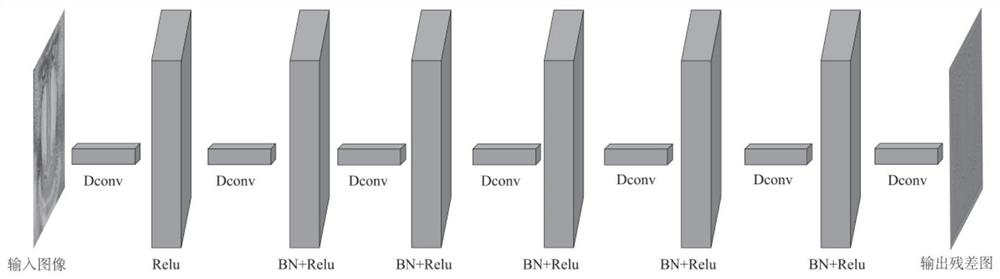
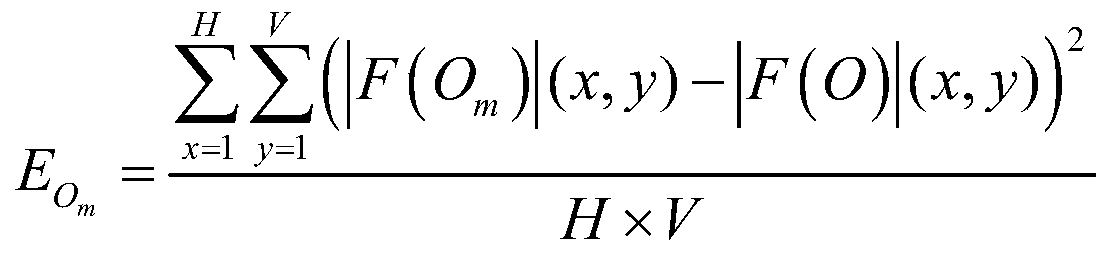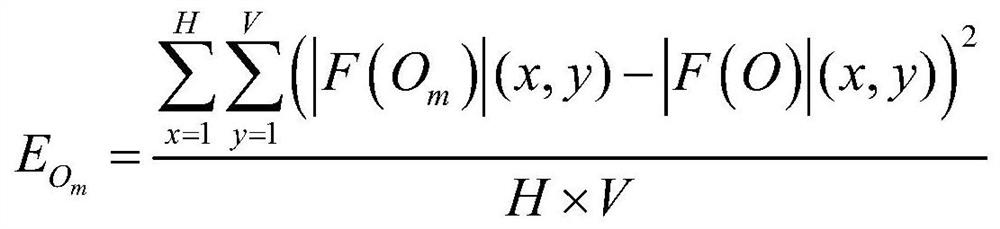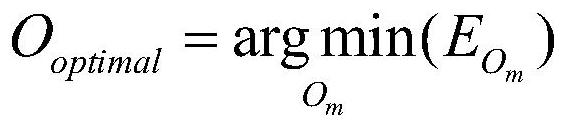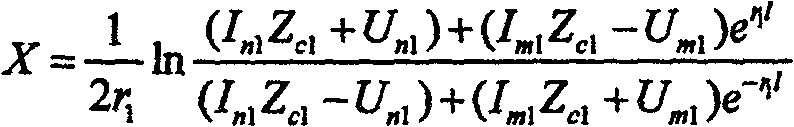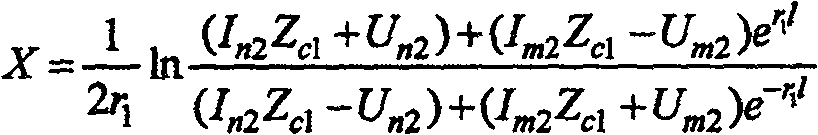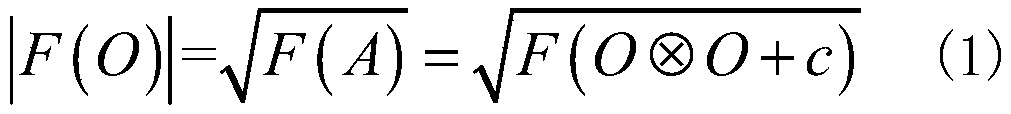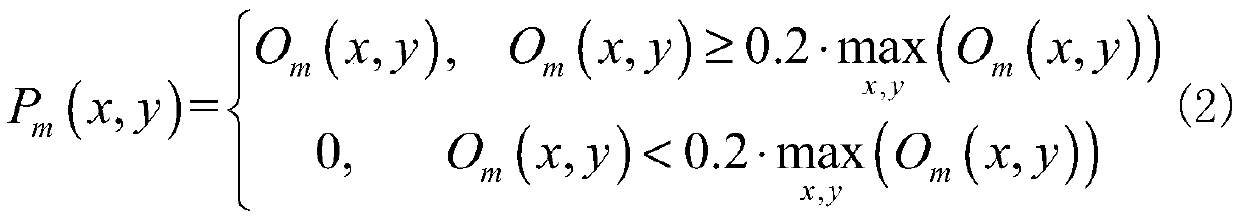Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Fourier phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
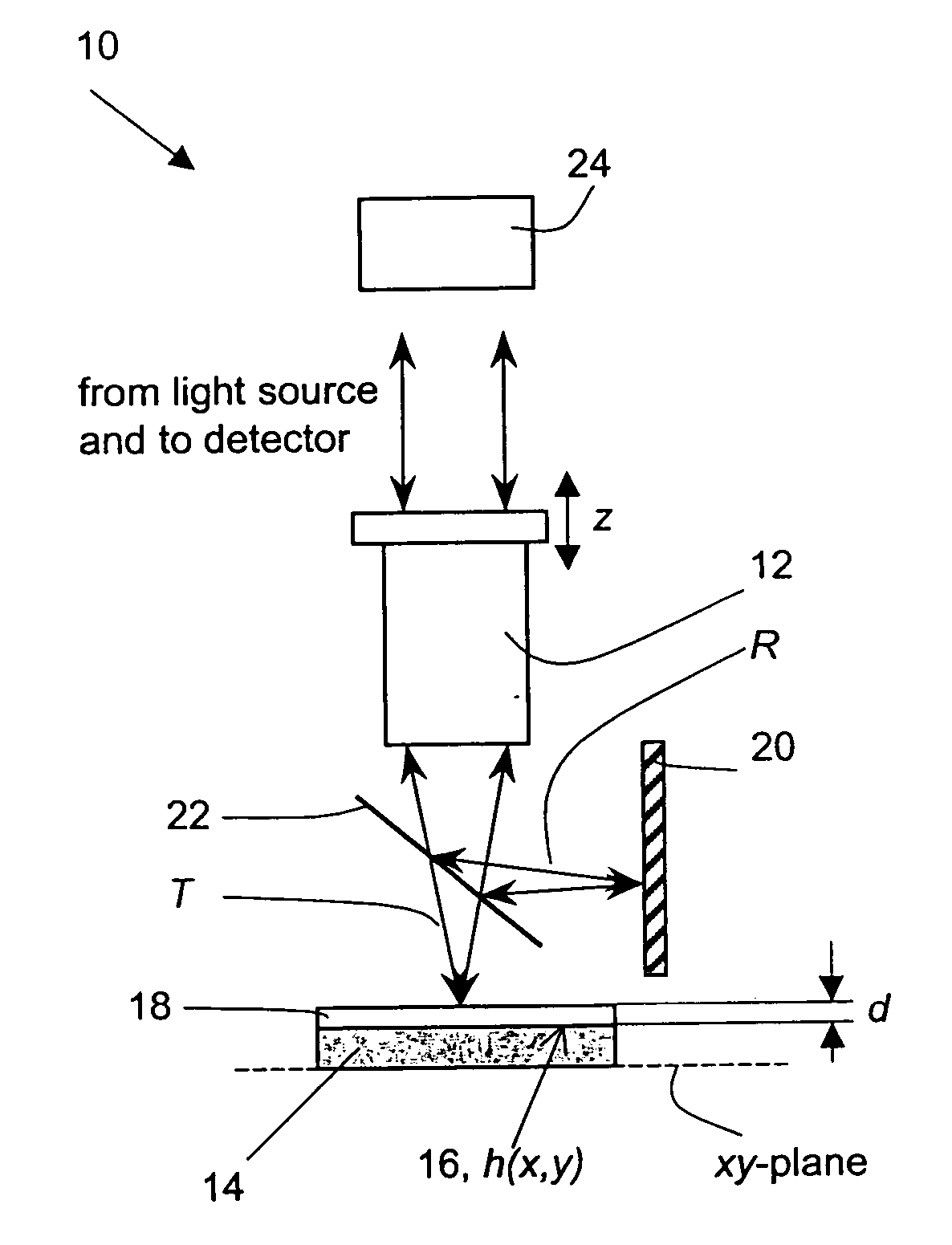
Measurement of thin films using fourier amplitude
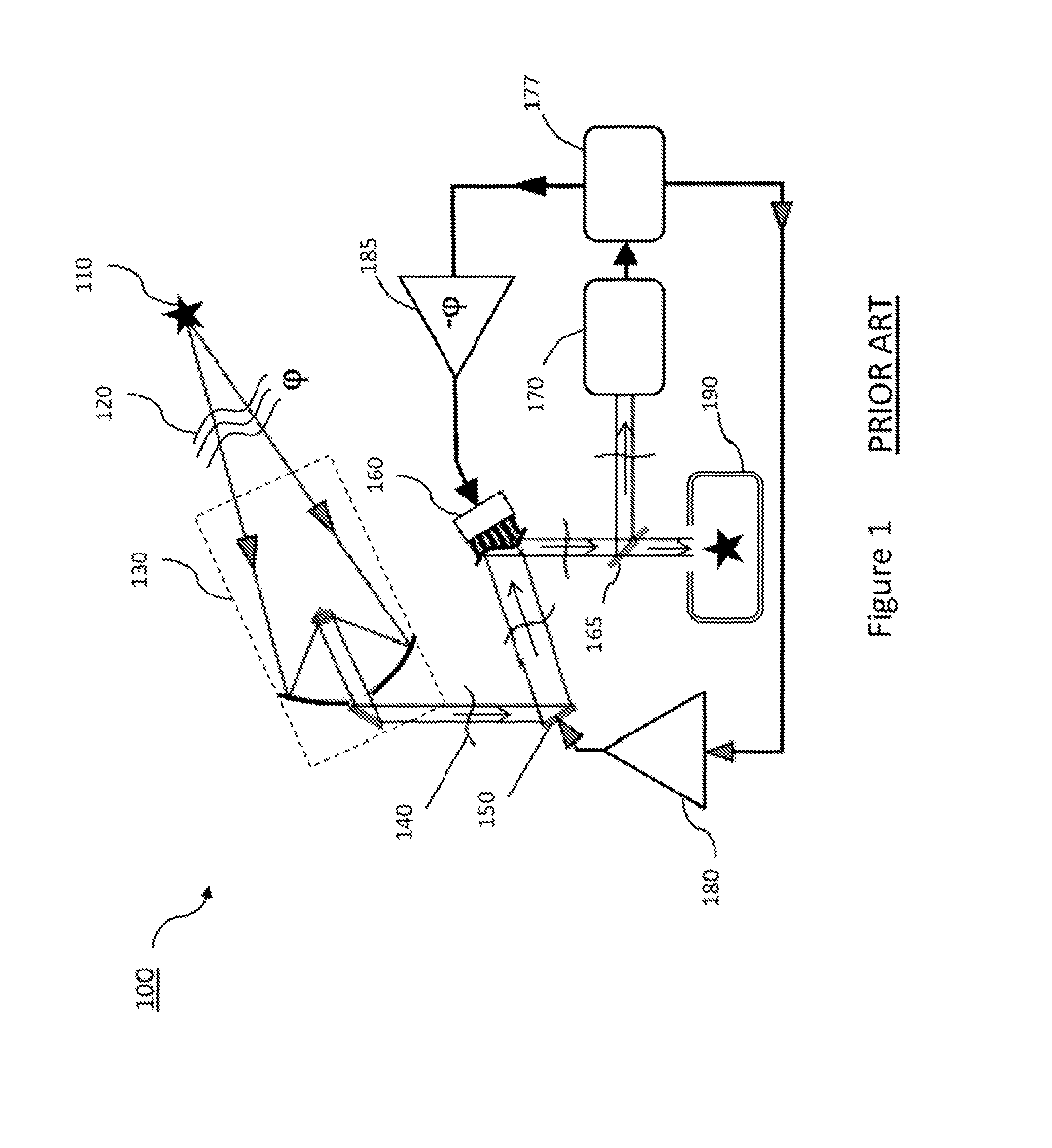
ActiveUS20070139656A1Robust resultPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansRefractive indexLength wave
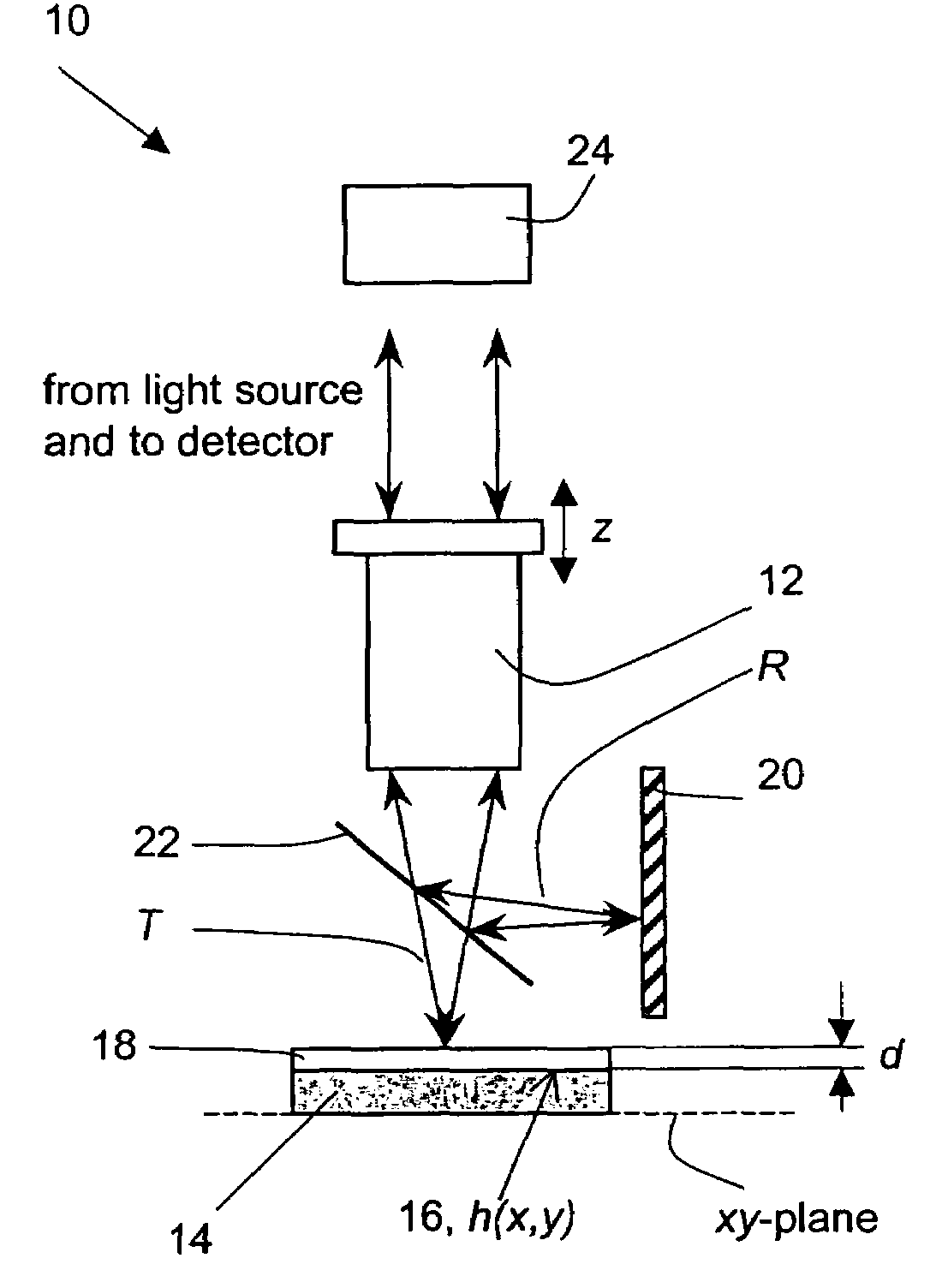
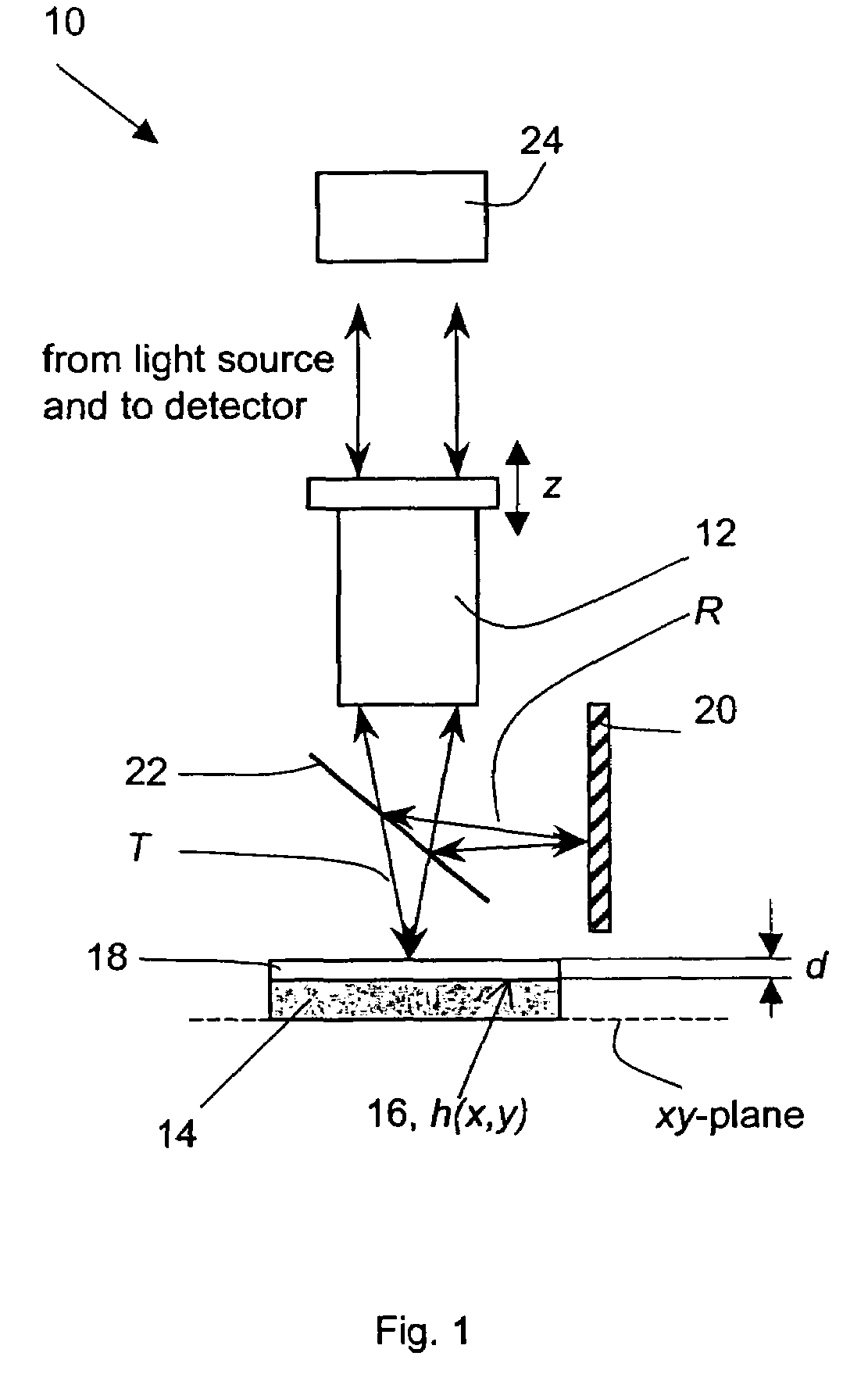
Thin-film thickness and refractive index are measured using the Fourier amplitude of a broadband interferometric spectrum. Due to the smooth nature of the Fourier amplitude as a function of wavelength, as compared to the fast varying Fourier phase conventionally used to measure thickness, increased stability and repeatability of measurement are achieved. As a result, measurements of ultra-thin films with thickness below 100 nm are possible with reliable results.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
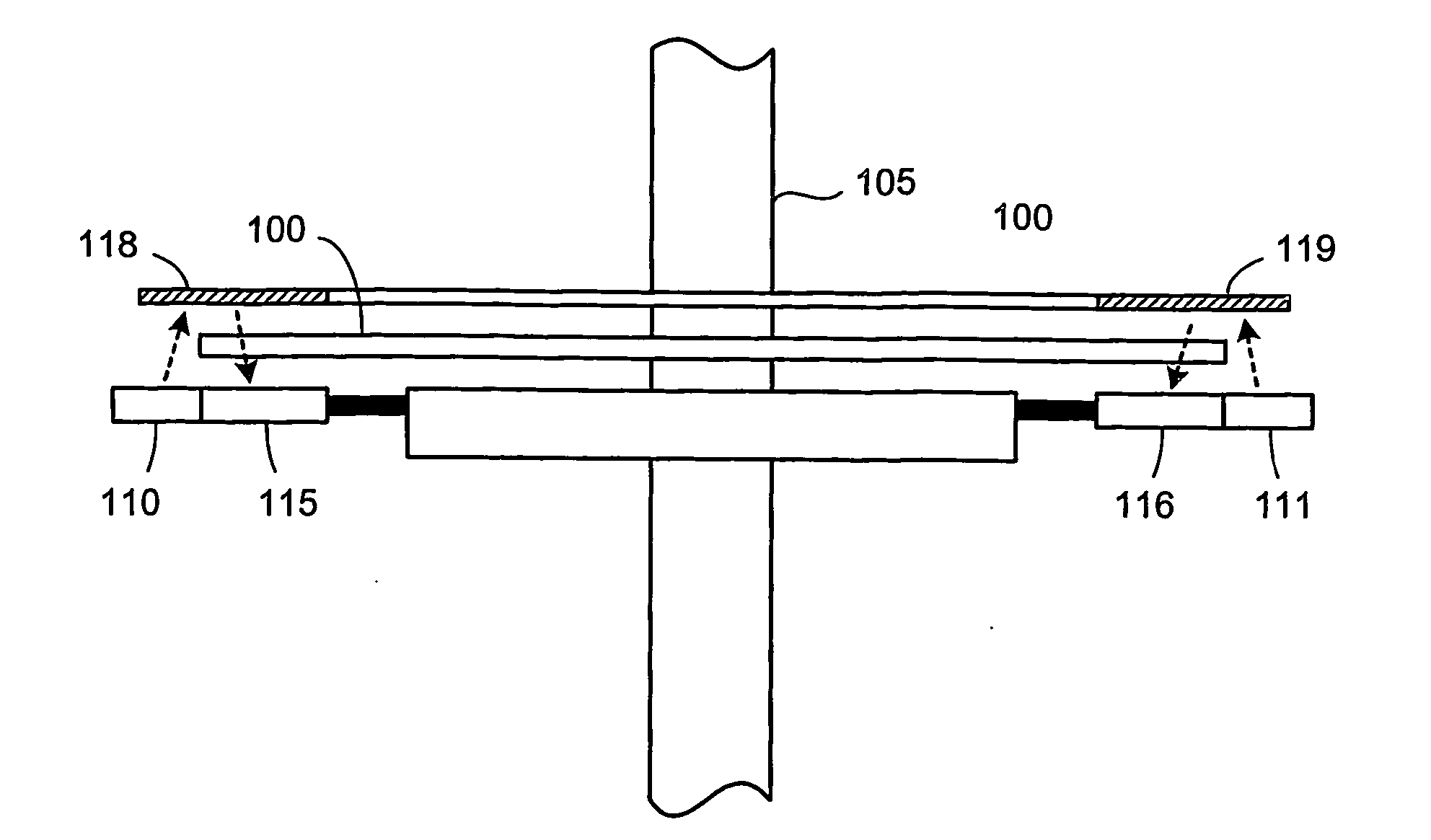
Method and apparatus for absolute optical encoders with reduced sensitivity to scale or disk mounting errors
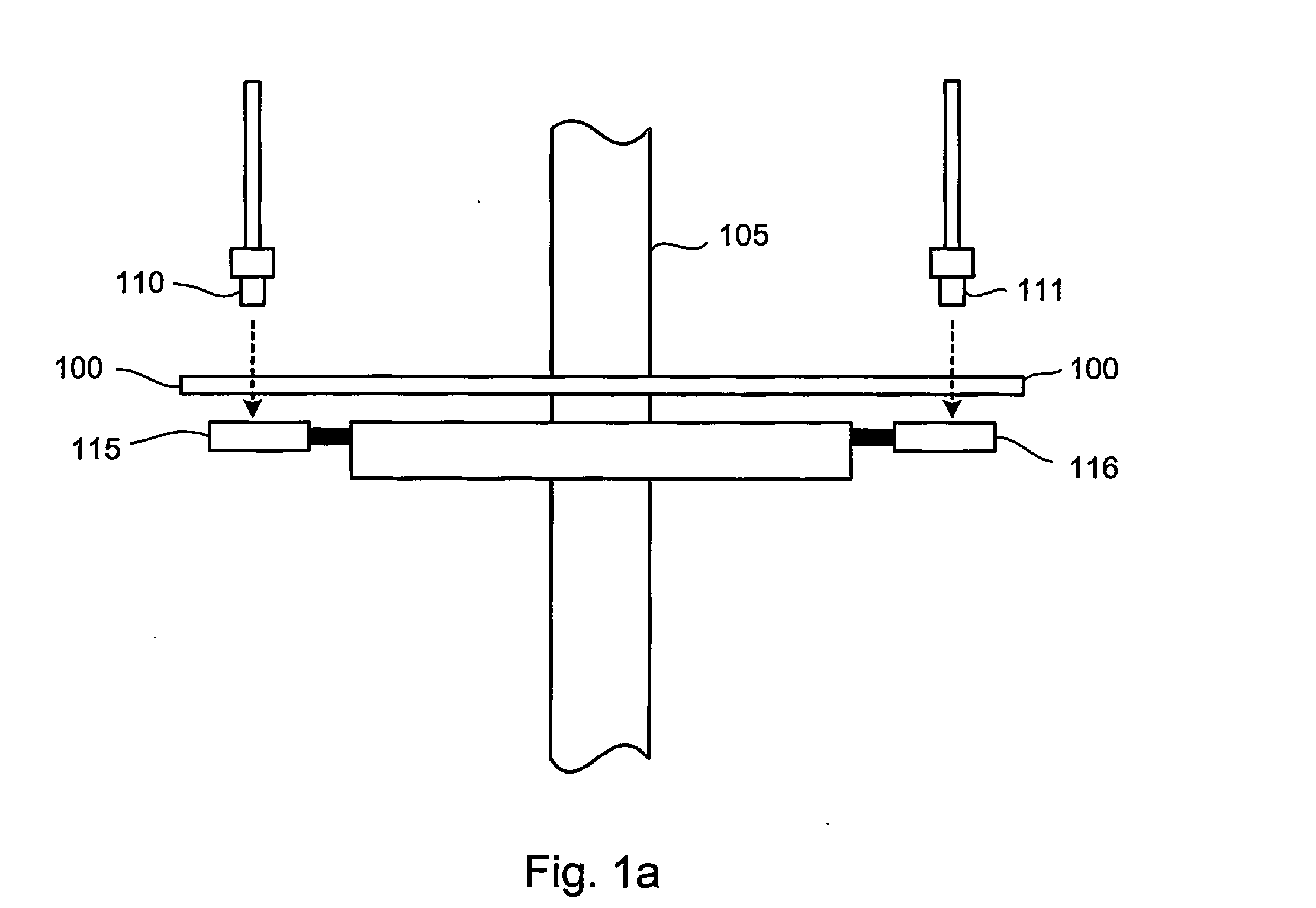
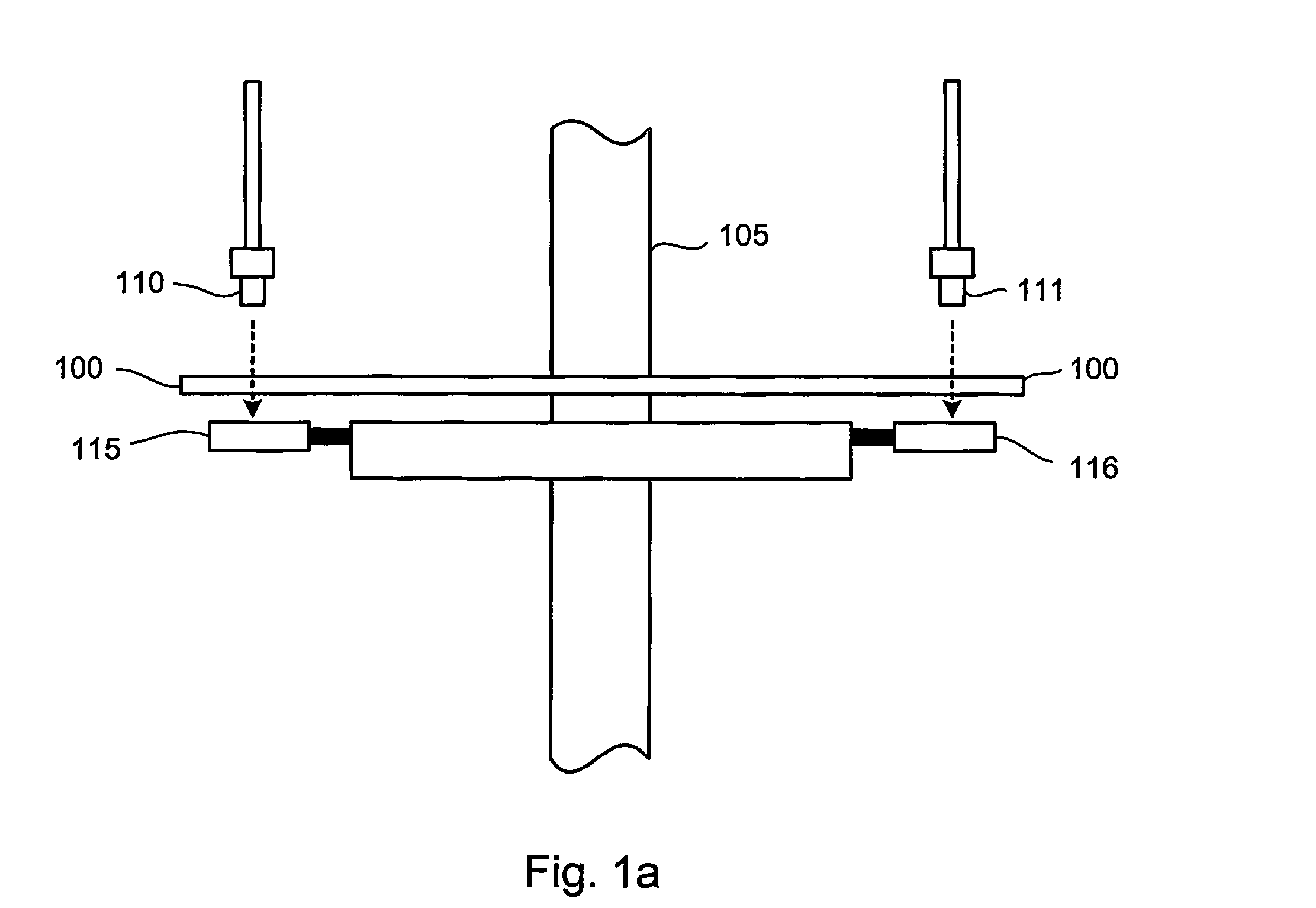
ActiveUS20060243895A1Material analysis by optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyOrbitImage code
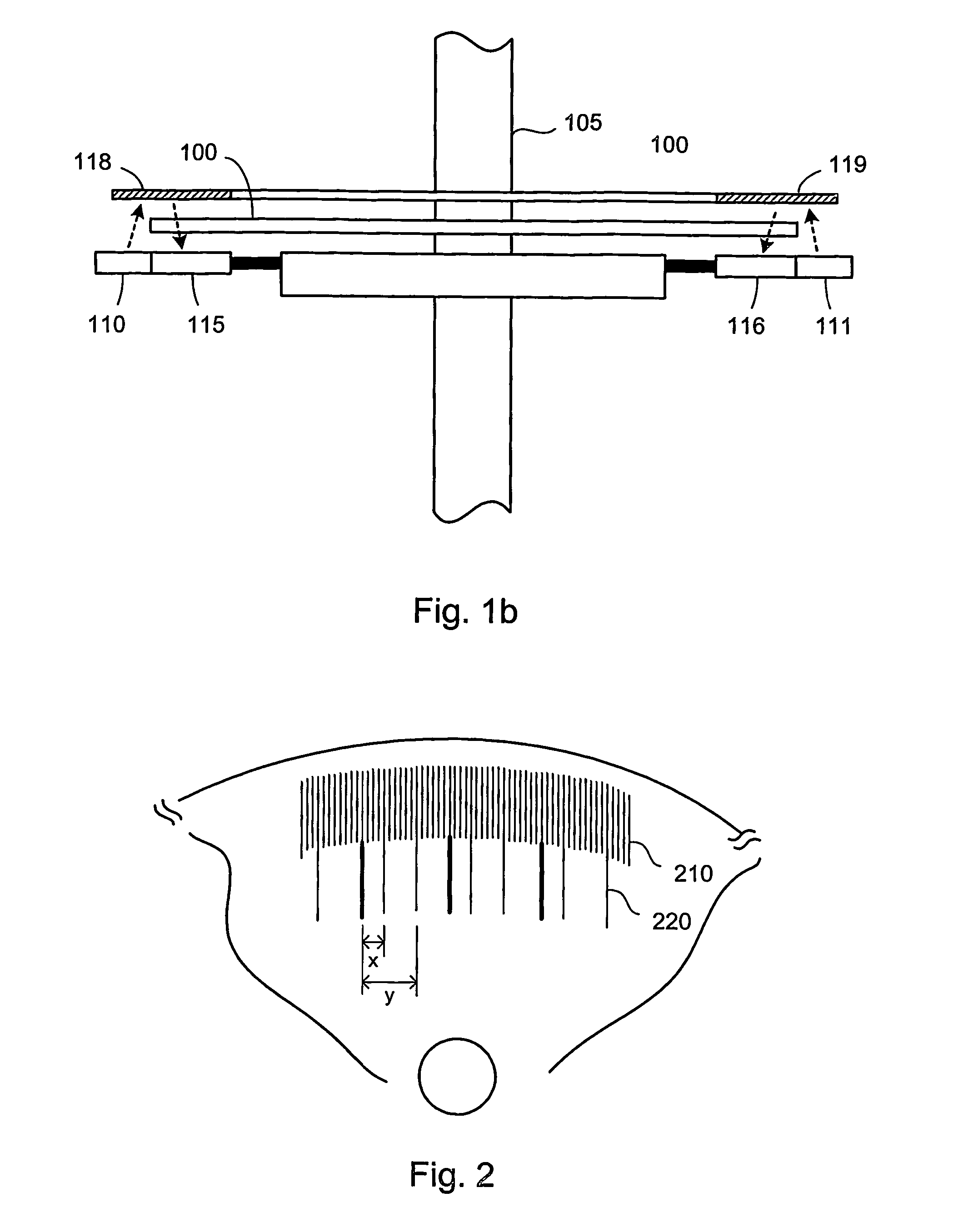
An absolute optical encoder apparatus for measuring an absolute position comprises an optical disk or scale element (100) having both incremental and absolute code tracks formed thereon. In the embodiment, a photoemitter light source (110, 111) illuminates the tracks onto a CCD area array sensor (115, 116) such that an image is formed from a pixel matrix having of rows and columns. Two