Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3517results about How to "Heavy load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
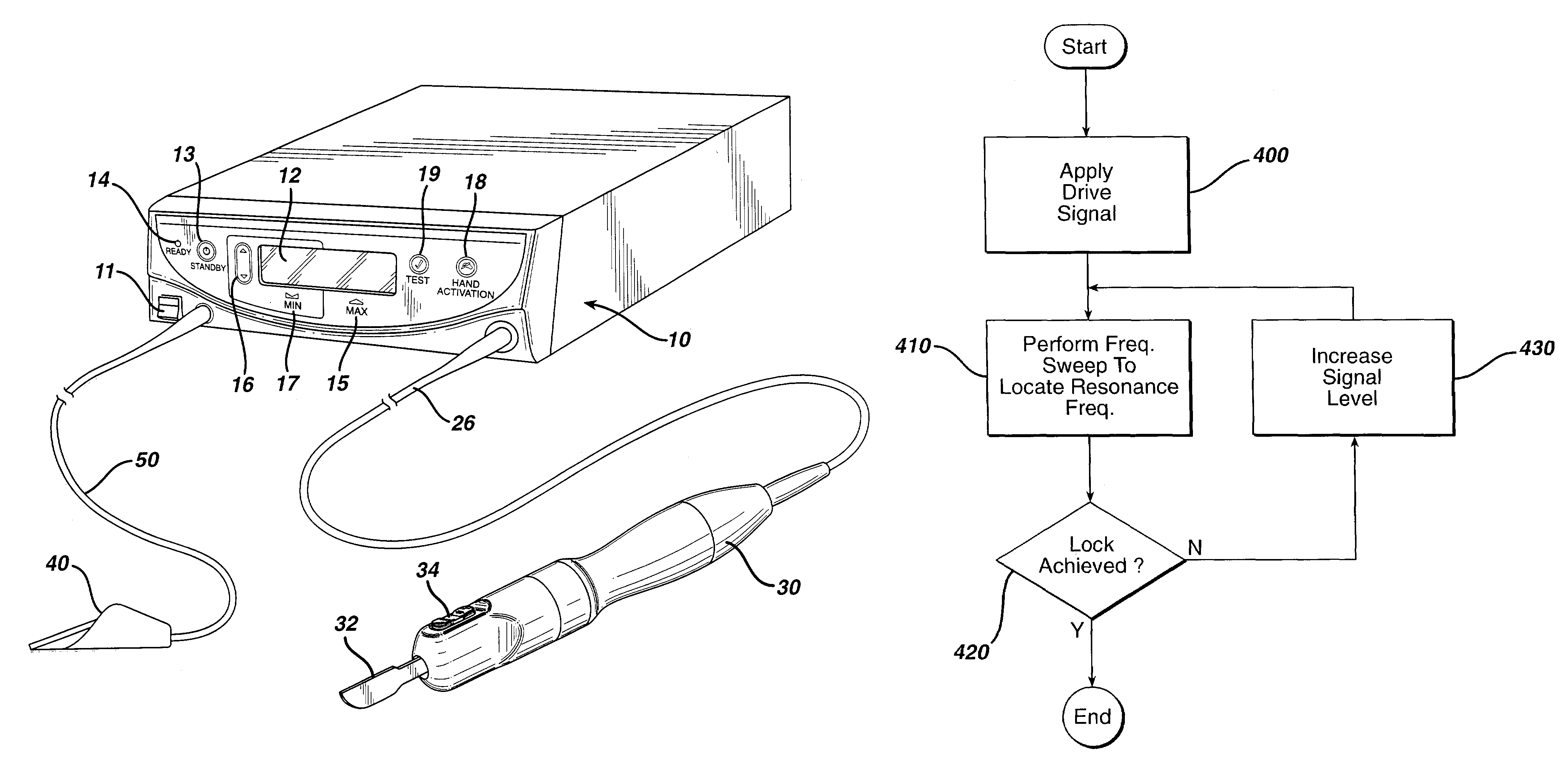
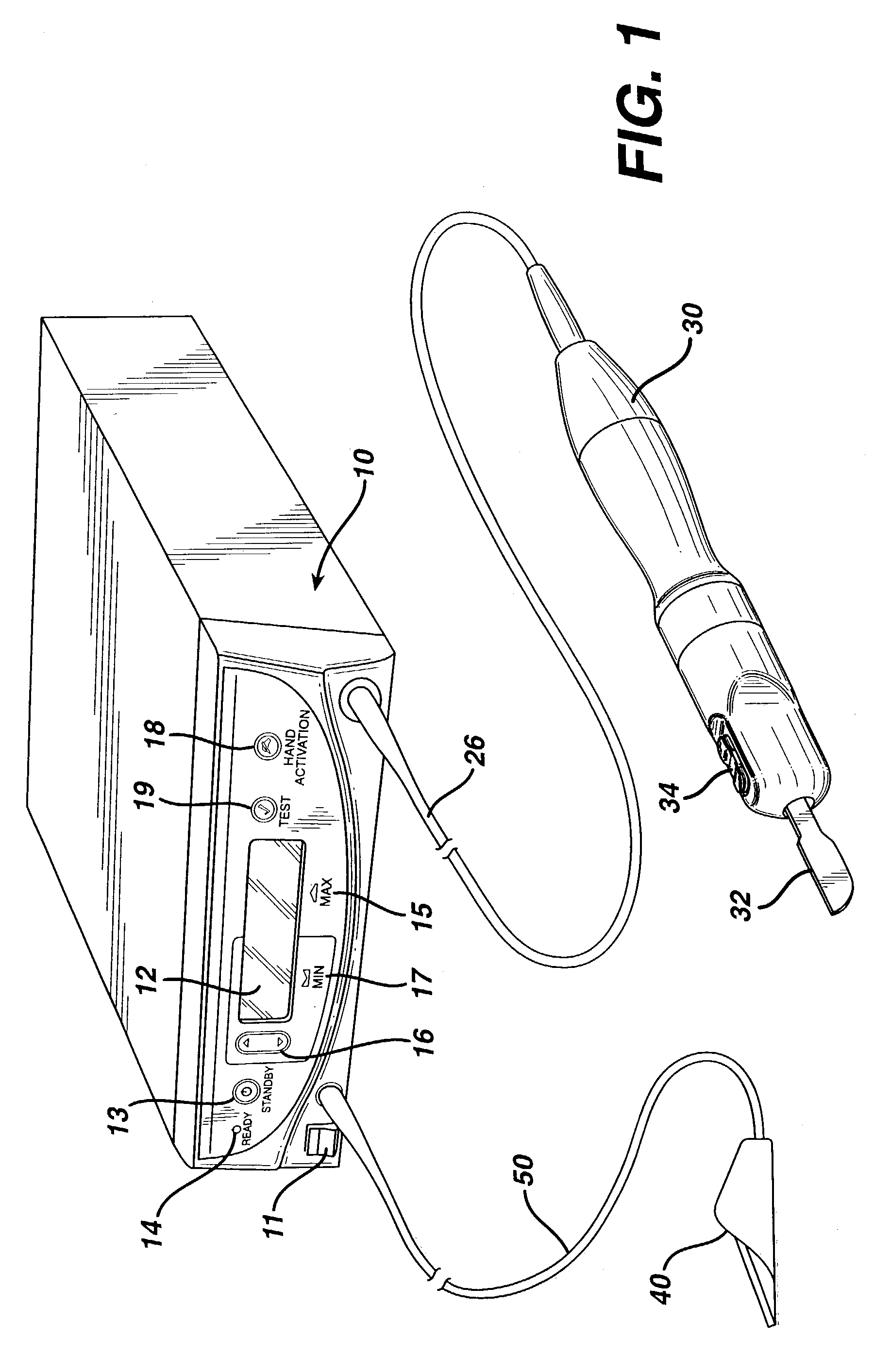
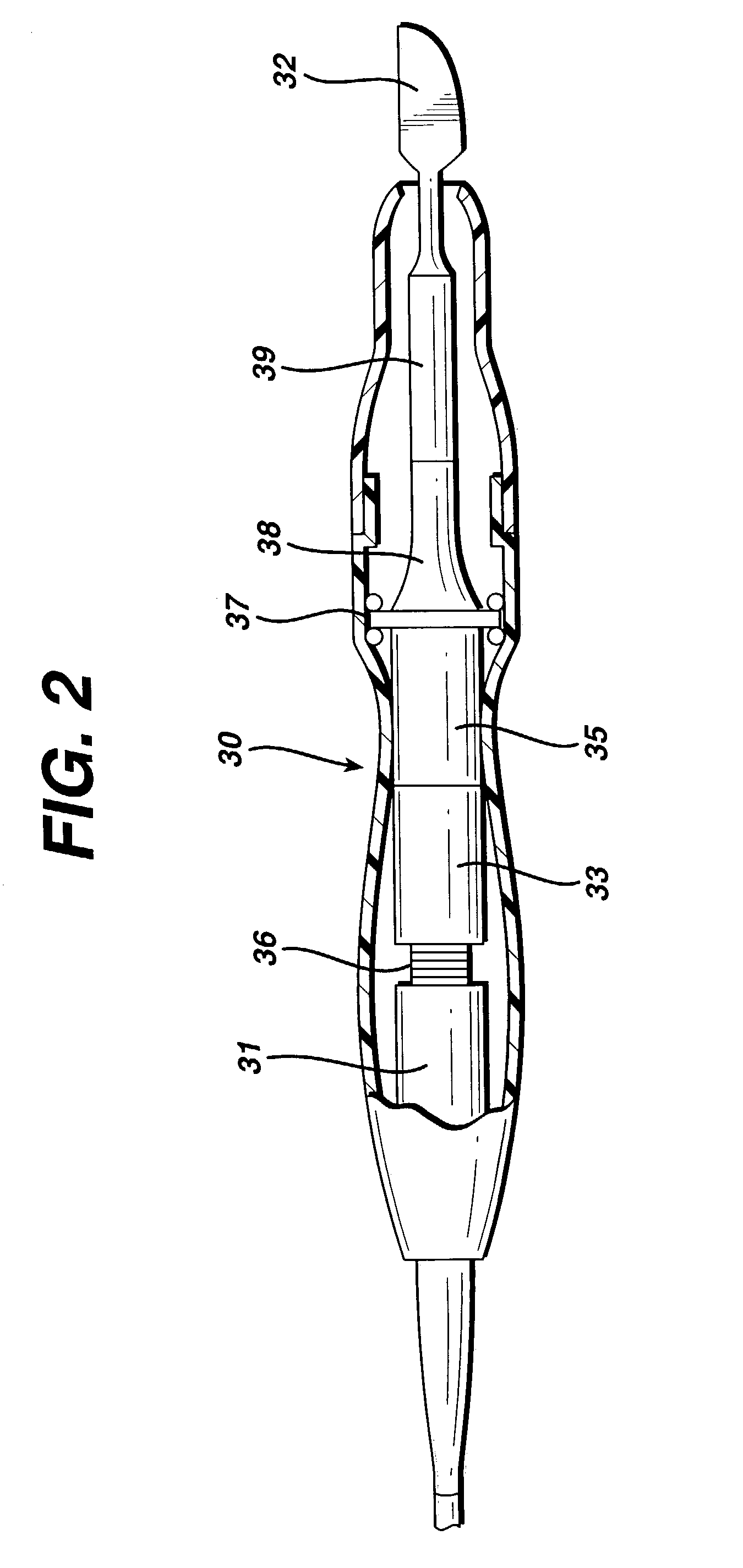
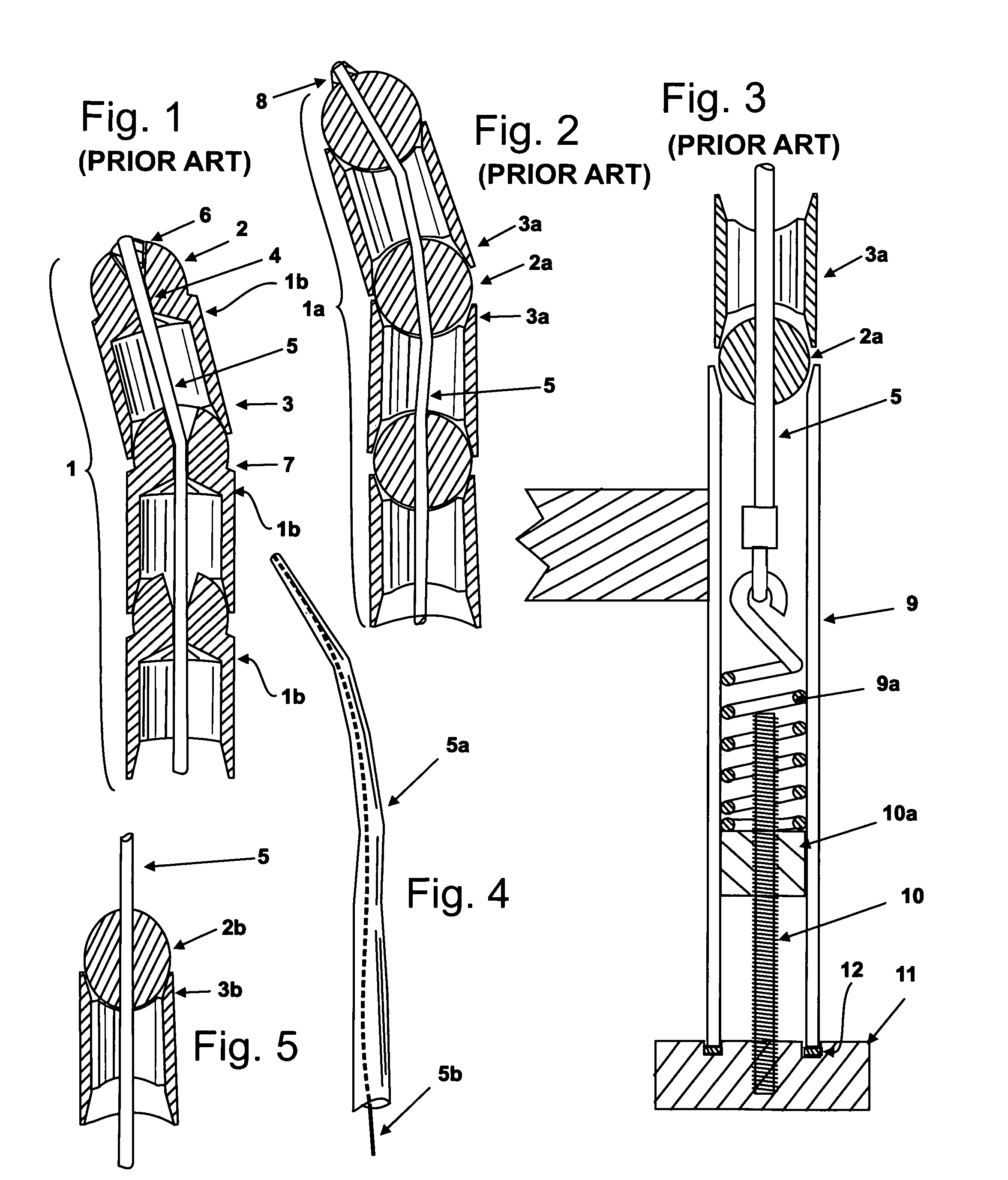
Method for driving an ultrasonic system to improve acquisition of blade resonance frequency at startup
InactiveUS7179271B2Increase load capacityImprove abilitiesSurgeryElectrical measurementsDriving currentResonance
The ability of an ultrasonic system to sweep and lock onto a resonance frequency of a blade subjected to a heavy load at startup is improved by applying a high drive voltage or a high drive current while systematically increasing the level of the applied signal. Increasing the drive signal to the hand piece results in an improved and more pronounced “impedance spectrum.” That is, under load, the increased drive signal causes the maximum phase margin to become higher and the minimum / maximum impedance magnitude to become more pronounced. Increasing the excitation drive signal to the hand piece / blade at startup significantly alleviates the limiting factors associated with ultrasonic generators, which results in an increase of the maximum load capability at startup.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Gradient porous implant
ActiveUS20070150068A1Optimize performanceOptimizes various mechanical and biological requirements of the implants performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantPorous metalMedical treatment
An implantable medical device includes a porous metal foam or foam-like structure having pores defined by metal struts or webs wherein the porous structure has directionally controlled pore characteristics. The pore characteristics controlled include one or more of the metal structure porosity, pore size, pore shape, pore size distribution and strut thickness. The pore characteristics may vary in one or more directions throughout the structure. Preferably the pore characteristics are controlled to match the porous metal structure to various mechanical and biological requirements of different regions of the structure in order to optimize aspects of the implants performance and may vary not only over the surface of the porous structure but through the depth of the porous structure. The thickness of the porous metal structure may also be modified to establish a thickness profile that optimizes mechanical and biological requirements of the implants performance. Acetabular cup embodiments of the invention are described. Various methods of manufacturing implants having directionally controlled pore characteristics are described.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Gradient porous implant
ActiveUS7578851B2Optimizes various mechanical and biological requirements of the implants performanceIncreasing the thicknessAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantPorous implantMedical device
An implantable medical device includes a porous metal foam or foam-like structure having pores defined by metal struts or webs wherein the porous structure has directionally controlled pore characteristics. The pore characteristics controlled include one or more of the metal structure porosity, pore size, pore shape, pore size distribution and strut thickness. The pore characteristics may vary in one or more directions throughout the structure. Preferably the pore characteristics are controlled to match the porous metal structure to various mechanical and biological requirements of different regions of the structure in order to optimize aspects of the implants performance and may vary not only over the surface of the porous structure but through the depth of the porous structure. The thickness of the porous metal structure may also be modified to establish a thickness profile that optimizes mechanical and biological requirements of the implants performance. Acetabular cup embodiments of the invention are described. Various methods of manufacturing implants having directionally controlled pore characteristics are described.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
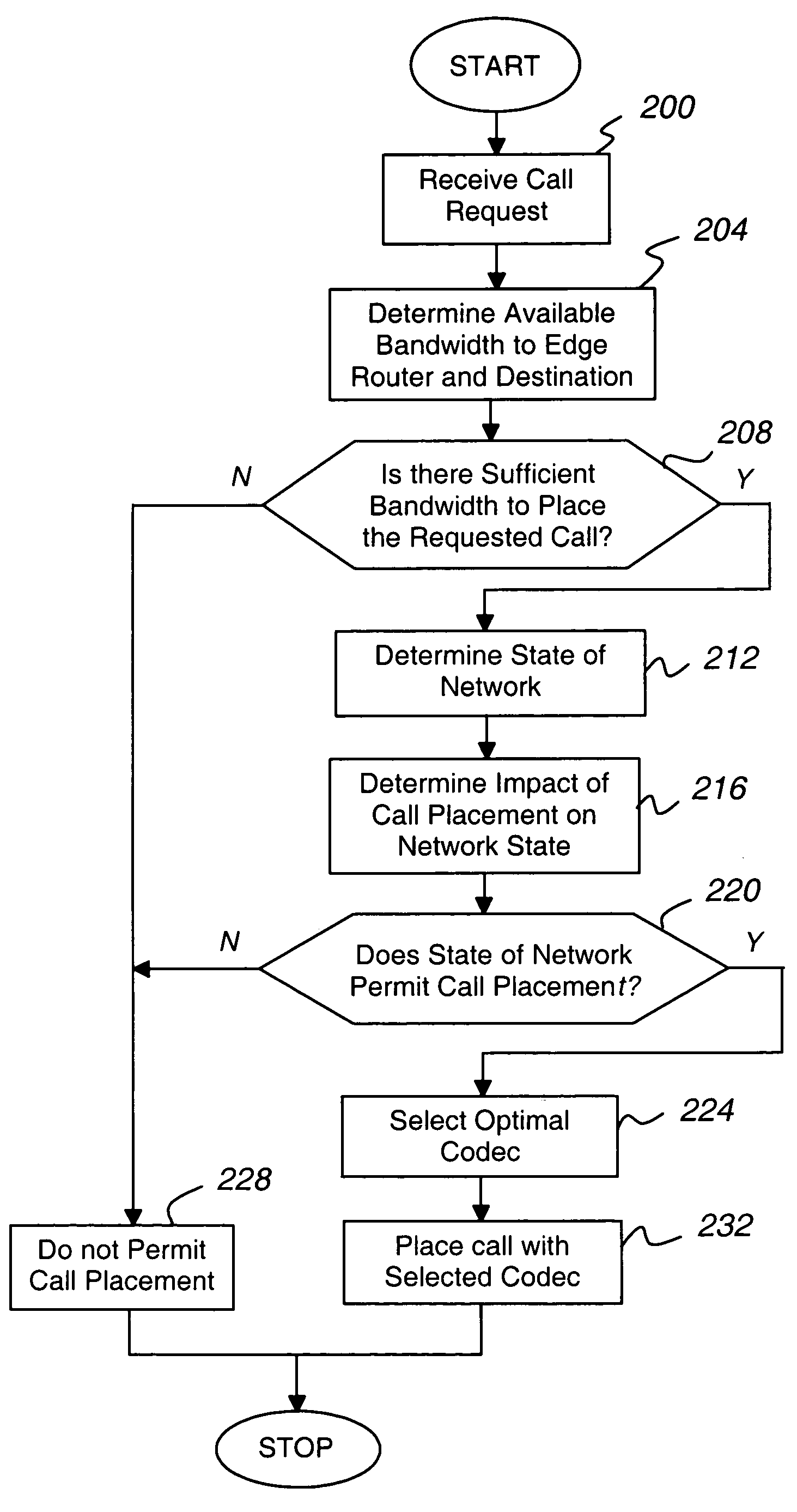
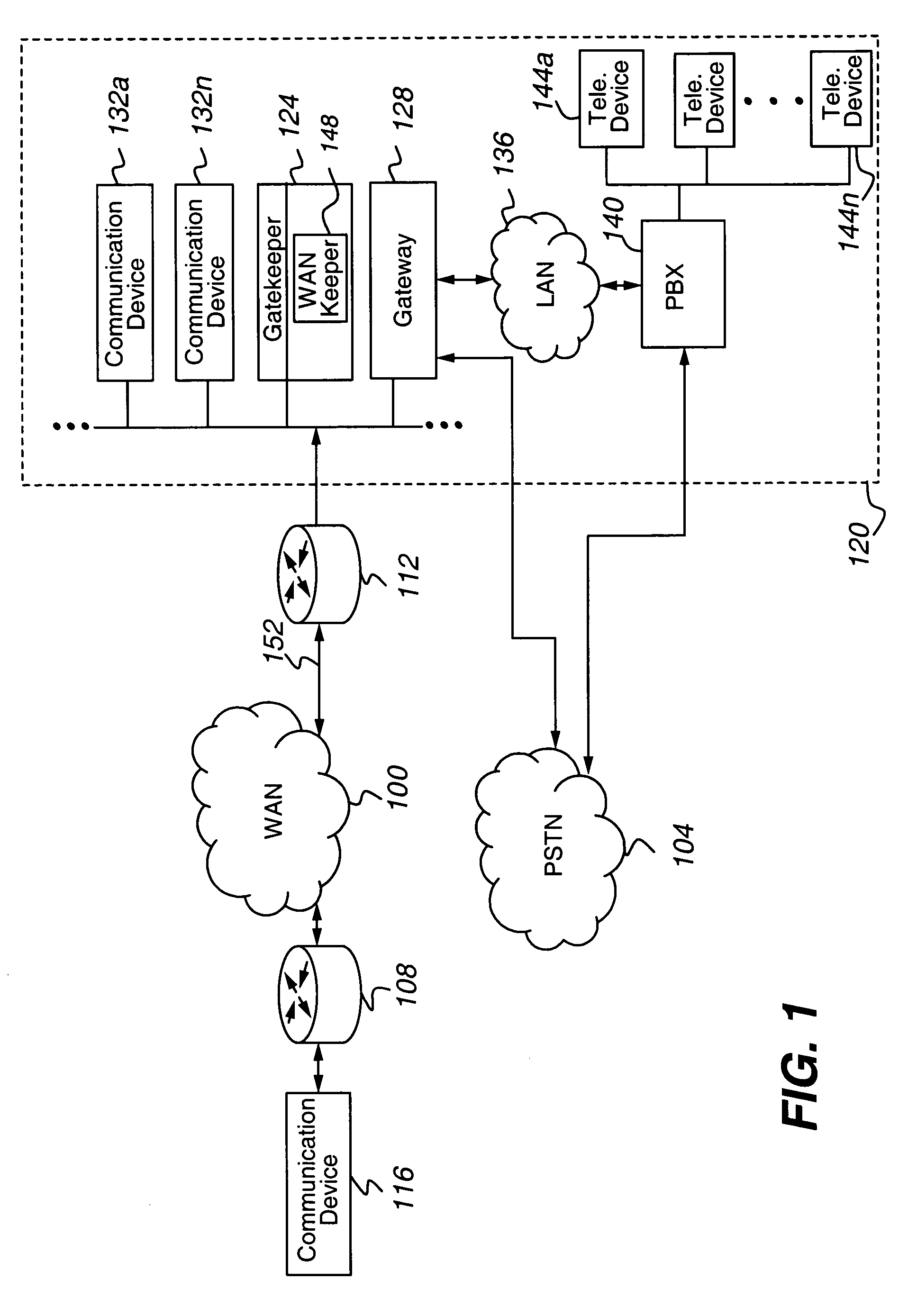
WAN keeper efficient bandwidth management
ActiveUS7643414B1Efficient use ofEnoughInterconnection arrangementsError preventionQuality of serviceLive voice
The present invention is directed to a call admission controller that is operable to: (a) determine at least one of (i) a bandwidth utilization level for a first path including a first link; (ii) an available bandwidth level for the first path; and (iii) one or more Quality of Service or QoS metrics for the first path; (b) compare the at least one of (i) a bandwidth utilization level; (ii) an available bandwidth level; and (iii) one or more Quality of Service or QoS metrics to one or more selected thresholds to determine whether a new live voice communication may be set up with a first selected codec; and (iii) when a new live voice communication may not be set up with the first selected codec, perform at least one of the following operations: (i) select a second different codec from among a plurality of possible codecs for the new live voice communication, wherein the second codec has a lower bit rate than the first codec; (ii) change an existing live voice communication from the first codec to the second codec; and (iii) redirect the new live voice communication from the first path to a second different path, wherein the second path does not include the first link.
