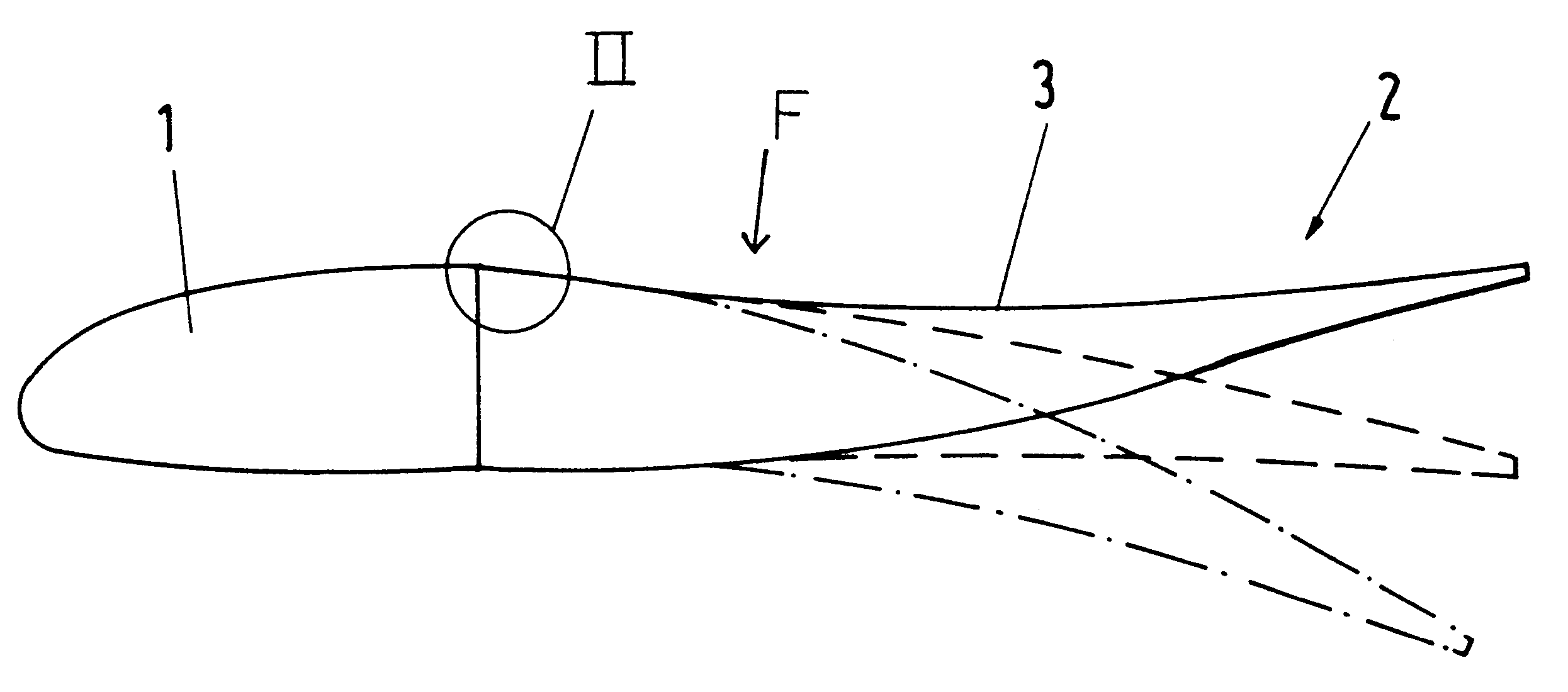
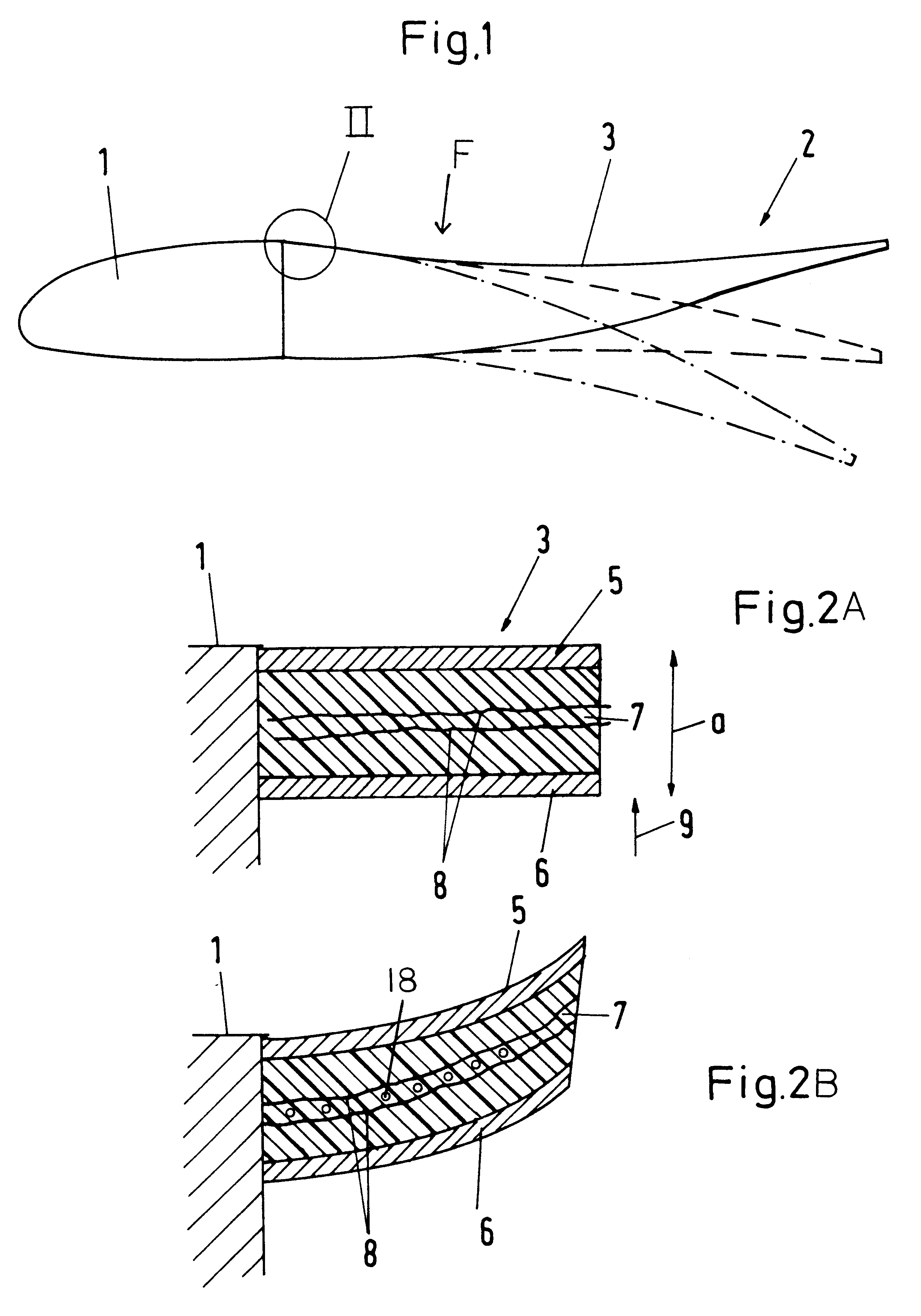
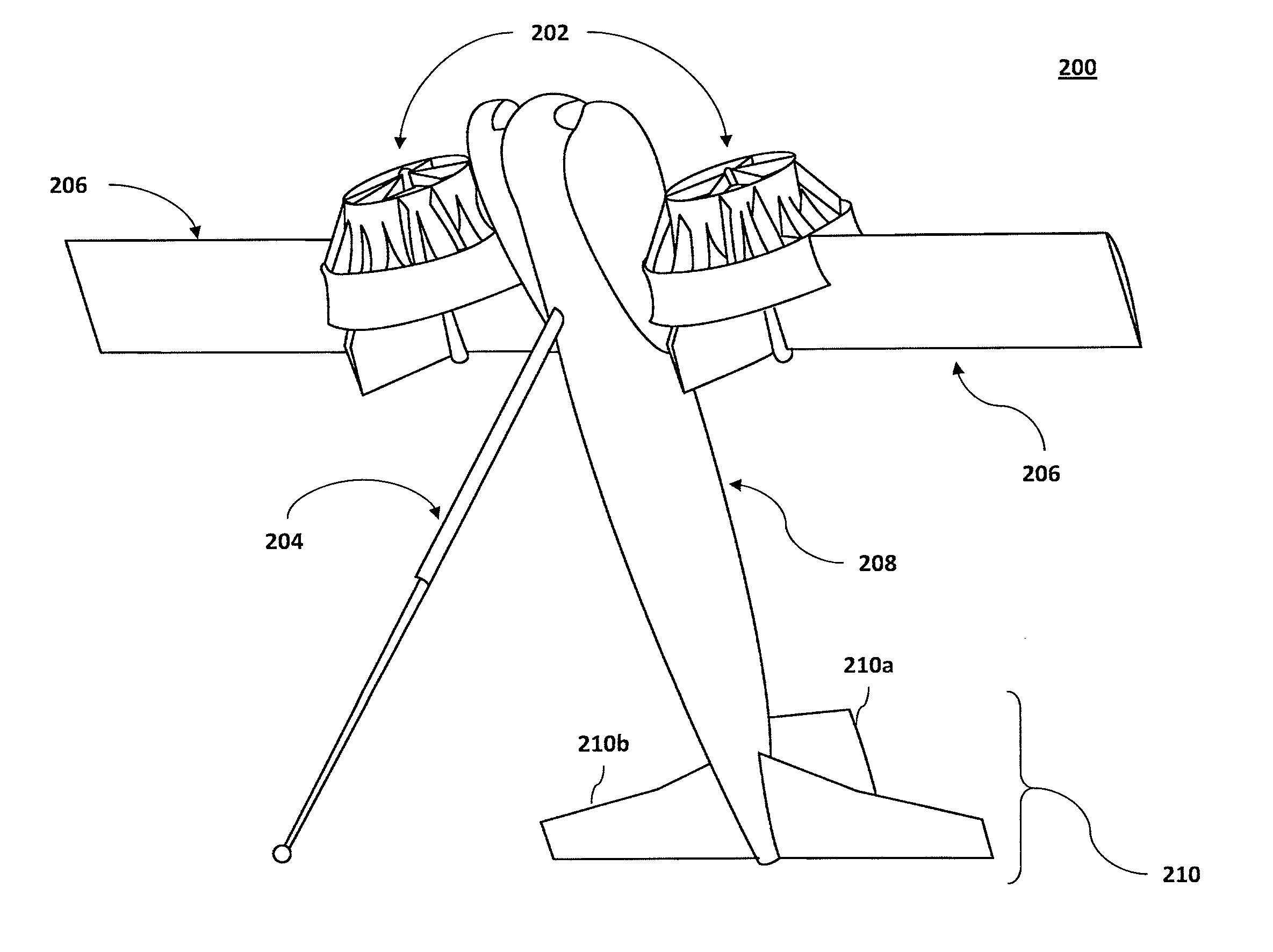
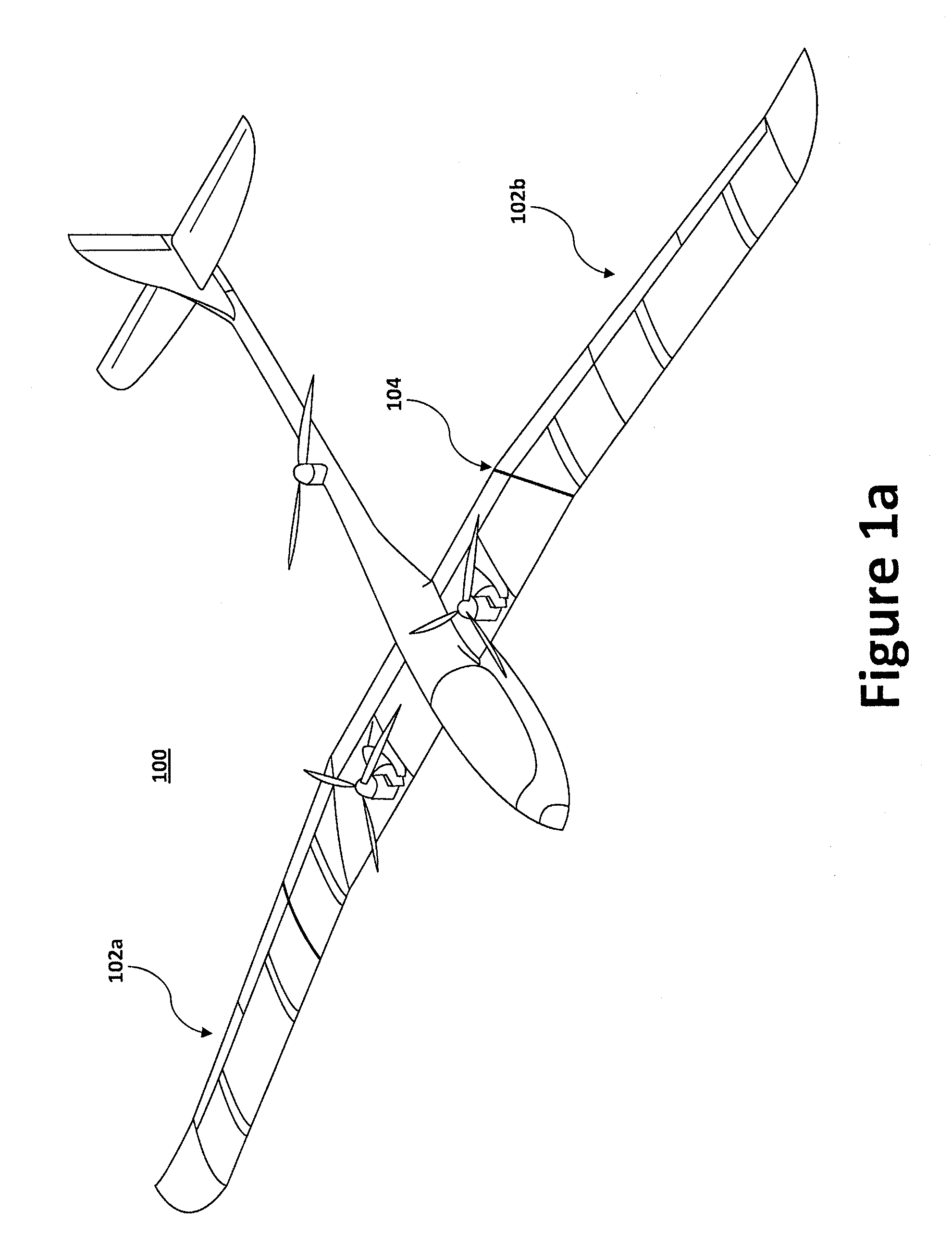
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3119results about "Wing adjustments" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
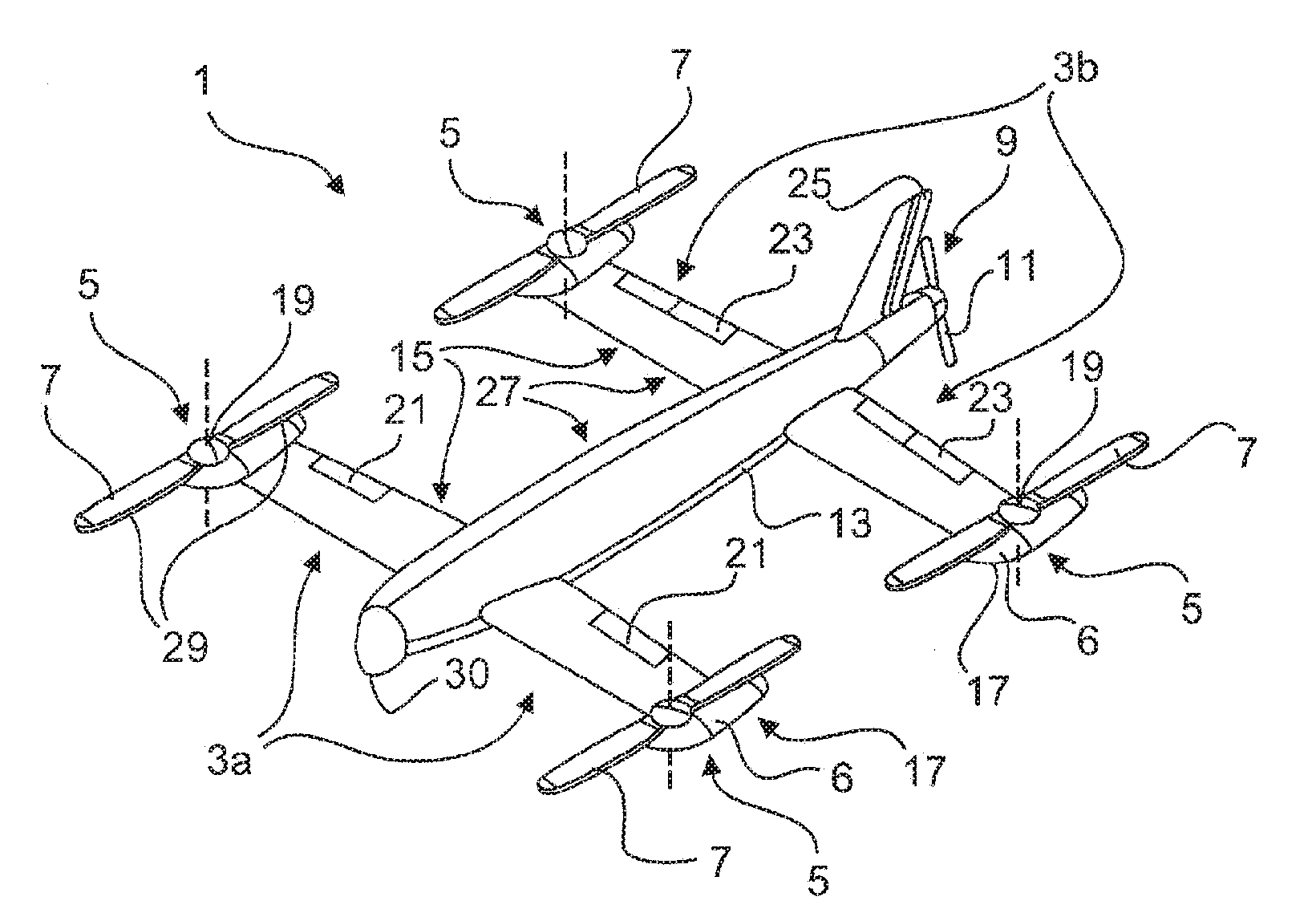
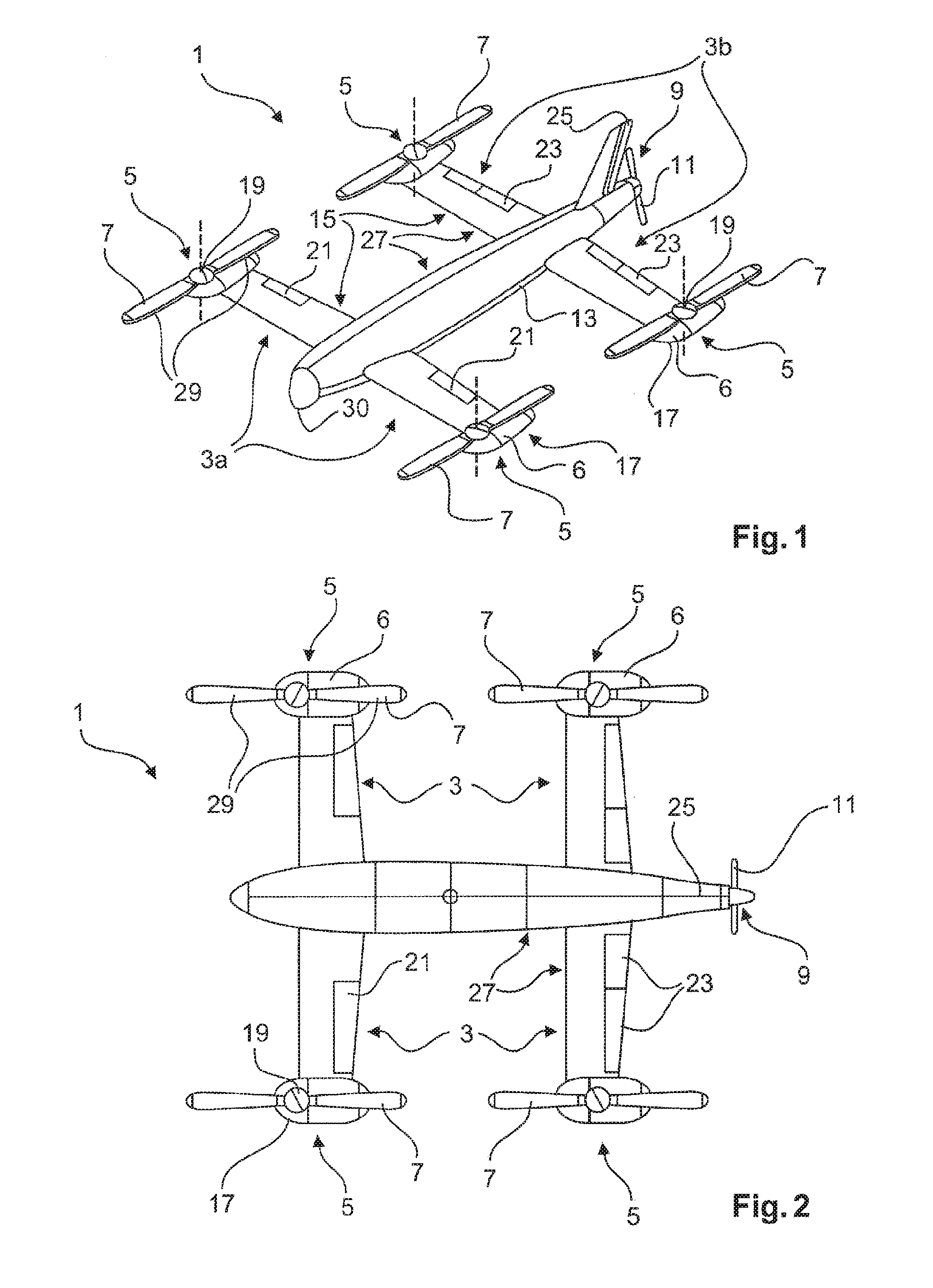
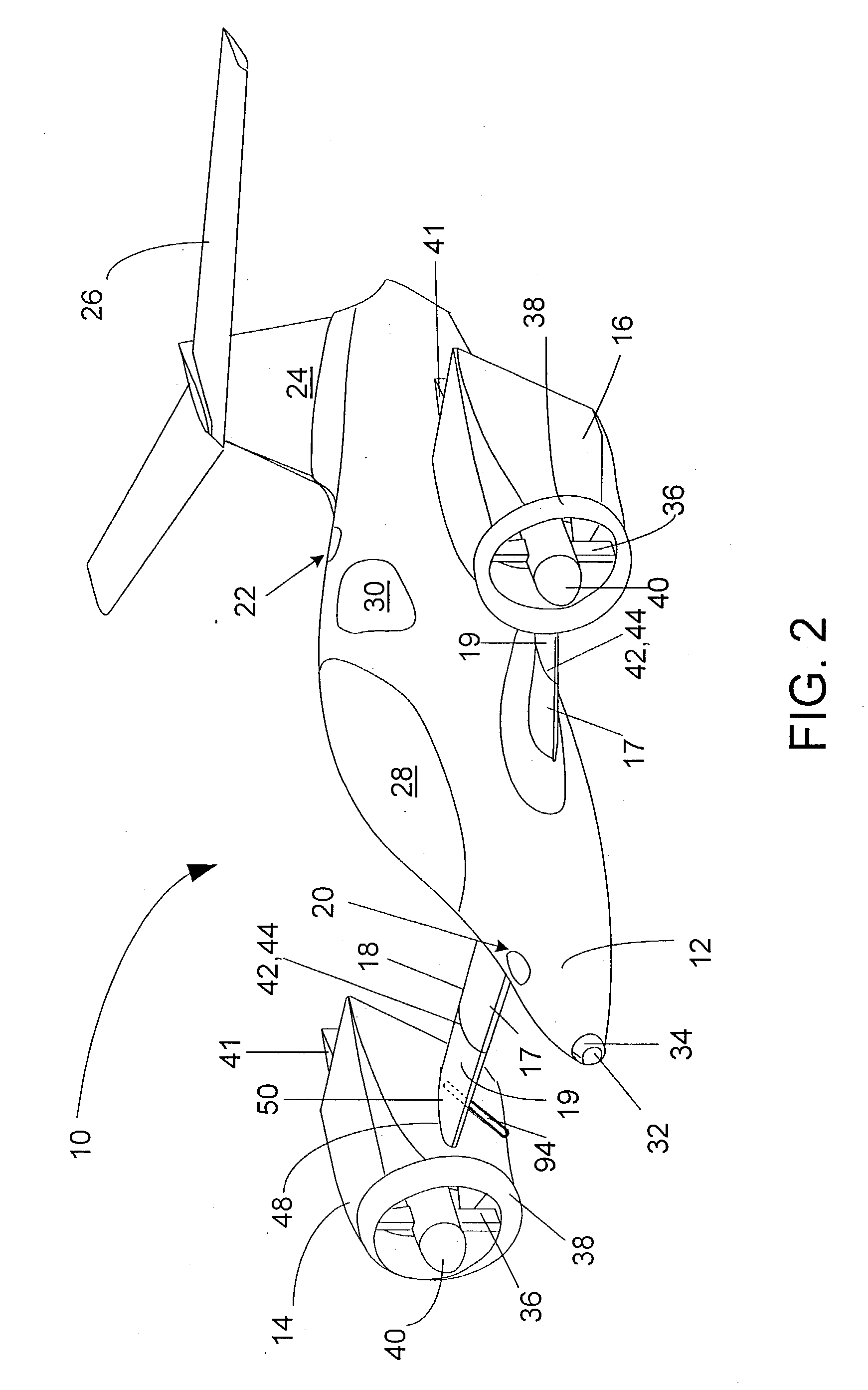
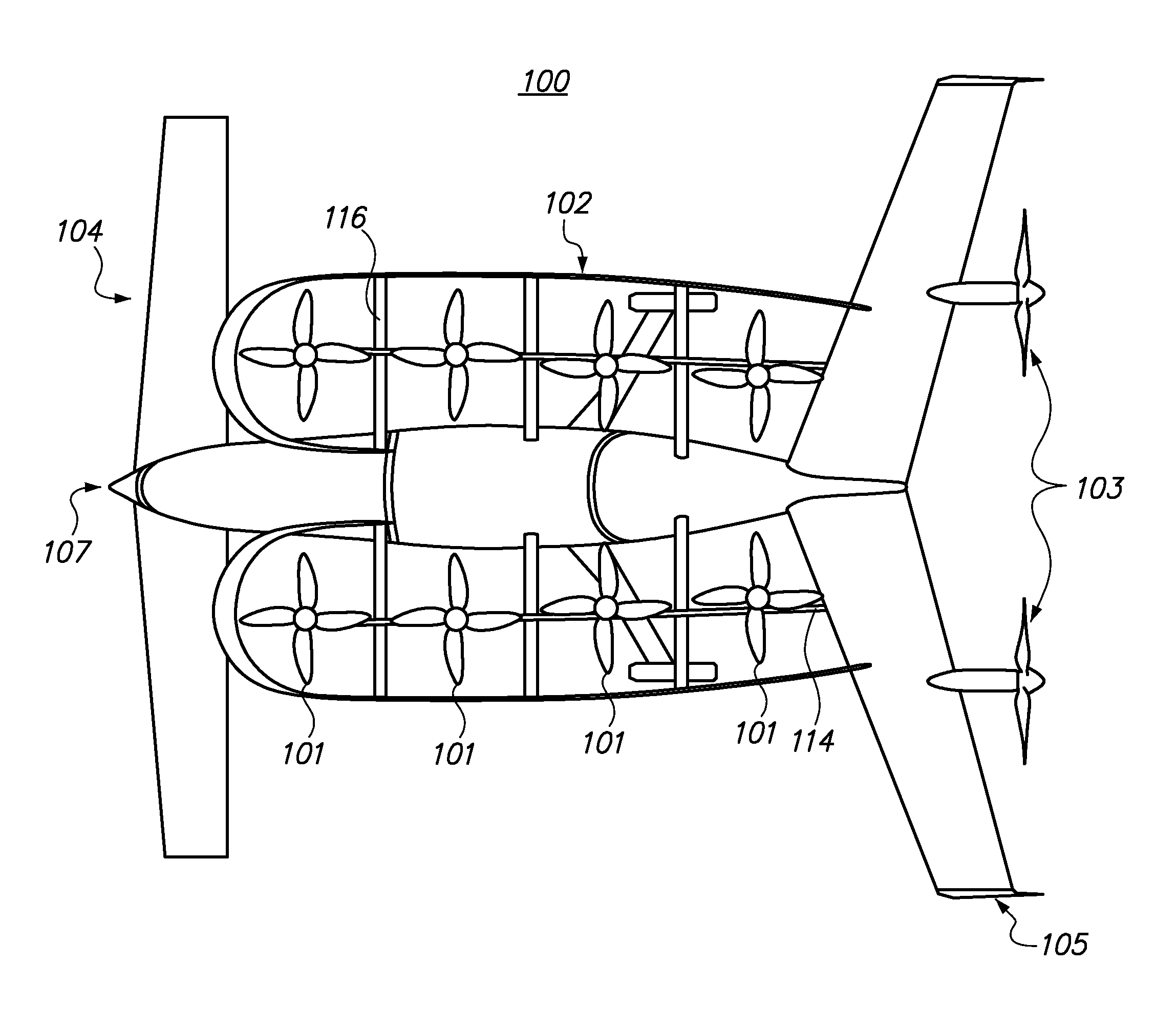
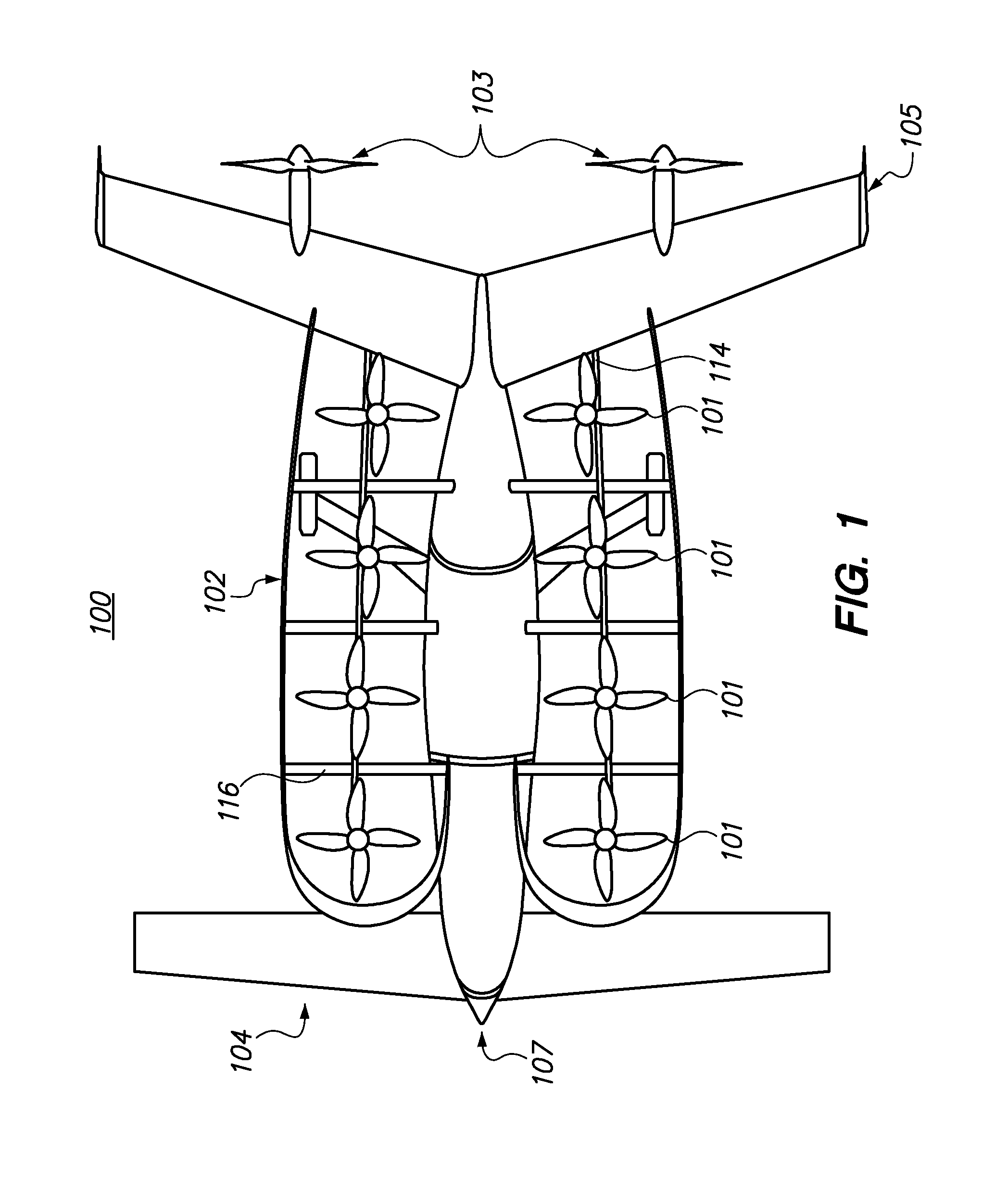
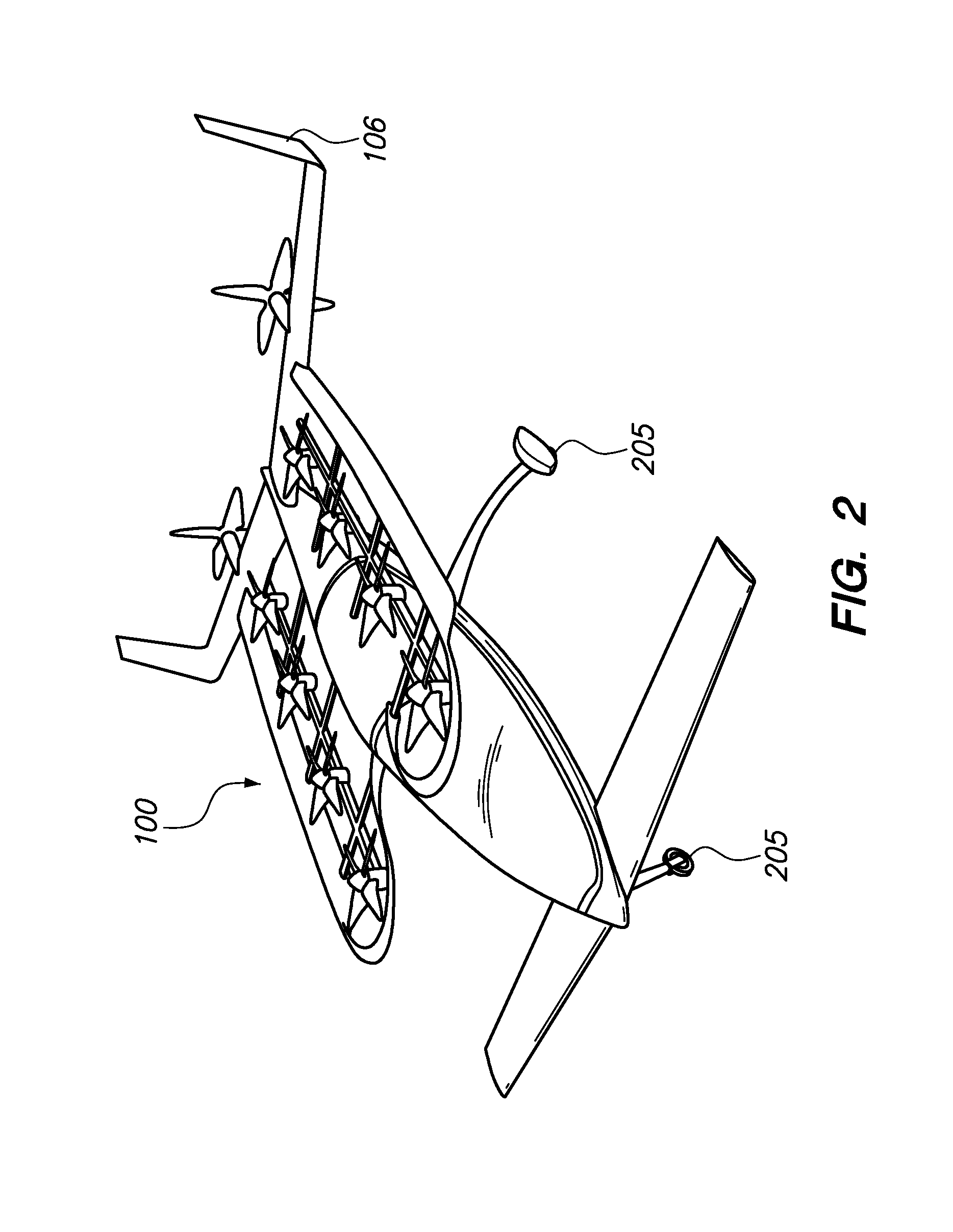
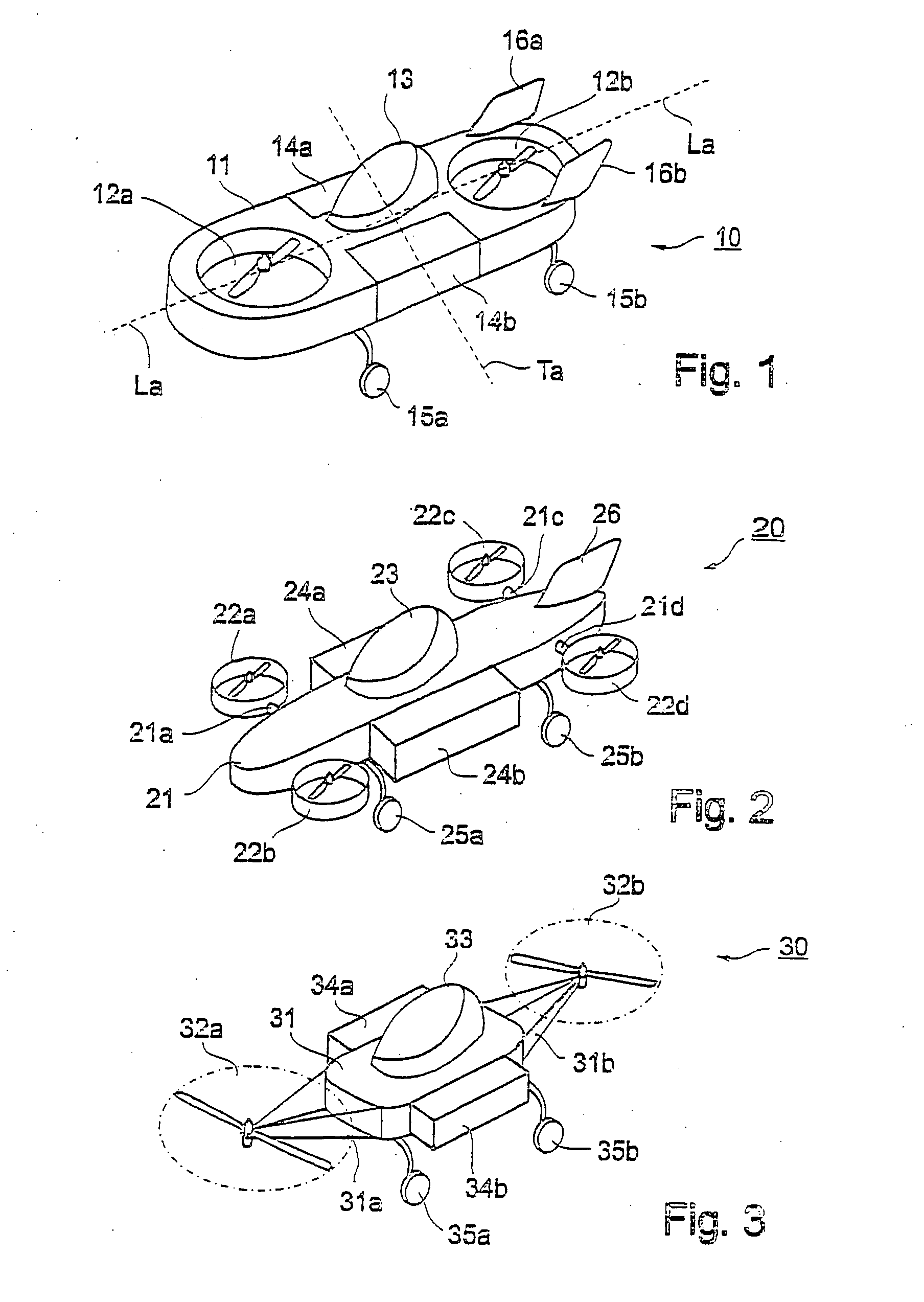
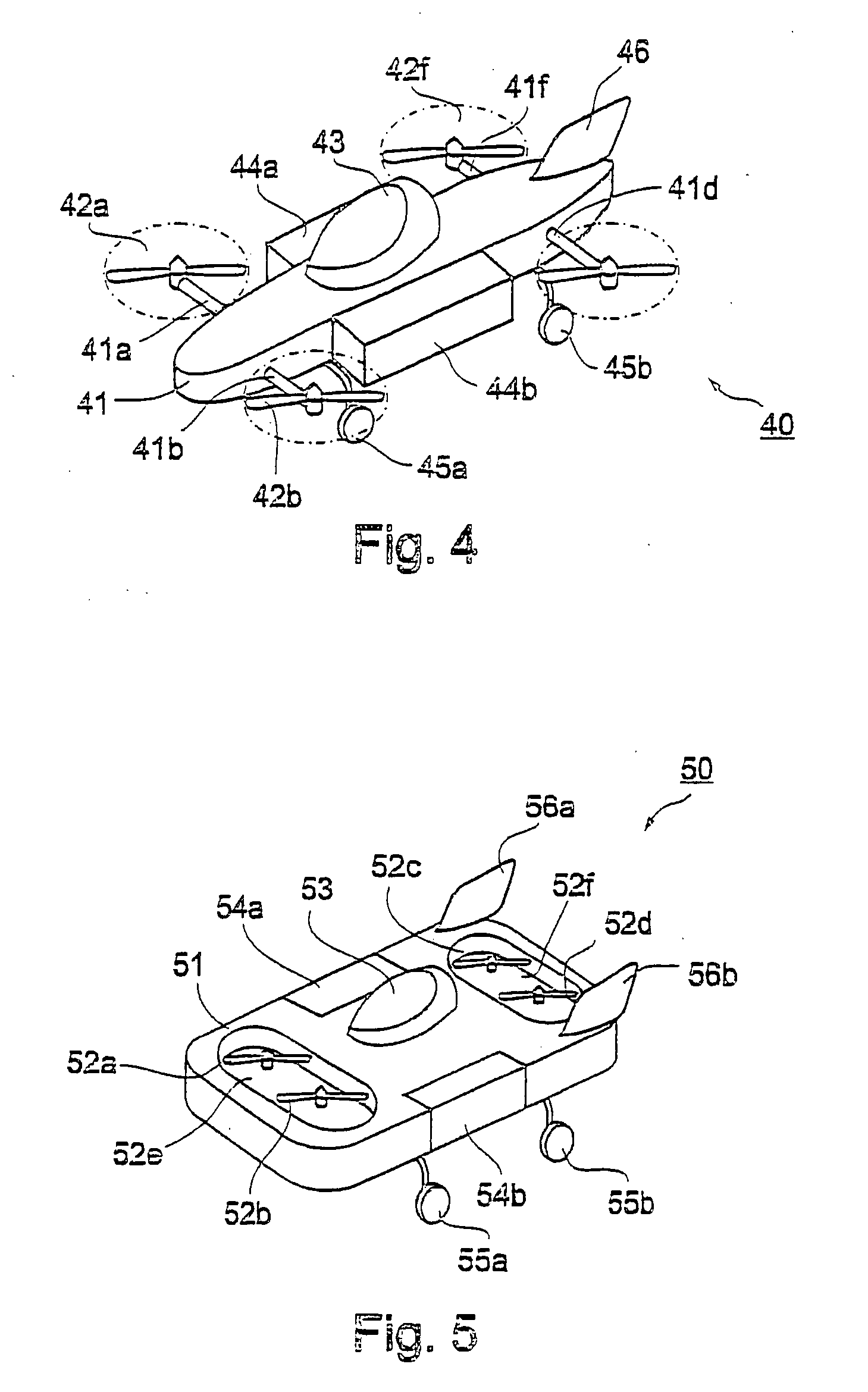
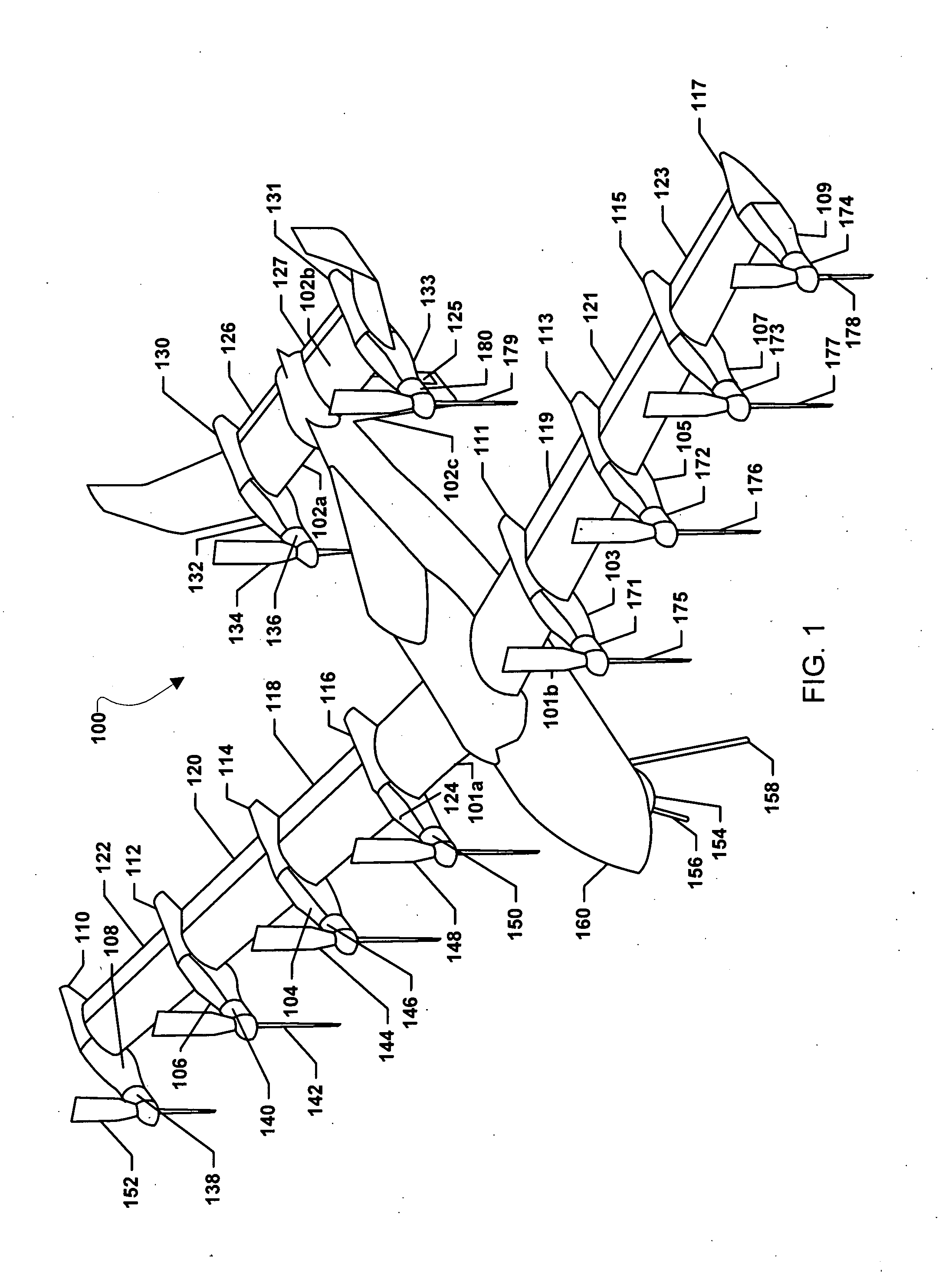
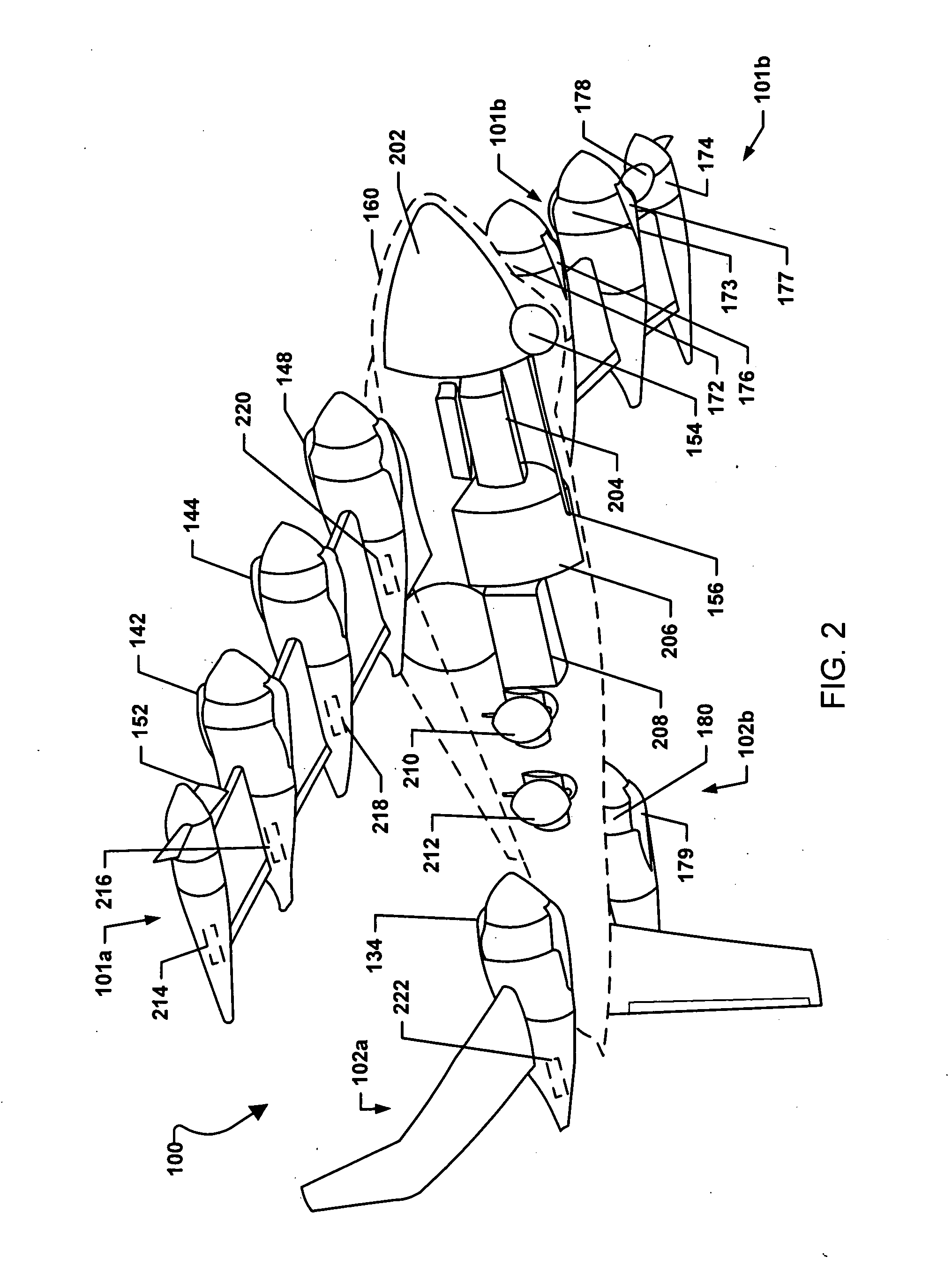
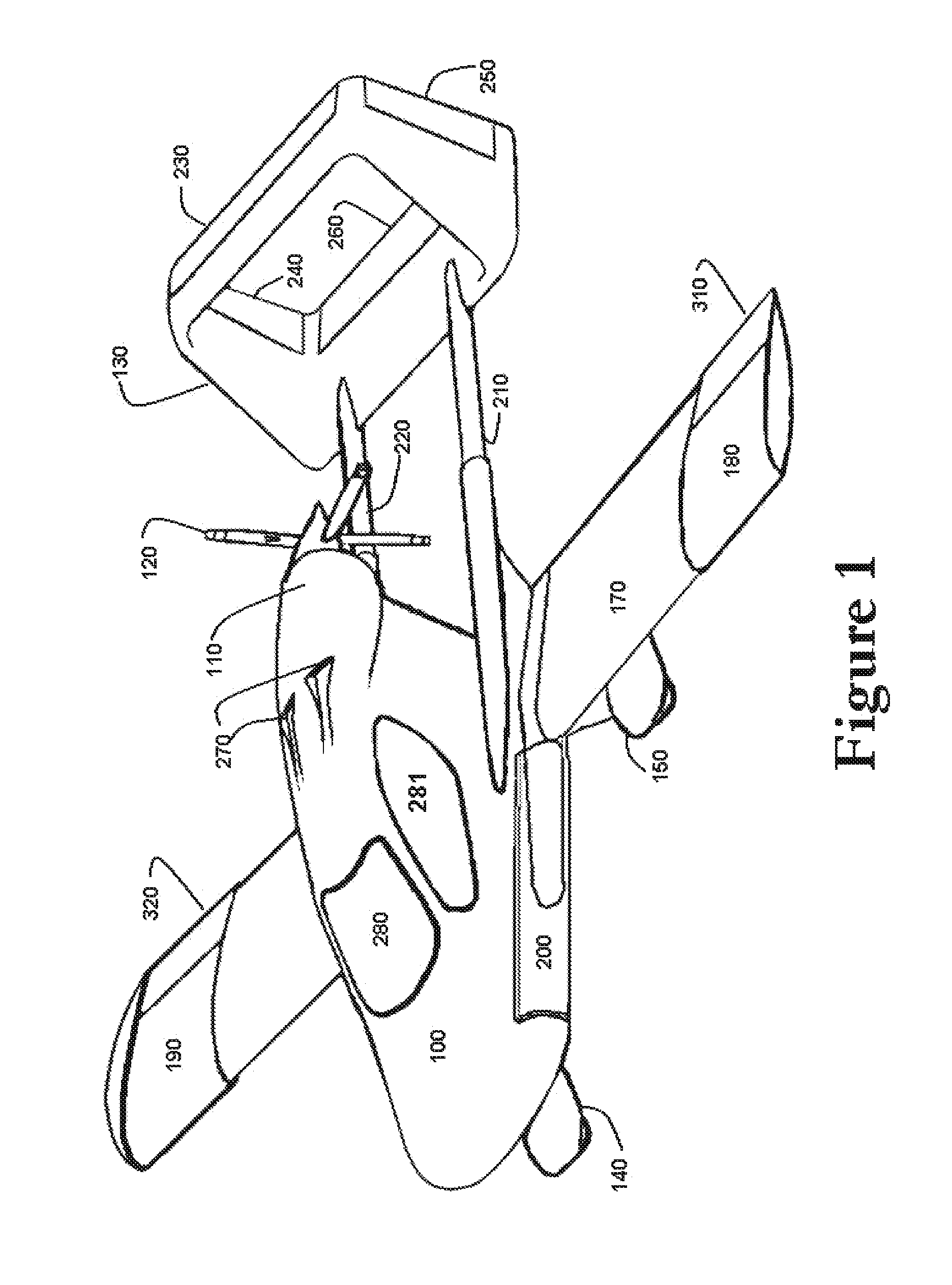
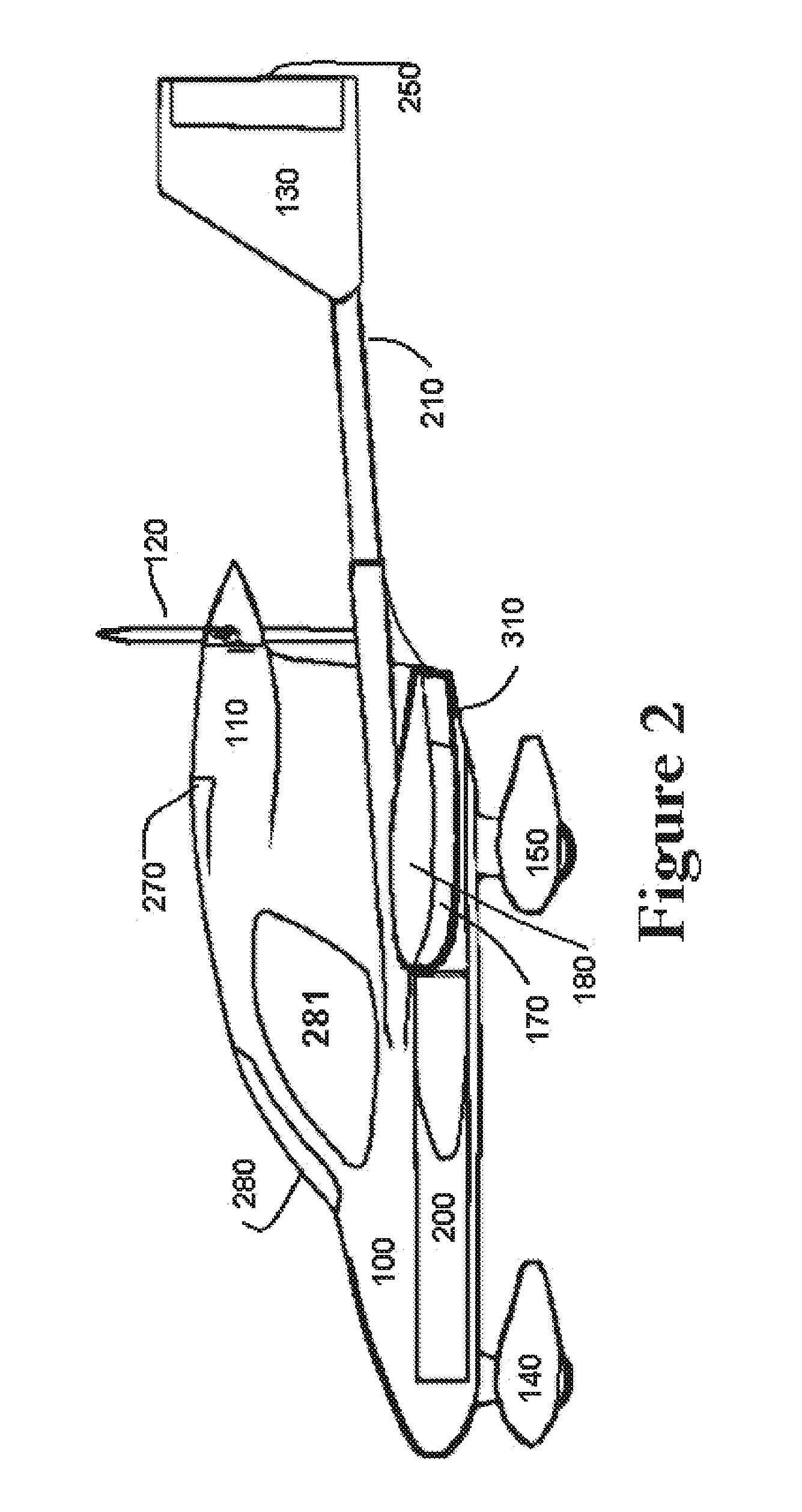
Aircraft Capable of Vertical Take-Off
ActiveUS20160207625A1Good hover characteristicIncrease cruising speedAircraft stabilisationUnmanned aerial vehiclesJet aeroplaneQuadcopter
The invention relates to an aircraft which can both take off and land vertically and can hover and also fly horizontally at a high cruising speed. The aircraft has a support structure, a wing structure, at least three and preferably at least four lifting rotors and at least one thrust drive. The wing structure is designed to generate a lifting force for the aircraft during horizontal motion. To achieve this the wing structure has at least one mainplane provided with a profile that generates dynamic lift. The wing structure is preferably designed as a tandem wing structure. Each of the lifting rotors is fixed to the support structure, has a propeller and is designed to generate a lifting force for the aircraft by means of a rotation of the propeller, said force acting in a vertical direction. The thrust drive is designed to