Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Flank milling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
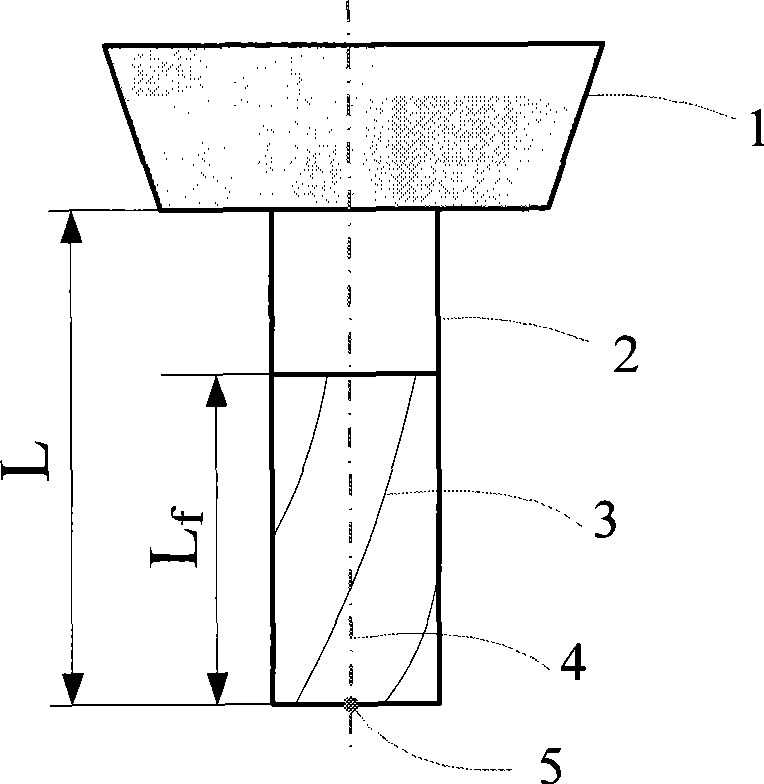
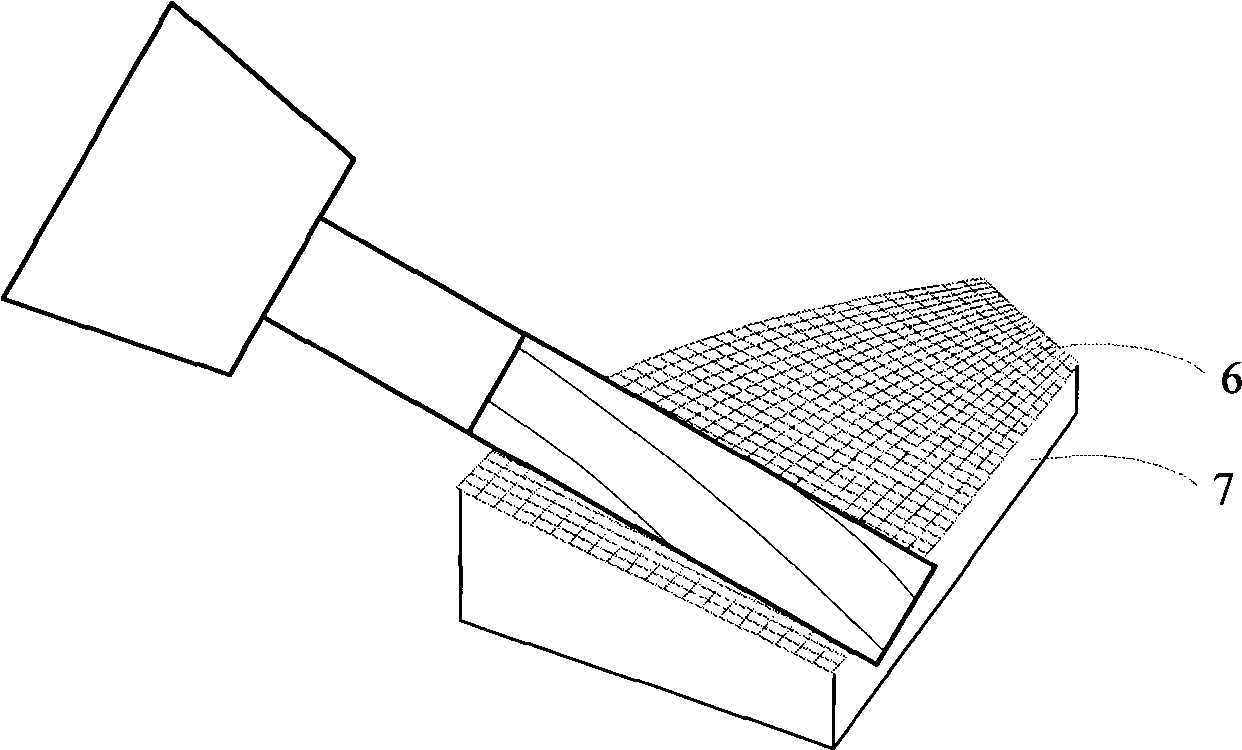
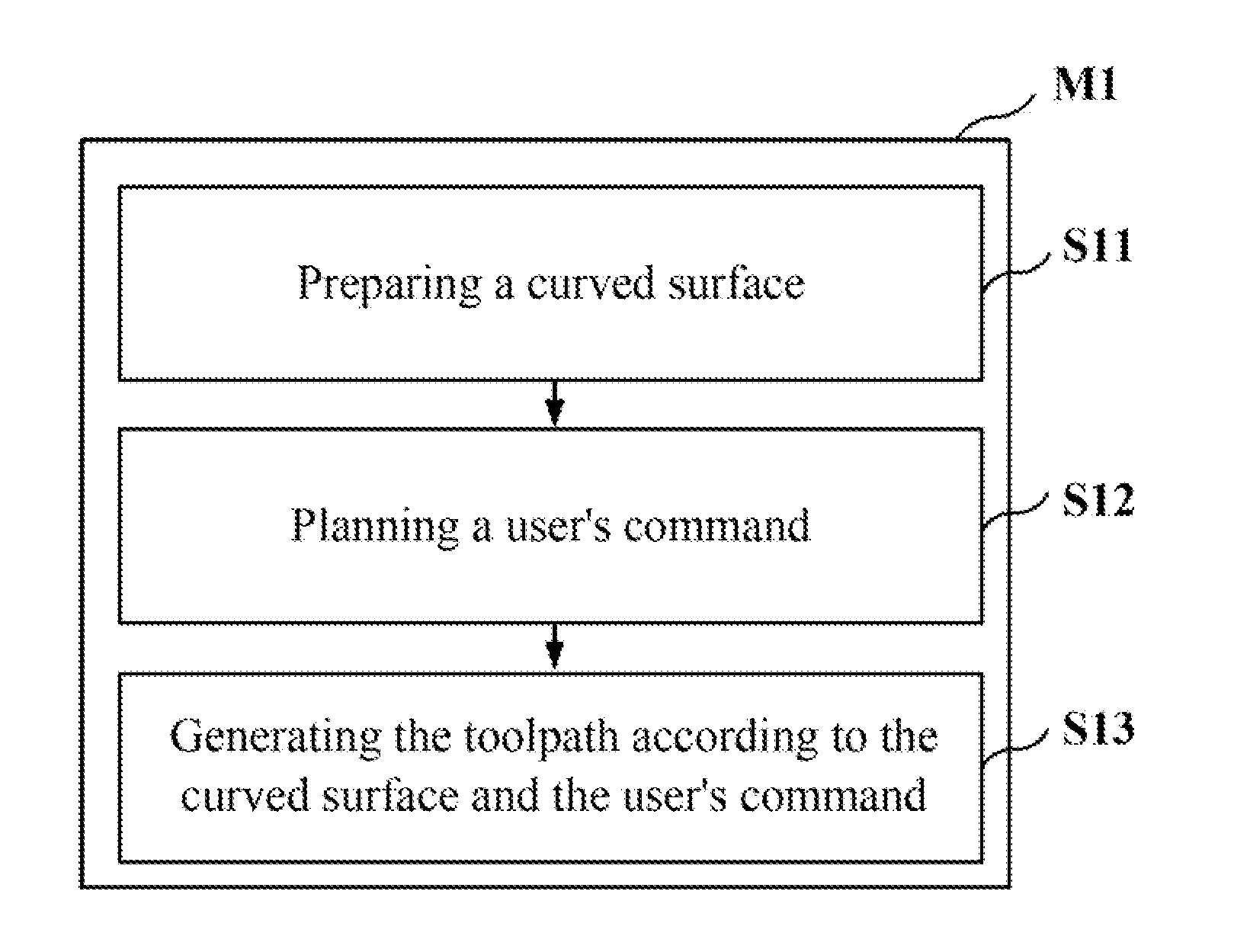
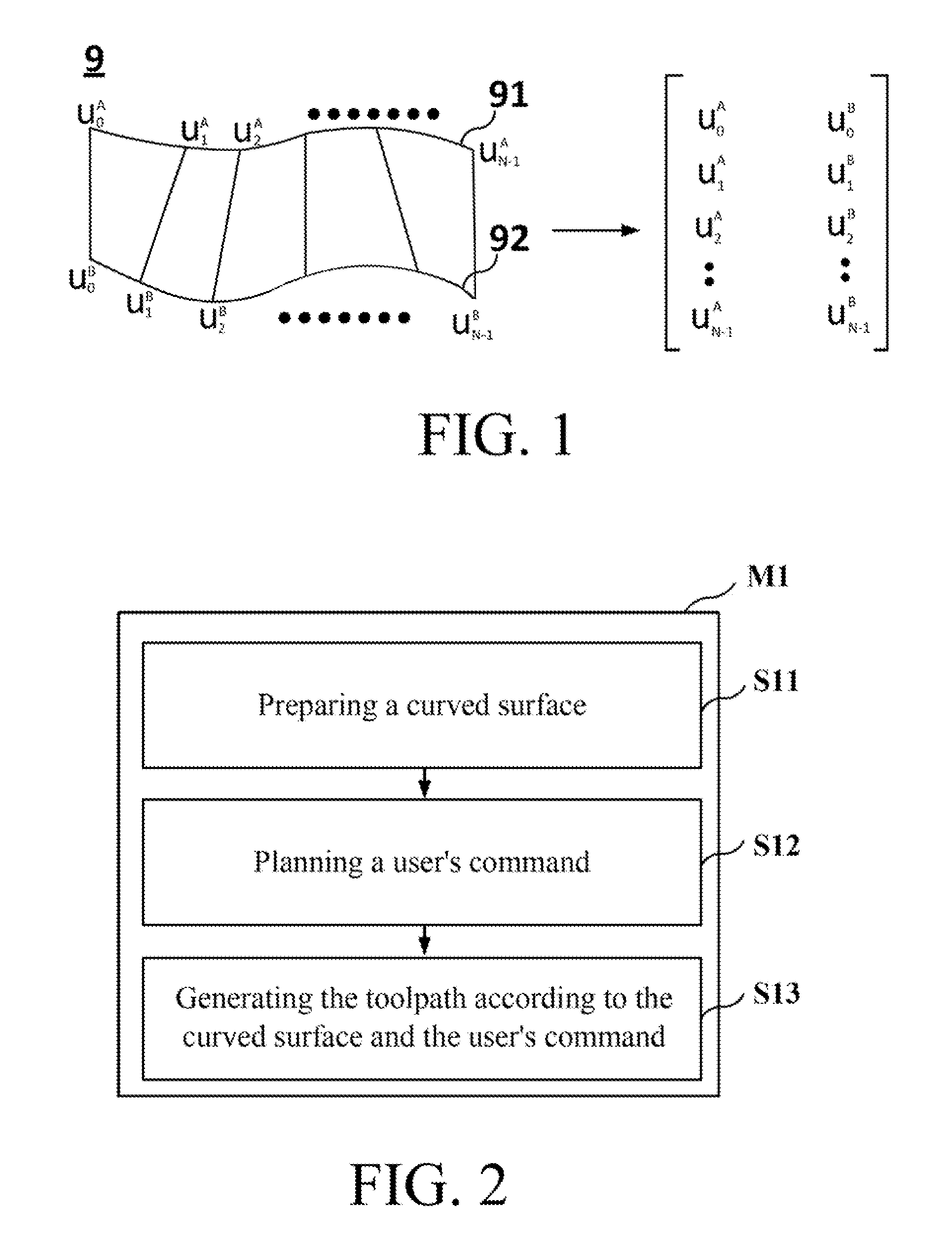
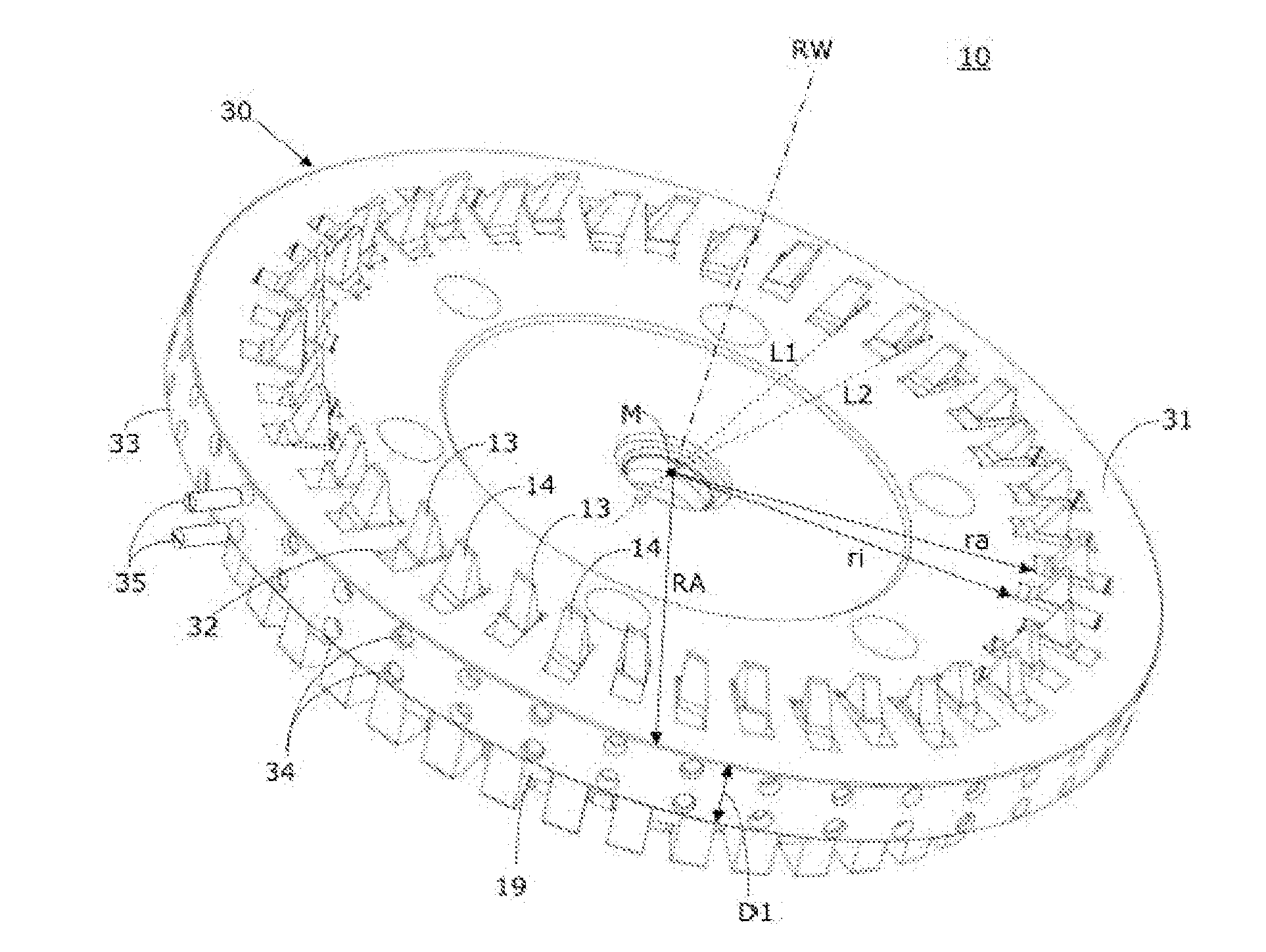
Five-axis flank milling system for machining curved surface and toolpath planning method thereof
ActiveUS20150032250A1Reduces uneven modificationQuality improvementSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical controlCutter locationMachined surface
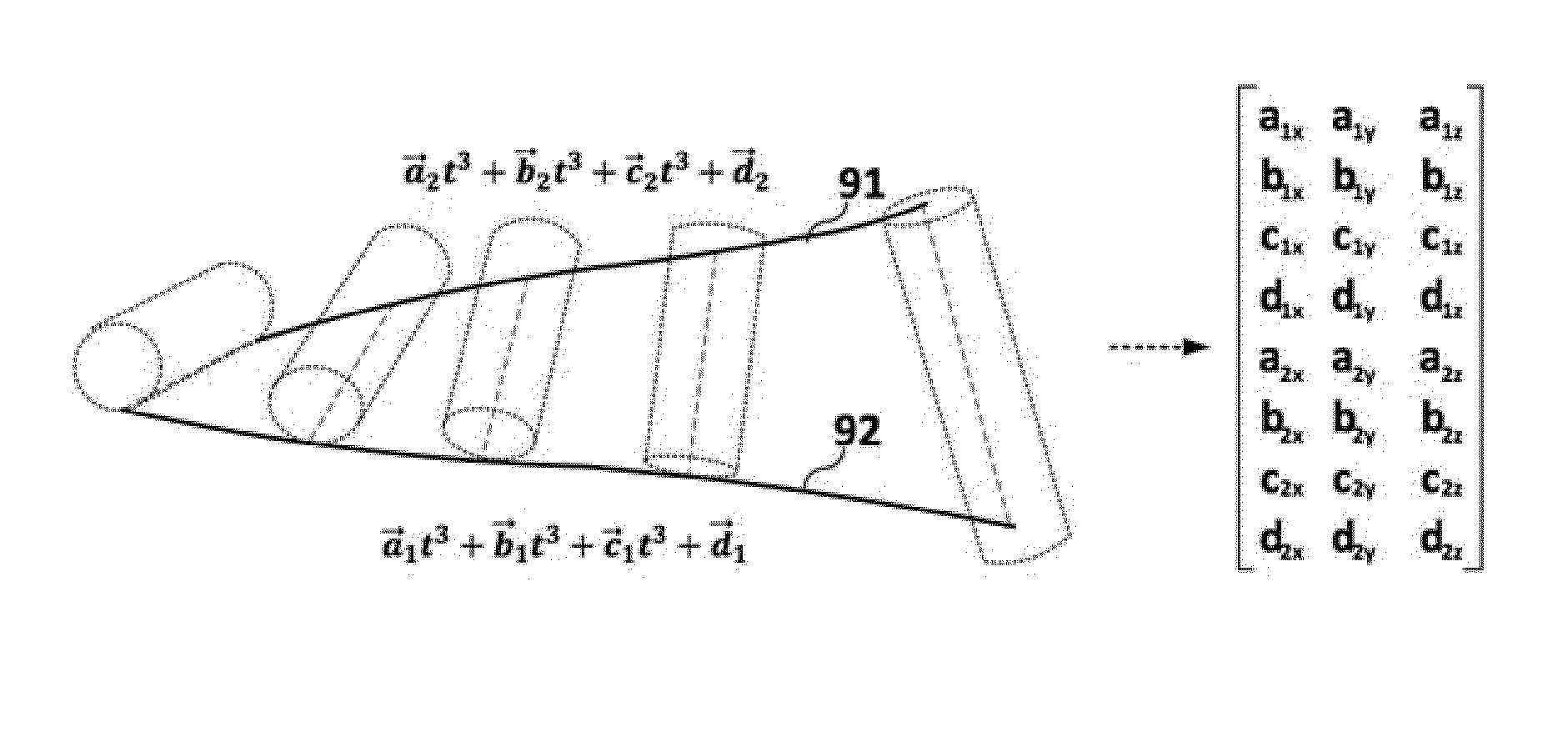
This invention provides a novel tool path planning method for five-axis flank milling by imposing the constraints of curve interpolation on the tool path. The tool motion is described in the form of spline curves during its optimization-driven calculation process, instead of discrete cutter locations in CNC linear interpolation. The coefficients of the curve equations are generated by minimizing accumulated geometrical errors on the machined surface using optimization algorithms. The continuity imposed by the spline motion reduces uneven modifications of cutter locations during the optimization process. The resultant tool path yields superior.