutting force to be applied to the workpiece when the tool engages the workpiece that is substantially the same as a desired cutting force.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
Shear Seal Blowout Preventer
ActiveUS20100319906A1Minimize cutting forcePrevent pressure leaksDrilling rodsFluid removalCoiled tubingEngineering
A shear / seal ram provides a knife edge at the shearing edge and the knife edge is inclined to minimize the cutting force required and to leave a clean cut edge. The knife edge is presented in an opening of the ram, thus the opening is positioned at the axis of the BOP, and consequently the coiled tubing, before the coiled tubing is run through the BOP. A biasing means, such as for example a Bellville spring, forces a sealing sleeve against the underside of the ram to prevent leakage of pressure from below the BOP. Similarly, a plurality of biasing means, referred to herein as “skates”, forces the ram down against the sealing sleeve to seal pressure from above the BOP.
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO LP
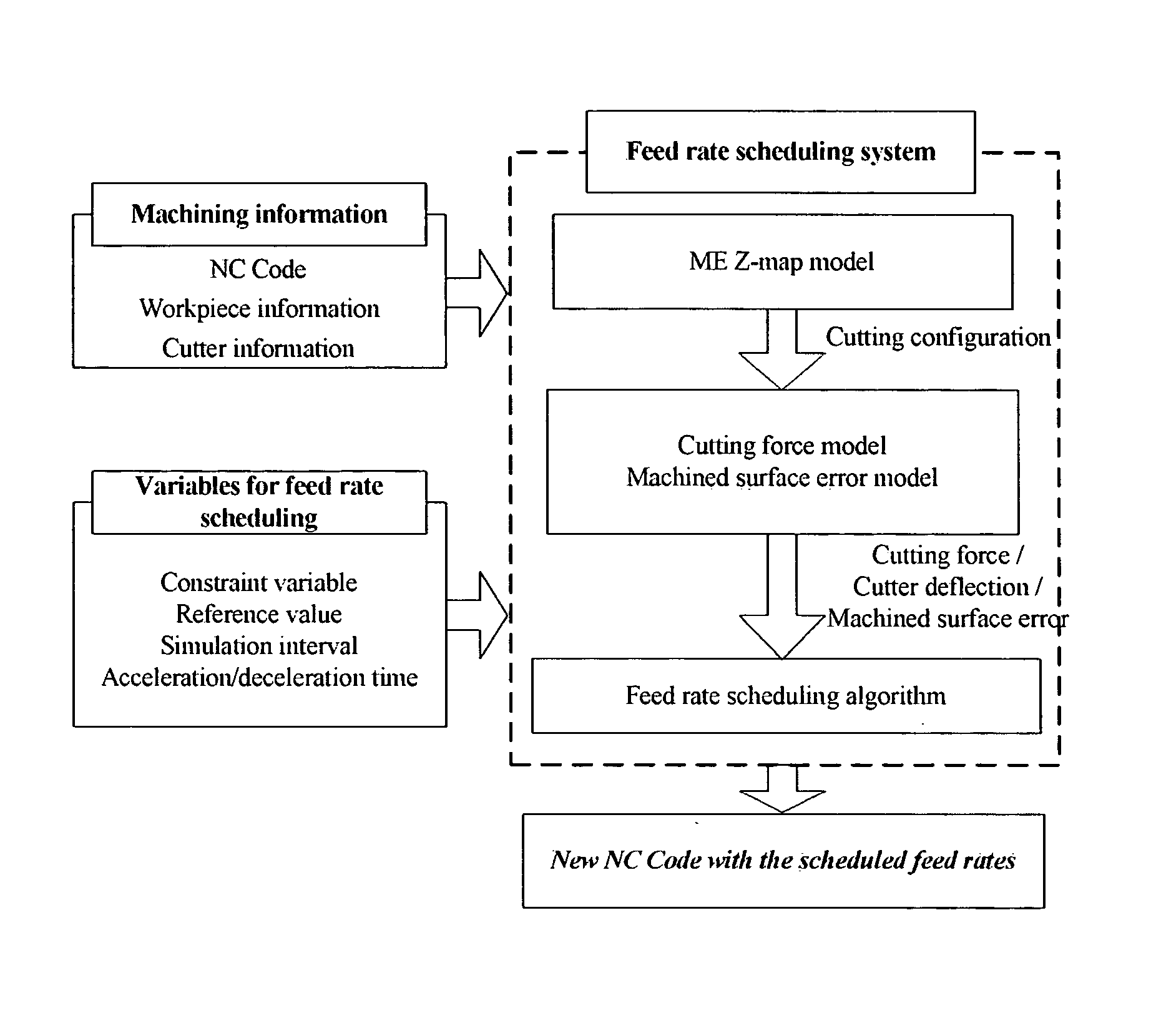
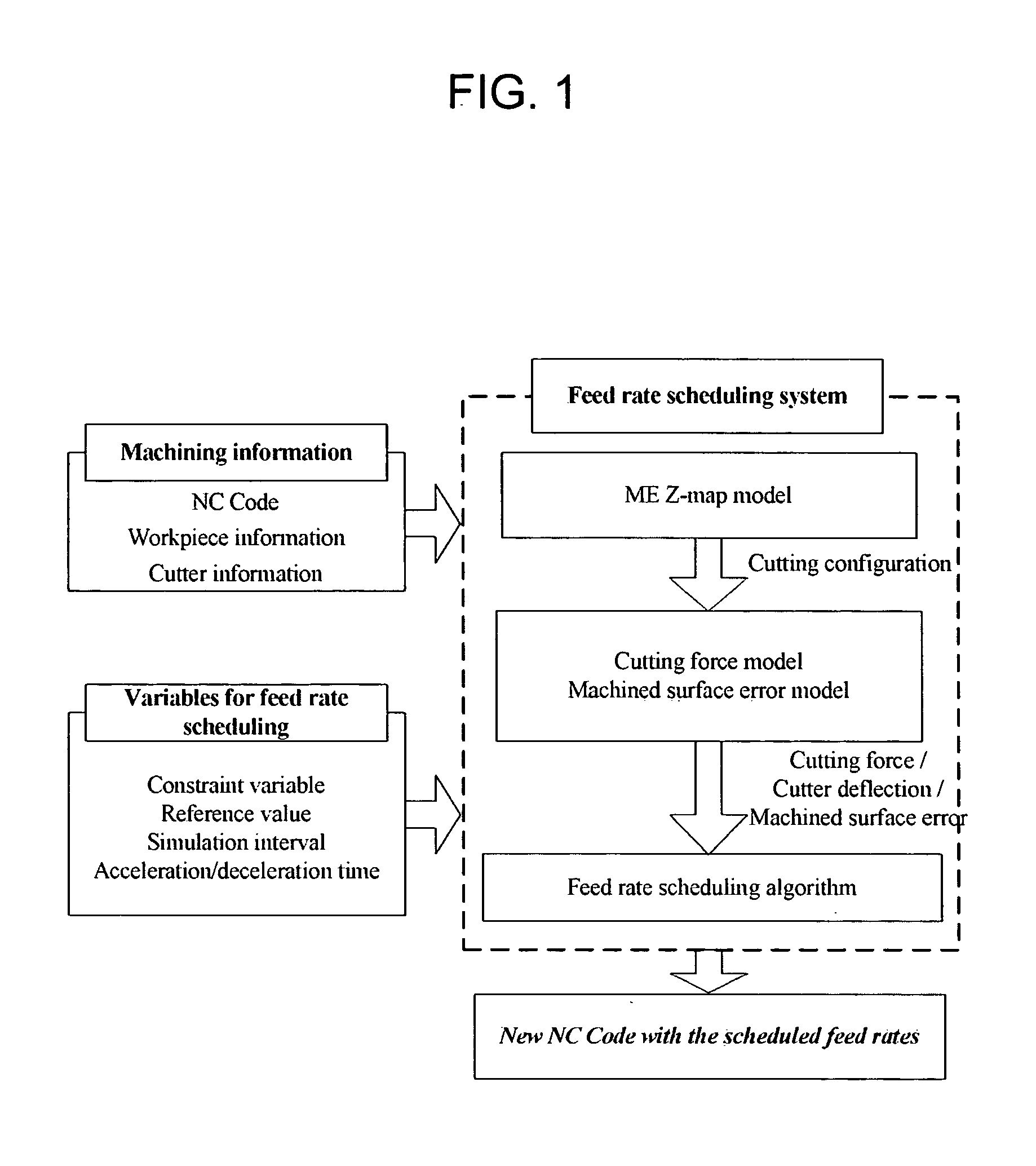
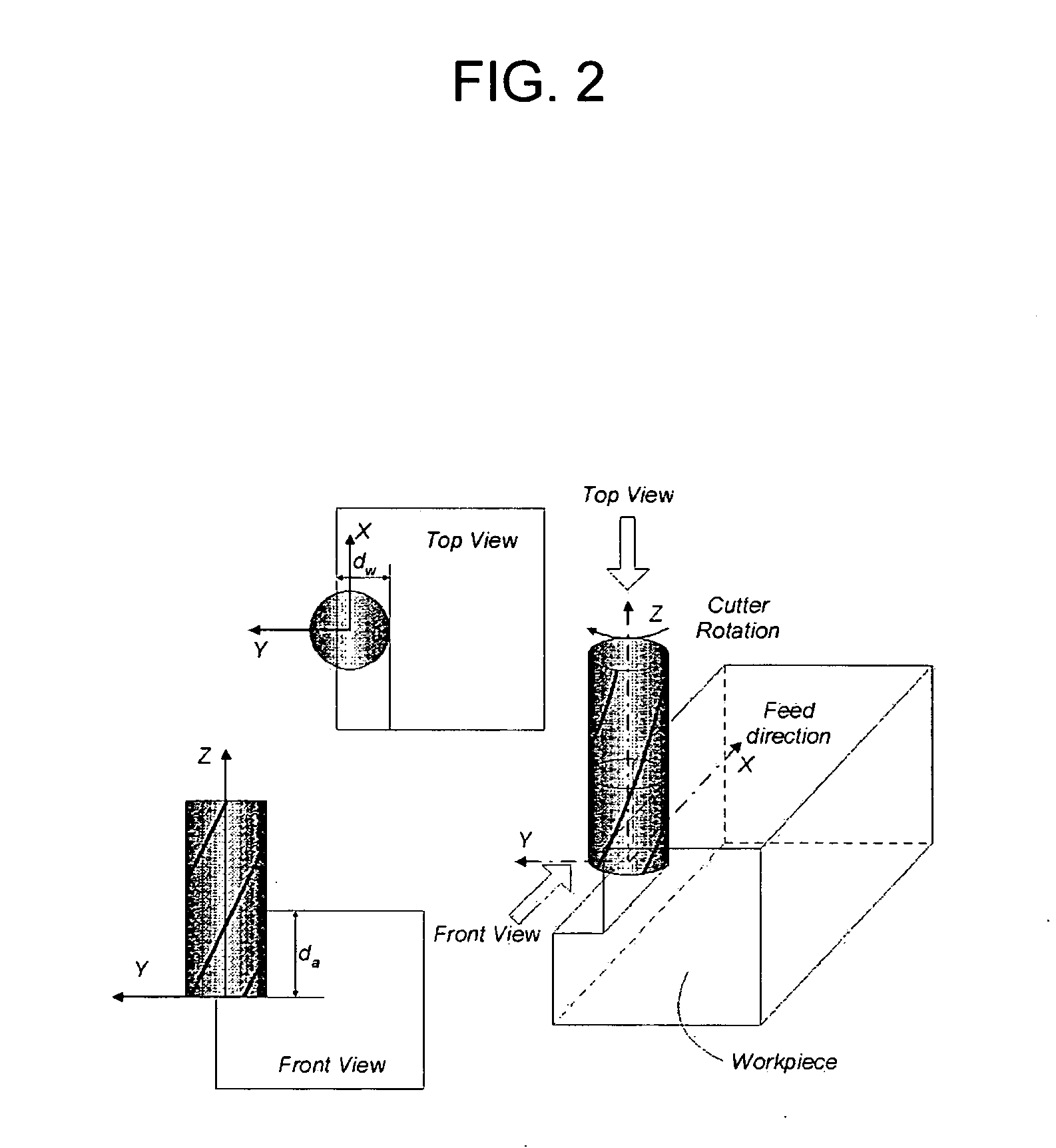
Off-line feed rate scheduling for reduction of machining time and enhancement of machining accuracy in CNC machining
InactiveUS20050113963A1Improve machining precisionIncrease productivityComputation using non-denominational number representationNumerical controlMachined surfaceSpecific rotation
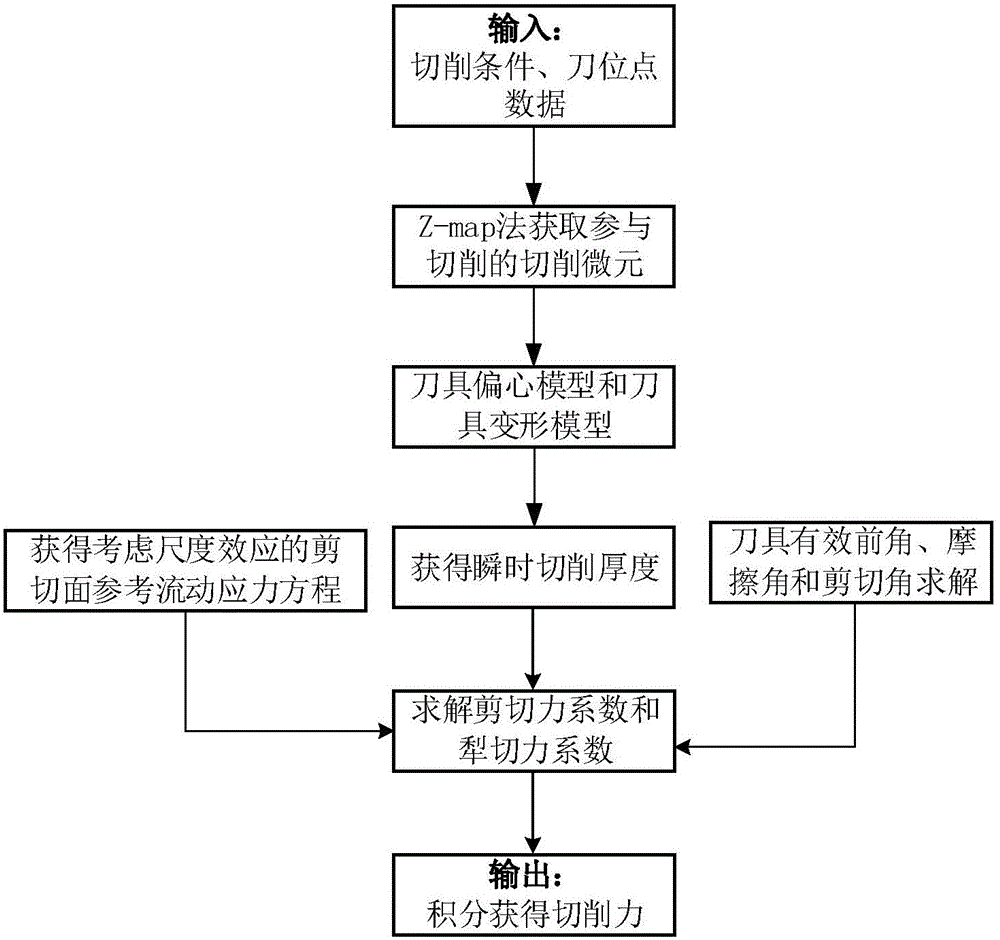
An off-line feed rate scheduling method of a CNC machining process includes selecting a constraint variable and inputting a reference value related to the constraint variable; estimating a cutting configuration where a maximum constraint variable value (CVV) occurs through ME Z-map modeling; receiving the estimated cutting configuration and estimating a specific rotation angle (φs) where the maximum constraint variable value occurs through constraint variable modeling; calculating a feed rate that satisfies the reference value of the constraint variable at the estimated specific rotation angle; and applying the calculated feed rate to the NC code. Cutting force or machined surface error may be selected as a constraint variable depending on machining conditions.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Reciprocating saw blade with tapered tang stem
InactiveUS7600458B2Facilitates effective and efficient engagementIncrease resistanceMetal sawing devicesMetal sawing toolsEngineeringCutting force
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Industrial robot cutting and processing system applied to auxiliary assembly of airplane as well as method
InactiveCN101372079ARealize cutting functionMeet the machining accuracy requirementsMeasurement/indication equipmentsLarge fixed membersEngineeringLaser tracker
