Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
666results about How to "Improve aerodynamic efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
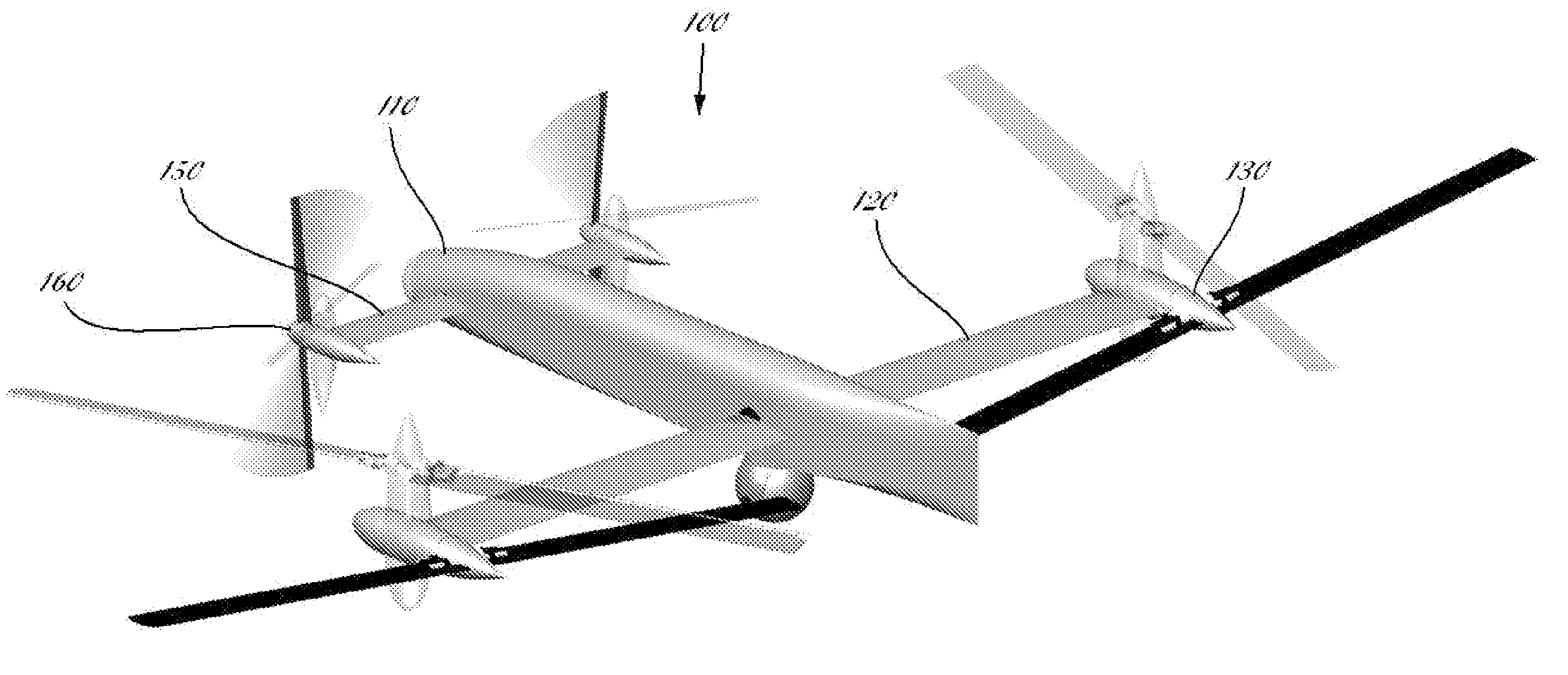
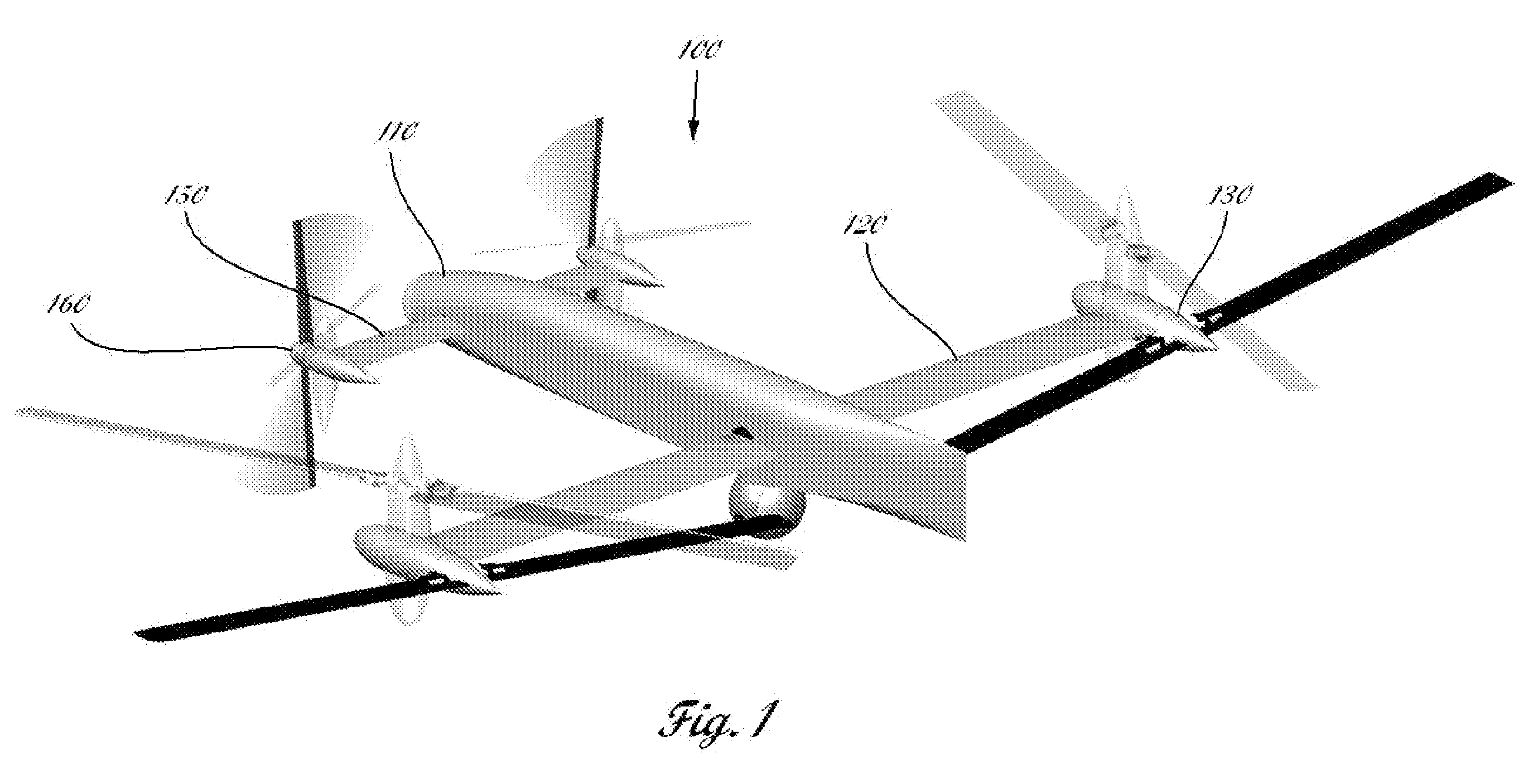
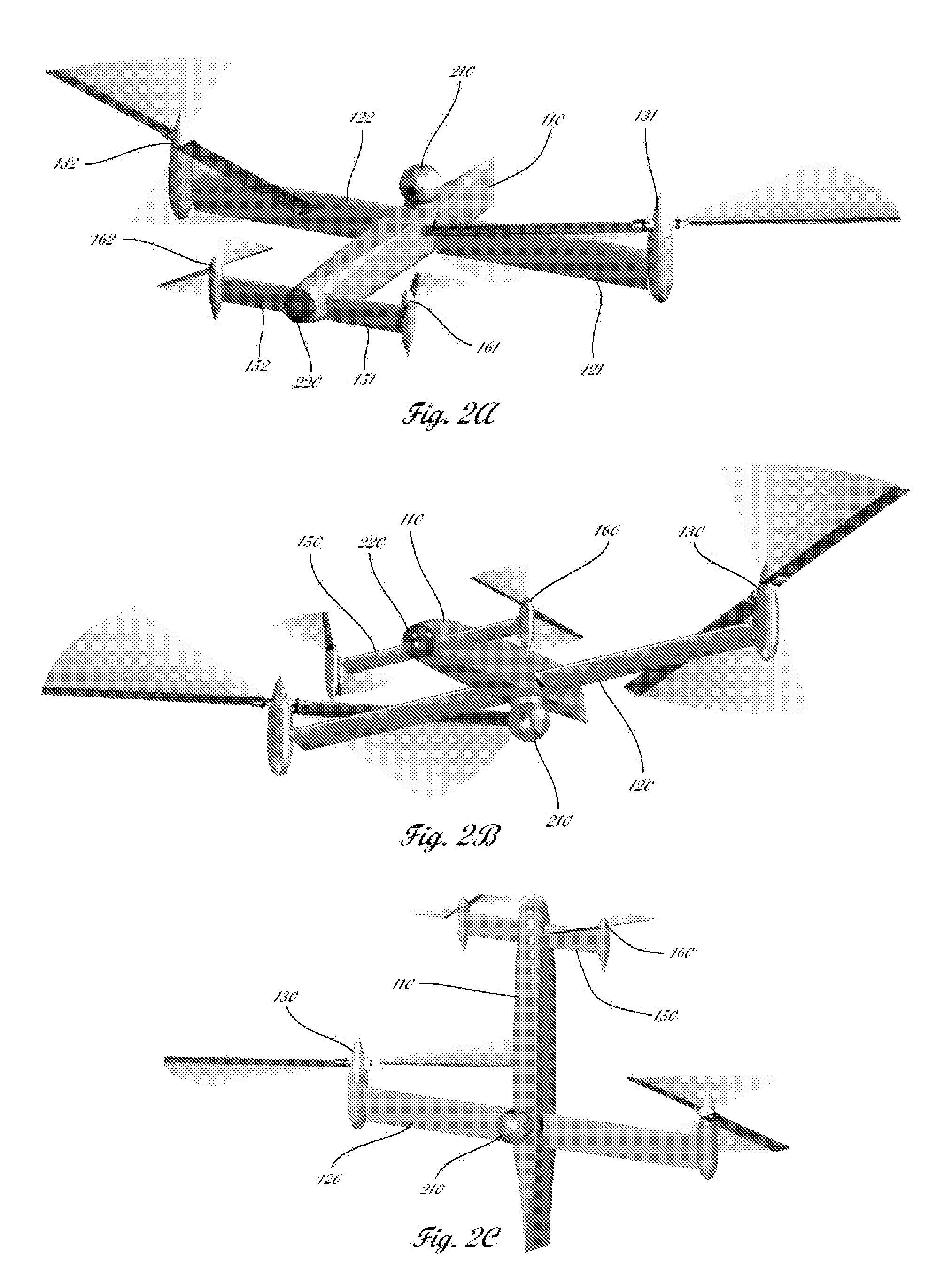
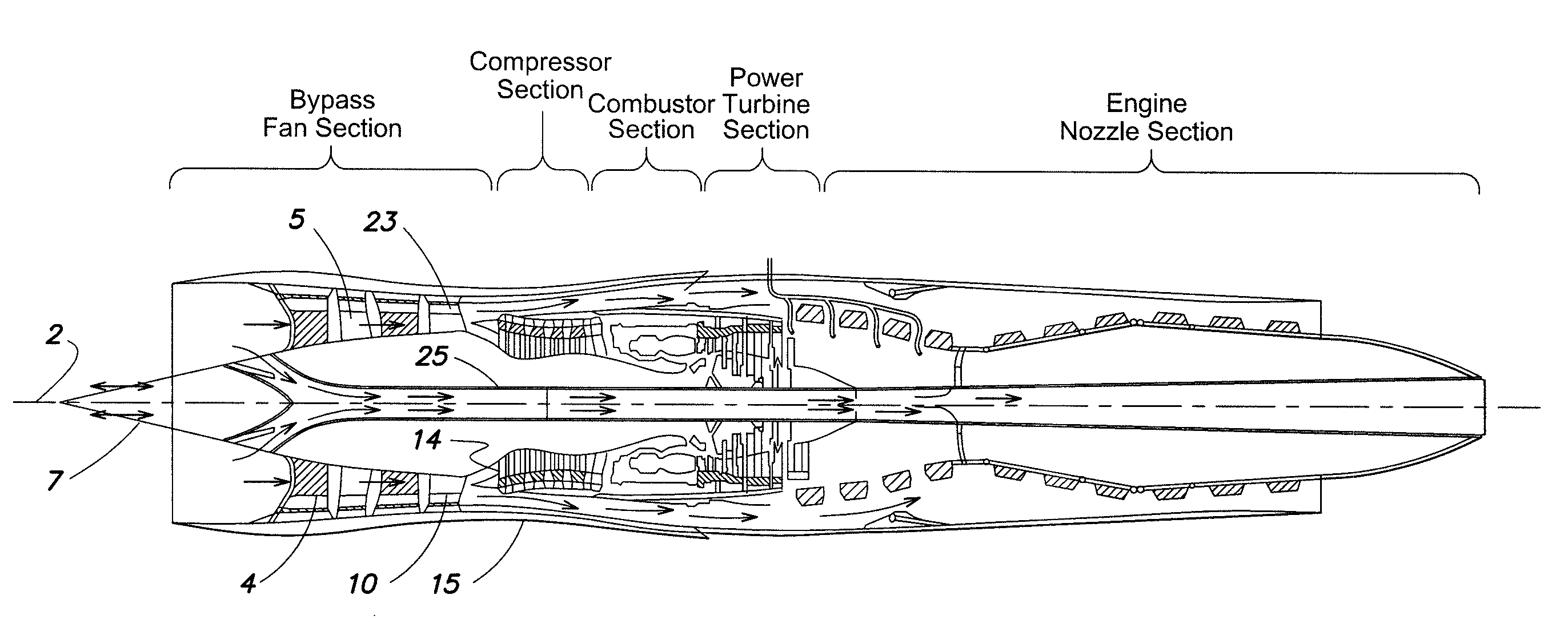
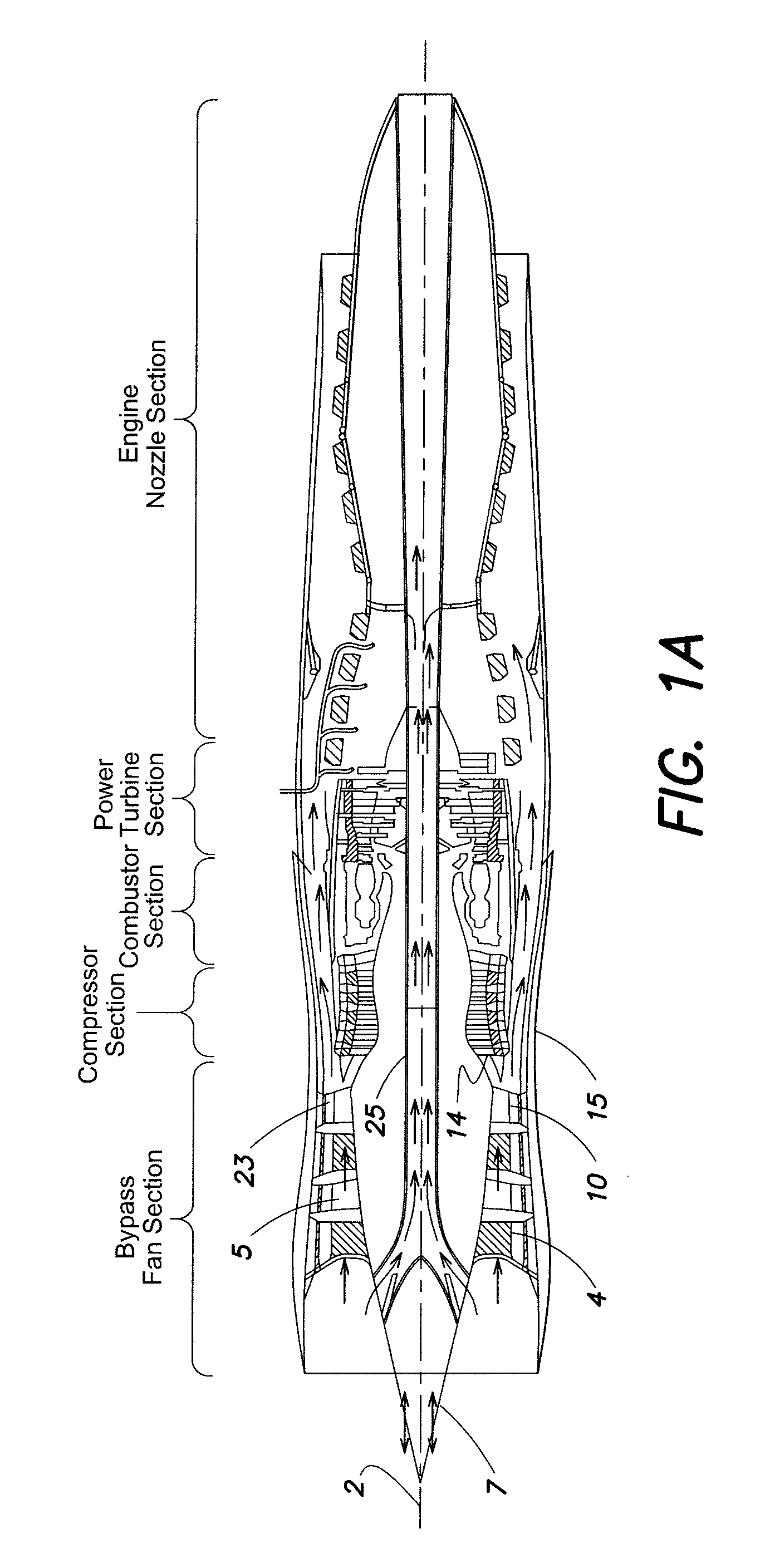
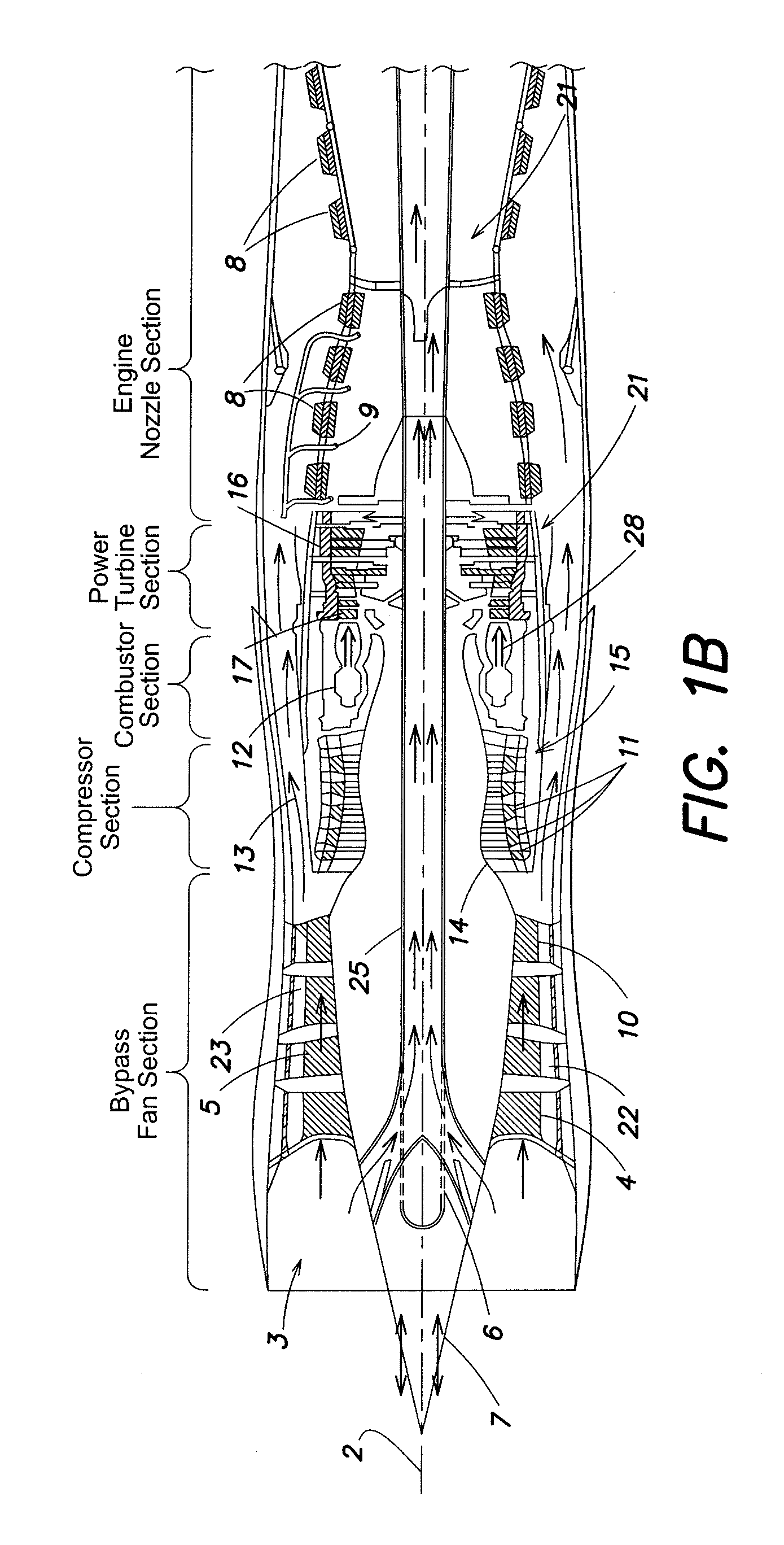
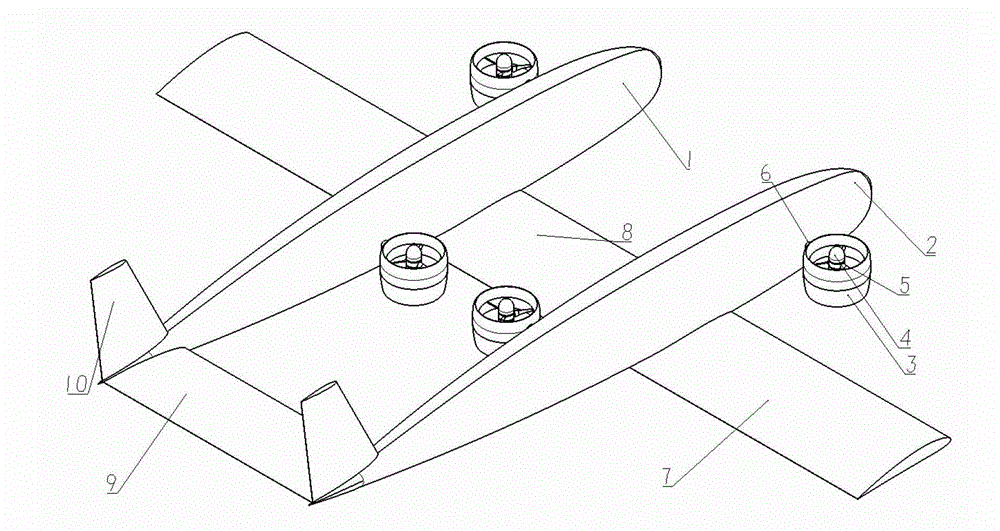
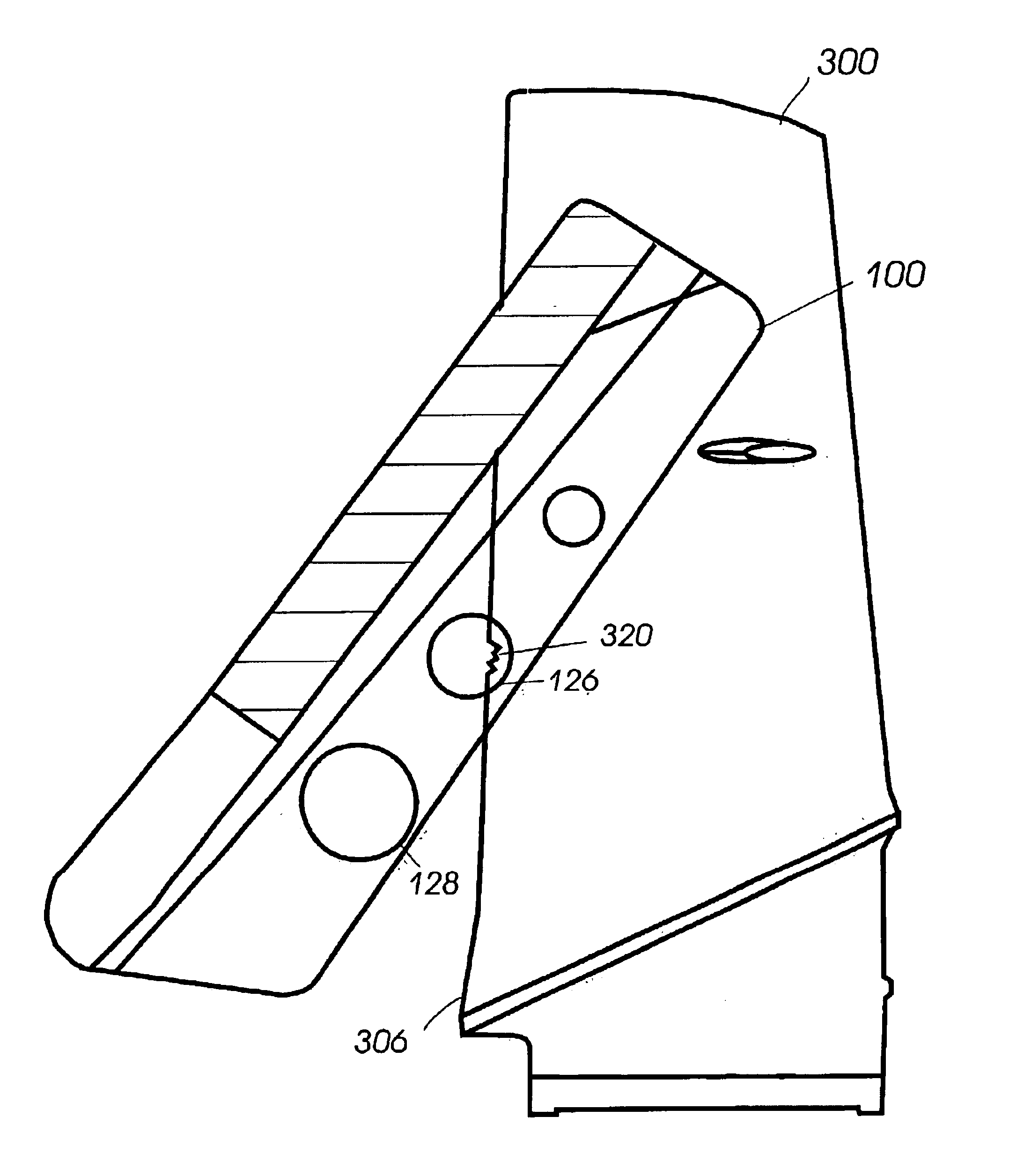
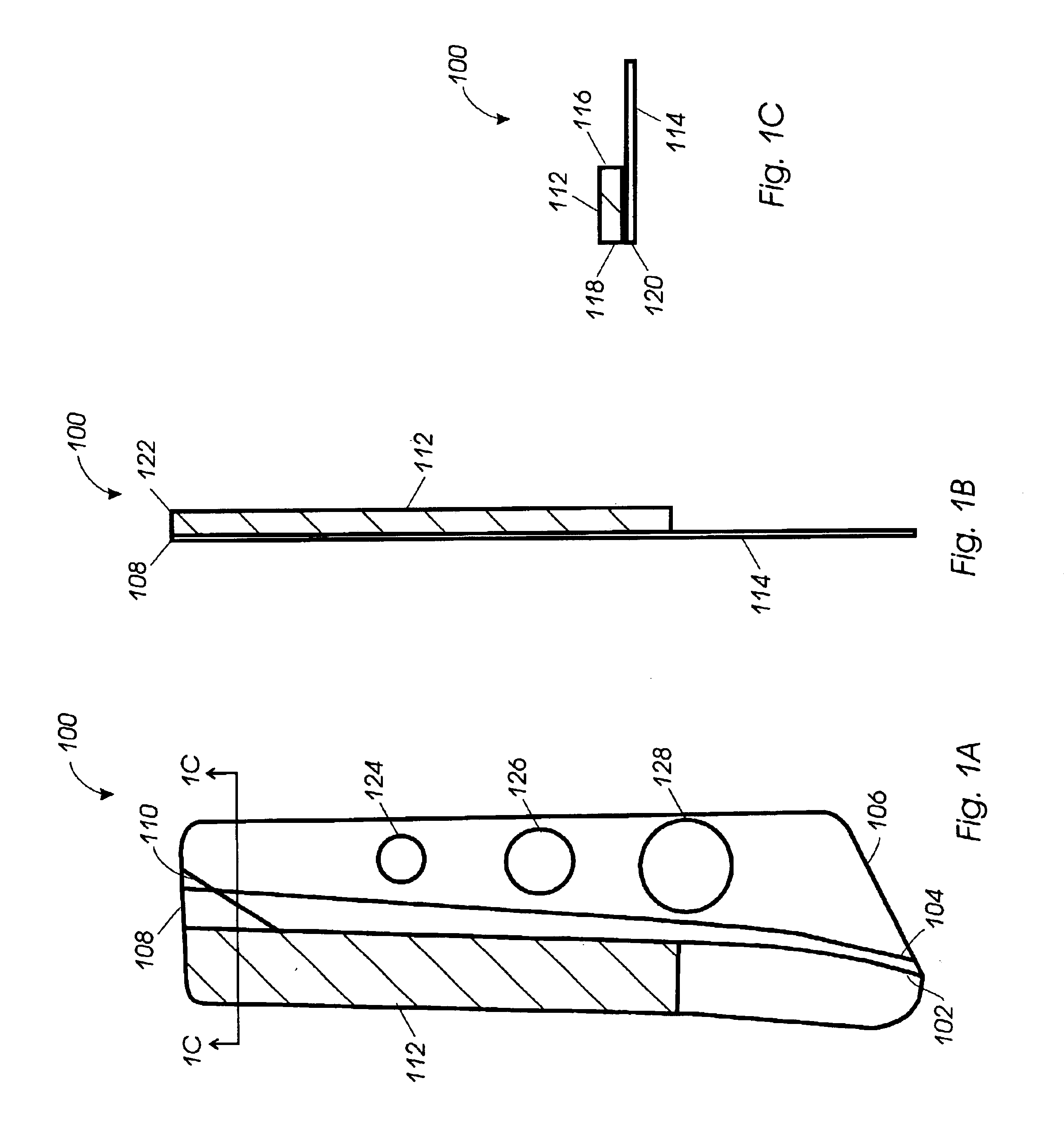
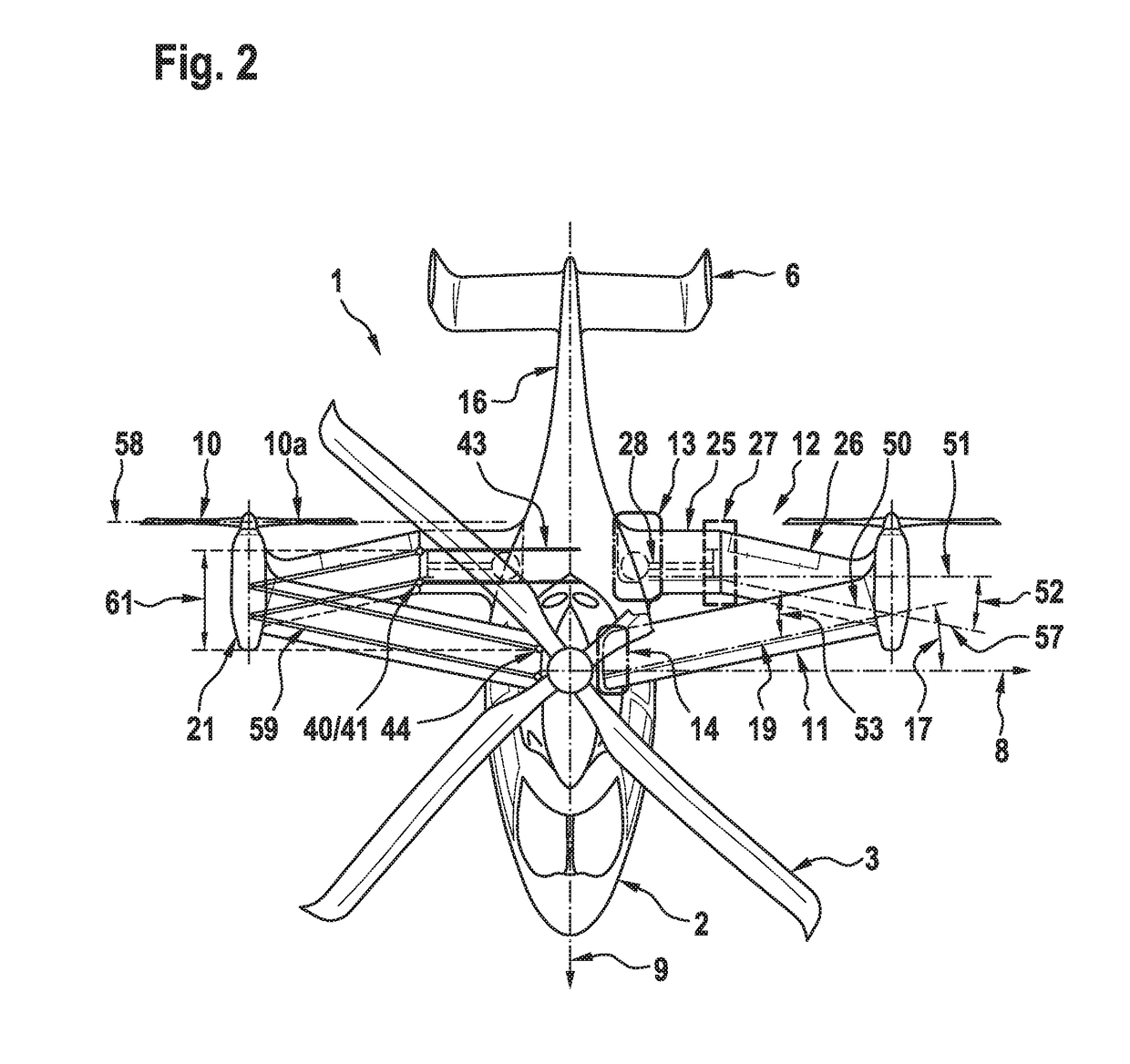
Quad tilt rotor aerial vehicle with stoppable rotors
InactiveUS20110001020A1Eliminate needIncrease vehicle aerodynamic efficiencyUnmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftFlight vehicleFuselage
The disclosed invention consists of several improvements to well known Quad Tilt-Rotor (QTR) aircraft. The first is that during a wing-borne flight, one pair of tilt-rotors, which can be substantially larger than the other pair, is feathered and stopped. This can promote vehicle aerodynamic efficiency and can be utilized to increase vehicle speed. Second is that the wings are not attached to the fuselage at a fixed angle of incidence like on conventional QTR aircraft, but can also be tilted in respect to the fuselage independently of the tilt-rotors. Furthermore, each rotor and each wing can be tilted with respect to fuselage to any tilt-angle without limit, which gives the vehicle unprecedented ability to position the fuselage in any attitude in respect to the vehicle direction of flight.
Owner:FORGAC PAVOL
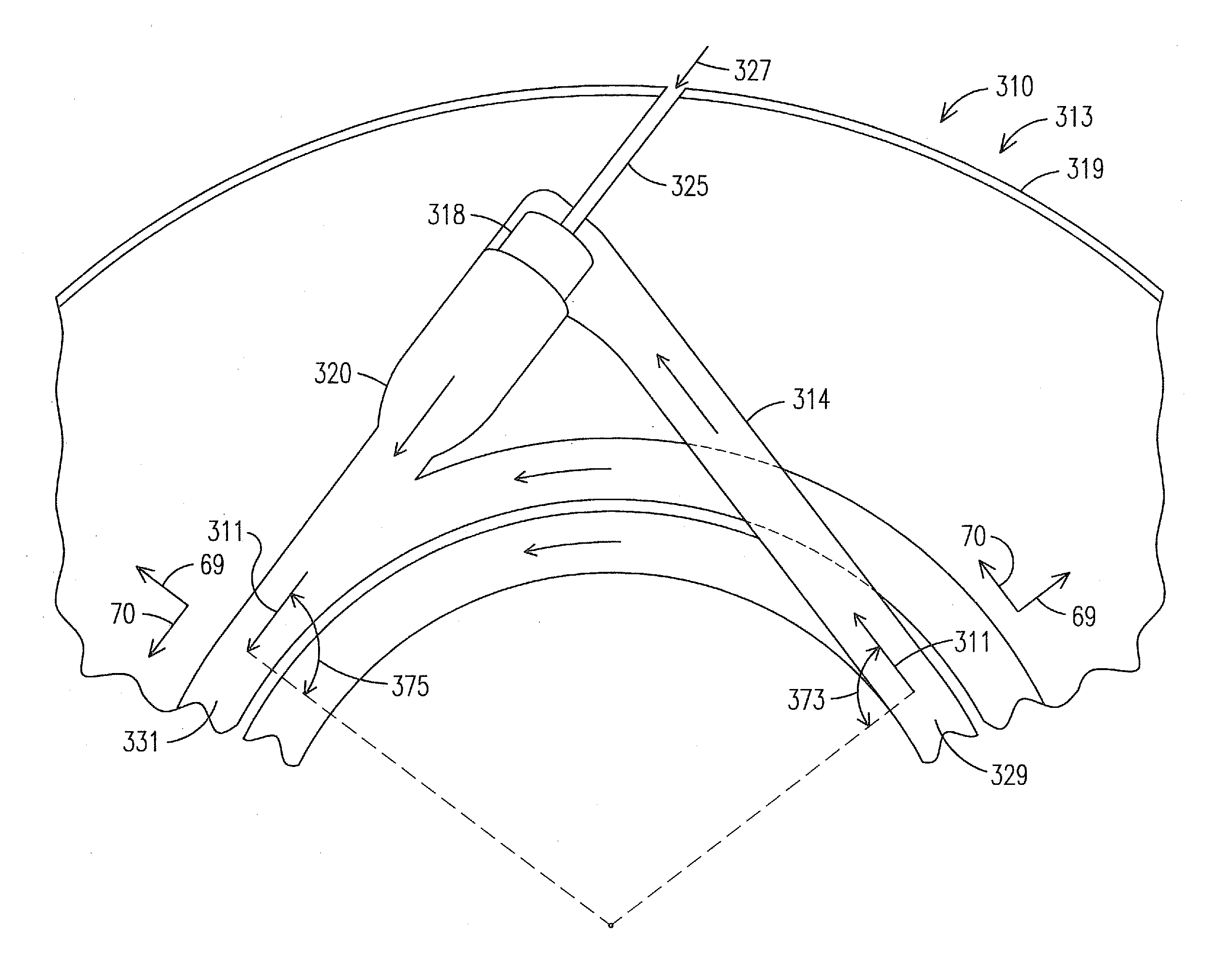
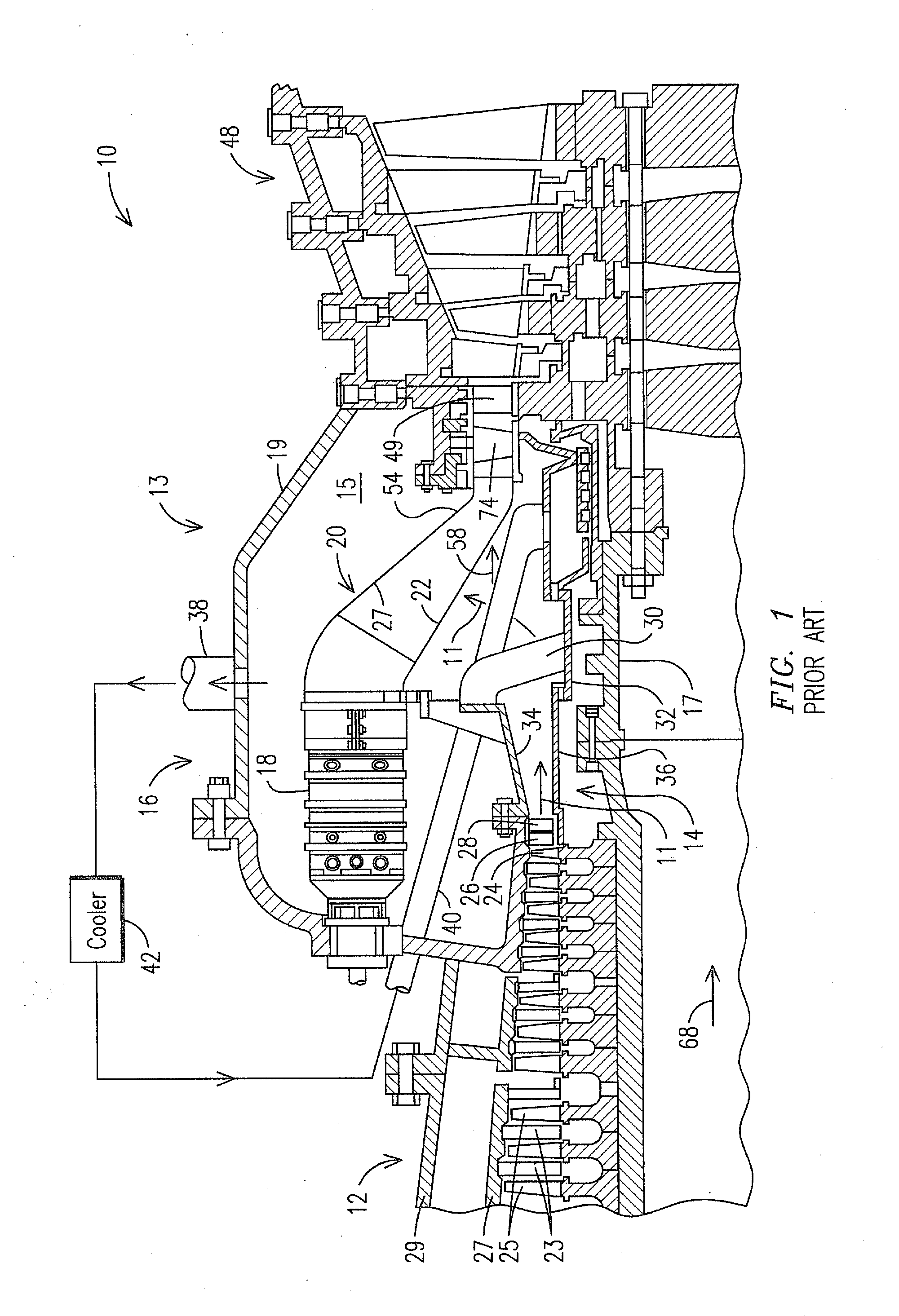
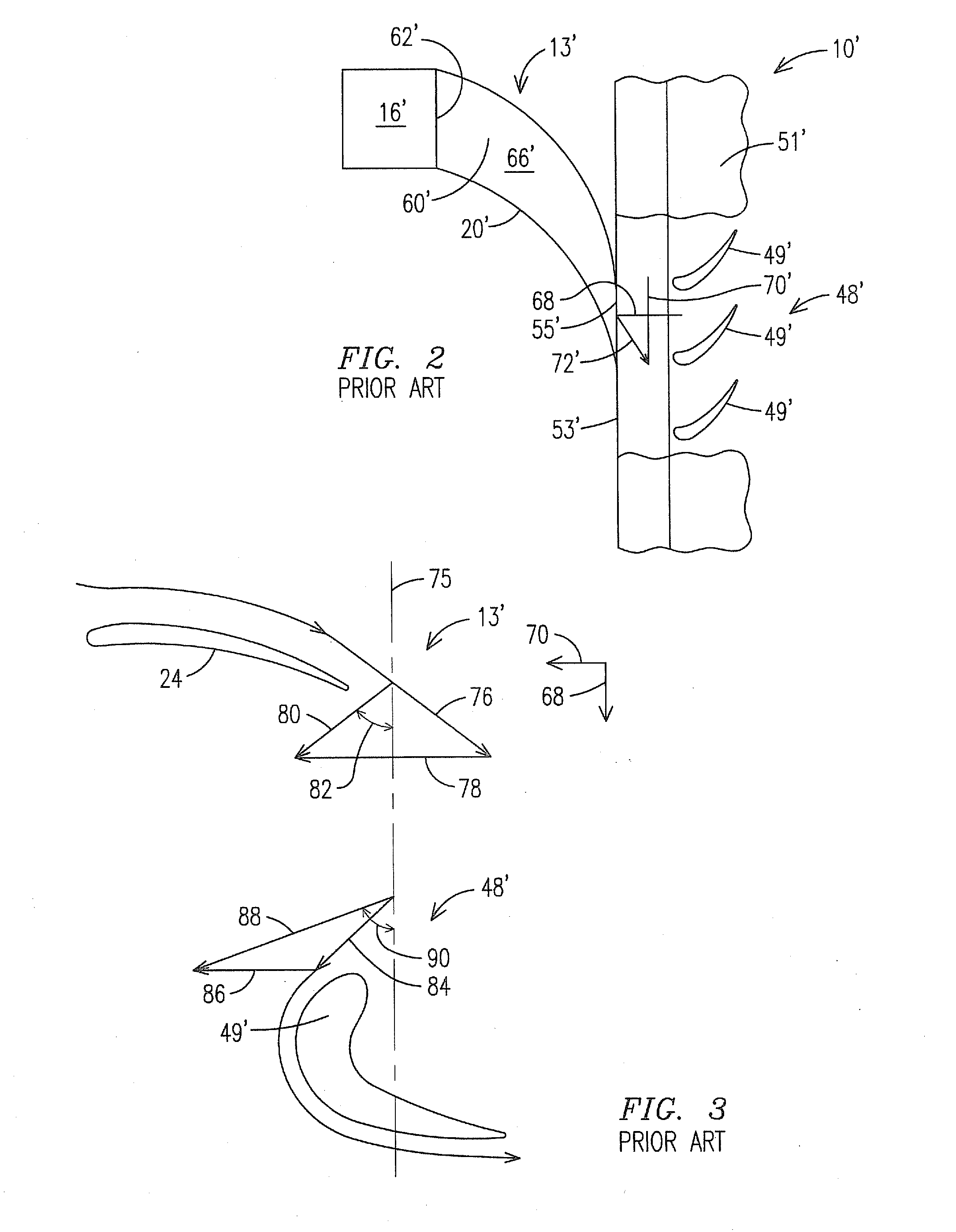
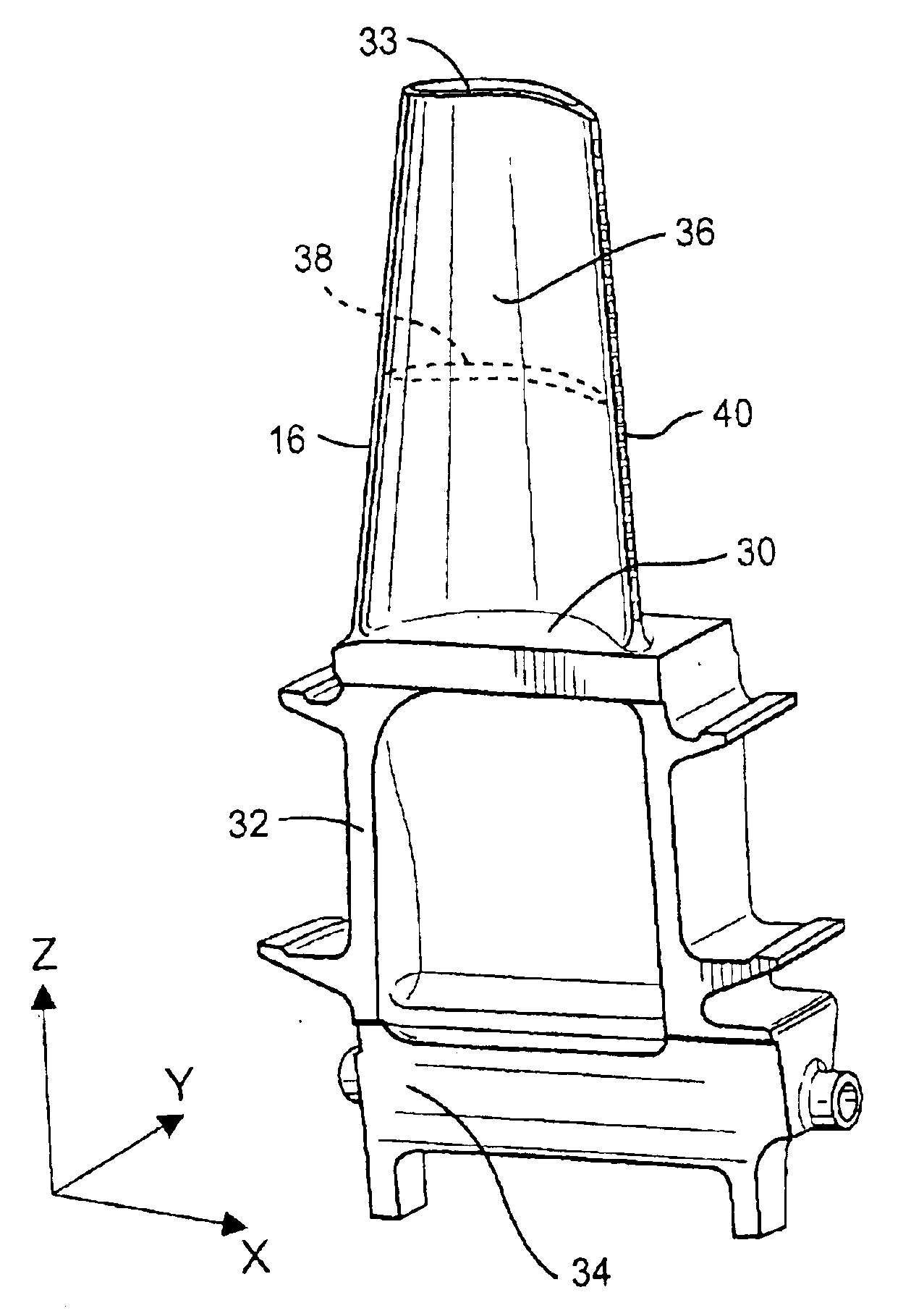
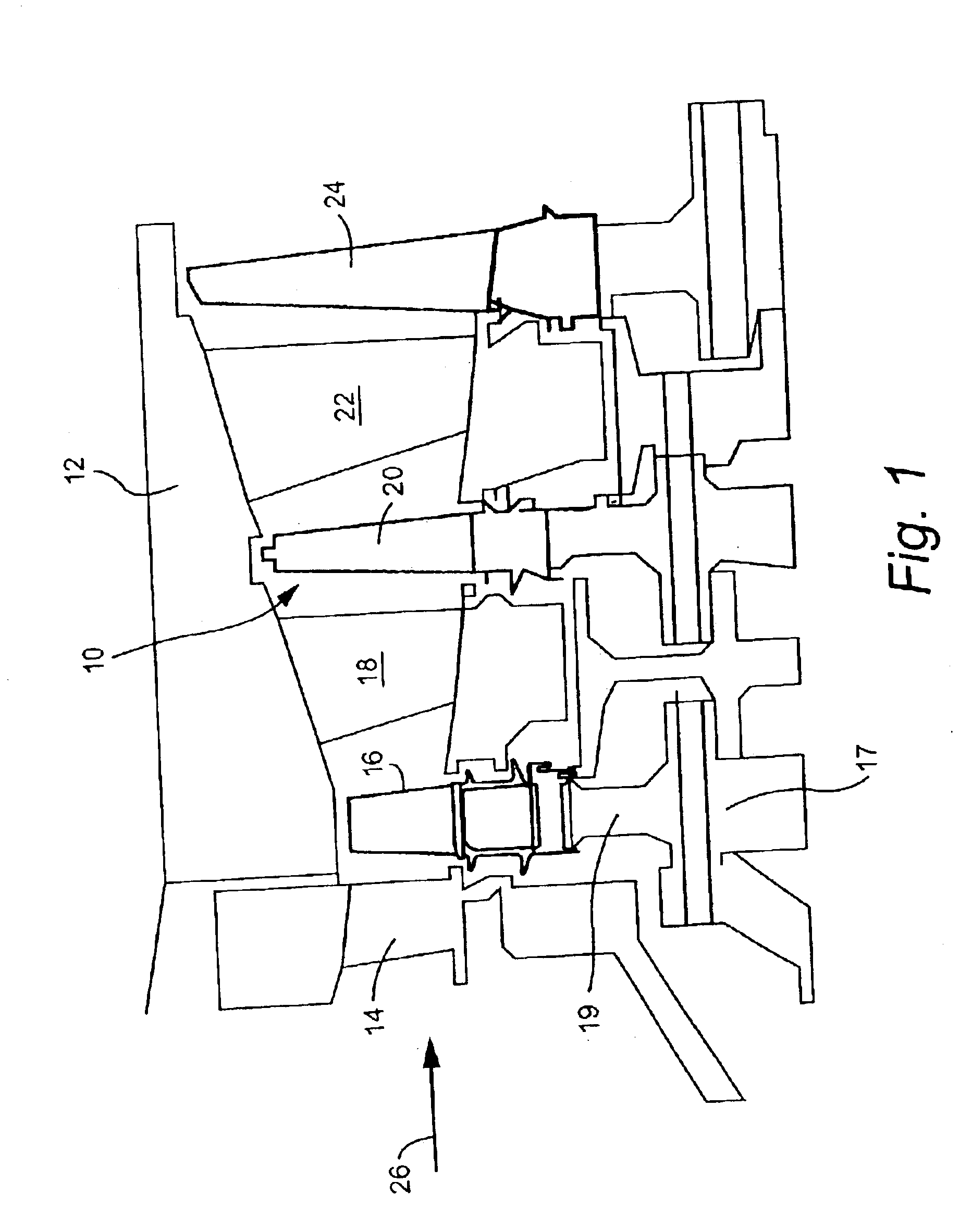
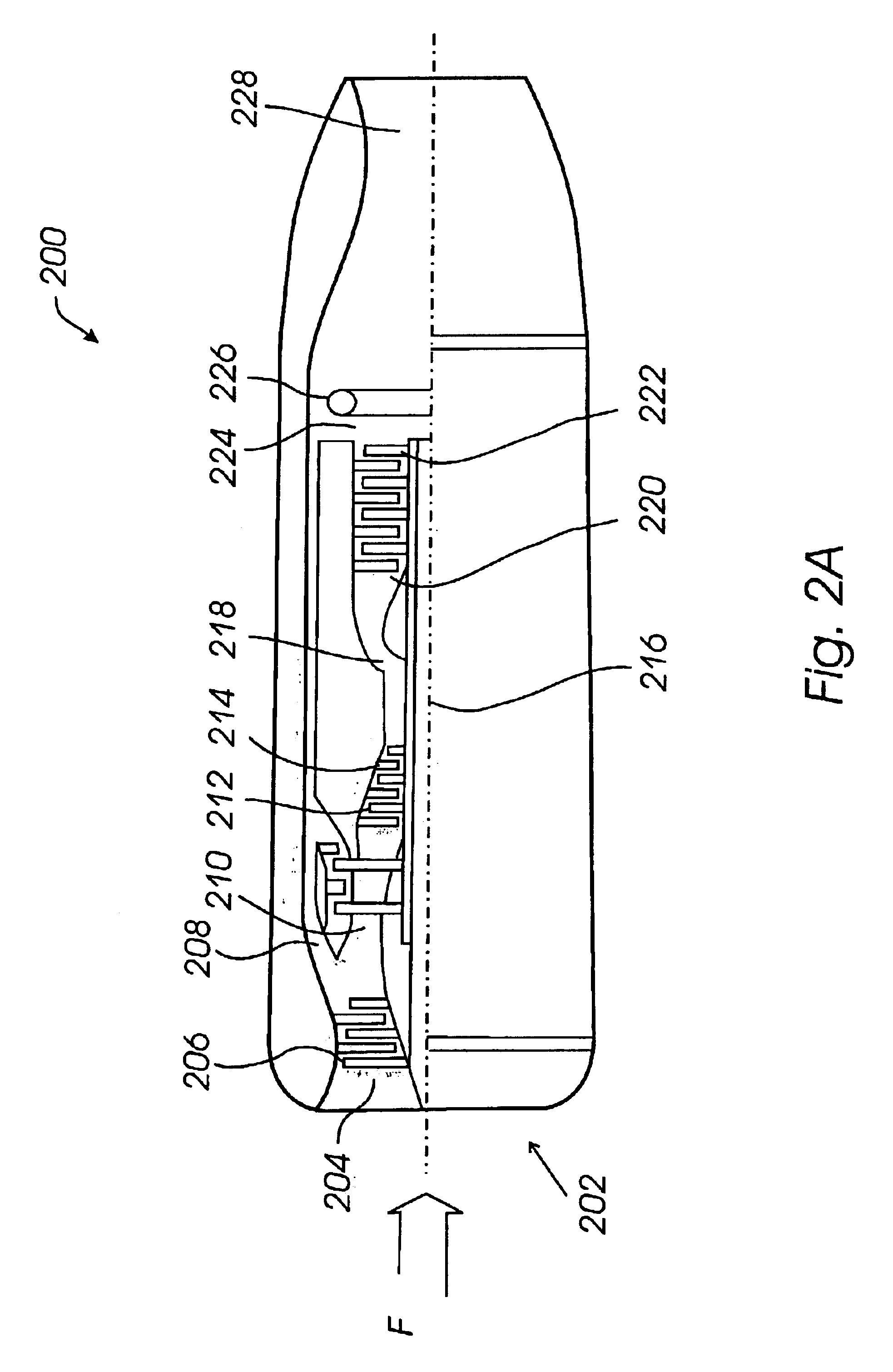
Mid-section of a can-annular gas turbine engine with an improved rotation of air flow from the compressor to the turbine
InactiveUS20130219853A1Easy to operateReduce lossesContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustorTurbine
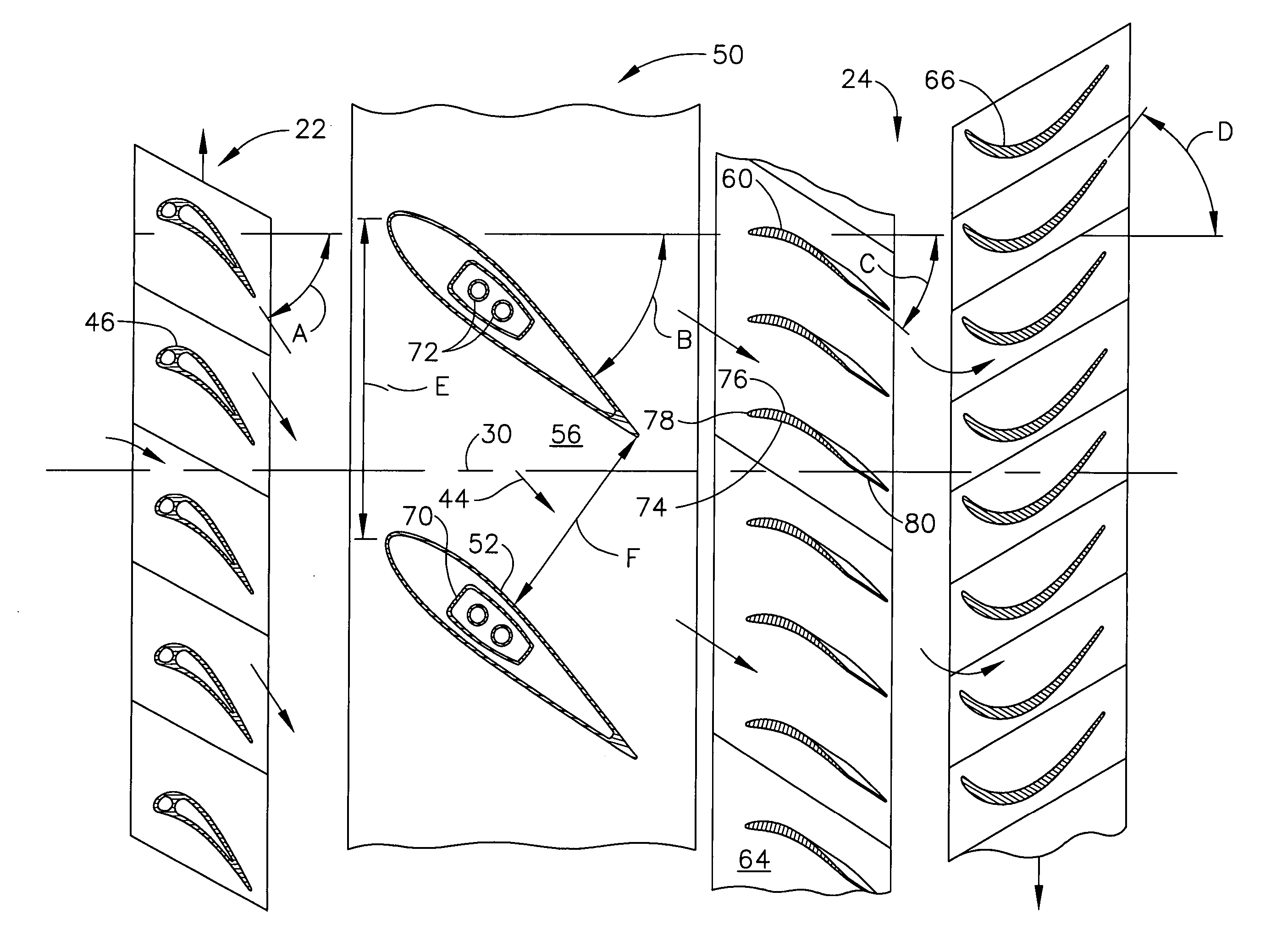
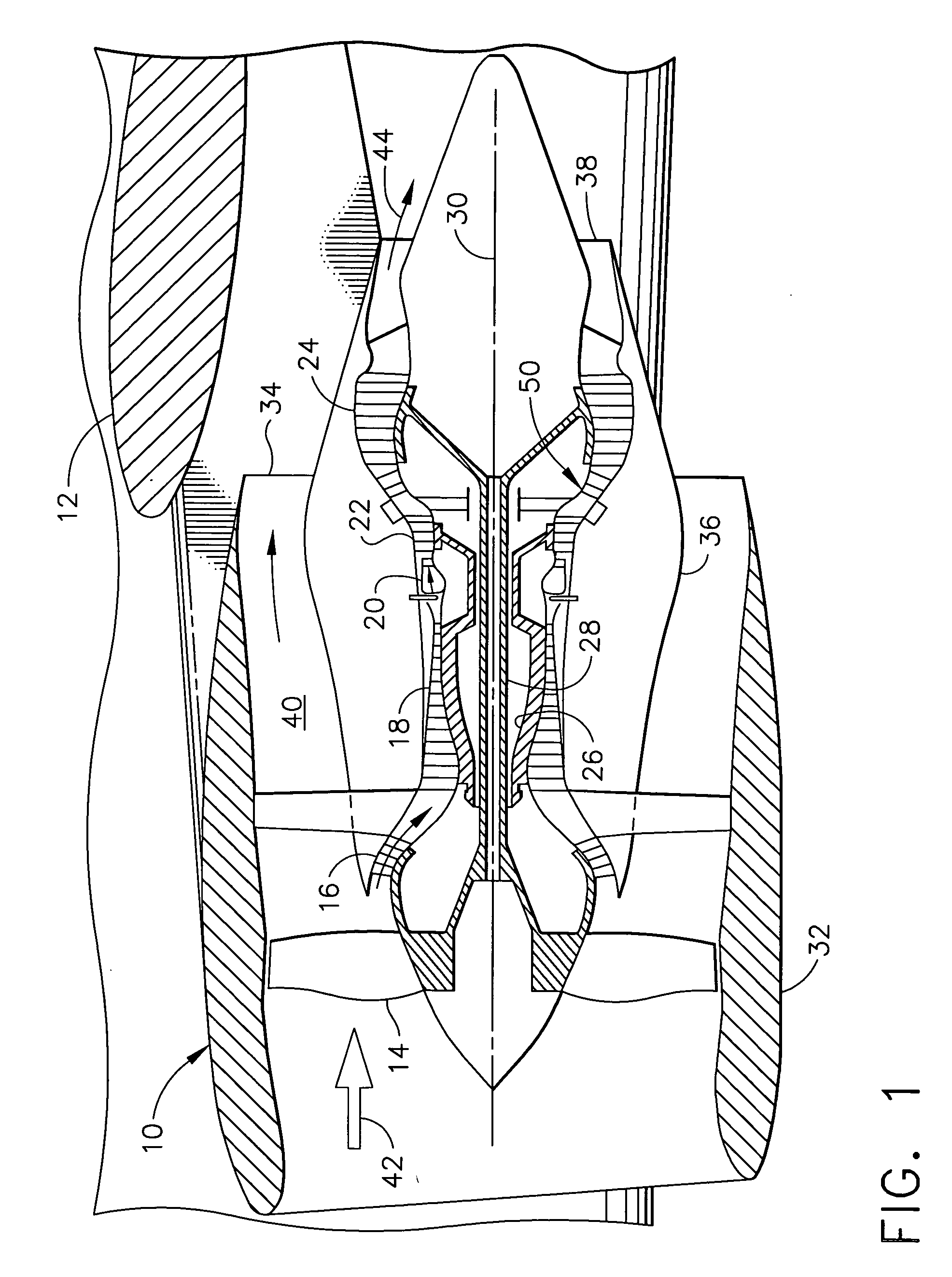
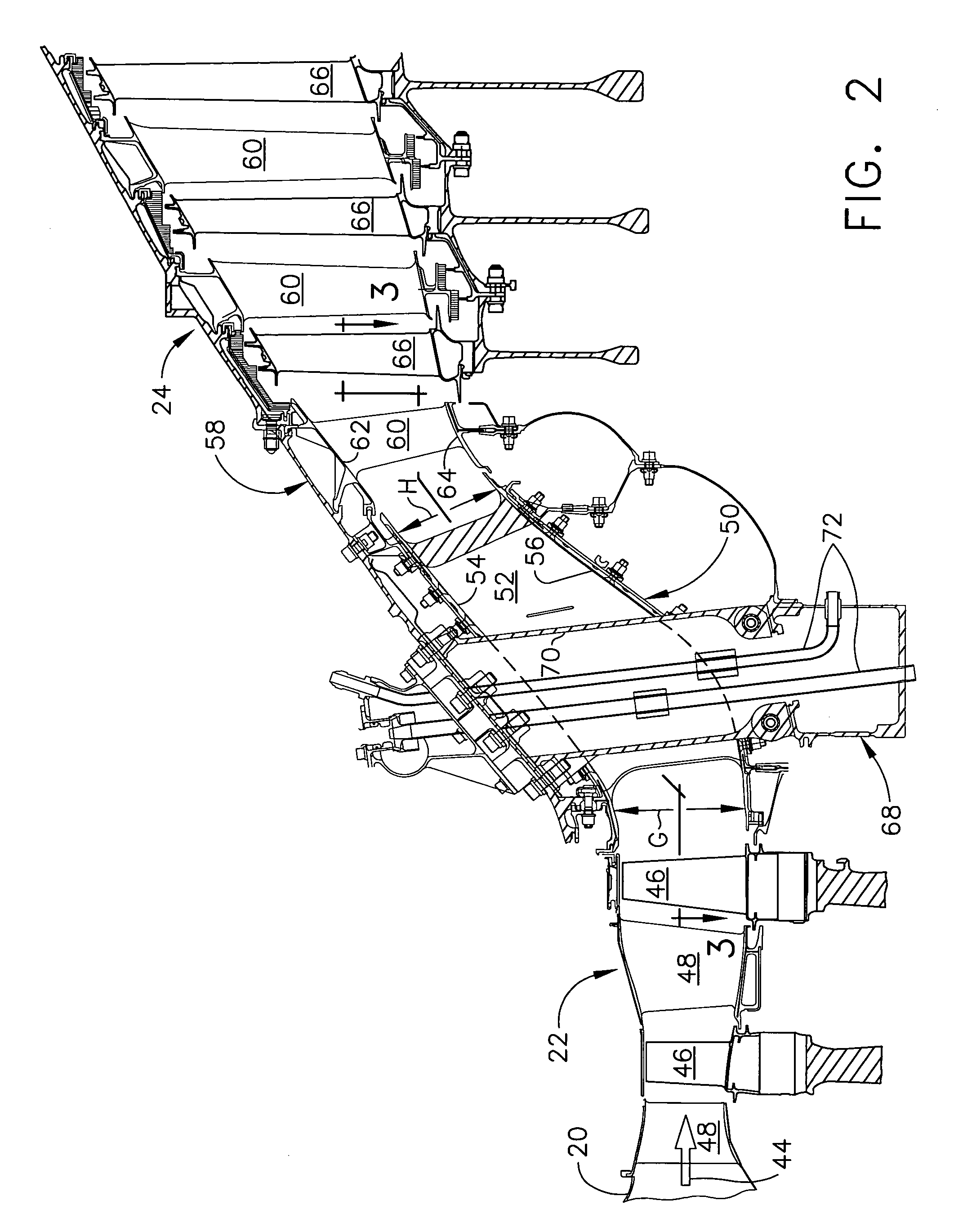
A midframe portion (313) of a gas turbine engine (310) is presented and includes a compressor section with a last stage blade to orient an air flow (311) at a first angle (372). The midframe portion (313) further includes a turbine section with a first stage blade to receive the air flow (311) oriented at a second angle (374). The midframe portion (313) further includes a manifold (314) to directly couple the air flow (311) from the compressor section to a combustor head (318) upstream of the turbine section. The combustor head (318) introduces an offset angle in the air flow (311) from the first angle (372) to the second angle (374) to discharge the air flow (311) from the combustor head (318) at the second angle (374). While introducing the offset angle, the combustor head (318) at least maintains or augments the first angle (372).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Airfoil shape for a turbine bucket