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Off-line planning method for cutting feed rate of five-shaft numerical control side milling machining
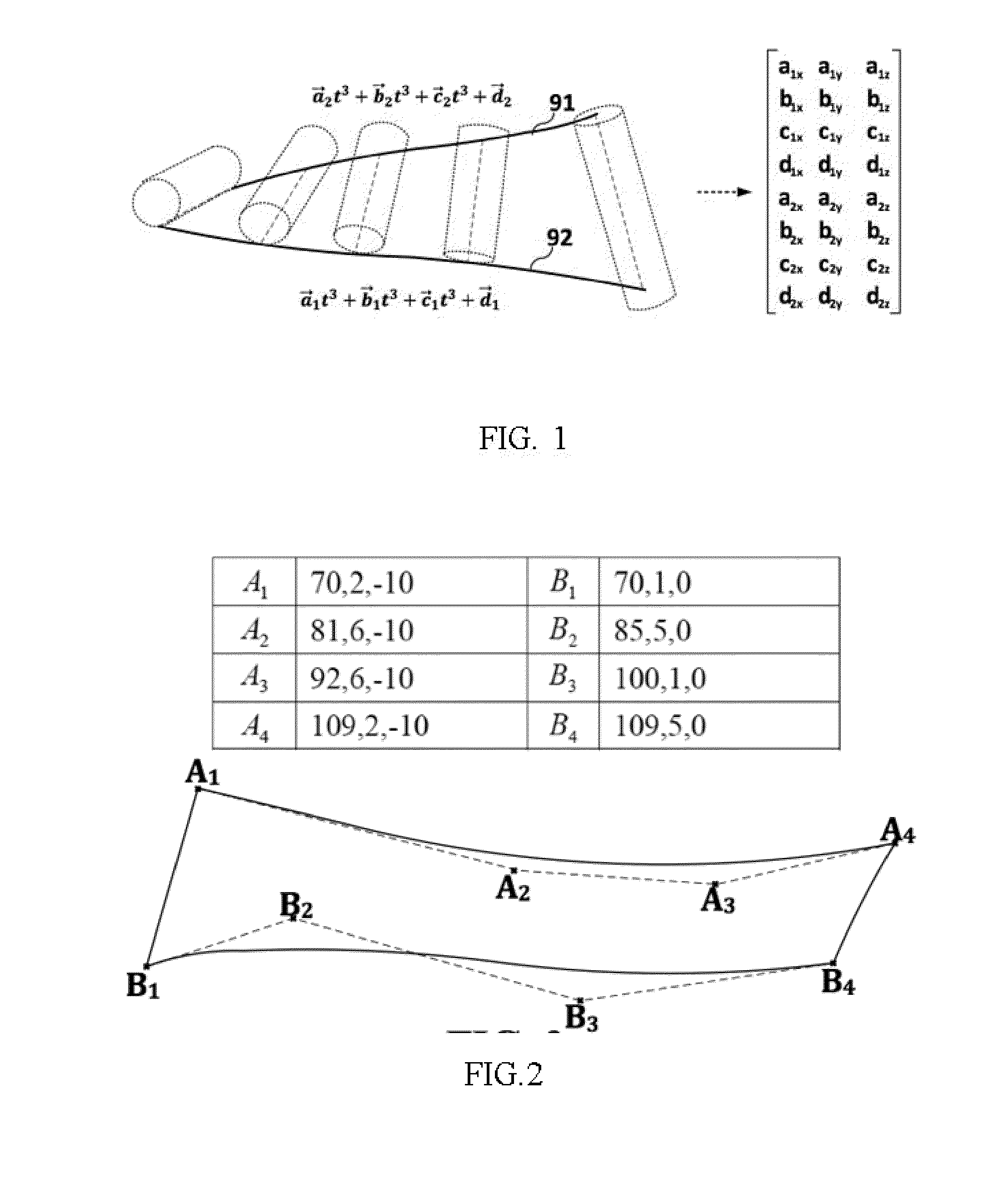
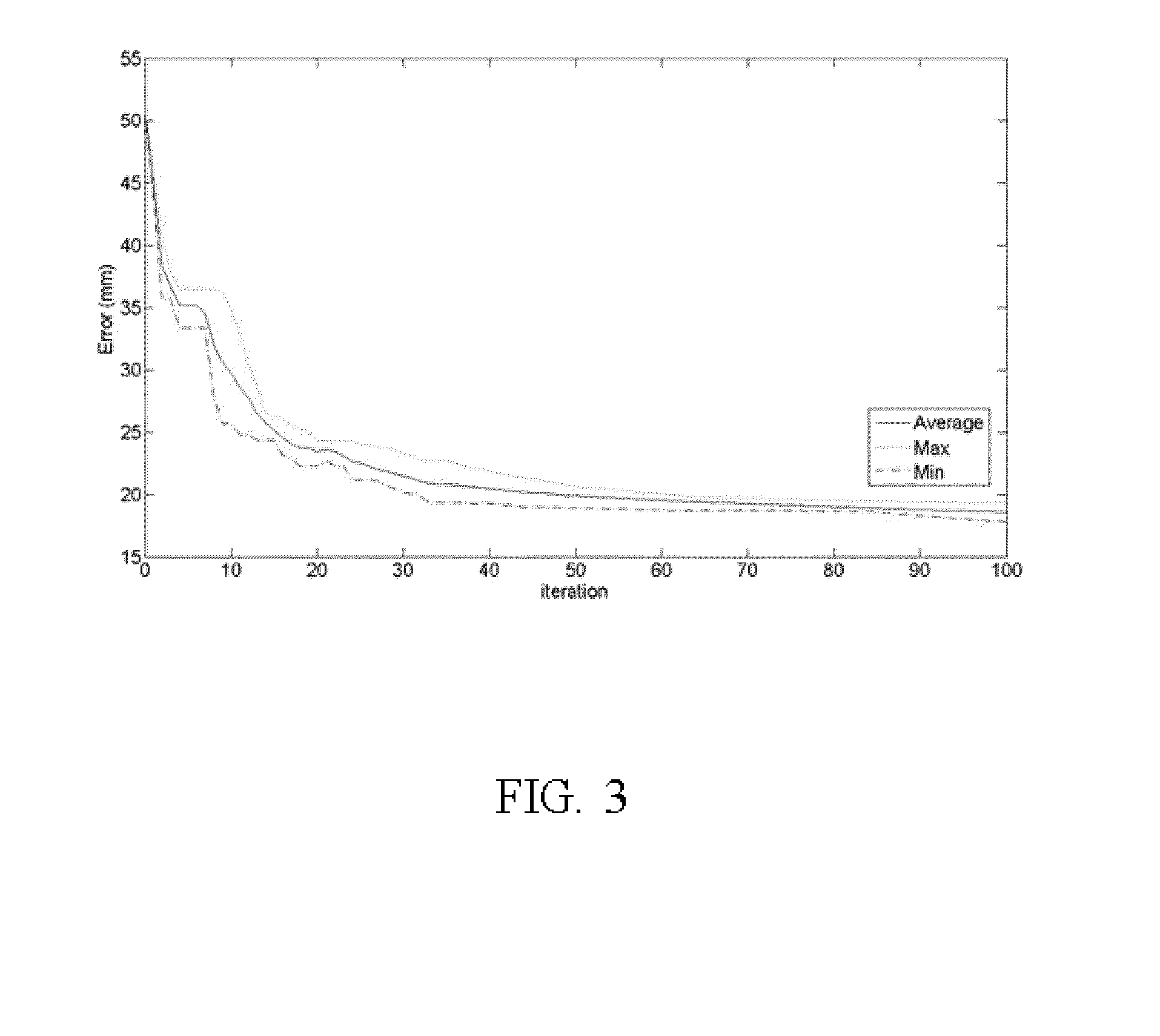
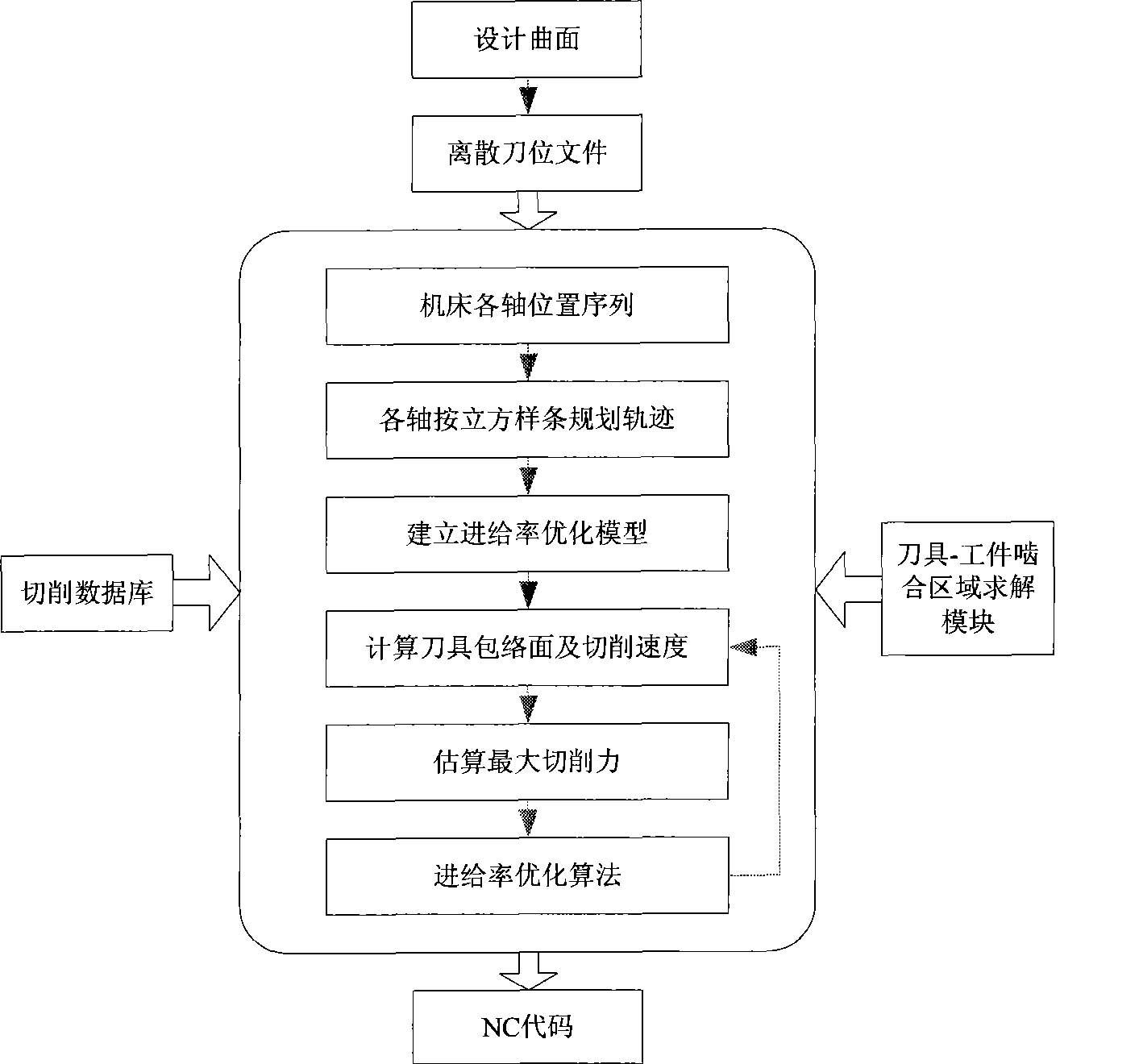
The invention relates to a 5-axis NC flank milling machining feed rate off-line planning method, which carries out 5-axis NC flank milling machining feed rate off-line planning on the basis of various axis cubic spline polynomial interpolation. By establishing an optimizing model which takes time sequences between adjacent position points of various axes as design variables, takes the minimum sum of running time sequences between adjacent position points of various axes as an objective function, takes limits of speeds, accelerations and jerks of various axes of a machine tool as restriction, and simultaneously takes the maximum cutting force in the cutting process of a tool is smaller than a threshold value as restriction, the method adopts global optimization algorithm to solve and obtain the optimal feed rate. The method is suitable for free-form surface rough machining and ruled surface or similar ruled surface semifinishing.