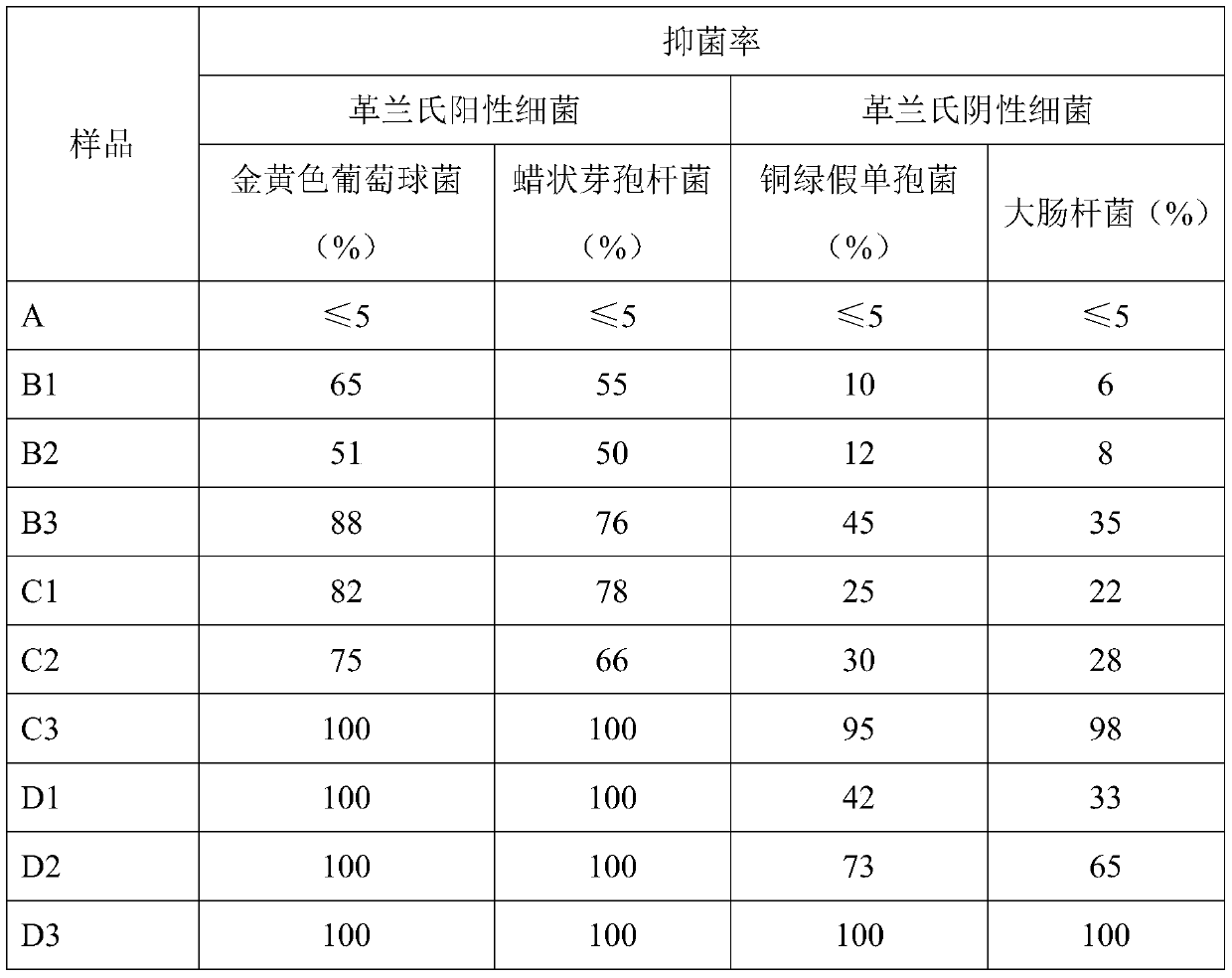
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69 results about "Bioactive composite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical device with porous surface containing bioerodable bioactive composites and related methods
InactiveUS20050119723A1Reduced responseImproving device-tissue interfaceStentsLiquid surface applicatorsActive agentNanoparticle
An implantable medical device includes a porous surface with a composite material located within the pores that includes a bioerodable material in combination with a bioactive agent. The composite material is adapted to erode upon exposure to the body of a patient, thus releasing the bioactive agent into the patient, whereas the porous surface remains on the device. In one embodiment, the composite material includes micro- or nano-particles that are deposited within the pores. In a further embodiment, the porous surface is an electrolessly electrochemically deposited material. Certain tie layer and other surface modification aspects are described to enhance various aspects of the bioactive composite surface. The bioactive composite surface is of particular benefit when provided on an endolumenal stent assembly in a manner adapted to elute anti-restenosis or anti-thrombosis agents or combinations thereof.
Owner:MEDLOGICS DEVICE CORP
Metallic structures incorporating bioactive materials and methods for creating the same
ActiveUS20060062820A1Reduce riskStructuredMaterial nanotechnologySurgeryInsertion stentElectroless deposition
Disclosed herein are methods to create medical devices and medical devices including bioactive composite structures. The methods include using template-assisted electro- or electroless deposition or codeposition methods for providing implantable medical devices coated with bioactive composite structures and also include layering deposited or codeposited metal layers with layers of bioactive materials. In one use, the implantable medical devices of the present invention include stents with bioactive composite structure coatings.
Owner:CELONOVA BIOSCIENCES INC
Methods and devices for enhanced adhesion between metallic substrates and bioactive material-containing coatings
InactiveUS20070073390A1Reduce riskExcellent Adhesive PropertiesVolume/mass flow measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsMedical deviceMetallic substrate
Disclosed herein are methods to create medical devices and medical devices including bioactive composite structures with enhanced adhesion characteristics. The bioactive composite structures are prepared using anchors that are electrochemically codeposited into a metallic layer that is formed on the surface of implantable medical device followed by the adhesion of a bioactive material-containing coating to the substrate and anchors.
