Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1866results about "Multiplex code allocation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multicarrier Sub-Layer for Direct Sequence Channel and Multiple-Access Coding
InactiveUS20070211786A1Low costImprove system performanceSecret communicationMultiplex code generationUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
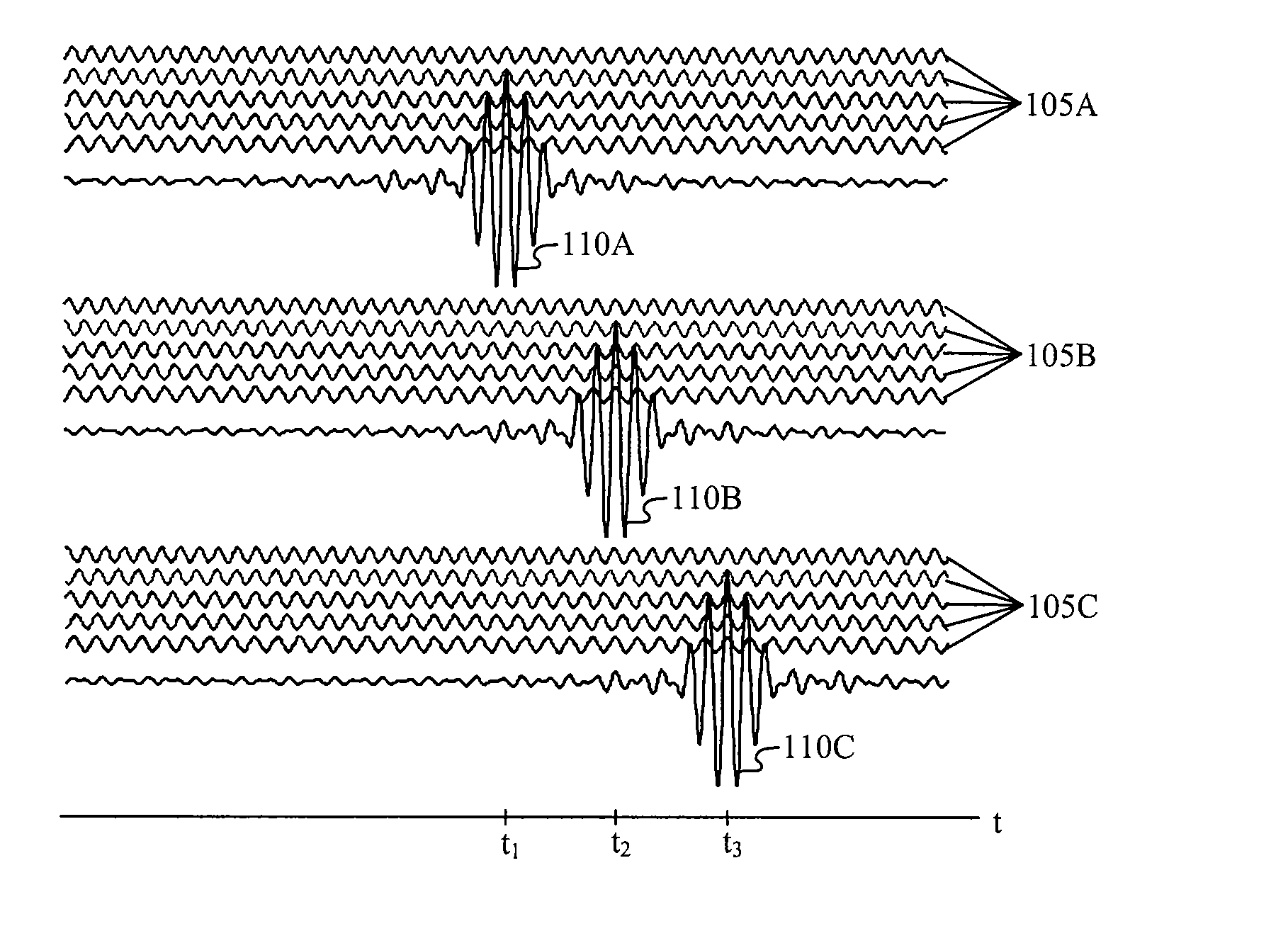
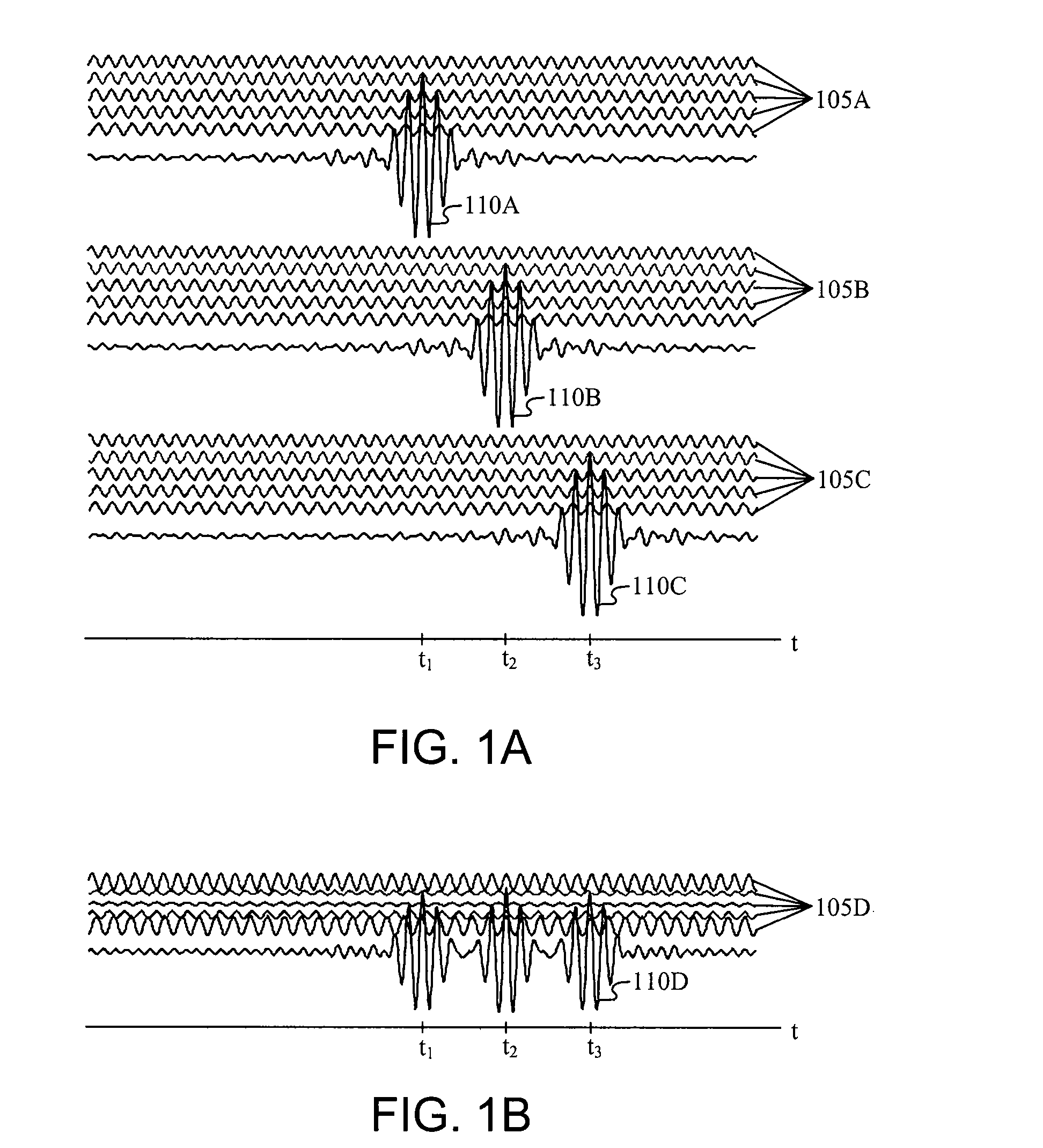
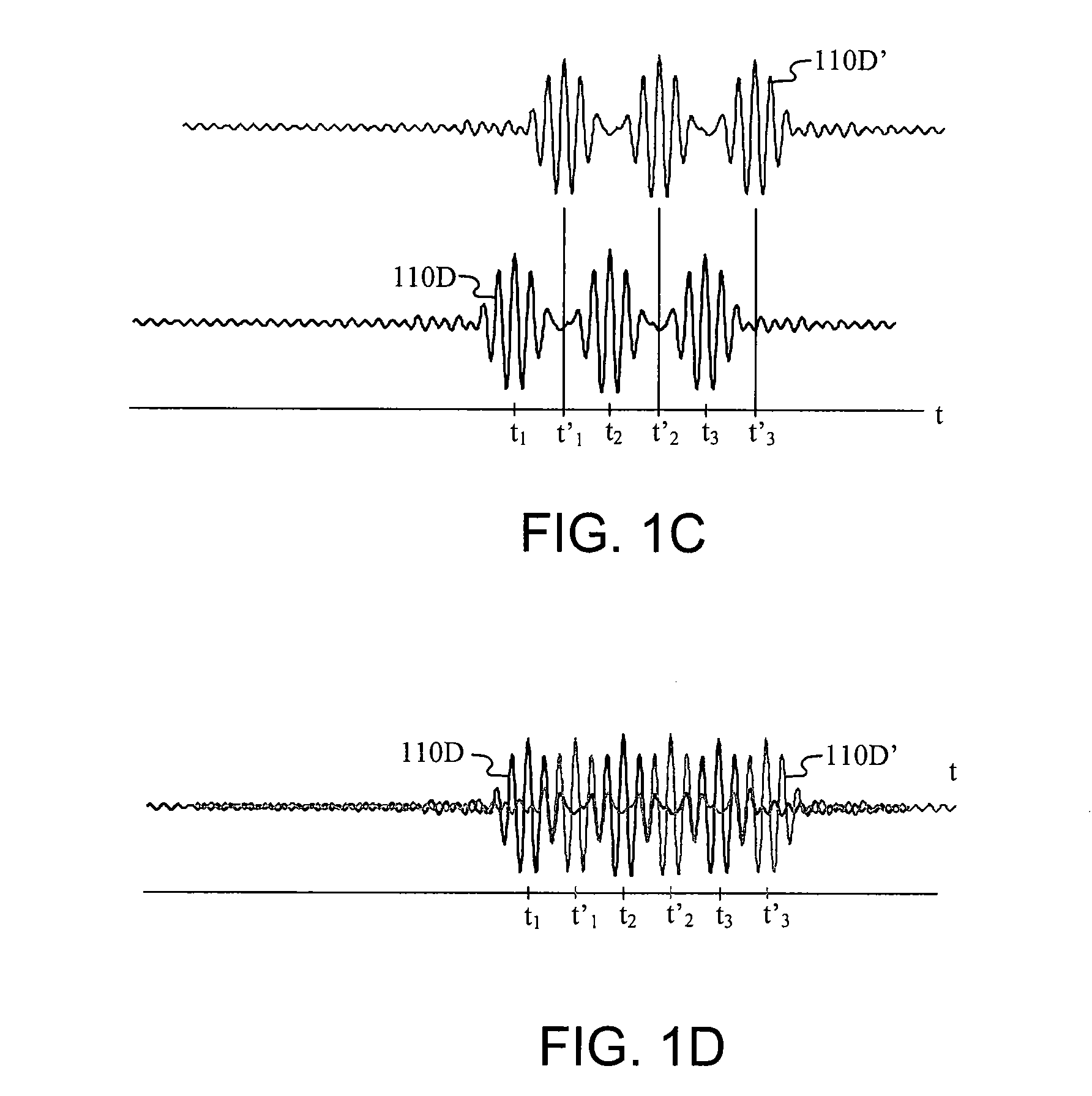
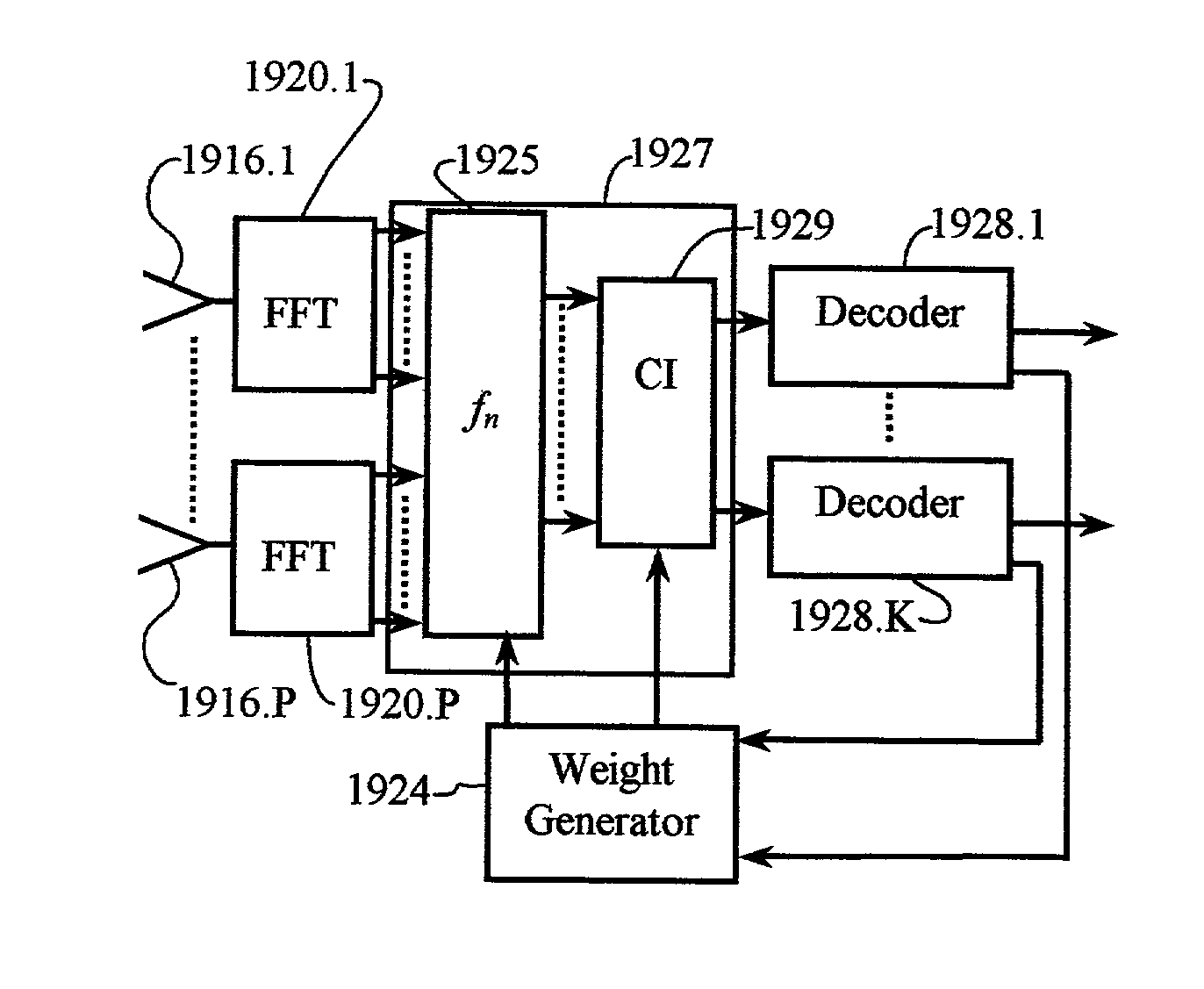
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Multicarrier sub-layer for direct sequence channel and multiple-access coding
InactiveUS7430257B1Low costPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
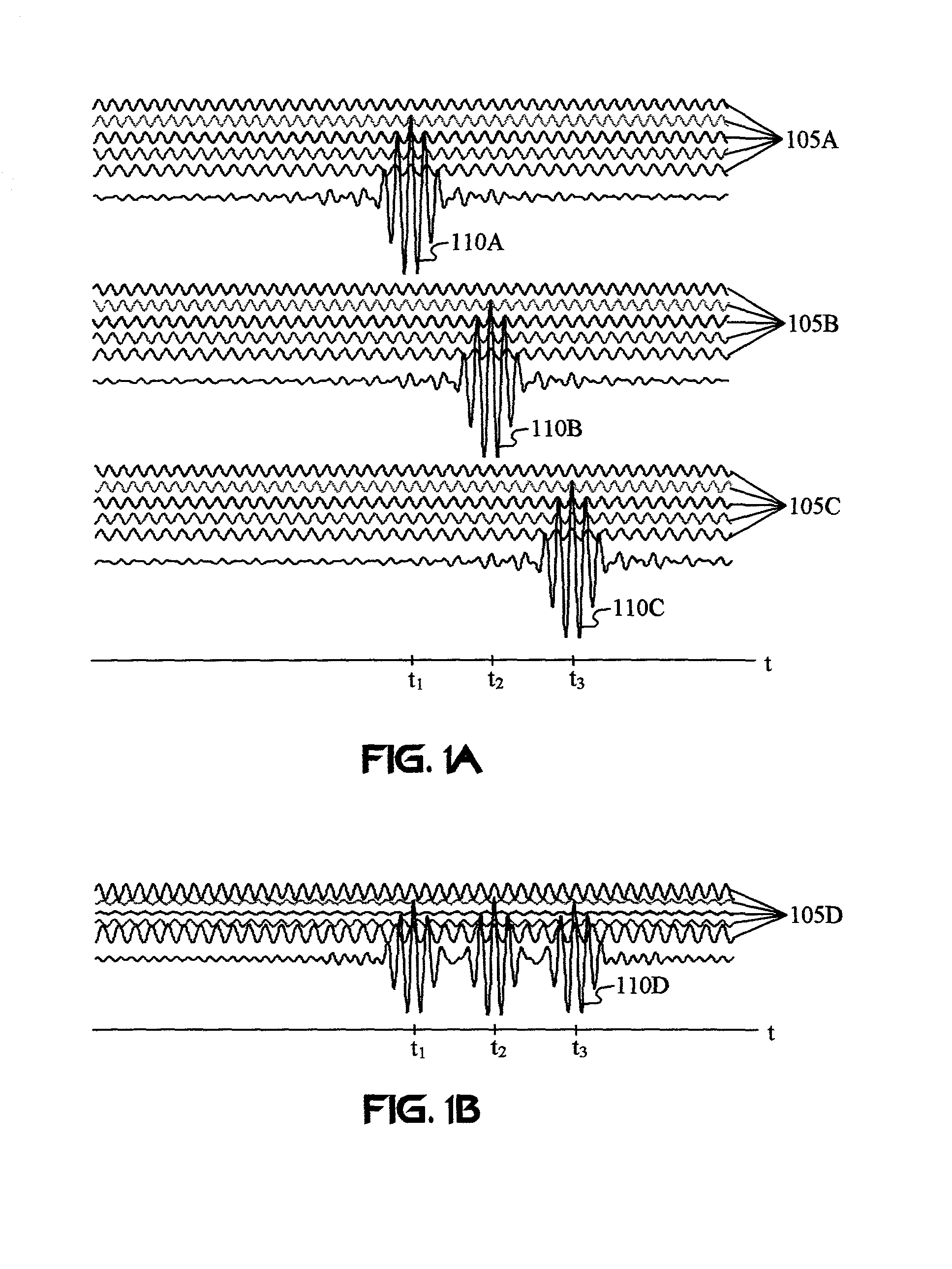
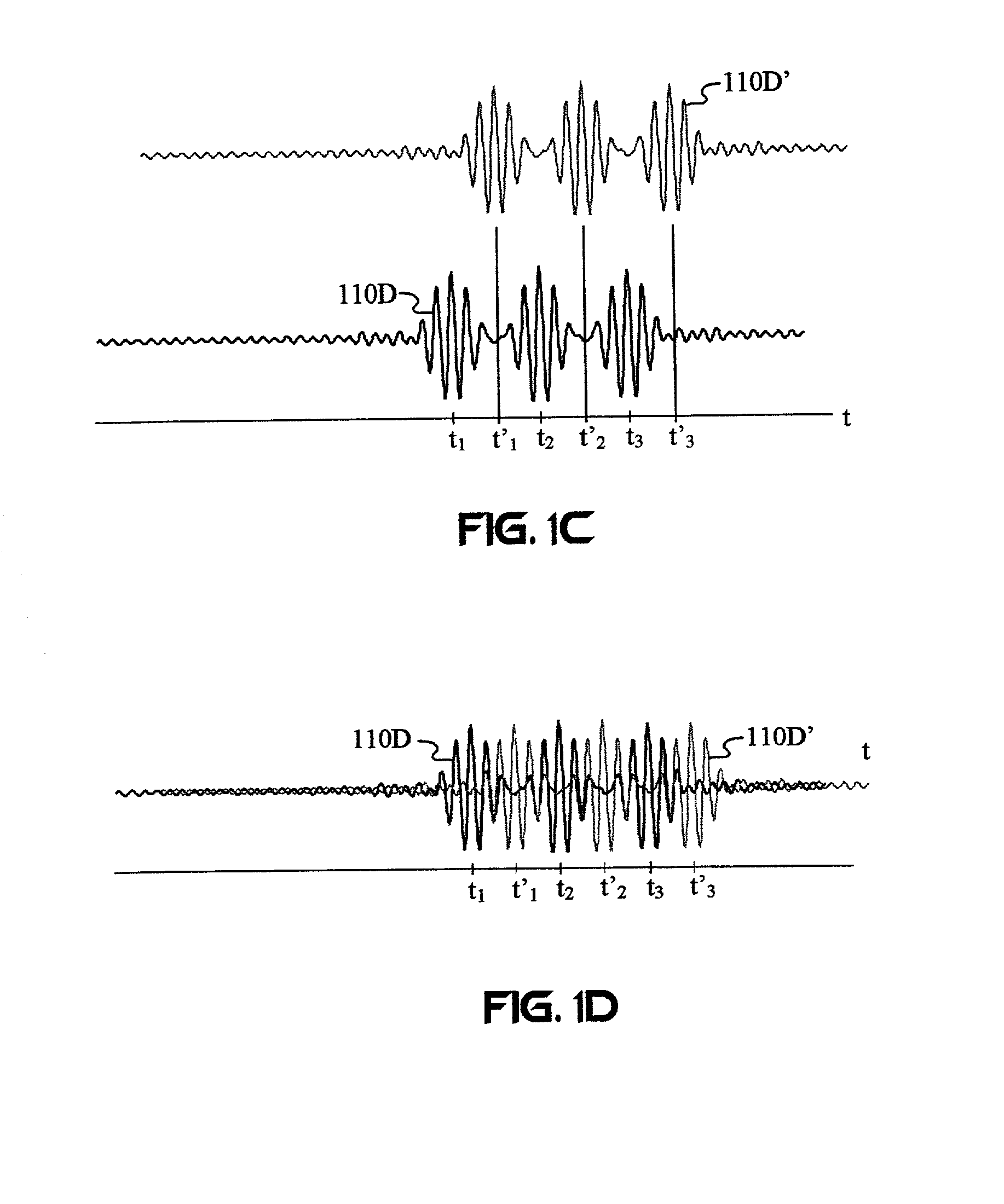
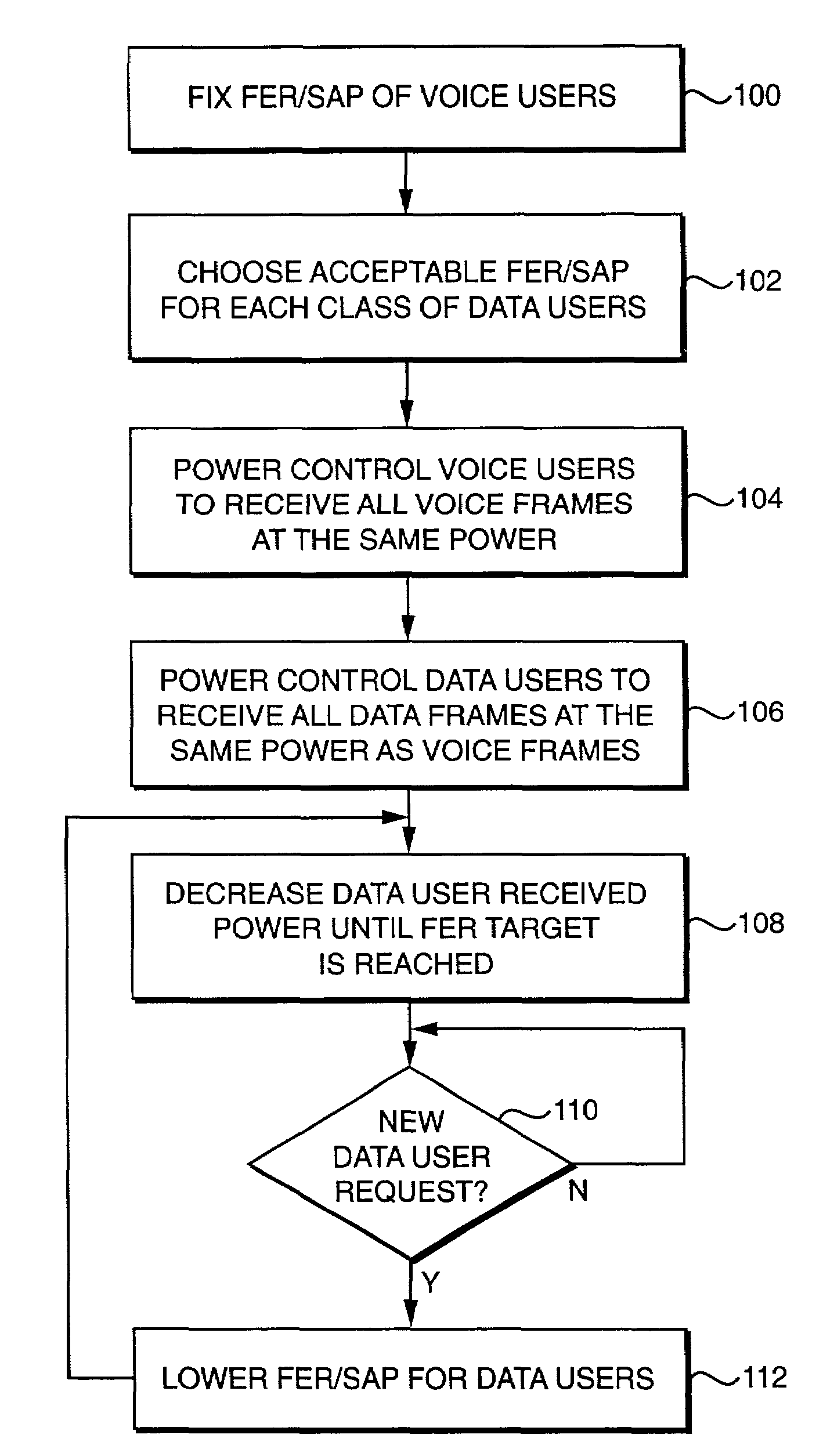
