Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2544results about "Vertical landing/take-off aircrafts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
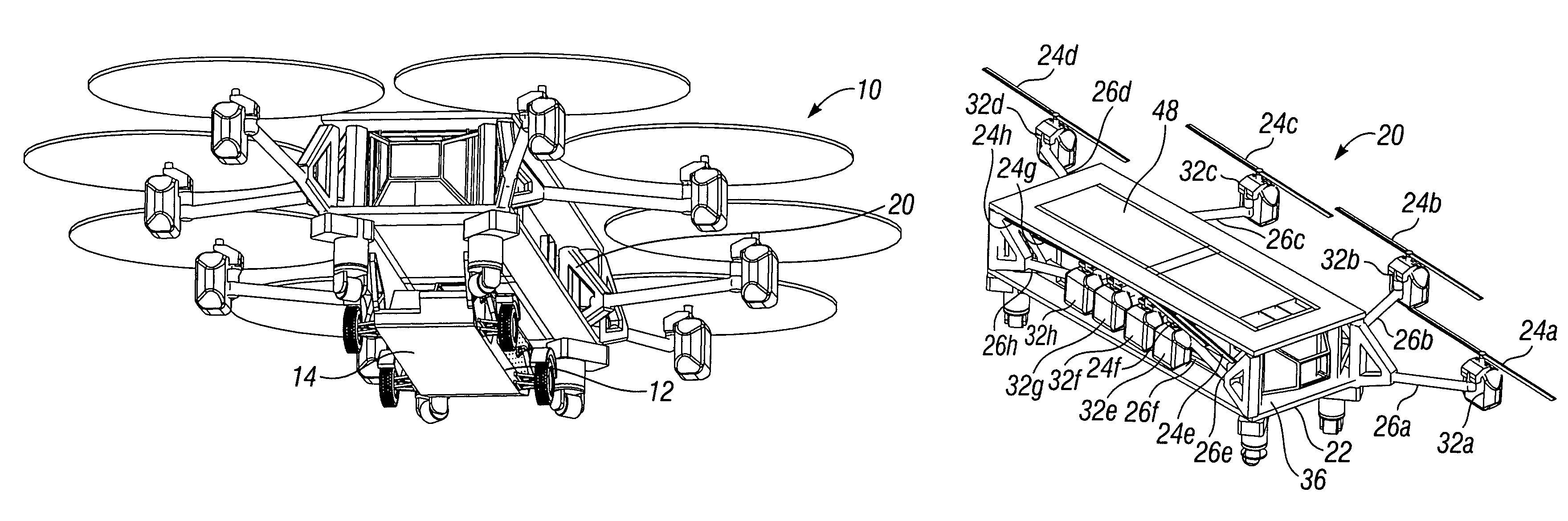
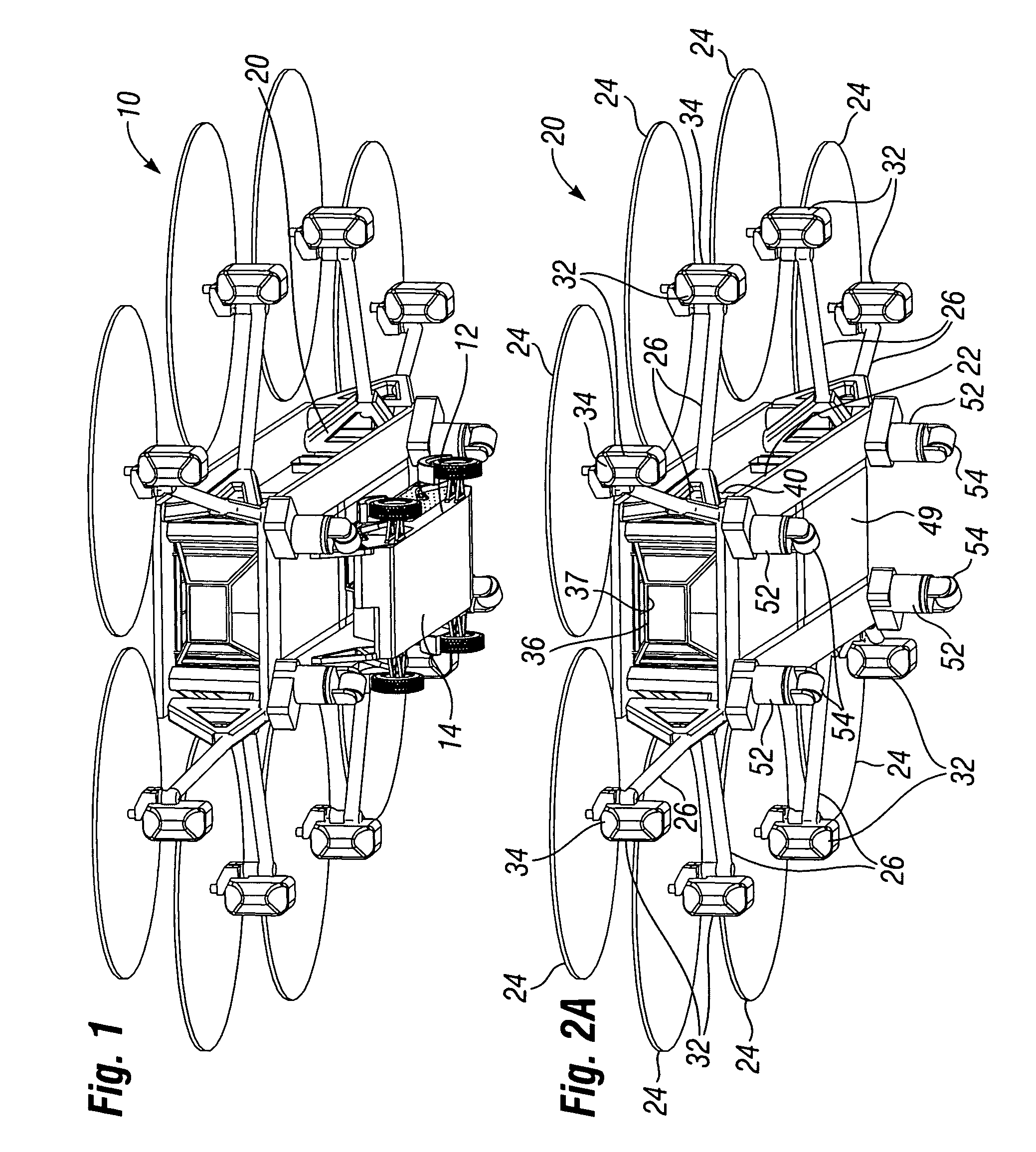
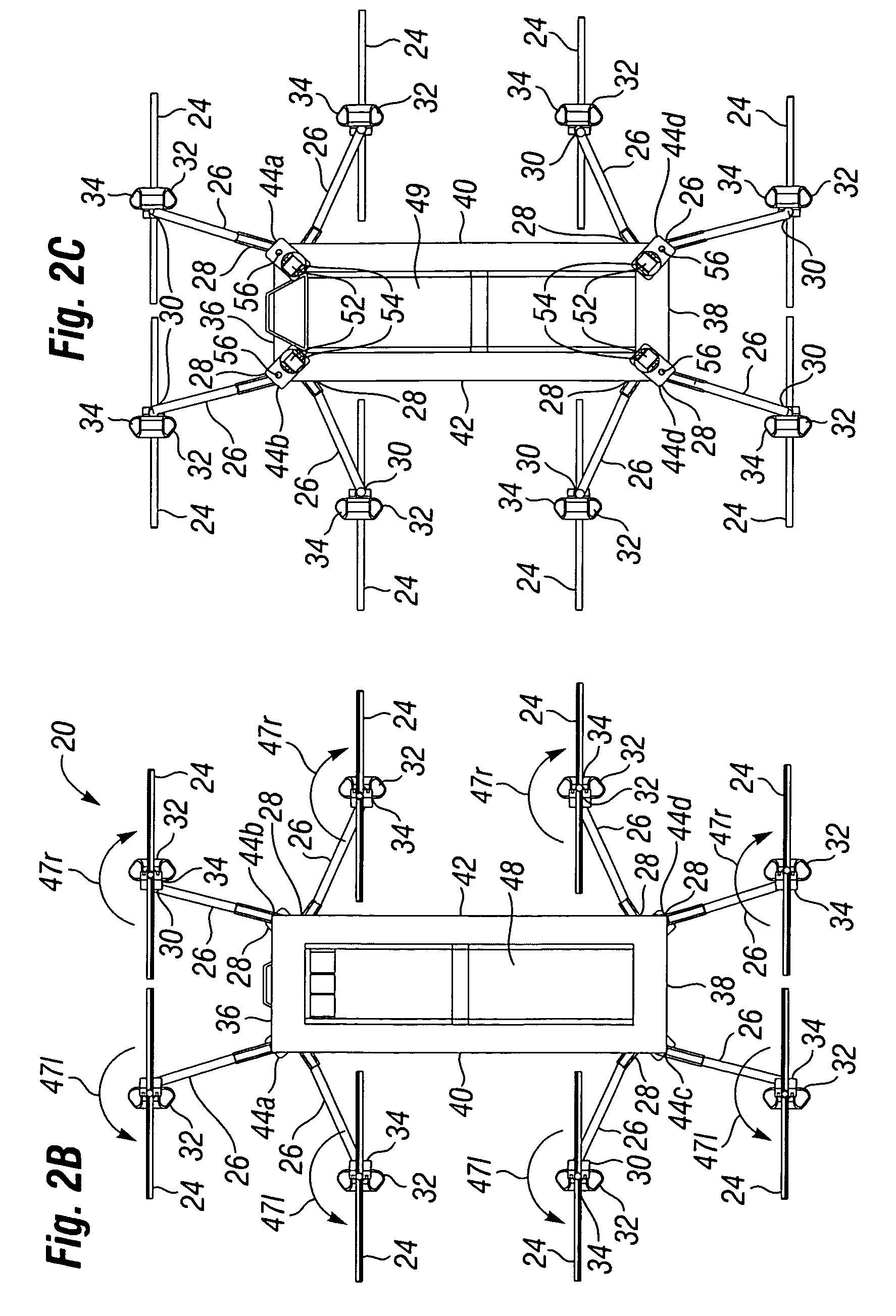
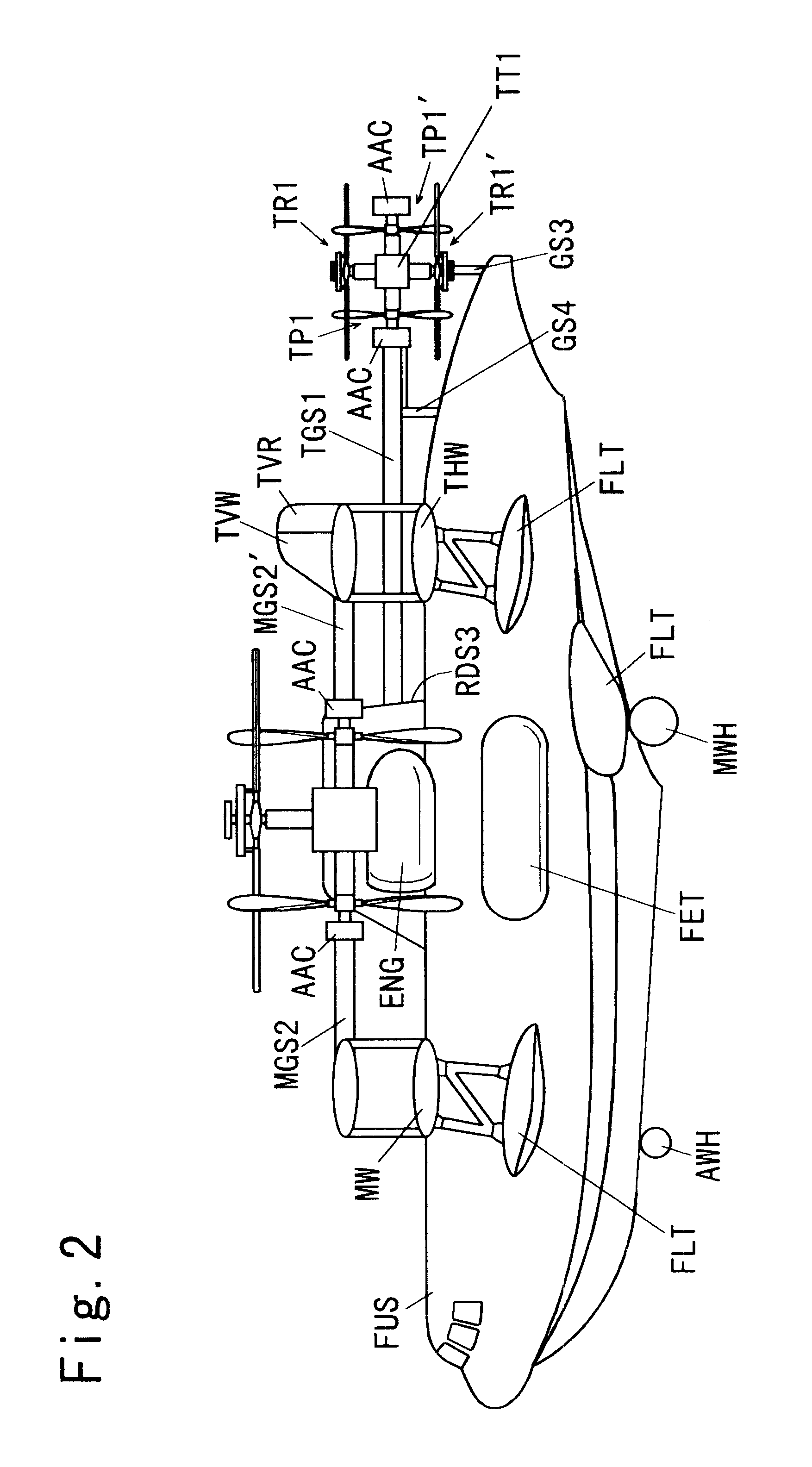
Autonomous Payload Parsing Management System and Structure for an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
InactiveUS20110084162A1Improve versatilityIncrease in sizeStatic/dynamic balance measurementRemote controlled aircraftManagement systemControl logic
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) for making partial deliveries of cargo provisions includes a UAV having one or more ducted fans and a structural interconnect connecting the one or more fans to a cargo pod. The cargo pod has an outer aerodynamic shell and one or more internal drive systems for modifying a relative position of one or more cargo provisions contained within the cargo pod. Control logic is configured to, after delivery of a partial portion of the cargo provisions contained within the cargo pod, vary a position of at least a portion of the remaining cargo provisions to maintain a substantially same center of gravity of the UAV relative to a center of gravity prior to delivery of the partial portion. Other center of gravity compensation mechanisms may also be controlled by the control logic to aid in maintaining the center of gravity of the UAV.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Power line sentry charging
A rechargeable battery energized unmanned aerial vehicle having surveillance capability and an ability to clandestinely collect propulsion and other energy needs from a conveniently located and possibly enemy owned energy transmission line. Energy collection is by way of a parked vehicle engagement with the transmission line in a current flow dependent, magnetic field determined, rather than shunt, voltage dependent, conductor coupling. Surveillance during both a parked or docked condition and during aerial vehicle movement is contemplated.
Owner:US SEC THE AIR FORCE THE
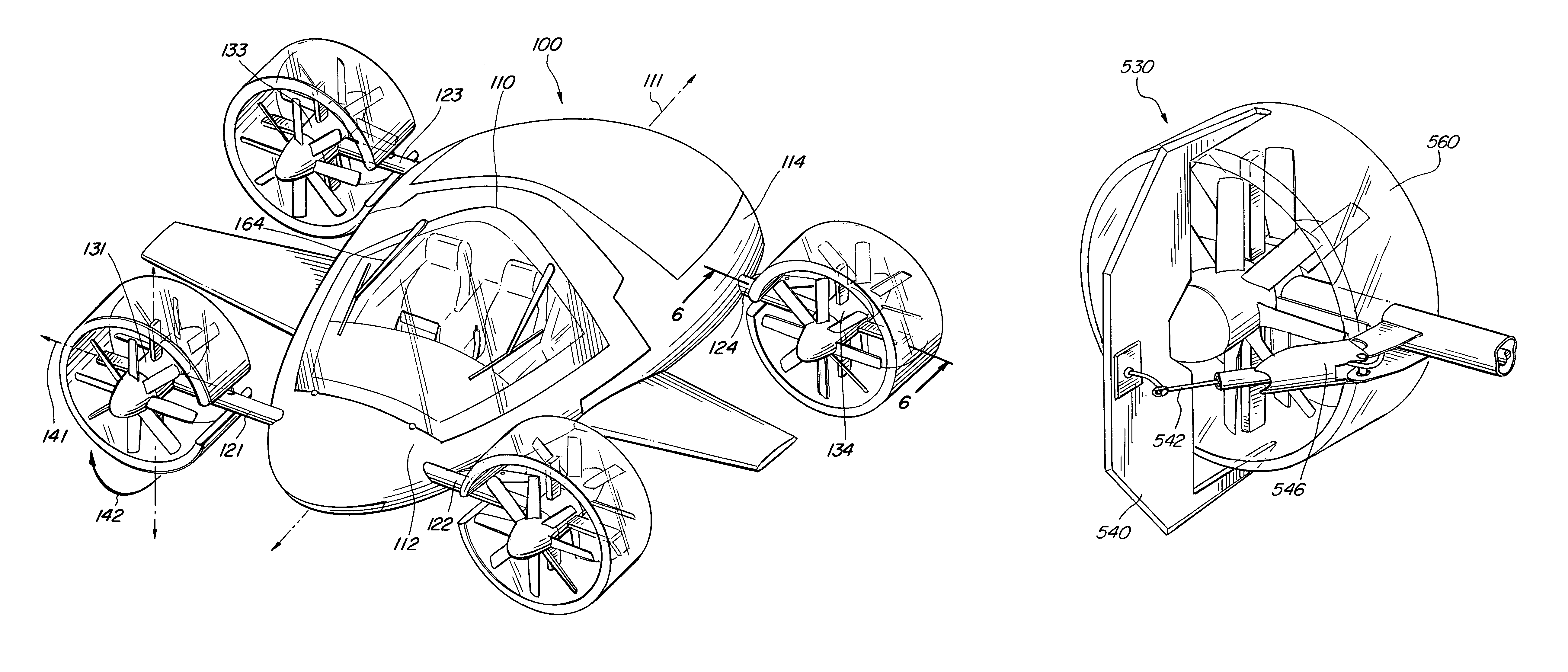
Modular flying vehicle
InactiveUS20090008499A1Reduce the required powerSteady fallAircraft navigation controlUnmanned aerial vehiclesFlight vehiclePropeller
The invention is a modular vehicle having an air vehicle that can be coupled to cargo containers, land vehicles, sea vehicles, medical transport modules, etc. In one embodiment the air vehicle has a plurality of propellers positioned around a main airframe, which can provide vertical thrust and / or horizontal thrust. One or more of the propellers may be configured to tilt forward, backward, and / or side-to-side with respect to the airframe.
Owner:SHAW DONALD ORVAL
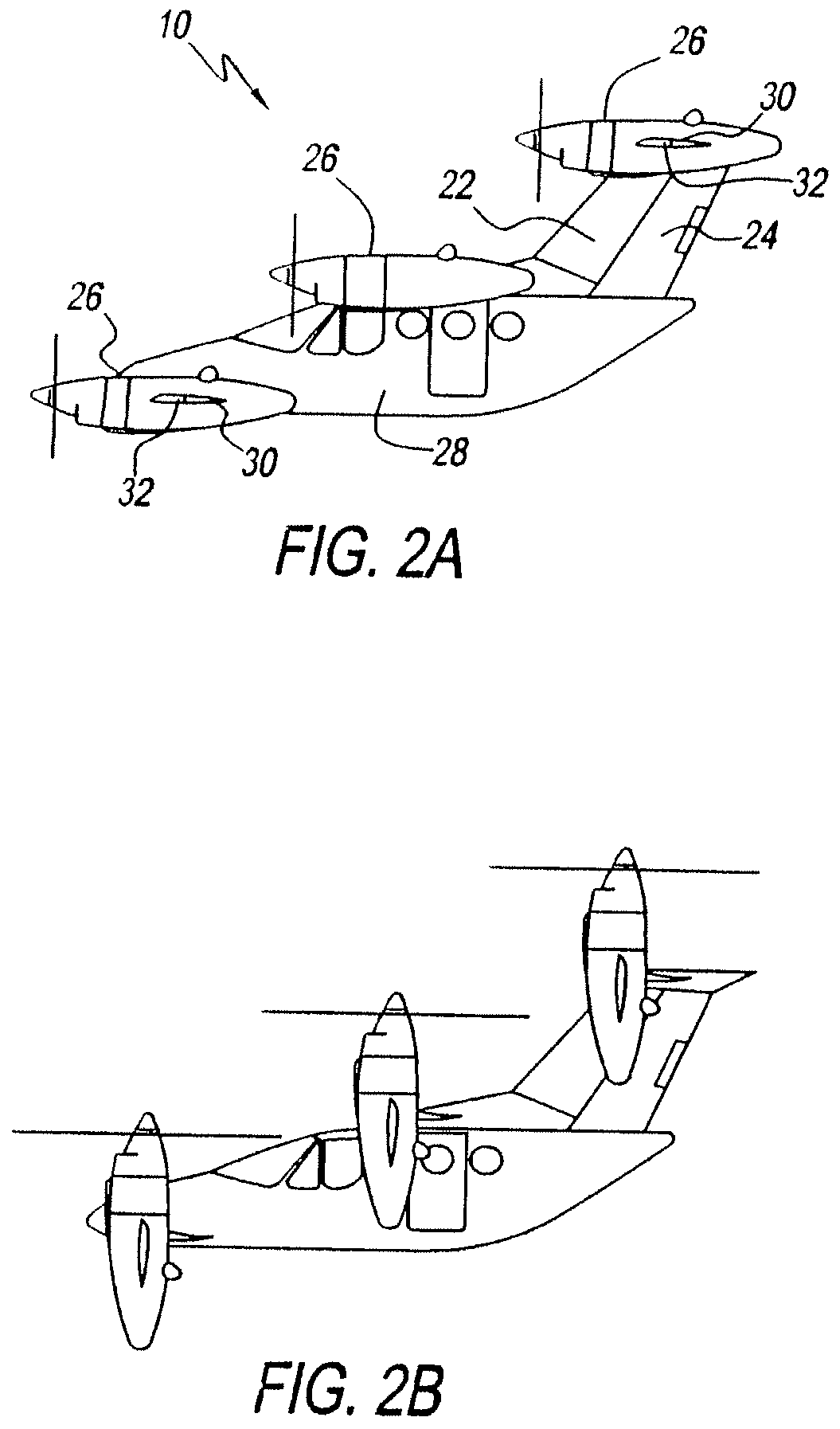
Ducted fan vertical take-off and landing vehicle
InactiveUS20060226281A1Process controlSafe travelVertical landing/take-off aircraftsRotocraftGear wheelFlight vehicle
A vertical take-off and landing vehicle comprised of a fuselage having a front, a rear, and two lateral sides and a set of four thrusters set to the front, the left, the right, and the rear of said fuselage. The thrusters are either independently powered thrusters or could utilize a single power source. The thrusters, which are ducted fan units capable of providing a vertically upward force to the aircraft, are provided with such redundancy that the aircraft can hover with up to two thrusters inoperative. The thrusters are comprised of a set of two counter rotating propellers both of which creates lift. The two counter rotating propellers cancel out the torque effect normally created by using only one propeller. The Ducted fan units being movable between a first position in which they provide vertical lift and a second position in which they provide horizontal thrust using a set of servos and gears.
Owner:WALTON JOH PAUL CHRISTOPHER
Quad tilt rotor aerial vehicle with stoppable rotors
InactiveUS20110001020A1Eliminate needIncrease vehicle aerodynamic efficiencyUnmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftFlight vehicleFuselage
The disclosed invention consists of several improvements to well known Quad Tilt-Rotor (QTR) aircraft. The first is that during a wing-borne flight, one pair of tilt-rotors, which can be substantially larger than the other pair, is feathered and stopped. This can promote vehicle aerodynamic efficiency and can be utilized to increase vehicle speed. Second is that the wings are not attached to the fuselage at a fixed angle of incidence like on conventional QTR aircraft, but can also be tilted in respect to the fuselage independently of the tilt-rotors. Furthermore, each rotor and each wing can be tilted with respect to fuselage to any tilt-angle without limit, which gives the vehicle unprecedented ability to position the fuselage in any attitude in respect to the vehicle direction of flight.
Owner:FORGAC PAVOL
Sky hopper
InactiveUS7472863B2Increase shaft powerAircraft navigation controlToy aircraftsSkyExternal combustion engine
A vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft design particularly suitable as a full-sized aircraft or remote controlled (RC) model aircraft is disclosed. The invention employs lightweight, high strength materials to reduce the power requirements of the propulsion plant. A preferred system of the invention comprises one internal combustion engine able to spit shaft power to four fan units. The fan units further employ counter rotating fan blades for stability. Separate horizontal and vertical tilting mechanisms delivered to the fan units are additionally disclosed. A variation in design is further included wherein electric motors provide the necessary shaft power.
