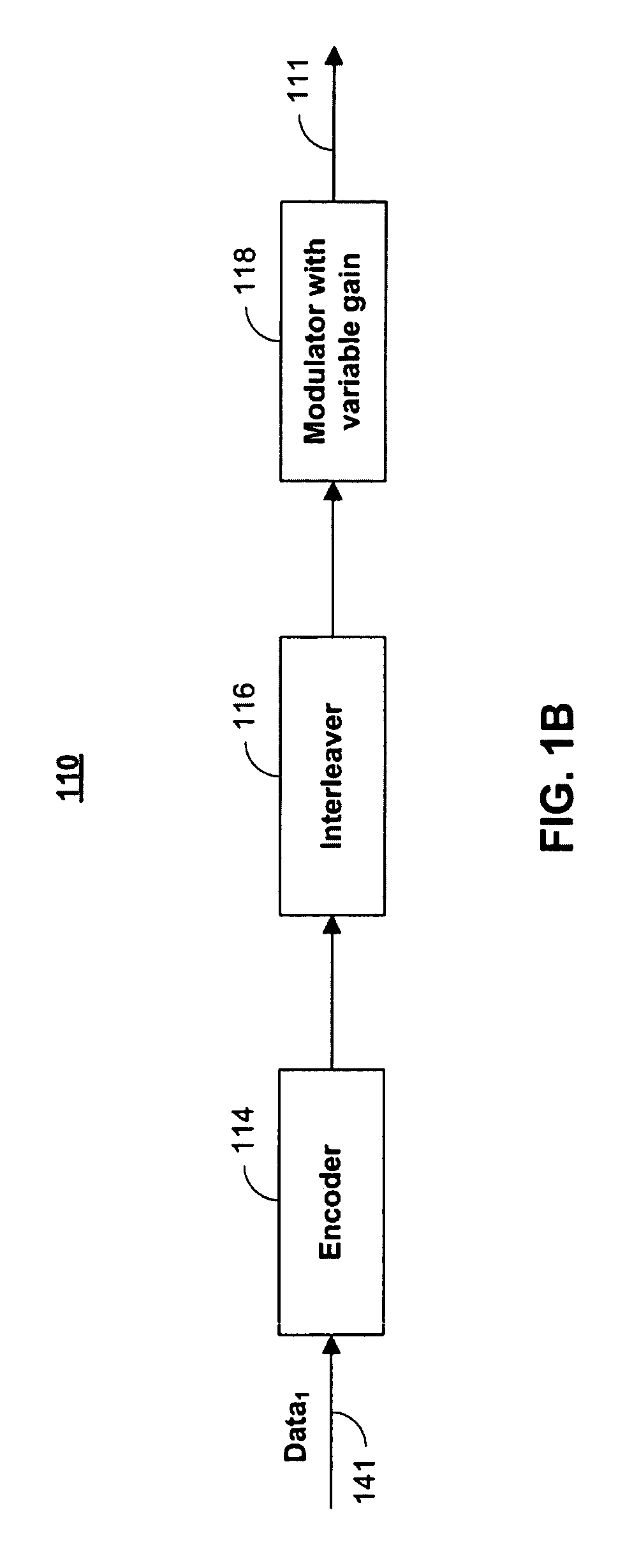
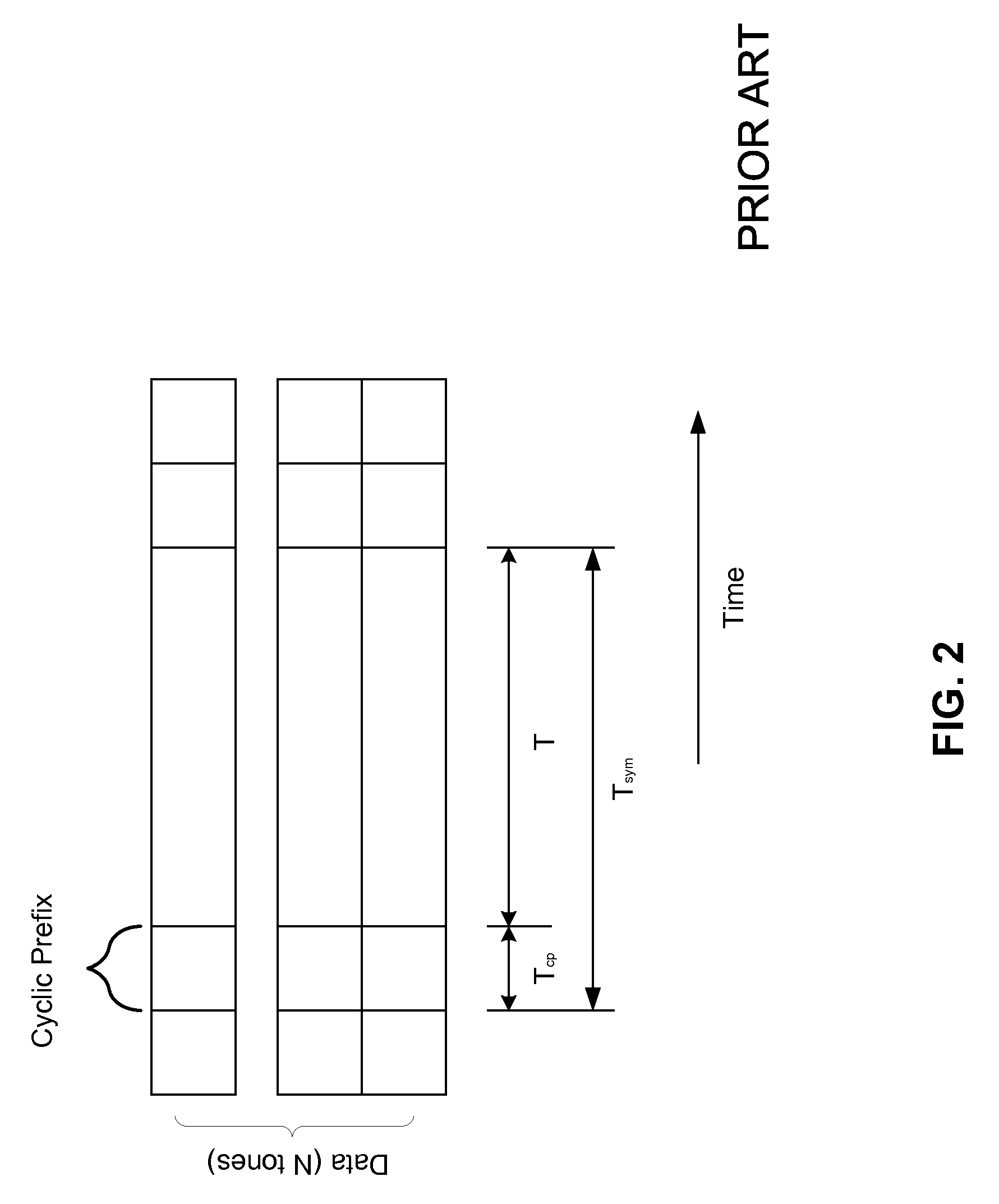
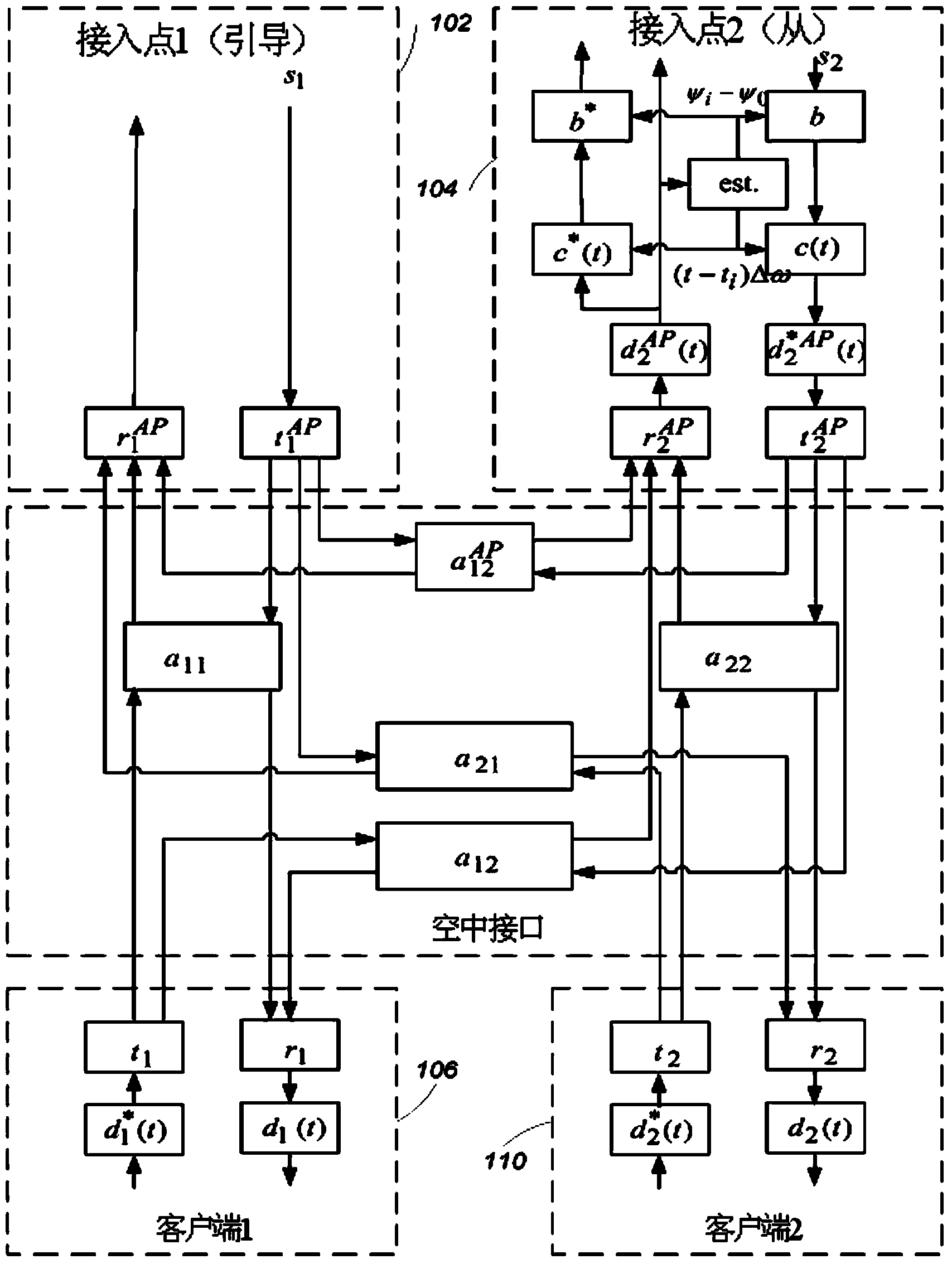
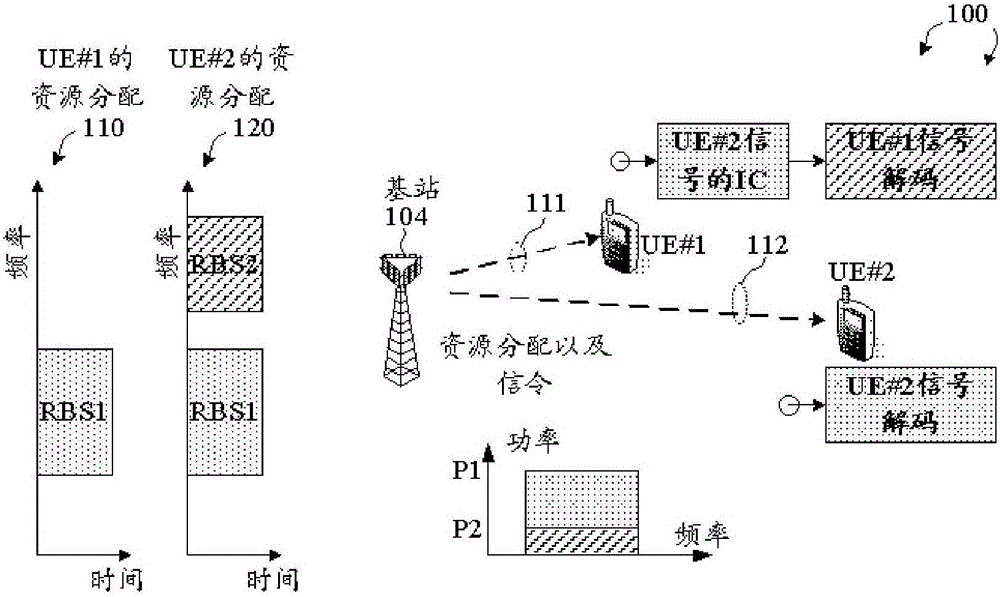
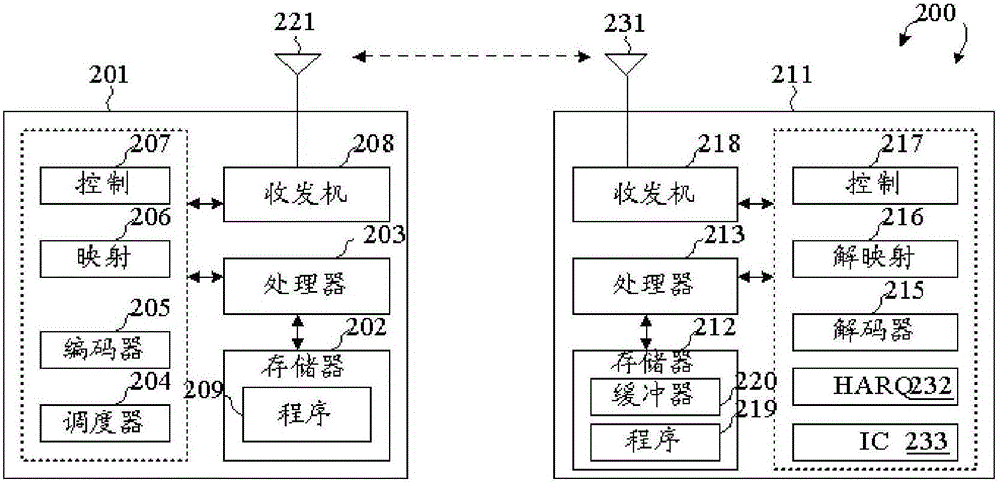
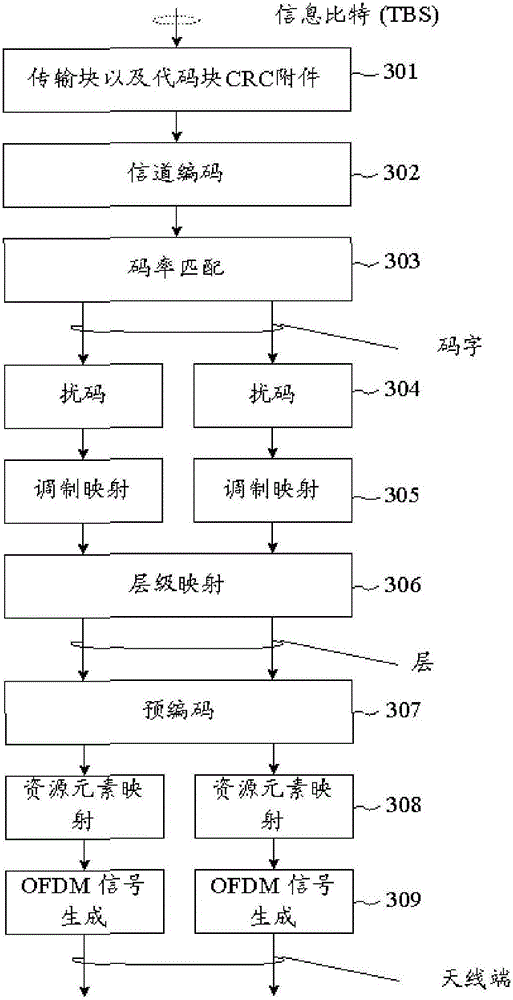
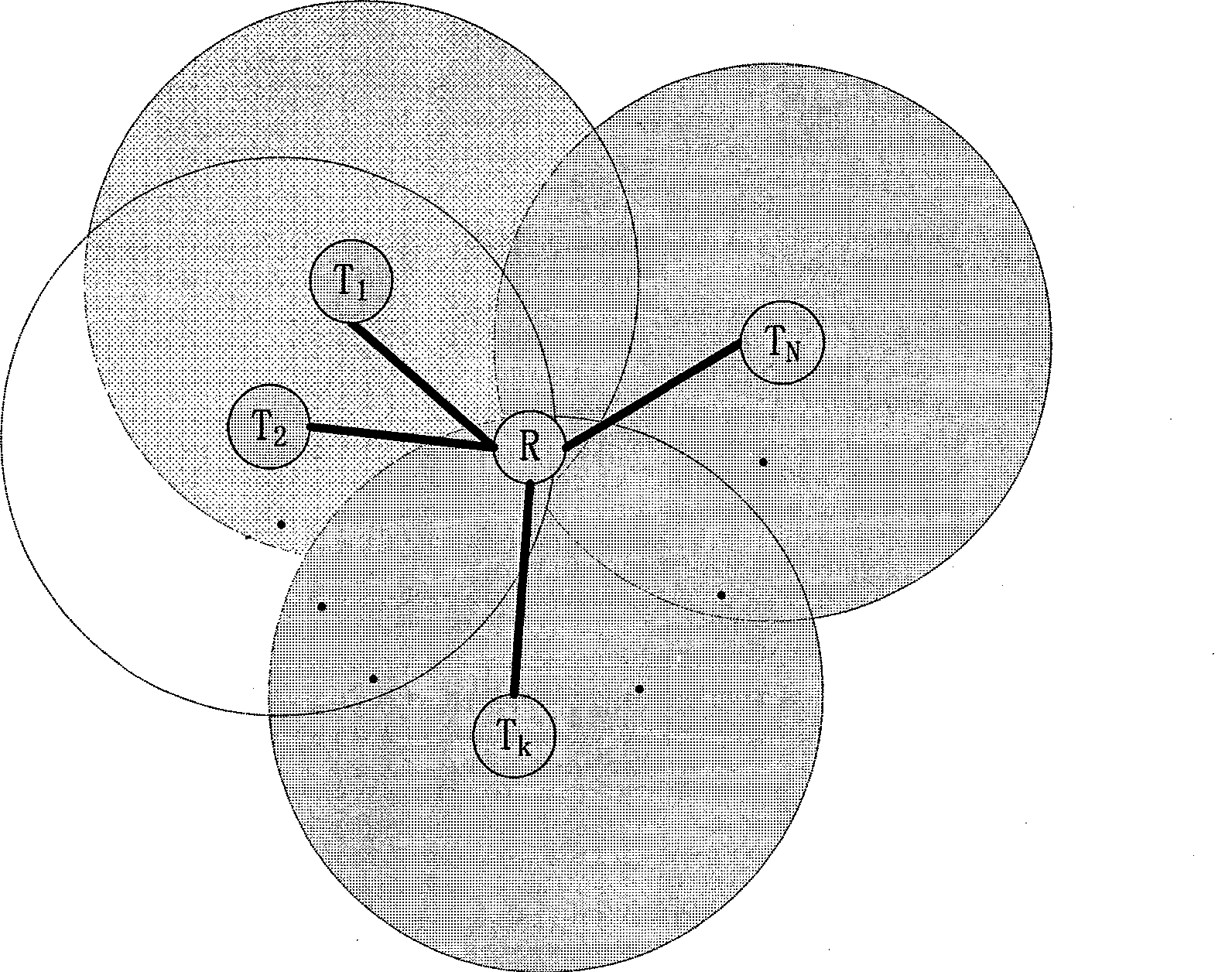Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
213 results about "Superposition coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
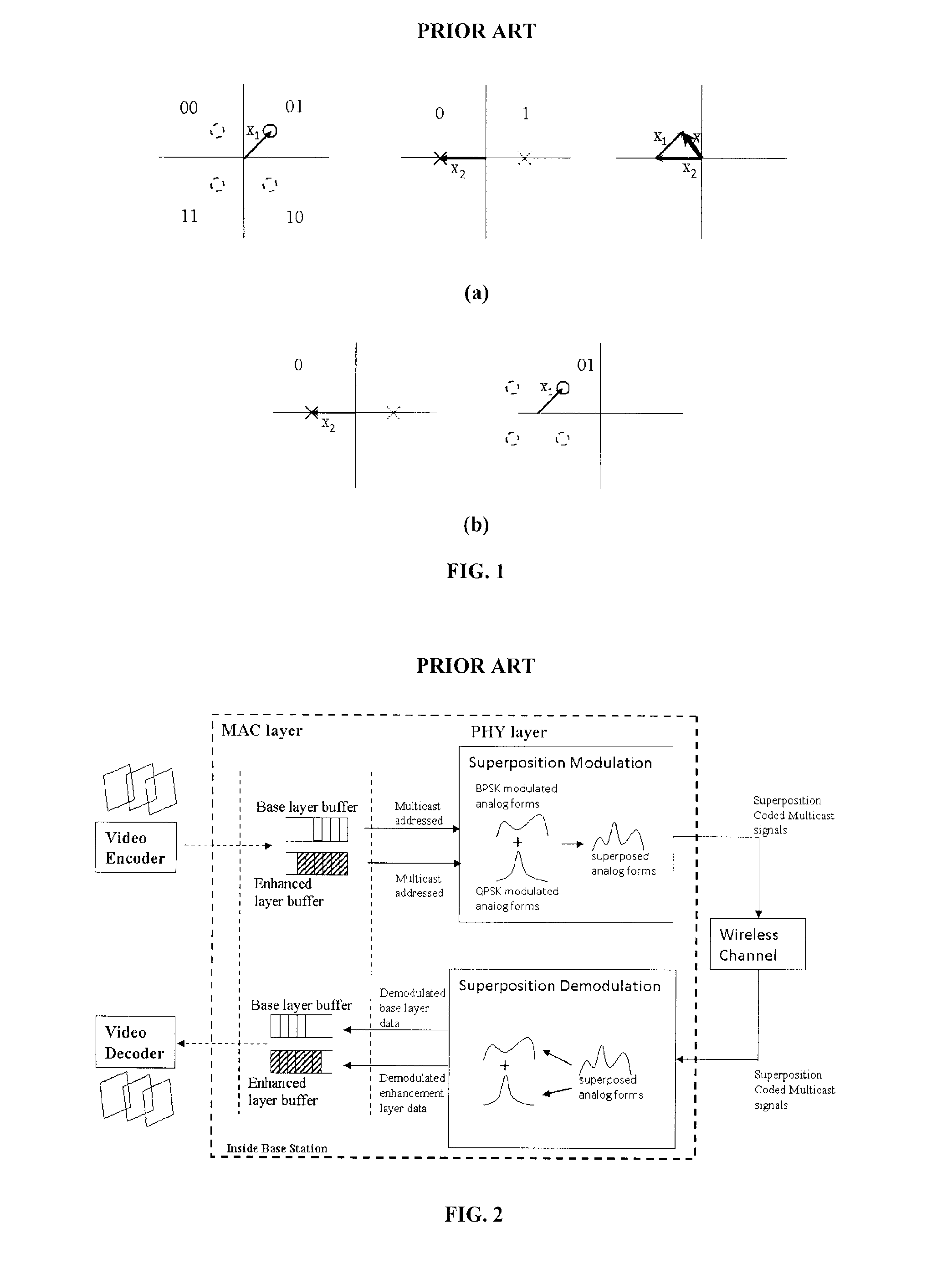
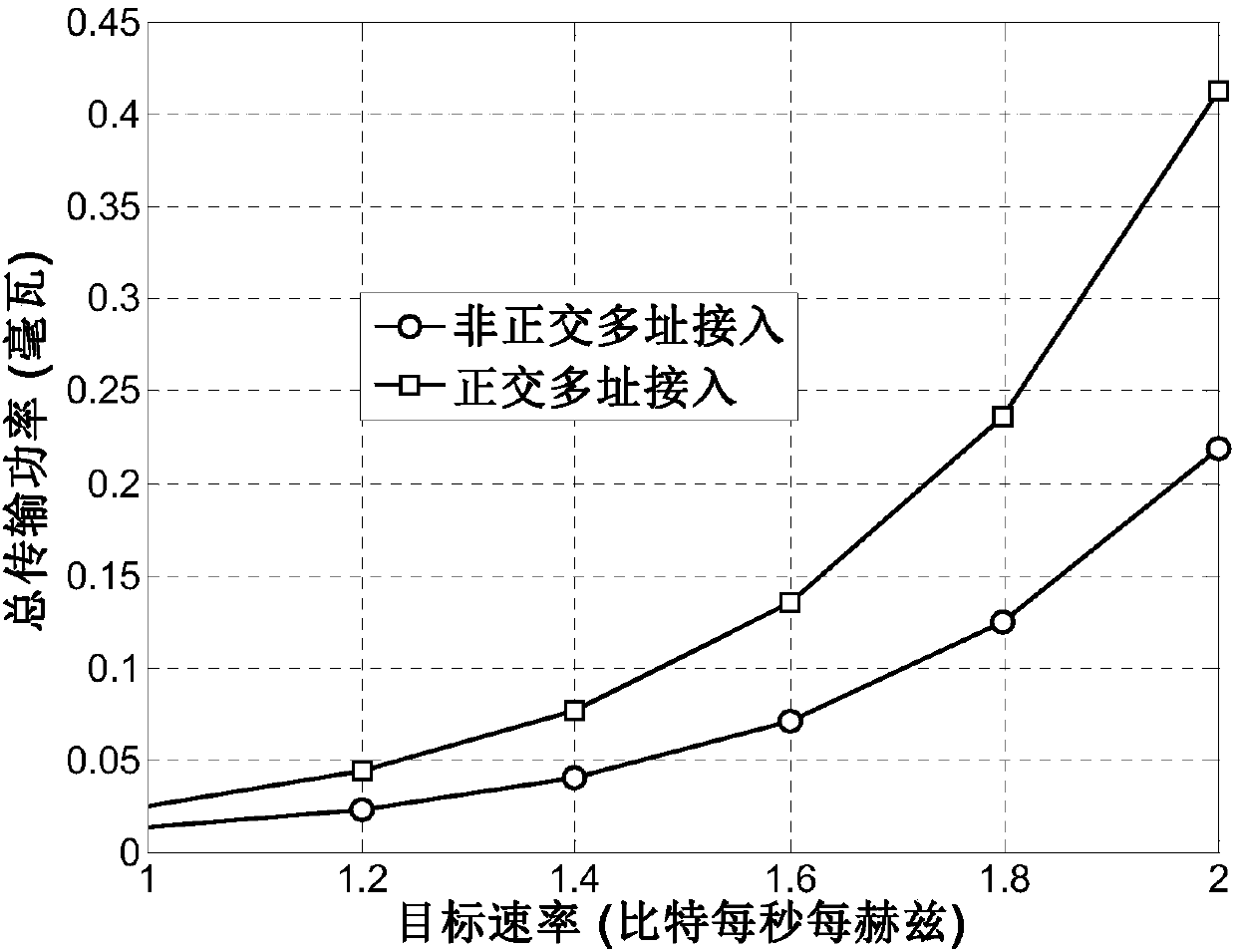
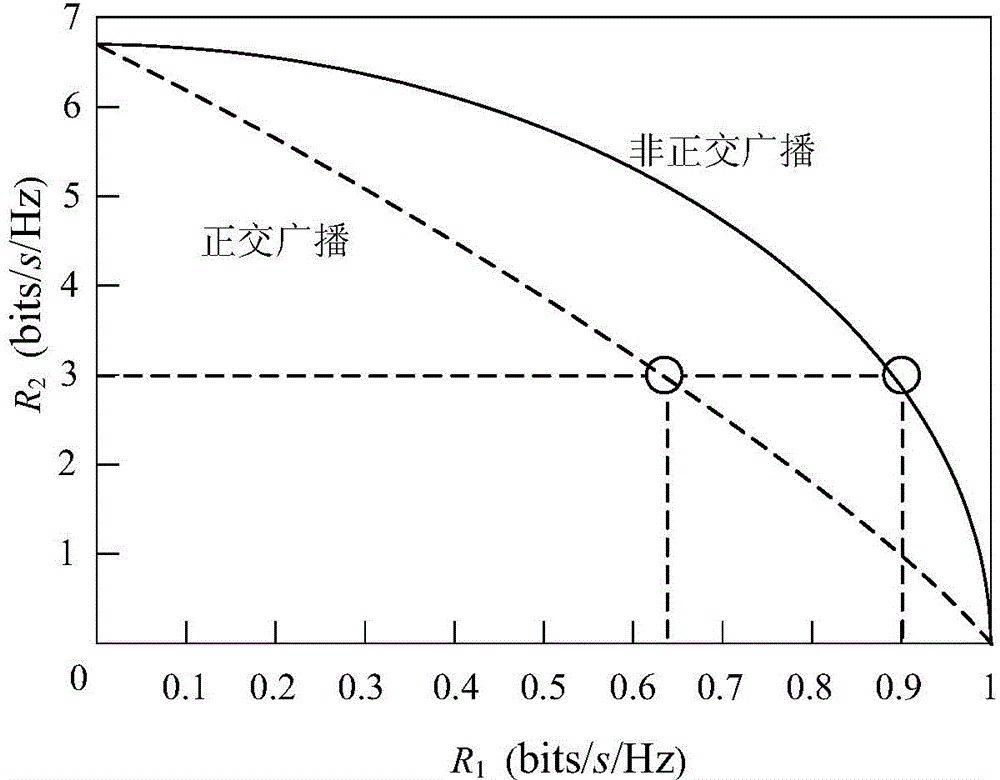
The key idea of superposition coding is to treat the message for decoder 2 as a common message that can be decoded by both receivers. Naturally, superposition coding is optimal in case where a strictly dominating relationship exists between the two channels, such as degraded, less noisy, and more capable condition.
