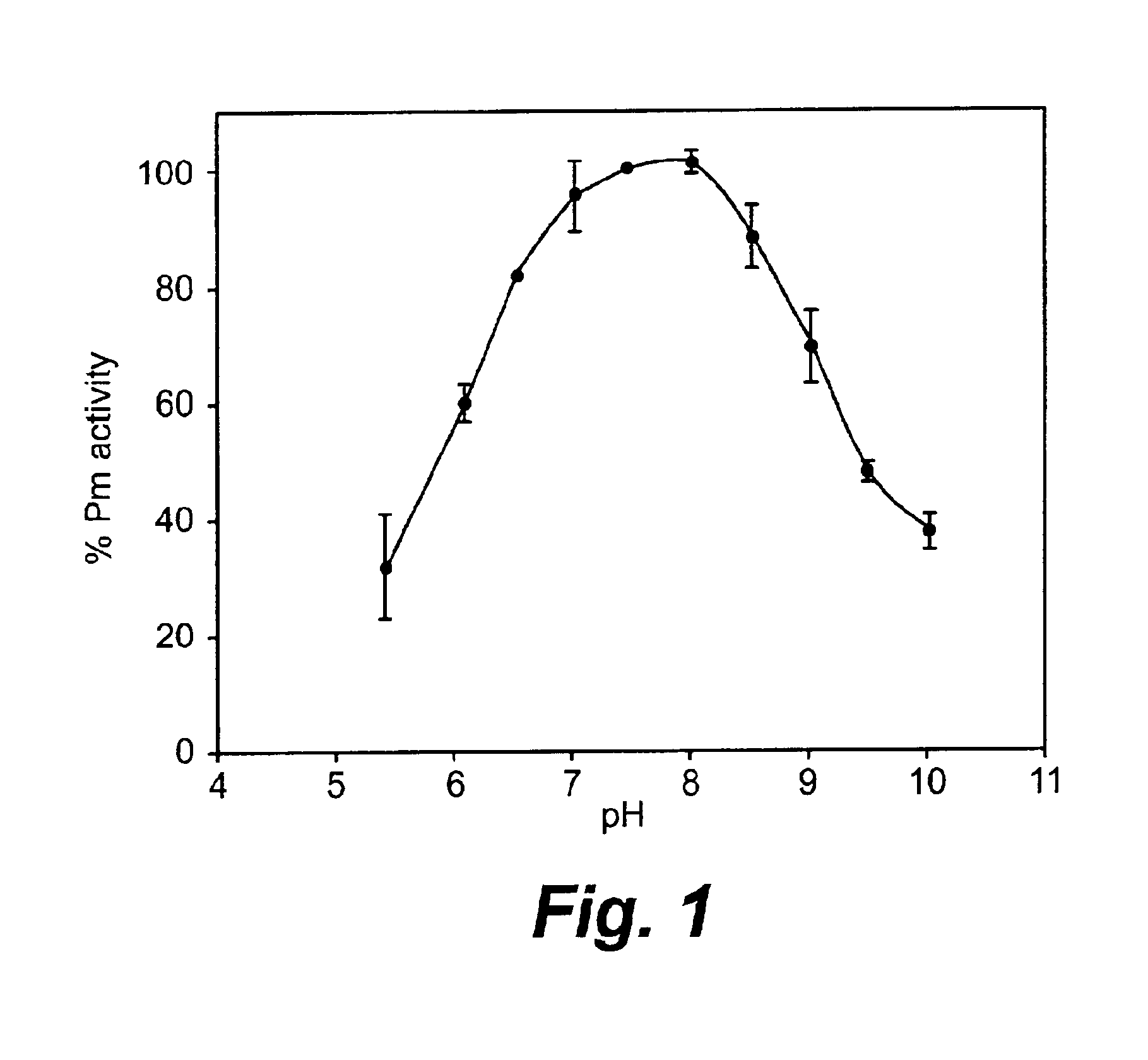
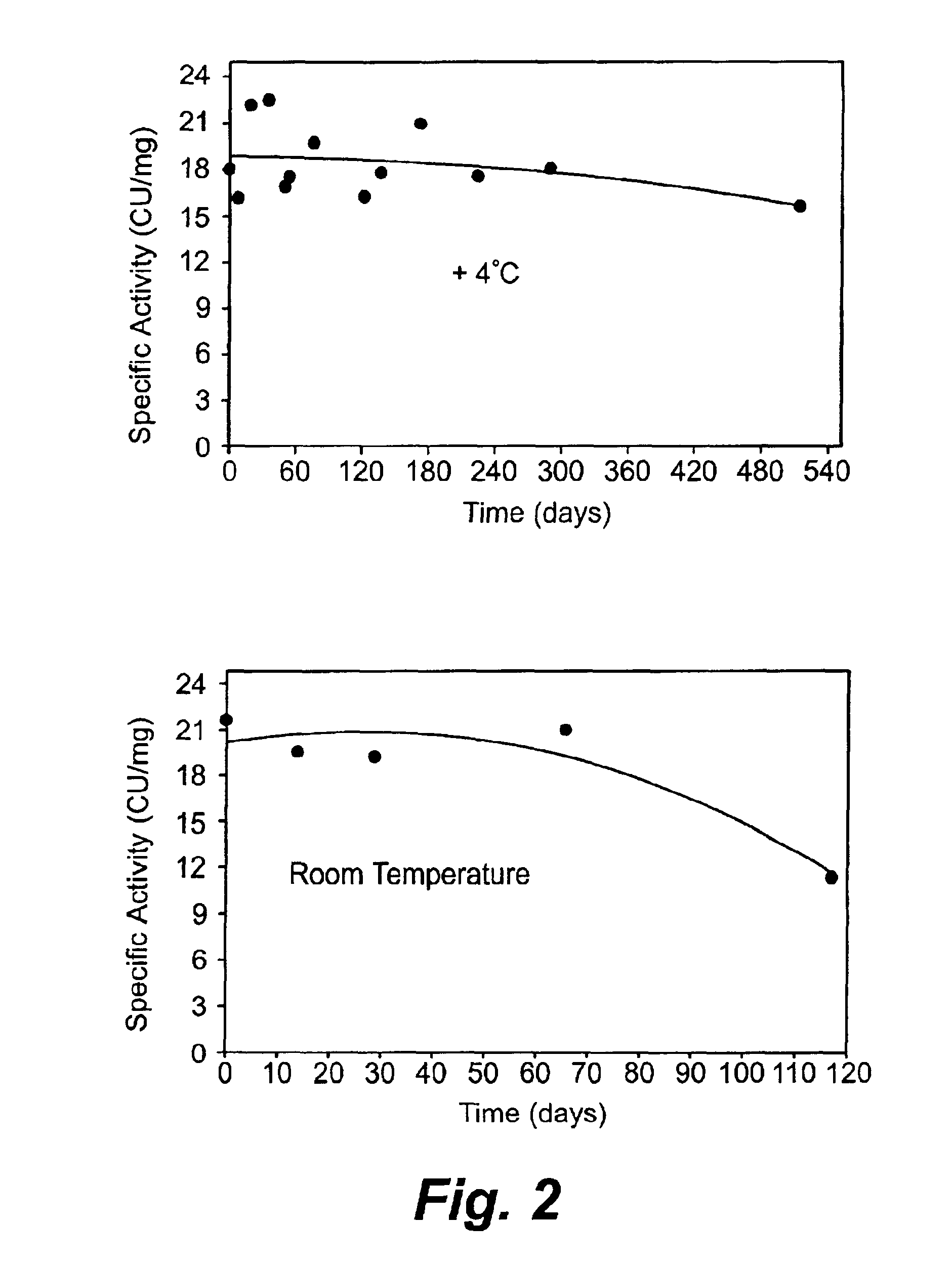
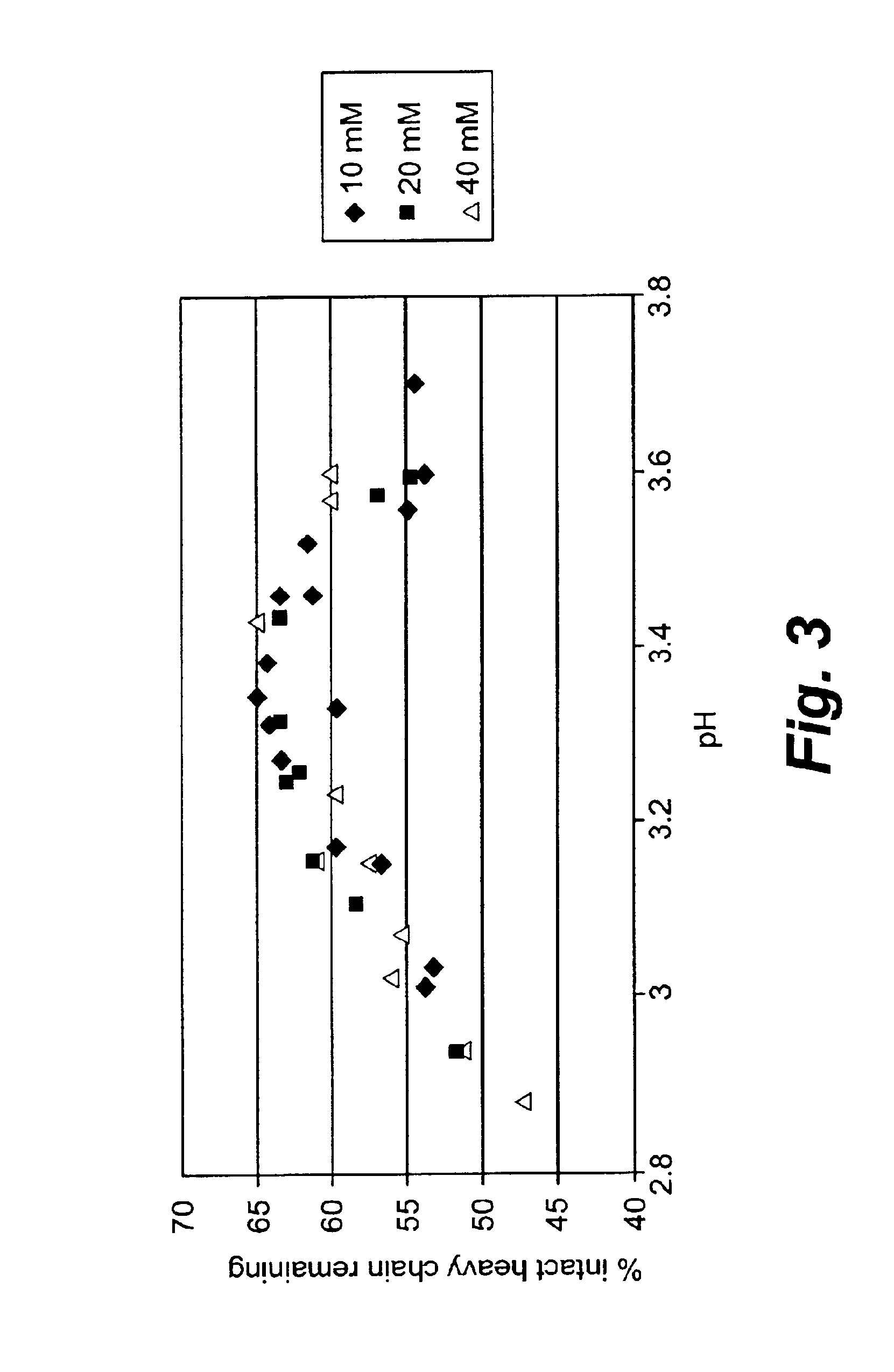
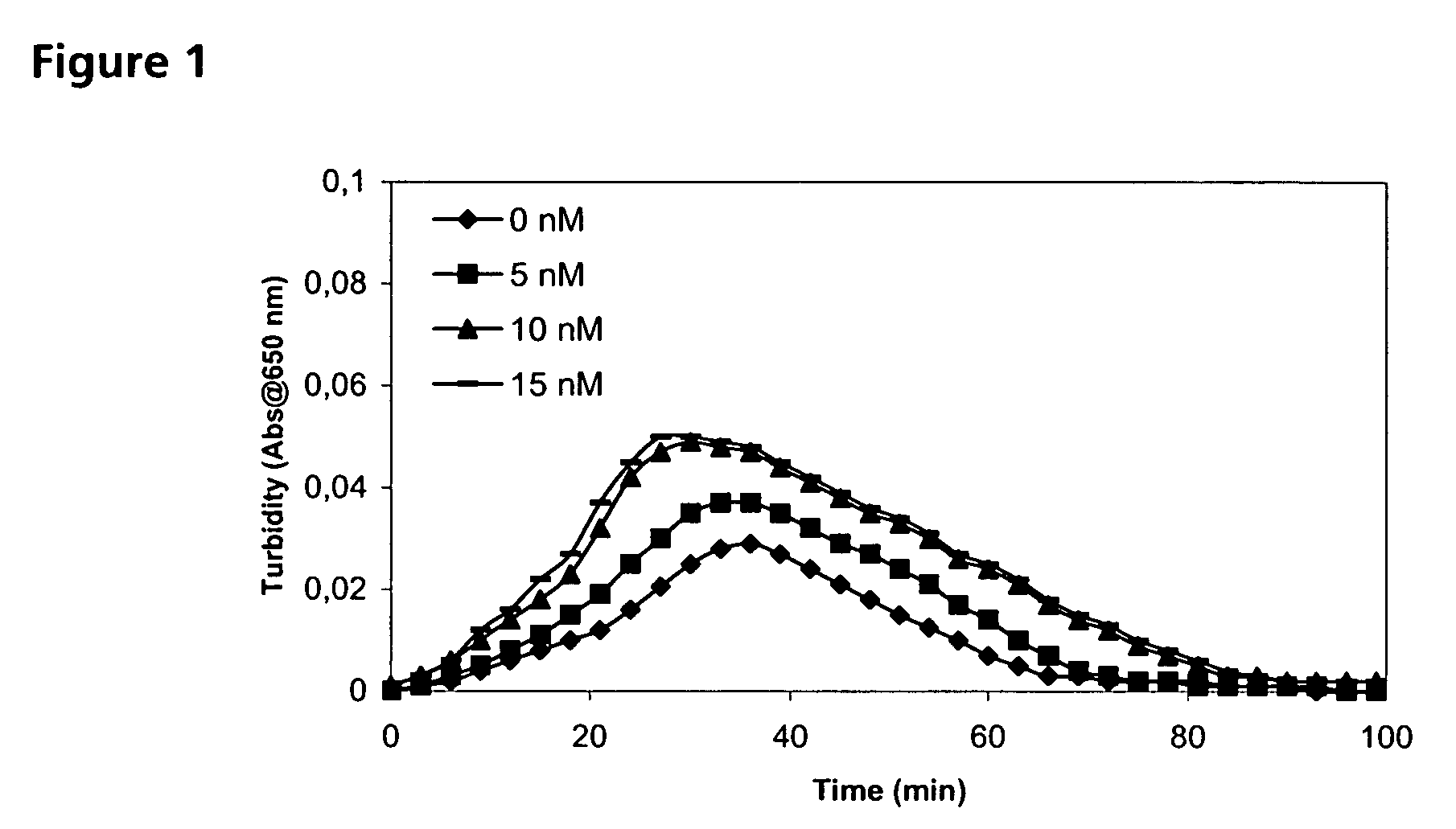
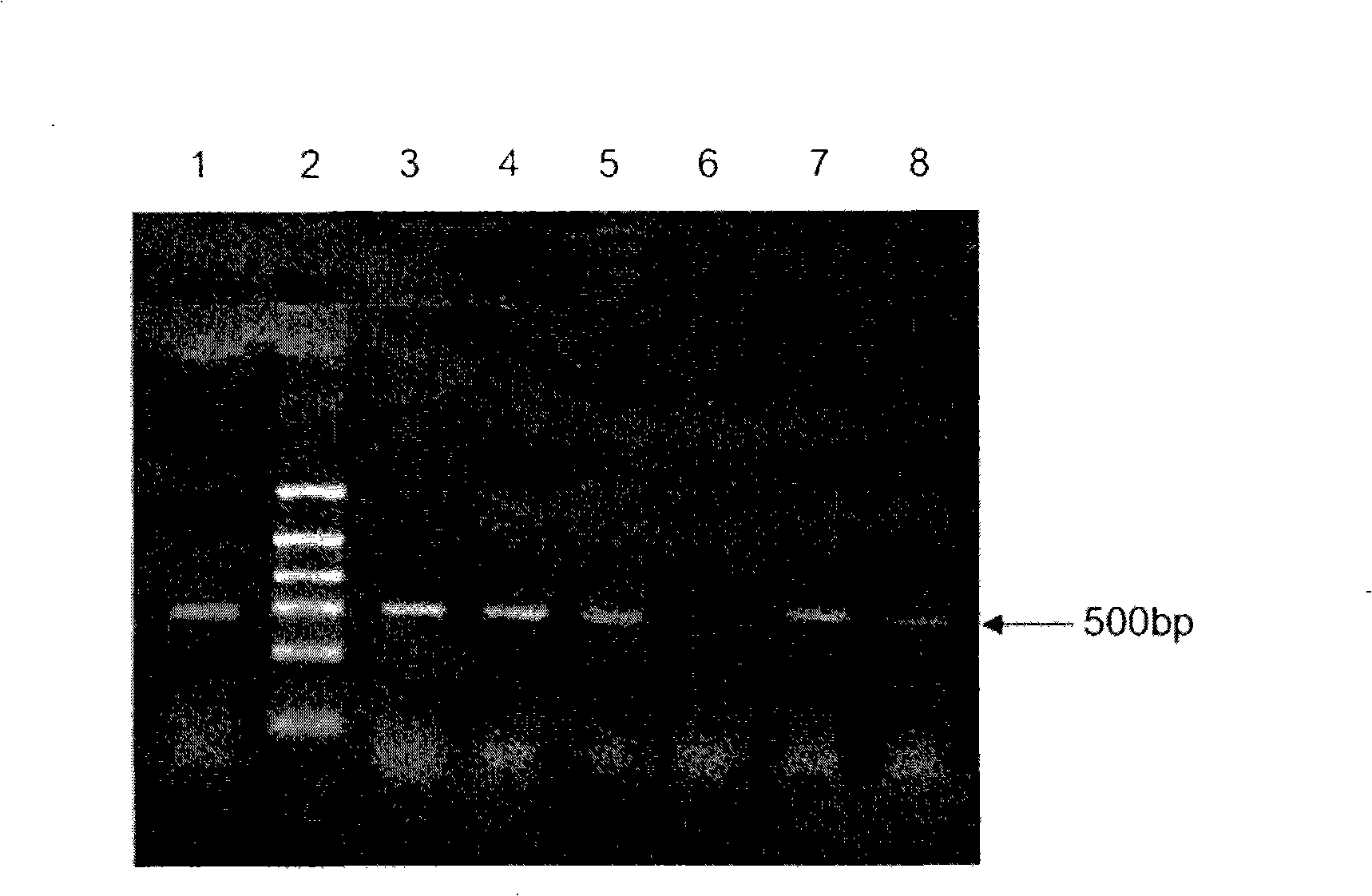
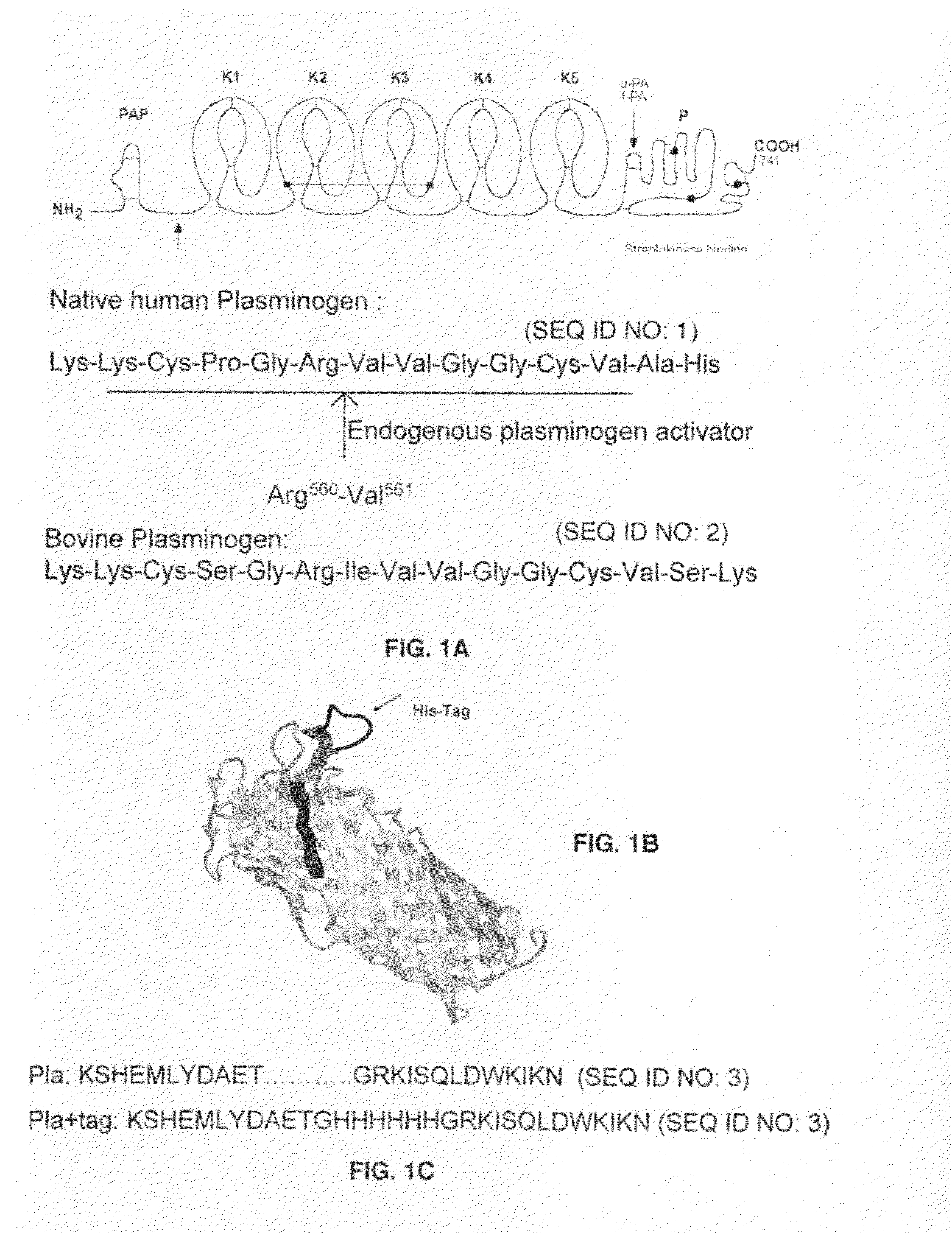
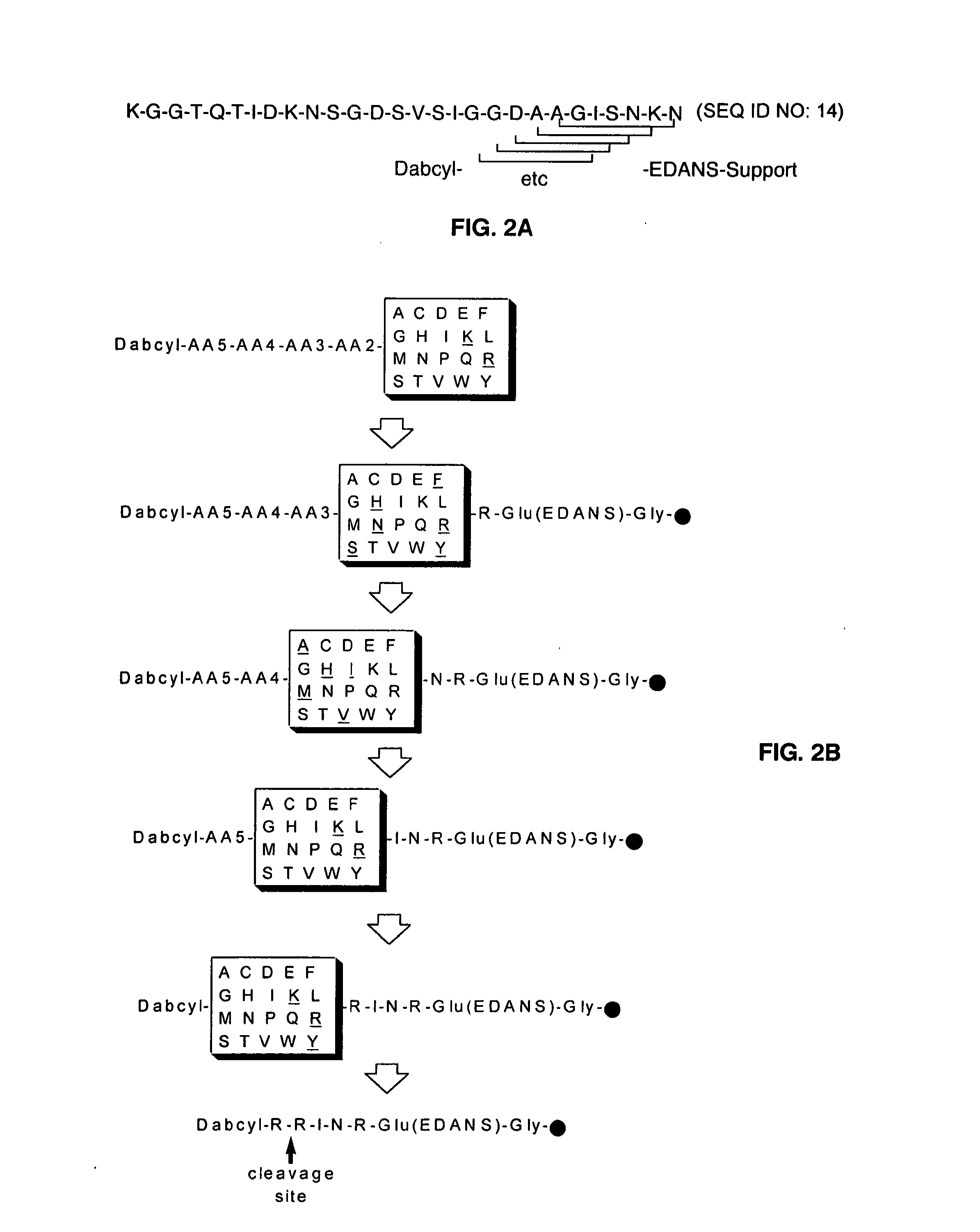
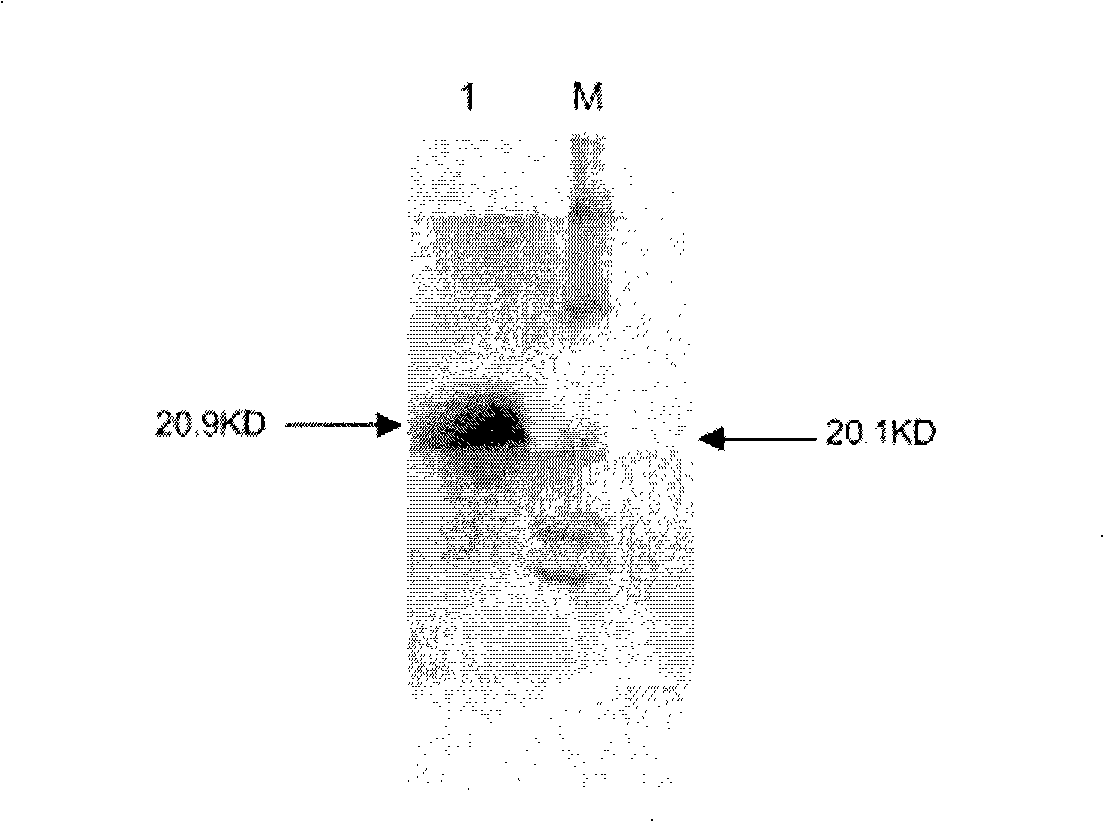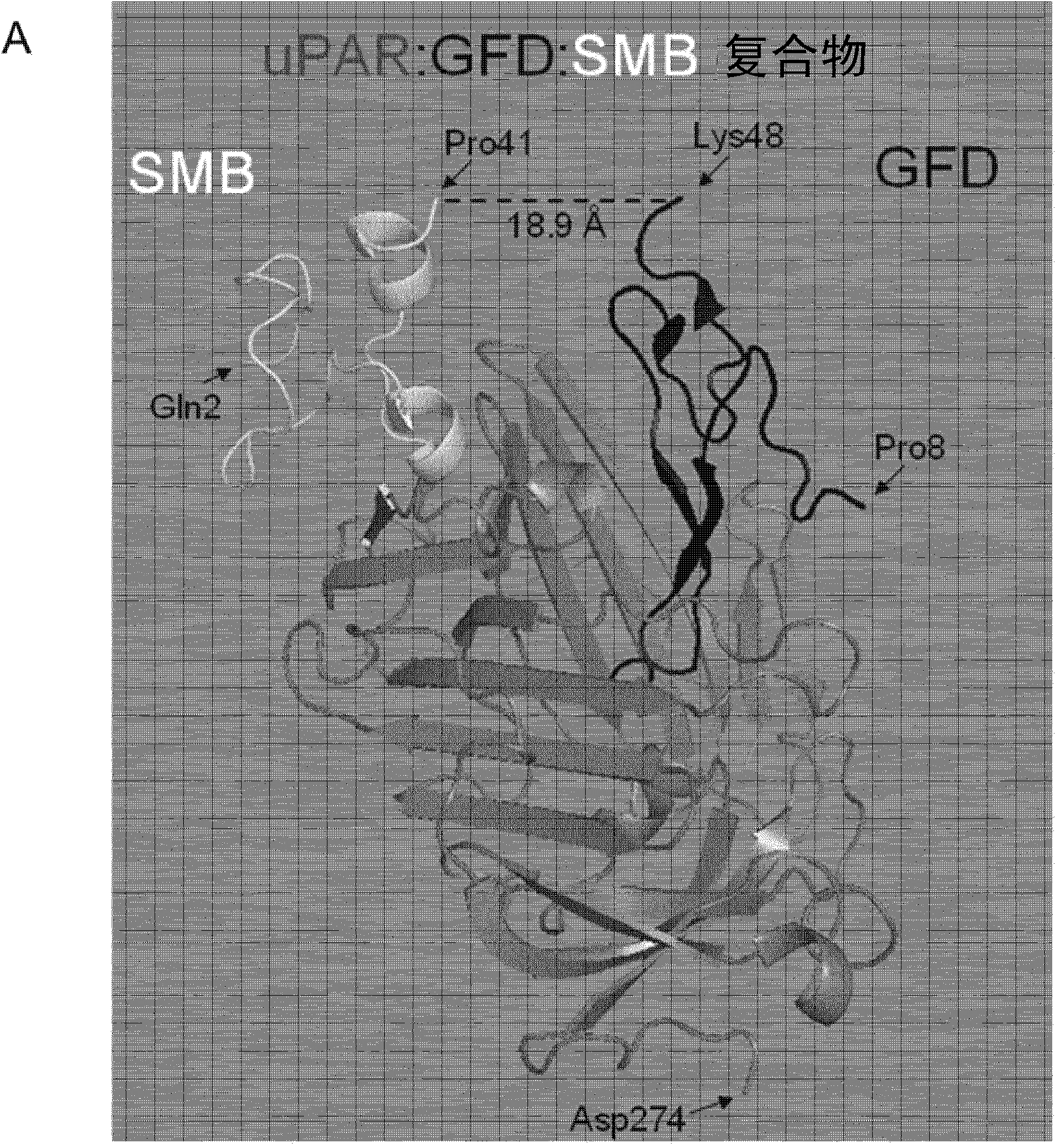Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
136 results about "PLG - Plasminogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
PLG plasminogen [ (human)] Gene ID: 5340, updated on 5-Feb-2017. Summary. The protein encoded by this gene is a secreted blood zymogen that is activated by proteolysis and converted to plasmin and angiostatin. Plasmin dissolves fibrin in blood clots and is an important protease in many other cellular processes while angiostatin inhibits ...
Methods for producing heterologous disulfide bond-containing polypeptides in bacterial cells
InactiveUS6083715AEfficient productionFold preciselyBacteriaUnicellular algaeMolecular biologyDisulfide bond
Disclosed are methods and compositions for producing heterologous disulfide bond containing polypeptides in bacterial cells. In preferred embodiments the methods involve co-expression of a prokaryotic disulfide isomerase, such as DsbC or DsbG and a gene encoding a recombinant eukaryotic polypeptide. Exemplary polypeptides disclosed include tissue plasminogen activator.
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
Removal of plasmin(ogen) from protein solutions
A method for specifically removing or isolating plasmin(ogen) or plasmin in presence of fibrinogen from a mixture containing plasmin(ogen) or plasmin by contacting the mixture with a rigid amino acid wherein the amino group of the amino acid and the carboxylic group of the amino acid are about 6–8 Angstroms, preferably about 7 Angstroms apart and the rigid amino acid is covalently bound to the support via the amino group of the amino acid.
Owner:OMRIX BIOPHARM
Leader sequences for use in production of proteins
InactiveUS20070141666A1Efficient secretionEasy to handlePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesDNA constructTissues types
This invention encompasses novel leader sequences for production of proteins. More specifically, the invention relates to DNA constructs encoding leader sequences comprising an immunoglobulin signal peptide fused to a tissue-type plasminogen activator propeptide, and to DNA constructs encoding leader sequences comprising a truncated human tissue-type plasminogen activator propeptide. The invention further relates to the use of these DNA constructs for producing proteins in mammalian cells.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