Owner:PAK STEVE
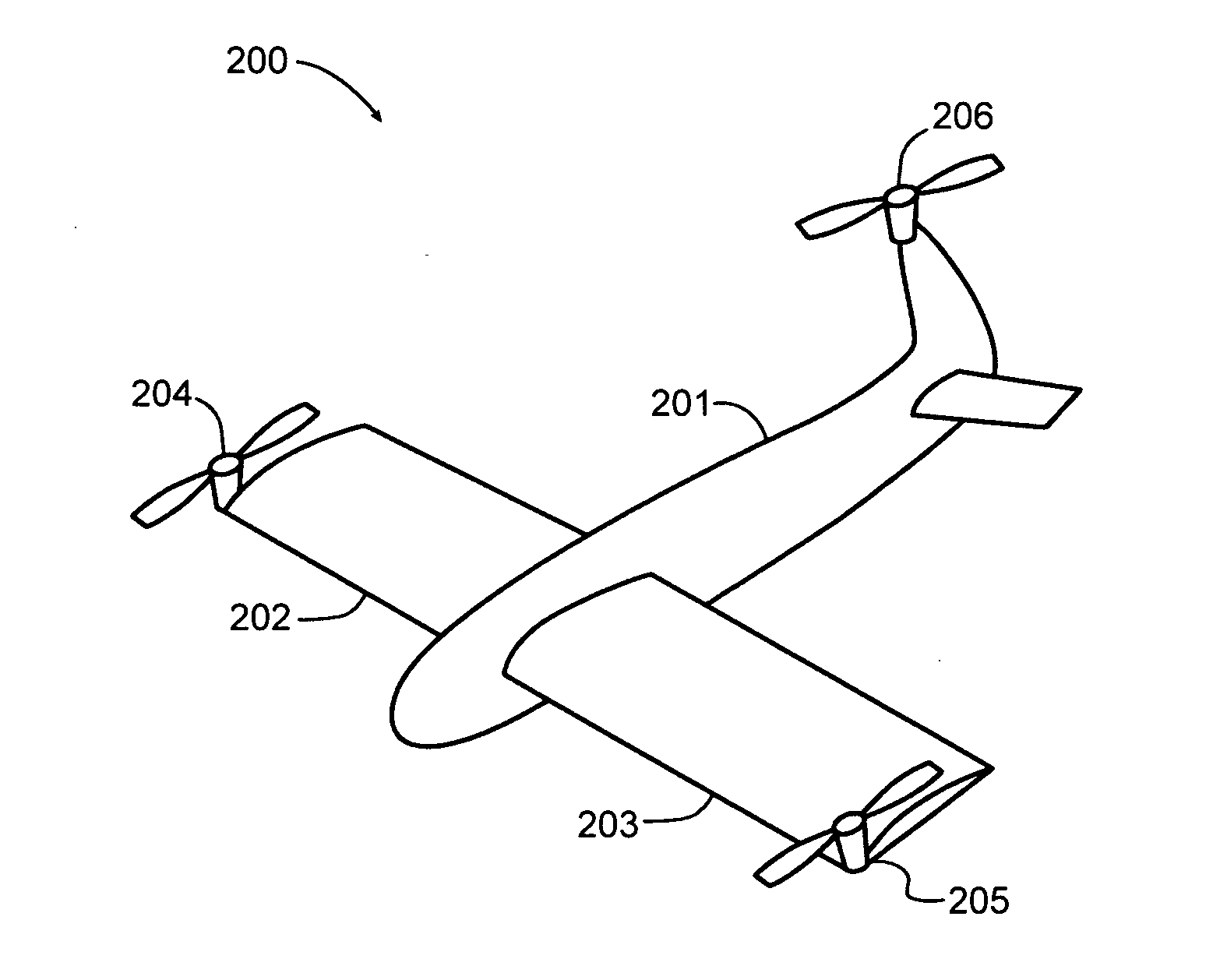
Personal Aircraft
ActiveUS20130020429A1Easy to controlMinimize disturbanceAircraft power plantsPropellersJet aeroplanePropeller
Owner:WISK AERO LLC
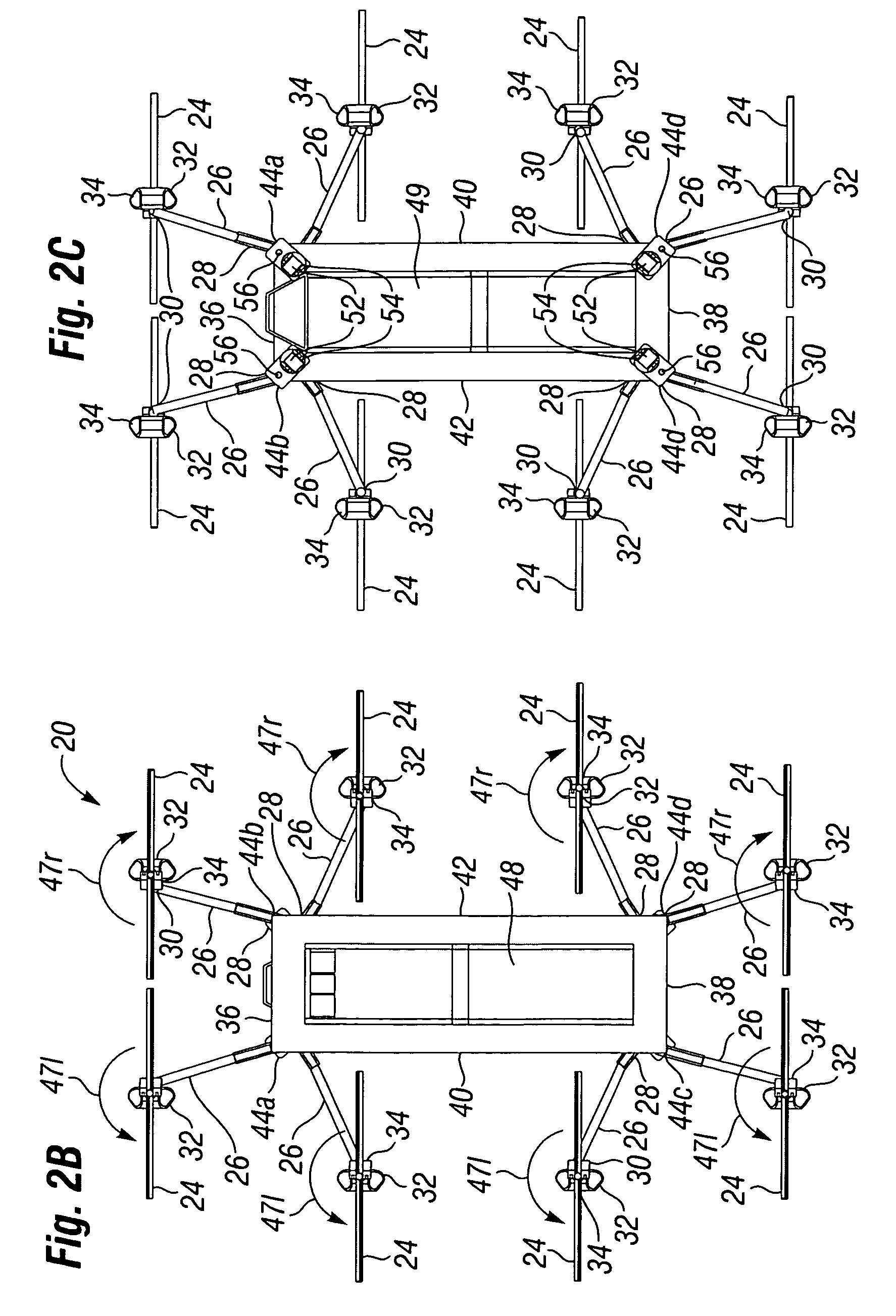
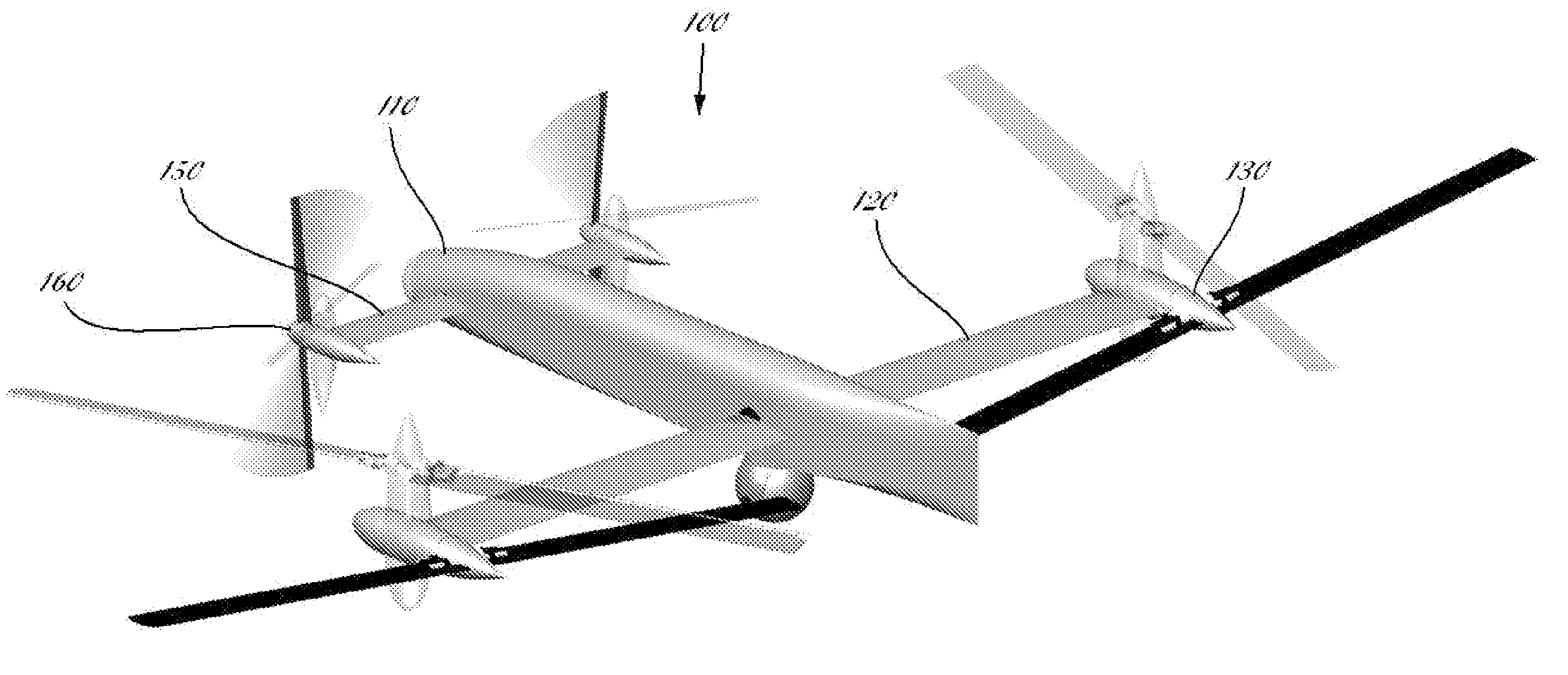
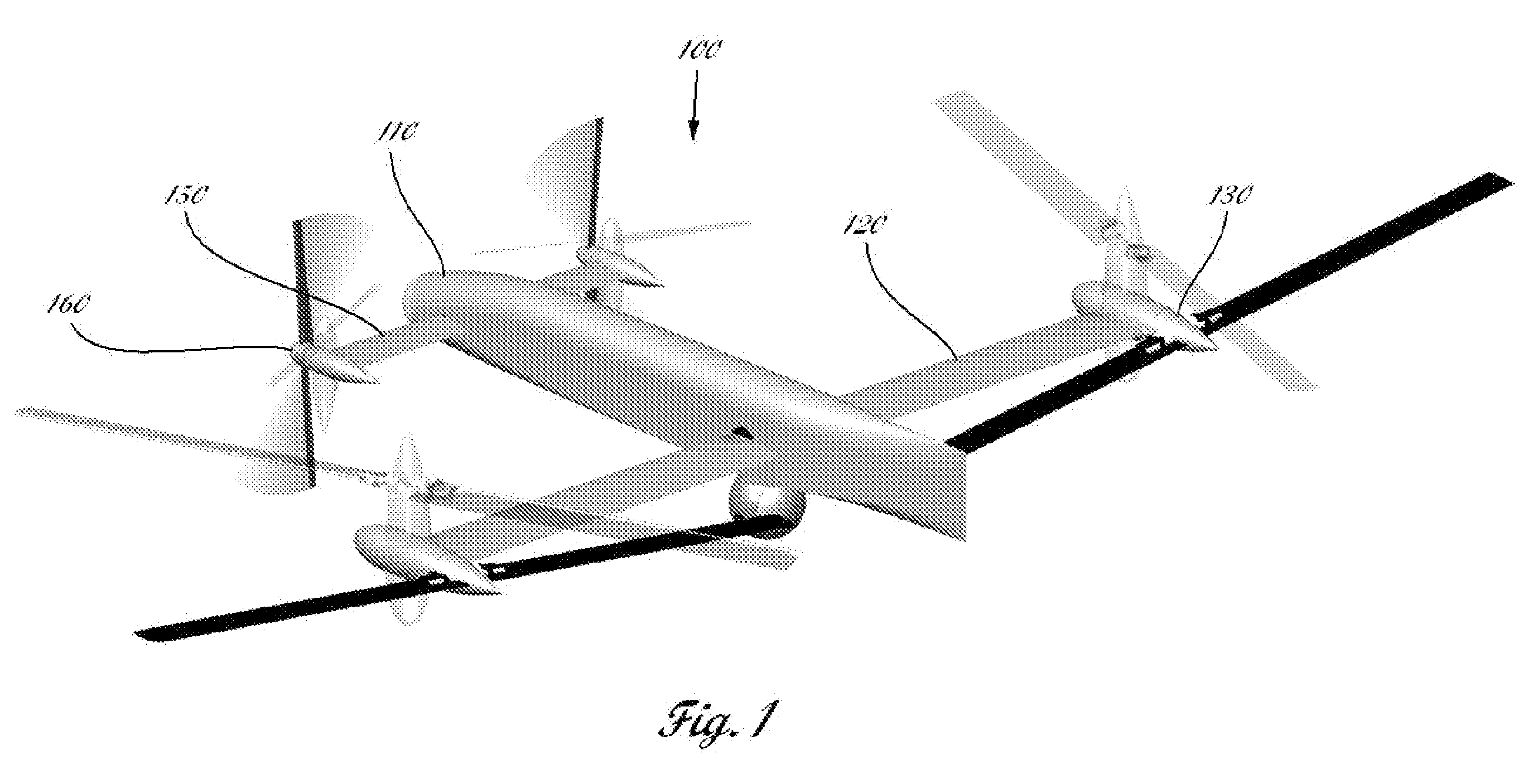
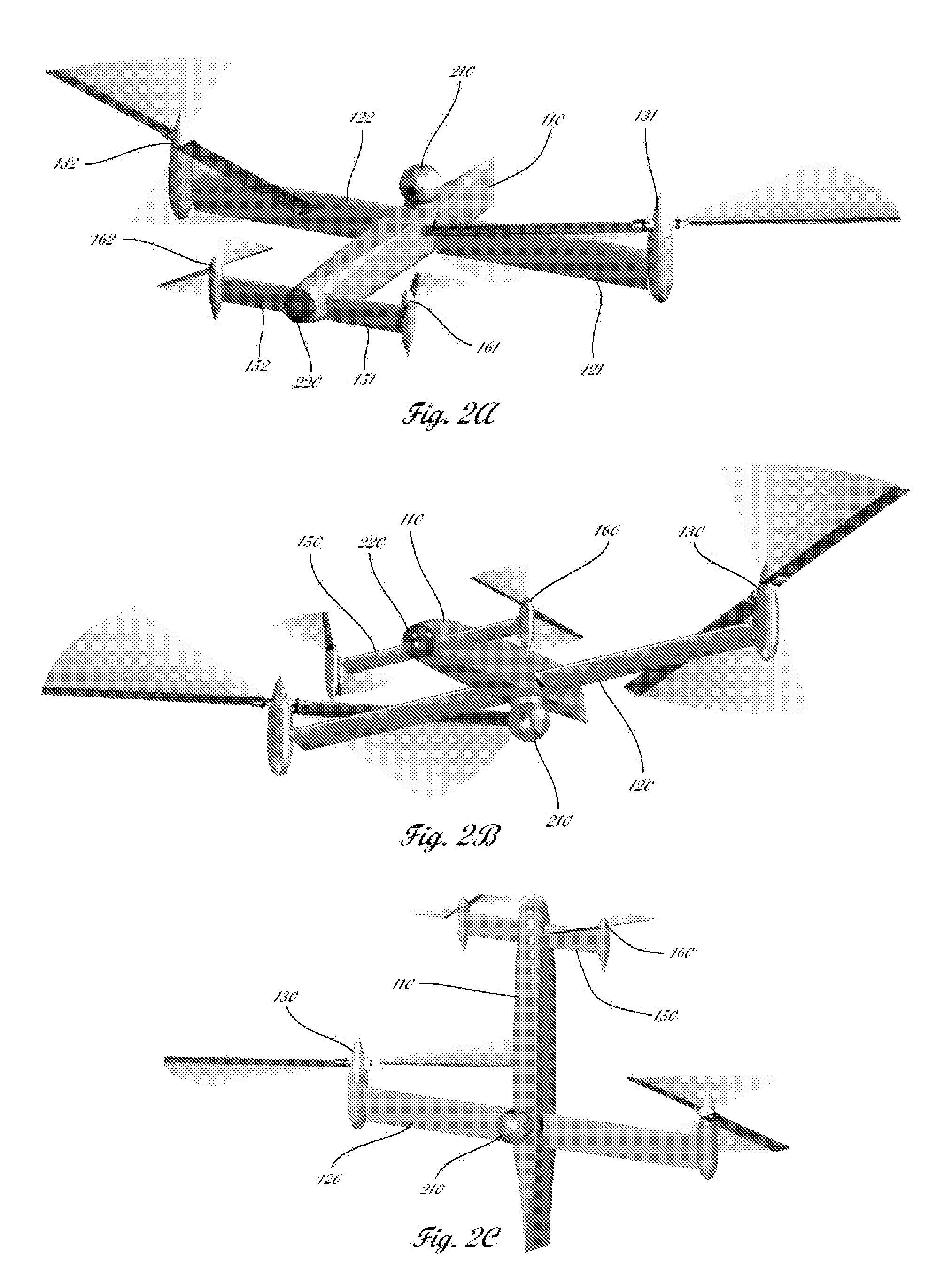
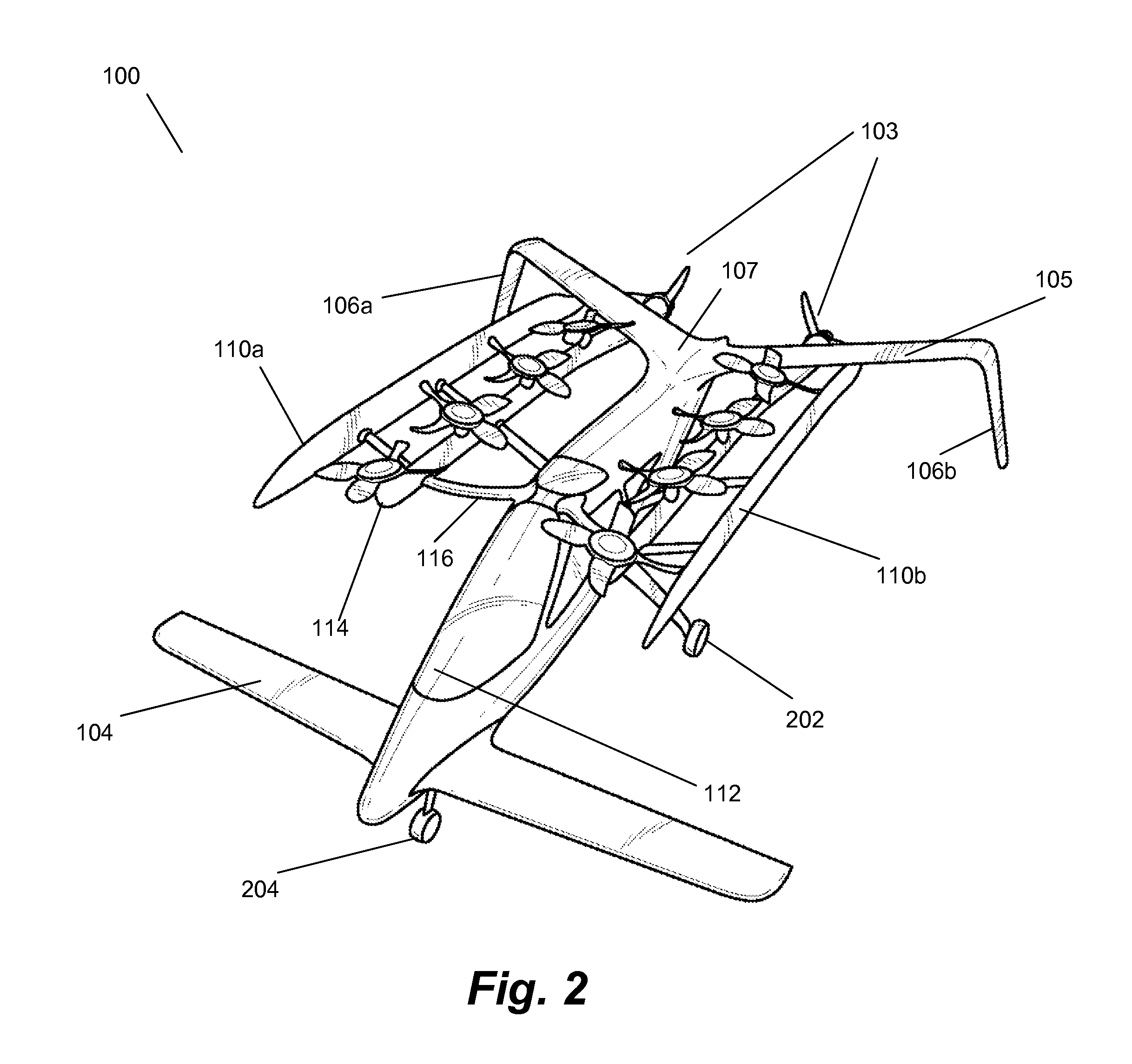
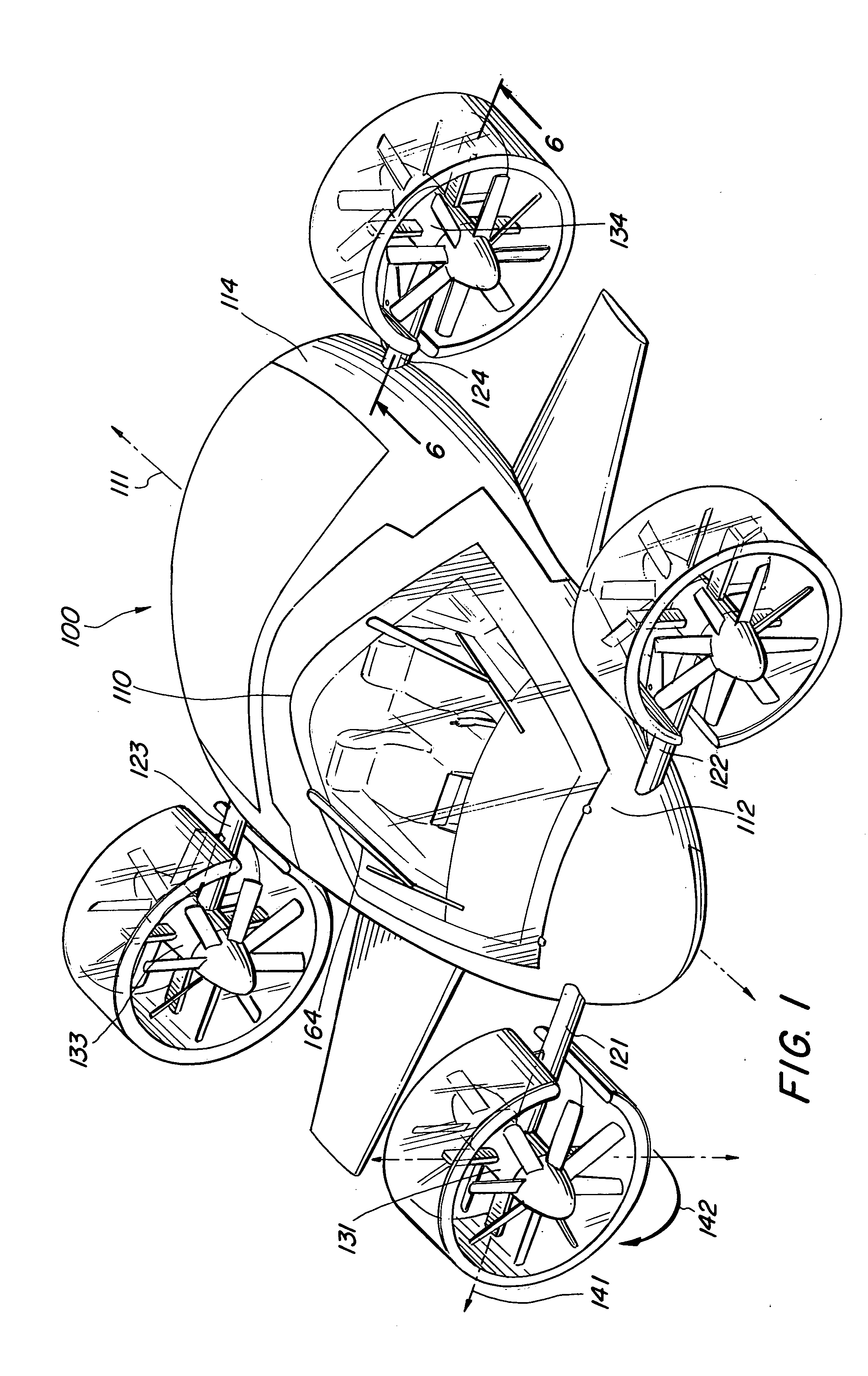
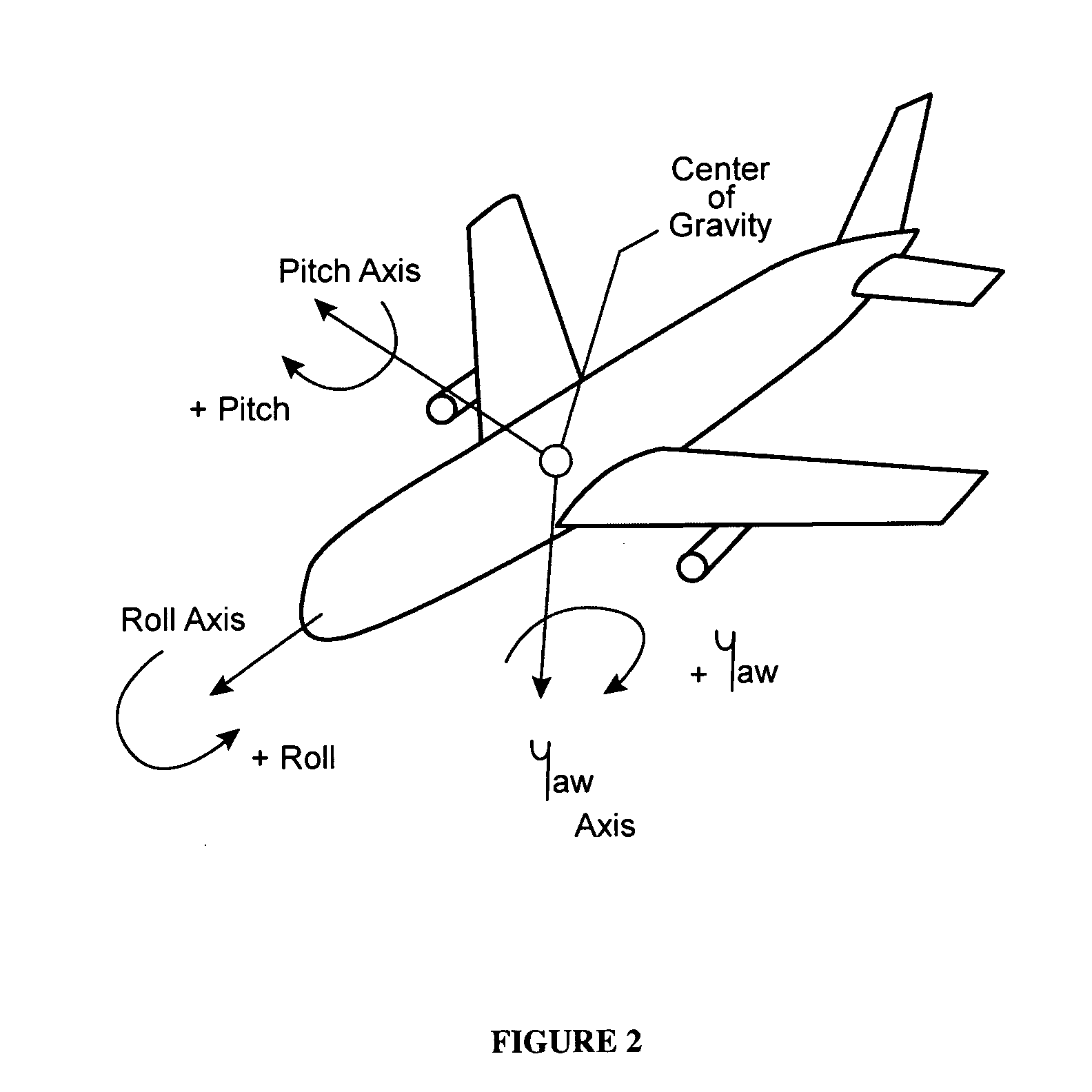
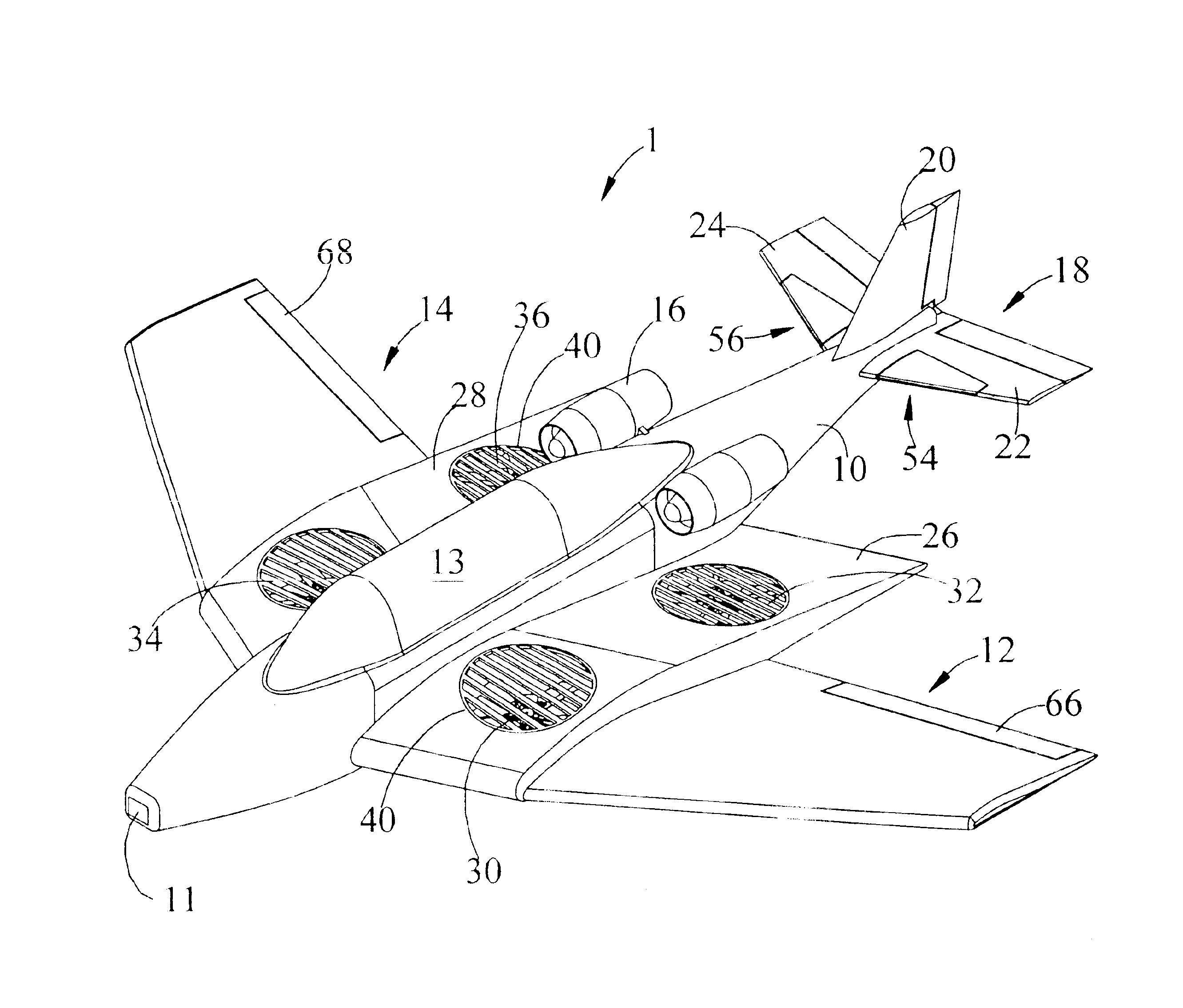
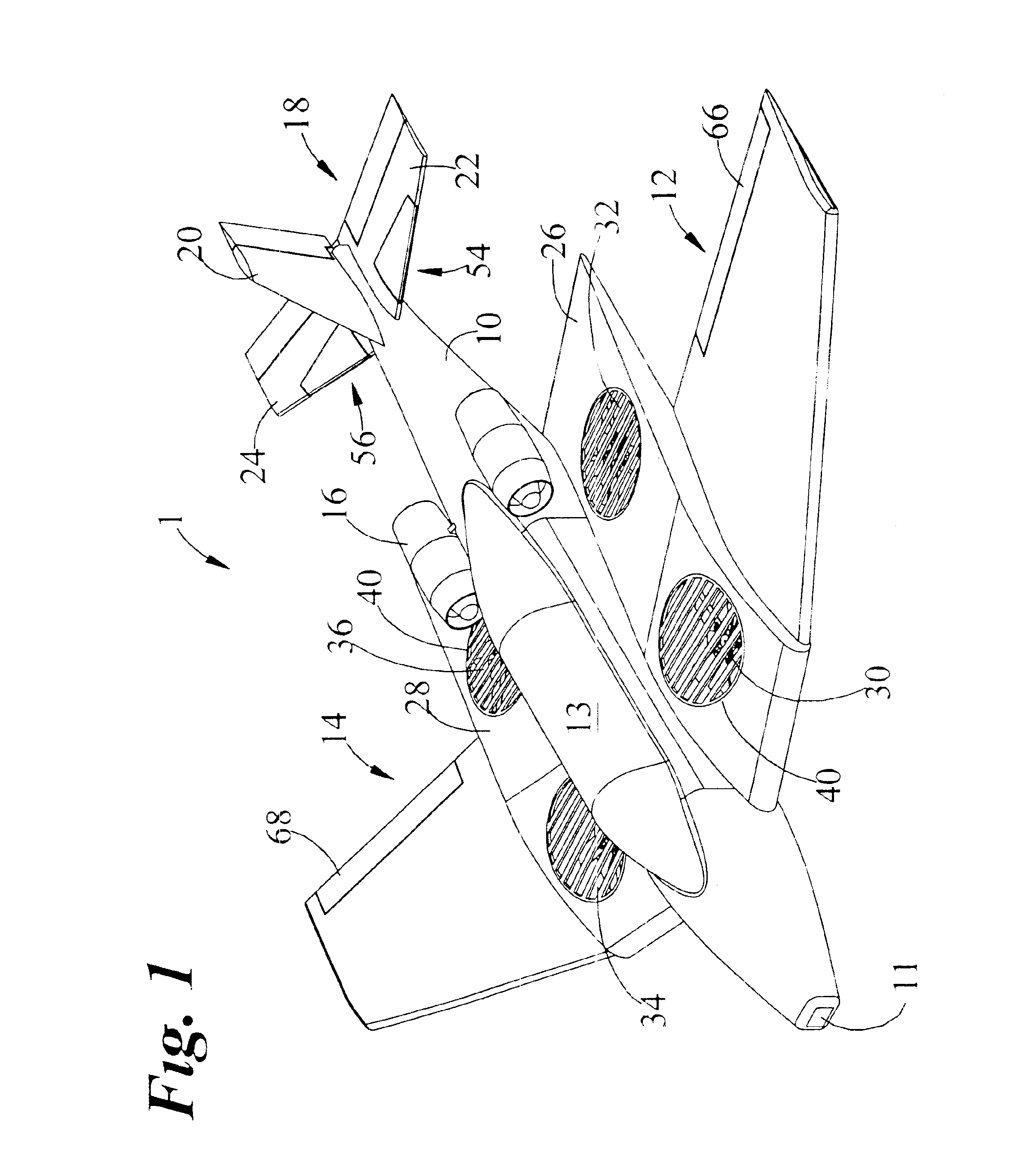
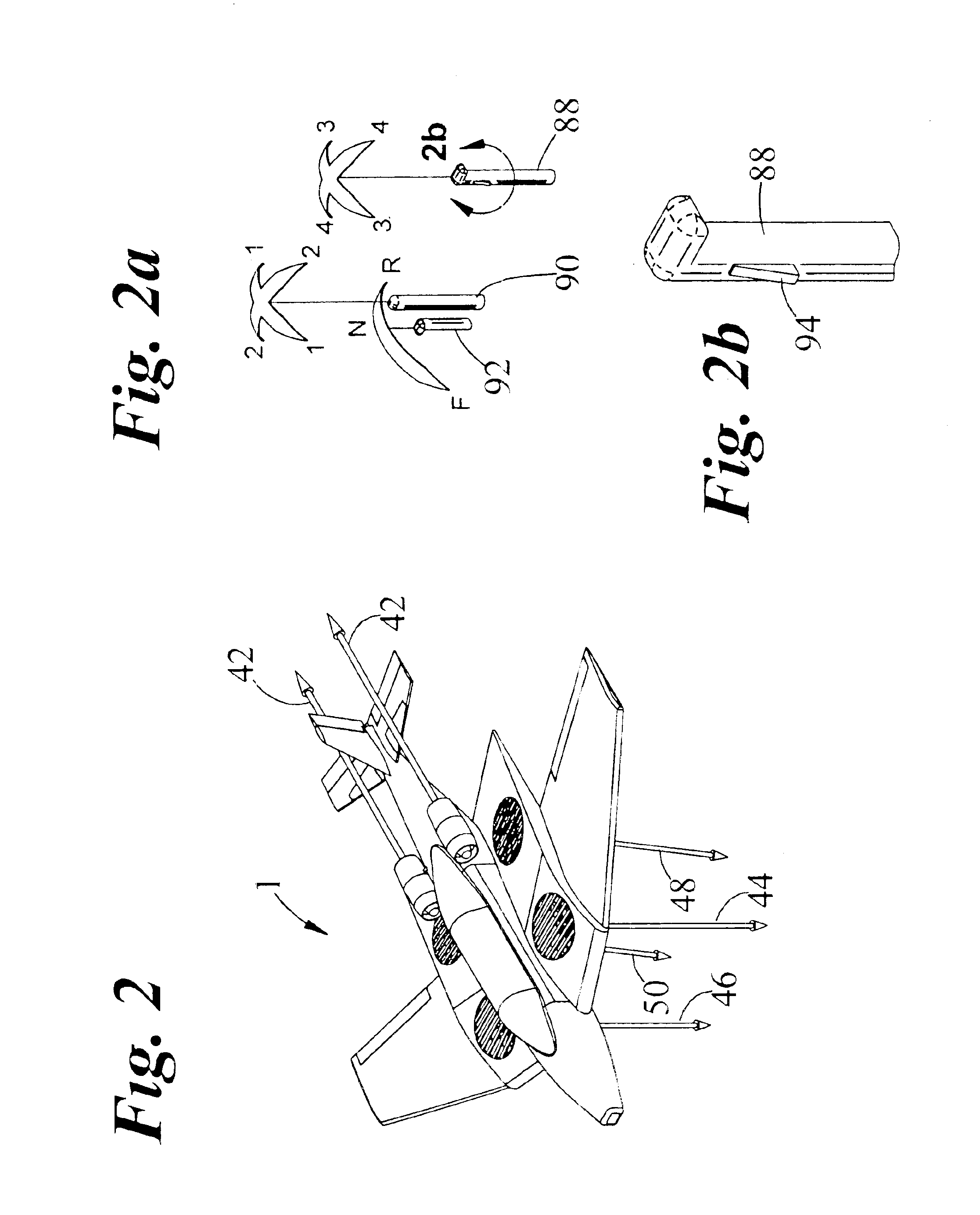
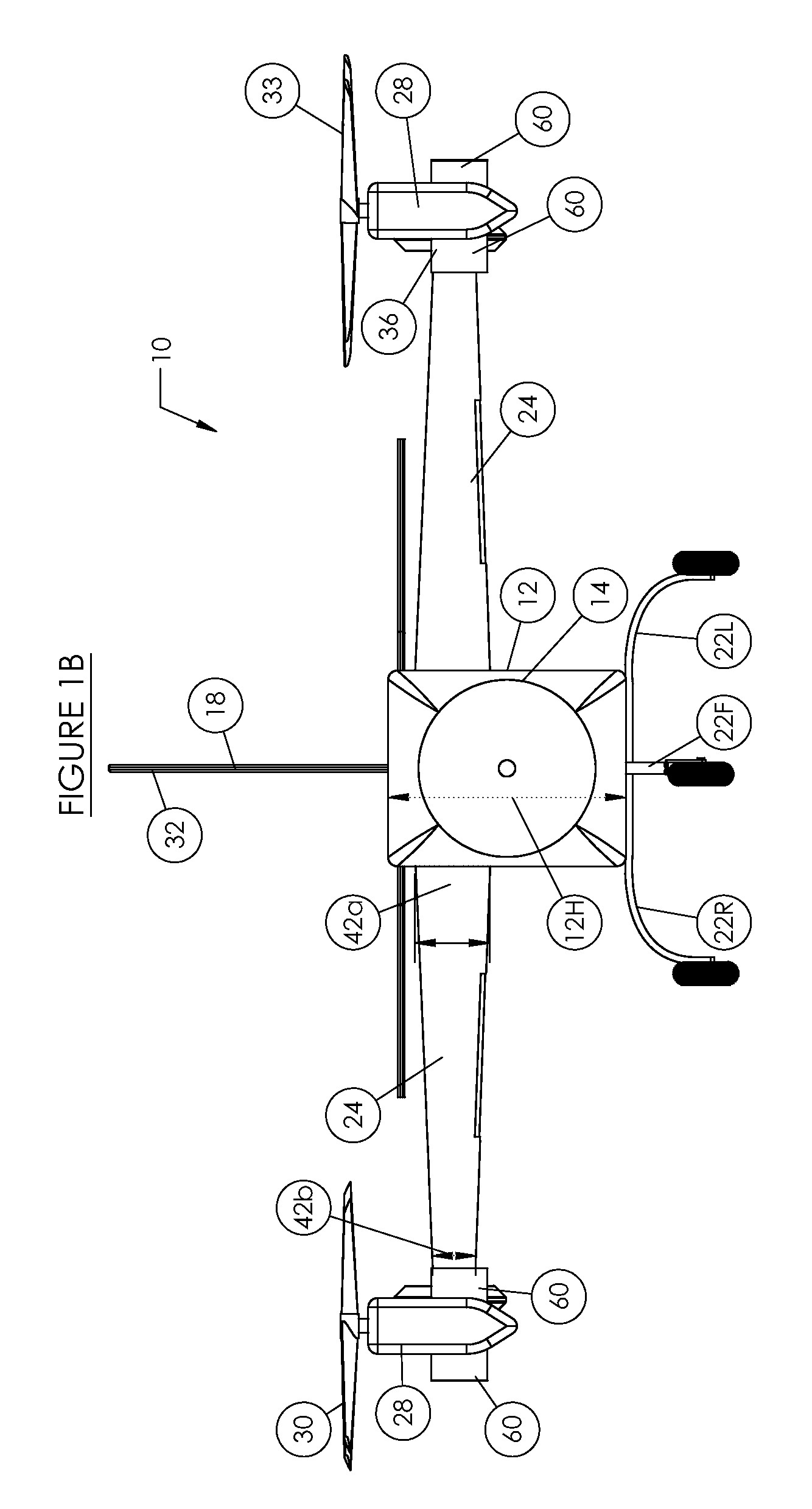
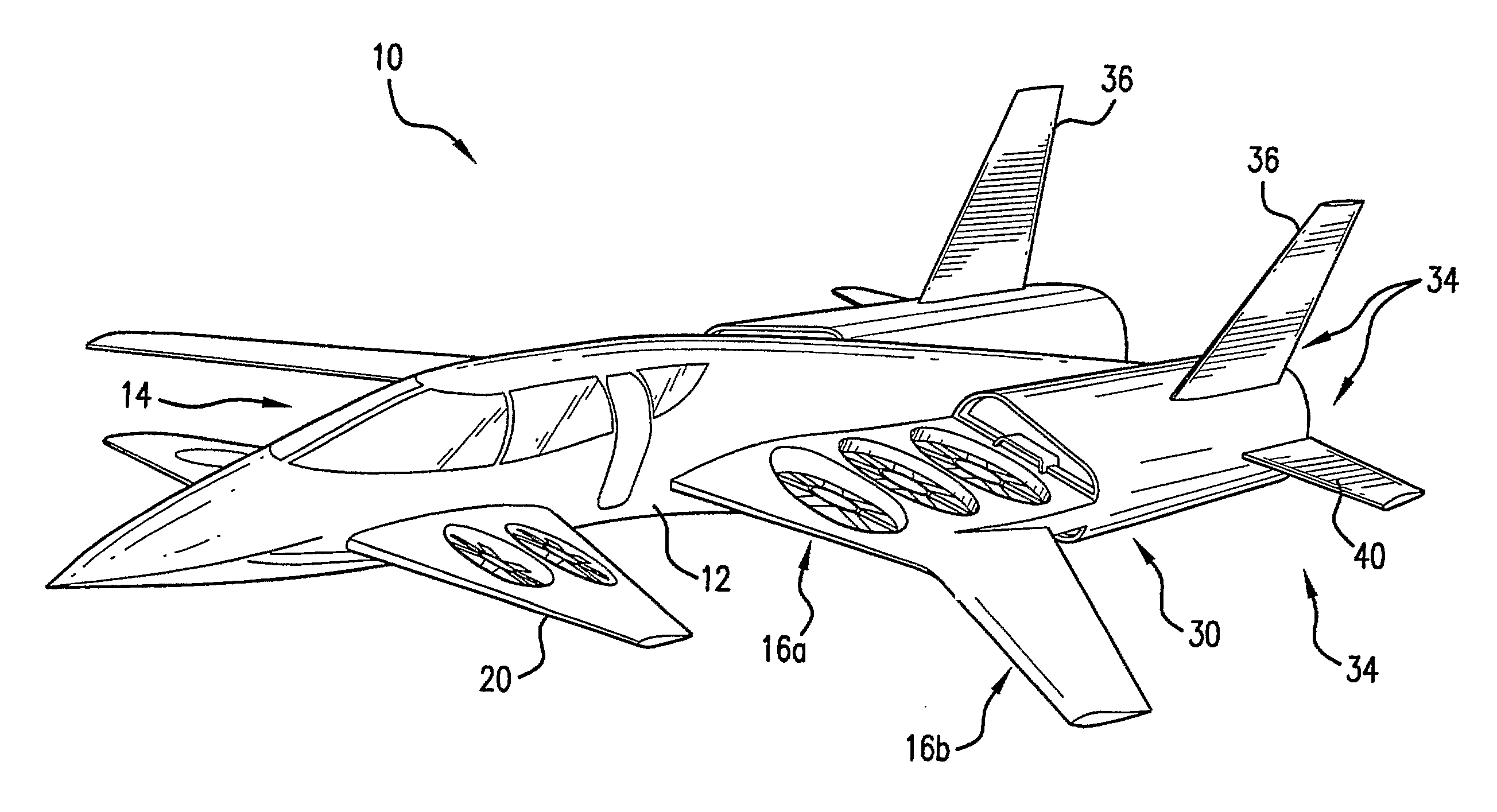
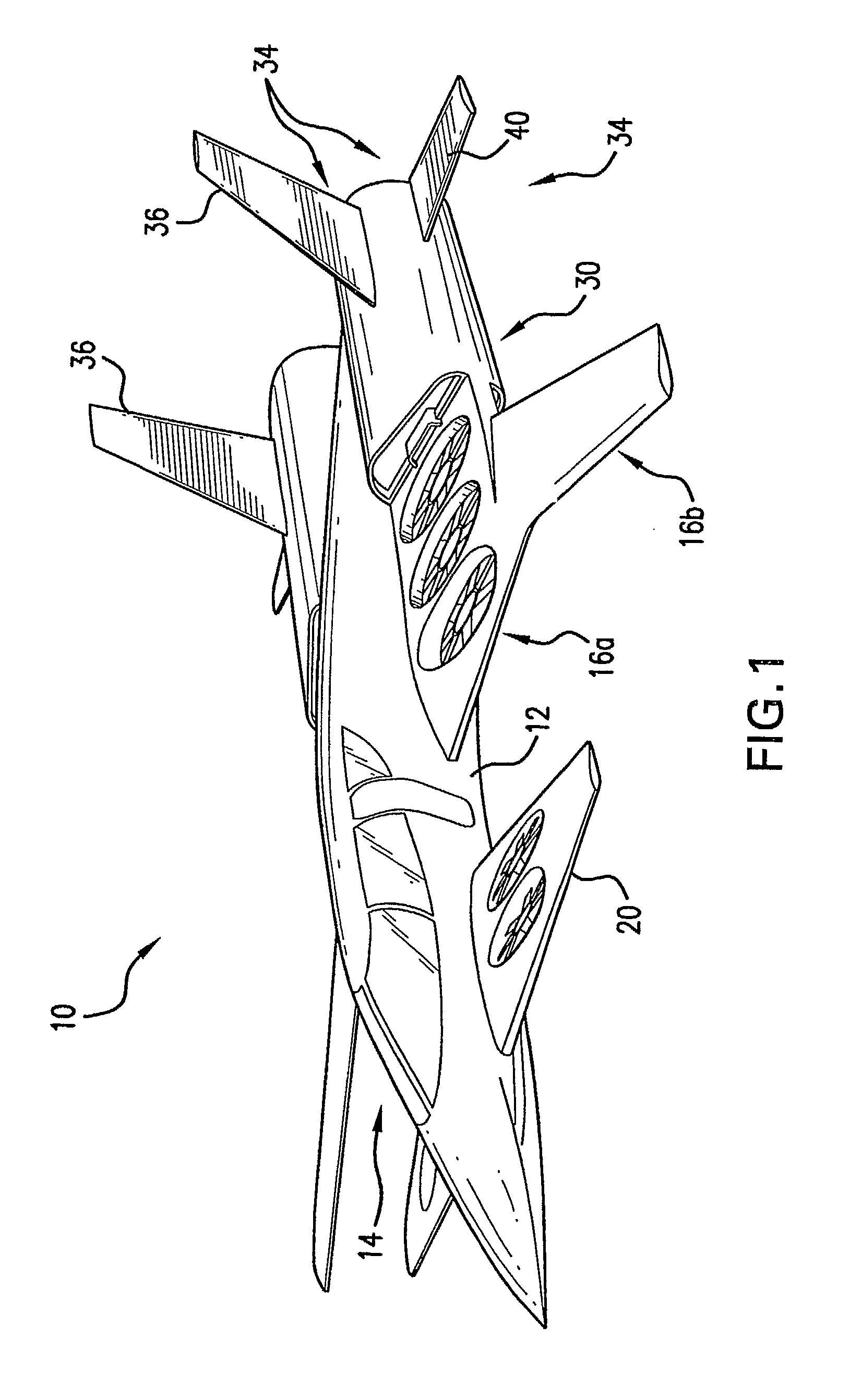
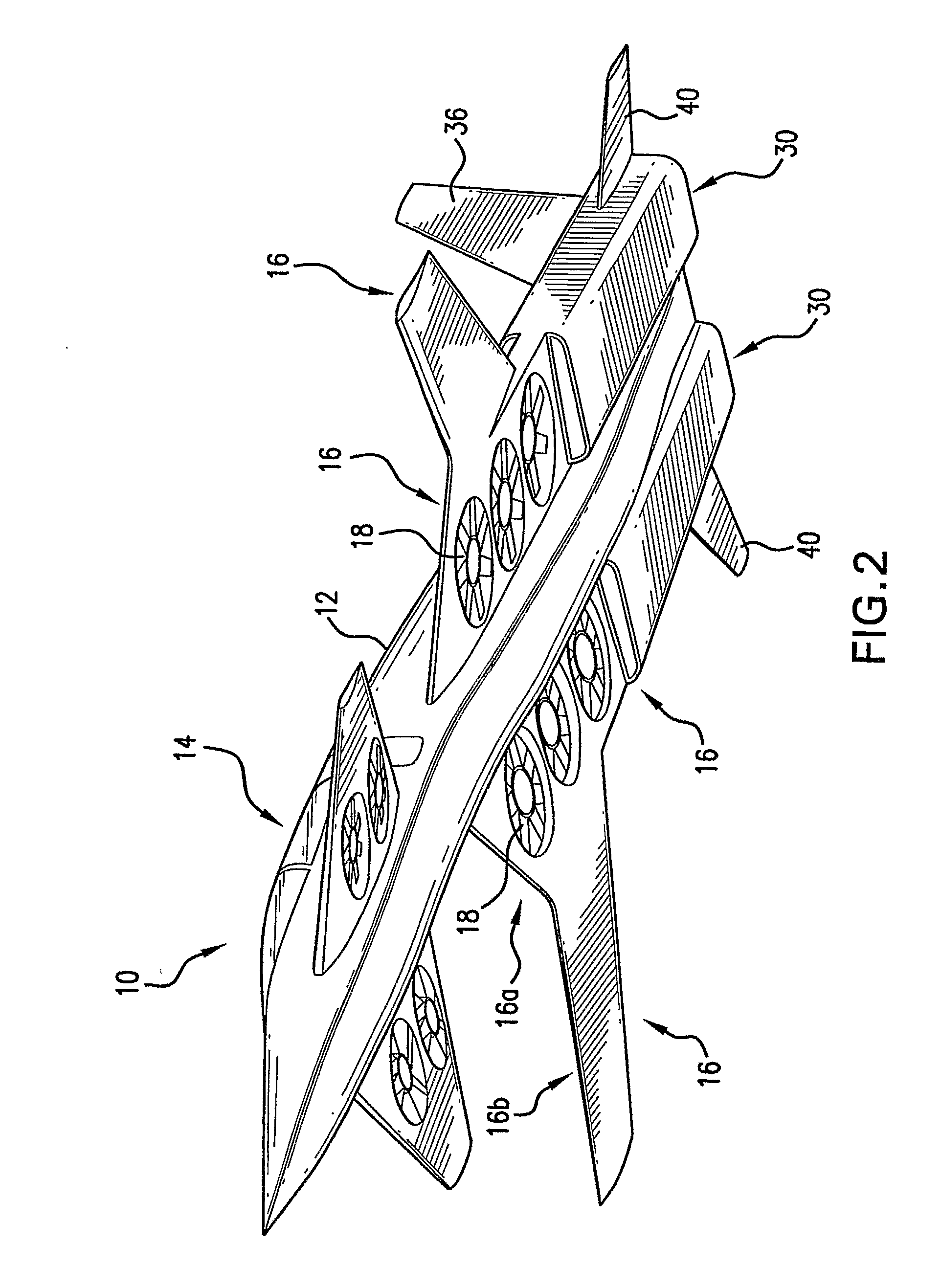
Vertical take-off and landing aircraft
ActiveUS9120560B1Remote controlled aircraftVertical landing/take-off aircraftsJet aeroplaneFixed wing
A vertical take-off and landing aircraft includes a fixed wing airframe having opposed left and right wings extending from left and right sides, respectively, of a fuselage having opposed leading and trailing extremities and an empennage located behind the trailing extremity. Four fixed, open and horizontal, vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) thrust rotors are mounted to the airframe in a quadrotor pattern for providing vertical lift to the aircraft, and a vertical, forward thrust rotor is mounted to the trailing extremity of the fuselage between the trailing extremity of the fuselage and the empennage for providing forward thrust to the aircraft. The four VTOL thrust rotors are coplanar being and operating in a common plane that is parallel relative to, and being level with, top surfaces of the left and right wings in and around a region of each of the four VTOL thrust rotors.
Owner:L3HARRIS UNMANNED SYST INC
Vertical takeoff and landing aircraft
InactiveUS6892980B2Superior and stable maneuverabilityEasy to operateAircraft navigation controlPropellersJet aeroplaneTurbofan
A vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft is superior in maneuverability, safety, and mobility. The aircraft has turbofan engines with separate core engines having fan engines used commonly for cruising and lifting up. The thrust from the fan engines can be directed to all directions by supporting the fan engines of the turbofan engines with separate core engines with biaxial support so that the fan engines are rotatable in the direction of pitching and rolling. The fan engines are mounted on both sides of each of front and rear sings. With this construction, the VTOL aircraft can cruise and hover by tilting the fan engines about the two axes while using the fan engines commonly for cruising and hovering.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Sky hopper
InactiveUS20060016930A1Increase shaft powerAircraft navigation controlToy aircraftsSkyRemote control
A vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft design particularly suitable as a full-sized aircraft or remote controlled (RC) model aircraft is disclosed. The invention employs lightweight, high strength materials to reduce the power requirements of the propulsion plant. A preferred system of the invention comprises one internal combustion engine able to spit shaft power to four fan units. The fan units further employ counter rotating fan blades for stability. Separate horizontal and vertical tilting mechanisms delivered to the fan units are additionally disclosed. A variation in design is further included wherein electric motors provide the necessary shaft power.
Owner:PAK STEVE
Controlled take-off and flight system using thrust differentials
InactiveUS20110042508A1Aircraft navigation controlUnmanned aerial vehiclesLevel flightFlight vehicle
A manned / unmanned aerial vehicle adapted for vertical takeoff and landing using the same set of engines for takeoff and landing as well as for forward flight. An aerial vehicle which is adapted to takeoff with the wings in a vertical as opposed to horizontal flight attitude which takes off in this vertical attitude and then transitions to a horizontal flight path. An aerial vehicle which controls the attitude of the vehicle during takeoff and landing by alternating the thrust of engines, which are separated in least two dimensions relative to the horizontal during takeoff. An aerial vehicle which uses a rotating platform of engines in fixed relationship to each other and which rotates relative to the wings of the vehicle for takeoff and landing.
