Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
84 results about "Thoracic bone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
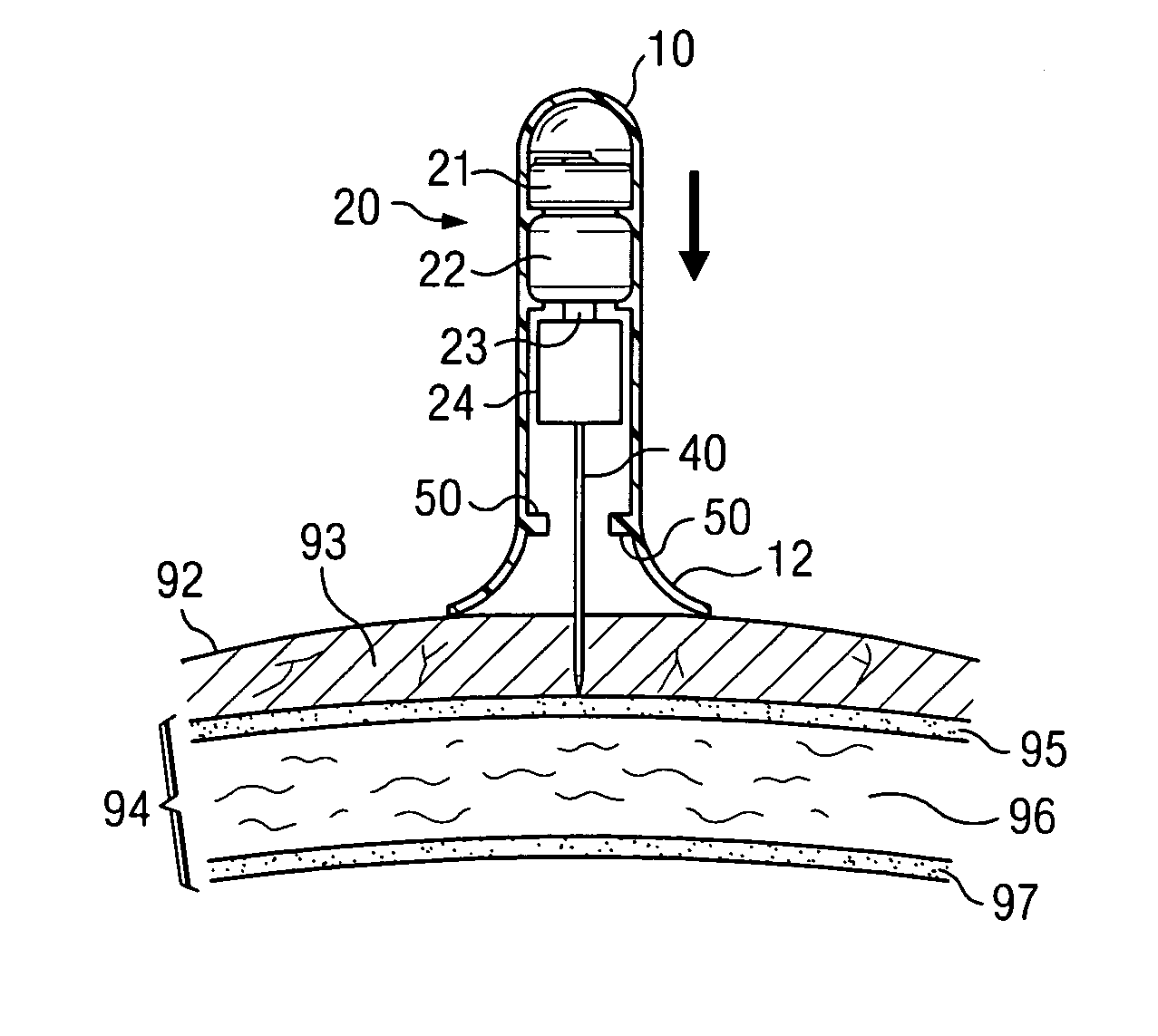
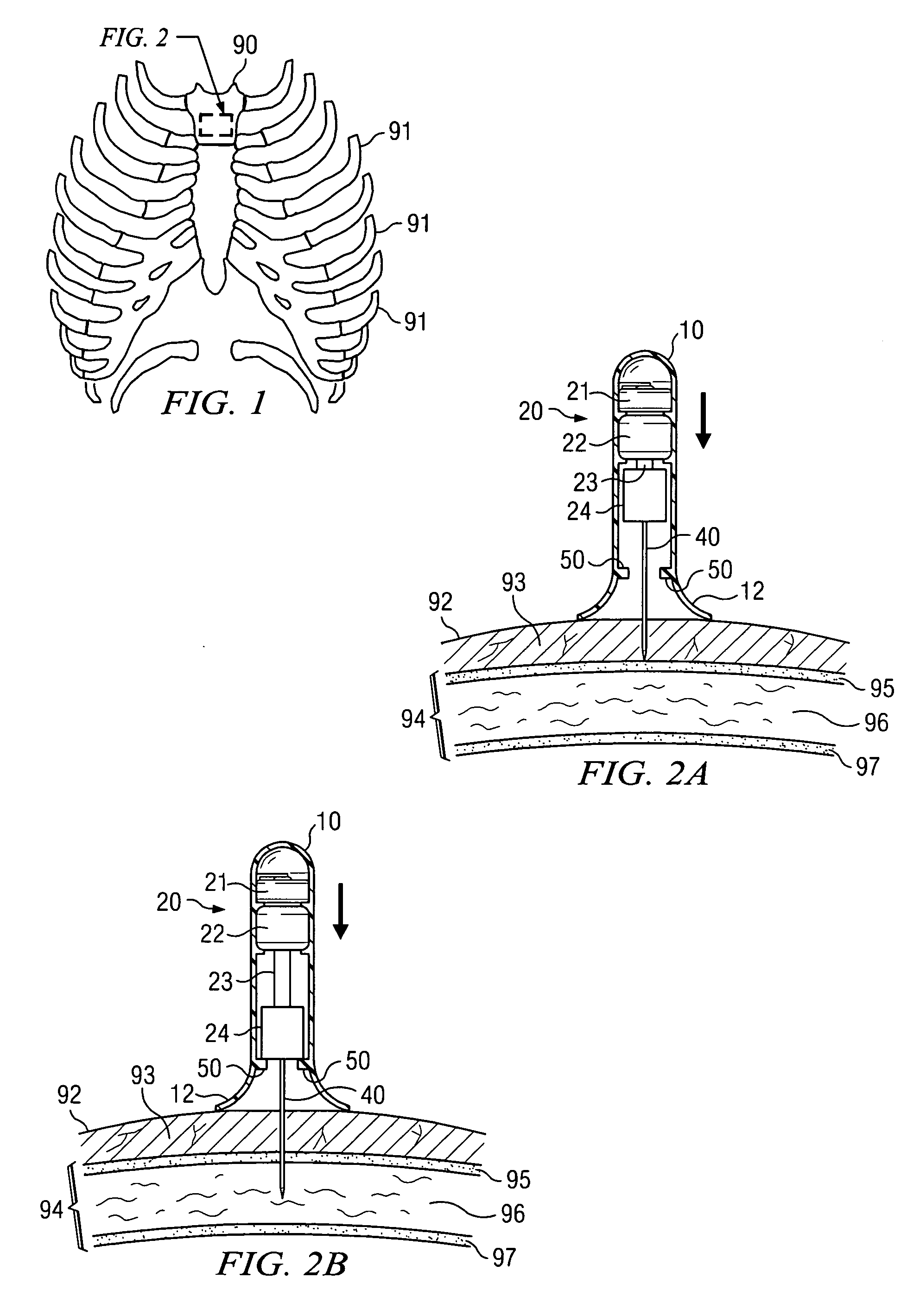
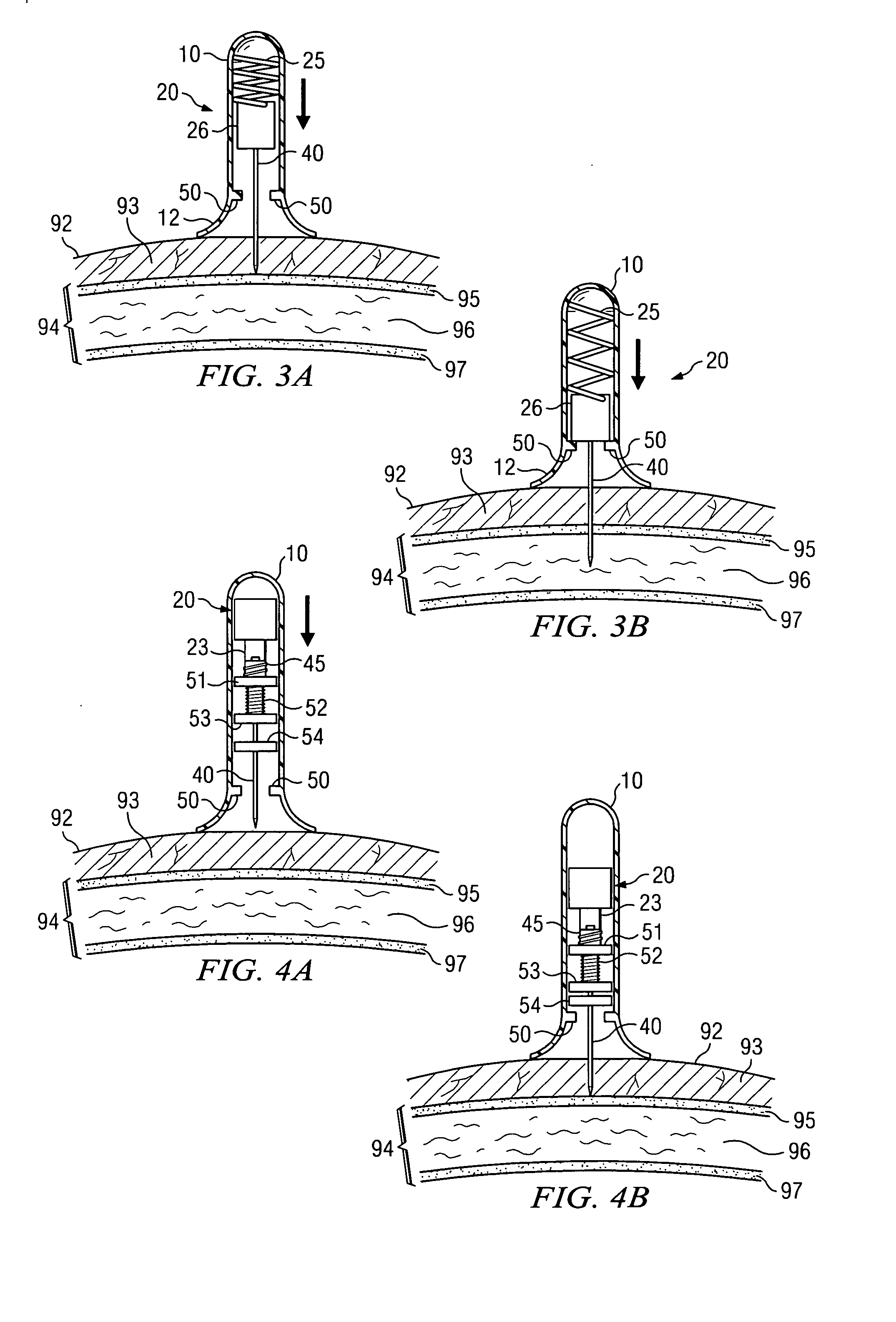
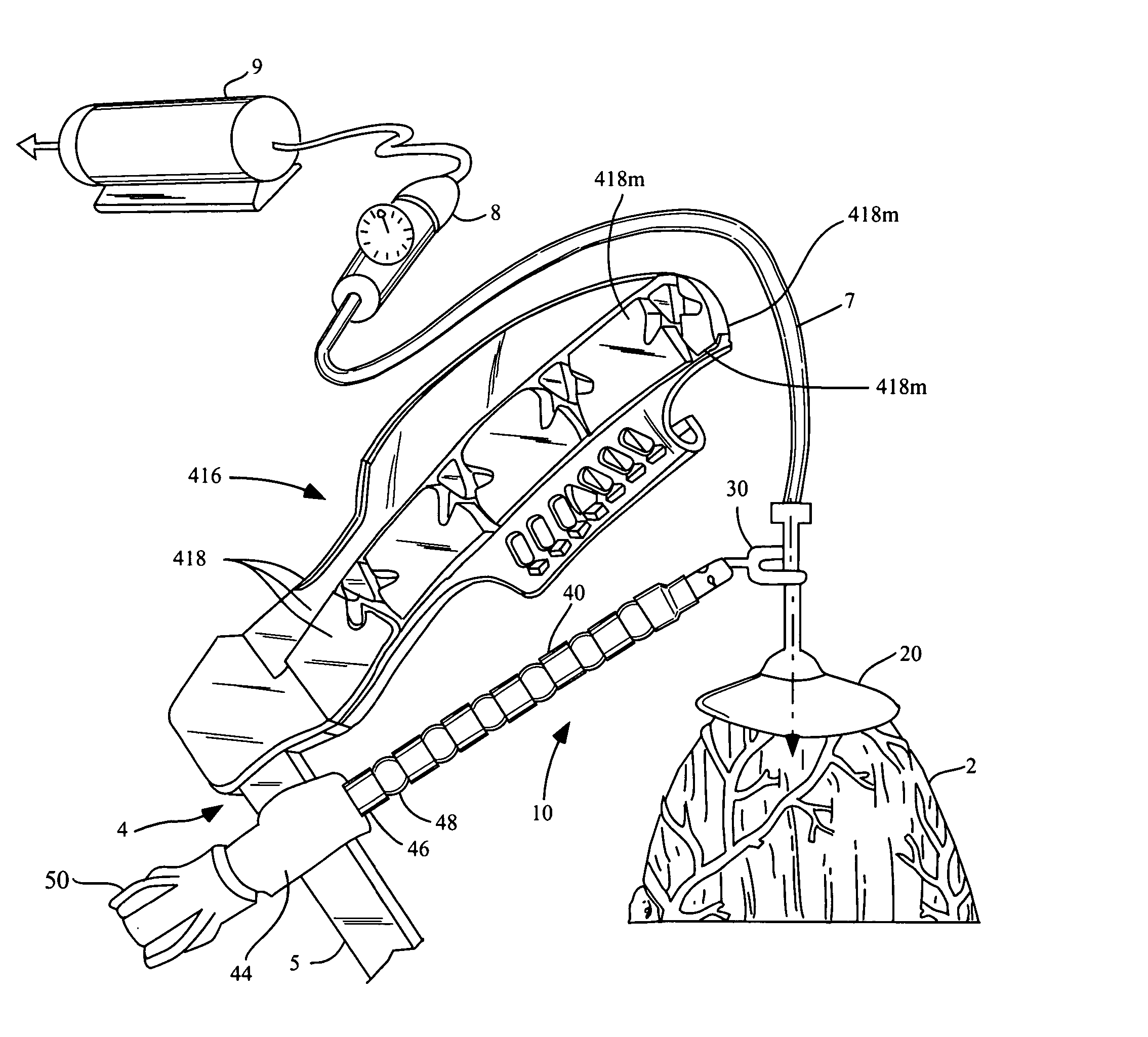
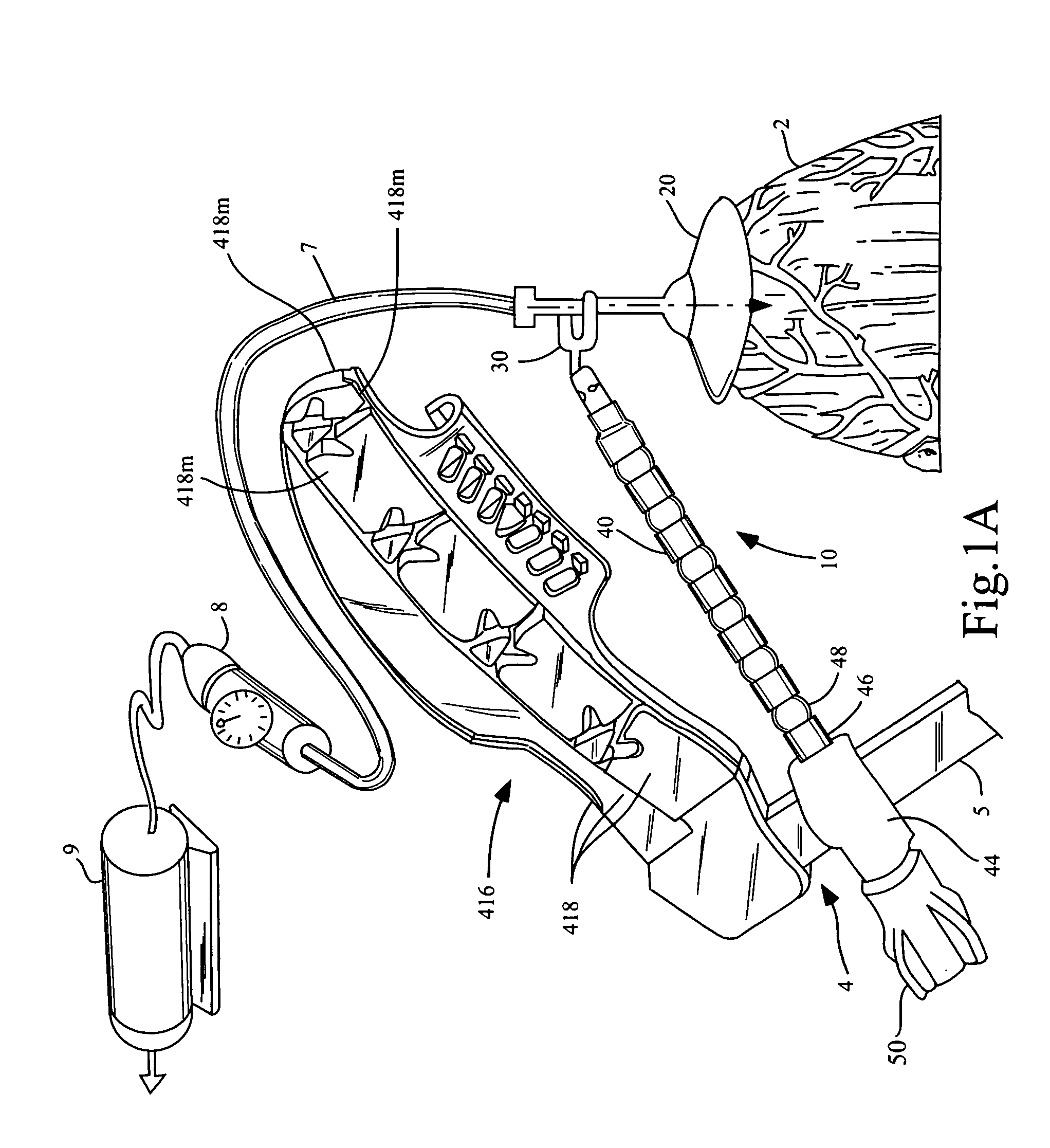
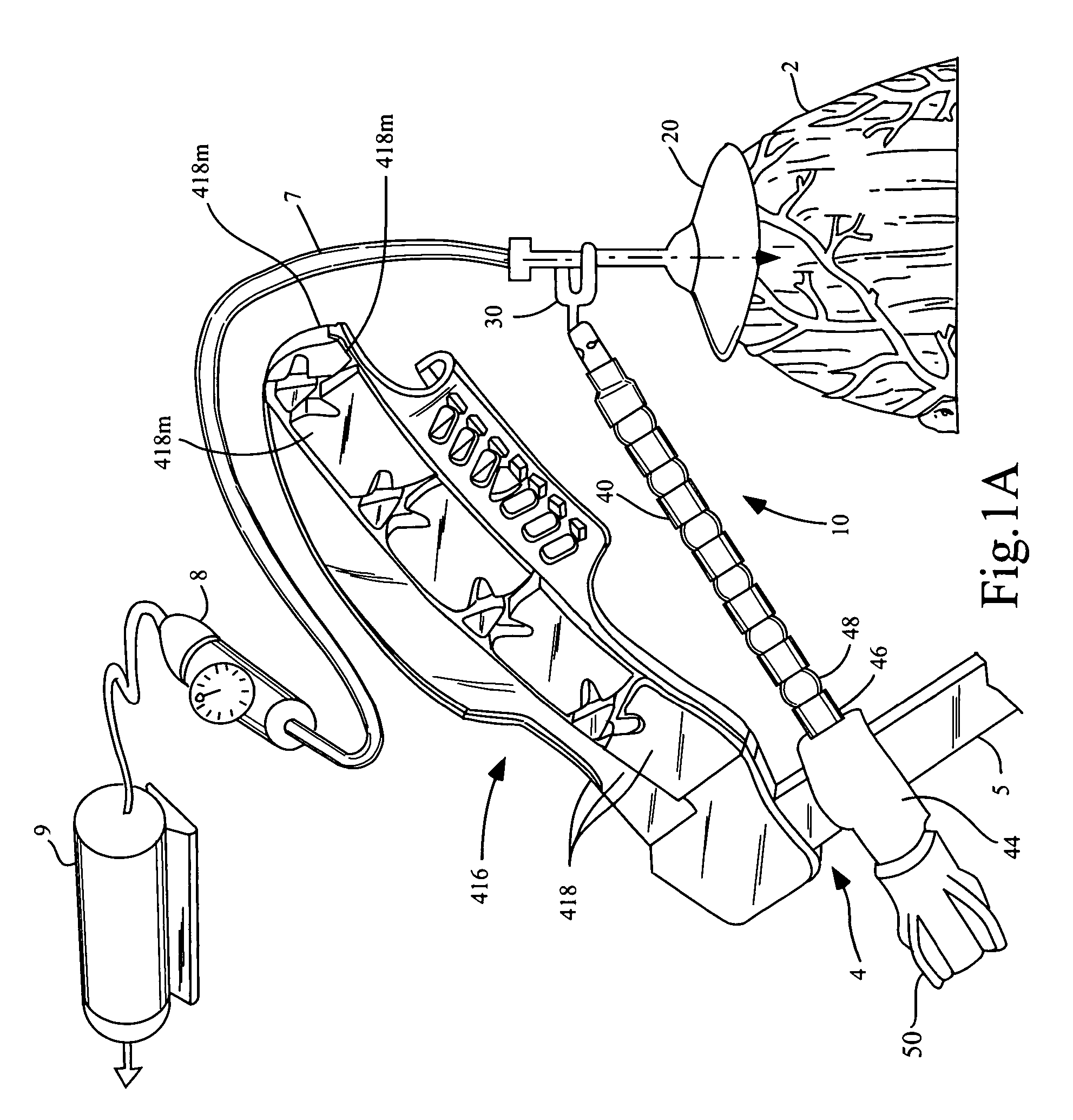
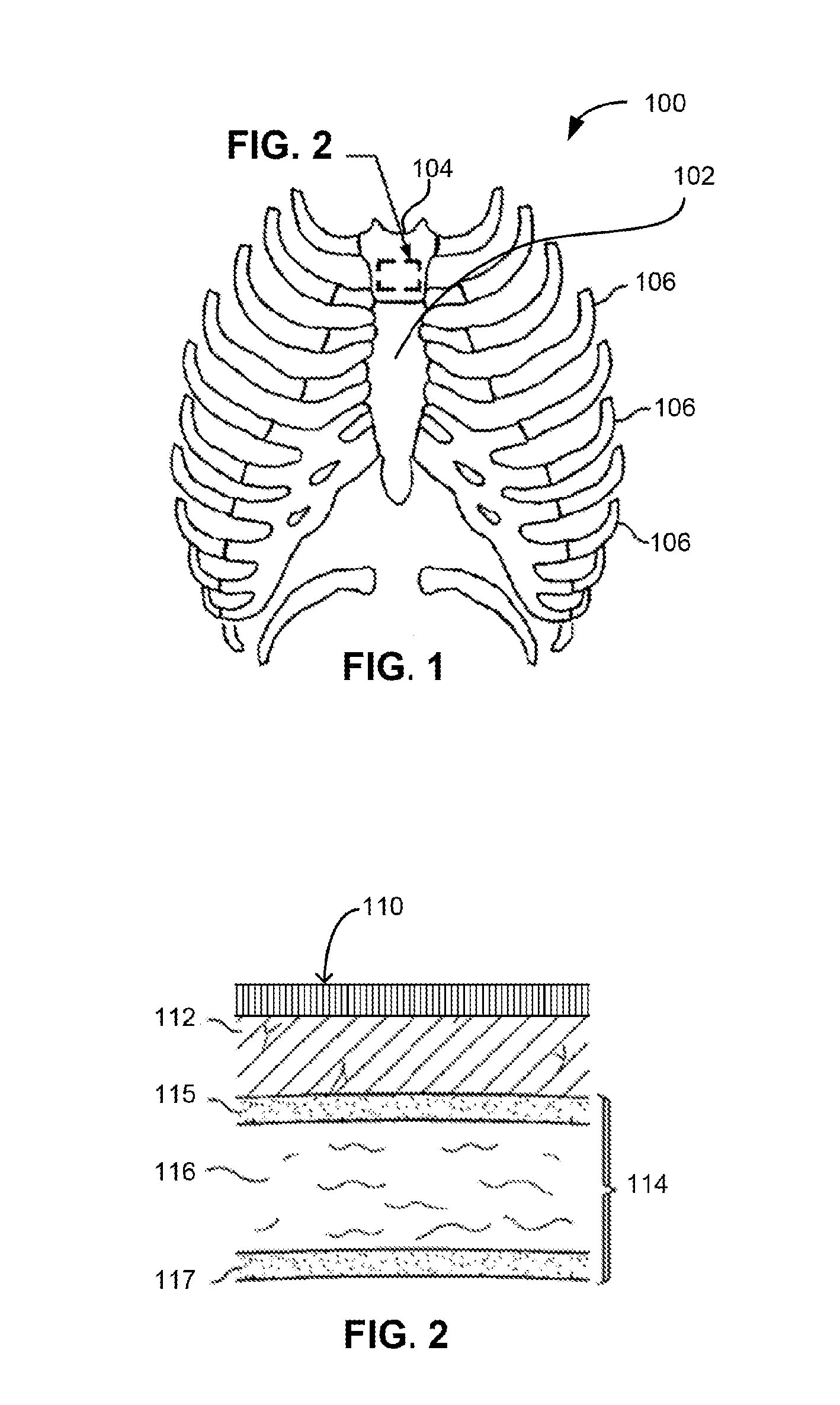
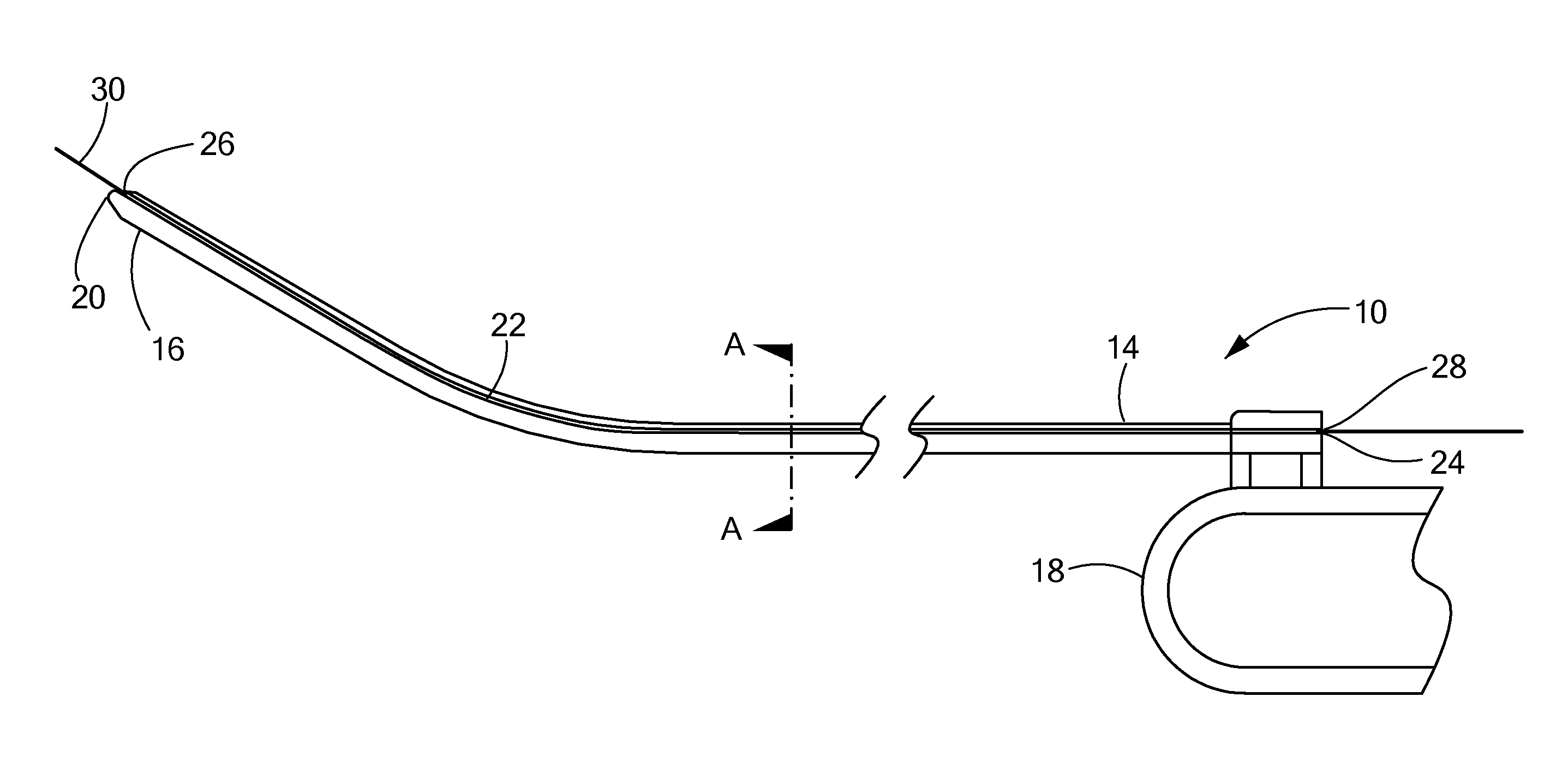
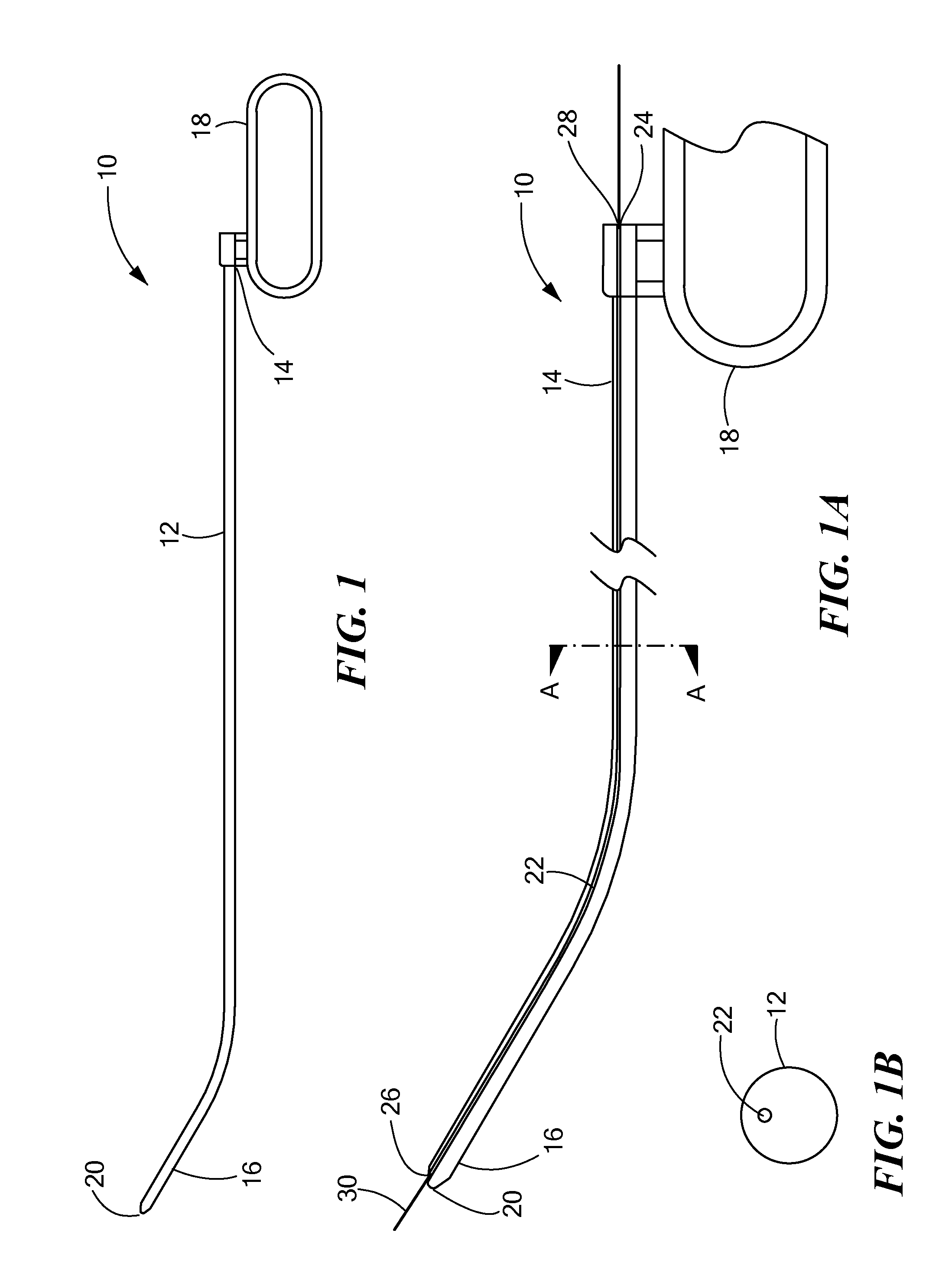
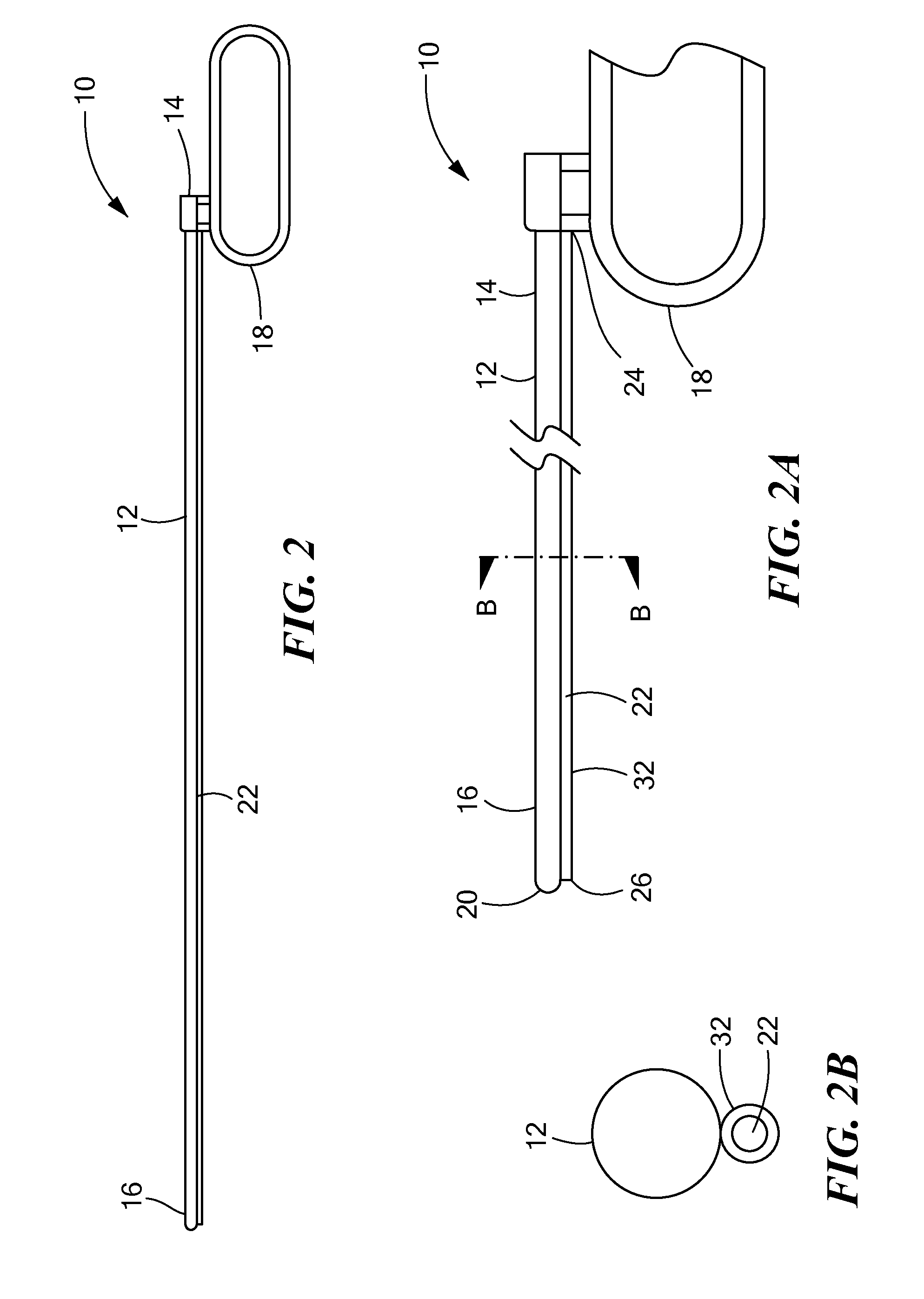
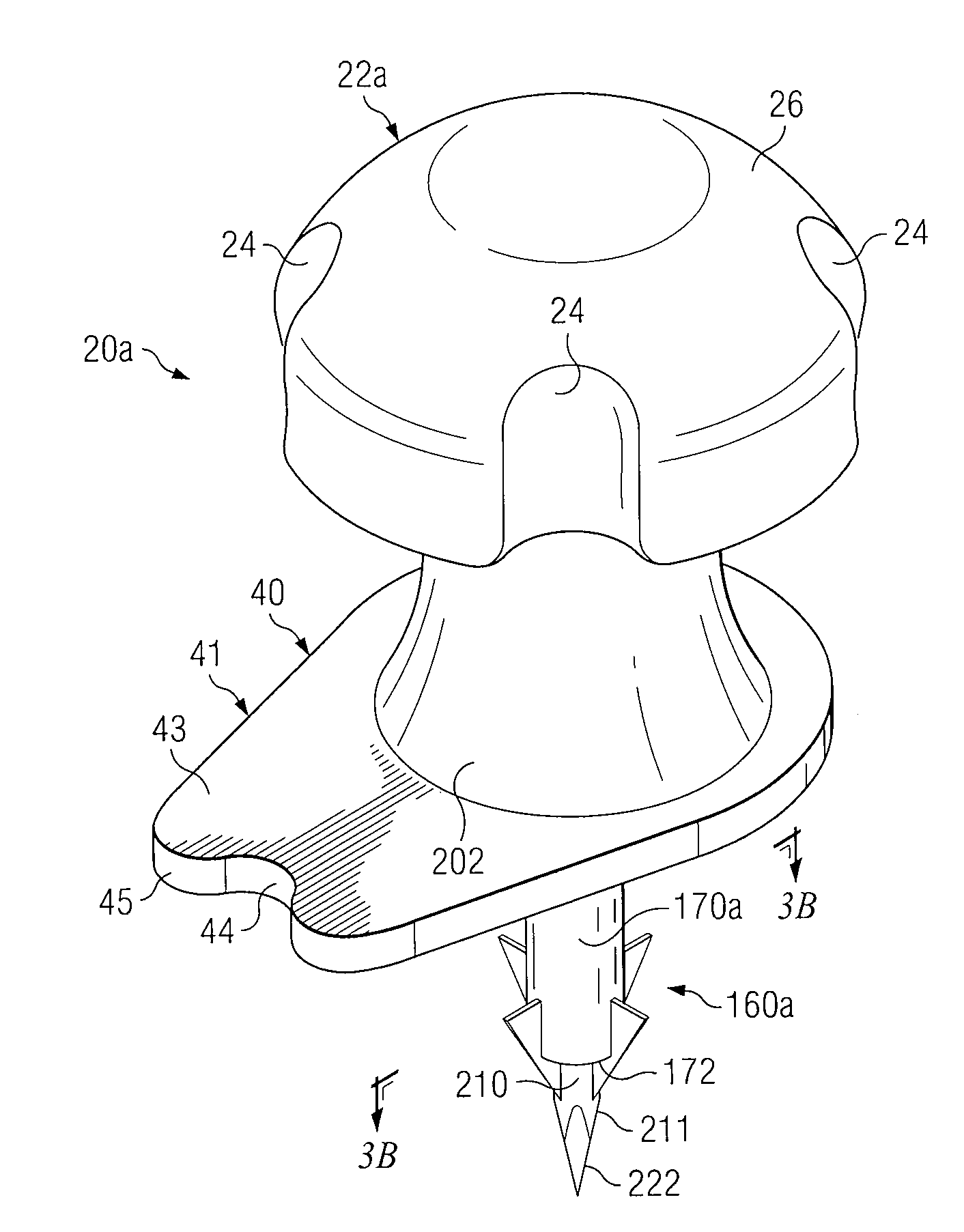
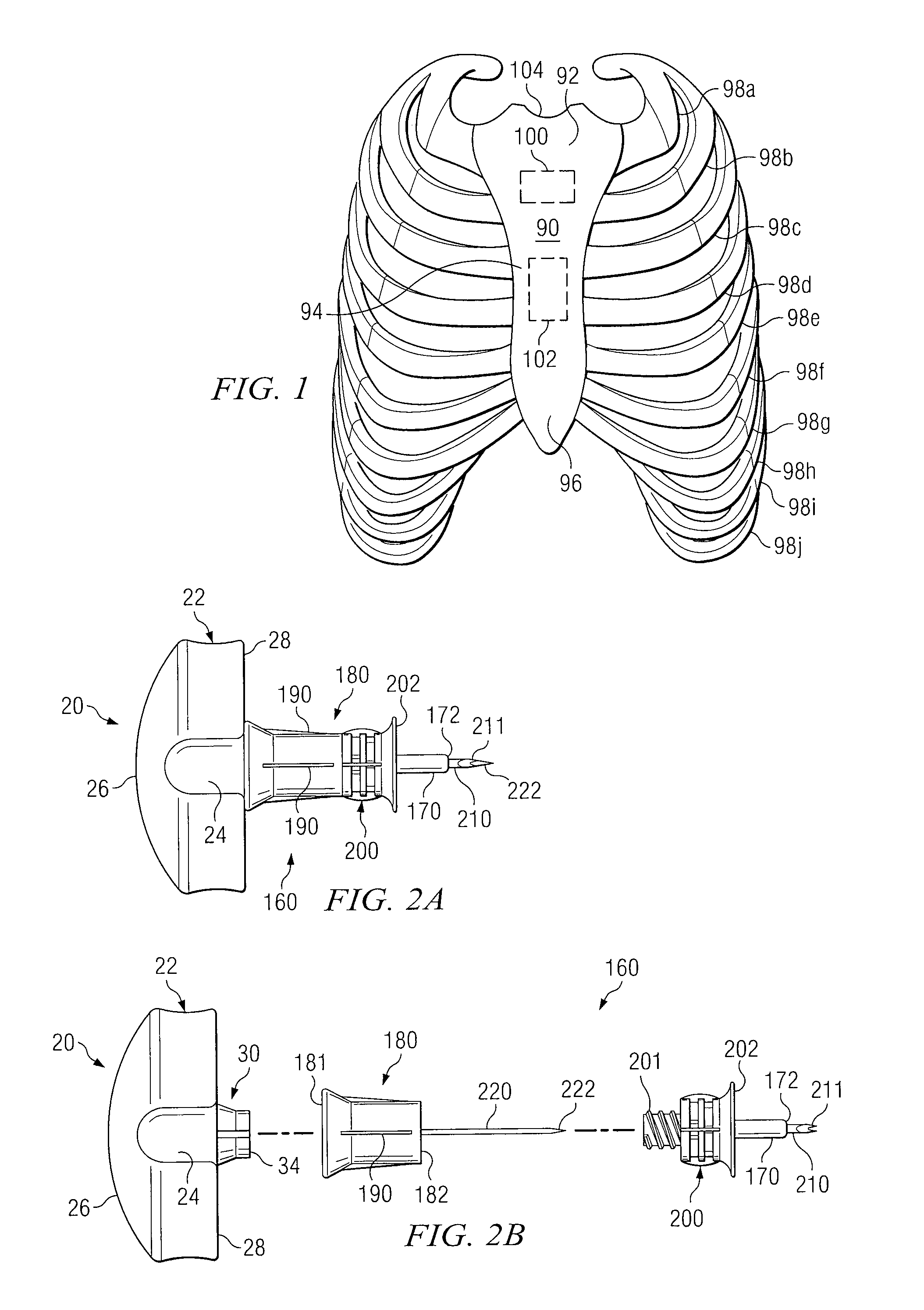
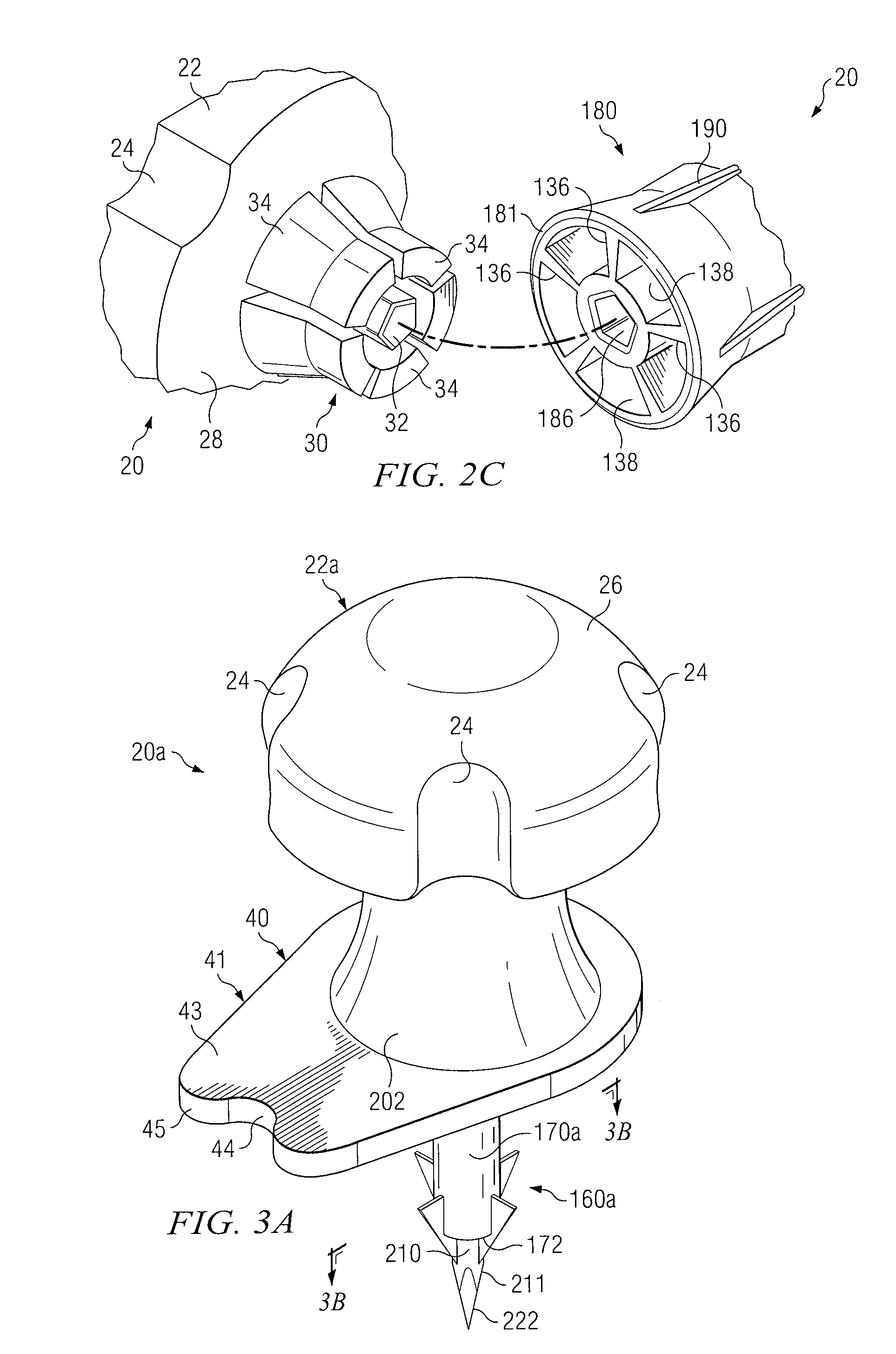
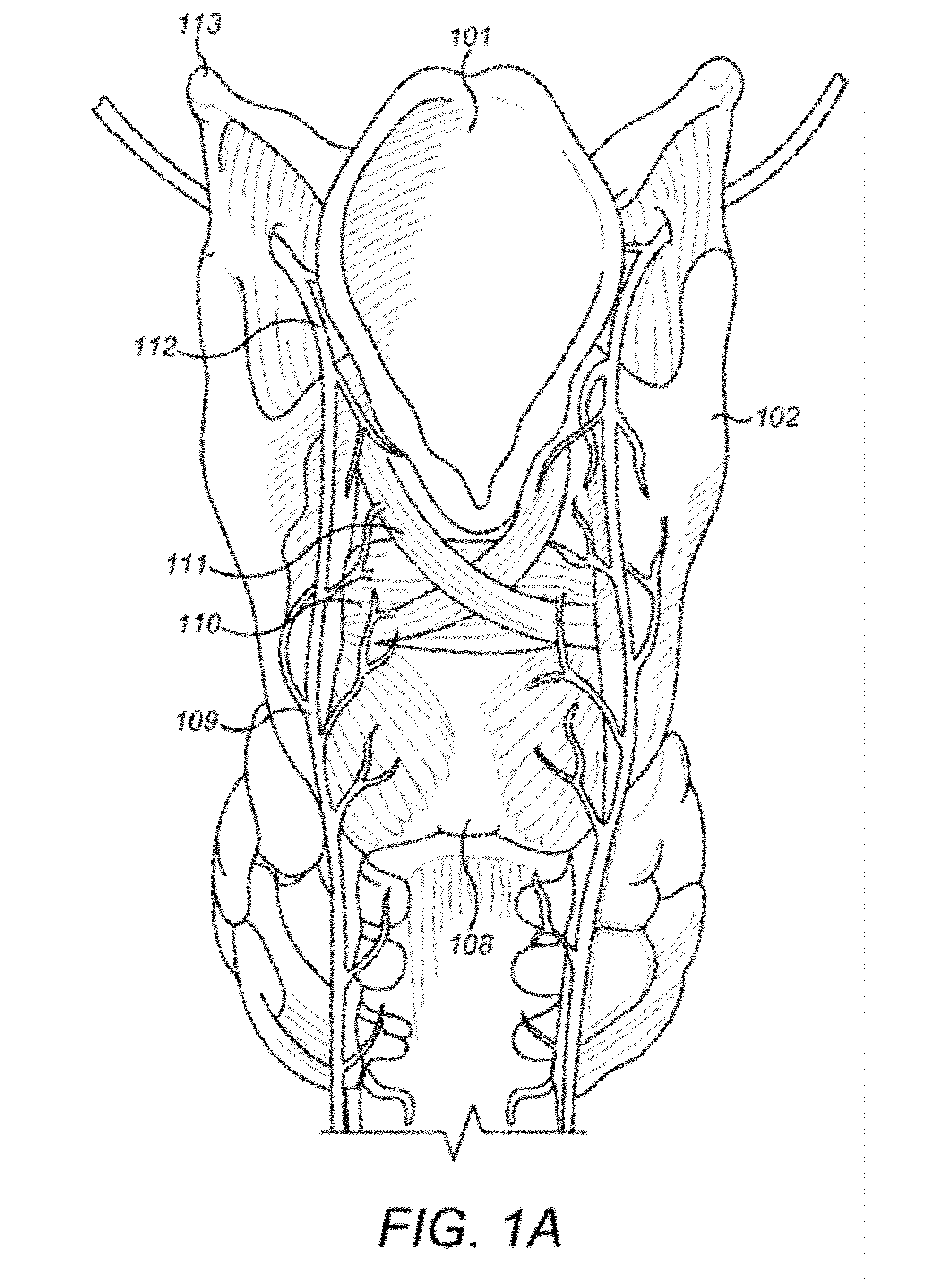
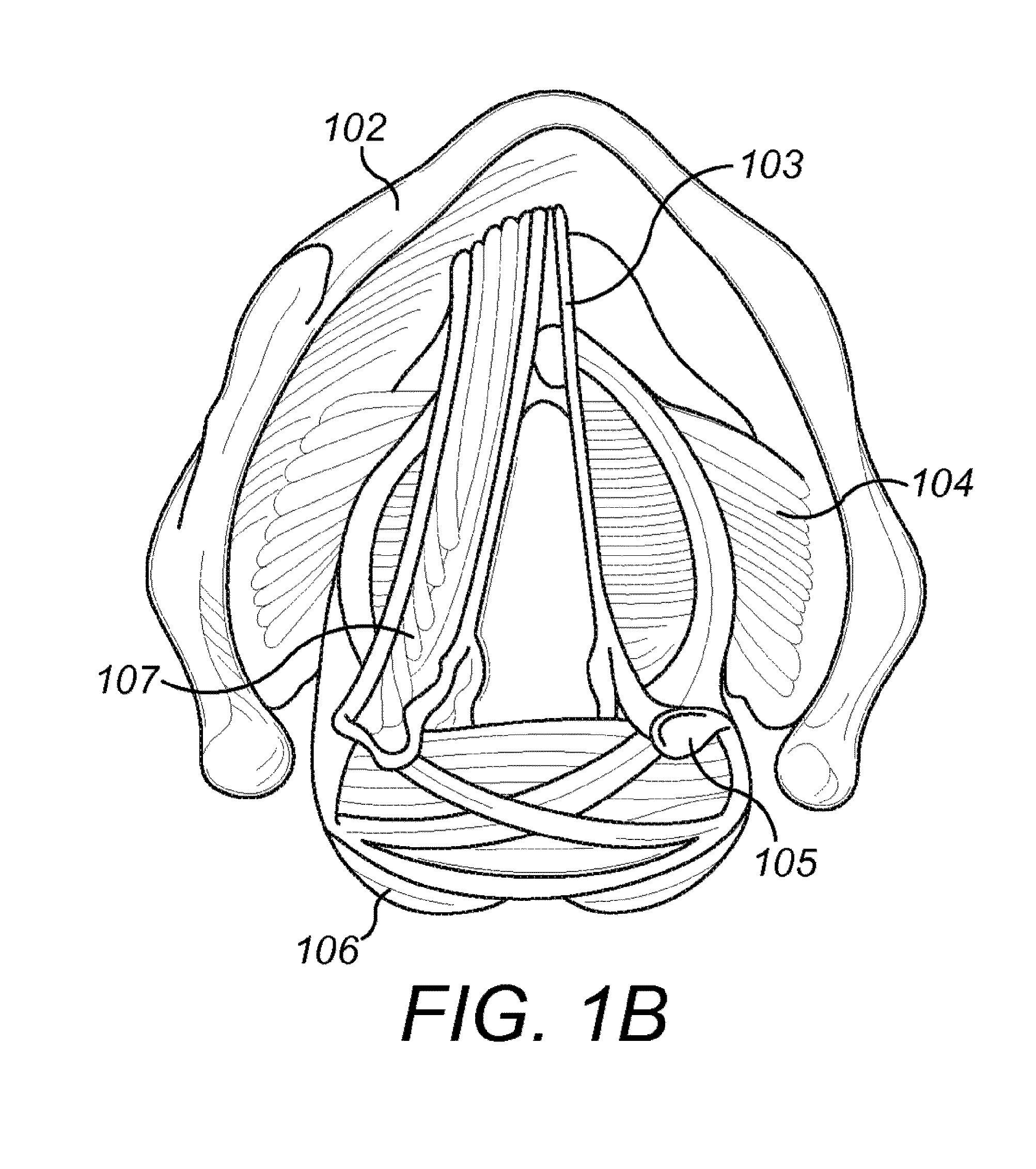
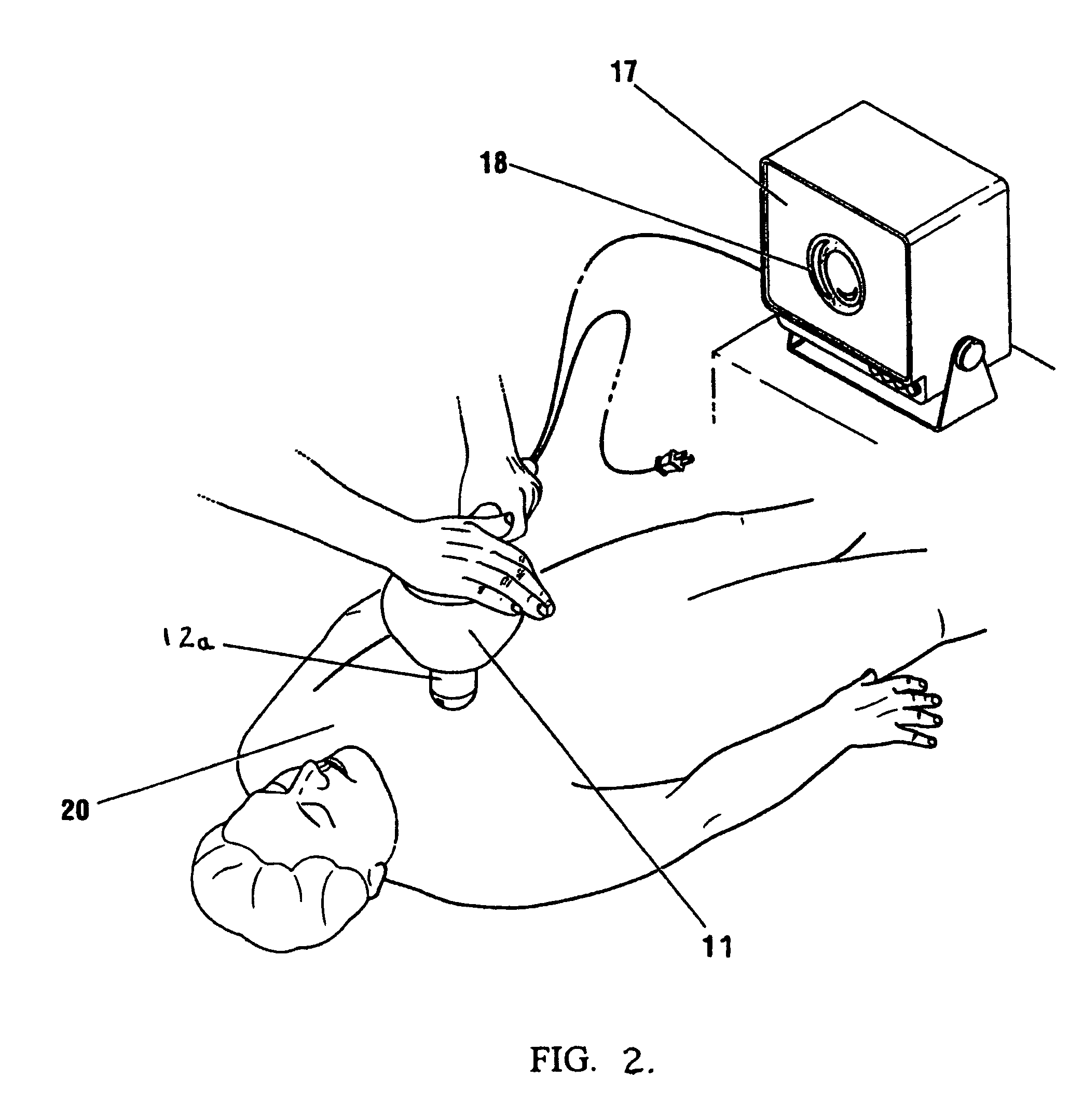
Apparatus and method for accessing the bone marrow of the sternum
ActiveUS20050131345A1Easy accessSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsThoracic boneBiomedical engineering
An apparatus and method for accessing the bone marrow of a human's sternum is provided. The apparatus includes a tissue penetrator configured to penetrate the sternum, a trigger mechanism configured to engage when the tissue penetrator contacts the sternum and a depth control mechanism operable to limit the penetration of the tissue penetrator into the sternum to a pre-selected depth.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Sternotomy splinting assembly, kit and method for use
InactiveUS20090163949A1Promote healingRelieve painSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisThoracic boneMedicine
Herein disclosed is a simple, passive splinting system for sternotomy patients designed to provide a continuous yet readily adjustable, compressive tangential stabilizing force to the ribcage so as to promote healing of a median sternotomy incision while minimizing patient pain.
Owner:ROLNICK MICHAEL A +2
Cerclage system for bone
Cerclage system, including methods, devices, and kits, for stabilizing bone, such as a sternum. The cerclage system may include a wire or cable that encircles bone, and a bone plate to which segments of the wire or cable lock. The cerclage system also or alternatively may include a tensioner for applying tension to a wire or cable.