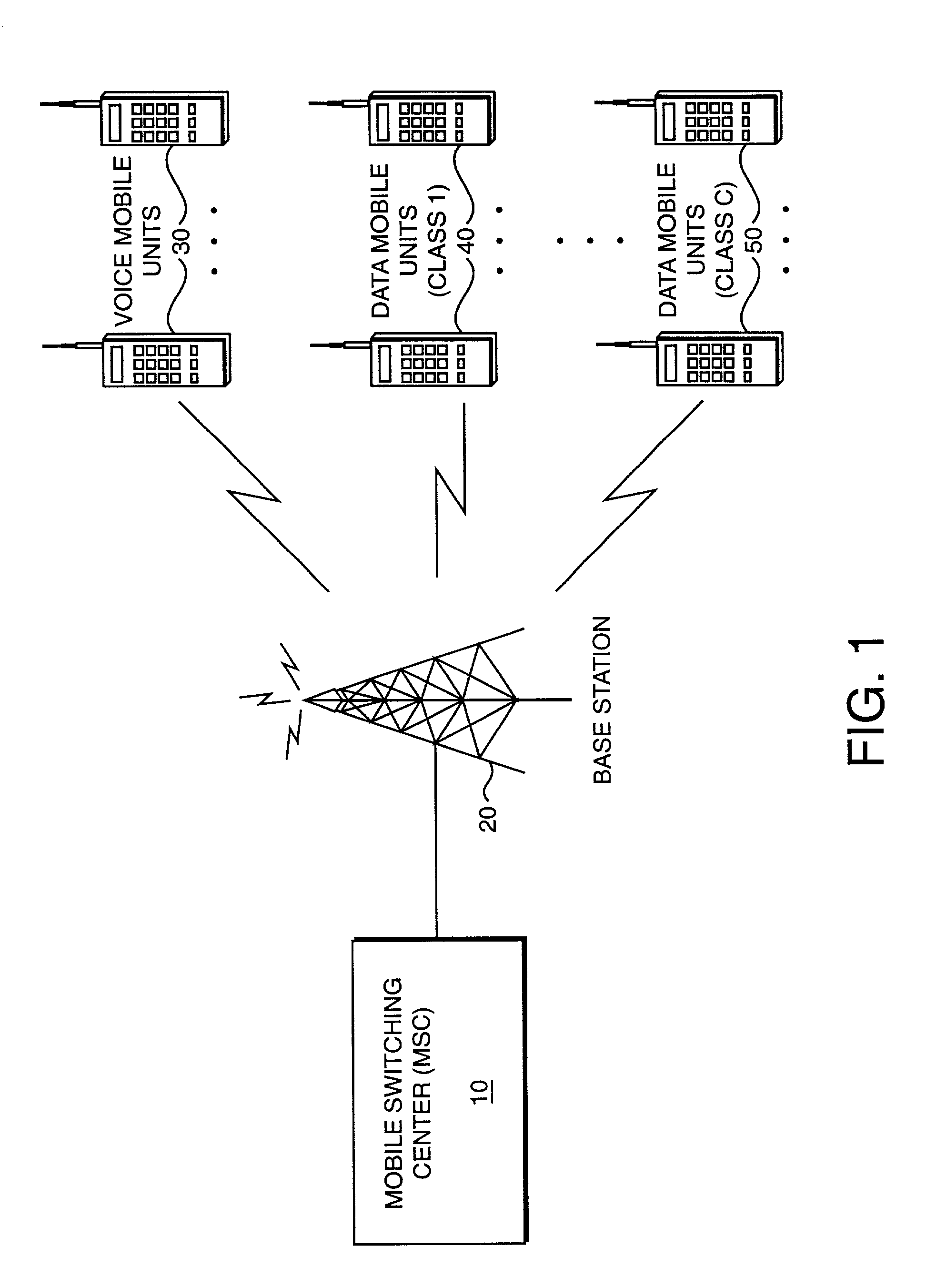
Capacity enhancement for multi-code CDMA with integrated services through quality of service and admission control
With the addition of high-speed data traffic to traditional CDMA cellular networks, there is a need to efficiently utilize system capacity so that the quality of service of existing voice and low-speed data users is maintained while new high-speed data users are added to the network. Methods and systems are presented that control allocation of power to users, quality of service requirements, and / or user activity levels to enhance capacity utilization. These methods and systems are based on a method for estimating the capacity of a CDMA carrier with both voice and data users using an interference-based analysis of the reverse link. In particular, the methods enhance capacity utilization