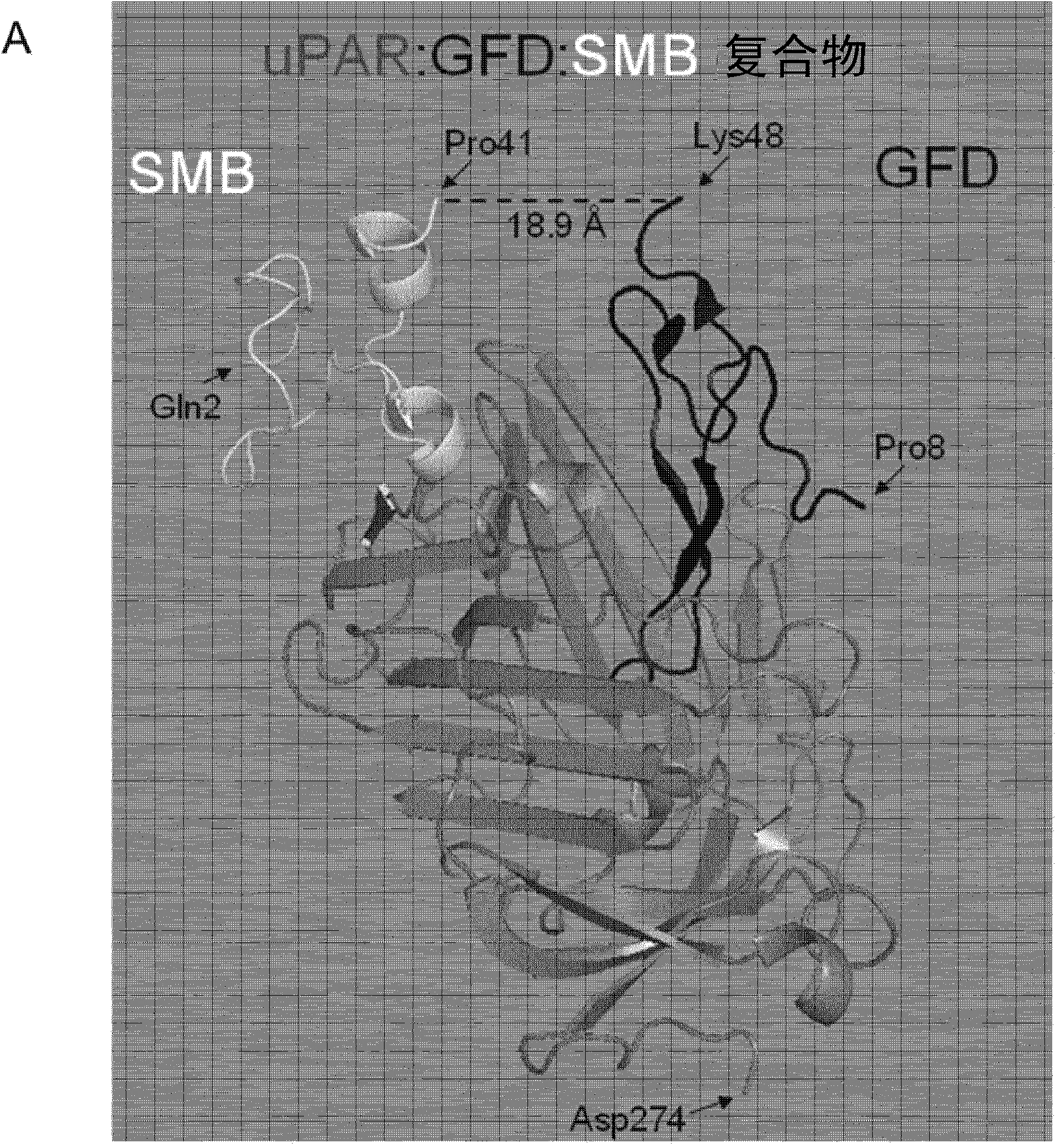UPAR-antagonists and uses thereof
A molecular and dimer technology, applied in the field of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor inhibitors, can solve the problems that the importance of interaction is not discussed, and achieve the effect of excellent drug properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] The invention will now be described by way of a non-limiting example with reference to the following figures.
