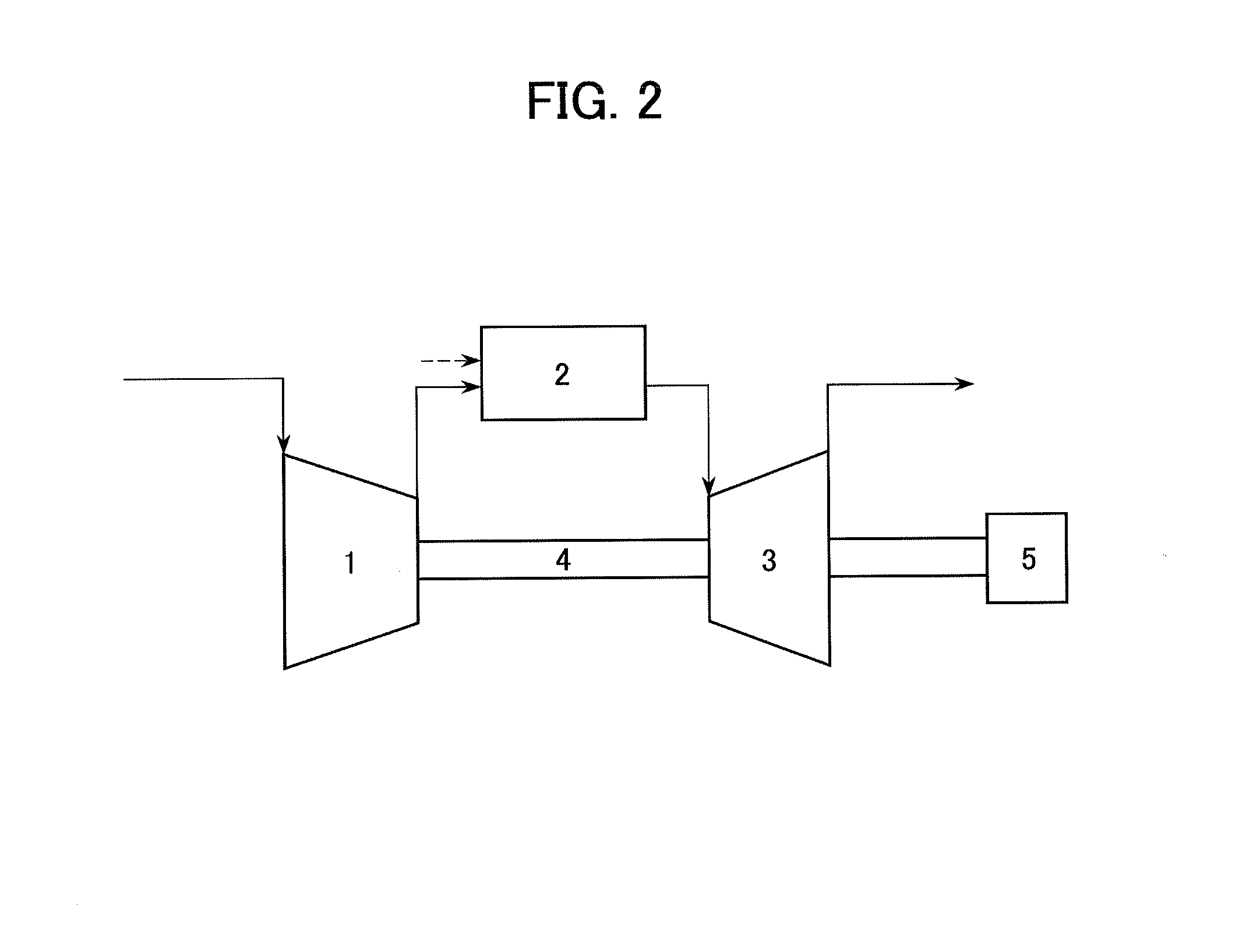
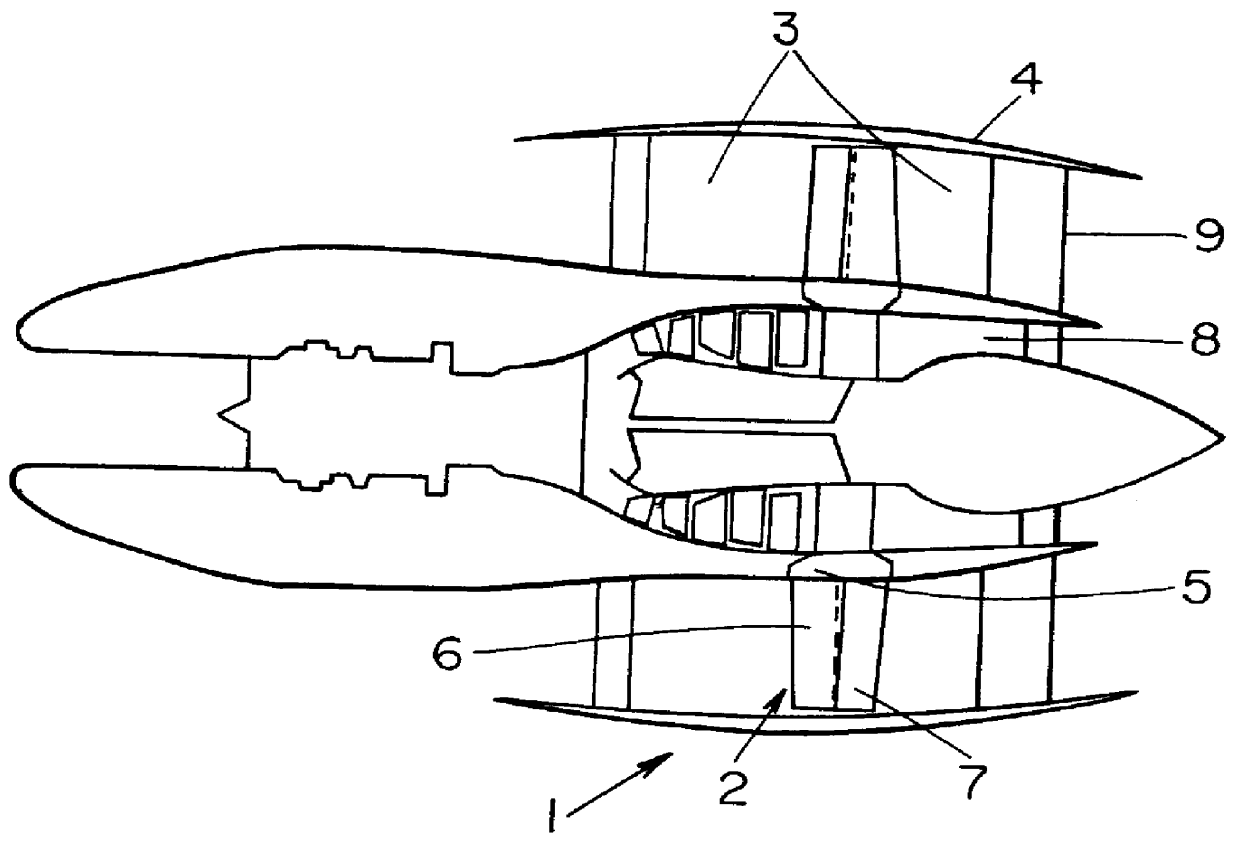
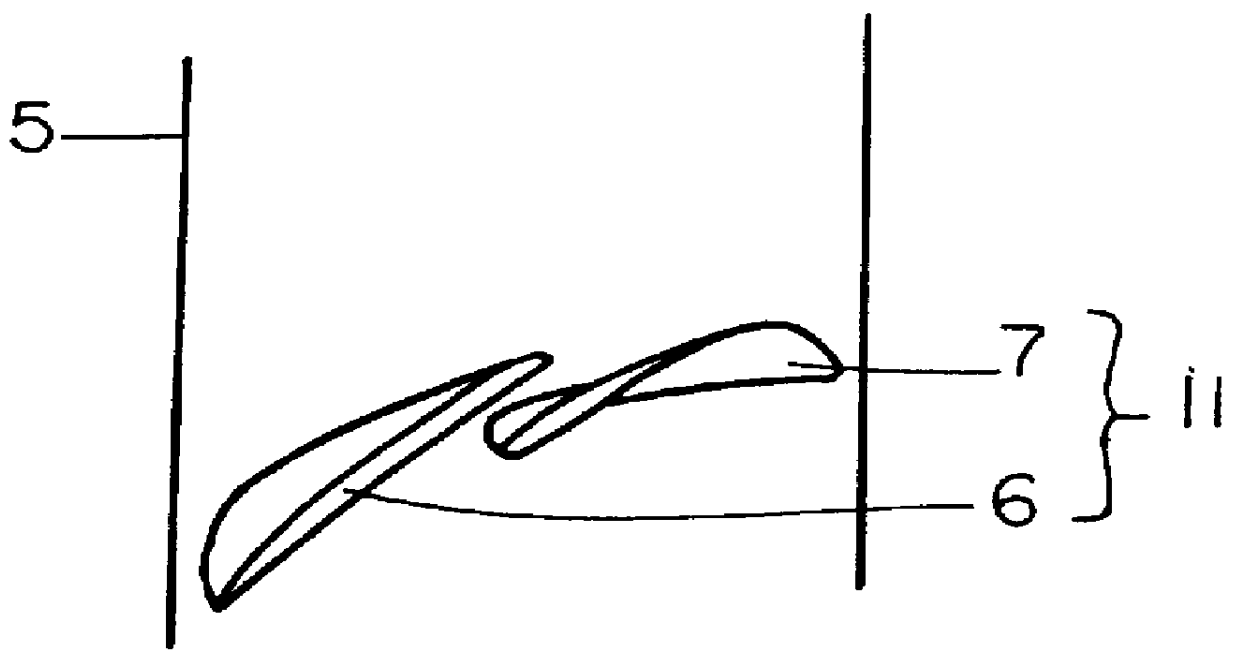
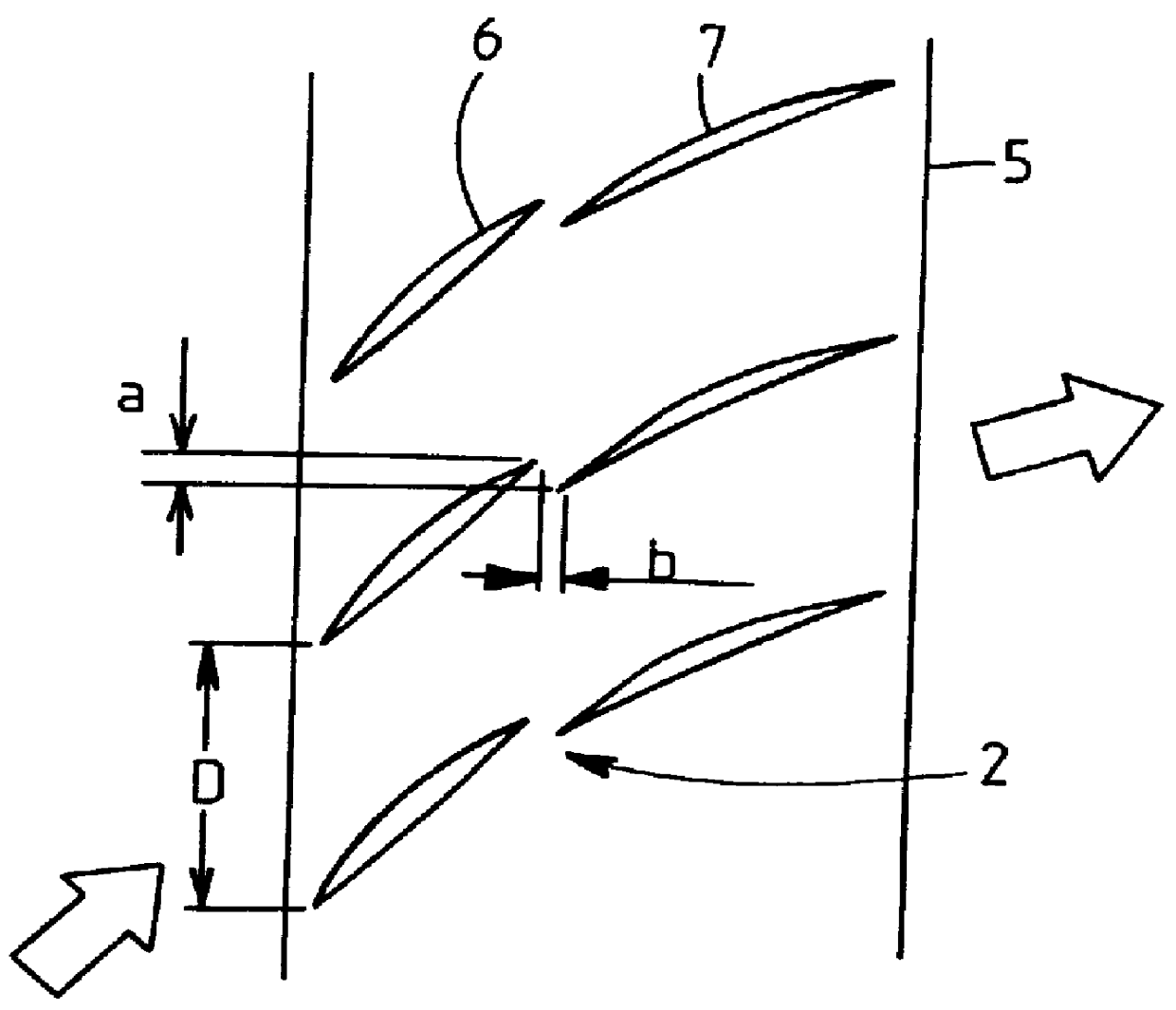
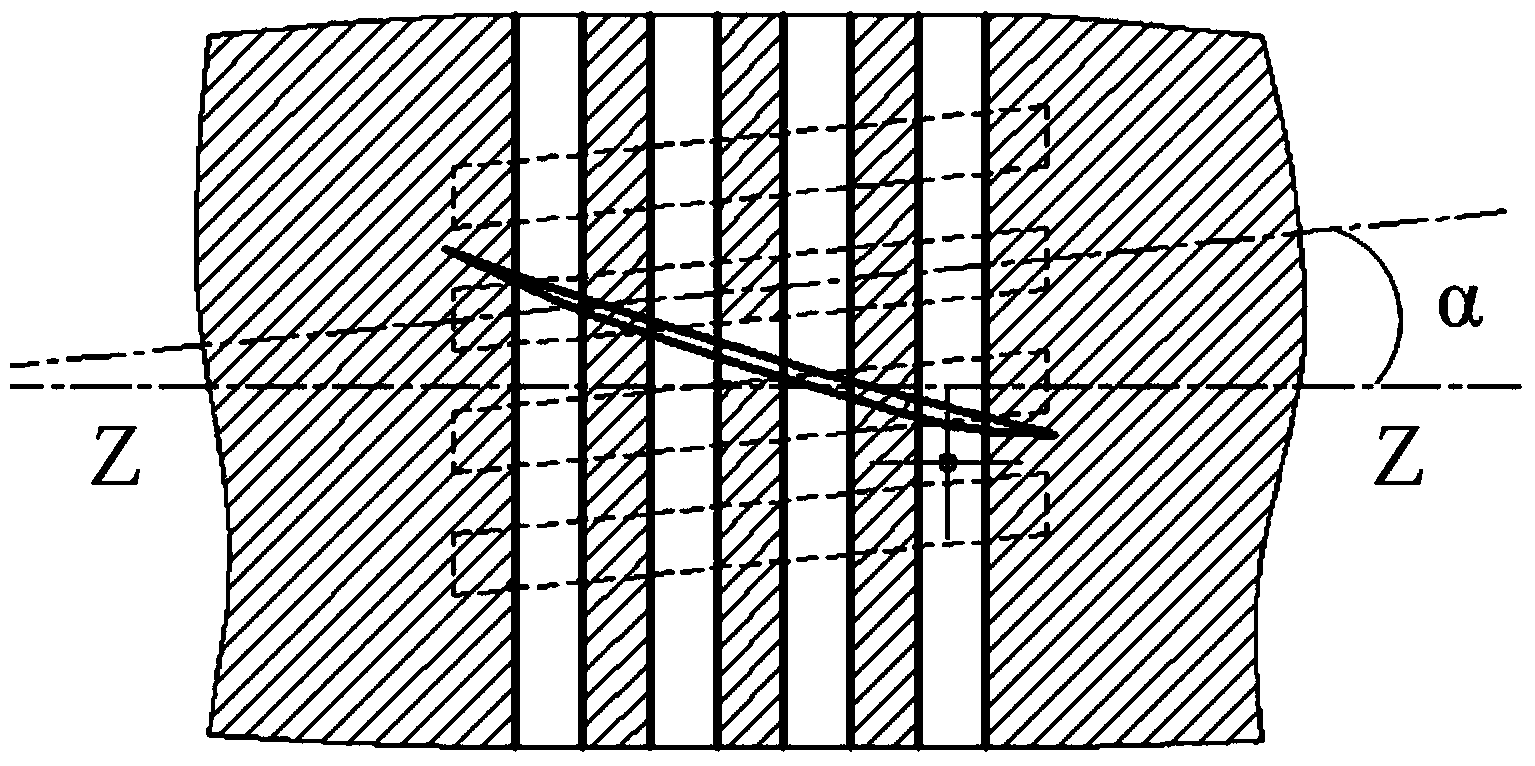
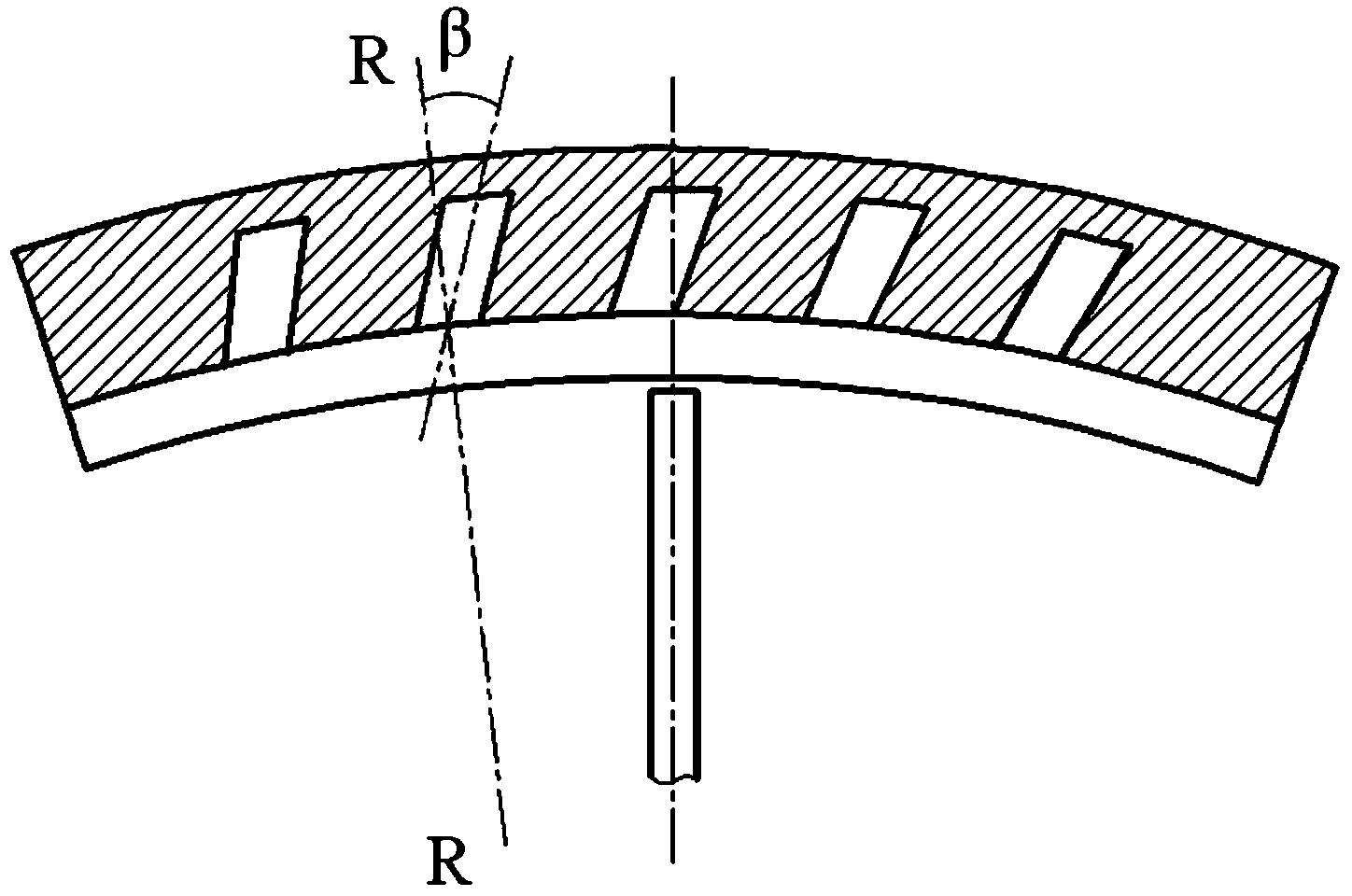
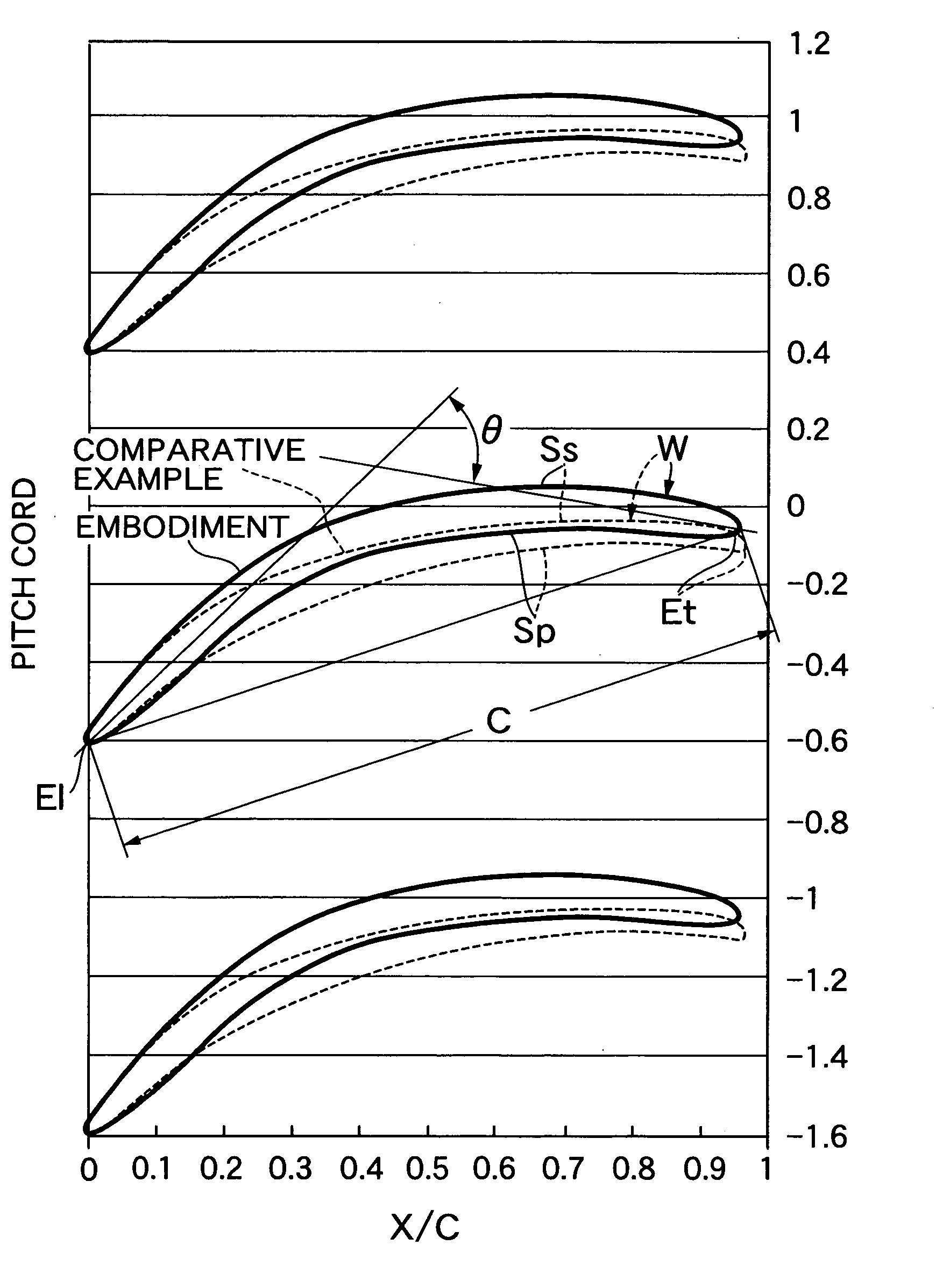
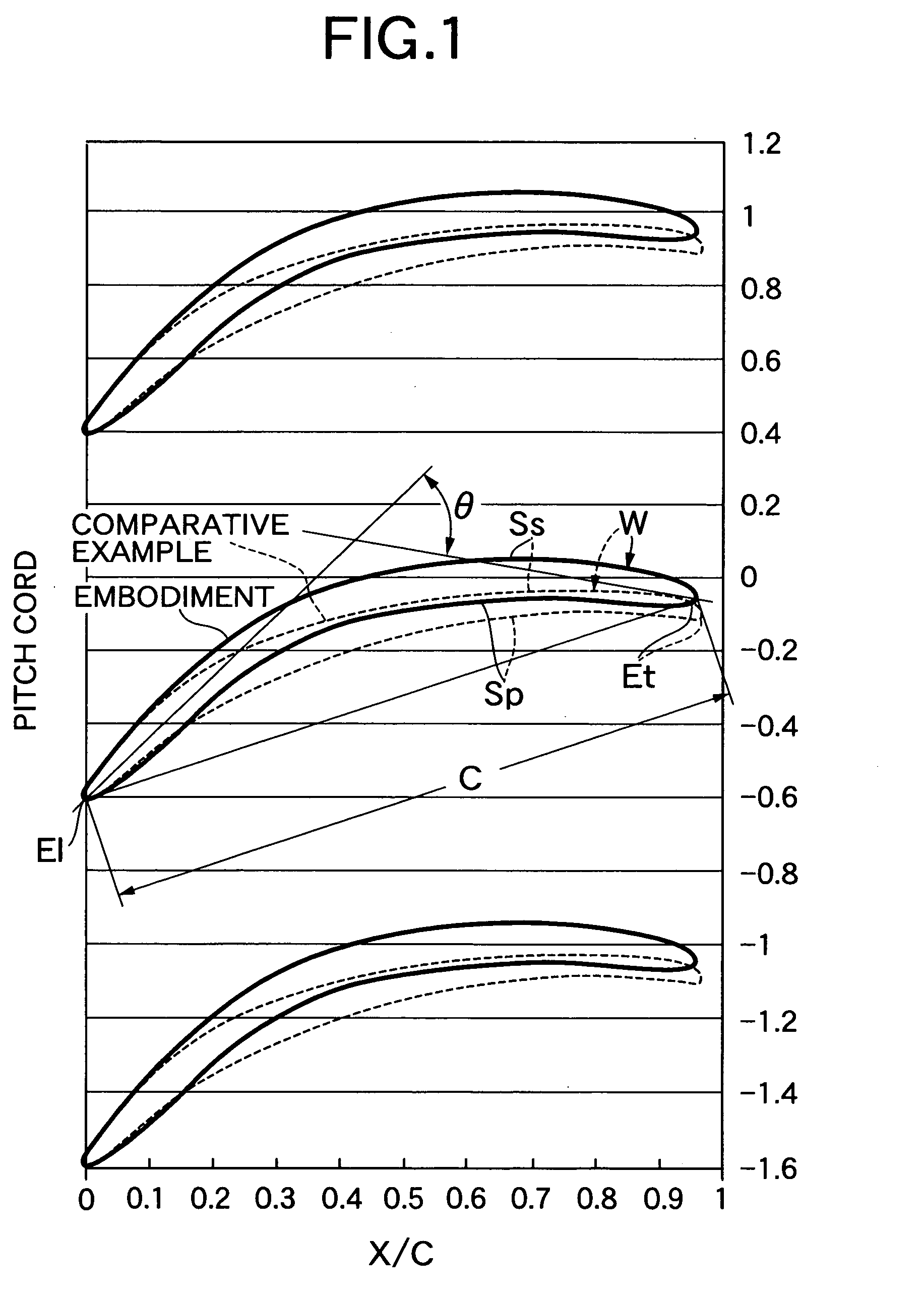
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
130results about "Supersonic fluid pumps" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
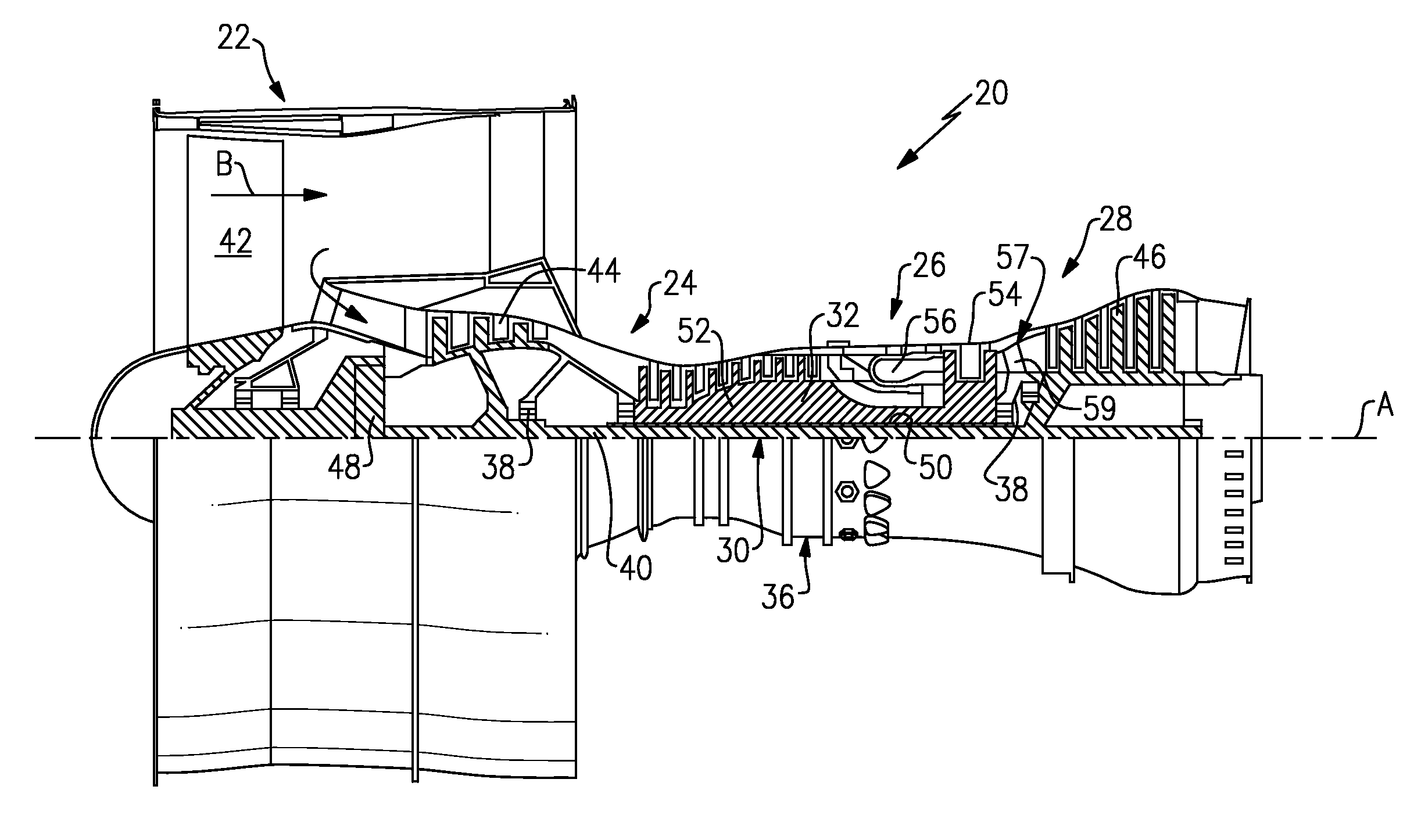
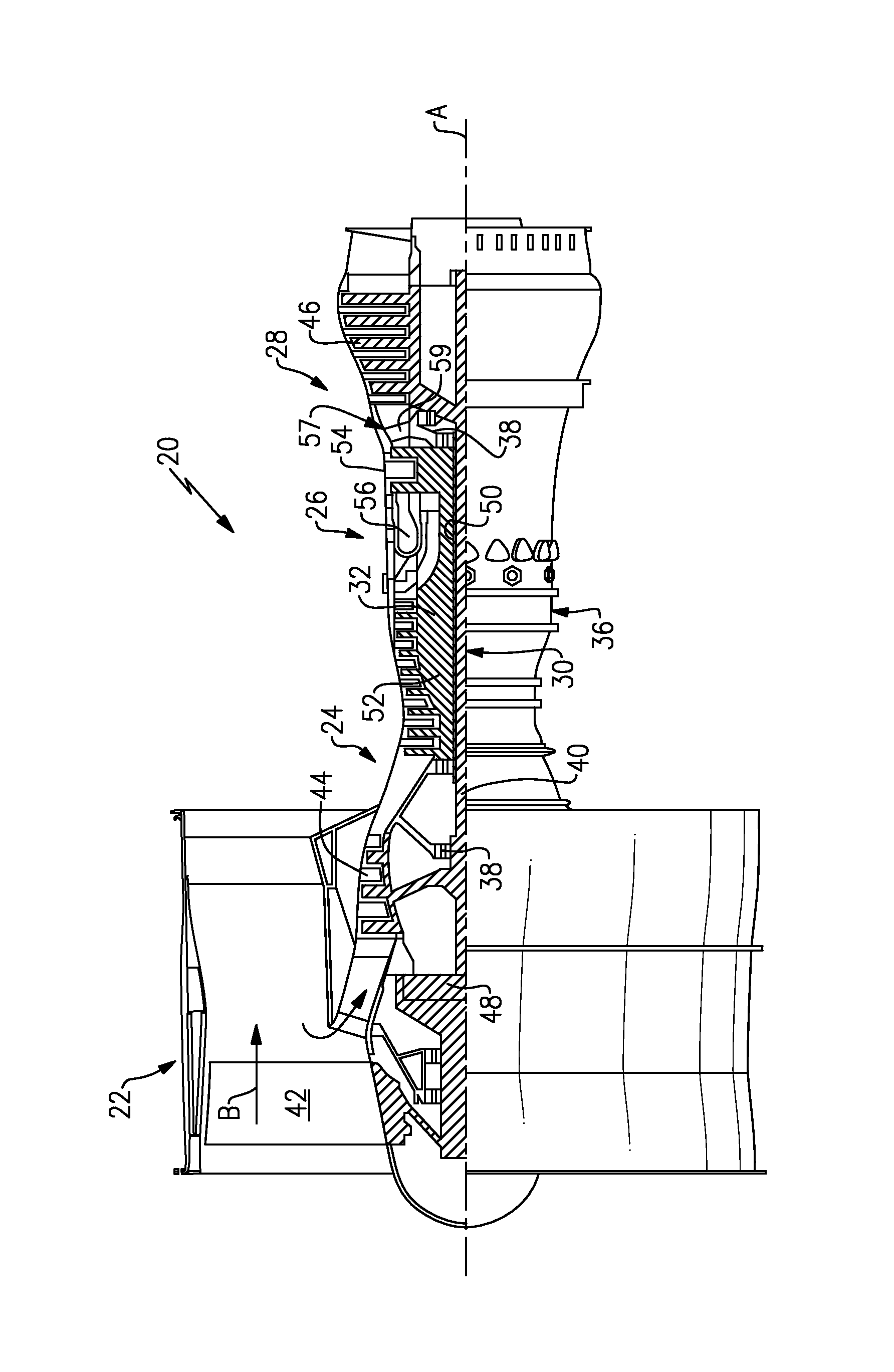