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
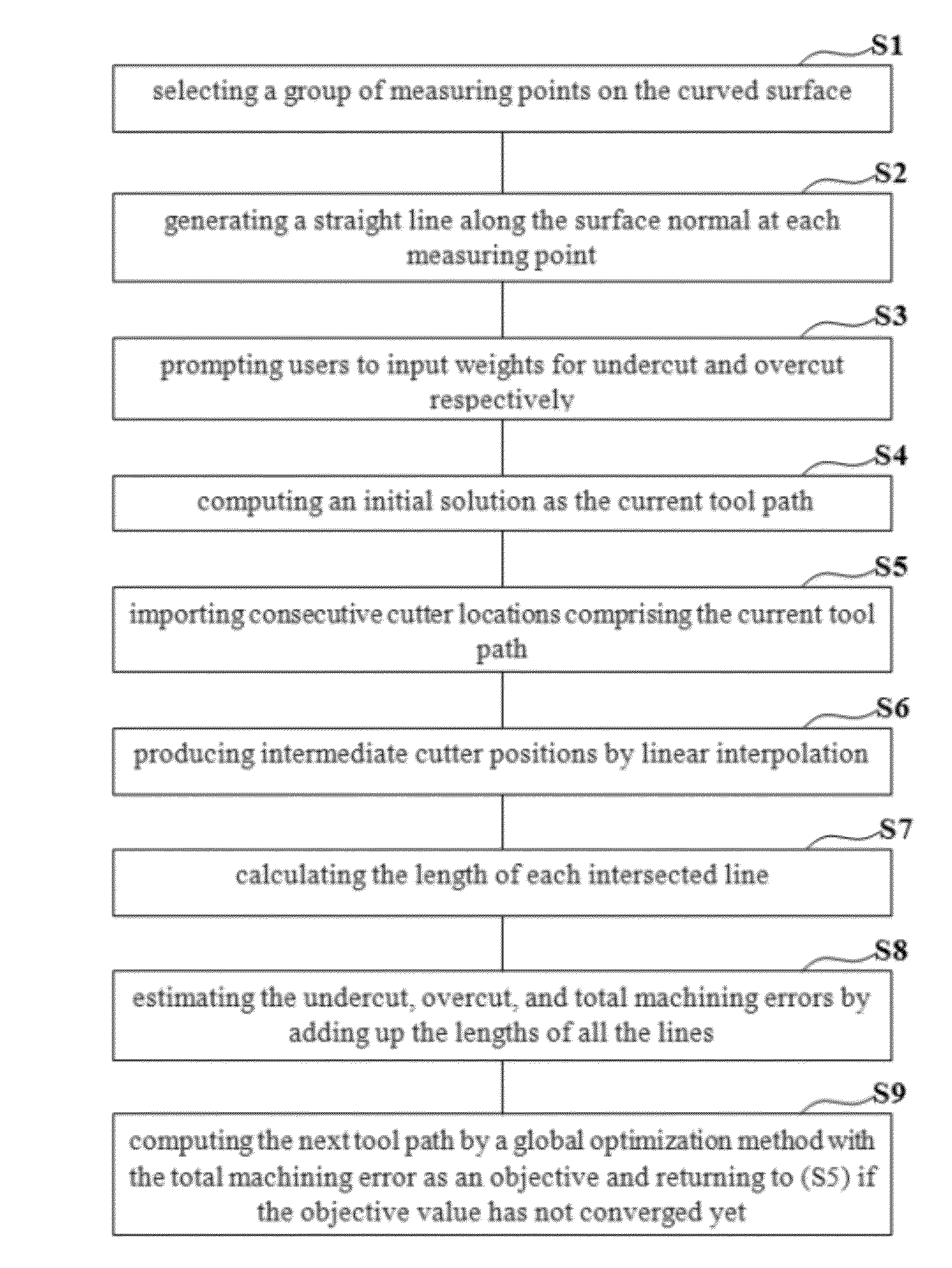
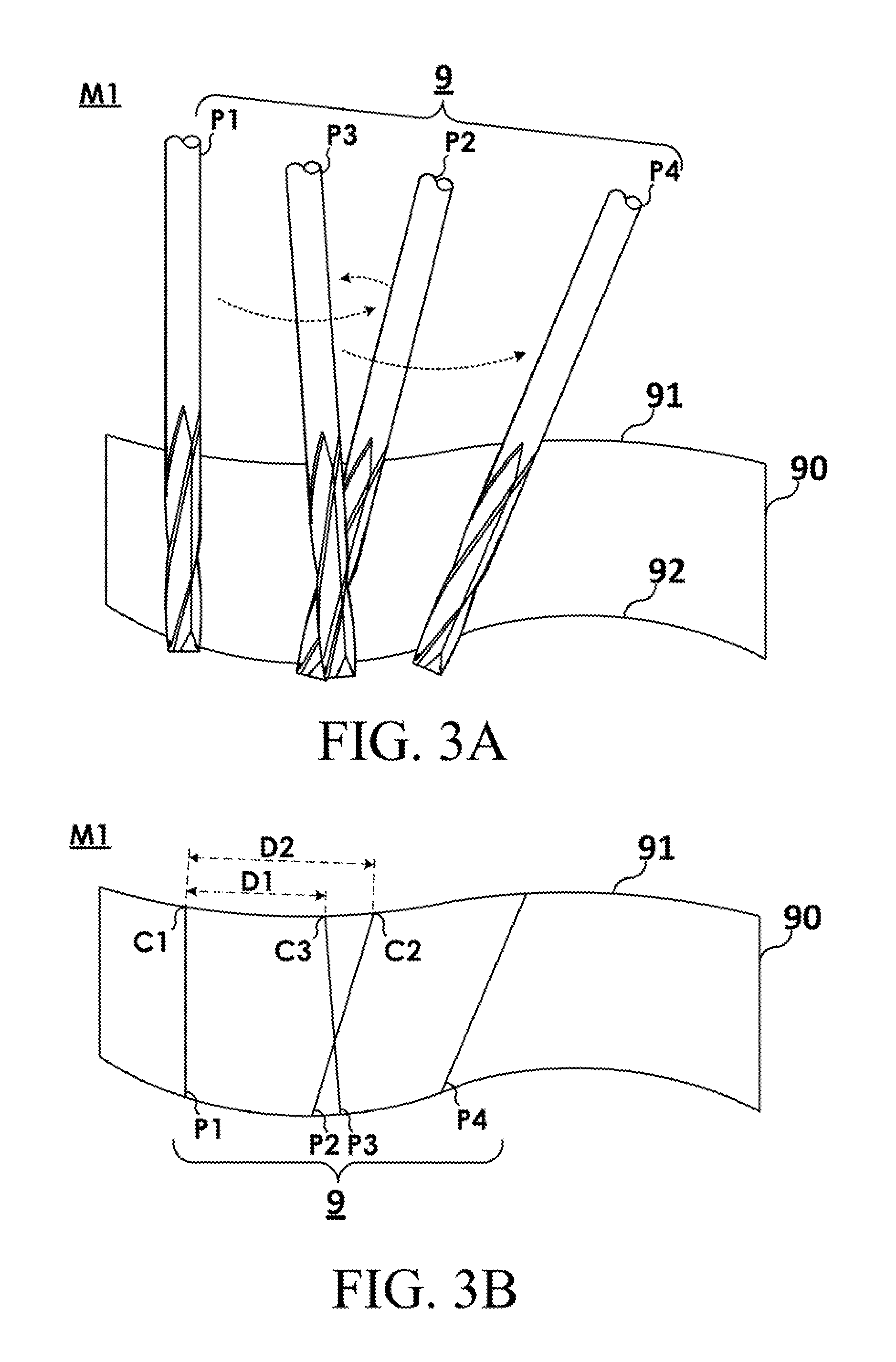
Five-axis flank milling system for machining curved surface and the tool-path planning method thereof
InactiveUS20120265331A1Error minimizationProgramme controlComputer aided designCutter locationPlanning method
The invention discloses a five-axis flank milling system for machining curved surface and the method thereof, the system is capable of generating a tool path that minimizes the undercut error, overcut error, or the total machining error. The amount of the overcut, undercut, or total machining errors can be precisely controlled by adjustment of the cutter locations contained in a tool path. This invention is to transform tool path planning in five-axis flank milling into an optimal matching problem. The proposed mechanism of the invention significantly improves the manufacturing capability of five-axis flank milling. It enhances the machining quality by reducing various machining errors and provides a systematic approach to precise control of machining error in five-axis flank milling.