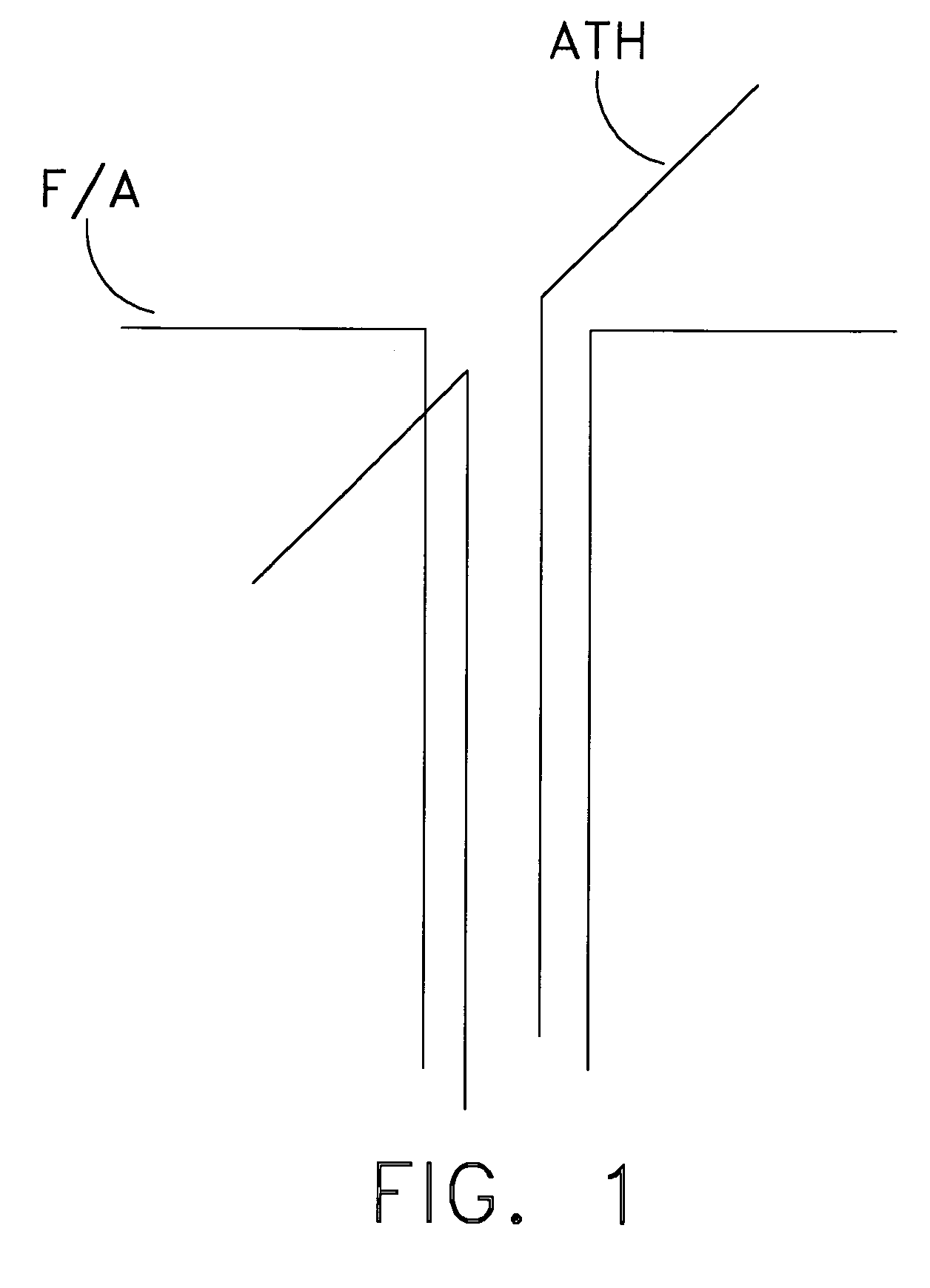Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
66 results about "Pole frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
“Poles” refers to the North and South pole of a magnetic rotor. A motor with a single pole pair (one North, one South) will rotate nominally at the AC supply frequency. So a 2-pole motor with a 60 Hz supply rotates 60 times per second or 3600 rpm (rotations per minute).
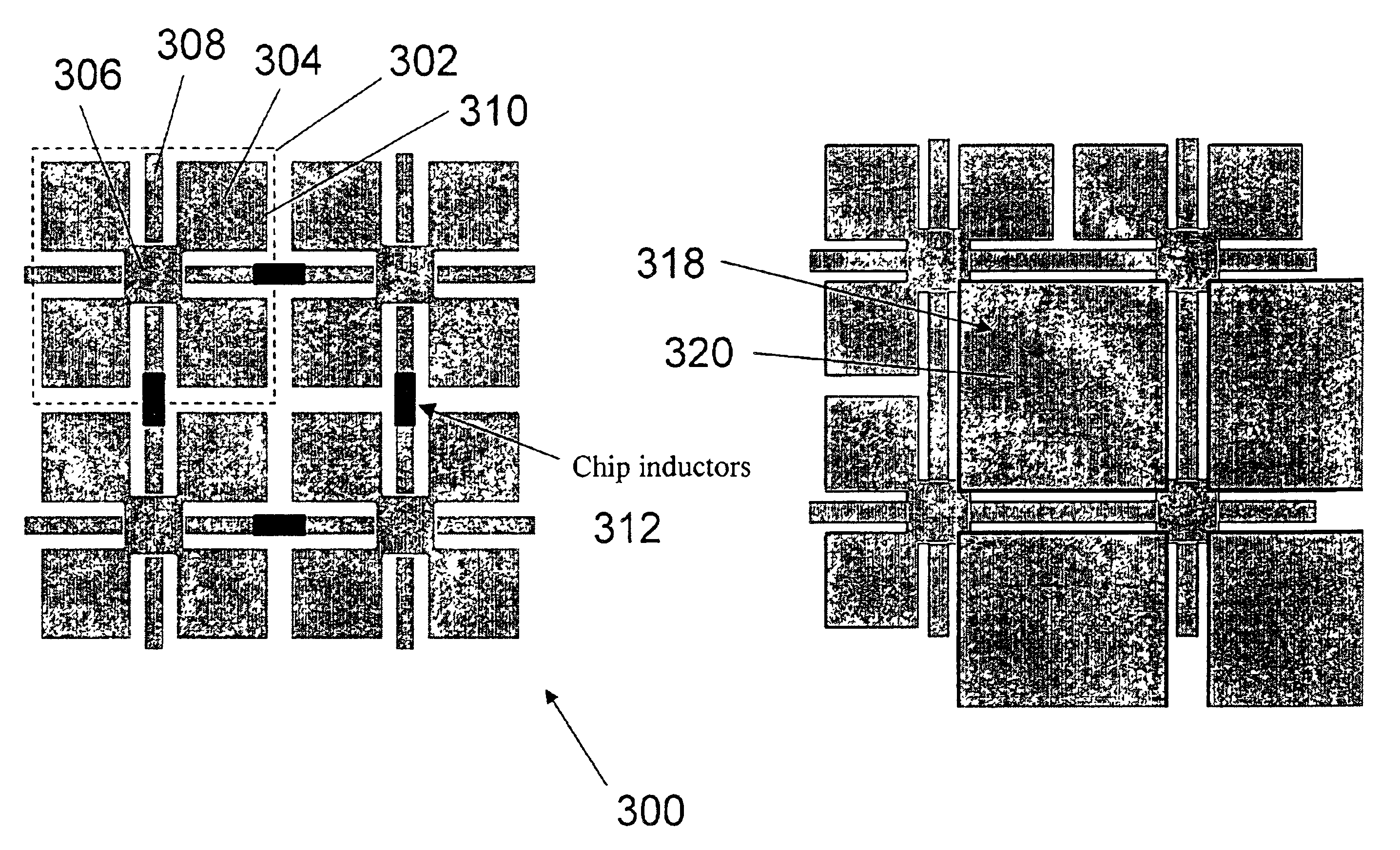
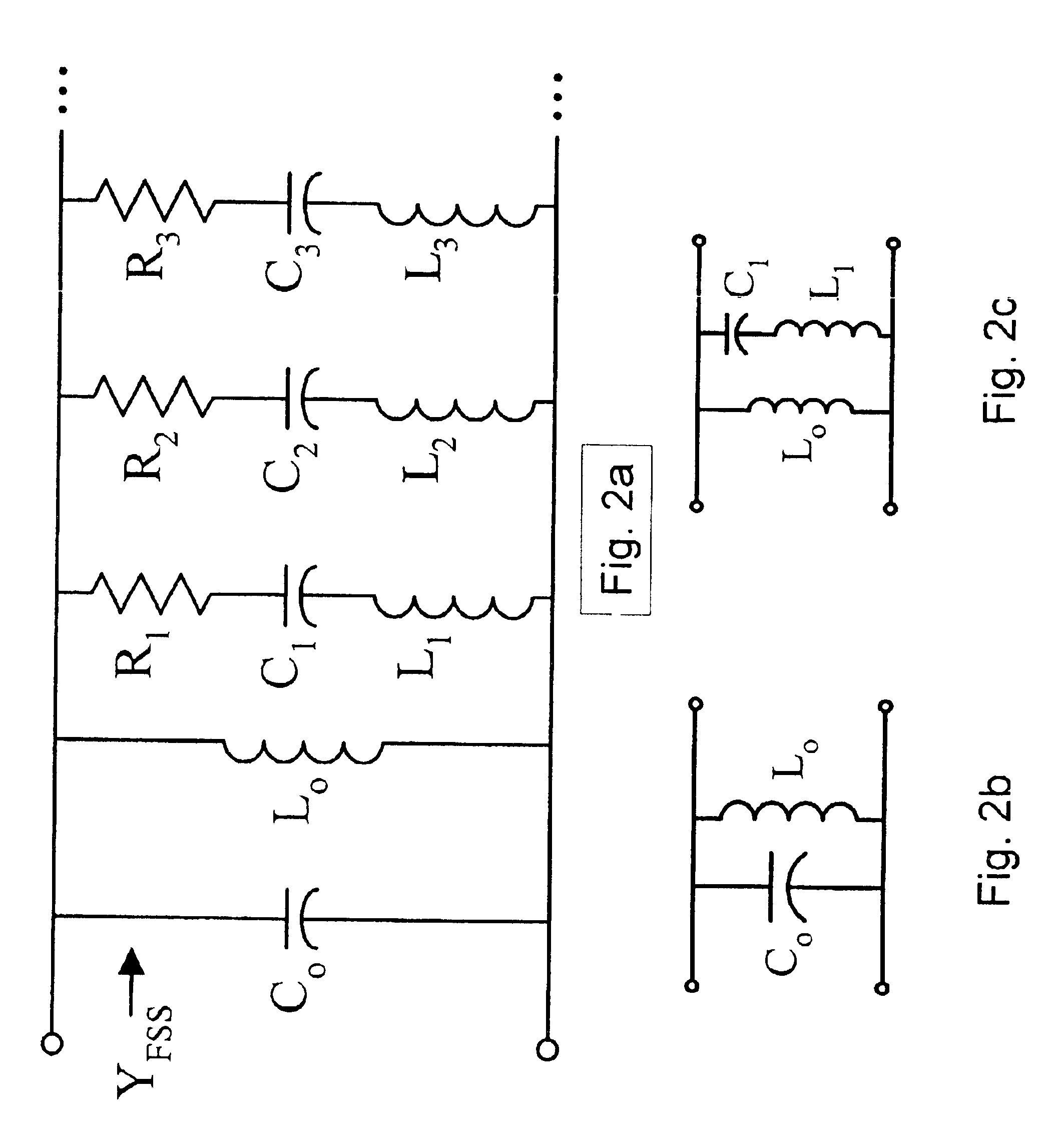
Low frequency enhanced frequency selective surface technology and applications
ActiveUS7071889B2Reduce physical sizeHigh surfaceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsWave structureCapacitance
DC inductive FSS technology is a printed slow wave structure usable for reduced size resonators in antenna and filter applications of wireless applications. It is a dispersive surface defined in terms of its parallel LC equivalent circuit that enhances the inductance and capacitance of the equivalent circuit to obtain a pole frequency as low as 300 MHz. The effective sheet impedance model has a resonant pole whose free-space wavelength can be greater than 10 times the FSS period. A conductor-backed DCL FSS can create a DC inductive artificial magnetic conductor (DCL AMC), high-impedance surface with resonant frequencies as low as 2 GHz. Lorentz poles introduced into the DCL FSS create multi-resonant DCL AMCs. Antennas fabricated from DCL FSS materials include single-band elements such as a bent-wire monopole on the DCL AMC and multi-band (dual and triple) shorted patches, similar to PIFAs with the patch / lid being a DCL FSS.
Owner:OAE TECH INC
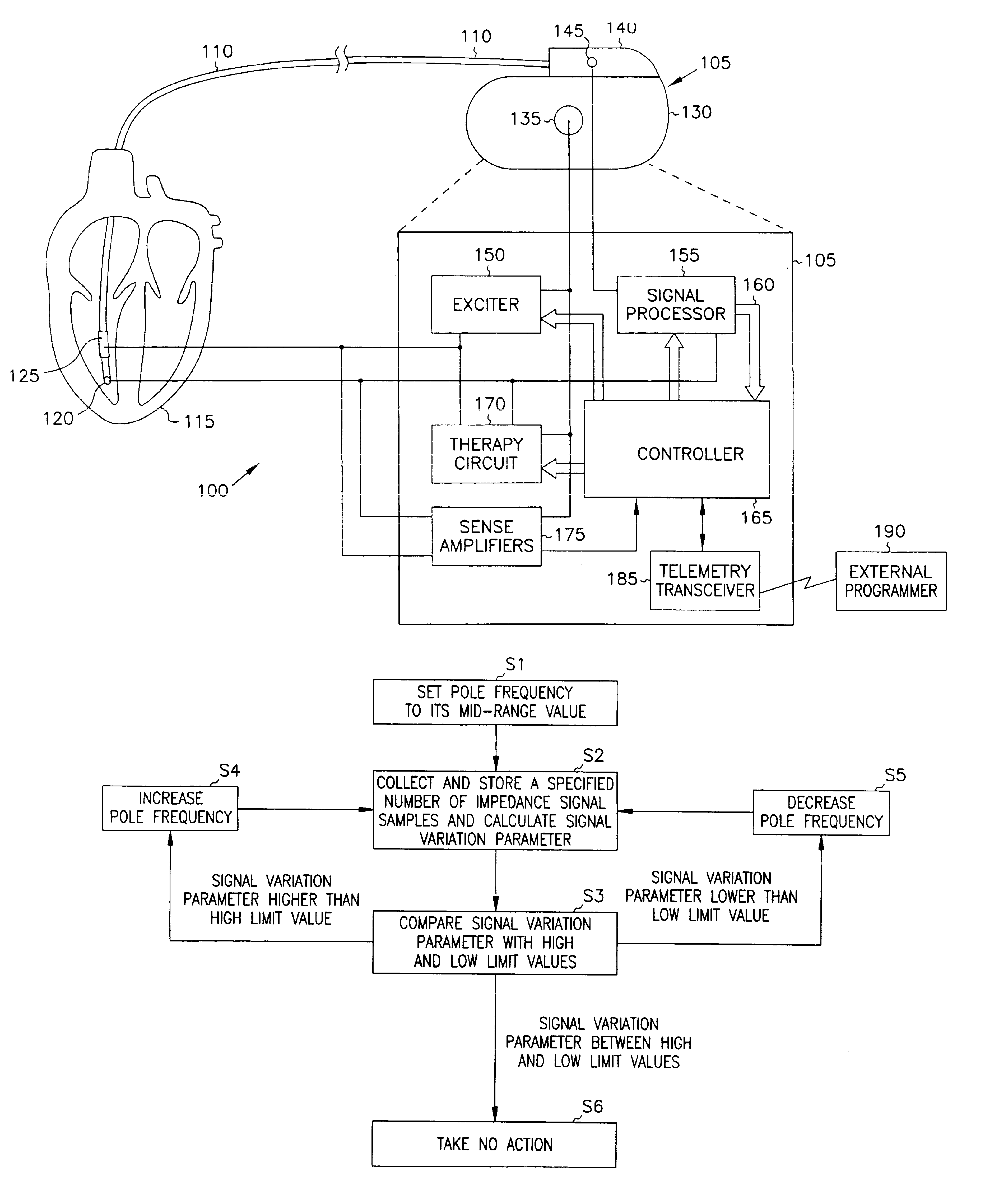
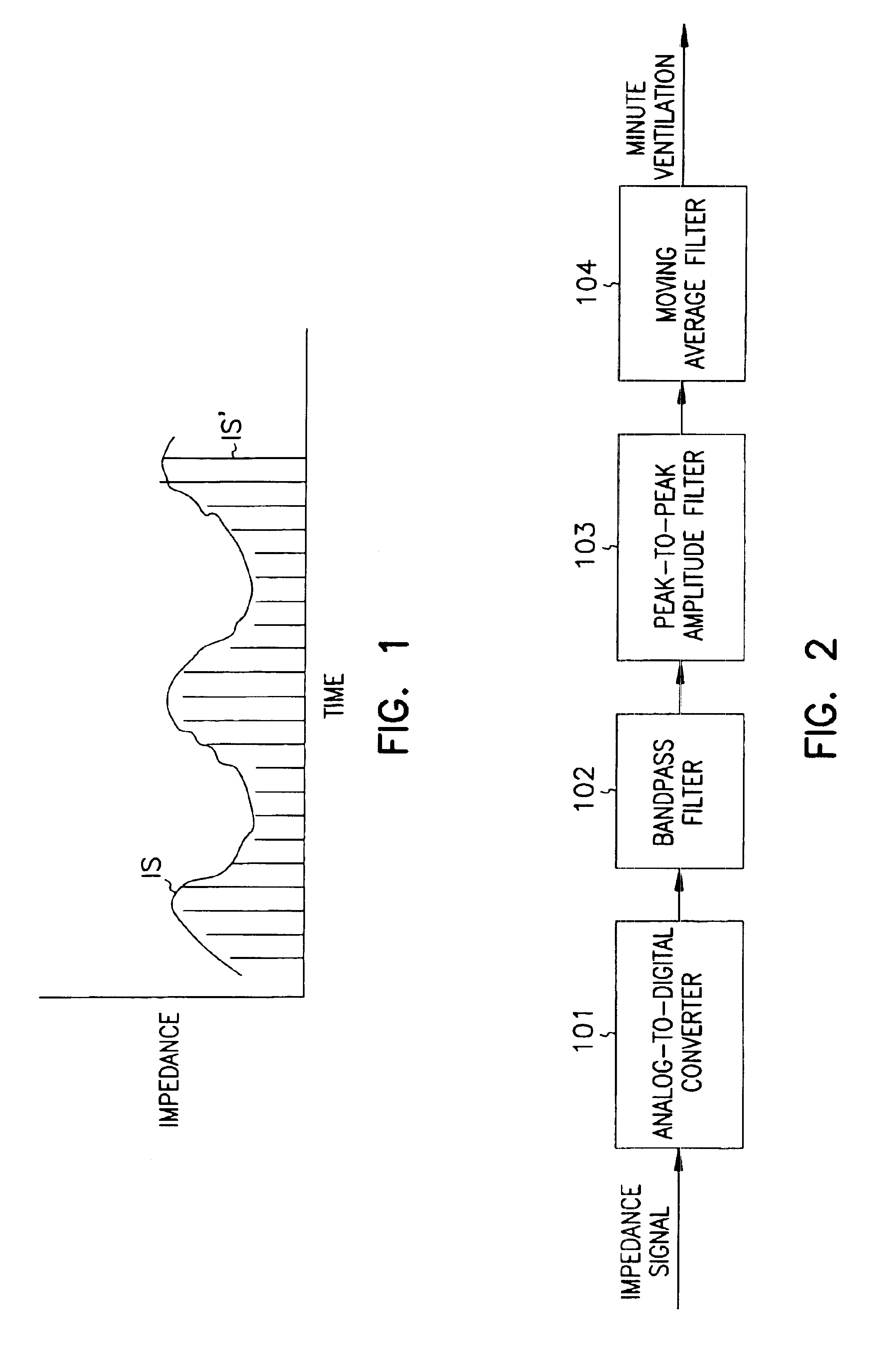
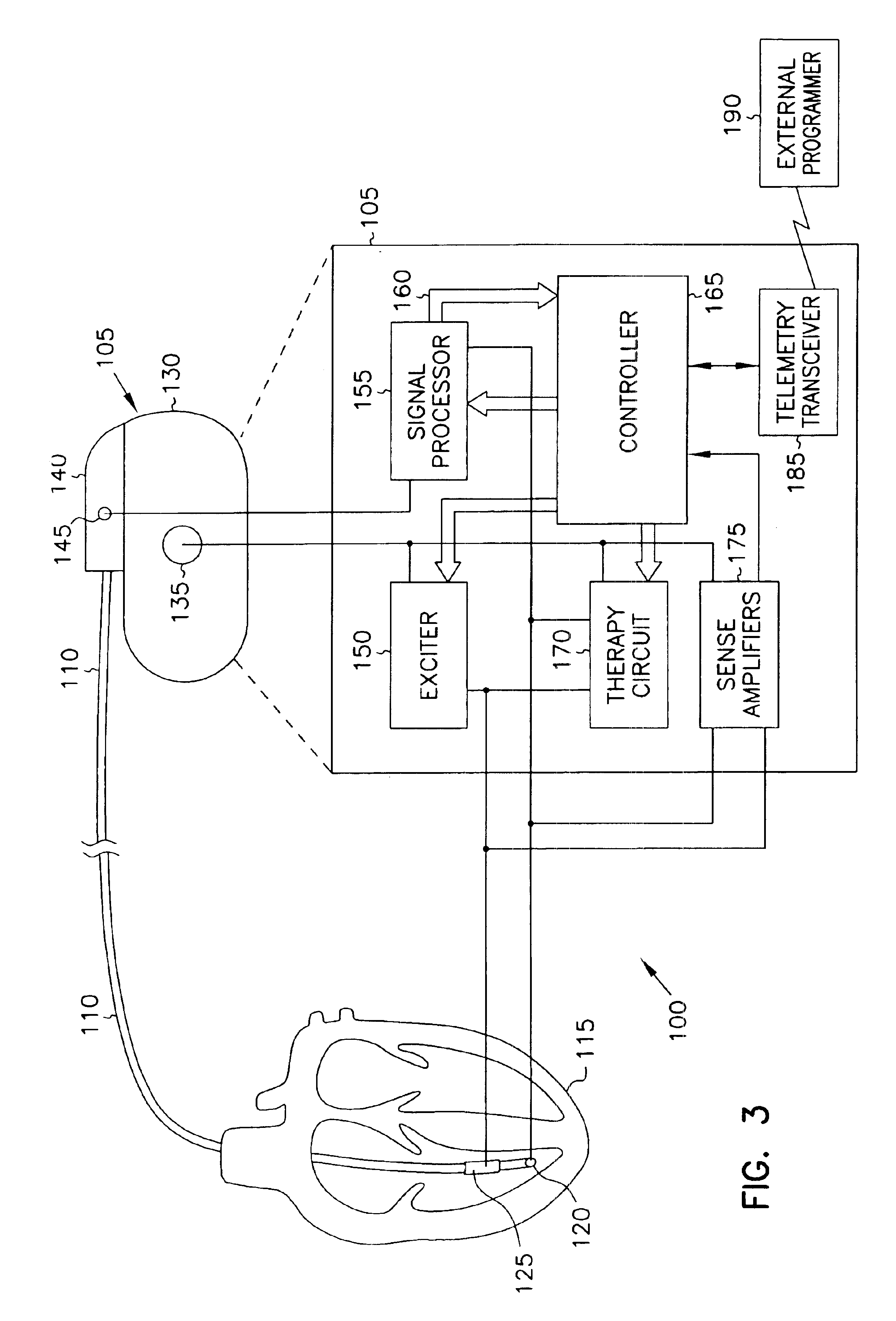
Minute ventilation sensor with automatic high pass filter adjustment
A minute ventilation sensing device in which transthoracic impedance is measured to generate an impedance signal from which a ventilation signal is derived, where the ventilation signal is proportional to minute ventilation. An adaptive high pass filter is used to filter the impedance signal into a ventilation band. The pole frequency of the high pass filter is adjusted in accordance with changes in a calculated signal variation parameter.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
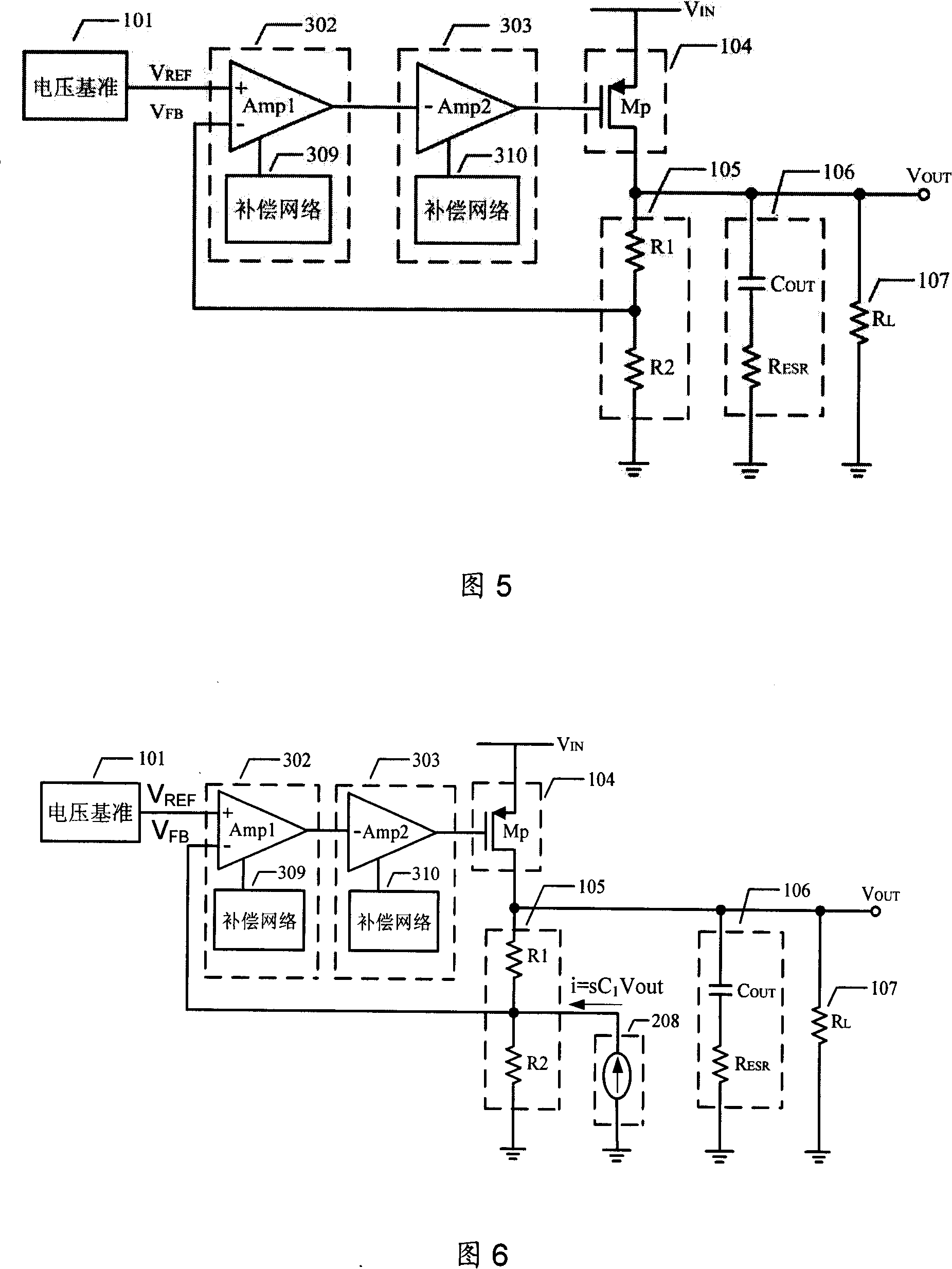
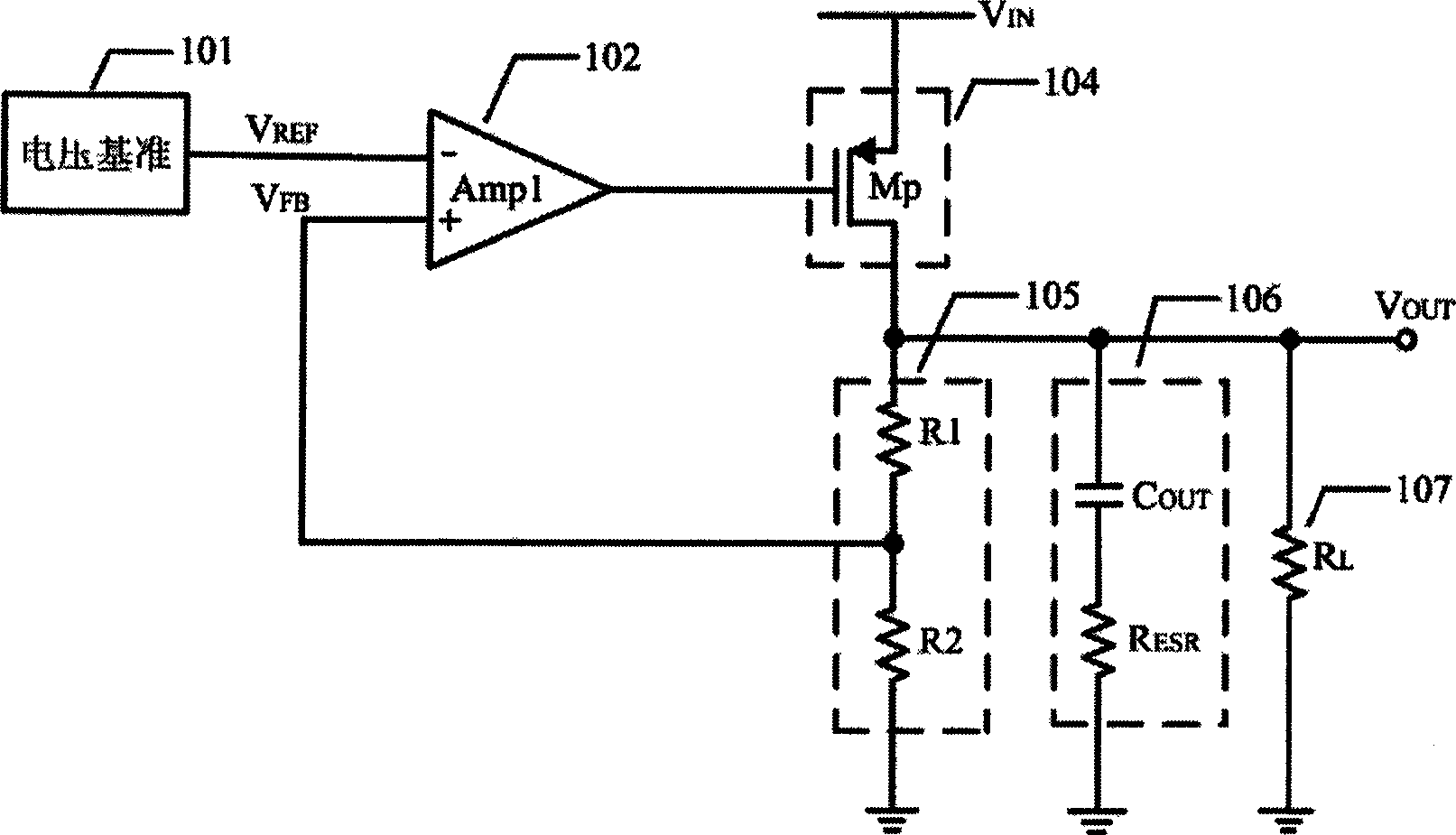
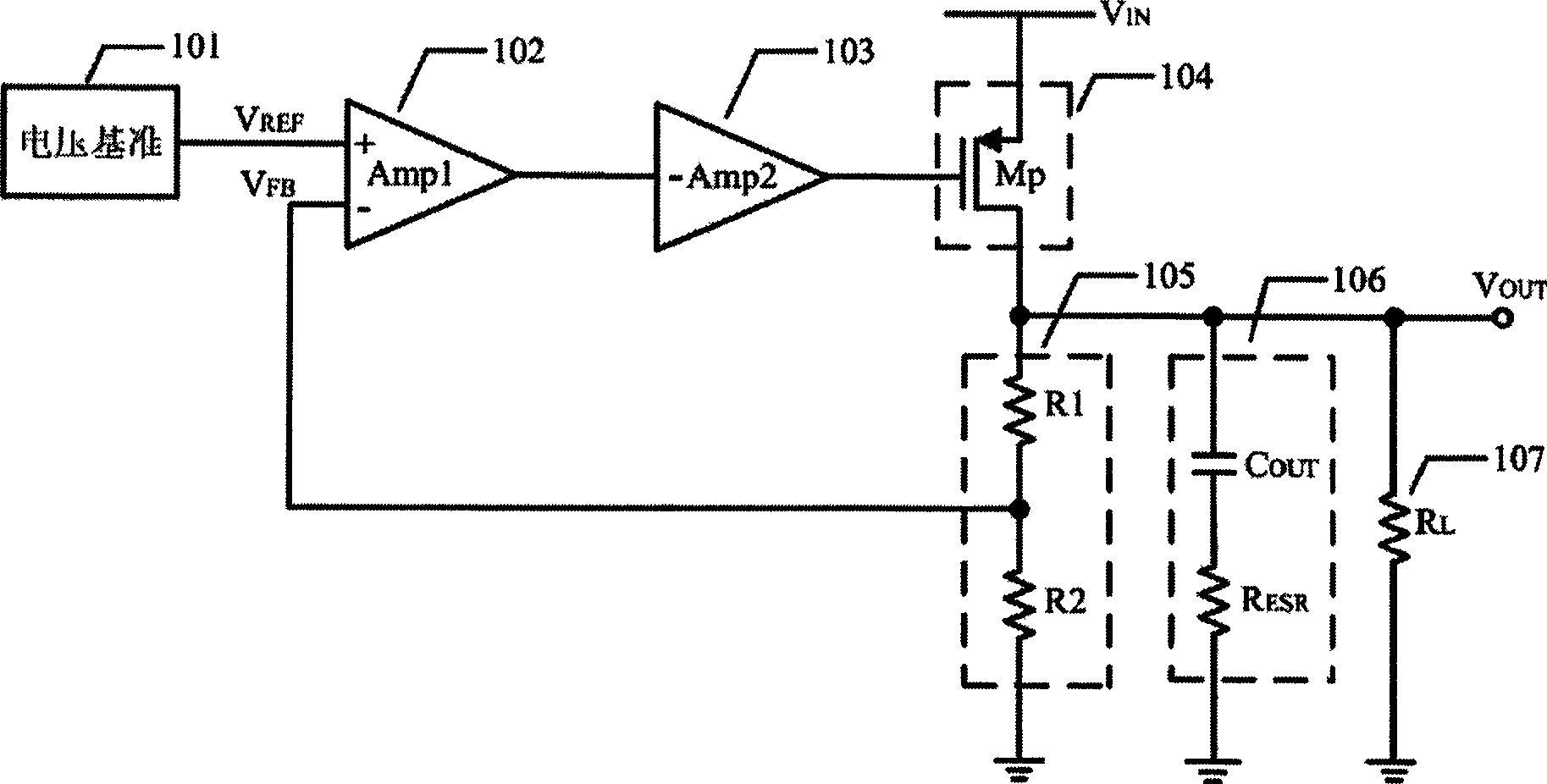
Low pressure difference linearity voltage stabilizer for enhancing performance by amplifier embedded compensation network
InactiveCN101140478AImprove performanceIncrease phase marginElectric variable regulationCapacitanceLinear regulator
A low voltage differential linear regulator utilizes an embedded compensation network in an amplifier to improve performance, which embeds a compensation network composed of resistances and capacitances into an amplifier to increase one or a plurality of pole-zero pairs with their pole-zero frequency lower than pole frequency in a transfer function of a feedback loop without changing static operating point of the amplifier and increasing static current. Frequency of the pole-zero pairs can be accurately confirmed to enhance stability of the feedback loop of the low voltage differential linear regulator, expand loop unit gain bandwidth and increase phase margin and DC and low-frequency gain of the loop, thus enhancing performance of the low voltage differential linear regulator.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +2
