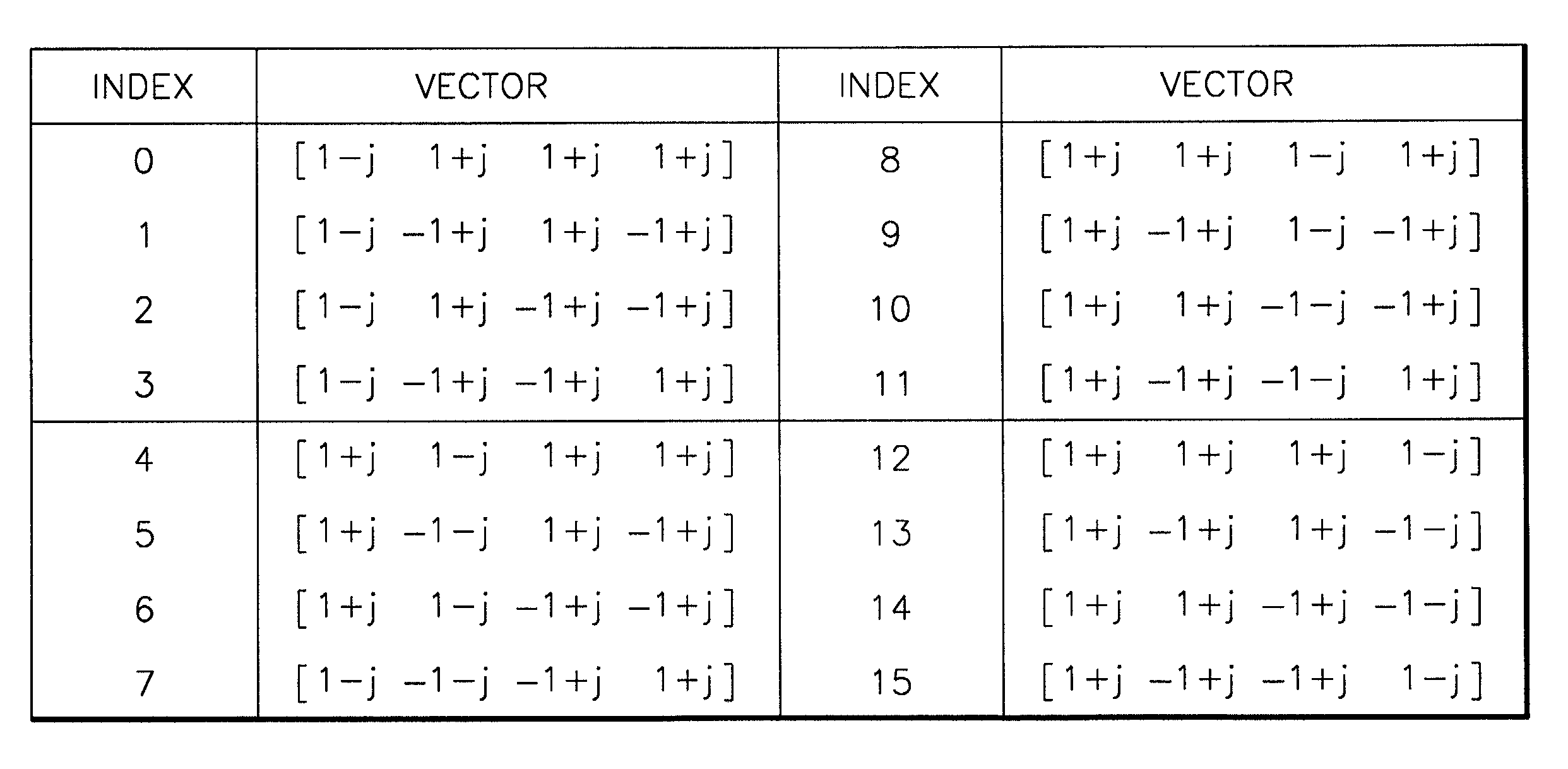Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
769 results about "Transmit diversity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
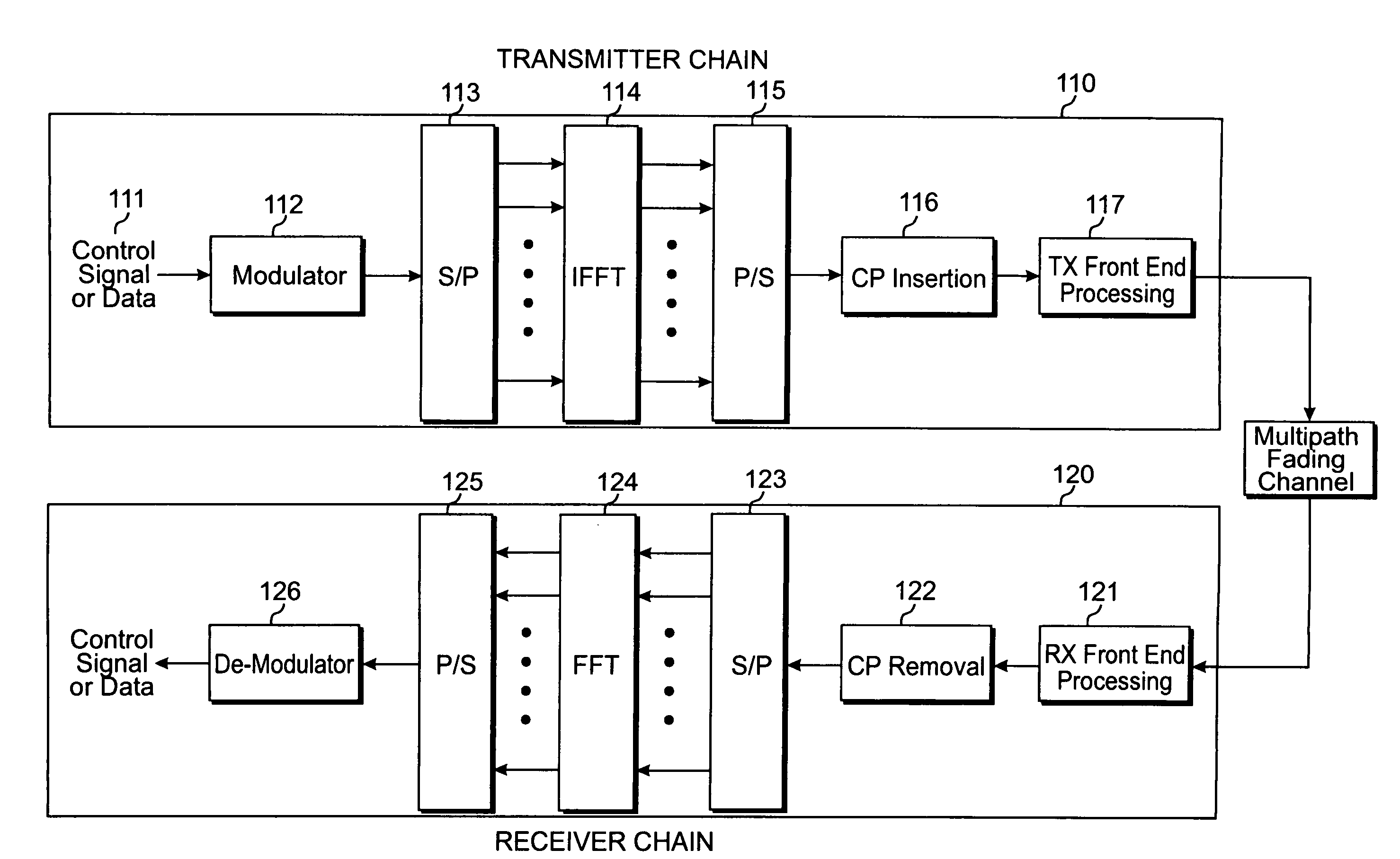
Transmit diversity is radio communication using signals that originate from two or more independent sources that have been modulated with identical information-bearing signals and that may vary in their transmission characteristics at any given instant.
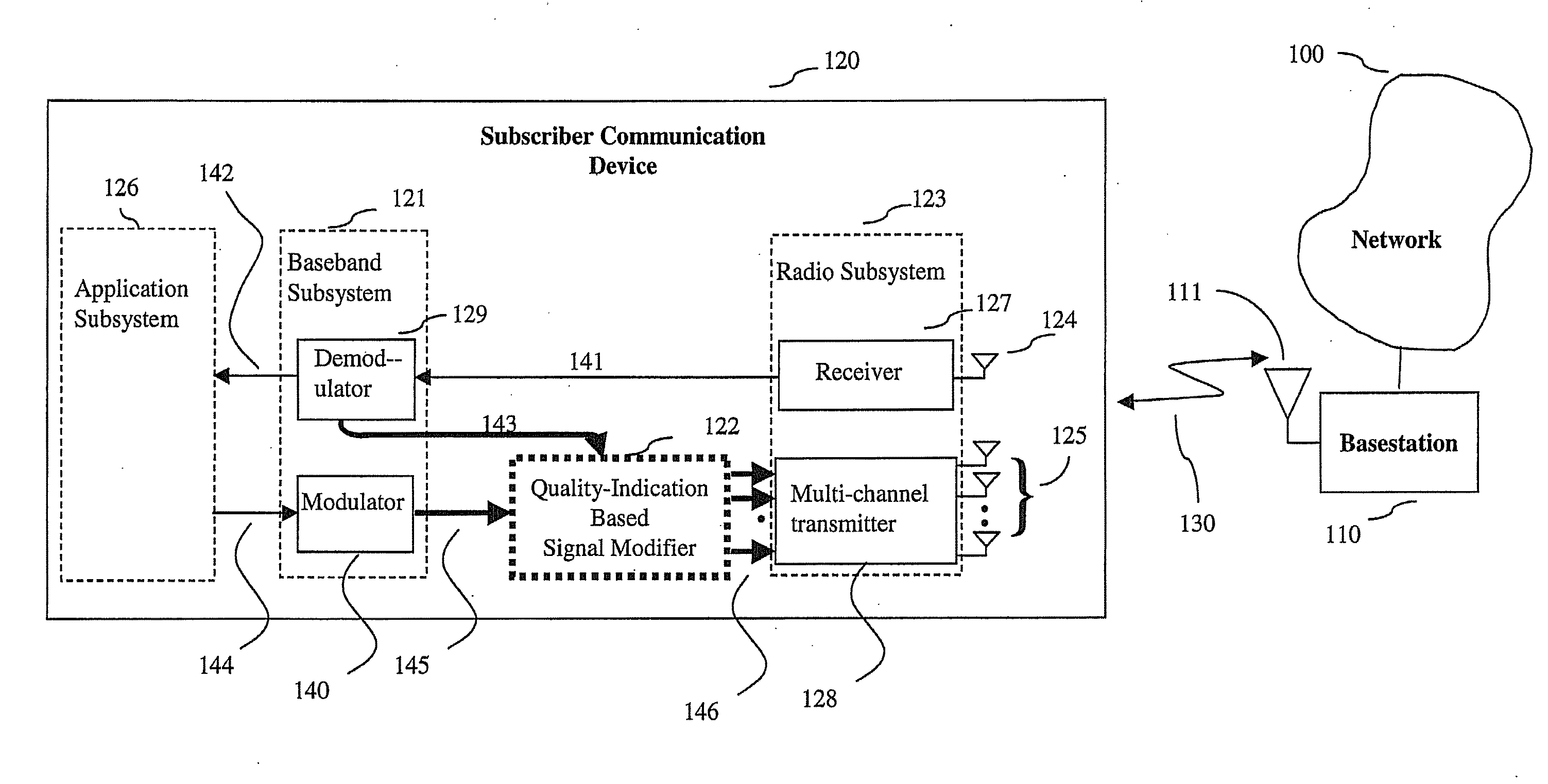
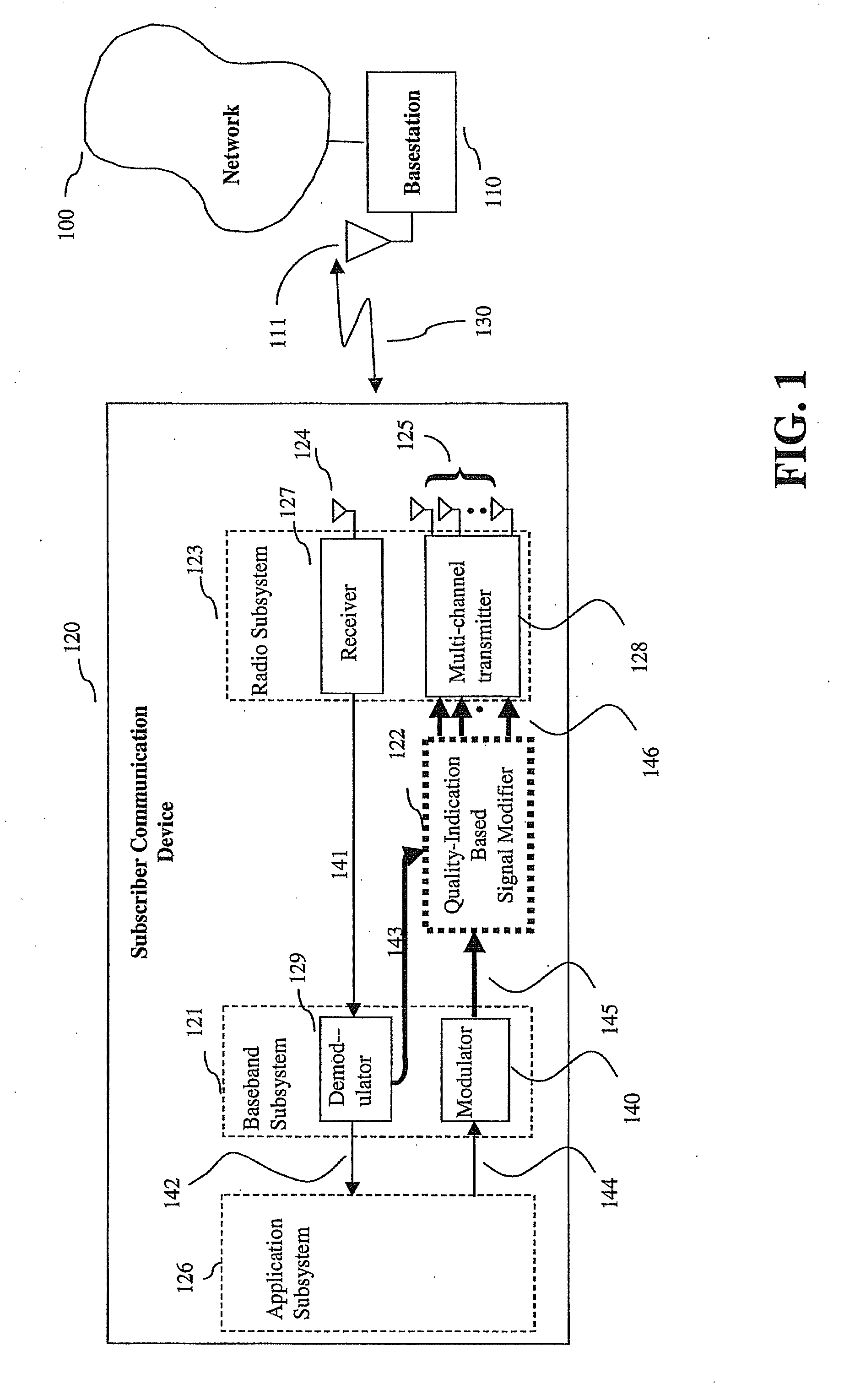
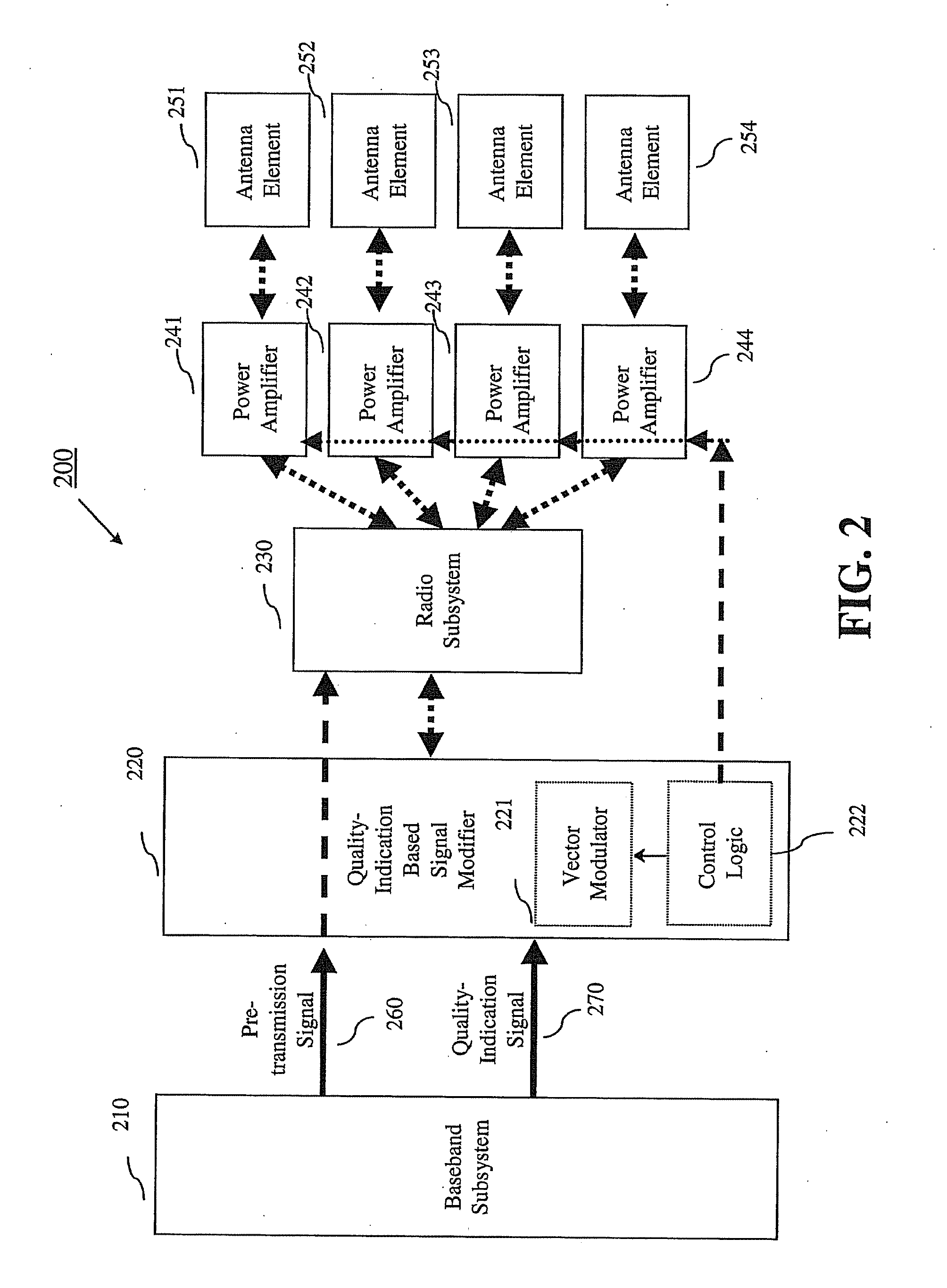
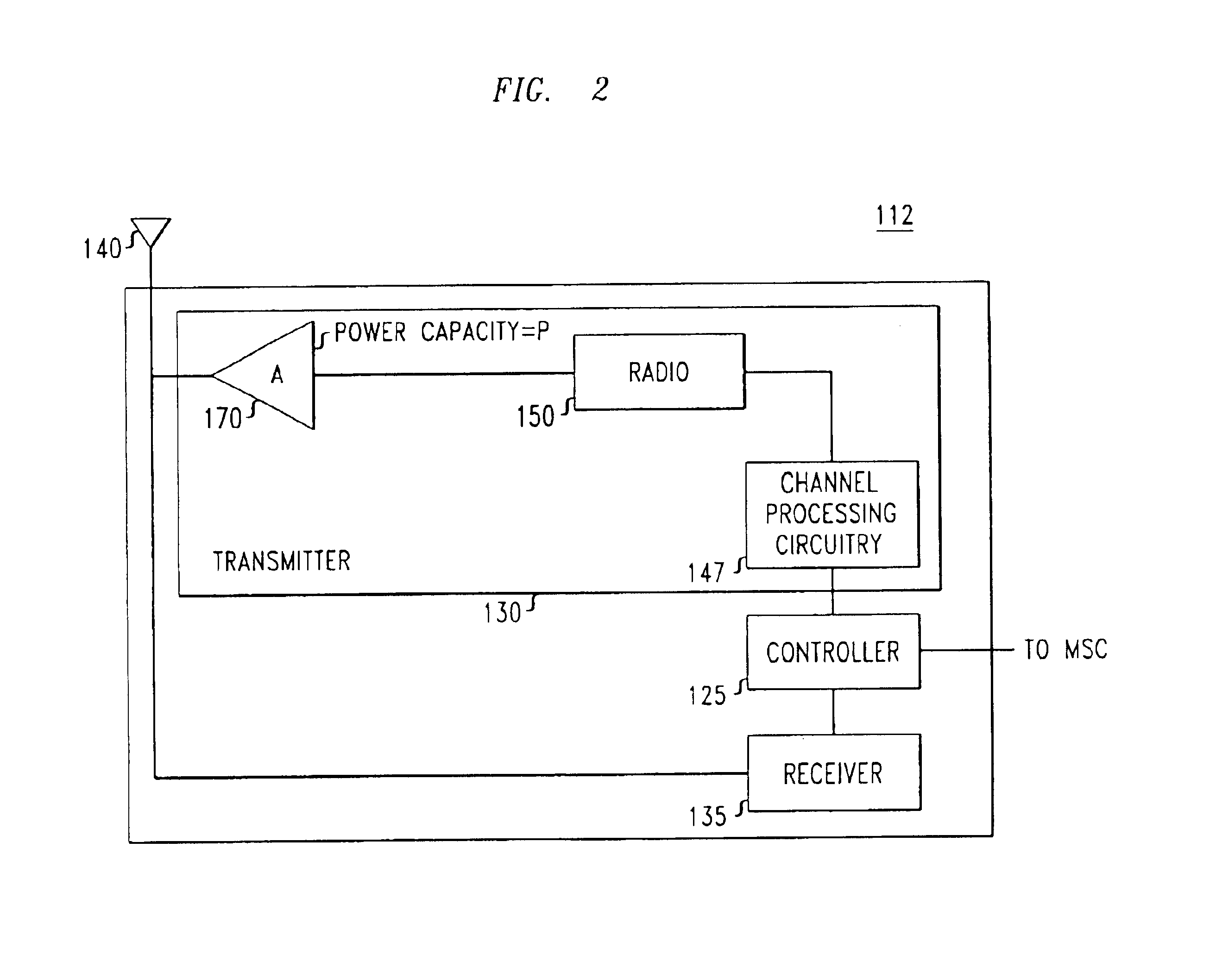
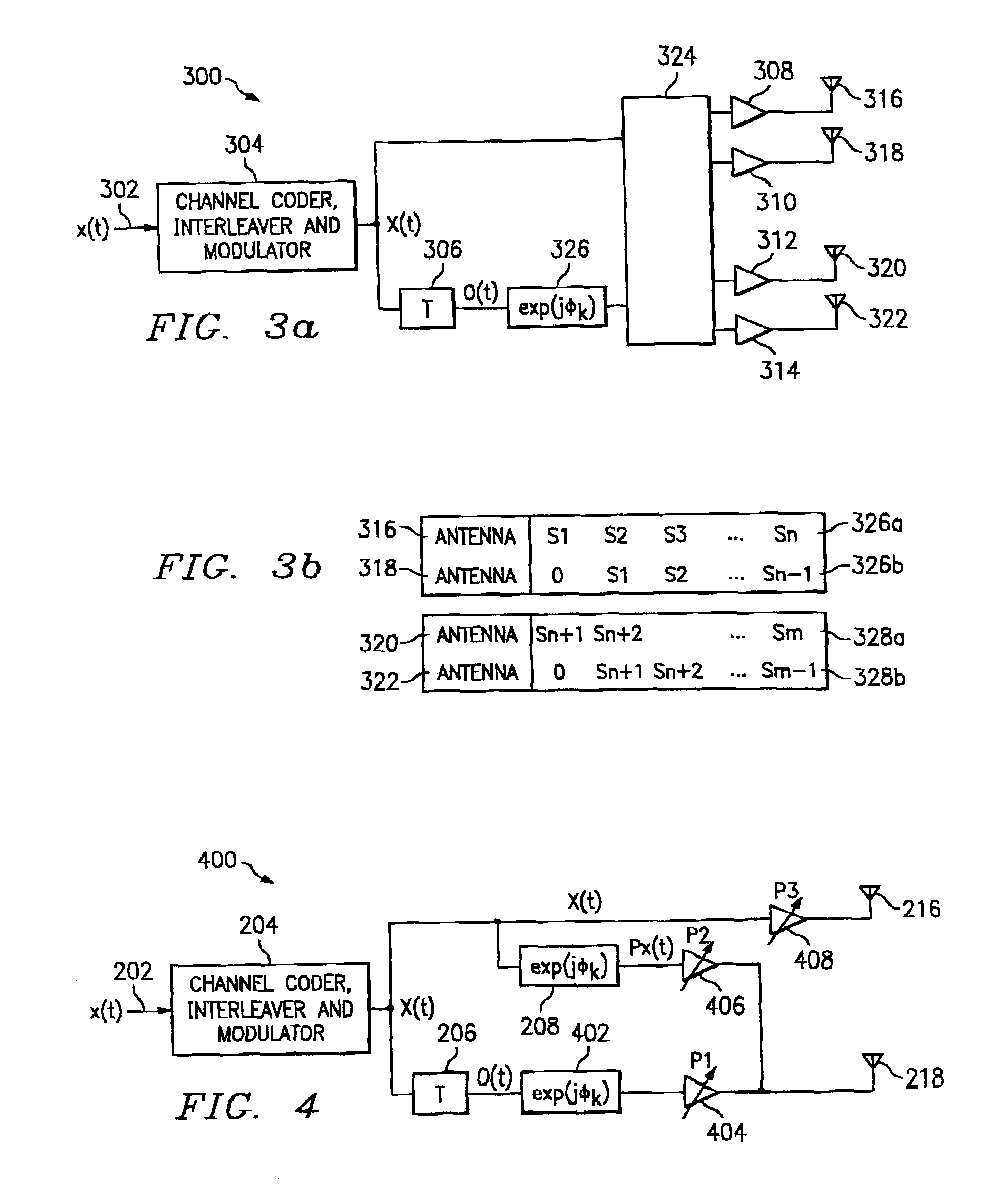
System, method and apparatus for mobile transmit diversity using symmetric phase difference
InactiveUS20100266063A1Easy to receiveQuality improvementPower managementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase differenceDiversity scheme
Communication is performed for a first communication device having a set of antenna elements. A quality-indication signal is received from a second communication device (e.g., a basestation). A complex weighting is calculated based on the quality-indication signal. A pre-transmission signal is modified based on the complex transmit diversity weighting to produce a set of modified-pre-transmission signals, wherein the modifications are symmetric by making approximately half the magnitude of the transmit diversity modification to one signal in a first direction, and approximately half the magnitude of the transmit diversity modification to the other signal in a second direction, opposite the first direction. Each modified pre-transmission signal from the set of modified-pre-transmission signals is uniquely associated with an antenna element from the set of antenna elements. The set of modified-pre-transmission signals is sent from the set of antenna elements to produce a transmitted signal.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
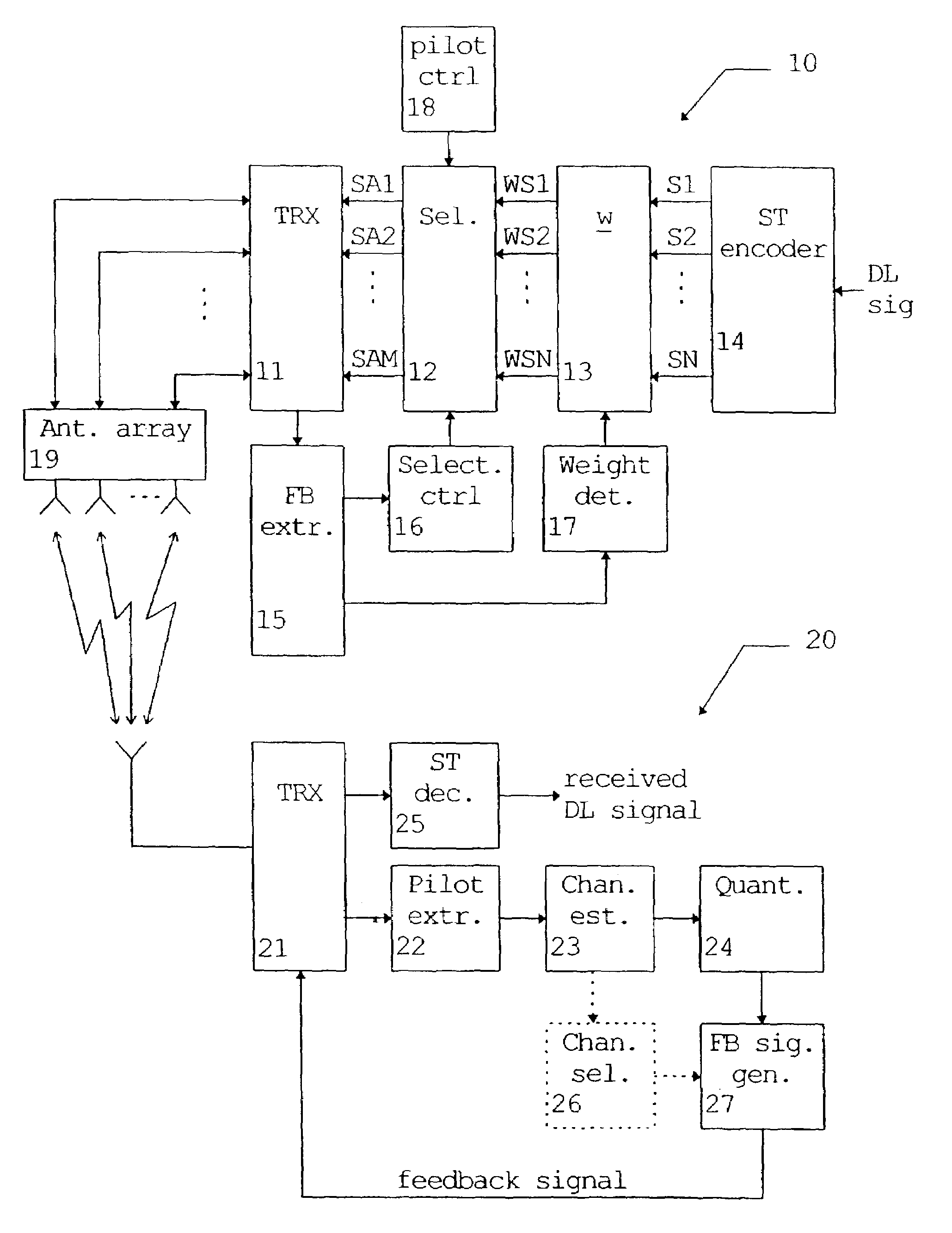
Multi-antenna transmission method and system
InactiveUS7403748B1Improve transmission gainImprove channel estimation performanceSpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumSignal quality
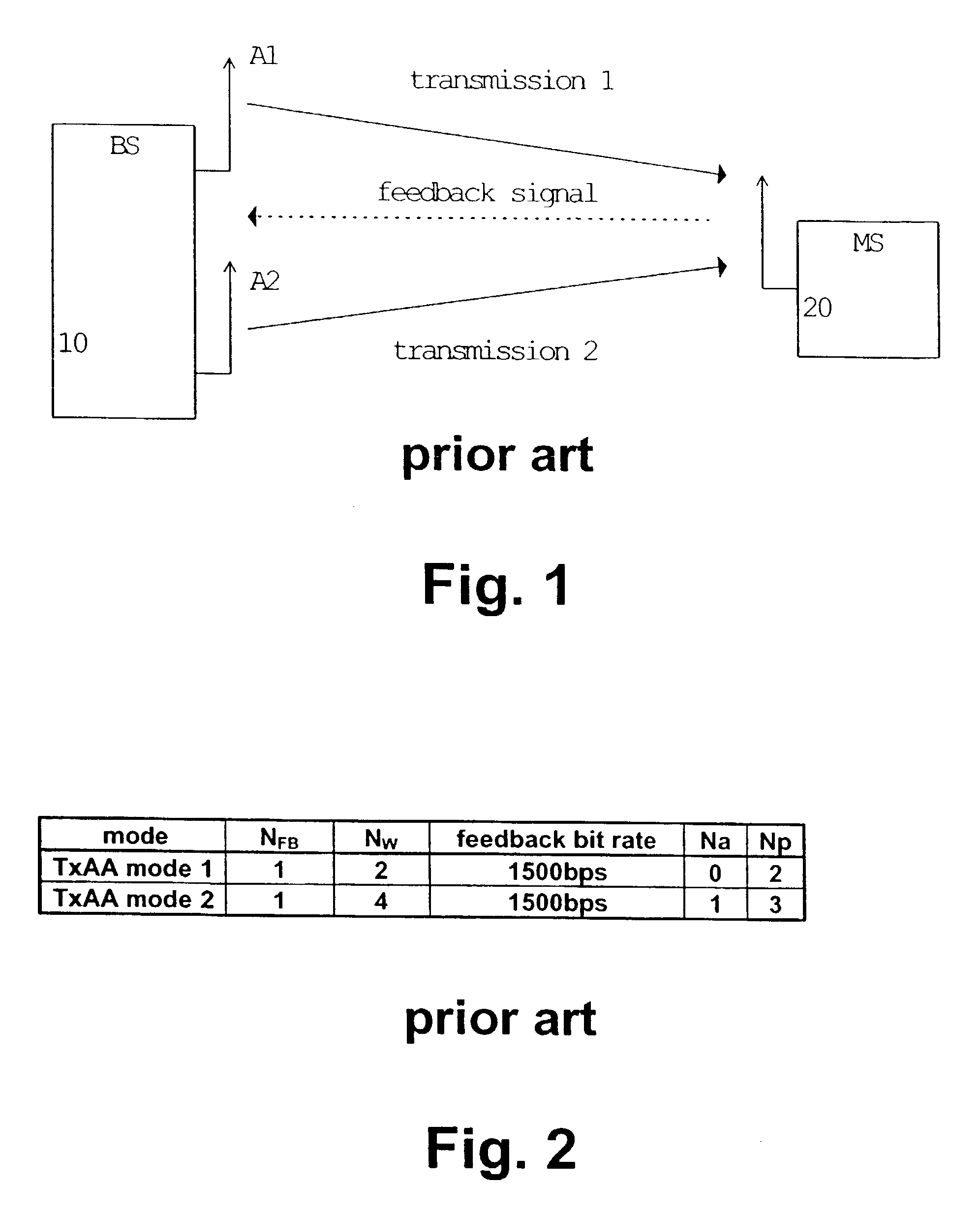
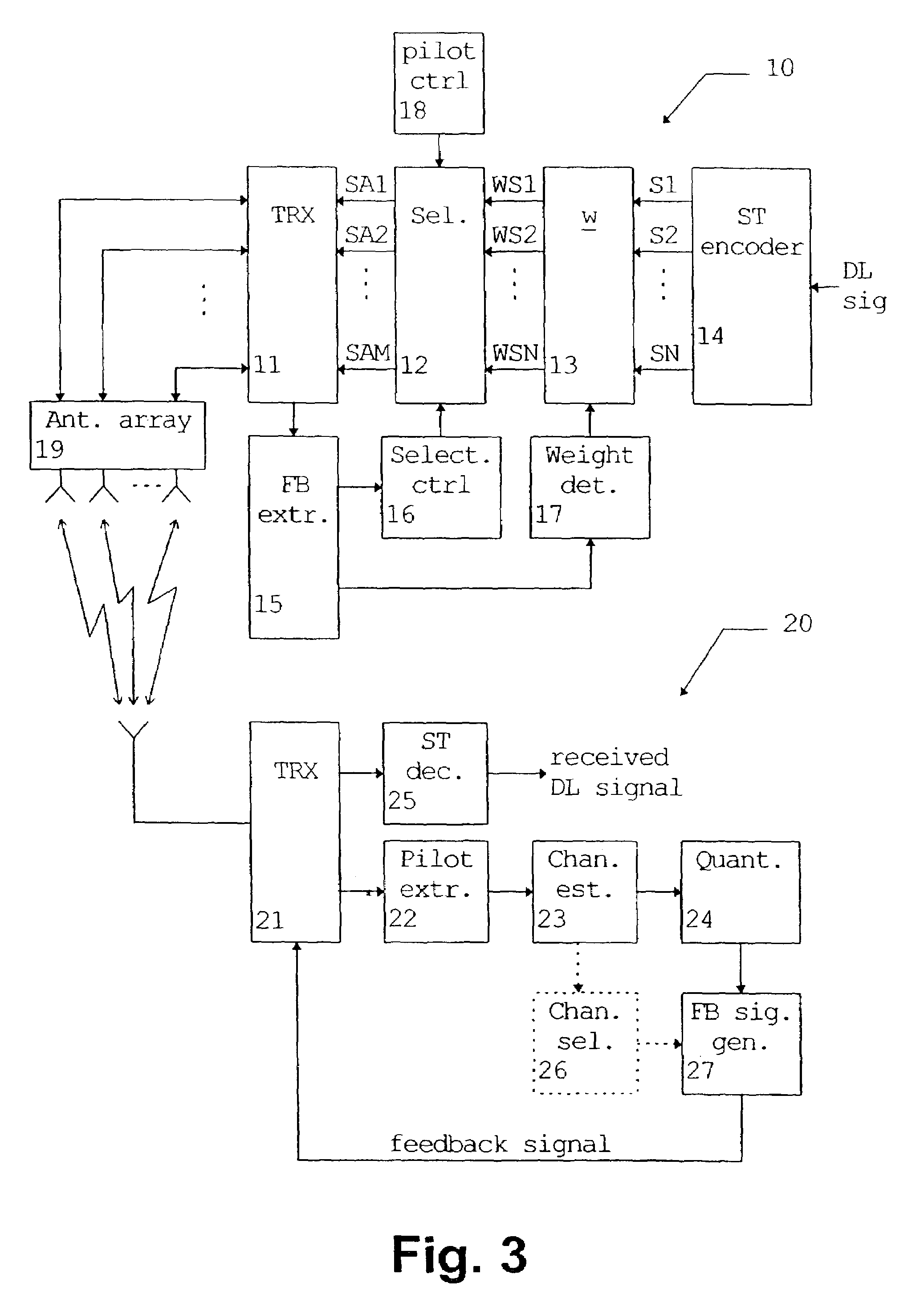
The present invention relates to a method and system for transmitting a transmission signal from an antenna array (19) to a receiving means (20) of a wireless communication system, wherein a signal quality measurement is performed at the receiving means (20) for predetermined antennas or beams of said antenna array (19). Based on a feedback information derived from the signal quality measurement, at least two of the predetermined antennas or beams of the antenna array (19) are selected. The selected antennas or beams are used for transmitting said transmission signal according to a transmit diversity or beamforming scheme. Thus, spectral efficiency and diversity gain can be enhanced by using only selected ones of the predetermined antennas or beams.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Polarization-adaptive antenna transmit diversity system
InactiveUS6411824B1Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityPolarization diversityCommunications system
A duplex polarization adaptive system is described. The system provides polarization diversity for base station antennas under both receive and transmitting conditions. Since the base station provides polarization diversity in both transmit and receive modes, no polarization diversity is needed in the handheld unit. Even though the handheld unit does not provide polarization diversity, a duplex communication system, that uses polarization diversity for both the uplink and the downlink is provided, because the base station provides polarization diversity for the uplink and the downlink paths. By installing the two-way diversity at the base station, the overall cost of implementing diversity is reduced because one base station can typically serve many handsets. The base station antenna determines the polarization state of signals received from a remote unit, such as a handheld unit, using a polarization diverse antenna system. The base station then transmits using the same polarization state. The system is compatible with time-division duplex systems.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
