Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1452 results about "Suction surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A suction cup, also known as a sucker, is a device or object that uses the negative fluid pressure of air or water to adhere to nonporous surfaces, creating a partial vacuum.
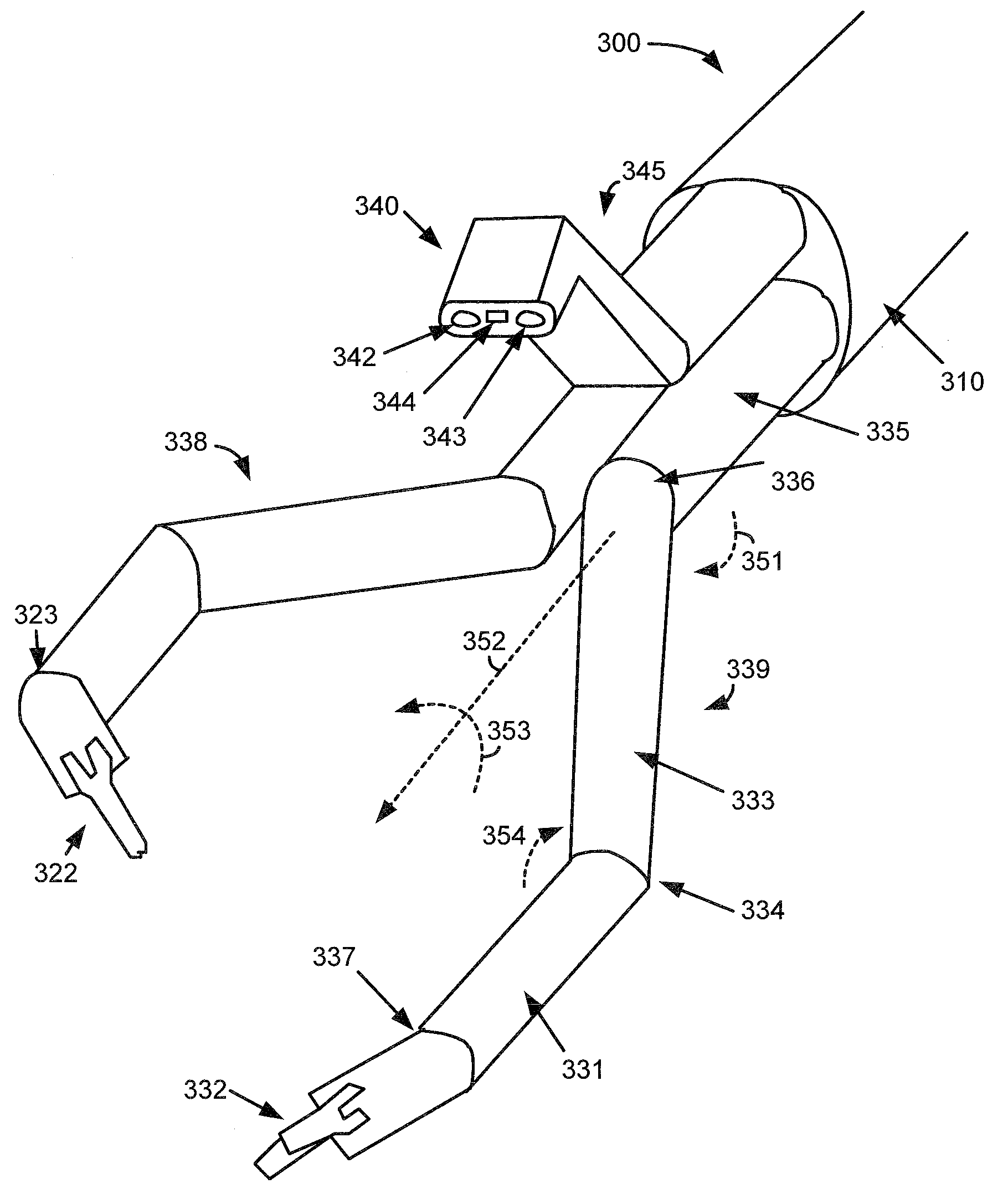
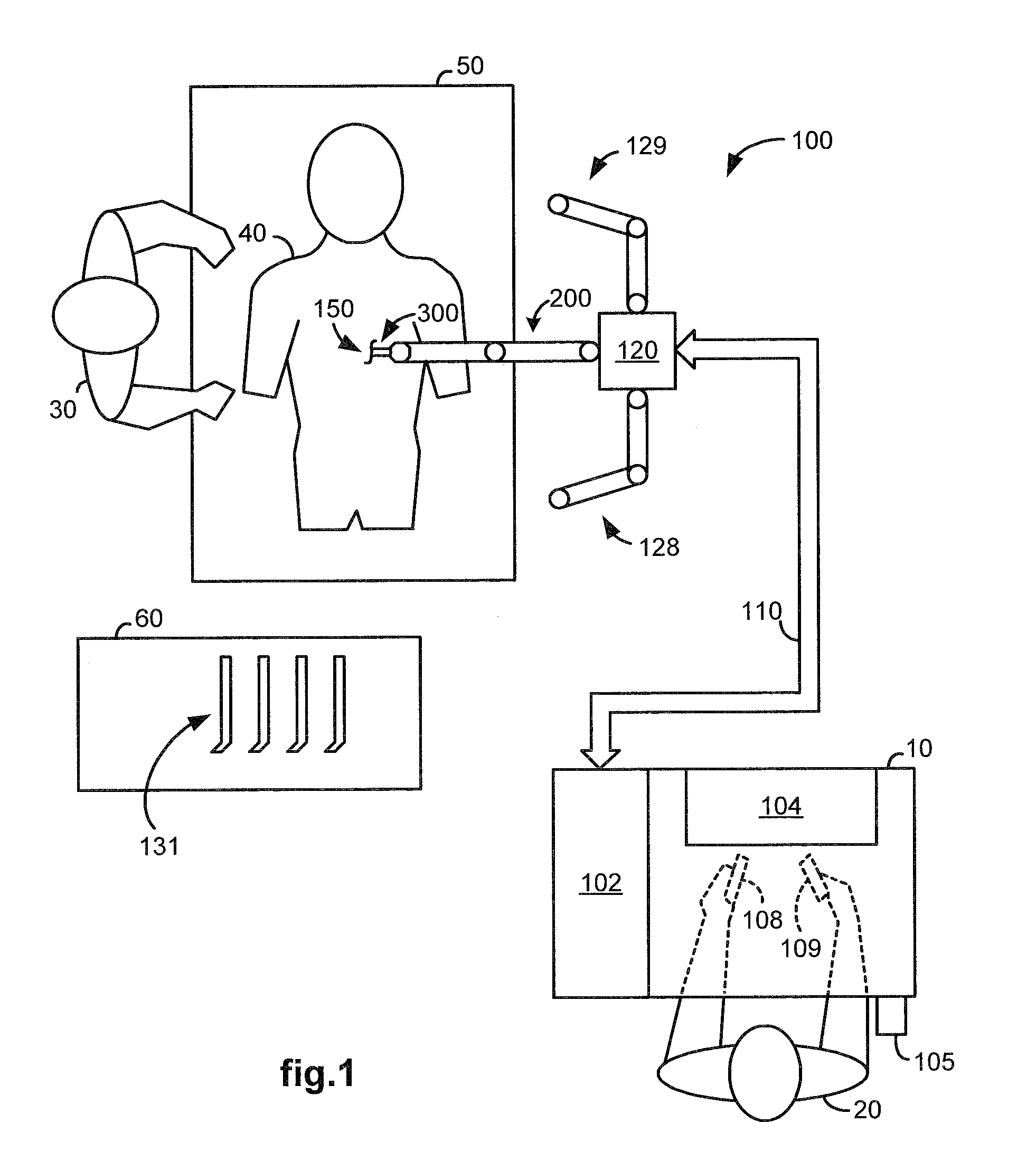
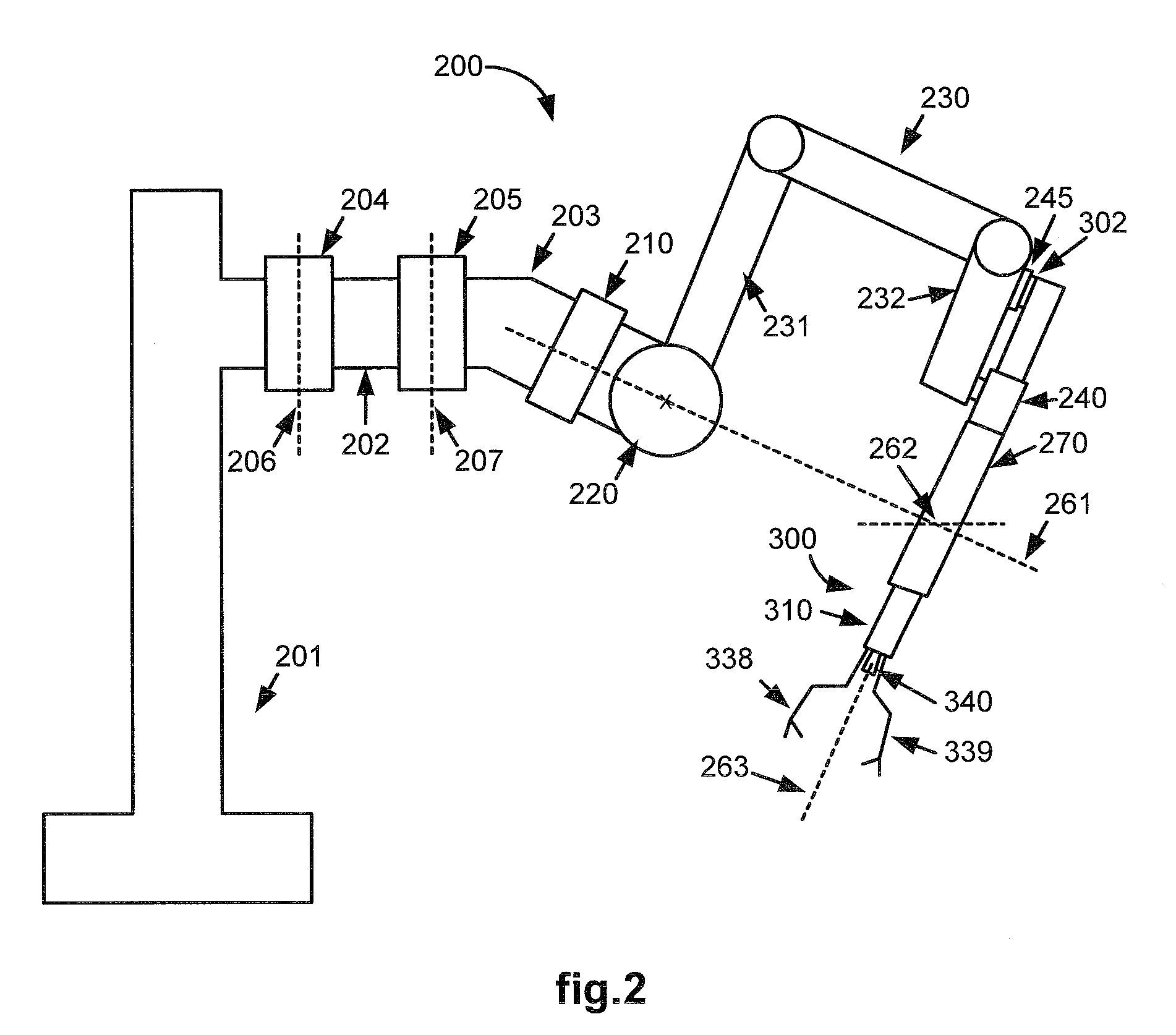
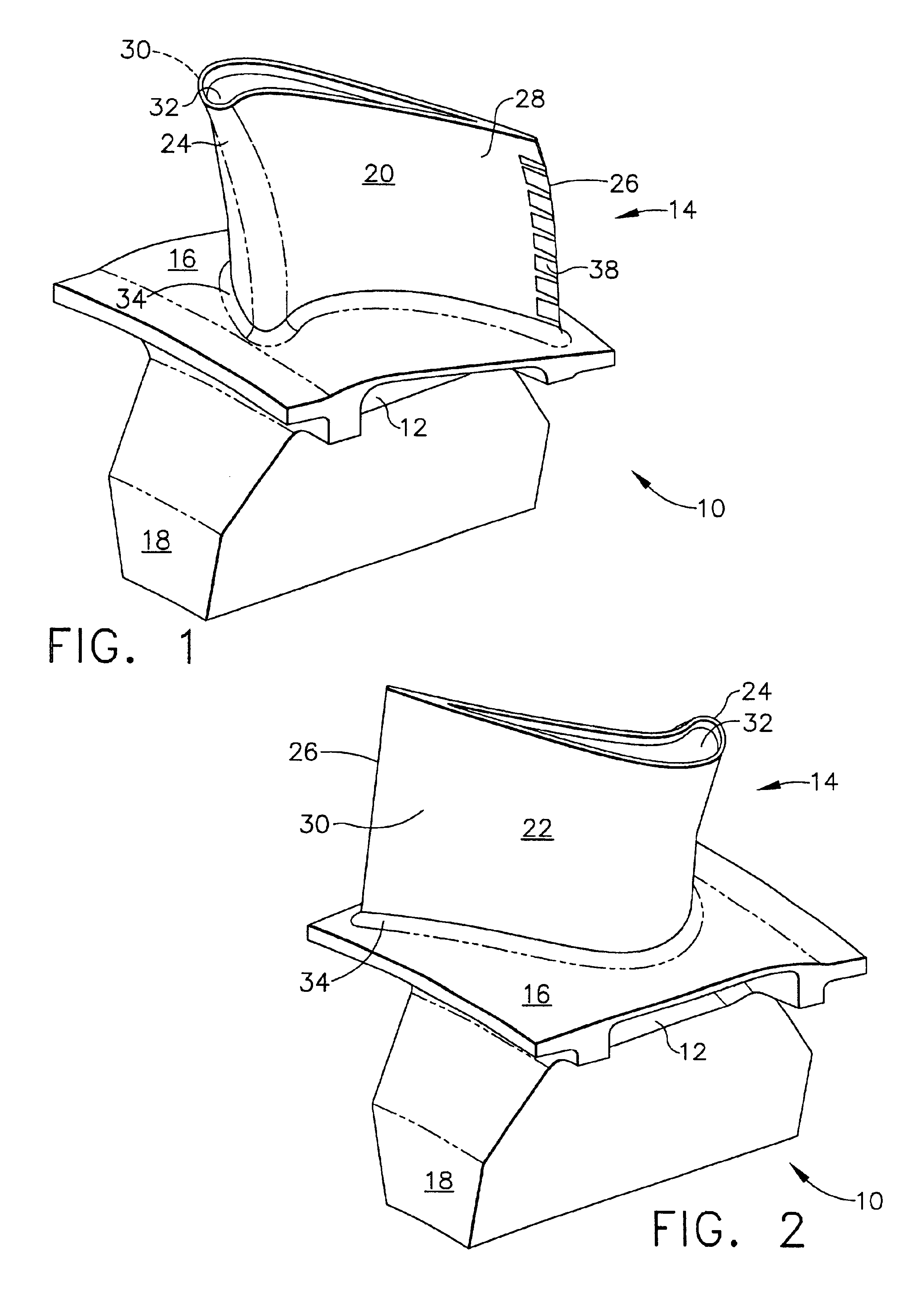
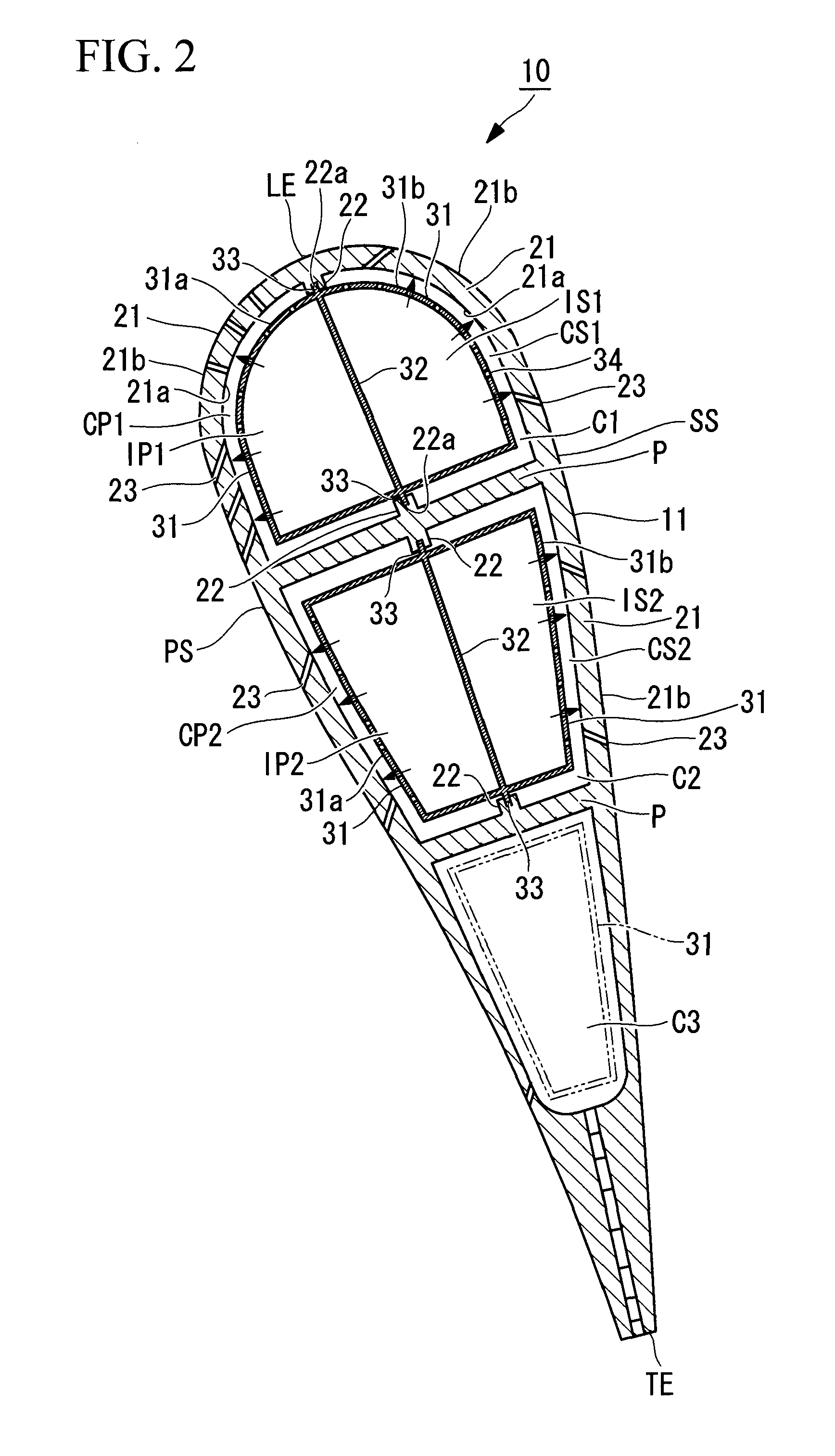
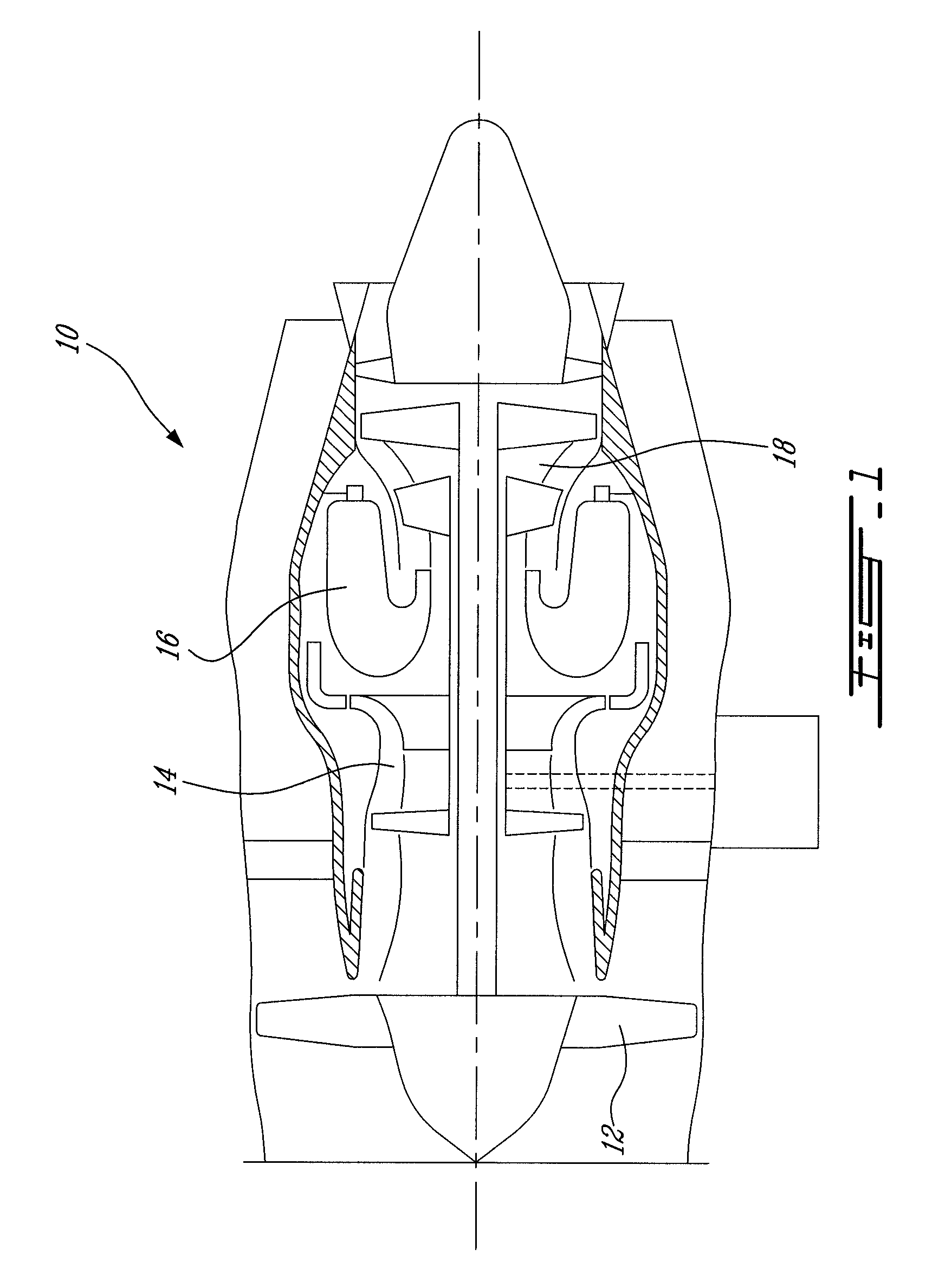
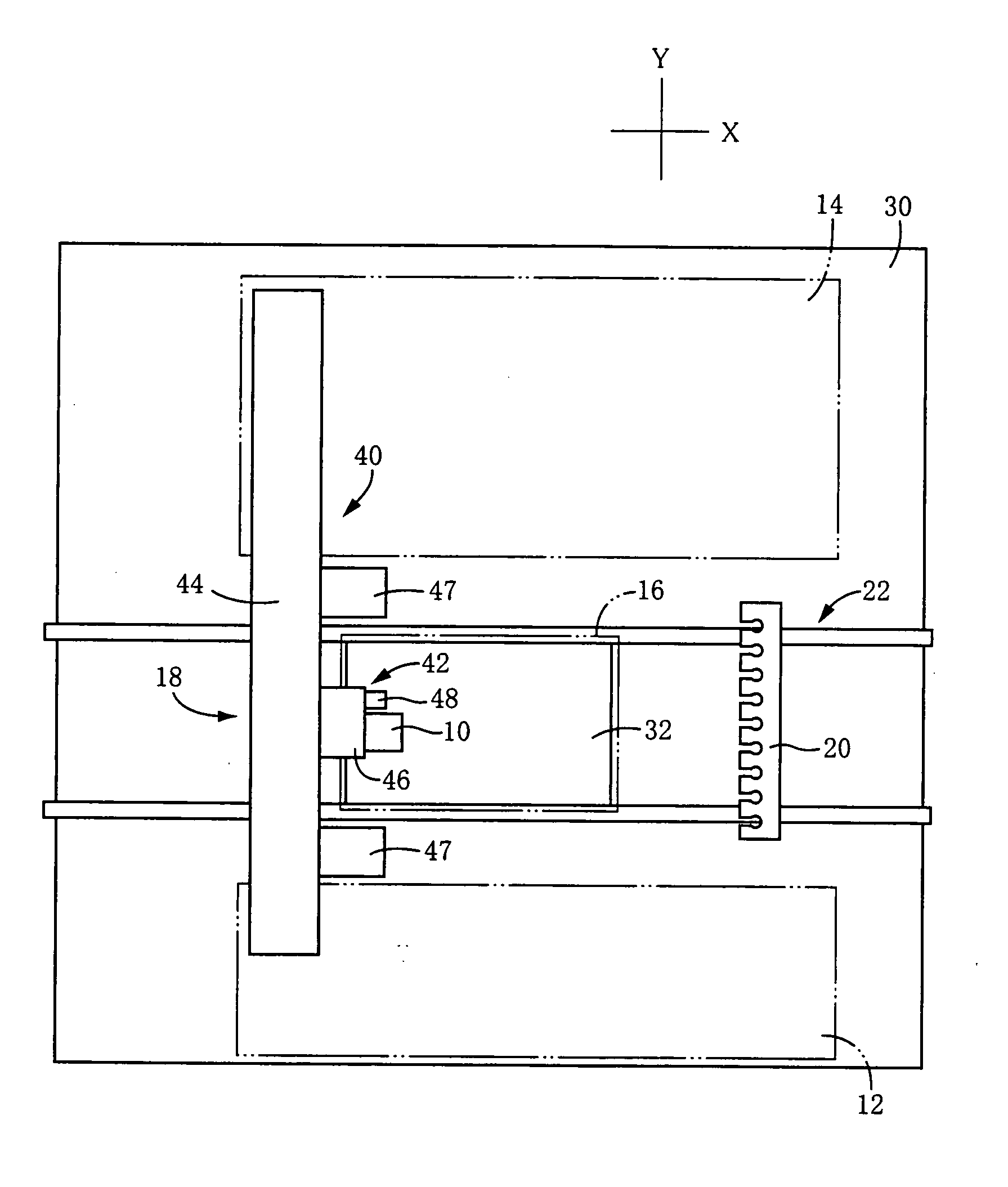
Extendable suction surface for bracing medial devices during robotically assisted medical procedures
Medical devices robotically manipulated by a medical robotic system for performing a medical procedure on a patient are bundled together as a bundled unit and inserted into the patient through a single entry port. Bracing of the bundled unit at a surgical site is performed by extending a suction surface disposed at a distal end of the bundled unit towards a bracing surface at the surgical site and applying a suction force between the suction surface and the bracing surface. The suction surface is ring-shaped with holes distributed about the ring so that controllably extendable and retractable tubes coupled at distal ends to the holes provide suction to the suction surface when coupled at proximal ends to a vacuum source.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
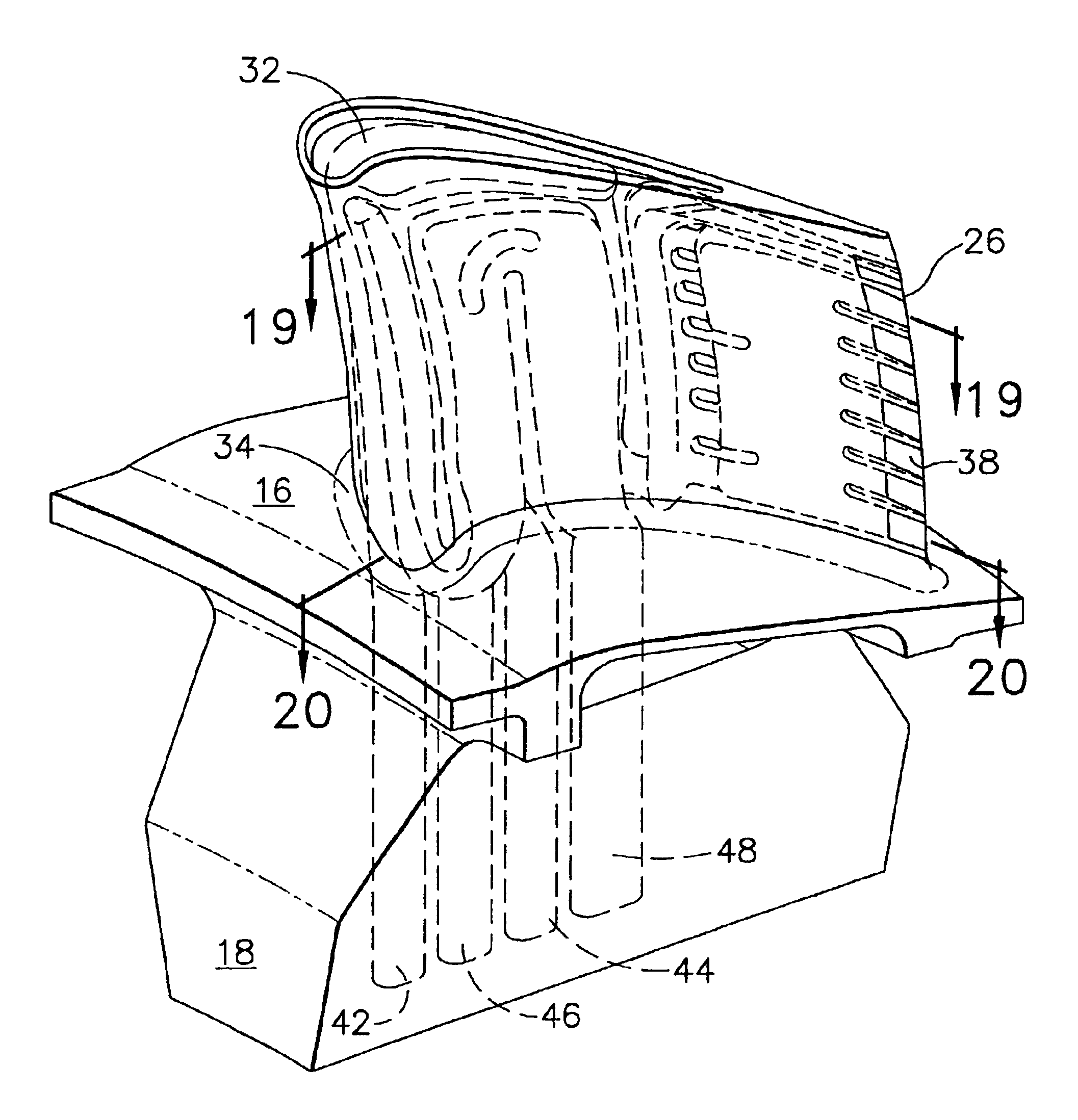
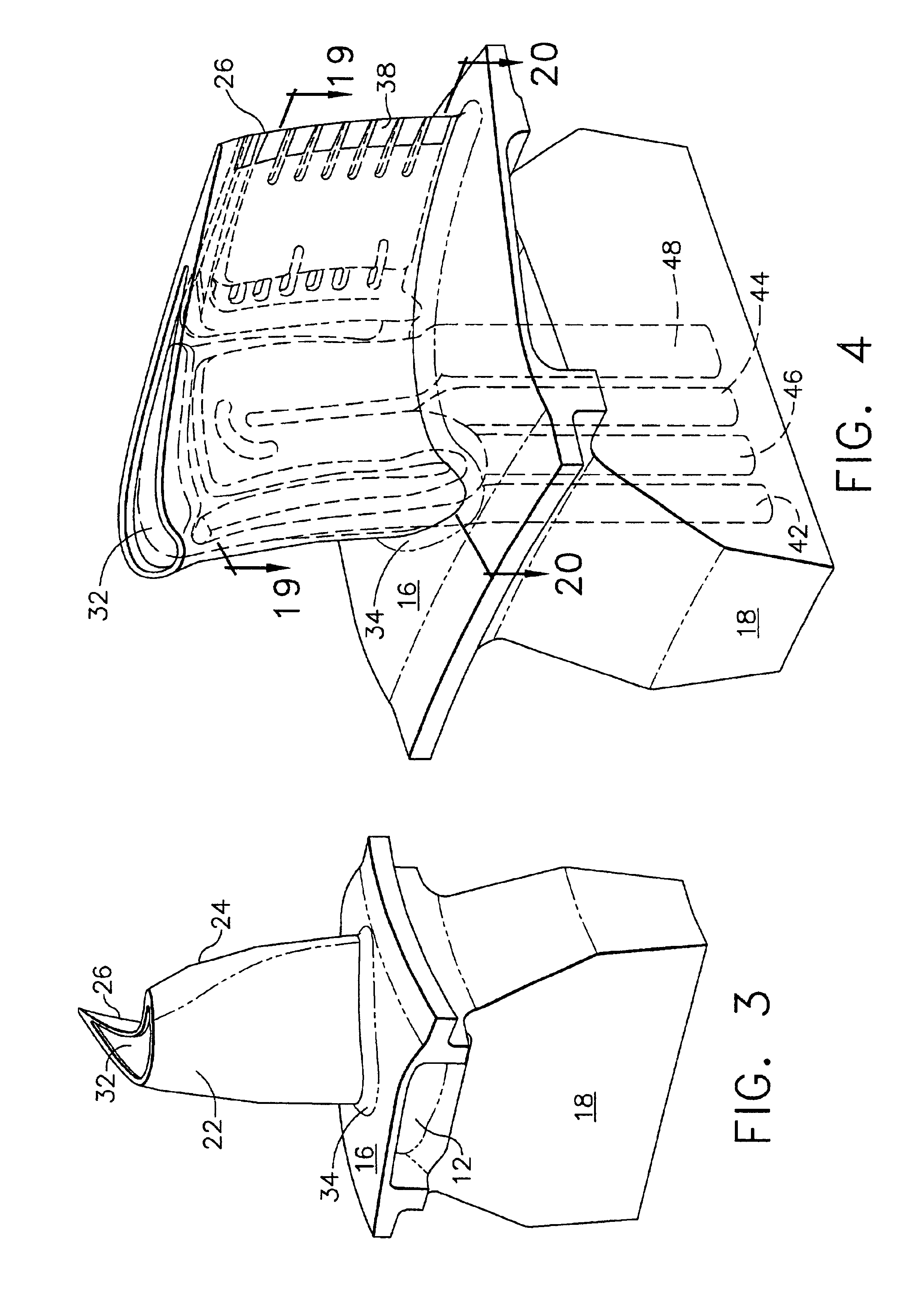
High effectiveness cooled turbine vane or blade
InactiveUS6974308B2Improve cooling efficiencyEasy to manufacturePump componentsEngine fuctionsSuction stressConventional casting
A robust multiple-walled, multi-pass, high cooling effectiveness cooled turbine vane or blade designed for ease of manufacturability, minimizes cooling flows on highly loaded turbine rotors. The vane or blade design allows the turbine inlet temperature to increase over current technology levels while simultaneously reducing turbine cooling to low levels. A multi-wall cooling system is described, which meets the inherent conflict to maximize the flow area of the cooling passages while retaining the required section thickness to meet the structural requirements. Independent cooling circuits for the vane or blade's pressure and suction surfaces allow the cooling of the airfoil surfaces to be tailored to specific heat load distributions (that is, the pressure surface circuit is an independent forward flowing serpentine while the suction surface is an independent rearward flowing serpentine). The cooling air for the independent circuits is supplied through separate passages at the base of the vane or blade. The cooling air follows intricate passages to feed the serpentine thin outer wall passages, which incorporate pin fins, turbulators, etc. These passages, while satisfying the aero / thermal / stress requirements, are of a manufacturing configuration that may be cast with single crystal materials using conventional casting techniques.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