detector line rows (410, 420) of the pixel matrix are each read out from the portion of the matrix comprising the incremental and absolute code tracks respectively. Inaccurate mounting of the disk or scale element can cause fluctuations in the period of the code tracks resulting from the rotation of the disk or movement of the scale element. The mounting inaccuracies are compensated for either by matching the spatial frequency by dynamically changing row of detector line read from the incremental image of the code track or by altering the numerical value of the pattern period used in the Fourier phase algorithm. The absolute position is numerically calculated from the imaged code tracks.
Owner:TRIMBLE INC
Method and apparatus for absolute optical encoders with reduced sensitivity to scale or disk mounting errors
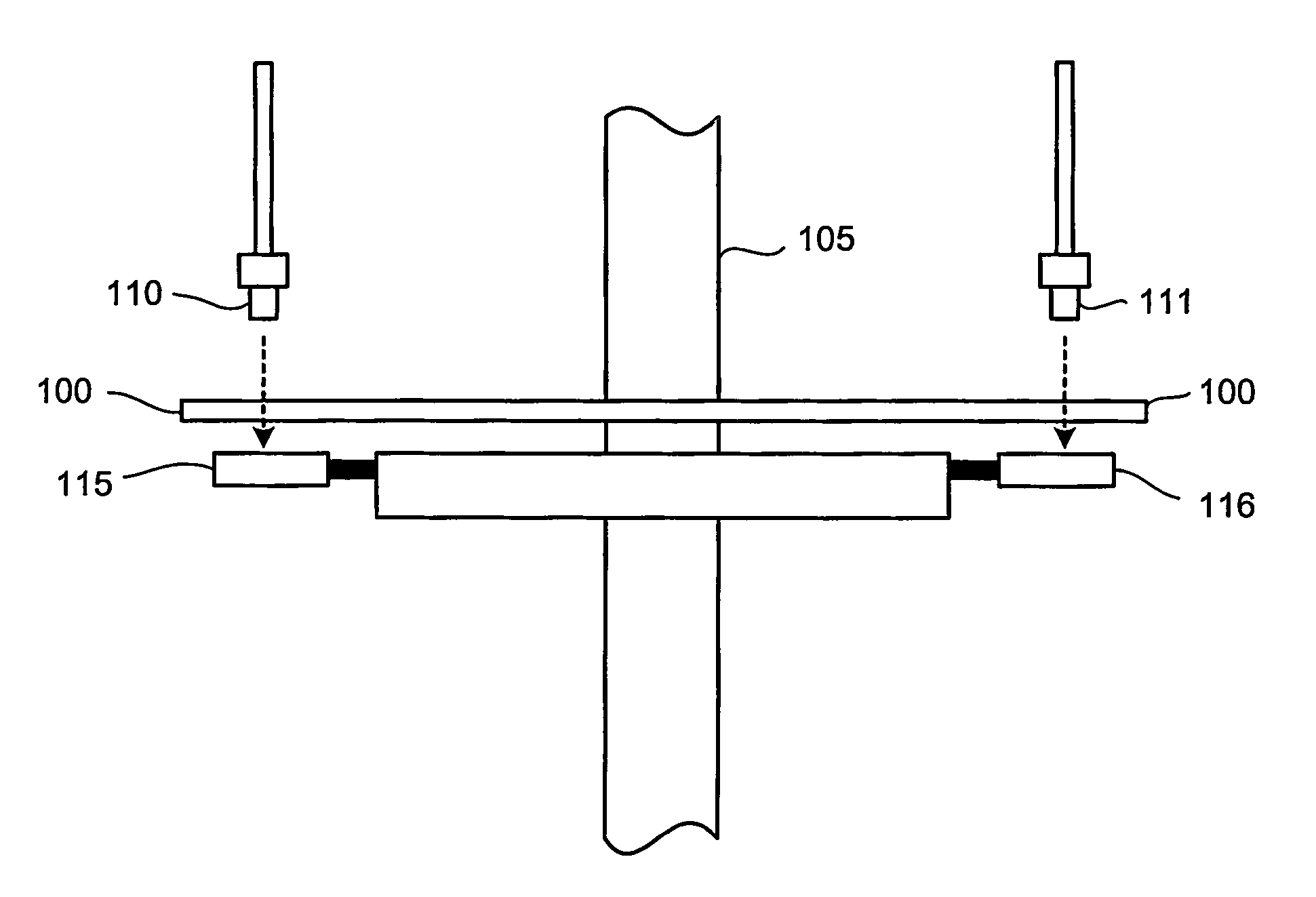
ActiveUS7589313B2Material analysis by optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyImage codePixel matrix
An absolute optical encoder apparatus for measuring an absolute position comprises an optical disk or scale element (100) having both incremental and absolute code tracks formed thereon. In the embodiment, a photoemitter light source (110, 111) illuminates the tracks onto a CCD area array sensor (115, 116) such that an image is formed from a pixel matrix having of rows and columns. Two detector line rows (410, 420) of the pixel matrix are each read out from the portion of the matrix comprising the incremental and absolute code tracks respectively. Inaccurate mounting of the disk or scale element can cause fluctuations in the period of the code tracks resulting from the rotation of the disk or movement of the scale element. The mounting inaccuracies are compensated for either by matching the spatial frequency by dynamically changing row of detector line read from the incremental image of the code track or by altering the numerical value of the pattern period used in the Fourier phase algorithm. The absolute position is numerically calculated from the imaged code tracks.