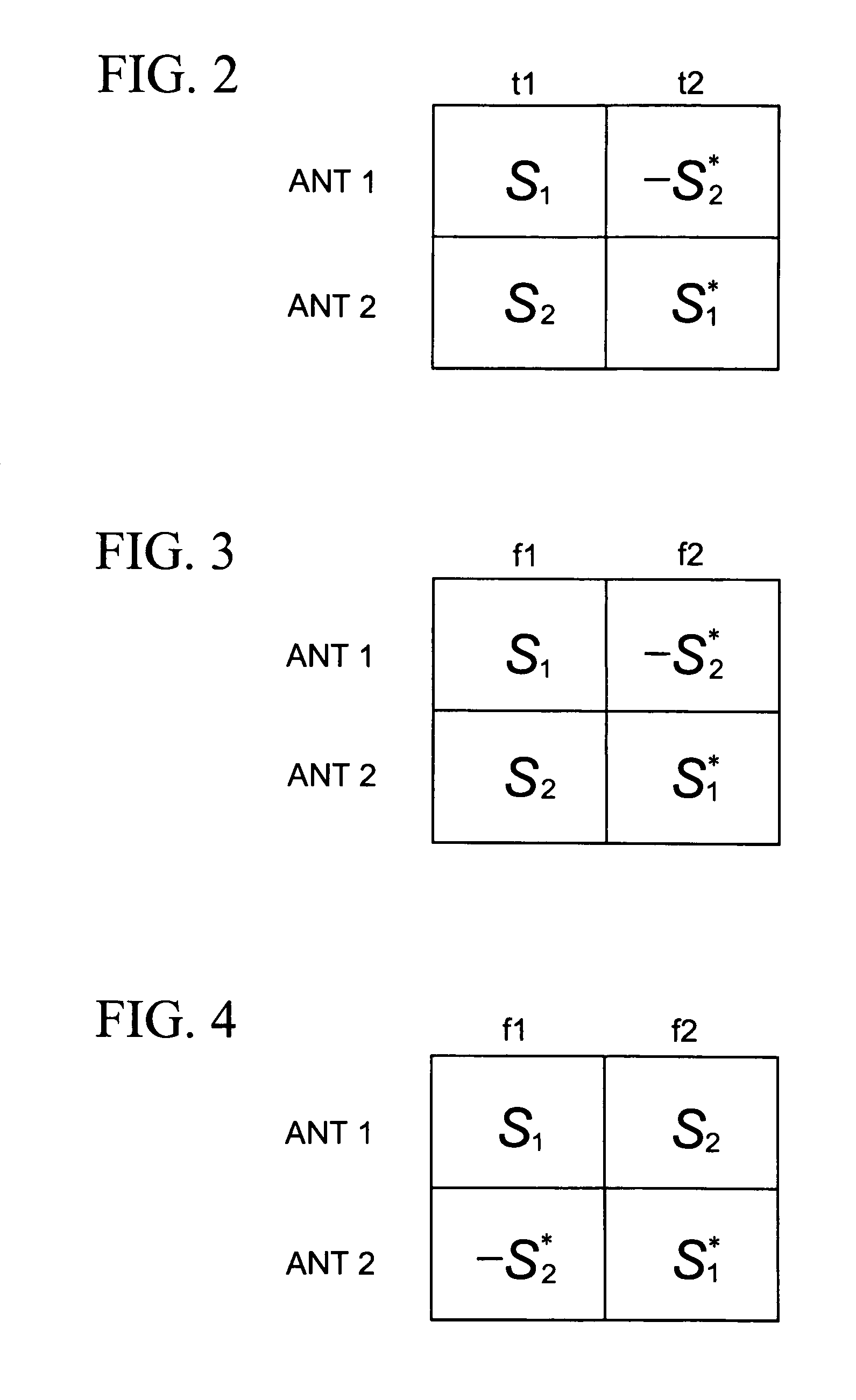
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing transmit diversity system for frequency-selective fading channels
InactiveUS7020072B1Reduce complexityIncrease transmission diversitySpatial transmit diversityFrequency-division multiplexReverse orderSignal on
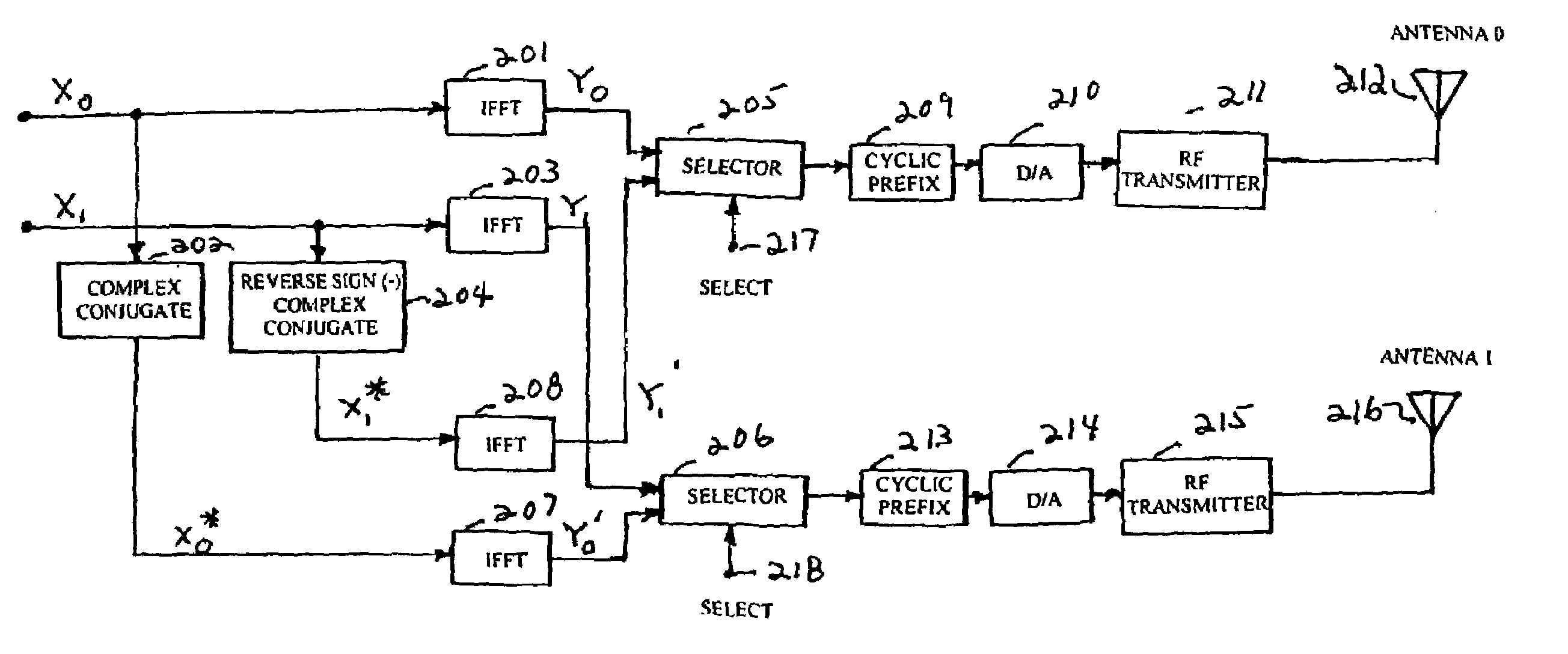
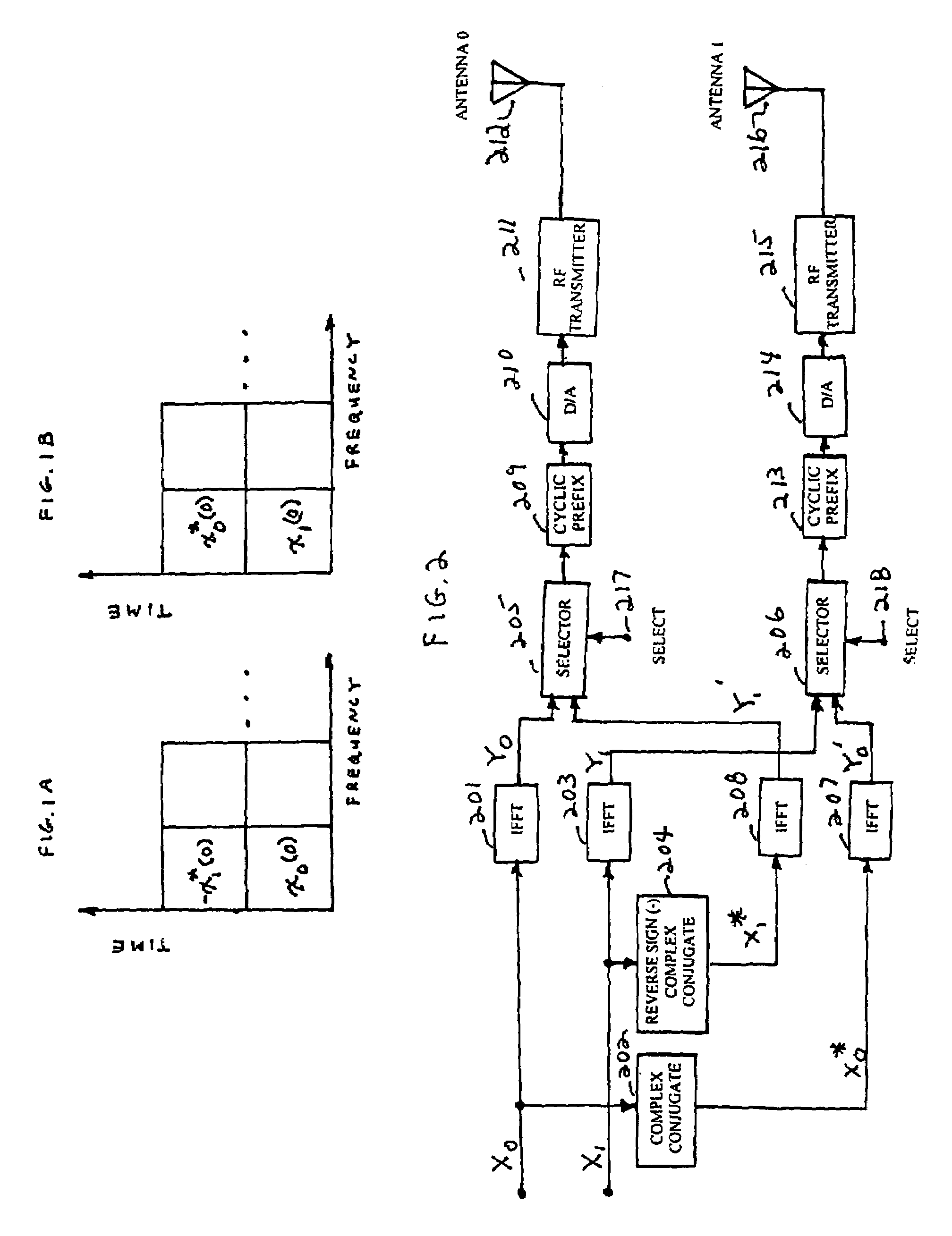
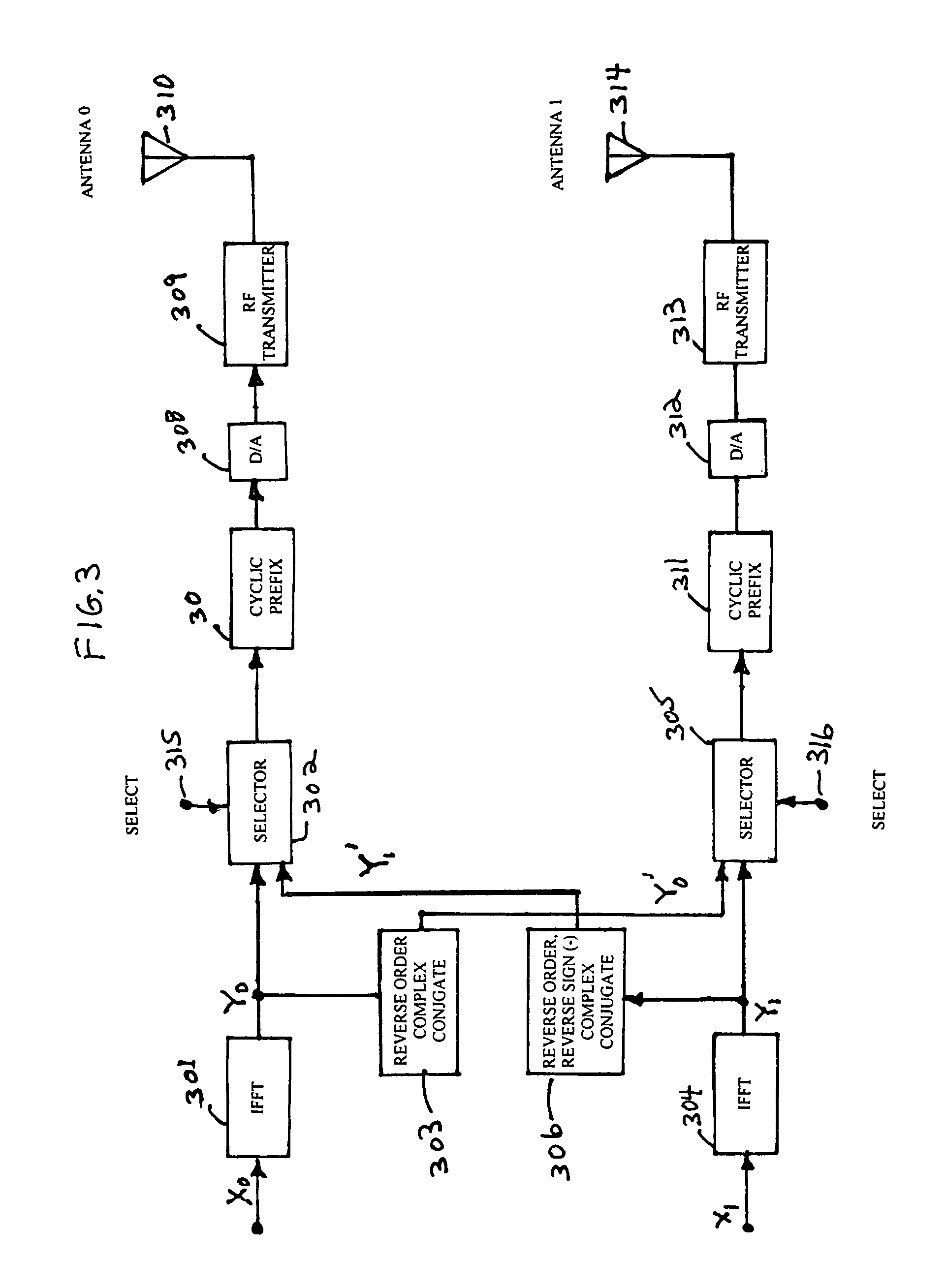
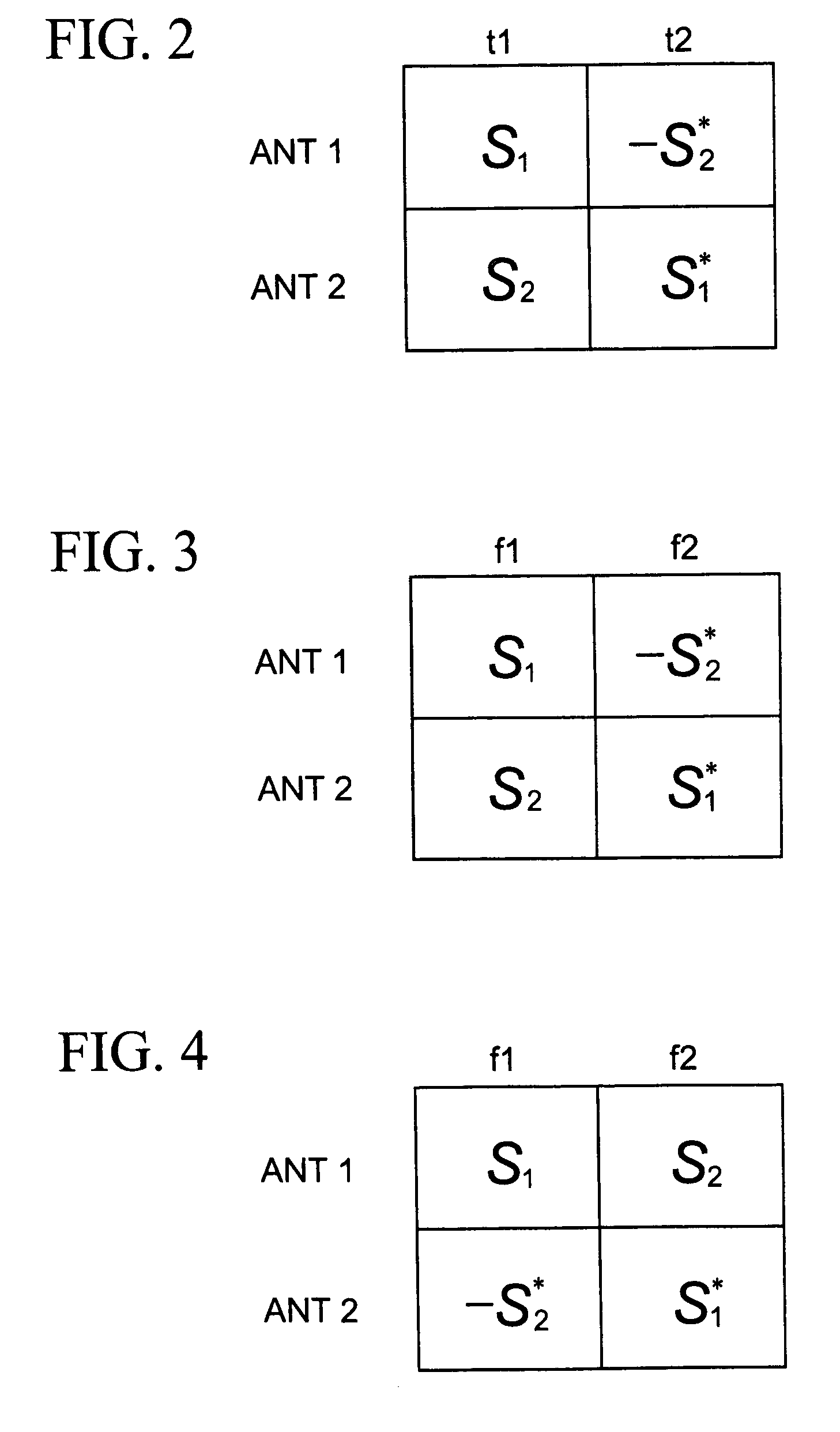
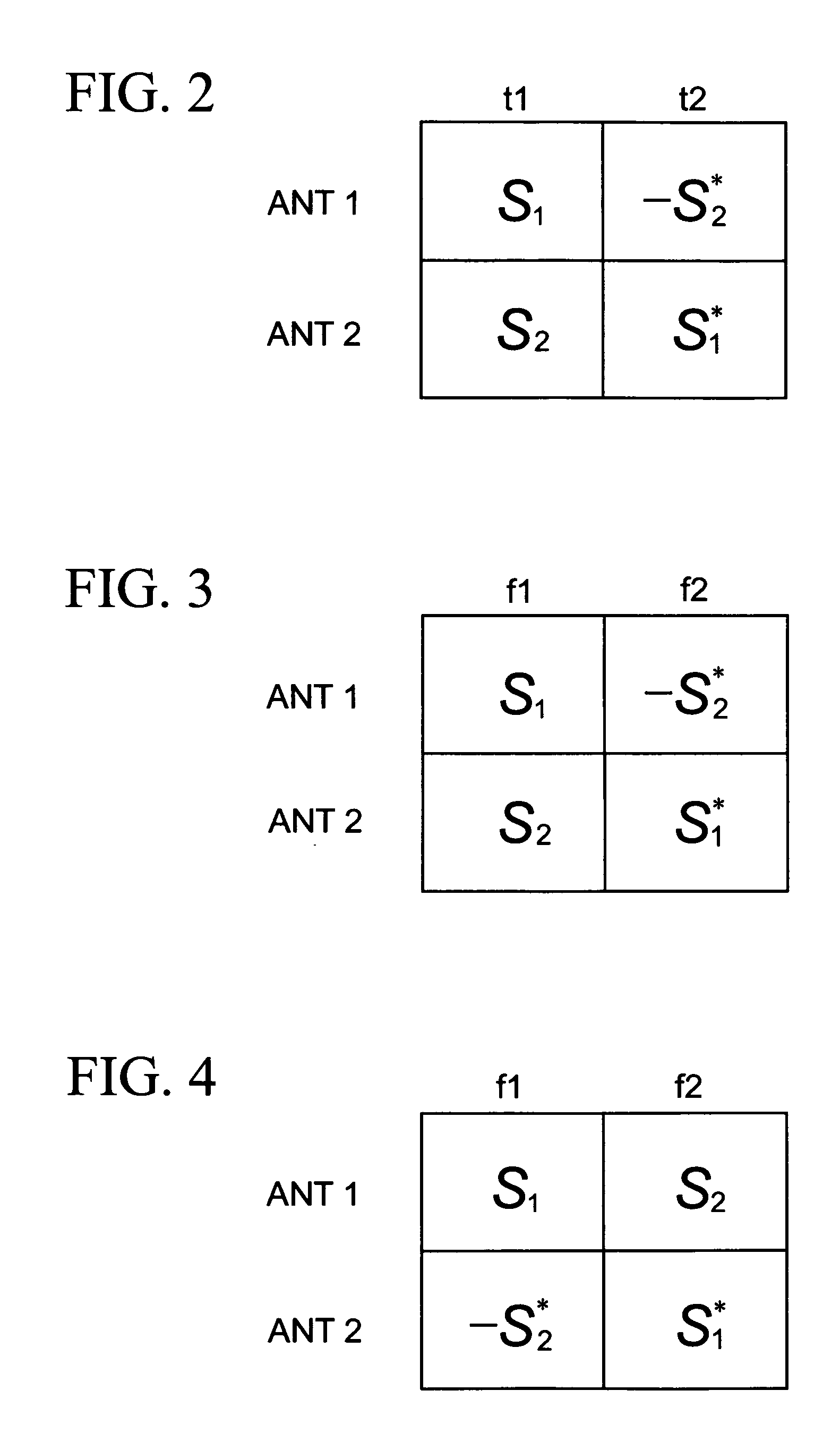
Wireless communications for frequency-selective fading channels is realized by employing a system including orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) in combination with an at least two antenna transmit diversity arrangement. Specifically, OFDM converts a multipath channel into a plurality of narrowband subchannels each having flat fading. Then, the signals on the same frequency subchannels of the at least two antennas are grouped together. Considering a first frequency subchannel, during a first OFDM time interval, a first signal and a second signal are transmitted on the first frequency subchannel from a first antenna (0) and from a second antenna (1), respectively. During a second OFDM time interval, a reverse sign (−) complex conjugate of the second signal and a complex conjugate of the first signal are transmitted from the first antenna and the second antenna, respectively. In a specific embodiment of the invention, reduced complexity in the implementation is realized by a reverse order complex conjugate and a reverse order, reverse sign (−) complex conjugate and judicious selection of the processed data signals in order to transmit the appropriate ones of the signals during the first and second OFDM intervals. Again, if the channel remains constant over the two OFDM intervals, diversity combination is realized for each frequency subchannel. In another embodiment of the invention, antenna-group hopping is employed in conjunction with pairing in time of the OFDM frequency subchannel signals to realize increased transmit diversity without rate loss.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method of transmitting data in multiple antenna system
ActiveUS20090059844A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsSignal allocationCommunications systemControl channel
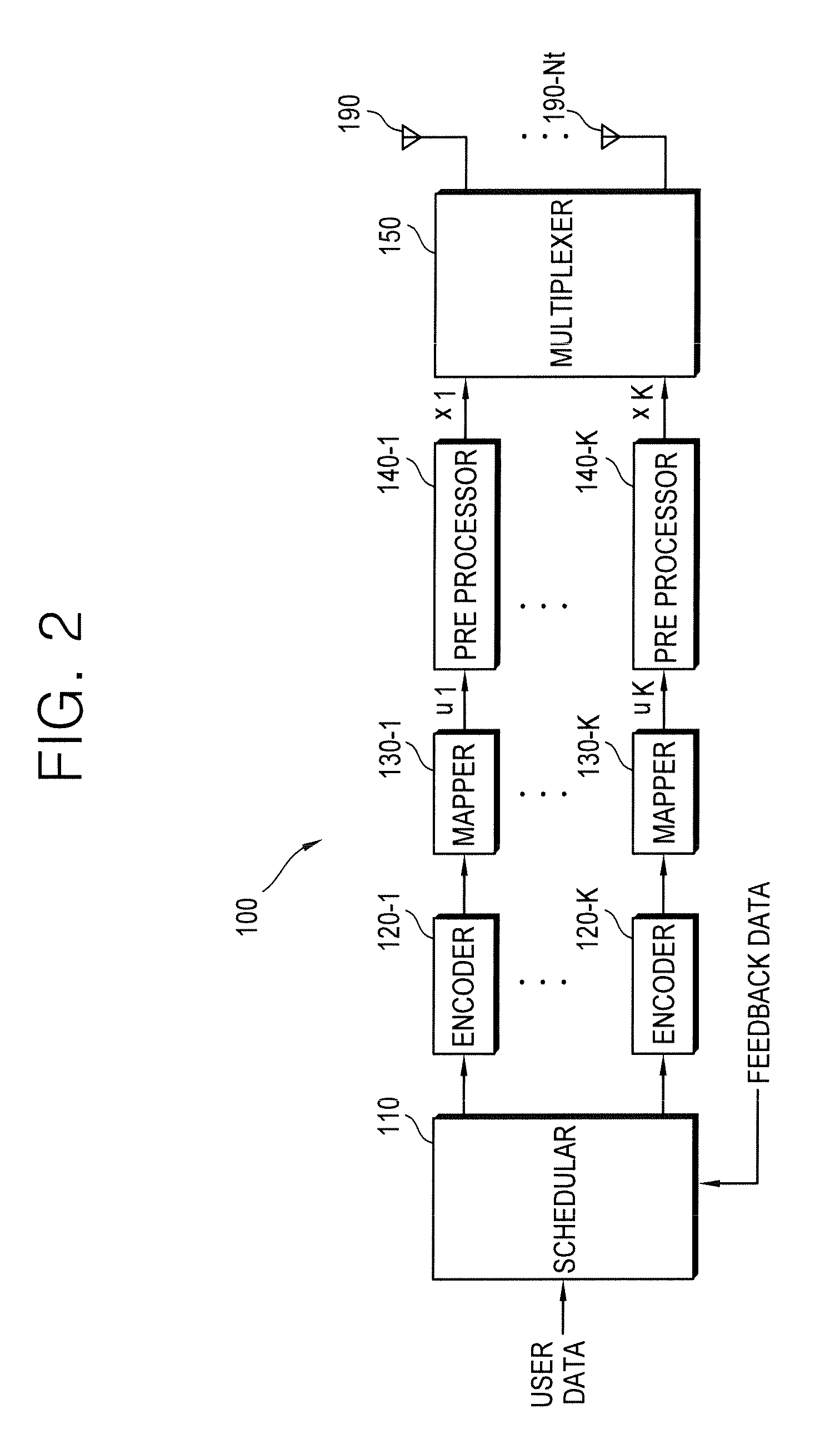
A method of transmitting data in a wireless communication system comprises receiving feedback data on an uplink data channel, the feedback data comprising a precoding matrix indicator (PMI), wherein the value of the PMI corresponds to an index in a codebook, transmitting a precoding scheme for downlink data on a downlink control channel, wherein the preceding scheme is determined as one of at least two of a transmit diversity irrespective of the received PMI, an acknowledgement indicating preceding according to the received PMI and a new PMI indicating that it is used in precoding downlink data to be transmitted, and transmitting the downlink data on a downlink data channel after applying precoding according to the determined preceding scheme.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Cooperative relay transmission method for wireless communication system
InactiveUS20070002766A1Increase transmission diversityImprove reception performanceSite diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemUplink transmission
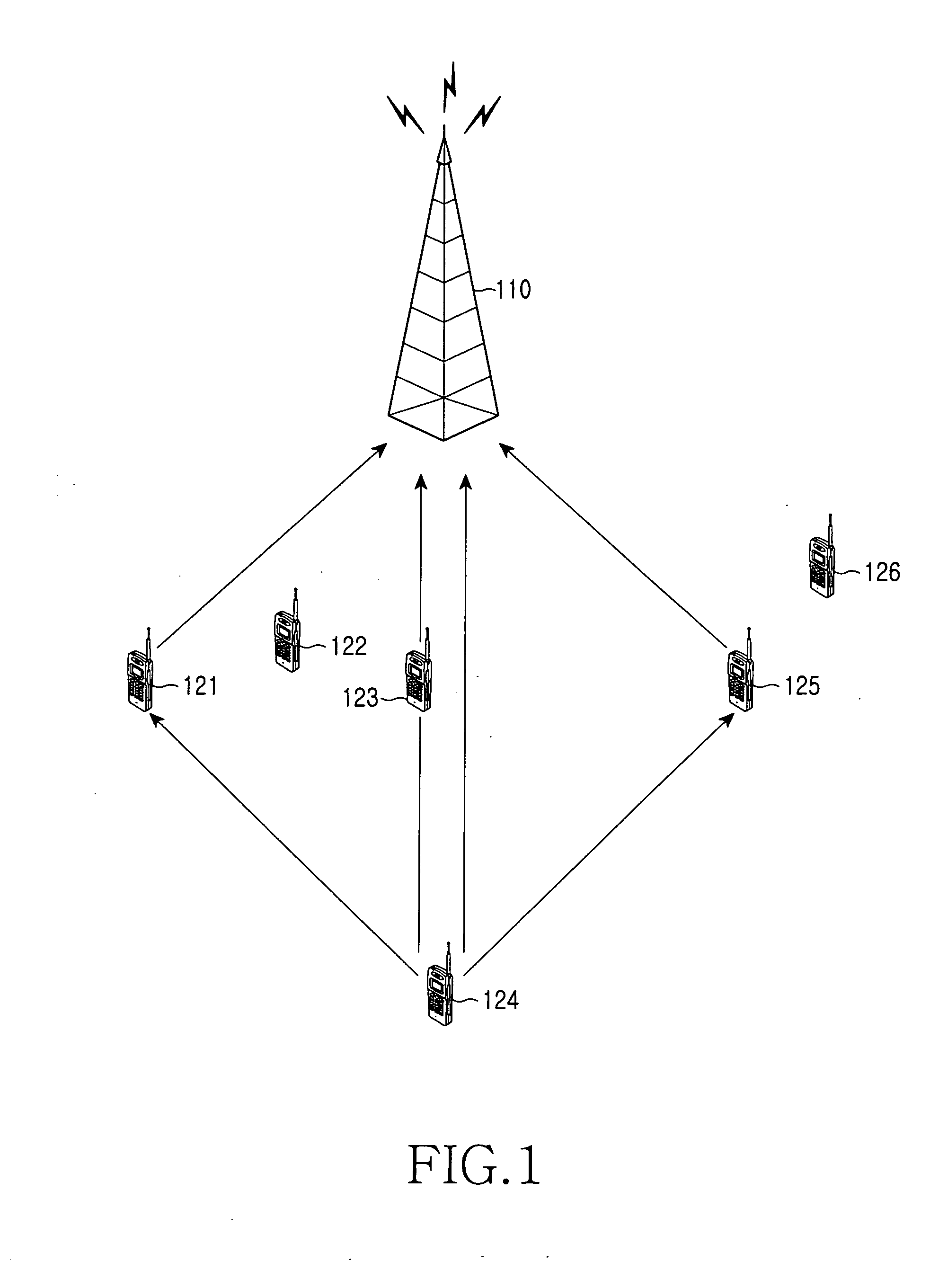
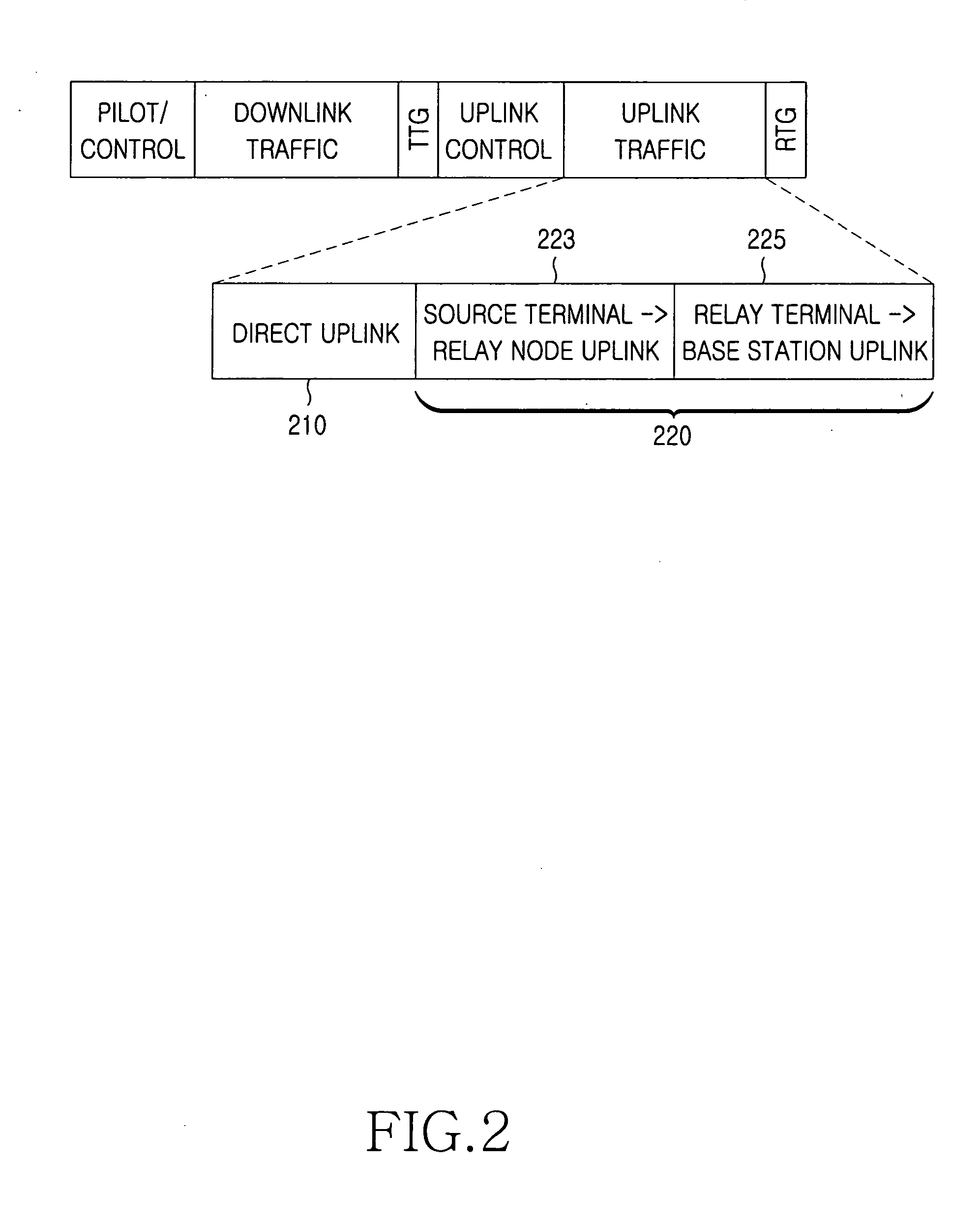
Disclosed is a method in a base station for providing a network access service to terminals. Where one of the terminals is selected as a source terminal and at least one of the other terminals is used as a relay node for relaying communication between the base station and the source terminal. Parameters for relay communication are initialized. A relay communication request message including that the parameters is transmitted. In response to the message, a terminal independently sets and performs the relay communication between the base station and the source terminal. Uplink signals are received from the source and relay terminals. The uplink signals received from the source and relay terminals are combined and decoded. A transmit diversity gain is obtained in uplink transmission of a terminal with a single antenna because relay nodes retransmit the source terminal's signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Pilot boosting and traffic to pilot ratio estimation in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20090041151A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationTime domainCommunications system