Owner:TRANSITION ROBOTICS INC
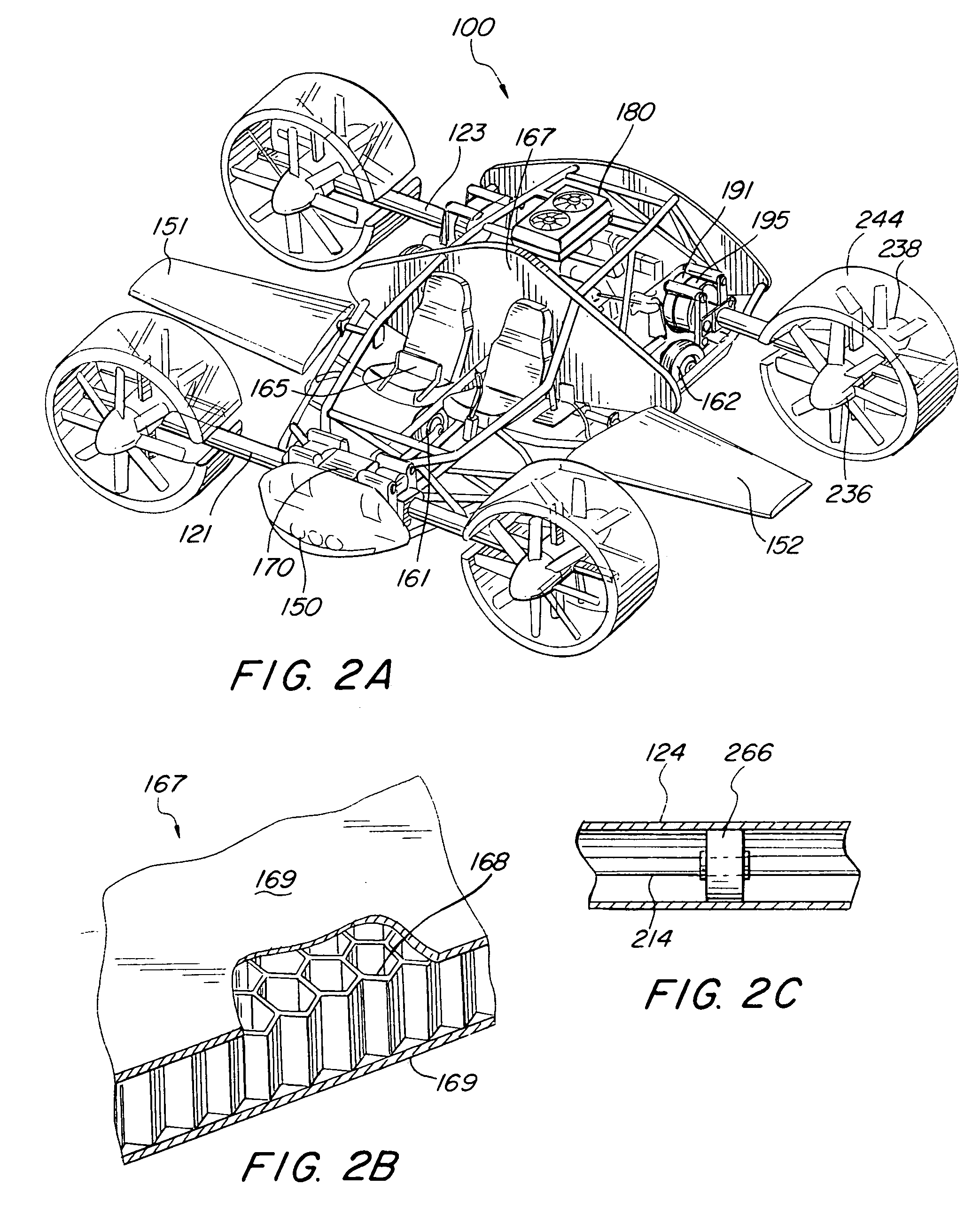
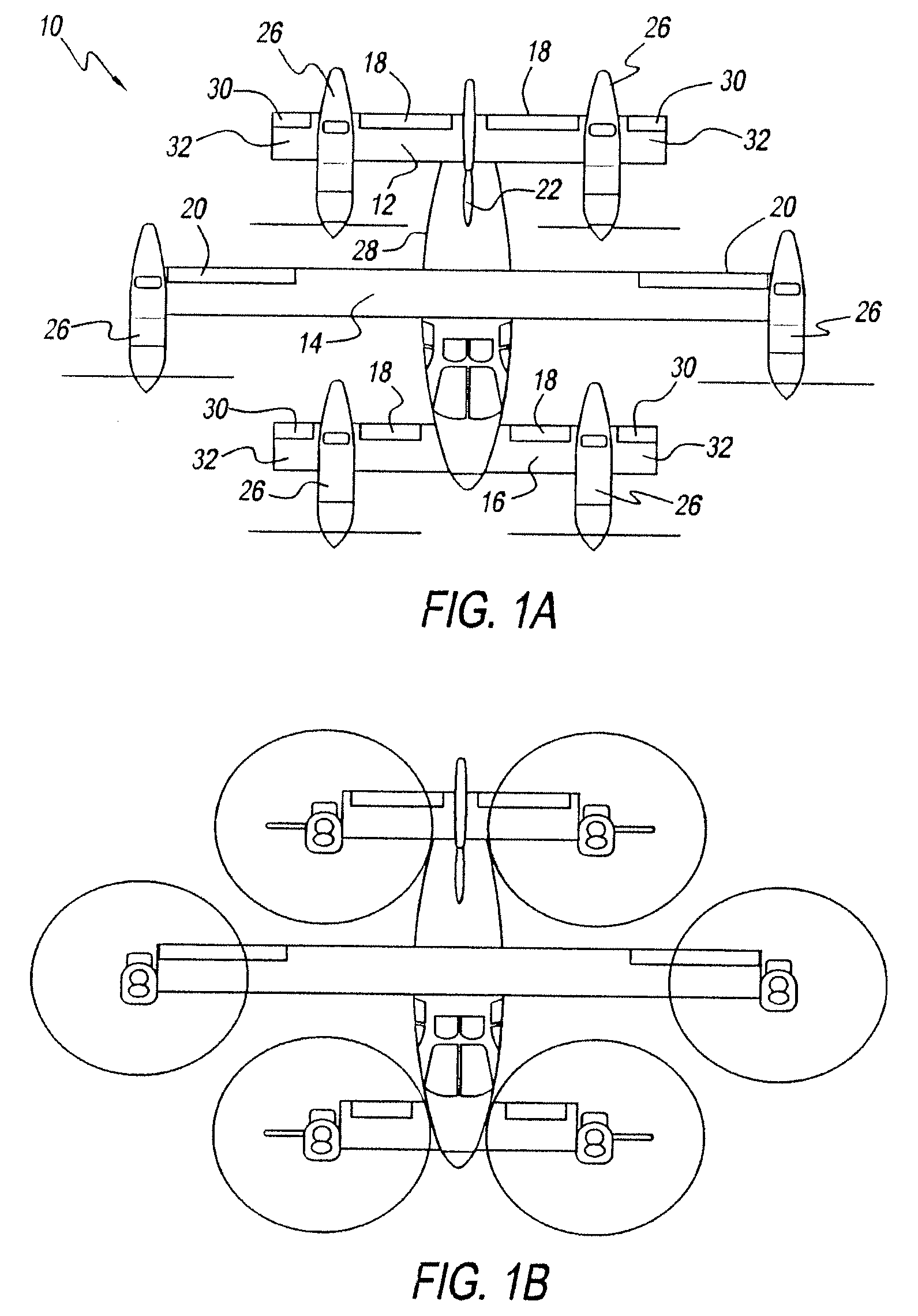
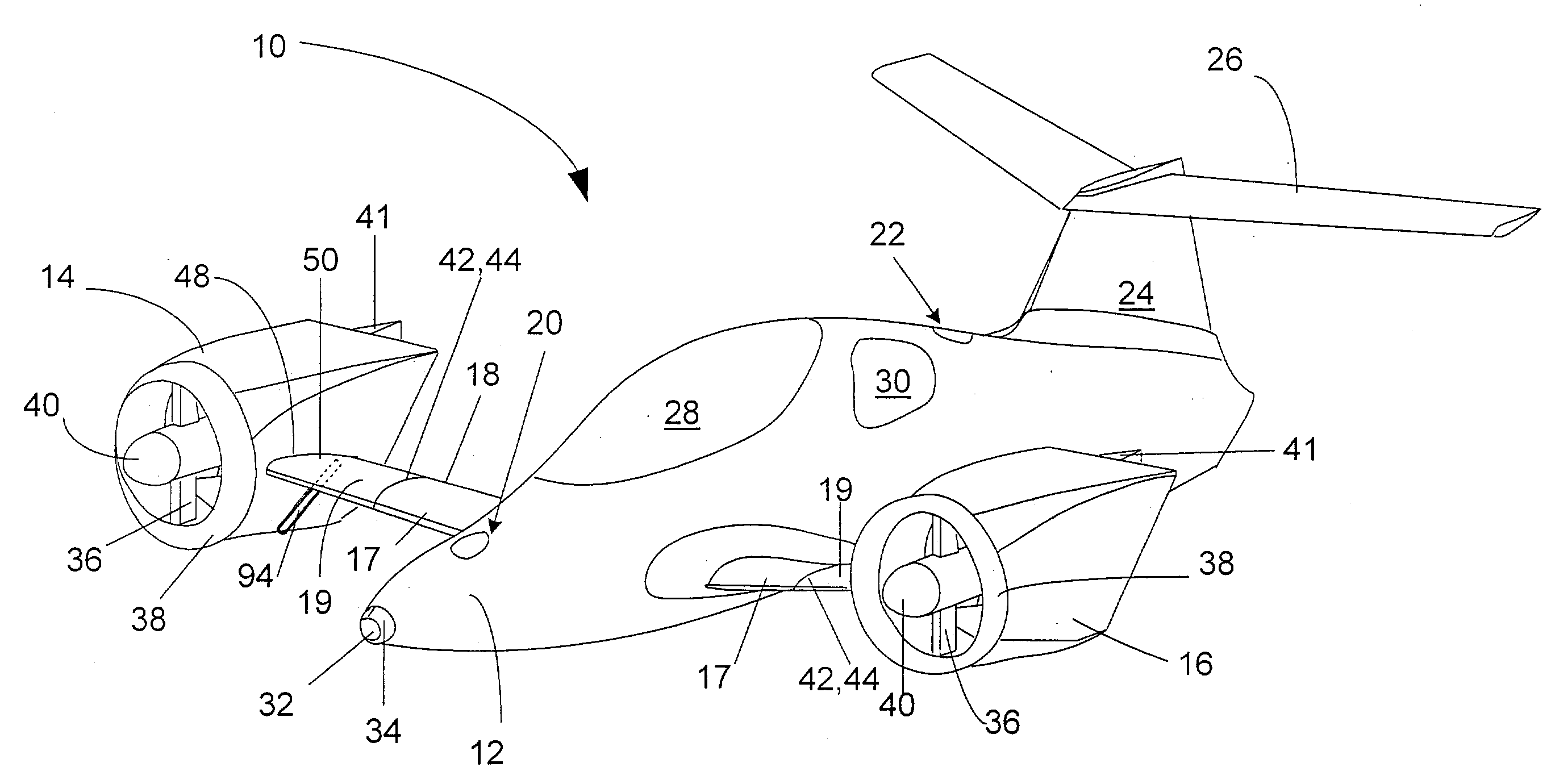
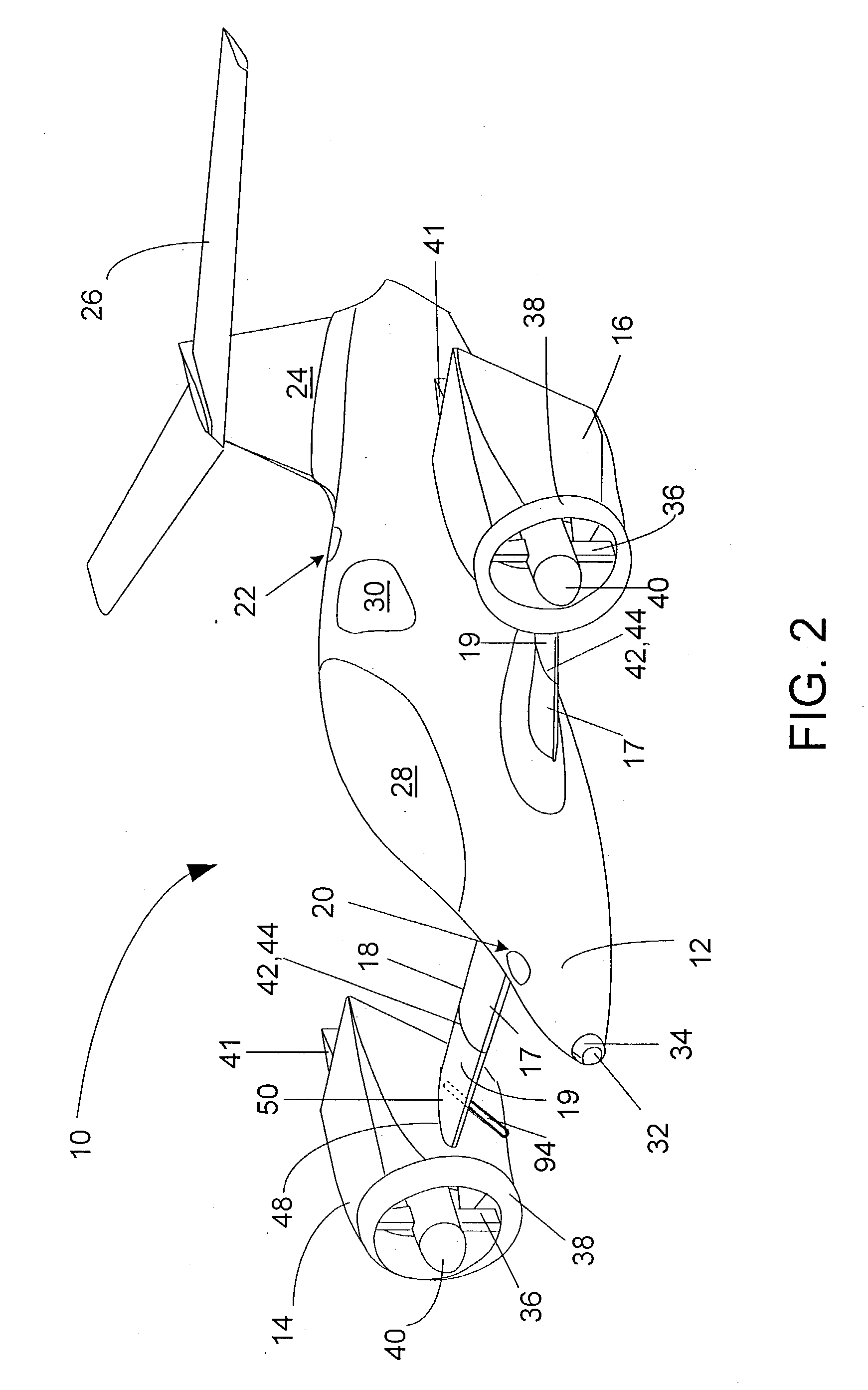
Vertical take-off and landing aircraft
ActiveUS6843447B2Improved hover stabilityAircraft navigation controlAircraft stabilisationEngineeringRight flank
A vertical take-off and landing aircraft includes a fuselage, a left wing, a right wing, at least one forward thruster, a horizontal stabilizer and a vertical stabilizer. The left and right wings extend from substantially a middle of the fuselage on left and right sides, respectively. The at least one forward thruster is preferably mounted to the fuselage, substantially behind the left and right wings. The horizontal stabilizer extends from a rear of the fuselage. The vertical stabilizer extends from a top of the fuselage at a rear thereof. At least two left lift rotors are retained in the left wing and at least two right lift rotors are retained in the right wing. A second embodiment of the VTOL aircraft includes a fuselage truncated behind the left and right wings with a twin tail empennage.
Owner:MORGAN AIRCRAFT LLC
Aircraft Capable of Vertical Take-Off
ActiveUS20160207625A1Good hover characteristicIncrease cruising speedAircraft stabilisationUnmanned aerial vehiclesJet aeroplaneQuadcopter
The invention relates to an aircraft which can both take off and land vertically and can hover and also fly horizontally at a high cruising speed. The aircraft has a support structure, a wing structure, at least three and preferably at least four lifting rotors and at least one thrust drive. The wing structure is designed to generate a lifting force for the aircraft during horizontal motion. To achieve this the wing structure has at least one mainplane provided with a profile that generates dynamic lift. The wing structure is preferably designed as a tandem wing structure. Each of the lifting rotors is fixed to the support structure, has a propeller and is designed to generate a lifting force for the aircraft by means of a rotation of the propeller, said force acting in a vertical direction. The thrust drive is designed to generate a thrust force on the support structure, said force acting in a horizontal direction. The lifting rotors can have a simple construction, i.e. they can have a simple rigid propeller for example, and a vertical take-off or hovering of the aircraft can be controlled, in a similar manner to quadcopters, by a simple control of the speeds of the lifting rotors. High cruising speeds can be achieved as a result of the additional horizontally acting thrust drive.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
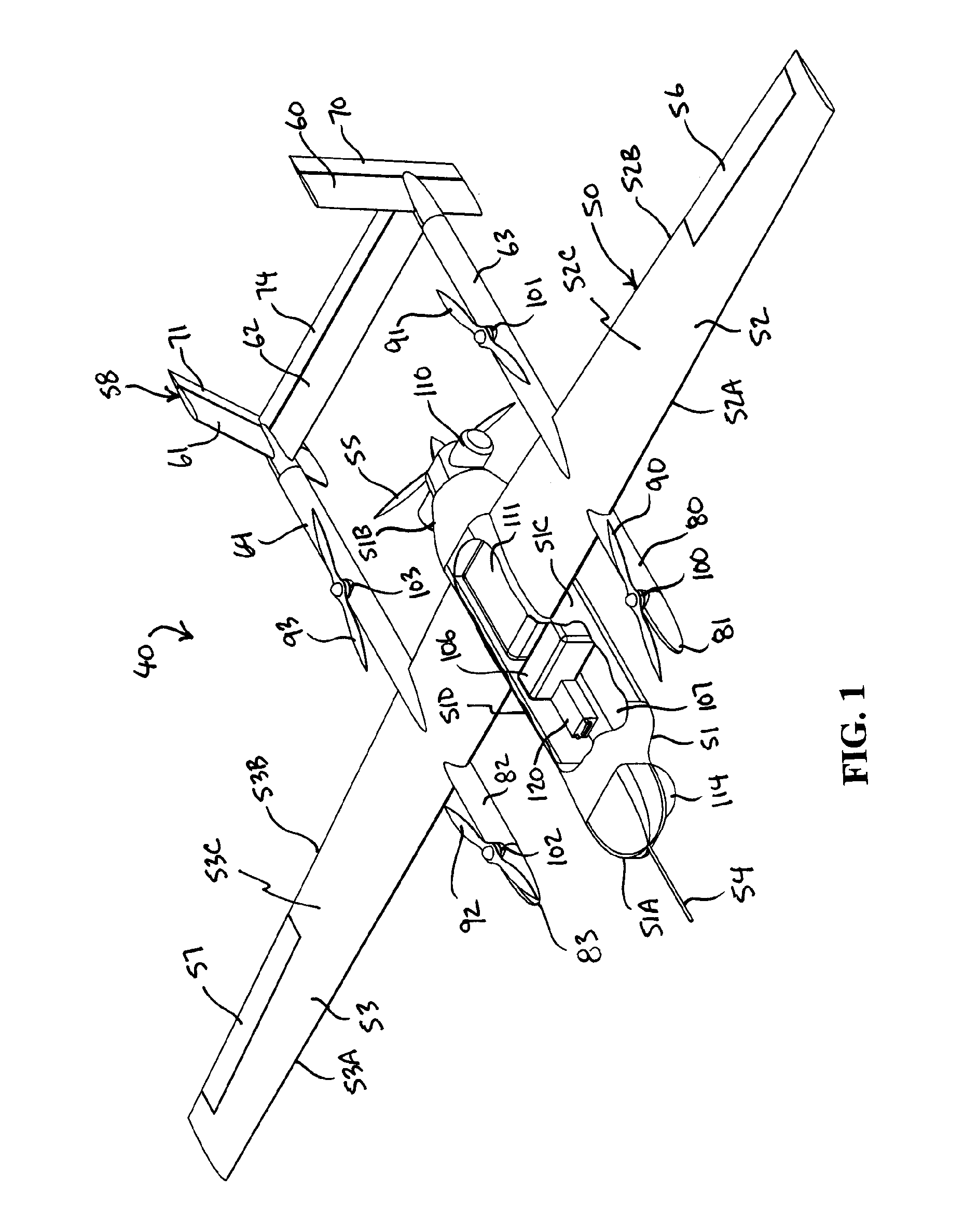
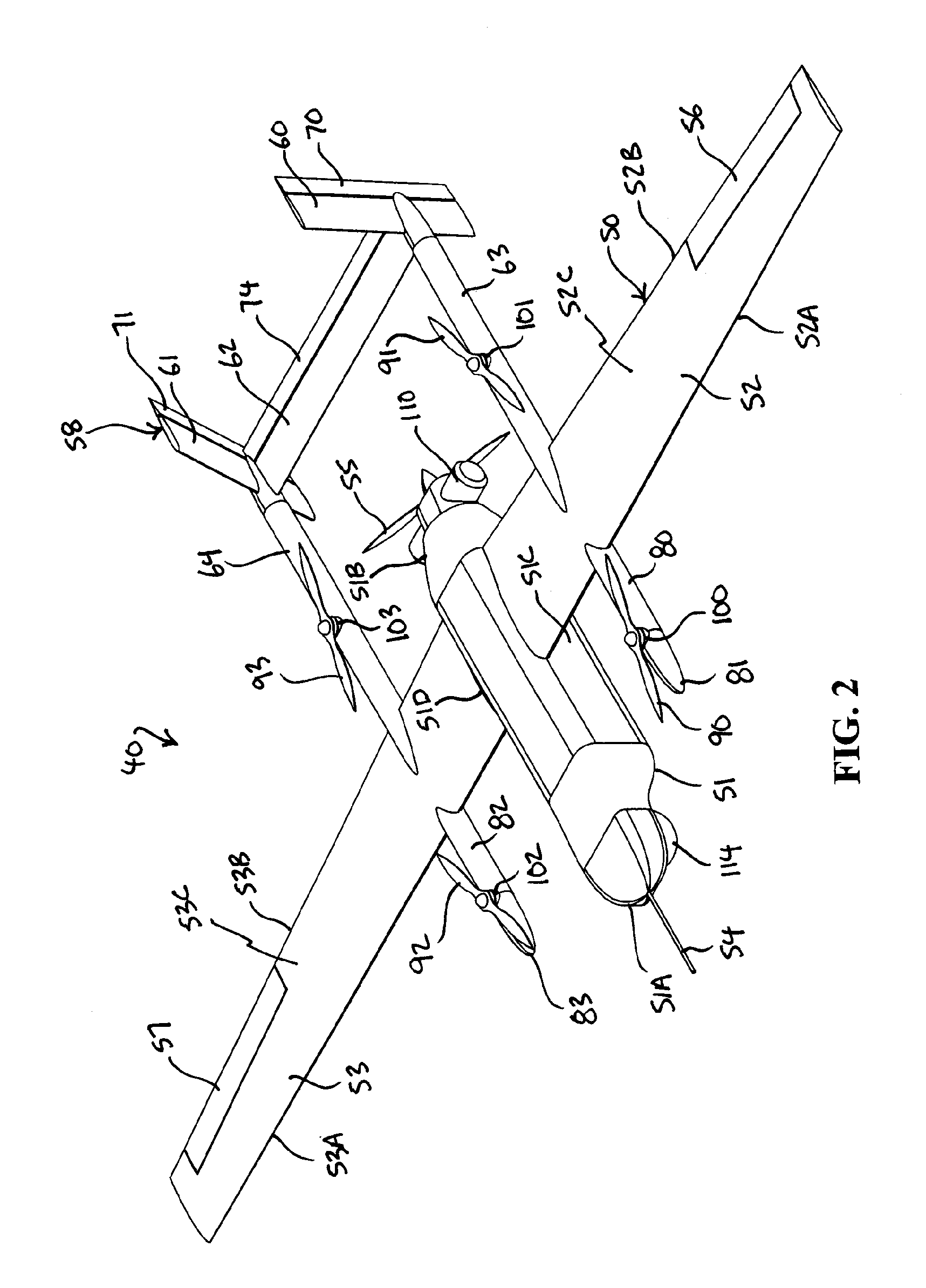
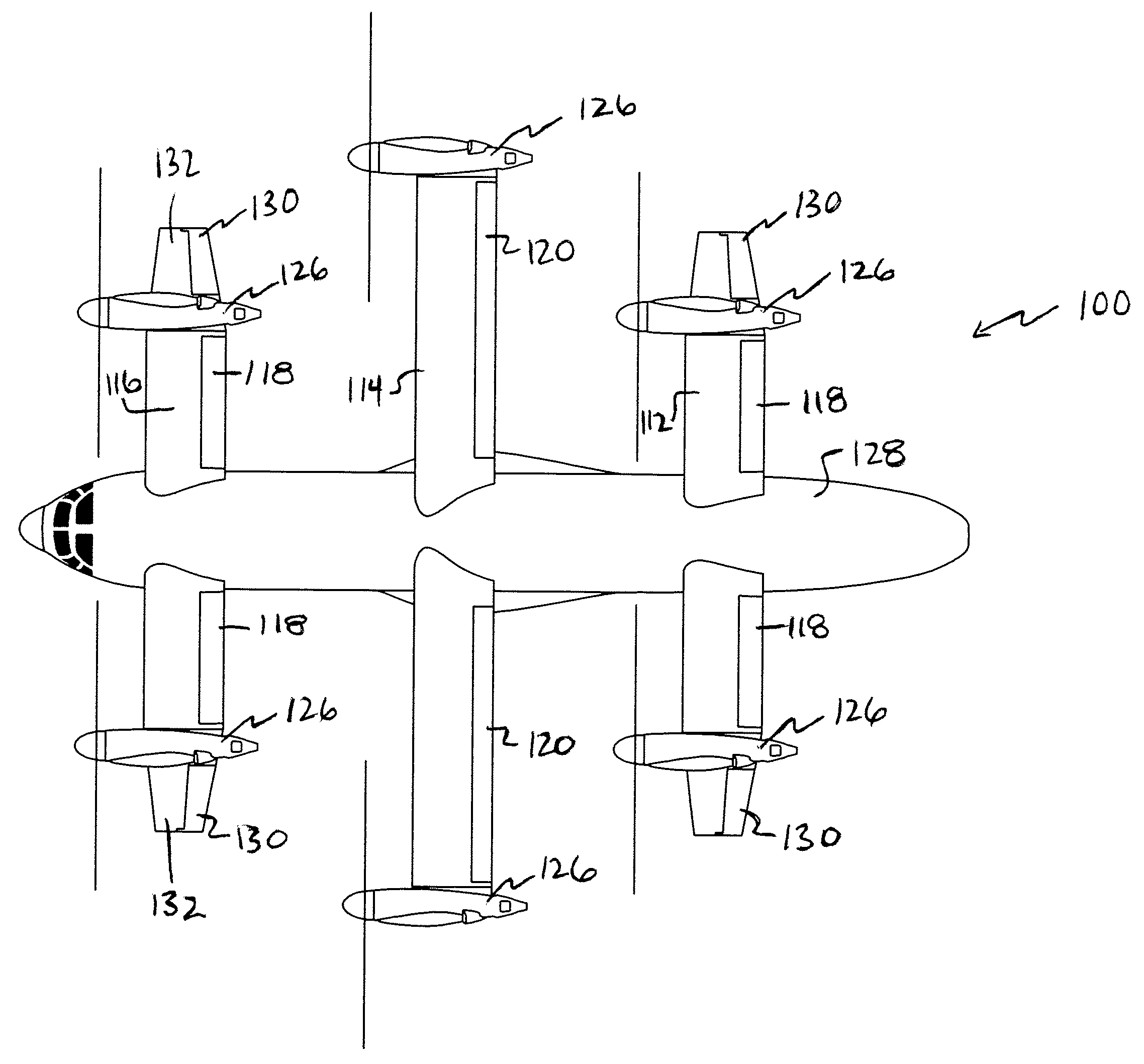
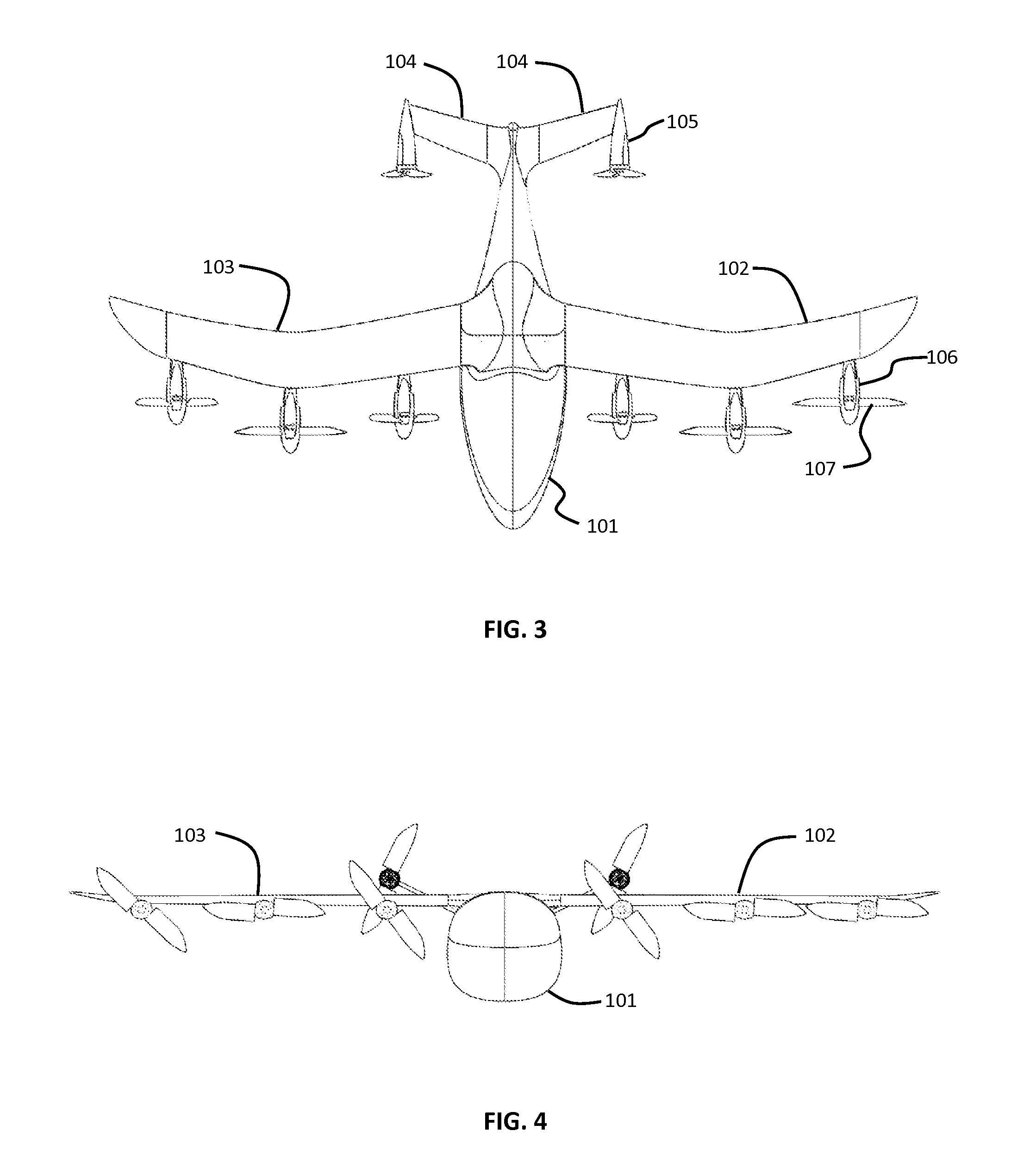
Three wing, six-tilt propulsion unit, VTOL aircraft
Owner:OLIVER VTOL
Modular flying vehicle
InactiveUS8453962B2Reduce the required powerSteady fallAircraft navigation controlUnmanned aerial vehiclesFlight vehicleModularity
The invention is a modular vehicle having an air vehicle that can be coupled to cargo containers, land vehicles, sea vehicles, medical transport modules, etc. In one embodiment the air vehicle has a plurality of propellers positioned around a main airframe, which can provide vertical thrust and / or horizontal thrust. One or more of the propellers may be configured to tilt forward, backward, and / or side-to-side with respect to the airframe.
Owner:SHAW DONALD ORVAL
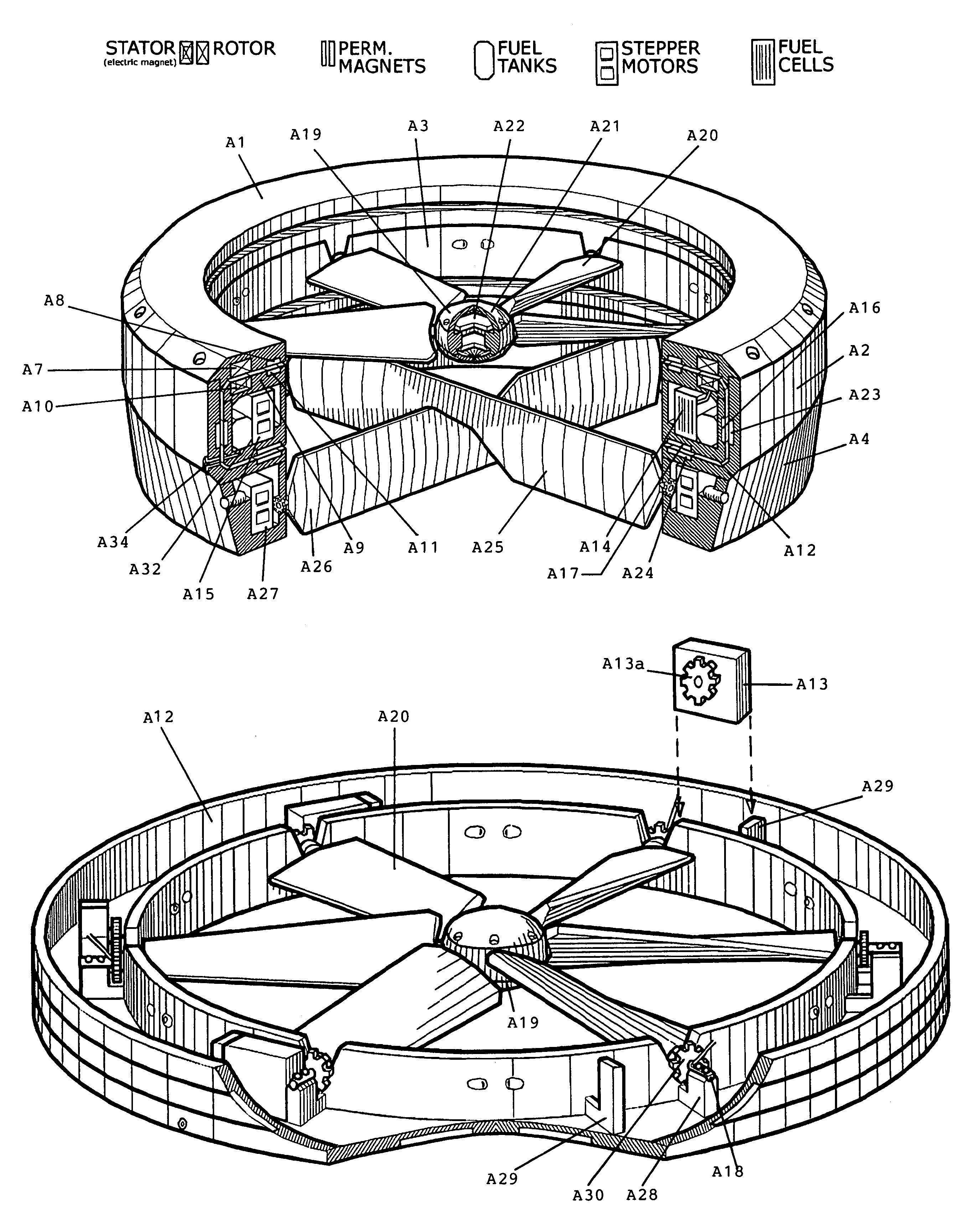
Quiet vertical takeoff and landing aircraft using ducted, magnetic induction air-impeller rotors
InactiveUS7032861B2Improve performanceImprove stabilityAircraft navigation controlUnmanned aerial vehiclesFlight control modesRudder
A hover aircraft employs an air impeller engine having an air channel duct and a rotor with outer ends of its blades fixed to an annular impeller disk that is driven by magnetic induction elements arrayed in the air channel duct. The air-impeller engine is arranged vertically in the aircraft frame to provide vertical thrust for vertical takeoff and landing. Preferably, the air-impeller engine employs dual, coaxial, contra-rotating rotors for increased thrust and gyroscopic stability. An air vane assembly directs a portion of the air thrust output at a desired angle to provide a horizontal thrust component for flight maneuvering or translation movement. The aircraft can employ a single engine in an annular fuselage, two engines on a longitudinal fuselage chassis, three engines in a triangular arrangement for forward flight stability, or other multiple engine arrangements in a symmetric, balanced configuration. Other flight control mechanisms may be employed, including side winglets, an overhead wing, and / or air rudders or flaps. An integrated flight control system can be used to operate the various flight control mechanisms. Electric power is supplied to the magnetic induction drives by high-capacity lightweight batteries or fuel cells. The hover aircraft is especially well suited for applications requiring VTOL deployment, hover operation for quiet surveillance, maneuvering in close air spaces, and long duration flights for continuous surveillance of ground targets and important facilities requiring constant monitoring.