Owner:TRIMBLE INC
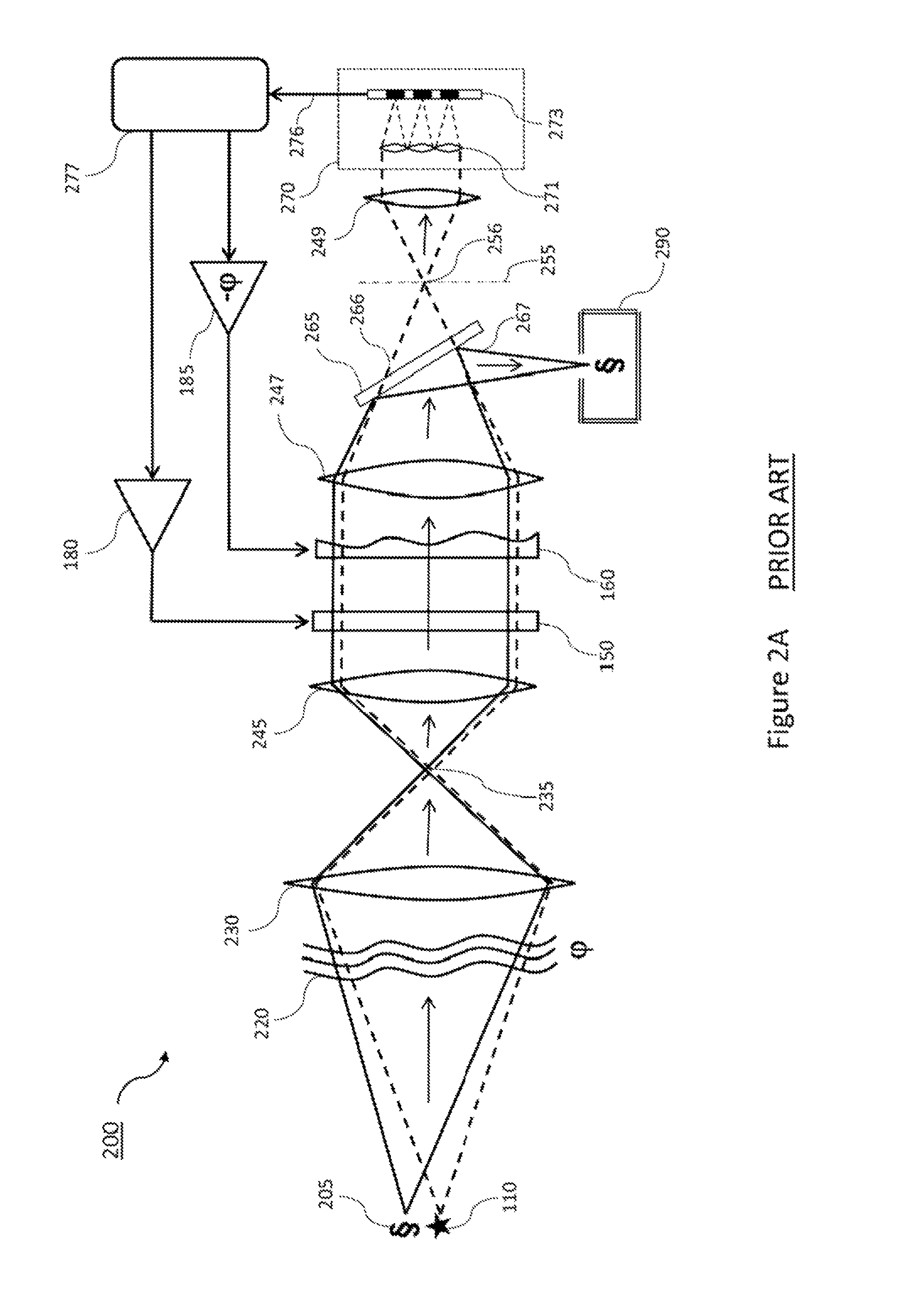
Measurement of thin films using fourier amplitude
ActiveUS7612891B2Robust resultPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansRefractive indexWide band
Thin-film thickness and refractive index are measured using the Fourier amplitude of a broadband interferometric spectrum. Due to the smooth nature of the Fourier amplitude as a function of wavelength, as compared to the fast varying Fourier phase conventionally used to measure thickness, increased stability and repeatability of measurement are achieved. As a result, measurements of ultra-thin films with thickness below 100 nm are possible with reliable results.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
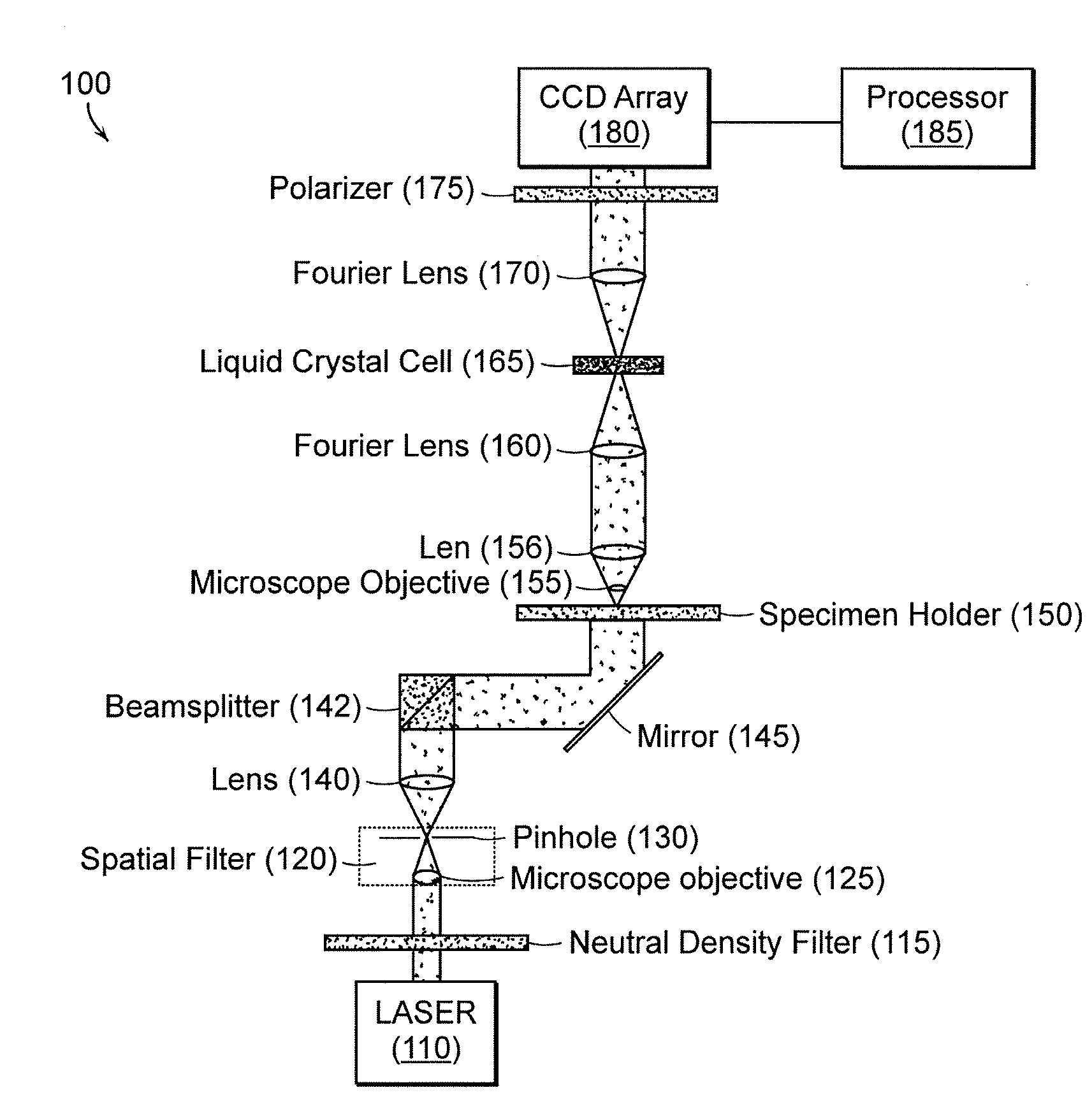
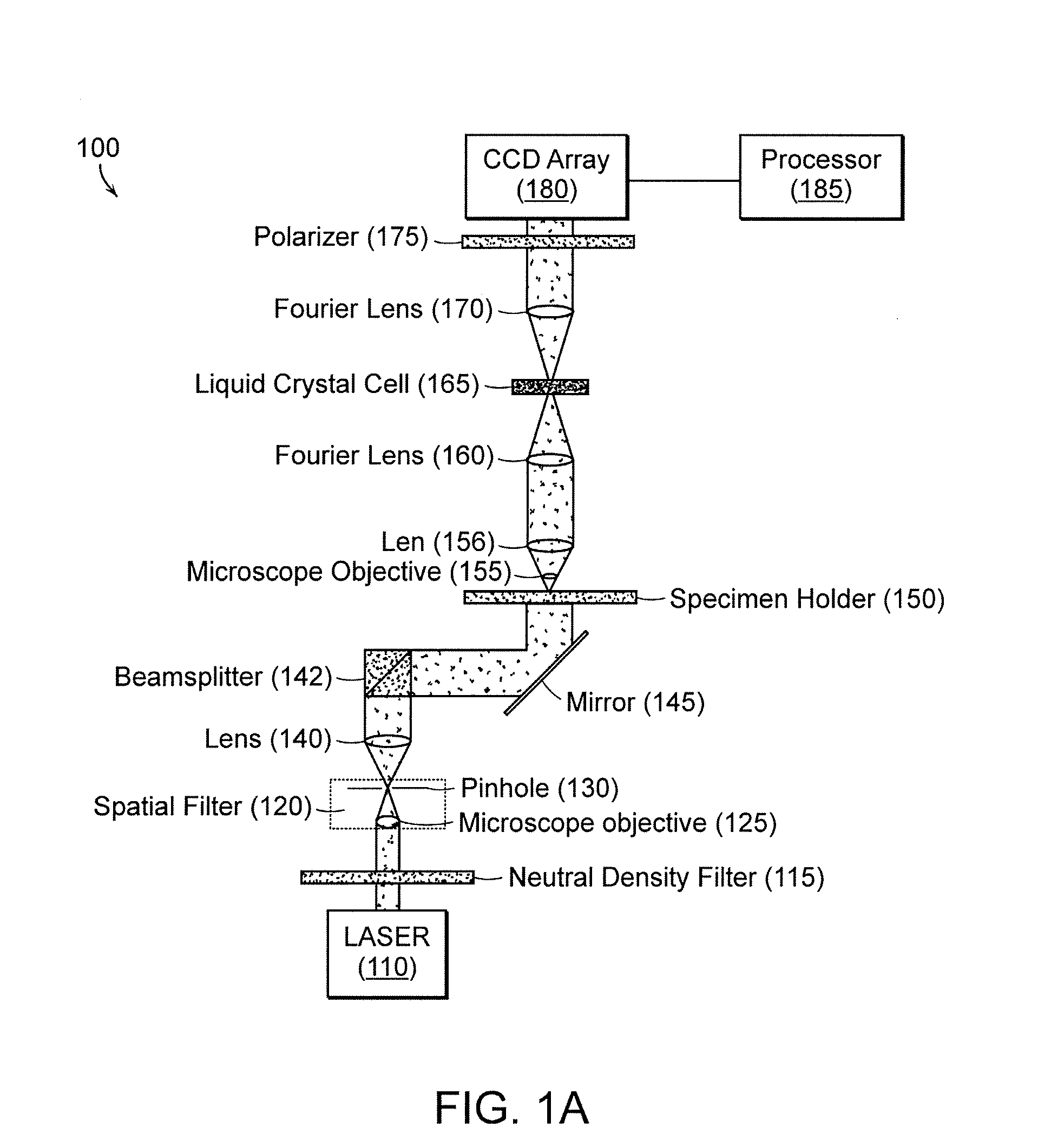
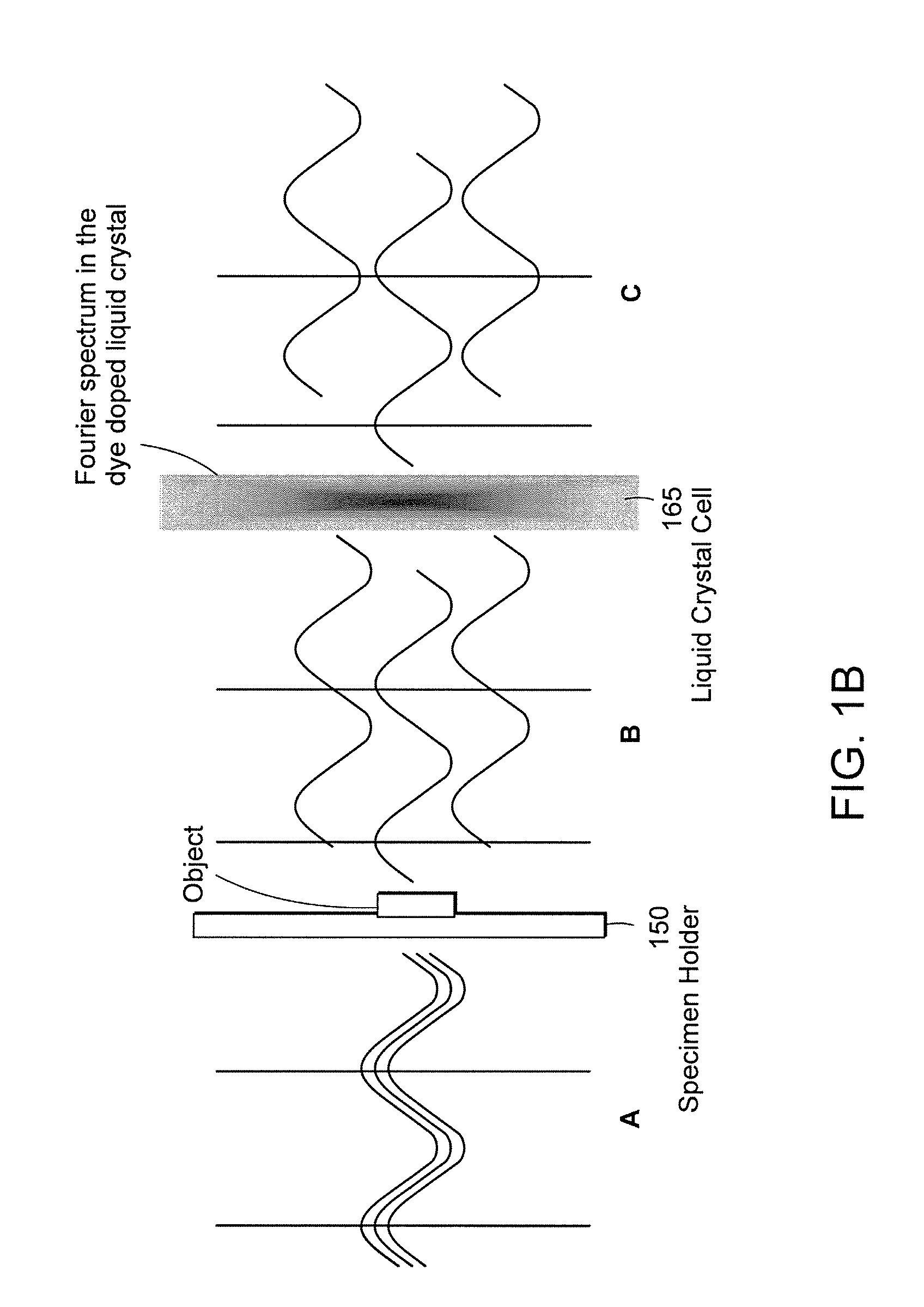
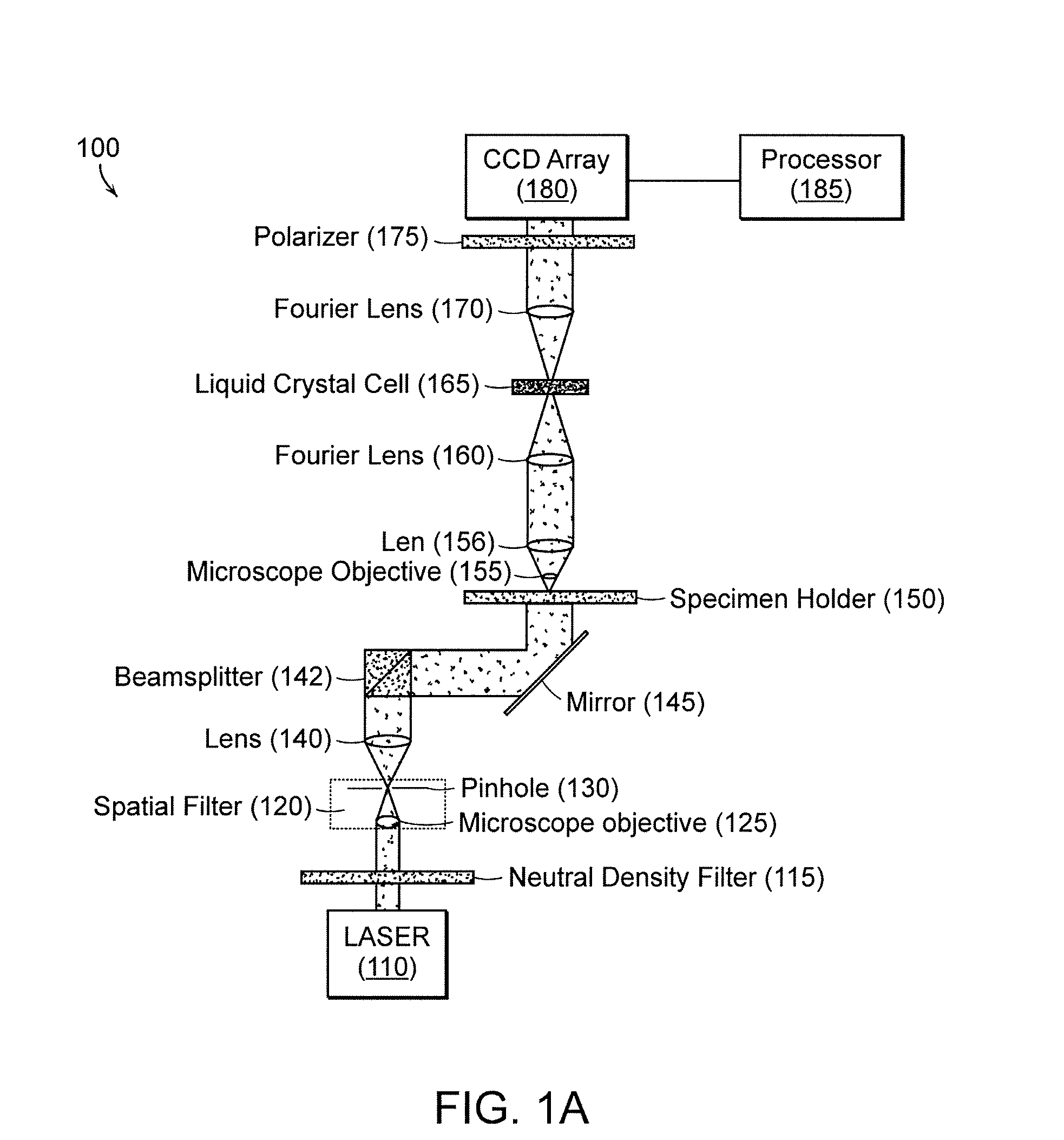
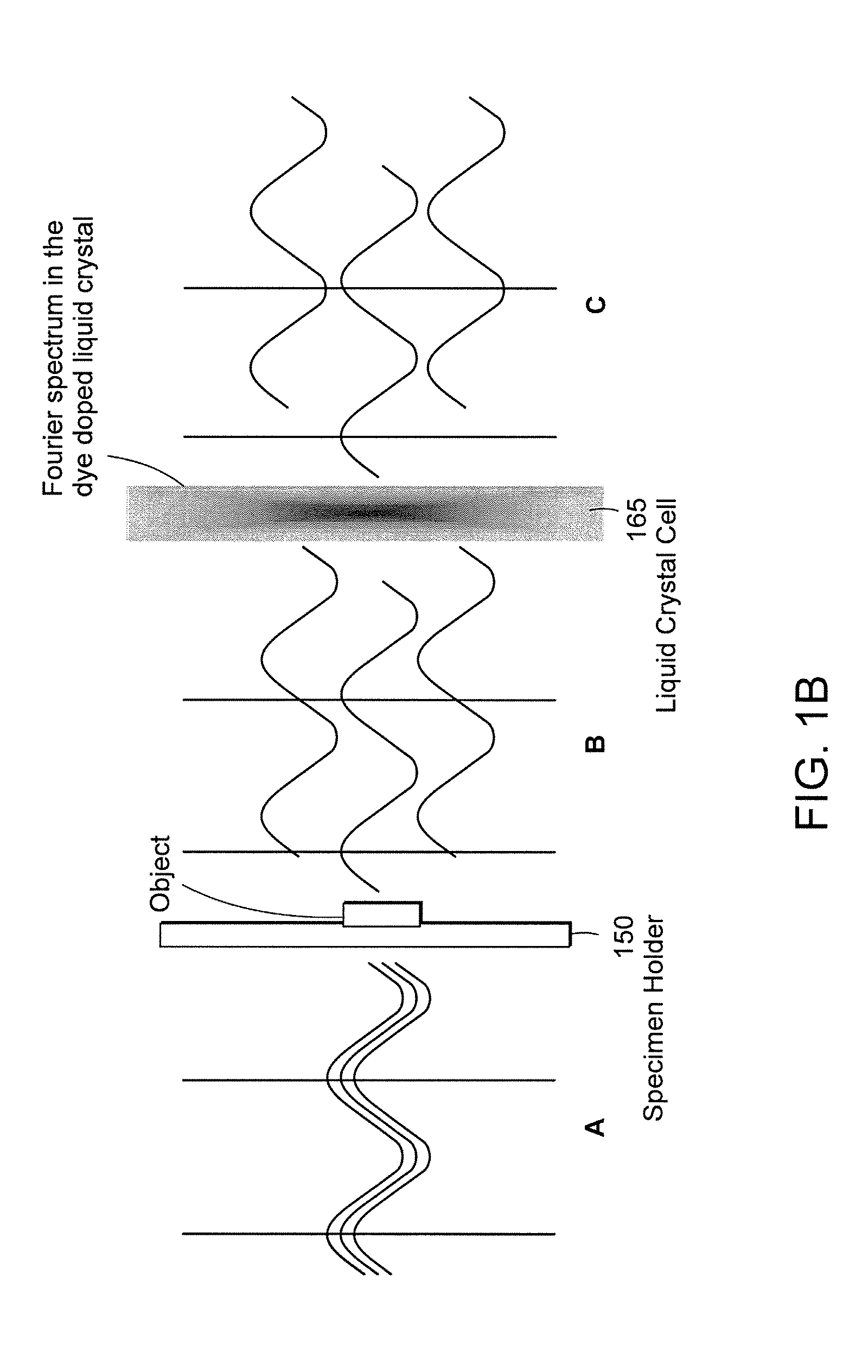
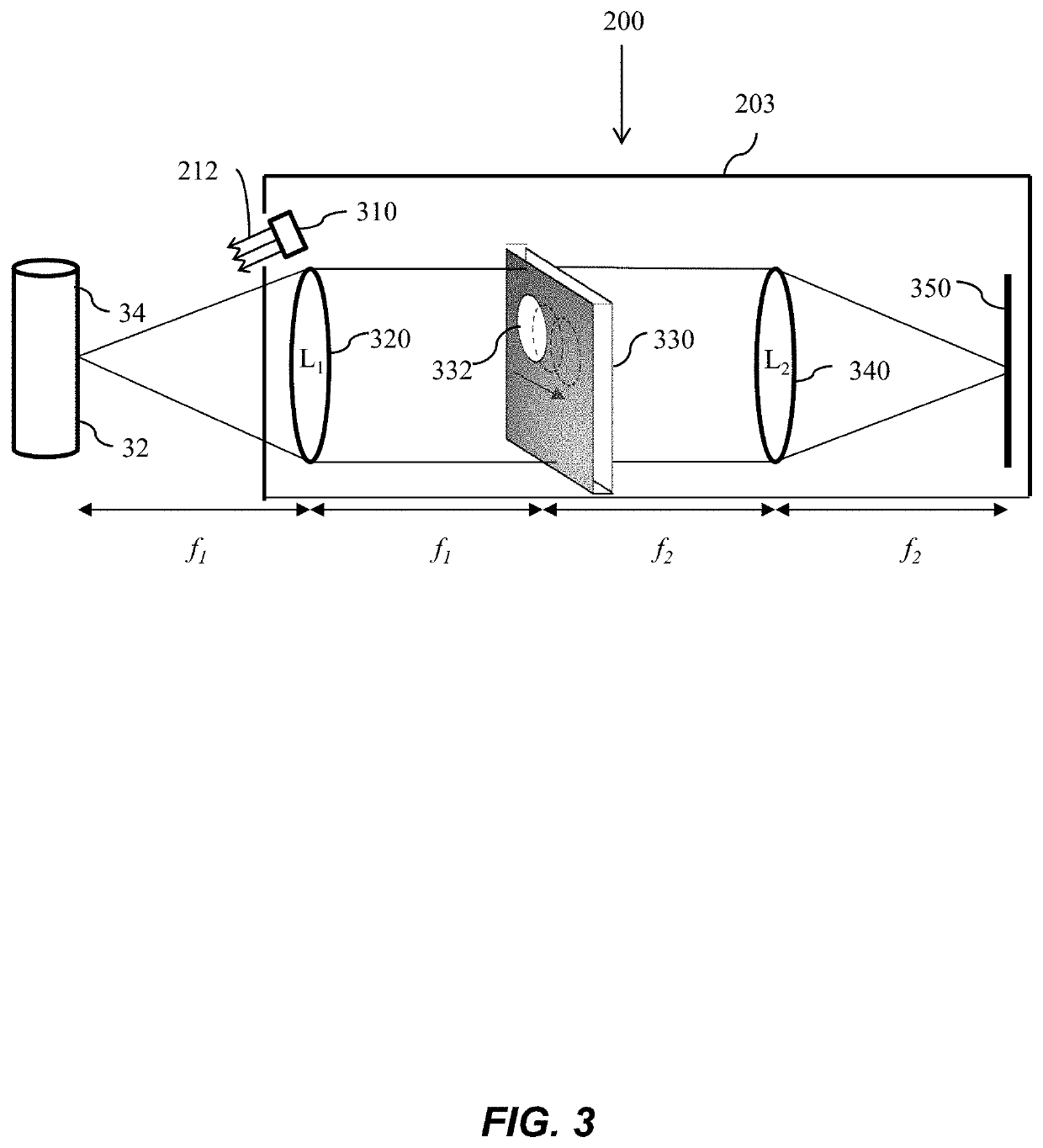
Systems and methods of all-optical fourier phase contrast imaging using dye doped liquid crystals
ActiveUS20080174860A1Reduce intensityNot to damageMicroscopesNon-linear opticsFourier transform on finite groupsDye doped
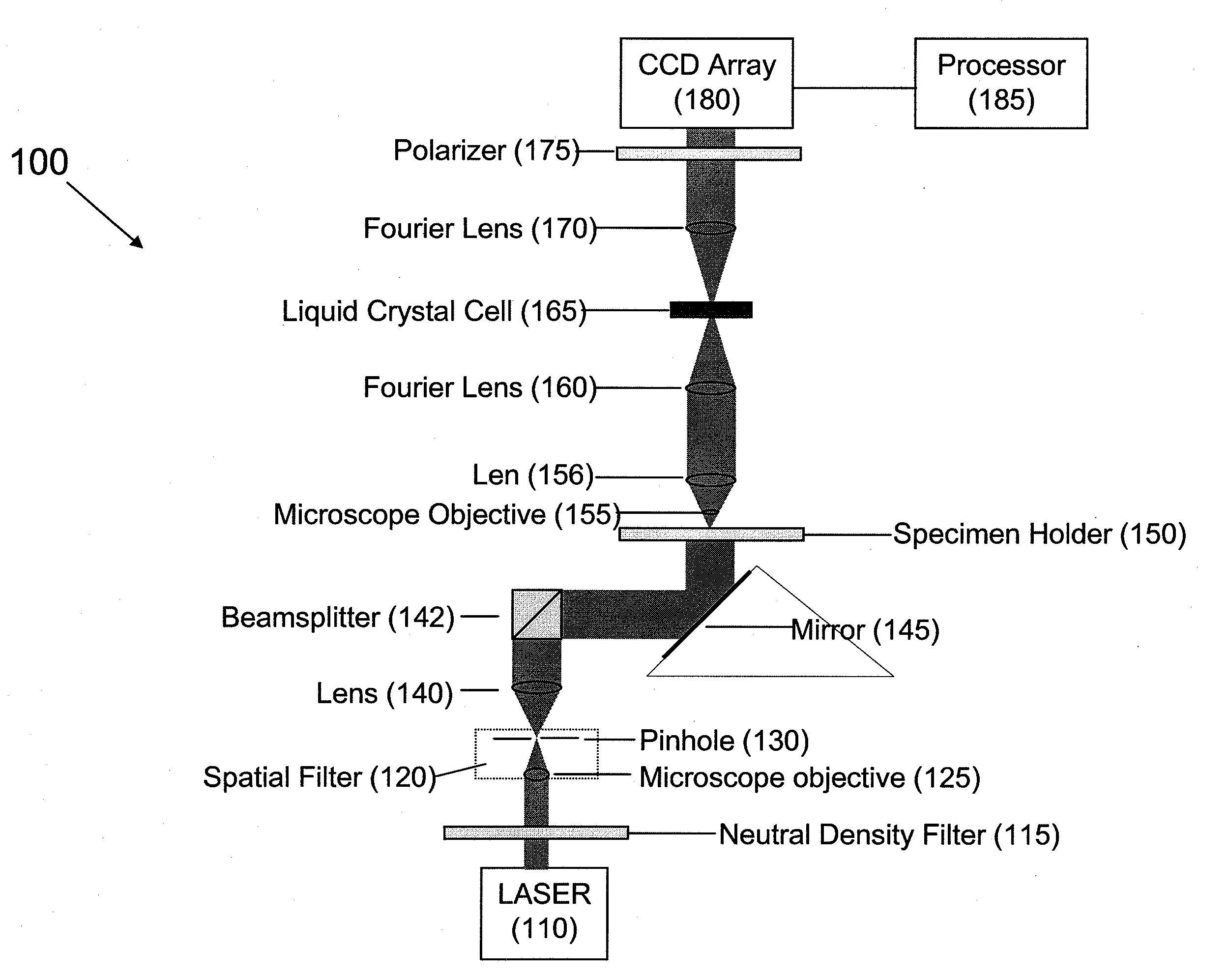
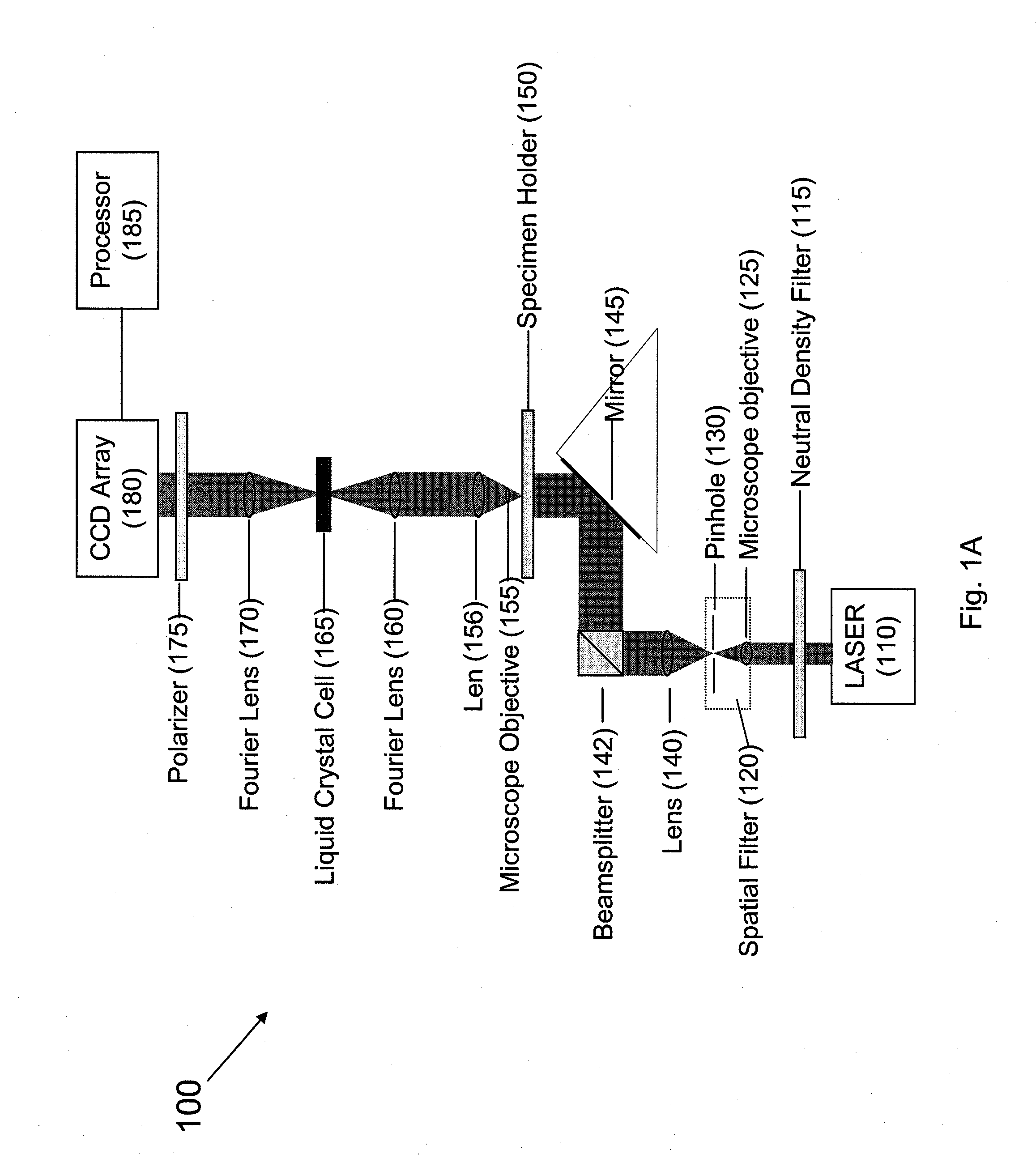
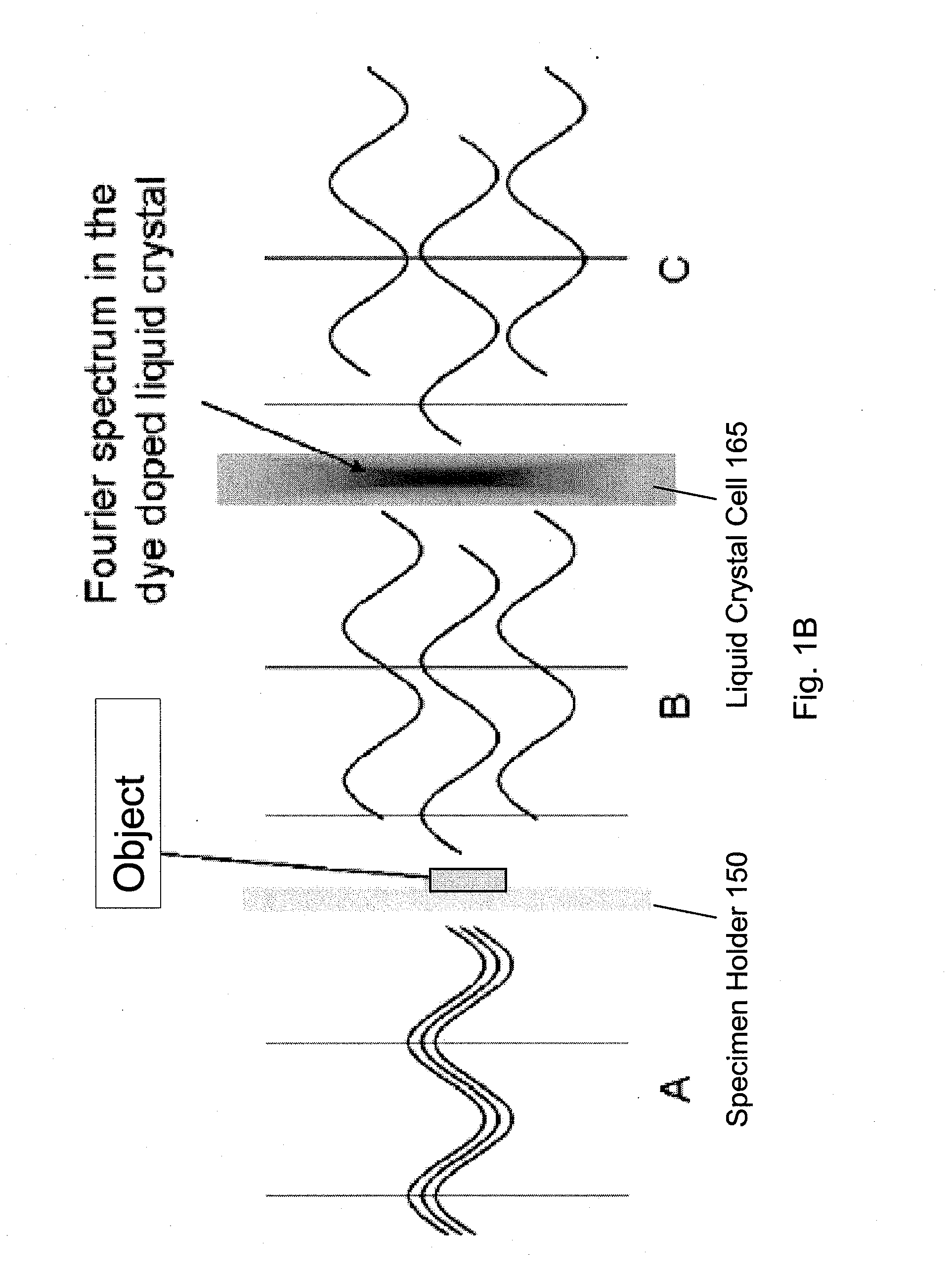
Under one aspect, a phase contrast imaging system includes a coherent light source emitting a coherent beam directed toward a sample area; a lens arranged to collect at least part of the beam from the sample area; an element Fourier transforming the collected beam in a Fourier plane; a liquid crystal cell in the Fourier plane that transmits at least part of the transformed beam, wherein the cell includes liquid crystal molecules having a phase transition temperature, and wherein at temperatures exceeding the phase transition temperature, light transmitted through the liquid crystal molecules obtains a different phase than light transmitted