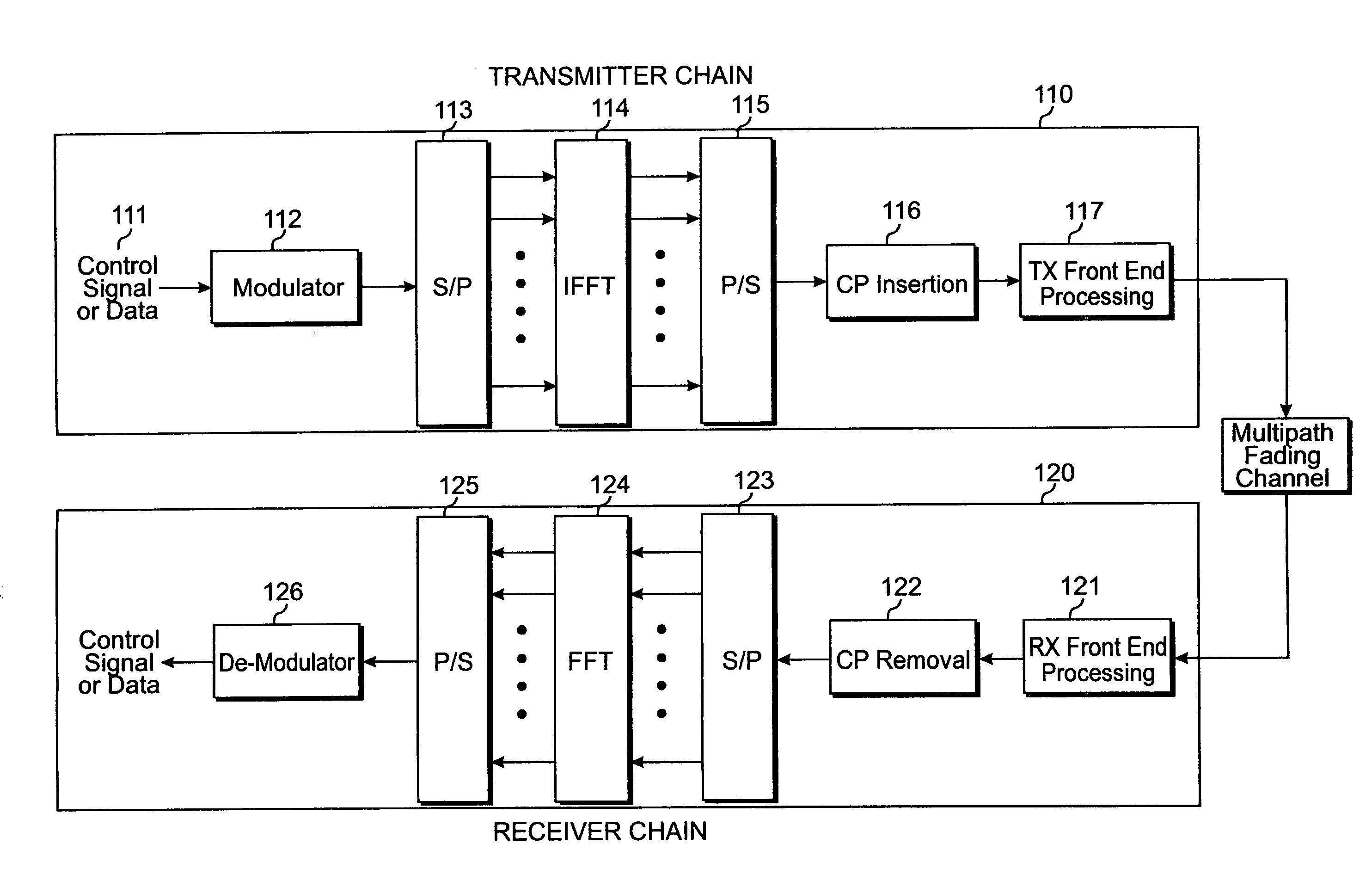
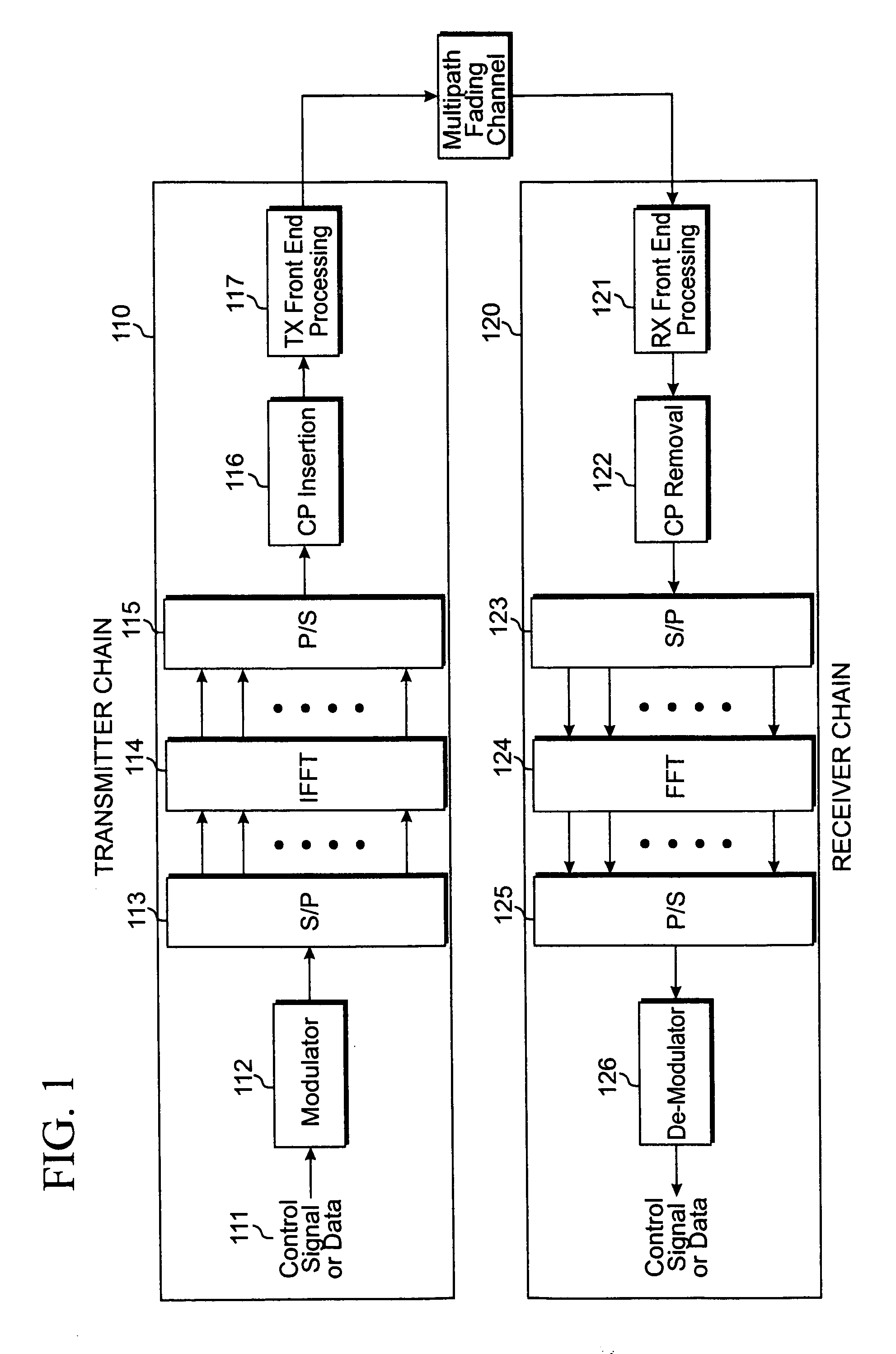
Methods and circuits for assigning pilot boosting factors and calculating traffic to pilot ratios in a wireless communication system. The data to be transmitted is first modulated to generate a plurality of data modulation symbols. The plurality of data modulation symbols and a plurality of reference signal symbols are mapped into transmission resources of each of a plurality of antennas in accordance with a transmit diversity scheme. The transmission resources of each of the antennas are divided into a plurality of subcarriers in a frequency domain and a plurality of time units in a time domain. Then, a power scaling factor are assigned for data modulation symbols on each of the antennas in dependence upon power levels of the reference signal symbols to maintain a fixed power level across the plurality of antennas in each time unit. Finally, the data modulation symbols and the reference signal symbols are transmitted via the plurality of antennas in accordance with the mapping scheme and the assigned scaling factors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
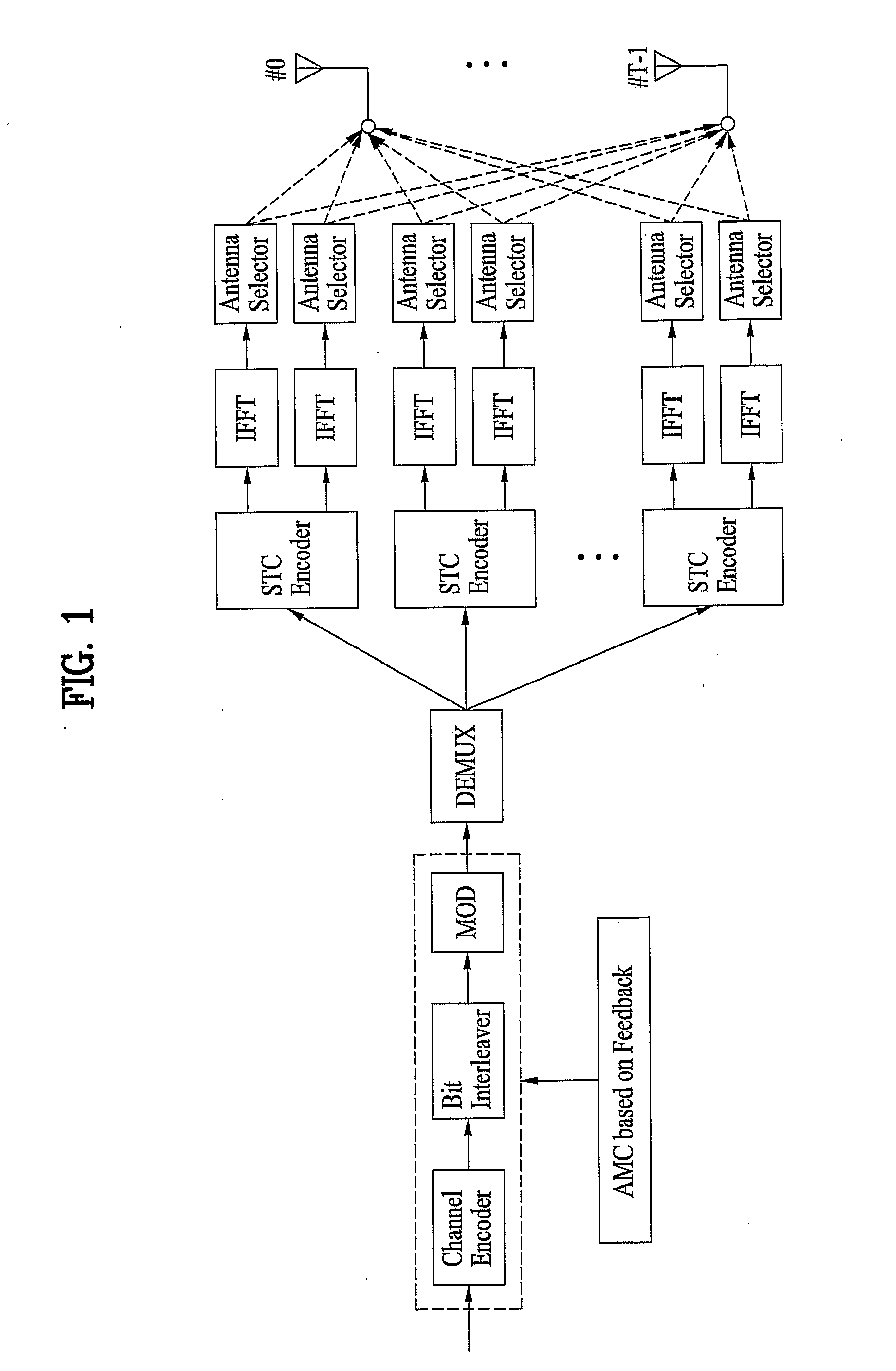
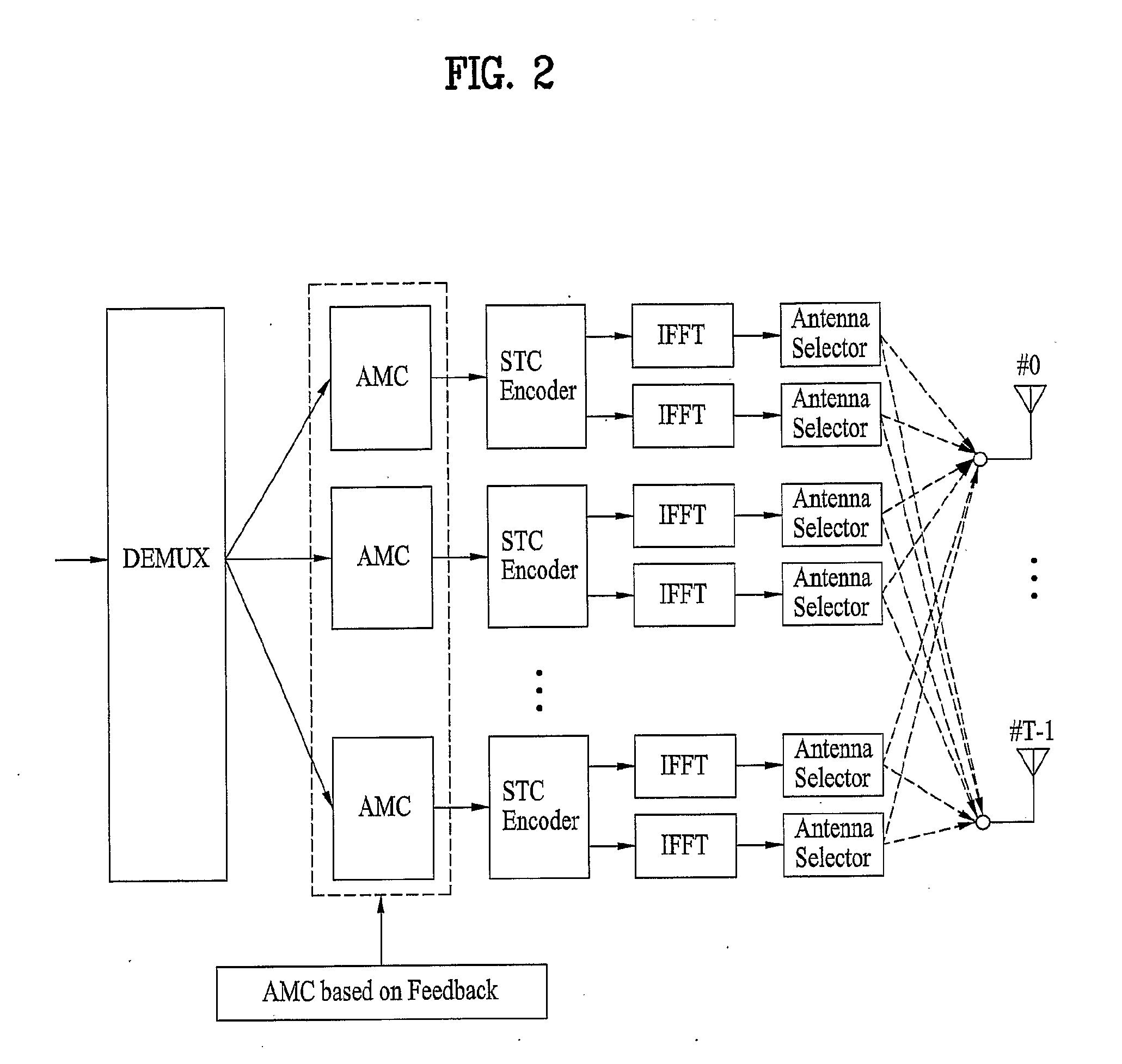
Method and apparatus for achieving transmit diversity and spatial multiplexing using antenna selection based on feedback information
InactiveUS20090316807A1Eliminate the problemSecret communicationRadio transmissionFast Fourier transformData stream
A method of achieving transmit diversity in a wireless communication system is disclosed. The method comprises encoding and modulating data stream based on feedback information, demultiplexing symbols to at least one encoder block, encoding the demultiplexed symbols by the at least one encoder block, transforming the encoded symbols by at least one inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) block, and selecting antennas for transmitting the symbols based on the feedback information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Transmission symbols mapping for antenna diversity
InactiveUS20080304593A1Polarisation/directional diversityError detection/correctionTime domainBurst transmission
Methods and apparatus for transmitting data via multiple antennas by using antenna diversity. A transmission diversity scheme is established such that two transmission matrices that are in accordance with the space frequency block code combined with Frequency switched transmit diversity (SFBC+FSTD) scheme, are alternatively applied in either the frequency domain, or the time domain, or both of the frequency domain or then time domain. The symbols in the transmission matrices may be transmitted either as one burst in a primary broadcast channel (PBCH), or as discrete bursts in the primary broadcast channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmit diversity in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20080267310A1Spatial transmit diversitySecret communicationCommunications systemDiversity scheme
A method for transmitting data via multiple antennas by modulating data to be transmitted into a plurality of modulated symbols, encoding each pair of modulated symbols from among said plurality of symbols in accordance with a transmission diversity scheme to result in a plurality of N by N matrices, with each N by N matrix corresponding to each pair of modulated symbols, generating a M by M code matrix comprised of the plurality of N by N matrices, orthogonally spreading the M by M code matrix to generate an output matrix, generating a plurality of row-permuted matrices by exchanging at least one pair of rows in the output matrix, and transmitting the symbols in the plurality of row-permuted matrices via a plurality of antennas by using either a space time transmission diversity scheme, a space frequency transmission diversity scheme, or a combination of a space time transmission diversity scheme and a space frequency transmission diversity scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Closed loop transmit diversity method and apparatus using complex basis vector sets for antenna selection