Orthogonal superposition coding for direct-sequence communications
ActiveUS7317750B2Efficient processingImprove signal to noise ratioTransmission path divisionInter user/terminal allocationFrequency spectrumSuperposition coding
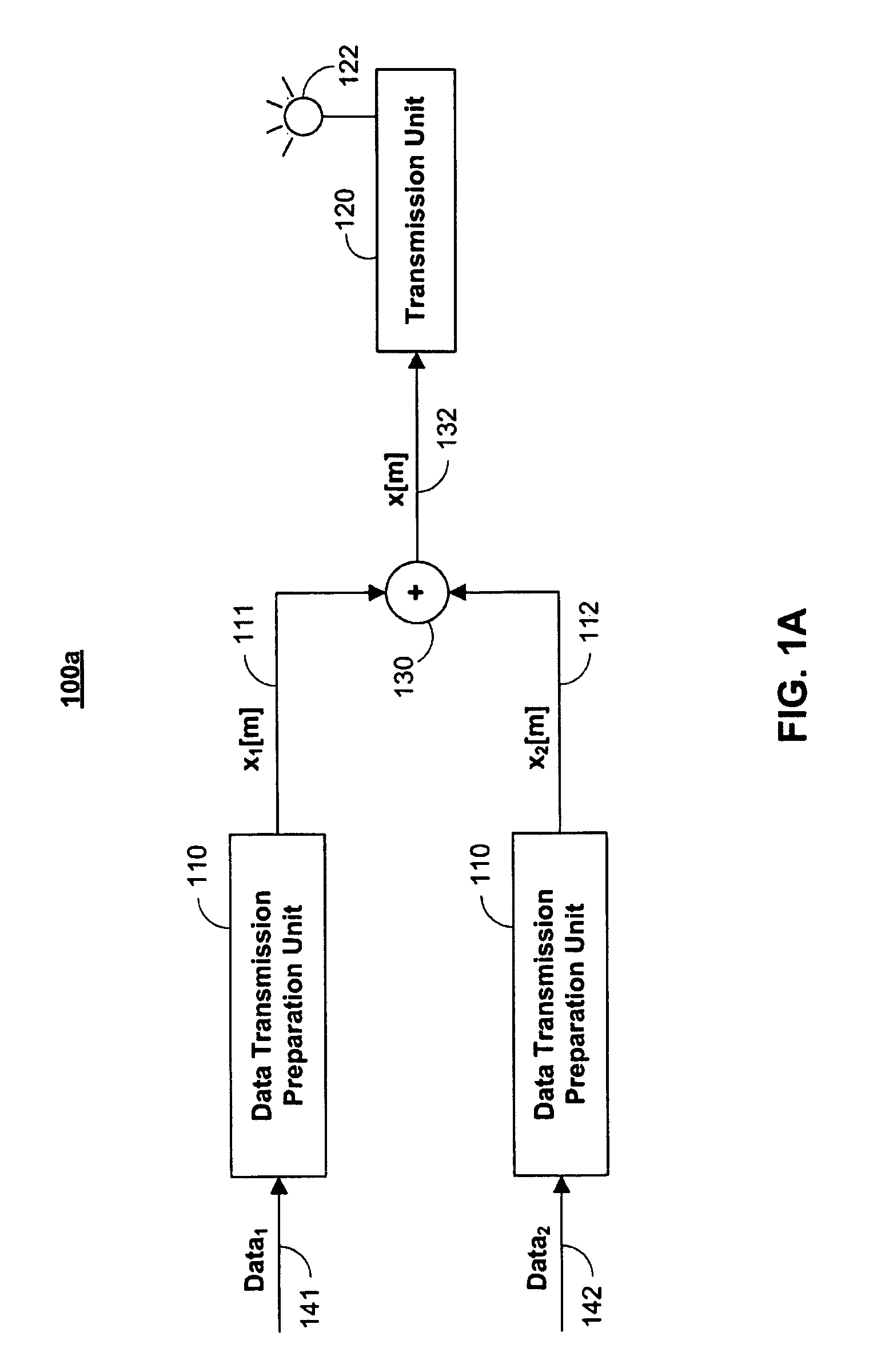
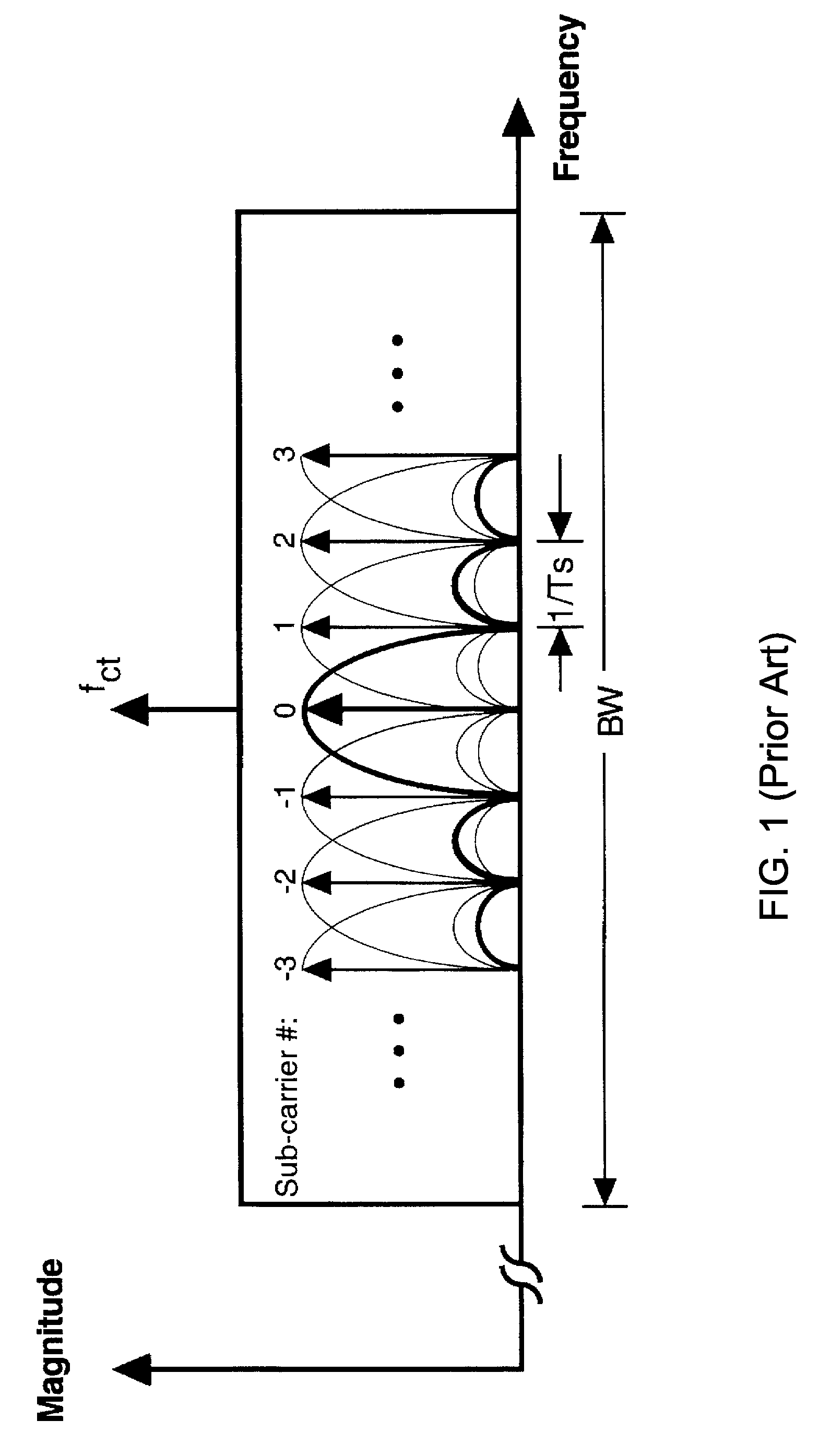
An adaptation to Carrier Interferometry synthesis and analysis provides for complex coding and decoding in a sliding window transform. Coding and decoding functionality can be extended to spatial processing in systems employing multiple transceiver elements. Poly-amplitude codes permit successive interference cancellation in spatial and frequency-domain processing. Handoffs in cellular systems are facilitated by selecting spectral / base station combinations that optimize link performance.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
System, method, and computer program for superposition coded multicast with a single modulation scheme
InactiveUS20110222462A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionModulated-carrier systemsSuperposition codingWireless data
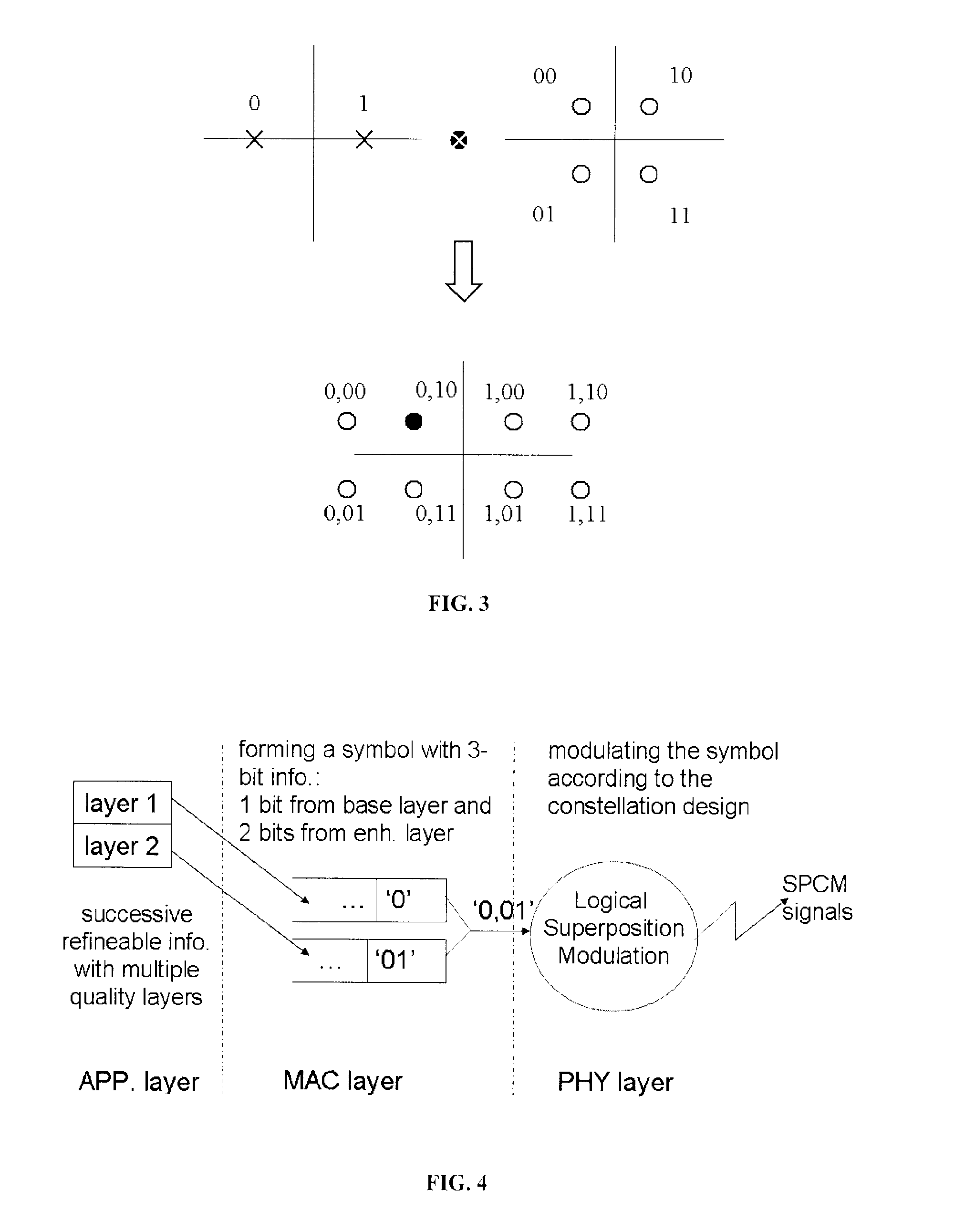
A cross-layer design architecture is provided for logical superposition coded (SPC) modulation for last-hop wireless data, aiming to overcome the effects of multi-user channel diversity in wireless video multicast. The proposed approach generates a logical SPC modulated signal by mapping successively refined information bits onto layered modulation through dynamic energy allocation and phase keying assignment, which mimics the superposition process for multiple modulated signals in convention hardware-based SPC modulation. At the receiver end, the received logical SPC signal is decoded by implementing a software-based approach on common demodulators without going through the signal-interference cancellation (SIC) process that is necessary in the conventional approach. The approach presented provides comparable or even better overall system throughput than by using the conventional hardware and SIC-based SPC modulation under various scenarios of different histograms of user channel conditions and power allocations for base and enhancement layer information.
Owner:HO PIN HAN +1
A robust system and method for wireless data multicasting using superposition modulation
InactiveUS20100296428A1Resource management arrangementsBroadcast transmission systemsSuperposition codingData stream
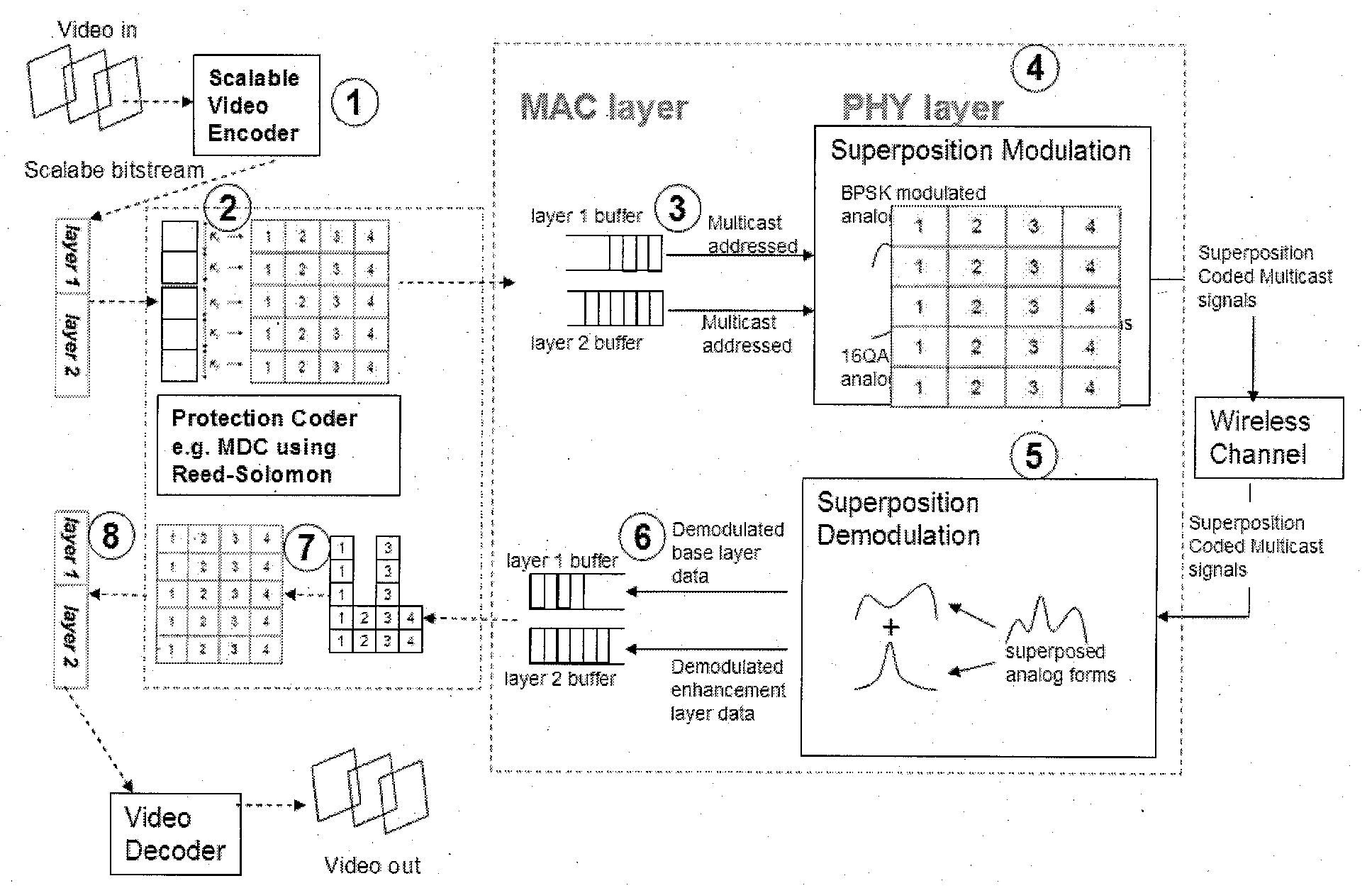
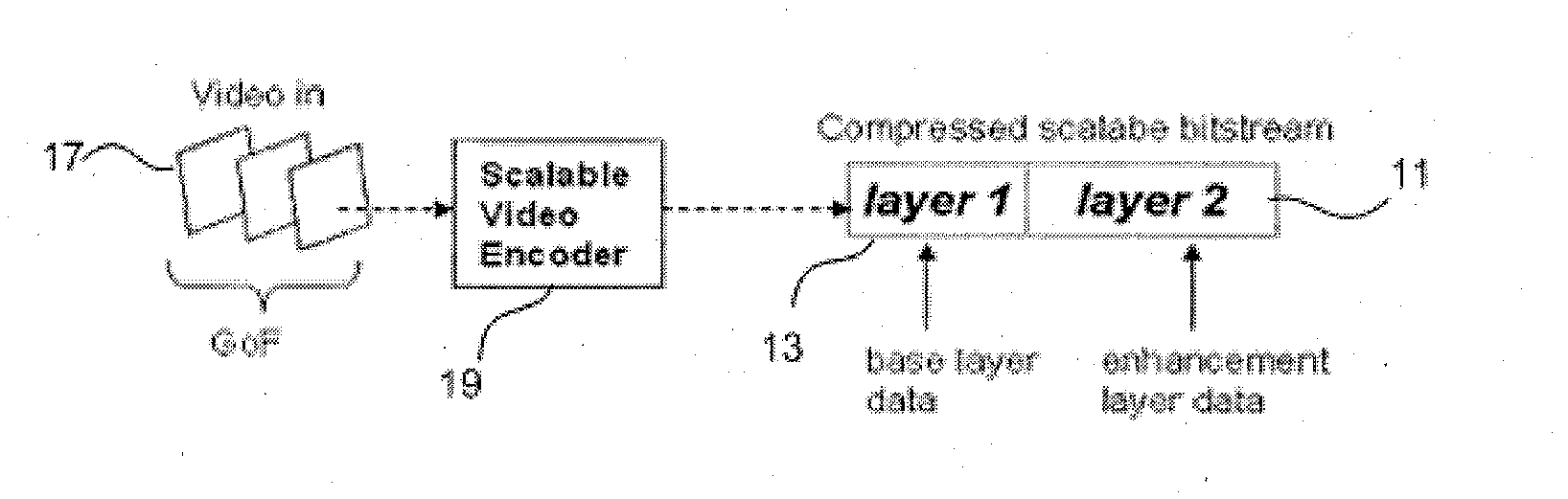
A method for transmitting data over a wireless network to a plurality of receivers connected to the wireless network is provided consisting of applying a superposition coded multicast or broadcast so as to create a multi-resolution multicast or broadcast signal to transmit data to the plurality of receivers as a scalable multicast or broadcast. The method consists of separating the data into one or more quality layers; converting the data in each quality layer into individual protected layer data streams by applying a protection or robustness means; modulating each said protected layer data stream using a modulation means, the modulations means for each said protected layer data stream not necessarily being the same; superimposing the modulated data of all layers into a single broadcasting or multicasting transmission block; and transmitting the single broadcasting or multicasting transmission block to the plurality of receivers linked to the wireless network.