Owner:AVAYA INC
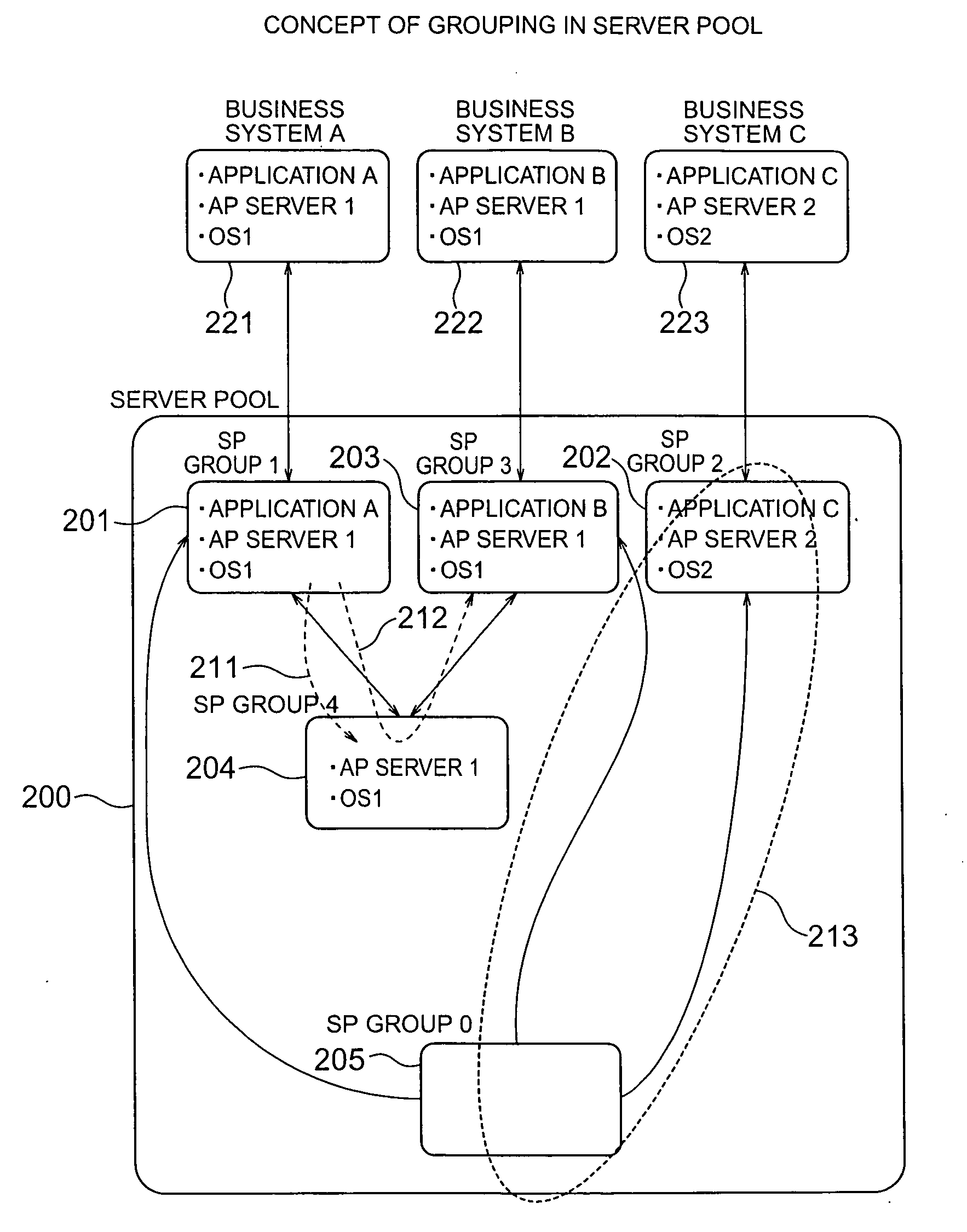
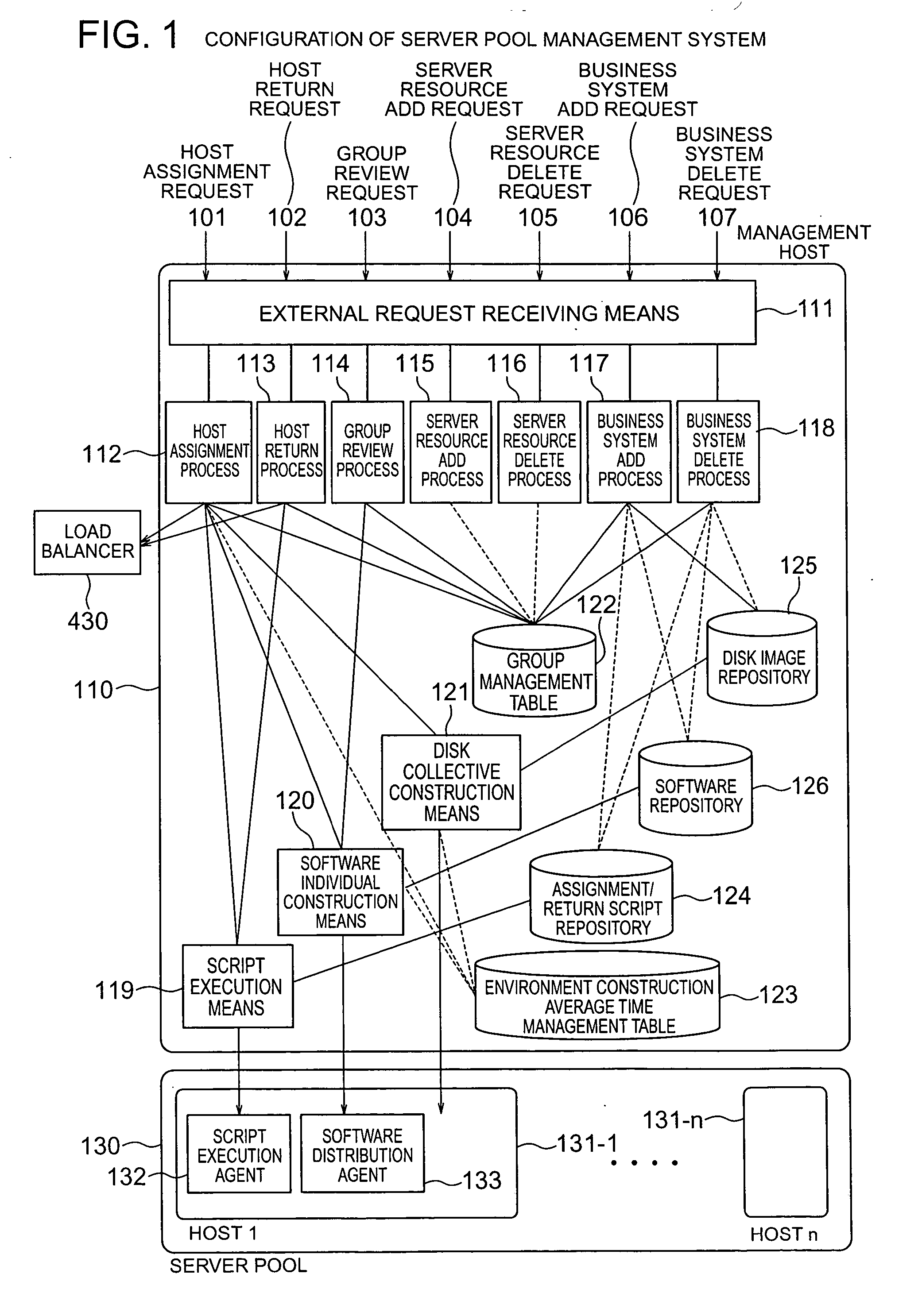
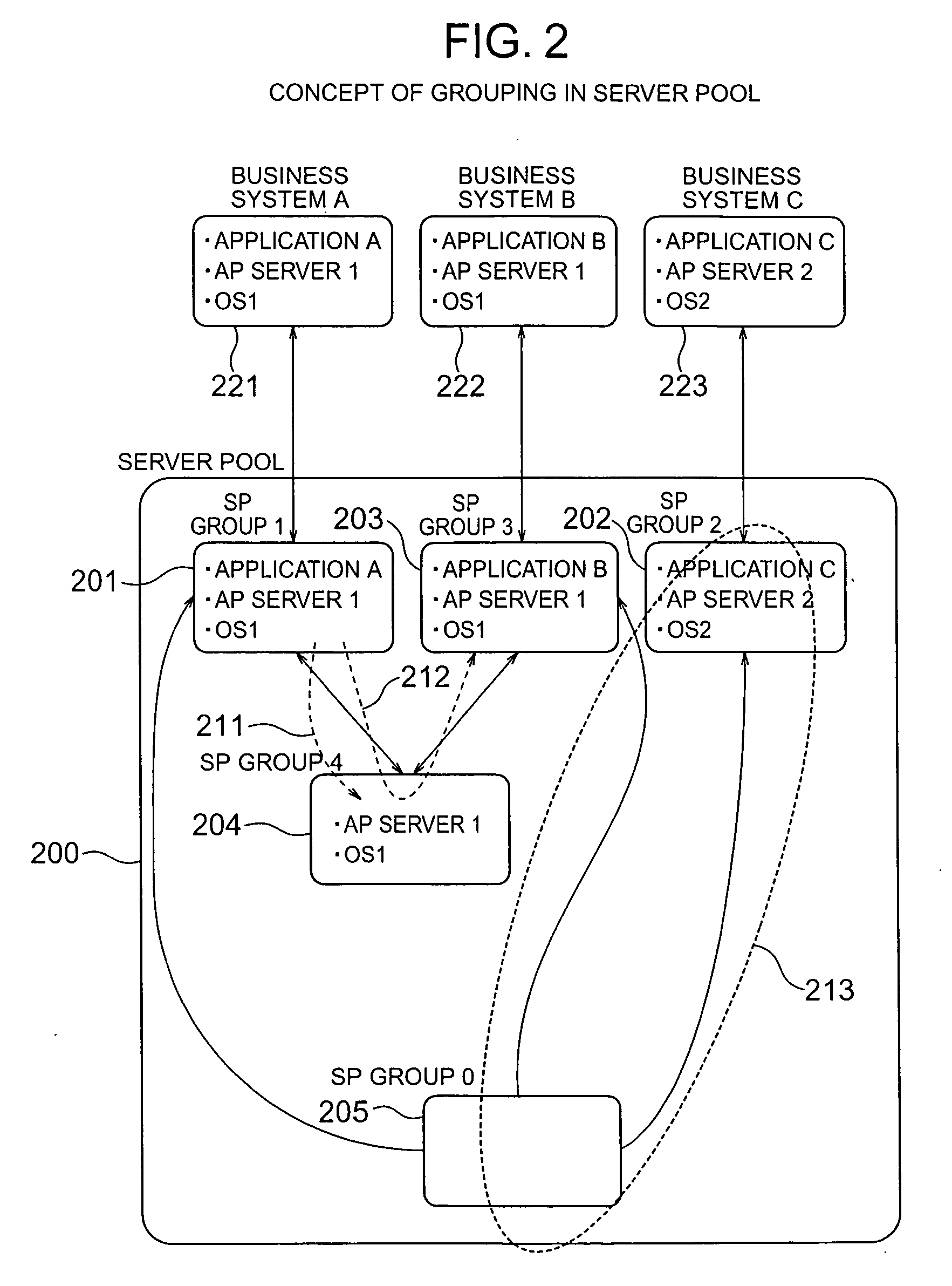
Server pool management method
InactiveUS20070094396A1Reduce buildHeavy loadDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsSoftwareSoftware engineering
Standby computers are dynamically divided into groups according to the difference between the software thereof and the software required of a business system. When a computer is made available, the standby computers divided into groups by software structure are searched and an appropriate one is extracted to quickly complete the construction of the software environment. An active computer, if to be transferred to standby mode, is associated with the group having the same software structure as the business system with which the active computer has thus far operated. The active / standby states of the computers are monitored, and the standby computers are changed thereby to widen the possible range of application to other business systems, removing copy operation of disk images from the active computer to the standby computers.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
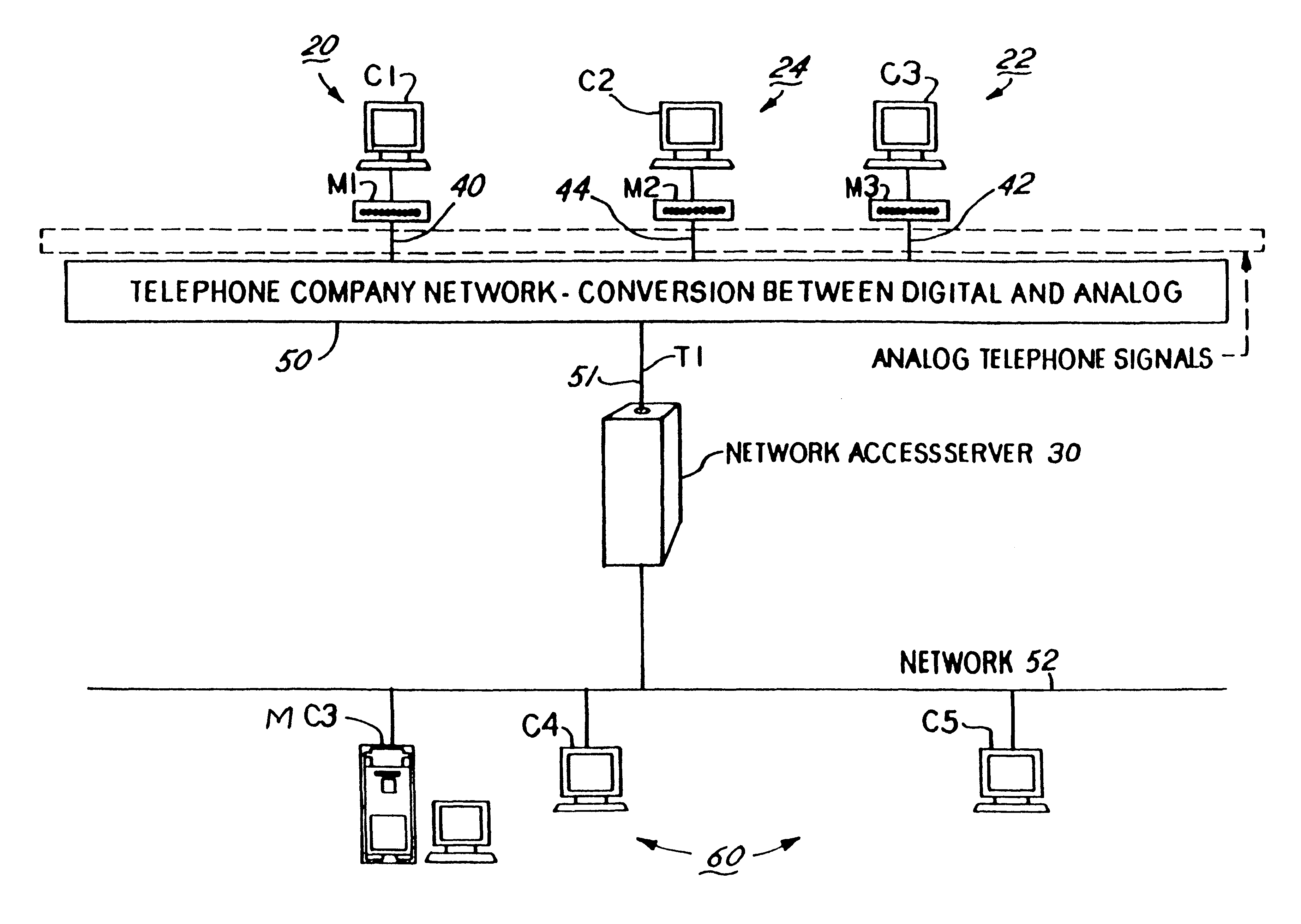
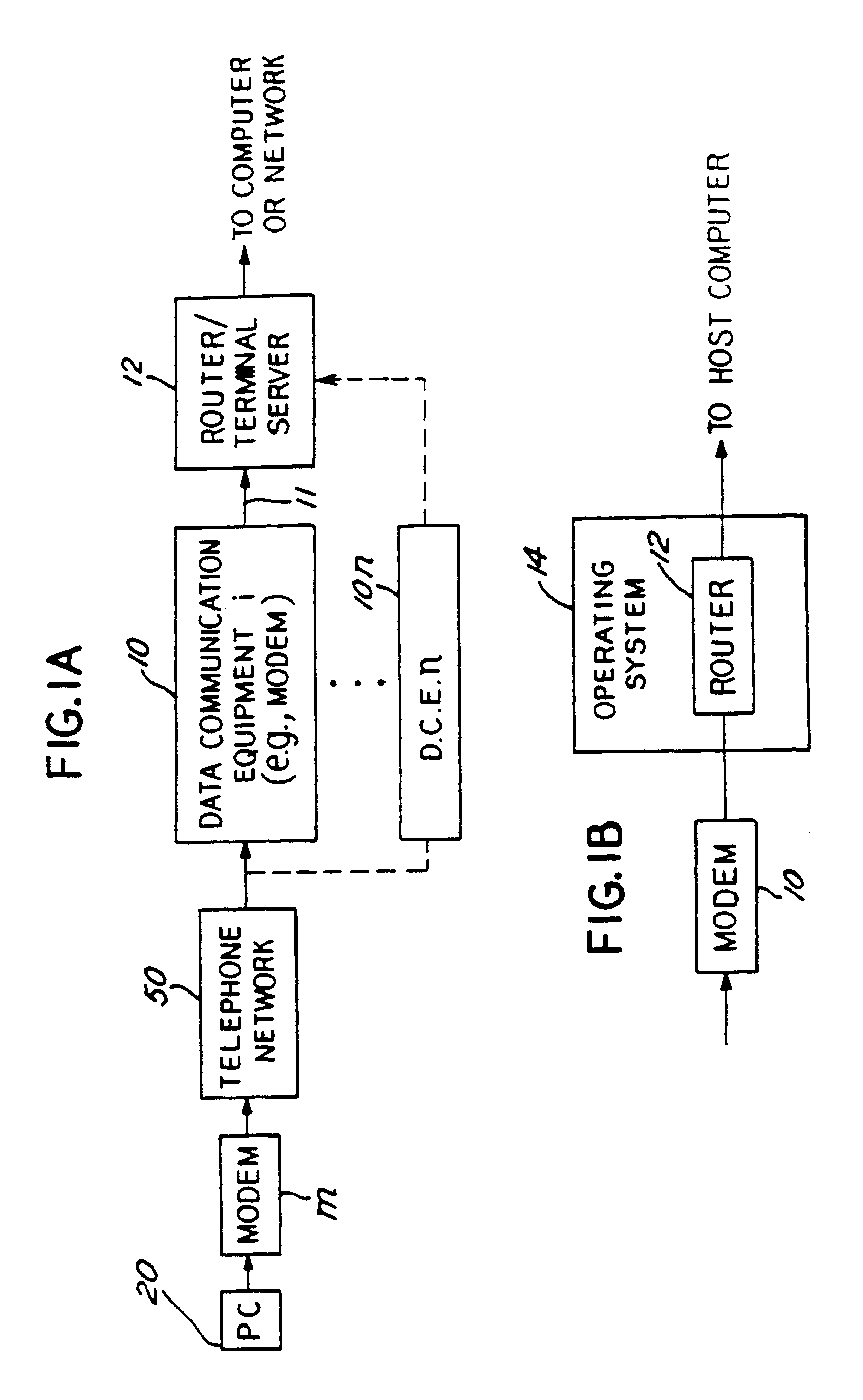
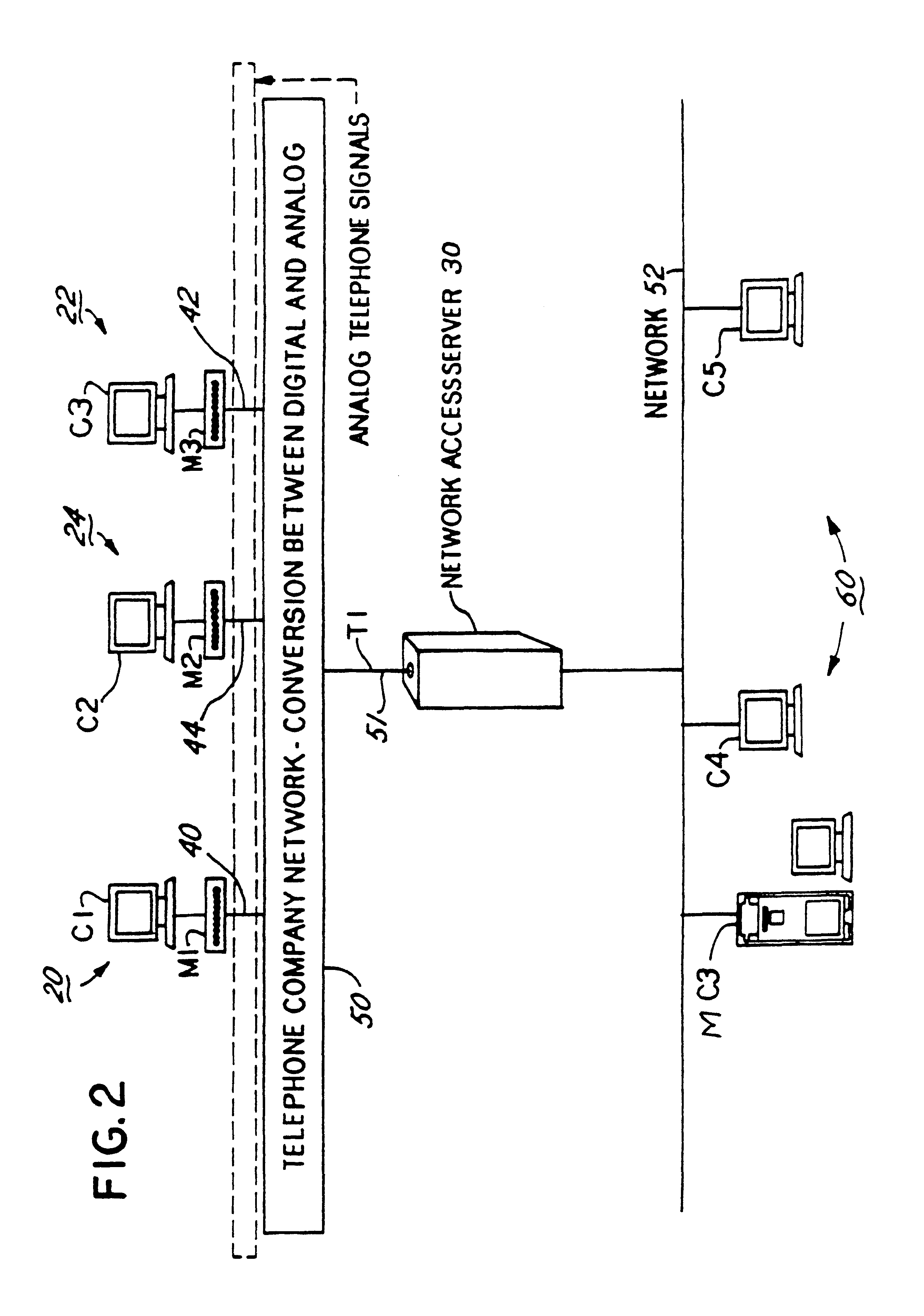
Distributed processing of high level protocols, in a network access server
InactiveUS6304574B1Introduces latency and delayHeavy loadTelephone data network interconnectionsTime-division multiplexNetwork access serverModem device
A method and apparatus for distributing protocol processing among a plurality of computing platforms. Data communications equipment such as Remote Access Devices, Communication Servers, Terminal Servers, and Dial-up Routers provide single user or large-scale multiple user communication access to various computing environments. The equipment costs and performance of such access equipment is related to the amount of CPU processing capability and memory required to support the desired number of serial communication links. It is common to use protocols that terminate in their entirely in the same processing machine. This invention encompasses methods developed to increase the cost / performance capabilities of the communication equipment that supports these serial links, primarily by means of distributing the protocol processing for higher level protocols across multiple computing platforms, including devices such as modems. Examples of such higher level protocols include PPP, SLIP and RTP.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
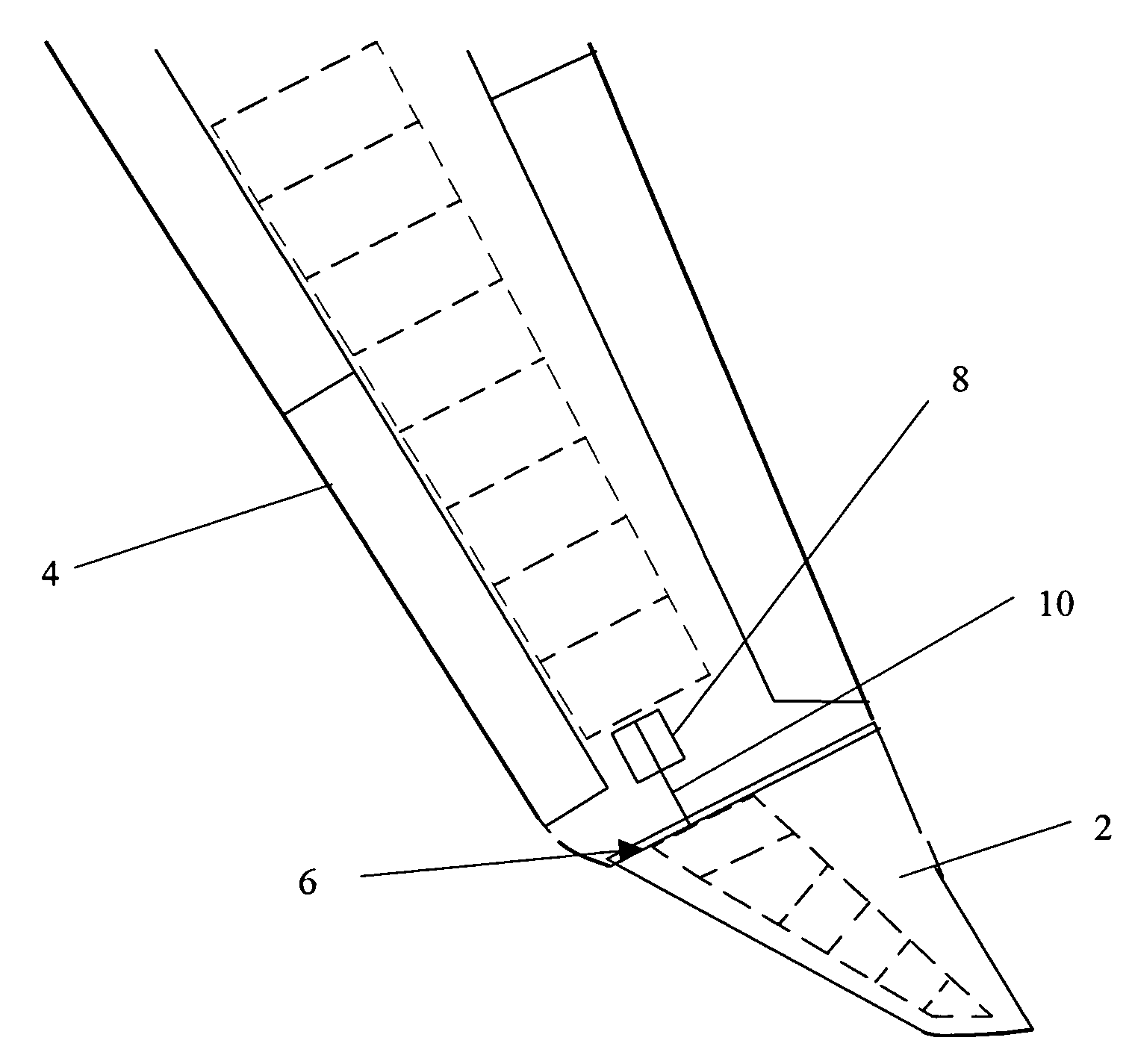
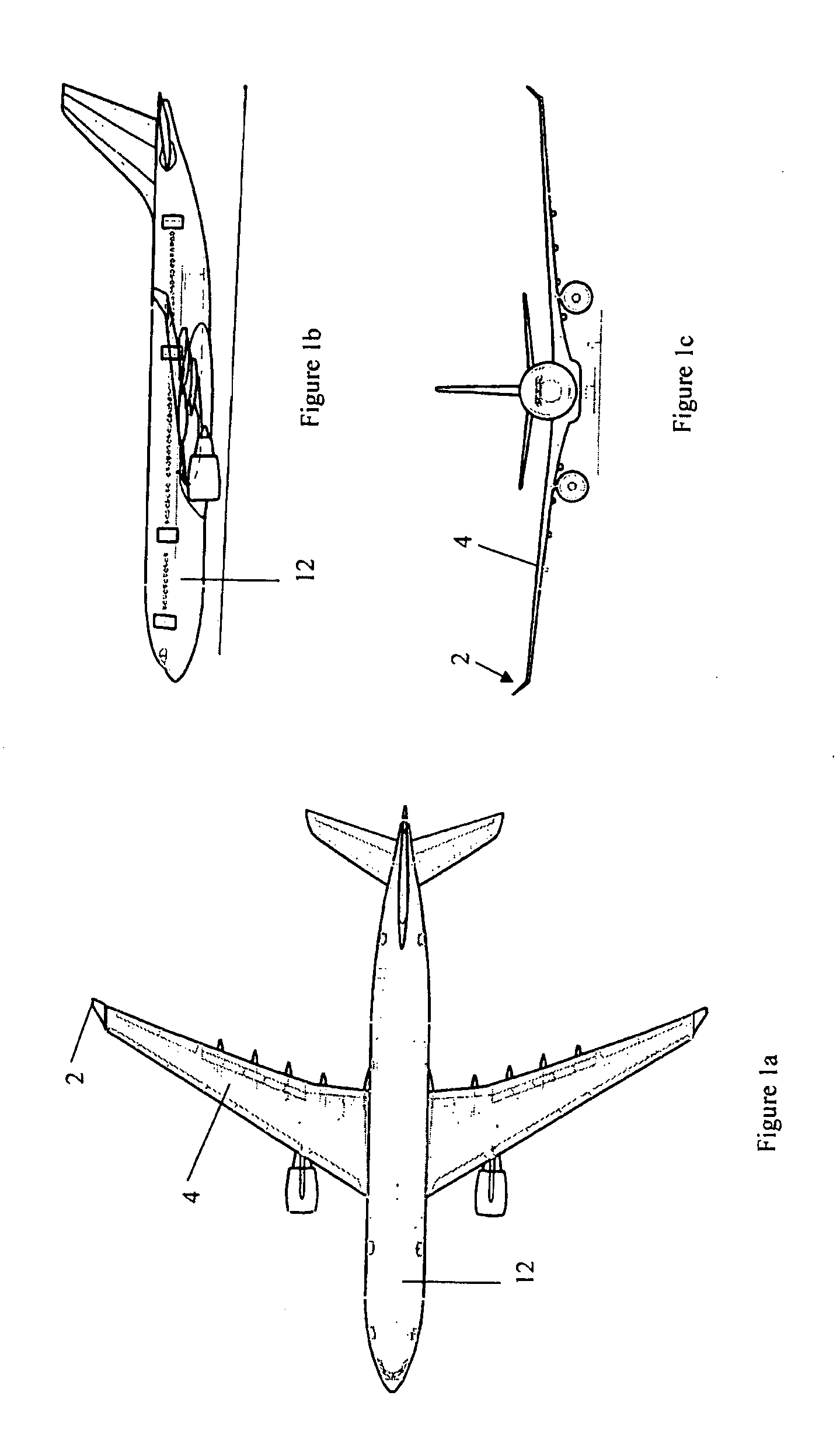
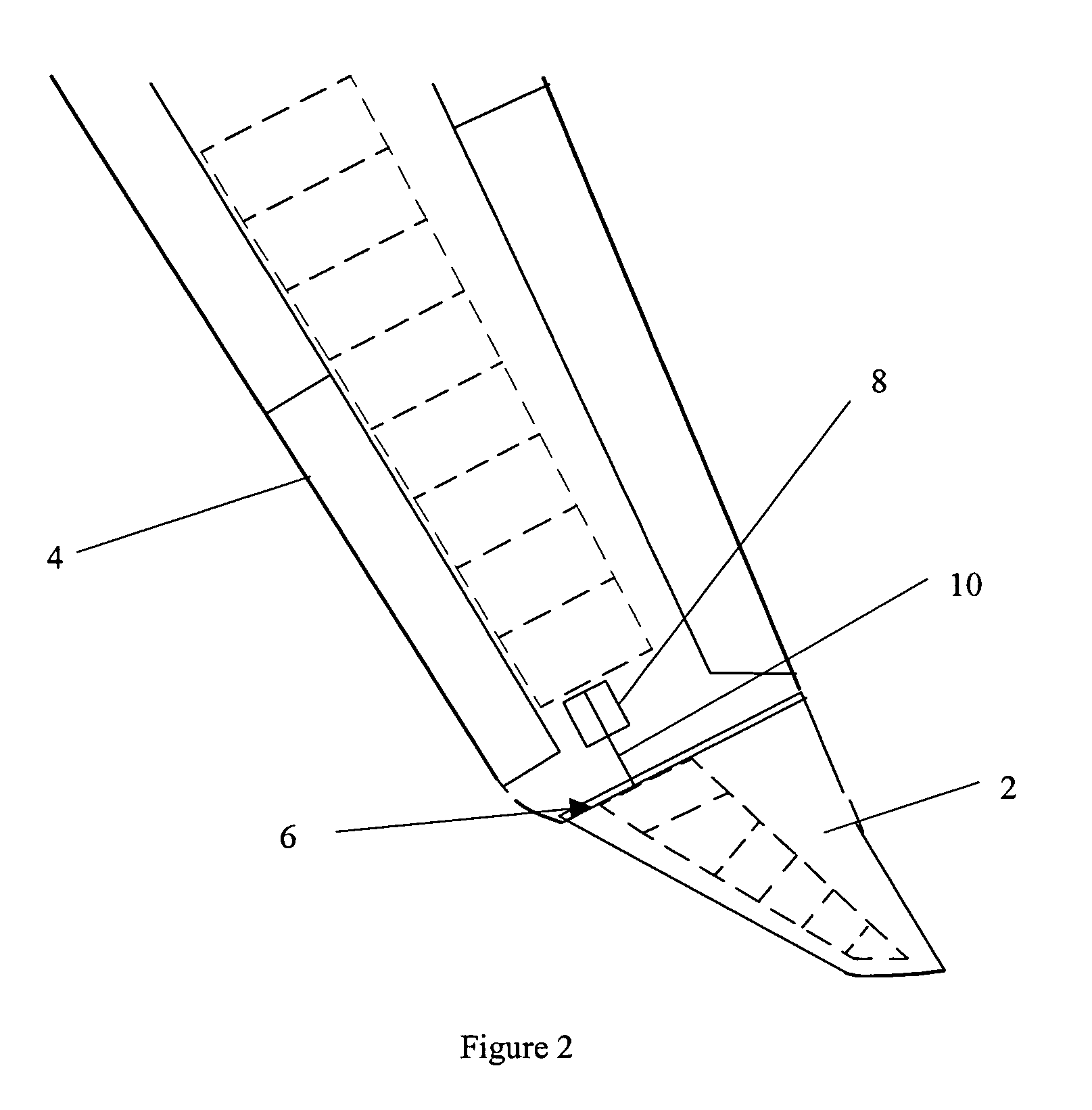
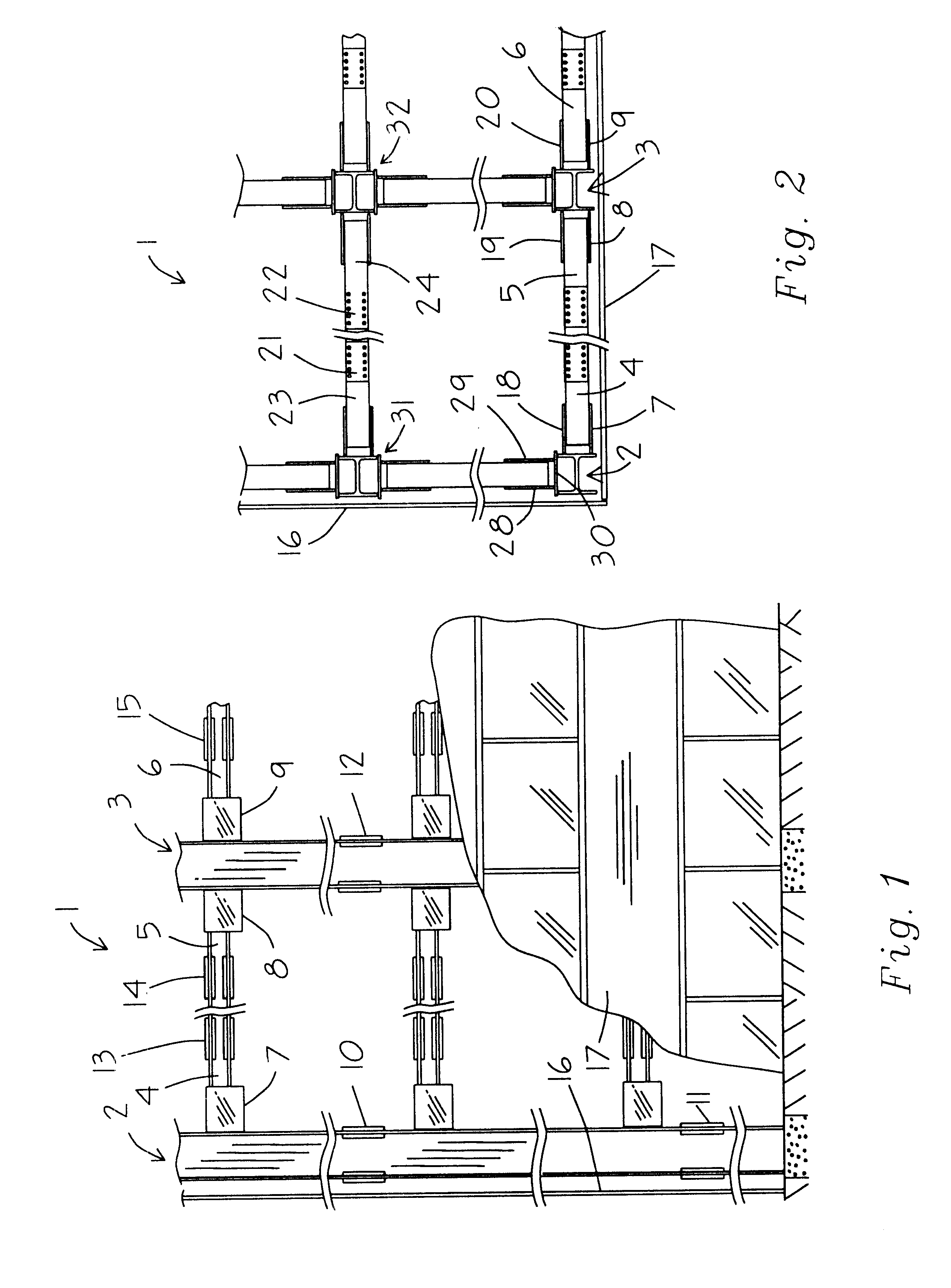
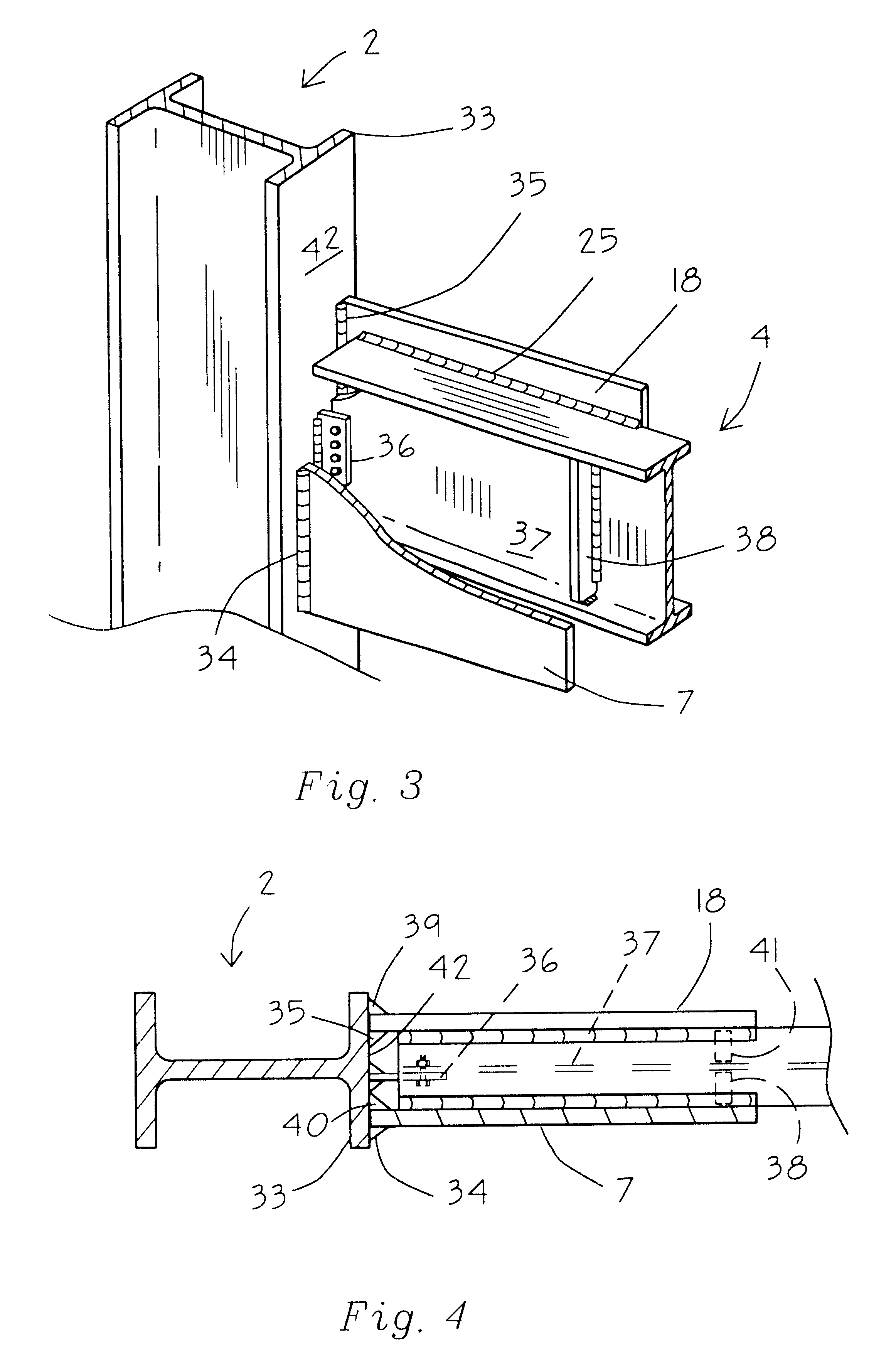
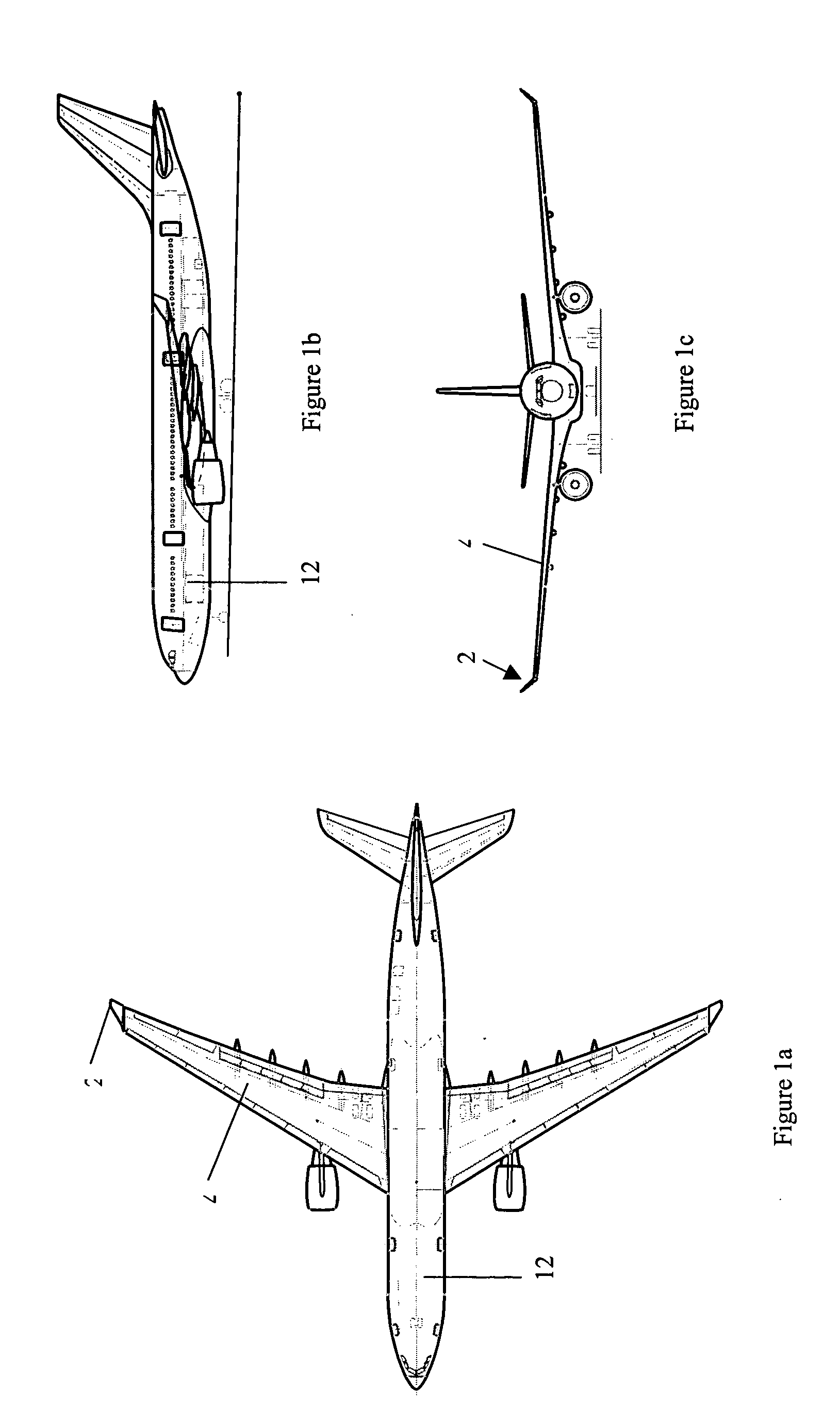
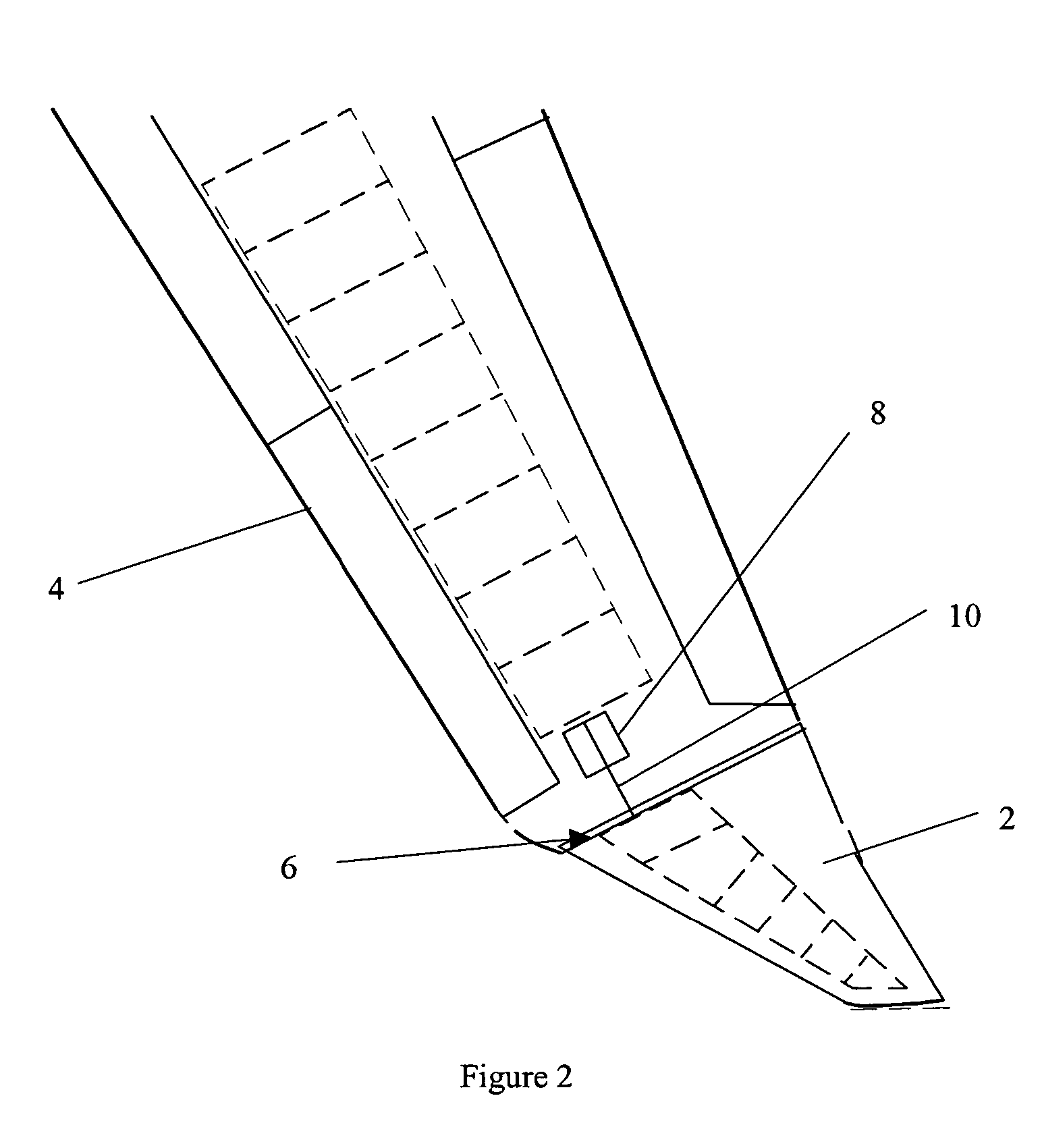
Wing tip device
ActiveUS7275722B2Reduce the total massCareful designInfluencers by generating vorticesWingsHigh loadAirplane
An aircraft comprises a wing tip device, for example a winglet, a raked-tip device, a wing tip fence or a planar wing extension, mounted in the region of the tip of a wing on the aircraft. The wing tip device is rotatably moveable between a first position and a second position, in which the upward lift produced by the wing or the wing tip device is reduced. During flight, the bending moment at the root of the aircraft wing therefore changes in dependence on the position of the wing tip device. The maximum bending moment in the aircraft wing sustained during high-load conditions is thereby reduced, allowing the structural mass of the aircraft to be reduced.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