InactiveUS7116723B2Overcome imbalanceSpatial transmit diversityAntenna arraysLow speedCommunications system
A transmission antenna diversity method, and a base station apparatus and a mobile station apparatus therefor in a mobile communication system are provided. In the transmission antenna diversity method, channel information is measured from signals received through the plurality of antennas used in the base station, and a channel information matrix is output. The channel information matrix is transformed according to a transform matrix composed of a complex basis vector set. Reception power with respect to the plurality of antennas is calculated based on the transformed channel information matrix. Antenna selection information obtained based on the calculated reception power is transmitted to the base station as feedback information for controlling transmission antenna diversity. Therefore, power is equally distributed to transmitting antennas, excellent performance is maintained at a high speed of movement, and reliable channel adaptation is accomplished at a low speed of movement of the mobile station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device and method for transmitting and receiving data by a transmit diversity scheme using multiple antennas in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050037718A1Maximizes transmission capacityMaximize capacitySpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsEngineeringMobile communication systems
In a mobile communication system, receivers measure channel characteristics using a received reference channel signal. The receivers determine a weight which has orthogonality with respect to each of a preset number of weight vectors in the mobile communication system and has the highest signal-to-interference-and-noise ratio, and feedback the weight and the corresponding signal-to-interference-and-noise ratio to the transmitter. The transmitter interprets the feedback information output from the receivers and determines receivers having feedback information which are orthogonal to each other and have the maximum throughput as an addition capacity when transmitted simultaneously, and determines weights based on the feedback information of the receivers having the maximum throughput. By applying the determined weights to the antennas using a well-known beam forming scheme, data can be transmitted to each of the determined receivers. Therefore, the present invention can maximize the efficiency in transmission capacity even with a simple transmitting and receiving structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Beam forming and transmit diversity in a multiple array radio communications system
ActiveUS7372911B1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionCommunications systemRadio reception
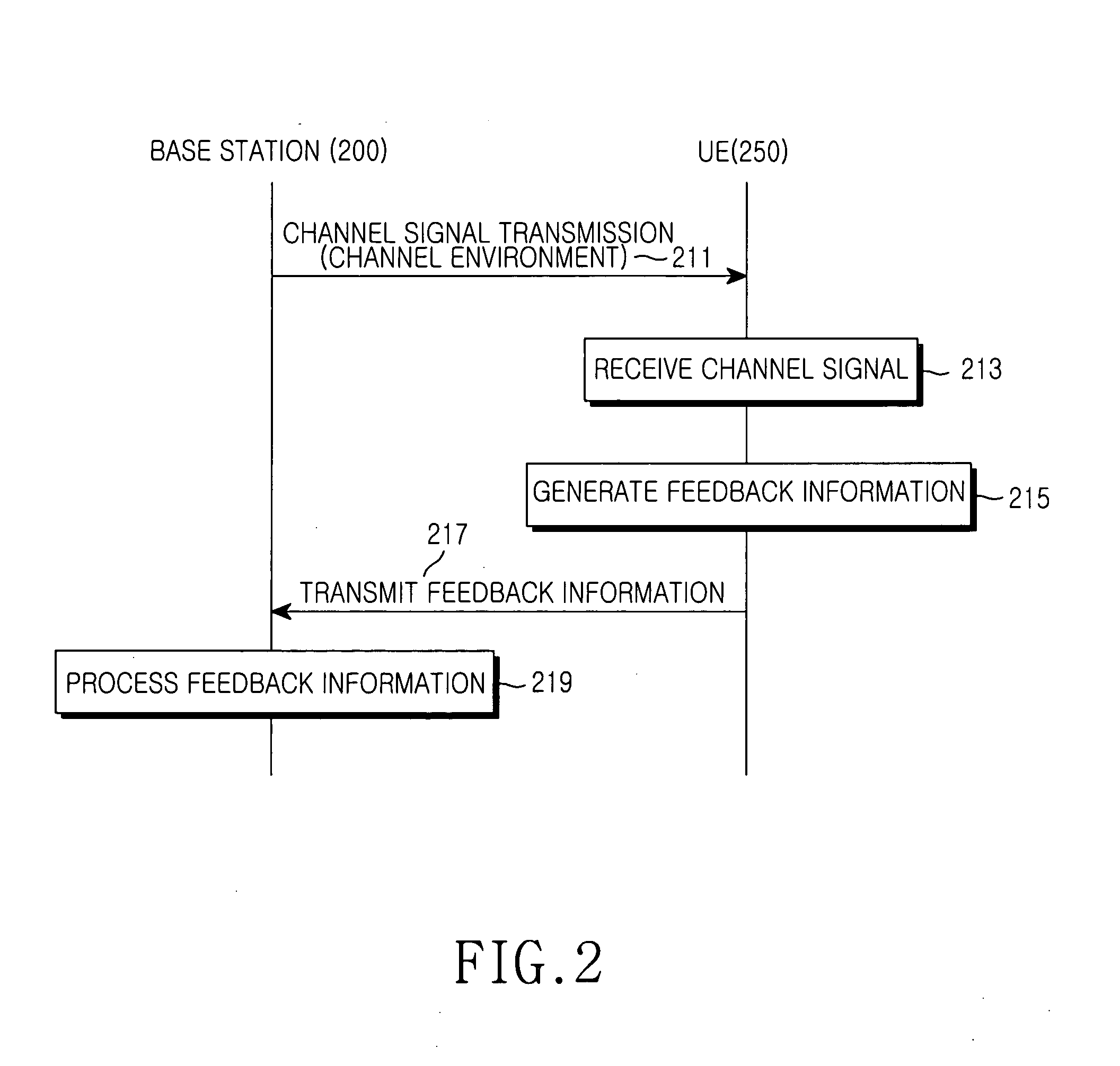
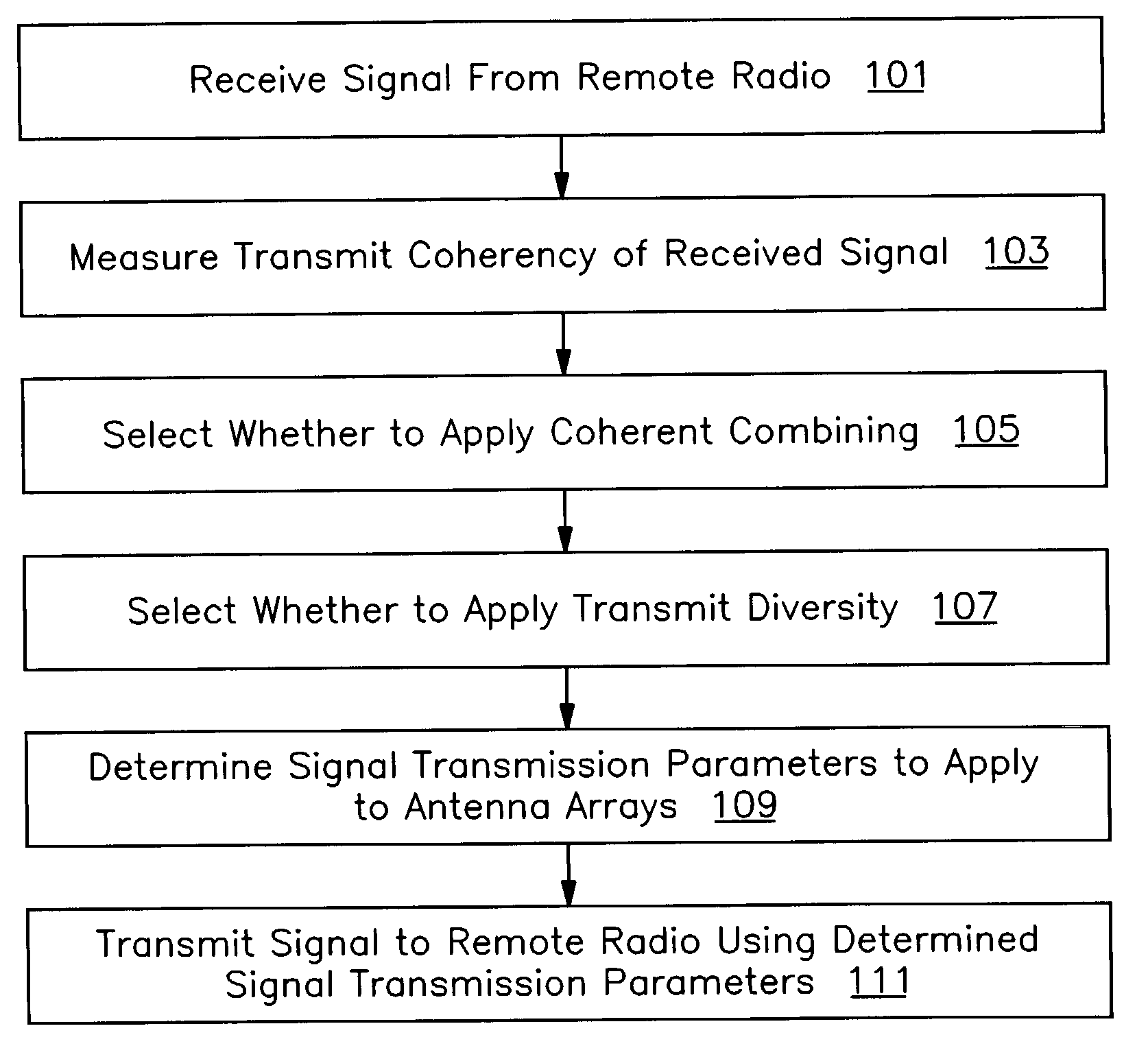
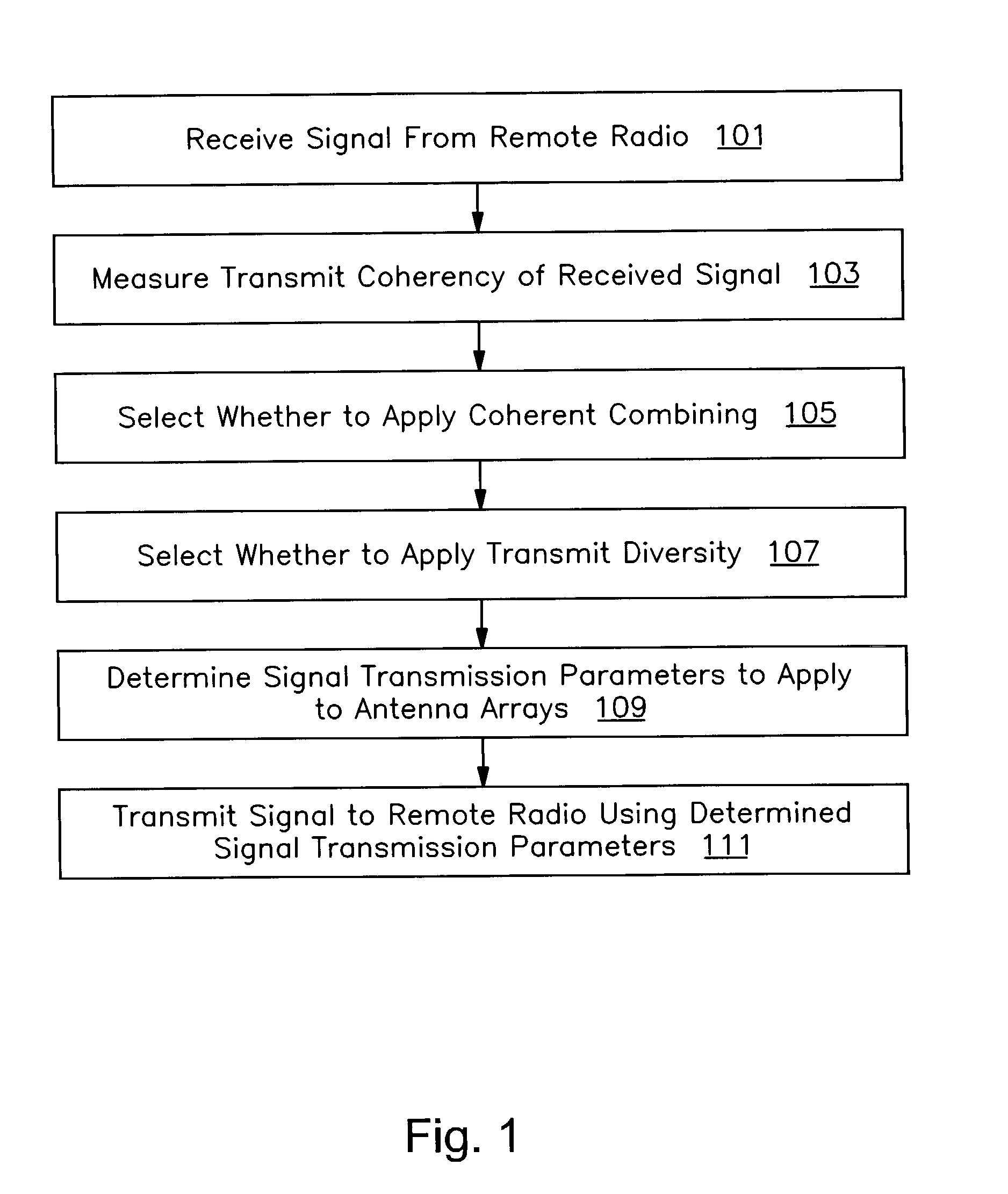
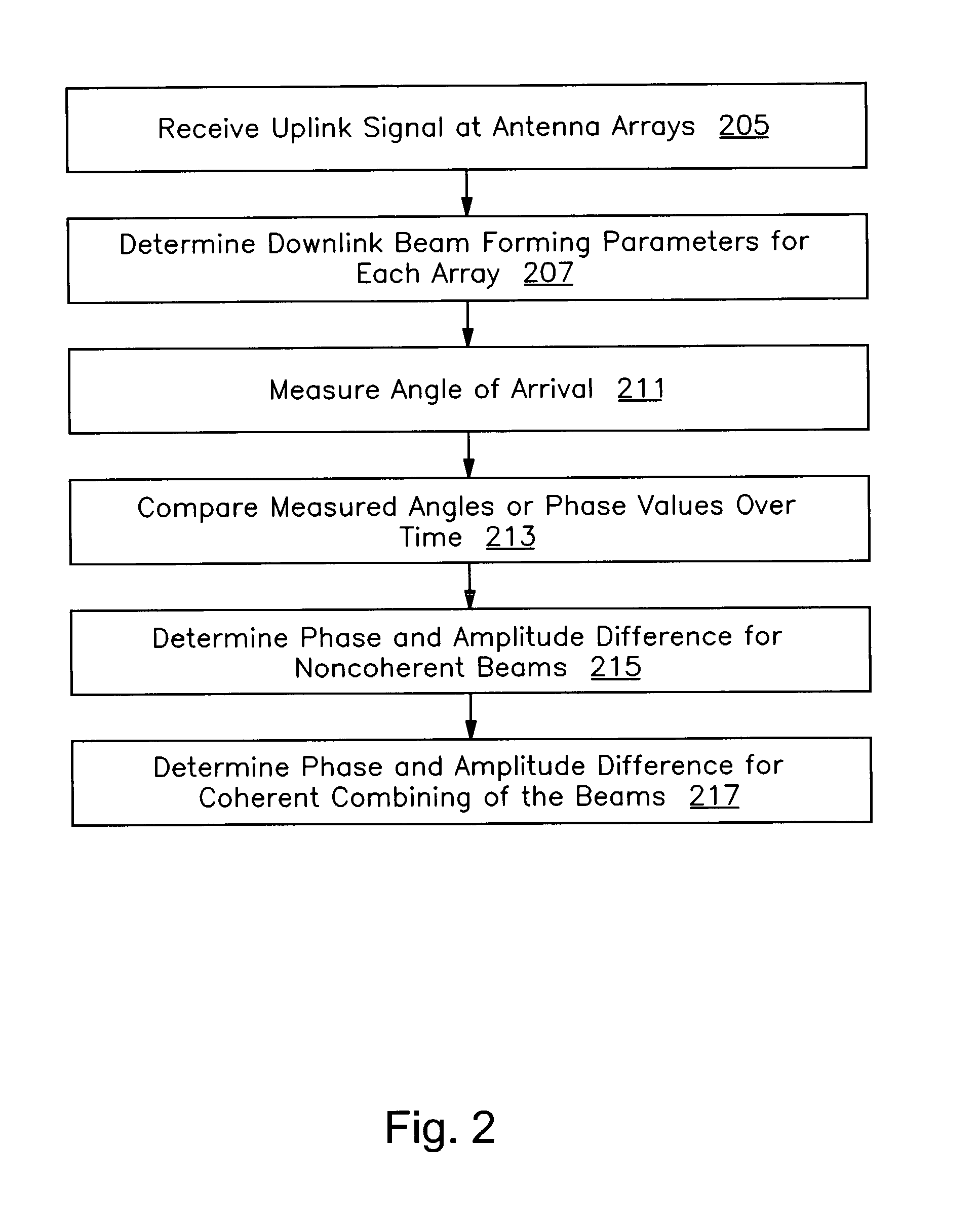
A method and apparatus are provided for selecting transmission parameters for multiple transmit antenna arrays. In one embodiment, the invention includes receiving a signal from a remote radio, measuring the transmit coherency of the received signal, selecting, based on the transmit coherency, whether to apply coherent combining to signals transmitted to the remote radio using each of two transmit antenna arrays to each form a beam to coherently combine with each other beam upon receipt by the remote radio, selecting, based on the transmit coherency, whether to apply transmit diversity to signals transmitted to the remote radio using each of the two transmit antenna arrays as diversity antennas. The embodiment further includes determining signal transmission parameters to apply to the two antenna arrays for transmissions to the remote radio based on the selections, and transmitting a signal to the remote radio from the two transmit antenna arrays by applying the determined signal transmission parameters to the two transmit antenna arrays.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Power amplifier sharing in a wireless communication system with amplifier pre-distortion
InactiveUS6859643B1Reduce difficultyCompensation for non-linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower managementAudio power amplifierSystems design