Mutant human plasminogen kringle5, preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a mutant human plasminogen kringle5 gene mK5 and an amplification primer of the mK5 gene, the mutant human plasminogen kringle5 gene modified by adding glutathione-S-transferase before the gene mK5, and a method for preparing protein mK5 recombinant protein of two gene codes, glutathioneS transferase (GST)-mK5 fusion protein and two proteins, wherein the mK5 gene and the GST-mK 5 gene can be applied to preparing medicaments for treating angiogenesis diseases. By the invention, the number of exogenous amino acid in the recombinant K5 protein molecules obtained by a gene engineering method is remarkably reduced, the K5 bioactivity of the obtained mK5 is improved, while the mK5 activity of the GST-mK5 fusion protein is maintained, the stability and water solubility of the protein are improved, the purification steps of an expressed product are simplified, and the purity of the product is improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Enzyme producing plasma protein fragment having inhibitory activity to metastasis and growth of cancer and plasma protein fragment produced by fragmentation by said enzyme
InactiveUS20070117180A1Inhibit growthLess effectOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderMiniplasminogenHigh homology
An aspartic enzyme having a high homology with a cathepsin D precursor, which is a protein having the N-terminal amino acid sequence LVRIPLHKFT (SEQ ID NO: 1) and showing a molecular weight of about 45 kDa in non-reductive SDS electrophoresis and can degrade plasma proteins, typically plasminogen, to produce plasma protein fragments having an inhibitory activity to metastasis and growth of cancer; the plasma protein fragments having an inhibitory activity to metastasis and growth of cancer which is prepared via the degradation with the above enzyme; a process for preparing the protein fragments which comprises degrading plasma proteins with the above enzyme; and a medicament for treating and preventing metastasis and growth of cancer which comprises as a major ingredient the above enzyme or the plasma protein fragments.
Owner:MORIKAWA WATARU +5
Method of thrombolysis by local delivery of reversibly inactivated acidified plasmin
InactiveUS6964764B2Formula stableReduce capacityPeptide/protein ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsWhole bodyThrombus
Methods of thrombolysis that allow the use of a fibrinolytic composition comprising reversibly inactivated acidified plasmin and the localized delivery of the plasmin to a vascular thrombotic occlusion are disclosed. Further disclosed is a method for administering a therapeutic dose of a fibrinolytic composition substantially free of plasminogen activator to a human or animal having a vascular thrombotic occlusion. The fibrinolytic composition includes a reversibly inactivated acidified plasmin substantially free of plasminogen activator. Intravascular catheter delivery of the fibrinolytic composition directly into or in the immediate vicinity of the thrombus is disclosed to minimize the systemic degradation of fibrin while retaining the maximum plasmin activity against the thrombus.