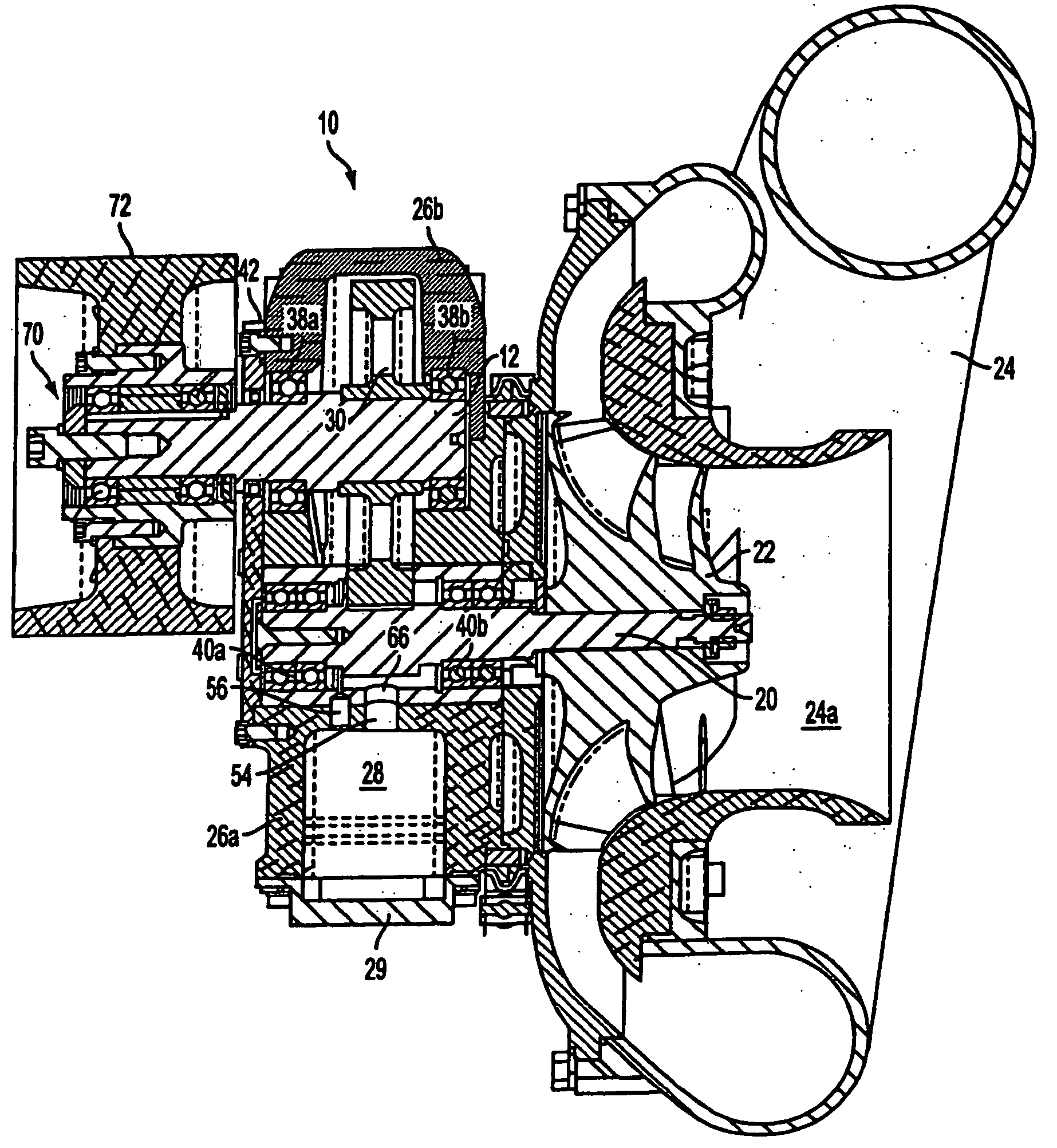
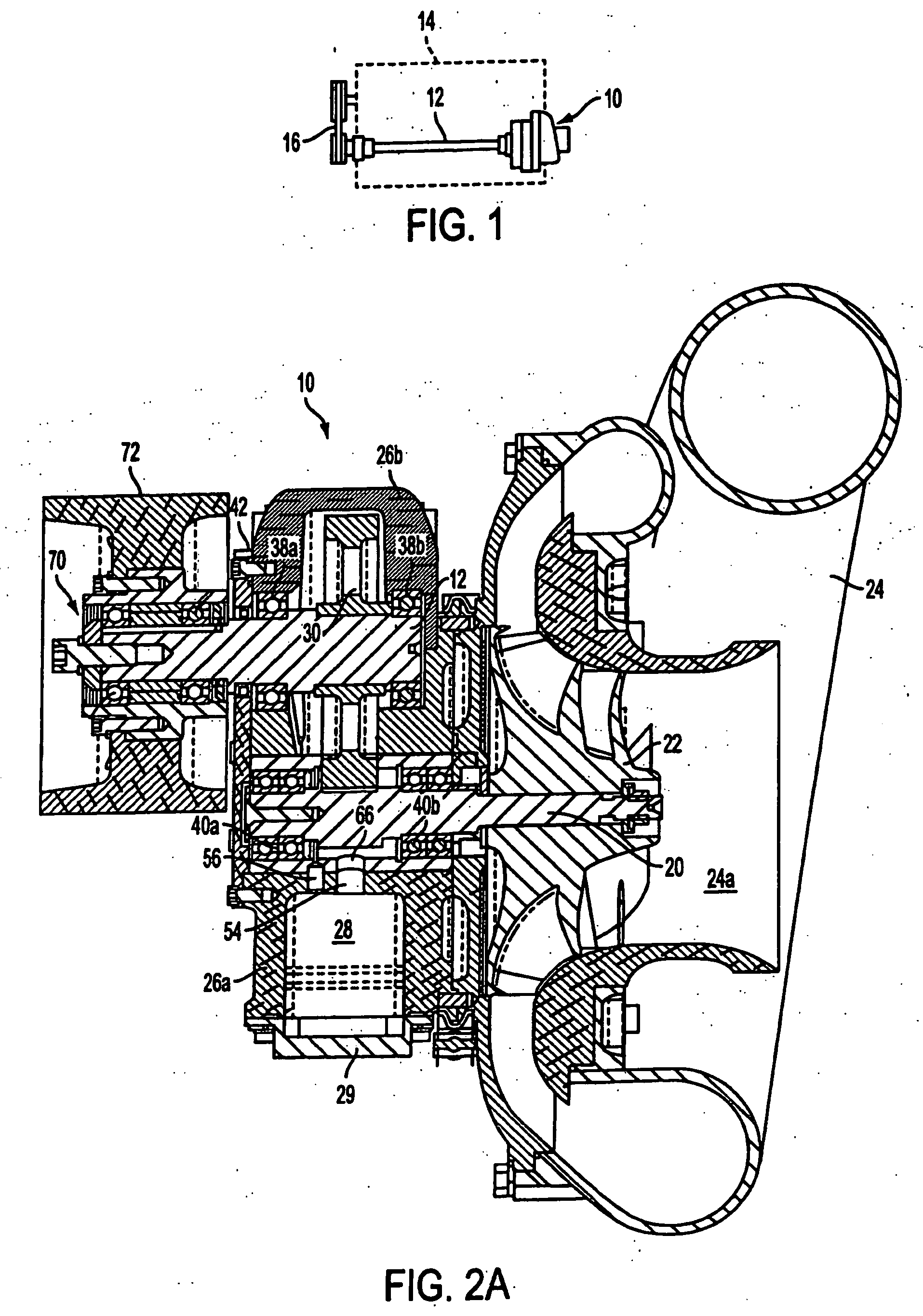
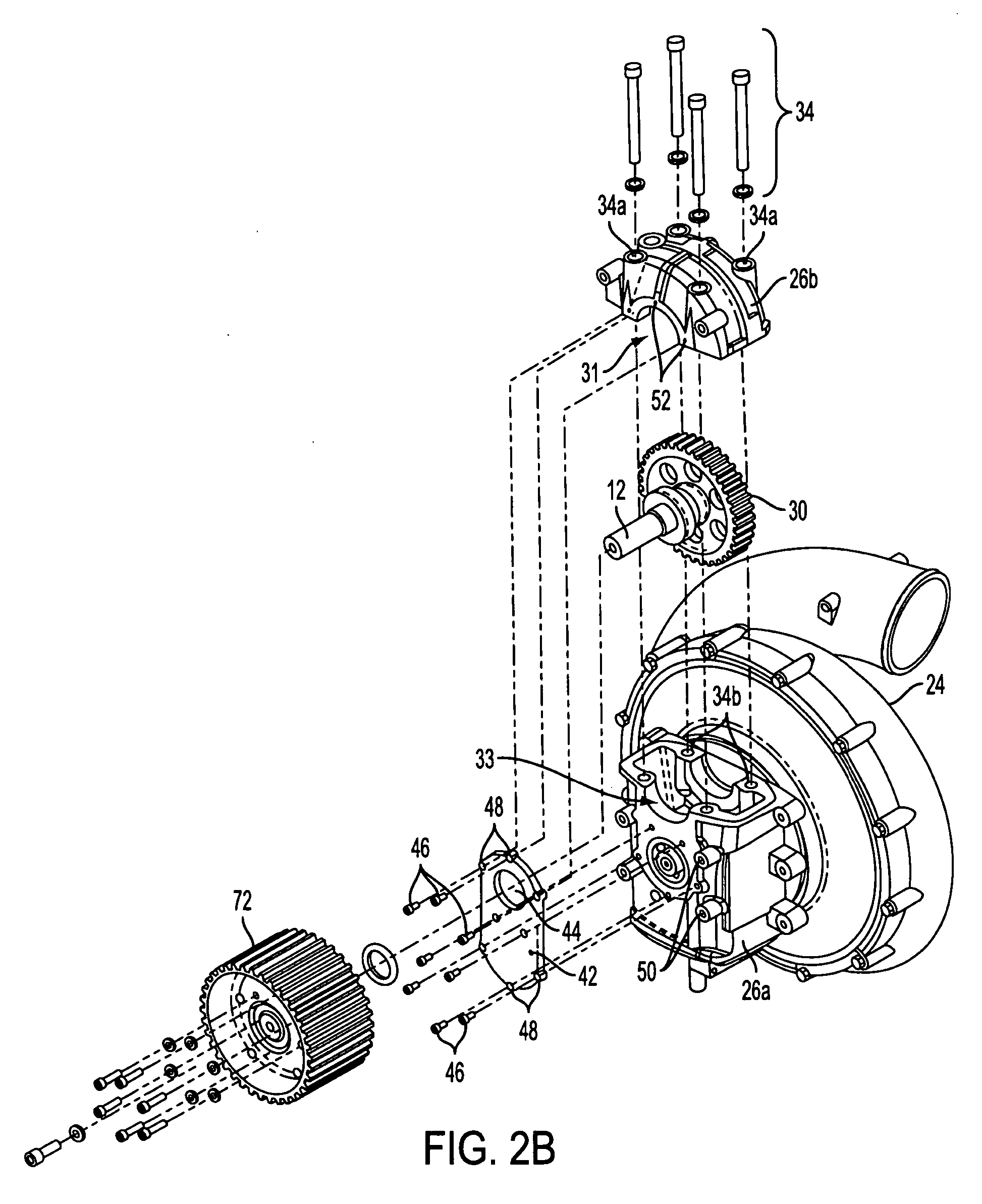
Low noise turbine for geared turbofan engine
A gas turbine engine is utilized in combination with a gear reduction to reduce the speed of a fan relative to a low pressure turbine speed. The gas turbine engine is designed such that a blade count in the low pressure turbine multiplied by the speed of the low pressure turbine will result in operational noise that is above a sensitive range for human hearing. A method and turbine module are also disclosed.