Owner:ACUTE INNOVATIONS
Intraosseous Device And Methods For Accessing Bone Marrow In The Sternum And Other Target Areas
ActiveUS20070270775A1Reduce eliminateVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsMedical devicesThoracic boneDepth of penetration
Apparatus and methods are provided to access bone marrow at various target areas. Such apparatus may include an intraosseous device operable to penetrate bone at a selected target area and a depth limiter operable to control depth of penetration of the intraosseous device into bone and associated bone marrow. A manual driver and a guide may be included to optimize optimum insertion of the intraosseous device at a selected insertion site on a sternum.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
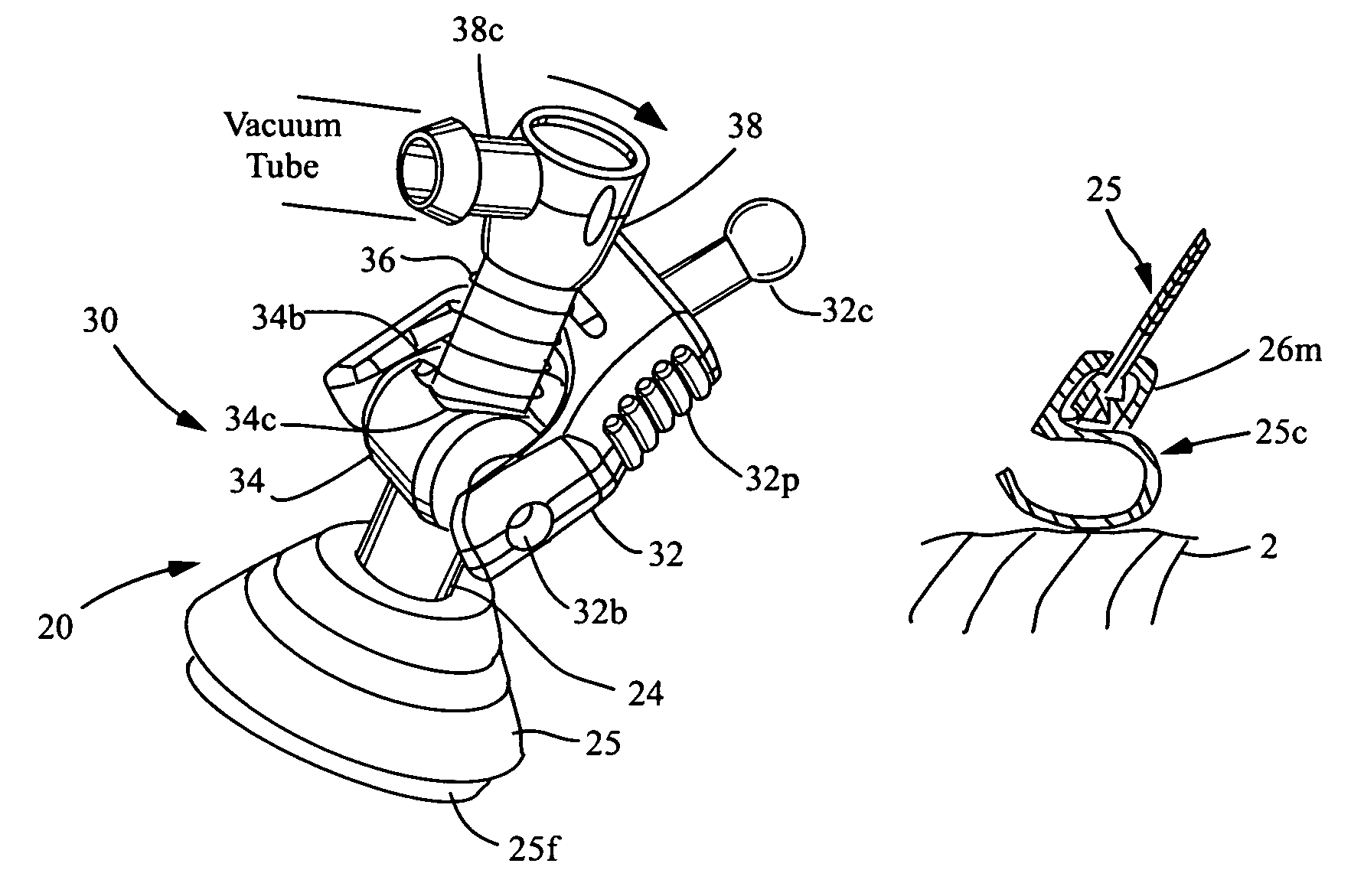
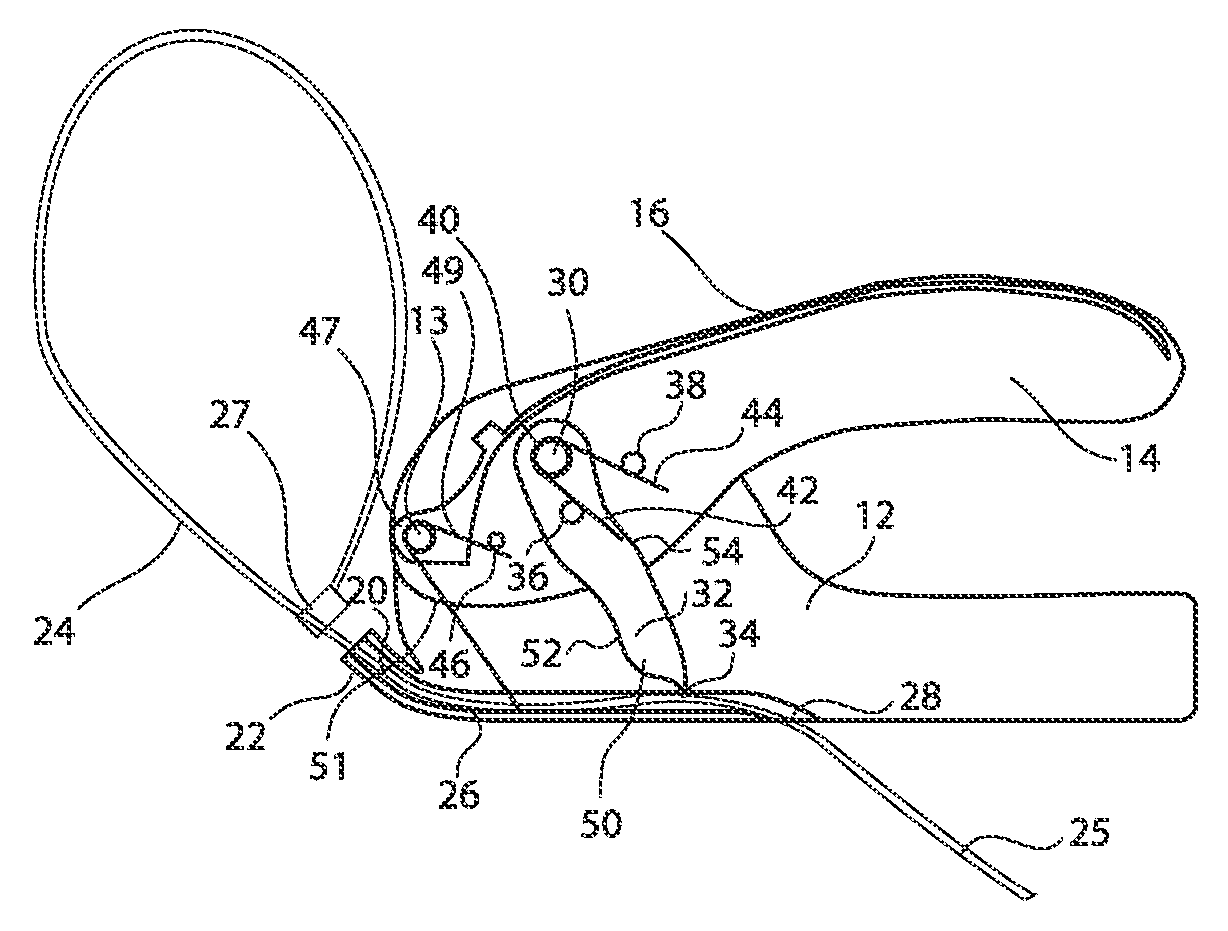
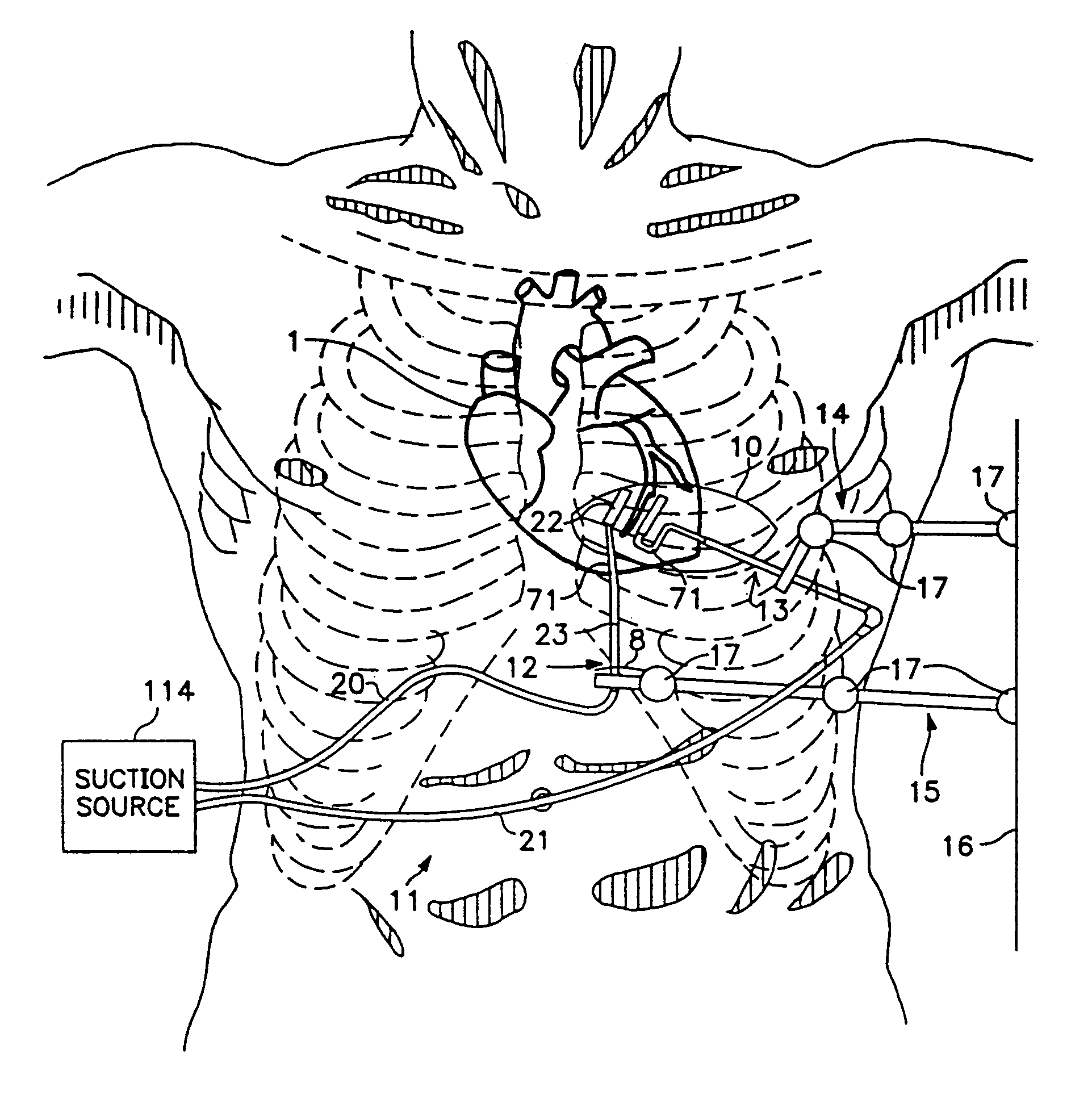
Organ manipulator apparatus
InactiveUS20050010197A1Prevent kinkingReduce creationDiagnosticsIntravenous devicesCoronary arteriesThoracic bone
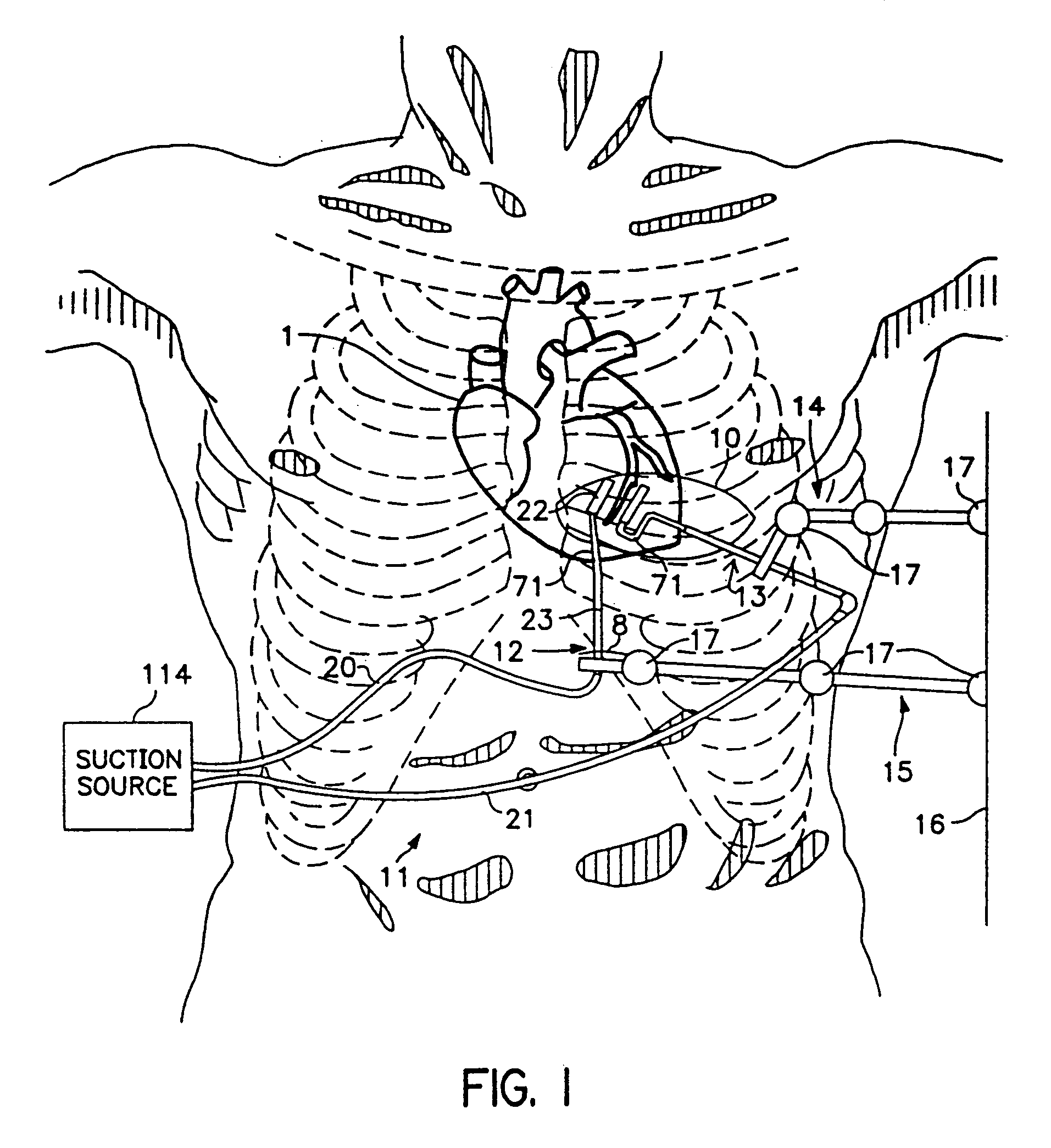
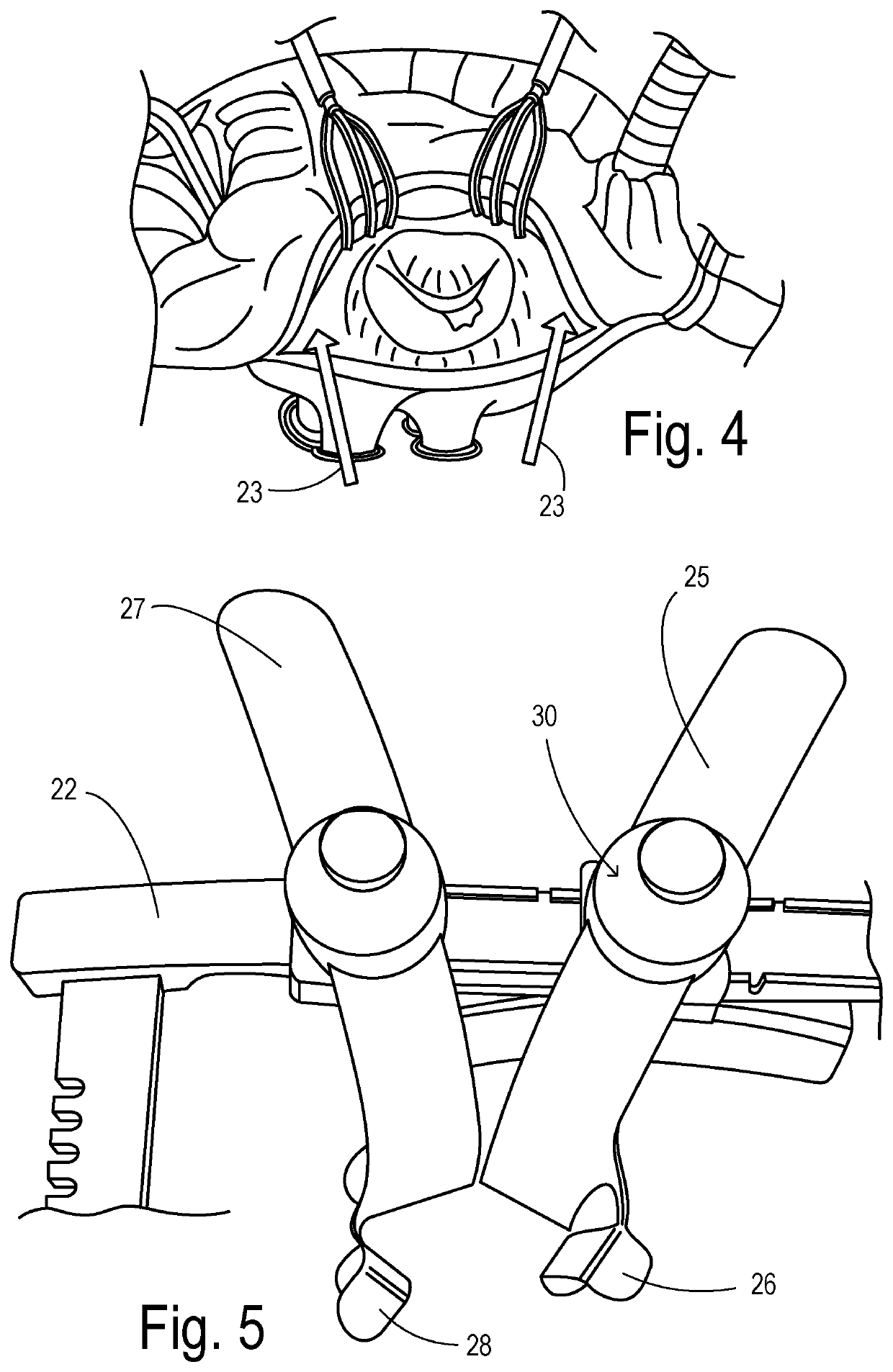
Organ manipulation devices for atraumatically grasping the surface of an organ and repositioning the organ to allow access to a location on the organ that would otherwise be substantially inaccessible. Methods of accessing a beating heart, retracting the heart using an organ manipulation apparatus, and stabilizing a surgical target area with a stabilizer. Both the organ manipulator and stabilizer are fixed to a stationary object which may be a sternal retractor. A system for performing beating heart coronary artery bypass grafting includes a sternal retractor, organ manipulator and stabilizer.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Organ manipulator apparatus
InactiveUS7479104B2Reduce creationDiagnosticsIntravenous devicesThoracic boneCoronary Artery Bypasses
Organ manipulation devices for atraumatically grasping the surface of an organ and repositioning the organ to allow access to a location on the organ that would otherwise be substantially inaccessible. Methods of accessing a beating heart, retracting the heart using an organ manipulation apparatus, and stabilizing a surgical target area with a stabilizer. Both the organ manipulator and stabilizer are fixed to a stationary object which may be a sternal retractor. A system for performing beating heart coronary artery bypass grafting includes a sternal retractor, organ manipulator and stabilizer.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
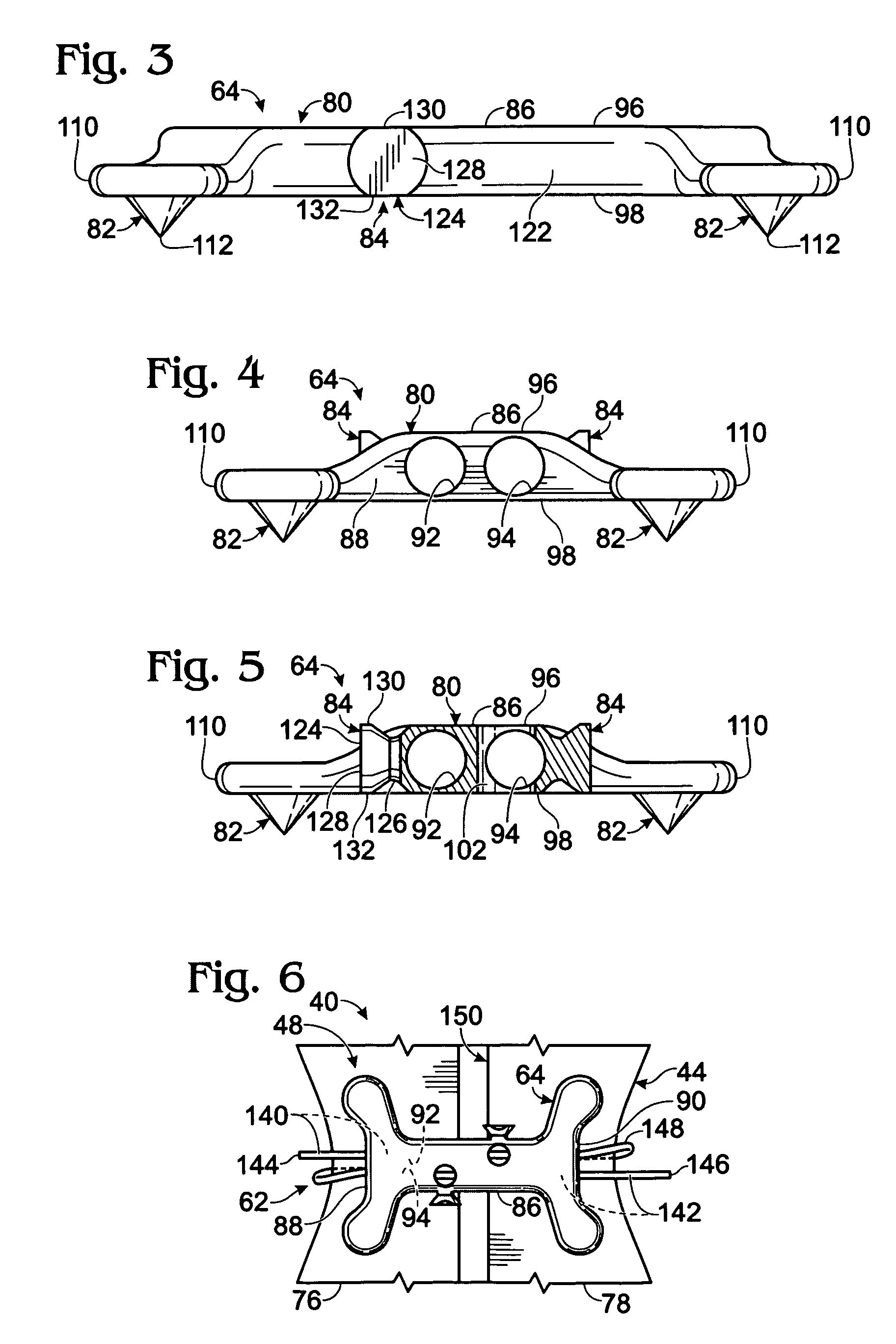
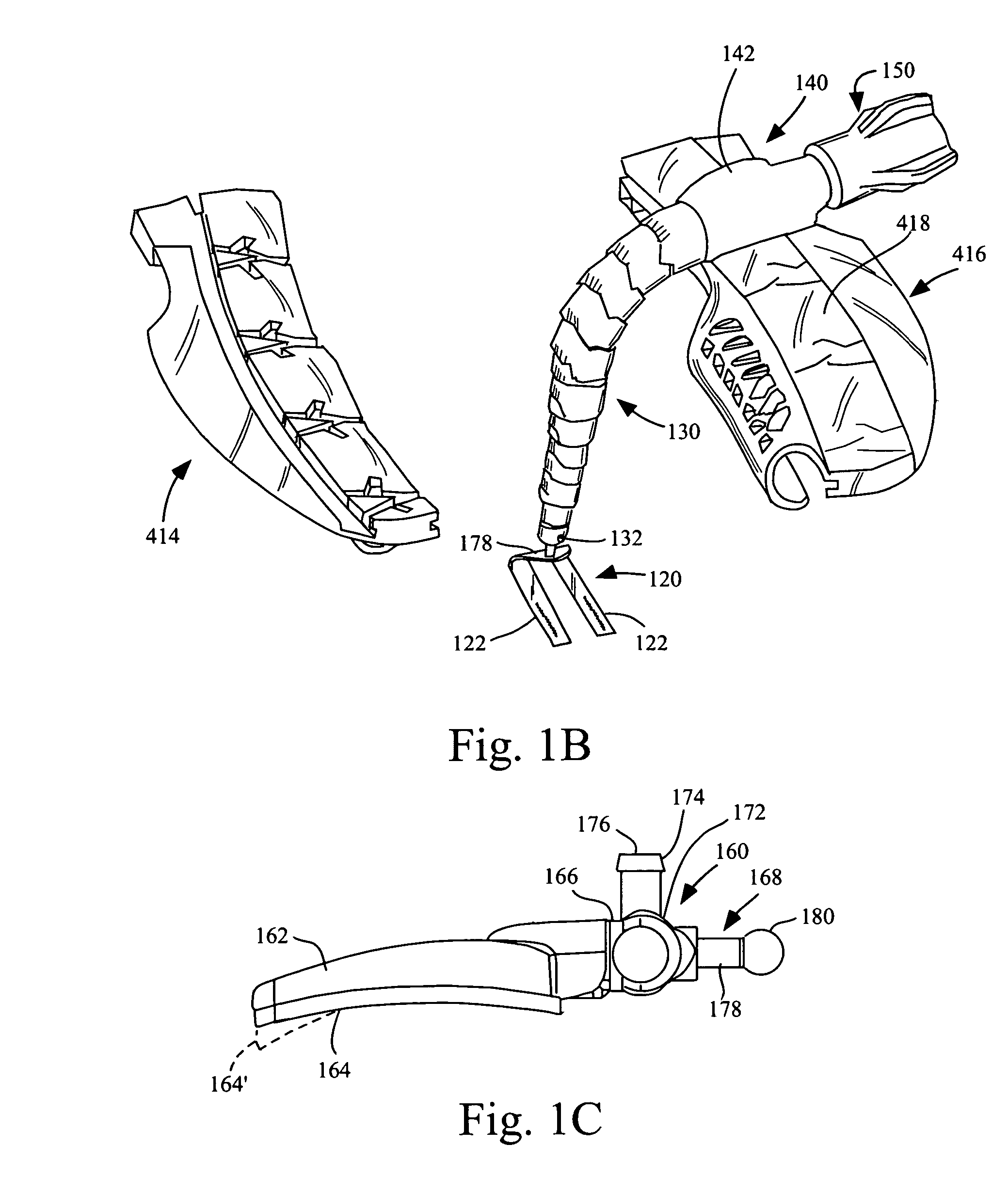
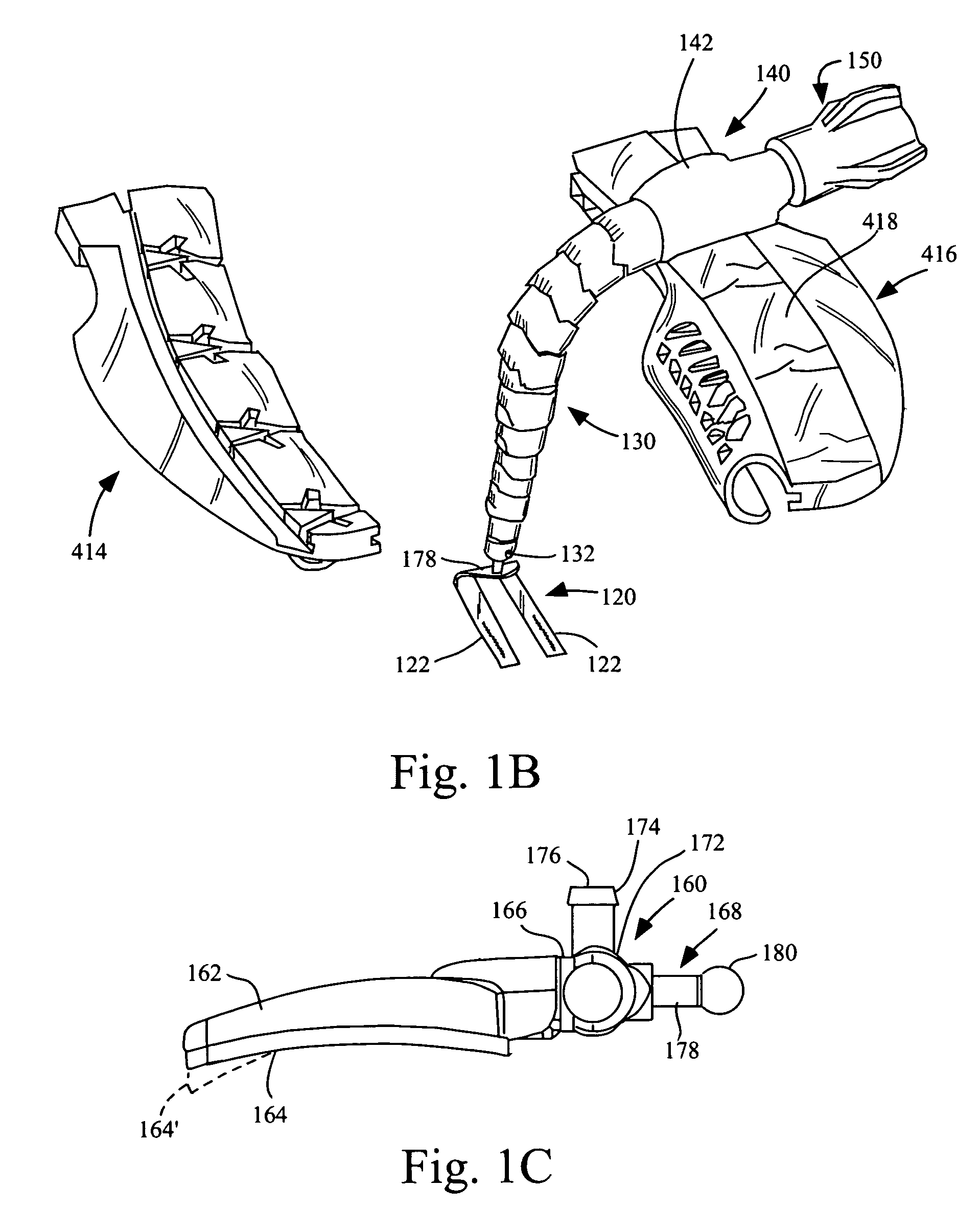
Thoracic closure device and methods
A thoracic closure device. The device has a handle member, a base member, and a feed path, and is designed to accept and, with a ratcheting mechanism, tension a toothed closure tie. A guide member is also provided, and assists in the placement of a closure tie prior to tensioning. Methods of closing a median sternotomy using toothed closure ties are also disclosed.