Owner:GRIFOLS THERAPEUTICS LLC
Pharmaceutical composition comprising factor VII polypeptides and tissue plasminogen inhibitors
InactiveUS20050266006A1Effective treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsTPA InhibitorsBleeding episodes
The present invention relates to a composition comprising factor VII or a factor VII-related polypeptide and a tPA inhibitor, and the use thereof for treating bleeding episodes.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Inhibitors of urokinase and blood vessel formation
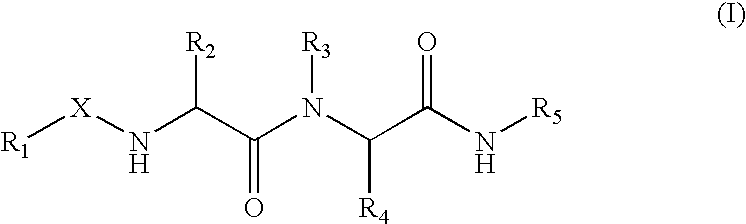
InactiveUS6432922B1Positive maintenanceInhibition effectSenses disorderAntipyreticPLG - PlasminogenArginine
Novel compounds having activity inhibitors of urokinase and in reducing or inhibiting blood vessel formation are provided. These compounds have an arginine or arginine mimic aldehyde or an arginine ketoamide group at P1. These compounds are useful in vitro for monitoring plasminogen activator levels and in vivo in treatment of conditions which are ameliorated by inhibition of or decreased activity of urokinase and in treating pathologic conditions wherein blood vessel formation is related to a pathologic condition.
Owner:DENDREON PHARMA INC
Functional mutant of human plasminogen, its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102199587AGood for renaturationExtended half-lifeSenses disorderNervous disorderPichia pastorisEukaryotic plasmids
A functional mutant of human plasminogen disclosed in the invention, respectively, is hPLG-delta K: human plasminogen protein Pro<544>-Asn<791> polypeptide; Pro<559> in RGD-hPLG-delta K: hPLG-delta K is mutated to Asp<559>; and Gly<560> in RHP-hPLG-delta K: hPLG-delta K polypeptide is mutated to His<560>. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the functional mutant. The product is obtained by using a plasmid containing a full-length cDNA sequence of human plasminogen as a template to carry out a PCR to construct a plasmid and using Pichia Pastoris expression. The functional mutant has a dual-function of fibrinolysis and inhibiting platelet aggregation or inhibiting fibrin monomer polymerization.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Fusion protein of urokinase type plasminogen activator a chain and melittin and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101337992AAvoid stickingInhibit migrationFungiPeptide/protein ingredientsMelittinProtein C
The invention provides a fusion protein formed by the combination of urokinase-type plasminogen activator a chain and melittin, the preparation method thereof, and the application of the fusion protein in tumor treatment.