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
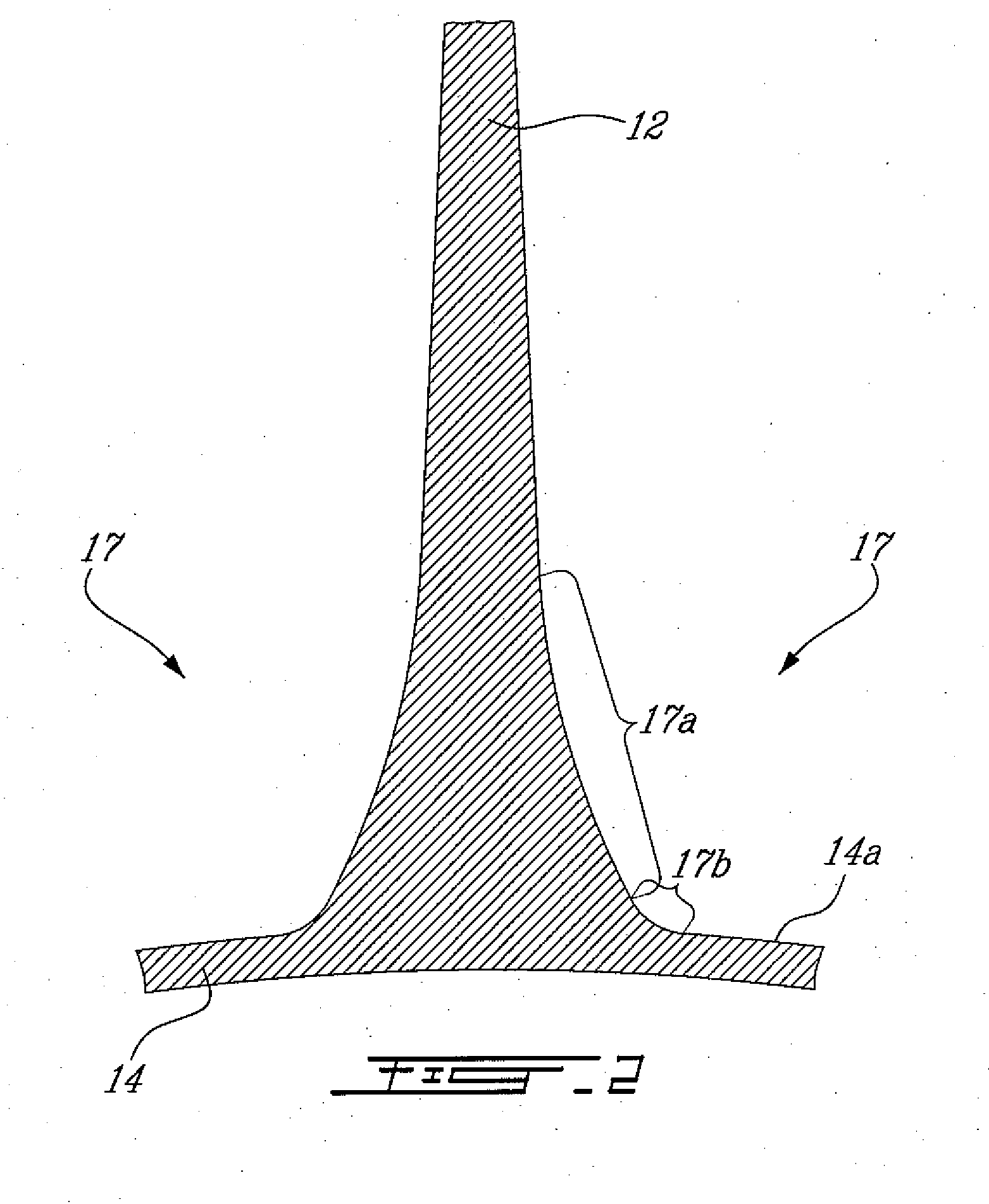
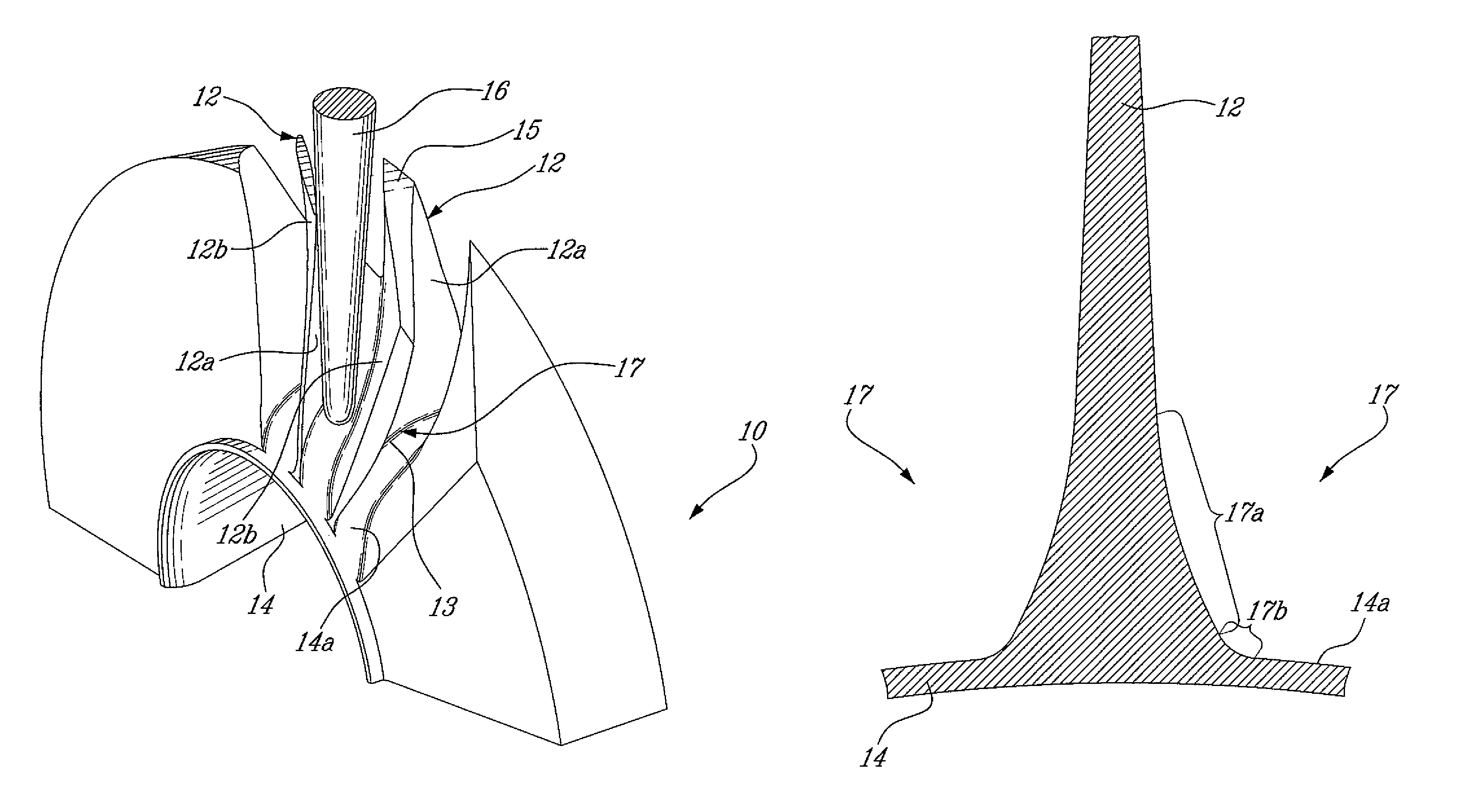
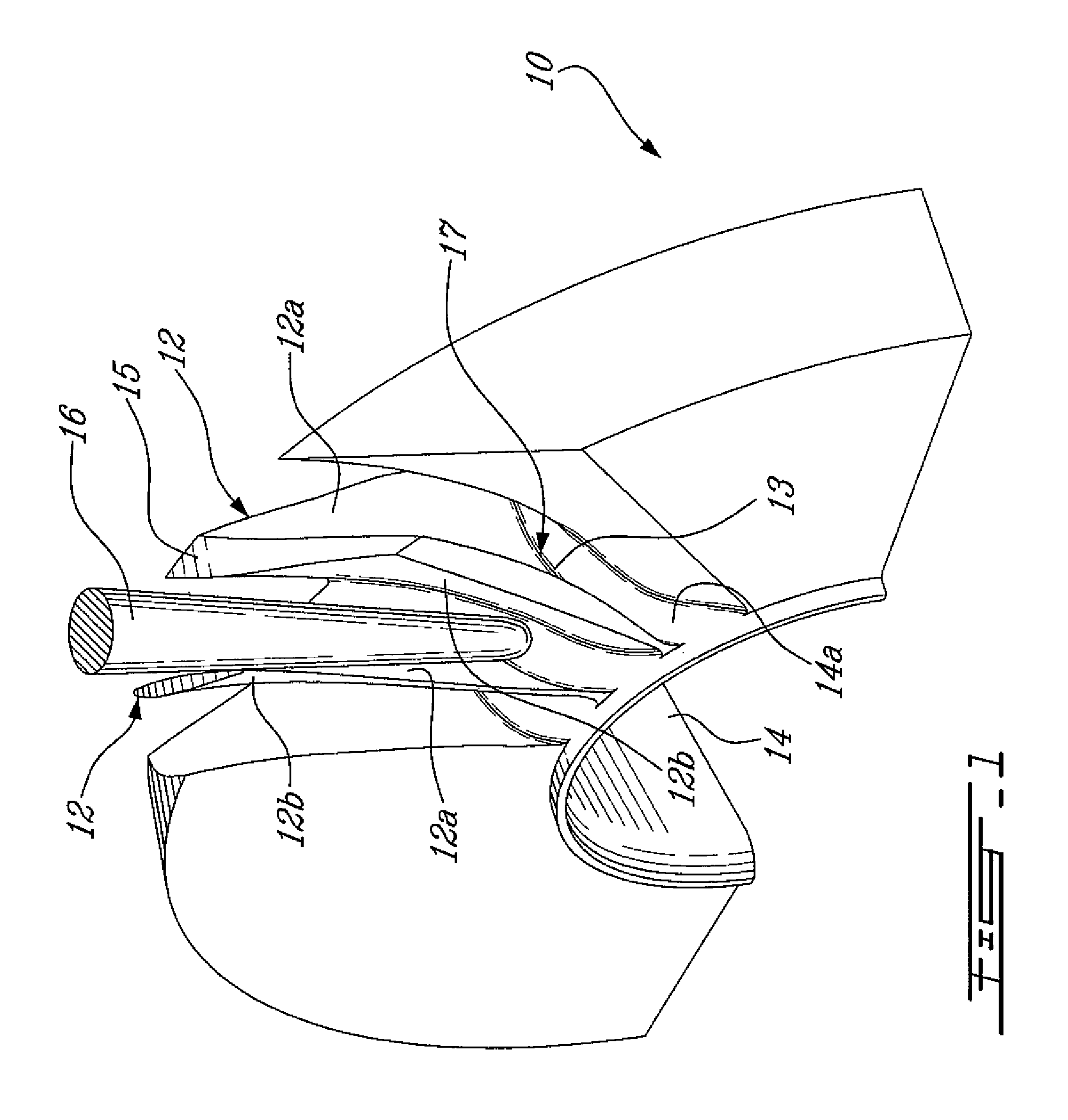
Method of machining airfoil root fillets
An airfoil root fillet having a predetermined compound curve profile can be flank milled with a single flank milling cutter having a generally conical flank milling portion and a rounded tip portion defining a compound curve.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Method of machining airfoil root fillets
An airfoil root fillet having a predetermined compound curve profile can be flank milled with a single flank milling cutter having a generally conical flank milling portion and a rounded tip portion defining a compound curve.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
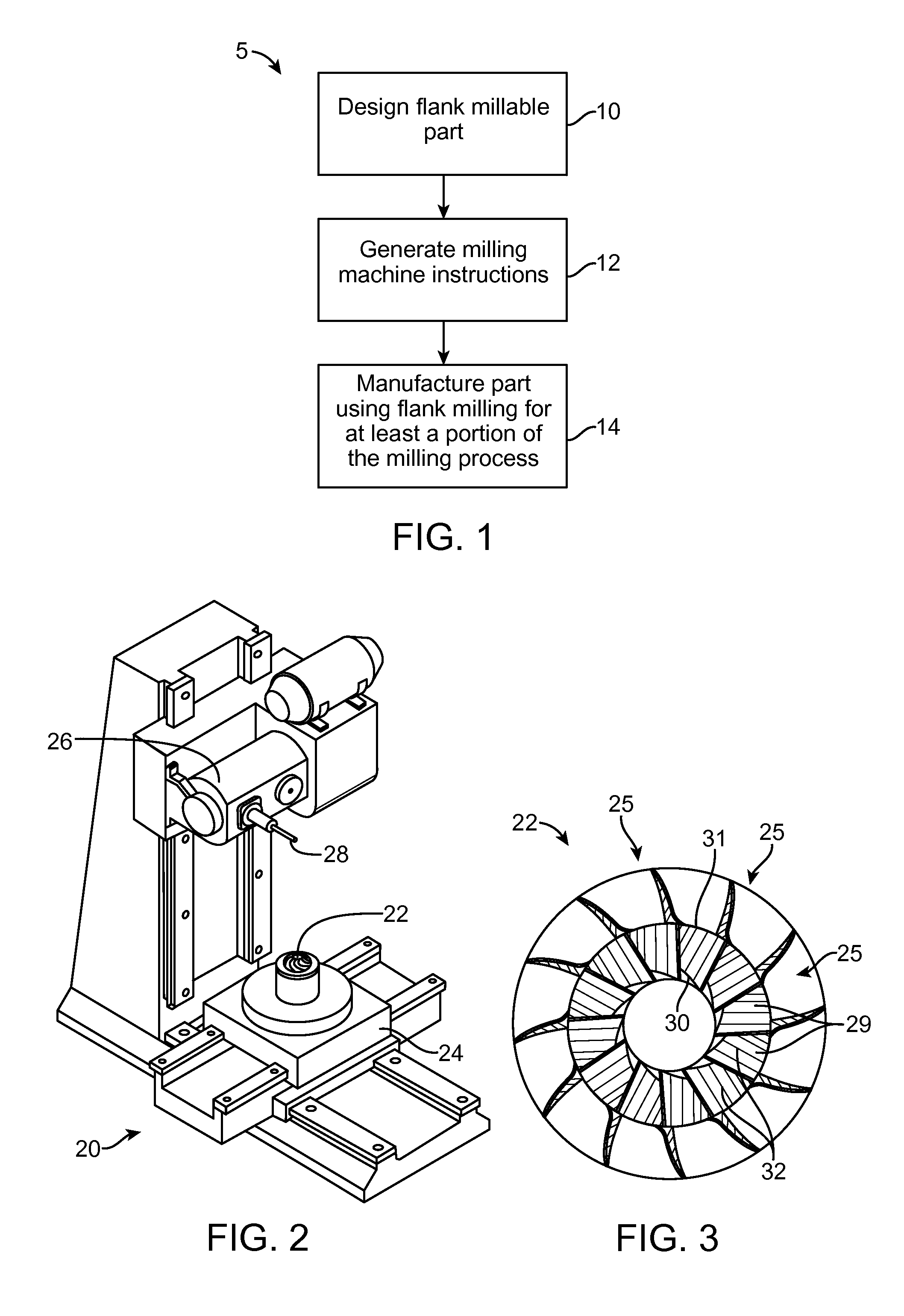
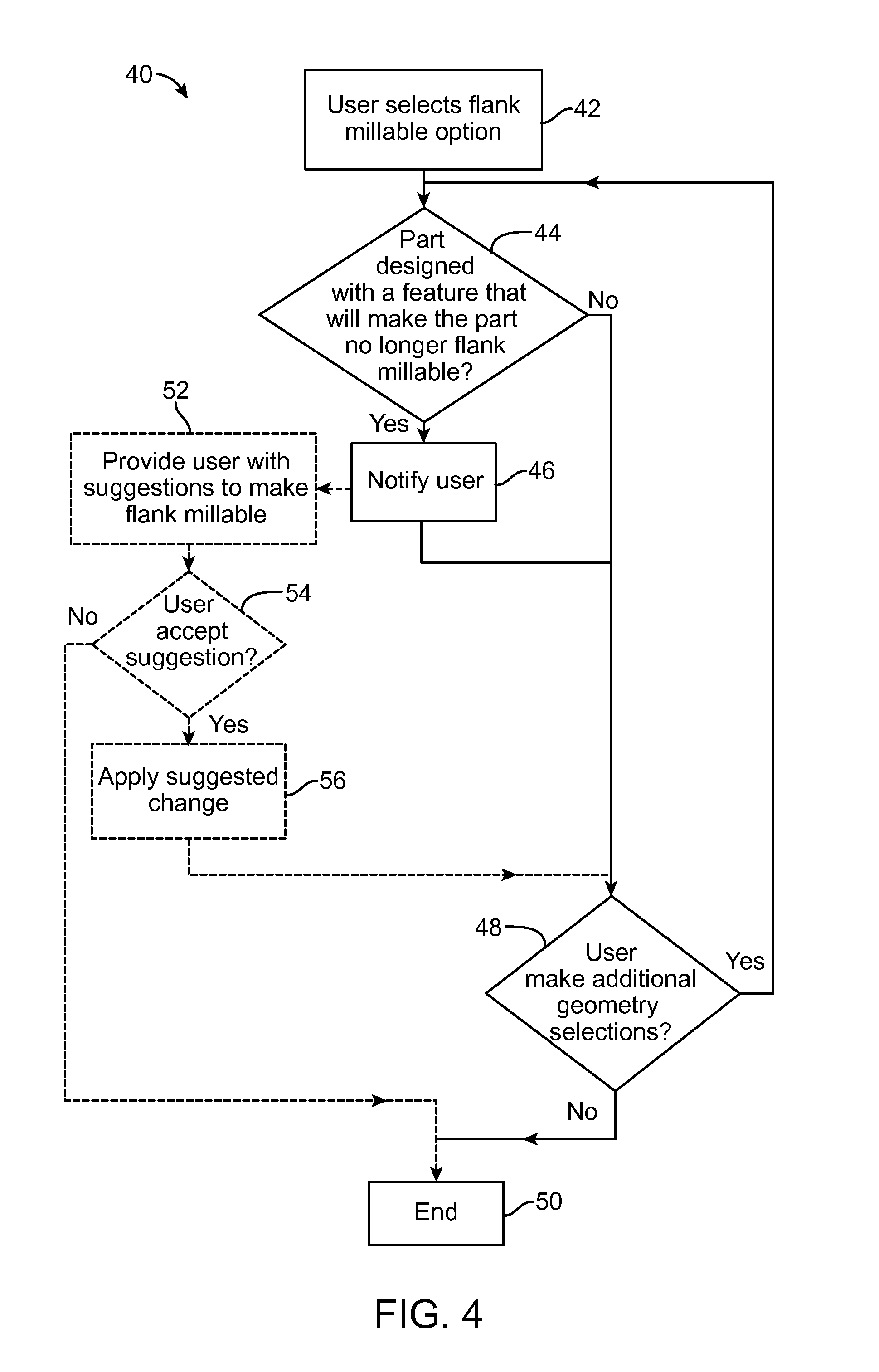
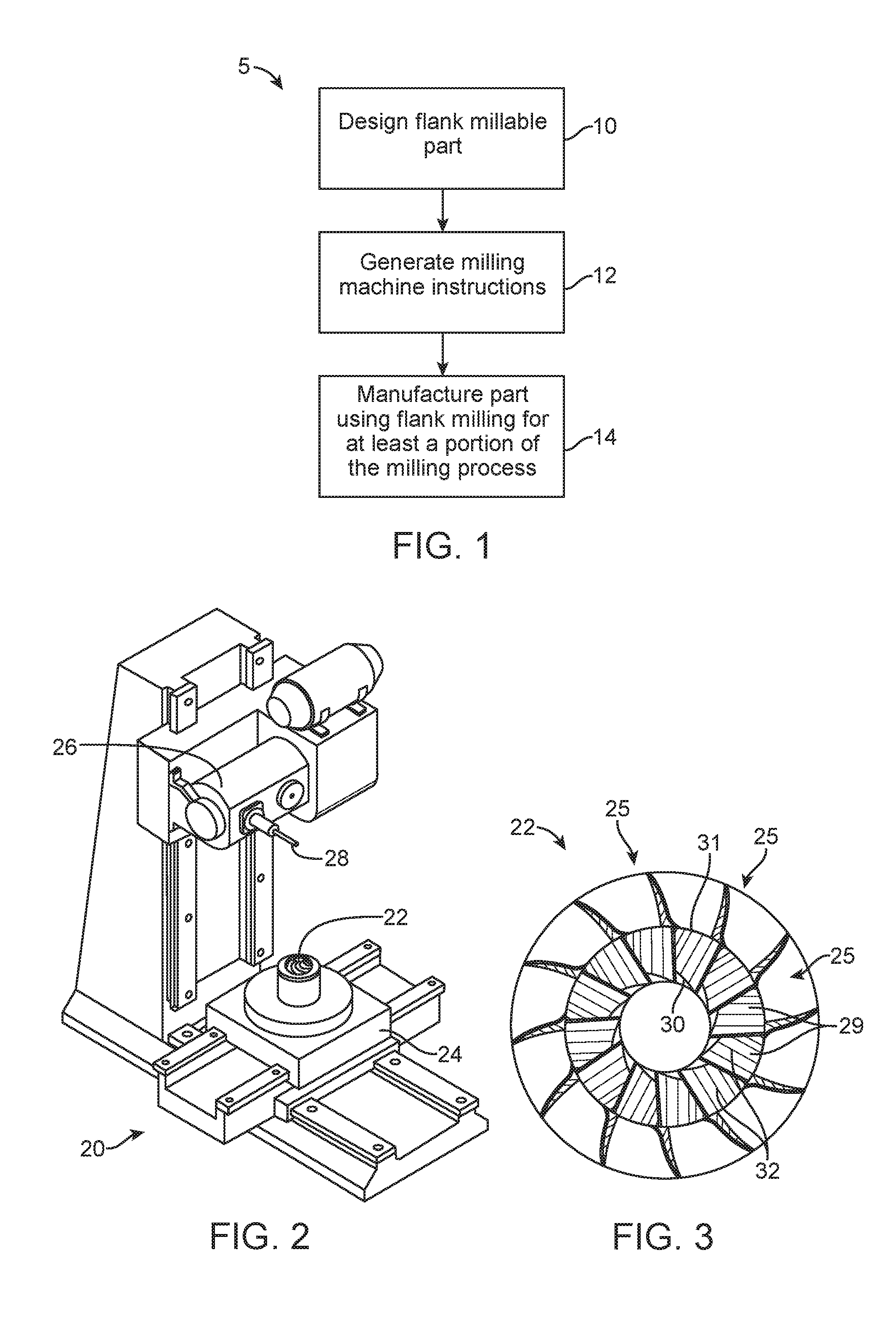
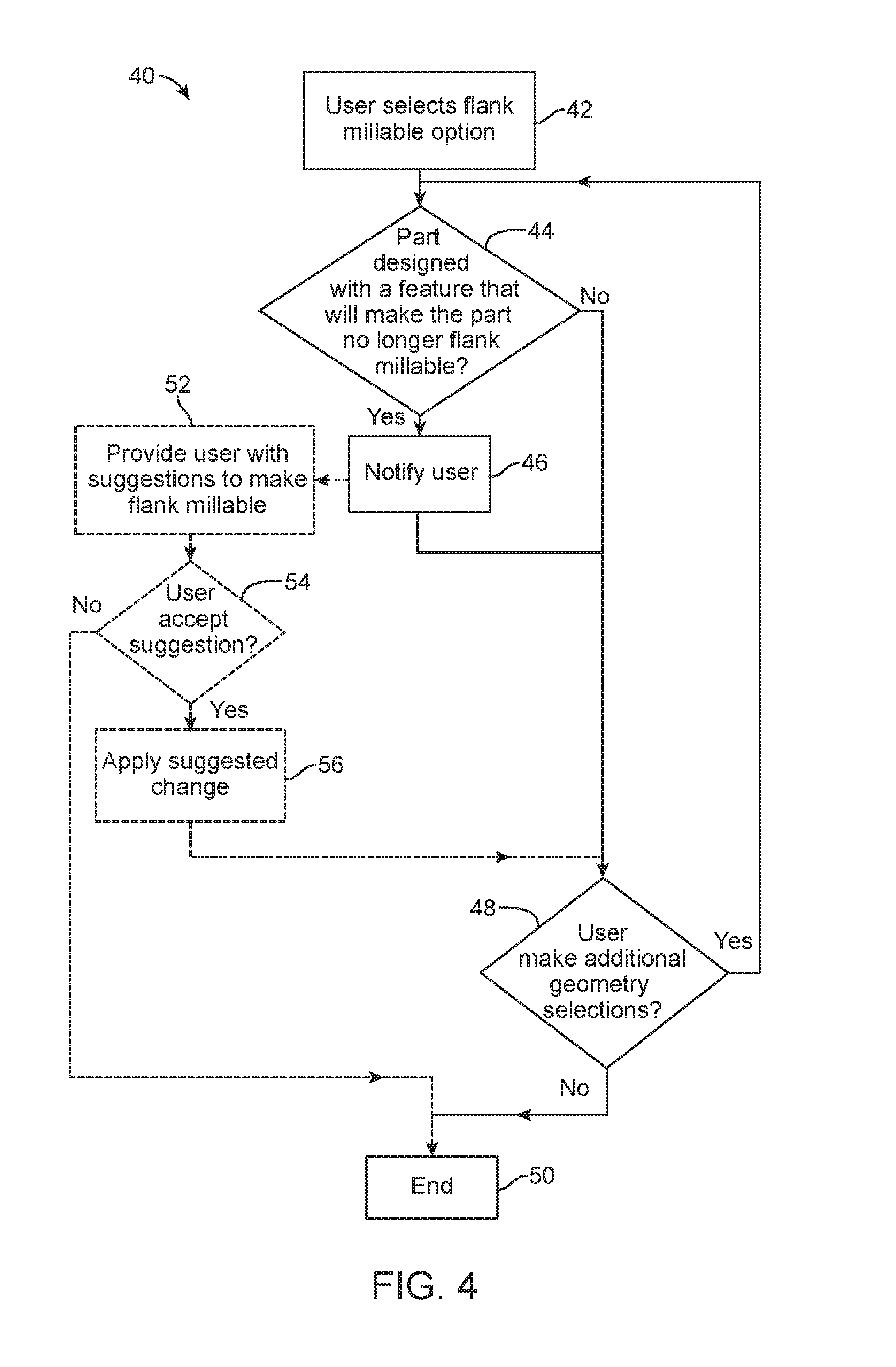
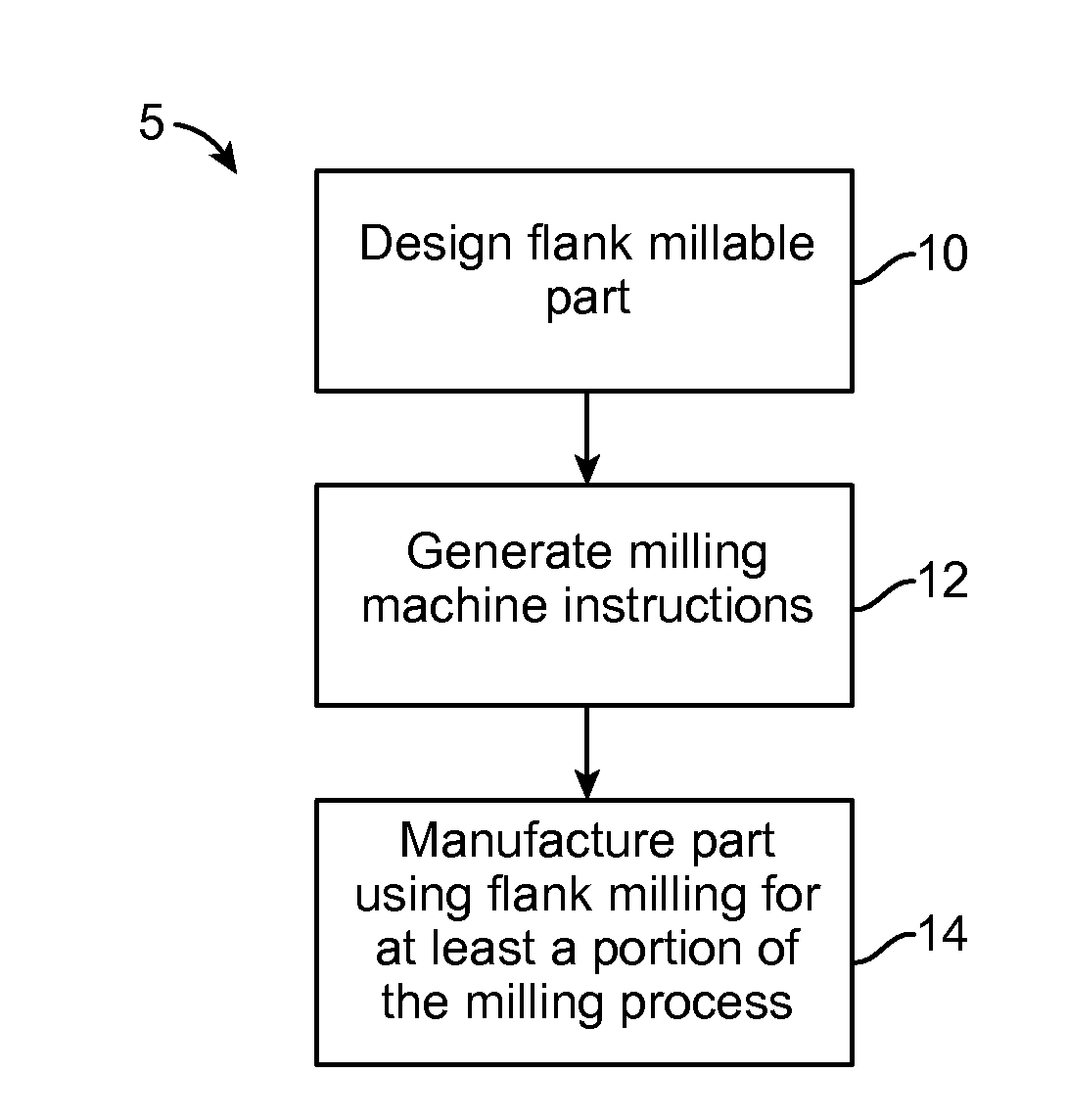