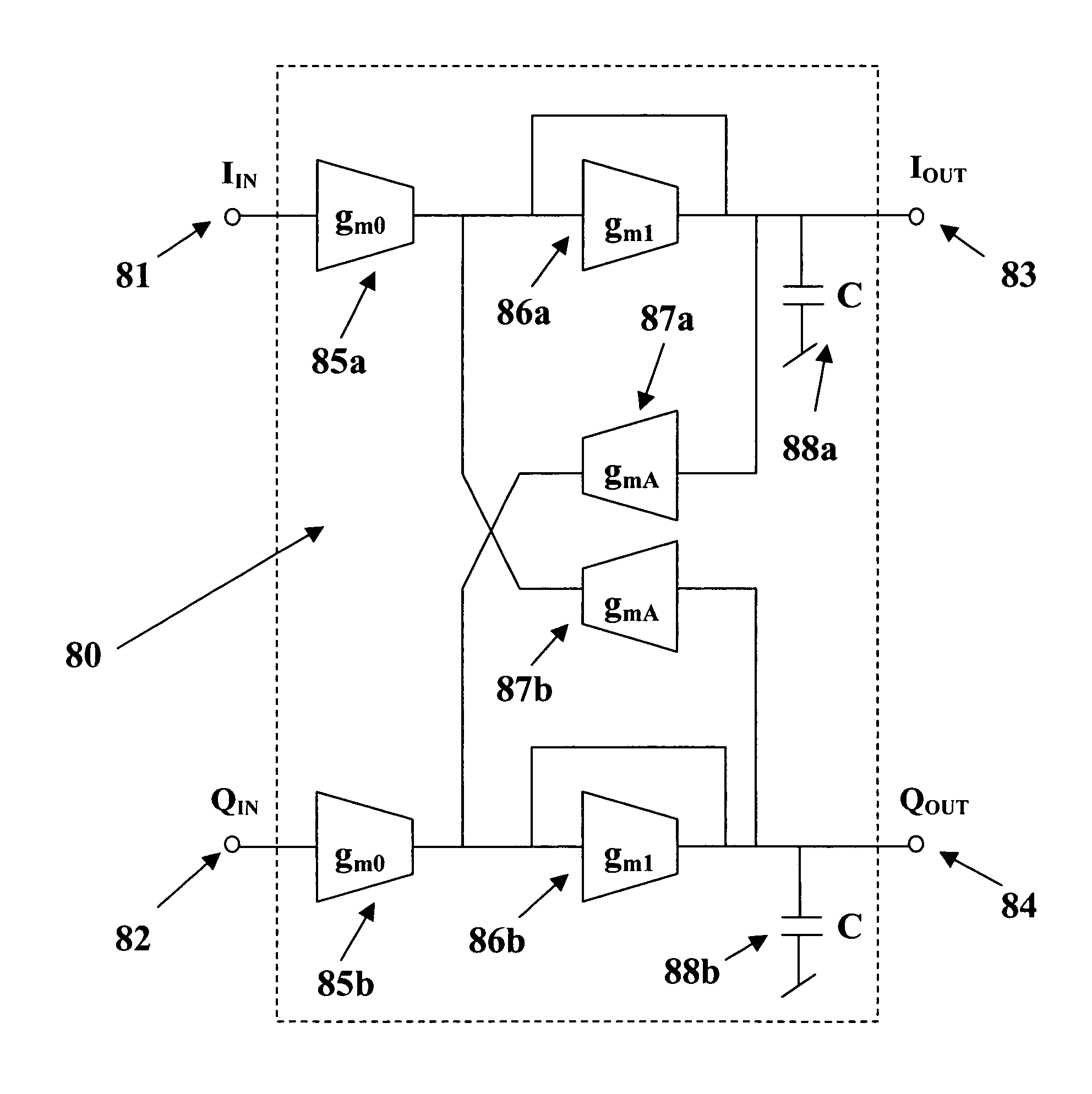
Synthesis method for an active polyphase filter
InactiveUS7098731B1Improve the level ofOscillations generatorsTransmissionElectrical conductorSynthesis methods
A fully-integrated continuous-time active complex bandpass IF filter that may contain transmission zeros yielding much sharper roll-off than that of an all-pole filter is implemented using transconductors and capacitors only. Each of the filter second-Order sections realizes a pair of complex poles and a may realize a double imaginary axis zero. Since the transconductors are electronically tunable the positions of filter zeros and poles are adjustable using an automatic tuning system. In each filter section the value of different transconductors are modified to separately change the pole frequency, its Q-factor and the zero frequency. Each pole and zero are separately tuned, which achieves a higher level of tuning accuracy than in case where all poles and zeros were adjusted simultaneously.
Owner:WYSZYNSKI ADAM S
Method and apparatus for compensating an amplifier
InactiveUS6924701B1Increased unity-gain bandwidthDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsAudio power amplifierCascode
A method and apparatus for compensating an amplifier is disclosed which significantly improves the unity gain bandwidth of the amplifier. In an embodiment of the invention the amplifier includes at least one compensated pair of cascode coupled transistors including: an input transistor, a cascode transistor, and a bypass element. The input transistor exhibits a first transition frequency. The cascode transistor is cascode coupled to the input transistor. The cascode transistor exhibits a second transition frequency less than or equal to the first transition frequency of the input transistor. The bypass element couples across a corresponding current interface of the cascode transistor to substantially bypass the cascode transistor at a pole frequency thereof.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
High-power LDO circuit without externally setting capacitor
ActiveCN105242734AGuaranteed output powerHigh power outputElectric variable regulationCapacitanceElectricity
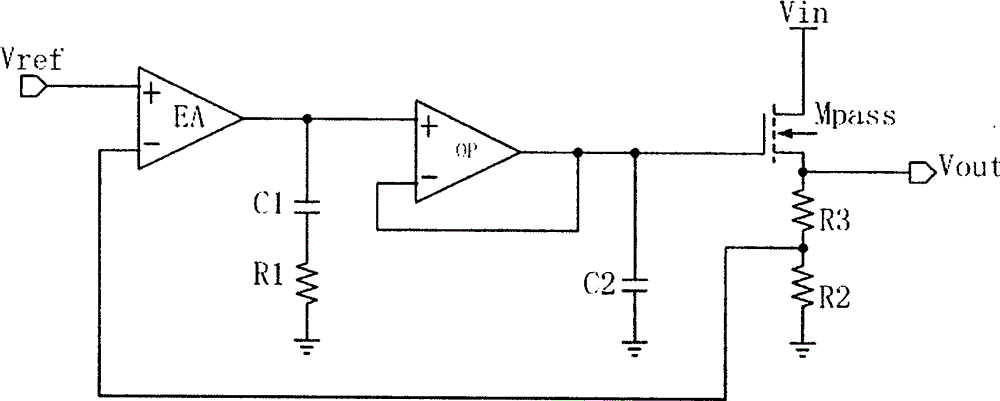
The invention relates to the technical field of power sources, and discloses a high-power LDO circuit without externally setting a capacitor, wherein the high-power LDO circuit provided herein is characterized in that the high-power LDO circuit is constituted of an error amplifier EA, an operational amplifier OP, two capacitors C1 and C2, three resistors R1, R2 and R3 and on N-type MOS pipe; the C2 is a built-in capacitor loaded by a gate end of Mpass of the N-type MOS pipe for reducing dominant pole frequency of a loop circuit of the LDO circuit; and at the same time, the capacitor C1 and the resistor R1 are added on an output end of the error amplifier EA to produce a zero point to offset the influence of the secondary dominant pole, thus ensuring the stability of a system. According to the invention, an internal loop circuit is set to compensate a circuit, thus ensuring that the system can still work stably without externally compensating capacitance at a large amount; and at the same time, by using the NMOS as a power device, the response speed of the system is improved, thus ensuring the output power of the LDO. The high-power LDO circuit provided herein is mainly used for supplying electricity for chips like central processing units with high performance, digital signal processors, programmable logic device and converters with high performance.