in a multi-code CDMA network architecture, in which several codes are allocated to a single high-speed data user for parallel transmission.
Owner:VERIZON LAB
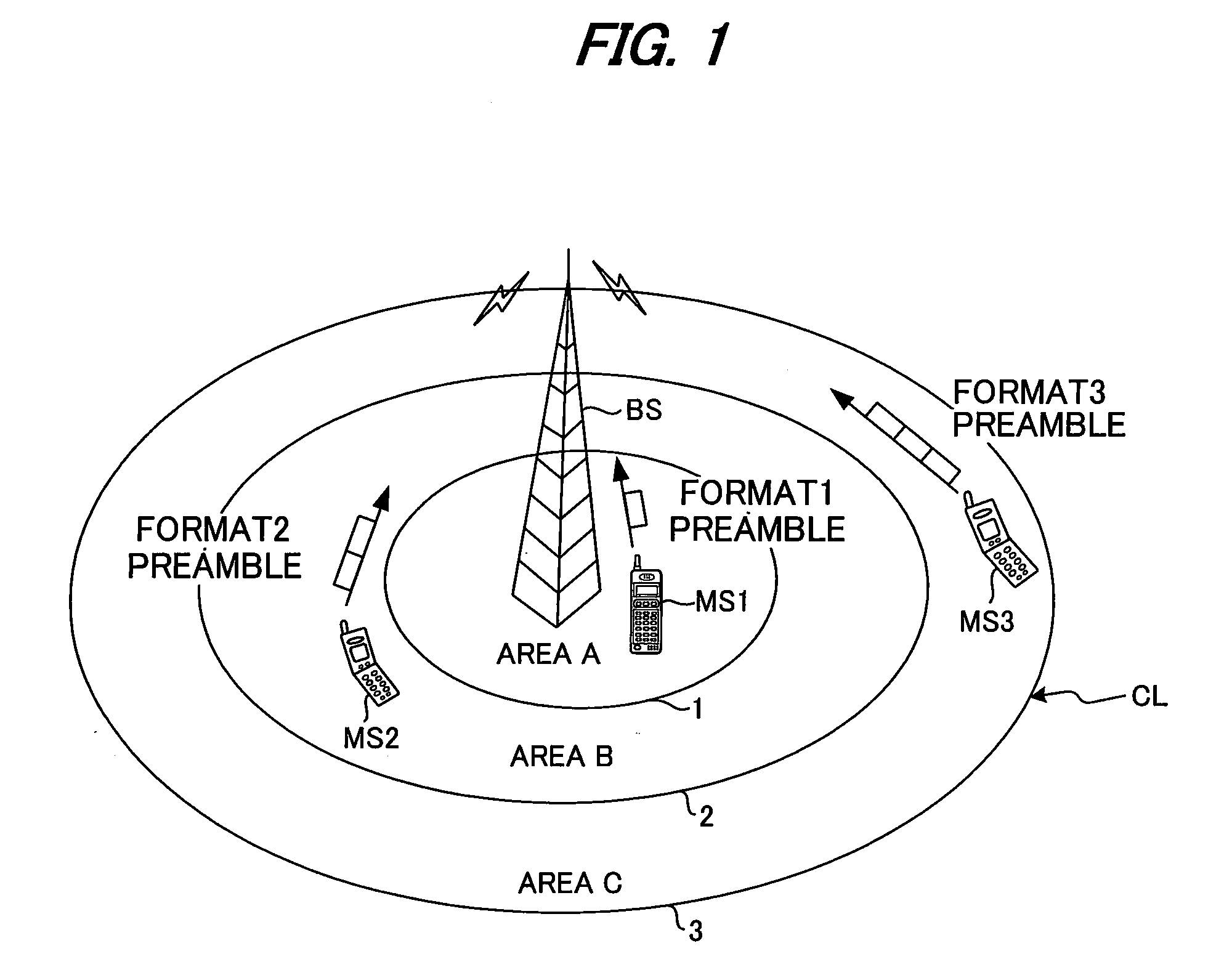
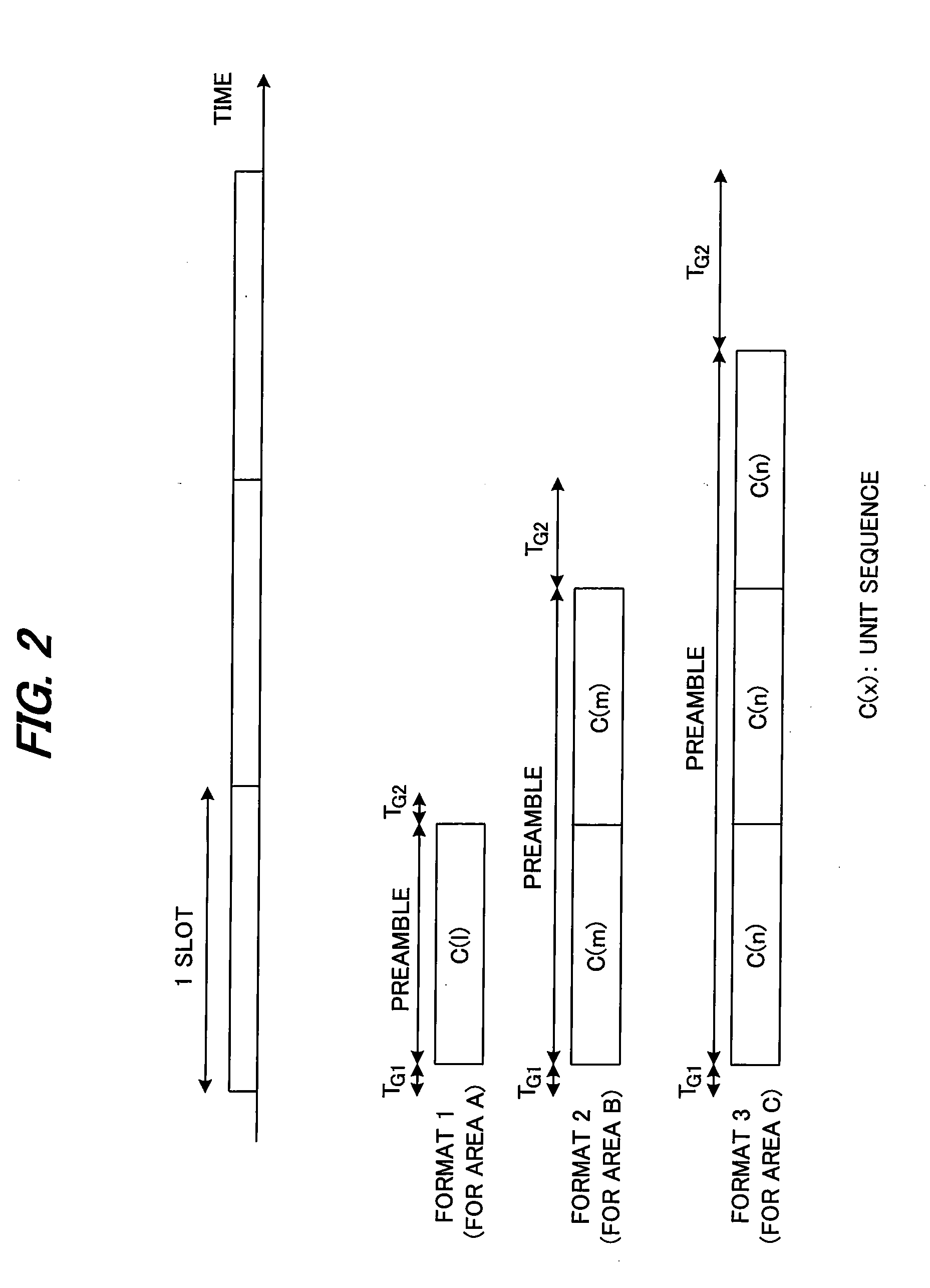
Method and apparatus for improved long preamble formats in a multiple antenna communication system
ActiveUS7742390B2Modulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCommunications systemTransmitter antenna
Methods and apparatus are provided for improved long preamble formats in a multiple antenna communication system having N antennas. According to one aspect of the invention, a preamble having a legacy portion and a high throughput portion is transmitted (or received) on each of the N transmit antennas, wherein the legacy portion comprises a legacy long training field and the high throughput portion comprises at