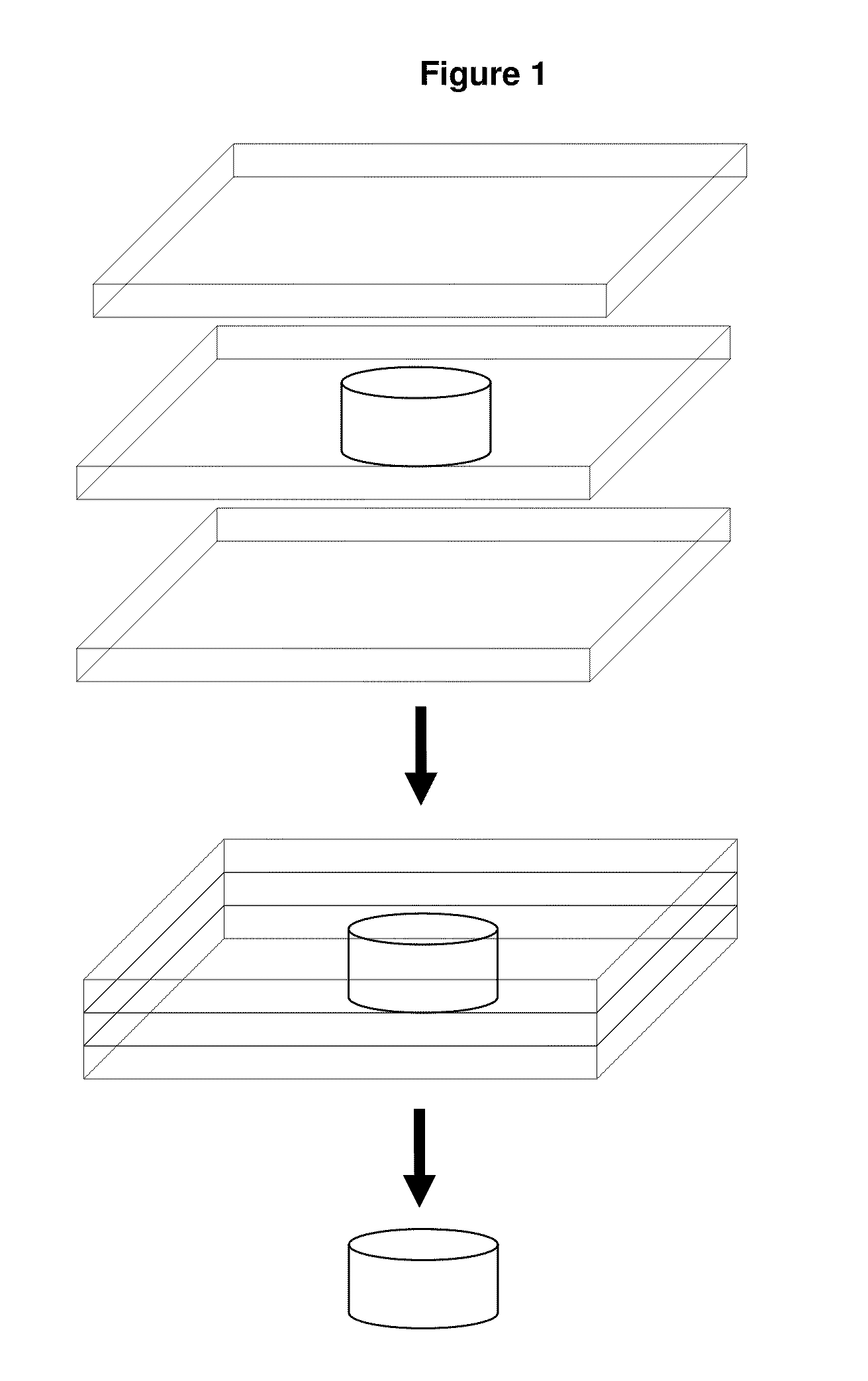
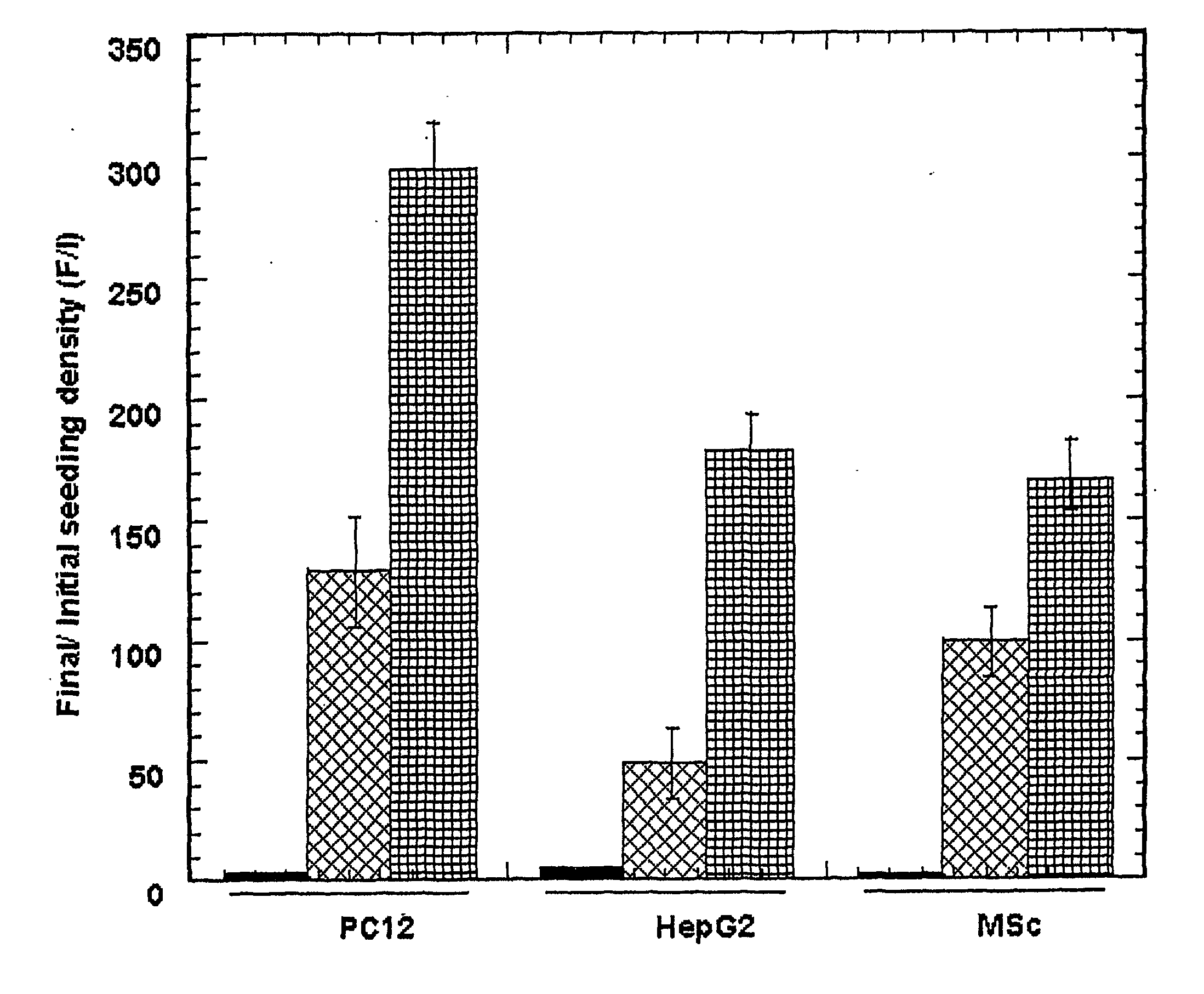
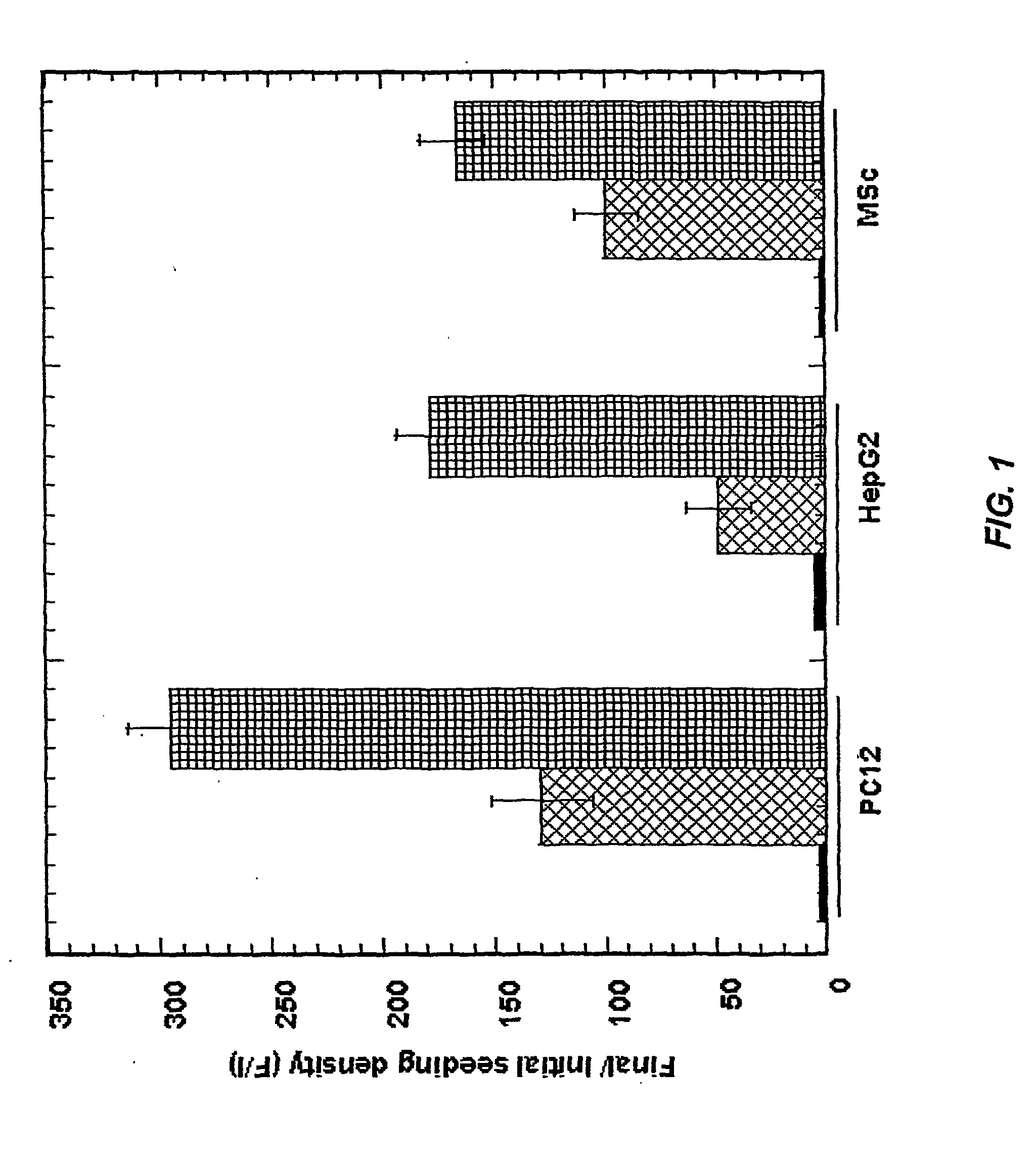
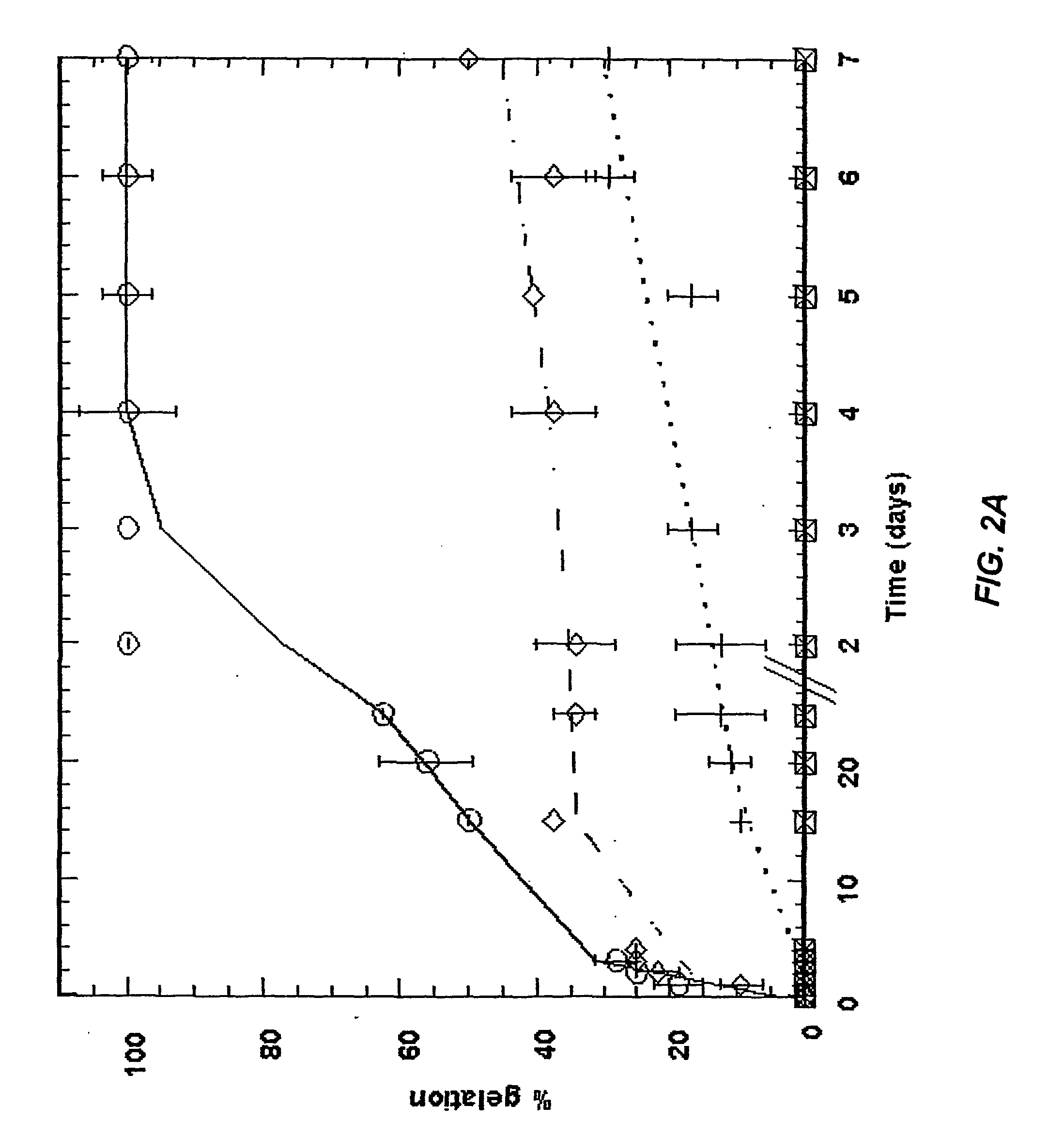
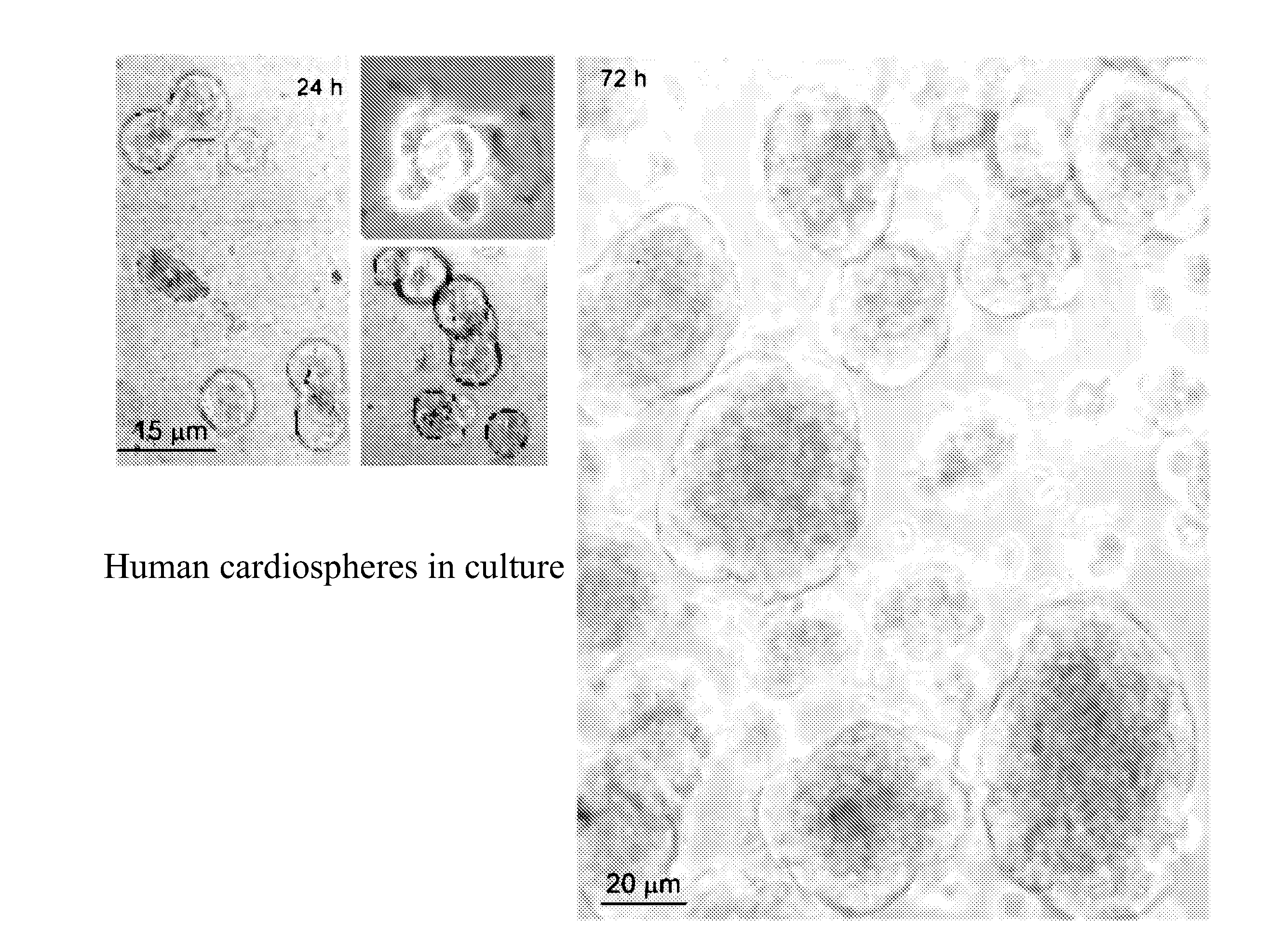
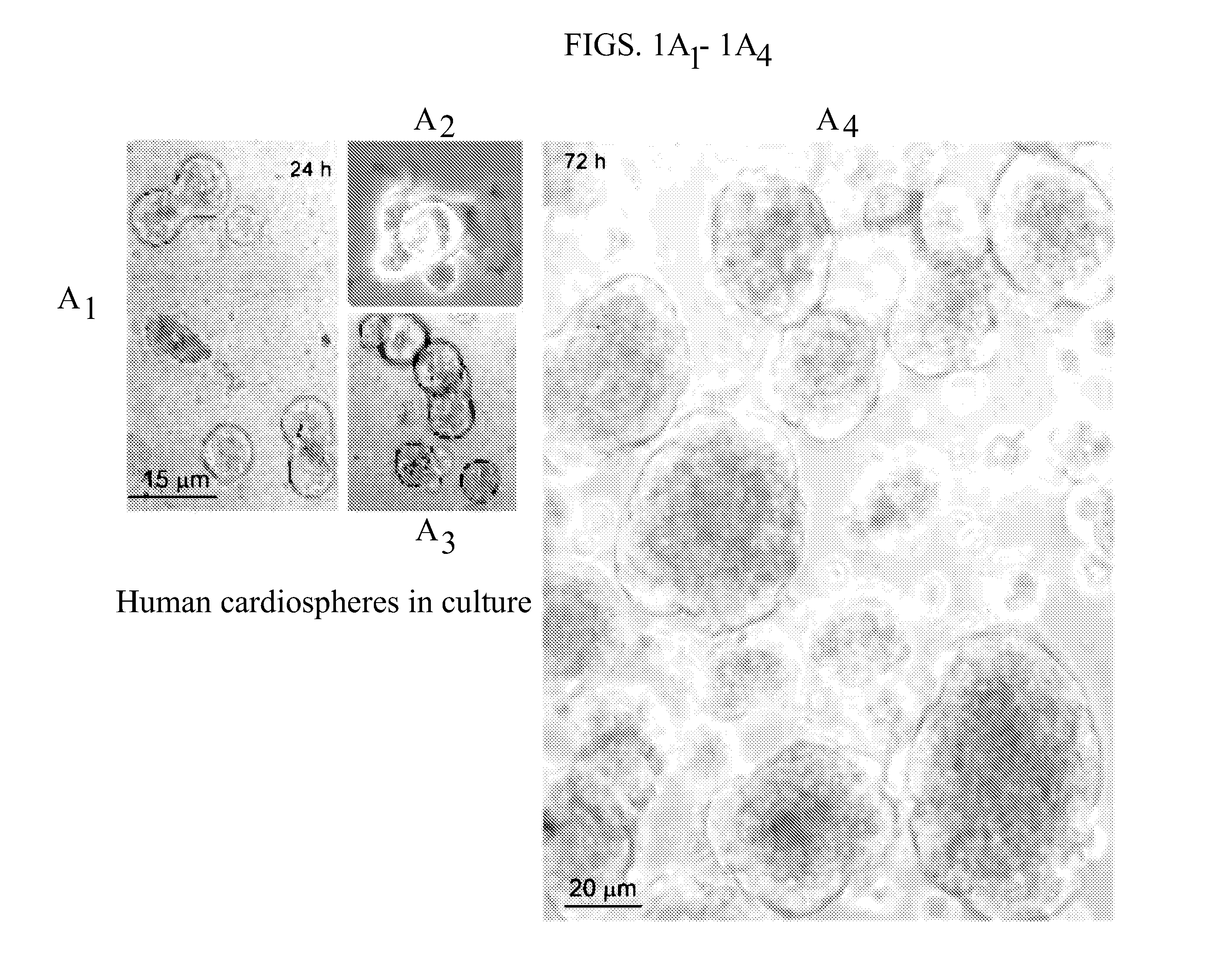
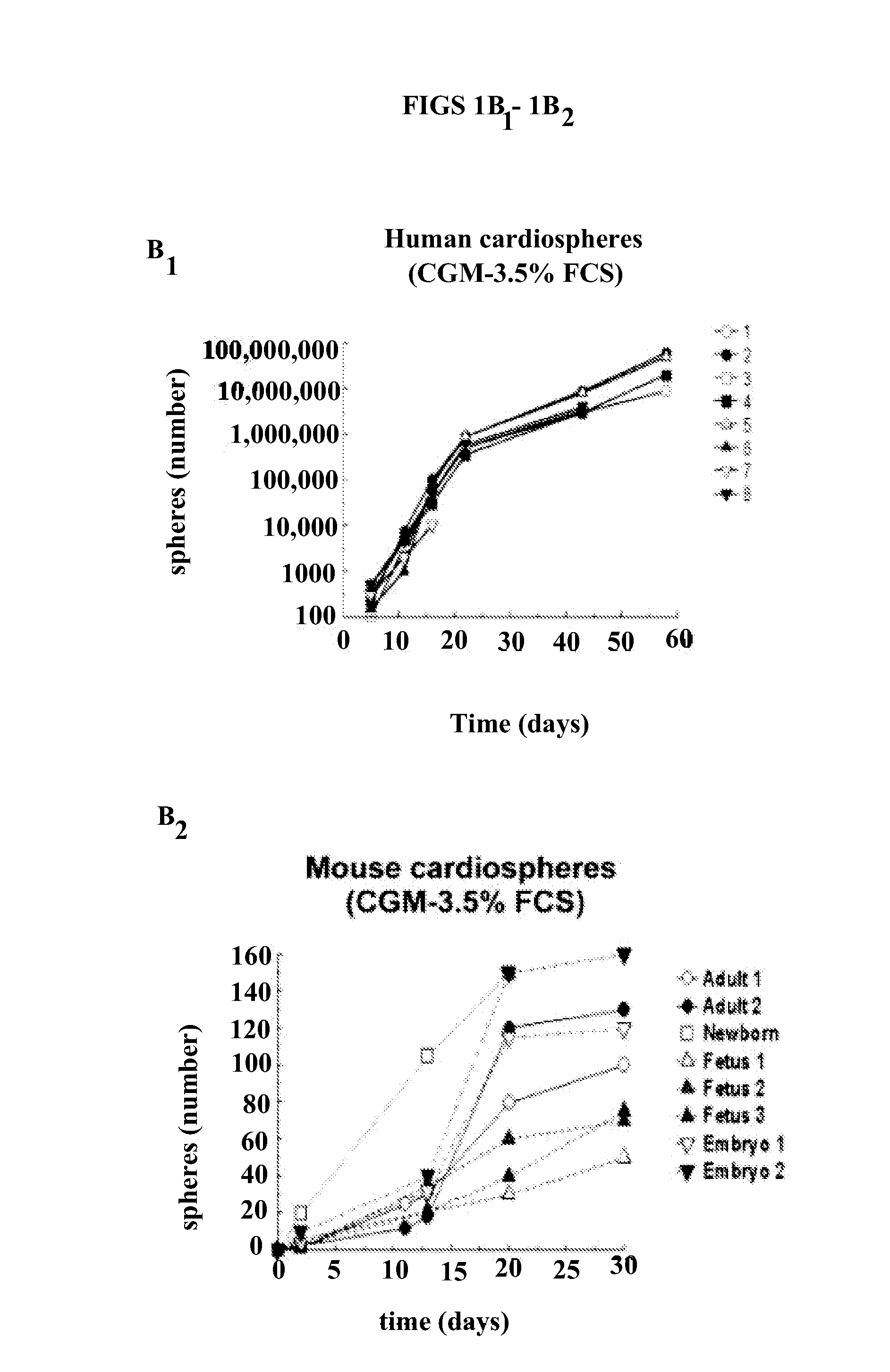
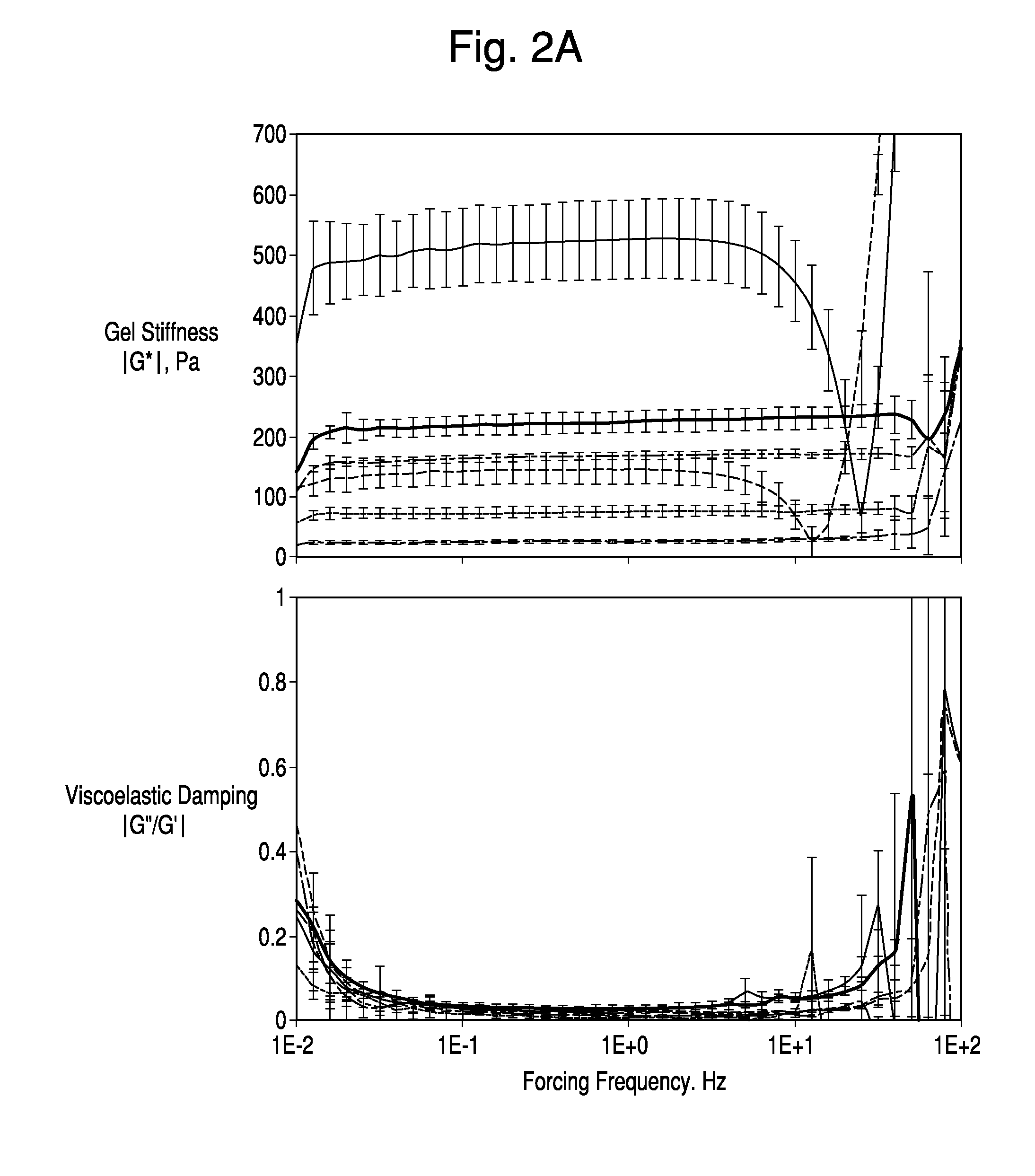
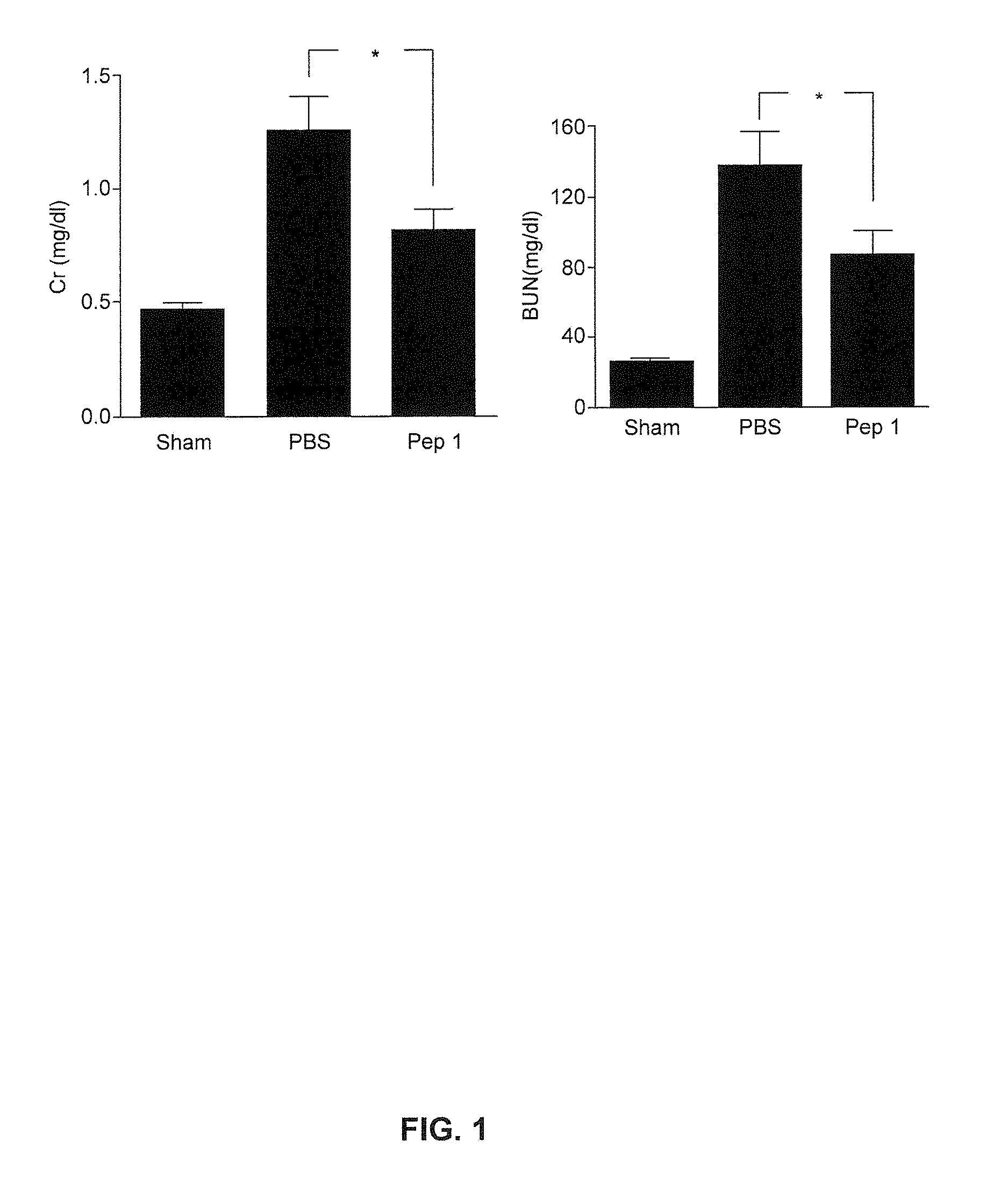
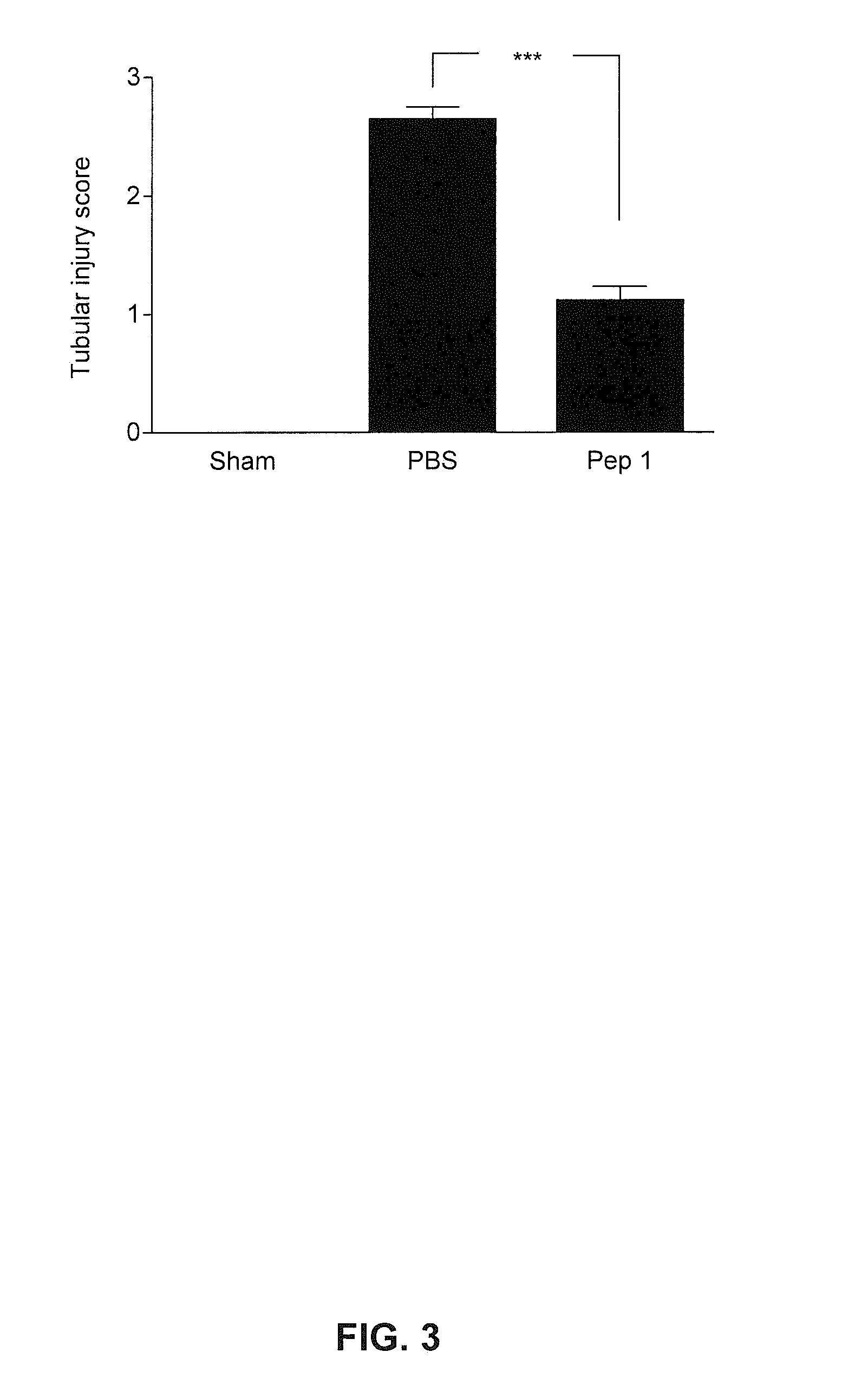
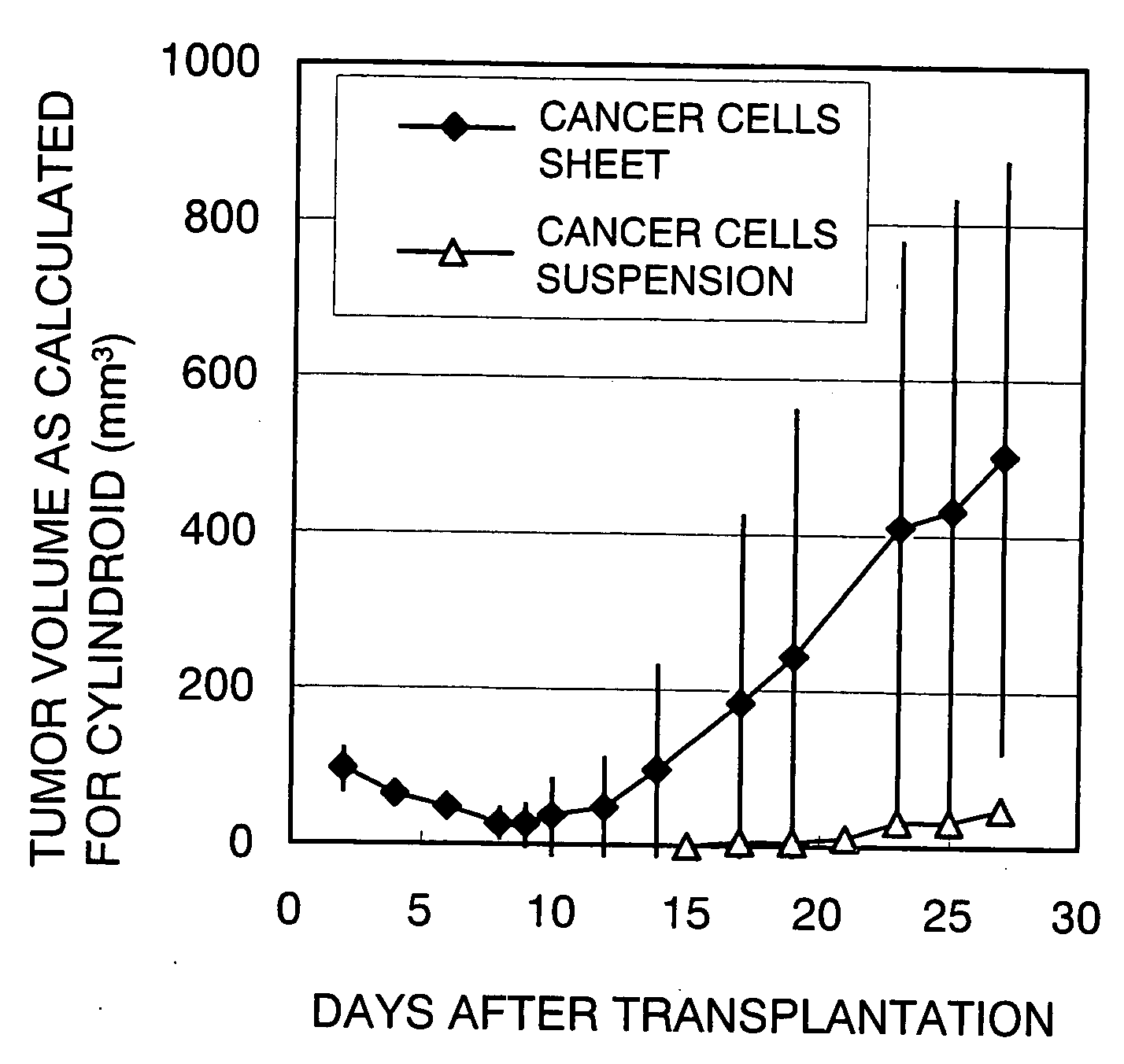
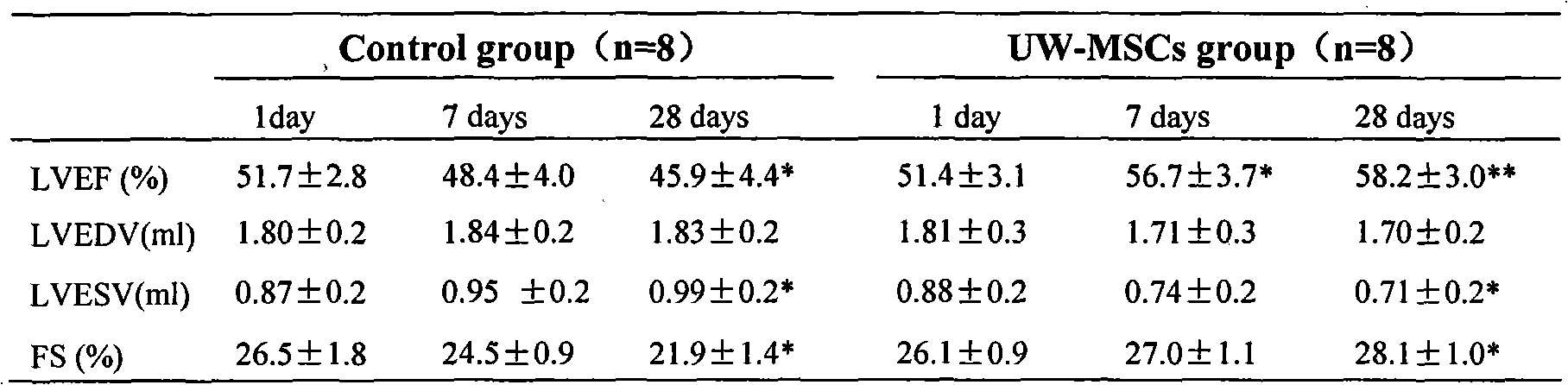Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
199 results about "Cells transplantation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and device for treating osteoarthritis, cartilage disease, defects and injuries in the human knee
InactiveUS7022506B2Heart defibrillatorsMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsHuman useCells transplantation
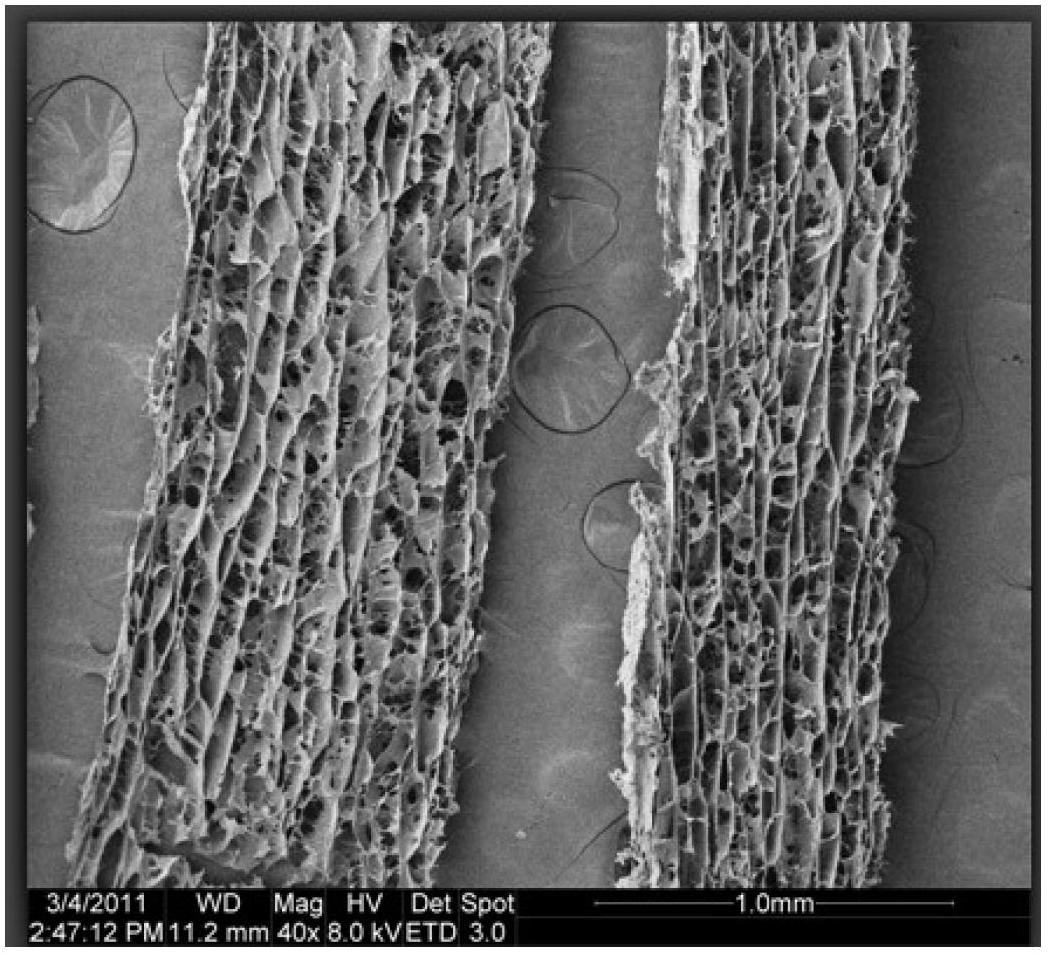
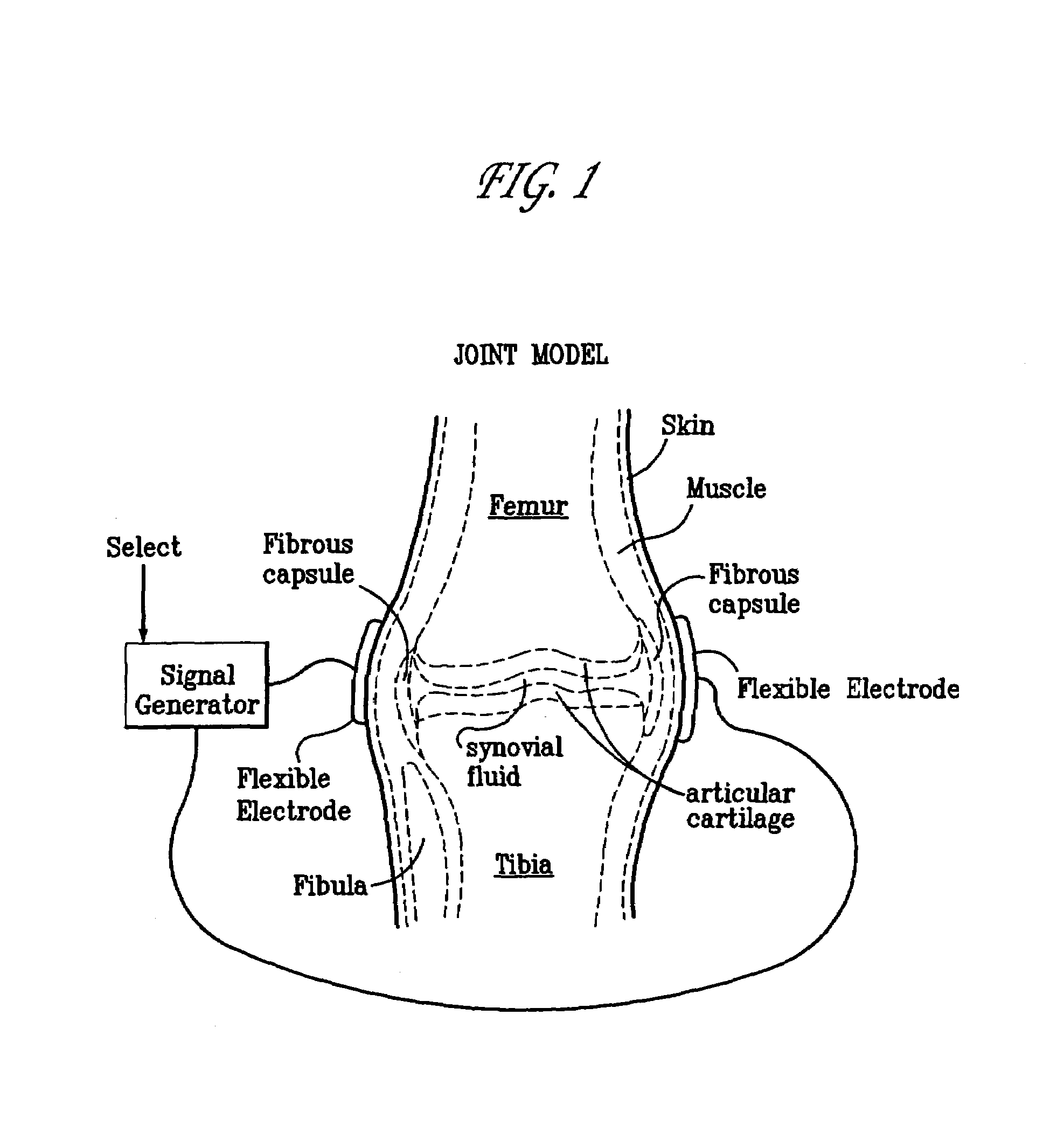
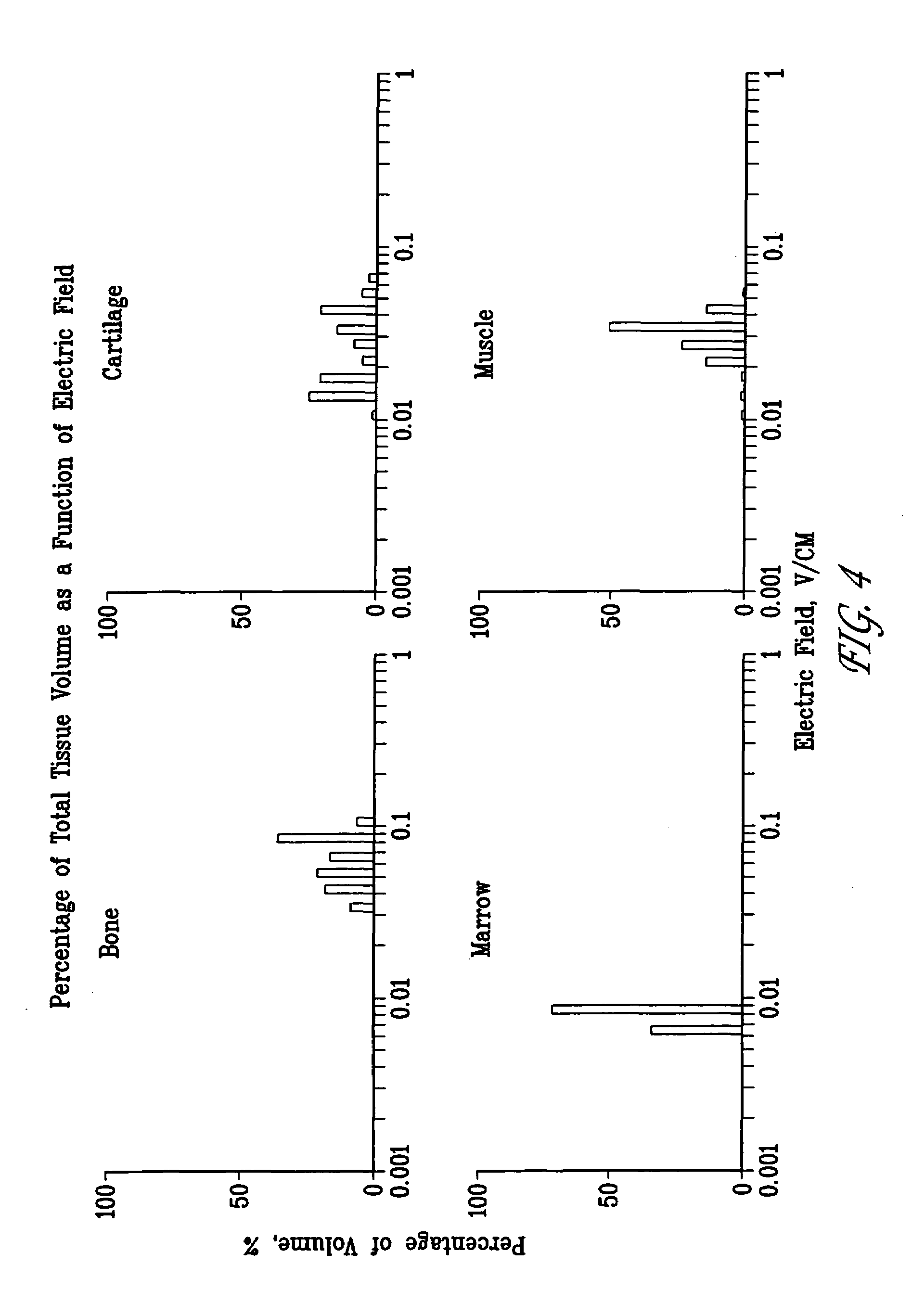
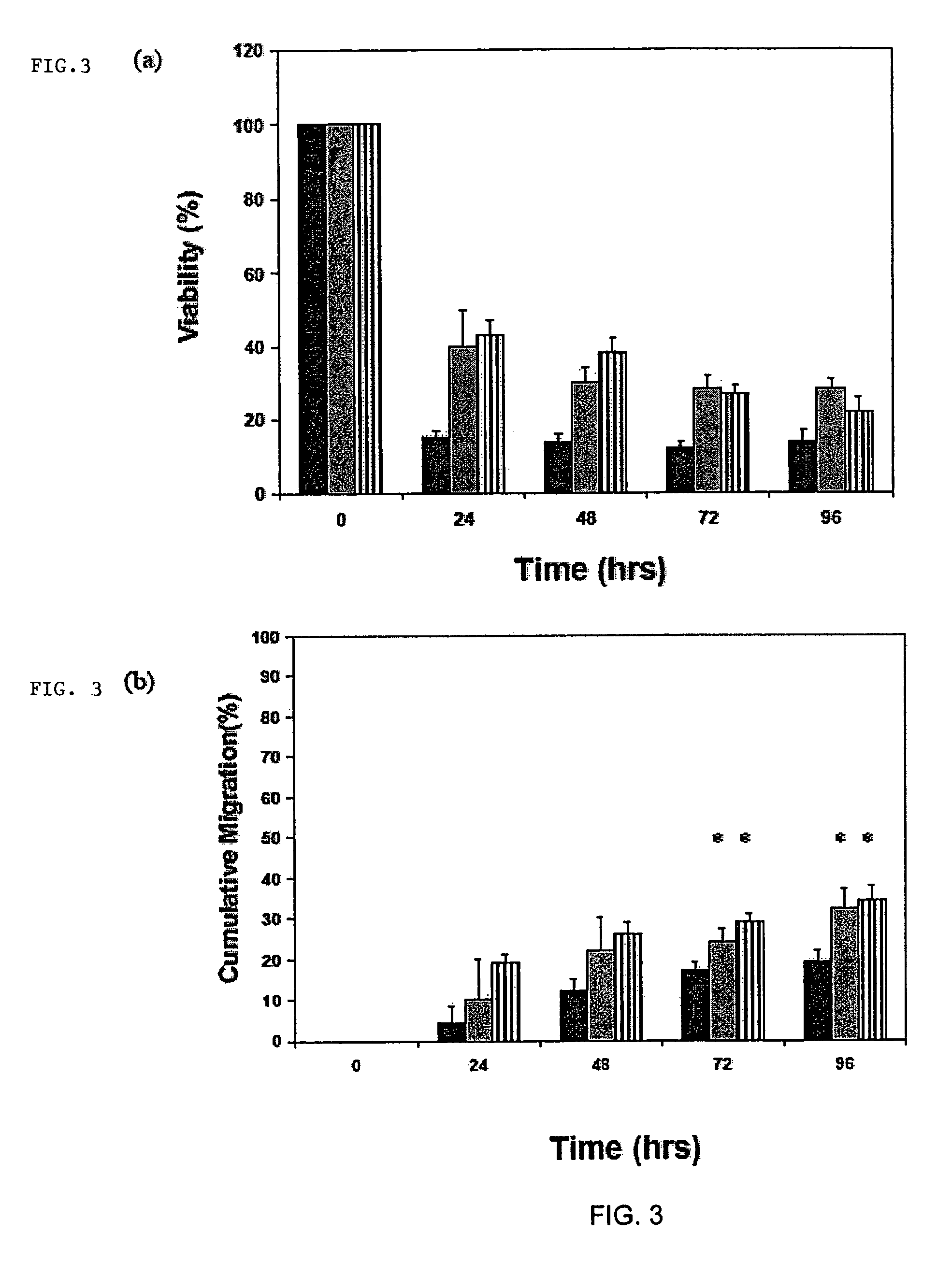
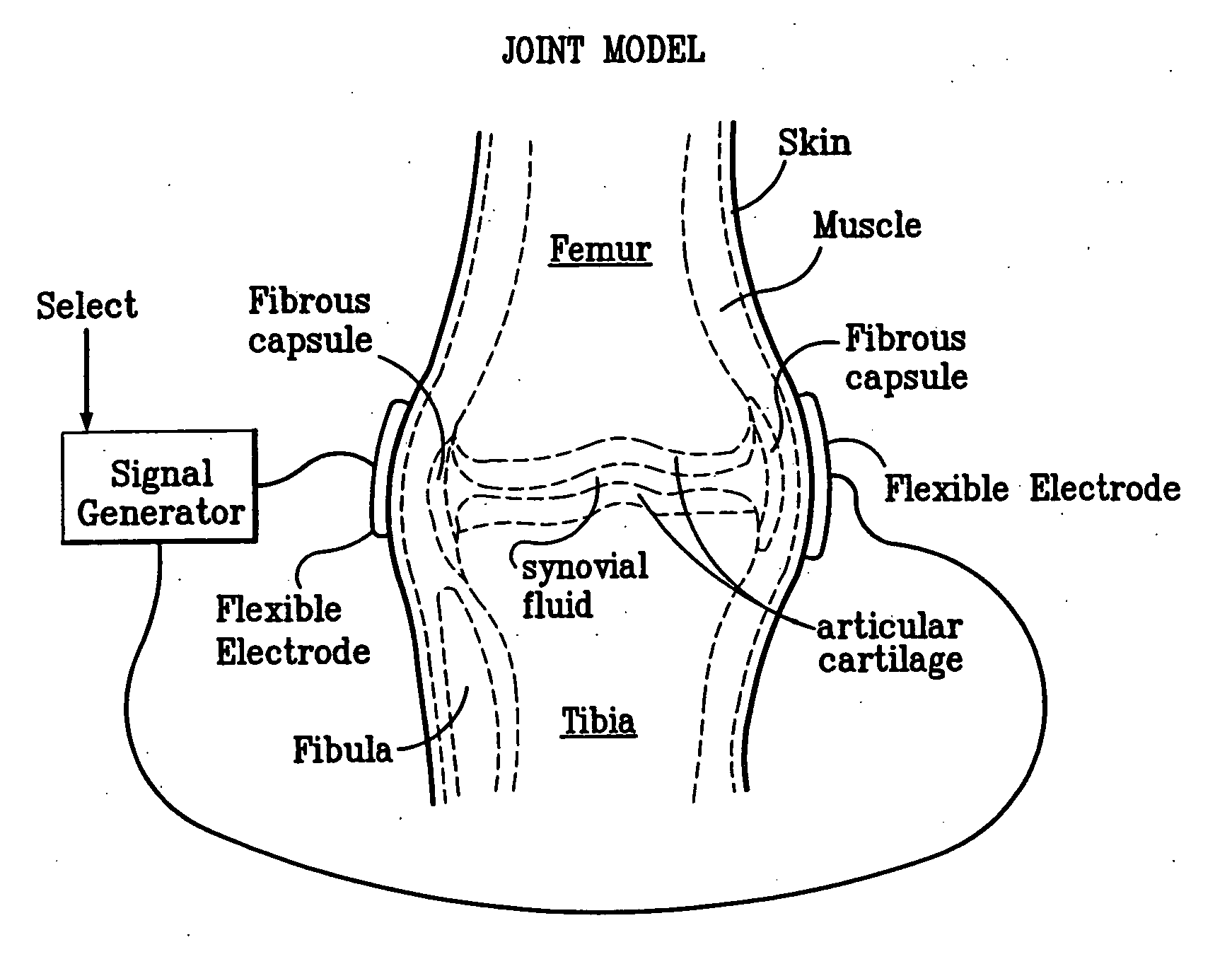
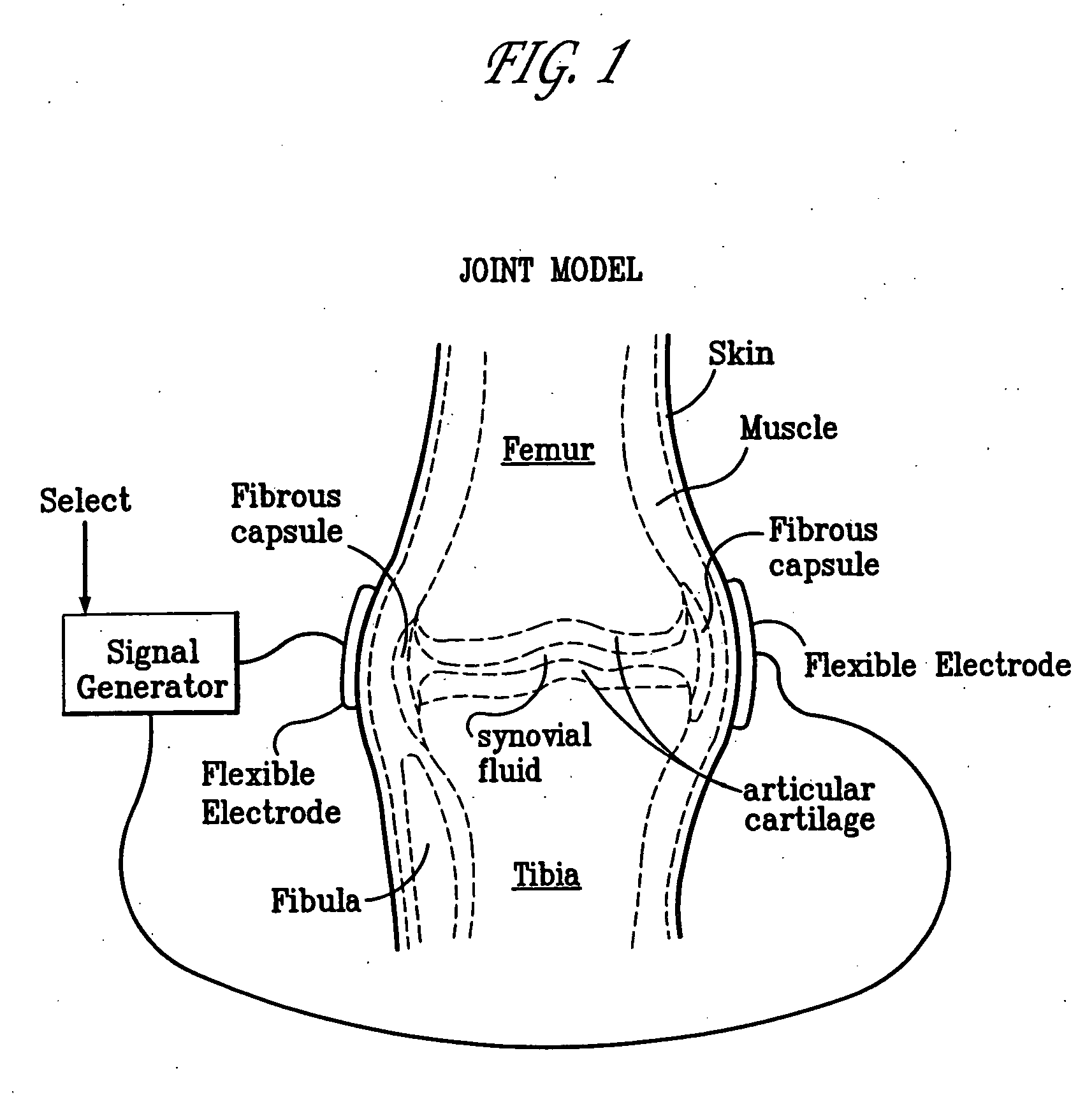
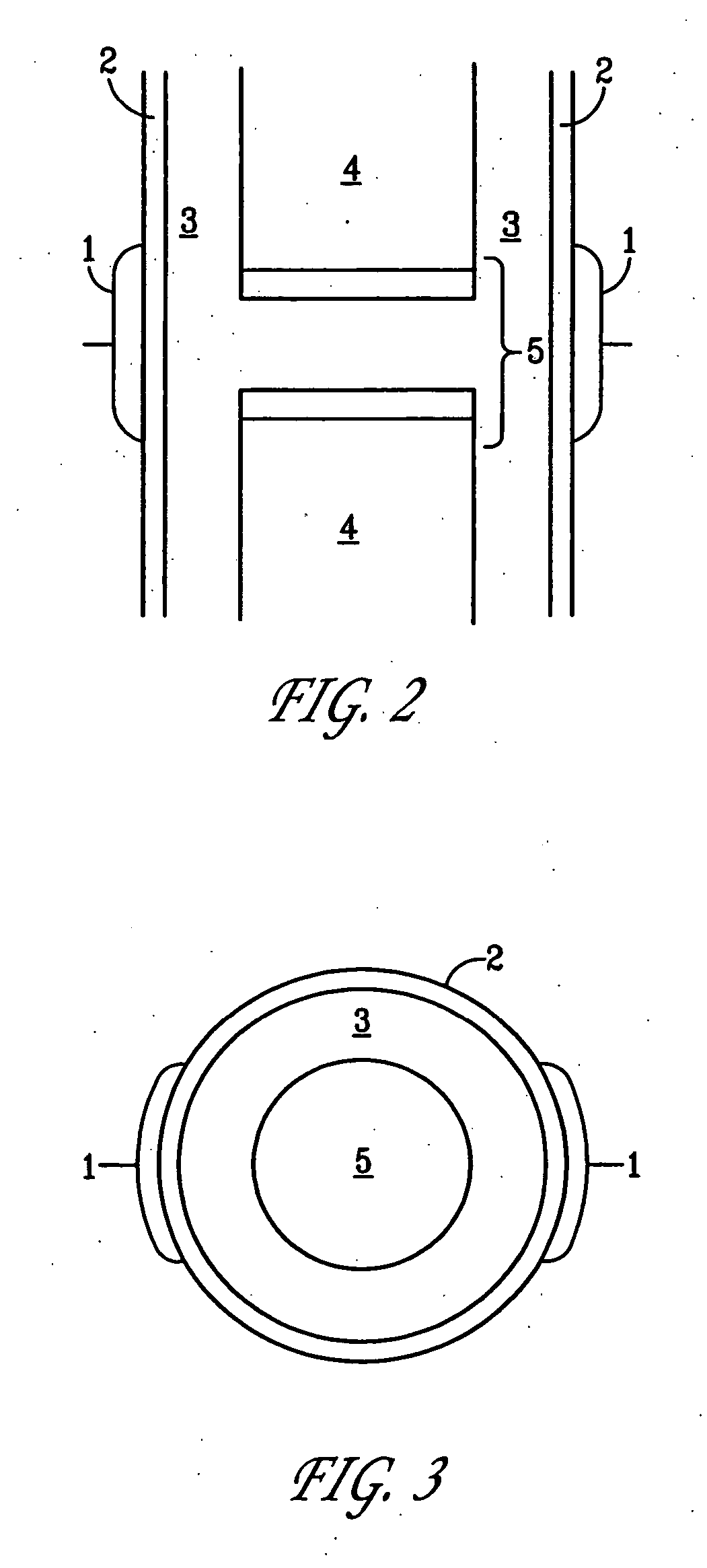
A method of determining the voltage and current output required for the application of specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals to diseased articular cartilage in the treatment of osteoarthritis, cartilage defects due to trauma or sports injury, or used as an adjunct with other therapies (cell transplantation, tissue-engineered scaffolds, growth factors, etc.) for treating cartilage defects in the human knee joint and a device for delivering such signals to a patient's knee. An analytical model of the human knee is developed whereby the total tissue volume in the human knee may be determined for comparison to the total tissue volume of the diseased tissue in the animal model using electric field and current density histograms. The voltage and current output used in the animal model is scaled based on the ratio of the total tissue volume of the diseased tissue of the human to the total tissue volume of the diseased tissue in the animal model and the resulting field is applied to the diseased tissue of the human using at least two electrodes applied to the knee or a coil or solenoid placed around the knee. The voltage of the signal applied to the electrodes, coil or solenoid is varied based on the size of the knee joint; larger knee joints require larger voltages to generate the effective electric field.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Scaffolds for cell transplantation