Owner:吉林圣元科技有限责任公司
Substrate peptide sequences for plague plasminogen activator and uses thereof
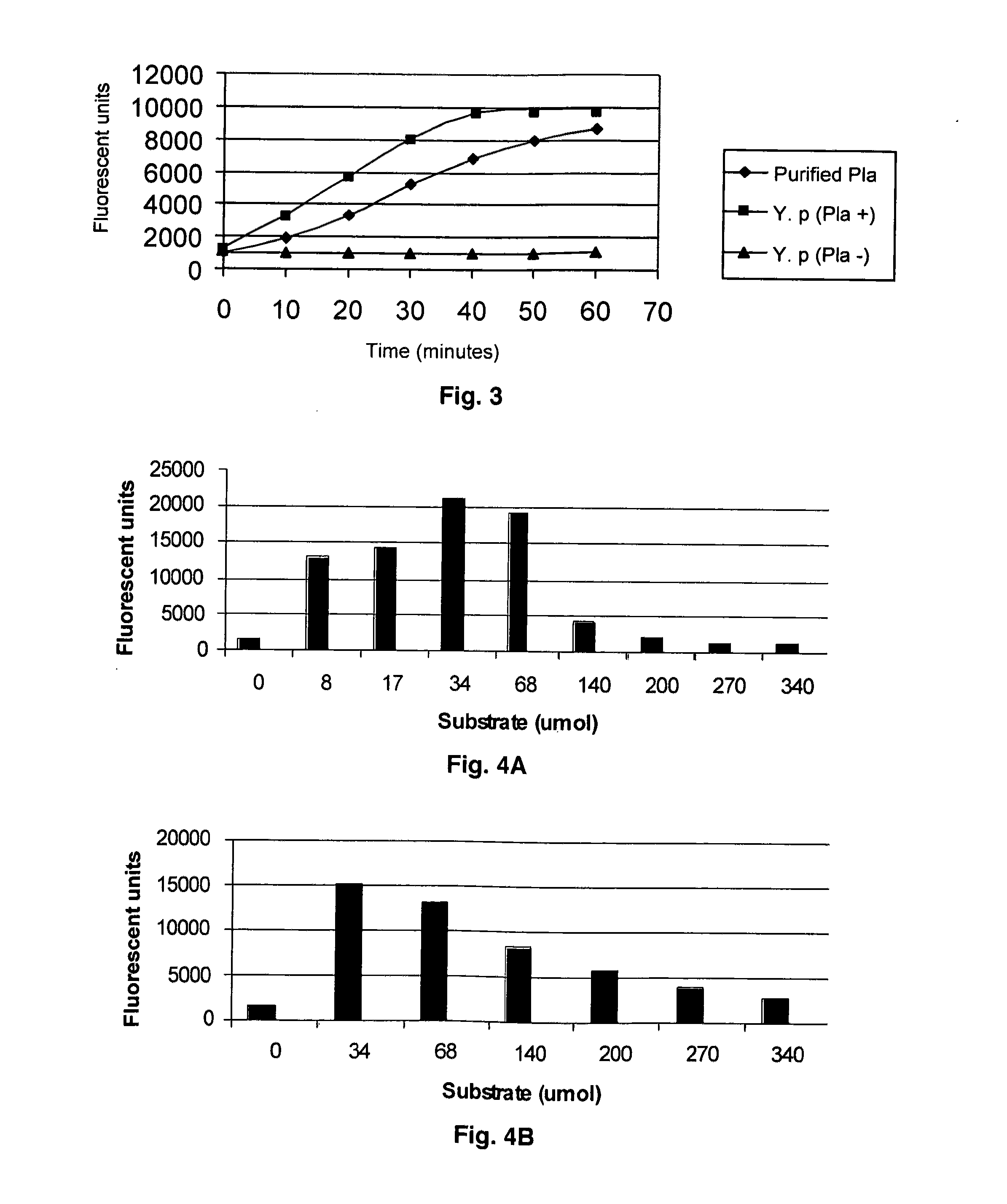
The present invention is directed to peptide sequences that were identified from combinatorial libraries and could serve as substrates of plague plasminogen activator (Pla). Another aspect of the present invention is drawn to peptides derived from the substrates for Pla as a result of chemical modifications leading to specific inactivation of the proteolytic activity of Pla. Additionally, the present invention is directed to the use of the substrates identified herein in the detection of bacteria expressing omptin family of proteases which includes Y. pestis. Furthermore, the present invention is also directed to the use of the inhibitors identified herein in the prevention and treatment of infection caused by these bacteria.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Title inhibitors of urokinase
InactiveUS6576613B1Promote cell adhesionImprove cell adhesionSenses disorderDipeptide ingredientsZymogenPLG - Plasminogen
Novel inhibitors of urokinase are provided which have an arginine or arginine mimic aldehyde or an arginine ketoamide group at P1. These compounds are useful in vitro for monitoring plasminogen activator levels and in vivo in treatment of conditions which are ameliorated by inhibition of or decreased activity of urokinase.
Owner:DENDREON PHARMA INC
Variants of plasminogen and plasmin
InactiveUS20120114630A1Excellent long-term storage stabilityReducing circulating fibrinogenSenses disorderFungiProteinase activityPlasmin
The invention relates to variants of plasminogen and plasmin comprising one or more point mutations in the catalytic domain which reduce or prevent autocatylic destruction of the protease activity of plasmin. Compositions, uses and methods of using said variants of plasminogen and plasmin are also disclosed.
Owner:THROMBOGENICS NV
Combination treatment with t-PA variant and low molecular weight heparin
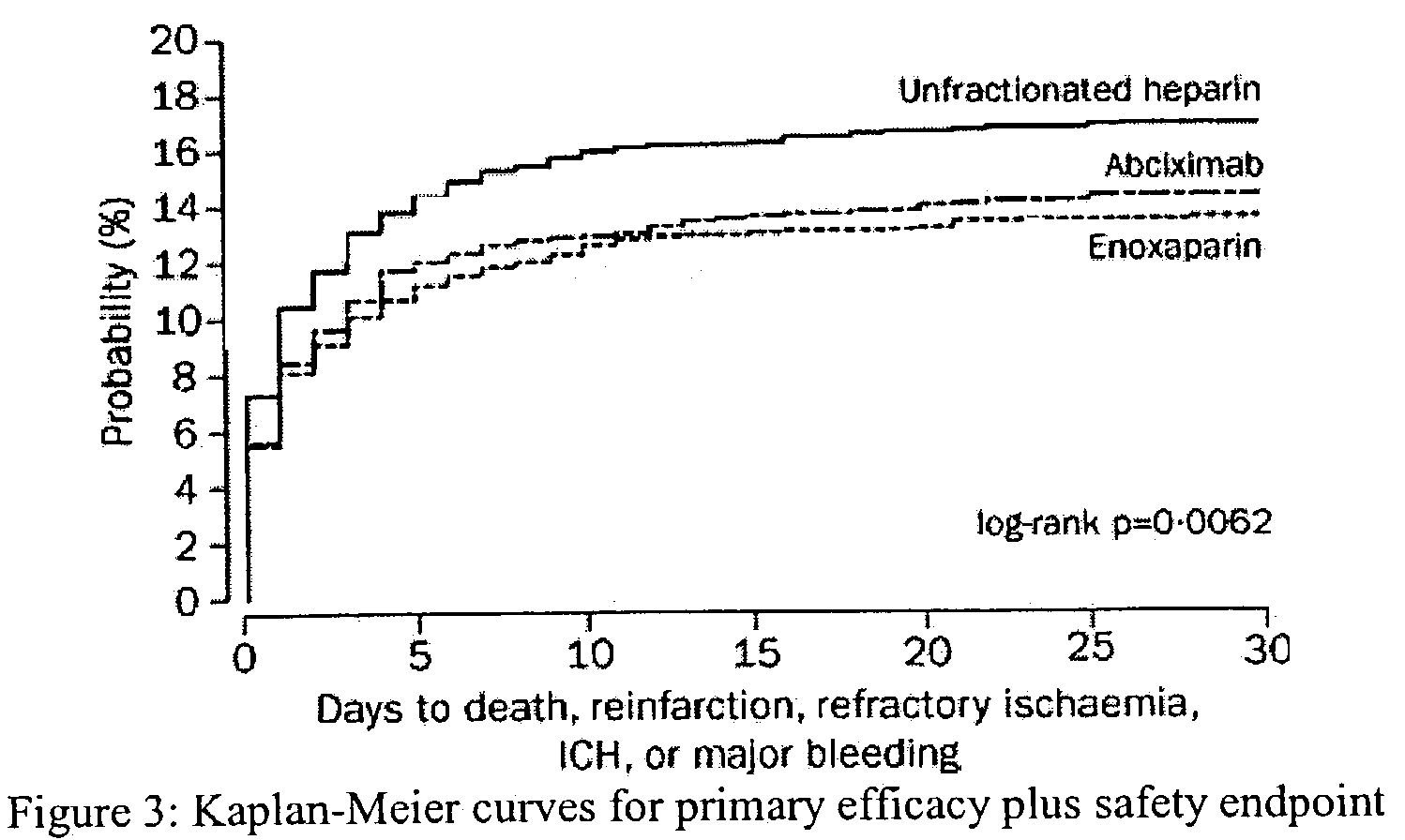
InactiveUS7084118B2Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeRetained fibrin bindingData processing applicationsFibrinogenPLG - PlasminogenRegimen
The invention concerns an improved therapeutic regimen for the treatment of thrombolytic disorders, such as acute myocardial infarction (AMI). In particular, the present invention concerns the treatment of thrombolytic disorders, e.g. AMI, with a combination of a tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) variant having improved fibrin specificity and extended plasma half-life when compared with wild-type human t-PA and a low molecular weight heparin.