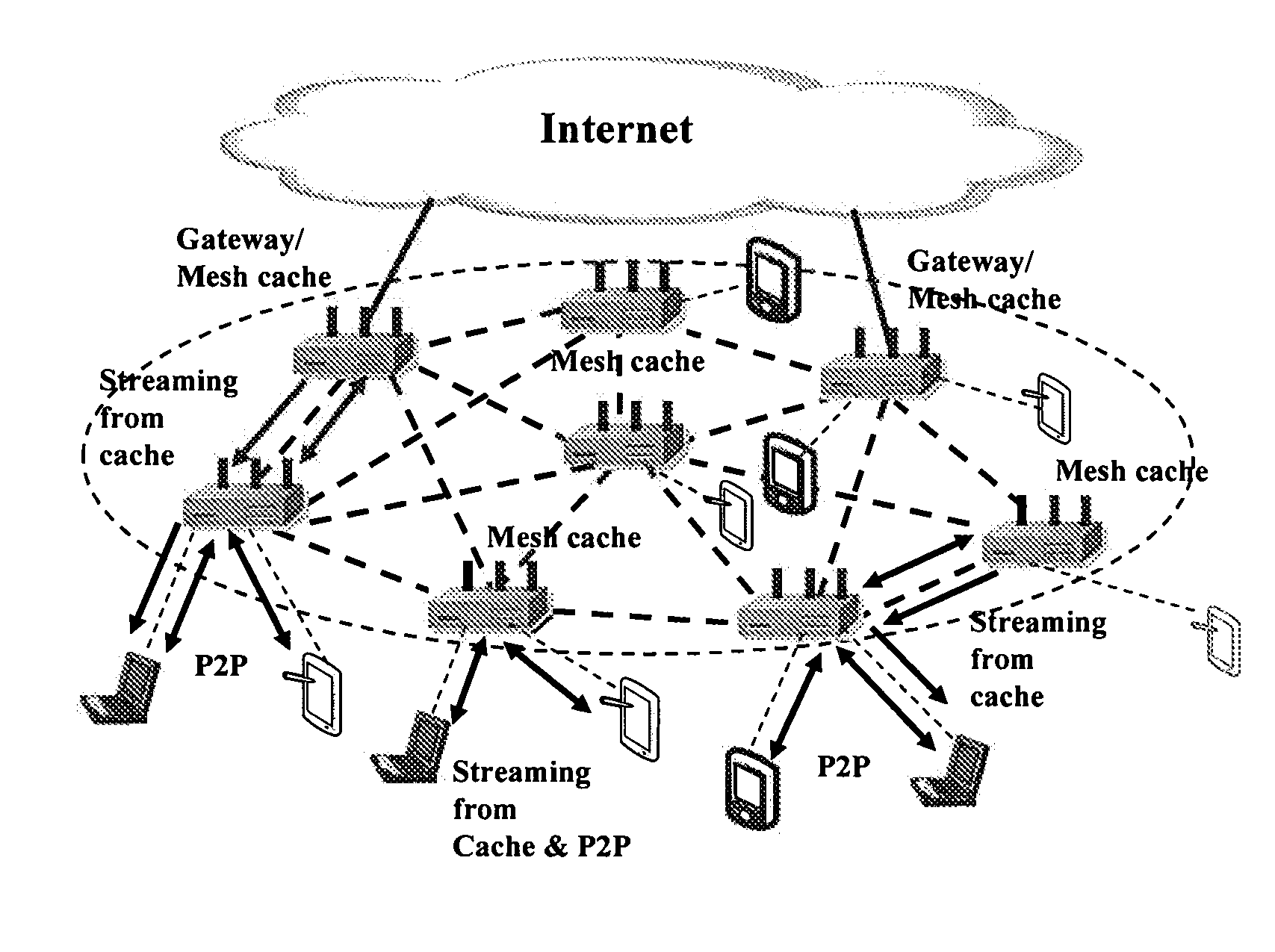
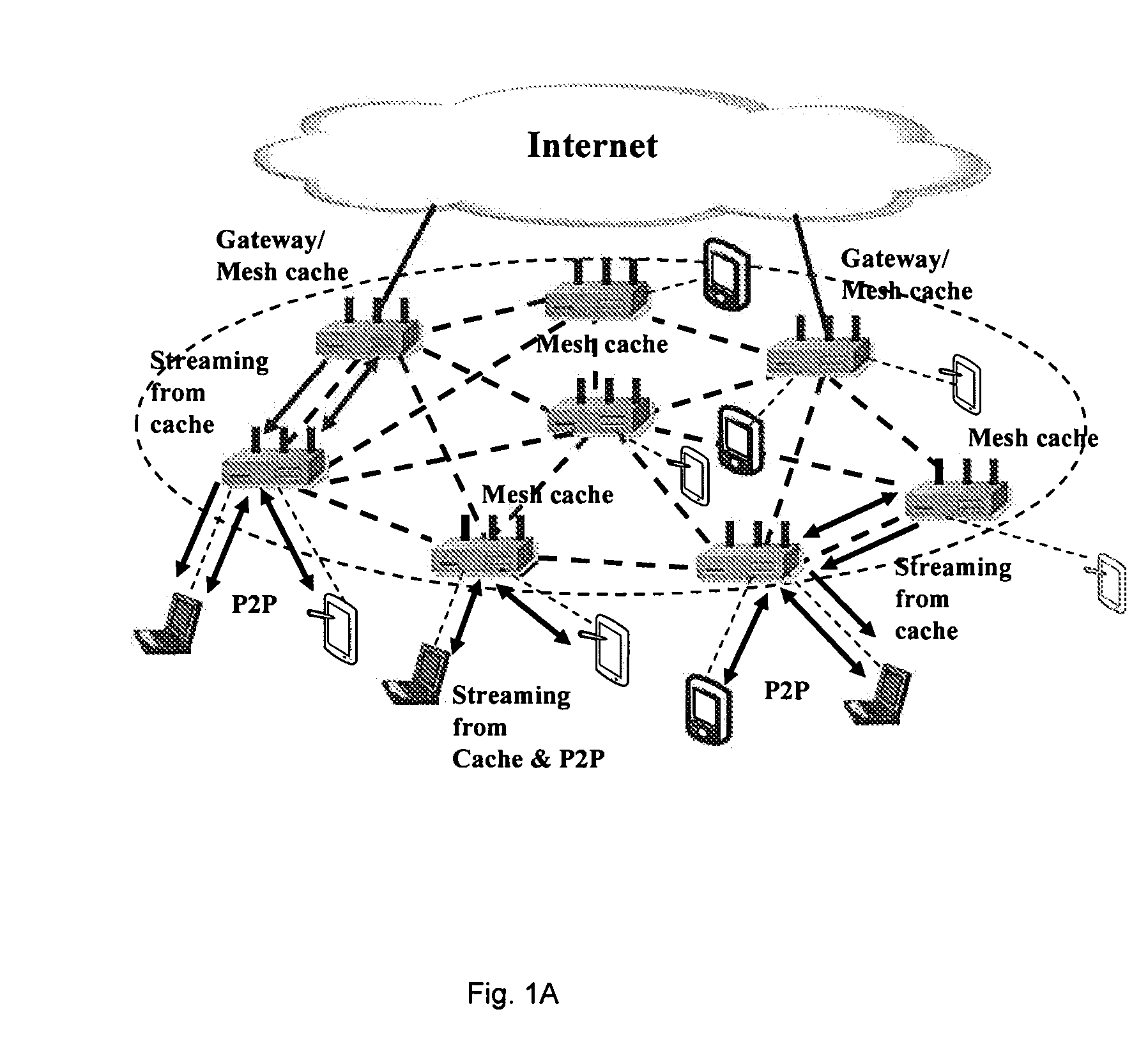
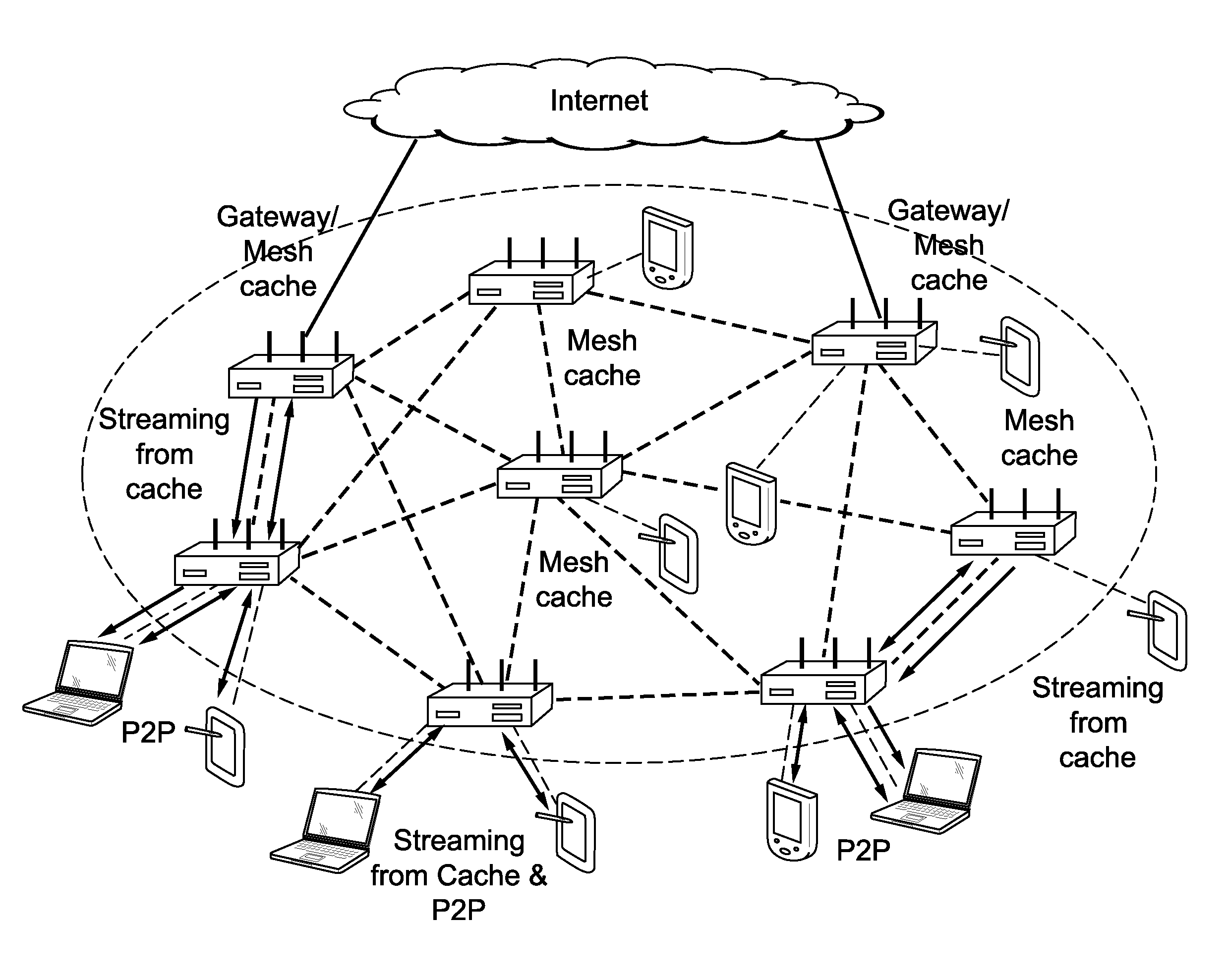
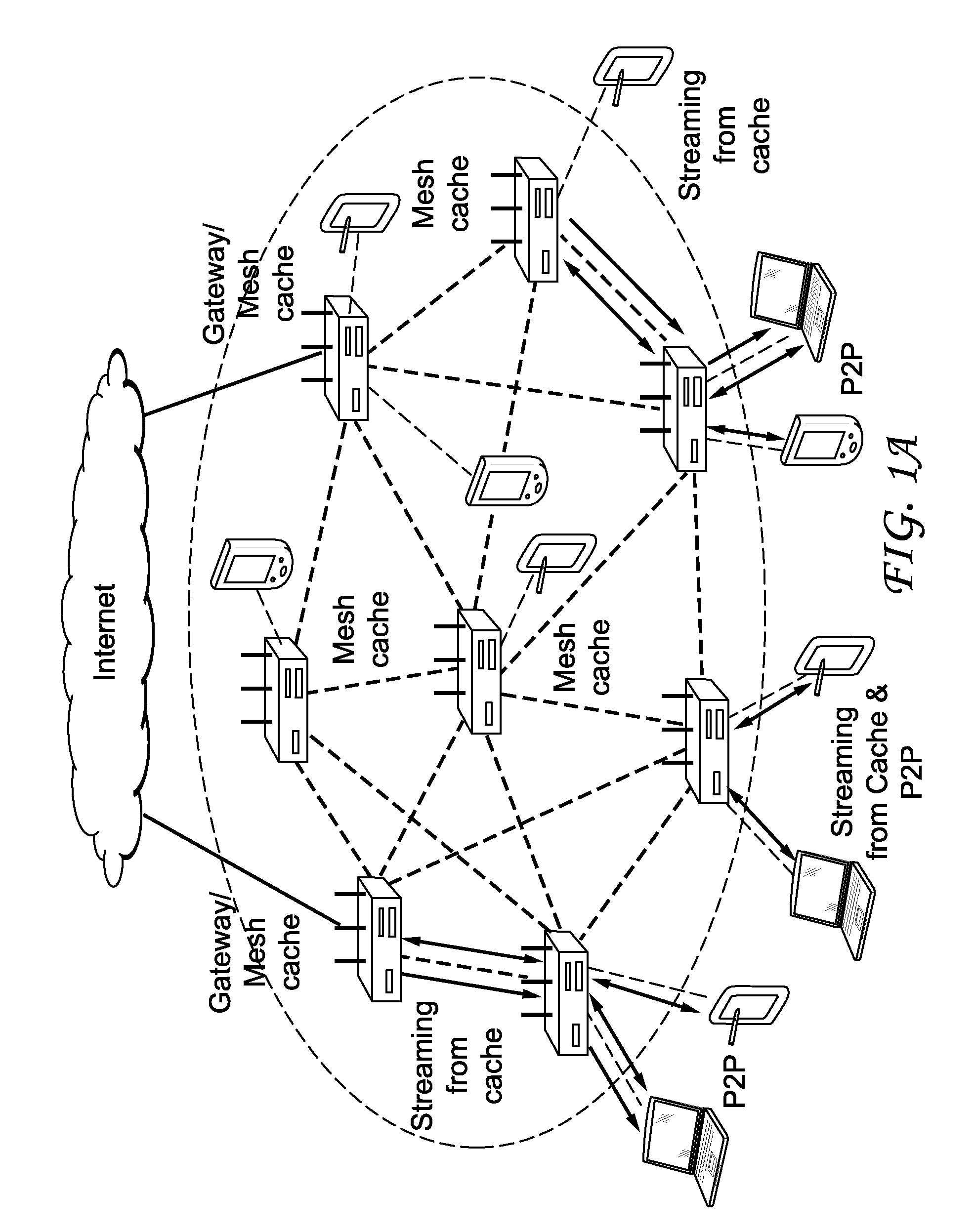
Unified cache and peer-to-peer method and apparatus for streaming media in wireless mesh networks
InactiveUS20110225312A1Reduce in quantityImprove good performanceSpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceMissing data
A method and apparatus are described including determining a number of clips to be streamed, requesting a selection of a mesh cache server to meet quality of service requirements for streaming the determined number of clips, establishing a streaming route responsive to the mesh cache server selection, receiving the number of streamed clips from the selected mesh cache server if the request is granted, joining a peer-to-peer network, downloading a next clip via the peer-to-peer network, requesting a selection of a mesh cache server to meet quality of service requirements for complimentary streaming any data missing from the next clip, receiving any data missing from the next clip via complimentary streaming if the request for complimentary streaming is granted and continuing to download any missing data of the next clip that has at least one of not passed its playback deadline and not been requested via complimentary streaming.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Matrix for transdermal drug delivery
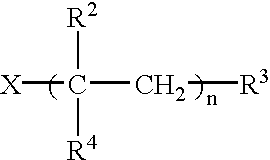
InactiveUS7097853B1Remove cleanHeavy loadMedical devicesAdhesive dressingsMacromonomerPressure sensitive
A transdermal drug delivery device involving a macromonomer-containing acrylate or methacrylate copolymer, a softener, and a drug. Also a pressure sensitive skin adhesive involving a macromonomer containing acrylate or methacrylate copolymer and a softener.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
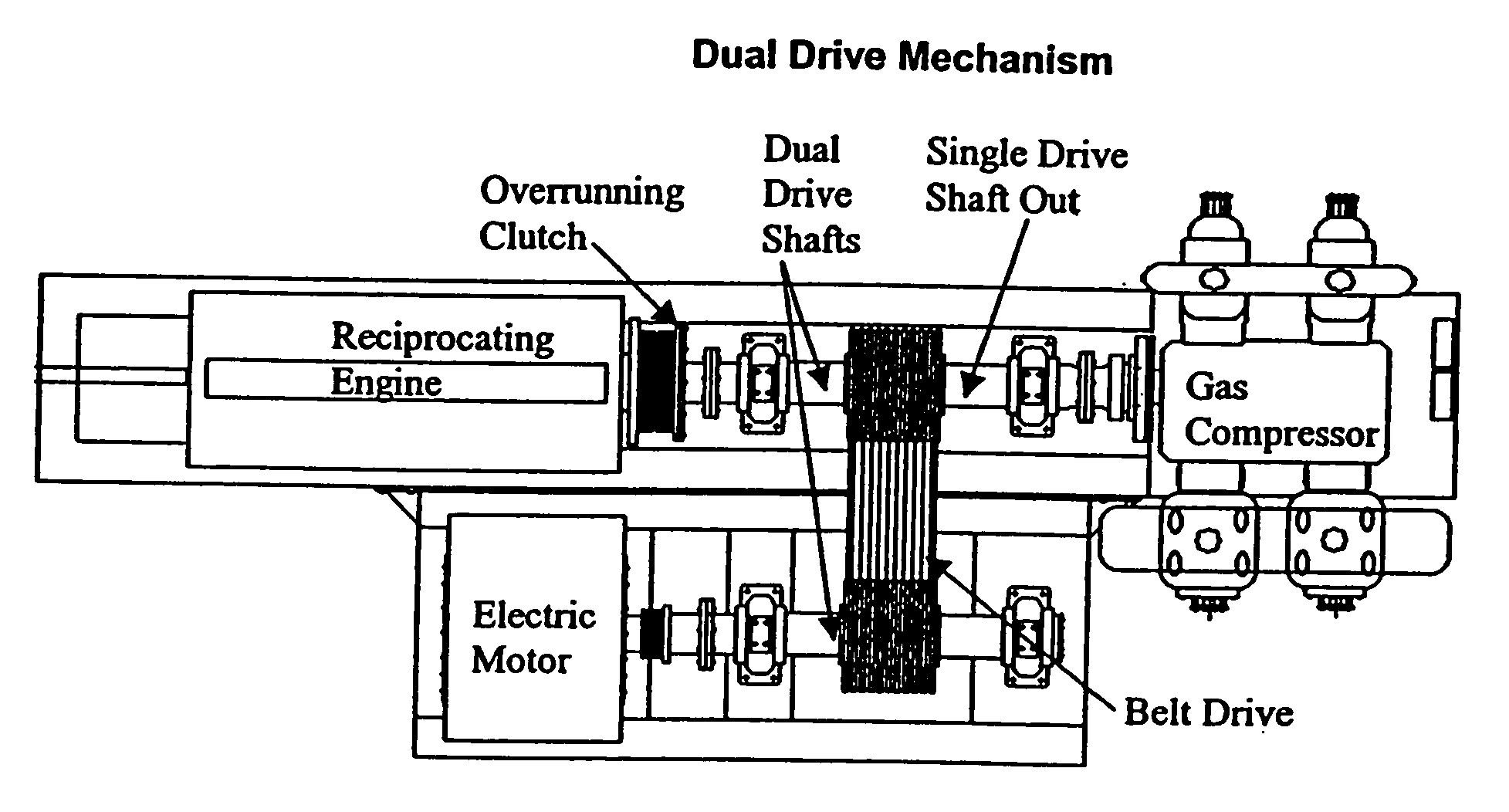
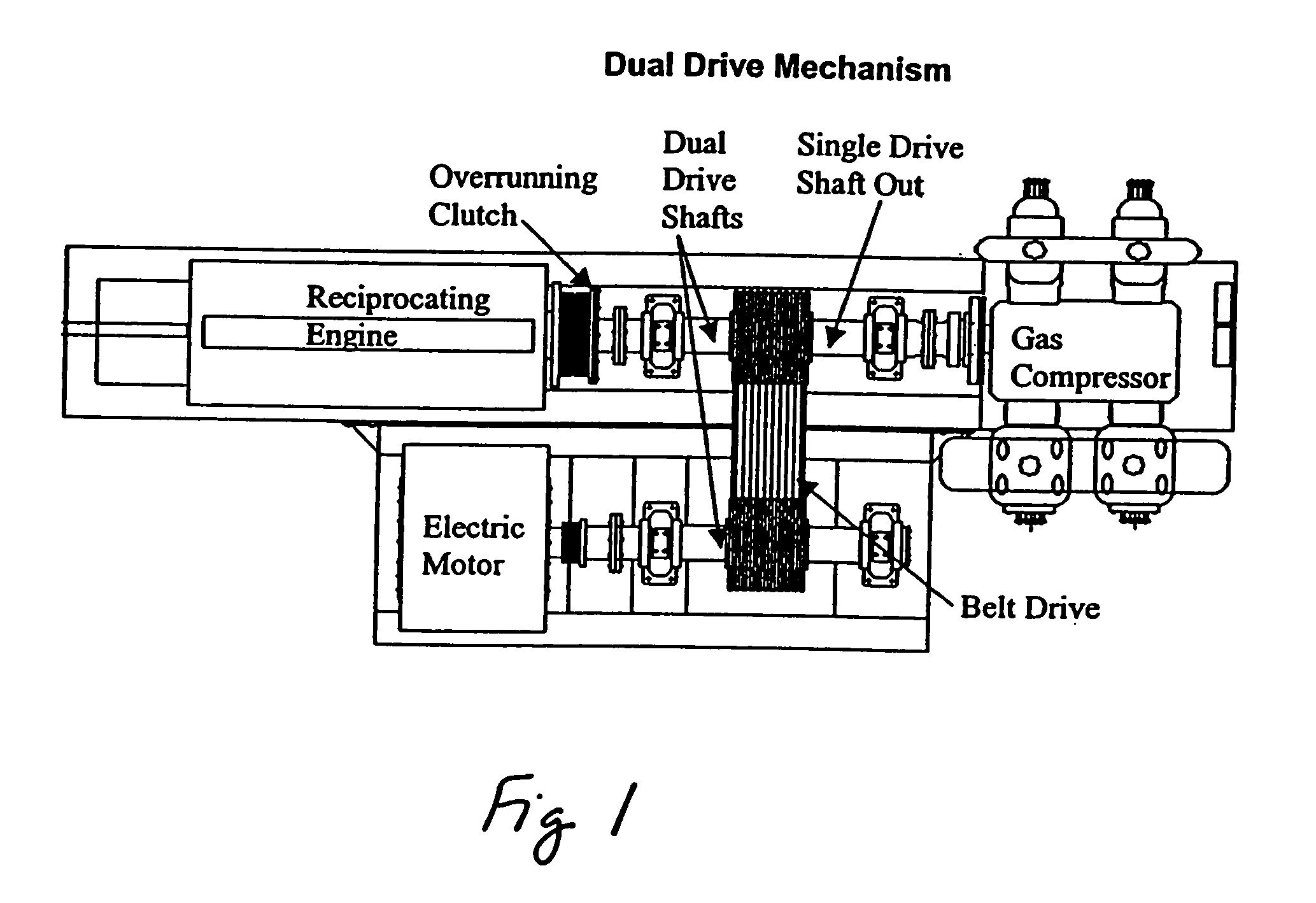
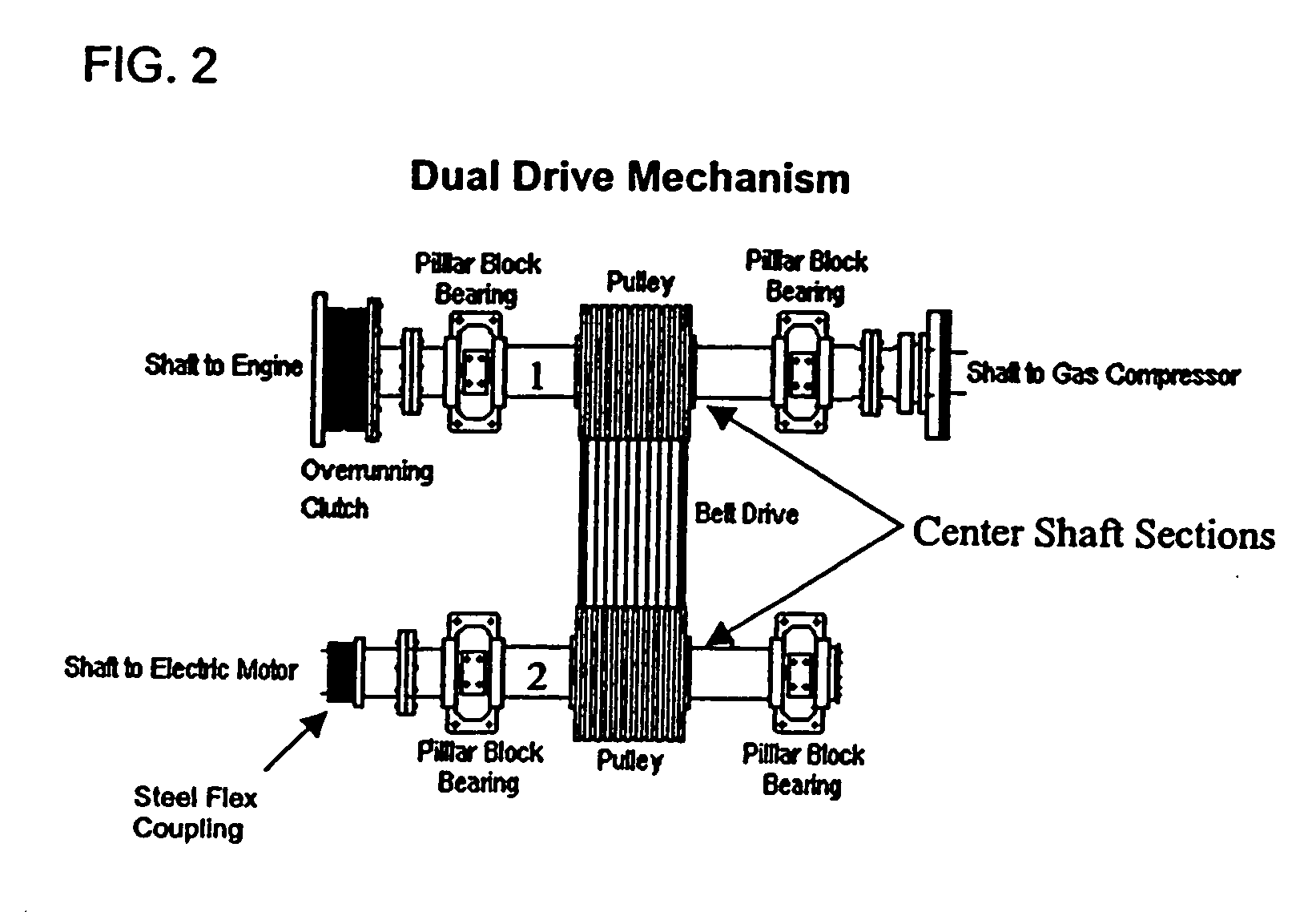
Gas compressor dual drive mechanism
InactiveUS20050196298A1Increase redundancyIncrease productivityPiston pumpsPositive-displacement liquid enginesGas compressorElectric power
A dual drive mechanism for a gas compressor includes a pulley and belt drive system to provide power to a gas compressor using either an electric motor or a reciprocating engine. The source of the power can be chosen by the operator of the system depending on a number of variables, including the cost of electric power.
Owner:MANNING JOHN B
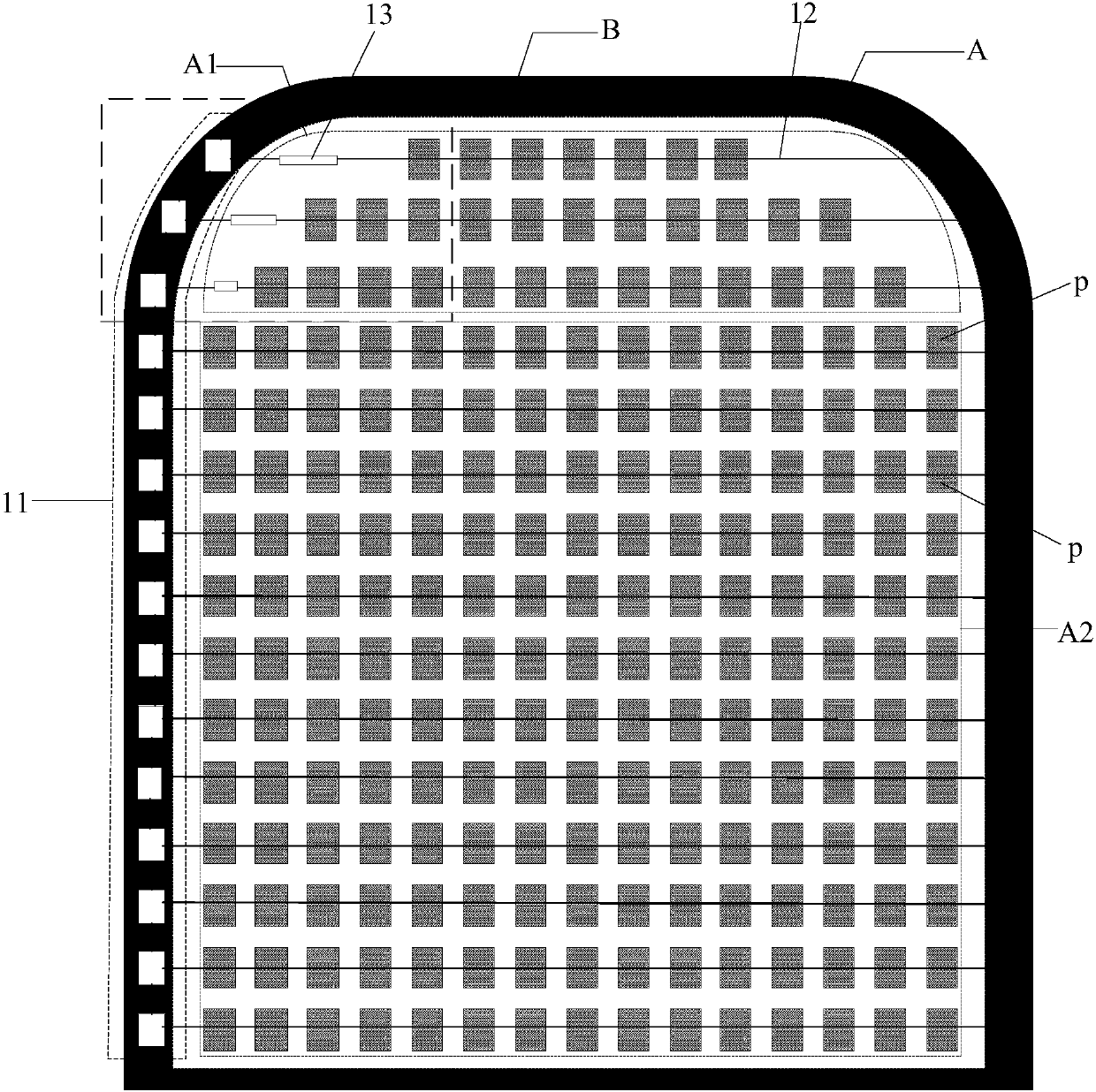
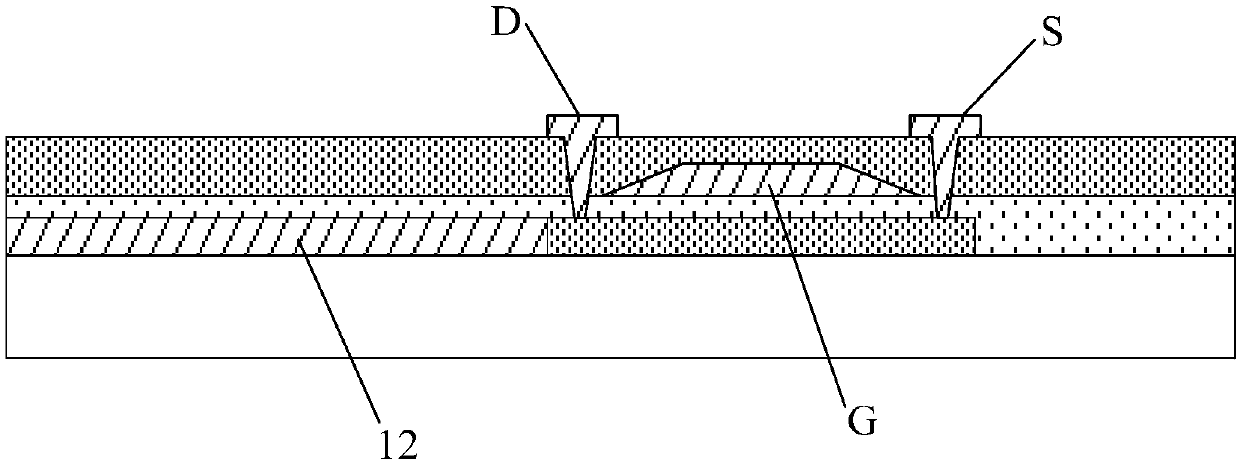
Display panel and display device
ActiveCN107610636AImprove display uniformityHeavy loadStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceDisplay device