least N high throughput long training fields, wherein the N high throughput long training fields are transmitted in N time slots using an N×N orthogonal matrix. The orthogonal matrix can be, for example, one or more of a Walsh matrix and a Fourier matrix. The N time slots can optionally comprise a single symbol.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
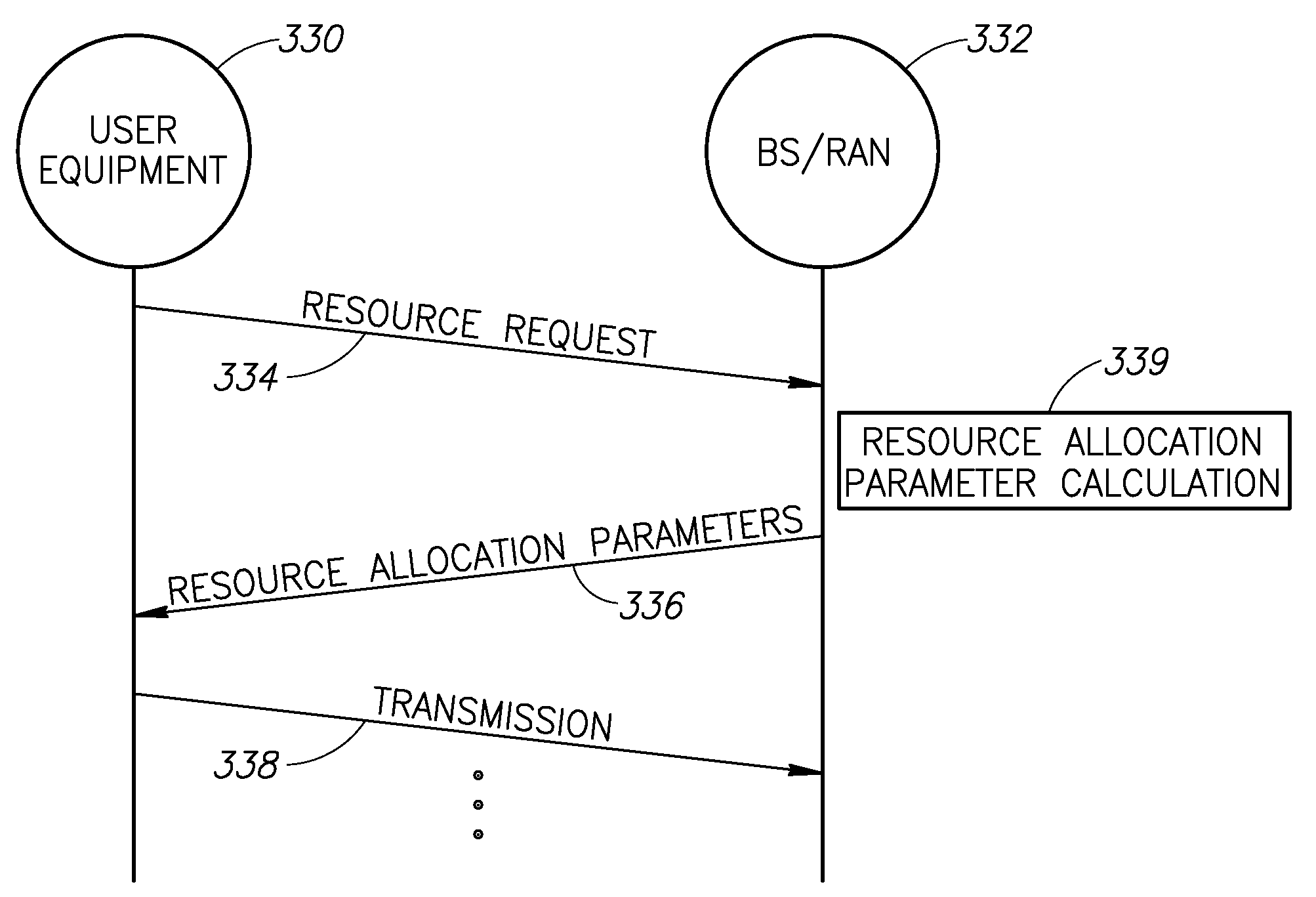
Resource allocation apparatus and method in an orthogonal frequency division multiple access communication system
InactiveUS20080233966A1Reduce Inter-Cell InterferenceMechanism suitableTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationCommunications systemControl channel
A novel and useful method and system for resource allocation in OFDM communication systems. The mechanism reduces inter-cell interference by randomizing the inter-cell interference