Owner:SANDERS JR JOHN K +3
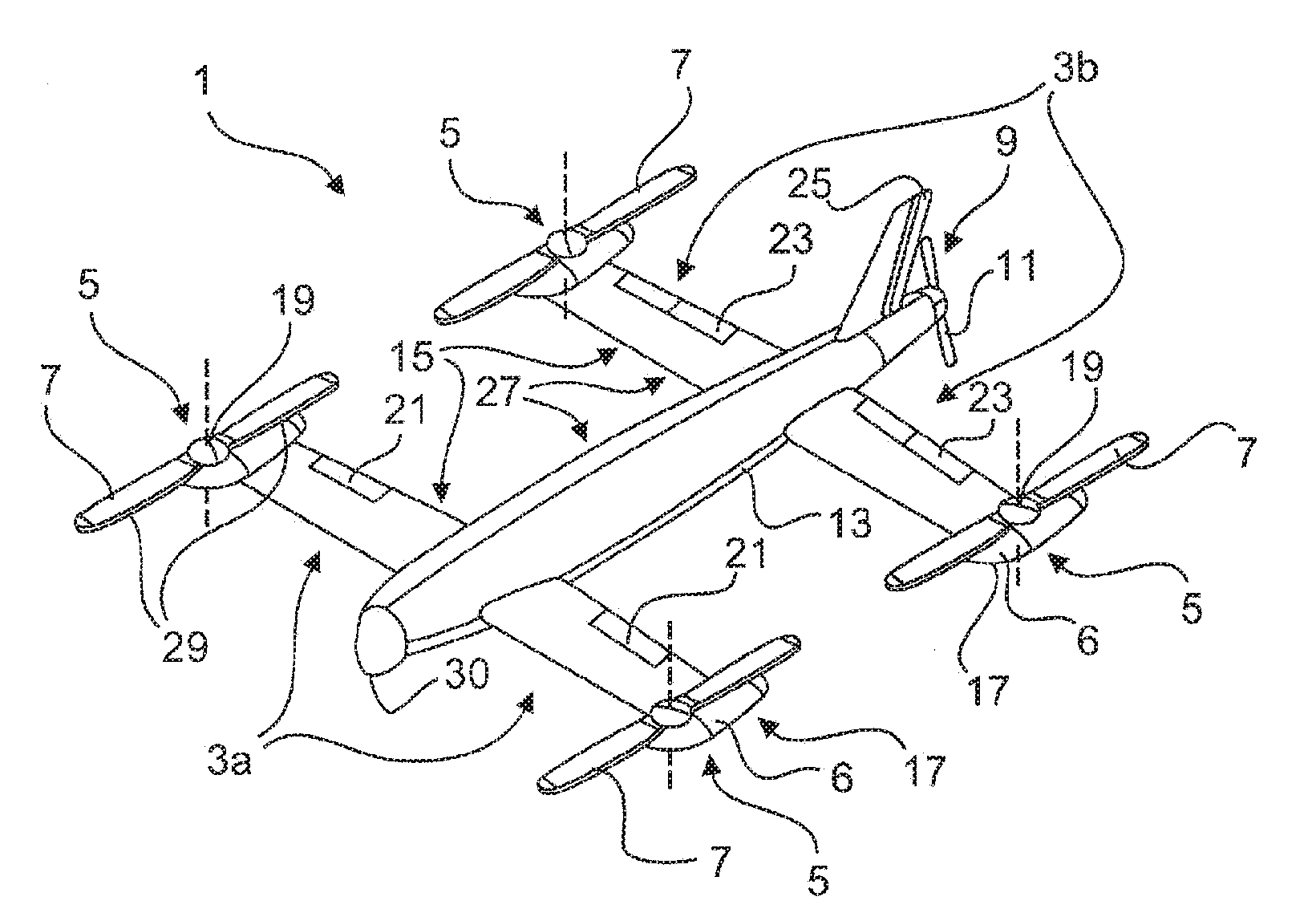
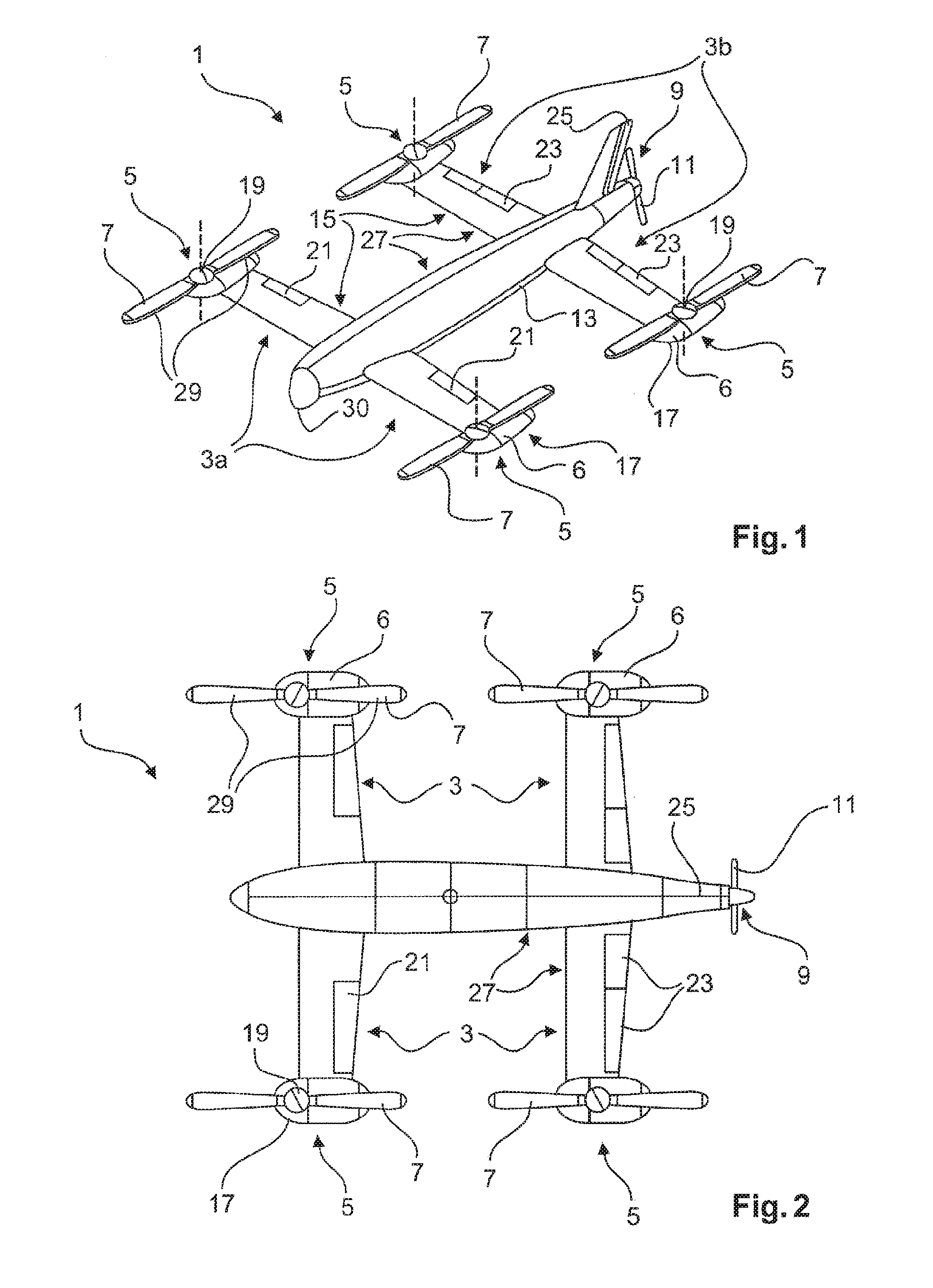
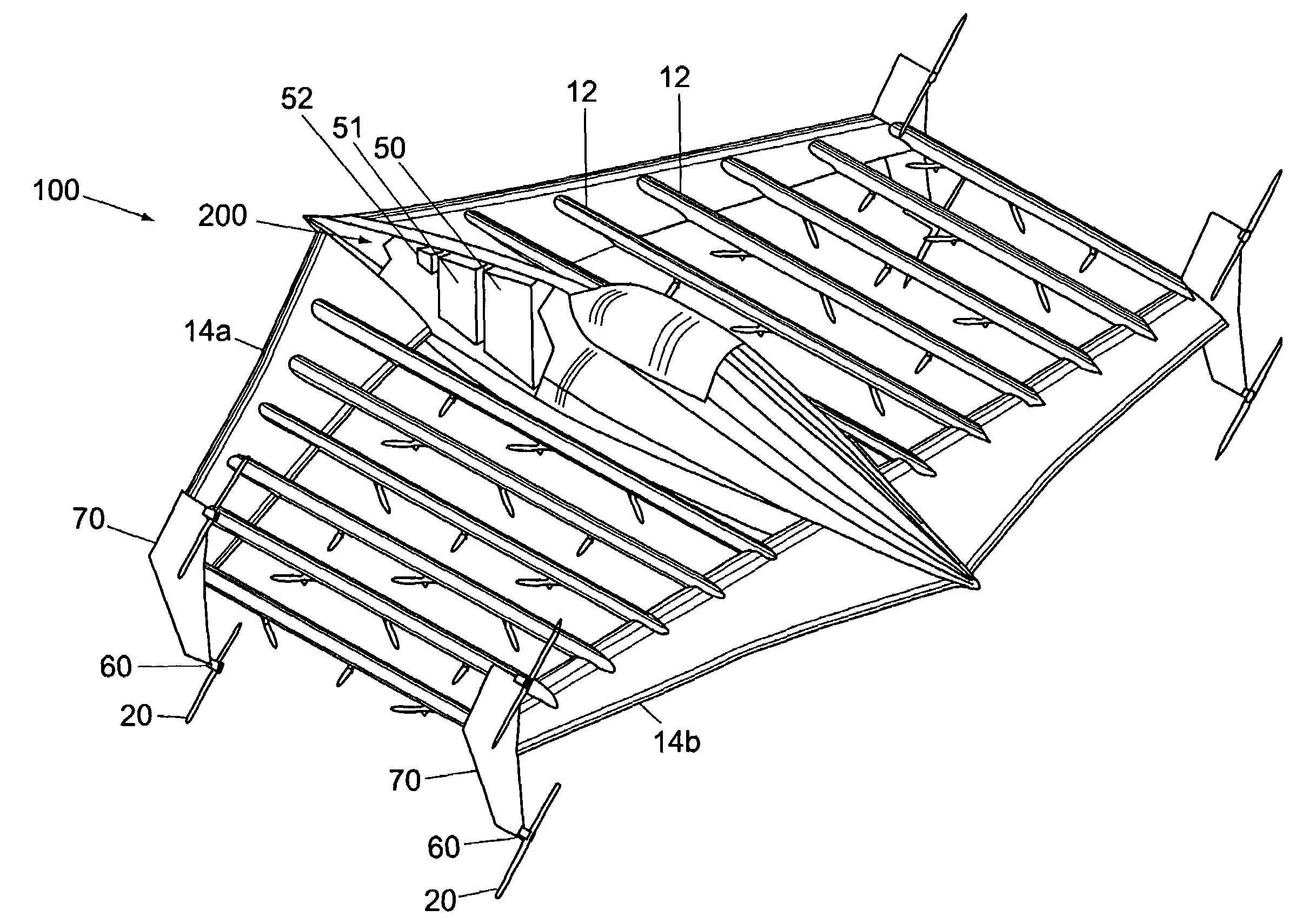
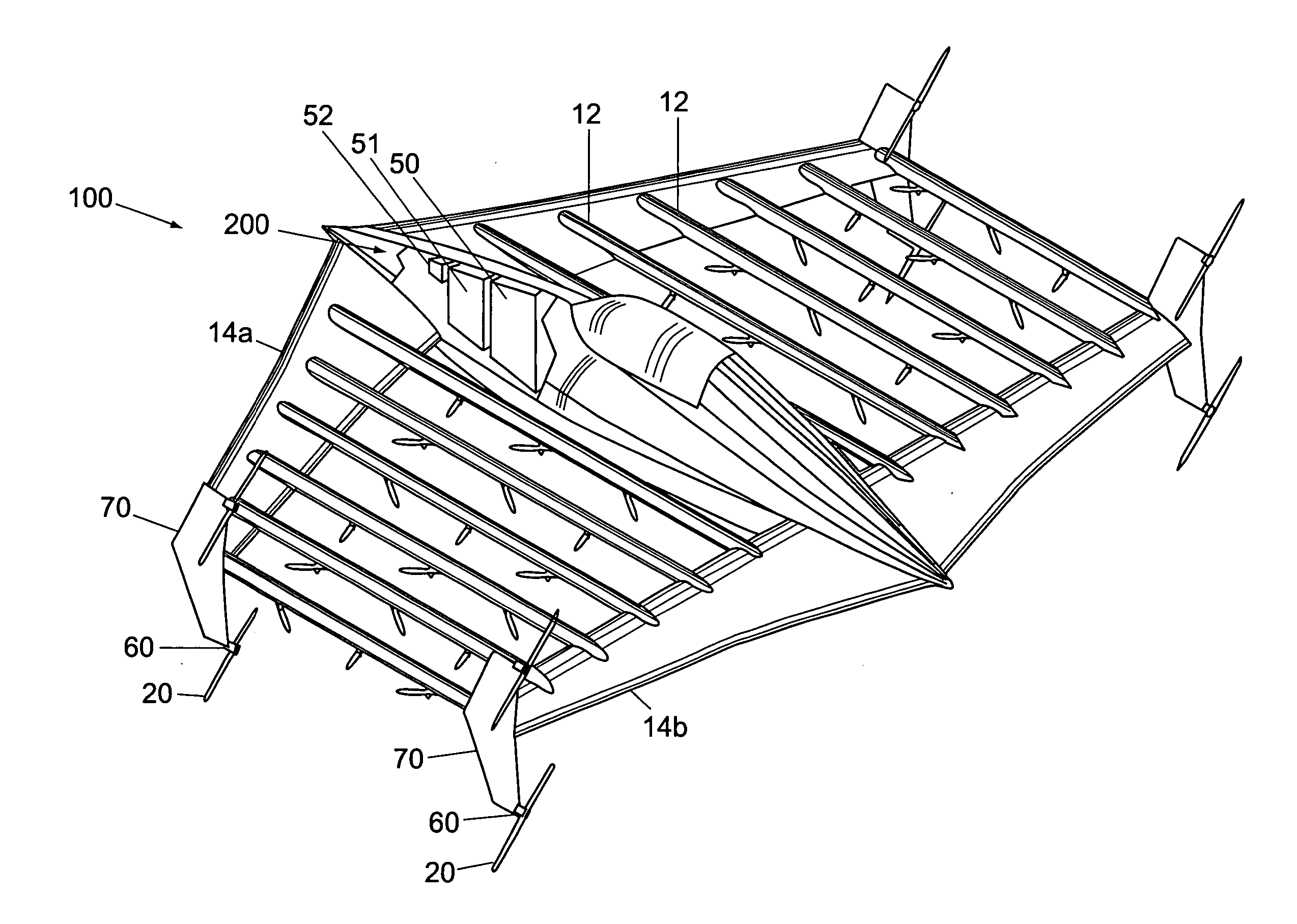
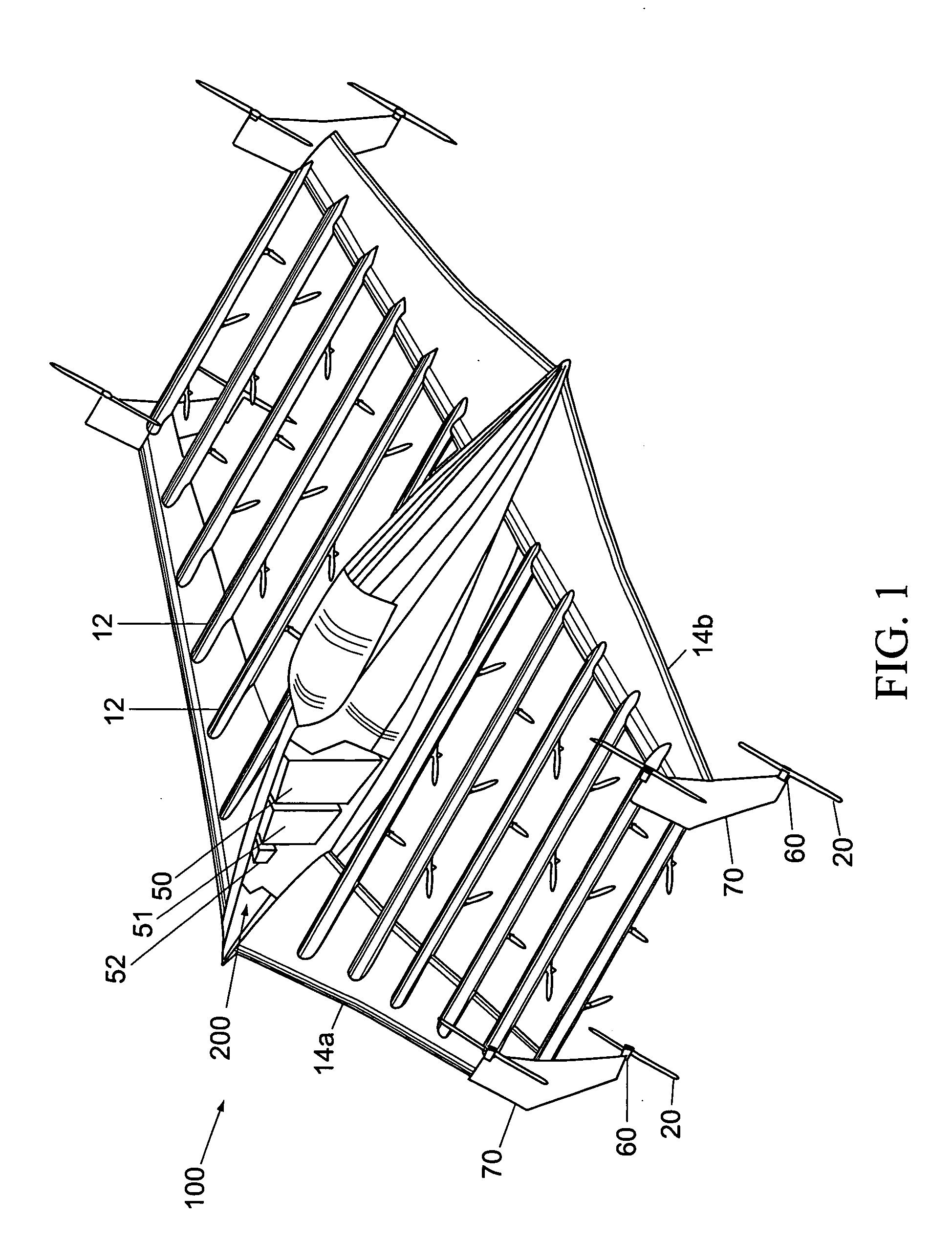
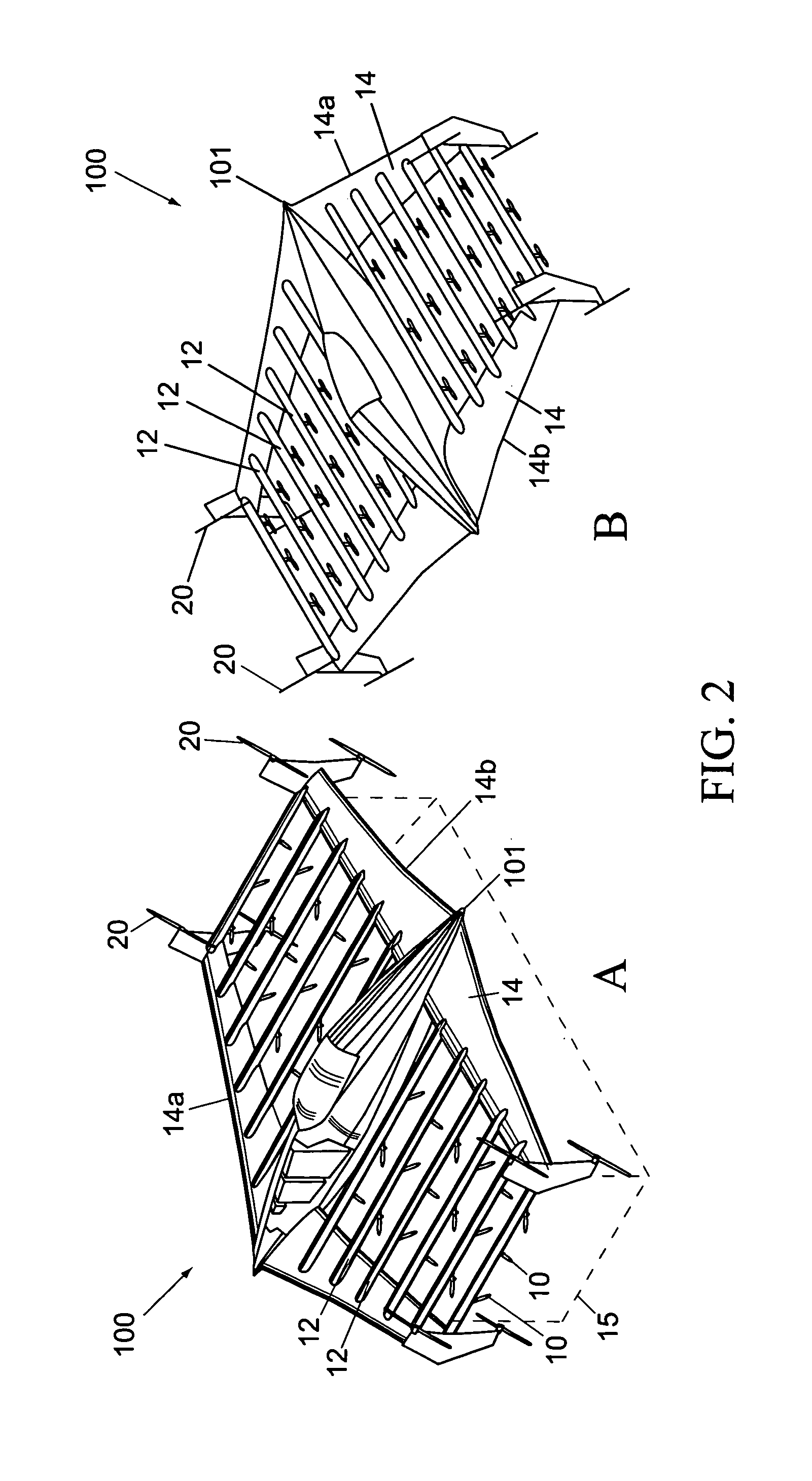
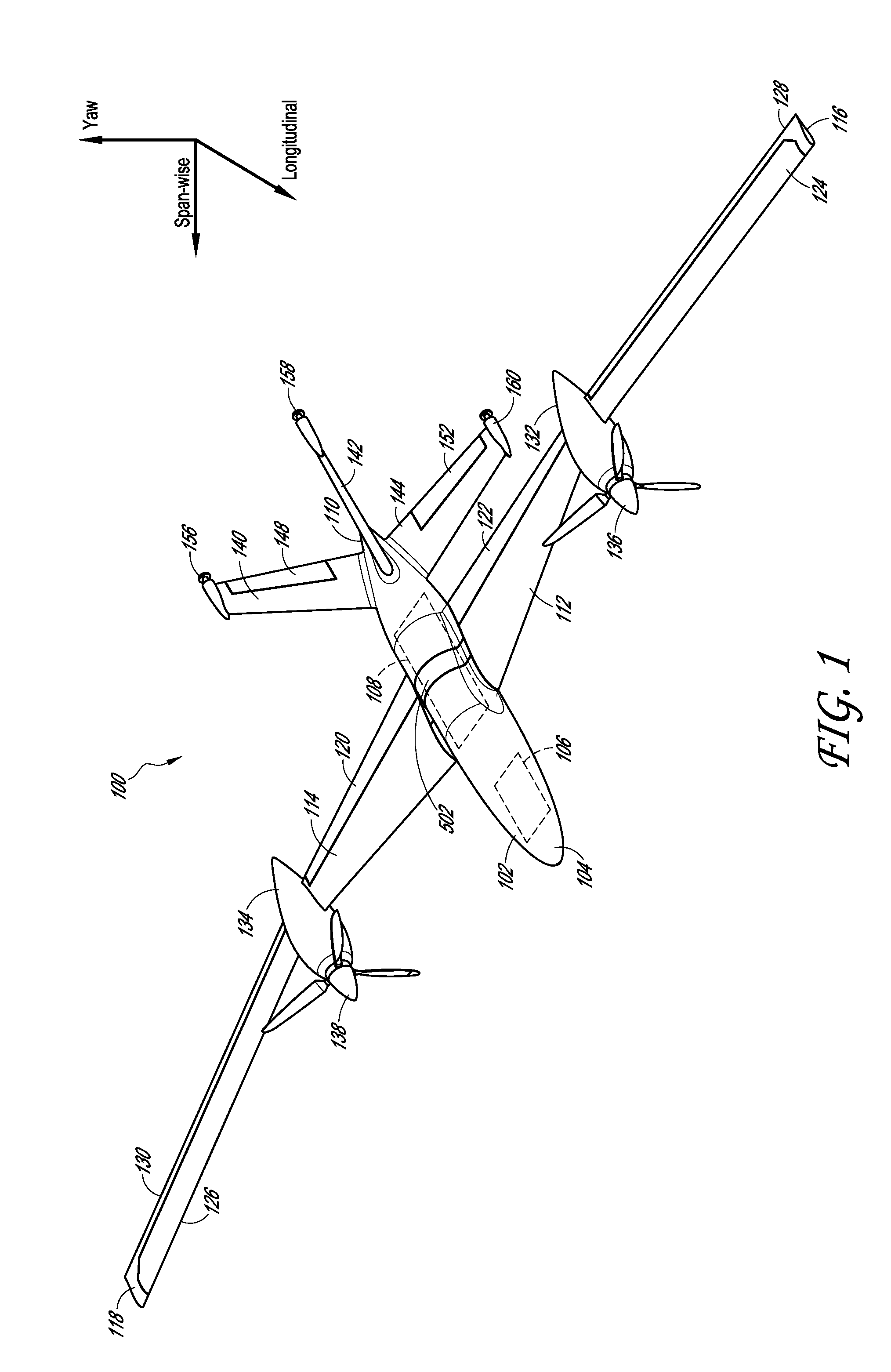
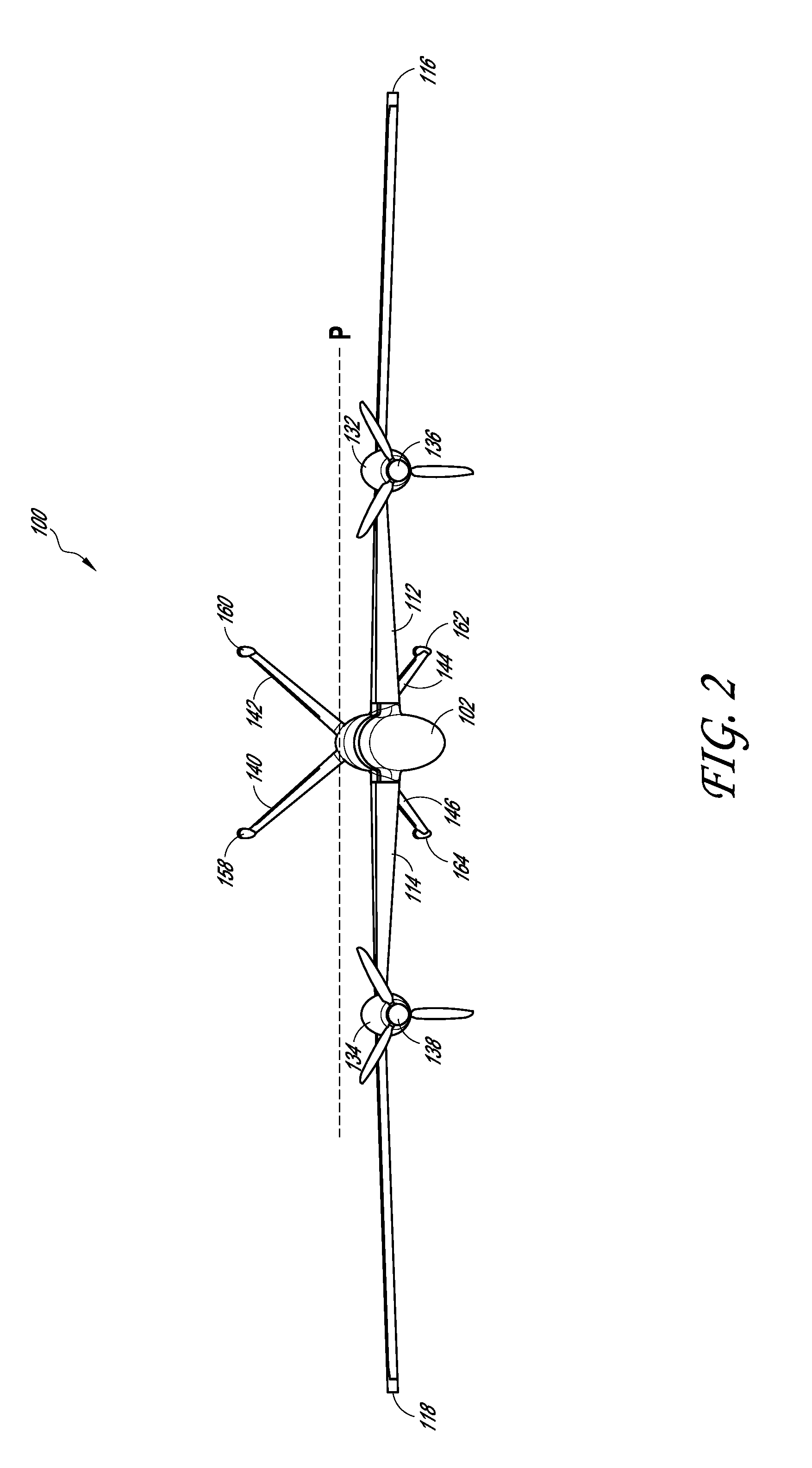
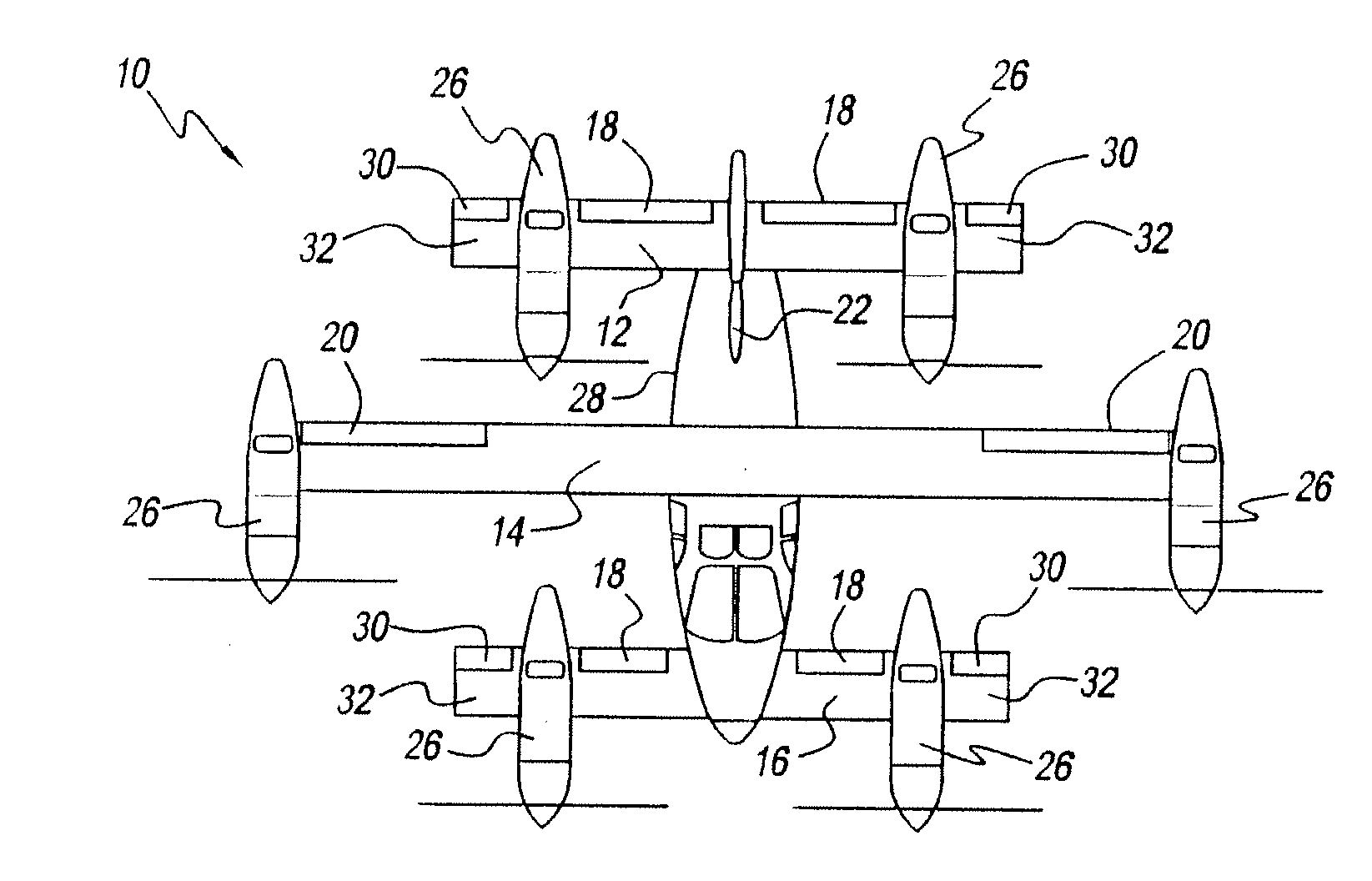
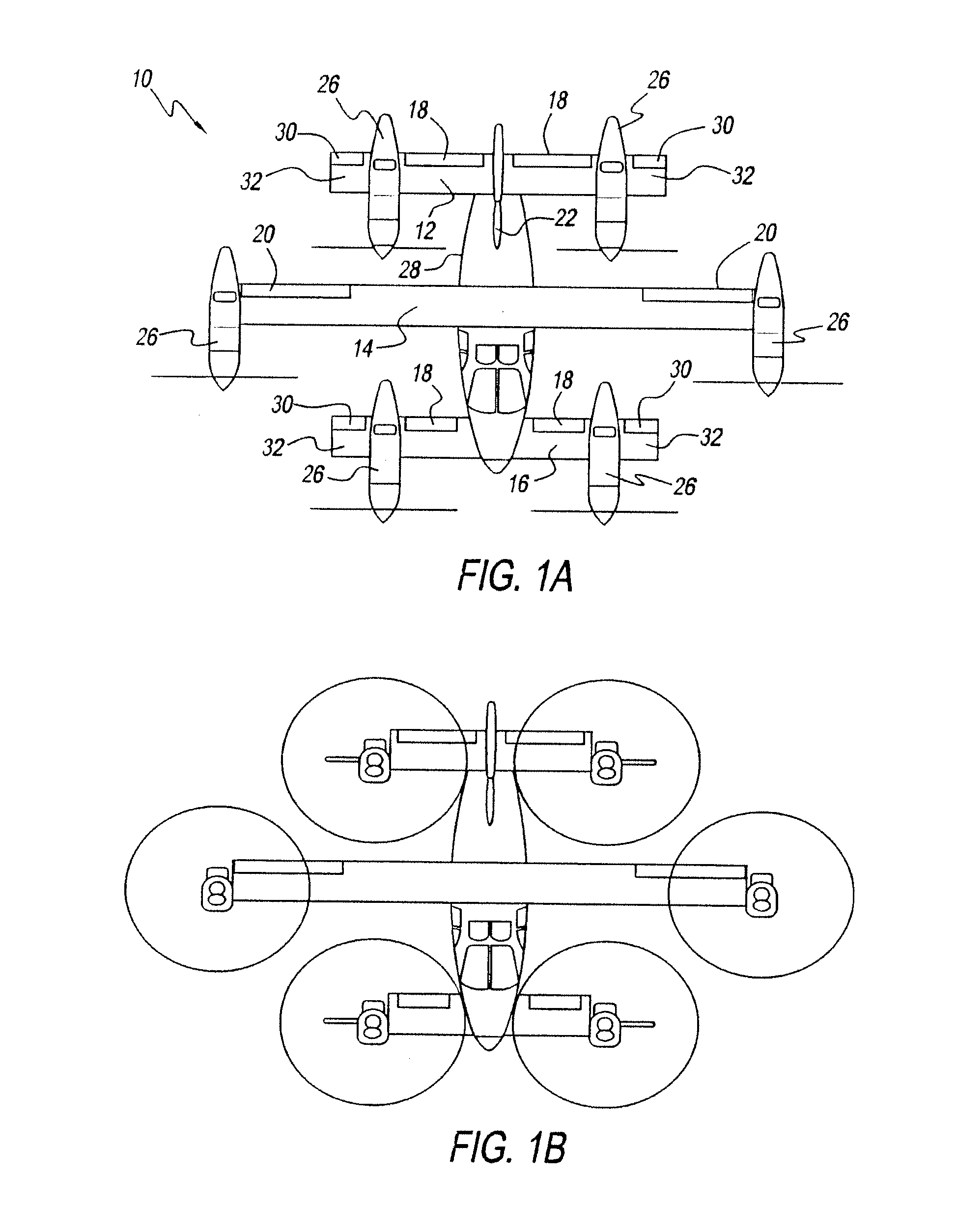
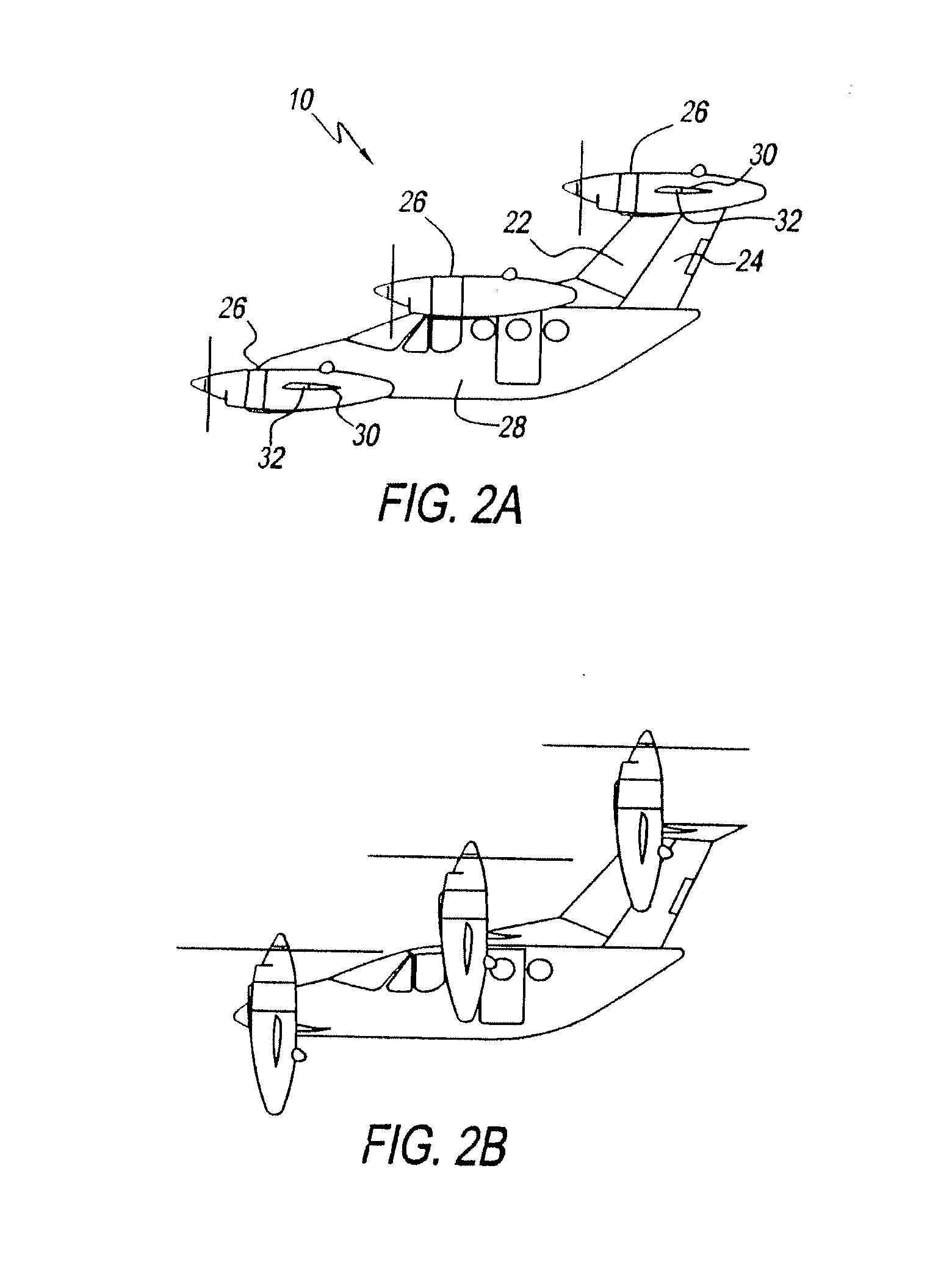
Vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft with distributed thrust and control
InactiveUS7159817B2Highly efficient forward flightImprove reliabilityAircraft navigation controlVertical landing/take-off aircraftsJet aeroplaneMotor controller
An aircraft having a vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) propulsion system. The aircraft includes a fuselage, the VTOL propulsion system, at least one forward thruster, a power source used for both the VTOL propulsion system and forward thruster, fore and aft wings and a plurality of spars attached to and spanning the space between the two wings. The VTOL propulsion system includes a plurality of VTOL cells (including a motor, motor controller, and propeller) attached in a spaced relation along each spar. The VTOL cells are used exclusively for vertical flight or hovering and are powered down as the aircraft develops forward flight velocity and corresponding wing lift. During forward flight the VTOL propellers are articulated to allow the aircraft to take on a low drag configuration. The present invention is suitable for use in manned or un-manned aircraft of any scale.
Owner:VANDERMEY TIMOTHY +1
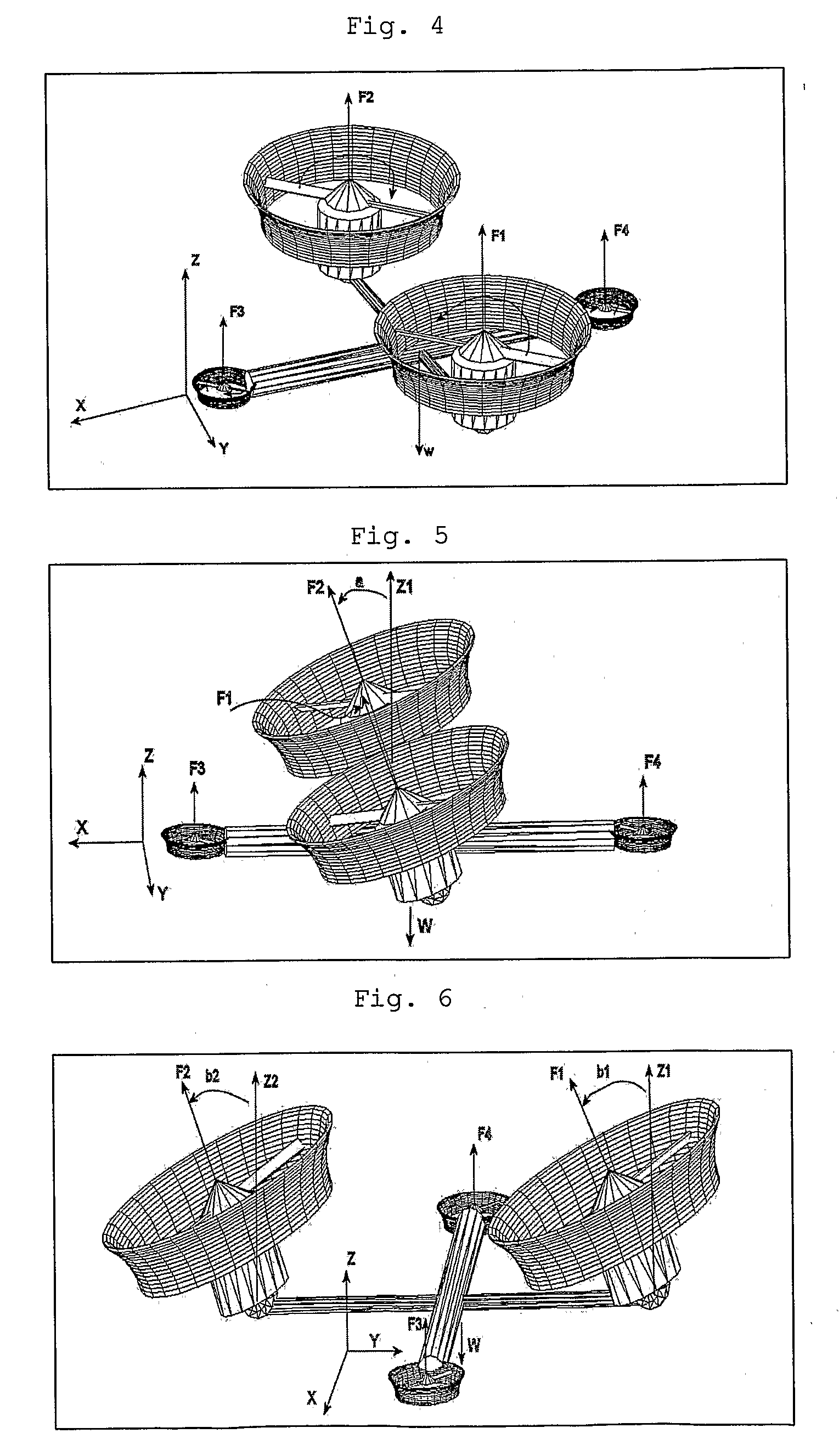
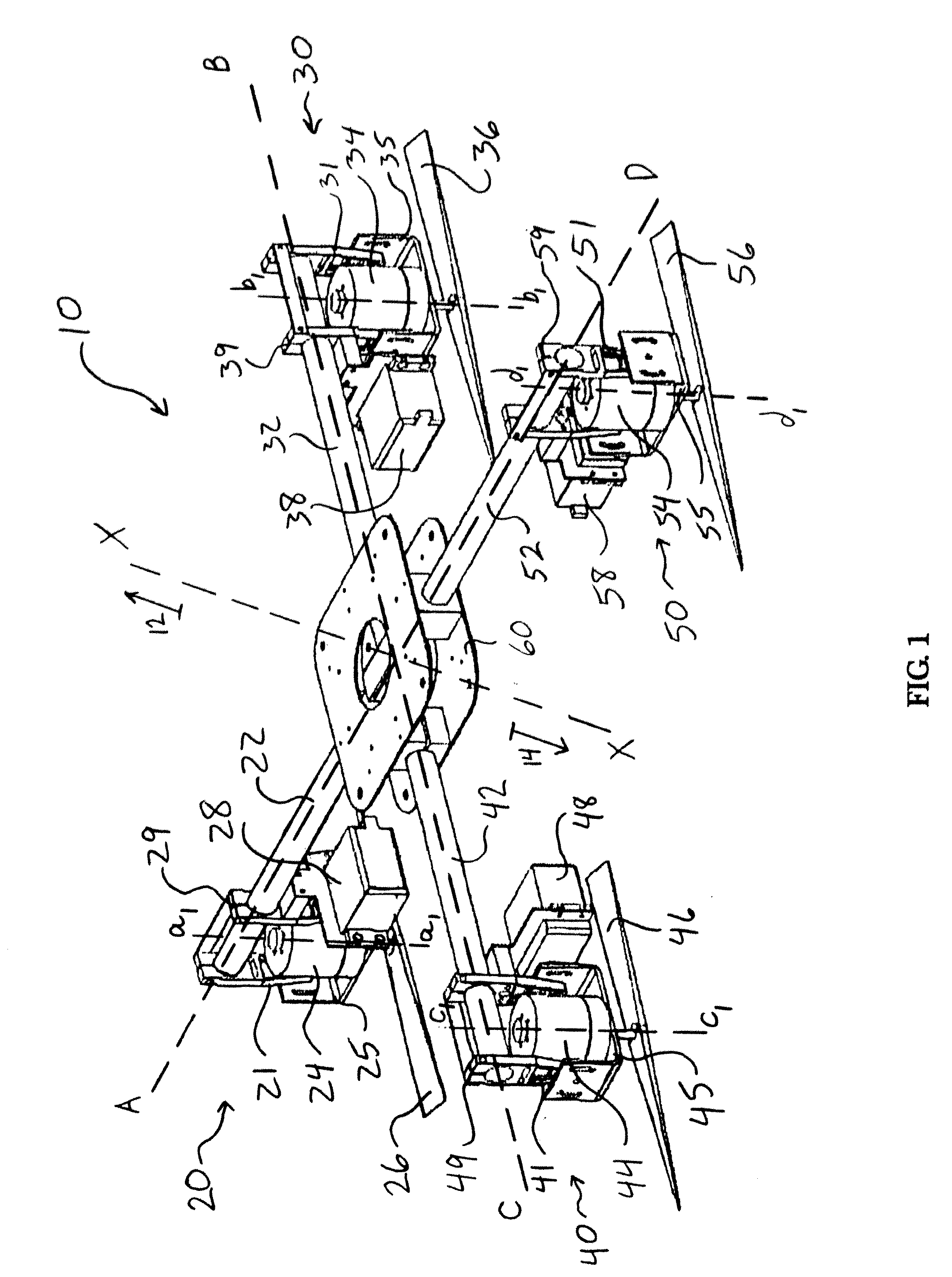
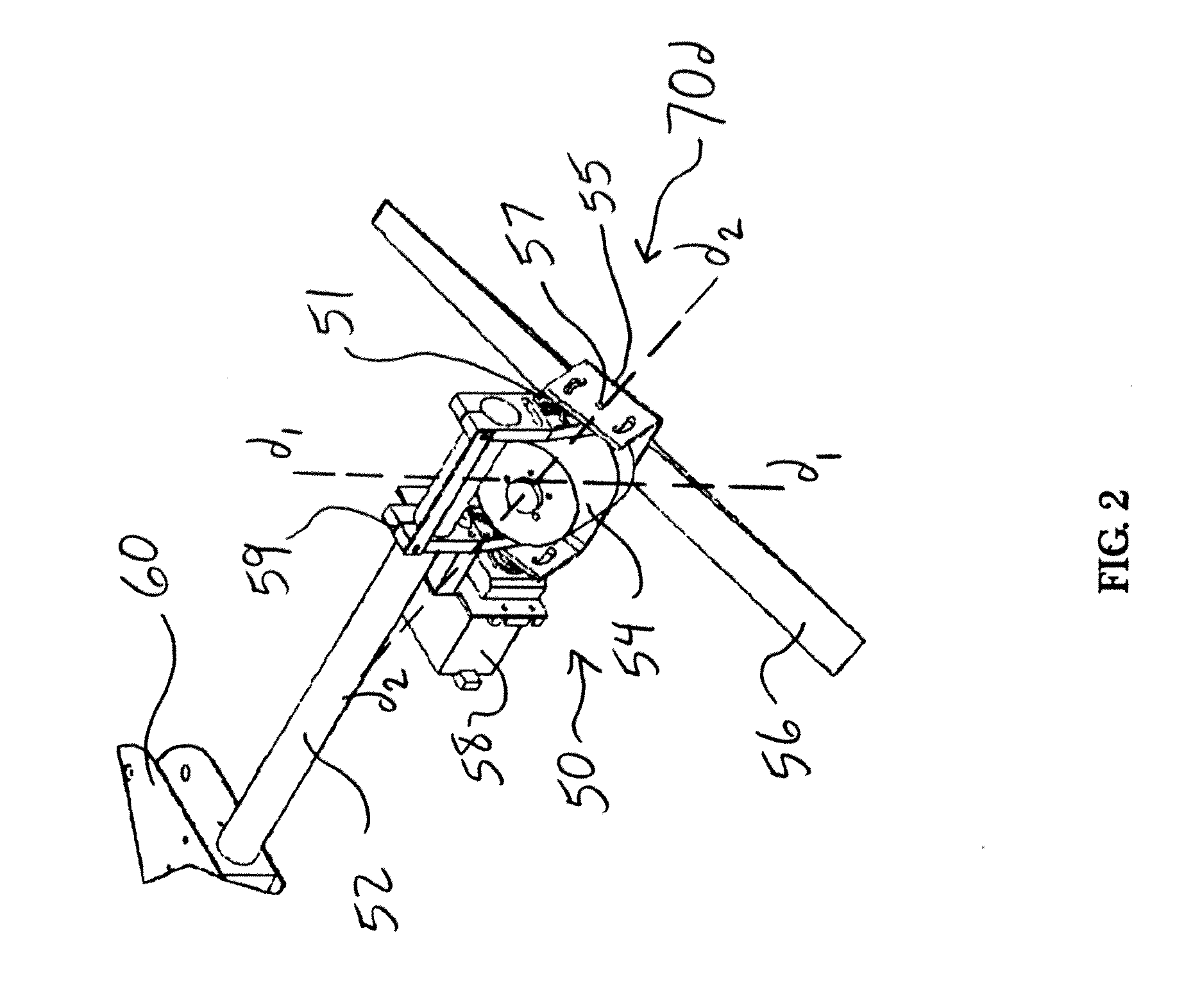
System and Process of Vector Propulsion with Independent Control of Three Translation and Three Rotation Axis
ActiveUS20100301168A1Reduces the passenger's discomfortEasy to controlCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsControl systemVector control system
The present invention relates to a propulsion system of a vertical takeoff and landing aircraft or vehicle moving in any fluid or vacuum and more particularly to a vector control system of the vehicle propulsion thrust allowing an independent displacement with six degrees of freedom, three degrees of translation in relation to its centre of mass and three degrees of rotation in relation to its centre of mass. The aircraft displacement ability using the propulsion system of the present invention depends on two main thrusters or propellers and which can be tilted around pitch is (I) by means of tilting mechanisms and, used to perform a forward or backward movement, can be tilted around roll axis (X) by means of tilting mechanisms and, used to perform lateral movements to the right or to the left and to perform upward or downward movements (Z), the main thrusters being further used to perform rotations around the vehicle yaw axis (Z) and around the roll is (X). The locomotion function also uses one or two auxiliary thrusters or propellers and mainly used to control the rotation around the pitch axis, these thrusters or propellers and being fixed at or near the longitudinal is of the vehicle, with there thrust perpendicular or nearly perpendicular to the roll and pitch axis of the vehicle.
Owner:RAPOSO SEVERINO
Vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft with distributed thrust and control
InactiveUS20060151666A1Highly efficient forward flightImprove reliabilityAircraft navigation controlVertical landing/take-off aircraftsFlight vehicleElectric machinery
