Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
464 results about "Stimulation Parameter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
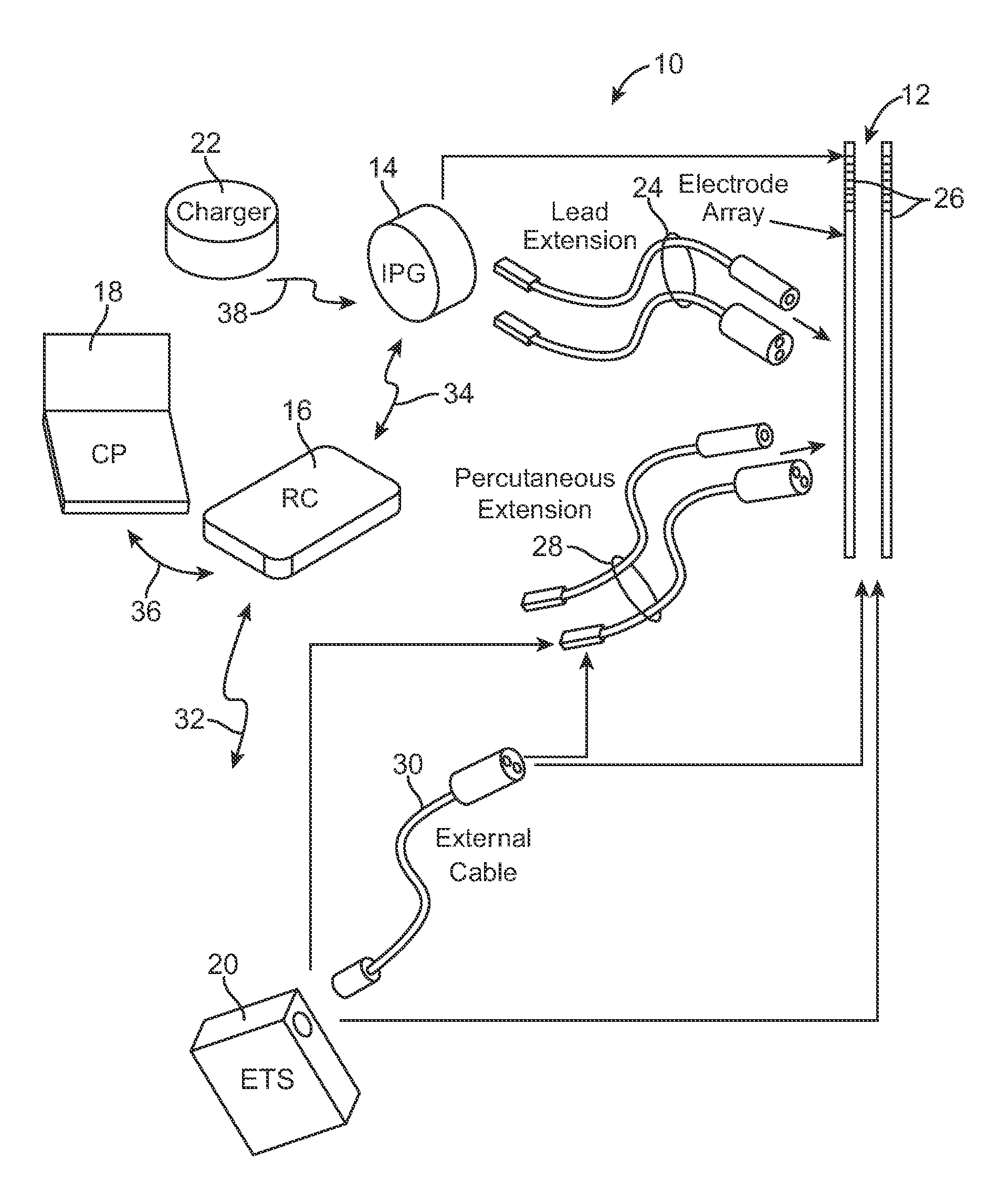
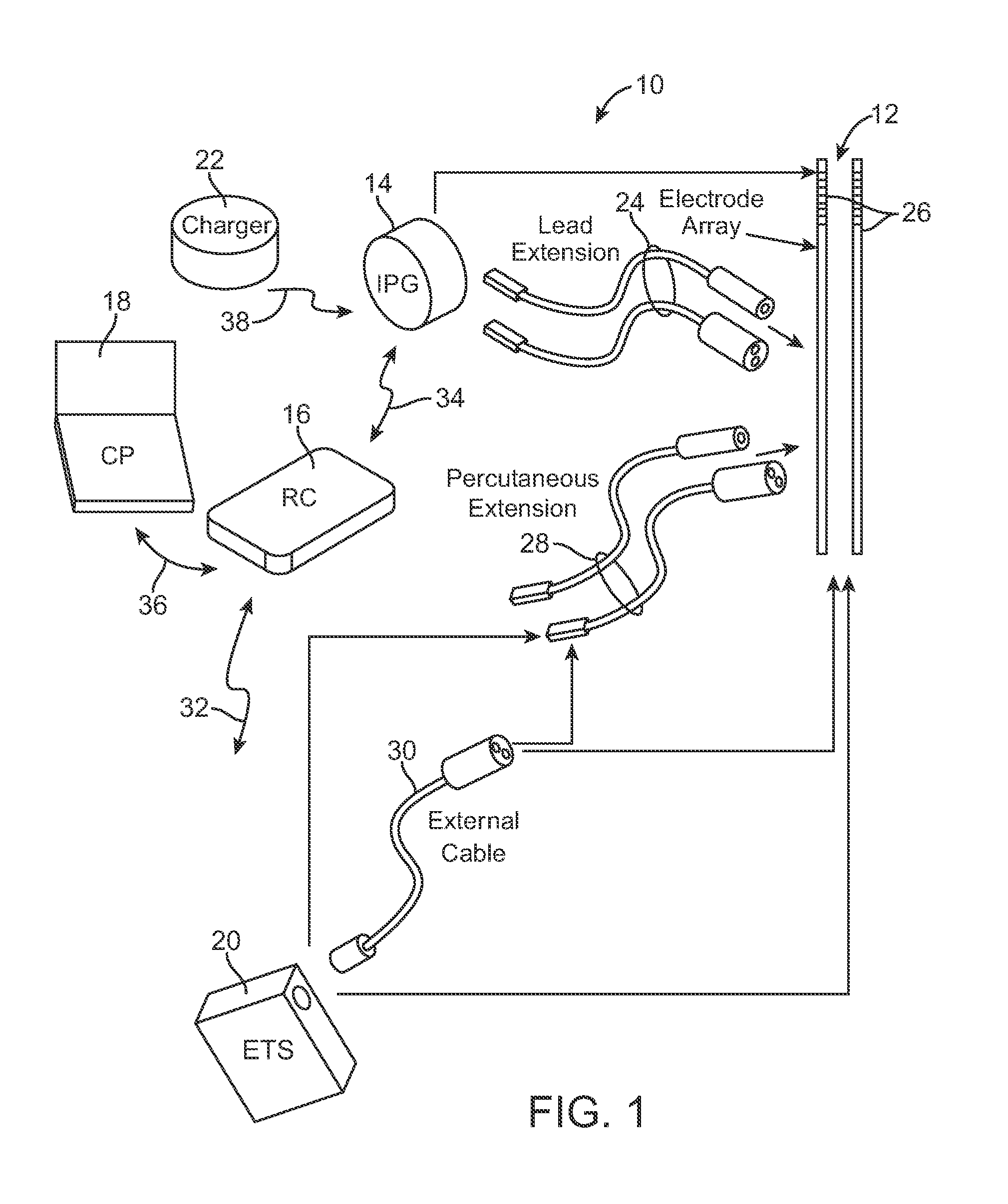
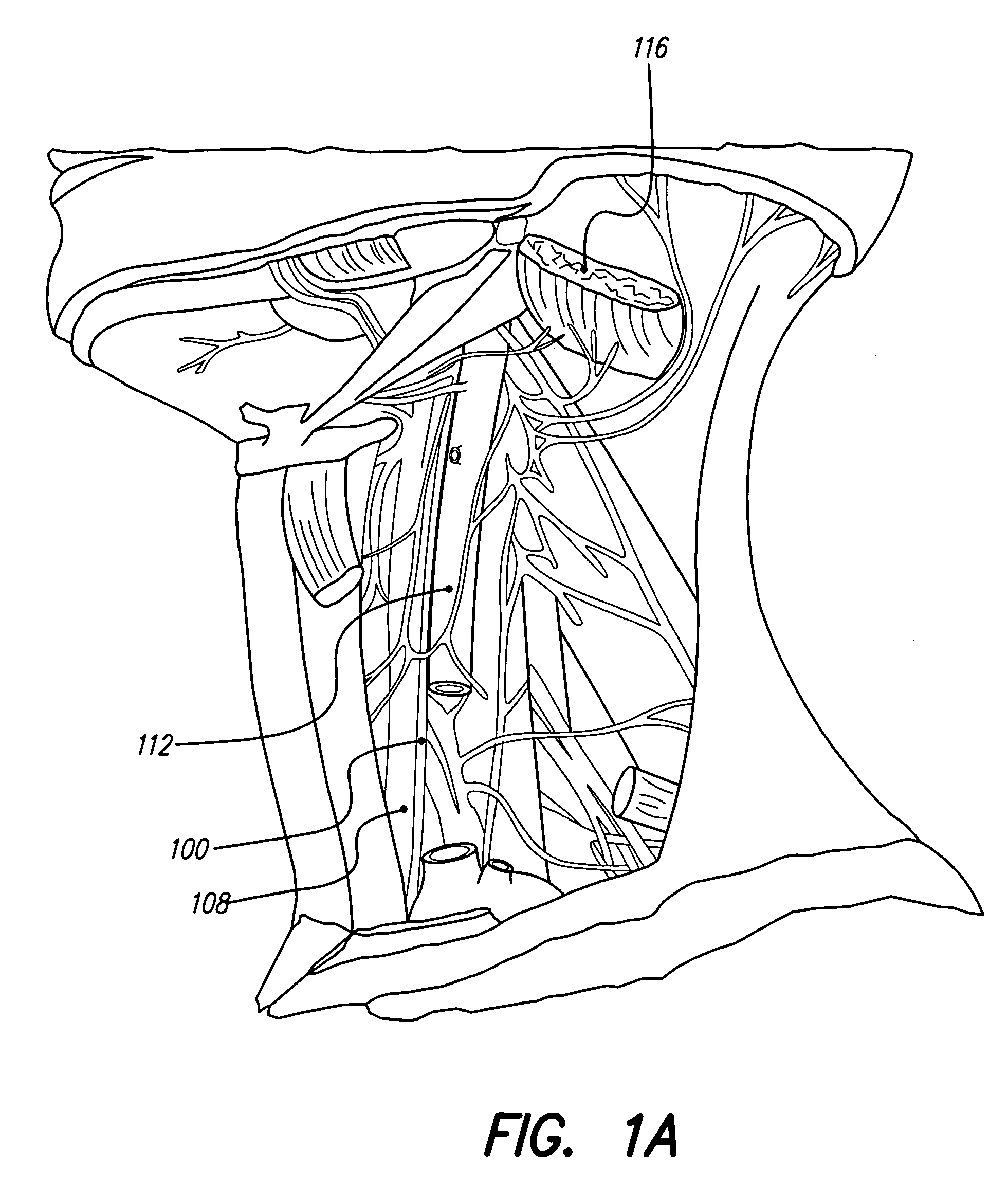
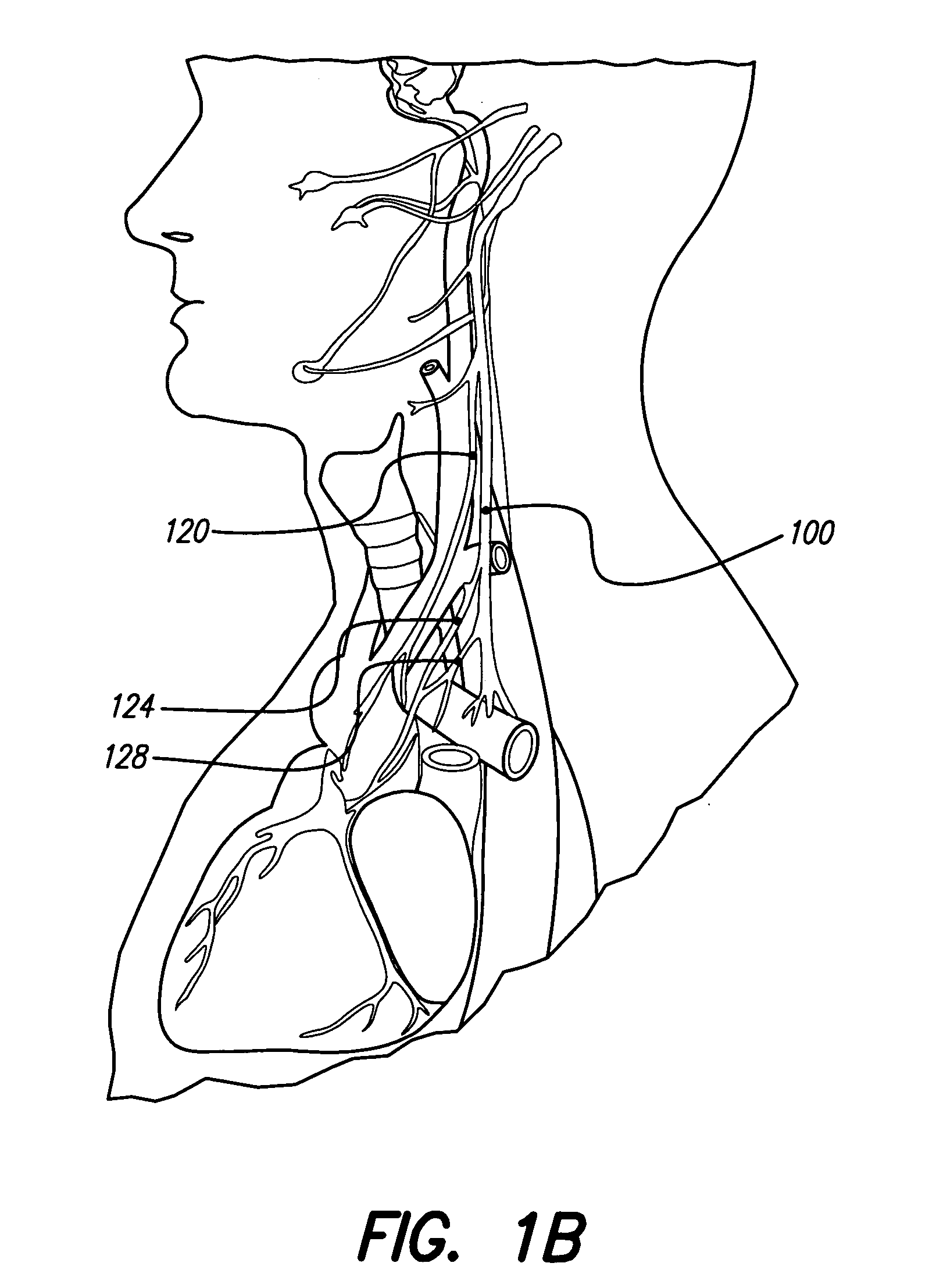
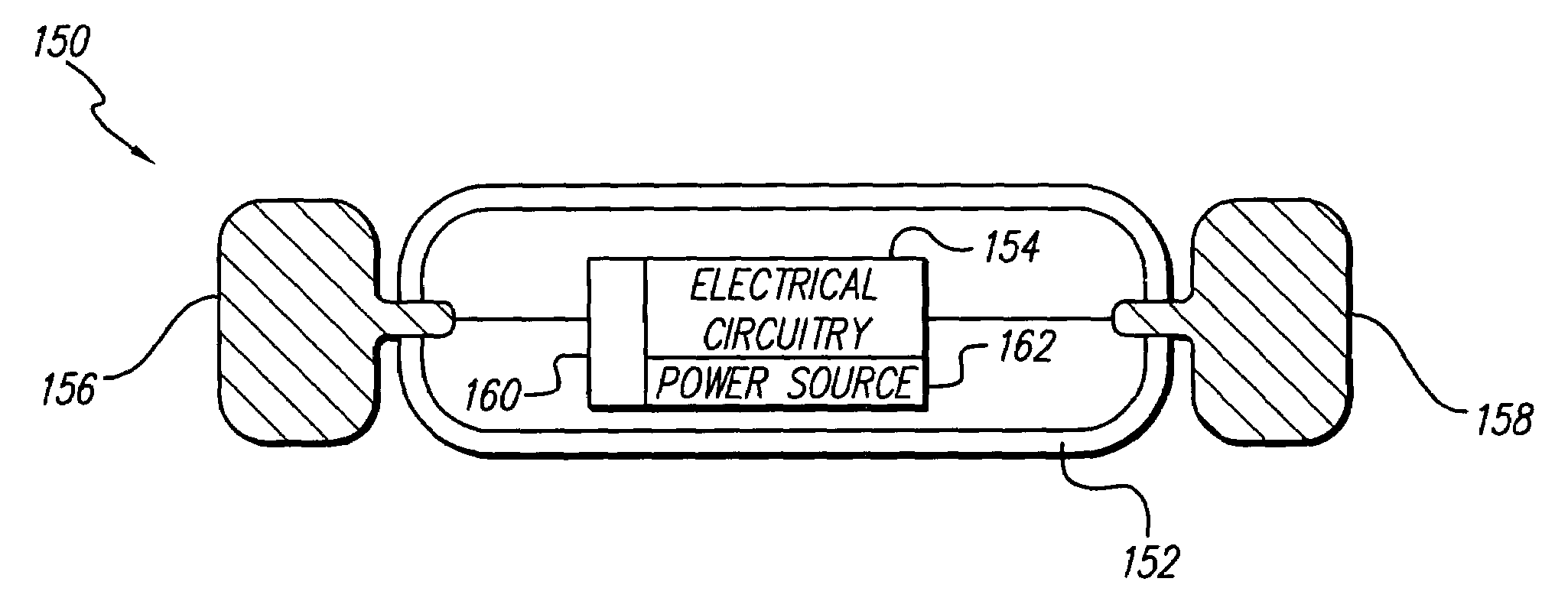
Systems and methods for modulation of circulatory perfusion by electrical and/or drug stimulation
InactiveUS6845267B2Minimal discomfortAvoid the needElectrotherapyPharmaceutical delivery mechanismElectrical batteryClosed loop
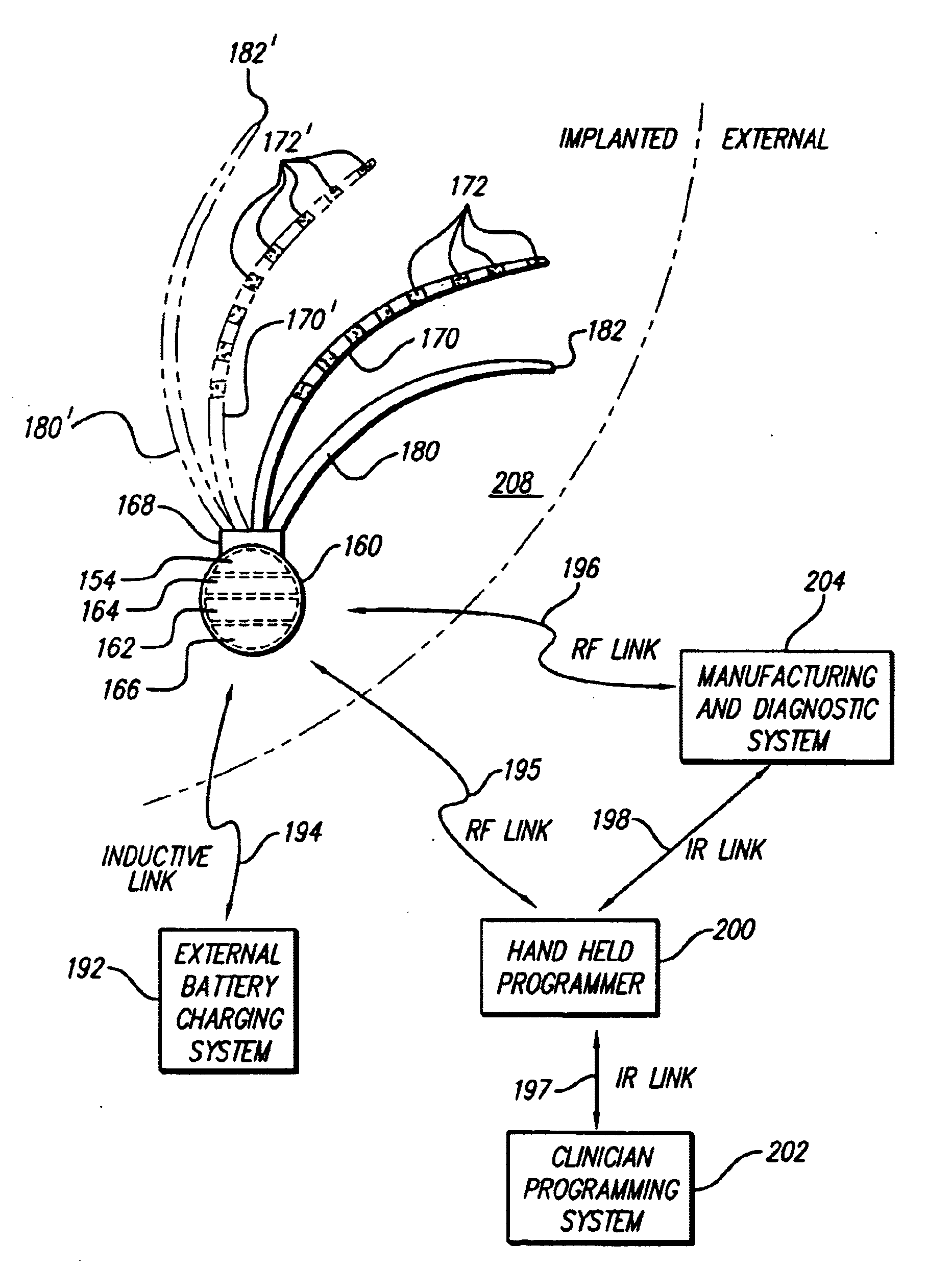
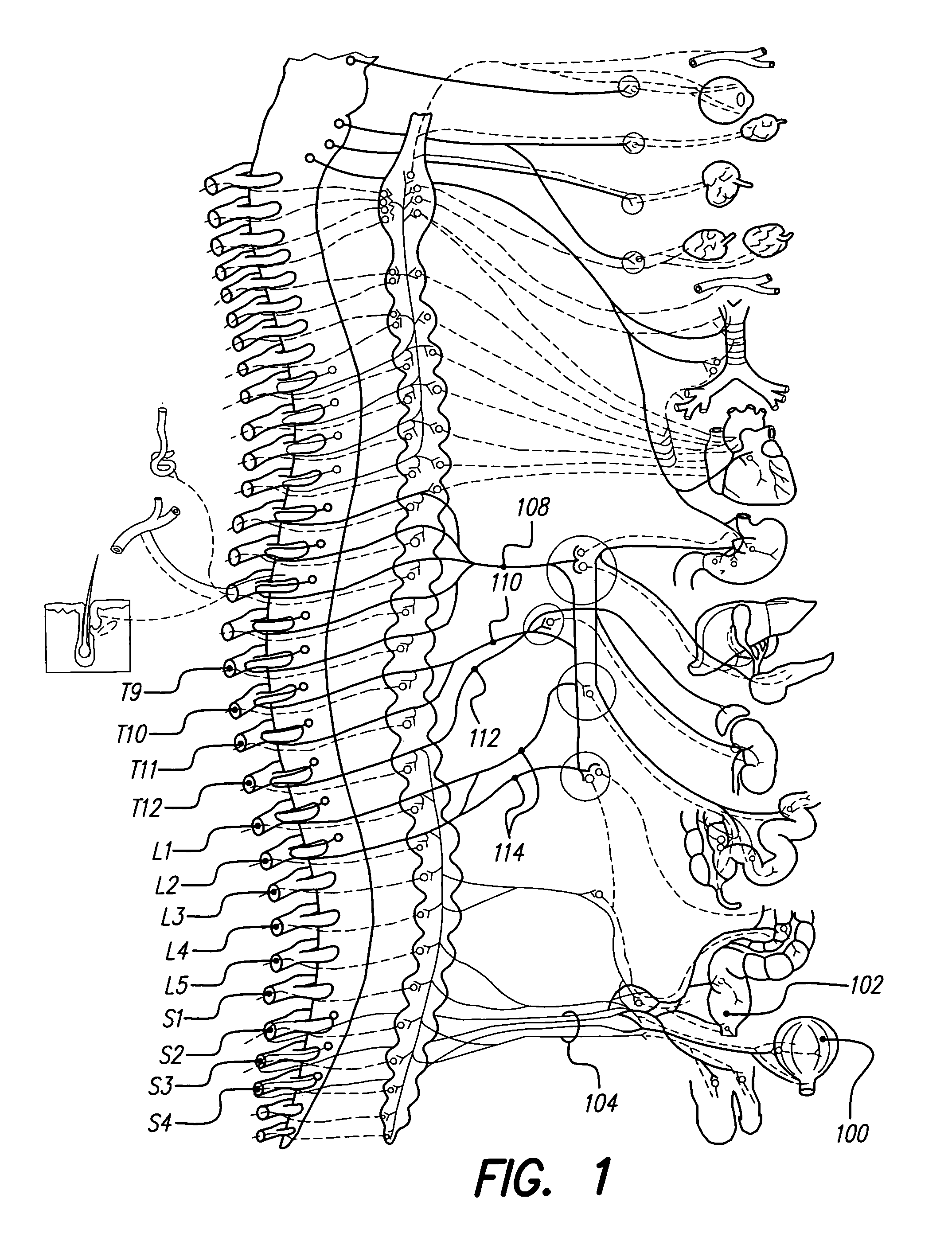
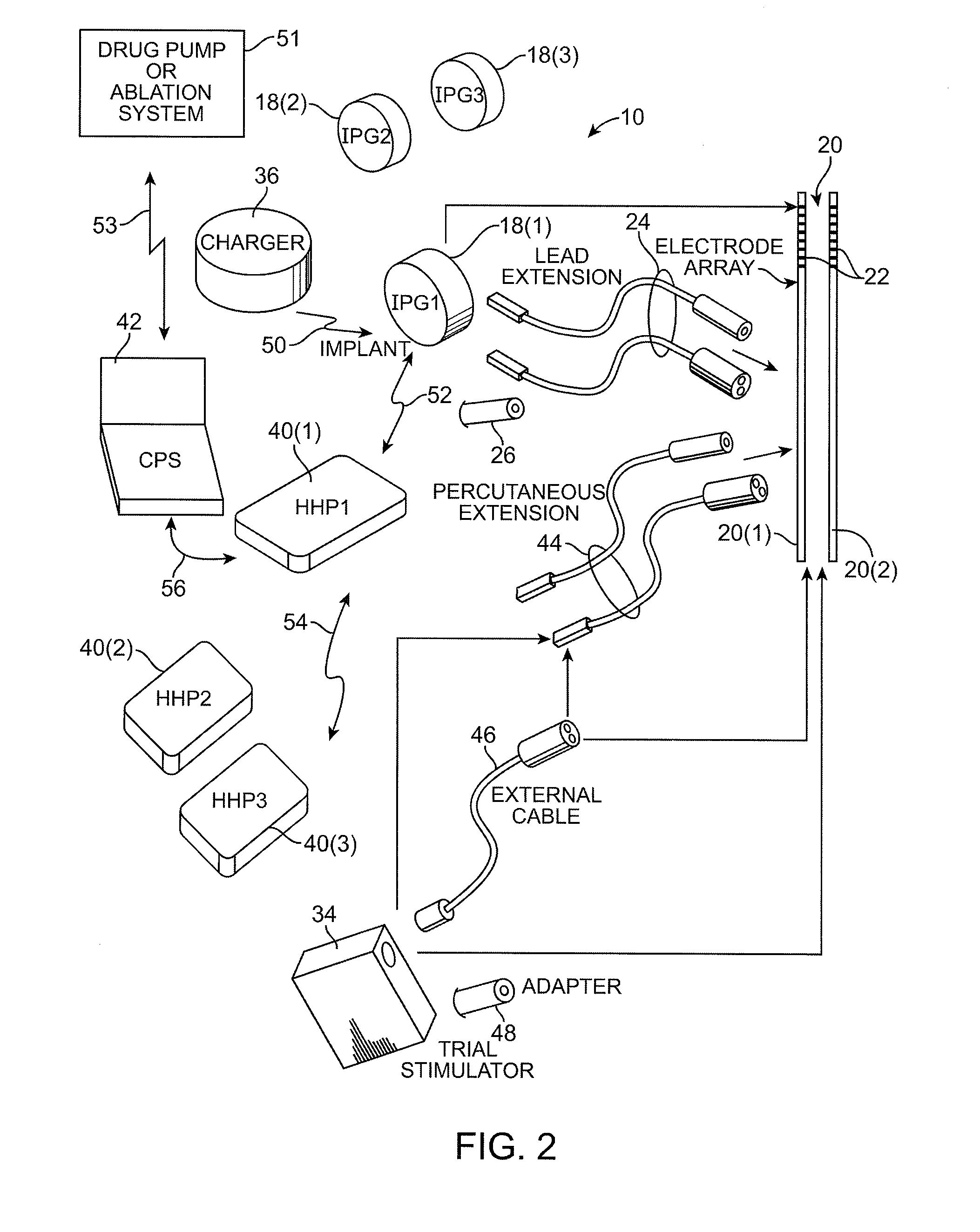
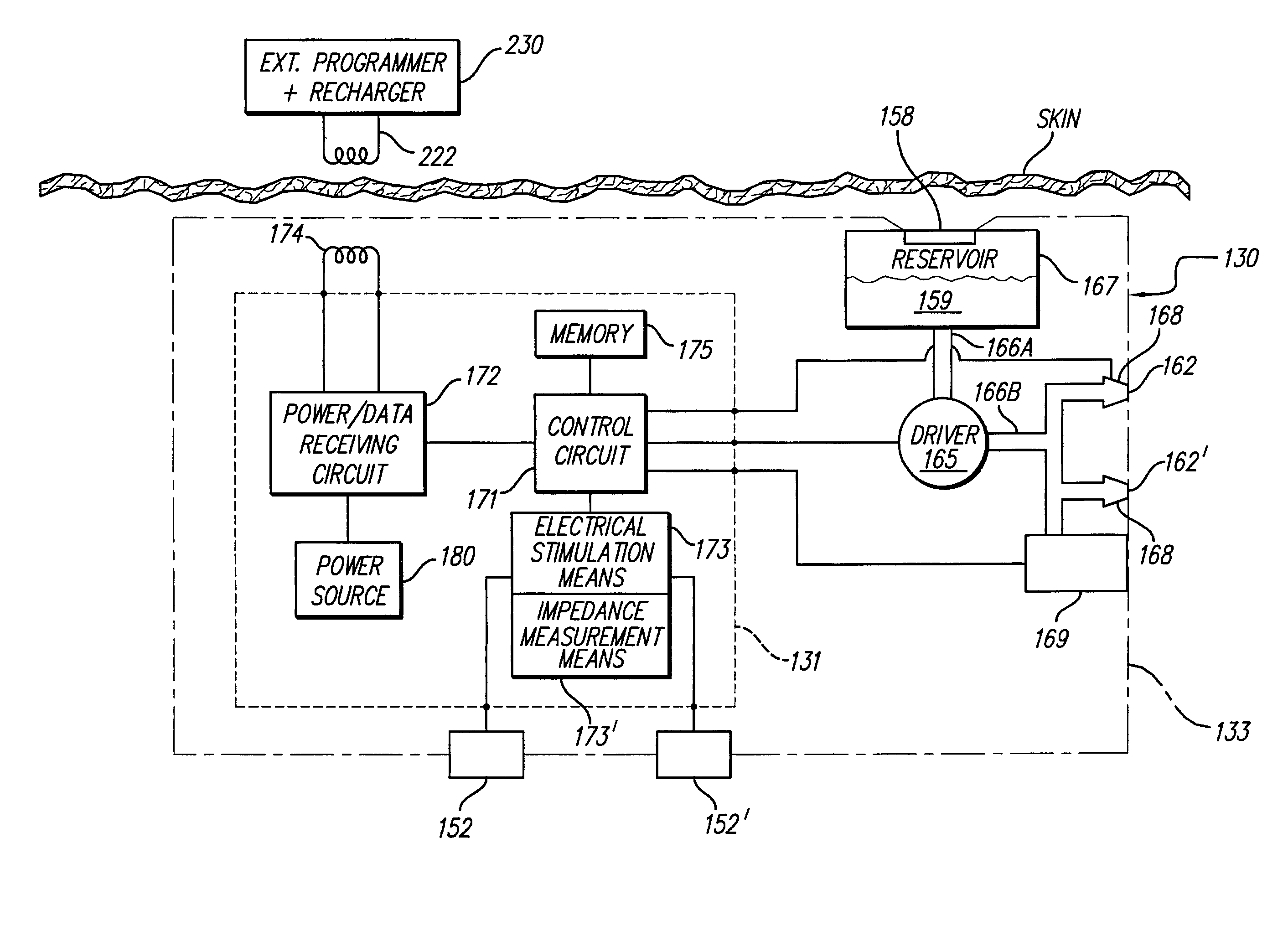
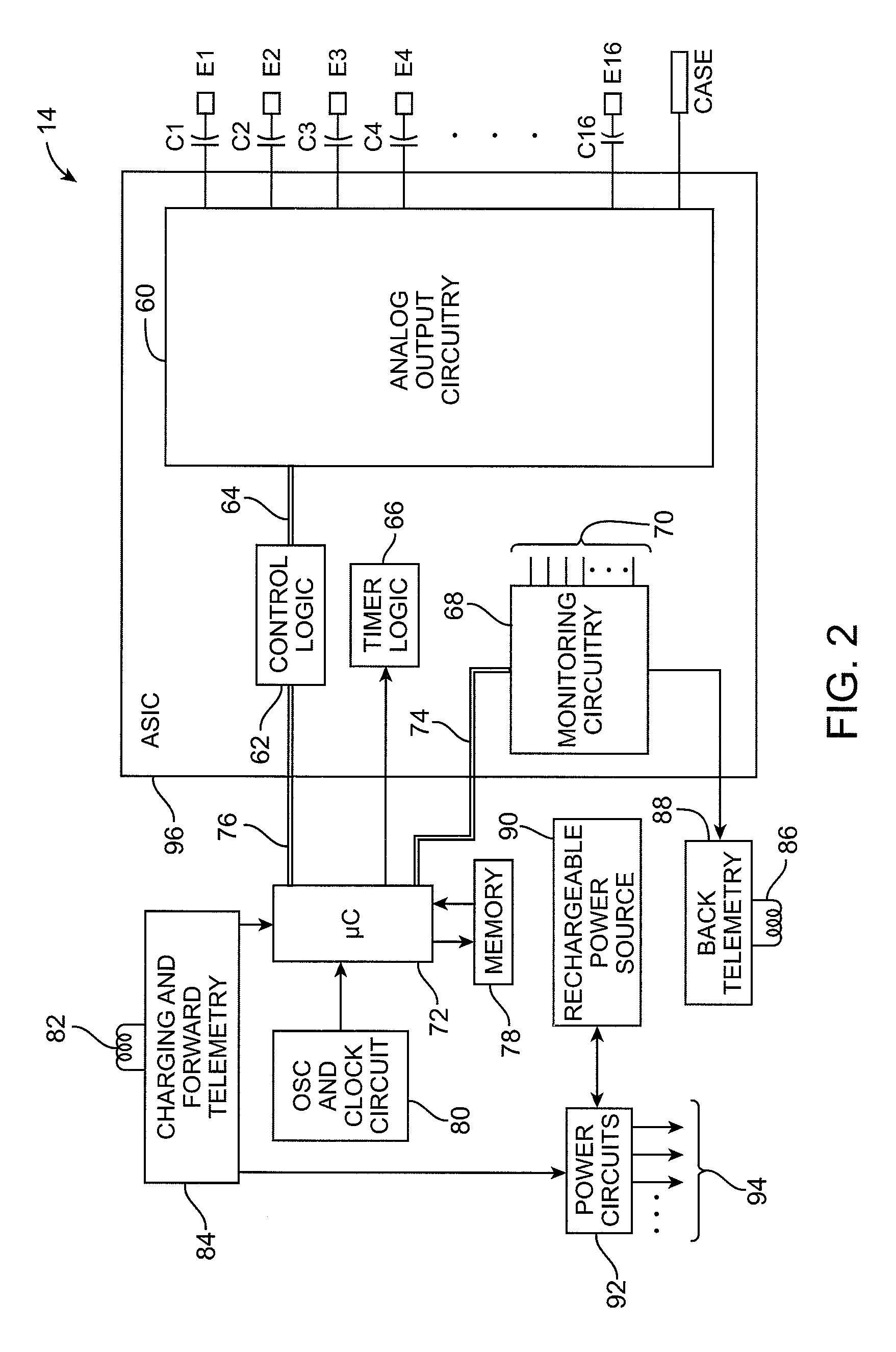
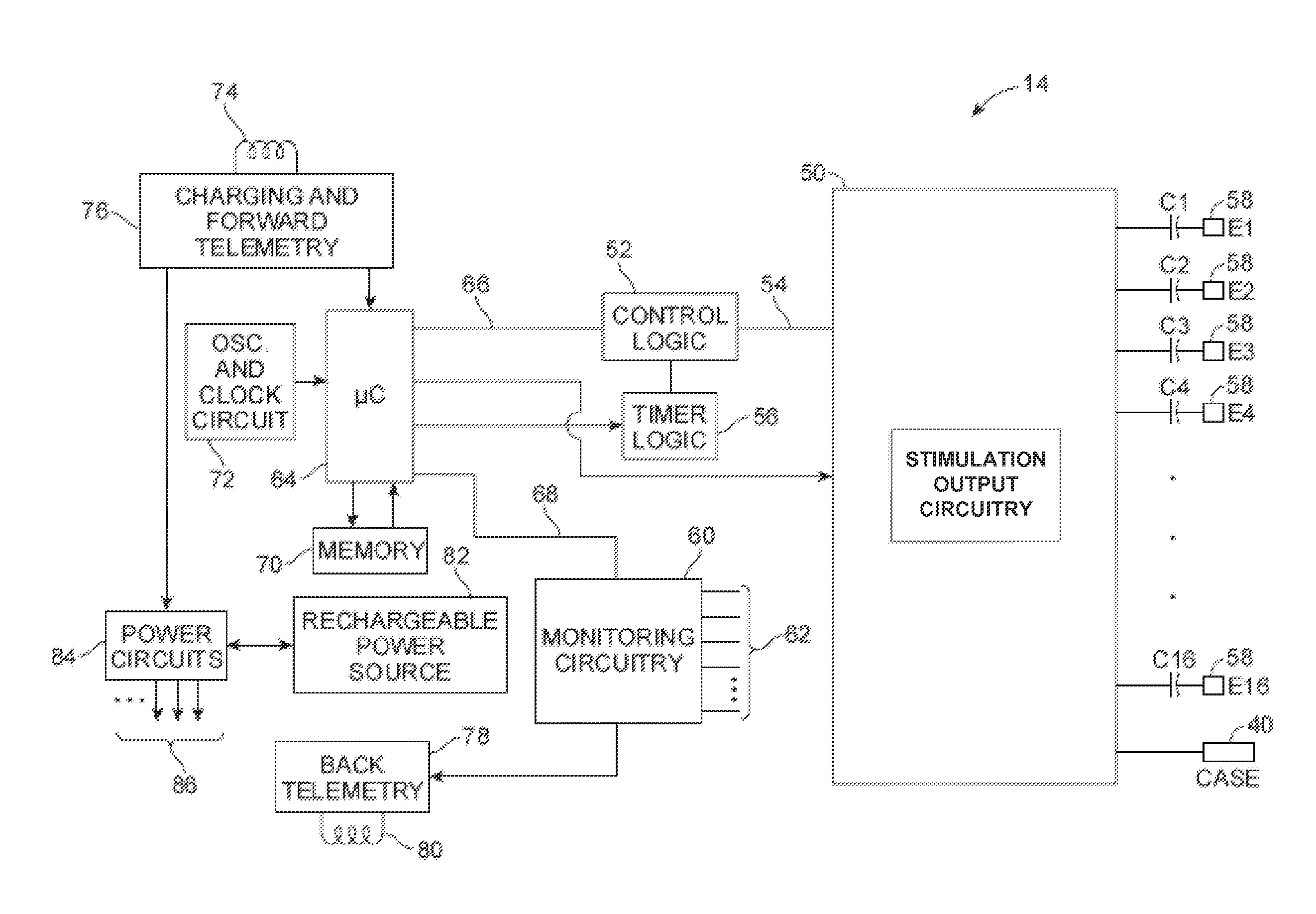
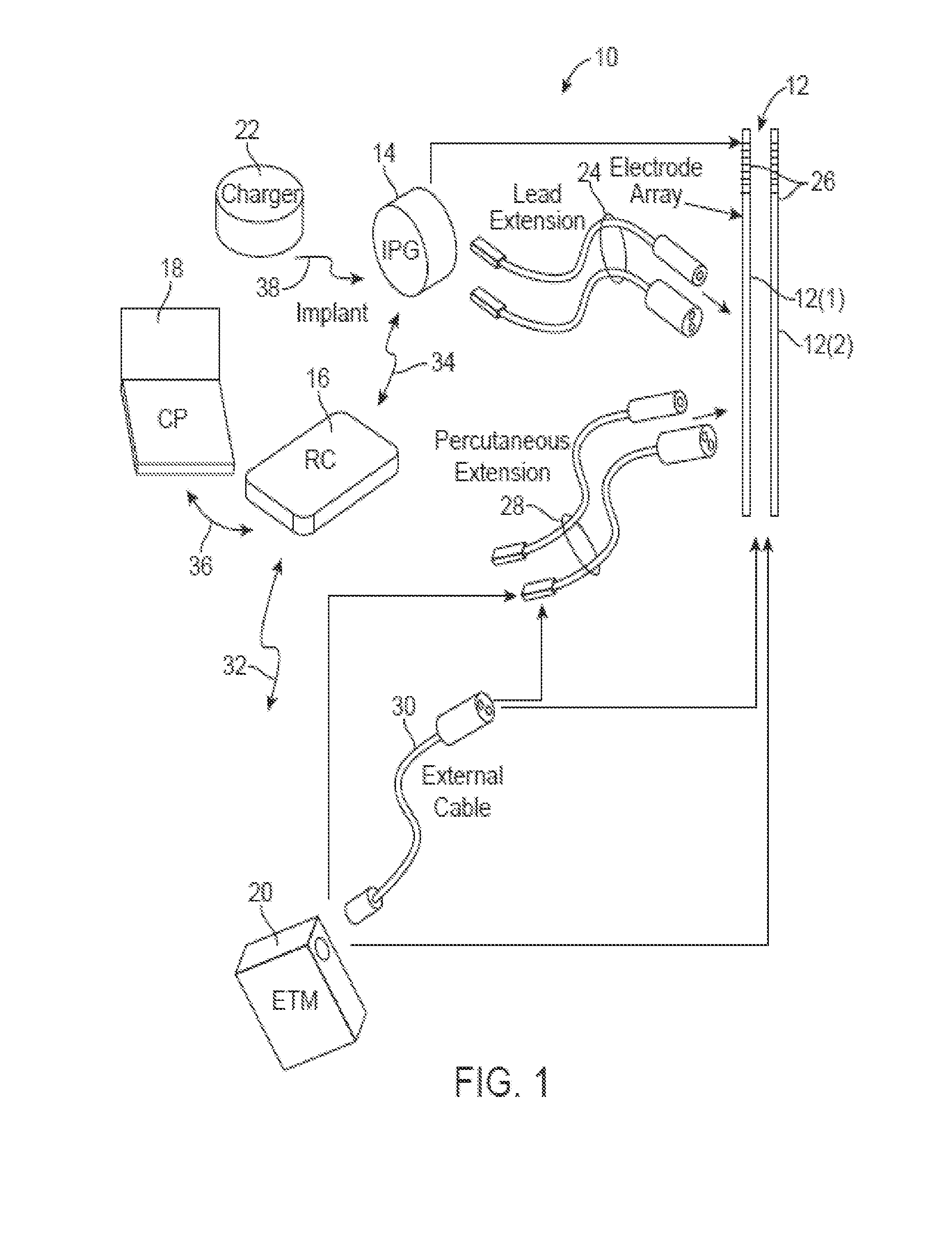
One or more implantable system control units (SCU) apply one or more stimulating drugs and / or electrical pulses to one or more predetermined areas affecting circulatory perfusion. The SCU preferably includes a programmable memory for storing data and / or control parameters, and preferably uses a power source / storage device, such as a rechargeable battery. If necessary, periodic recharging of such a power source / storage device is accomplished, for example, by inductive coupling with an external appliance. The SCU provides a means of stimulating a nerve(s) or other tissue with electrical and / or infusion pulses when desired, without the need for external appliances during the stimulation session. When necessary, external appliances are used for the transmission of data to and / or from the SCU(s) and / or for the transmission of power. In a preferred embodiment, the system is capable of open- and closed-loop operation. In closed-loop operation, at least one SCU includes a sensor, and the sensed condition is used to adjust electrical and / or drug stimulation parameters.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
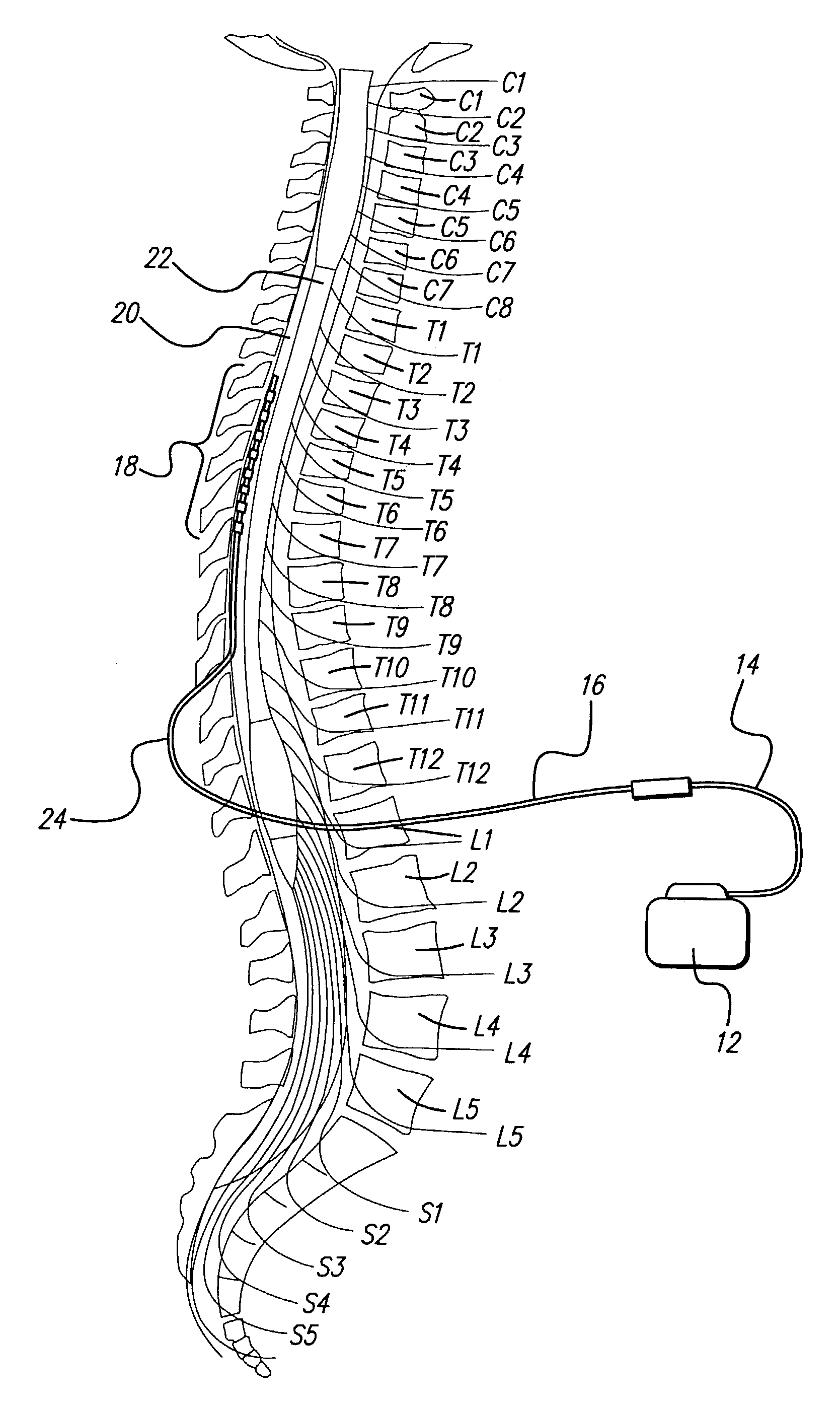
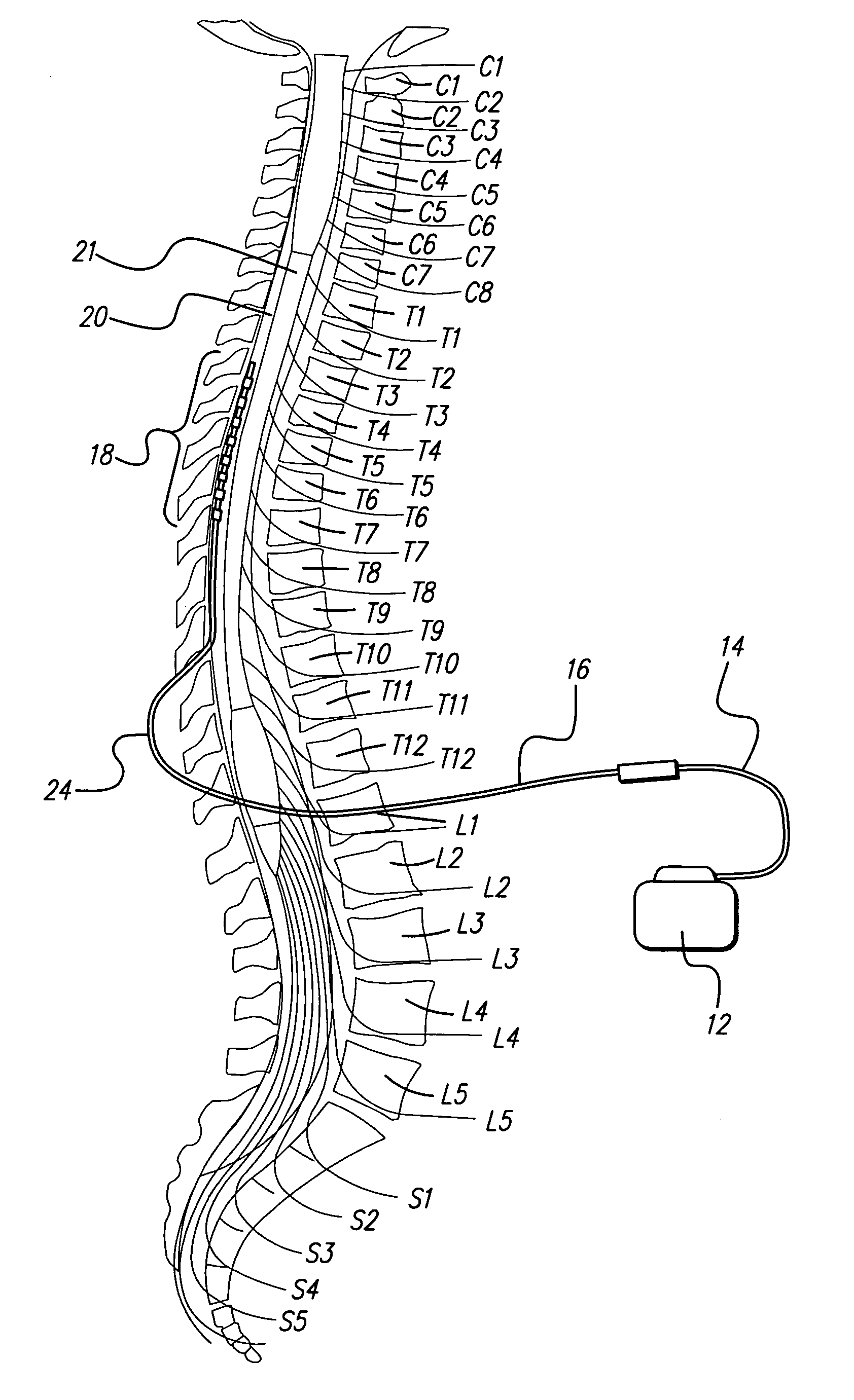
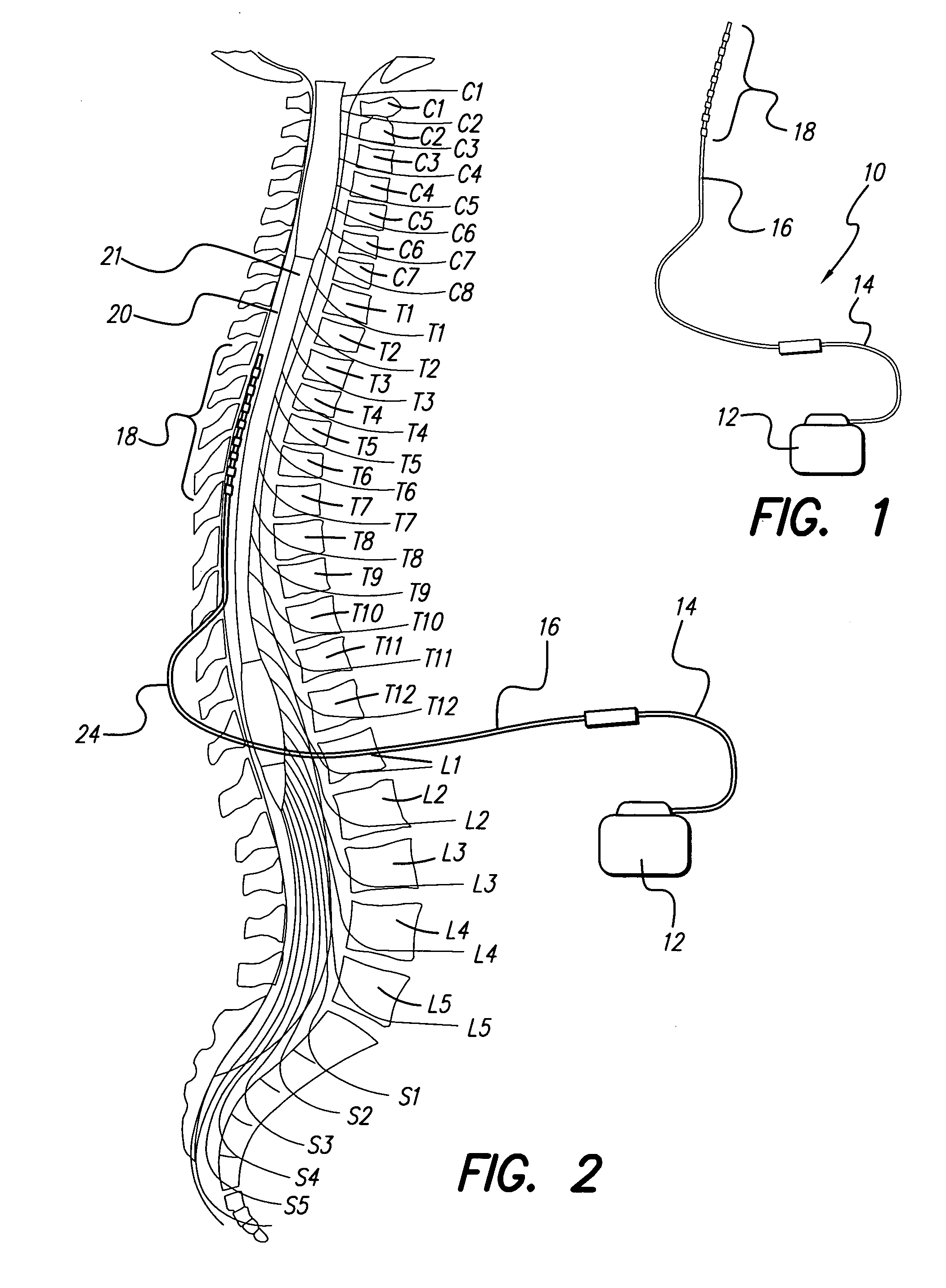
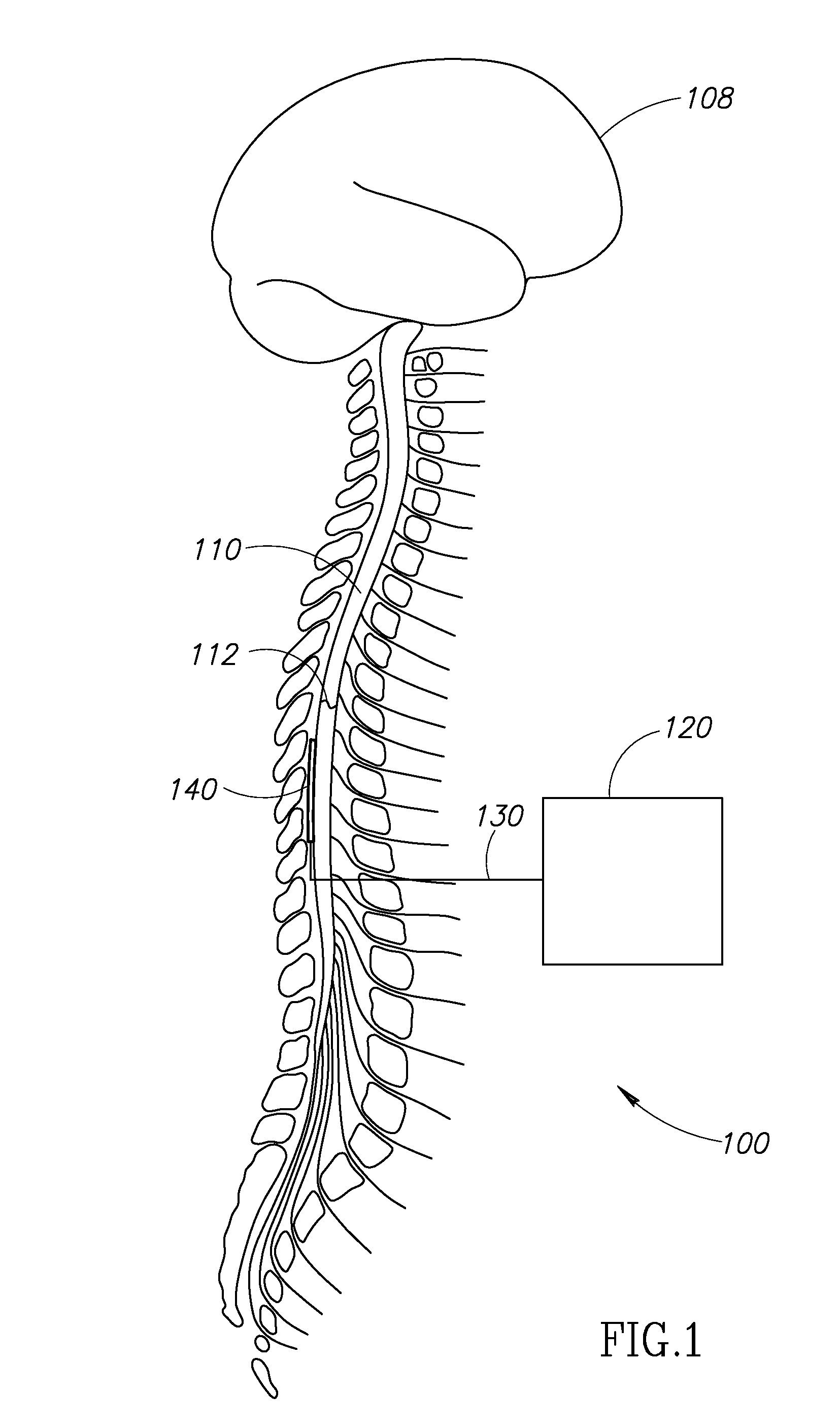
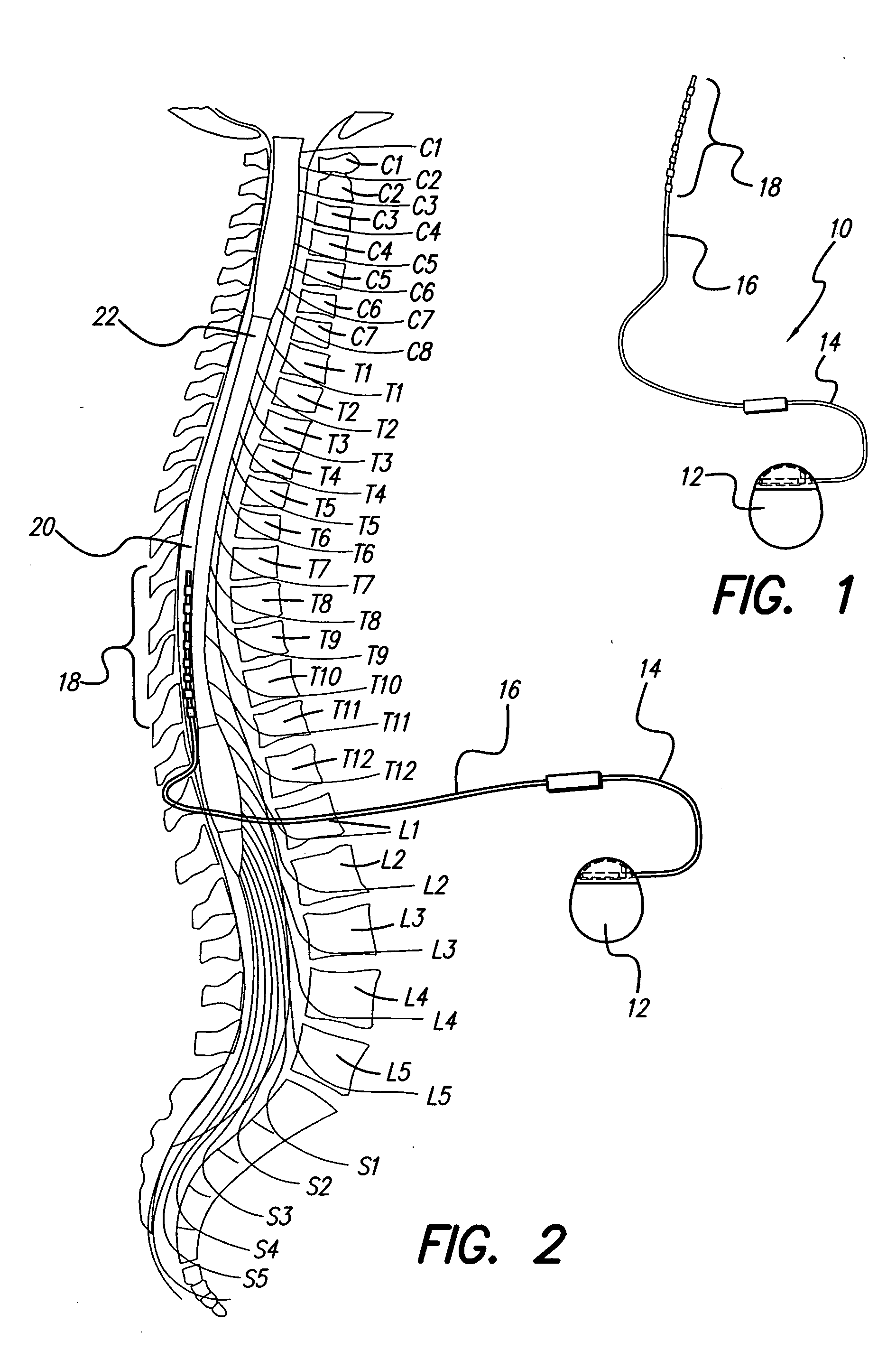
Fully implantable microstimulator for spinal cord stimulation as a therapy for chronic pain
An implantable stimulator(s), small enough to be located near or within an area of the spine responsible for sensations in a region experiencing chronic pain uses a power source / storage device, such as a rechargeable battery. Periodic recharging of such a power source / storage device is accomplished, for example, by inductive coupling with an external appliance. The small stimulator provides a means of stimulating a nerve(s) or other tissue