Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
260results about How to "Increase mass flow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
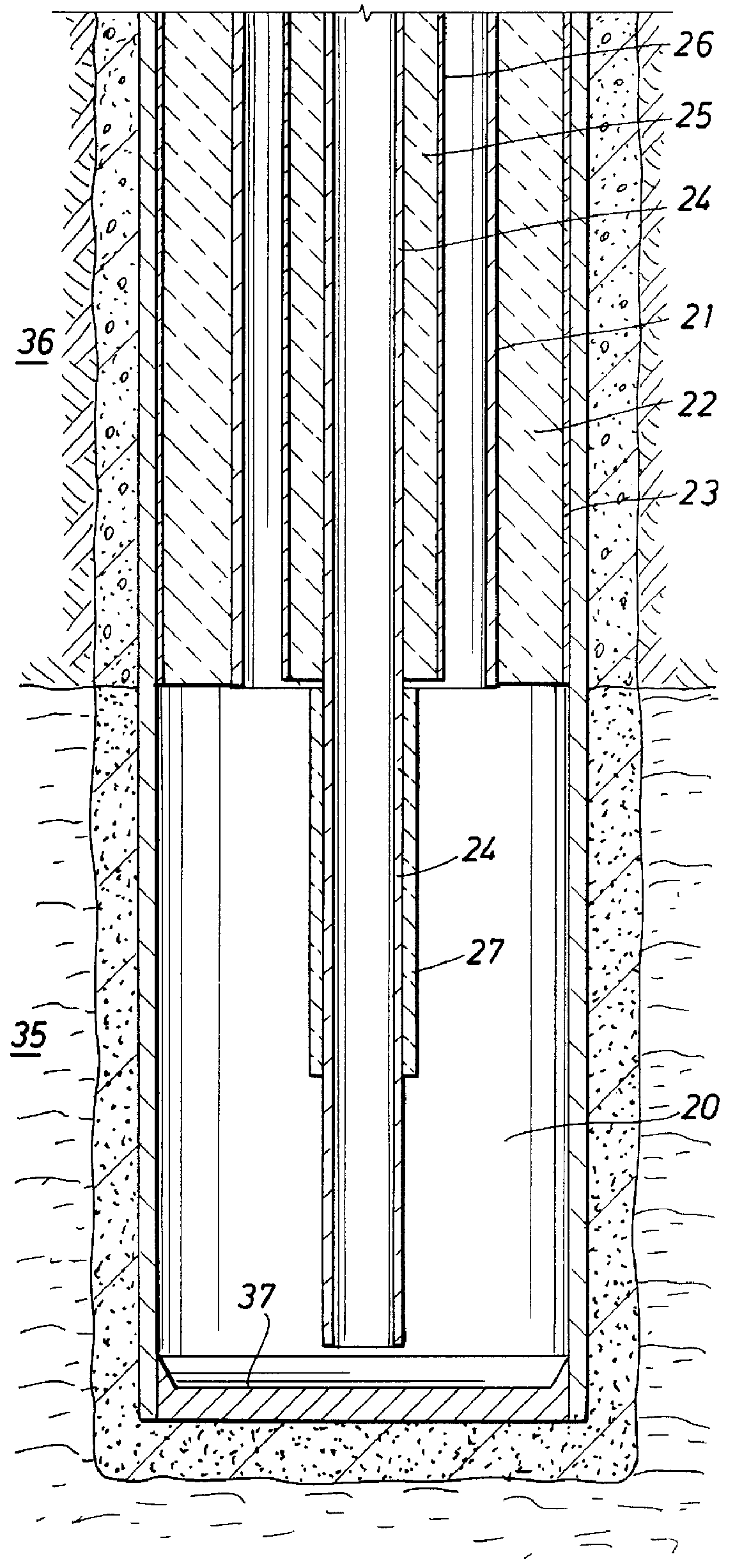
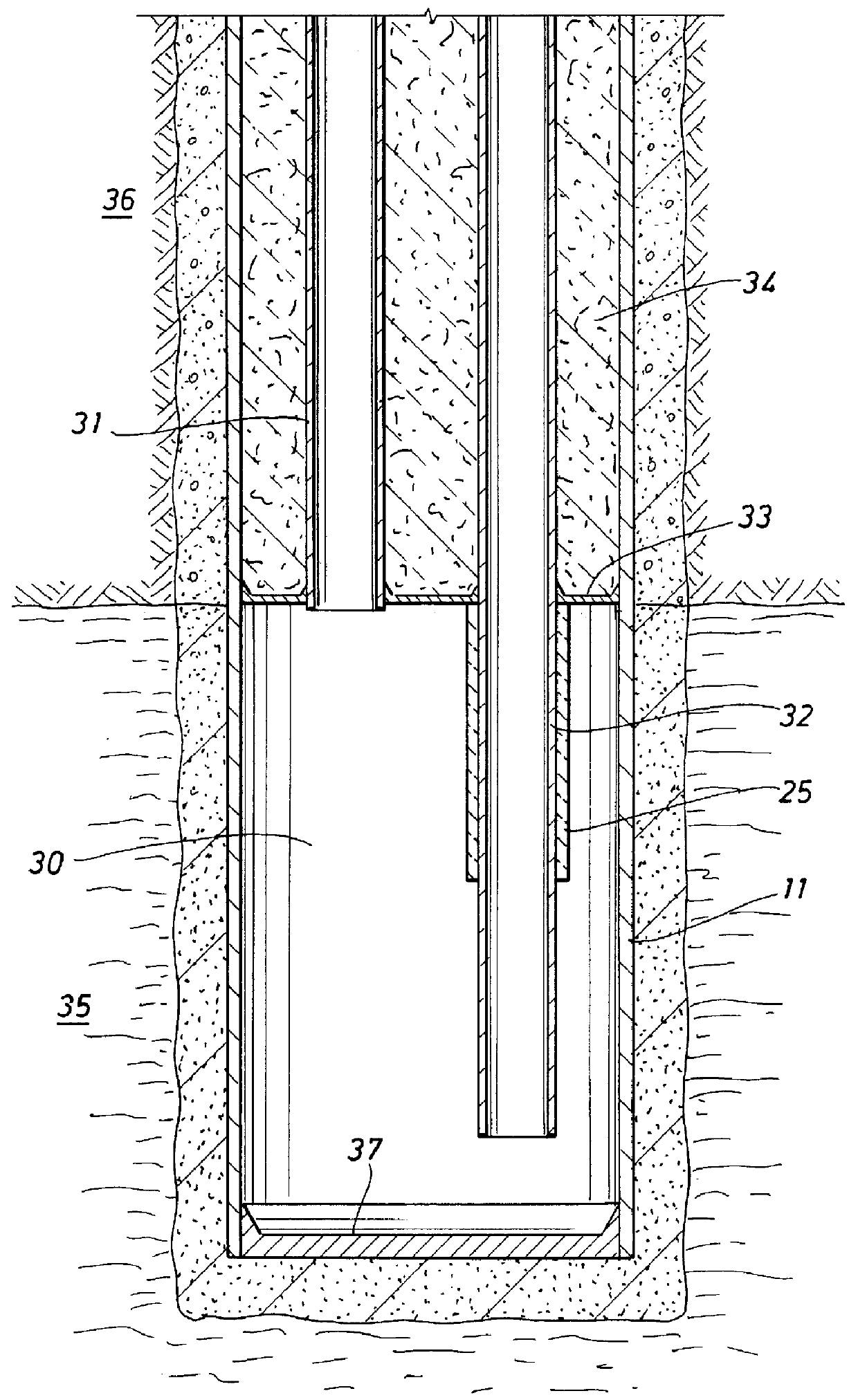
Heater well method and apparatus
InactiveUS6079499AImprove efficiencyImprove completenessInsulationFluid removalGeomorphologyWellbore
A method and apparatus is disclosed for heating of formations using fired heaters. The method includes the steps of: providing a wellbore within the formation to be heated, the wellbore comprising a casing within the formation to be heated, a tubular defining, in the inside of the tubular, a flowpath for hot gases from the surface to a point in the wellbore near the bottom of the formation to be heated, and a volume between the tubular and the casing providing a flowpath for hot gases from near the bottom of the formation to be heated to the top of the formation to be heated, wherein the flowpaths are in communication with each other near the bottom of the formation to be heated and the volume between the casing and the tubular at the top of the formation to be heated is in communication with a point above the surface, and insulation for a portion of the length of the wellbore within the formation to be heated between the flowpath for hot gases from the surface to the point in the wellbore near the bottom of the formation to be heated and the flowpath for hot gases from near the bottom of the formation to be heated to the surface; and supplying a flow of hot gases to the flowpath for hot gases from the surface to a point in the wellbore near the bottom of the formation to be heated.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
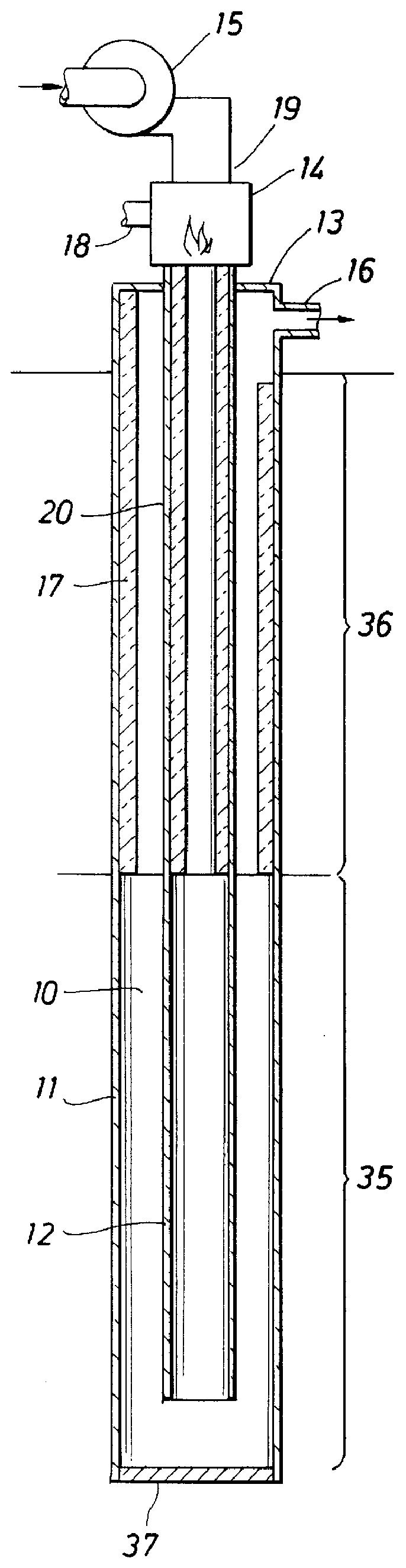
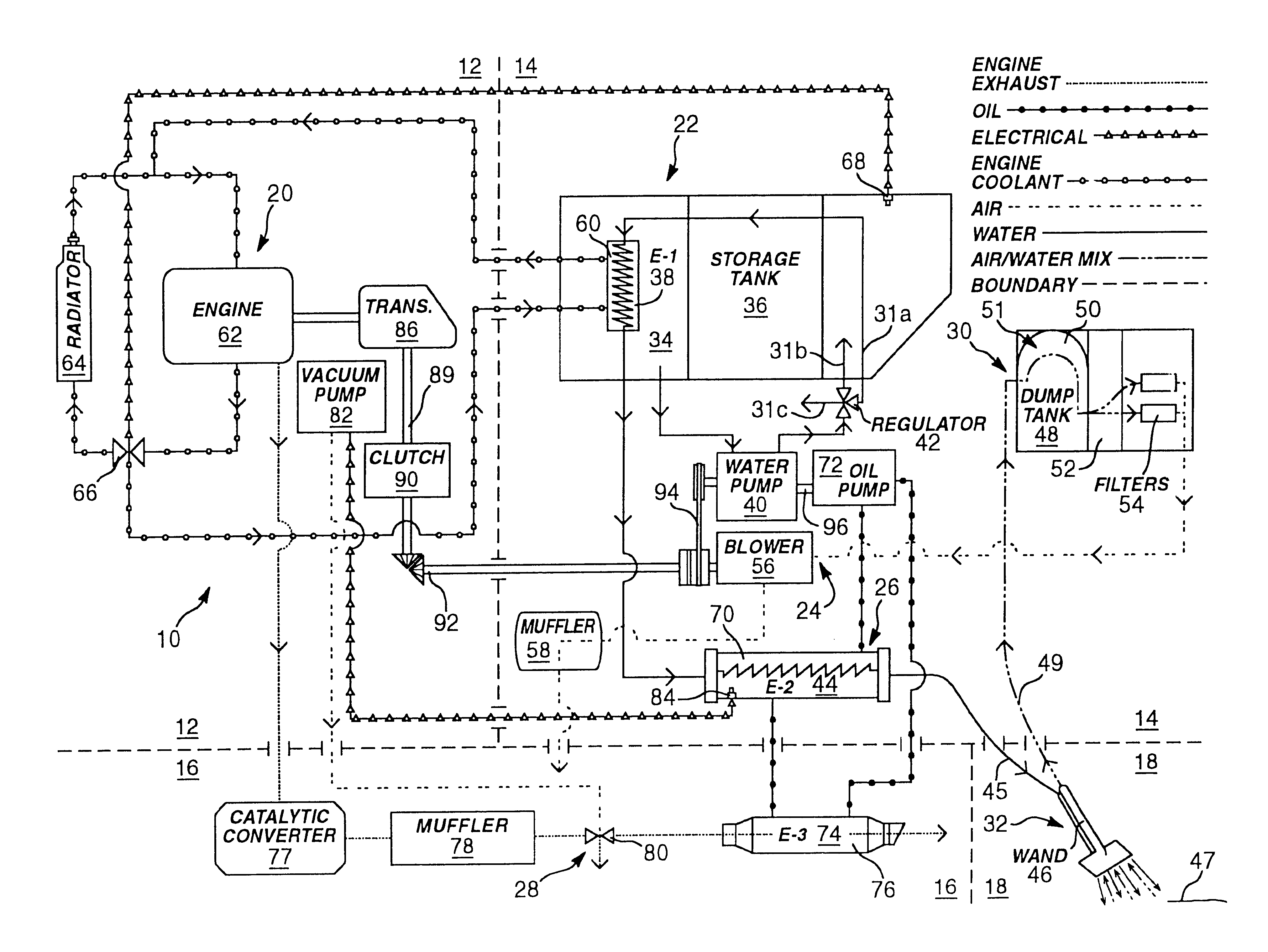
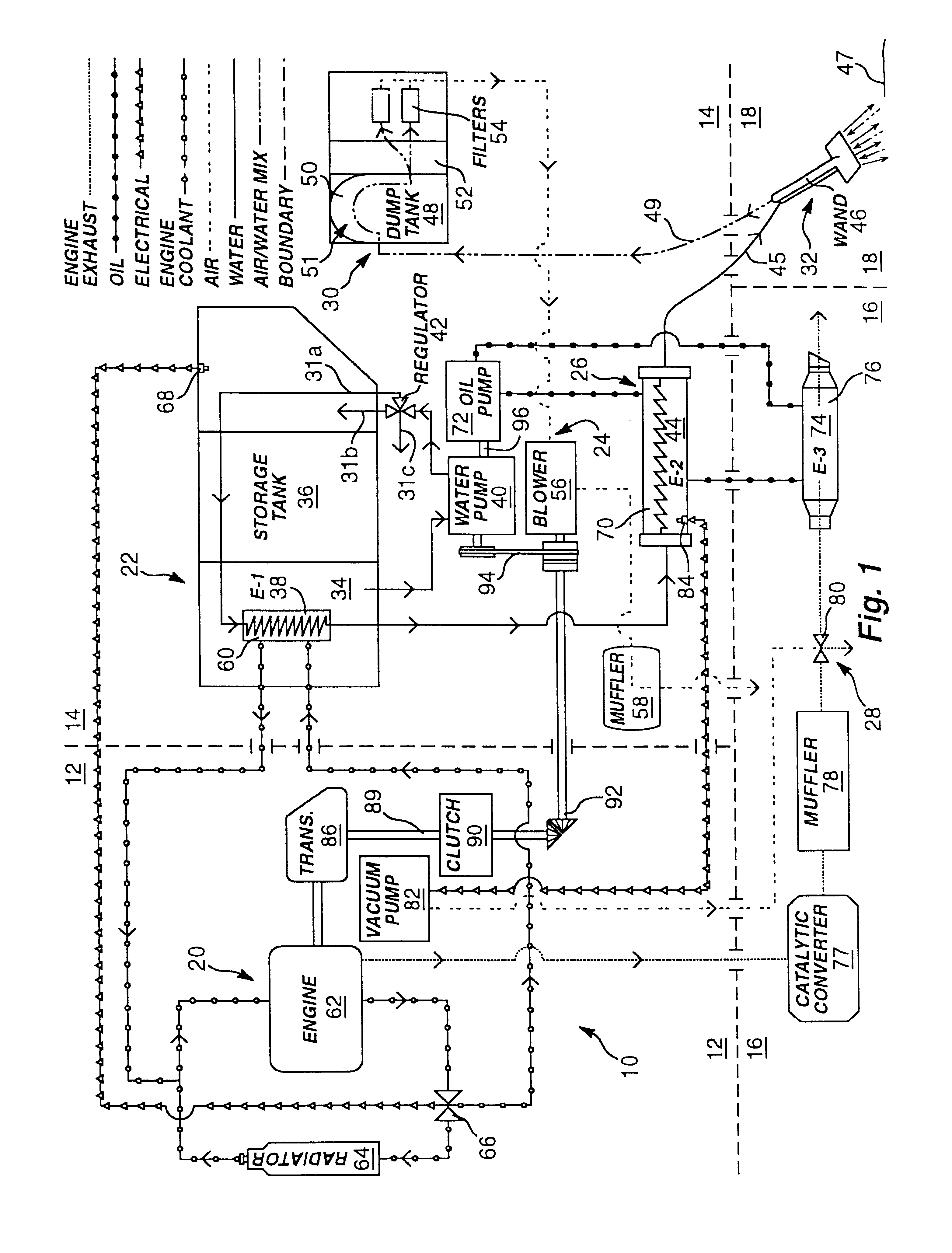
Portable high-temperature, high-pressure washing plant
InactiveUS6675437B1Reliable outputIncrease temperatureInternal combustion piston enginesRecuperative heat exchangersProcess engineeringThermal contact
A washing system for high temperature cleaning applications, such as carpet-cleaning, is disclosed that provides a consistent cleaning fluid temperature. The washing system utilizes multiple heat exchangers and multiple heat paths. The heating and power source is provided by a medium duty, diesel cycle engine. Multi-stage heating involves heat transfer from the engine's coolant to the cleaning fluid and heat transfer from the exhaust of the engine to the cleaning fluid via an intermediate medium. The system also includes a fluid clutch used to engage a power takeoff from the engine to operate the pump and blower of the washing plant. A failsafe source cutoff diverts the exhaust flow from thermal contact with an intermediate heat transfer oil.