Owner:DEVICE EVOLUTIONS
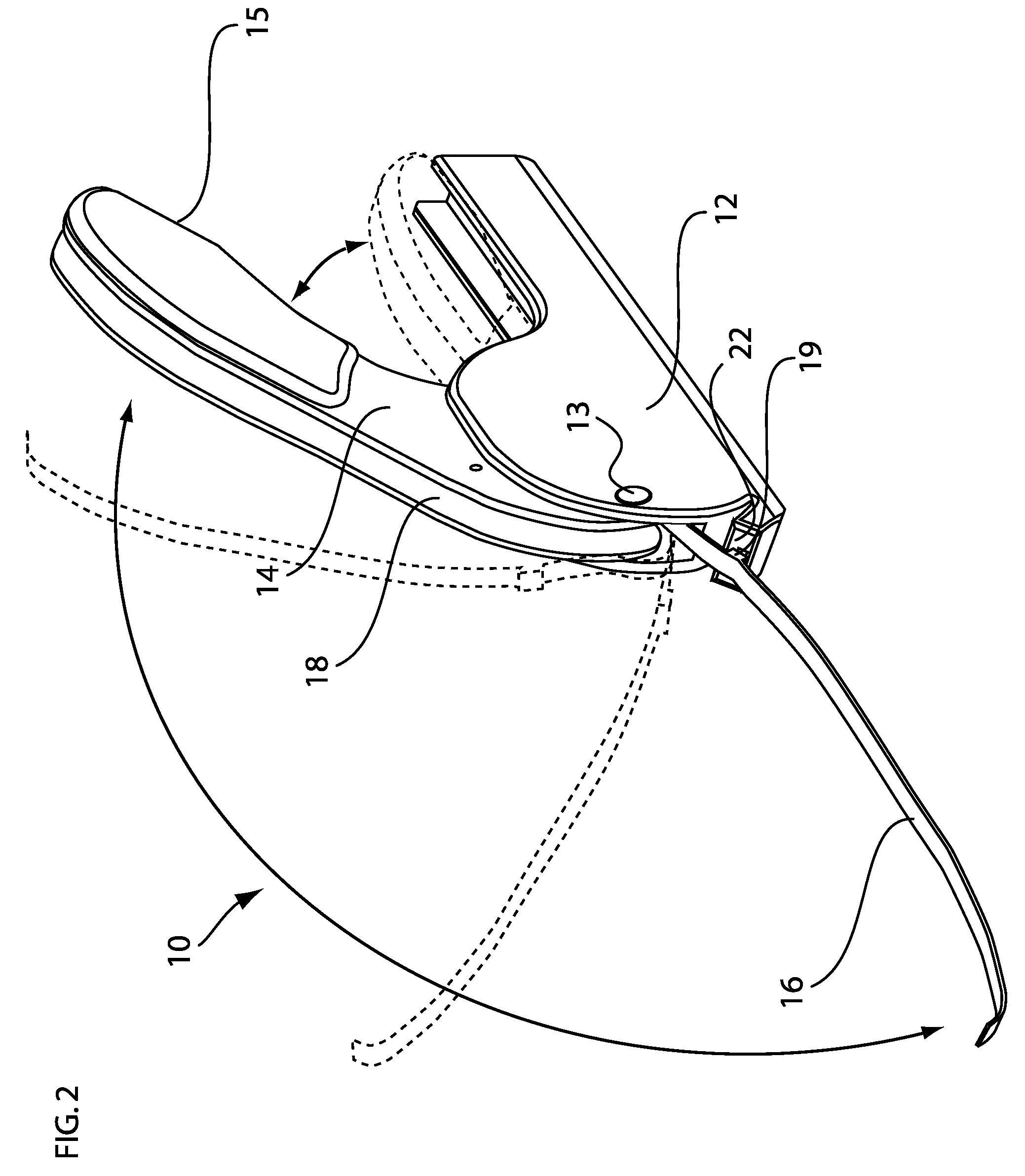
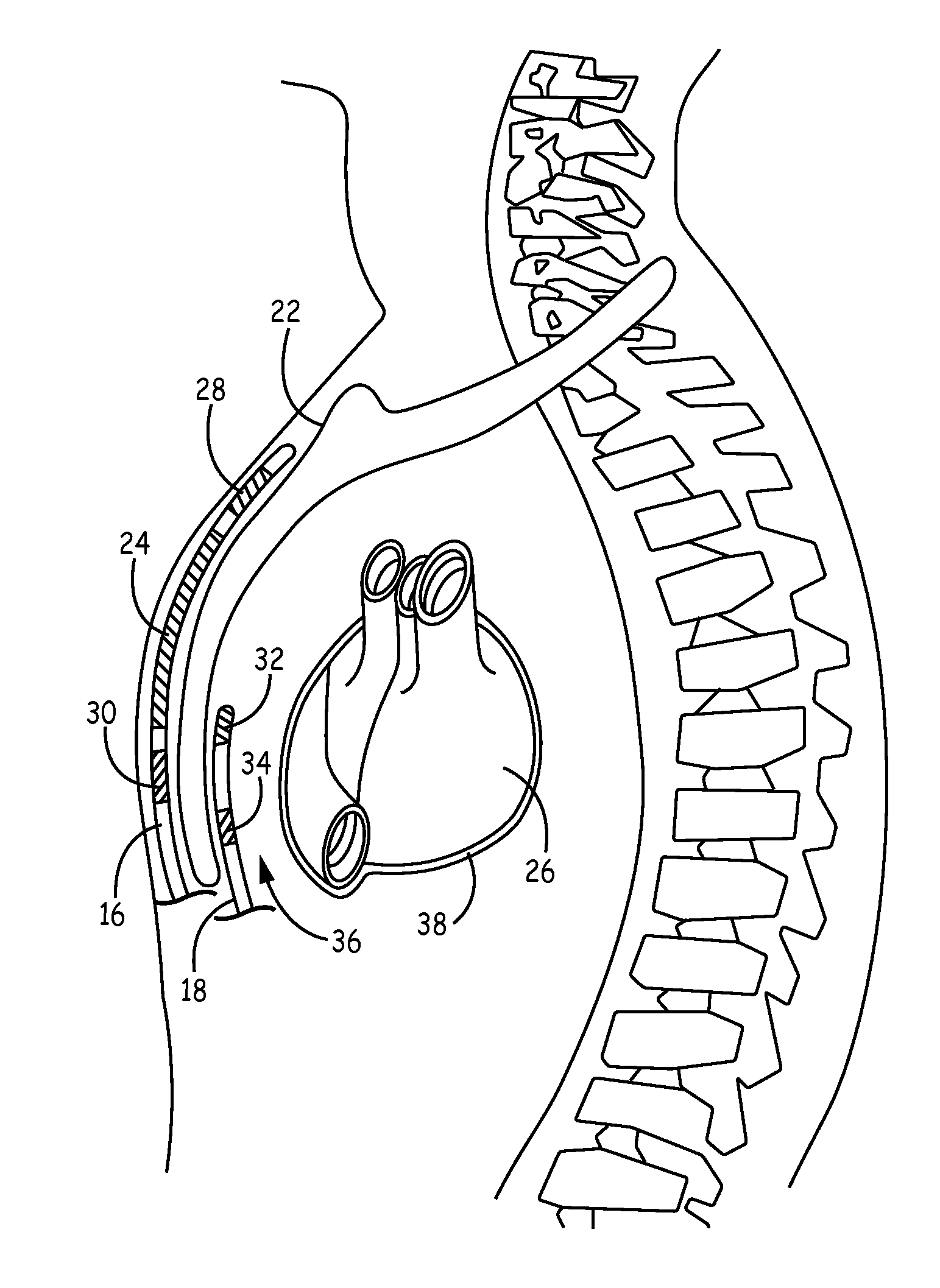
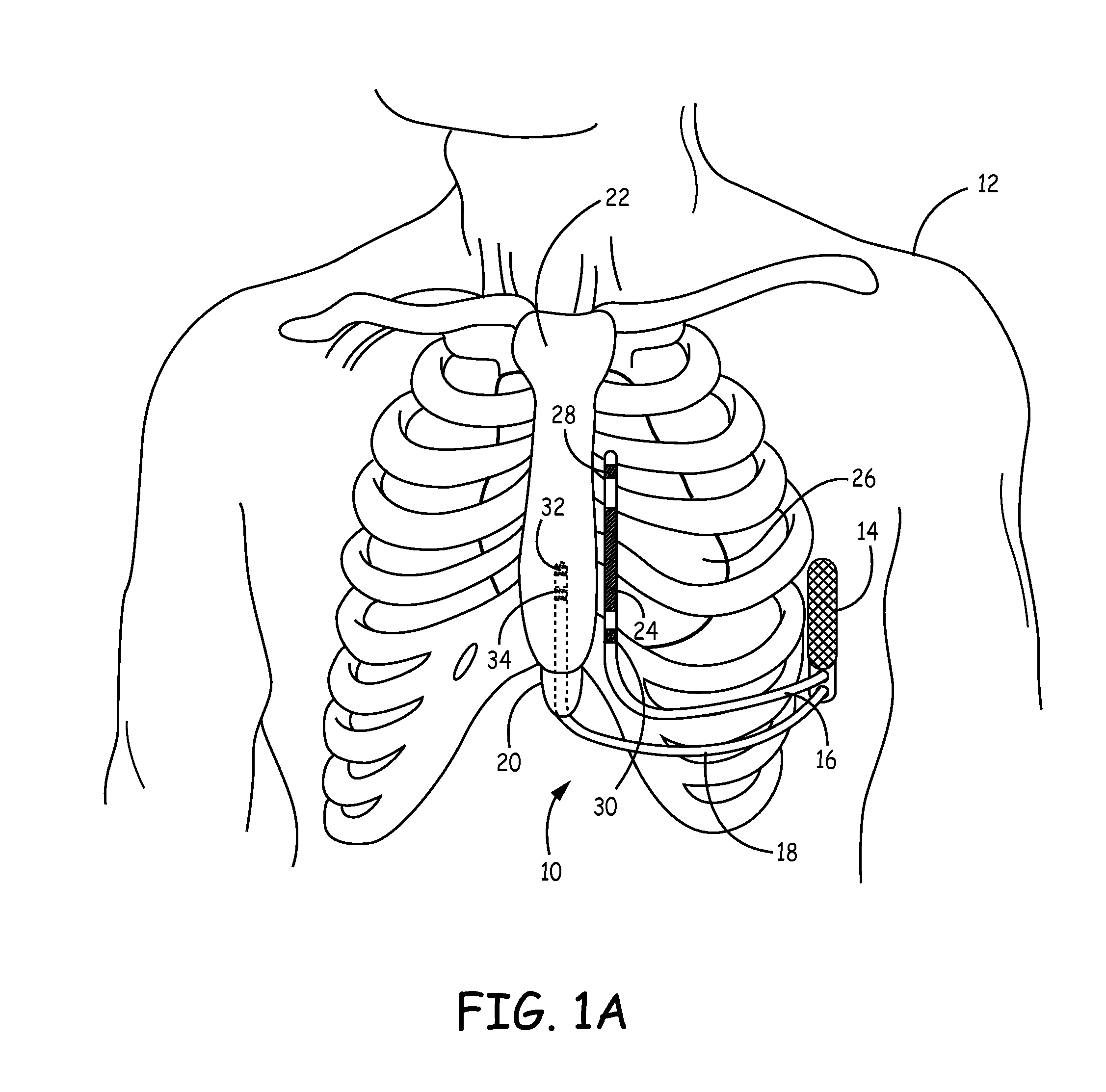
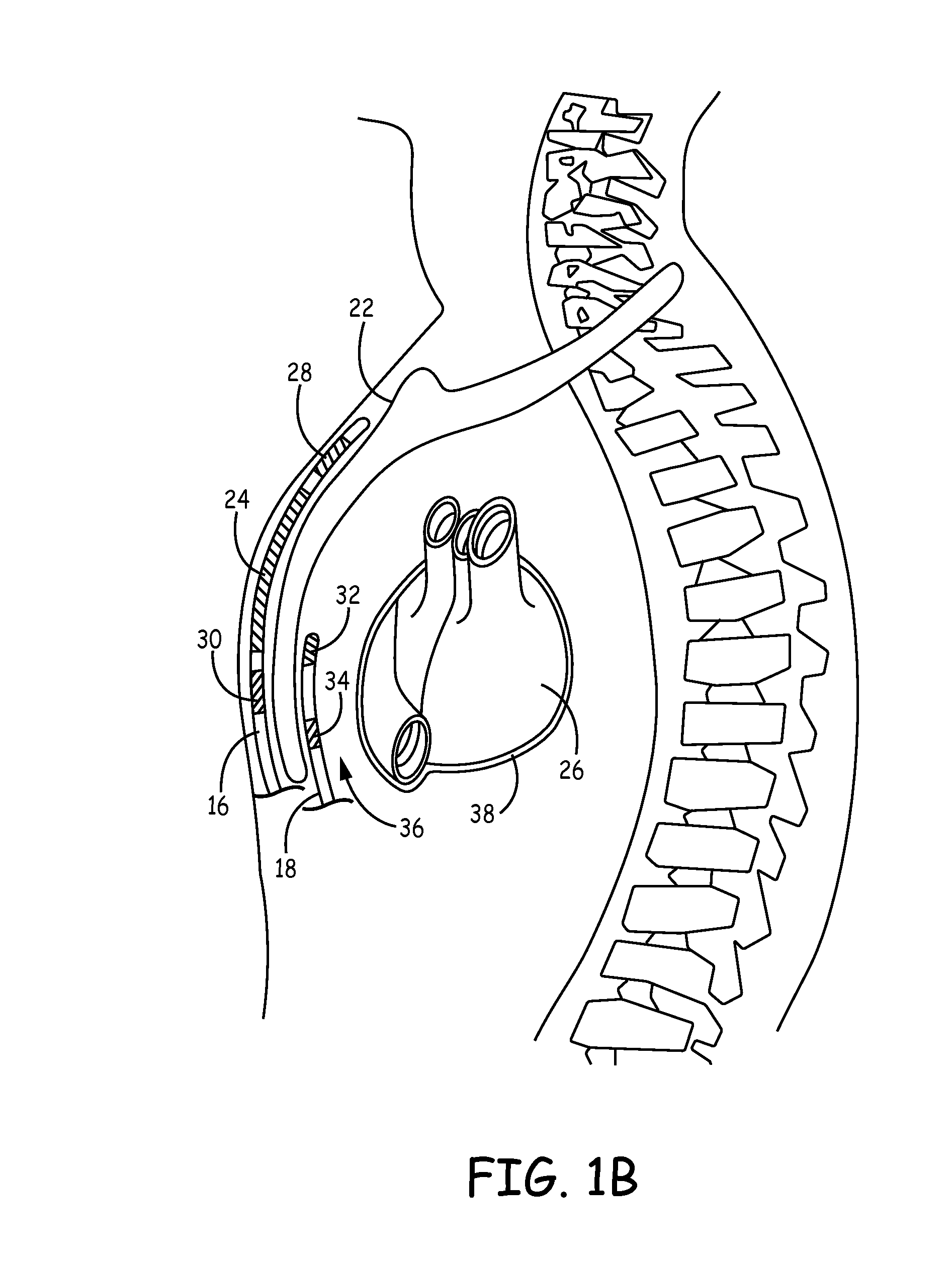
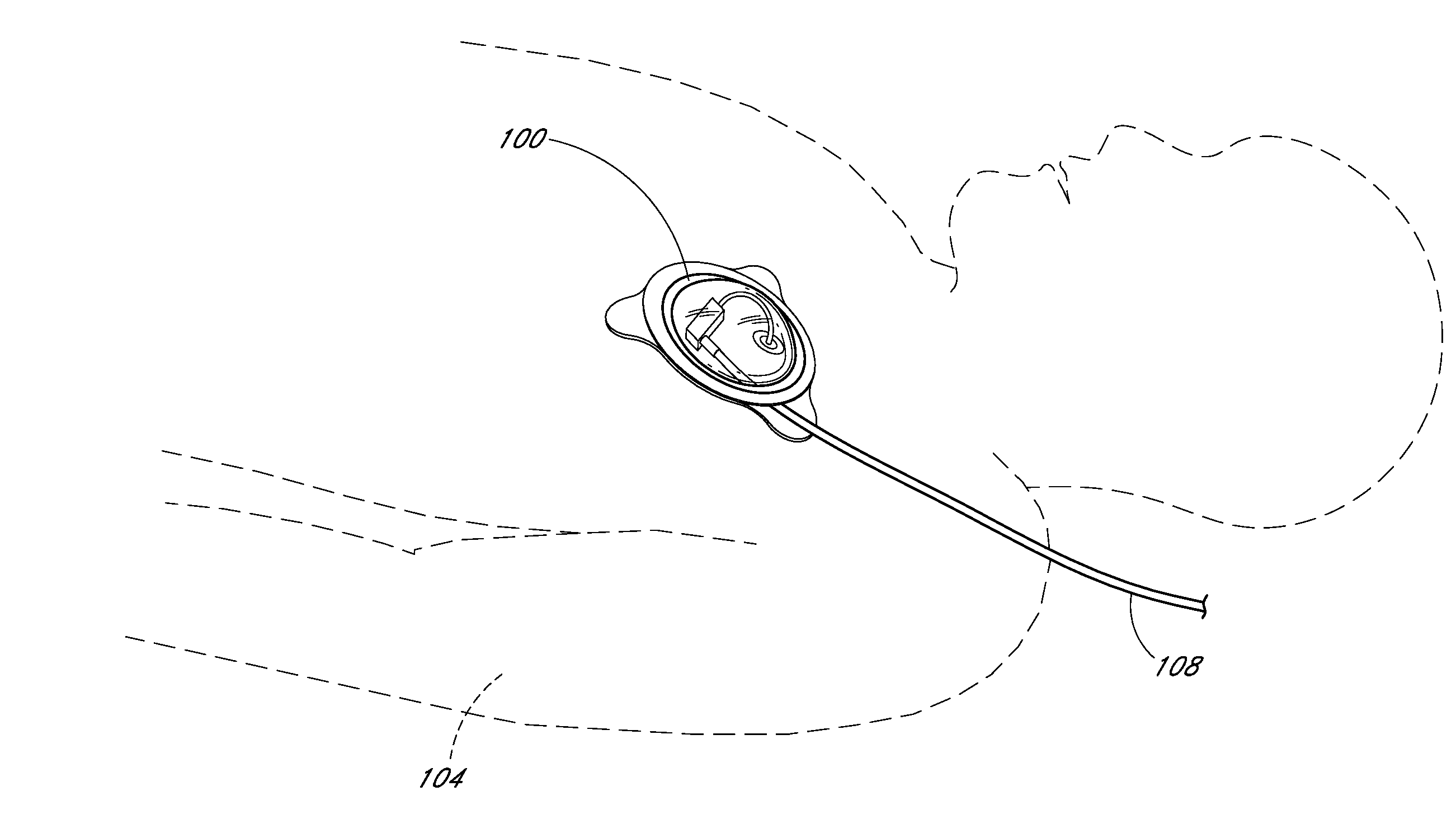
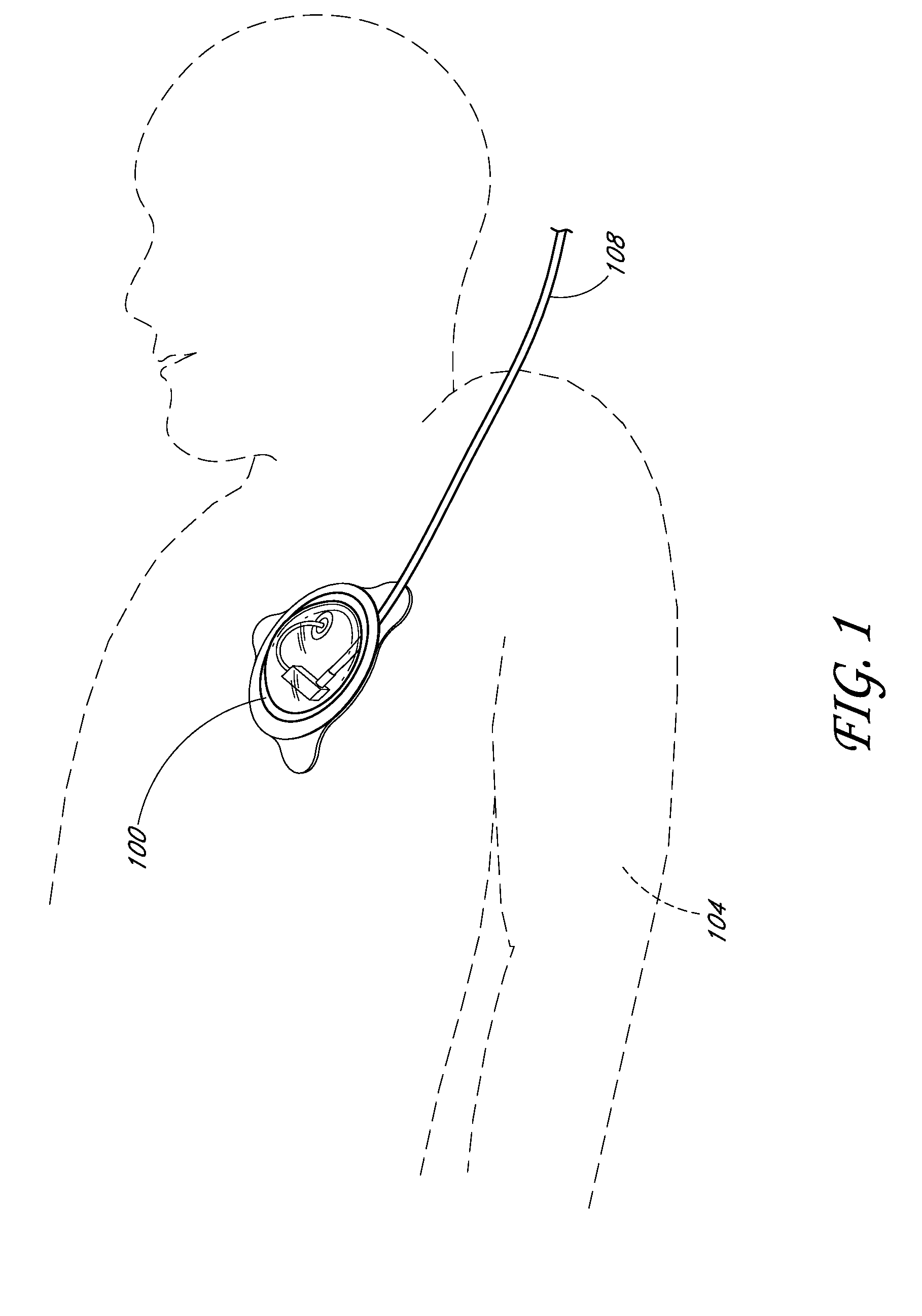
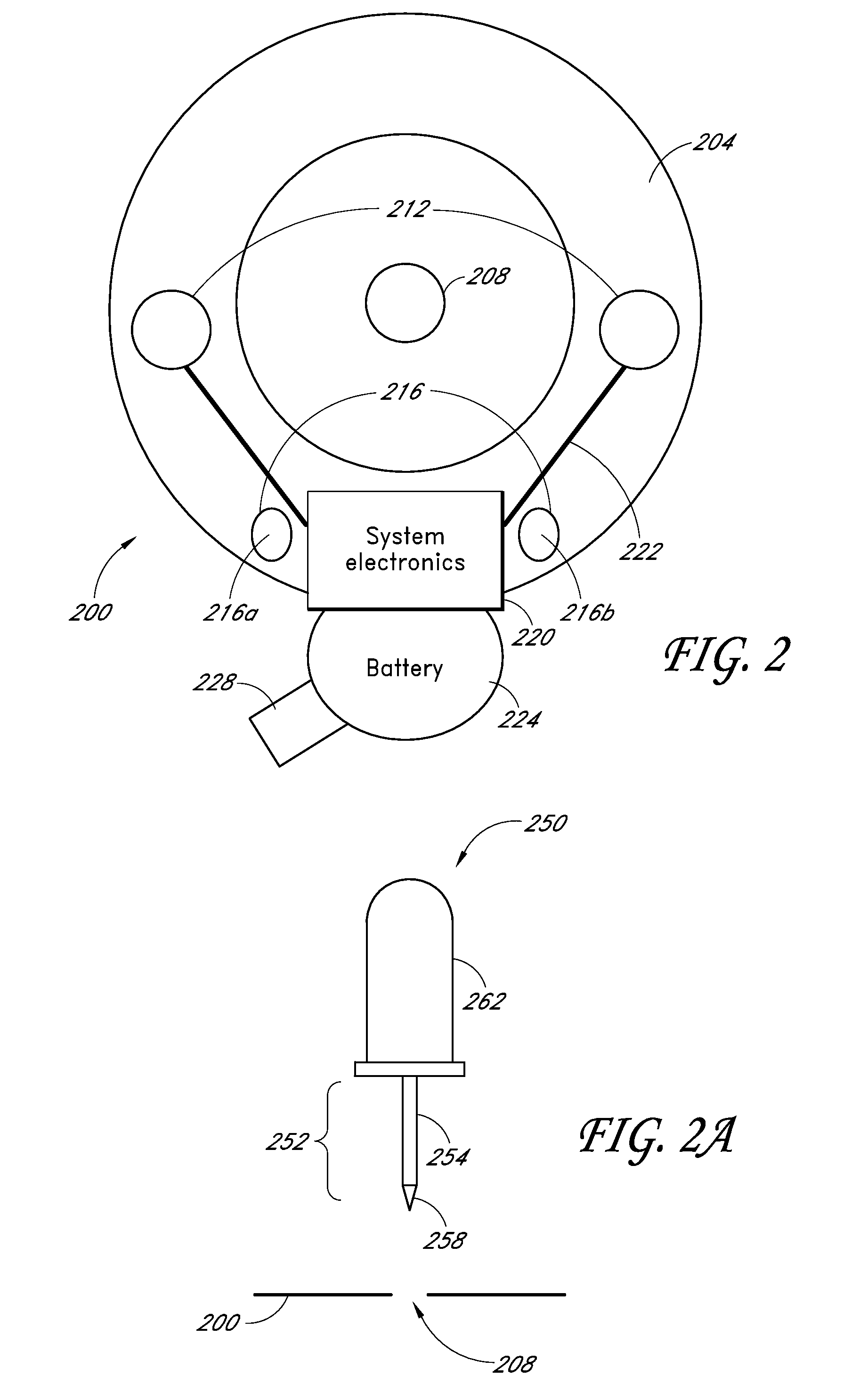
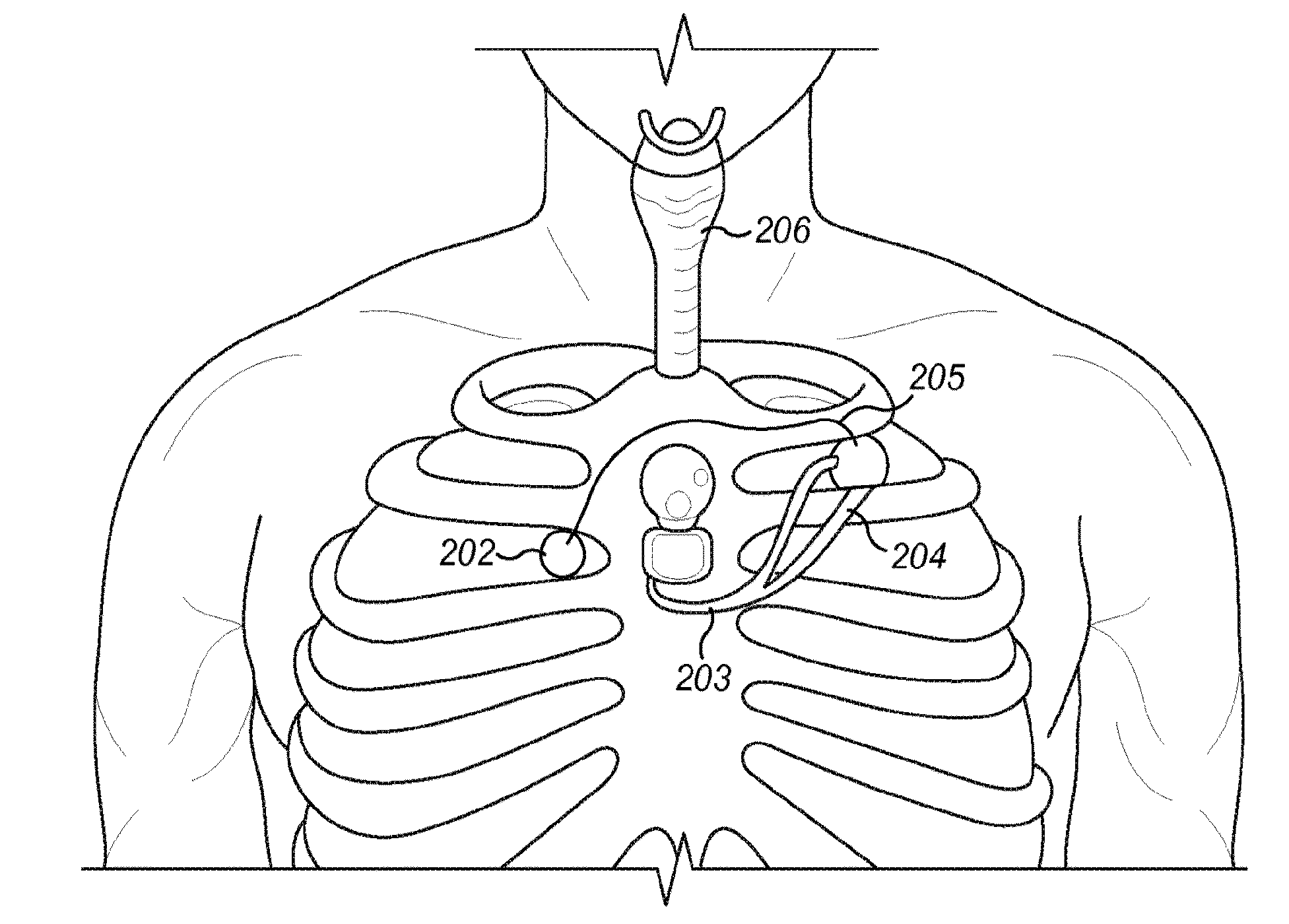
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) system including substernal pacing lead
An implantable cardiac defibrillator (ICD) system includes an ICD implanted subcutaneously in a patient, a defibrillation lead having a proximal portion coupled to the ICD and a distal portion having a defibrillation electrode configured to deliver a defibrillation or cardioversion shock to a heart of the patient, and a pacing lead that includes a distal portion having one or more electrodes and a proximal portion coupled to the ICD. The distal portion of the pacing lead is implanted at least partially along a posterior side of a sternum of the patient within the anterior mediastinum. The ICD is configured to provide pacing pulses to the heart of the patient via the pacing lead and provide defibrillation shocks to the patient via the defibrillation lead. As such, the implantable cardiac system provides pacing from the substernal space for an extravascular ICD system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
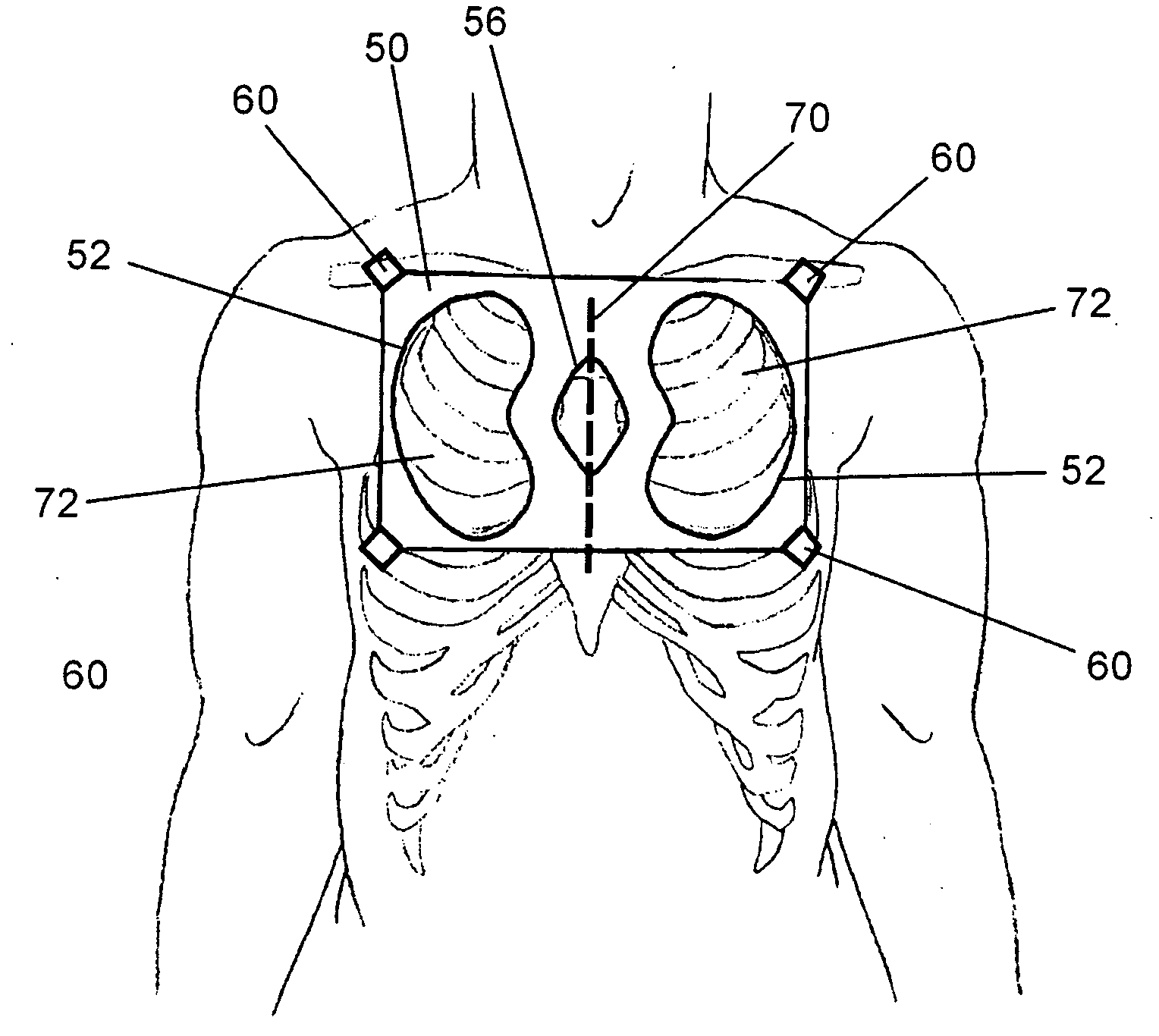
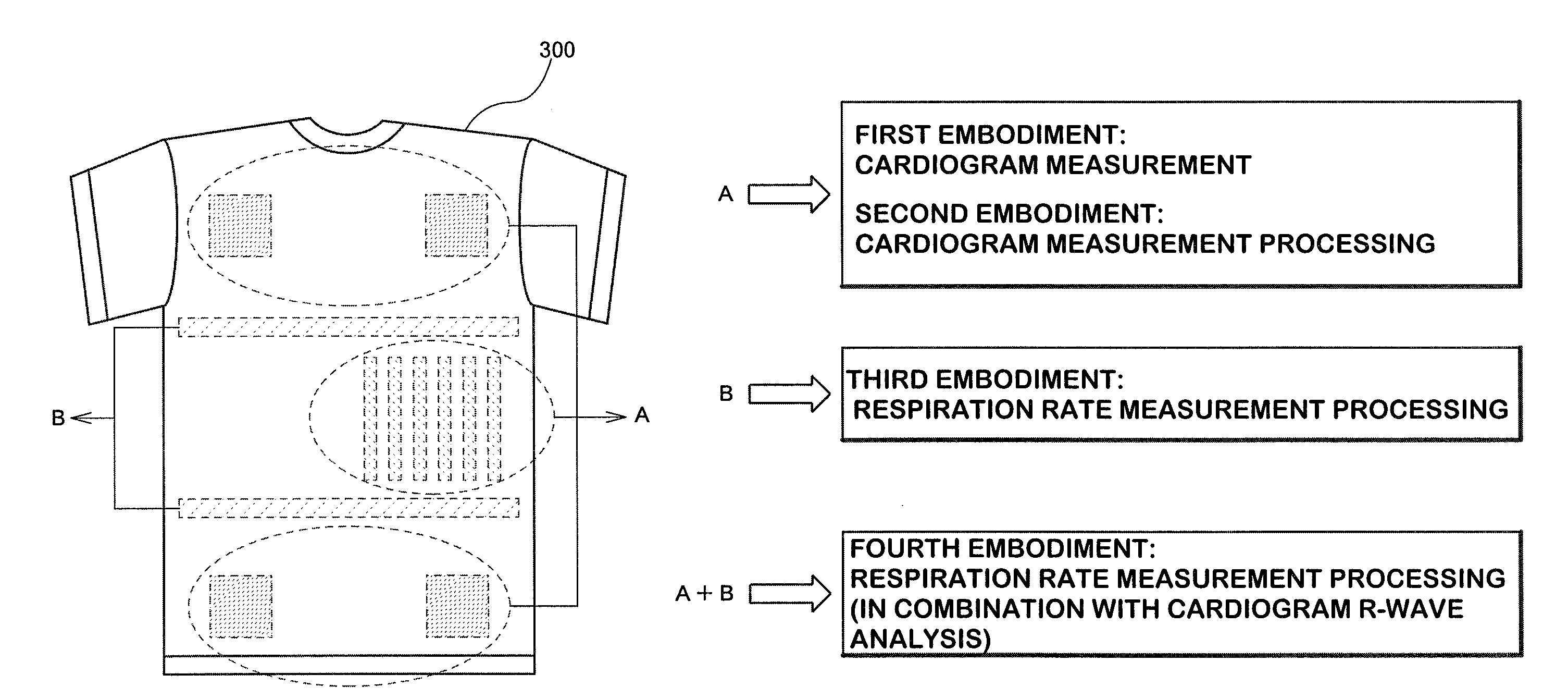
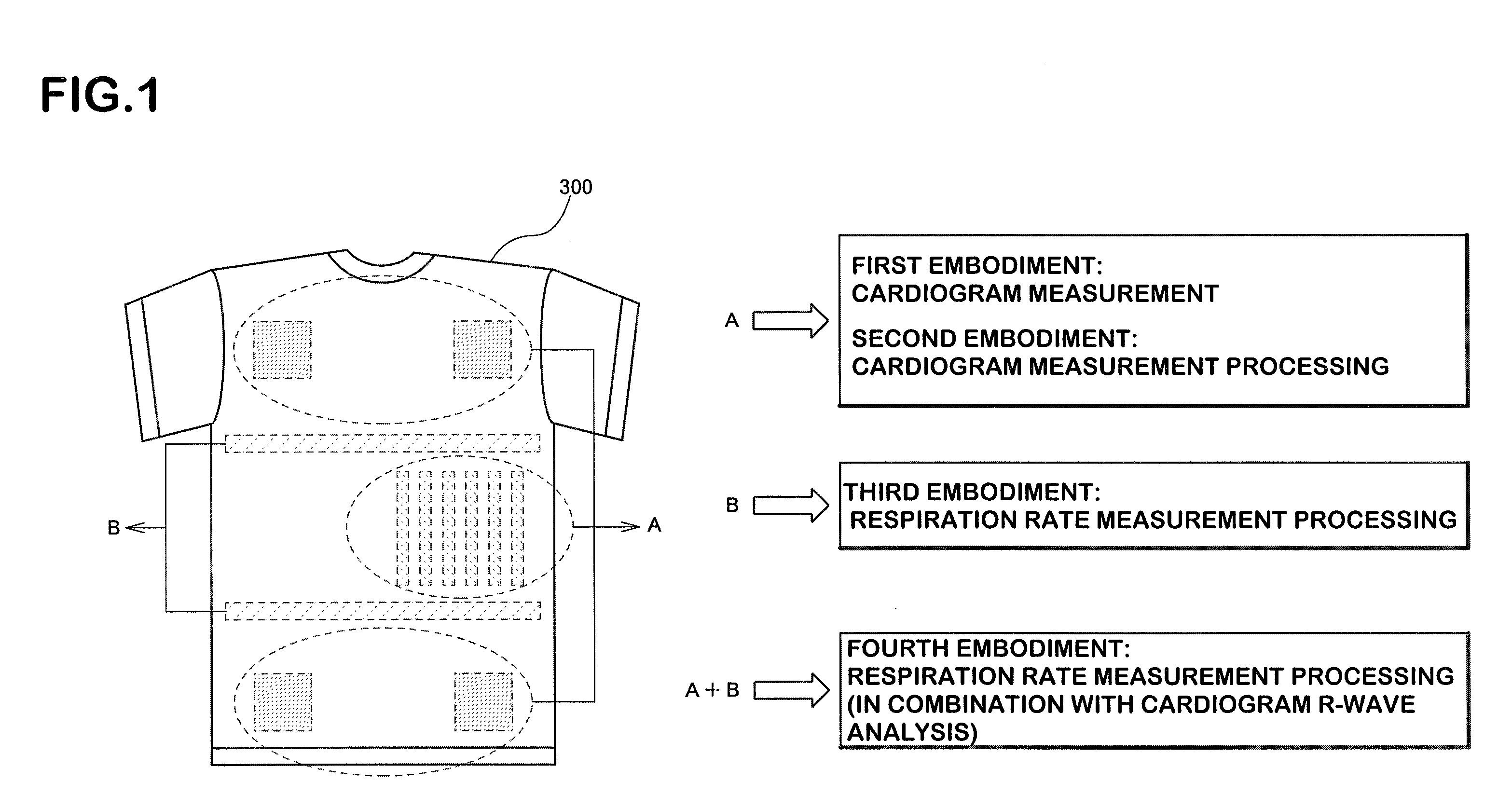
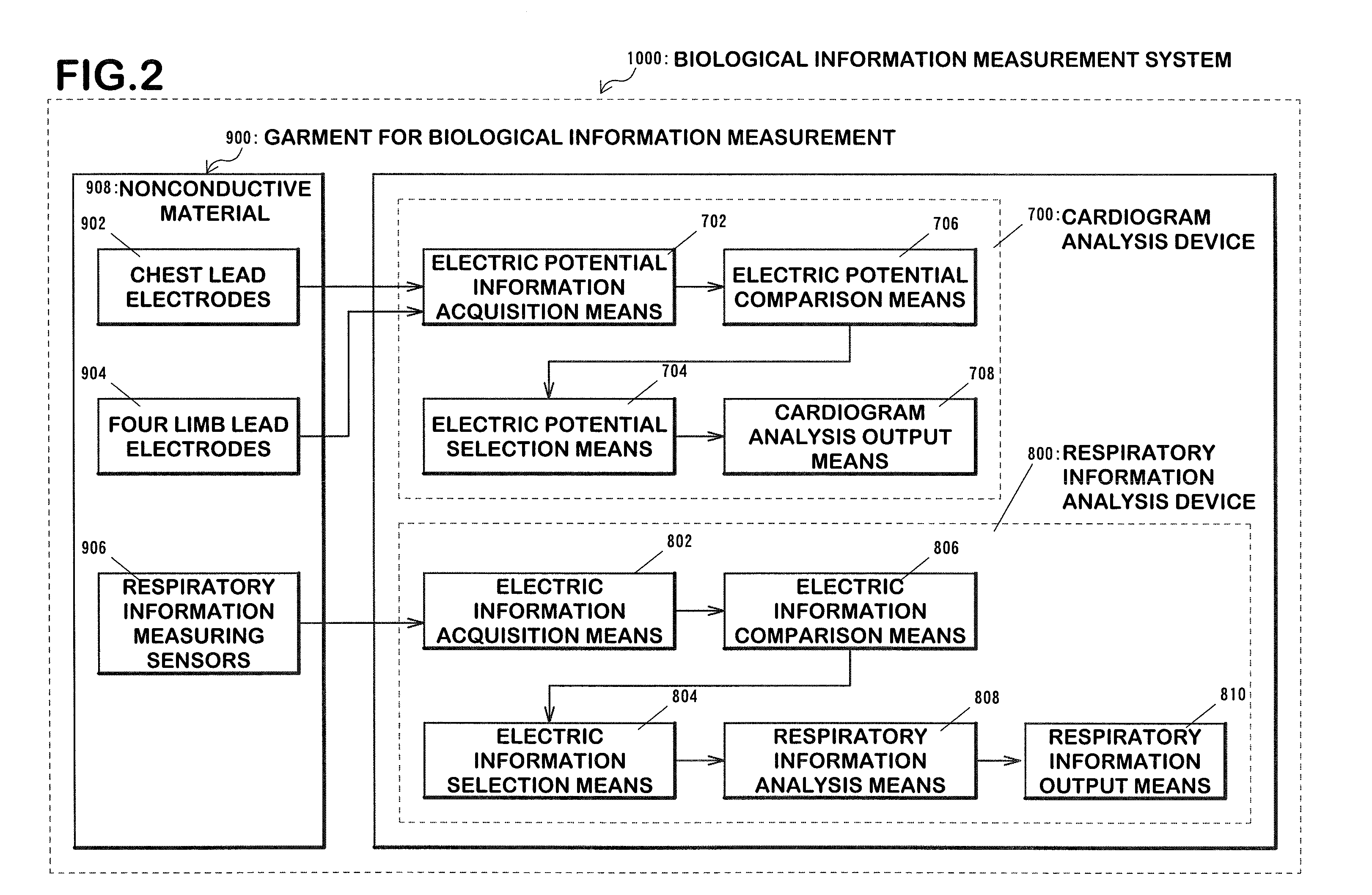
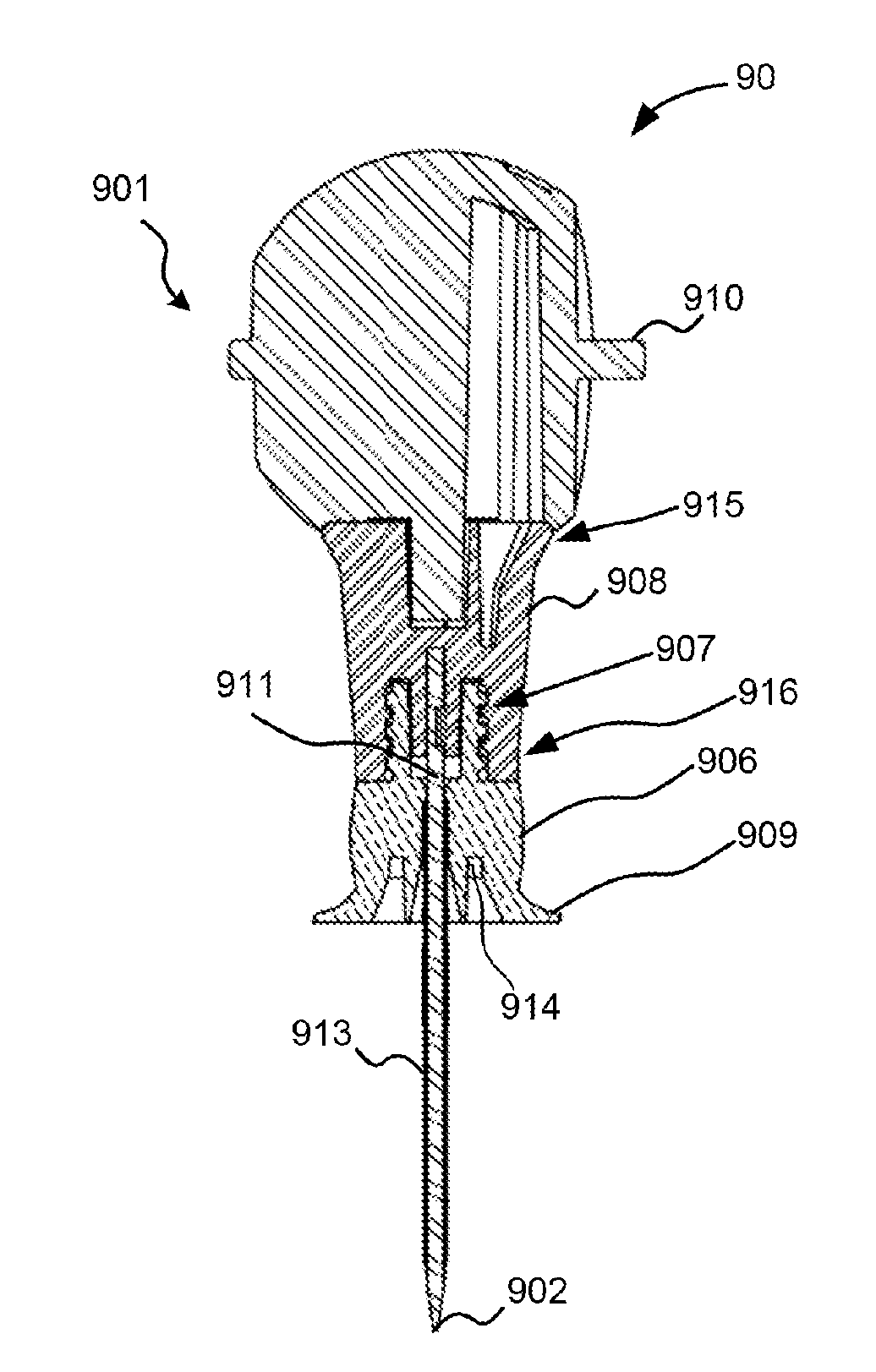
Garment for bioinformation measurement having electrode, bioinformtion measurement system and bioinformation measurement device, and device control method
ActiveUS20090012408A1Simple structureMeasurement accuracyElectrocardiographyCatheterPresternal regionMeasurement device
The present invention provides a garment for measuring biological information, a biological information measurement system, a biological information measurement device and a method of controlling thereof capable of measuring biological information with accuracy regardless of variations of the constitution of each examinee. When an examinee wears a biological information measurement shirt 301, four limb electrodes 351 and 352 are arranged at positions so that the electrodes cover the body surface other than around the clavicle of the examinee. At that time, four limb electrodes 362 and 363 are assigned to positions so that they cover about the pelvis of the examinee. Also, during the use of the shirt, chest electrodes 353˜358 cover from the body surface (around lower part of left side of the body) of a presternal region around the left thorax of an examinee for a perpendicular direction of the body axis (a direction perpendicular to the length of the shirt) and the electrodes are assigned so as to cover from the body surface around the fourth rib to that around the sixth rib.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
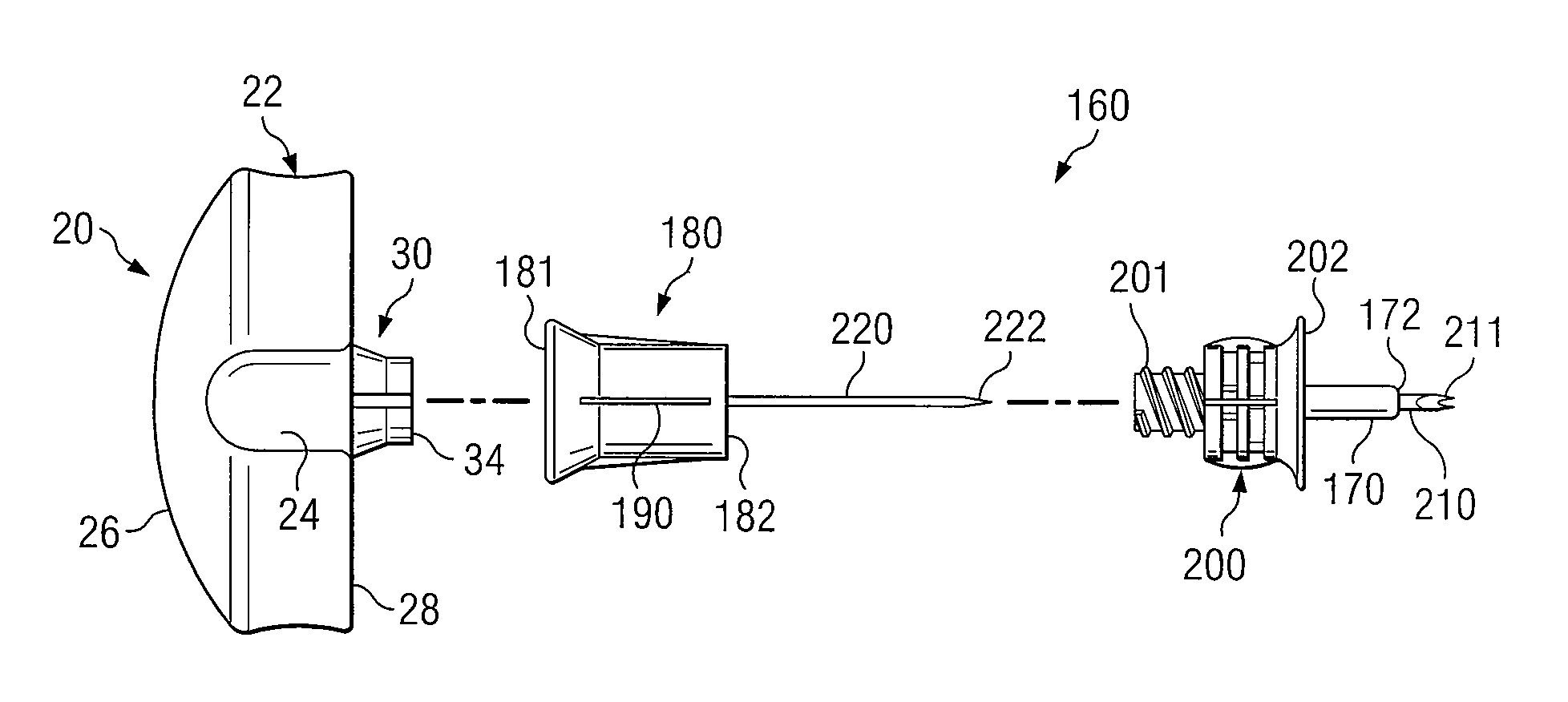
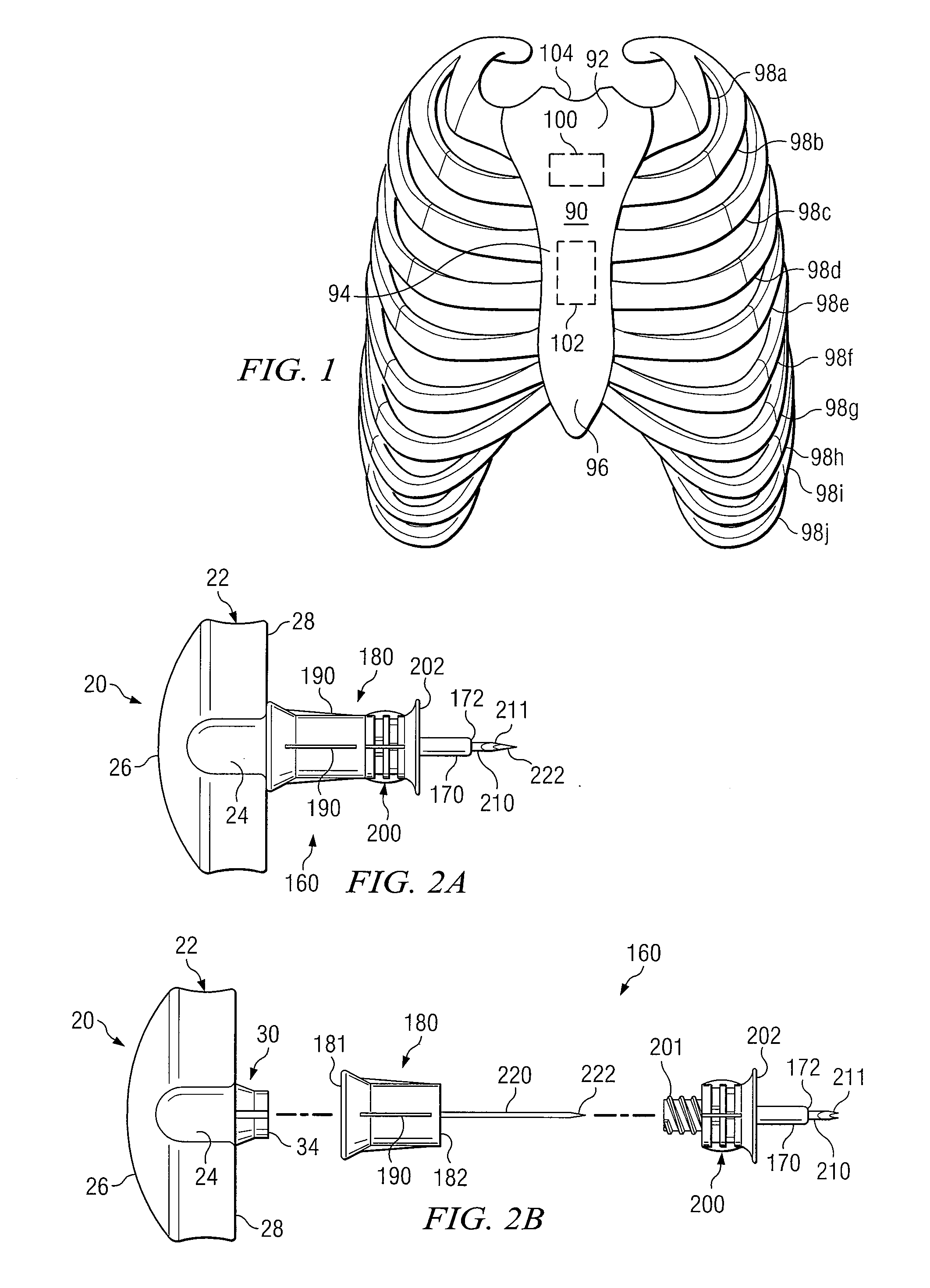
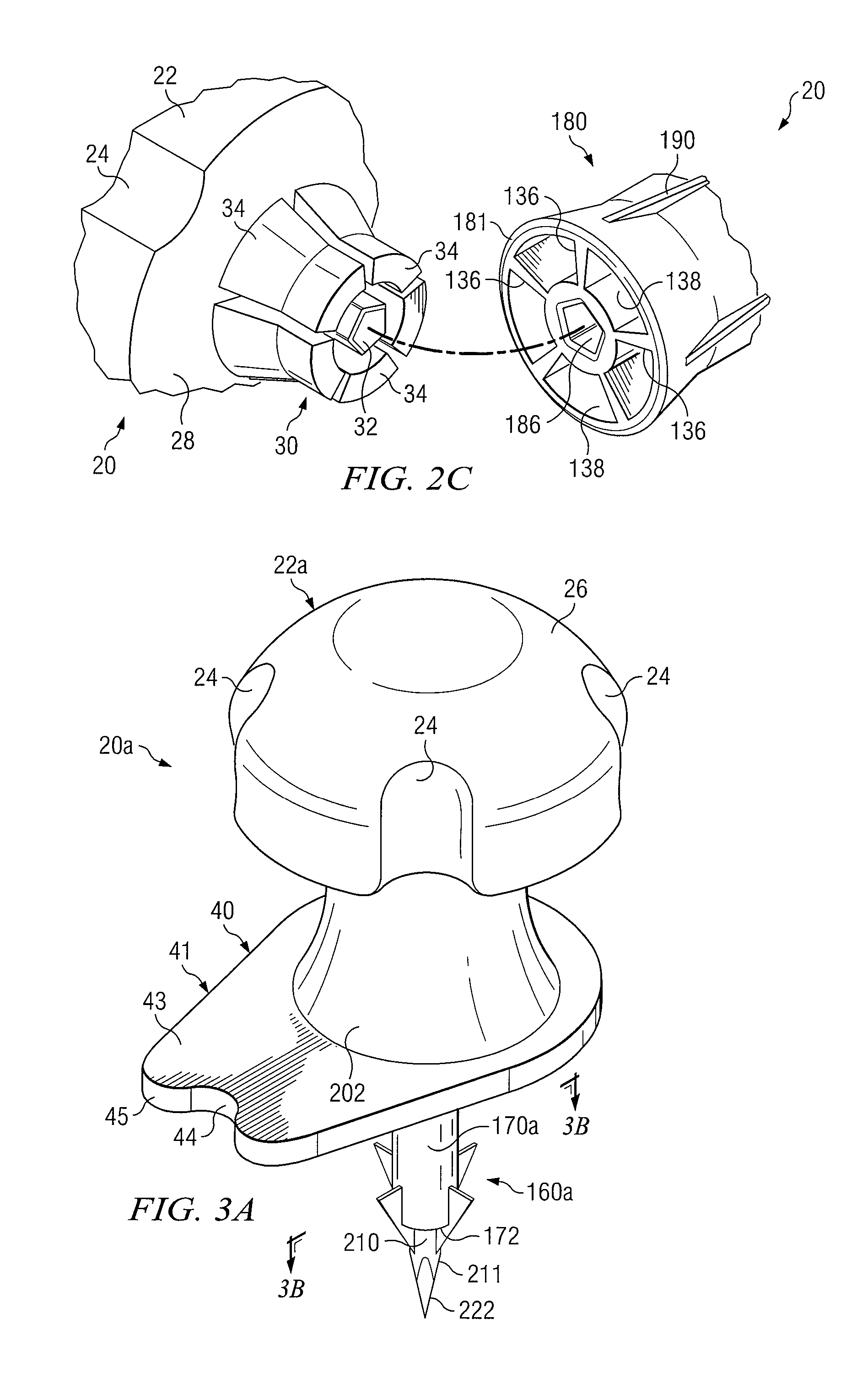
Sternal locators and associated systems and methods
Apparatuses, systems, and methods for sternal locators for placement of an intraosseous device into the sternum of a human patient.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Protecting biological structures, including the great vessels, particularly during spinal surgery
InactiveUS20050126576A1Improve barrier propertiesAvoid formingRestraining devicesSurgeryIntracranial surgeryThoracic bone
Natural and / or synthetic materials to form a strong barrier between the skeletal system and the great vessels. In the preferred embodiments, a natural or synthetic material is used to prevent scar tissue from forming around the vessels and / or to act as barrier placed between the vessels and the skeletal system, including the spine. Devices according to the invention may also be used over the dura and nerves following laminectomy procedures, between the sternum and the pericardium or heart following cardiac procedures, in intra-abdominal procedures such as intestinal or vascular surgery, over the brain in intra-cranial surgery, over the ovaries or other organs or tissues in the female genitourinary system, over the prostate or other organ or tissues in the male genitourinary system, or in other surgeries on humans or animals.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
Biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material and a preparation method thereof. The material is applied to the bone surface or bone section of a human body or an animal, and is characterized in that the biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material is modified starch prepared by modifying natural starch serving as a raw material, and comprises one or more than two of modified starch granules, modified starch sponges, modified starch films, modified starch foams or modified starch glues, wherein the molecular weight of the modified starch is 15,000 to 10,000,000, and the water absorption rate is 1 to 100 times; in the natural starch serving as the raw material, the content of the amylopectin is at least no less than 70 percent of the total amount of the raw material. The invention fulfills the aim of stopping bleeding through direct spraying, daubing and pasting the biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material to touch the bone bleeding surface of wound; meanwhile, the biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material has a function of promoting bone healing, and can be used in the bleed stopping in the sternotomy of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, spinal surgeries and joint surgeries of orthopedics department, Craniotomy and maxillo-facial surgery and the bleed stopping in the process of trauma care.
Owner:纪欣
Rib auto-demarcating method and device
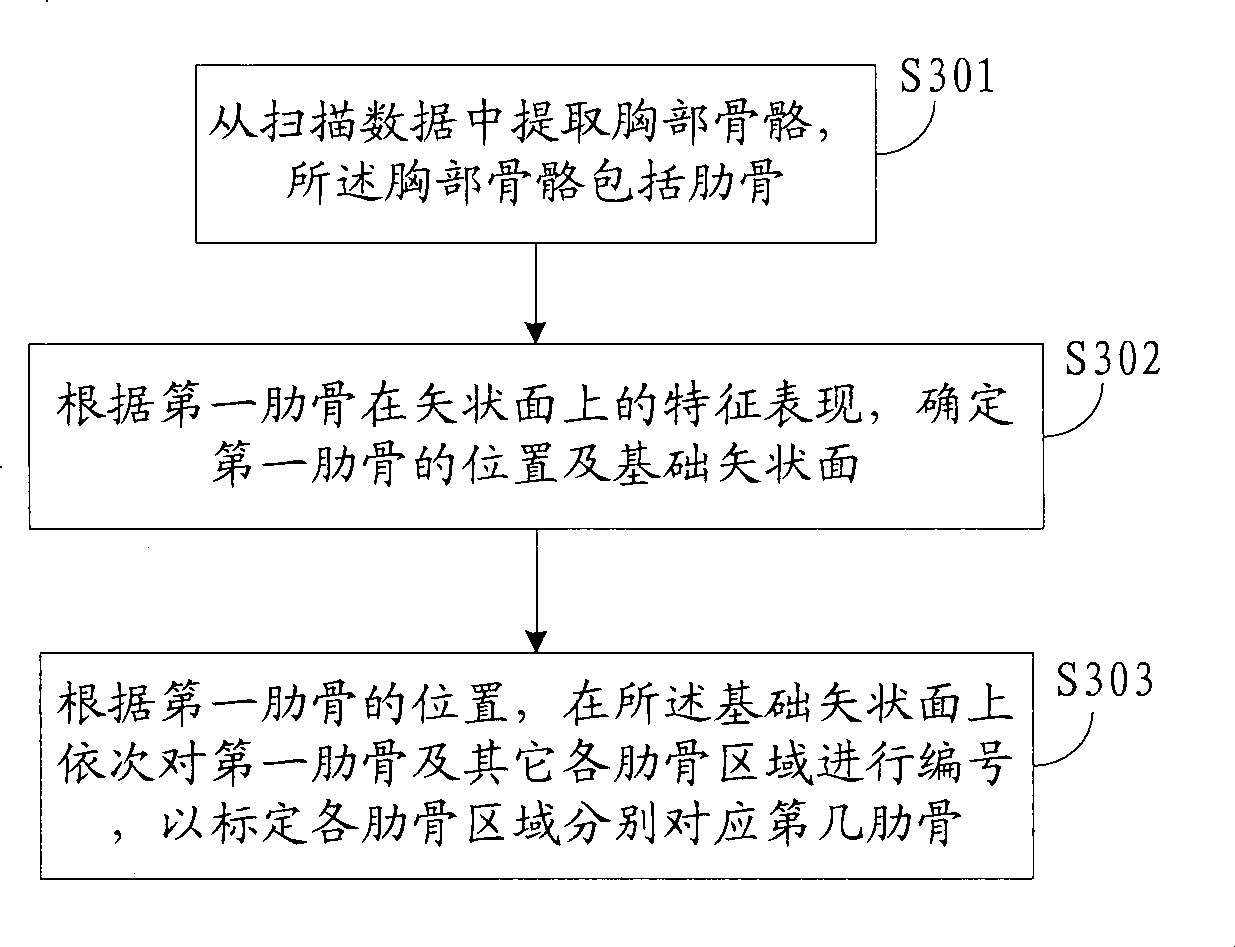
ActiveCN101452577AEasy to determinePrecise positioningImage analysisComputerised tomographsThoracic boneSagittal plane
The invention discloses an automatic rib marking method, which comprises: extracting thoracic bones from scan data, wherein the thoracic bones comprise ribs; according to the feature representation of a first rib on a sagittal plane, determining the position of the first rib and a basic sagittal plane; according to the position of the first rib, coding the first rib and other rib regions on the basic sagittal plane to mark the sequence number of the ribs corresponding to the rib regions. The invention also discloses an automatic rib marking device. The method can accurately mark the rib regions according to the feature presentation of the ribs on the sagittal plane; in addition, the method can obtain ideal rib outlines easily, facilitate the initial seed points of the ribs and consequently complete the positioning of the whole ribs accurately.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
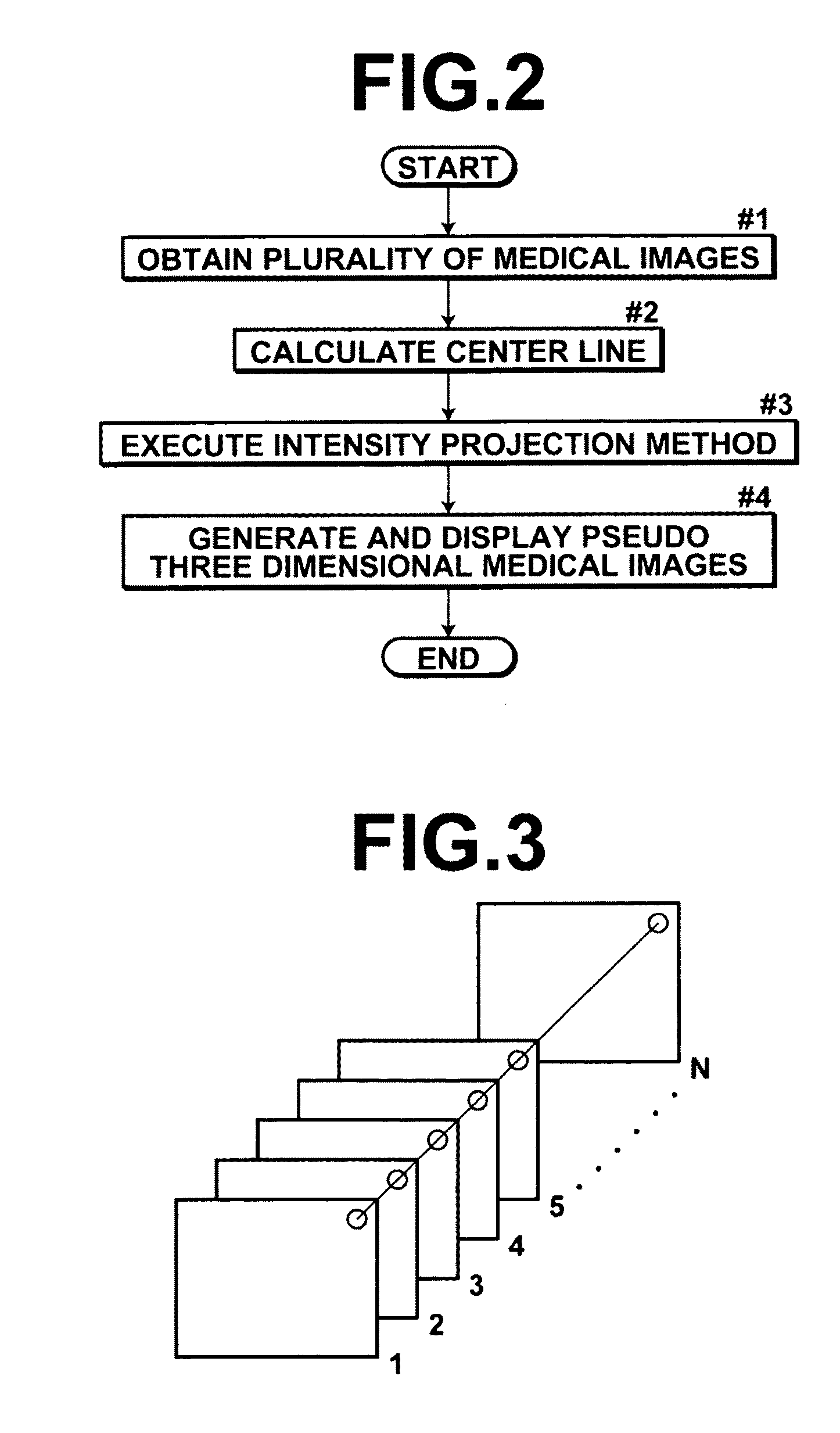
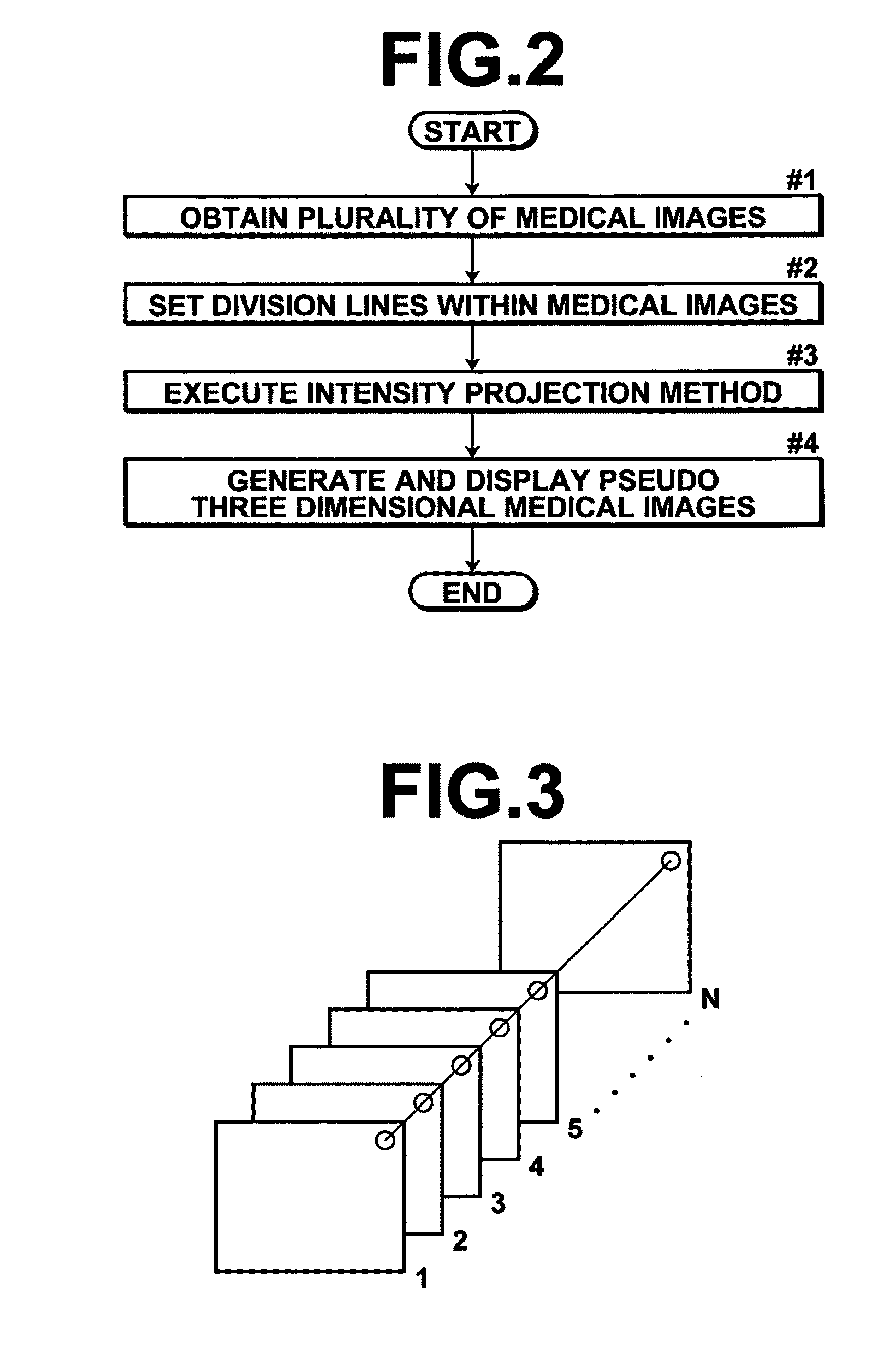
Image processing method, image processing apparatus, and image processing program
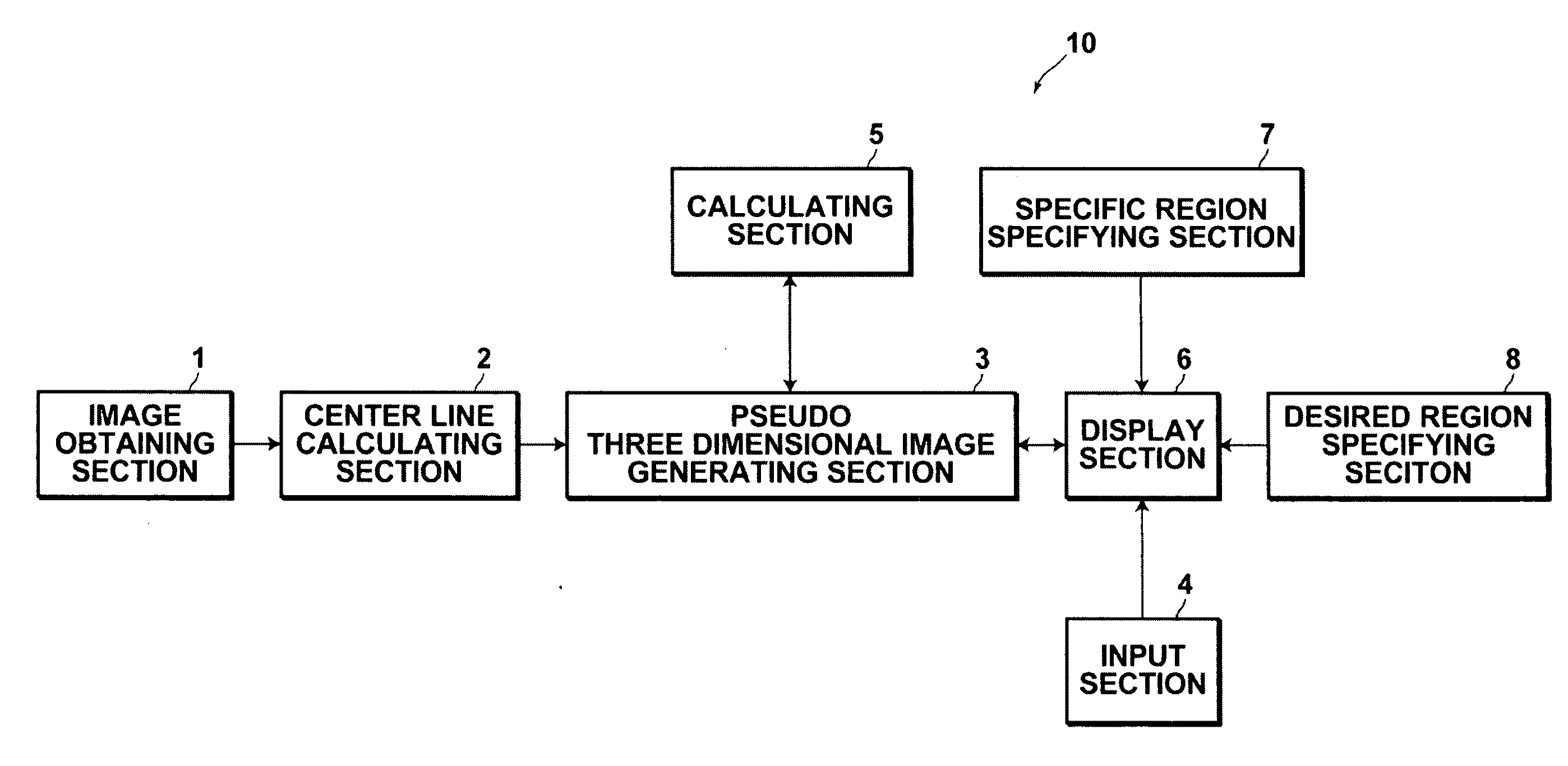
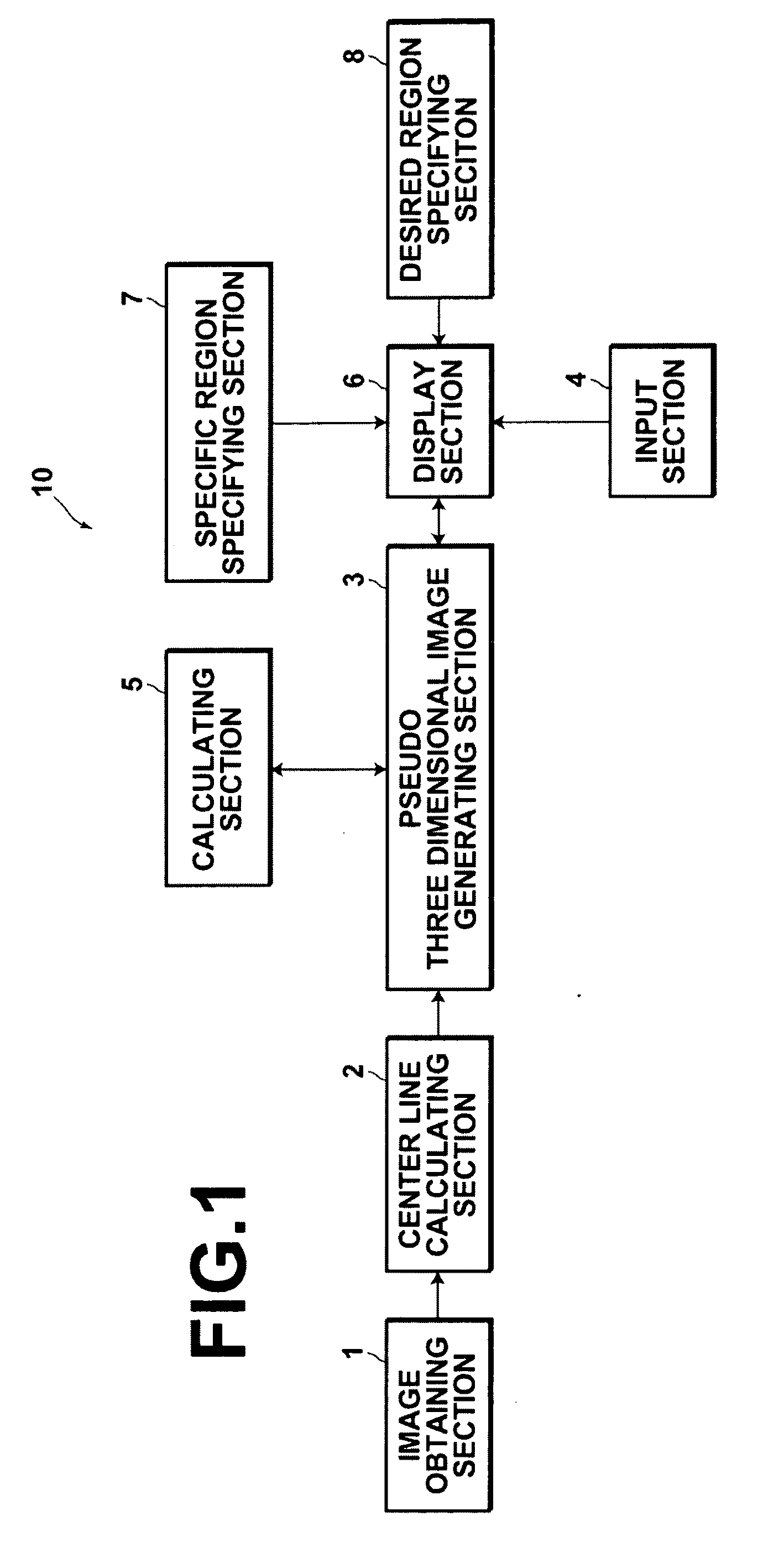
InactiveUS20100177945A1Easy diagnosisEasy to understandImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImaging processingThoracic bone
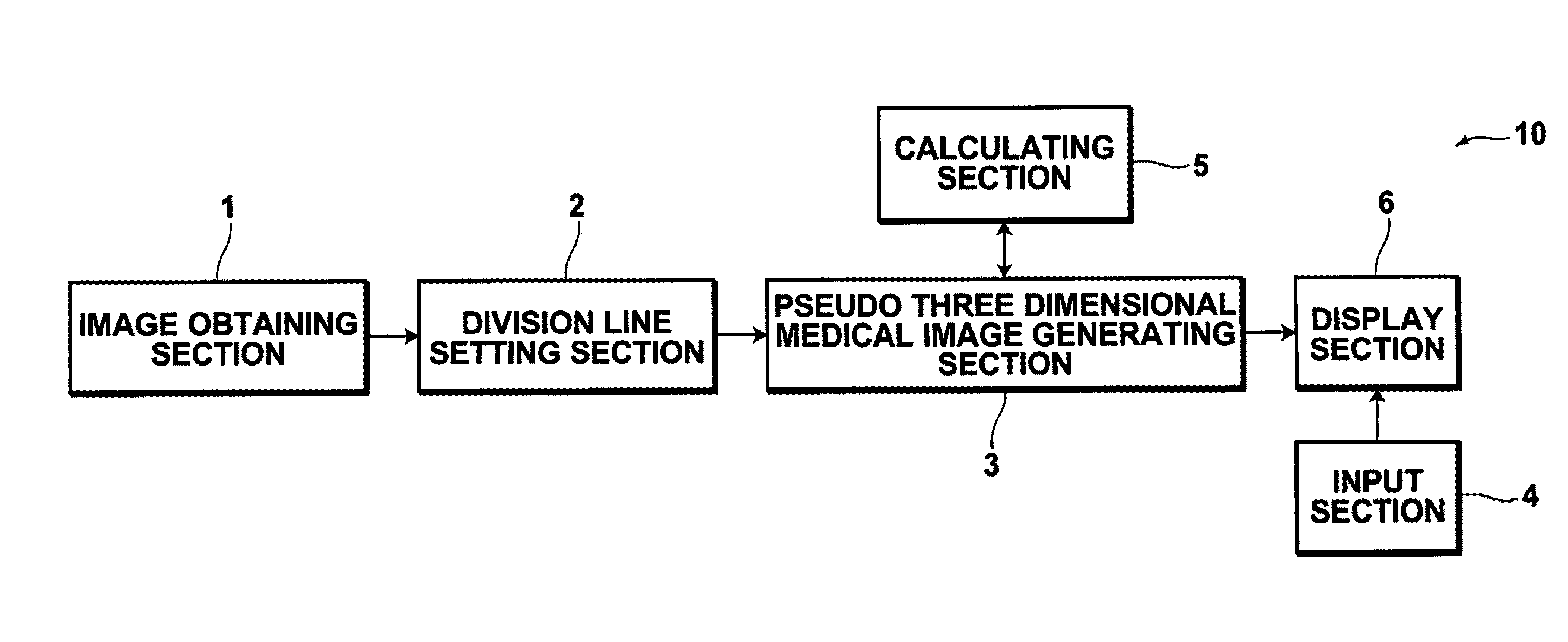
An image processing apparatus includes: an image obtaining section for obtaining medical images (axial images), which are imaged in advance, that represent transverse cross sections of a subject; a center line calculating section, for calculating a center line that connects the centers of subject regions within the medical images; a pseudo three dimensional medical image generating section, for generating a planar exploded pseudo three dimensional medical image, by executing an intensity projection method on image data constituted by at least a plurality of the subject regions from the center line radially outward toward the surface of the subject's body such that thoracic bones in the front to back direction of the projection direction of the subject are not displayed in an overlapping manner; and a display section, for displaying at least one of the pseudo three dimensional medial image and the plurality of medical images.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Over-the-wire delivery of a substernal lead
A method for implanting a medical lead. The method includes advancing a tunneling tool posteriorly proximate the caudal end of the sternum toward a first location. The tunneling tool is advanced superiorly underneath the sternum through the anterior mediastinum from the first location to a second location cranial to the first location. A guidewire is advanced from the first location to the second location. A medical lead is slid along at least a portion of the guidewire, the medical lead at least substantially spanning the distance between the first location and the second location.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Intraosseous device and methods for accessing bone marrow in the sternum and other target areas
Apparatus and methods are provided to access bone marrow at various target areas. Such apparatus may include an intraosseous device operable to penetrate bone at a selected target area and a depth limiter operable to control depth of penetration of the intraosseous device into bone and associated bone marrow. A manual driver and a guide may be included to optimize optimum insertion of the intraosseous device at a selected insertion site on a sternum.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Method and apparatus for temporarily immobilizing a local area of tissue