Owner:广州市力驰微电子科技有限公司
Low drop-out voltage regulator with wide bandwidth power supply rejection ratio
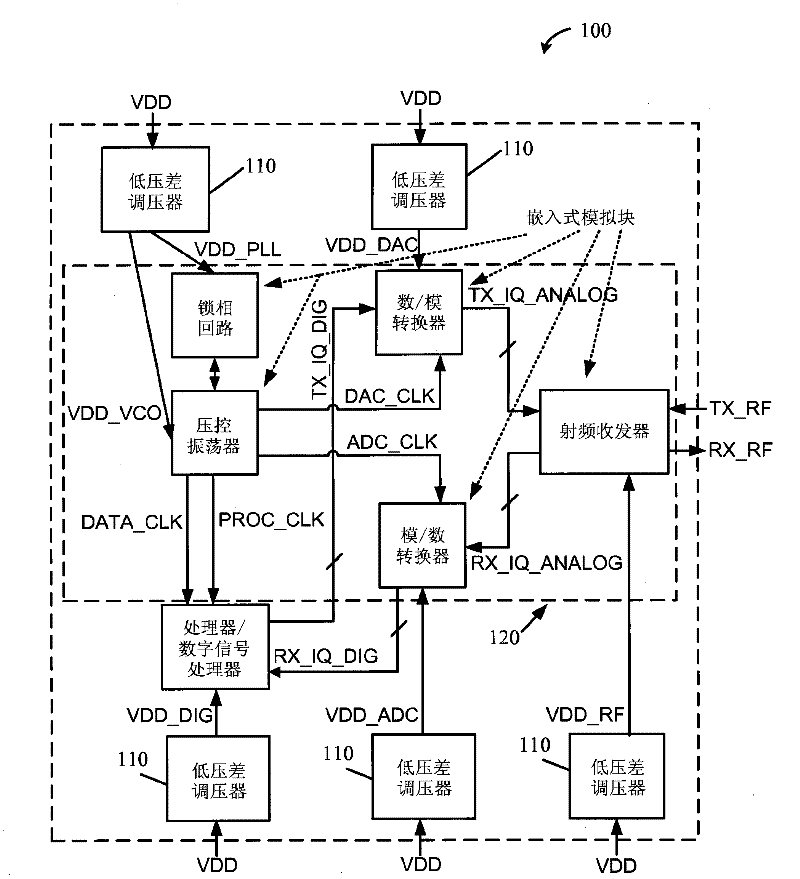
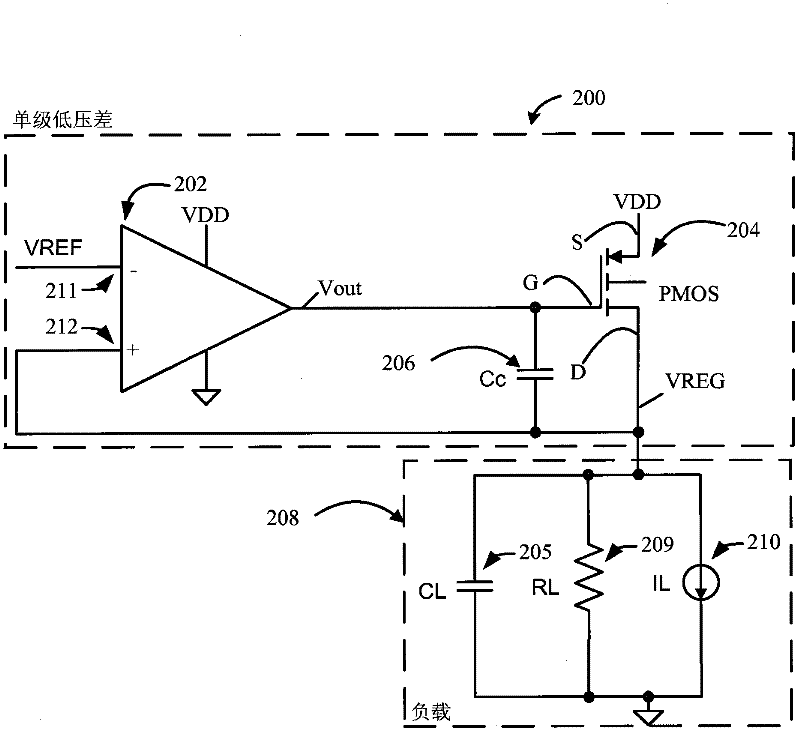
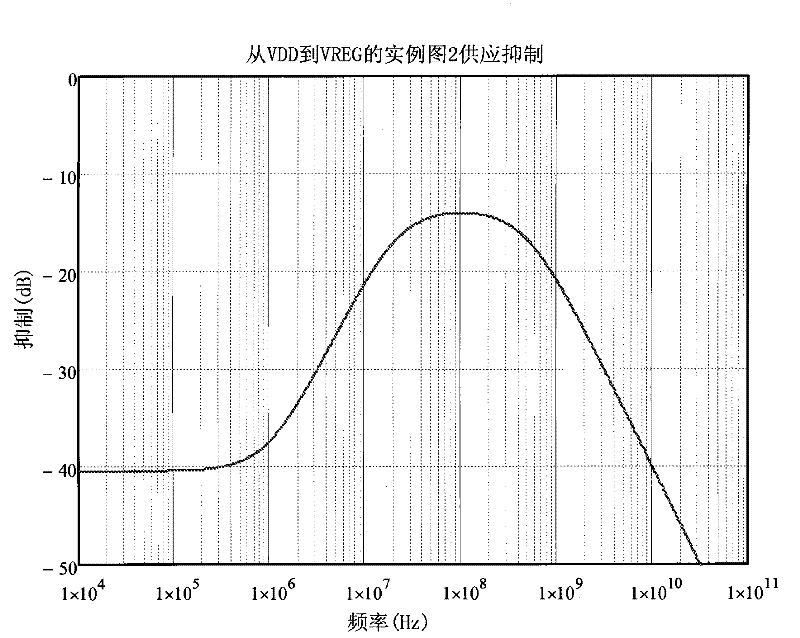
A low drop-out (LDO) voltage regulator with a wide bandwidth power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) is described. In one aspect, the LDO voltage regulator includes two individual voltage regulator circuit stages. A first stage voltage regulator circuit output is at an intermediate voltage (VINT) between an input supply voltage (VDD) and a final regulated output voltage (VREG). A second stage voltage regulator circuit output is at the final regulated output voltage (VREG) and is optimized for noise-sensitive analog circuits across a wide operating bandwidth. The first stage voltage regulator circuit has a zero frequency while the second stage voltage regulator circuit has a matching pole frequency to minimize the AC response from VDD to VREG across all frequencies.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
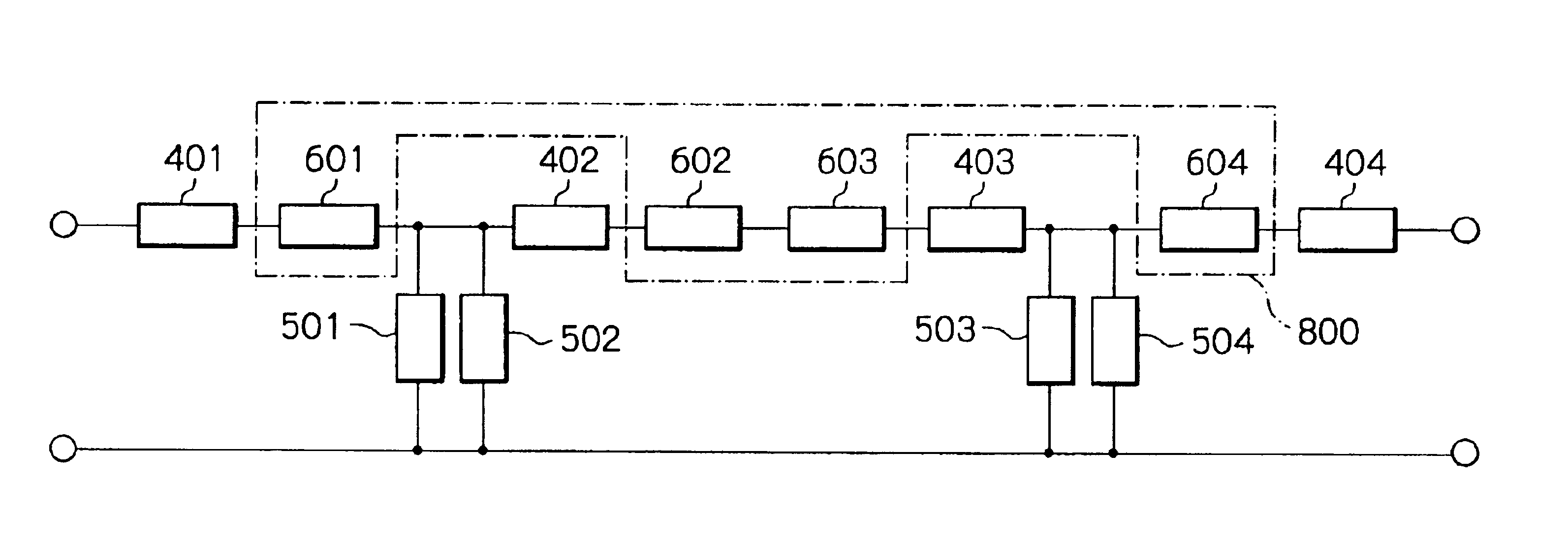
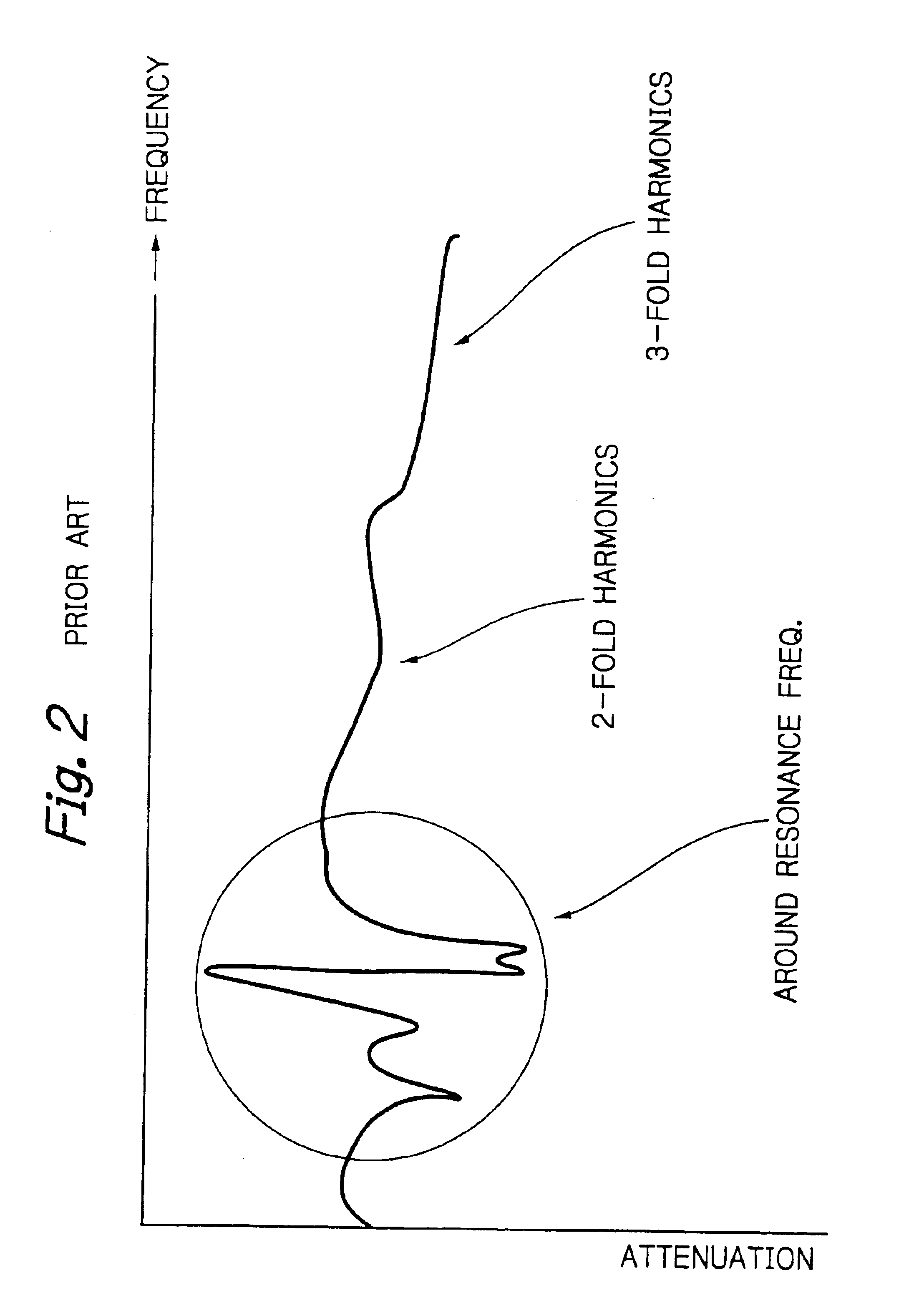
SAW filter with an improved attenuation characteristic at a frequency any multiple of an attenuation pole frequency at one or both sides of a pass band
InactiveUS6844795B2Low insertion lossImprove the attenuation effectPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksUltrasound attenuationCapacitance
A SAW (Surface Acoustic Wave) filter includes serial arm resonators and parallel arm resonators interconnected in pairs in a multiple-stage, ladder configuration. A resonating device is serially connected to any one of the serial arm resonators and has an attenuation pole frequency higher than that of the serial arm resonator. At the attenuation pole frequency of the serial arm resonator, the resonating device functions as capacitance without performing attenuation. The resonating device has an antiresonance frequency 1.8 times or more but 2.2 times or less, or 2.7 times or more but 3.3 times or less, as high as the antiresonance frequency of the serial arm resonator.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
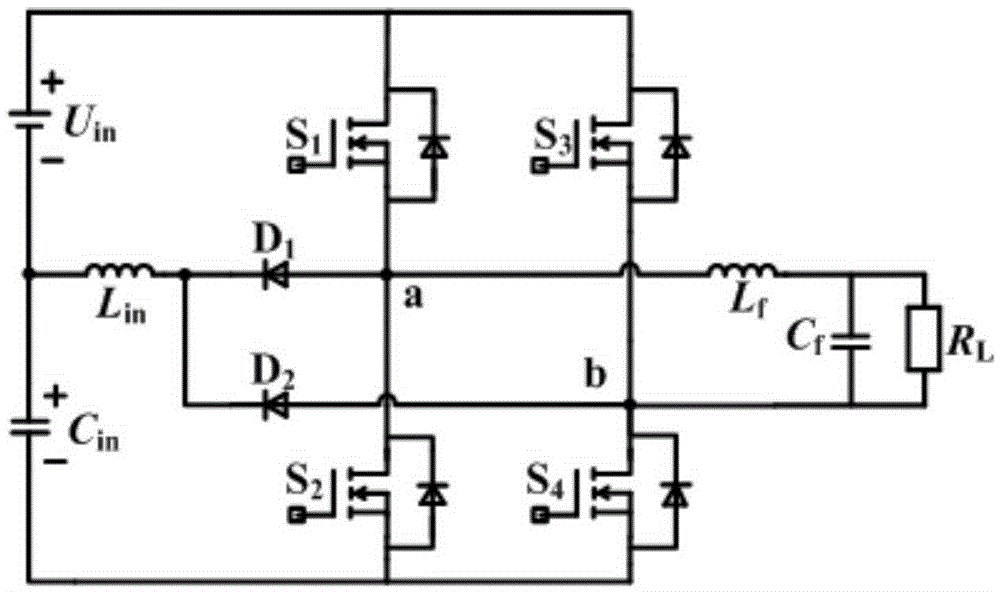
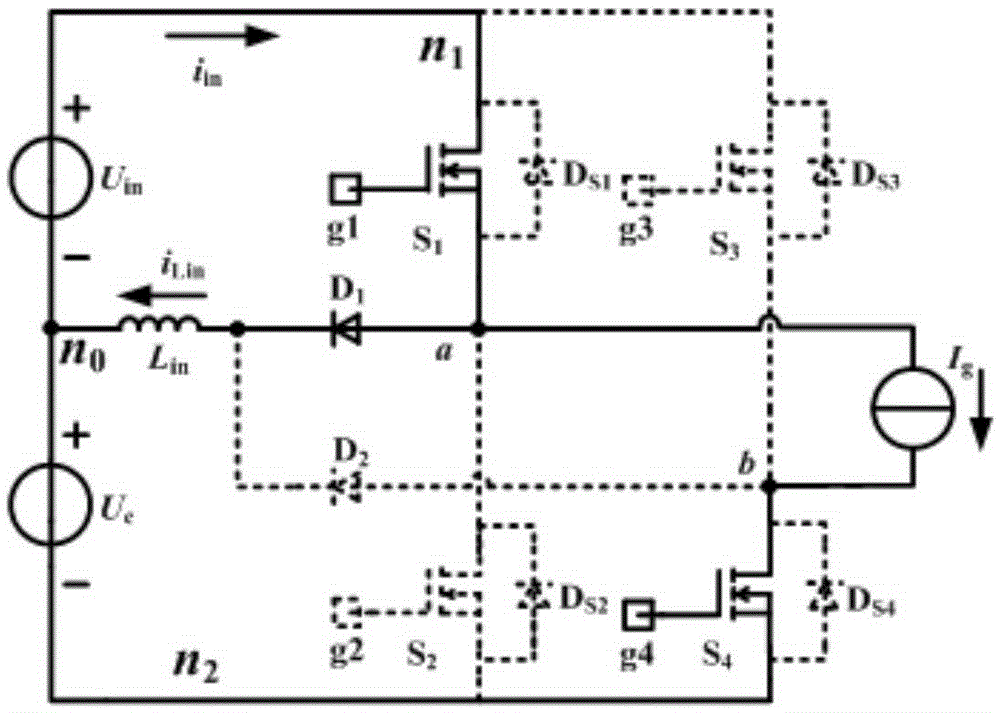
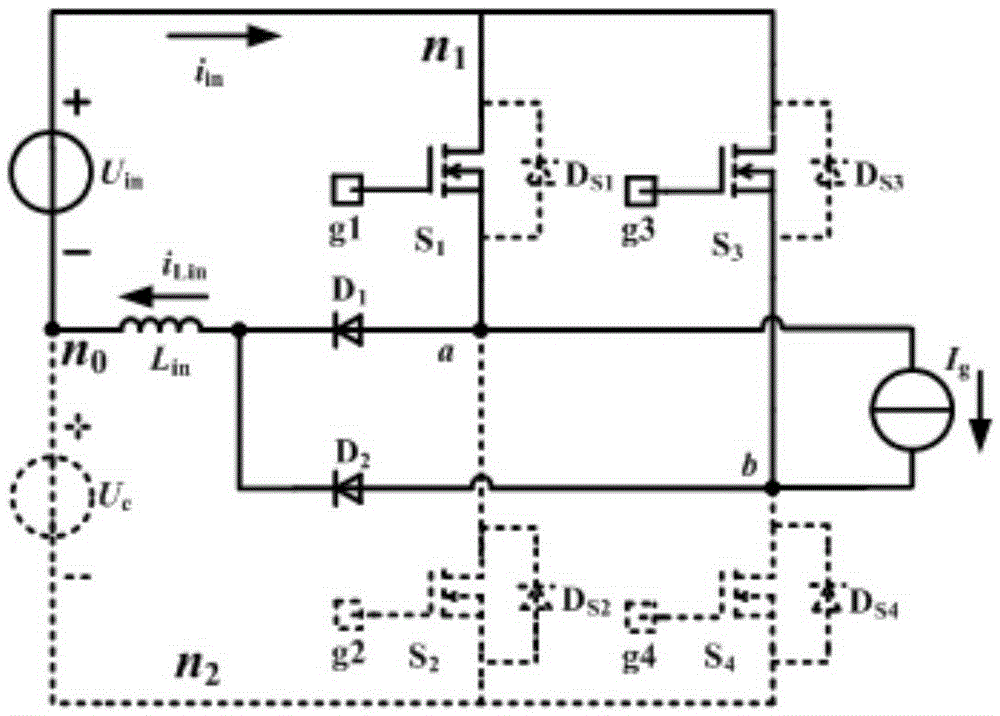
A high-gain Buck-Boost integrated inverter and a control method
The invention discloses a high-gain Buck-Boost integrated inverter and a control method. A switch tube S1 and a switch tube S2 in the inverter are in series connection to form a first bridge arm circuit. A switch tube S3 and a switch tube S4 are in series connection to form a second bridge arm circuit. The first bridge arm circuit and the second bridge arm circuit are in parallel connection to form a full-bridge circuit. A junction point a of the switch tube S1 and the switch tube S2 is connected to an anode of a diode D1. A junction point b of the switch tube S3 and the switch tube S4 is connected to an anode of a diode D2. Cathodes of the diode D1 and the diode D2 are together connected to one end of a boost inductor Lin. The other end of the boost inductor Lin is connected to one end of a capacitor Cin. A filter circuit is also connected between the junction point a and the junction point b. When the inverter of the present invention is compared with a traditional full-bridge inverter, only two diodes and one boost inductor are added to the inverter of the invention; the inverter of the invention employs one-pole frequency multiplication SPWM modulation so as to simultaneously realize a direct current voltage pumping function and an inversion function. Accordingly, the inverter has advantages of high efficiency, a high integrated level, convenient control, a simple structure, low cost, etc.
Owner:上海骋海新能源科技有限公司
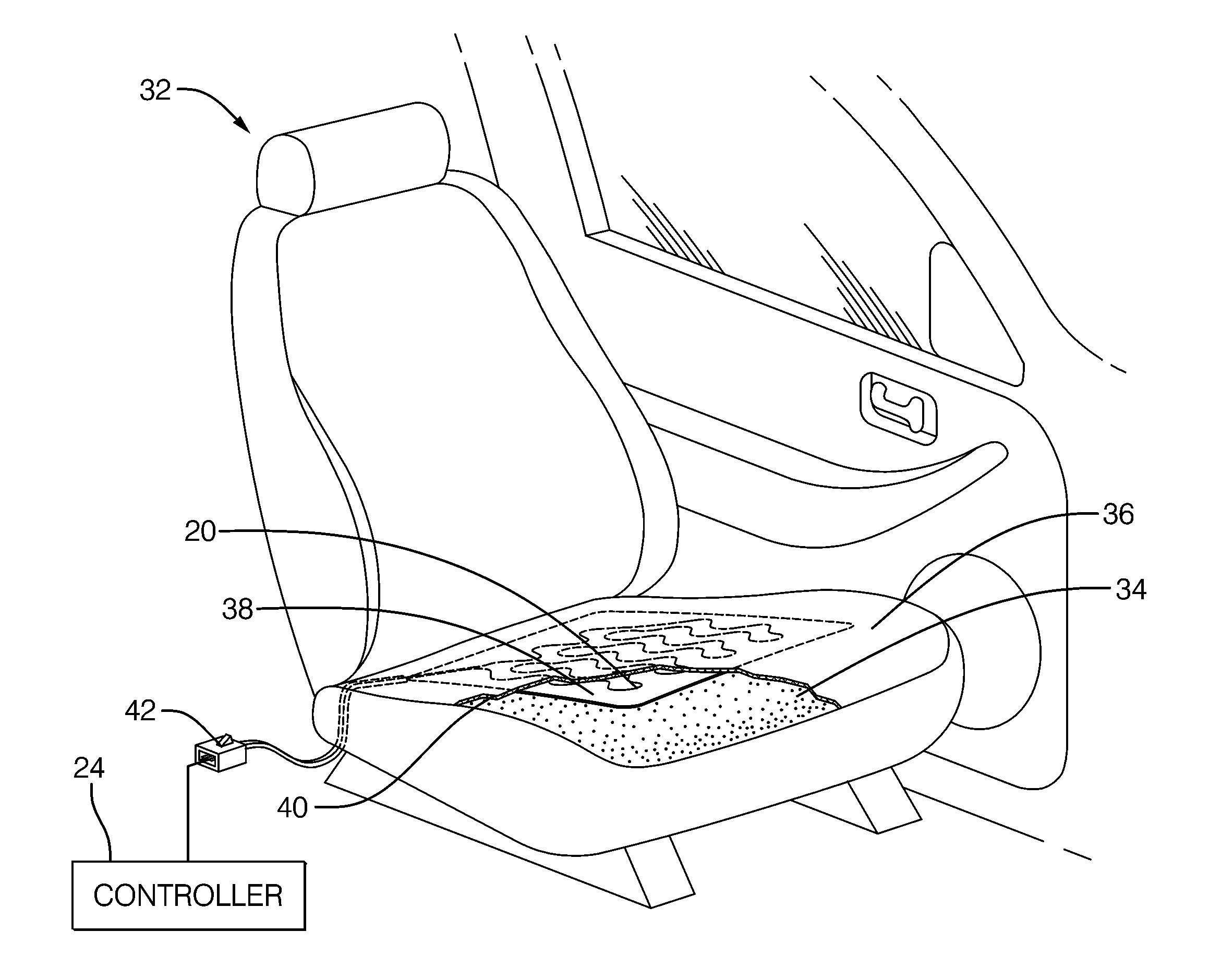
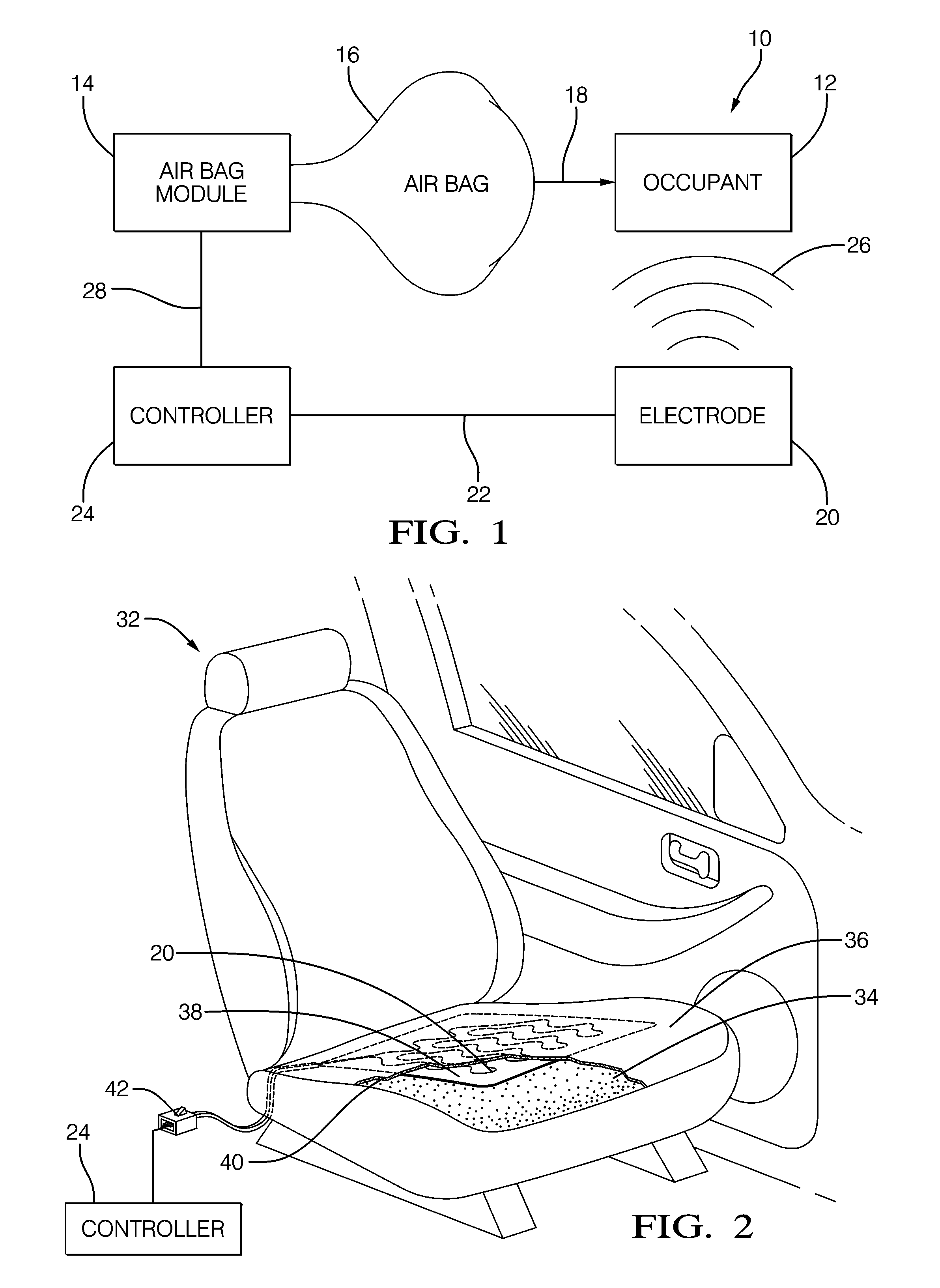
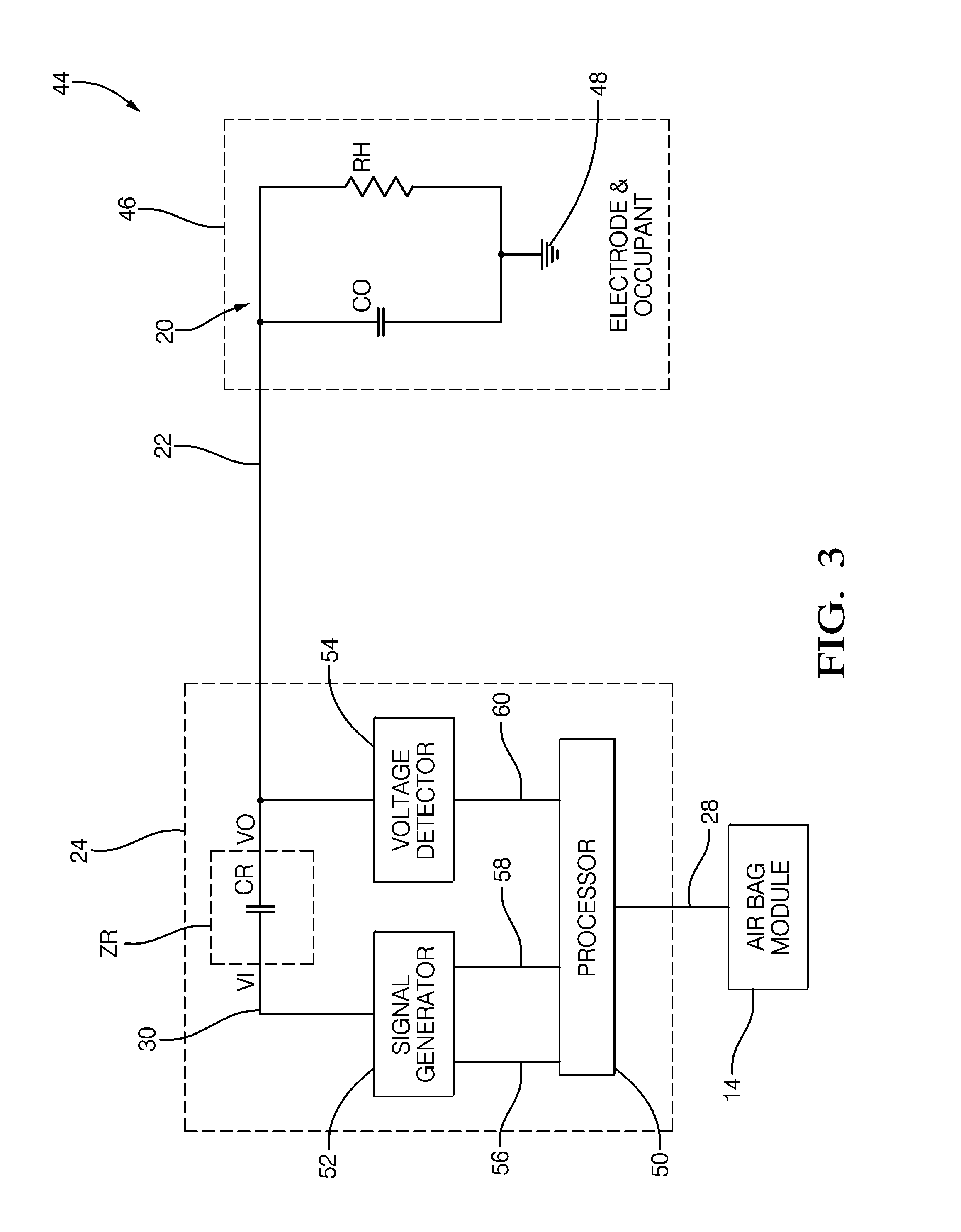
Occupant detection system and method
InactiveUS20110190980A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceDigital data processing detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceUltrasound attenuation
An occupant detection system, a controller for an occupant detection system and a method of detecting an occupant. The presence or absence of the occupant varies the dielectric properties of an area proximate an electrode to influence the electrical impedance of the electrode. The electrode impedance is determined by determining electrical characteristics of a filter formed by a reference impedance device and the electrode. The pole frequency and absolute attenuation of the filter are determined based on a relative ratio of the excitation signal magnitude and the electrode signal magnitude, at two distinct frequencies. A lookup table may be used to determine the pole frequency and absolute attenuation based on the relative ratio, and thereby determine an occupant presence based on the electrode impedance.