generate a thrust force on the support structure, said force acting in a horizontal direction. The lifting rotors can have a simple construction, i.e. they can have a simple rigid propeller for example, and a vertical take-off or hovering of the aircraft can be controlled, in a similar manner to quadcopters, by a simple control of the speeds of the lifting rotors. High cruising speeds can be achieved as a result of the additional horizontally acting thrust drive.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Apparatus and methods for variable sweep body conformal wing with application to projectiles, missiles, and unmanned air vehicles
InactiveUS6923404B1Improve aerodynamic efficiencyImprove aerodynamic performanceAircraft stabilisationUnmanned aerial vehiclesBody axisUncrewed vehicle
An unmanned air vehicle (“UAV”) apparatus is configured to have a body and a body-conformal wing. The body-conformal wing is configured to variably sweep from a closed position to a fully deployed position. In the closed position, the body-conformal wing span is aligned with the body axis and in the fully deployed position the body-conformal wing span is perpendicular to the axial direction of the body. Delivery of the UAV comprises the steps of: positioning the span of a body conformal wing in alignment with the axis of the body of the UAV; initiating the flight of the UAV; and adjusting the sweep angle of the body-conformal wing as a function of the current speed, altitude, or attack angle of the UAV, with the adjustment starting at a 0 degree position and varying between a closed position and a fully deployed position. The UAV also has a control mechanism configured to variably adjust the sweep of the body-conformal wing to achieve a high lift over drag ratio through out the flight path of the UAV.