The invention discloses an industrial robot cutting processing system and a method applied to aircraft auxiliary assembly, comprising a six-axis joint typed industrial robot, a robot controller, an operation panel, a high speed electric mainshaft, a tool clamping process device, a tool quick exchanger, a target installation flange and a laser tracker; high speed cutting technique is adopted; process methods and hole preparing process of boring, reaming by milling and final reaming are sequentially carried out so as to improve the diameter precision of the hole; meanwhile, the cutting force can be controlled by finishing the reaming hole; rough milling is carried out firstly, fine milling is subsequently carried out; furthermore, the cutting depth is not more than 0.15mm during the fine milling process, thus ensuring the planeness of the processing surface; the industrial robot cutting processing system can realize various cutting processes of the soft metal (such as aluminium alloy) as follows: boring, hole enlarging, reaming, dimpling, surface milling, cutting, etc. The invention integrates normal robot, high speed electric mainshaft, quick exchanger, etc., and can solve the cutting process problems of operations such as fine processing, skin cutting, and the like of radar cover installation hole in the field of aircraft assembly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
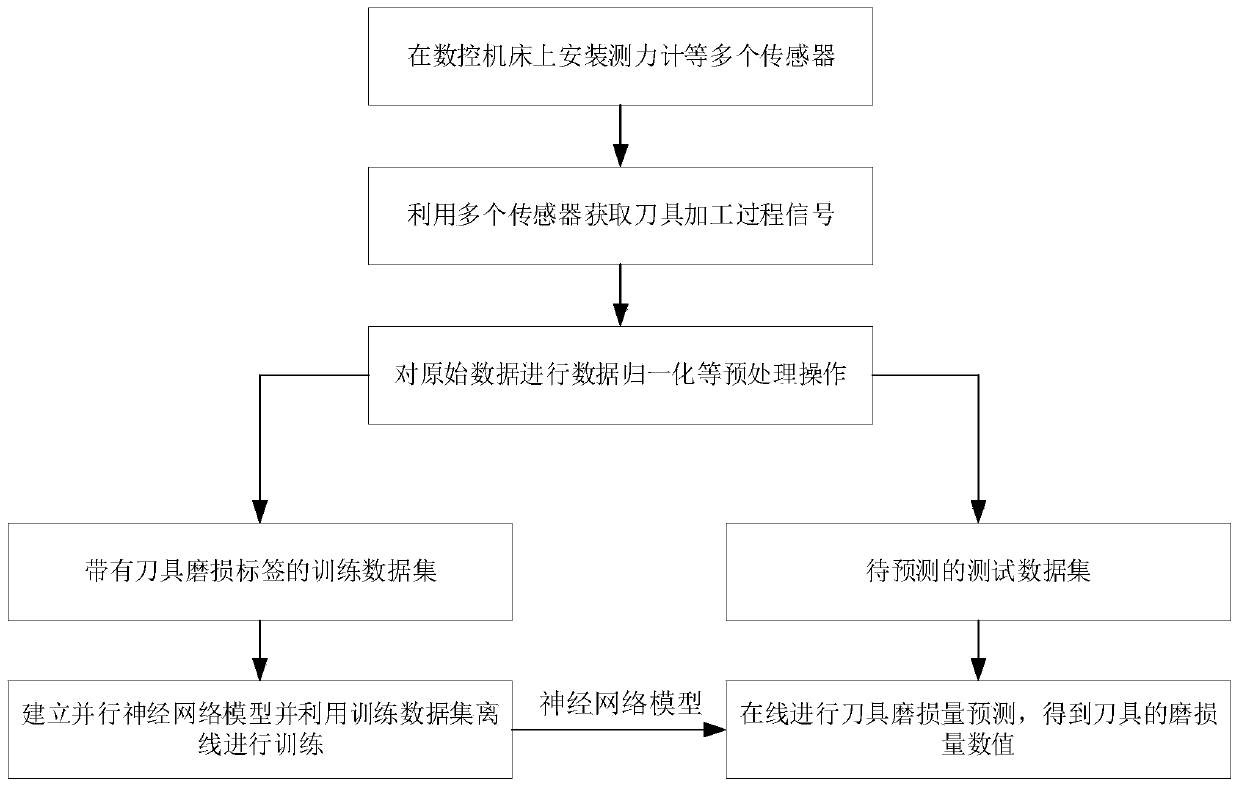
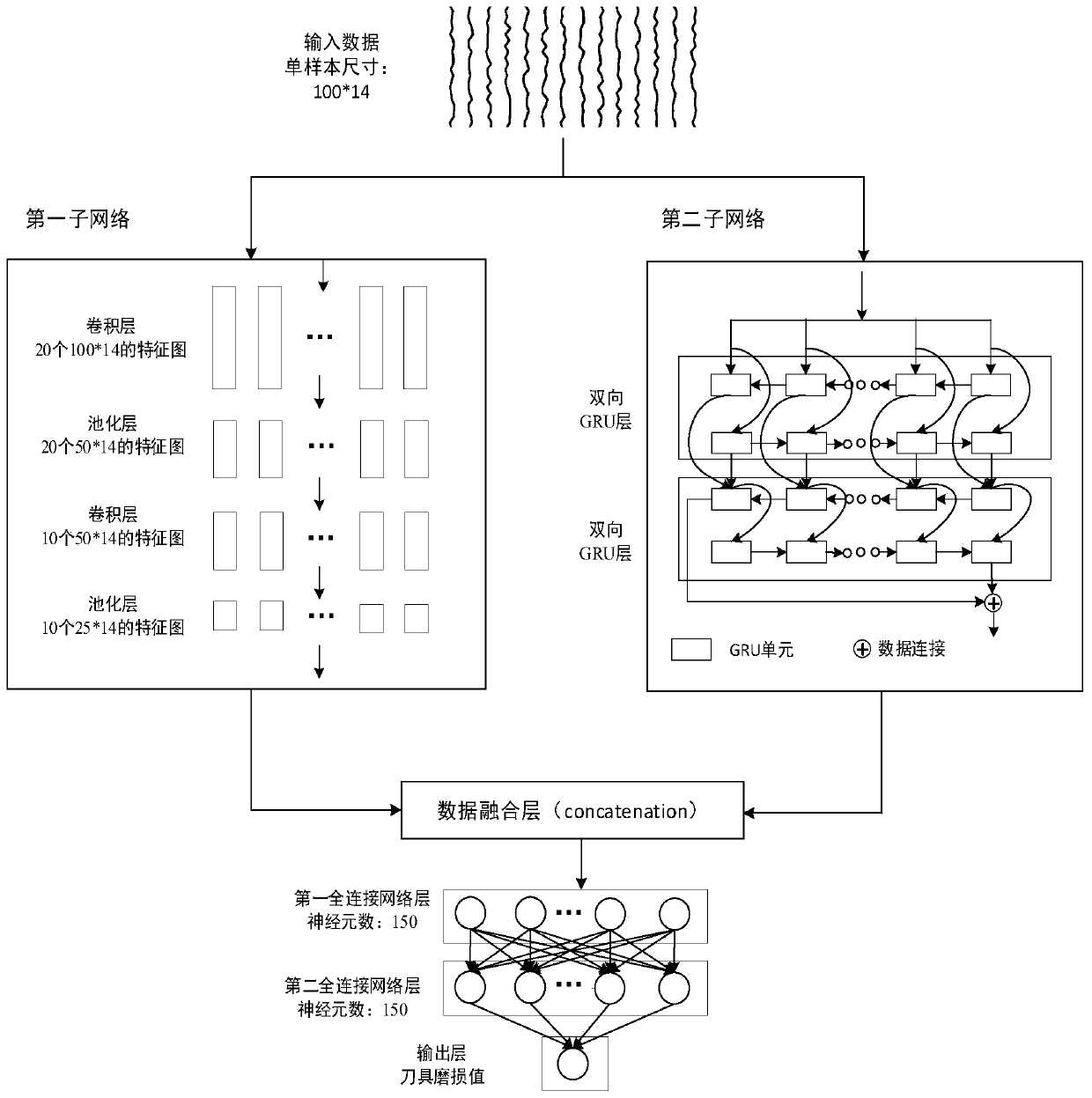
Tool wear condition prediction method of numerical control machine tool based on parallel deep neural network
ActiveCN109822399AStrong feature extraction abilityEffective mining of time series featuresMeasurement/indication equipmentsNumerical controlEngineering
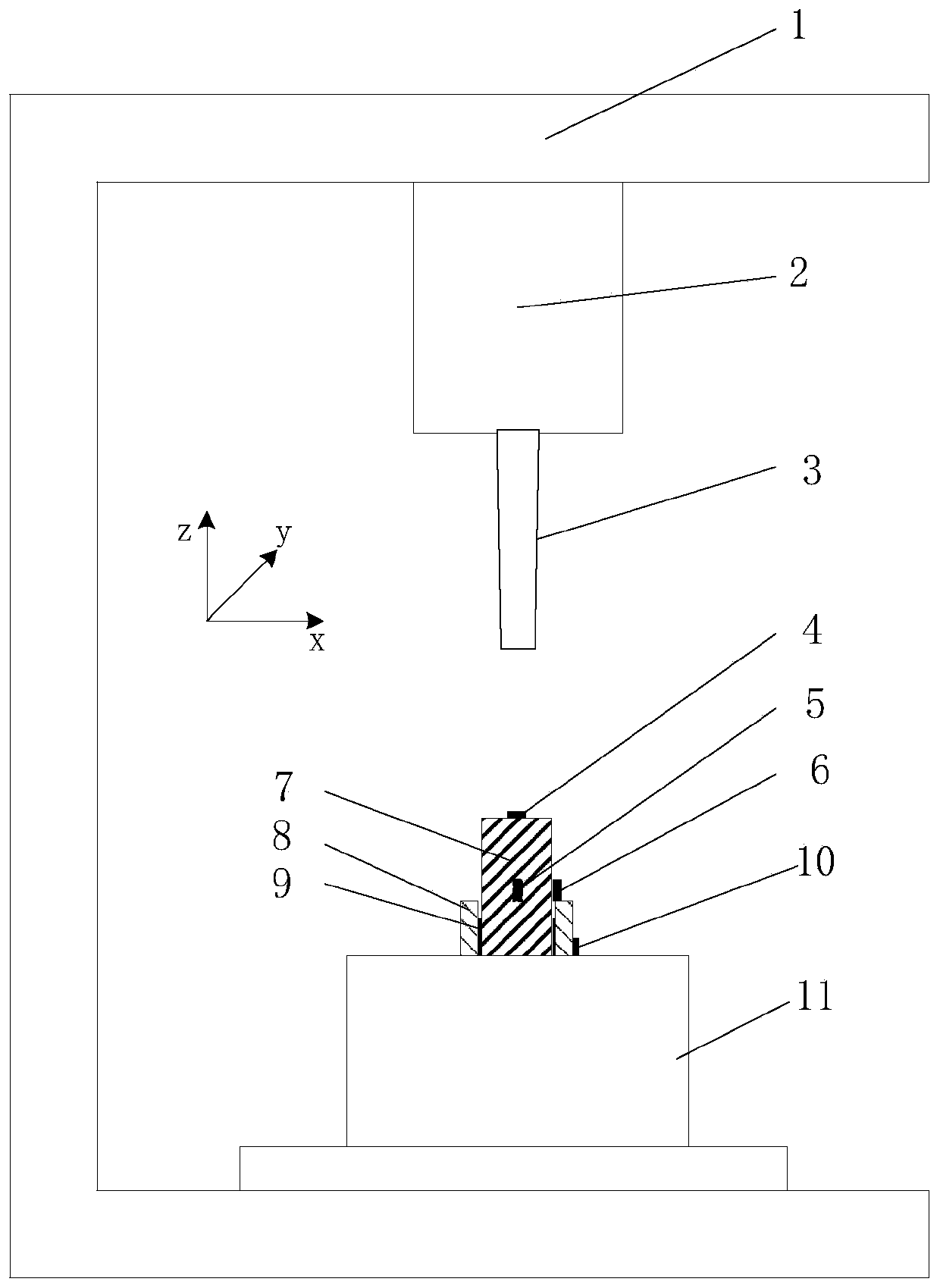
The invention discloses a tool wear condition prediction method of a numerical control machine tool based on a parallel deep neural network. A dynamometer, an acceleration sensor and an acoustic sensor are installed on a workbench and a fixture of the numerical control machine tool; a milling experiment is conducted, the cutting force and vibration and acoustic signals of a milling process are collected so as to obtain multisensor data, and the wear capacity of a tool is collected; pretreatment is performed so as to obtain training data and to-be-tested data; a parallel deep neural network model is established; the treated training data and the label of the wear capacity of the tool are input into an offline training model in the parallel deep neural network model; and the to-be-tested multisensor data are introduced into the trained model so as to predict the wear capacity of the tool in real time and on line. According to the method, the implied characteristics during tool processingof the numerical control machine tool are fully mined, and the wear capacity of the tool can be predicted in real time. The method has the advantage of wide applicability and can be widely applied tovarious numerical control machine tools.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
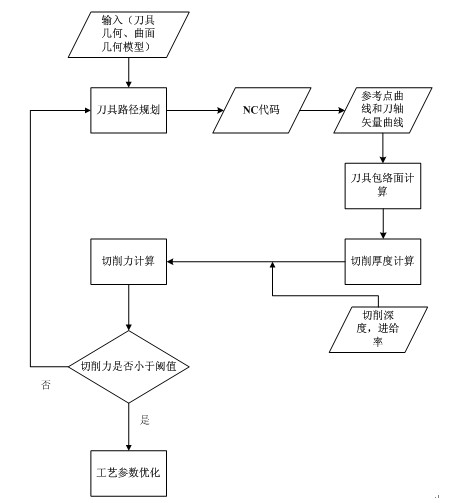
Five-axis side milling machining process parameter design method
InactiveCN102129232AAccurate transient cutting thicknessImprove accuracyNumerical controlNumerical controlAnalytical expressions