Owner:DELPHIH TECH
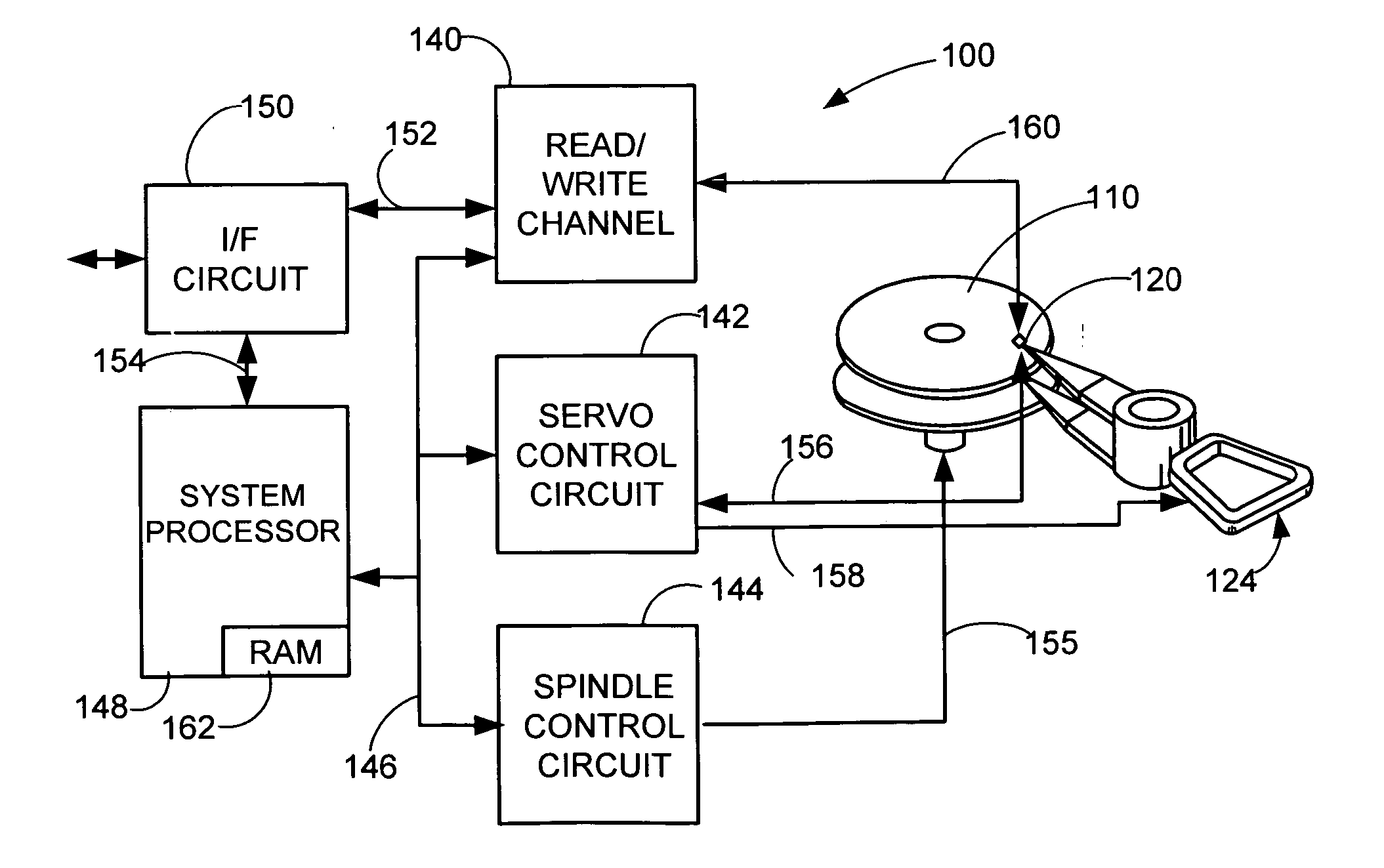
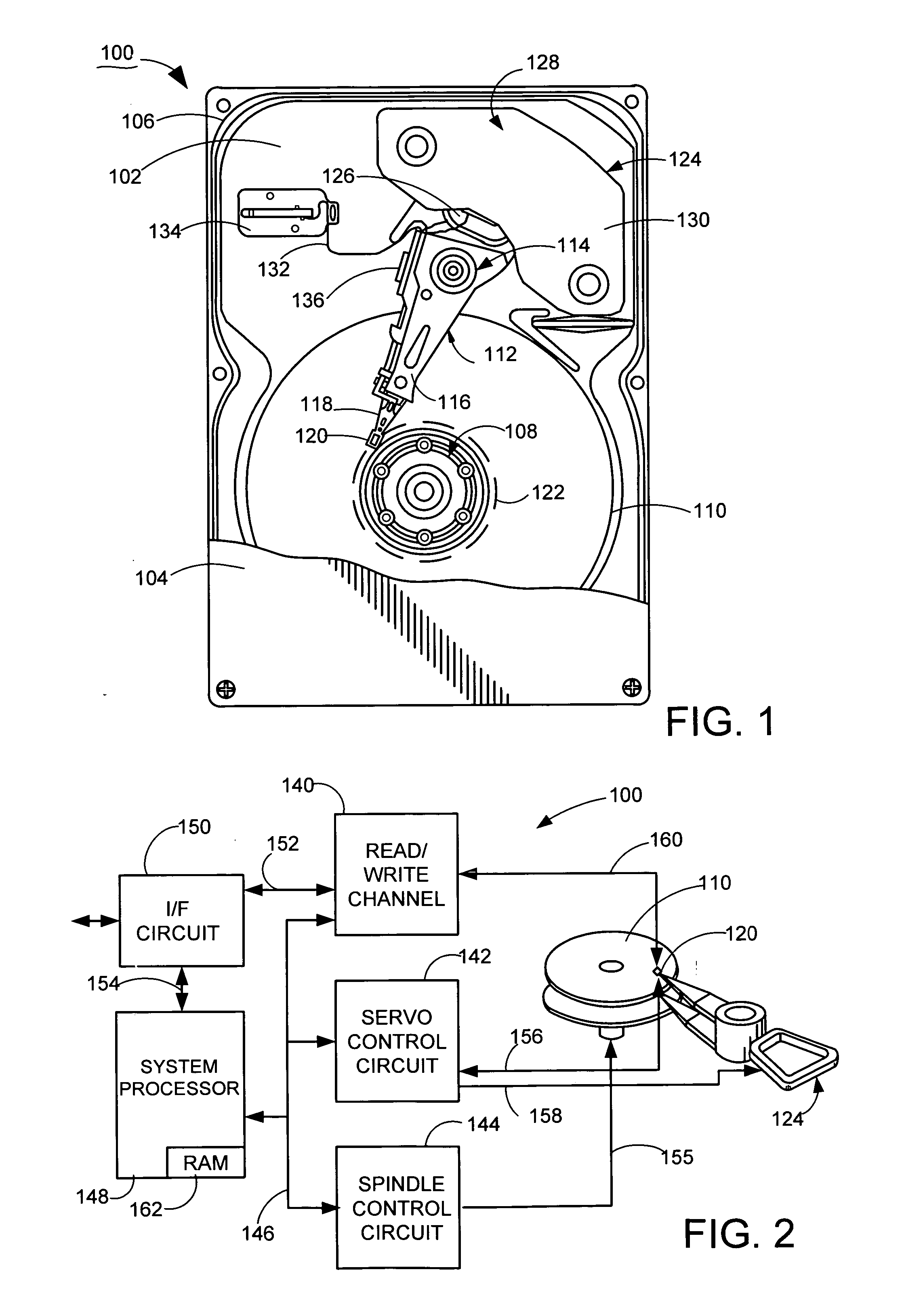
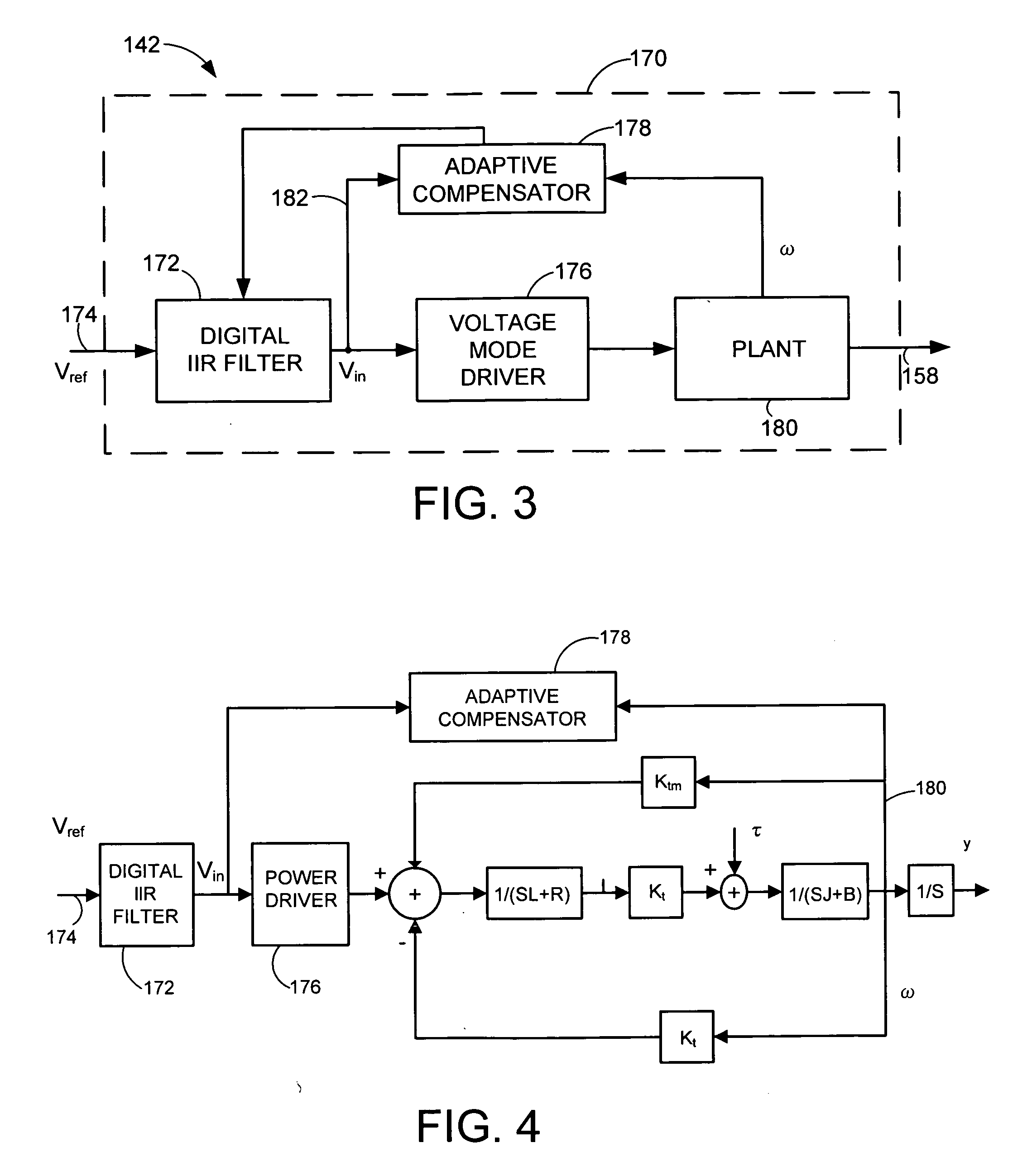
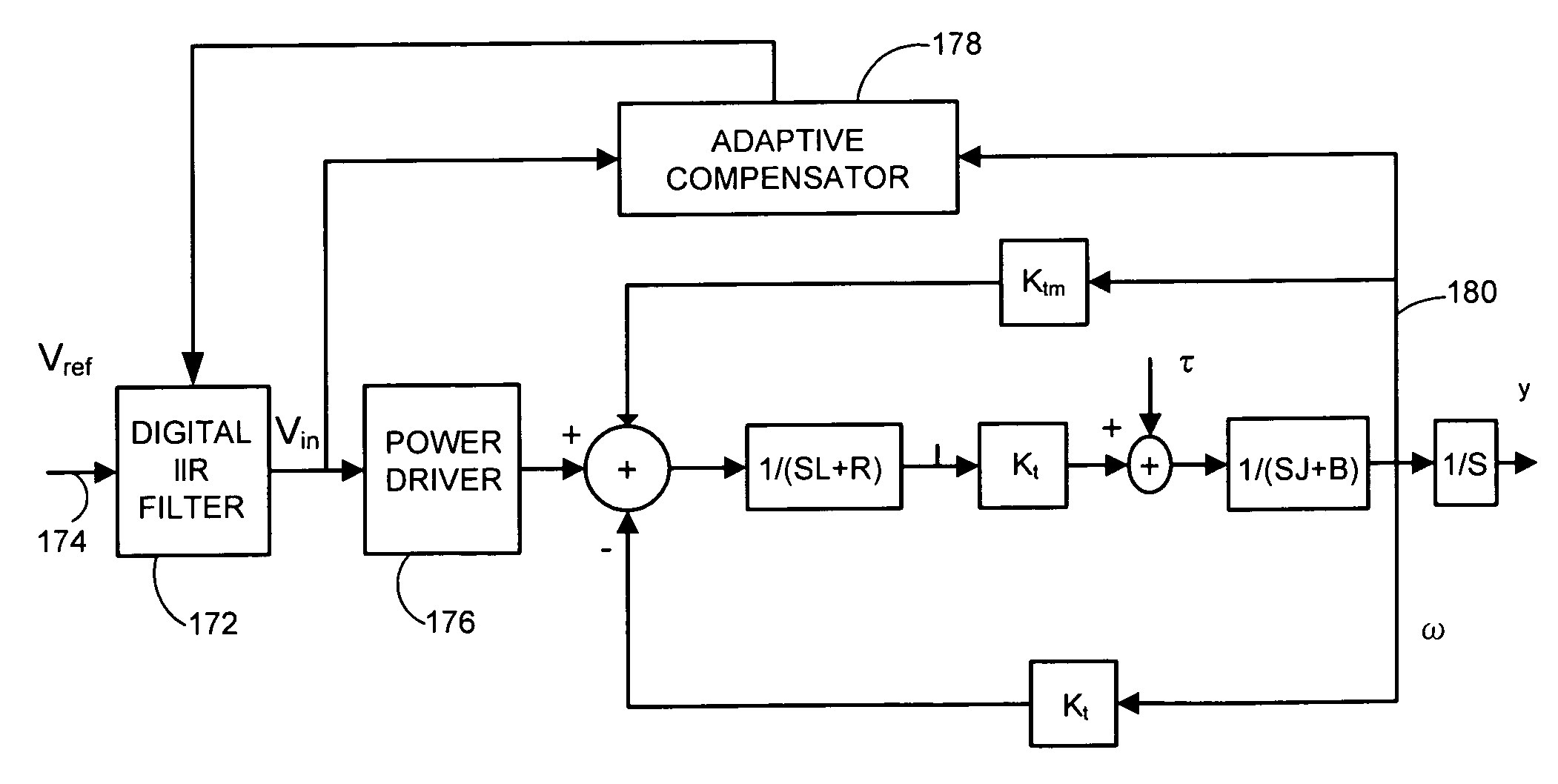
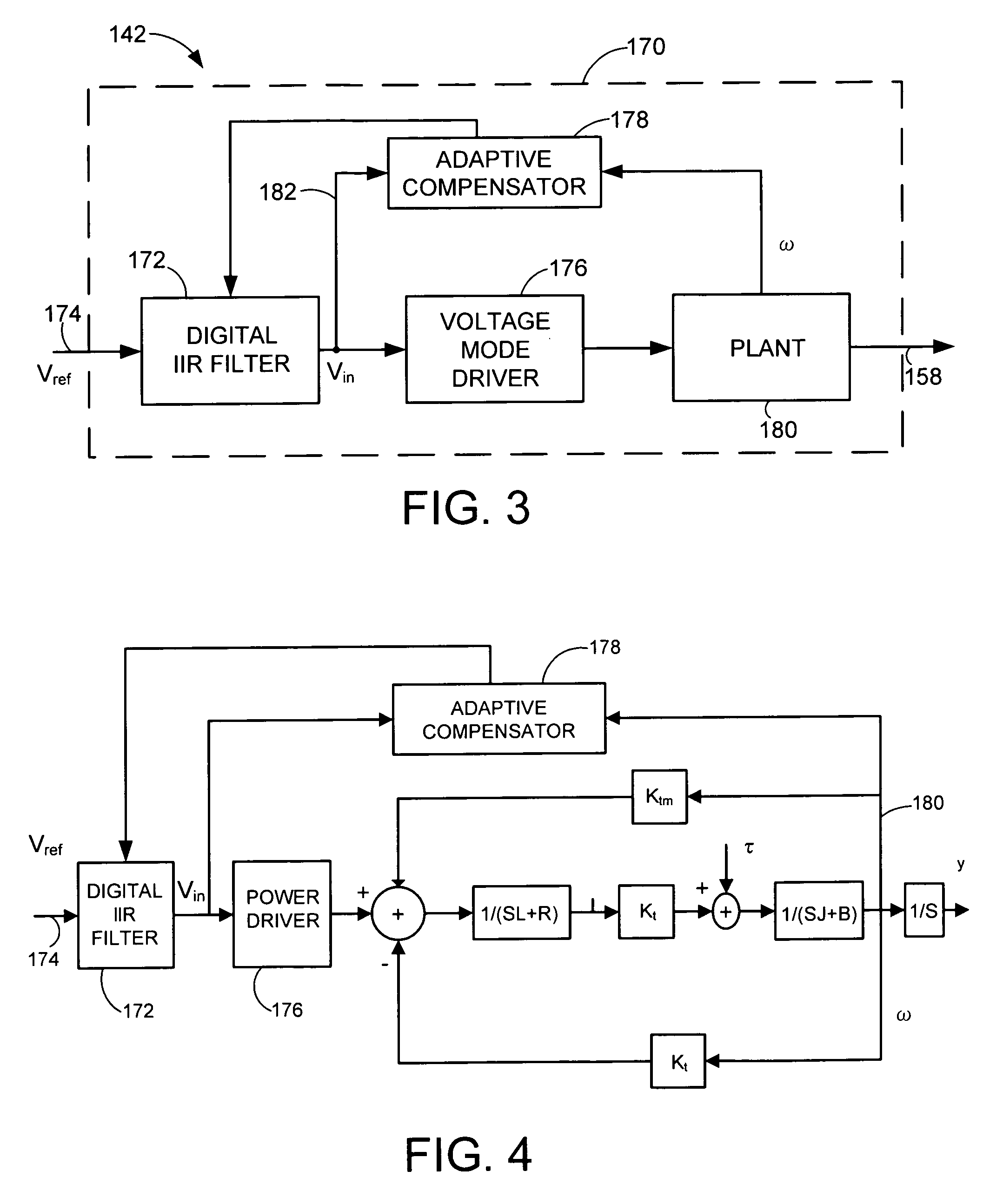
Adaptive voltage-mode controller for a voice coil motor
InactiveUS20070013337A1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageElectrical resistance and conductanceIir filtering
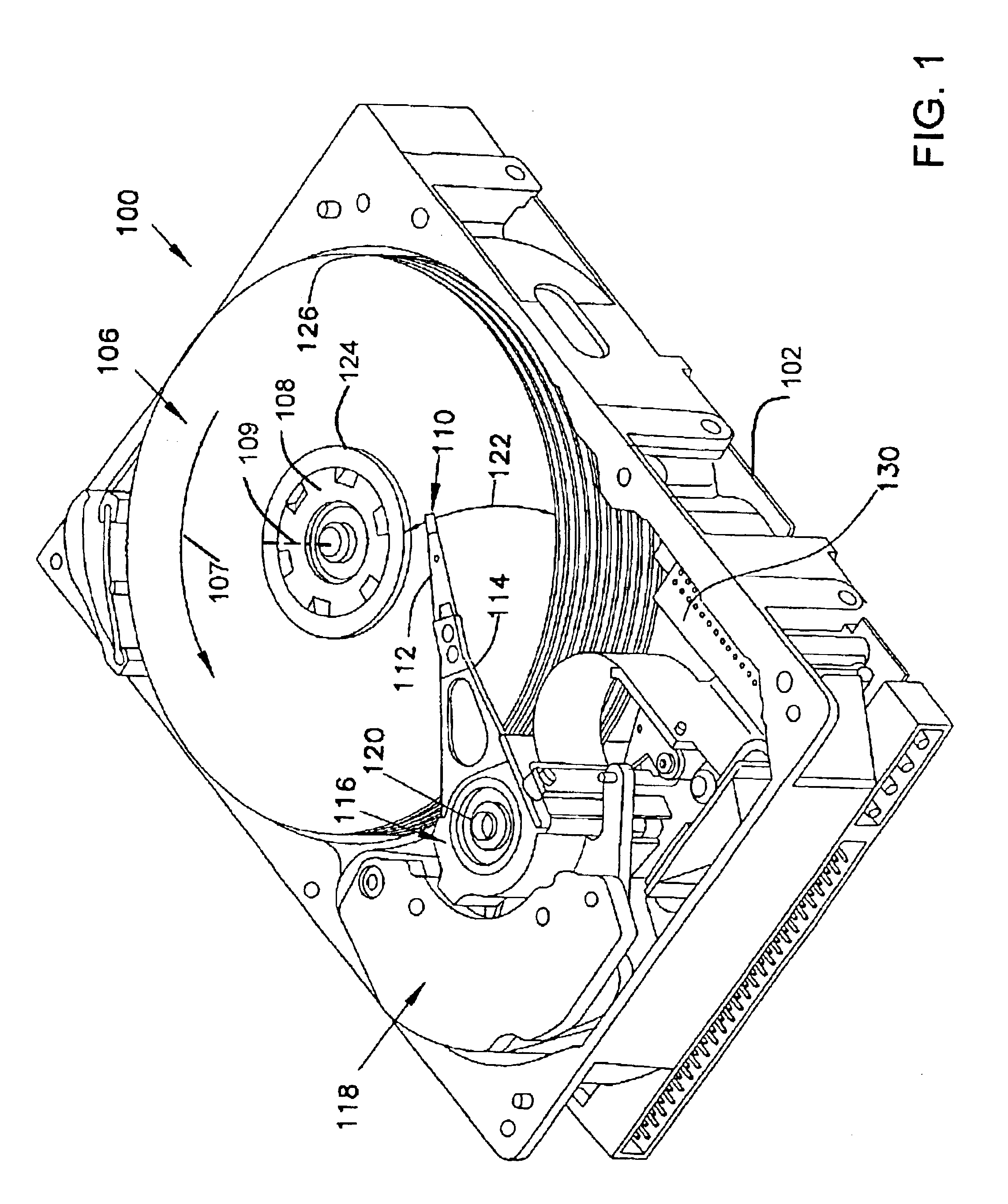
A voltage-mode VCM controller is provided comprising an Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) filter that modifies a servo control voltage signal to a voltage driver in response to an adaptive compensator that configures the IIR filter in relation to an observed VCM velocity and an actual VCM velocity. An associated method is provided comprising modeling a velocity response of a VCM to a voltage input; inputting the observed velocity and an actual VCM velocity to an adaptive compensator that computes a gain and a VCM response pole frequency in relation to the VCM resistance and inductance; configuring an IIR filter in relation to the computed gain and pole frequency values; and using the IIR filter to modify a voltage command from a servo controller to a power driver.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
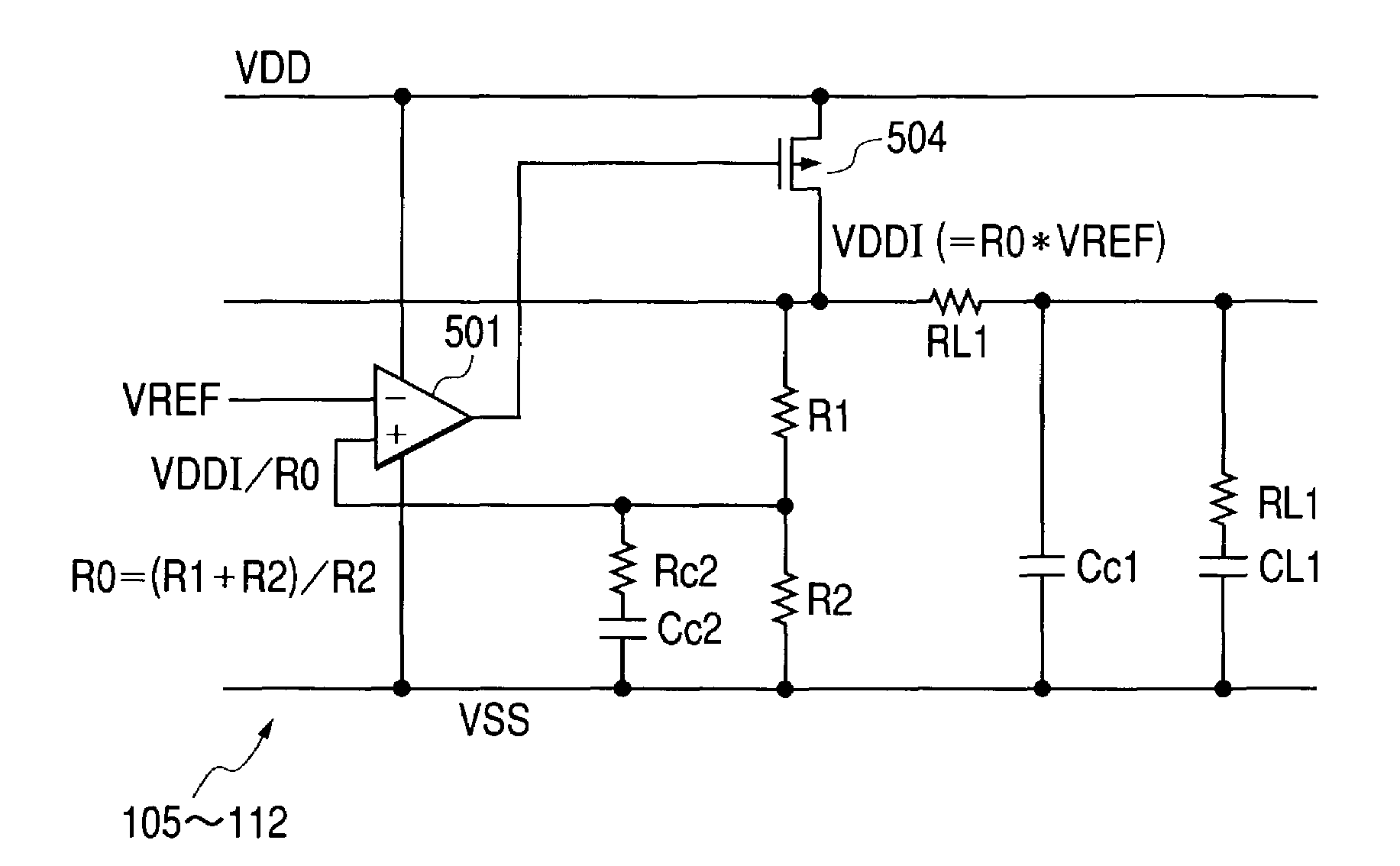
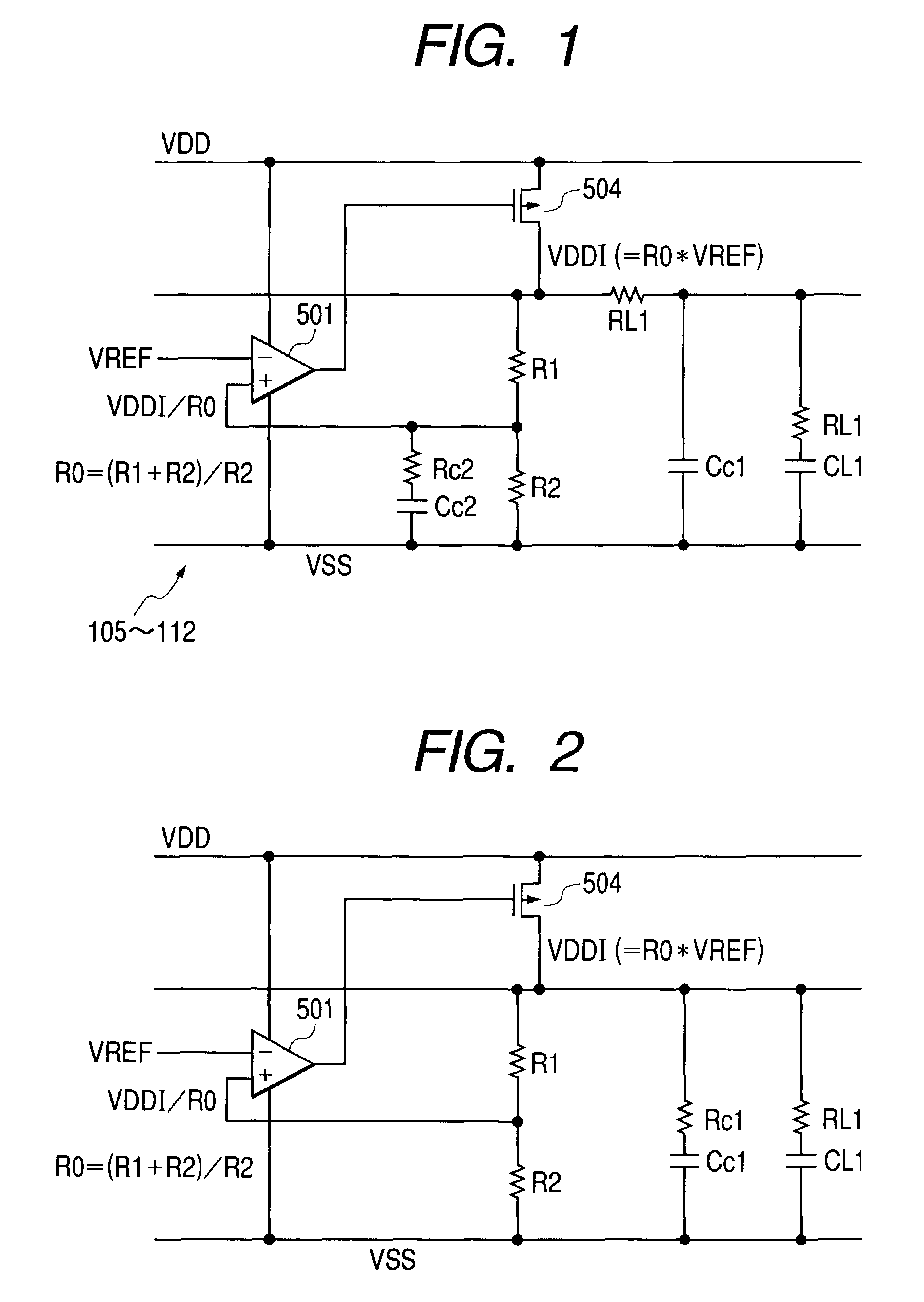
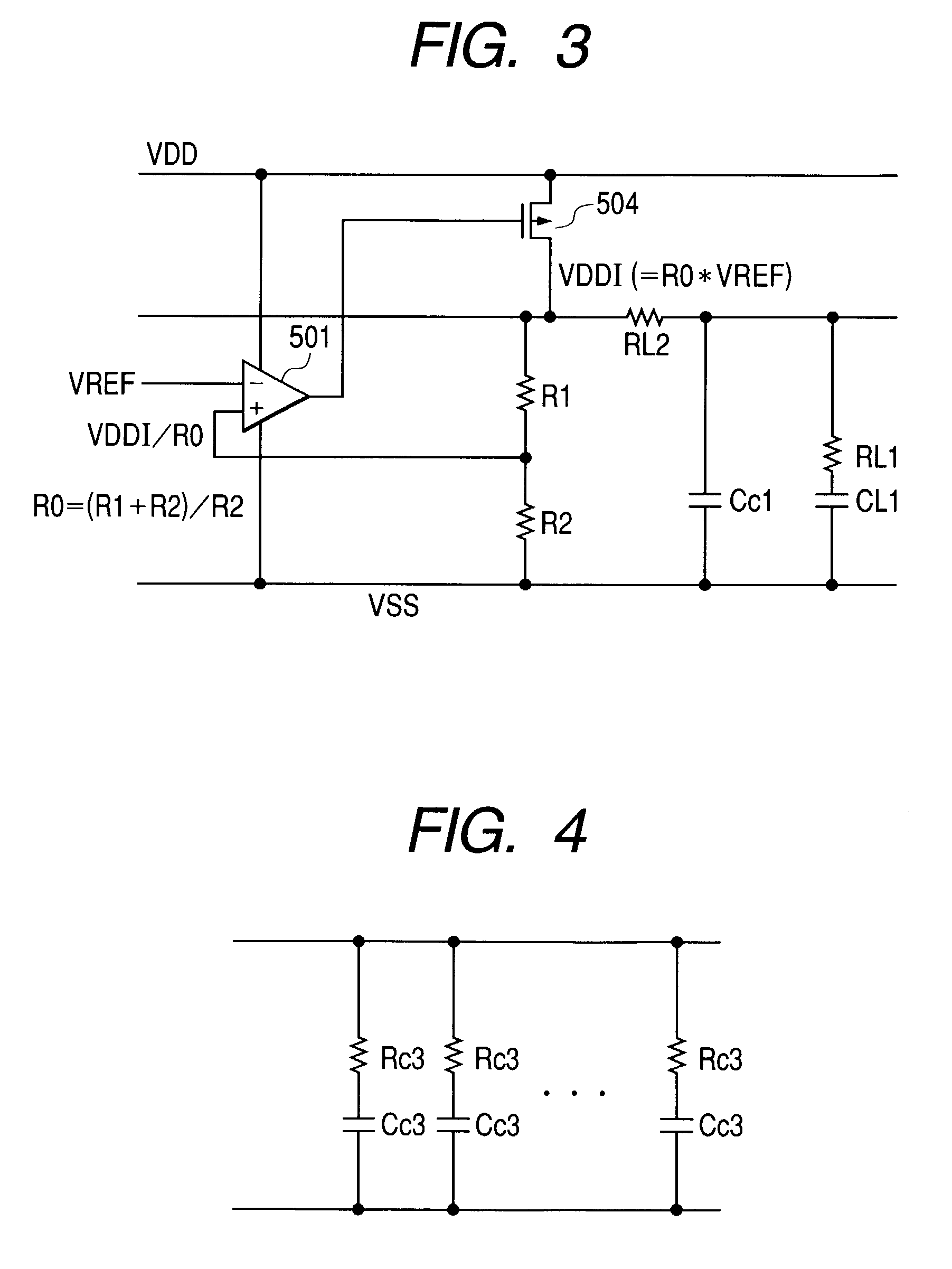
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
ActiveUS7208924B2Reduces chip occupancy areaDecrease drain conductanceAc-dc conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsHigh resistanceCapacitance
The invention intends to provide a technique that achieves a sufficient phase margin with ease. The circuit includes a power supply circuit that is formed with a phase compensating resistor and a phase compensating capacitor, between a second input terminal of a differential amplifier and a low supply voltage. Thereby, the first pole frequency in the overall gain is determined by the first pole frequency in the voltage-dividing resistor stage in the Bode diagram for the pole / zero compensation, which is shifted to a lower frequency. Also, the zero point cancels the first pole frequency in the differential amplifier stage, which reduces the phase delay to secure the phase margin. And, since the phase compensating resistor can take a considerably high resistance, the same characteristic can be achieved with a low capacitance of the phase compensating capacitor; thereby, the phase compensation becomes possible with a resistor and a capacitor having a smaller size than the pole / zero compensation with the internal supply voltage.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
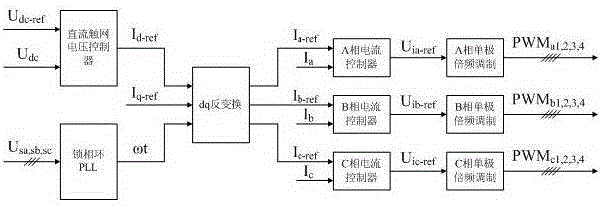
Closed-loop control method of subway energy feedback device
ActiveCN105162160AImprove control accuracyAc-dc conversionPower supply linesLow voltageControl signal
The invention relates to a closed-loop control method of a subway energy feedback device. The method comprises the following steps that 1) a target voltage value Udc-ref of a DC contact net is arranged manually, the voltage Udc of the DC contact net is detected in real time, and a voltage controller of the DC contact net compares the Udc-ref with the Udc to obtain deltaU; 2) three phases of voltage transformers PT1, PT2 and PT3 detect sampling electrical-network voltages Usa, Usb and Usc of three phase lines at the step-up side respectively, and the sampling electrical-network voltages Usa, Usb and Usc are calculated by a phase-locked loop PLL to obtain an electrical-network synchronization signal omegat needed by dq reverse transformation; 3) an axis-q reactive current instruction lq-ref is set according to a reactive scheduling requirement issued by a peripheral superior control system; and 4) three phases of control output Uia-ref, Uib-ref and Uic-ref are input to a three-phase scheduling module for single-pole frequency multiplication modulation to obtain three phases of pulse signals, and each phase includes 4 paths. Thus, the frequency is multiplied at the low-voltage ends of the voltage transformers, correct three-phase AC is fed to the middle-voltage AC electrical network, and the voltage of the DC contact net is stabilized.