experienced in each cell. The mechanism effectively spreads the resource allocation in each cell in a random manner resulting in statistical-like inter-cell interference behavior. In many cases, use of the mechanism is sufficient to obviate the need for frequency planning between cells. A formula or hardware permutation machine is used to generate a random list of indices. The indices are then used to assign user data to the system resources. One or more parameters defining the random index generator at the transmitter are forwarded to the receiver to enable the local generation of an exact copy of the list of indices generated at the transmitter, thus enabling the DL and UL at the receiver while minimizing the required control channel signaling.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
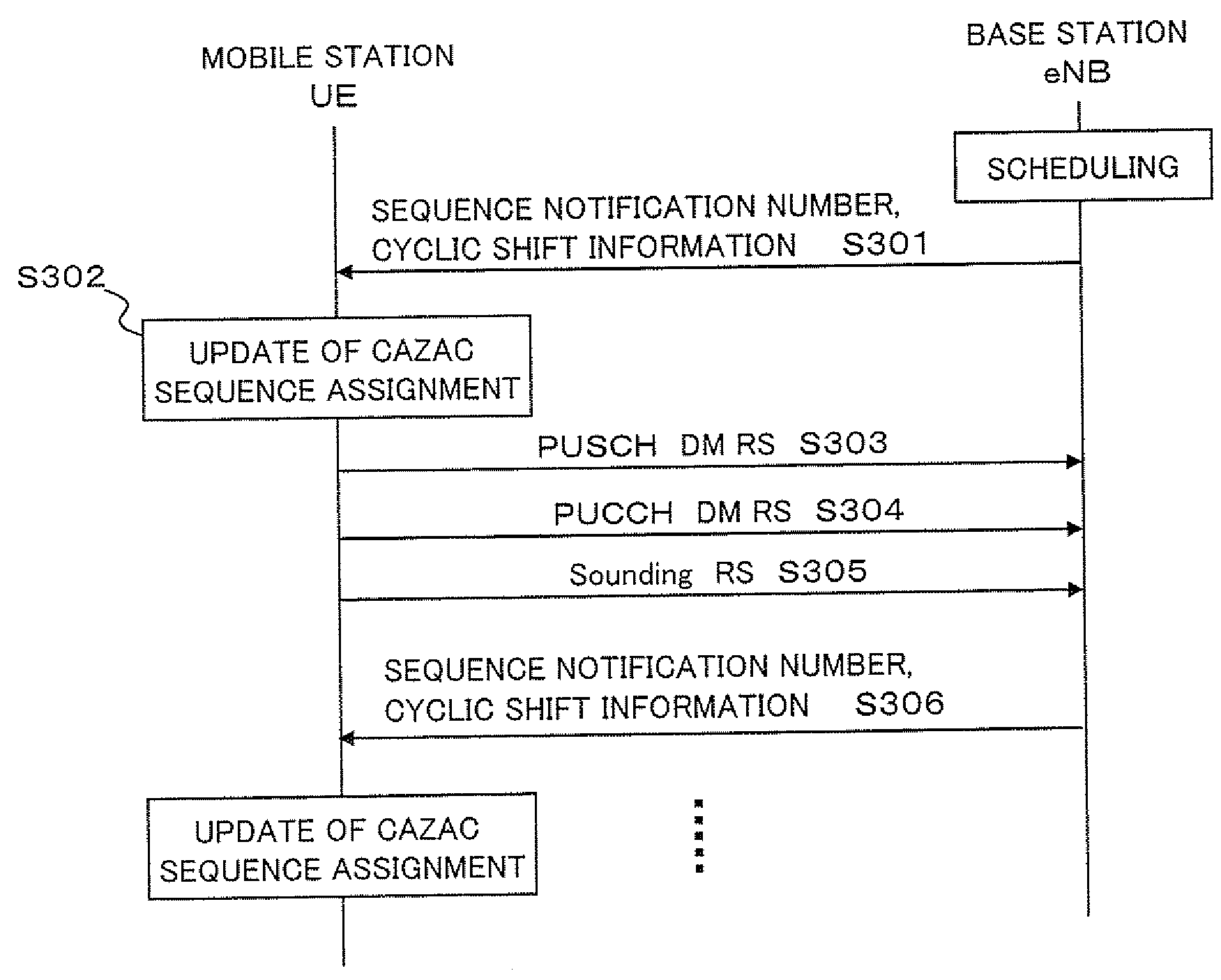