The invention discloses a five-axis side milling machining process parameter design method, belongs to the technology of numerical control (NC) machining, and solves the problem that real machining conditions cannot be reflected in cutting force calculation in the conventional process parameter design method. The method comprises the following steps of: tool path planning, cutting force calculation and process parameter optimization; in the tool path planning step, an NC code is generated by using computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software; in the cutting force calculation step, first, a continuous tool path is generated from the NC code; then, a cutting thickness is obtained; and finally, the cutting force is calculated according to the cutting thickness; and in the process parameter optimization step, whether the calculated cutting force is not greater than a design threshold is judged; if the calculated cutting force is not greater than the design threshold, the NC code, the cutting depth and a feed rate are taken as input parameters; and otherwise, an NC code is regenerated. In the method, the real machining conditions are reflected by utilizing a tool enveloping surface analytical expression and the obtained transient cutting thickness is more accurate, so that the accuracy of the calculation of the cutting thickness and the cutting force is improved, and reliable assurance is provided for precisely and efficiently machining a spatial curved surface.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
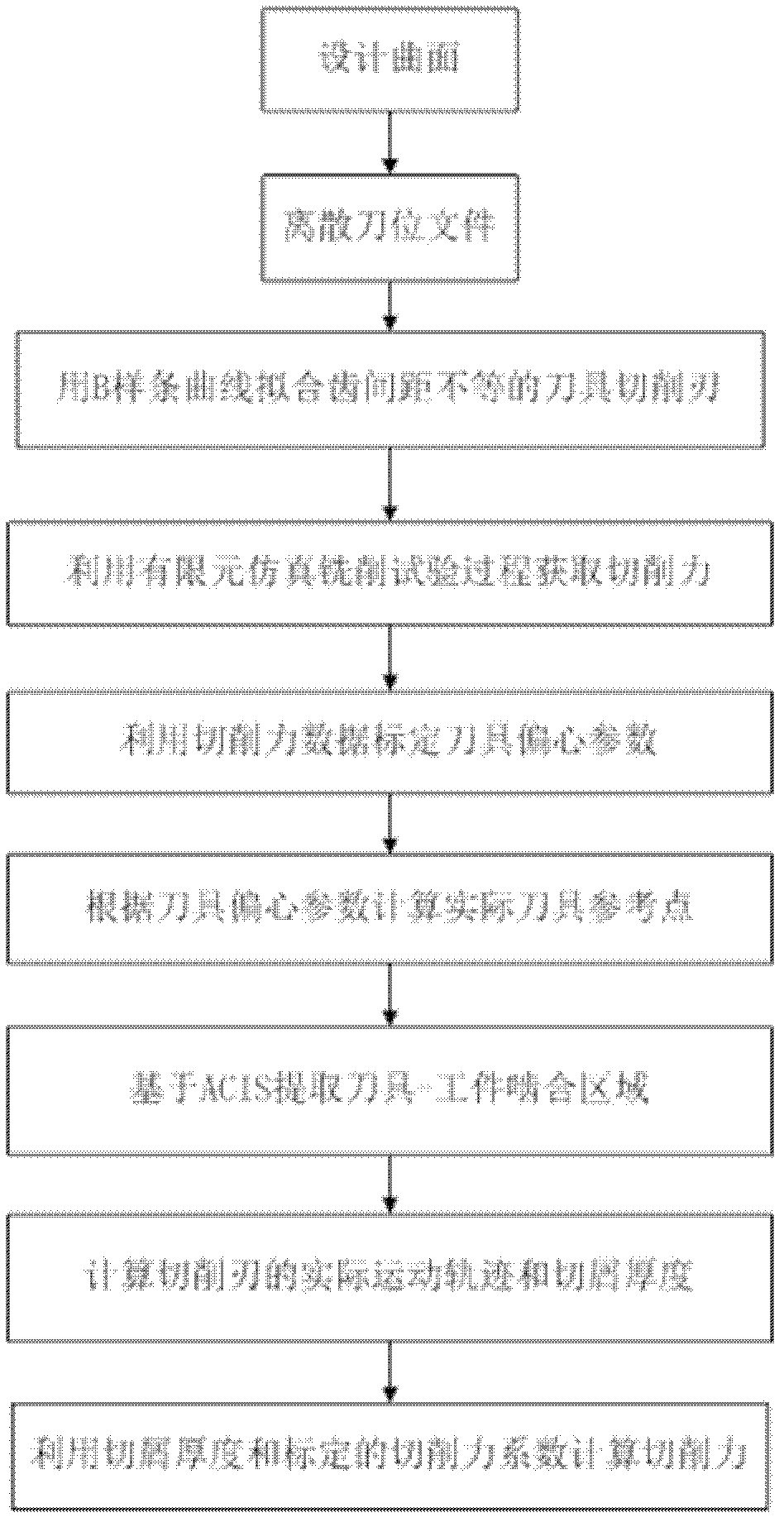
Five-axis side milling cutting force predicting method based on ACIS platform
The invention discloses a five-axis side milling cutting force predicting method based on an ACIS platform, and is used for solving the problem that the real machining condition cannot be reflected in conventional cutting force calculation. The method comprises the following steps of: fitting the edge of a cutter with unequal space width through a B spline, simulating by a finite element method to acquire a cutting force, calibrating dynamic eccentric parameters of the cutter by using the cutting force data, correcting cutter position data by using the eccentric parameters of the cutter to acquire actual cutter reference points, extracting an instantaneous cutter-workpiece engagement region by using the actual cutter reference points and using ACIS as a platform, calculating the actual movement locus and the instantaneous cutting thickness of the edge by using the actual cutter reference points, and calculating the instantaneous cutting force by using the calculated cutting thickness and the calibrated cutting force coefficients. According to the method, the instantaneous cutting thickness is calculated by using the actual movement locus of the edge, so that the real machining condition is reflected, and the predicting accuracy of the cutting force is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
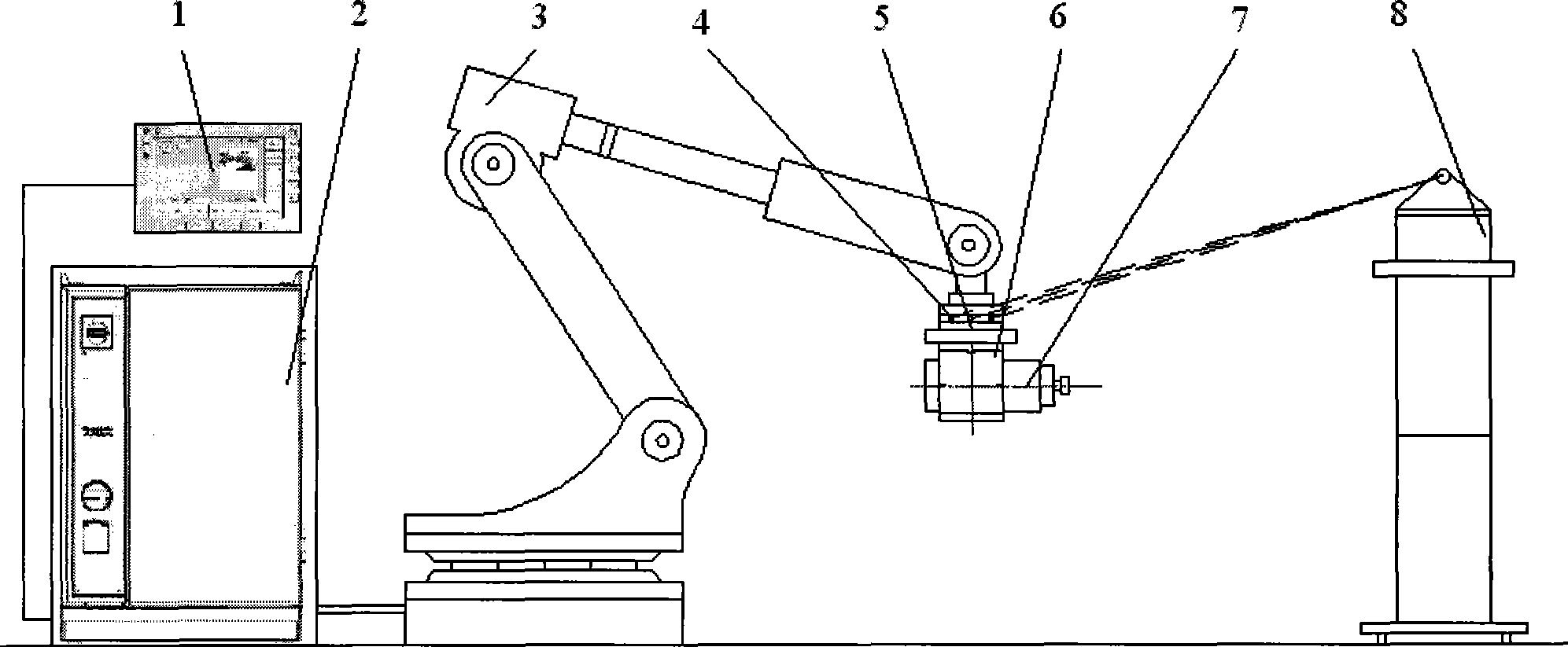