through the liquid crystal molecules obtains at temperatures below the phase transition temperature; and an element inversely Fourier transforming the transmitted beam to provide an image. Part of the transformed beam has an intensity sufficient to heat a portion of the liquid crystal molecules above the phase transition temperature.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
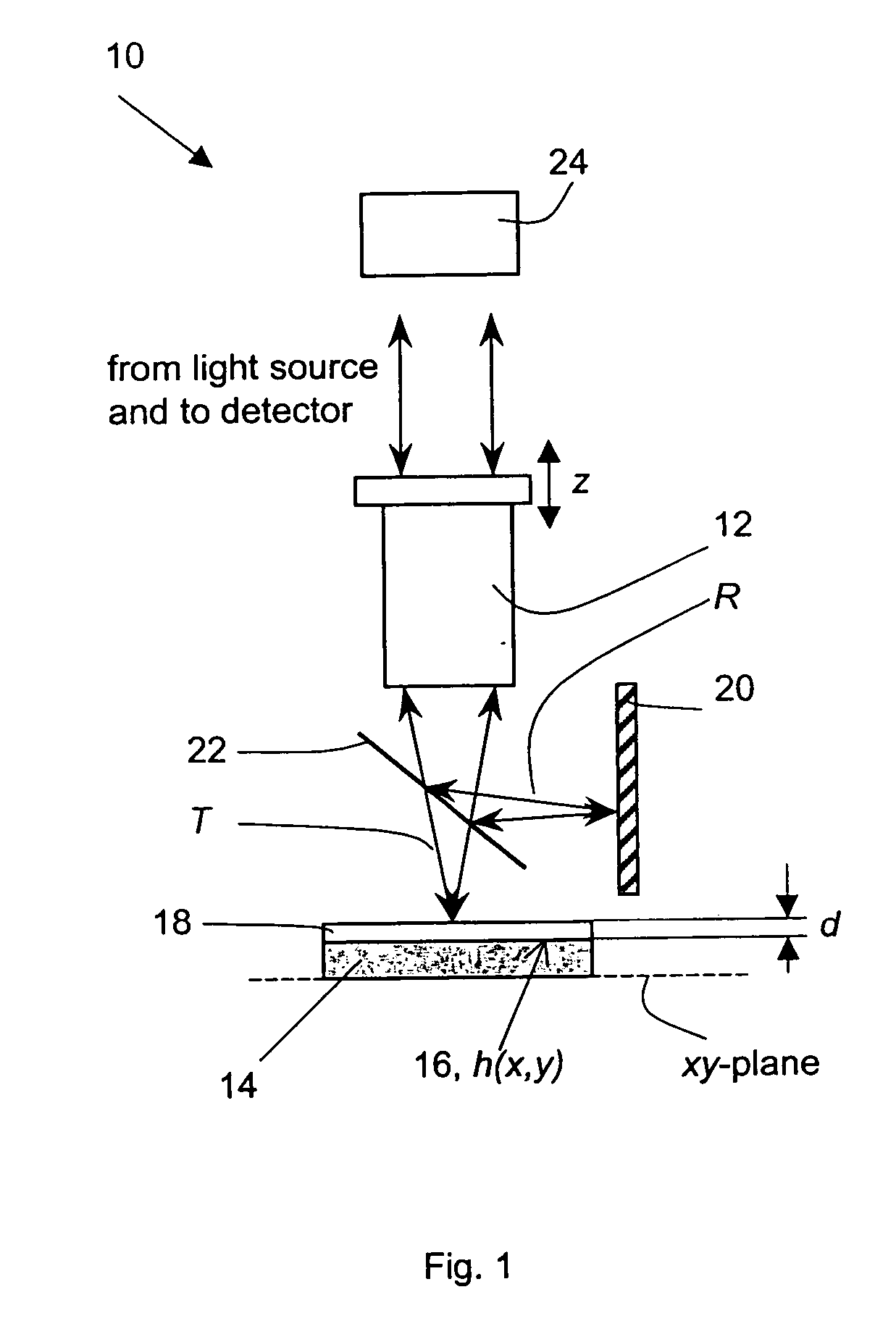
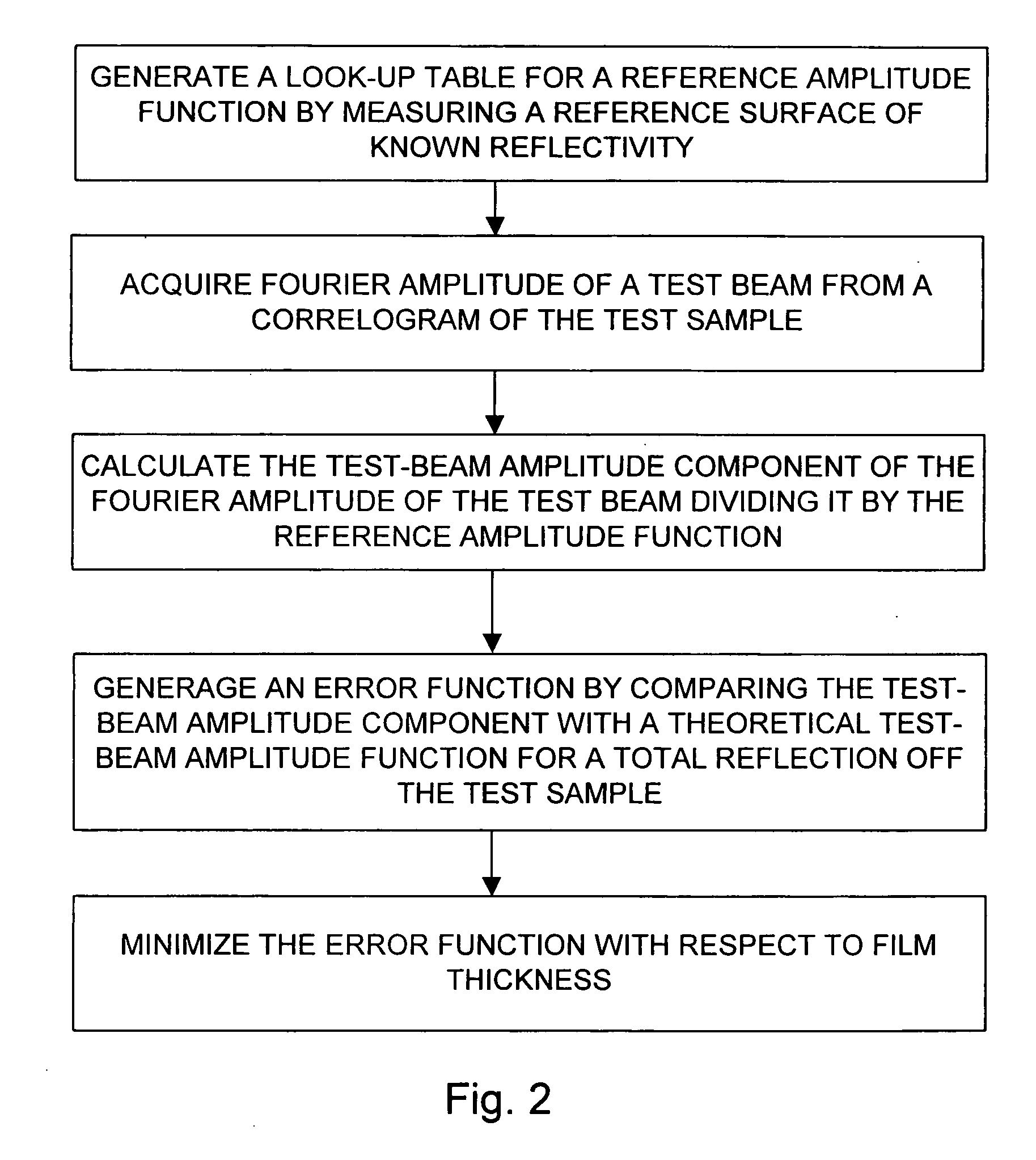
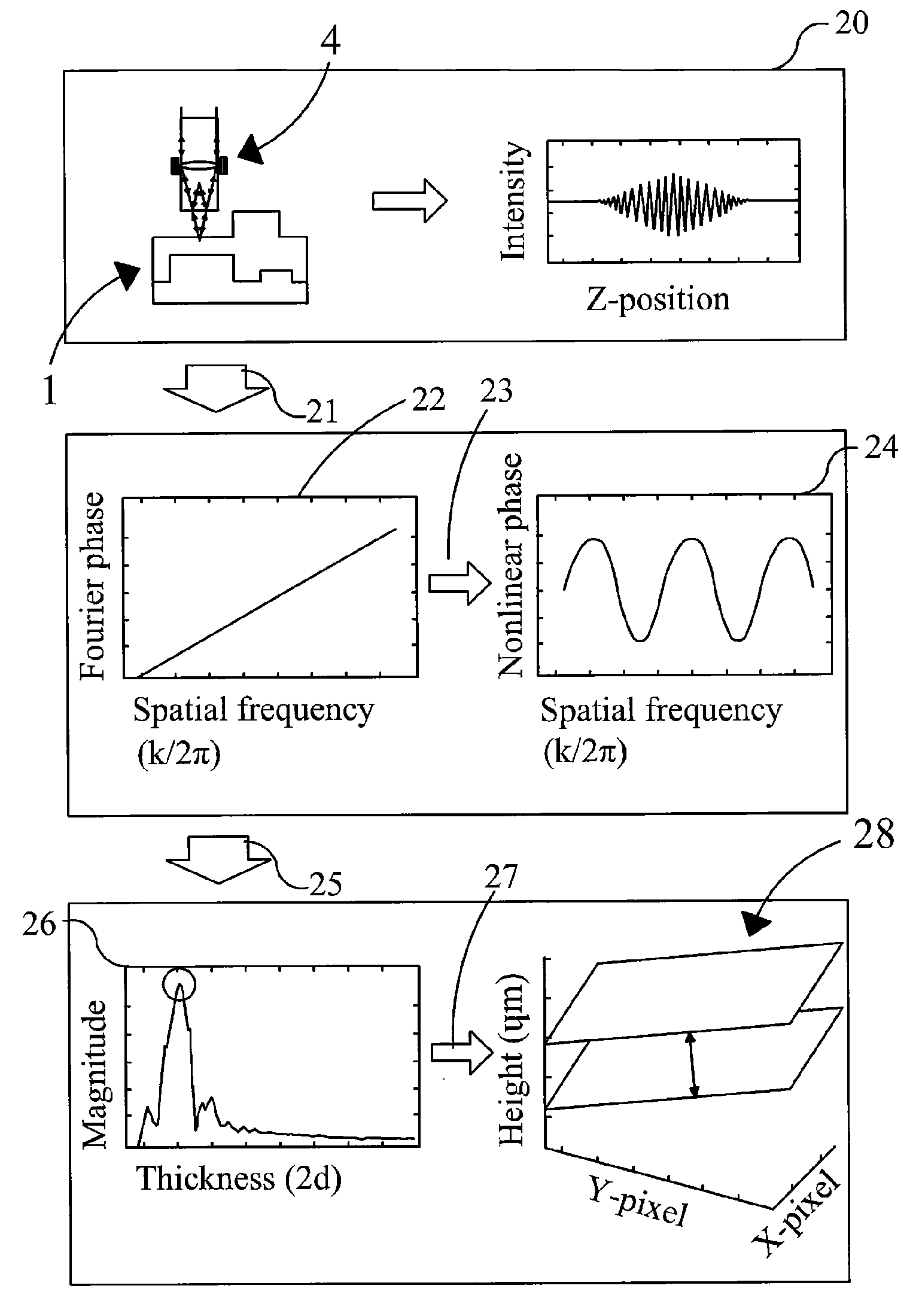
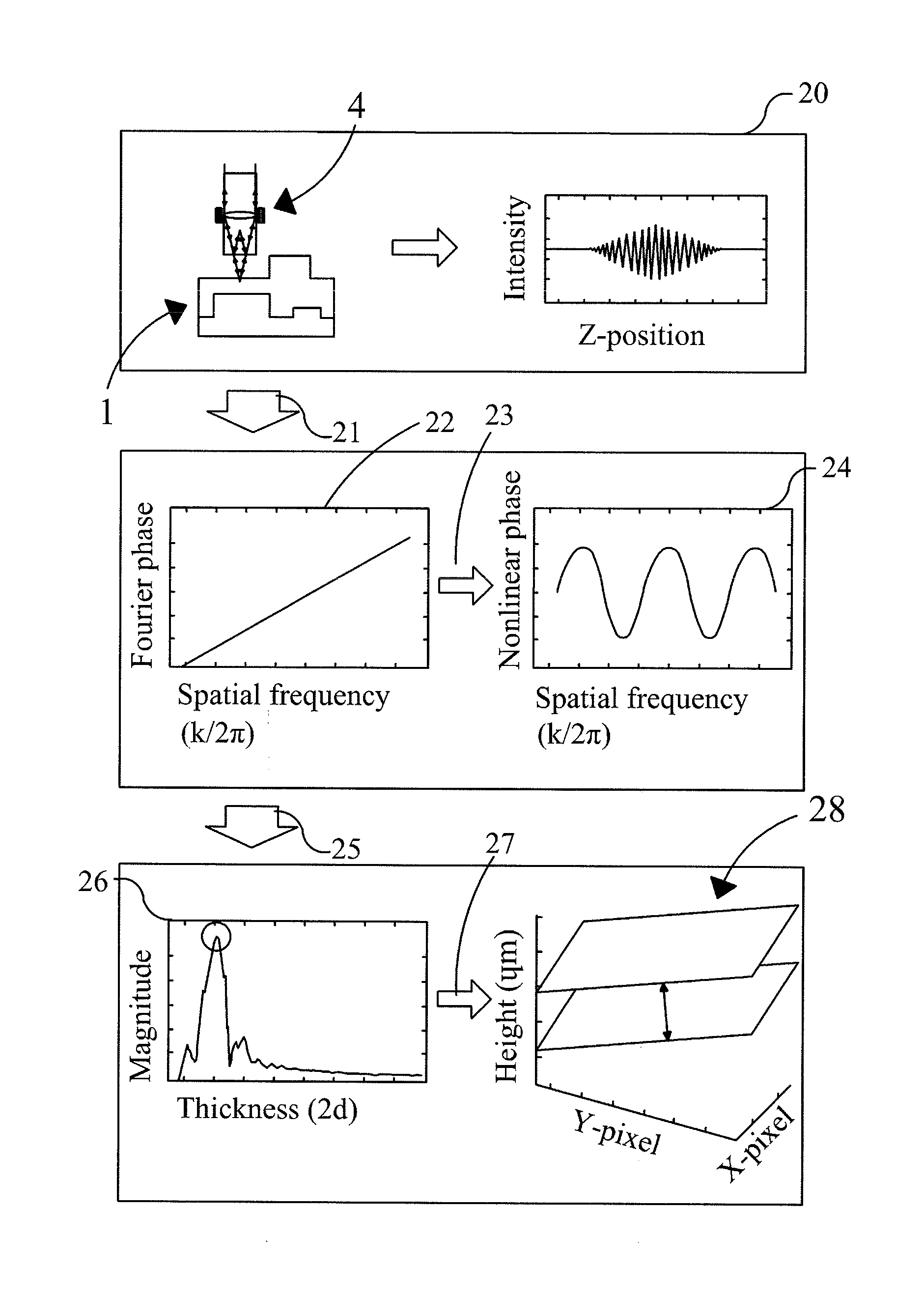
Method and apparatus for performing film thickness measurements using white light scanning interferometry
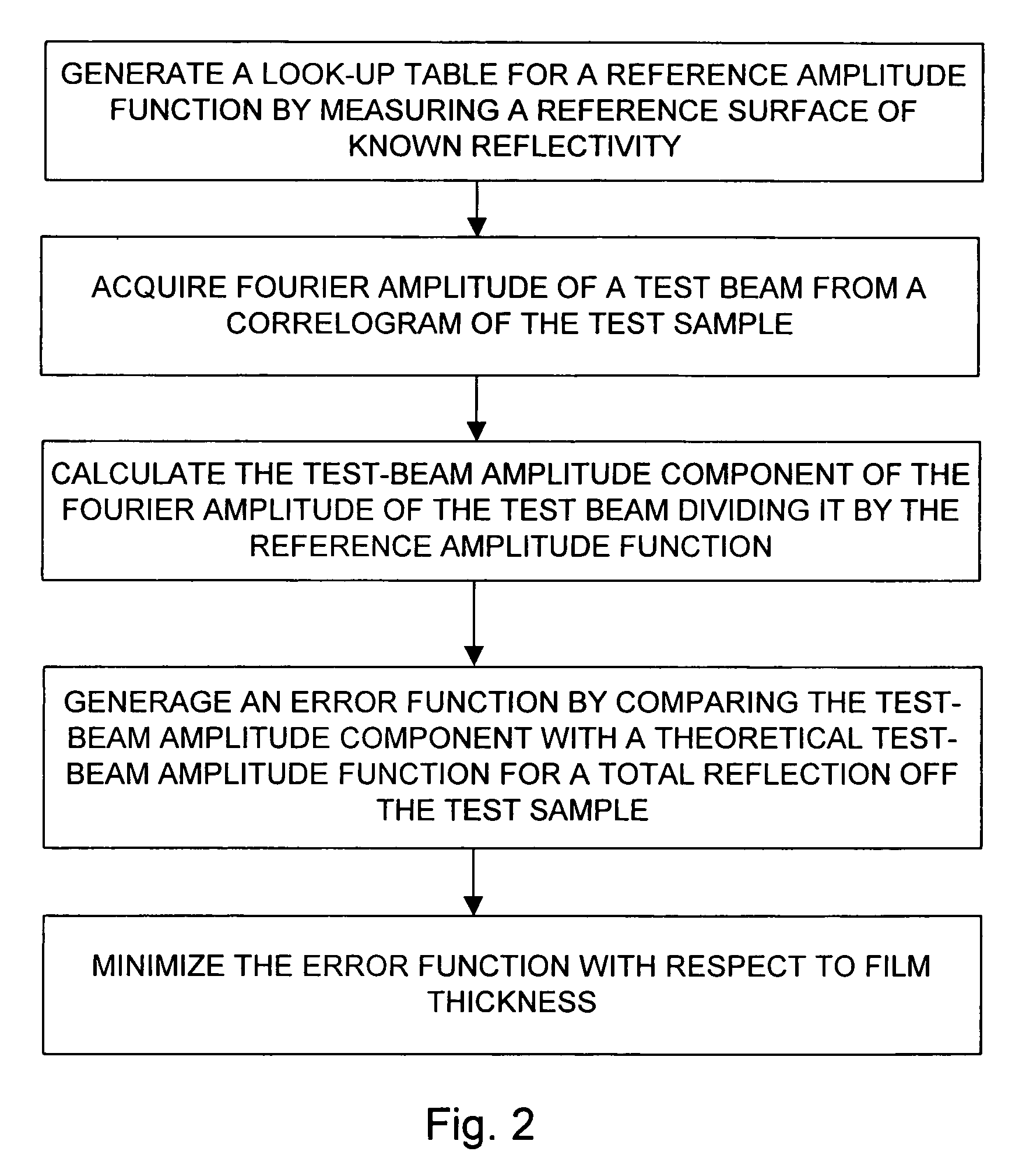
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for measuring the thickness of a transparent film by broad band interferometry, comprising the steps of preparing a correlogram of the film by an interferometer, applying a Fourier transformation to said correlogram to obtain a Fourier phase function, removing a linear component thereof, applying a second integral transformation to the remaining non-linear component to obtain an integral amplitude function of said non-linear component, identifying the peak location of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the film as the double value of the abscissa at said peak location considering a refractive index of a film which is dependent on wavelength. The last two steps may be replaced by identifying the peak locations of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the films as the double values of the abscissas at the peak locations.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
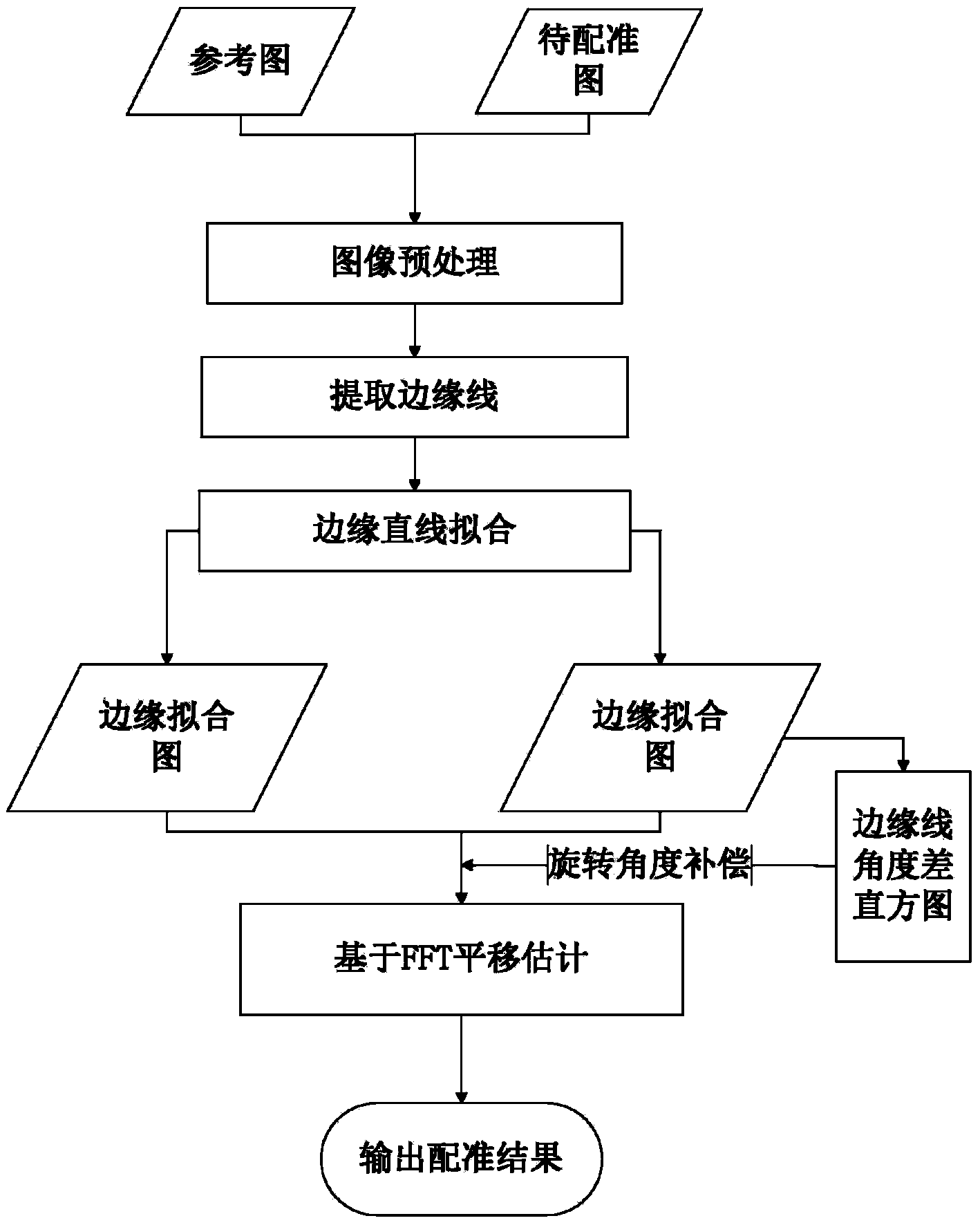
SAR image registration method based on straight lines and FFT
InactiveCN103839262AAvoid problems with severe noise effectsReduce the impact of noiseImage analysisPhase correlationComputation complexity