ActiveUS8067237B2Enhance cell viabilityIncrease successBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologyCells transplantation
A device that includes a scaffold composition and a bioactive composition with the bioactive composition being incorporated into or coated onto the scaffold composition such that the scaffold composition and / or a bioactive composition controls egress of a resident cell or progeny thereof. The devices mediate active recruitment, modification, and release of host cells from the material.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Method and device for treating osteoarthritis, cartilage disease, defects and injuries in the human knee
InactiveUS20060190043A1ElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsHuman useArticular cartilage
A method of determining the voltage and current output required for the application of specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals to diseased articular cartilage in the treatment of osteoarthritis, cartilage defects due to trauma or sports injury, or used as an adjunct with other therapies (cell transplantation, tissue-engineered scaffolds, growth factors, etc.) for treating cartilage defects in the human knee joint and a device for delivering such signals to a patient's knee. An analytical model of the human knee is developed whereby the total tissue volume in the human knee may be determined for comparison to the total tissue volume of the diseased tissue in the animal model using electric field and current density histograms. The voltage and current output used in the animal model is scaled based on the ratio of the total tissue volume of the diseased tissue of the human to the total tissue volume of the diseased tissue in the animal model and the resulting field is applied to the diseased tissue of the human using at least two electrodes applied to the knee or a coil or solenoid placed around the knee. The voltage of the signal applied to the electrodes, coil or solenoid is varied based on the size of the knee joint; larger knee joints require larger voltages to generate the effective electric field.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
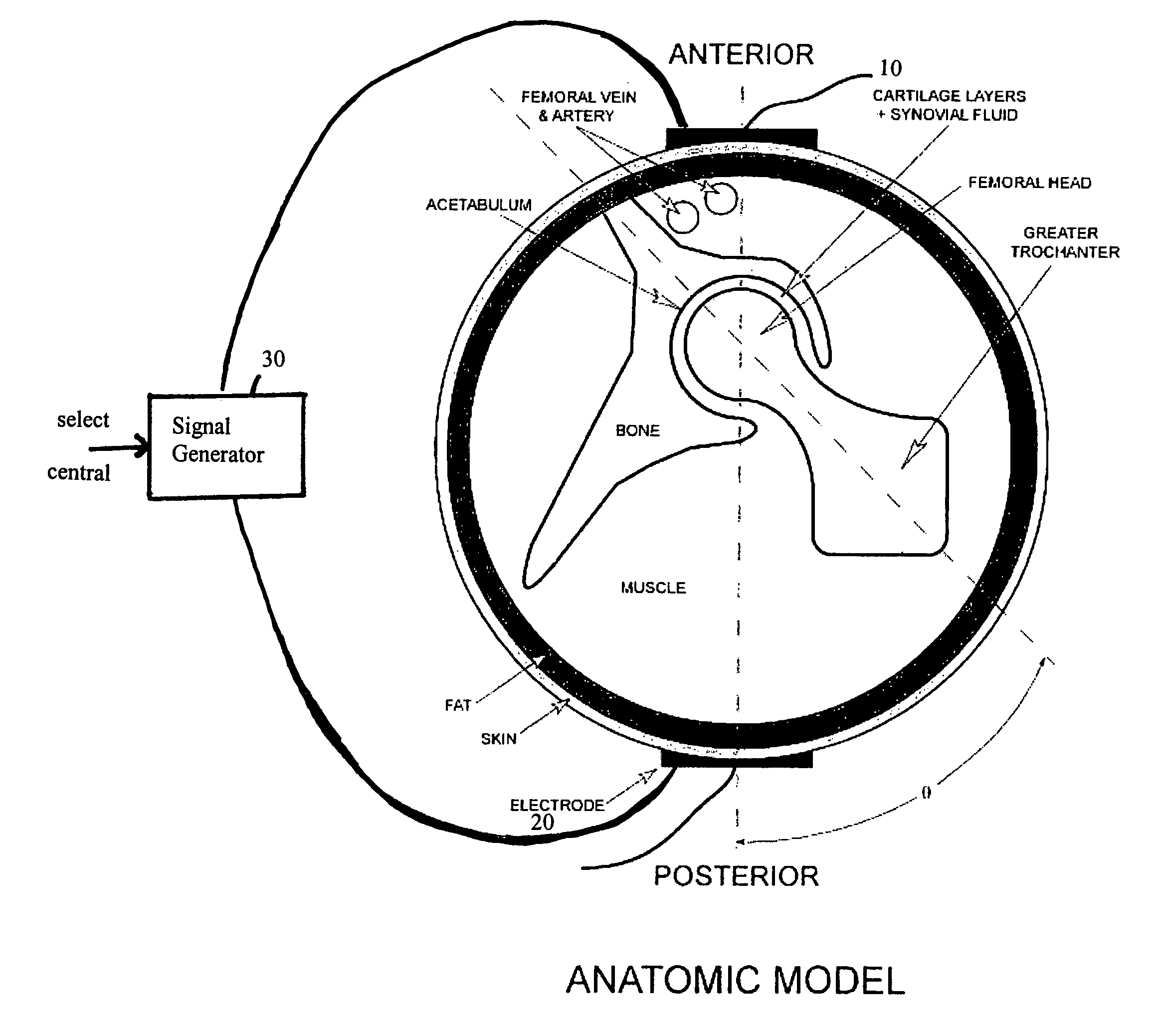
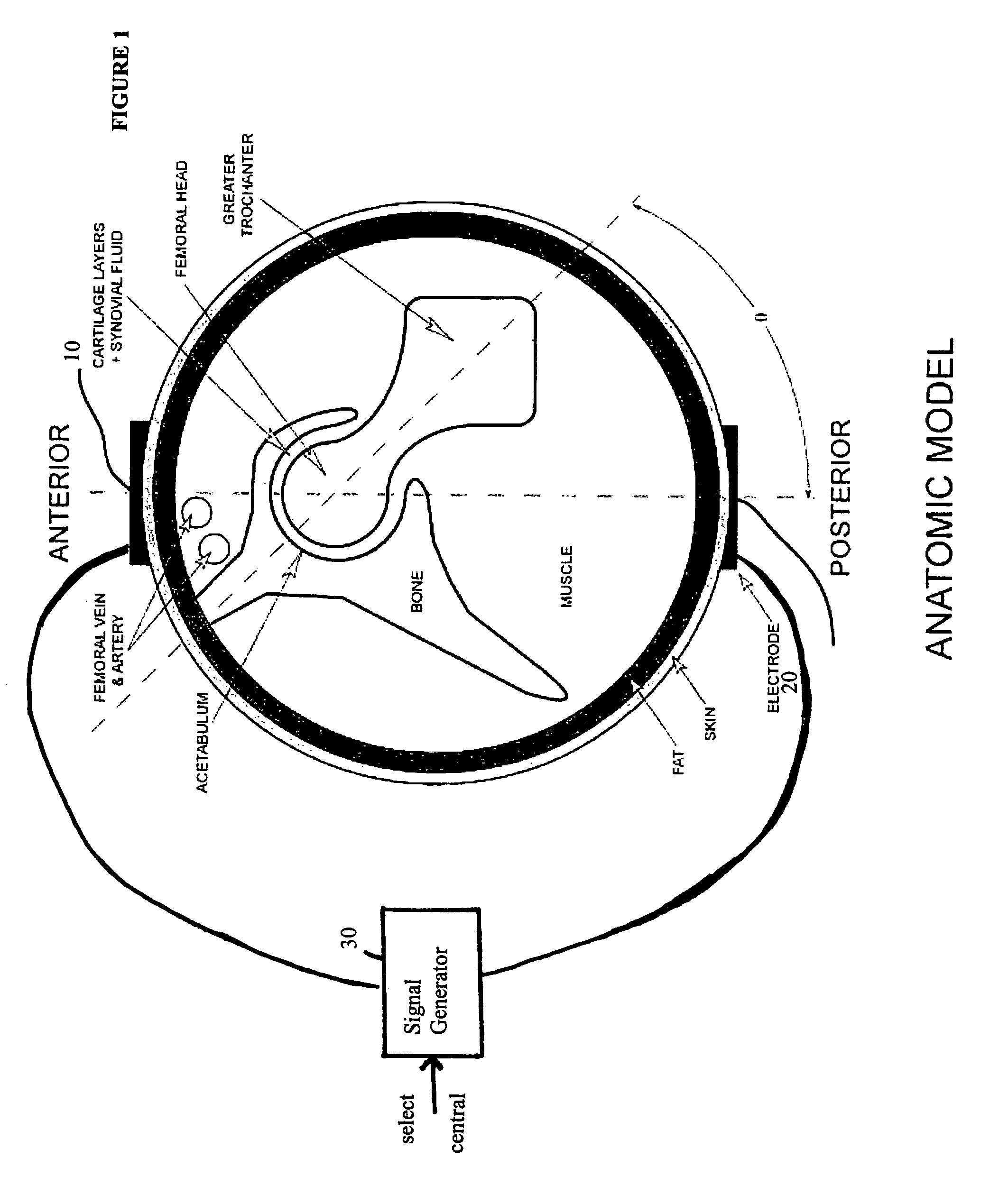
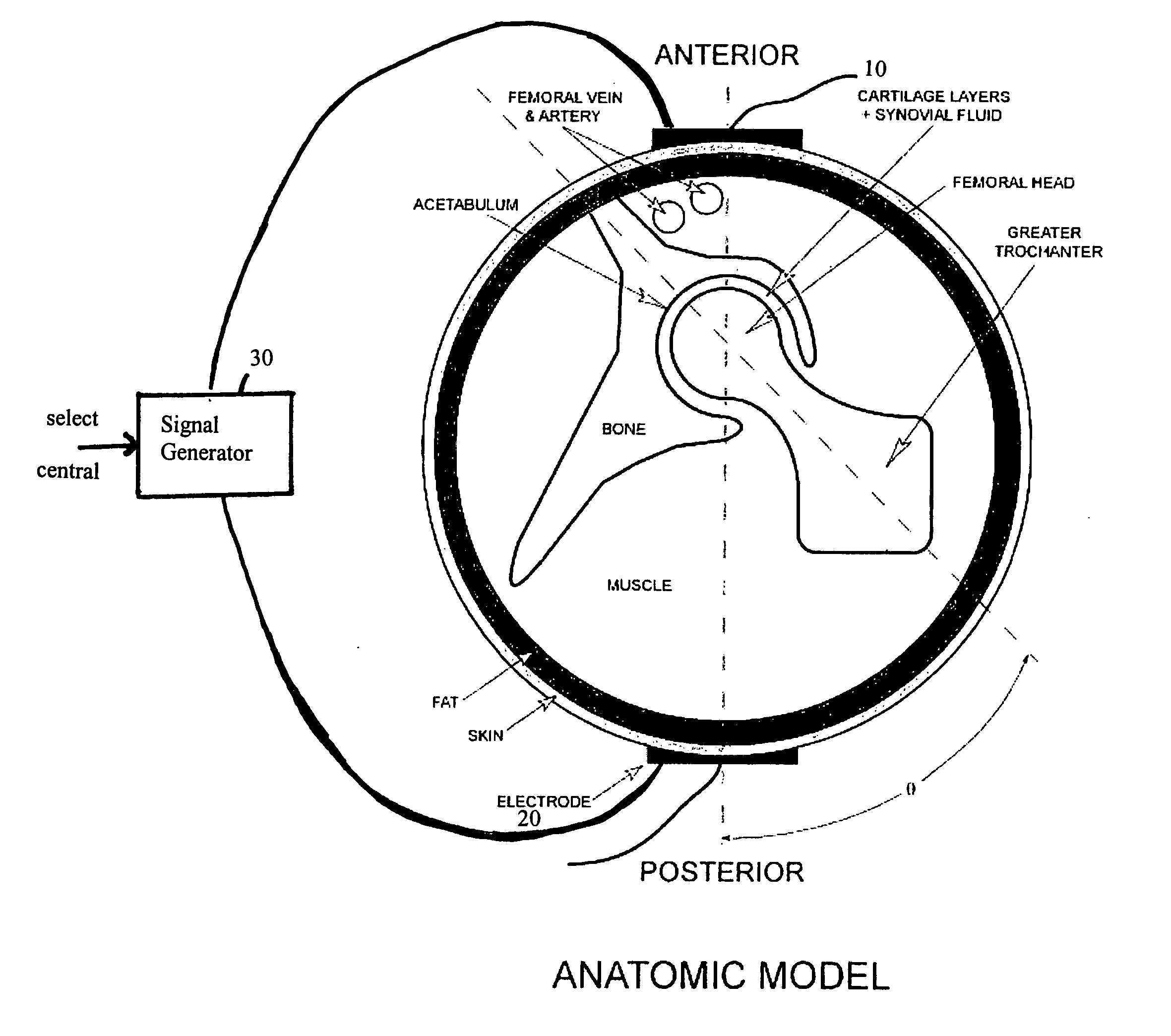