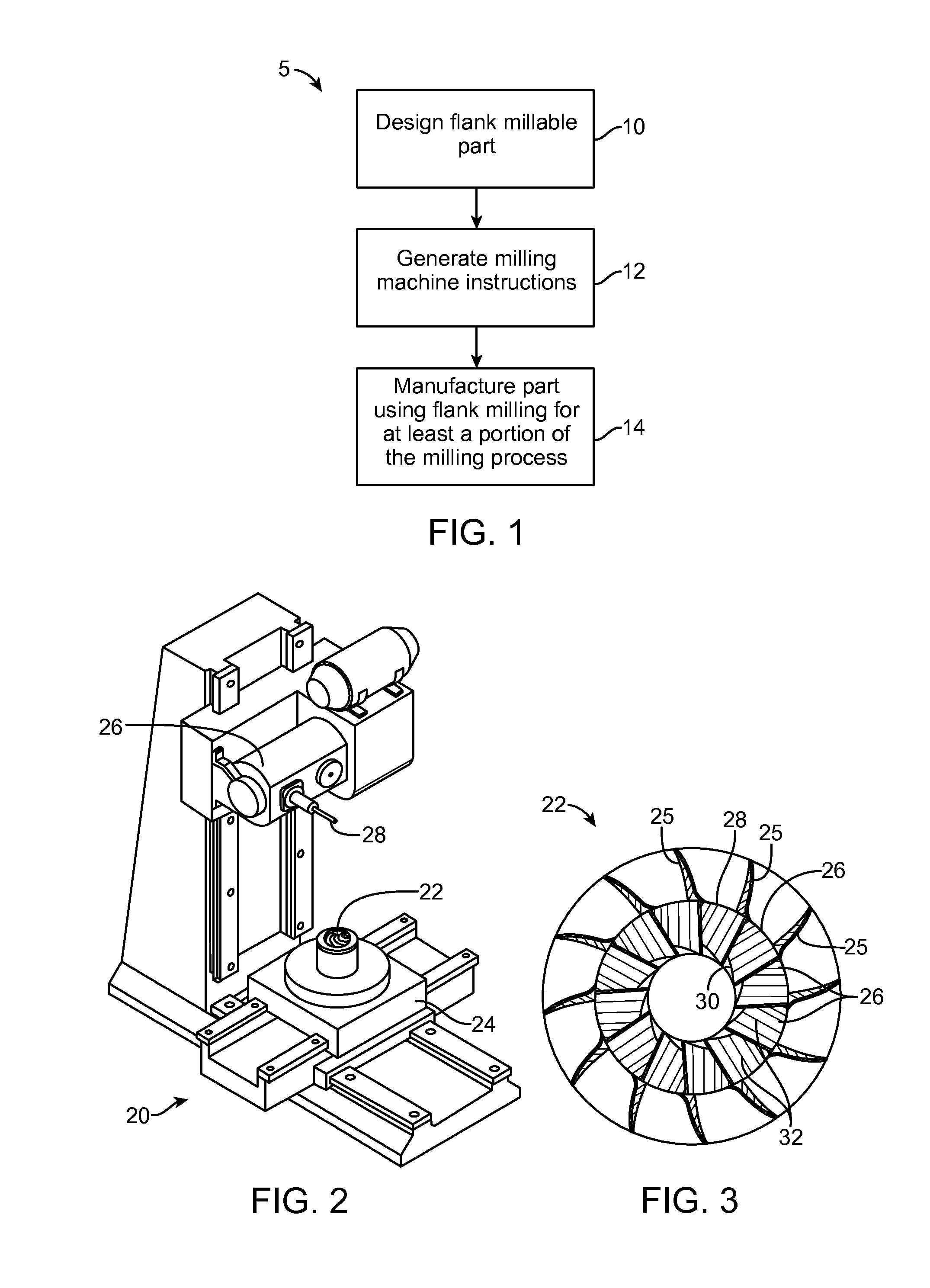
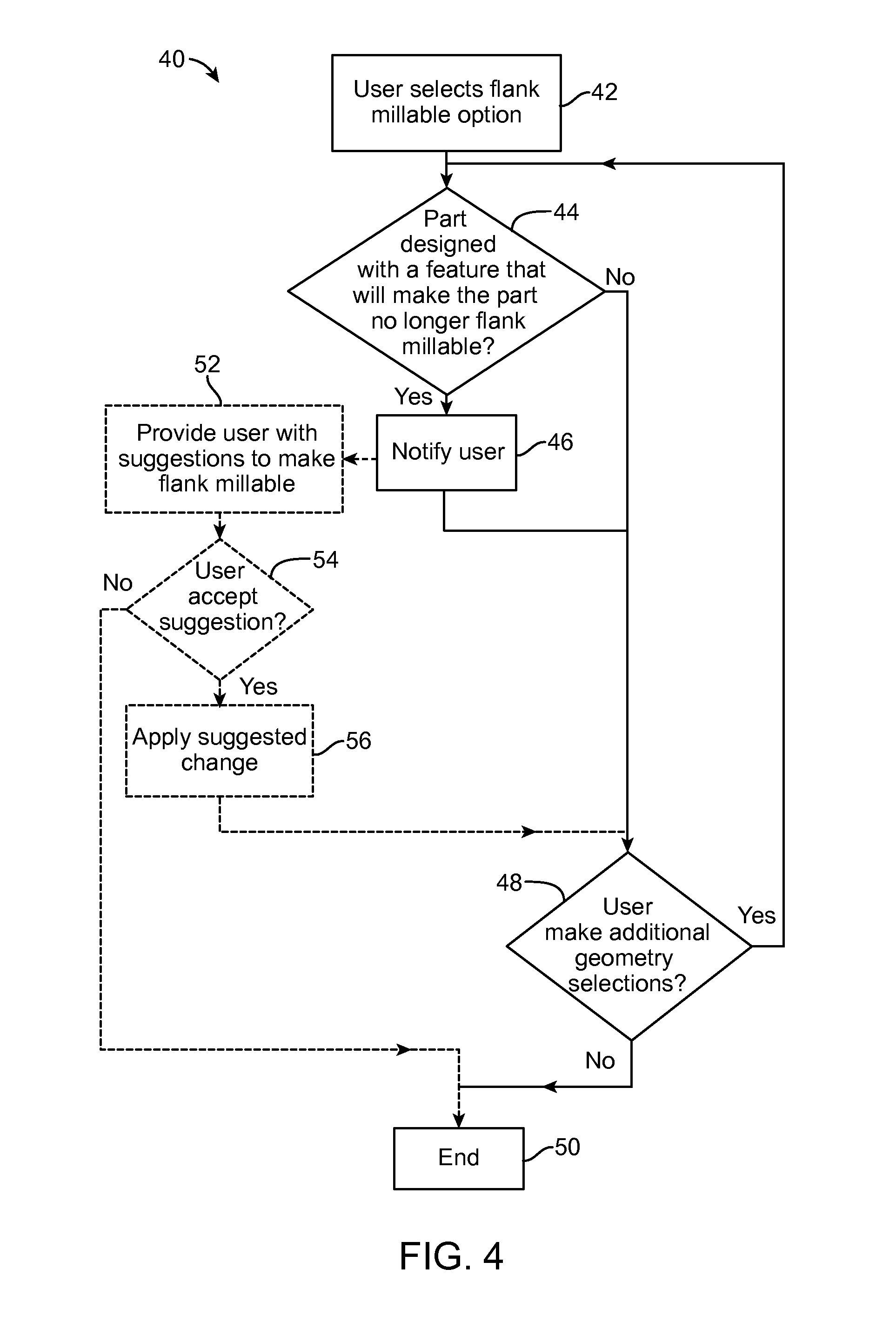
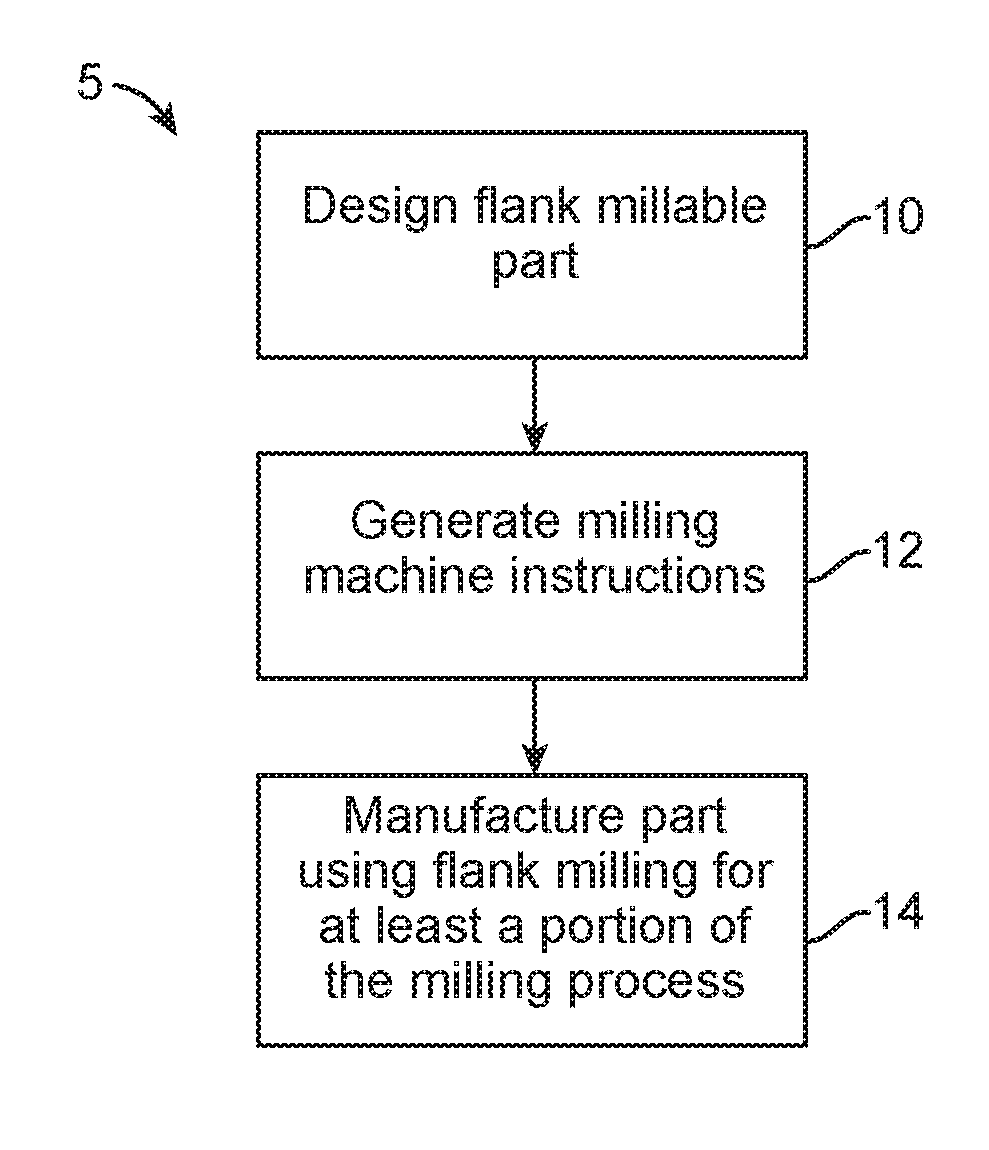
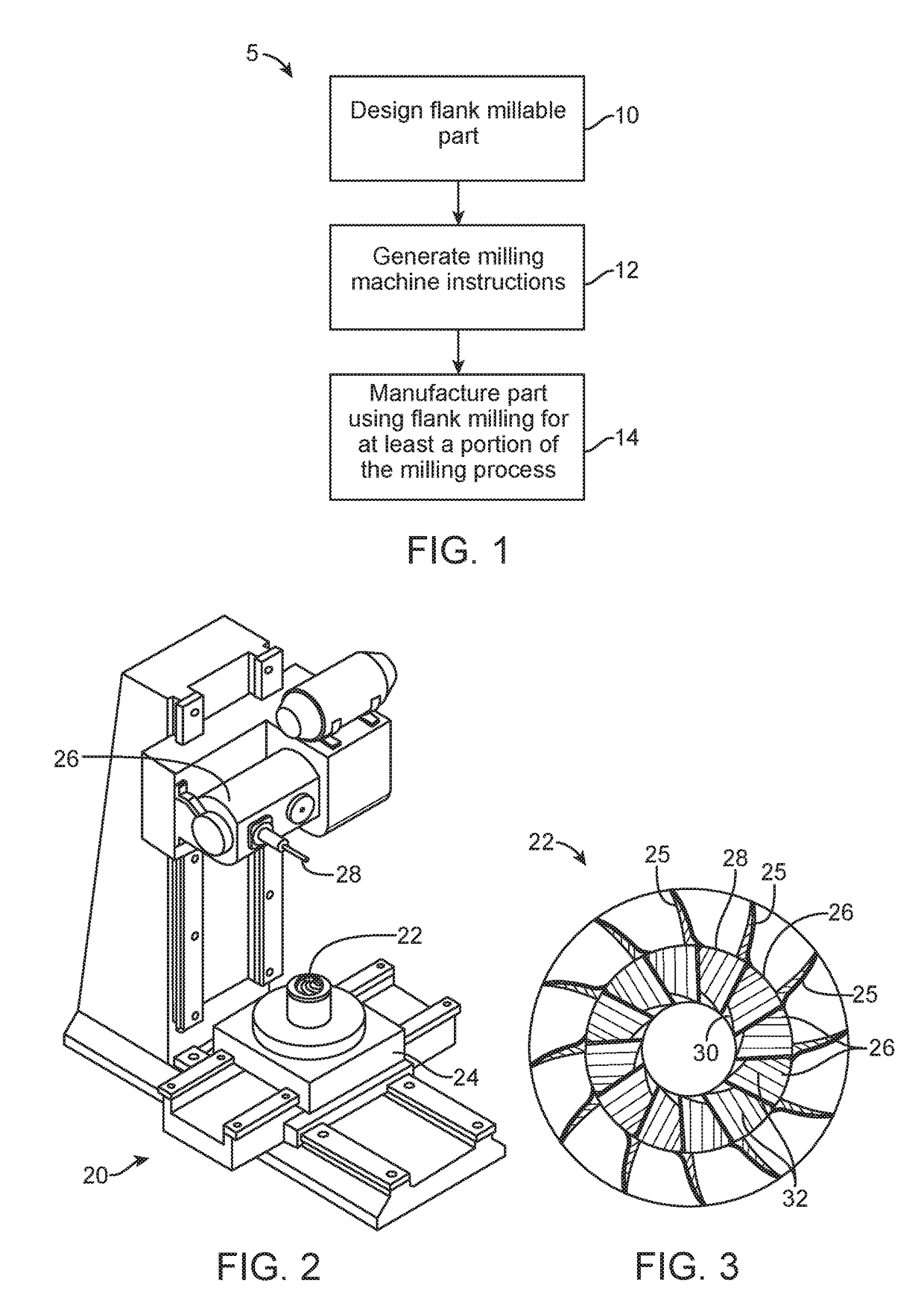
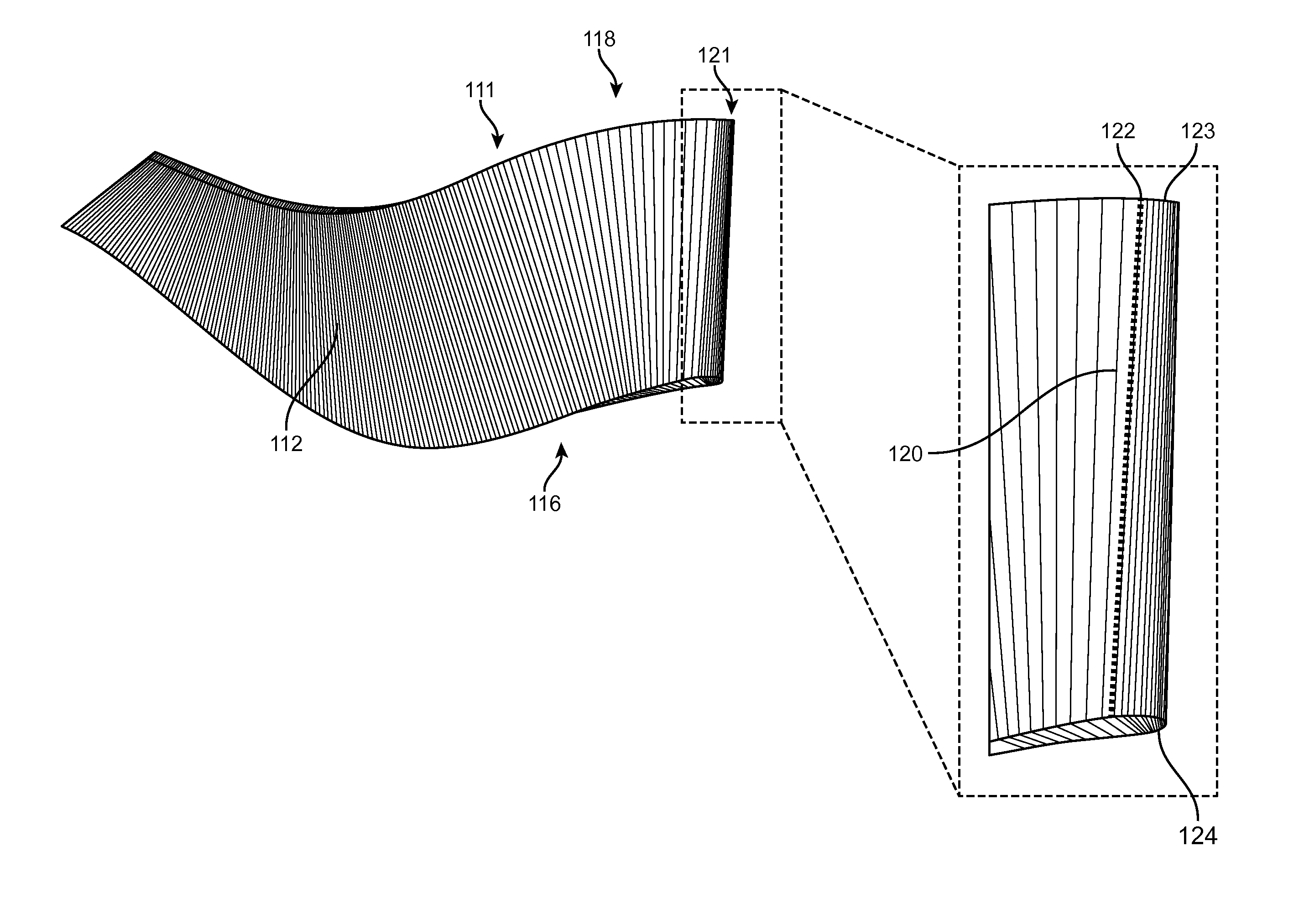
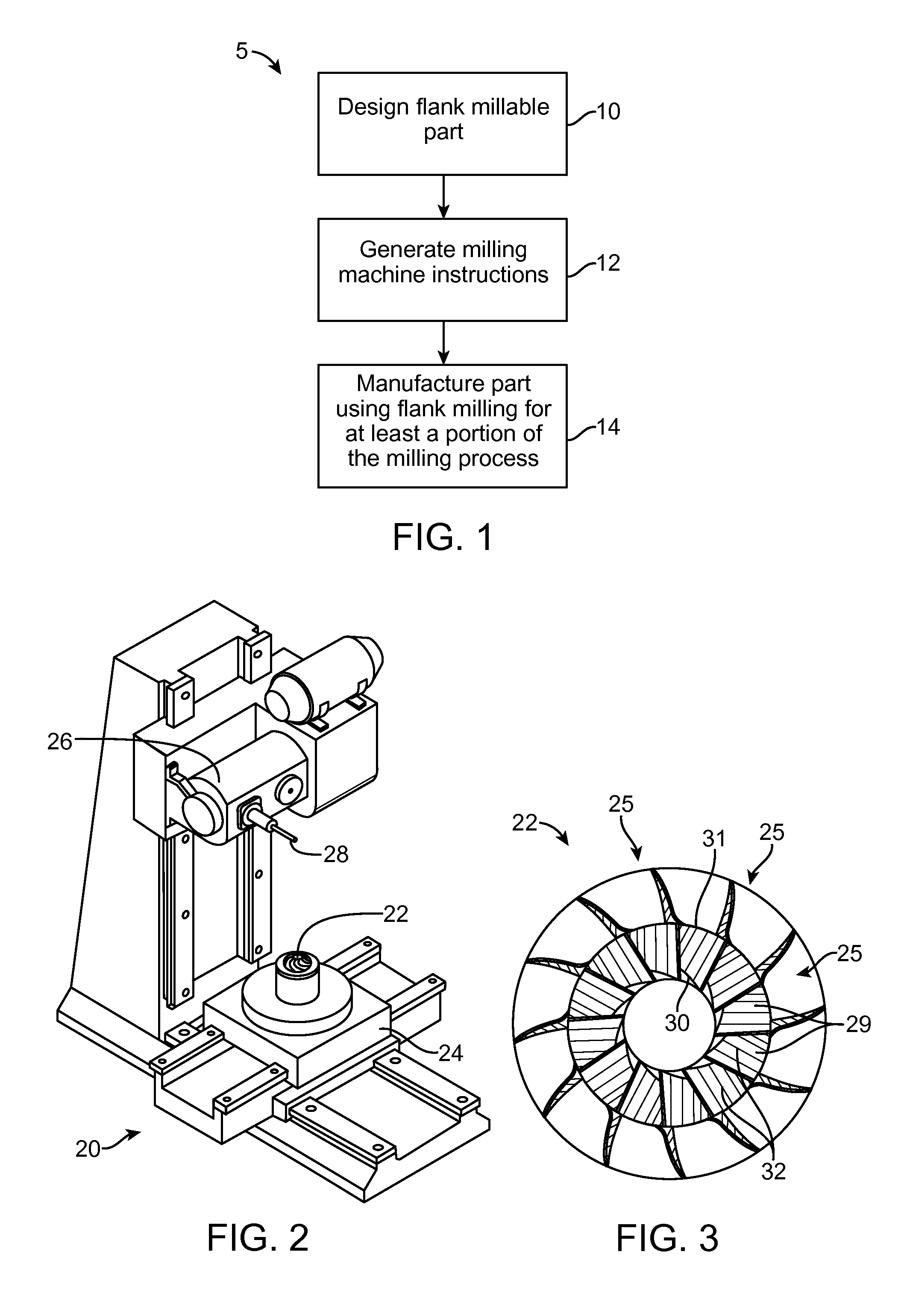
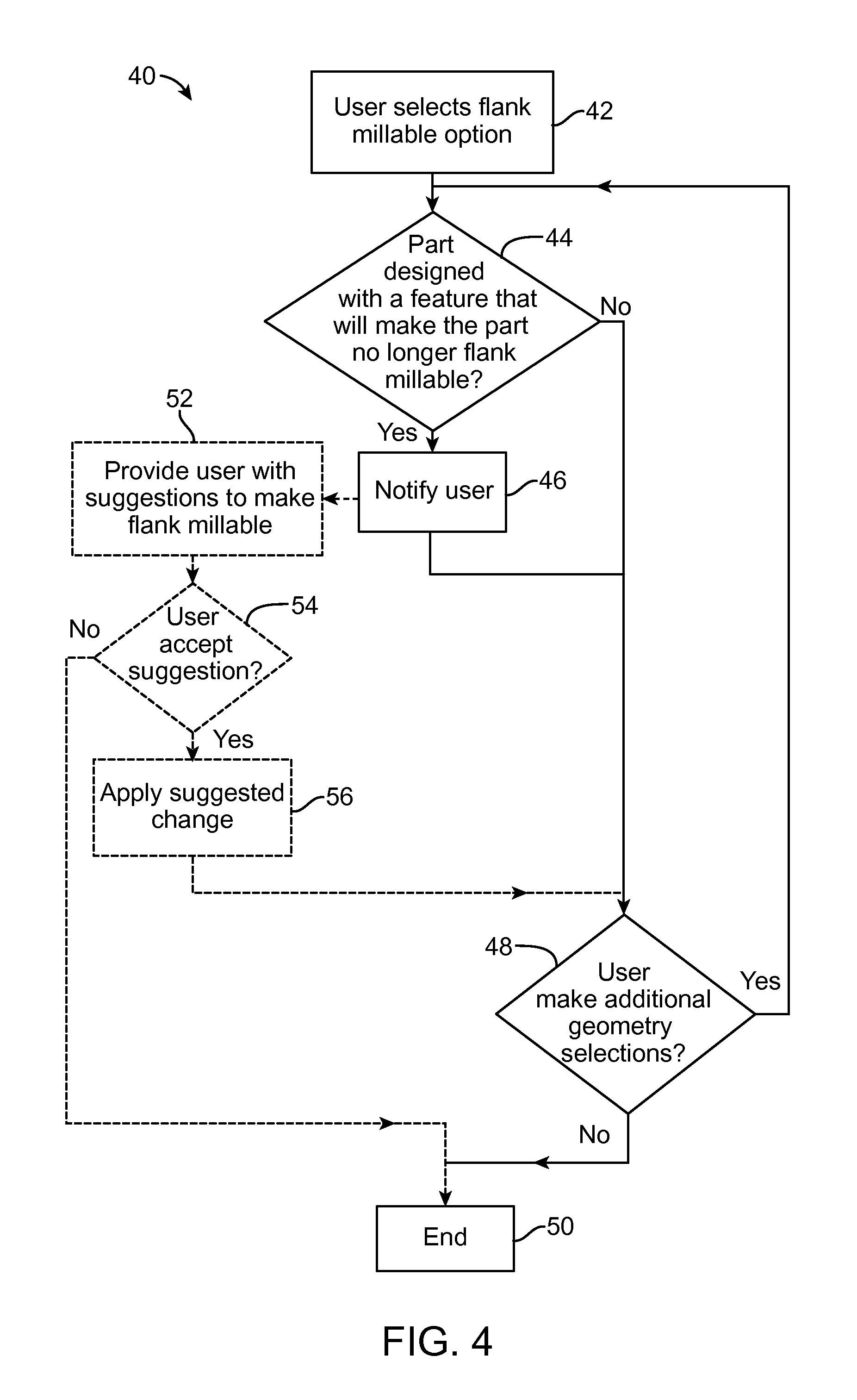
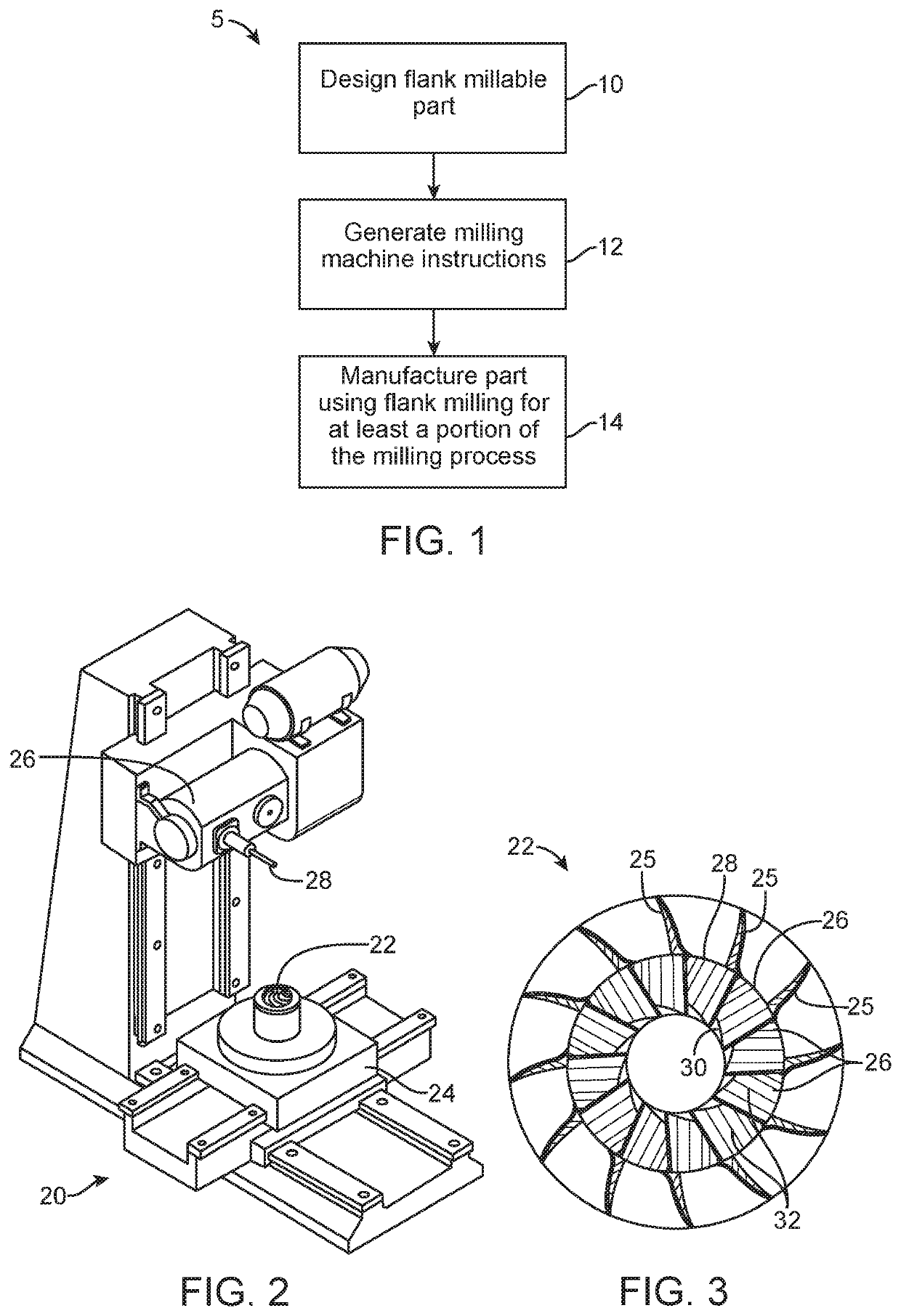
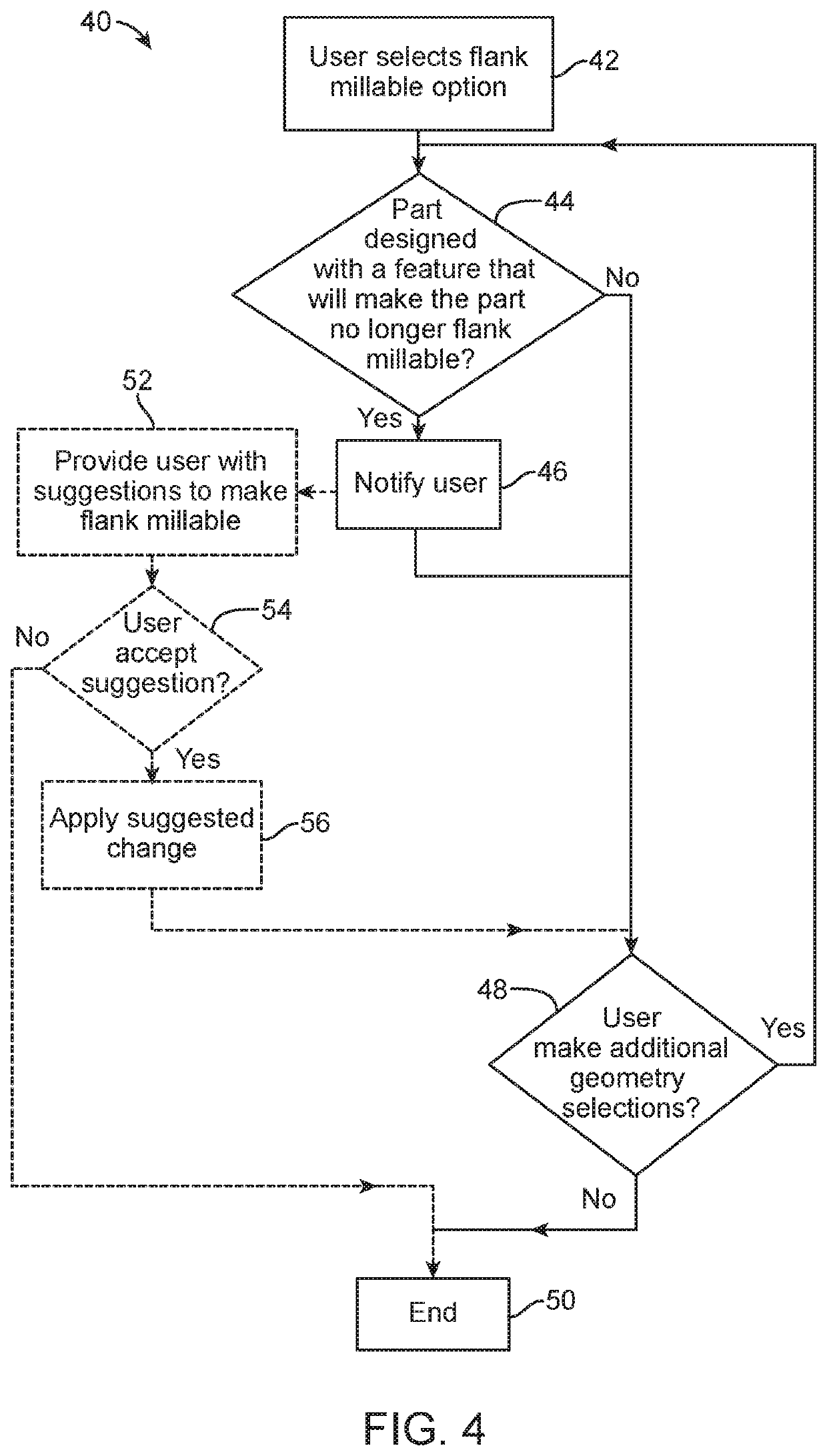
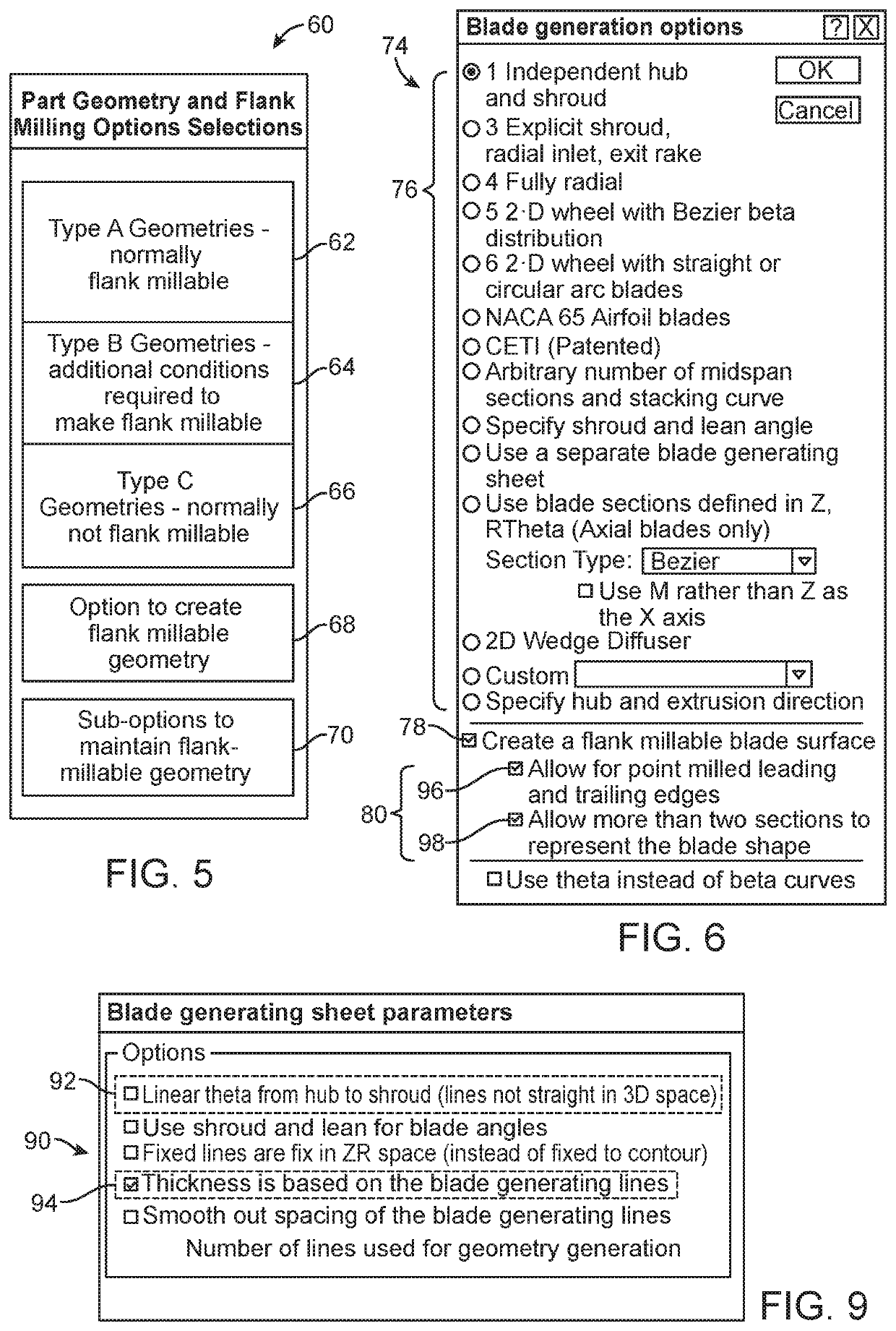
Methods, Systems, and Devices for Designing and Manufacturing Flank Millable Components
Methods, systems, and devices for designing and manufacturing flank millable components. In one embodiment, devices, systems, and methods for designing a flank millable component are provided, in which a user is notified when a component geometry option is selected that will result in the component not being flank millable. In another embodiment, the user is prevented from selecting a geometry option that would result in the component not being flank millable. In yet another embodiment, devices, systems, and methods are provided for manufacturing a component with a flank milling process, in which optimized machine instructions are determined that minimize milling machine motion.