The invention discloses a display panel and a display device. A display area comprises a first display region and a second display region. Each of the first display region and the second display region comprises a plurality of pixels in array distribution. The number of at least one line of pixels of the first display region is smaller than the number of any line of pixels of the second display region. The display panel comprises a grid drive circuit, a plurality of scanning signal lines and resistance compensation units. At least one scanning signal line provides scanning signals to one lineof the pixels. The resistance compensation units, namely metal or metal oxide wires, are connected with the scanning signal lines of the first display region. Through connection between the scanning signal lines of the first display region and the resistance compensation units, load of the scanning signal lines connected with the resistance compensation units can be increased, so that load differences among the scanning signal lines of the first display region and load differences among the scanning signal lines of the second display region are reduced, display uniformity of the display panelis improved, and display effect is enhanced.
Owner:WUHAN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Unified cache and peer-to-peer method and apparatus for streaming media in wireless mesh networks
InactiveUS20110225311A1Reduce throughputQuality improvementBroadcast transmission systemsData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceRouting table
A method and apparatus are described including receiving a route request message to establish a streaming route, determining a cost of a reverse route and traffic load introduced by the requested streaming route, discarding the route request message if one of wireless interference constraints for the requested streaming route cannot be satisfied and quality of service requirements for the requested streaming route cannot be satisfied, pre-admitting the route request message if wireless interference constraints for the requested streaming route can be satisfied and if quality of service requirements for the requested streaming route can be satisfied, adding a routing table entry responsive to the pre-admission, admitting the requested streaming route, updating the routing table and transmitting a route reply message to an originator if requested content is cached, updating the route request message and forwarding the updated route request message if the requested content is not cached, receiving a route reply message and deleting the pre-admitted routing table entry if a time has expired.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
Display panel and display device
The present invention discloses a display panel and a display device. A display area is divided into a first display area and a second display area, when the number of pixels of one row of pixels in the second display area is smaller than the number of pixels of one row of the pixels in the first display area, the load of a scanning signal line connected with the row of the pixels in the second display area is smaller than the load of a scanning signal line connected with the row of the pixels in the first display area, and through adoption of a mode of connecting at least one of each scanning signal line connected with each row of the pixels in the second display area with a compensation capacitor, the load of the scanning signal lines connected with the compensation capacitor can be increased, and the load difference from the scanning signal lines in the first display area can be reduced so as to improve the problems that the loads of the scanning signal lines are different to cause uneven data writing-in and uneven display.