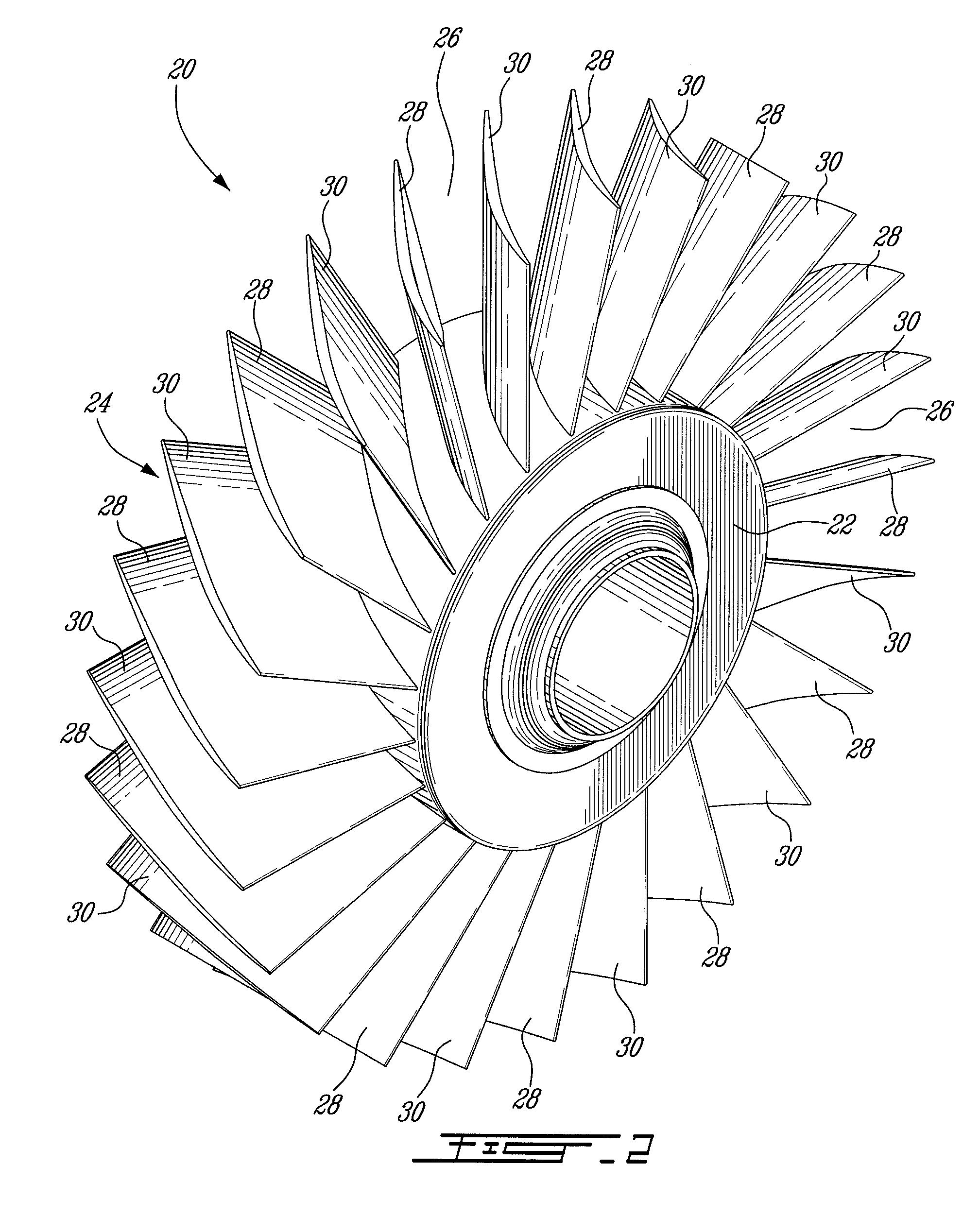
Impeller for axial flow pump
A rotor for an axial-flow blood pump has blades projecting outwardly from a hub and channels between the blades. The blades incorporate hydrodynamic bearing surfaces capable of suspending the rotor during operation. The rotor has a configuration which provides superior pumping action and reduced shear of blood passing through the pump. The forwardly facing pressure surfaces of the blades may include outflow corner surface at their downstream ends. The outflow corner surfaces desirably slope rearwardly and intersect the rearwardly-facing suction surfaces of the blades at outflow ends of the blades.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Turbine vane and gas turbine
ActiveUS20110123351A1Improve cooling effectAvoid deformationEngine fuctionsBlade accessoriesLeading edgeSuction stress
An airfoil part includes a plurality of cooling chambers that are spaces into which the inside of the airfoil part is partitioned, from a leading edge side to a trailing edge side, by a partition wall, that extend in a vane-longitudinal-section direction, and that include division parts on inner walls of a body; insert cylinders that are disposed in the cooling chambers and that have a plurality of impingement holes; and film holes that are provided in the body. The insert cylinders include partitioning parts that extend from the leading edge side to the trailing edge side and that extend in the vane-longitudinal-section direction. The insides of the insert cylinders are partitioned into pressure-surface-side insert spaces close to a pressure surface and suction-surface-side insert spaces close to a suction surface.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Impeller for axial flow pump
A rotor for an axial-flow blood pump has blades projecting outwardly from a hub and channels between the blades. The blades incorporate hydrodynamic bearing surfaces capable of suspending the rotor during operation. The rotor has a configuration which provides superior pumping action and reduced shear of blood passing through the pump. The forwardly facing pressure surfaces of the blades may include outflow corner surface at their downstream ends. The outflow corner surfaces desirably slope rearwardly and intersect the rearwardly-facing suction surfaces of the blades at outflow ends of the blades.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
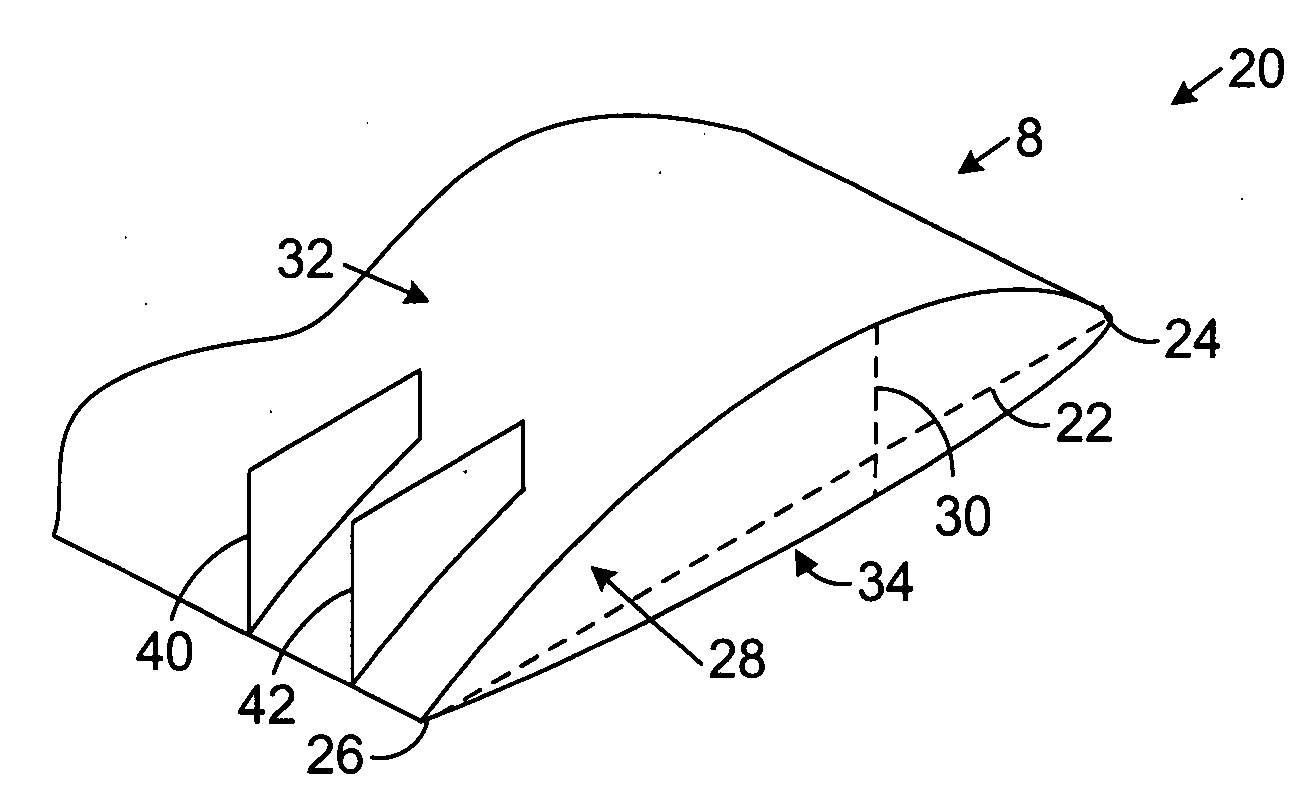
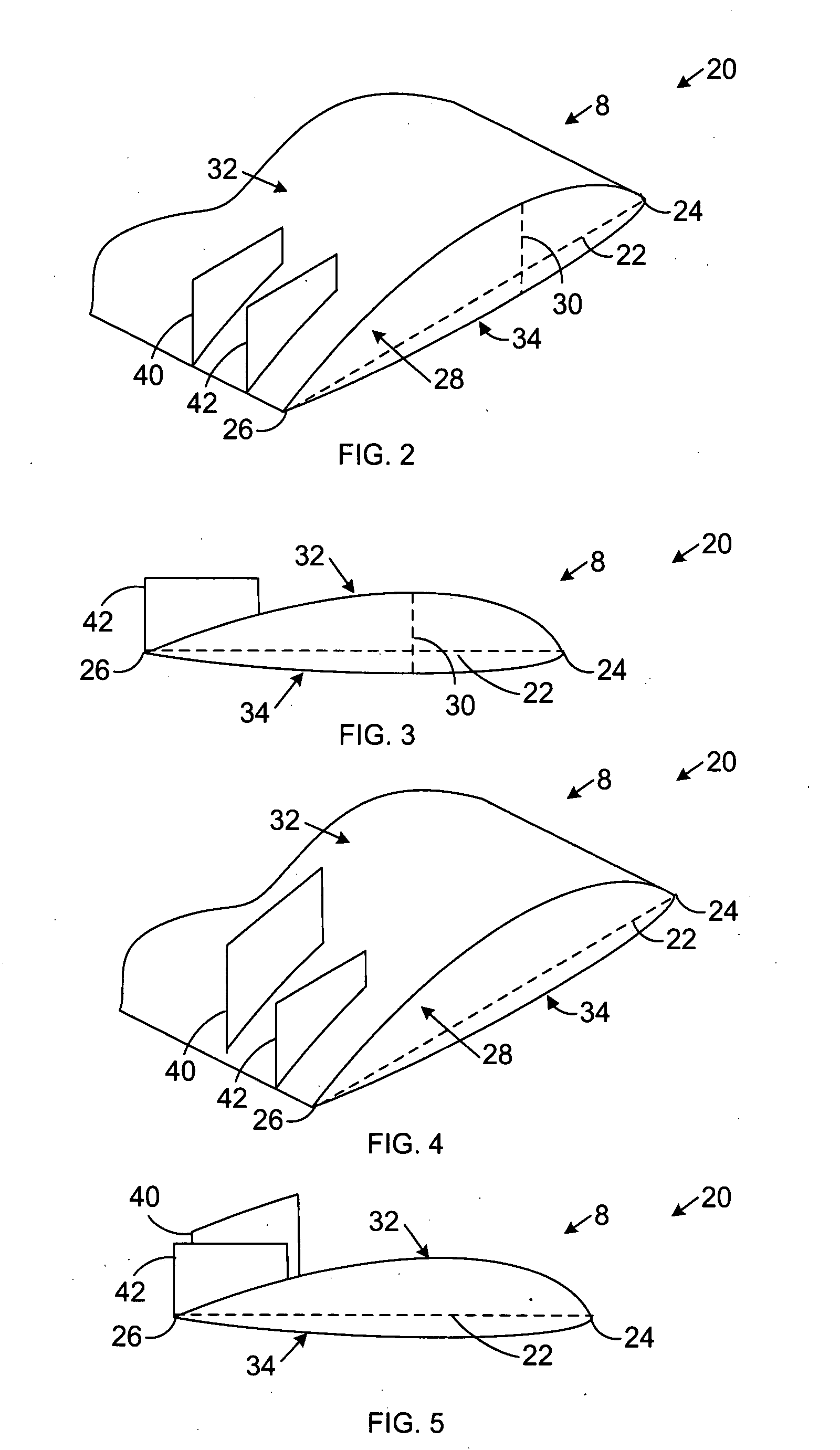
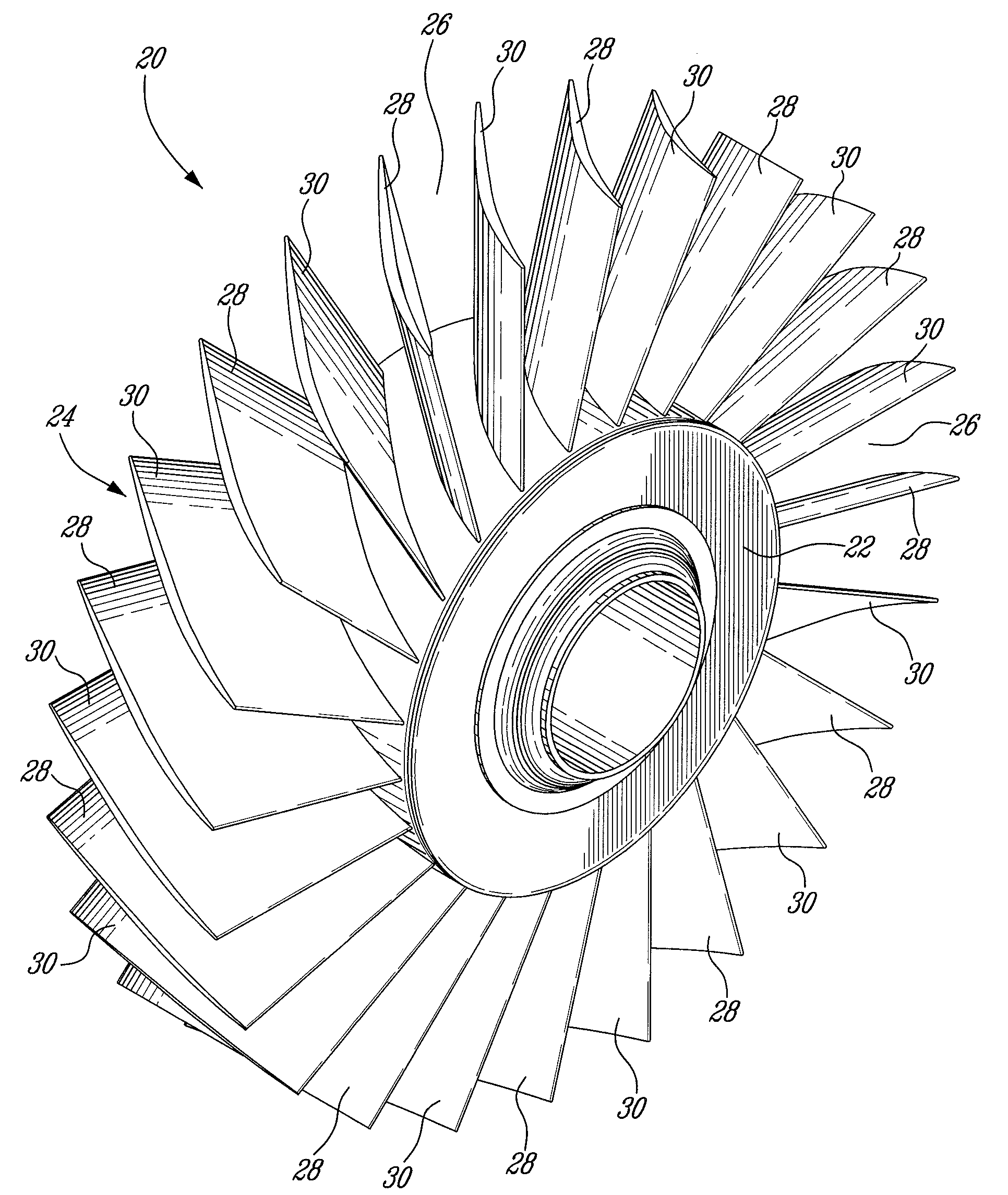
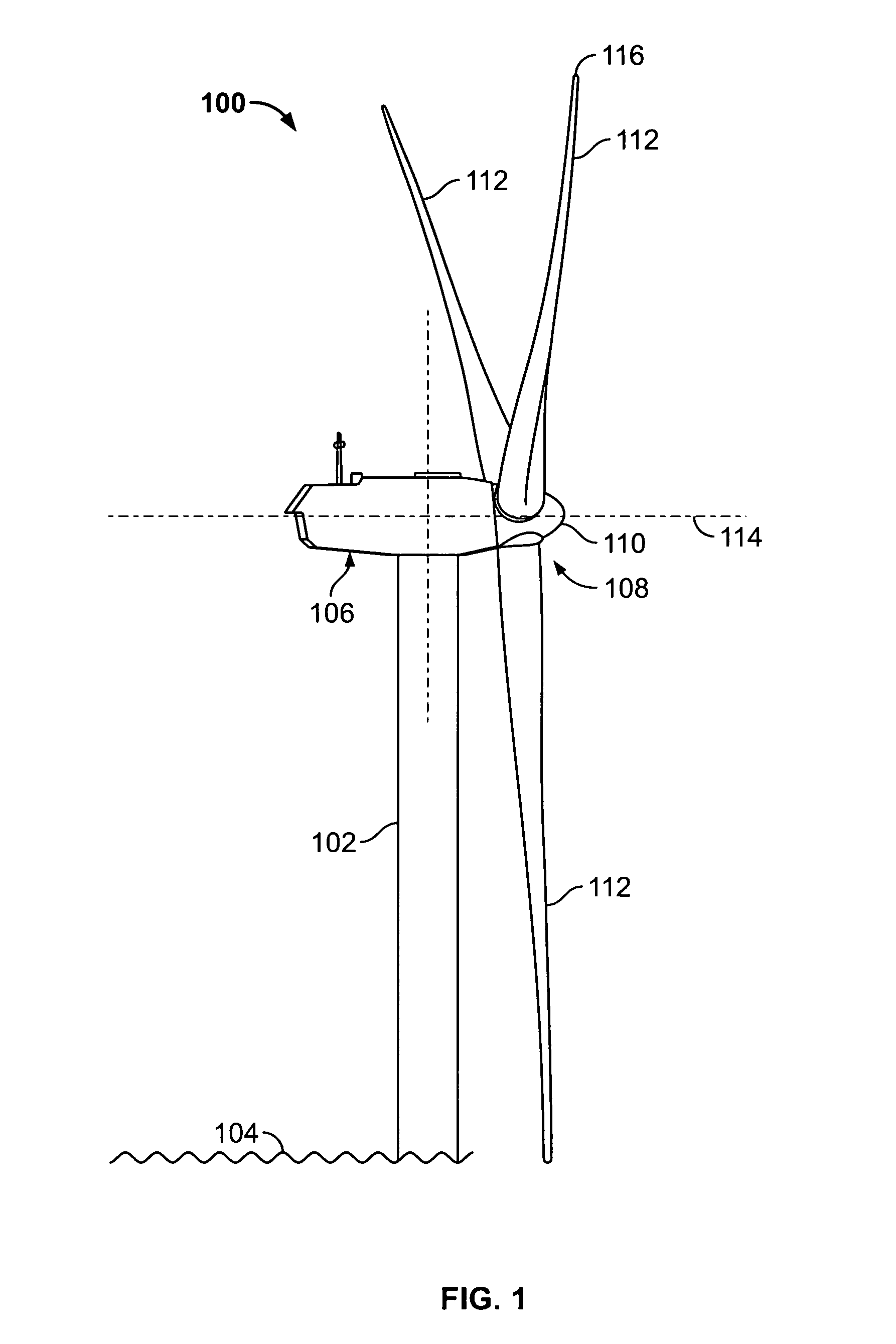
Wind turbine blade tip vortex breakers
A wind turbine includes a tower supporting a drive train with a rotor, at least one blade extending radially from the rotor; and a plurality of substantially flat flaps extending substantially perpendicular from a suction surface of the blade and along different chord lines near a tip of the blade for capturing and directing tip vortices toward a trailing edge of the blade.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Compressor aerofoil