Owner:MTU AERO ENGINES GMBH +1
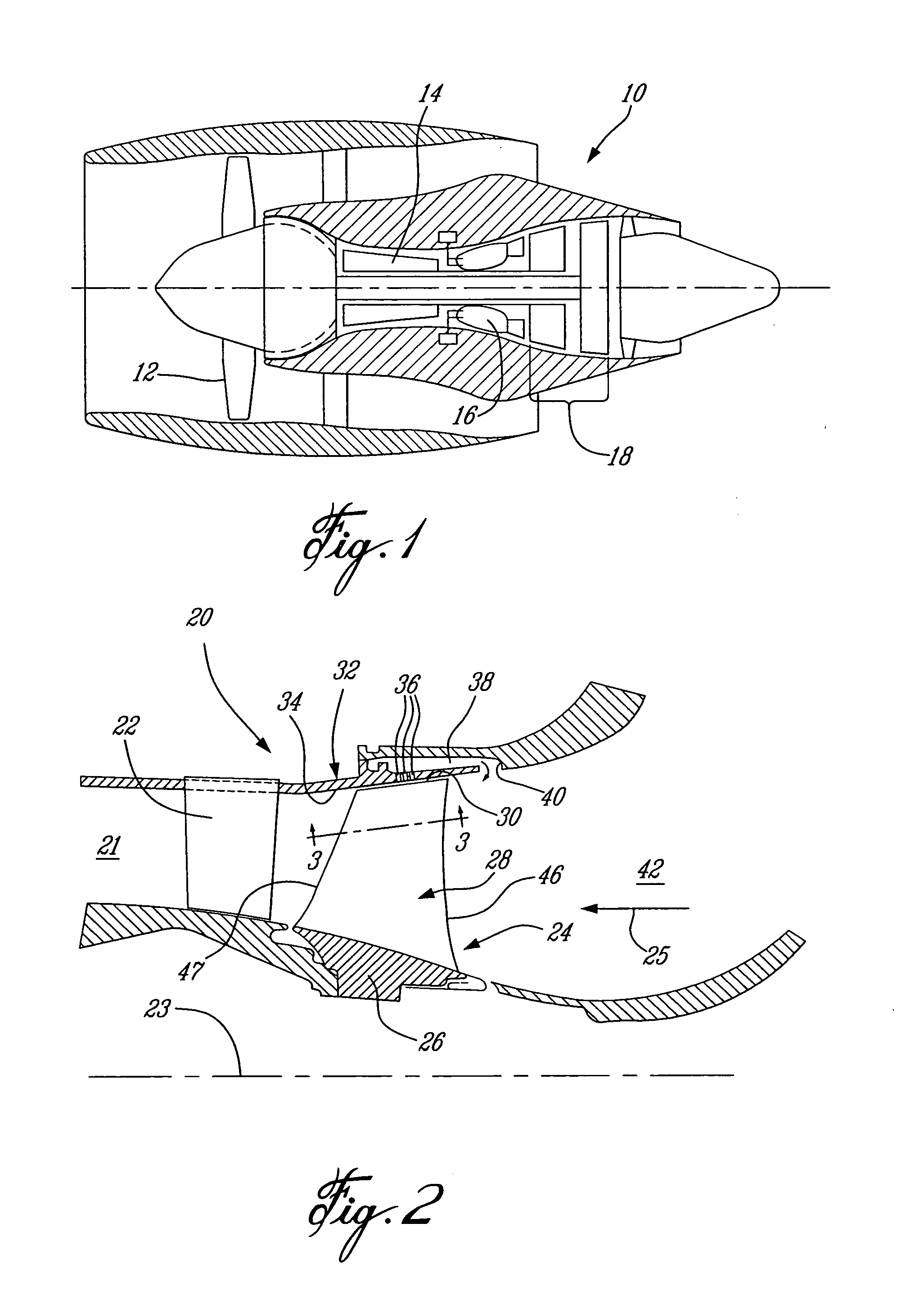
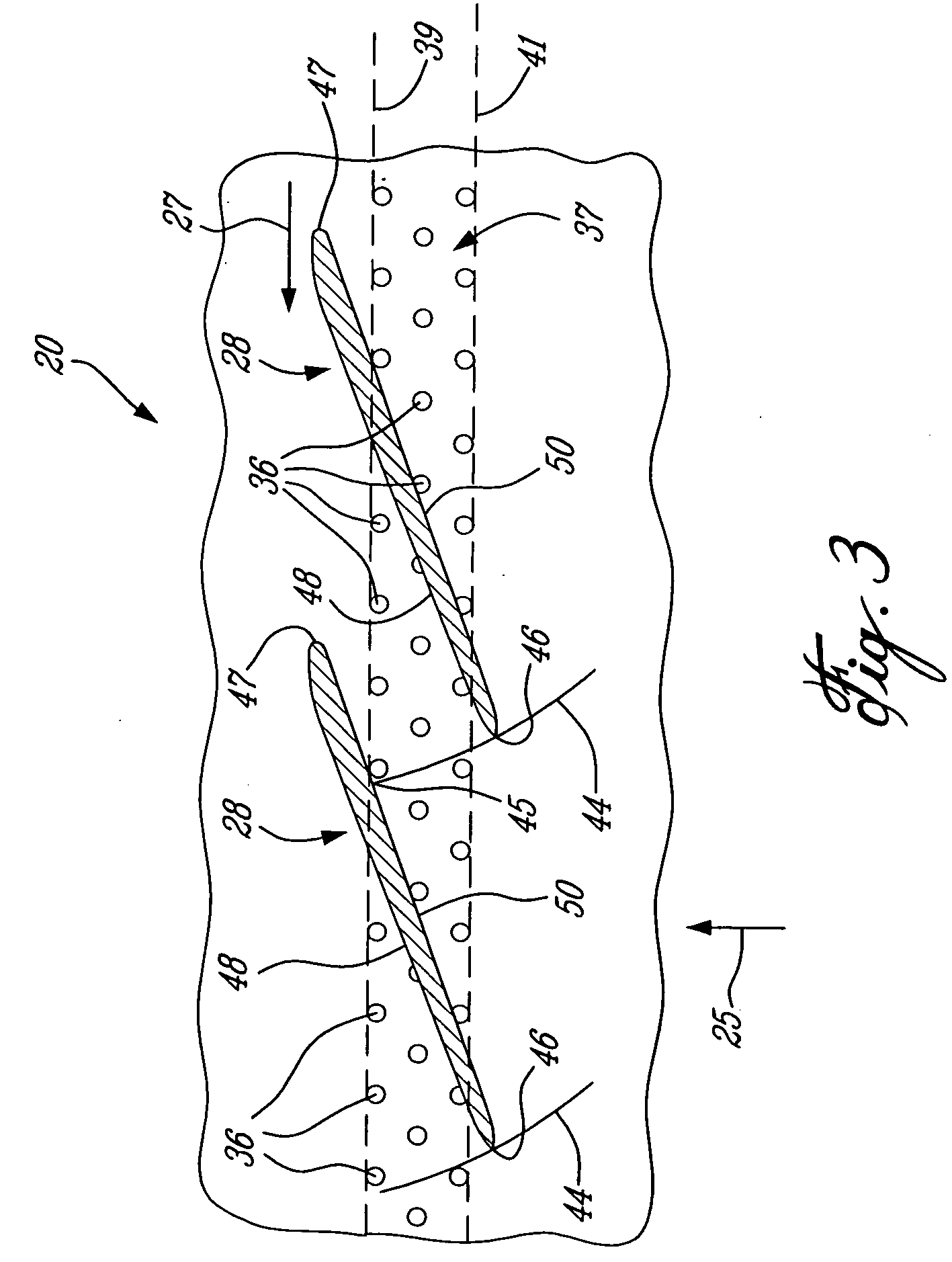
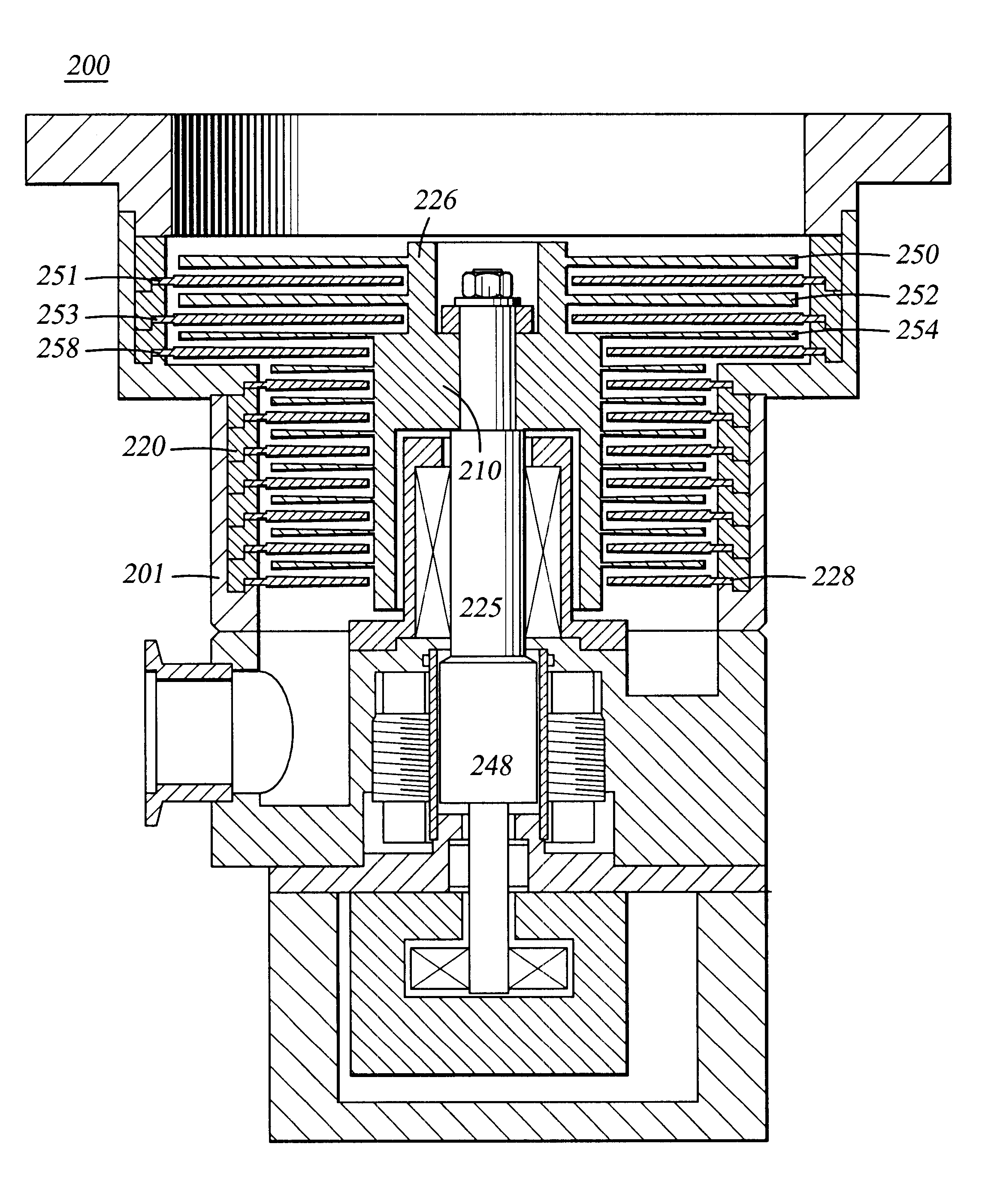
Jet engine inlet-fan system and design method
InactiveUS20060179818A1Improve performanceIncrease pressureSupersonic fluid pumpsEfficient propulsion technologiesJet engineDesign methods
A supersonic aircraft engine axial fan that includes a rotating blade row having blades that receive a supersonic entry flow in the absolute frame and decelerate the flow to a lower supersonic or subsonic velocity exit flow while adding work to the flow to increase stagnation pressure. It is preferred that the lower velocity be subsonic. When the fan is combined with a suitably designed inlet, the propulsion system is compact and lighter in weight than conventional engines for supersonic aircraft.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Tone noise reduction in turbomachines
ActiveUS8177496B2Carefully controlledSupersonic fluid pumpsEngine manufactureClassical mechanicsEngineering
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Transonic compressor rotors with non-monotonic meanline angle distributions
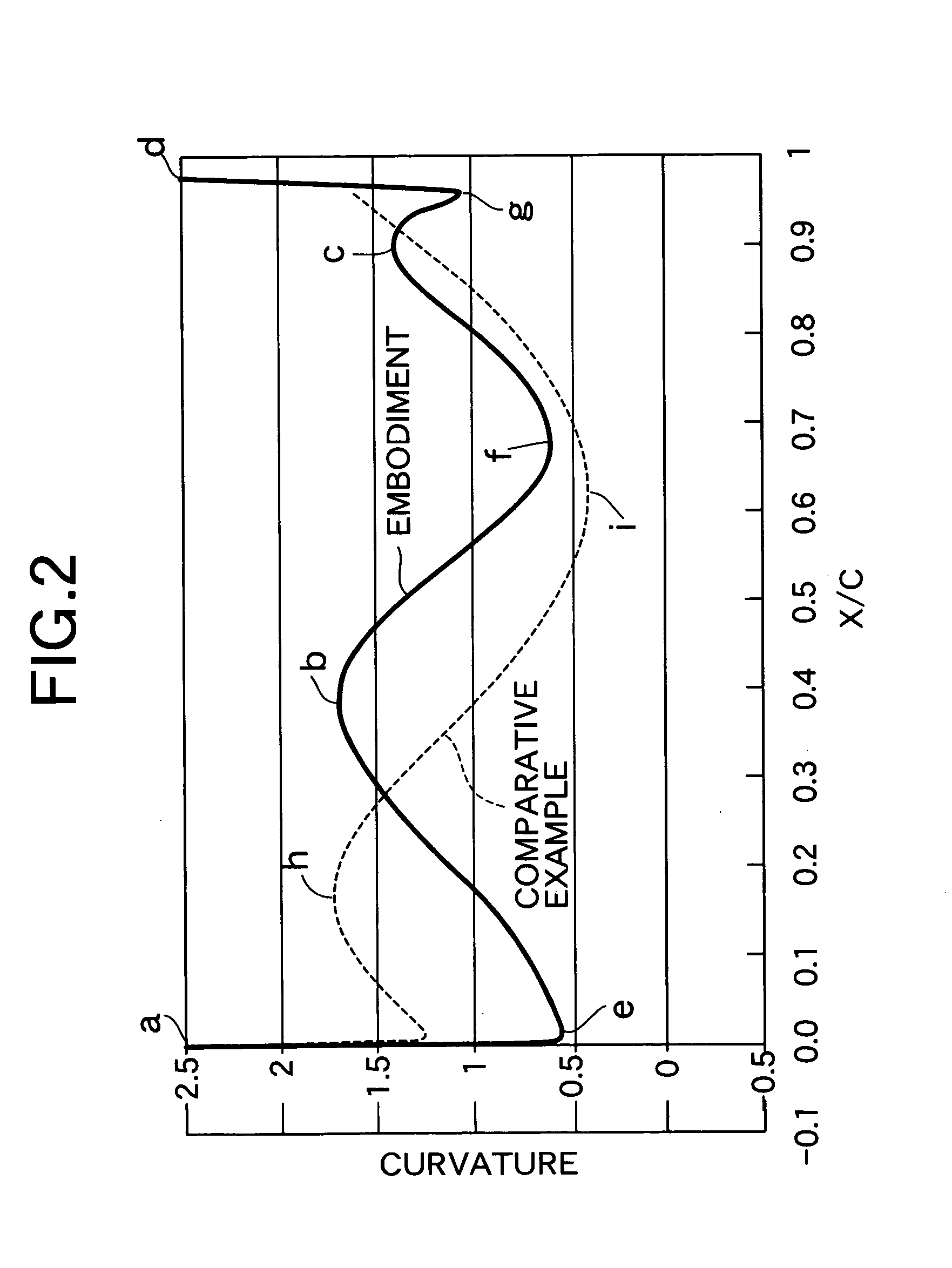
InactiveUS20080118362A1Improve efficiencySimple designSupersonic fluid pumpsPump componentsShock waveLeading edge