InactiveUS6854961B2Improve performanceReduction of thermalEngine manufactureOther chemical processesTurbine bladeEngineering
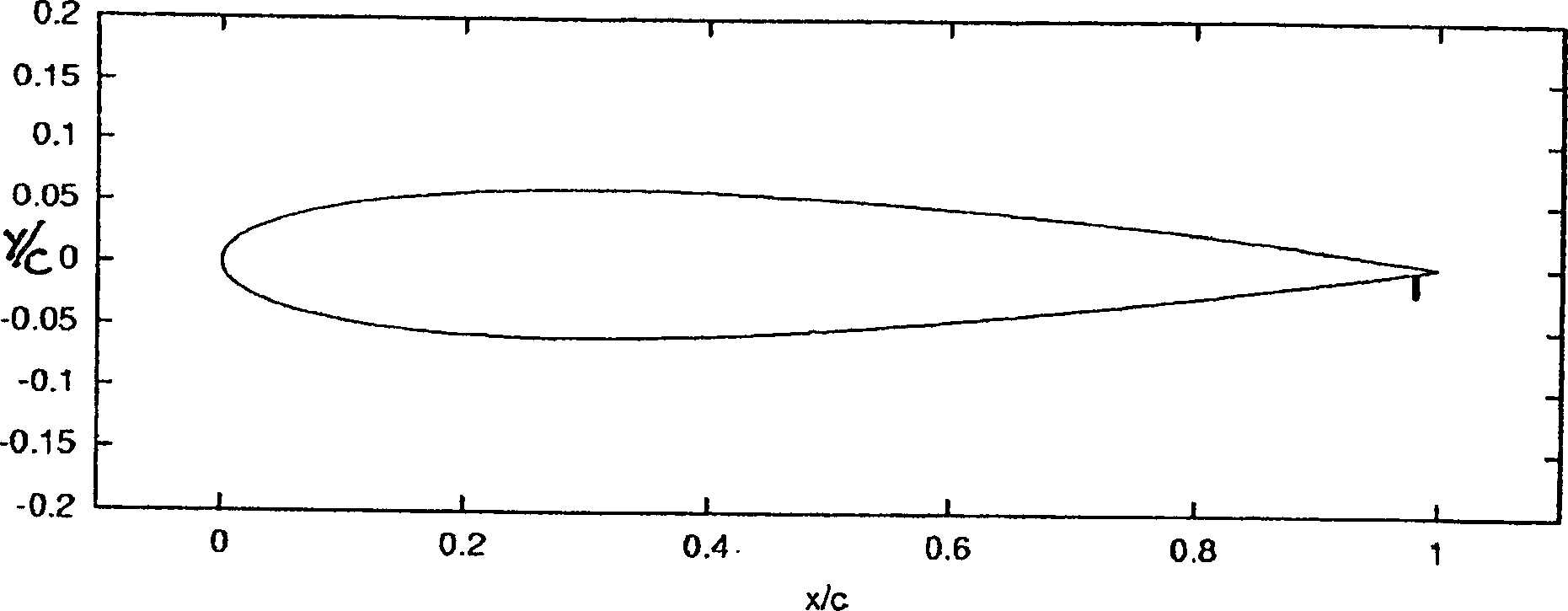
First stage turbine buckets have airfoil profiles substantially in accordance with Cartesian coordinate values of X, Y and Z set forth Table I wherein X and Y values are in inches and the Z values are non-dimensional values from 0 to 1 convertible to Z distances in inches by multiplying the Z values by the height of the airfoil in inches. The X and Y values are distances which, when connected by smooth continuing arcs, define airfoil profile sections at each distance Z. The profile sections at each distance Z are joined smoothly to one another to form a complete airfoil shape. The X, Y and Z distances may be scalable as a function of the same constant or number to provide a scaled up or scaled down airfoil section for the bucket. The nominal airfoil given by the X, Y and Z distances lies within an envelop of ±0.055 inches in directions normal to the surface of the airfoil.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
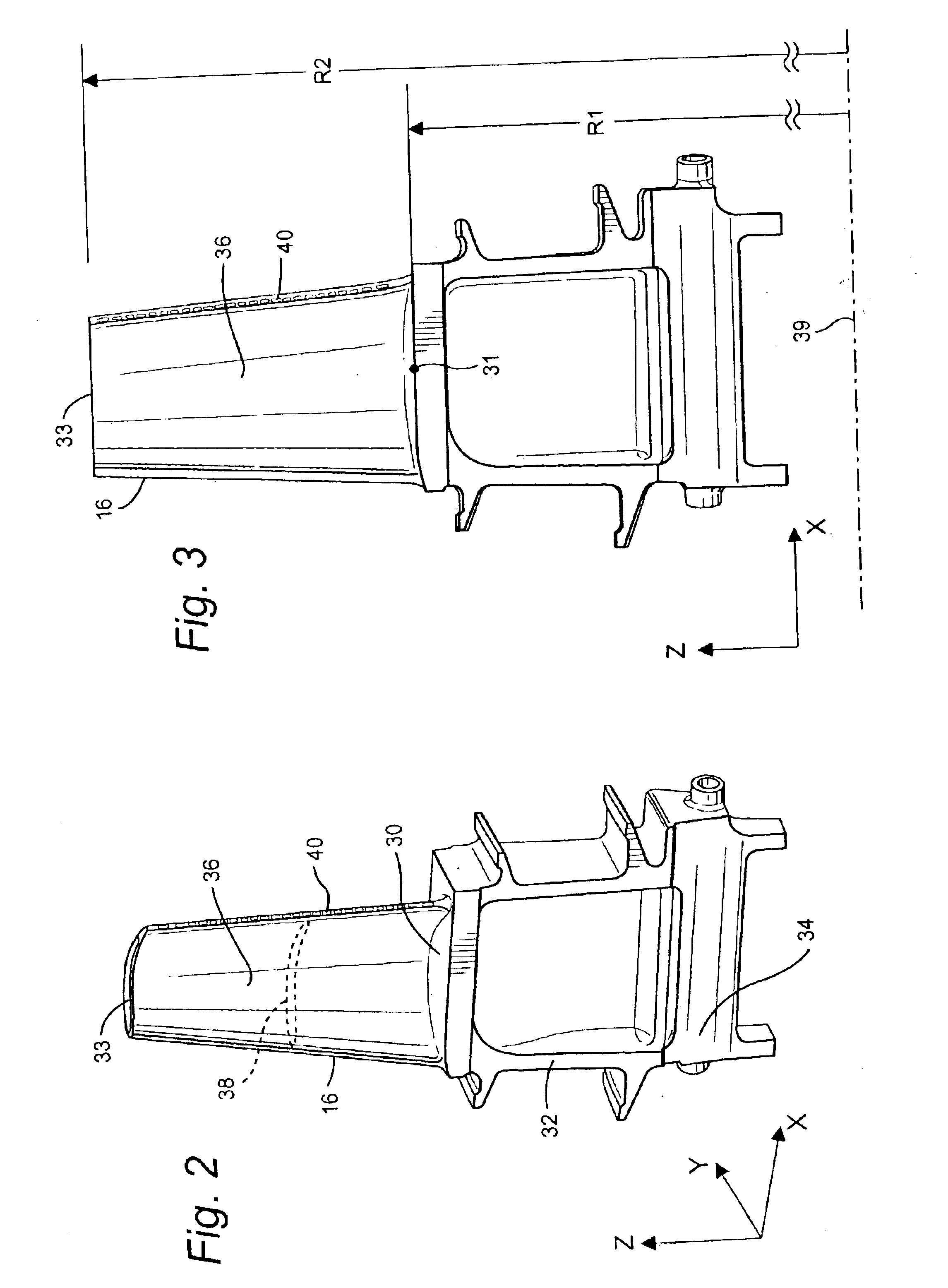
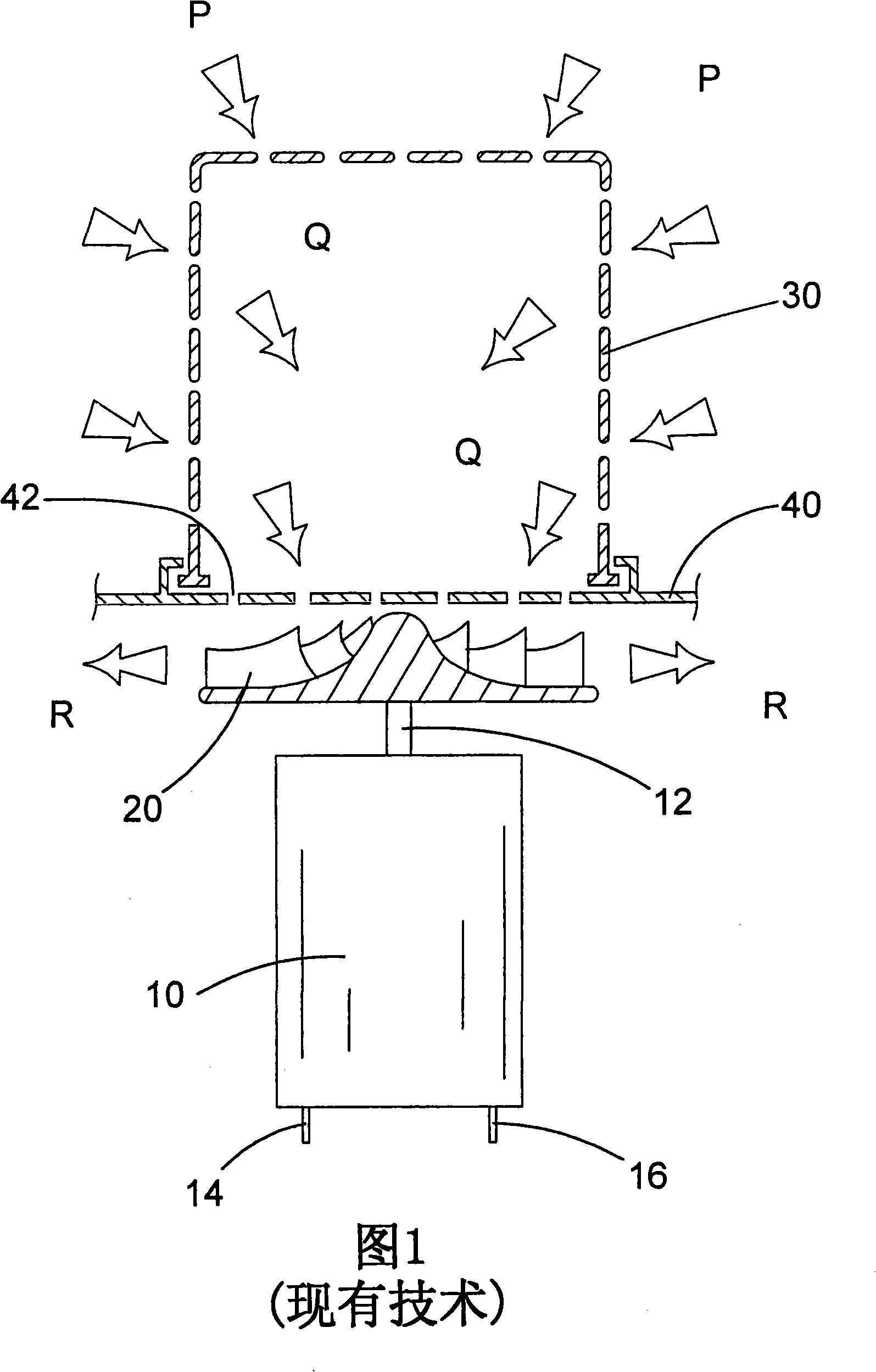
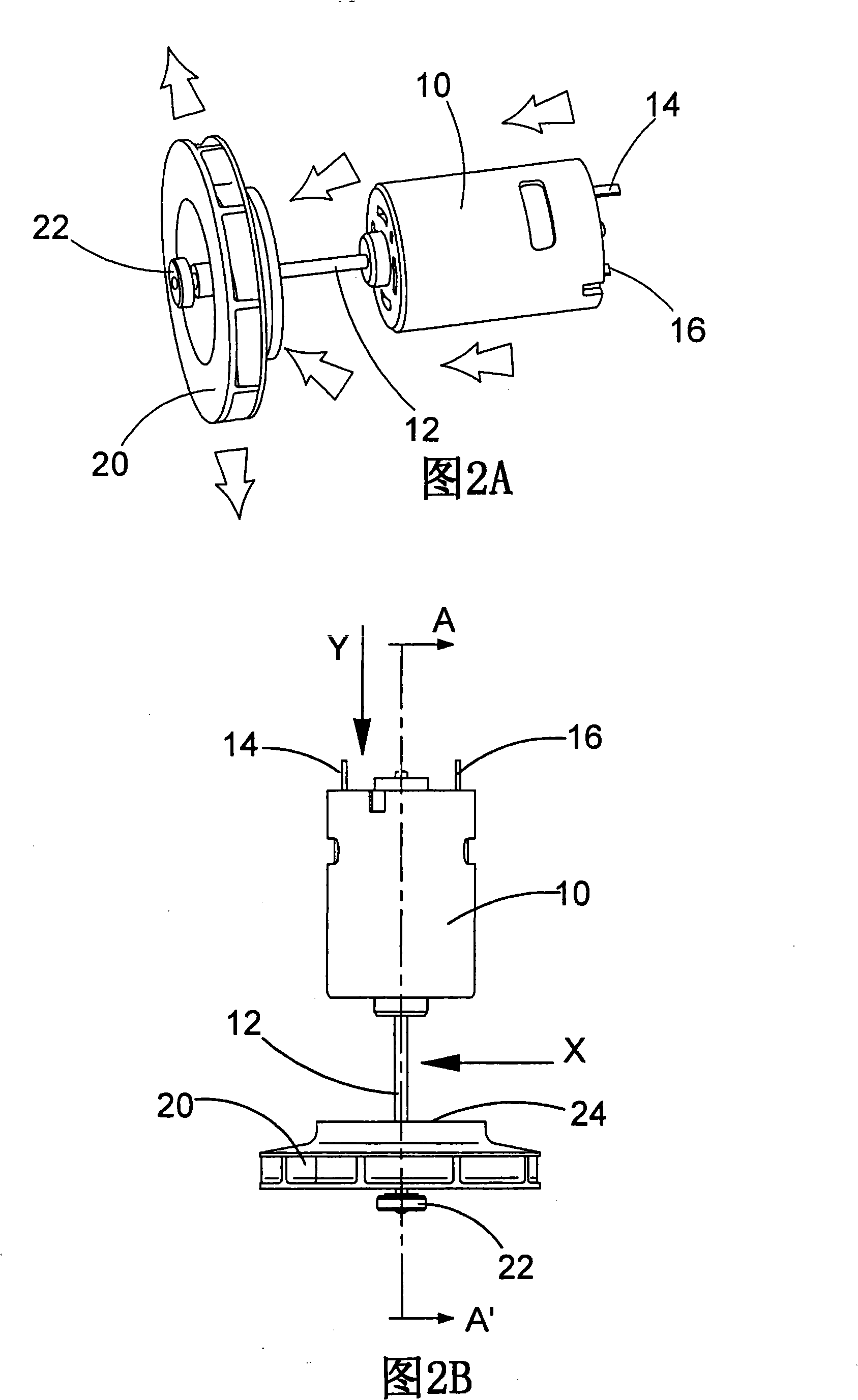
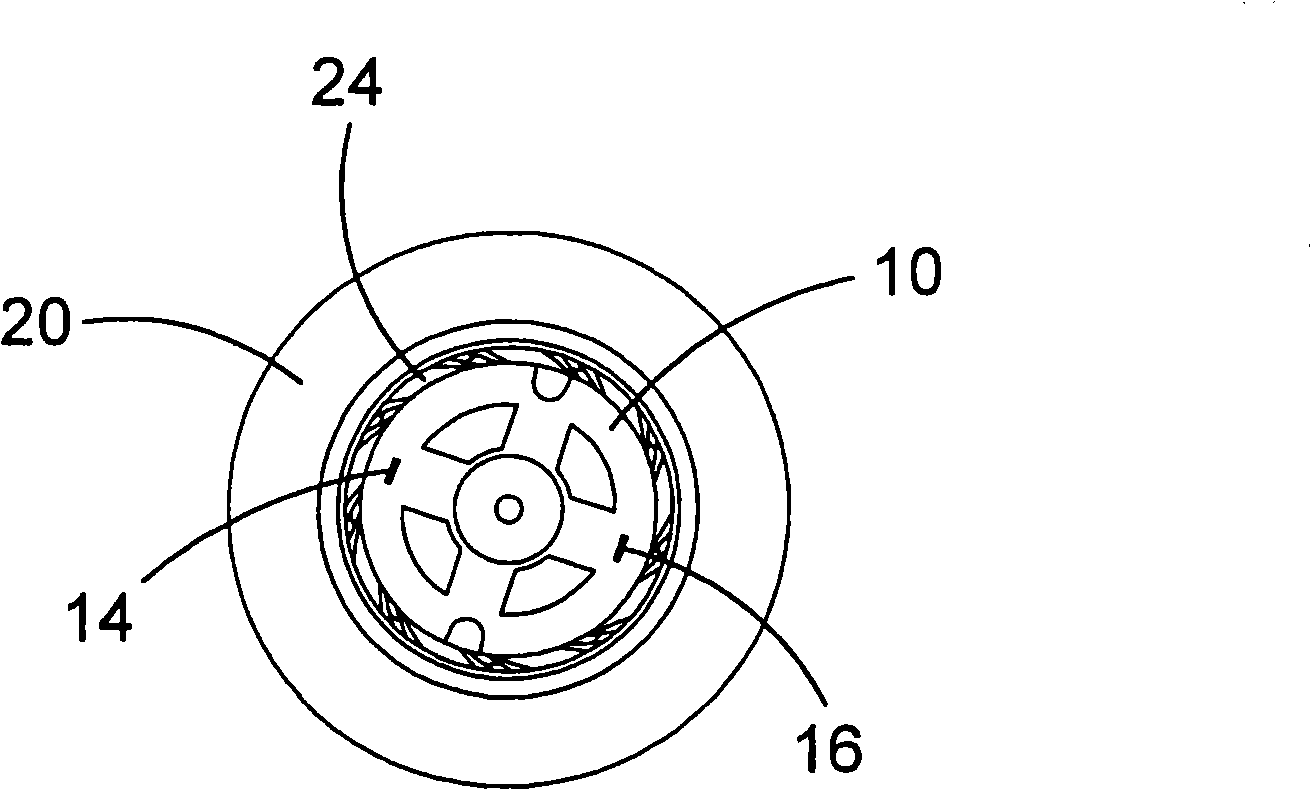
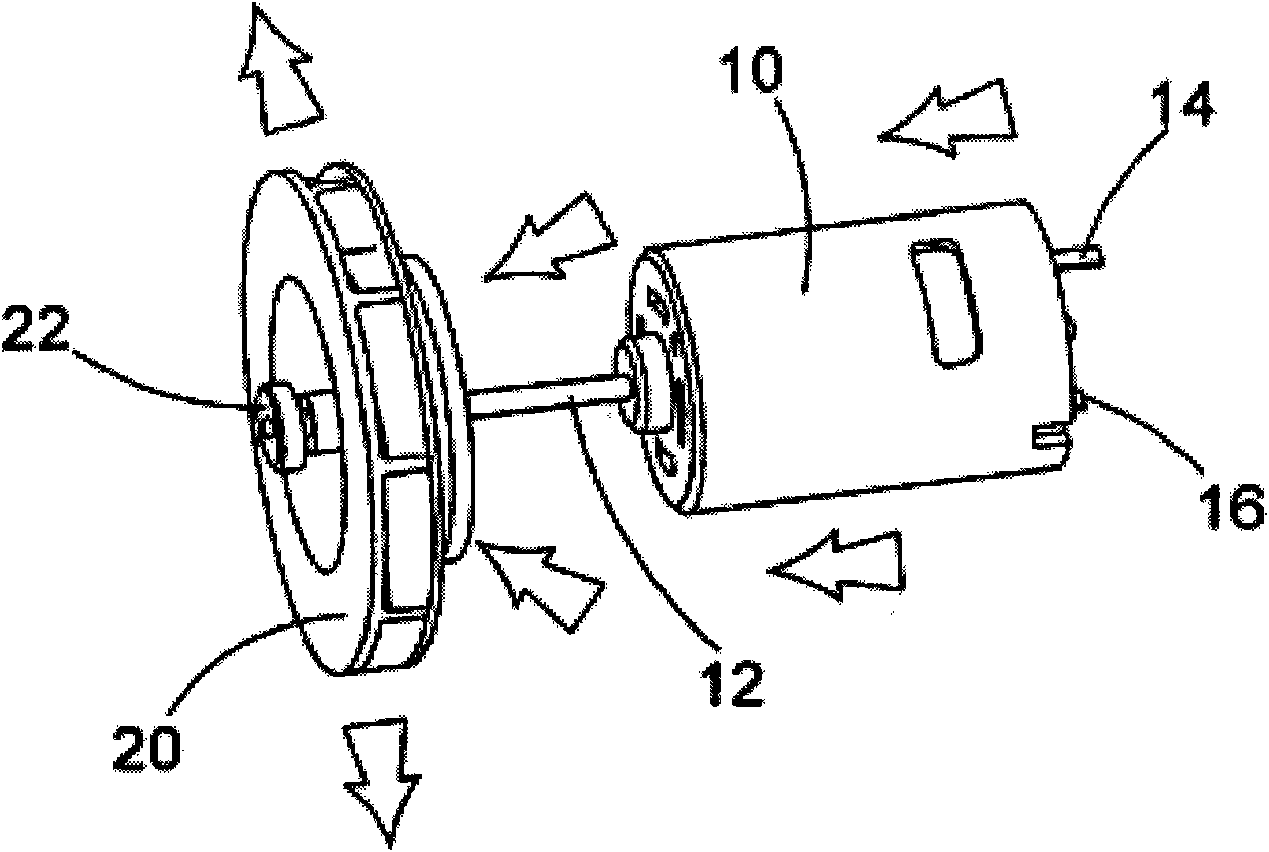
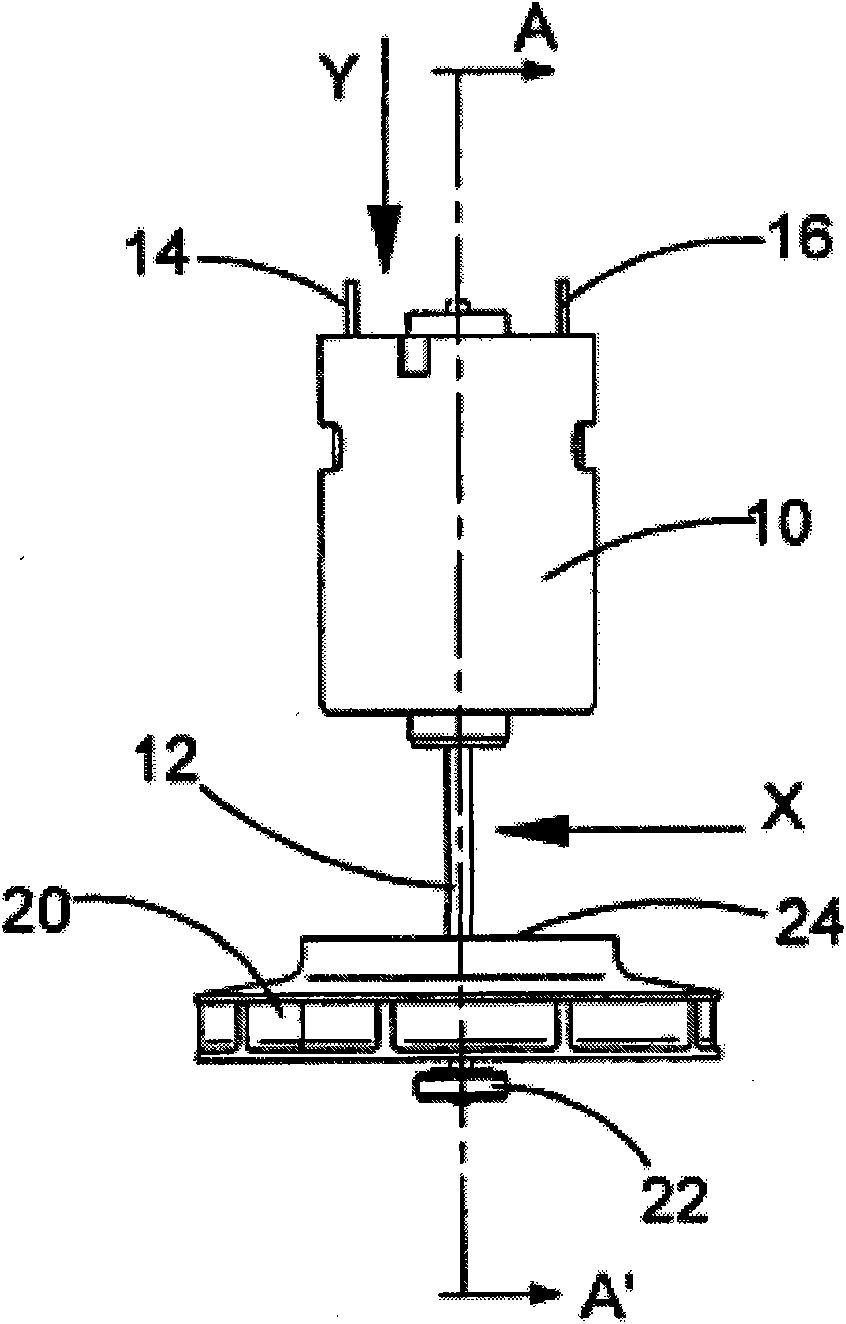
Motor, fan and filter arrangement for a vacuum cleaner
InactiveCN101288572AExhaust freeFreedom to guideCleaning filter meansSuction filtersSide effectControl theory
In a first aspect, the present invention provides a motor, fan and filter arrangement for a vacuum cleaner, comprising: a motor (10); a fan (20) connected to an output shaft (12) of the motor and having an axial intake; and a filter (30, 230, 330); wherein the fan (20) is arranged with its axial intake facing the motor (10); and the motor (10) is housed within the filter (30, 230, 330). Such an arrangement makes much more efficient use of space than a conventional arrangement and allows the motor to be positioned within the filter in a reversed direction in comparison to conventional arrangements, so that clear air from the filter can be drawn over the motor before encountering the fan. This also has the beneficial side-effect of cooling the motor with the filtered air.; In a second aspect, the present invention also provides vacuum cleaners (100, 200, 300) comprising such a motor, fan and filter arrangement. Preferred embodiments of such vacuum cleaners are described, including a pivotable stick vac and different hand-holdable vacuum cleaners.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
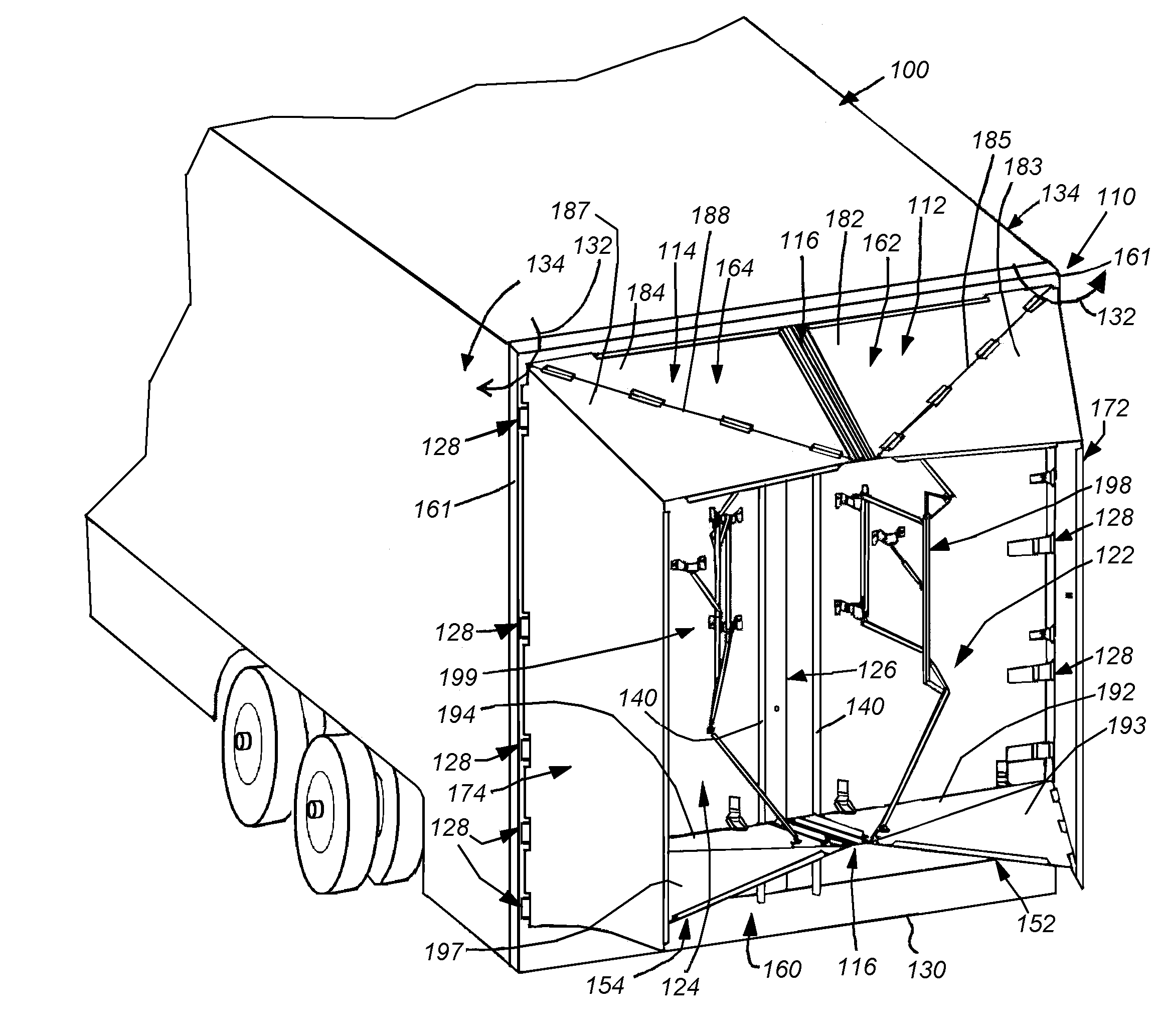
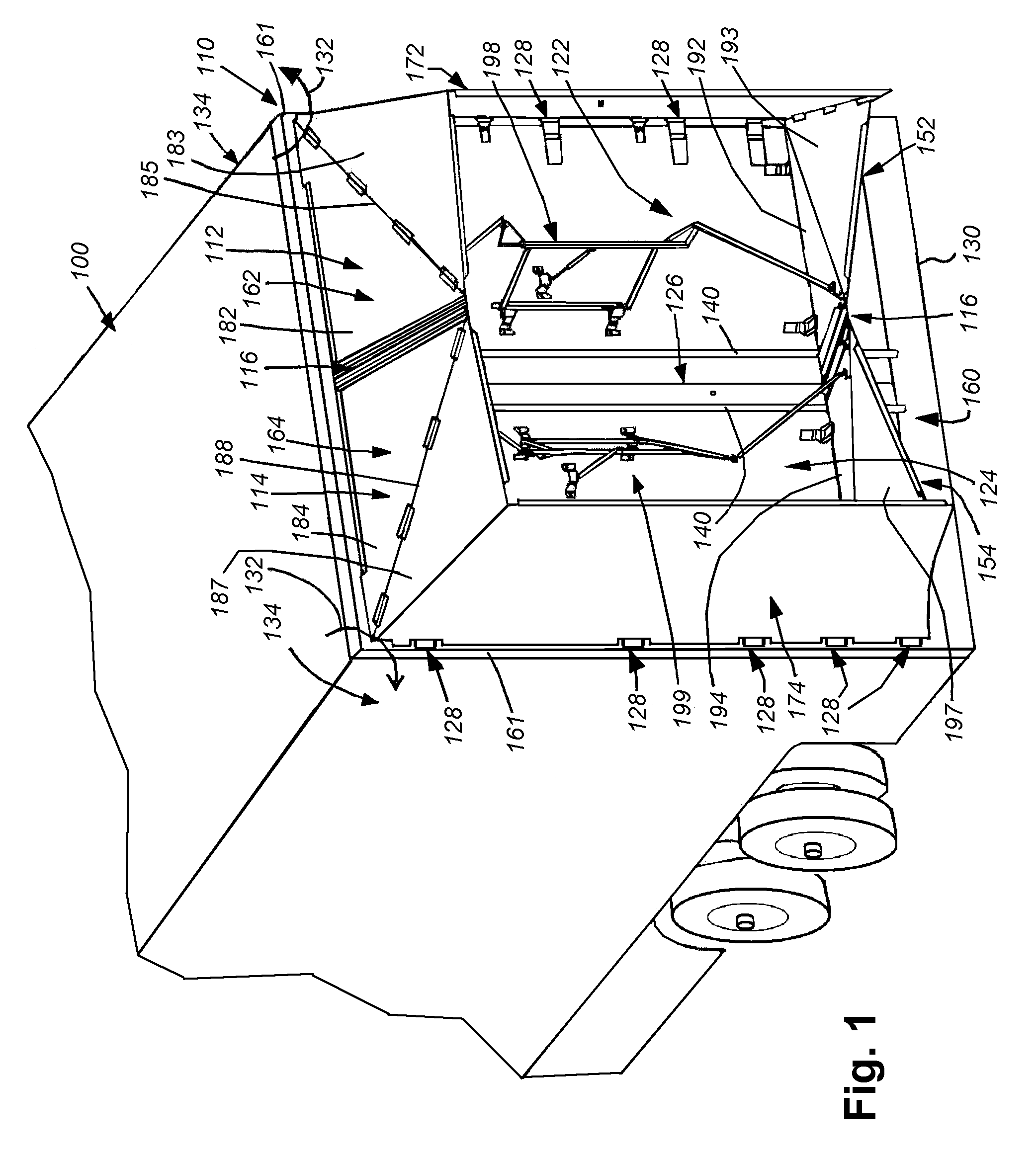
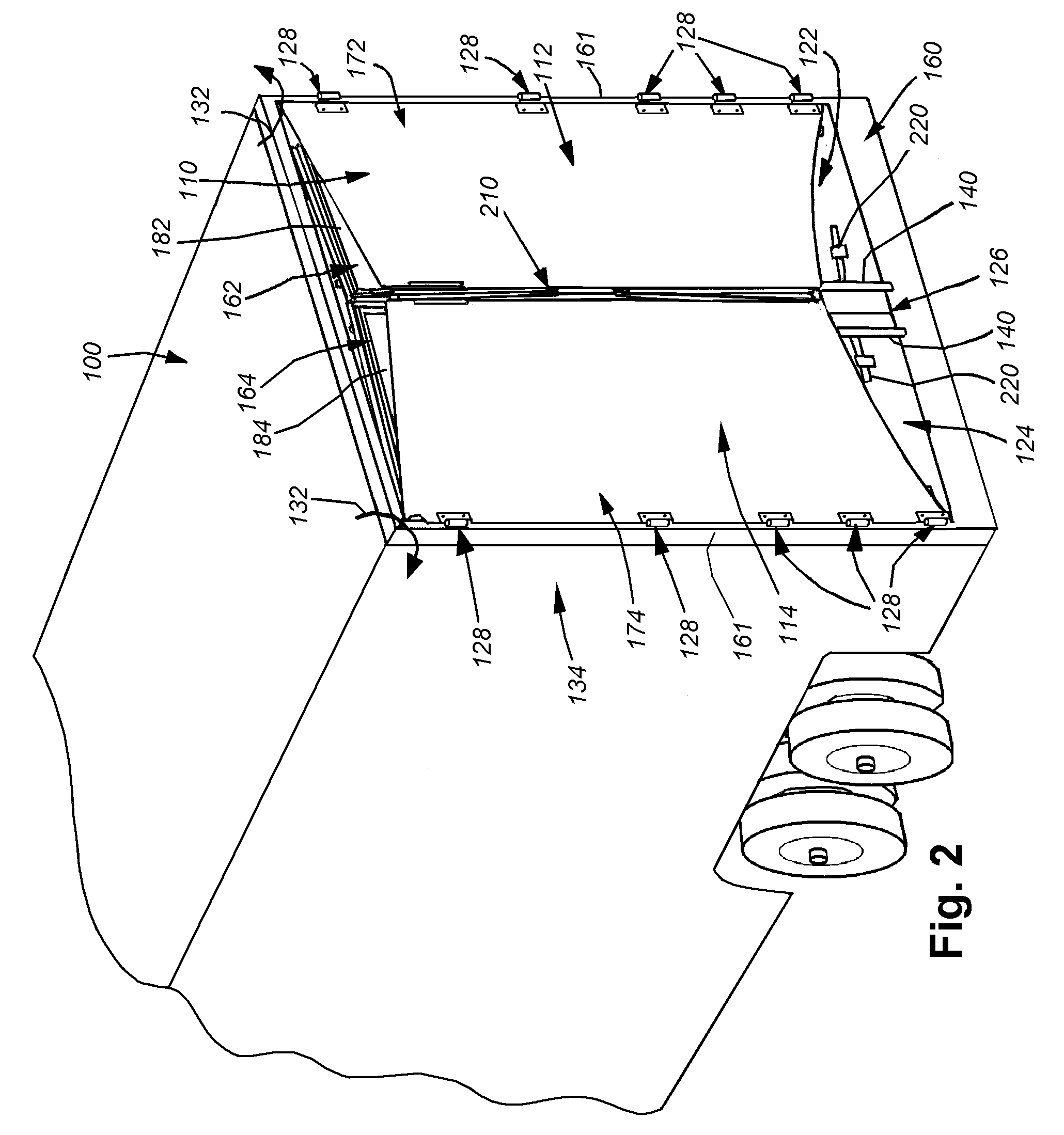
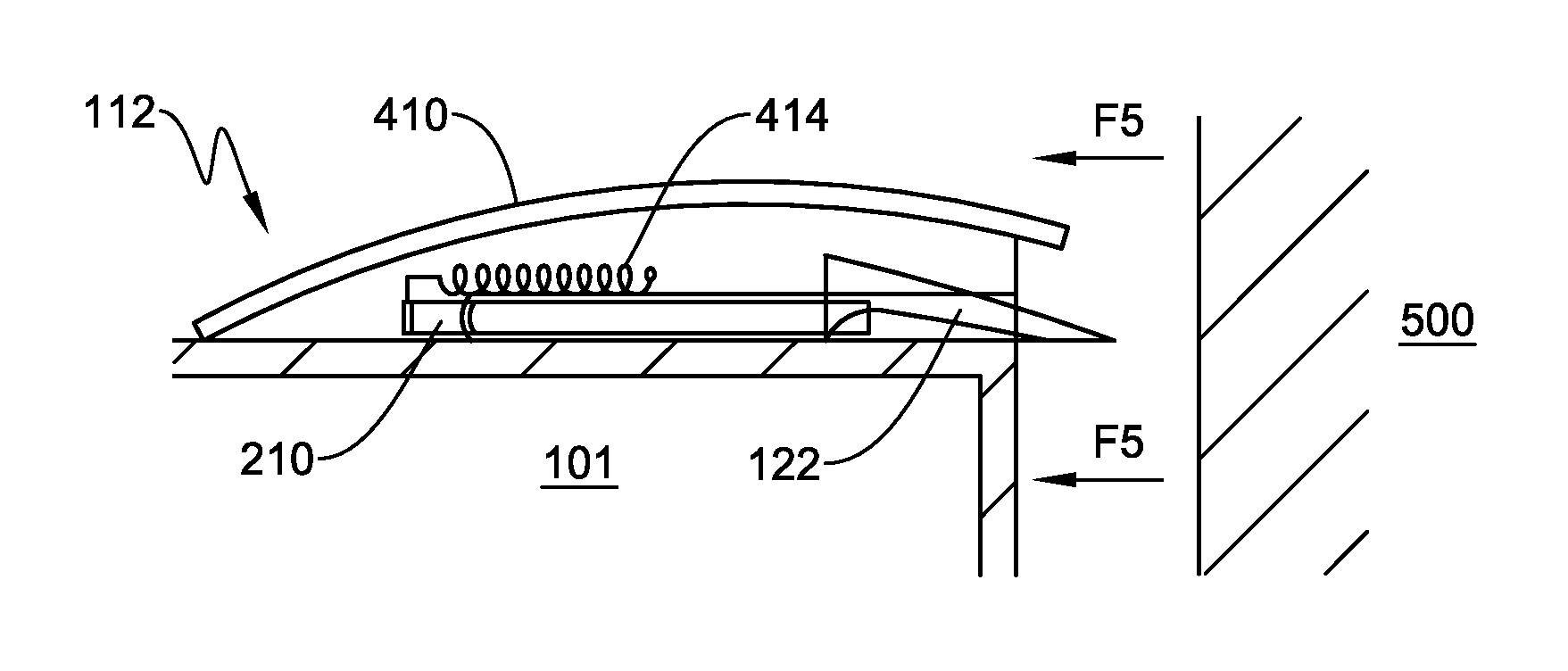
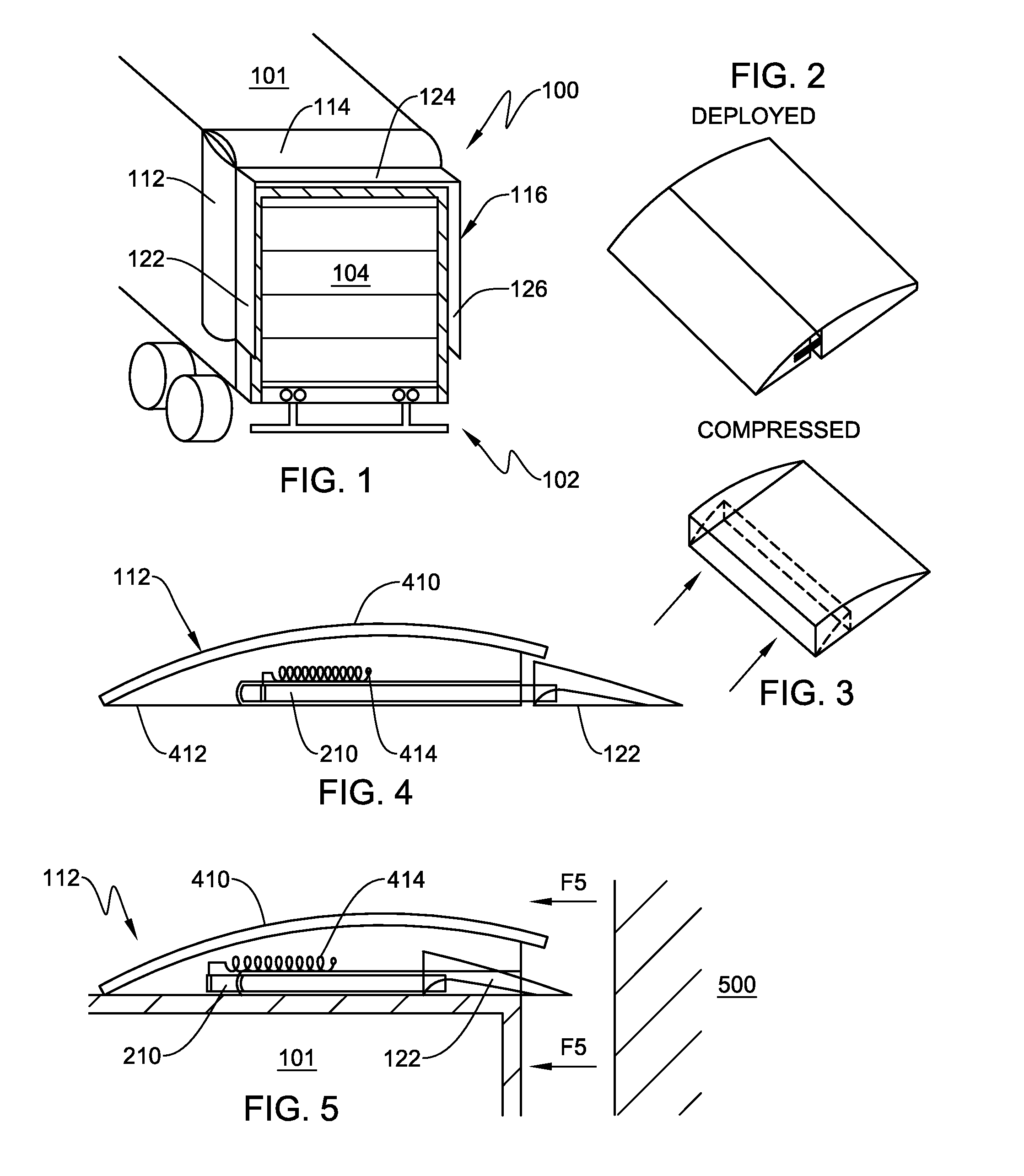