Owner:WUHAN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
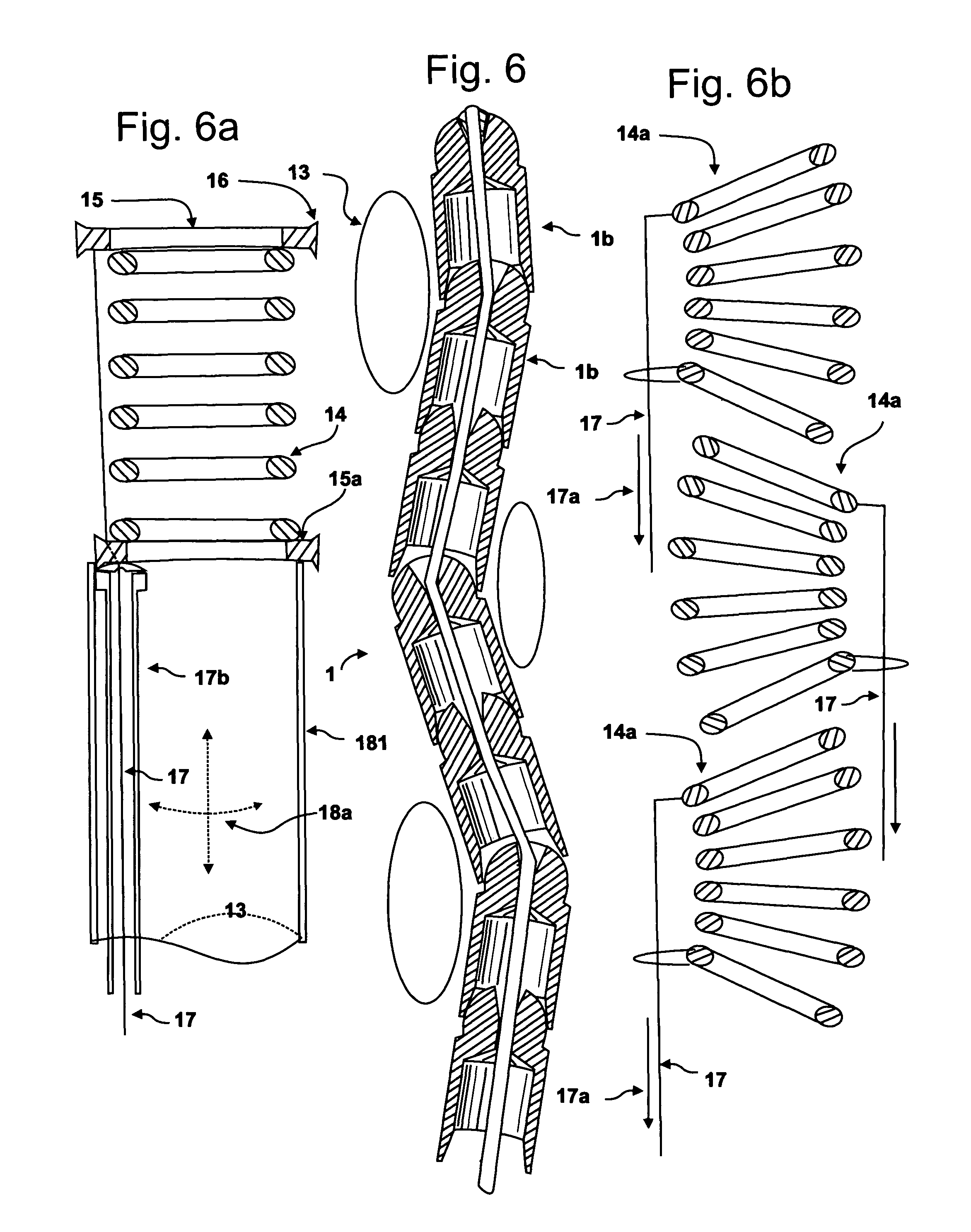
Medical instrument for milling a curved path in bone and procedure
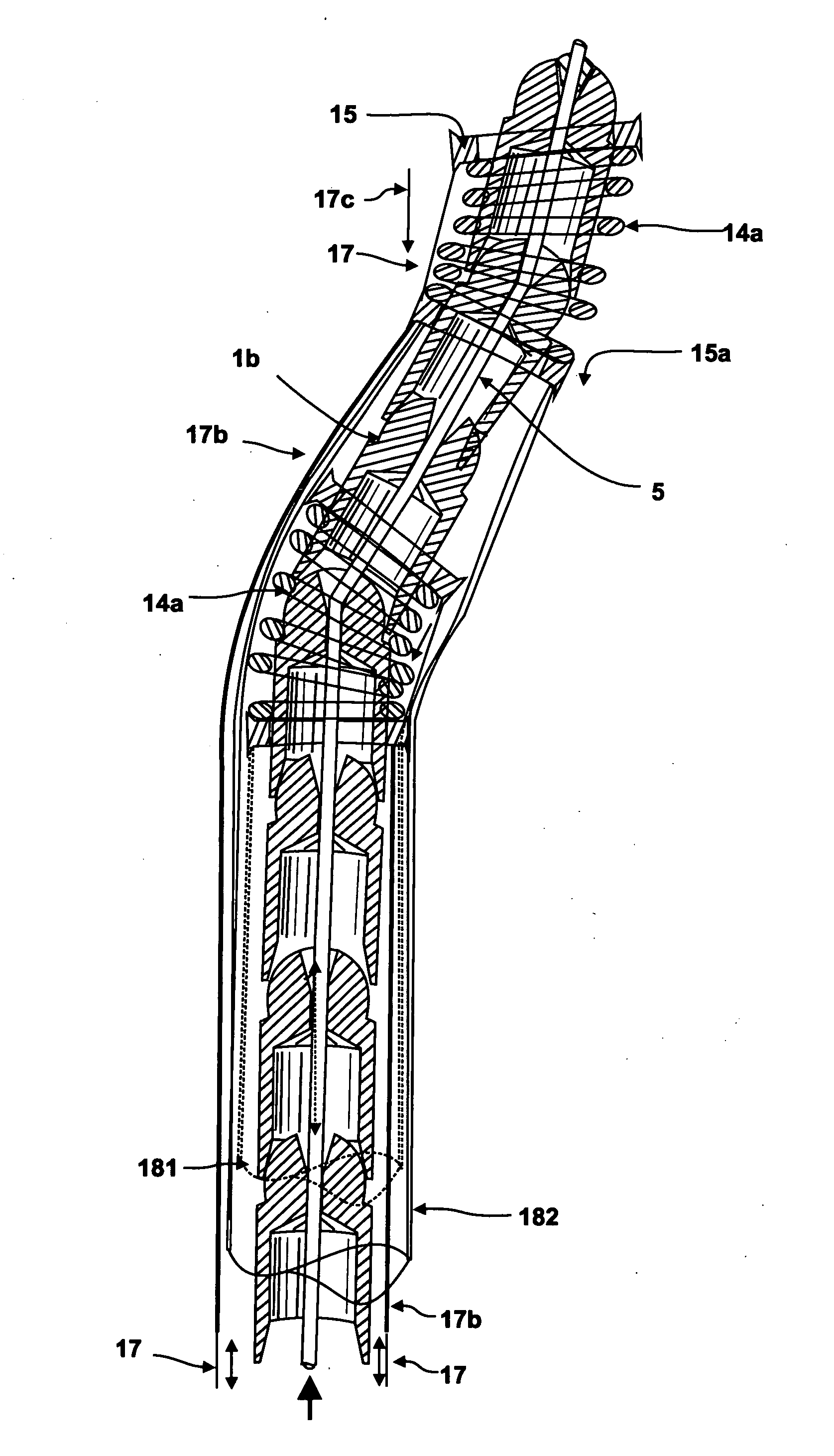
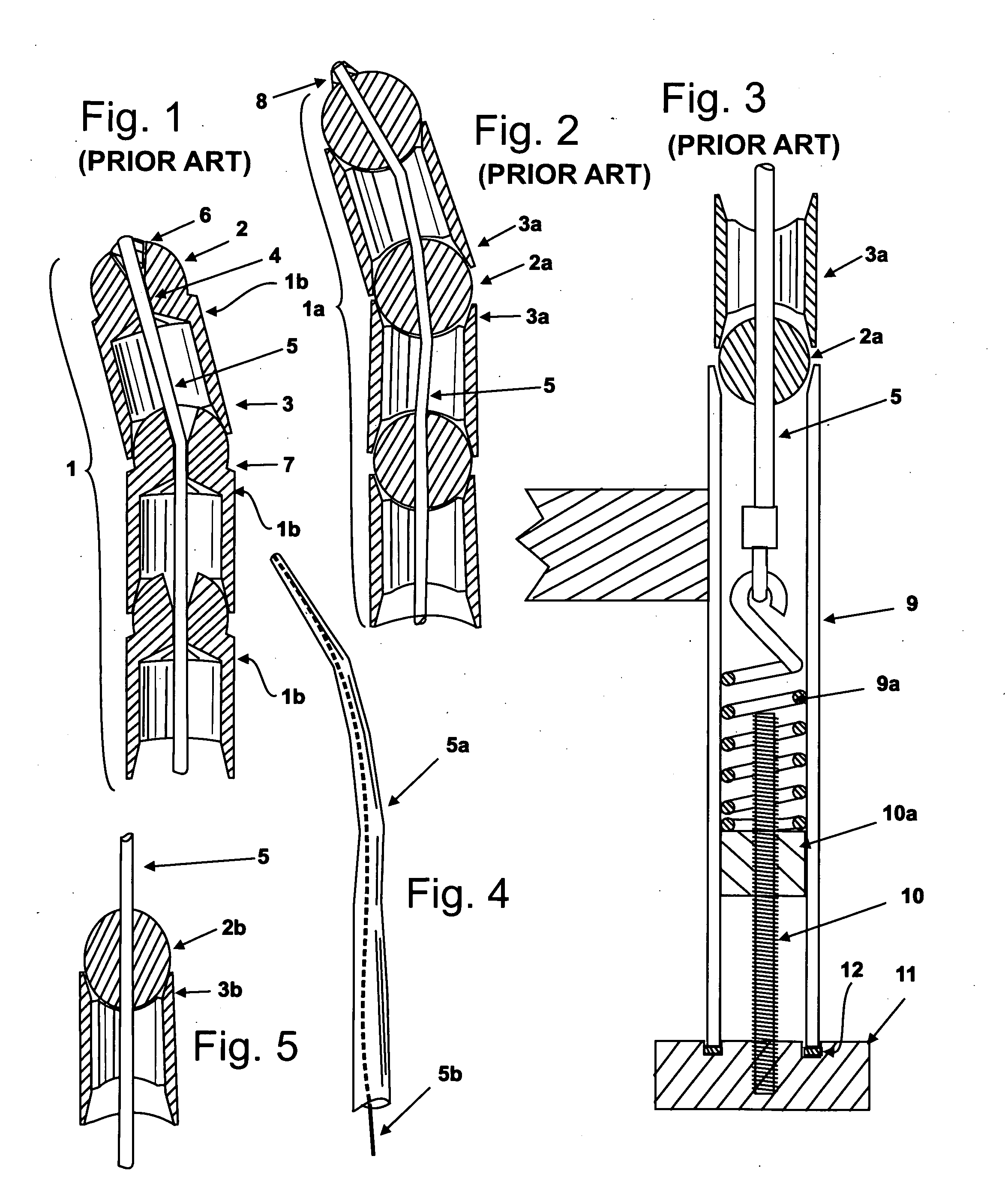
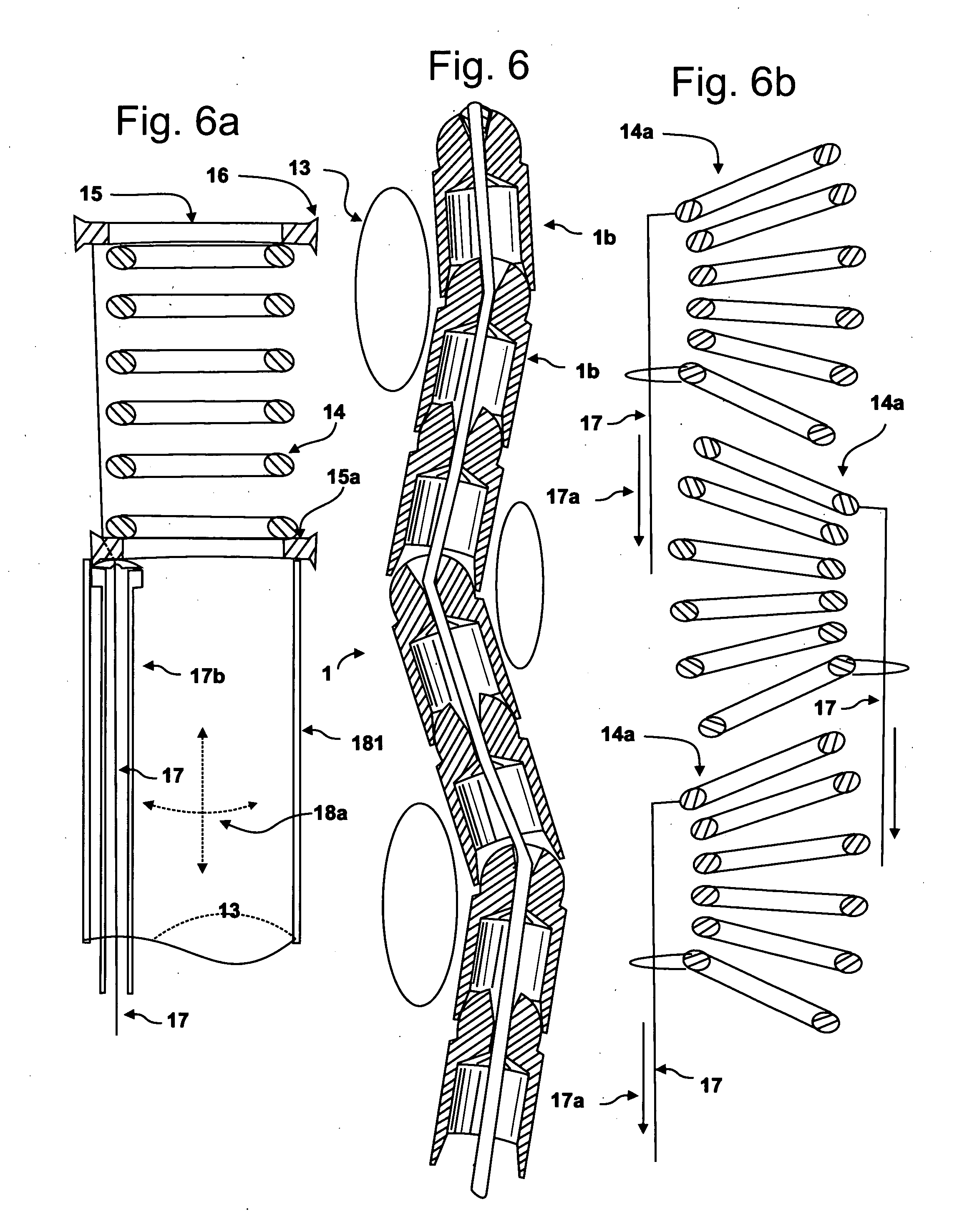
A medical instrument and procedure is adapted to mill bone along a curve and with respect to at least two angles of orientation with respect to an input source of rotary motion. Particularly, the medical instrument is a bone milling apparatus that is configured to mill bone along a predetermined curved path or curve. The bone milling apparatus includes a reamer that is rotatable about a curved shaft which is retained by a frame. The shaft has a predetermined curve that corresponds to a desired milling curve. The reamer is comprised of a plurality of interconnected segments, with each segment having cutting surfaces such that each segment is a cutter. The reamer is thus flexible with respect to the interconnection between the individual segments.
Owner:DEPUY ORTHOPAEDICS INC
Snaking robotic arm with movable shapers
ActiveUS8224485B2Overcome difficultiesMaking the articulable column sufficiently stiffProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlRobotic armEngineering
Owner:TITAN MEDICAL INC
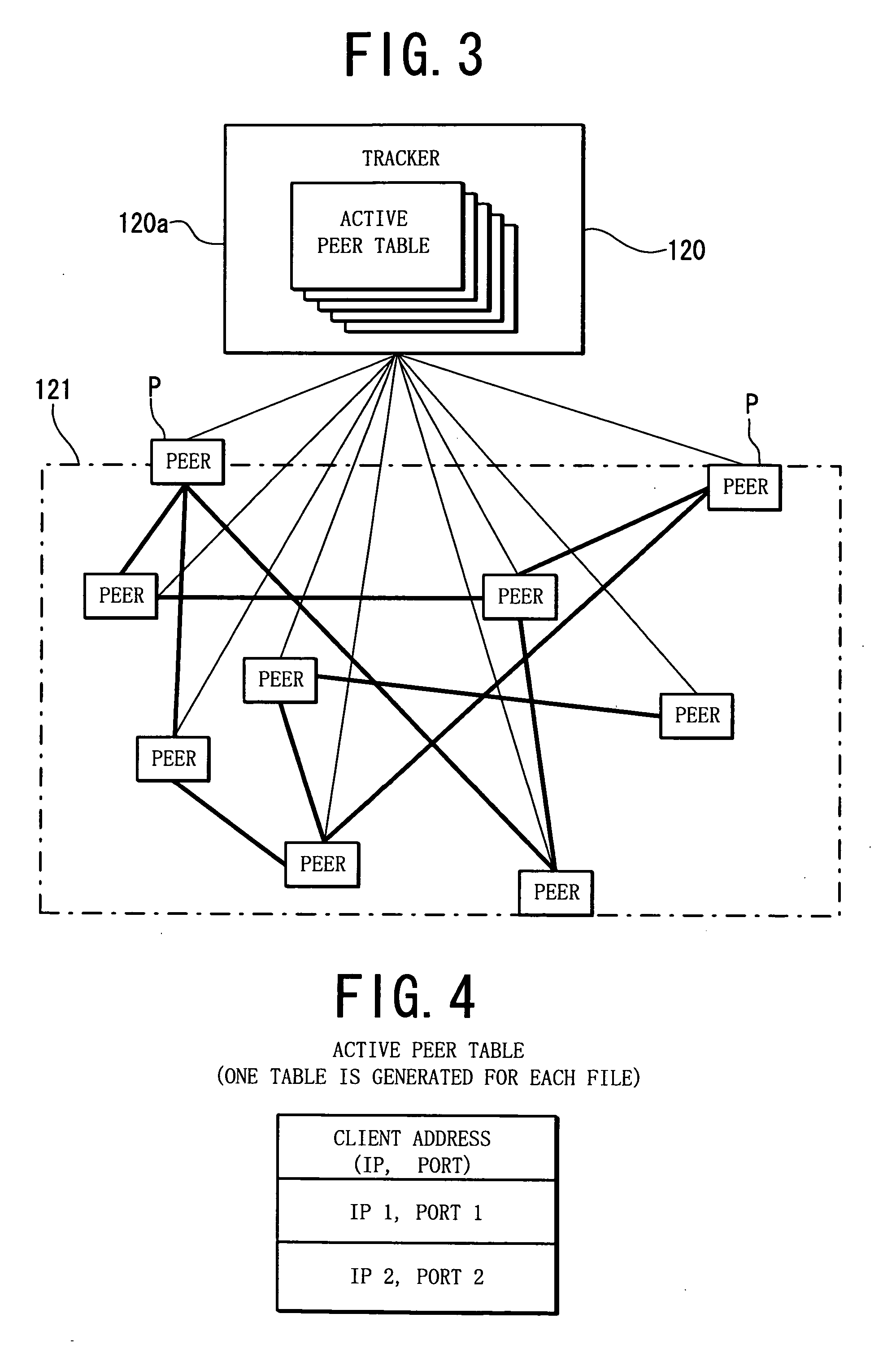
Download method for file by bit torrent protocol
InactiveUS20070028133A1Easy loadingIncrease investmentTransmissionRedundant hardware error correctionBit torrentSeeder
The present invention relates to the improvement of the Bit Torrent protocol, which is one of the P2P protocols. A seeder flag is added to the active peer table. First a super seeder having the original is activated, and the super seeder is stopped when the total value of the seeder flags (number of activated seeders) reaches a certain level. The super seeders are activated only when the seeders having the original of a file are insufficient on the network, and are stopped when excessive. By this dynamic control, the number of activated processes of the super seeders can be decreased.
Owner:GRID SOLUTIONS INC
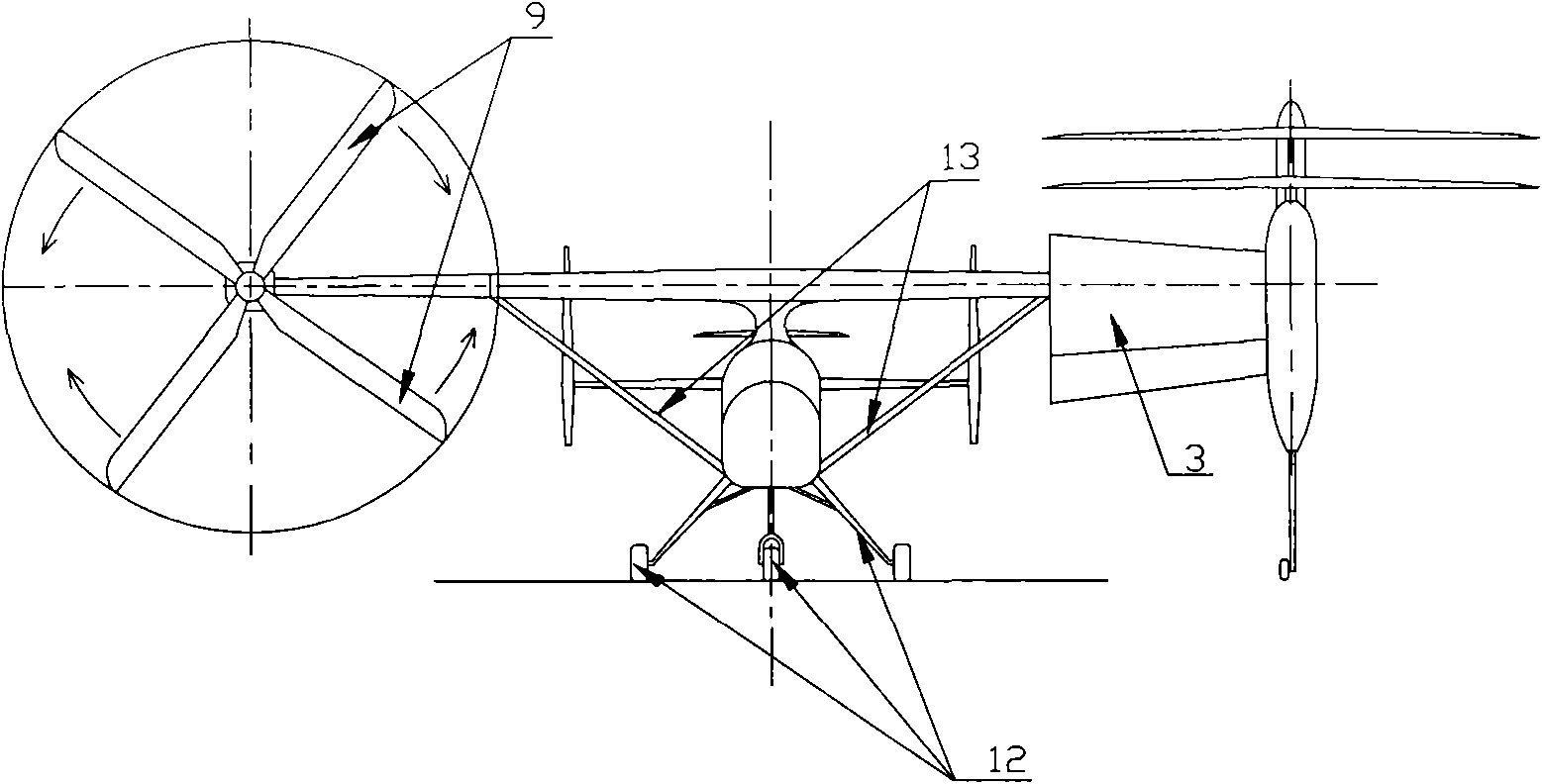
Tilt rotor aircraft adopting parallel coaxial dual rotors
The invention relates to a tilt rotor aircraft adopting parallel coaxial dual rotors, which comprises a fuselage, wings, an empennage, a pitch control scull system, a landing gear, a power and fuel system, a transmission system, a rotor system, a rotor nacelle and a tilt system, wherein the wings are arranged at the center section of the fuselage; the empennage and the pitch control scull system are arranged at the tail of the fuselage; the landing gear is positioned at the belly of the fuselage; the power and fuel system is arranged inside the center section of the fuselage and is connected with the rotor system and the pitch control scull system through the wings and the transmission system in the fuselage; the rotor system is arranged on the rotor nacelle at the tip of the wings; partial wing which is fixedly connected with the rotor nacelle and simultaneously can tilt is arranged at the inner side of the rotor nacelle; and the tilt system is arranged in the wings and is connected with the rotor nacelle and the partial wing which can tilt. The tilt rotor aircraft is mainly characterized by adopting the pitch control scull system, the parallel coaxial dual rotors and the partialwing which can tilt to realize flight status transformation and conventional taxiing and landing, thereby improving the forward speed and the propulsive efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
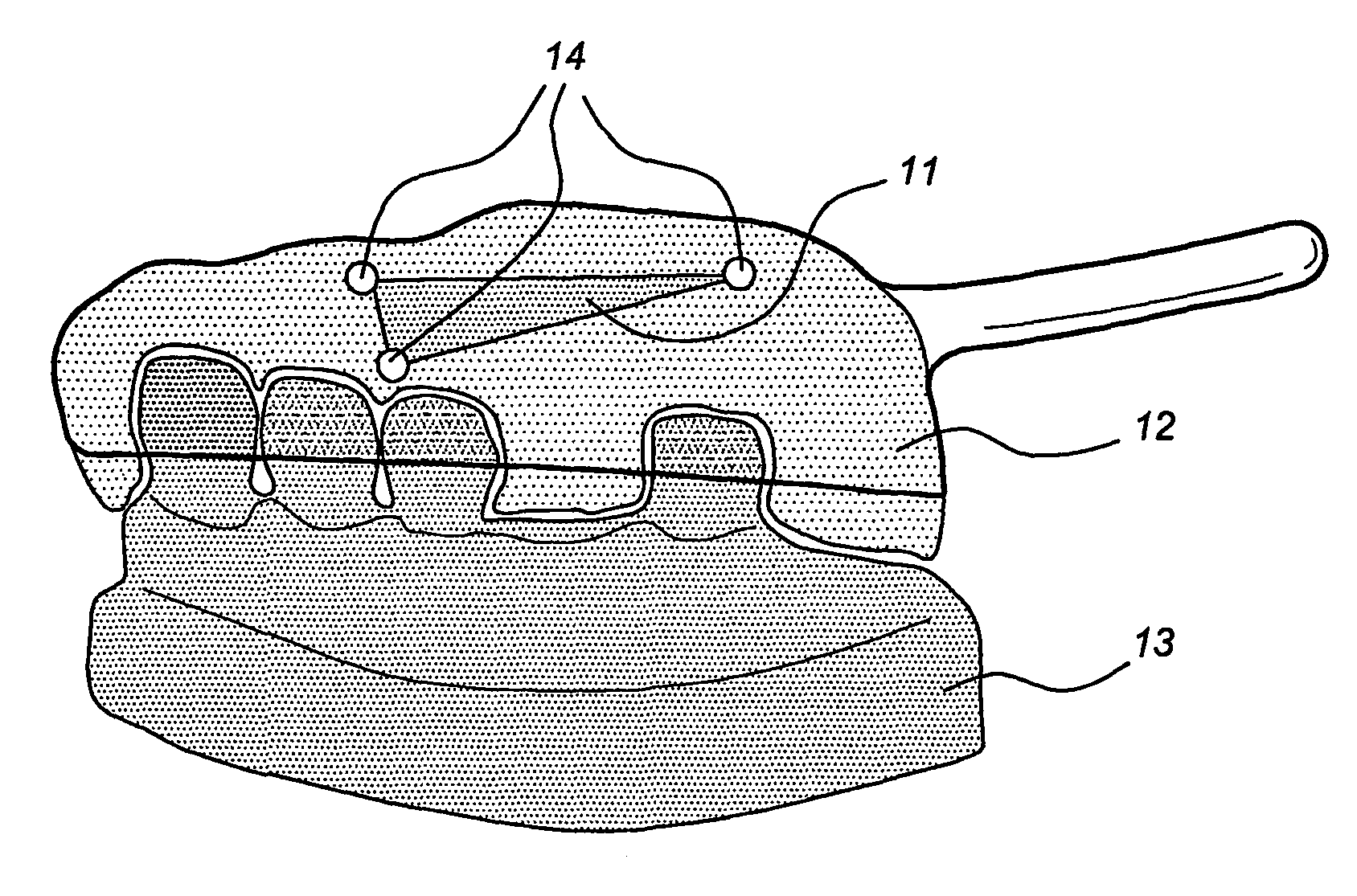
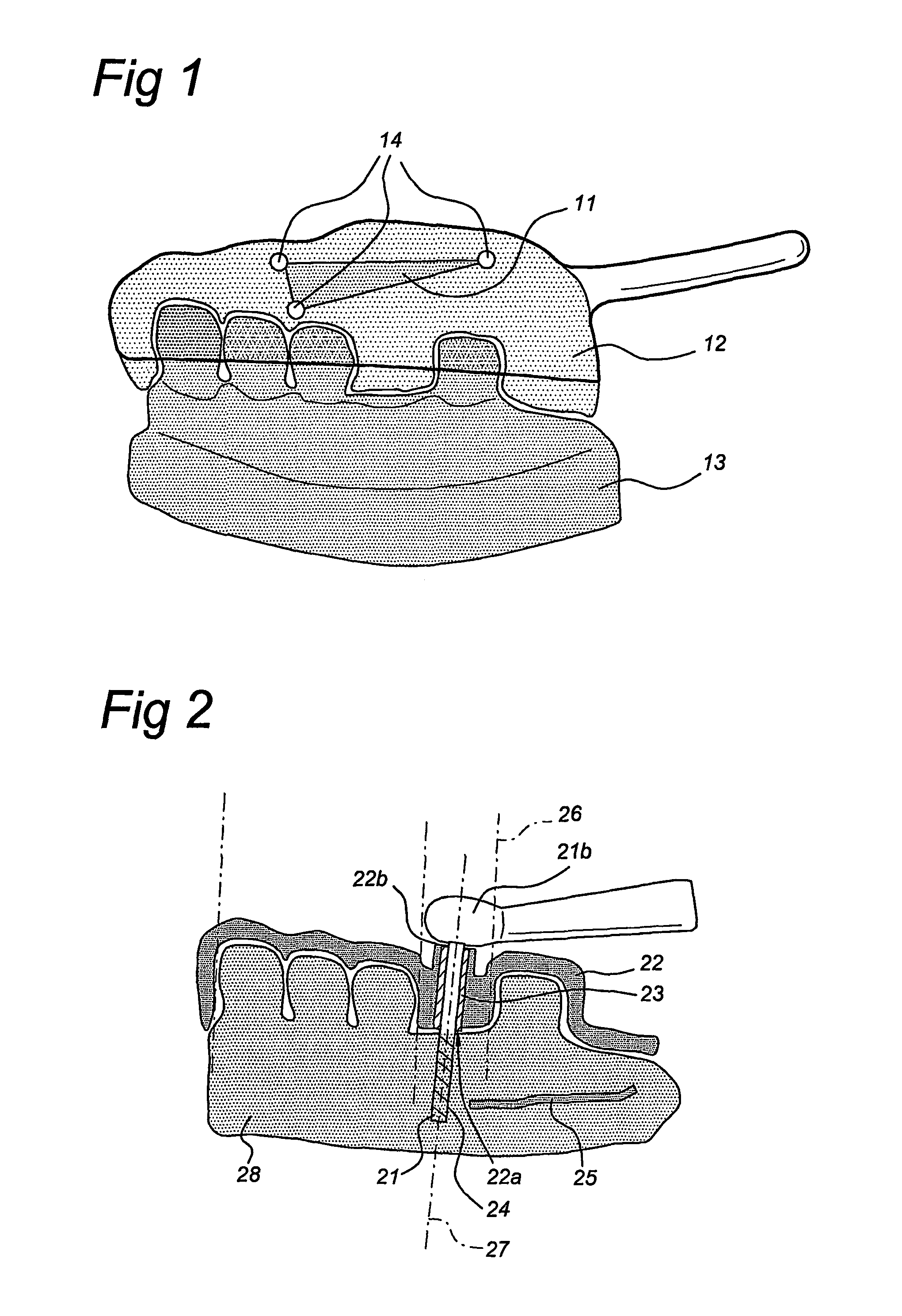
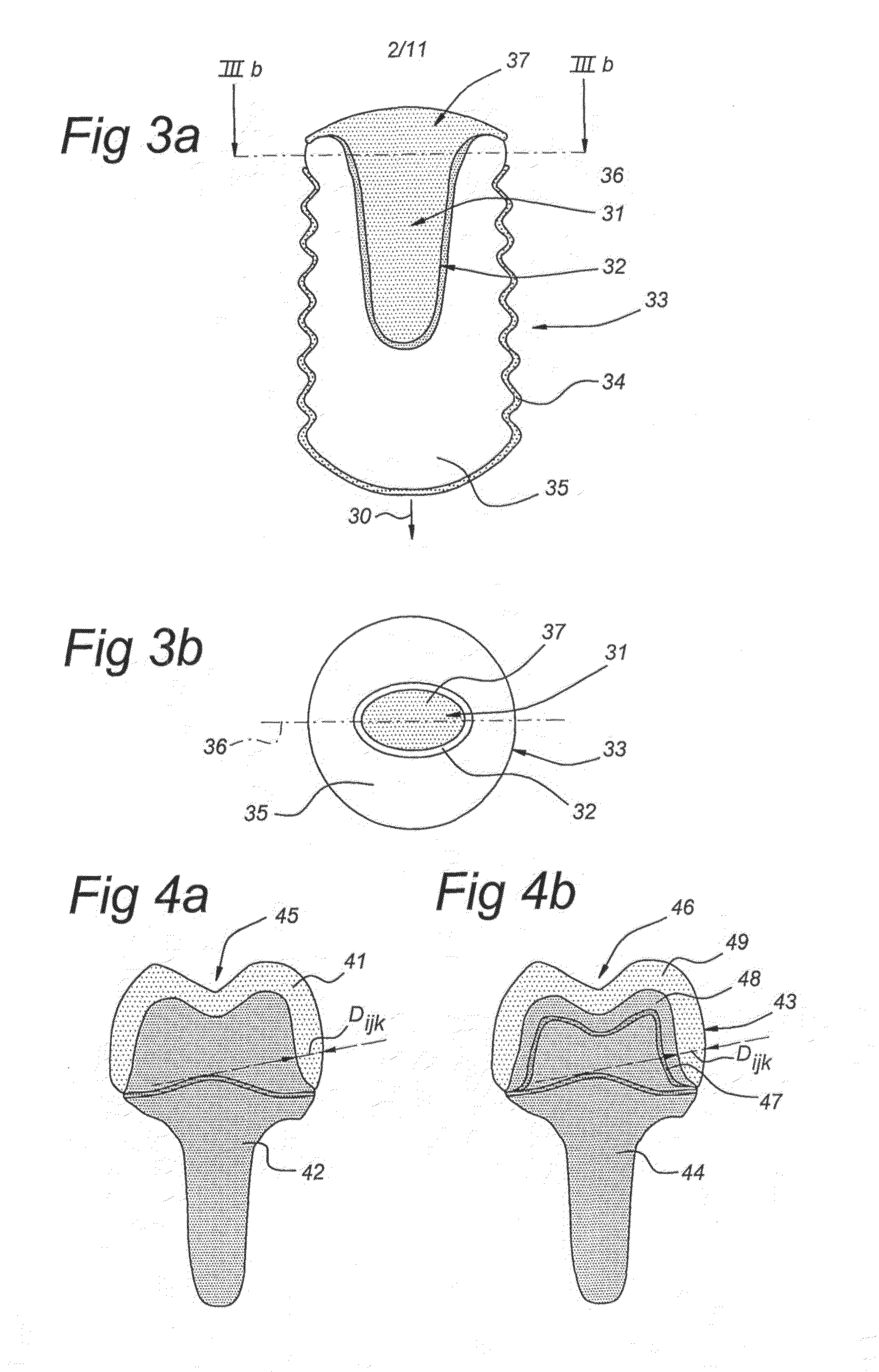
Method of manufacturing and installing a ceramic dental implant with an aesthetic implant abutment
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a tooth prosthesis, for insertion in a jawbone, including an implant and an abutment on top of the implant. The method includes: defining a shape of the prosthesis and its location in the jawbone by using first data from a first CT scan image of the jawbone and second data from a second image of a gypsum cast, correlating first and second data by extracting from the first data first position reference data of a first reference in the first image, and from the second data second position reference data of a second reference in the second image, the second reference being identical to the first reference; performing a geometric transformation on the second data and / or the first data to have a coincidence of the second image with the first image and to combine the first and second data into composite scan data.