ActiveUS20110206527A1Improve efficiencyEngine manufacturePump componentsInteraction energyEngineering
An aerofoil (52) for a compressor comprising a suction surface (56) and a pressure surface (58) with a thickness distribution defined therebetween, the aerofoil further comprising a first local maximum in the thickness distribution and a second local maximum (54) in the thickness distribution, the second local maximum (54) being downstream of the first local maximum and the second local maxima being formed by a first region of concave curvature in the suction surface between the first and second local maxima, wherein the second local maximum is disposed such that in use a boundary layer upstream of the second local maximum on the suction surface is thinned by the second local maximum, and in addition the boundary layer may be sufficiently thinned so that an interaction of an upstream flow feature with the thinned boundary layer is capable of generating a turbulent spot with a calmed region downstream of the turbulent spot.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
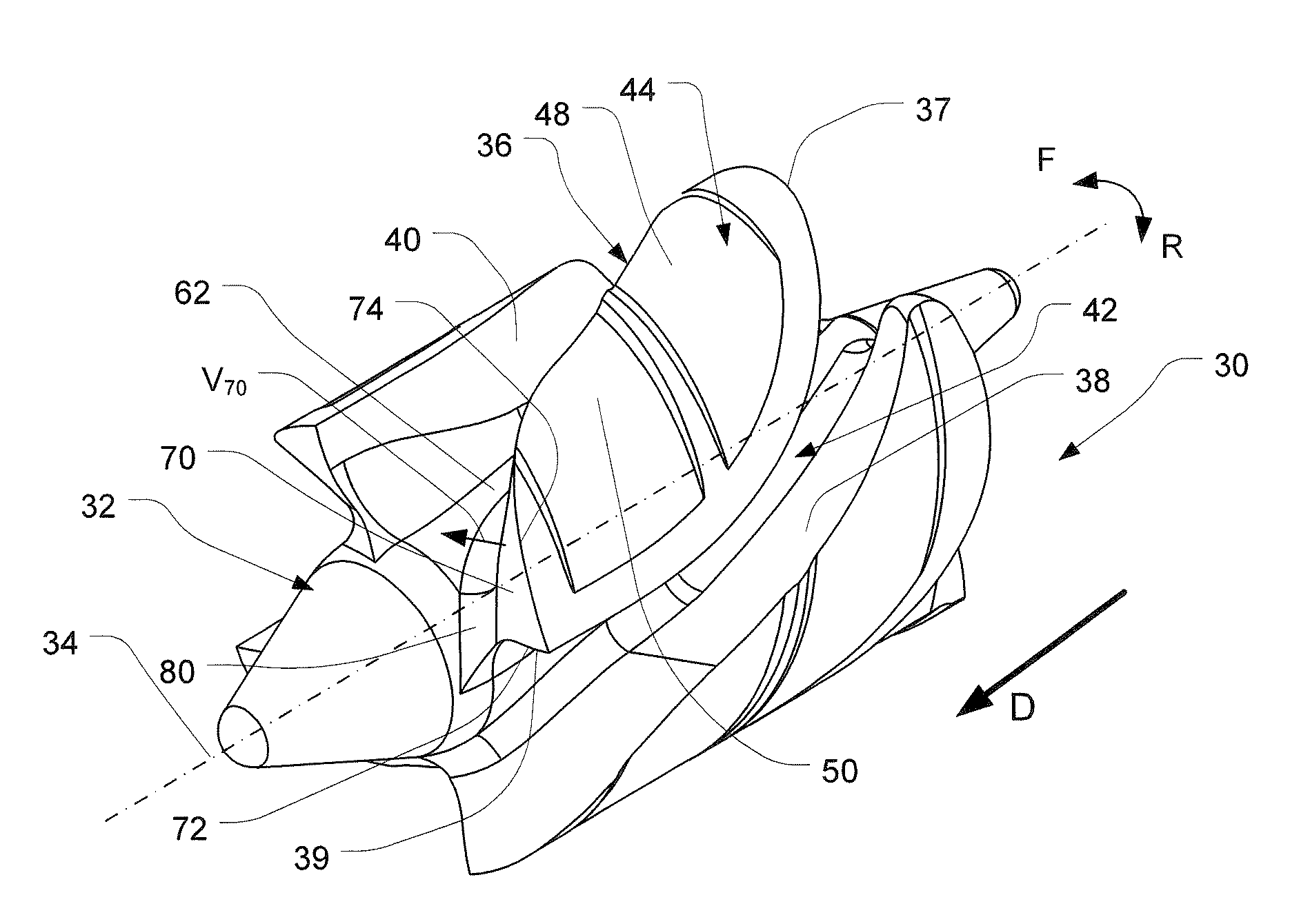
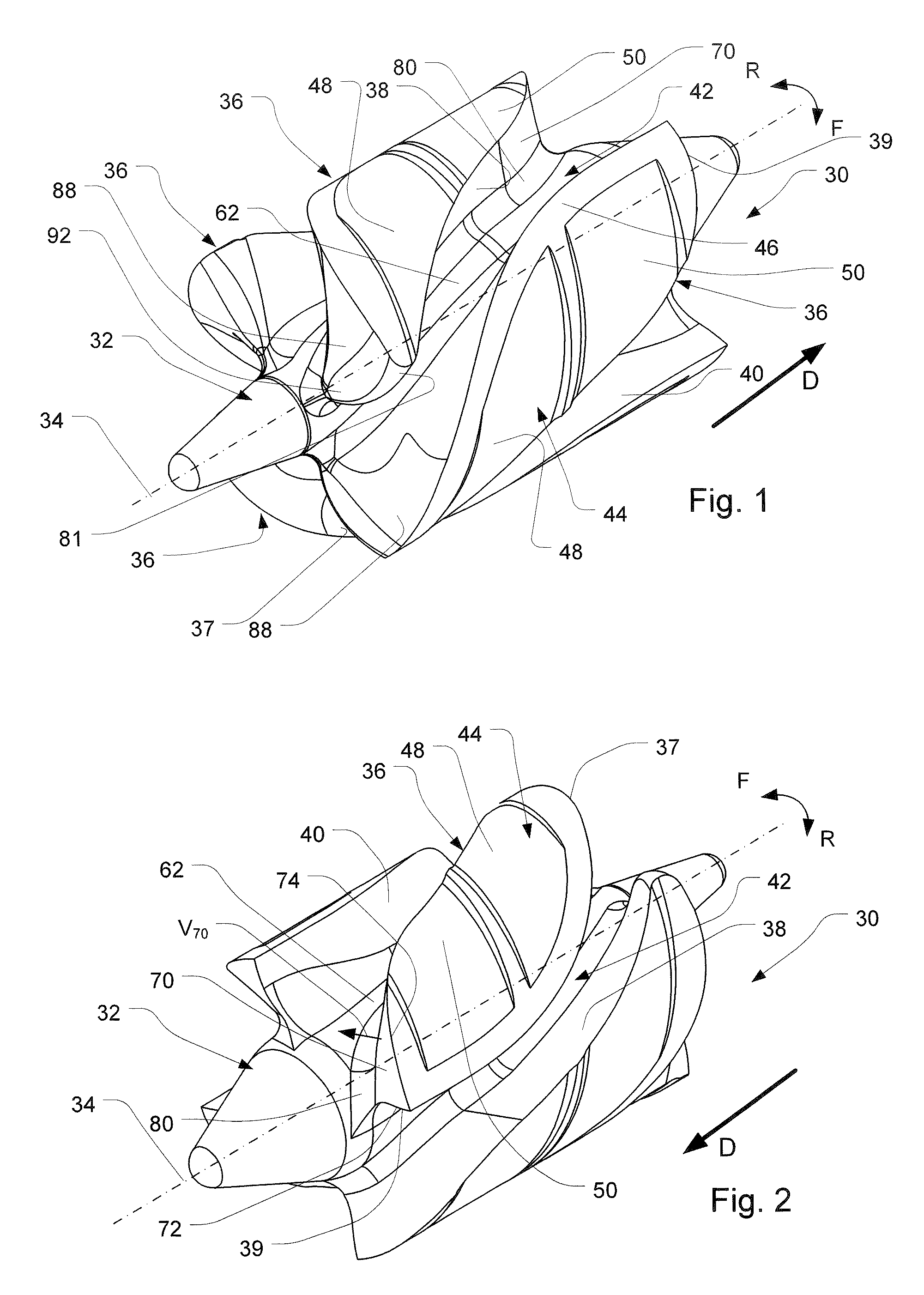
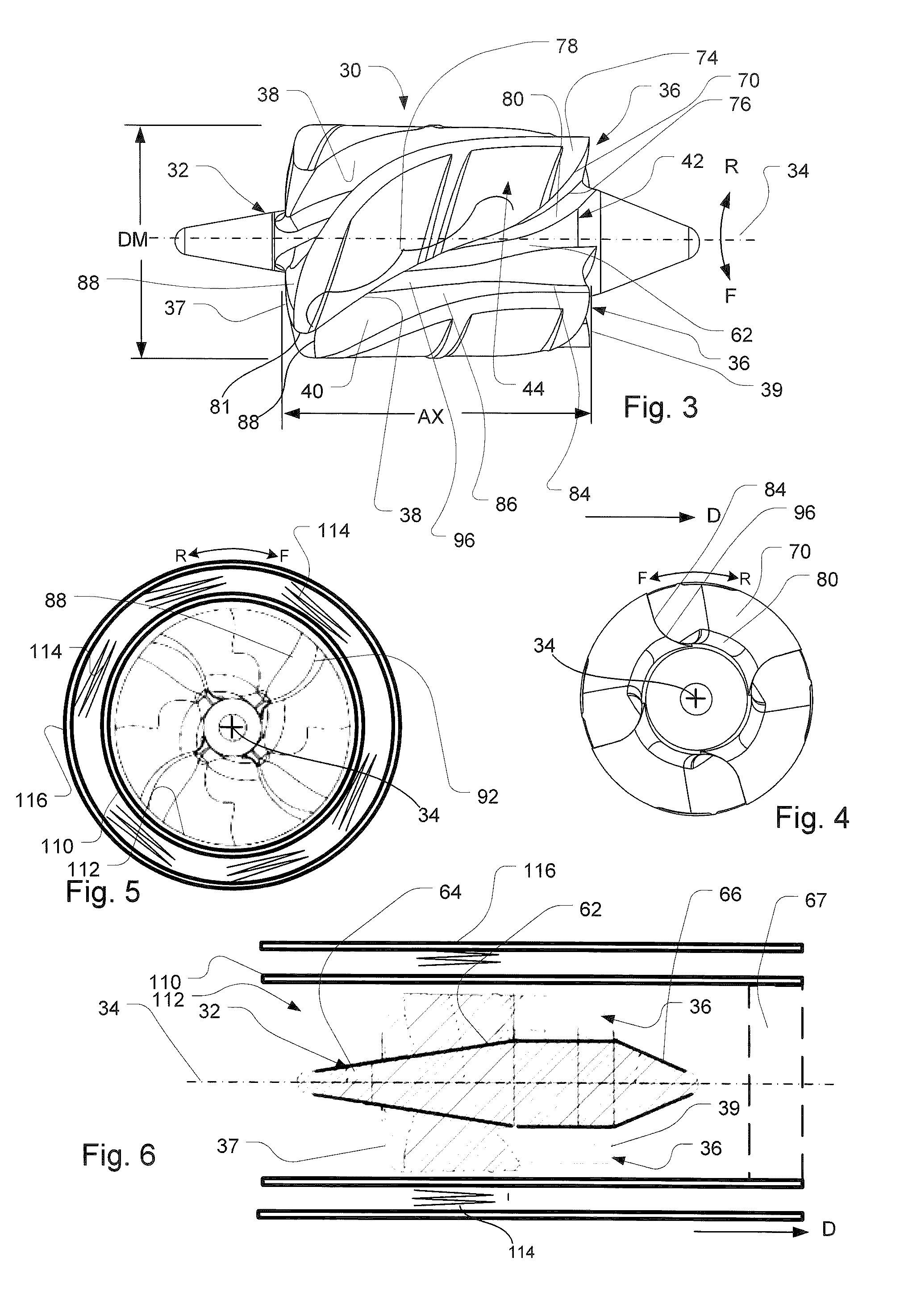
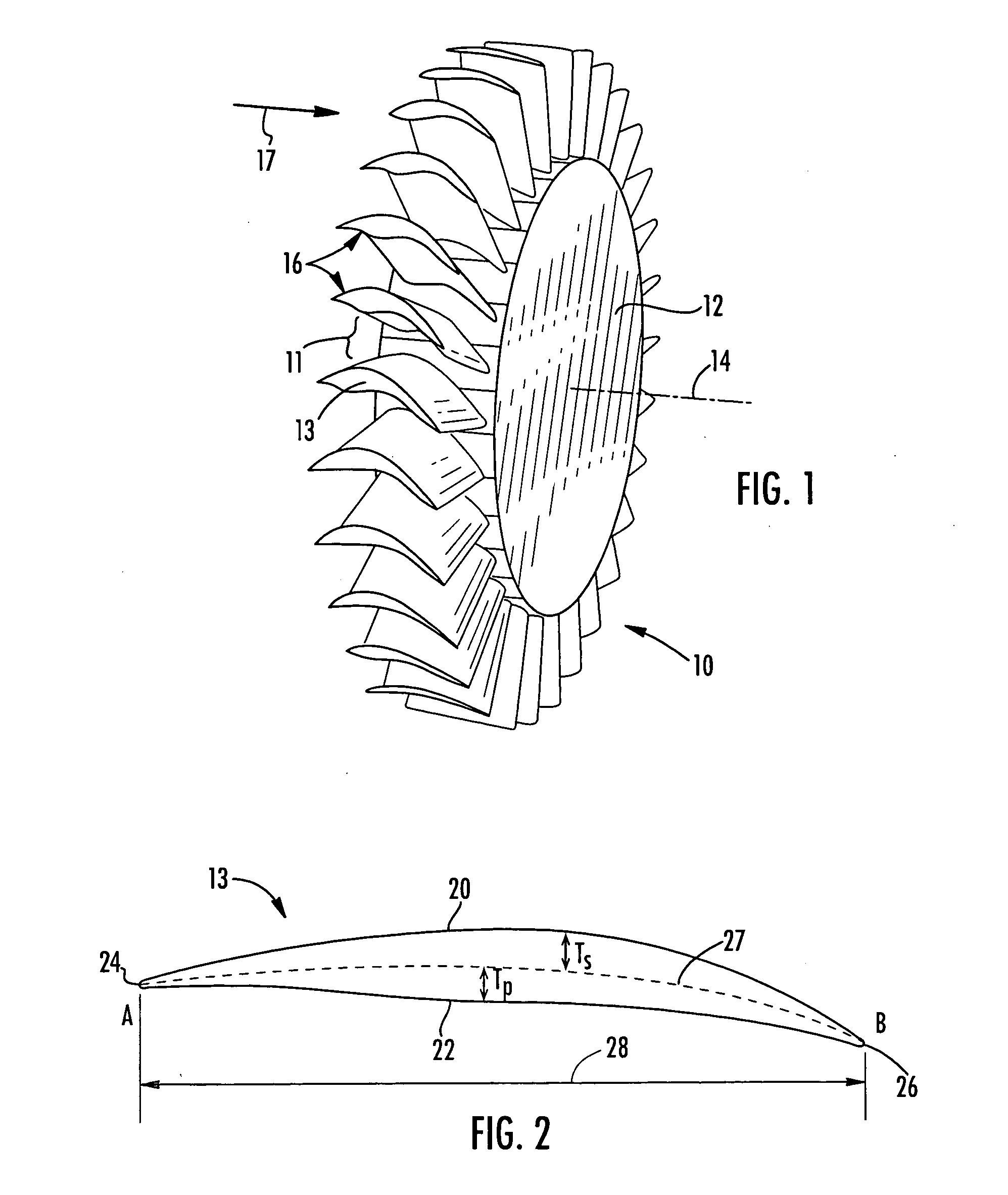
Intentionally mistuned integrally bladed rotor
A frequency mistuned integrally bladed rotor (IBR) for a gas turbine engine comprises a hub and a circumferential row of blades of varying frequency projecting integrally from the hub. Each blade in the row alternate with another blade having a different pressure surface definition but similar suction surface, leading edge and trailing edge definitions.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
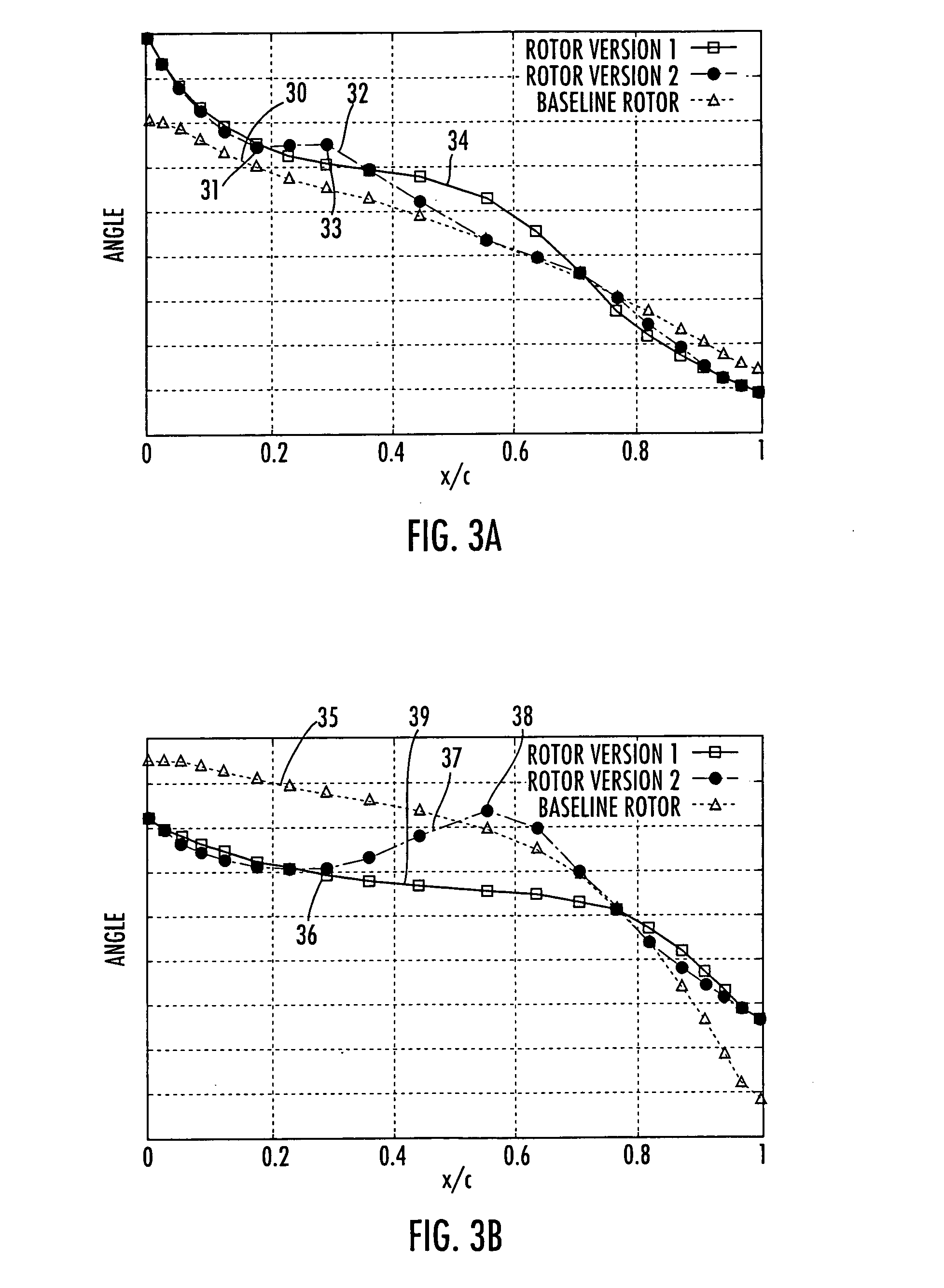
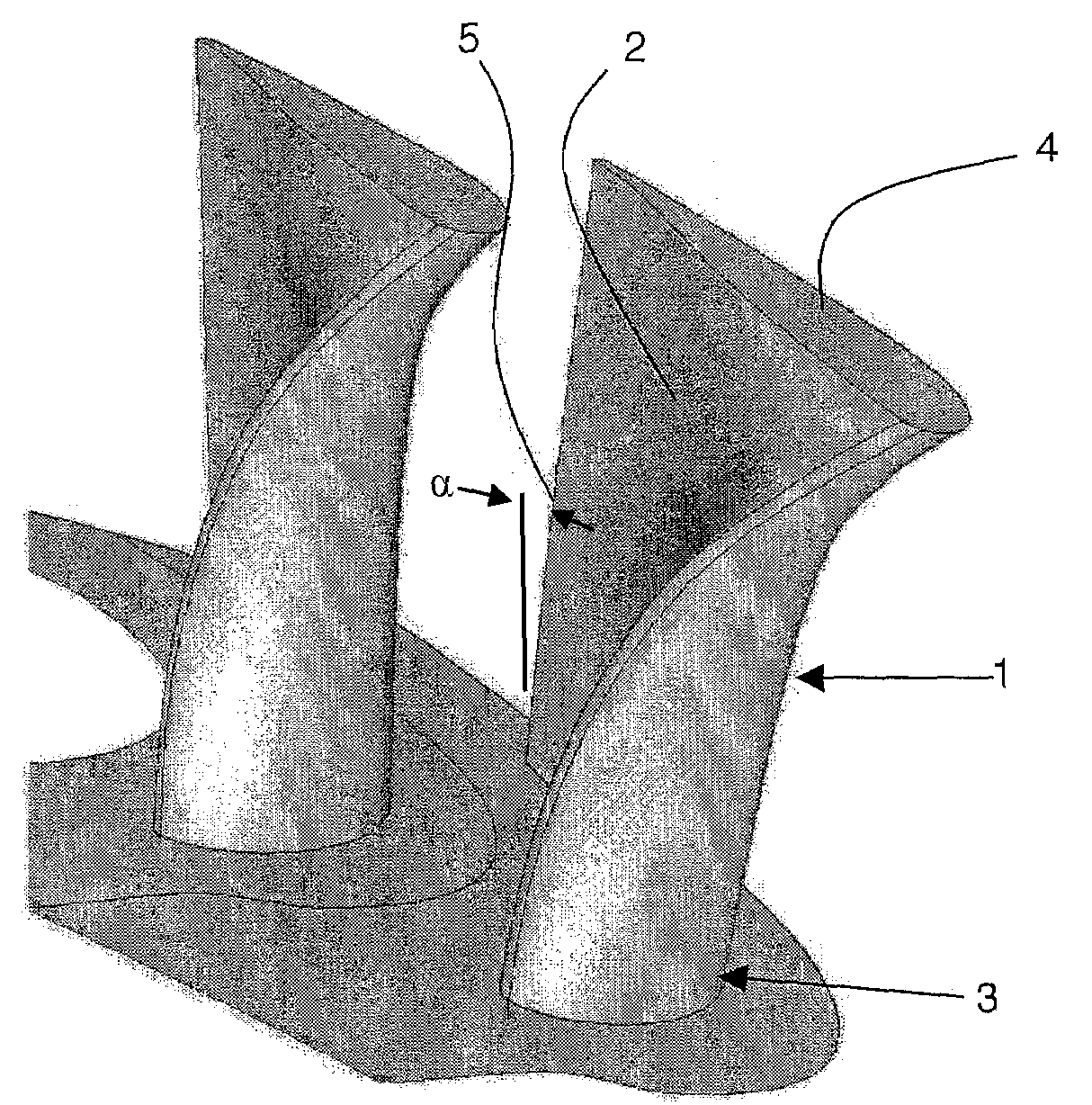
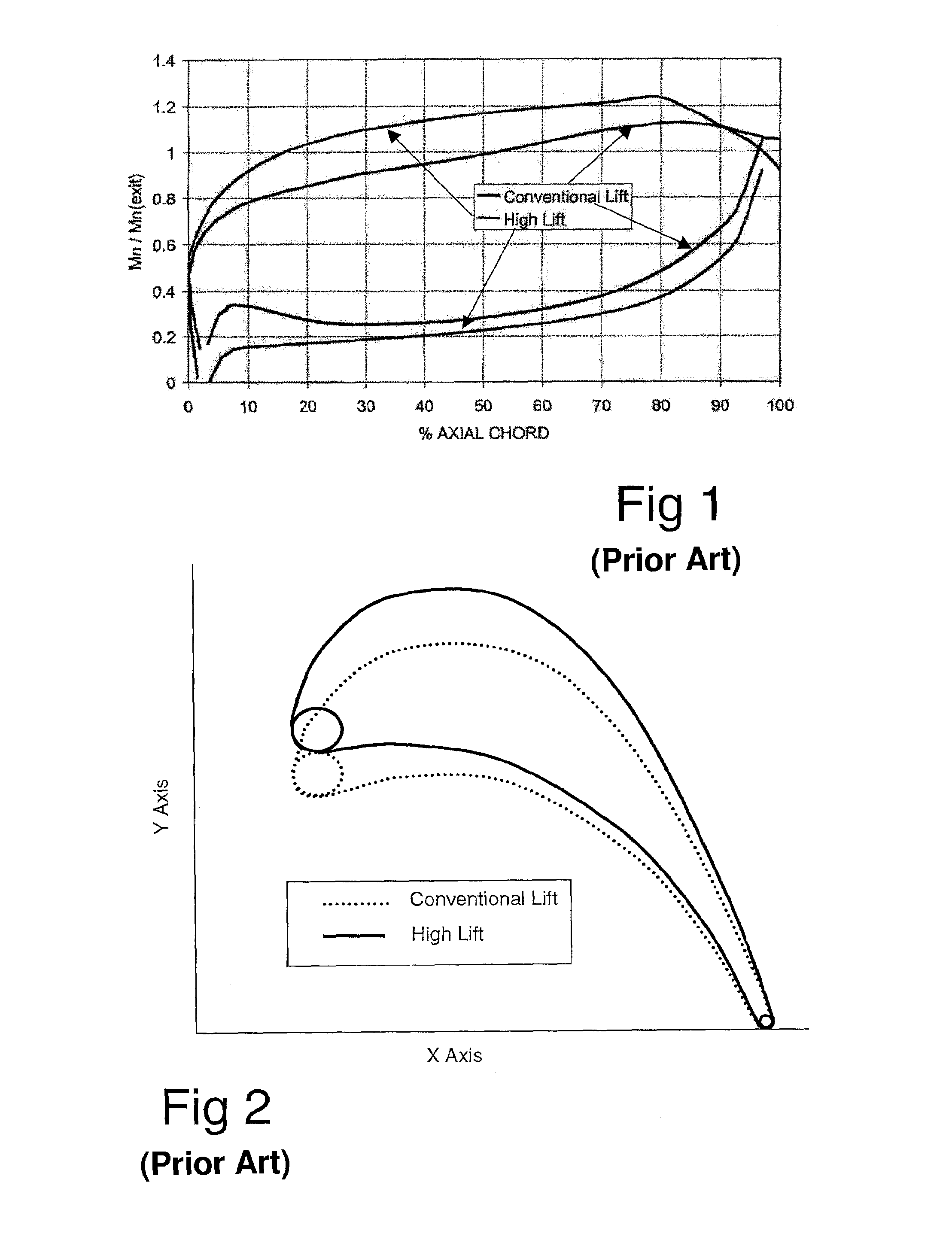
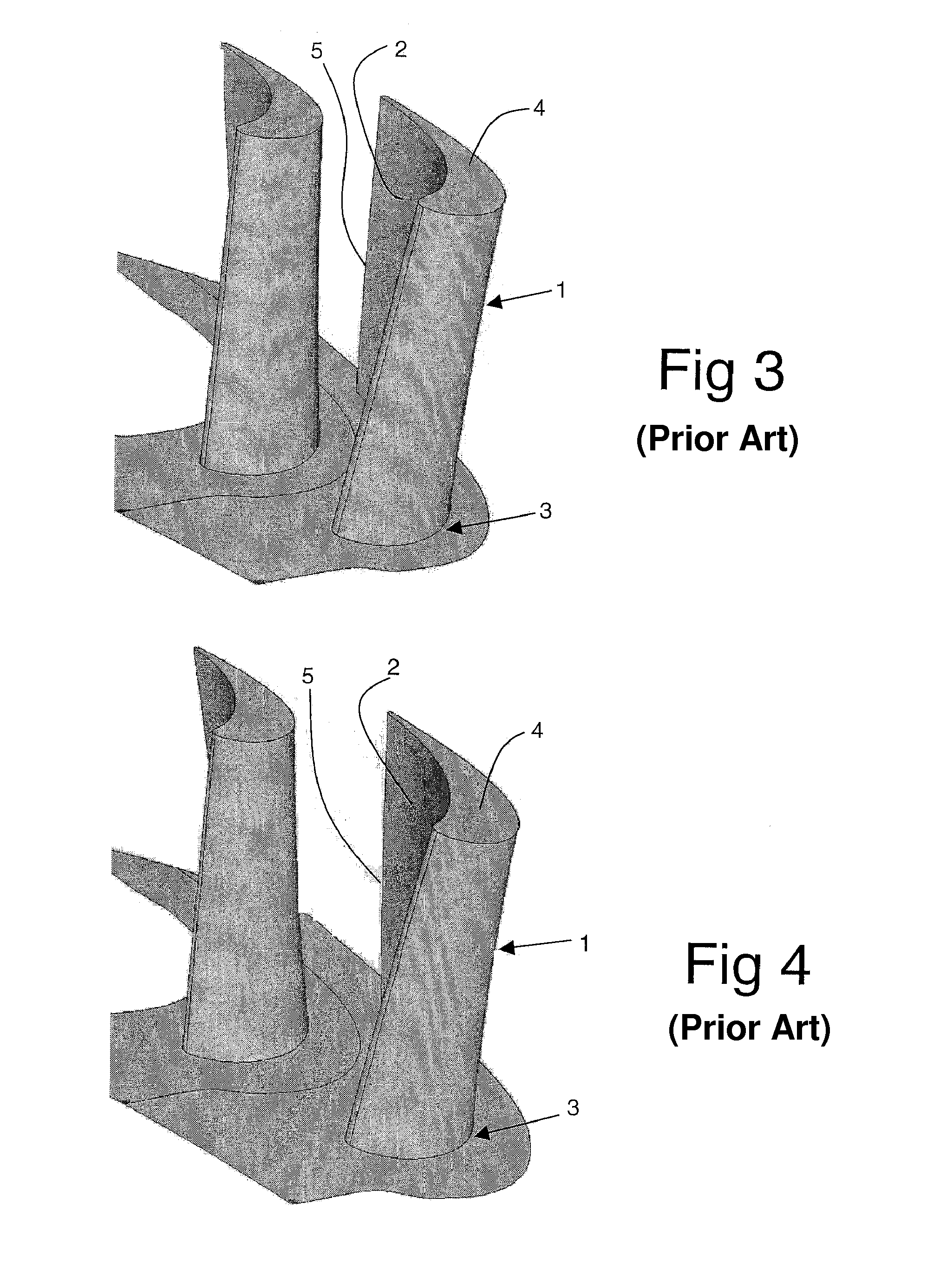
Transonic compressor rotors with non-monotonic meanline angle distributions
InactiveUS20080118362A1Improve efficiencySimple designSupersonic fluid pumpsPump componentsShock waveLeading edge
Airfoils are provided having non-monotonic meanline angle distributions and local negative camber along a length of the meanline between a point on a leading edge of the airfoil and a point on the trailing edge of the airfoil. The improved airfoil shape decreases the peak of a Mach number of a shock wave that develops in a passage between adjacent airfoils and attenuates or eliminates the shock wave at the suction surface of the airfoil within the passage. A blade constructed by this type of airfoil provides improved fluid flow in the passages between the airfoils, increased efficiency and an improved stall margin, among other benefits.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Intentionally mistuned integrally bladed rotor
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Suction cup and suction cup device
Owner:SONY CORP
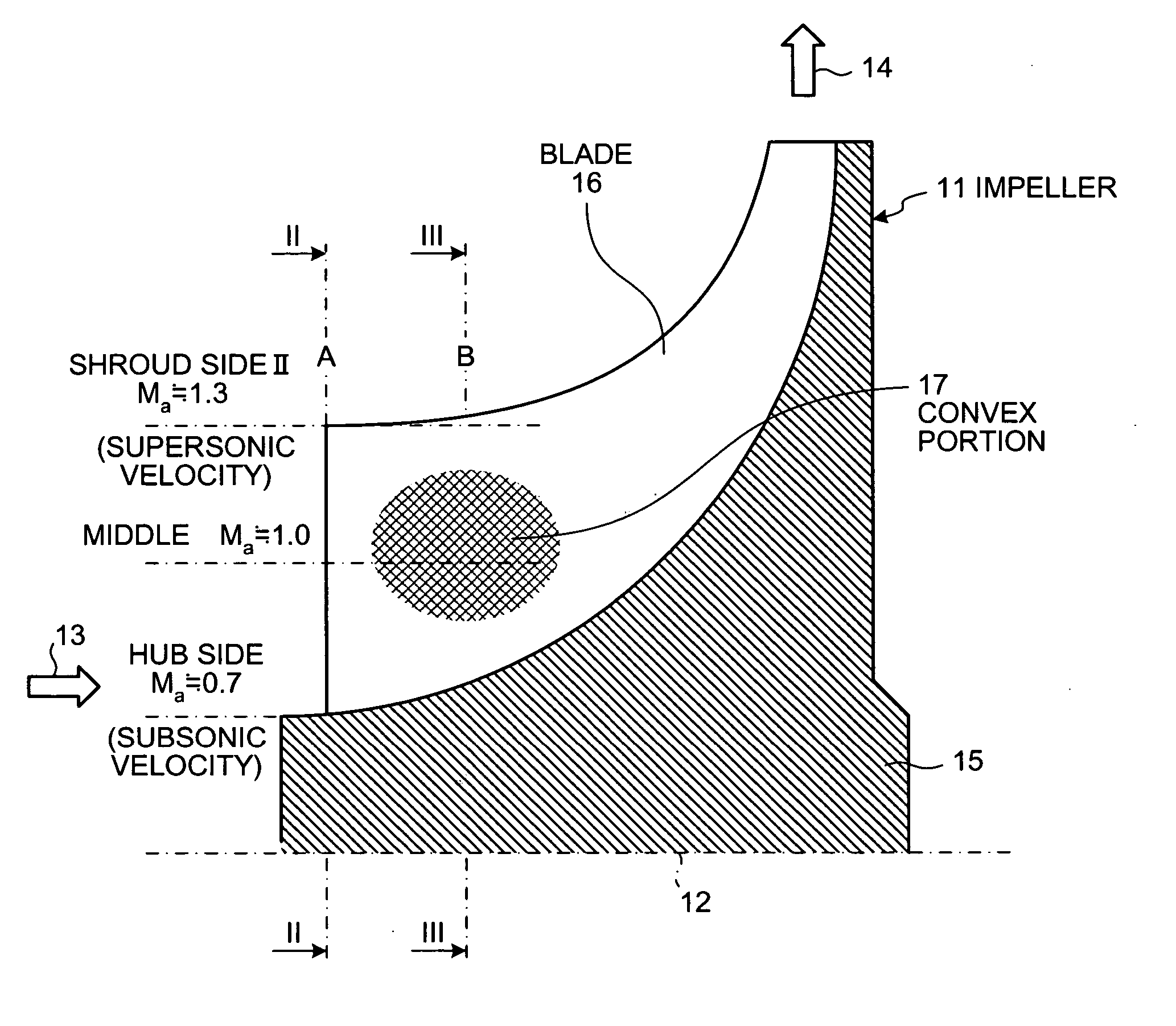
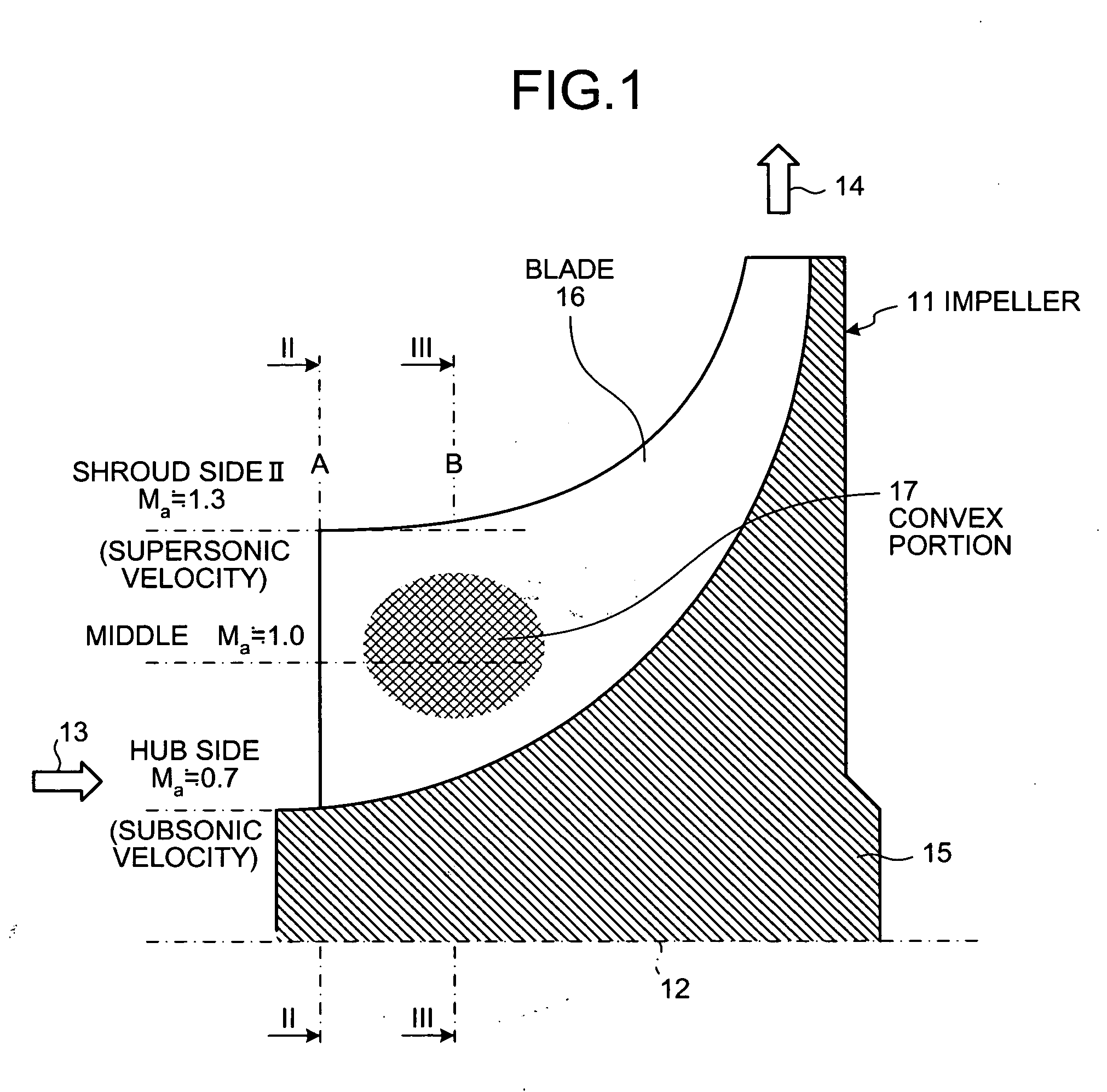
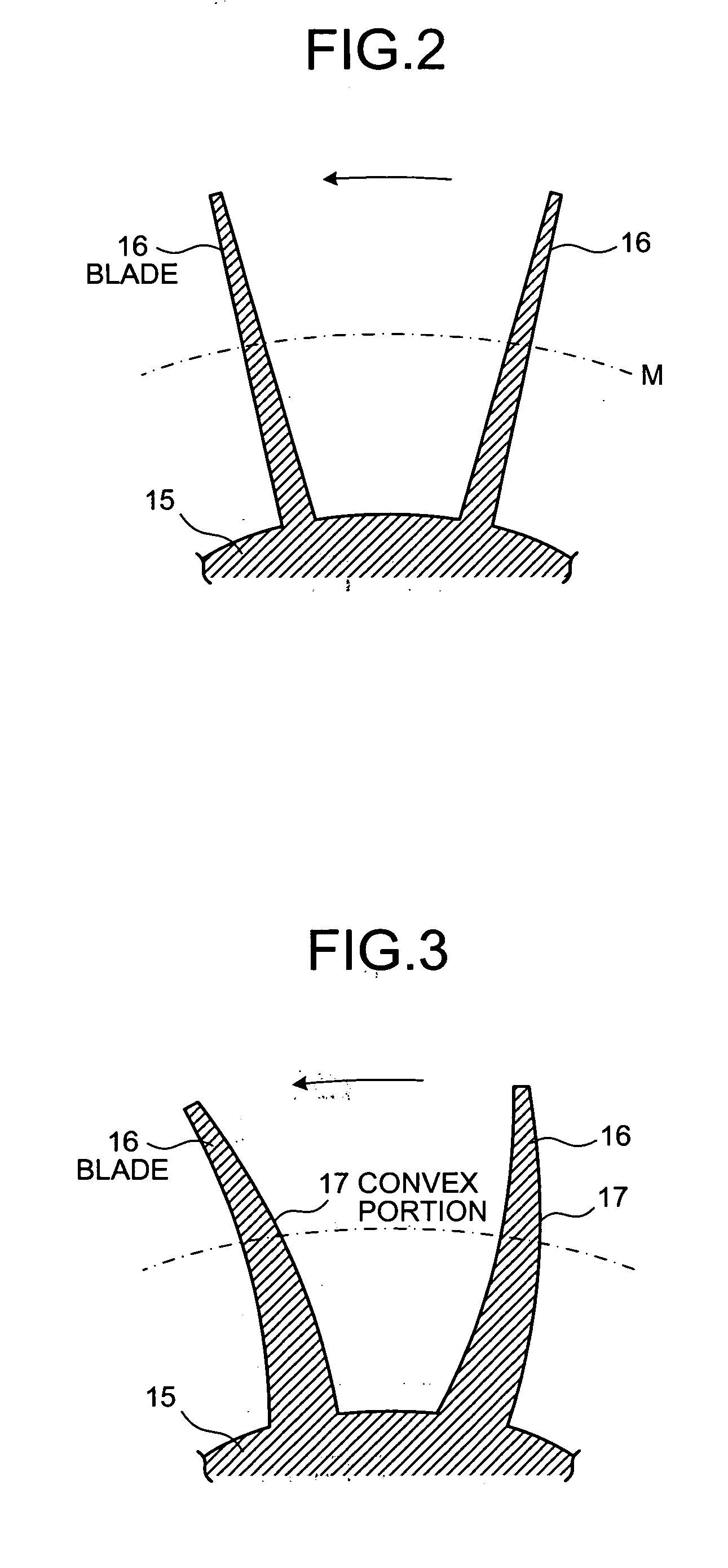