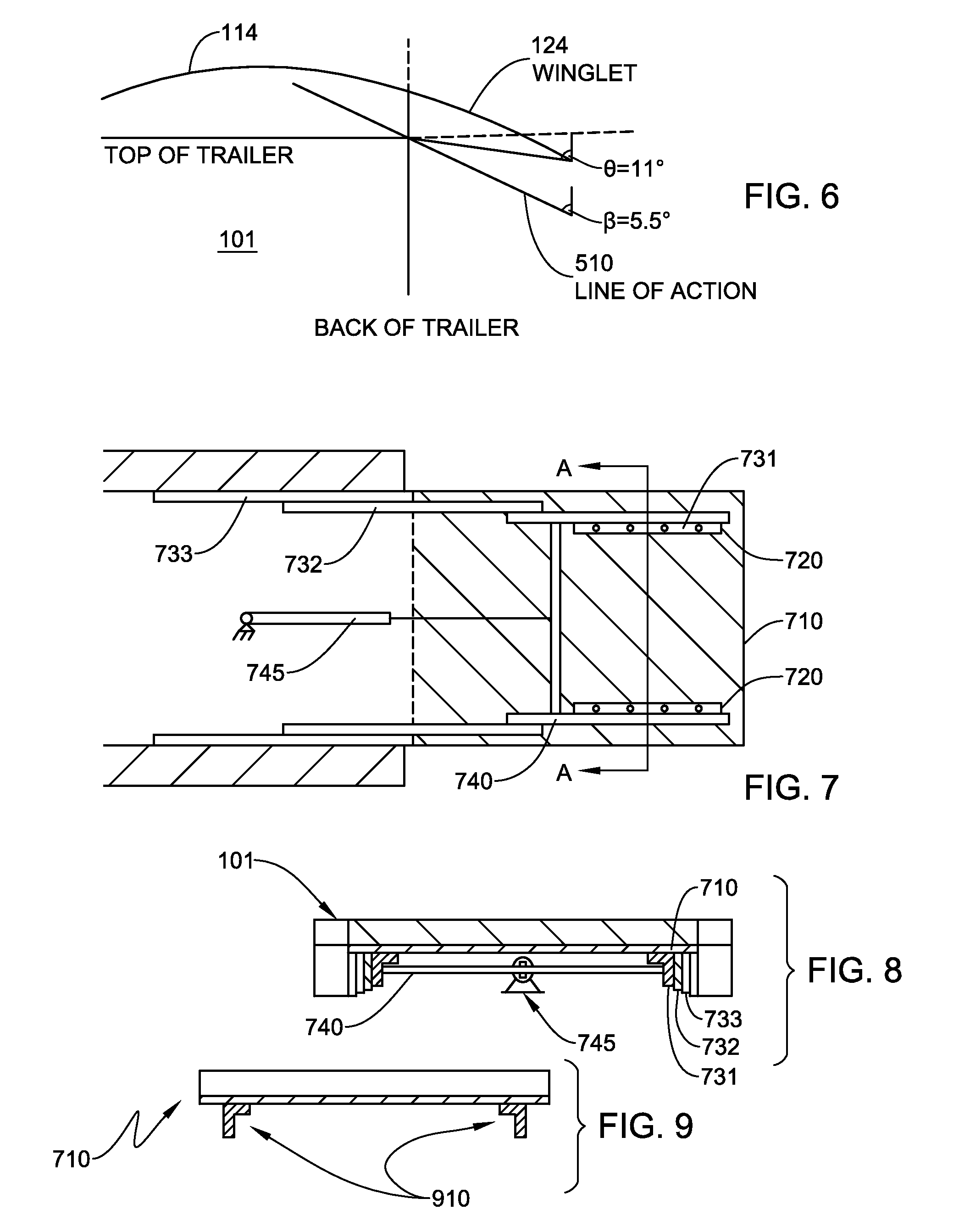
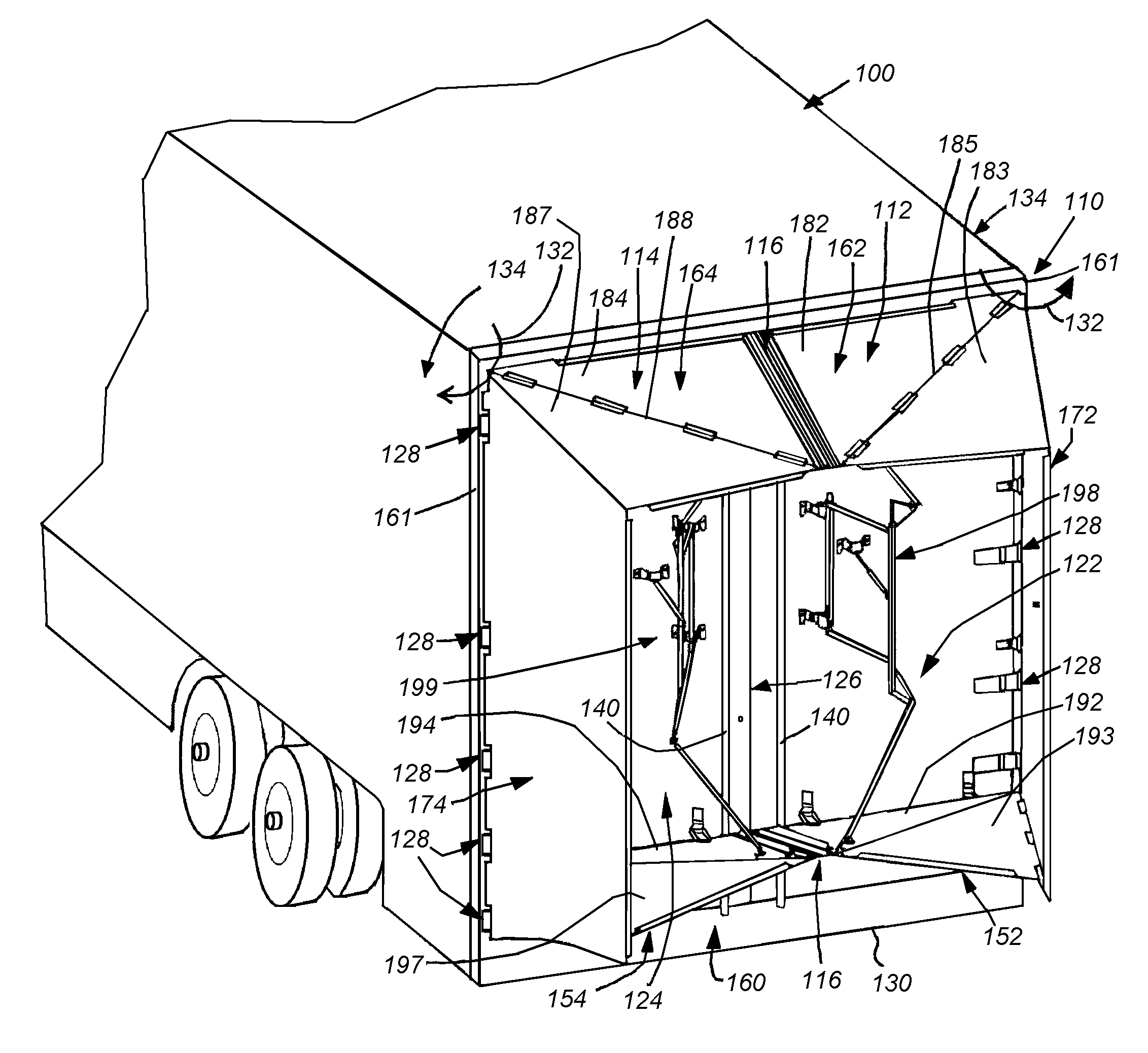
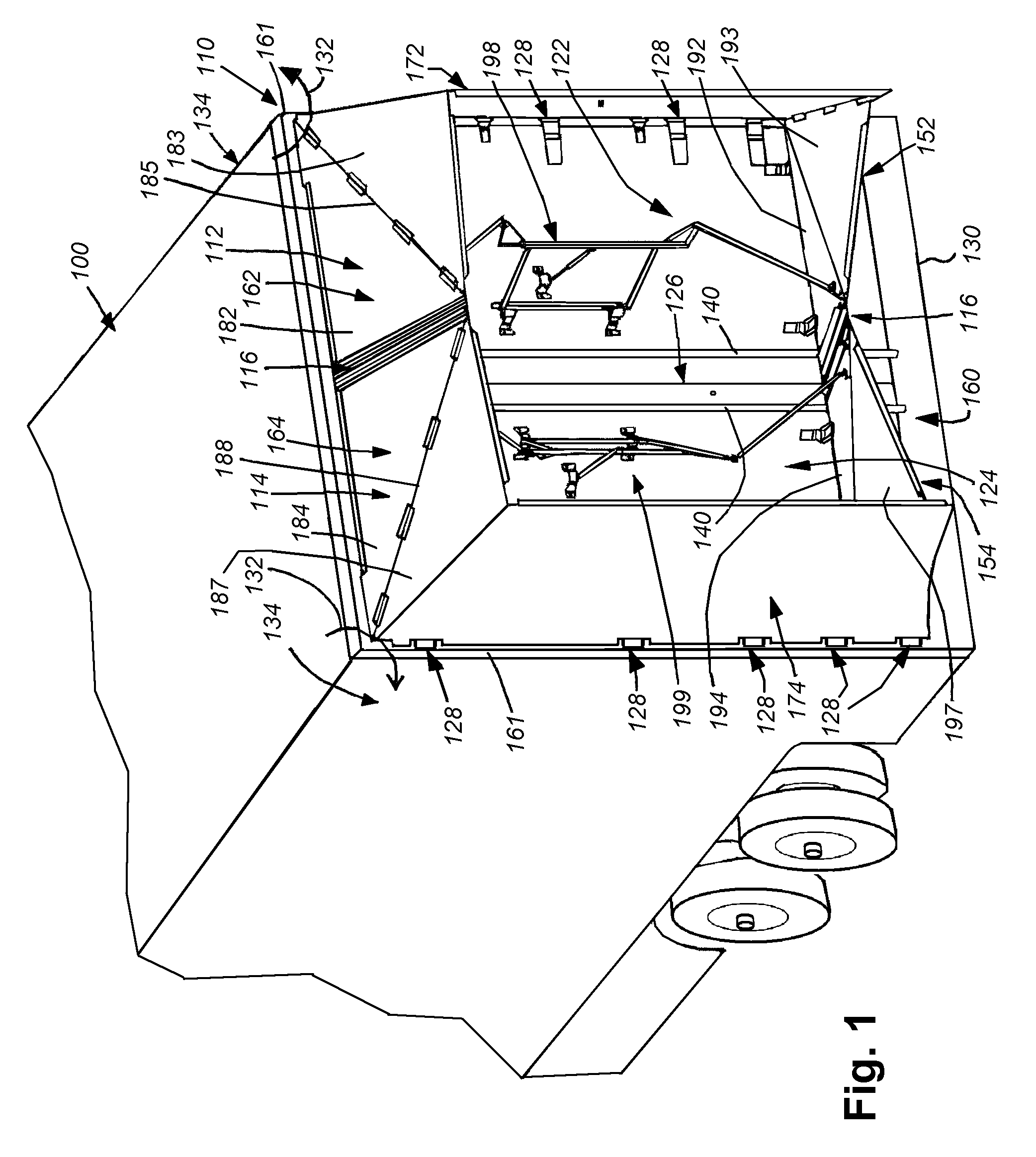
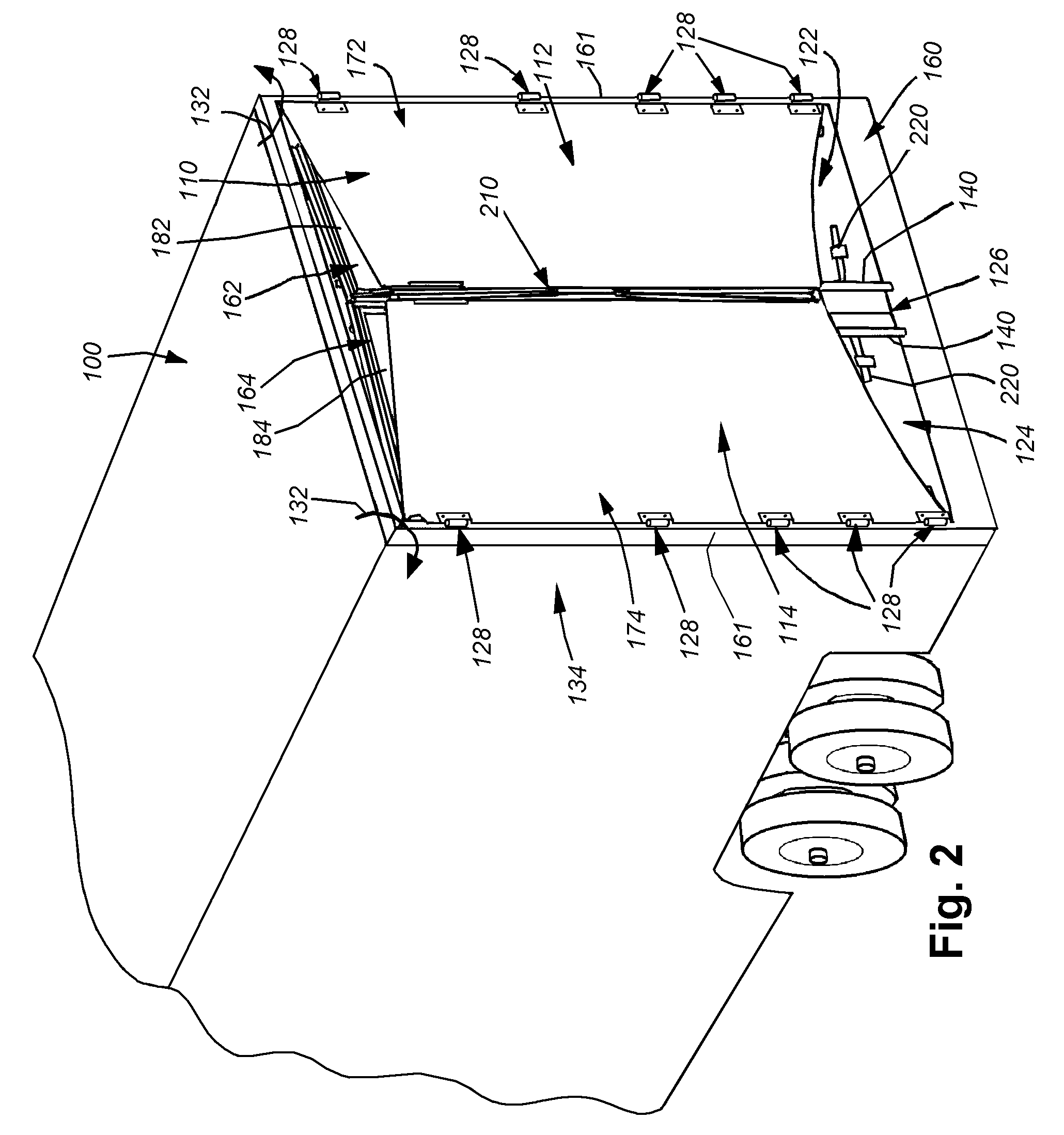
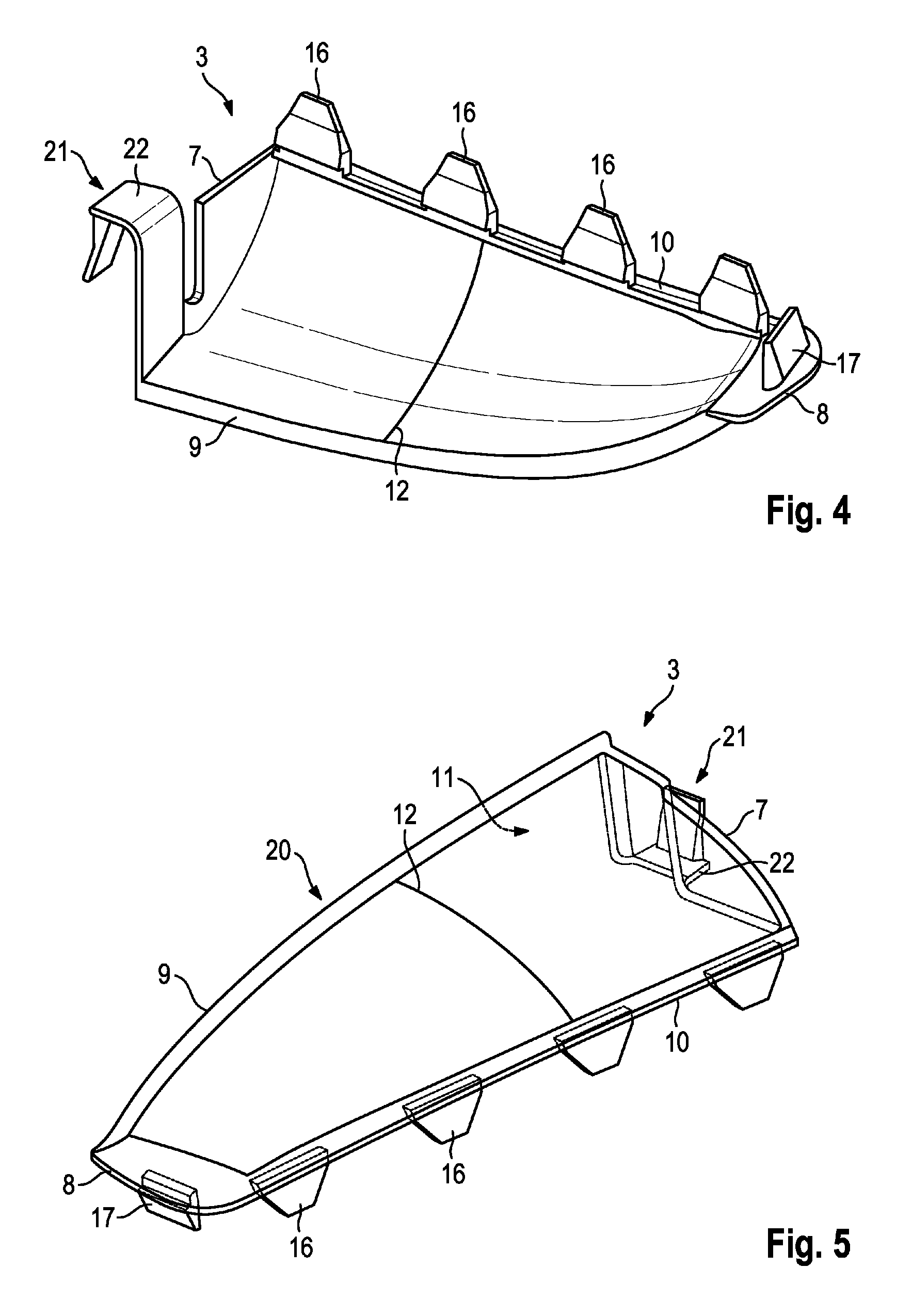
Rear-mounted aerodynamic structure for truck cargo bodies
This invention provides a foldable / retractable and unfoldable / deployable, rearwardly tapered aerodynamic assembly for use on the rear trailer bodies and other vehicles that accommodate dual swing-out doors. The aerodynamic assembly includes a right half mounted on the right hand door and a left half mounted on a left hand door. Each half is constructed with a side panel, top panel and bottom panel, which each form half of an overall tapered box when deployed on the rear of the vehicle, the bottom panels and top panels being sealed together at a pair of overlapping weather seals along the centerline. The panels are relatively thin, but durable, and are joined to each other by resilient strip hinges. The top and bottom panels are also hinged to form two sections along diagonal lines to facilitate folding of all panels in a relatively low-profile stacked orientation. This low profile allows the doors to be swung through approximately 270 degrees to be secured to the sides of the body in a manner that does not interfere with adjacent doors or bodies in, for example a multi-bay loading dock. A swing arm assembly and gas spring biases the panels into a deployed position that can be refolded by grasping the side panel and rotating it inward toward the door surface. The top and bottom panels are partly inwardly folded when deployed to define external valleys using a stop assembly. This ensures that the panels fold readily when desired without the two sections of the panels “locking up”.
Owner:STEMCO PROD INC
Rear-mounted retractable aerodynamic structure for cargo bodies
An aerodynamic structure attached to the sides and top of a truck cargo body (either a stand-alone trailer or a “straight truck” with the cab and cargo area as a fixed vehicle) at the aftmost region, which rear typically contains a rolling door assembly, which rolls upwardly. An aerodynamic structure is permanently attached to the sides and top of the trailer in a manner that extend past the aftmost plane of the truck cargo body and retract to the aftmost plane of the truck cargo body when subjected to a force, allowing this device to be backed into structures. The retracted orientation allows for the rear of the trailer to be fully accessible for loading and unloading, and does not reduce the size of the opening of the trailer. The various embodiments of the invention allow for automated deployment once the force used to compress the structure is removed.
Owner:STEMCO LP
Golf ball with improved flight performance
InactiveUS6945880B2Improve aerodynamic efficiencyIncrease flight distanceGolf ballsSolid ballsEngineeringGolf Ball