The technique of amplifier sharing is implemented in a system designed to accommodate transmit diversity. In one embodiment of the invention, the amplifiers are shared 1) to amplify a first and a second diversity-encoded signal, each of which represents the information a first signal that is to be transmitted using transmit diversity, and 2) to amplify a second signal to be transmitted without using transmit diversity. The first and second diversity-encoded signals are used to form a first and a second composite signal. Each composite signal is amplified in a different one of two power amplifiers. Each amplified composite signal is then used to form an amplified first diversity-encoded signal and an amplified second diversity-encoded signal. The first and second composite signals can also be formed using the second signal. Each composite signal is then amplified in a different one of the two power amplifiers and the two amplified composite signals are used to form an amplified second signal. In another embodiment of the invention, the first and second composite signals can be formed in the digital domain. Each composite signal is digitally pre-distorted and then modulated onto a transmission frequency signal, such as an RF signal. Each pre-distorted composite signal is then amplified in the respective amplifier.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Device and method for transmitting and receiving data by a transmit diversity scheme using multiple antennas in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS7366253B2Maximize capacitySpatial transmit diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsEngineeringMobile communication systems
In a mobile communication system, receivers measure channel characteristics using a received reference channel signal. The receivers determine a weight which has orthogonality with respect to each of a preset number of weight vectors in the mobile communication system and has the highest signal-to-interference-and-noise ratio, and feedback the weight and the corresponding signal-to-interference-and-noise ratio to the transmitter. The transmitter interprets the feedback information output from the receivers and determines receivers having feedback information which are orthogonal to each other and have the maximum throughput as an addition capacity when transmitted simultaneously, and determines weights based on the feedback information of the receivers having the maximum throughput. By applying the determined weights to the antennas using a well-known beam forming scheme, data can be transmitted to each of the determined receivers. Therefore, the present invention can maximize the efficiency in transmission capacity even with a simple transmitting and receiving structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmit diversity for acknowledgement and category 0 bits in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20080267158A1Use minimizedSimple and efficient transmit diversitySignal allocationCode division multiplexCommunications systemCarrier signal
A method of transmitting acknowledgement / nonacknowledgement (ACK / NACK) signals including multiplexing ACK / NACK signals; and repeatedly transmitting for predetermined times the multiplexed signal with each of repetitions of transmitting the multiplexed signal being spread in a frequency domain and being mapped to a plurality of discrete resource units each having a pair of neighboring subcarriers and a predetermined number of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) control symbols.A method for transmitting Category 0 bits, including modulating the Category 0 bits; repeatedly transmitting the modulated Category 0 bits with each of repetitions of transmitting the modulated Category 0 bits being spread in a frequency domain and being mapped to a plurality of discrete resource units each having a pair of subcarriers and a predetermined number of OFDM control symbols; and mapping the modulated Category 0 bits by a frequency selective transmit diversity (FSTD).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hopped delay diversity for multiple antenna transmission
InactiveUS7065156B1Spatial transmit diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDiversity schemeComputer science