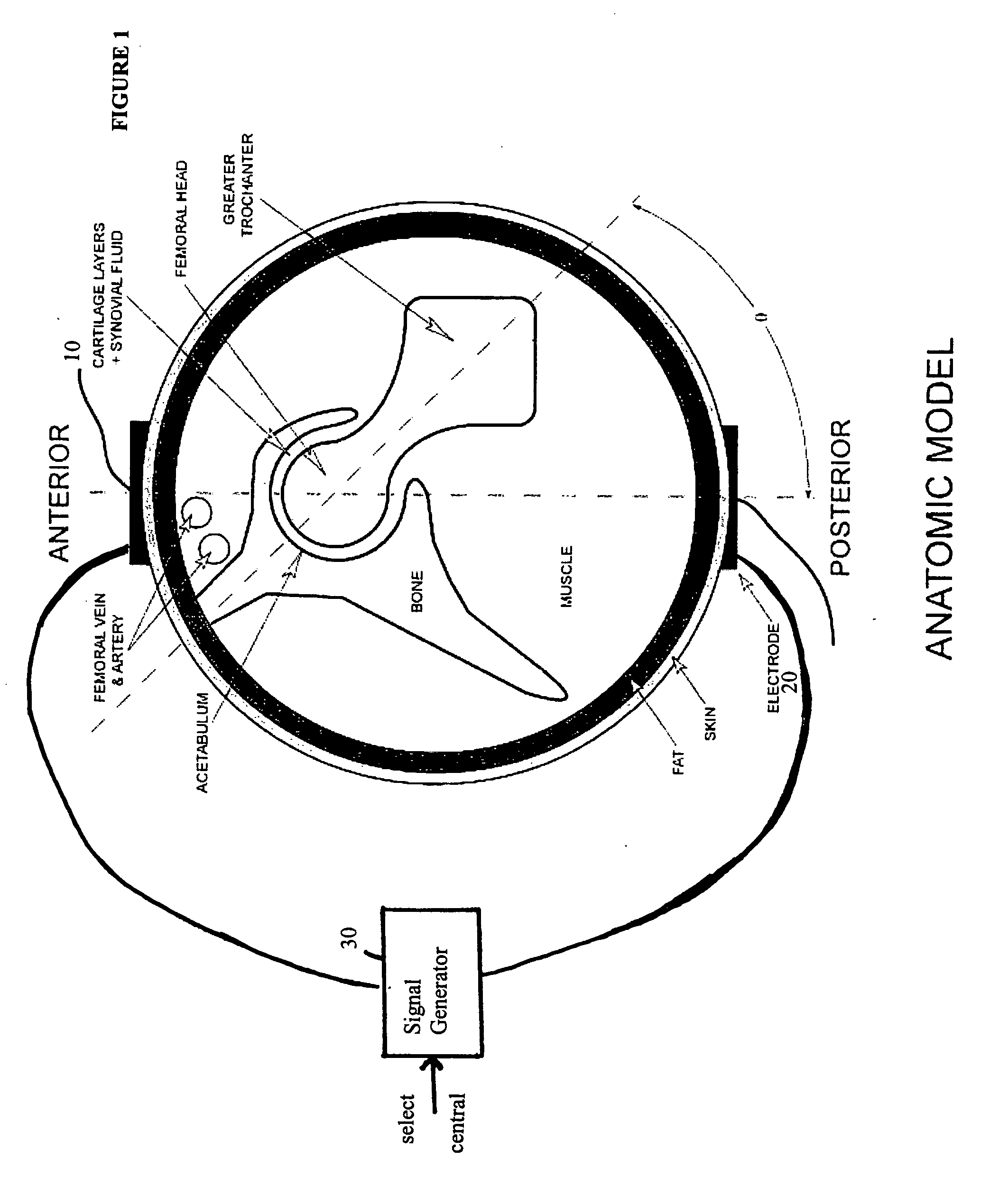
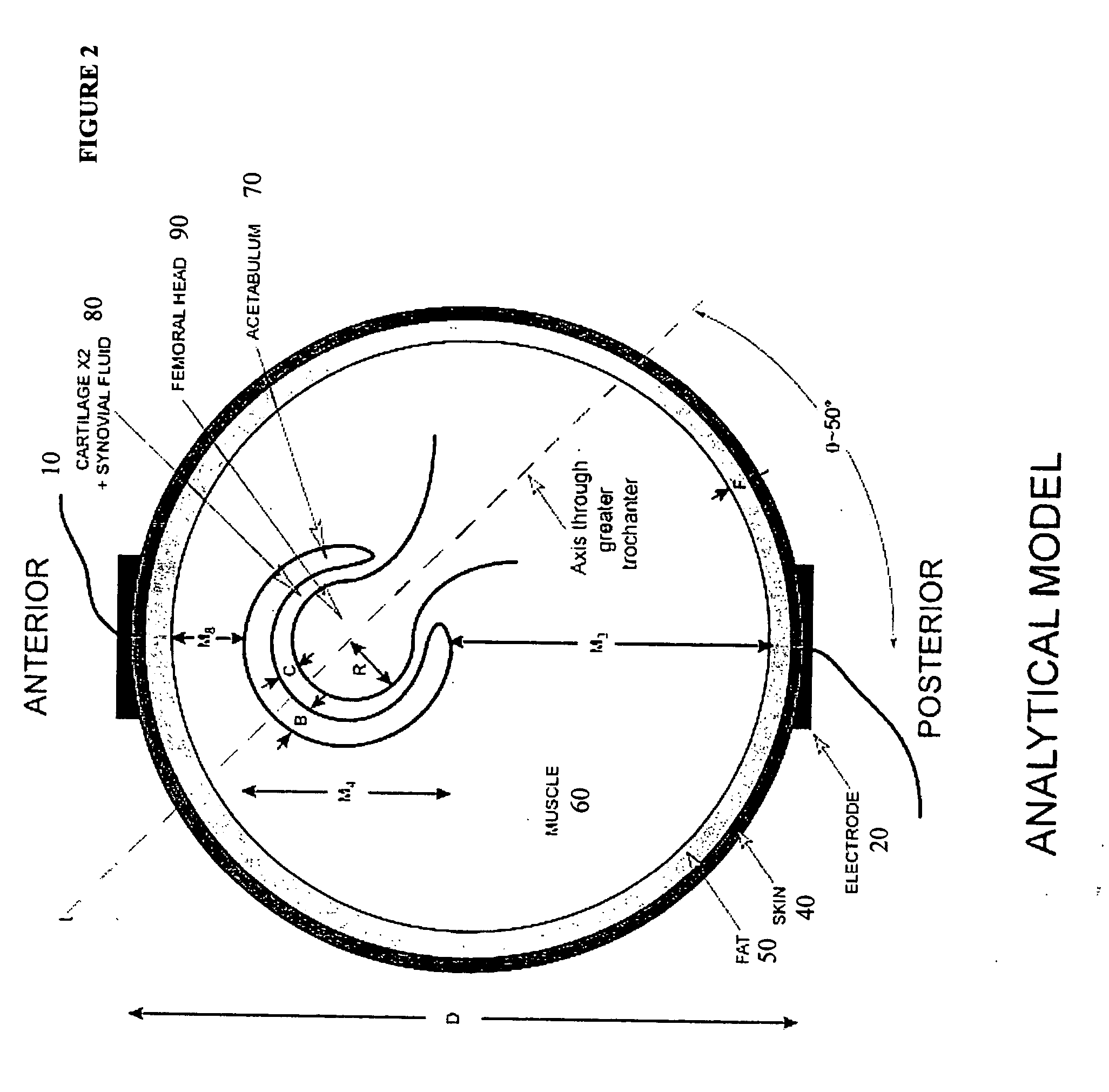
Method and device for treating osteoarthritis and cartilage disease, defects, and injuries in the human hip
A method of determining the voltage and current required for the application of specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals to diseased articular cartilage in the treatment of osteoarthritis, cartilage defects due to trauma or sports injury, or used as an adjunct with other therapies (cell transplantation, tissue-engineered scaffold, growth factors, etc.) for treating cartilage defects in the human hip joint and a device for delivering such signals to a patient's hip. Anatomic, analytical, and planar circuit models are developed to determining the impedances, conductivities, and current flows in the human hip joint and its surrounding soft tissues and skin that are required to produce a 20 mV / cm electric field in the synovium and articular cartilage of the human hip. The voltage of the signal applied to the surface electrodes or to a coil(s) or solenoid is varied based on the size of the hip joint; larger hip joints require larger voltages to generate the effective electric field.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Embryonic or stem-like cell lines produced by cross species nuclear transplantation
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of a species different from the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for the production of isogenic embryonic stem cells, in particular human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. These embryonic or stem-like cells are useful for producing desired differentiated cells and for introduction, removal or modification, of desired genes, e.g., at specific sites of the genome of such cells by homologous recombination. These cells, which may contain a heterologous gene, are especially useful in cell transplantation therapies and for in vitro study of cell differentiation.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
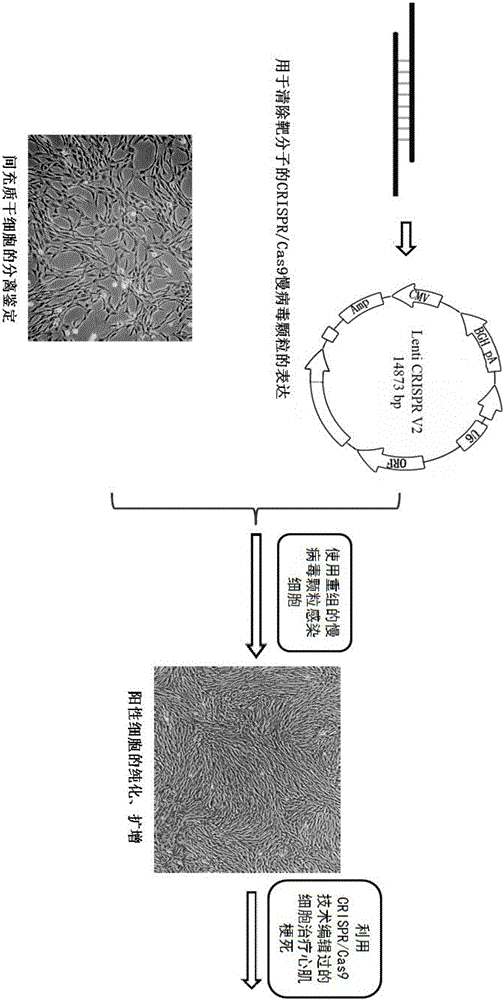
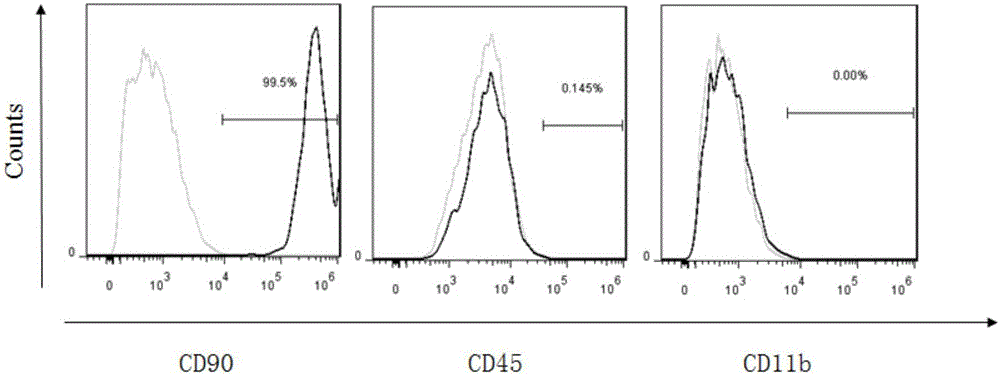
Preparation method of allogenic mesenchymal stem cells by CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) technique editing and IGF (insulin-like growth factor) optimization and application of allogenic mesenchymal stem cells in treating myocardial infarction