Owner:NANJING APAITEK TECH
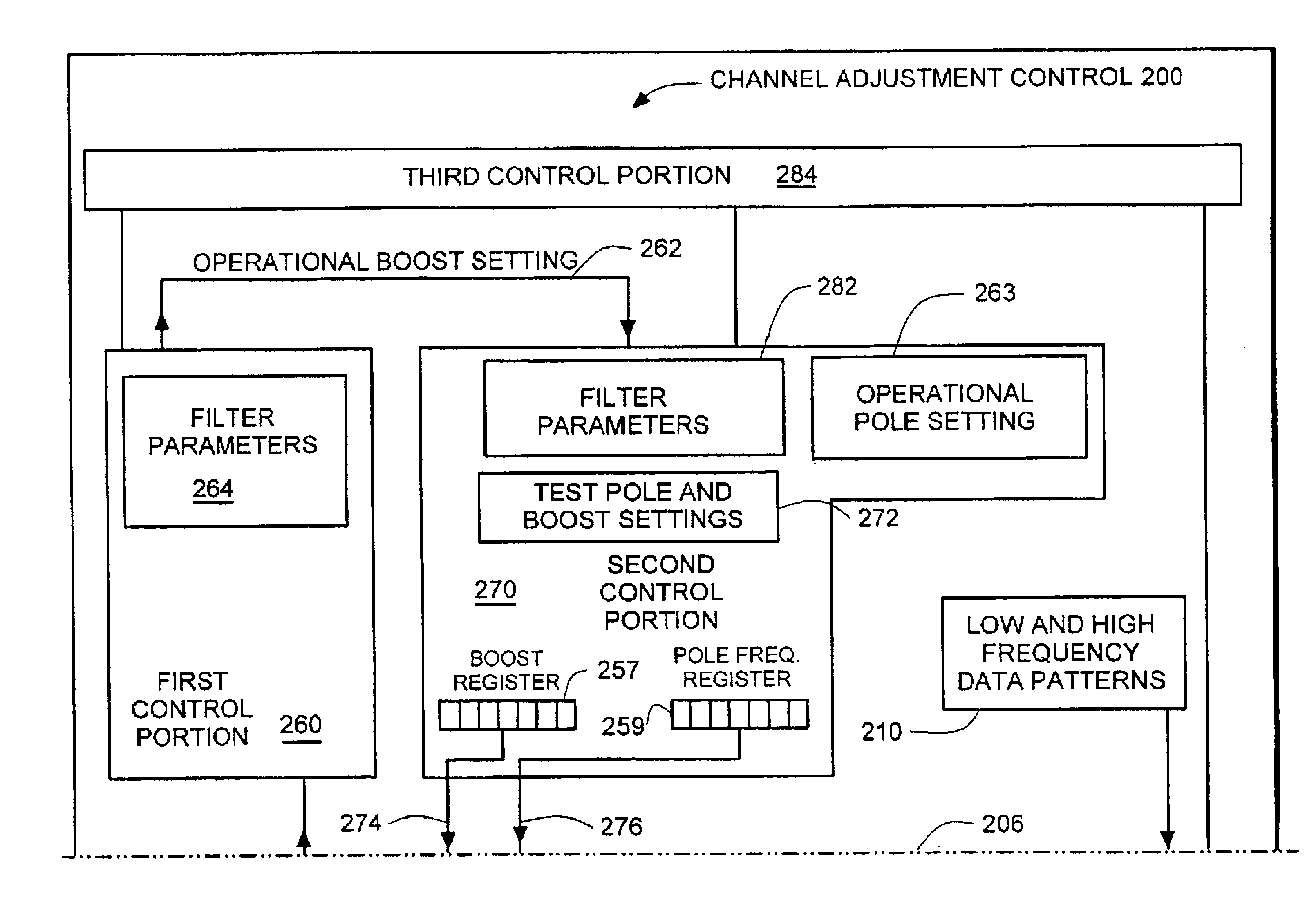
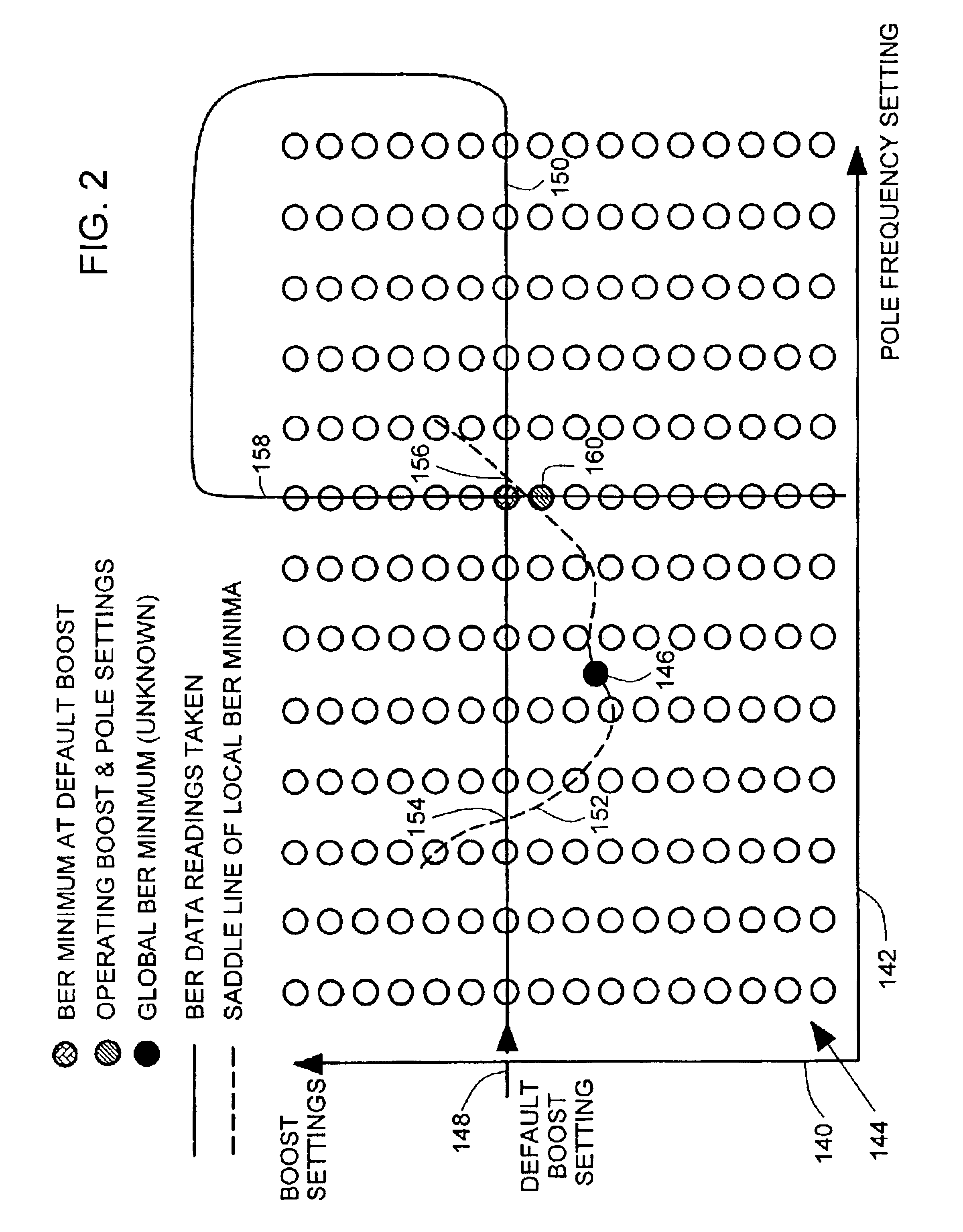
Adjustment of pole frequency and boost settings of a filter in a channel
InactiveUS6862152B2Reduce bit error rateModification of read/write signalsRecord information storageAudio power amplifierProcessor register
A channel adjustment control adjusts a channel to reduce bit error rate in a disc drive. Variable gain register settings are read and compared to filter characteristics to provide an operational boost register setting for an adjustable gain amplifier in the channel. An operational pole register setting is provided based on the operational boost register setting and known parameters of the adjustable low pass filter. Low and high frequency data patterns are applied while the channel adjustment control reads the variable gain register settings.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
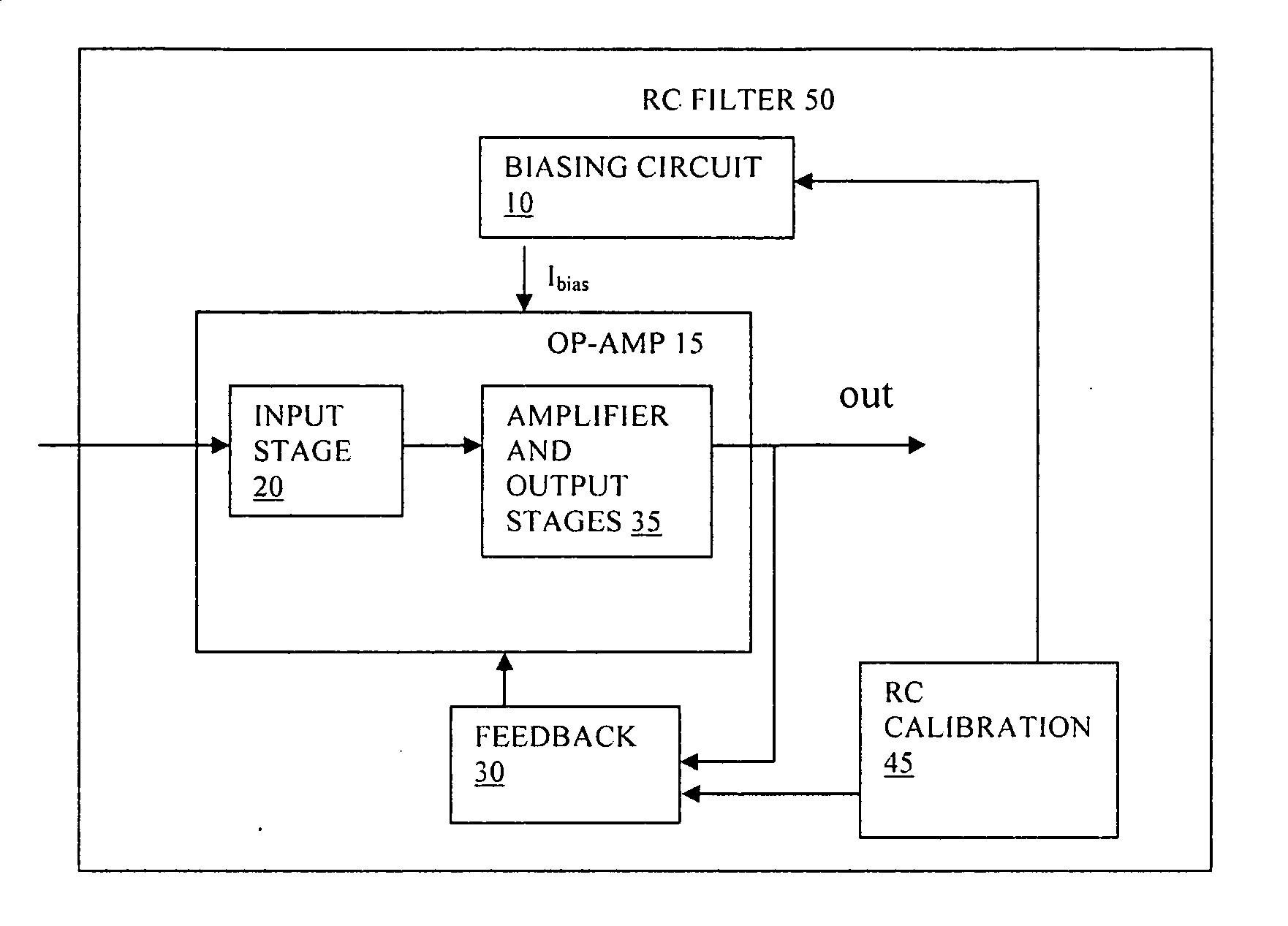
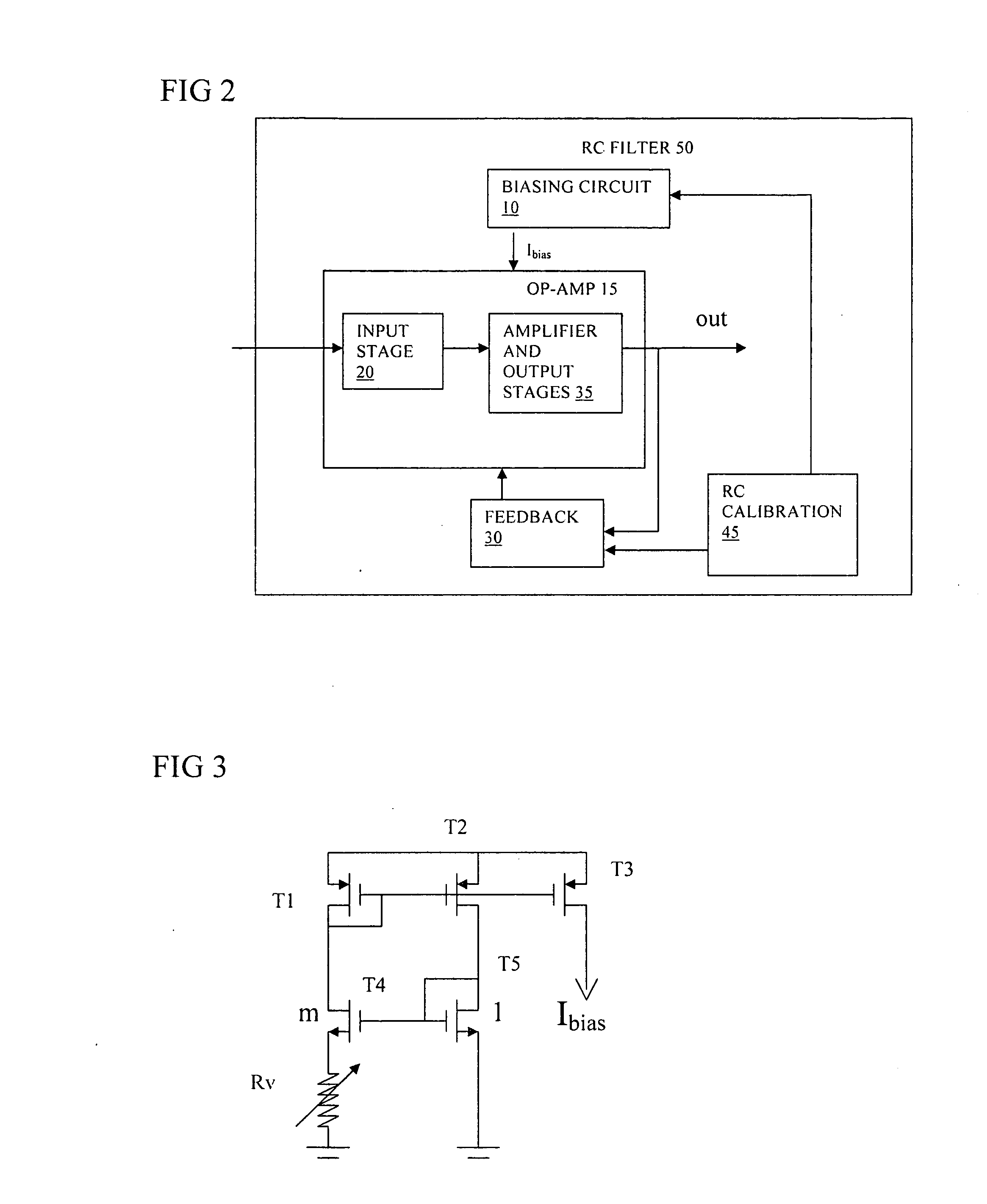
Bandwidth calibration of active filter
InactiveUS20080100373A1Decrease gain bandwidthReduce the required powerActive element networkAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierOperational transconductance amplifier
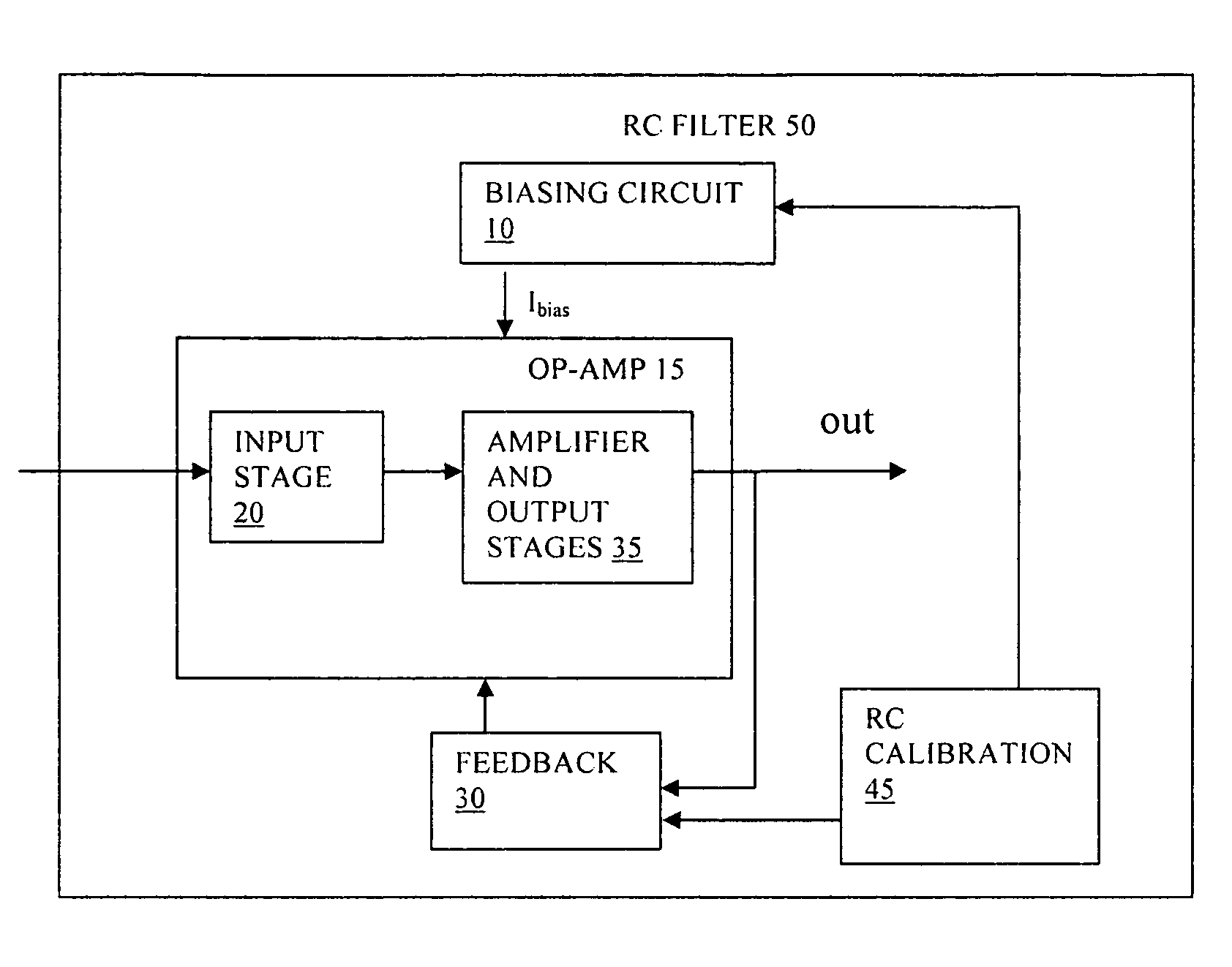
An active RC filter has an op-amp and a biasing circuit arranged to bias the op-amp to set a gain bandwidth product of the op-amp according to a desired pole frequency of the filter. The biasing circuit is operable according to an output of an RC calibration circuit. The op-amp can be an OTA transconductance amplifier, and the biasing circuit can be arranged to maintain a constant product of R and transconductance at an input of the transconductance amplifier. This biasing can help to set the pole frequency more accurately and can thus reduce the need for bandwidth margin to be provided to allow for manufacturing process variations.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
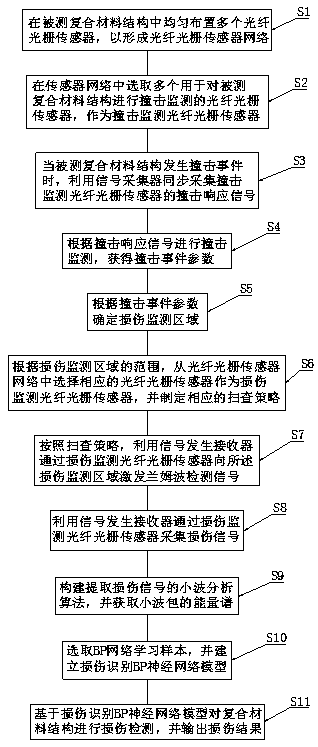
Composite material damage detection method based on wavelet analysis
InactiveCN107870205ARealize intelligent identification of damageSolve nonlinear problemsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalFeature vectorGrating
The invention discloses a composite material damage detection method based on wavelet analysis. The method only monitors damage in a damage monitoring zone related to damage in a composite material structure without monitoring damage of the whole detected composite material structure covered with a whole optical fiber grating sensor network through the whole optical fiber grating sensor network sothat the roll poling frequency of an optical fiber grating sensor for damage monitoring is greatly reduced, the quantity of the signals of damage needing to be collected and processed is reduced andthe damage monitoring efficiency is effectively improved. A composite material damage signal is analyzed and pre-processed through a wavelet packet so that a damage signal energy spectrum is obtained.The method extracts feature vectors and is accurate and effective. Through a BP neural network model and training, a network having the function of the composite material damage identification mode is obtained, thereby realizing damage intelligent identification, solving some nonlinear problems, realizing damage identification and positioning and degree determination and being effective and feasible.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
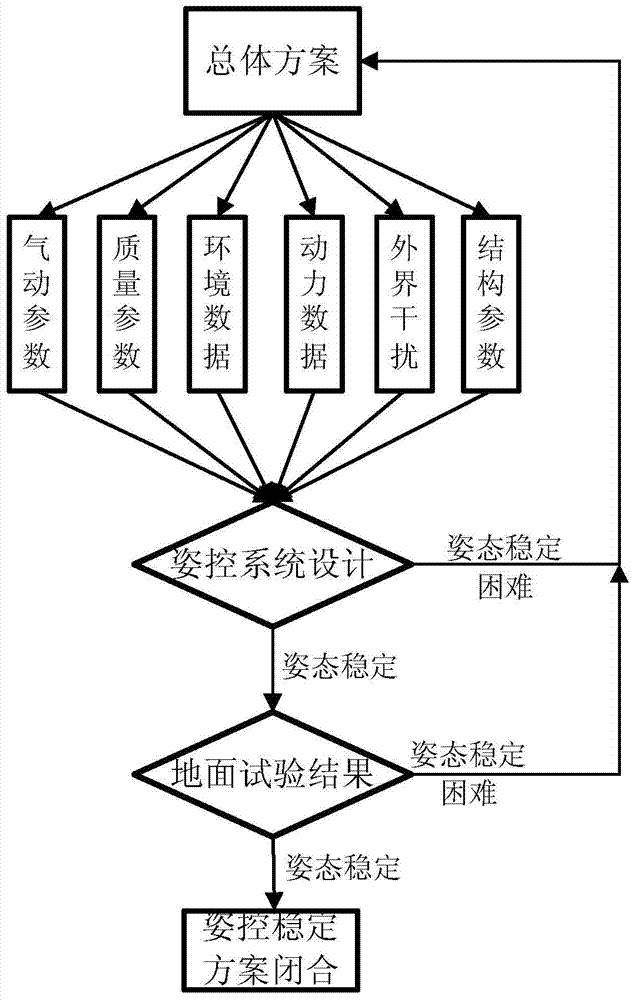
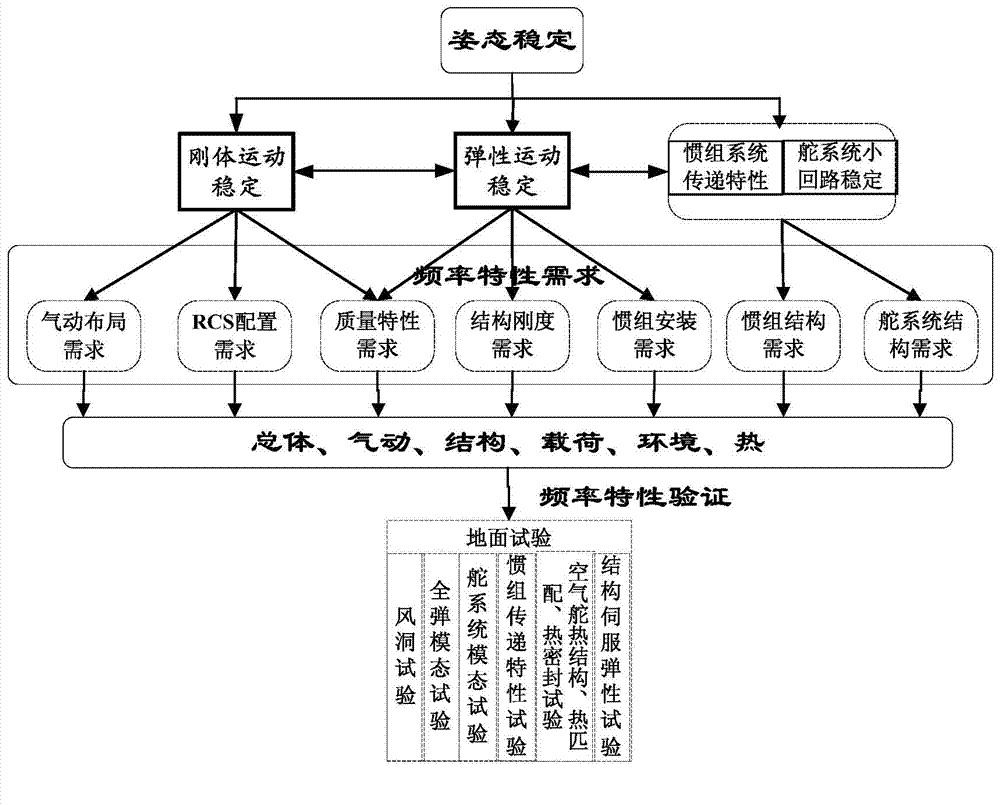
Frequency management method for stable postures of hypersonic aircraft
ActiveCN103587718AReduce complexityMitigating indicators such as high performanceAircraft components testingAccelerometerGyroscope