when desired, without the need for external appliances during the stimulation session. When necessary, external appliances are used for the transmission of data to and / or from the stimulator(s) and for the transmission of power, it necessary. In a preferred embodiment, the system is capable of open- and closed-loop operation. In closed-loop operation, at least one implant includes at least one sensor, and the sensed condition is used to adjust stimulation parameters.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
System and method for converting tissue stimulation programs in a format usable by an electrical current steering navigator
A method, computer medium, and system for programming a controller is provided. The controller controls electrical stimulation energy output to electrodes, and stores a set of programmed stimulation parameters associated with the electrodes. The programmed stimulation parameter set is compared with sets of reference stimulation parameters, each of the reference sets of stimulation parameters being associated with the electrodes. If an identical match is determined between the programmed stimulation parameter set and any one of the reference stimulation parameter sets exists based on the comparison, the identically matched stimulation parameter set is selected as an initial stimulation parameter set. If an identical match does not exist, a best between the programmed stimulation parameter set and the reference stimulation parameter sets is determined and selected as the initial stimulation parameter set. The controller is then programmed with a new set of programmable stimulation parameters based on the initial stimulation parameter set.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
System and method for determining appropriate steering tables for distributing stimulation energy among multiple neurostimulation electrodes
A method, computer medium, and system for programming a control device are provided. The control device is configured for controlling electrical stimulation energy provided to a plurality of electrode leads that are physically implanted within a patient in a side-by-side lead configuration. Electrical energy is conveying from the electrode leads to create a stimulation region within the patient. The stimulation region is automatically shifted along the electrode leads (e.g., by selecting and using at least one navigation table) in accordance with an electrical current shifting pattern that is based on a stagger of the side-by-side lead configuration. At least one stimulation parameter set is selected based on the effectiveness of the shifted stimulation region, and the control device is programmed with the selected stimulation parameter set(s).