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing, and particularly provides an SAR image registration method based on straight lines and an FFT to mainly solve the problems that an existing technology is poor in registration effect and high in computing complexity. The method comprises the first step of inputting two SAR images and detecting the straight lines of the two images through a margin fitting method, the second step of carrying out statistics on the detected straight lines according to a slope difference histogram and calculating rotating parameters, the third step of carrying out the Fourier transform on a reference image and a rotated image to be registered to obtain a Fourier transform diagram, the fourth step of calculating horizontal movement parameters through the Fourier phase correlation method, and the fifth step of enabling the horizontally-moved and rotated image to be registered to coincide with the reference image and finishing the registration. The SAR image registration method has the advantages that the effect degree on the registration of the SAR images from noise is small, the registration result of the SAR images with abundant linear features is stable, the registration effect is better, speed is high, and the computing complexity is low, and the SAR image registration method can be used for pattern recognition, automatic navigation and computer vision and remote sensing image process.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
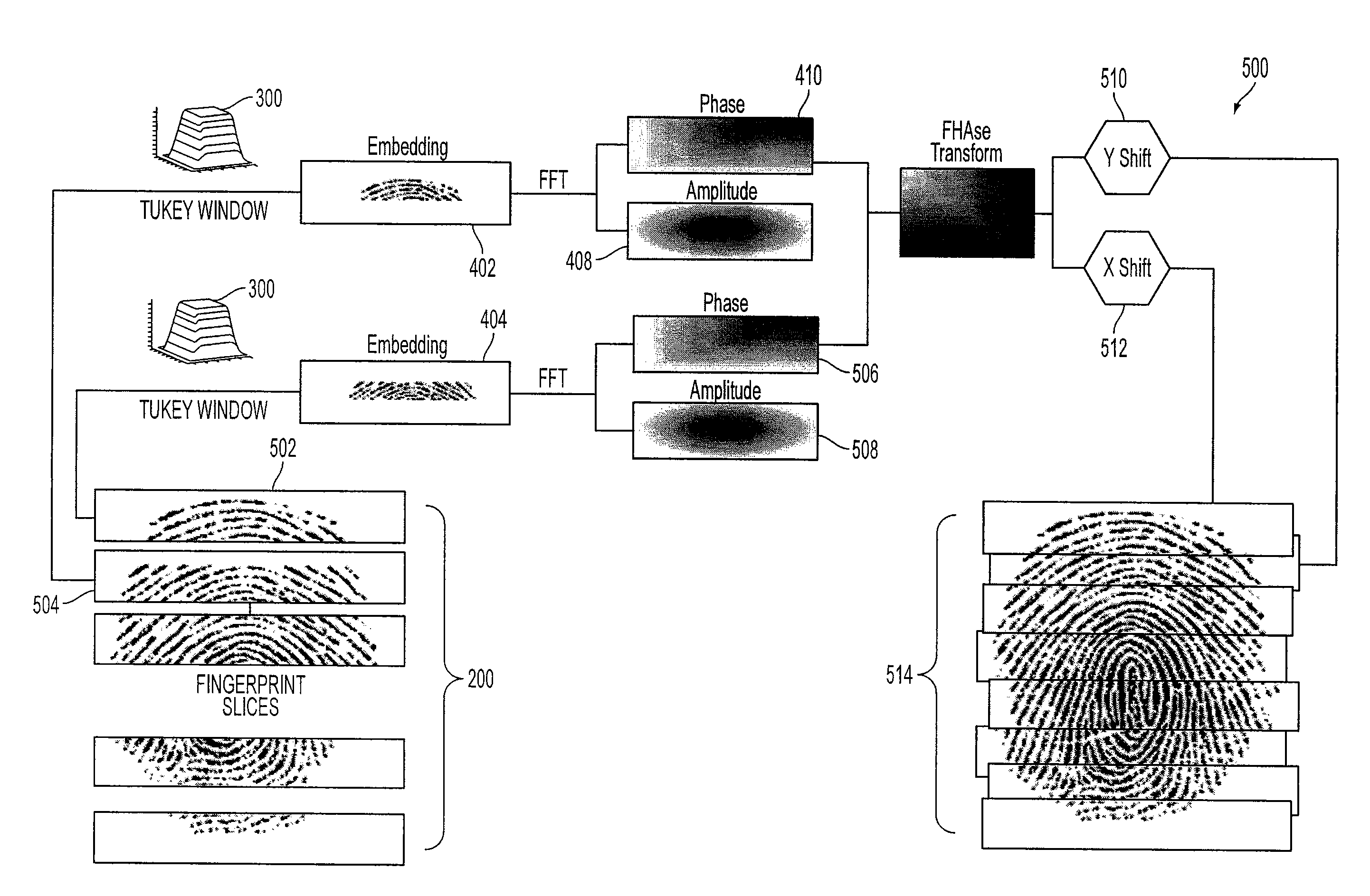
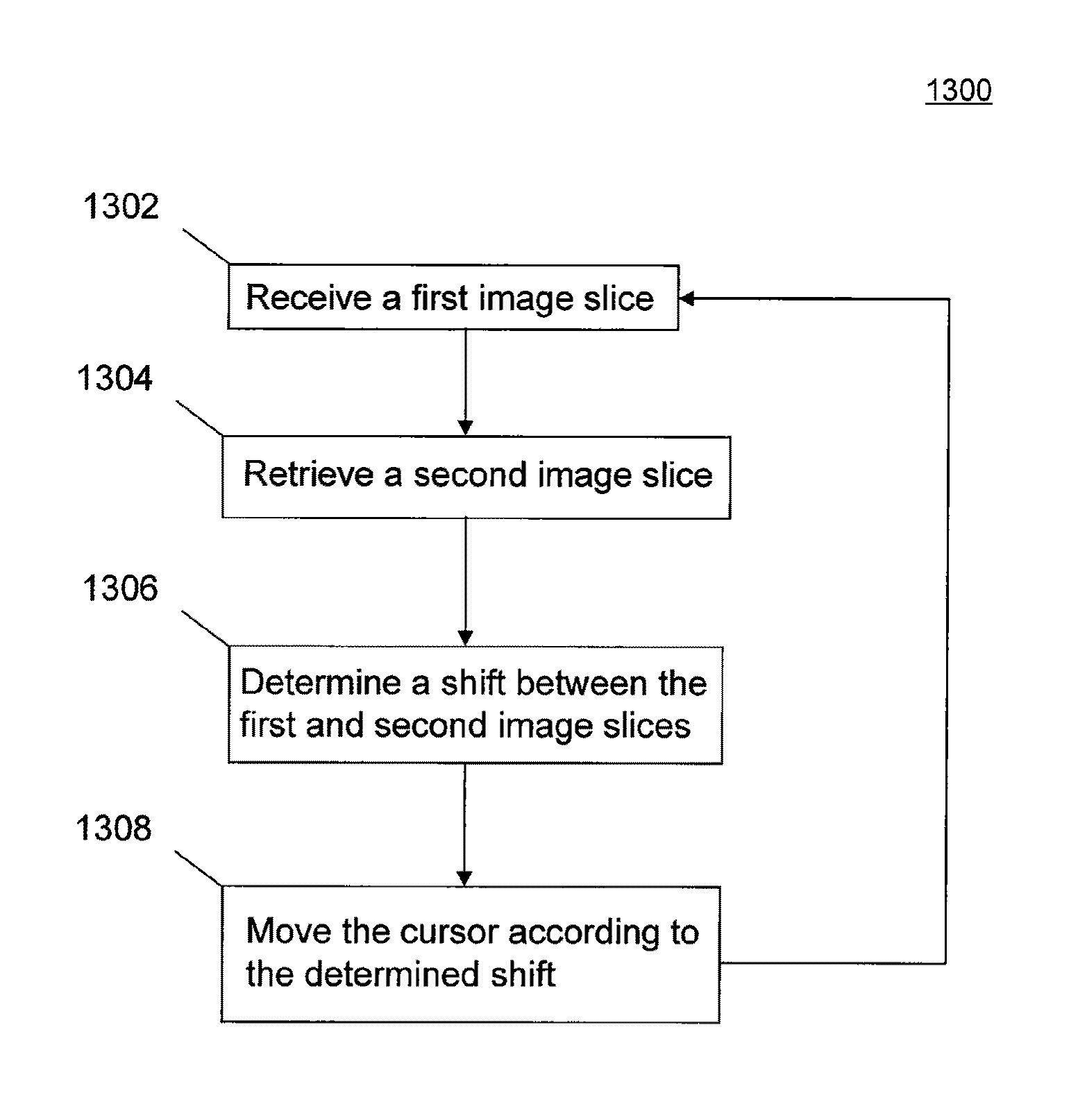
Method and system for swipe sensor image alignment using fourier phase analysis
InactiveUS20090175539A1Noise levelAccurate measurementImage enhancementImage analysisImage alignmentComputer science
Provided is a method for analyzing image slices. The method includes transforming a first slice and a second slice to frequency domain and determining shift data between the first slice and the second slice from only the phase component of the transformed first and second slices.