Owner:BLUE LINE EQUIP
Method for utilizing gas reserves with low methane concentrations and high inert gas concentrations for fueling gas turbines
InactiveUS6907737B2Improve flammabilityLow costSolidificationLiquefactionProcess engineeringCurrent technology
The invention is directed to a method of fueling gas turbines from natural gas reserves with relatively low methane concentrations. The invention uses such reserves to generate electric power. The invention permits the use of these reserves at significantly lower cost than by producing pipeline natural gas to fuel gas turbines to generate electric power. These reserves currently generally are used only after the removal of impurities to produce pipeline natural gas quality turbine fuel. The latter current technology is capital intensive, and at current natural gas prices, economically unattractive. The process of the invention can remove the impurities from the gas from the natural gas reserve necessary for protection of the environment, and leaves inert gasses in the fuel in an amount which will increase the output of a gas turbine for the generation of power by about 5 to about 20%.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6595183B1Increase mass flowIncrease torqueValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust valveTop dead center
A multicylinder internal combustion engine with an exhaust-driven turbocompressor and with a divided exhaust flow has at least two exhaust valves and one intake valve per cylinder. A first exhaust valve is connected to a first exhaust manifold which leads to the turbine of the compressor, while a second exhaust valve is connected to a second exhaust manifold which opens downstream of the turbine. In the top dead center position of the piston, the second exhaust valve and the intake valve are open at the same time for a period. The synchronization between these valves is such that the length of the period during which they are open together increases with the engine speed when the engine is driven at high load. In this way, the possibilities are improved of the engine providing good torque over a wide engine speed range.
Owner:SAAB AUTOMOBILE AB
Triple Cycle Power Plant
InactiveUS20080034727A1High power outputQuality improvementGas turbine plantsSteam engine plantsPower stationNuclear engineering
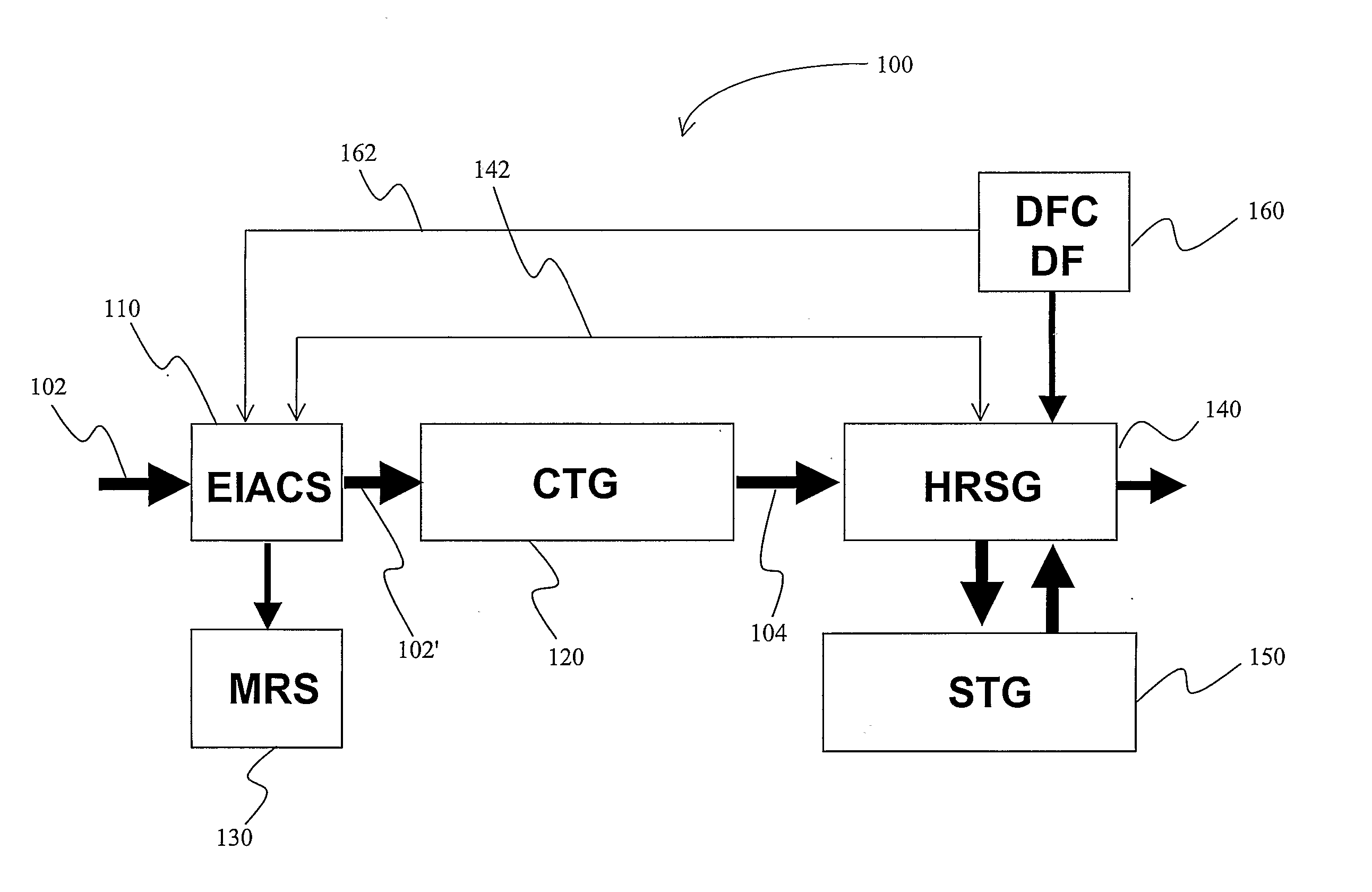
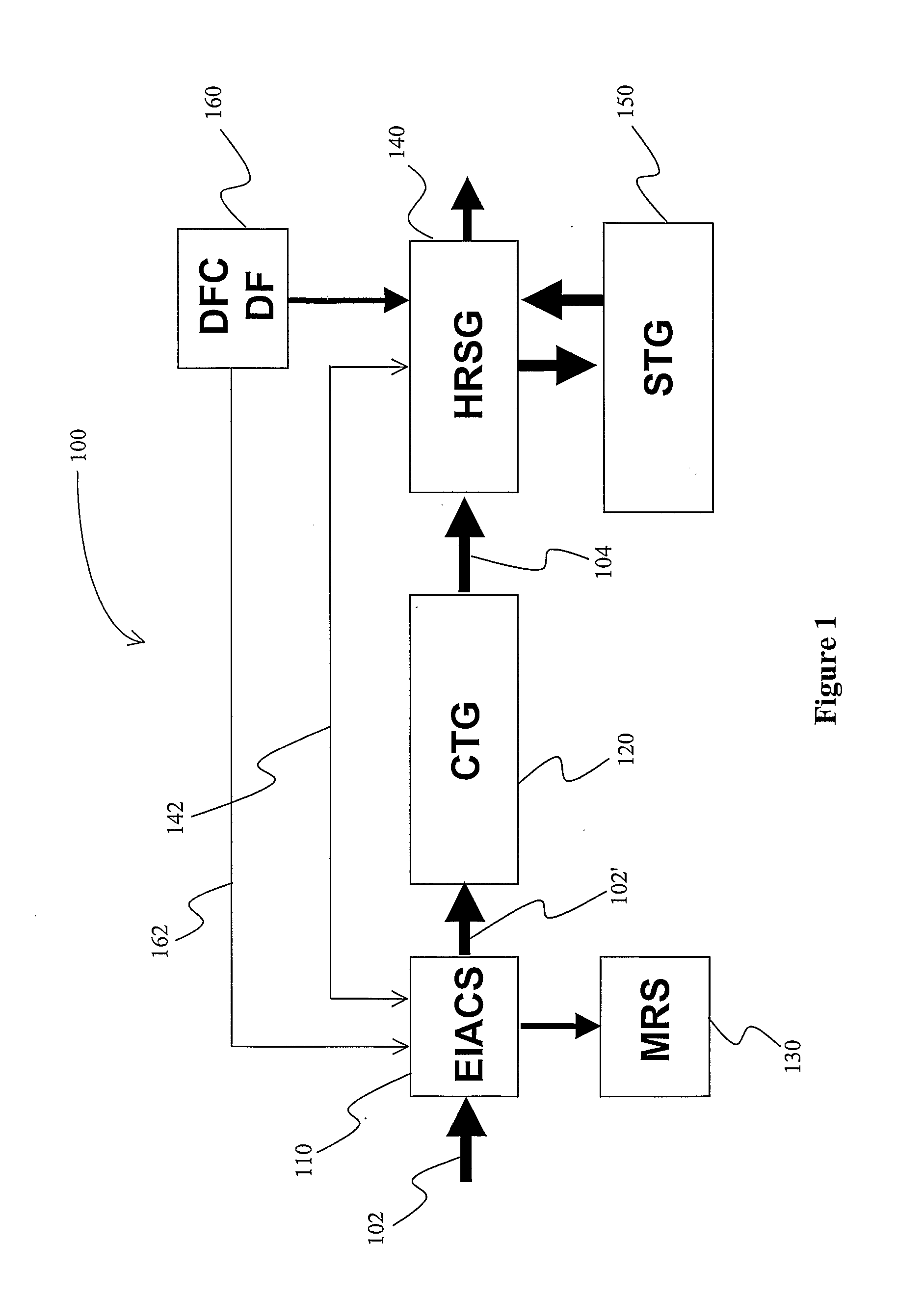
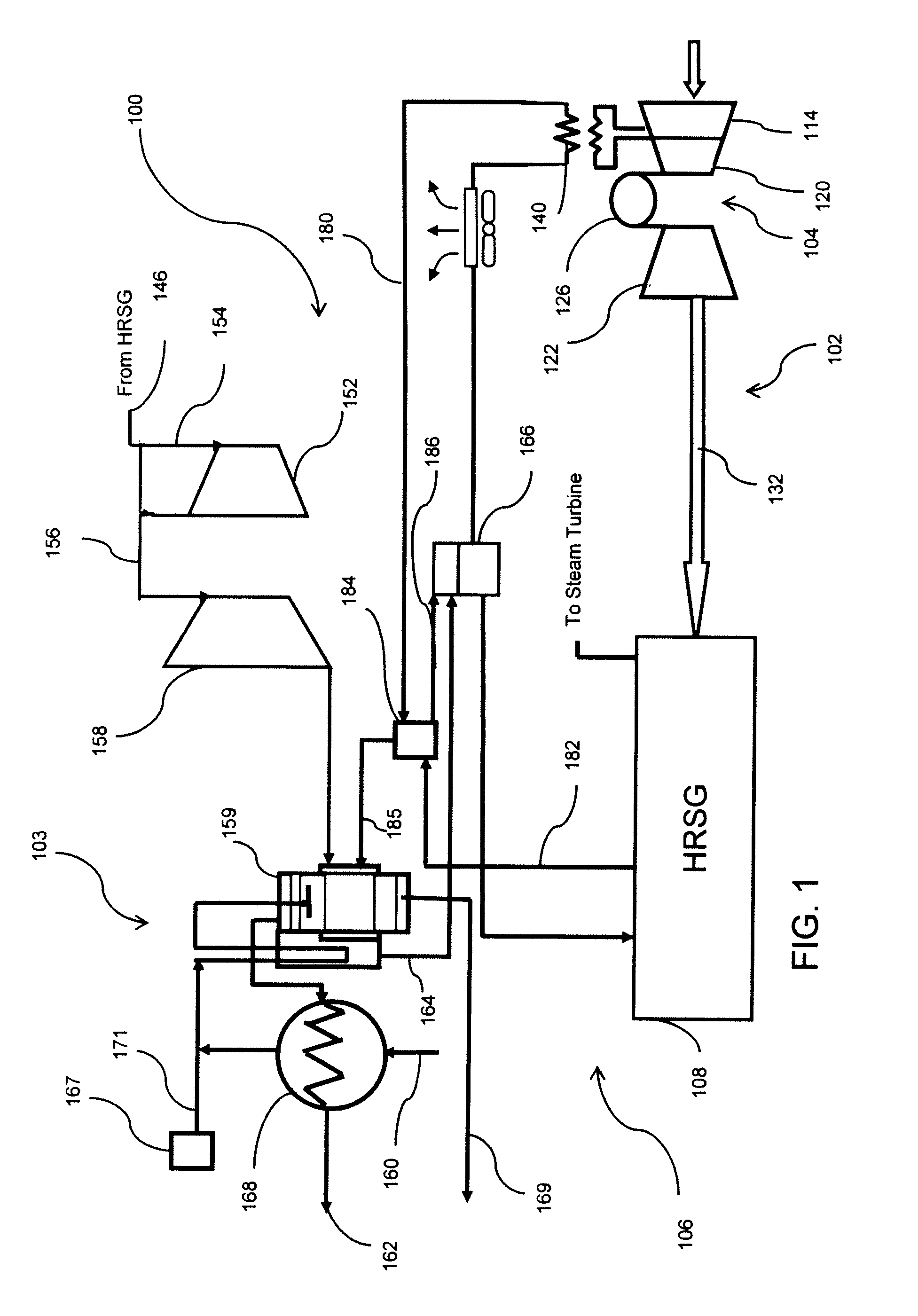
Abstract: A refrigeration cycle is integrated into a combined cycle power plant to form a triple cycle power plant in which gas turbine generator inlet air is chilled and dehydrated to increase the mass flow of the inlet air, and in which duct firing in HRSG is increased in dependence of the increased mass flow. In further preferred integration aspects, the heat from the inlet chiller refrigerant is provided to the HRSG.
Owner:FLUOR TECH CORP
Waste heat driven desalination process
InactiveUS20110147195A1Improved power generationIncrease massDrying using combination processesGeneral water supply conservationHeat recovery steam generatorExhaust gas
Disclosed is a process for improving the efficiency of a combined-cycle power generation plant and desalination unit. The process includes supplying exhaust gases from a gas turbine set used to generate electrical power to a heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) and then directing the steam from the HRSG to a steam turbine set. Salinous water is supplied into an effect of the desalination unit. Steam exhausted from the steam turbine set is utilized in the effect of the desalination unit to produce a distillate vapor and brine from the effect by heat exchange. Additionally, steam is introduced steam from at least one additional heat source from the combined-cycle power generation plant to the effect to increase the mass flow rate of steam into the effect. In one embodiment, the additional heat source is an intercooler heat exchanger. Heated water from the intercooler heat exchanger is provided to a reduced atmosphere flash tank, and the steam flashed in the flash tank is provided to the effect.
Owner:BL TECH INC
Jet engine inlet-fan system and design method
InactiveUS20060179818A1Improve performanceIncrease pressureSupersonic fluid pumpsEfficient propulsion technologiesJet engineDesign methods
A supersonic aircraft engine axial fan that includes a rotating blade row having blades that receive a supersonic entry flow in the absolute frame and decelerate the flow to a lower supersonic or subsonic velocity exit flow while adding work to the flow to increase stagnation pressure. It is preferred that the lower velocity be subsonic. When the fan is combined with a suitably designed inlet, the propulsion system is compact and lighter in weight than conventional engines for supersonic aircraft.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Dual evaporator for indoor units and method therefor
InactiveUS6116048AImprove cooling effectIncrease temperatureEvaporators/condensersAir conditioning systemsEngineeringRefrigerant
A dual (or multi) sectional evaporator system comprising first and second (or more) evaporator sections capable of cooling the air supply through the evaporator. The first evaporator section is positioned upstream of the second evaporator section (second upstream of the third and so on). However, the warmest refrigerant passes through the first evaporator section and the coldest refrigerant passes through the second evaporator section (or last evaporator section if more than two sections), such that the air supply is precooled prior to reaching the second (or last) evaporator. Providing a two (or more) passes of refrigerant through the dual (or multi) sectional evaporator system increases the superheat temperature out of the first evaporator up to about 25 degrees Fahrenheit, and / or increases the mass flow of refrigerant because of the increased heat exchange efficiency provided by counterflow heat exchange. Moreover, in the preferred embodiment for an A-coil or slant coil, the second evaporator section is positioned over the top of the first evaporator section such that the second evaporator overlays the first evaporator section in order to maximize the use of available space. Also, A-coil or slant coil forms of the present invention are configured such that they include contoured cut-out shaped corner portions wherein the squared corners of the evaporators are substantially eliminated thereby eliminating the dead air flow spaces typically associated with other known evaporators. The elimination of the dead air space allows the system to operate at a lower fan speed as well as allows the system to be constructed and operate within smaller confines.