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Treatment of movement disorders with drug therapy
ActiveUS7155279B2Increase excitementPrevent movementElectrotherapyDiagnosticsTherapeutic exerciseMedicine
Introducing one or more stimulating drugs to the vagus nerve and / or one or more branches of the vagus nerve to treat movement disorders uses at least one implantable system control unit (SCU) with an implantable pump with at least one infusion outlet. Optional electrical stimulation may additionally be supplied by an implantable signal / pulse generator (IPG) with one or more electrodes. In certain embodiments, a single SCU provides one or more stimulating drugs and the optional electrical stimulation. In some embodiments, one or more sensed conditions are used to adjust stimulation parameters.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Fully implantable neurostimulator for autonomic nerve fiber stimulation as a therapy for urinary and bowel dysfunction
An implantable stimulator(s), small enough to be located near or adjacent to an autonomic nerve(s) innervating urinary and / or gastrointestinal structures, uses a power source / storage device, such as a rechargeable battery. Periodic recharging of such a power source / storage device is accomplished, for example, by inductive coupling with an external appliance. The small stimulator provides a means of stimulating a nerve(s) or other tissue when desired, without the need for external appliances during the stimulation session. When necessary, external appliances are used for the transmission of data to and / or from the stimulator(s) and for the transmission of power, if necessary. In a preferred embodiment, the system is capable of open- and closed-loop operation. In closed-loop operation, at least one implant includes at least one sensor, and the sensed condition is used to adjust stimulation parameters.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Multimodal neurostimulation systems and methods
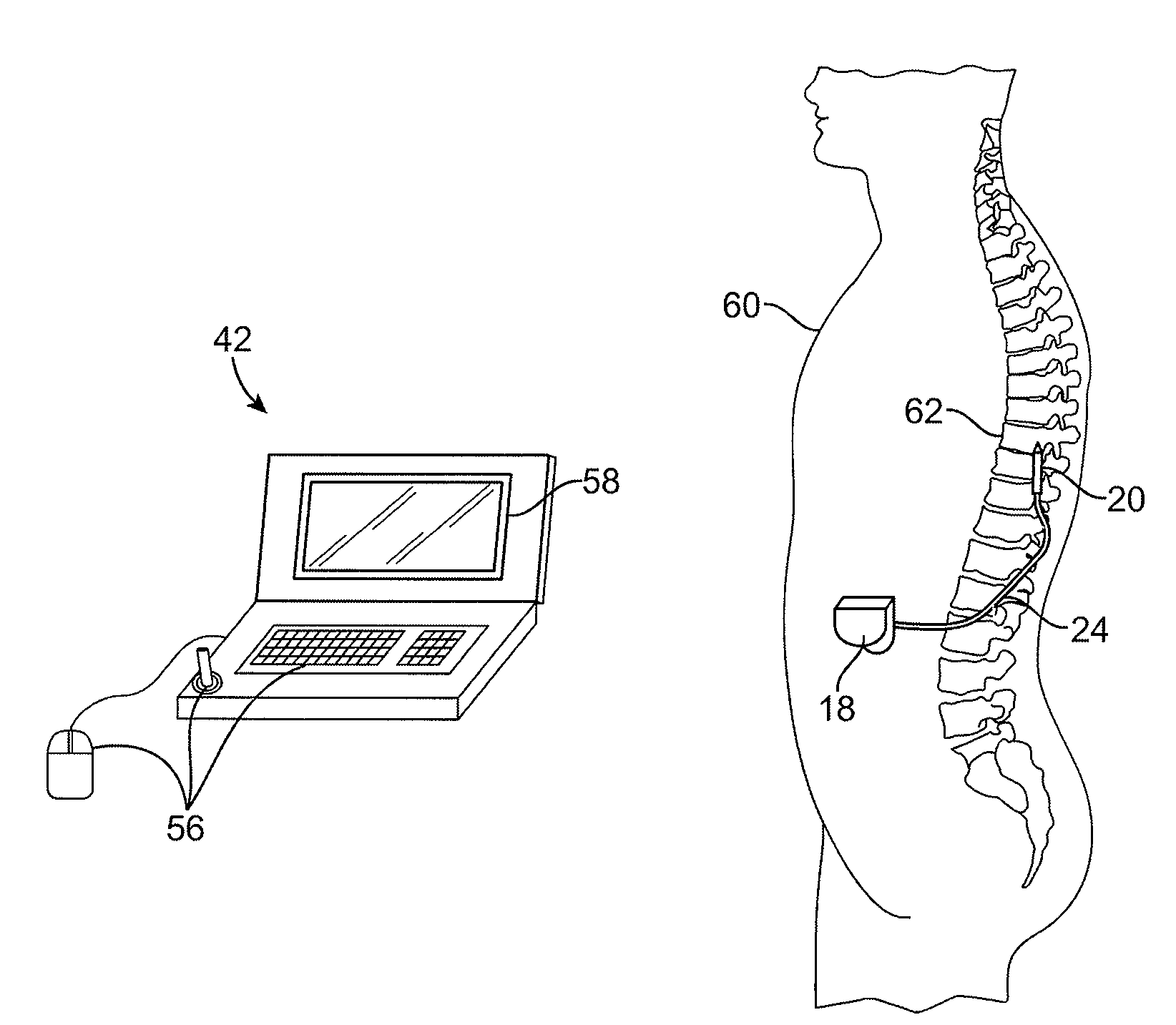
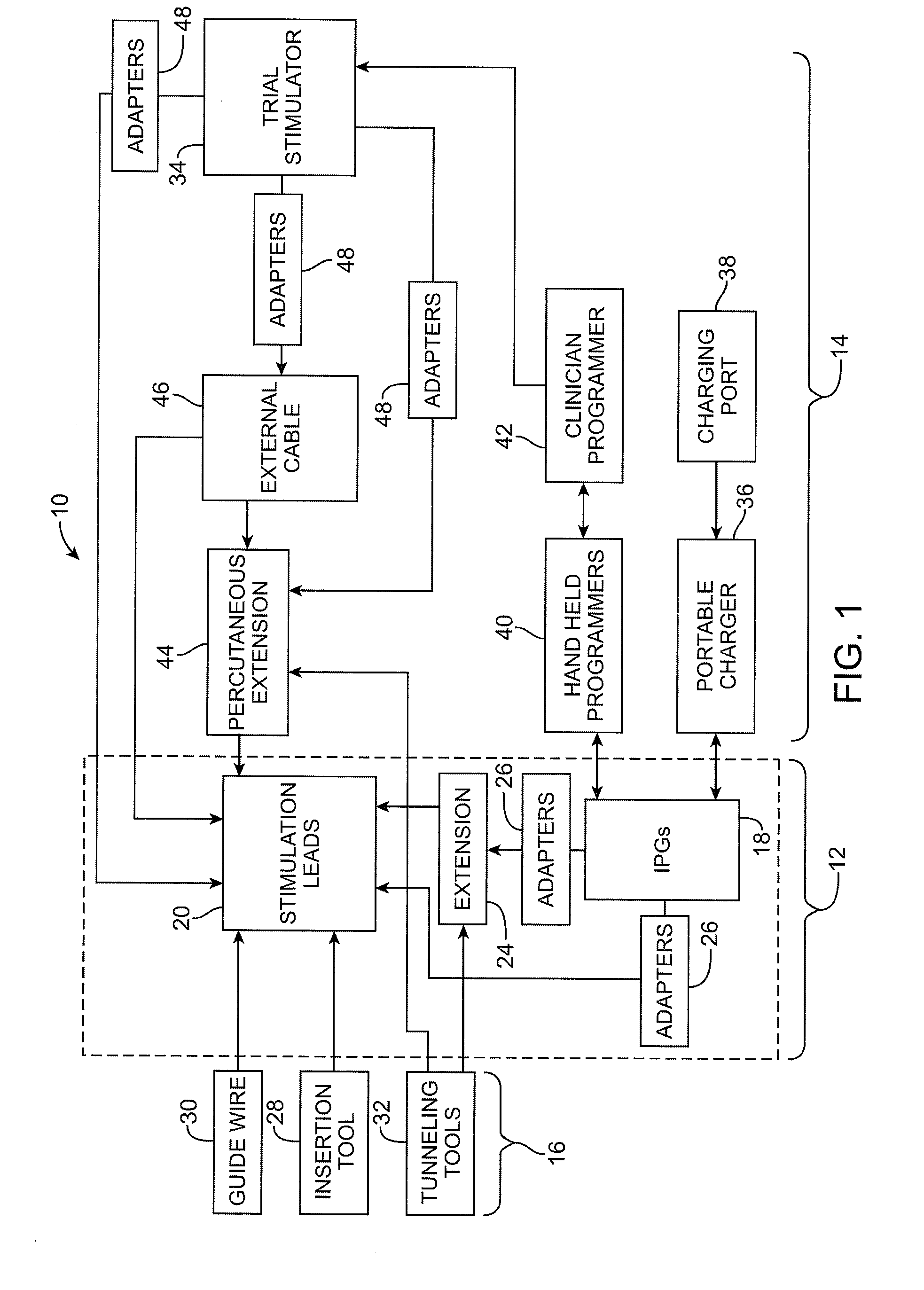
A system for performing a neurostimulation trial comprises an external trial stimulator capable of delivering stimulation energy to a plurality of electrodes carried by one or more stimulation leads. The external trial stimulator is configurable to operate in a plurality of stimulation energy delivery modes to respectively emulate one of different neurostimulator types. The system may further comprise a programmer capable of configuring the external trial stimulator to operate in one of the stimulation energy delivery modes. The programmer may be capable of generating a first programming screen capable of allowing a first set of stimulation parameters to be defined for the first neurostimulator type, and a second programming screen capable of allowing a second set of stimulation parameters to be defined for a second neurostimulator type.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Methods for implanting a spinal cord stimulator