A golf ball is provided that has improved aerodynamic efficiency, resulting in increased flight distance for golfers of all swing speeds, and more particularly for golfers possessing very high swing speeds, such as those who can launch the balls at an initial speed greater than 160 miles per hour and more particularly at initial ball speed of about 170 miles per hour or higher. The golf ball of the present invention combines lower dimple count with multiple dimple sizes to provide higher dimple coverage and improved aerodynamic characteristics.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Golf ball with improved flight performance
InactiveUS20050079931A1Improve aerodynamic efficiencyIncrease flight distanceGolf ballsSolid ballsGolf BallFlight distance
A golf ball is provided that has improved aerodynamic efficiency, resulting in increased flight distance for golfers of all swing speeds, and more particularly for golfers possessing very high swing speeds, such as those who can launch the balls at an initial speed greater than 160 miles per hour and more particularly at initial ball speed of about 170 miles per hour or higher. The golf ball of the present invention combines lower dimple count with multiple dimple sizes to provide higher dimple coverage and improved aerodynamic characteristics.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Rear-mounted aerodynamic structure for truck cargo bodies
This invention provides a foldable / retractable and unfoldable / deployable, rearwardly tapered aerodynamic assembly for use on the rear trailer bodies and other vehicles that accommodate dual swing-out doors. The aerodynamic assembly includes a right half mounted on the right hand door and a left half mounted on a left hand door. Each half is constructed with a side panel, top panel and bottom panel, which each form half of an overall tapered box when deployed on the rear of the vehicle, the bottom panels and top panels being sealed together at a pair of overlapping weather seals along the centerline.
Owner:STEMCO PROD INC
Novel turbine and blades
InactiveUS20110027084A1Increase power generationReduce speedPropellersPump componentsSelf limitingRotational axis
A variable axis turbine may include multiple nested rotatable rotor assemblies. The turbine may be self-starting in slow fluid conditions while simultaneously self-limiting in fast fluid conditions. The turbine may provide omni-directional energy recovery and be self-balancing. The nested rotatable rotor assemblies may be configured to rotate independently of each other, but along the same rotational axis. Each outer nested rotor blade set may direct fluid onto the inner rotor blade sets in an aerodynamically beneficial manner. Each rotor blade set may be interconnected with a rotating generator hub that encloses a rotating generator element that rotates along with a corresponding rotor blade set for electric power generation. The blades may be “smart blades” that are sufficiently flexible to be self-configuring during rotation and soft enough to partially absorb sound. The blades may have a variable hardness and a two or more dimensional twist.