Owner:MEDLOGICS DEVICE CORP
Metallic structures incorporating bioactive materials and methods for creating the same
InactiveUS20060115512A1Reduce riskEconomical and scaleableStentsSurgeryInsertion stentMedical device
Disclosed herein are methods to create medical devices and implantable medical devices with an electrochemically engineered porous surface that contains one or more bioactive materials to form bioactive composite structures. The bioactive composite structures are prepared using electrochemical codeposition methods to create metallic layers with pores that can be loaded with bioactive materials. In one use, the implantable medical devices of the present invention include stents with bioactive composite structure coatings.
Owner:MEDLOGICS DEVICE CORP
Metallic structures incorporating bioactive materials and methods for creating the same
InactiveUS20060051397A1Reduce riskEconomical and scaleableSurgeryCatheterElectrophoresisMedical device
Disclosed herein are methods to create medical devices and medical devices including bioactive composite structures. The methods include using electroless and electrophoretic deposition and codeposition methods for providing implantable medical devices coated with bioactive composite structures. In one use, the implantable medical devices of the present invention include stents with bioactive composite structures.
Owner:MEDLOGICS DEVICE CORP
Metallic structures incorporating bioactive materials and methods for creating the same
One embodiment of the invention is directed to a method comprising providing an electrochemical solution comprising metal ions and a bioactive material such as bioactive molecules, and then contacting the electrochemical solution and a substrate. A bioactive composite structure is formed on the substrate using an electrochemical process, where the bioactive composite structure includes a metal matrix and the bioactive material within the metal matrix.
Owner:MEDLOGICS DEVICE CORP
Bioabsorbable and bioactive composite material and a method for manufacturing the composite
InactiveUS20100121463A1Increase strength valueIncrease toughness valueSurgeryProsthesisFiberPolymer chemistry
The present invention relates to a bioabsorbable and bioactive composite material for surgical musculoskeletal applications comprising a bioabsorbable polymeric matrix material which is reinforced with bioabsorbable polymeric fibers and bioabsorbable ceramic fibers. The surgical bioabsorbable polymeric matrix material is reinforced with the bioabsorbable polymeric fibers and the bioabsorbable ceramic fibers from which at least a portion is longer than 150 μm. The invention also relates to a method for manufacturing a bioabsorbable and bioactive composite material.