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA SA (US) +2
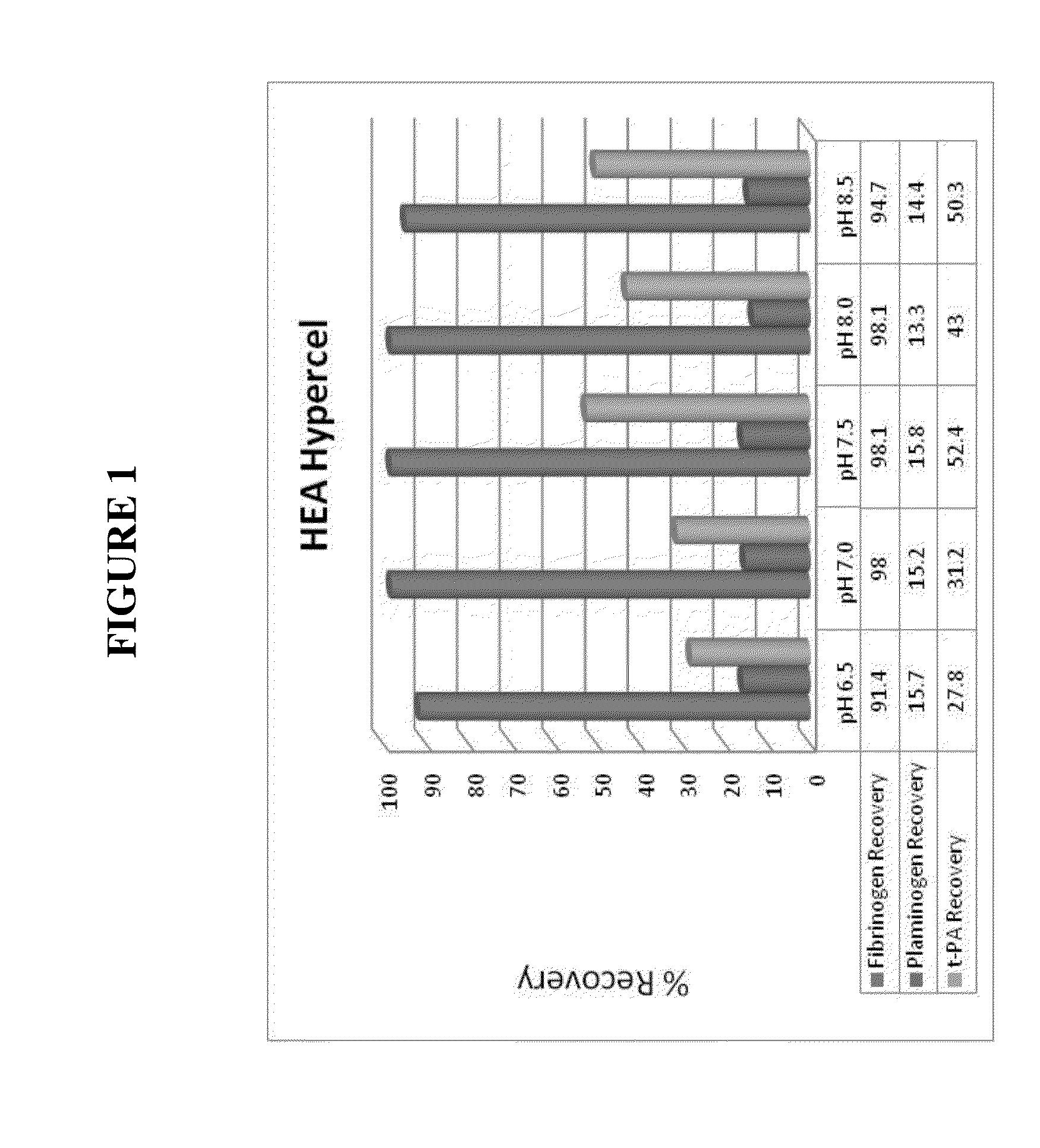
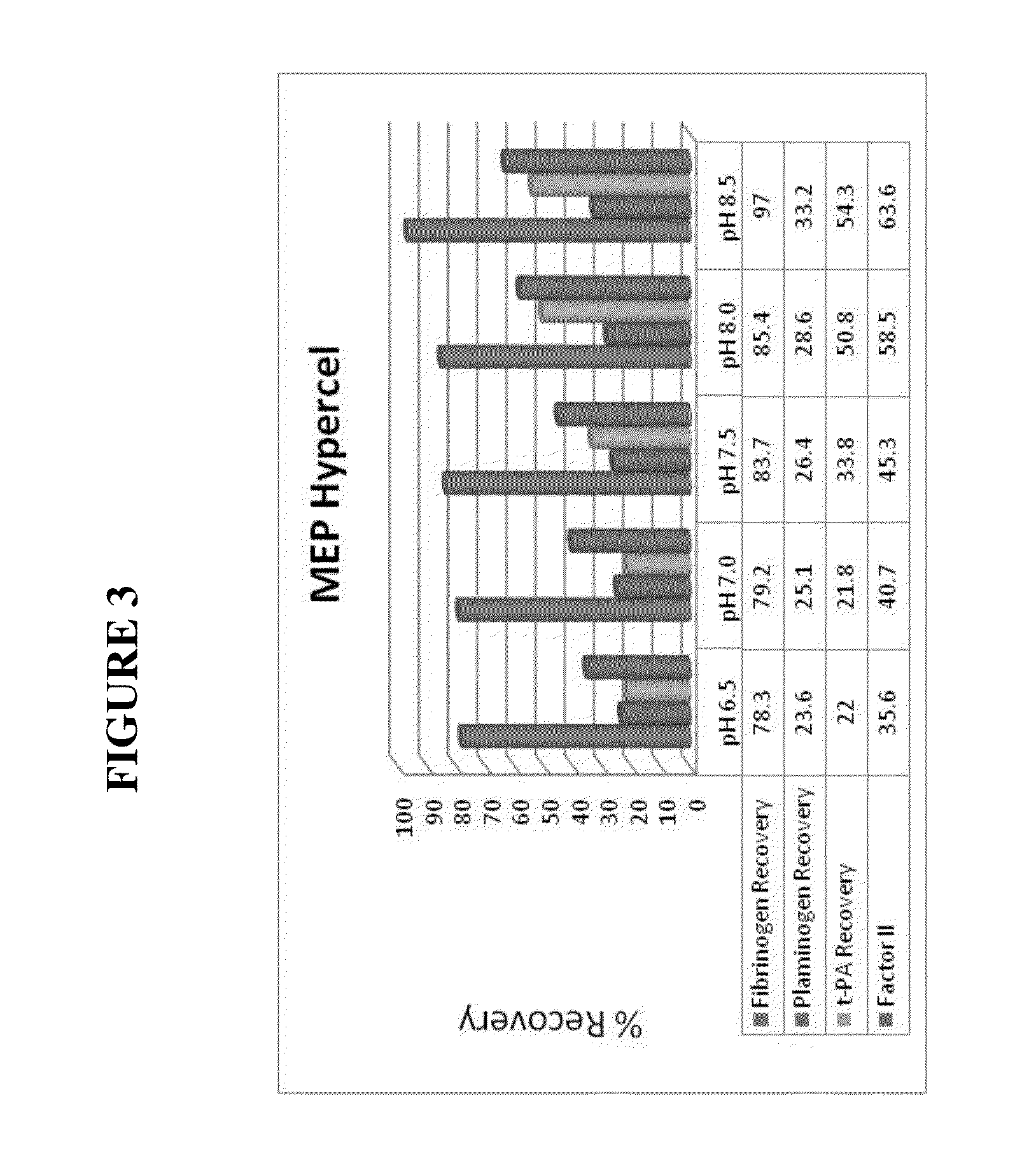
Method of purifying therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS20140154233A1Reduce concentrationLower Level RequirementsFactor VIIFibrinogenFactor VIII vWFTherapeutic protein
The present invention relates generally to a method of reducing the level of plasminogen and / or tissue plasminogen activator and / or other protease(s) in a solution comprising fibrinogen and / or Factor VIII and / or von Willebrand factor (VWF), the method comprising: (i) passing a feedstock comprising fibrinogen and / or Factor VIII and / or VWF through a hydrophobic charge-induction chromatographic resin under conditions selected such that the plasminogen and / or tissue plasminogen activator and / or other protease(s) is bound to the resin; and (ii) recovering the solution comprising fibrinogen and / or Factor VIII and / or VWF which passes through the resin; wherein the concentration of the plasminogen and / or tissue plasminogen activator and / or protease(s) in the recovered solution is reduced by at least 50% compared to the feedstock. Also provided are solutions and pharmaceutical formulations comprising the fibrinogen and / or Factor VIII and / or VWF recovered by such methods, and uses thereof.
Owner:CSL BEHRING GMBH
Recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator, and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN103159860AHigh expressionImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgeryHalf-lifeTissues types
The invention discloses a recombinant TNK-tPA-Fc fusion protein, and a preparation method and application thereof. The protein orderly contains human TNK-tPA, a flexible peptide joint and human IgG natural or variant Fc. The fusion protein has invitro and invivo biological activity similar to human TNK-tPA, and greatly prolonged plasma half-life.
Owner:LONGBIO PHARM (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Biomarkers useful in liver fibrosis diagnosis
InactiveUS20100136579A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMetalloproteinaseGastroenterology
Identification of urokinase-type plasminogen, matrix metalloproteinase 9, and β-2-microglobulin as novel biomarkers associated with liver fibrosis and uses thereof in diagnosing liver fibrosis.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