Machine tool spindle reliability test bed based on mixed loading of electro-hydraulic servo and dynamometer
ActiveCN102889983ATrigger failureExposure to failureMachine part testingElectro hydraulicAxial force
The invention relates to a test device of a machine tool spindle, in particular to a machine tool spindle reliability test bed based on mixed loading of electro-hydraulic servo and a dynamometer, and aims to solve the problem that the conventional machine tool spindle reliability test device cannot truly simulate dynamic cutting force loading, static cutting force loading and cutting torque loading. The machine tool spindle reliability test bed mainly comprises a machine tool spindle supporting part, a torque loading part and a cutting force loading part, wherein the machine tool spindle supporting part is formed by combining a spindle box base plate (14) and an iron gasket (15); the torque loading part consists of a loading rod (12), an elastic diaphragm coupler (9) and the dynamometer (8), which are coaxially assembled; and the cutting force loading part employs two loading modes, namely a cutting resultant force loading mode and a cutting axial force and radial force separated loading mode. By performing reliability test for simulating true working conditions on the tested machine tool spindle, the failure of a product is stimulated and exposed, and practical basic data are provided for reliability growth and evaluation of the product.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Cutting tool having cutting insert secured by non-penetrating abutment of a threaded fastener
A cutting insert is retained in a cutting tool through a combination of resilient clamping and abutment by a threaded fastener. The threaded fastener, which abuts but does not penetrate cutting insert, pre-loads the cutting insert against cutting forces, by biasing the cutting insert against a jaw of the cutting tool.
Owner:ISCAR LTD
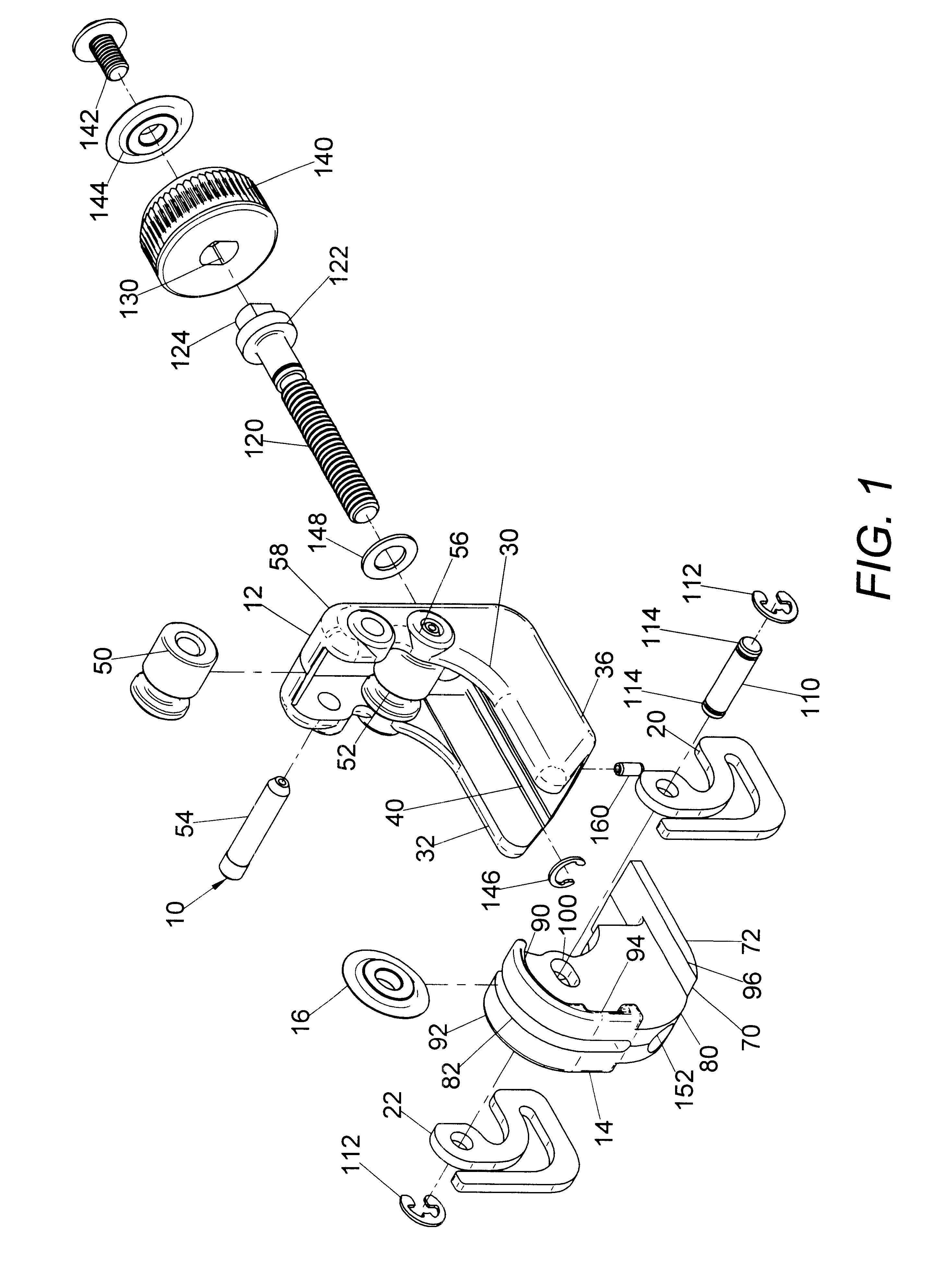
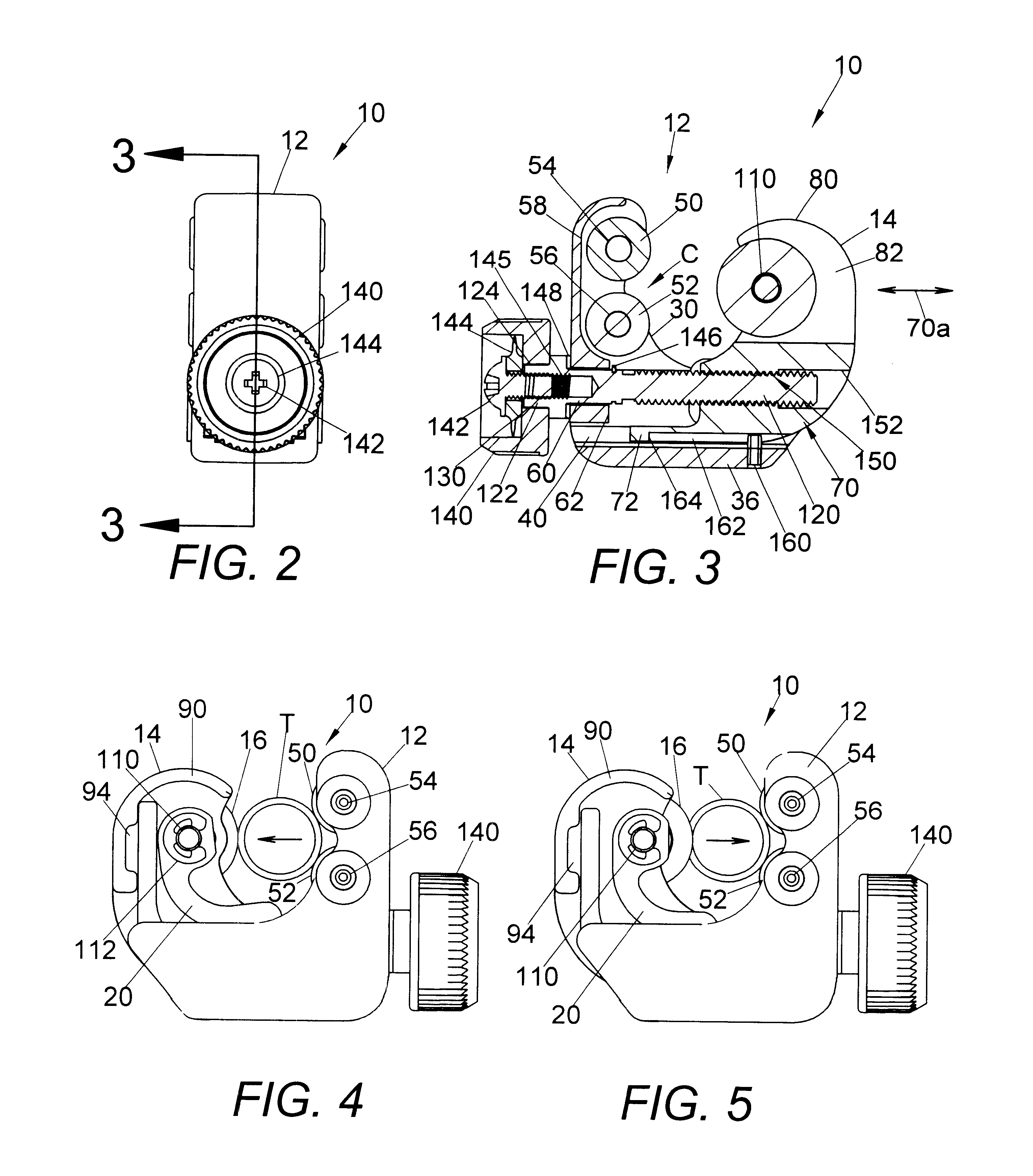
Tube cutter
InactiveUS6393700B1Reduce actionMaintain abilityTube shearing machinesMetal working apparatusEngineeringCutting force
A tube cutter for cutting a circular tube having a central tube axis, the cutter comprising: a housing with first and second parallel rollers defining a cradle for receiving a tube cut with the tube axis generally parallel to the axes of the rollers, a cutter head reciprocally mounted on the housing for sliding linearly in a direction toward and away from the rollers, the cutter head having a base and an upstanding arm supporting a cutter wheel rotatable about an axis generally parallel to the axes of the rollers and facing the tube in the cradle, a spring element biasing the cutter wheel in the stated direction and toward the rollers, and a threaded shaft between the housing and cutter head, and rotatable to move the cutter head linearly toward the housing, whereby the cutter wheel engages the tube and the spring element creates a cutting force pushing the cutter wheel against the tube for cutting the tube.