Owner:ZONA TECH
Mechanical meta-materials
ActiveUS20060192465A1Minimize sizeMinimize massEfficient propulsion technologiesCatheterMechanical metamaterialEngineering
The present invention provides meta-materials with an actively controllable mechanical property. The meta-material includes a deformable structure and a set of activation elements. The activation elements are controllable between multiple states. The meta-material includes a first value for a mechanical property when one or more of the activation elements is in the first activation state and includes a second value for the mechanical property when the activation elements have been activated to the second activation state. In one aspect, the meta-material resembles a composite material where the connectivity between the component materials or shape and arrangement of the component materials is dynamically controllable so as to affect a mechanical property of the meta-material.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
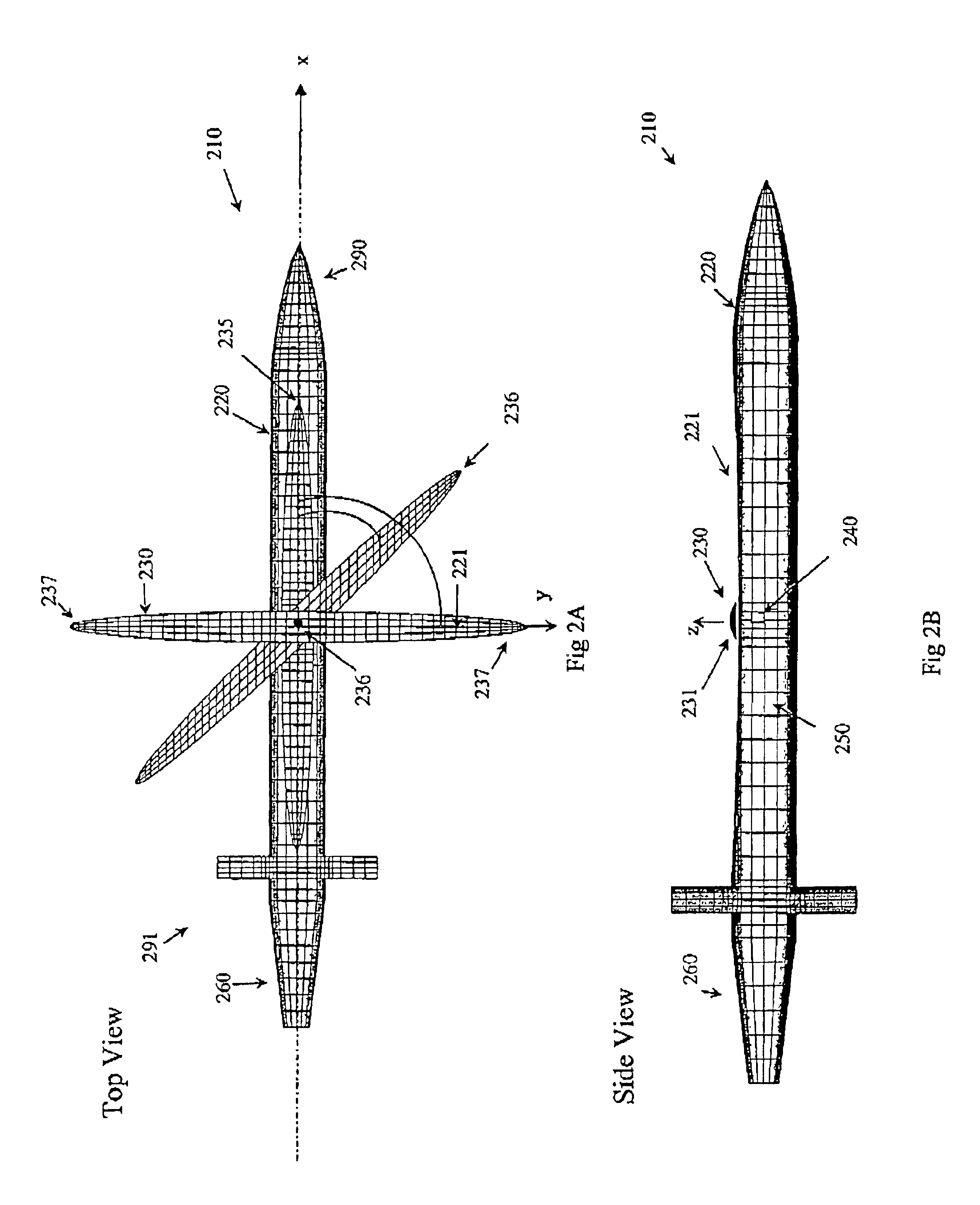
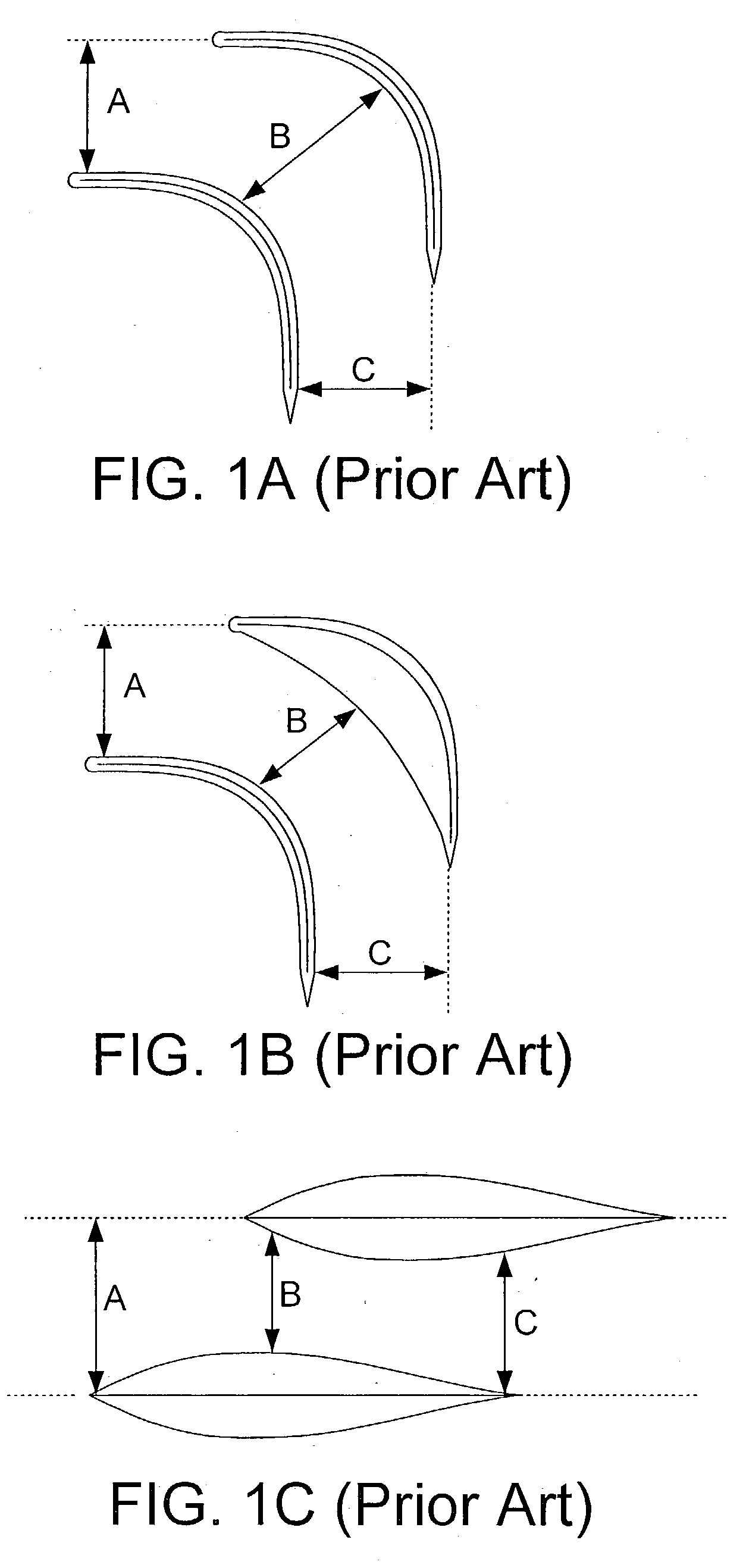
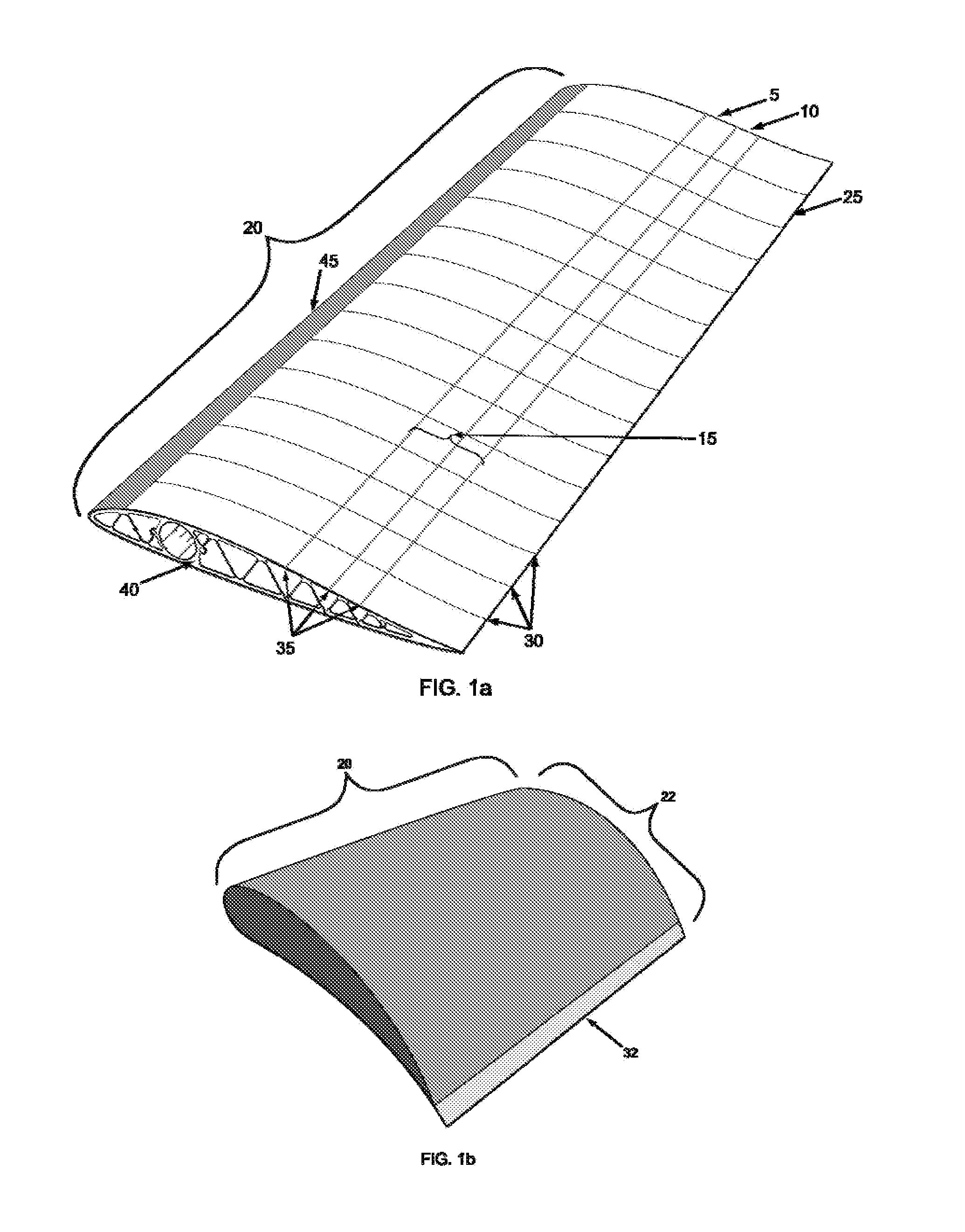
Subsonic aircraft with backswept wings and movable wing tip winglets
InactiveUS6345790B1Optimized aerodynamic streamline contourRaise the ratioInfluencers by generating vorticesAircraft stabilisationWingspanAirplane
A subsonic aircraft having backswept lifting wings is equipped with individually rotatable winglets at the wing tips thereof, in order to reduce drag during cruise flight, to minimize the dangers posed by wing tip vortices to following aircraft during take-off and landing, and to minimize the total wingspan during ground operations, with respective different positions of the winglets. A streamline-shaped rotation body made up of at least two individually rotatably supported rotation segments is mounted on the wing tip of each lifting wing. A respective winglet is mounted on each respective rotation segment. Each rotation segment with its associated winglet is individually rotatable about a rotation axis of the rotation body extending substantially parallel to the aircraft lengthwise axis. Thereby, each winglet is individually pivotable to any selected pivot angle relative to a horizontal plane extending through the rotation axis. Each winglet and its associated rotation segment is rotatable through an angular range between maximum end limits of at least +90° (vertically upward) and at least -90° (vertically downward) relative to the horizontal plane.
Owner:DAIMLER CHRYSLER AEROSPACE AIRBUS
Ducted fan VTOL vehicles
InactiveUS7857253B2Easy constructionConveniently performedAircraft navigation controlParachutesTransverse axisPropeller
A vehicle including a fuselage having a longitudinal axis and a transverse axis, two Ducted Fan lift-producing propellers carried by the fuselage on each side of the transverse axis, a pilot's compartment formed in the fuselage between the lift-producing propellers and substantially aligned with one side of the fuselage, a payload bay formed in the fuselage between the lift-producing propellers and opposite the pilot's compartment, and two pusher fans located at the rear of the vehicle. Many variations are described enabling the vehicle to be used not only as a VTOL vehicle, but also as a multi-function utility vehicle for performing many diverse functions including hovercraft and ATV functions. Also described is an Unmanned version of the vehicle. Also described are unique features applicable in any single or multiple ducted fans and VTOL vehicles.
Owner:URBAN AERONAUTICS
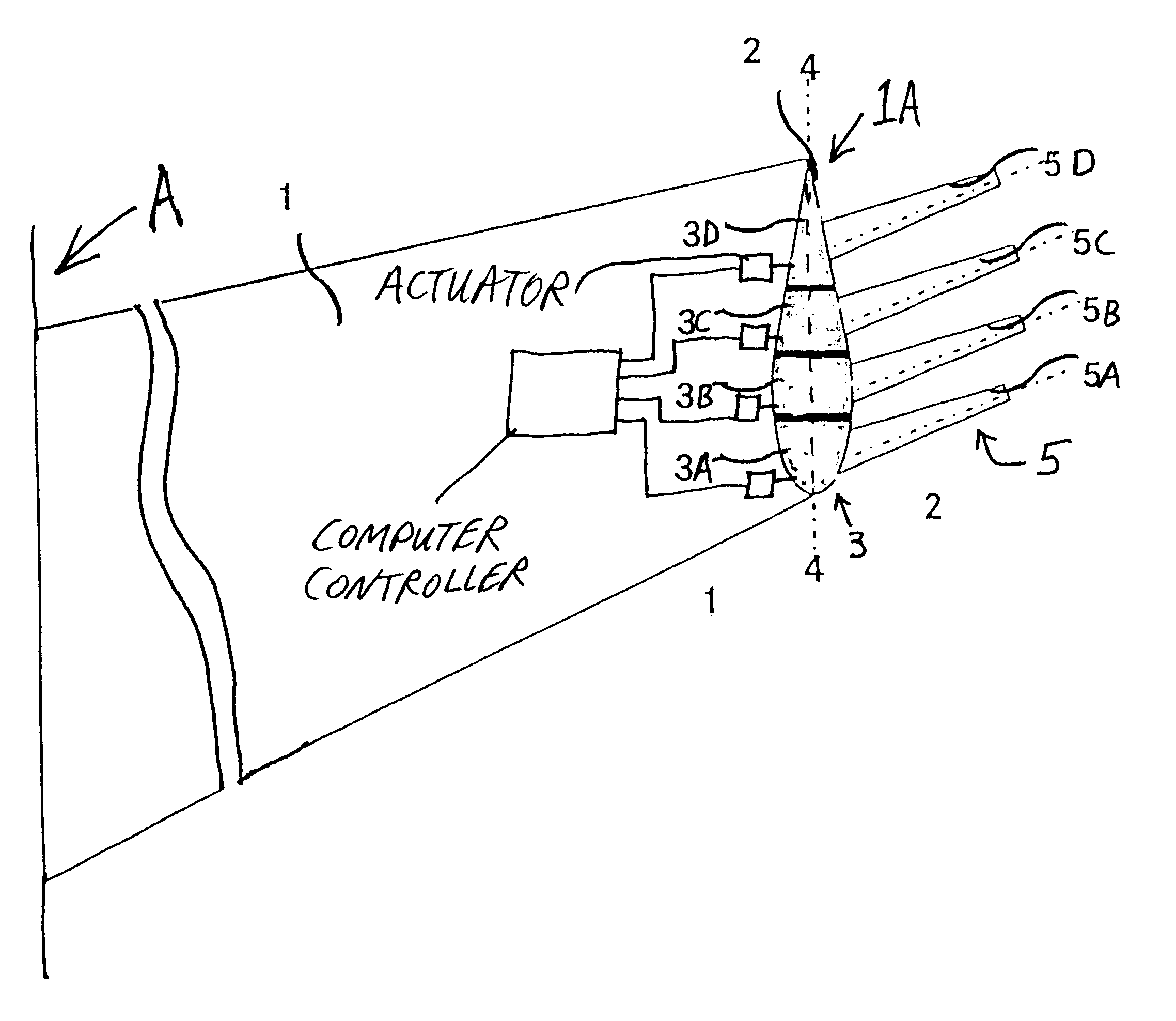
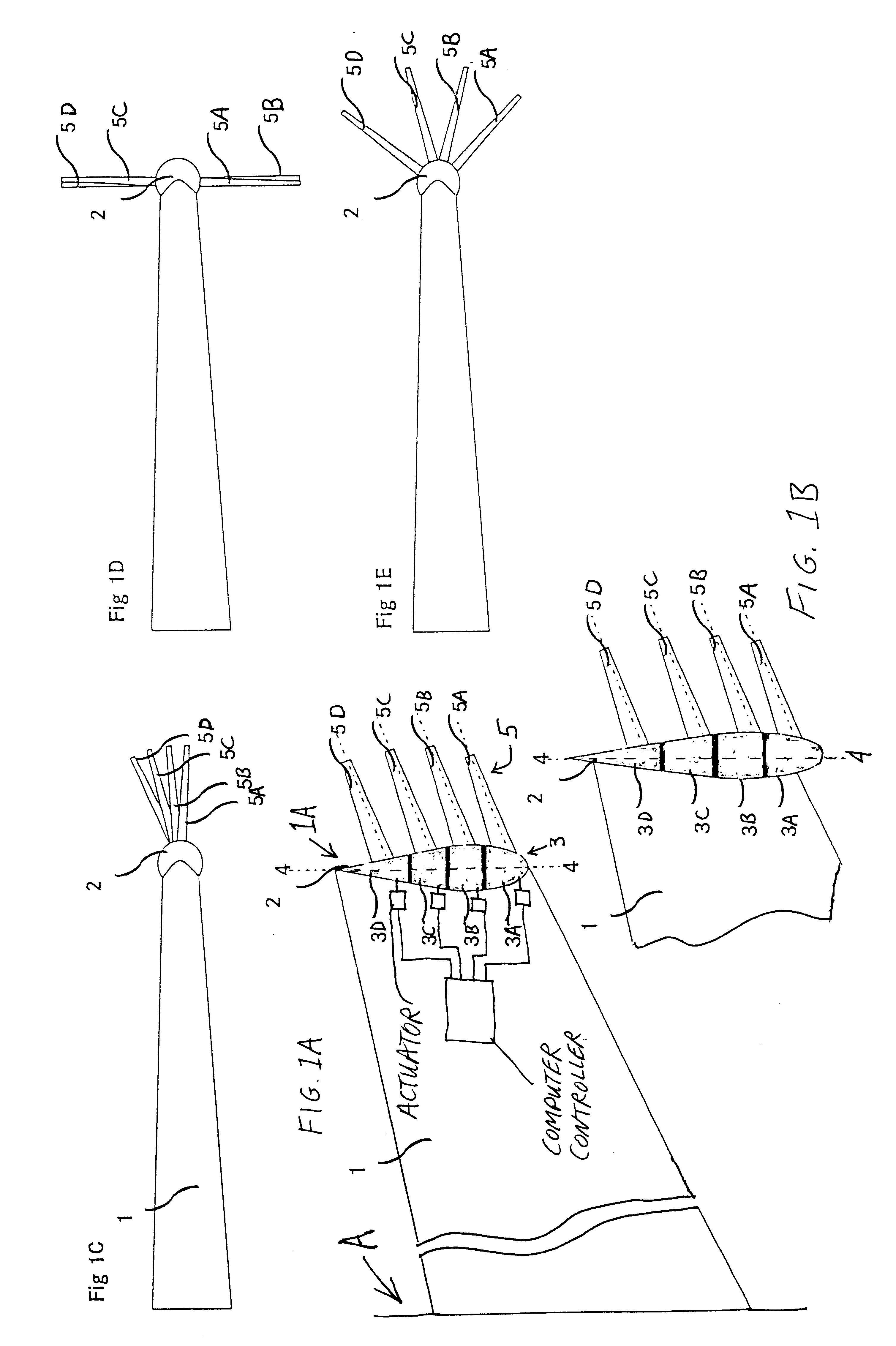
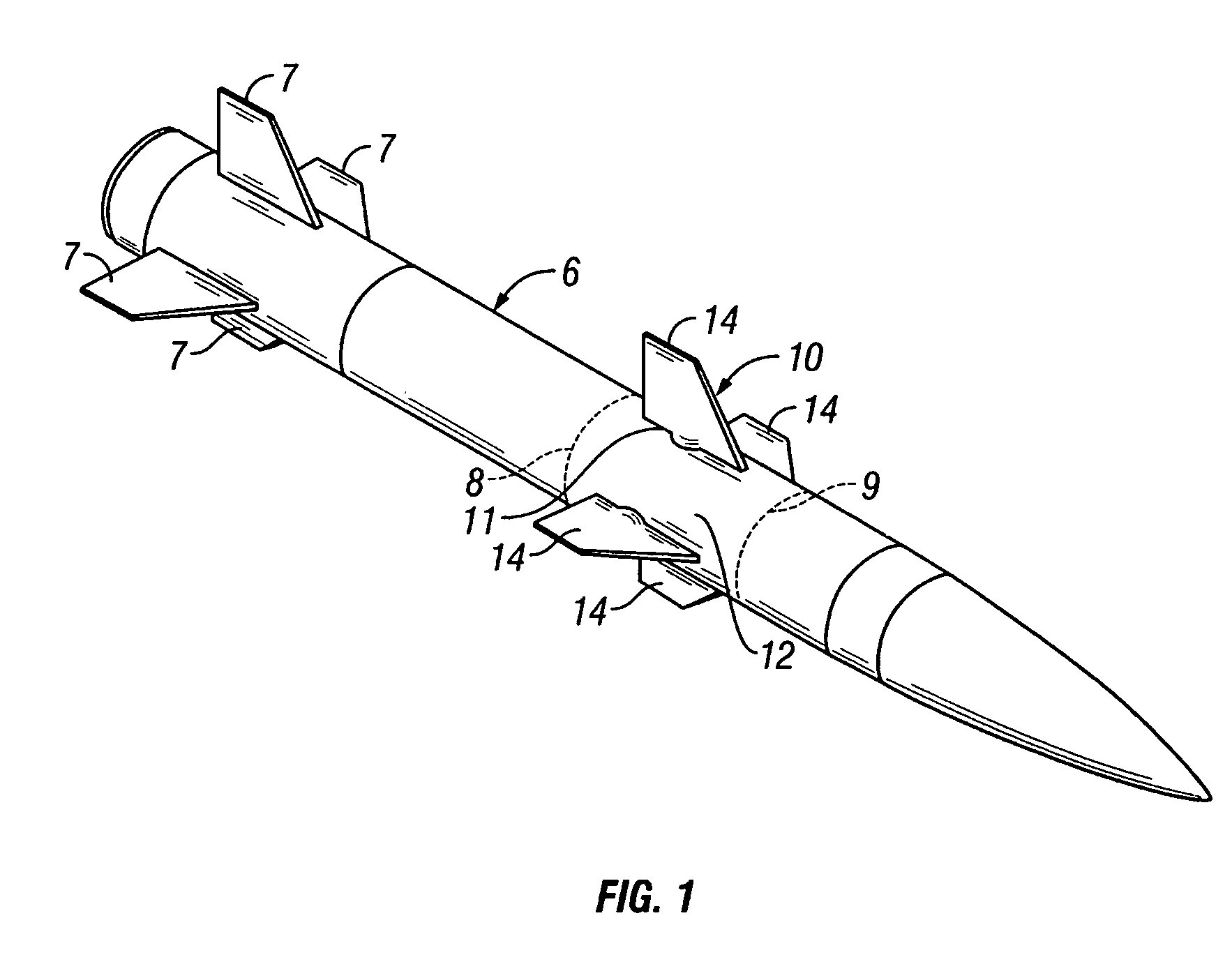
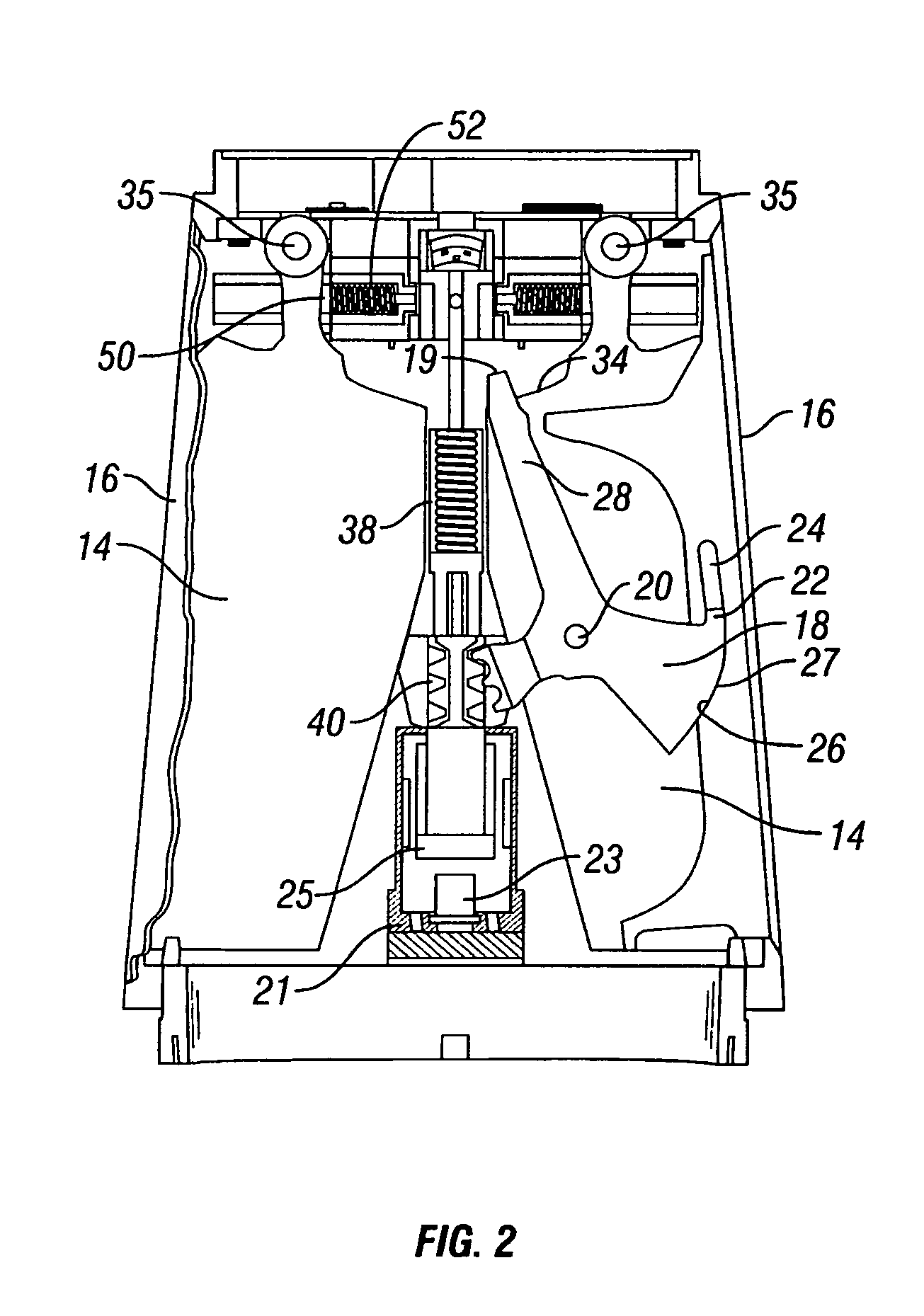
Cover ejection and fin deployment system for a gun-launched projectile
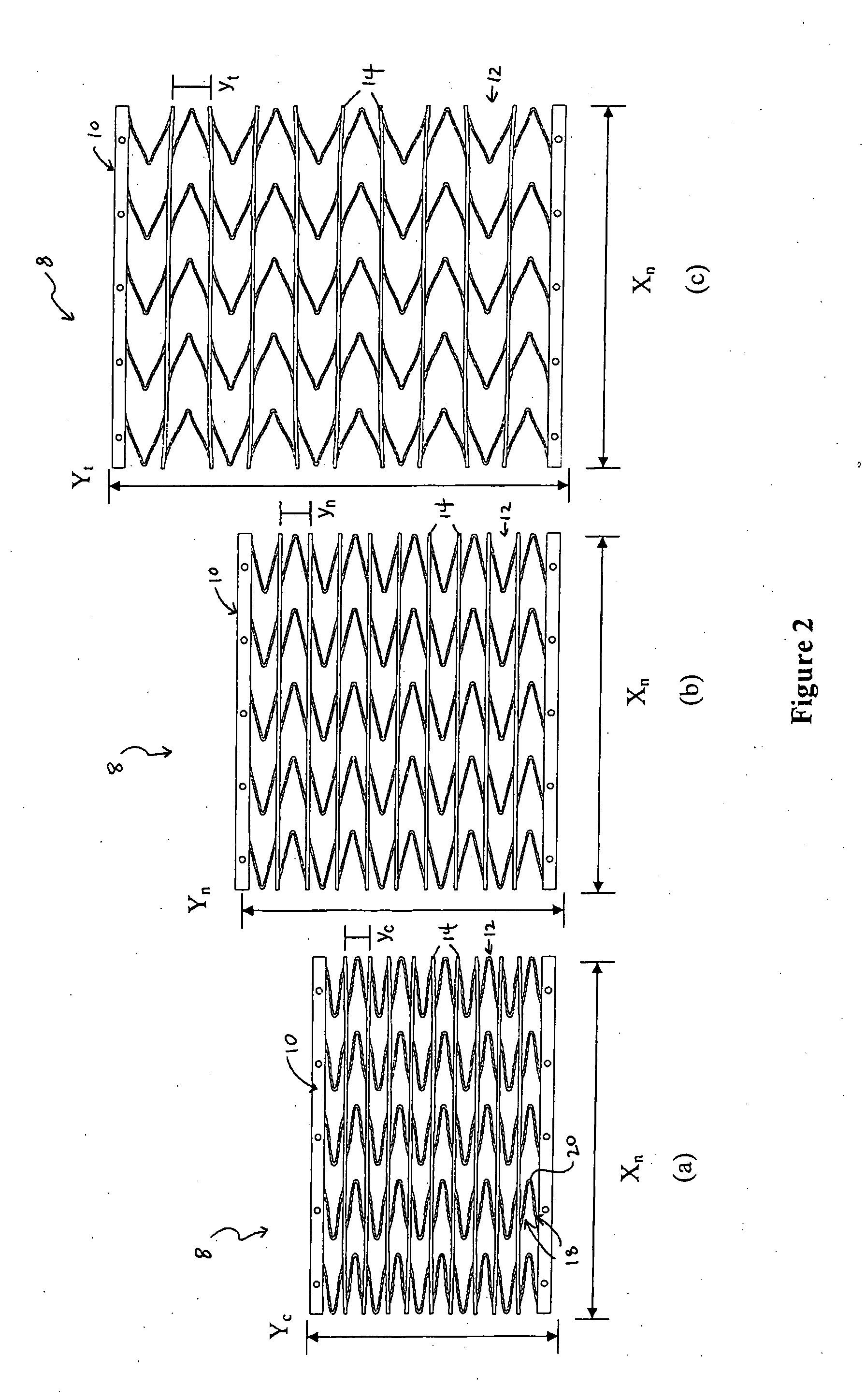
InactiveUS6880780B1Control rateSufficient velocityWing adjustmentsSelf-propelled projectilesActuatorCam
A fin cover release and deployment system designed for high G forces of gun-launched missiles. In one embodiment, a pyrotechnic actuator drives actuator arms to first release and eject the fin slot covers, followed by deployment of the fins radially outward to the steering position. Following complete ejection of the covers, the fins are driven outwardly by cam surfaces along the latch arms, followed by a spring and wedge mechanism installed interiorly of the fin steering shaft to lock the fins in the fully deployed state. In another embodiment, a motor and rotating threaded shaft replace the pyrotechnic actuator.