ActiveCN105985985AImprove anti-apoptotic abilityPromote homingUnknown materialsFermentationAntigenInflammatory factors
The invention belongs to the field of allogenic mesenchymal stem cells, and particularly relates to a preparation method of allogenic mesenchymal stem cells by CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) technique editing and IGF (insulin-like growth factor) optimization and application of the allogenic mesenchymal stem cells in treating myocardial infarction. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out separation by density gradient centrifugation to obtain allogenic single karyocytes, and carrying out adherent culture to obtain mesenchymal stem cells; designing a mesenchymal stem cell surface antigen B2M-gRNA and an inflammatory factor TNF-alpha-gRNA; establishing recombinant slow virus particles, and transfecting the mesenchymal stem cells; optimizing the mesenchymal stem cells by using IGF-1; and preparing drugs for treating myocardial infarctions by using the modified and optimized mesenchymal stem cells. The CRISPR / Cas9 technique is utilized to remove the antigens capable of causing immunological rejection and the inflammatory factors capable of causing inflammatory reaction on the mesenchymal stem cell surface, and the IGF-1 is utilized to enhance the apoptosis resistance of the mesenchymal stem cells and promote the homing of the mesenchymal stem cells, thereby providing a new technical scheme for preparing drugs for treating cardiovascular diseases in clinic. The prepared allogenic mesenchymal stem cells can not cause immunological rejection after cell transplantation.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Retinal pigment epithelial cell cultures on amniotic membrane and transplantation
InactiveUS7824671B2Promotes growth and differentiationMaintenance of morphological appearanceBiocideSenses disorderSurgical GraftRetinal pigment epithelial cell
The present invention relates to a composition for implantation in the subretinal space of an eye, the composition including amniotic membrane, which may be cryopreserved human amniotic membrane, and a plurality of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells or RPE equivalent cells present at the amniotic membrane. The amniotic membrane may be intact, epithelially denuded, or otherwise treated. The invention includes the use of amniotic membrane for the culturing of RPE cells thereon, forming a surgical graft for replacement