Airfoils are provided having non-monotonic meanline angle distributions and local negative camber along a length of the meanline between a point on a leading edge of the airfoil and a point on the trailing edge of the airfoil. The improved airfoil shape decreases the peak of a Mach number of a shock wave that develops in a passage between adjacent airfoils and attenuates or eliminates the shock wave at the suction surface of the airfoil within the passage. A blade constructed by this type of airfoil provides improved fluid flow in the passages between the airfoils, increased efficiency and an improved stall margin, among other benefits.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
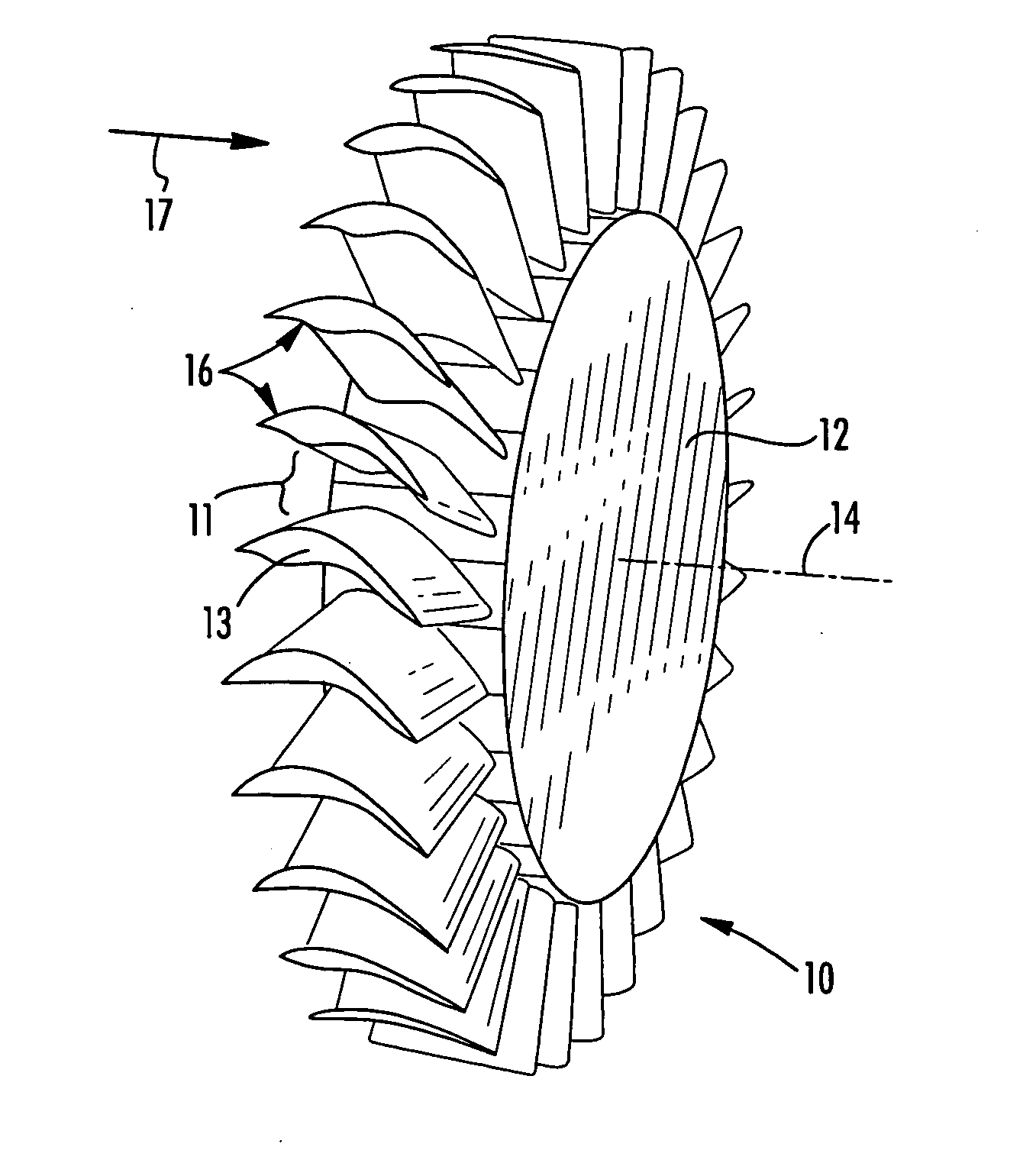
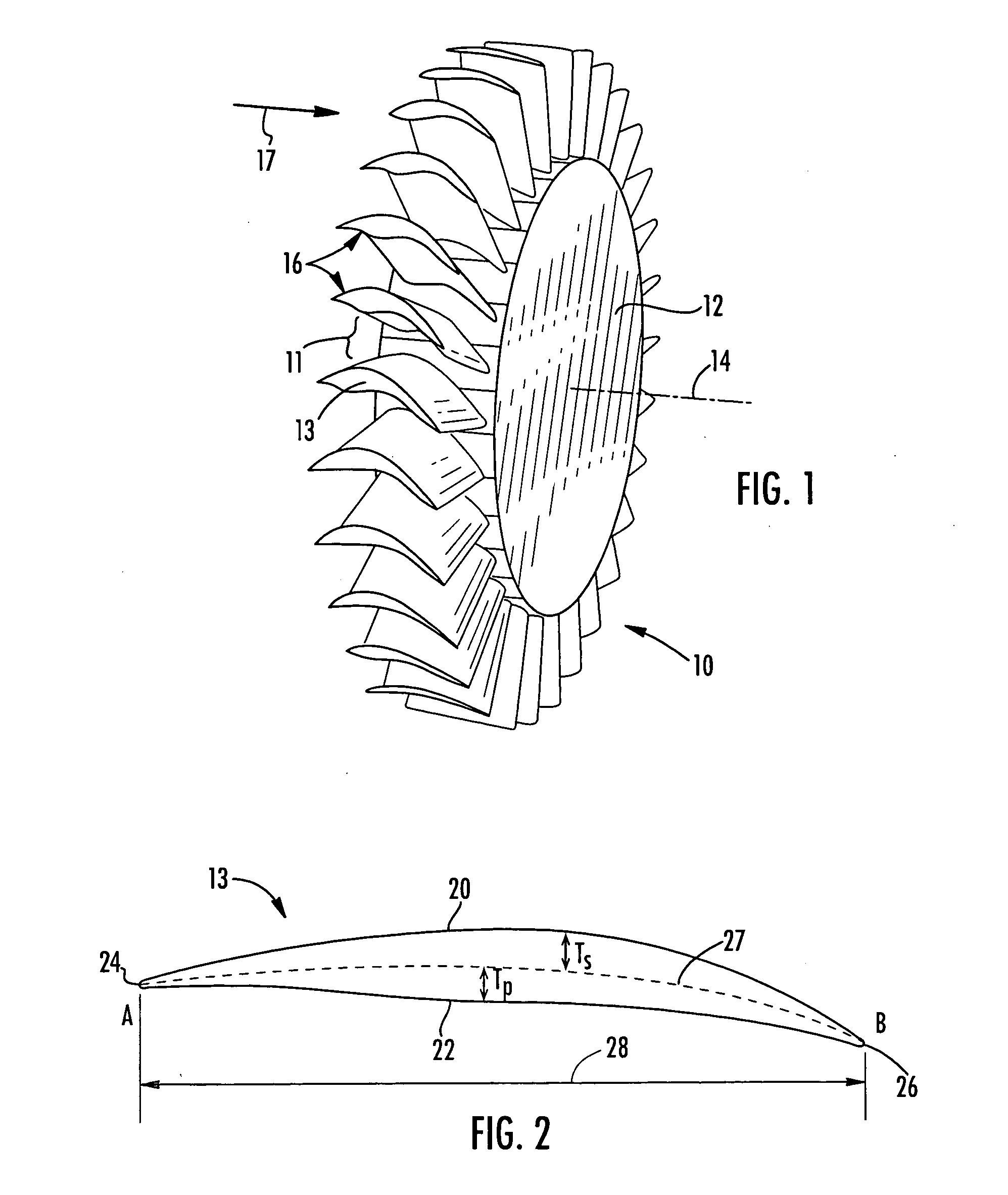
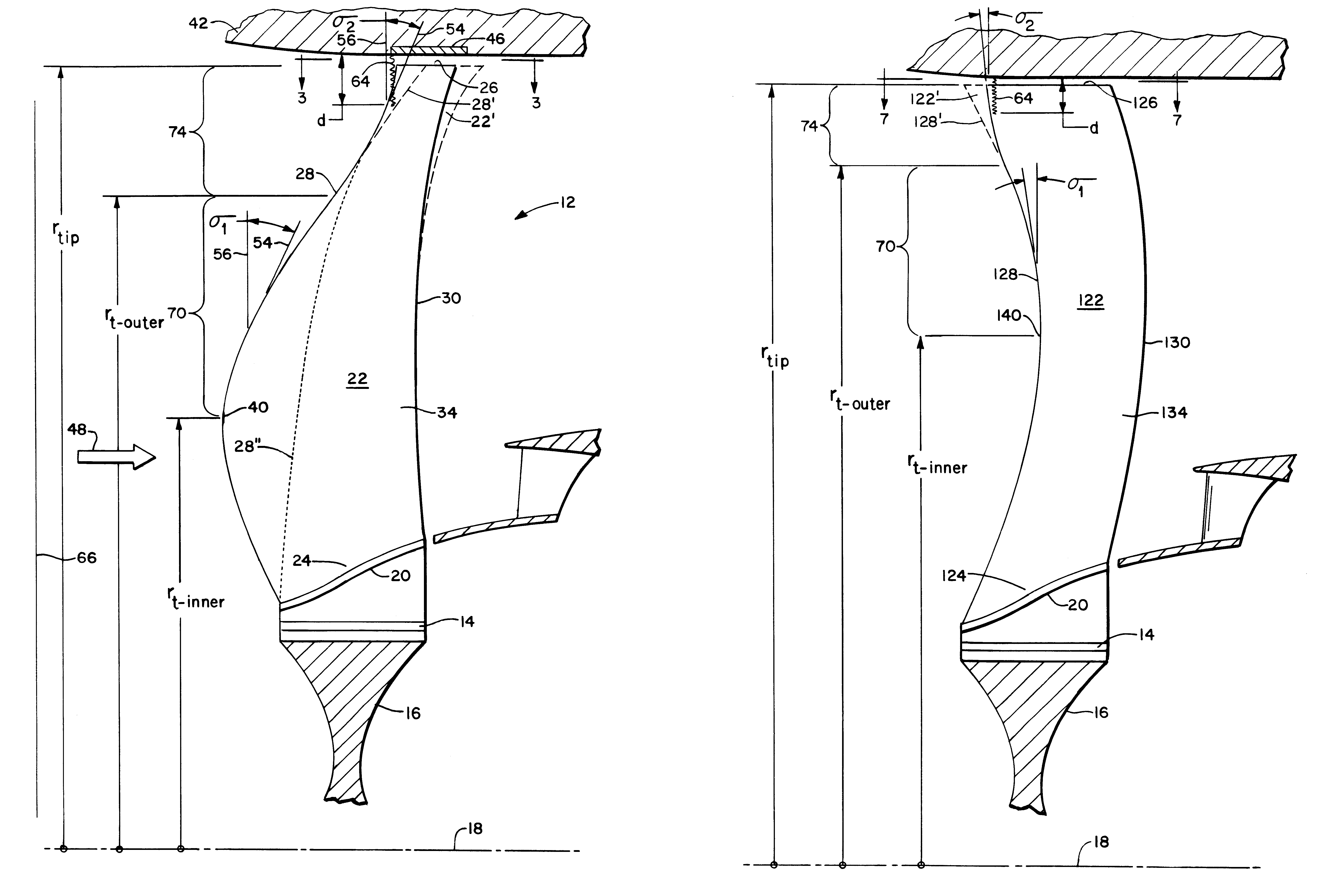
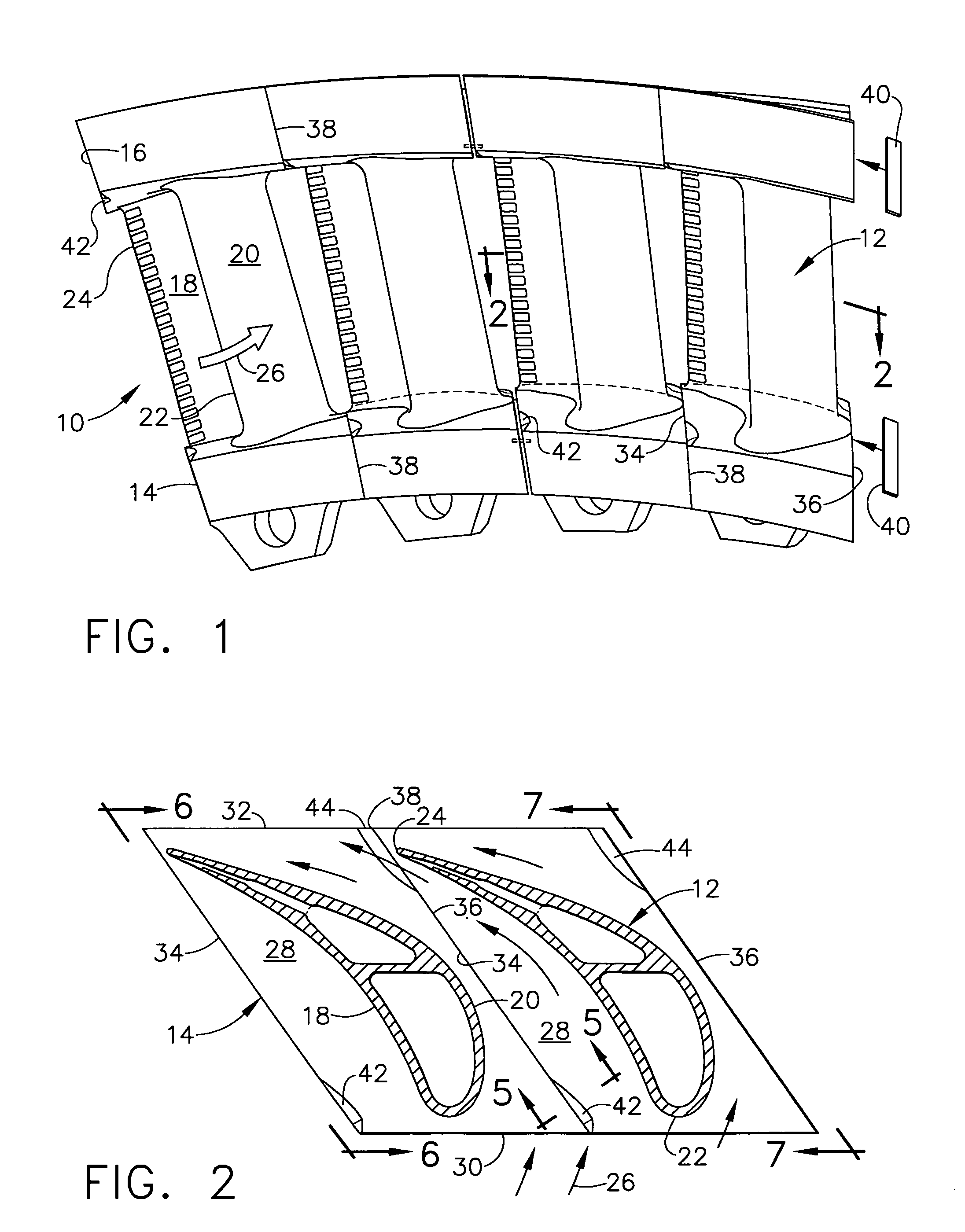
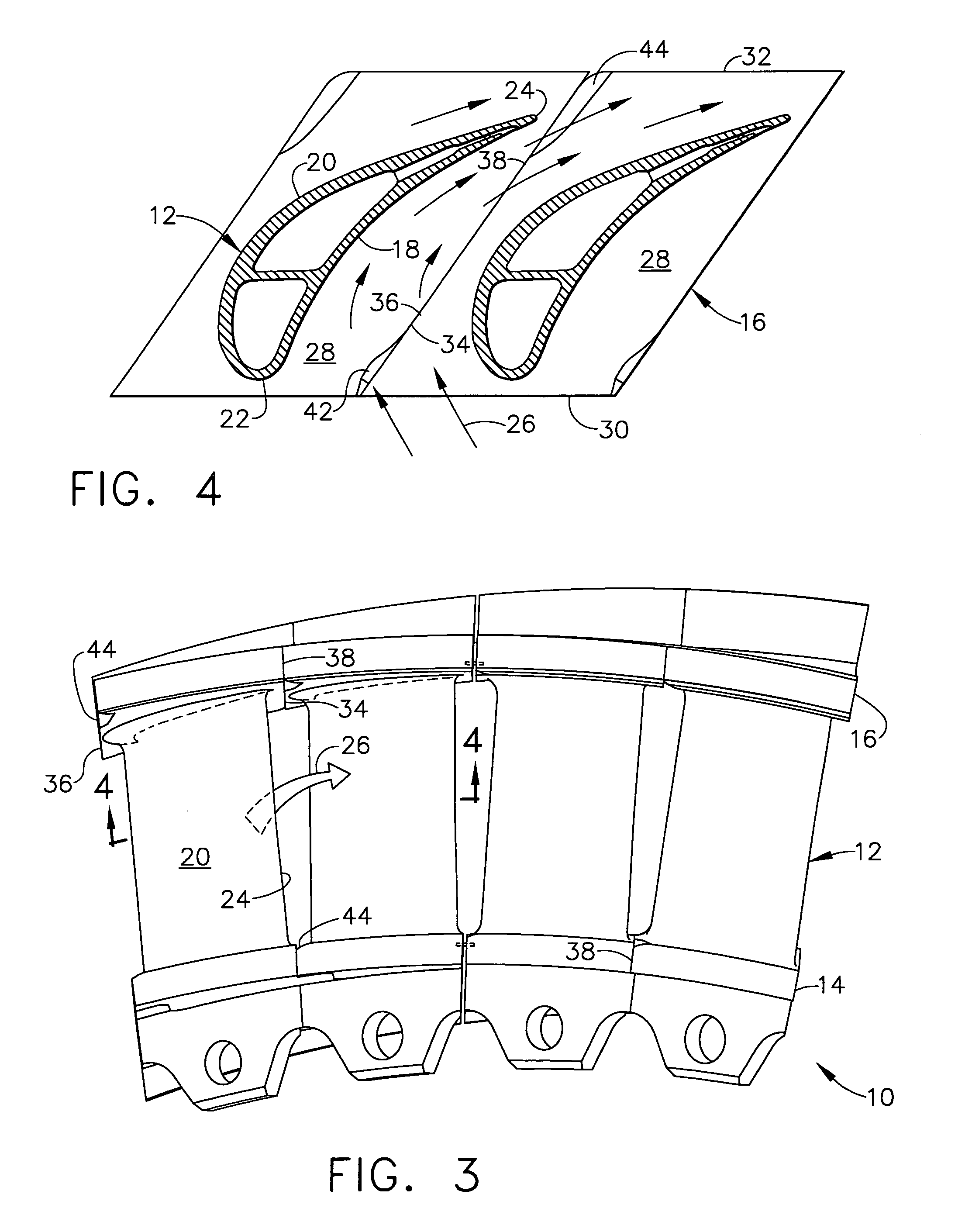
Swept turbomachinery blade
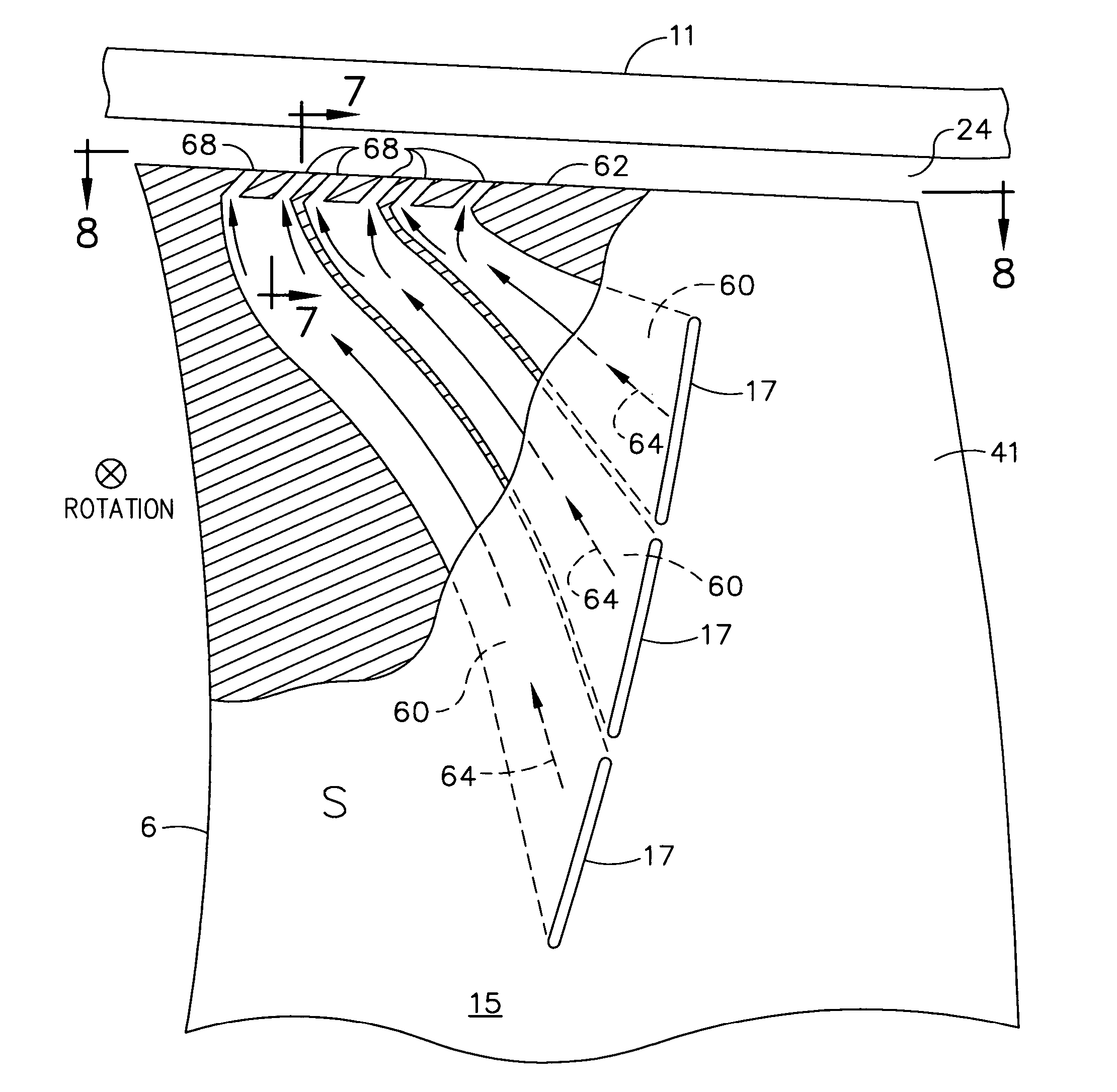
InactiveUSRE38040E1Maximize engine efficiencyReduce in quantityPropellersSupersonic fluid pumpsEngineeringTransition point
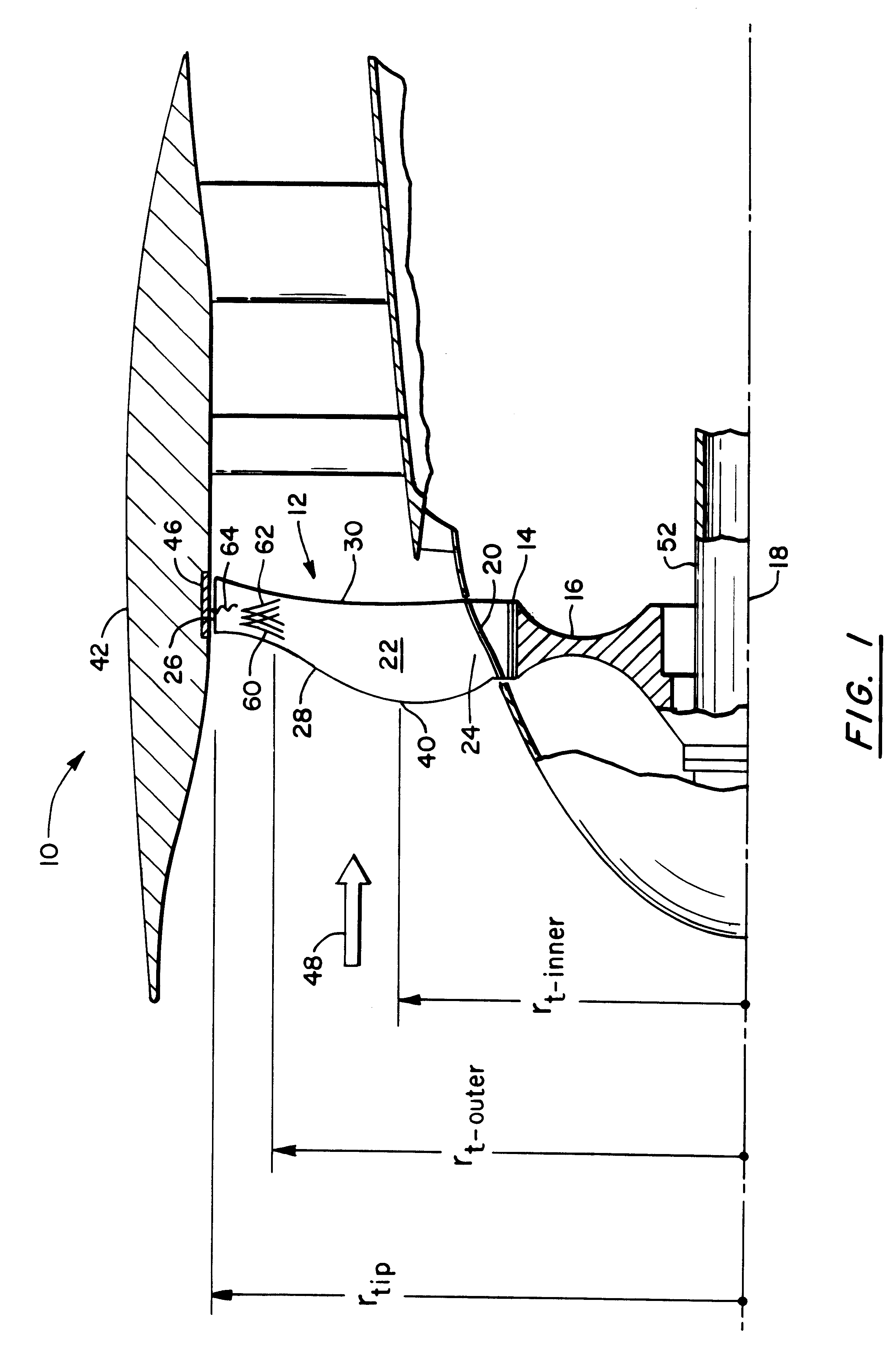
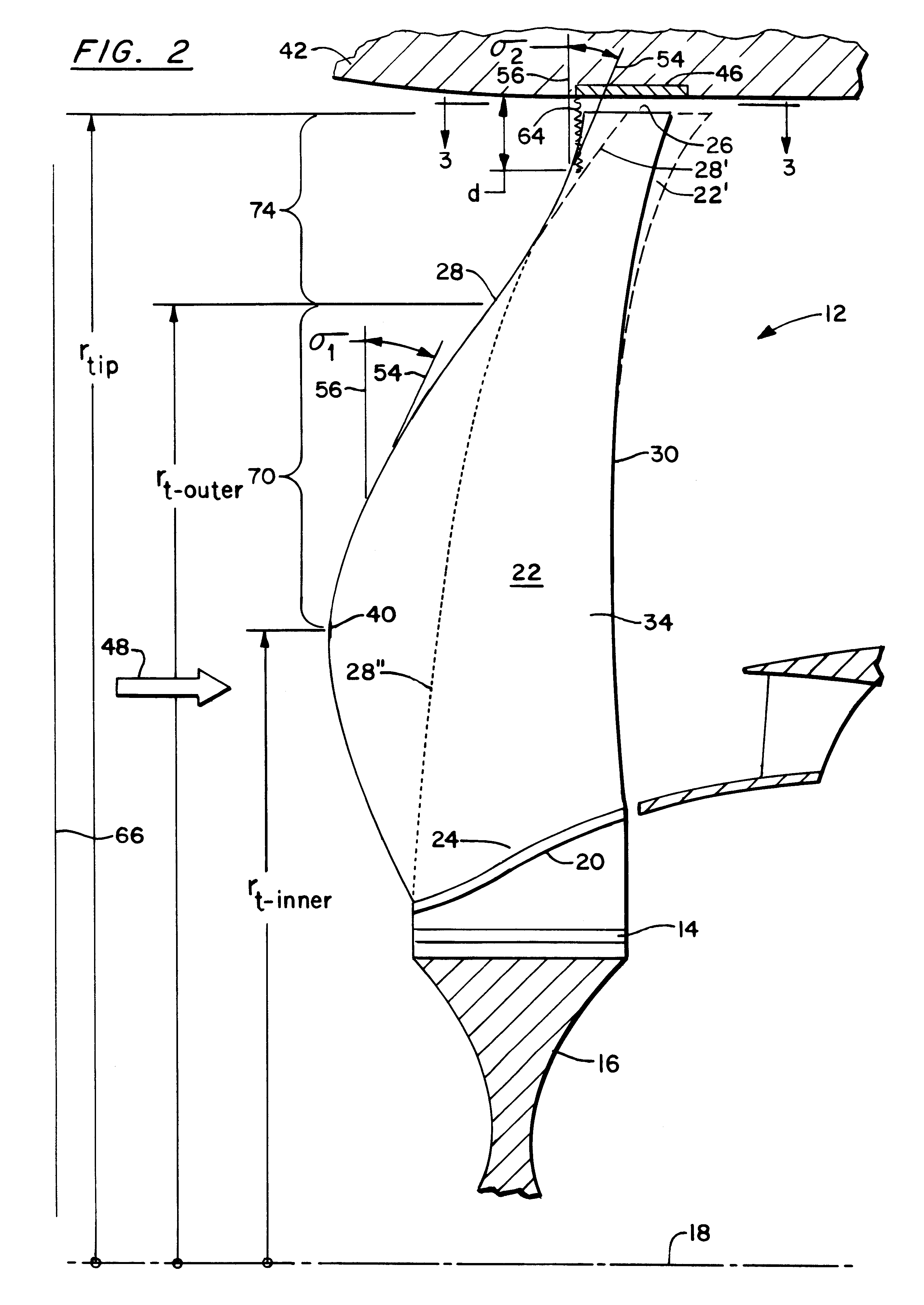
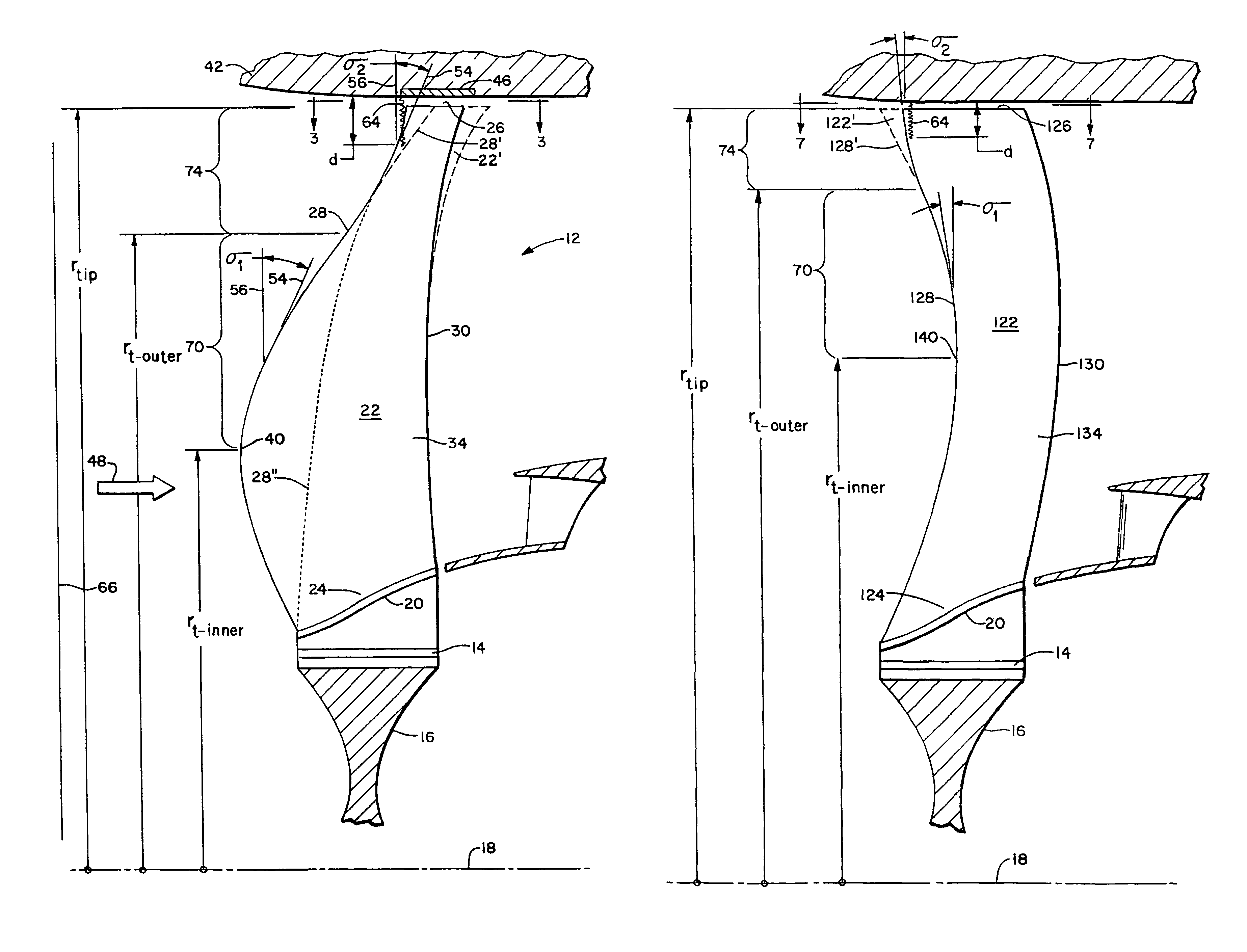
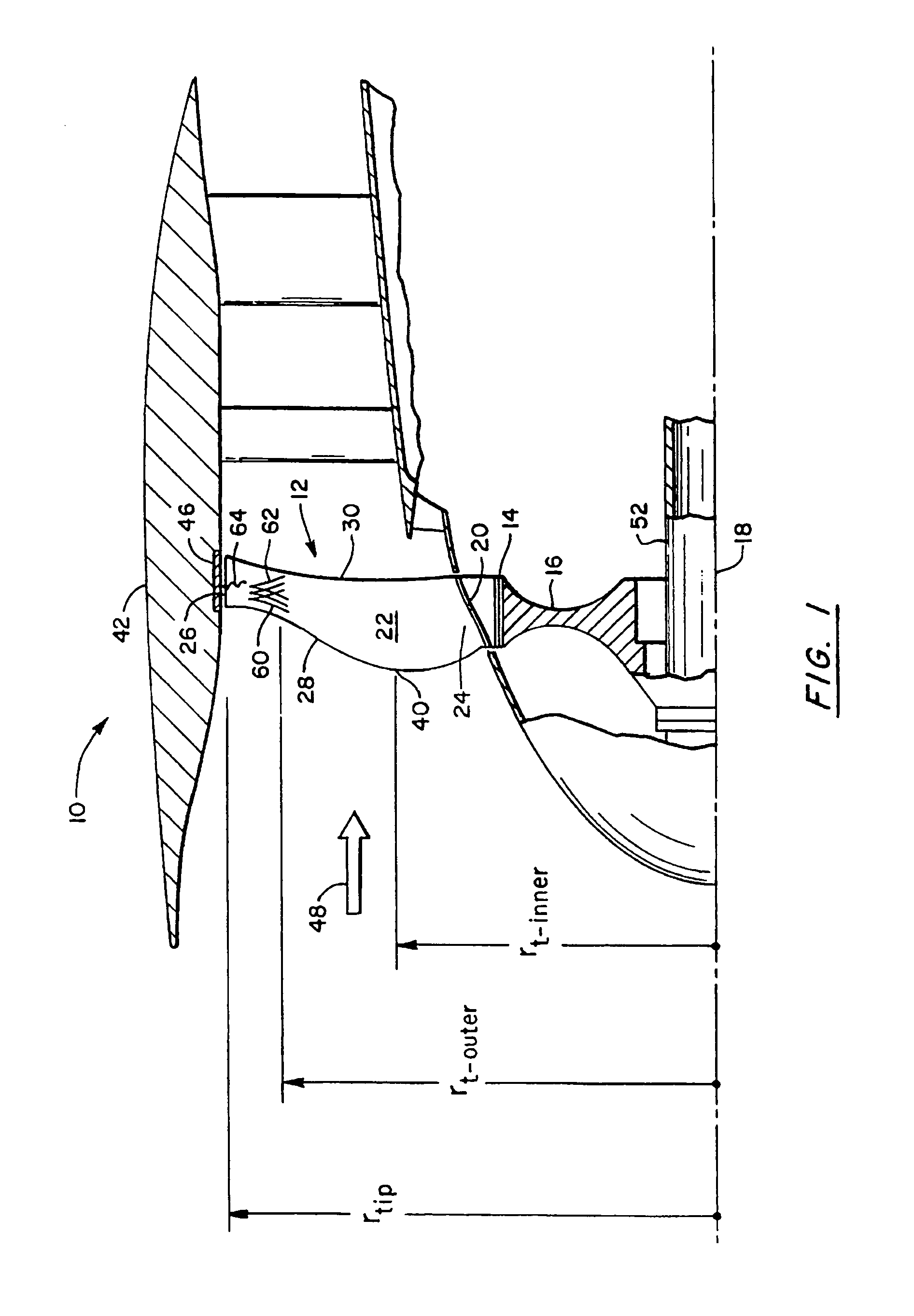
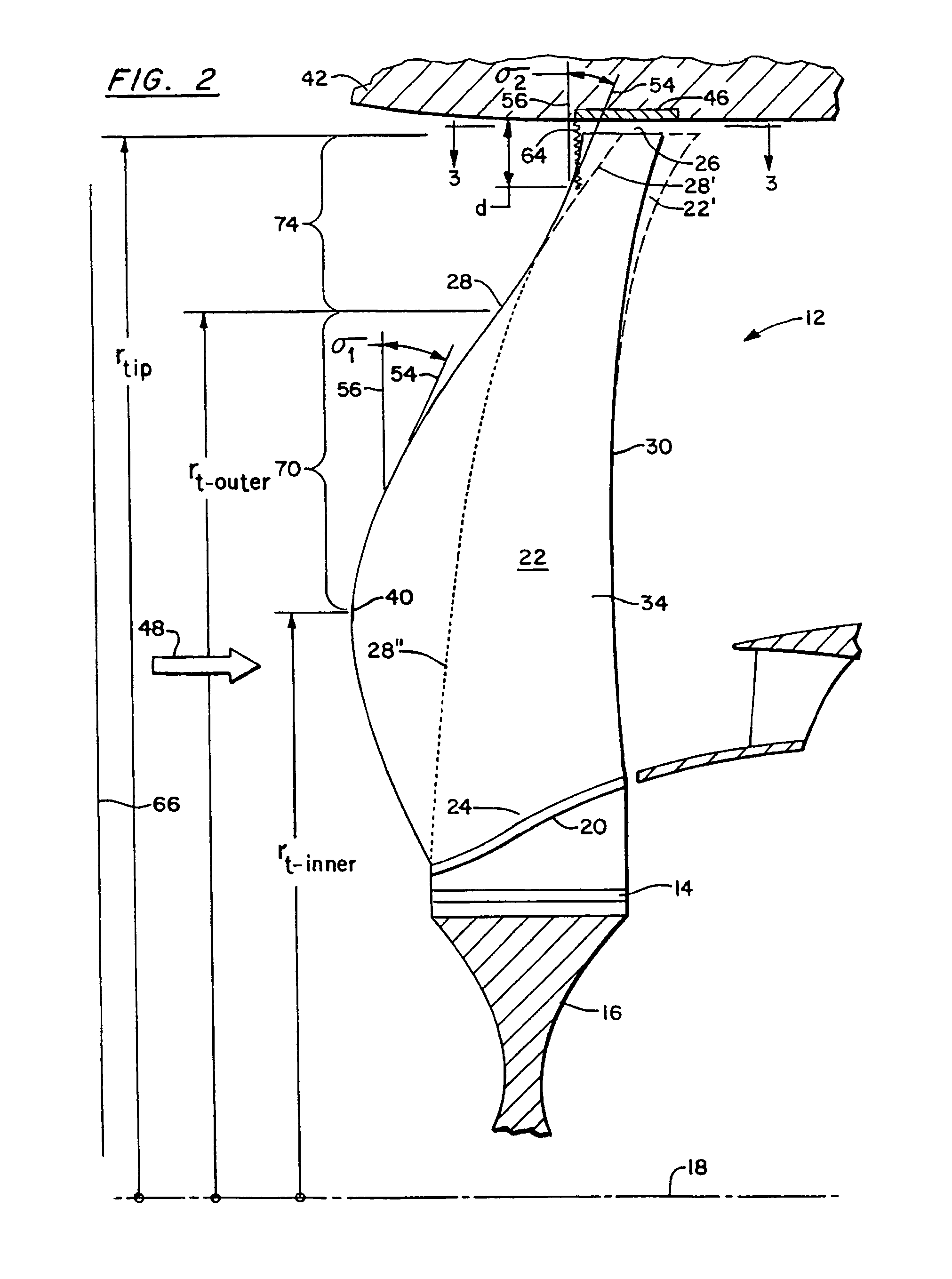
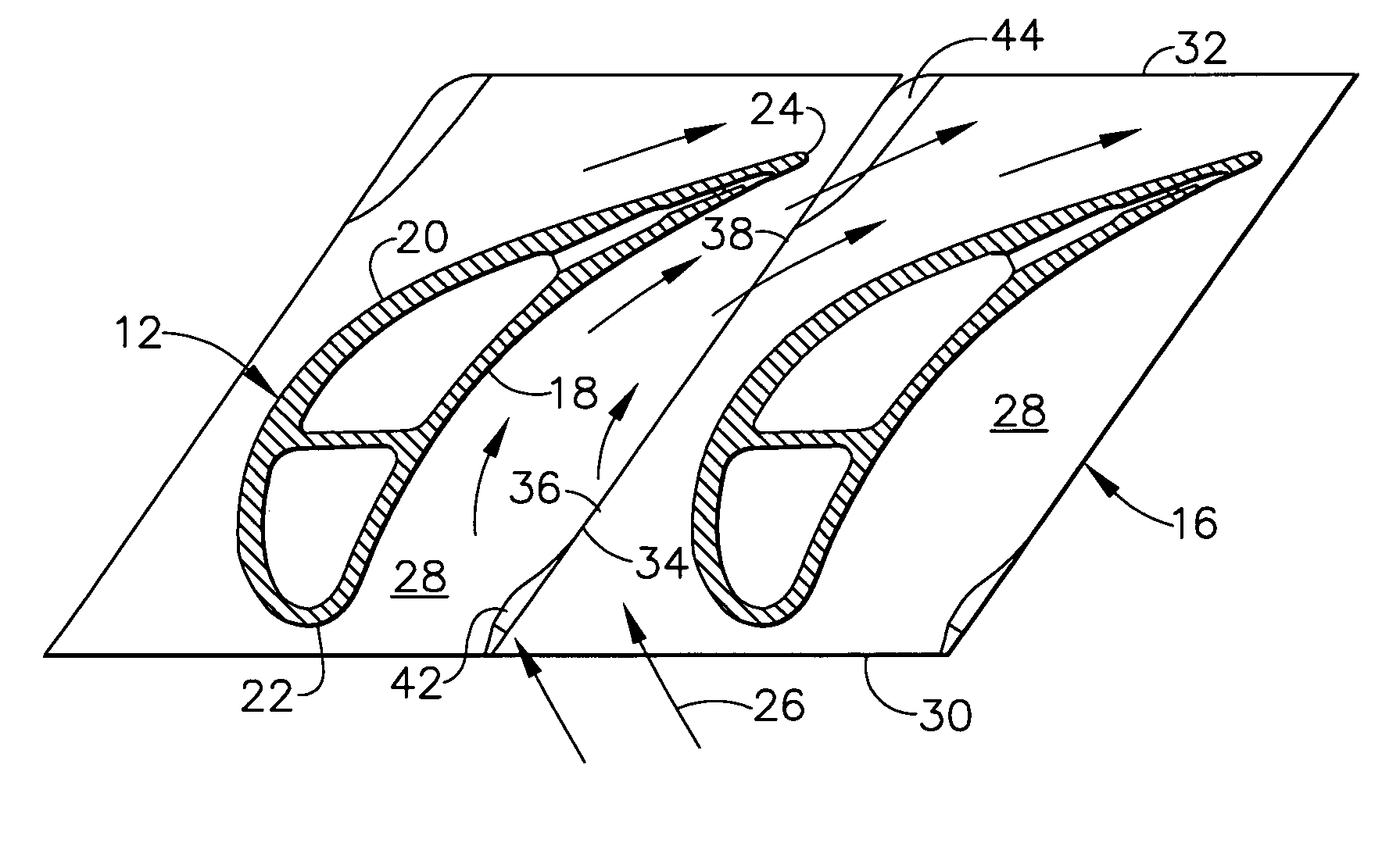
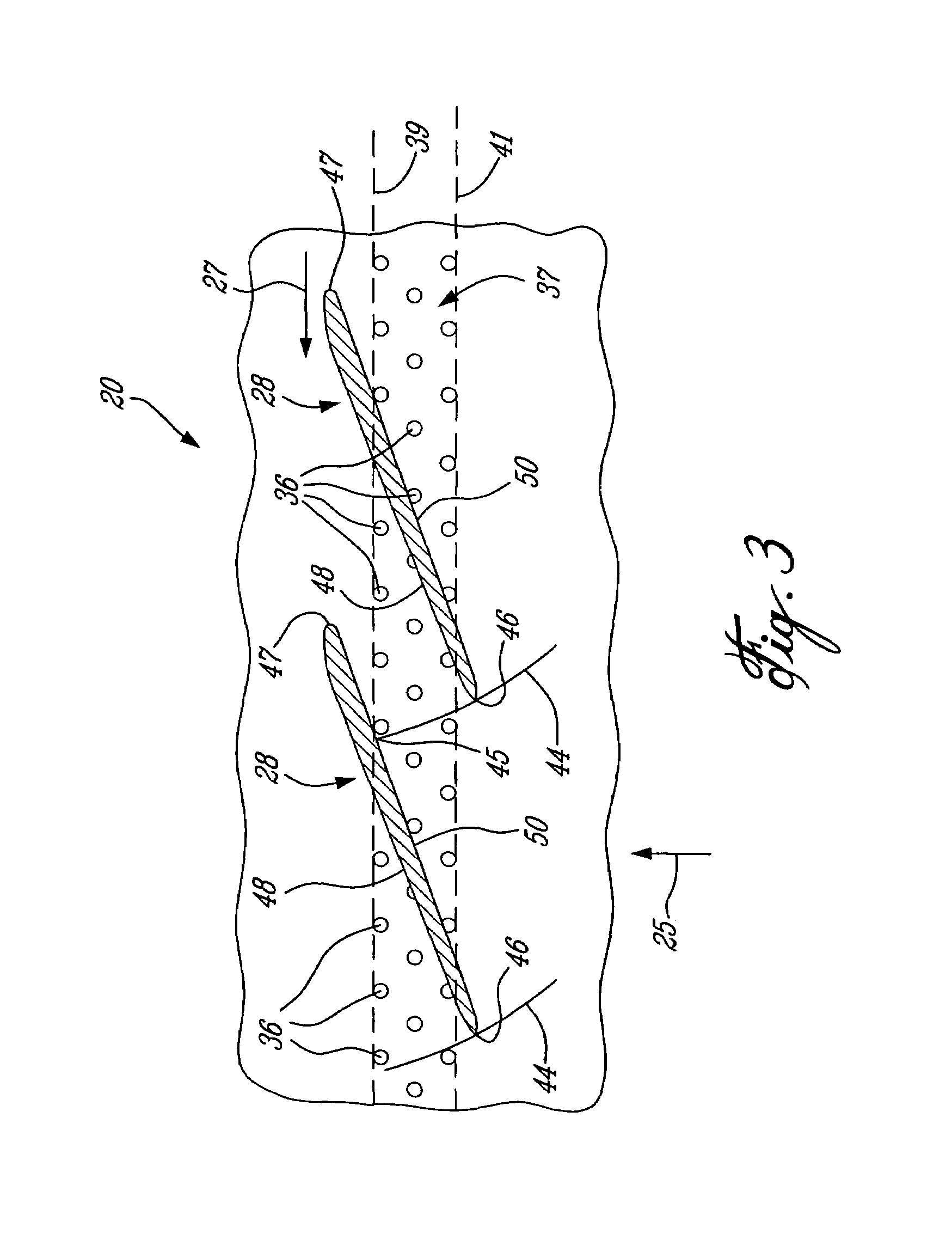
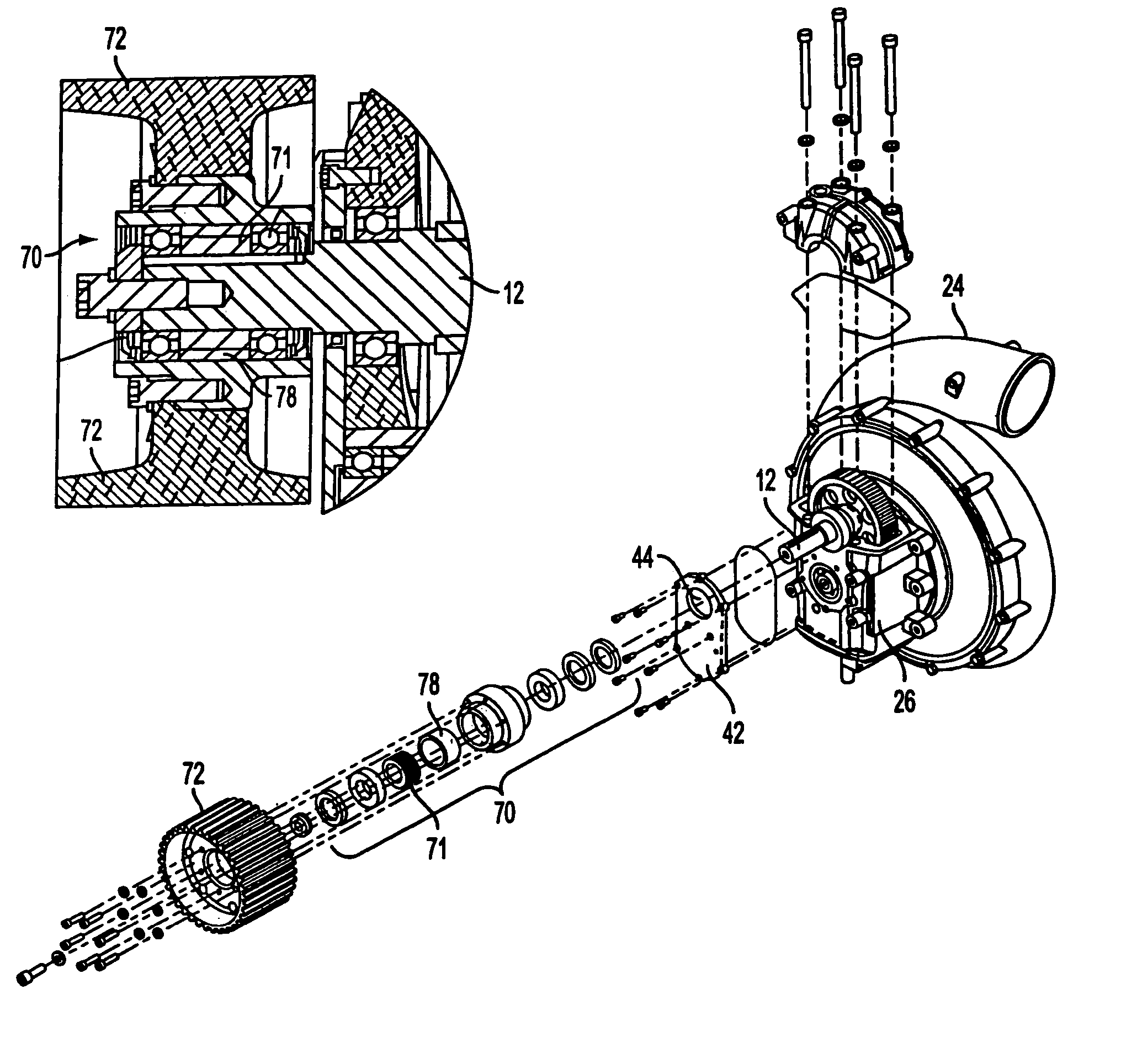
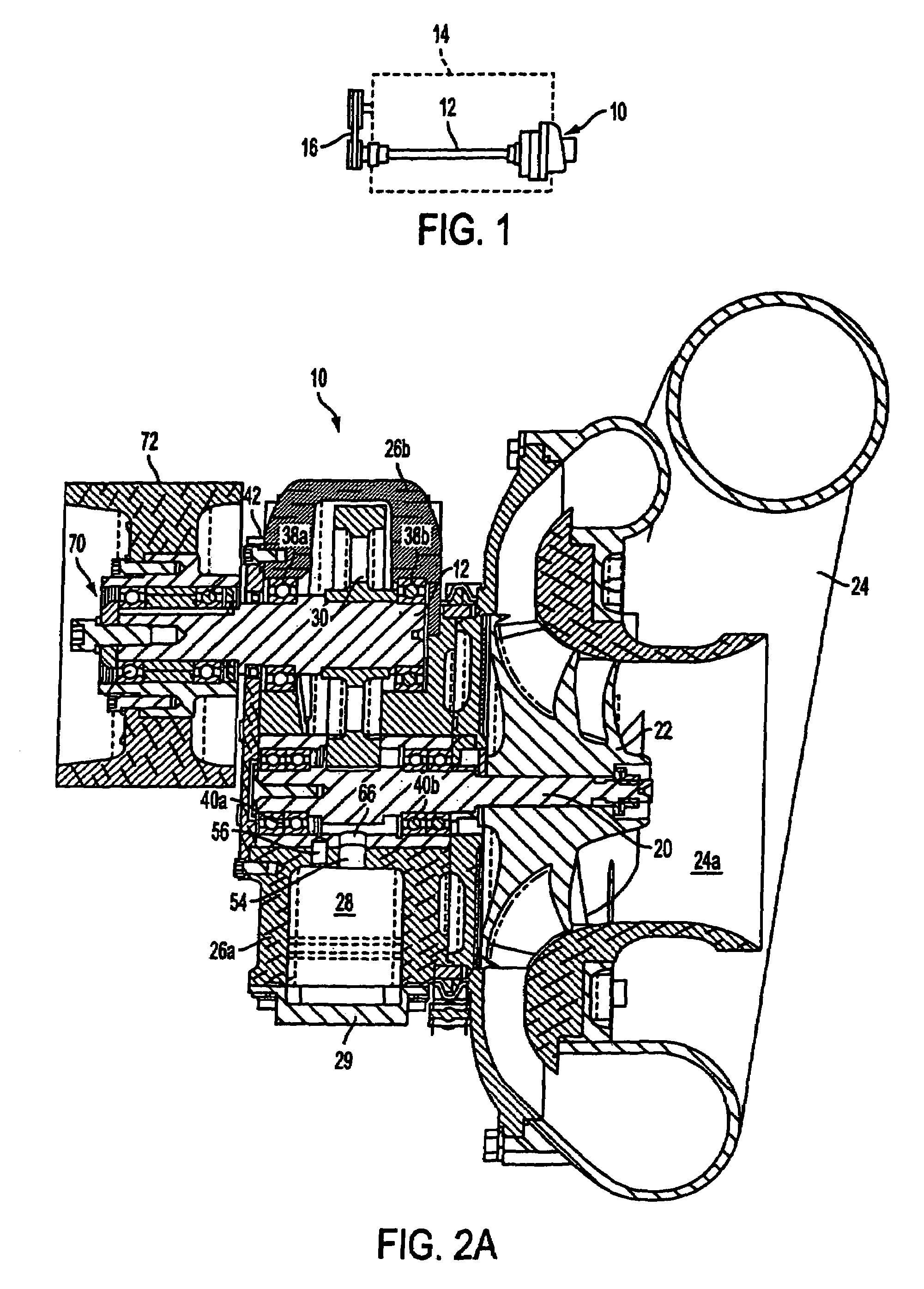
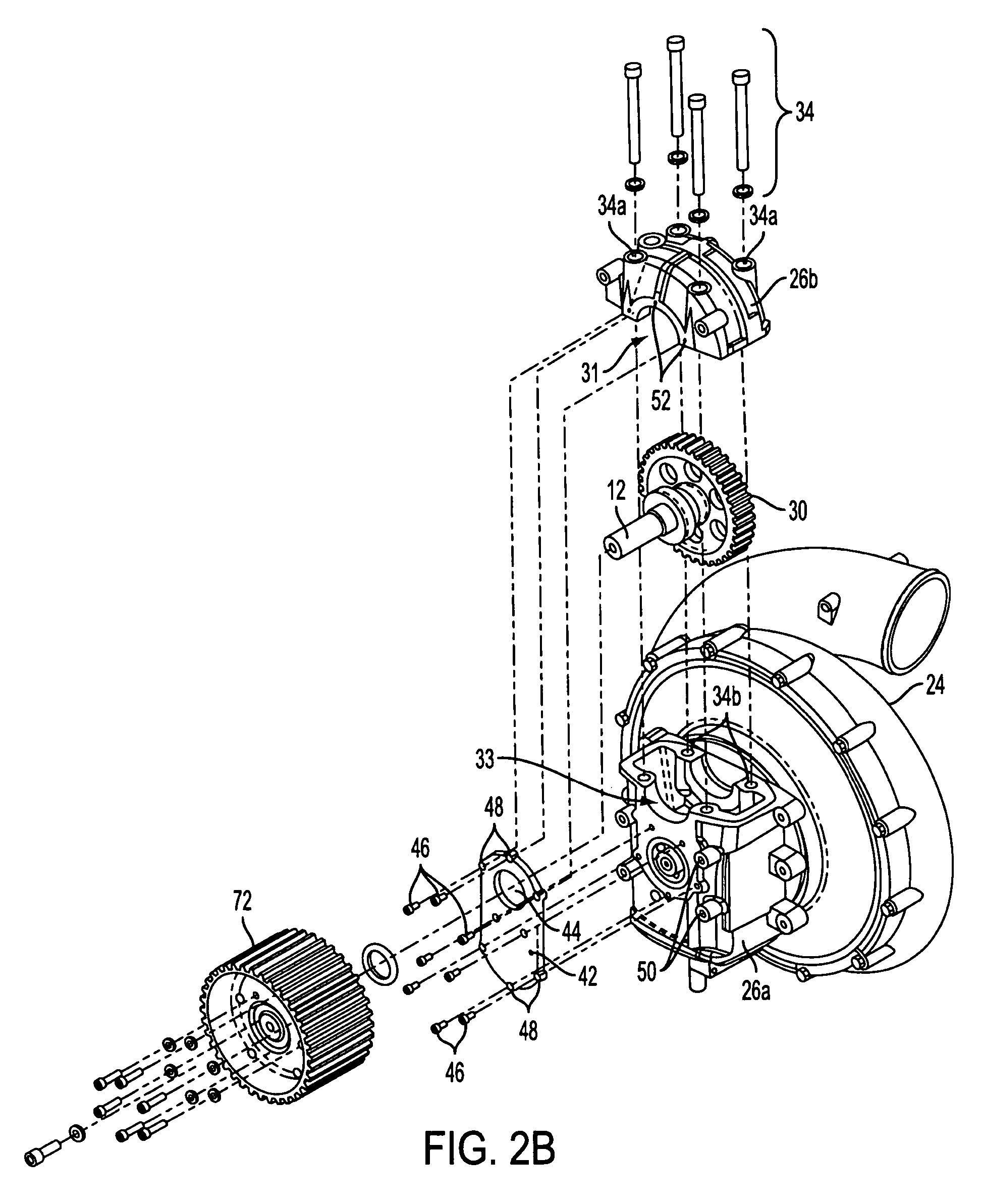
A swept turbomachinery blade for use in a cascade of such blades is disclosed. The blade (12) has an airfoil (22) uniquely swept so that an endwall shock (64) of limited radial extent and a passage shock (66) are coincident and a working medium (48) flowing through interblade passages (50) is subjected to a single coincident shock rather than the individual shocks. In one embodiment of the invention the forwardmost extremity of the airfoil defines an inner transition point (40) located at an inner transition radius rt-inner. The sweep angle of the airfoil is nondecreasing with increasing radius from the inner transition radius to an outer transition radius rt-outer, radially inward of the airfoil tip (26), and is nonincreasing with increasing radius between the outer transition radius and the airfoil tip.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Low noise compressor rotor for geared turbofan engine
A gas turbine engine comprises a fan and a turbine section having a first turbine rotor. The first turbine rotor drives a compressor rotor. A gear reduction effects a reduction in the speed of the fan relative to an input speed from a fan drive turbine rotor. The compressor rotor has a number of compressor blades in at least one of a plurality of rows of the compressor rotor. The blades operate at least some of the time at a rotational speed. The number of compressor blades in at least one row and the rotational speed are such that the following formula holds true for at least one row of the compressor rotor:(the number of blades×the rotational speed) / (60 seconds / minute)≧5500 Hz; andthe rotational speed being in revolutions per minute.A compressor module and a method of designing a gas turbine engine are also disclosed.