Owner:CONCEPTS ETI
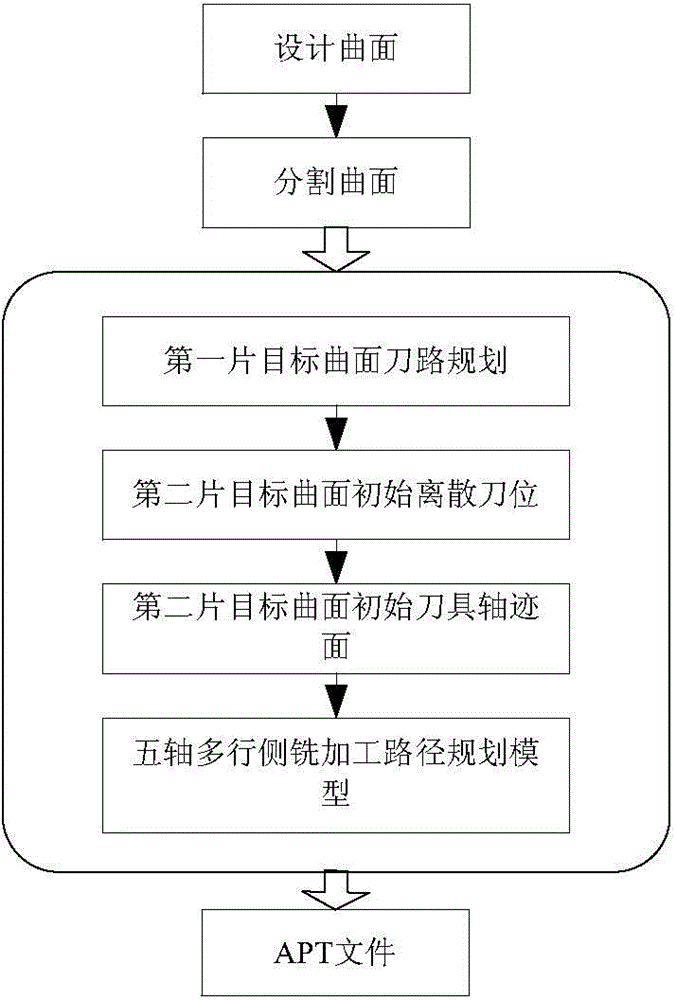
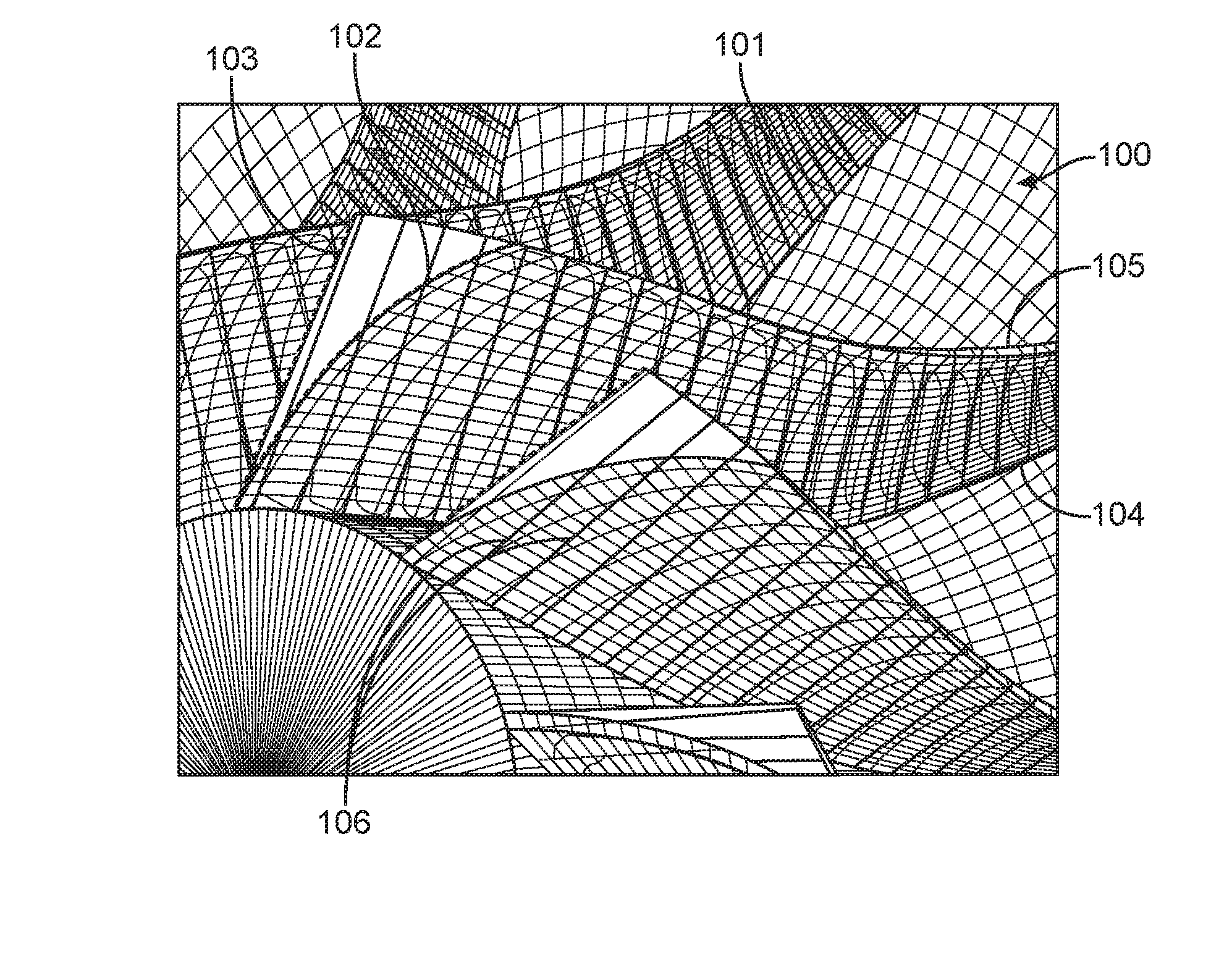
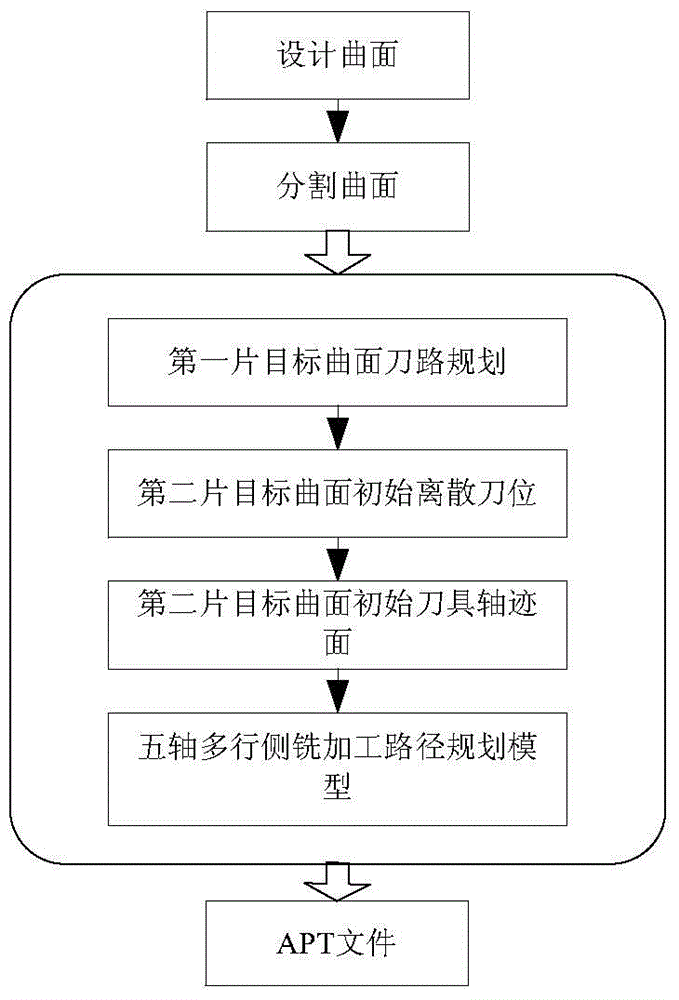
Five-axis multi-row flank milling cutter position planning method
The invention provides a five-axis multi-row flank milling cutter position planning method. The method includes the first step of deducing cutting direction continuity conditions of envelope curved surfaces of two adjacent rows of cutters according to the two-parameter sphere congruence envelope theory, the second step of conducting segmentation design on the curved surfaces according to a curved surface parameter line to obtain multiple target curved surfaces, the third step of planning the cutter axial trace surface of the first target curved surface, the fourth step of sampling points on a top curved line of the cutter axial trace surface of the first target curved surface and calculating cutter center reference points of discrete cutter positions of the second target curved surface, the fifth step of calculating the directions of the cutter axes of the discrete cutter positions according to the linear constraint of the directions of the cutter axes, the sixth step of interpolating the discrete cutter positions to obtain the initial cutter axial trace surface of the second target curved surface, and the seventh step of establishing a five-axis multi-row flank milling cutter path planning model and obtaining the axial trace surface of the optimized second target curved surface. Through the five-axis multi-row flank milling cutter position planning method, the problem that geometric errors between the cutter envelope surfaces and the target curved surfaces approach a control error in the process of continuous splicing and layered machining of the two cutter envelope curved surfaces in the cutting direction is solved, and the method is applicable to flank milling of free-form surfaces and ruled surfaces or curved surfaces similar to the ruled surfaces.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Five-axis flank milling system for machining curved surface and a toolpath planning method thereof
InactiveUS20130144425A1Minimize machining errorRemove restrictionsProgramme controlSpecial data processing applicationsCutter locationPlanning approach
The present invention discloses a five-axis flank milling system for machining a curved surface and a tool-path planning method. The method generates a tool path comprising a series of cutter locations by optimization with minimizing machining errors. The tool path planning method includes a reciprocating tool path planning method and a multi-pass tool path planning method. The reciprocating tool path planning method eliminates the “forward only” limitation. The tool is allowed to move backward in certain regions, producing smaller machining errors compared with forward only cutter movement. Furthermore, the multi-pass tool path planning method computes various tool paths applied to finish milling multiple times. Each path can be chosen to be generated by minimizing undercut error, overcut error, or the total machining error. The machining errors are reduced in a progressive manner, resulting in better machining quality than single pass tool path.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Method for Gear Pre-Cutting of a Plurality of Different Bevel Gears and Use of an According Milling Tool
Soft milling bevel gear teeth on multiple similar bevel gears using a universal hobbing tool with a set of bar cutters comprising a plurality of pairs of inner and outer cutting edges, having four machining phases: 1) simultaneous milling machining a first bevel gear's convex inner and concave outer flanks with the pairs; 2) milling finishing pre-machining either the concave outer flanks with the outer cutting edges the convex inner flanks with the inner cutting edges without employing respective other cutting edges; 3) using the same tool with the same set of cutter bars to pre-tooth a second similar bevel gear, including simultaneous milling machining the gear's convex inner and concave outer flanks; 4) milling finishing pre-machining on the second gear either the concave outer flanks with the outer cutting edges or the convex inner flanks with the inner cutting edges without employing respective other cutting edges.
Owner:KLINGELNBERG AG
Methods, Systems, and Devices for Designing and Manufacturing Flank Millable Components
Methods, systems, and devices for designing and manufacturing flank millable components. In one embodiment, devices, systems, and methods for designing a flank millable component are provided, in which a user is notified when a component geometry option is selected that will result in the component not being flank millable. In another embodiment, the user is prevented from selecting a geometry option that would result in the component not being flank millable. In yet another embodiment, devices, systems, and methods are provided for manufacturing a component with a flank milling process, in which optimized machine instructions are determined that minimize milling machine motion.
Owner:CONCEPTS ETI
Methods, Systems, And Devices For Designing and Manufacturing Flank Millable Components
Methods, systems, and devices for designing and manufacturing flank millable components. In one embodiment, devices, systems, and methods for designing a flank millable component are provided, in which a user is notified when a component geometry option is selected that will result in the component not being flank millable. In another embodiment, the user is prevented from selecting a geometry option that would result in the component not being flank millable. In yet another embodiment, devices, systems, and methods are provided for manufacturing a component with a flank milling process, in which optimized machine instructions are determined that minimize milling machine motion.
Owner:CONCEPTS ETI
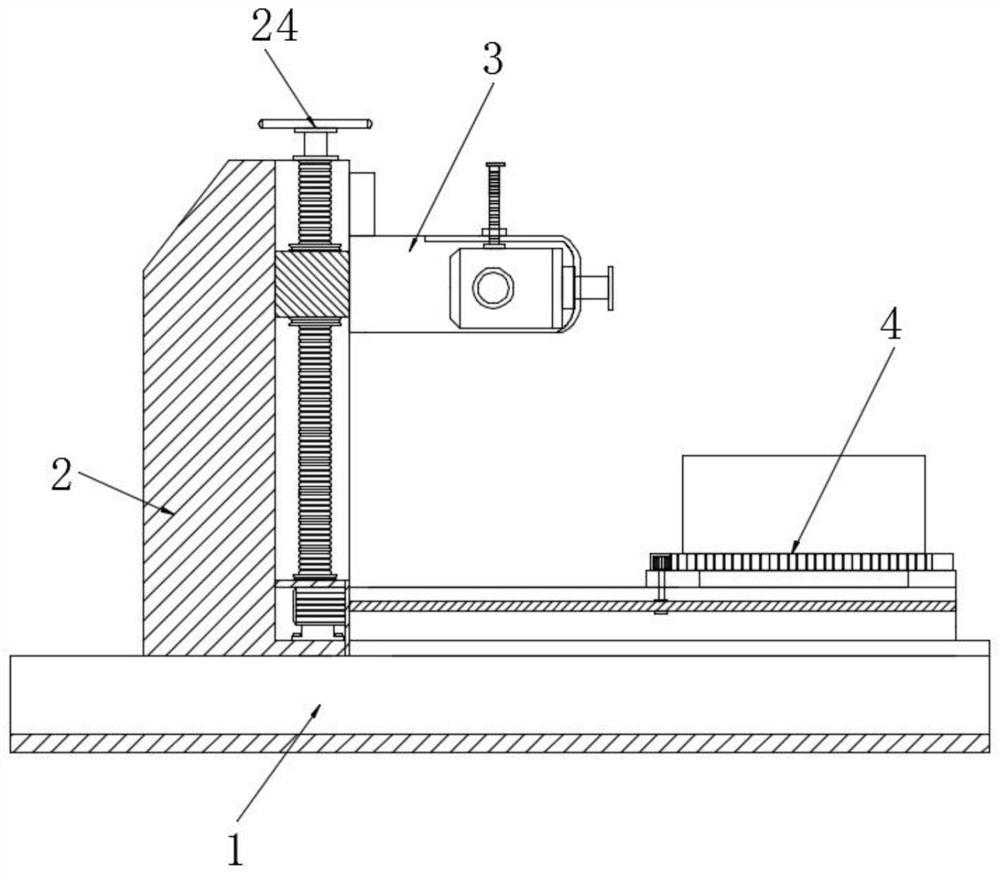
Screw type sleeve part side milling multi-station adjustable manual clamp and method
PendingCN107717553AFully fixedNo secondary damagePositioning apparatusMetal-working holdersSet screwMachine building
The invention belongs to the field of mechanical manufacturing of disc sleeve part side milling and particularly relates to a screw type sleeve part side milling multi-station adjustable manual clampand method. A positioning device, a clamping device and a knife setting device are all arranged on a clamp body. The positioning device and the clamping device are arranged in parallel, and the knifesetting device is disposed on one side of the positioning device and one side of the clamping device. A positioning block of the positioning device and a positioning pin are arranged at intervals. Thepositioning pin is fixed to a supporting plate, the positioning block penetrates the supporting plate and is connected with a positioning block push plate, and a set screw is fixed to the positioningblock through a screw base. The screw type sleeve part side milling multi-station adjustable manual clamp has the advantages that disc sleeve parts of various sizes and shapes can be fully fixed, large plane and positioning pin combination and positioning block positioning are adopted, the positioning is reliable, and parts are not subjected to secondary damage. Through the knife setting device capable of being lifted in a stepless mode, multi-time milling can be achieved by one-time clamping, manual fastening dismantling is convenient, a plurality of workpieces can be clamped in one time forsimultaneous machining, and the screw type sleeve part side milling multi-station adjustable manual clamp greatly improves production efficiency and reduces labor intensity.
Owner:TIANJIN CHENGJIAN UNIV
Machining equipment
PendingCN111215904ASpeed up production scheduleIncrease productivityOther manufacturing equipments/toolsLarge fixed membersEngineeringRaised floor
The invention discloses machining equipment. A height milling device, an edge milling device, a turnover device and a hole forming device are integrated on a production line so that foot piece heightmachining, side face edge milling, drilling and other machining treatment can be performed on the single production line for targets such as raised floors. Accordingly, the production time interval can be accelerated, and the production efficiency can be improved.
Owner:ベロテクノロジーズドンタイカンパニーリミテッド
Processing equipment
PendingCN111558833ASpeed up production scheduleIncrease productivityOther manufacturing equipments/toolsMilling equipment detailsRaised floorManufacturing line
The invention discloses processing equipment. A height milling device, a multi-tasking device, a turnover device and a hole forming device are integrated on a production line, so that footstand heightmachining, side face edge milling, surface groove milling, drilling and other machining treatments can be carried out on a target object of a raised floor on a single production line, the productiontime is shortened, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:ベロテクノロジーズドンタイカンパニーリミテッド
Five-axis flank milling system for machining curved surface and toolpath planning method thereof
ActiveUS9785137B2Reduces uneven modificationQuality improvementSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical controlMachined surfaceCutter location
This invention provides a novel tool path planning method for five-axis flank milling by imposing the constraints of curve interpolation on the tool path. The tool motion is described in the form of spline curves during its optimization-driven calculation process, instead of discrete cutter locations in CNC linear interpolation. The coefficients of the curve equations are generated by minimizing accumulated geometrical errors on the machined surface using optimization algorithms. The continuity imposed by the spline motion reduces uneven modifications of cutter locations during the optimization process. The resultant tool path yields superior.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Pull rod machining technology
The invention discloses a pull rod machining technology. The pull rod machining technology includes the steps of 1, cutting materials by a laser cutting machine to form an L-shaped product outline preliminarily according to the drawing size; 2, subjecting the cut product to positioning and machining by a milling machine; 3, using the milling machine for hole milling; 4, further machining the materials by the milling machine; 5, using the milling machine for milling an elongated slot in the surface in which an R20 circular arc is positioned; 6, using the milling machine for side face hole milling; 7, subjecting the materials to linear cutting; 8, subjecting the materials to finish milling, namely, finish machining according to drawing requirements on the size and shape; 9, rounding off the materials according to drawing requirements; 10, subjecting a machined product to surface polishing; 11, product inspection and warehousing. The pull rod machining technology has the advantages that production requirements are met, precision and strength of the produced pull rod are improved to meet the requirements, defective percentage is decreased and production cost is lowered.
Owner:SUZHOU FUMAI PRECISION MACHINERY
Methods, Systems, and Devices For Designing and Manufacturing Flank Millable Components
Methods, systems, and devices for designing and manufacturing flank millable components. In one embodiment, devices, systems, and methods for designing a flank millable component are provided, in which a user is notified when a component geometry option is selected that will result in the component not being flank millable. In another embodiment, the user is prevented from selecting a geometry option that would result in the component not being flank millable. In yet another embodiment, devices, systems, and methods are provided for manufacturing a component with a flank milling process, in which optimized machine instructions are determined that minimize milling machine motion.
Owner:CONCEPTS ETI
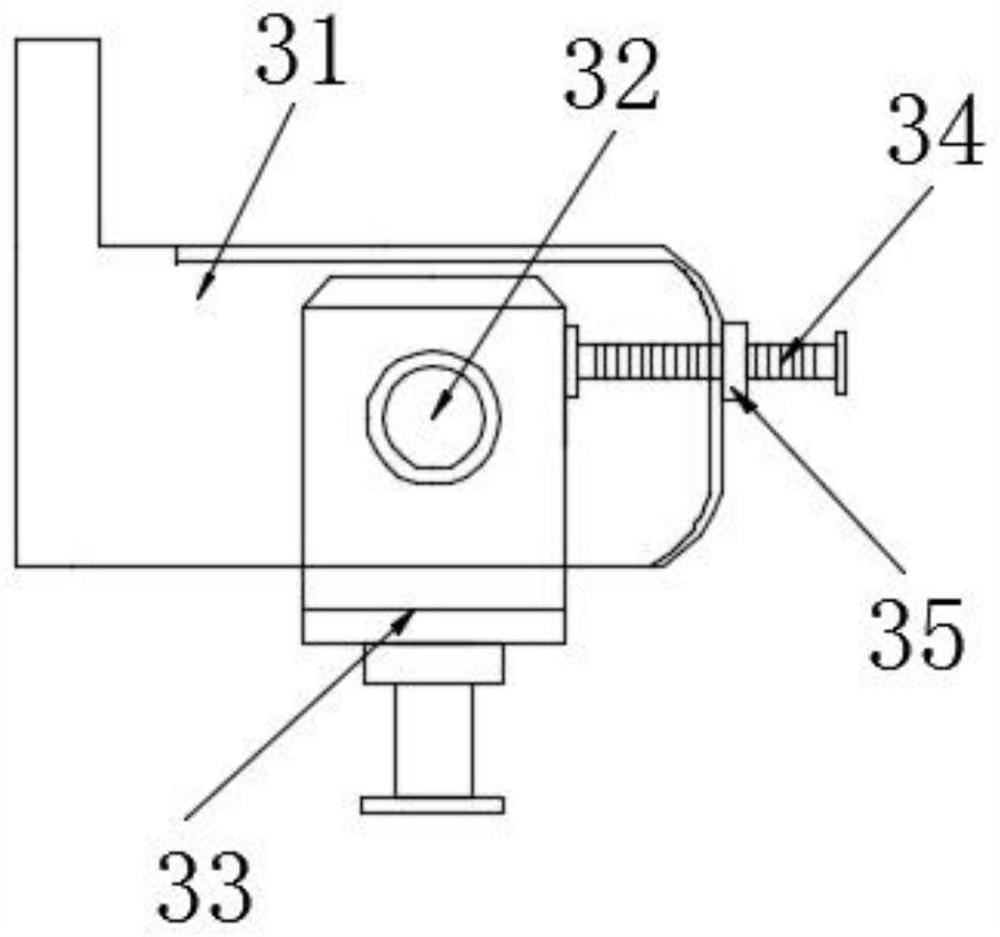
Groove milling device for kitchen cooking utensils
InactiveCN111975072AEasy to useIncrease flexibilityMilling equipment detailsPositioning apparatusMachiningFlank milling
The invention discloses a groove milling device for kitchen cooking utensils. The groove milling device for the kitchen cooking utensils comprises a main body rack, a two-way groove milling machiningmechanism and a machining table assembly. A lifting adjusting frame is perpendicularly fixed to one side of the surface of the main body rack. The two-way groove milling machining mechanism is fixedlyinstalled on the lifting adjusting frame, and the lifting adjusting frame is assembled to be used for driving the two-way groove milling machining mechanism to conduct lifting adjustment. The two-waygroove milling machining mechanism comprises a U-type machining frame and a groove milling machining head. The groove milling machining head is rotatably arranged on the U-type machining frame through a rotary shaft. By means of the groove milling device for the kitchen cooking utensils, it is achieved that top groove milling machining and side-face groove milling machining are conducted on cooking utensils and workpieces; flexibility of groove milling machining is improved prominently; multiple kinds of groove milling machining requirements can be met; there is no need for replacing or disassembling the groove milling machining head; and in the meantime, adaptive regulating of position can be conducted by the machining table assembly according to top groove milling machining or side-facegroove milling machining requirements so that the groove milling device for the kitchen cooking utensils is more convenient when used.