InactiveUS20050119713A1Decrease excitement of targeted nerve rootsIncrease the areaElectrotherapyElectric power transmissionSpinal column
Methods for implanting spinal cord stimulators are provided, including implanting at least one electrode in an anterolateral area of the spine. Stimulation provided by the stimulator(s) may be used to treat patients with chronic pain. The stimulator(s) use a power source / storage device, such as a rechargeable battery. Periodic recharging of such a power source / storage device is accomplished, for example, by inductive coupling with an external applience. The stimulators provide means of stimulating a nerve(s) or other tissue when desired, without the need for external appliances during the stimulation session. When necessary, external appliances are used for the transmission of data to and / or from the stimulator(s) and for the transmission of power, if necessary. In a preferred embodiment, the system is capable of open- and closed-loop operation. In closed-loop operation, at least one implant includes at least one sensor, and the sensed condition is used to adjust stimulation parameters.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
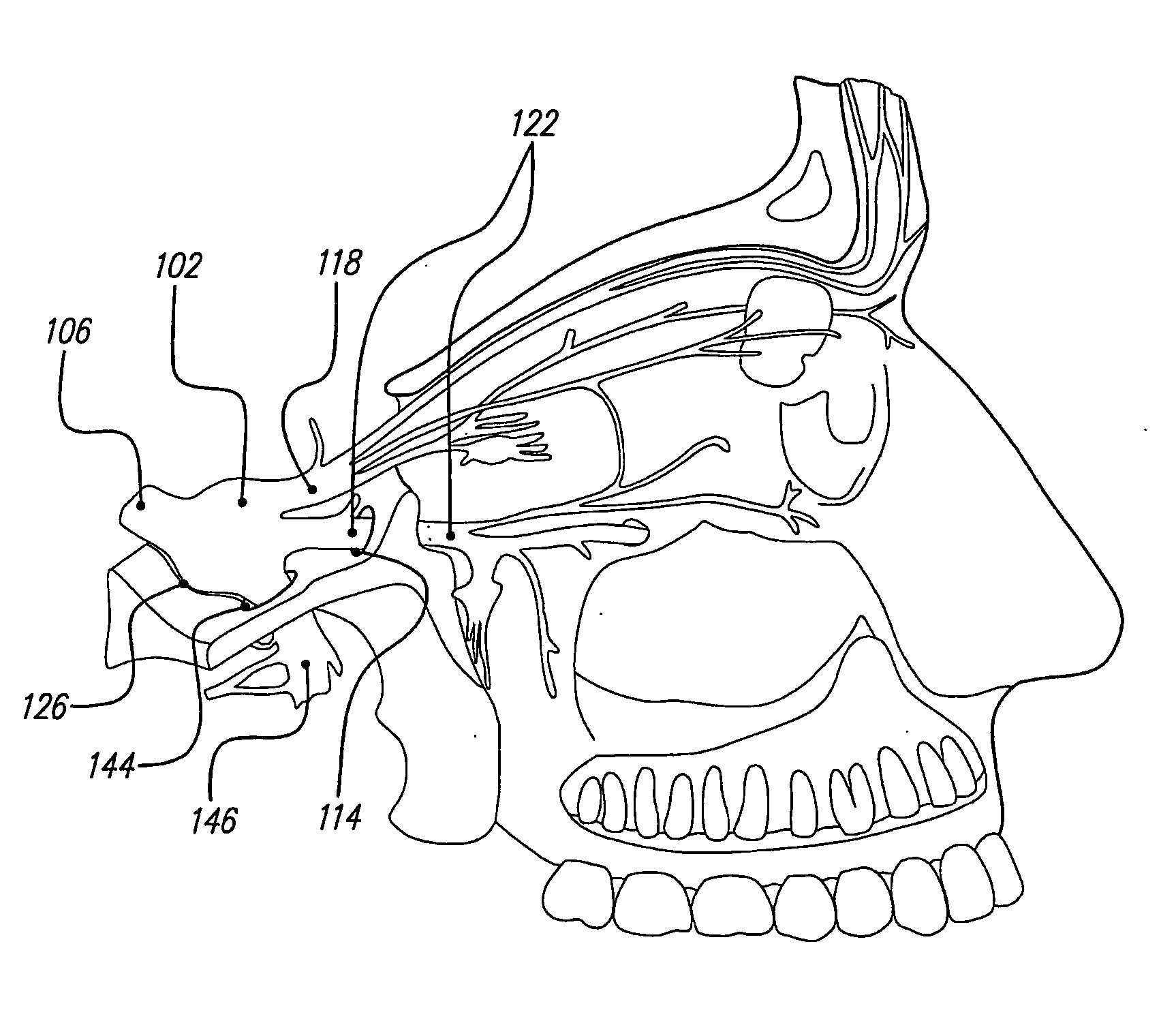
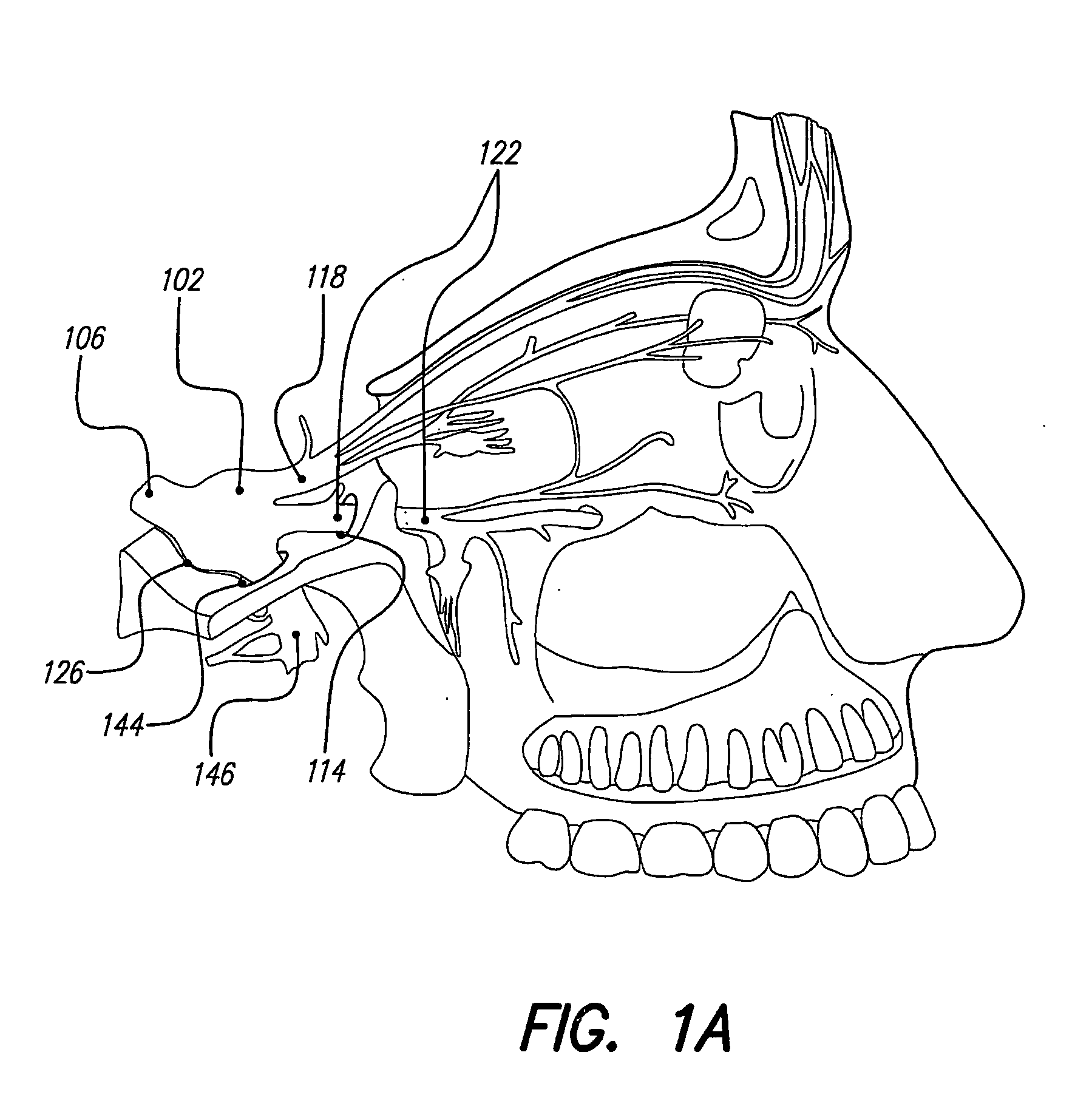
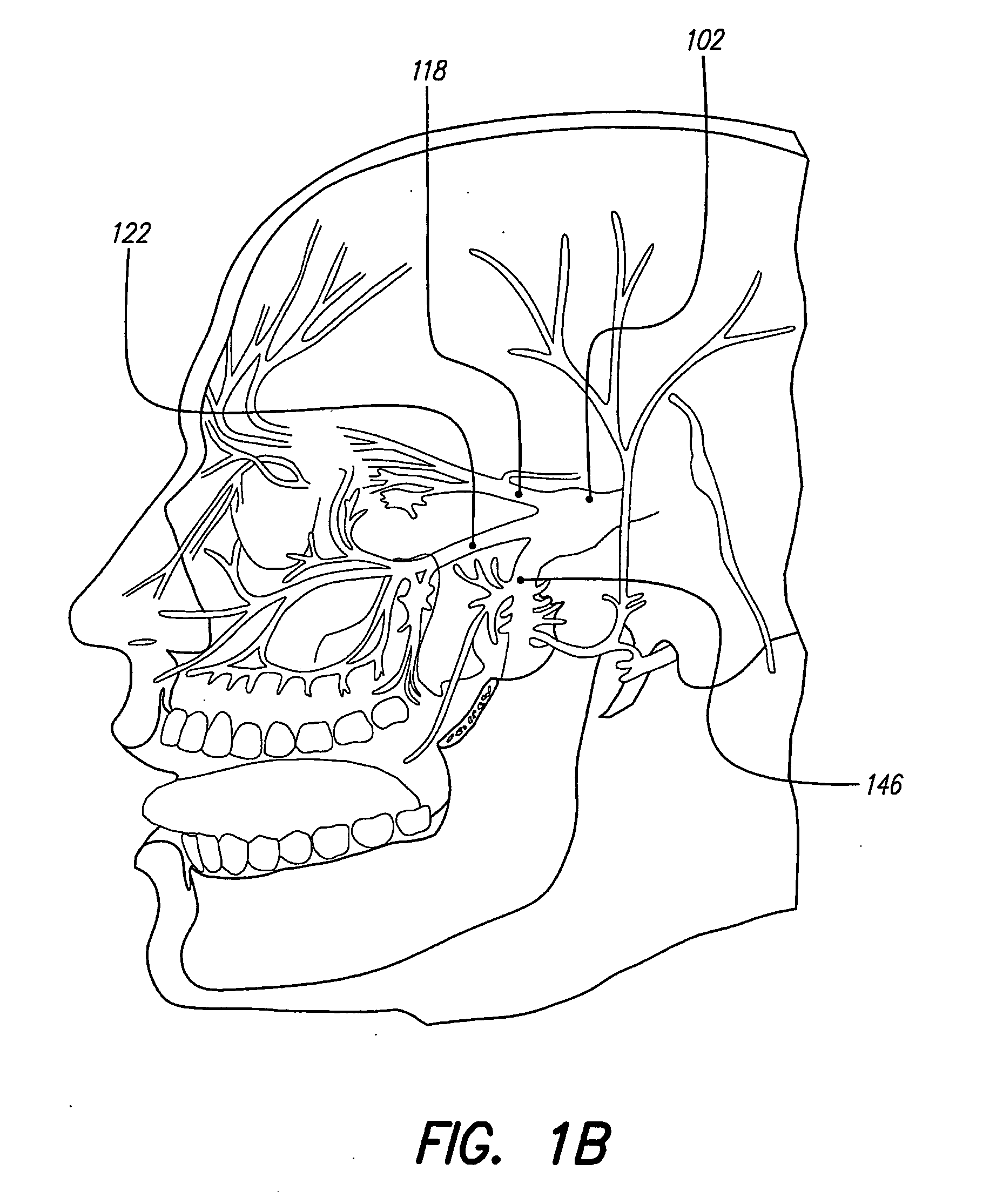
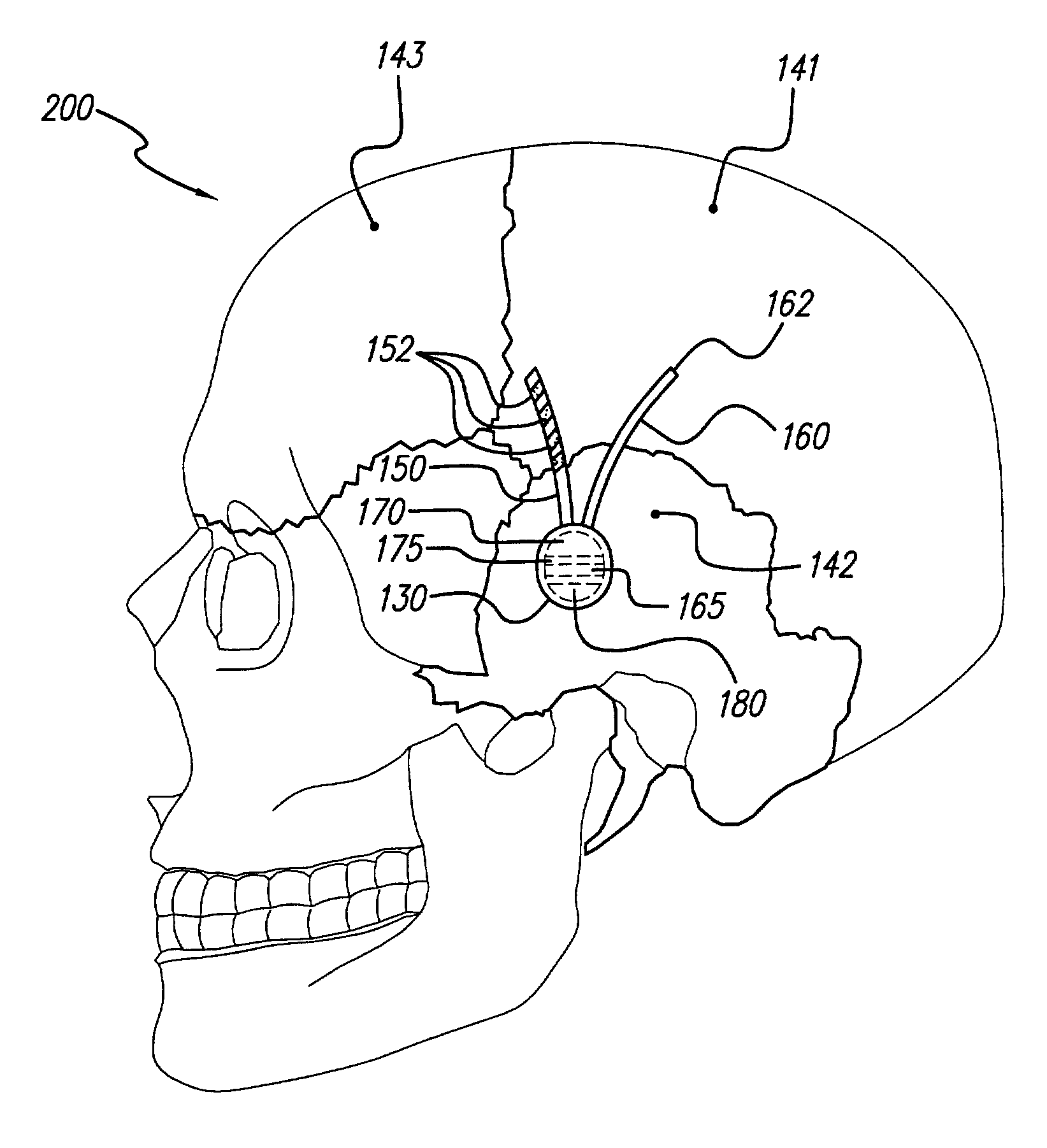
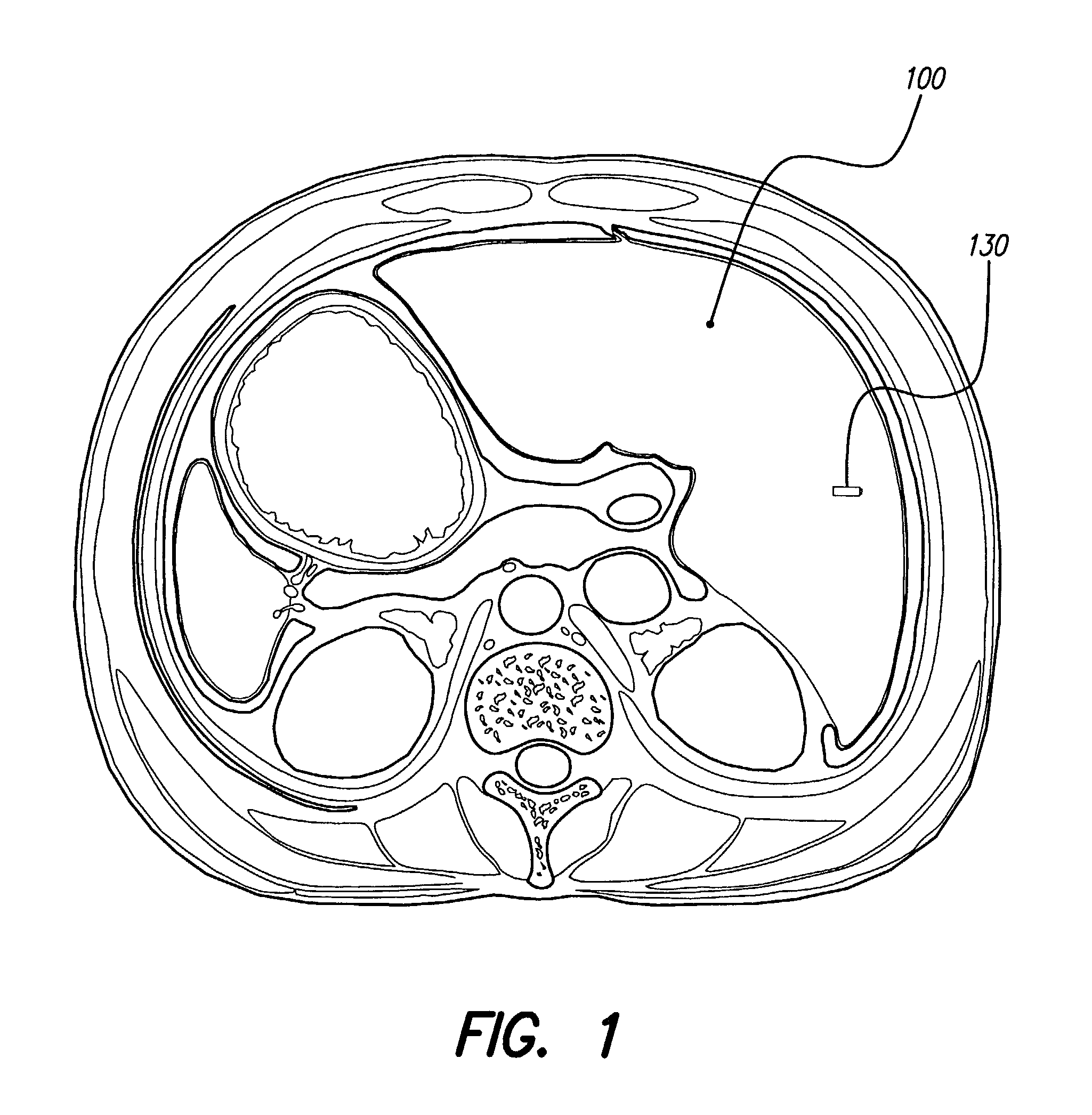
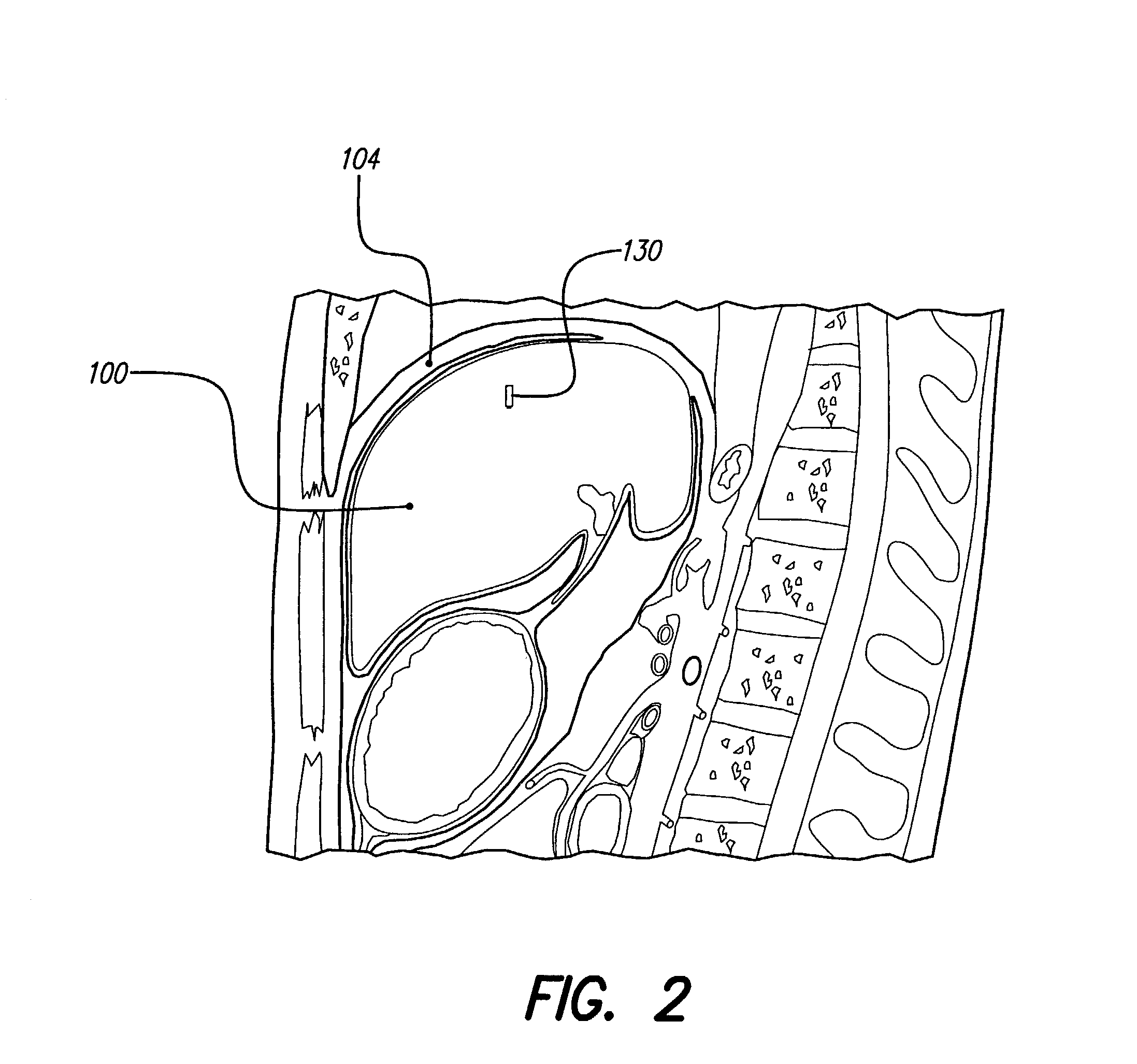
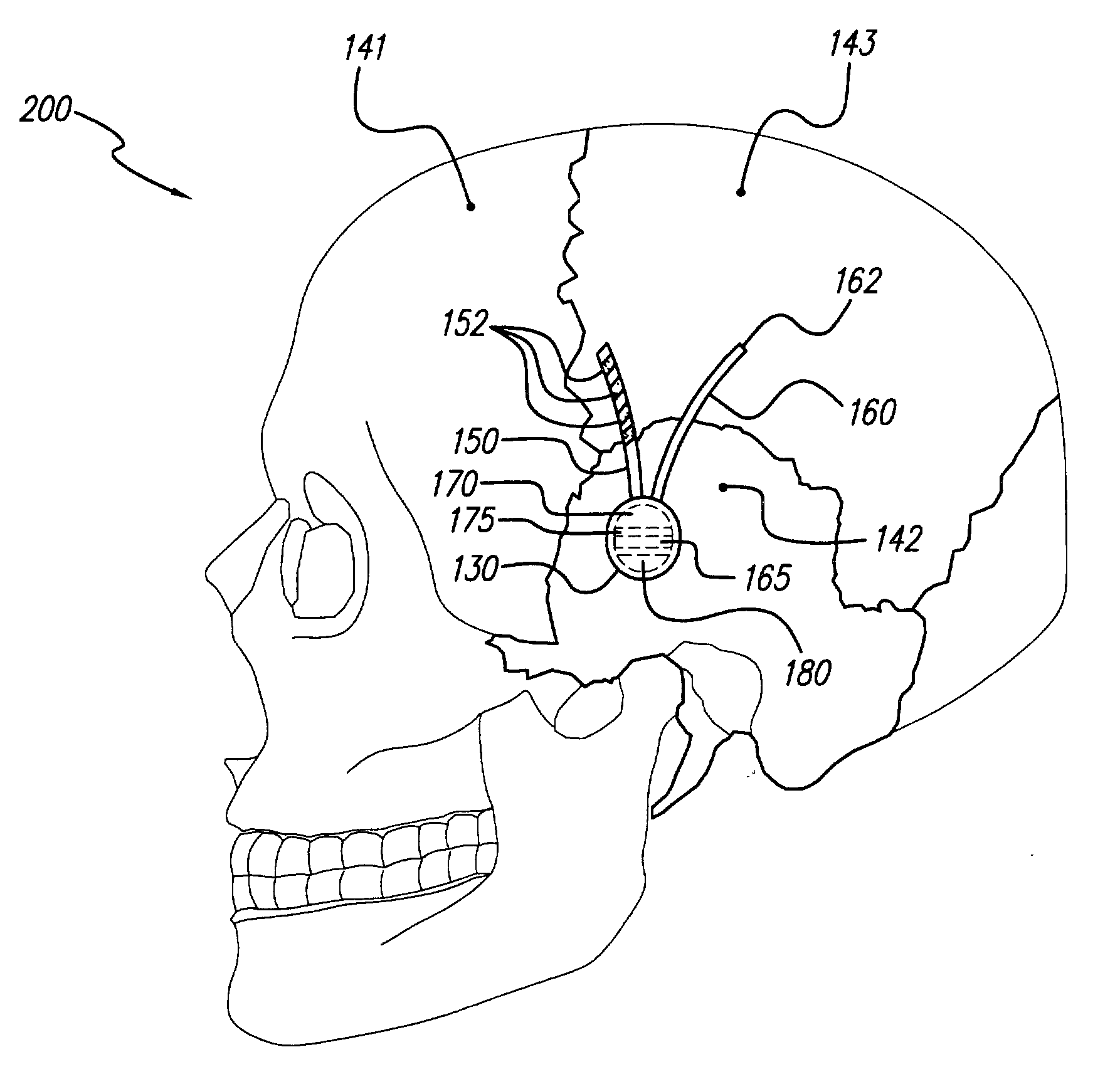
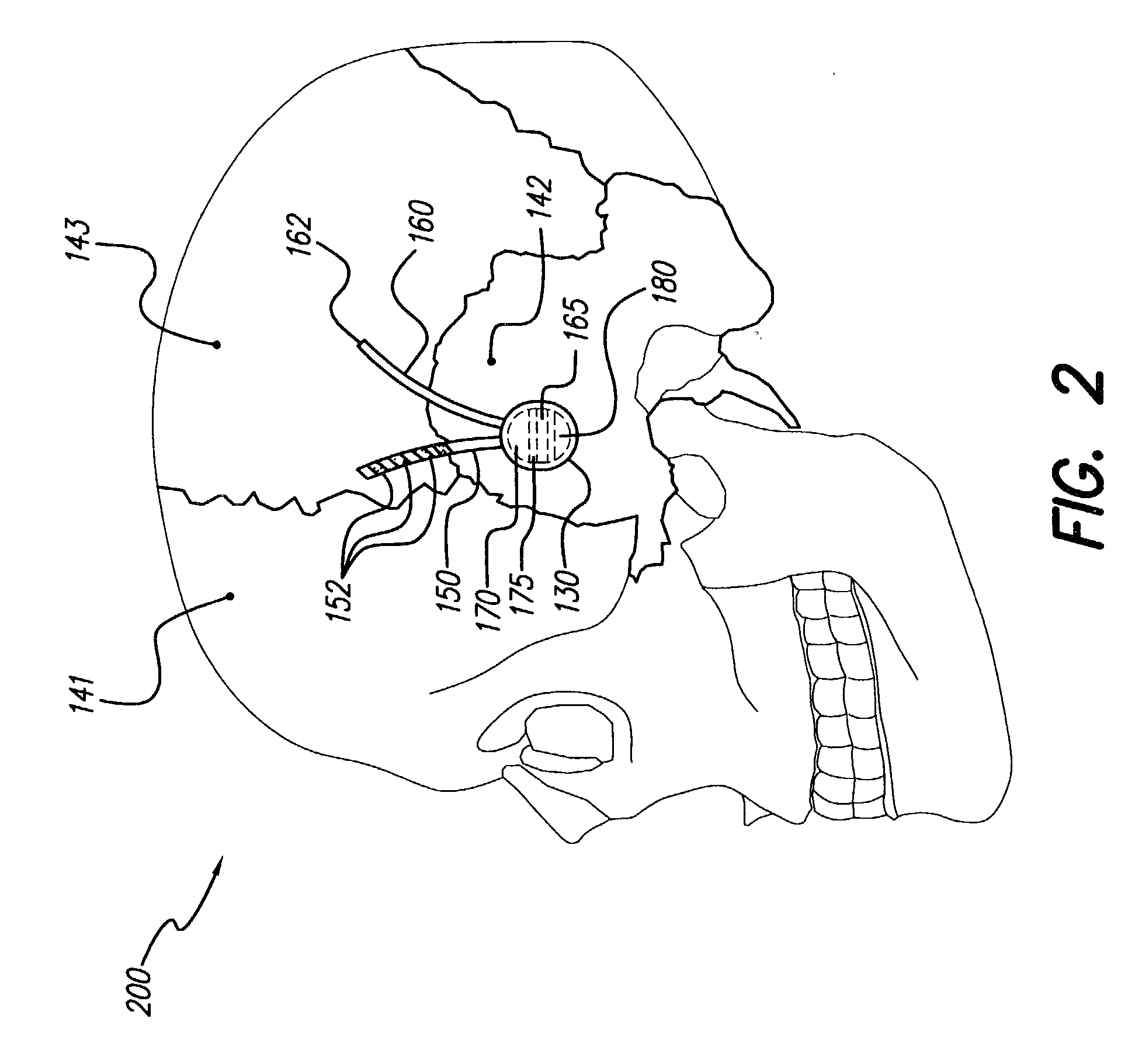
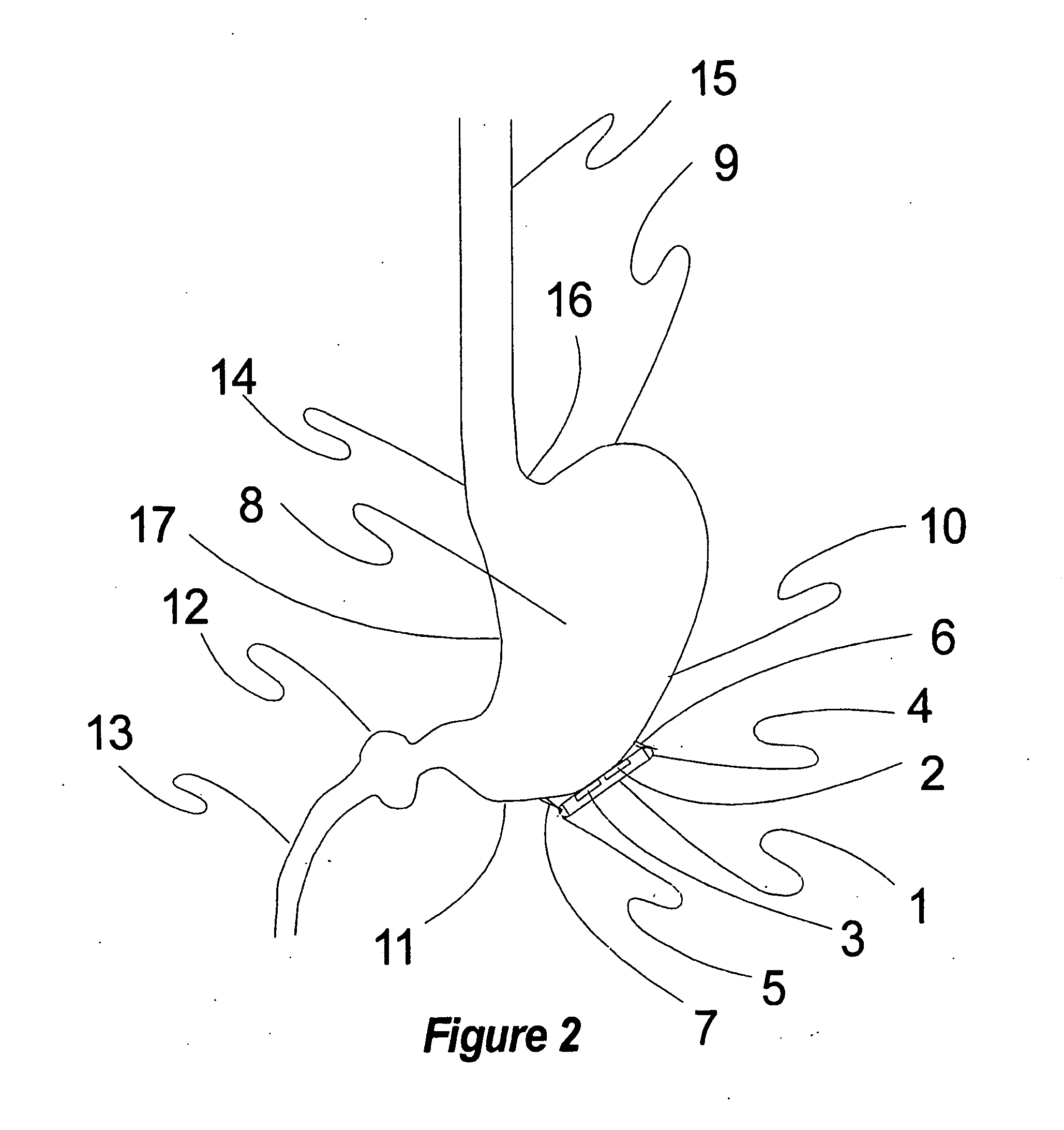
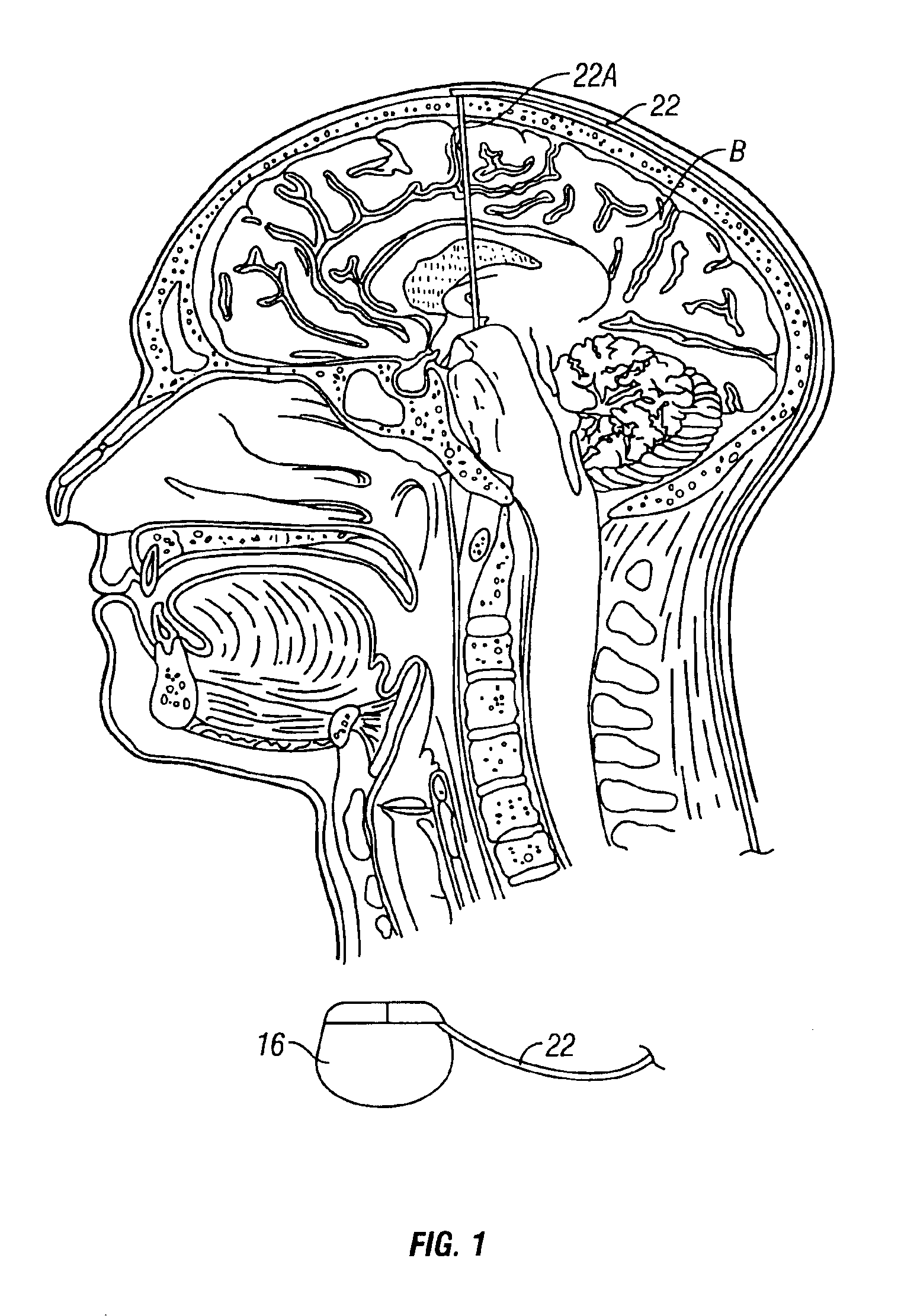
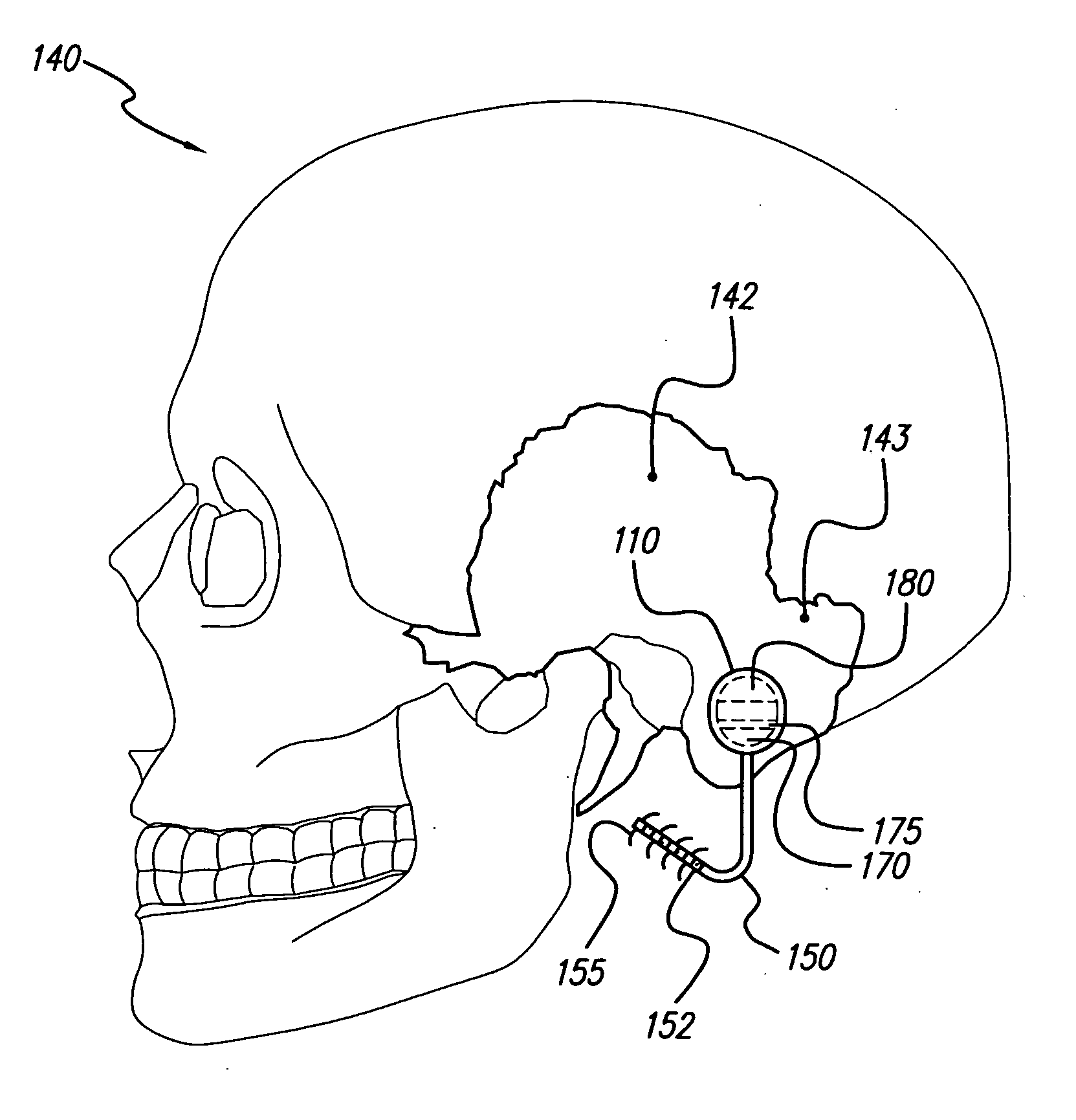
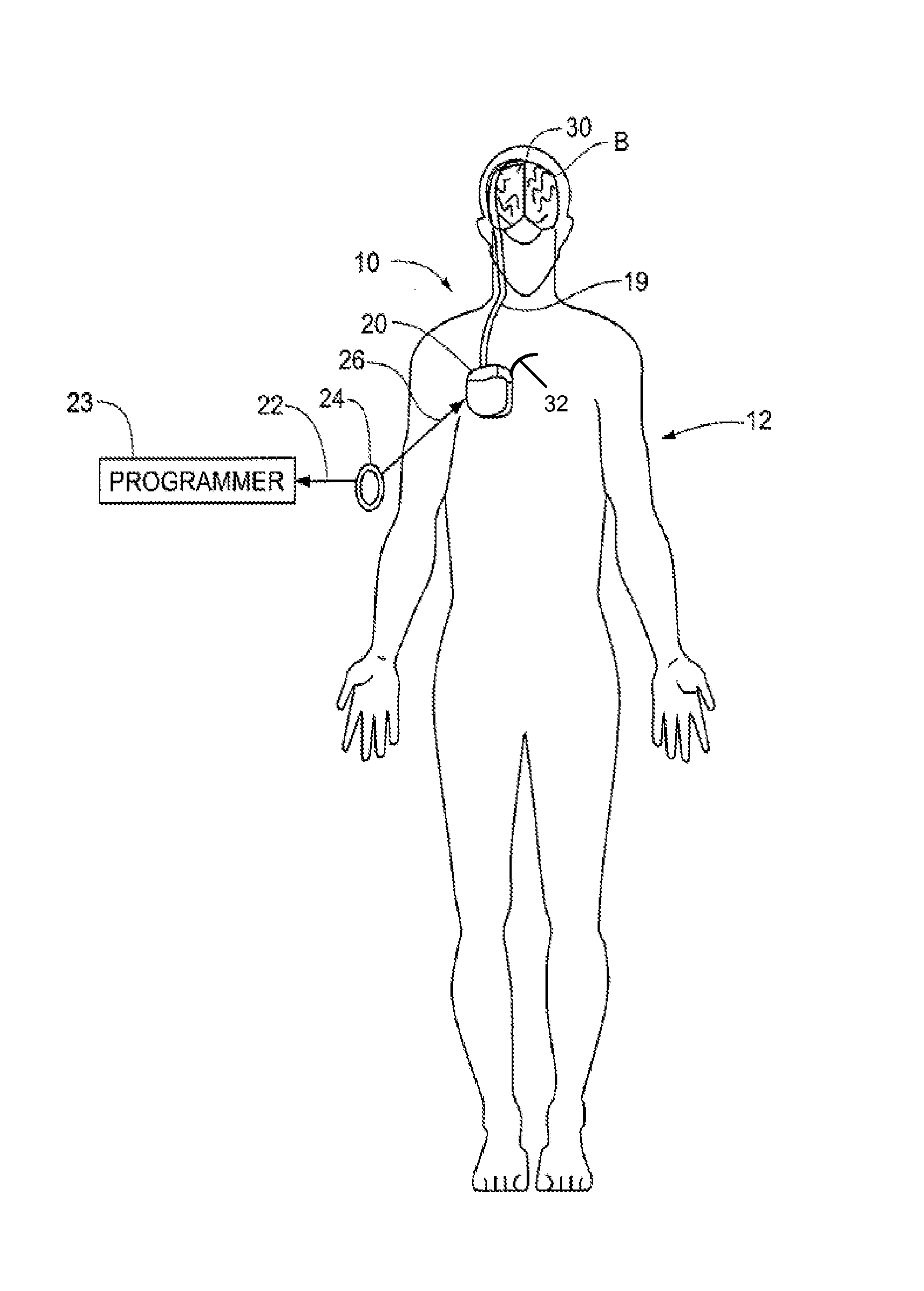
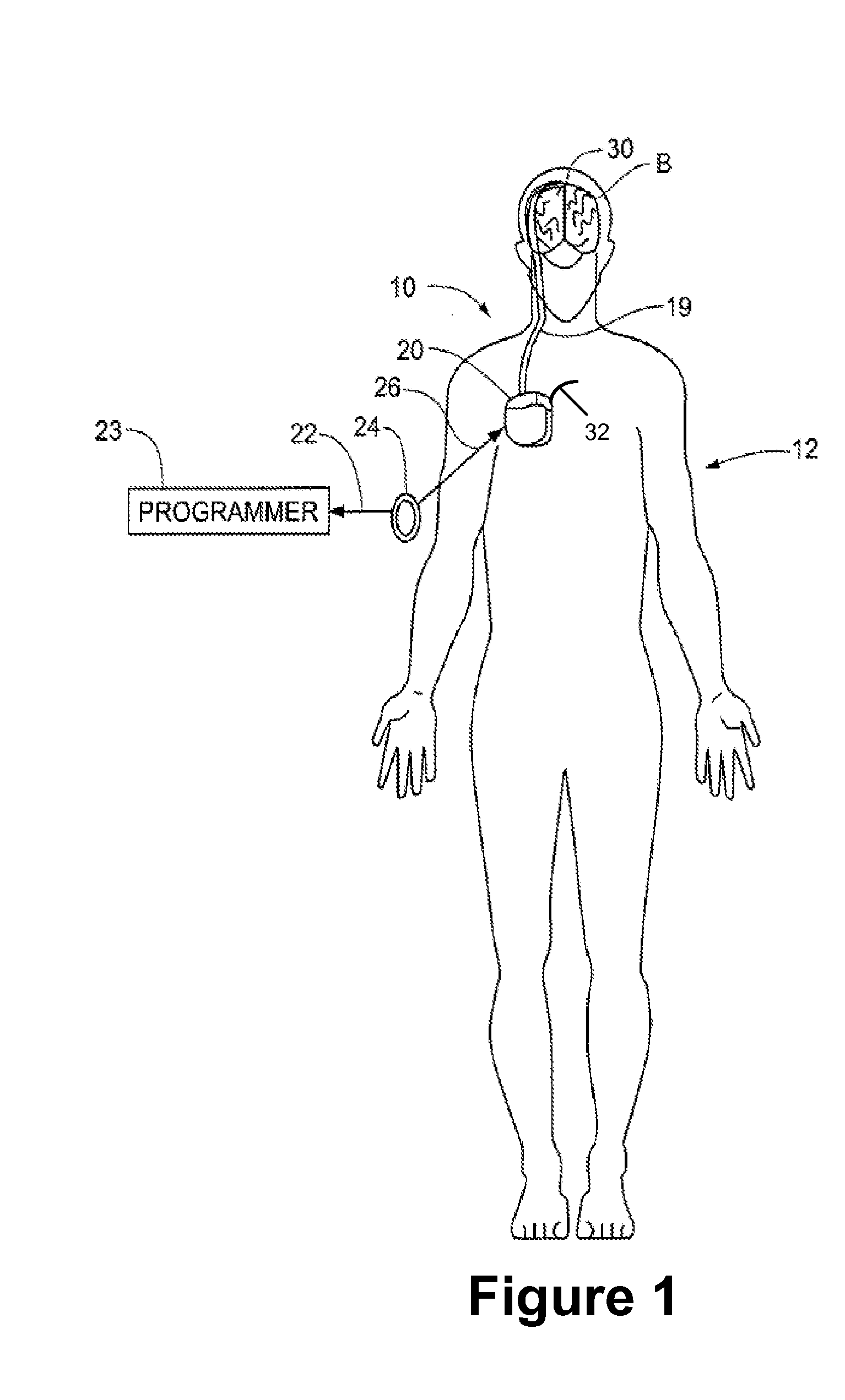
Skull-mounted electrical stimulation system and method for treating patients
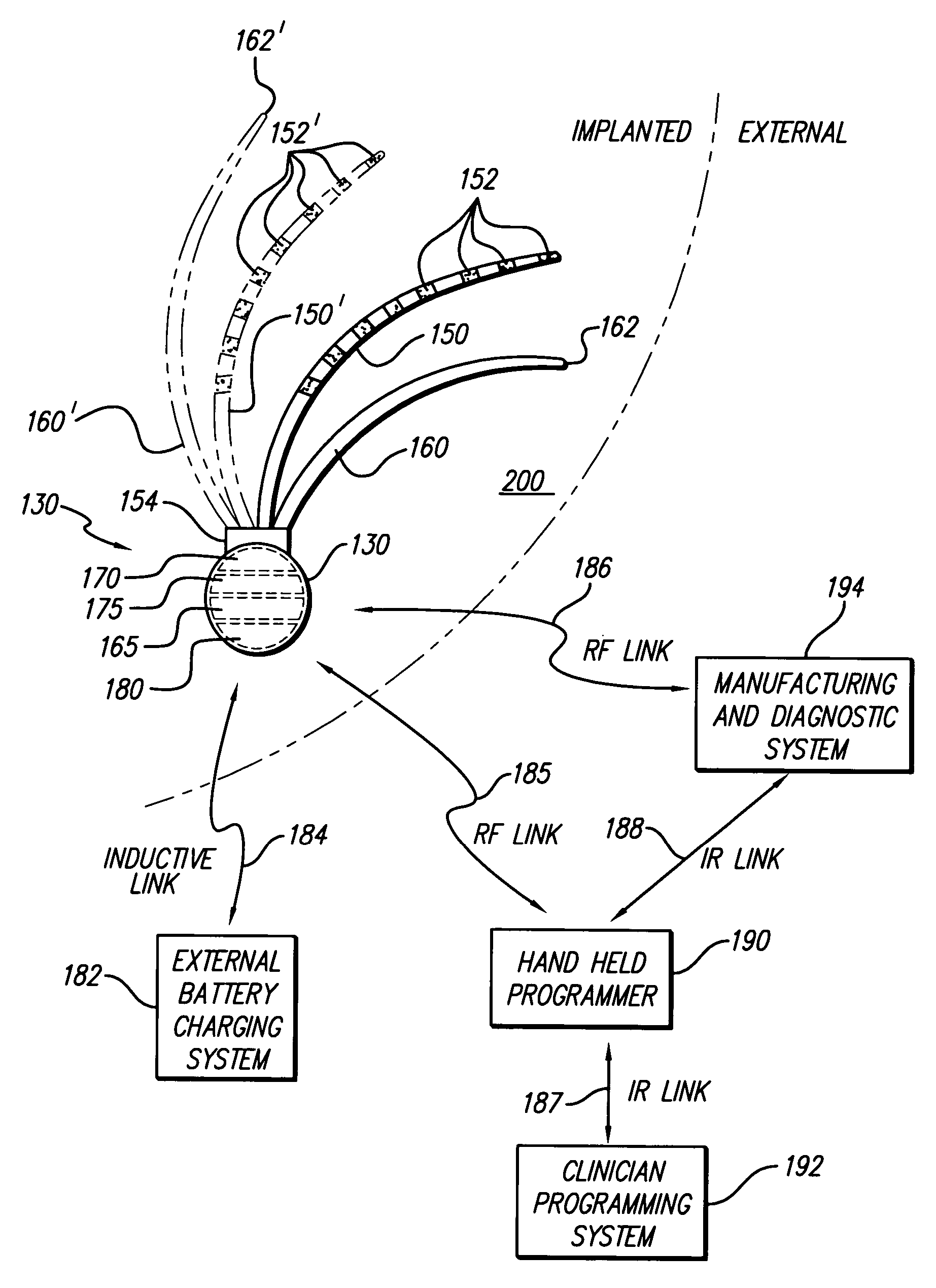
ActiveUS20060293723A1Extension of timeMinimal discomfortHead electrodesMedical devicesDrugs infusionClosed loop
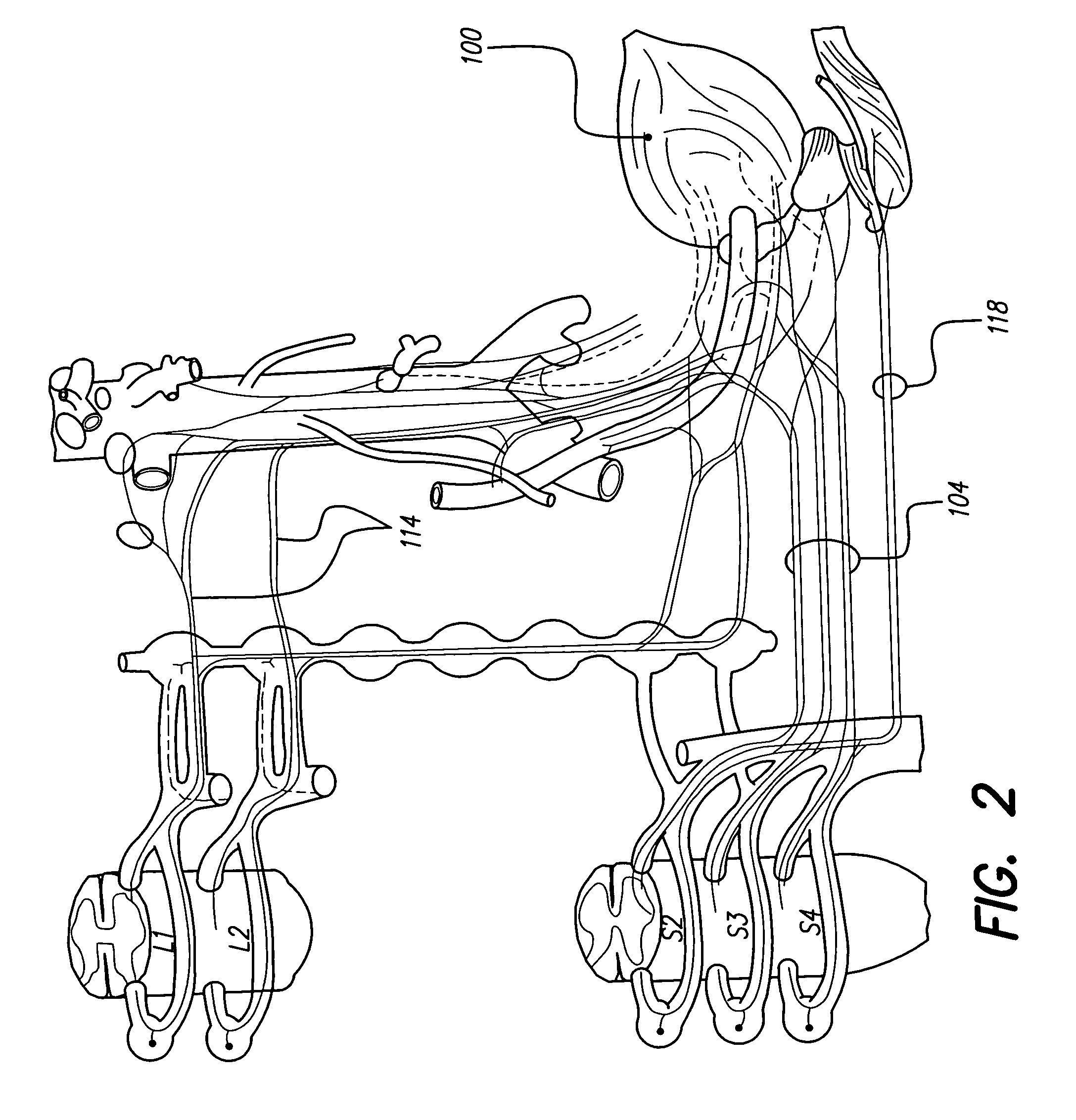
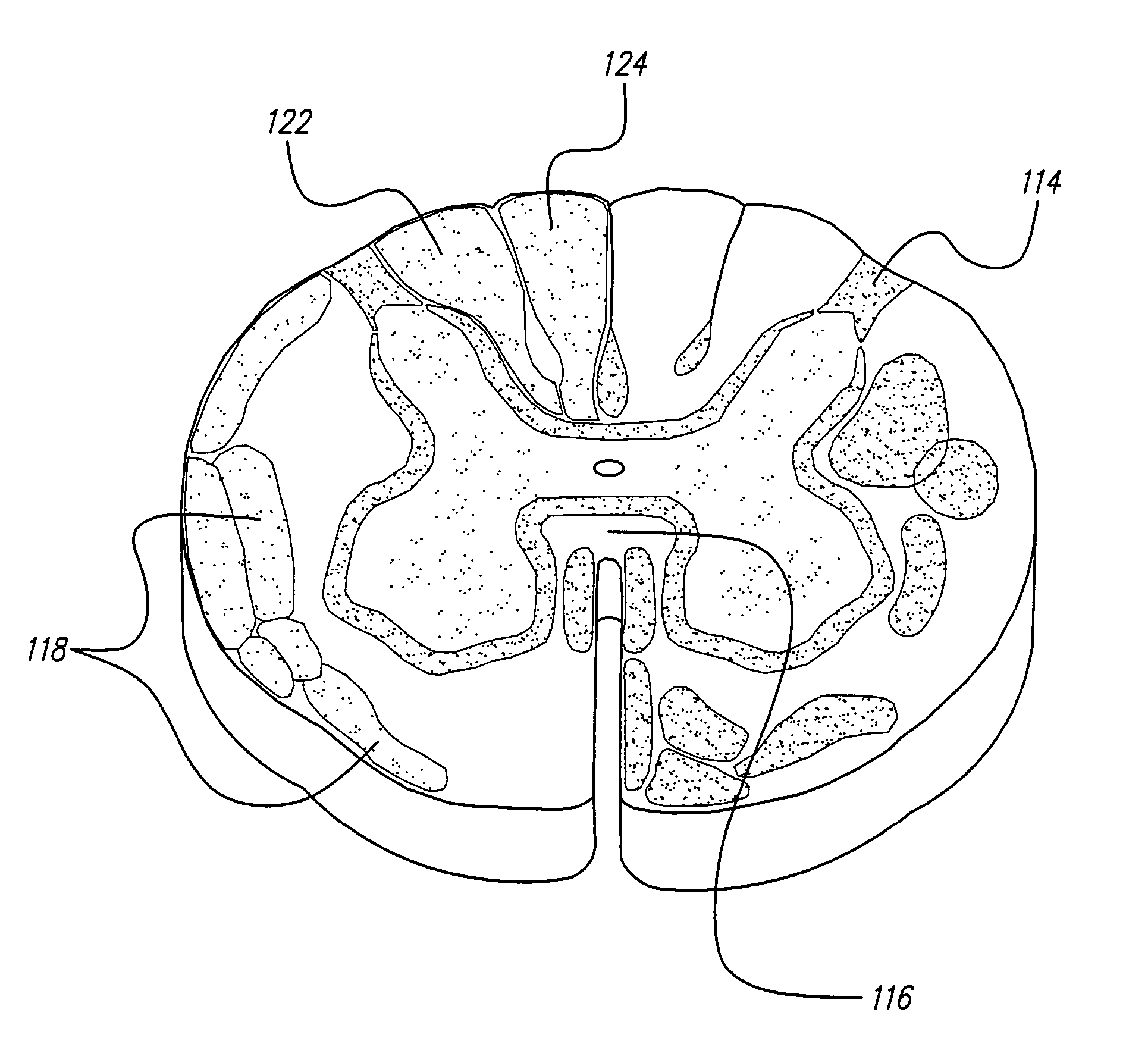
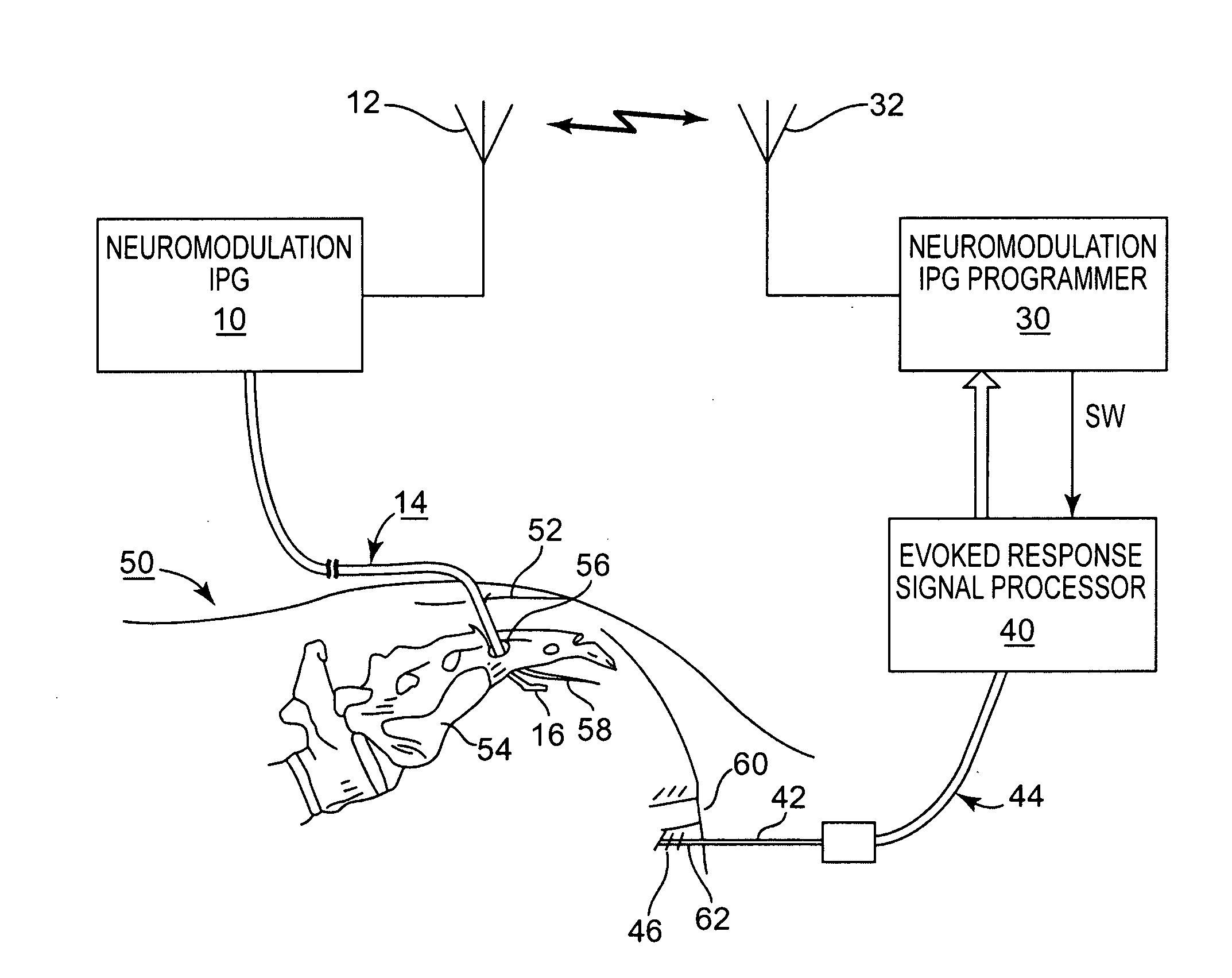
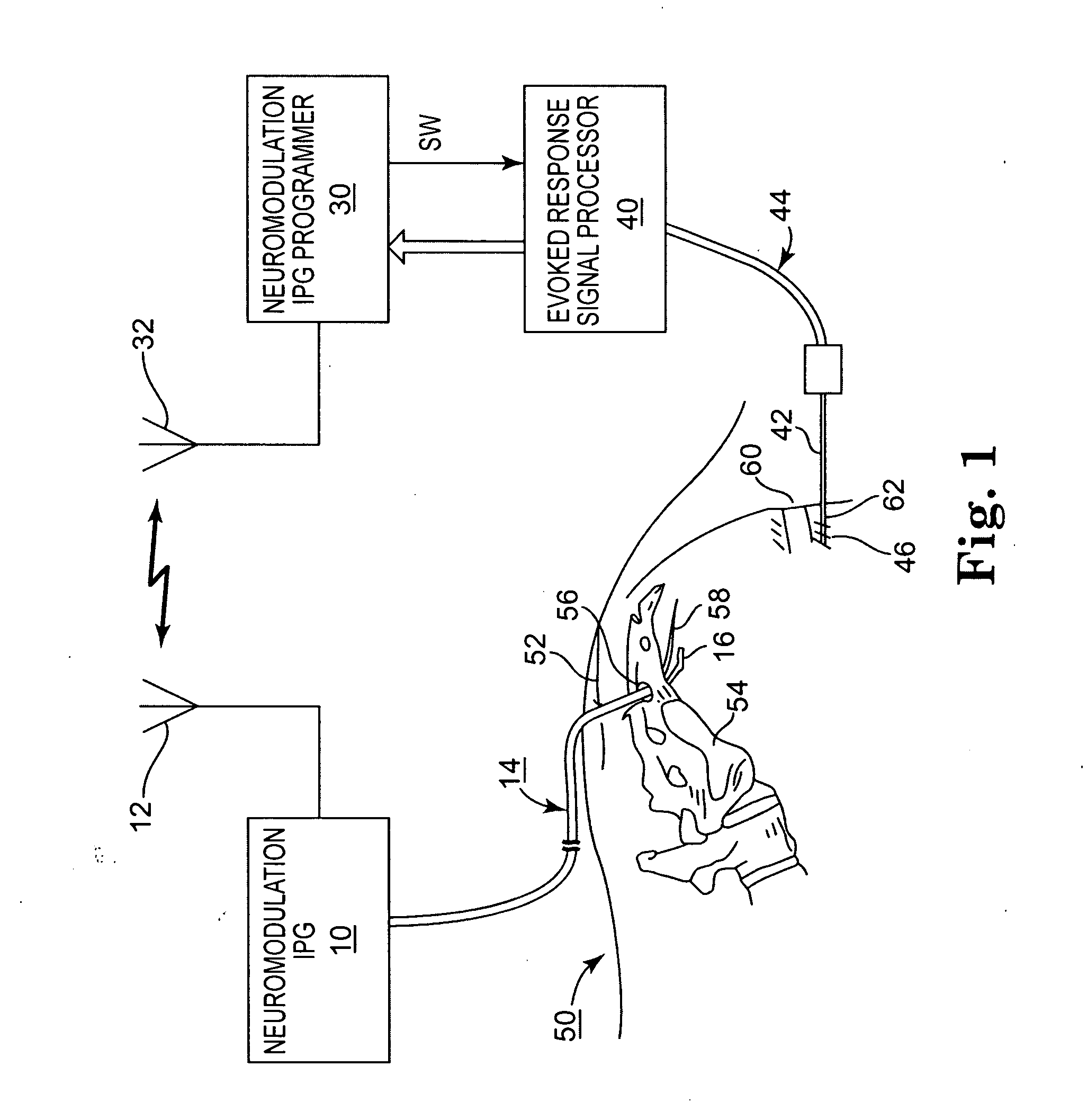
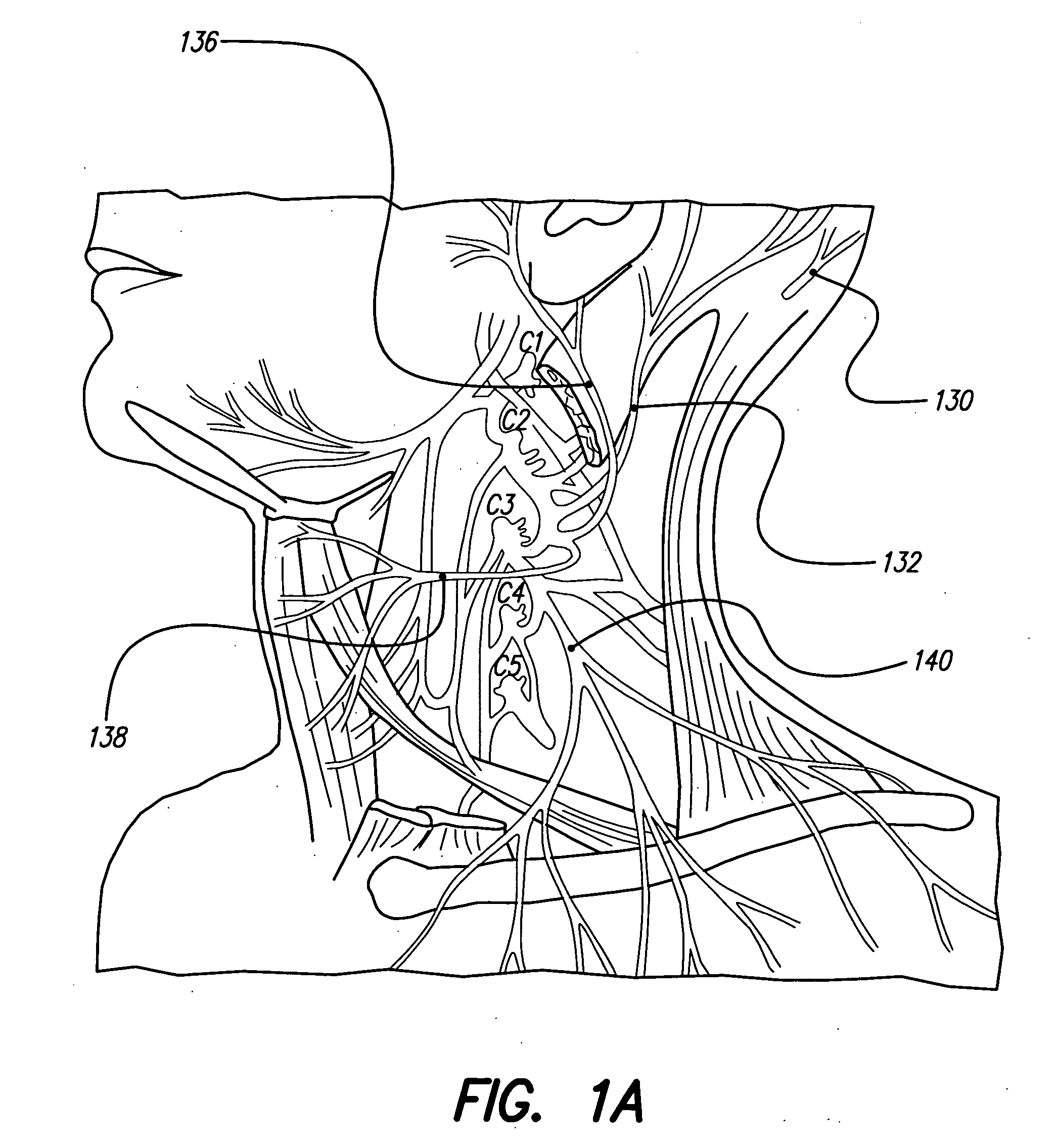
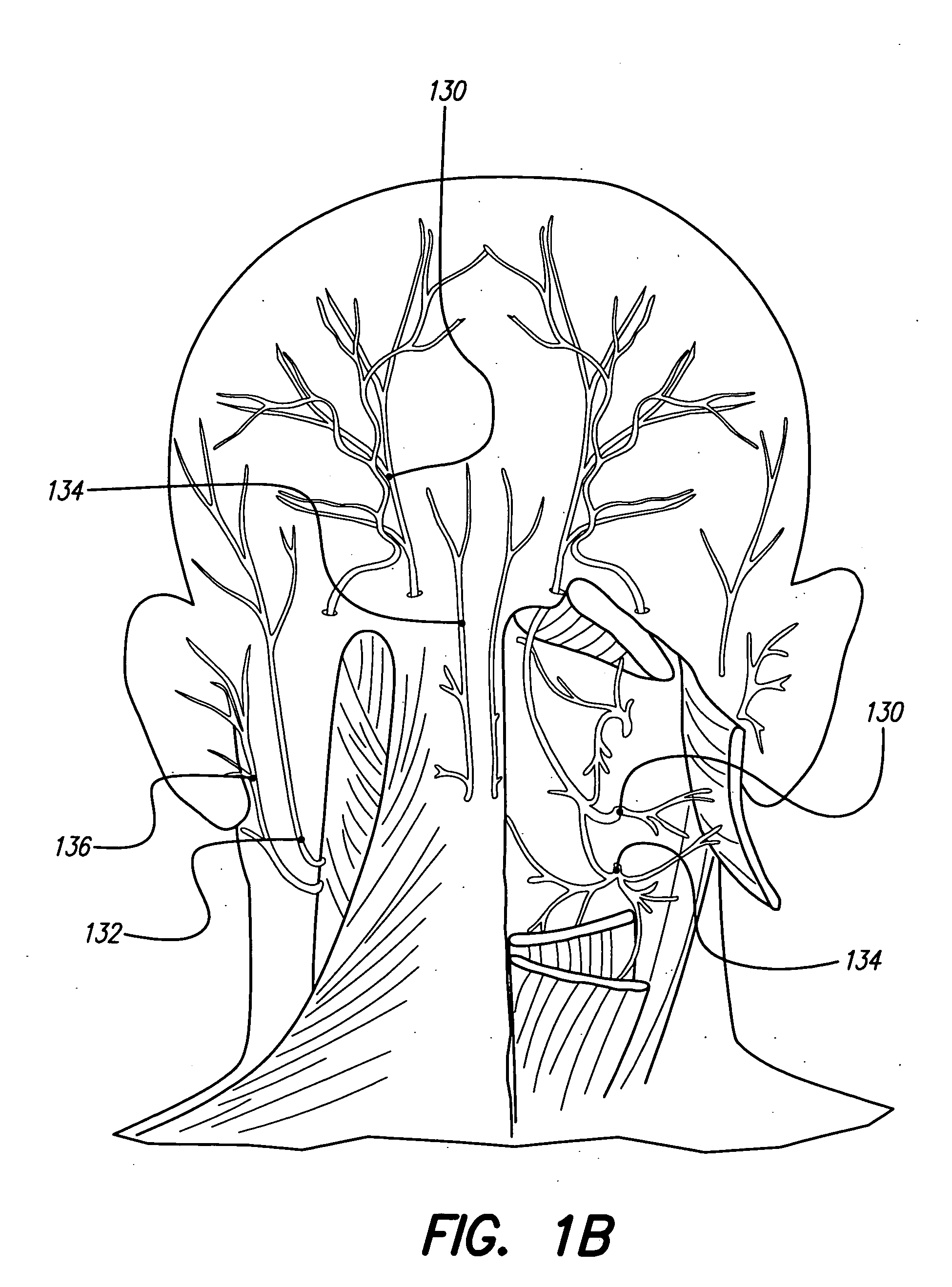