Owner:WARNER DAVID B
Hybrid lift air vehicle
InactiveUS20120273608A1Improve aerodynamic efficiencyImprove fuel efficiencyRigid airshipsHybrid airshipsFlight vehicleLighter than air
A hybrid lift air vehicle for carrying and transporting a load, comprising an envelope having a generally ellipsoidal shape adapted to receive a volume of lighter-than-air gas, at least two variable thrust vertical thrusters in secure engagement with the envelope and at least two variable thrust lateral thrusters in secure engagement with the envelope, means for temporarily securely engaging the load to the envelope wherein the volume of lighter-than-air gas has a buoyancy that offsets at least 25% of the weight of the air vehicle when unloaded, wherein the thrust from the at least two vertical thrusters may be varied to raise and lower the air vehicle and the load when engaged, and wherein the thrust from the at least two lateral thrusters may be varied to maneuver and transport the raised air vehicle and the load when engaged.
Owner:JESS PETER E +1
Motor, fan and filter arrangement for a vacuum cleaner
InactiveCN101897558AExhaust freeFreedom to guideCleaning filter meansSuction filtersSide effectControl theory
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Air guiding device
ActiveUS8297685B2Reduce air resistanceRealize automatic adjustmentVehicle seatsWindowsRest positionEngineering
Owner:DR ING H C F PORSCHE AG
Multi-freedom degree bird-like flapping wing air vehicle
InactiveCN106043692ACompact structureReduce the stress areaOrnithoptersElevation angleAerodynamic drag
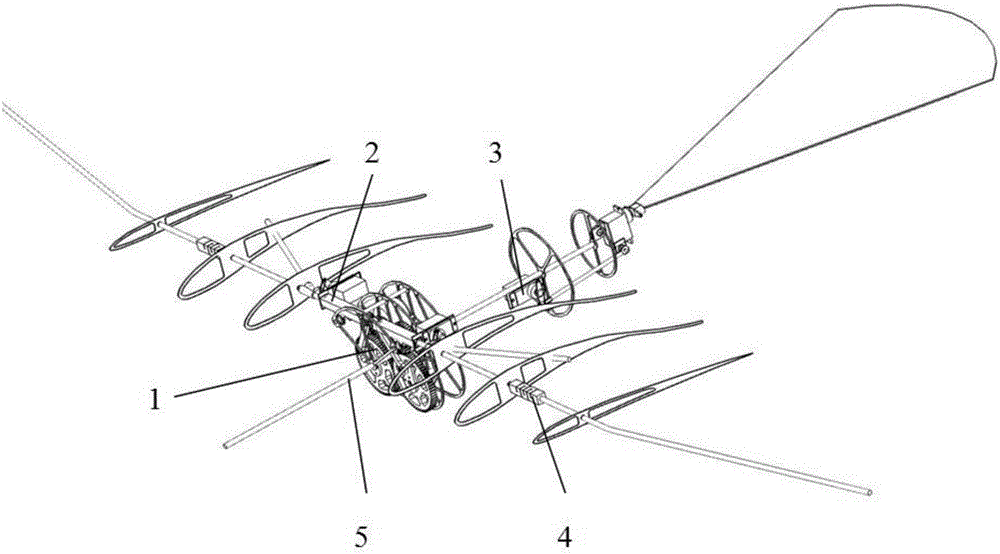
The invention relates to a multi-freedom degree bird-like flapping wing air vehicle. The multi-freedom degree bird-like flapping wing air vehicle comprises a driving mechanism, two twisting mechanisms, an empennage mechanism, two flexible joint structures and a machine frame. The multi-freedom degree bird-like flapping wing air vehicle is simple and compact in structure, and fully-symmetrical flapping wing movement can be realized. Two rubber flexible grooved mechanisms are arranged, so that the flapping wing air vehicle can fly like a bird; flapping wings are curved and folded, so that when the flapping wings flap upwards, a stressed area is reduced, and the resistance is reduced; when the flapping wings flap downwards, the wing extending area is the largest; besides, outer wings can also be passively bent in a flight direction by air resistance, so that great lifting force and great thrust are generated; steering engines are adopted to control inner wing rods so as to change the elevation angle of the flapping wings, the multi-freedom degree bird-like flapping wing air vehicle conforms to the effect that upward flapping resistance is less than downward flapping lifting force in aerodynamics, and the aerodynamic efficiency is improved; the two steering engines are utilized to control the deflection of the empennage, so that operating and controlling of the flight attitude of the flapping wing air vehicle are facilitated. The multi-freedom degree bird-like flapping wing air vehicle disclosed by the invention can be used in the fields of models, aerial photography monitoring, information collecting, disaster searching and rescuing, airport bird expelling and the like.