Owner:HO PIN HAN
Superposition coding based preamble designs for co-existing radio access technologies
Methods, systems, and devices are described for wireless communication at a device. A device may distinguish a preamble sent from a device configured for a first RAT (e.g., WLAN, Wi-Fi, etc.) from a preamble sent from a device configured for a second RAT (e.g., LTE, LTE-A, LTE-U, etc.). A wireless device associated with a second RAT may transmit a dual-use preamble over a contention-based frequency channel. The dual-use preamble may function as a valid preamble for a first RAT and may be received and decoded by devices associated with the first RAT in addition to devices associated with the second RAT. The dual-use preamble may also include a signature associated with the second RAT. The signature may be embedded with the preamble such that it minimizes interference with the valid preamble and be detected by devices associated with the second RAT.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
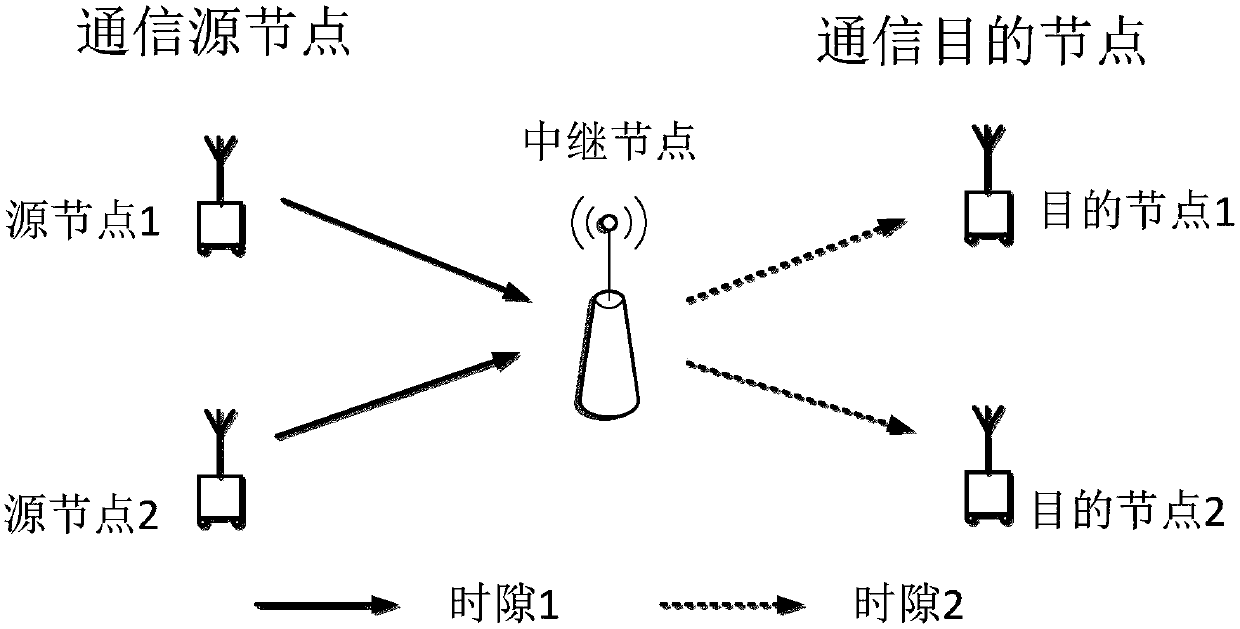
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving data using multi-user superposition coding in a wireless relay system
InactiveUS20080227388A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsActive radio relay systemsSuperposition codingComputer science
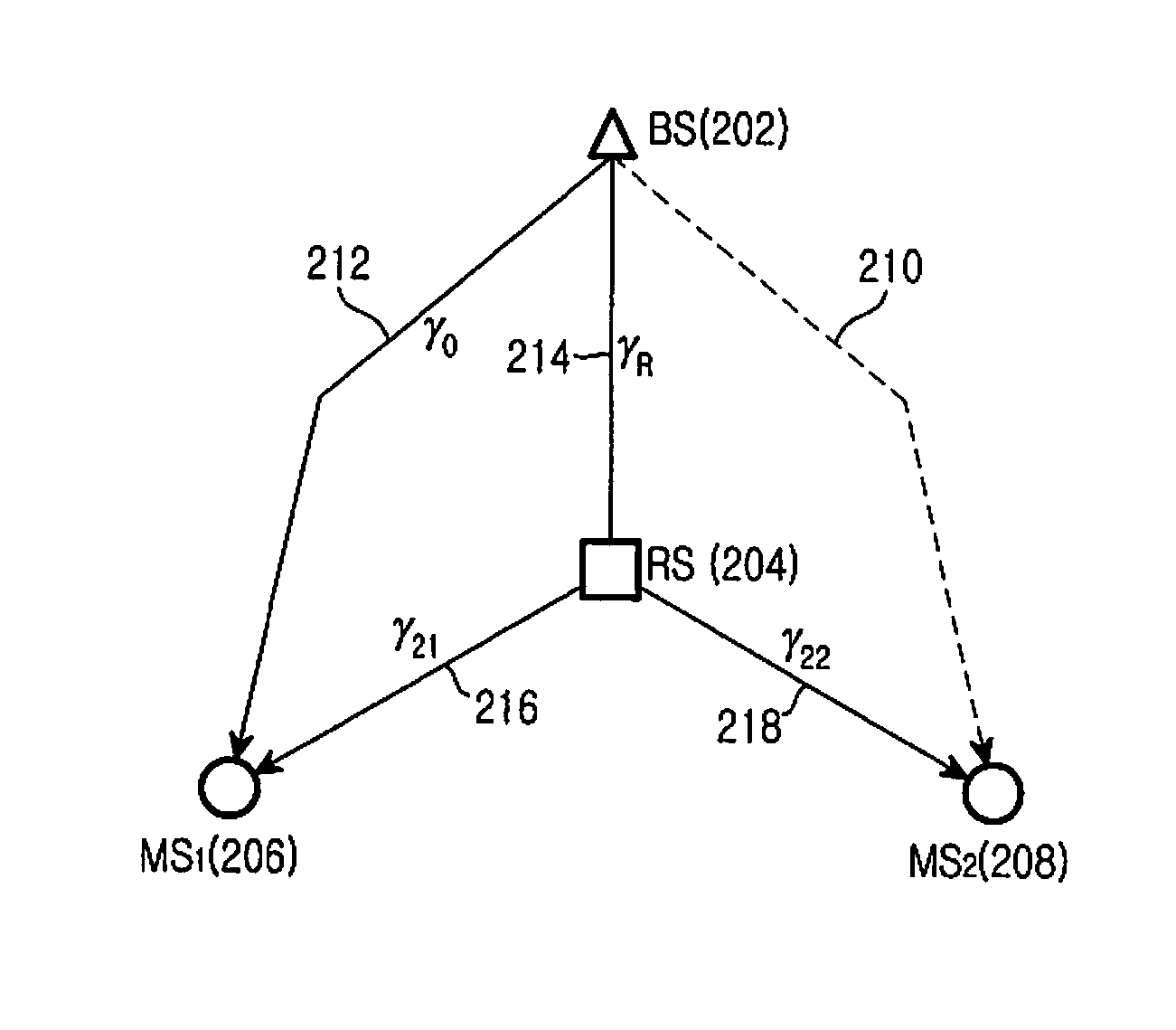
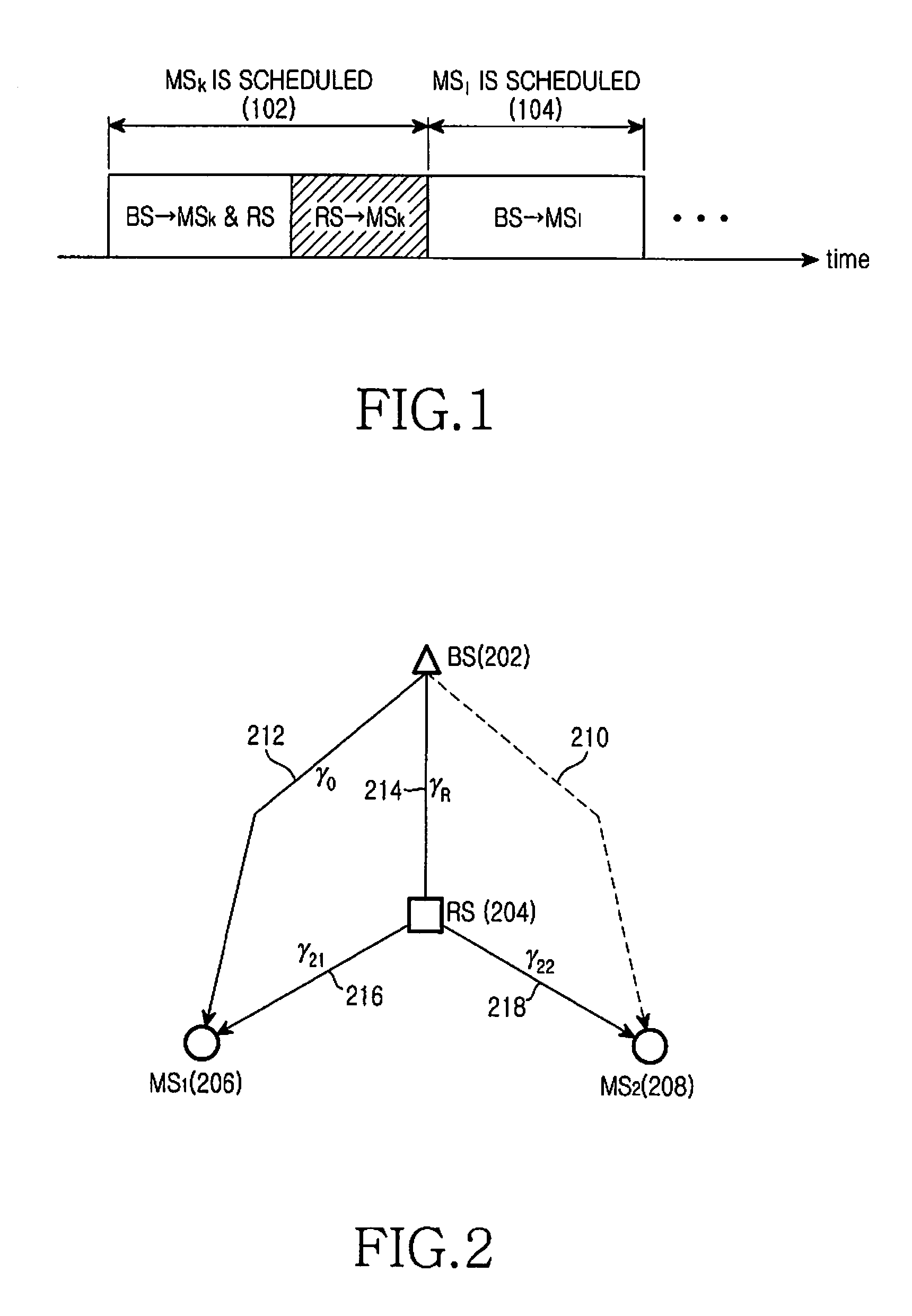
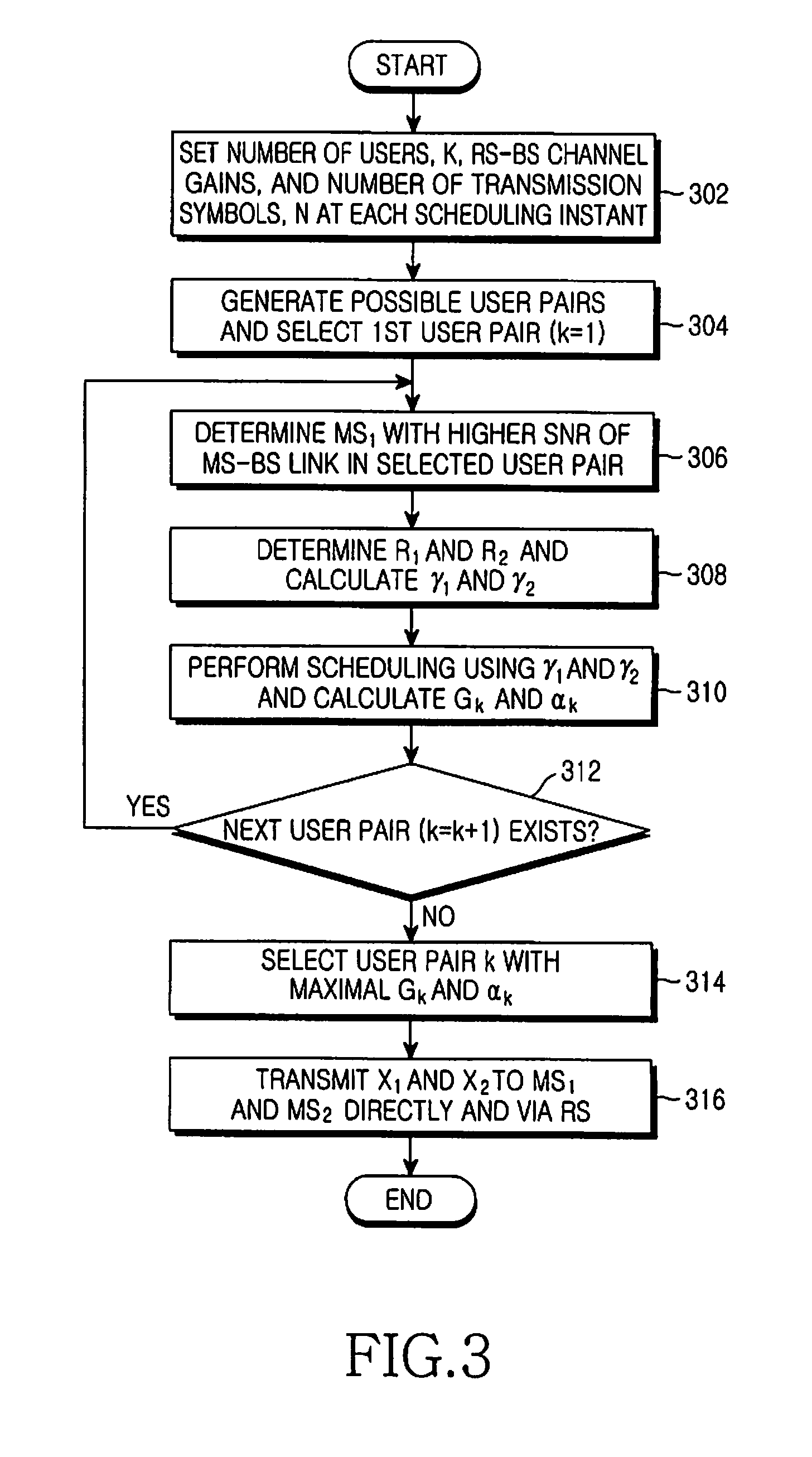
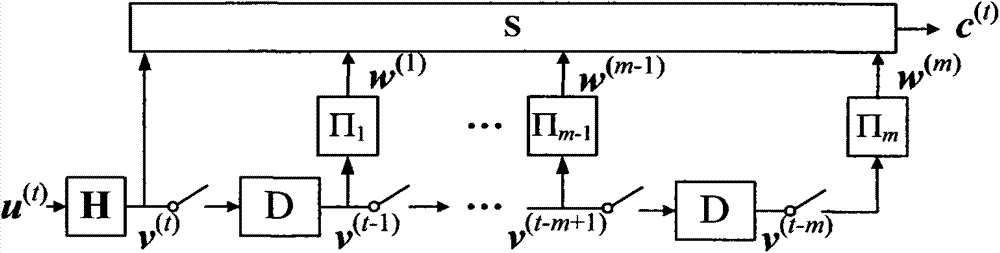
A method and apparatus for joint unicast using multi-user superposition coding in a wireless relay system are provided. A BS superposition-encodes first and second data messages directed to first and second MSs, respectively, scheduled at a current scheduling instant. The first and second data messages carry first and second information bit streams for the first and second MSs, respectively. The first MS has a relatively good direct link to the BS, and the second MS has a relatively bad direct link to the BS. The superposition-coded data is transmitted to the first MS and an RS connected between the BS and the first and second MSs. The RS receives the superposition-coded data from the BS, extracts the second information bit stream by decoding the superposition-coded data, and transmits a third data message carrying the second information bit stream to the first and second MSs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for multi-code-rate coding based on grouped Markov superposition coding
ActiveCN103888151AImprove error correction performanceError correction/detection using convolutional codesError detection onlySuperposition codingBinary information
The invention belongs to the field of digital communication and digital storage, and particularly relates to a method for multi-code-rate coding based on grouped Markov superposition coding. The method is used for coding a binary information sequence shown in a specification to a codon shown in the specification, wherein the length of the binary information sequence conforms to the formula: K=kBL, the length of the codon is nB(L+m[k]), n is larger than 1, k ranges from 1 to n-1, namely, a code rate set is {1 / n, 2 / n,..., (n-1) / n}, L is the number of kB sequence groups of the same length, and mk is the memory span of each sub code with the code rate being k / n. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, the information sequence is divided into L groups shown in the specification with the equal length and a sequence shown in the specification with the length of nB is initiated when t is equal to -1, -2,...,-(mk-1), -mk; then, when t is equal to 0, 1, ...L-1, a sequence shown in the specification with the length being kB is divided into B groups and the B groups are sent to conversion defined by an n-dimensional matrix H for coding, so that a coding sequence shown in the specification with the length of nB is obtained and combined with elements shown in the specification, and the tth sub sequence shown in the specification of the codon shown in the specification is calculated. The method for multi-code-rate coding is simple in design, wide in code rate range and superior in performance.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Self-adapting fountain code multicast transmission system based on modulation
InactiveCN101562781AImprove applicabilityImprove transfer rateError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementInformation processingSuperposition coding
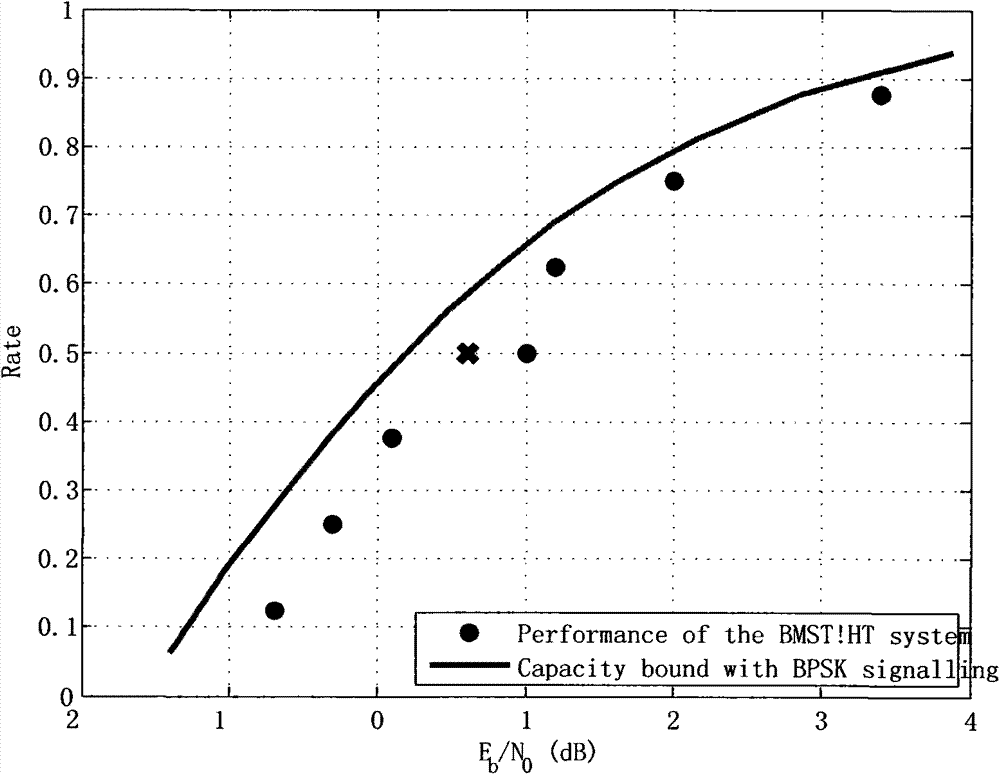
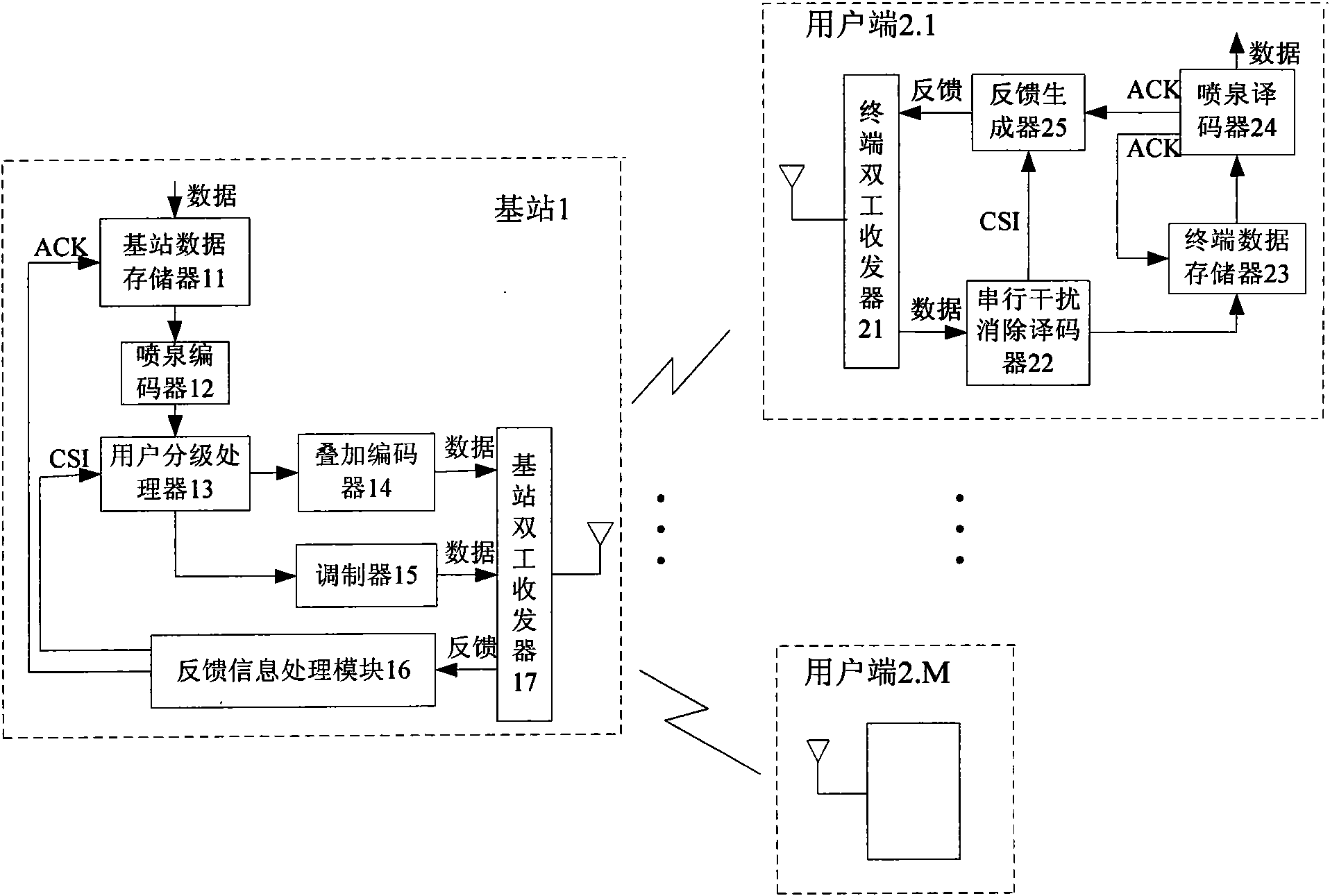
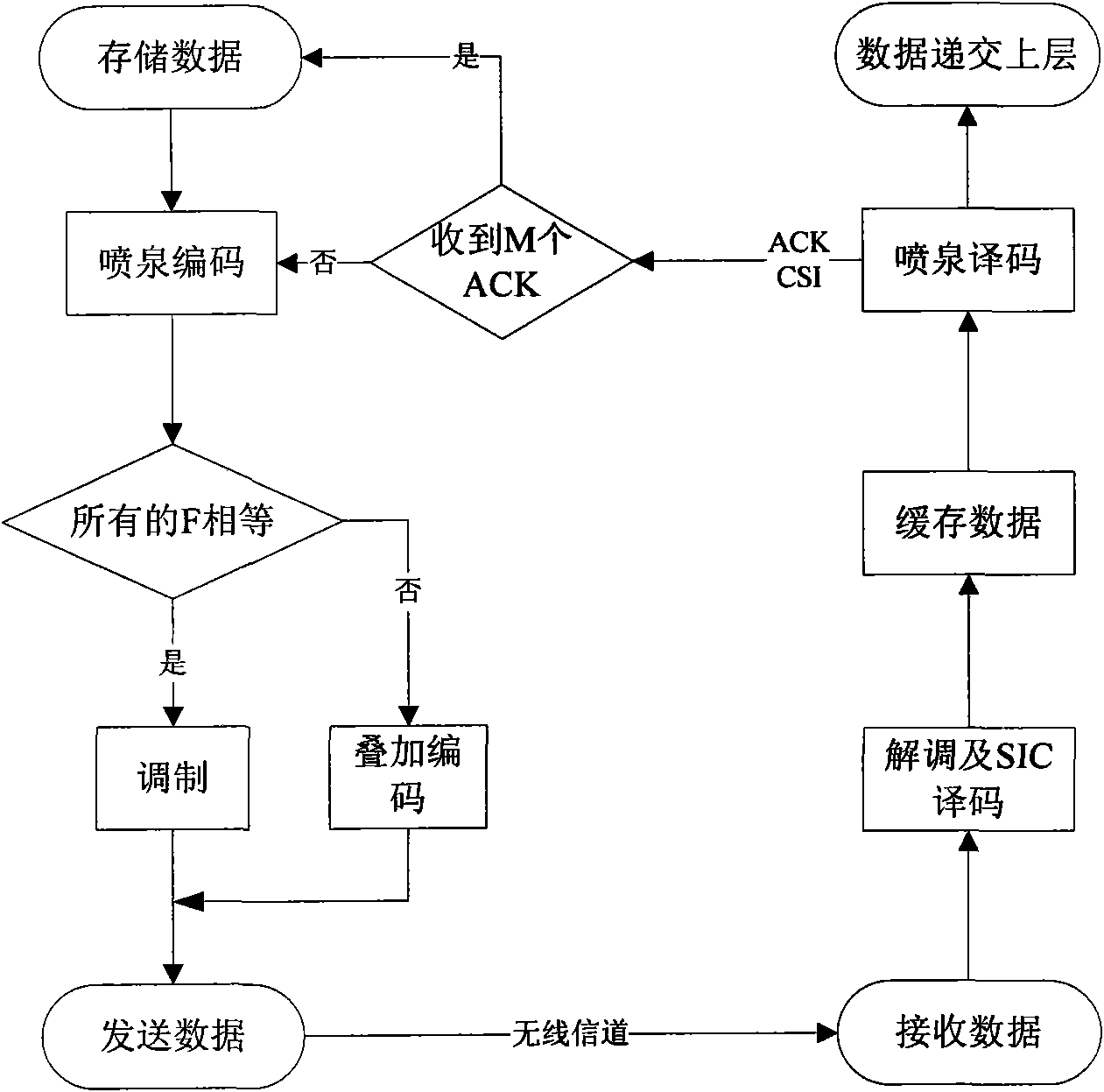
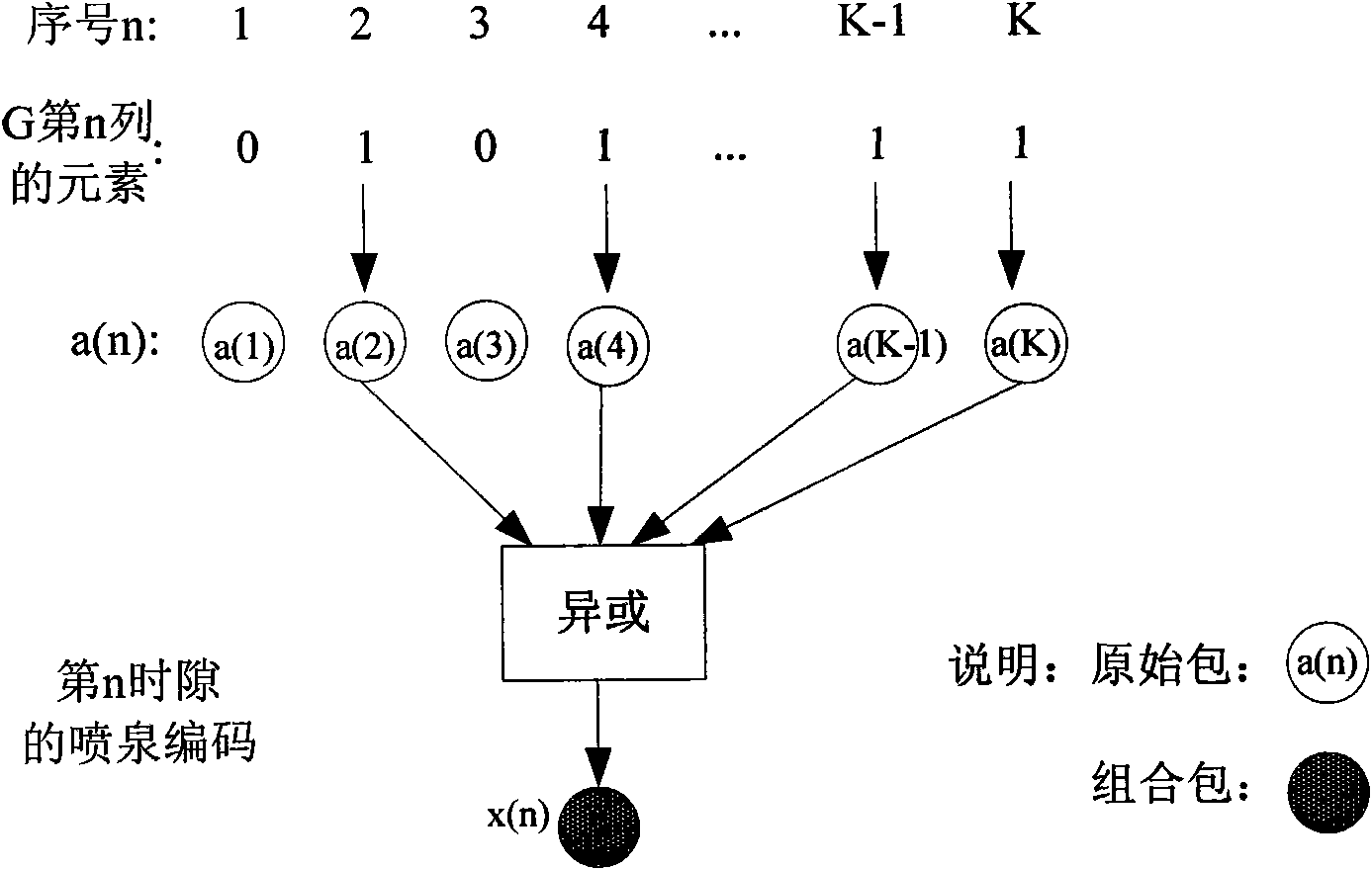
The invention discloses a self-adapting fountain code multicast transmission system based on modulation, which comprises a base station and a plurality of user sides. The base station comprises a base station data memory, a fountain coder, a user classification processor, a superposition coder, a modulator, a base station duplex transceiver and a feedback information processing module; and each user side comprises a terminal duplex transceiver, a serial interference cancellation decoder, a terminal data memory, a fountain decoder and a feedback generator. In a correcting and deleting channel, a mode of digital fountain codes is adopted for transmission so as to reduce the feedback in a multicast environment and improve the throughput rate of the system. According to a multi-user channel state, modulation modes are self-adaptively switched and selected. When the performance difference among the users is small, a common modulation mode is adopted; and when the performance difference among the users is large, superposition coding for different user information is carried out through power distribution so that the system still can keep good transmission performance. The combination of the digital fountain code and the superposition coding exerts the advantages of the digital fountain code and improves the performances.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Collaborative communication method and collaborative communication system based on non-orthogonal multiple access
InactiveCN108601088ASimultaneous accessImprove spectral efficiencySource coding adaptationSignalling characterisationInformation recoverySuperposition coding