Centrifugal compressor and manufacturing method for impeller
InactiveUS20050260074A1Fall in efficiencyFall in performancePropellersSupersonic fluid pumpsEngineeringFront edge
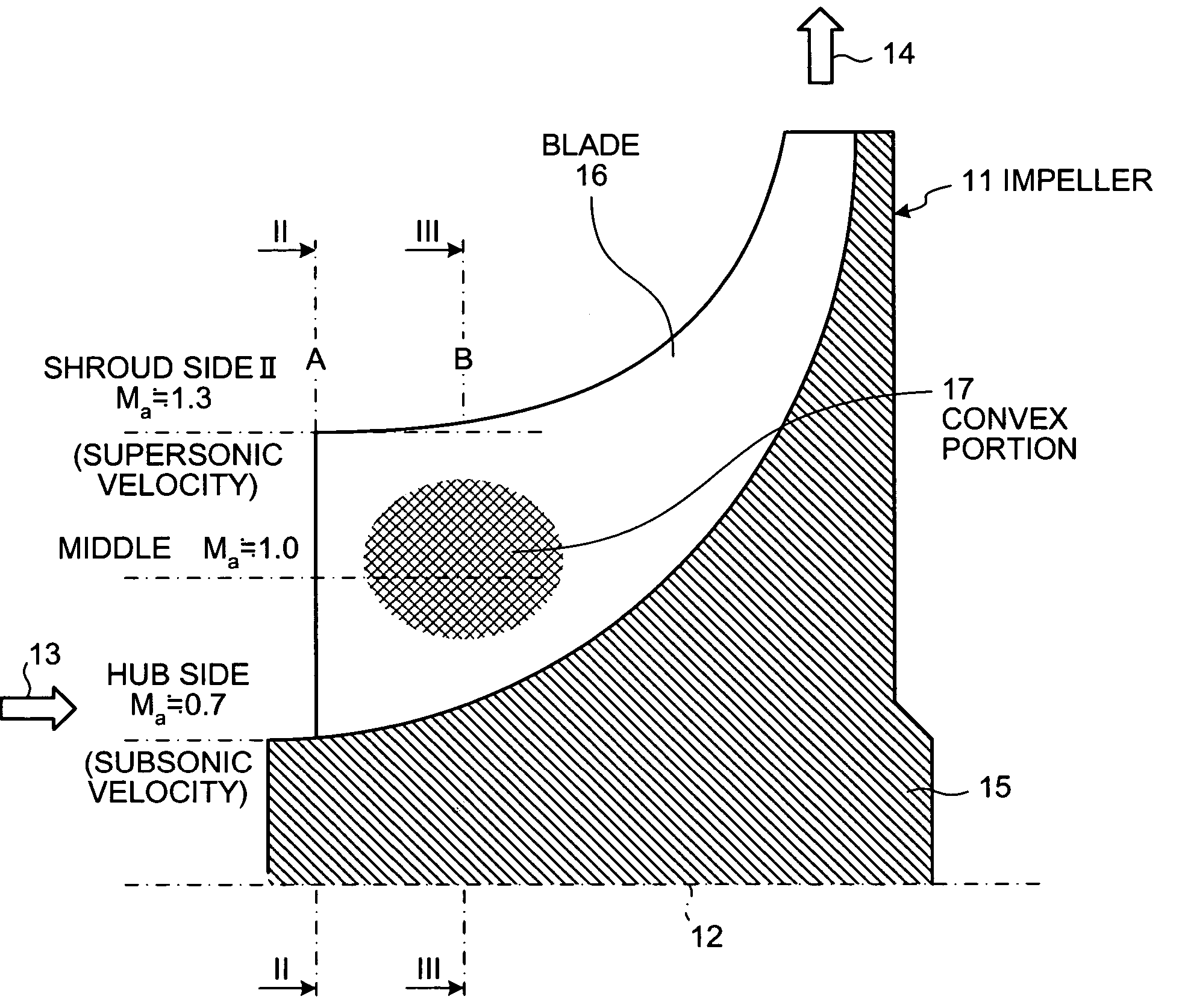
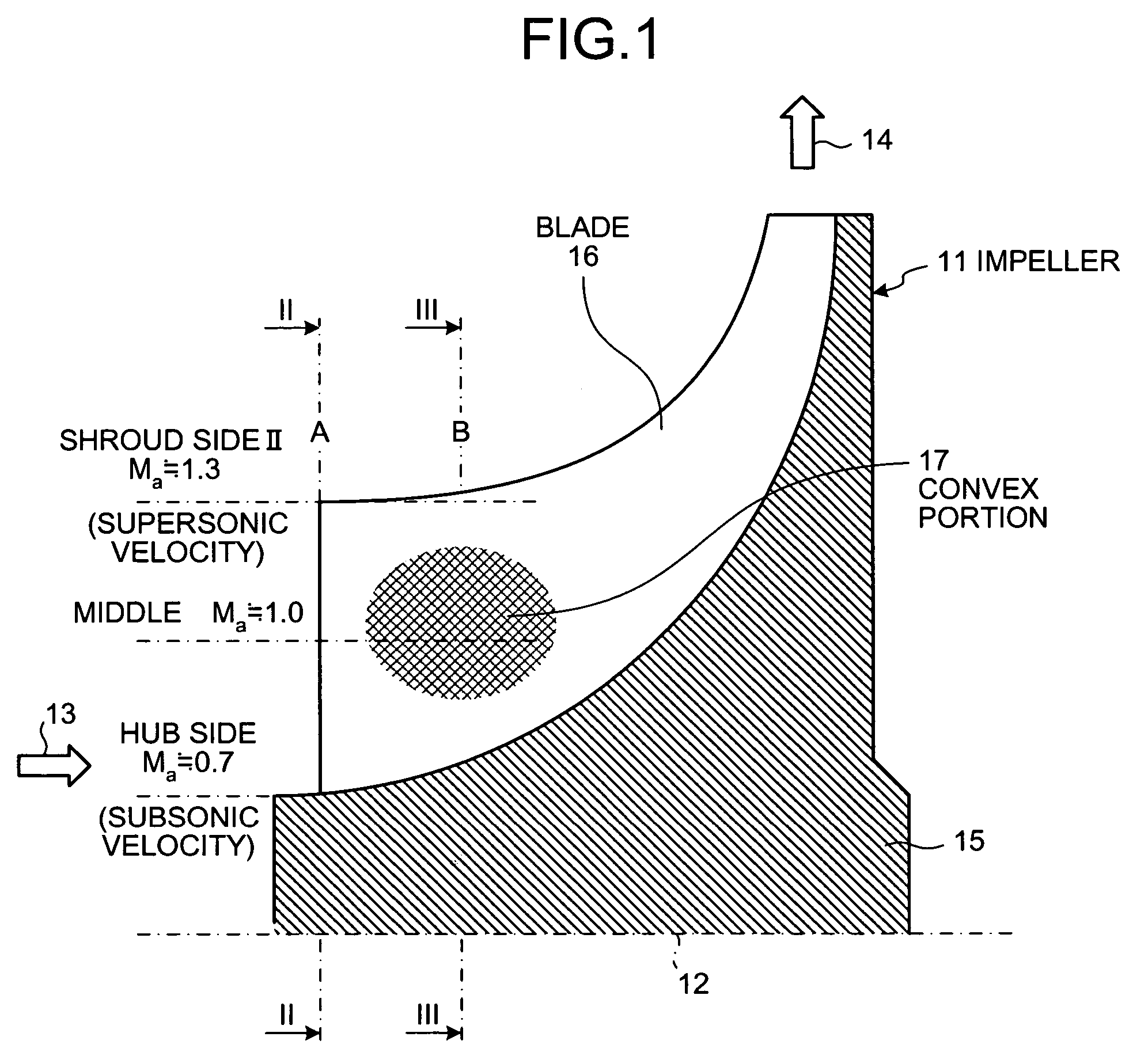
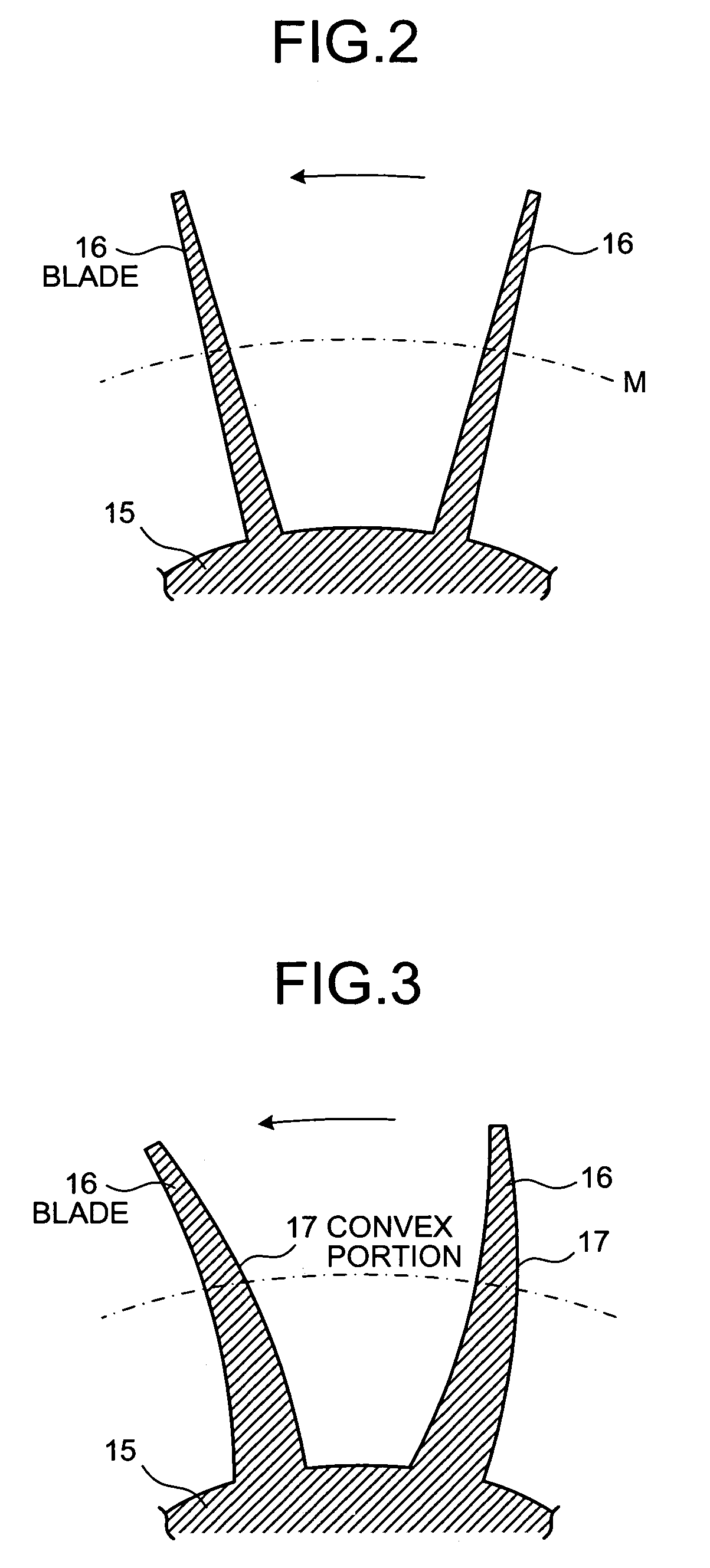
On a suction surface side of a blade in an impeller, a convex portion is formed to assume a curved line from a front edge portion to a throat portion substantially in the middle in a radial direction, and this convex portion is formed to be flat assuming a curved line from the throat portion toward a rear edge portion, whereby this convex portion is formed in a position where a relative inlet velocity of fluid into the impeller is Mach number Ma≅1.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Turbine blade having squealer
ActiveUS20100111704A1Decrease in efficiency of gas can be preventedLow efficiencyEngine fuctionsBlade accessoriesLeading edgeTurbine blade
A turbine blade of the invention includes an air foil including a plurality of cooling flow passages through which a cooling medium flows from a leading edge region to a trailing edge region, a top plate which forms the apex of the air foil, has a heat-resistant coating applied on the upper surface thereof, and includes a plurality of cooling holes, and a squealer which protrudes radially outward from the blade from the top plate, and is formed so as to extend from a leading edge end to a starting end of the trailing edge region along a suction-surface-side blade wall in a peripheral direction of the blade.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Method and apparatus for fabricating wind turbine components
A method of assembling a wind turbine blade includes forming a preform pressure surface member and a preform suction surface member. The method also includes forming at least one of a leading edge and a trailing edge. One method of forming the leading edge or the trailing edge includes coupling a preform cap member to one of a portion of the preform pressure surface member and a portion of the preform suction surface member. At least a portion of one of the preform pressure surface member and the preform suction surface member overlap at least a portion of the preform bond cap member. Another method of forming the leading edge or the trailing edge includes coupling the preform pressure surface member to the preform suction surface member wherein at least a portion of the preform pressure surface member overlaps at least a portion of the preform suction surface member.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
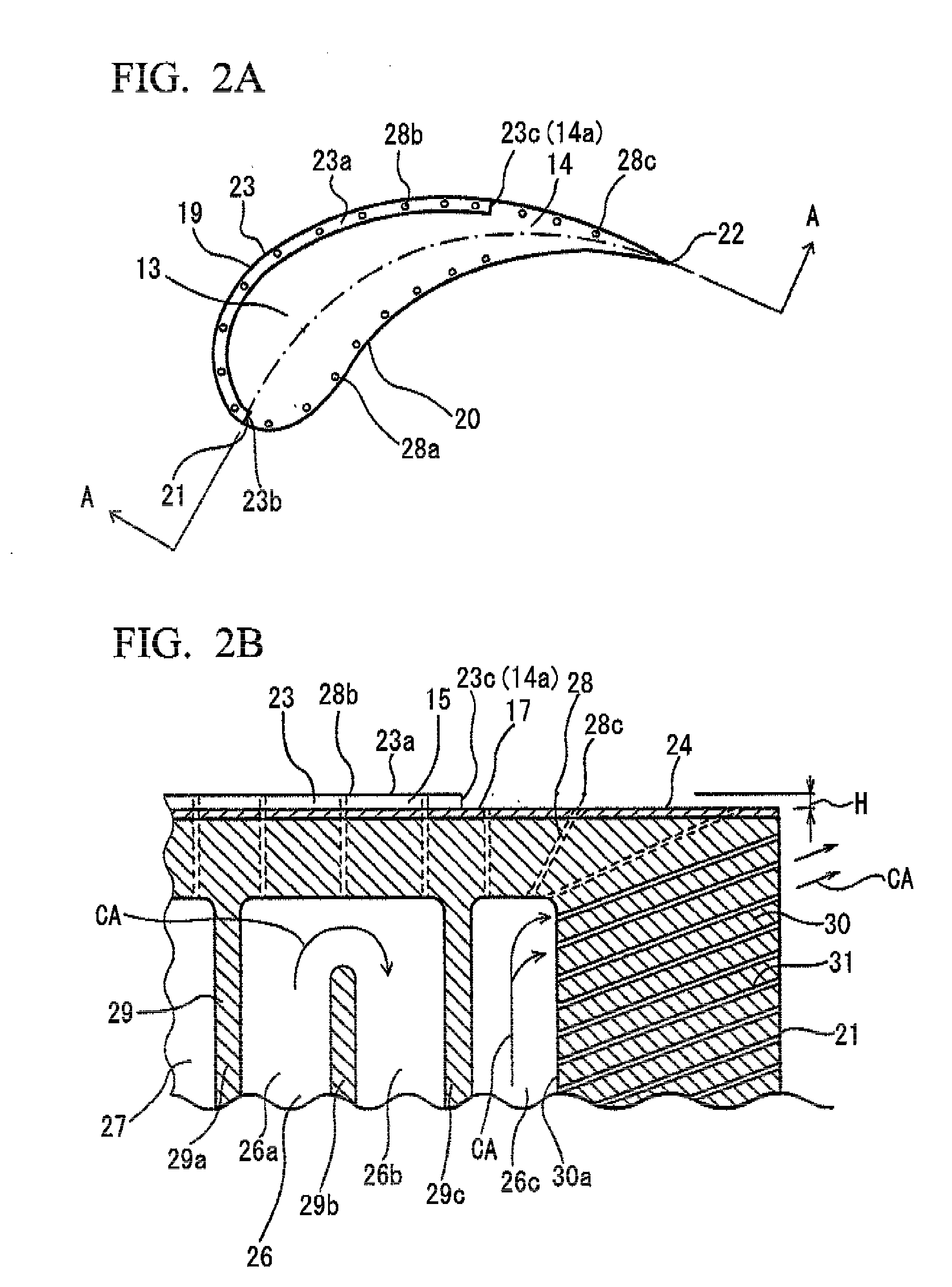
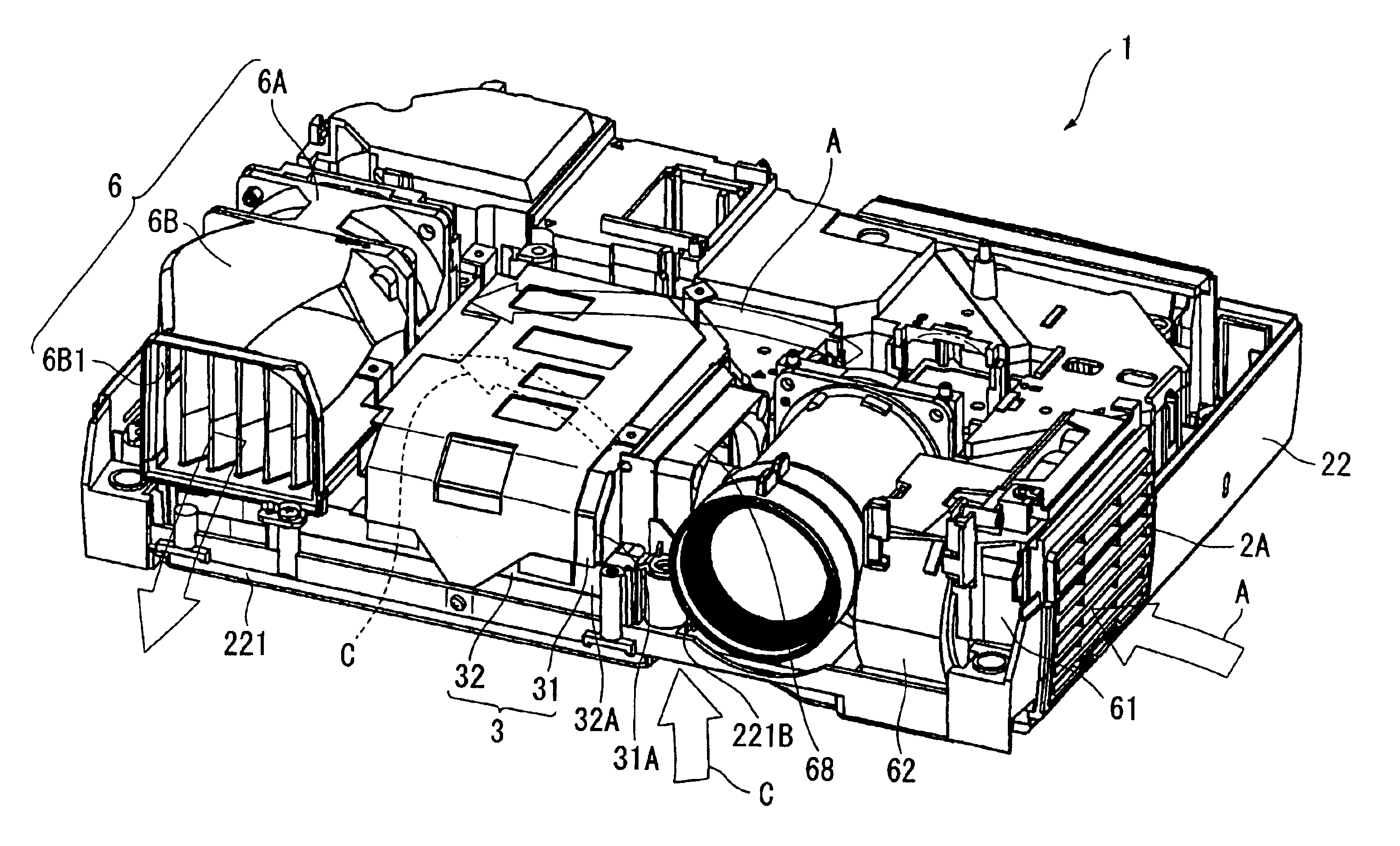
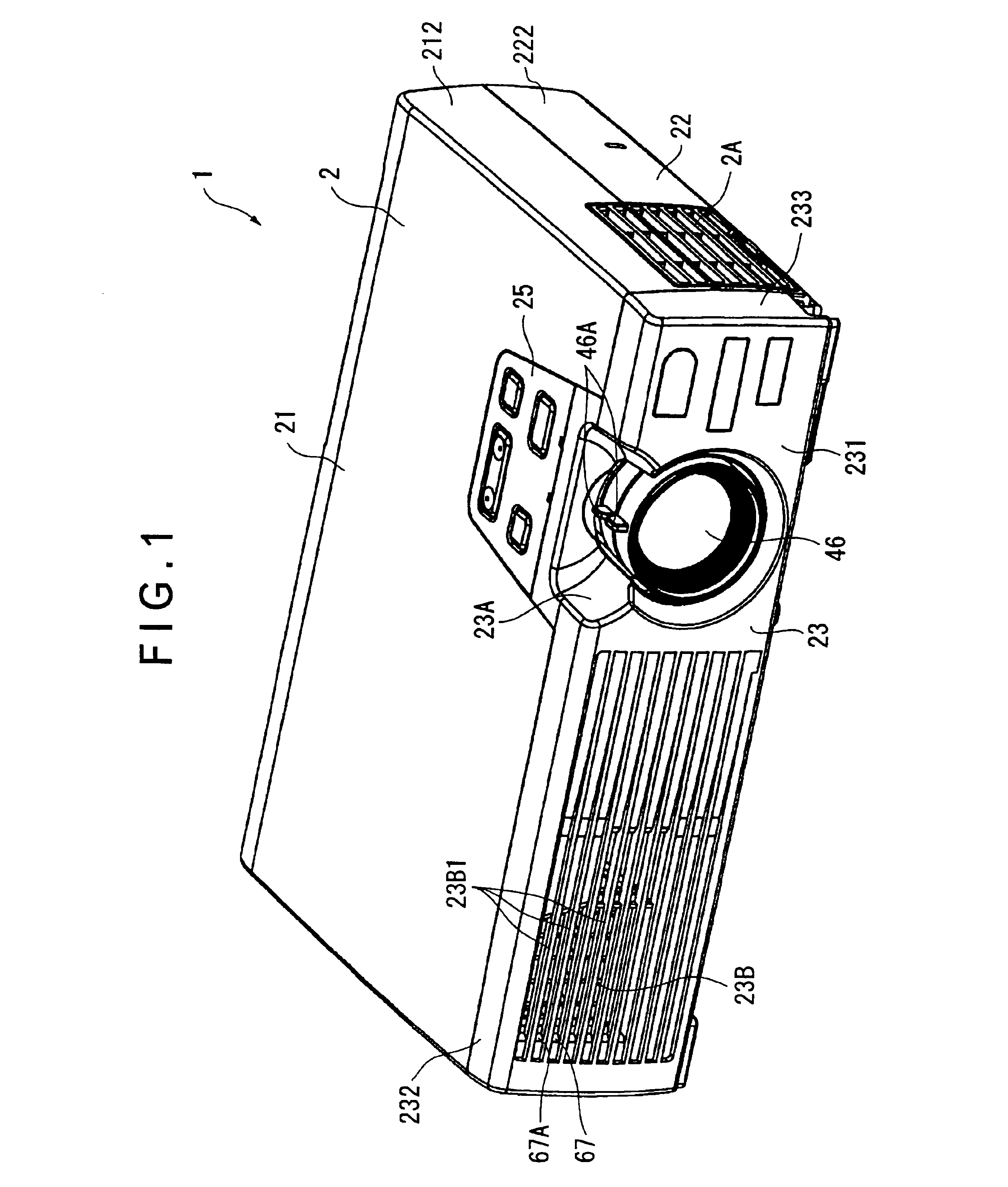
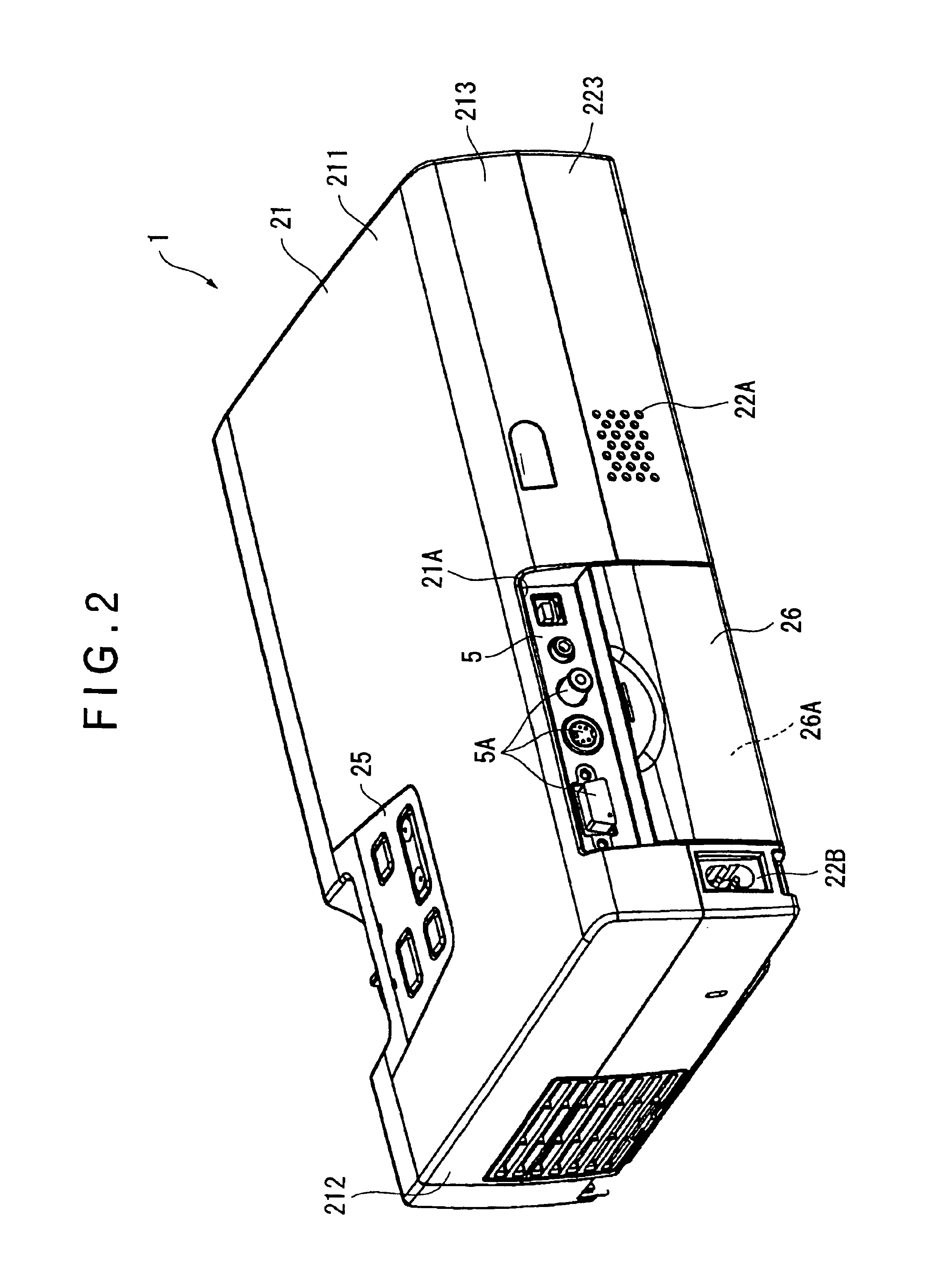
Projector provided with cooling mechanism
InactiveUS6793343B2Reduce the soundImprove cooling efficiencyTelevision system detailsProjectorsEngineeringProjection lens