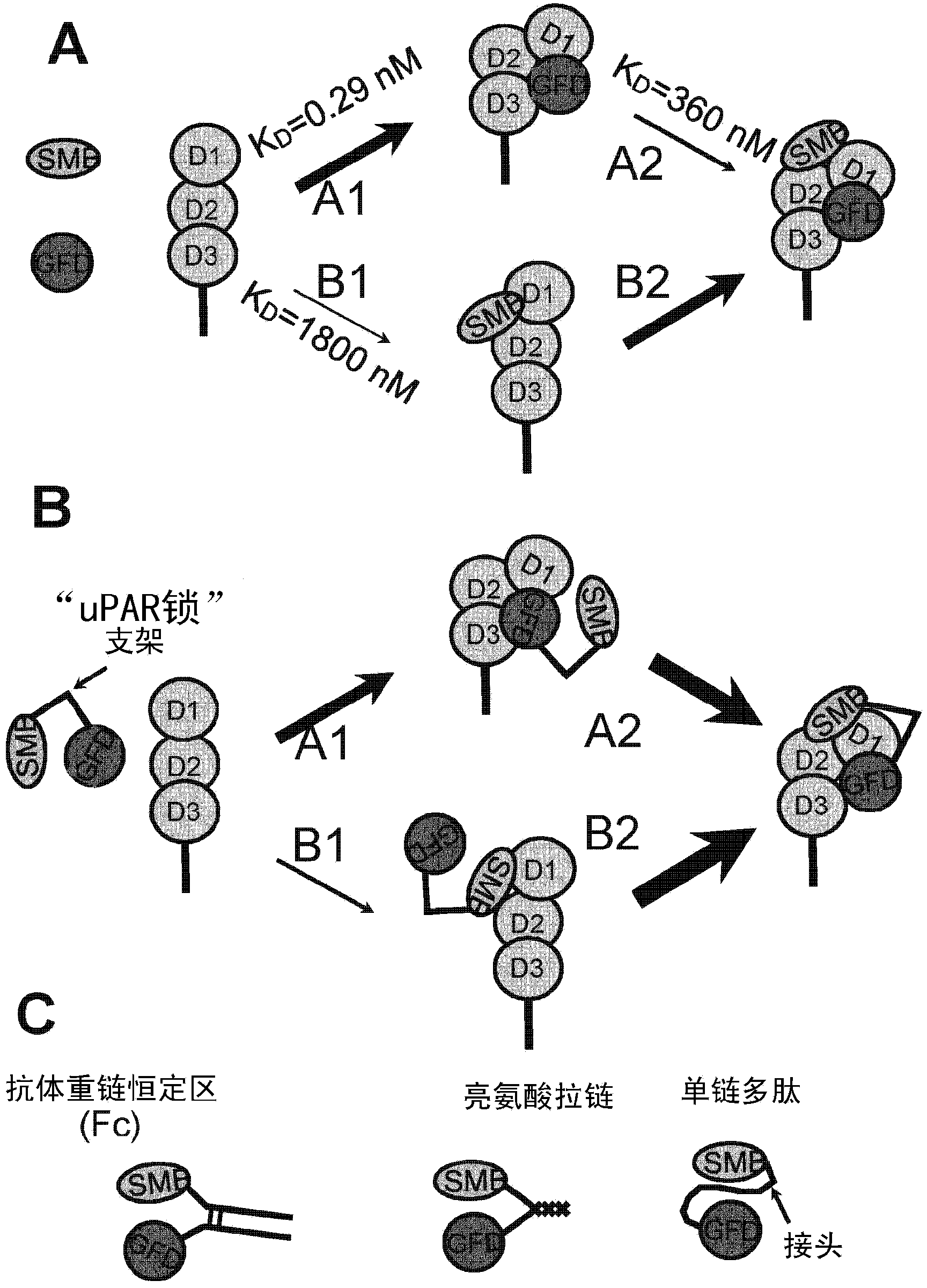
[0045] figure 1 .Sketch showing the forced-proximity concept of the uPAR lock.
[0046] The function of uPAR in extracellular proteolysis mediated by uPA binding can be competitively inhibited by receptor binding to the growth factor-like domain (GFD) of uPA. The somatomodulin B domain (SMB) of VN can be exploited to competitively inhibit the function of uPAR in signal transduction mediated by VN binding. D1, D2 and D3 below are uPAR domains.