Owner:湖南华军厨房设备有限公司
Methods, systems, and devices for designing and manufacturing flank millable components
Methods, systems, and devices for designing and manufacturing flank millable components. In one embodiment, devices, systems, and methods for designing a flank millable component are provided, in which a user is notified when a component geometry option is selected that will result in the component not being flank millable. In another embodiment, the user is prevented from selecting a geometry option that would result in the component not being flank millable. In yet another embodiment, devices, systems, and methods are provided for manufacturing a component with a flank milling process, in which optimized machine instructions are determined that minimize milling machine motion.
Owner:CONCEPTS ETI
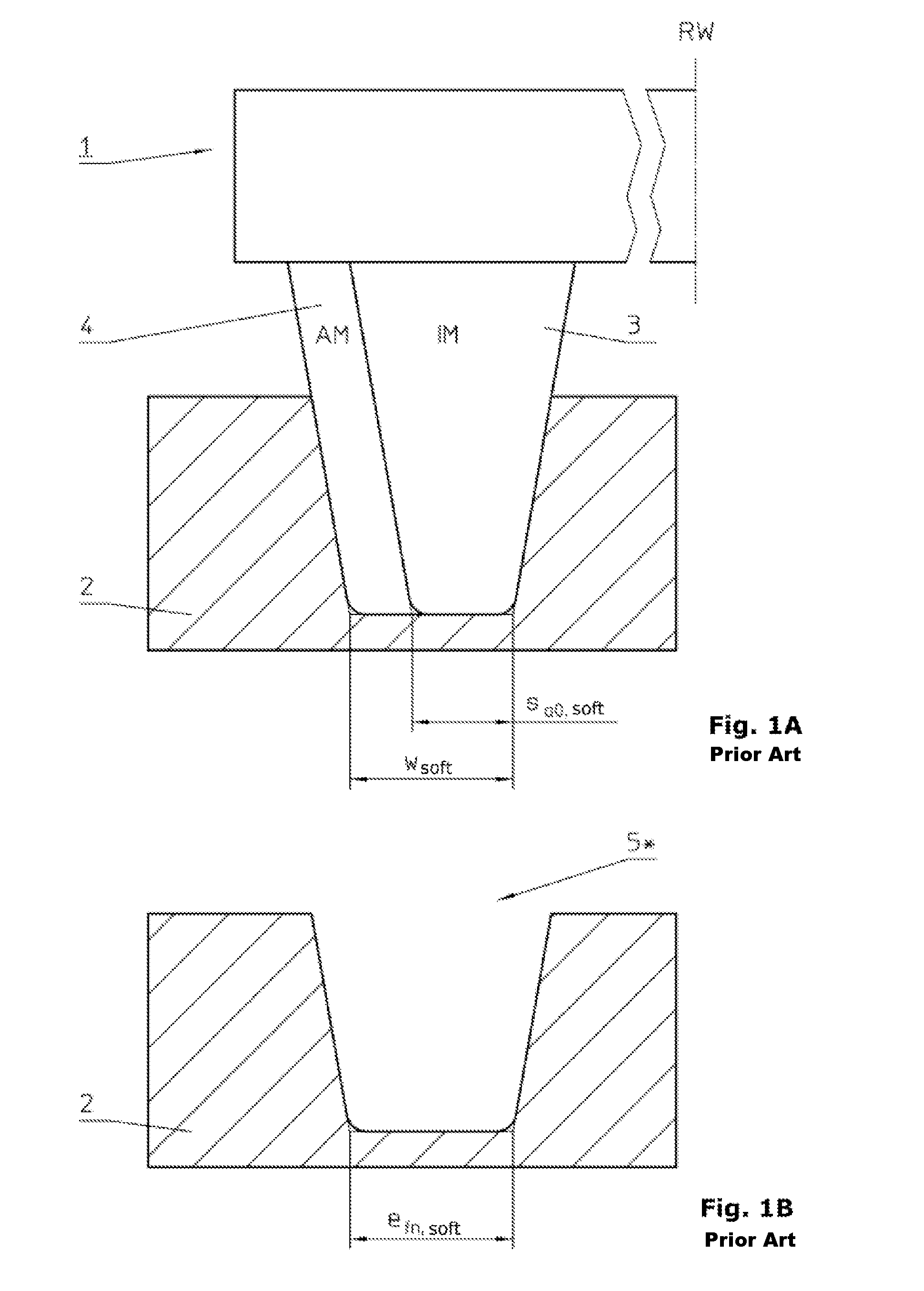
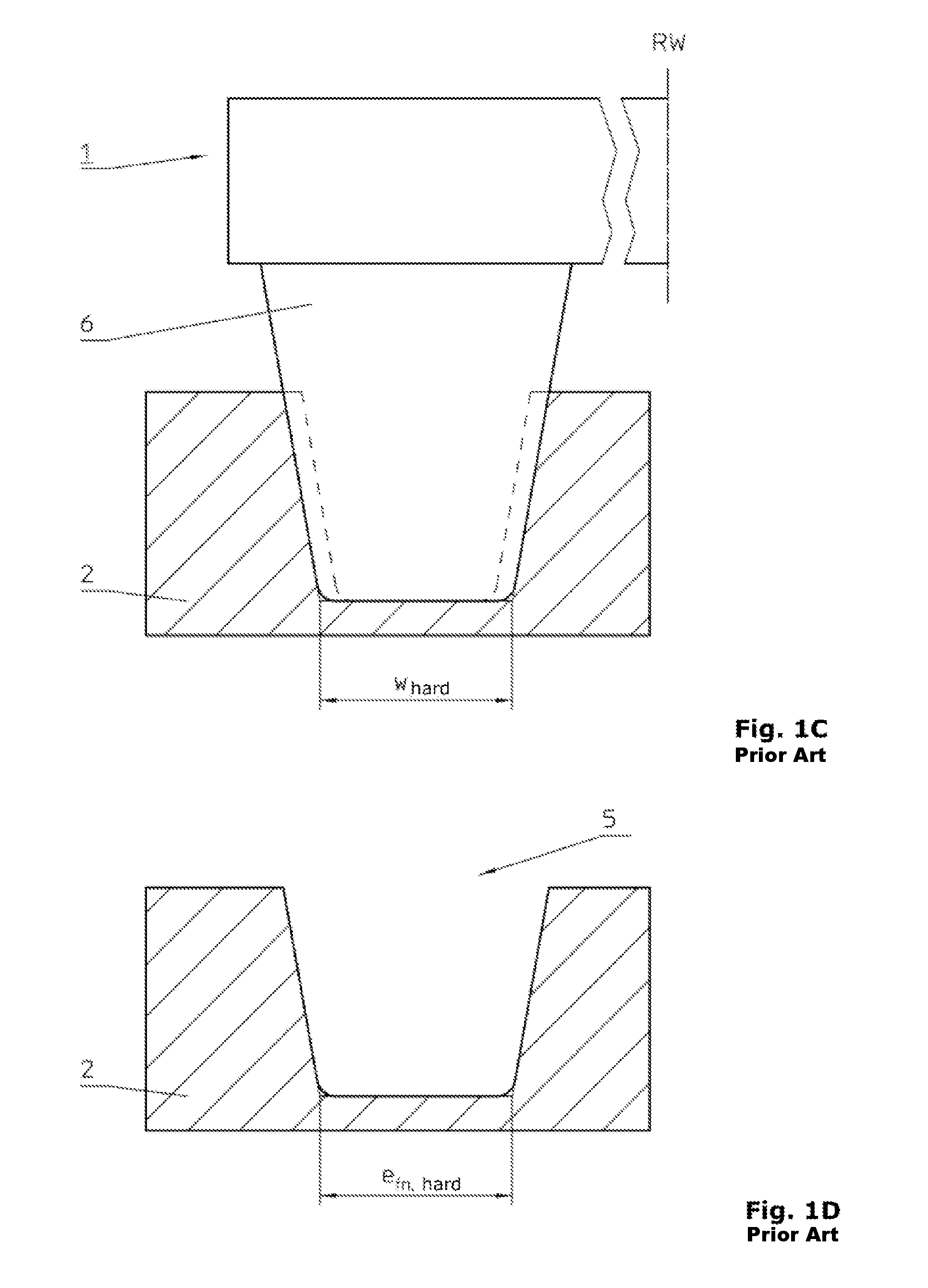
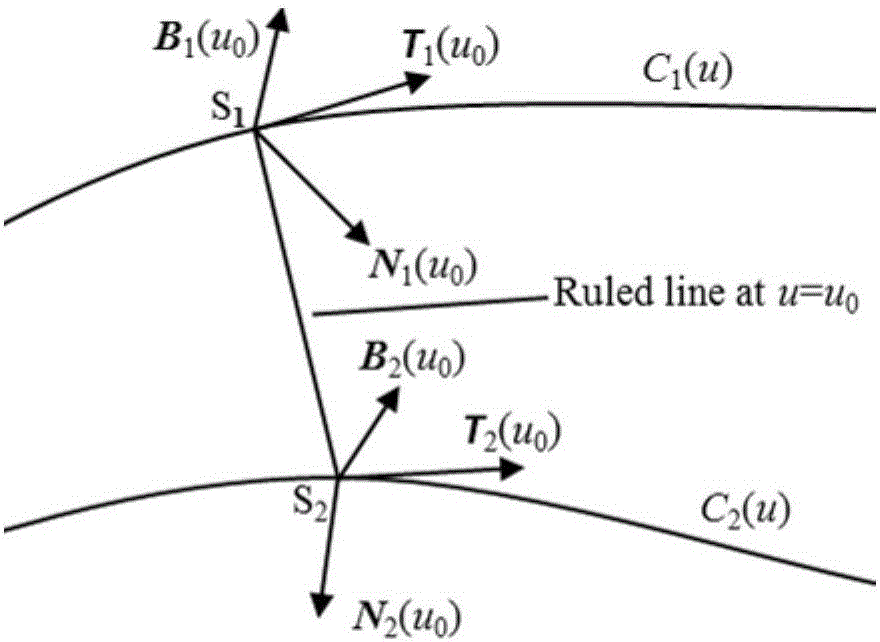
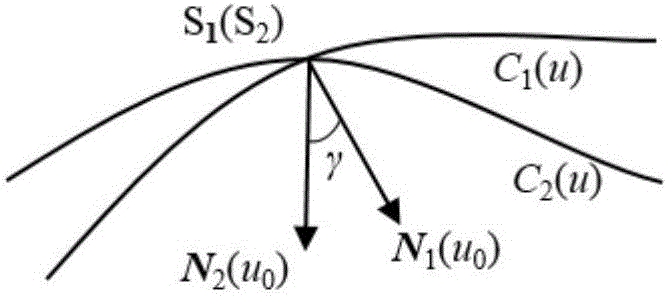
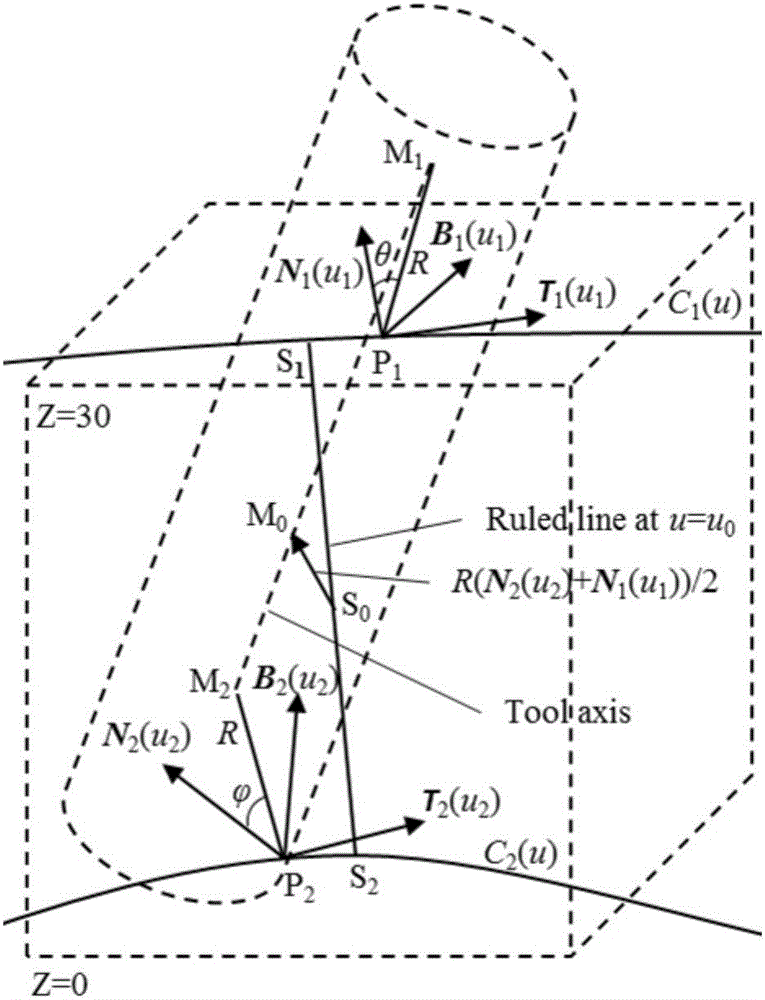
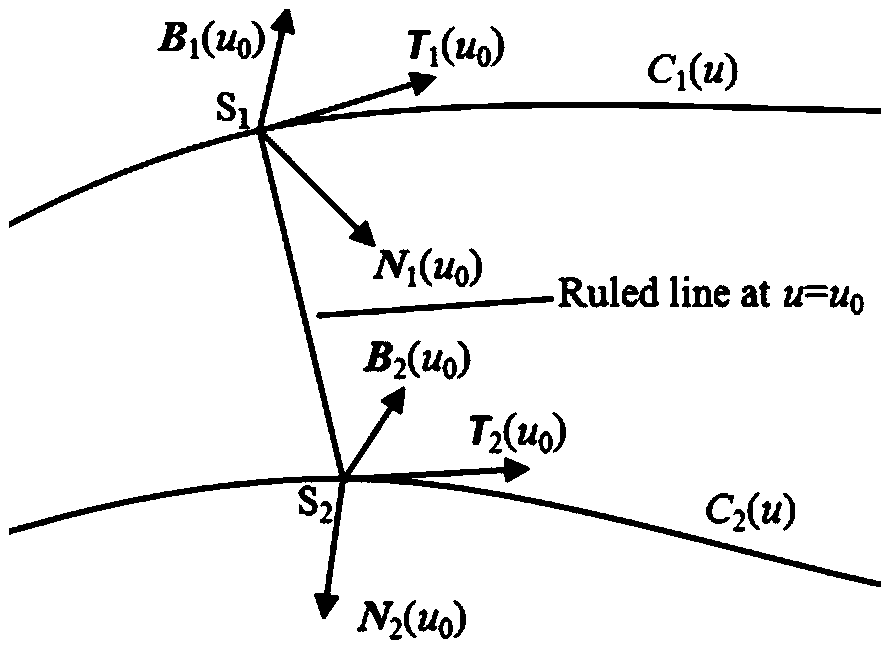
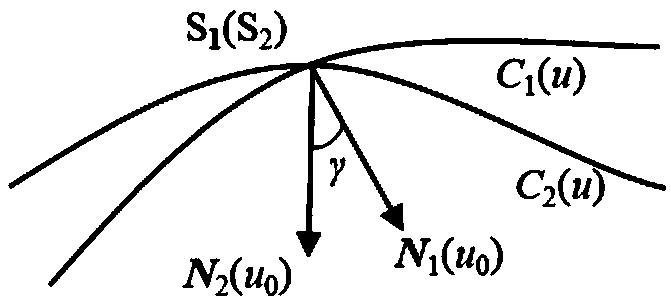
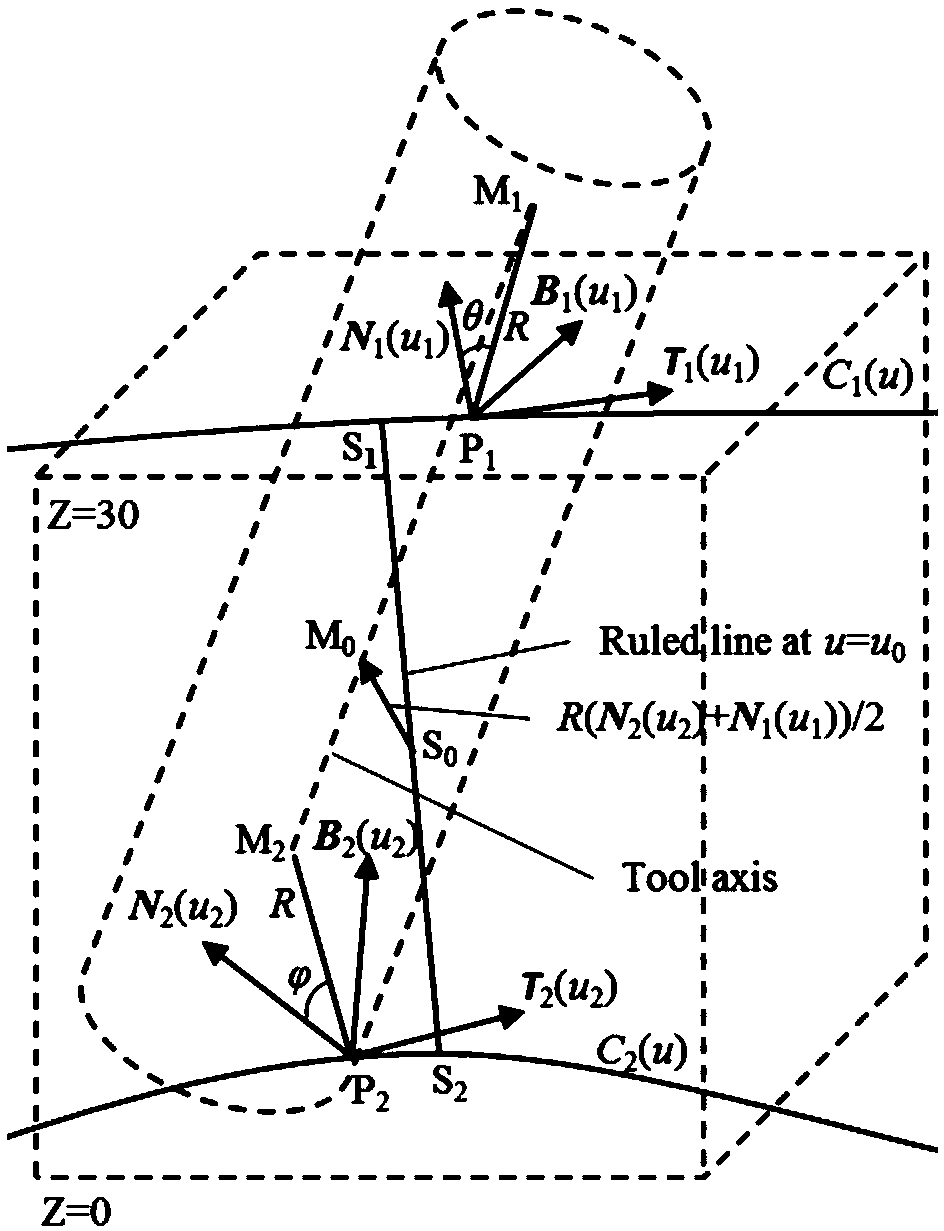
Cutter positioning method for flank milling non-unfoldable ruled surface
ActiveCN106227153AEfficient determinationEffective side millingProgramme controlComputer controlCutter locationEngineering
The invention relates to a cutter positioning method for flank milling a non-unfoldable ruled surface. The method comprises the steps that the non-unfoldable ruled surface of a part to be machined is selected, wherein upper and lower boundary curves are C1(u) and C2(u); any one straight generatrix S1S2 on the ruled surface is selected, wherein a corresponding parameter value is u0; unknown parameters u1 and u2 are selected near the generatrix S1S2, wherein the unit tangent vector of the upper boundary curve at a P1 point is T1(u1), the unit tangent vector of the lower boundary curve at a P2 point is T2(u2), the unit vector of a main normal line at the P1 point is N1(u1), the unit vector of a binormal at the P1 point is B1(u1), the unit vector of the main normal line at the P2 point is N2(u2), and the unit vector of the binormal at the P2 point is B2(u2); a relation equation about a M1 point and a M2 point on the cutter axis and the P1 point and the P2 point is determined; after two constraint conditions are added into the equation, four unknown variables u1, u2, theta and phi are solved, then values of the M1 point and the M2 point are calculated, a cutter-axis vector of the cutter is obtained, and the cutter location attitude is determined by combining the cutter tip point M2; all the parameters are traversed along the boundary curves according to the increasing sequences and the appropriate parameter interval till the cutter location attitude of the whole ruled surface is completed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for manufacturing a thin-walled part
ActiveUS20210178495A1Improve machine efficiencyEasy to wearWorkpiecesMilling equipment detailsTurbine bladeMachine tool
A method for manufacturing a thin-walled part having curved surfaces, in particular a turbine blade by a machine tool comprising roughing process and semi-finishing process. At least one of the roughing process and the semi-finishing process is accomplished by flank milling.