A light source is disposed at an end of an optical unit (4) formed approximately in planarly-viewed L-shape and an axial-flow fan (6A) is disposed so that suction surface thereof opposes the light source, where an exhaust duct (6B) connected with the axial-flow fan (6A) and extending toward a front side of a projector (1) along a side of a lower case is disposed on the exhaust side of the axial-flow fan (6A), so that the axial-flow fan (6A) is spaced apart from an exhaust hole formed on the front side of the projector (1) and the exhaust flow from the axial-flow fan (6A) becomes parallel to an image projecting direction of a projection lens.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Impeller for centrifugal compressors
InactiveUS6905310B2Interference minimizationMinimizes separationPropellersRotary propellersSuction stressAerodynamic load
In an impeller for centrifugal compressors comprising a plurality of blades each having a base end attached to a central hub, each of the blades is given with a thickness which increases progressively toward a hub end thereof, and a suction surface side of the blade is given with a greater thickness increase rate with respect to a neutral plane than a pressure surface side of the blade. Thereby, the inter-blade channel is narrowed locally in the region near the hub end of the suction surface of each blade, and this locally reduces the aerodynamic loading on the blade. In particular, the surge property is improved, and the generation of radially outwardly directed secondary flows can be minimized. This allows the distribution of aerodynamic loading in the radial direction or from the tip end to the hub end of each blade to be controlled at will, and enables the optimum design of the impeller.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
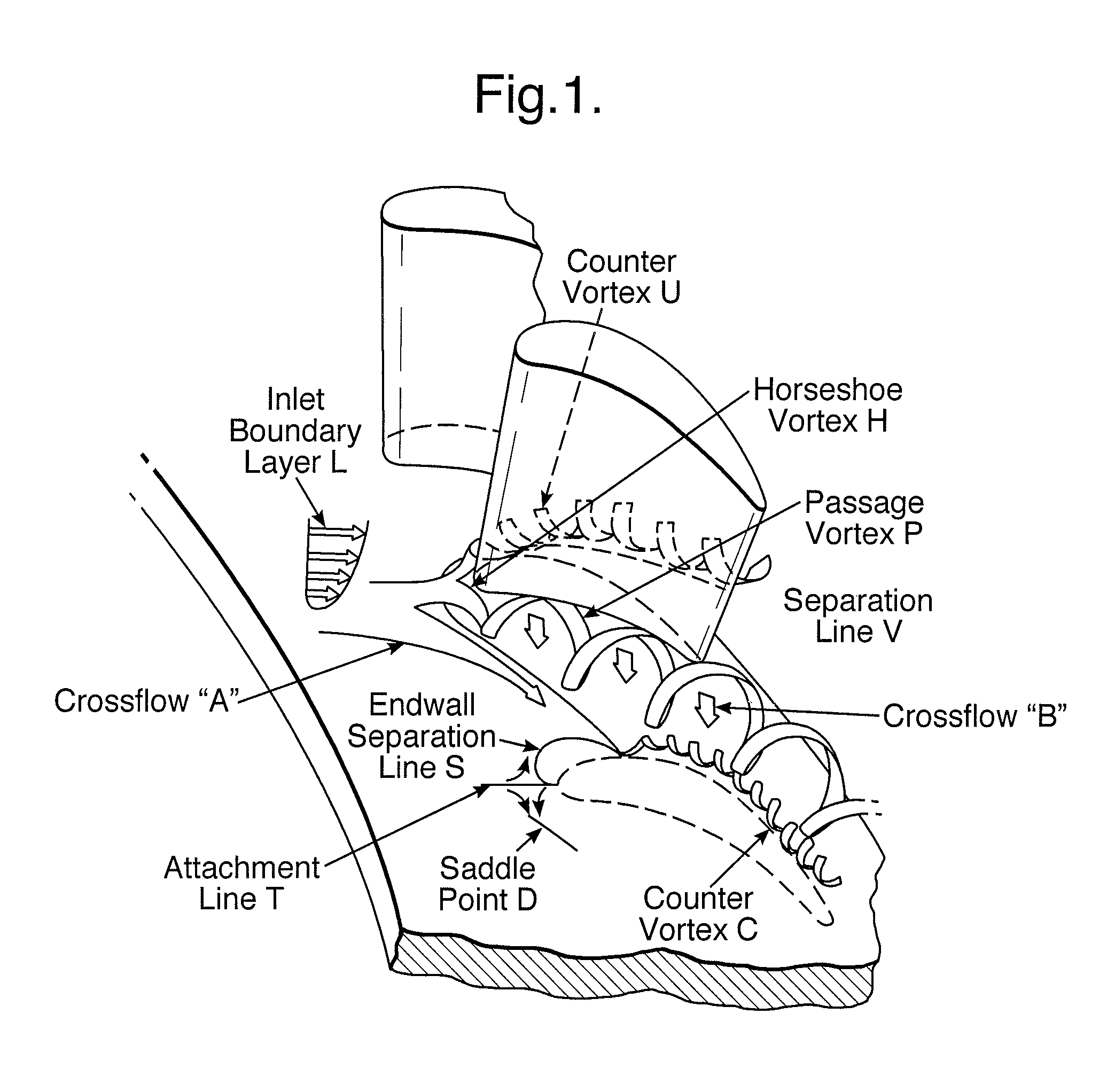
Aerofoil members for a turbomachine
A circumferential row of aerofoil members span an annular duct for carrying a flow of compressible fluid. The duct is centered on the axis of a turbomachine. Pressure and suction surfaces of neighboring aerofoil members bound respective sectoral passages which receive the flow of compressible fluid. The row of aerofoil members includes at least one radial endwall to which the tangent to the trailing edge of each aerofoil member at midspan is substantially orthogonal. Each aerofoil member has reverse compound lean. Each aerofoil member further has a leading edge which has a position at the endwall which is upstream of its position at midspan. The endwall at each sectoral passage has a non-axisymmetrical cross-section formed by a region that, in meridional section, is convexly profiled immediately adjacent the pressure surface and a region that, in meridional section, is concavely profiled immediately adjacent the suction surface.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Substrate holder and substrate holding method
ActiveUS20100267317A1Durable surfaceDegree of vacuum is decreasedPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesFluid supplySuction surface