Owner:MTU AERO ENGINES GMBH
Swept turbomachinery blade
InactiveUSRE43710E1Minimize the aerodynamic losses and efficiency degradationMaximize efficiencyPropellersSupersonic fluid pumpsEngineeringTransition point
A swept turbomachinery blade for use in a cascade of such blades is disclosed. The blade (12) has an airfoil (22) uniquely swept so that an endwall shock (64) of limited radial extent and a passage shock (66) are coincident and a working medium (48) flowing through interblade passages (50) is subjected to a single coincident shock rather than the individual shocks. In one embodiment of the invention the forwardmost extremity of the airfoil defines an inner transition point (40) located at an inner transition radius rt-inner. The sweep angle of the airfoil is nondecreasing with increasing radius from the inner transition radius to an outer transition radius rt-outer, radially inward of the airfoil tip (26), and is nonincreasing with increasing radius between the outer transition radius and the airfoil tip.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
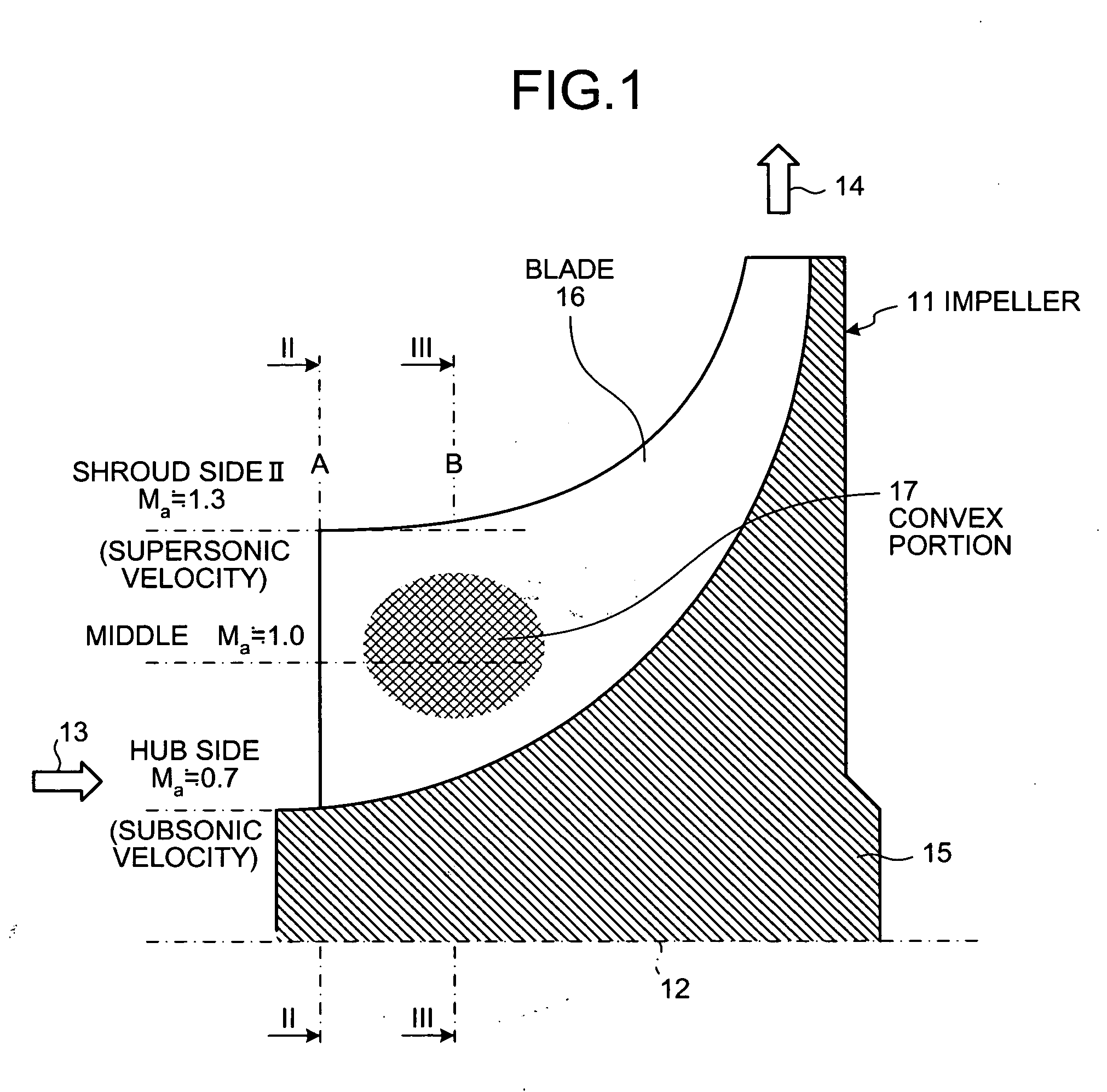
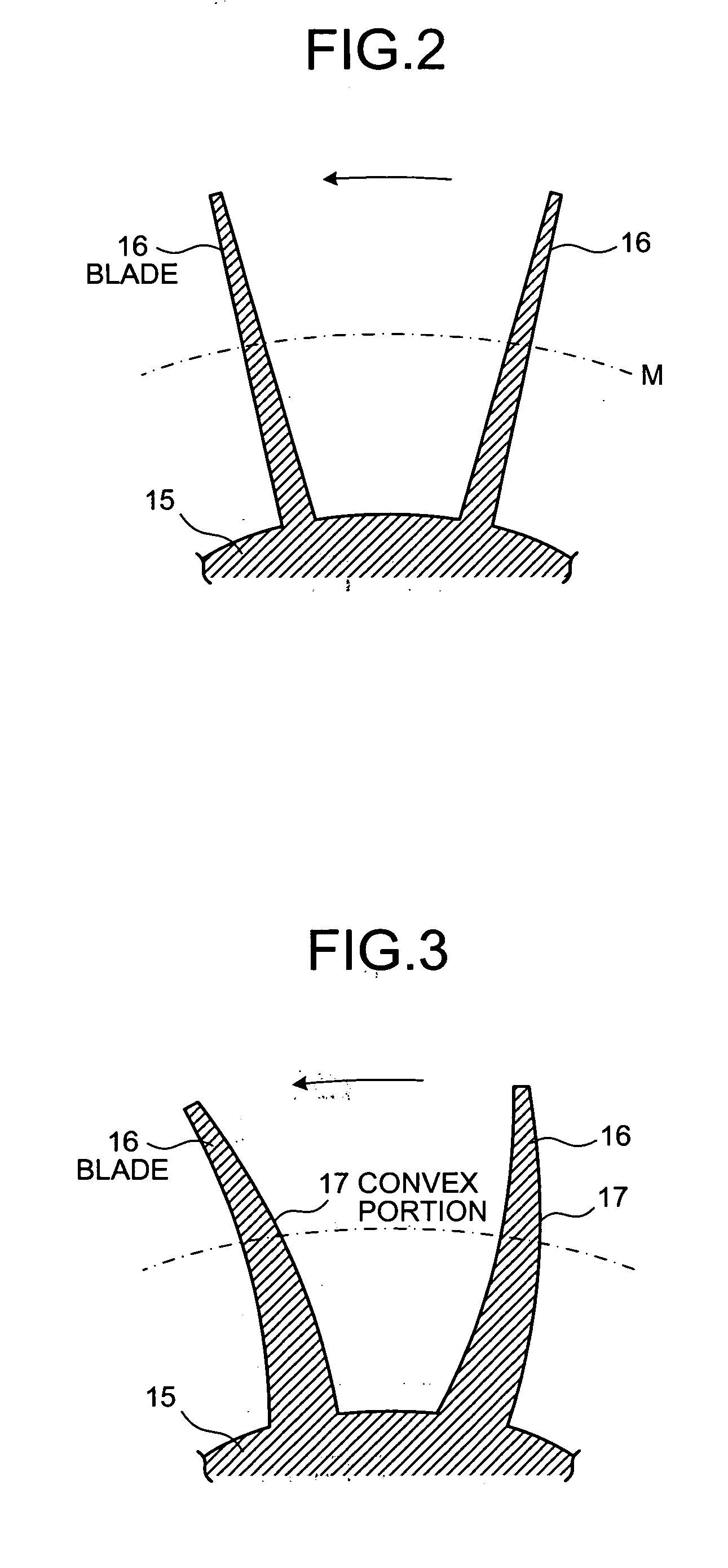
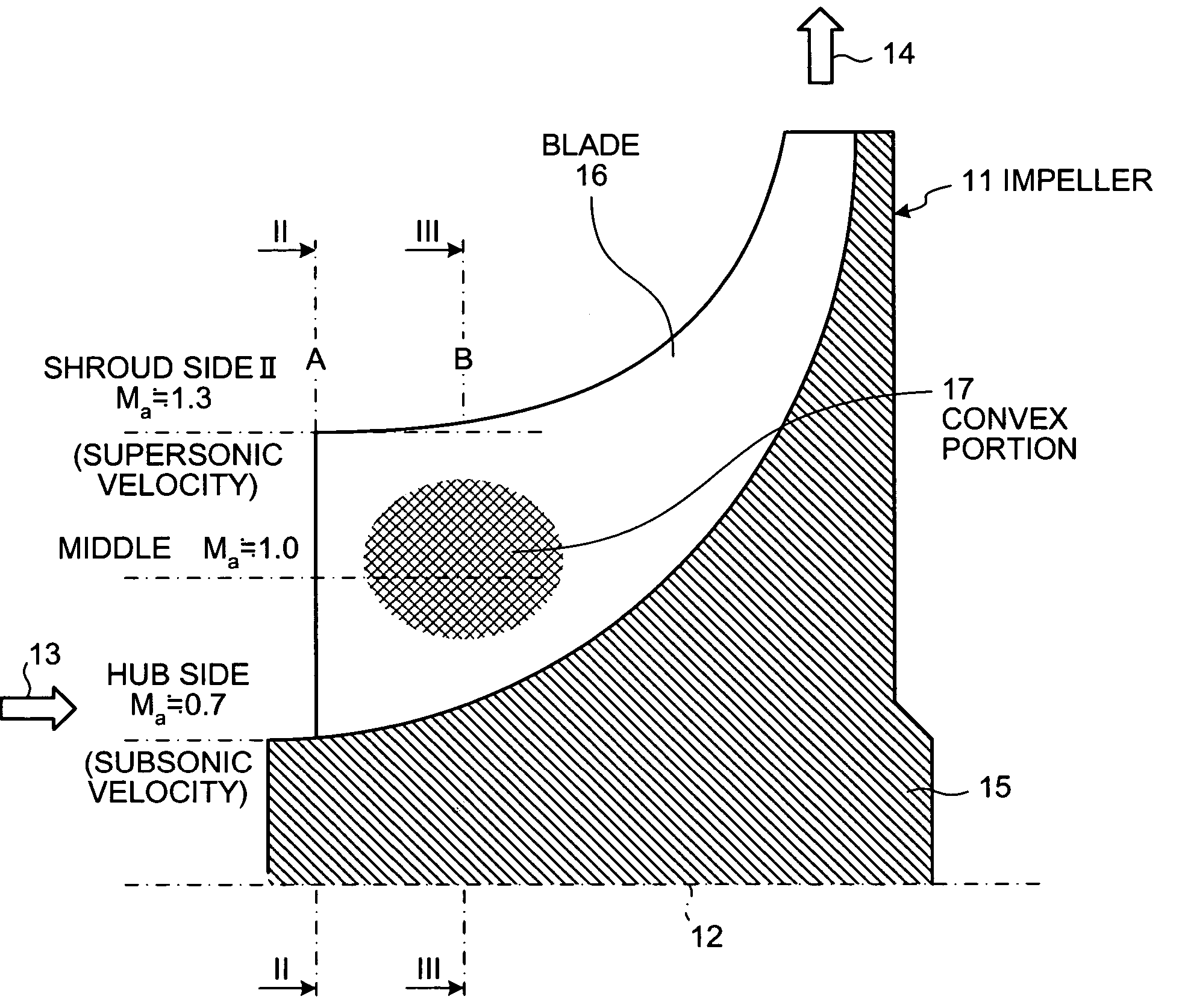
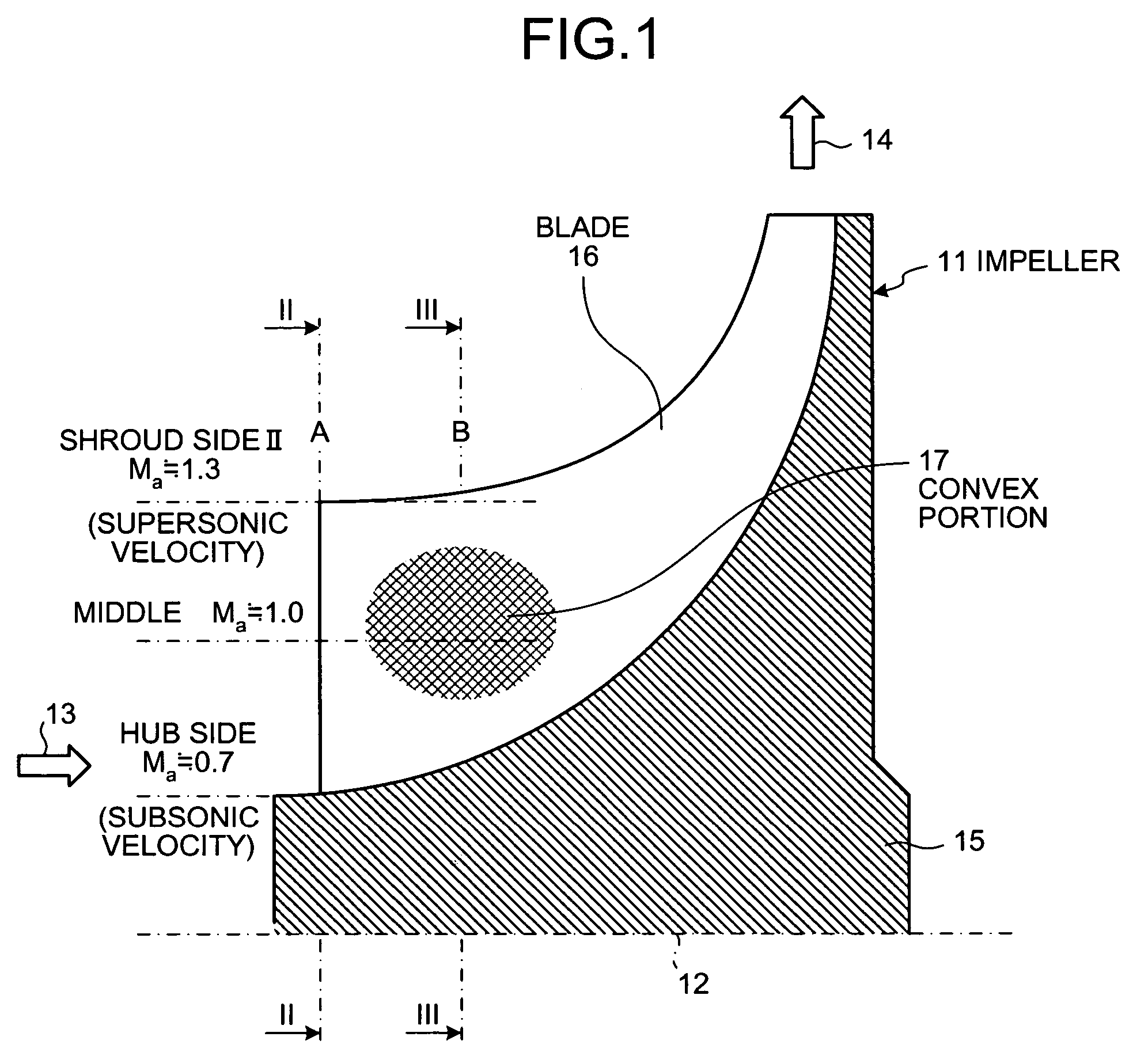
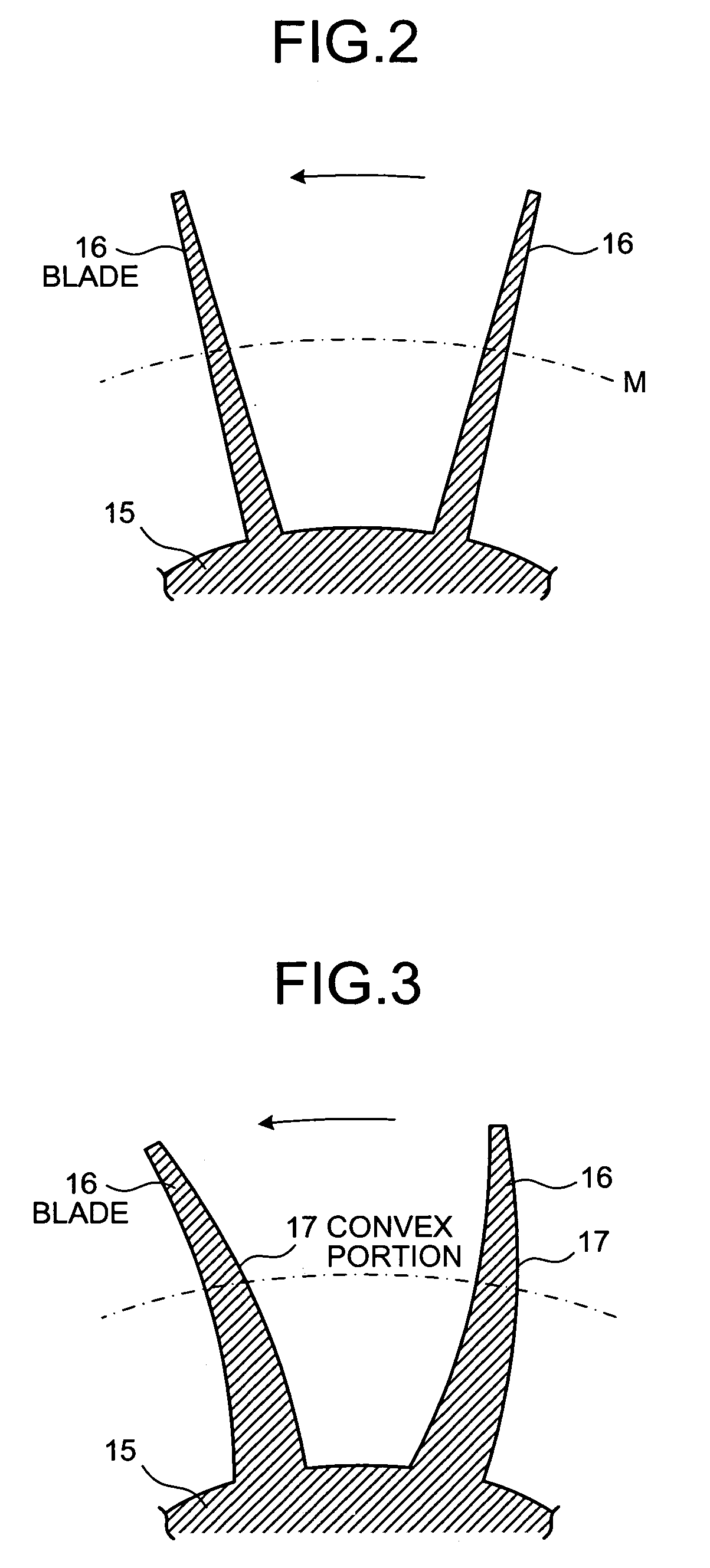
Centrifugal compressor and manufacturing method for impeller
InactiveUS20050260074A1Fall in efficiencyFall in performancePropellersSupersonic fluid pumpsEngineeringFront edge
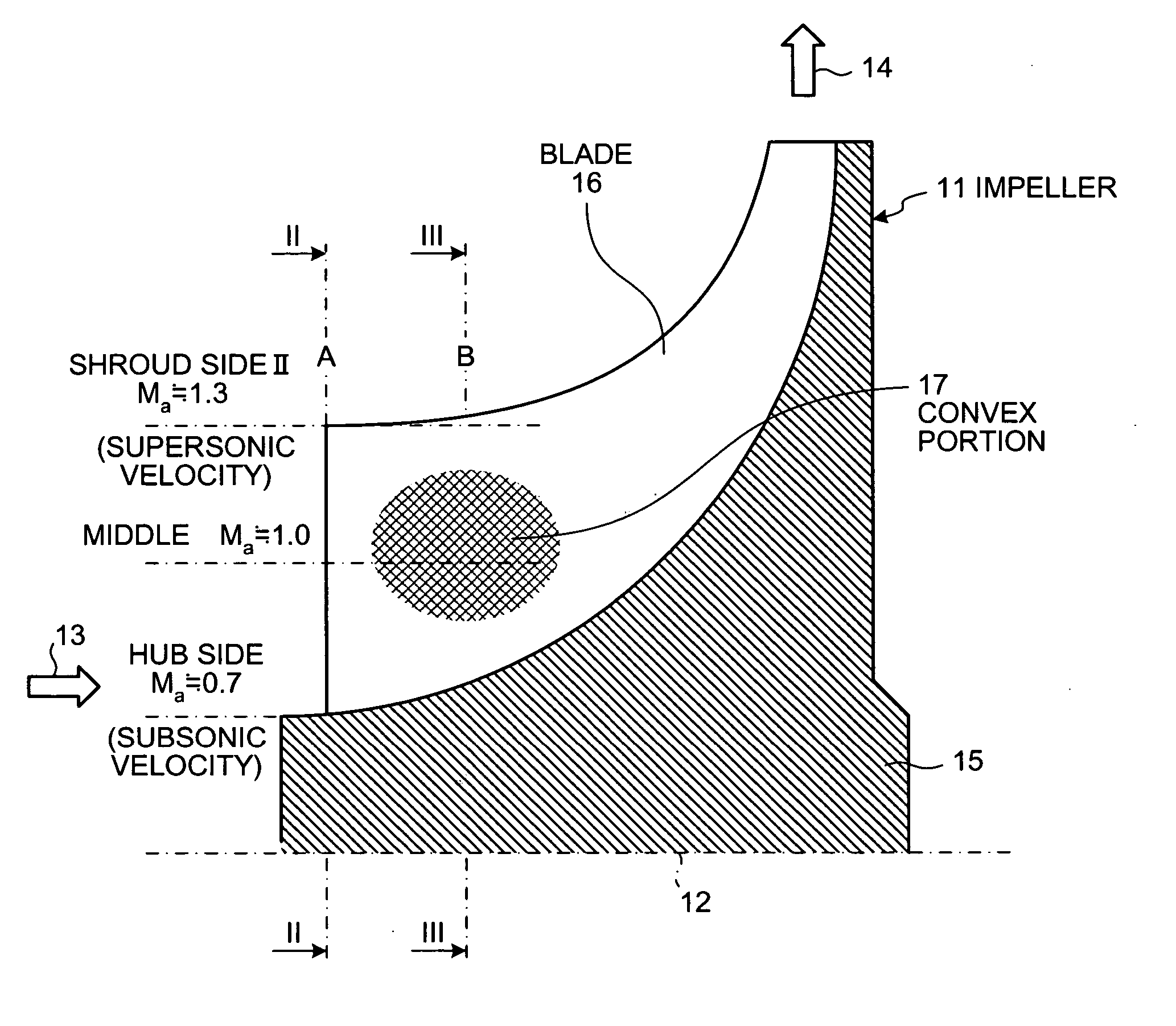
On a suction surface side of a blade in an impeller, a convex portion is formed to assume a curved line from a front edge portion to a throat portion substantially in the middle in a radial direction, and this convex portion is formed to be flat assuming a curved line from the throat portion toward a rear edge portion, whereby this convex portion is formed in a position where a relative inlet velocity of fluid into the impeller is Mach number Ma≅1.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Transonic Blade
ActiveUS20130259668A1Increase stall marginReduce lossesSupersonic fluid pumpsPump componentsLeading edgeEngineering
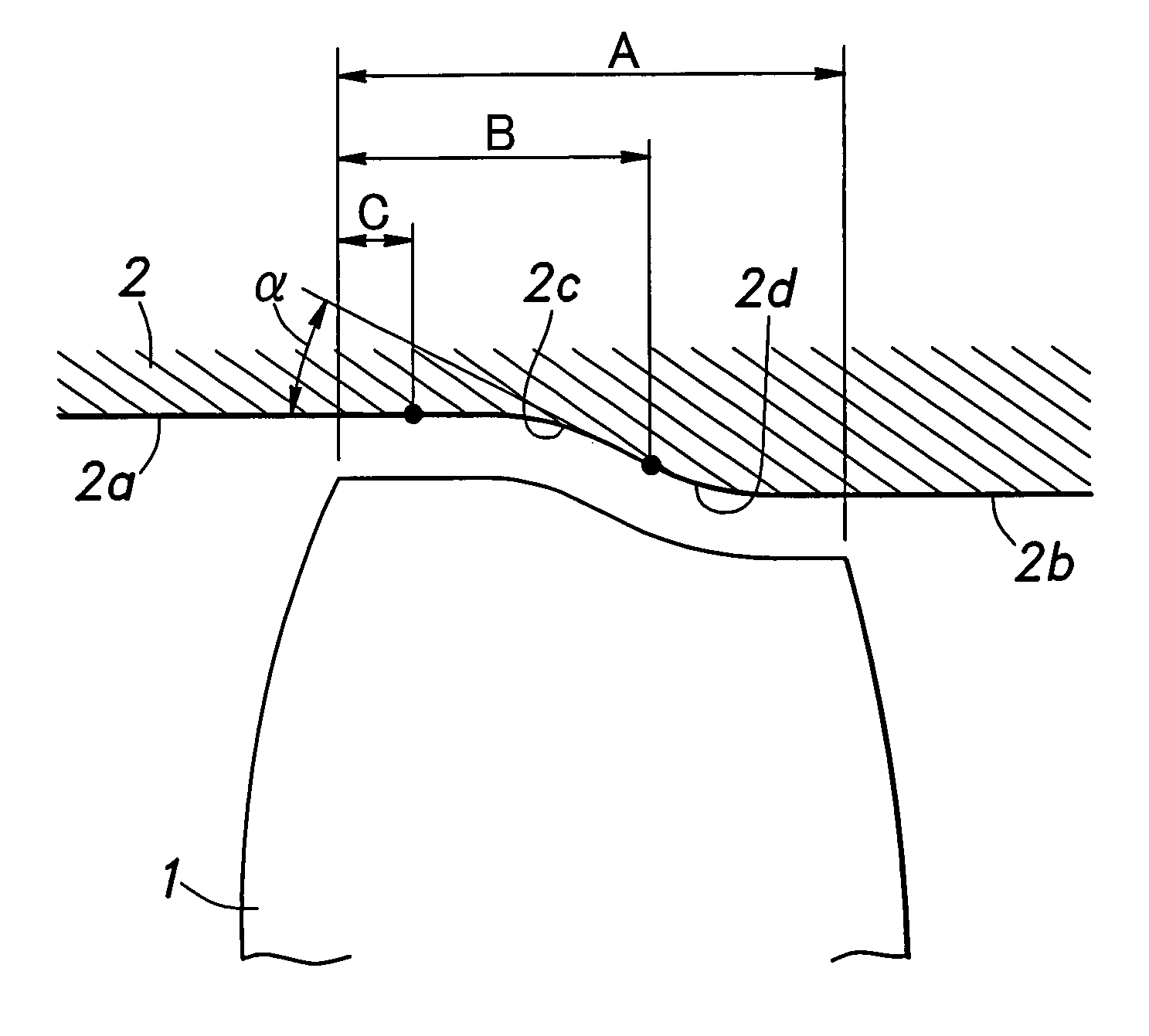
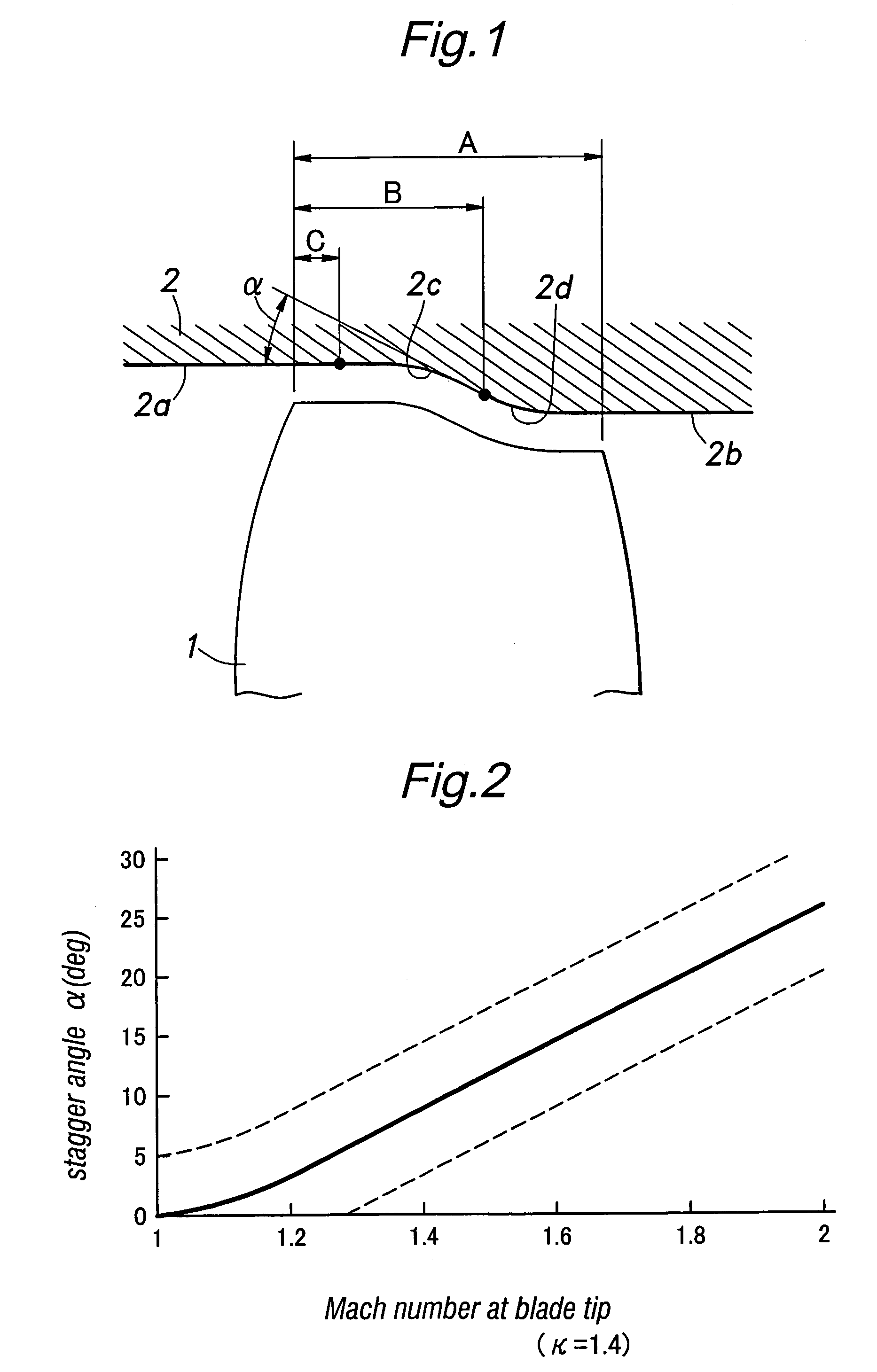
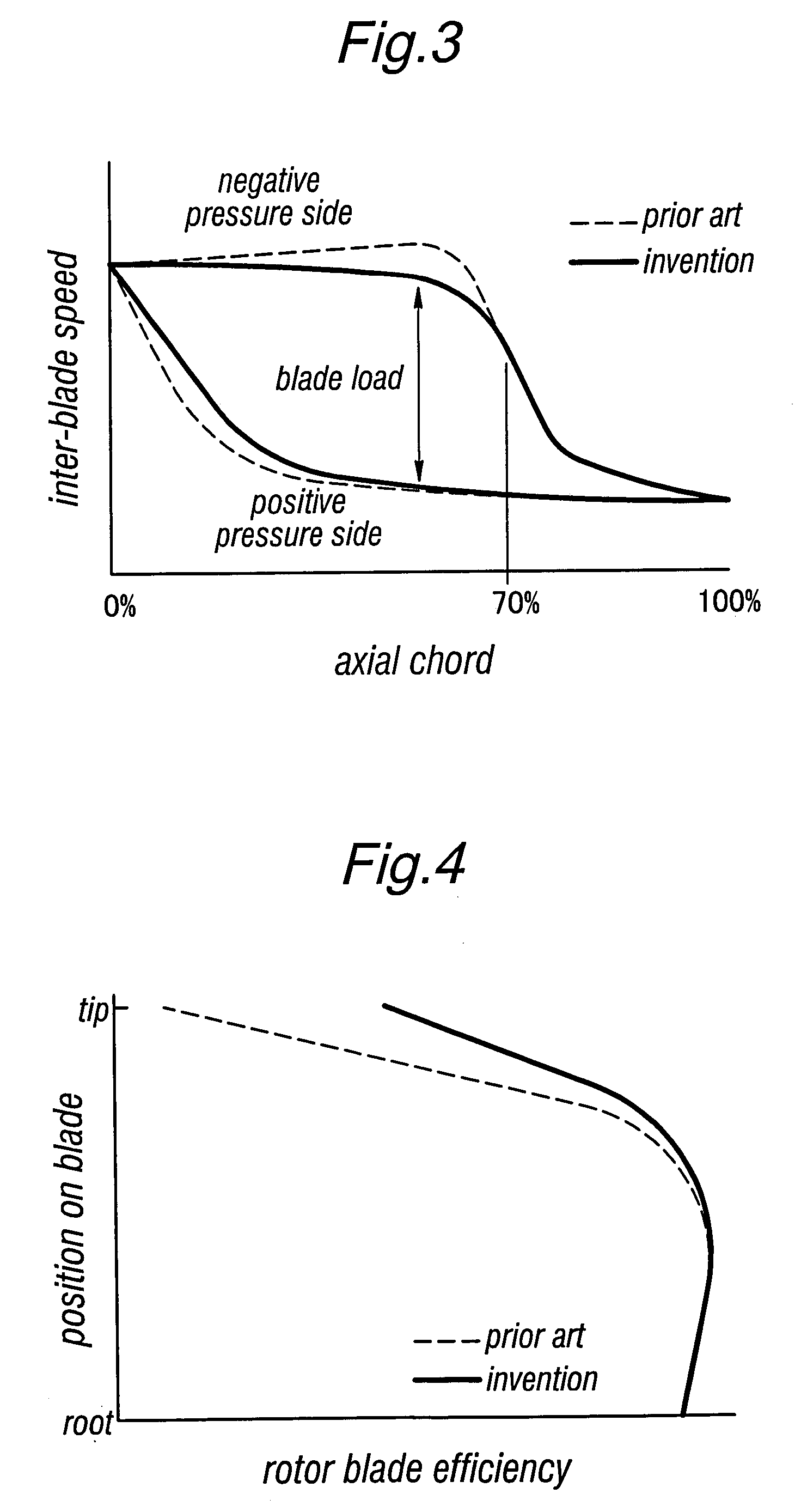
The present invention provides a transonic blade that concurrently achieves reduction in shock loss at a design point and improvement in stall margin in blades operating in a flow field of transonic speed or higher in an axial-flow rotating machine. A cross-sectional surface at each of spanwise positions of the blade is shifted parallel to a stagger line connecting a leading edge with a trailing edge of the blade. A stacking line is shifted toward an upstream side of working fluid. The stacking line connects together respective gravity center positions of blade cross-sectional surfaces at spanwise positions in a range from a hub cross-sectional surface joined to a rotating shaft or an outer circumferential side casing of a rotating machine to a tip cross-sectional surface lying at a position most remote from the hub cross-sectional surface in a spanwise direction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Structure of output section of jet propulsion engine or gas turbine
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
Axial flow compressor
InactiveUS7004722B2Improve efficiencyWide operatingSupersonic fluid pumpsPump componentsAxial compressorEngineering
At least part of the inner circumferential wall of the outer casing is provided with a concave surface opposing the rotor blade tips as seen in a longitudinal section. Typically, each of the rotor blades is provided with aerofoil section, and the compressor is designed as a transonic axial flow compressor. Thereby, a compressive wave is produced upstream of the shockwave so that the Mach number of the flow entering the shockwave can be reduced. As a result, the shockwave is made less severe, and the shockwave loss can be reduced. In particular, because the concave surface is provided in the casing wall as opposed to the case where the concave surface is provided in the negative pressure side of the rotor blade, the reduction in the performance owing to the change in the angle of the airflow entering the passage defined by the concave surface under a partial load condition can be avoided.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Bullnose step turbine nozzle
A turbine airfoil includes opposite pressure and suction sides extending in span from a flowpath surface. The flowpath surface has chordally opposite forward and aft edges and laterally opposite first and second endfaces corresponding with the airfoil pressure and suction sides. The flowpath surface joins the first endface at the forward edge in a forward bullnose and joins the second endface at the aft edge in an aft bullnose, with the bullnoses varying in radius from the opposite edges.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for aerodynamically self-enhancing rotor blades
InactiveUS7320575B2Improve performanceImprove stabilitySupersonic fluid pumpsRotary propellersEngineeringAerodynamics
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Tone noise reduction in turbomachines
ActiveUS20080181769A1Improve the attenuation effectReduce noiseSupersonic fluid pumpsEngine manufactureClassical mechanicsEngineering
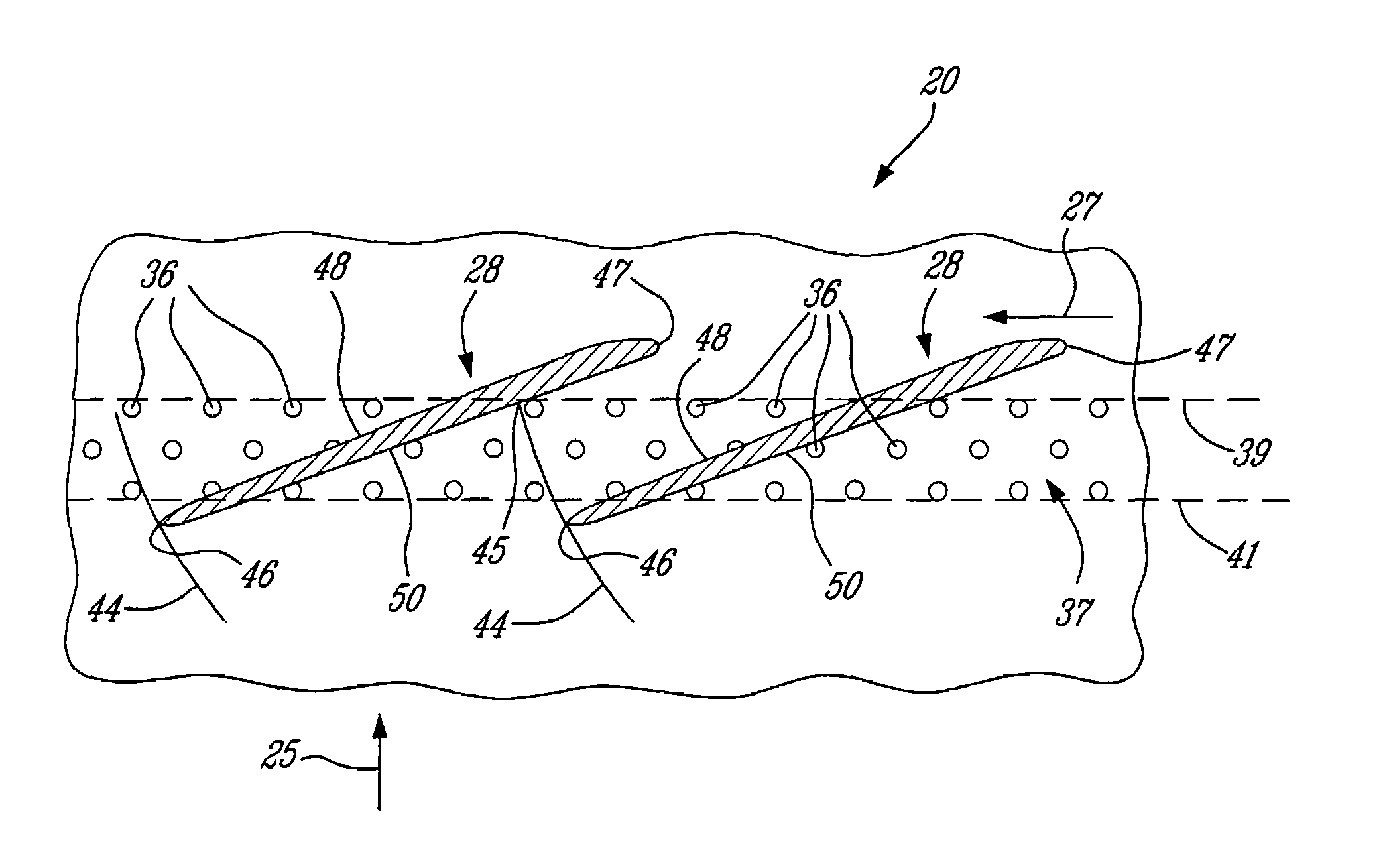
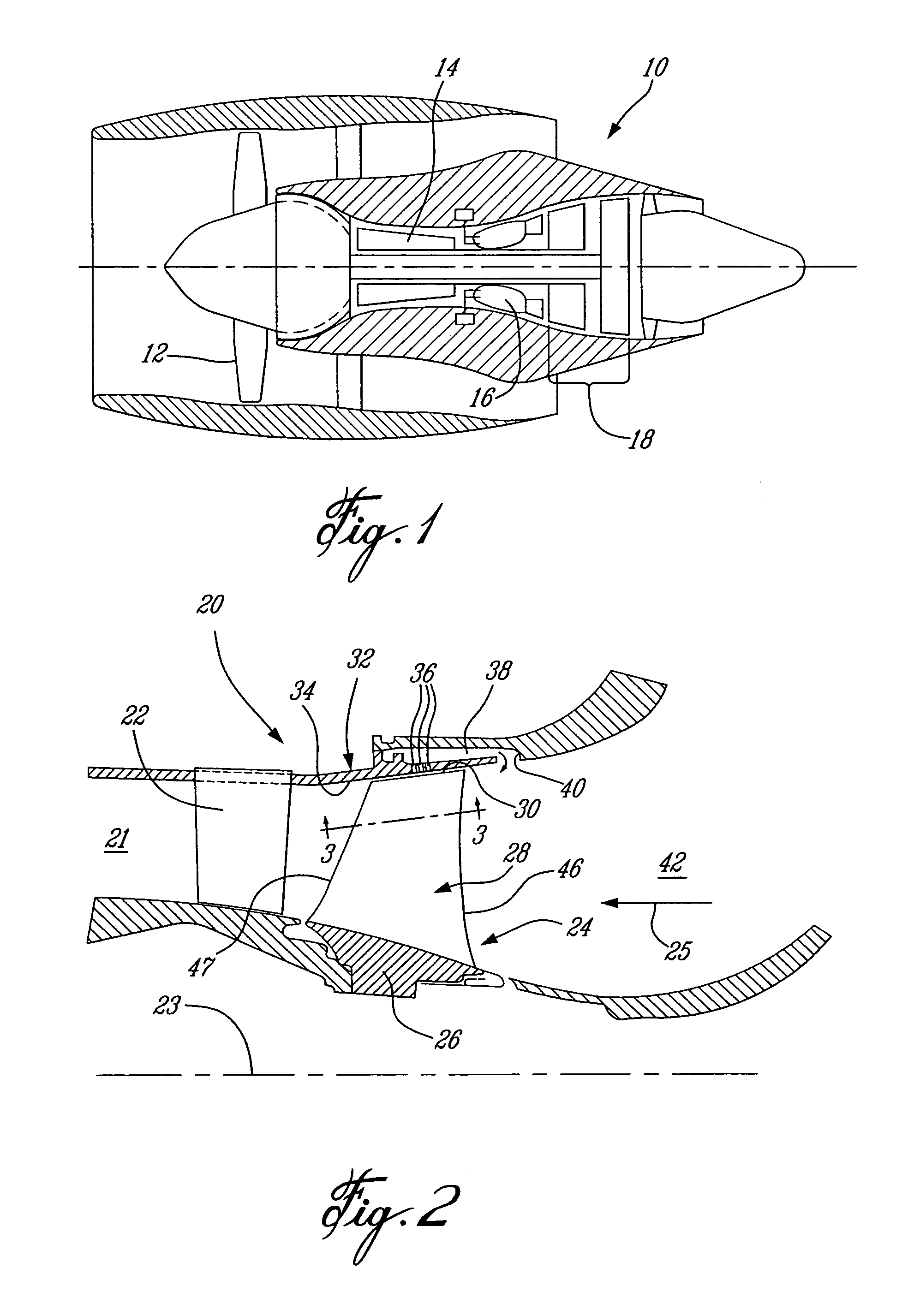
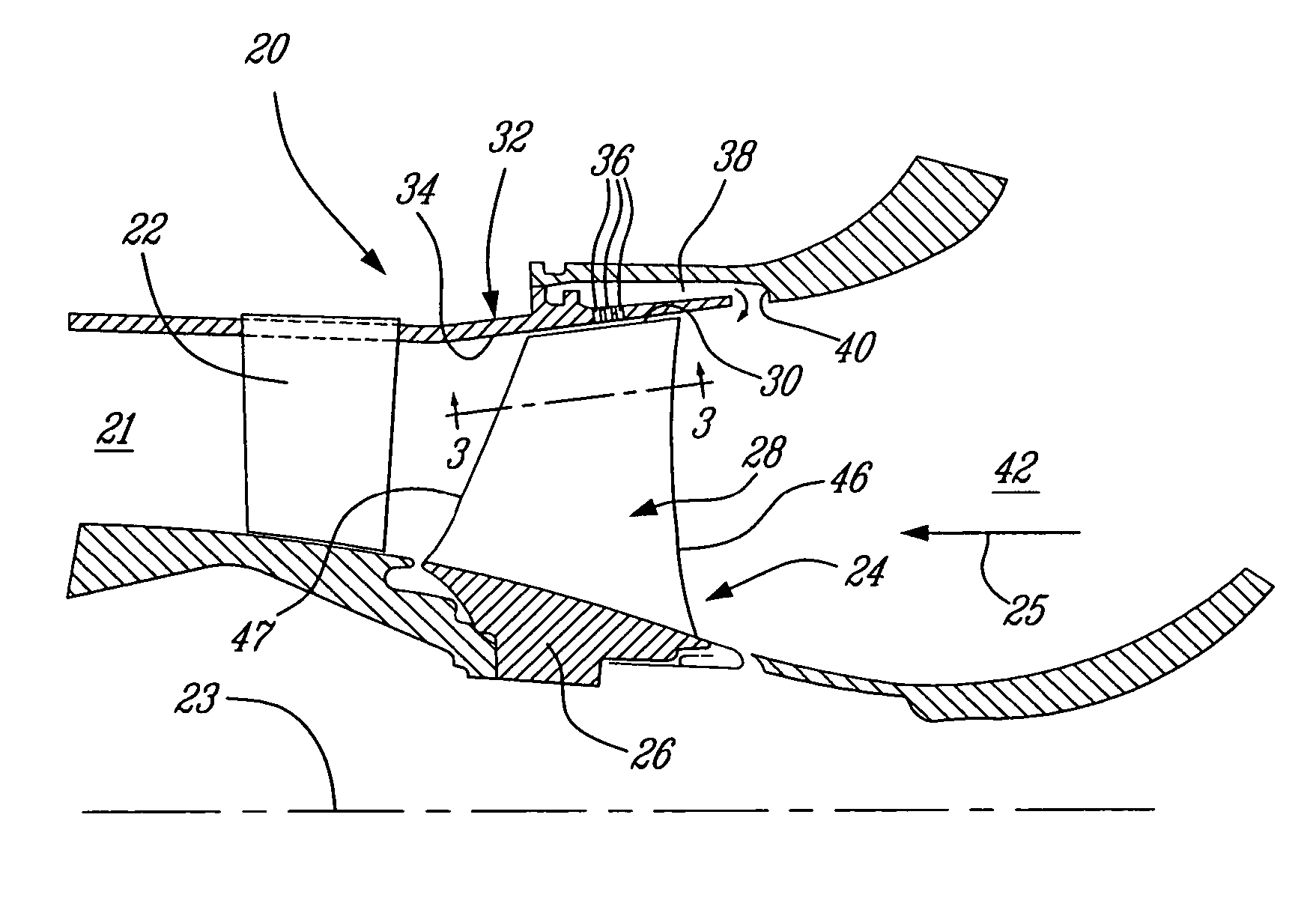