of Bruch's membrane as a substrate, and for the transplanting of RPE cells to the subretinal space. The composition does not elicit immunological reactions to alloantigens or to RPE specific autoantigens; and exerts anti-inflammatory, and angiogentic, and anti-scarring effects. The invention includes methods and kits for making or using composites including amniotic membrane and RPE cells. Also disclosed is a device for harvesting RPE cells.
Owner:TISSUETECH INC
Cell transplantation
ActiveUS20100104542A1Avoid damageReduce cell deathBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical compositionFat grafting
The present invention provides polymers for use in preventing damage to the membranes of cells in fat grafts. Mixing of a triblock copolymer such as poloxymer P188 with adipocytes or adipose tissue to be transplanted into a subject is thought to stabilize the membranes of the cells leading to more successful fat transplantation in soft tissue reconstruction or augmentation. Such methods may also be used in the transplantation of adult stem cells or other cells derived from fat tissue. Other agents such as lipoic acid may also be added to the polymer / cell compositions for cell transplantation.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
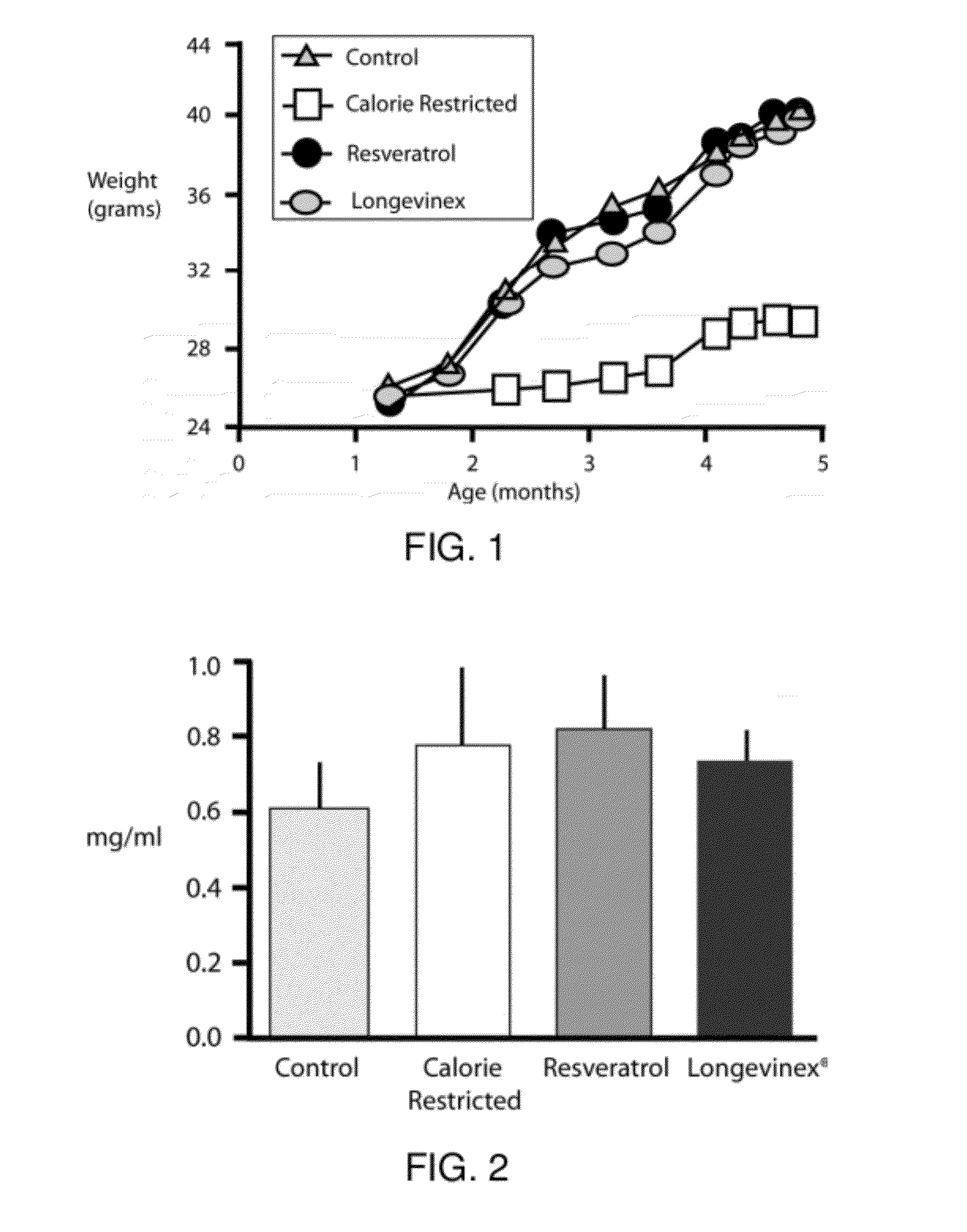
Resveratrol-Containing Compositions And Methods Of Use
A resveratrol-containing composition capable of providing a therapeutic benefit to a subject such as modulation of a biological activity, improving cell transplantation therapy, or improving macular degeneration or dystrophy treatments. The compositions comprise trans-resveratrol, a metal chelator, and one or more additional antioxidants such as phenolic antioxidants or vitamin D.
Owner:RESVERATROL PARTNERS
Method for Cell Implantation
InactiveUS20090214614A1High-quality repairQuality improvementPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue defectTissue engineering
The present invention provides for a method for tissue engineering by cell implantation that involves the use of a scaffold in situ at the site of a defect, where the therapeutic cells are fixed in place into the scaffold only once the scaffold is inserted at the site of the tissue defect, thereby locking not only the cells to the scaffold, but also the scaffold to the tissue defect. The invention also provides a kit of parts suitable for performing the method of the invention.