A system and method for applying electrical stimulation or drug infusion to nervous tissue of a patient to treat epilepsy, movement disorders, and other indications uses at least one implantable system control unit (SCU) (110), including an implantable signal / pulse generator (IPG) and one or more electrodes (152, 152′). The IPG is implanted in the mastoid area (143) of the skull (140) and communicates with at least one external appliance (230), such as a Behind-the-Ear (BTE) unit (100). In a preferred embodiment, the system is capable of open- and closed-loop operation. In closed-loop operation, at least one SCU includes a sensor, and the sensed condition is used to adjust stimulation parameters.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Treatment of pain by brain stimulation
InactiveUS7013177B1Treating and preventing painIncrease excitementHead electrodesElectricityMedicine
Systems and methods for introducing one or more stimulating drugs and / or applying electrical stimulation to the brain to alleviate pain use at least one implantable system control unit (SCU), producing electrical pulses delivered via electrodes implanted in the brain and / or producing drug infusion pulses, wherein the stimulation is delivered to targeted areas in the brain. In some embodiments, one or more sensed conditions are used to adjust stimulation parameters.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Enhancement of neural signal transmission through damaged neural tissue via hyperpolarizing electrical stimulation current
ActiveUS7877136B1Enhanced signalSpread the wordElectrotherapyArtificial respirationElectricityPower flow
Methods and systems of enhancing transmission of a neural signal through damaged neural tissue include providing a stimulator, programming the stimulator with one or more stimulation parameters configured to enhance transmission of a neural signal through the damaged neural tissue, and applying a hyperpolarizing electrical stimulation current with the stimulator to the damaged neural tissue in accordance with the one or more stimulation parameters.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Testing Efficacy of Therapeutic Mechanical or Electrical Nerve or Muscle Stimulation
InactiveUS20070265675A1Rule out the possibilityReduce complicationsElectrotherapyMuscle tissuePelvic nerve
Methods and apparatus for testing of the efficacy of therapeutic stimulation of pelvic nerves or musculature to alleviate one of incontinence or sexual dysfunction are disclosed. A therapy delivery device is operable in a therapy delivery mode and a test mode and an evoked response detector is employed in the test mode to detect the evoked response to applied test stimuli. The test stimuli parameters of the test stimulation regimen are adjusted prior to delivery of each test stimulation regimen, and the evoked responses to the applied test stimulation regimens are compared to ascertain an optimal test stimulation regimen. The therapy stimulation regimen parameters are selected as a function of the test electrical stimulation parameters causing the optimal evoked response.