Owner:BIORETEC
Bioactive composite implants
A composite spinal implant device including collagen and / or synthetic fibers impregnated with a bioactive formulation is disclosed. Also disclosed are methods of making the composite spinal implant devices, surgeries using the device, and kits containing the device.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Broad-spectrum bioactive composite foliar fertilizer and its preparation method
InactiveCN102464502AGuaranteed stabilityImprove the durability of fertilizer effectOrganic fertilisersSodium acetateDisease
The invention relates to a broad-spectrum bioactive composite foliar fertilizer and its preparation method. The preparation method of the broad-spectrum bioactive composite foliar fertilizer comprises: (by weight of solid substances) mixing 14.2% of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 14.2% of urea, 17.7% of brown sugar, 30% of composite amino acid powder, 7.1% of salt, 9.1% of fulvic acid, 0.4% of sodium acetate, 0.2% of magnesium sulfate, 7.6% of trace elements, and molasses with a concentration of 2.5ml / L, a composite liquid strain of equivalent lactic acid bacteria, yeasts, actinomycetes, aspergilli and phosphorus bacteria and with a concentration of 10ml / L, as well as sterile water at a temperature of 35DEG C, and conducting microaerobic fermentation for 192-288h, then adding photosynthetic bacteria with a concentration of 1ml / L for stirring, leaving the mixture to 48-96h of illumination, then adjusting the PH value, thus obtaining a bioactive composite foliar fertilizer. The bioactive composite foliar fertilizer of the invention can promote crop photosynthesis, activate the activity of each enzyme, enhance disease prevention and antibacterial properties of plants, and improve the stress resistance of plants. Characterized by no pollution, no public hazard, lasting fertilizer effect, the fertilizer of the invention can strengthen seedlings, resist diseases, enhance output, improve agricultural product quality, and bring products to market about 7-15 days earlier, thus improving agricultural economic benefits.
Owner:江苏邦德生物科技发展有限公司
Bioactive Load-Bearing Composites
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Bioactive load-bearing composites
Owner:ORTHOVITA INC