Owner:SONAVATION INC
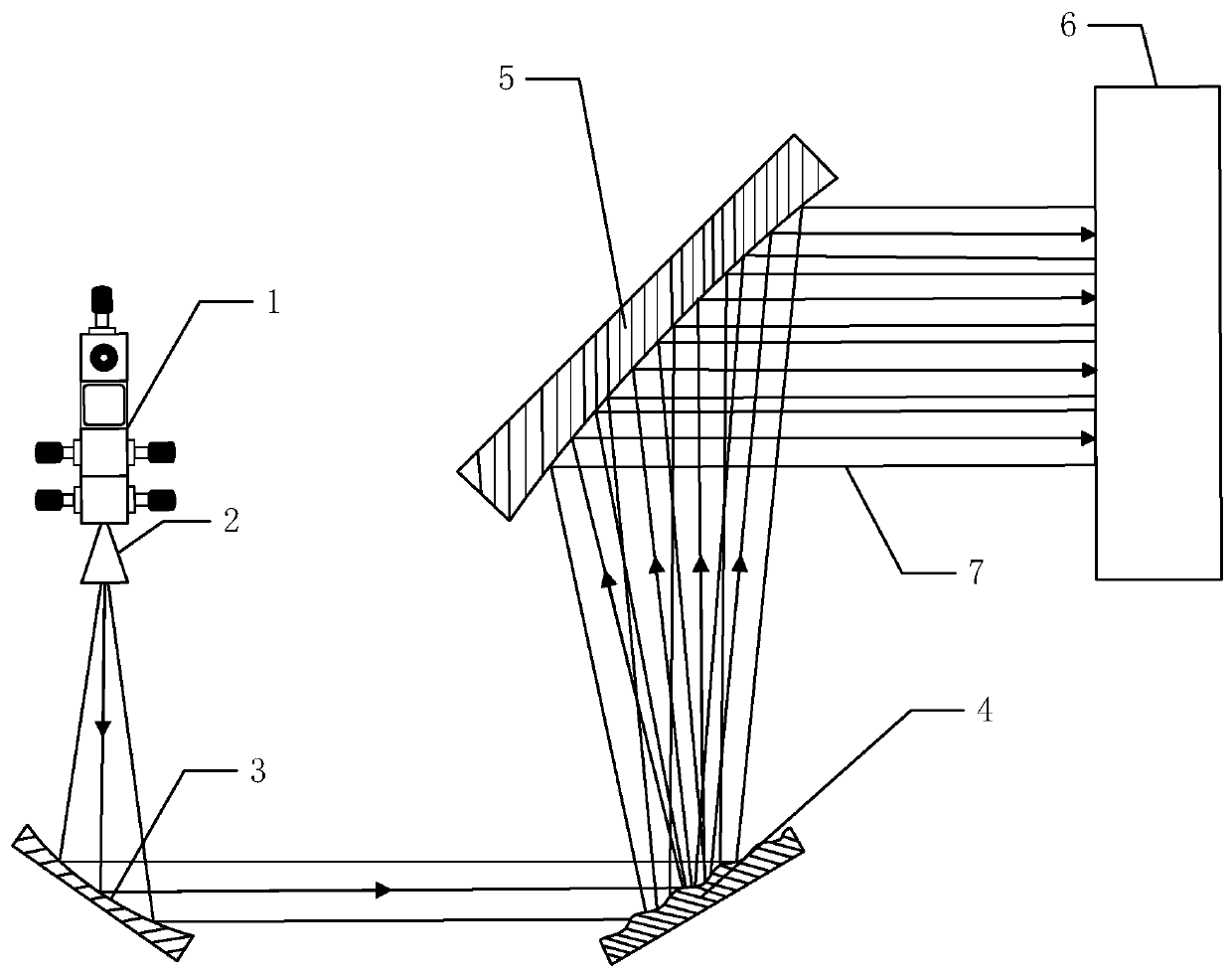
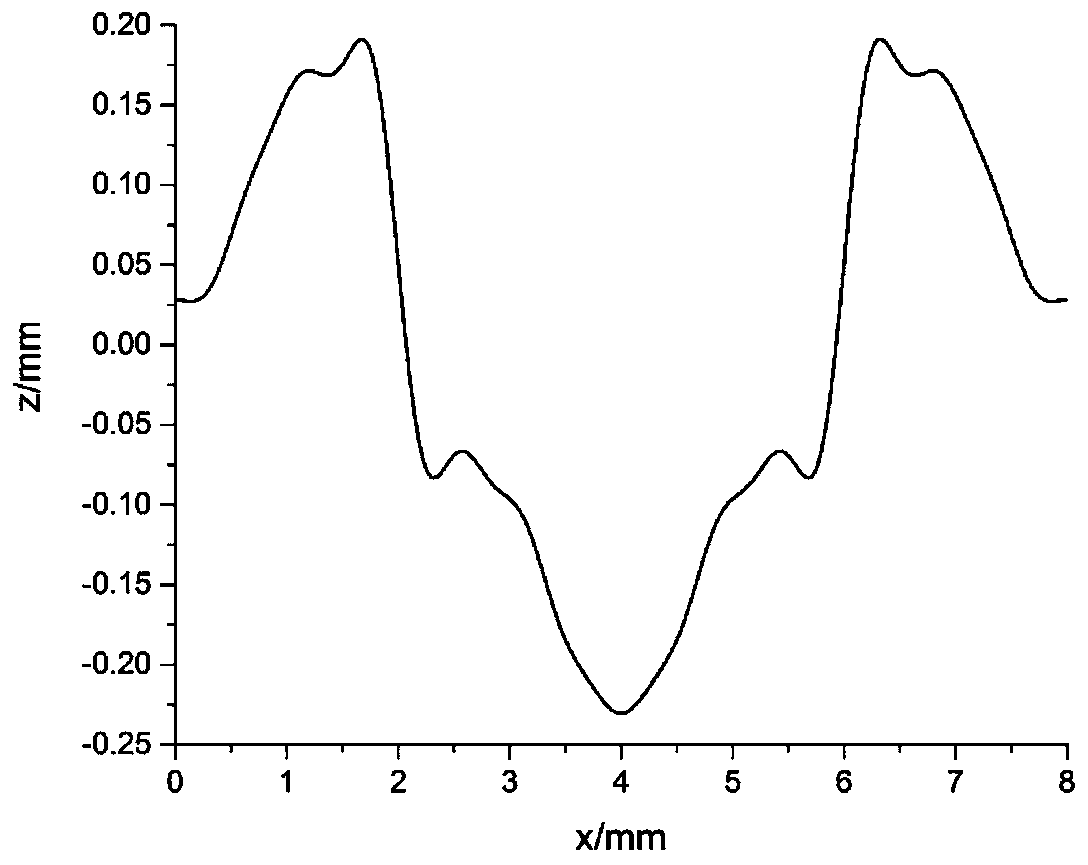
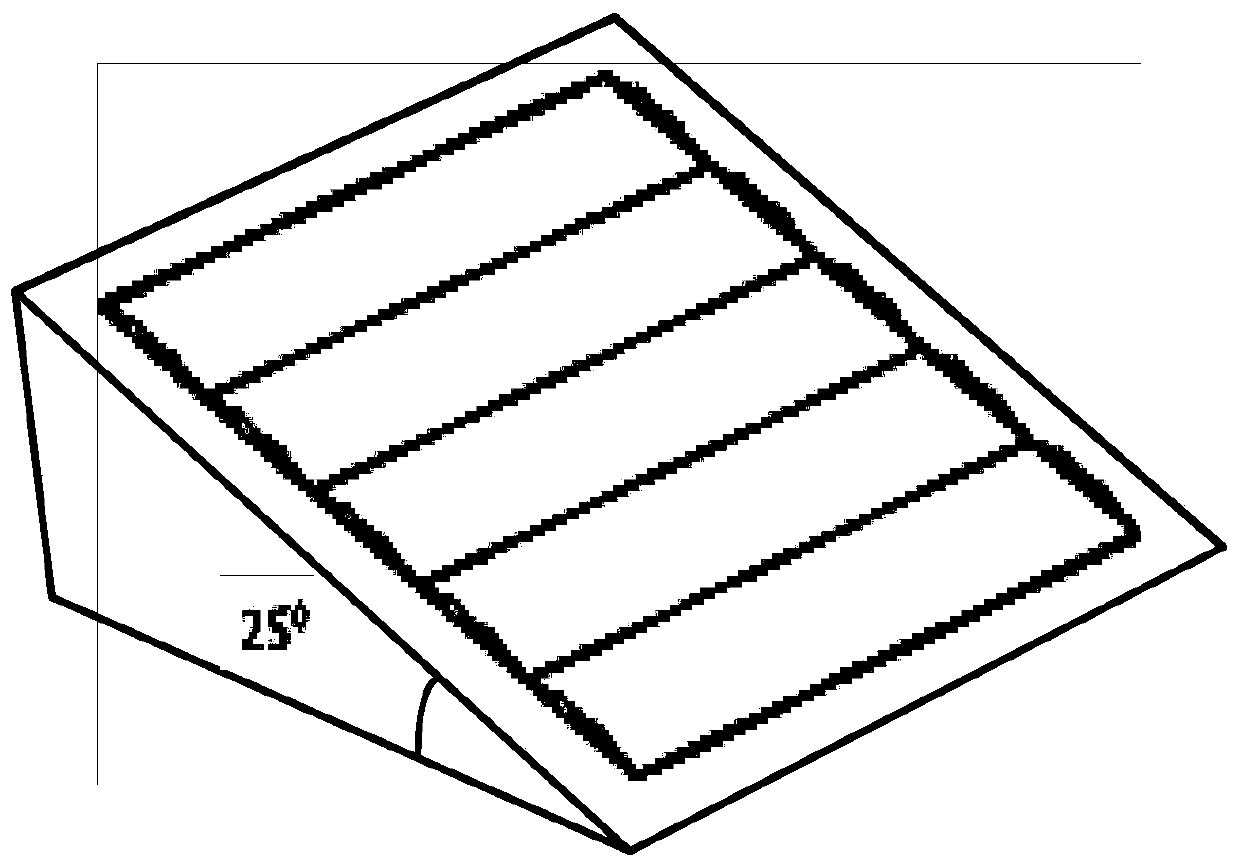
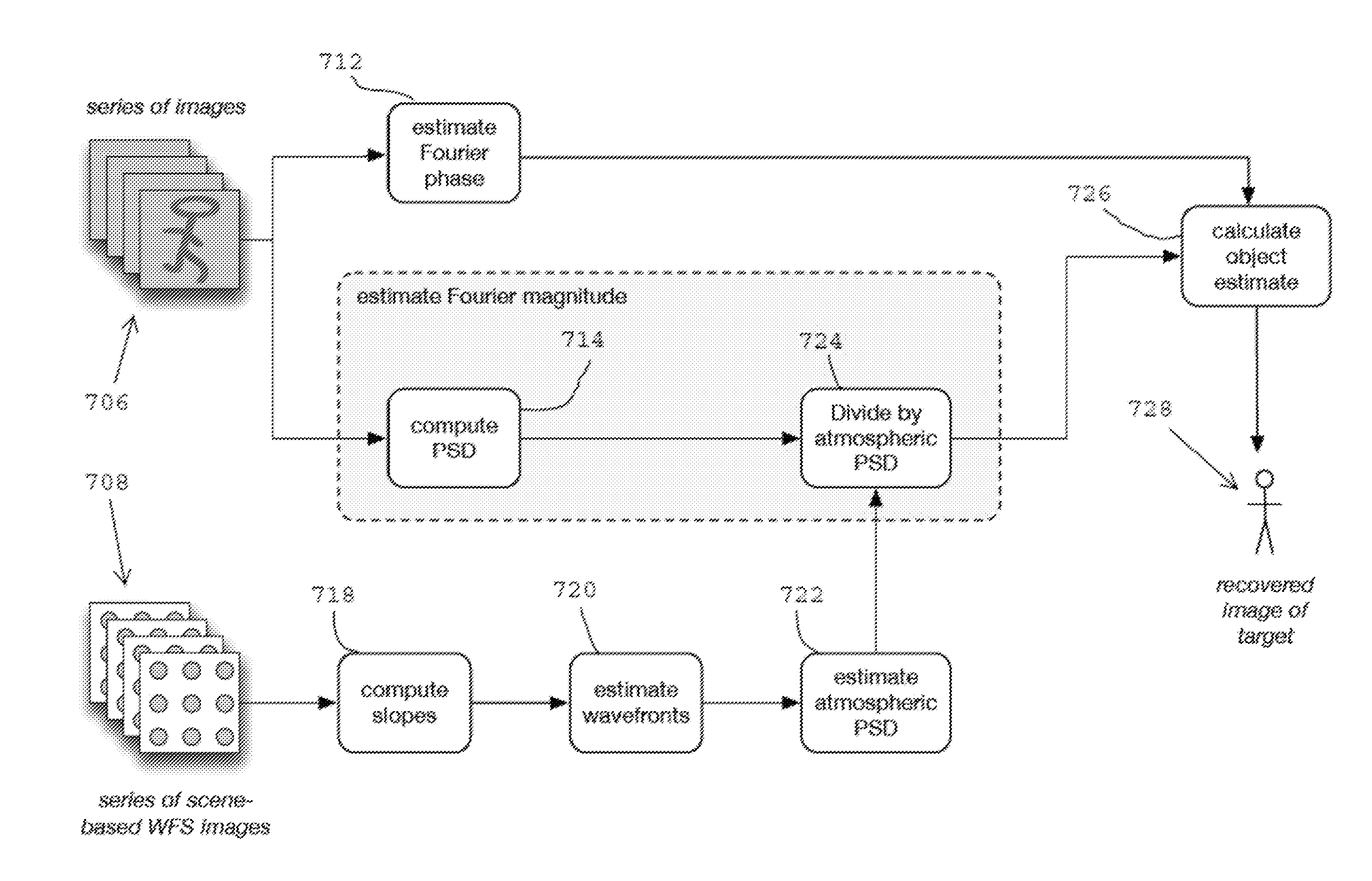
Measurement of wave-front aberration in a small telescope remote imaging system using scene-based wave-front sensing
InactiveUS20140270565A1High-resolution imageImage enhancementGeometric image transformationWavefront sensorHigh resolution image
Reference-free compensated imaging makes an estimation of the Fourier phase of a series of images of a target. The Fourier magnitude of the series of images is obtained by dividing the power spectral density of the series of images by an estimate of the power spectral density of atmospheric turbulence from a series of scene based wave front sensor (SBWFS) measurements of the target. A high-resolution image of the target is recovered from the Fourier phase and the Fourier magnitude.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
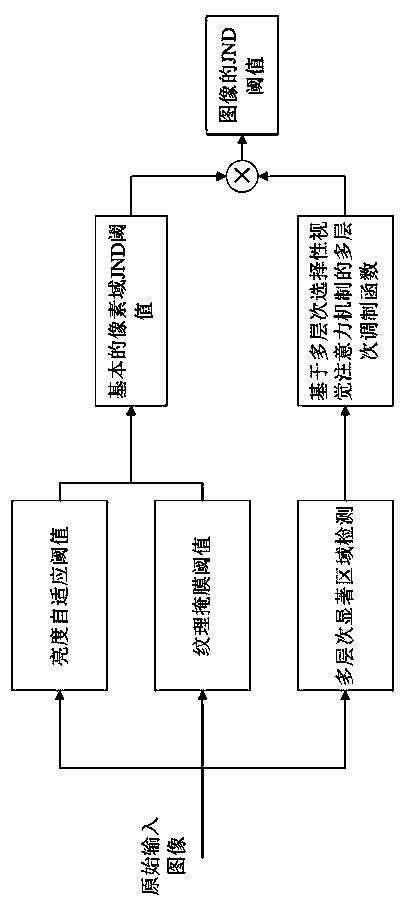
Level selection visual attention mechanism-based image JND threshold calculating method in pixel domain
InactiveCN103607589AMuch noiseGuaranteed visual subjective qualityDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionMasking threshold
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of image / video coding, relates to a level selection visual attention mechanism-based image just-noticeable-distortion (JND) threshold calculating method in a pixel domain. According to the technical scheme, the provided method comprises the following steps: S1, calculating a background brightness adaptive threshold for an original input image; S2, calculating an edge-based texture masking threshold for an image; S3, adding the brightness adaptive threshold obtained in the step S1 and the texture masking threshold obtained in the step S2 and subtracting a superposed portion of the two threshold so as to obtain a basic JND threshold; S4, according to the size of the input image, setting a level value of level selection; S5, carrying out downsampling on the original input image at different resolution ratios and carrying out saliency map detection on the image at the different resolution ratios by utilizing a quaternion fourier phase spectrum (PQFT) saliency detection method; and S6, carrying out sampling on the saliency map at different resolution ratios so as to obtain the resolution ratio of the original image. According to the invention, more noises can be accommodated; and a good visual quality is realized.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
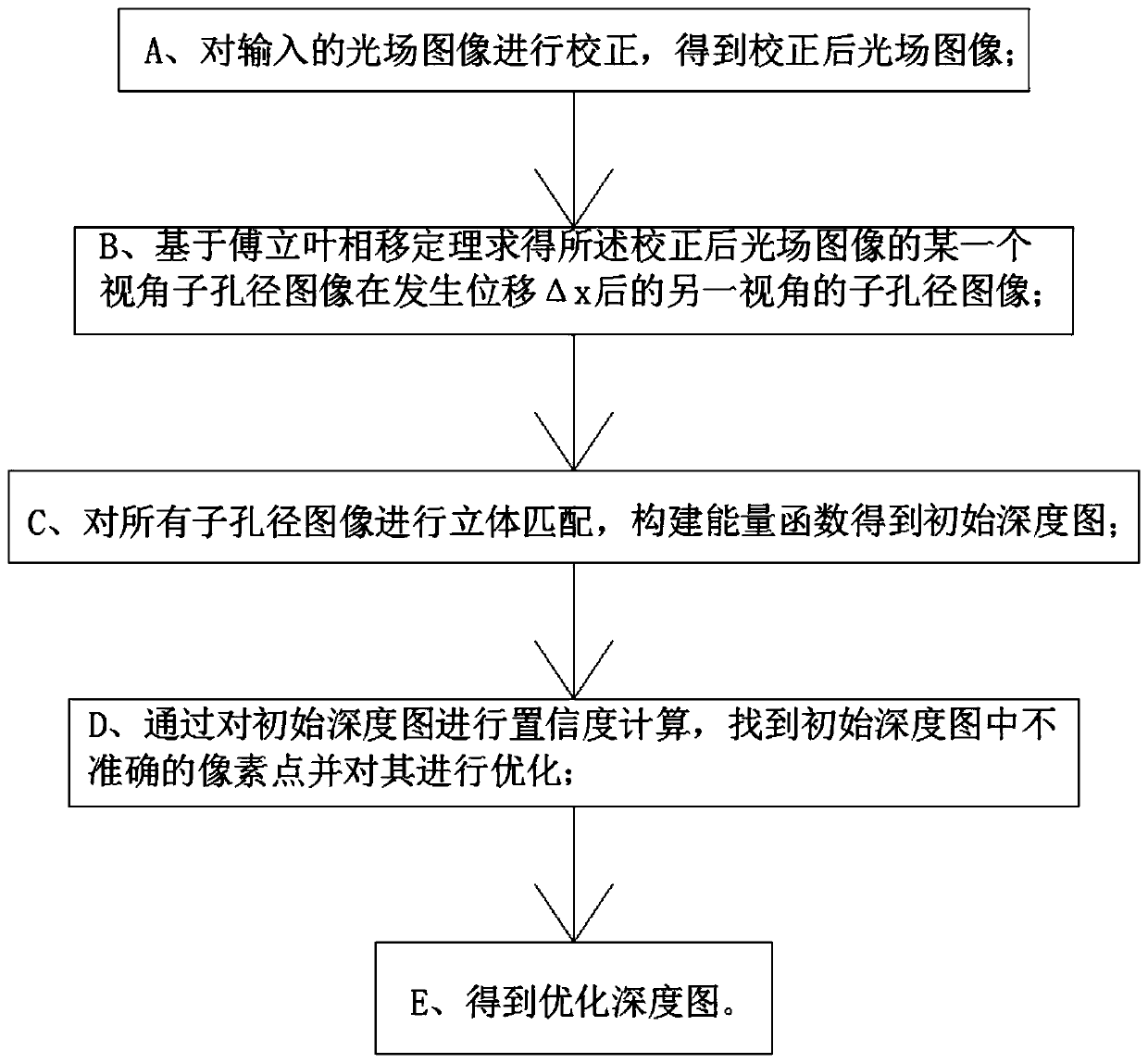
Light field depth estimation method based on splitting iteration algorithm
ActiveCN110276795AFix too narrowConstraint smoothnessImage enhancementImage analysisStereo matchingEstimation methods
The invention discloses a light field depth estimation method based on a splitting iteration algorithm, and belongs to the field of computer vision and light fields. The method comprises the following steps: A, correcting an input light field image to obtain a corrected light field image; B, obtaining a sub-aperture image I (x + [delta]x) of the other view angle of the corrected light field image I (x) after the displacement [delta]x occurs based on the Fourier phase shift theorem; C, performing stereo matching on all the sub-aperture images, and constructing an energy function to obtain an initial depth map; D, performing confidence calculation on the initial depth map, finding out inaccurate pixel points in the initial depth map, and optimizing the initial depth map; and E, obtaining an optimized depth map. According to the method, the problem that the baseline between the sub-aperture images is too narrow is effectively solved, the matching quality is improved, and the accuracy degree of the depth map is ensured as much as possible in the calculation process of the initial depth map.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Systems and methods of all-optical Fourier phase contrast imaging using dye doped liquid crystals
ActiveUS7738047B2Reduce intensityNot to damageMicroscopesNon-linear opticsFourier transform on finite groupsDye doped
Under one aspect, a phase contrast imaging system includes a coherent light source emitting a coherent beam directed toward a sample area; a lens arranged to collect at least part of the beam from the sample area; an element Fourier transforming the collected beam in a Fourier plane; a liquid crystal cell in the Fourier plane that transmits at least part of the transformed beam, wherein the cell includes liquid crystal molecules having a phase transition temperature, and wherein at temperatures exceeding the phase transition temperature, light transmitted through the liquid crystal molecules obtains a different phase than light transmitted through the liquid crystal molecules obtains at temperatures below the phase transition temperature; and an element inversely Fourier transforming the transmitted beam to provide an image. Part of the transformed beam has an intensity sufficient to heat a portion of the liquid crystal molecules above the phase transition temperature.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Method and apparatus for performing film thickness measurements using white light scanning interferometry
ActiveUS20120218560A1Accurate measurementImprove accuracyUsing optical meansLinear componentAmplitude function
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for measuring the thickness of a transparent film by broad band interferometry, comprising the steps of preparing a correlogram of the film by an interferometer, applying a Fourier transformation to said correlogram to obtain a Fourier phase function, removing a linear component thereof, applying a second integral transformation to the remaining non-linear component to obtain an integral amplitude function of said non-linear component, identifying the peak location of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the film as the double value of the abscissa at said peak location considering a refractive index of a film which is dependent on wavelength. The last two steps may be replaced by identifying the peak locations of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the films as the double values of the abscissas at the peak locations.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Systems and Methods of All-Optical Fourier Phase Contrast Imaging Using Dye Doped Liquid Crystals
InactiveUS20100245694A1Reduce intensityNot to damageStatic indicating devicesMicroscopesFourier transform on finite groupsPhase contrast microscopy
An assembly for converting a microscope into a phase contrast microscope includes a first optical Fourier element that Fourier transforms light from a coherent light source, a cell in the Fourier plane arranged to receive light from the first optical Fourier element, a second optical Fourier element arranged to receive light from the cell and inversely Fourier transform the received light to provide an image, an image sensor that detects the image and generates an electronic representation of the image, and an adaptor capable of coupling the first and second Fourier elements, the cell, and the image sensor to the microscope such that the first Fourier element Fourier transforms light collected by the microscope objective. The cell includes liquid crystal molecules having a phase transition temperature, wherein at temperatures exceeding the phase transition temperature, light transmitting through the liquid crystal molecules obtains a different phase than light transmitting through the liquid crystal molecules at temperatures below the phase transition temperature.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Novel shear beam imaging system and target image acquisition method
ActiveCN107656288ASimple structureImprove image signal-to-noise ratioElectromagnetic wave reradiationLight beamTwo step
The invention discloses a novel shear beam imaging system and a target image acquisition method. The novel shear beam imaging system applies a Fourier phase extraction technology to a traditional shear beam imaging technology, so that it becomes possible to remove the two steps of beam frequency shift and fringe demodulation in the traditional shear beam imaging system, the structure of the shearbeam imaging system is simplified, the imaging signal-to-noise ratio is improved, and the complexity of an image reconstruction algorithm is reduced. Moreover, the performance of the shear beam imaging system is greatly improved, and engineering implementation of the system is facilitated.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
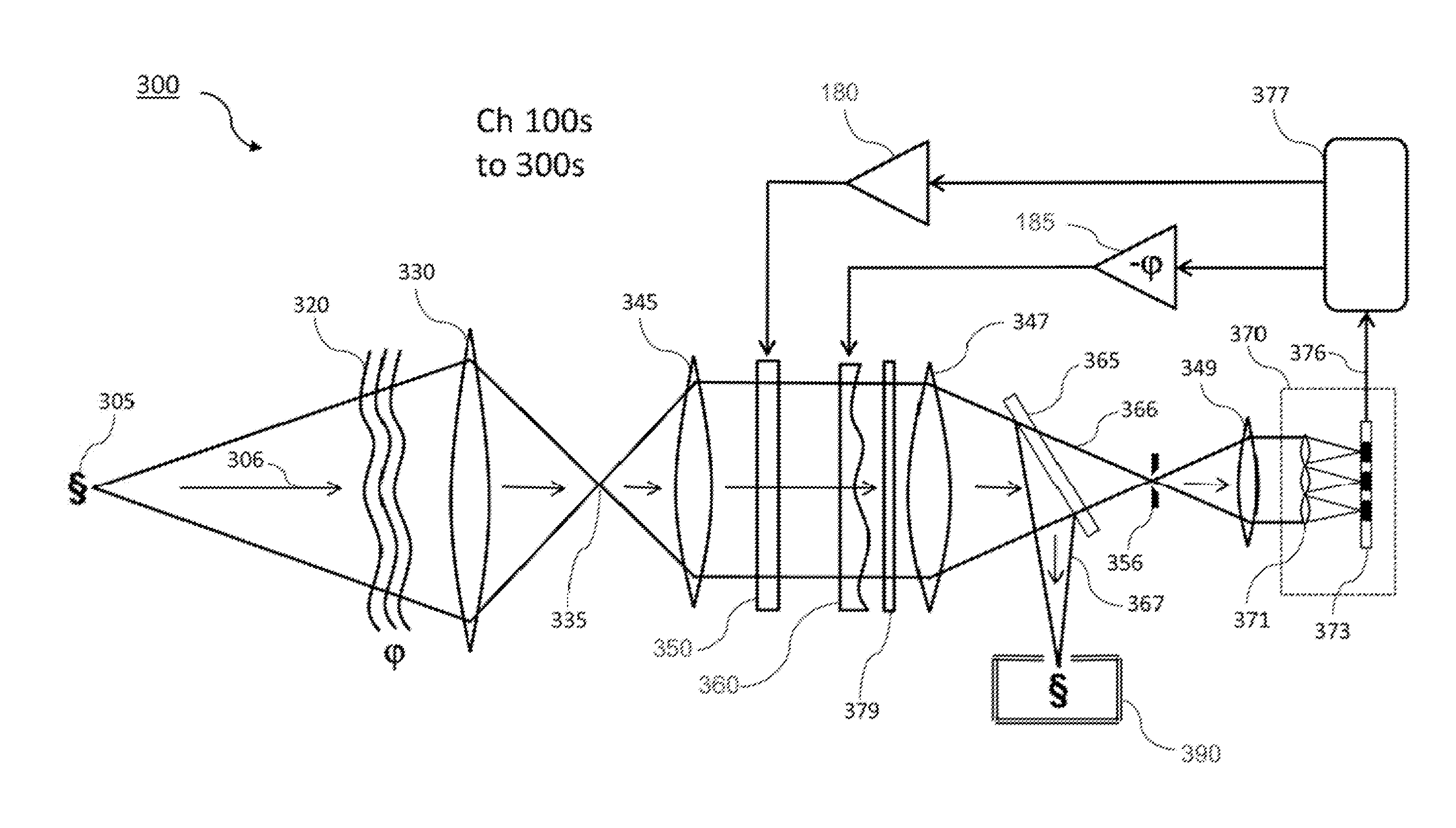
Free orientation fourier camera
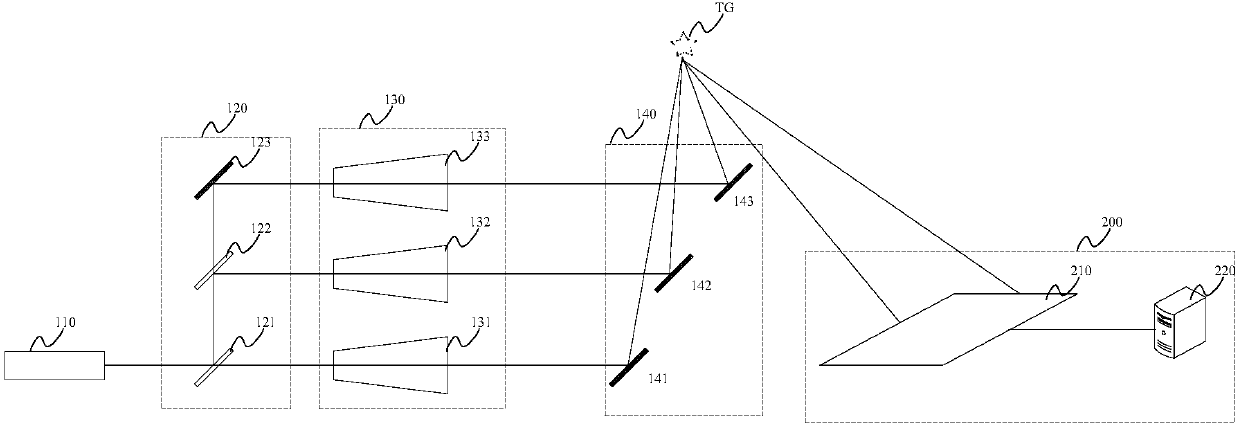
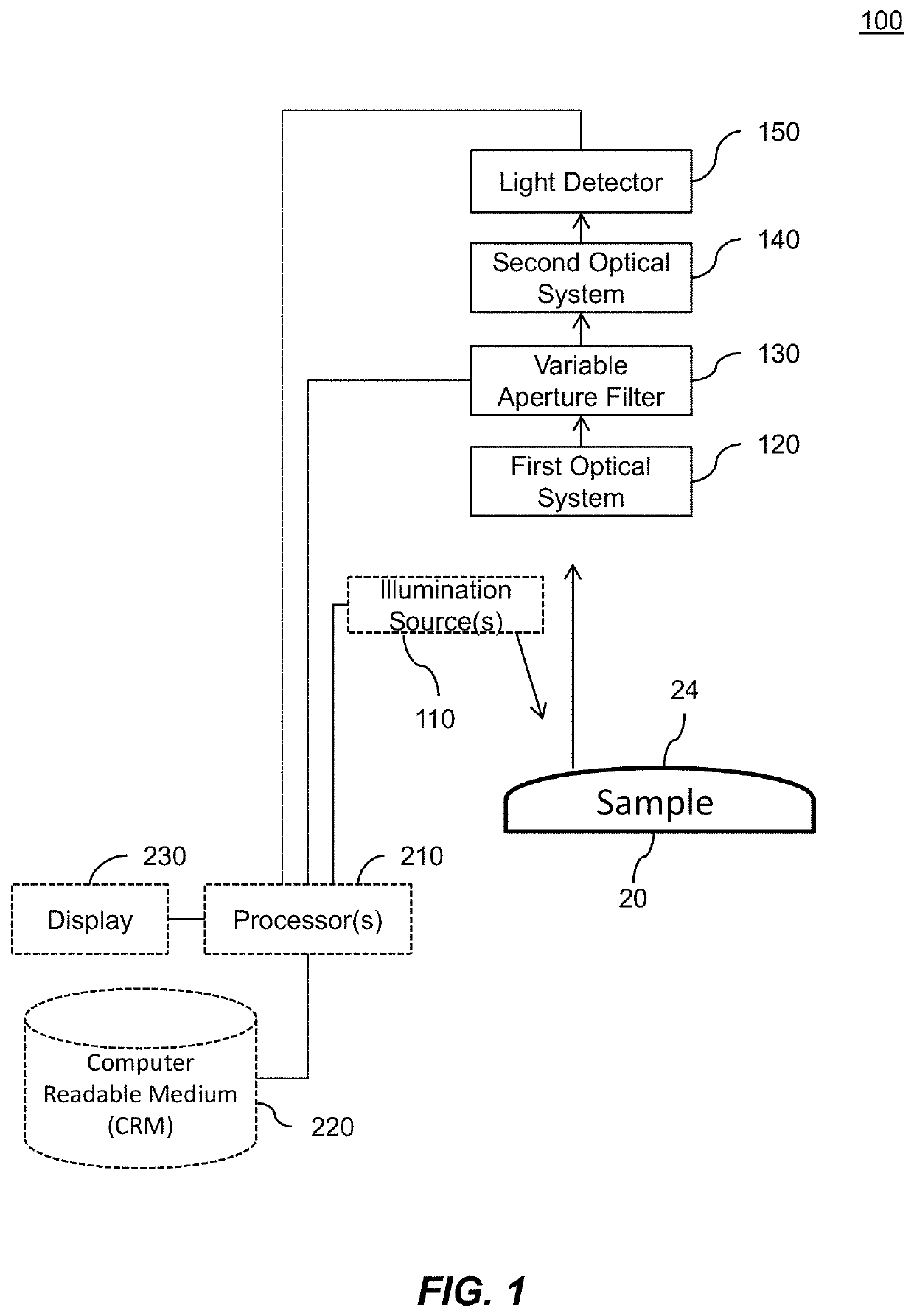
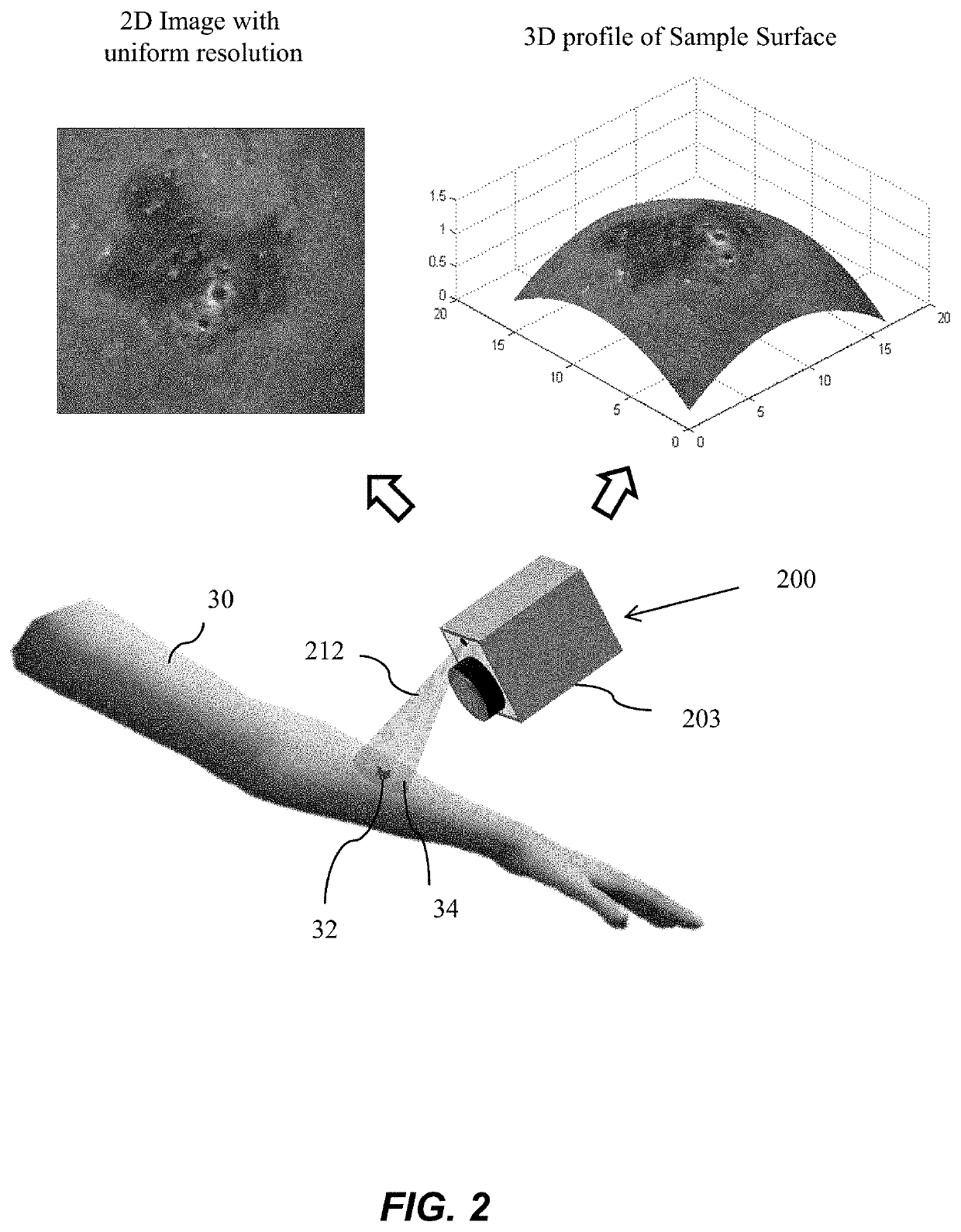