Owner:OLIVE TREE PATENTS 1 +1
Apparatus and related methods for turbine cooling
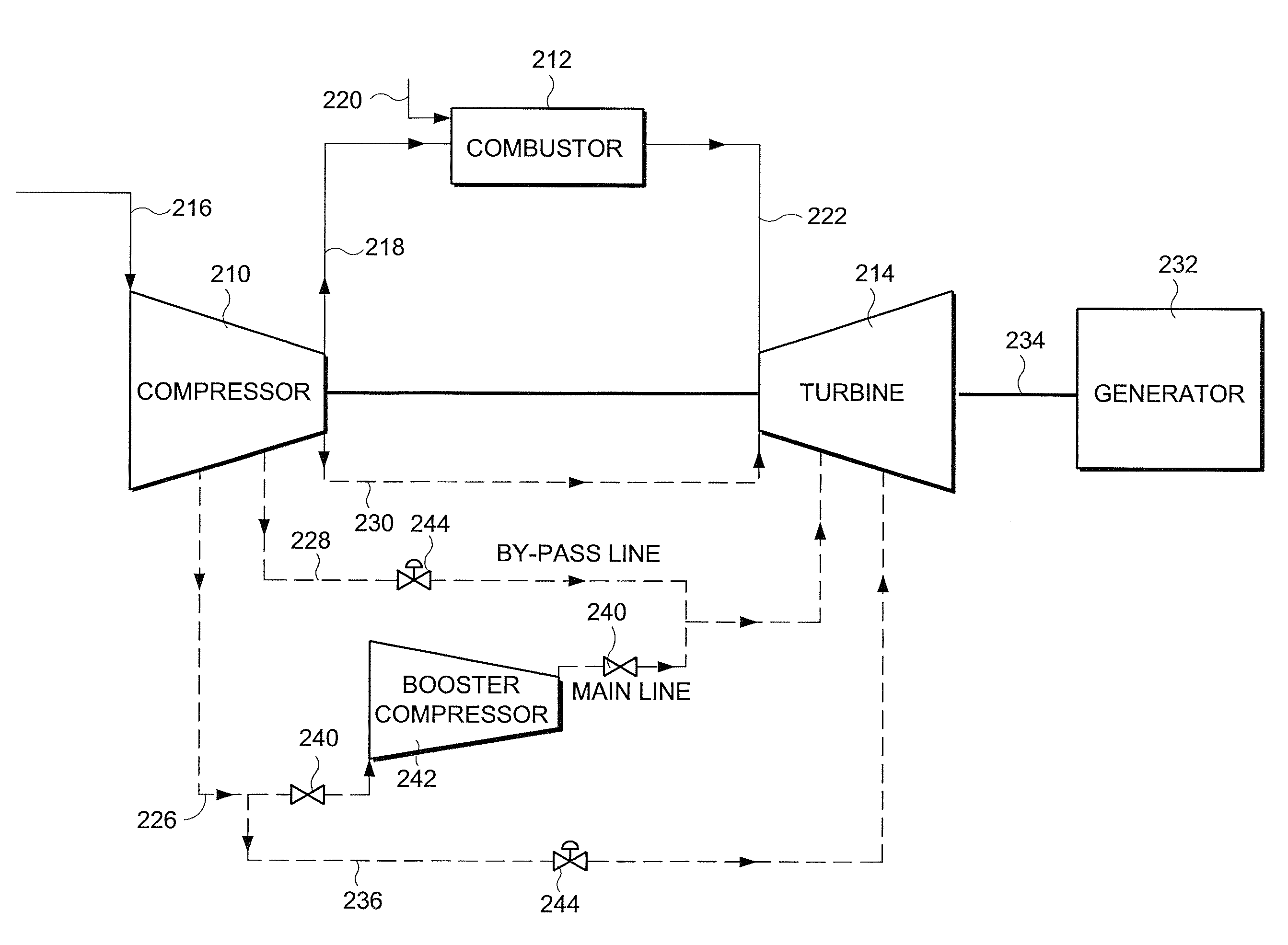
InactiveUS20090196736A1LessIncrease mass flowPump componentsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingTurbineGas turbines
An apparatus and a method for cooling and / or sealing a gas turbine by selectively boosting the pressure of air extracted at a lower extraction stage is provided. The pressure of the extracted air is boosted by an external compressor before it becomes available for cooling and / or sealing the turbine components. A bypass line includes a higher extraction stage providing air for cooling the turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method of operating an aircraft system
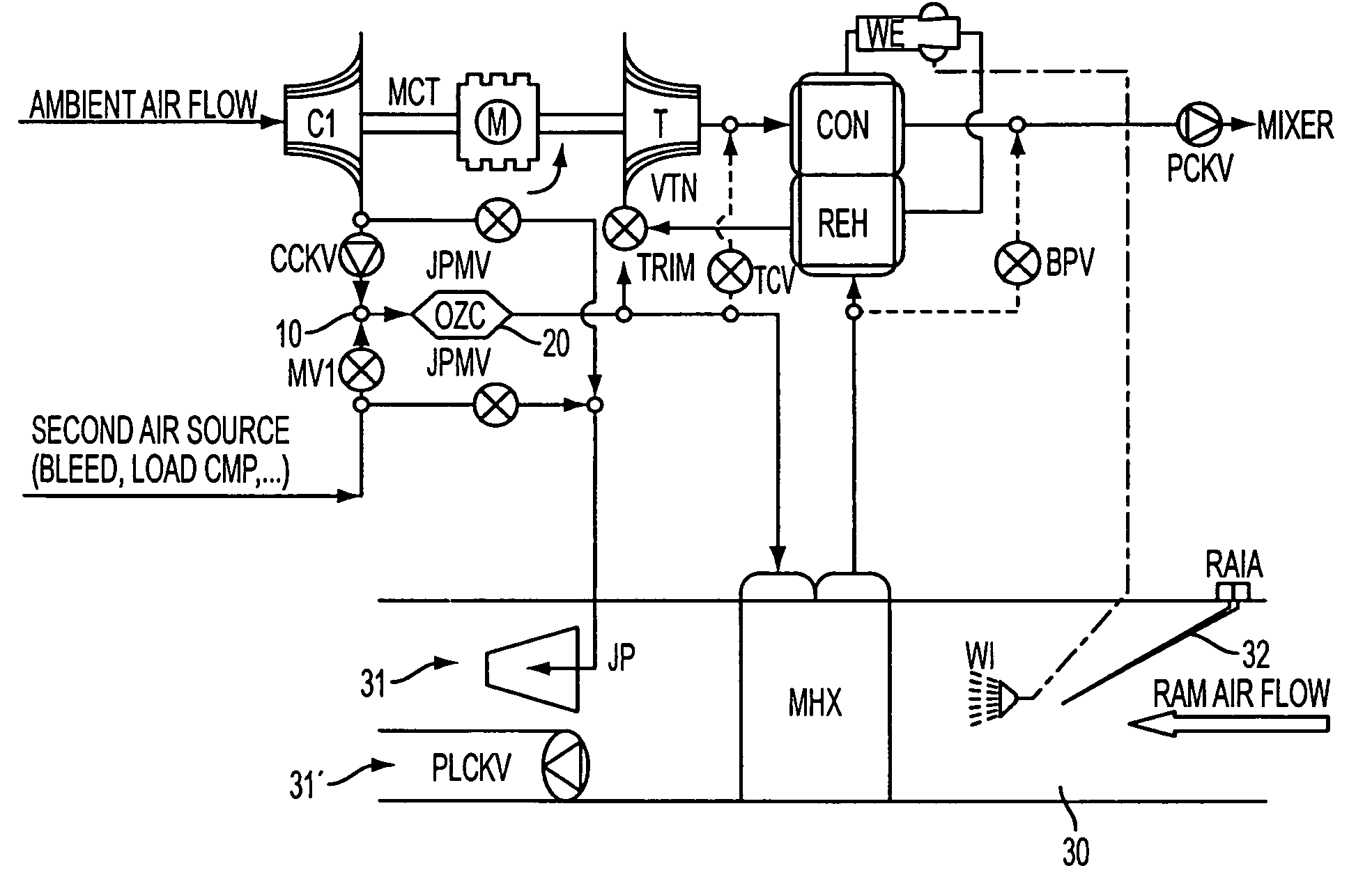
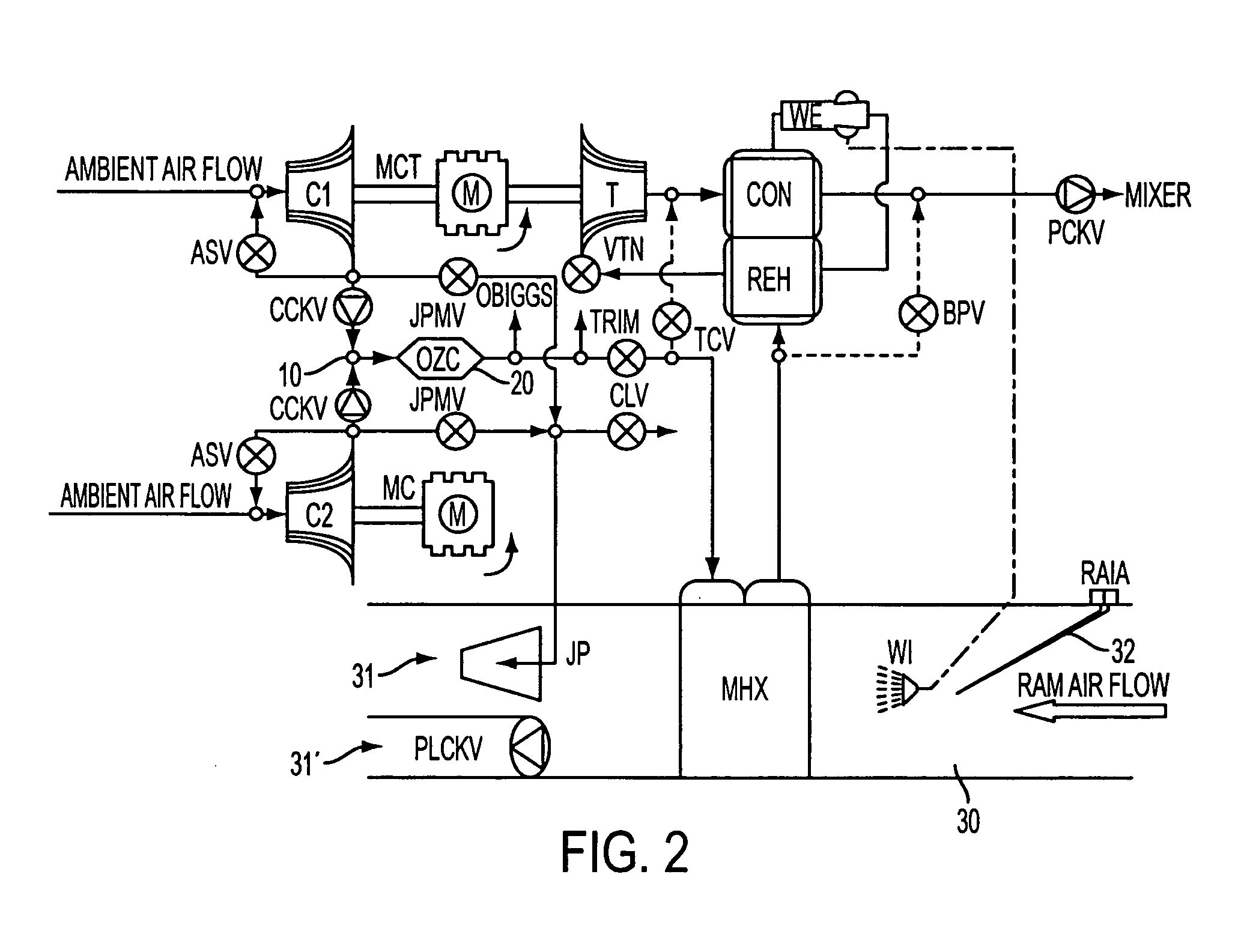
ActiveUS20090117840A1Reduced mass flowReduce capacityDomestic cooling apparatusAir-treatment apparatus arrangementsFlight vehicleOperation mode
The present disclosure relates to a method of operating an aircraft system, in particular for the purpose of fresh air supply, air-conditioning and pressurization of an aircraft cabin, having a first compressed air source formed by a first compressor charged with ambient air, ram air and / or precompressed air and driven by means of at least one motor and / or of at least one turbine and whose outlet is in direct or indirect communication with an aircraft cabin, said aircraft system having at least one second compressed air source whose outlet can be connected directly or indirectly to the aircraft cabin, wherein only the first compressed air source is in communication with the aircraft cabin in a first operating mode, wherein both the first and the second compressed air sources are in communication with the aircraft cabin in a second operating mode, and wherein the selection of the operating mode depends on the pressure of the ambient air such that the first operating mode is set at a high pressure of the ambient air and the second operating mode is set at a pressure of the ambient air lower in comparison.
Owner:LIEBHERR AEROSPACE LINDENBERG
Hydrocarbon gas conversion system and process for producing a synthetic hydrocarbon liquid
InactiveUS6130259AEliminates high capital costCost effectiveCombustion enginesGas turbine plantsLiquid productCombustion chamber
A system and process are provided for converting a light hydrocarbon gas to a synthetic heavier hydrocarbon liquid. The system includes an autothermal reformer, a Fischer-Tropsch reactor and a Brayton cycle that are structurally and functionally integrated. In the practice of the process, a mixture of a hydrocarbon feed gas, a compressed air feed and process steam is fed to the autothermal reformer to produce a synthesis gas. The synthesis gas is fed to the Fischer-Tropsch reactor where it is catalytically reacted to produce heavy hydrocarbons. The outlet from the Fischer-Tropsch reactor is separated into water, a low heating value tail gas, and the desired hydrocarbon liquid product. The water is pressurized and heated to generate process steam. The tail gas is heated and fed with compressed air and steam to the Brayton cycle having a combustor and a series of power turbines and compressors. The tail gas and air feed are burned in the combustor to produce a combustion gas that is used to drive a power turbine linked by a shaft to an air compressor, thereby driving the air compressor. The system further includes a plurality of heat exchangers that enable heat to be recovered from the outlet of the autothermal reformer. The recovered heat is used to make the process steam as well as to preheat the hydrocarbon feed gas before it is fed to the autothermal reformer, preheat the synthesis gas before it is fed to the Fischer-Tropsch reactor and preheat the tail gas before it is fed to the combustor.
Owner:REG SYNTHETIC FUELS LLC +1
Method and apparatus for producing carbon dioxide
InactiveUS6537514B1High coefficientIncrease mass flowNitrogen purification/separationCarbon compoundsIonCarbon dioxide
In a method for the production of carbon dioxide, an oxygen-containing first process gas is flowed along a cathode side of a first oxygen selective ion transport membrane. The membrane is at operating conditions effective to transport a first permeate oxygen portion from the cathode side to an opposite anode side. A carbon-containing second process gas is flowed along the anode side at a flow rate effective to provide a stoichiometric surplus of oxygen on combination with the first permeate oxygen portion. A first mixture of a second process gas and the first permeate oxygen portion is combusted such that substantially all of the second process gas is converted into a second mixture of water and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide is separated from such second mixture.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Apparatus and method for controlling fluid flows for pneumatic conveying
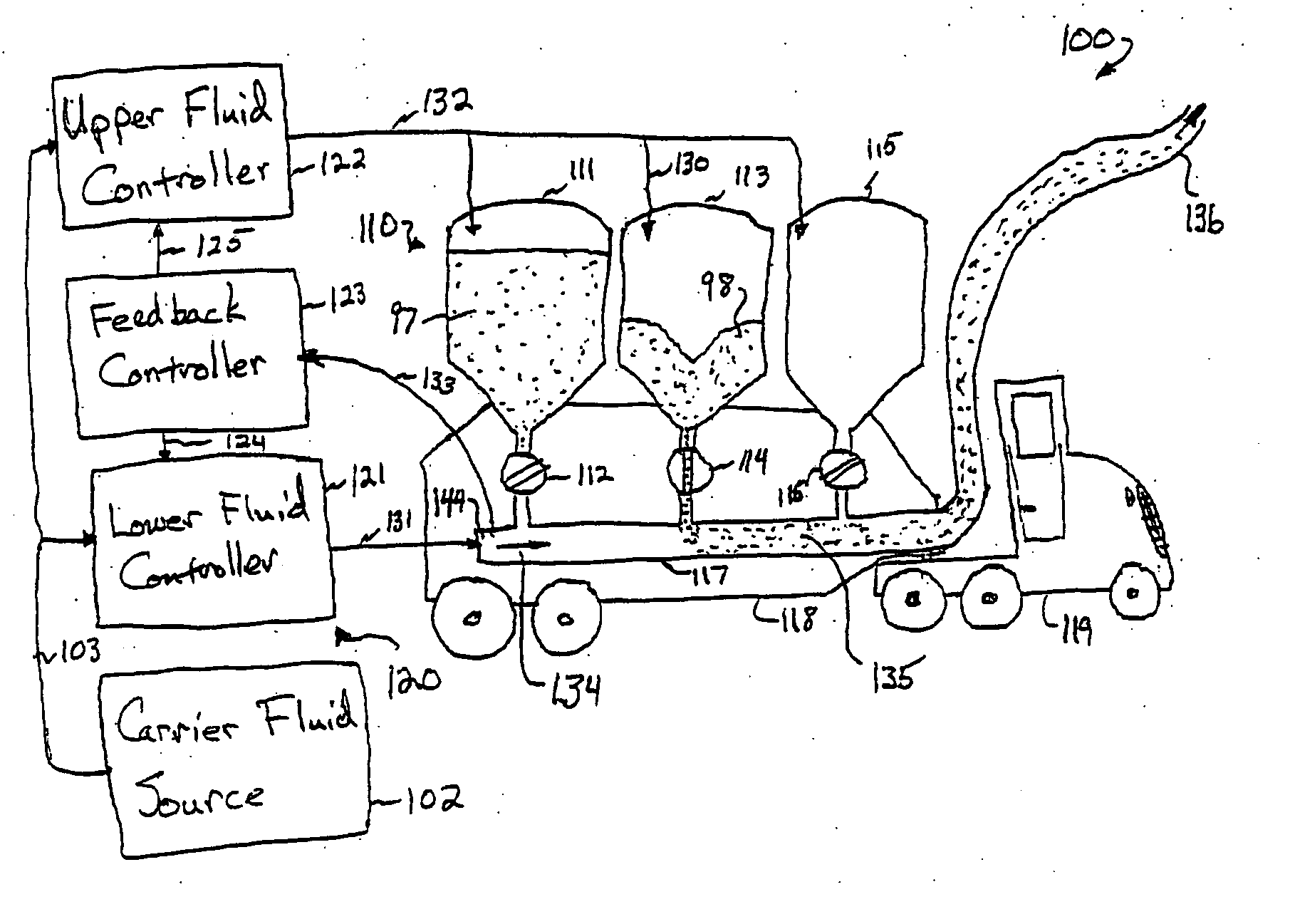
InactiveUS7101120B2Increase mass flowIncrease pressureLoading/unloading vehicle arrangmentBulk conveyorsLine tubingRotary valve
A system and method providing automatic adjustment of flows used to empty dry material from a pressure pot or hopper. In some embodiments, based on pressure increases in the conveying line that receives the dry material, the flow of conveying-fluid to the conveying line automatically increases and / or the flow of pressurization fluid to the hopper that assists pushing dry material out of the hopper automatically decreases and / or rotary-valve speed controlling dry-material rates from the hopper automatically slows. In some embodiments, one or more discretely or continuously adjustable critical-flow venturies (CFVs) automatically adjust mass flow of fluid based on, e.g., pintle position set by a pneumatic cylinder controlled by conveying-line pressure. Each pintle moves in and out of its CFV throat, adjusting throat area, thus setting the rate of flow. In some embodiments, pintle cross-sectional area is linearly proportional to distance from the tip of the pintle.