Owner:GF MACHINING SOLUTIONS AG
Method for manufacturing a thin-walled part
ActiveUS11338374B2Improve machine efficiencyEasy to wearWorkpiecesMilling equipment detailsTurbine bladeMachine tool
Owner:GF MACHINING SOLUTIONS AG
Side hole machining machine
PendingCN112719913AEnsure consistencyEasy to buyOther manufacturing equipments/toolsEngineeringMachine
The invention discloses a side hole machining machine which comprises a machine frame, a servo transverse hole milling mechanism for machining a side hole in a workpiece, a vibration disc feeding mechanism for automatic feeding, a material taking mechanism for obtaining the workpiece in the feeding mechanism, and a carrying mechanism for conveying the workpiece obtained by the material taking mechanism to the servo transverse hole milling mechanism; the vibration disc feeding mechanism, the material taking mechanism, the carrying mechanism and the servo transverse hole milling mechanism are all installed on the machine frame, and a first working face and a second working face are arranged on the machine frame, the vibration disc feeding mechanism and the material taking mechanism are installed on the first working face, and the carrying mechanism and the servo transverse hole milling mechanism are both installed on the second working face. A vibration disc is used for feeding, the material taking mechanism and the carrying mechanism are used for conveying products to the servo transverse hole milling mechanism, a high-speed main shaft is driven by the servo transverse hole milling mechanism to mill holes in the side faces of workpieces, and a material box collects the workpieces subjected to hole milling.
Owner:贵州顺安科技有限公司
A tool positioning method suitable for side milling of non-developable ruled surfaces
ActiveCN106227153BEfficient determinationEffective side millingProgramme controlComputer controlCutter locationEngineering
The invention relates to a cutter positioning method for flank milling a non-unfoldable ruled surface. The method comprises the steps that the non-unfoldable ruled surface of a part to be machined is selected, wherein upper and lower boundary curves are C1(u) and C2(u); any one straight generatrix S1S2 on the ruled surface is selected, wherein a corresponding parameter value is u0; unknown parameters u1 and u2 are selected near the generatrix S1S2, wherein the unit tangent vector of the upper boundary curve at a P1 point is T1(u1), the unit tangent vector of the lower boundary curve at a P2 point is T2(u2), the unit vector of a main normal line at the P1 point is N1(u1), the unit vector of a binormal at the P1 point is B1(u1), the unit vector of the main normal line at the P2 point is N2(u2), and the unit vector of the binormal at the P2 point is B2(u2); a relation equation about a M1 point and a M2 point on the cutter axis and the P1 point and the P2 point is determined; after two constraint conditions are added into the equation, four unknown variables u1, u2, theta and phi are solved, then values of the M1 point and the M2 point are calculated, a cutter-axis vector of the cutter is obtained, and the cutter location attitude is determined by combining the cutter tip point M2; all the parameters are traversed along the boundary curves according to the increasing sequences and the appropriate parameter interval till the cutter location attitude of the whole ruled surface is completed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Tool position planning method for five-axis multi-row side milling
ActiveCN104007697BResolving Approximation Control ErrorsNumerical controlStructural engineeringFlank milling
The invention provides a five-axis multi-row flank milling cutter position planning method. The method includes the first step of deducing cutting direction continuity conditions of envelope curved surfaces of two adjacent rows of cutters according to the two-parameter sphere congruence envelope theory, the second step of conducting segmentation design on the curved surfaces according to a curved surface parameter line to obtain multiple target curved surfaces, the third step of planning the cutter axial trace surface of the first target curved surface, the fourth step of sampling points on a top curved line of the cutter axial trace surface of the first target curved surface and calculating cutter center reference points of discrete cutter positions of the second target curved surface, the fifth step of calculating the directions of the cutter axes of the discrete cutter positions according to the linear constraint of the directions of the cutter axes, the sixth step of interpolating the discrete cutter positions to obtain the initial cutter axial trace surface of the second target curved surface, and the seventh step of establishing a five-axis multi-row flank milling cutter path planning model and obtaining the axial trace surface of the optimized second target curved surface. Through the five-axis multi-row flank milling cutter position planning method, the problem that geometric errors between the cutter envelope surfaces and the target curved surfaces approach a control error in the process of continuous splicing and layered machining of the two cutter envelope curved surfaces in the cutting direction is solved, and the method is applicable to flank milling of free-form surfaces and ruled surfaces or curved surfaces similar to the ruled surfaces.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
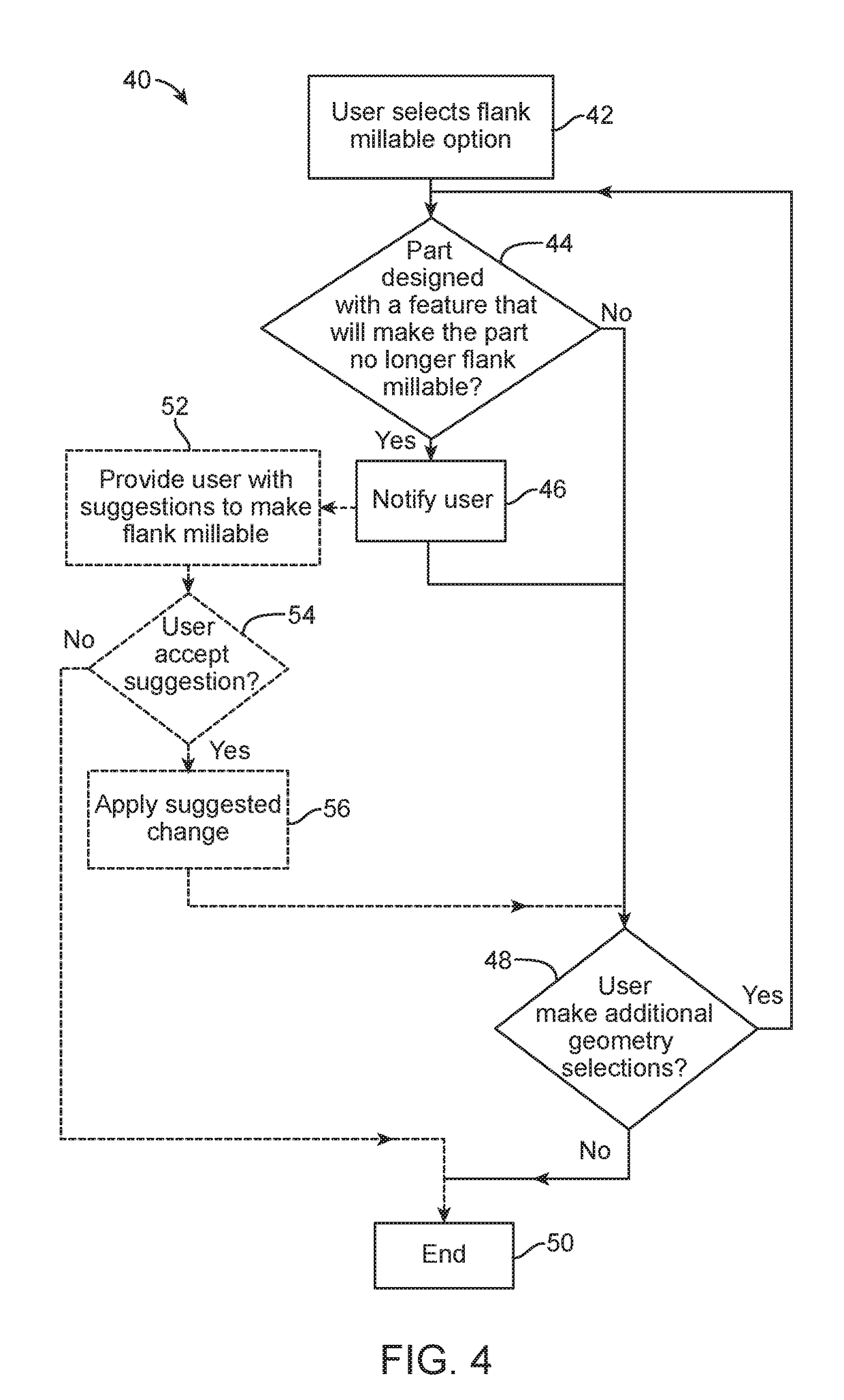
Methods, systems, and devices for designing and manufacturing flank millable components
Flank milling checks during a computer automated design process which may include notifying a user when a component geometry option is selected that will result in the component not being flank millable. In some examples, the user is prevented from selecting a geometry option that would result in the component not being flank millable. In some examples, devices, systems, and methods are provided for manufacturing a component with a flank milling process, in which optimized machine instructions are determined that minimize milling machine motion.
Owner:CONCEPTS ETI
Novel drill bit for high-precision internal threads and using method of novel drill bit
ActiveCN114378379AReduce milling resistanceEasy loadingThread cutting toolsMilling cutterMachine tool control
The invention discloses a novel drill bit for high-precision internal threads and a using method thereof. The novel drill bit comprises a supporting rod inserted into the control end of a machine tool, and a cutter used for forming the high-precision internal threads is arranged on the side, away from the control end of the machine tool, of the supporting rod; the cutter comprises a side wall cutting edge arranged on the side, away from the machine tool control end, of the supporting rod, a plurality of side face milling cutting edges are formed around the side wall cutting edge at equal intervals, an end face milling cutter is arranged on the side, away from the supporting rod, of the side wall cutting edge, and a plurality of end face milling cutting edges are formed in the surface of the end face milling cutter. A combined end face milling cutter and a side wall cutting edge are creatively combined, the novel milling cutter rotates in the radial direction to form cutting power, meanwhile, a machine tool controls radial feeding and radial track movement, the end face milling edge is used for machining a hole in the surface of a workpiece in the radial feeding process, and the side wall single milling edge is optimally increased to be two or more. The milling resistance of each single blade is reduced; one-time machining of the threads is achieved through combination of the two methods, and efficiency is improved by more than one time.
Owner:ZHENJIANG ZHENGKAI ELECTRONICS
A high-efficiency side edge finish milling method based on the mathematical model of Niemann worm gear
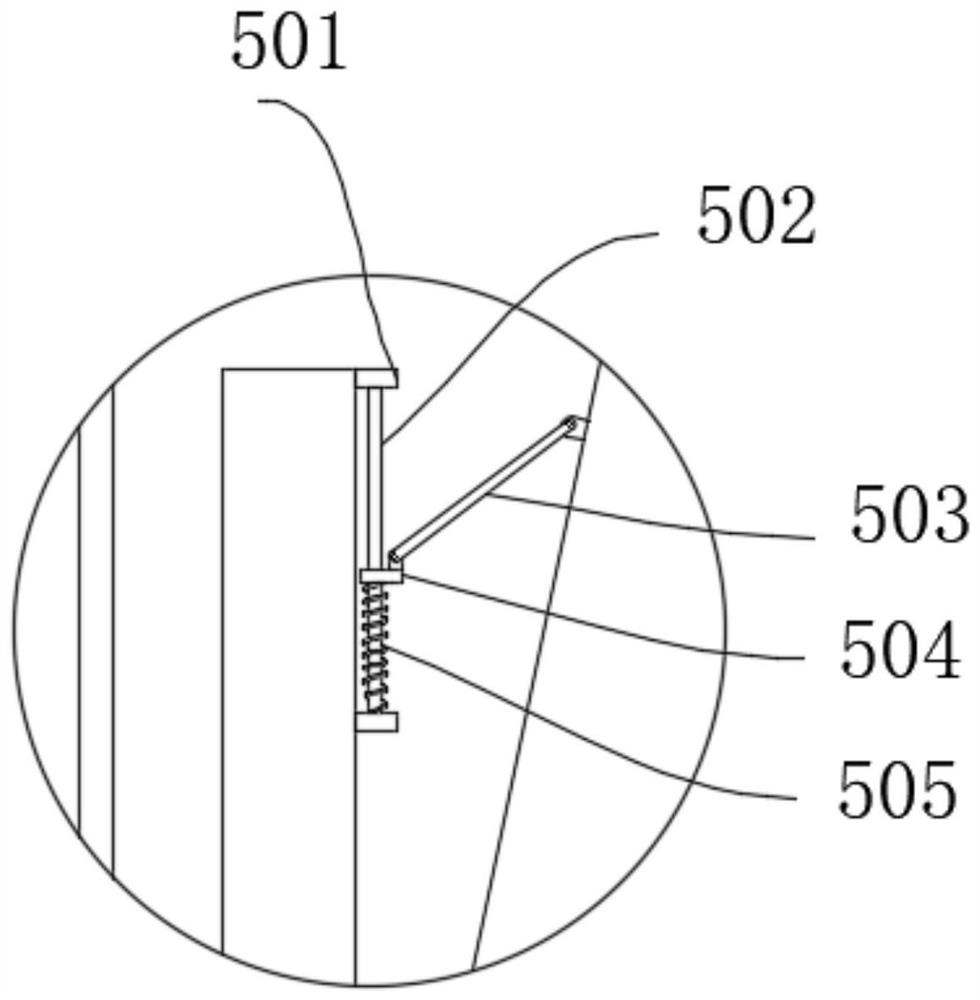
ActiveCN109604738BReduce the number of passesImprove processing efficiencyMilling equipment detailsWorm wheelsMilling cutterCutter location
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Milling force prediction method for five-axis CNC side milling
ActiveCN103955169BImprove accuracyEfficiencyProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlField methods
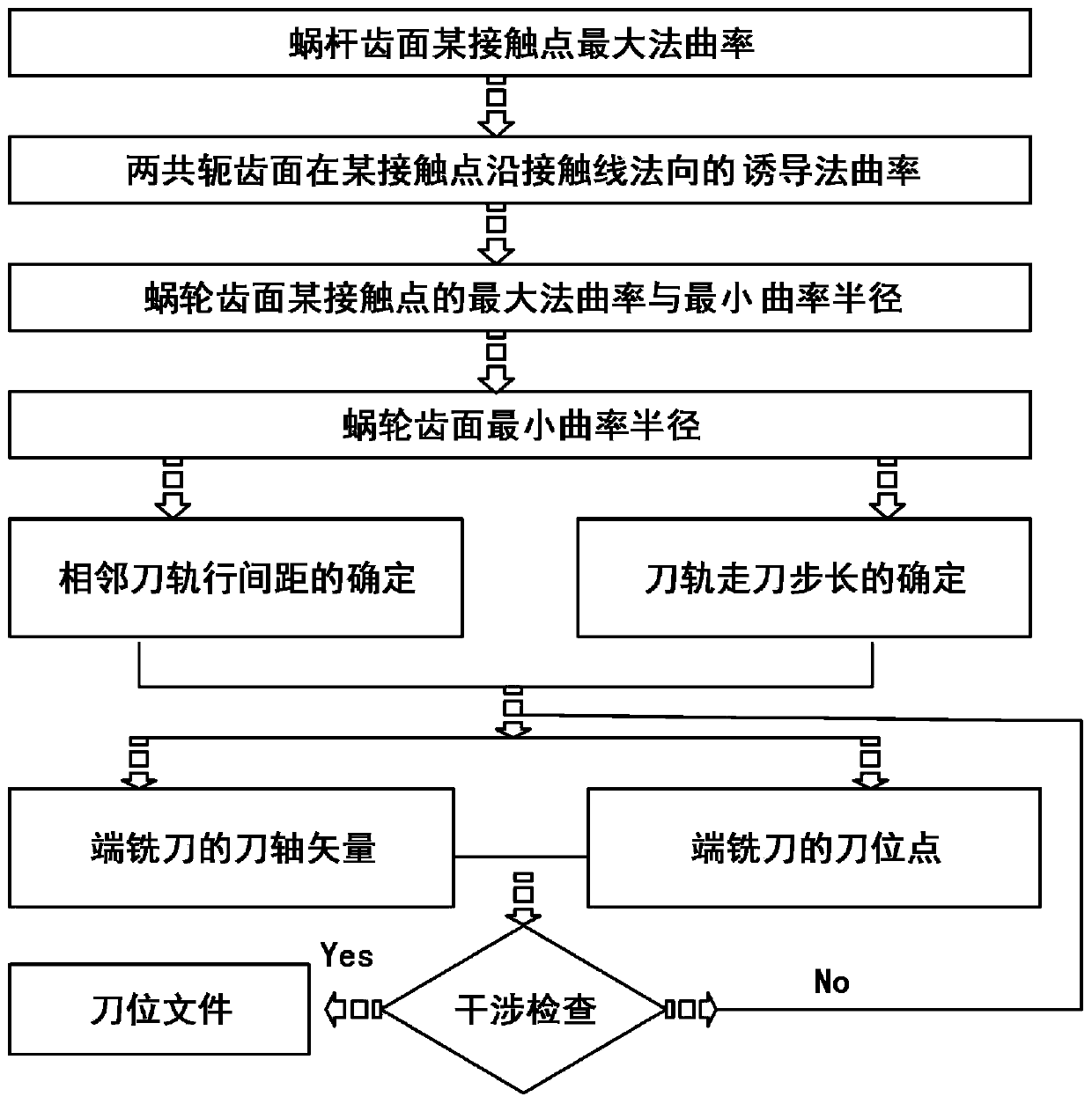
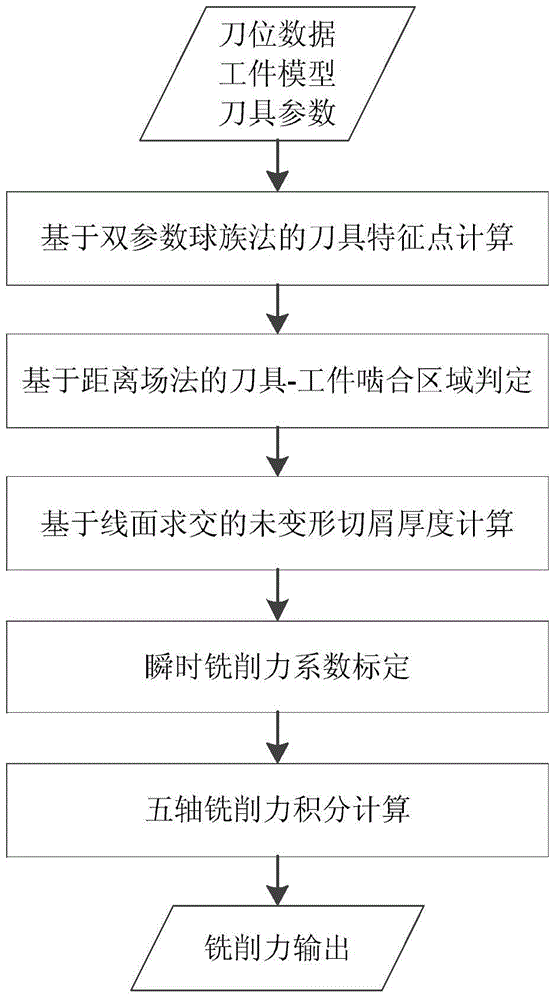
The invention provides a method for predicting milling force of five-axis numerical control side milling. The method comprises the steps that firstly, the current cutter spacing cutter-workpiece meshing area is acquired based on the distance field method, points and normal directions on a cutting edge of the current cutter spacing are converted to a previous cutter spacing cutter coordinate system, the analytical expression of a non-transformation cuttings thickness is obtained according to the line and face intersection method, and milling force coefficients are acquired through three-axis single-tooth milling experiment calibration; secondly, the cutter is dispersed into a plurality of slice infinitesimals in the axial direction, and the tangential milling force, the radial milling force and the axial milling force of the slice infinitesimals are obtained through calculation according to cutter geometrical parameter information, cutter-workpiece meshing area information, non-transformation cutting thicknesses calculated value and the milling force coefficients; lastly, the force coordinates are converted into the X-axis direction, the Y-axis direction and the Z-axis direction, and integration is carried out on the slice infinitesimals in the axial direction to obtain the five-axis side milling force predicting value at current time. By means of the method, the accuracy and efficiency of prediction and calculation on the milling force of five-axis side milling are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Strip material side face milling and pressing limiting device
PendingCN113427584AAvoid displacementReasonable designCane mechanical workingProfiling/shaping machinesMilling cutterCutter location
The invention relates to a strip material side face milling and pressing limiting device. The problems that in the prior art, a milling cutter position adjusting device is not flexible enough to use, and the strip positioning effect is poor are solved. The strip material side face milling and pressing limiting device comprises two milling cutters which are horizontally and adjacently arranged at the upper end of a milling box body, and a milling channel which is formed between the two milling cutters and is used for strip materials to pass through, wherein a milling cutter position adjusting mechanism capable of adjusting the distance between the two milling cutters and / or the perpendicularity of at least one of the two milling cutters is arranged between the milling cutters, and a strip pressing limiting mechanism used for limiting the side face of the strip material and / or the upper end of the strip material is arranged in the milling channel. The device has the advantages that the positions of the milling cutters can be flexibly adjusted, and a milled strip material can be peripherally and adaptively pressed and positioned.
Owner:江浩
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com