Certain aspects pertain to Fourier camera systems and methods. In one aspect, a Fourier camera comprises a first optical system, a second optical system, a variable aperture filter, and a light detector. The first optical system configured to receive illumination reflected from a curved sample surface. The variable aperture filter configured to move an aperture to a plurality of aperture locations in a Fourier plane, wherein the aperture filters light from the first optical system to the second optical system. The light detector configured to receive light from the second optical system, and configured to acquire a plurality of raw intensity images of the curved sample surface corresponding to the plurality of aperture locations, wherein the raw images are iteratively updated in overlapping regions in Fourier space to generate a focused, substantially uniform resolution image of the curved sample surface, and wherein the overlapping regions correspond to the plurality of aperture locations.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
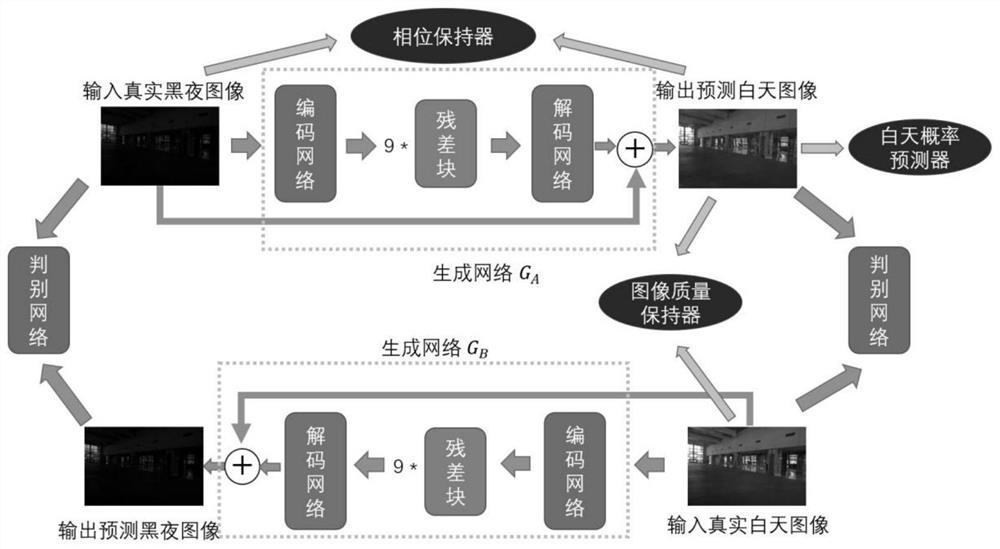
Night image enhancement method and system based on cyclic generative adversarial residual network and QTP loss item
ActiveCN113610736AEnsure content consistencyEnhancement effect is goodImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionReference image
The invention provides a night image enhancement method based on a cyclic generative adversarial residual network and QTP loss items, and respectively improves problems faced by an unsupervised night image enhancement task through loss items of three dimensions of QTP. According to the invention, mixed loss comprises the loss items of the cyclic adversarial network, and three added parts, namely quality loss, task loss and perception loss, wherein the quality part solves a blurred image or false color problem by enhancing similarity between a reference image and an enhancement result quality score; the task part solves a problem of an insufficient enhancement effect from a perspective of constraining an enhancement result to have a higher daytime probability, namely, maximizing the daytime probability; and the perception part limits missing semantic information after domain transformation through a method of keeping Fourier phase spectrum of images before and after night enhancement to be consistent, and ensures content consistency of a night image and an enhanced image. In addition, a learnable and more ideal night image enhancement model is obtained by fusing new loss functions.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Method and apparatus for performing film thickness measurements using white light scanning interferometry
ActiveUS8804129B2Increase speedFast processingSpectral/fourier analysisPhase-affecting property measurementsAmplitude functionLinear component
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for measuring the thickness of a transparent film by broad band interferometry, comprising the steps of preparing a correlogram of the film by an interferometer, applying a Fourier transformation to said correlogram to obtain a Fourier phase function, removing a linear component thereof, applying a second integral transformation to the remaining non-linear component to obtain an integral amplitude function of said non-linear component, identifying the peak location of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the film as the double value of the abscissa at said peak location considering a refractive index of a film which is dependent on wavelength. The last two steps may be replaced by identifying the peak locations of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the films as the double values of the abscissas at the peak locations.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
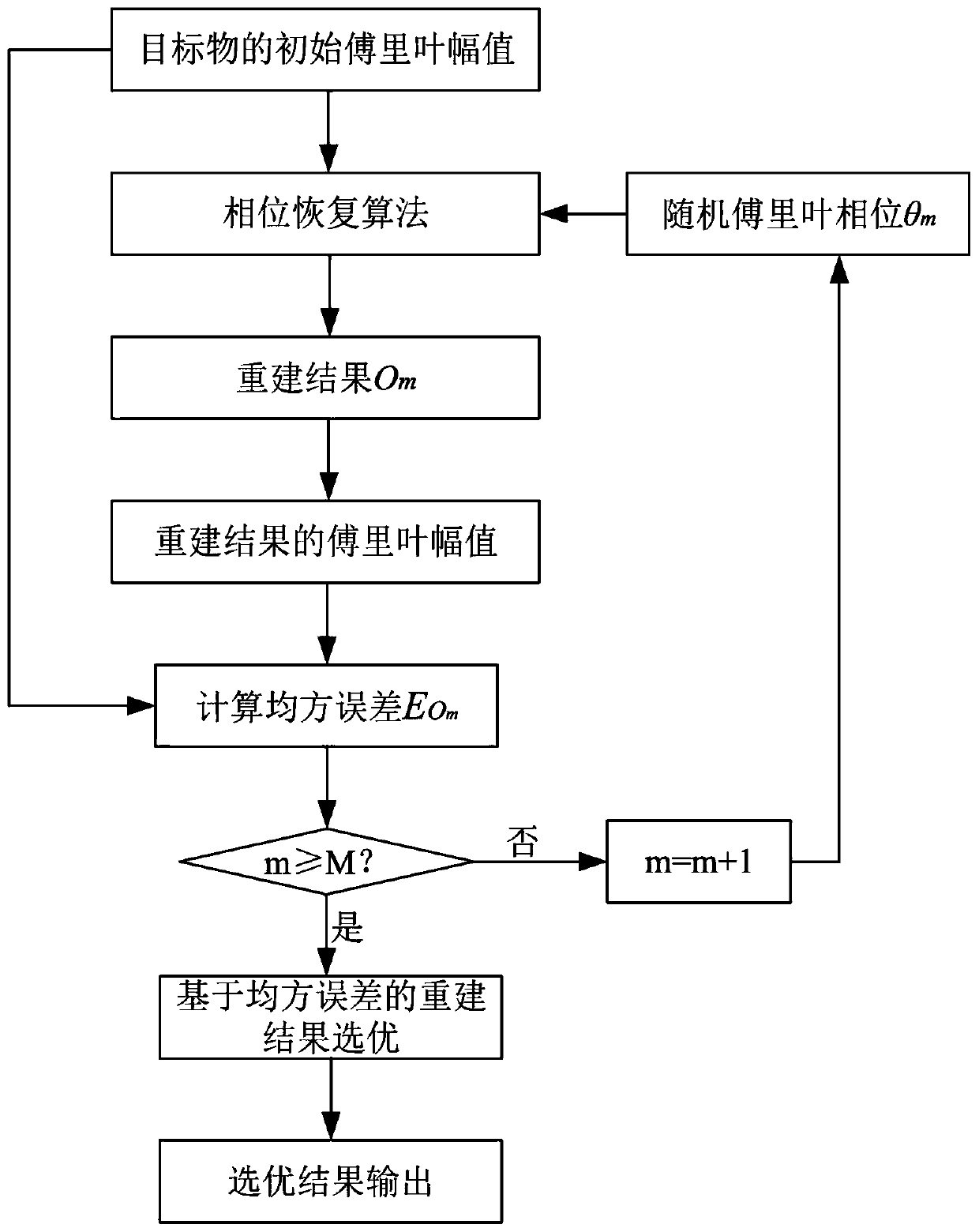
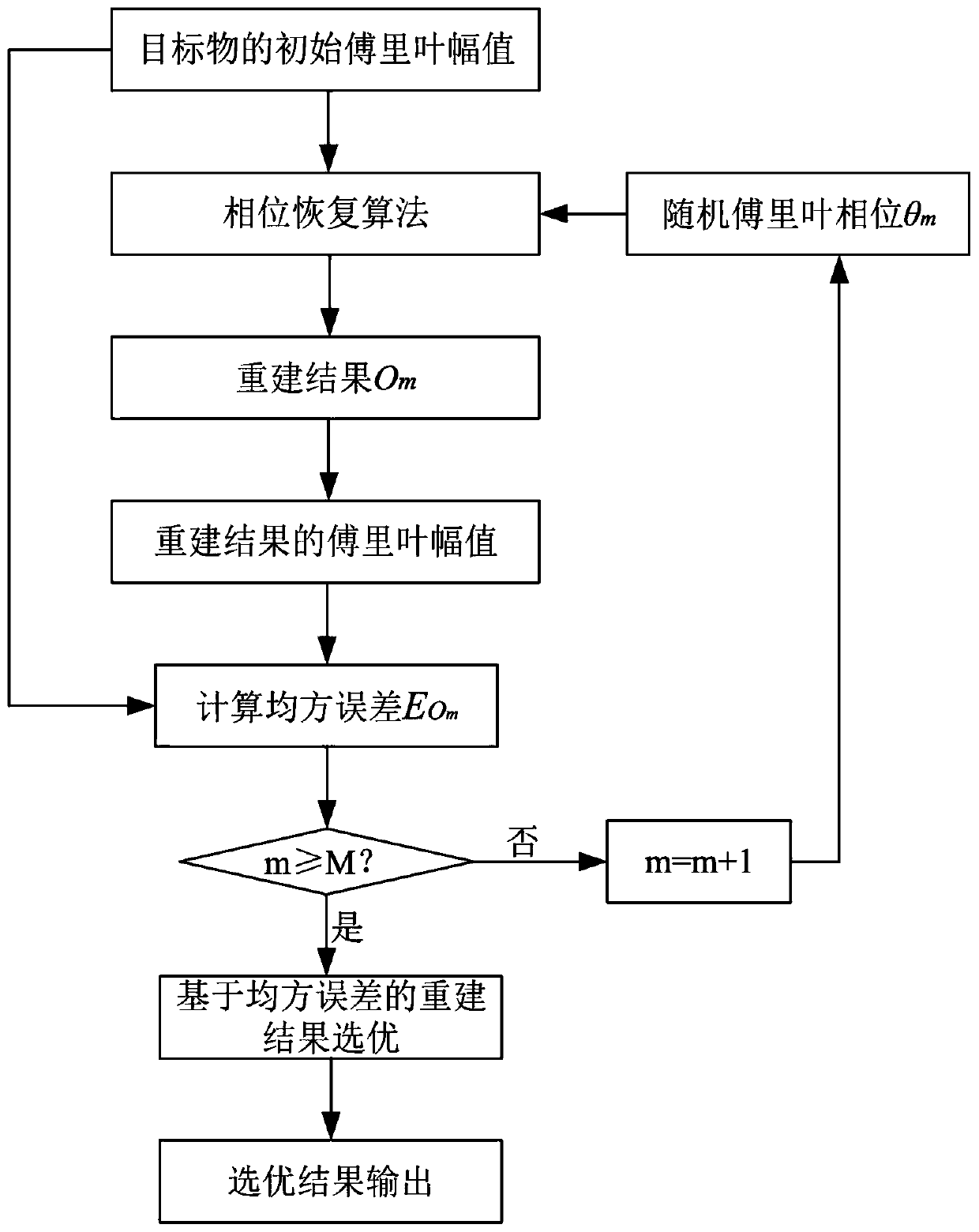
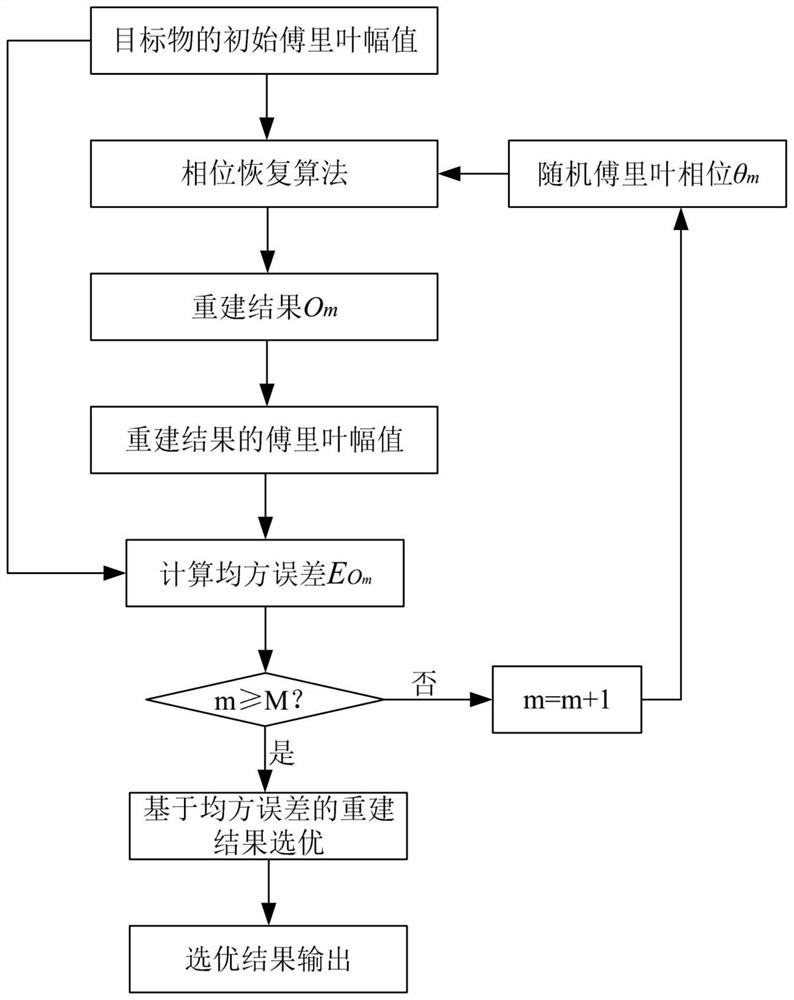
Phase recovery improved algorithm based on MSE optimization
The invention discloses a phase recovery improved algorithm based on MSE optimization, and the algorithm comprises the following steps of A1, taking a random Fourier phase as an input, obtaining a reconstruction result of a phase recovery algorithm, and calculating a mean square error between a Fourier amplitude of the reconstruction result and an initial Fourier amplitude of a target object; A2,taking a plurality of different random Fourier phases as input, and repeating the step A1 to obtain a plurality of corresponding reconstruction results and a plurality of corresponding mean square errors; and A3, taking the mean square error as an evaluation index of the quality of a reconstruction result, and selecting an optimal reconstruction result from a plurality of reconstruction results asa final output to realize the phase recovery of the target object. According to the invention, the stable phase recovery can be realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
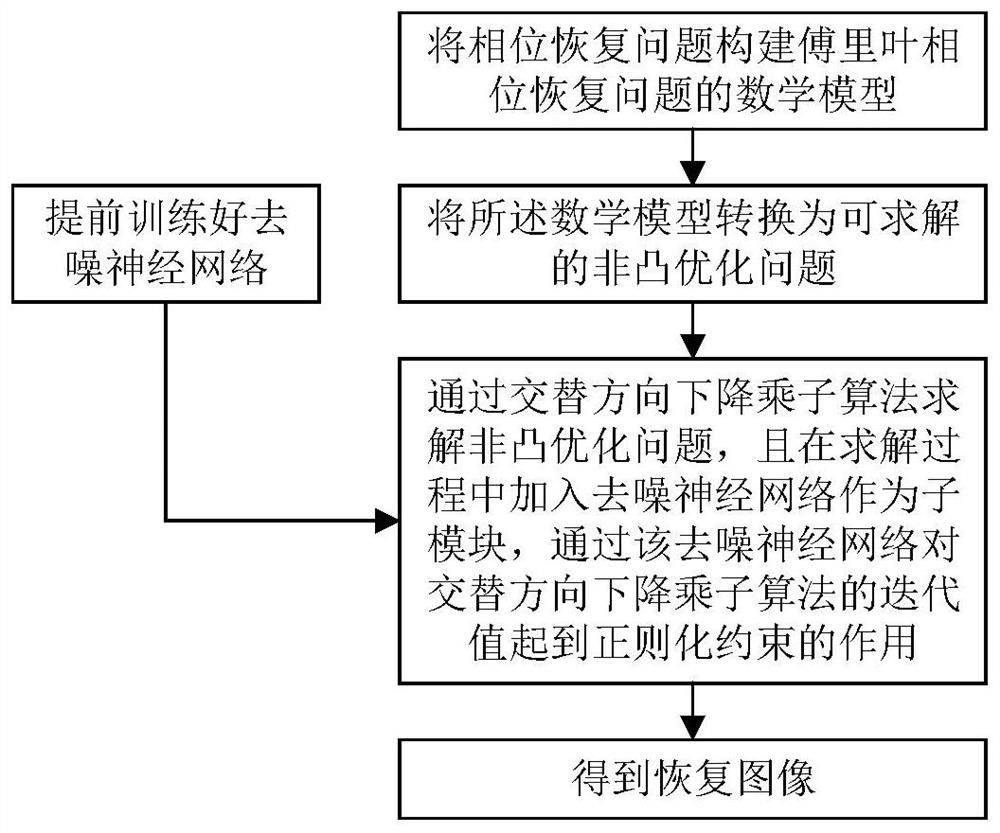
Fourier phase recovery method and system based on plug-and-play neural network
PendingCN112597433AIn line with the lawImprove image qualityImage enhancementNeural architecturesMathematical modelSimulation
The invention discloses a Fourier phase recovery method and system based on a plug-and-play neural network. The Fourier phase recovery method based on the plug-and-play neural network comprises the steps of constructing a mathematical model of a Fourier phase recovery problem for the phase recovery problem; converting the mathematical model into a solvable non-convex optimization problem. The non-convex optimization problem is solved through an alternating direction descent multiplier algorithm, a denoising neural network trained in advance is added in the solving process to serve as a sub-module of the alternating direction descent multiplier algorithm, the denoising neural network plays a regularization constraint role on an iterative value of the alternating direction descent multiplieralgorithm, and finally a restored image is obtained. According to the method, the defects that an existing classical algorithm is sensitive to an initial value, poor in robustness and the like can beovercome, and a high-quality image can be recovered from low-signal-to-noise-ratio phase-free measurement.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Fourier phase grating terahertz wave beam splitter
The invention discloses a Fourier phase grating terahertz wave beam splitter. The splitter comprises a two-dimensional Fourier phase grid, a support frame, a rotating table, a disc, a base, a height adjusting knob and a rotating shaft, the four corners of the two-dimensional Fourier phase grid are fixed to the support frame through screws, the lower end of the support frame is fixed to the rotating table through position pins, the rotating table is fixed to the upper end of the disc through a height adjusting knob and a height adjusting insertion hole, and the disc is fixed to the upper end ofthe base through a metal column and a fixing hole. The upper end of the rotating shaft sequentially penetrates through the through hole in the middle of the disc and the through hole in the middle ofthe rotating table to match the round hole in the middle of the lower end of the supporting frame. On the premise that high diffraction efficiency is guaranteed, the beam splitter is simple in structure, the angle and the height can be adjusted, and the complexity and the cost of a system suitable for the beam splitter are reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Terahertz wave beam splitting system
ActiveCN111024642ASimple structureEasy to processOptical detectionMaterial analysis by optical meansGaussian beamBeam splitting
The invention discloses a terahertz wave beam splitting system. The device comprises a frequency source frequency multiplier module, a Gaussian beam shaping horn antenna, a one-dimensional Fourier phase grating, a thermoelectric detector and two 90-degree offset parabolic mirrors, the output end of the frequency source frequency multiplier module is electrically connected with the input end of a Gaussian beam shaping horn antenna; an output signal is coupled to a free space through a Gaussian beam shaping horn antenna; the beam waist position of an output signal coincides with the focus of the90-degree offset parabolic mirror A, the output signal is sent to the surface of the one-dimensional Fourier phase grating through collimation of the 90-degree offset parabolic mirror A and is bunched through the 90-degree offset parabolic mirror B, and the thermoelectric detector can scan and receive the bunched signal. The terahertz wave beam splitting system can avoid using a plurality of terahertz frequency sources, reduces the complexity of a terahertz array receiver, and is simple in structure, convenient to process, low in cost and high in diffraction efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Measurement of wave-front aberration in a small telescope remote imaging system using scene-based wave-front sensing