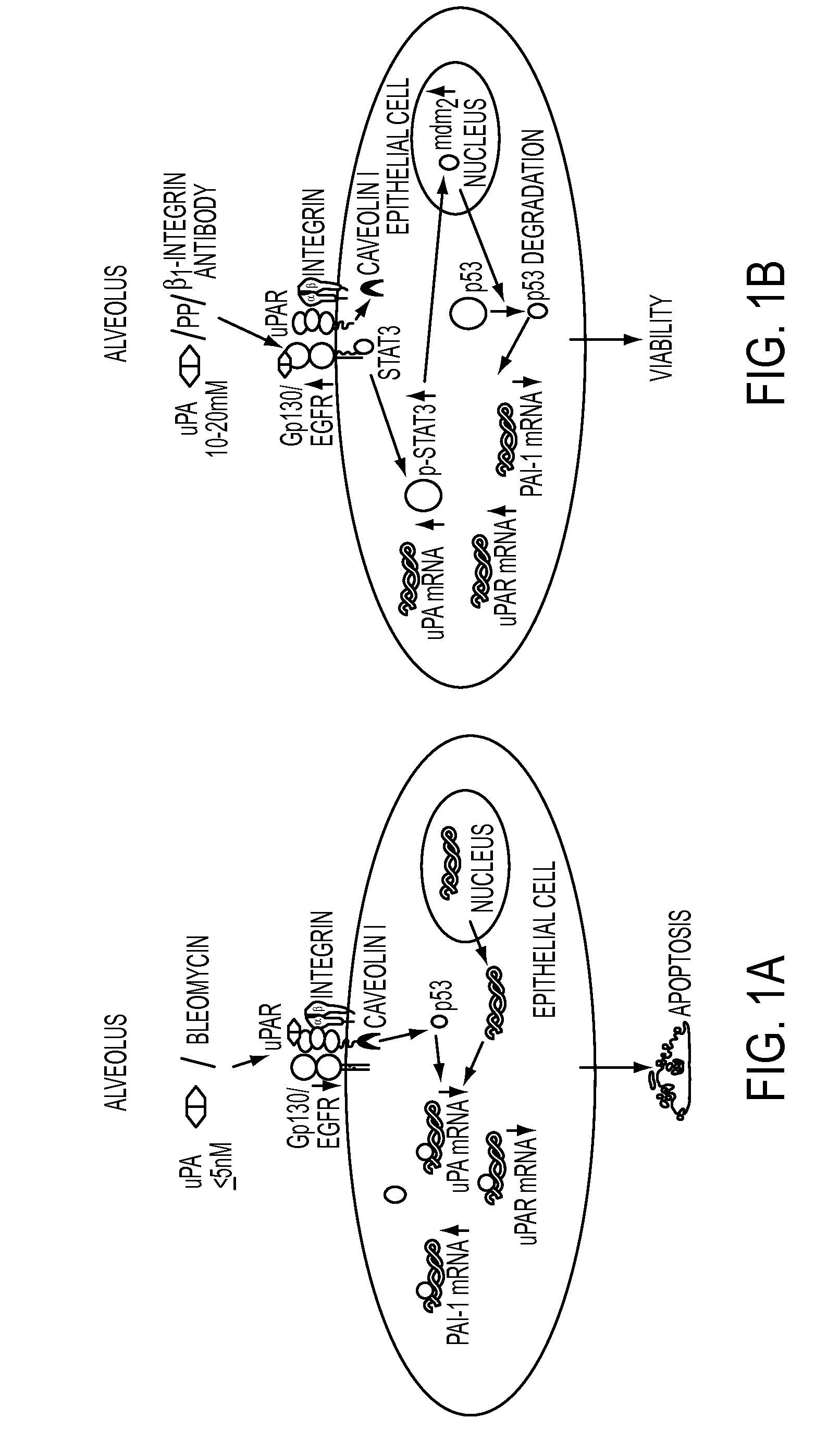
Peptide inhibition of lung epithelial apoptosis and pulmonary fibrosis
ActiveUS8697840B2High expressionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsZymogenReceptor
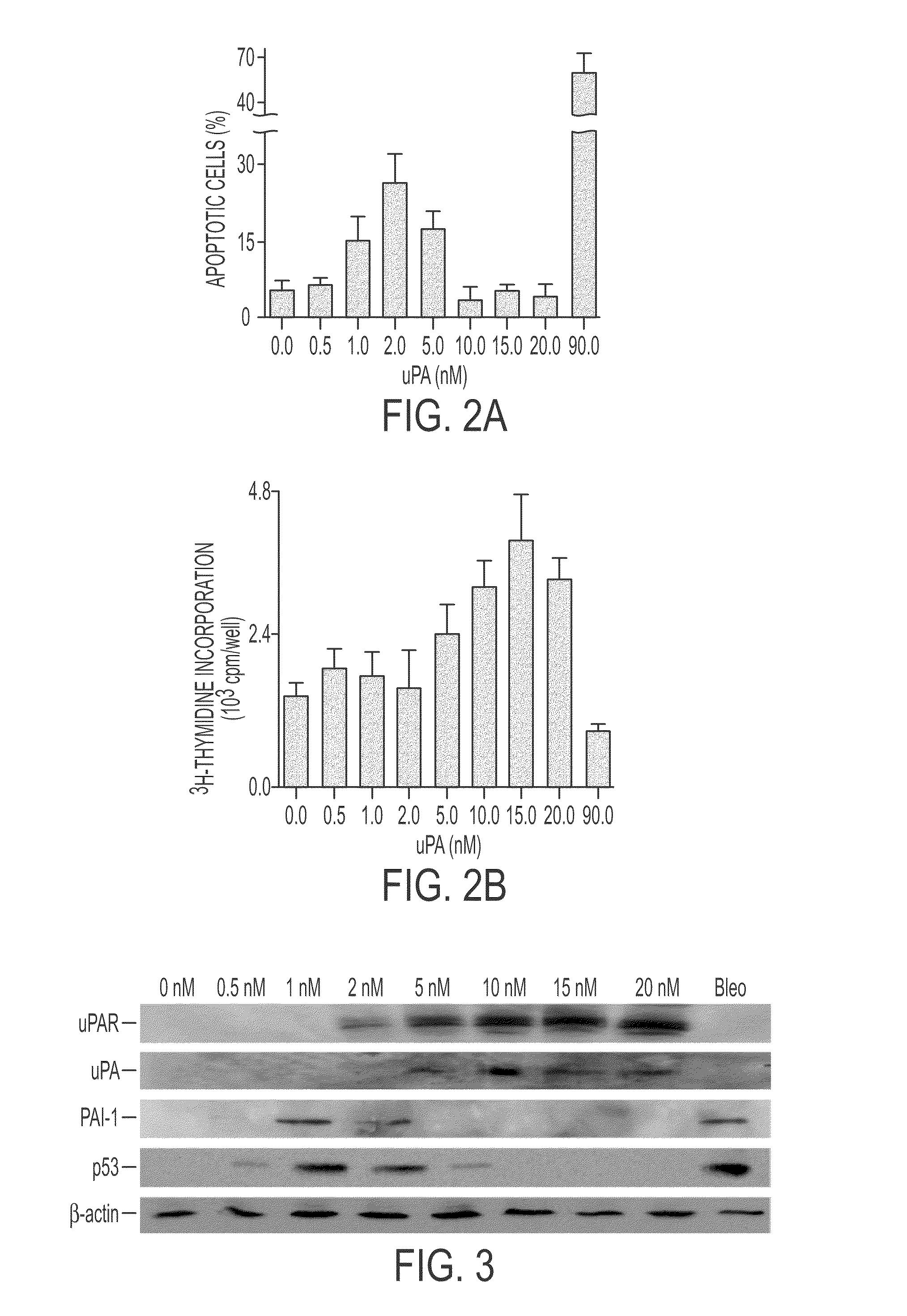
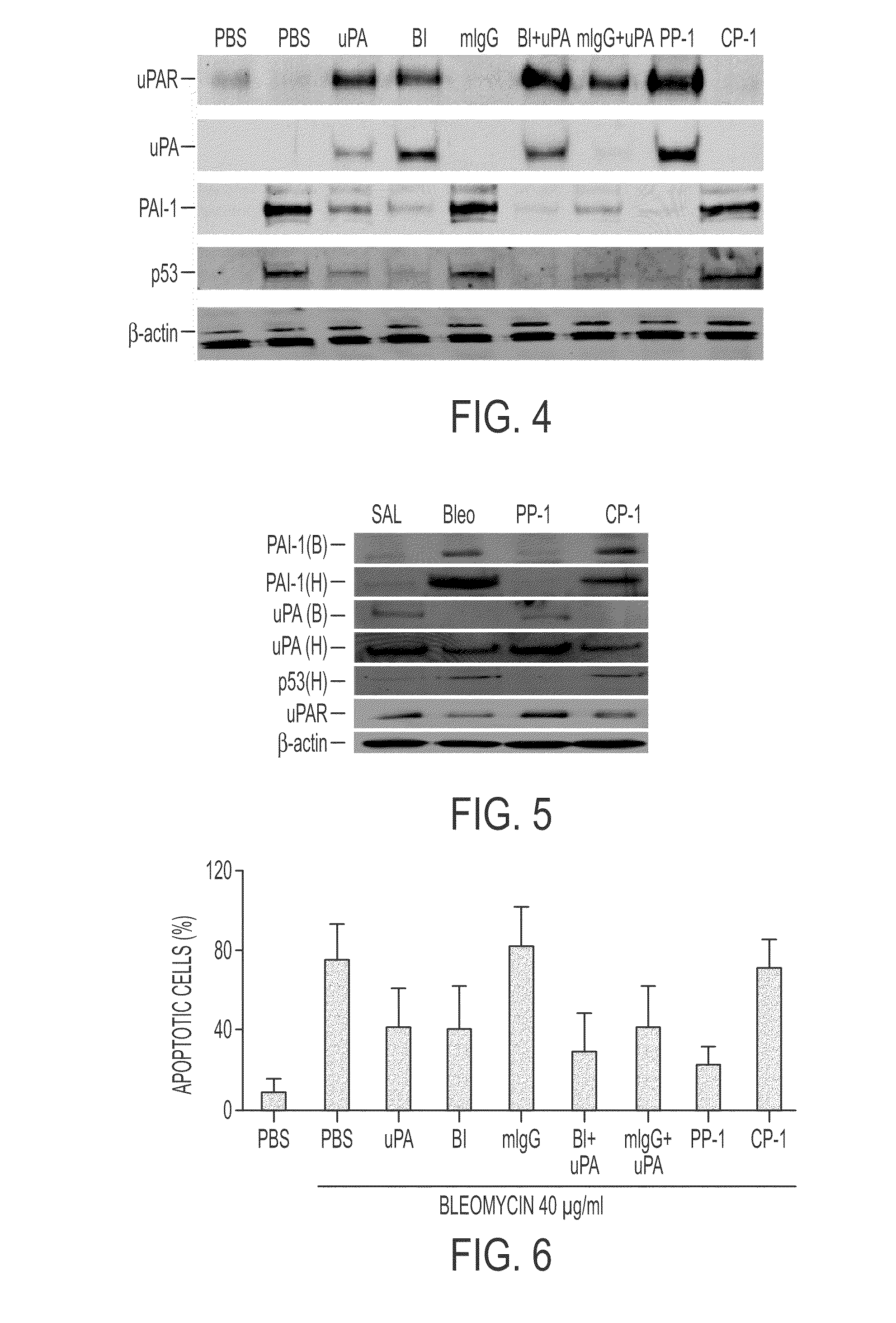
During lung injury, p53 expression increases, inducing plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) while inhibiting expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and its receptor (uPAR), resulting in apoptosis of lung epithelial cells (LECs). In the bleomycin lung injury model, p53 and PAI-1 are induced while uPA and uPAR are inhibited. A 20 residue peptide DGIWKASFTTFTVTKYWFYR termed PP-1 (the Cav-1 scaffolding domain) or peptide NYHYLESSMTALYTLGH, termed PP-2, protected LECs from bleomycin-induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo and prevented subsequent pulmonary fibrosis by attenuating lung epitheilial damage. Pharmaceutical compositions, peptide multimers and deliverable polypeptides comprising the above peptides are dislcosed. The peptides and functional variants, peptide multimers, cell-targeted polyepeptides and pharmaceutical compositions are used in methods for inhibiting apoptosis of injured or damaged lung epithelial cells and for treating acute lung injury and consequent pulmonary fibrosis.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for preventing and treating lipid metabolism disorders and related diseases thereof
InactiveUS20190328850A1Reduce riskLow-density lipoprotein levelPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseLipid Metabolism Disorder
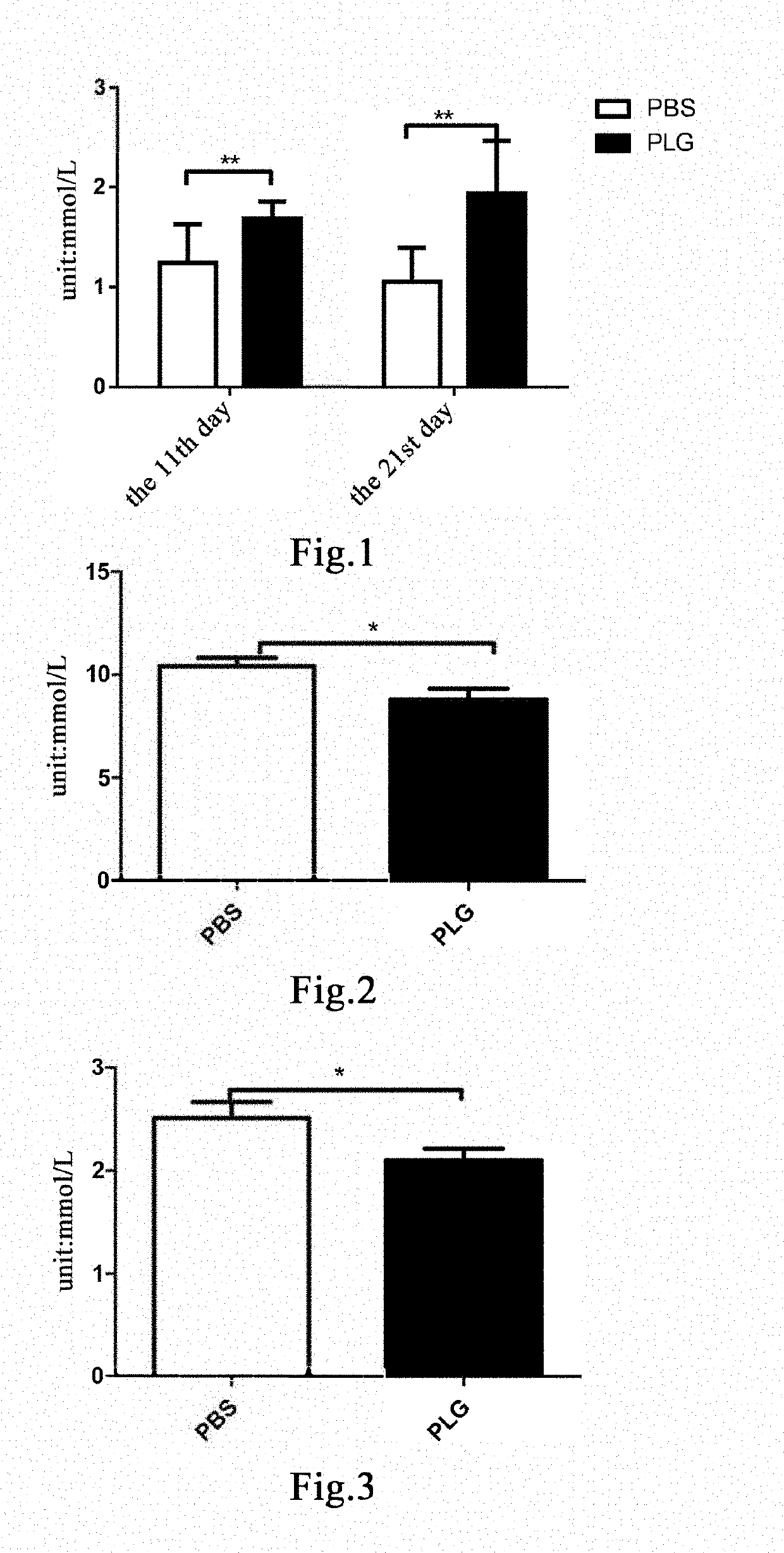
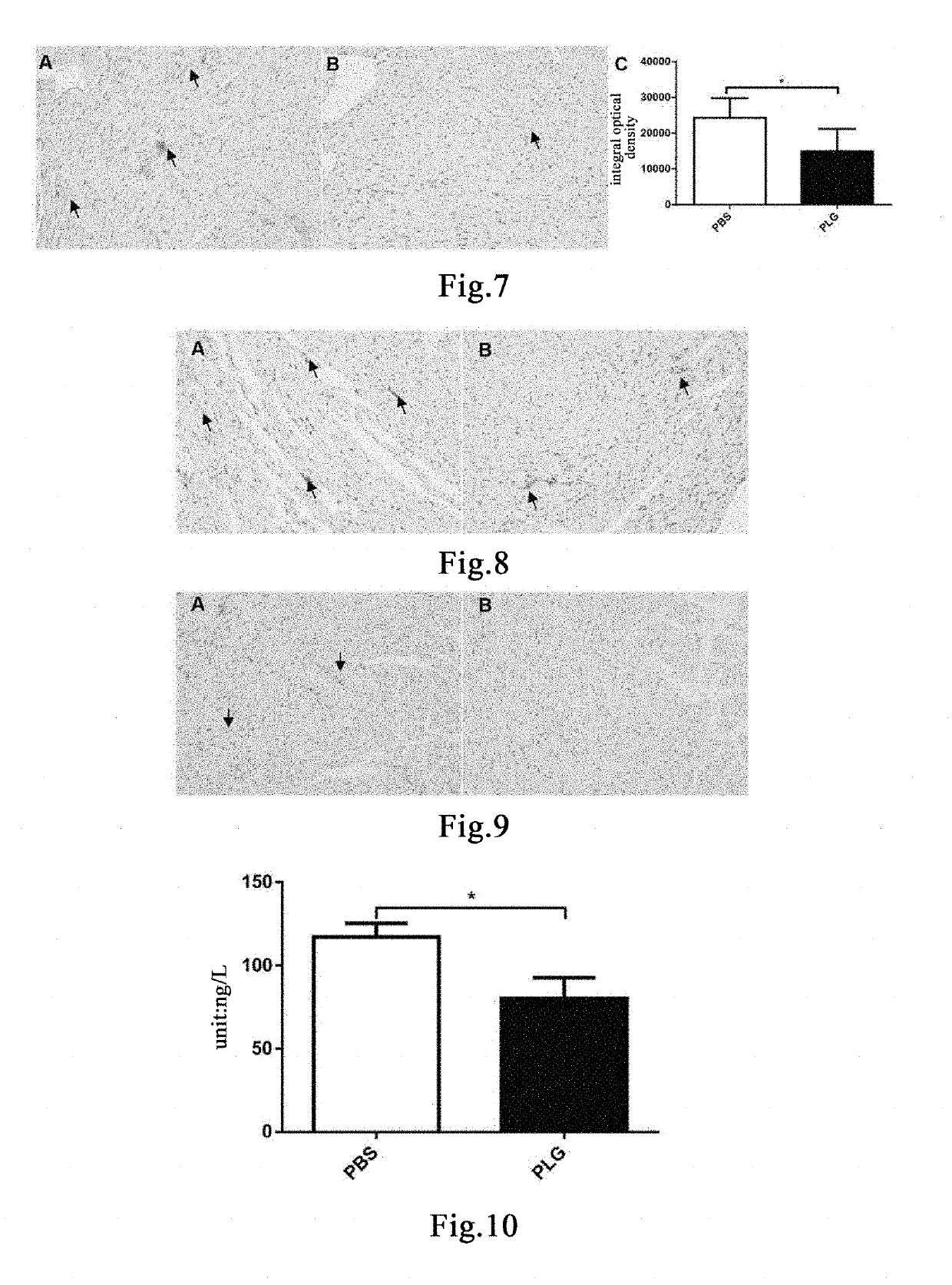
The present invention relates to a method for preventing and / or treating a fat metabolism disorder and its related conditions, comprising administering an effective amount of plasminogen to a subject susceptible to or suffering from a fat metabolism disorder and its related conditions, to reduce an abnormal fat deposition at various sites of the body, thereby achieving the purpose of preventing and / or treating a fat metabolism disorder and its related conditions or complications.