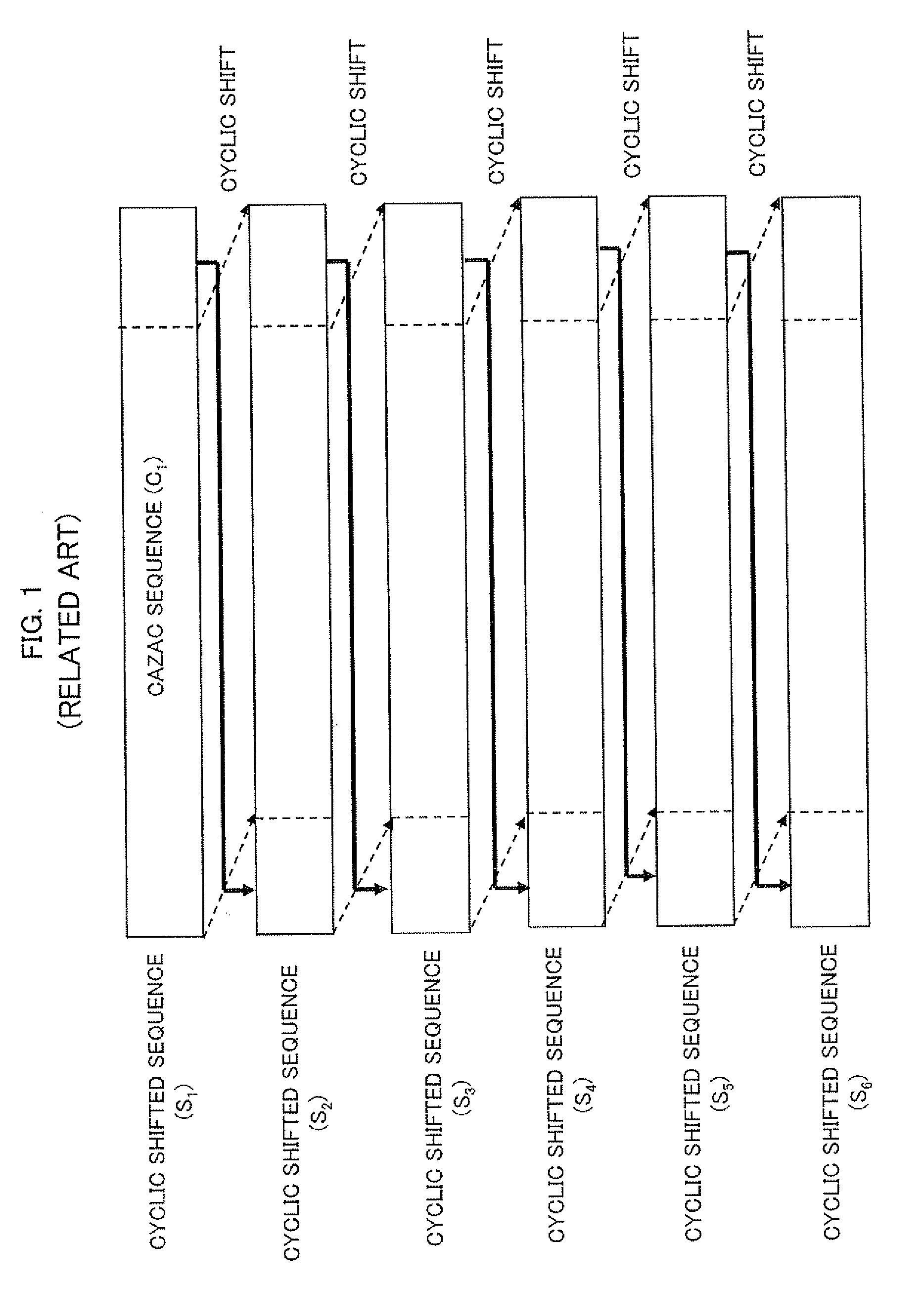
Method and device for assigning reference signal sequences in mobile communications system
ActiveUS20080318608A1Reduce impactIncrease the number ofModulated-carrier systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemOrthogonal sequence
A reference signal sequence assignment method and device are provided by which the influence of inter-cell interference can be reduced and the number of usable cyclic shifted sequences per sector can be increased. In a mobile communications system with a structure including multiple cells each including multiple sectors, a sequence assignment method is employed by which pseudo-orthogonal sequences used for reference signals are assigned to cells or sectors. According to this method, the multiple pseudo-orthogonal sequences are assigned to cells or sectors by using multiple repetition patterns.