A method and apparatus for providing hopped delay diversity for multiple antenna transmissions. In the method and apparatus, an input symbol stream is offset in time by M symbol periods to generate or offset symbol stream. The offset input stream may be offset so as to lead or lag the original input symbol stream. The original input symbol stream is then transmitted on a first set of N antennas and the offset input symbol stream is transmitted on a second set of N antennas, with transmit diversity techniques applied to the transmissions from the first and second set of N antennas.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
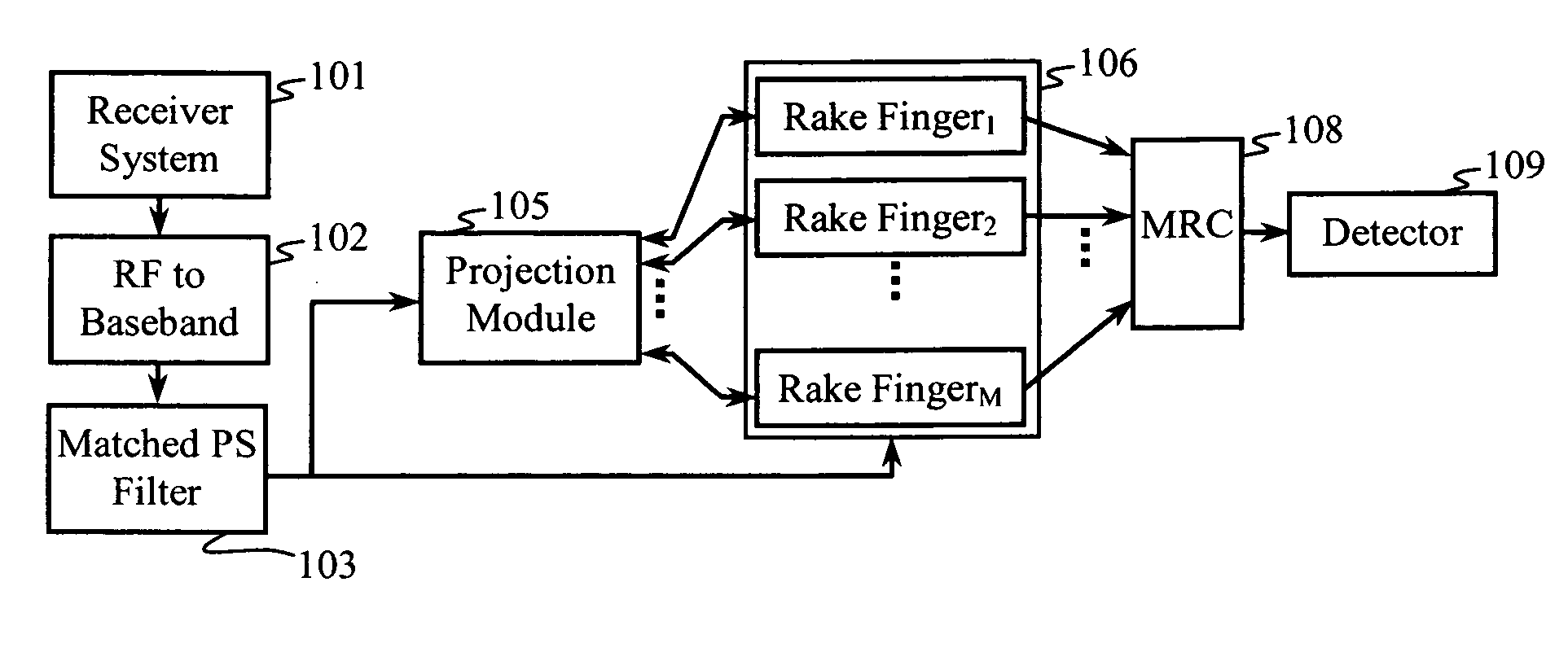
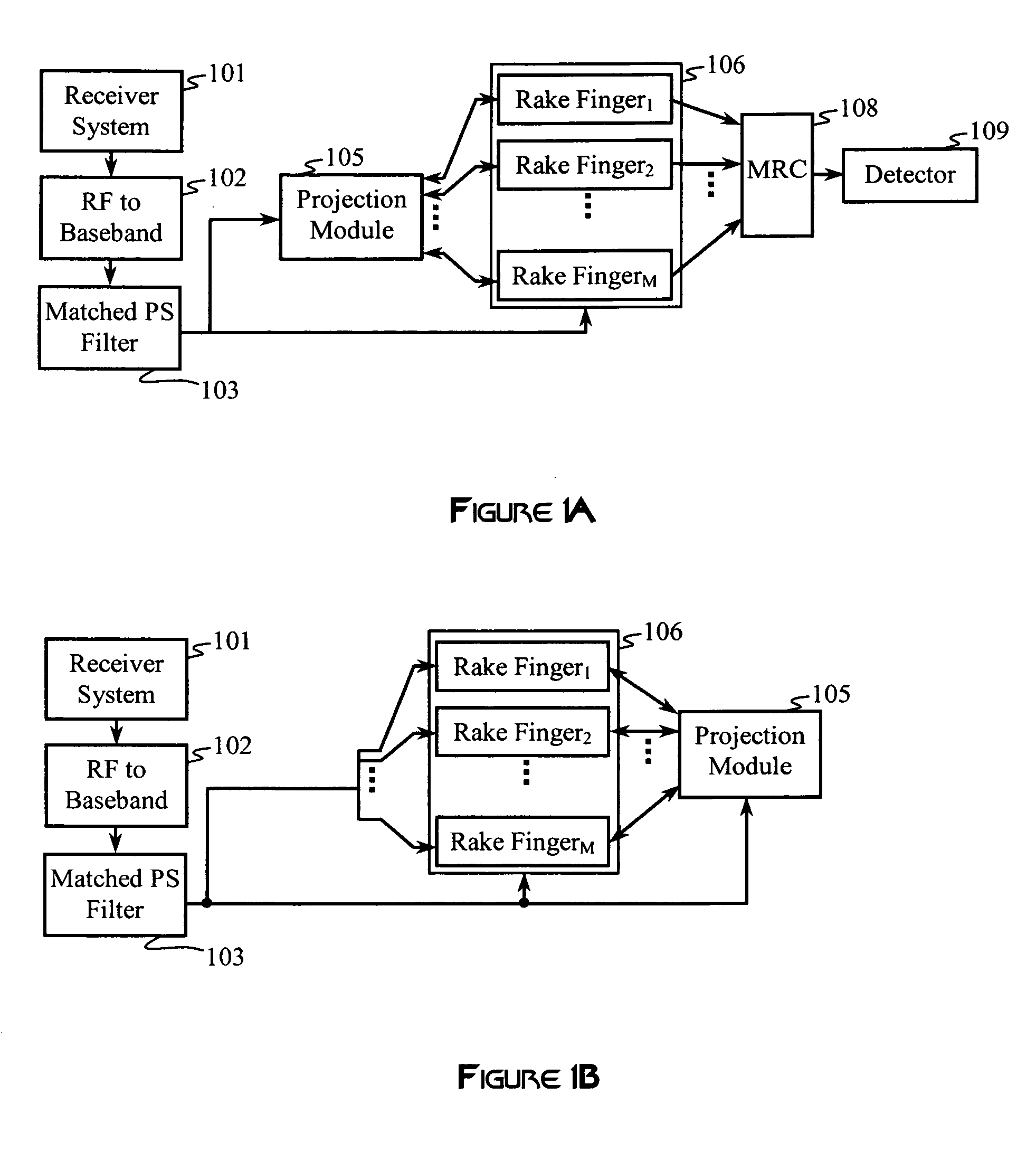
Construction of projection operators for interference cancellation
InactiveUS20050180364A1Reduce in quantityReduce complexitySecret communicationRadio transmissionTime domainTransceiver
Interference cancellation is performed in a CDMA receiver by projecting a received signal onto a subspace that is orthogonal to a signal selected for removal. An interference matrix or a combined interference vector is used to construct an interference-canceling projection operator. Confidence weights may be provided to components of the interference matrix or the interference vector based on estimation errors or relative strengths of interfering signals. Complexity reduction of the orthogonal projection operator may be achieved by providing for simplifying approximations that remove terms and operations. A linear transformation operator may be applied to the rows and / or columns of the interference matrix or the interference vector prior to construction of the orthogonal projection. Interference cancellation techniques may be configured for processing signals in a transmit-diversity system or a receive-diversity system using time and / or frequency-domain implementations and space and / or wave-number implementations of the transceiver.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
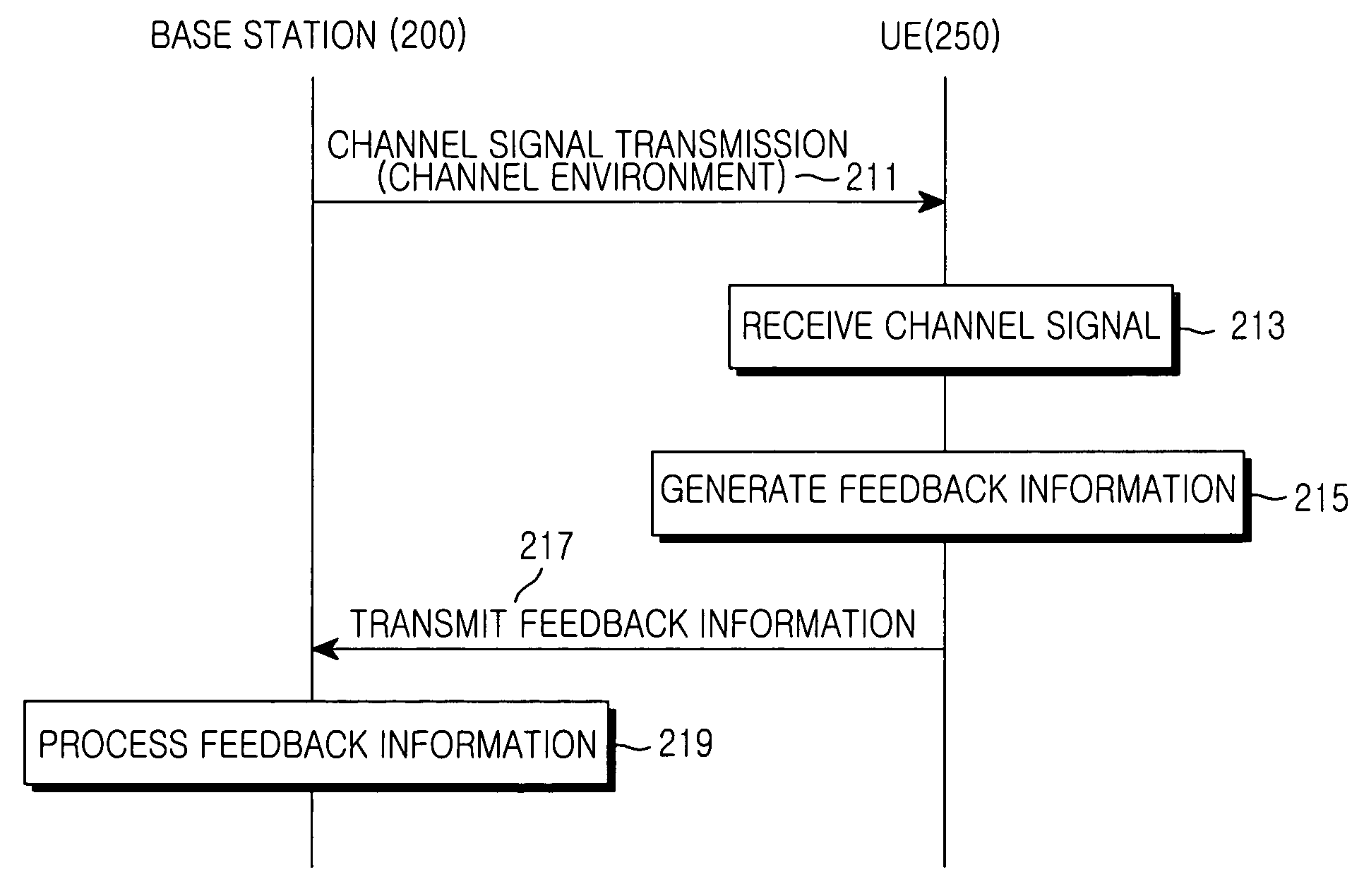
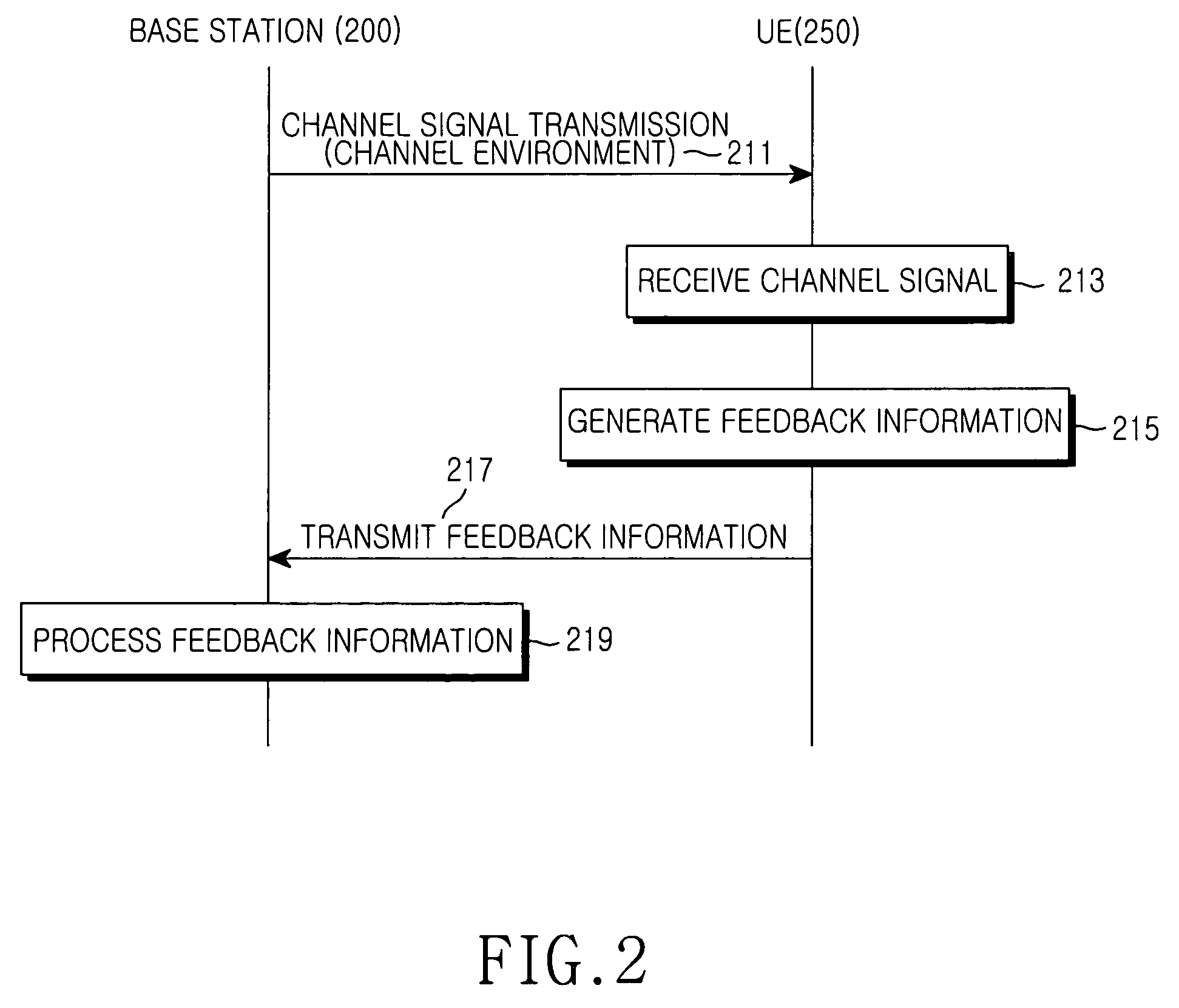
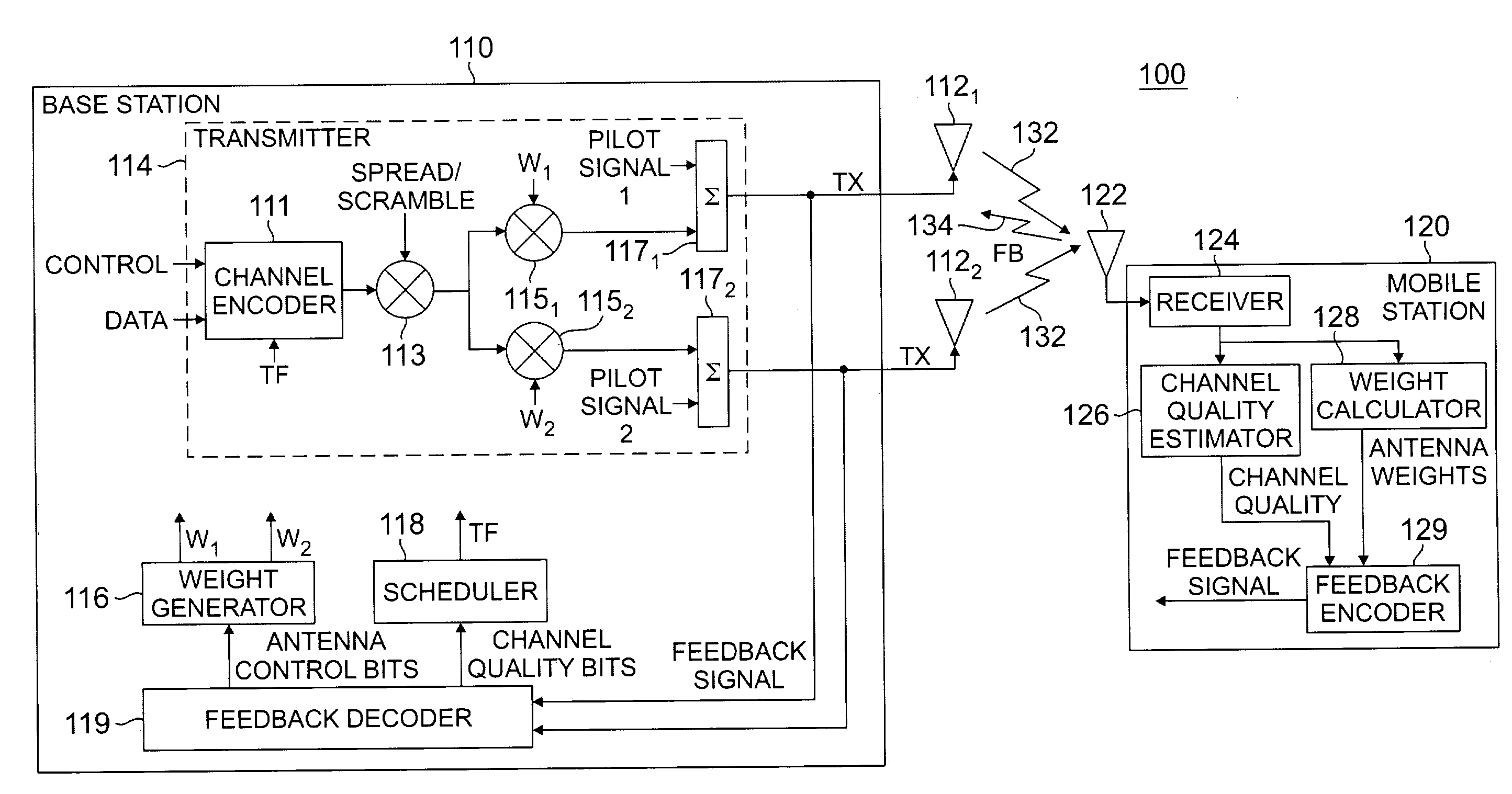
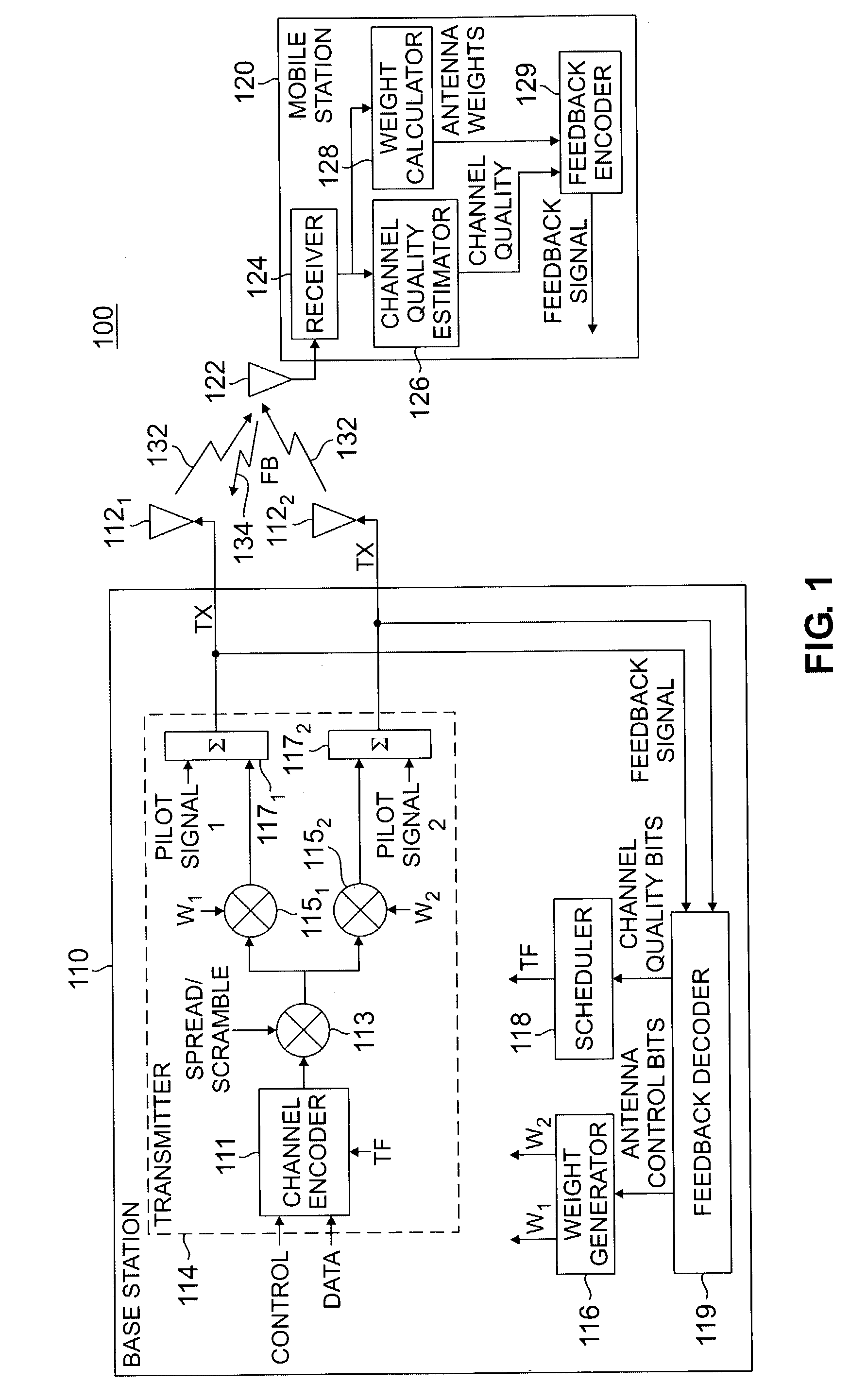
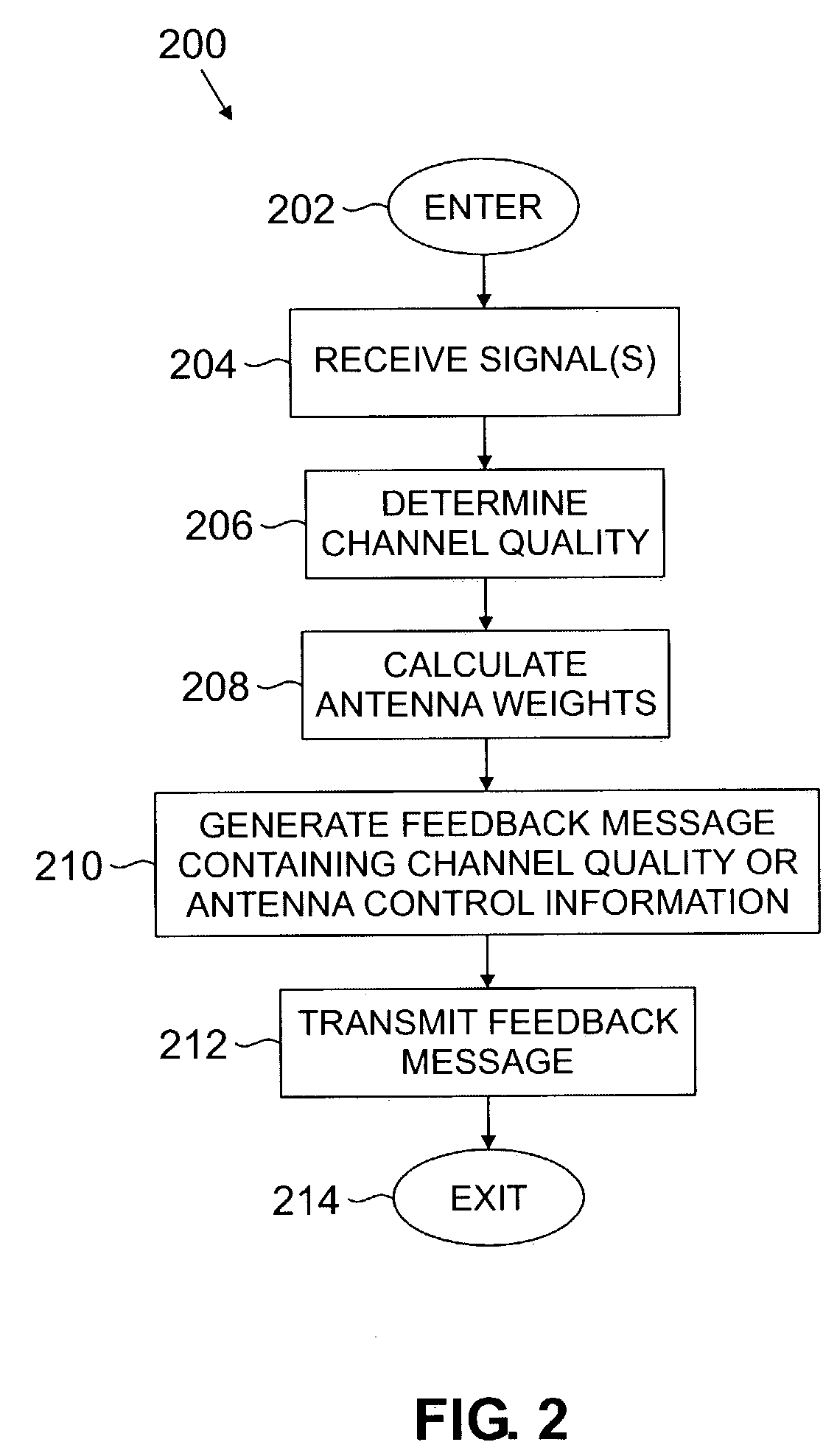
Method and apparatus for feedback error detection in a wireless communications systems
Errors in closed loop transmit diversity (CLTD) feedback signaling may be detected and / or corrected by a mobile station, according to aspects of the present invention, based on signals received from a base station. The mobile station is generally configured to compute antenna weights to be applied at the base station and feed back corresponding antenna control bits to the base station, as in conventional CLTD systems. However, rather than automatically process subsequent transmissions received from the base station as if the base station properly received the antenna control bits and applied the computed antenna weights, the mobile station attempts to determine the antenna weights actually applied at the base station, and uses these determined antenna weights for processing the subsequent transmissions. Accordingly, even if a feedback signaling error occurred, resulting in the base station using the wrong antenna weights, the mobile station may properly process the transmissions. According to some aspects of the present invention, the base station transmits (feeds forward) antenna control bits actually received from the mobile station on a feed forward channel, and the mobile station processes subsequent transmissions using antenna weights generated based on the fed forward antenna control bits.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Transmit diversity fo base stations
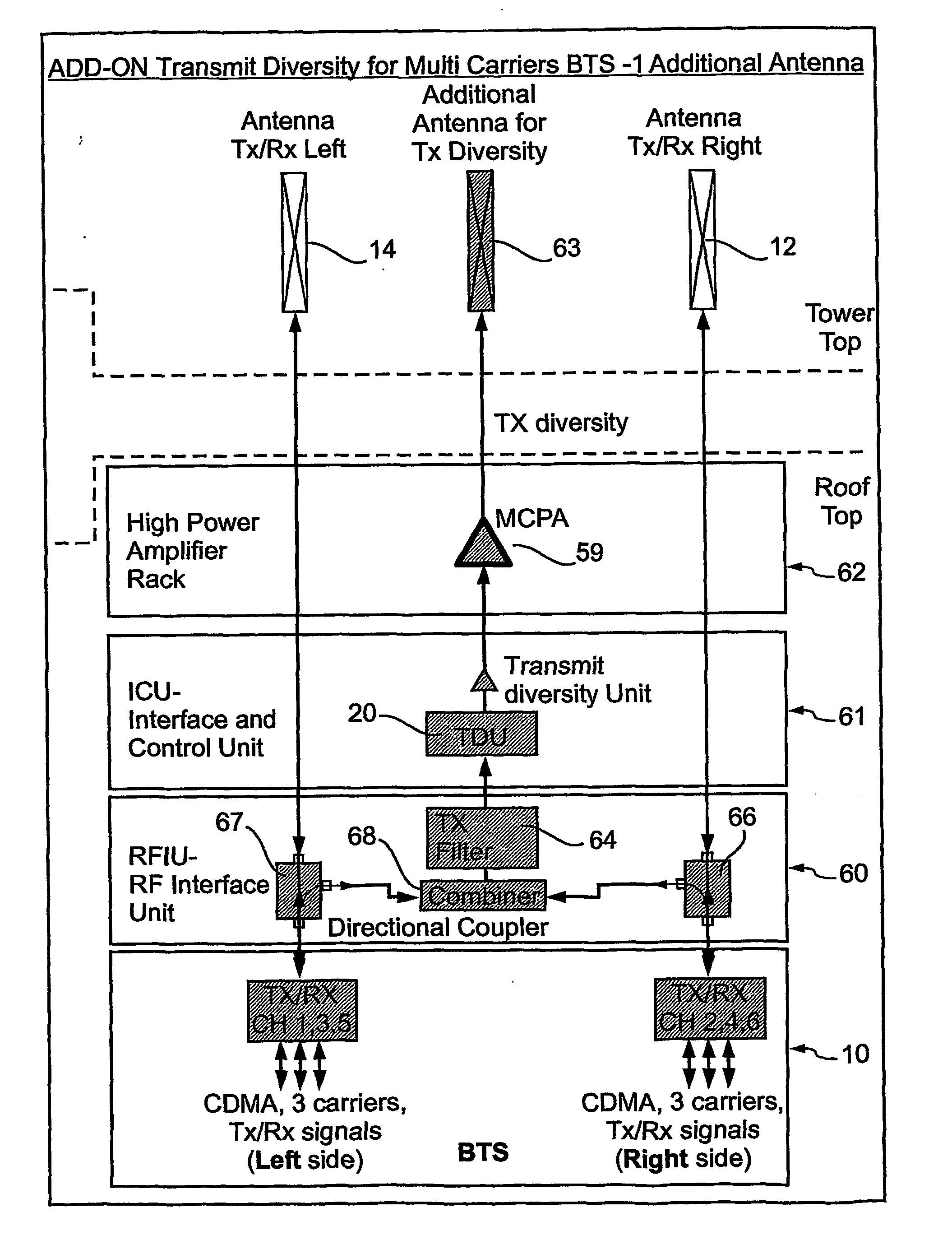
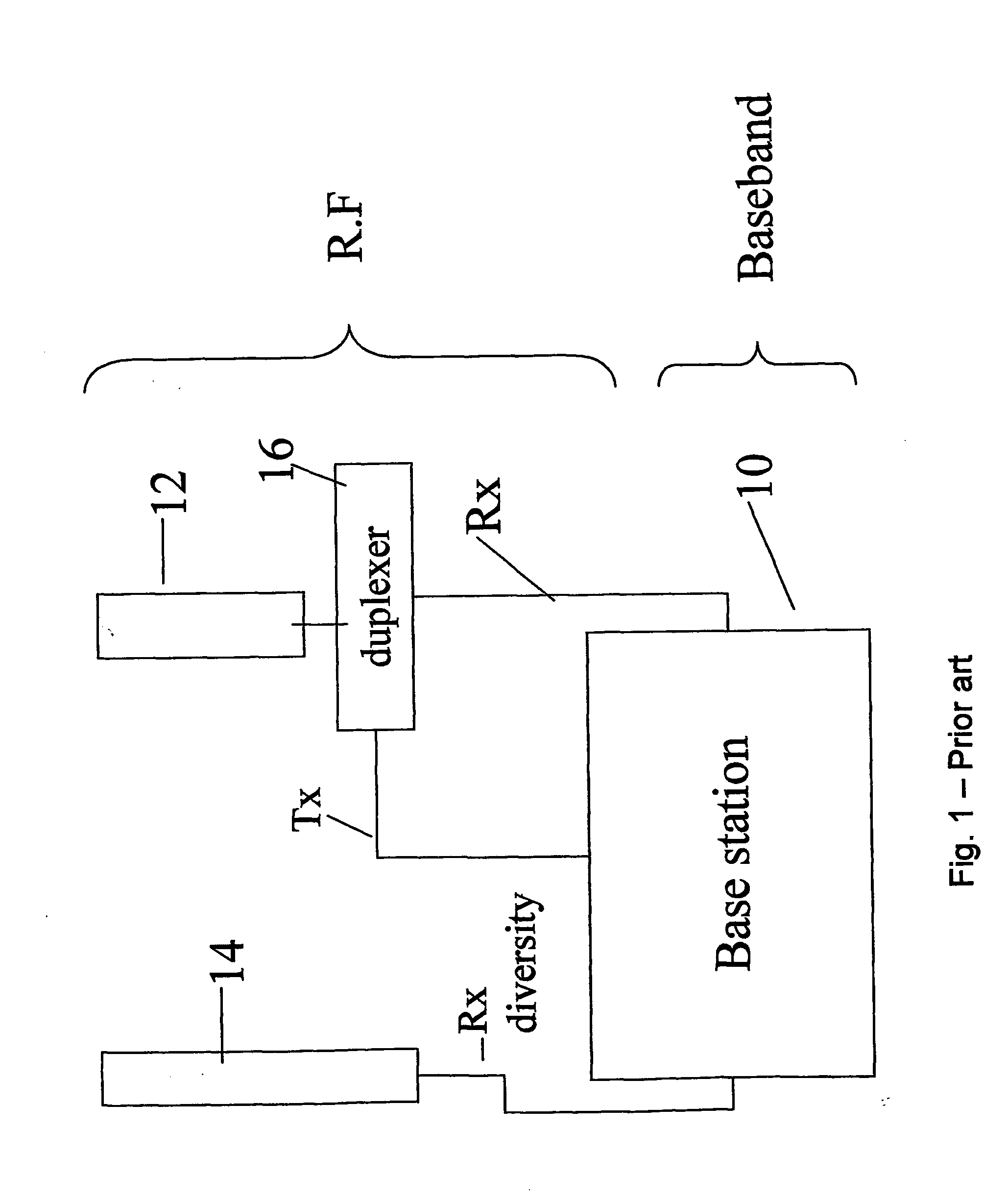
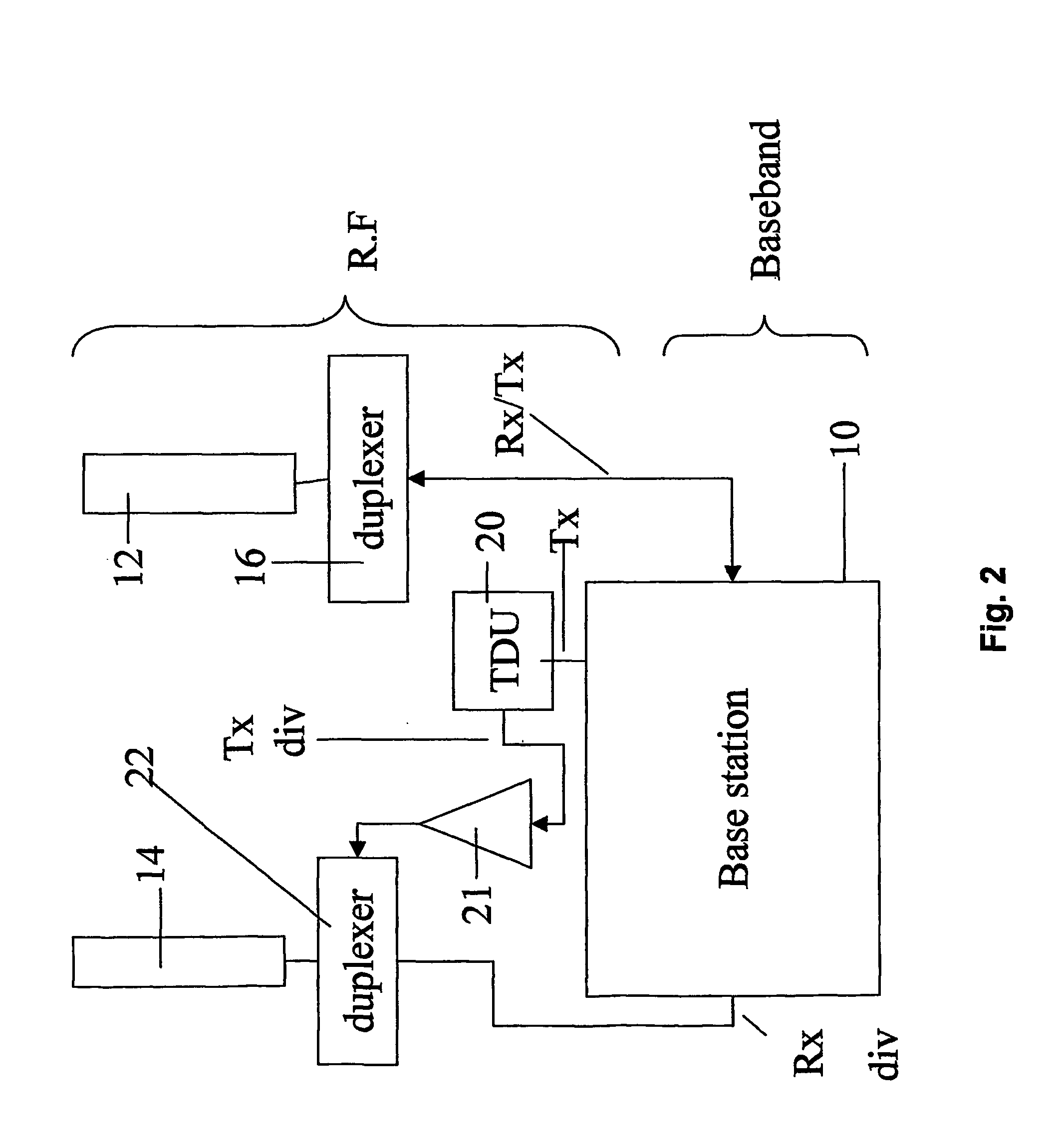
InactiveUS20060052065A1Capability to receiveSpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentAir interfaceRadio frequency
A method and corresponding upgrade kit, for enhancing a base station (10) having a CDMA air interface and a passive antenna (12) with receive space diversity capability so as to provide the base station with transmit diversity capability. The method comprises attaching a radio frequency interface unit to an R.F. output of the base station to obtain a sample of a main R.F. signal, attaching a diversity unit (20) to the radio frequency interface unit to generate a transmit diversity signal, and connecting the diversity unit to the passive antenna to transmit the transmit diversity signal.
Owner:CELLETRA
High rate transmit diversity transmission and reception