The invention discloses a collaborative communication method based on non-orthogonal multiple access, and the method comprises the following steps: a relay node receives a source node signal and channel state information; the relay node decodes the source node signal through successive interference cancellation to obtain a decoded signal; superposition coding is executed for the coded signal according to a power distribution coefficient, the relay node sends the superposed signal to a plurality of destination nodes simultaneously through performing downlink non-orthogonal multiple access withthe plurality of destination nodes; the destination nodes perform decoding and information recovery for the superposed signal through successive interference cancellation; according to channel state information and user requirements, transmitting power and the power distribution coefficients of all the nodes are calculated, and a plurality of source nodes send the obtained information to the relaynode through performing uplink non-orthogonal multiple access with the relay node. In the method and the system provided by the invention, the non-orthogonal multiple access technology is used, userrate is satisfied, total consumption of the system is minimized, the number of access users is expanded effectively, spectrum efficiency of the system is promoted, and power consumption of the systemis reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Communication system for supporting primary user and secondary user
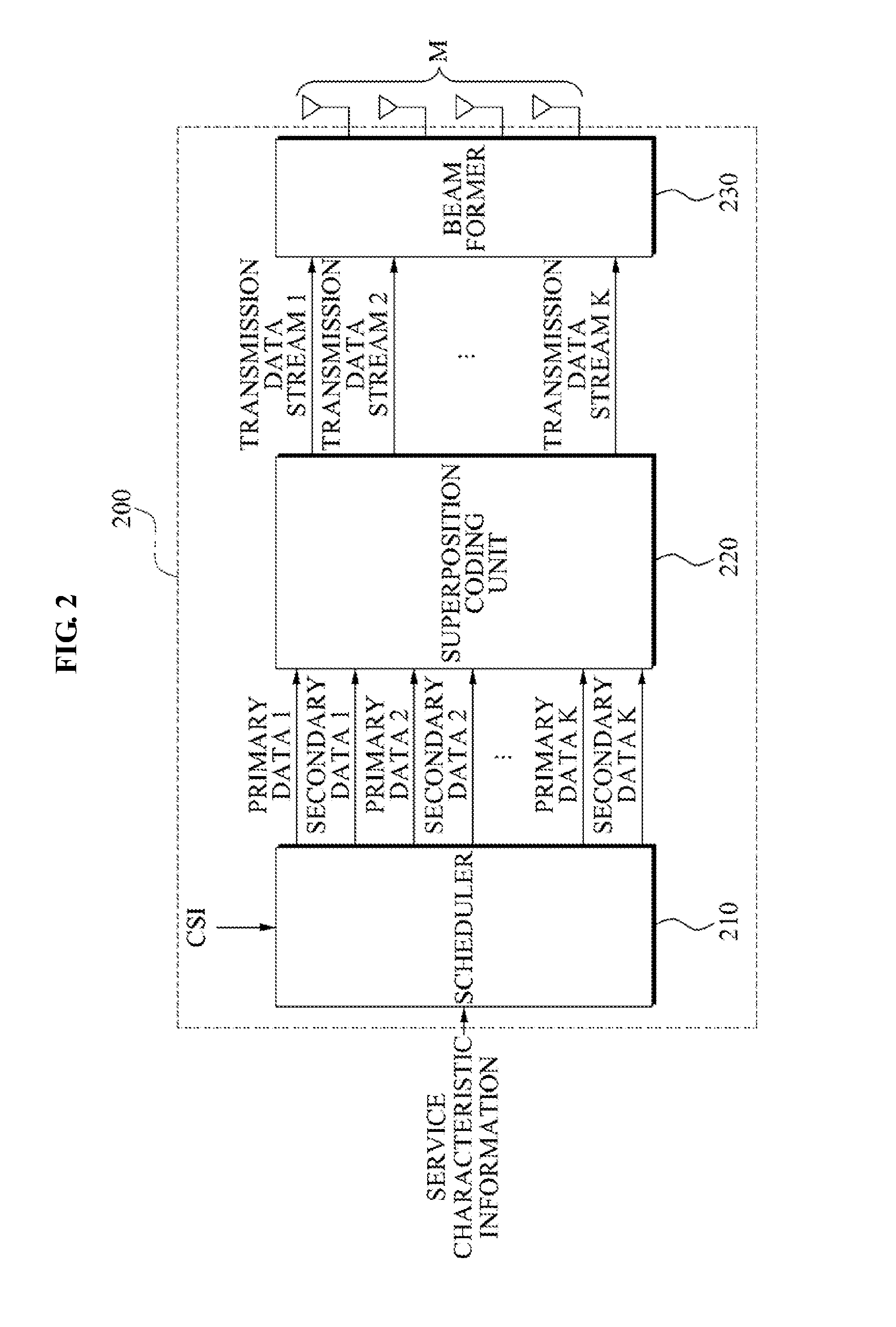
ActiveUS20100041406A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsInter user/terminal allocationSuperposition codingBase station
A communication system for supporting a primary user and a secondary user is provided. A base station of a communication system, includes a scheduler to group at least one primary user and at least one secondary user corresponding to each of the at least one primary user according to characteristics of services desired by users, a superposition coding unit to perform superposition coding for primary data associated with the at least one primary user and secondary data associated with the at least one secondary user to generate a transmission data stream, and a beamformer to perform beamforming for the transmission data stream.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of OFDM communication using superposition coding
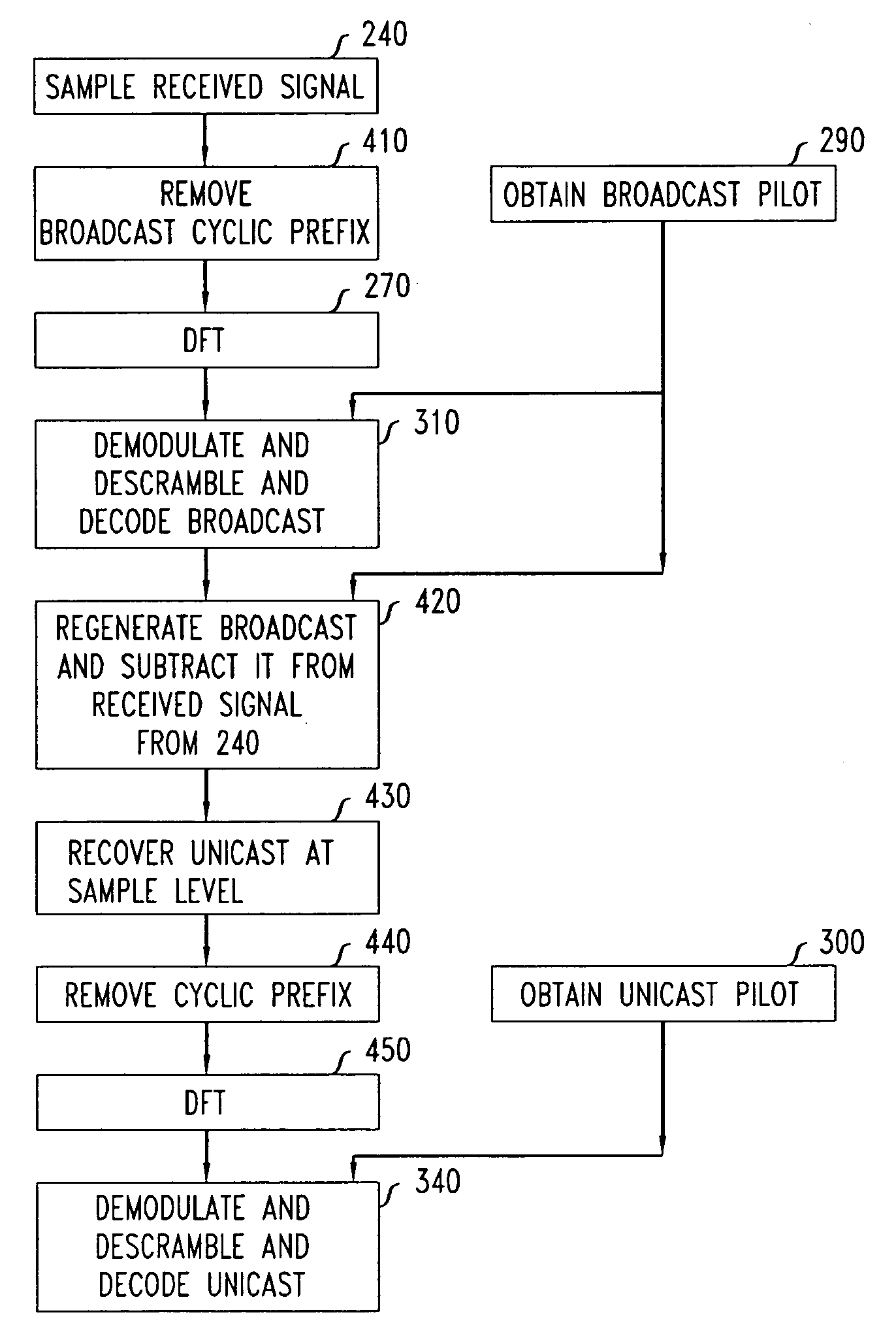
ActiveUS20080062857A1Improve network performanceModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionSuperposition codingData rate
Improvements are provided in an OFDM network that uses superposition coding. A broadcast signal and e.g. a unicast signal are each subjected to OFDM modulation including processing by an IDFT, combined, and transmitted using non-orthogonal transmission resources. In one approach, the respective signals are combined after instead of before the IDFT processing. In specific examples, a respective cyclic prefix is appended to each signal after the IDFT processing but before the respective signals are combined. In another approach, a broadcast pilot signal and e.g. a unicast pilot signal are transmitted concurrently with the broadcast and unicast information signals. The pilot signals are transmitted using the same time and subcarrier resources, but are made more distinguishable by combining each with a respective scrambling or spreading code. In specific examples, embodiments, the unicast pilot signal is used for estimating the data rate for transmission of further unicast information signals.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Dynamic cooperative relay transmission method based on power domain non-orthogonal multiple access technology
InactiveCN108512585AImprove spectral efficiencyLarge capacityPower managementSite diversitySuperposition codingLeast mean square error
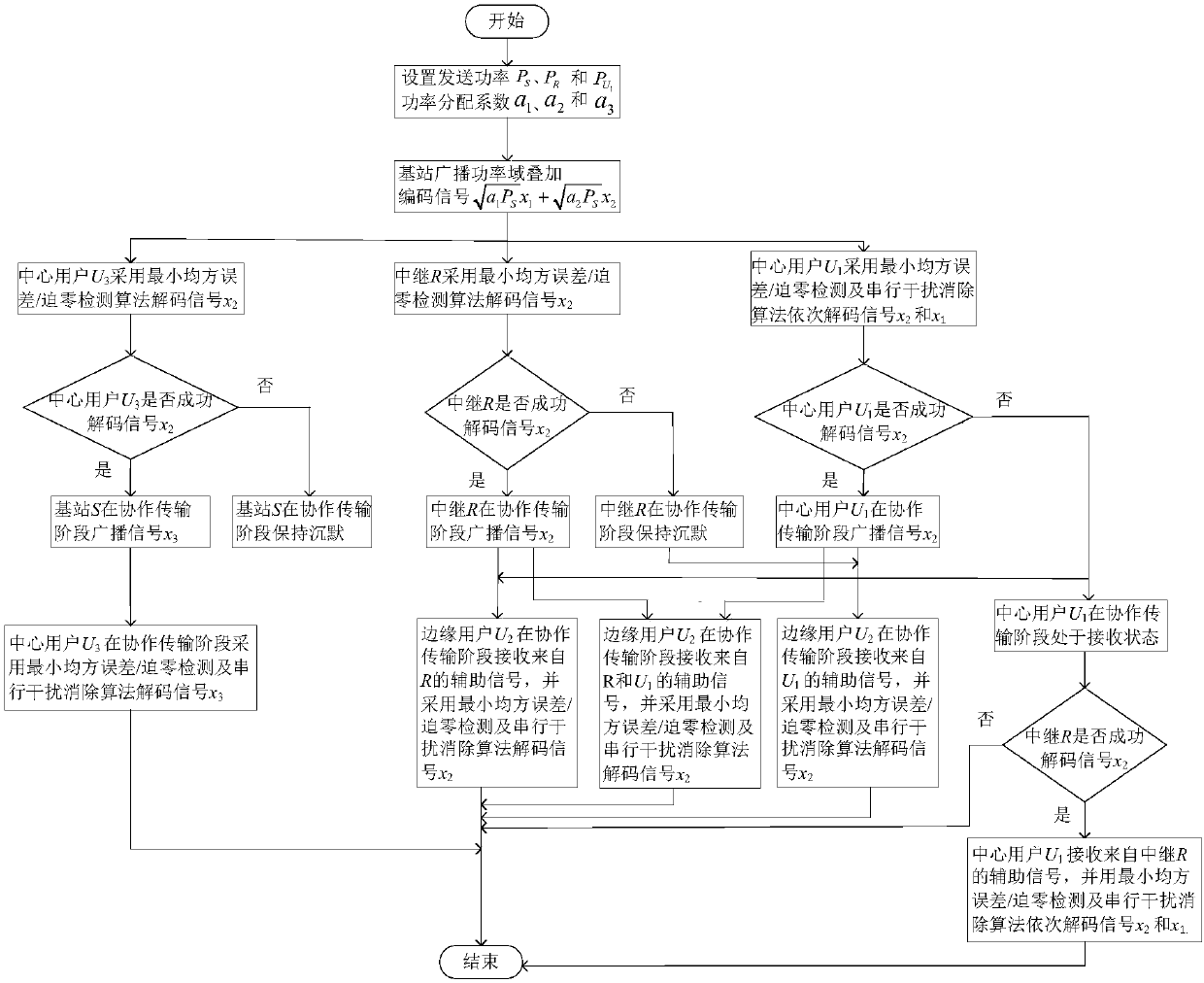
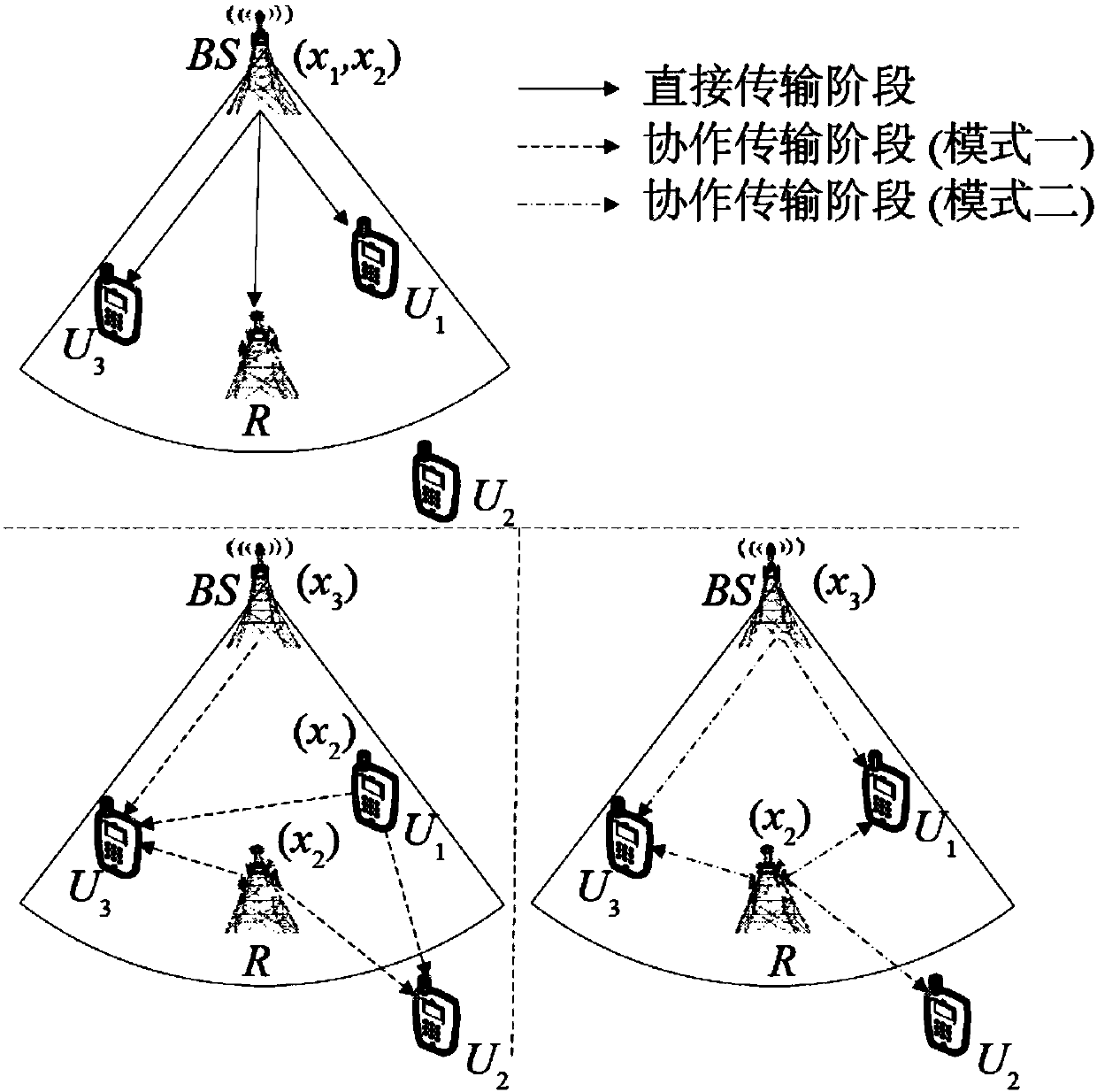
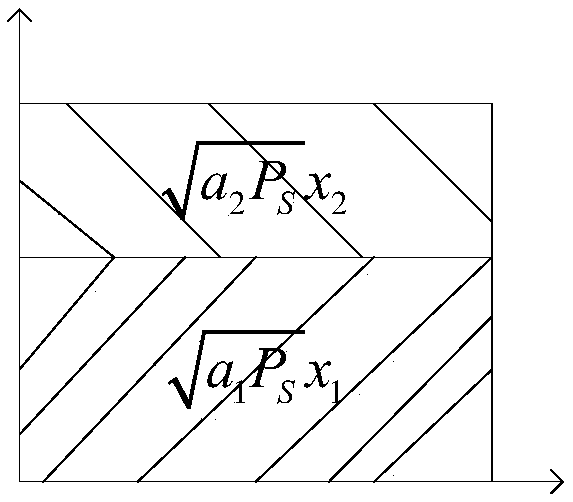
The invention discloses a dynamic cooperative relay transmission method based on power domain non-orthogonal multiple access technology, and relates to a dynamic cooperative relay transmission method.The purpose of the invention is to solve the problems of base station slot resource waste of the existing cooperative transmission scheme based on the power domain non-orthogonal multiple access technology and low edge user reliability of the direct relay cooperative transmission scheme based on the power domain non-orthogonal multiple access technology. The process is: in a direct transmission phase, a base station S broadcasts a superposition coding signal xs of information x1 required by a central user U1 and information x2 required by an edge user U2, performing: the U1, a U3, and a relayR respectively decode x2 received signals by adopting a least mean square error algorithm, and then U1 decodes x1 using a serial interference cancellation algorithm; in a cooperative transmission phase, the S broadcasts x2 information required by the U3, the R broadcasts x2, and the U1 broadcasts x2 according to a dynamic protocol, respectively: U3 decodes x3 the received signals using MMSE; andthe U2 decodes x2 the received signals using maximum ratio combining and MMSE. The method is used in the field of wireless cooperative relay transmission.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Superposition coding and orthogonal multiplexing combined downlink multiuser transmission method
InactiveCN104486035AReduce complexityReduce receiving delayError preventionTransmission path multiple useMultiplexingSuperposition coding
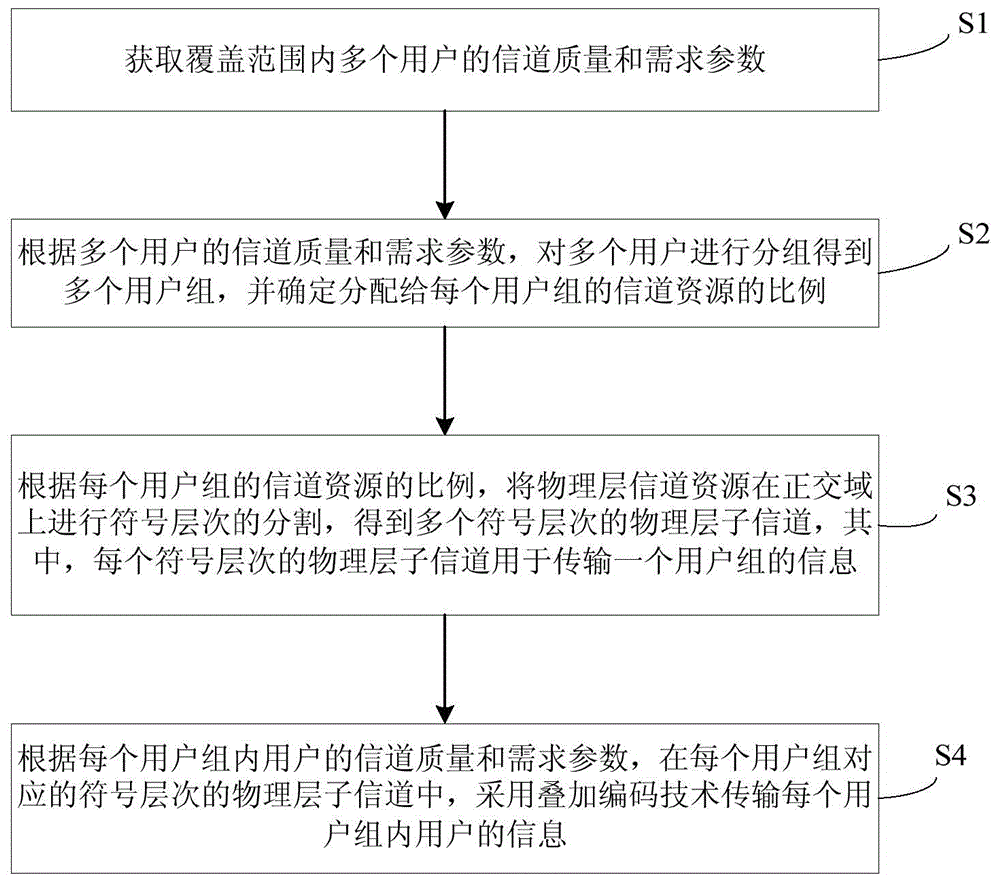