Owner:JURKOVICH JOHN C
System and method for controlling a power generating system
InactiveUS20070158947A1Fuel efficiencyLimit power outputMechanical energy handlingFree piston enginesControl theoryElectric power
This invention overcomes the disadvantages of the prior art by providing a power generating system particularly suitable for field use in remote locations, which is fuel-efficient, relatively quiet, tolerant of dust, capable of operating on low grade logistics and diesel-like fuels and capable of generating between 500 W and 2 KW of continuous electrical power. This generating system employs a two-cycle MICE generator having a piston that operates within a cylinder, and an interconnected, axially moving piston shaft that oscillates an alternator coil within a magnetic core. The piston shaft is attached to, and resisted by, the free end of a strong spring with a second, opposing end fixed to the MICE casing. To control operation of the MICE generator a dual clipper circuit is operatively connected with the alternator coil. The clipper circuit senses the current and at least two voltage levels and applies at least two respective loads in response to the sensed voltage levels and current so as to (a) prevent overstroke of the piston and (b) control power output of the alternator coil. The MICE generator also includes a fuel intake preheater that selectively heats fuel / air mixture entering the casing and a controller that senses load on the alternator coil varies a level of preheating to thereby control a level of power output.
Owner:AERODYNE RES
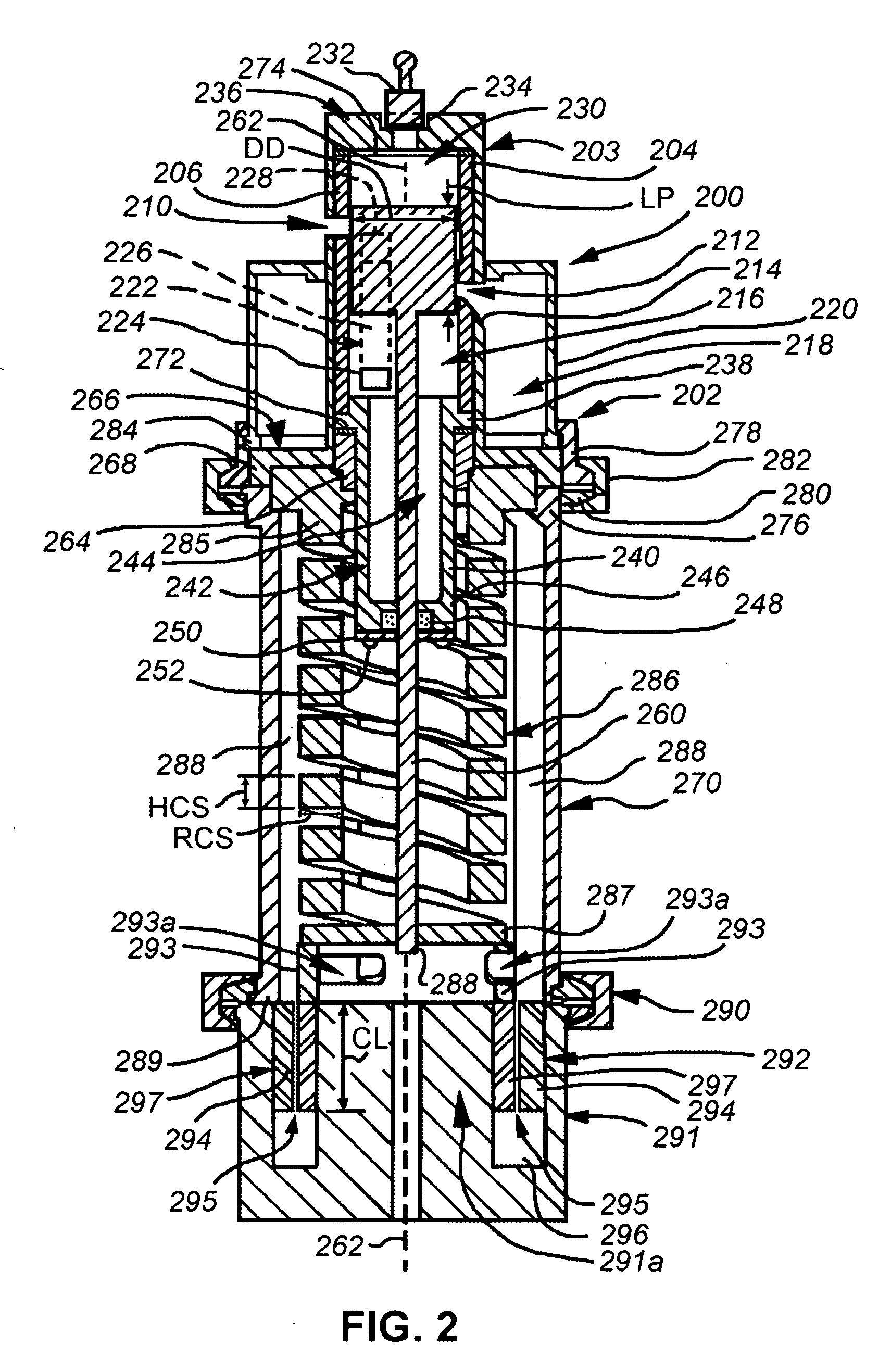
Very low temperature refrigeration system having a scroll compressor with liquid injection
ActiveUS7234310B2Improve efficiencyIncrease mass flowCompressorCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEngineeringRefrigeration
Disclosed is a very low temperature or cryogenic refrigeration system with a scroll compressor and utilizing a mixed refrigerant that decreases refrigerant discharge temperature by refrigerant injection into the compressor.
Owner:EDWARDS VACUUM LLC
Method for operating a gas turbine group
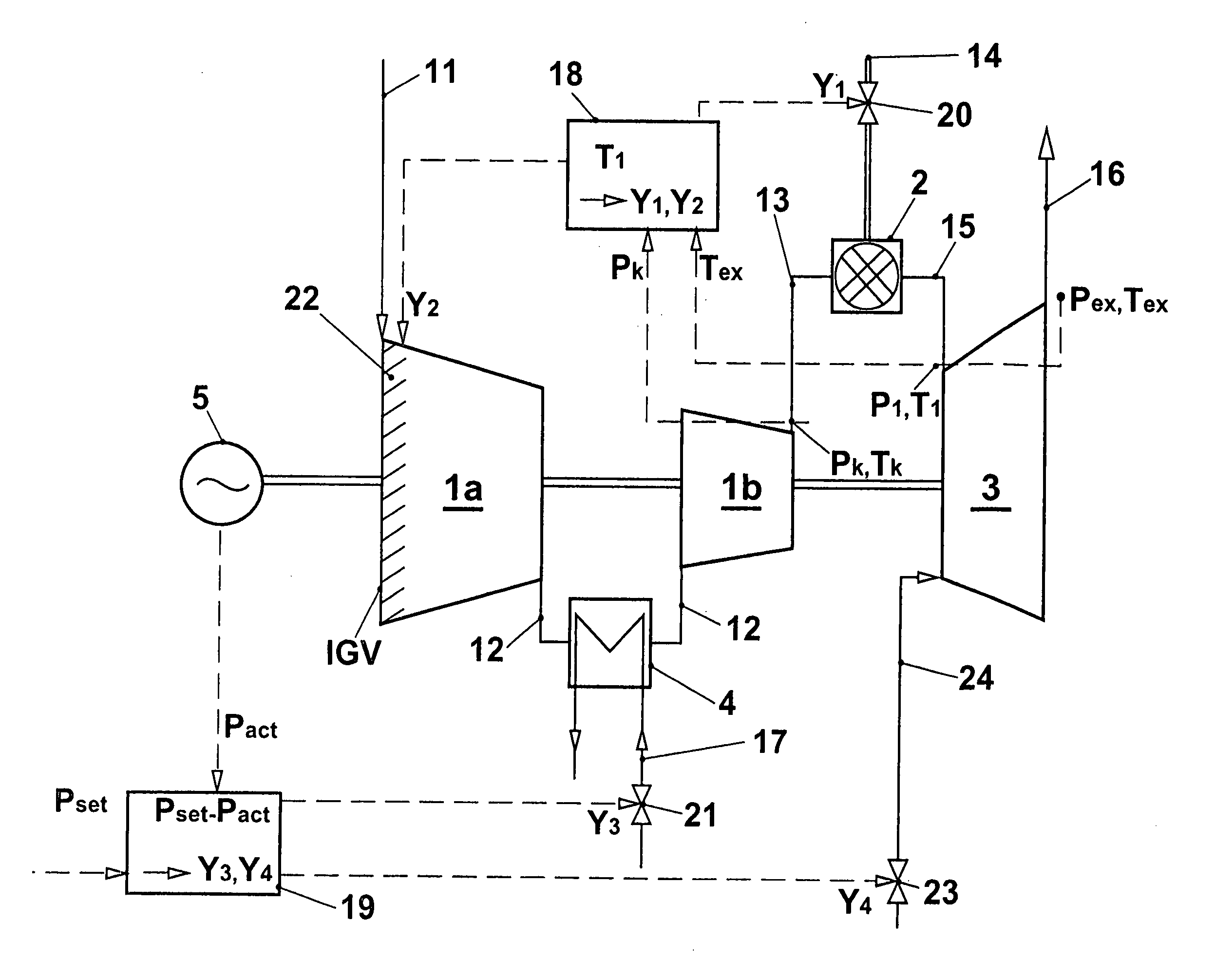
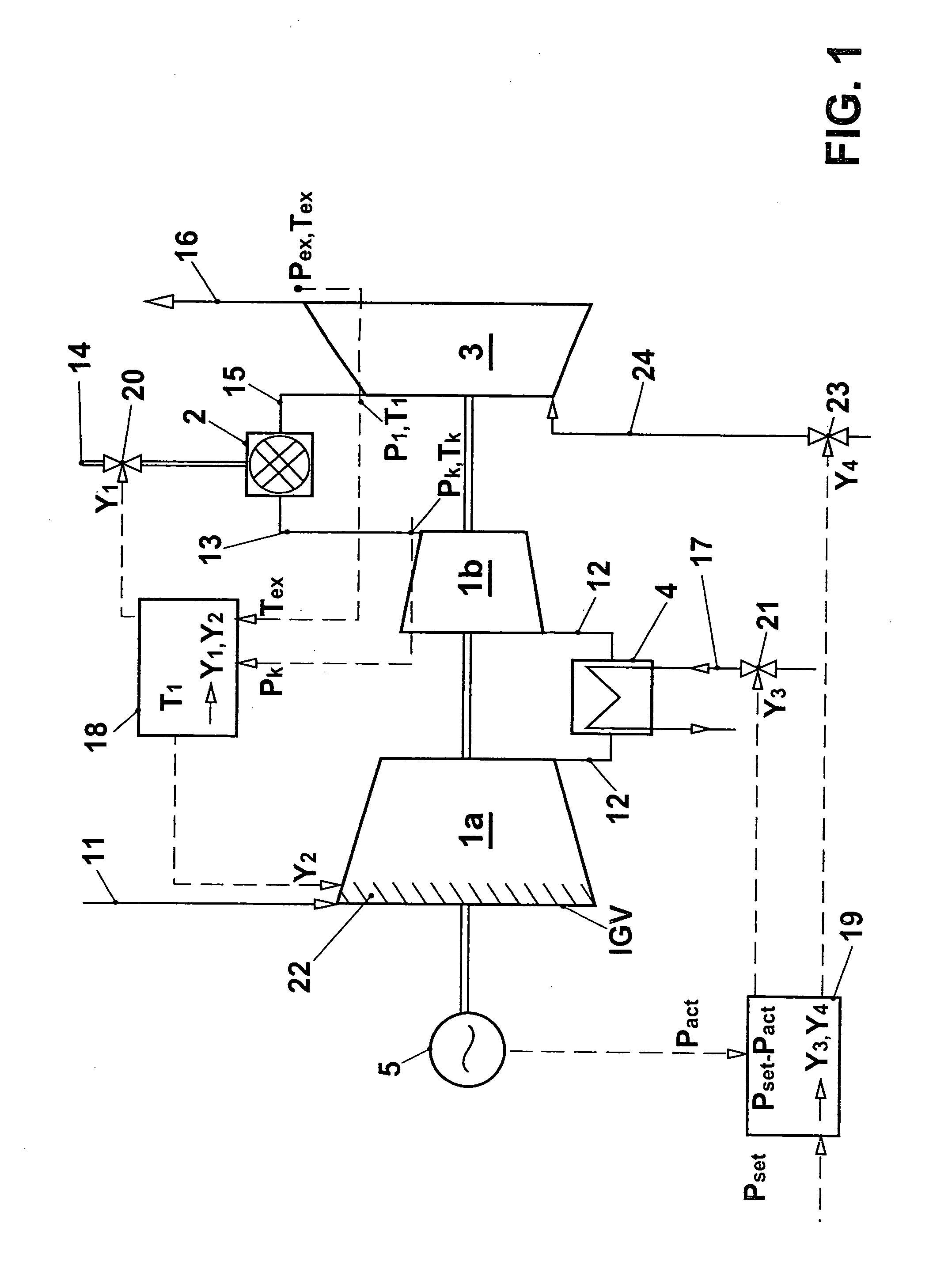
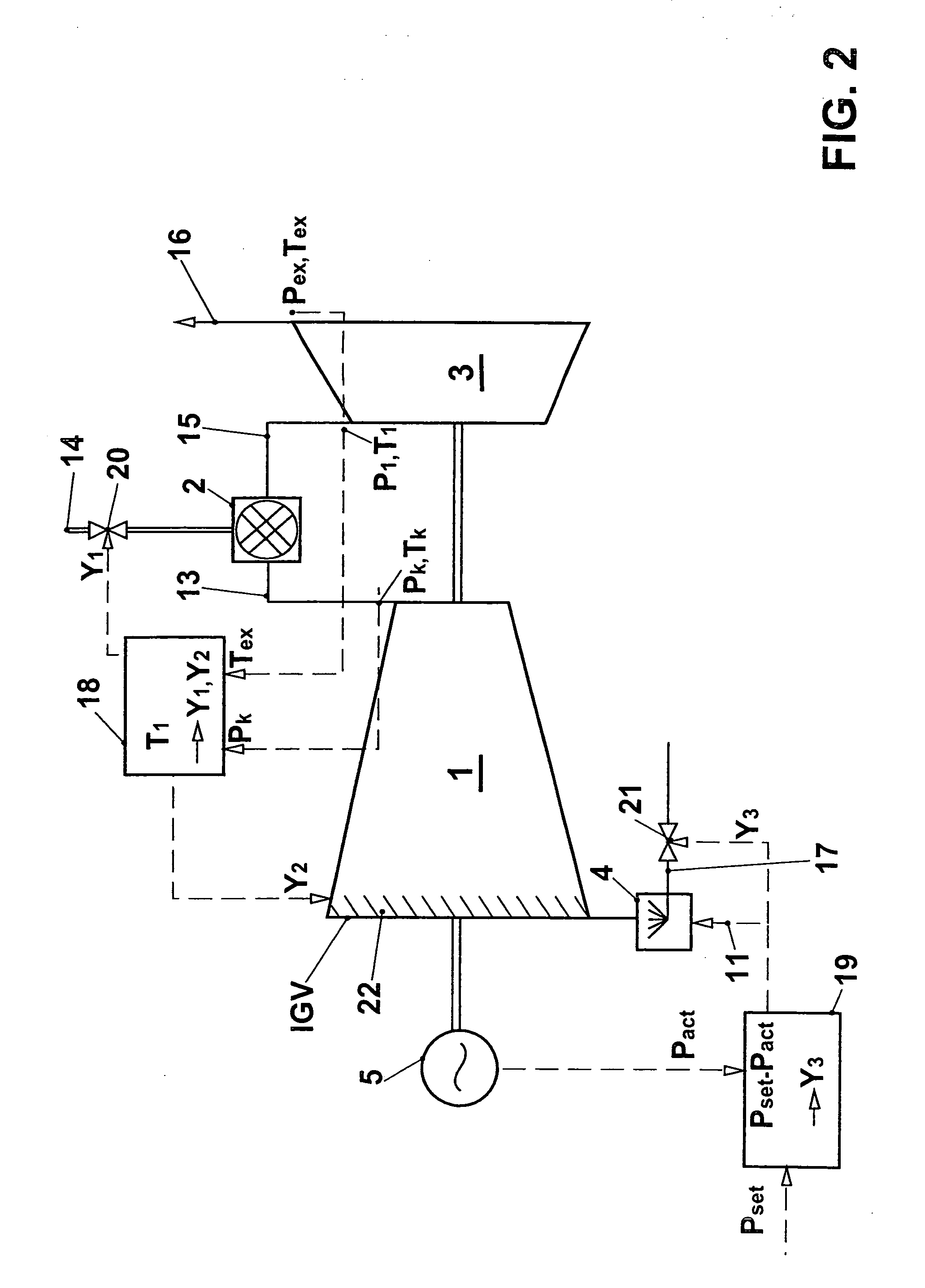