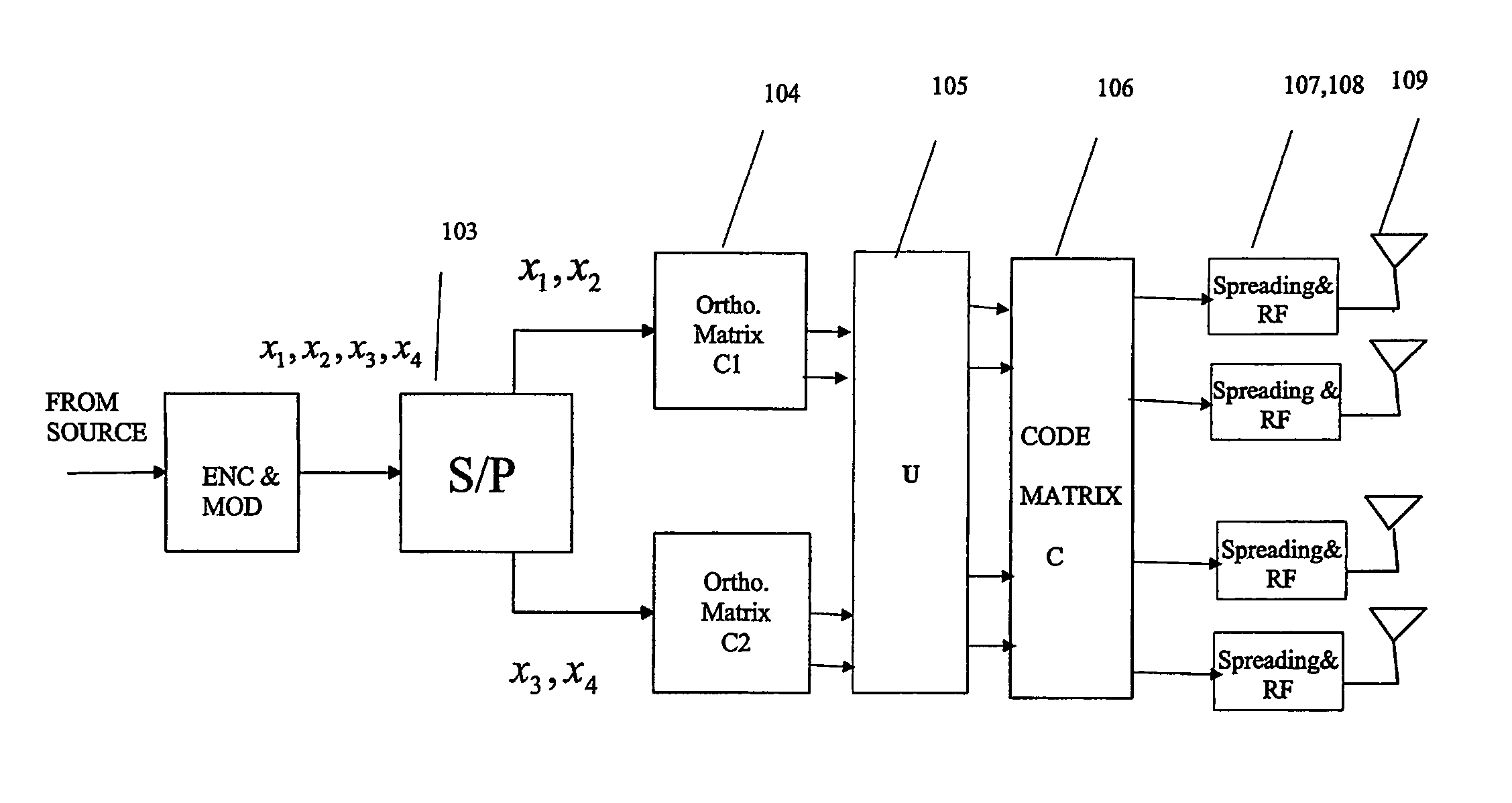
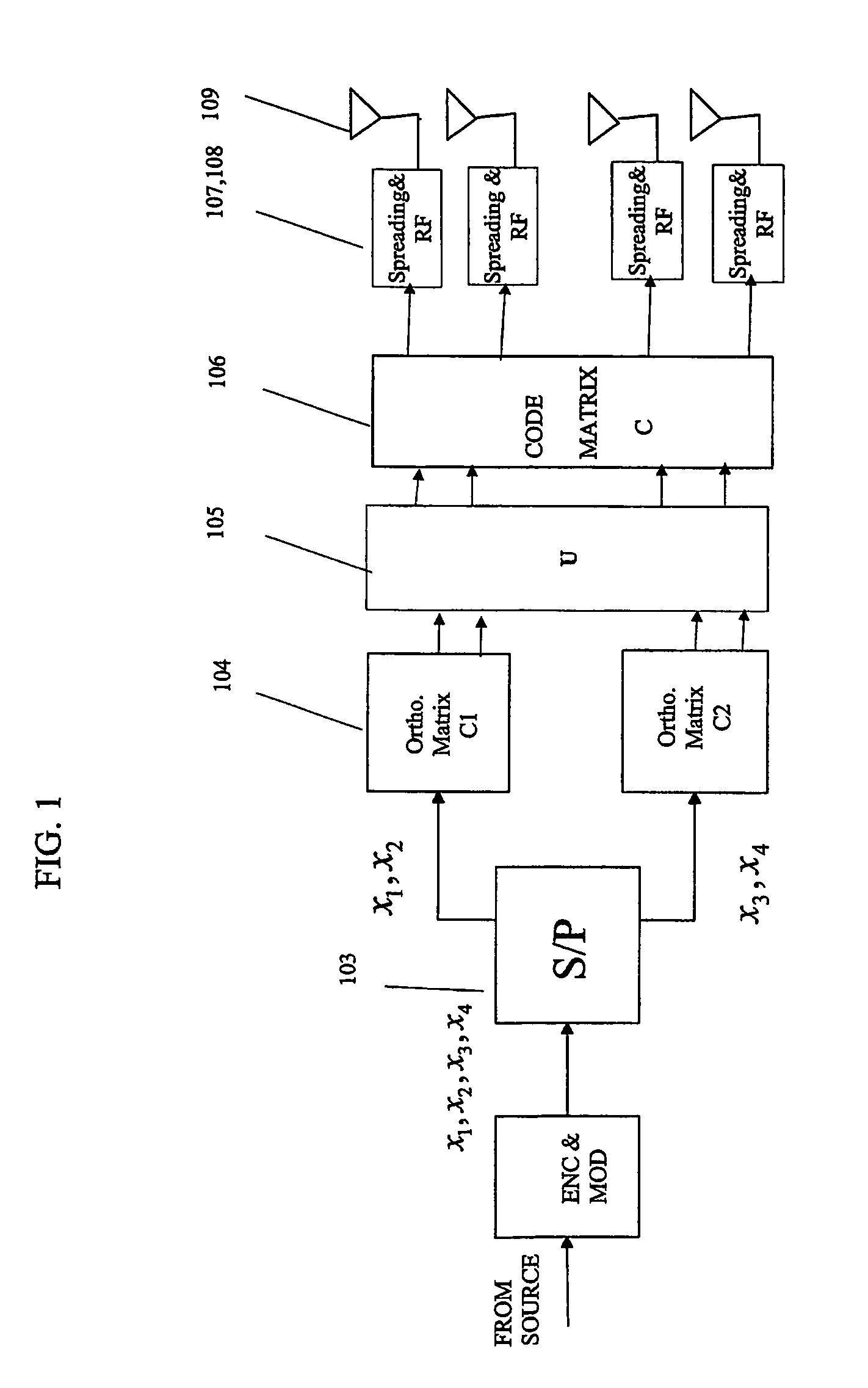
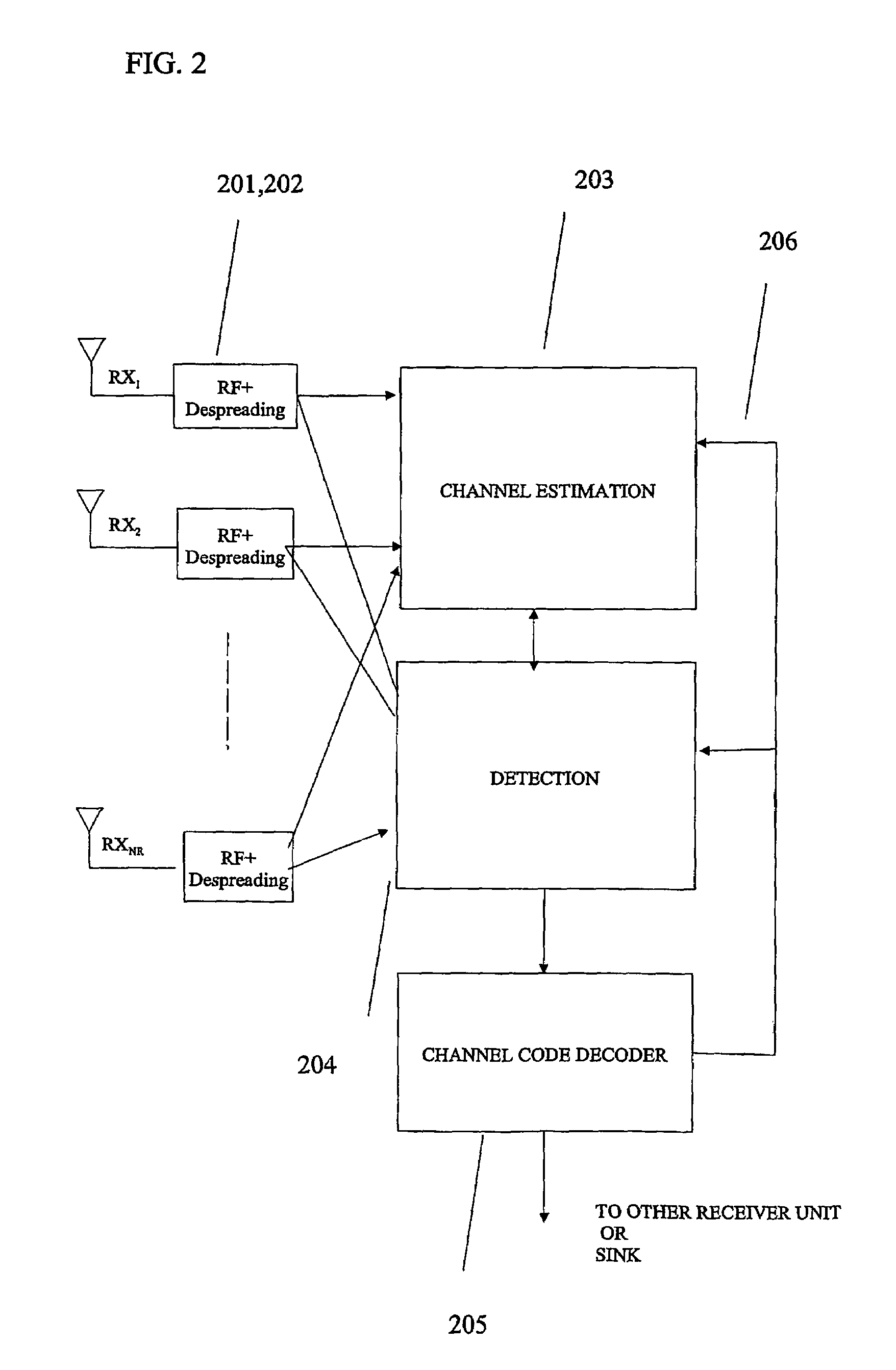
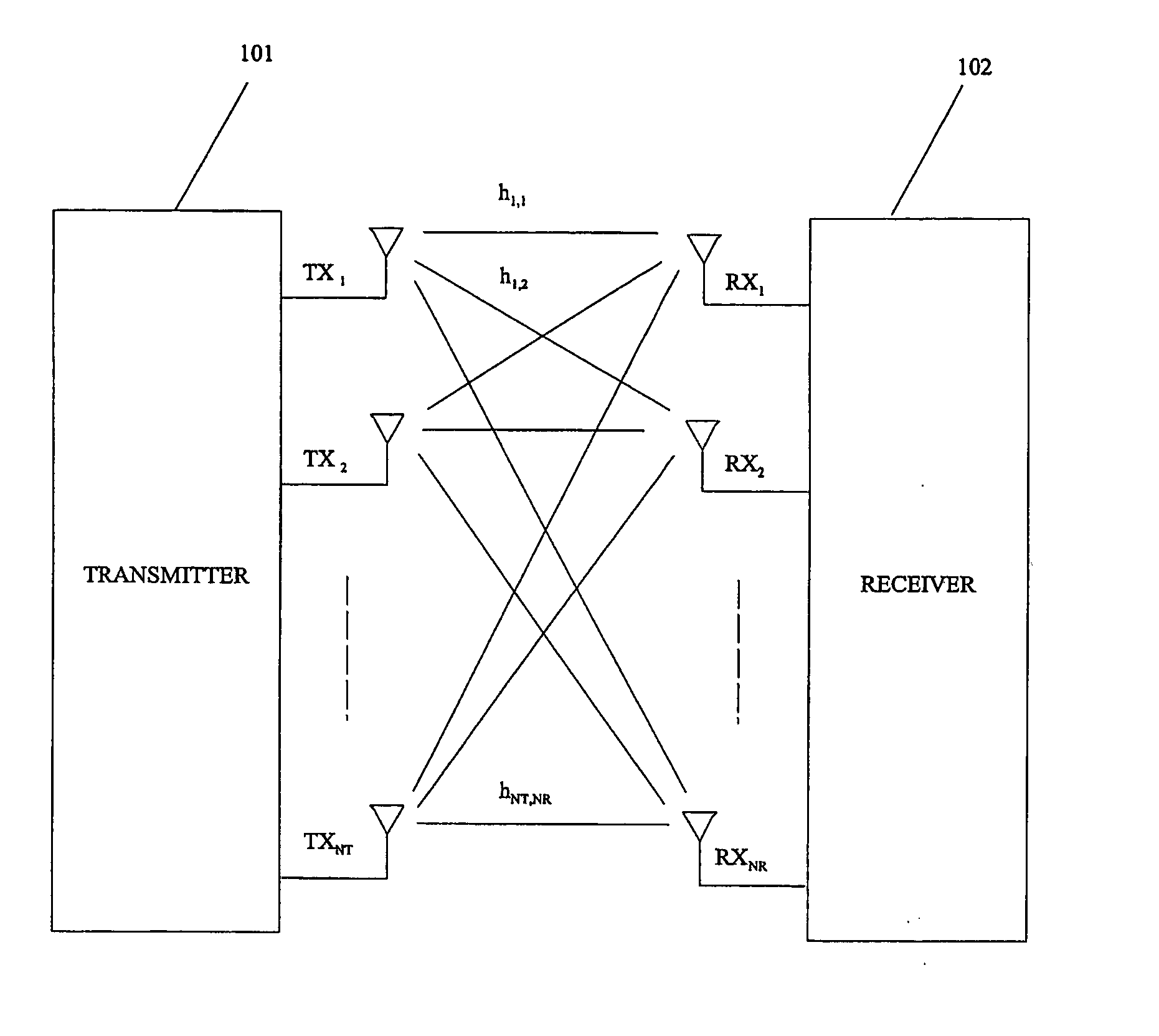
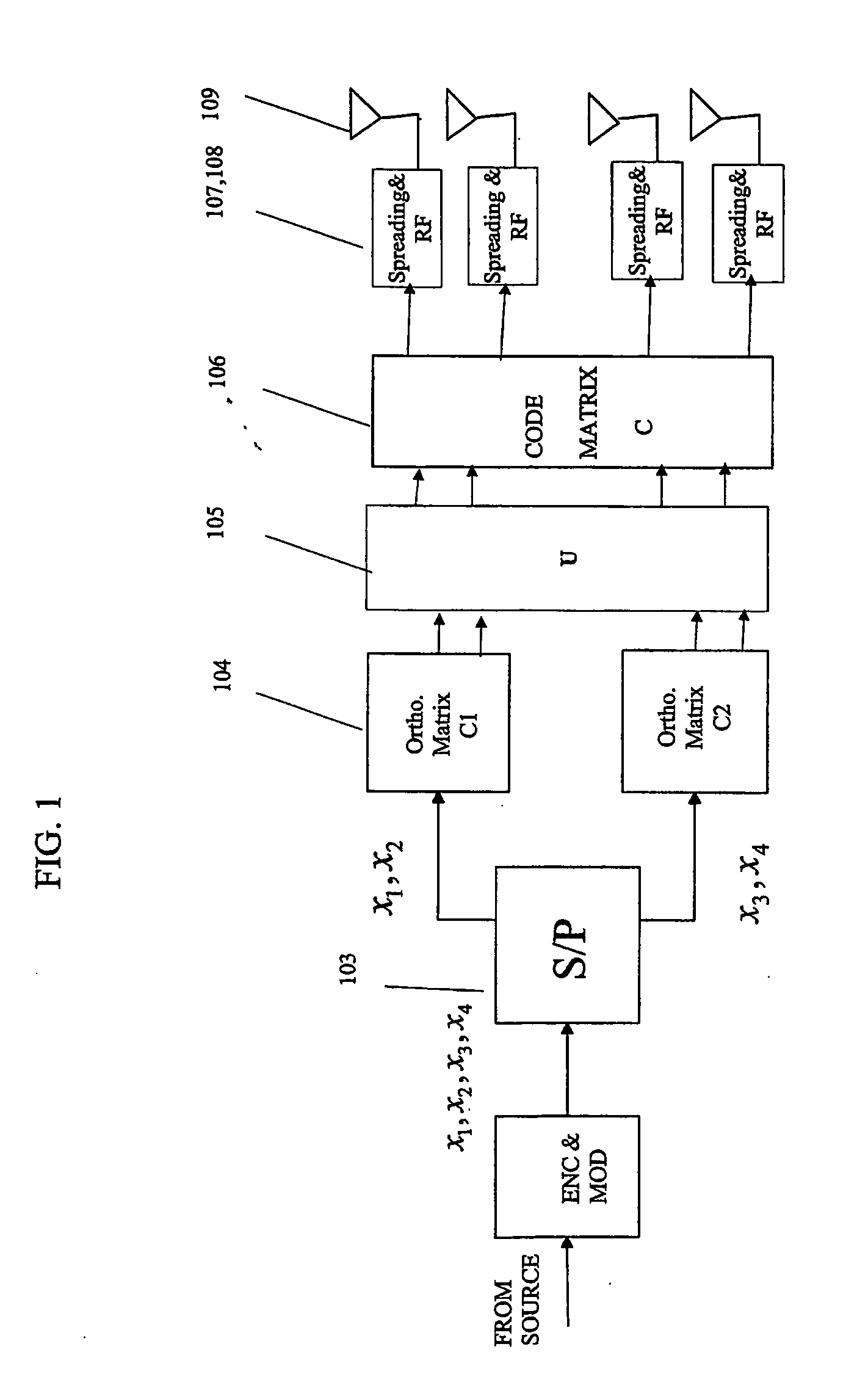
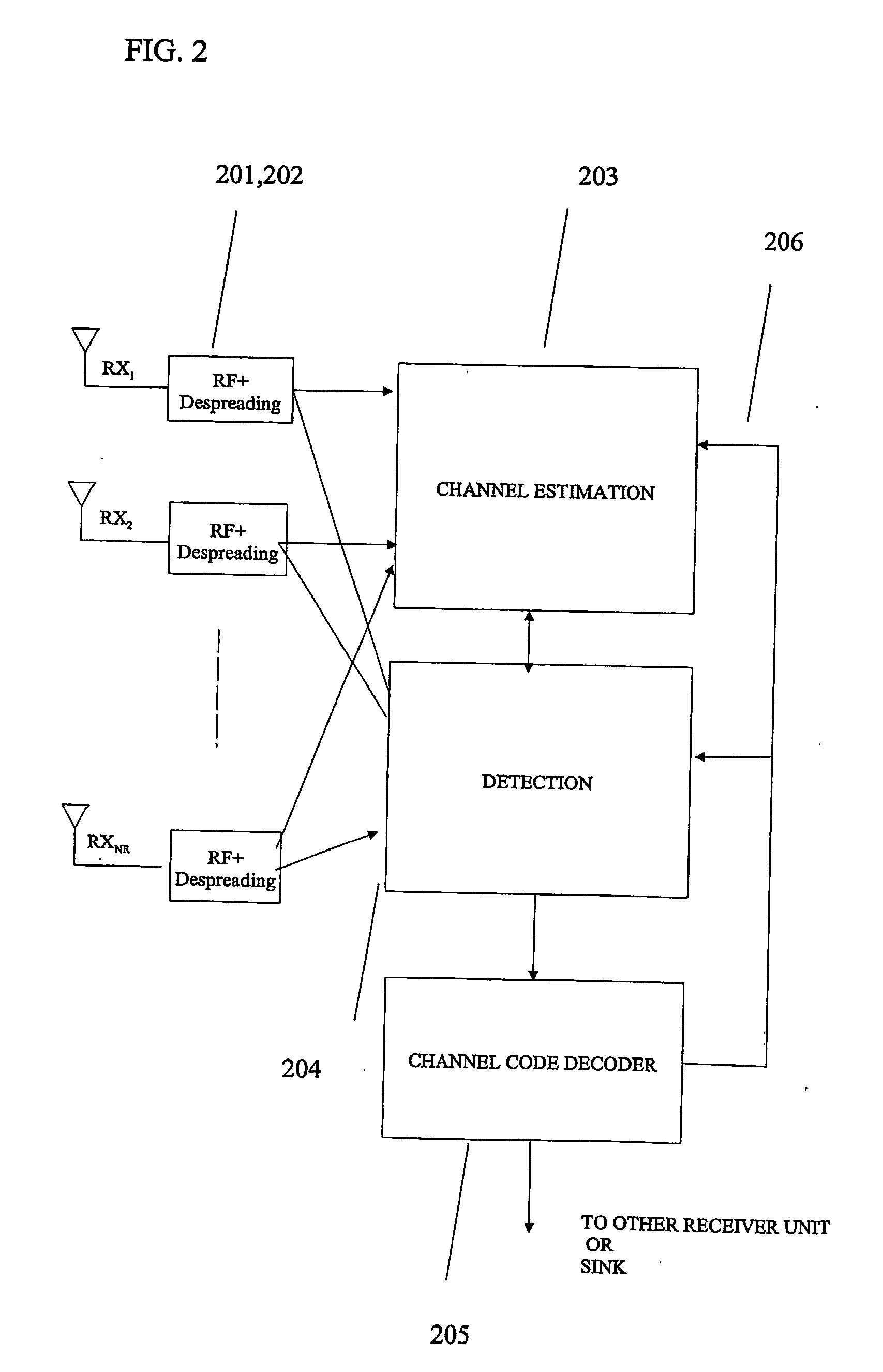
The performance and symbol rate in a wireless mobile system are increased by forming a transmission code matrix using transformed orthogonal codes, in such a way that the code is robust to channel statistics and operates well in both Ricean and (correlated) Rayleigh channels. Furthermore, the invention enables high symbol rate transmission using multiple transmit antennas, and one or multiple receive antennas, and obtains simultaneously high diversity order and high symbol or data rate.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Transmission methods for downlink ACK/NACK channels
A method from transmitting data via multiple antennas. In this method, four information bits to be transmitted are multiplexed by using either one of a code division multiplexing scheme or a second code division multiplexing scheme combined with a real and imaginary multiplexing scheme, to generate a code division multiplexed symbol including four vectors. Then, the code division multiplexed symbol is repeatedly transmitted by alternatively applying two transmit diversity schemes via four transmission antennas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Communication system and method using transmit diversity
InactiveUS20060148415A1Improving downlink capacityIncrease capacitySpatial transmit diversityError preventionCommunications systemDiversity scheme
Influencing the transmission of signals from a transmitting device to a receiving device in a communication system comprising at least one transmitting device and at least one receiving device is disclosed. In a receiving station received transmission signals are processed and a feedback signal to be transmitted to a transmitting device is generated on the basis of the processed signals. Then, transmit weights to be applied to transmission signals are determined in accordance with the feedback signal.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Adaptive transmit diversity with quadrant phase constraining feedback
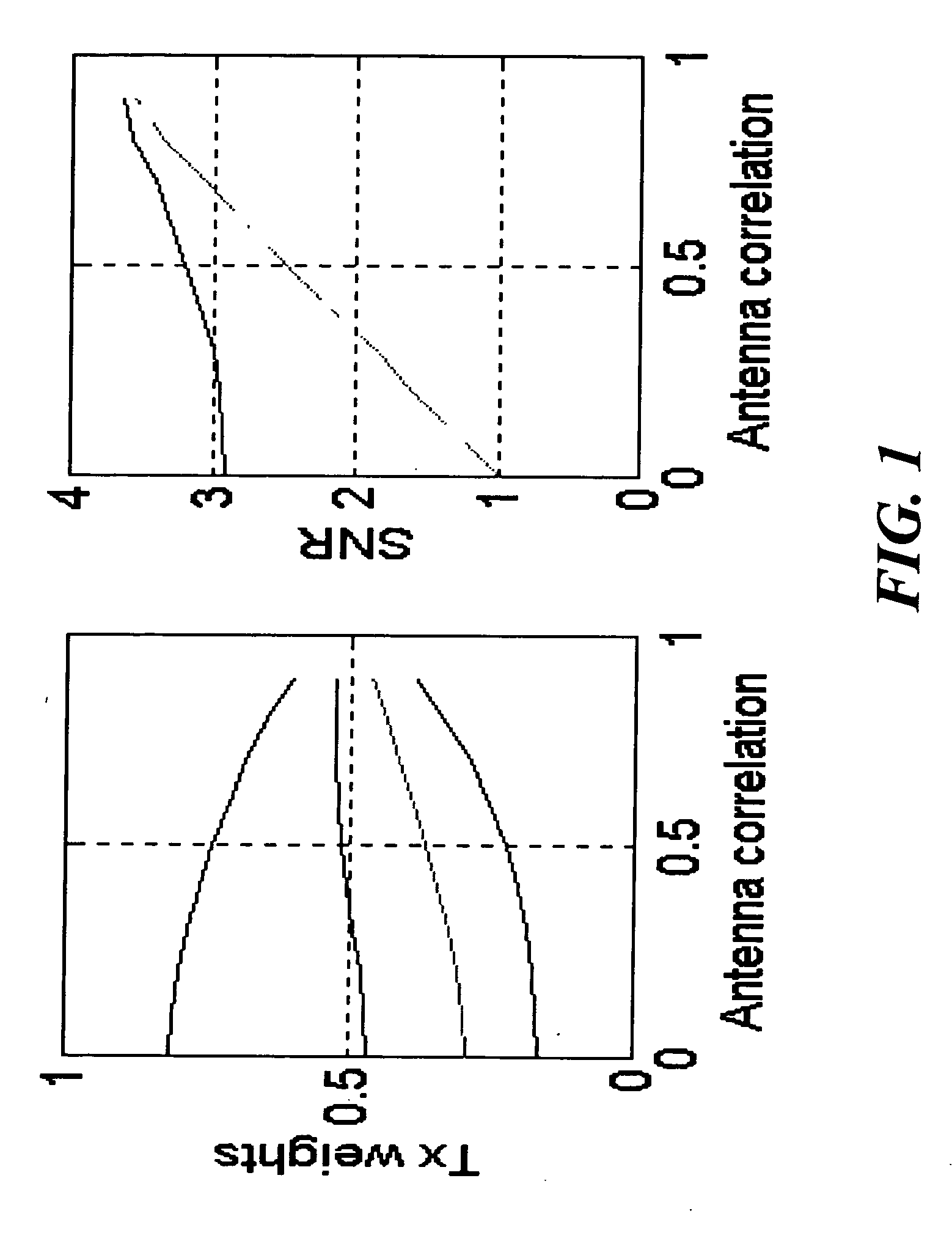
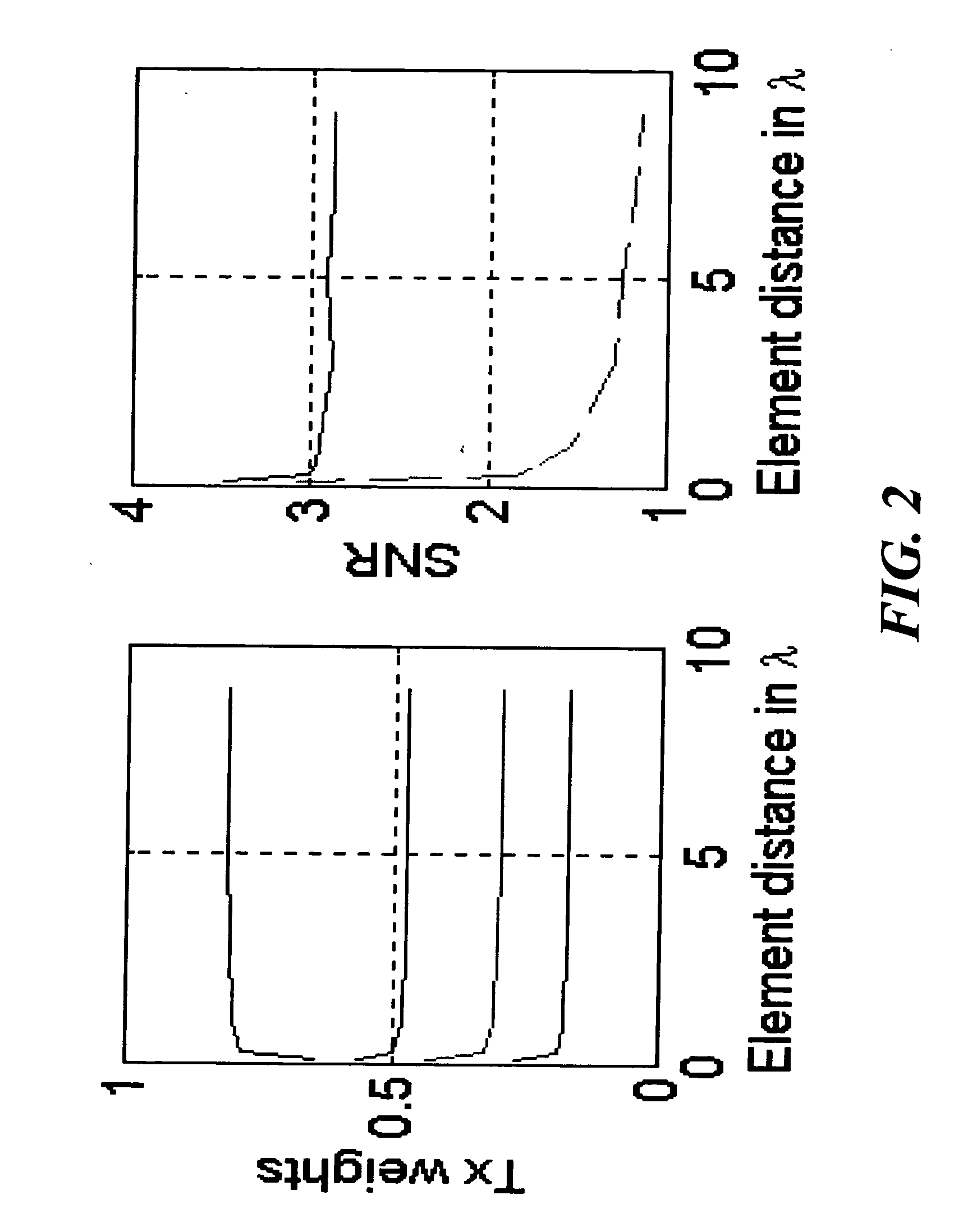
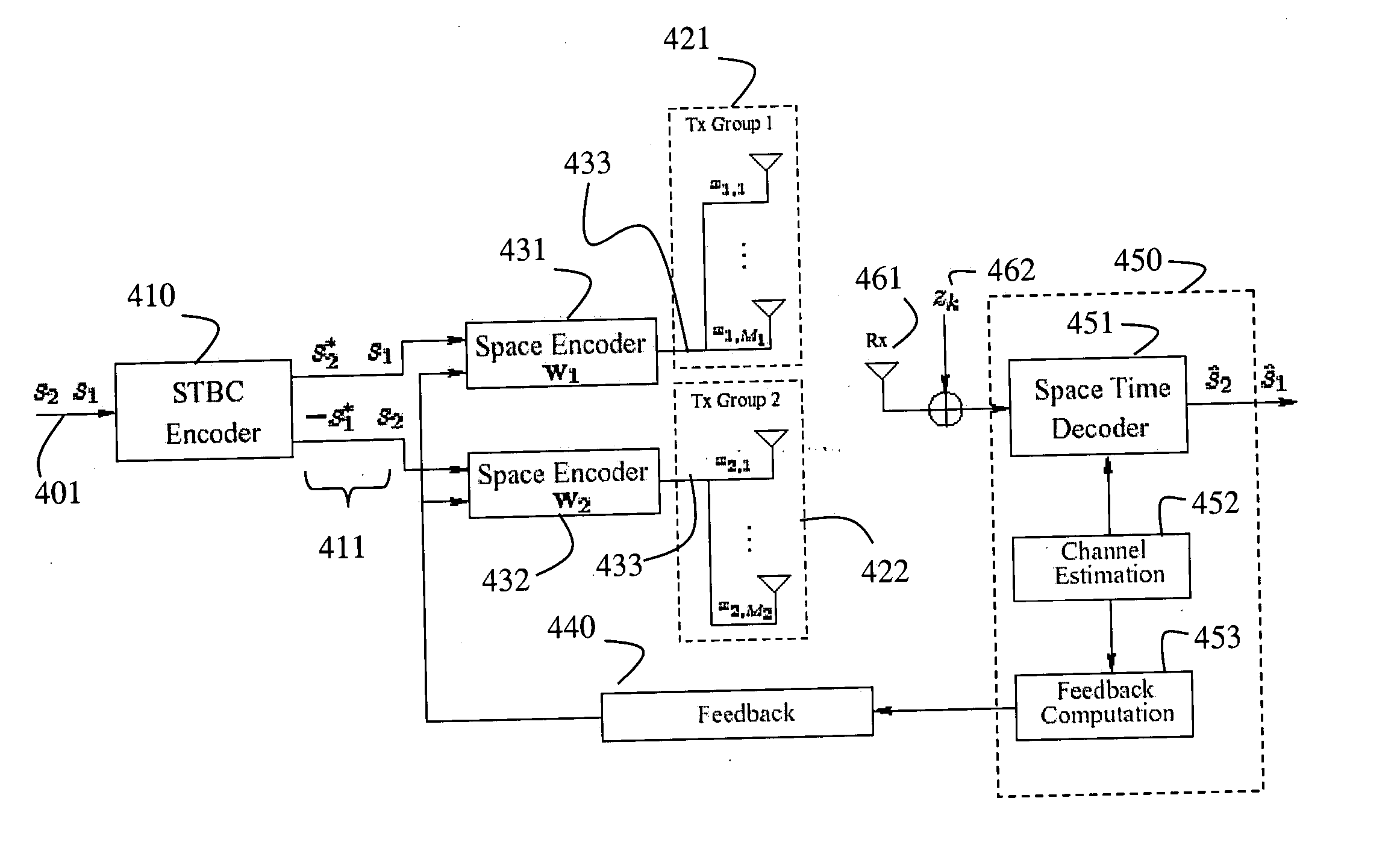
InactiveUS20050048933A1Feedback is intuitiveImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityElectromagnetic wave modulationCommunications systemData stream
A wireless communication system includes a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter includes multiple groups of transmit antennas. Input symbols are generated and then orthogonal space-time block is encoded to produce a data stream for each group of transmit antennas. Each data stream is adaptively linear space encoded to produce an encoded signal for each transmit antenna of each group according to feedback information for the group. The receiver includes a single receive antenna, a module for measuring a phase of a channel impulse response for each transmit antenna. The feedback information is determined independently for each group of transmit antennas from the channel impulse responses. The feedback information for each group of transmit antennas is sent to the transmitter.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
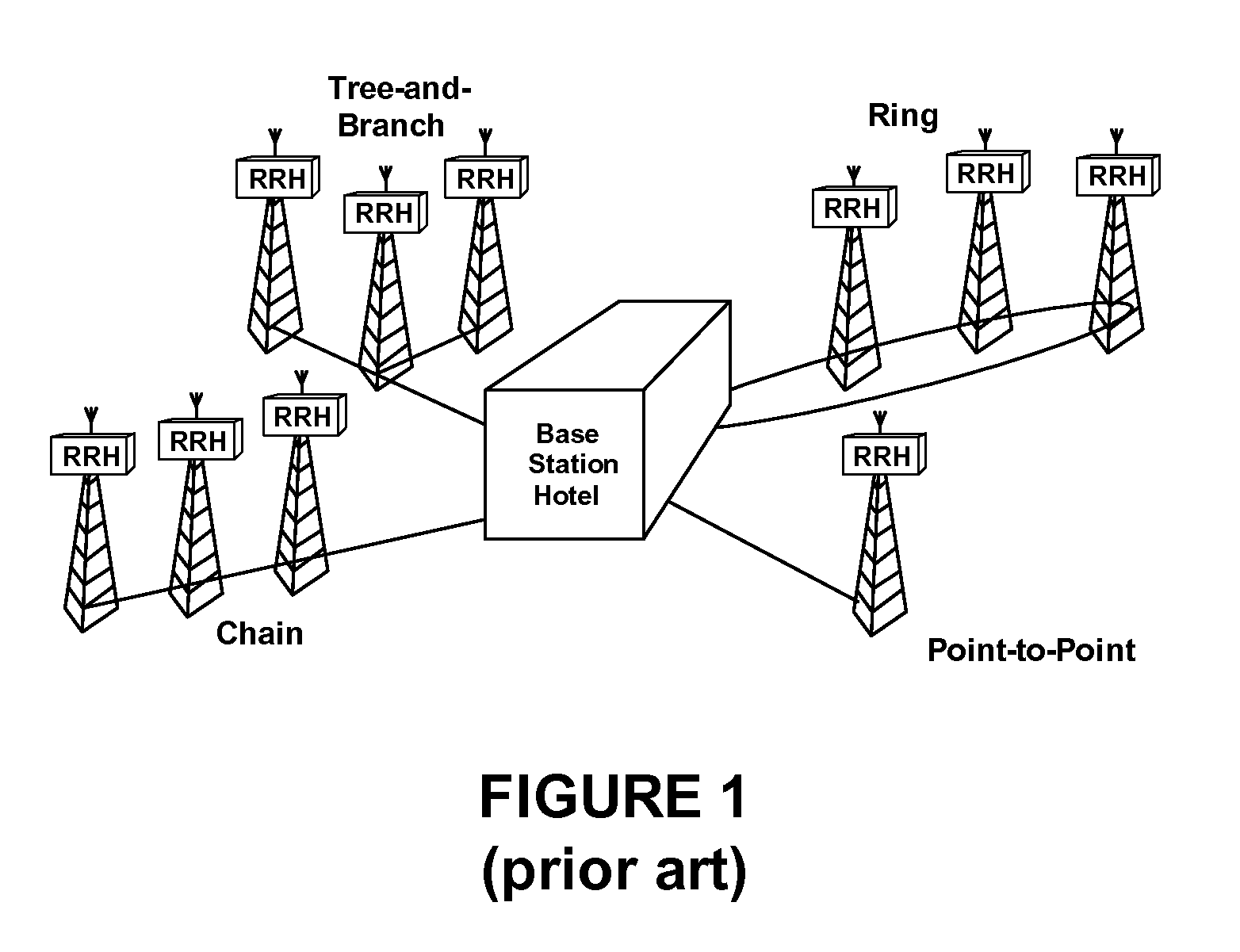
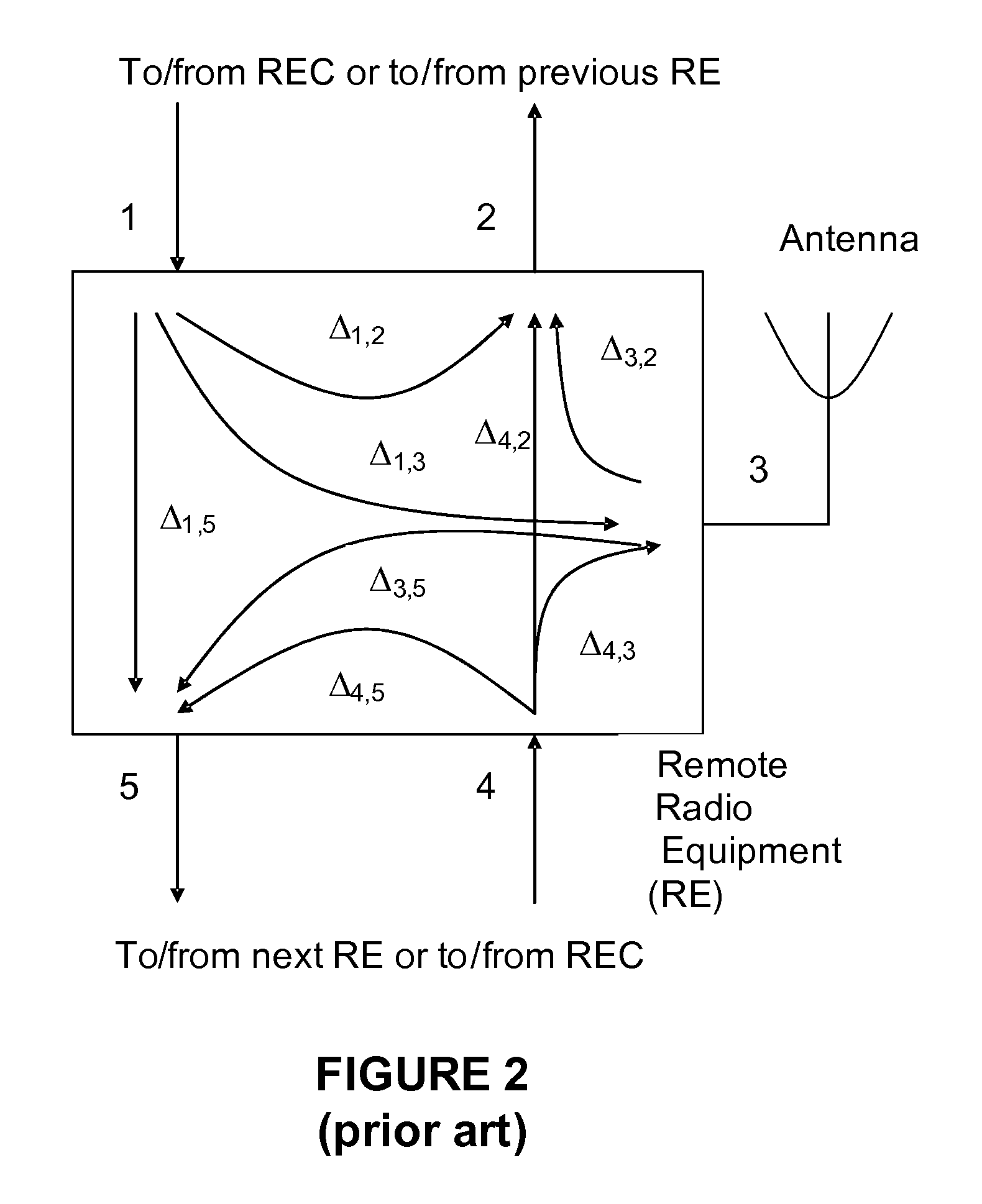
Delay measurements and calibration methods and apparatus for distributed wireless systems
InactiveUS7940667B1High delay measurement accuracyReduce significant maintenance costSynchronisation arrangementError preventionDiversity schemeComputer science
Delay measurement and delay calibration methods and apparatus are described for use within distributed wireless base stations employing a remote radio head topology. The methods and apparatus are usable in any system that requires accurate delay measurement and / or constant delay through an electronic device. The methods and apparatus for measuring delay embody a highly accurate distributed delay measurement architecture that handles multiple delay paths within distributed wireless base stations employing a remote radio head topology. The method and apparatus are amenable to implementation with current integrated circuit technology. The methods and apparatus for calibrating electronic delay within distributed base stations employing a remote radio head topology are useful for implementing distributed wireless base stations where transmit diversity is desired. Using the methods disclosed herein, delay within a distributed wireless base station can be measured and calibrated to achieve very deterministic delay characteristics at the system level.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOLUTIONS (US) INC