An aircraft having a vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) propulsion system. The aircraft includes a fuselage, the VTOL propulsion system, at least one forward thruster, a power source used for both the VTOL propulsion system and forward thruster, fore and aft wings and a plurality of spars attached to and spanning the space between the two wings. The VTOL propulsion system includes a plurality of VTOL cells (including a motor, motor controller, and propeller) attached in a spaced relation along each spar. The VTOL cells are used exclusively for vertical flight or hovering and are powered down as the aircraft develops forward flight velocity and corresponding wing lift. During forward flight the VTOL propellers are articulated to allow the aircraft to take on a low drag configuration. The present invention is suitable for use in manned or un-manned aircraft of any scale.
Owner:VANDERMEY TIMOTHY +1
Quad tilt rotor vertical take off and landing (VTOL) unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) with 45 degree rotors
InactiveUS20130105635A1Maintain balance and stabilityIncreased payload capacityUnmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftFlight vehicleClassical mechanics
A system and method to control the stability and direction of a quad tilt vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) by manipulating the rotational speed of propellers at each rotor while simultaneously tilting the rotors in a 45 degree configuration related to a central axis for directional control. Each rotor is attached to a tilting mechanism configured to be symmetrically aligned at a 45 degree angle from a central axis to manipulate a directional angle of each rotor along a first and second axis. The first and fourth rotors are aligned on the first axis while the second and third rotors are aligned on the second axis. A controller includes a first control loop for manipulating the rotational speed of the propellers to control the aircraft balance and a second control loop for controlling lateral movement by tilting the rotors along the first and second axis.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH II DESIGN & DEV BUREAU
Aerodynamically efficient lightweight vertical take-off and landing aircraft with pivoting rotors and stowing rotor blades
ActiveUS20150266571A1Reduce resistanceReduce drag in all flight modesPropellersEfficient propulsion technologiesLevel flightFlight vehicle
An aerial vehicle adapted for vertical takeoff and landing using a set of wing mounted thrust producing elements and a set of tail mounted rotors for takeoff and landing. An aerial vehicle which is adapted to vertical takeoff with the rotors in a rotated, take-off attitude then transitions to a horizontal flight path, with the rotors rotated to a typical horizontal configuration. The aerial vehicle uses different configurations of its wing mounted rotors and propellers to reduce drag in all flight modes.
Owner:JOBY AERO INC
Long endurance vertical takeoff and landing aircraft
An aircraft for use in fixed wing flight mode and rotor flight mode is provided. The aircraft can include a fuselage, wings, and a plurality of engines. The fuselage can comprise a wing attachment region further comprising a rotating support. A rotating section can comprise a rotating support and the wings, with a plurality of engines attached to the rotating section. In a rotor flight mode, the rotating section can rotate around a longitudinal axis of the fuselage providing lift for the aircraft similar to the rotor of a helicopter. In a fixed wing flight mode, the rotating section does not rotate around a longitudinal axis of the fuselage, providing lift for the aircraft similar to a conventional airplane. The same engines that provide torque to power the rotor in rotor flight mode also power the aircraft in fixed wing flight mode.