Owner:AMS RES CORP
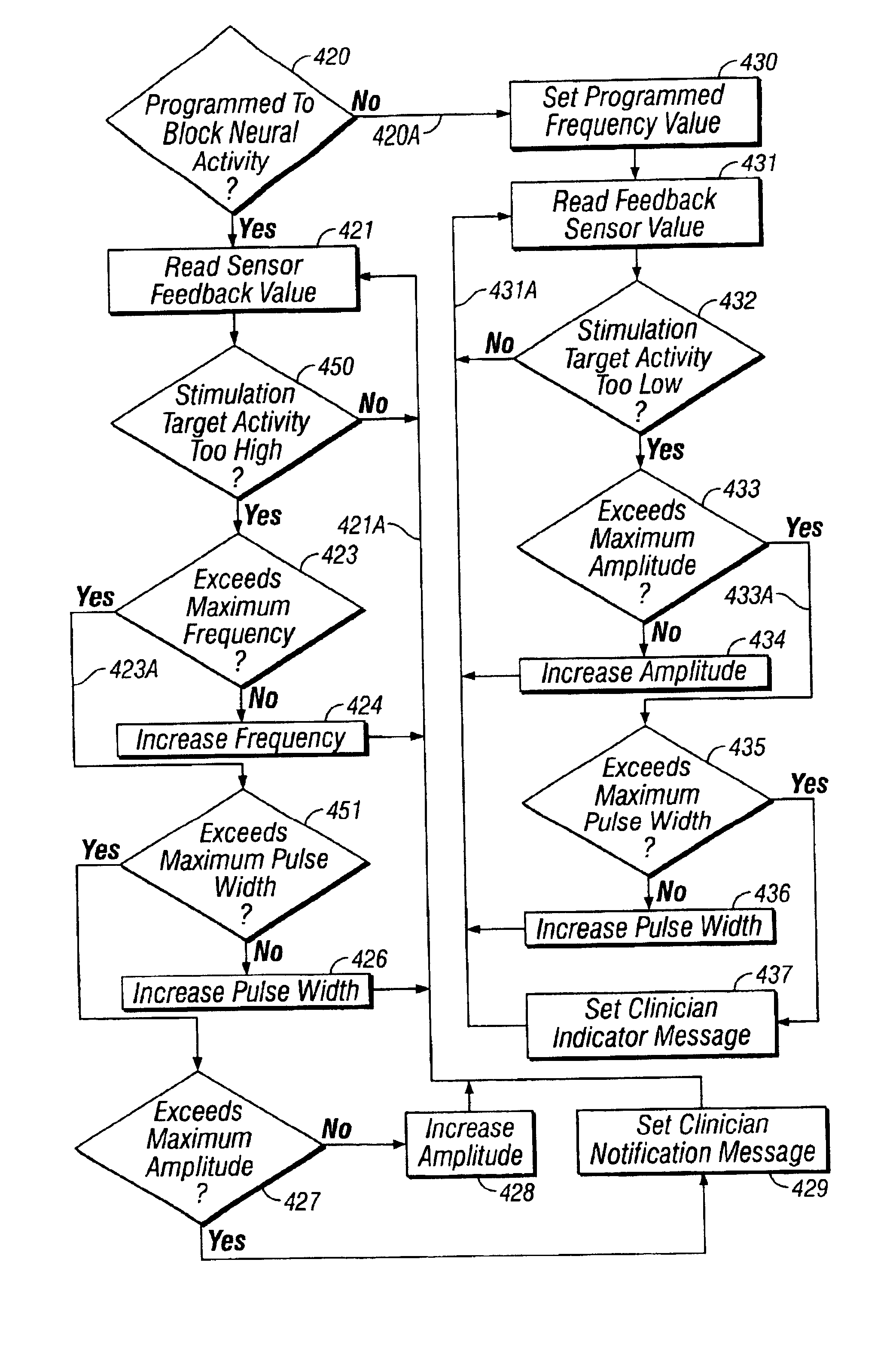
Method for determining stimulation parameters
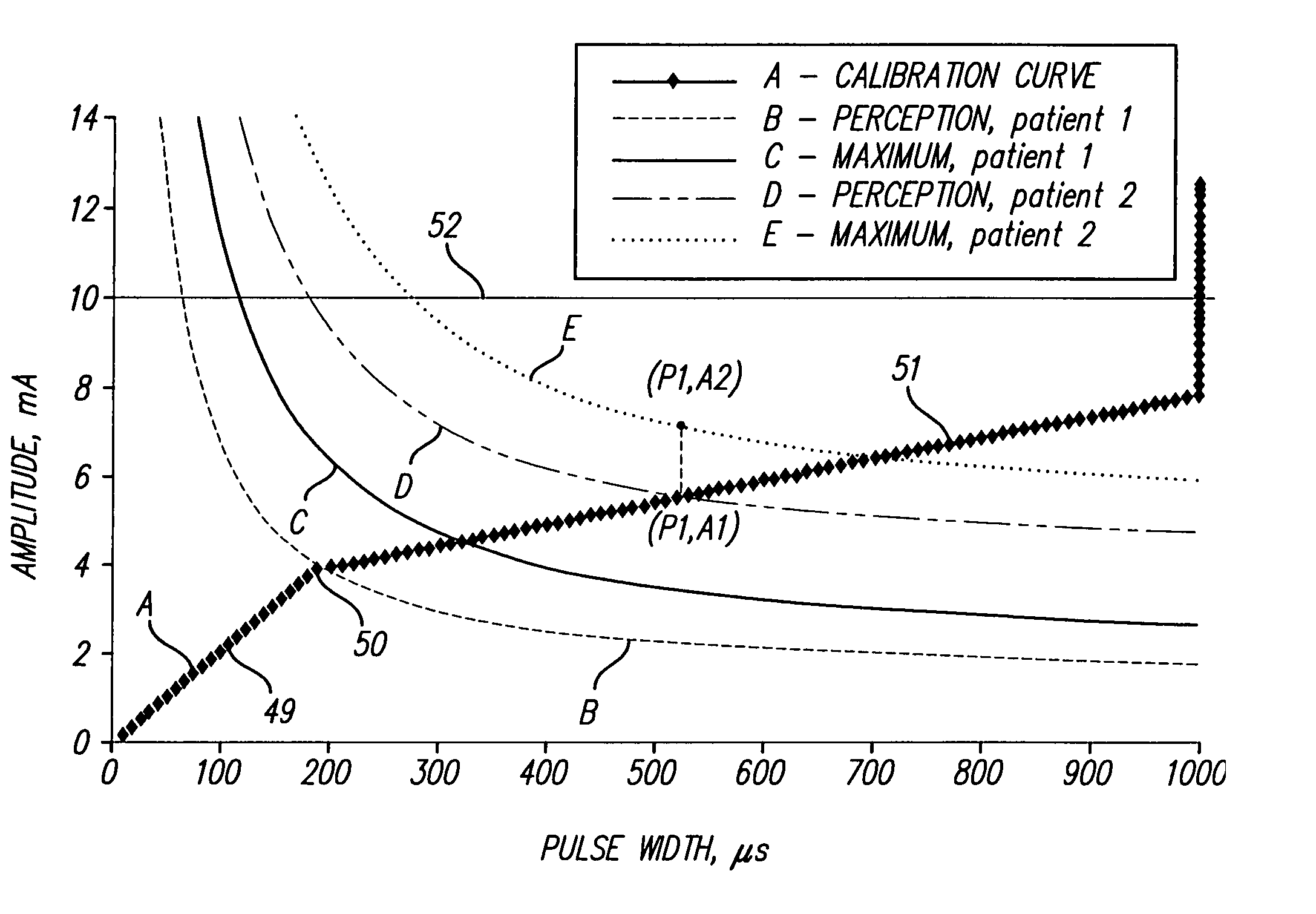
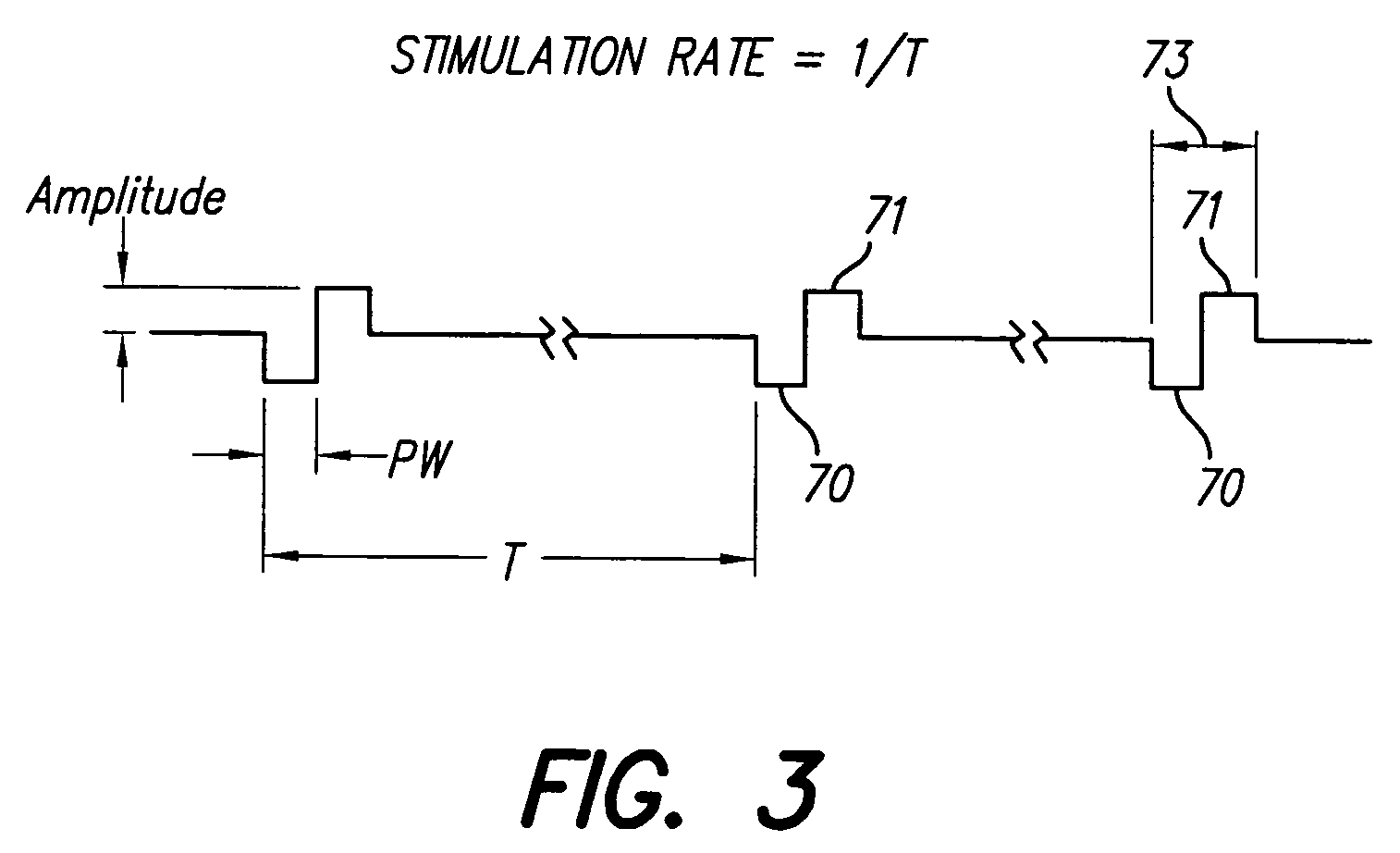
InactiveUS7174215B2Efficiently determinedElectrotherapyArtificial respirationMedicineCalibration curve
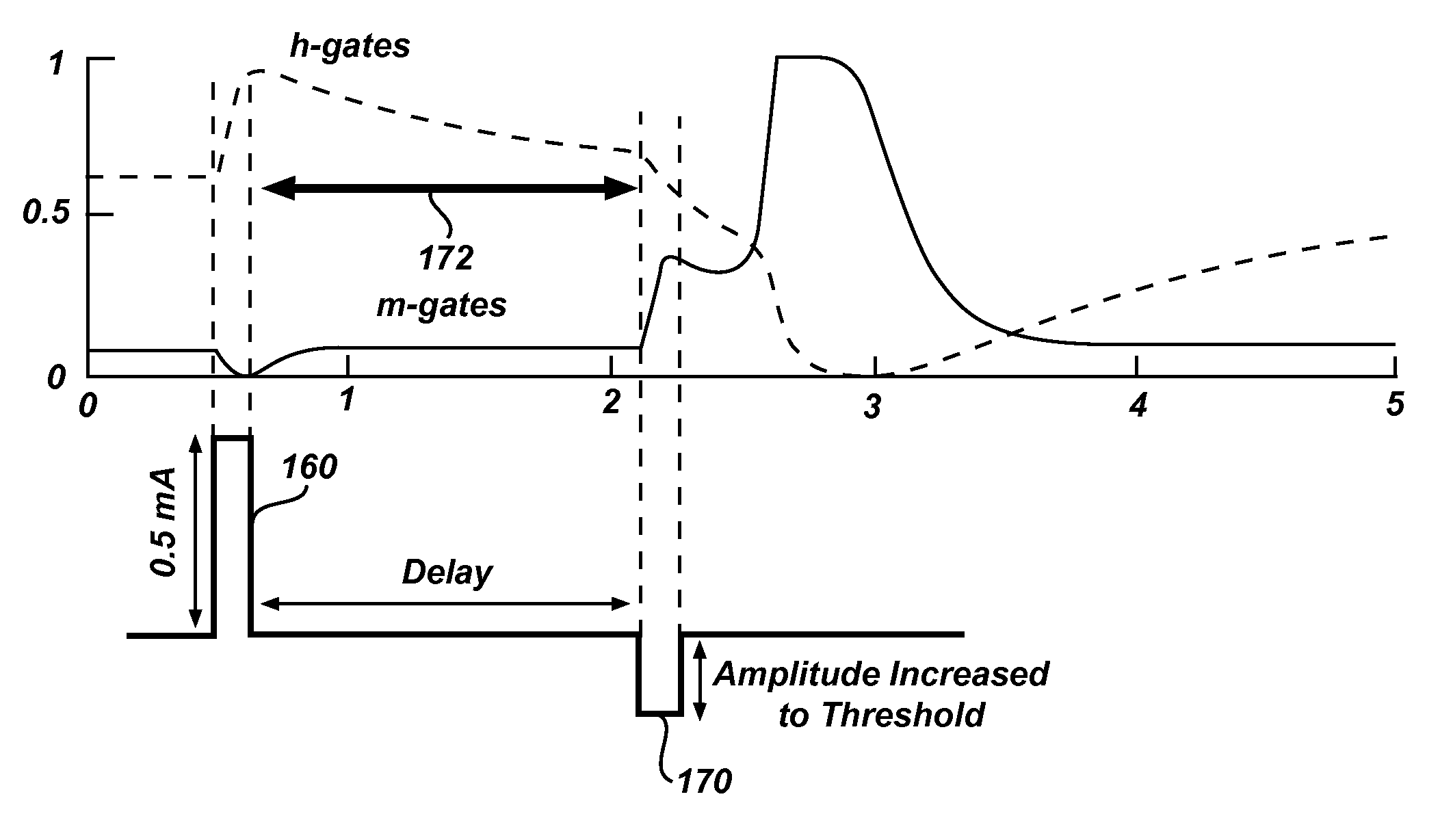
A method is provided for determining optimal stimulus pulsewidth and stimulus amplitude for stimulating nerves with at least one electrode (17). The method comprises: providing a predetermined calibration curve comprising a set of pulsewidth and amplitude values; and delivering sets of pulsewidths and amplitude values which are part of the calibration curve to the at least one electrode (17) to determine at least the optimal pulsewidth. A pulsewidth (70) and an amplitude can be efficiently selected that is efficacious and provides an ample clinical usage range (UR).
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
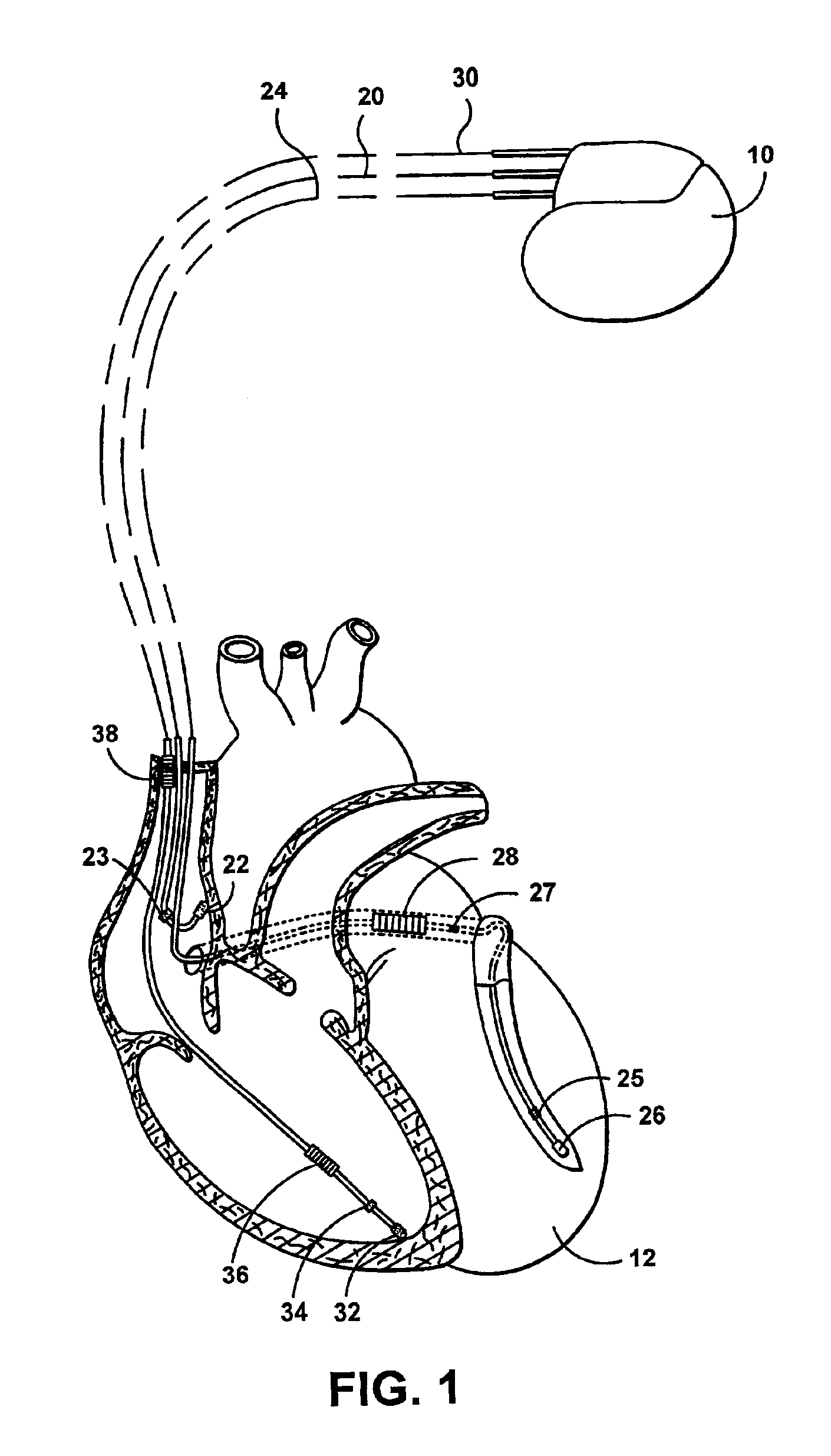
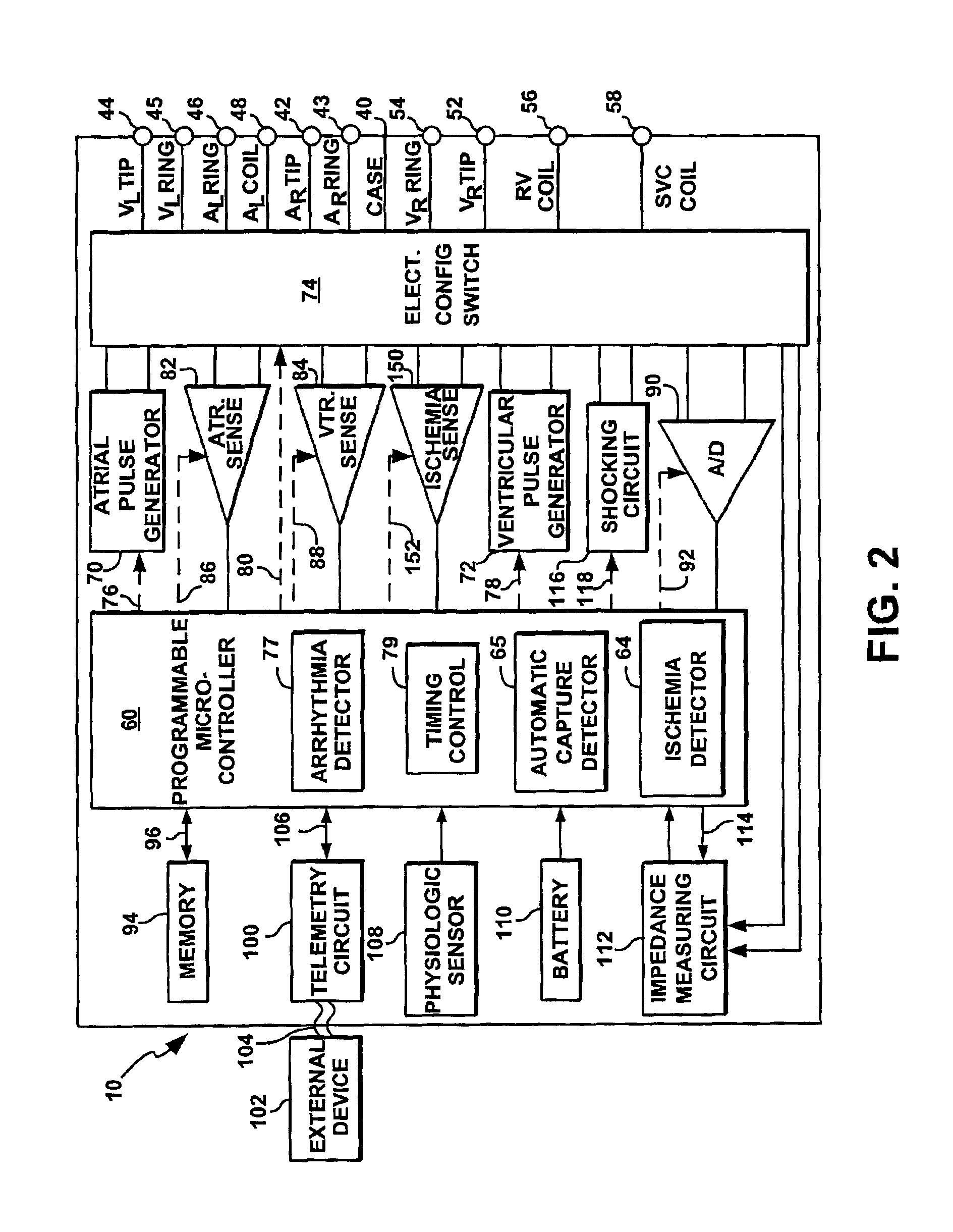
Cardiac stimulation device for optimizing cardiac output with myocardial ischemia protection
InactiveUS6865420B1Reduce demandReduce detectionHeart stimulatorsCardiac muscleIntracardiac Electrogram
A cardiac stimulation device and method detect myocardial ischemia and provide a response for alleviating the ischemia. Myocardial ischemia is detected by identifying changes in the ST-segment of the intracardiac electrogram (EGM) sensed using large sensing electrode surfaces created by electrically coupling one or more cardiac electrodes or by using larger surface area shocking coils. Myocardial ischemia monitoring is performed when stimulation parameters are adjusted for increasing cardiac output, causing an increased metabolic demand to be placed on the myocardium itself. When myocardial ischemia is detected, stimulation parameters are re-adjusted to reduce the demand placed on the myocardium and thereby alleviate the ischemia.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
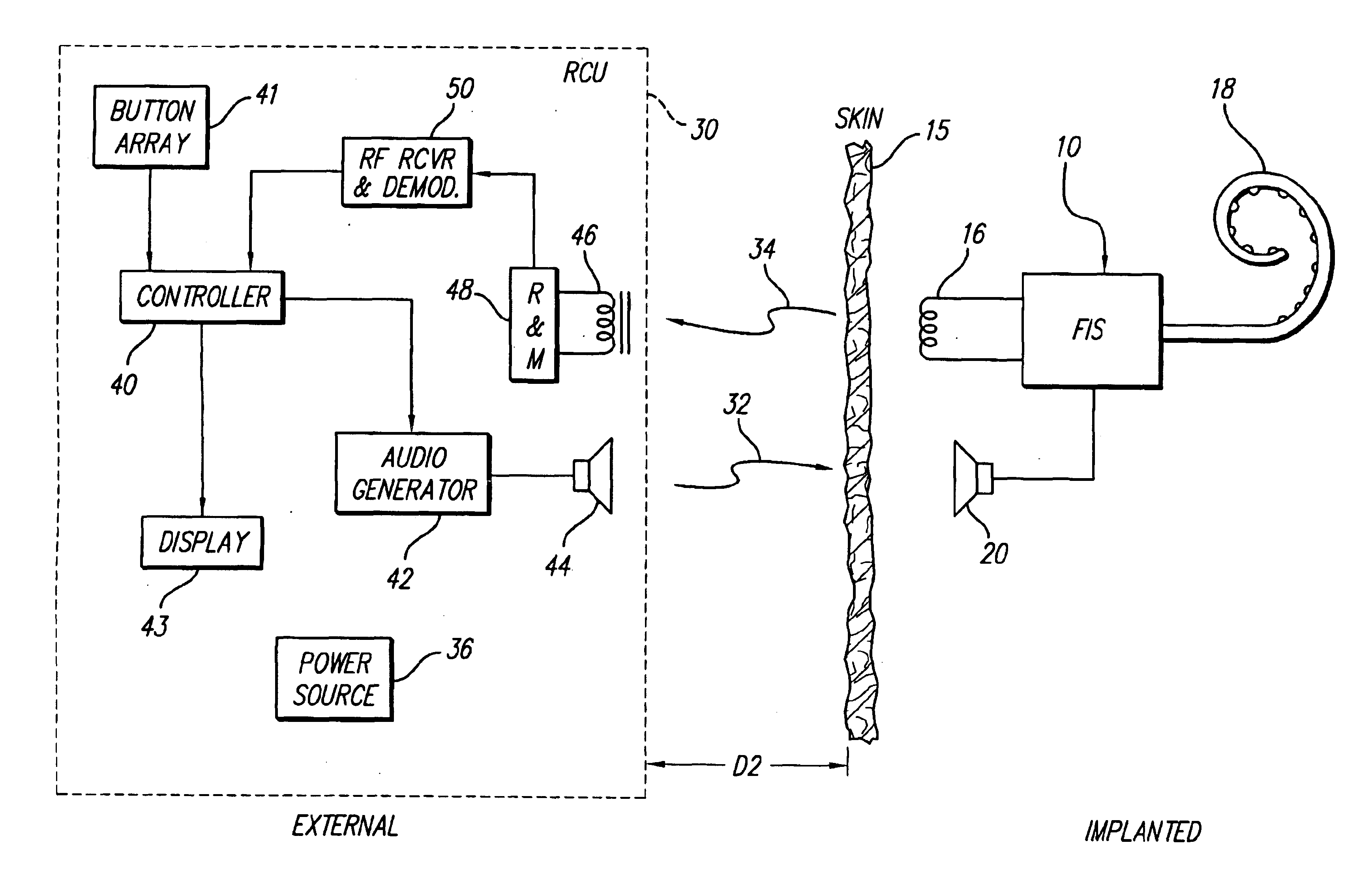
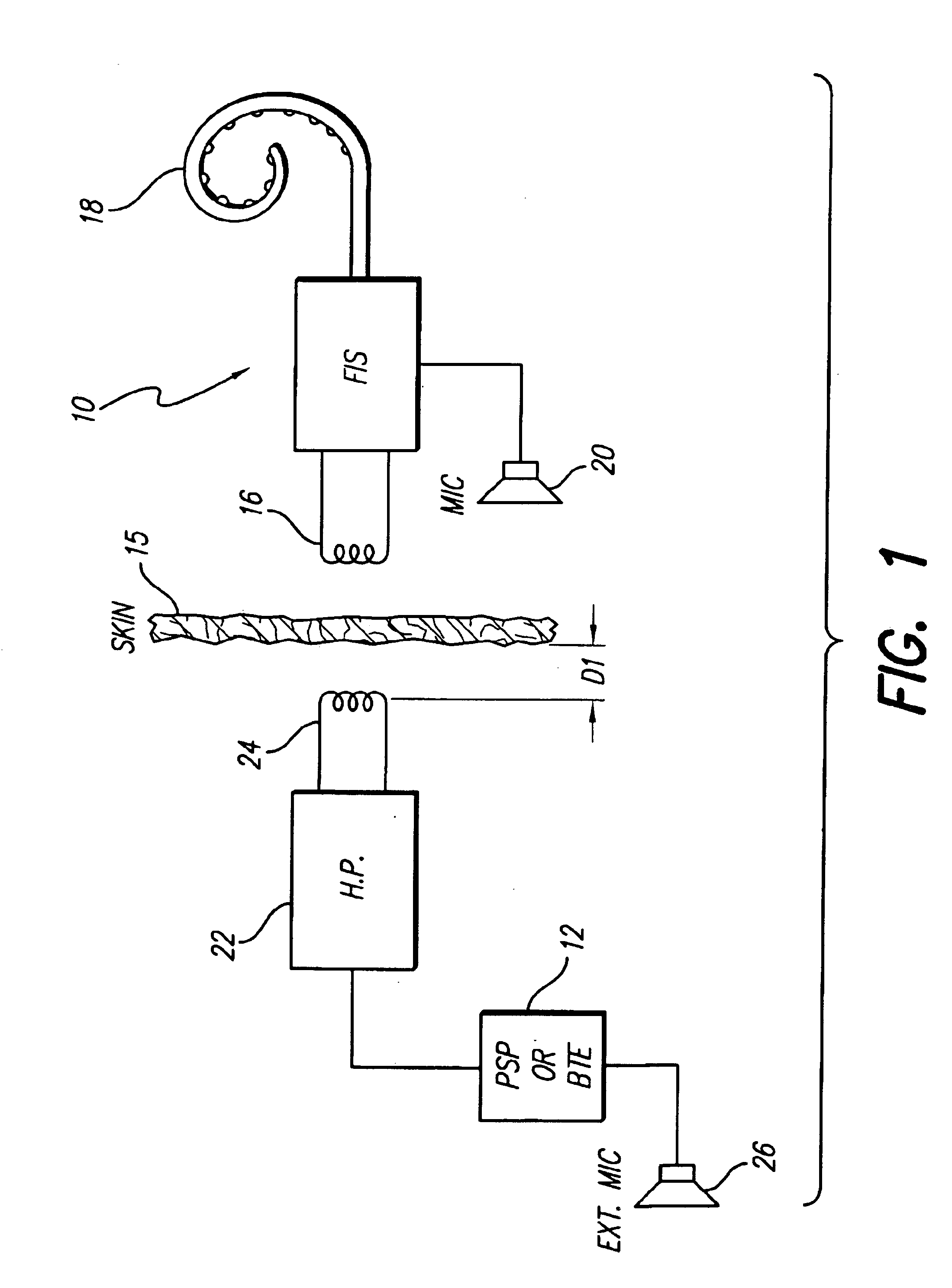
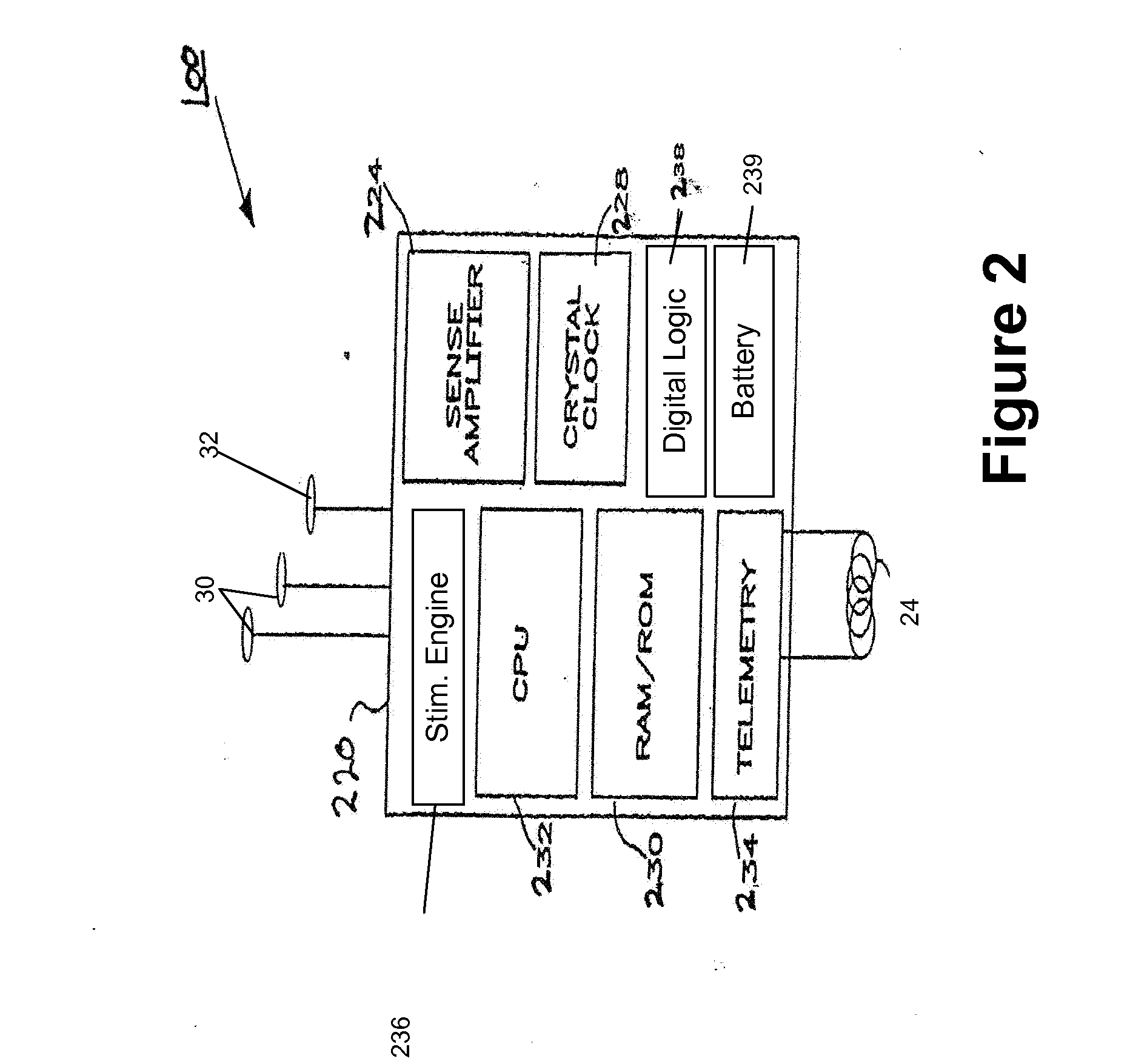
Implantable neural stimulator system including remote control unit for use therewith
InactiveUS6842647B1Reliable transmissionElectrotherapyImplantable hearing aidsControl signalRemote control
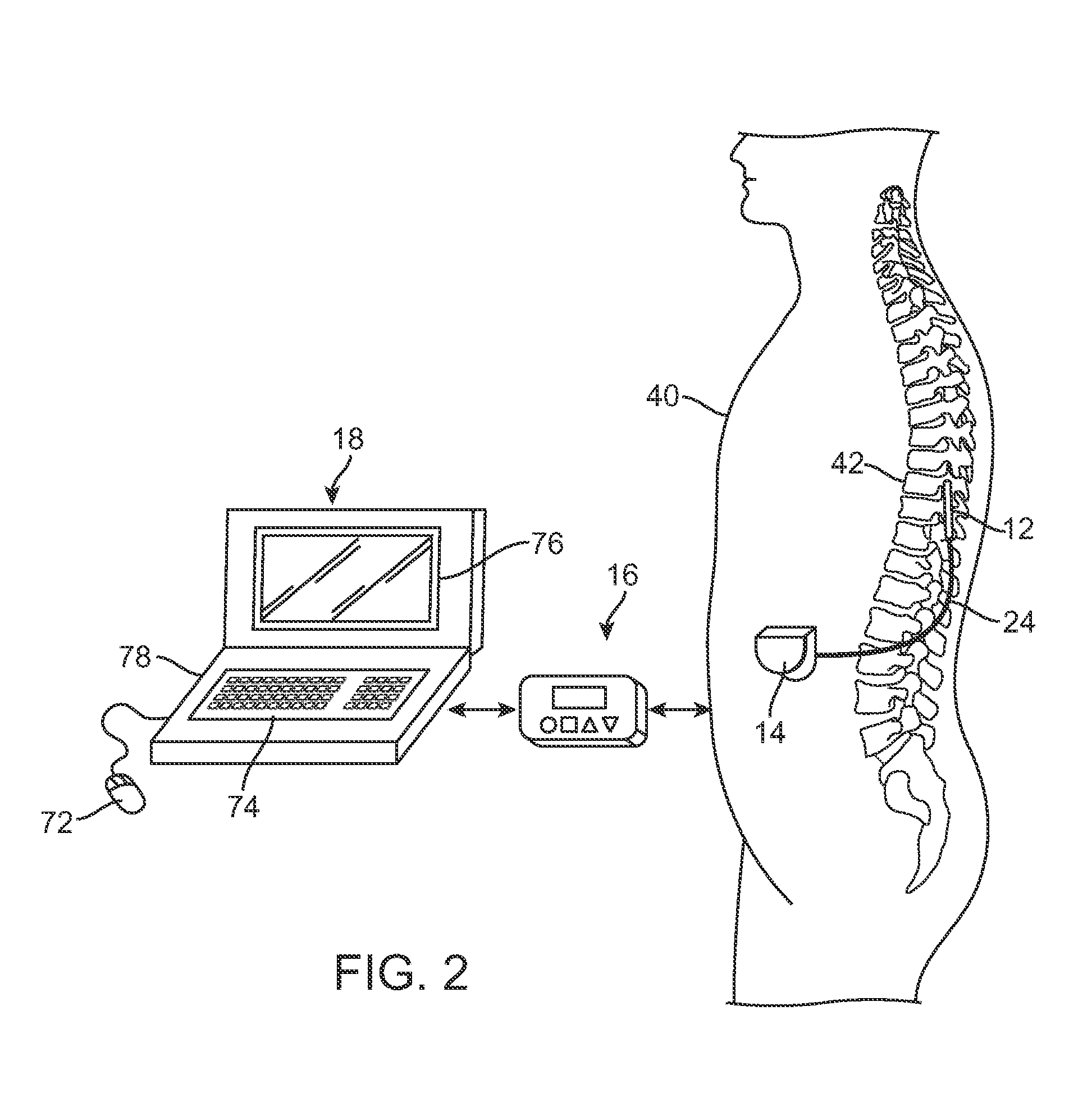
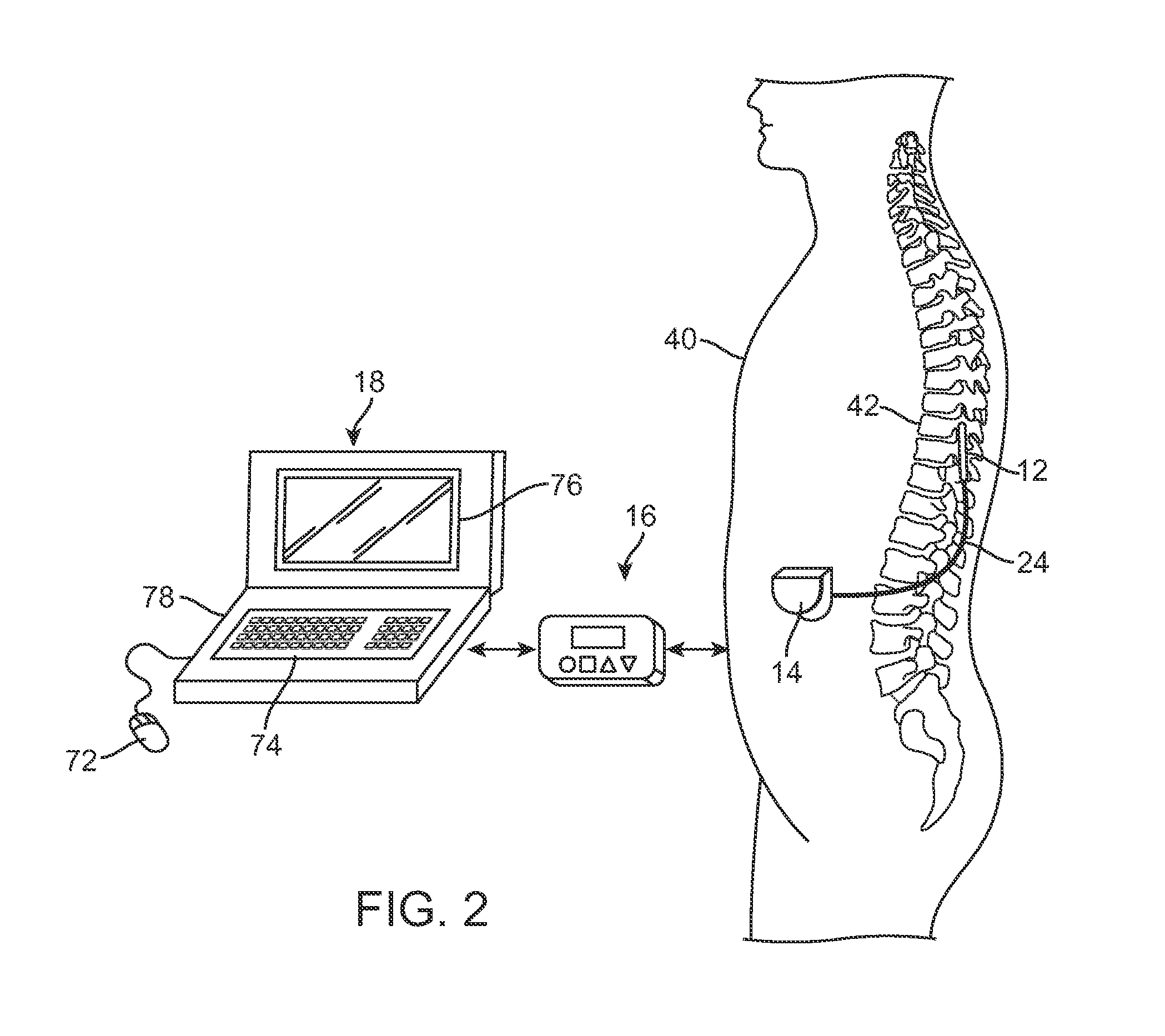
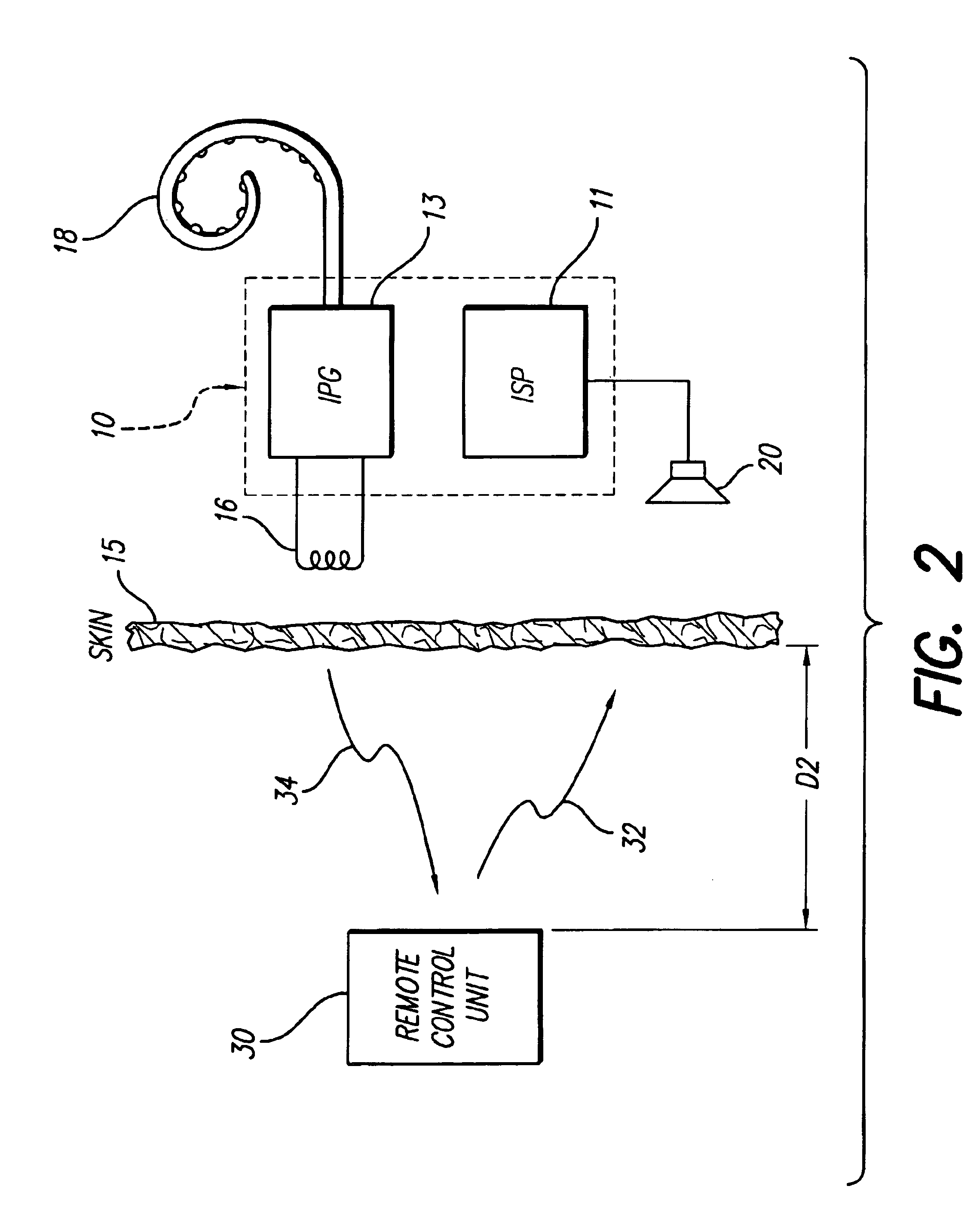
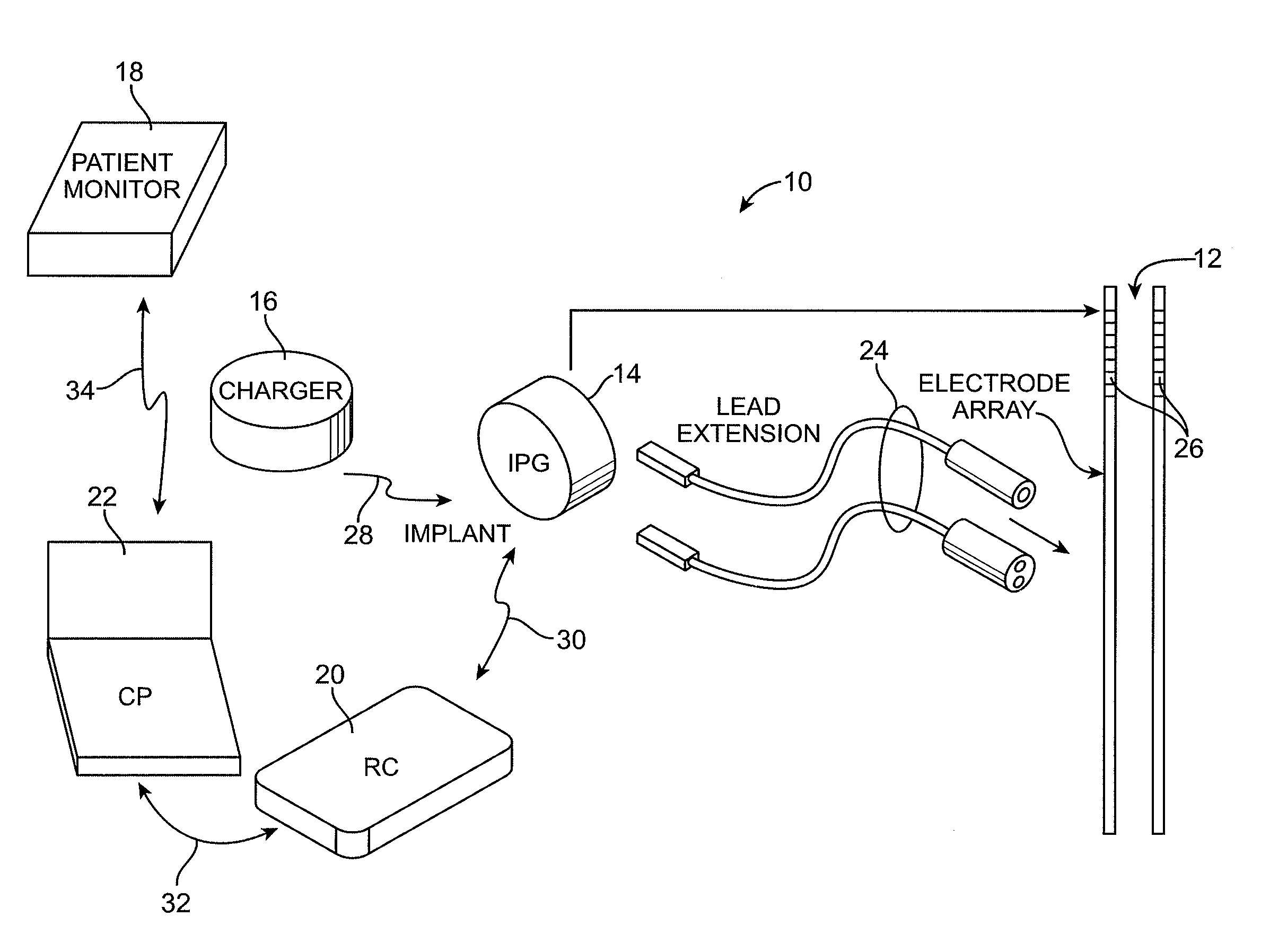
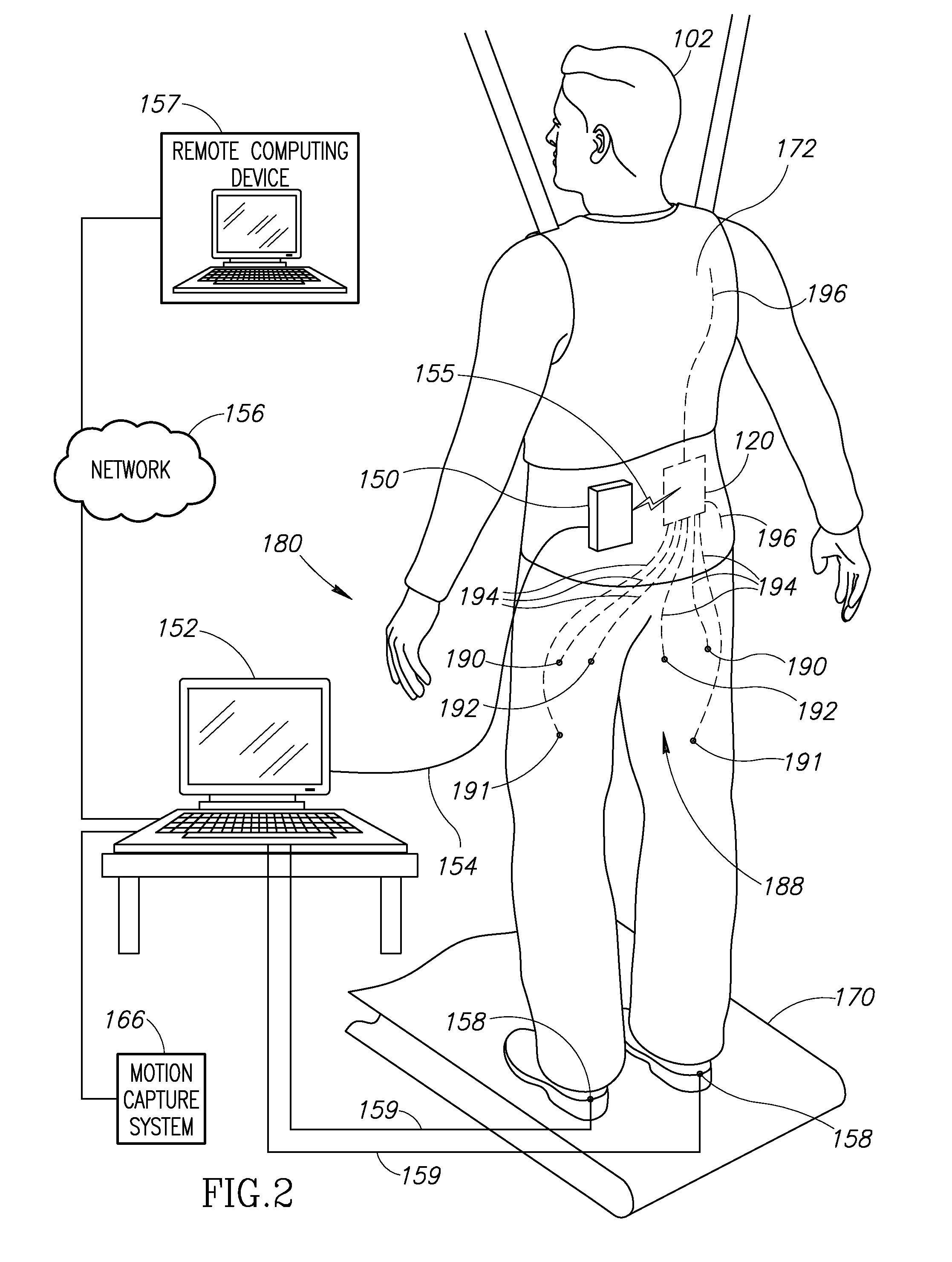
An implantable neural stimulation system, such as an auditory Fully Implantable System (FIS), includes: (1) an implanted device capable of providing desired tissue or nerve stimulation; and (2) a remote control unit that provides a mechanism for readily controlling the implant device, i.e., for selectively adjusting certain stimulation parameters associated with the tissue stimulation of the implanted device. The remote control unit uses a first signal path to send signals to the implant device, and a second signal path to receive signals from the implant device. The combination of these two signal paths provides a full-duplex channel between the remote control unit and the implant device through which air appropriate control and status signals may be sent and received. In one embodiment, the first signal path comprises an audio signal path through which audio control signals, e.g., a tone sequence or a 32-bit word FSK modulated between 300 and 1200 Hz, are sent; and the second signal path comprises a RF signal path through which a BPSK, QPSK or FM modulated RF signal is received. The full-duplex channel allows operation of the remote control unit, i.e., allows signals to be successfully sent to and received from the implant device, from as far away as 45-60 cm from the implant device.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
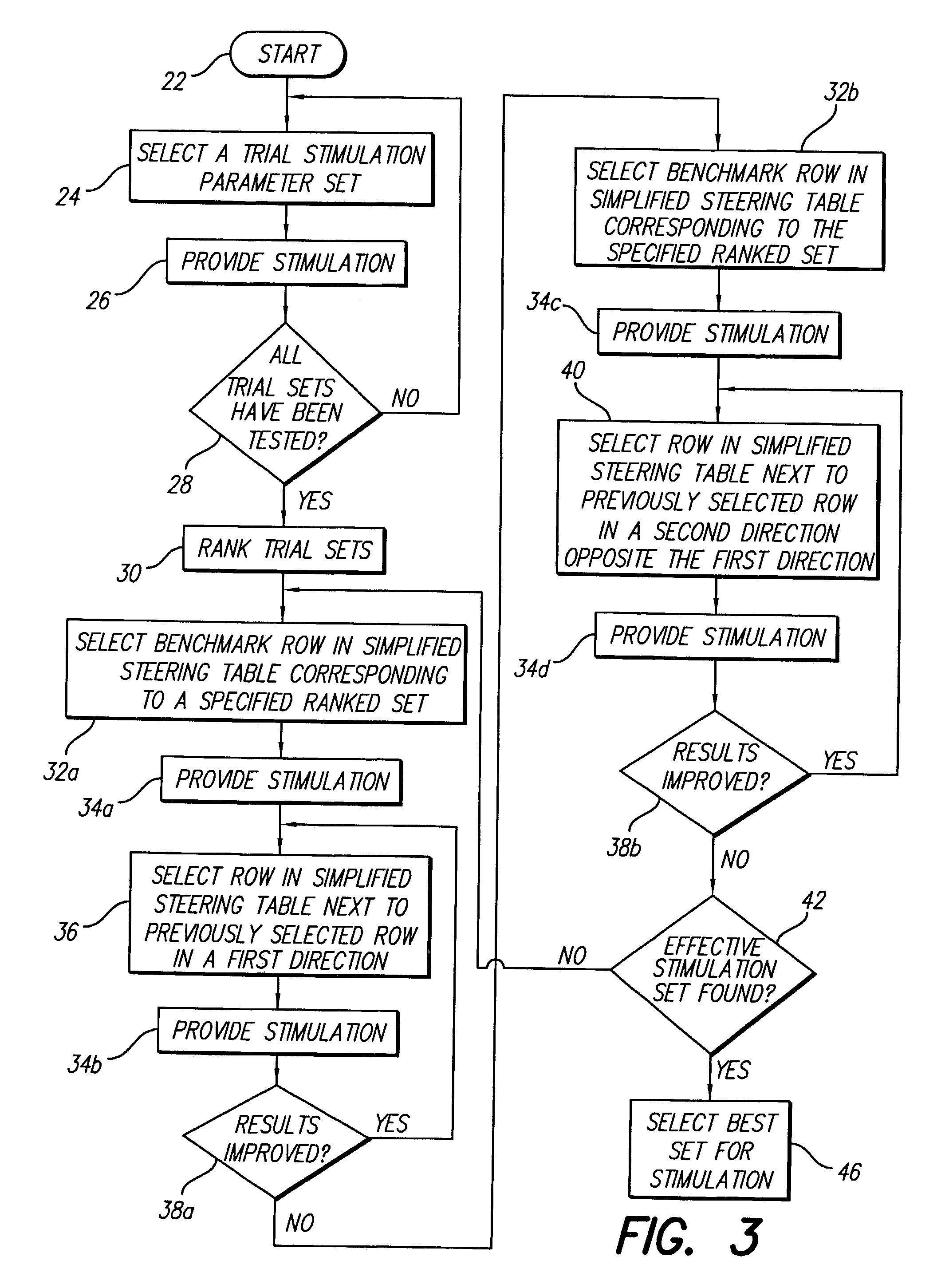
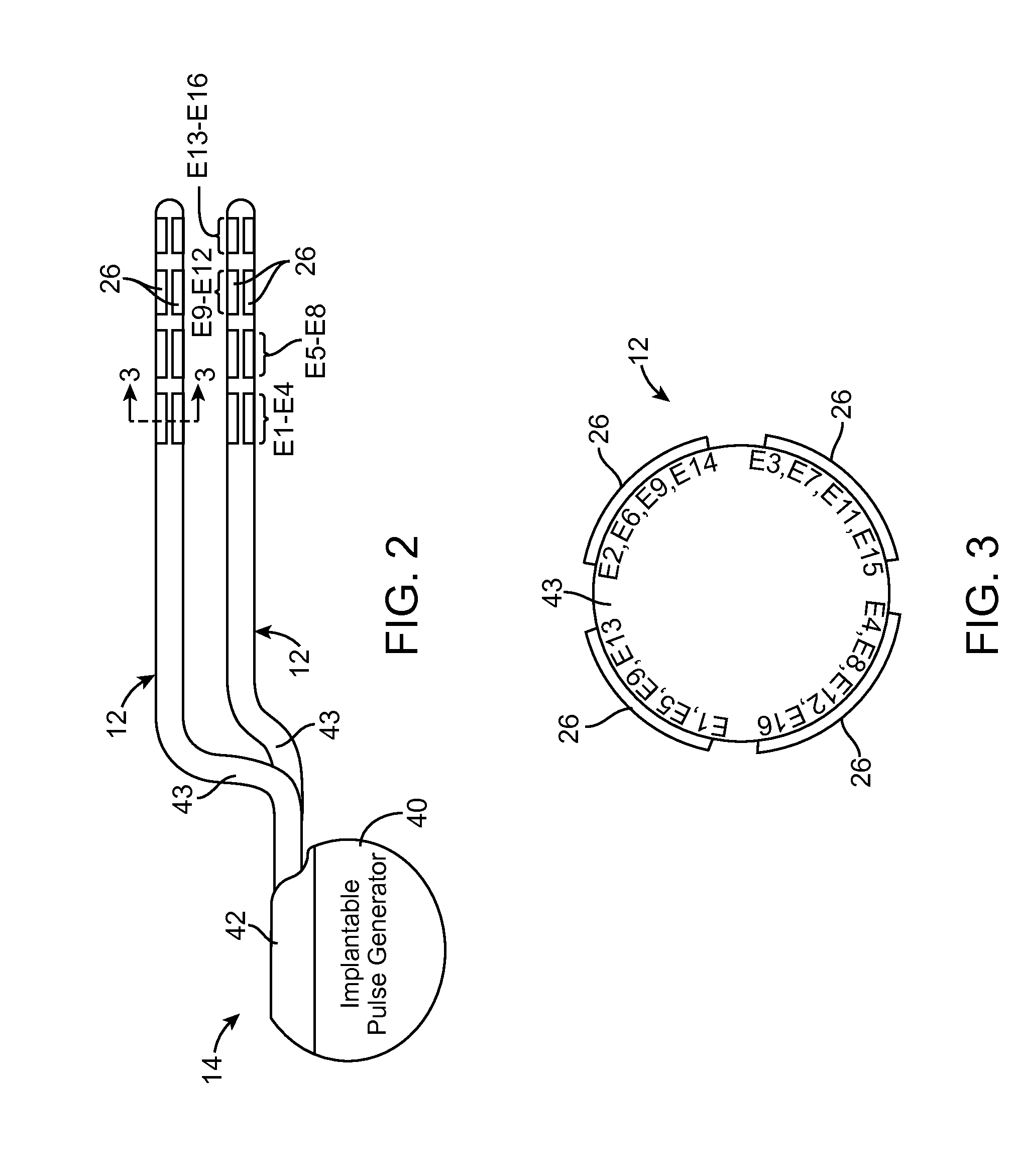
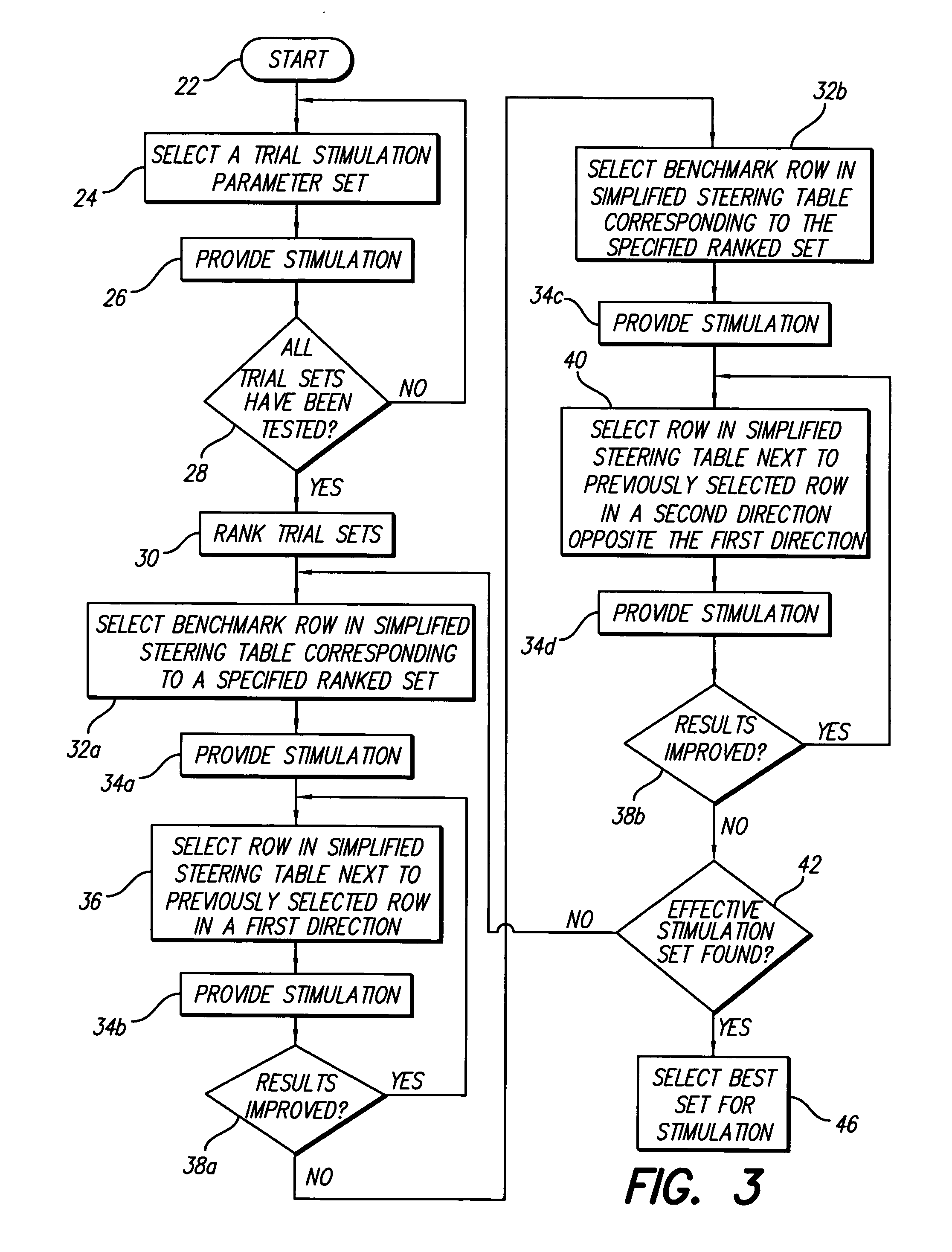
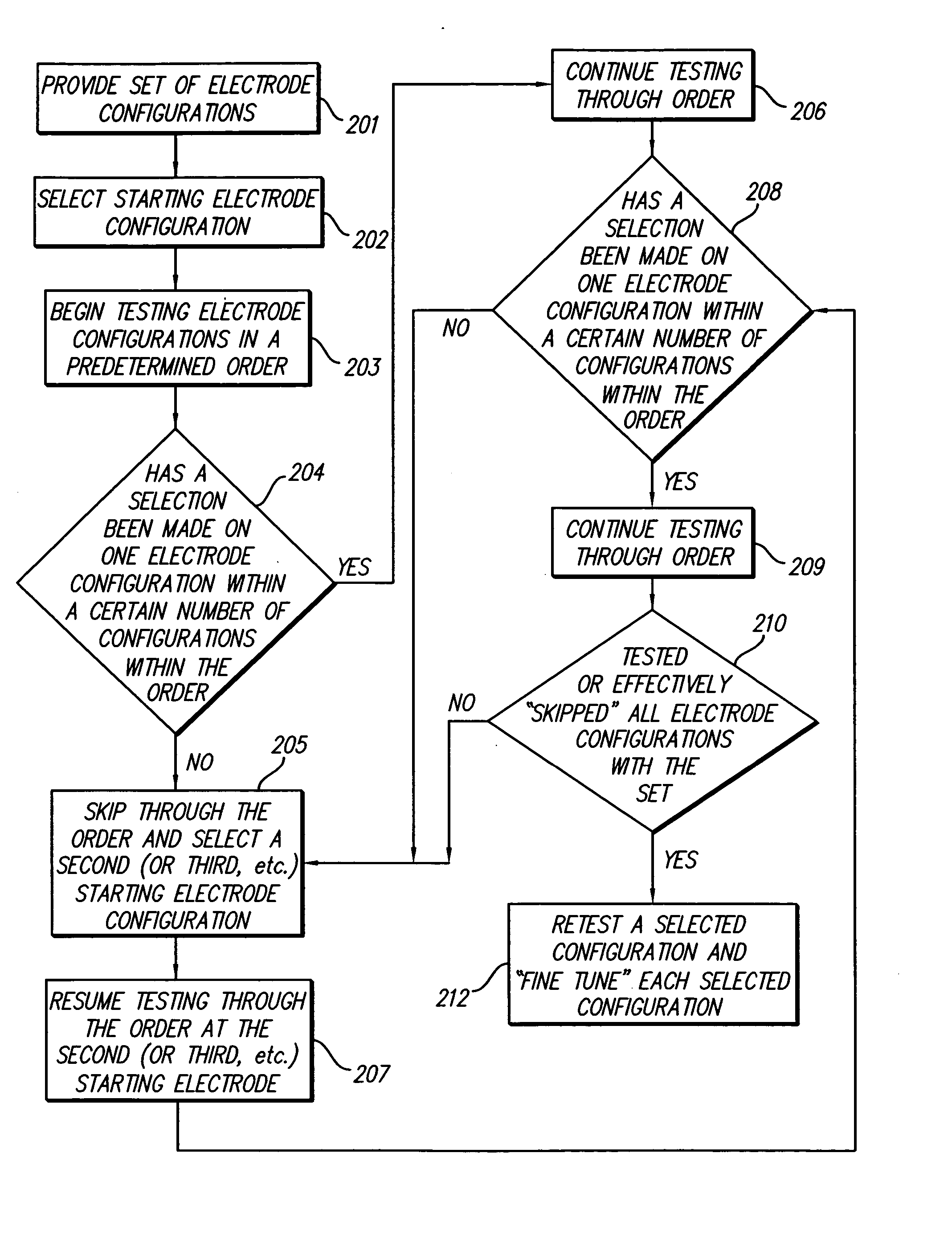
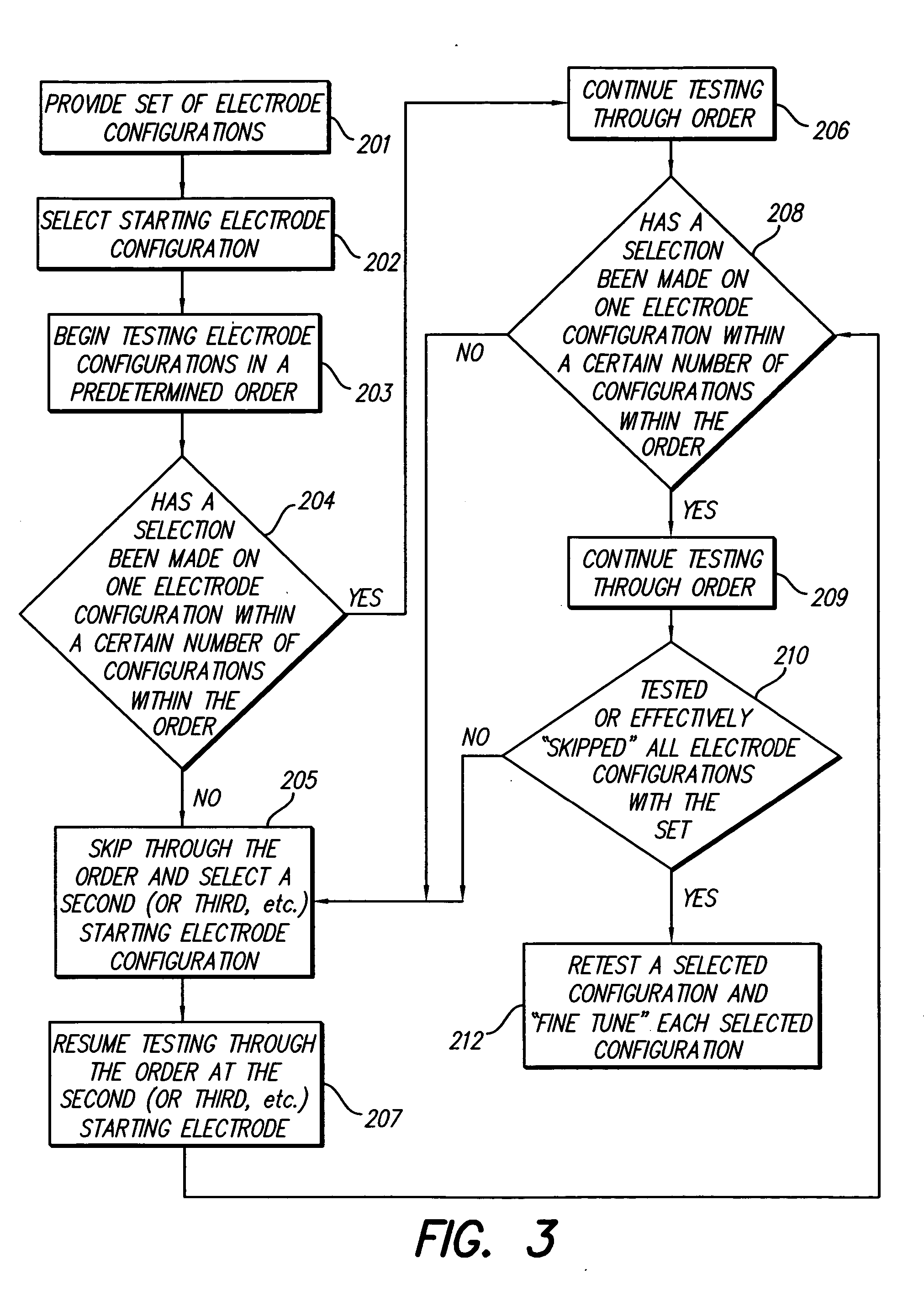
Method for optimizing search for spinal cord stimulation parameter settings
A method for selecting Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) stimulation parameter sets guides a clinician towards an effective set of stimulation parameters. The clinician first evaluates the effectiveness of a small number of trial stimulation parameter sets from a Measurement Table. Based on the patient's assessment, the trial stimulation sets are ranked. Then the clinician selects a starting or benchmark row in a Steering Table corresponding to the highest ranked trial stimulation parameter set. The clinician moves either up or down from the starting row, testing consecutive parameter sets. When a local optimum is found, the clinician returns to the benchmark row, and tests in the opposite direction for another local optimum. This process of searching for optimum parameter sets is repeated for a new starting row in the Steering Table that is selected based on the next ranked trial set from the Measurement Table.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Variation of neural-stimulation parameters
InactiveUS7050856B2Reduce lossesOvercomes shortcomingInternal electrodesExternal electrodesSide effectMedicine
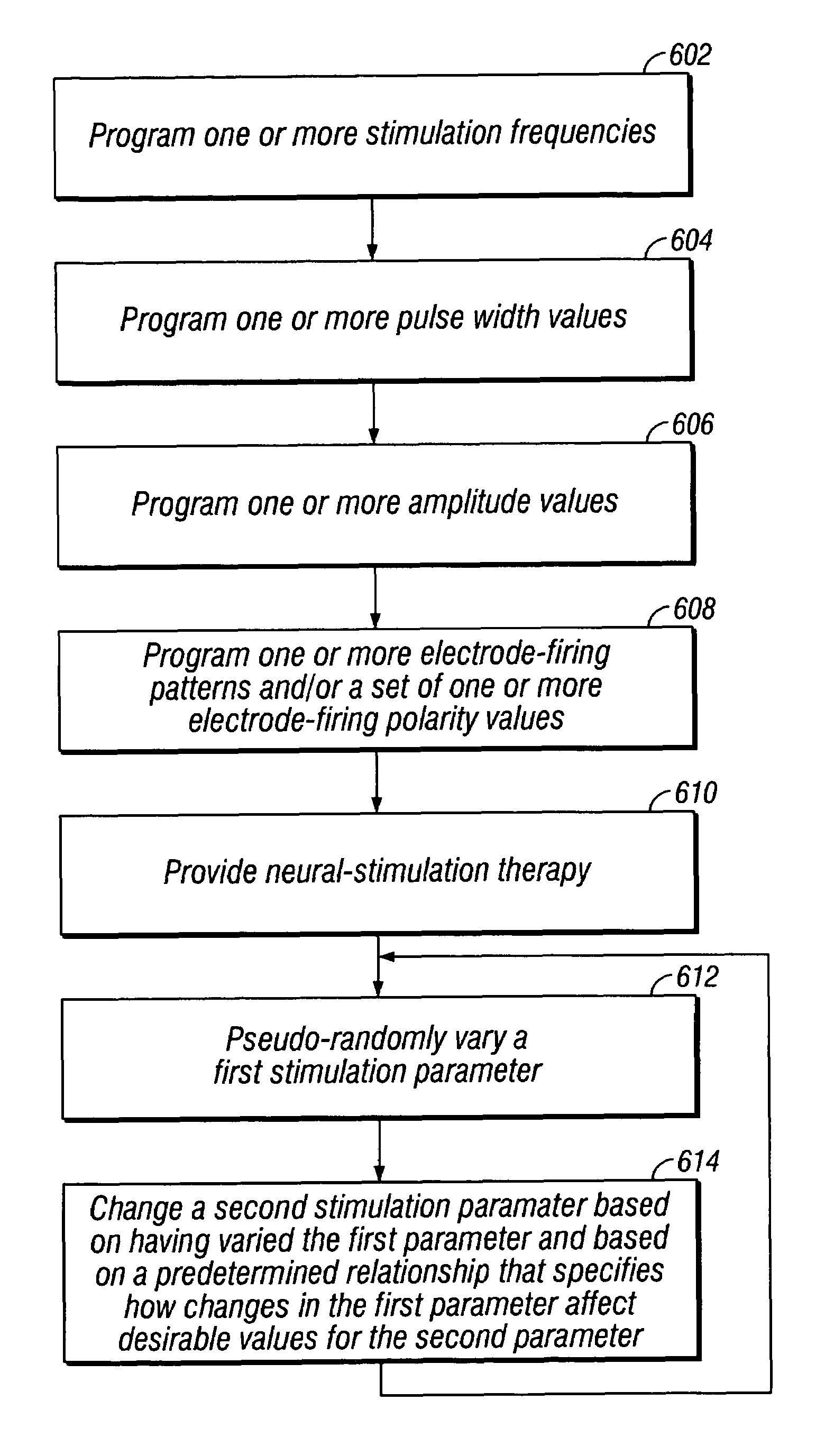
Techniques for varying stimulus parameters used in neural stimulation to improve therapy efficacy, minimize energy consumption, minimize undesired side effects, and minimize loss of therapeutic effectiveness due to physiologic tolerance to stimulation. Neural stimulation is provided having a stimulation amplitude, a stimulation frequency, a stimulation pulse duration, an electrode-firing pattern, and a set of electrode-firing-polarity conditions. At least one of the stimulation parameters is pseudo-randomly varied. A second stimulation parameter is changed based upon having pseudo-randomly varied the first stimulation parameter and based upon a predetermined relationship specifying how changes in the first parameter affect desirable values for the second parameter.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Monitoring, preventing, and treating rejection of transplanted organs