Owner:INTERFACE BIOTECH
Method and device for treating osteoarthritis and cartilage disease, defects, and injuries in the human hip
A method of determining the voltage and current required for the application of specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals to diseased articular cartilage in the treatment of osteoarthritis, cartilage defects due to trauma or sports injury, or used as an adjunct with other therapies (cell transplantation, tissue-engineered scaffold, growth factors, etc.) for treating cartilage defects in the human hip joint and a device for delivering such signals to a patient's hip. Anatomic, analytical, and planar circuit models are developed to determining the impedances, conductivities, and current flows in the human hip joint and its surrounding soft tissues and skin that are required to produce a 20 mV / cm electric field in the synovium and articular cartilage of the human hip. The voltage of the signal applied to the surface electrodes or to a coil(s) or solenoid is varied based on the size of the hip joint; larger hip joints require larger voltages to generate the effective electric field.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Uses of immunologically modified scaffold for tissue prevascularization cell transplantation
This invention provides method of making and using of a porous 3 dimensional cyclic RGD peptide-modified alginate scaffold that can be loaded with different cell types and / or growth factors for implantation at sites of tissue damage to promote tissue regeneration. The cyclic RGD peptide promotes vascular formation of the host tissue, cell binding and survival of seeded cells. Scaffolds with growth factors but without cells can also be implanted to create a vascular bed in which cells are transplanted at a later time point.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Non-disruptive three-dimensional culture and harvest system for anchorage-dependent cells
InactiveUS20040023370A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNon destructiveCell division
A non-disruptive three-dimensional culture system allows cell growth and proliferation in three dimensions, permitting cell splitting without subjecting cells to disruptive conditions that affect cell structure and functions. An extracellular matrix provides a good environment for culturing or co-culturing anchorage-dependent cells. The cells cultured this manner can be readily used in such applications as cell transplantation, tissue engineering seeding of cells on scaffolds, and other applications that require immediate availability of functioning cells.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Cardiac stem cell populations for repair of cardiac tissue
InactiveUS20120021019A1Convenient amountIncrease the number ofBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsTissue biopsyCardiac Stem Cell
Method for the isolation, expansion and preservation of cardiac stem cells from human or animal tissue biopsy samples to be employed in cell transplantation and functional repair of the myocardium or other organs. Cells may also be used in gene therapy for treating cardiomyopathies, for treating ischemic heart diseases and for setting in vitro models to study drugs.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI ROMA LA SAPIENZA
Multi-aperture nerve repairing tube and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102688110AGood tissue compatibilityImprove plasticityTubular organ implantsCylindromaSpinal nerve
The invention relates to a multi-aperture nerve repairing tube and a preparation method and application thereof. The multi-aperture nerve repairing tube is a cylinder with a length-diameter ratio of 0.1-1, and multiple microtube channels are axially distributed in parallel inside; and the ratio of the diameter of each microtube channel to the diameter of the cylinder is 0.04-0.2. The multi-aperture nerve repairing tube provided by the invention has good histocompatibility, proper and controllable degradation absorbability, low antigenicity and good plasticity and mechanical properties. The multi-aperture nerve repairing tube provided by the invention can effectively promote the repair of the injured spinal nerve, and also can be used as a cell transplantation carrier to carry different nerve growth factors and stem cells for repairing the spinal nerve injury. The multi-aperture nerve repairing tube provided by the invention is favorable for the intrusion, differentiation and growth of the nerve cell; and the tubular biomaterial is connected with the far and near broken ends of the nerve, and can induce the axon of the regenerated nerve to grow from the near end to the far end along the tube cavity and stimulate the growth of the neuron of the organism. The multi-aperture nerve repairing tube can be used for promoting the repair of spinal nerves.
Owner:TIANXINFU (BEIJING) MEDICAL APPLIANCE CO LTD
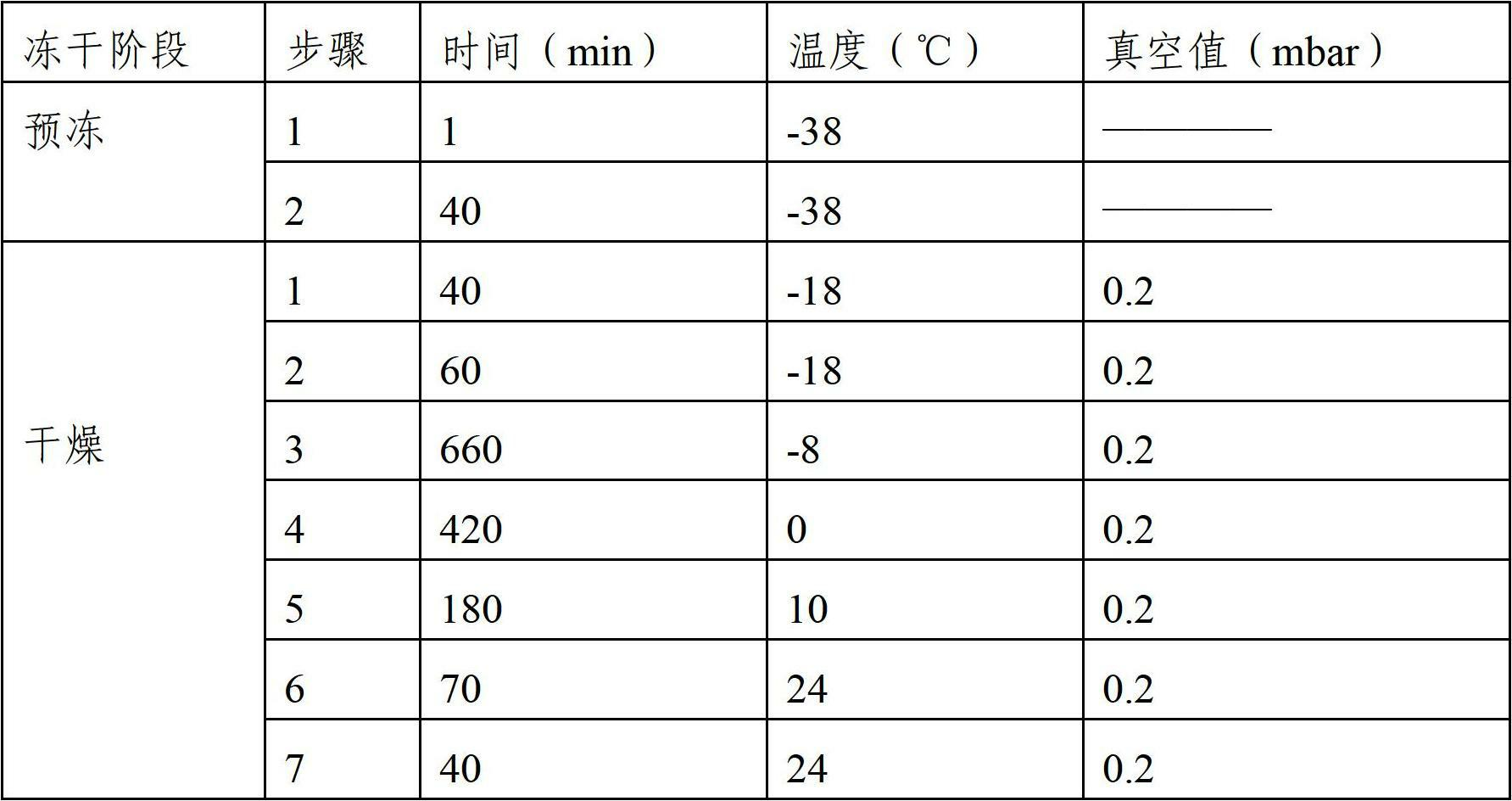
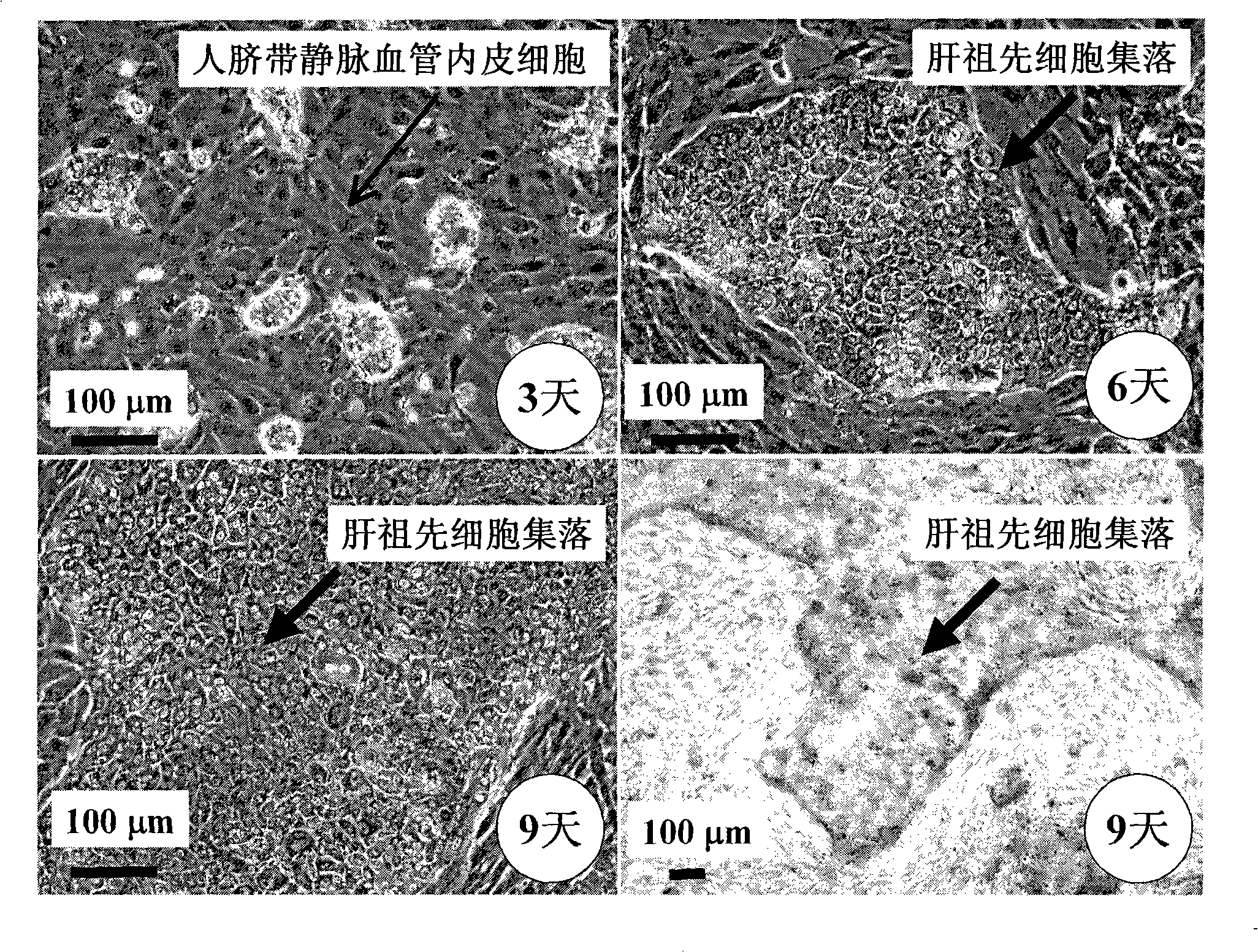
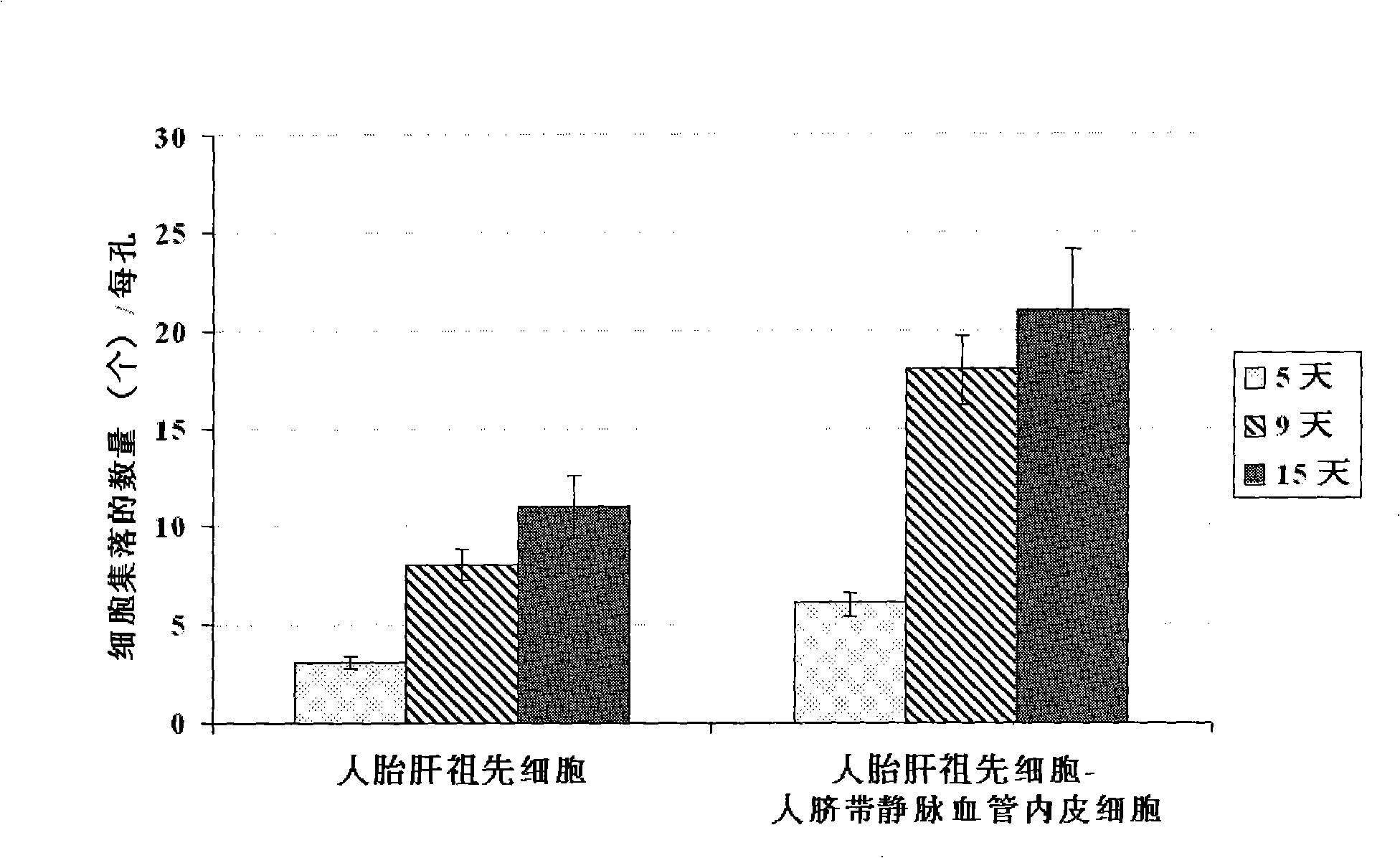
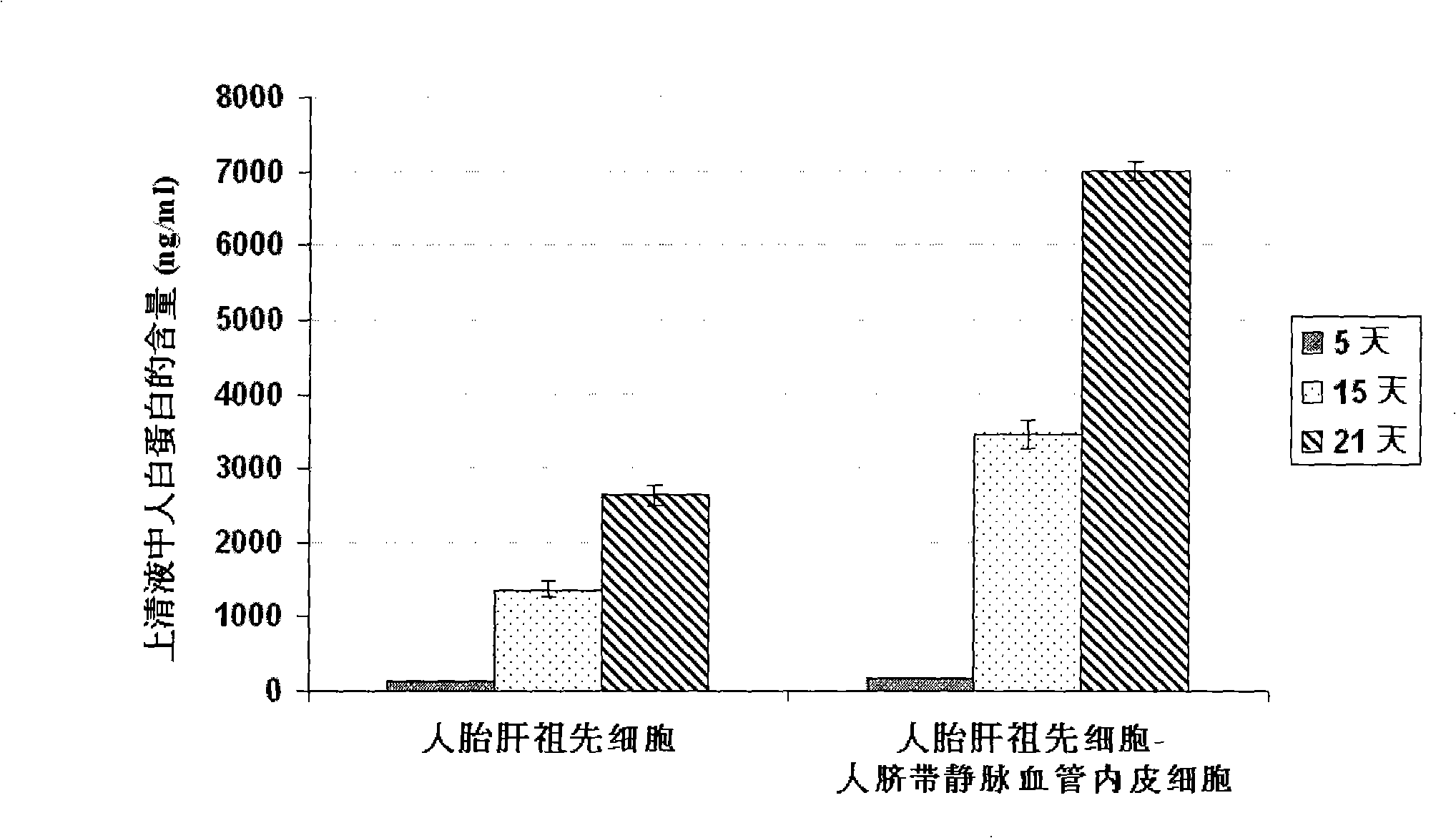
In vitro culture-amplified human liver progenitor cell and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101275121AAccelerate self-renewalConvenient sourceArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The present invention provides a preparing method of a human hepatic progenitor cell which is amplified and cultivated in vitro, including: a. separating the human hepatic progenitor cell; b. co-cultivating a feeder cell and the human hepatic progenitor cell separated from the step a by a medium having no serum on an extracellular matrix containing human fibrin sealant or other analogues, obtaining a human hepatic progenitor cell colony by amplification. The human hepatic progenitor cell colony is easy to separate from the surface of human fibrin sealant by the simple gelatinolytic band process, purified or / and subcultured by further single cell preparation technology process such as enzymatic degradation etc. The human hepatic progenitor cell prepared by the method is hepatic progenitor cell treatment, including a cell transplantation and a bioartificial liver support system, providing excellent human hepatocyte source for cytotoxicity test platform in the drug screening, virus infection and drug screening platform etc.