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Variable camber continuous aerodynamic control surfaces and methods for active wing shaping control
ActiveUS9227721B1Improve various performance metricNo additional benefitAircraft controlWing shapesLeading edgeControl signal
An aerodynamic control apparatus for an air vehicle improves various aerodynamic performance metrics by employing multiple spanwise flap segments that jointly form a continuous or a piecewise continuous trailing edge to minimize drag induced by lift or vortices. At least one of the multiple spanwise flap segments includes a variable camber flap subsystem having multiple chordwise flap segments that may be independently actuated. Some embodiments also employ a continuous leading edge slat system that includes multiple spanwise slat segments, each of which has one or more chordwise slat segment. A method and an apparatus for implementing active control of a wing shape are also described and include the determination of desired lift distribution to determine the improved aerodynamic deflection of the wings. Flap deflections are determined and control signals are generated to actively control the wing shape to approximate the desired deflection.
Owner:NASA
Magnetic advanced generation jet electric turbine
ActiveUS8365510B2Maximizes propulsion efficiencyImprove combustionGas turbine plantsEnergy production using magneto-hydrodynamic generatorsAviationElectric power system
Supersonic Magnetic Advanced Generation Jet Electric Turbine (S-MAGJET) described herein, and a subsonic derivative, MAGJET, integrate a gas power turbine, superconducting electric power and propulsion generation, and magnetic power flux field systems along with an ion plasma annular injection combustor which utilizes alternative petroleum-based fuel and combustion cycles to create a hybrid turbine turbomachine for aerospace propulsion. The propulsion unit is able to achieve a dramatic increase in horsepower, combustion and propulsion efficiency, and weight reduction. In addition, the turbomachinery structures may be disposed within an exo-skeleton architecture that achieves an increase in thrust to weight ratio with a concomitant increase in fuel efficiency and power generation over traditional gas turbine technology today. The engine continuously adjusts the temperature, pressure and mass airflow requirements using an electromagnetic power management system architecture. Engine performance may be controlled across the entire desired flight envelope, whether subsonic, transonic or supersonic flight conditions.