Owner:CYRTINA DENTAL GROUP BV
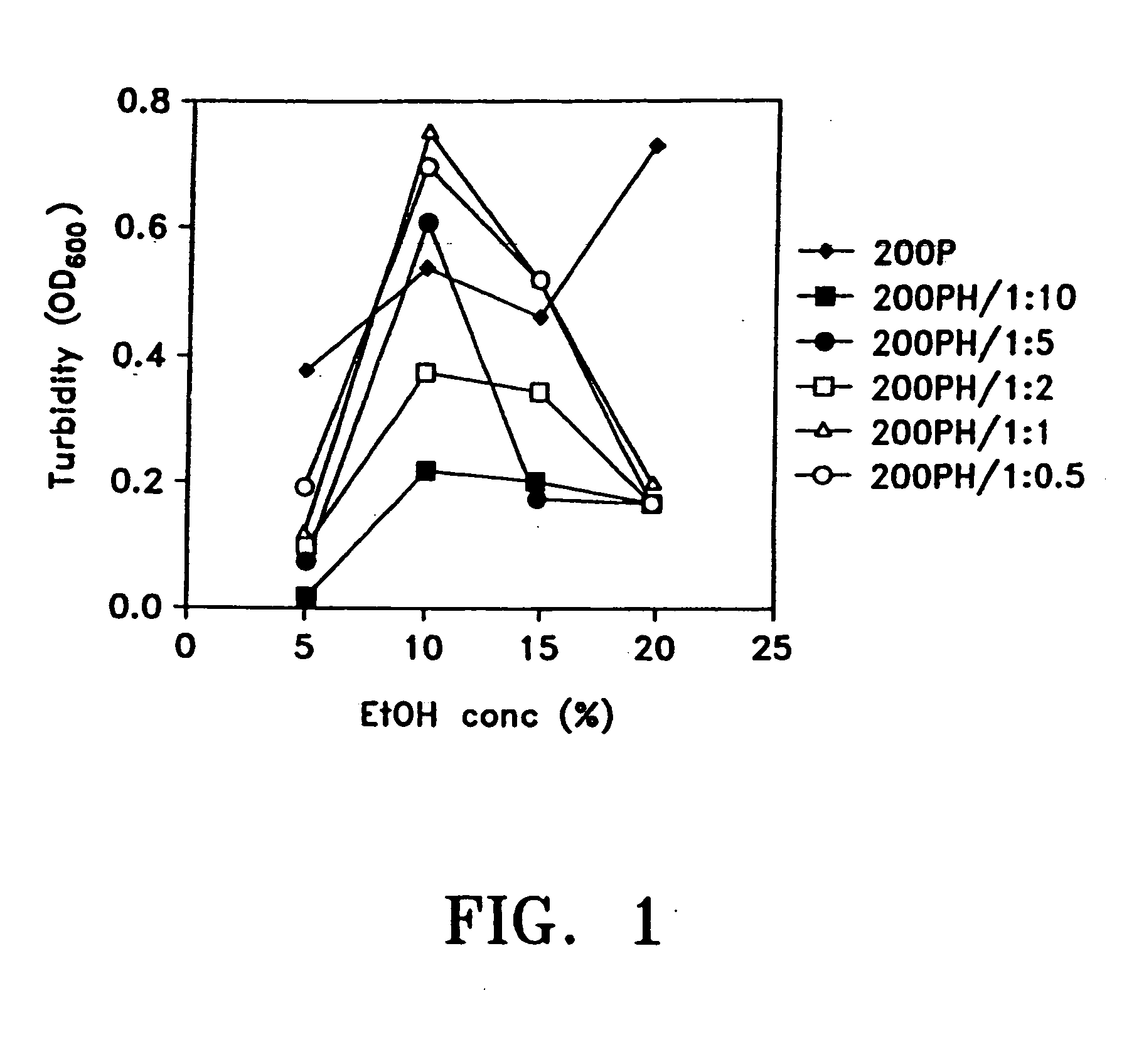
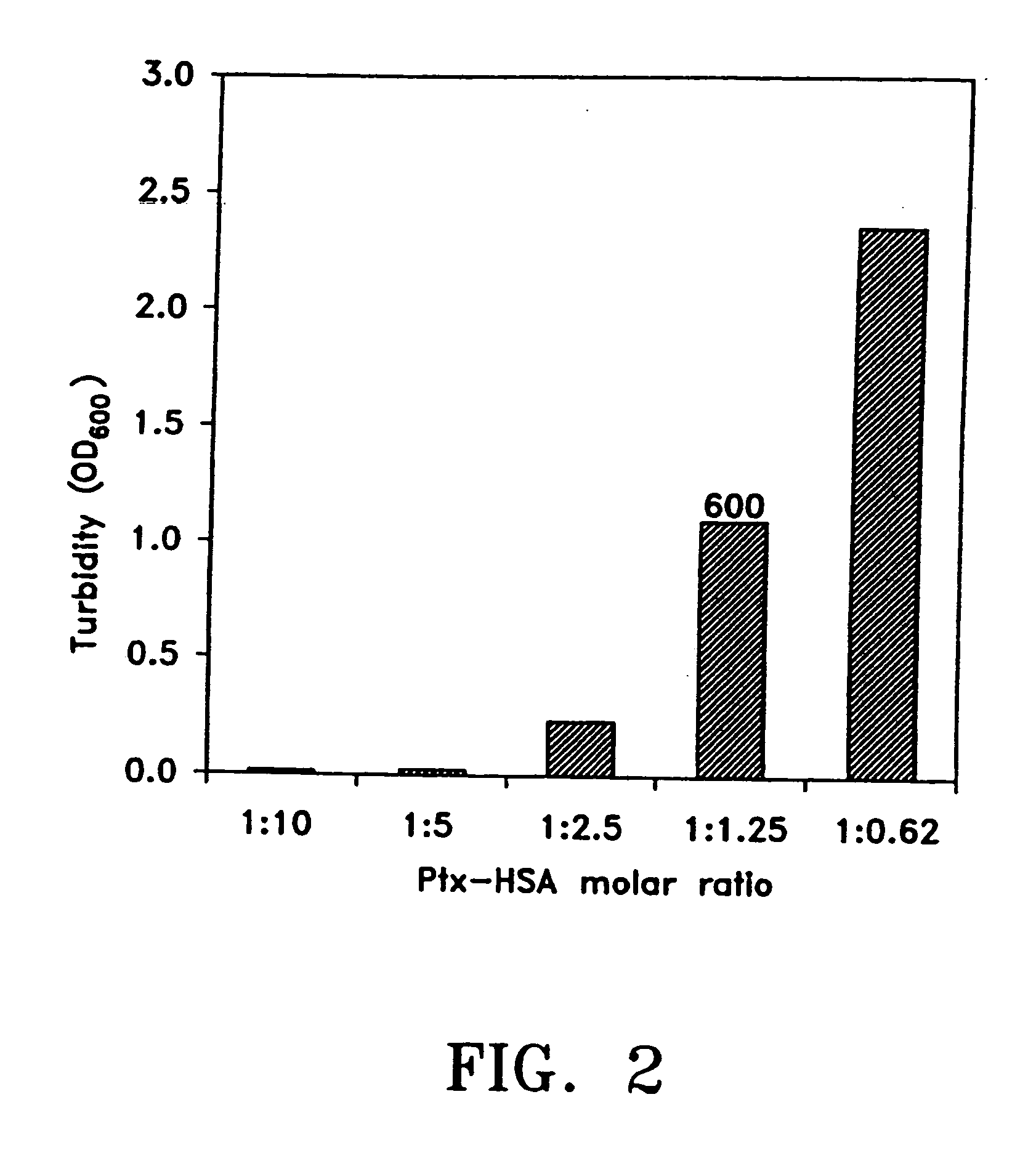
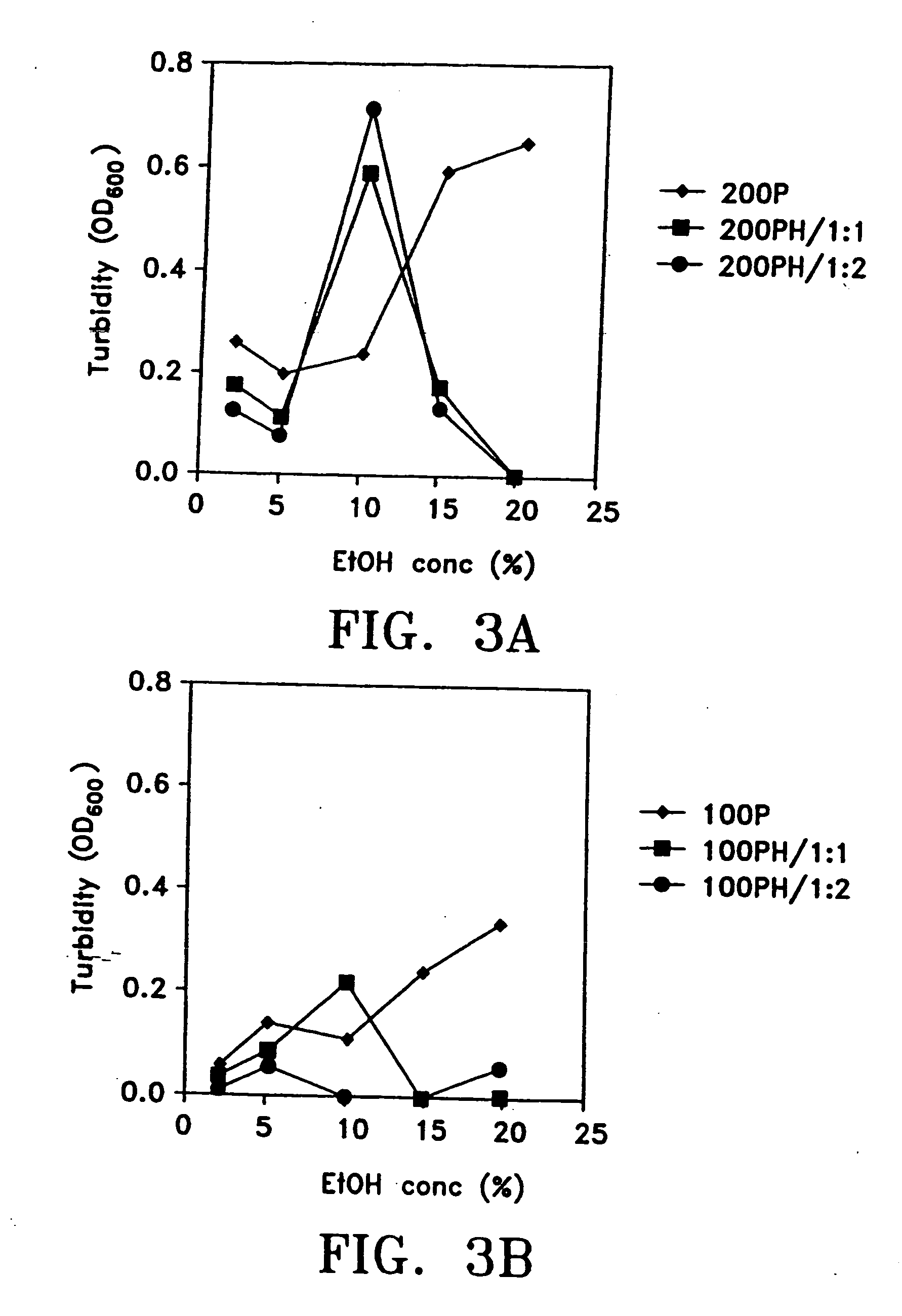
Pharmaceutically acceptable composition comprising an aqueous solution of paclitaxel and albumin
InactiveUS20050282734A1Prevent restenosisFree of organic solventsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsOrganic solventSerum protein albumin
An optically clear, pharmaceutically acceptable aqueous composition comprising paclitaxel or a derivative thereof, serum albumin and a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle, wherein the composition comprises no more than 10% organic solvent and has a pH of about 3.0 to about 4.8, is described. The serum albumin can be fatted or defatted, and the composition can optionally be lyophilized or optionally lyophilized and reconstituted. At least 70% of the paclitaxel is bound to serum albumin, the ratio of paclitaxel to albumin is at least about 1:5, and the concentration of paclitaxel is at least about 25 μg / ml. Methods of making and using this composition an also provided.
Owner:KADIMA TENSHUK A +6
Snaking Robotic Arm with Movable Shapers
ActiveUS20100030377A1Easy constructionOvercome difficultiesProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlRobotic armEngineering
Presented is a method and apparatus comprising one or more robotic members which are curvaceous or snake-like; having movable shapers through which may pass an articulable column having successive joints formed of alternating ball and socket members. The shapers can be directed up and down the articulable column, to create virtually any radius of curvature, in any direction. The robotic member may also include discrete microelectronic mechanical devices (MEMS) shapers with embedded addressable controllers. Thus the device, with computerized control is capable of negotiating a tortuous path to access the site of a given operation and to retreat along the same path, without injury to the body in which the arm is directed. Once at the work site, the articulating columns, or parts of them, may be put in compression, causing them to become rigid.
Owner:TITAN MEDICAL INC
Gusset plates connection of beam to column
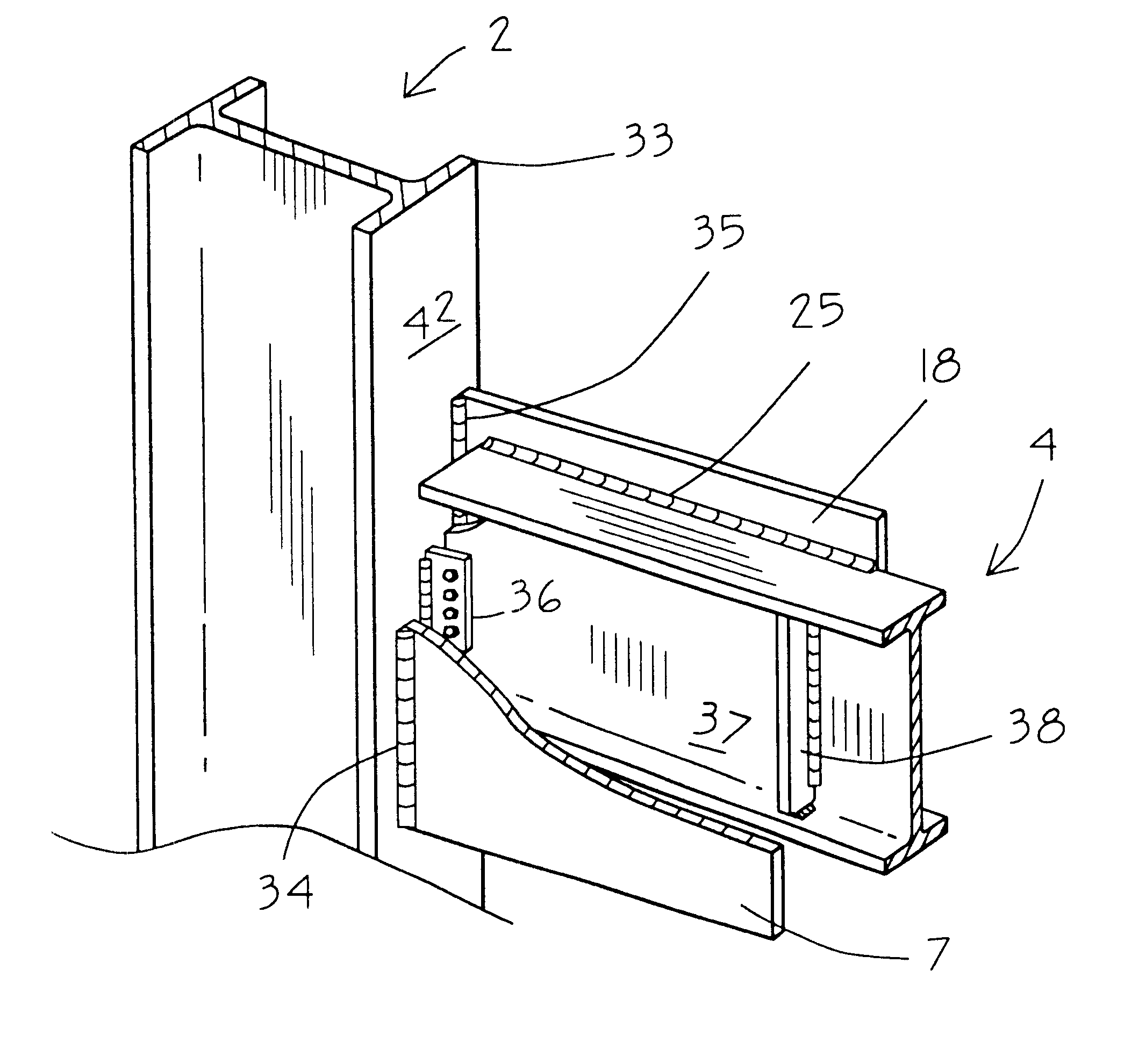
InactiveUS6591573B2Improve rendering capabilitiesImprove stabilityBuilding roofsArched girdersGusset plateEngineering
This invention relates to columnar, "primary support" for a building or other heavy structure, in which a beam is connected to a column in a strong, moment-resisting connection comprised of two gusset plates welded to a flange or the face of the flange of the column and welded to the beam or attached to cover plates fixedly attached to the beam.