Owner:EMERSON ELECTRIC CO
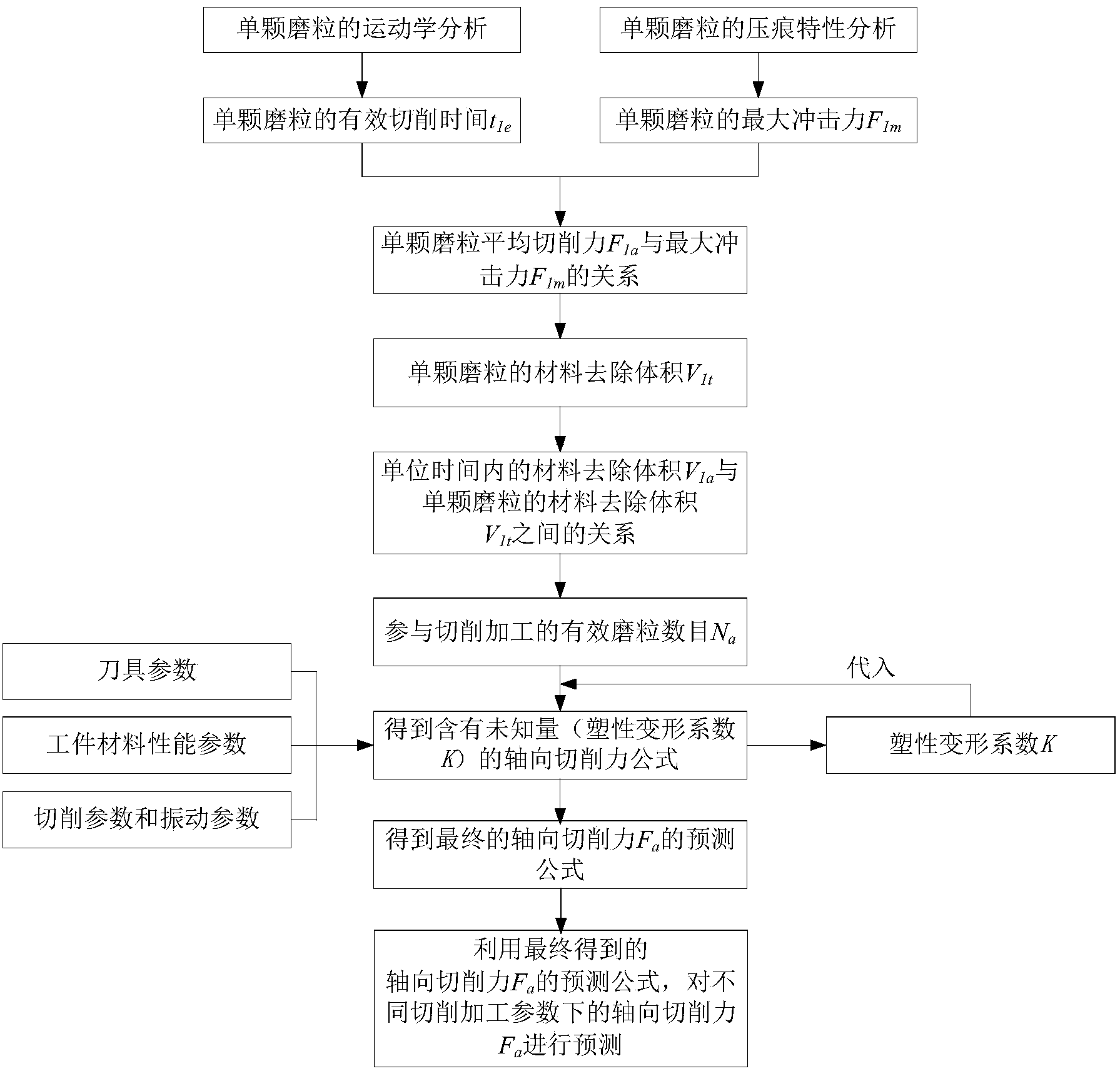
Method for predicting axial direction cutting force of supersonic vibration auxiliary grinding for fragile materials
InactiveCN103753357AComply with removal volumeIn line with the actual processing conditionsGrinding feed controlOctahedronKinematics
The invention provides a method for predicting the axial direction cutting force of supersonic vibration auxiliary grinding for fragile materials. The method includes the steps that the kinematics characteristics and the indentation characteristics of a single abrasive grain are analyzed under the supersonic vibration auxiliary action, the effective cutting time of the single abrasive grain, the relation of the average cutting force and the maximum impact force of the single abrasive grain, the material removal size and the number of effective abrasive grains participating in machining within a vibration period are determined, the relation of axial direction cutting force and cutter parameters, workpiece material performance parameters, cutting parameters and vibration parameters is established ultimately, the number of the effective abrasive grains participating in machining and the plastic deformation removal of materials are comprehensively considered, a octahedron material removal size calculation method is put forward, a predicator formula of the axial direction cutting force Fa is established, the formula is more close to the real machining condition, and therefore the precision for predicting the axial direction cutting force of supersonic vibration auxiliary grinding for fragile materials is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Precision numerical control milling method for thin-wall parts
InactiveCN101602122AReduce stiffnessGuaranteed machining accuracyMilling equipment detailsNumerical controlEngineering
The invention discloses a precision numerical control milling method for thin-wall parts, and provides a processing method for reducing the milling deformation of the thin-wall parts and improving processing precision and surface quality. When a thin-wall part is finished by fine processing through end milling, the machining allowances of the side wall and a web plate are larger than those of the prior process, and are between 2 and 5mm respectively; when the side wall is processed, the axial depth ap is between 0.2 and 0.8mm, and the radial cutting width is 60 to 80 percent of the diameter of a cutting tool; and when the web plate is processed, the axial depth ap is between 2 and 5mm, and the radial cutting width ae is 10 to 20 percent of the diameter of the cutting tool. The processing method effectively slows down the reduction of the self-rigidity of workpieces and control the cutting force in the thin-wall direction when the processing efficiency is ensured, thereby effectively reducing and controlling the processing deformation of the thin-wall parts, and ensuring the processing precision and surface quality of the parts.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
Cutting insert and shim for heavy machining operations
A combination of a cutting insert and a shim. The cutting insert and shim have two opposing end surfaces with two identical opposing major side surfaces and two identical opposing minor side surfaces extending between the minor side surfaces. Each end surface of the insert has two lowered abutment members, each having a shim abutment surface for contacting the shim. One end surface of the shim has two raised abutment members, each having an insert abutment surface for contacting the insert. The abutment surfaces contact each other in an area where high cutting forces occur so as to help distribute the loads encountered in the cutting operation, as well as provide protection of the insert pocket in case of insert failure.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