In-situ forming injectable bioactive composite hydrogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106806943AIncrease moisture contentHigh mechanical strengthPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAbsorbent padsBone formationCell migration
The invention relates to in-situ forming injectable bioactive composite hydrogel as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The composite hydrogel is formed by mixing sodium alga acid, amino acids and silicate bioceramics containing two or more than two multivalent cations serving as raw materials and performing in-situ forming, wherein the raw materials respectively comprise the following components by weight volume: 1.5-2% of sodium alga acid, 1-20% of silicate bioceramics and 0.25-2% of amino acids. According to the composite hydrogel disclosed by the invention, the inorganic component silicate bioceramics have the effect of promoting cell migration, bone formation, vascularization and other biological activities and can serve as a reinforced phase inside the hydrogel for improving the mechanical strength of the composite hydrogel, so that the composite hydrogel can provide a physical support and a good chemical environment for regeneration and reconstruction of tissues.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
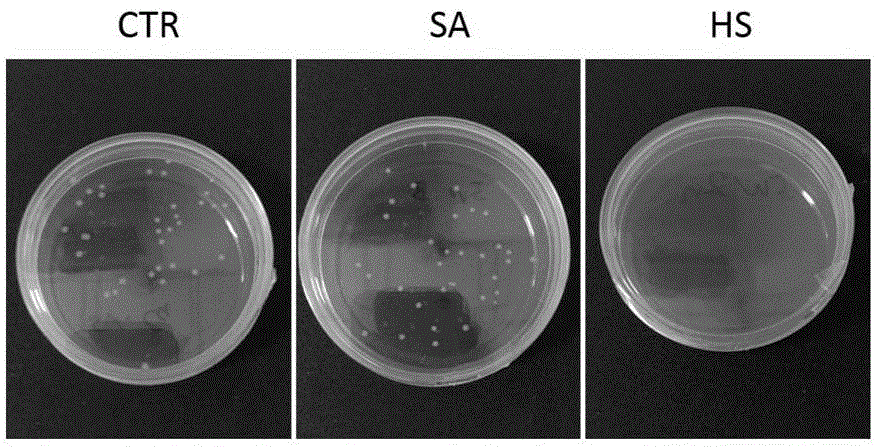
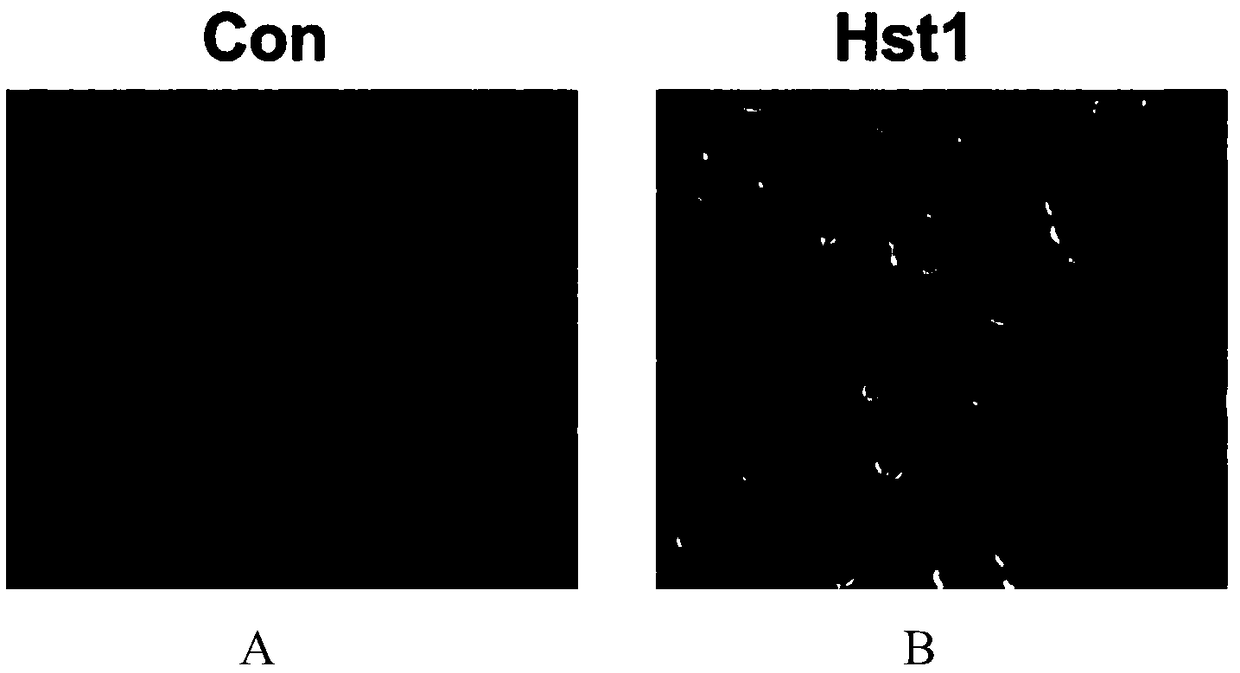
Application of histatin 1 (Hst1) polypeptide in preparation of composite materials for promoting repair of large-area skin defects
ActiveCN108785657AImprove adhesionPromote repairPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticFiberCell adhesion
The invention discloses application of histatin 1 (Hst1) polypeptide in preparation of composite materials for promoting repair of large-area skin defects. The Hst1 polypeptide is found to have the characteristics of promoting cell adhesion and vascularization and inhibiting inflammatory response. The Hst1 polypeptide can be loaded on a variety of biological materials, and can be prepared into dressing, injection, ointment, powder, hydrogel, membranes, sponges, fiber scaffold materials and the like, which can effectively promote the healing of the large-area skin defects, by being compounded with bioactive composite materials, wherein large-area skin defects include traumas, burns, skin ulcer caused by tumor resection or diabetes, and the like. The Hst1 polypeptide provided by the invention is human-derived polypeptide, and has good biocompatibility and biosafety. When being used for the preparation of the composite materials for promoting the repair of the large-area skin defects, theHst1 polypeptide has an important medical value and a good industrialization prospect.