Owner:TALENGEN INTERNATIONAL LIMITED
Activation of Recombinant Diphtheria Toxin Fusion Proteins by Specific Proteases Highly Expressed on the Surface of Tumor Cells
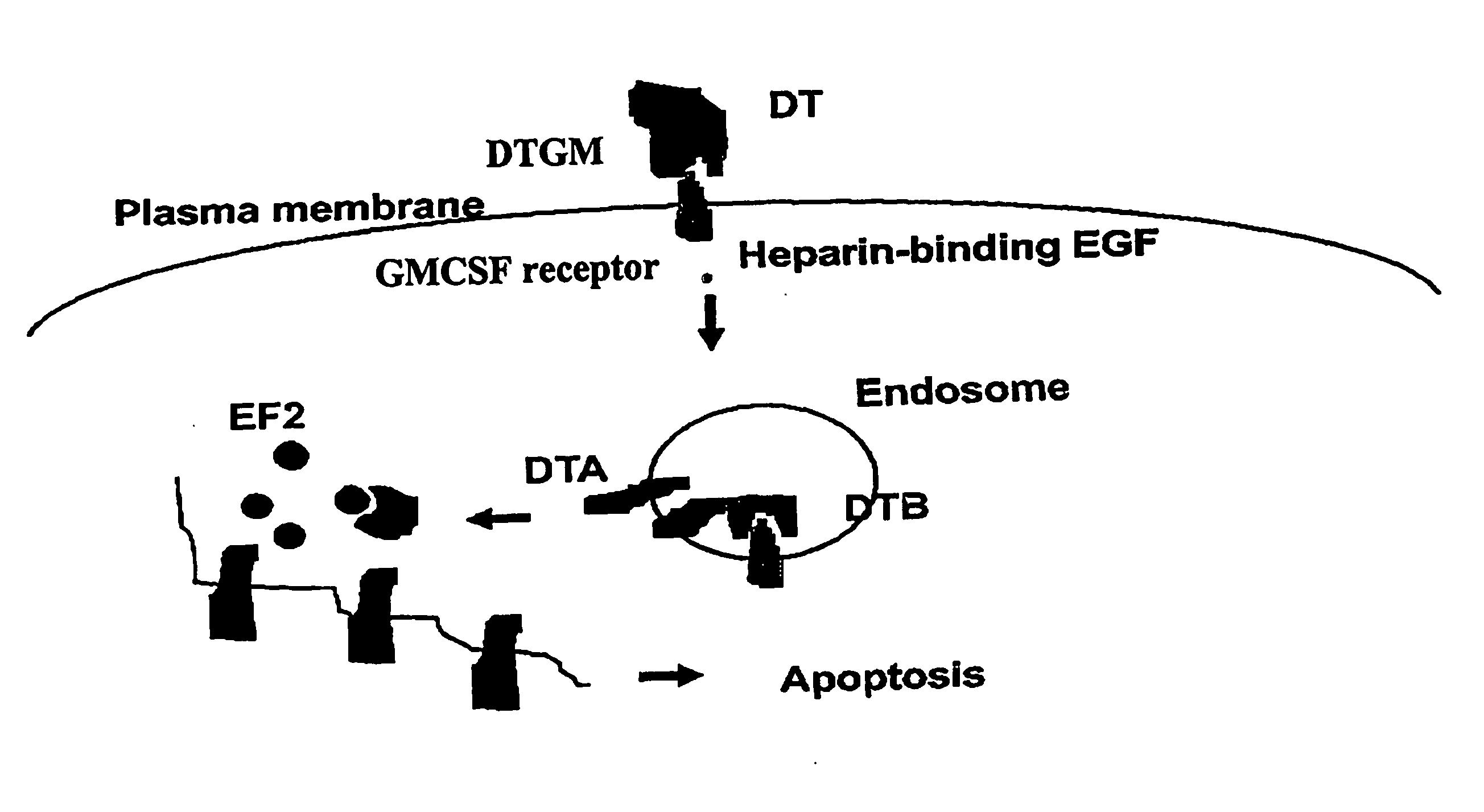
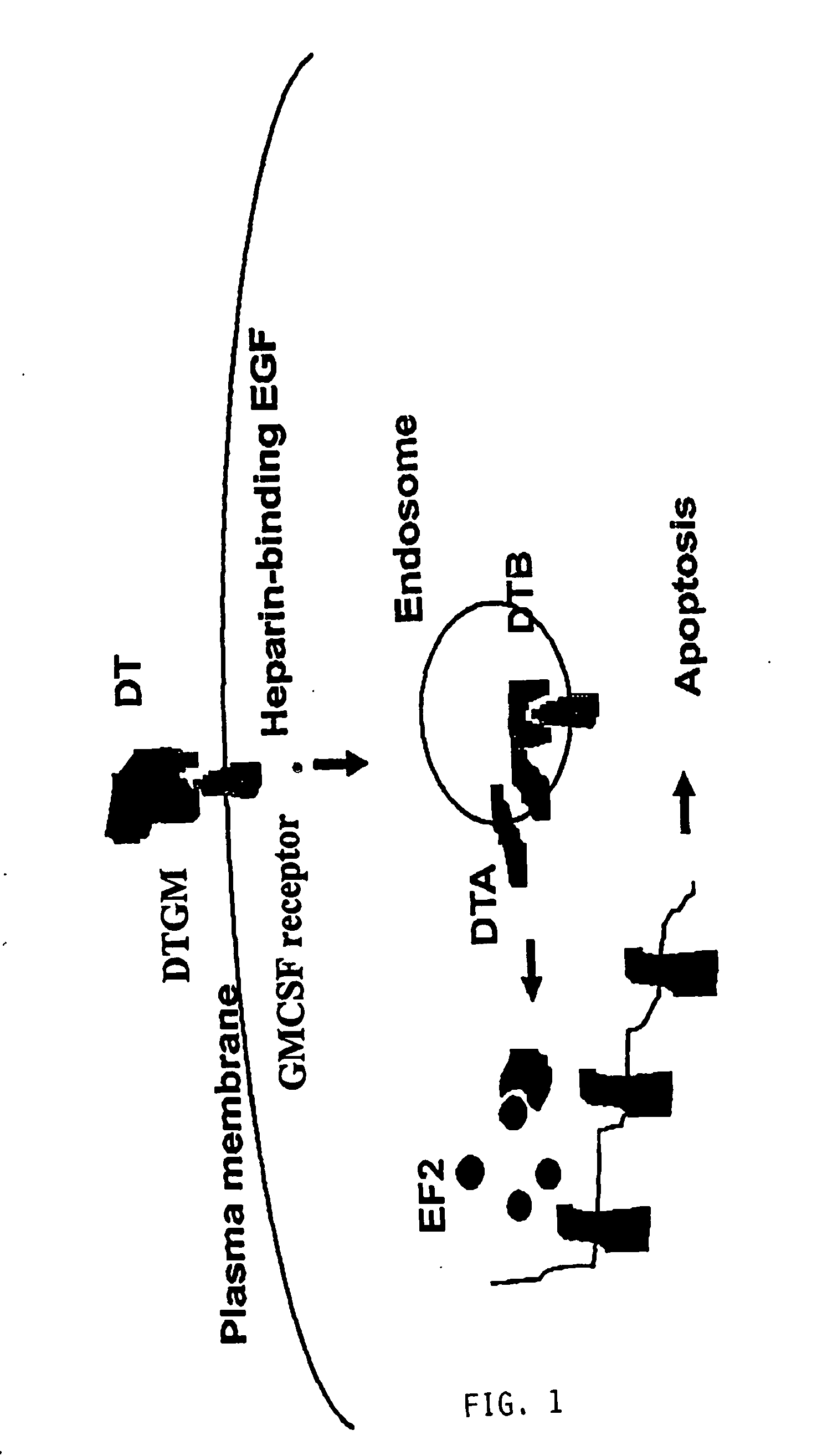
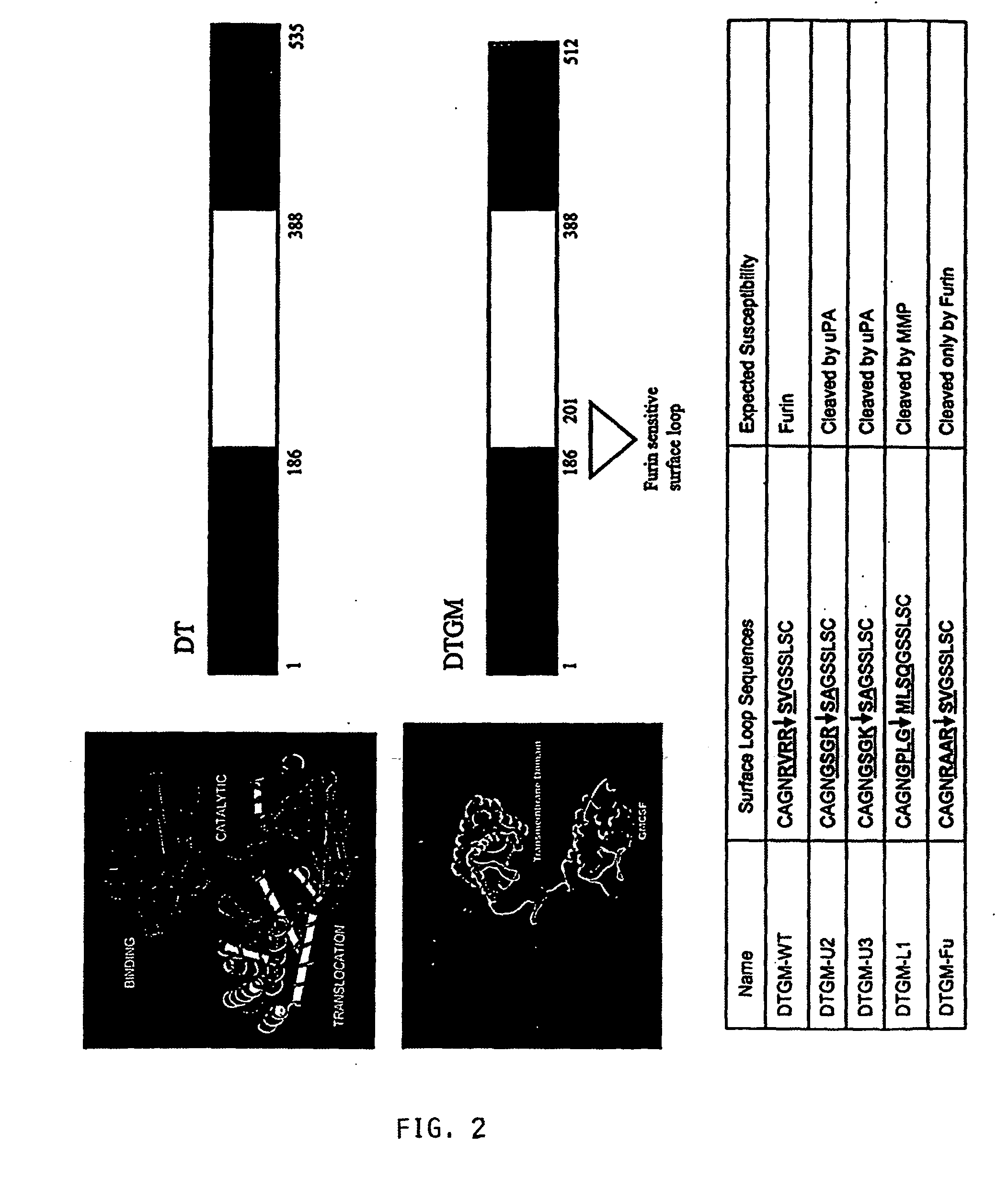
The present invention provides compositions and methods for inhibiting abnormal cell growth. In particular, the invention provides nucleic acids encoding Diphtheria toxin fusion proteins comprising residues 1-388 of Diphtheria toxin, wherein the native furin cleavage site has been substituted for a matrix metalloproteinase or plasminogen activator cleavage site, and a heterologous polypeptide and the polypeptides encoded by such nucleic acids. In addition, the invention provides methods of treating cancer by administering such polypeptides.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Producing new fibrinolysin from rhizopchin
The present invention relates to the extraction of fibrinolysin as new type of thromboliytic medicine from rhizopchin. The fibrinolysin has molecular weight 30.5 KD, isoelectric point 8.5, and double effects of directly dissolving thrombus and activating human plasminogen. The production process includes three stages, of culture of rhizopchin including slant culture, seed culture and fermentation culture; and separating and purifying fermented liquid to obtain fibrinolysin. The product is safe, non-toxic and cheap and the production process uses cheap agricultural side product as main material and is a liquid fermentation process. The purification process includes microfiltering to eliminate thallus, decolorizing with ion exchange resin, salting out, ultrafiltering to eliminate salt and hybrid protein and ion exchanging to purify. The present invention has short technological process, low cost and high production efficiency.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibitors and methods of use thereof
The invention relates to plasminogen activator-1 (PAI-1) inhibitor compounds and uses thereof in the treatment of any disease or disorder associated with elevated PAI-1. The invention includes, but is not limited to, the use of such compounds to prevent or reduce thrombosis and fibrosis, to promote thrombolysis, and to modulate lipid metabolism and treat diseases or disorders associated with elevated PAI-1, cholesterol, or lipid levels.