Owner:DZYNE TECH
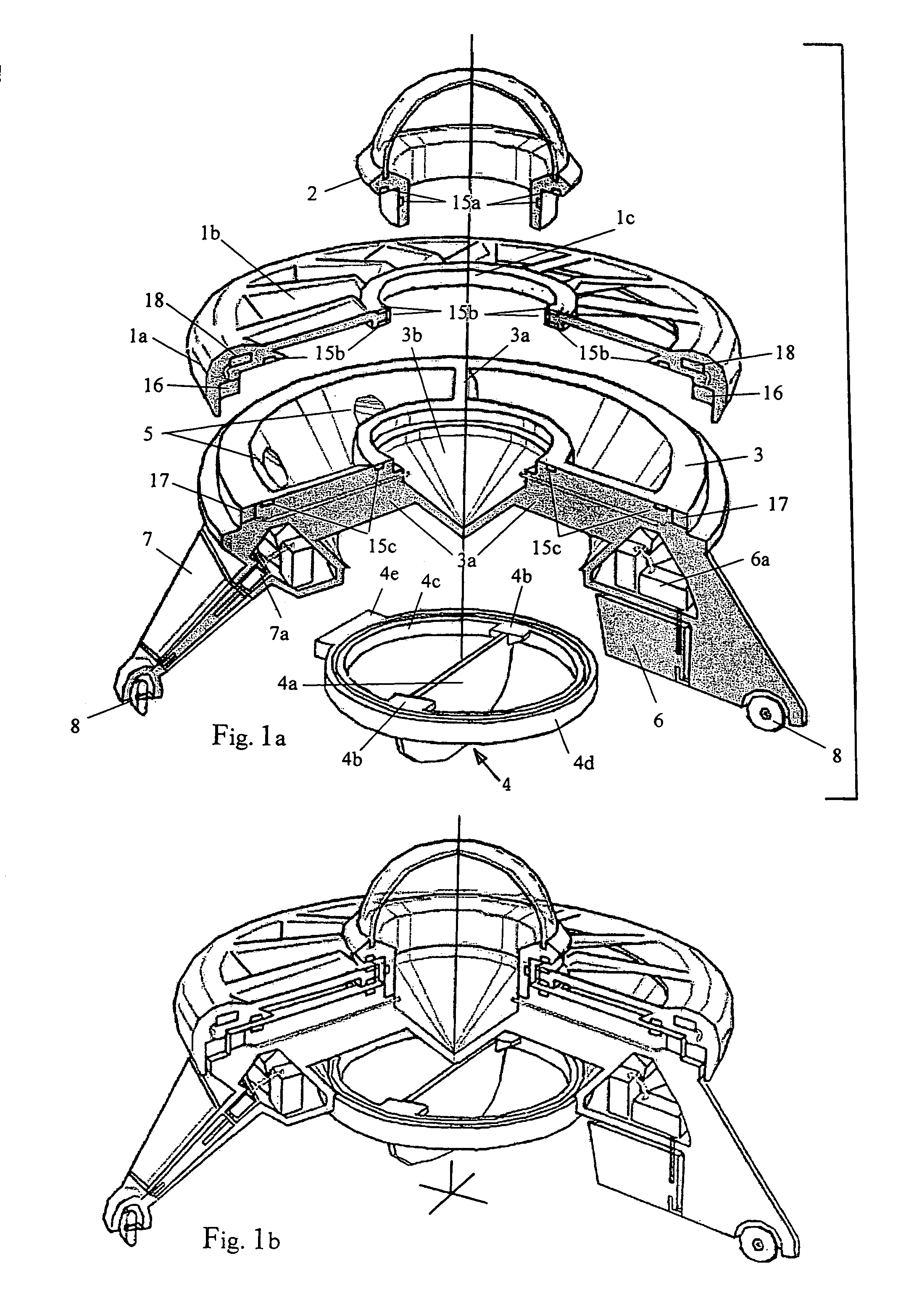
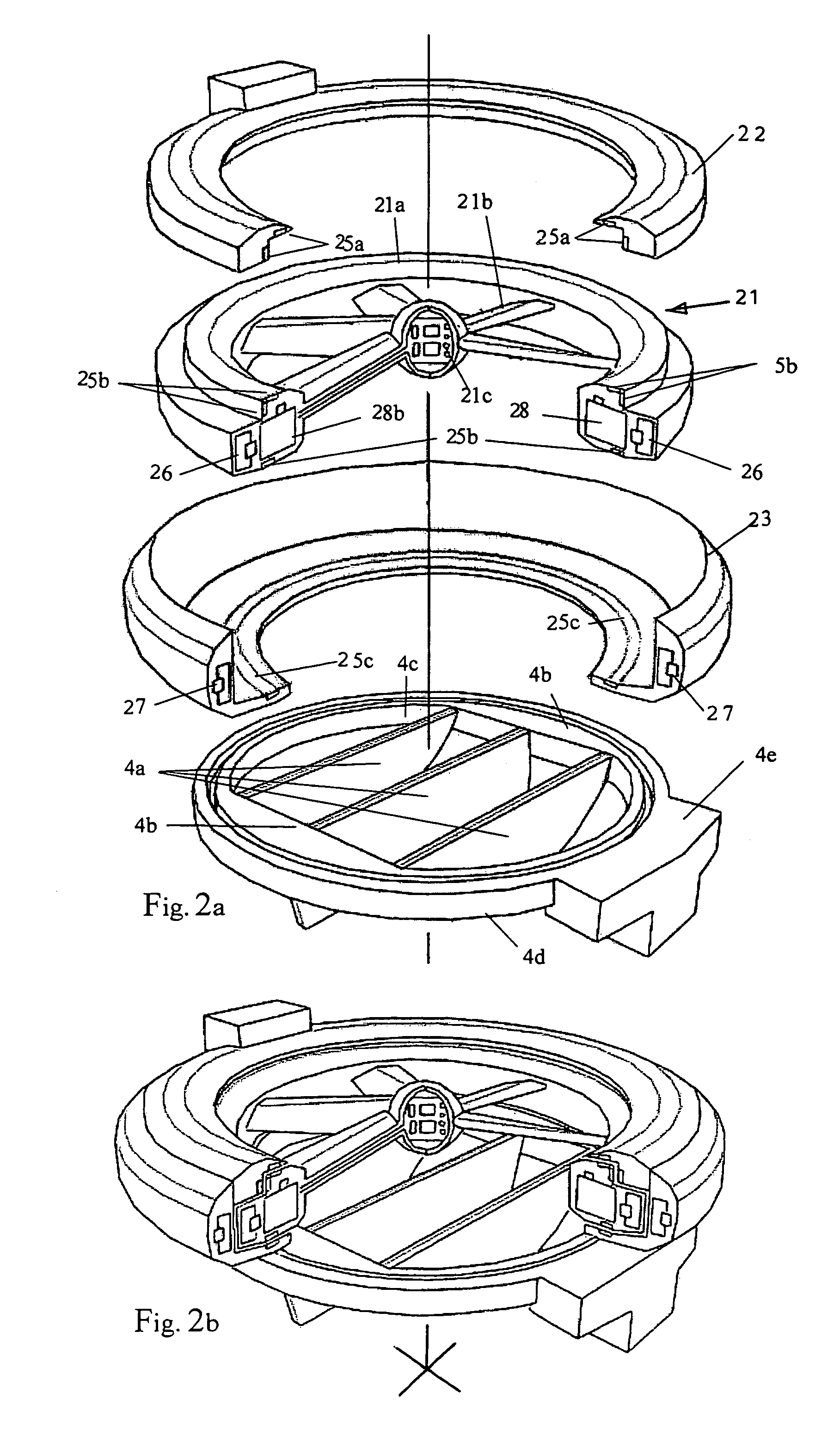
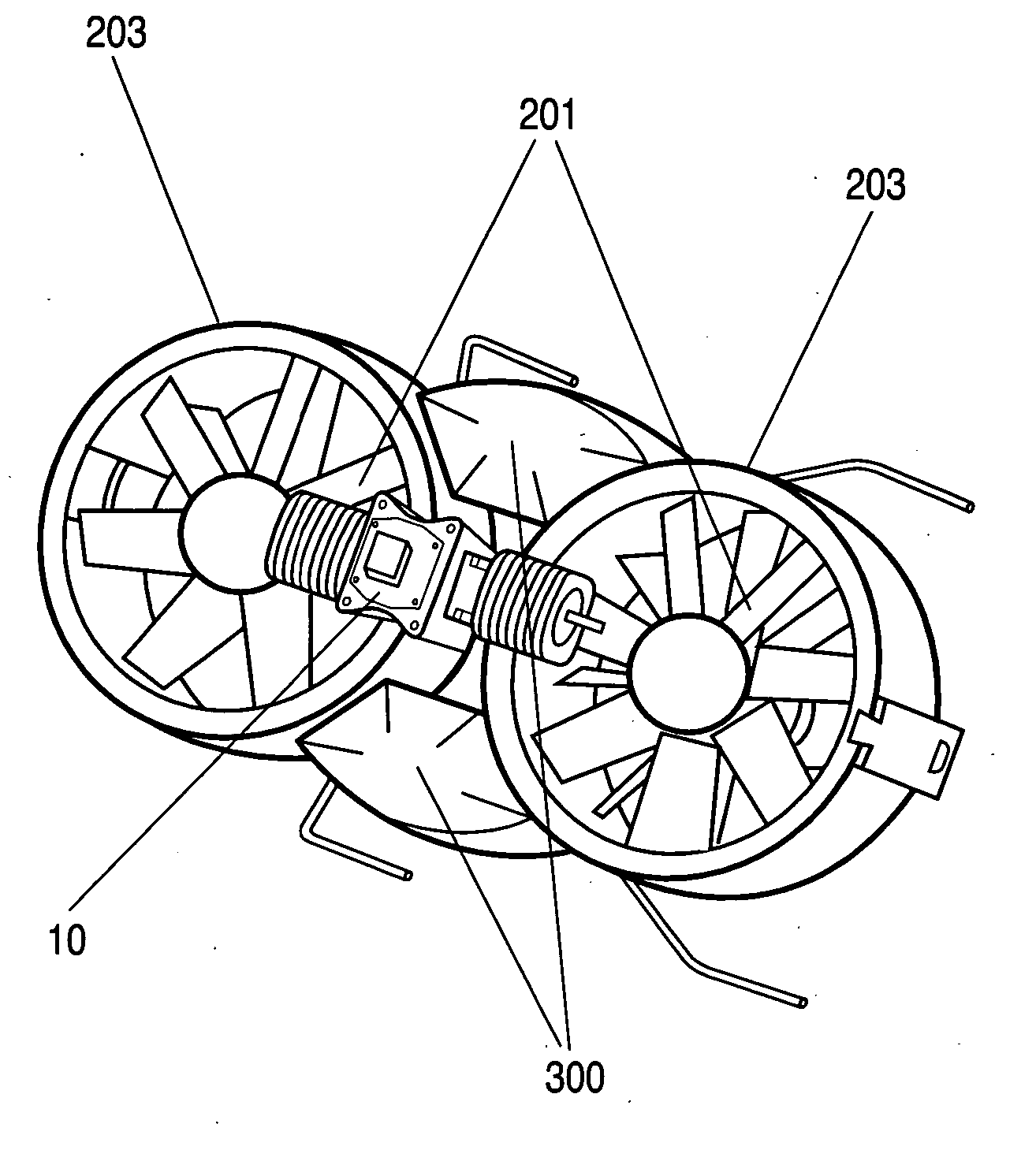
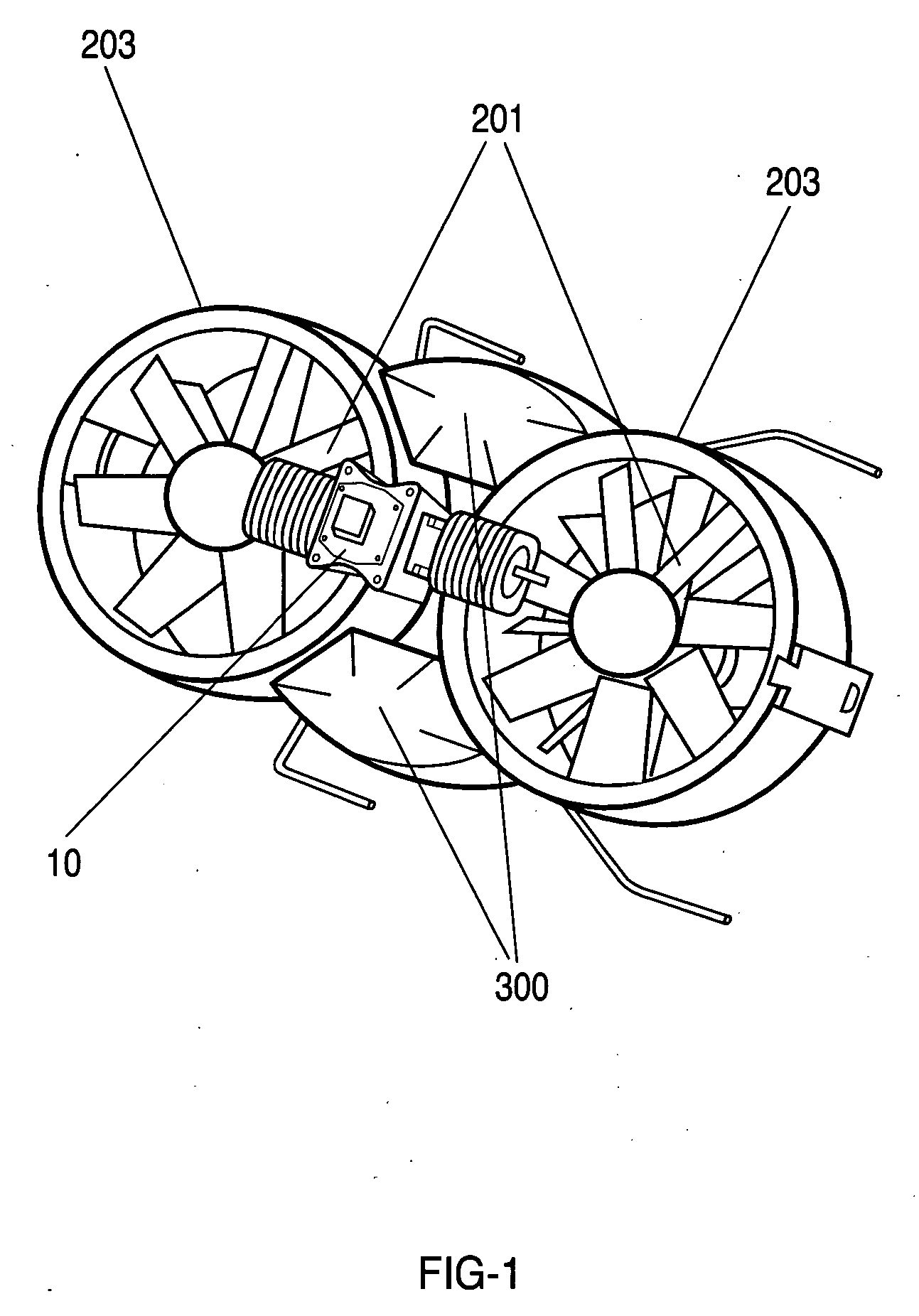
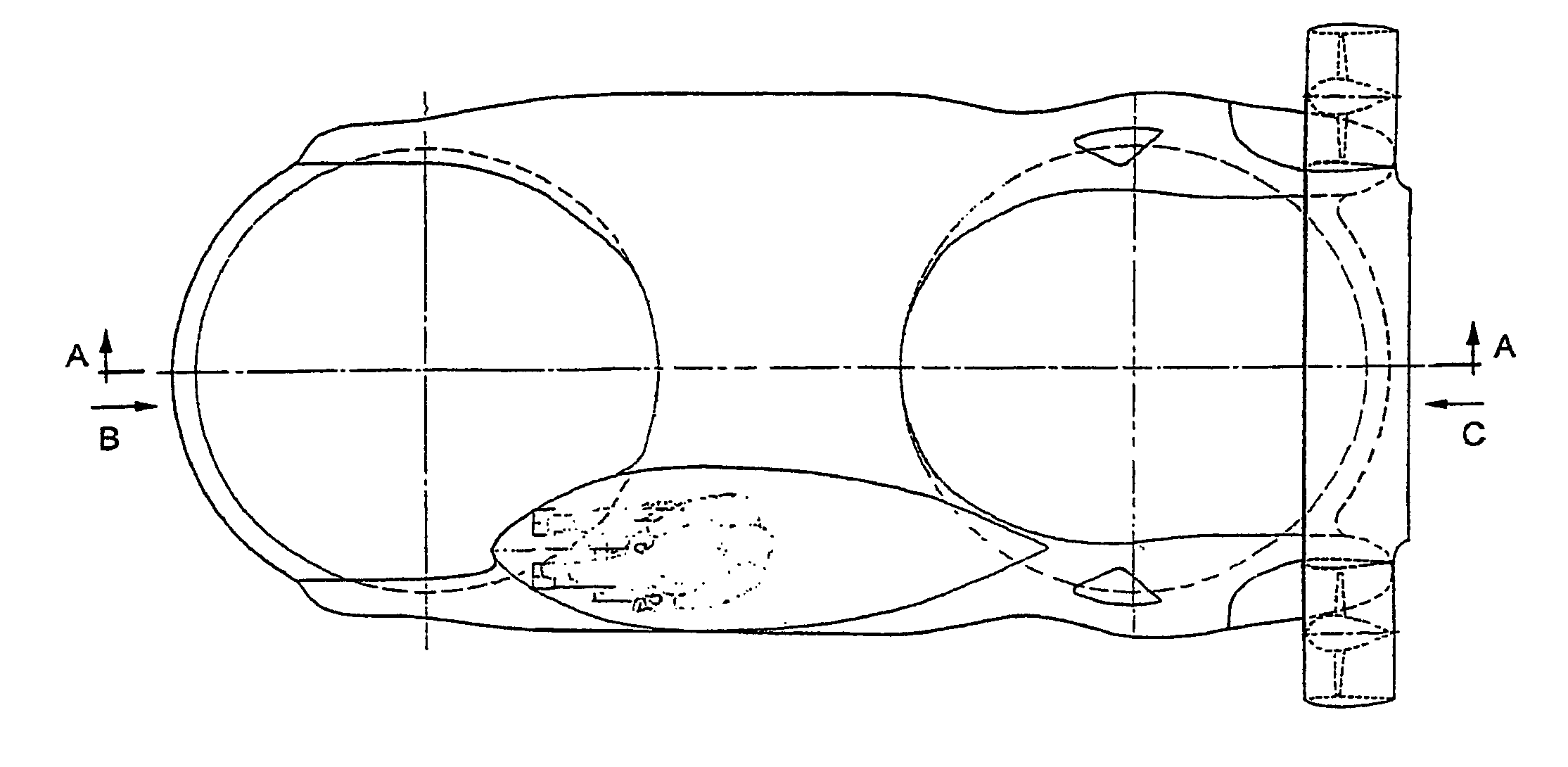
Double ducted hovering air-vehicle
InactiveUS20060192047A1Improve lifting performanceHeavy loadPower plant arrangements/mountingUnmanned aerial vehiclesAviationGear wheel
A dual ducted fan arrangement in which the duct components, engine, and avionics / payload pods are capable of being quickly disassembled to fit within common backpacking systems.. Each duct is identical in fan, stator, and control vane design. Assembly connections between ducted fans and electronic modules are also identical. An engine or APU drives the dual ducted fans through a splined shaft to a differential or through electric motors. Energy is transferred to the ducted fans by a single gear mounted to the stator hub. Relative speeds of the individual ducted fans are controlled through separate frictional or generator load control braking mechanisms on each of the splined shafts between the differential and ducted fans. In the electric motor case relative speed is through electronic speed control. The fans are counter rotating for torque balancing. The electronic module locations are vertically variable for longitudinal center of gravity for variations in payloads.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Aircraft and torque transmission
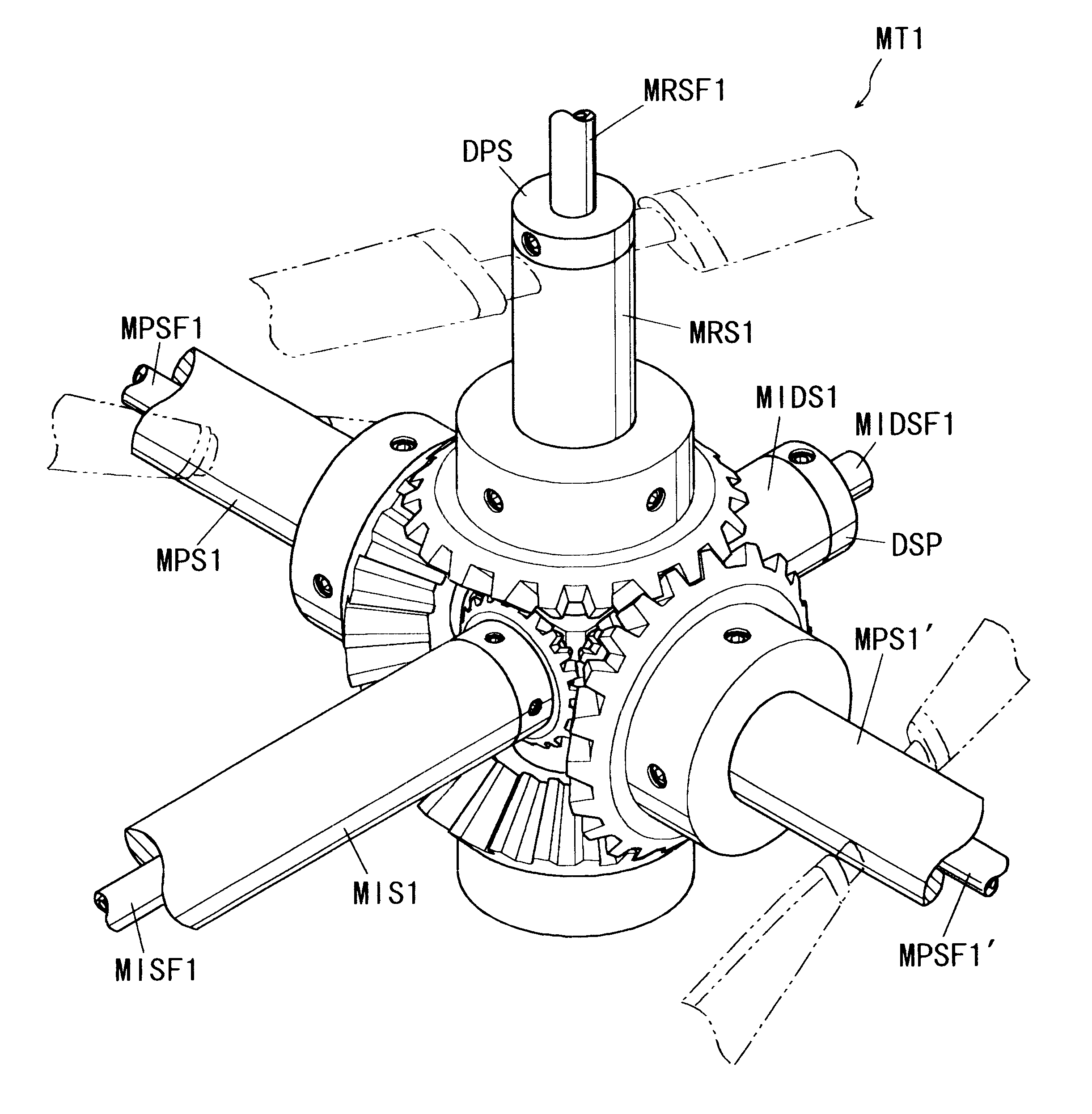
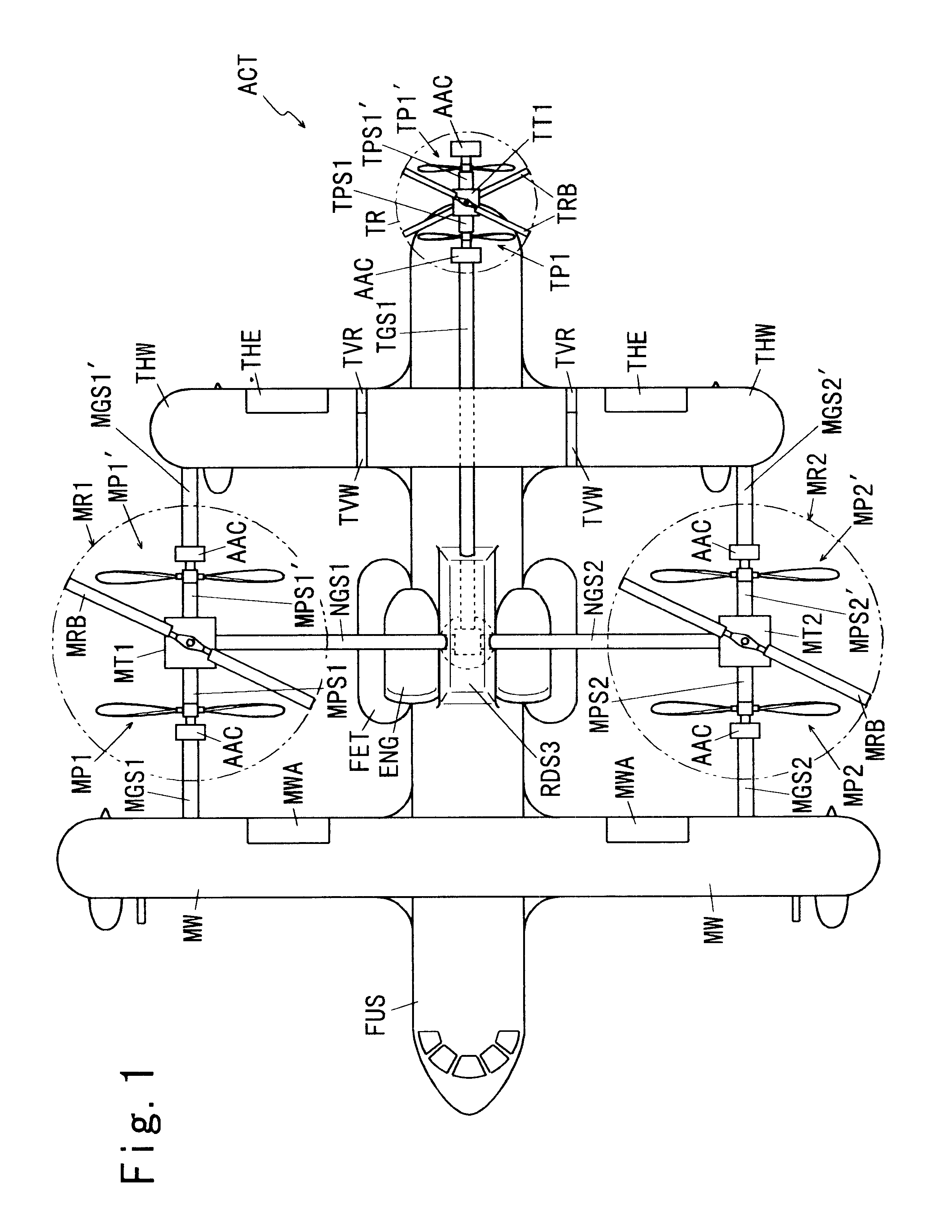
InactiveUS6467726B1Satisfactory stability and controllabilityReduce rotationAircraft navigation controlToothed gearingsFlight directionGear wheel
An aircraft including an airframe having a fuselage which extends longitudinally, and having fixed wings including a main wing, a horizontal tail wing and a vertical tail wing. A propeller-rotor torque transmission has a bevel gear which transmits the rotation of an input shaft simultaneously to a propeller shaft and to a rotor shaft. An engine gearbox supplies the above-mentioned input shaft with rotationalal motive power. The aircraft further includes a propeller collective pitch controller, a rotor collective pitch controller, an engine power controller which controls the output of the above-mentioned engine gearbox for the purpose of changing the rotational speed of the input shaft, and a flight control system having a directional (yaw) control system which controls the flight direction of the aircraft by controlling the positions of the above-mentioned control surfaces.
Owner:HOSODA ROKURO
Ducted fan VTOL vehicles
InactiveUS7857253B2Easy constructionConveniently performedAircraft navigation controlParachutesTransverse axisPropeller
A vehicle including a fuselage having a longitudinal axis and a transverse axis, two Ducted Fan lift-producing propellers carried by the fuselage on each side of the transverse axis, a pilot's compartment formed in the fuselage between the lift-producing propellers and substantially aligned with one side of the fuselage, a payload bay formed in the fuselage between the lift-producing propellers and opposite the pilot's compartment, and two pusher fans located at the rear of the vehicle. Many variations are described enabling the vehicle to be used not only as a VTOL vehicle, but also as a multi-function utility vehicle for performing many diverse functions including hovercraft and ATV functions. Also described is an Unmanned version of the vehicle. Also described are unique features applicable in any single or multiple ducted fans and VTOL vehicles.