The invention relates to a frequency management method for stable postures of a hypersonic aircraft. The method sequentially comprises the steps that (1), information of various frequencies is collected; (2) when a rigid motion transmission band is larger than first-order elastic vibration frequency by more than 10 times, and an elasticity amplitude stabilizing method is adopted; (3), a rate gyroscope is led in to a place where the vibration mode slope is zero; (4) when shaking zero frequency is larger than pole frequency, shaking stability is improved through feedback of an accelerometer or additional arrangement of an anti-shaking board; (5), a transmission band of a steering engine is 5-10 times of the rigid motion transmission band; (6), an inertia unit transmission band is 10-20 times of rigid motion bandwidth; (7), the structural stiffness of an executing mechanism and a sensitive mechanism is kept to be more than 5 times of a single-engine bandwidth; (8), main frequency of external disturbance is prevented from being coupled with inherent frequency of a structural part; (9), ground tests of various frequency characteristics are carried out, and the stable postures of the hypersonic aircraft are ensured. According to the frequency management method for the stable postures of the hypersonic aircraft, repeated schemes are avoided, development schedule is accelerated, and system interfaces are made to be clear and comprehensively optimum.
Owner:BEIJING LINJIN SPACE AIRCRAFT SYST ENG INST +1
Adaptive voltage-mode controller for a voice coil motor
InactiveUS7199964B2Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageIir filteringMode control
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Simulation filament impedance circuit, LED lamp tube, and LED illuminating system
ActiveCN106102255AThe equivalent impedance value is reducedLow equivalent impedanceElectrical apparatusElectric circuit arrangementsEngineeringZero frequency
The invention provides a simulation filament impedance circuit, an LED lamp tube, and an LED illuminating system. The simulation filament impedance circuit has pole frequency and zero frequency. The pole frequency is smaller than the zero frequency. When input frequency is smaller than the pole frequency, the equivalent impedance value of the simulation filament impedance circuit remains unchanged, and is a first equivalent impedance value. When the input frequency is greater than the pole frequency and smaller than the zero frequency, the equivalent impedance value of the simulation filament impedance circuit is lowered along with the rising of the input frequency. When the input frequency is greater than the zero frequency, the equivalent impedance value of the simulation filament impedance circuit remains unchanged, and is a second equivalent impedance value. The first equivalent impedance value is greater than the second equivalent impedance value. By adopting the simulation filament impedance circuit provided by the invention, requirements of IEC standard tests are satisfied, and the conversion efficiency of the lamp tube is not affected.
Owner:OPPLE LIGHTING
A high-gain two-stage operational transconductance amplifier with a cross structure
PendingCN109728786AReduce noiseInput Common Mode Level LowAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlCapacitanceDamping factor
The invention discloses a high-gain two-stage operational transconductance amplifier with a cross structure, relates to the technical field of operational transconductance amplifiers, solves the problems of low gain, low output pole frequency and poorer circuit stability of the existing amplifier. the technical scheme includes that the operational transconductance amplifier comprises a two-stage amplifying circuit, a damping factor control module circuit and a biasing circuit for providing bias voltage for a circuit structure, Wherein the first stage of the two-stage amplifying circuit is a PMOS tube differential input amplifying circuit, and the second stage of the two-stage amplifying circuit is a complementary push-pull driving circuit of a common-source gain stage; The damping factor control module circuit is connected with the output end of the PMOS tube differential input amplification circuit; A first capacitor C1 used for forming a Miller compensation path is arranged between the output end and the input end of the complementary push-pull driving circuit of the common-source gain stage, the circuit can be stabilized, and under the condition that the whole circuit is in lowpower consumption, the effects of improving the gain, the common-mode rejection ratio and the power supply rejection ratio of the circuit are achieved.