A substrate holder is a mechanism for holding a substrate, to be polished, by vacuum suction. The substrate holder includes a substrate-holding stage having a suction surface for the substrate, and a fluid passage selectively coupled to a vacuum source and a fluid supply source. The suction surface has a plurality of closed sections surrounded by convexities, and the fluid passage includes a plurality of communication passages which are in fluid communication with the plurality of closed segments respectively and independently.
Owner:EBARA CORP
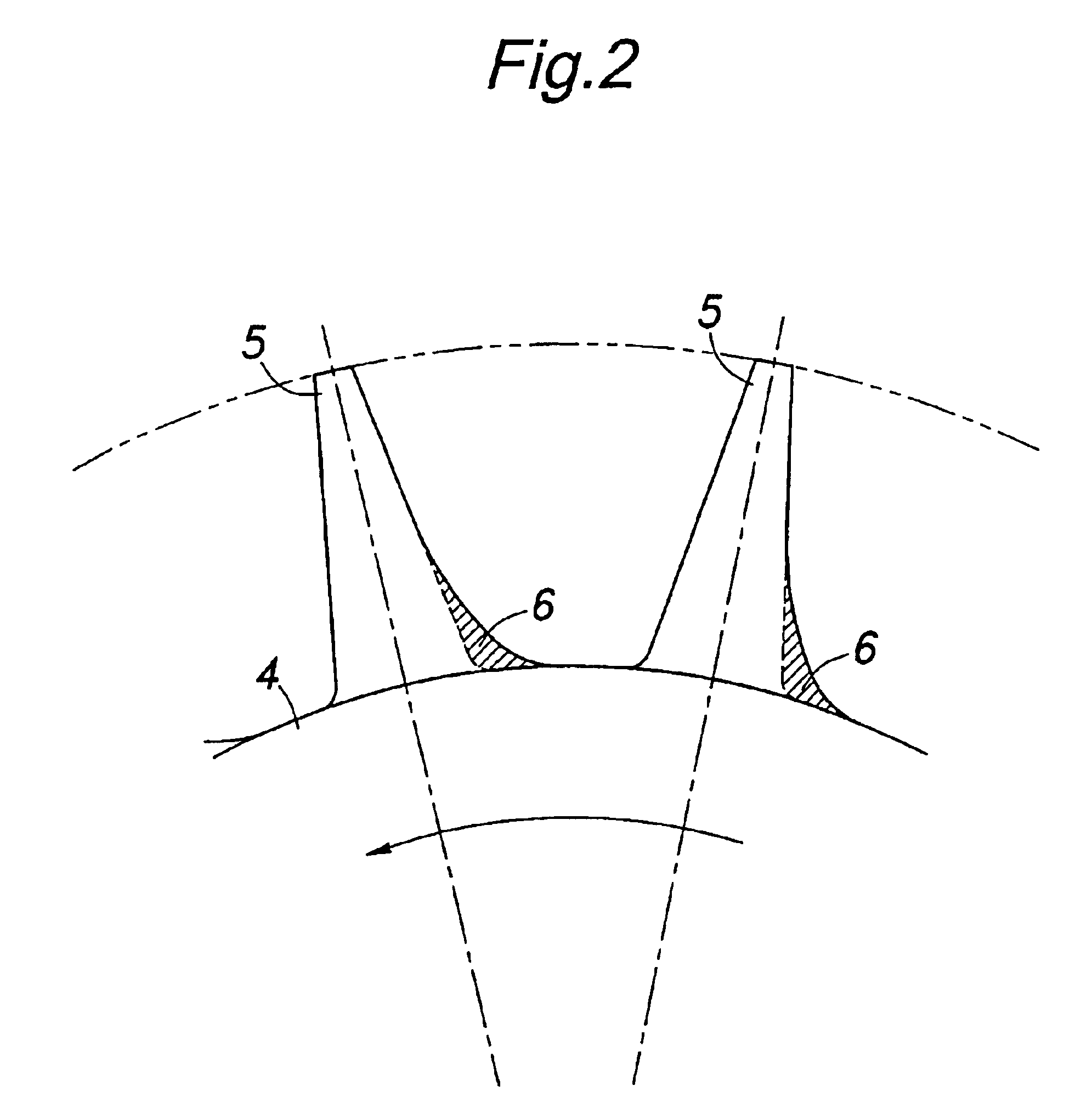
Turbine blade cascade endwall
ActiveUS20100196154A1Improve performanceReduce secondary flow lossEngine manufacturePump componentsSuction stressTurbine blade
Provided is a turbine blade cascade endwall that is capable of suppressing a vortex generated on a suction surface of a turbine stator blade and that is capable of reducing secondary-flow loss due to this vortex. A turbine blade cascade endwall that is positioned on a tip side of a plurality of turbine stator blades arranged in a ring form is provided with a pressure gradient alleviating part that alleviates a pressure gradient generated in the blade height direction at a suction surface of the turbine stator blades due to a clearance leakage flow, leaking out of a gap between a tip of a turbine rotor blade located on the upstream side of the turbine stator blades and a tip endwall disposed facing the tip of this turbine rotor blade.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Substrate holding device
ActiveUS20120235335A1Hold steadySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWork holdersEngineeringSuction surface
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
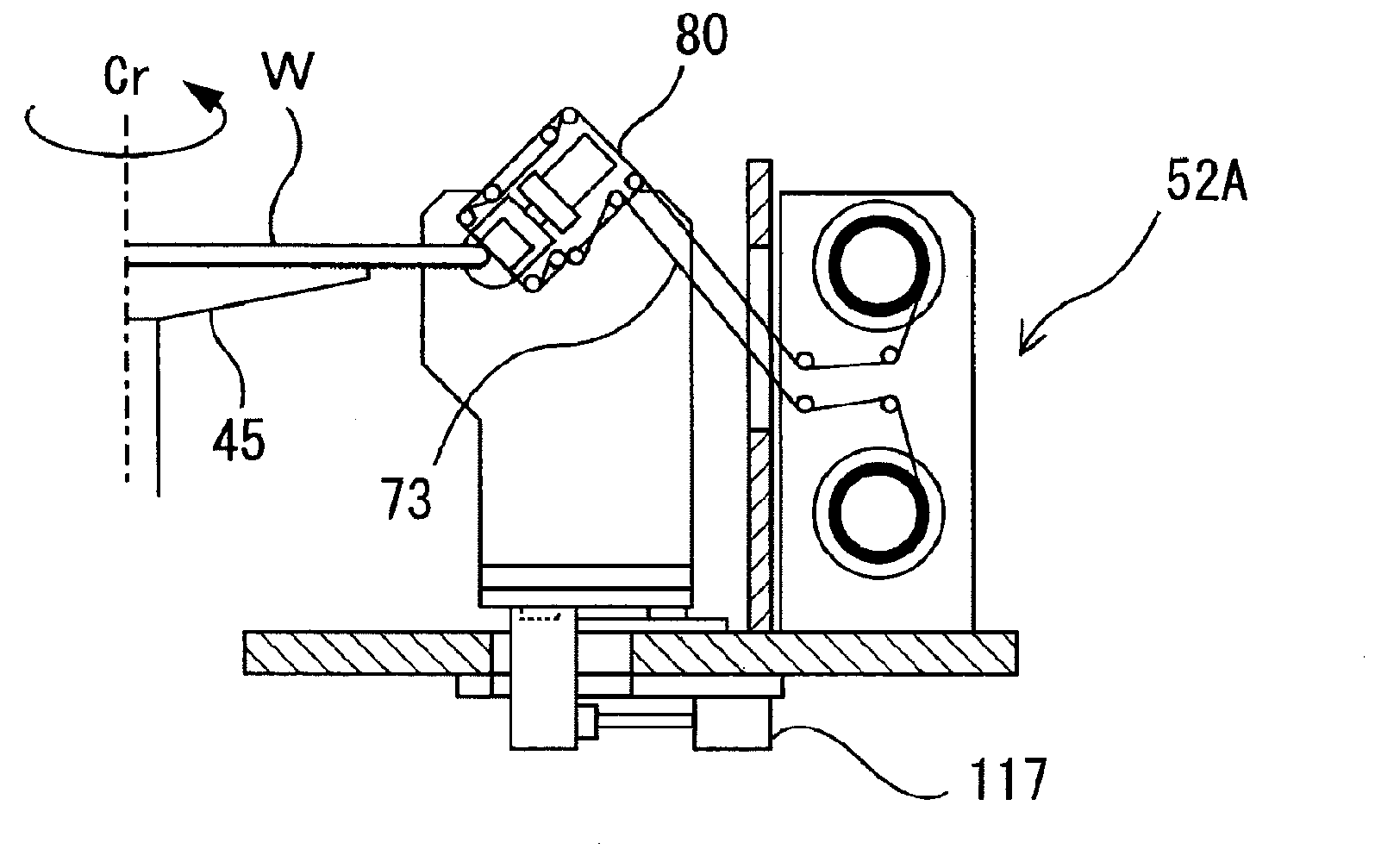
Electronic-component holding apparatus, electronic-component mounting system, and electronic-component mounting method
ActiveUS20060207090A1Attach and detachGood adhesionPrinted circuit assemblingMetal working apparatusSpool valvePositive pressure
An electronic-component holding apparatus, an electronic-component mounting system, and an electronic-component mounting method each of which assures that a nozzle head holding at least one suction nozzle is easily attached to, and detached from, a head holding member, are provided. A suction surface 130 of a head holding member 52 is held in close contact with a to-be-sucked surface 200 of a revolver head 56, so as to define a head-related negative-pressure chamber 204 that holds the revolver head 56 by utilizing suction based on a negative pressure. The revolver head 56 is rotated, and moved upward and downward, with the head holding member 52. The revolver head 56 has twelve suction nozzles 212 and twelve valve devices 264. Owing to the upward and downward movements of the head holding member 52, a lever drive member 510 engages a pivotable lever 224, a first spool valve 280, and a second spool valve 310, so as to move mechanically a corresponding suction nozzle 212 upward and downward and switch mechanically a corresponding valve device 264 to an arbitrary one of its negative-pressure supply state and its positive-pressure supply state, so that the corresponding suction nozzle 212 holds and mounts an electronic component.