[0047] (A) GFD and SMB domains as competitive uPAR antagonists
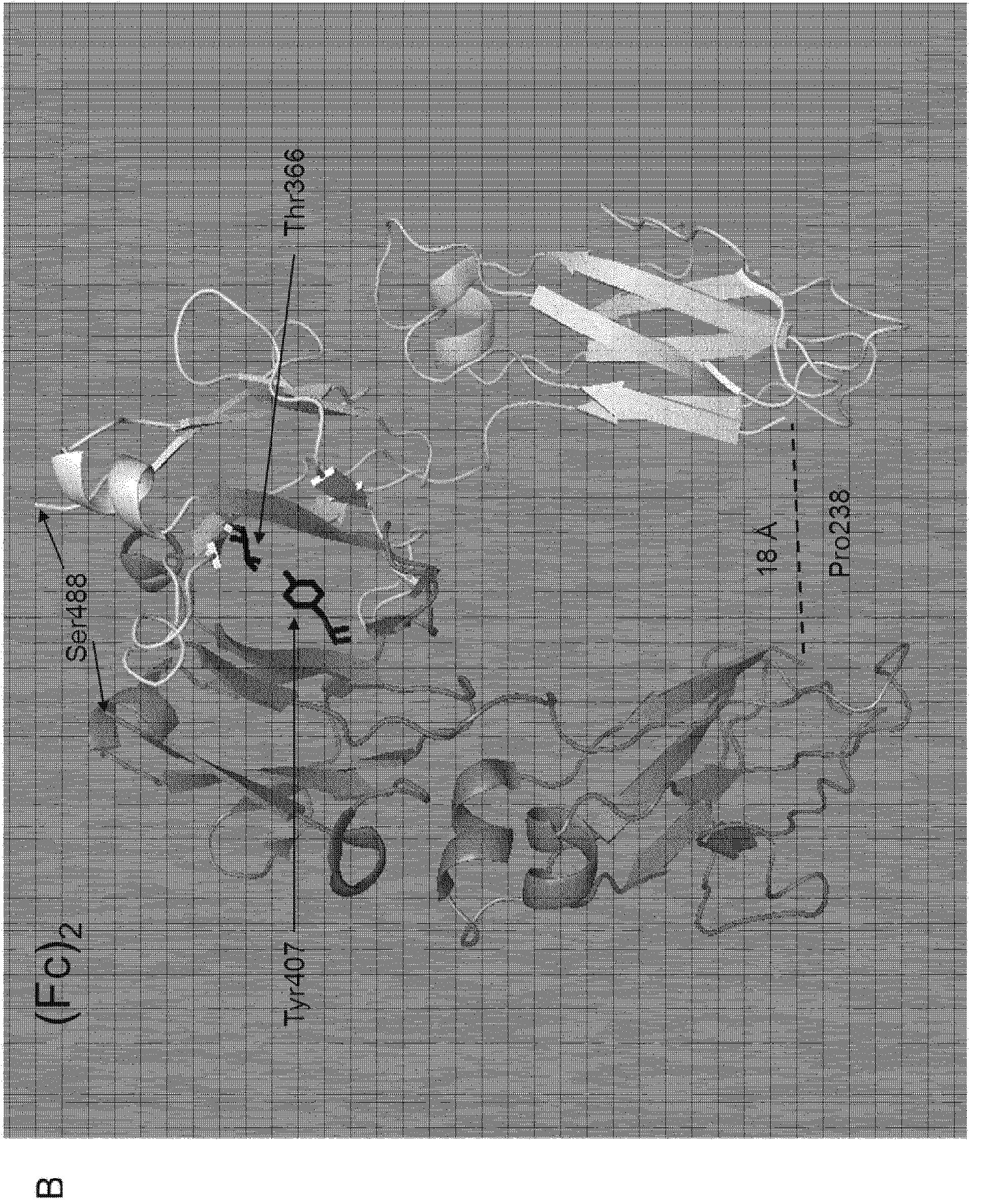
[0048] Blocking uPAR function using a mixture of isolated GFD and SMB requires two sequential first-order intermolecular binding reactions (1 and 2), and two pathways can be used depending on whether GFD or SMB first binds to the receptor (A and B). The overall stability of the ternary uPAR:GFD:SMB complex and thus receptor inhibition is limited by t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com