Owner:GANNAN NORMAL UNIV
Amplification circuit
ActiveCN104821795ADifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
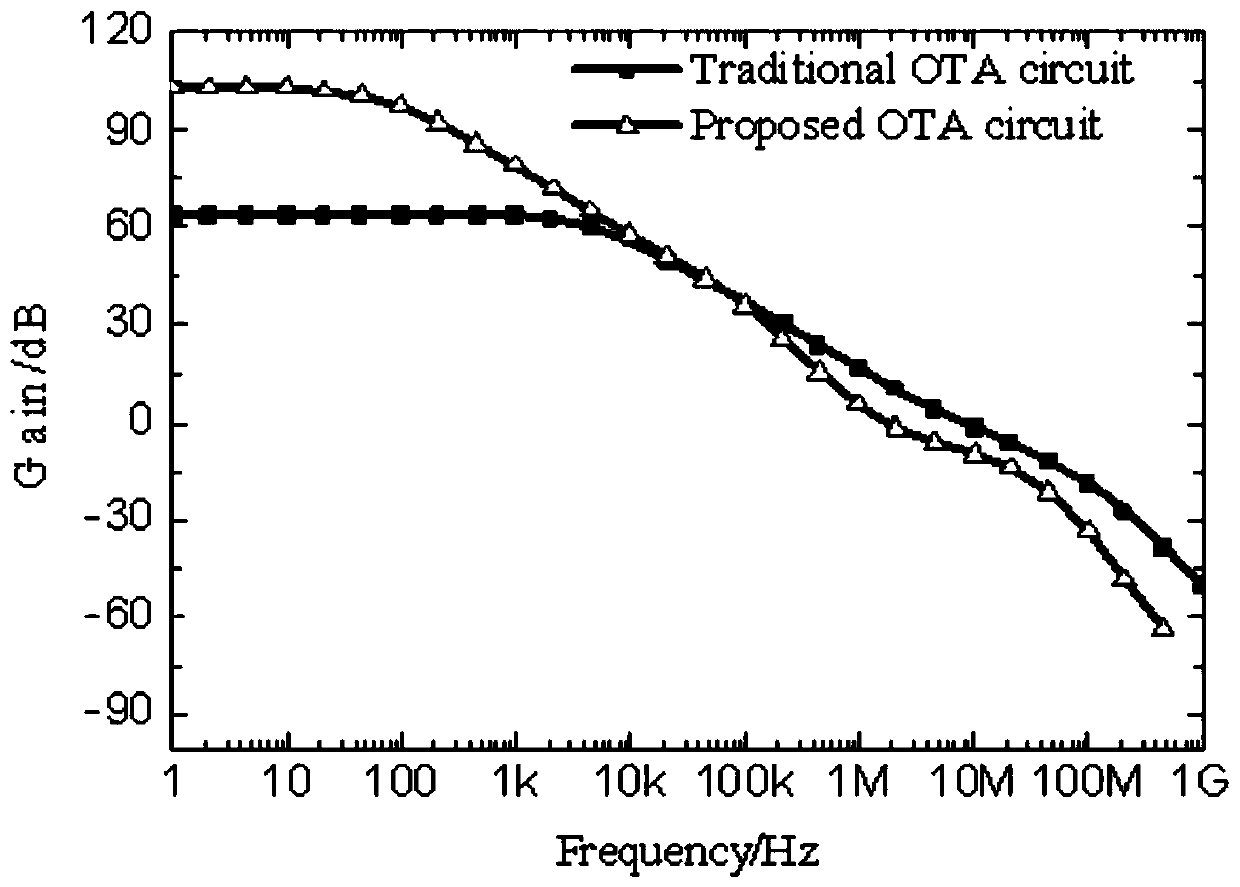
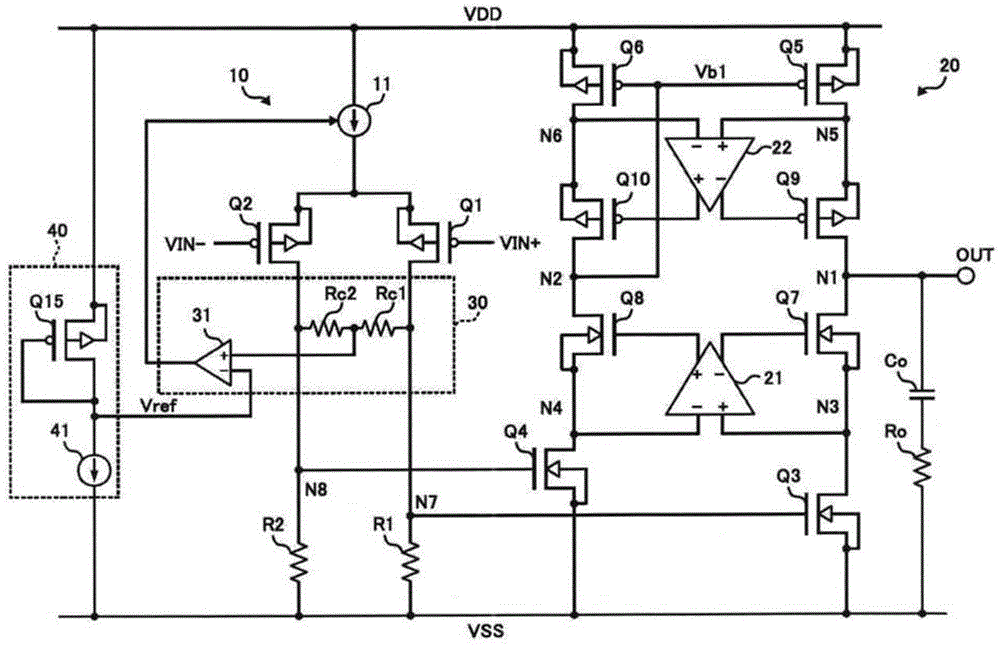
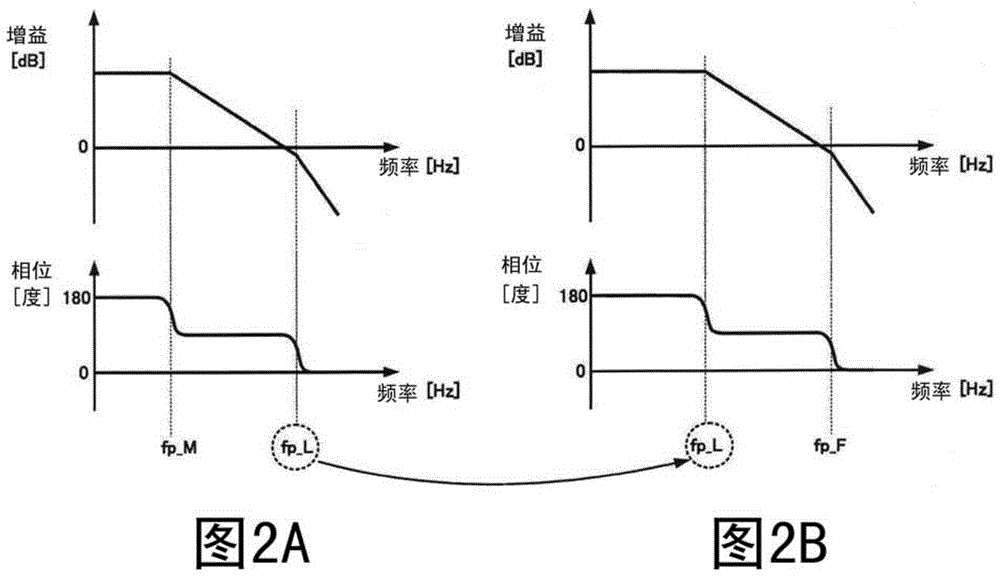
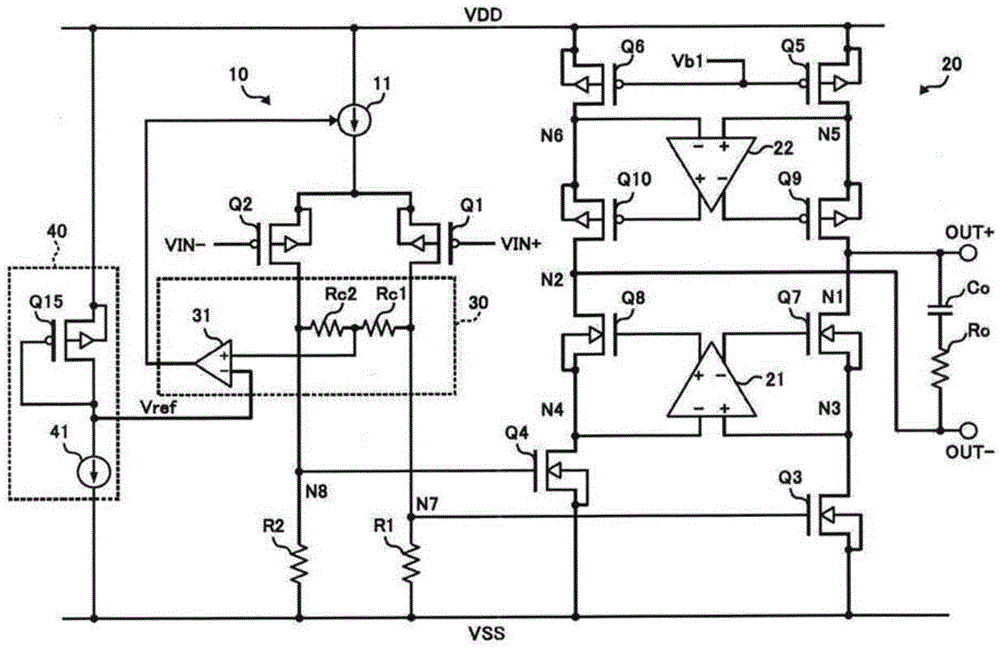
The invention provides an amplification circuit which can act in a high speed during connection with a capacitive load. A second amplification stage 20 has a large output resistance. A pole frequency fp_L caused by the output resistance and an output capacitance (a capacitor C0) becomes the lowest pole frequency in a transfer function. When the amplification circuit is compared with a previous amplification circuit wherein the upper limit of a frequency band is limited by a pole frequency fp_L caused by output resistance and output capacitance, the pole frequency limiting the upper limit of a frequency band is raised, and so the lowest pole frequency in the transfer function can be raised to a higher frequency.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Bandwidth calibration of active filter
InactiveUS7692484B2Reduce pole frequency variationCalibrates the gain bandwidth of the op-ampActive element networkAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierEngineering
An active RC filter has an op-amp and a biasing circuit arranged to bias the op-amp to set a gain bandwidth product of the op-amp according to a desired pole frequency of the filter. The biasing circuit is operable according to an output of an RC calibration circuit. The op-amp can be an OTA transconductance amplifier, and the biasing circuit can be arranged to maintain a constant product of R and transconductance at an input of the transconductance amplifier. This biasing can help to set the pole frequency more accurately and can thus reduce the need for bandwidth margin to be provided to allow for manufacturing process variations.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
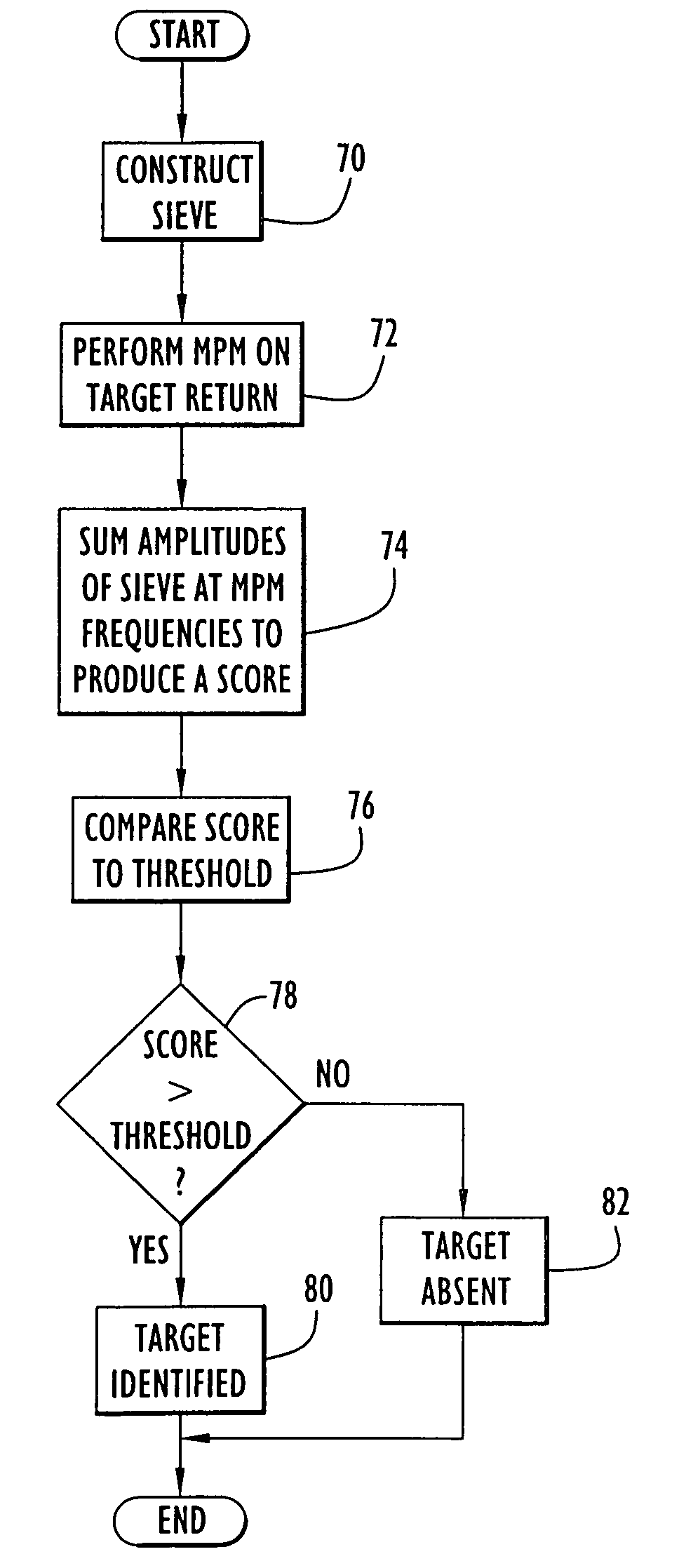
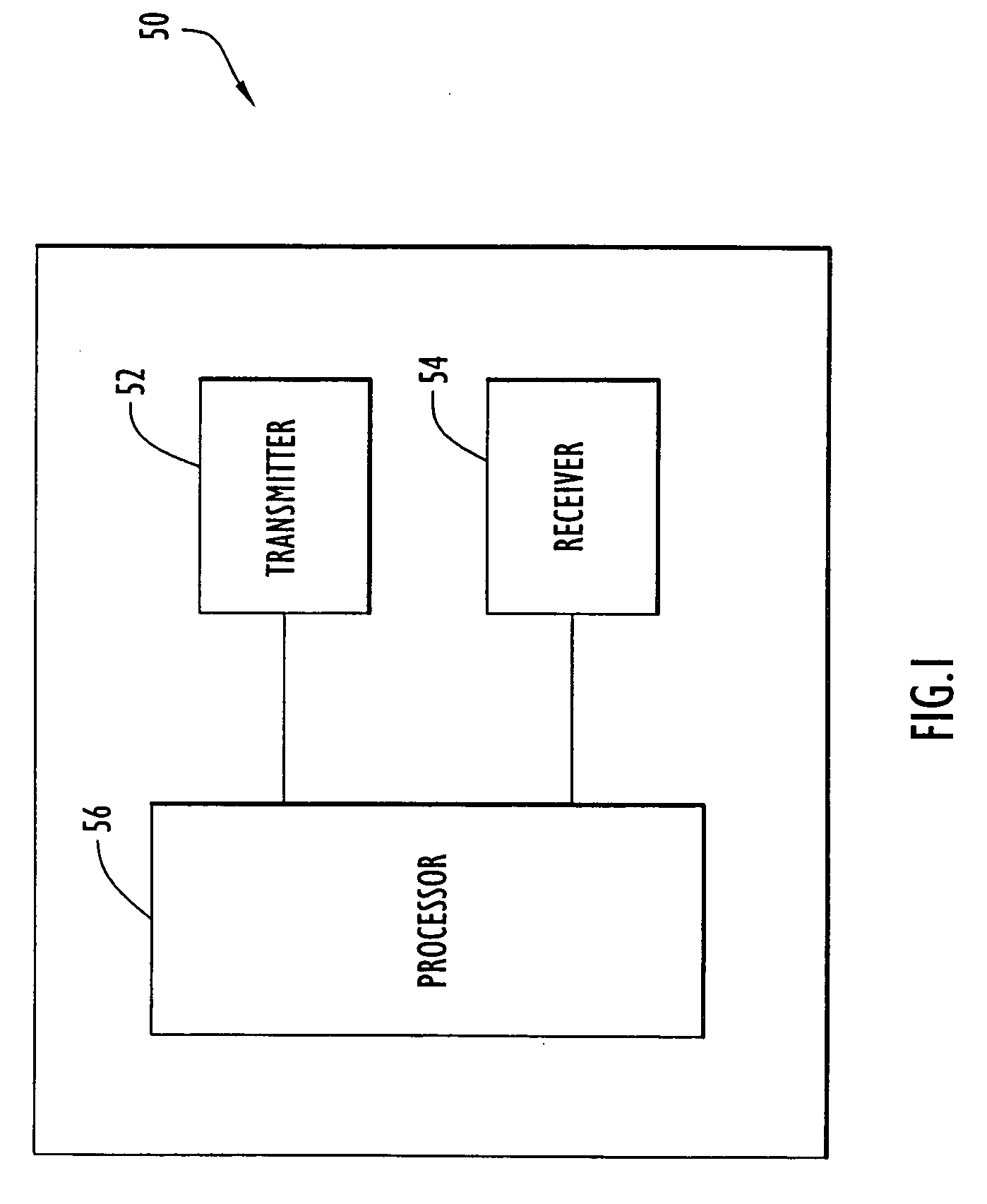
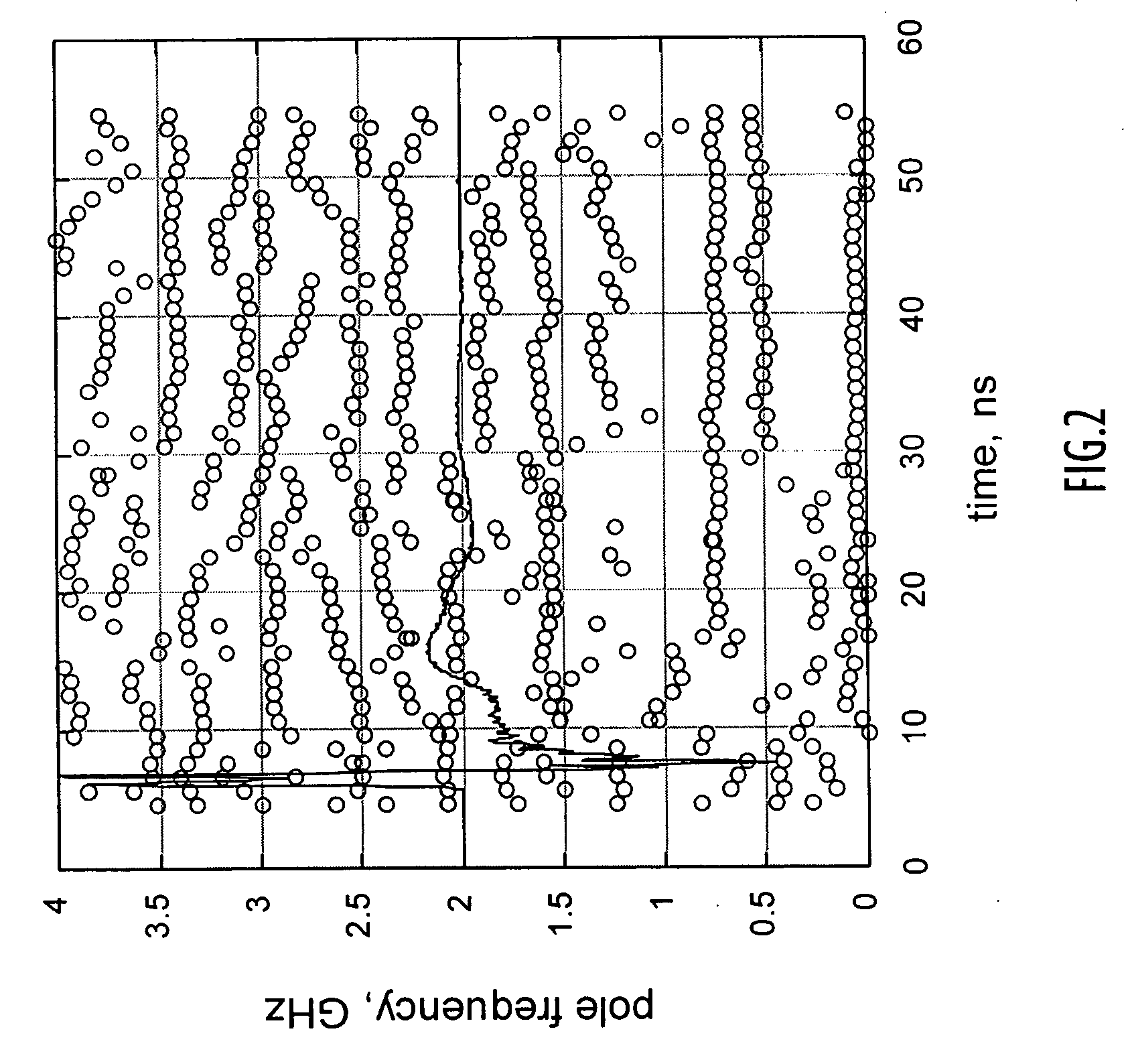
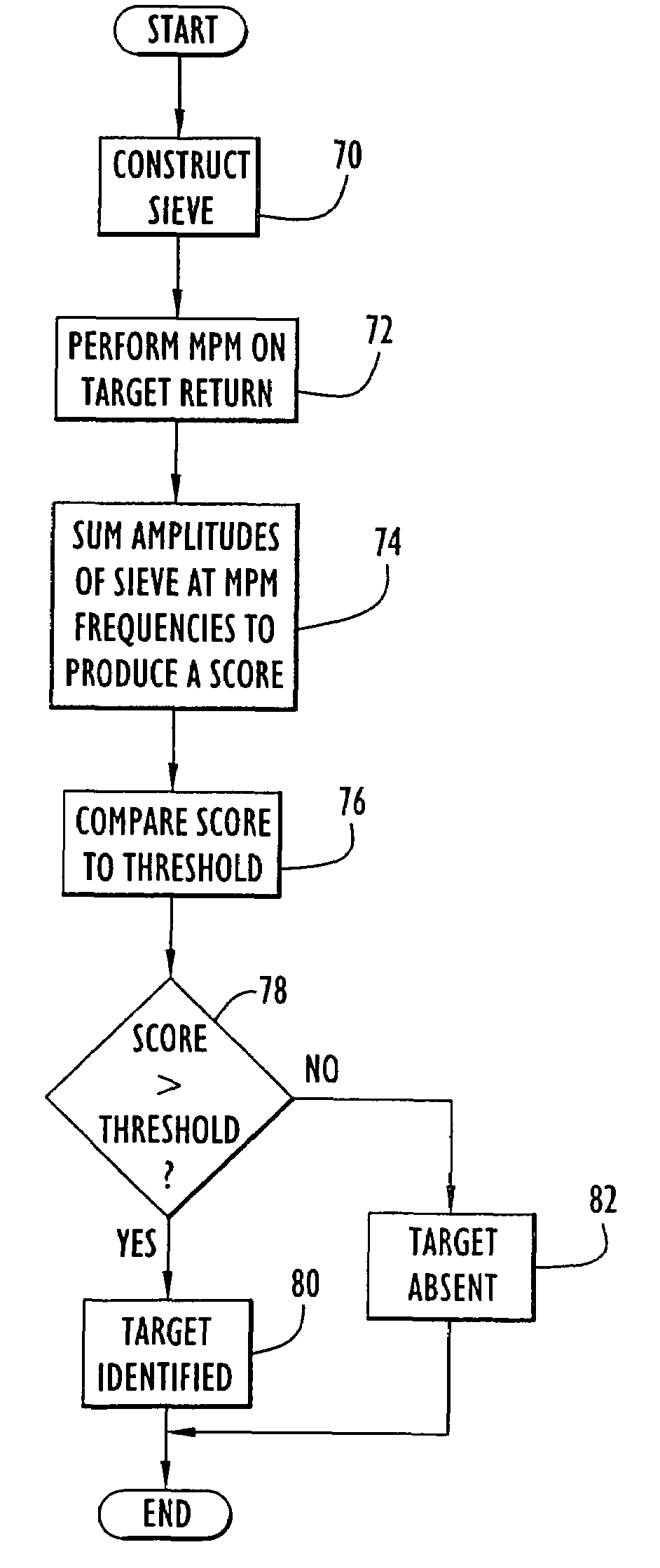
Method and apparatus for target discrimination within return signals
A template representing a desired target is applied to response signals from an area including a plurality of targets and illuminated by electromagnetic radiation. The response signals include poles or damped sinusoids representing resonances (e.g., resonant frequencies) distinctly associated with each of the targets within the area. An embodiment of the present invention utilizes pole or damped sinusoid frequencies of a desired target to construct the template or comb-like pattern that is compared to the mixture of pole frequencies within the response signals from the area. The comparison yields a resulting score that indicates the presence of the desired target within the area.
Owner:PERATON INC
Method and apparatus for target discrimination within return signals
A template representing a desired target is applied to response signals from an area including a plurality of targets and illuminated by electromagnetic radiation. The response signals include poles or damped sinusoids representing resonances (e.g., resonant frequencies) distinctly associated with each of the targets within the area. An embodiment of the present invention utilizes pole or damped sinusoid frequencies of a desired target to construct the template or comb-like pattern that is compared to the mixture of pole frequencies within the response signals from the area. The comparison yields a resulting score that indicates the presence of the desired target within the area.