Owner:MITEK HLDG INC
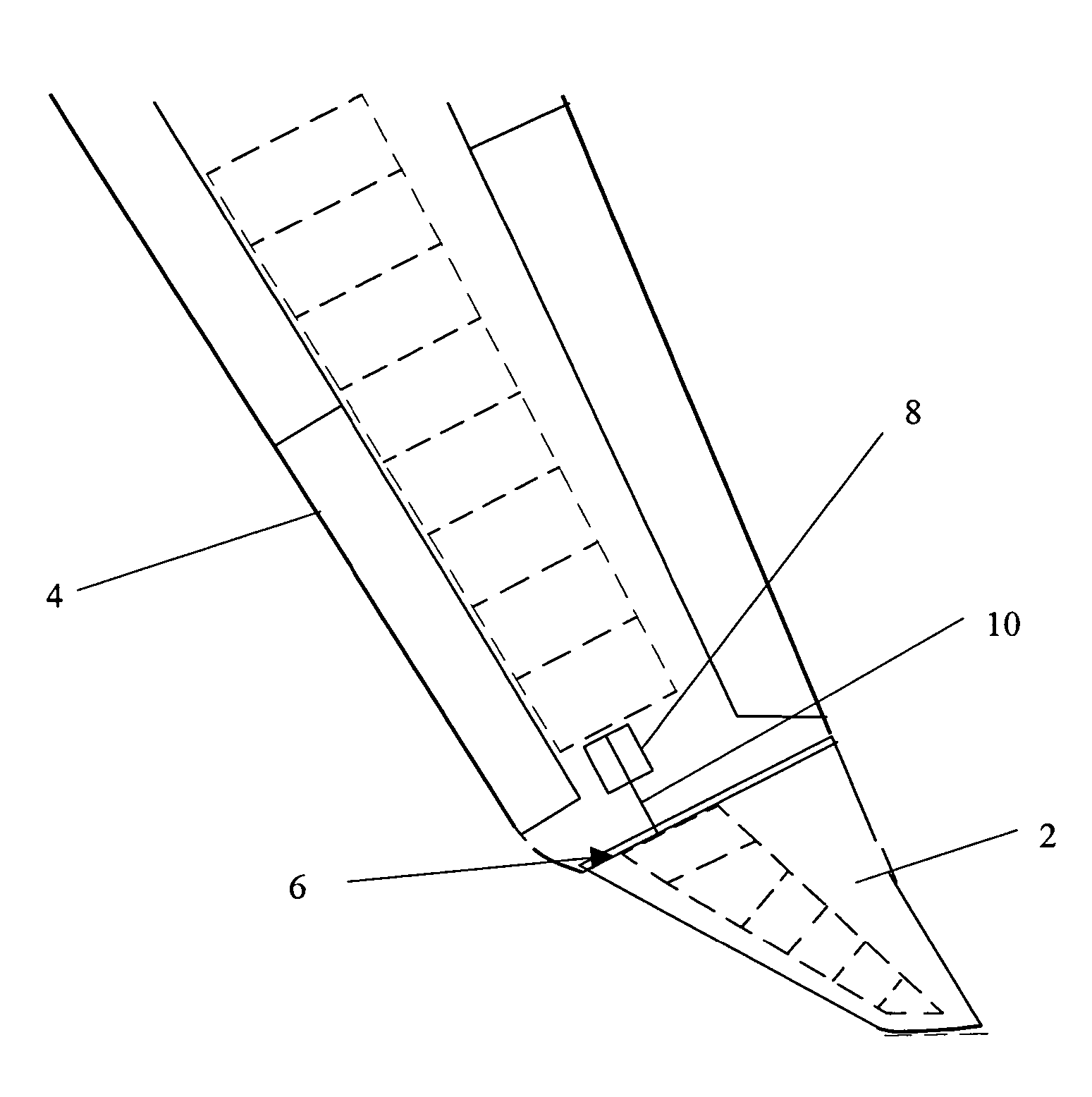
Wing tip device
ActiveUS20050133672A1Reduce the impactUndesirable oscillationInfluencers by generating vorticesWingsFlight vehicleWingtip device
An aircraft comprises a wing tip device, for example a winglet, a raked-tip device, a wing tip fence or a planar wing extension, mounted in the region of the tip of a wing on the aircraft. The wing tip device is rotatably moveable between a first position and a second position, in which the upward lift produced by the wing or the wing tip device is reduced. During flight, the bending moment at the root of the aircraft wing therefore changes in dependence on the position of the wing tip device. The maximum bending moment in the aircraft wing sustained during high-load conditions is thereby reduced, allowing the structural mass of the aircraft to be reduced.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
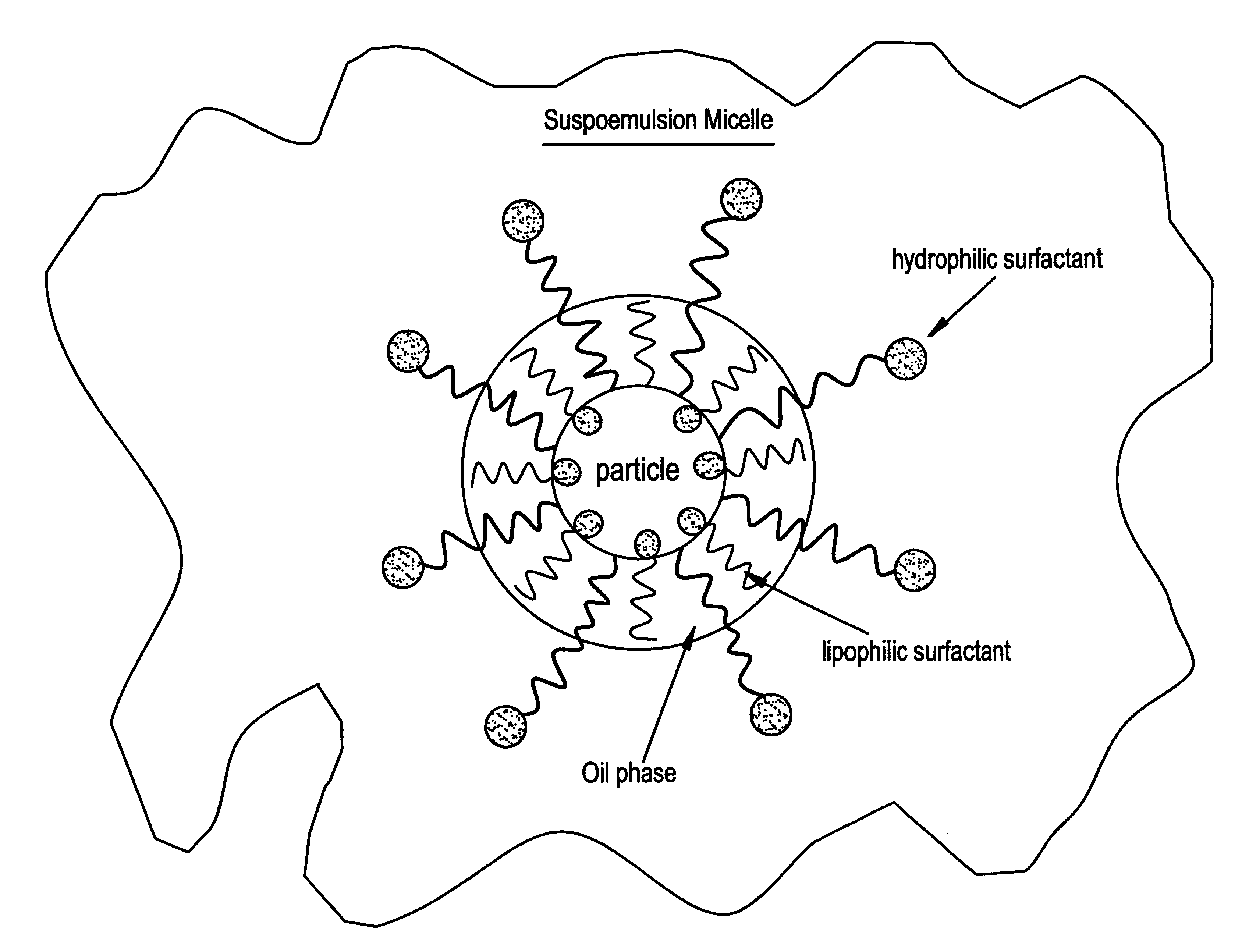
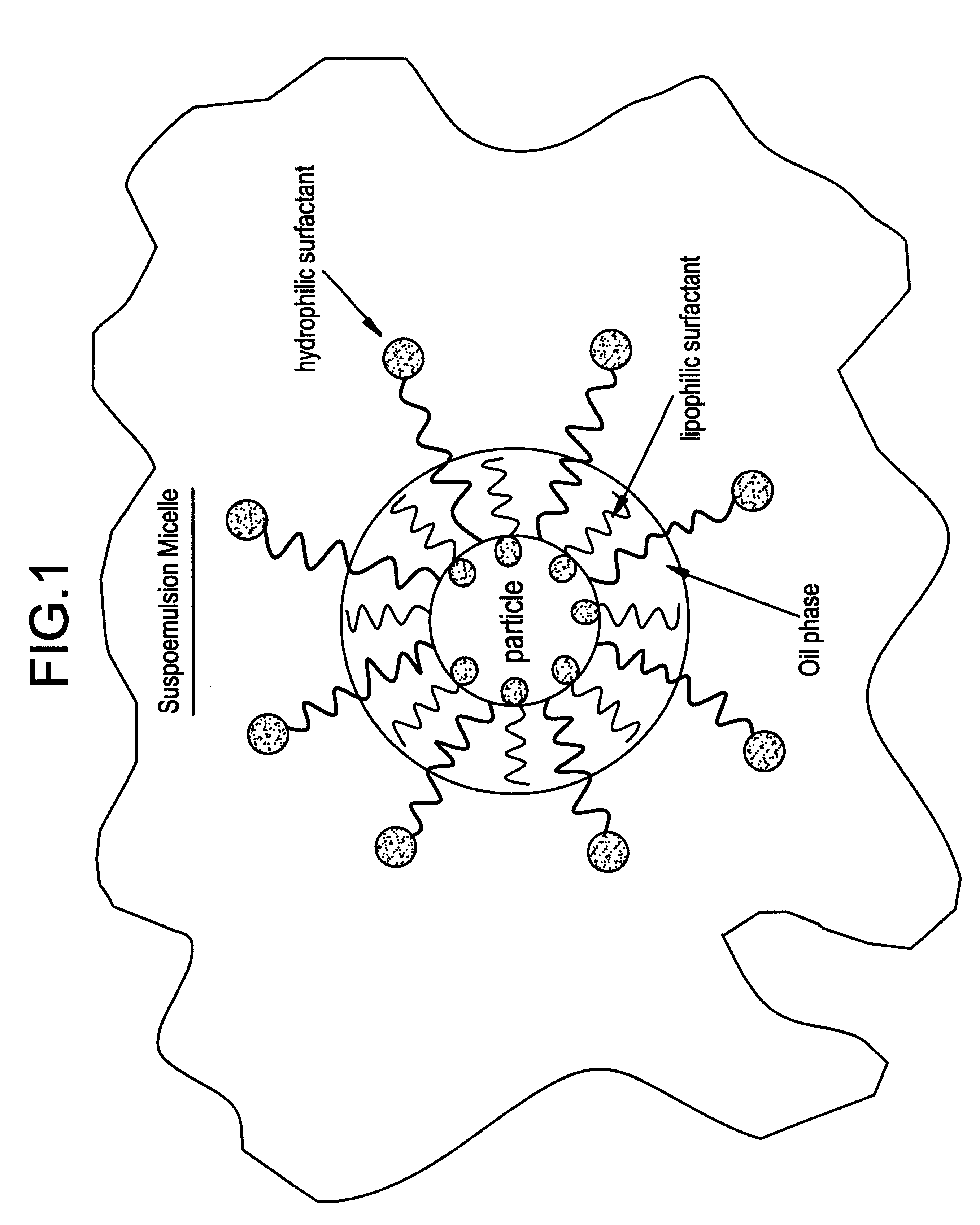
Suspoemulsion system for delivery of actives
InactiveUS6358909B1Heavy loadInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCationic surface-active compoundsOrganic chemistryChemistry
An oil-in-water suspoemulsion system is provided for the delivery of actives for laundering, cleaning or surface treatment, in which the suspoemulsion includes a major portion of water as a continuous phase, at least one Active, and an encapsulate including an oil, and at least first and second nonionic surfactants, the first and second nonionic surfactants having a HLB of at least about 3, the encapsulate substantially completely coating the active and suspending it within the aqueous phase.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
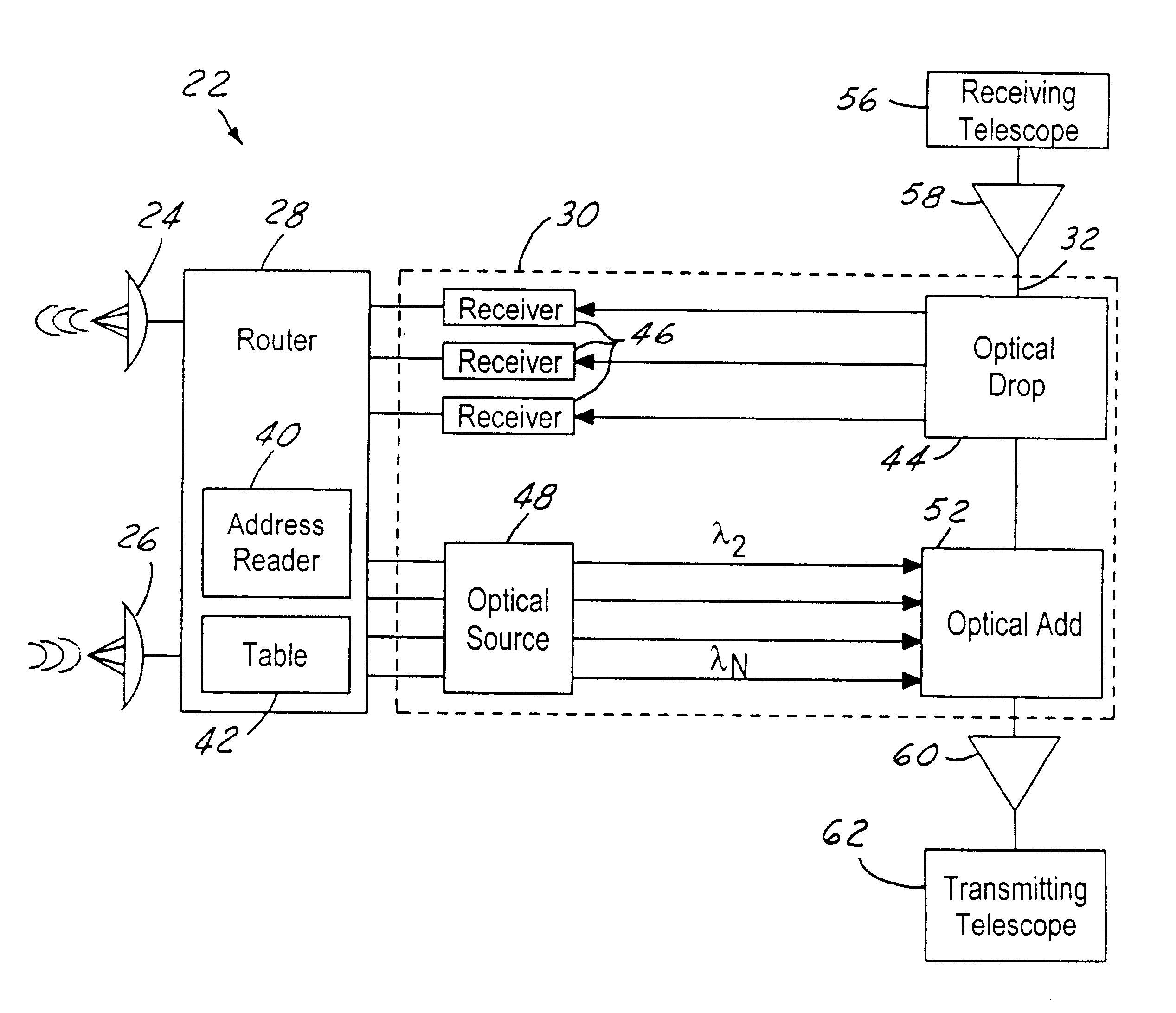
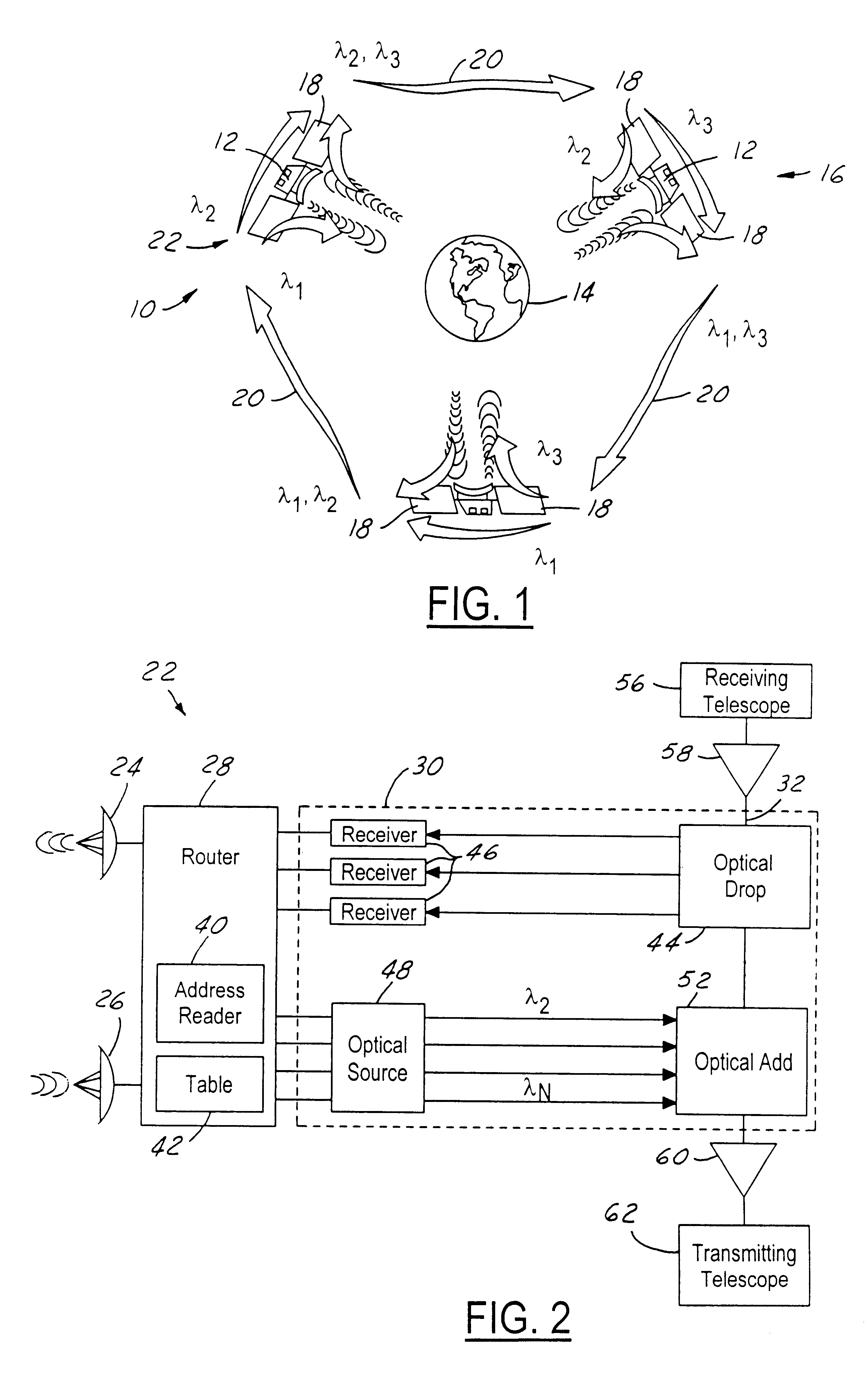
Ring architecture for an optical satellite communication network with passive optical routing
InactiveUS6912075B1Reduce power consumptionReduce weightSatellite communication transmissionOptical multiplexFiberLength wave
A node for satellite system communications between a ground station and a satellite includes a fiber optic bus on the satellite. An optical drop is coupled to the bus. The optical drop resolves an optical signal destined to the given satellite from the optical bus. An uplink and downlink receive and transmit communications from a ground terminal. A router is coupled to the optical drop and the uplink and downlink. An address reader and a table are used by the router to determine the destination of the received RF signals. The received RF signals are converted to optical signals by an optical source. The optical source has a wavelength that corresponds with the destination satellite. The optical signals are transmitted to an adjacent satellite by an optical transmitter such as a transmitting telescope.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
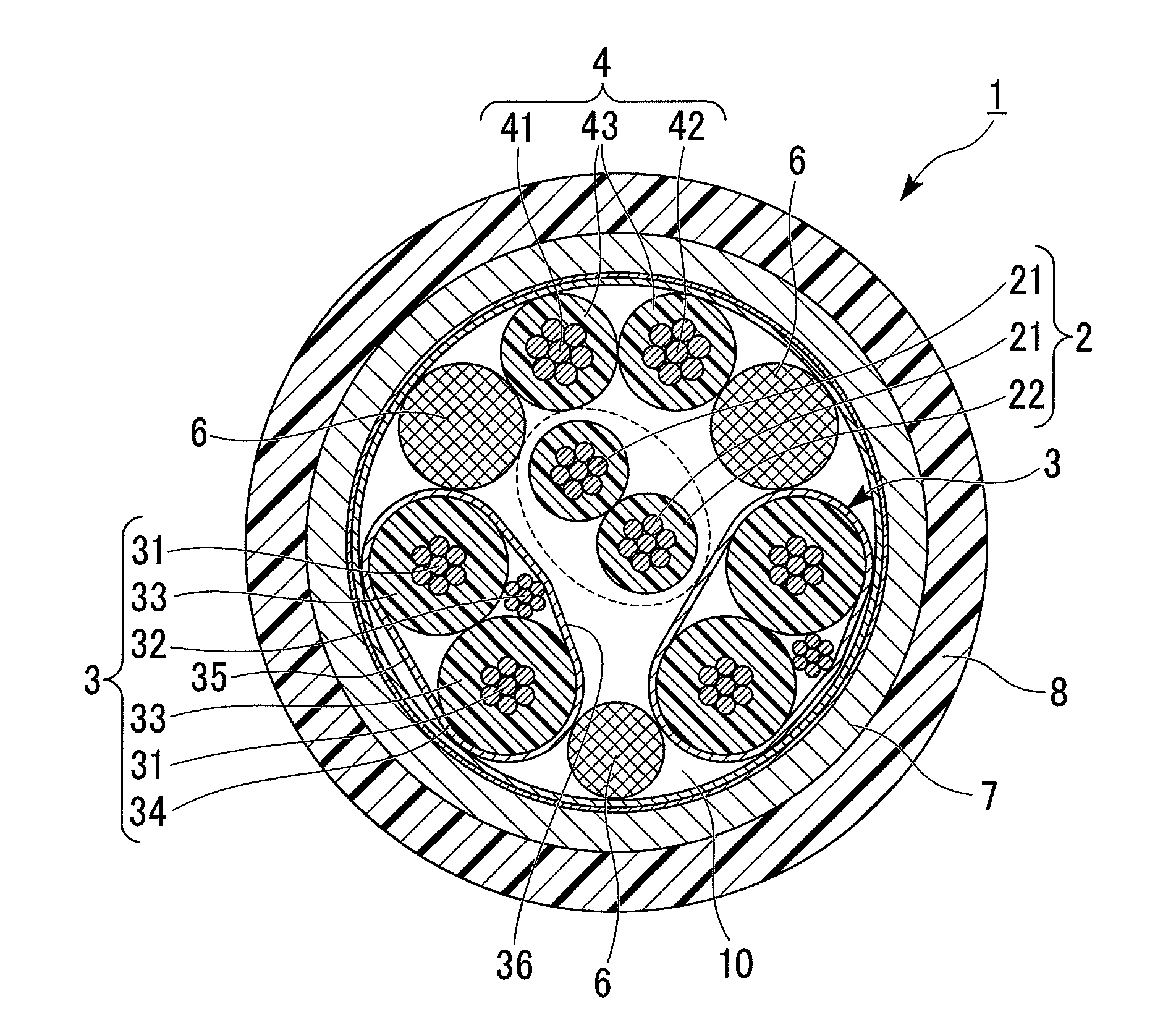
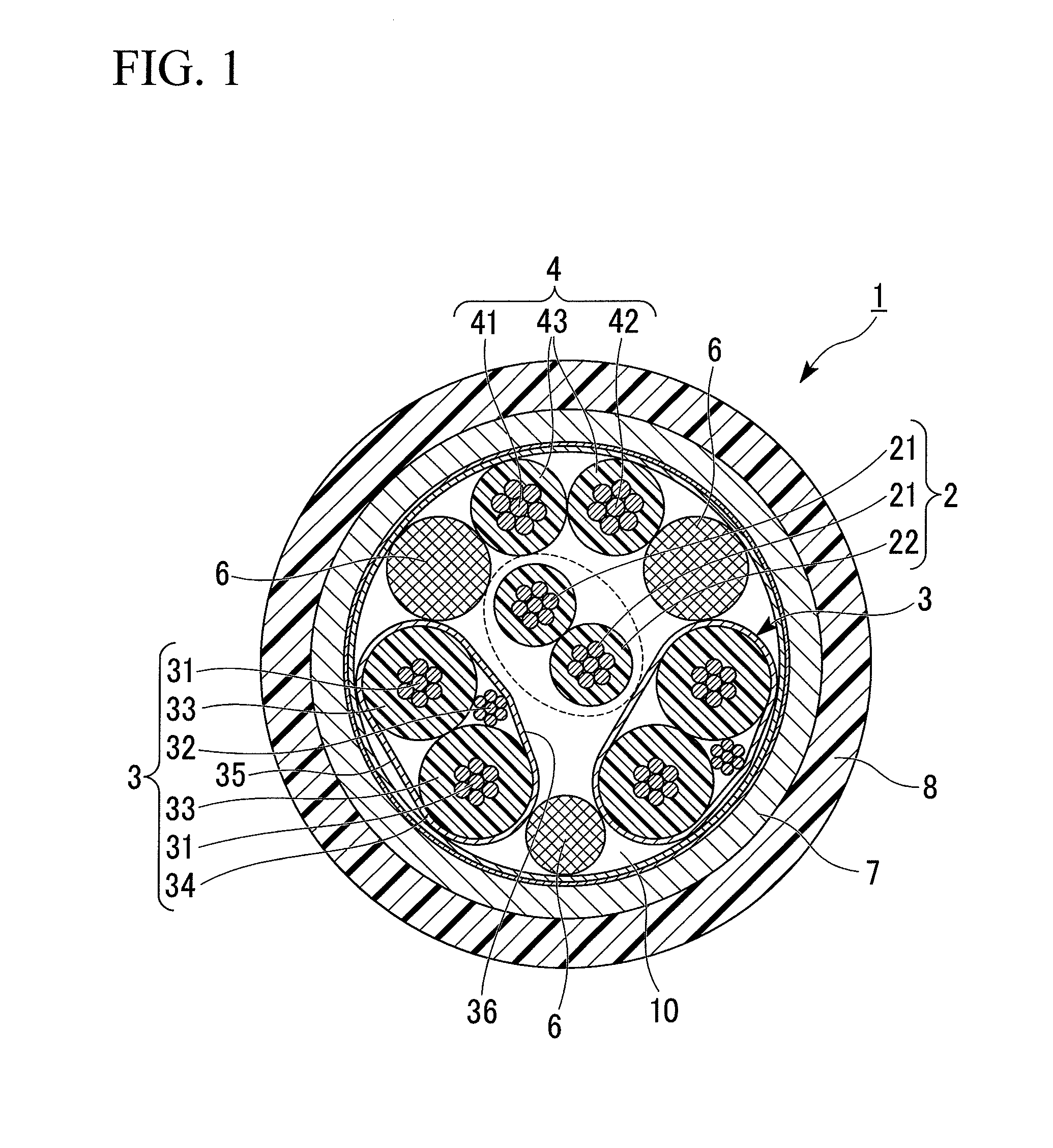
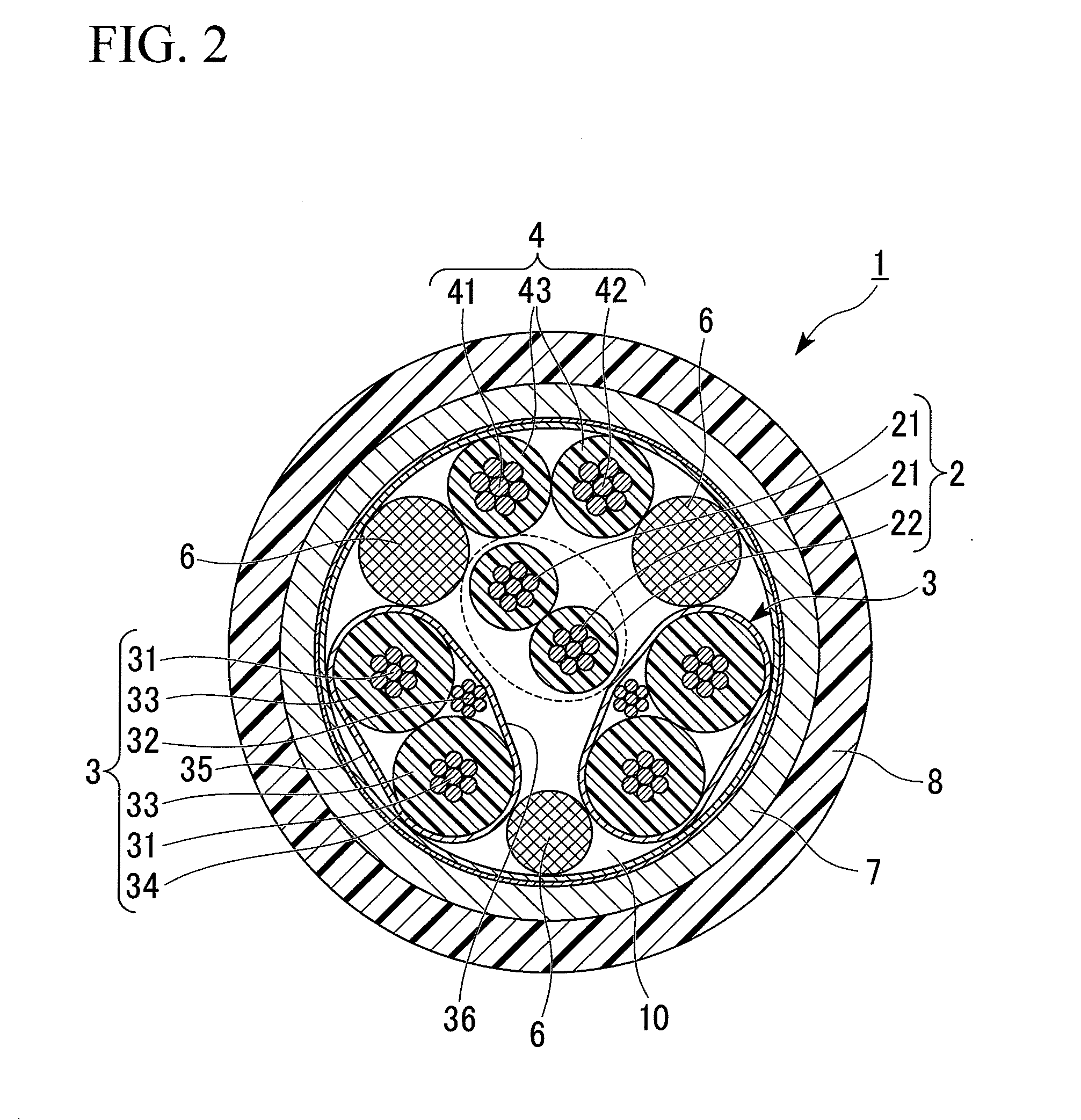
Transmission cable
InactiveUS20110278043A1Avoiding characteristicHeavy loadPower cables including communication wiresInsulated cablesEngineeringTwisted pair
A transmission cable of the invention includes a twisted-pair signal wire; a plurality of signal wire pairs; and a power wire pair. The twisted-pair signal wire, the plurality of signal wire pairs, and the power wire pair are bundled together so that the twisted-pair signal wire is surrounded by the plurality of signal wire pairs and the power wire pair when viewed in cross-section vertical to a longitudinal direction thereof.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
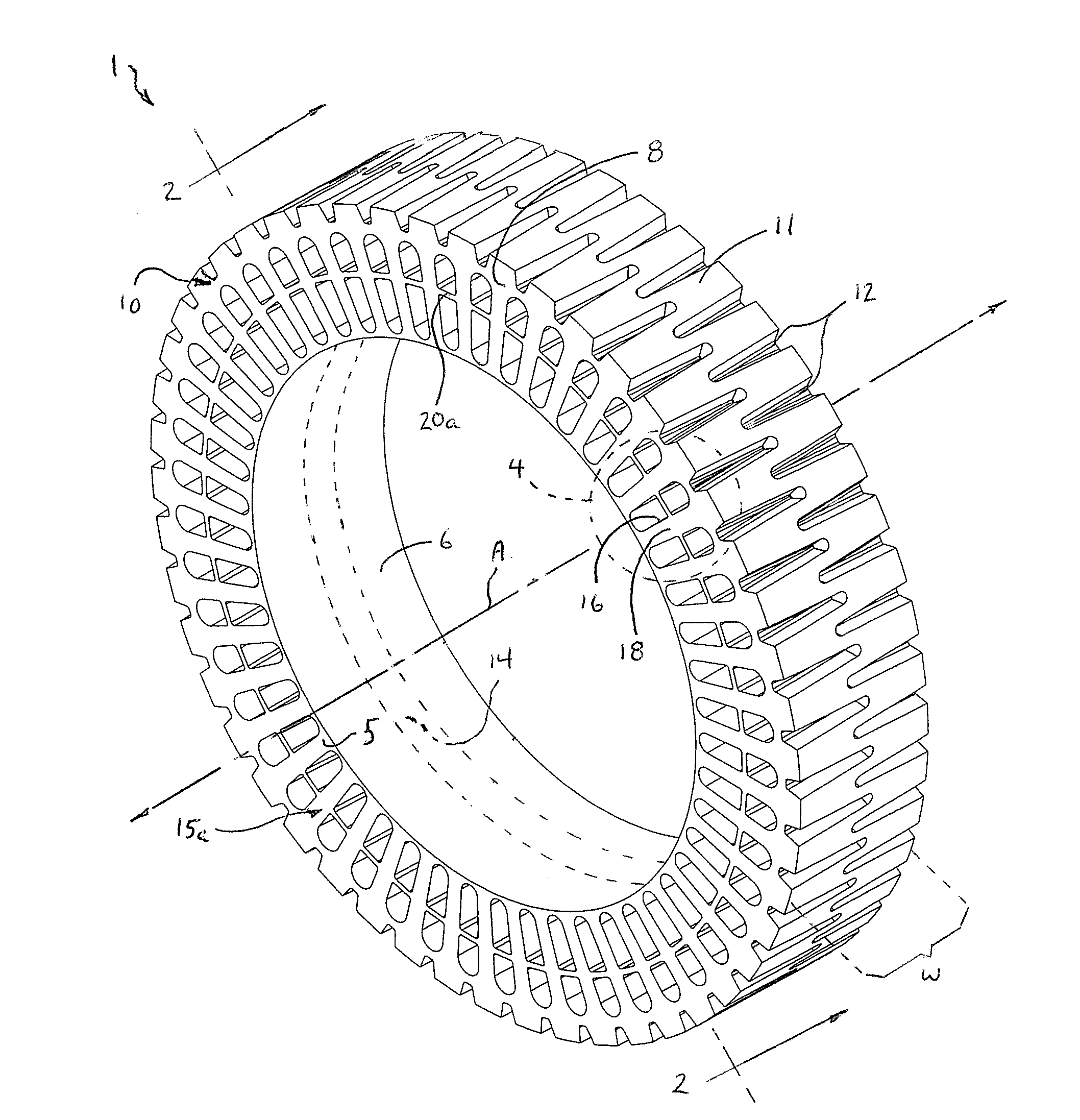
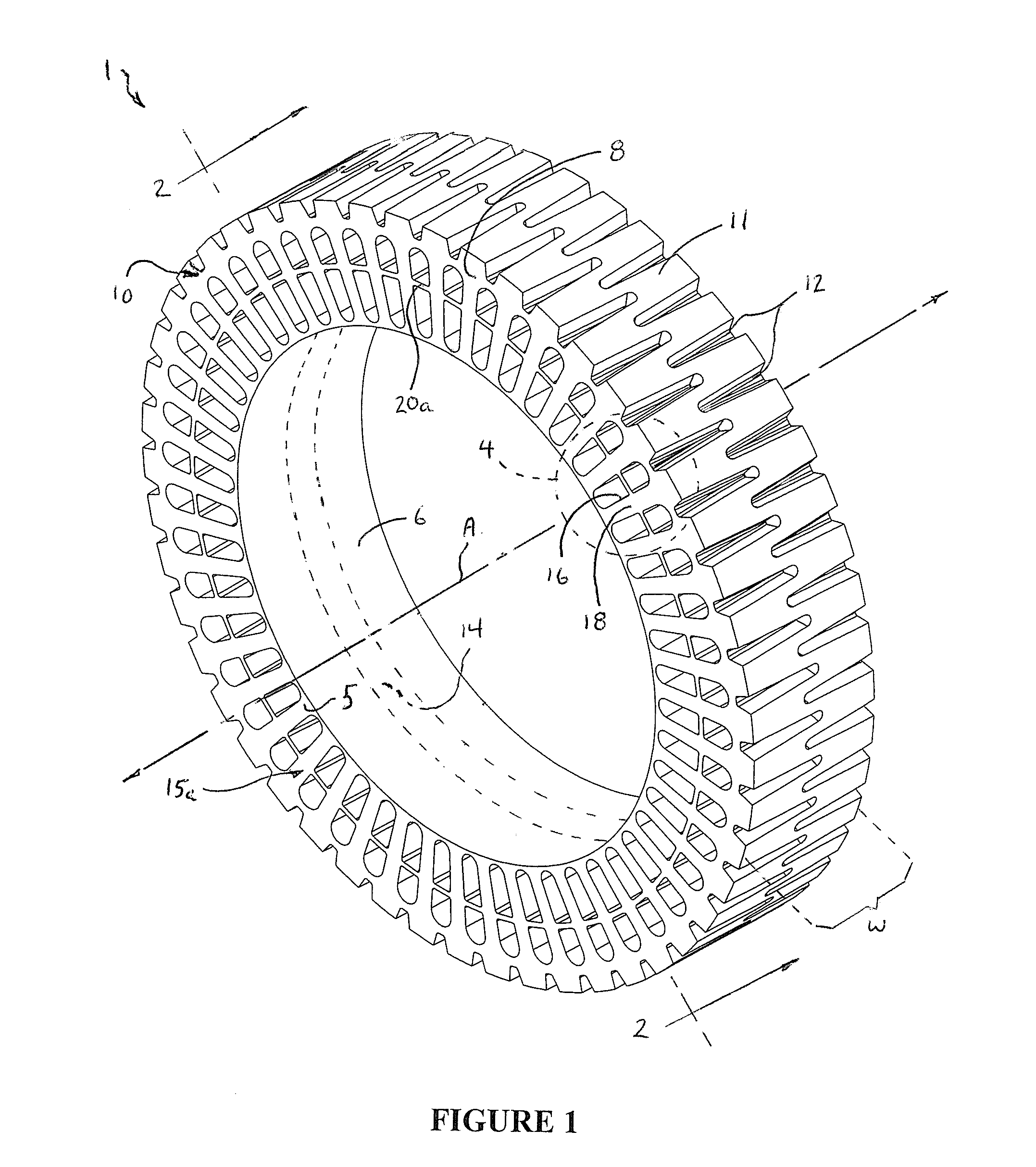
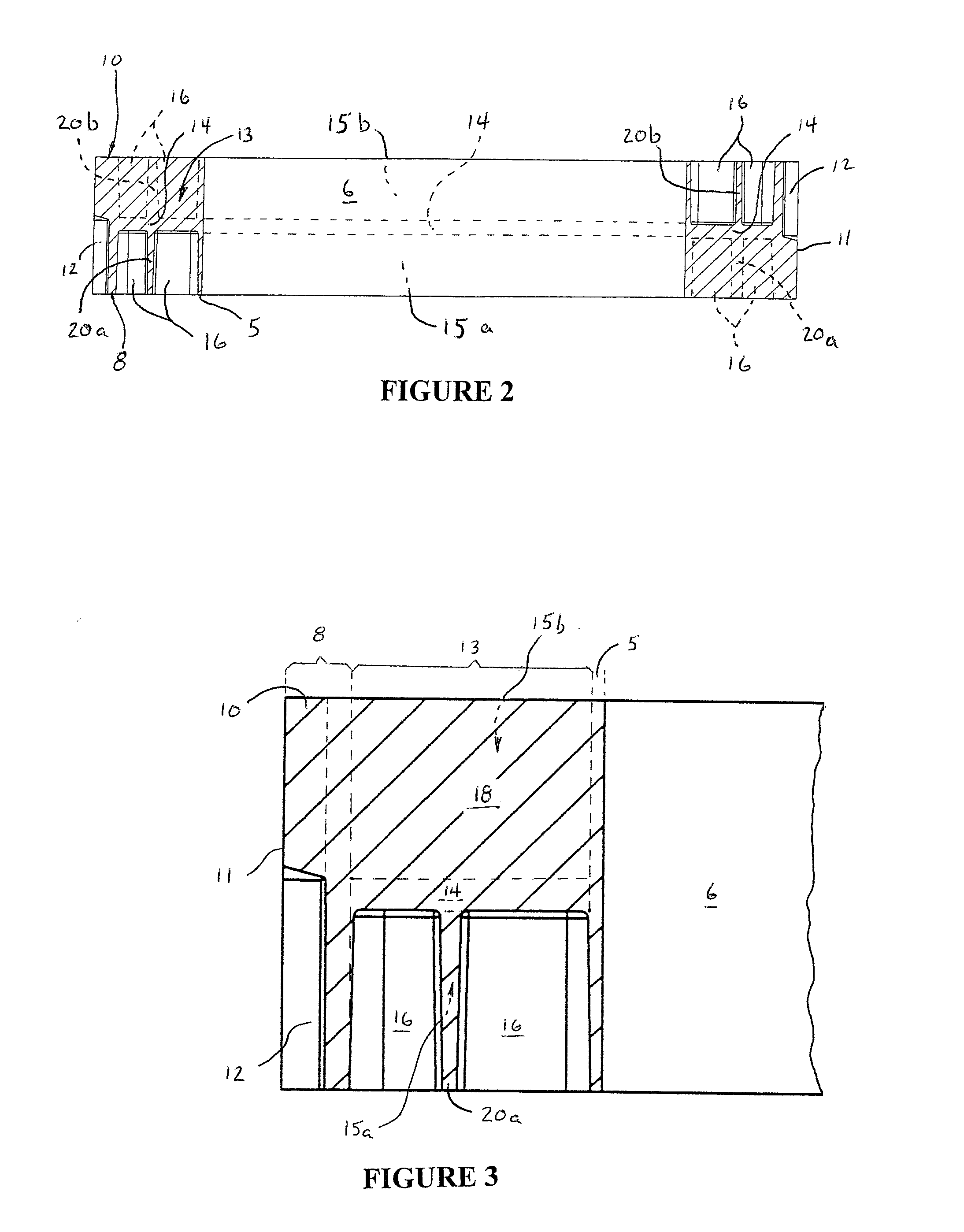
Non-pneumatic tire with annular spoke reinforcing web
InactiveUS20120234444A1Increased bending stiffnessIncrease the maximum loadNon-inflatable tyresLoad carryingEngineering