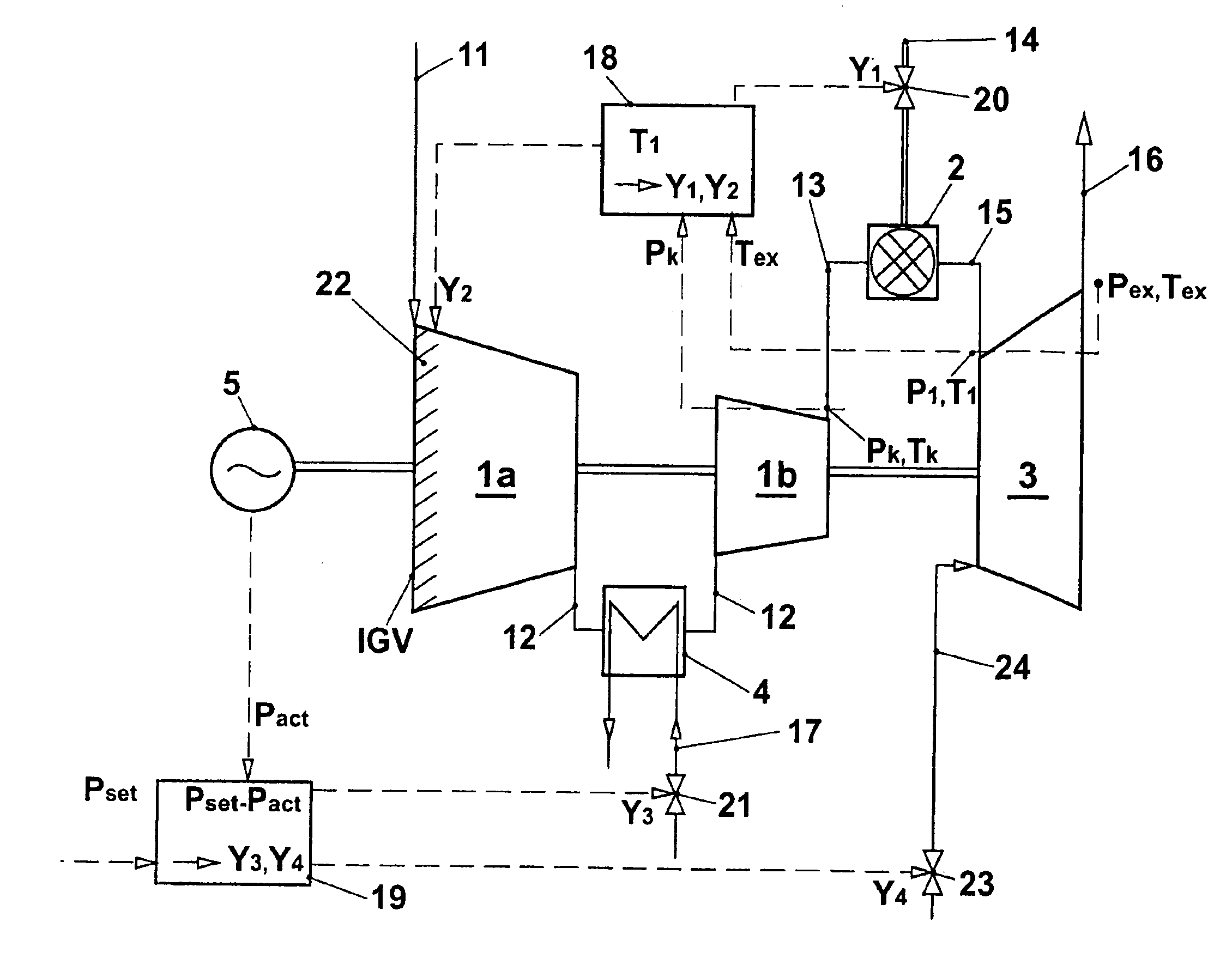
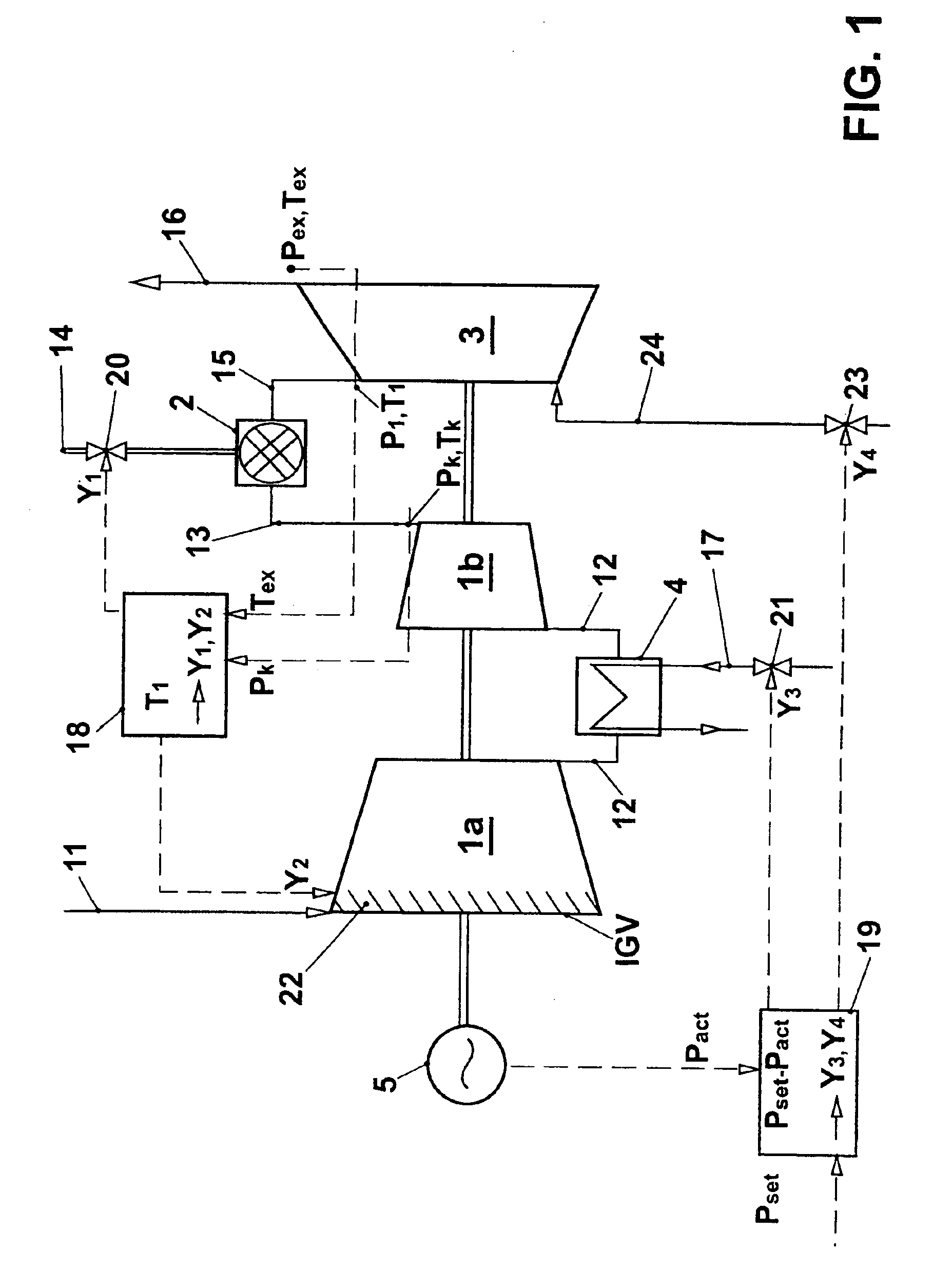
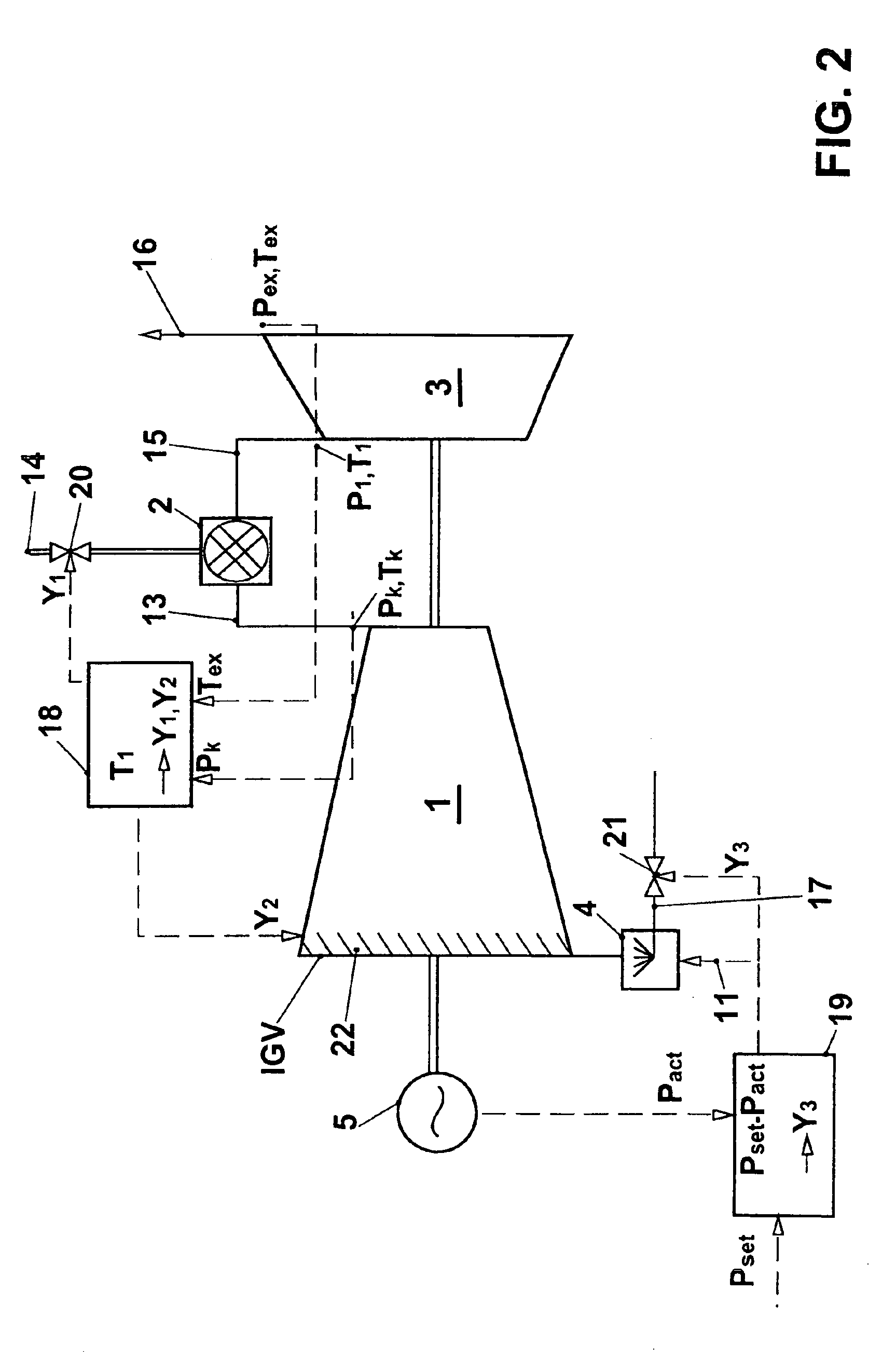
InactiveUS20050109033A1Increase powerReduces compressor outlet temperatureEngine fuctionsGas turbine plantsCooling powerLimit value
A gas turbine group is provided with at least one cooling apparatus for cooling the working medium before and / or during the compression. The cooling power of the cooling apparatus can be adjusted by suitable means. A controller controls the cooling power of the cooling apparatus as a function of a control deviation in the useful power of the gas turbine group. The cooling controller interacts with other controllers of the gas turbine group in such a way that the gas turbine group is itself always operated at least close to its full load operating state. In this context, it is preferable for the inlet guide vane row of the compressor to be maximally open, and for the hot-gas temperature on entry into the turbines to be controlled so that it is constantly at an upper limit value.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA IP UK LTD
Apparatus and method for controlling fluid flows for pneumatic conveying
InactiveUS20060056924A1Increase mass flowIncrease pressureLoading/unloading vehicle arrangmentBulk conveyorsLine tubingRotary valve
A system and method providing automatic adjustment of flows used to empty dry material from a pressure pot or hopper. In some embodiments, based on pressure increases in the conveying line that receives the dry material, the flow of conveying-fluid to the conveying line automatically increases and / or the flow of pressurization fluid to the hopper that assists pushing dry material out of the hopper automatically decreases and / or rotary-valve speed controlling dry-material rates from the hopper automatically slows. In some embodiments, one or more discretely or continuously adjustable critical-flow venturies (CFVs) automatically adjust mass flow of fluid based on, e.g., pintle position set by a pneumatic cylinder controlled by conveying-line pressure. Each pintle moves in and out of its CFV throat, adjusting throat area, thus setting the rate of flow. In some embodiments, pintle cross-sectional area is linearly proportional to distance from the tip of the pintle.