InactiveUS7048683B2Improve performanceWithout significant deterioration of the pumping function of the beating heartDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsThoracic boneCardiac surface
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Image processing method, image processing apparatus, and image processing program
InactiveUS20100150418A1Easy to understandCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsThoracic boneImaging processing
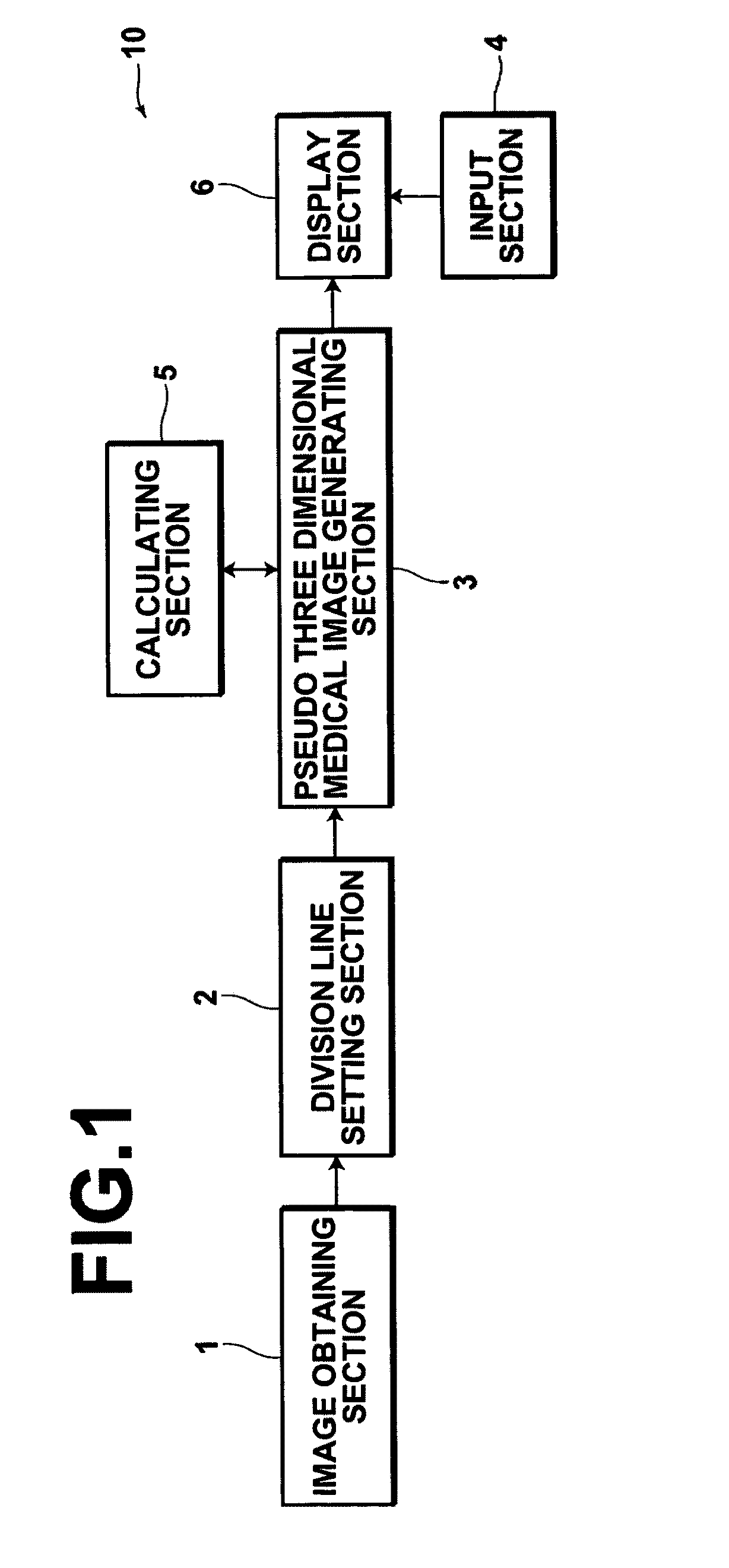
An image processing apparatus includes: an image obtaining section for obtaining medical images that represent transverse cross sections of a subject, and a division line setting section, for setting division lines within each medical image that divide subject regions representing the subject front to back, such that thoracic bones in the front to back direction of the projection direction of the subject are not displayed in an overlapping manner within the pseudo three dimensional images. A pseudo three dimensional medical image generating section generates a first pseudo three dimensional medical image based image data representing subject regions toward first sides of the division lines within the medical images, and generates a second pseudo three dimensional medical image based on image data representing subject regions toward second sides of the division lines within the medical images, by executing intensity projection methods.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Percussion assisted angiogenesis
InactiveUS20080275343A1EnablingSignificant positive effectUltrasound therapyOrgan movement/changes detectionThoracic boneResonance
The present invention relates to a new non-invasive method for inducing angiogenesis and more particularly coronary angiogenesis wherein an operator applies localized percussion upon the upper torso proximate an ischemic myocardial region, whereby the percussive forces penetrate to cause sheer stresses to the endothelium of the coronaries which lie thereupon, and thereby cause new coronary growth by virtue of endogenous liberation of beneficial angiogenic mediators. A pair of vibratory contacts are advantageously applied to rib-spaces to either side of the sternum (or alternatively to the upper back), where-after percussion is applied at the resonance frequency of the heart / epimyocardium at a displacement amplitude of 0.1 mm-15 mm (preferably greater than 1 mm), such as to maximize an internal oscillatory effect. The system is also adaptable for cerebral and peripheral vasculature applications. Ultrasonic imaging may optionally be utilized to direct percussive therapy.
Owner:SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY +1
Patient status sensor
ActiveUS8273053B2Less likely to failEfficient use ofMedical devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringThoracic boneTrauma victims
Owner:PYNG MEDICAL CORP
Respiration Sensors For Recording Of Triggered Respiratory Signals In Neurostimulators
InactiveUS20150283382A1Promote breathing effortElectrotherapyArtificial respirationThoracic boneRespiratory signal
A respiration implant system includes a parasternal respiration sensor is configured for intramuscular placement into parasternal muscle of the implanted patient to develop a respiration signal representing respiration activity of the implanted patient. A movement sensor develops a patient movement signal representing movement of the implanted patient. A pacing processor receives the respiration signal from the respiration sensor and the movement signal from the movement sensor to generate a respiration pacing signal synchronized with the respiration activity of the implanted patient. A stimulating electrode delivers the respiration pacing signal from the pacing processor to respiration neural tissue of the implanted patient to promote the breathing effort of the implanted patient.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
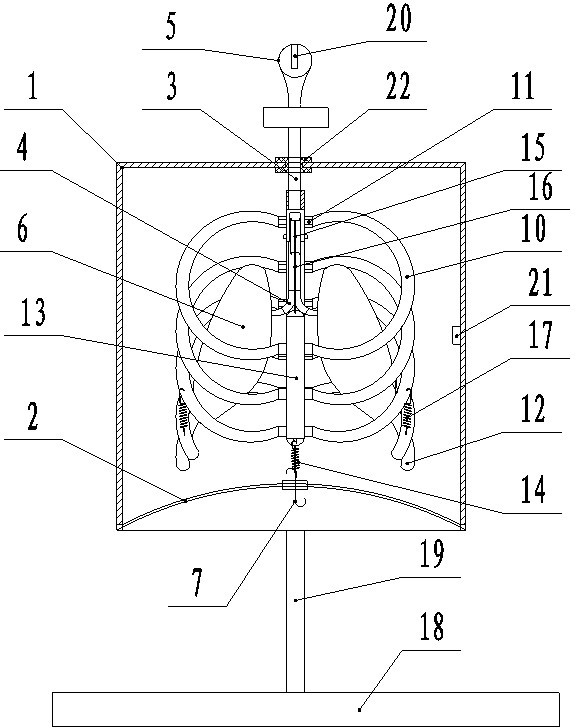
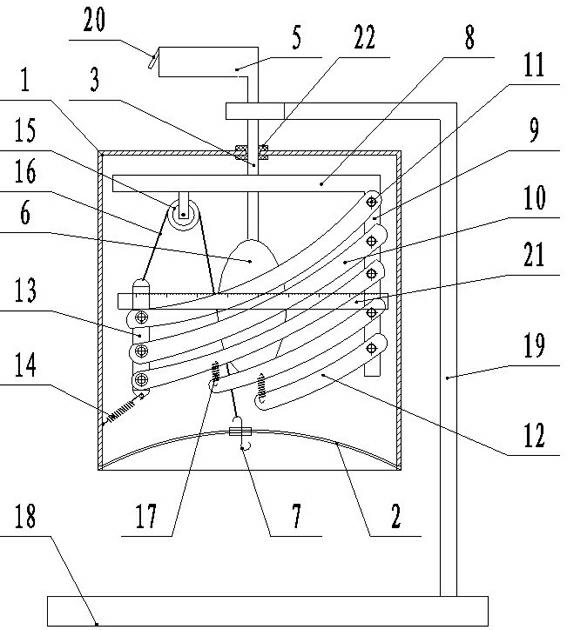
Human breathing demonstration instrument
The invention provides a human breathing demonstration instrument, which comprises a simulative thorax, simulative lungs and a simulative skeleton; the simulative skeleton is arranged in the simulative thorax, and comprises a vertical rod as the spinal column and curved rods as the ribs, the curved rods are curved, one end of each of each pair of curved rods is articulated with the vertical rod through a bolt, and the other ends of each pair of curved rods are articulated with a connecting rod as the sternum through bolts; the connecting rod is vertically arranged, the lower end of the connecting rod is connected with a restoring spring, the other end of the restoring spring is connected with a housing, and the restoring spring can downwardly pull the connecting rod; the upper end of the connecting rod is connected with a string, and the string passes through a pulley arranged on a cross rod, and is connected with a hook. The human breathing demonstration instrument not only can demonstrate the entry of the air into the lungs, the expansion and contraction of the lungs, the motion of the diaphragms and the expansion and contraction of the thorax when the human body breathes, but also can demonstrate the motion of the ribs, the sternum and other thoracic bones.