Owner:NEC CORP
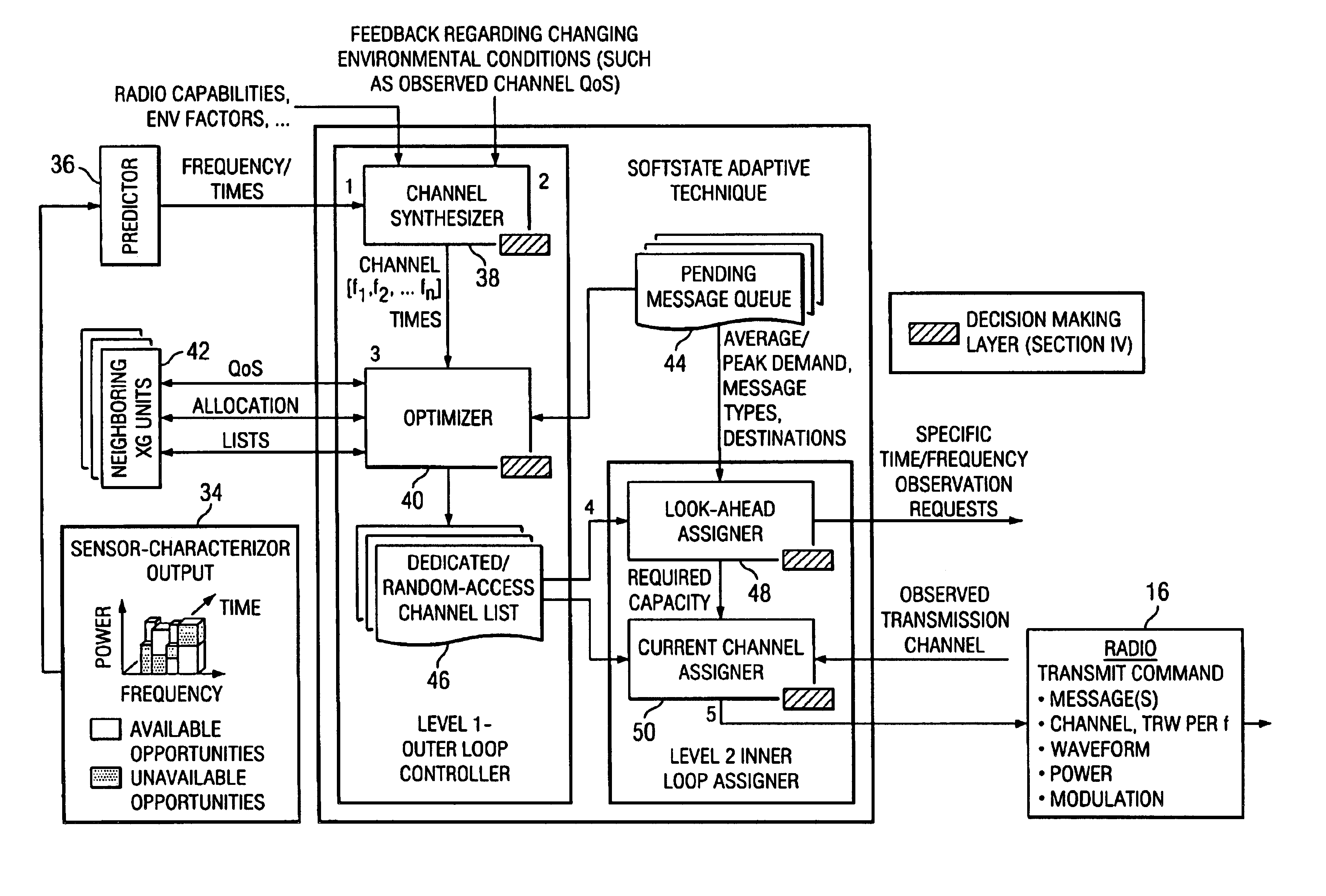
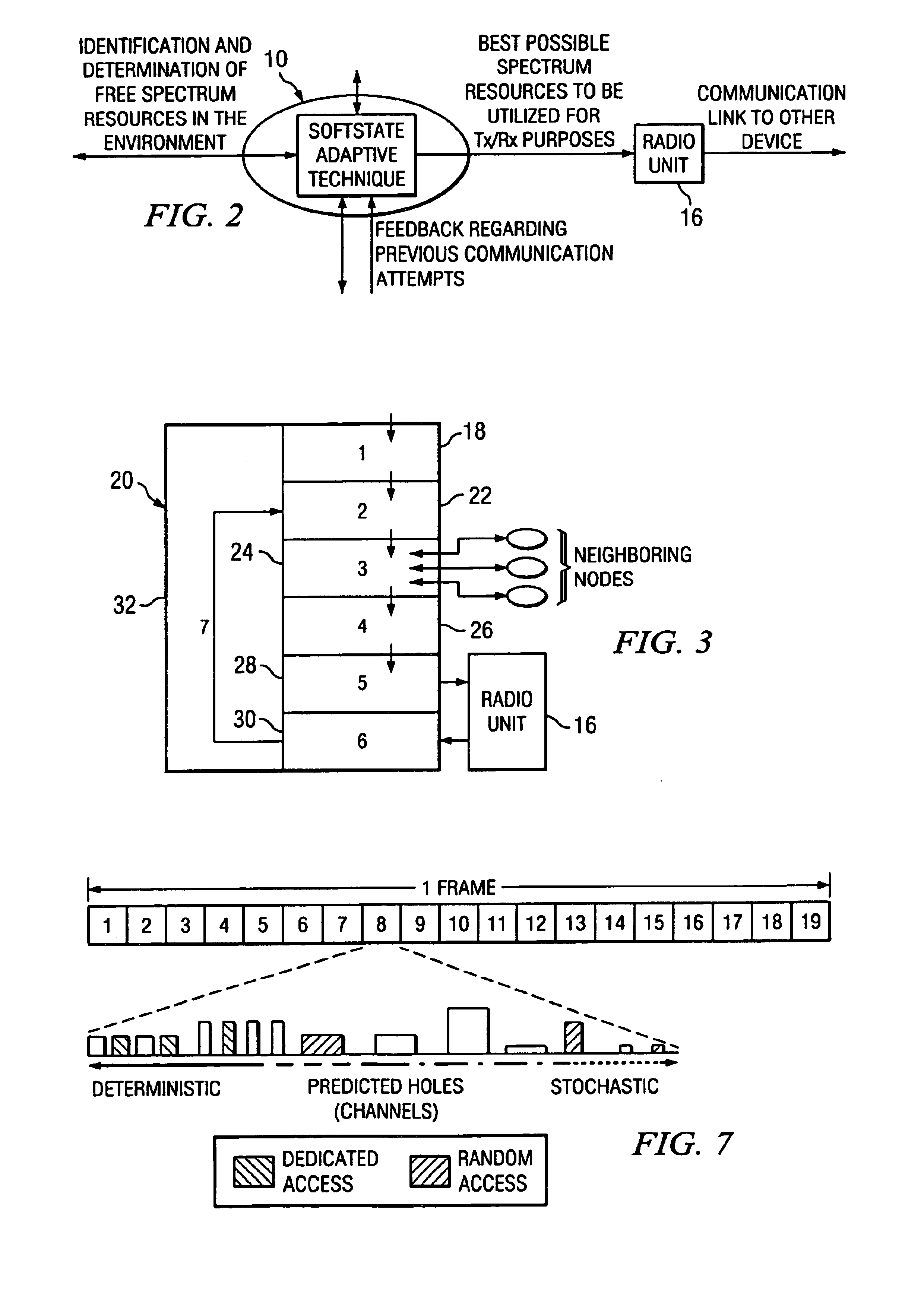
Dynamic wireless resource utilization
InactiveUS6990087B2Increase profitImprove efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsResource utilization
In one embodiment, a method for dynamic wireless resource utilization includes monitoring a wireless communication resource; generating wireless communication resource data; using the wireless communication resource data, predicting the occurrence of one or more holes in a future time period; generating hole prediction data; using the hole prediction data, synthesizing one or more wireless communication channels from the one or more predicted holes; generating channel synthesis data; receiving data reflecting feedback from a previous wireless communication attempt and data reflecting a network condition; according to the received data and the channel synthesis data, selecting a particular wireless communication channel from the one or more synthesized wireless communication channels; generating wireless communication channel selection data; using the wireless communication channel selection data, instructing a radio unit to communicate using the selected wireless communication channel; and instructing the radio unit to discontinue use of the selected wireless communication channel after the communication has been completed.