Owner:JURKOVICH JOHN C
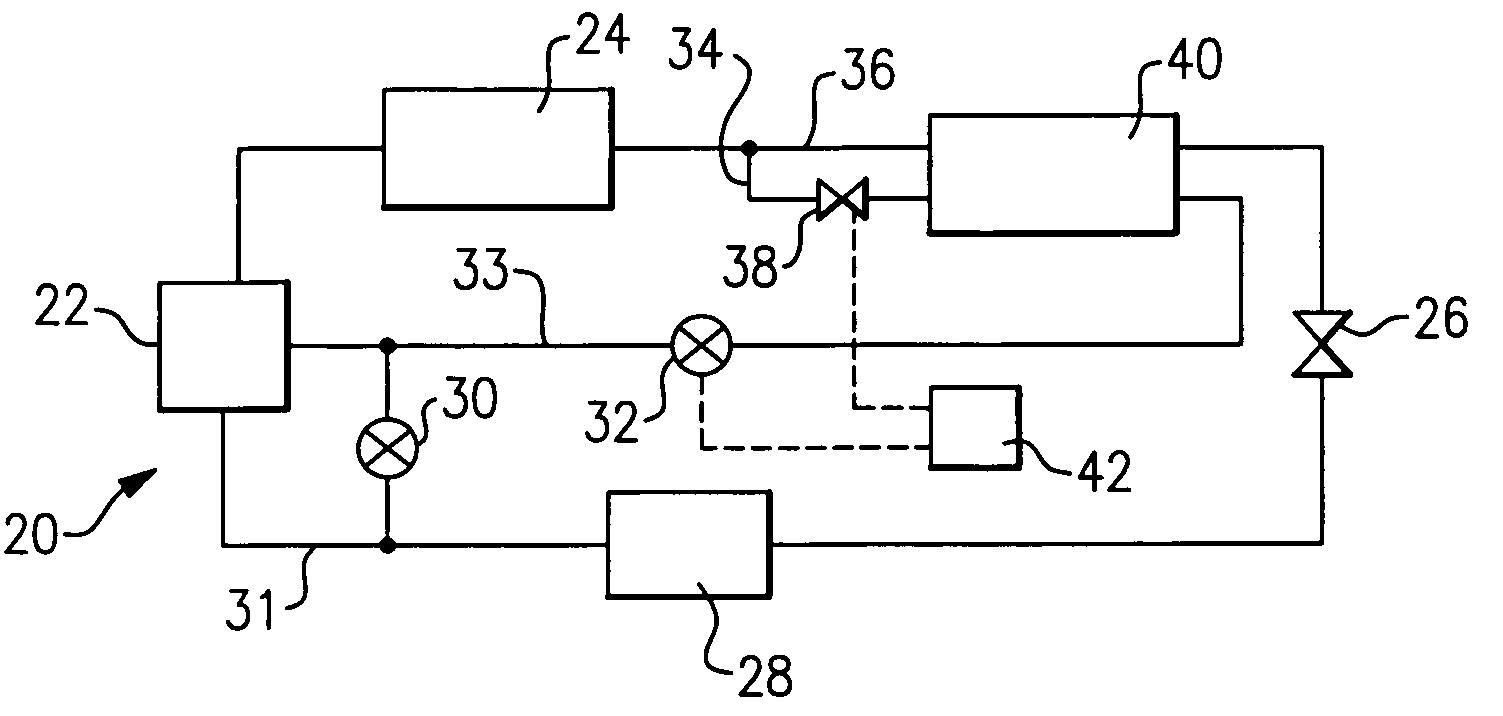
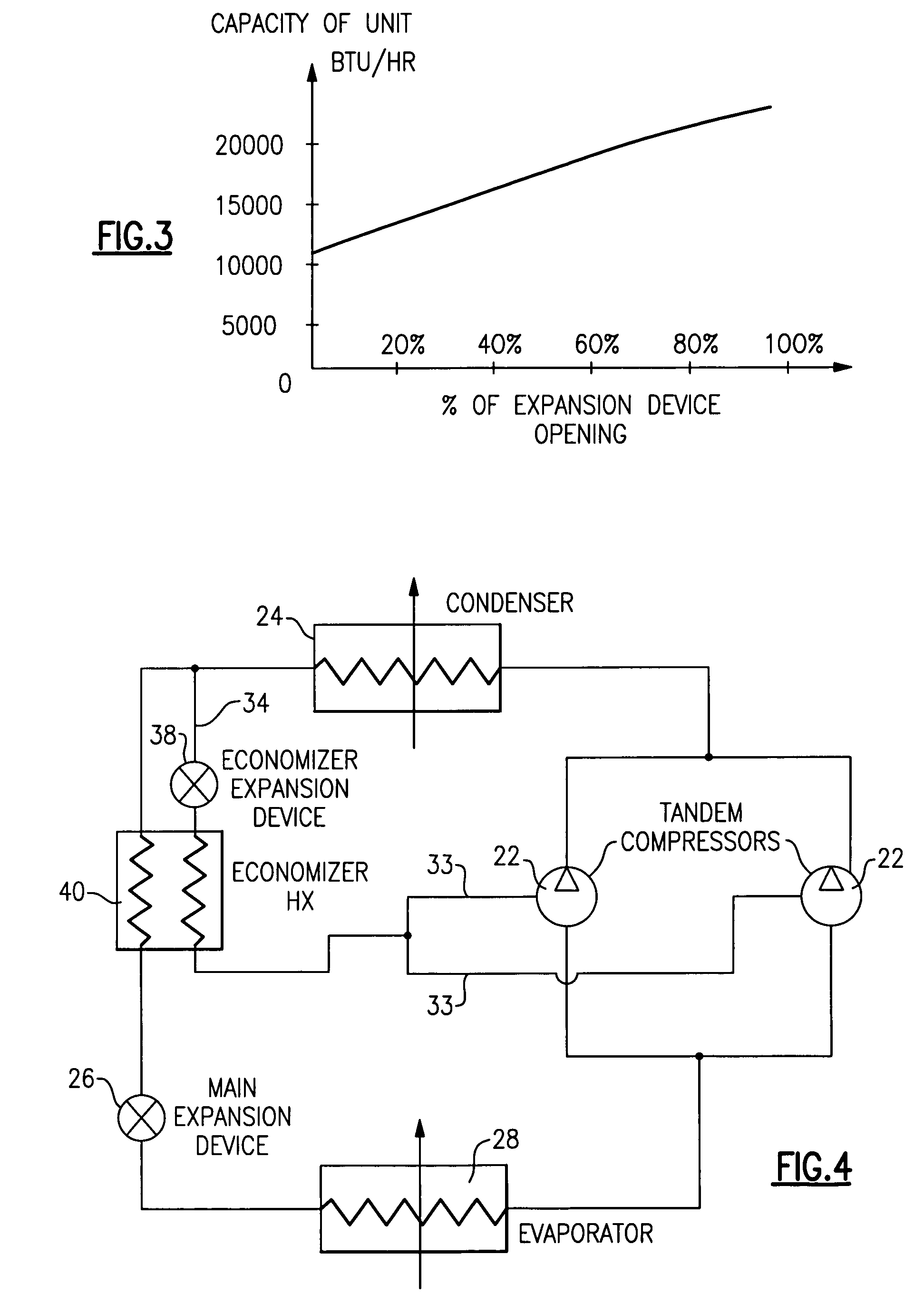
Control scheme for multiple operating parameters in economized refrigerant system
InactiveUS20050235689A1Reduce the amount requiredReduced mass flowFluid circulation arrangementRefrigeration safety arrangementTemperature controlControl theory
A refrigerant cycle is provided with an economizer circuit. The amount of refrigerant passing through the economizer circuit can be gradually modulated by an expansion device whose position can be easily adjusted from fully open to fully closed or disengaged. In the past, economizer circuits have either been fully engaged or fully disengaged. Modulation of economizer flow allows for variable capacity operation. This improves unit operating efficiency, minimizes unit cycling and prevents compressor overloading at extreme of operating conditions. It also allows for head pressure and discharge temperature control.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Oxidation-reduction active mass and chemical-looping combustion method
InactiveUS20110054049A1Maximize productionIncrease mass flowCatalytic crackingCarbon compoundsOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
The invention relates to a method for chemical-looping redox combustion on an active mass including a binder, in form of a fluidized-bed catalytic cracking catalyst containing silica and alumina, and a metal oxide active phase. The active mass is obtained by impregnating metal salts on a new or used catalytic cracking catalyst. Advantageously, the invention applies to the sphere of CO2 capture.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE +1
Method and device for reutilization of natural gas pipe network pressure energy in gas turbine working domain
InactiveCN101280723AHigh outputImprove economyTurbine/propulsion fuel heatingGas turbine plantsCold airCombustion chamber
The invention relates to a recycling method for natural gas pipe network pressure energy in the gas turbine working field and a device thereof, aiming at solving the problem of the loss of energy in the depressurization of high-pressure natural gas. The technical proposal is that the cold air flow and the hot air flow generated after the high-pressure natural gas is depressurized through a vortex tube are respectively outputted, the cold air flow after absorbing the inverse air in a heat exchanger and the heat of the exhaust gas of the gas turbine and being heated up joins with the hot air flow and enters a combustion chamber of the gas turbine set; the air cooled by the heat exchanger enters a compressor of the gas turbine set for boosting pressure and then is introduced to the combustion chamber of the gas turbine set; in the combustion chamber, the natural gas is combusted with the air to lead the gas turbine to work and drive energy-consumed equipment. The method of the invention selects the vortex tube to complete the depressurization and pressure adjustment of the natural gas and utilizes the low temperature natural gas flow to cool the intake air of the compressor to increase the mass flow of the intake air, thereby greatly increasing the output of the gas turbine and the economy and effectively utilizing the pressure energy.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Combustion system with steam or water injection
InactiveUS20100077943A1Reducing and eliminating conventional FGRReduce the amount requiredEmission preventionBoiler controlCombustion systemFlue gas
A combustion system having a furnace arranged and disposed to receive solid fuel and oxygen and combust the solid fuel and oxygen to form a flue gas. The system includes a heat exchanger arrangement arranged and disposed to receive heat from the flue gas, where the heat exchanger arrangement has a predetermined heat exchange capacity. A water injection arrangement is arranged and disposed to provide water to the flue gas to controllably adjust the flue gas mass flow rate and temperature to provide the predetermined heat exchange capacity.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Method for controlling an engine braking device and engine braking device
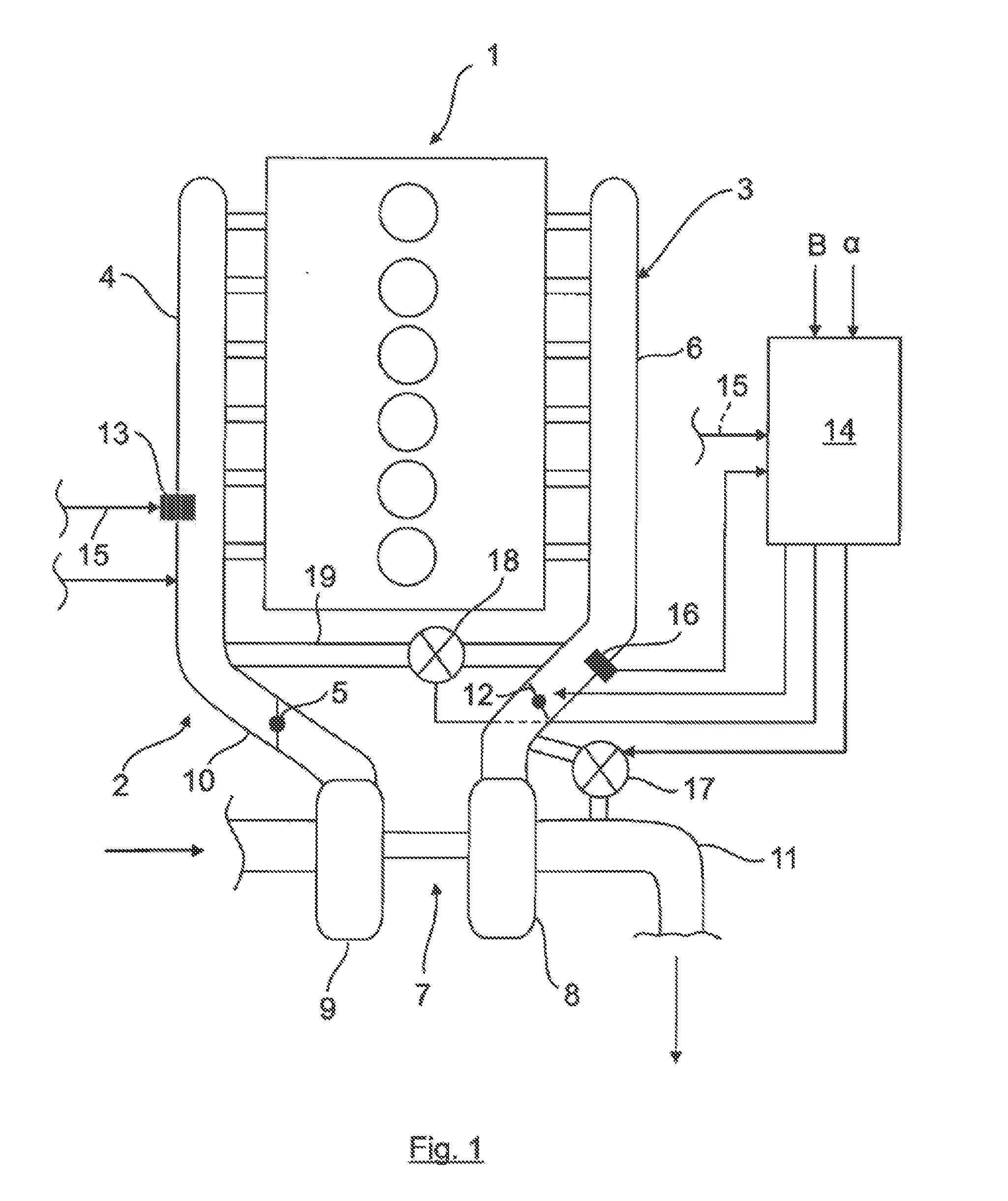
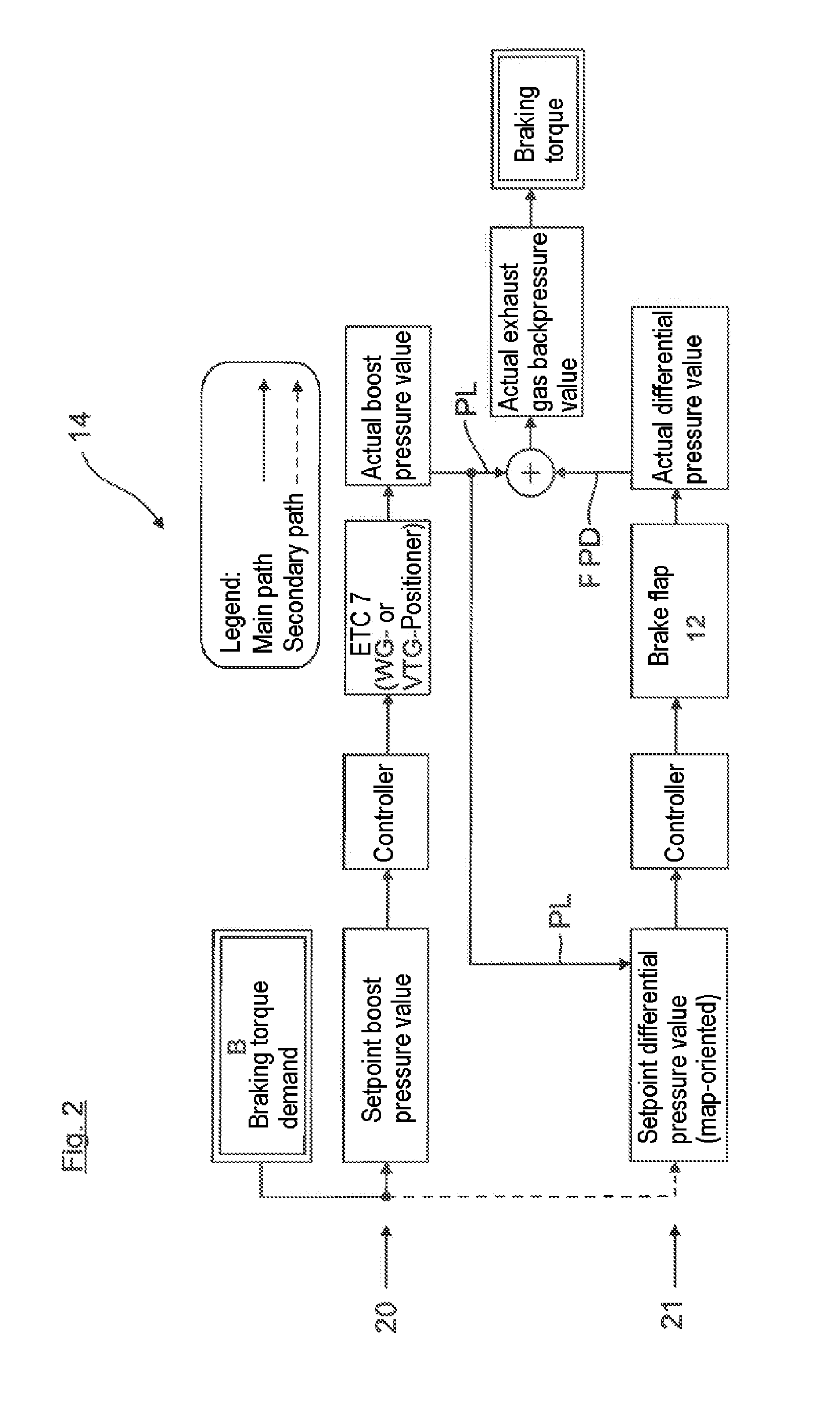
ActiveUS20160169127A1Increase boost pressureReduced exhaust gas flow rateValve arrangementsInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionTurbocharger
The invention relates to a method for controlling an engine braking device for a combustion engine in motor vehicles, wherein the engine braking device has an intake system, an exhaust system, gas exchange valves associated with the combustion engine, exhaust turbo-charging by at least one exhaust turbocharger integrated into the exhaust system and the intake system, and an engine braking unit, wherein the engine braking unit has a decompression brake, which influences at least one outlet valve of the gas exchange valves and is dependent on the exhaust gas backpressure, and a brake flap, which is arranged in the exhaust system. To achieve a precisely controllable engine braking power in the engine braking mode, the demanded braking torque is controlled in accordance with the boost pressure of the exhaust turbocharger and with the exhaust gas backpressure upstream of the brake flap, which is arranged directly upstream of an exhaust turbine of the exhaust turbocharger. A suitable engine braking device is furthermore proposed.