Owner:GEN DYNAMICS ORDNANCE & TACTICAL SYST +1
Vertical take-off and landing vehicles
A VTOL vehicle including a fuselage with two foldable wings, two tiltable nacelles attached to the wings, a vertical stabilizer, a horizontal stabilizer, and two auxiliary thrusters. Each nacelle contains a system of vanes located at the rear opening thereof, and actuators are provided for extending and retracting the vanes in conjunction with nacelle tilting mechanisms to deflect the airflow over a predetermined range of angles from the horizontal. Each nacelle also contains two rotary engines, each of which directly drives a fan. The fans face each other and operate in counter-rotating directions at the same rotational speed. An alternative embodiment includes two additional nacelles attached to the fuselage instead of having the auxiliary thrusters. A redundant computerized flight control system maintains stability of the vehicle as it transitions from one flight mode to another.
Owner:MOLLER INT
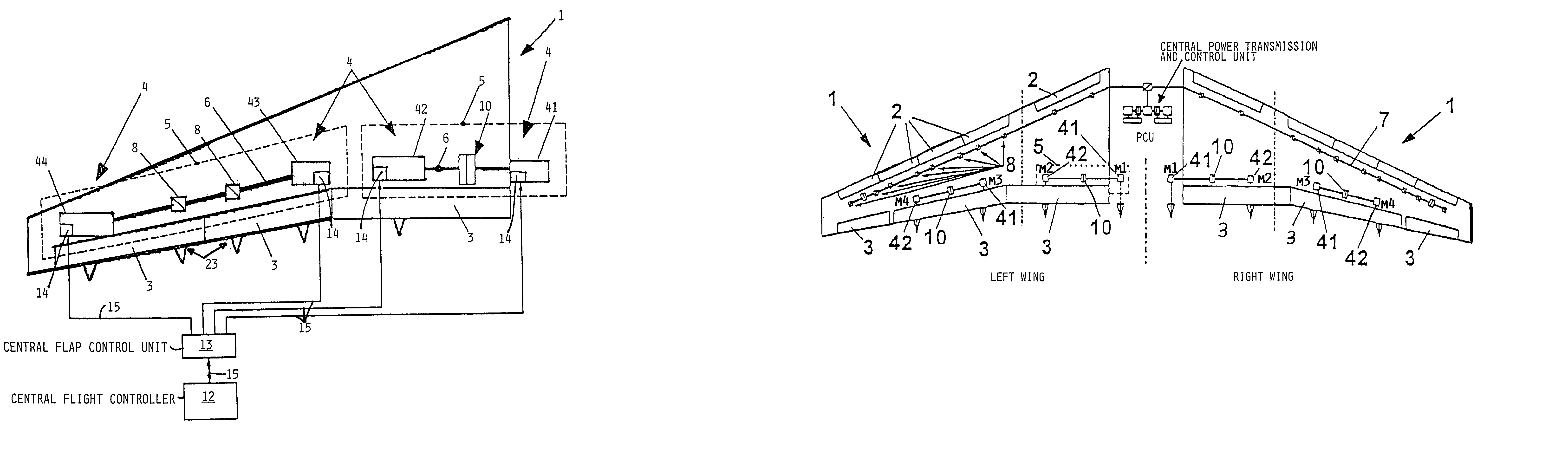
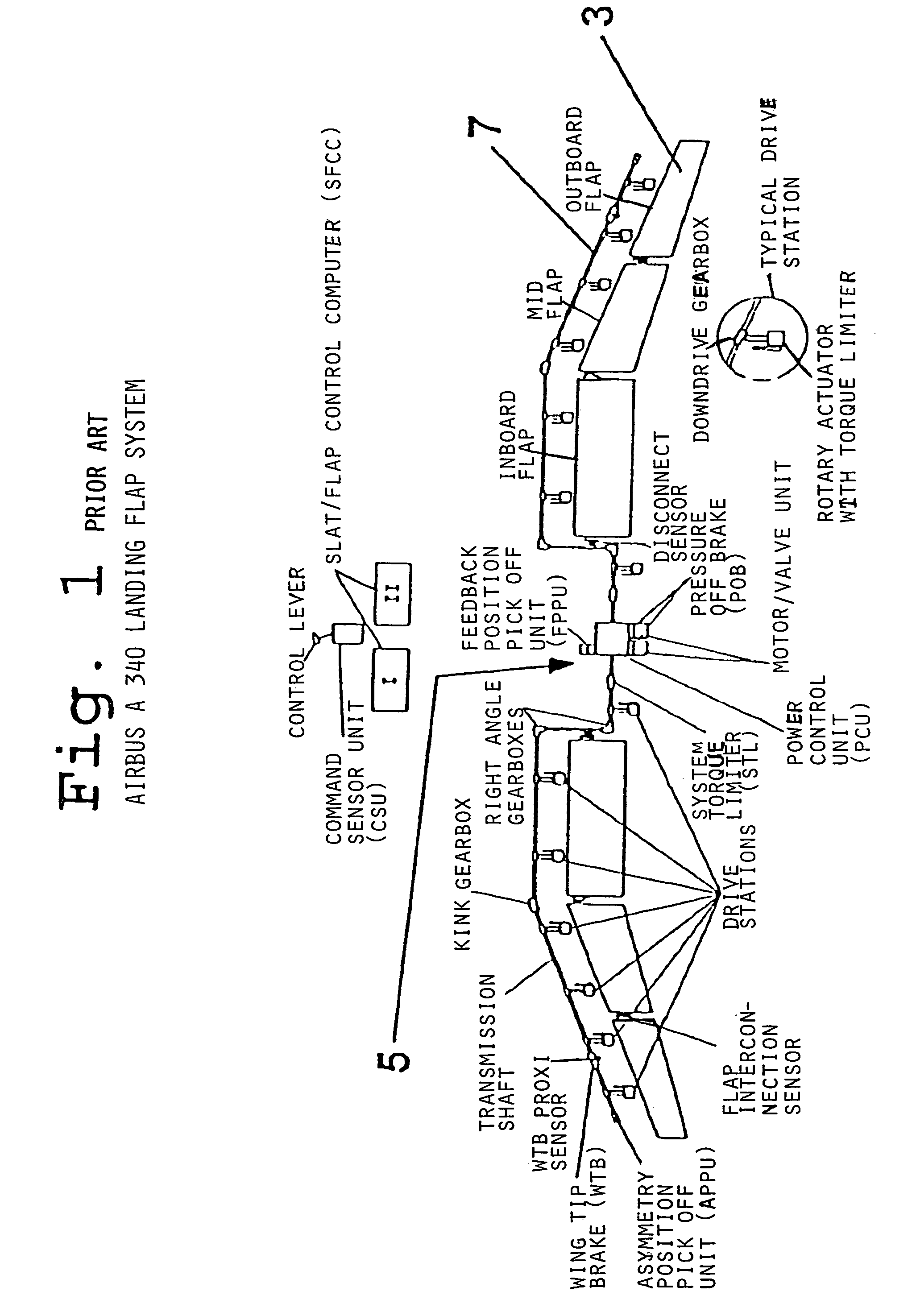
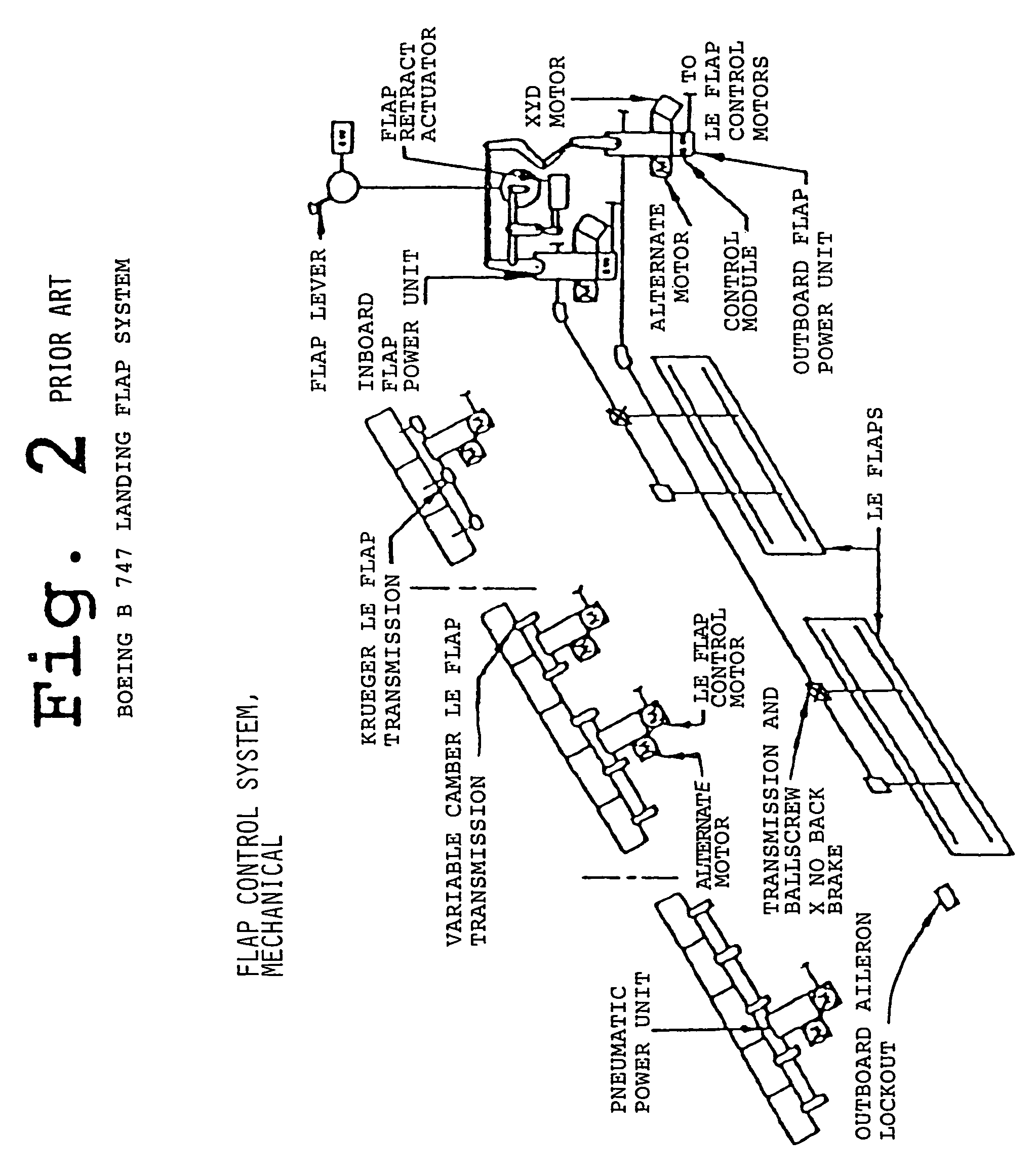
Adaptive flap and slat drive system for aircraft
ActiveUS7048234B2Improve usabilityImprove adaptabilityAircraft stabilisationWith power amplificationEngineeringControl theory
A drive station includes two drives connected via drive transmissions to one or more flaps or slats of a flap / slat group. The drives may be mechanically coupled to a rotational shaft, with a shaft brake arranged thereon. Guide transmissions are connected to the shaft and to respective flaps or slats of the flap / slat group. Alternatively, the two drives are not mechanically coupled, but are merely electrically or electronically synchronized. Each flap / slat group can be actuated individually and independently of the other groups by actuation commands provided by a central control unit connected to the drives and to a flight controller. Position sensors provide actual position feedback. Each flap / slat is driven by two transmissions, namely two drive transmissions, or two guide transmissions, or one drive transmission and one guide transmission. A redundant drive path is ensured if a component fails.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
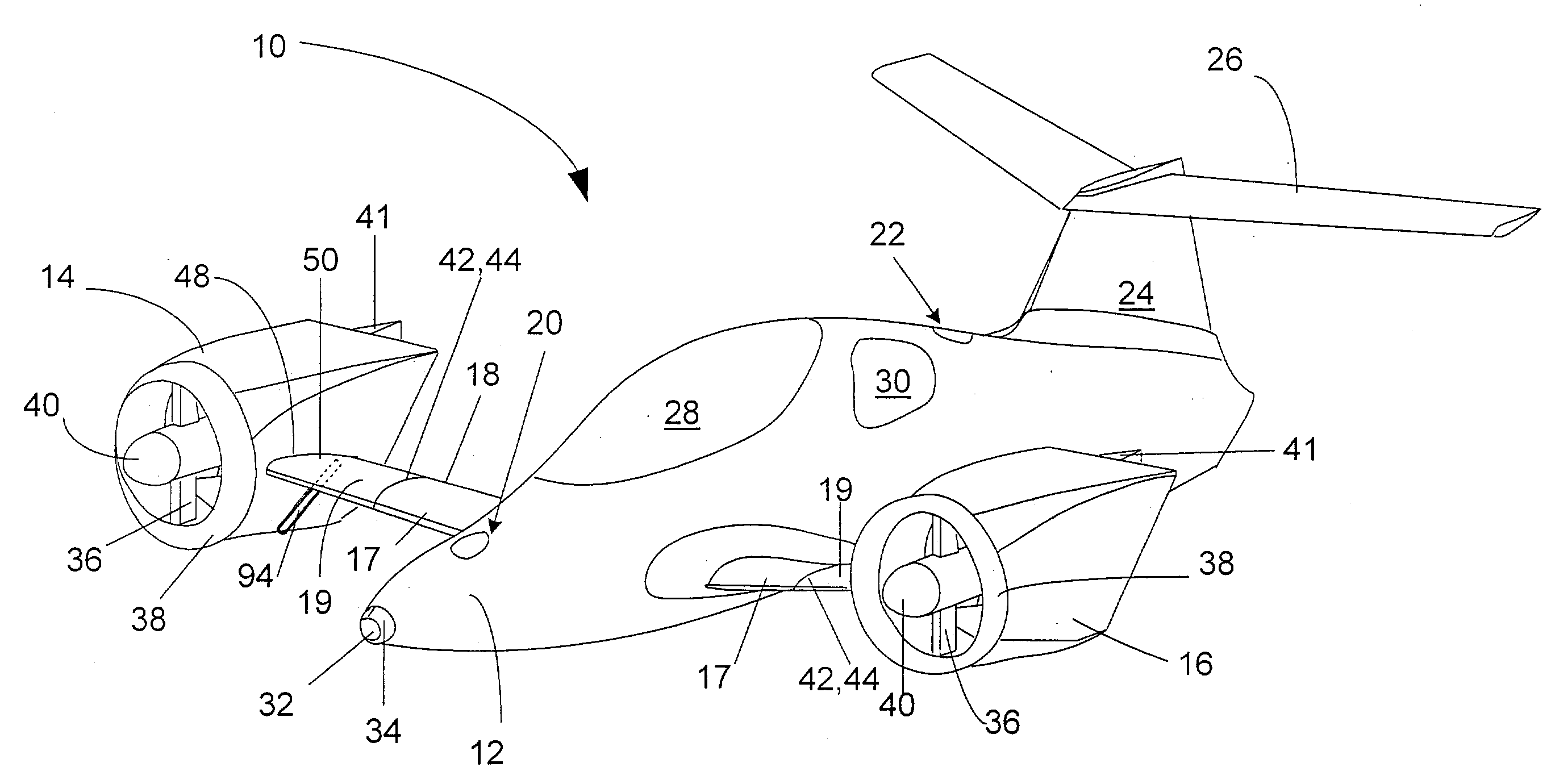
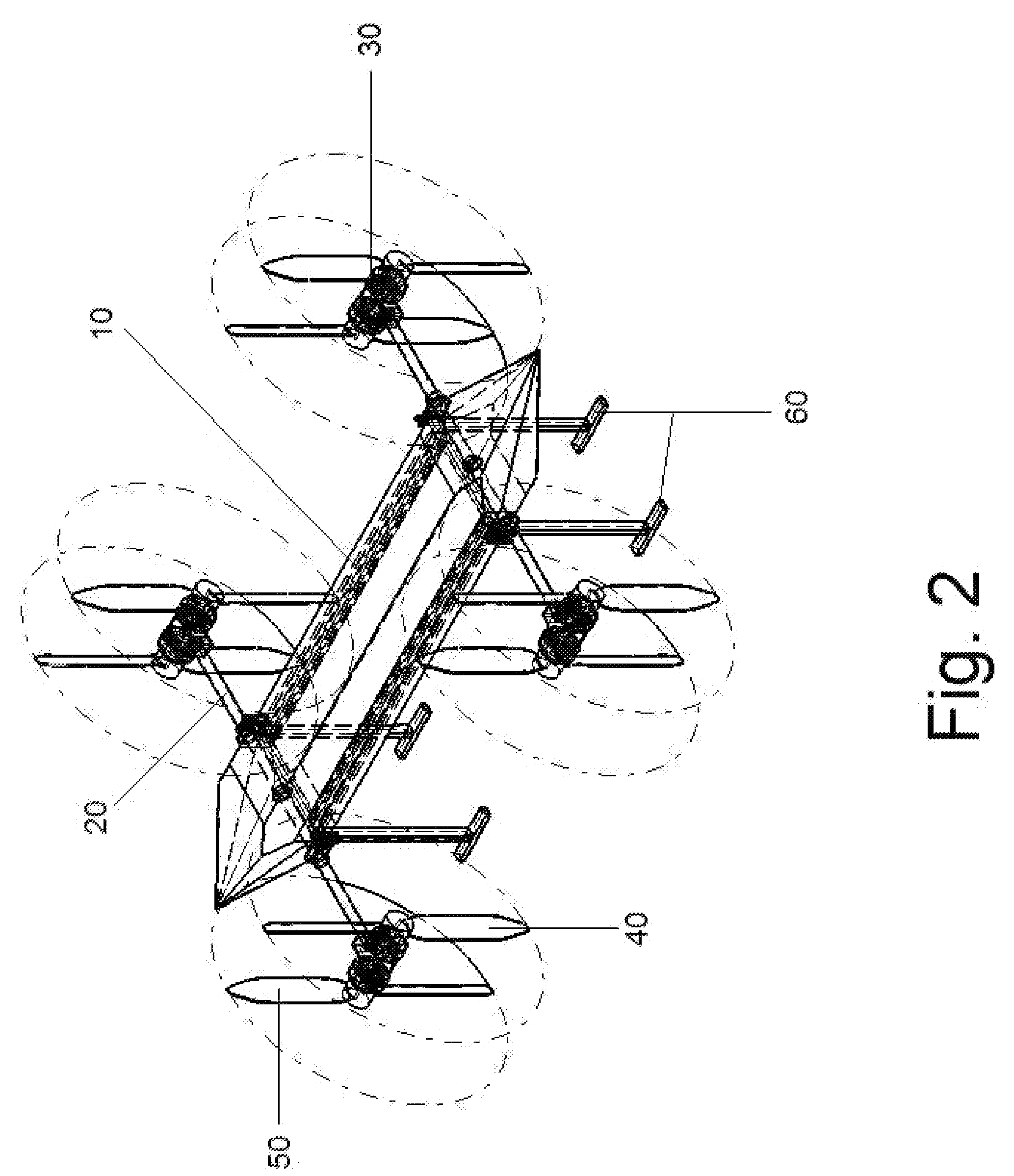
Personal Aircraft
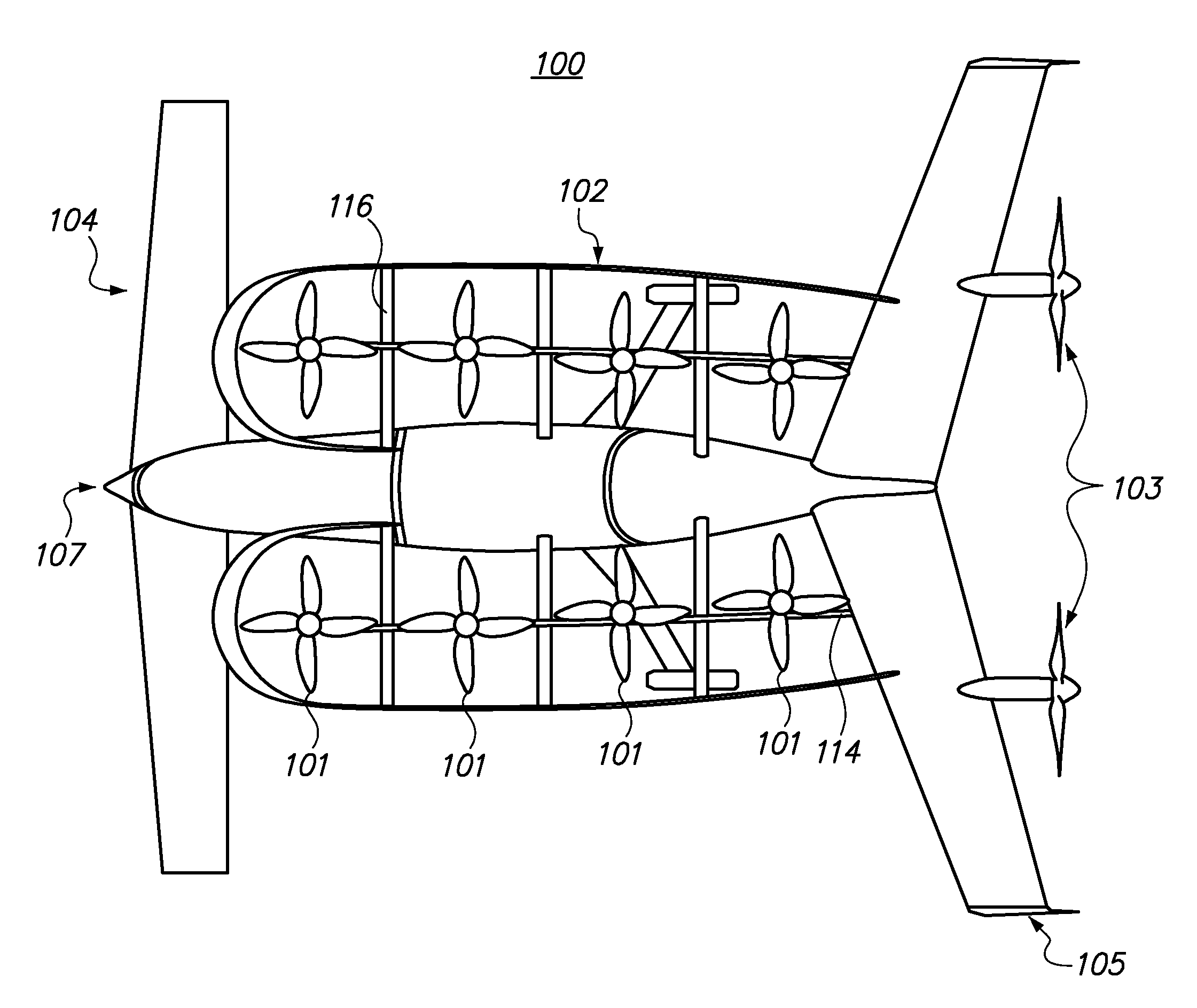
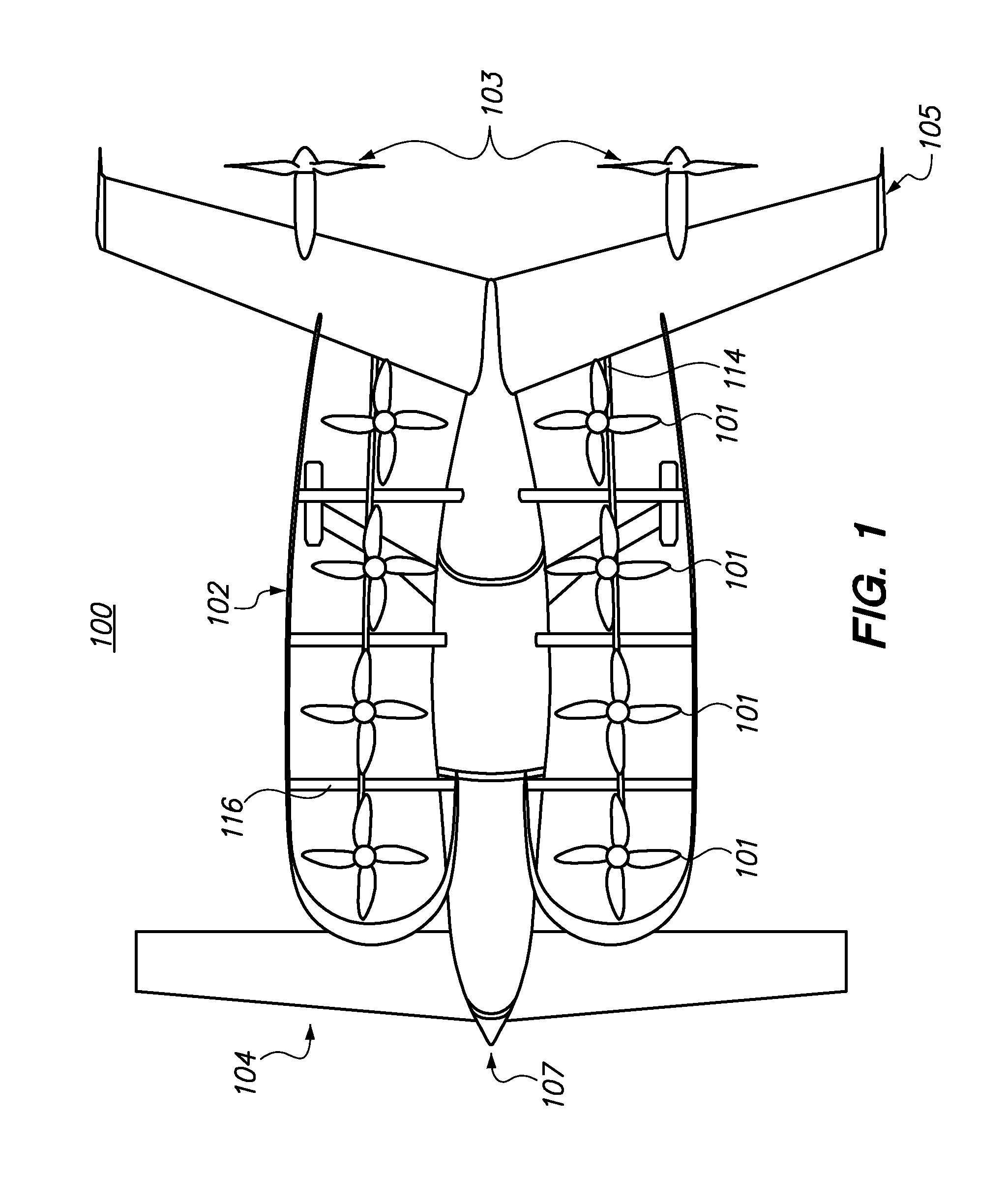
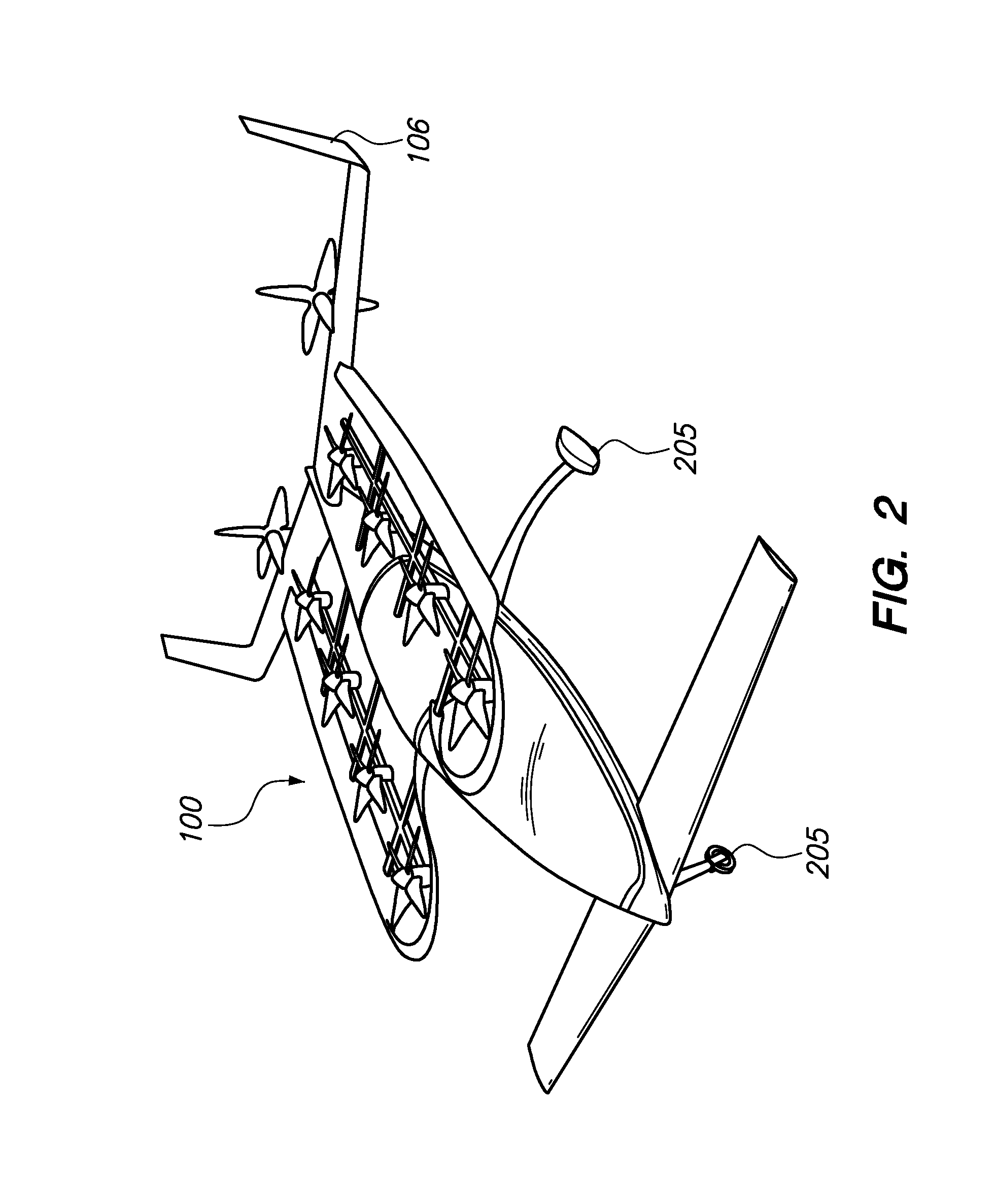
ActiveUS20120012692A1Easy to controlImprove compactnessPower installationsEfficient propulsion technologiesLevel flightPropeller
A safe, quiet, easy to control, efficient, and compact aircraft configuration is enabled through the combination of multiple vertical lift rotors, tandem wings, and forward thrust propellers. The vertical lift rotors, in combination with a front and rear wing, permits a balancing of the center of lift with the center of gravity for both vertical and horizontal flight. This wing and multiple rotor system has the ability to tolerate a relatively large variation of the payload weight for hover, transition, or cruise flight while also providing vertical thrust redundancy. The propulsion system uses multiple lift rotors and forward thrust propellers of a small enough size to be shielded from potential blade strike and provide increased perceived and real safety to the passengers. Using multiple independent rotors provides redundancy and the elimination of single point failure modes that can make the vehicle non-operable in flight.
Owner:WISK AERO LLC
Ducted fan VTOL vehicles
InactiveUS20080054121A1Improve flight characteristicsReduce momentum dragAircraft navigation controlParachutesFlight vehicleFuselage
A VTOL vehicle comprising a fuselage having forward and aft propulsion units, each propulsion unit comprising a propeller located within an open-ended duct wall wherein a forward facing portion of the duct wall of at least the forward propulsion unit is comprised of at least one curved forward barrier mounted for horizontal sliding movement to open the forward facing portion to thereby permit air to flow into the forward facing portion when the VTOL vehicle is in forward flight.
Owner:URBAN AERONAUTICS
Air vehicle having rotor/scissors wing
InactiveUS6669137B1Easy to convertEfficiently and effectively flyJet type power plantsEfficient propulsion technologiesLow speedReverse order
An air vehicle, such as a manned or unmanned air vehicle, has a fuselage, a rotor / scissors wing, and a scissors wing. At helicopter mode, the rotor / scissors wing rotates to make the air vehicle fly like a helicopter to achieve vertical and / or short take-off and landing, hovering, and low speed flying. At airplane mode, the rotor / scissors wing and scissors wing form a scissors wings configuration to maximize the air vehicle's flying efficiency at a wide range of speed and flying conditions by adjusting the yaw angle of the rotor / scissors wing and scissors wing. During the conversion from helicopter mode to airplane mode, the scissors wing generates lift to offload the rotating rotor / scissors wing and eventually the offloaded rotor / scissors wing's rotating speed is slowed and stopped so that the rotor / scissors wing can be locked at a specific position and the conversion can be achieved. In a reverse order, the air vehicle can convert from airplane mode to helicopter mode. Either turbofan or turbojet engine, or turboshaft / turbofan convertible engine can be used to power the air vehicle.
Owner:CHEN ZHUO
Personal aircraft
ActiveUS8393564B2Easy to controlImprove compactnessPower installationsEfficient propulsion technologiesJet aeroplanePropeller