Owner:FUJI MASCH MFG CO LTD
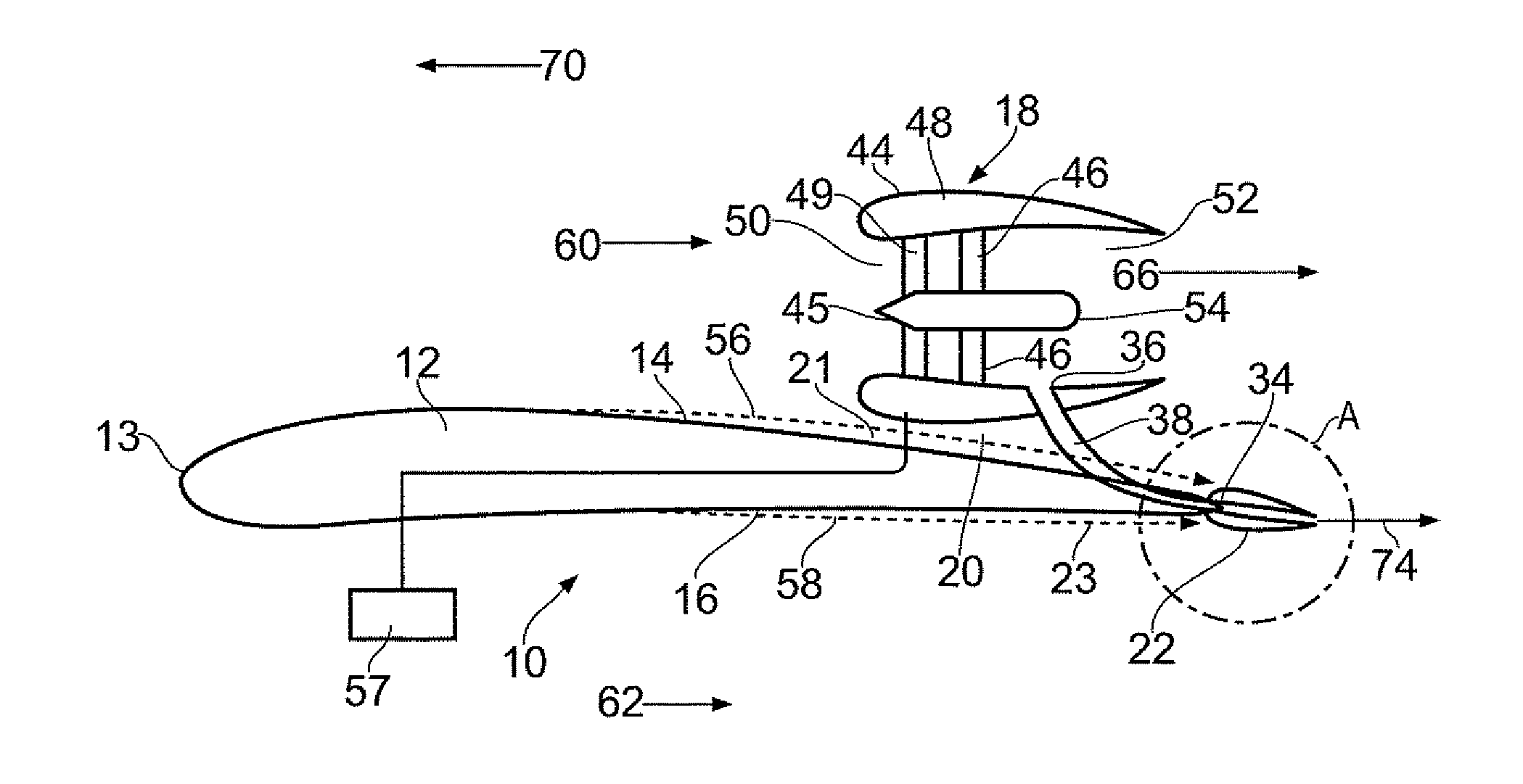
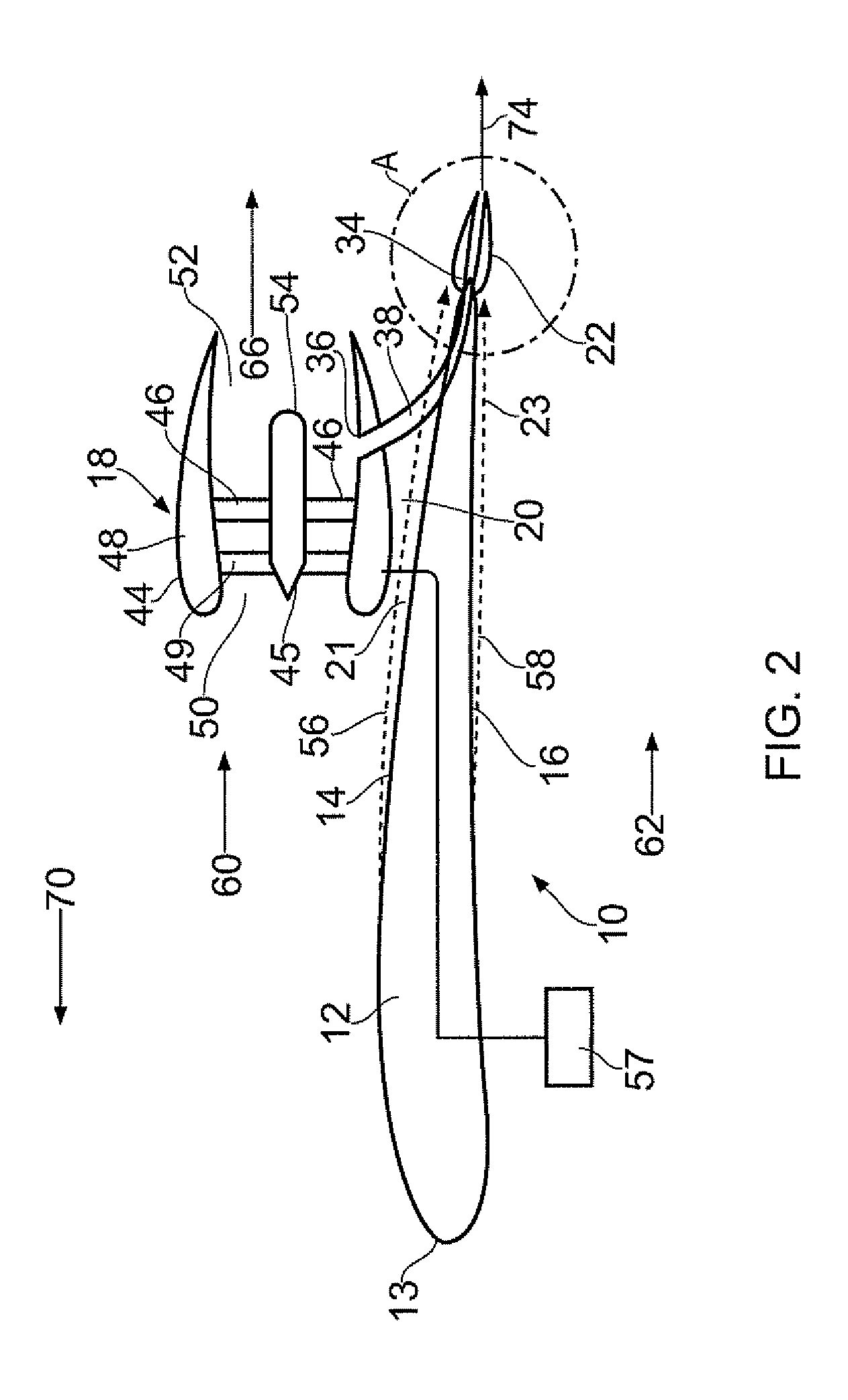
Aircraft
InactiveUS20130336781A1Improve aerodynamic efficiencyPropellersPump componentsJet aeroplaneSuction stress
An aircraft includes a propulsive fan arrangement having an intake and an exhaust. The fan arrangement is mounted adjacent a gas washed surface of the aircraft in the form of a suction surface of a wing. The intake is separated from the suction surface to define a channel therebetween. The aircraft further includes a Venturi device positioned downstream of the fan exhaust to draw boundary layer air through the channel.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
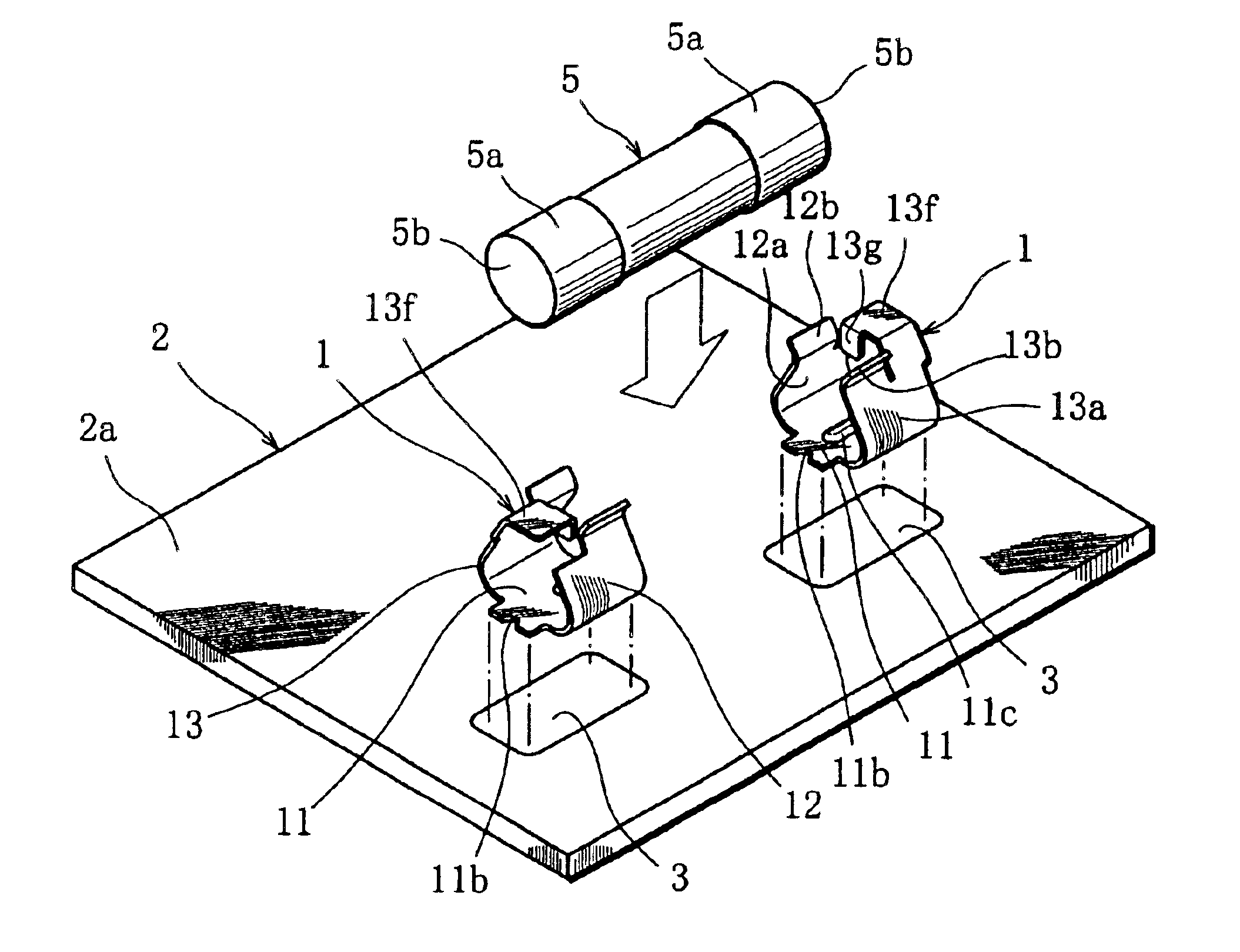
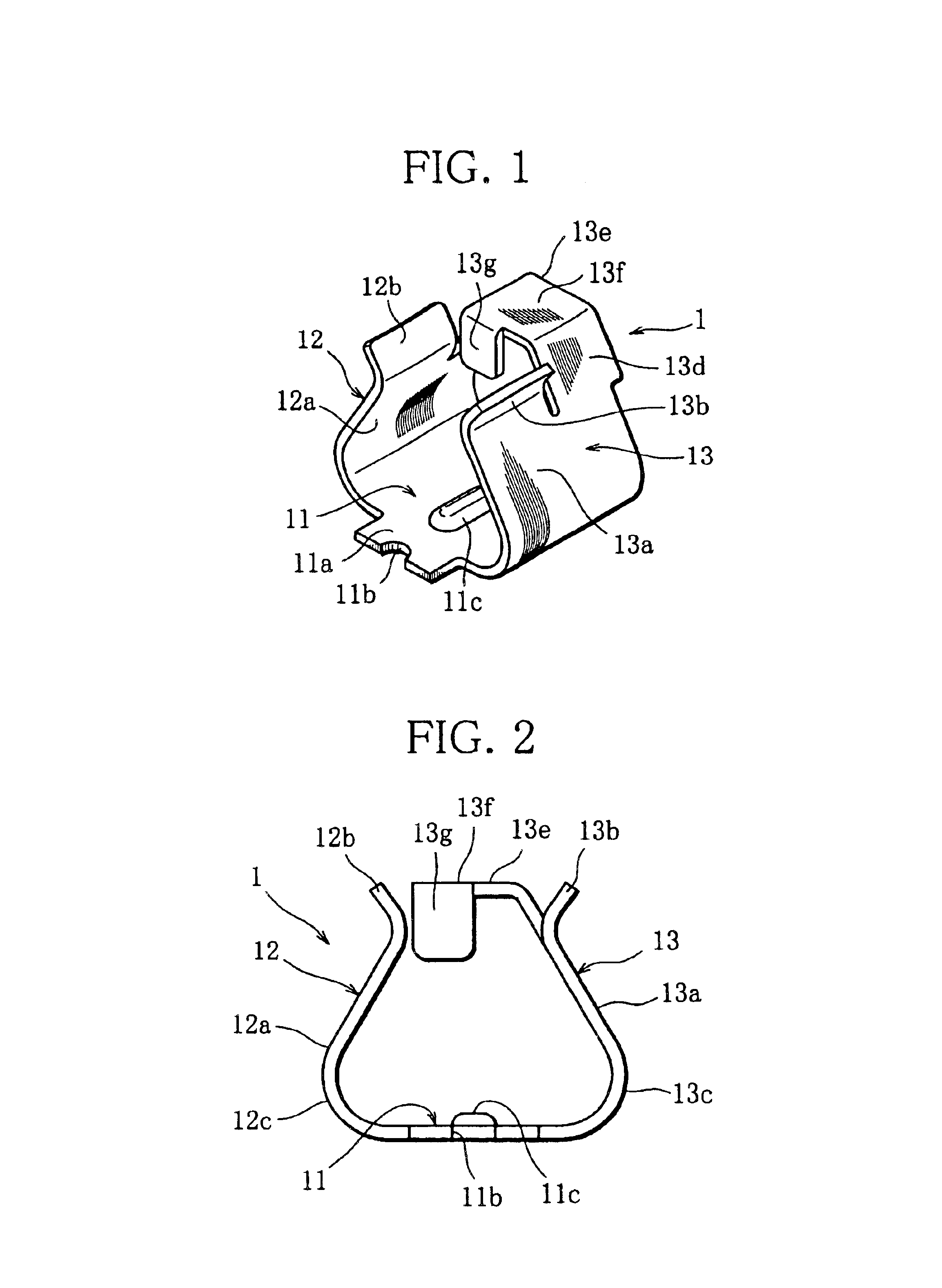
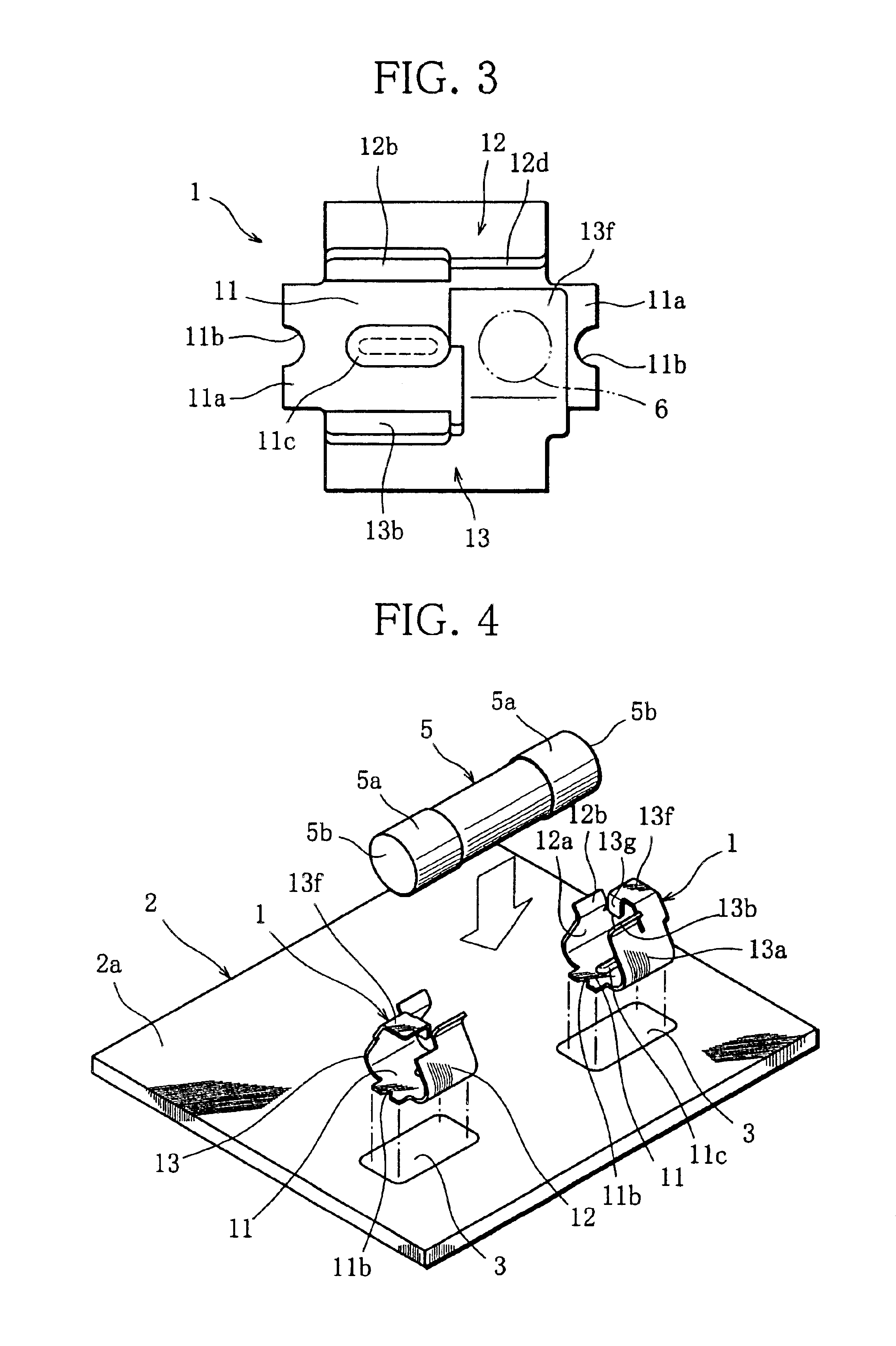
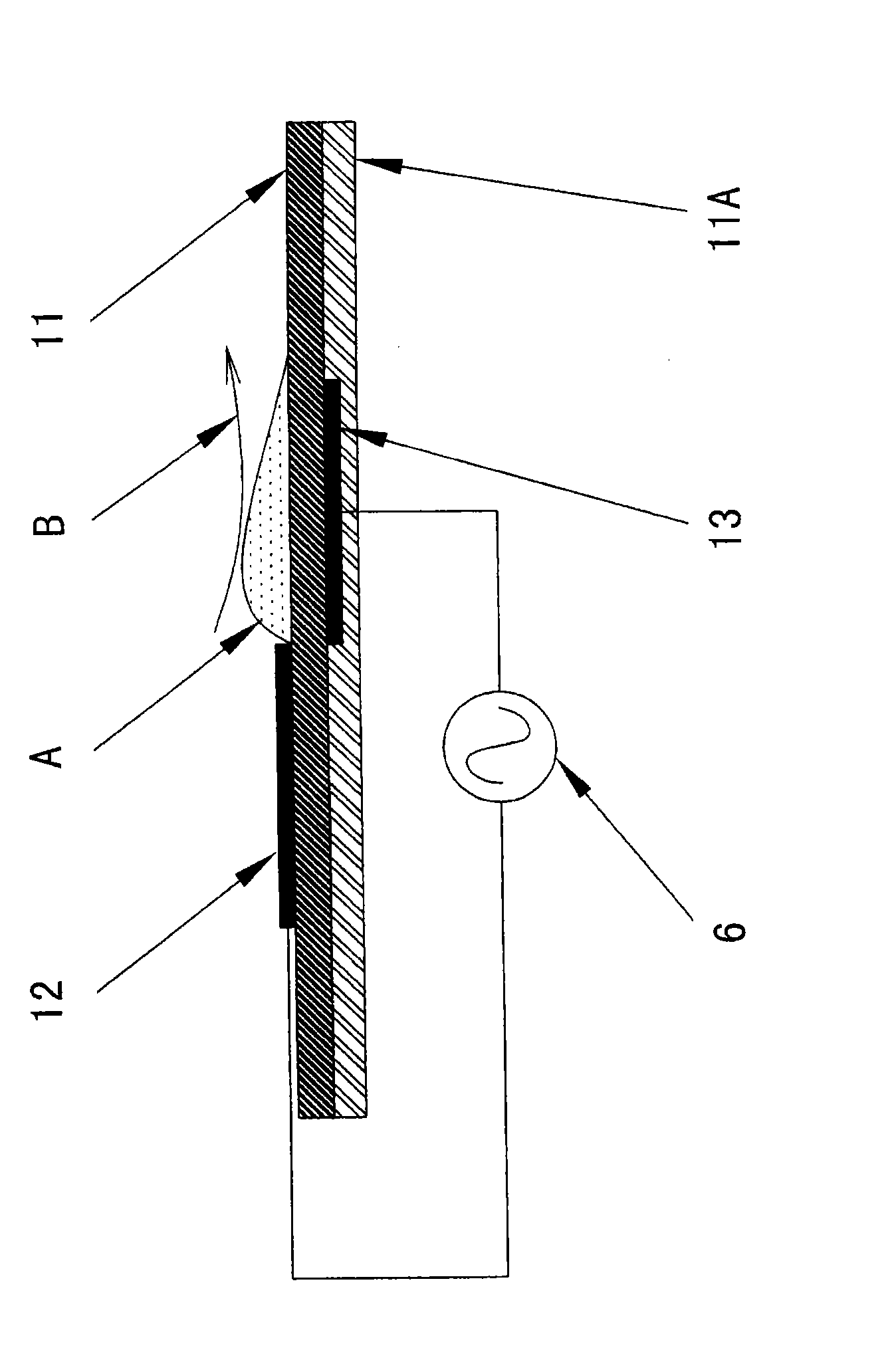
Fuse holder component
ActiveUS6837755B1Easy to installImprove solder resistancePrinted circuit assemblingContact member assembly/disassemblySurface mountingEngineering
A fuse holder component includes a bottom plate fixed to a printed board, and first and second side plates whose main body portions individually extend from side edges of the bottom plate. The second side plate includes a suction portion extending through an extension portion from the main body portion and provided with a suction surface to which a suction nozzle of a mounter is accessible. A pair of fuse holder components, surface-mounted on the printed board by using the mounter, constitute a fuse holder that stably holds a glass-tube fuse.