A blade for a turbomachine extends in use, in a radial direction relative to the axis of the turbomachine. The turbomachine has at least one operating condition which generates supersonic fluid flow at the blade. The blade is adapted to provide, at the supersonic operating condition, a leading edge sweep angle which varies such that successive radial positions (i) to (iii) along the leading edge are at respective sweep angle turning points. Position (i) is the radially inner and position (iii) the radially outer of the positions. Position (i) is at or radially outward of the 30% span position, where 0% span is the radially innermost point of the leading edge and 100% span is the radially outermost point of the leading edge.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Centrifugal compressor and manufacturing method for impeller
InactiveUS7517193B2Fall in efficiency and performance is preventedIncrease rangeSupersonic fluid pumpsPropellersEngineeringFront edge
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Compressor for an aircraft engine
ActiveUS7207772B2Relieve pressureNot to damageSupersonic fluid pumpsPropellersLeading edgeEngineering
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE DEUT LTD & CO KG
Shockwave-induced boundary layer bleed
An apparatus and method is provided for improving efficiency of a transonic gas turbine engine compressor by bleeding off a shockwave-induced boundary layer from the gas flow passage of the compressor using an array of bleed holes having a downstream edge aligned with a foot of an oblique shock wave which originates on the leading edge of an adjacent transonic rotor blade tip.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Compressor for an aircraft engine
ActiveUS20050214113A1Reduce vibrationSatisfies requirementSupersonic fluid pumpsPropellersLeading edgeEngineering
On a compressor with compressor blades, a flow transition fixation mechanism (4) is provided on the suction side (2), approximately parallel to the leading edge (3) and upstream of the compression shocks acting upon the blade, which prevents the transition point from the laminar to the turbulent boundary layer flow from oscillating, thus suppressing oscillation of the compression shocks and their coupling effect with the natural frequencies of the compressor blades.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE DEUT LTD & CO KG
Supercharger
InactiveUS7128061B2Easy to manufactureEasy to serviceSupersonic fluid pumpsPump componentsImpellerRotational axis
A centrifugal supercharger is provided. One embodiment of the supercharger comprises a two-piece housing wherein a parting area is substantially aligned with a rotational axis of a drive- or impeller shaft. Another embodiment comprises a sleeve, or intermediate member disposed substantially between the housing and a bearing assembly(s) located within the supercharger housing. Another embodiment comprises a disengagement device located between the supercharger impeller and the engine. The disengagement device allows selective disengagement of the impeller from the engine. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:VORTECH ENG
Shockwave-induced boundary layer bleed
An apparatus and method is provided for improving efficiency of a transonic gas turbine engine compressor by bleeding off a shockwave-induced boundary layer from the gas flow passage of the compressor using an array of bleed holes having a downstream edge aligned with a foot of an oblique shock wave which originates on the leading edge of an adjacent transonic rotor blade tip.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
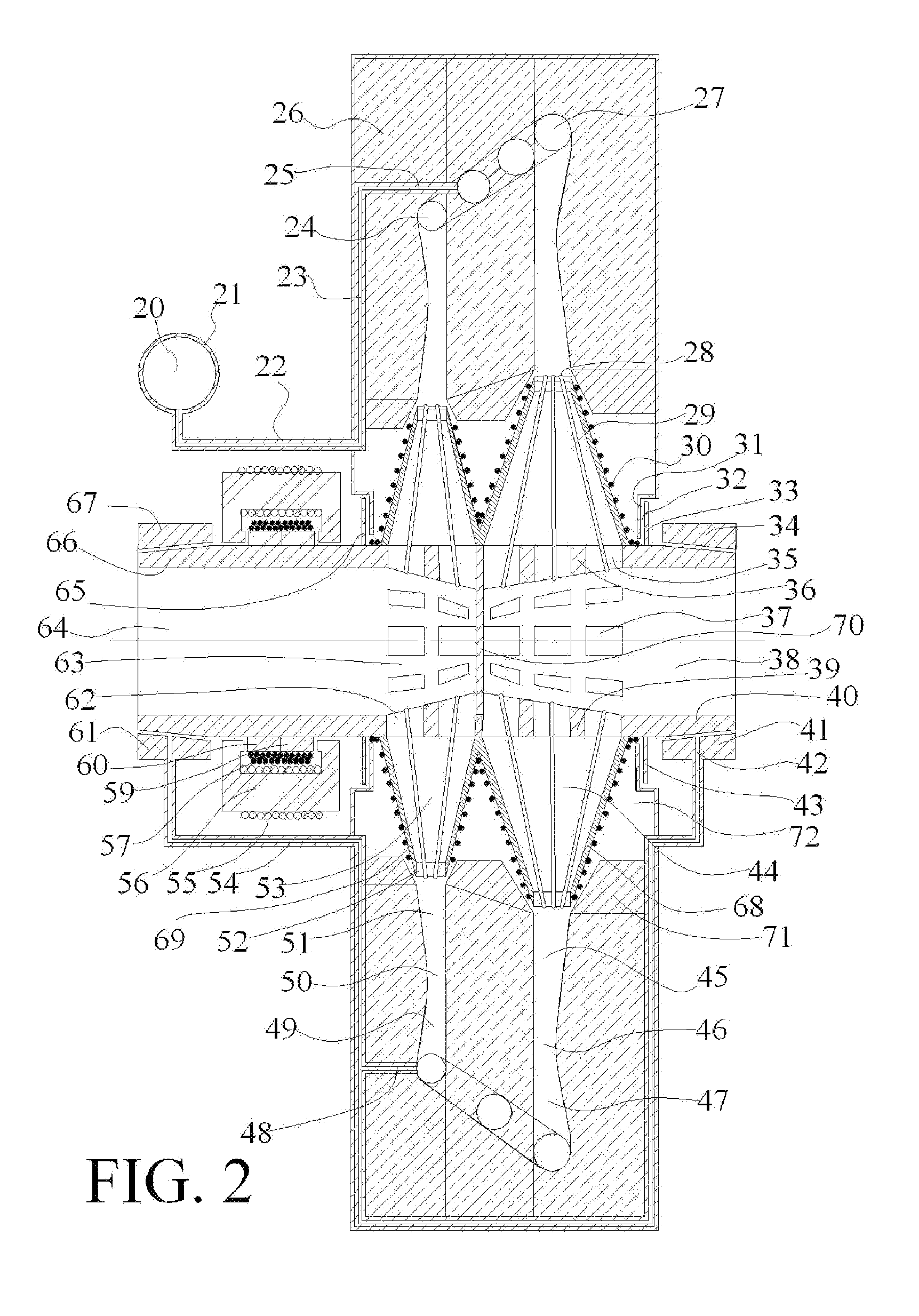
Turbo-molecular pump having enhanced pumping capacity
In one aspect, a vacuum processing system comprising a vacuum processing chamber and a turbo-molecular pump disposed on the vacuum processing chamber is provided. The turbo-molecular pump comprises a casing having an inlet port and an outlet port, a stator disposed on an inner wall of the casing, a rotor disposed in the stator, and a motor extending coaxially with the rotor, wherein at least the first stage of the pump is enlarged with no correspondingly larger pump components other than the corresponding upper portion of the housing.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods and apparatus for aerodynamically self-enhancing rotor blades
InactiveUS20060067821A1Improve aerodynamic performanceImprove performanceSupersonic fluid pumpsPump componentsEngineeringAerodynamics
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Transonic airfoil and axial flow rotary machine
ActiveUS8133012B2Improve efficiencyLow efficiencySupersonic fluid pumpsPropellersEngineeringMechanical engineering
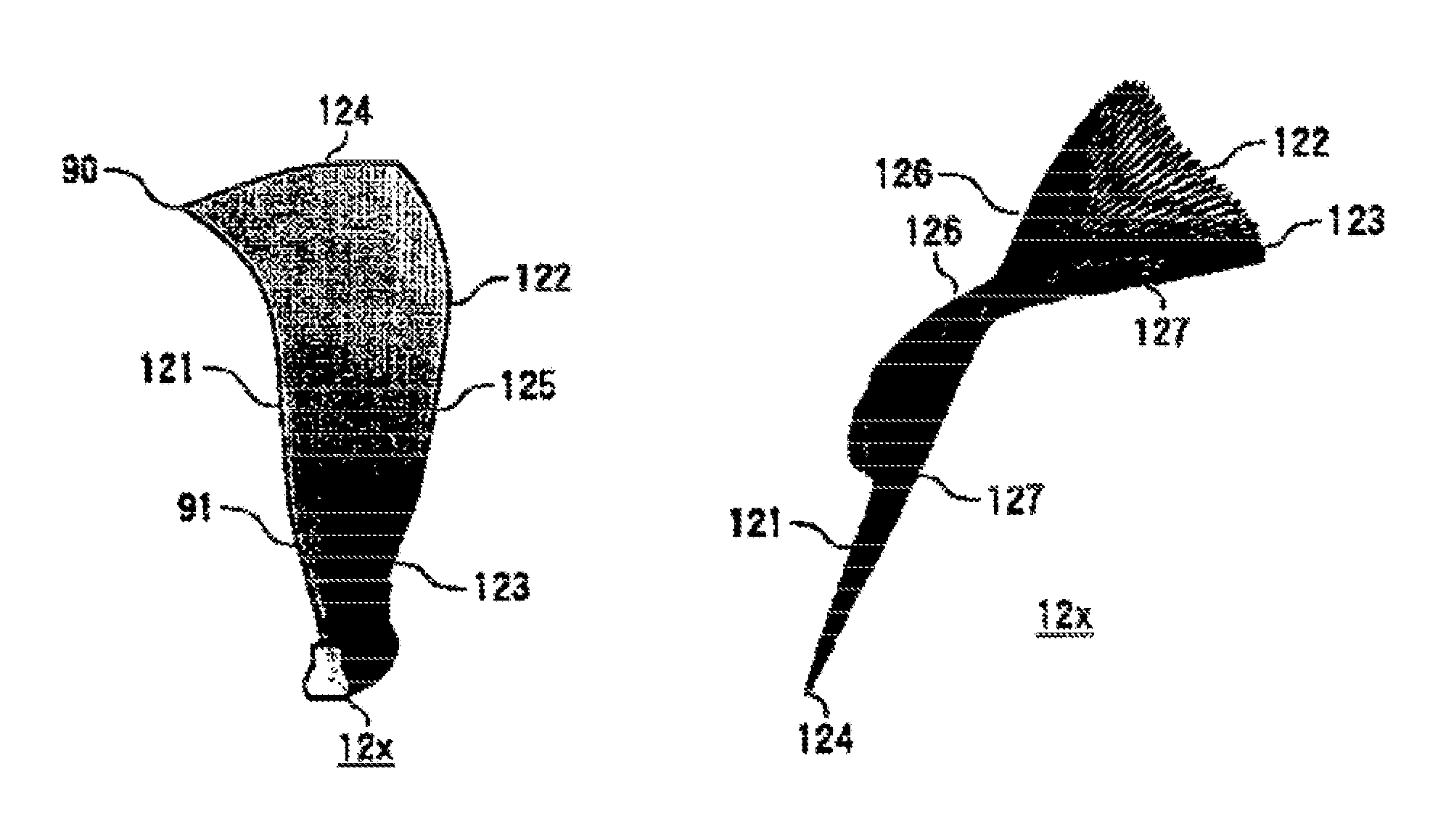
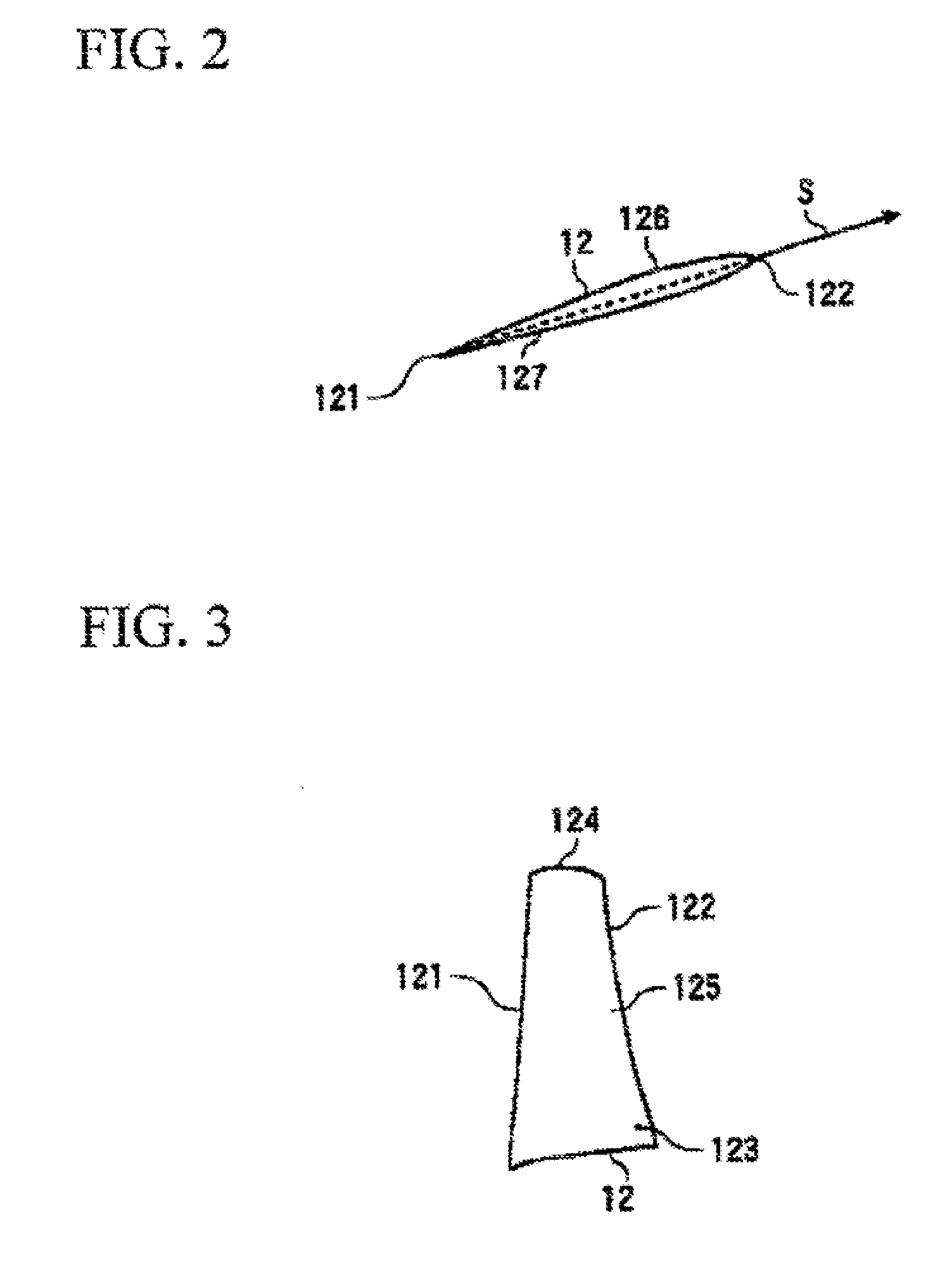
Sectional profiles close to a tip 124 and a part between a midportion 125 and a hub 123 are shifted to the upstream of an operating fluid flow in a sweep direction. Accordingly, an S shape is formed in which the tip 124 and the part between the midportion 125 and the hub 123 protrude. As a result, it is possible reduce various losses due to shook, waves, thereby forming a transonic airfoil having an excellent aerodynamic characteristic.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Treatment and flow control method for gas compressor casing with scattered seam type circumferential grooves
ActiveCN104373388AIncrease stall marginImprove stable working rangeSupersonic fluid pumpsPump componentsImpellerLow speed