Owner:EASTERN MICHIGAN UNIVERSITY +1
Ligands binding the complex of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uppa) and its receptor (upar) that inhibit downstream upar interactions: identification and use in diagnosis or therapy
Antibodies or other ligands specific for the binary uPA-uPAR complexes, for ternary complexes comprising uPA-uPAR and for complexes of uPAR and proteins other than uPA such as integrins inhibit the interaction of uPA and uPAR with additional molecules with which the complexed interact. Such antibodies or other ligands are used in diagnostic and therapeutic methods, particularly against cancer.
Owner:ATTENUON LLC
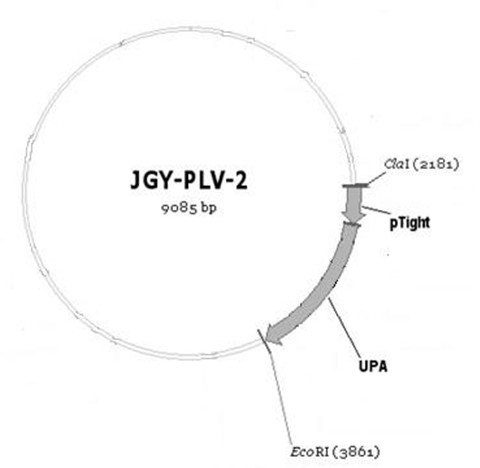
PAlb-uPA slow virus vector and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102628063AReduce mortalityLow response backgroundFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionUrokinase Plasminogen ActivatorHepatic inflammation
The invention discloses a PAlb-uPA slow virus vector, which contains an albumin promoter PAlb, a urokinase plasminogen activator gene uPA, a tetracycline trans-acting factor rtTA / rtTA2S-M2 of the albumin promoter PAlb and a PTight promoter for regulating and controlling the urokinase plasminogen activator gene uPA. The invention further discloses a preparation method and an application of the PAlb-uPA slow virus vector. The preparation method is simple; the obtained slow virus vector can be used for preparing a urokinase fibrinolysis protease mouse liver injury model; and an effective research platform is provided for the clinical research of a human hepatitis virus infection mechanism and an anti-virus medicament.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Human blood-derived products having decreased fibrinolytic activity and uses thereof in hemostatic disorders
ActiveUS20190192564A1Reduced fibrinolytic activityAvoid delayPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsHemostatic DisordersPlasmin
The present invention provides therapeutic products with decreased fibrinolytic activity of t-PA-deficient and / or plasminogen-deficient blood products, as well as compositions, kits and methods using the same in treating bleeding associated with hereditary or acquired bleeding disorders. The invention further provides extracorporeal apparatus for blood or blood products Plasmapheresis aimed to prevent or treat bleeding disorders.
Owner:PLAS FREE LTD
Mimic peptide of human plasminogen activator and preparation thereof
InactiveCN1680430AWith anti-thrombolytic functionLow immunogenicityMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesSurface displayProtein target
Human plasminogen activator analog peptide and its production are disclosed. It is based on protein molecule interaction critical theory and uses solvent of streptokinase and glycosylzyme as mechanism. It is carried out by taking human plasminogen as target protein by surface displaying technology of phagicin random polypeptide base, biological elutriating, screening, obtaining polypeptide sequence with mu Pg high affinity, and solid-phase synthesizing the analog peptide. Its advantages include small molecular weight, low immunity, simple process and easy control of product output, purity and activity. It can be used to prepare oral preparation and prevent thrombogenesis.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Modified plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 molecule and methods based thereon
InactiveUS20100184667A1Reduce cancer cell growthInhibit primaryPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderUrokinase Plasminogen ActivatorVitronectin
The present invention relates to a modified plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) molecule that displays CN an increased in vivo half-life of the active form of PAI-1, but is deficient in one or more functional activities as compared to the wild-type PAI-1 protein. The modified PAI-1 molecule that displays an increased half-life further displays at least one of the following funtional characteristics: (i) decreased binding activity to at least one of the following molecules: urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA), tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and vitronectin (Vn); and (ii) decreased specific activity against at least one of the following molecules: uPA, tPA and Vn. The invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising modified PAI-1 molecules and methods of using these pharmaceutical compositions for treatment.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
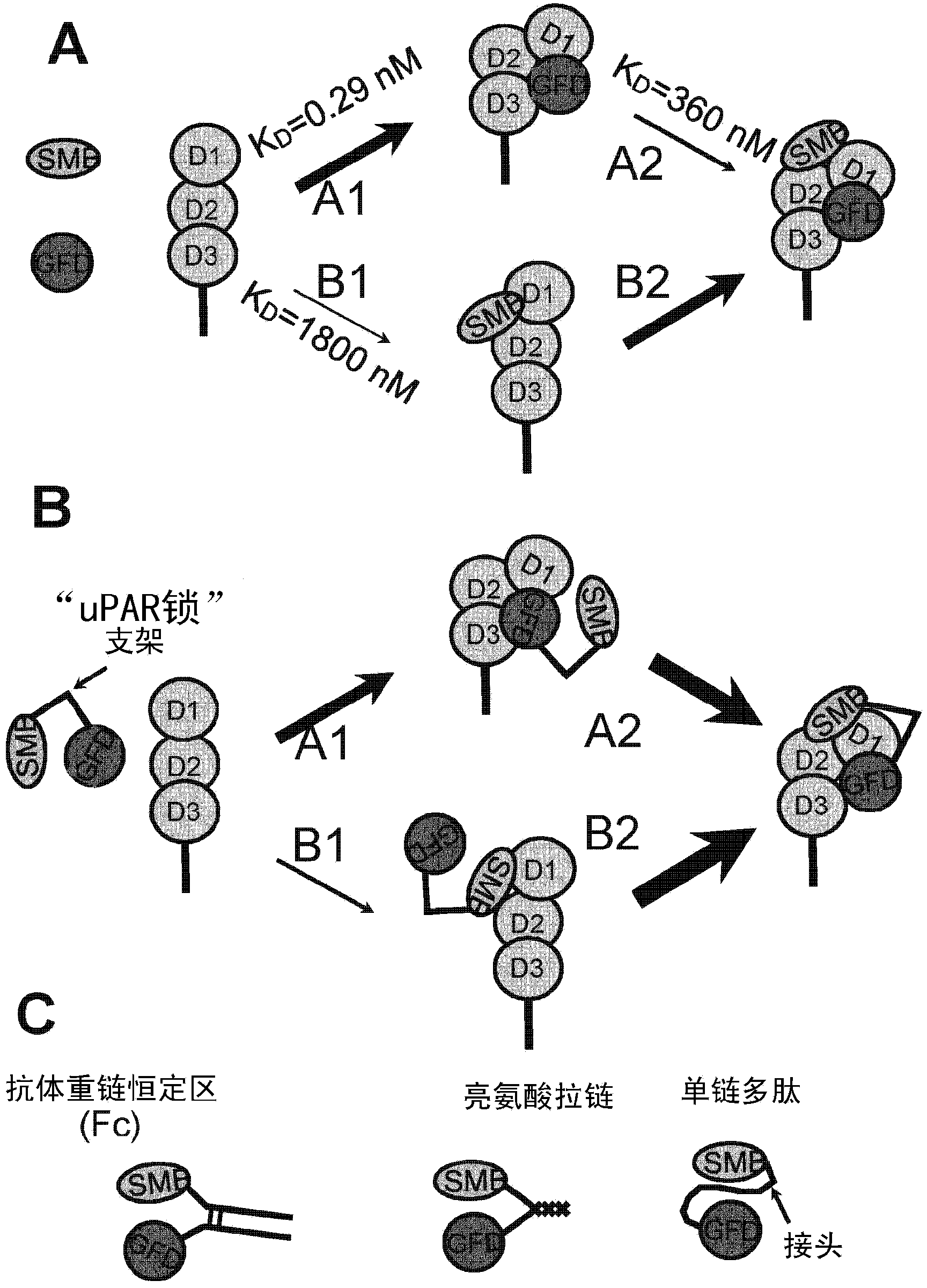
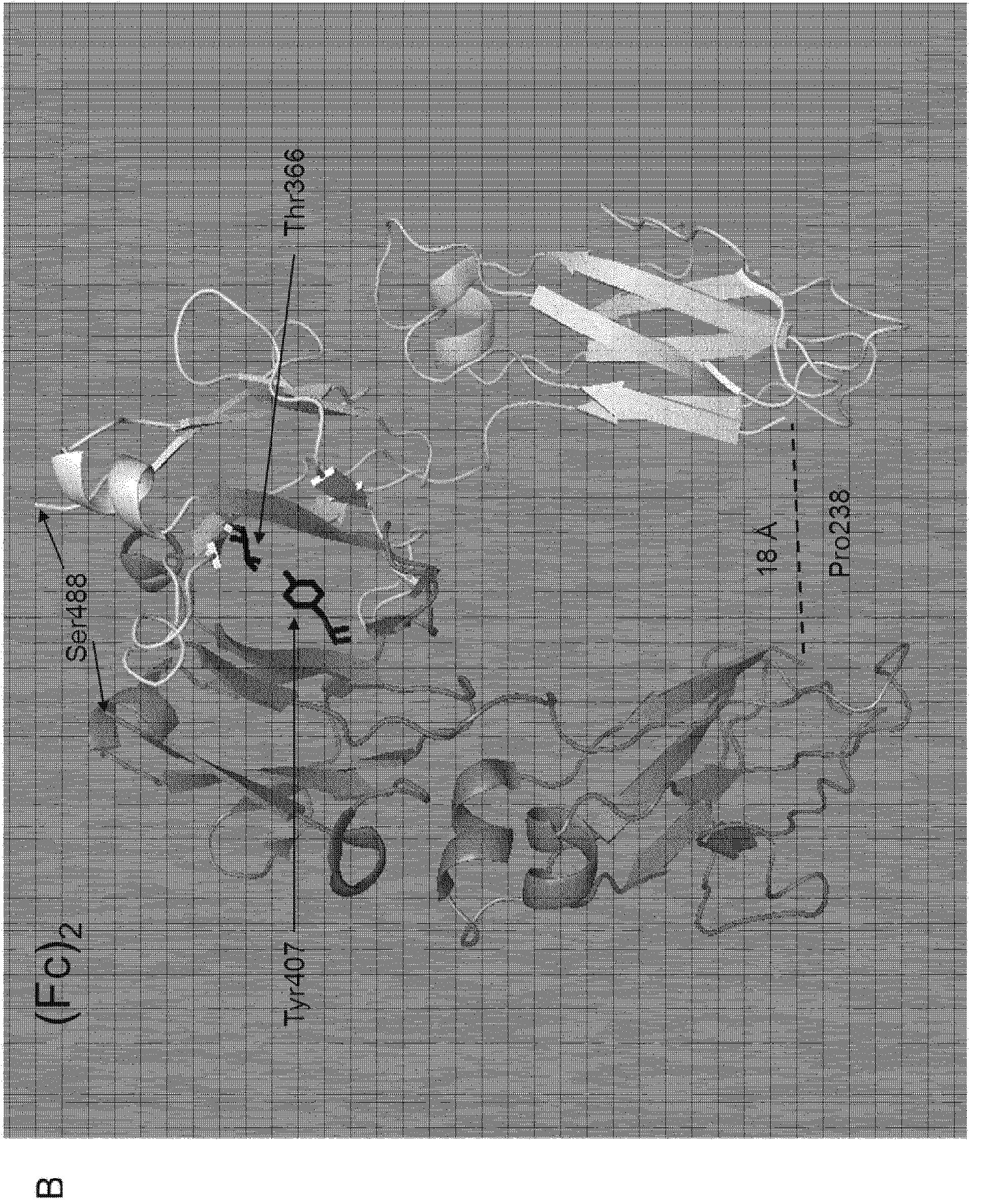
UPAR-antagonists and uses thereof
InactiveCN103391787AExcellent drug propertiesVarious clinical applicationsConnective tissue peptidesHydrolasesCell-Extracellular MatrixVitronectin
The invention relates to inhibitors of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR). The generated inhibitors are bivalent uPAR-ligands containing the receptor binding domains of the extracellular protease urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and of the extracellular matrix protein vitronectin (VN), in different configurations, linked by a scaffold. The present invention also refers to the above molecules for use as a medicament, in particular for treatment of cancer, and for diagnostic purposes.
Owner:IFOM FOND INST FIRC DI ONCOLOGIA MOLECOLARE
Renaturation separation purification method of tissue plasminogen activator mutant
InactiveCN1556206AHigh yieldReduce manufacturing costPeptide preparation methodsEnzymesEscherichia coliPurification methods
A process for renaturating, separating and purifying the mutant of tissue plasminogen activator features that the imidazole and urea are used to make the tissue plasminogen activator 'Ruitipu enzyme' be correctly folded in order to have activity and make it be renaturated, separated and purified simultaneously.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Compound and method for regulating plasminogen activation and cell migration
InactiveUS20070053894A1Prevents and reduces capillary tube formationDecrease and prevents and delayPeptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsDiseaseBiological activation
The invention relates to novel regulators of plasminogen activation and their use for regulating cell migration, plasminolysis, angiogenesis, fibrinolysis, for treating cancer and thrombo-embolic diseases such as heart stroke. Furthermore, the present invention relates to novel pharmaceutical compositions form regulating cell migration, plasminolysis, angiogenesis and for treating cancer. In particular, the present invention relates to a method of regulating the activation of plasminogen comprising contacting a solution of pro-urokinase (uPA) or tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and plasminogen with melanotransferrin (p97) for a time sufficient to effect regulation thereof.
Owner:TRANSFERT PLUS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com