Owner:KYOSHIN KOGYO CO LTD
Control system and control method for plasma excitation for cascade internal flow
ActiveCN101666343AReduce flow lossImprove running stabilityPump componentsFluid dynamicsControl systemEngineering
The invention relates to a control system and a control method for plasma excitation for cascade internal flow, which are performed under the control of a computer. By applying the plasma excitation with appropriate intensity at different positions of a cascade suction surface, on one hand, the system and the method can play a role in inhibiting the flow separation of the cascade suction surface,and on the other hand, the system and the method can improve the flow state of a cascade wake to play a role in reducing the flow loss.
Owner:江苏中国科学院能源动力研究中心 +1
Suction apparatus, polishing apparatus, semiconductor device, and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
ActiveUS20090060688A1Reduce the impactEasy to flattenGrinding drivesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingForeign matterEngineering
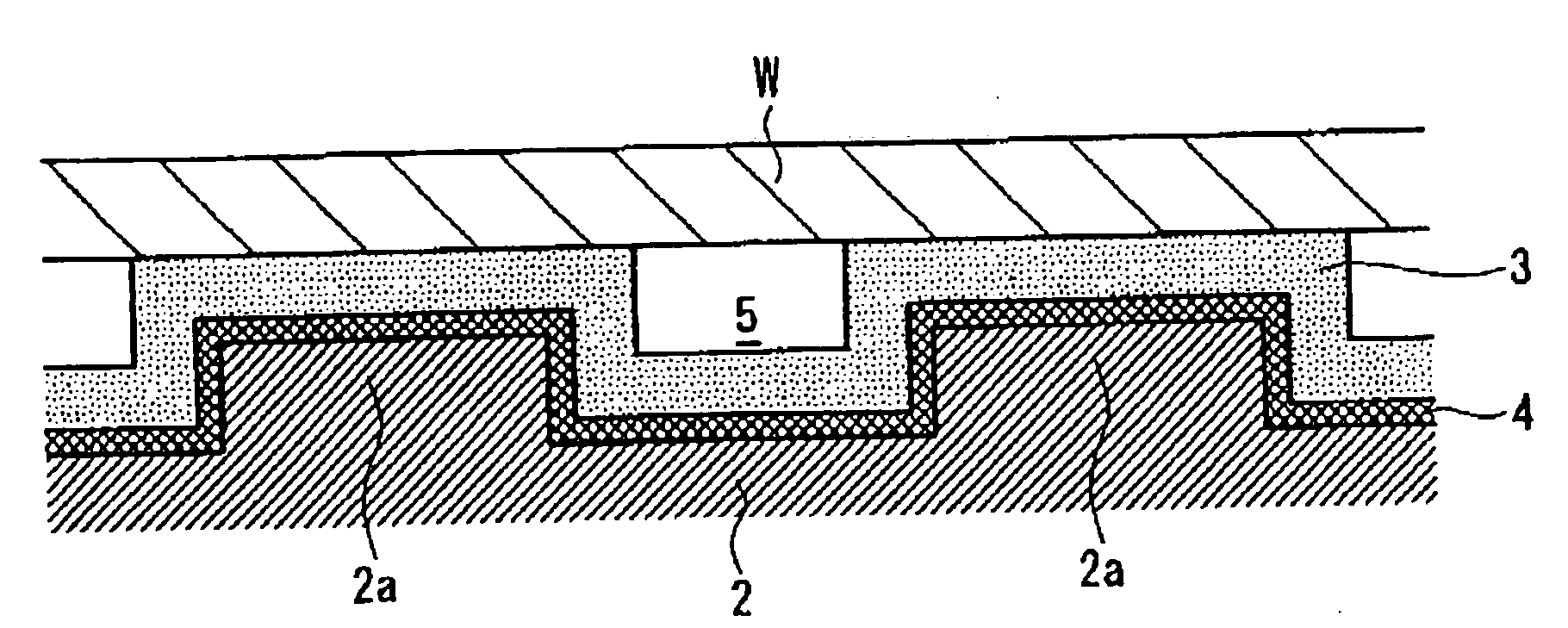
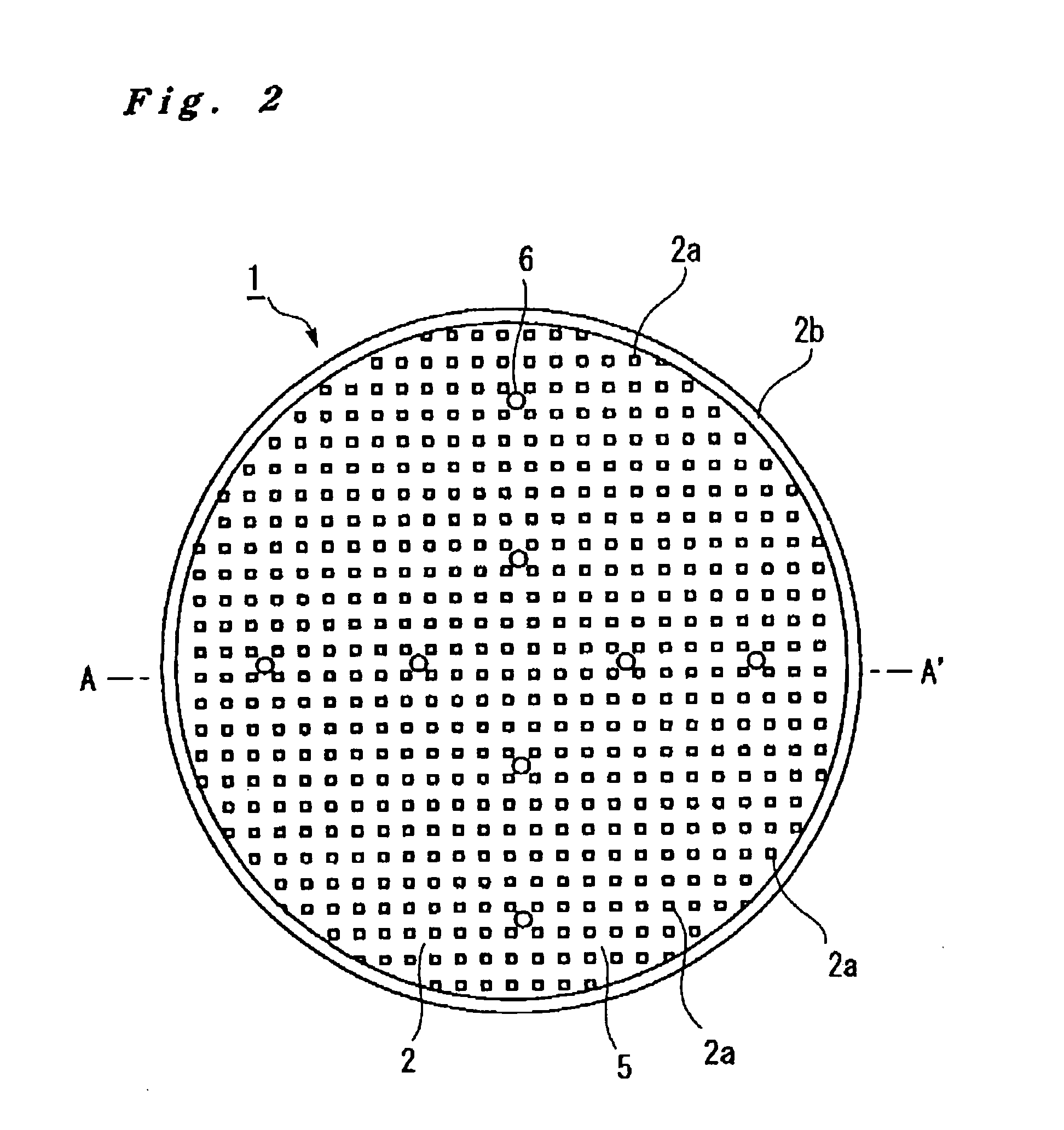
A suction apparatus 1 holds a wafer W by performing vacuum-suctioning on the wafer W. The suction apparatus 1 comprises a suction substrate 2. The suction substrate 2, which is rigid, comprises a plurality of pin-like protrusions 2a formed so that the tip-end faces (upper surfaces) thereof are the same height. An elastic coating layer is coated by way of an undercoat layer 4 on the tip-end faces of the protrusions 2a. When the wafer W is suctioned, even if a foreign matter is interposed between the wafer W and the suction surface, because the foreign matter embeds itself into the coating layer 3, the planarization of the wafer W is improved. In addition, because the coating layer 3 can be made comparatively thinner, undulations in the wafer W can be reduced and, to that end, the planarization of the wafer W in the suctioned state can be improved.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Device and method for handling fragile objects, and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20030062734A1Gripping headsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSurface level
A handler for applying a vacuum holding force to an object is provided. The handler generally includes a body having a plurality of levels of openings including a holding surface level and a suction surface level, and optionally one or more intermediate levels. In general, the openings decrease in size (e.g., effective diameter) from the suction surface level to the holding surface level. Further the openings at the suction surface level are in fluid communication with at least a portion of the openings at the holding surface level.
Owner:FARIS SADEG M
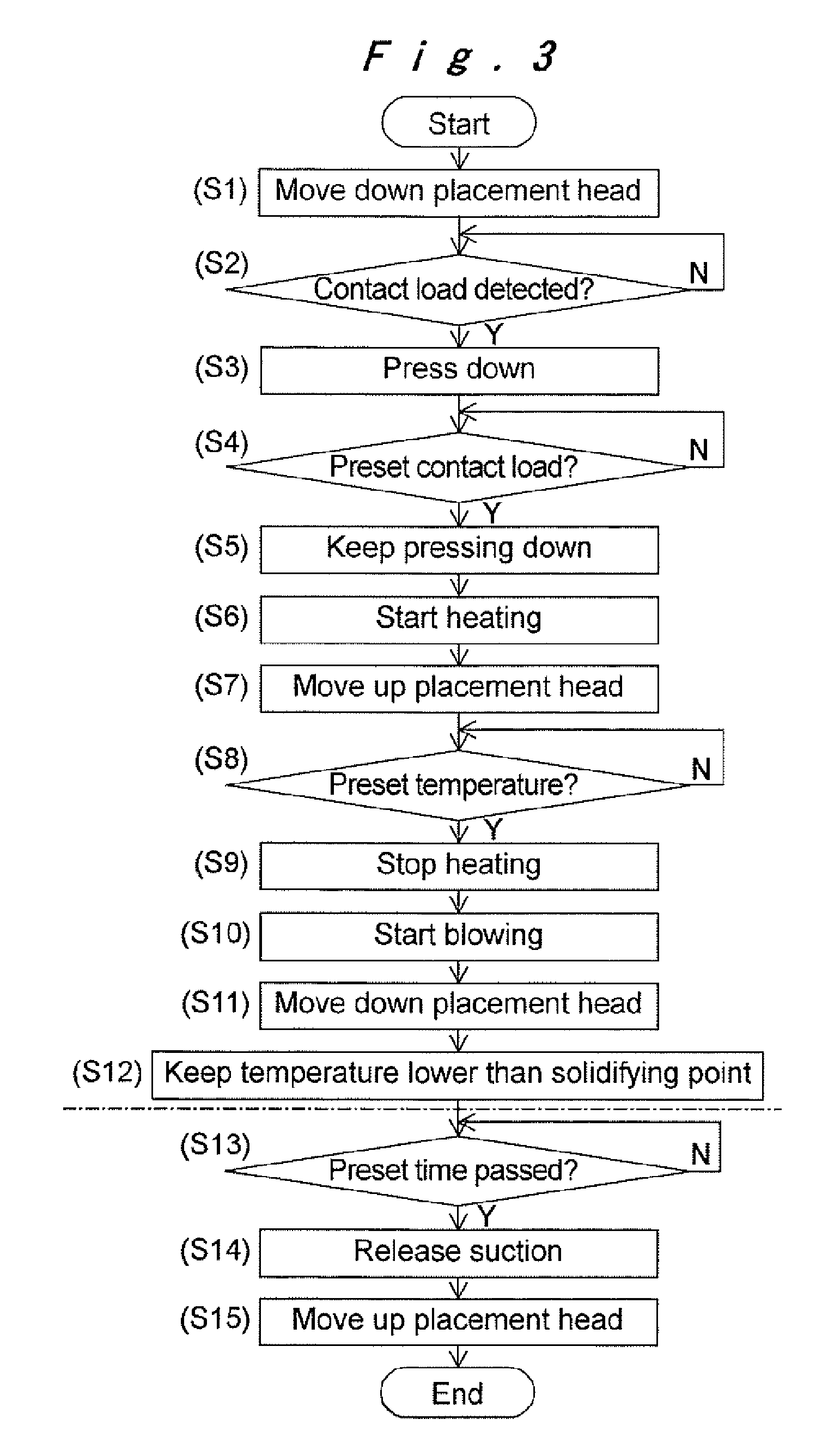
Component mounting method and component mounting apparatus
InactiveUS20070181644A1Avoid bond failureFlatness is easy to guaranteeCooking-vessel materialsPrinted circuit assemblingSuction stressEngineering
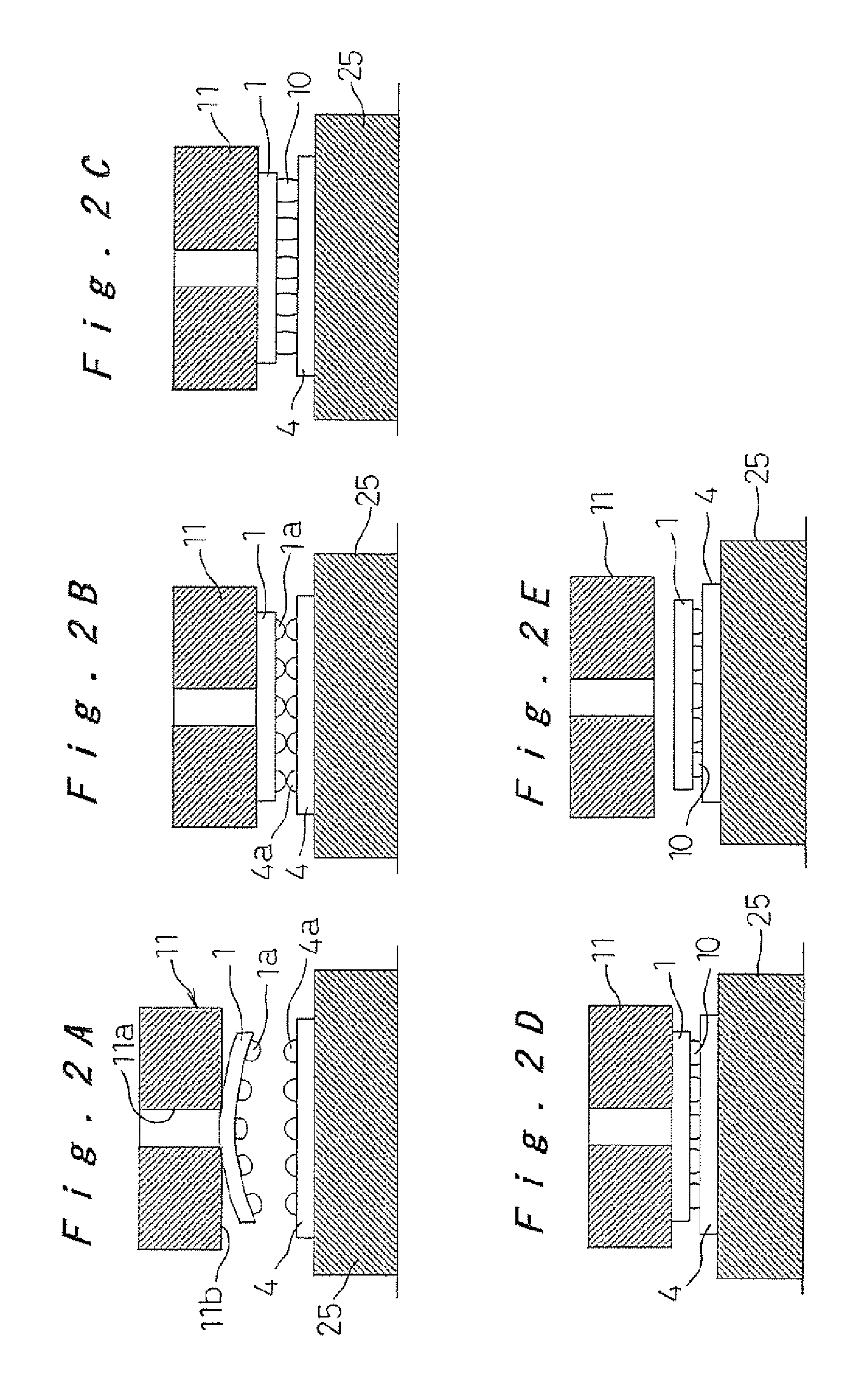
A method and an apparatus for mounting electronic components that enables precise mounting of electronic components, such as deformation-prone thin IC chips or fine-pitch and high-pin-count IC chips, on a substrate. Thin IC chips, which conventionally tend to lose flatness because of warping that occurs during production or deformation that occurs when picked up with a suction nozzle, are pressed against a substrate (4) with a preset load using a suction nozzle with a flat suction surface (11b) so as to correct deformation; the suction nozzle (11) is controlled to move up to make up for a decrease in the distance between the oppositely spaced IC chip and the substrate (4) that is caused by thermal expansion due to the heating for melting solder bumps (1a) on the electrodes; and the suction nozzle (11) is controlled to move down to mitigate the effect of a pulling-apart force applied to the molten parts as the thermally expanded parts cool down and contract.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Turbine rotor blade for gas turbine engine
InactiveUS7217101B2Reduce leakage lossReduce manufacturing costPropellersEngine manufactureLeading edgeTurbine blade
A rotor blade for a gas turbine engine includes a blade root (3) and an aerofoil projecting therefrom, the aerofoil having a leading edge and a trailing edge (5), a generally concave pressure surface (2) and a generally convex suction surface (1). The aerofoil shape of the blade varies in section along the length thereof such that:the chord-wise convex curvature of the rear suction surface decreases towards the tip (4) of the blade;the convex curvature of the early to mid suction surface increases towards the tip;the stagger of the aerofoil section increases towards the tip; andthe trailing edge (5) is a straight line.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
Sheet feeding device, sheet feeding unit and image forming apparatus connected with the sheet feeding unit with a controlled floating air blowing mechanism
A sheet feeding device may include a sucking and conveying mechanism having a suction surface, which sucks sheets stacked on a sheet stacking table, from an upper surface of the sheets, sucks an uppermost sheet to be sucked on the suction surface, and conveys the uppermost sheet onto a sheet conveyance path; a floating air blowing mechanism which blows floating air against the sheets from a side surface of the stacked sheets; a sheet position detecting sensor which detects an upper surface height position of the sheets stacked, and detects a floating state of the sheets floated; and a controller which judges the floating state of the sheets detected in a floating state detecting period in connection with a blowing of the floating air, and controls an air volume of floating air blown from the floating air blowing mechanism based on the floating state of the sheets.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
Centrifugal compressor and manufacturing method for impeller
InactiveUS7517193B2Fall in efficiency and performance is preventedIncrease rangeSupersonic fluid pumpsPropellersEngineeringFront edge
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com