InactiveUS8995787B2Image enhancementGeometric image transformationWavefront sensorHigh resolution image
Reference-free compensated imaging makes an estimation of the Fourier phase of a series of images of a target. The Fourier magnitude of the series of images is obtained by dividing the power spectral density of the series of images by an estimate of the power spectral density of atmospheric turbulence from a series of scene based wave front sensor (SBWFS) measurements of the target. A high-resolution image of the target is recovered from the Fourier phase and the Fourier magnitude.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Navigation using fourier phase technique
InactiveUS8358803B2Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer visionComputer science
Owner:SONAVATION INC
Method and apparatus for performing film thickness measurements using white light scanning interferometry
InactiveUS20120191412A1Accurate measurementImprove accuracyDigital computer detailsUsing electrical meansAmplitude functionLinear component
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for measuring the thickness of a transparent film by broad band interferometry, comprising the steps of preparing a correlogram of the film by an interferometer, applying a Fourier transformation to said correlogram to obtain a Fourier phase function, removing a linear component thereof, applying a second integral transformation to the remaining non-linear component to obtain an integral amplitude function of said non-linear component, identifying the peak location of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the film as the double value of the abscissa at said peak location considering a refractive index of a film which is dependent on wavelength. The last two steps may be replaced by identifying the peak locations of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the films as the double values of the abscissas at the peak locations.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
An Improved Phase Recovery Algorithm Based on mse Selection
The invention discloses an improved phase recovery algorithm based on MSE selection, which includes the following steps: A1, taking random Fourier phase as input, obtaining the reconstruction result of the phase recovery algorithm, and calculating the Fourier amplitude and the reconstruction result The mean square error between the initial Fourier amplitudes of the target; A2. Repeat step A1 with multiple different random Fourier phases as input to obtain corresponding multiple reconstruction results and corresponding multiple mean square errors; A3 . Using the mean square error as an evaluation index of the quality of the reconstruction result, selecting the optimal reconstruction result from the plurality of reconstruction results as the final output, so as to realize the phase recovery of the target object. The invention can realize stable phase recovery.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
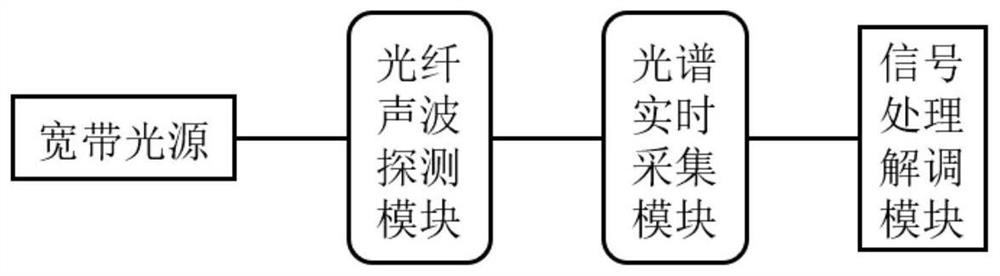
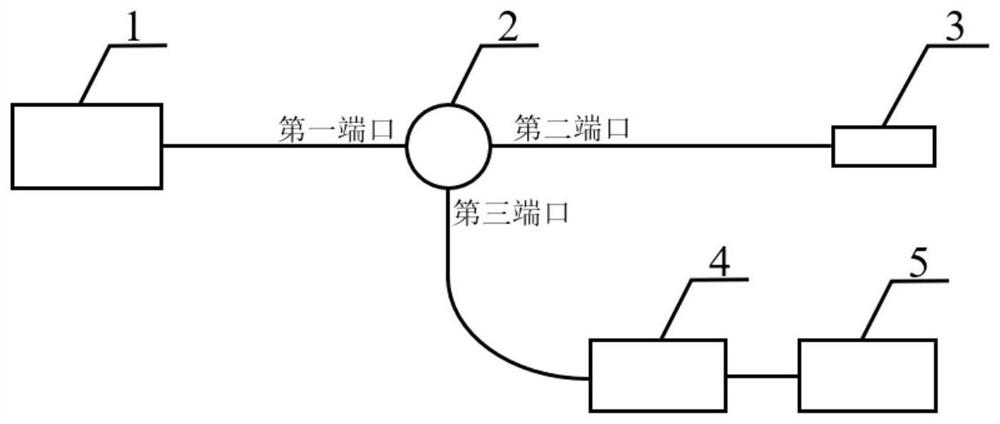
FP interference type sound wave detector and sound wave detection method
ActiveCN114543971ANo change in structureNo change in sizeSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansFrequency spectrumDynamic range
The invention discloses an FP interference type sound wave detector and a sound wave detection method, and belongs to the technical field of sound wave detection, and the FP interference type sound wave detector comprises a light source, an optical fiber circulator, an FP sensing head, a spectrum real-time acquisition module and a signal processing demodulation module. The FP sensing head is composed of an optical fiber collimator, a ceramic ferrule, a metal sleeve and a thin film, and the optical fiber collimator is designed to a certain extent. By using the improved Fourier phase demodulation algorithm, the spectral phase variation in direct proportion to the cavity length variation can be obtained, and the improved demodulation algorithm greatly widens the dynamic range of the detection system. For an extrinsic high-fineness FP sensor, the phase demodulation method provided by the invention can realize phase multiplication by performing Fourier phase demodulation at a high-order characteristic frequency peak on a Fourier spectrum of a spectrum, so that the phase sensitivity of the sensor is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for measuring power-transmission circuit double-ended distance by distributing parameter
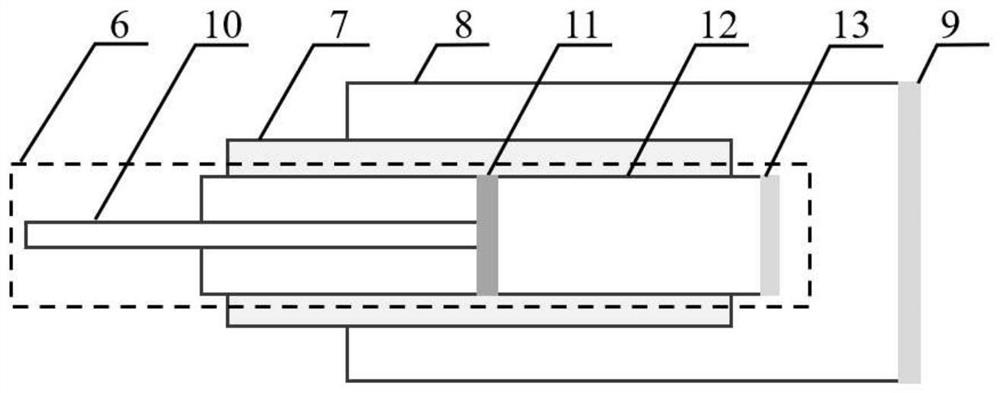
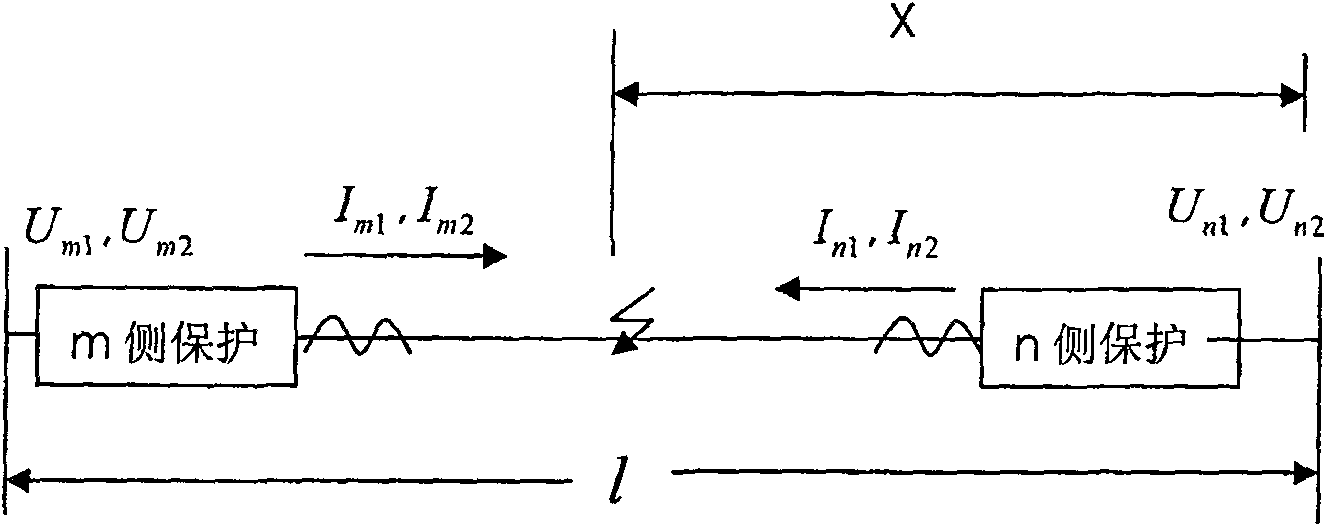
The invention relates to a method for relay protection in the field of power systems. Disclosed is a method of synchronizing sampling current and voltage at both ends of a power system, using distributed parameter long-line equations, and realizing double-terminal fault location according to the method that the positive-sequence or negative-sequence voltages at both ends of the fault point are equal. The method includes the following main steps: the line protection device samples the secondary current of the current transformer and the secondary voltage of the voltage transformer on the side of the line to obtain the corresponding instantaneous values of current and voltage, and obtains the three-phase current and the three-phase current on the side through the Fourier algorithm. The Fourier form of the phase voltage, and the phasor form of the current and voltage obtained by receiving the synchronous sampling of the opposite side protection through the optical fiber communication network and filtering and calculating, using the condition that the positive sequence voltage or negative sequence voltage on both sides of the fault point is equal, the protection is obtained. The distance from the installation to the reference point. The method is not affected by the power supply impedance and transition resistance of the line operation mode. Theory and practice have proved that the method can greatly improve the accuracy of fault location of transmission lines.
Owner:BEIJING SIFANG JIBAO AUTOMATION +1
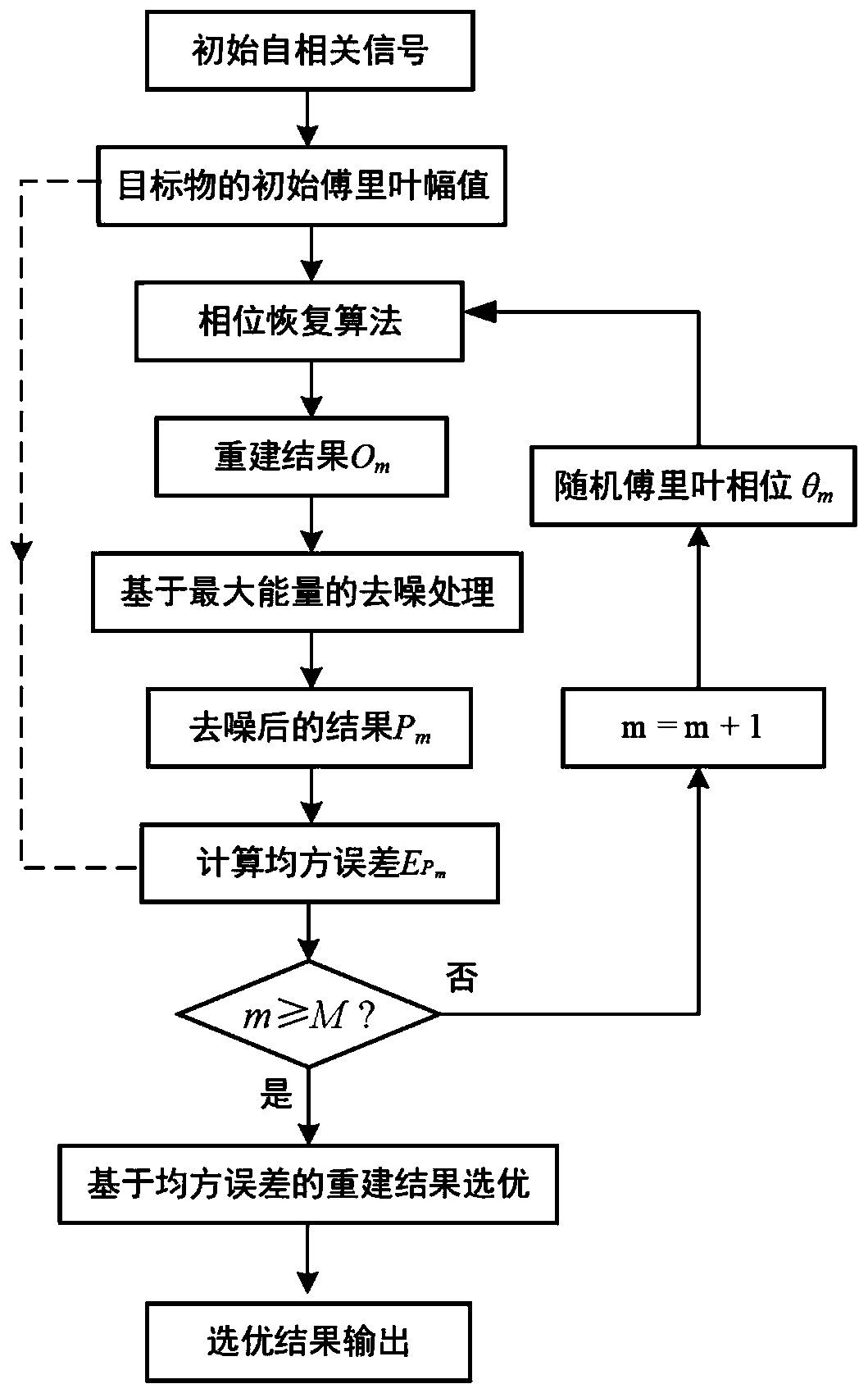
Phase recovery improvement method and device for autocorrelation signal with interference
ActiveCN111325682APhase recovery stabilizationImage enhancementHigh level techniquesAlgorithmEngineering
The invention discloses a phase recovery improvement method and device for an autocorrelation signal with interference, and the method comprises the steps: extracting the initial Fourier amplitude ofa target object from a known target object autocorrelation signal, and obtaining a phase recovery reconstruction result through employing a random Fourier phase as an input; performing spatial domaindenoising processing on the reconstruction result, assigning zero to a part smaller than the maximum energy setting percentage of the reconstruction result to obtain a denoised reconstruction result,and calculating a mean square error between the Fourier amplitude of the denoised reconstruction result and the initial Fourier amplitude of the target object; repeating the above steps by taking a plurality of different random Fourier phases as inputs to obtain a plurality of denoised reconstruction results and a plurality of mean square errors; and taking the mean square error as an evaluation index of the quality of the reconstruction result, selecting an optimal reconstruction result from the plurality of denoised reconstruction results as final output, and realizing phase recovery of thetarget object. According to the invention, stable phase recovery can be realized for an autocorrelation signal with interference.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
A Novel Shearing Beam Imaging System and Target Image Acquisition Method
ActiveCN107656288BSimple structureImprove image signal-to-noise ratioElectromagnetic wave reradiationImage reconstruction algorithmMechanical engineering
The present application discloses a novel sheared beam imaging system and target imaging acquisition method, wherein the novel sheared beam imaging system applies the Fourier phase extraction technology to the traditional sheared beam imaging technology, thereby removing the traditional The two steps of beam frequency shifting and fringe demodulation in the cut-beam imaging system become possible, and then realize the purpose of simplifying the structure of the cut-beam imaging system, improving the imaging signal-to-noise ratio and reducing the complexity of the image reconstruction algorithm, which greatly The performance of the shearing beam imaging system is improved and its engineering realization is facilitated.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com