A safe, quiet, easy to control, efficient, and compact aircraft configuration is enabled through the combination of multiple vertical lift rotors, tandem wings, and forward thrust propellers. The vertical lift rotors, in combination with a front and rear wing, permits a balancing of the center of lift with the center of gravity for both vertical and horizontal flight. This wing and multiple rotor system has the ability to tolerate a relatively large variation of the payload weight for hover, transition, or cruise flight while also providing vertical thrust redundancy. The propulsion system uses multiple lift rotors and forward thrust propellers of a small enough size to be shielded from potential blade strike and provide increased perceived and real safety to the passengers. Using multiple independent rotors provides redundancy and the elimination of single point failure modes that can make the vehicle non-operable in flight.
Owner:WISK AERO LLC
Vertical take-off and landing vehicle with increased cruise efficiency
Systems, methods, and devices are provided that combine an advance vehicle configuration, such as an advanced aircraft configuration, with the infusion of electric propulsion, thereby enabling a four times increase in range and endurance while maintaining a full vertical takeoff and landing (“VTOL”) and hover capability for the vehicle. Embodiments may provide vehicles with both VTOL and cruise efficient capabilities without the use of ground infrastructure. An embodiment vehicle may comprise a wing configured to tilt through a range of motion, a first series of electric motors coupled to the wing and each configured to drive an associated wing propeller, a tail configured to tilt through the range of motion, a second series of electric motors coupled to the tail and each configured to drive an associated tail propeller, and an electric propulsion system connected to the first series of electric motors and the second series of electric motors.
Owner:NASA
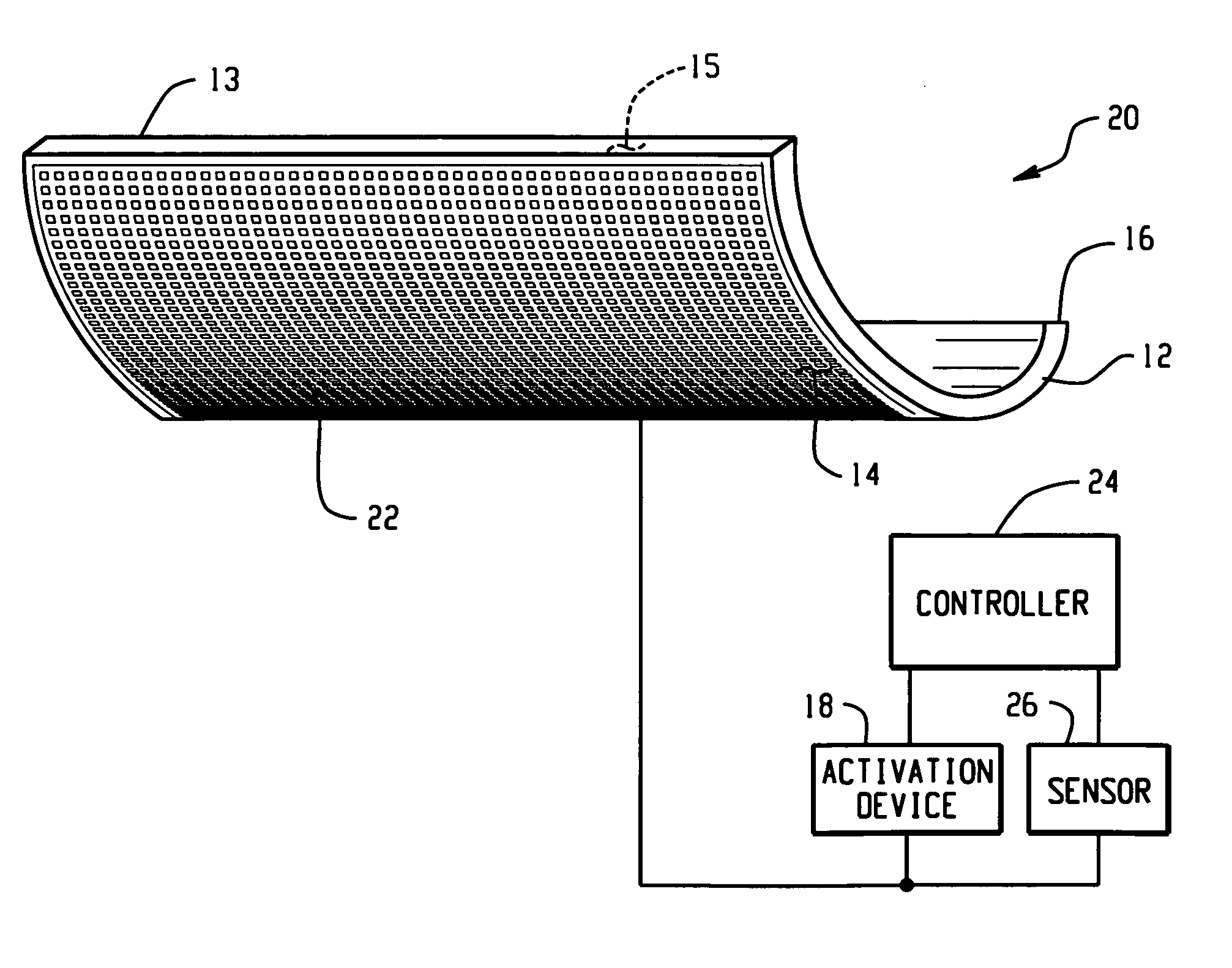
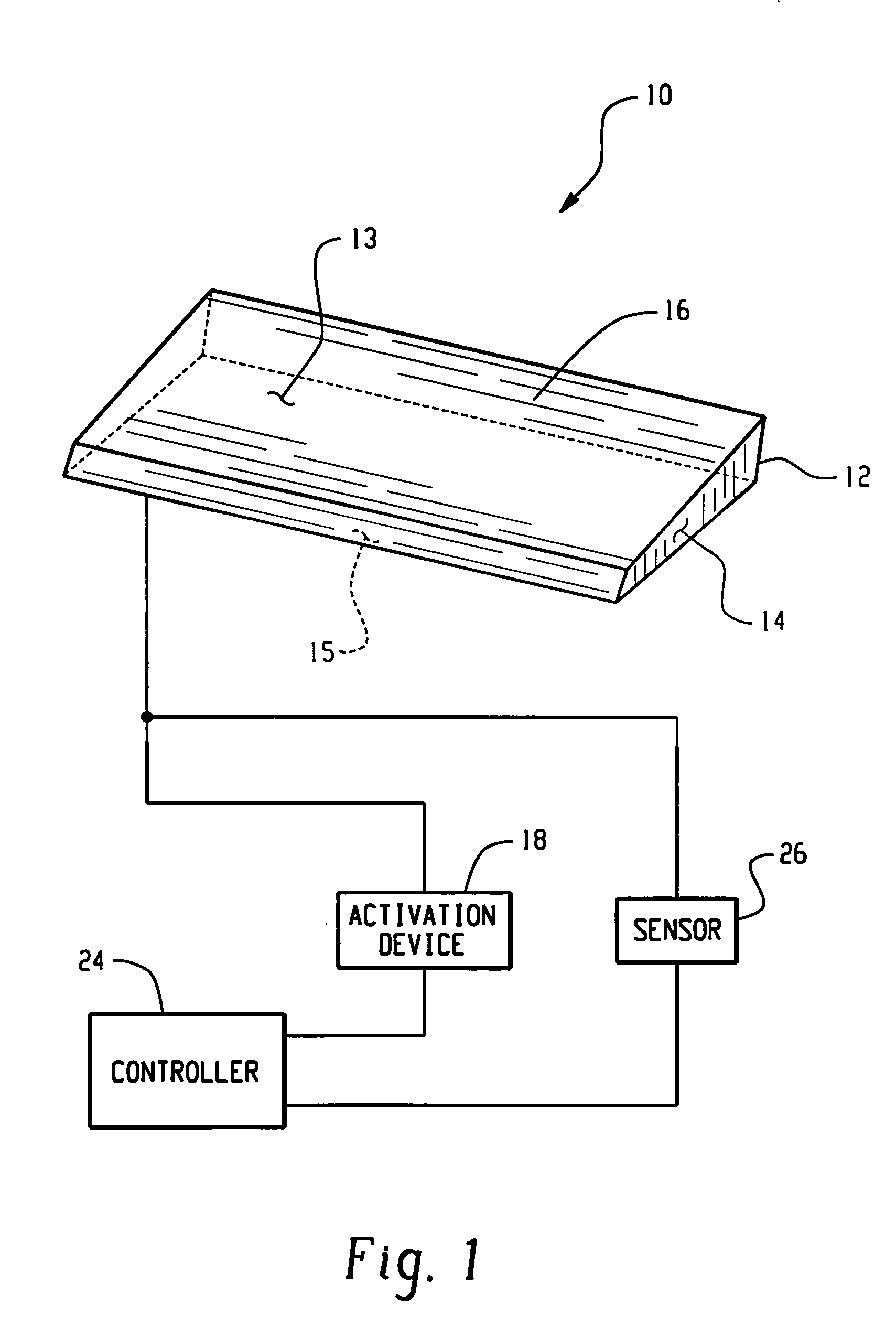
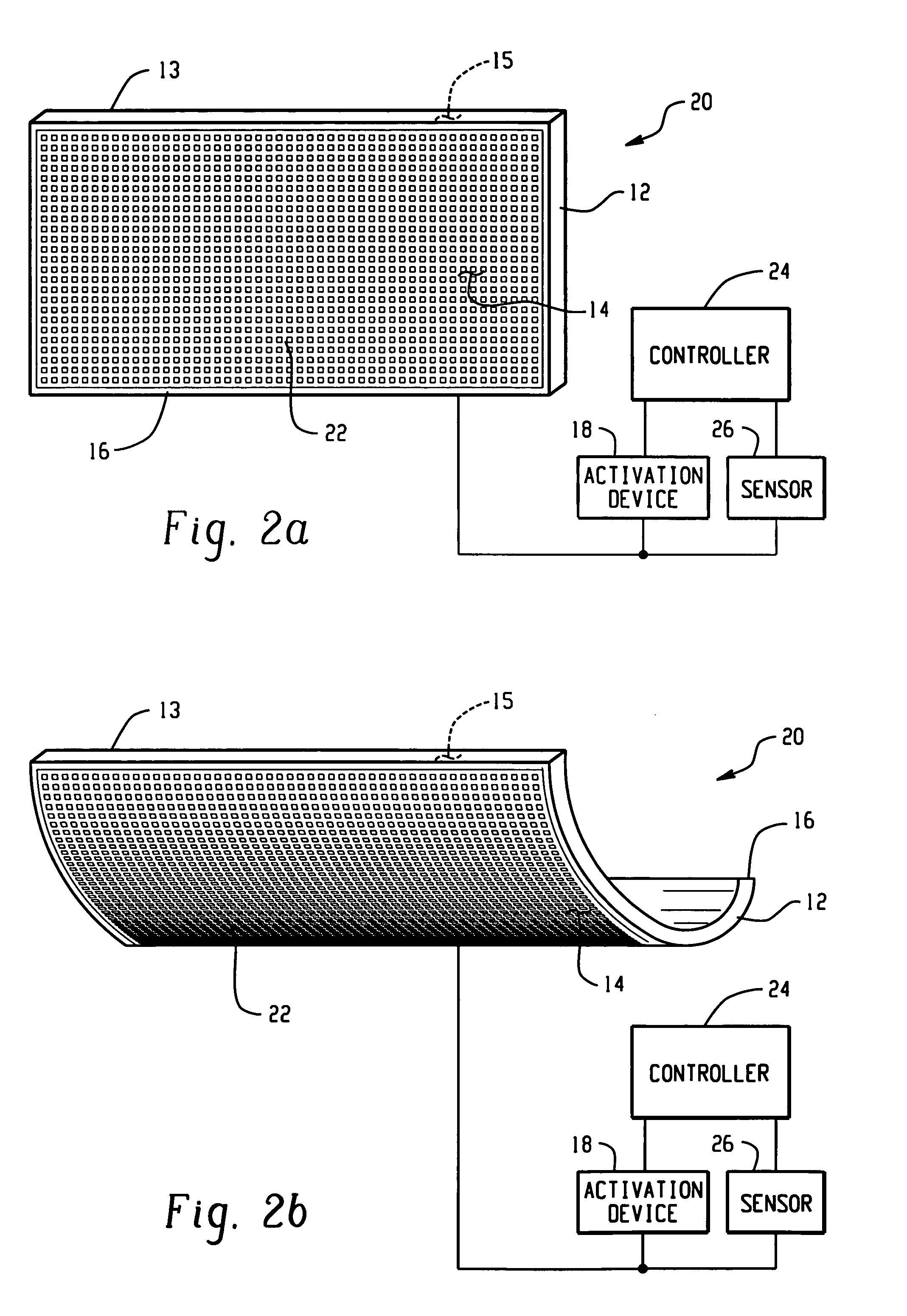
Airflow control devices based on active materials
An airflow control device comprises a body and an active material in operative communication with the body. The active material, such as shape memory material, is operative to change at least one attribute in response to an activation signal. The active material can change its shape, dimensions and / or stiffness producing a change in at least one feature of the airflow control device such as shape, dimension, location, orientation, and / or stiffness to control vehicle airflow to better suit changes in driving conditions such as weather, ground clearance and speed, while reducing maintenance and the level of failure modes. As such, the device reduces vehicle damage due to inadequate ground clearance, while increasing vehicle stability and fuel economy. An activation device, controller and sensors may be employed to further control the change in at least one feature of the airflow control device such as shape, dimension, location, orientation, and / or stiffness of the device. A method for controlling vehicle airflow selectively introduces an activation signal to initiate a change of at least one feature of the device that can be reversed upon discontinuation of the activation signal.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
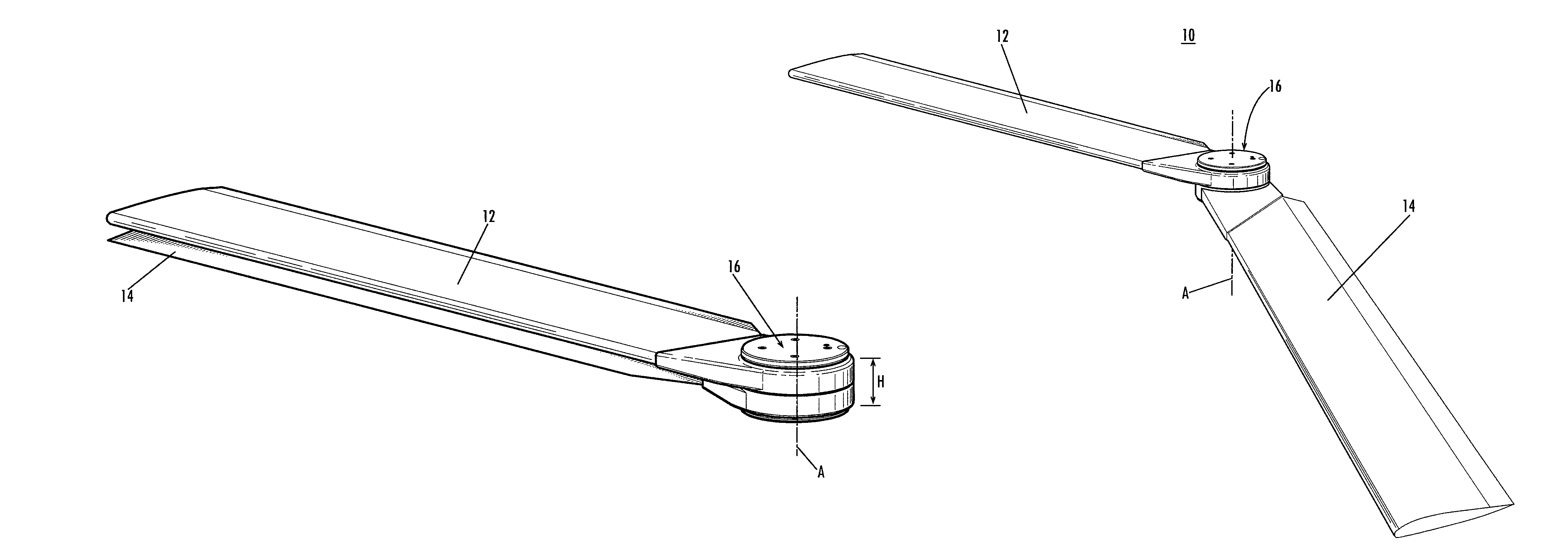
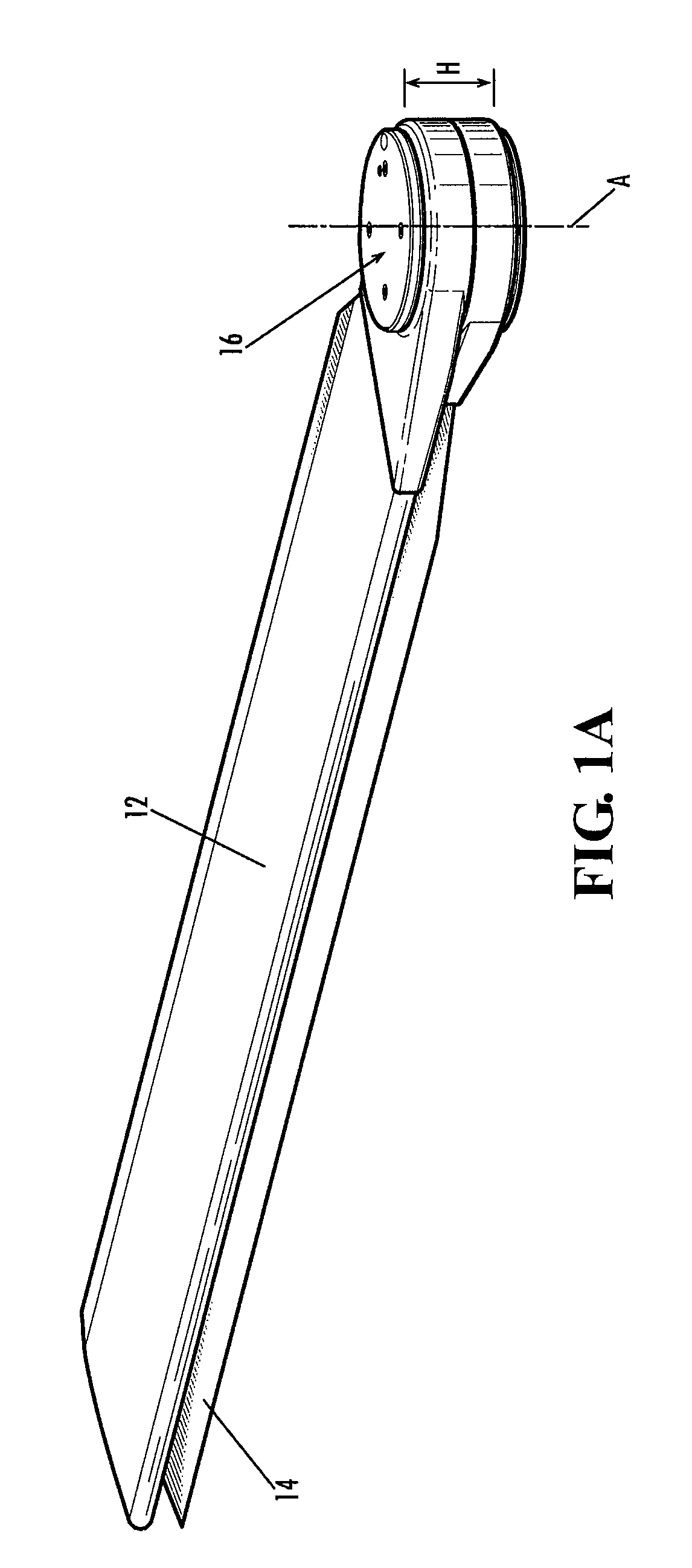
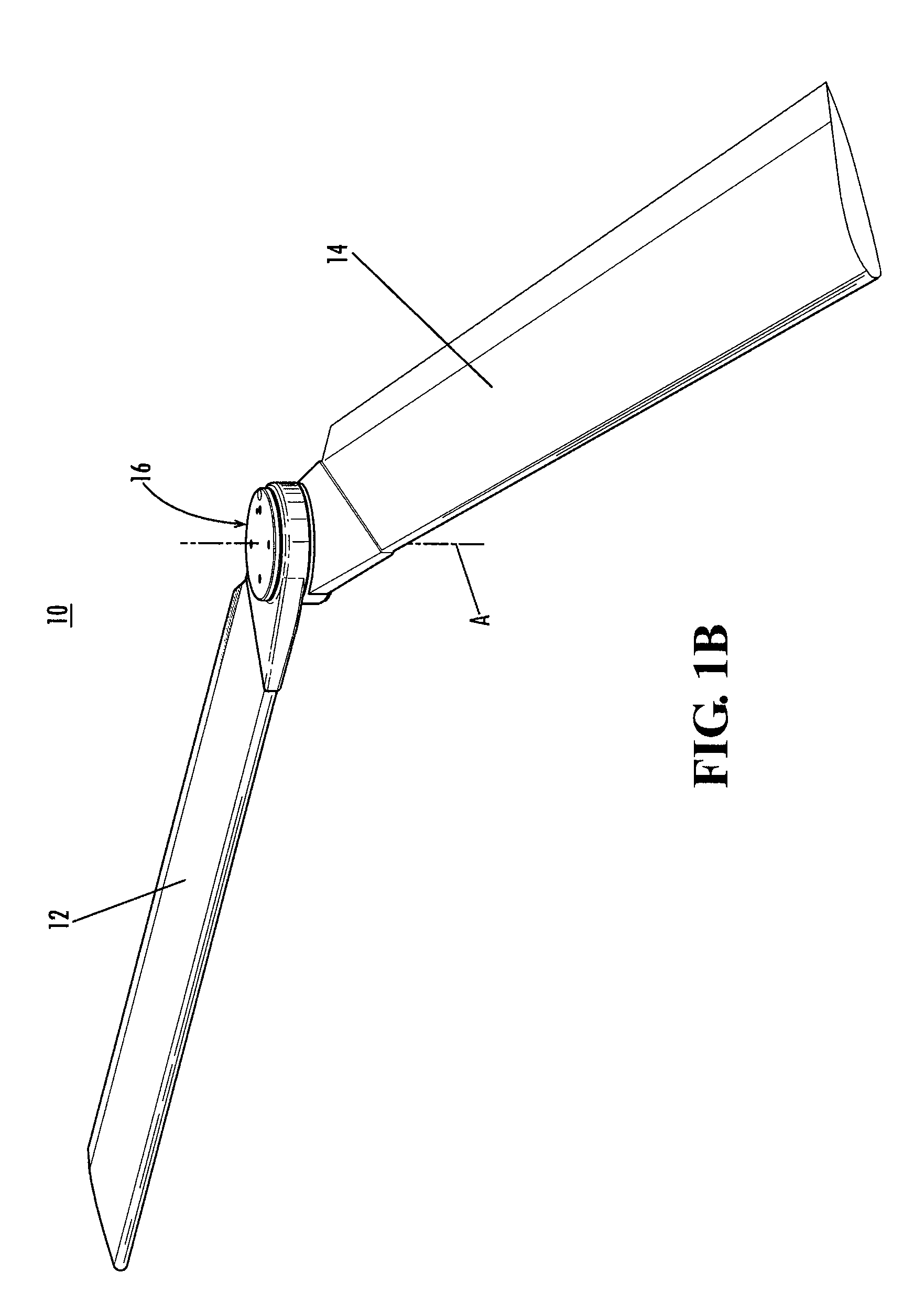
Mechanism for folding, sweeping, and locking vehicle wings about a single pivot
A wing pivot mechanism that is configured to pivot two wings about a single pivot axis of a vehicle, such as an aircraft. The wing pivot mechanism includes a hub, a set of gears positioned at least partially within an interior region of the hub, and two wings that are rotatably connected to the hub. Each wings includes a gear surface extending therefrom. Each gear of the hub assembly engages a gear of a respective wing such that rotation of the gears of the hub assembly causes rotation of the gears of the wings and pivoting of the wings about the single pivot axis in opposite rotational directions between a stowed position and a deployed position. A releasable locking mechanism is provided for locking the wings in a fixed rotational position in both the deployed position and the stowed position.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Load carrying structure having variable flexibility
InactiveUS6182929B1Simple wayReduce stiffnessPropellersPump componentsShape-memory alloyOperating temperature range
A load carrying structure having a selectively rigid or flexible characteristic includes a thermoplastic material (7) having a softening temperature above the operating temperature range of the load carrying structure, and a heating arrangement (8) provided to selectively heat the thermoplastic material to above its softening temperature. During normal operation, the thermoplastic material is in a rigid state and the overall load carrying structure is rigid to the prevailing loads. By activating the heating arrangement to heat the thermoplastic material to at least its softening temperature, the thermoplastic material and therewith the load carrying structure becomes flexible so that it may be deformed to a different configuration by applying a deforming load. Once the desired deformed configuration is achieved, the heating arrangement is deactivated, and the thermoplastic material is allowed to cool below its softening temperature so that it once again becomes rigid and rigidly fixes the new deformed configuration. The deforming force may be applied by any actuating mechanism, or for example by arranging shape memory alloys in connection with the thermoplastic material.