Owner:SONIC BLUE AEROSPACE
Longitudinal-line-type dual-culvert vertical-lifting air-ground vehicle
ActiveCN101559702AImprove aerodynamic efficiencyAvoid harmAircraft convertible vehiclesRotocraftControllabilityDucted propeller
The invention relates to the field of air-ground dual-dwelling vehicle technology, in particular to a longitudinal-line-type dual-culvert vertical-lifting air-ground vehicle. The vehicle comprises a vehicle body, a driving cabin and vehicle wheels that are arranged on the vehicle body; the front end and the rear end of the vehicle body are respectively provided with a ducted propeller; each ducted propeller comprises a culvert, an airscrew and a bracket; the rotation shaft of the airscrew is arranged vertically; the airscrew is provided with an automatic inclining device; two airscrews are driven to rotate reversely by an engine of the vehicle body; the vehicle can be driven on road by the vehicle wheels and can realize vertical lifting and flying by the lifting force provided by the rotation of two vertical ducted propellers; the flying, landing, suspending, heading, withdrawing and rotating are realized by adjusting the rotation speed difference of the two ducted propellers and / or the elevation of the oars; the controllability is good and the structure is simple; the culverts protect the airscrews and the passerby simultaneously and avoid the passerby from being harmed by the airscrews, thus having high safety performance.
Owner:谢雁洲
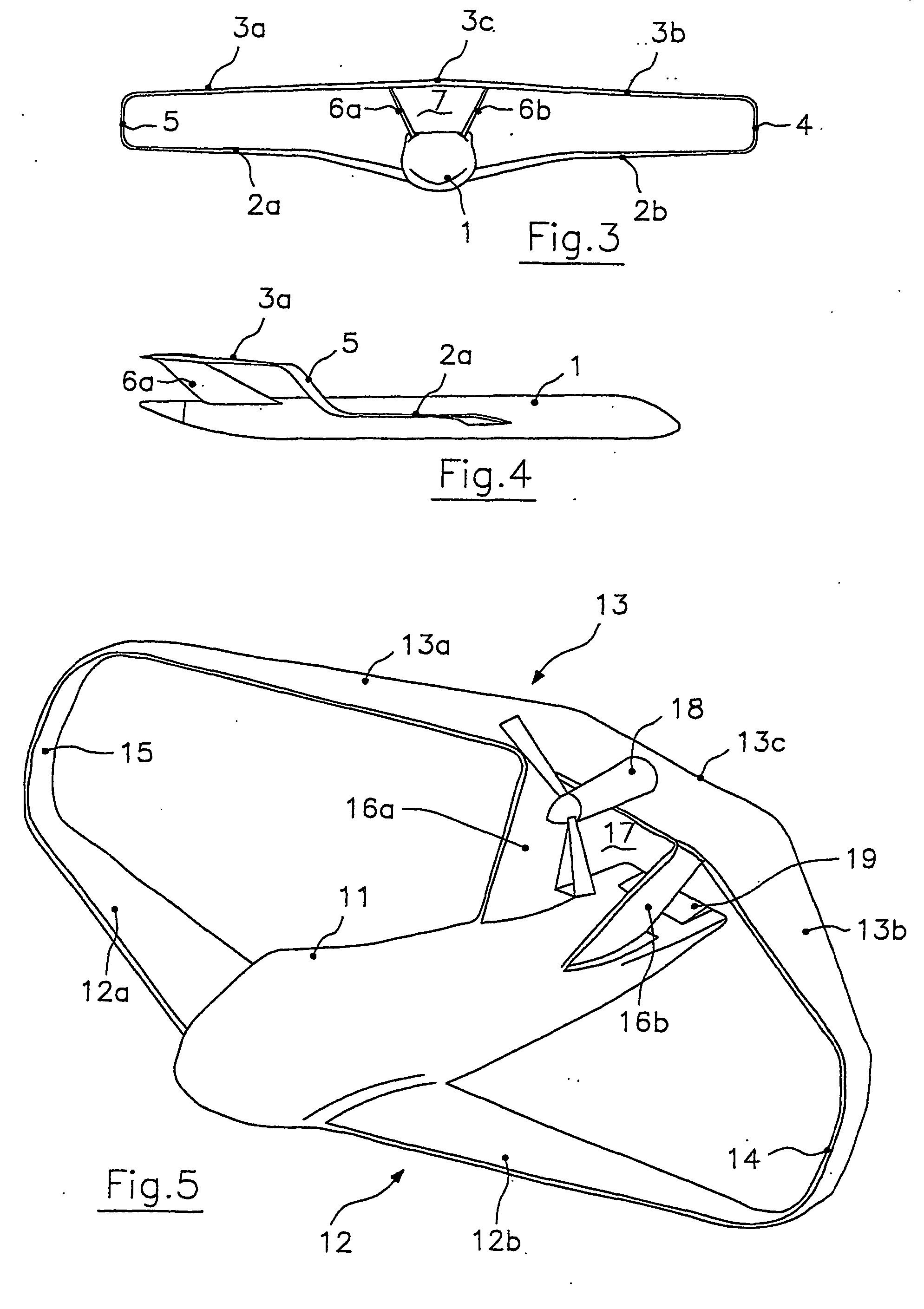
Swept-wing box-type aircraft with high fligh static stability
InactiveUS20060144991A1Stable flightImprove aerodynamic efficiencyWing adjustmentsCanard-type aircraftAirplaneLift system
Swept-wing box-type aircraft comprising a fuselage and a lifting system formed by two substantially horizontal wings. One of the wings has a positive sweep angle, while the other has a negative sweep angle, the wings lying in planes spaced apart from one another and joined by two vertical wings extending from their ends. The positively swept wing is the front wing and extends from the bottom of the fuselage, whereas the negatively swept wing is the rear wing and extends generally continuously above the fuselage, the fuselage being provided with a pair of fins at its tail section. The fins are joined at their ends to the rear wing, the fins, the rear wing and the fuselage defining an aerodynamic channel along which the surface of the fuselage is substantially flat.
Owner:FREDIANI ALDO
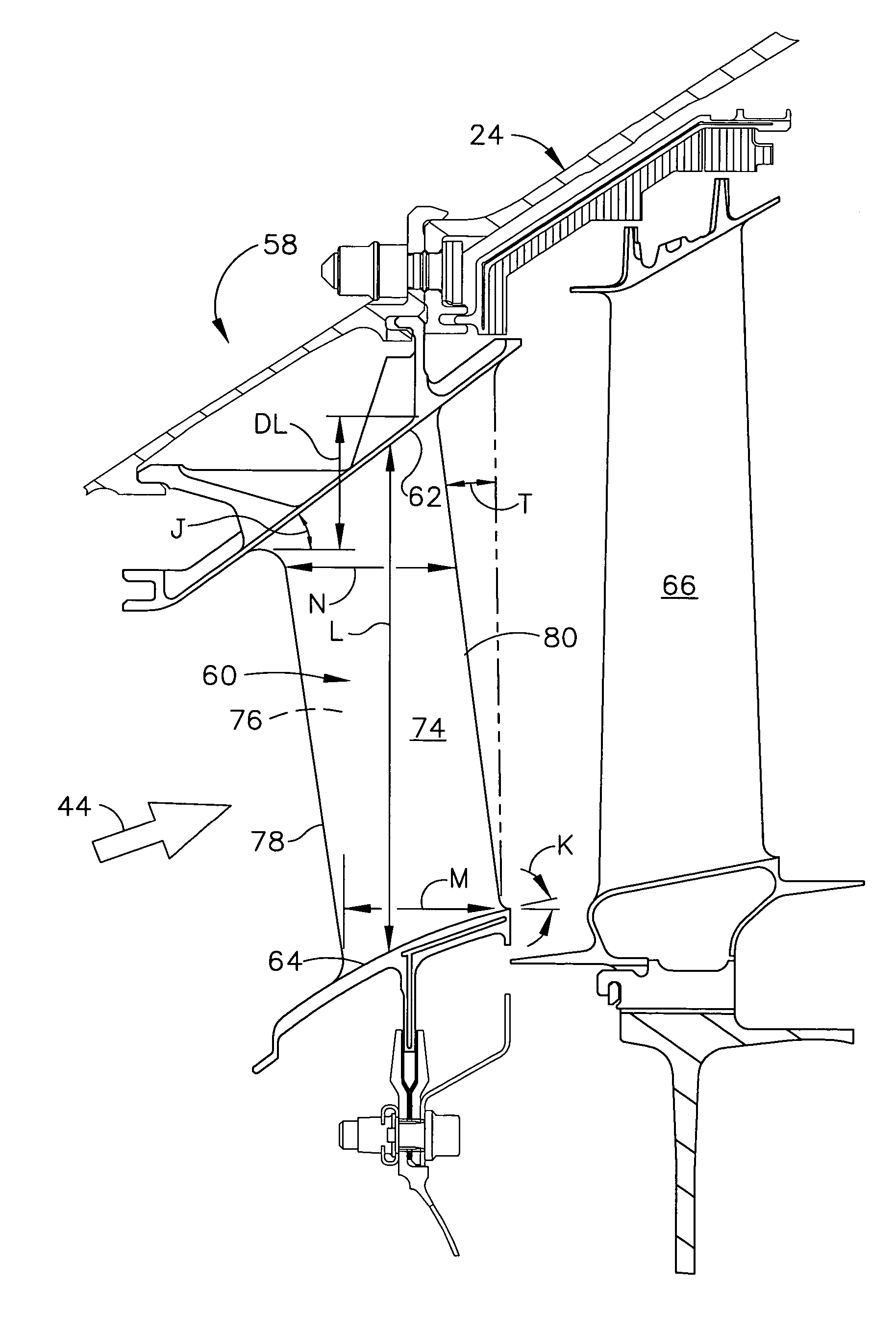
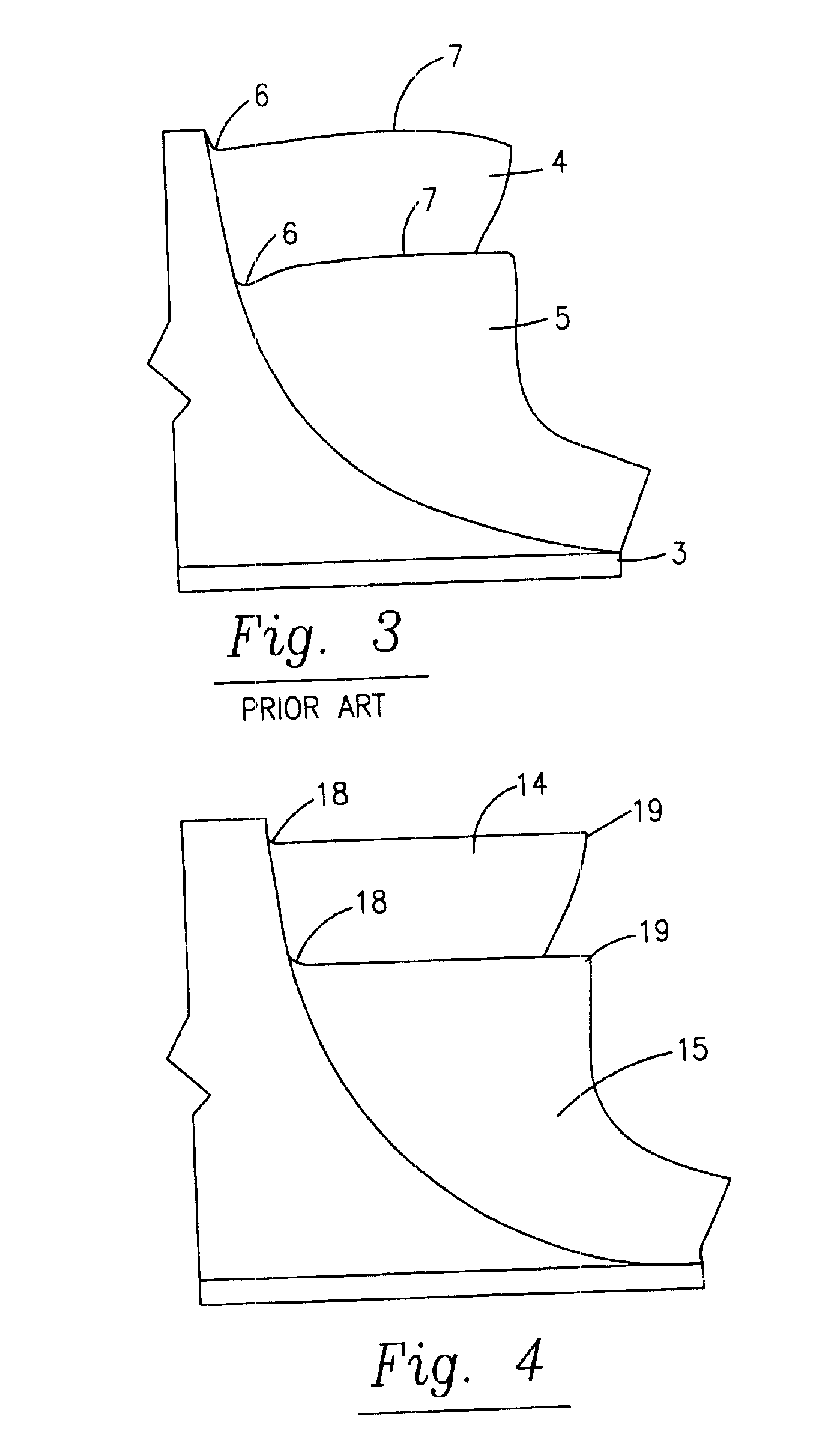
Forward tilted turbine nozzle
ActiveUS7510371B2Improve aerodynamic efficiencyEngine manufacturePump componentsCombustionTrailing edge
A turbine nozzle includes a row of vanes joined to radially outwardly inclined outer and inner bands. Each vane has camber and an acute twist angle for importing swirl in combustion gases discharged at trailing edges thereof. The trailing edges are tilted forwardly from the inner band to the outer band for increasing aerodynamic efficiency.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Pneumatic layout of vertical taking-off and landing aircraft with tilted duct
InactiveCN103144769AImprove aerodynamic efficiencyCompact structureVertical landing/take-off aircraftsFlight vehicleGravitation
The invention discloses a pneumatic layout of a vertical taking-off and landing aircraft with a tilted duct. The pneumatic layout is characterized in that front duct fans are symmetrically arranged at the outer sides of the head parts of all the aircraft bodies; rear duct fans are symmetrically arranged at the inner sides of the middle parts of all the aircraft bodies; and all the duct fans are respectively connected with transmission components in the aircraft bodies by duct rotating shafts in the transmission components. The axial distance between protection points of the axial lines of all the duct rotating shafts on the axial lines of the aircraft bodies and the center of gravity of the whole aircraft along the aircraft bodies is 1.125 times of the chord length of wings. In the pneumatic layout, the duct fans can rotate around the duct rotating shafts; when the aircraft takes off or lands vertically, the duct fans are positioned at the vertical 90-degree position, the thrust vector is upward; in the transition stage, the duct fans rotate forwards around the duct rotating shafts; and in the cruise stage, the duct fans are positioned at a horizontal 0-degree position, and the thrust vector is forward, so that vertical taking off and landing and high-speed cruise flying are realized. The pneumatic layout disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high pneumatic efficiency, compact structure, strong reliability, strong maneuverability, flexible operation, long voyage and low noise and the like.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method of making turbocharger including cast titanium compressor wheel
InactiveUS6904949B2Improve aerodynamic efficiencyComplex designPropellersRotary propellersWaxImpeller
A method of making an air boost device, wherein a compressor wheel incorporated therein is re-designed to permit die inserts (20), which occupy the air passage and define the blades (4, 5) during a process of forming a wax pattern (21) of a compressor wheel, to be pulled without being impeded by the blades. This modified blade design enables the automated production of wax patterns (21) using simplified tooling. These wax patterns (21) can be used in a large-scale investment casting process, and produce an economical cast titanium compressor wheel which performs aerodynamically at high boost pressure / RPM.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
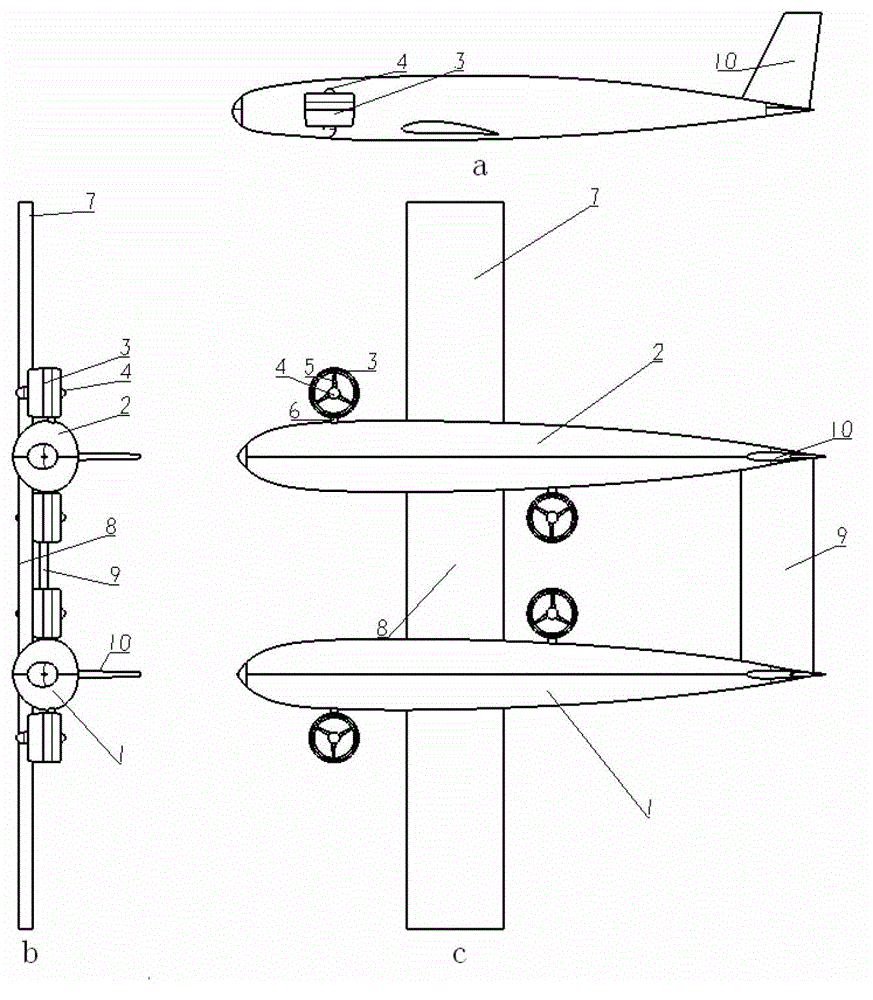
Solar drone
ActiveCN104890859AImprove the force characteristicsReduce structural weightWingsPower plant typeHigh liftSolar cell
The invention relates to the field of drone design, in particular to a solar drone. The solar drone comprises a front wing, a rear wing, power systems, an energy system, task load pods and the like, wherein the front wing and the rear wing are connected with each other through a left drone body and a right drone body; and the power systems, the energy system and the task load pods are disposed on the drone bodies. The solar drone has the advantages that the drone adopts a serial-wing double-drone-body layout, front wing stress features are improved favorably, and structural weight is reduced; a lifting layout is used, all lifting faces provide positive lifting force, the pneumatic efficiency of the pneumatic layout can be increased, and high lifting force and high lift-drag ratio are achieved easily; a full-motion operating face is used, the area of the lifting faces where solar cells can be laid is maximized, and a large amount of energy conversion is achieved; and further, the front wing is not provided with the operating face, influence on structural design can be eliminated, and structural weight is reduced.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
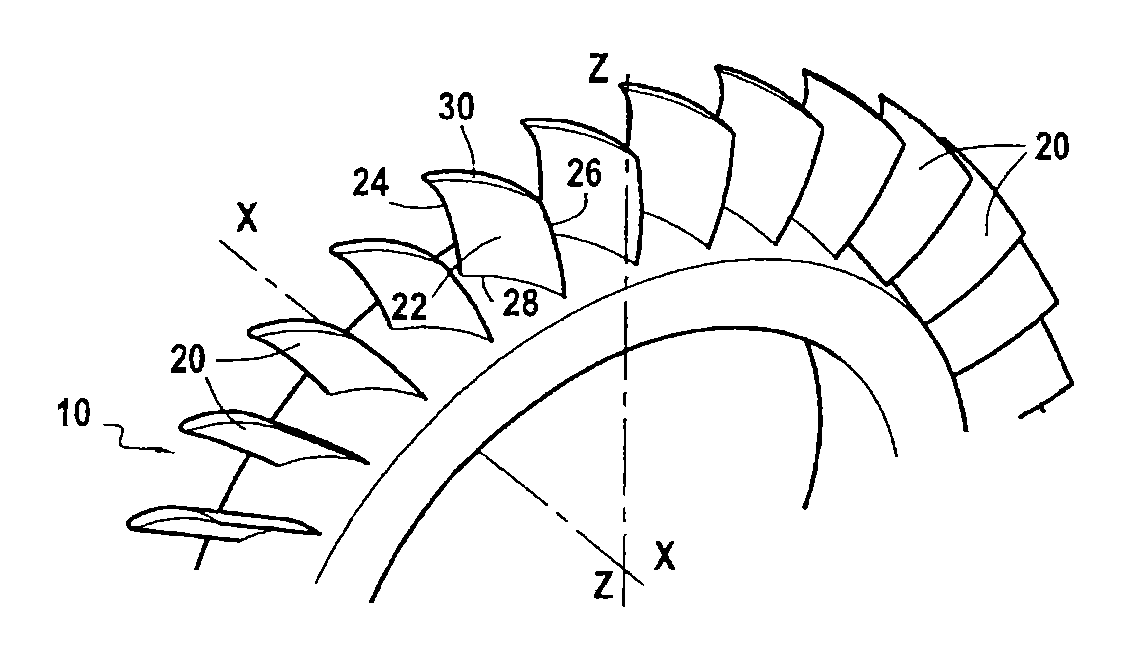
Turbine engine blade, in particular for a one-piece bladed disk
ActiveUS20140341749A1Easy to controlImprove aerodynamic efficiencyPropellersEngine manufactureLeading edgeTrailing edge
A turbine engine blade comprising an airfoil extending axially between a leading edge and a trailing edge and extending radially between a root and a tip. The leading edge of the airfoil presents a sweep angle that is positive and that increases continuously from the root to a first radial height of the airfoil situated in the range 20% to 40% of the total radial height of the airfoil as measured from the root to the tip, and decreases continuously from this first radial height of the airfoil to the tip.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Apparatus and method for inspecting and marking repair areas on a blade
InactiveUS6910278B2Accurate visual inspection of damaged areaImprove aerodynamic efficiencyPump componentsEngine fuctionsStress pointMarking out
A template for assessing damaged areas on a blade includes a set of marks indicating the maximum areas of damage allowed on an edge, as well as the tip of a blade. A guide enables the template to be aligned in proper position against the blade for accurate visual inspection of the damaged areas. One or more blend guides are included to allow the inspector to mark a blend area around the damage to enable maintenance personnel to smooth sharp, jagged edges of the damaged areas, thereby relieving stress points on the blade and improving the aerodynamic efficiency of the blade. The template is fabricated with transparent material that allows the blade to be viewed when the template is overlayed on the blade. A mechanism such as a clip, a sleeve, or magnetic attraction can be included on the template to retain the template on the blade during inspection.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
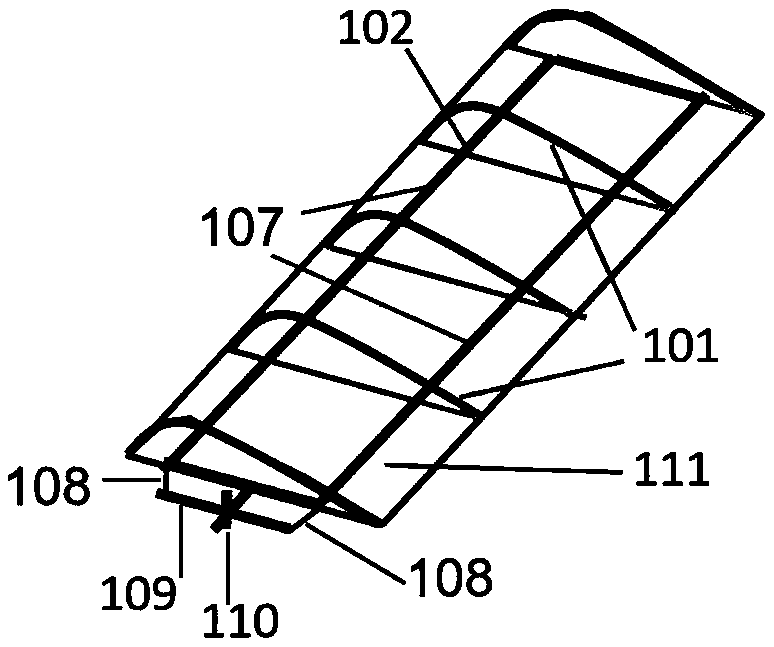
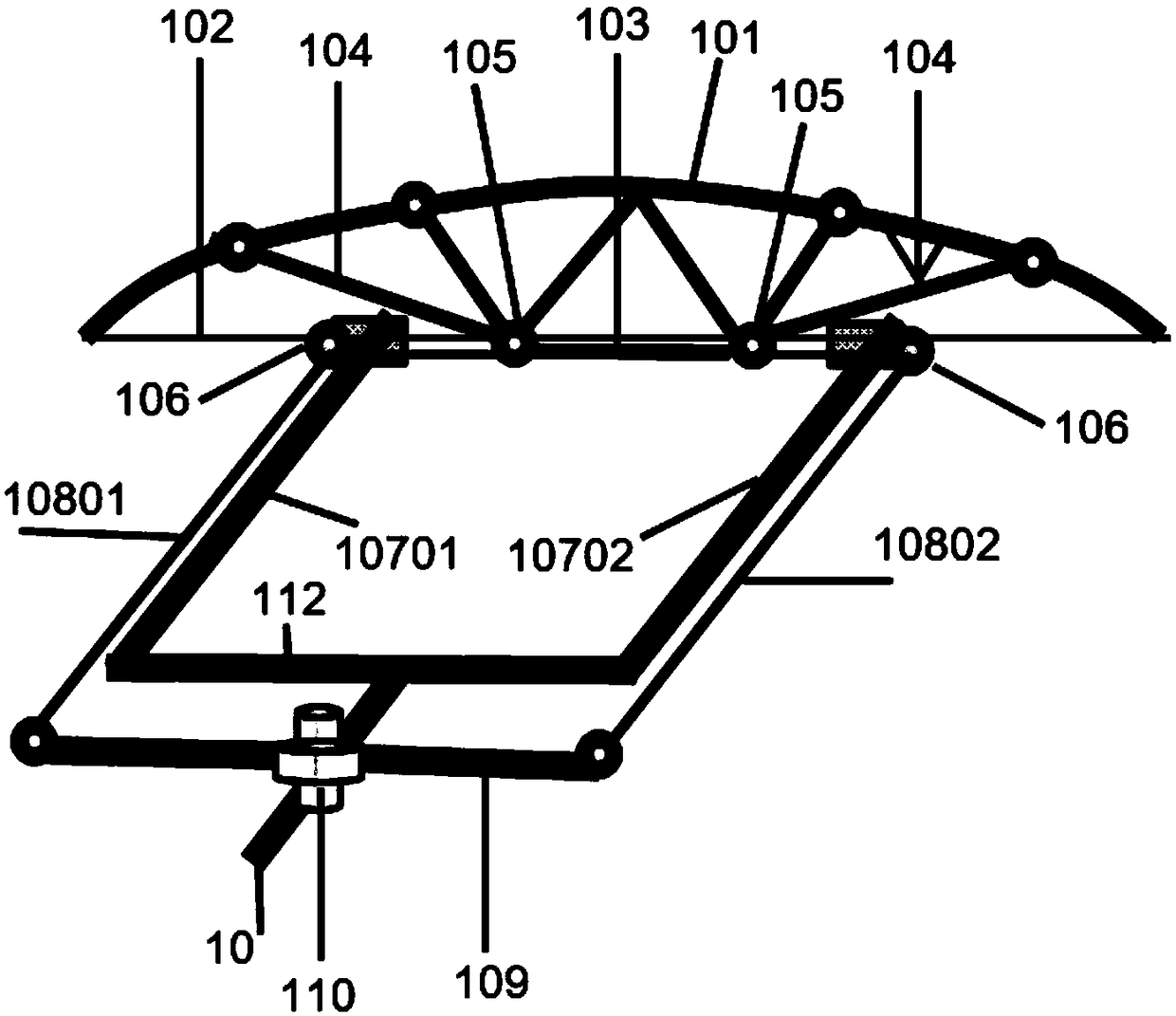
Wing with self-adaptive variable camber trailing edge
The invention discloses a wing with a self-adaptive variable camber trailing edge. The wing comprises a main wing, a rear beam and a variable camber trailing edge section, wherein the variable camber trailing edge section is connected with the main wing through the rear beam; the variable camber trailing edge section comprises an upper surface skin and a lower surface skin; the first end of the upper surface skin and the first end of the lower surface skin are respectively connected with the rear beam; the other end of the upper surface skin and the other end of the lower surface skin are connected through a rigid trailing edge; the parts, close to the rigid trailing edge, of the upper surface skin and the other end of the lower surface skin, are connected through a sliding mechanism; the sliding mechanism is connected with the rear beam through a shape memory driving part. By adopting the technical scheme, compared with a conventional similar wing, the wing with the self-adaptive variable camber trailing edge has the advantages of simple structure, light weight, low research and manufacturing cost, high flying performance and the like, the aerodynamic performance of an aircraft is greatly improved, the aerodynamic efficiency of the aircraft is improved, the oil consumption is reduced, and the use cost of the aircraft in the whole service life is lowered.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Compound rotorcraft
ActiveUS20170197709A1Improve aerodynamic efficiencyReduction of the dihedral angle of the lower wingWing shapesSpars/stringersPropellerFixed wing
A compound rotorcraft with a fuselage and at least one main rotor, the fuselage comprising a lower side and an upper side that is opposed to the lower side, the at least one main rotor being arranged at the upper side, wherein at least one propeller is provided and mounted to a fixed wing arrangement that is laterally attached to the fuselage, the fixed wing arrangement comprising at least one upper wing that is arranged at an upper wing root joint area provided at the upper side of the fuselage and at least one lower wing that is arranged at a lower wing root joint area provided at the lower side of the fuselage, the upper and lower wings being at least interconnected at an associated interconnection region.