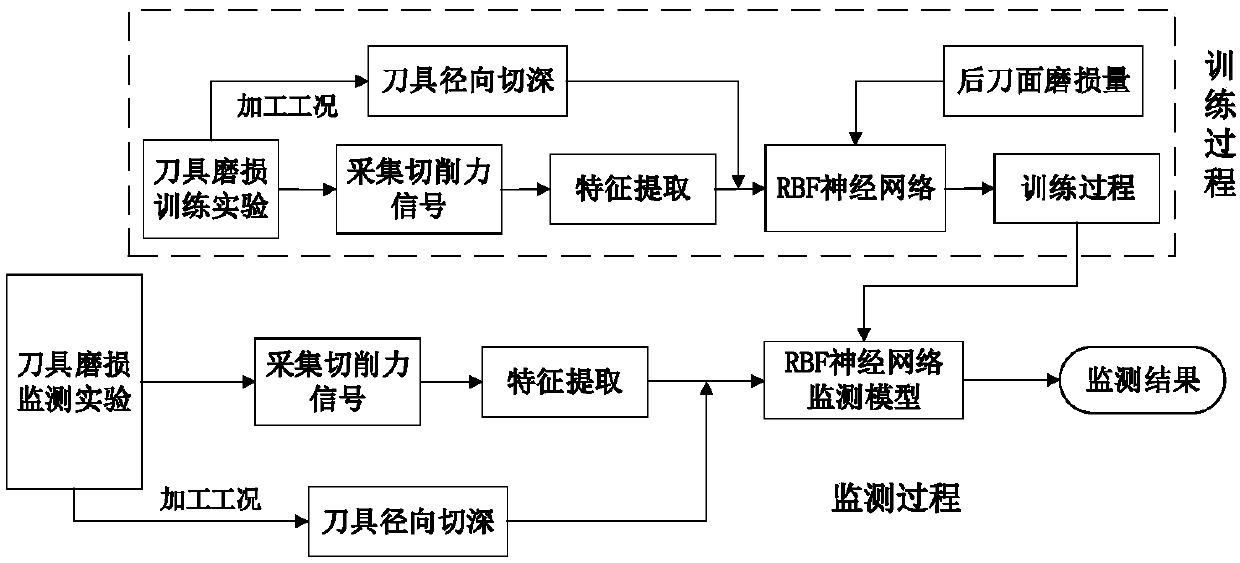
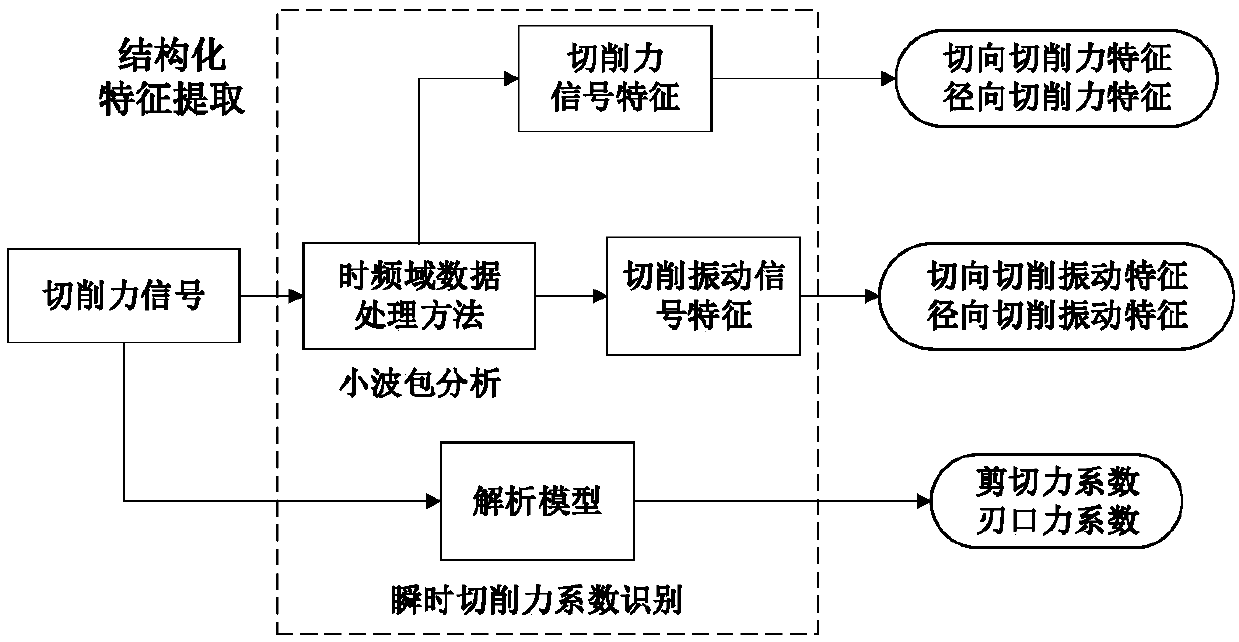
Cutter abrasion online monitoring method based on wavelet packet analysis and radial basis function (RBF) neural network
ActiveCN108356606AAchieve the effect of online monitoringIncrease costMeasurement/indication equipmentsHidden layerTangential force
The invention relates to a cutter abrasion online monitoring method based on wavelet packet analysis and a radial basis function (RBF) neural network. The method comprises the steps that shear force coefficients and cutting edge force coefficients of tangential force and radial force in different cutter abrasion states are calibrated by means of an instantaneous cutting force coefficient recognition method; and by analyzing the correlation between cutting force coefficients and cutter abrasion, the coefficients are taken as cutter abrasion characteristic parameters and input into a RBF neutralnetwork model after being subjected to normalization processing. An input layer of a RBF neutral network monitoring model training process comprises cutting force characteristics, cutting vibration characteristics, the shear force coefficients and the cutting edge force coefficients after being subjected to normalization processing; and an output layer comprises the cutter rear cutter surface abrasion capacity after being subjected to normalization processing; a hidden layer comprises neurons obtained through radial basis function iterative optimization; and it is verified that the RBF neuralnetwork monitoring model has the advantages of high response speed and high recognition precision through cutter abrasion monitoring experiments.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Off-line planning method for cutting feed rate of five-shaft numerical control side milling machining
The invention relates to a 5-axis NC flank milling machining feed rate off-line planning method, which carries out 5-axis NC flank milling machining feed rate off-line planning on the basis of various axis cubic spline polynomial interpolation. By establishing an optimizing model which takes time sequences between adjacent position points of various axes as design variables, takes the minimum sum of running time sequences between adjacent position points of various axes as an objective function, takes limits of speeds, accelerations and jerks of various axes of a machine tool as restriction, and simultaneously takes the maximum cutting force in the cutting process of a tool is smaller than a threshold value as restriction, the method adopts global optimization algorithm to solve and obtain the optimal feed rate. The method is suitable for free-form surface rough machining and ruled surface or similar ruled surface semifinishing.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
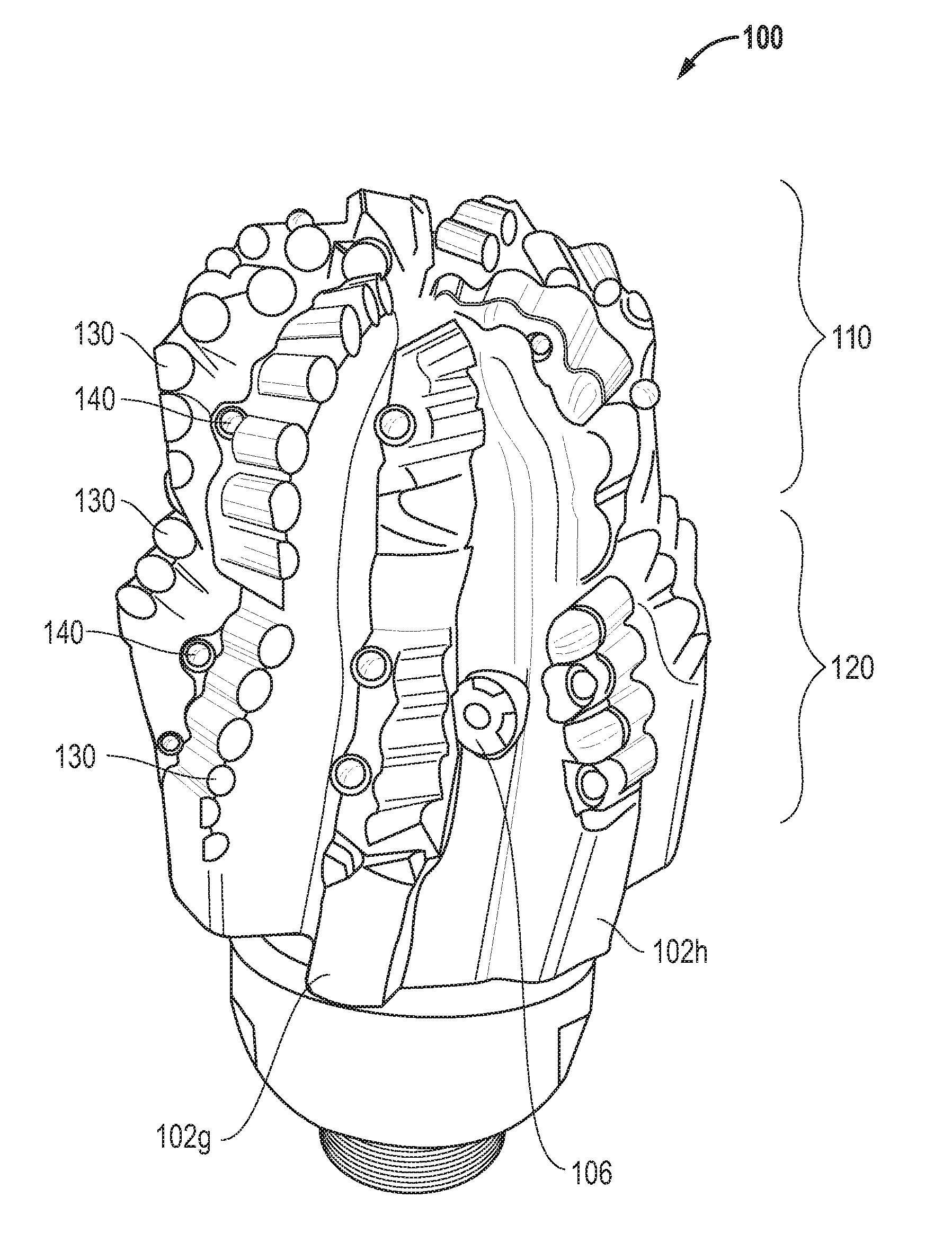
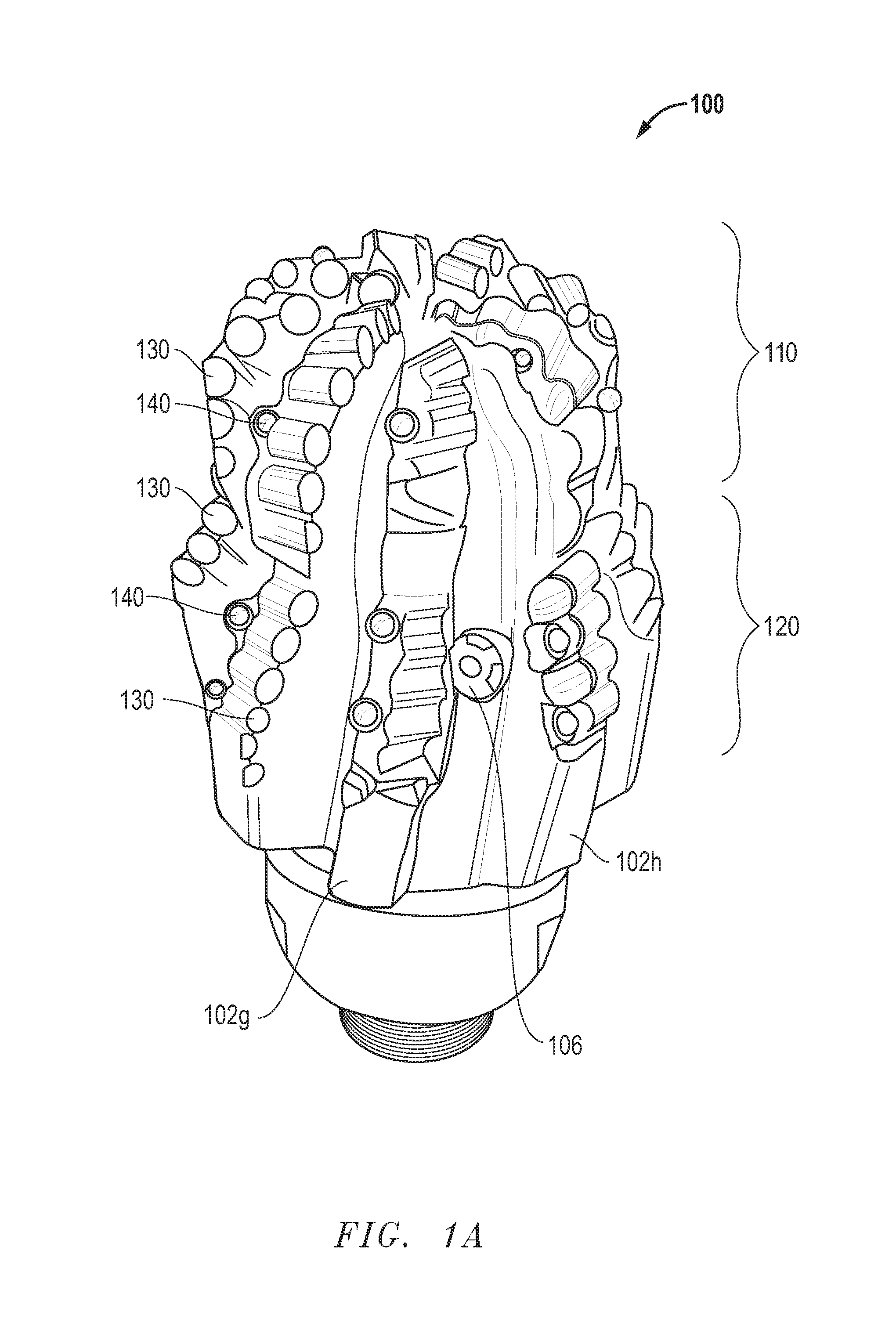
Fixed cutter drill bit
InactiveUS7726415B1Maintaining and restoring bit stabilityMaintain relatively stableEarth drilling toolsDrill bitsReamerCutting force
The fixed cutter drill bit disclosed utilizes a unique piloting section and reaming section carefully designed to impart several specific operational advantages. In the piloting section, cutting structures have been arranged so as to create offsetting cutting forces that result in a net zero imbalance during operation. Furthermore, the piloting section utilizes carefully placed shock studs which aid in protecting the primary cutting structure. In addition, the location of the fluid supply nozzles on the body of the reamer section serves to indicate the occurrence of a catastrophic cutting structure failure below the pilot gage.