The invention discloses a superposition coding and orthogonal multiplexing combined downlink multiuser transmission method which comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring channel quality and requirement parameters of a plurality of users in a coverage range; S2, according to the channel quality and the requirement parameters of the plurality of users, carrying out grouping on the plurality of users to obtain a plurality of user groups, and determining a ratio of channel resources distributed to each user group; S3, according to the ratio of the channel resources distributed to each user group, carrying out symbolic level division on the physical layer channel resources on an orthogonal domain to obtain a plurality of symbolic level physical layer sub-channels; S4, according to the channel quality and the requirement parameters of users in each user group, in the symbolic level physical layer sub-channel corresponding to each user group, transmitting information of the users in each user group by adopting a superposition coding technology. Relative to the optimal SC (superposition coding) technology, the superposition coding and orthogonal multiplexing combined downlink multiuser transmission method has the advantage of greatly reducing implementation complexity of a terminal and time delay of the user information; relative to a conventional orthogonal multiplexing technology, the superposition coding and orthogonal multiplexing combined downlink multiuser transmission method has the advantage that the total system transmission rate is obviously promoted.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods and apparatus for providing receivers for use in superposition coded multi-user systems
InactiveUS7876784B1Reduce complexityLess complexTime-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSuperposition codingComputer science
Methods and apparatus provide low-complexity receivers for use in superposition coded multi-user systems. In a downlink scenario, a superposition coded signal that includes data unique to first and second users is compared with every permutation of the bit positions of the transmitted signal. The values of the received signal that are nearest to the transmitted signal are located to extract the data unique to the first user. In an uplink scenario, a superposition coded signal that includes data unique to the first and second users is compared with every permutation of the bit positions of transmitted signals corresponding to the first and the second users. The values of the received signal that are nearest to the transmitted signal corresponding to the first user are located to extract the data unique to the first user simultaneously with the extraction of the data unique to the second user.
Owner:MARVELL INT LTD
Cooperative beam forming method, apparatus and base station
ActiveUS20110305164A1Improve performanceImprove stand-alone performanceSite diversityError preventionMultiplexingSuperposition coding
The present invention proposes a method, device and base station for cooperative beam forming based on MBMS fixed grid of beams GoB. The cooperative beam forming method comprises following steps: grouping users into cell central user group and cell edge user group (S701); performing cell central user group multiplexing based on superposition coding (S702); performing cooperative beam forming operation based on fixed grid of beams GoB for cell edge user group (S703).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Receiver and signal processing method thereof
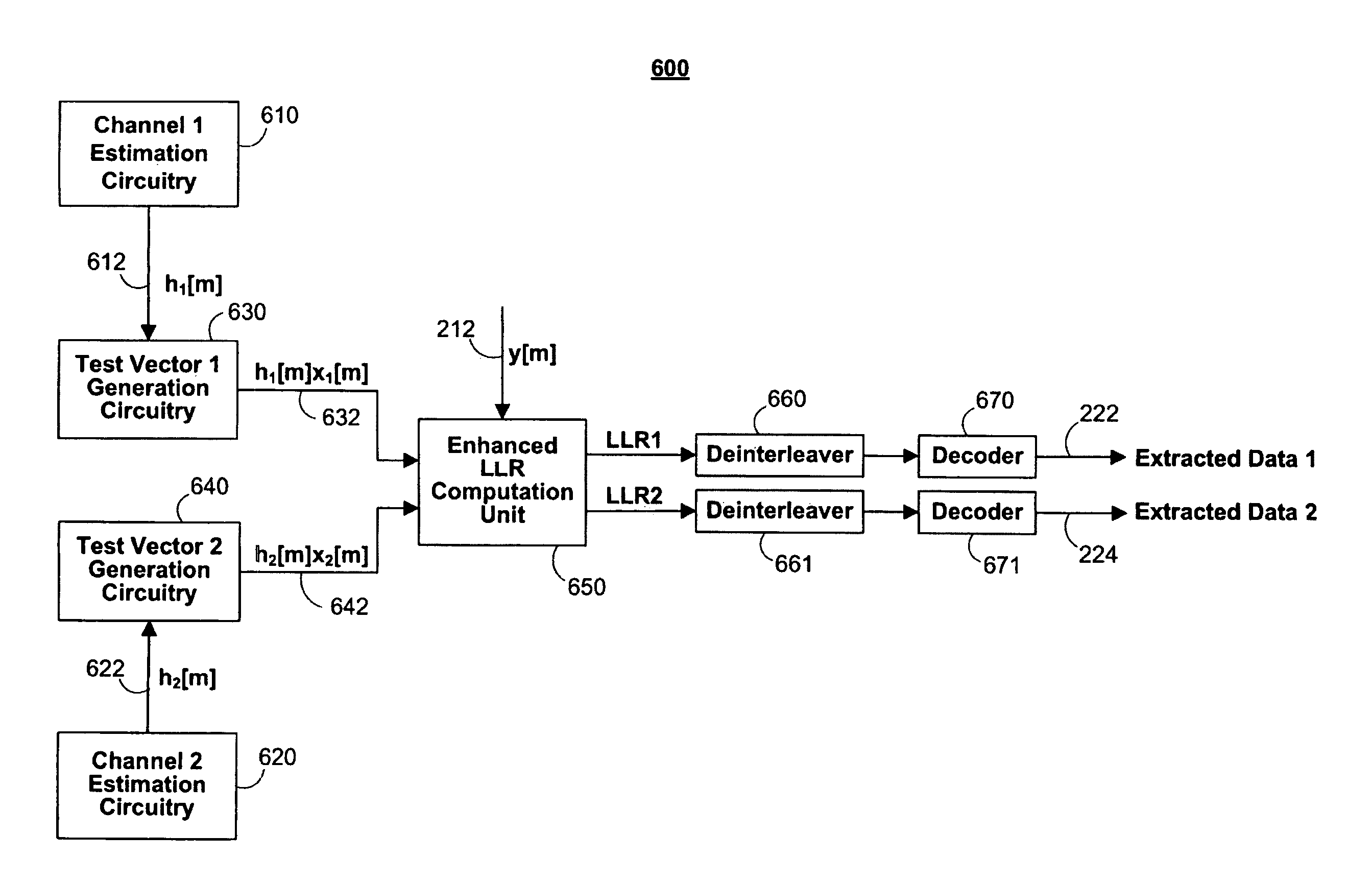
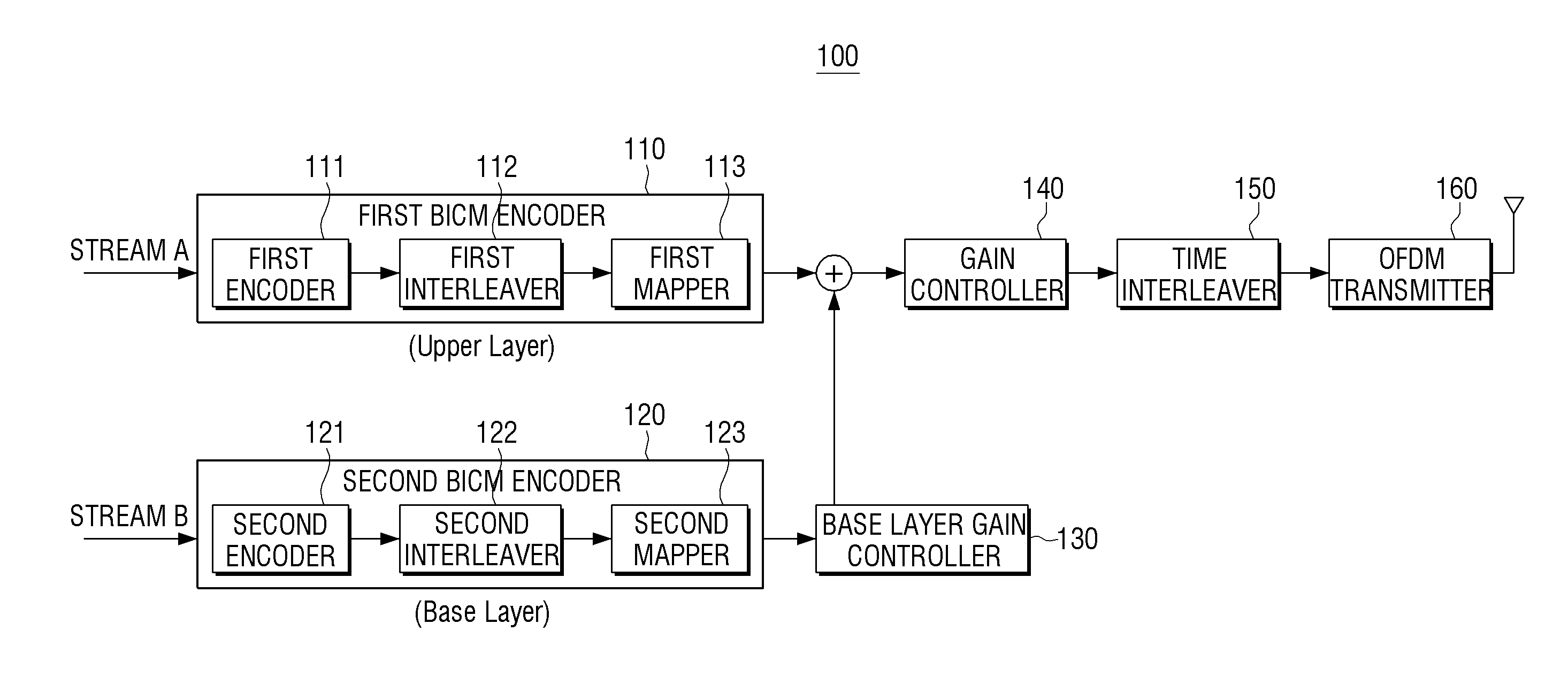
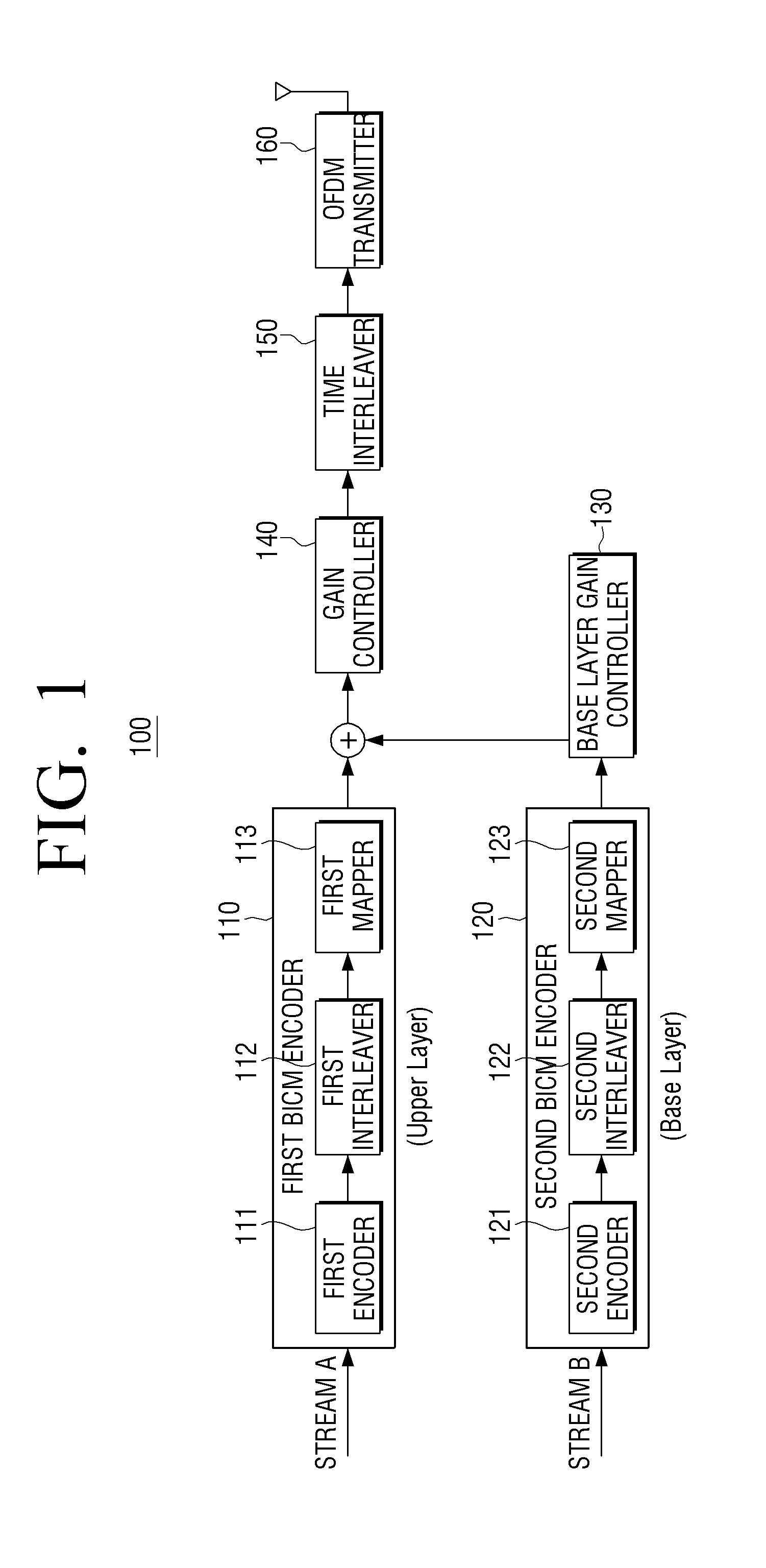
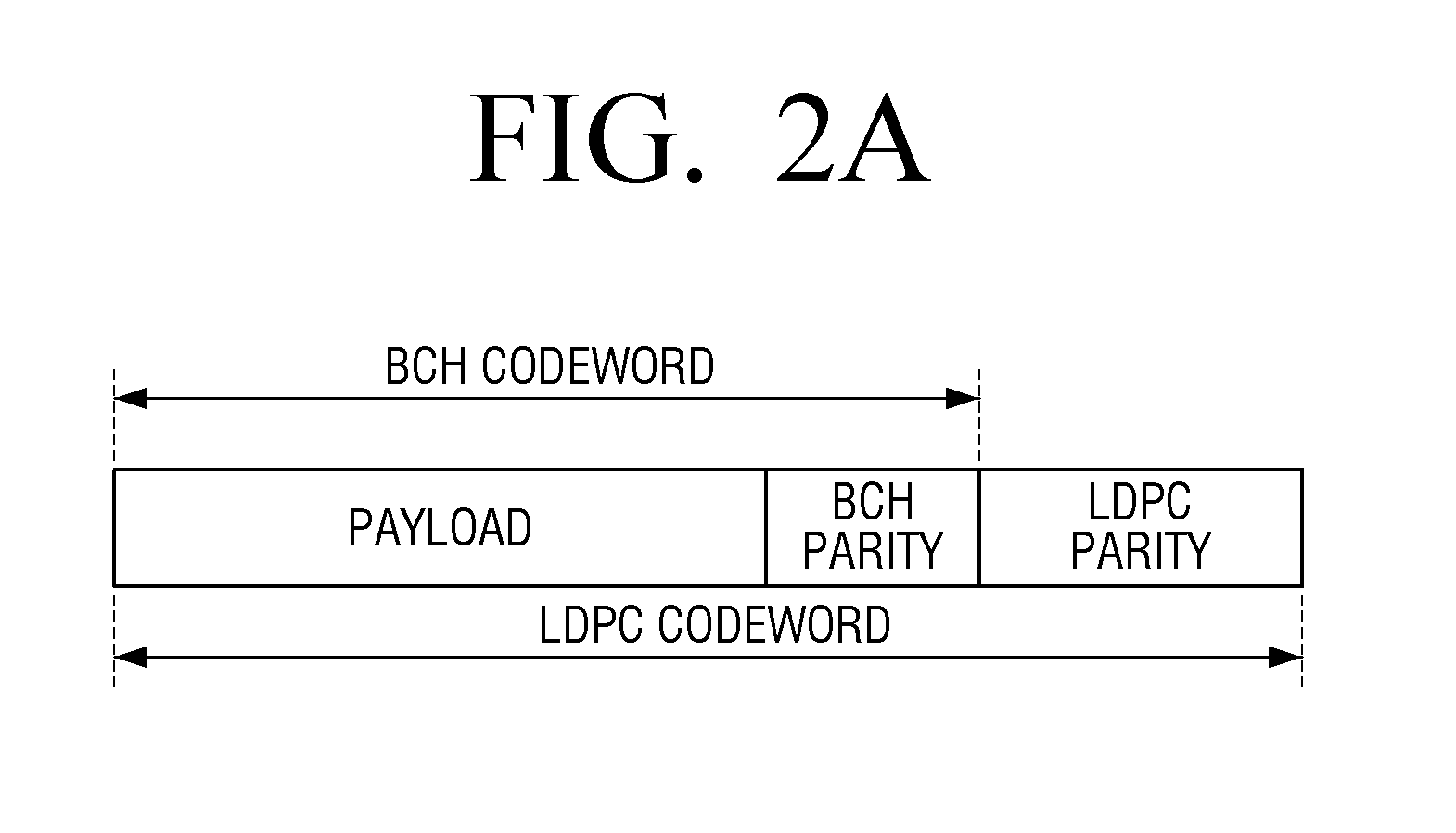
ActiveUS20160352462A1Faster base layer signal recoveryShorten the timeError correction/detection using concatenated codesError correction/detection using LDPC codesSuperposition codingBit interleaved coded modulation
Provided is a receiver which includes at least one processor configured to control or execute: a first Bit-Interleaved Coded Modulation (BICM) decoder configured to generate a first output signal corresponding to an upper layer signal by processing a first input signal which includes a superposition coding signal generated at a transmitter by superimposing the upper layer signal and a lower layer signal; a parity generator configured to generate at least one parity based on a result of the processing of the first input signal by the first BICM decoder; and a second BICM decoder configured to generate a second output signal corresponding to the lower layer signal by processing a second input signal which is generated using the parity generated by the parity generator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
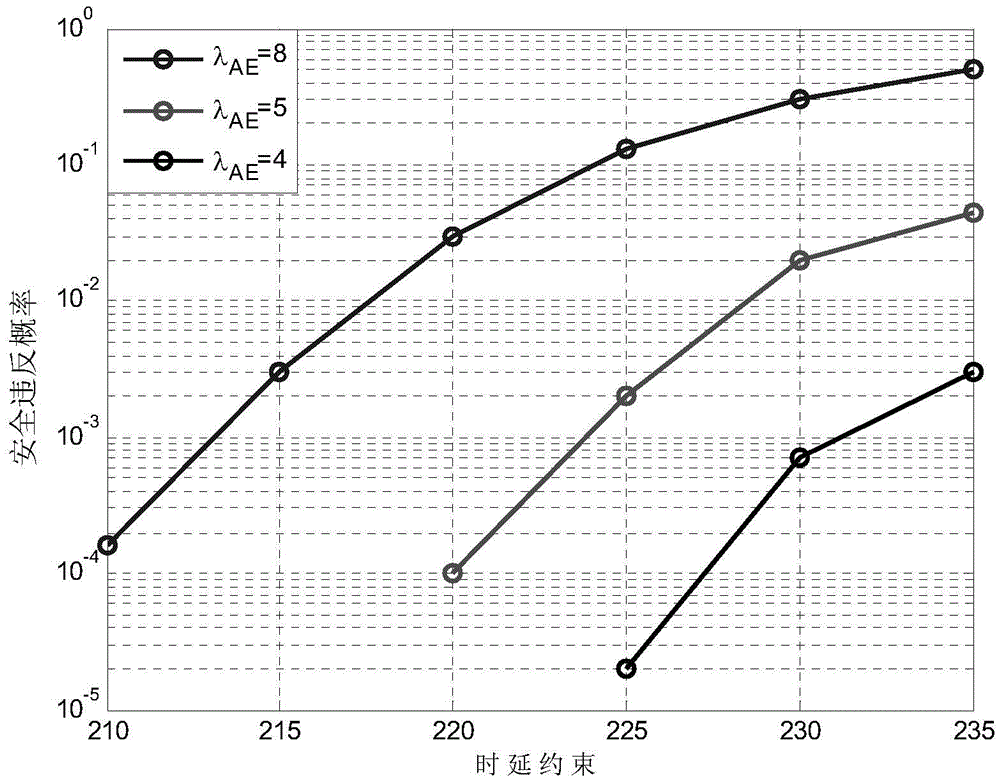
Wireless information and power transfer system maximum safety rate optimization method based on NOMA
ActiveCN108495337AOptimize power distributionMaximum safe transmission ratePower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemSuperposition coding
The invention discloses a wireless information and power transfer system maximum safety rate optimization method based on NOMA; the method comprises the following steps: firstly, a wireless information and power transfer system based on the NOMA is provided, the system is provided with a cell base station BS, M information receivers IRs and K energy receivers ERs, wherein the ER obtains energy from a radio frequency signal transmitted by the BS and eavesdrops on the information sent by the BS to the IR; according to the principle of the NOMA technology, the information transmitted by the BS tothe IR transmits a signal through a superposition coding technology, and the expression is as follows: formula; in the formula, am is the signal transmission power distribution coefficient of the mthIR, P is the signal transmission total power of the BS, xm is the confidential information of the mth IR, and sigma 2 is the additive gaussian white noise; and an optimization parameter AM is adjusted according to the method, certain energy can be provided for the ER, and a certain information rate is provided for the IR; and the purpose of providing the maximum safety information rate is provided for the IR in the case of the ER eavesdropping on information.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Superposition coding in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS8085819B2Lower latencyReduce transmission delayError prevention/detection by using return channelPower managementCommunications systemSuperposition coding
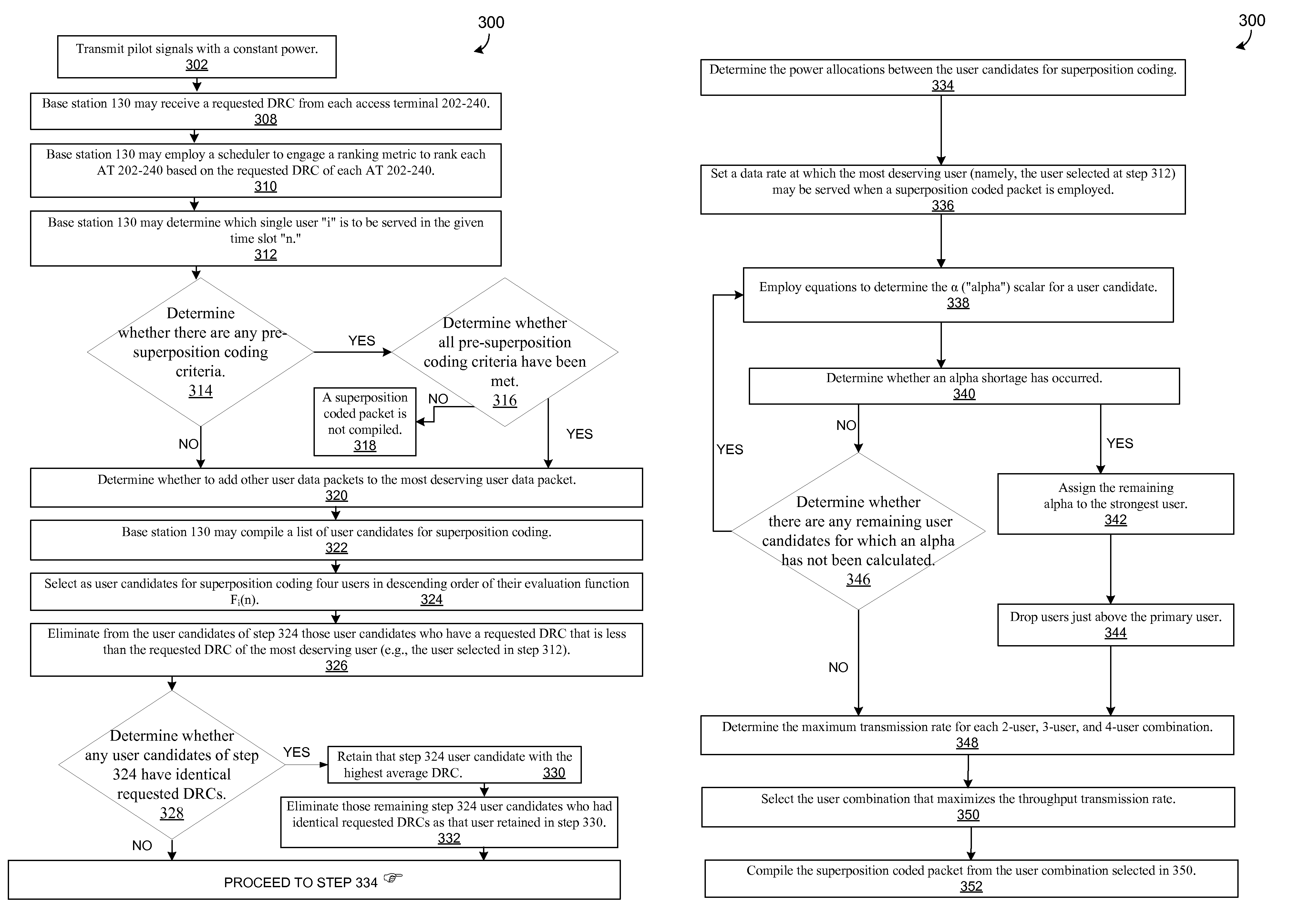
The present patent application comprises a method and apparatus to compile a superposition coded packet by compiling user candidates for superposition coding, ranking the user candidates based on a result of an evaluation function, selecting a deserving user candidate from among the user candidates, and compiling a superposition coded packet by adding other user data packets to a packet of the deserving user data packet, wherein the data packets for the user candidates may conform to a plurality of different formats and wireless communication standards.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Distributed decoding forwarding bidirectional relay selection method under dissymmetrical speeds