Owner:AIRBUS HELICOPTERS DEUT GMBH
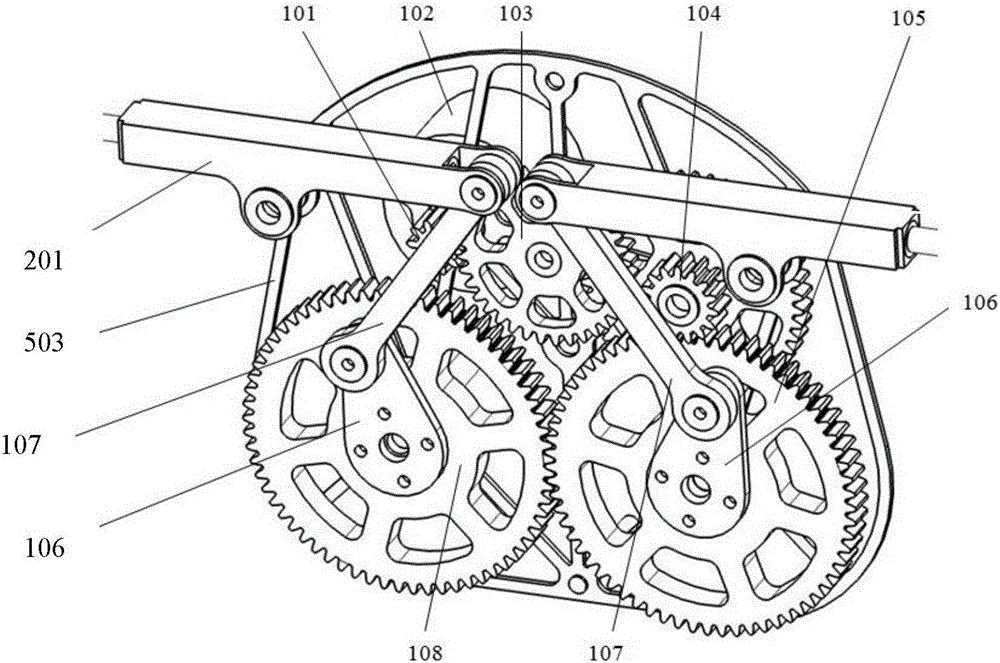
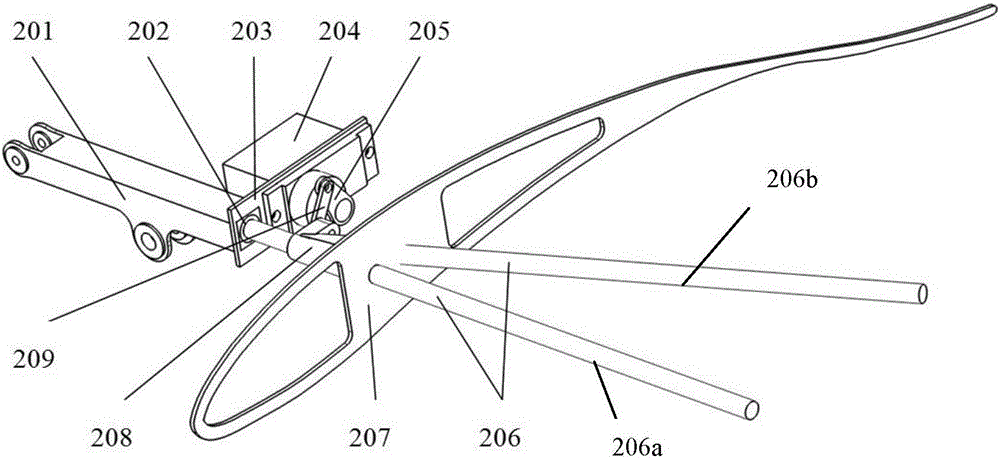
Minitype ornithopter wing driving mechanism with changeable wing area
The invention discloses a minitype ornithopter wing driving mechanism with changeable wing area, and belongs to the technical field of minitype ornithopters. The minitype ornithopter wing driving mechanism comprises a machine body frame, a driving motor, a follow-up gear, a synchronizing gear as well as a front crank, a rear crank, a front connecting rod, a rear connecting rod, a fixe rocking arm, a sliding block rocking arm, a humerus, an ulna, a middle finger bone, a little finger bone, an ulna muscle tendon and a radius which are symmetrically arranged on the two sides of the machine body frame, wherein modulus and tooth number of the follow-up gear and the synchronizing gear are same, the follow-up gear and the synchronizing gear can reversely and synchronously move, and the rear crank and the rear connecting rod can drive the sliding block rocking arm to simultaneously realize fore-and-back movement in upper-down waving manner, so that a wing is driven to transform. The minitype ornithopter wing driving mechanism provided by the invention has the advantages that the structure is simple, the cost is low, the complex movements of wing waving and wing area deformation are simultaneously realized; a wing skeleton drives a patagium to slack in upward waving, and the wing area is small; the patagium is tightened in downward waving, the wing area is enlarged, and the aerodynamic efficiency and flight efficiency are further improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Forward tilted turbine nozzle
ActiveUS20060275111A1Improve aerodynamic efficiencyEngine manufacturePump componentsCombustionTrailing edge
A turbine nozzle includes a row of vanes joined to radially outwardly inclined outer and inner bands. Each vane has camber and an acute twist angle for importing swirl in combustion gases discharged at trailing edges thereof. The trailing edges are tilted forwardly from the inner band to the outer band for increasing aerodynamic efficiency.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Control of power, loads and/or stability of a horizontal axis wind turbine by use of variable blade geometry control
InactiveCN1780983AReduce loadReduce aerodynamic noiseWind motor controlEngine fuctionsTurbine bladeHorizontal axis
The present invention relates to a design concept according to which, by using active geometry control (for example, smart materials or embedded mechanical actuators), or using passive geometry control (for example caused by the loading and / or deformation of the blade) changes), or a combination of these two methods, allows rapid changes in the blade geometry to control the power, load and / or stability of the wind turbine. In particular the invention relates to a wind turbine blade, a wind turbine and a method of controlling a wind turbine.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
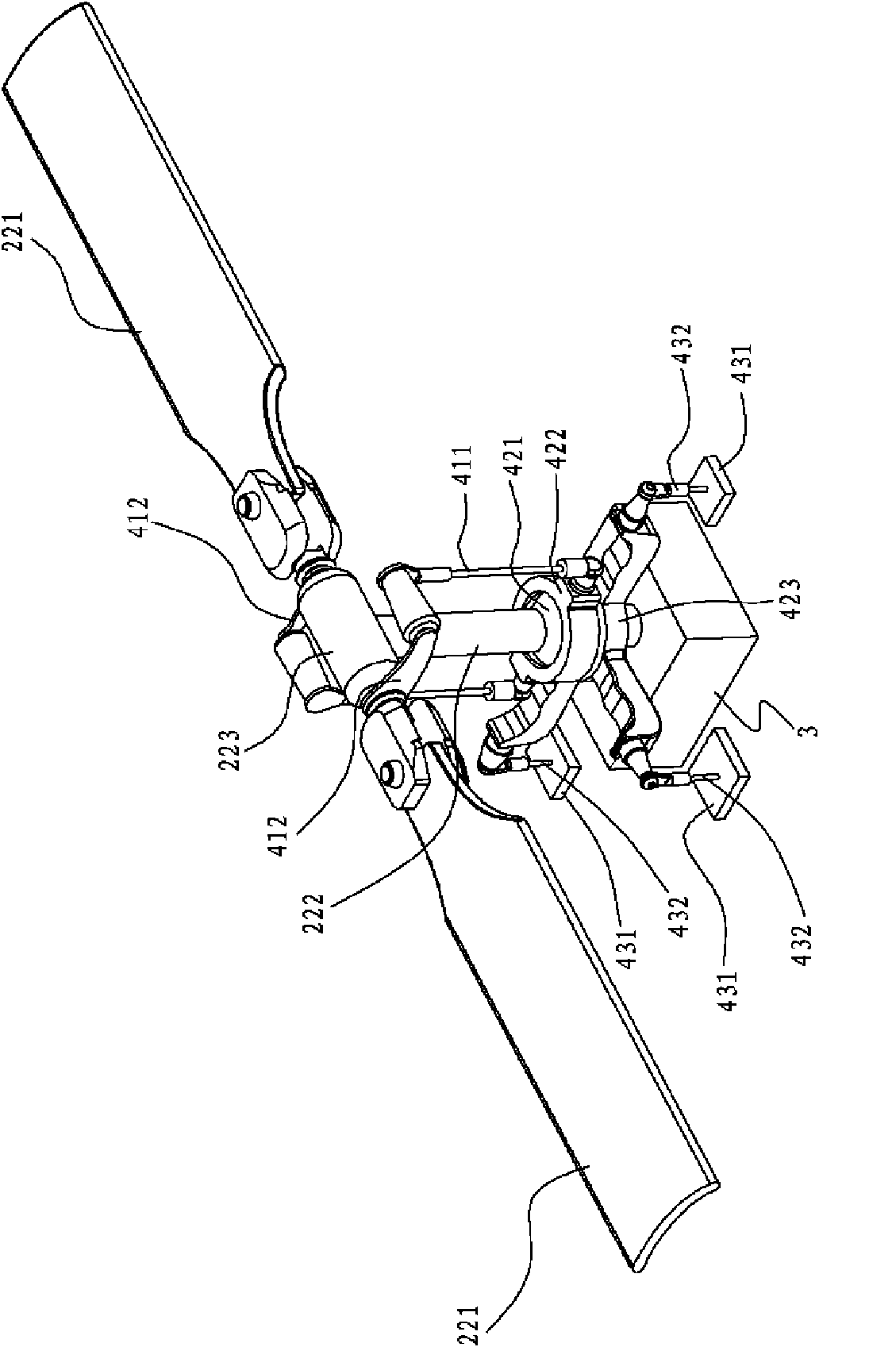
A bionic aircraft which realizes the conversion of a flapping rotor and a flapping wing flight mode based on a deformable wing
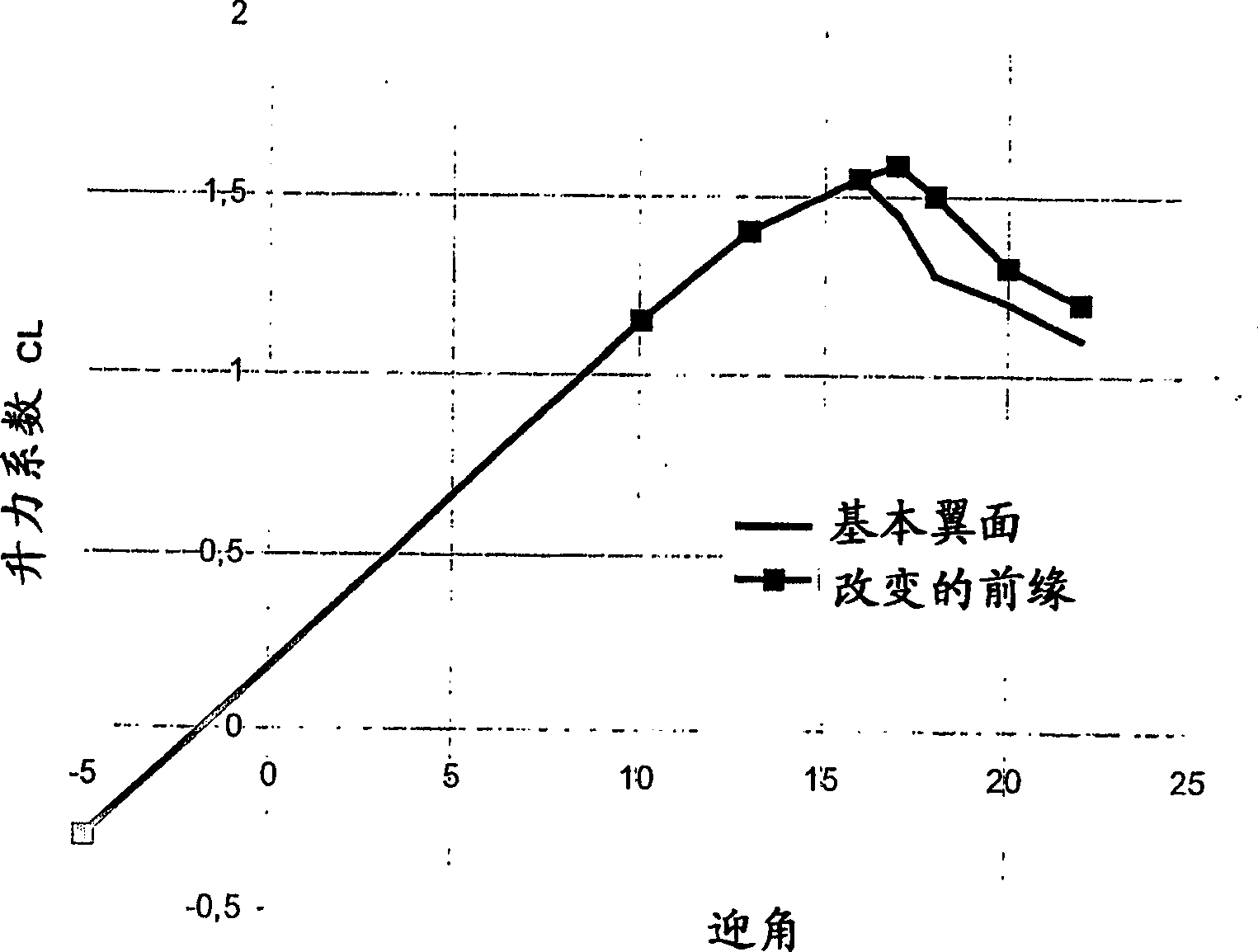
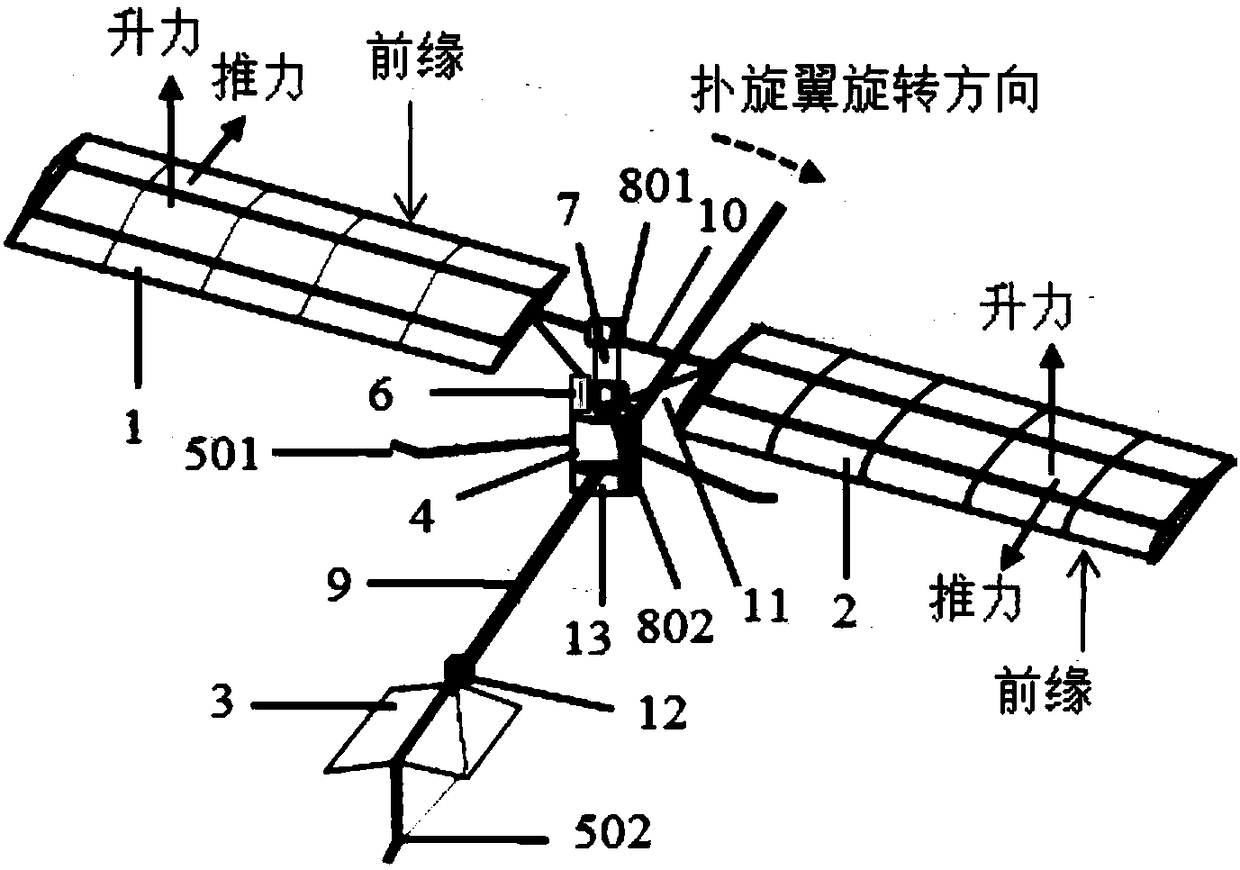
The invention discloses a bionic aircraft which realizes the conversion of a flapping rotor and a flapping wing flight mode based on a deformable wing, and belongs to the technical field of bionic aircraft design. When it is in vertical take-off, landing and hovering, it is a flapping rotor flight mode, and its structure is characterized by that the flapping wings on both sides are mounted in an axisymmetric manner, that is, the airfoils on both sides are antisymmetrical; When in forward flight or gliding, the flapping wing or fixed wing flight mode is characterized by symmetrical mounting ofthe flapping wing on both sides in a fixed wing symmetrical manner, i.e., symmetrical wing profiles on both sides. At that same time, an elastic bow beam is adopt, In the structural design of deformable wing rib composed of chord and multi-bar mechanism, when the shape of deformable wing is changed, by rotating the tie rod installed at the root of wing and the cable connecting each wing rib, the multi-bar mechanism is pulled to force the connected bow beam to produce the elastic deformation required, that is, the overall structure of the airfoil is kept unchanged, but the leading edge and thetrailing edge of the deformable wing are interchanged. The invention simplifies the driving mechanism and the integral configuration of the aircraft, and remarkably improves the aerodynamic efficiencyand the lift coefficient.
Owner:陕西斯凯迪物联科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com