Owner:赵泽洪
Device and method for determining image quality of a radiogram image
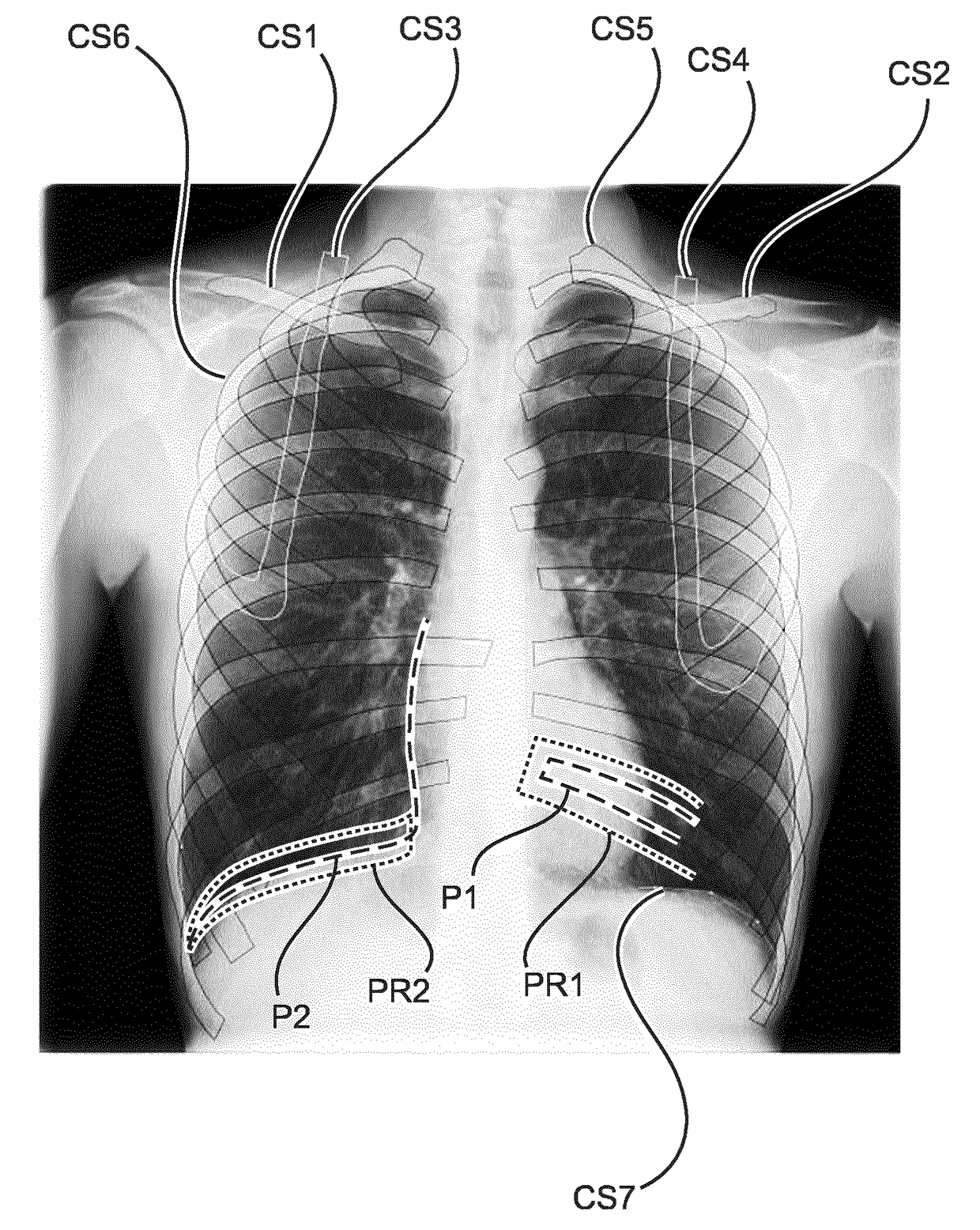
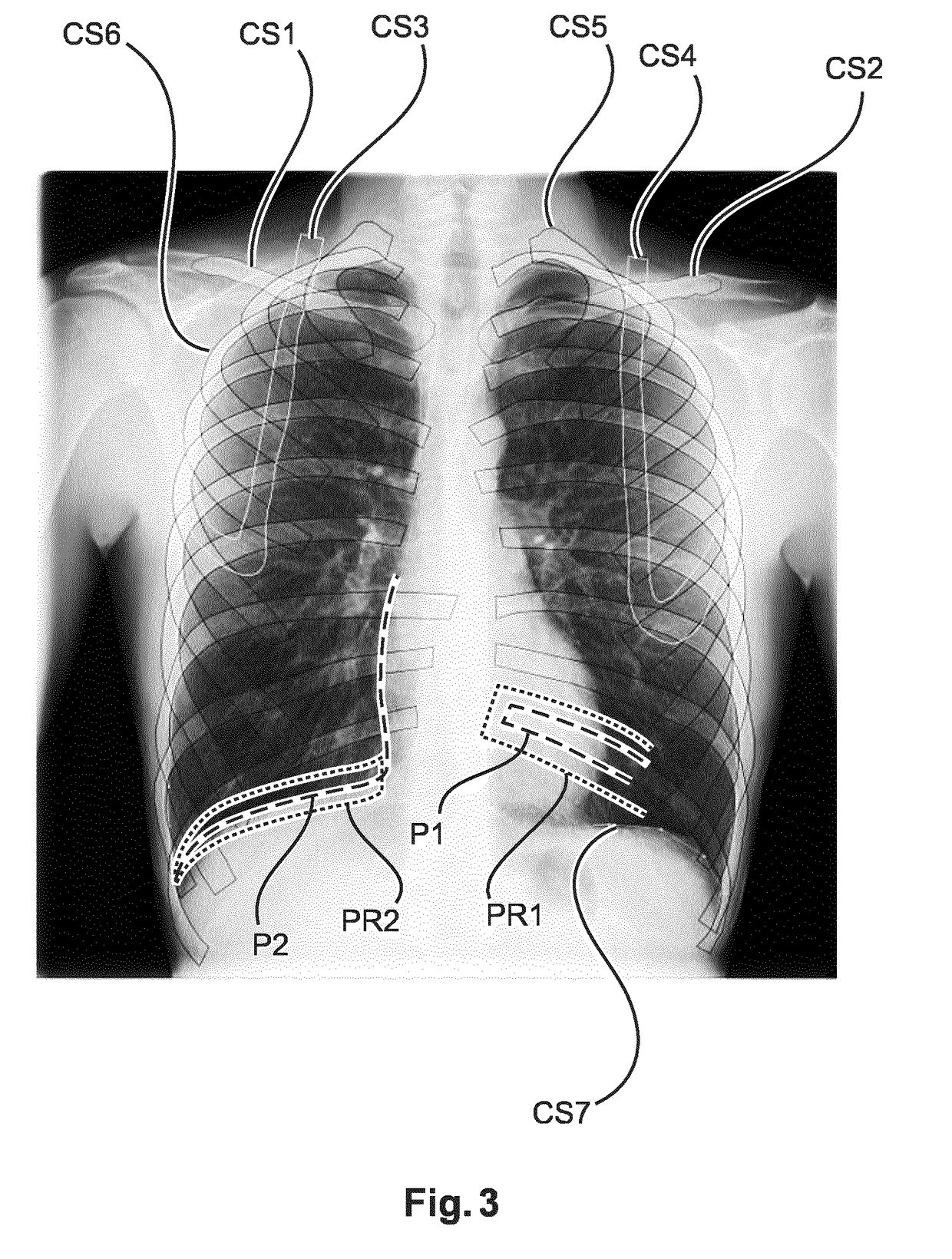
The present invention relates to a device (1) for determining image quality of a radiogram image, the device comprising: an acquiring module (10), which is configured to acquire the radiogram image; a segmentation module (20), which is configured to segment a thoracic bone structure on the acquired radiogram image into segmented thoracic bone structure contours and a tissue structure on the acquired radiogram image into segmented tissue structure contours; and a quality-determination module (30), which is configured to determine a image quality coefficient for the acquired radiogram image based on a comparison of a first position of the segmented thoracic bone structure contours with a second position of the segmented tissue structure contours.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
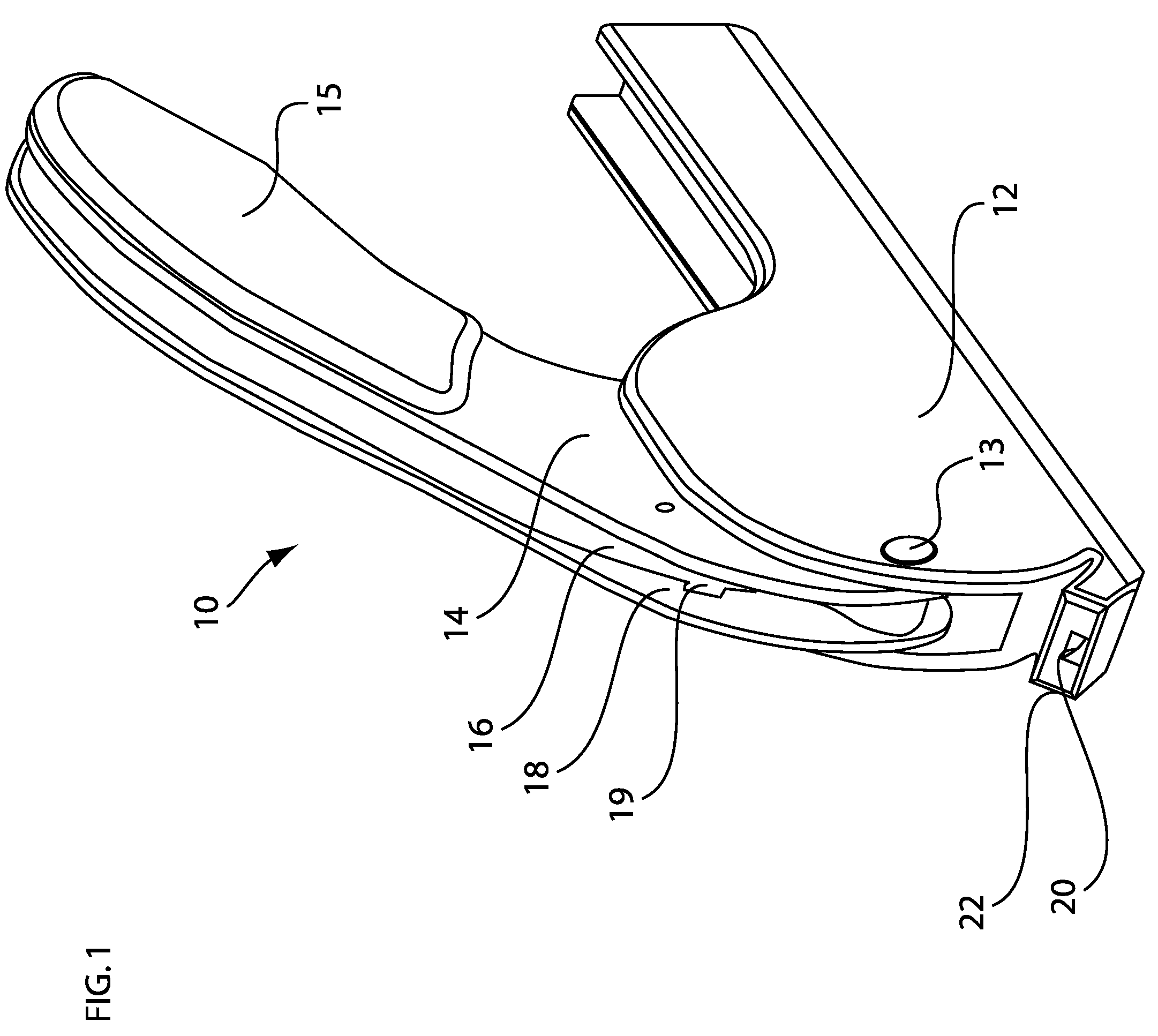
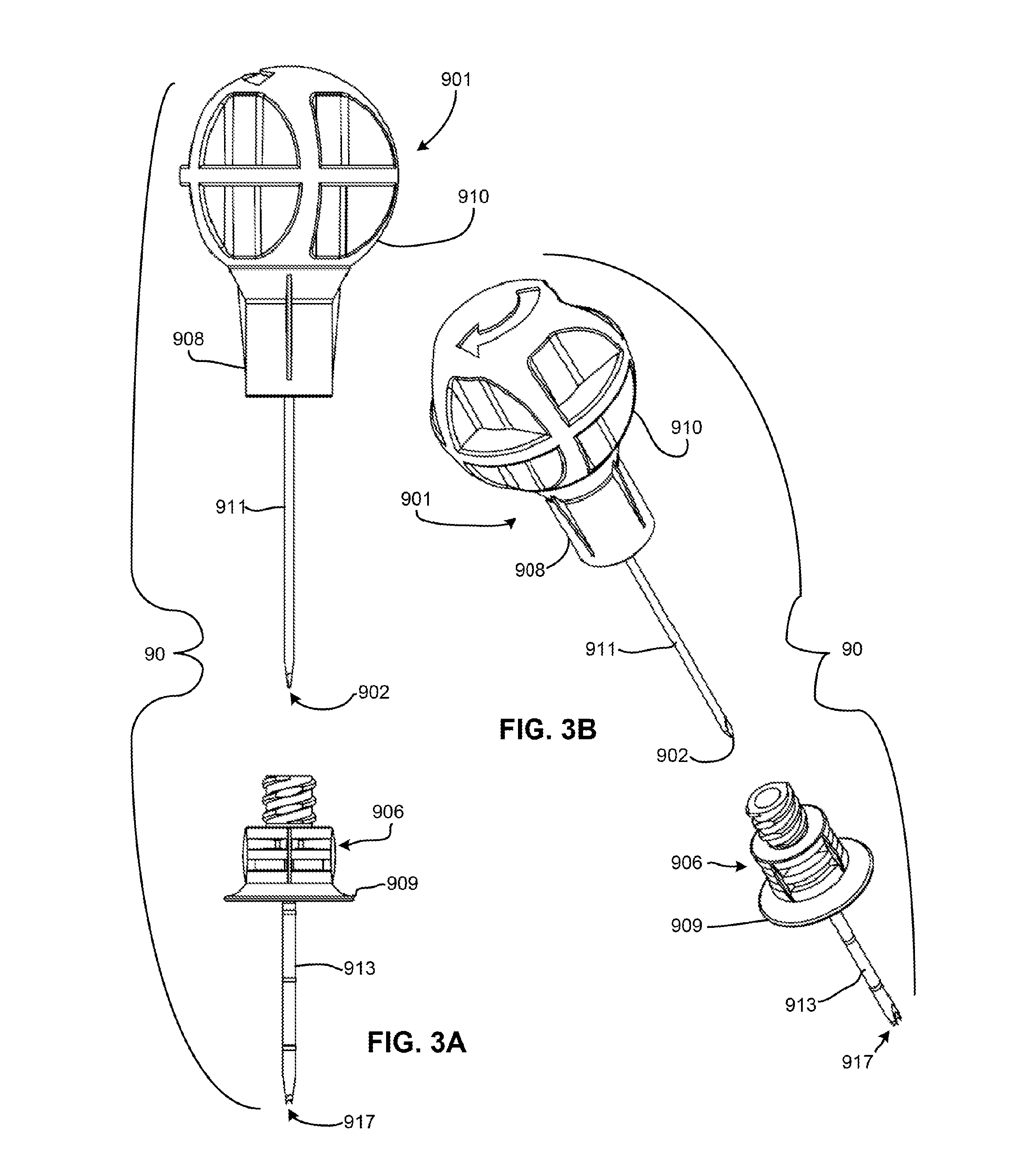
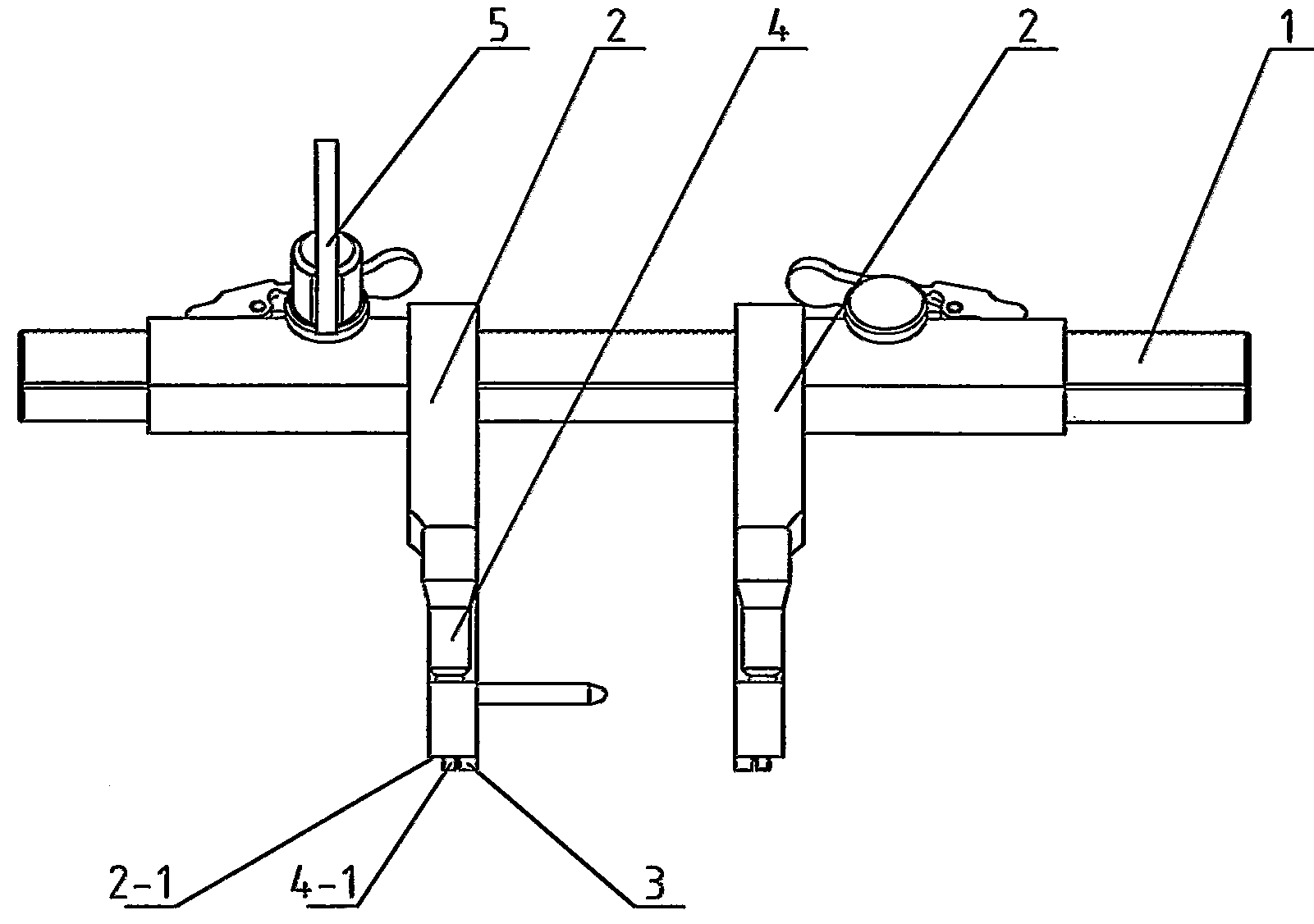
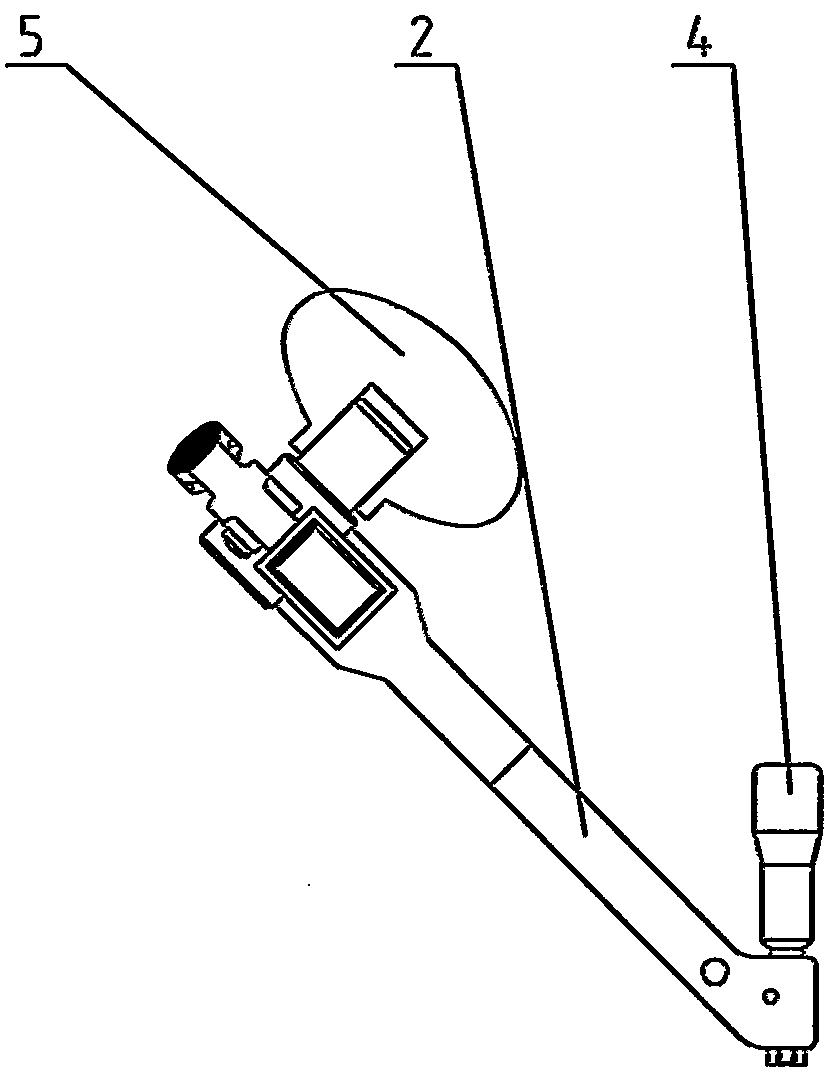
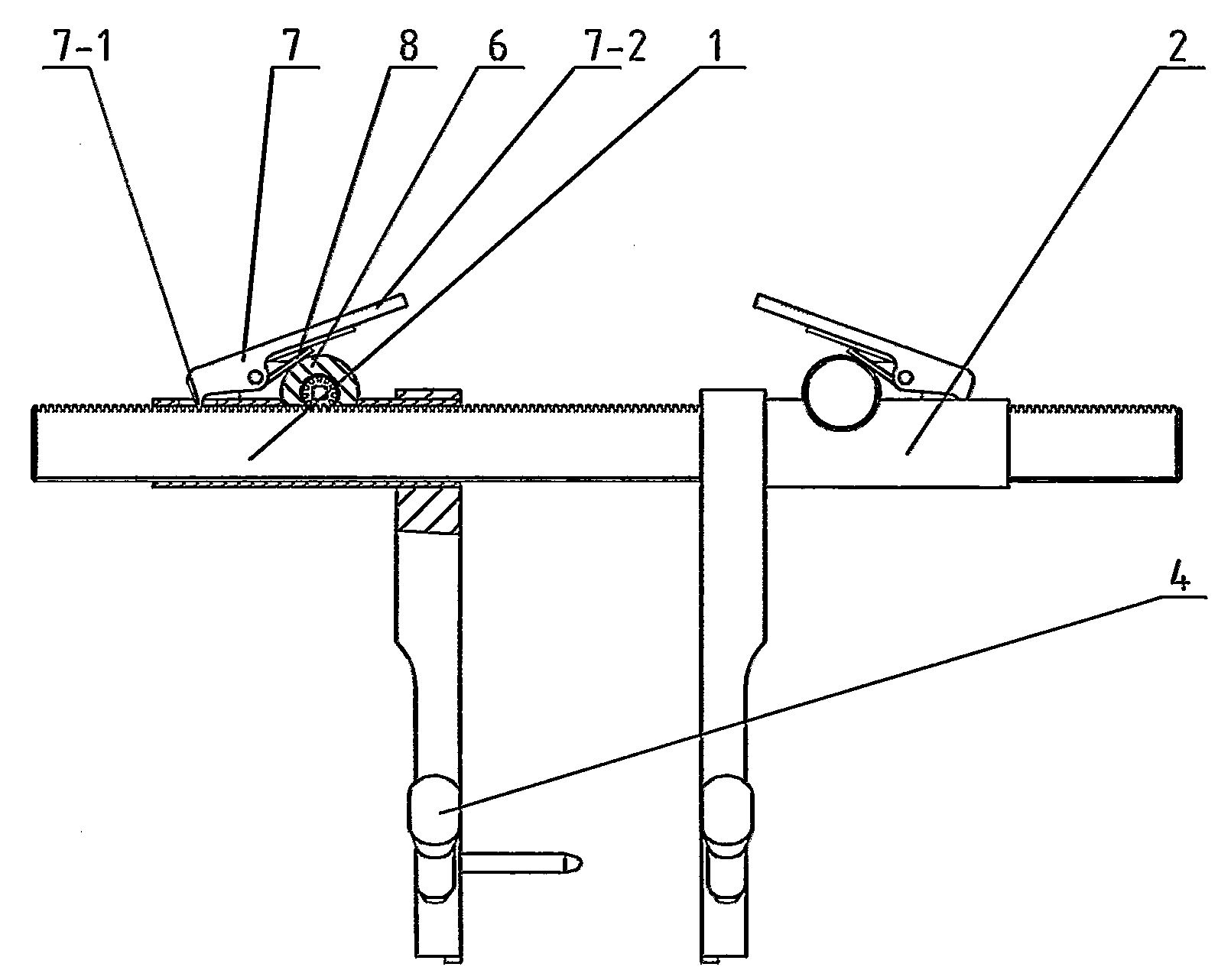
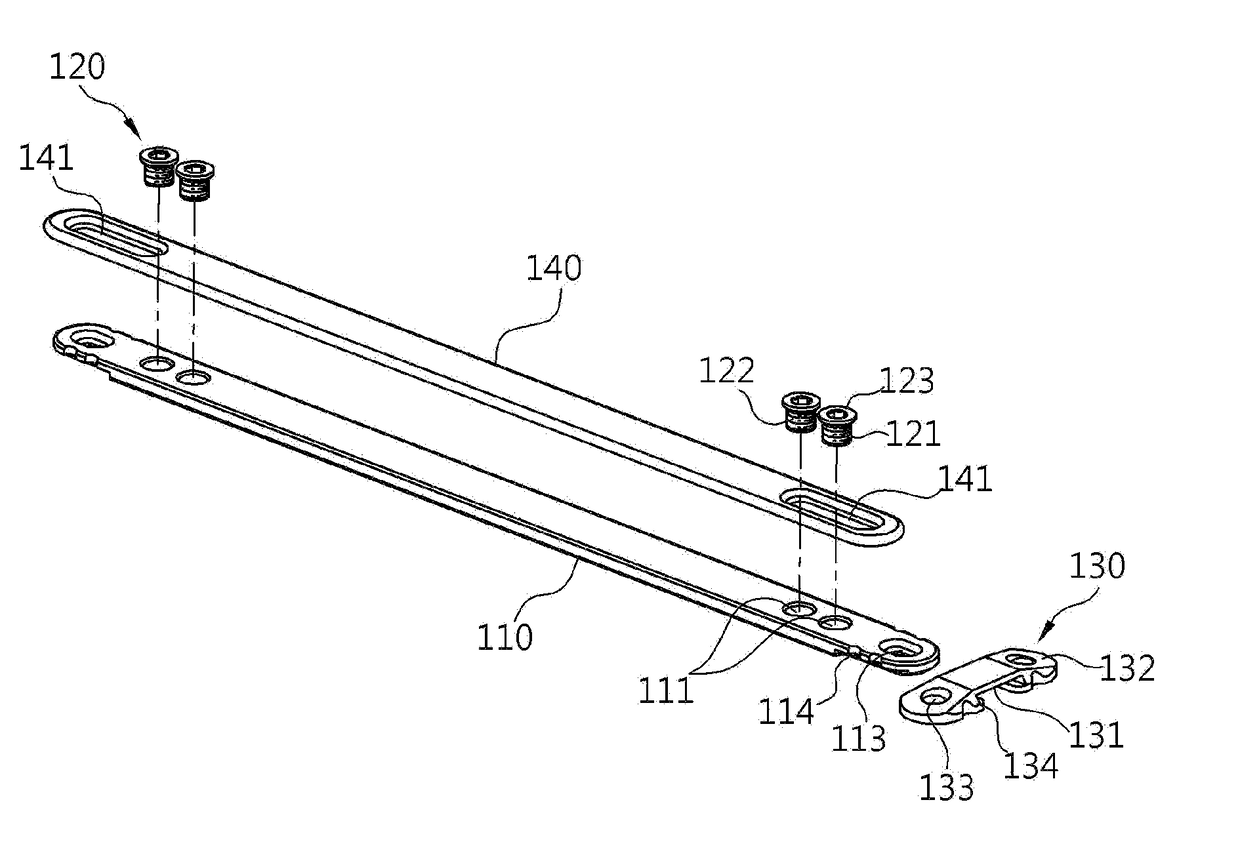
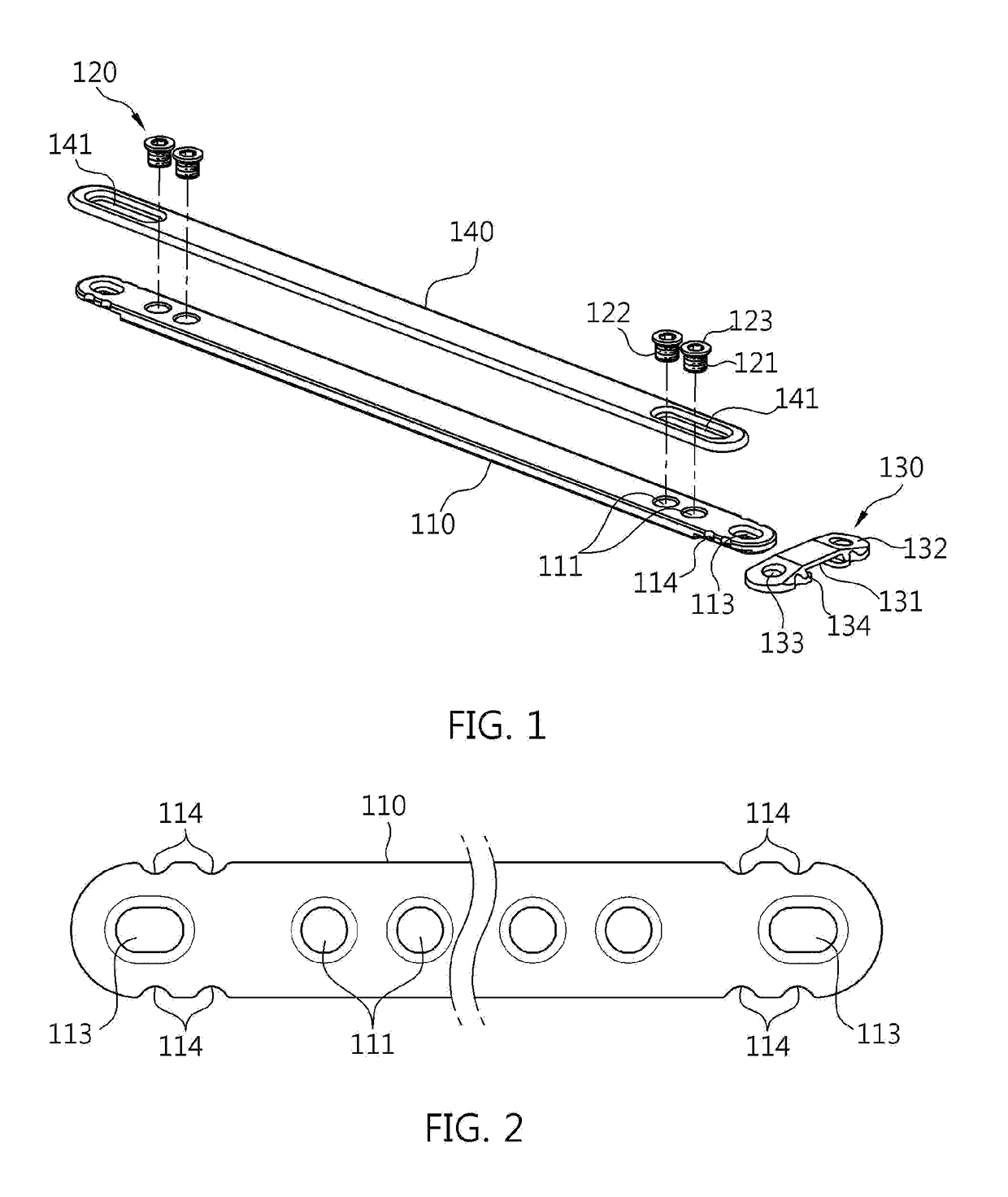
Installation tool for sternum closing fixator
The invention discloses an installation tool for a sternum closing fixator. The installation tool comprises a rack and two retractor arms. The retractor arms are sleeved on the rack, each retractor arm is provided with a non-return mechanism capable of limiting the retractor arm to move correspondingly to the rack, one of the retractor arms is provided with a driving mechanism capable of driving the same to move correspondingly to the rack, and the bottom of each retractor arm is provided with a positioning boss and a fixing screw which are capable of mutually matching with the sternum closing fixator. The installation tool can be used for positioning and fixing the sternum closing fixator so as to have sternum evenly fixed, degree of tightness is controllable, operation is facilitated and fixation is stable.
Owner:CHANGZHOU WASTON MEDICAL APPLIANCE CO LTD
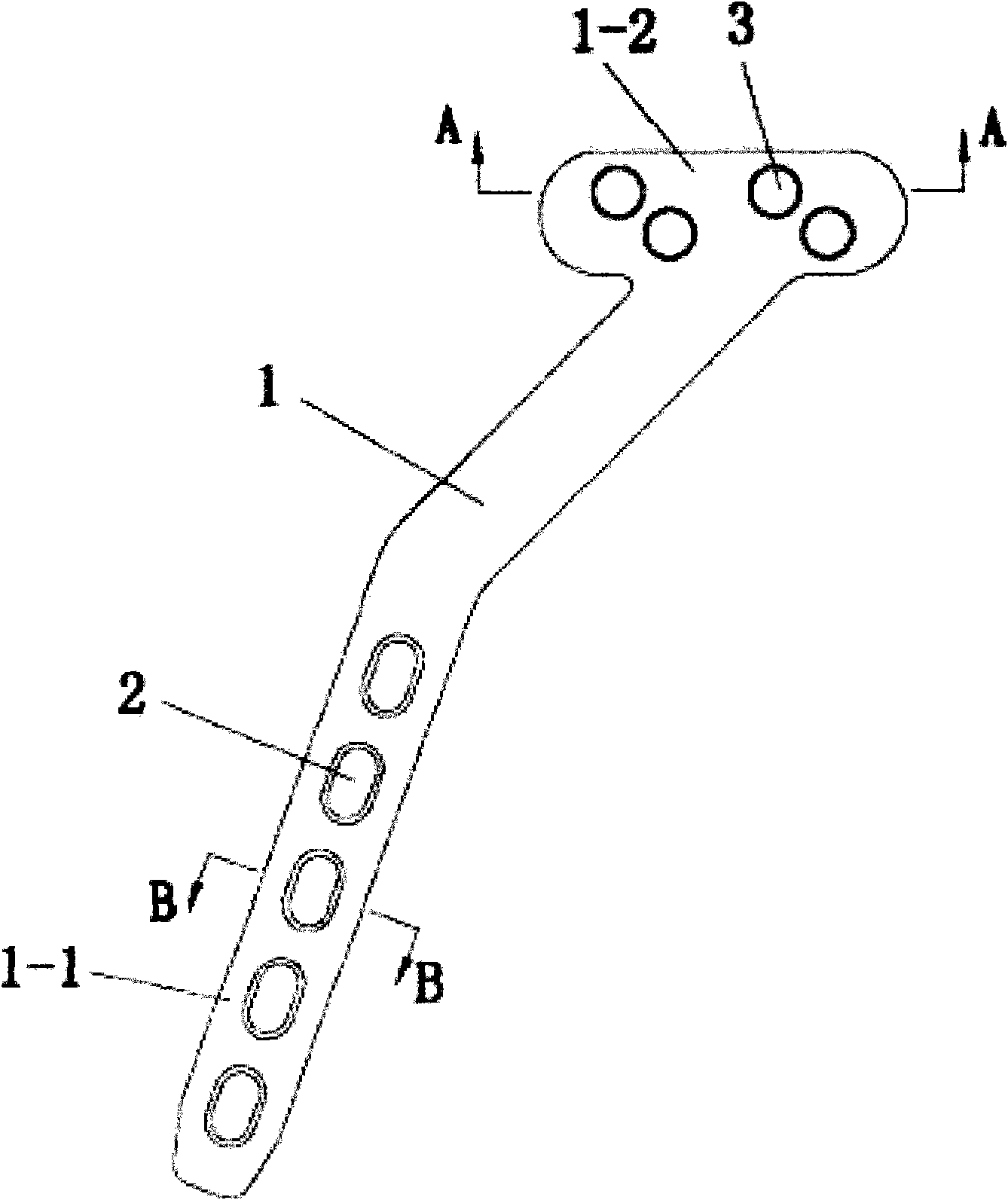
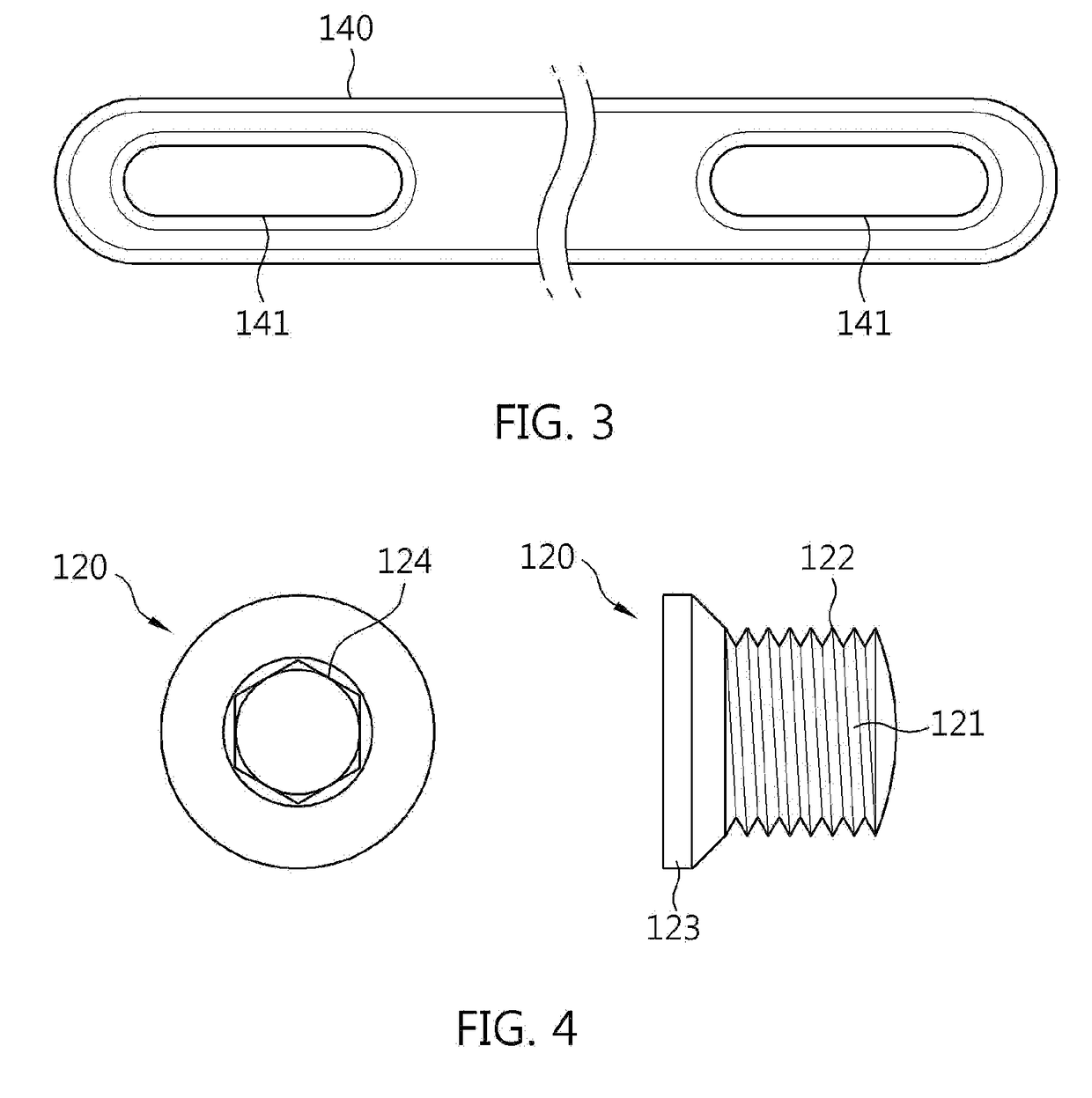
Anatomical plate for sternoclavicular joints
InactiveCN103462678AImprove gripStrong and reliable internal fixationBone platesThoracic boneMedicine
An anatomical plate for sternoclavicular joints, four pieces as a group, comprises a steel plate, which is of a flat sheet structure, the bending of the steel plate is matched with the position between the proximal clavicle and the sternum, one end of the steel plate is a fixed end fixed on the proximal clavicle, the fixed end is provided with a group of (three or five) clavicle-fixing holes using ordinary cortical bone screws, which correspond to the structure of the proximal clavicle, the other end of the steel plate is a fixed end fixed on the sternum, the fixed end is provided with a group of sternum-fixing holes, three in each row, which correspond to the front structure of the manubrium, and screws screwed down in the sternum-fixing holes have a certain angle. The anatomical plate ensures that a simple and reliable internal fixing material according with anatomical features is provided for sternoclavicular joint dislocation and proximal clavicle fracture, so that an effective clinical treatment method is provided for patients with sternoclavicular joint dislocation and proximal clavicle fractures. The anatomical plate is thin, the postoperative appearance is attractive, the screws can be fixed at an angle in the holes, and thereby the holding force of the screws is greatly enhanced.
Owner:张振武
Orthopedic apparatus for pectus excavatum
Disclosed is an orthopedic apparatus for pectus excavatum, the orthopedic apparatus including: a primary pectus bar inserted behind a concave sternum for pectus deformity repair; a secondary pectus bar inserted in front of the sternum to be in parallel with the primary pectus bar; and a locking member provided at a junction between the primary pectus bar and the secondary pectus bar to lock the primary pectus bar relative to the secondary pectus bar. According to the present invention, the primary pectus bar inserted behind the concave sternum is fixed through the secondary pectus bar that is inserted in front of the sternum, whereby it is possible to prevent the primary pectus bar from rotating or moving during the long period of correction, thereby accurately performing sternum repair.