ActiveCN103067127AImprove performanceError preventionRadio relay systemsChannel state informationSuperposition coding
A distributed decoding forwarding bidirectional relay selection method under dissymmetrical speeds is suitable for a decoding forwarding bidirectional relay system adopting superposition coding. The method is based on a passive selection method for achieving relay selection after source nodes send data. In overall consideration of nonsymmetry of target speeds of the tow source nodes in a network, by means of using of balancing technique, according to channel state information, the best bidirectional relay selection is carried out, and system performance optimation under any business types and link characteristics can be achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Differential new user selection access method applicable to non-orthogonal multi-access system
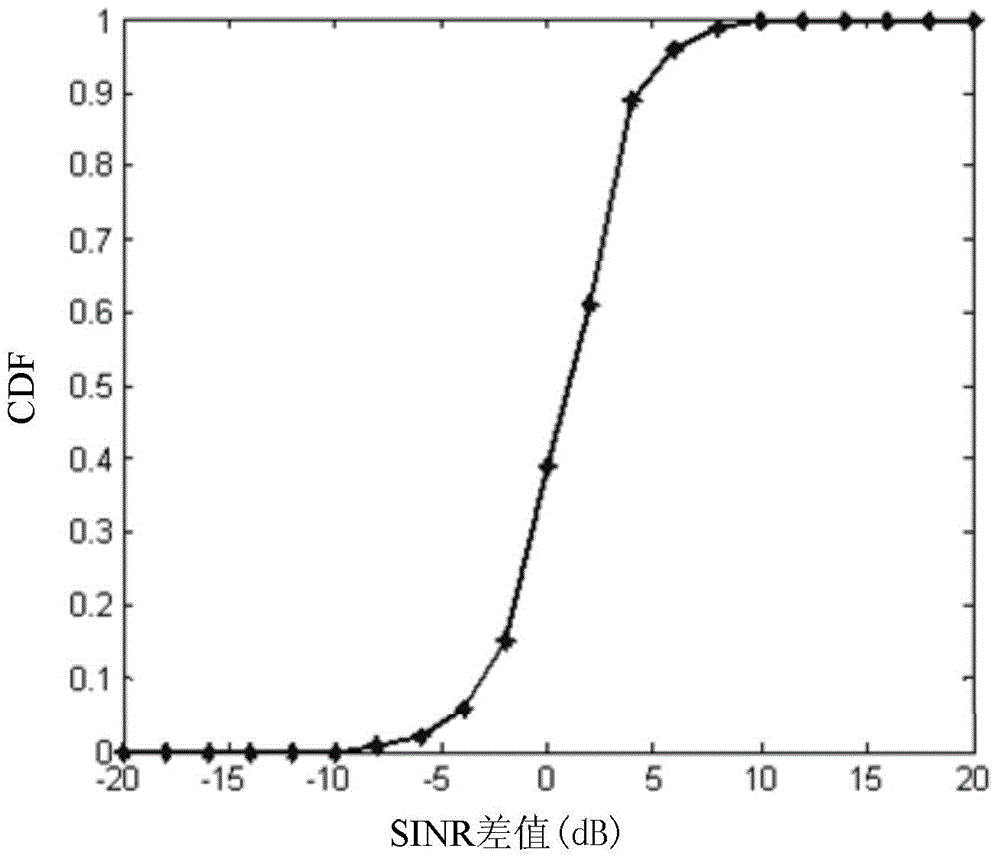
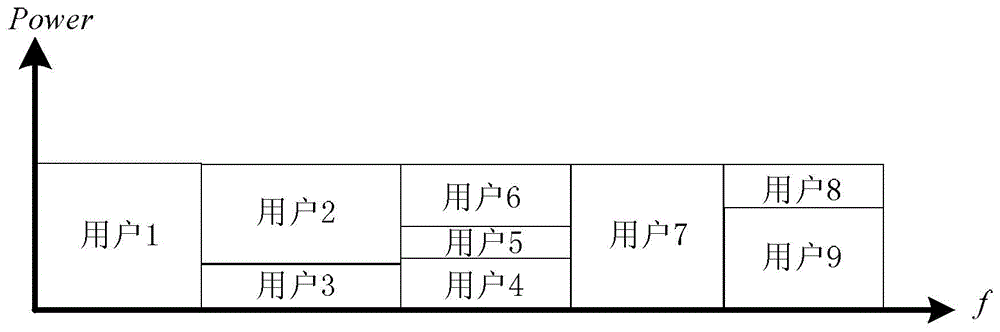
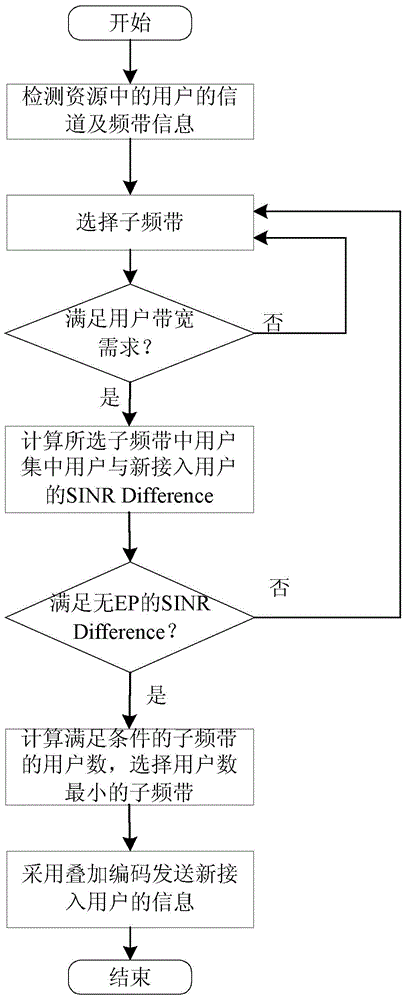
InactiveCN104980389AMeet access requirementsMeet needsMulti-frequency code systemsResource poolSuperposition coding
The invention provides a differential new user selection access method applicable to a non-orthogonal multi-access system, and relates to differential new user selection access technology applicable to non-orthogonal multi-access systems. The differential new user selection access method is used for enabling new users in the non-orthogonal multi-access system to better access the network. The method comprises the following steps: a first step, establishing an information resource pool of a full-band candidate user set; a second step, selecting sub-bands which satisfy bandwidth requirements; a third step, sequentially calculating differences of signal to interference plus noise power ratios; a fourth step, calculating a ratio A<l> of the number of users, satisfying preset standards, of each sub-band to the total number of candidate users of the sub-band, and sorting the ratios A<l> from small to large; a fifth step, carrying out selection according to the expression described in the specification; and a sixth step, carrying out non-orthogonal coding on the new access user information and other candidate user information through superposition coding, and conducting signal transmission. The differential new user selection access method provided by the invention is applicable to the differential new user selection access of the non-orthogonal multi-access system, and can satisfy the demand of a 5G new user access solution in the future.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Packet Markov superposition coding method by taking binary BCH code as component code, and decoding method
ActiveCN106059596AKeep basic code rateSimplify the design processCyclic codesComputer architectureSuperposition coding
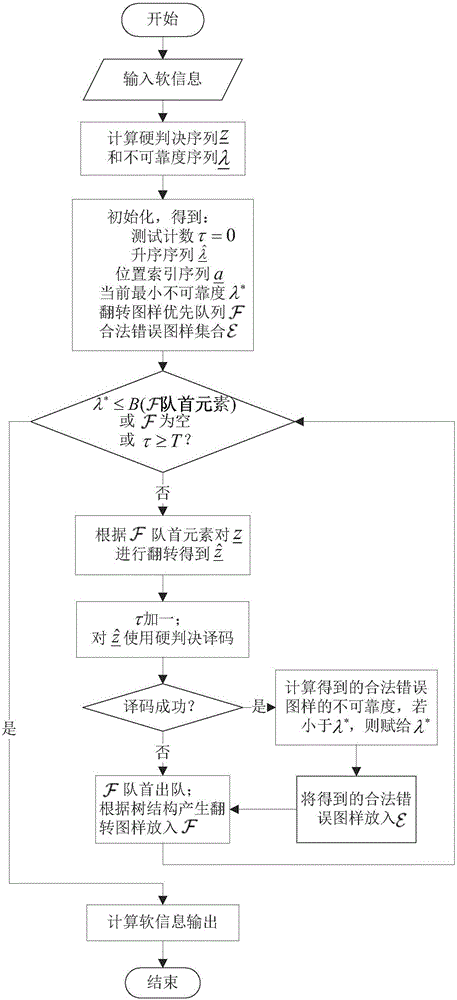
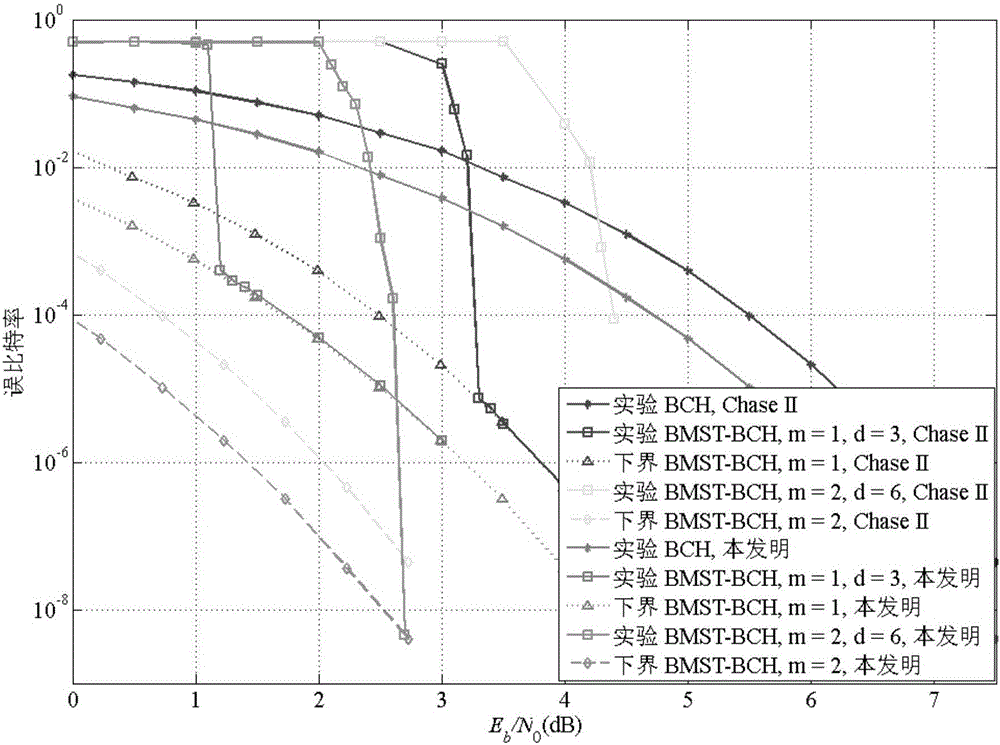
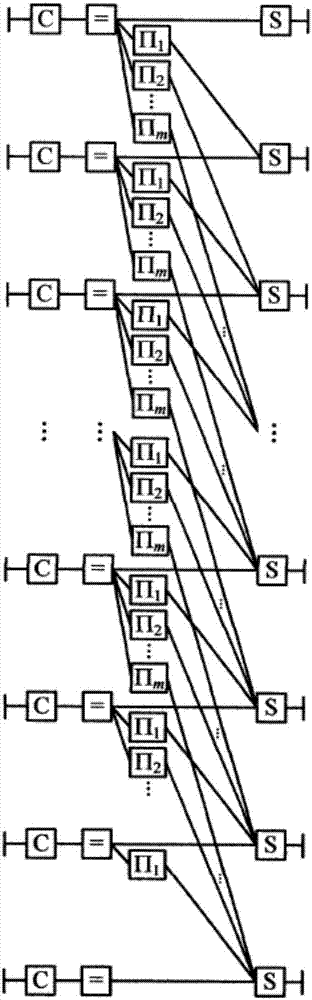
The invention belongs to the field of digital communication and digital storage, and discloses a packet Markov superposition coding method by taking a binary BCH code as a component code, and a decoding method. The binary BCH code having the code length of n, the information bit length of k and the error correcting capability of tmin is used as the component code; and a binary information sequence (u)u( / u) having the length of K=kBL is coded into a code (u)c( / u) having the length of N=nB(L+m). The invention further provides a soft iteration decoding method applicable to the packet Markov superposition coding method by taking the binary BCH code as the component code. The soft iteration decoding method comprises the following steps of: generating a turnover pattern according to a tree structure, judging whether a test process is ended or not and whether soft information output is calculated or not by using the lower bound of the unreliability of a potential legal error pattern, etc. According to the packet Markov superposition coding method and the decoding method thereof provided by the invention, the value of the coding memory length m is {1,2,3}; the net coding gain, which is greater than 10 dB, is provided at the bit error rate performance, which is as low as 10-10 to 10-15; and thus, the packet Markov superposition coding method and the decoding method thereof provided by the invention can be applied to a communication system having low bit error rate requirements, such as optical fibre communication.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Hard decision iterative decoding method for packet Markov superposition coding
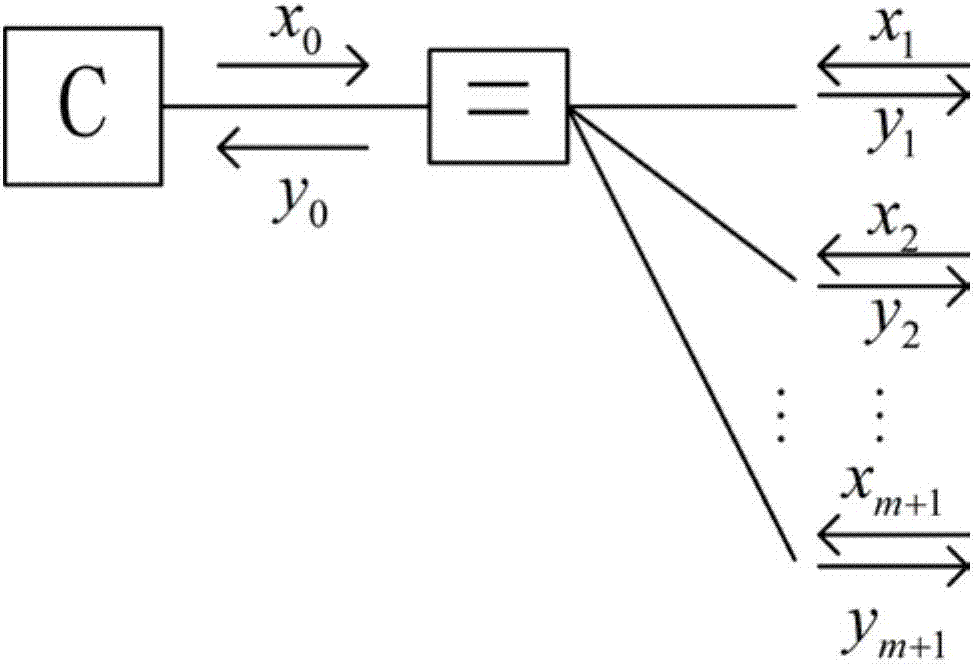
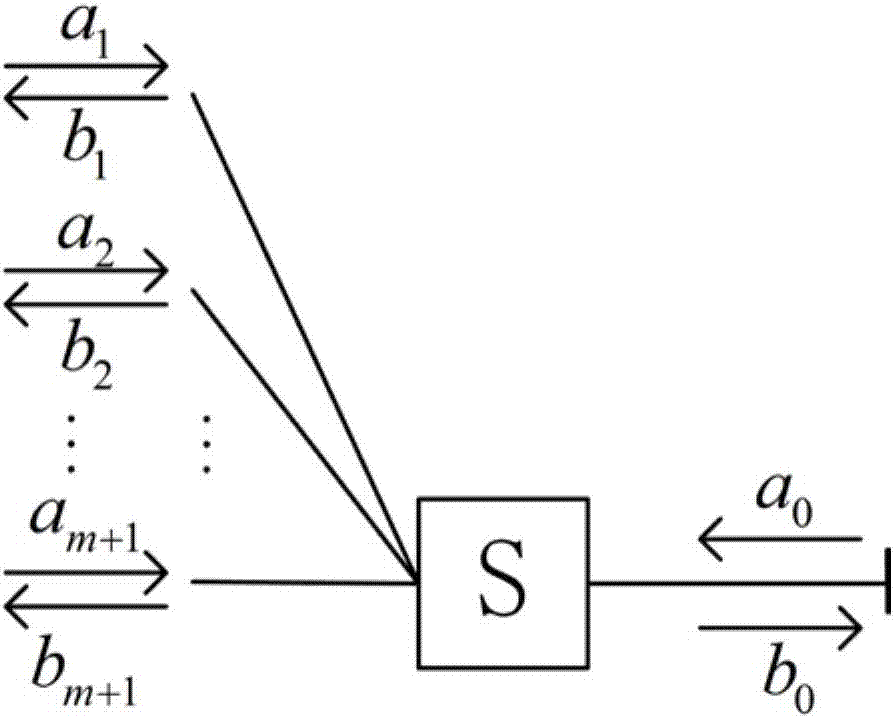
ActiveCN106992841AGood error correction performanceThe method steps are simpleError correction/detection using convolutional codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsSuperposition codingBinary information
The invention discloses a hard decision iterative decoding method for packet Markov superposition coding, and belongs to the fields of digital communication and digital storage. The hard decision iterative decoding method is used for recovering superposition-coded L groups of binary information sequences (as shown in the original PDF) with kB lengths from (L+m) hard decision vectors (as shown in the original PDF) with nB lengths corresponding to packet Markov superposition coding with a memory of m, which is constructed by a binary component code coder with a k-length input and an n-length output and for a hard decision iterative decoding method with a decoding delay as d, only {0, 1, e} is used as iterative information, wherein the e represents a state ''delete'', and a receiving end receives groups (as shown in the original PDF) of hard decision vectors and then starts decoding, so that estimation (as shown in the original PDF) of transmission information (as shown in the original PDF) is acquired. The invention further provides processing methods for each node processor in the hard decision iterative decoding method. The hard decision iterative decoding method for the packet Markov superposition coding, provided by the invention, has excellent performances, low complexity and simpleness in implementation, and can be applied to communication systems, such as optical fiber communication and the like, with the low bit error rate and low decoding time delay requirements.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