Owner:HANGZHOU HUIBO SCI & TECH CO LTD
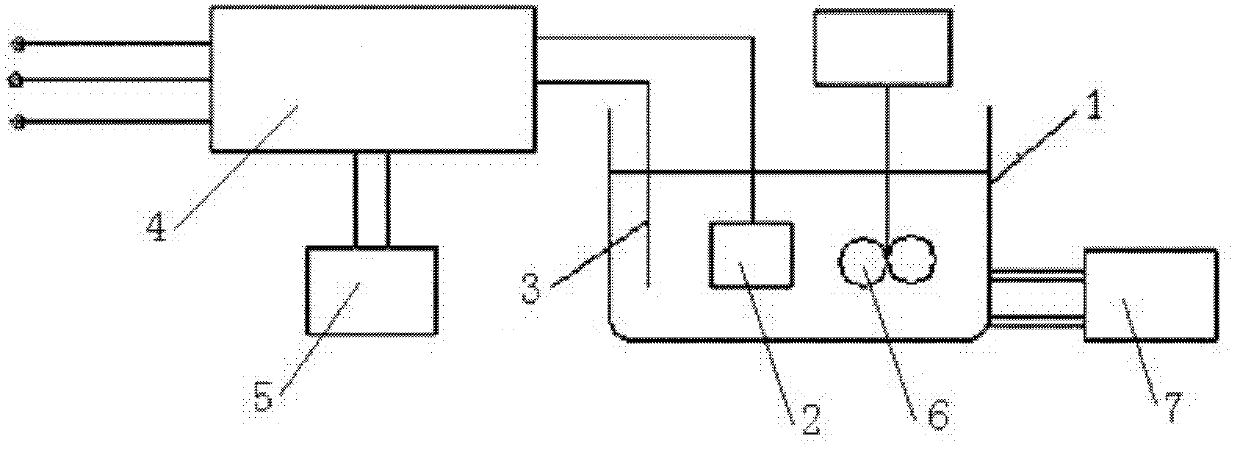
Method for preparing bioactive composite film layer containing hydroxyapatite on titanium metal surface
InactiveCN102605410AContent changeImprove bindingElectrolytic inorganic material coatingSurface reaction electrolytic coatingMicro arc oxidationElectrolysis
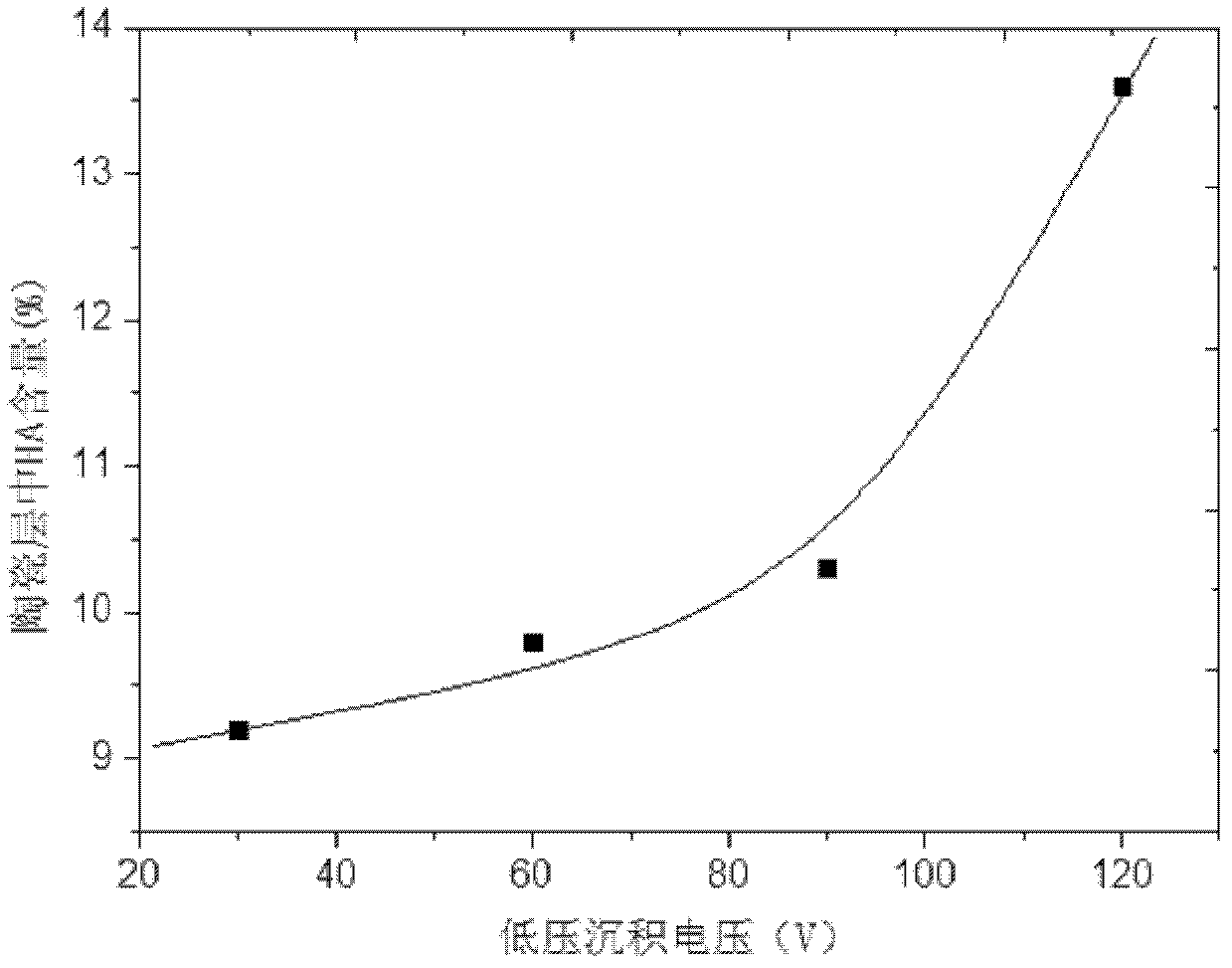
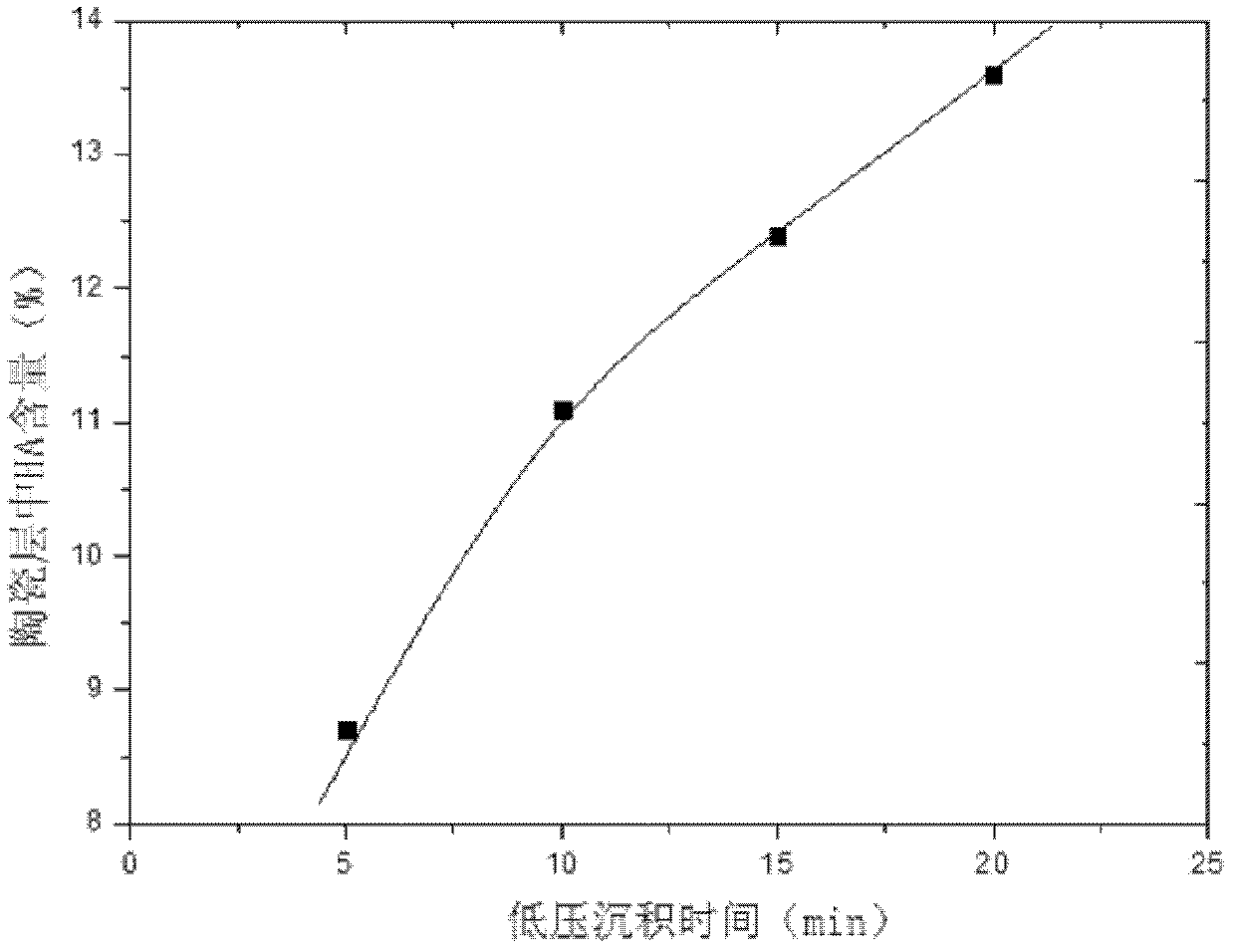
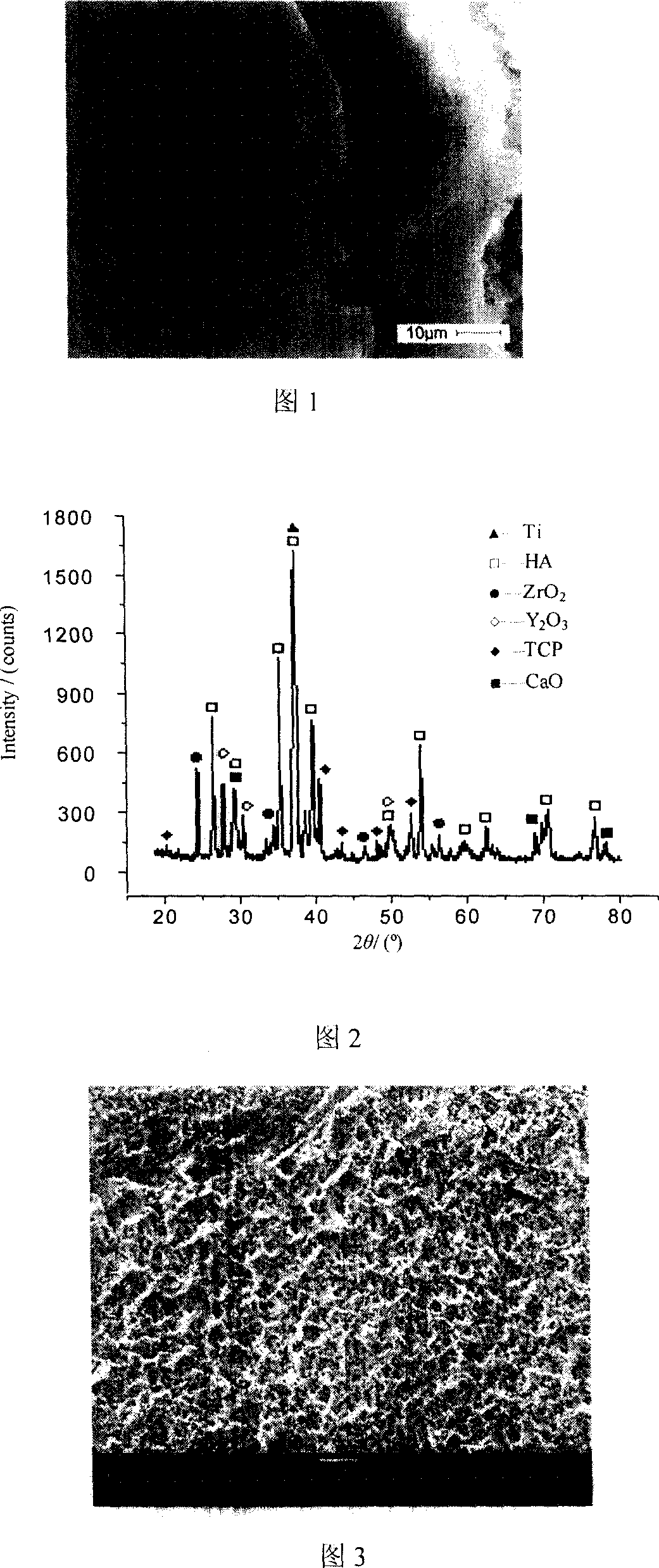
The invention provides a method for preparing a bioactive composite film layer containing hydroxyapatite on a titanium metal surface. The method comprises the following steps: preparing an electrolytic solution containing hydroxyapatite firstly; then applying voltage to the titanium metal through a power supply for low-voltage deposition and differential arc oxidation treatment, wherein at the low-voltage deposition stage: the voltage is controlled at 30V-120V and the deposition time is 5-20 minutes, and at the differential arc oxidation stage: the voltage is controlled at 450V-600V, the deposition time is 10 minutes and the frequency of the power supply is 200kHz, and the duty ratio is 10%; and growing a layer of HA (hydroxyapatite)-TiO2 composite ceramic layer on the surface of a titanium metal test sample after low-voltage deposition and differential arc oxidation. The method has the beneficial effects that the ceramic layer containing HA particles is prepared on the titanium test sample in the electrolyte solution, the process that the HA particles are deposited on the titanium metal test sample surface is simplified, and the content of HA in the film layer is changed through regulating the content of HA in the electrolyte solution or the deposition voltage and time.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Bioactive composites of polymer and glass and method for making same
The present invention relates to a method of preparing a bioactive composite, the method comprising the steps of a) adding in a solid state a biocompatible polymer and a bioactive glass to an extruder to form an extrudable material; b) applying energy to the extrudable material to at least the melting temperature of the biocompatible polymer to melt mix the biocompatible polymer and bioactive glass; and c) extruding a bioactive composite.