Owner:PERATON INC
Omni-azimuthal pattern generator for VLF and LF communication
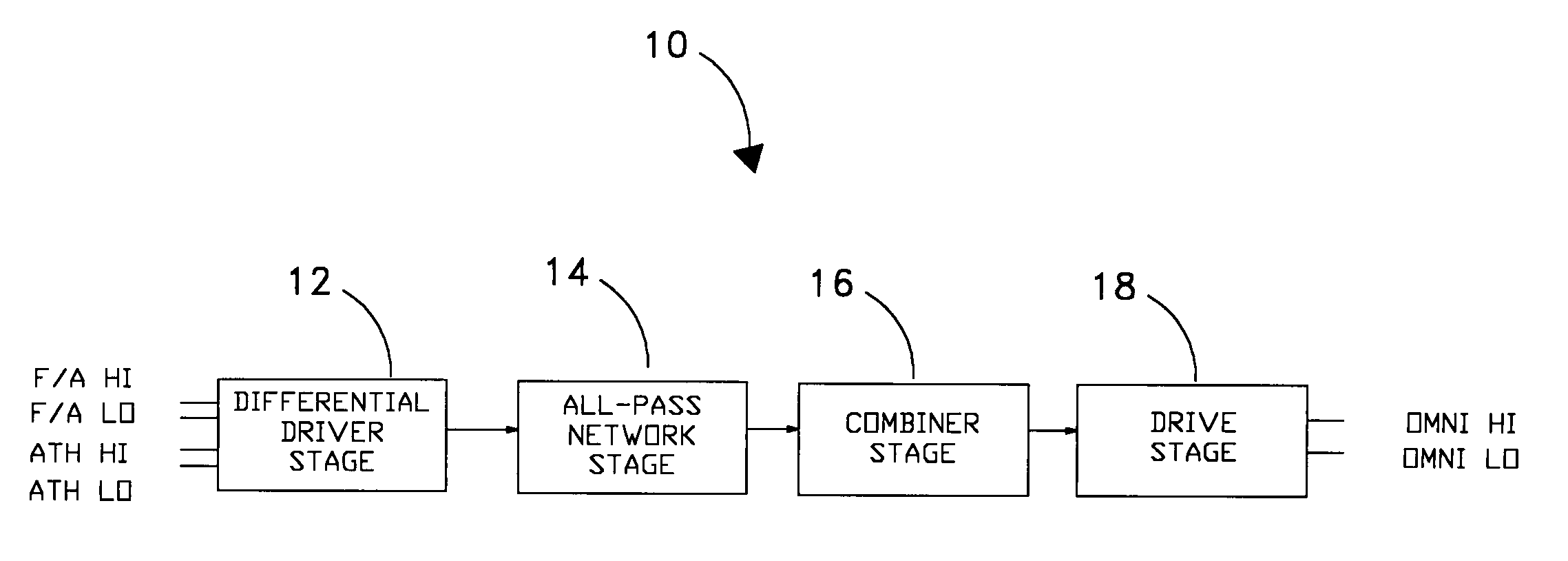
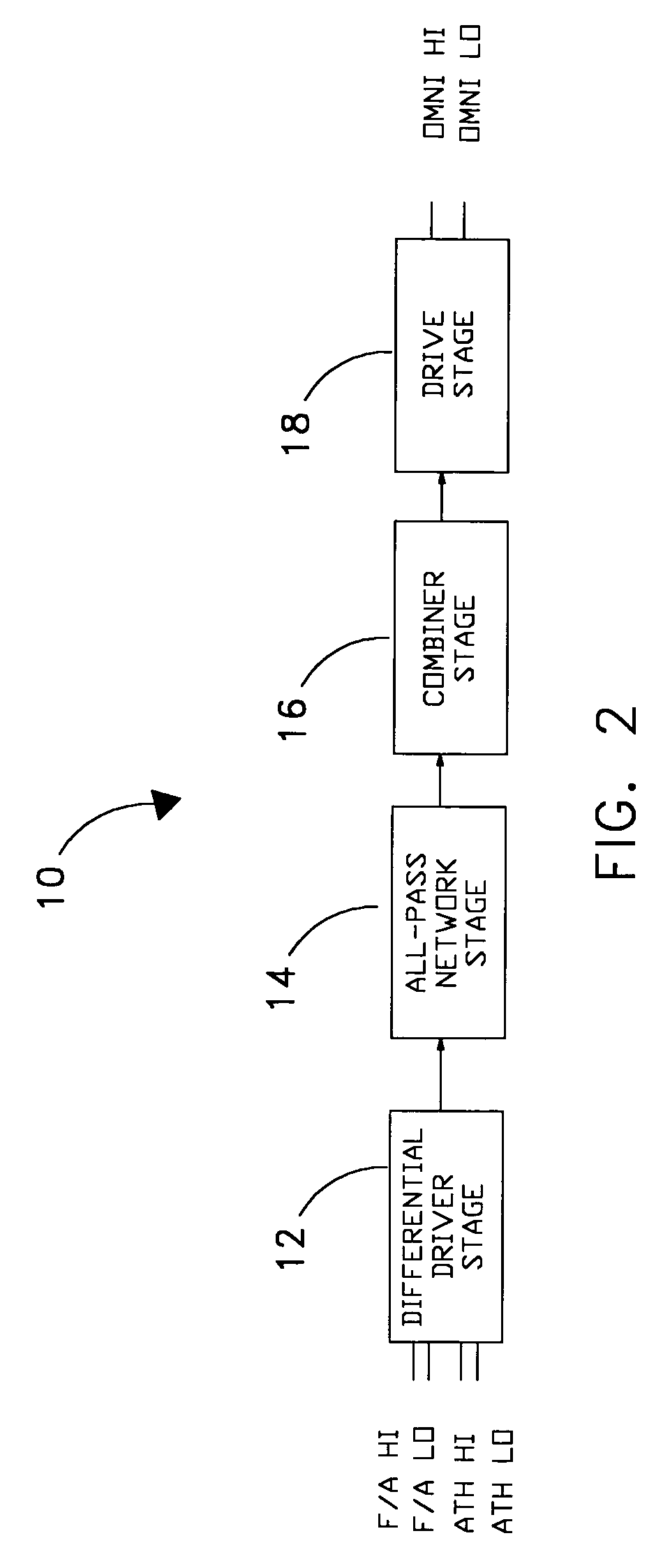
ActiveUS7106269B1Easy to receivePolarisation/directional diversityIndividually energised antenna arraysPhase shiftedRelative phase
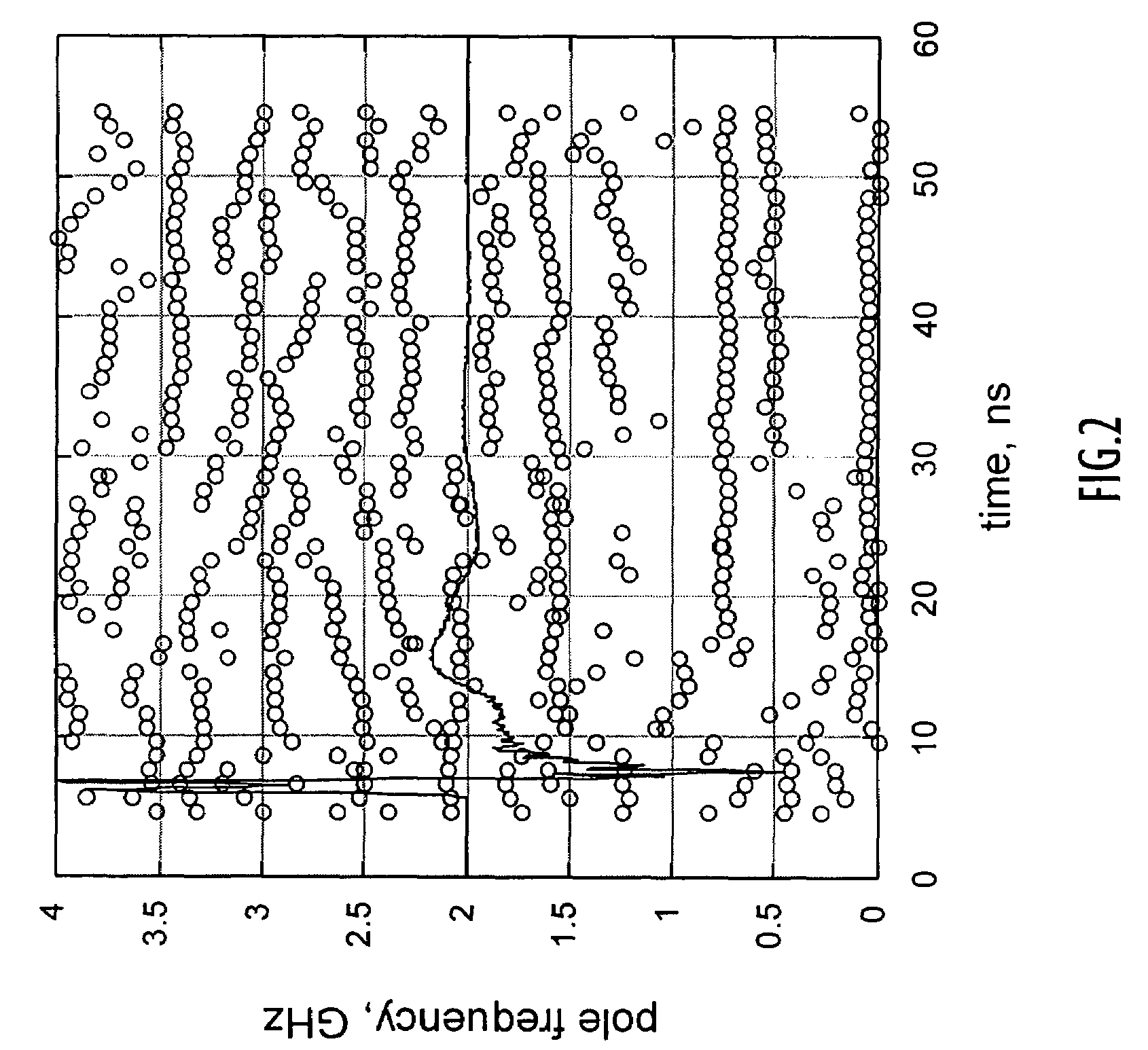
A relative phase shift is induced in the signals of a pair of identical orthogonal antennas such that when the signals are combined the signals are 90 degrees out of phase. This is done in order to eliminate the null along the axis between the two dipole moments of the antennas such that the system has equally good reception from all azimuth angles over a broad range of frequencies. The phase shift is accomplished with the use of single pole operational amplifier circuits whose pole frequencies are adjusted by means of a potentiometer prior to implementation of the antenna system.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
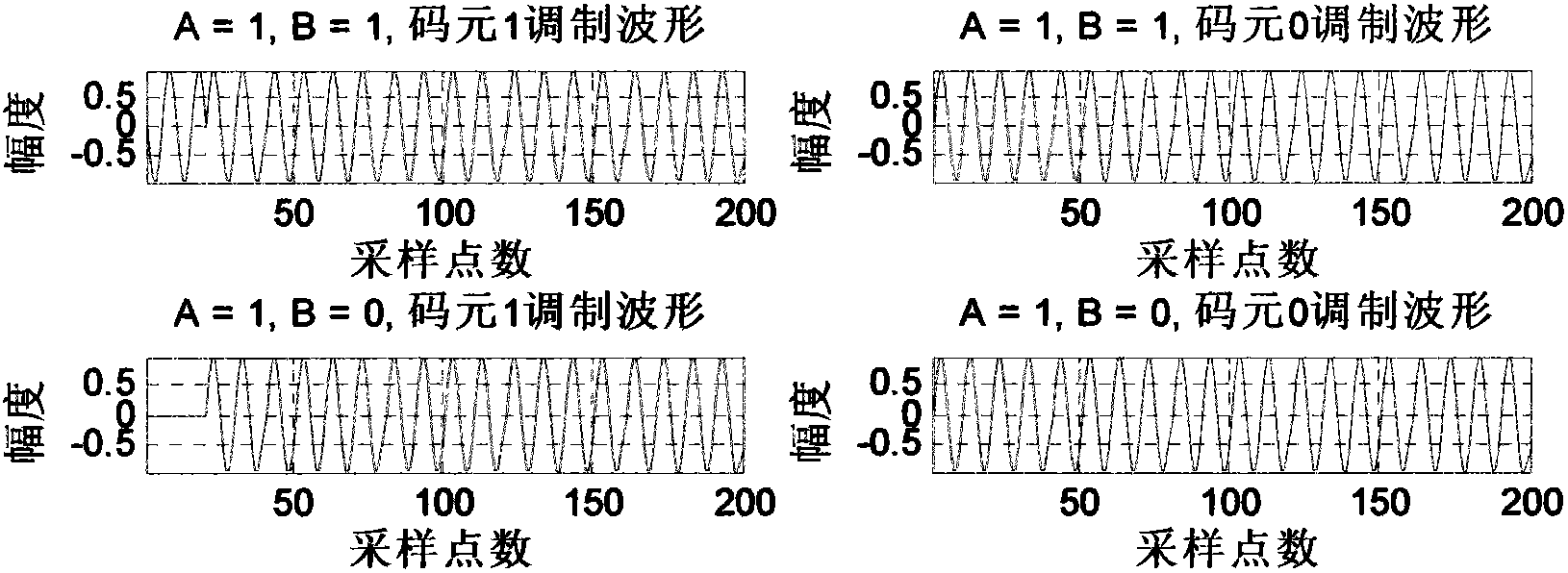
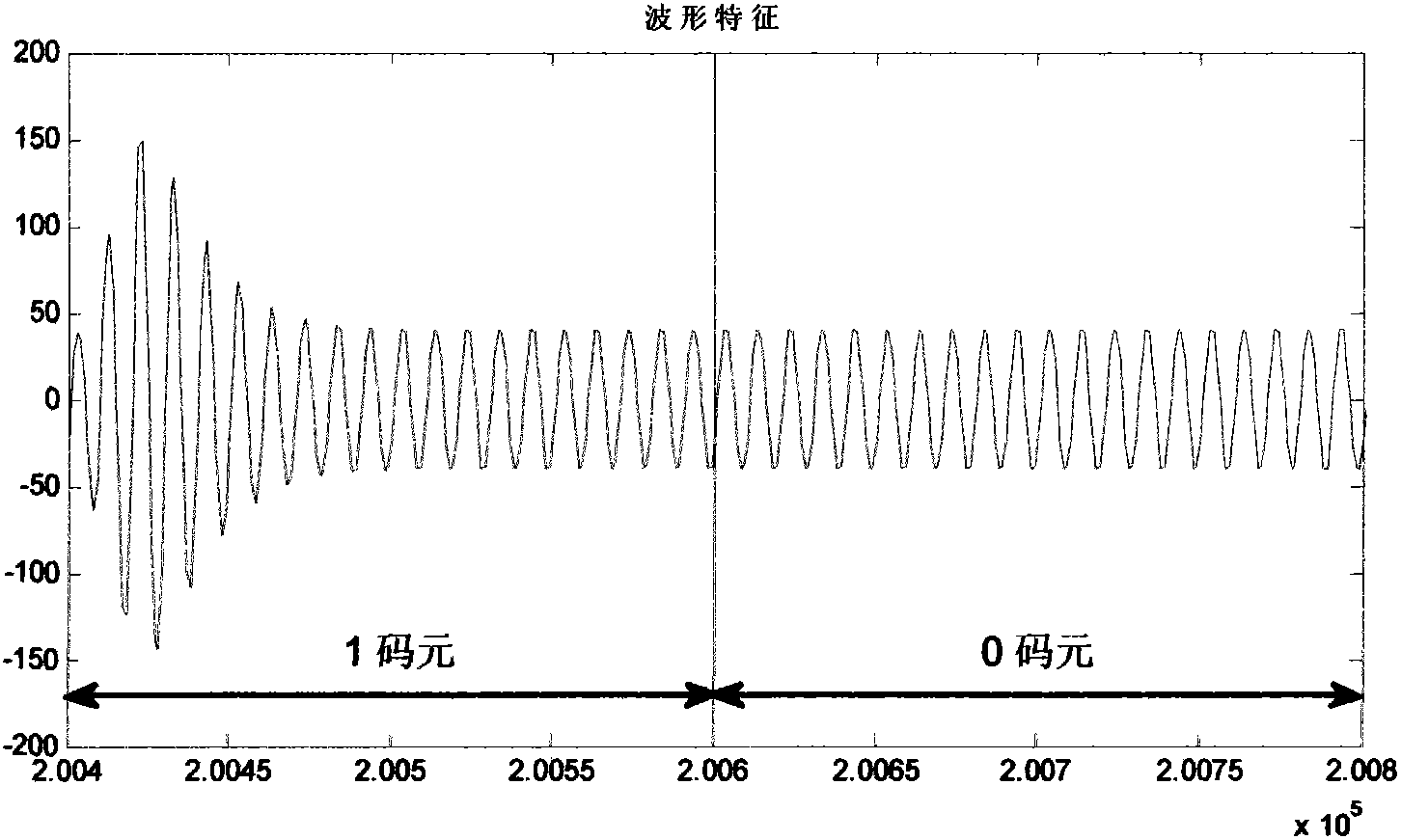
Geometric feature discrimination demodulator based on EBPSK (Extended Binary Phase Shift Keying) signal impulse filter response
ActiveCN102882823AImprove demodulation performanceReduce consumptionPhase-modulated carrier systemsDiscriminatorEngineering
The invention provides a geometric feature discrimination demodulator based on EBPSK (Extended Binary Phase Shift Keying) signal impulse filter response, which comprises a digital impulse filter and a geometric feature discriminator, wherein the digital impulse filter consists of a pair of conjugate zeroes and at least two pairs of conjugate poles, the signal carrier frequency of the digital impulse filter is higher than the zero frequency but lower than all pole frequencies, the close degree between the zero frequency and the pole frequencies at least reaches to 10-3 magnitude of the signal carrier frequency, the geometric feature discriminator extracts and memorizes the geometric feature and the internal relation of signal waveforms enhanced through the impulse filter by use of an artificial neural network sorter, and makes a united decision on all corresponding sampling points of output waveforms of the EBPSK impulse filter within n (n is greater than or equal to 1) code element periods, thus, the demodulator can still keep the good demodulating performance in complex working conditions such as high Gaussian white noise, intersymbol interference and channel fading, and has strong robustness and adaptivity.
Owner:苏州东奇信息科技股份有限公司
Frequency spectrum recognition method for groundwater runoff dynamic information
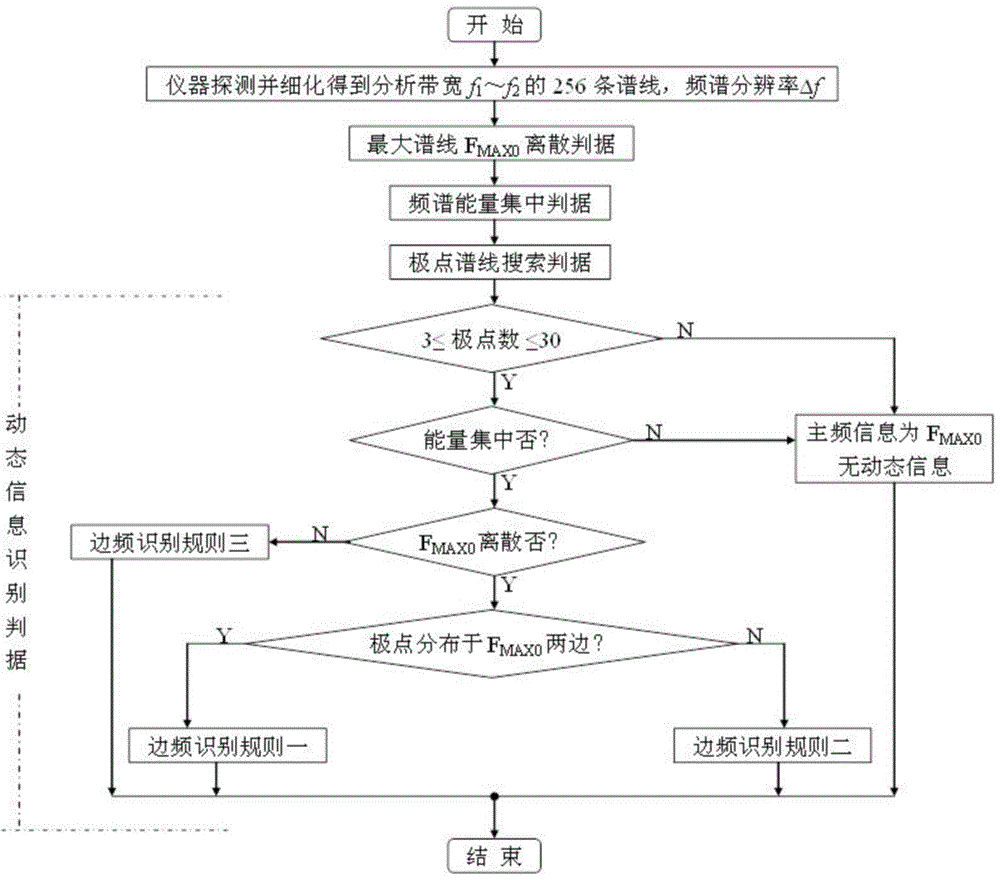
ActiveCN105929457ASolve the problem that it is difficult to identify the dynamic information of underground runoffWater resource assessmentElectric/magnetic detectionFrequency spectrumLine search
The invention discloses a frequency spectrum recognition method for groundwater runoff dynamic information, and the method comprises the steps: receiving a natural electric field signal through a detection instrument; carrying out refining and obtaining 256 spectrum lines with the analysis bandwidth f1-f2 and the resolution delta f; obtaining a judgment whether there is groundwater runoff dynamic information or not through a maximum spectrum line discrete criterion, a frequency spectrum energy concentration criterion, a pole frequency spectrum line search criterion and a dynamic information recognition criterion, and correspondingly giving the amplitudes and frequencies of main frequency information and dynamic information. The method starts from the research of the forming mechanism of the groundwater runoff dynamic information, employs a rule of combining the signal modulation principle and side frequency characteristics to automatically recognize the groundwater runoff dynamic information in a refined spectrum, gives full consideration to the impact from interference factors, can enable the recognition accuracy of the groundwater runoff dynamic information to reach 90% or more, and solves a problem that a conventional geophysical prospecting method is difficult to recognize the groundwater runoff dynamic information.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Phase-locked loop based on comb filter
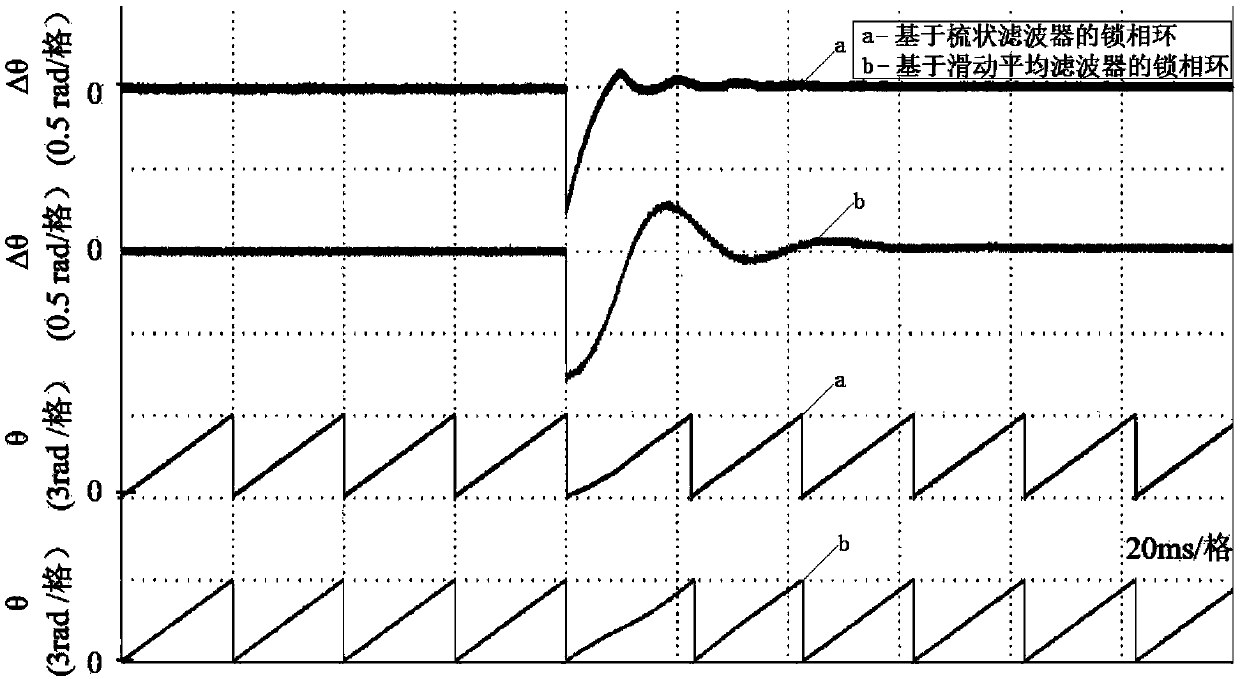
PendingCN107846218ASolve Phase LagSolve technical problems with small phase margPulse automatic controlHigh level techniquesMoving averageAverage filter
The embodiment of the invention discloses a phase-locked loop based on a comb filter. According to the phase-locked loop, a moving average filter in a traditional phase-locked loop is replaced by thecomb filter; the comb filter has a plurality of zero poles at non-origin positions. The distance among the zero poles is relatively low. When a signal frequency deviates from a zero frequency, signalsare hardly influenced due to mutual cancellation effect among the zero poles, so the phase lag at the position of the zero frequency can be effectively compensated. The phase margin of the comb filter is greater than the phase margin of the moving average filter, so the technical problem that the phase lag exists at the position of the zero pole frequency of the current phase-locked loop and thephase margin of the current phase-locked loop is relatively low is solved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Low pressure difference linearity voltage stabilizer for enhancing performance by amplifier embedded compensation network
InactiveCN100527039CImprove performanceIncrease low frequency gainElectric variable regulationLinear regulatorCapacitance
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +2
Ultrasonic amplitude-change pole with frequency modulation sucker
ActiveCN112427283APrevent looseningImprove adsorption capacityMechanical vibrations separationMagnetic holding devicesUltrasonic machiningEngineering
The invention relates to an ultrasonic amplitude-change pole, in particular to an ultrasonic amplitude-change pole with a frequency modulation sucker. The problem that stable frequency modulation is difficult to achieve through a traditional ultrasonic amplitude-change pole frequency modulation technology is solved. The ultrasonic amplitude-change pole with the frequency modulation sucker comprises an ultrasonic amplitude-change pole body and further comprises the frequency modulation sucker. The frequency modulation sucker comprises a cylindrical magnetic conductive sleeve, a cylindrical yoke, M arc-groove-shaped permanent magnets, M arc-groove-shaped electromagnets, a cylindrical shell, a circular-ring-shaped top cover and a circular-ring-shaped bottom cover, and M is a positive integerand is greater than or equal to 2, wherein a cylindrical section of the ultrasonic amplitude-change pole body faces upwards, and two symmetrical guide grooves are formed in the side face of the cylindrical section of the ultrasonic amplitude-change pole body in the axial direction; and the lower ends of the two guide grooves are closed, and the upper ends of the two guide grooves penetrate throughthe upper end face of the cylindrical section of the ultrasonic amplitude-change pole body. The ultrasonic amplitude-change pole is suitable for ultrasonic machining.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com