A non-pneumatic tire is provided with an annular reinforcing web that reduces the bending of compression spokes formed in the tire and reduces stresses and strains in the tire. The non-pneumatic tire includes an inner hoop member having an inner surface that defines the inner diameter of the tire, and an outer hoop member having a tread groove region that defines the outer diameter of the tire. A disc-shaped central web portion connects the inner and outer hoop members. A plurality of elongated, radially aligned cavities on either side of the central web defines integrally-formed compression spokes which connect the inner and outer hoop members. The annular reinforcing web is located on and affixed to either side of the central web portion and interconnects a mid portion of each spoke to a mid portion of the spokes on either side of it. Preferably, the annular reinforcing web is reinforced with fiber webbings on its outer side for added strength. The annular reinforcing web allows the tire to be made with less polyurethane material with no reduction in load carrying capability.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Cellulose acylate, cellulose acylate film, and method for production and use thereof
InactiveUS20060222786A1Good optical performanceImprove thermal stability performanceLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingCelluloseSulfur
A cellulose acylate solution containing a cellulose acylate which satisfies 2.5≦A+B≦3, 0≦A≦2.5, 0.3≦B≦3 (wherein A is the substitution degree of an acetyl group, and B is the sum of the substitution degrees of an acyl group having 3 to 7 carbon atoms) and whose content of sulfur atoms of residual sulfate moiety S is such that 50 ppm<S<500 ppm. When solution casting is carried out using this solution, a cellulose acylate film having good surface state and low peel-off load can be produced.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Metallic structures incorporating bioactive materials and methods for creating the same
InactiveUS20060115512A1Reduce riskEconomical and scaleableStentsSurgeryInsertion stentMedical device
Disclosed herein are methods to create medical devices and implantable medical devices with an electrochemically engineered porous surface that contains one or more bioactive materials to form bioactive composite structures. The bioactive composite structures are prepared using electrochemical codeposition methods to create metallic layers with pores that can be loaded with bioactive materials. In one use, the implantable medical devices of the present invention include stents with bioactive composite structure coatings.
Owner:MEDLOGICS DEVICE CORP
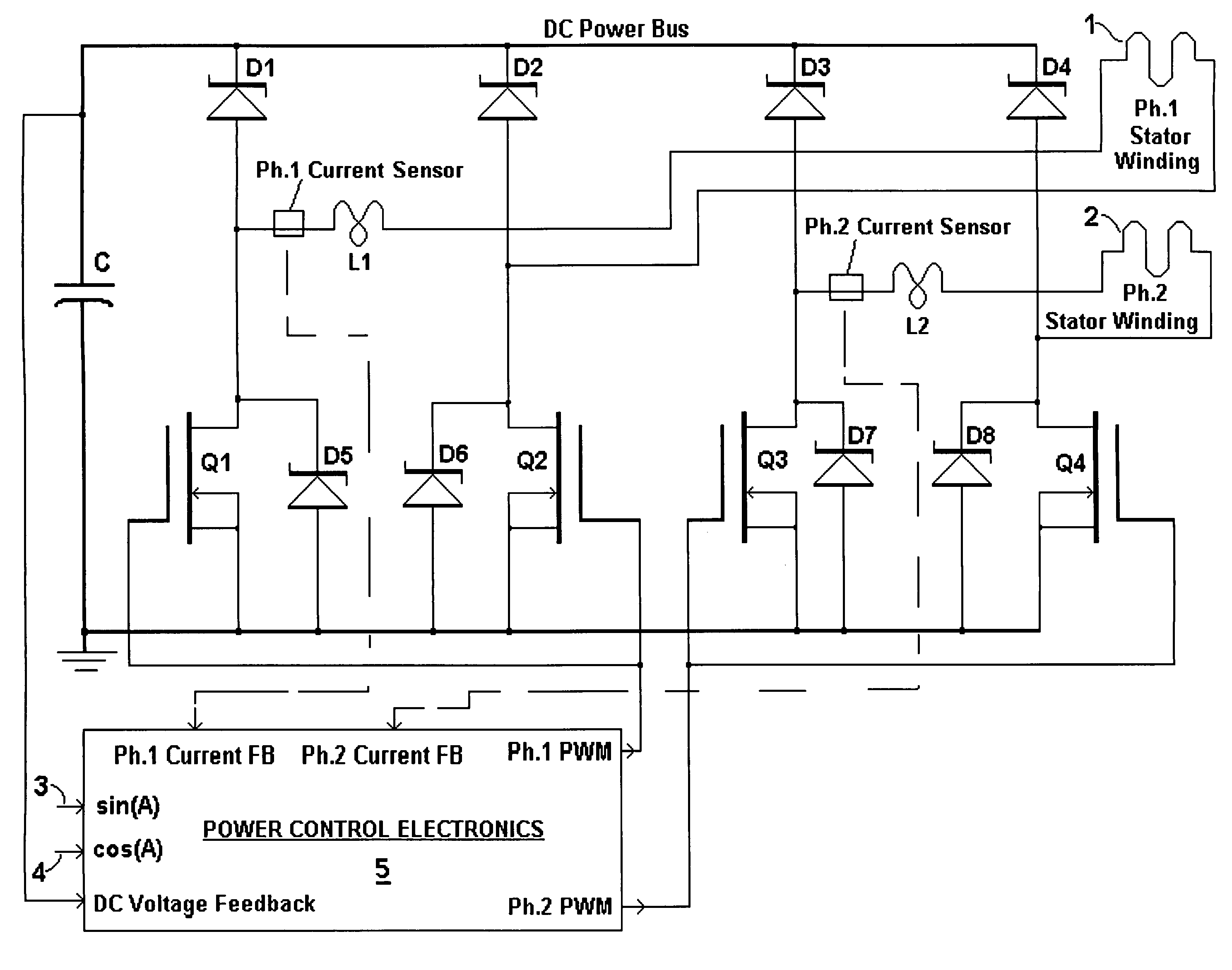
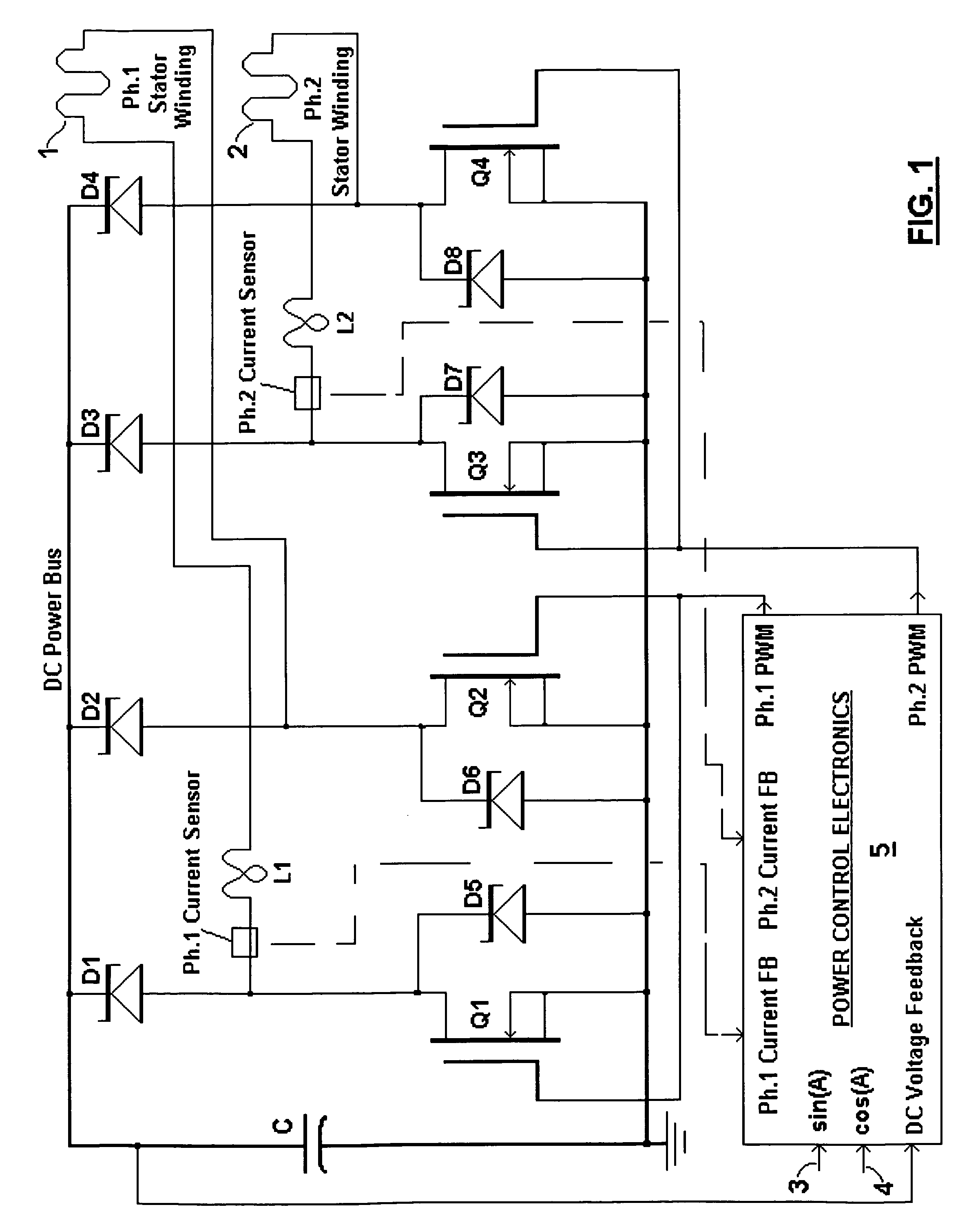
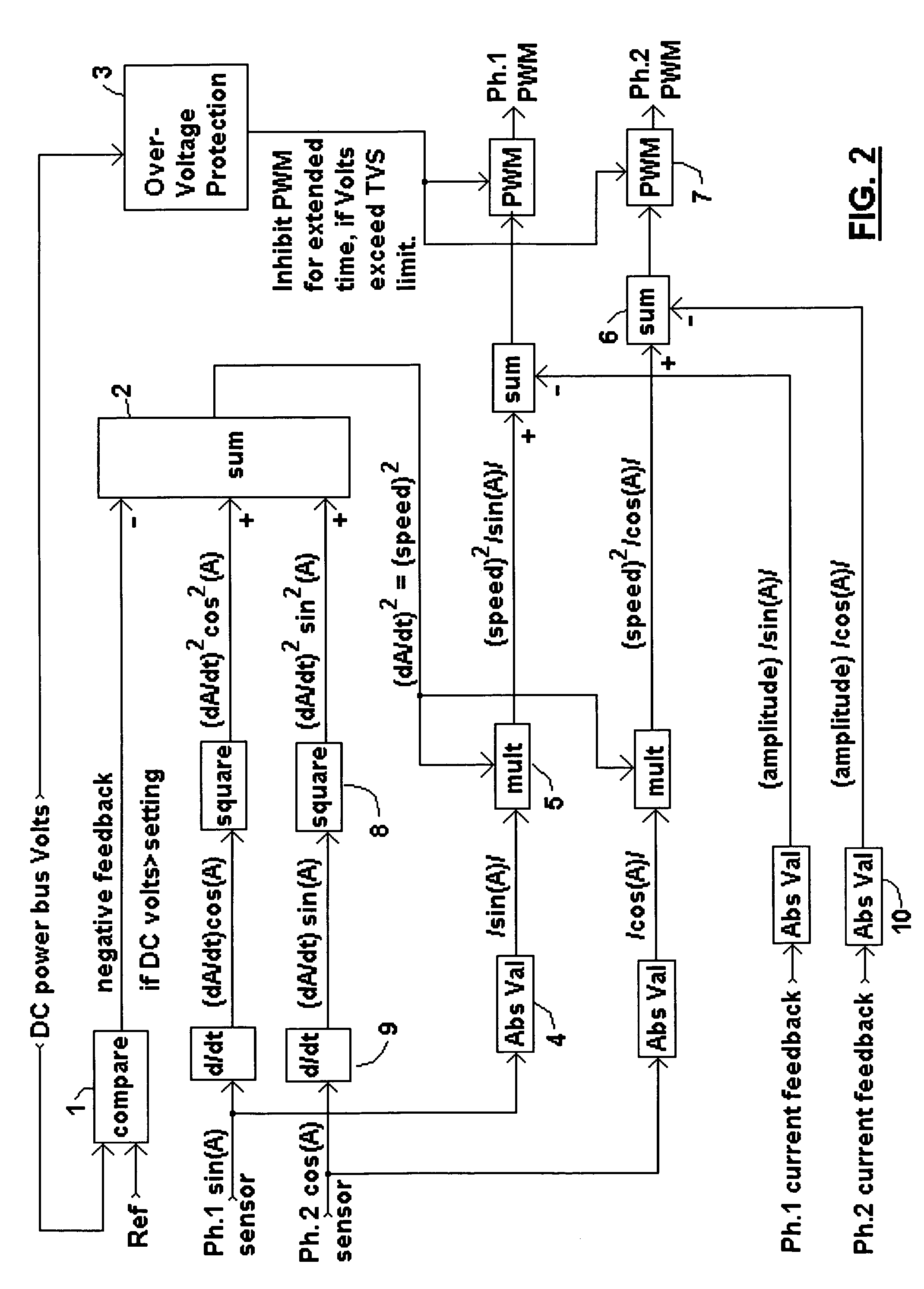
Broad-speed-range generator
InactiveUS7646178B1Harvest sustainable mechanical powerWide speed rangeWindingsMagnetic circuitPower controlPower over
A brushless generator with permanent-magnet multi-pole rotor disks and coreless stator winding disks includes integral electronics to efficiently generate regulated DC current and voltage from shaft input power over a broad speed range. Its power rating is scalable, and it incurs no cogging torque, or friction from gearing. Integral power control electronics includes high-frequency pulse-width-modulated boost regulation, which provides regulated current at requisite voltage over its broad speed range. A main embodiment to produce DC power at widely variable speeds includes signal processing so output power varies according to the third power of speed. A version for use with vertical-axis wind turbines has a relatively large diameter to facilitate a large number of poles. Combined boost-regulation, zero cogging torque, and no gearing, enable a wide speed range, for better power quality and higher wind energy yields. An alternate embodiment is intended to produce DC power from a variety of shaft drive sources, with selectable shaft torque.
Owner:FRADELLA RICHARD B
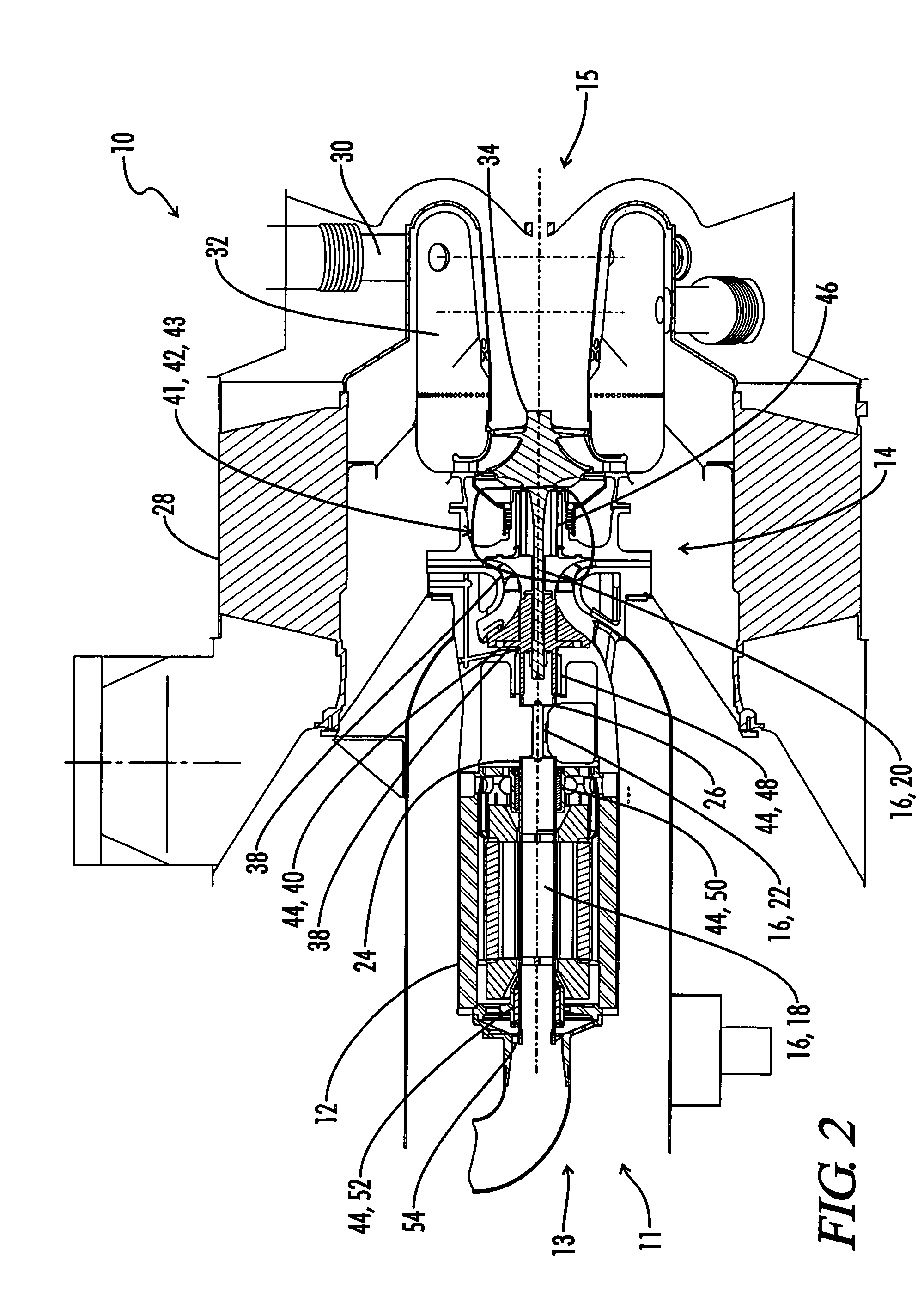
Rotor and bearing system for a turbomachine
ActiveUS7112036B2Reduce wear and temperatureHeavy loadPump componentsPiston pumpsImpellerDrive shaft
A rotor and bearing system for a turbomachine. The turbomachine includes a drive shaft, an impeller positioned on the drive shaft, and a turbine positioned on the drive shaft proximate to the impeller. The bearing system comprises one gas journal bearing supporting the drive shaft between the impeller and the turbine. The area between the impeller and the turbine is an area of increased heat along the drive shaft in comparison to other locations along the drive shaft. The section of the drive shaft positioned between impeller and the turbine is also a section of the drive shaft that experiences increased stressed and load in the turbomachine. The inventive bearing machine system positions only one radial bearing in this area of increased stress and load.
Owner:CAPSTONE GREEN ENERGY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com