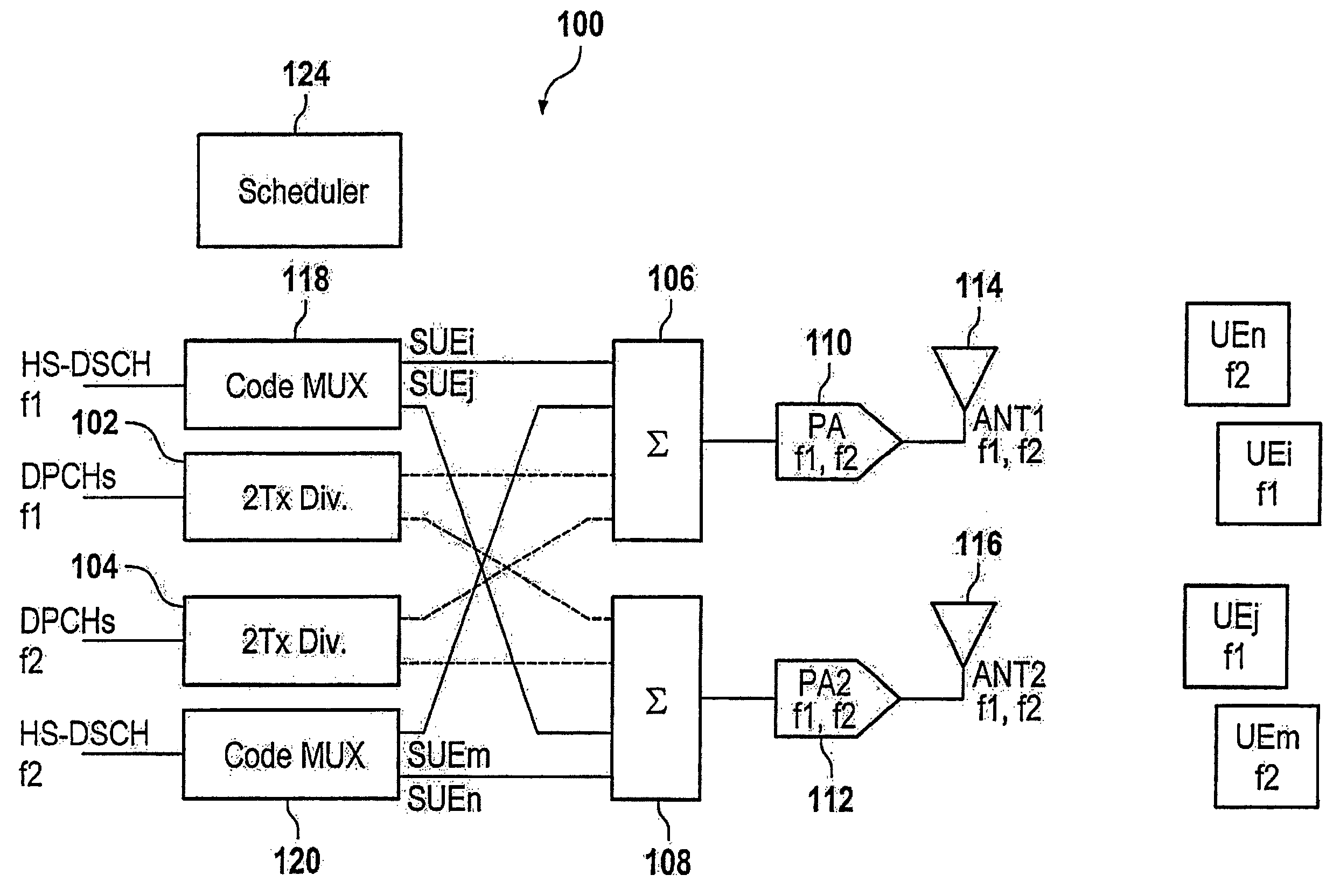
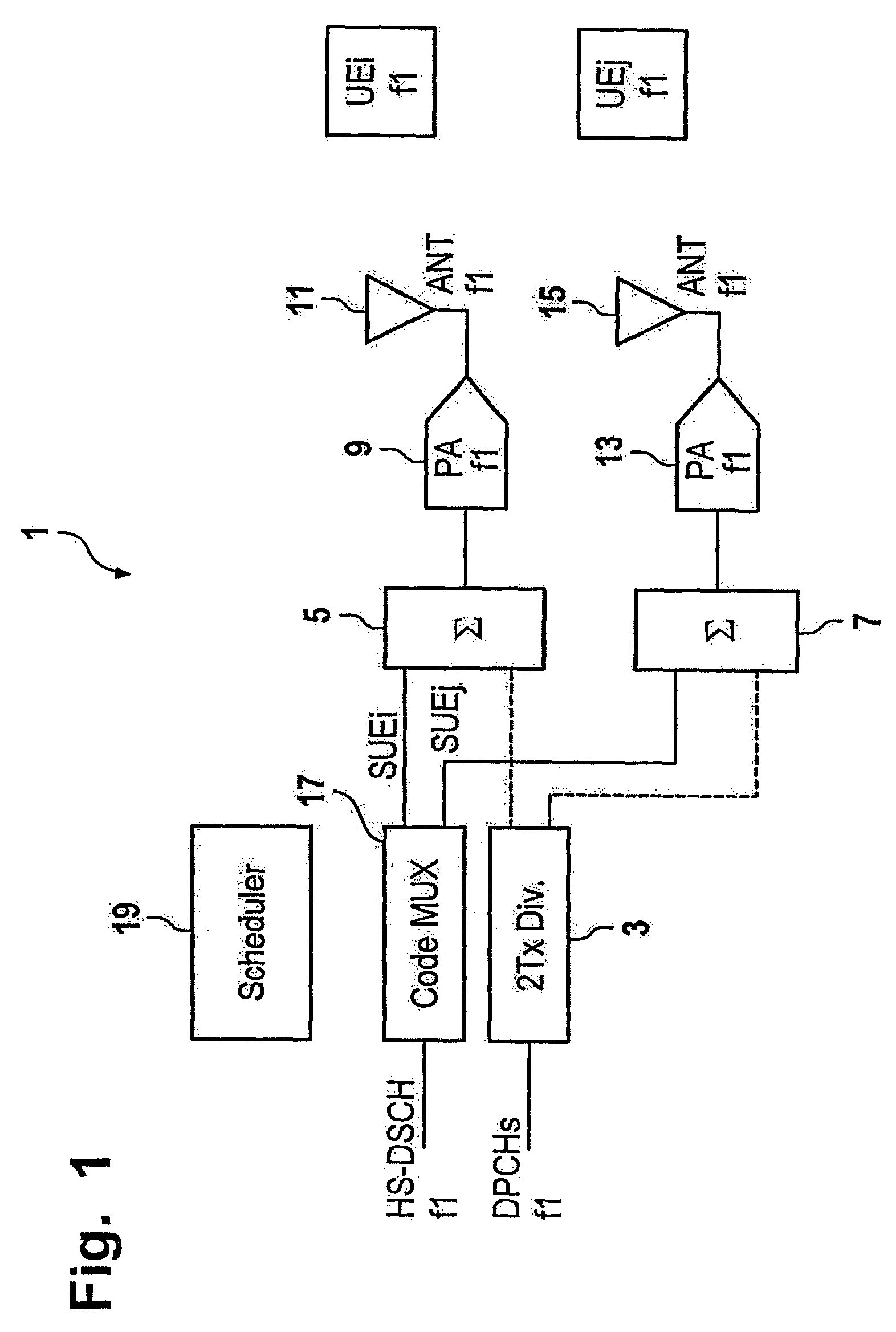
Telecommunication system with transmit and multi-user diversity
ActiveUS7890114B2Easy to useSpatial transmit diversityTime-division multiplexMultiplexingDiversity scheme
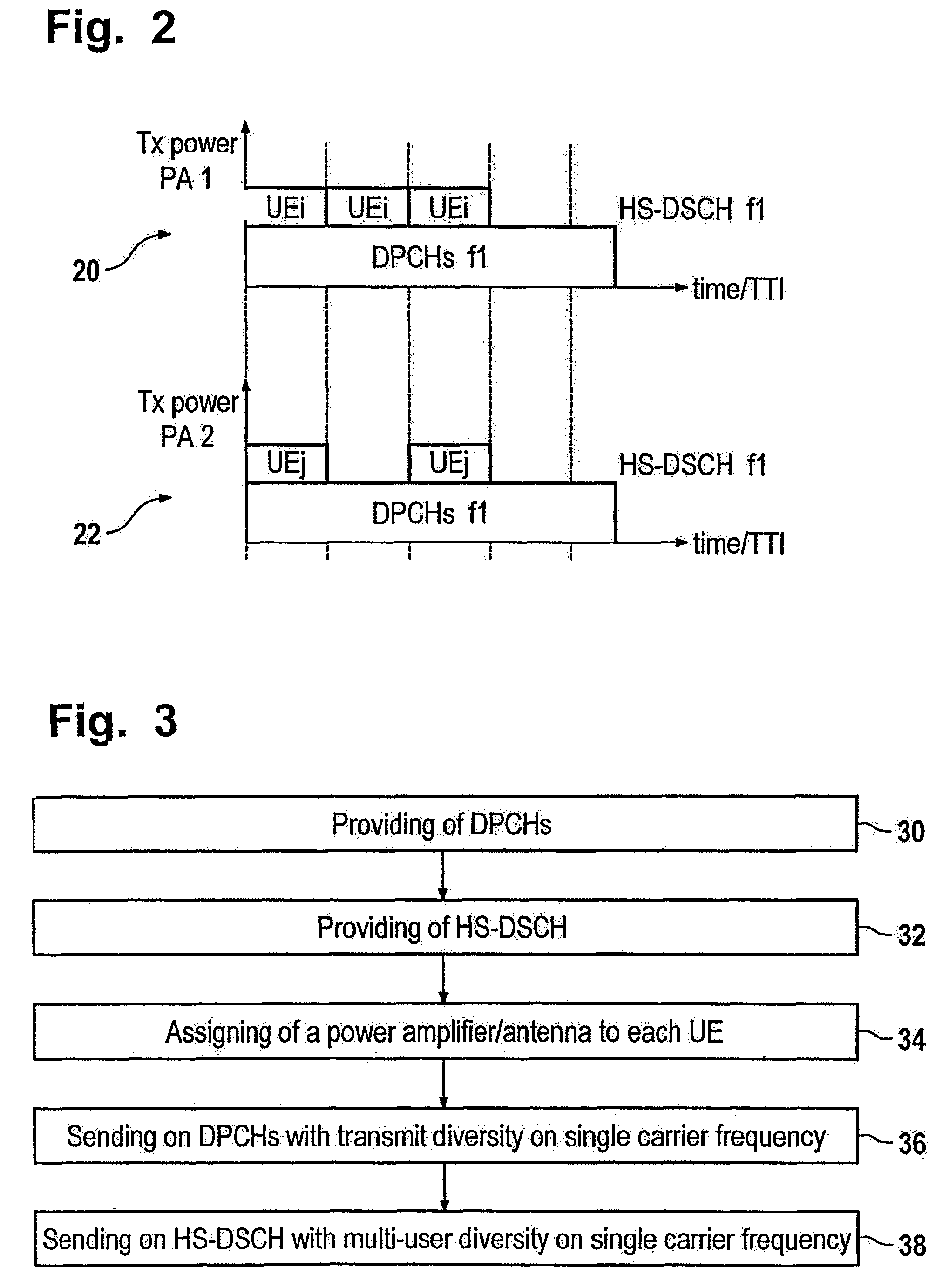
The present invention relates to a method of sending first and second signals to a plurality of user equipments, the method comprising the steps of providing of a dedicated channel for each one of the plurality of user equipments, providing of a code-multiplexed shared channel for the plurality of user equipments, assigning of an antenna of a set of antennas to each one of the user equipments, sending of one of the first signals to one of the plurality of user equipments on one of the dedicated channels on a carrier frequency by applying transmit diversity, sending of one of the second signals to one of the plurality of user equipments on the code-multiplexed shared channel on the carrier frequency by applying multi-user diversity.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High rate transmit diversity transmission and reception
The performance and symbol rate in a wireless mobile system are increased by forming a transmission code matrix using transformed orthogonal codes, in such a way that the code is robust to channel statistics and operates well in both Ricean and (correlated) Rayleigh channels. Furthermore, the invention enables high symbol rate transmission using multiple transmit antennas, and one or multiple receive antennas, and obtains simultaneously high diversity order and high symbol or data rate.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Communication system having a flexible transmit configuration
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
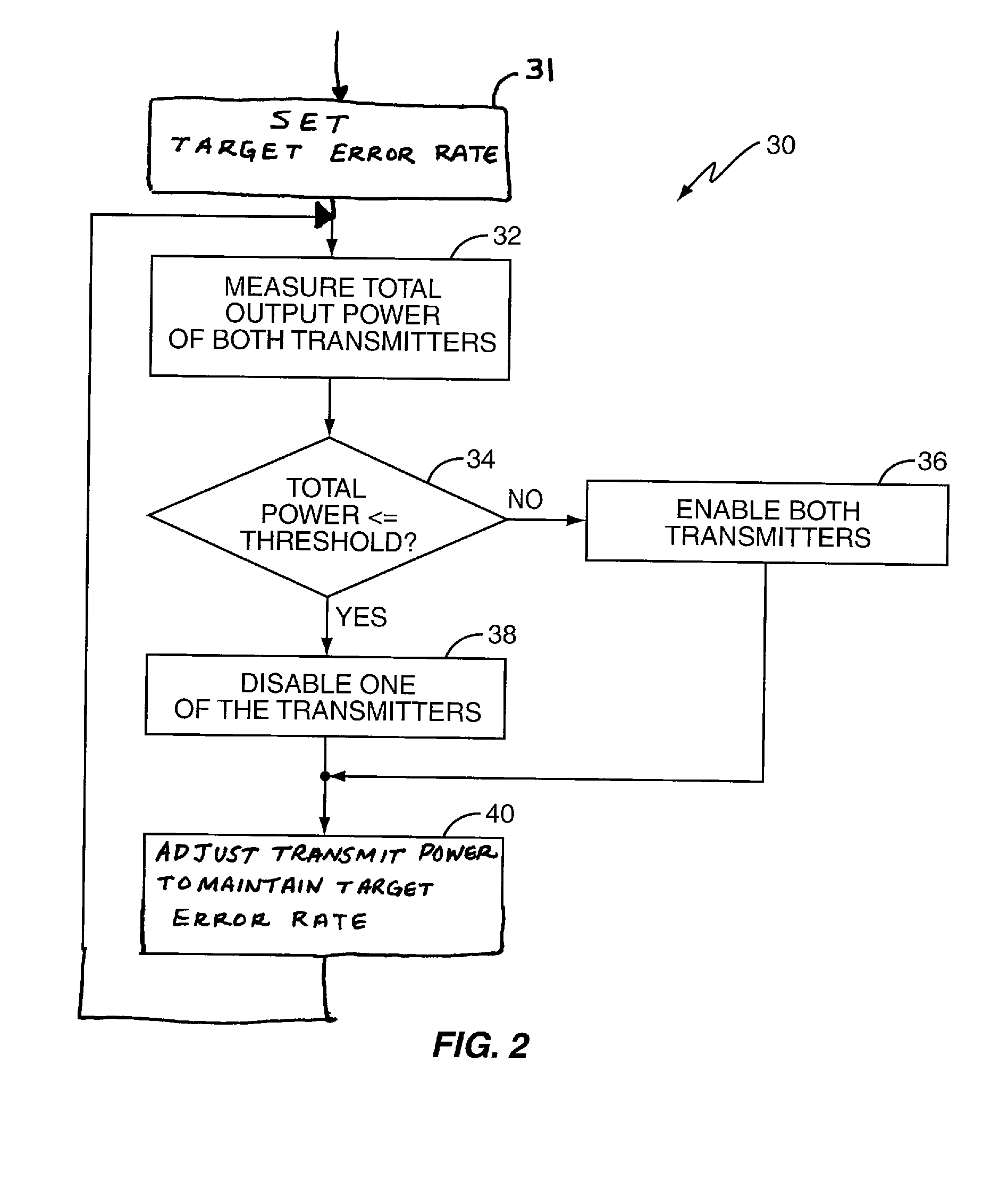
WCDMA Power Saving with Transmit Diversity
InactiveUS20080151798A1Reduce power consumptionEnabling and disabling transmit diversityPower managementSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringComputer terminal
A mobile terminal reduces its power consumption by selectively switching between a diversity mode and a non-diversity mode. The mobile terminal monitors the total output power of two or more of its transmitters, and selectively switches between the diversity mode and the non-diversity mode based on the total output power. The mobile terminal may also selectively switch between the diversity and non-diversity modes based on a difference in output power levels between the two or more transmitters.
Owner:SONY MOBILE COMM INC
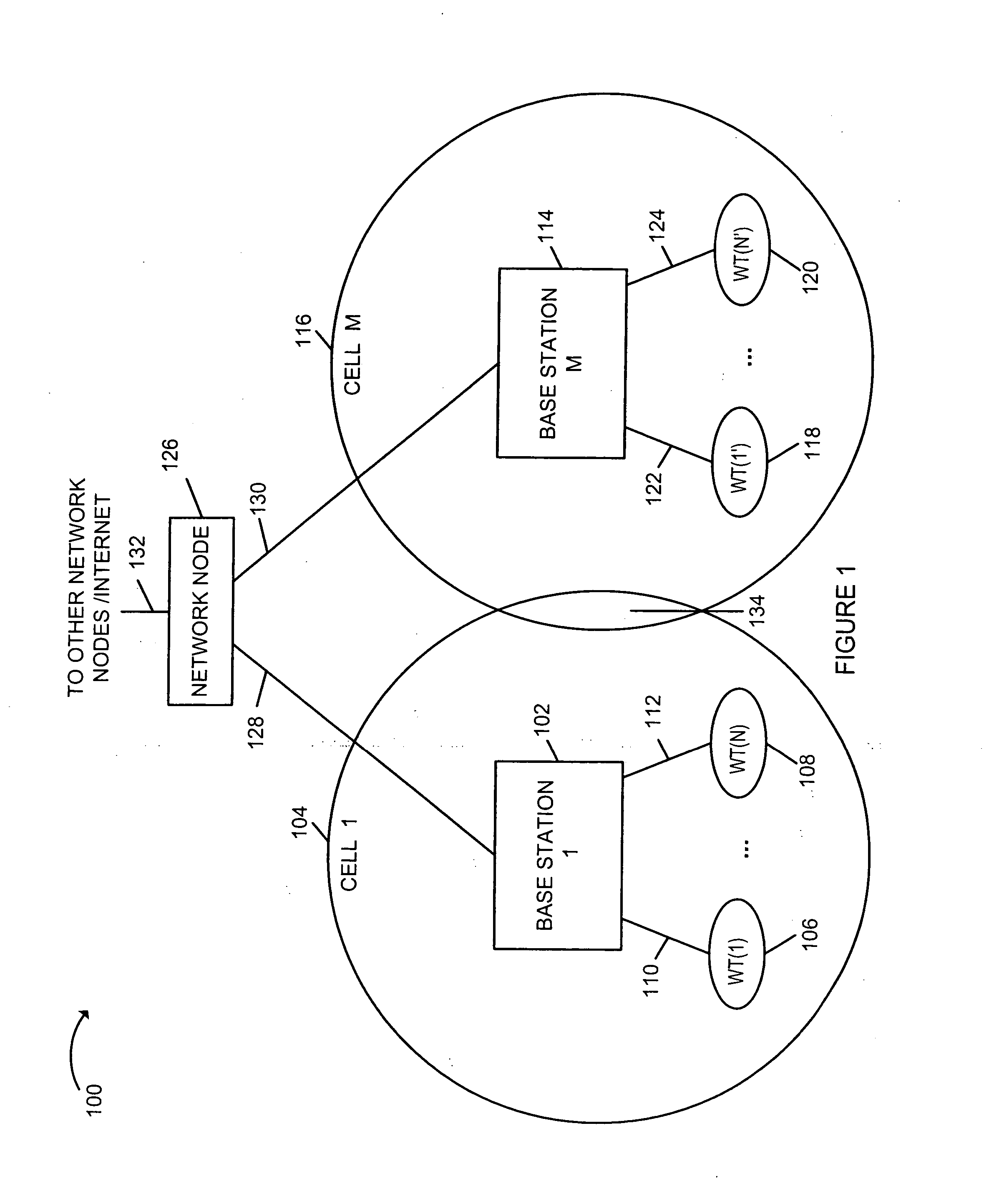
Methods and apparatus of providing transmit diversity in a multiple access wireless communication system
ActiveUS20050003768A1Lower latencyImproved versionSpatial transmit diversityFrequency-division multiplexCommunications systemDiversity scheme
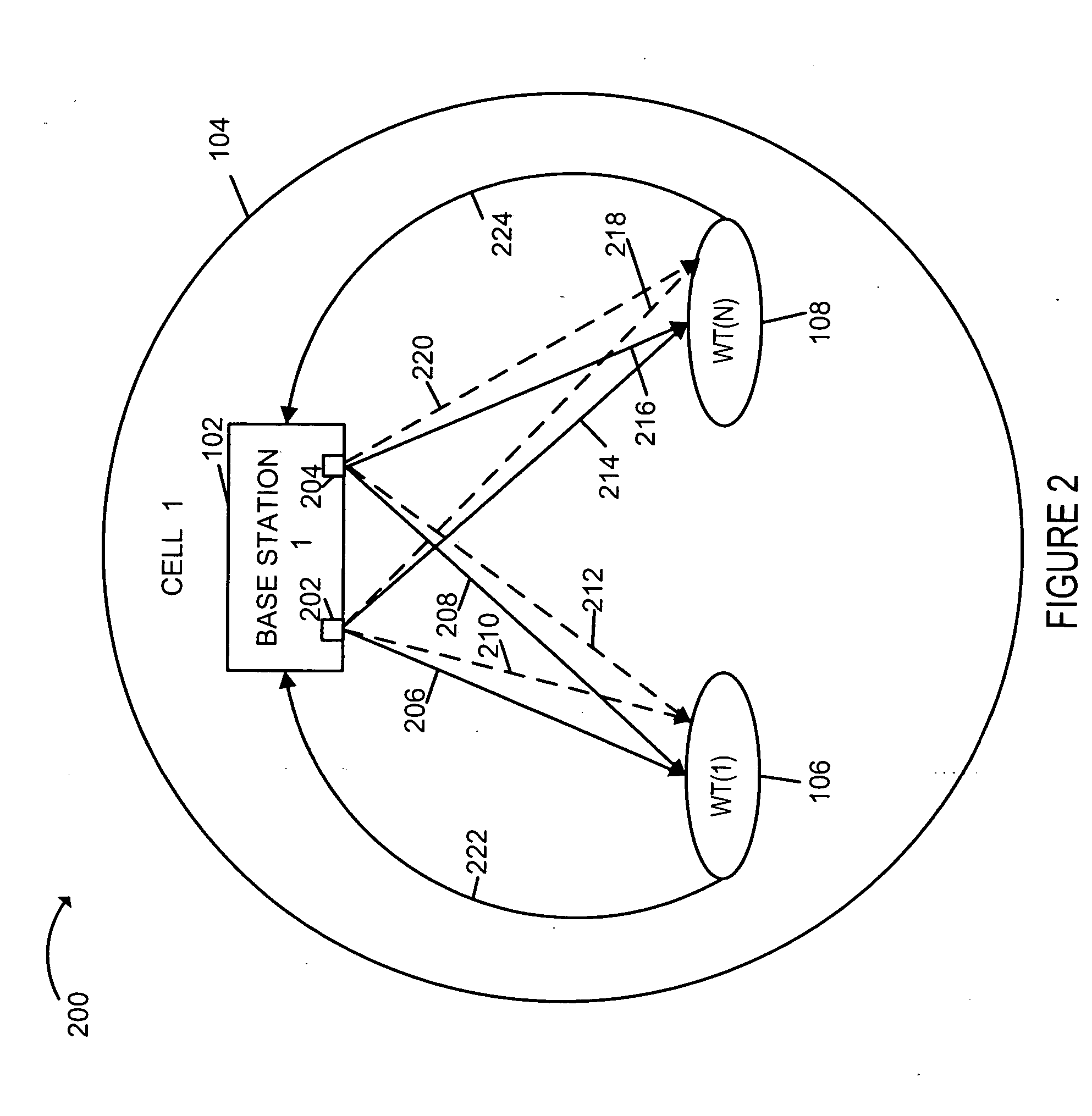
Methods and apparatus for providing channel diversity to wireless terminals (WTs) in a manner that reduces the latency between the time a WT encounters satisfactory channel conditions are described. A plurality of communications channels with different physical characteristics are maintained in a cell by a base station (BS). Each WT monitors multiple channels and maintains multiple channel estimates at the same time so that rapid switching between channels is possible. Channel quality information is conveyed from each WT to the BS. The WT or BS selects a channel based on the measured channel quality. By supporting multiple channels and by introducing periodic variations into the channels in various embodiments, the time before a WT encounters a channel with good or acceptable channel conditions is minimized even if the WT does not change location. Multiple antennas are used at the BS to support numerous channels simultaneously, e.g., by controlling antenna patterns.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com