Owner:INST FUER VERBUNDWERKSTOFFE GMBH +1
System, apparatus and method for long endurance vertical takeoff and landing vehicle
InactiveUS20130206921A1High aspect ratioAircraft stabilisationUnmanned aerial vehiclesWing configurationVertical take off and landing
A vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft according to an aspect of the present invention comprises a fuselage, an empennage having an all-moving horizontal stabilizer located at a tail end of the fuselage, a wing having the fuselage positioned approximately halfway between the distal ends of the wing, wherein the wing is configured to transform between a substantially straight wing configuration and a canted wing configuration using a canted hinge located on each side of the fuselage. The VTOL aircraft may further includes one or more retractable pogo supports, wherein a retractable pogo support is configured to deploy from each of the wing's distal ends.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
Ducted fan VTOL vehicles
InactiveUS20070034739A1Improve life characteristicsEasy constructionAircraft navigation controlParachutesTransverse axisPropeller
A vehicle including a fuselage having a longitudinal axis and a transverse axis, two Ducted Fan lift-producing propellers carried by the fuselage on each side of the transverse axis, a pilot's compartment formed in the fuselage between the lift-producing propellers and substantially aligned with one side of the fuselage, a payload bay formed in the fuselage between the lift-producing propellers and opposite the pilot's compartment, and two pusher fans located at the rear of the vehicle. Many variations are described enabling the vehicle to be used not only as a VTOL vehicle, but also as a multi-function utility vehicle for performing many diverse functions including hovercraft and ATV functions. Also described is an Unmanned version of the vehicle. Also described are unique features applicable in any single or multiple ducted fans and VTOL vehicles.
Owner:URBAN AERONAUTICS
Tri-Rotor Aircraft Capable of Vertical Takeoff and Landing and Transitioning to Forward Flight
ActiveUS20160200436A1Increase rangeImprove enduranceAircraft stabilisationUnmanned aerial vehiclesJet aeroplanePropeller
Systems, methods, and devices provide a vehicle, such as an aircraft, with rotors configured to function as a tri-copter for vertical takeoff and landing (“VTOL”) and a fixed-wing vehicle for forward flight. One rotor may be mounted at a front of the vehicle fuselage on a hinged structure controlled by an actuator to tilt from horizontal to vertical positions. Two additional rotors may be mounted on the horizontal surface of the vehicle tail structure with rotor axes oriented vertically to the fuselage. For forward flight of the vehicle, the front rotor may be rotated down such that the front rotor axis may be oriented horizontally along the fuselage and the front rotor may act as a propeller. For vertical flight, the front rotor may be rotated up such that the front rotor axis may be oriented vertically to the fuselage, while the tail rotors may be activated.
Owner:NASA
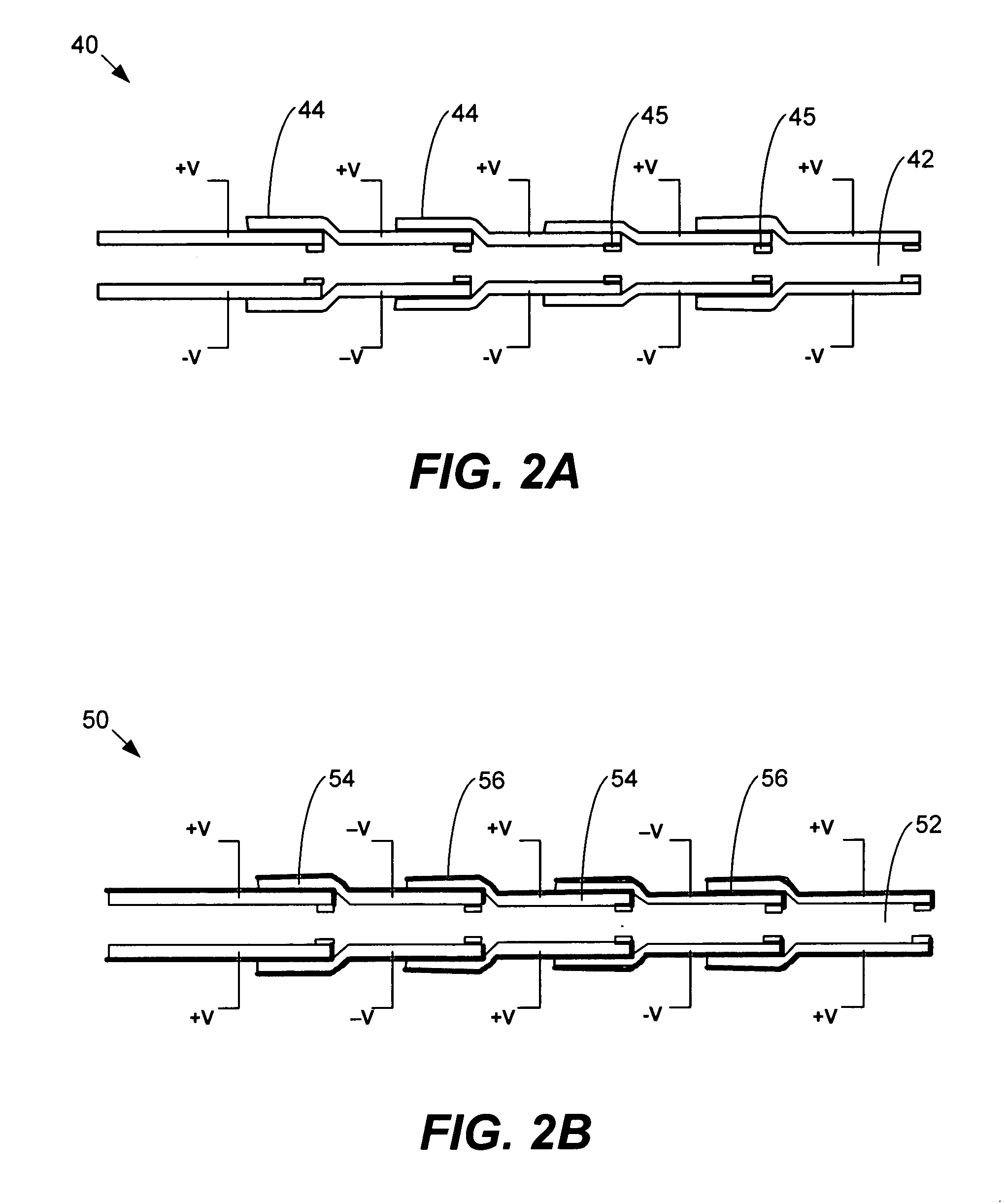
Surface deformation electroactive polymer transducers
InactiveUS20080289952A1Augments out-of-plane deflectionsIncrease awarenessPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEfficient propulsion technologiesPolymeric surfaceVisibility
The present invention provides electroactive polymer transducers that produce out-of-plane deflections. The transducers form a set of surface features based on deflection of an electroactive polymer. The set of surface features may include elevated polymer surface features and / or depressed electrode surface features. Actuation of an active area may produce the polymer deflection that creates one or more surface features. A passive layer may operably connect to a polymer. The passive layer may comprise a thicker and softer material to amplify polymer thickness changes and increase surface feature visibility.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Passive adaptive structures
ActiveUS20110084174A1Reduce quality problemsMinimizing weight penaltyPropellersRotary propellersMorphingAerodynamic drag
Morphing an aerodynamic body's geometry in situ can optimize its aerodynamic properties, increasing range, reducing fuel consumption, and improving many performance parameters. The aerodynamic load exerted on the body by the flow is one such parameter, typically characterized as lift or drag. It is the aim of the present disclosure to teach the use of passive adaptive morphing structures to manage these aerodynamic loads.
Owner:CORNERSTONE RES GROUP
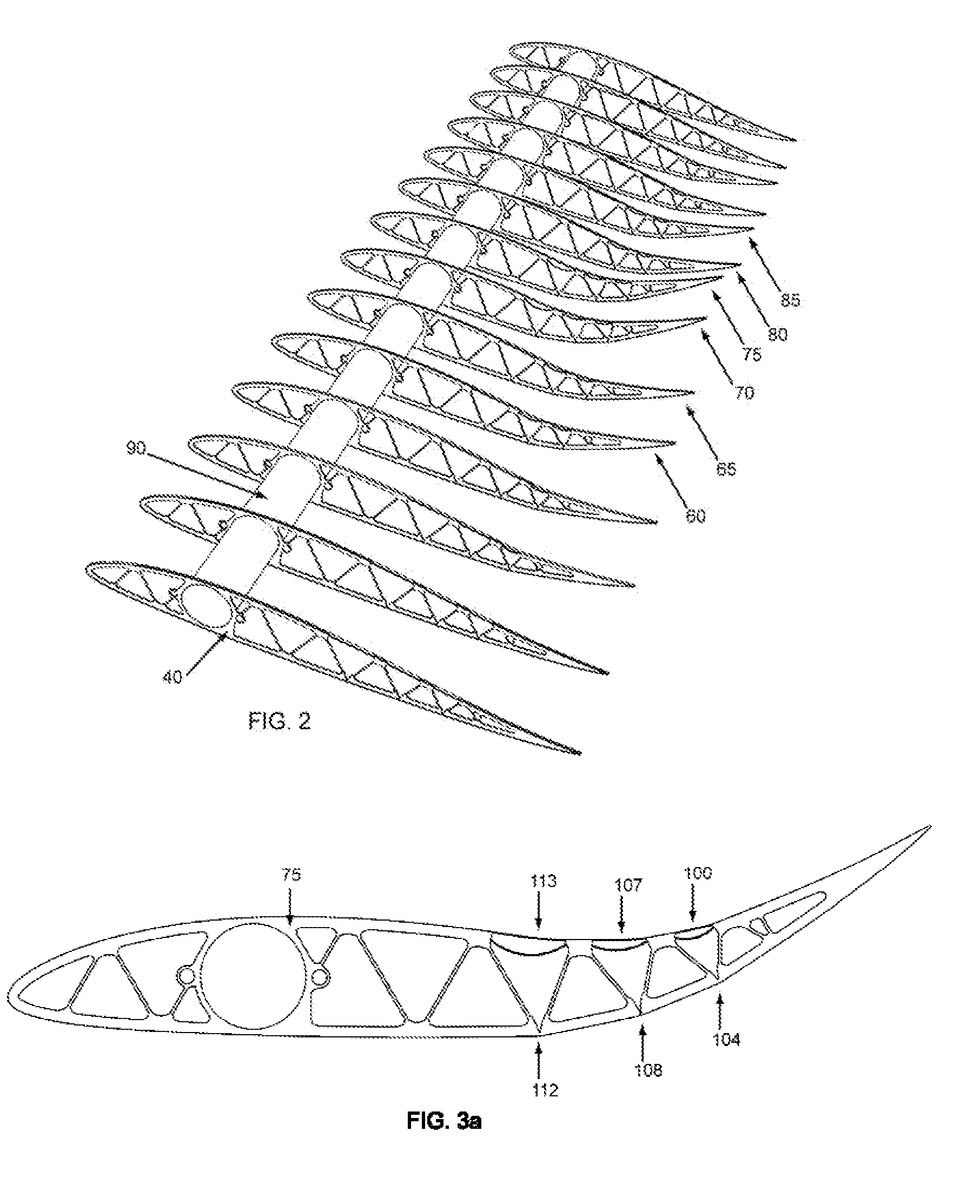
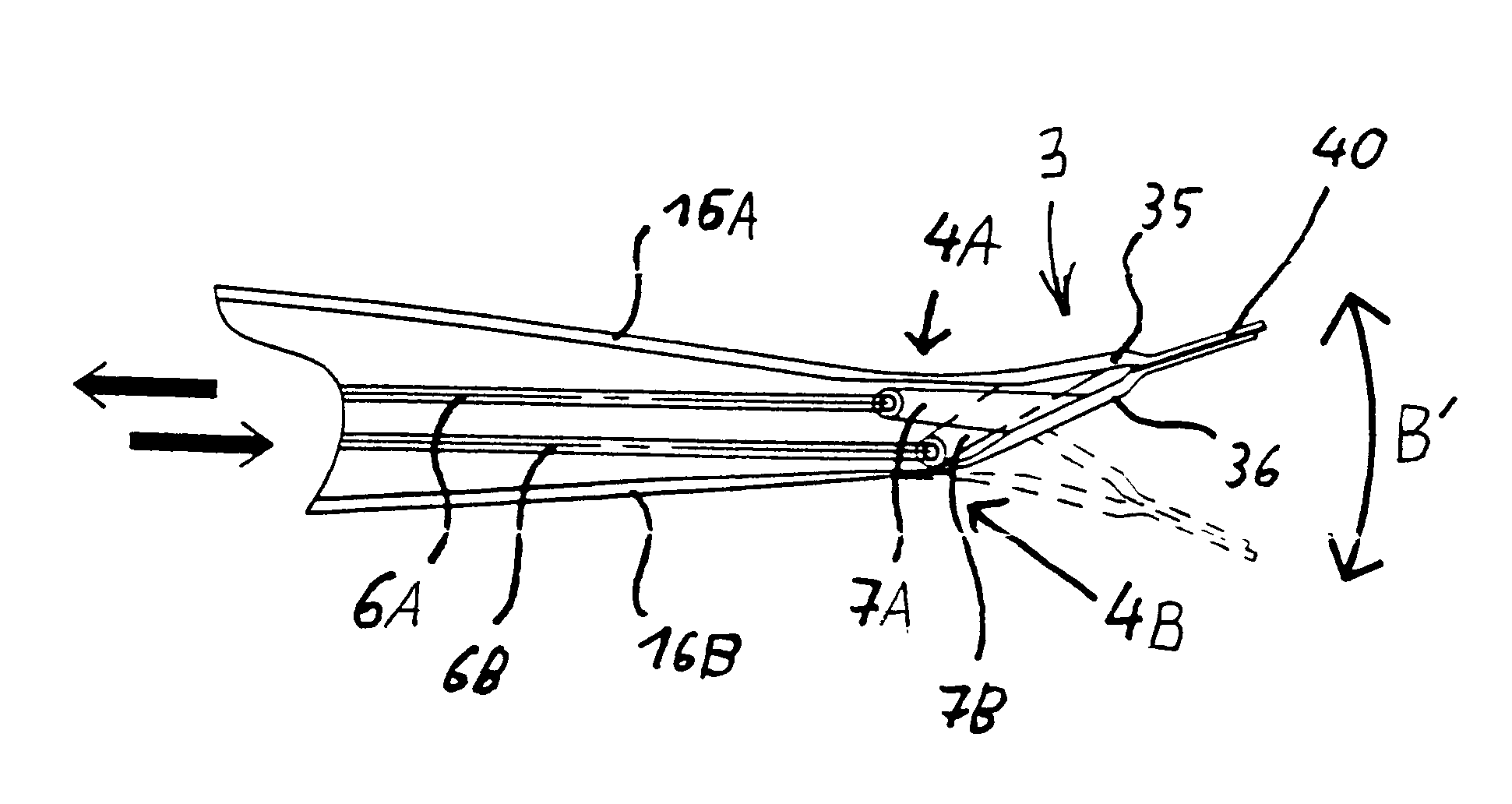
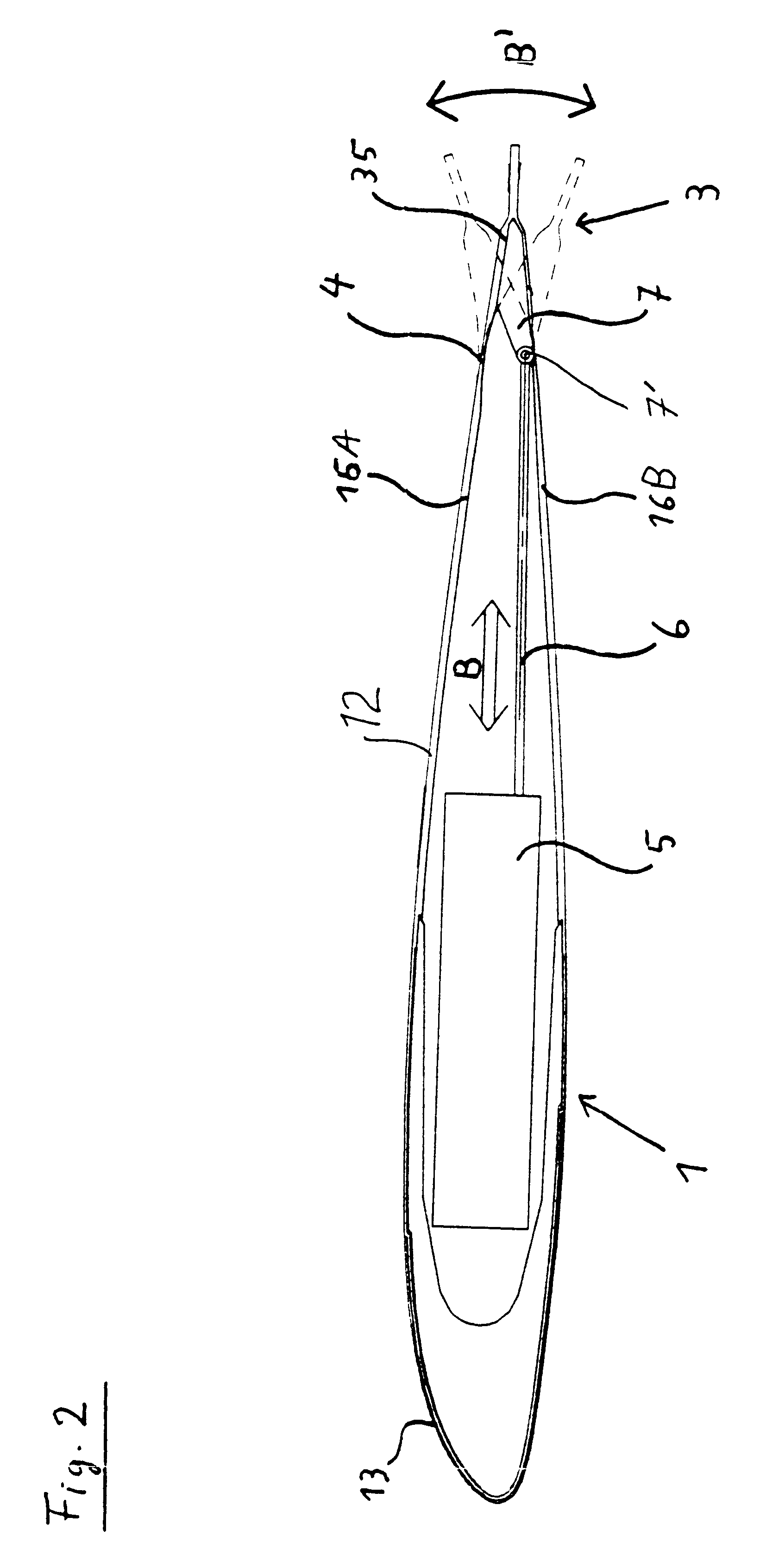
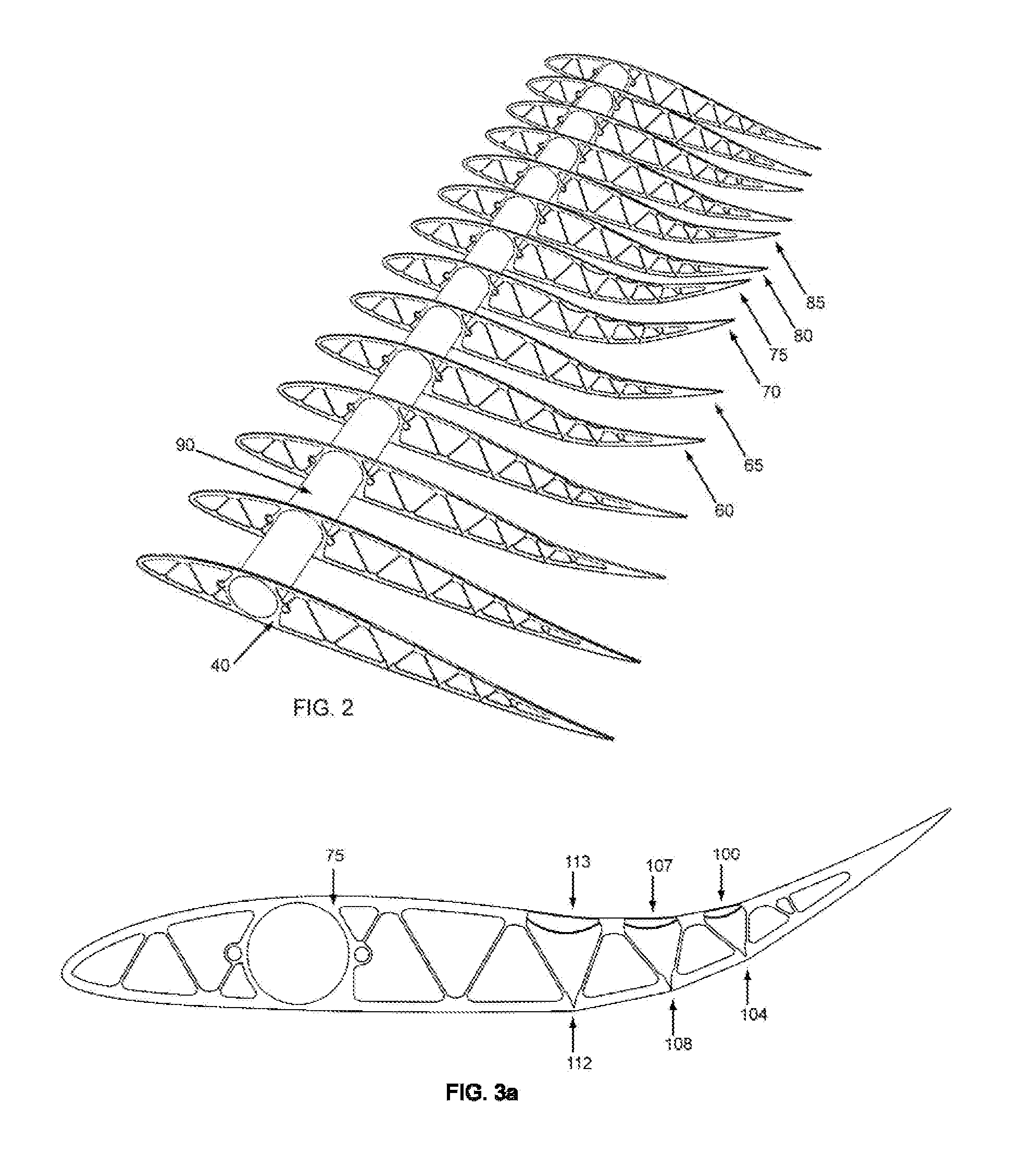
Helicopter rotor blade with a movable flap
InactiveUS6168379B1Durable and wear-resistant flexiblyImprove inspectionPropellersAircraft stabilisationPiezoelectric actuatorsFiber-reinforced composite
A helicopter rotor blade includes a main airfoil body (12) and a movable control flap (3) incorporated in the trailing edge profile of the airfoil body. The flap (3) is movably connected to the main airfoil body (12) by a flexibly bendable junction element (4), and is actuated by a piezoelectric actuator unit (5) via a push / pull rod (6) and a lever arm (7), whereby the control flap is deflected relative to the main airfoil body. The junction element (4) is preferably a continuous integral fiber-reinforced composite component having a flexible bending portion (42) with a reduced thickness in comparison to the adjoining portions, whereby the reinforcing fibers extend continuously through the joint in the direction of the connection between the main airfoil body and the flap.