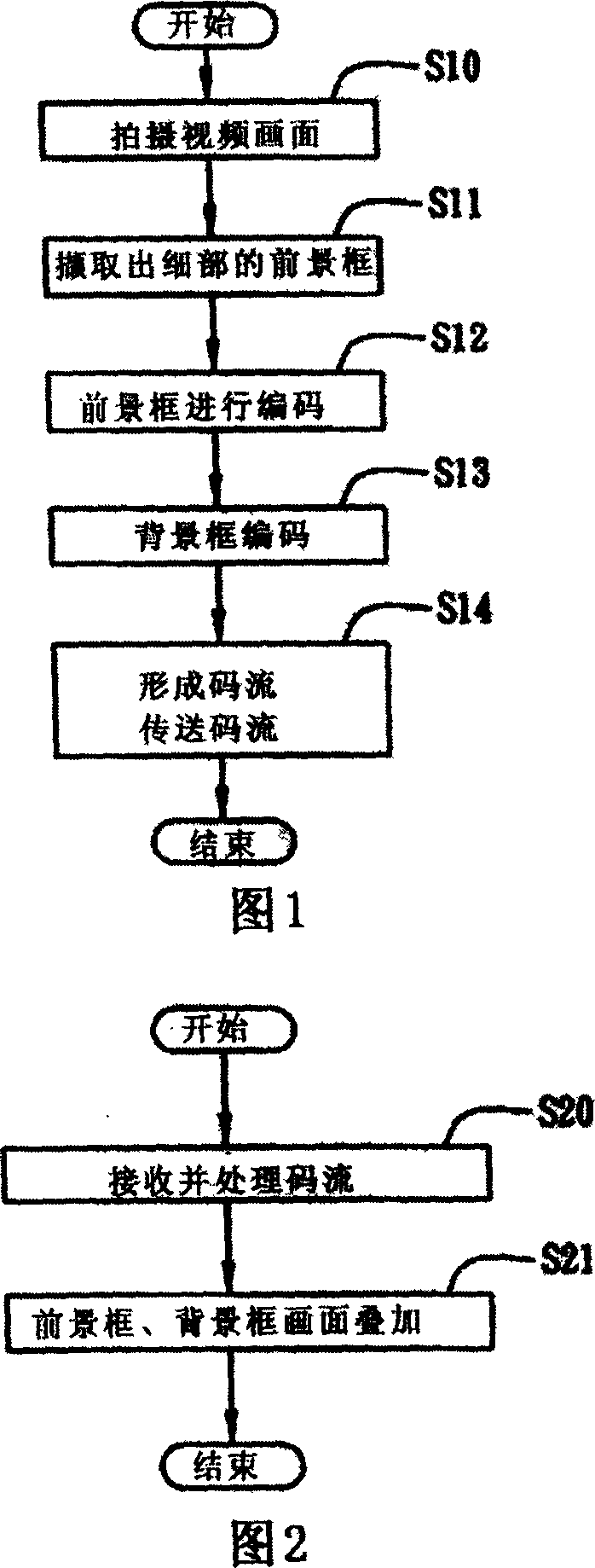
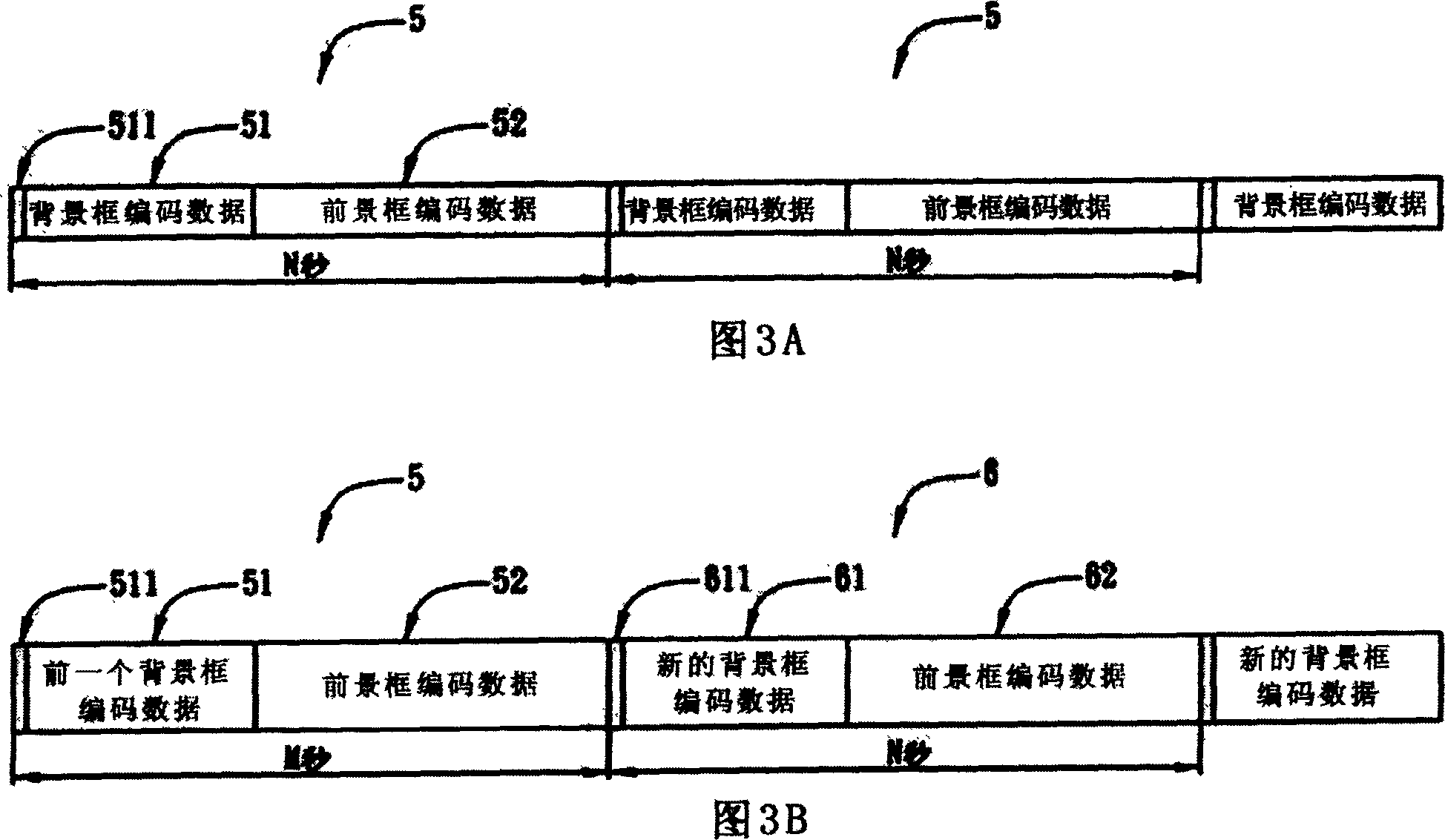
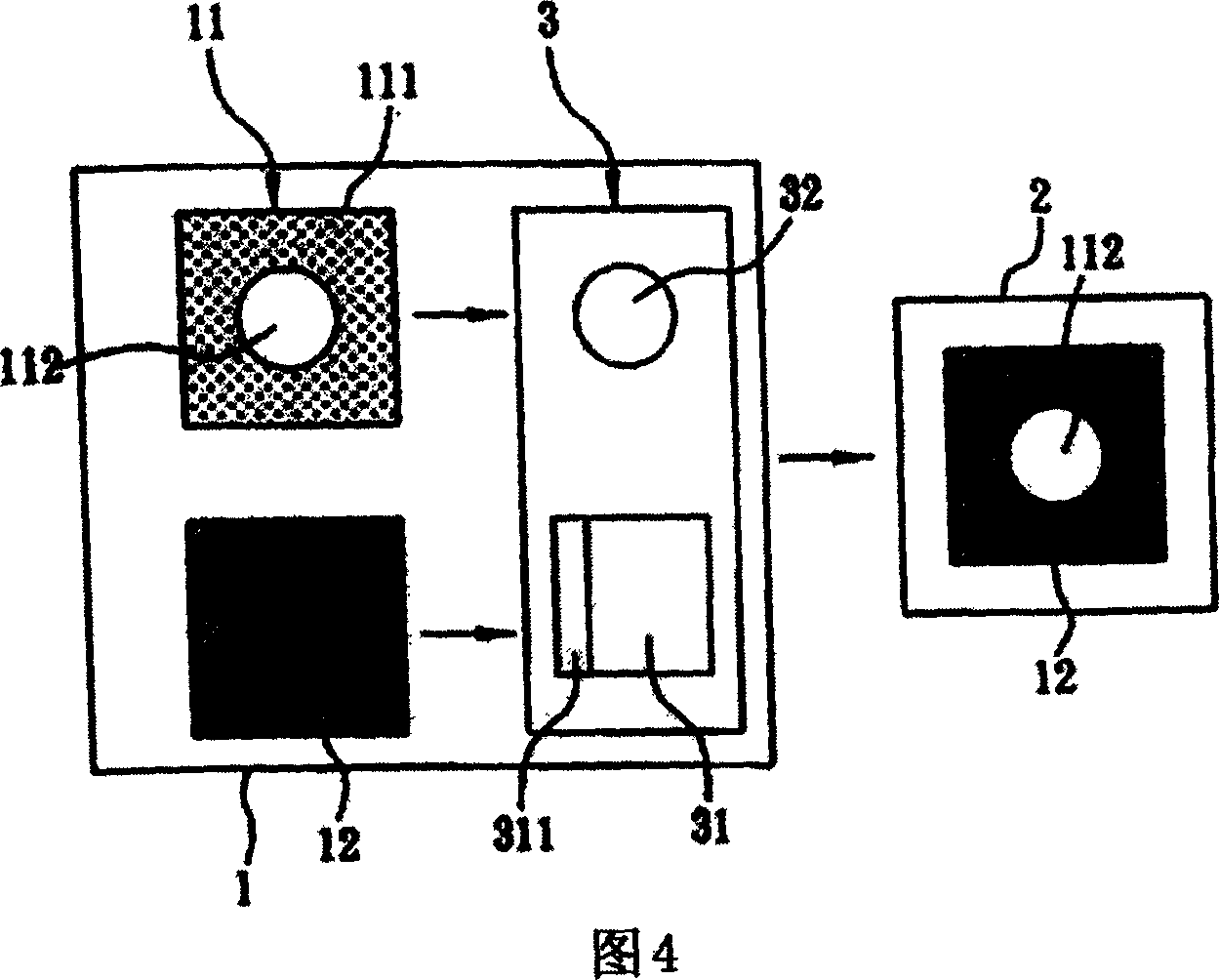
Video-picture composition code transmission method
InactiveCN1980334AReduce code rateReduce computationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSuperposition codingComputer graphics (images)
Through each own electronic communication device, sending client end and receiving client end carries out communication process with video service. Foreground frame of the sending client end segments video image frame shot and picks up detail part, and then foreground frame and background frame encodes video image frame and transfers it to the receiving client end. Since background frame is changeless before background is replaced, thus, the code of the background is needed to transferred to the receiving client end just once. In the invention, video frame is divided into foreground frame and background frame. Encoding and decoding foreground frame and background frame are carried out respectively. The invention realizes diversified video image frames providing high amusement effect. Features are: lowering encoded code rate, reducing operation quantity and limitation of communication bandwidth.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
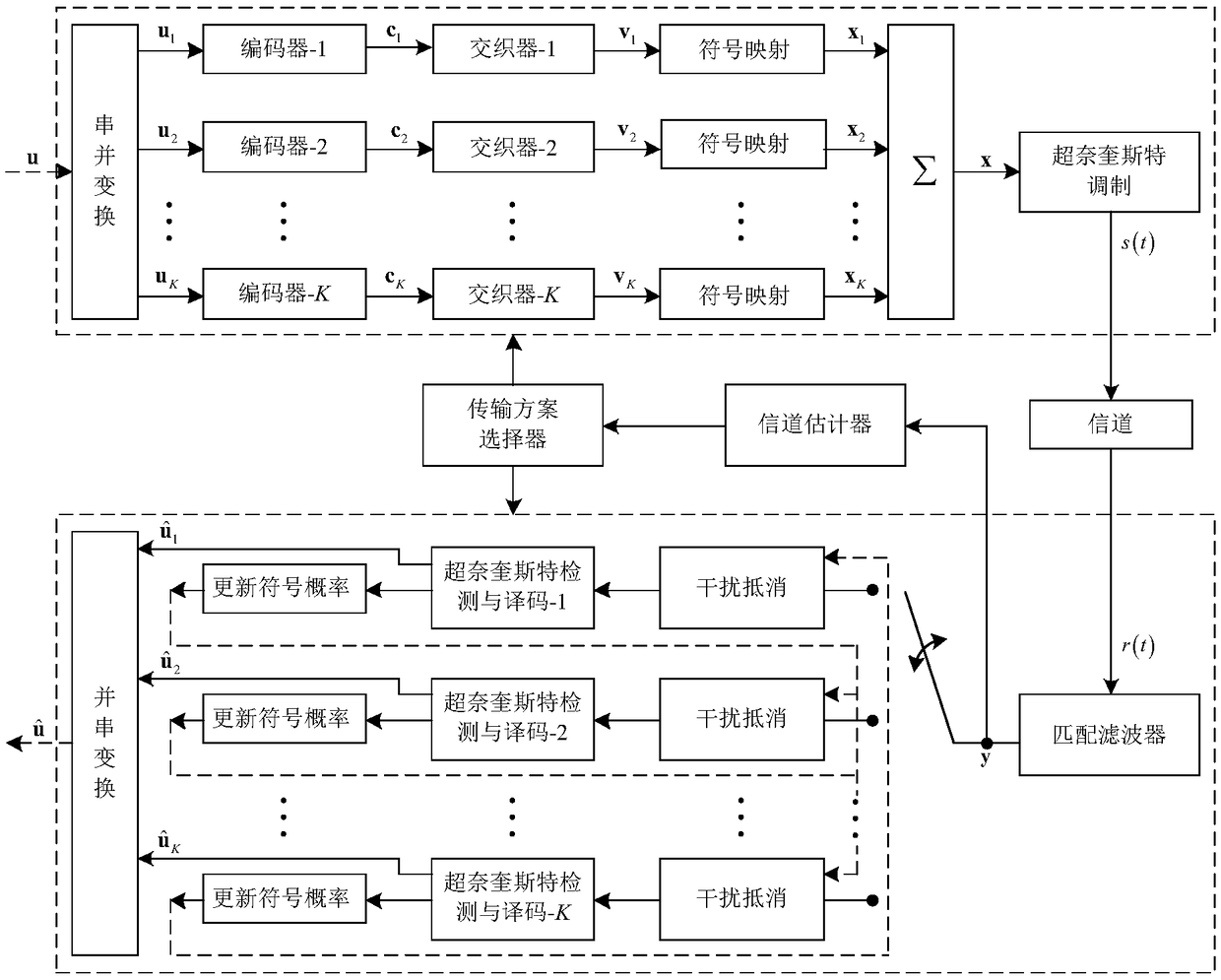
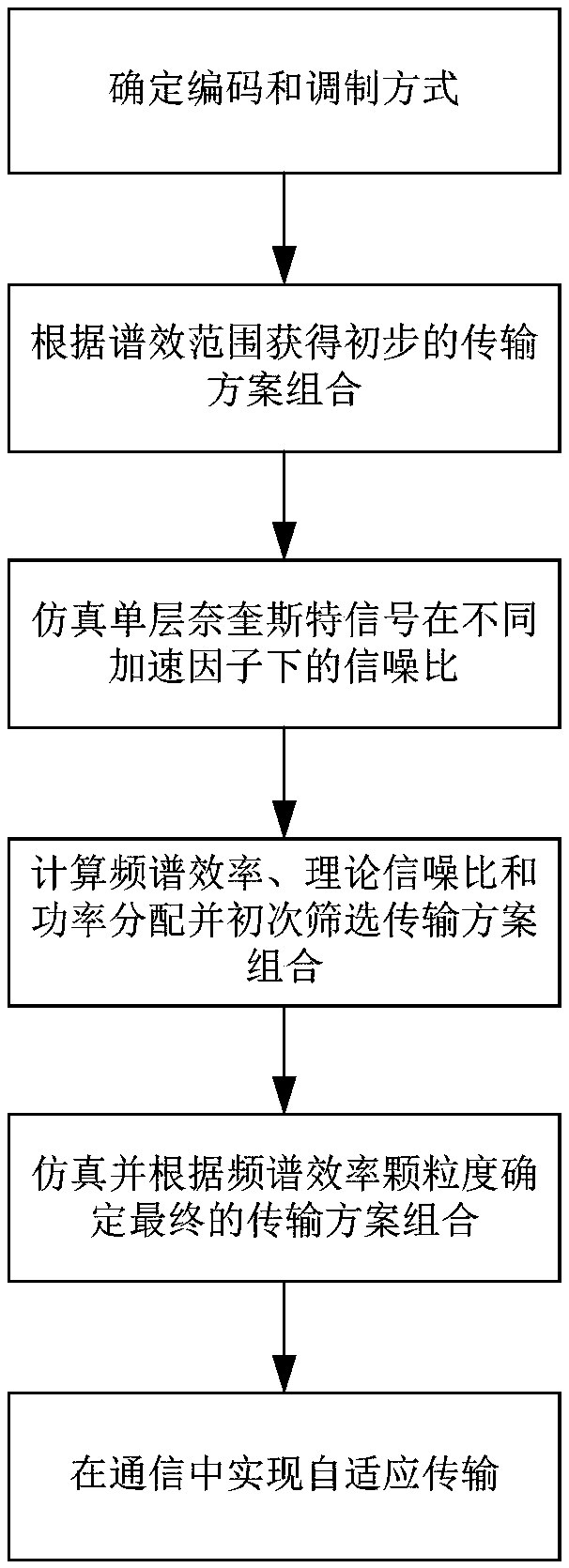
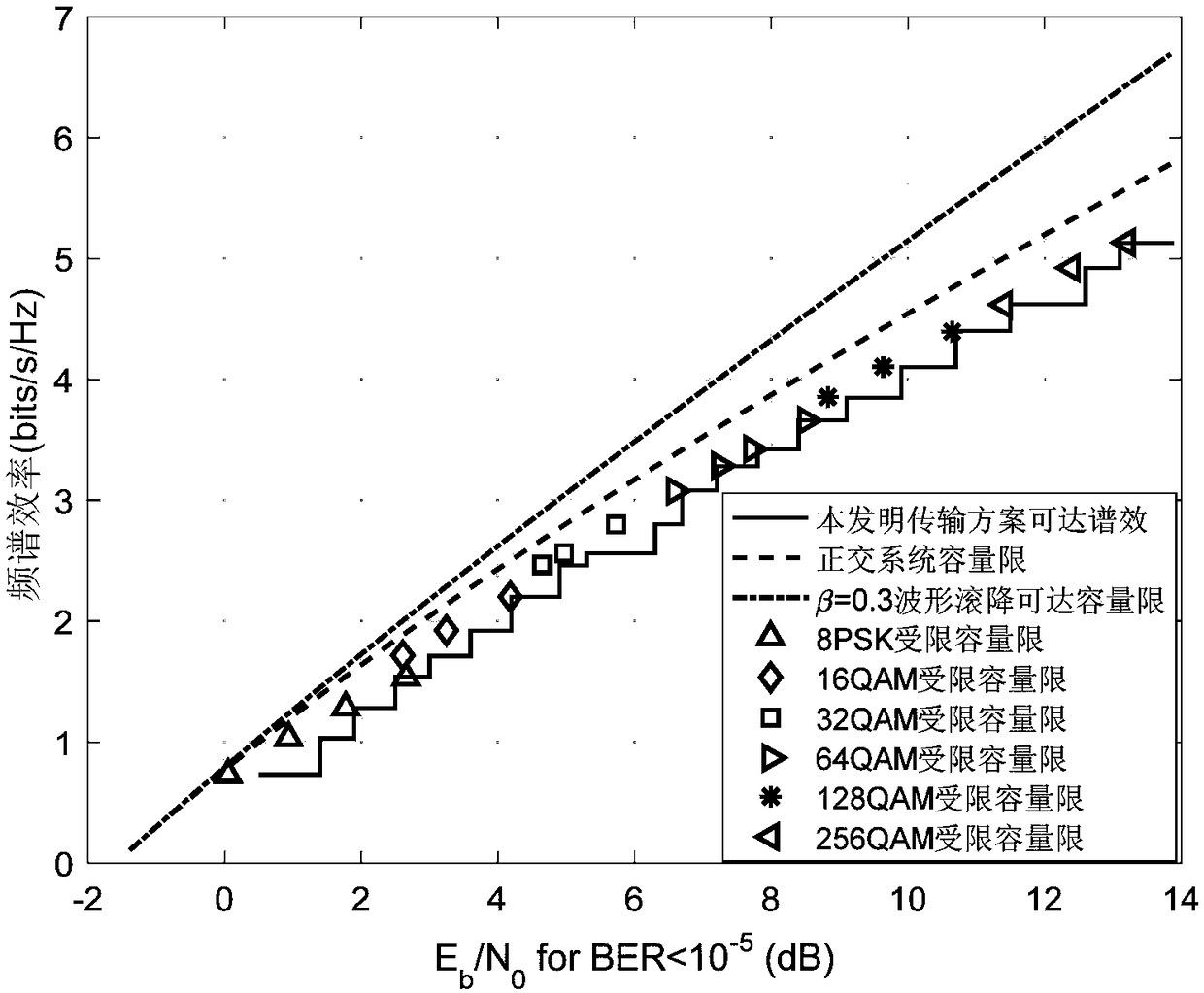
Adaptive system and method of super-Nyquist based on superposition coded modulation
ActiveCN109150409AOvercome limitationsAvoid code rate compatibility issuesTransmission monitoringChannel coding adaptationSuperposition codingFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a super Nyquist adaptive system and a super Nyquist adaptive method based on the superposition coding modulation, which solves the problems of code rate compatibility and highcomplexity caused by high-order modulation and multiple code rates in prior art. The invention realizes adaptive coded modulation by changing the number of layers of a superposition coded modulation module and the acceleration factor of a Nyquist modulation module. The steps of the method are as follows: determining the coding and modulation mode; obtaining a preliminary transmission scheme combination; simulating a single-layer super-Nyquist signal for obtaining a signal-to-noise ratio; performing primary selection of an initial transmission scheme combination; simulating and determining thefinal combination of multiple transmission schemes available for selection; and realizing adaptive transmission in communication. As that transmission scheme is screened for the first time according to the theoretical signal-to-noise ratio, the simulation workload is reduced and the efficiency is improved. The adaptive system and the method support a large spectrum efficiency range and meet the requirement of the communication on the spectrum efficiency. The adaptive system and the method have low complexity and high flexibility, and are used in the wireless communication system such as the ground and the satellite.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Coherent transmission from distributed wireless transmitters
InactiveCN103988449AModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmission for post communicationMulti inputSuperposition coding
In one aspect, a distributed coherent transmission system enables transmissions from separate wireless transmitters with independent frequency or clock references to emulate a system where all the transmitters share a common frequency or clock reference. Differences in frequency and / or phase between transmitters are addressed by suitably precoding signals before modulation at one or more of the transmitters based on a synchronizing transmission from one of the transmitters (e.g., a master transmitter) received at a corresponding receiver sharing the frequency or clock reference with each of the one or more transmitters. Such a distributed coherent transmission system can allow N single-antenna transmitters with independent frequency or clock references to emulate a single N-antenna Multi Input Multi Output (MIMO) transmitter, or implement schemes such as distributed superposition coding or lattice codes that require coherence across separate transmitters.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Resource Allocation for Superposition Coding
When the codeword level interference cancellation (CW-IC) is used at the receiver in conjunction with the superposition coding scheme at the transmitter, in order to guarantee the success of signal reception, restrictions of scheduling decisions in resource allocation of superposed transport blocks may occur. A method to mitigate the scheduling restrictions is proposed. For a low-geometry UE in NOMA operation, one sub-band is used as the basic scheduling unit. As a result, data in resource blocks scheduled for NOMA operation and data in resource blocks scheduled for other non-NOMA operation correspond to different transport blocks. Therefore, a high-geometric UE only needs to decode the data scheduled for NOMA. The base station does not need to impose additional scheduling restrictions and signaling overhead.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
Method for applying combination of network encoding and constellation overlapped encoding in collaboration relay system
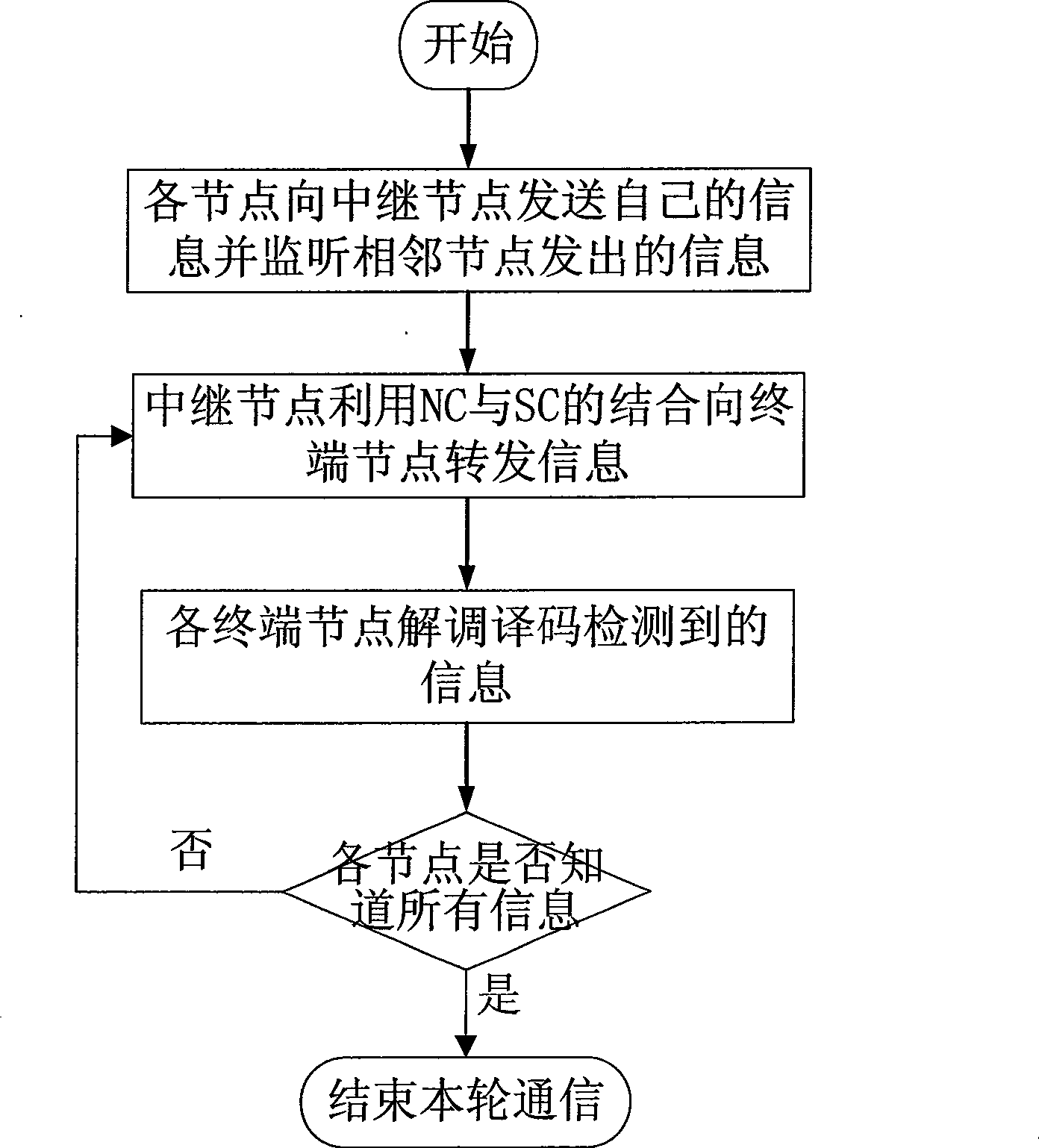
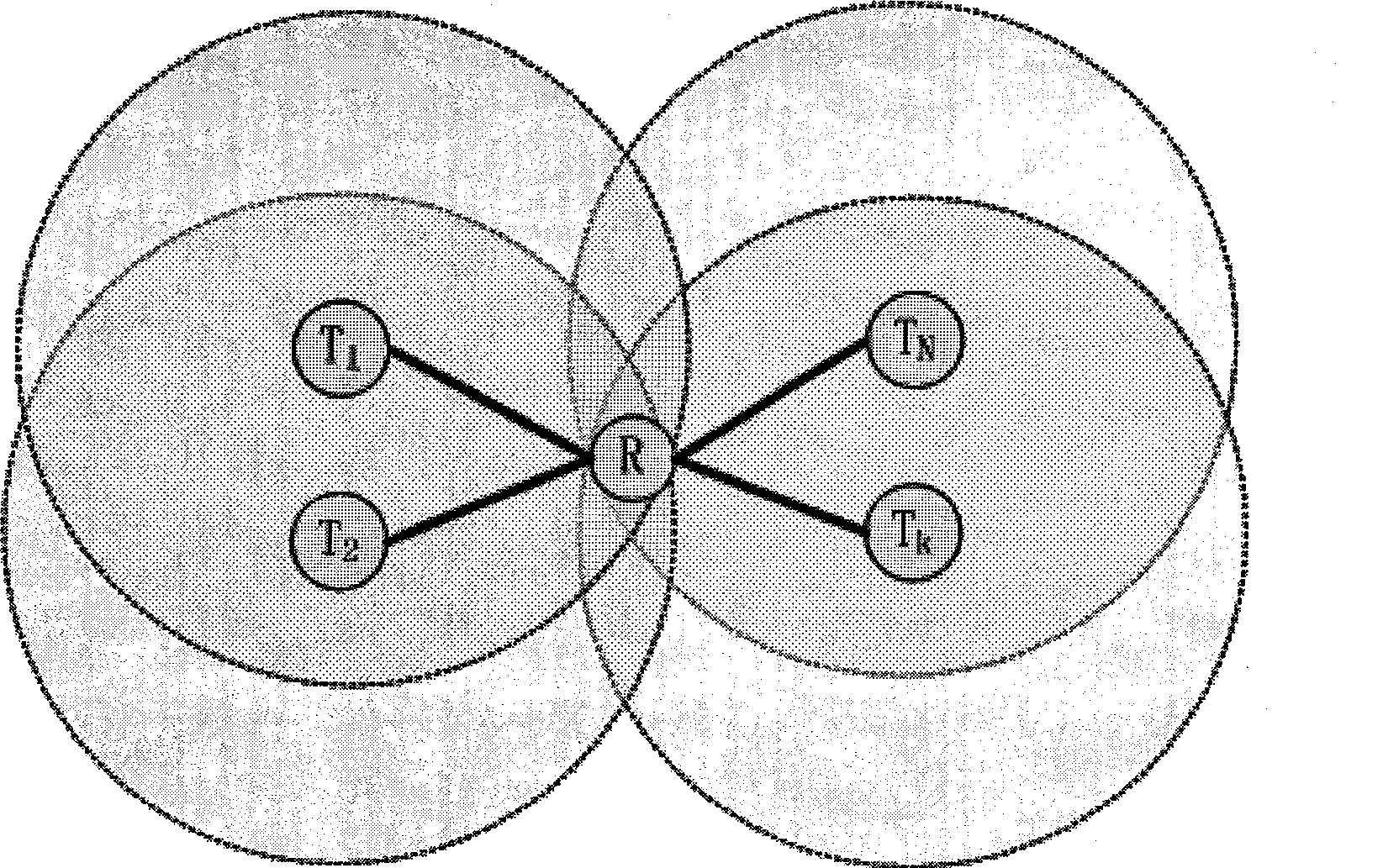
ActiveCN101394327ASave resourcesImprove throughputSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationSuperposition codingNetwork code