Owner:MAN TRUCK & BUS OESTERR
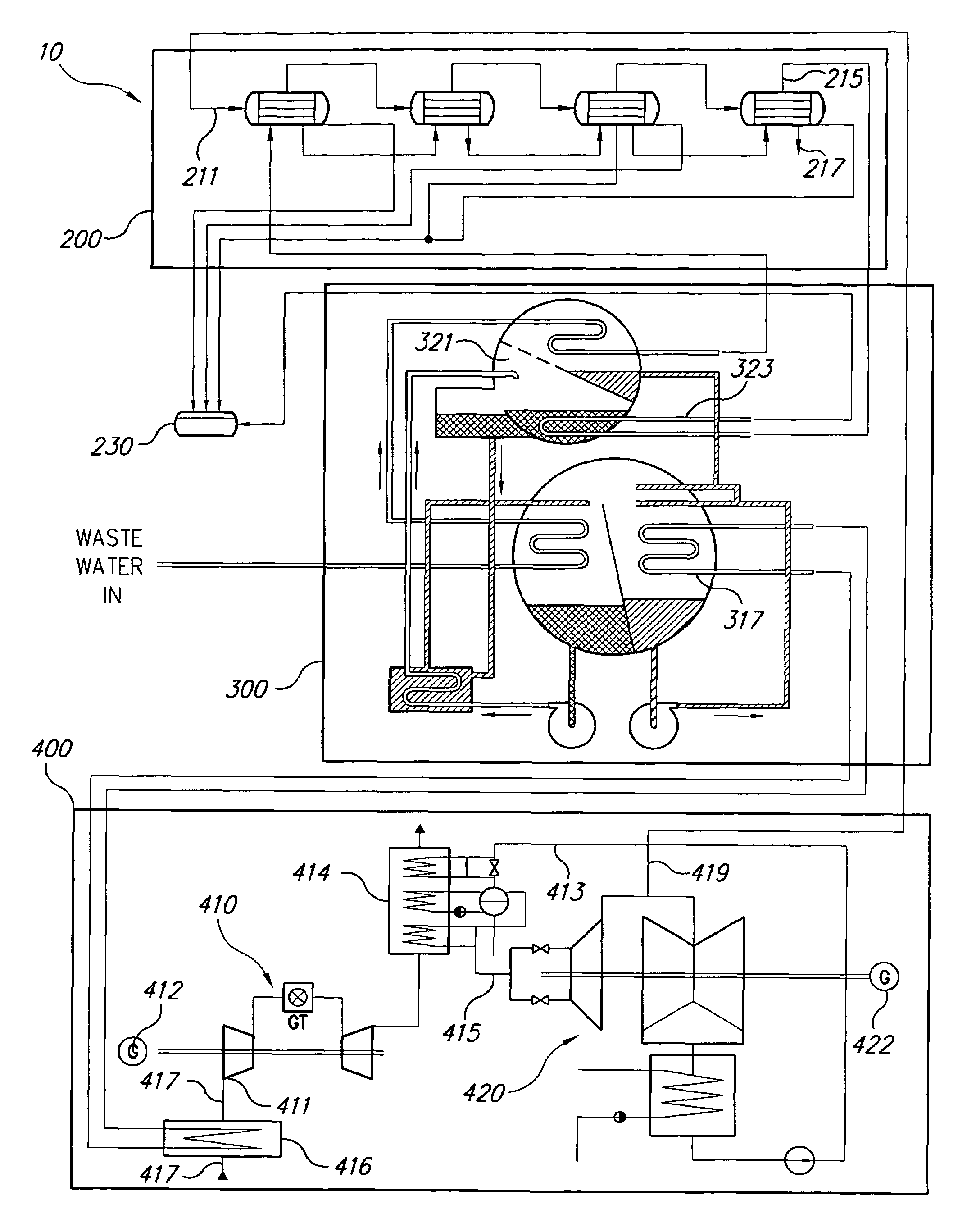
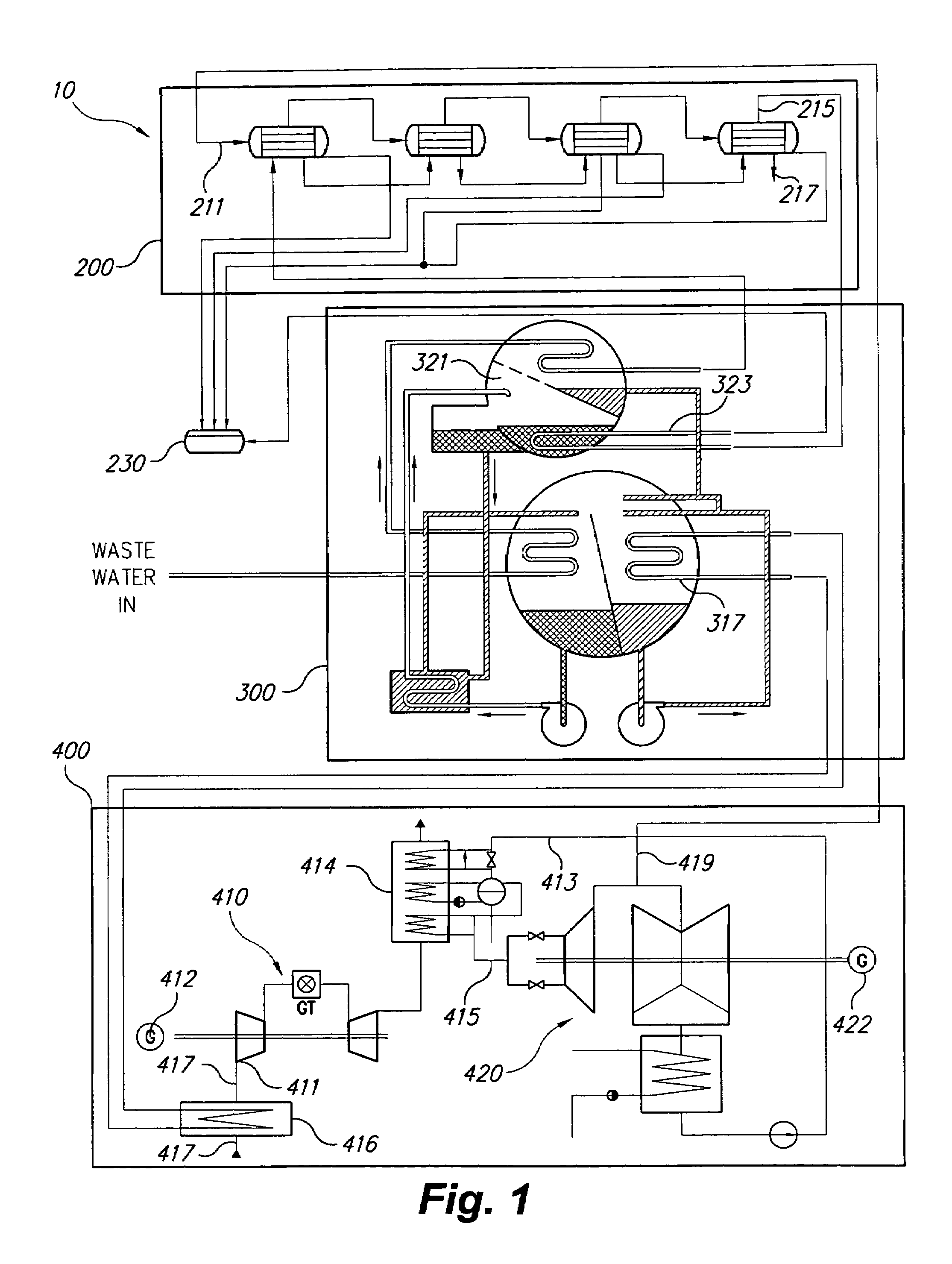
System for augmented electric power generation with distilled water output
InactiveUS7228682B2Minimize consumptionImprove system efficiencyGas turbine plantsWater/sewage treatmentDistillationChilled water
Owner:KASHLER YEFIM
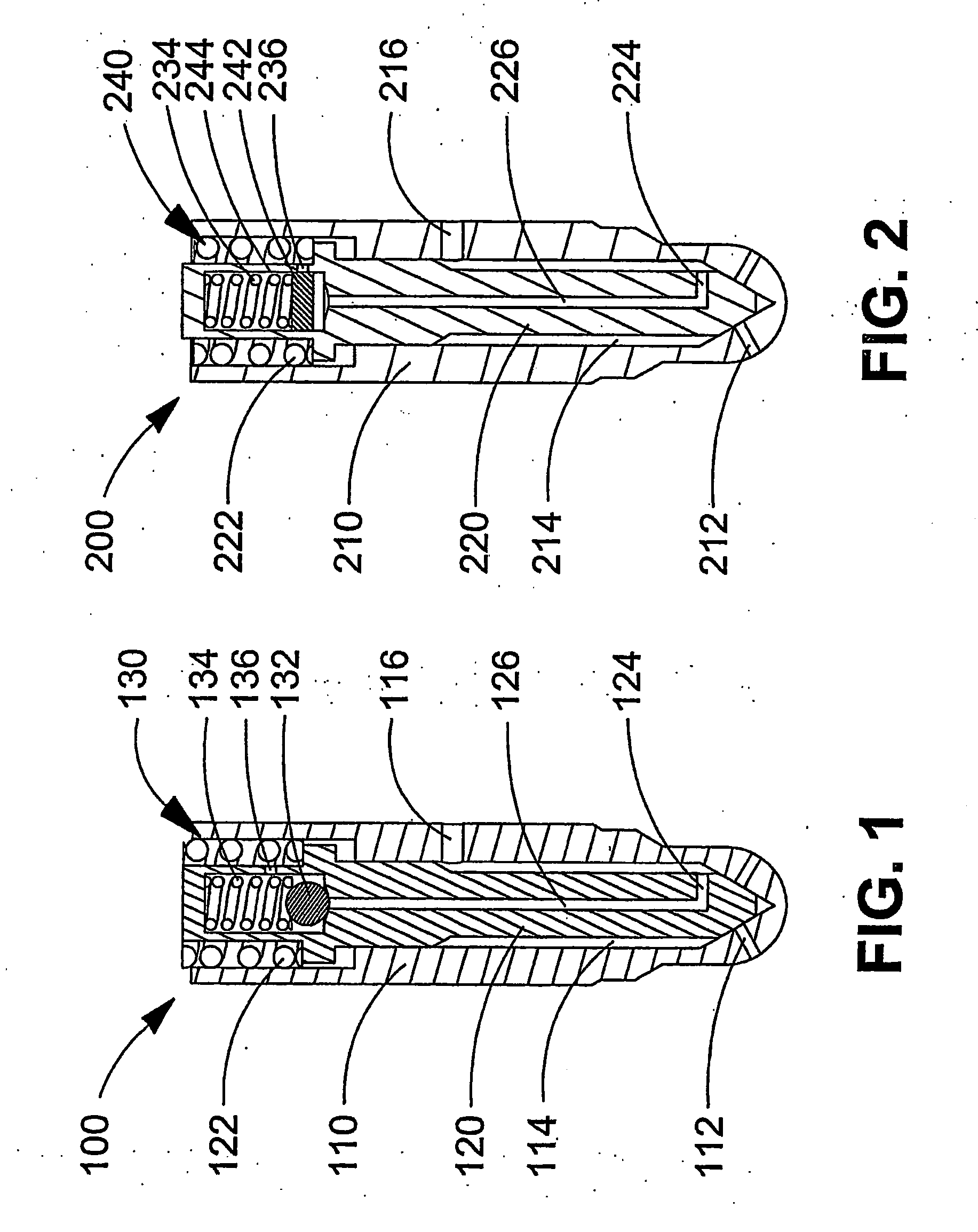
Liquid cooled fuel injection valve and method of operating a liquid cooled fuel injection valve
InactiveUS7090145B2Inexpensive and durableLarge displacementInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusCombustion chamberNuclear engineering
Owner:WESTPORT POWER
Multi-function simplex/prefilmer nozzle
InactiveUS6920749B2Straightforward to manufactureStraightforward to assembleBurnersSpray nozzlesThermodynamicsSpray nozzle
A multi-function spray nozzle for engine applications useful as a cooling device to introduce a fluid into the fluid stream of the engine, and as a cleaning device to introduce a fluid to clean internal components of the engine. The nozzle includes a multi-layered arrangement of etched plates defining flow paths for the first and second fluids. Non-radial feed slots direct the first fluid into a cylindrical swirl chamber. The swirling fluid exits the swirl chamber through a spray orifice or a prefilmer, depending on whether the nozzle is configured as a simplex or prefilmer nozzle. Other non-radial feed slots direct the second fluid inward, downstream of the first fluid, to create a fine dispersion of droplets for fluid stream cooling purposes. During cleaning, only the first fluid is introduced through the nozzle, which results in a larger droplet size suitable for cleaning purposes of the internal components of the engine.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Apparatus and related methods for turbine cooling
InactiveUS8096747B2LessIncrease mass flowPump componentsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingTurbineGas turbines
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for operating a gas turbo group
InactiveUS20040216462A1Speed up the flowReduce cooling powerContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionCombustion chamberProcess engineering
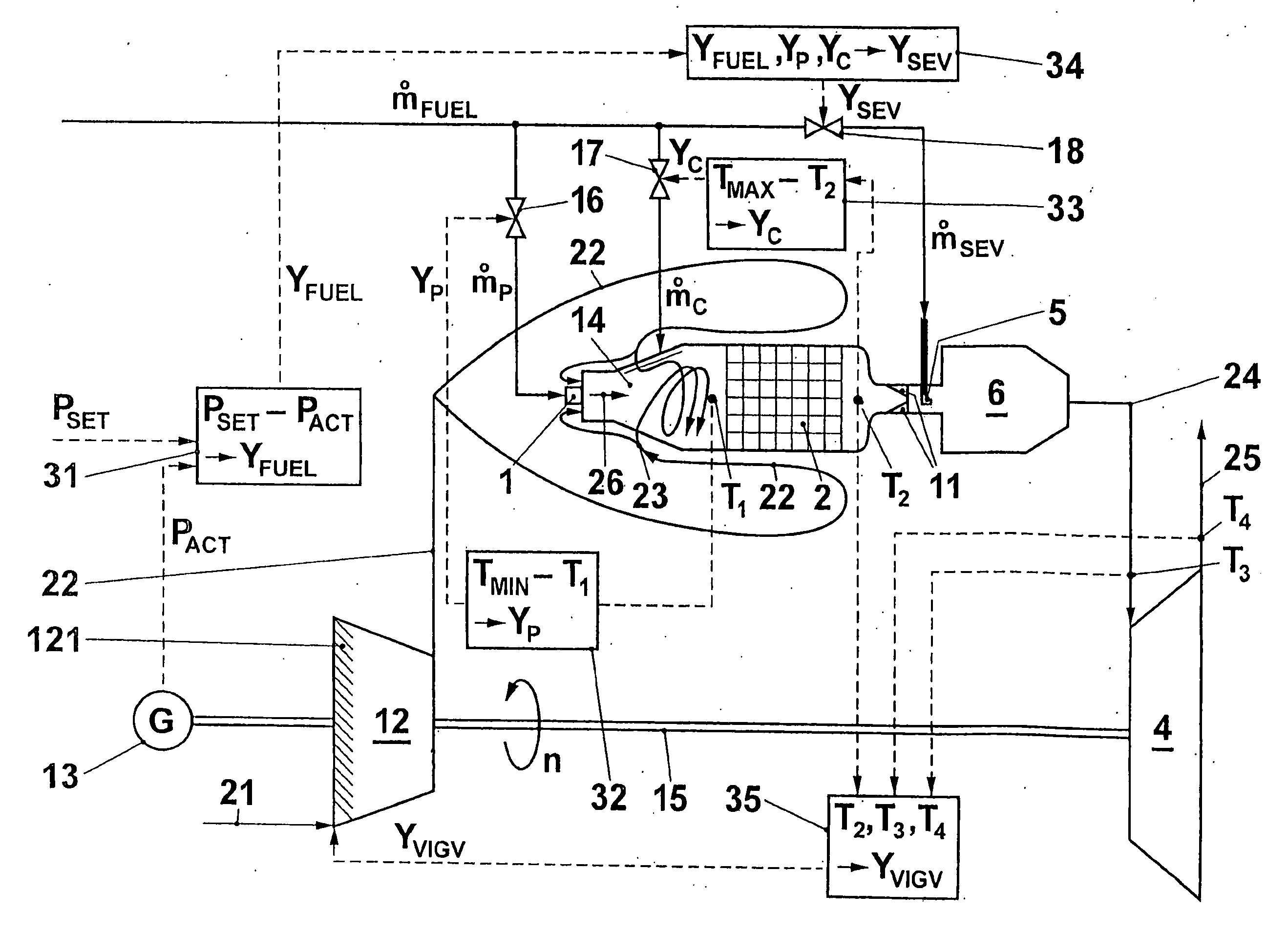
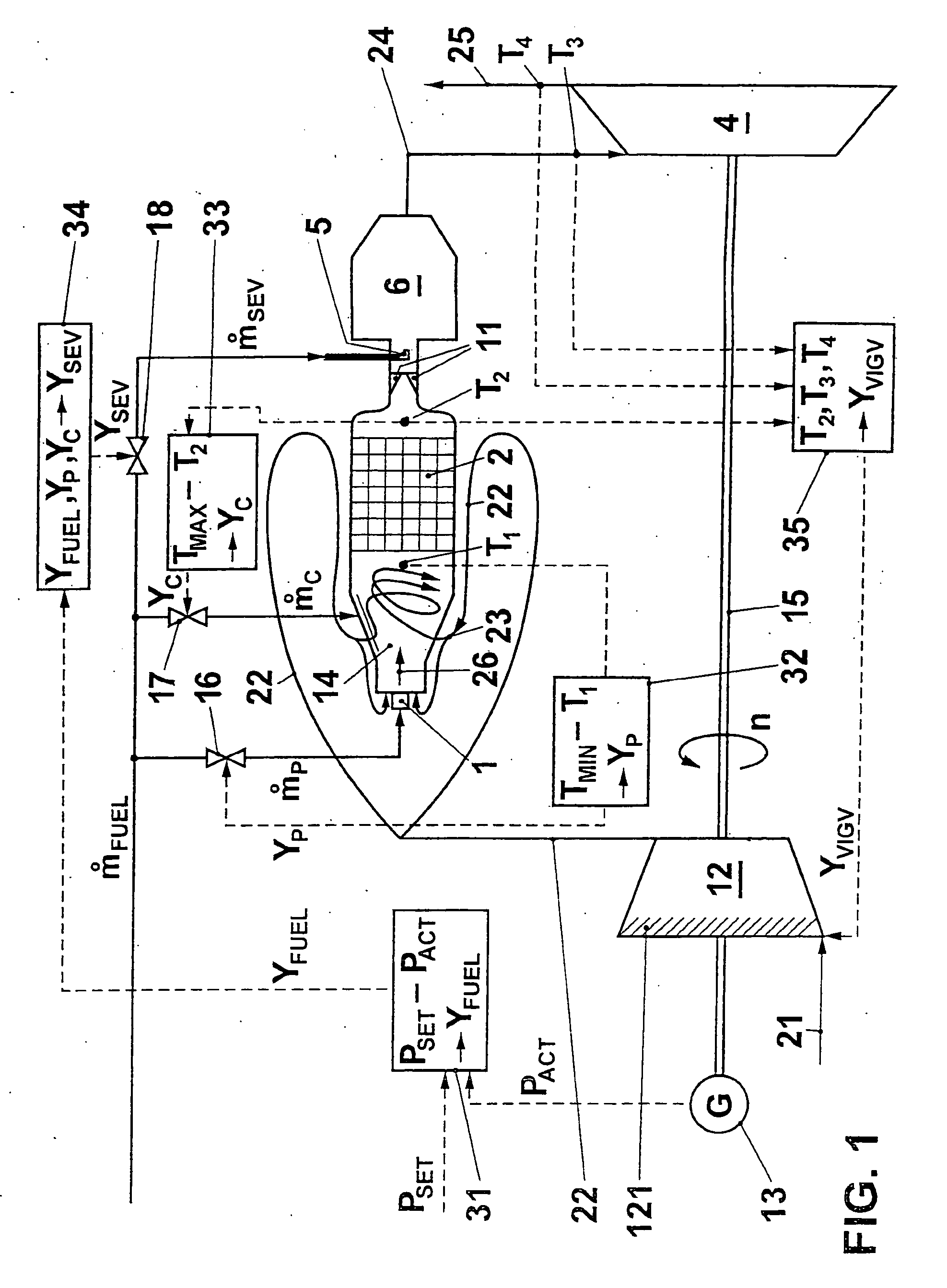
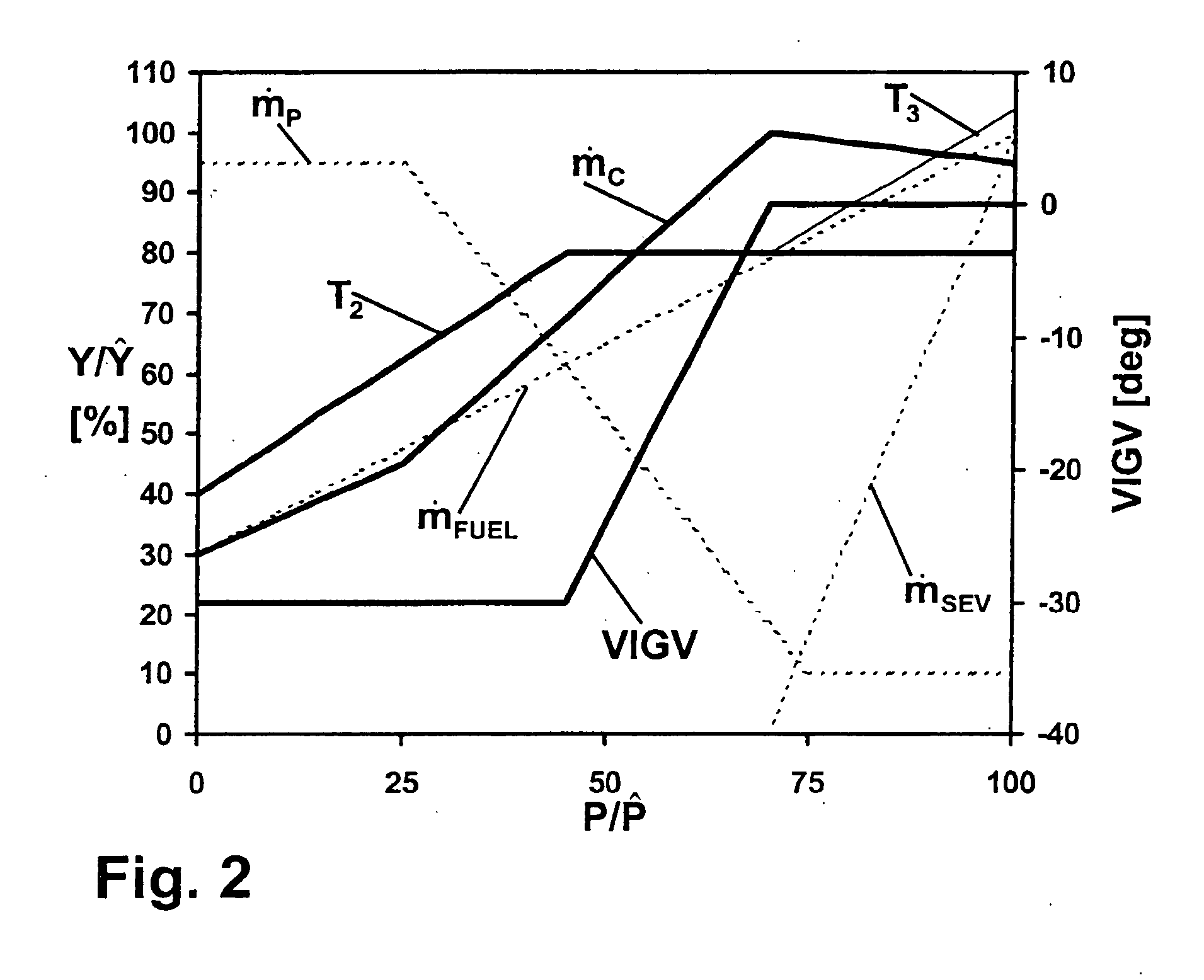
A gas turbo group has a combustion chamber comprising a catalytic burner stage (2), a preburner stage (1) located upstream from the catalytic burner stage, as well as a non-catalytic burner stage (11, 5, 6) located downstream from the catalytic burner stage. The preburner stage serves to always maintain a temperature (T1) at the inlet into the catalytic stage that corresponds at least to a minimum temperature (TMIN) necessary for operating the catalytic burner stage. According to the invention, the gas turbo group is operated so that the burner stage located downstream from the catalytic combustion chamber is taken into operation only when the temperature (T2) at the outlet from the catalytic stage has reached an upper limit in the presence of a maximum combustion air mass flow.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
Liquid cooled fuel injection valve and method of operating a liquid cooled fuel injection valve
InactiveUS20050224601A1Inexpensive and durableLarge displacementInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusCombustion chamberEngineering