Owner:芦银雪
Method for long-time in-vitro culturing and proliferating hepatic cells and application of method
ActiveCN105296418AEasy to storeEasy to transportMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsOrganismCells transplantation
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology and provides a method for long-time in-vitro culturing and proliferating hepatic cells. The method includes that mature hepatic parenchymal cells are induced to be hepatic cells with infinite proliferation capability in vitro. The hepatic cells obtained by the method can be used for toxicological and pharmacological evaluation of compounds and drug, study and diagnosis as well as treatment of hepatitis virus, hepatic cell transplantation therapy and preparation of bioartificial liver.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELLIVER BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Method for preparing a cell-derived extracellular matrix membrane
InactiveCN101563450ASkeletal disorderCell culture supports/coatingHigh concentrationCell-Extracellular Matrix
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a cell-derived extracellular matrix membrane, more particularly, to a method for preparing a chondrocyte-derived ECM membrane, the method comprising the steps of forming a suitable thickness of ECM membrane by culturing chondrocytes derived from animal cartilage at a high concentration in vitro, and drying it after decellularization process. The cell-derived ECM membrane scaffold according to the present invention is composed of extracellular matrix secreted by chondrocytes so that the membrane has excellent biocompatibility as well as an immune-previlage effect specific to cartilage. Since the membrane also has a suitable compressive strength, it can be used to replace periosteum for cartilage regeneration or artificial collagen membrane and used as dura mater transplant material, a natural ECM membrane for treating skin loss, materials for cell transplantation and a growth factor delivery vehicle.
Owner:REGENPRIME
Method of engrafting cells from solid tissues
A method of repairing diseased or dysfunctional organs or of establishing a model system of a disease state is provided. For repairing diseased organs, the method involves engraftment of cells from healthy tissue of the diseased or dysfunctional organ admixed with gel-forming biomaterials and nutrient medium, signaling molecules and extracellular matrix components that can be made insoluble rapidly upon transplantation to form a graft. In this way, the graft mimics the complexity of the native microenvironment with a minimum number of components that allow transplantation of cells to successfully engraft, expand and then rebuild part or the entirety of the diseased or dysfunctional organ. In the case of using grafting methods for establishing a disease model, diseased cells may be transplanted in the biomaterials and into experimental hosts.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Method for cell implantation
An endoscopic method for treating cartilage or bone defects in an animal, said method comprising the steps of: I) identifying the position of the defect, ii) applying cells selected from the group consisting of chondrocytes, chondroblasts, osteocytes and osteoblasts and combinations thereof into the cartilage or bone defect. In particular, the invention relates to a method for arthroscopic or endoscopic implantation of homologous or autologous cells into a defect of an animal body, the method comprising a step of I) arthroscopic or endoscopic application of a fluid to a cavity or surface containing the defect, and the steps of ii) application of the cells to the defect substantially simultaneously with a support material, the application being performed at the defect covered by the fluid, iii) mixing of the cells and the supporting material, iv) solidification of the supporting material so that the defect is covered by a mixture of cells and support material without any significant amount of fluid, and v) optionally, removal of the fluid from the cavity or surface by drainage or suction.
Owner:INTERFACE BIOTECH
Alginate-epsilon-polylysine microcapsules and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102101036AReduce surface roughnessGood biocompatibilityUnknown materialsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEpsilon-PolylysinePolyelectrolyte
The invention relates to a bioactive substance included alginate microcapsule product. The invention is characterized in that: the microcapsule product is a spherical microcapsule with diameter of 100 to 1,000 microns, and the structure of the microcapsule product comprises a microcapsule film and a core, wherein the microcapsule film is a polyelectrolyte composite hydrogel film formed by electrostatic complexing reaction of two macromolecular materials, namely alginate and epsilon-polylysine; and the core is a liquid or hydrogel environment containing a bioactive substance. The microcapsule product is mainly applied to cell transplantation, cell culture and included carriers of bioactive substances such as protein, polypeptide, enzyme, nucleic acid and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in the acute myocardial infarction cell transplantation therapy
ActiveCN101642469AImproved prognosisImprove proliferative abilityMammal material medical ingredientsTissue cultureDiseaseCells transplantation
The invention discloses an application of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in the acute myocardial infarction cell transplantation therapy; the application is suitable for ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction within one mouth or non ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction cases, a vascular remodeling is carried out to a patient who is attacked by the disease withinsix hours, after about four to six days, coronary perfusion is carried out to the patient; and the other patients who choose date to carry out vascular remodeling operation, the coronary perfusion iscarried out at the same time. The treating effect in the invention is superior to the bone mesenchymal stem cells transplantation.
Owner:PLA NAVY GENERAL HOSIPTAL
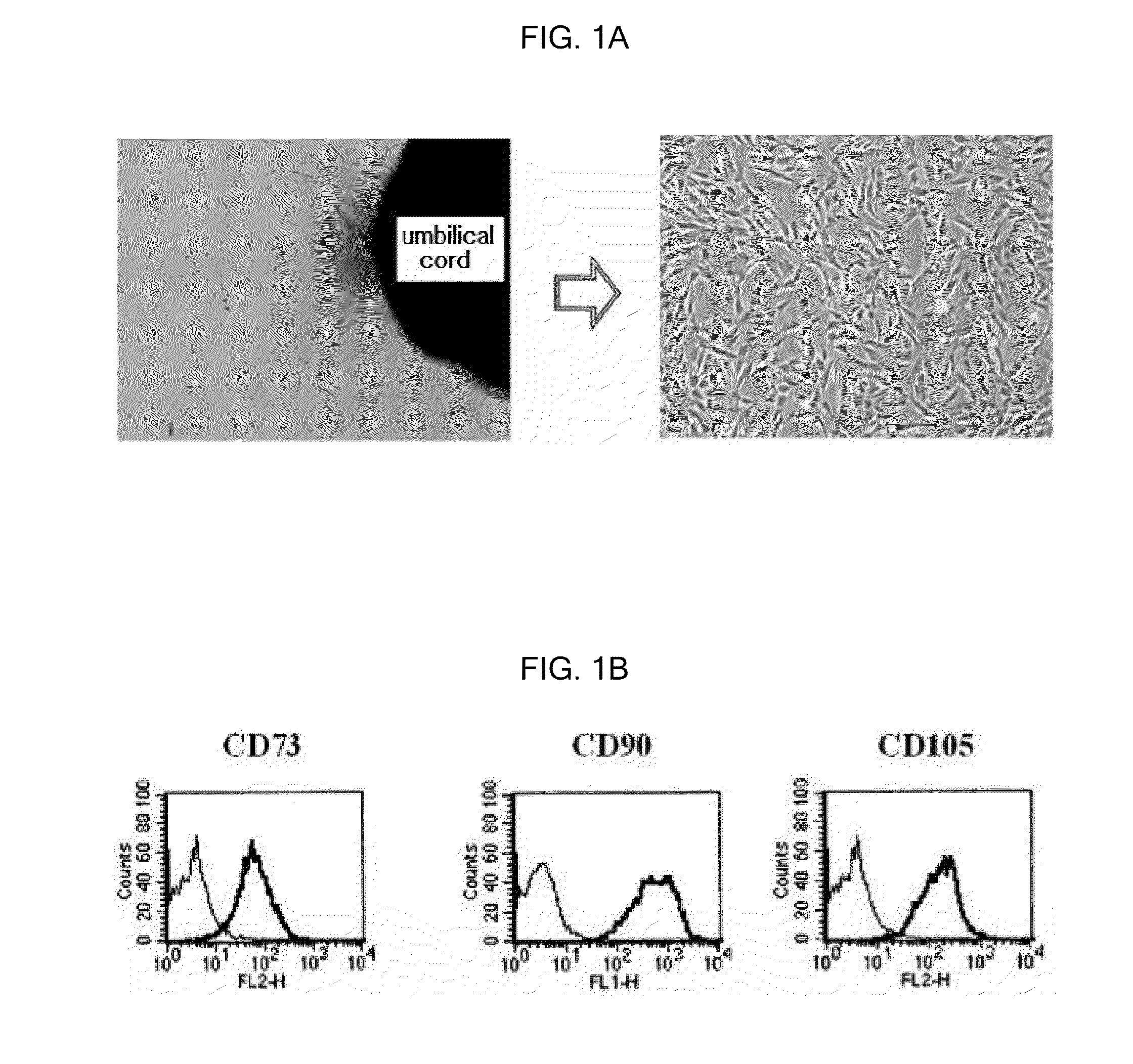
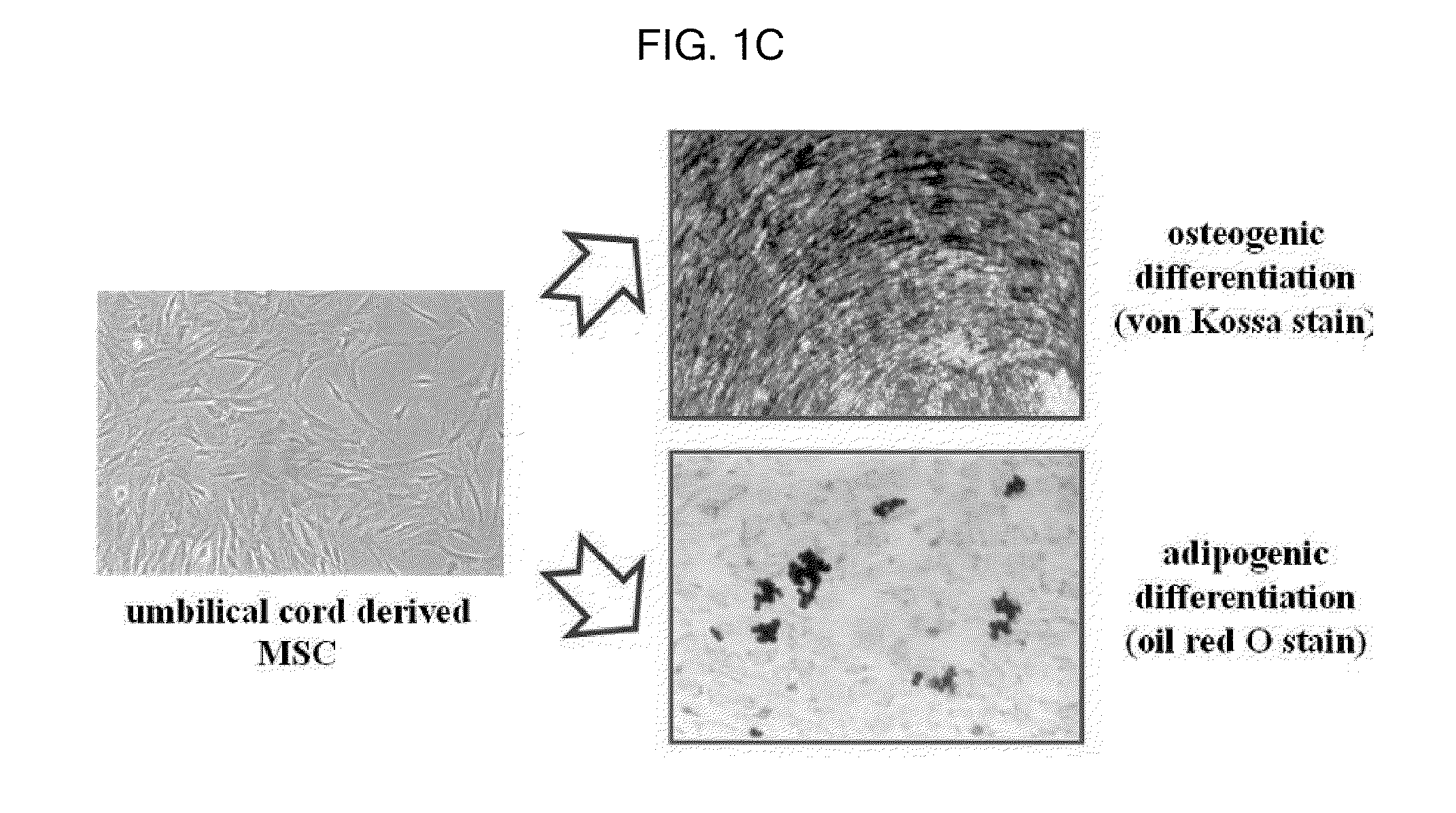
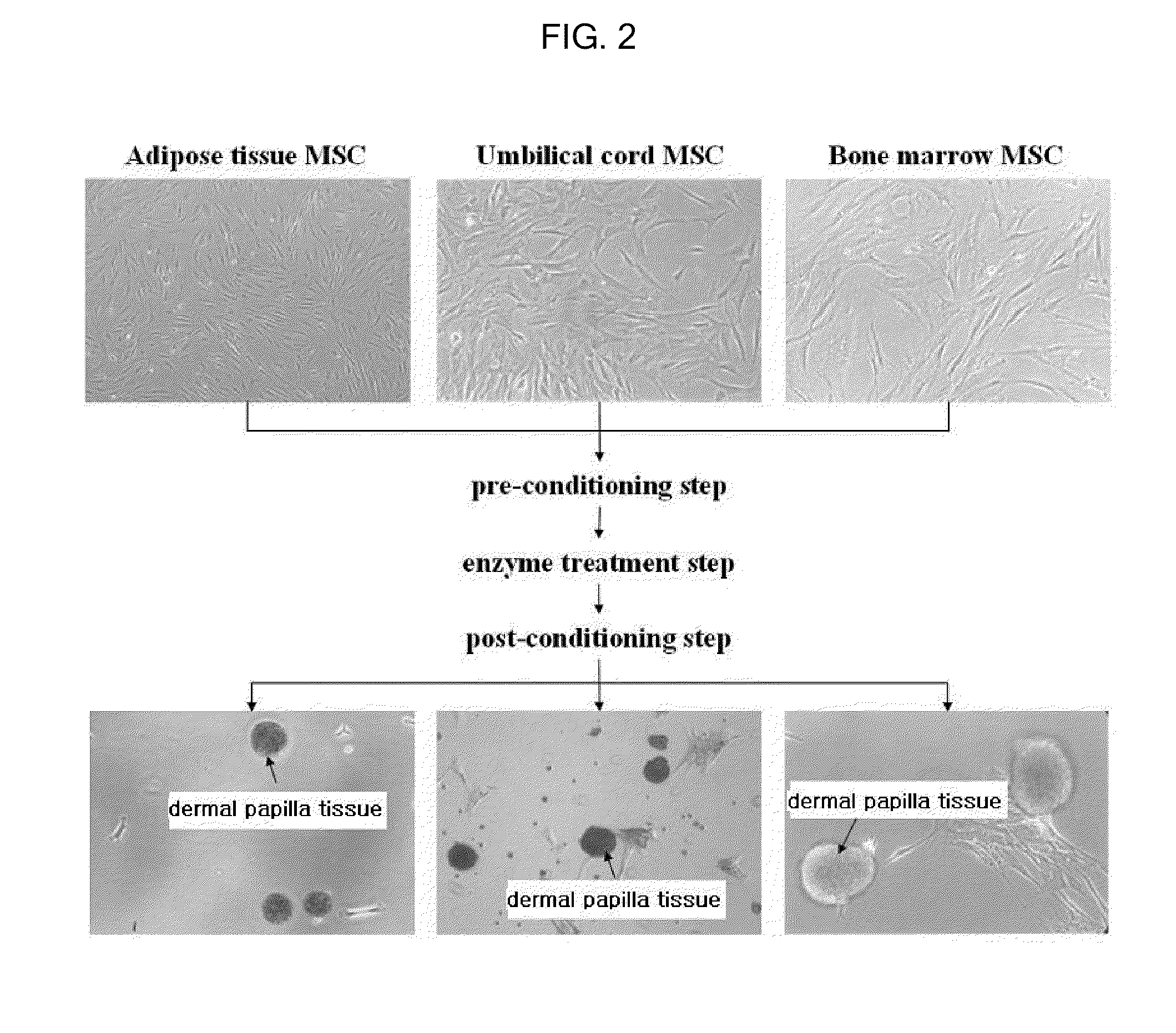
Method For The Preparation Of Dermal Papilla Tissue Employing Mesenchymal Stem Cells
A method for the preparation of dermal papilla tissue comprising the step of culturing mesenchymal stem cells in a medium having a specific composition is provided. The method makes it possible to form in vitro a quantity of dermal papilla tissues having hair follicle inducting ability and, accordingly, it can be effectively used for the treatment of alopecia through cell transplantation.
Owner:DONGGUK UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
Method for obtaining neural progenitor cells induced by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN101215545AResolve source issuesNervous system cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsProgenitorNerve cells
The invention provides a method for inducing mesenchymal stem cell in the bone marrow to obtain the nerve prosoma cell, which comprises the following steps: doing generation culture for the separated and purified mesenchymal stem cell in the bone marrow, switching stable generation mesenchymal stem cell into induction culture medium, inducing and culturing for 7-20 d, obtaining nerve prosoma cell. The induction culture medium is basic culture medium which is charged with growth factor, wherein the growth factor mainly comprises an epiderm growth factor (EGF), a base fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), an insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and a nerve nourishment factor 3 (NT-3). The invention provides a method for inducing mesenchymal stem cell in the bone marrow to obtain the nerve prosoma cell which can be differentiated into nerve cell and the nerve prosoma cell can be switched into inner ear hair cell and inner ear supporting cells, which provides experiment evidence for cochlear cell transplantation therapeutic sound perception nerve deafness and solves the problem of the transplantation cell resource.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Composition for Organ, Tissue, or Cell Transplantation, Kit, and Transplantation Method
ActiveUS20170058001A1Facilitate functioningImprove survivabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgical drugsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTActive ingredient
Disclosed are: a composition for organ, tissue or cell transplantation, containing, as an active ingredient, a peptide comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, a peptide having at least 80% sequence homology with the amino acid sequence, or a peptide which is a fragment thereof; a kit comprising the composition; or a method using the composition. By using the composition, the kit, or the method, the viability and / or function of an organ, tissue, or cell after transplantation are strengthened and an organ, tissue or cell isolated from a living body is preserved temporarily without damage.