An implantable system control unit (SCU) includes means for measuring tissue impedance or other condition to determine allograft health, in order to predict or detect allograft rejection. The SCU also includes at least two electrodes coupled to means for delivering electrical stimulation to a patient within whom the device is implanted, and may also include a reservoir for holding one or more drugs and a driver means for delivering the drug(s) to the patient. In certain embodiments, the system is capable of open- and closed-loop operation. In closed-loop operation, at least one SCU includes a sensor, and the sensed condition is used to adjust stimulation parameters. Alternatively, this sensory “SCU” sounds an alarm, communicates an alarm to an external device, and / or is responsive to queries regarding sensed information, such as tissue impedance.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Treatment of movement disorders by extra dural motor cortex stimulation
InactiveUS20060241717A1Increase excitementReduce excitementElectrotherapyArtificial respirationElectricityMedicine
System and methods for introducing one or more stimulating drugs and / or applying electrical stimulation to the cortex of the brain to treat movement disorders uses at least one implantable system control unit (SCU), specifically an implantable signal / pulse generator (IPG) or microstimulator with two or more electrodes in the case of electrical stimulation, and an implantable pump with one or more infusion outlets in the case of drug infusion. In certain embodiments, a single SCU provides both electrical stimulation and one or more stimulating drugs. In some embodiments, one or more sensed conditions are used to adjust stimulation parameters.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
User interface for segmented neurostimulation leads
An external control device for use with a neurostimulation system having a plurality of electrodes capable of conveying an electrical stimulation field into tissue in which the electrodes are implanted is provided. The external control device comprises a user interface having one or more control elements, a processor configured for generating stimulation parameters designed to modify the electrical stimulation field relative to one or more neurostimulation lead carrying the electrodes. The external control device further comprises output circuitry configured for transmitting the stimulation parameters to the neurostimulation system.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Method, apparatus, surgical technique, and stimulation parameters for autonomic neuromodulation for the treatment of obesity
InactiveUS20070162085A1Reduce or prevent conditionReducing and preventing symptomSpinal electrodesHead electrodesSplanchnic nervesAfferent Neurons
The present invention teaches a method and apparatus for physiological modulation, including neural and gastrointestinal modulation, for the purposes of treating several disorders, including obesity, depression, epilepsy, and diabetes. This includes chronically implanted neural and neuromuscular modulators, used to modulate the afferent neurons of the sympathetic nervous system to induce satiety. Furthermore, this includes neuromuscular stimulation of the stomach to effect baseline and intermittent smooth muscle contraction to increase gastric intraluminal pressure, which induces satiety, and stimulate sympathetic afferent fibers, including those in the sympathetic trunk, splanchnic nerves, and greater curvature of the stomach, to augment the perception of satiety.
Owner:DILORENZO BIOMEDICAL
System and method of treating stuttering by neuromodulation
Stuttering-treatment techniques using neural stimulation and / or drug delivery. One or more electrodes and / or a catheter are implanted adjacent to sites in the brain. A signal generator and the electrode deliver stimulation to a first site. A pump and the catheter deliver one or more therapeutic drugs to a second site. The first and second sites could be: the supplementary motor area, the centromedian circuit, the dorsomedial nuclei, the lateral prefrontal circuit, or other paramedian thalamic and midbrain nuclei. The stuttering treatment could be performed via periodic transcranial magnetic stimulation. A sensor, located near the patient's vocal folds, can be used for generating a signal responsive to activity of the patient's speech-producing muscles. A controller adjusts one or more stimulation parameters in response to the signal from the sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method for optimizing search for spinal cord stimulation parameter settings
InactiveUS20050209655A1Improve search efficiencyConstant level of paresthesiaSpinal electrodesSurgeryVolumetric Mass DensityPattern perception
Methods for selecting stimulation parameter sets guide a clinician towards an effective set(s) of stimulation parameters. The clinician first evaluates the effectiveness of a small number of trial stimulation parameters sets from a Measurement Table comprising for example, four stimulation parameter sets, measuring the perception threshold and maximum threshold levels. The maximum comfortable step size and desired field shift resolution are determined, and are used along with the measured threshold levels to determine an appropriate step size to use in the current steering process. In order to maintain paresthesia at a relatively constant level during the steering process, a Superposition Equalization (SEQ) algorithm is used to compensate for the physical characteristics of the lead array, i.e., electrode separation and size. A multiplier is determined and a modifying function is used to apply this multiplier to the electrode energy output during transition to maintain a relatively constant current density.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
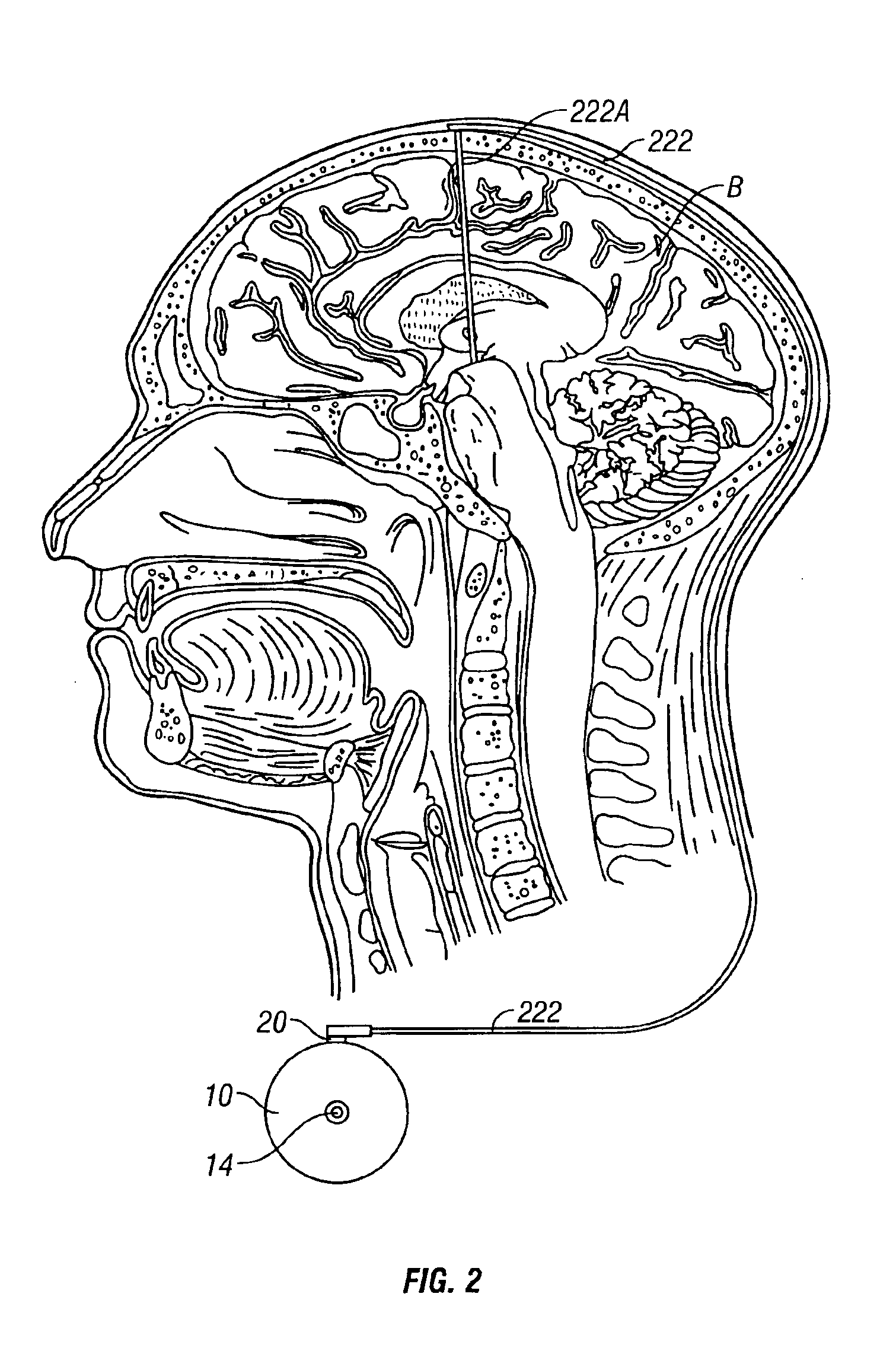
Skull-mounted electrical stimulation system
InactiveUS20050102006A1Substantial therapeutic benefitSignificant comprehensive benefitsElectrotherapyMedical devicesElectricityStimulation Parameter
Systems and methods for applying electrical stimulation to the brain to treat headaches and neuralgia use at least one implantable system control unit (SCU), specifically an implantable signal / pulse generator (IPG) with one or more electrodes. The IPG is implanted in the skull and communicates with at least one external appliance, such as a Behind-the-Ear (BTE) unit. In a preferred embodiment, the system is capable of open- and closed-loop operation. In closed-loop operation, at least one SCU includes a sensor, and the sensed condition is used to adjust stimulation parameters.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Automated fitting system for deep brain stimulation