Owner:ORTHOVITA INC
Metallic structures incorporating bioactive materials and methods for creating the same
InactiveCN1694770ARelease adjustableReduce the likelihood of separationSurgeryPharmaceutical containersBioactive moleculesMetal
One embodiment of the invention is directed to a method comprising providing an electrochemical solution comprising metal ions and a bioactive material such as bioactive molecules, and then contacting the electrochemical solution and a substrate. A bioactive composite structure is formed on the substrate using an electrochemical process, where the bioactive composite structure includes a metal matrix and the bioactive material within the metal matrix.
Owner:MEDLOGICS DEVICE CORP
Degradable bioactive composite ceramic microsphere stent material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106563170AHigh strengthAperture controllableTissue regenerationProsthesisEmulsionMicrosphere
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH +1
High-biological activity composite material for promoting bone regeneration repair and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103263691AImprove biological activityEfficient degradation abilityProsthesisCalcium silicateTooth Tissue
The invention discloses a high-biological activity composite material for promoting bone regeneration repair and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of respectively weighing 2 to 20wt% of foreign ion-doped calcium silicate powder, 40 to 60wt% of alpha-calcined gypsum powder and 20 to 40wt% of a mixed liquid, mixing them, stirring the mixture to obtain uniform paste, and carrying out hydration of the uniform paste to obtain the high-biological activity composite material which is a self-curing material. The high-biological activity composite material has self-curing performance, injectable performance, high strength and rapid degradation performance. The preparation method has simple processes. The high-biological activity composite material has excellent biological activity and degradability and can be used for fast and complete regeneration repair of bone defects in bone tooth tissue, root canal filling and slow-release carriers of bone disease-treatment drugs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for producing bioactive composites
ActiveUS8512732B2High bonding strengthBiocideInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsPorous substrateMicroparticle
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for producing bioactive composites having imparted thereto bioactivity, to thereby form and grow in vivo or in vitro a coating layer containing a calcium phosphate compound as the major component with a high adhesion strength on the surface of various types of porous substrates such as a porous shaped body comprising an organic polymer. The means for solving the problem is characterized by comprising at least (1) a step of immersing a porous substrate in a solution containing at least calcium ions and hydrogenphosphate ions, thereby distributing the solution to the inside of at least a part of the pores of the substrate, and (2) a step of depositing fine particles containing a calcium phosphate compound as the major component inside the pores into which the solution is introduced.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Preparation method of bioactive composite high-efficiency feed nutrient solution used for livestock and poultry
ActiveCN102334602AHigh substance contentAdjust and improve organ functionFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyAnimal science
The invention discloses a preparation method of bioactive composite high-efficiency feed nutrient solution used for livestock and poultry. The method comprises the following steps of: inoculating bacillus coprophilus, streptococcus thermophilus, saccharomyces cerevisiae and hansenulaanomala into culture mediums to obtain four seed solutions respectively; filling 0.6-1.5 percent by weight of each of four seed solutions into an active nutrient solution which is prepared from 10-18 percent by weight of cane molasses, 0.5-1.8 percent by weight of milt cream, 10-20 percent by weight of starch and pure water through fermentation; and the feed nutrient solution is obtained after fermentation. Through the feed nutrient solution, the problems of high probability of moistening and oxidation, low probability of absorption in bodies of livestock and poultry, low material utilization rate and the like existing in the use of a solid additive are improved; a huge number of organic compounds can be decomposed; antibiotic and ablastin are produced; a large amount of amino acid, protein, vitamins, various bioactive enzymes and the like is excreted; and the feed nutrient solution has the functions of adjusting and improving functions of organs in the bodies of the livestock and poultry, increasing content of nutritive materials of the livestock and poultry, improving immunity of organisms and promoting growth and development.
Owner:重庆富博生物技术有限公司
Bioactive composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108530851AImprove biological activityImprove mechanical propertiesProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingDrug biological activity
The invention relates to a bioactive composite material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the bioactive composite material, poly-citrate glycol ester is compoundedwith bioactive glass, or the poly-citrate glycol ester is further modified with a saline coupling agent, then good bioactivity, osteoconduction, biocompatibility and controllable biodegradability canbe achieved, meanwhile mechanical properties can be relatively improved, and in addition, the preparation method is simple in process and easy in production.