Owner:AIRBUS HELICOPTERS DEUT GMBH
Passive adaptive structures
ActiveUS20110042524A1Reduce quality problemsMinimizing weight penaltyPropellersControl initiation meansMorphingAerodynamic drag
Morphing an aerodynamic body's geometry in situ can optimize its aerodynamic properties, increasing range, reducing fuel consumption, and improving many performance parameters. The aerodynamic load exerted on the body by the flow is one such parameter, typically characterized as lift or drag. It is the aim of the present disclosure to teach the use of passive adaptive morphing structures to manage these aerodynamic loads.
Owner:CORNERSTONE RES GROUP
Tiltrotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
ActiveUS20160272312A1Improve mobilityUnmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftFuselageVoltage
The invention is directed toward a UAV having a plurality of rotors position on axles extending longitudinally from a fuselage. The axles articulate the rotors from a vertical position, where the rotors provide lift, to a horizontal position, where the rotors provide thrust. The UAV is configured such that the voltage provided to each rotor may be varied to adjust rotor speed, and thus thrust, independently, giving the UAV enhanced maneuverability.
Owner:AERO MACHINING LLC
Rapidly convertible hybrid aircraft and manufacturing method
InactiveUS20110036939A1Easy to convertAvoid many safety and emissionInfluencers by generating vorticesConvertible aircraftsCruise speedControl system
A hybrid fixed wing aircraft converts into a roadworthy vehicle in a matter of seconds therefore operating efficiently in both air and ground transportation systems. The single piece wing is mounted on a skewed pivot that is on the lower portion of the fuselage and is operated by a pushbutton operating system. The aircraft includes telescopic twin boom tail design that when extended allows good pitch stability and damping. The aircraft's wing area may be increased with additional telescopic wing tip segments. This allows an increase in aspect ratio, hence improving efficiency at high loads. This feature will also creates a reduction in induced drag at cruise speed by simply retracting the tips in flight. The vehicle has a unique synchronized control system that switches from flight to ground mode without input from the operator, thereby providing a natural interface for the operator.
Owner:EASTER WILLIAM CRAIG
Mechanism for folding, sweeping, and locking vehicle wings about a single pivot
A wing pivot mechanism that is configured to pivot two wings about a single pivot axis of a vehicle, such as an aircraft. The wing pivot mechanism includes a hub, a set of gears positioned at least partially within an interior region of the hub, and two wings that are rotatably connected to the hub. Each wings includes a gear surface extending therefrom. Each gear of the hub assembly engages a gear of a respective wing such that rotation of the gears of the hub assembly causes rotation of the gears of the wings and pivoting of the wings about the single pivot axis in opposite rotational directions between a stowed position and a deployed position. A releasable locking mechanism is provided for locking the wings in a fixed rotational position in both the deployed position and the stowed position.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
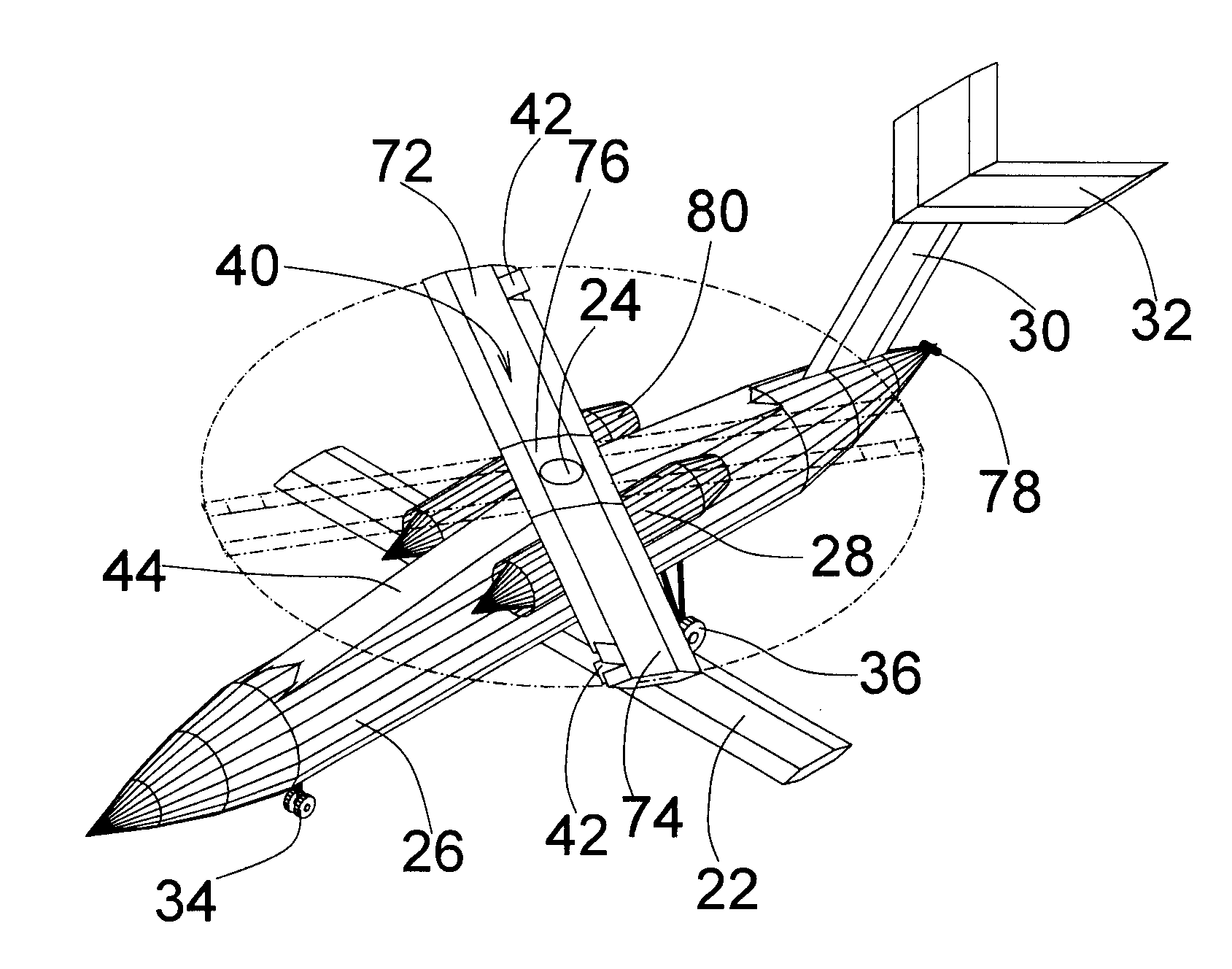
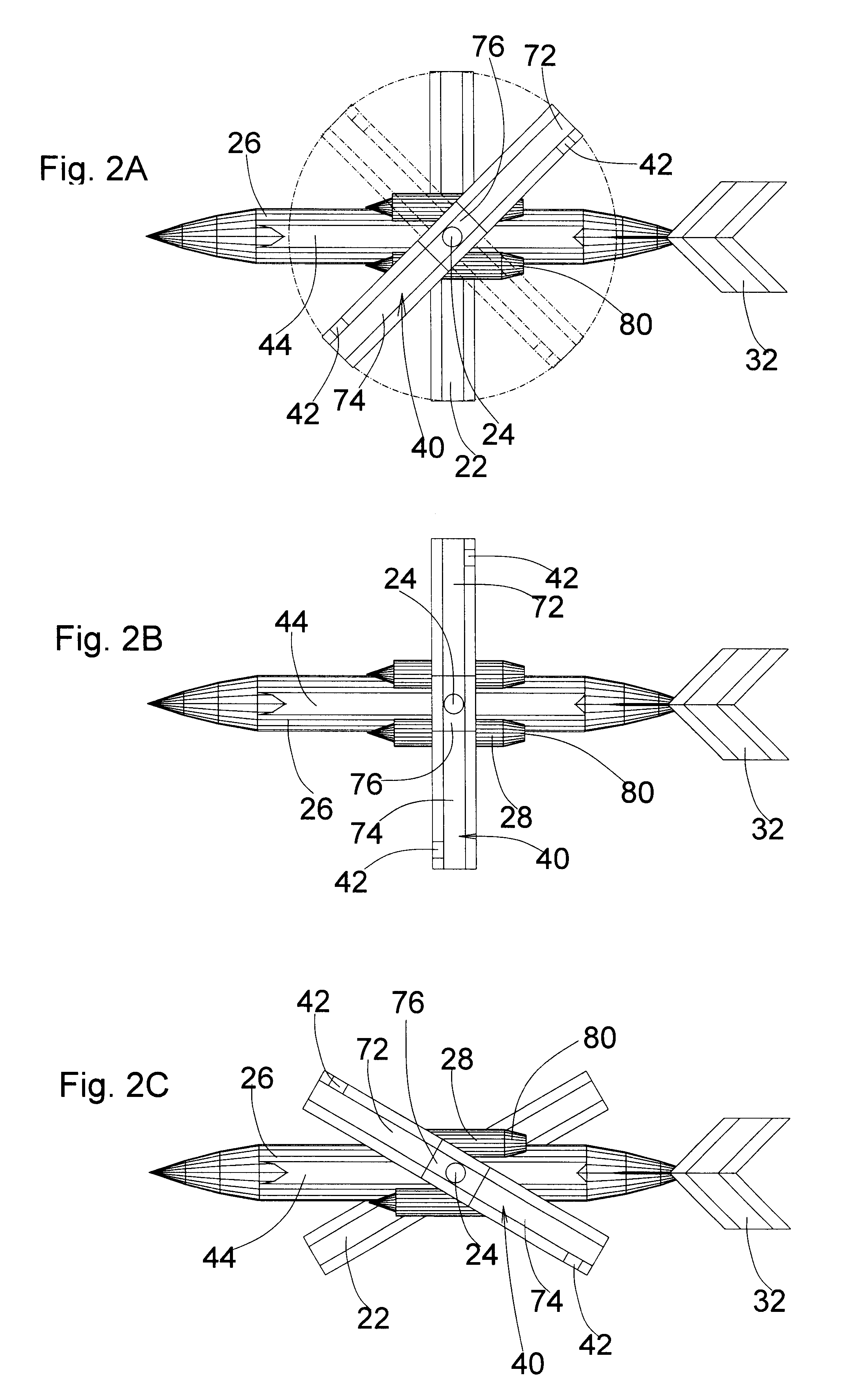
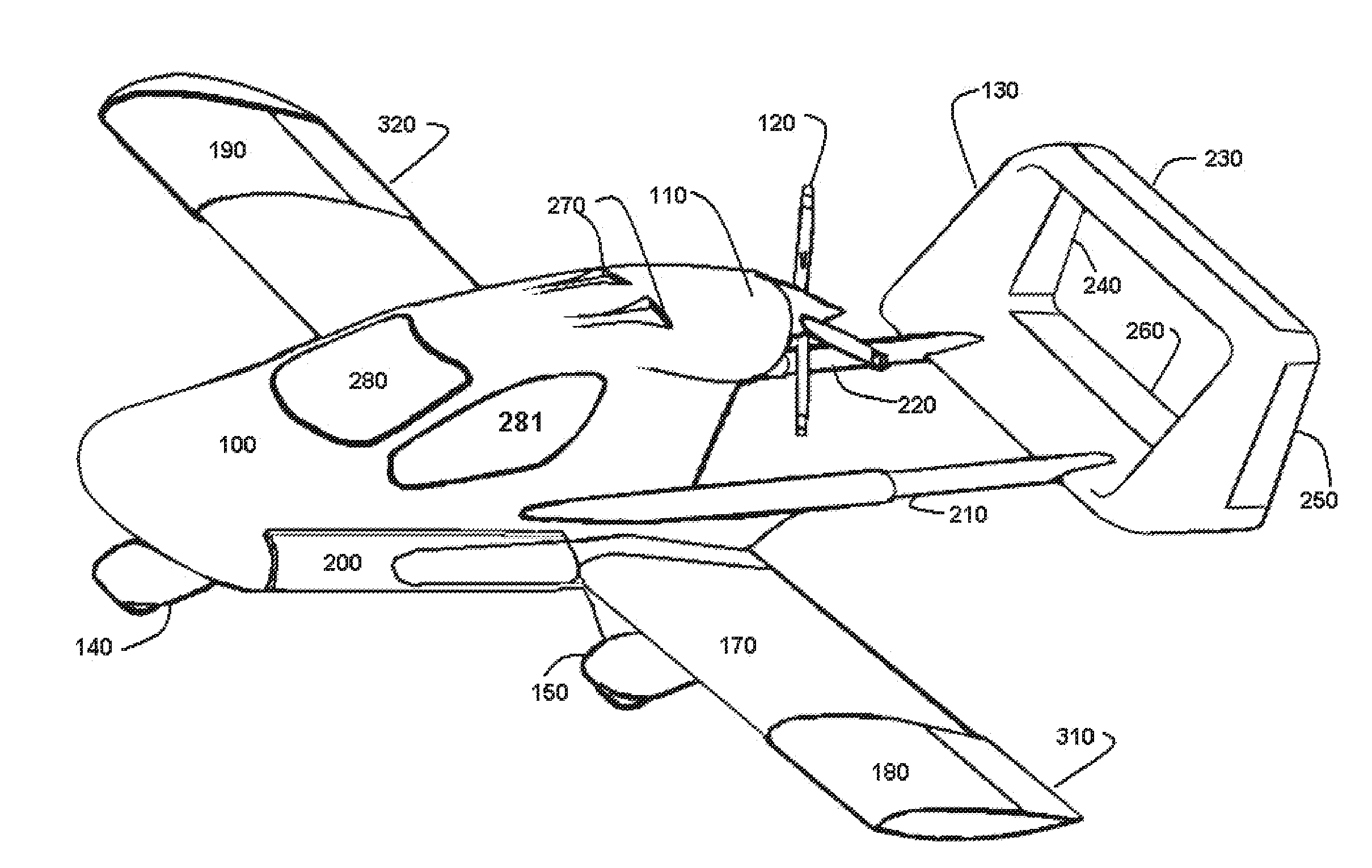
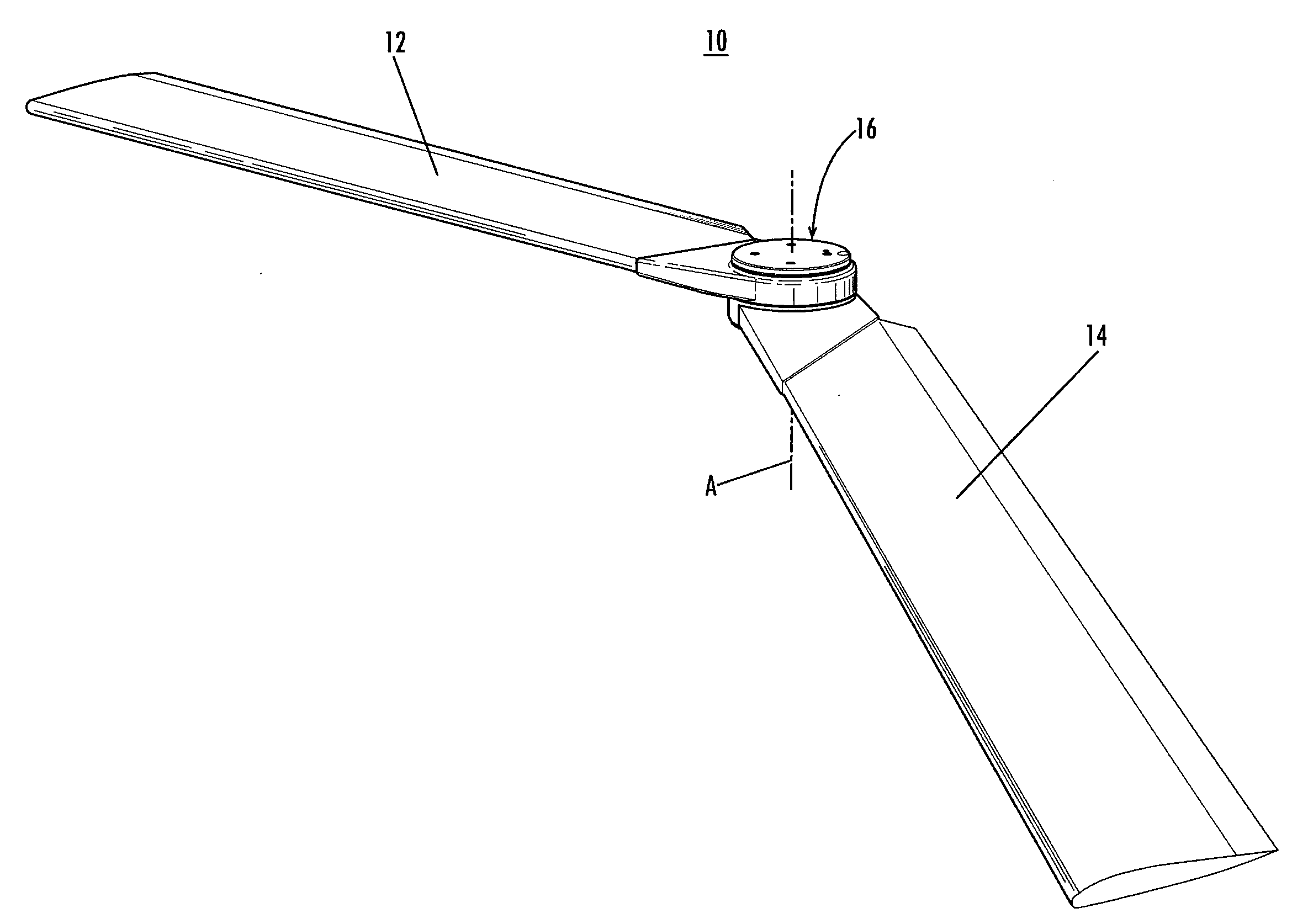
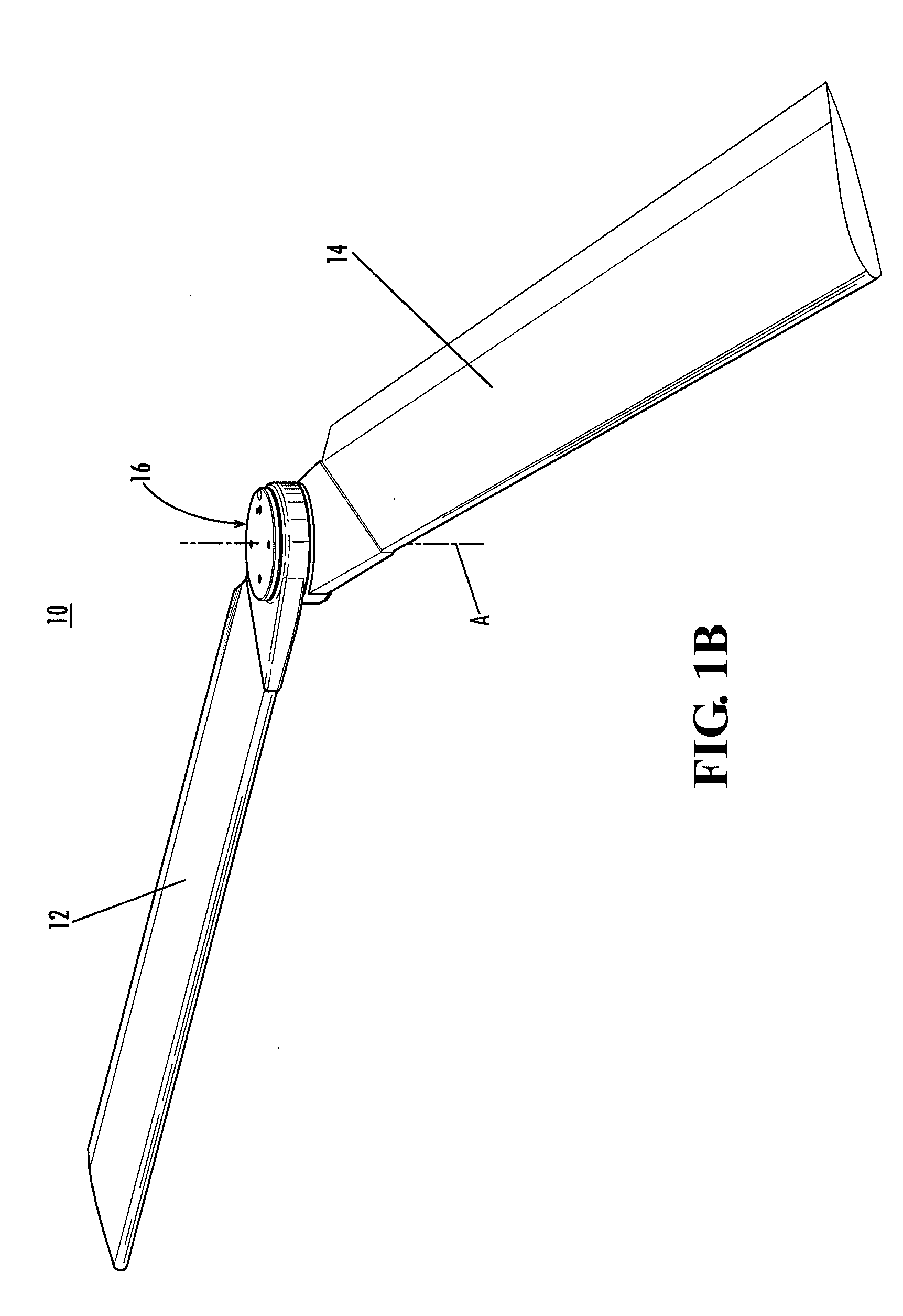
High Performance VTOL Aircraft
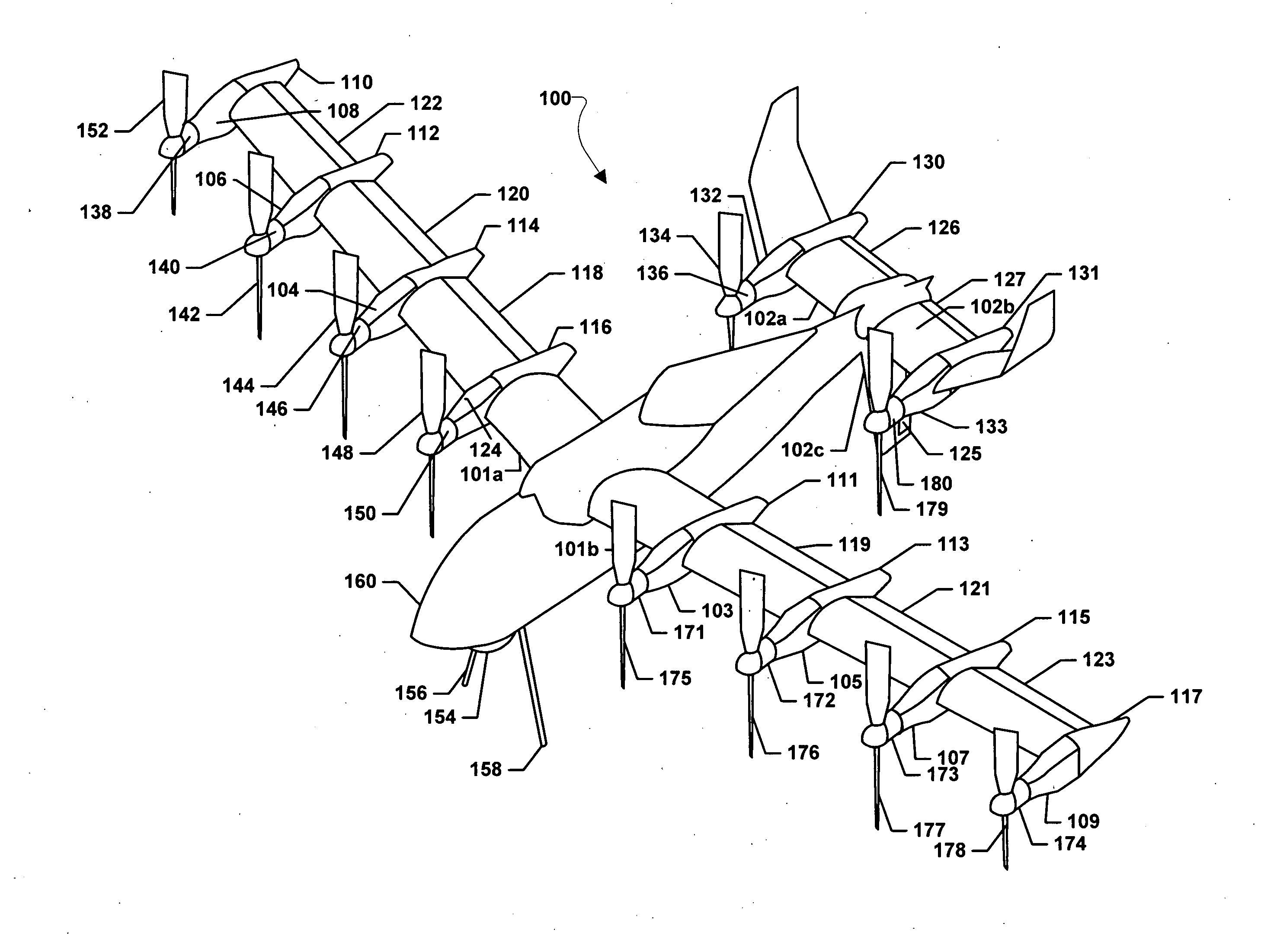
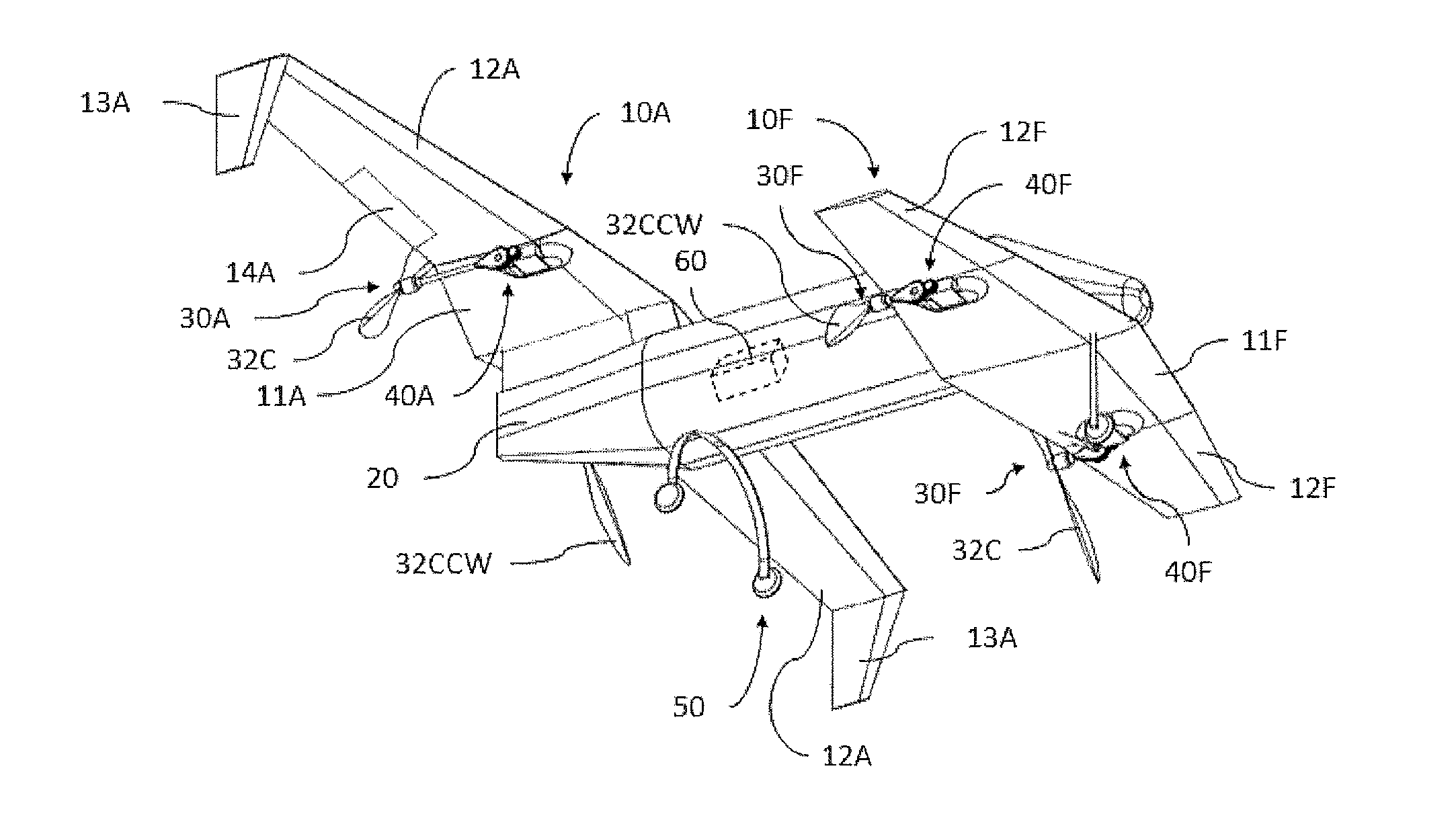
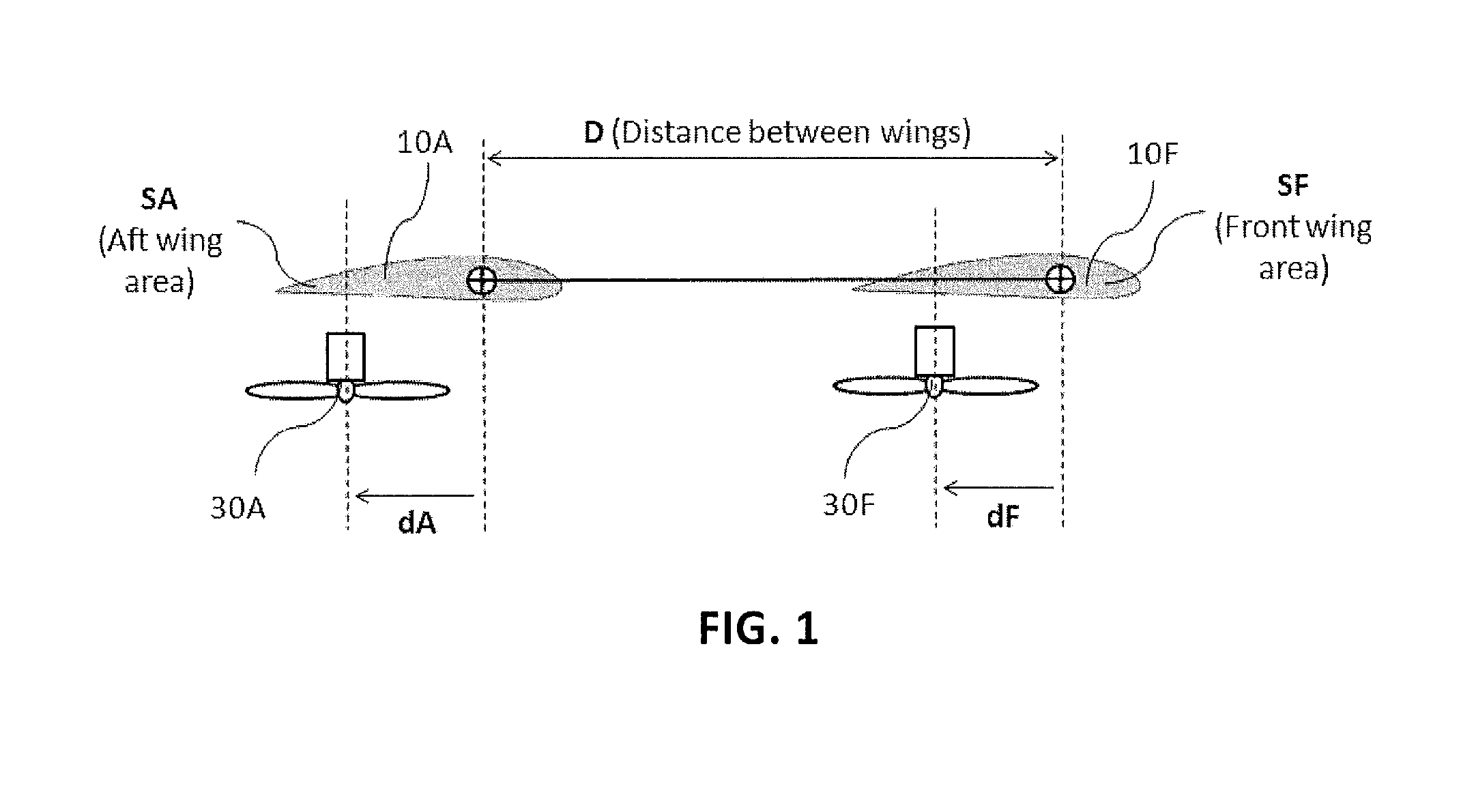
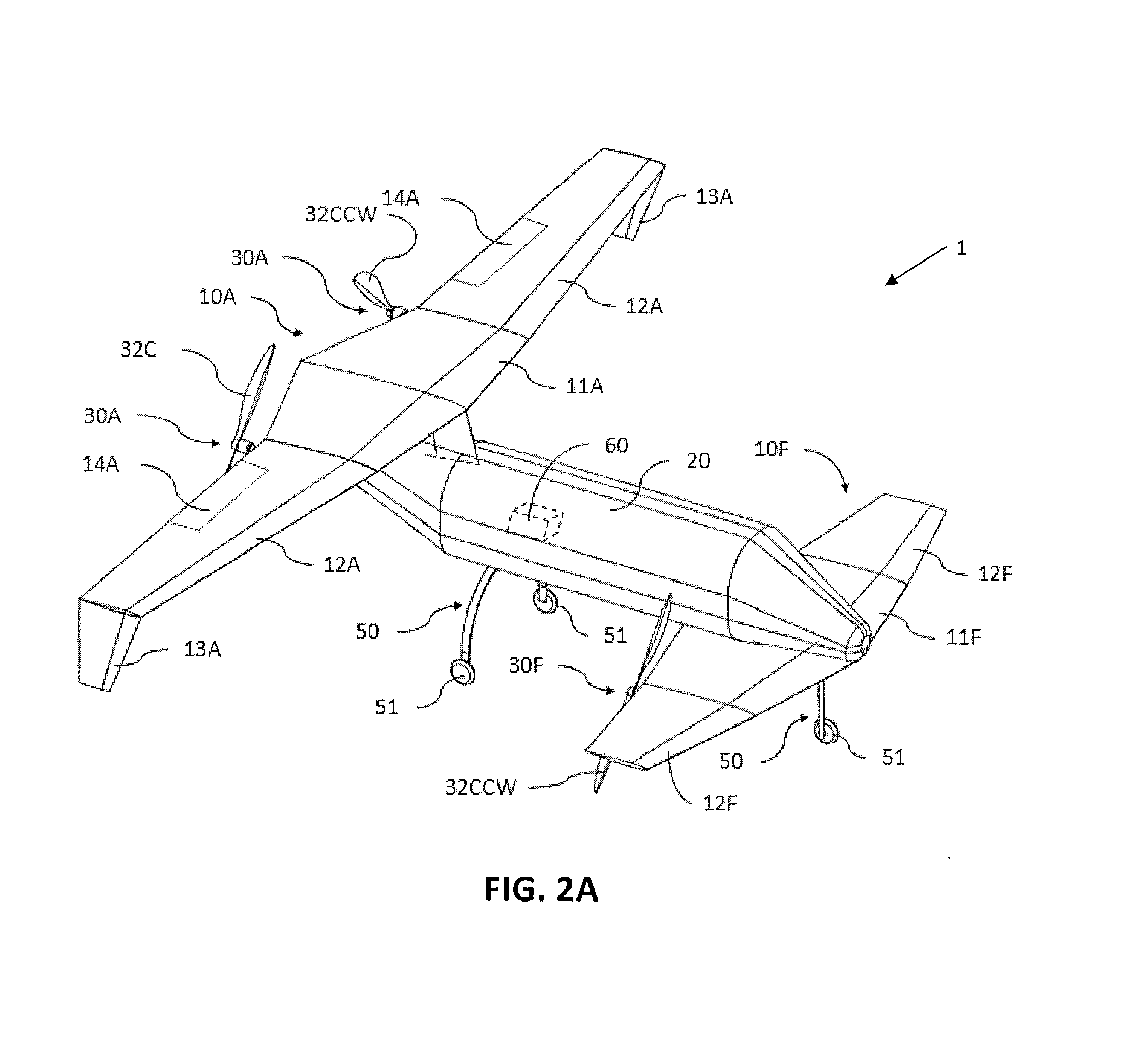
ActiveUS20150344134A1Maximize effective thrustMaximize useRemote controlled aircraftWing adjustmentsJet aeroplaneEngineering