Methods, systems, and external programmers provide therapy to a patient having a dysfunction. In one aspect, stimulation energy is conveyed from a neurostimulator to electrodes located within a tissue region of the patient, thereby changing the status of the dysfunction. A physiological end-function of the patient indicative of the changed status of the dysfunction is measured, and stimulation parameters are programmed into the neurostimulator based on the measured physiological end-function. In another aspect, electrodes are placed adjacent to a tissue region of the patient, and stimulation energy is conveyed from the electrodes to the tissue region in accordance with the stimulation parameters, thereby changing the status of the dysfunction. A physiological end-function of the patient indicative of the changed status of the dysfunction is measured, and the stimulation parameters are adjusted based on the measured physiological end-function.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
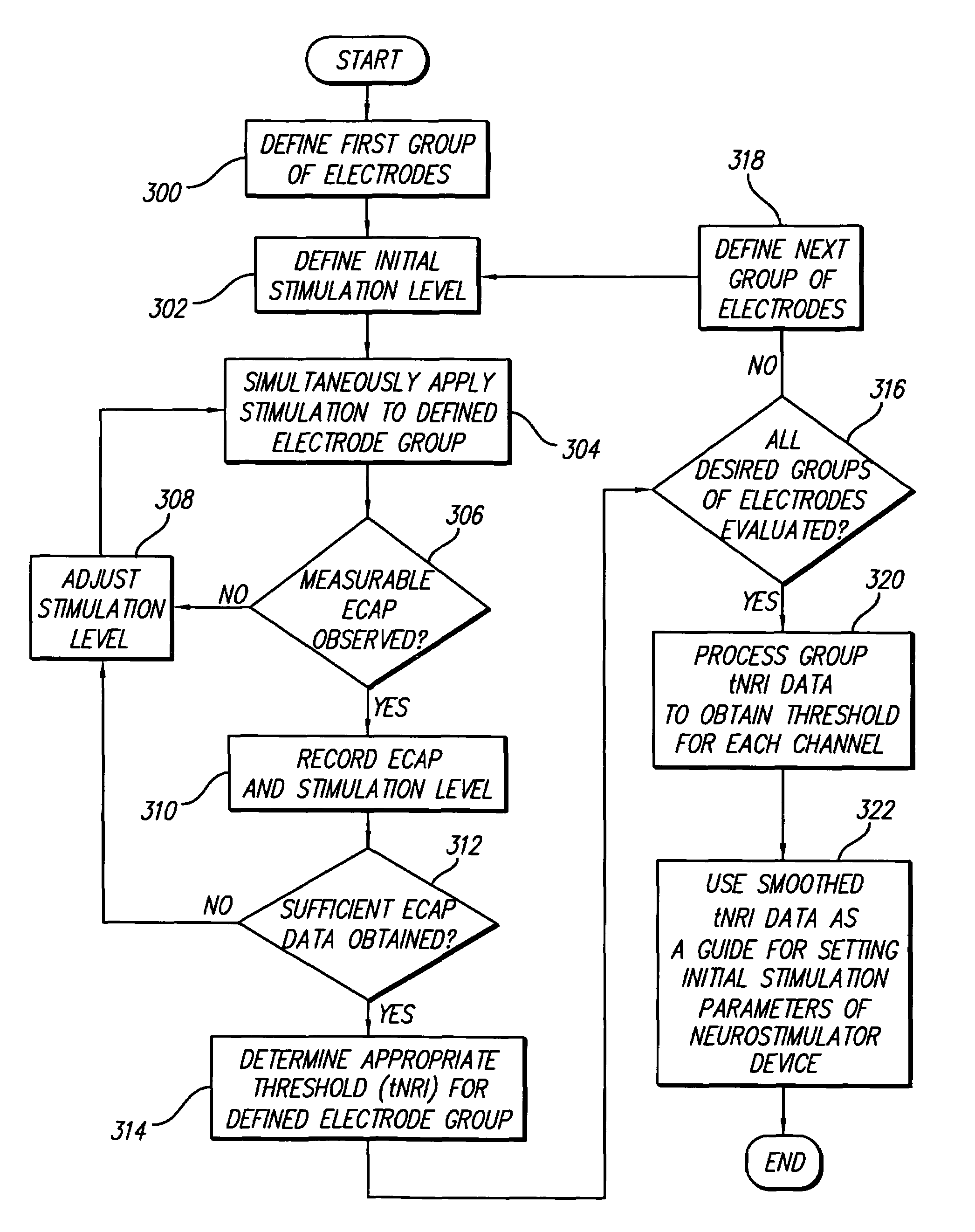
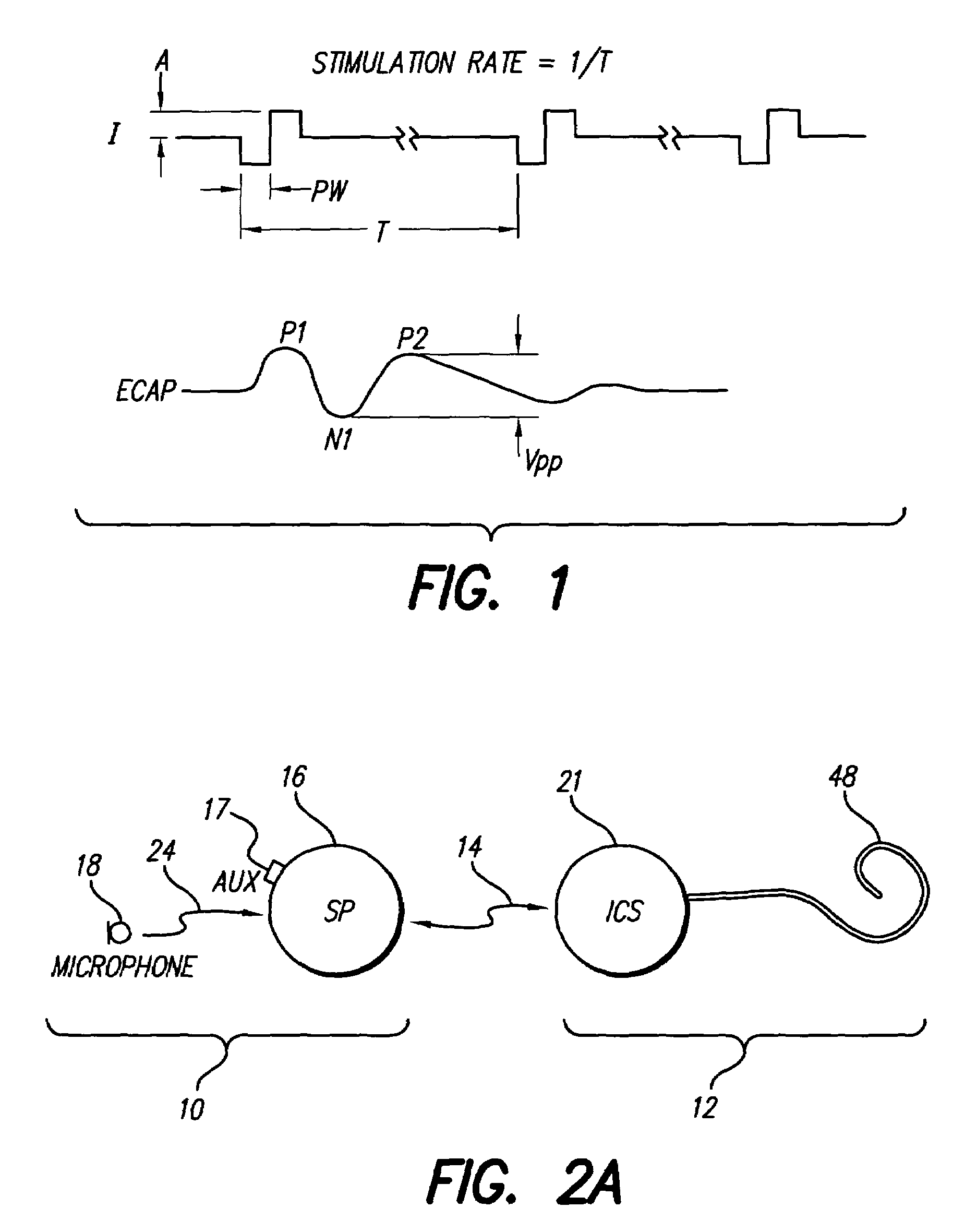
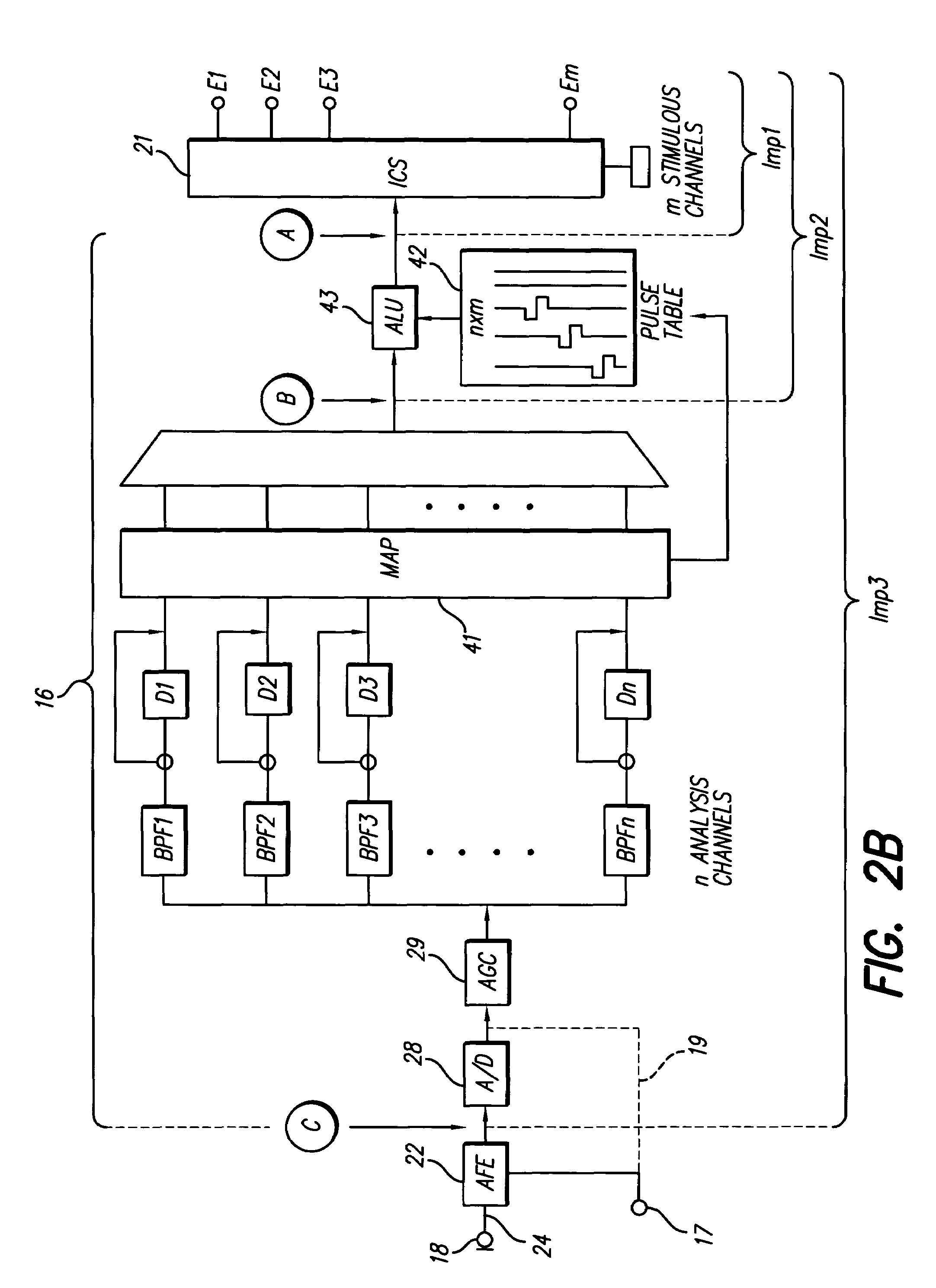
Method and system for generating a cochlear implant program using multi-electrode stimulation to elicit the electrically-evoked compound action potential
InactiveUS7206640B1Increase amplitudeConvenient recordingHead electrodesEvoked compound action potentialConfocal
A multichannel cochlear implant system spatially spreads the excitation pattern in the target neural tissue by either: (1) rapid sequential stimulation of a small group of electrodes, or (2) simultaneously stimulating a small group of electrodes. Such multi-electrode stimulation stimulates a greater number of neurons in a synchronous manner, thereby increasing the amplitude of the extra-cellular voltage fluctuation and facilitating its recording. The electrical stimuli are applied simultaneously (or sequentially at a rapid rate) on selected small groups of electrodes while monitoring the evoked compound action potential (ECAP) on a nearby electrode. The presence of an observable ECAP not only validates operation of the implant device at a time when the patient may be unconscious or otherwise unable to provide subjective feedback, but also provides a way for the magnitude of the observed ECAP to be recorded as a function of the amplitude of the applied stimulus. From this data, a safe, efficacious and comfortable threshold level can be obtained which may be used thereafter as the initial setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device, or to guide the setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
Evoked Response to Stimulation
InactiveUS20070244407A1ElectroencephalographyImplantable neurostimulatorsFunctional connectivityConfiguration design
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Neurostimulator
ActiveUS20140180361A1Improve performanceImprove neurological functionSpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringWave shapeWaveform shaping
A neurostimulator device for use with groups (e.g., more than four groups) of electrodes. The neurostimulator may include a stimulation assembly configured to deliver different stimulation to each of the groups. The neurostimulator may also include at least one processor configured to direct the stimulation assembly to deliver stimulation to the groups. The stimulation delivered to at least one of the groups may include one or more waveform shapes other than a square or rectangular wave shape. The processor may receive data from one or more sensors and use that data to modify the stimulation delivered. The neurostimulator may be configured to communicate with an external computing device. The neurostimulator may send data to and / or receive data and / or instructions from the computing device. The computing device may use information collected by one or more sensors to at least partially determine stimulation parameters to communicate to the neurostimulator.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +2
Neurostimulation system and method for automatically adjusting stimulation and reducing energy requirements using evoked action potential
A neurostimulation system comprising stimulation output circuitry configured for delivering stimulation pulses to target tissue in accordance with a set of stimulation parameters. The neurostimulation system comprises monitoring circuitry configured for continuously measuring action potentials evoked in the target tissue in response to the delivery of the stimulation pulses to the target tissue, memory configured for storing a characteristic of a reference evoked action potential, and at least one processor configured for initiating an automatic mode, in which a characteristic of the measured evoked action potentials is compared to the corresponding characteristic of the reference evoked action potential, and one or more stimulation parameter values in the set of stimulation parameters are adjusted to decrease or increase the energy level of the stimulation pulses, thereby evoking action potentials in the target tissue having substantially the same corresponding characteristic as the reference evoked action potential.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Method for programming implantable device
A method for selecting Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) stimulation parameter sets guides a clinician towards an effective set of stimulation parameters. The clinician first evaluates the effectiveness of a small number of trial stimulation parameters sets from a Measurement Table comprising for example, four stimulation parameter sets. Based on the patient's assessment, the trial stimulation parameter sets are ranked. Then the clinician selects a starting or benchmark row in a Steering Table corresponding to the highest ranked trial stimulation parameter set. The clinician moves either up or down form the starting row, testing consecutive parameter sets. The clinician continues as long as the patient indicates that the stimulation results are improving. When a local optimum is found, the clinician returns to the benchmark row, and tests in the opposite direction for another local optimum. If an acceptable set of stimulation parameters is found, the selection process is complete. If an acceptable set is not found, a new starting row in the Steering Table is selected based on the next ranked trial set from the Measurement Table, and the process of searching for local optima is repeated.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com