Owner:GEMVAX & KAEL
Method of Constructing Animal Having Cancer Cells Transplanted Thereinto
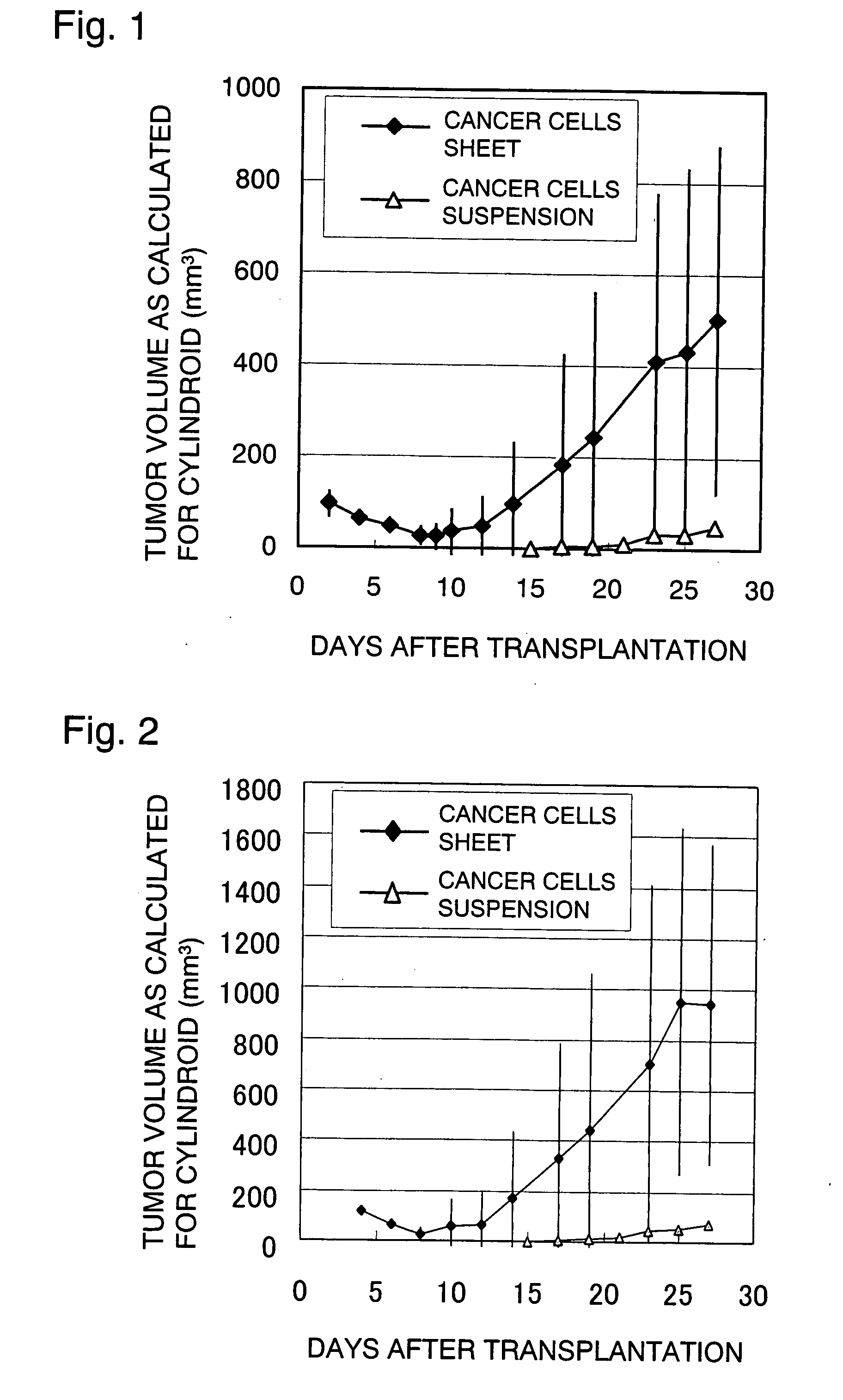
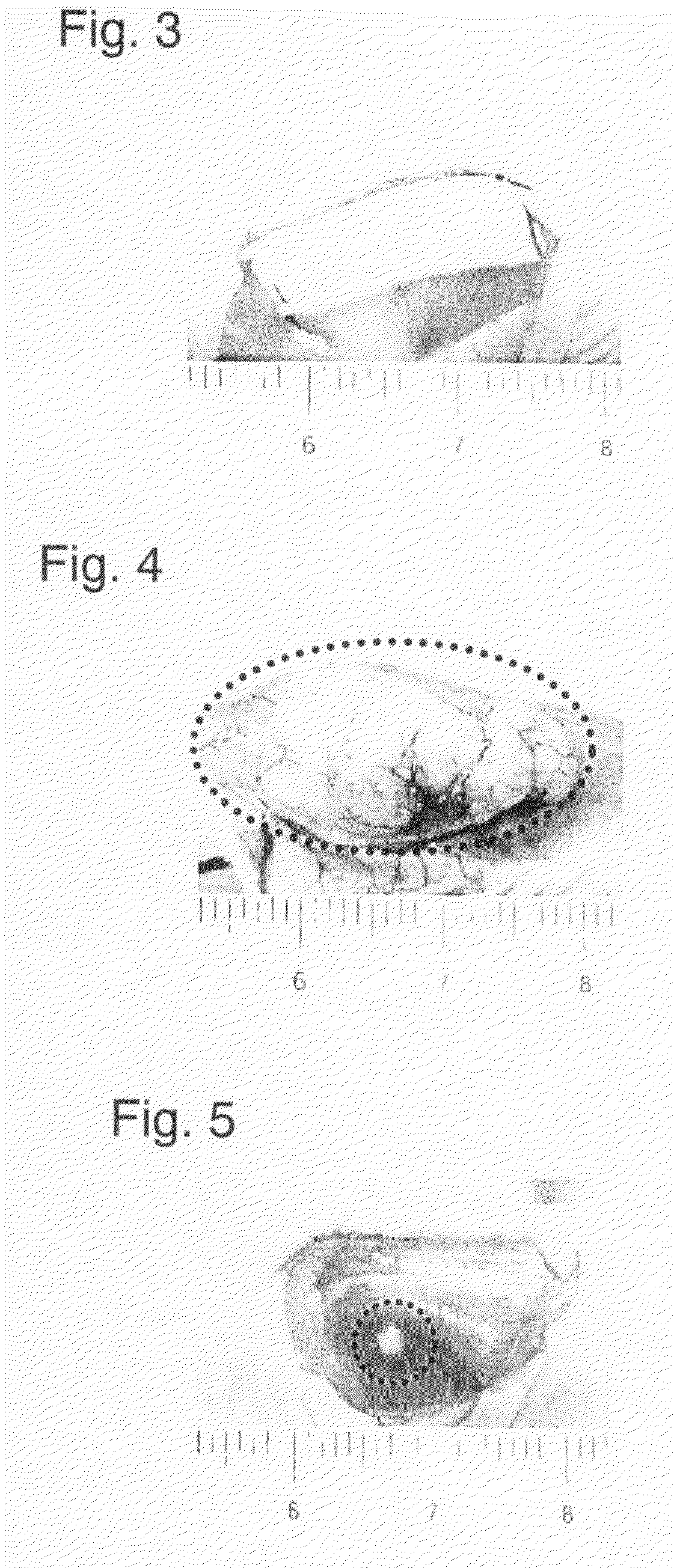
InactiveUS20080289052A1Efficient preparationPrevent leakageCompounds screening/testingTumor/cancer cellsCancer cellCells transplantation
A cell culture support is first prepared that is coated on a surface with a polymer the hydration force of which changes in a temperature range of 0-80° C.; cancer cells are then cultivated on the support in a temperature region where the polymer has weak hydration force; thereafter, the culture solution is adjusted to a temperature at which the polymer has a stronger hydration force, whereby the cultured cancer cells are detached; the detached cancer cells are then transplanted to a specified site of an animal on which transplantation is to be performed; this method is an efficient way of cancer cells transplantation.
Owner:CELLSEED
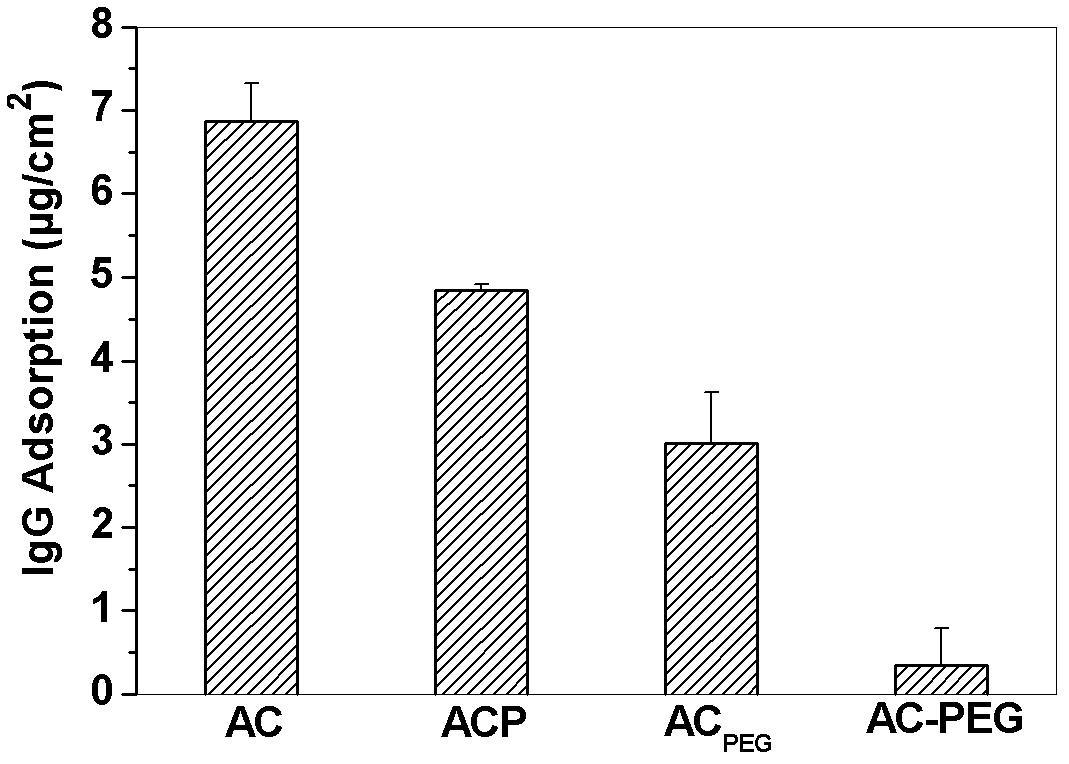
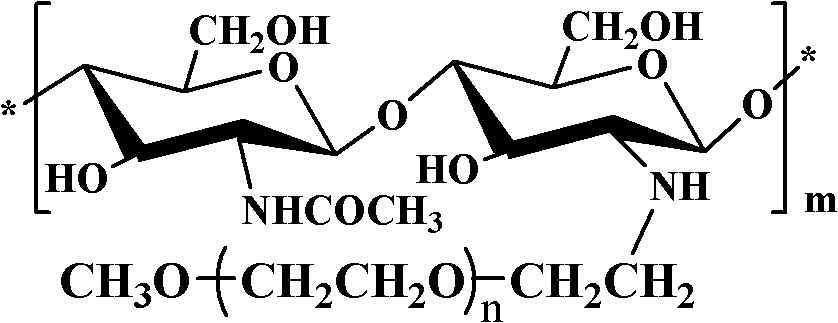
Alginate-chitosan microcapsule modified via PEG grafting and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN103301788AGood biocompatibilityIdeal anti-protein adsorption propertiesOn/in organic carrierMicroballoon preparationPolyelectrolyteAlginate chitosan
The invention relates to an alginate-chitosan microcapsule modified via in situ covalent PEG grafting. The structure of the microcapsule is divided into two parts, i.e., a microcapsule membrane and an inner core, wherein the microcapsule membrane is a polyelectrolyte composite hydrogel membrane formed by chitosan and alginate, the surface of the membrane is modified via in situ covalent PEG grafting, and the inner core is an alginate liquid or alginate hydrogel environment containing living cells. Because of resistance to protein adsorption, the microcapsule is applied to living cell encapsulation and used as an immunoisolation carrier for cell transplantation.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation and application of adipose-derived stem cell exosome in facial rejuvenation
InactiveCN108373996AAvoid harmCell dissociation methodsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismNew Zealand white rabbitFacial rejuvenation
The invention provides a preparation and application of an adipose-derived stem cell exosome in facial rejuvenation. The preparation method comprises the following steps: separation of adipose-derivedstem cell, extraction of the exosome and coating of adipose-derived stem cell exosome-nano collagen. By carrying out facial microscopic carving and face-lifting by virtue of the adipose-derived stemcell exosome-nano collagen, the superiorities of the adipose-derived stem cell exosome-nano collagen, compared with adipose-derived stem cell autoplastic transplantation, exosome injection or pure nano collagen, in skin reconstructive repairing and micro-face lifting are observed. Particularly, adipose-derived stem cells are separated, the exosomes of the adipose-derived stem cells are extracted,the nano collagen is fused with the separated exosome to form an adipose-derived stem cell exosome-nano collagen combined preparation, the combined preparation is injected into the skin an injured part of a New Zealand white rabbit, the promotion effect of the adipose-derived stem cell exosome-nano collagen, compared with a pure adipose-derived stem cell transplantation group, an exosome group andpure nano collagen, in the regeneration of injured skin is observed, and meanwhile, a user can observe whether the adipose-derived stem cell exosome is harmful to a human body.
Owner:王丽丽
Monocyte-origin multipotent cell momc
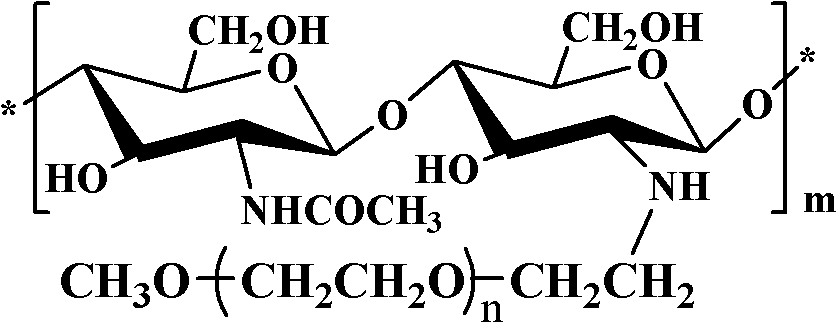
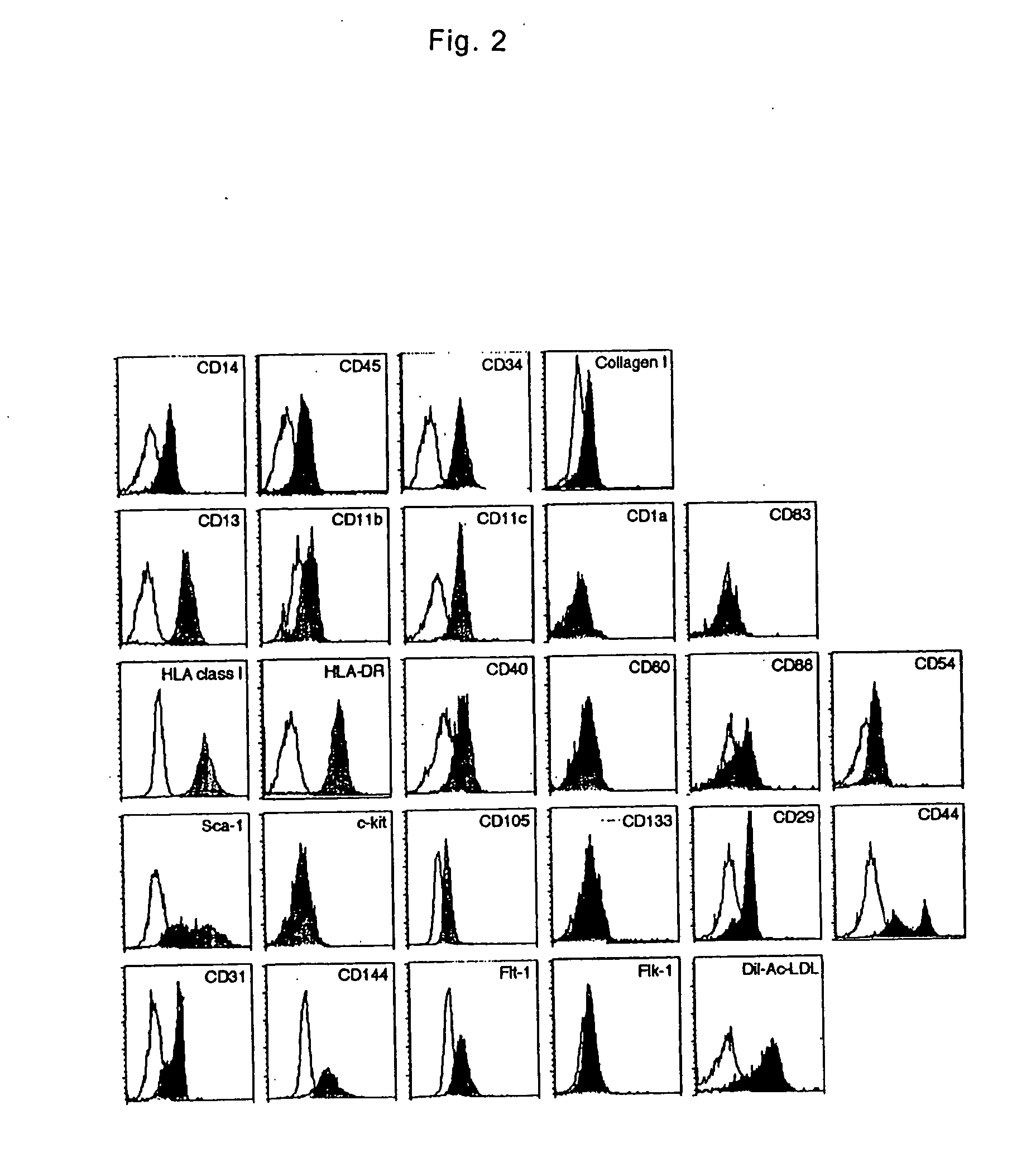
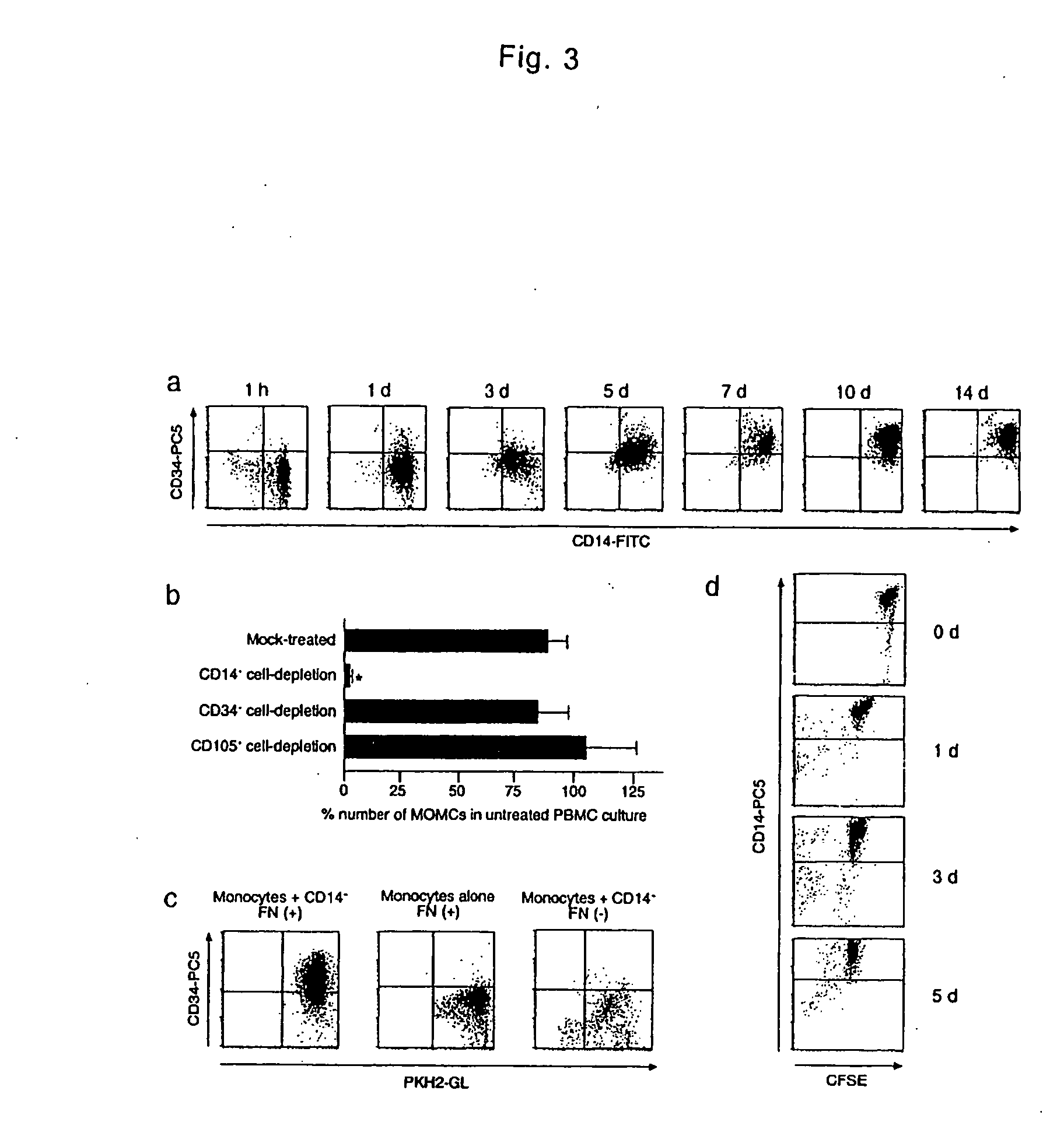
The present invention is to provide a multipotent cell wherein the sufficient amount necessary can be stably and conveniently supplied with a minimum invasion, that will not cause rejection at the time of cell transplantation, that has a potential to differentiate into various cells such as mesenchymal cells including bone, cartilage, skeletal muscle and fat, endothelial cells, myocardial cells, neurons, mesenchymal cells, myocardial cells, endothelial cells, neurons induced to differentiate from the multipotent cell, and a therapeutic agent / treating method comprising these as active ingredient. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PMBC) are cultured on fibronectin-coated plastic plates for 7 to 10 days. The generating cell population with a fibroblast-like morphology is derived from circulating CD14+ monocyte, with a unique phenotype of CD14+CD45+CD34+ type I collagen+. These cells have a potential to differentiate into mesenchymal cells including bone, cartilage, skeletal muscle and fat, endothelial cells, myocardial cells, and neurons under particular culture conditions.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Method for orienting inducing and differentiating heart pacemaker cell by embryo source pluripotent stem cell
Cell transplantation for constructing biological heart pacemaker is used embryo source dry / ancestral cell and adult mesogalia dry cell as cell sources. The process is carried out by oriented differentiation inducing for heart pacemaker cell by embryo source multifunctional dry cell, bone marrow adhering to obtain primary culture cell, clone culturing to obtain purifying system by diluting, applying paracrine factor endothelin-1 or nervous adjusting protein-1, extracellular matrix laminated adherent protein and fiber connecting protein etc. substrate glue, trans-dyeing pacemaker gene HCN4, and in-vitro inducing embryo source multifunctional dry cell. It is various and non-immunogenicity. It can be used to treat sick sinus syndrome.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com