The present disclosure relates to a high performance Vertical Takeoff and Landing (VTOL) aircraft for executing hovering flight, forward flight, and transitioning between the two in a stable and efficient manner. The VTOL aircraft provides a highly stable, controllable and efficient VTOL aircraft. The preferred comprises: (1) a pusher propeller configuration with strategic placement which maximizes the effective use of thrust, (2) four propellers which allow for the highly-controllable and mechanically simple control methods used in multirotor aircraft, (3) electric motors which create mechanically simple, lightweight and reliable operation, (4) and a tandem wing configuration which is stable, controllable and efficient in both hovering and forward flight. The VTOL aircraft is capable of full runway, short runway or vertical takeoffs or landings, having unobstructed forward view for camera and sensor placement; and providing a compact, mechanically simple and low-maintenance VTOL aircraft design.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Cellular support structures used for controlled actuation of fluid contact surfaces
InactiveUS20080035788A1Aircraft stabilisationWithout power ampliicationHoneycomb likeBiomedical engineering
An assembly for controlling a vehicle, including a fluid contact surface constructed and arranged to act against a fluid passing over the fluid contact surface; and a support structure coupled to the fluid contact surface. The support structure is constructed and arranged to expand or contract between a first position and a second position, such that a first dimension of the support structure changes during movement of the support structure between the first position and the second position, while a second dimension of the support structure remains substantially constant during the movement of the support structure between the first position and the second position.
Owner:INNOVITAL LLC +2
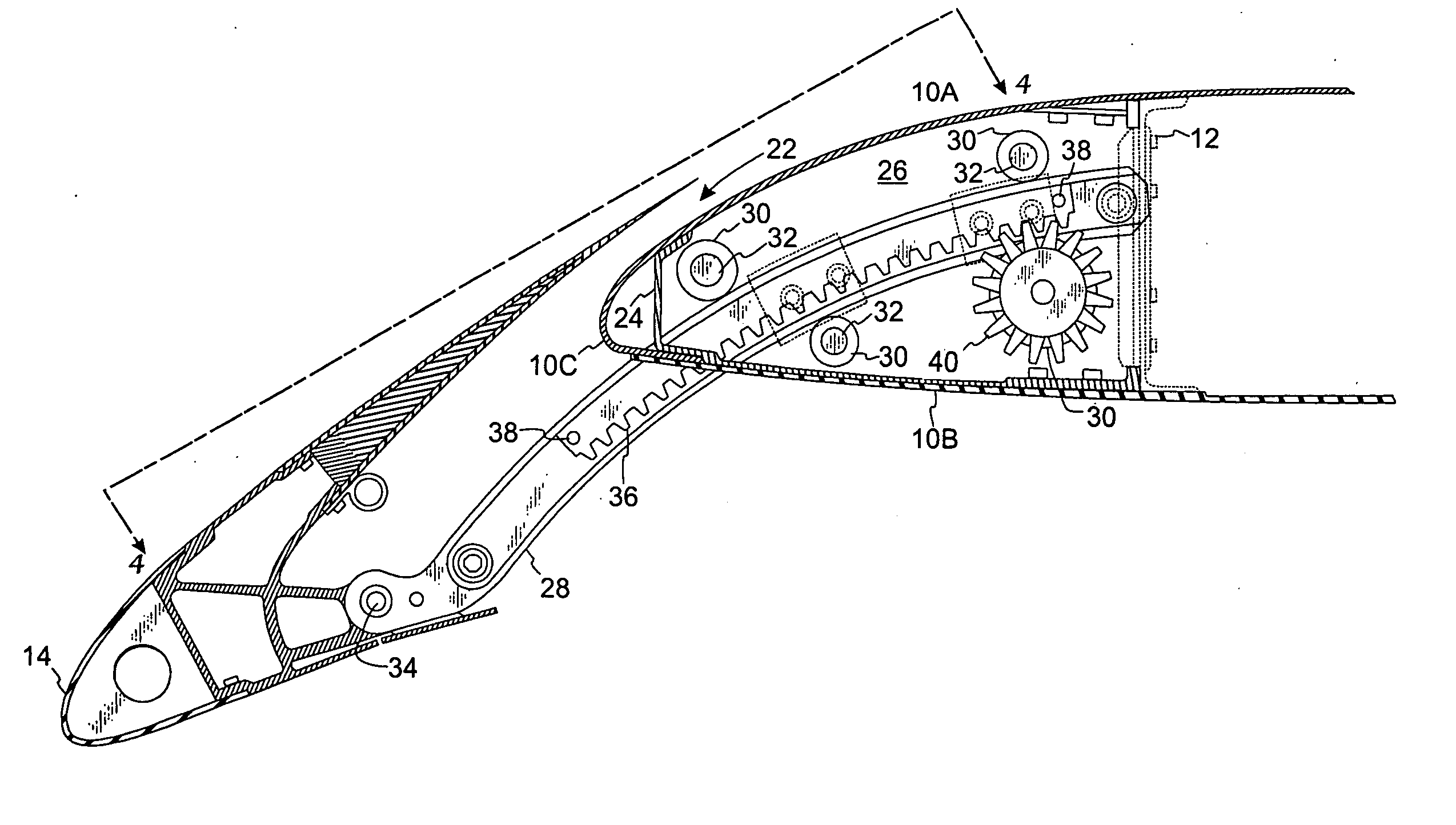
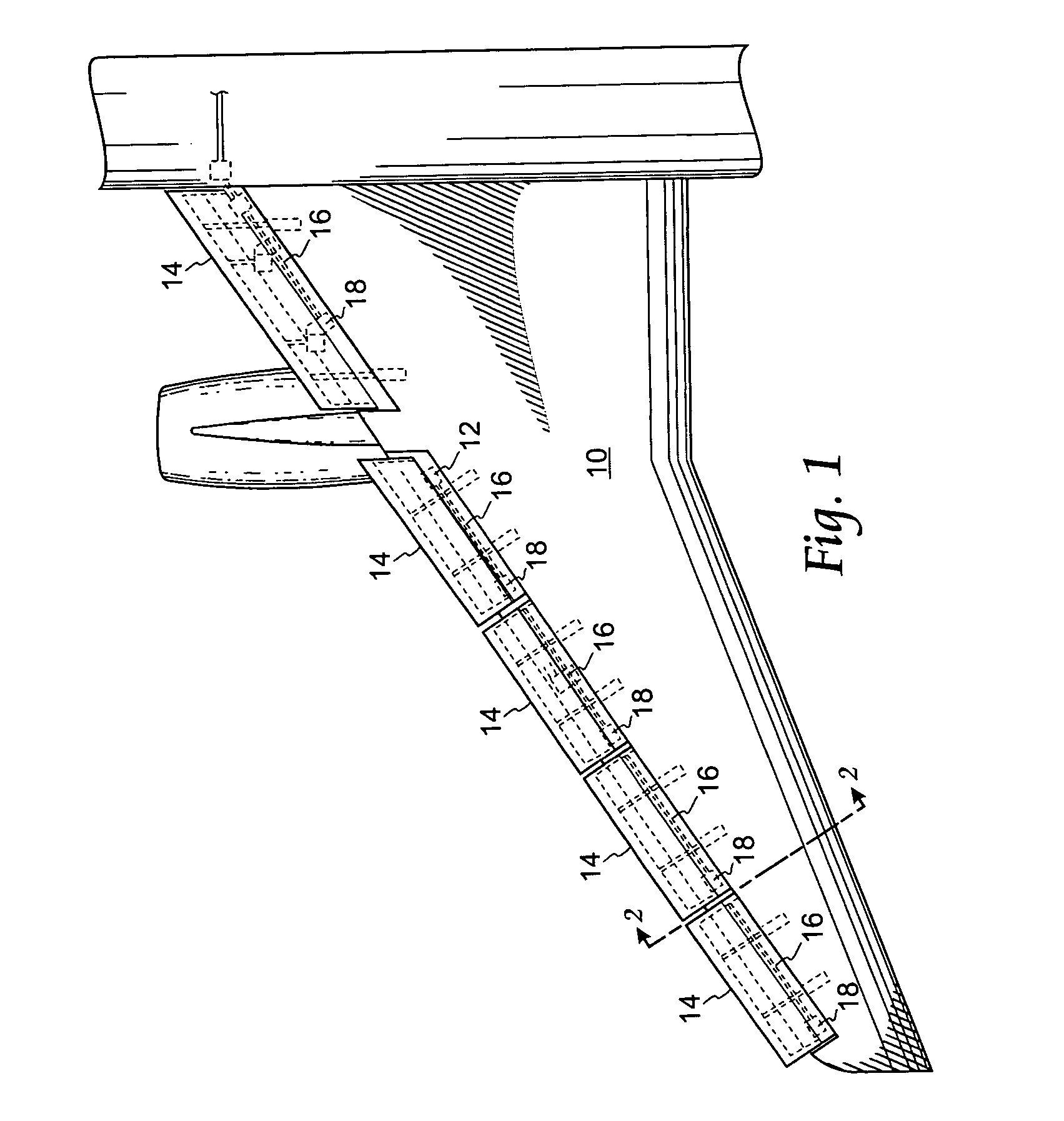
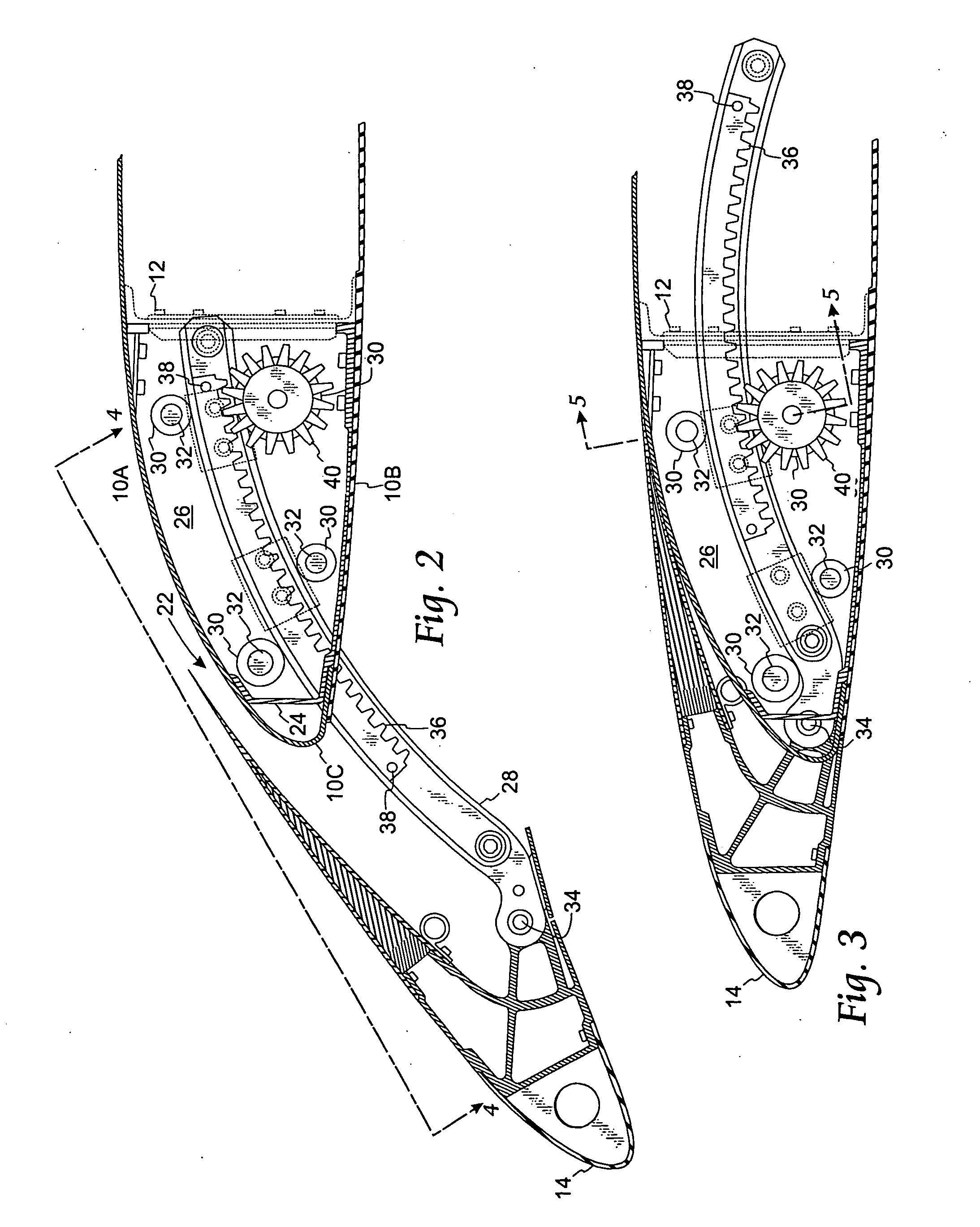
Wing leading edge slat system
A mechanism for extending and supporting a high-lift device relative to an airfoil has a pair of support ribs coupled to the airfoil. A carrier track is pivotally coupled to the high-lift device and positioned between the pair of support ribs. The carrier track has a slot opening along a lower length thereof. A gear rack is coupled within the slot opening. A pinion gear is positioned between the support ribs and below the carrier track. The pinion gear engages with the gear rack for extending the high-lift device relative to the airfoil. A plurality of rollers is rotateably coupled to the support ribs and in bearing contact with the carrier track. At least one roller is positioned above the carrier track and a second roller is positioned below the carrier track. The second roller is positioned concentrically with the pinion gear.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
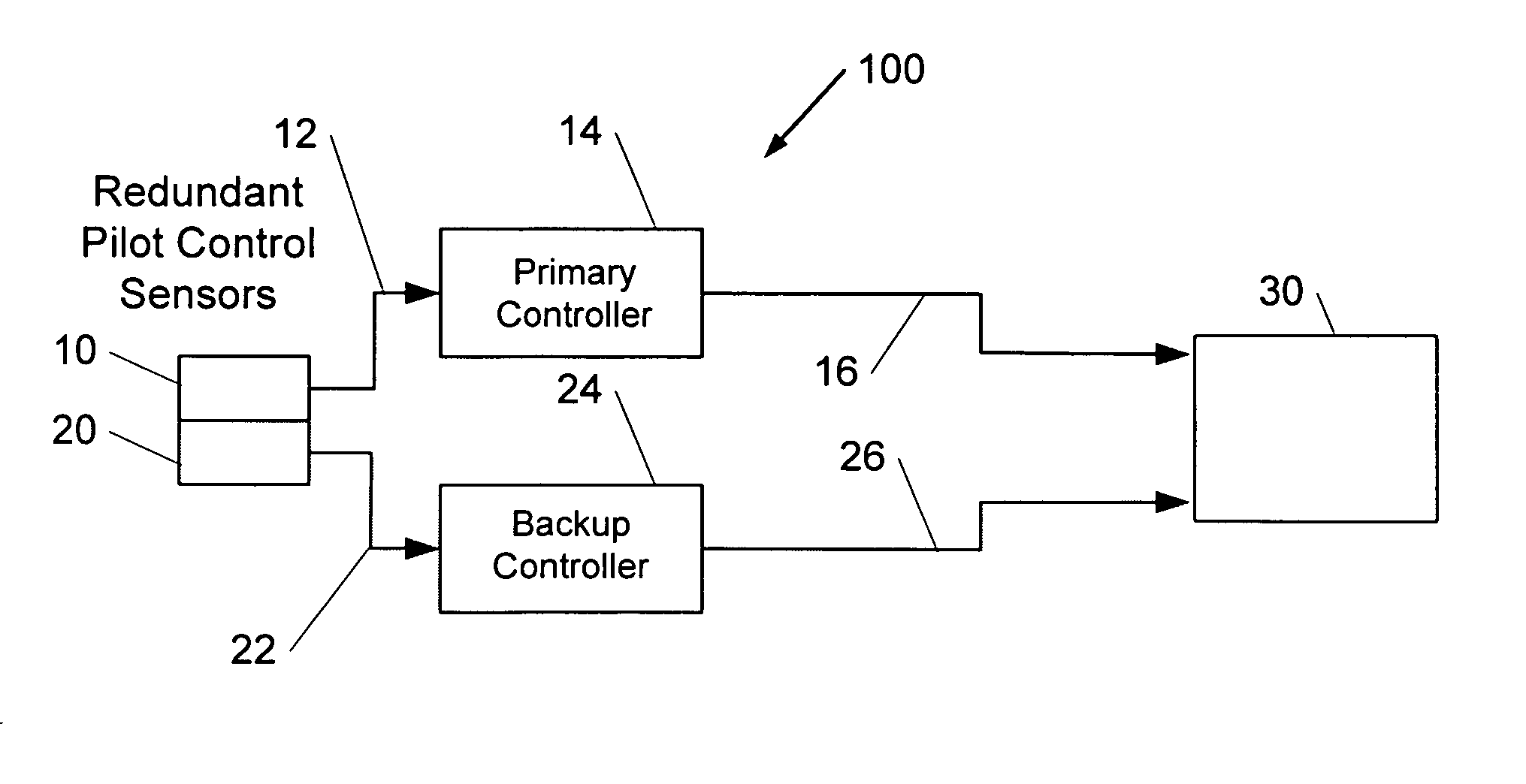
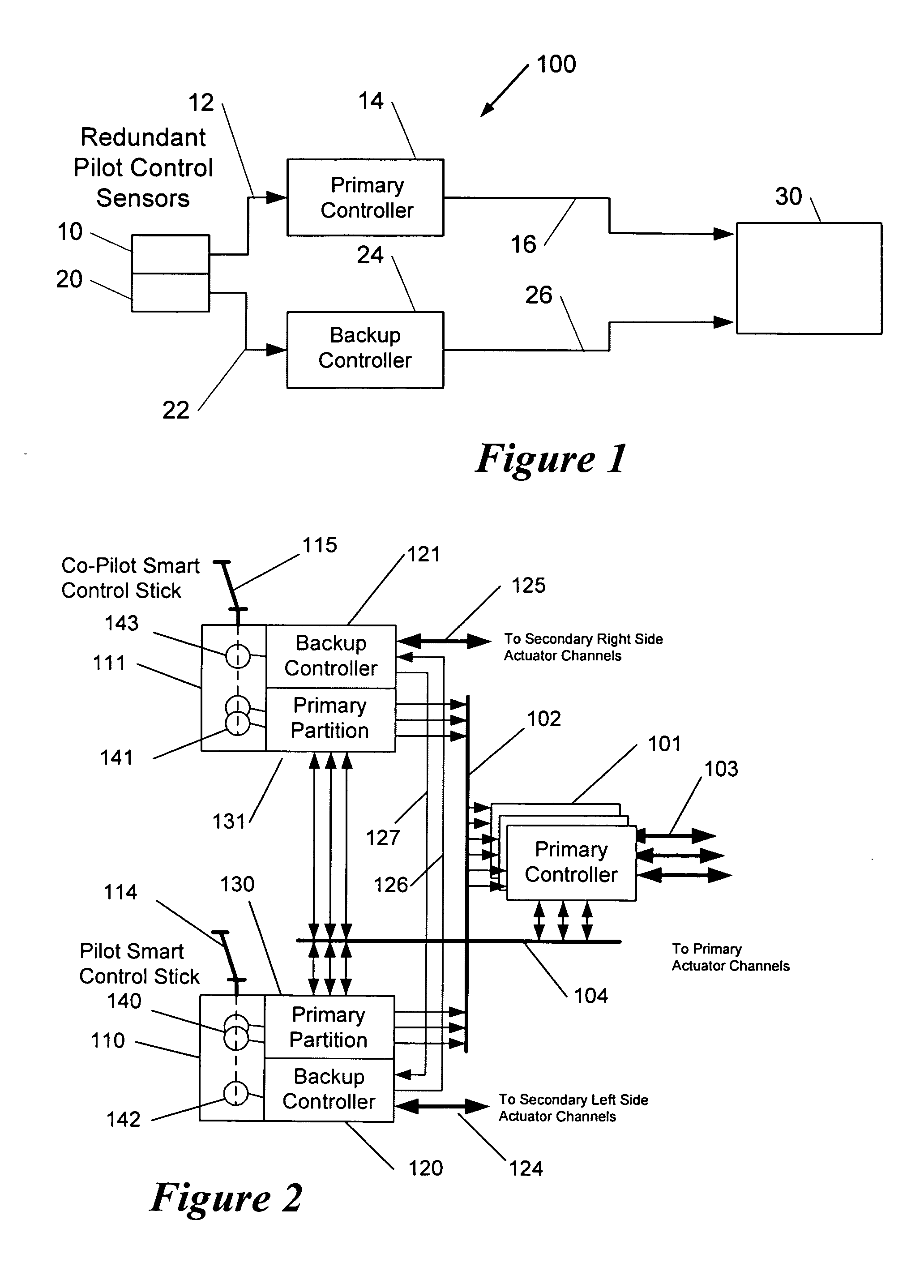
System and method for an integrated backup control system
ActiveUS20070164168A1Excess processing capacityAircraft stabilisationWith power amplificationJoystickControl signal
Embodiments of the invention relate to a flight control system for controlling an aircraft in flight having a backup control system integrated into an active control stick. The actuated control stick may include a processing unit that includes independent and separate hardware and / or software dedicated to the primary control system and the backup control system. For the primary control system, the processing unit may receive a sensed primary control stick signal and communicate with a primary processor, which may be configured to generate a primary control signal. For the backup control system, the processing unit may receive a sensed backup control stick signal and generate a backup control signal. The processing unit may also generate tactile signal for use by the actuated control stick to adjust the feel of a pilot's control stick.
Owner:GULFSTREAM AEROSPACE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com