Owner:CARETECH +1
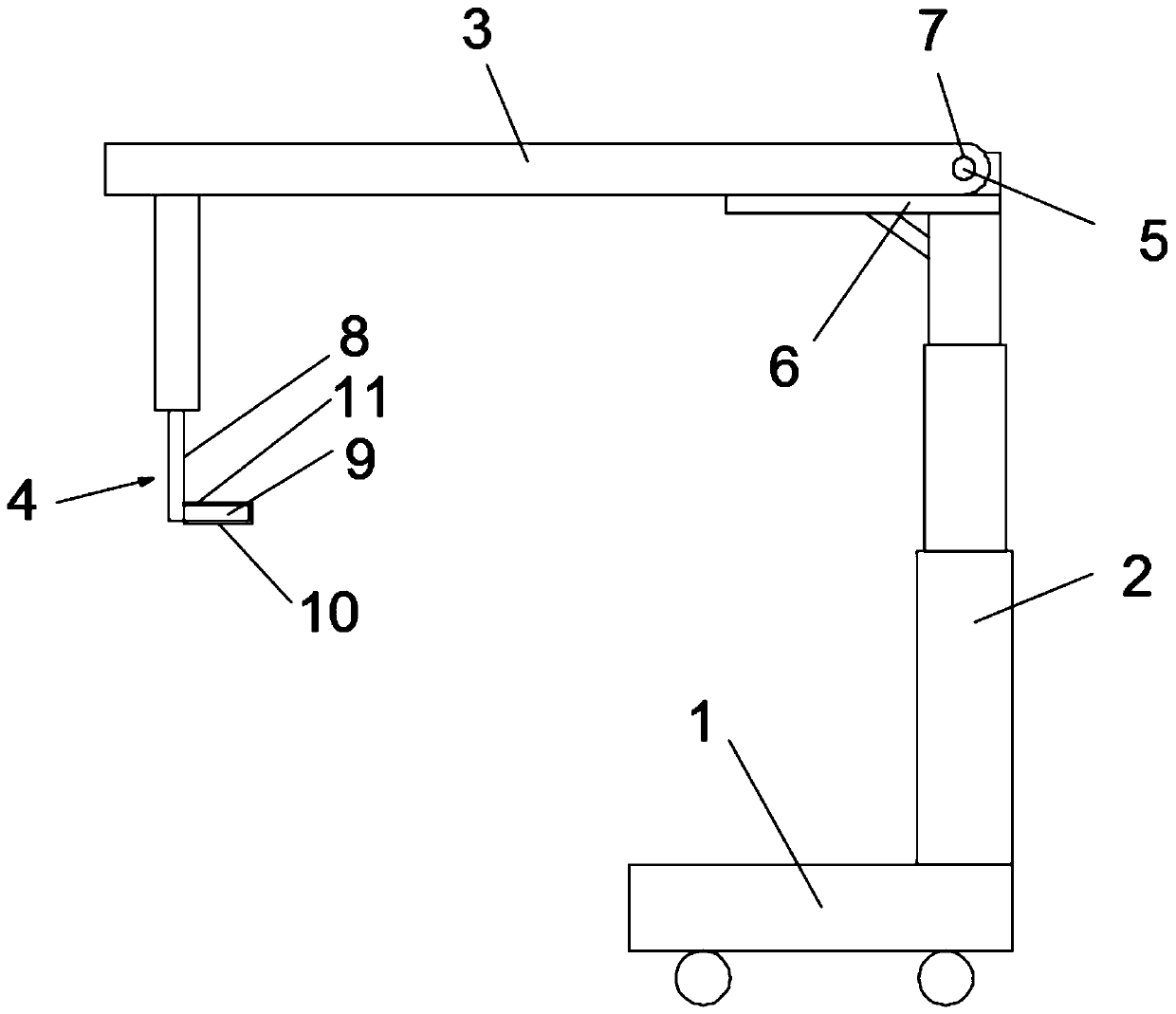
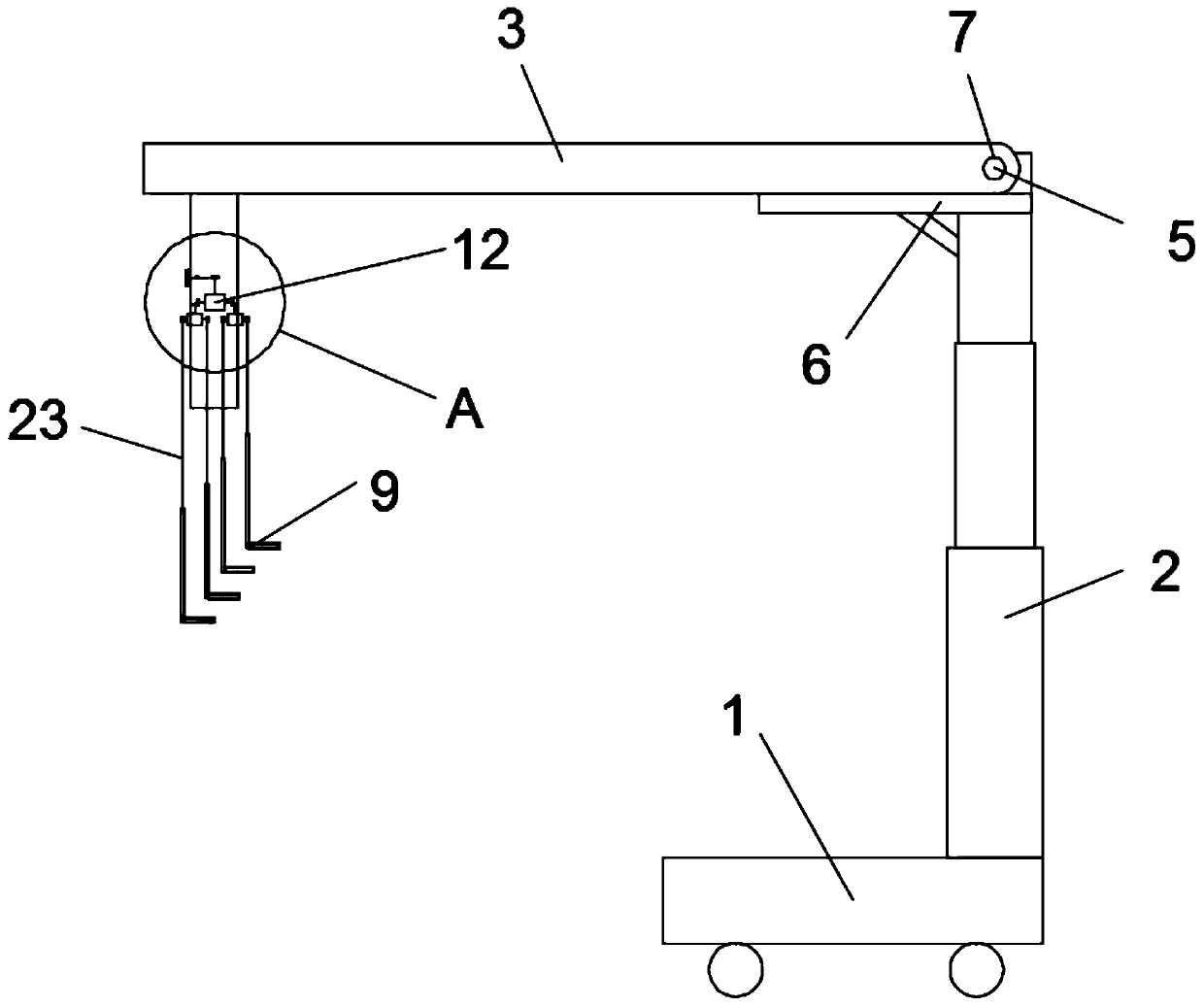
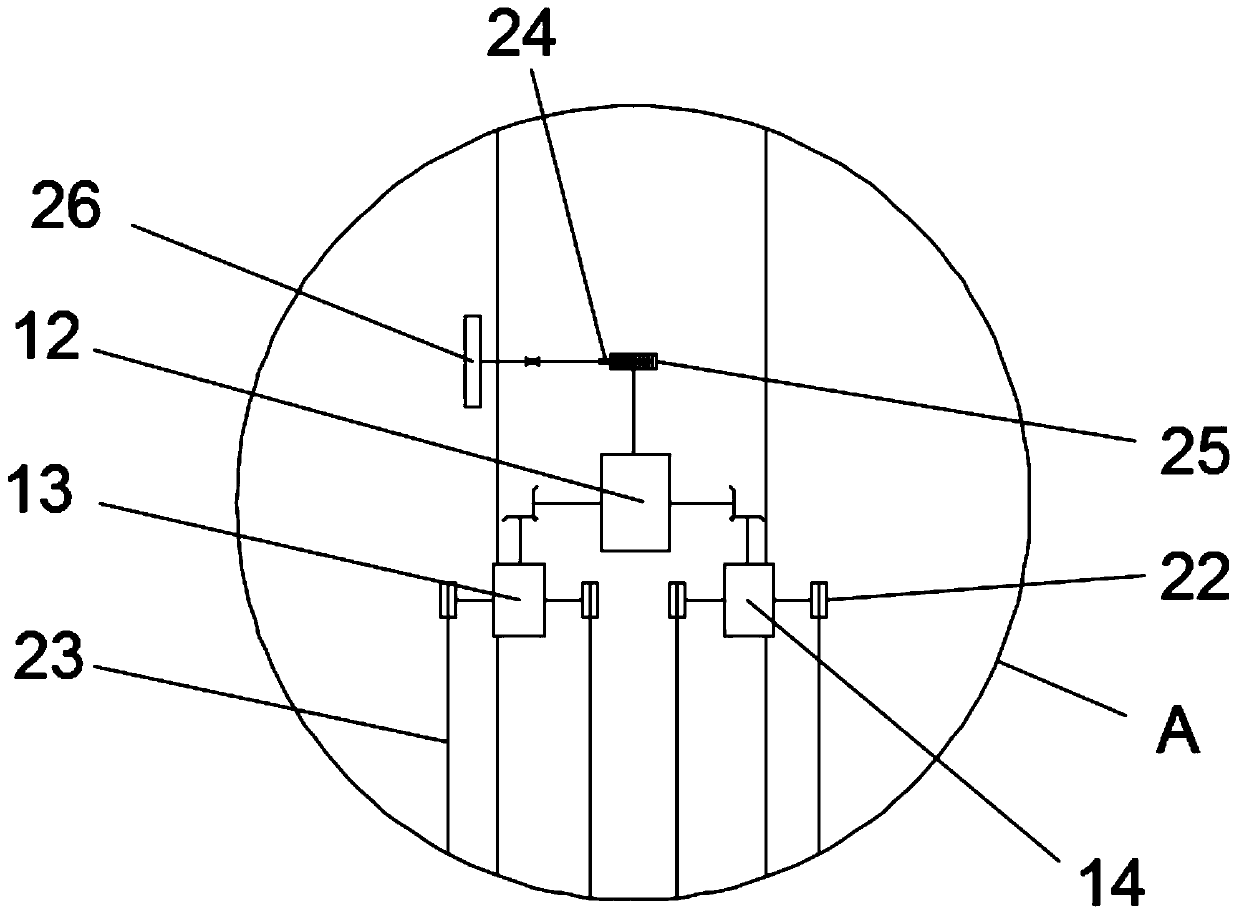
Breastbone drag hook
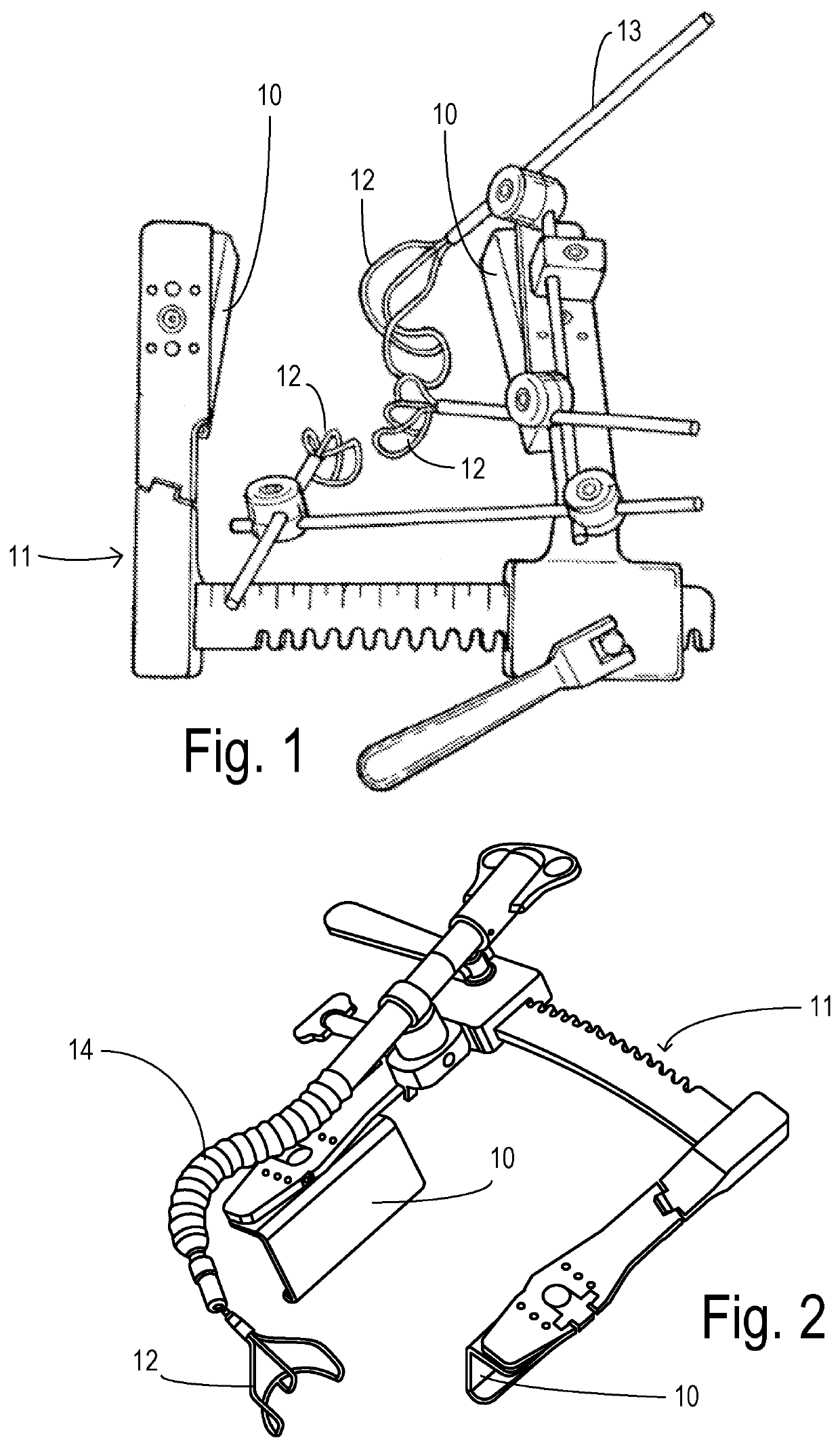
The invention discloses a breastbone drag hook. The breastbone drag hook comprises a base, an electric telescopic rod, a horizontal rod and drag hooks, wherein the lower end part of the electric telescopic rod is vertically fixed to the base, and a rotating shaft and a supporting plate are arranged at the upper end of the electric telescopic rod; an inserting hole which is inserted into the rotating shaft is formed in one end of the horizontal rod; the bottom of the horizontal rod is supported by the supporting plate; the drag hooks are connected with the horizontal rod; each drag hook comprises a connecting rod and a drawing claw; each drawing claw is mounted on the corresponding connecting rod, and is used for drawing the breastbone of a human body; a sterile disposable sleeve sleeves each drawing claw; and a plurality of gas storing bags which can be cut by a scalpel are arranged on the surface which is in contact with the breastbone of the human body, of the sleeve. According to the breastbone drag hook disclosed by the invention, during an operation, the gas storing bags which are pressed on blood vessels or nerves are cut by the scalpel, so that a sunken part is formed in thelocation of the breastbone drag hook, the situation that the blood vessels or the nerves are pressed is avoided; the horizontal rod does not cross an operating table, and the telescopic rod is also not arranged on the standing side of a doctor, so that the operation view field is greatly enlarged; and materials of components including the telescopic rod, the horizontal rod, the drawing claws andthe like can resist high temperature, so that the high-temperature sterilization condition of operation instruments is met, and the risk of operation infection is reduced.
Owner:李标 +4
Mitral valve retractor with side malleable retract feature and universal adjuster
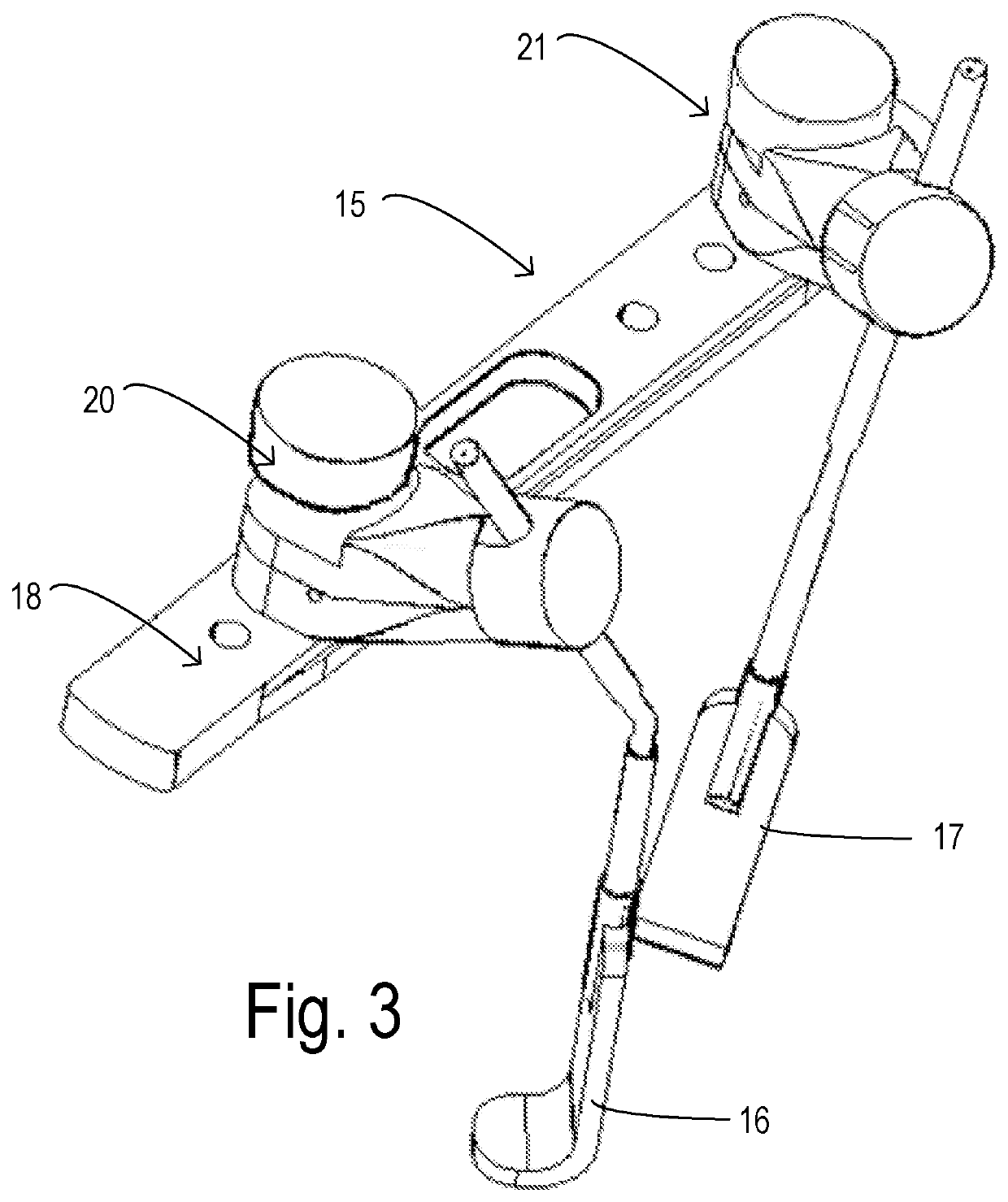
ActiveUS20200015799A1Fast and simple and secure adjustmentMaintains available spaceSurgerySurgical operationThoracic bone
A retraction apparatus increases flexibility of retracting tissues around a surgical site, such as during cardiac surgery including mitral valve repair or other surgical procedures. A holder is configured to mount to a fixed rail such as a sternal retractor. A rake element comprises a strap segment having a proximal end slidably received in a slot in the holder. The rake element has a primary rake finger at a distal end of the strap segment configured to grasp and retract tissue at a surgical site and a sub-finger extending perpendicularly via a bendable wing from a side of the primary rake finger adapted to retract adjacent tissue around the surgical site.
Owner:TERUMO CARDIOVASCULAR SYST CORP
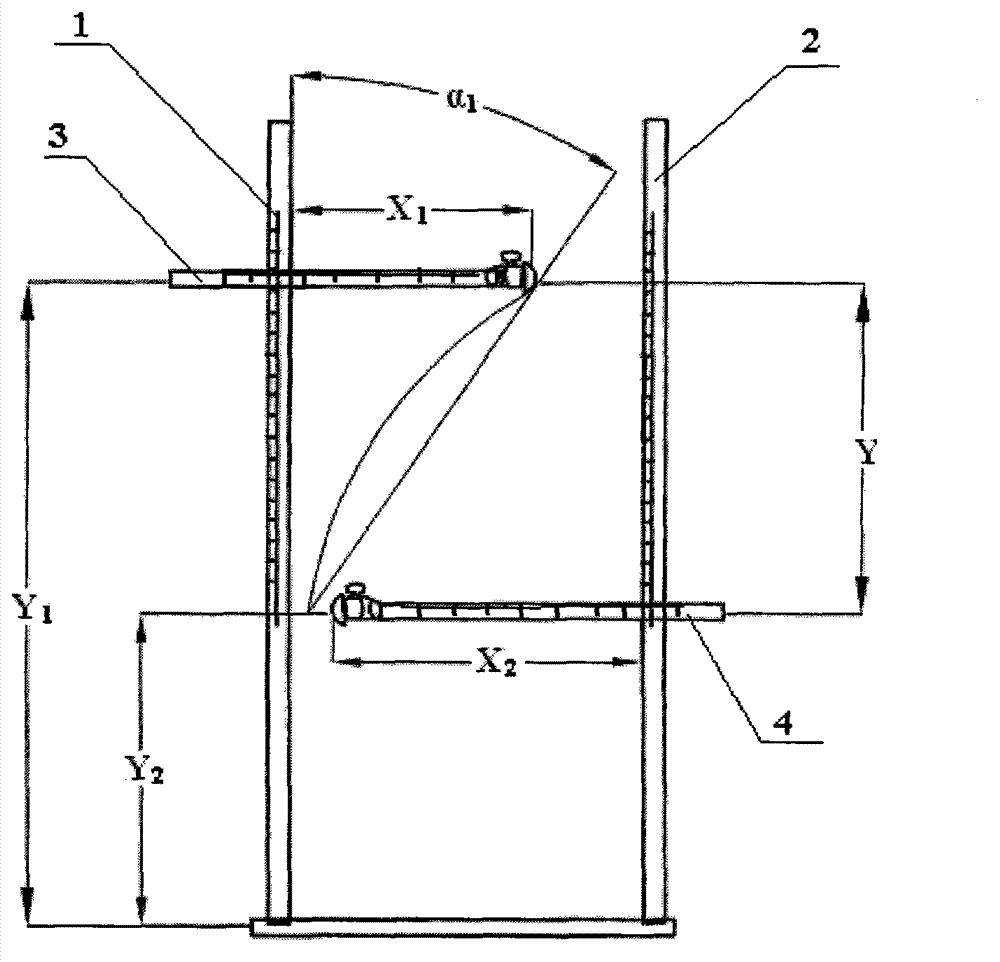
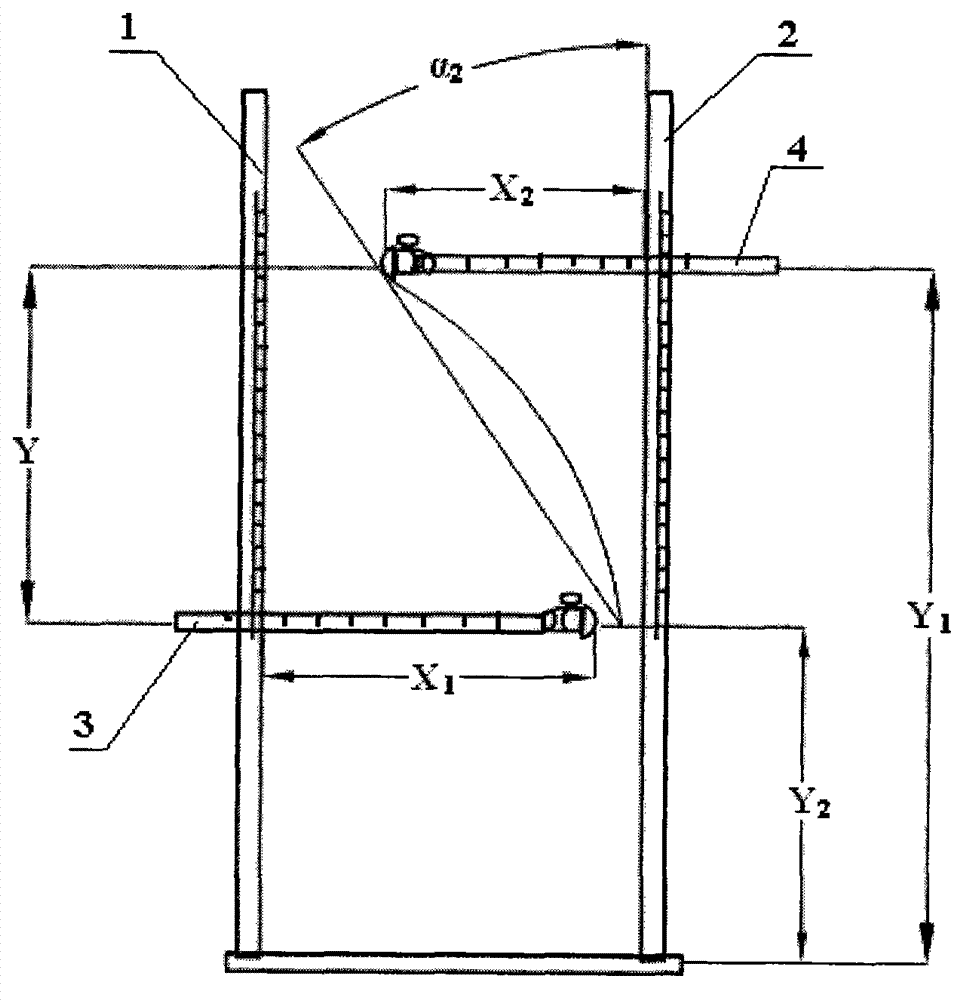
Testing method for lumbar vertebra stretching and buckling angles and application of testing method
ActiveCN102860829APracticalGuarantee the quality of filmingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationShoulder Blades
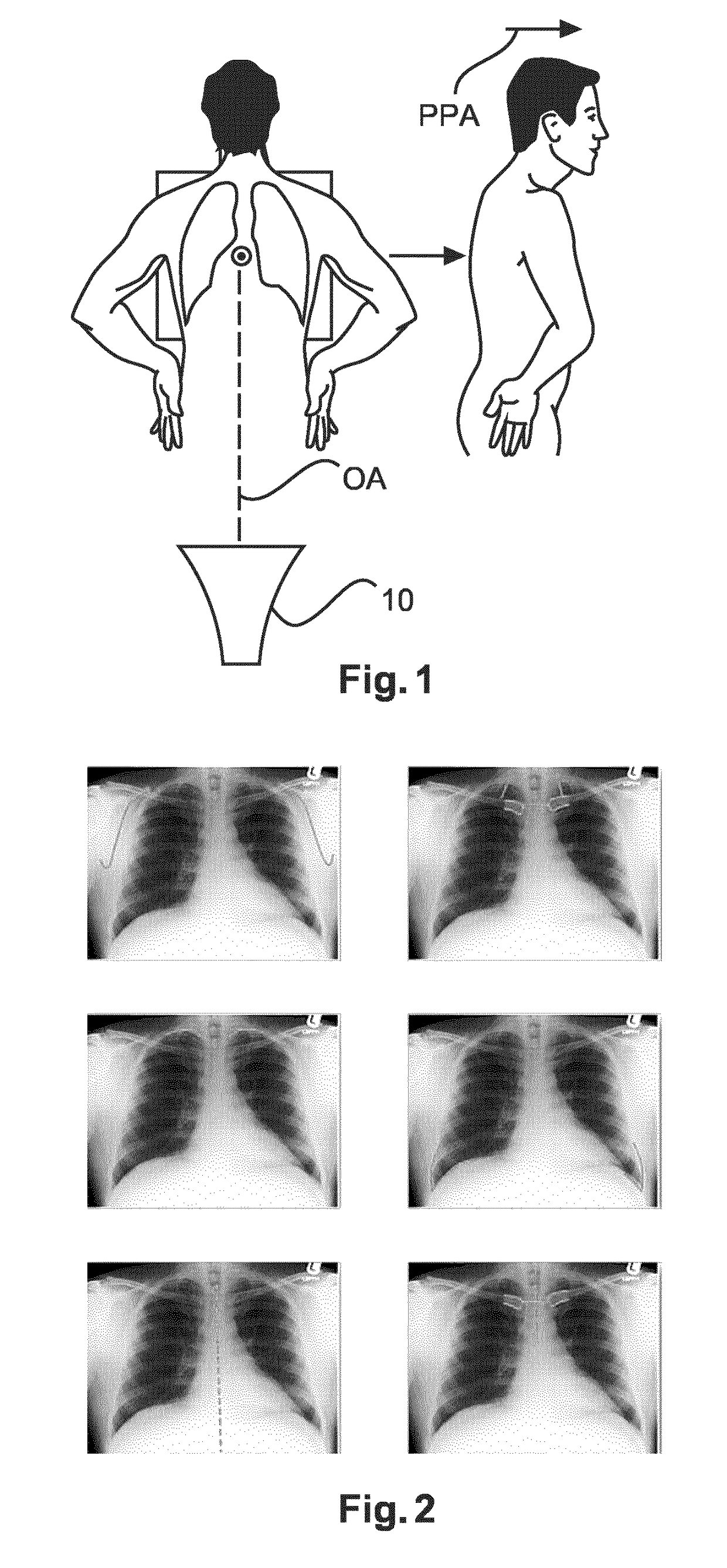
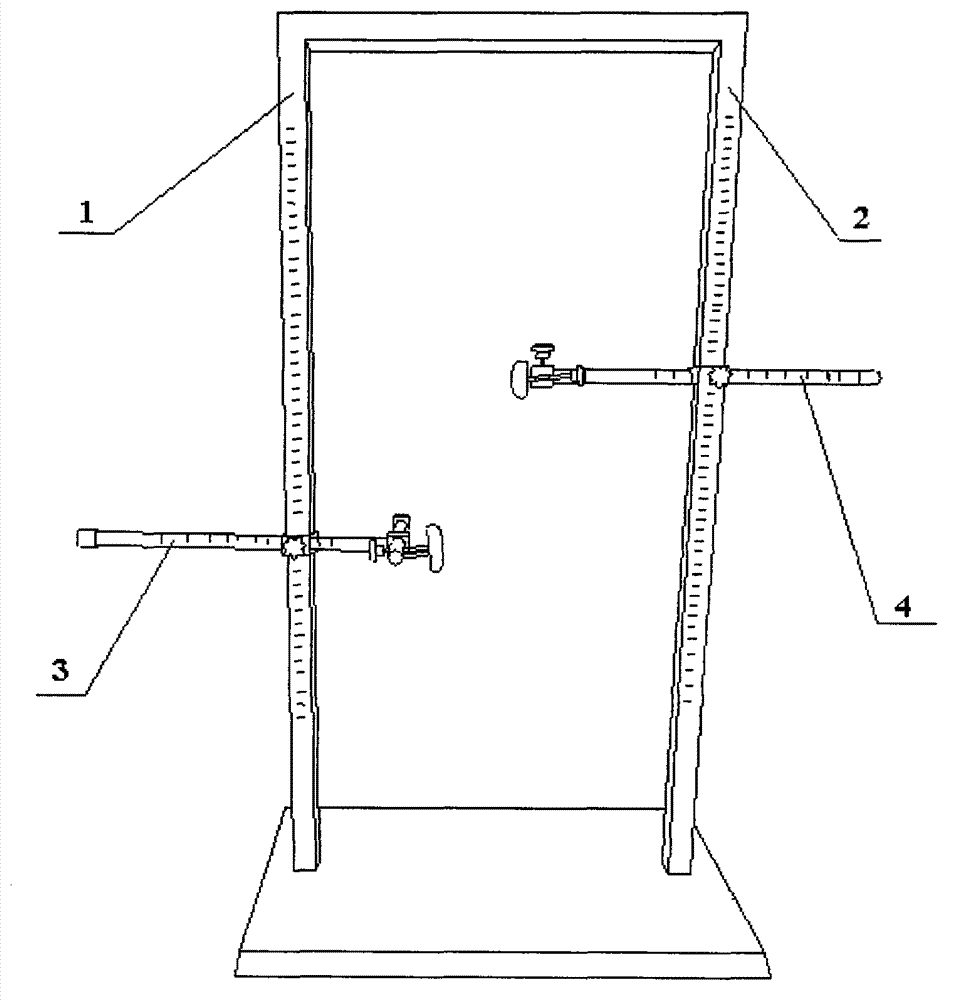
The invention discloses a testing method for lumbar vertebra stretching and buckling angles. The stretching and retracting angles comprise a stretching-position stretching angle alpha1 and a buckling-position buckling angle alpha2, an included angle between a plane built by upper portions of the mesosternum and the sacrum of a testee and a perpendicular plane is the stretching-position stretching angle alpha1, an included angle between a plane built by upper portions of a symphysis pubis position and shoulder blades on two sides of the testee and a perpendicular plane is the buckling-position buckling angle alpha2, a horizontal measuring device and a perpendicular measuring device are fixed or shifted to measure the alpha1 and the alpha2 of the testee. The invention further discloses application of the testing method in lumbar vertebra functional-position radiography. The functional positions of the lumbar vertebrae of patients can be determined by adjusting the horizontal measuring device and the perpendicular measuring device according to lumbar vertebra stretching and buckling angle values of different individual patients, subjective randomness of the patients when the lumbar vertebra functional positions are fixed is reduced, and the radiographic quality of the lumbar vertebra functional positions is guaranteed.
Owner:合肥市第三人民医院
Percussion assisted angiogenesis
InactiveUS8734368B2Induces and assists coronary angiogenesisEasy to useUltrasound therapyOrgan movement/changes detectionThoracic boneResonance
The present invention relates to a new non-invasive method for inducing angiogenesis and more particularly coronary angiogenesis wherein an operator applies localized percussion upon the upper torso proximate an ischemic myocardial region, whereby the percussive forces penetrate to cause sheer stresses to the endothelium of the coronaries which lie thereupon, and thereby cause new coronary growth by virtue of endogenous liberation of beneficial angiogenic mediators. A pair of vibratory contacts are advantageously applied to rib-spaces to either side of the sternum (or alternatively to the upper back), where-after percussion is applied at the resonance frequency of the heart / epimyocardium at a displacement amplitude of 0.1 mm-15 mm (preferably greater than 1 mm), such as to maximize an internal oscillatory effect. The system is also adaptable for cerebral and peripheral vasculature applications. Ultrasonic imaging may optionally be utilized to direct percussive therapy.
Owner:SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com