Owner:OTS INT
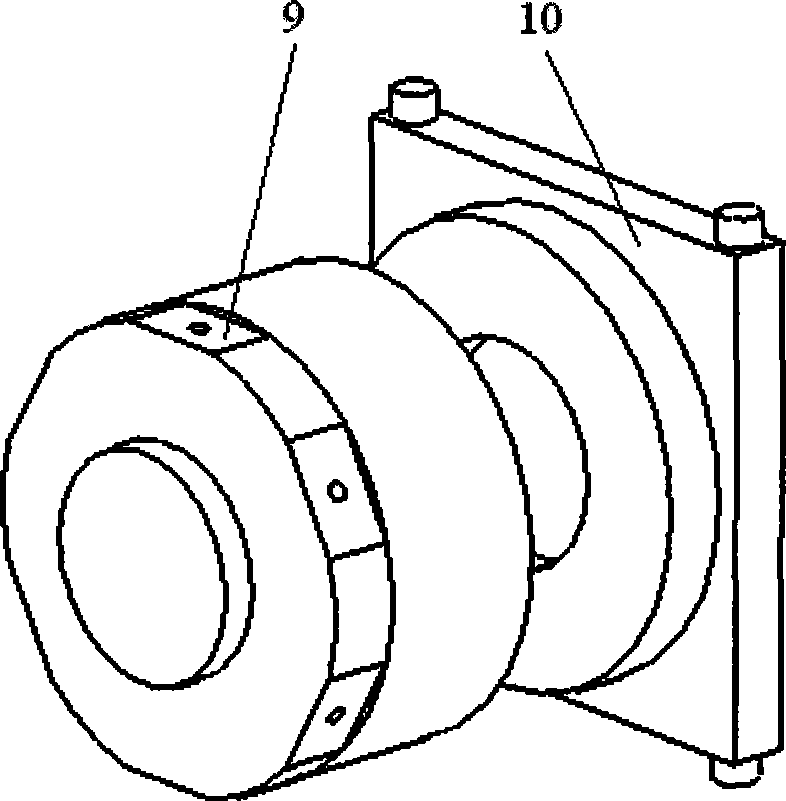
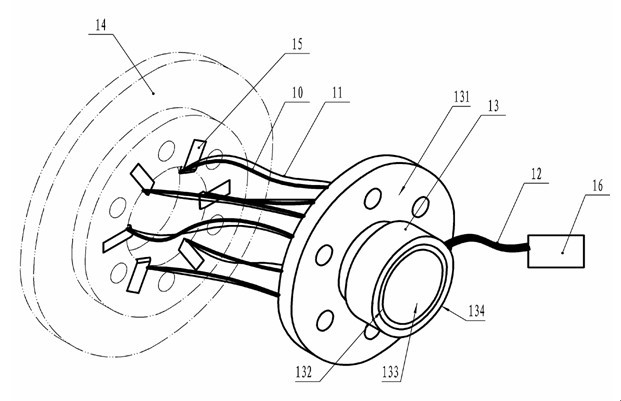
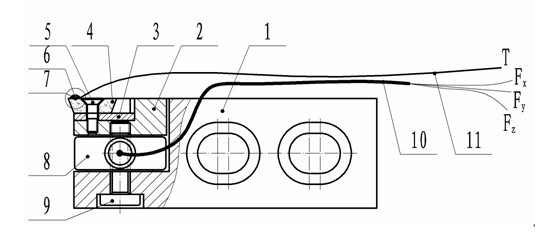
Device for measuring cutting force and cutting temperature of cutter holder type rotary milling blade
InactiveCN102554702ACompact structureEasy to manufactureMeasurement/indication equipmentsMeasurement deviceMilling cutter
The invention relates to a measuring device for monitoring cutting force and cutting temperature of various blades for rotary milling processing in a synchronous real-time online manner, which is formed by a three-directional piezoelectric force sensor, a film temperature sensitive element and a slip ring, belonging to the technical field of cutting. According to the invention, a simple and compact cutter holder type structure is adopted; the three-directional piezoelectric force sensor fastened between a cutter seat and a cutter holder by threads is used for measuring the cutting force; the film temperature sensitive element bonded near a cutter tip of a cutting area of a blade is used for measuring the cutting temperature; and a multi-channel through hole type slip ring is used as an electrical interface between a sensing device and a data collecting device. The measuring device has the characteristics of compact structure, excellent dynamic performance, high measuring accuracy, synchronous online measurement of the cutting temperature and the cutting force, easiness in preparation, installation and adjustment and low manufacturing cost, is suitable for synchronous online measurement of transient cutting force and cutting temperature of each cutter on a rotary milling cutter disc, and can also be used for synchronous measurement of the transient cutting force and the cutting temperature in a turning process.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cutting tool mode parameter uncertain curve five-shaft numerical control process parameter optimizing method
InactiveCN101493686AReach the goal of optimization of processing parametersImprove accuracyProgramme controlComputer controlMachining vibrationsNumerical control
The invention provides a method for optimizing uncertain curve-surface five-axis numerical control process parameter of the cutter modal parameters, belonging to the technical field of computer numerical control machining. The method for optimizing the machining process parameter comprises the steps as follows: firstly, the uncertain area of the cutter system modal parameter is obtained; a five-axis milling machining dynamic model is established; the input parameter of the model comprises a cutter system modal parameter area, a cutting force coefficient, a cutter geometry and a cutter path; the five-axis milling machining vibration stabilization curve is calculated; and by taking the five-axis milling machining vibration stabilization curve as a constraint, the process parameter optimization model is established and worked out by a sequence nonlinear planning method so as to obtain the optimized process parameter. As the invention considers the uncertainty of the cutter system modal parameter and is closer to the real machining condition, thus improving the exactness of the vibration prediction during the machining.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
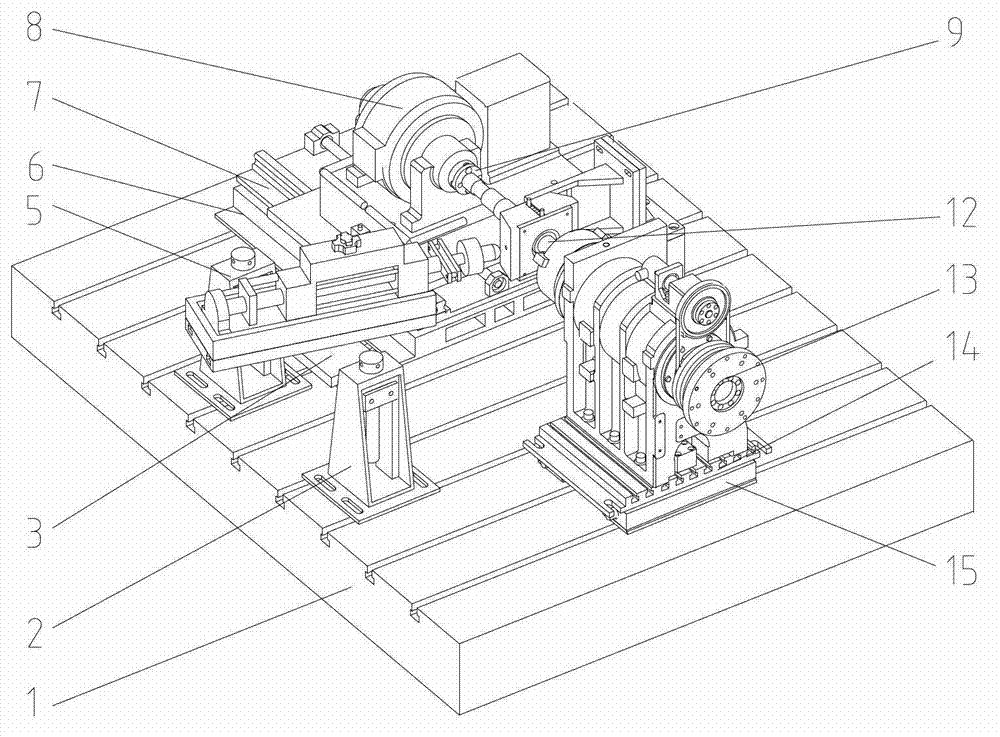
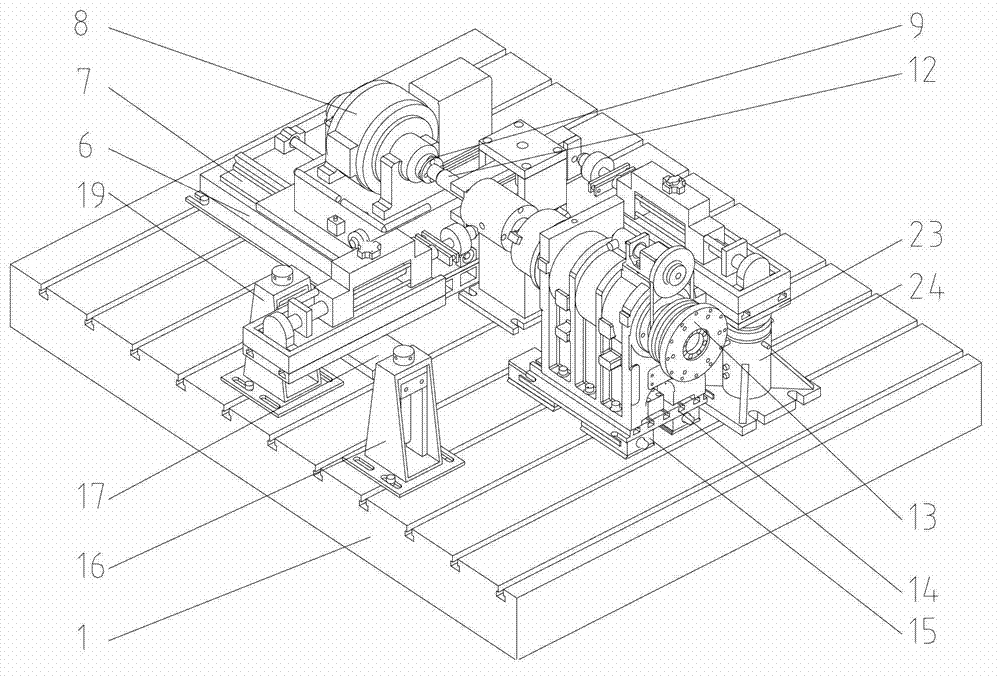
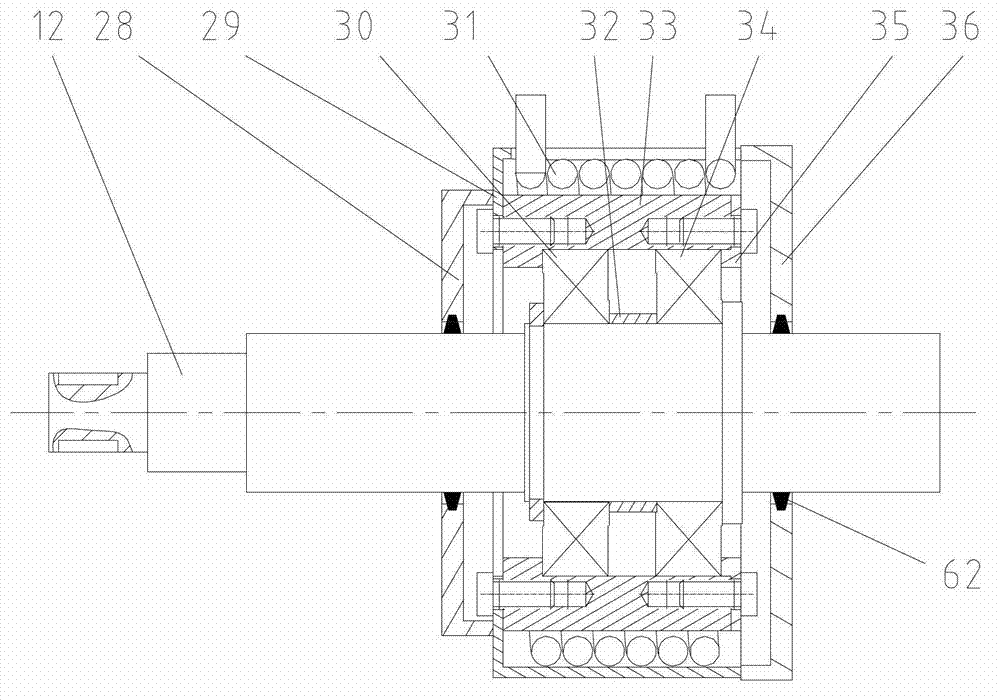
Reliability loading testing device and method for main shaft of numerically controlled lathe
InactiveCN104019986AThe reliability value is true and reliableLoad time adjustmentMachine part testingMotor driveControl system
The invention relates to a reliability loading testing device and a reliability loading testing method for a main shaft of a numerically controlled lathe. The testing device comprises a testing platform body and a control system, wherein the testing platform body is provided with a motor, a radial cutting force simulated loading device, an axial cutting force simulated loading device, a bearing loading unit and a torque loading system. The main shaft to be detected is fixedly arranged on the testing platform body through a main shaft box . The motor drives the main shaft to be detected by a belt; the radial cutting force simulated loading device, the axial cutting force simulated loading device and the torque loading system are used for applying a torque, a radial force and an axial force to the main shaft to be detected through the bearing loading unit. The invention creates a condition for simulating the main shaft under a cutting state of the lathe; a reliability loading test and a precision recession test on the main shaft of the numerically controlled lathe can be realized; an early-stage fault of the main shaft is exposed and a precision recession rule of the main shaft is grasped.