Owner:华魁科技泰州有限公司
Degradable biological composite material of phosphate containing calcium and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101417149BImprove performanceGuaranteed biocompatibilityProsthesisCalcium biphosphatePhosphate
The invention provides a degradable bioactivity composite containing calcium phosphate and a preparation method thereof. The composite consists of calcium phosphate and a multiple amino acid polymer; wherein, the weight percentage of inorganic composition is not more than 50 percent and the residual substance is the multiple amino acid polymer which is formed by the polymerization of caprolactam and at least 5 other amino acids; wherein, the molar ratio of the caprolactam in the polymer is 40-90 percent and the respective molar ratio of other single amino acid is not less than 0.5 percent. During preparation, the caprolactam is mixed with all amino acids and dehydration is carried out under the protection of inert gases and stirring, and pre-polymerization composition reaction and polymerization reaction are respectively carried out at the temperature of 210-250DEG C, thus obtaining the composite. The indexes of the prepared material such as mechanic performance, degradation period and the like can be adjusted and controlled according to the use requirements.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Natural high-polymer bioactive trauma repair material with function of releasing active ions and method for preparing natural high-polymer bioactive trauma repair material
ActiveCN107198794AEvenly dispersedControllable ion release concentrationTissue regenerationProsthesisBlood vesselBioactive composite
The invention relates to a natural high-polymer bioactive trauma repair material with a function of releasing active ions and a method for preparing the natural high-polymer bioactive trauma repair material. The method includes soaking natural high-polymer materials in silicate extract liquid for a period of time; taking the natural high-polymer materials out of the silicate extract liquid and drying the natural high-polymer materials to obtain the natural high-polymer bioactive trauma repair material with the function of controllably releasing the ions. The natural high-polymer bioactive trauma repair material and the method have the advantages that the natural high-polymer bioactive trauma repair material is creatively prepared by the aid of silicate extract liquid permeating processes, aqueous solution is used as a medium, silicate components with angiogenesis activity can be uniformly dispersed inside the natural high-polymer materials, granular agglomeration can be prevented, and accordingly the natural high-polymer bioactive trauma repair material which is a bioactive composite trauma repair material can be prepared; the inorganic ions are uniformly adsorbed and distributed in high-polymer matrixes, and the ion release concentration can be controlled.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method and application of bioactive composite film hemostasis dressing
ActiveCN104069535APromote healingGood biocompatibilityAbsorbent padsBandagesCross-linkBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a bioactive composite film hemostasis dressing. The preparation method of the bioactive composite film hemostasis dressing comprises the following steps: dissolving alginic acid in a sodium hydroxide solution to obtain a sodium alga acid solution, dissolving cross-linked hydroxypropylated starch in distilled water for pasting and obtaining a cross-linked hydroxypropylated starch paste solution, mixing the sodium alga acid solution with the cross-linked hydroxypropylated starch paste solution at a volume ratio of (1:1)-(3:1), adding fatty substances into the mixed solution for improving the barrier property of the film, preparing the bioactive composite film by using a tape casting method, and drying in vacuum. The film material prepared by the preparation method has good biocompatibility and biodegradability and has the special functions of inhibiting bacteria, stopping bleeding, promoting healing and the like; when the film material is contacted with a wound, the film material is capable of quickly absorbing water in the blood, keeping a humid environment and effectively sealing the hemorrhagic wound.
Owner:山东贝诺医药生物科技有限公司
Magnetron sputtering method for preparing HA/YSZ/polyimide bioactive composite material
InactiveCN1995450AHelp repairHelp rebuildVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringAtmospheric pressure