The invention discloses a treatment and flow control method for a gas compressor casing with scattered seam type circumferential grooves, and belongs to the field of turbo machines. The method comprises the steps that the circumferential grooves are firstly formed in the blade tip casing of a gas compressor, then scattered seams are formed in the bottoms of the circumferential grooves, and the circumferential grooves are communicated through the scattered seams. According to the treatment and control method for the casing, the pressure difference in a blade channel can be effectively utilized, fluid nearby a pressure face can be transported to the position nearby a suction face through the circumferential grooves, and fluid of the downstream portion of the blade channel can be conveyed to the upstream portion through the seams in the bottoms of the circumferential grooves. Therefore, mass and momentum exchange between the fluid and main flow in the casing treatment structure can be promoted, a low-speed area caused by the leakage vortex of a blade tip can be effectively reduced, overflowing of leakage flow nearby the front edge of the blade tip is postponed, and therefore the stable work range of the gas compressor can be widened.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-turning and high-transonic blade
A high-turning and high-transonic blade for use in a blade cascade of an axial-flow compressor, wherein a distribution of flow speed on an extrados at a leading edge of the blade has a supersonic region of a substantially constant flow speed in the rear of a first large value of the flow speed and inside a position corresponding to 15% of a chord length from the leading edge. The supersonic region is established so that a value obtained by the division of a difference between Mach numbers at front and rear ends of the supersonic region by a chord-wise length of the supersonic region is smaller than 1, and the maximum Mach number in the supersonic region is smaller than 1.4. A first large shock wave is positively generated at a position where the flow speed assumes a first maximum value, whereby a second shock wave generated in the supersonic region of the substantially constant flow speed in the rear of such a position can be weakened. Thus, boundary layer separation due to the second shock wave can be suppressed, to thereby remarkably reduce the pressure loss of a following flow on the blade.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Turbo-molecular pump having enhanced pumping capacity
In one aspect, a vacuum processing system comprising a vacuum processing chamber and a turbo-molecular pump disposed on the vacuum processing chamber is provided. The turbo-molecular pump comprises a casing having an inlet port and an outlet port, a stator disposed on an inner wall of the casing, a rotor disposed in the stator, and a motor extending coaxially with the rotor, wherein at least the first stage of the pump is enlarged with no correspondingly larger pump components other than the corresponding upper portion of the housing.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Supercharger
ActiveUS20050092307A1Easy to manufactureEasy to serviceSupersonic fluid pumpsPump componentsRotational axisImpeller
A centrifugal supercharger is provided. One embodiment of the supercharger comprises a two-piece housing wherein a parting area is substantially aligned with a rotational axis of a drive- or impeller shaft. Another embodiment comprises a sleeve, or intermediate member disposed substantially between the housing and a bearing assembly(s) located within the supercharger housing. Another embodiment comprises a disengagement device located between the supercharger impeller and the engine. The disengagement device allows selective disengagement of the impeller from the engine. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:VORTECH ENG
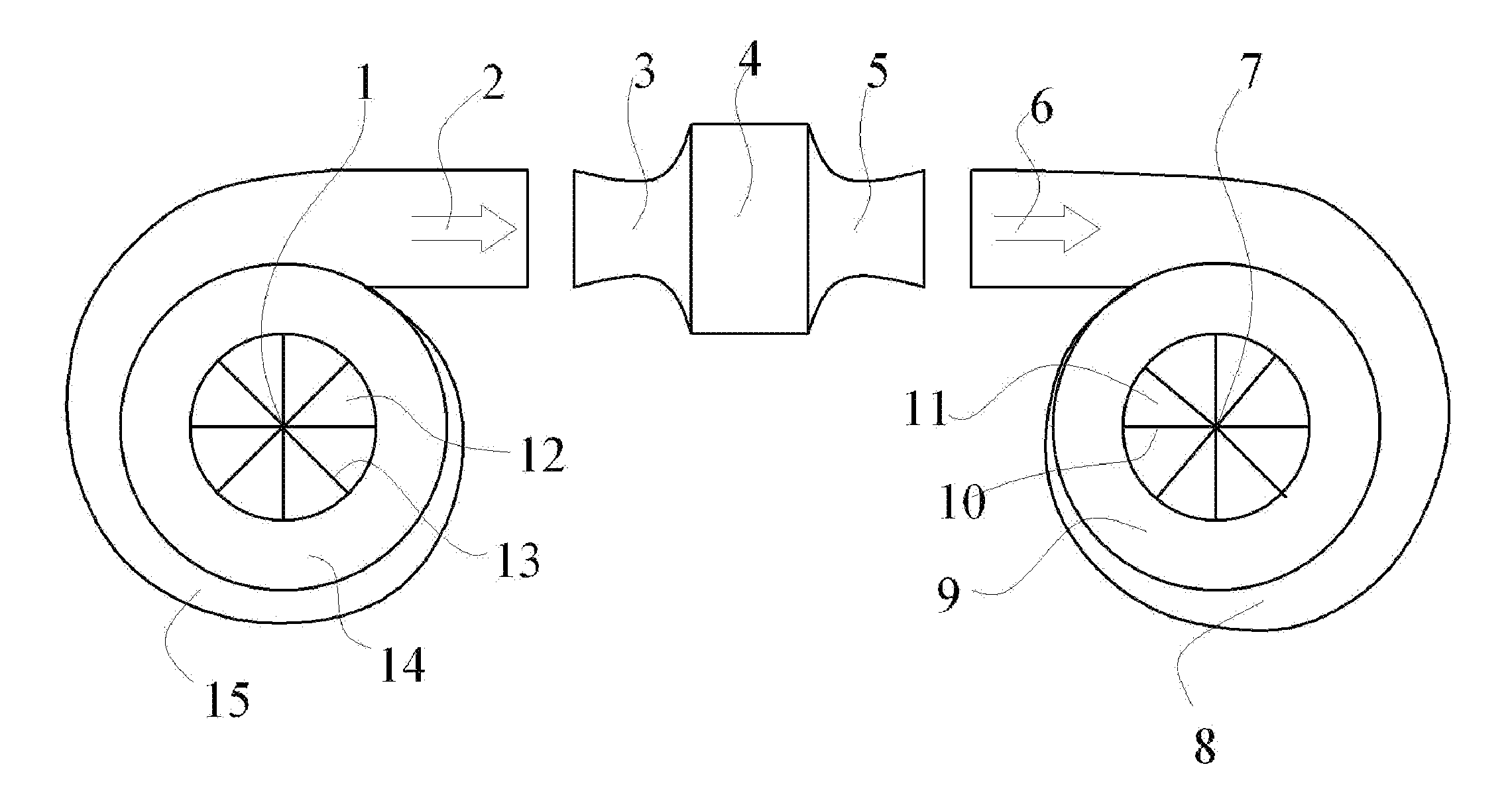
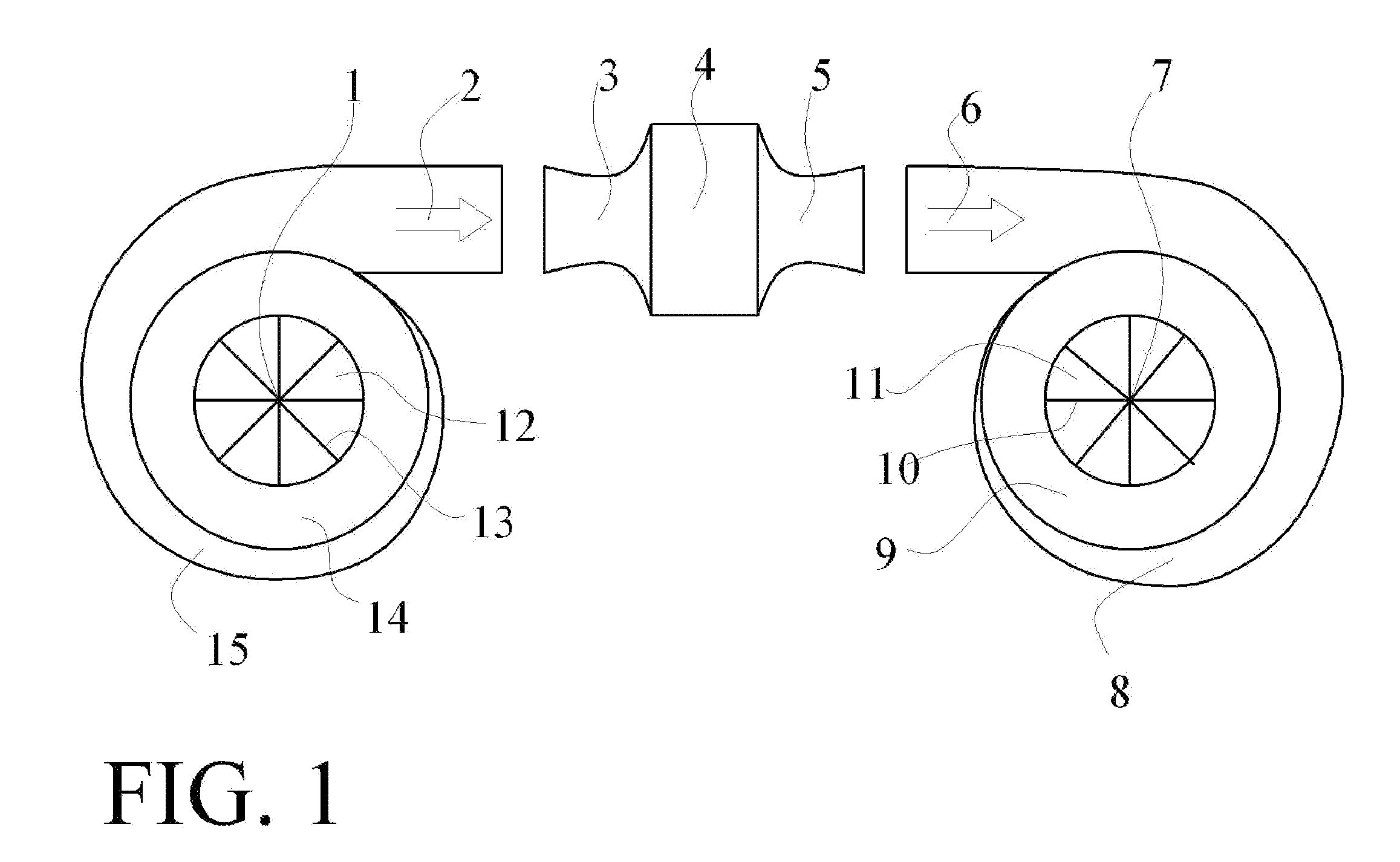
Subsonic and stationary ramjet engines
InactiveUS20090241549A1Eliminate wasteful dragHigh energy flowSupersonic fluid pumpsPropellersRamjetJet engine
A ramjet engine (3, 4, 5), flying at Mach 3 has 64% efficiency, and at Mach 4 has 76% efficiency. Ramjet engines are currently only used for supersonic flight and have not been used as stationary engines with mechanical output. The present invention, in addition to subsonic flight, can be operated as a stationary engine, and can expand the use of the ramjet engine for mechanical output in vehicles, power plants, and in generator sets for large buildings, homes, and industry. The present invention provides the means to use ramjet engines as stationary engines by building nearly adiabatic compressors (1, 2, 12, 13, 14, 15) and expanders (6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11) capable of (de-)compression ratios up to about 92:1 to supply the high energy gas / air required by ramjet engines, and shows how to replace de Laval nozzles with sonic converters (49, 50, 51) that convert supersonic to subsonic flow and sonic converters (45, 46, 47) that convert subsonic to supersonic flow without having choke areas.
Owner:AMICABLE INVENTIONS LLC
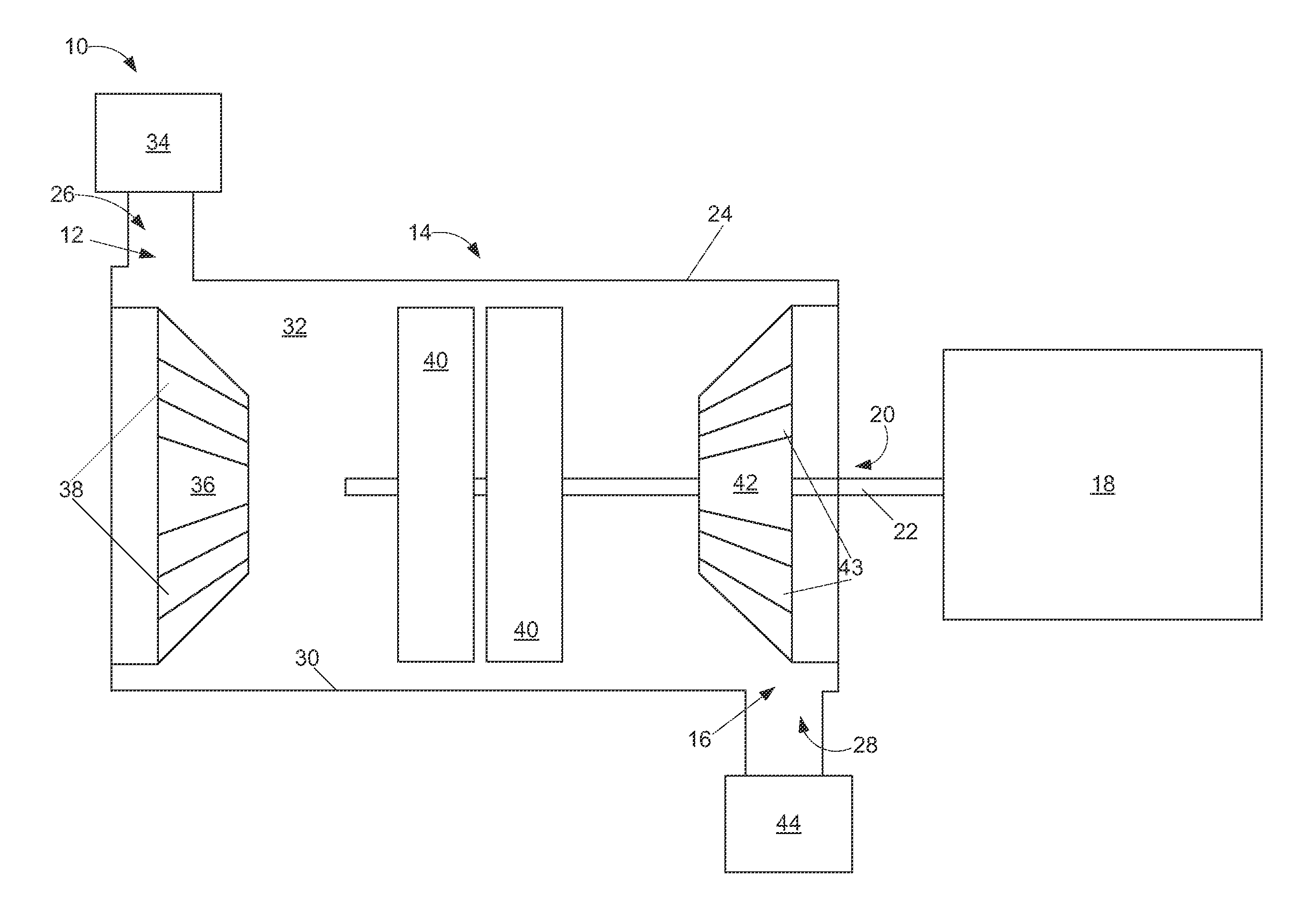
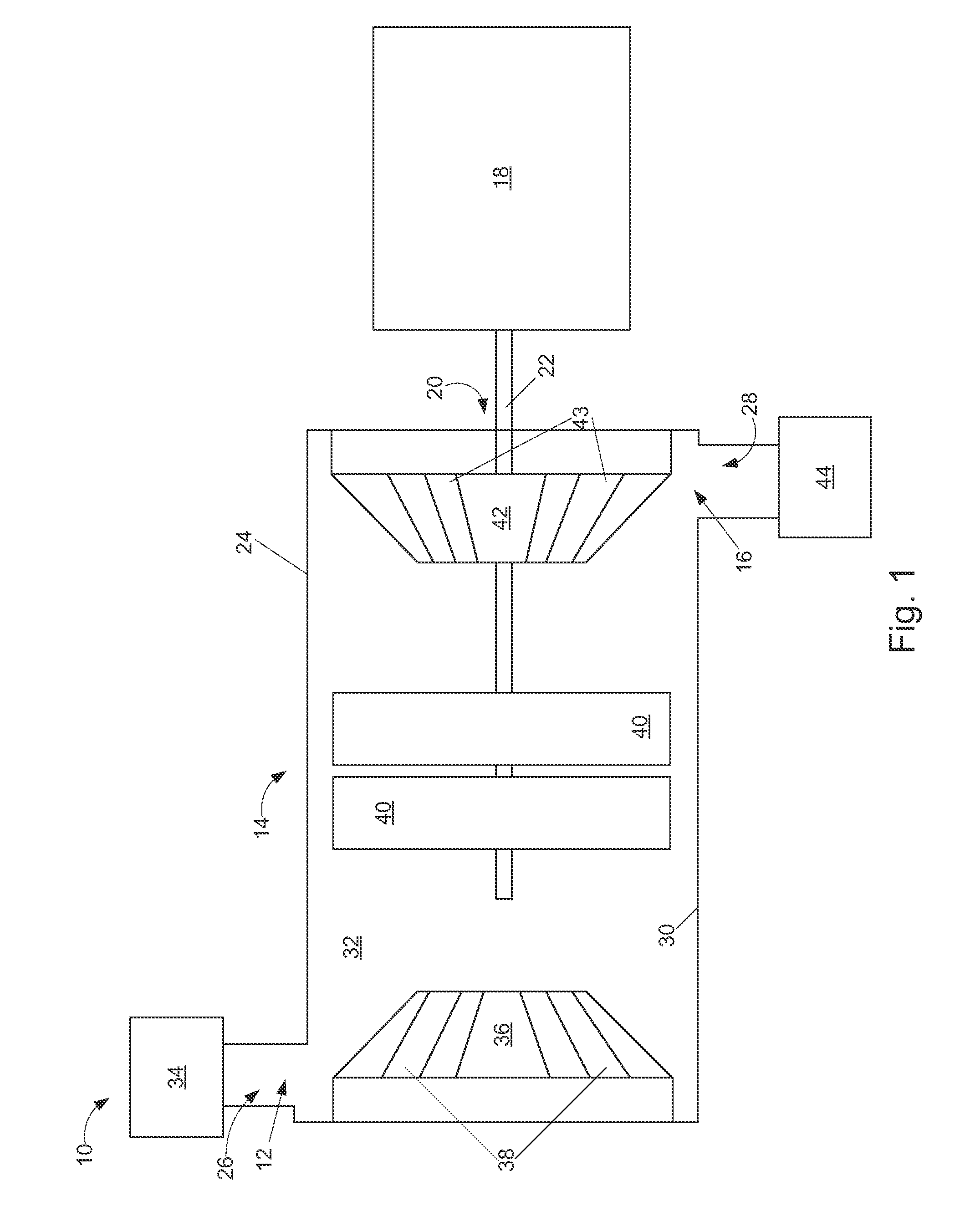
Supersonic compressor and method of assembling same
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Supersonic compressor
Owner:NUOVO PIGNONE TECH SRL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com