Owner:通用技术集团沈阳机床有限责任公司
Free-form surface micro-milling cutting force modeling method
ActiveCN105069257AAccurate application of free-form surface micro-millingImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsFree formEngineering
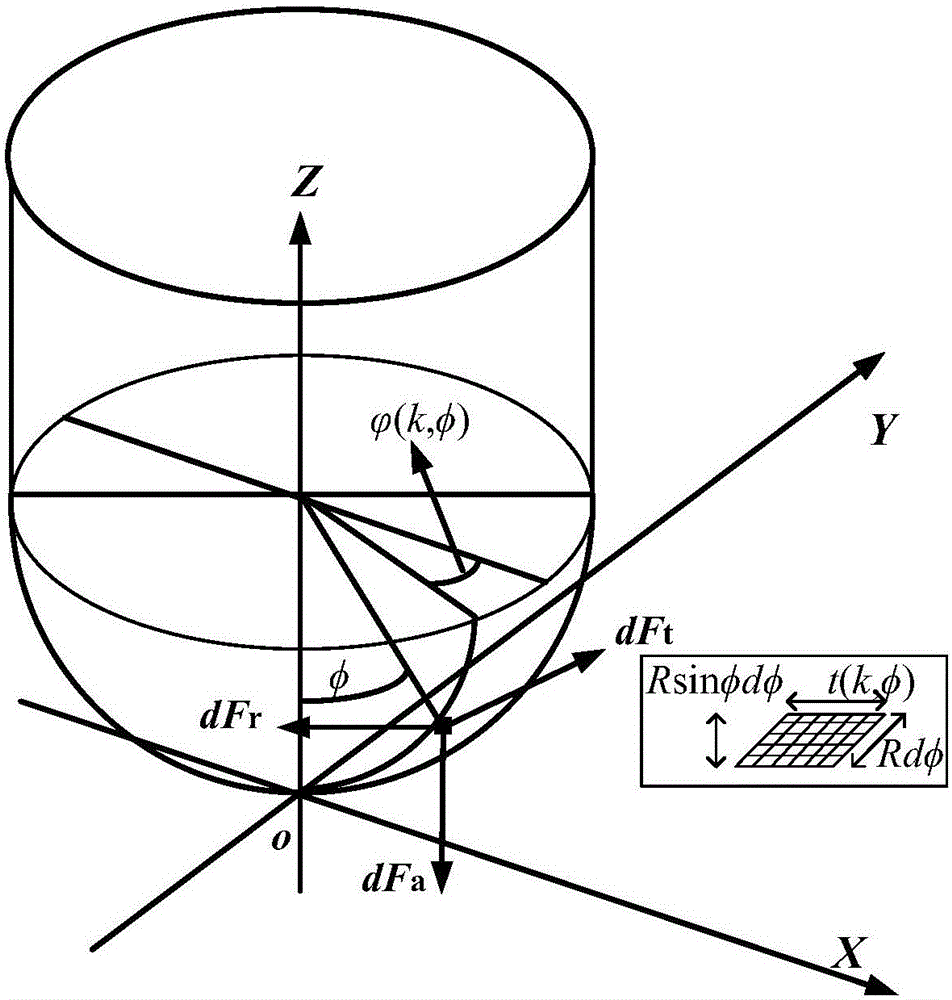
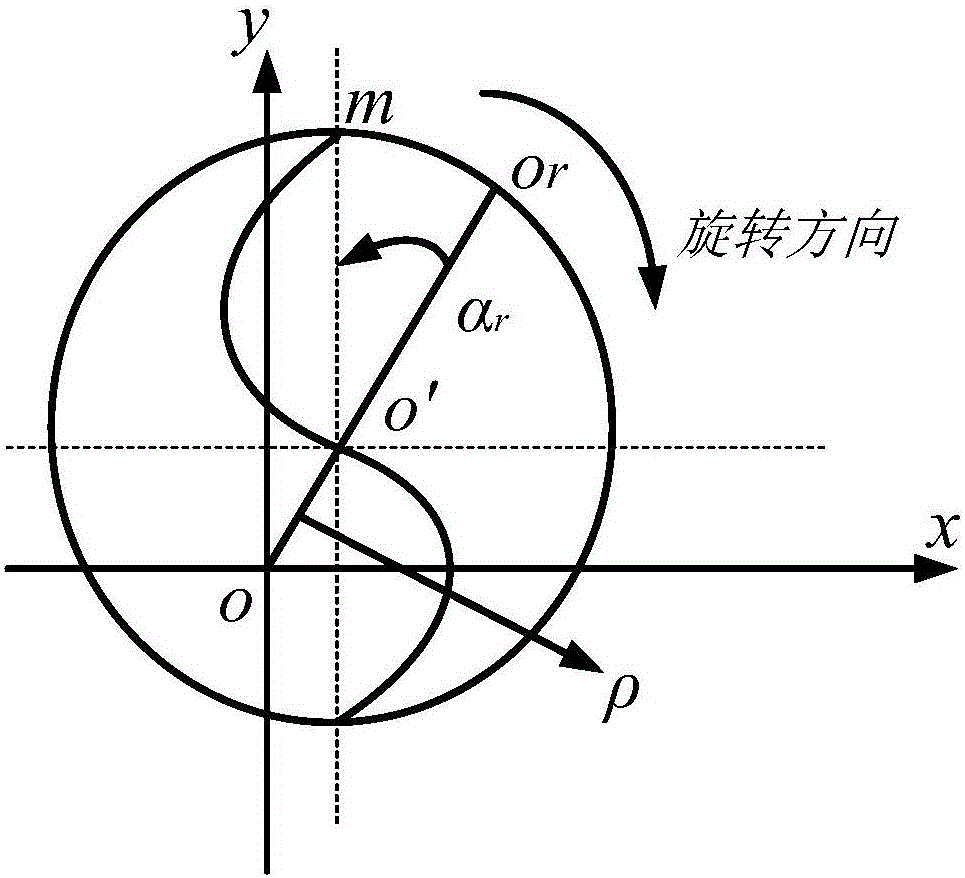
The invention discloses a free-form surface micro-milling cutting force modeling method. The free-form surface micro-milling cutting force modeling method comprises the following steps of (1) obtaining machining parameters including the radius R of a cutter, a helix angle beta of the cutter, the number Nf of cutting edges, the feed amount ft of each tooth, an eccentric distance p of the cutter and the initial eccentric angle alpha of the cutter, (2) dispersing the cutting edges of the cutter in the axial direction to form a series of cutting micro-elements and obtaining cutting micro-elements involved with cutting, (3) calculating the instantaneous cutting thickness of the cutting micro-element P (k, phi) with an axial angle phi of the current cutting edge, (4) calculating the cutting force of the micro-element P (k, phi) and (5) calculating the sum of the parameters obtained in the steps (3) and (4) and the cutting forces of the micro-elements involved with cutting to obtain the cutting force of the cutter. By means of the free-form surface micro-milling cutting force modeling method, the micro-milling cutting force of a free-form surface can be efficiently and accurately predicted.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Contact-type reliability test bed capable of conducting mixed loading on electric main shaft
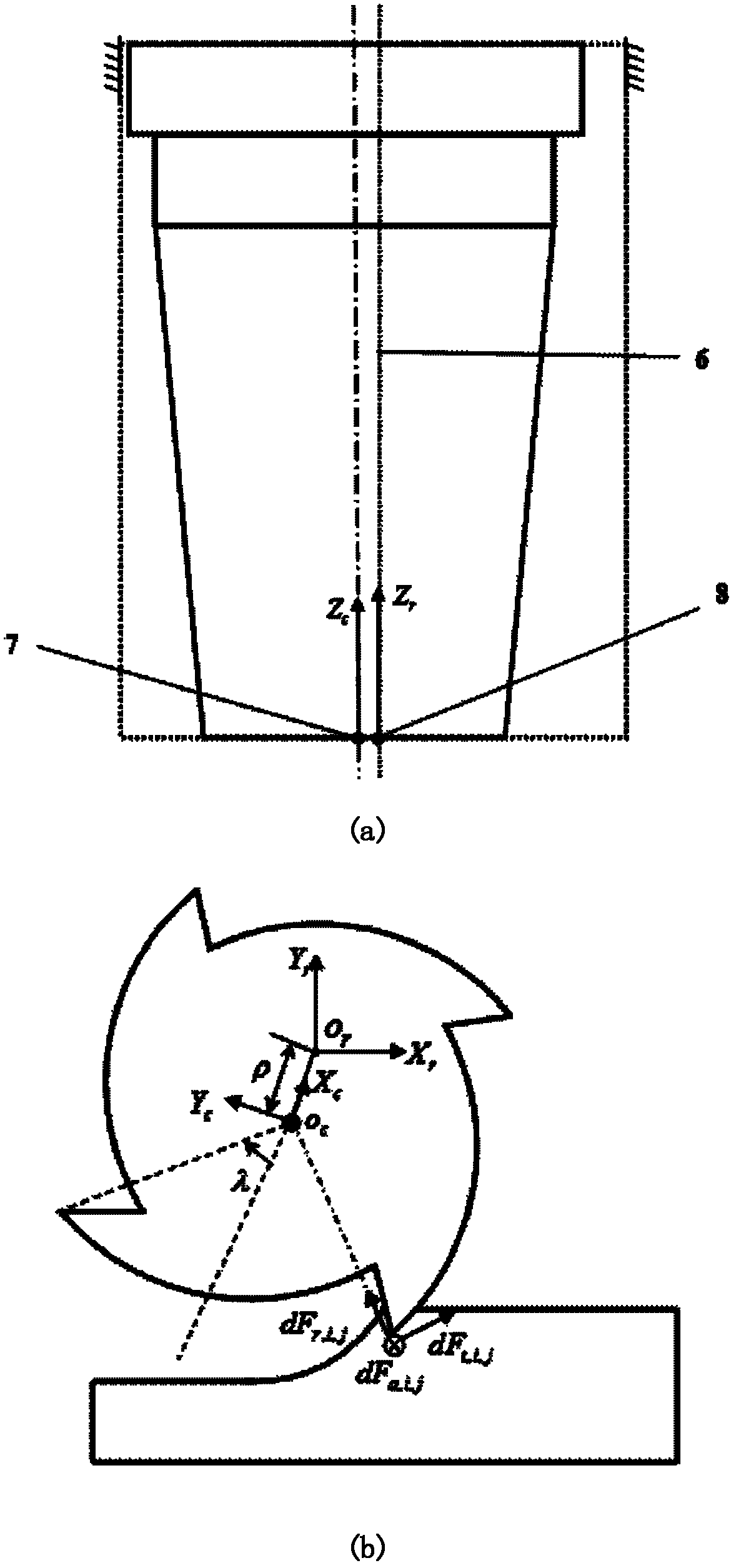
The invention discloses a contact-type reliability test bed capable of conducting mixed loading on an electric main shaft. The test bed is composed of the electric main shaft, a connecting shaft unit, a torque loading device, a radial force electromagnetic loading device, an axial force electromagnetic loading device and a swing arm device. The test bed can load an axial force, a radial force and a torque on the electric main shaft at the same time, control the magnitudes of the three forces in a coordinate mode to simulate cutting forces in different magnitudes and different directions, really and reliably simulate the cutting forces of the electric shaft in practical working conditions, and provide a test foundation for reliability acceleration tests of the electric shaft.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com