A liquid cooled fuel injection valve is operable to inject fuel directly into a combustion chamber through a nozzle orifice provided in an injector tip. The fuel injection valve further comprises a cooling system for draining fuel from a fuel cavity disposed within the injector tip and a drain valve that opens when pressure within the fuel cavity is greater than a predetermined set point. Fuel drained through the cooling system is directed to a drain system that may be combined with drain passages typically found in fuel injection valves. In a preferred embodiment, the drain valve is disposed within the fuel injection valve.
Owner:WESTPORT POWER
Method for operating a gas turbine group
InactiveUS7104071B2Increase powerIncrease mass flowEngine fuctionsGas turbine plantsCooling powerLimit value
A gas turbine group is provided with at least one cooling apparatus for cooling the working medium before and / or during the compression. The cooling power of the cooling apparatus can be adjusted by suitable means. A controller controls the cooling power of the cooling apparatus as a function of a control deviation in the useful power of the gas turbine group. The cooling controller interacts with other controllers of the gas turbine group in such a way that the gas turbine group is itself always operated at least close to its full load operating state. In this context, it is preferable for the inlet guide vane row of the compressor to be maximally open, and for the hot-gas temperature on entry into the turbines to be controlled so that it is constantly at an upper limit value.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA IP UK LTD
Flat pipe and heat exchanger
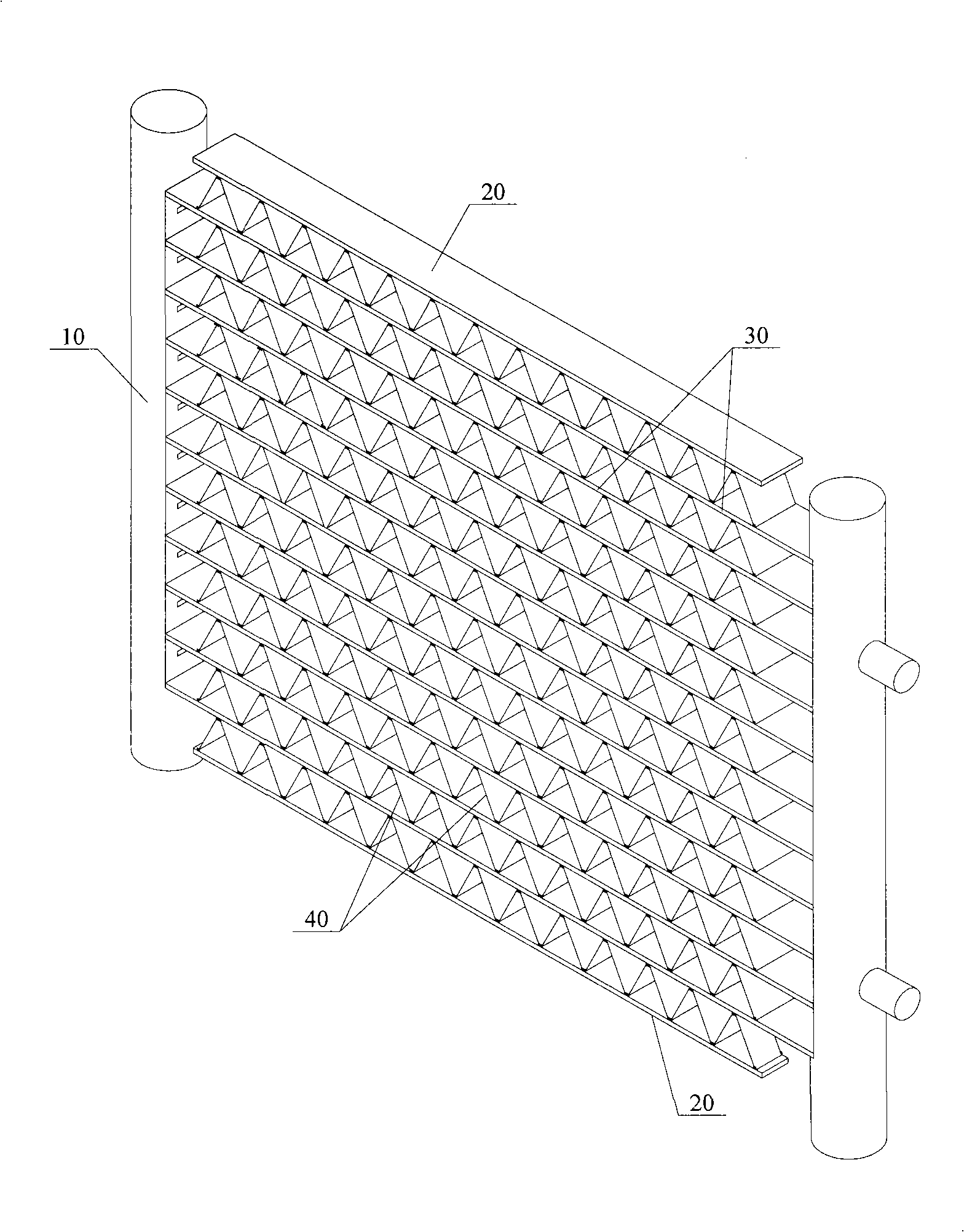
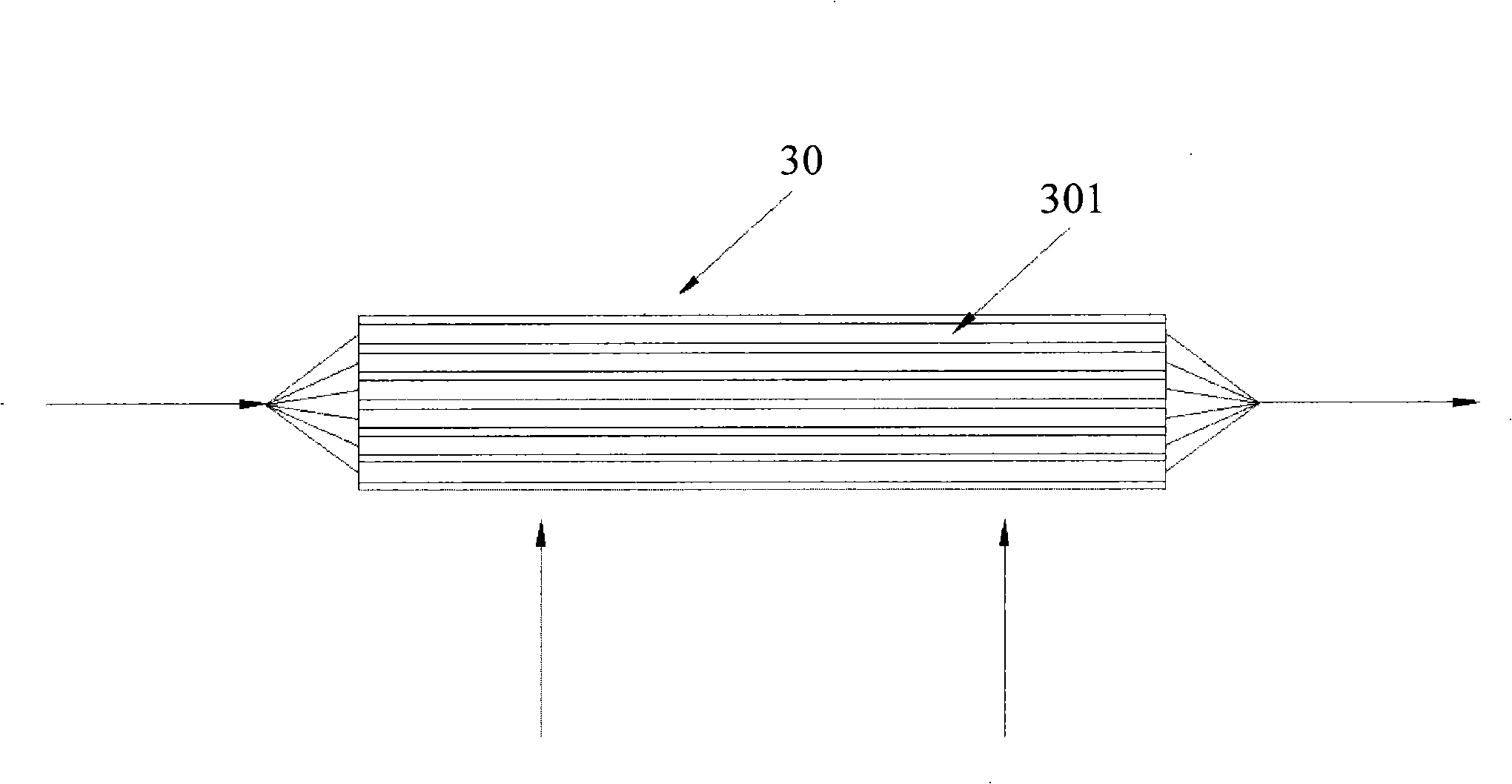
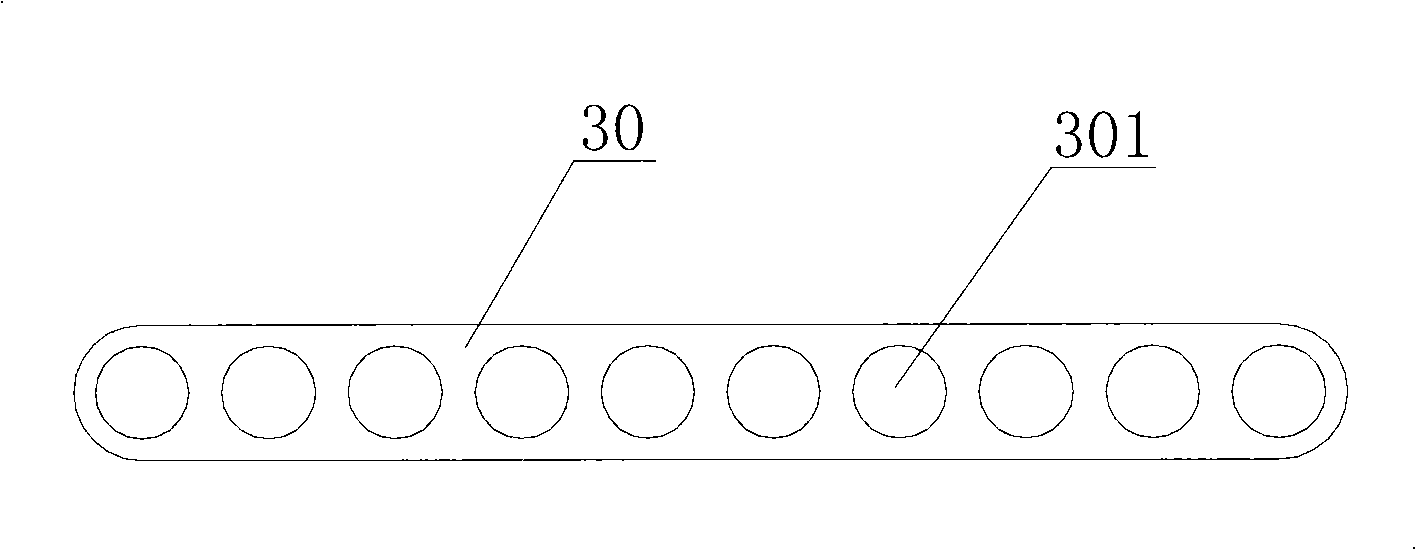
InactiveCN101526322AGive full play to the heat transfer performanceUniform stateStationary conduit assembliesTubular elementsPlate heat exchangerHeat transmission
The invention relates to the technical field of heat exchanger, in particular to a flat pipe which comprises not less than two through holes which extend along the lengthwise direction of the flat pipe. The through holes are arranged side by side along the width direction of the flat pipe. Two ends of the flat pipe along the width direction respectively form an external air influx entrance end and an external air outflux end. The section sizes of the through holes are reduced gradually along the direction from the external air influx entrance end of the flat pipe to the external air outflux end of the flat pipe. The through hole near the external air influx entrance end of the flat pipe has larger section size, larger heat transmission temperature difference, large heat exchange volume and larger mass flow. The through hole near the external air outflux end of the flat pipe has smaller section size, lower heat transmission temperature difference, less heat exchange volume and less mass flow. The invention brings the heat exchange performance of the flat pipe into play completely and improves the heat exchange efficiency of the heat exchanger further. The invention also provides a heat exchanger.
Owner:SANHUA(HANGZHOU) MICRO CHANNEL HEAT EXCHANGER CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com