The invention provides a technical proposal used in a cooperative relay system, which further optimizes system throughput by integrating two up-to-date communication technologies including network coding (NC) and cooperative superposition coding (SC) and designing to utilize the two technologies in saving system resources at the same time. The proposal is easy to implement and has flexible application ways. The invention effectively integrates the NC and the SC technologies during forwarding information at relay nodes. The technical proposal comprises the steps of performing network coding of information of as many demodulated nodes with relatively better channel conditions as possible and mapping to an SC basic constellation map, and mapping NC information on an additional constellation map and broadcasting to all nodes. The technical proposal greatly saves system resources, so as to remarkably improve the system throughput.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Secure image transmission method based on fountain code and self-adaptive resource distribution
ActiveCN105553618ARealize unequal security protectionSave transmission resourcesPower managementSignalling characterisationSuperposition codingFountain code
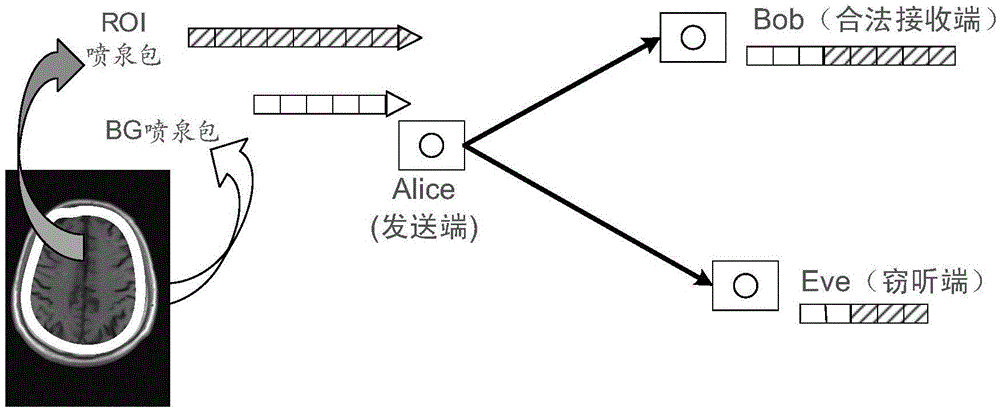
The invention discloses a secure image transmission method based on a fountain code and self-adaptive resource distribution. The invention aims at specifically ensuring the security of a region-of-interest in a medical image under delay constraint. Firstly, the image is subjected to region segmentation to extract the region-of-interest (ROI) and a background region (BG), thus two kinds of original data packages ROI and BG are obtained. Secondly, the type of the data package to be transmitted is selected according to the channel quality of a legal link and the receiving state identifiers of the two kinds of data packages. Then the self-adaptive resource distribution is performed according to the channel quality of the legal link, thus a legal receiving end achieves higher data package correct receiving rate. At last, the RS fountain code is performed on the original data package to be transmitted. In order to compensate relatively high time delay due to the fact that the BG package is transmitted when the channel quality is poor, the two kinds of packages are simultaneously transmitted in a superimposed coding manner when the channel quality is especially good. By simulation verifying, the secure image transmission method can well achieve key protection on the ROI in the image.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Detection method in hierarchical superposition coding generalized spatial modulation system
ActiveCN106254036AUniform performanceSpatial transmit diversityError preventionQuality of serviceSuperposition coding
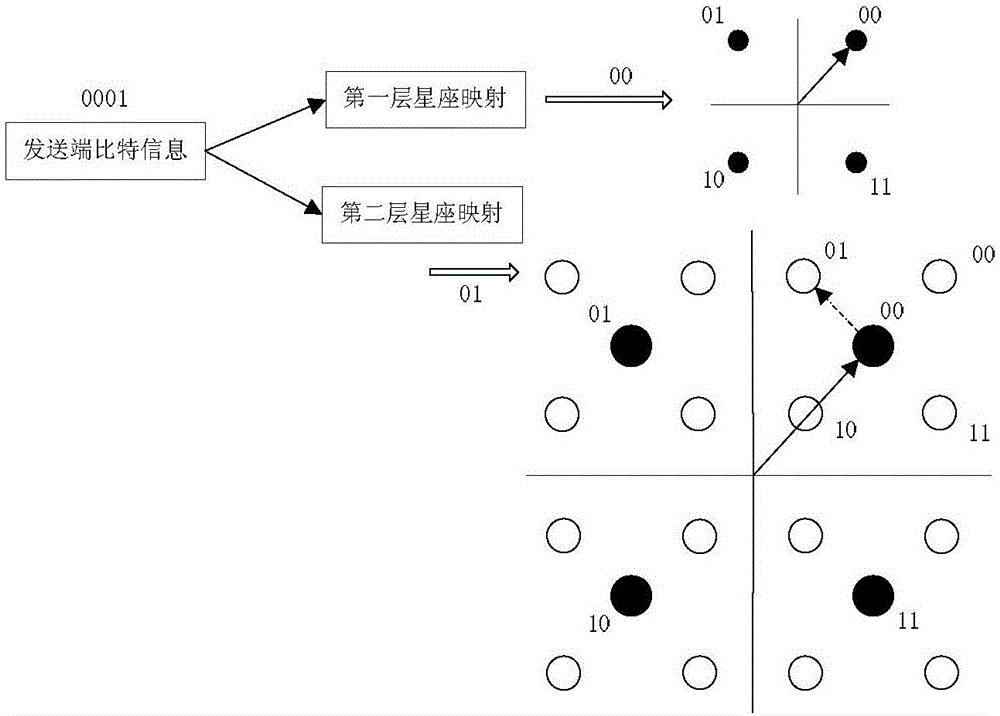
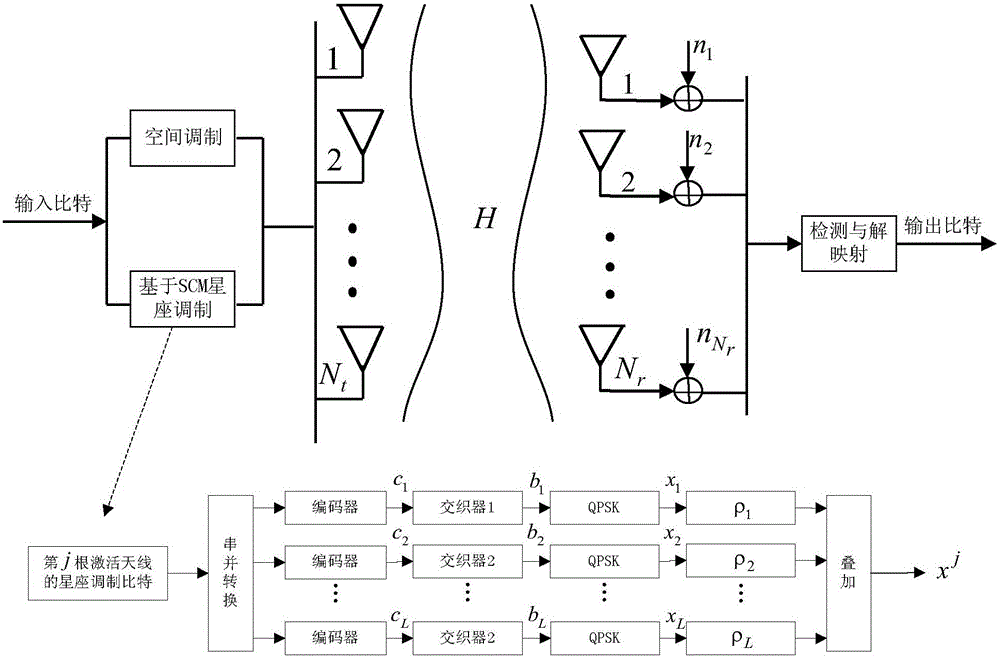
The invention discloses a detection method in a generalized spatial modulation system (SCM-GSM) adopting hierarchical superposition coding, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The hierarchical coding modulation (SCM) technology is adopted on constellation mapping to meet the different requirements of quality of service of different data services on the same transmission time slot, and a variety of business demands of a future 5G system can be met for flexibly. Based on the constellation modulation principle based on SCM, a receiving end proposes an iterative hierarchical detection (ILD) algorithm, the method can effectively reduce the search times of signal detection, and the system bit error rate (BER) performance is approximate to theoptimal maximum likelihood (ML) detection.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Superposition encoding method, decoding method, devices, transmitter and receiver
ActiveCN105703877ASolve the problem of low performanceImprove performanceError preventionPhase-modulated carrier systemsSuperposition codingComputer science
The invention discloses a superposition encoding method, a decoding method, devices, a transmitter and a receiver. The superposition encoding method comprises the following steps: modulating the information flow of first-kind users through a binary phase shift keying BPSK modulation approach to get a first modulation symbol; modulating the information flow of second-kind users through a second-kind modulation approach to get a second modulation symbol; allocating power for the first modulation symbol and the second modulation symbol; and superposing the first modulation symbol and the second modulation symbol after power allocation, wherein the constellation diagram of the superposed symbols is in gray mapping. According to the method, the problem that multiple users are of low performance when the multiple users are directly superposed in the related technologies is solved, and the performance of multiple users is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Multi-service broadcasting single-frequency network optimizing method based on superposition codes
ActiveCN104486641AReduce analysis design cycleEfficient use ofSelective content distributionSuperposition codingPhysical layer
The invention discloses a multi-service broadcasting single-frequency network optimizing method based on superposition codes. The multi-service broadcasting single-frequency network optimizing method comprises the following steps of S1, segmenting physical layer channels into a common subchannel and a local subchannel which are used for respectively transmitting common services and local services; S2, according to the networking information and service requirements, setting the initial values of transmitting base station parameters and subchannel transmitting parameters, and selecting one part of parameters as to-be-optimized parameters, including adjustable transmitting parameters of subchannels and adjustable parameters of a transmitting base station; S3, calculating the target function value corresponding to the overall receiving property of the target area, optimizing the adjustable transmitting parameters of the subchannels, and furthest optimizing the target function value; S4, performing optimum iteration on the adjustable transmitting parameters of the transmitting base station, and gradually updating the target function value by generations, so as to obtain the optimum adjustable parameters; S5, repeating the steps S2 to S5, selecting different initial values, so as to obtain a group of optimizing results. The multi-service broadcasting single-frequency network optimizing method has the advantages that the coverage requirement of the common services is guaranteed to meet, and the coverage effect of the local services is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com