Owner:URBAN AERONAUTICS
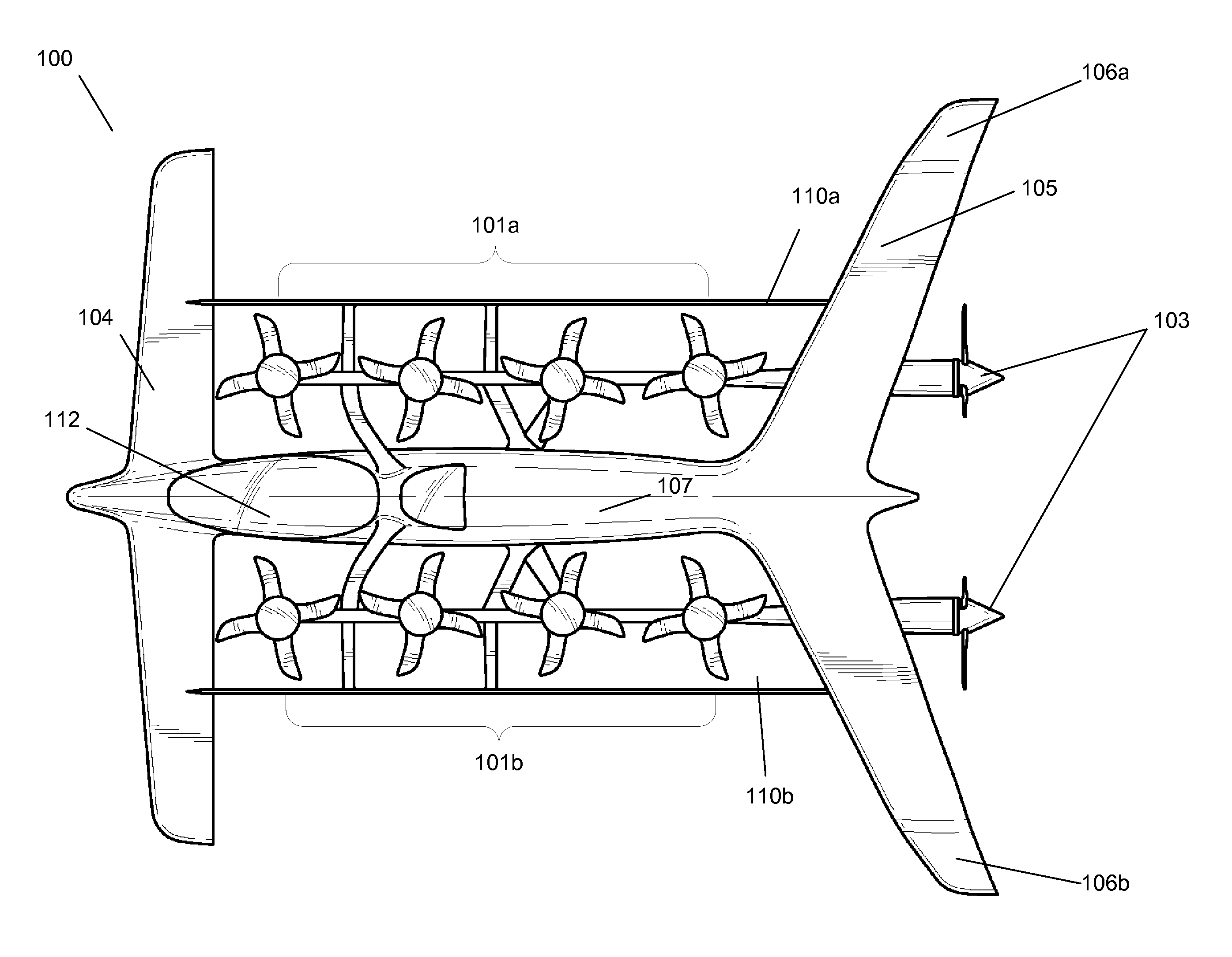
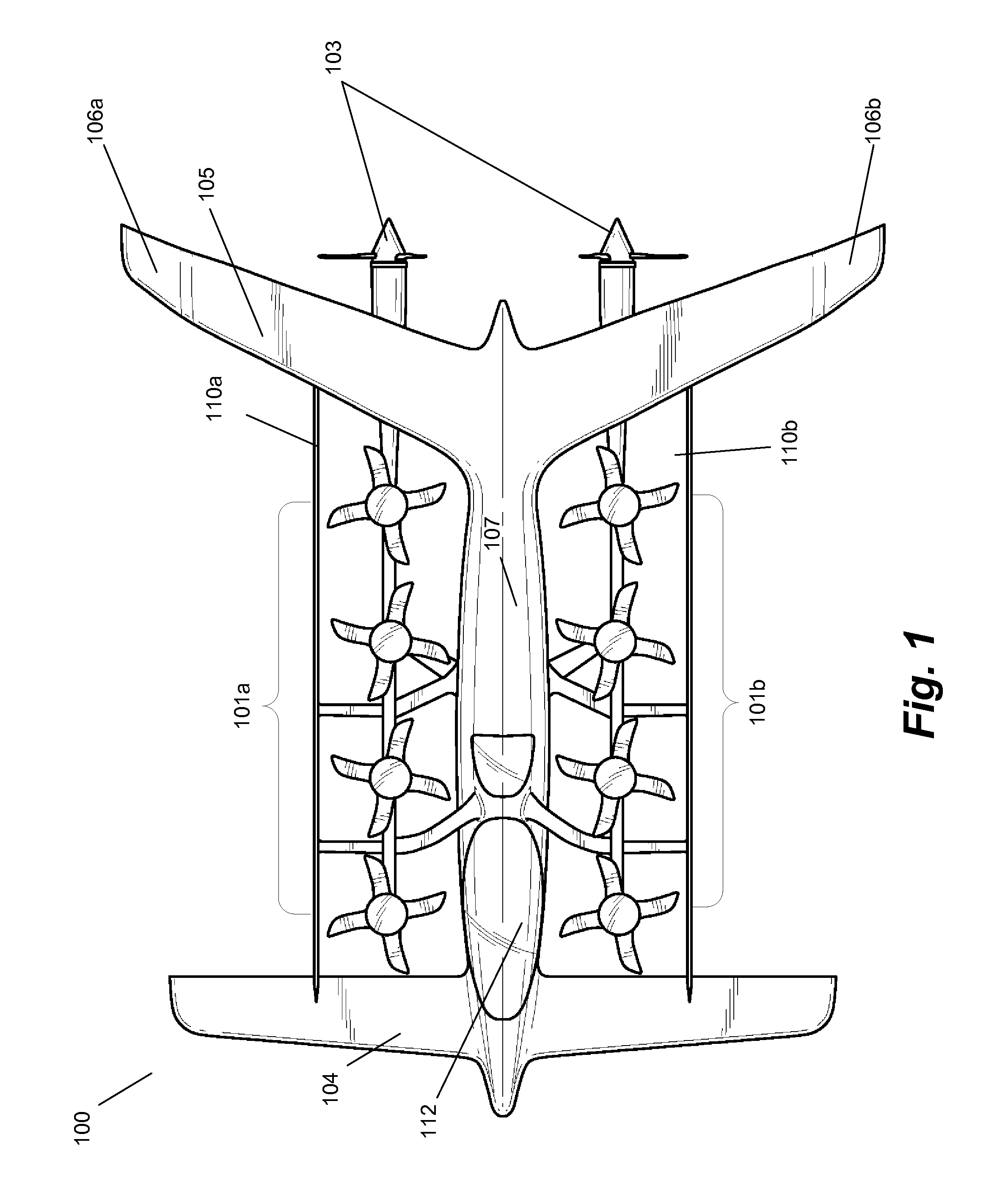
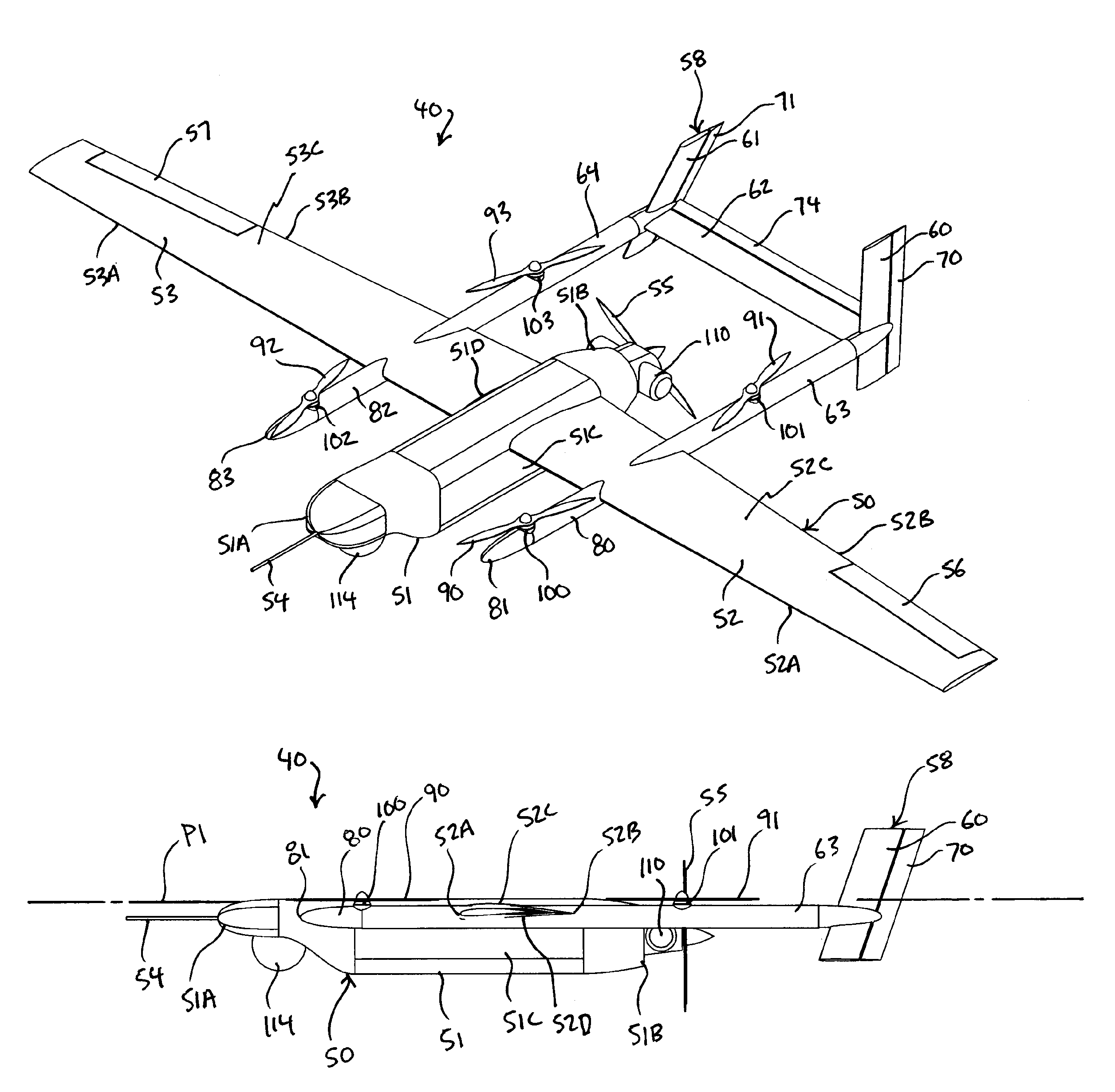
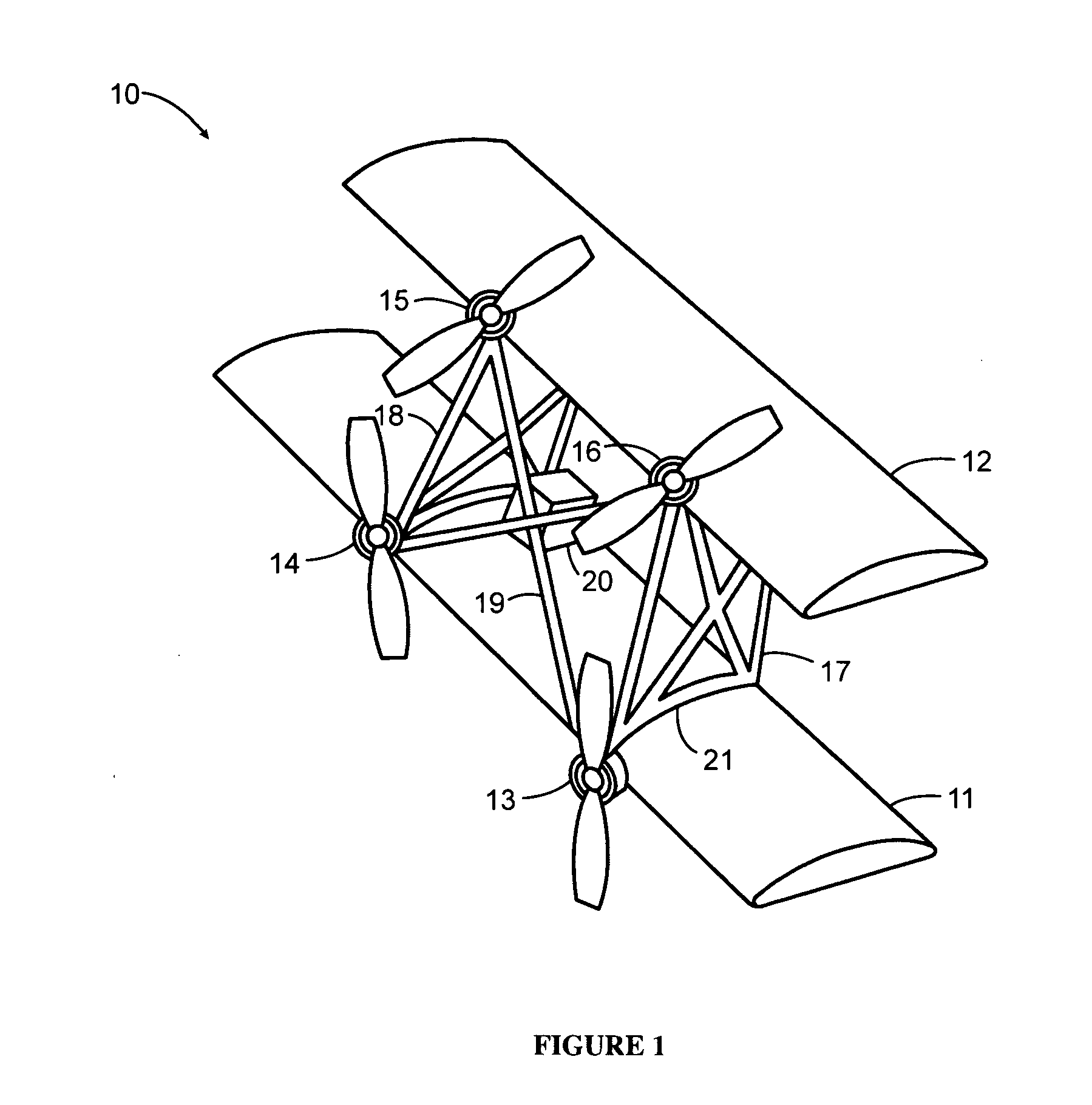
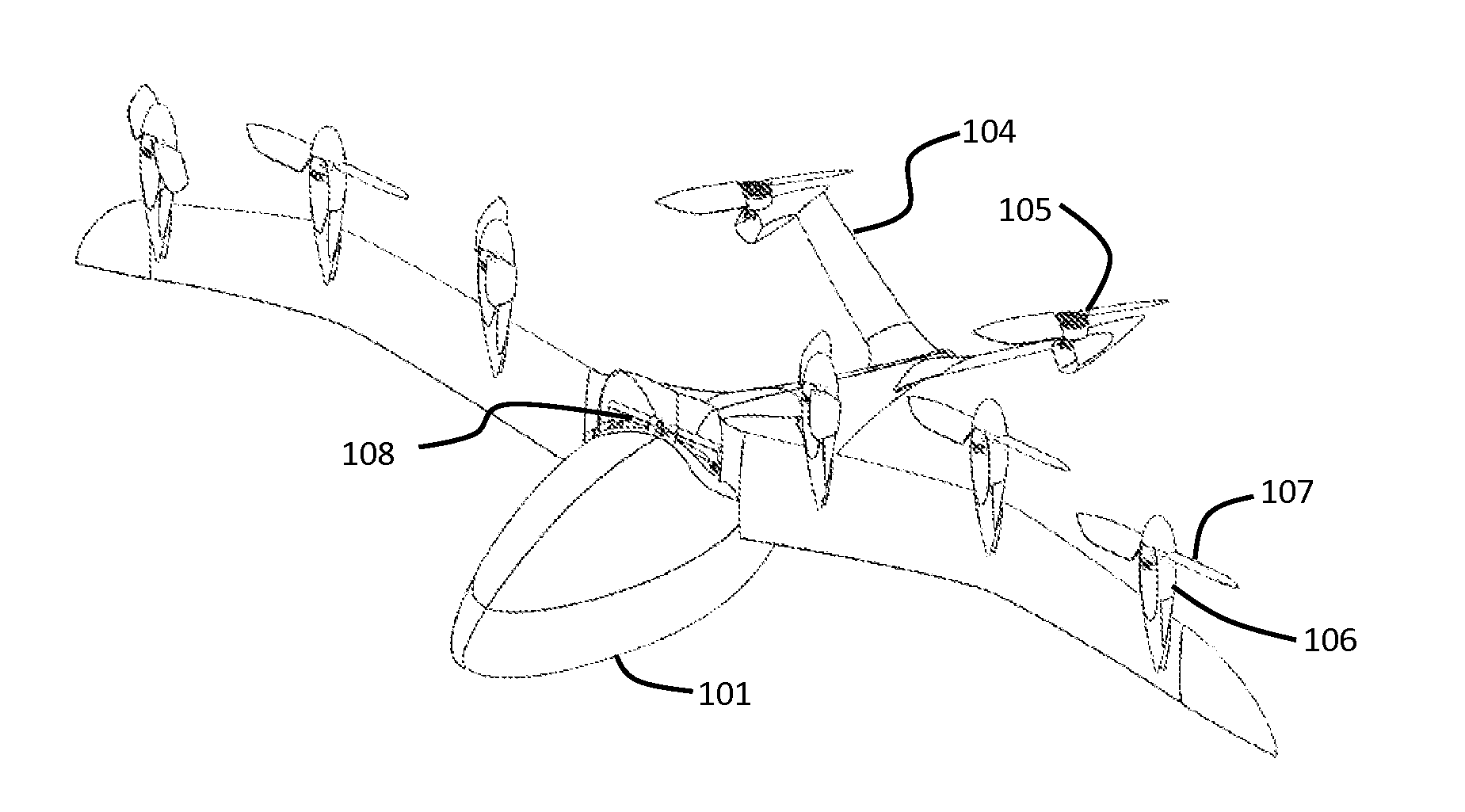
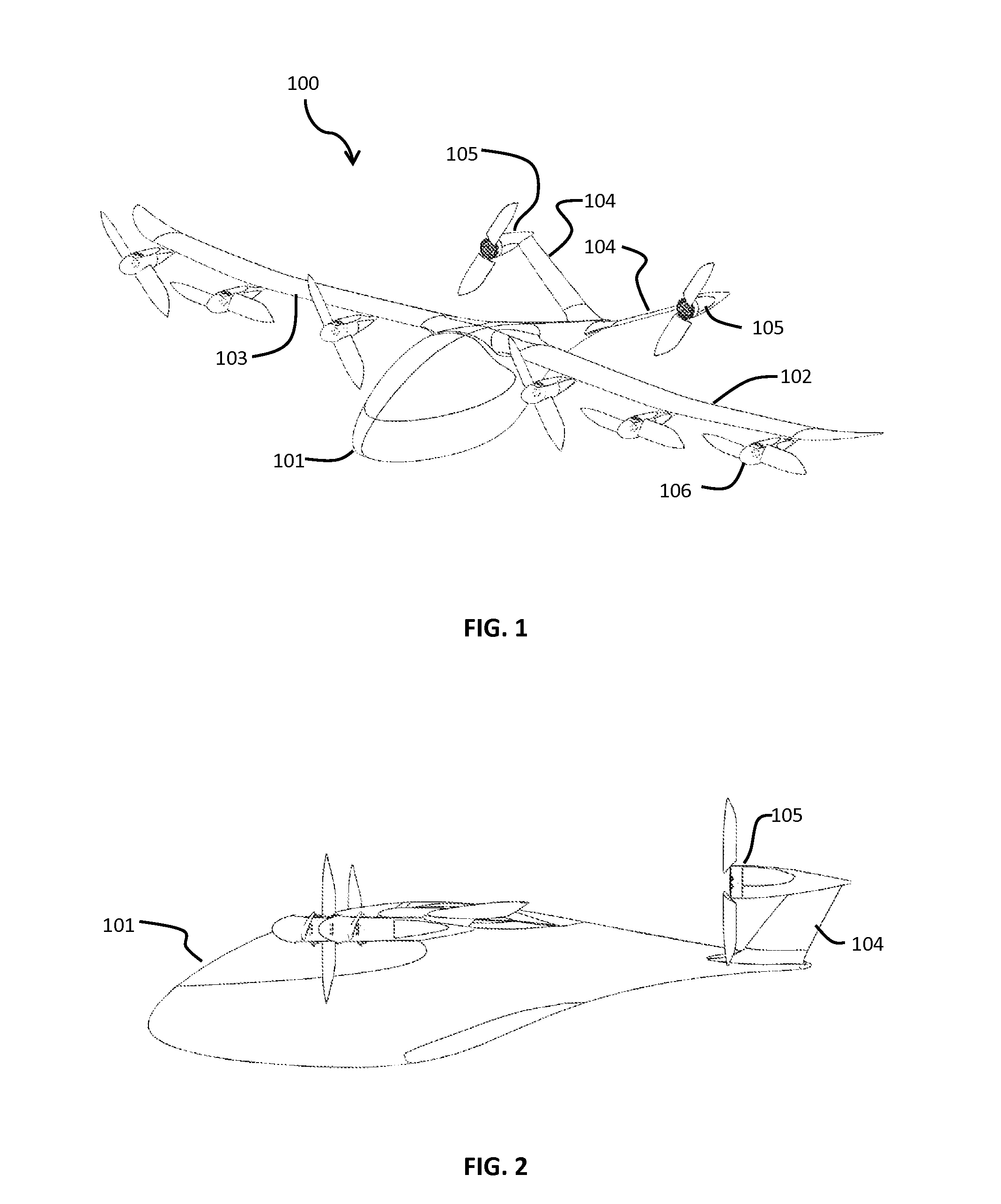
Three wing, six-tilt propulsion unit, vtol aircraft
A vertical takeoff and landing aircraft having at least three wings and at least six propulsion units, each of which are located radially from two adjacent propulsion units, by equal or substantially equal angles. The at least six propulsion units together being located symmetrically, or at substantially symmetric positions, about the approximate center of gravity of the aircraft, when viewed from above. A vertical stabilizer may or may not be employed. If no vertical stabilizer is employed, yaw control during horizontal flight may be achieved through differential thrust using the at least six propulsion units. Yaw control during vertical flight may be provided by a plurality of yaw control panels. Absent yaw control panels, yaw control during vertical flight may be provided using differential propulsion unit tilt angles.
Owner:OLIVER VTOL
Ducted vehicles particularly useful as VTOL aircraft
InactiveUS6568630B2Easy entryEasy exitAircraft navigation controlFlying saucersJet aeroplaneJet engine
A VTOL aircraft (or other vehicle such as a sea vehicle) includes a pair of elongated ducts on opposite sides of the vehicle body, and a plurality of powered propellers (or other propulsion units such as jet engines) mounted within and enclosed by each of the elongated ducts, such as to produce an upward lift force to the vehicle. Each of the elongated ducts has a short transverse dimension slightly larger than the diameter of the blades of each propeller enclosed thereby, and a large transverse dimension slightly larger than the sum of the diameters of the blades of all the propellers enclosed thereby.
Owner:URBAN AERONAUTICS
Aircraft with wings and movable propellers
ActiveUS9187174B2Reduce or eliminate propeller thrustVertical landing/take-off aircraftsRotocraftFlight vehiclePropeller
The invention is a flight vehicle, and methods of operation thereof, having wings and movable propeller assemblies which can be rotated to provide vertical and / or horizontal thrust. The propeller assemblies are configured to maximize available engine / propeller thrust and to prevent propwash from striking the wings of the aircraft.
Owner:SHAW DONALD ORVAL
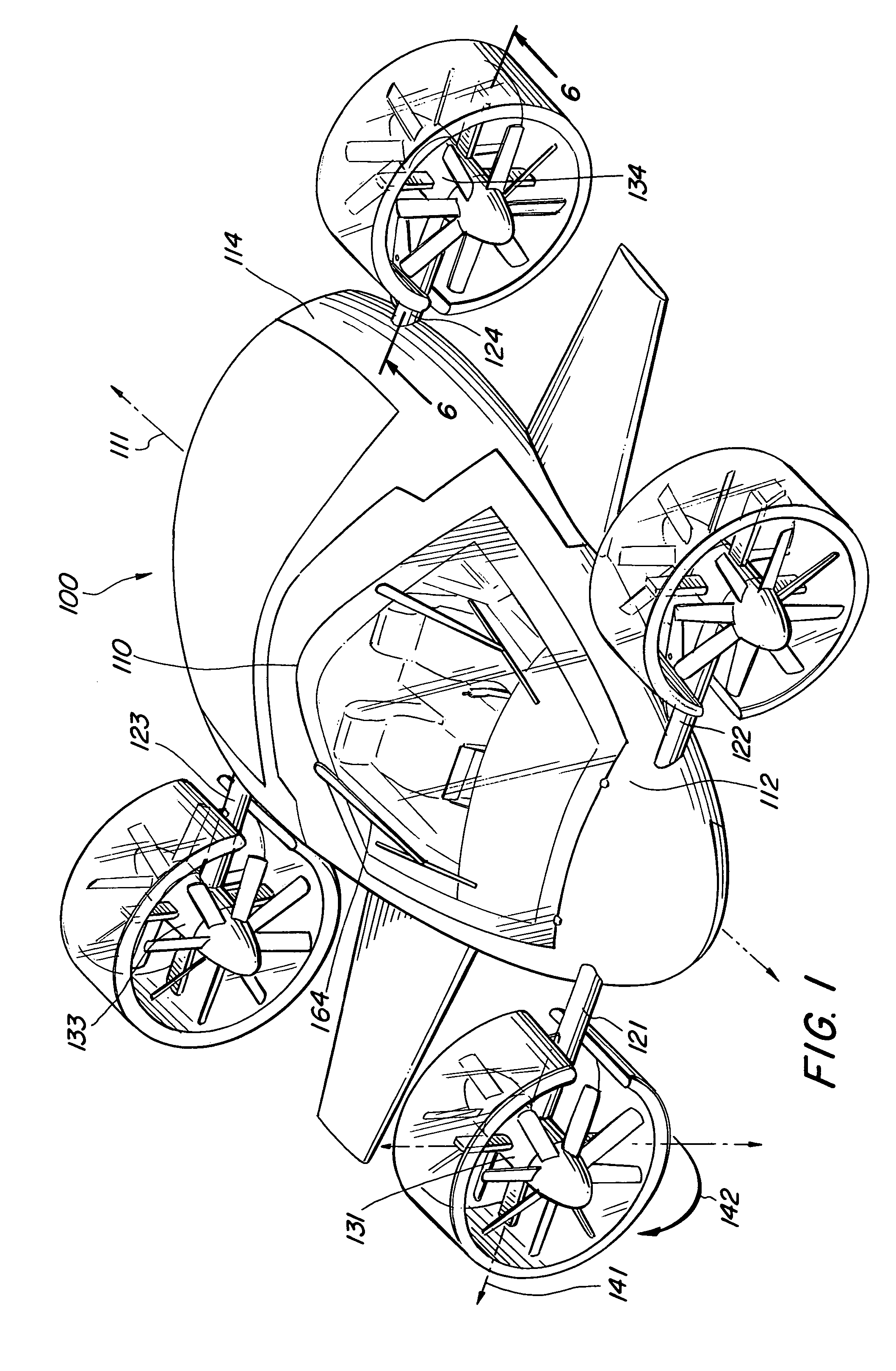
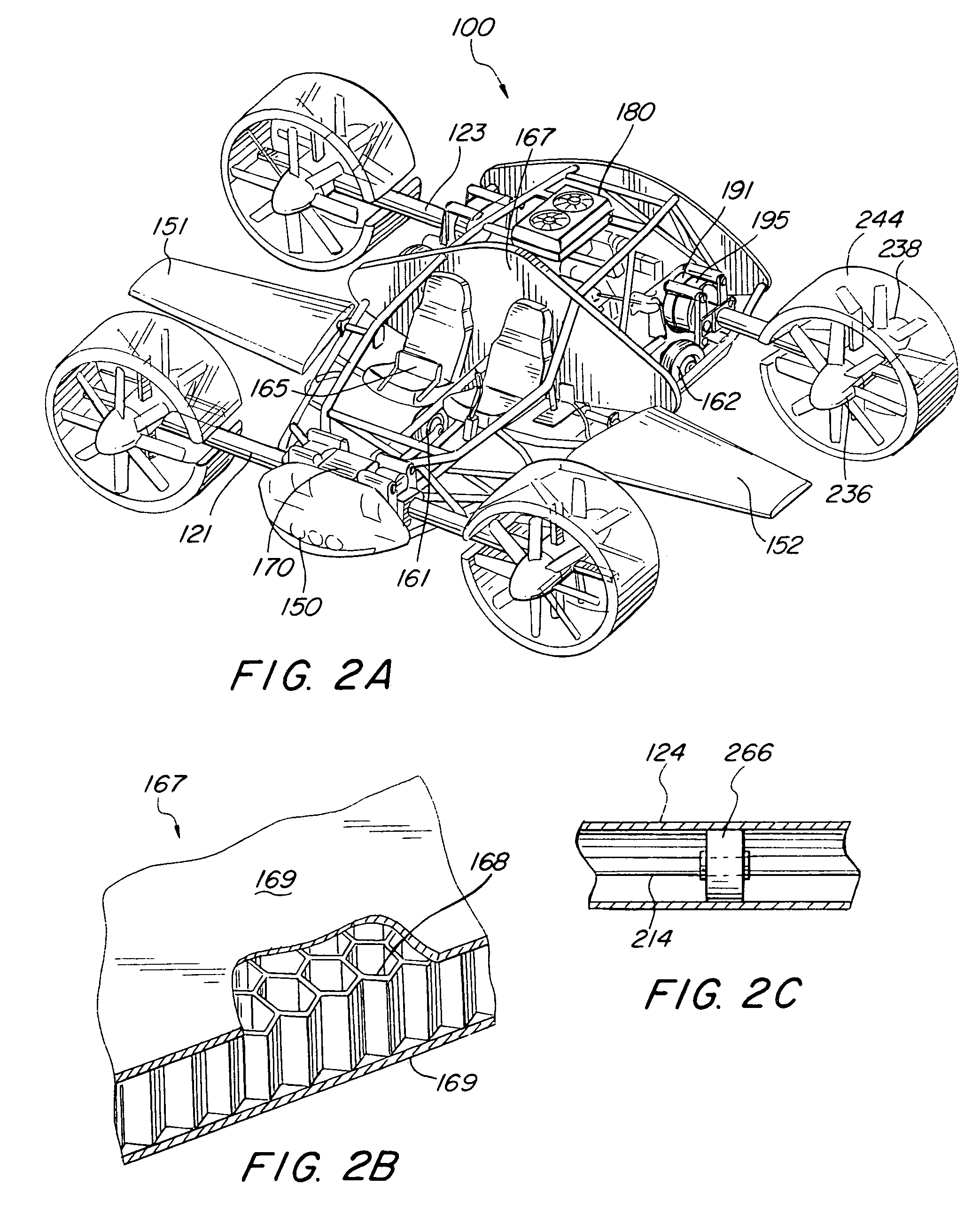
Vertical take-off and landing vehicles
A VTOL vehicle including a fuselage with two foldable wings, two tiltable nacelles attached to the wings, a vertical stabilizer, a horizontal stabilizer, and two auxiliary thrusters. Each nacelle contains a system of vanes located at the rear opening thereof, and actuators are provided for extending and retracting the vanes in conjunction with nacelle tilting mechanisms to deflect the airflow over a predetermined range of angles from the horizontal. Each nacelle also contains two rotary engines, each of which directly drives a fan. The fans face each other and operate in counter-rotating directions at the same rotational speed. An alternative embodiment includes two additional nacelles attached to the fuselage instead of having the auxiliary thrusters. A redundant computerized flight control system maintains stability of the vehicle as it transitions from one flight mode to another.
Owner:MOLLER INT
Hybrid jet/electric vtol aircraft
ActiveUS20130062455A1Improve efficiencyLess thrust capacityAircraft navigation controlEfficient propulsion technologiesJet aeroplaneElectricity
A fixed-wing VTOL aircraft features an array of electric lift fans distributed over the surface of the aircraft. A generator is (selectively) coupled to the gas turbine engine of the aircraft. During VTOL operation of the aircraft, the engine drives the generator to generate electricity to power the lifting fans. Power to the lifting fans is reduced as the aircraft gains forward speed and is increasingly supported by the wings.
Owner:SONIC BLUE AEROSPACE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com