The invention discloses a making method of biological active composite material of HA / YSZ / polyimide through magnetic control sputtering method, which comprises the following steps: adding 5-40% YSZ powder in the nanometer graded HA powder; making HA / YSZ target material in the vacuum through heat sintering method; cleaning PI base; drying; placing on the base on the carrier of sputtering chamber; extracting the chamber into vacuum; making the pressure below 10-4Pa; activating the surface of PI base surface; placing HA / YSZ target material and PI base in the sputtering chamber; extracting the sputtering chamber into vacuum between 3*10-4 and 5*10-4 Pa; adjusting Ar flow quantity; reducing vacuum degree of sputtering chamber to 2*10-1Pa-1*10-1Pa; adjusting sputtering power to do firing sputter for 6-8h; fetching the sample out of sputtering chamber at 100-200 deg. c; insulating 2-4h; cooling.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Bioactive composite material for bones as well as preparation method and application of composite material
ActiveCN112972773APromote generationEnabling activityTissue regenerationProsthesisOrganic acidAngiogenesis growth factor
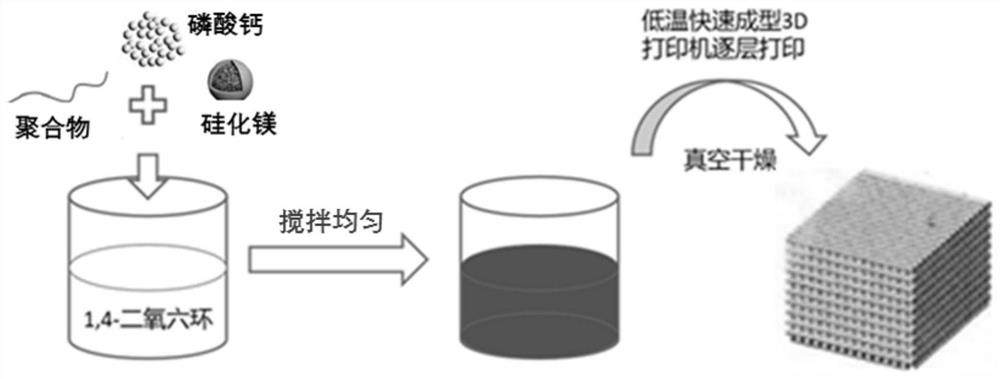
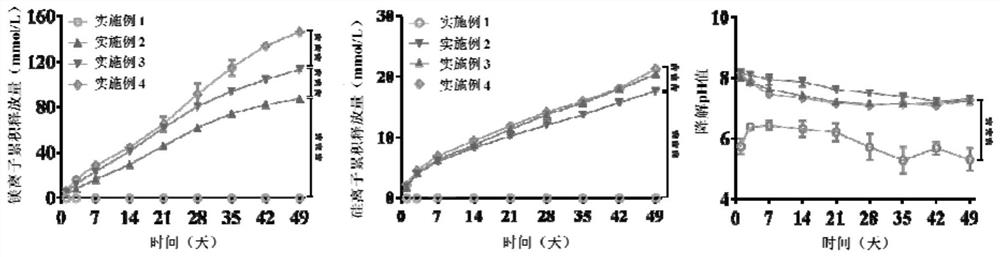
The invention relates to a bioactive composite material for bones as well as a preparation method and application of the bioactive composite material, in particular to a composite material for bones, which is characterized by comprising a substrate of a biodegradable polymer, and the substrate further comprises magnesium silicide; and the biodegradable polymer can be degraded in an aqueous solution environment to generate is micromolecular organic acids. The special effect of magnesium silicide acting on bone injury parts is found for the first time, a biodegradable polymer substrate is degraded in a physiological environment to generate micromolecular organic acids, and the surrounding environment of a stent is slightly acidic, so that degradation of magnesium silicide can be triggered, controllable long-acting release of magnesium ions and silicon ions along with the degradation process of the stent is realized, and osteogenic activity is promoted; and meanwhile, implantation parts are adjusted to form a hypoxic microenvironment, and angiogenesis is promoted. The magnesium silicide-containing composite material for bones shows bioactivity for promoting osteogenesis and vascularization, and can realize effective bone defect repair.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Magnetron sputtering method for preparing HA/YSZ/Ti6Al4V gradient bioactive composite material
ActiveCN1995449ALow costGradient coating thinVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringBioactive composite
The invention discloses a magnetic control sputtering method of HA / YSZ / Ti6Al4V gradient biological active composite material, which comprises the following steps: adding 20-80% YSZ powder in the HA powder; pressing; sintering; making composite target material of HA / YSZ; polishing Ti6Al4V base through gold phase sandpaper; spraying sand on the base surface; etching base through NaOH solution; placing HA target material, composite target material of HA / YSZ and Ti6Al4V base to presputter and clean for 20-40 min; transmitting Ti6Al4V base into main sputtering chamber with vacuum degree at 5*10-1-9*10-1Pa for 2-4h; sampling from main sputtering chamber; disposing in the heat disposing furnace at 300-500 deg. c; insulating 2-4 h.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Bioactive composite antibacterial soap and preparation method thereof
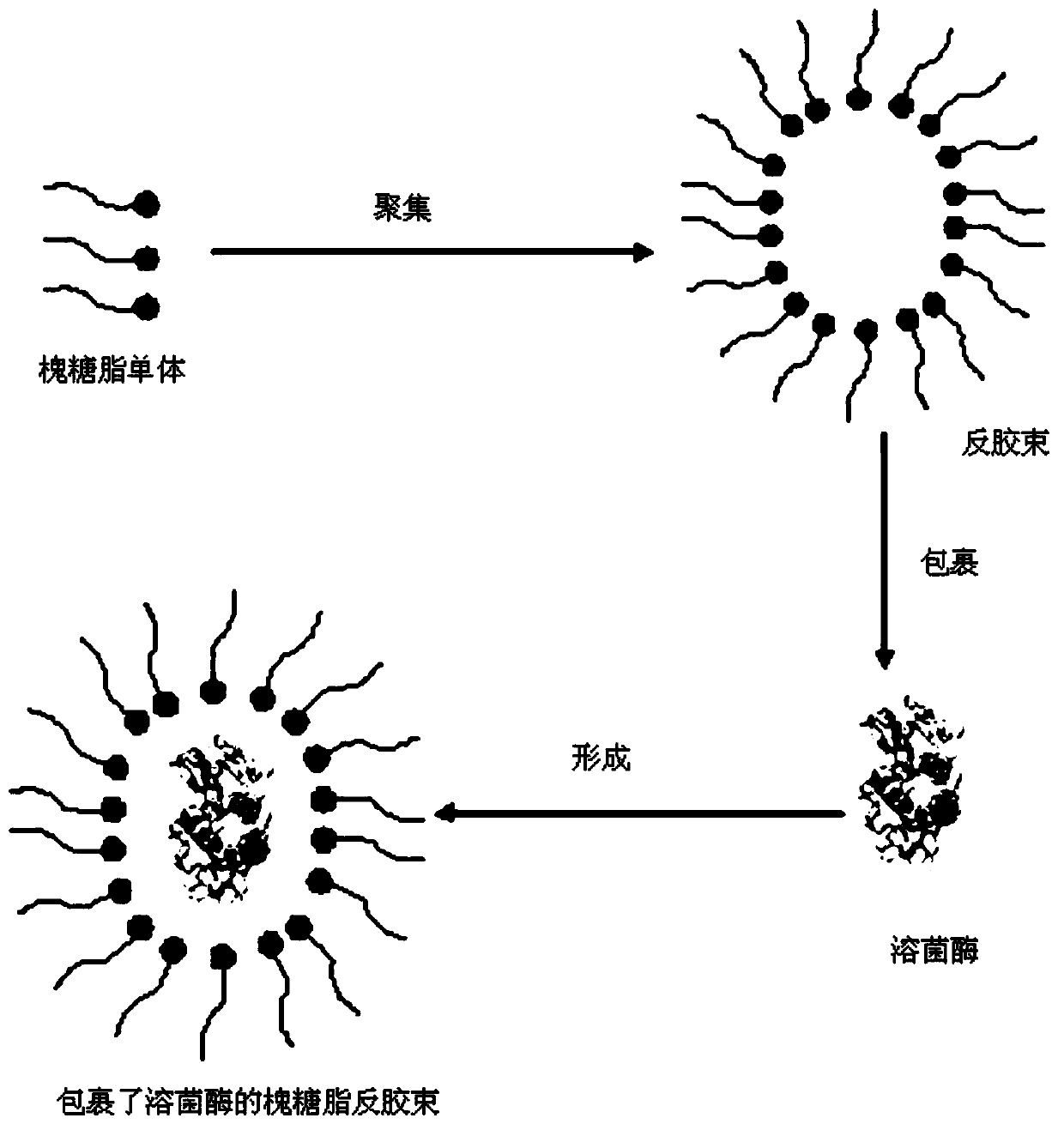
InactiveCN110331059AEfficient antibacterial effectBroad-spectrum antibacterialSurface-active non-soap compounds and soap mixture detergentsIrritationBoric acid
The invention discloses a bioactive composite antibacterial soap and a preparation method thereof. The antibacterial soap comprises, by mass, 89-98% of a vegetable soap base, 2-10% of an aqueous sophorolipid solution and 0.2-1% of an aqueous lysozyme solution; and the concentration of the aqueous sophorolipid solution is 750-950 g / L, and the concentration of the aqueous lysozyme solution is 100-120 g / L. The sophorolipid and lysozyme are added to the natural vegetable soap base to replace the antibacterial components such as phenols, boric acid, carbolic acid and the like in a traditional antibacterial soap, and a novel compounding technology for wrapping the lysozyme with a reverse micelle structure formed by the sophorolipid is used to prepare the composite antibacterial soap. The antibacterial soap has the advantages of efficient antibacterial effect, wide antibacterial spectrum, strong decontamination ability, good moisturizing effect, simple composition, no irritation, no odor, greenness and environmental protection.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com