Owner:POWERWAVE COGNITION INC
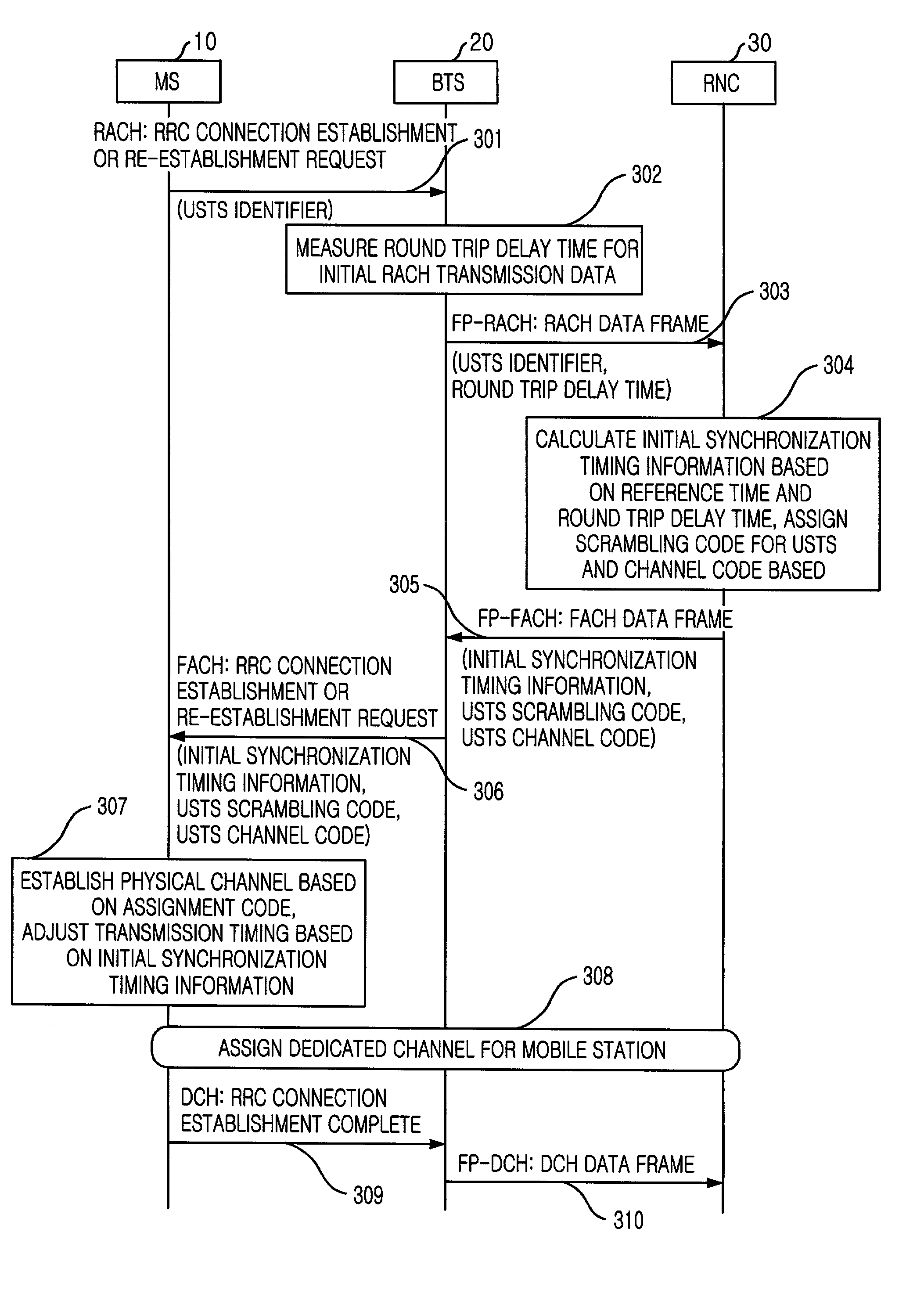
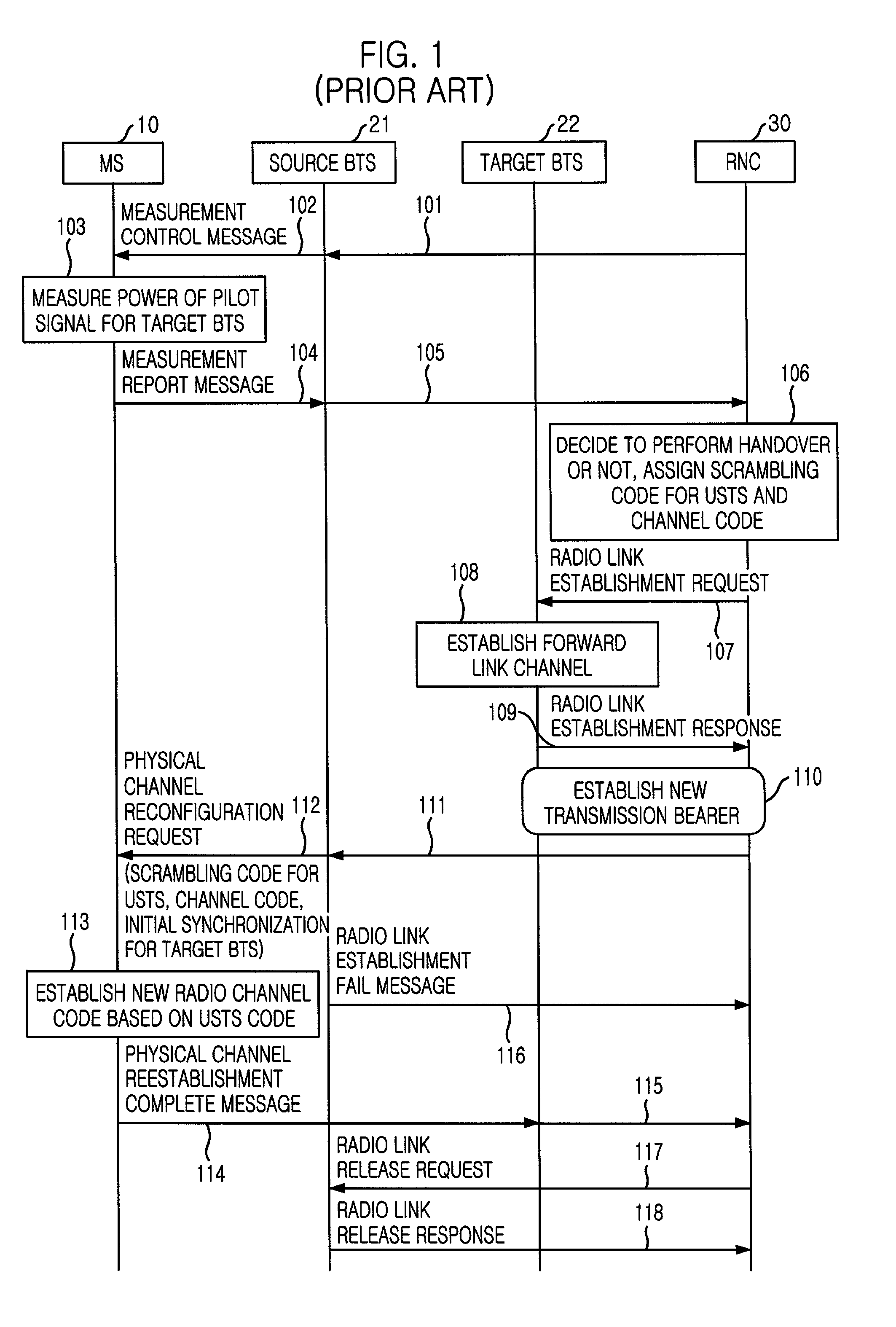
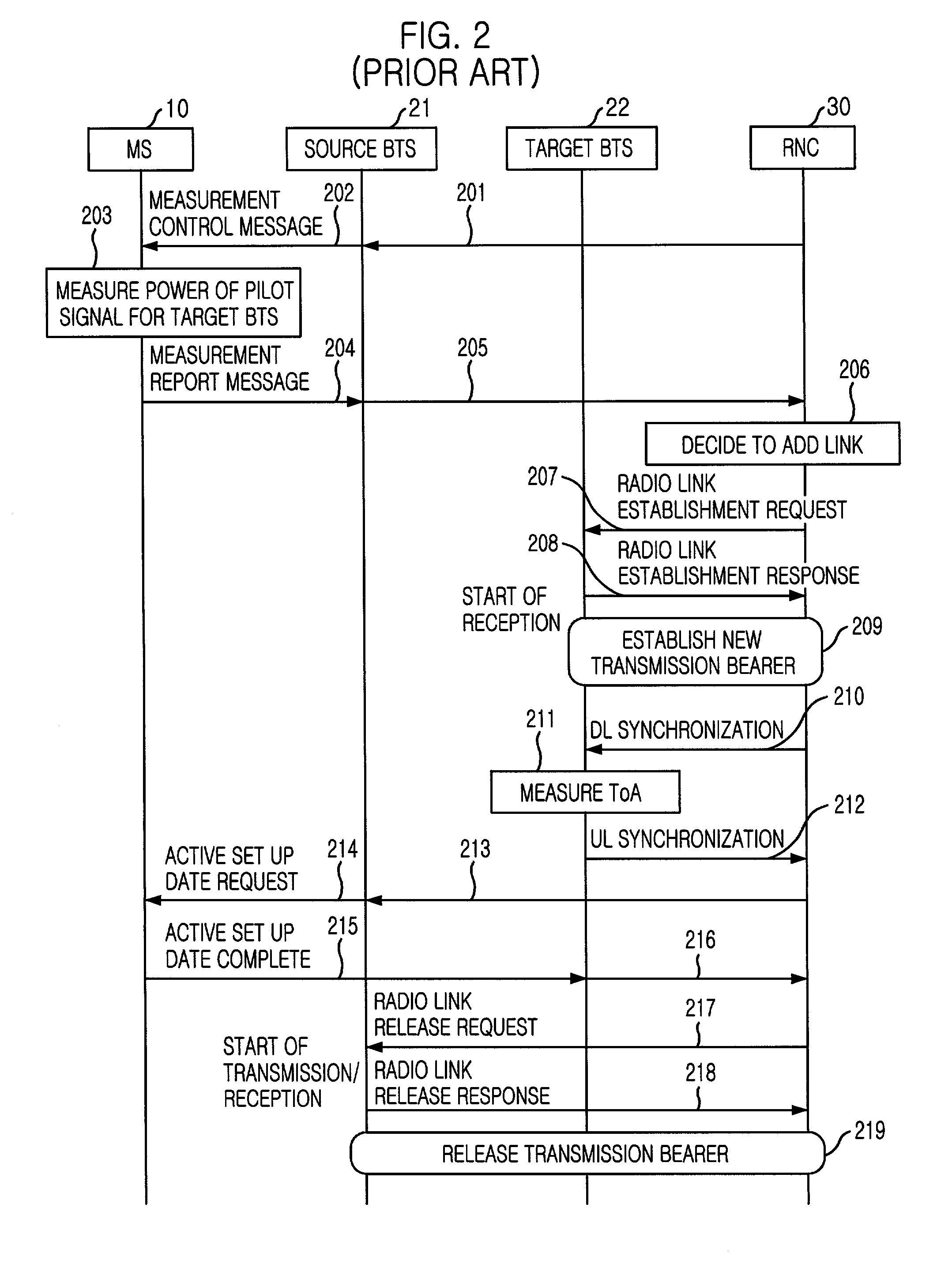
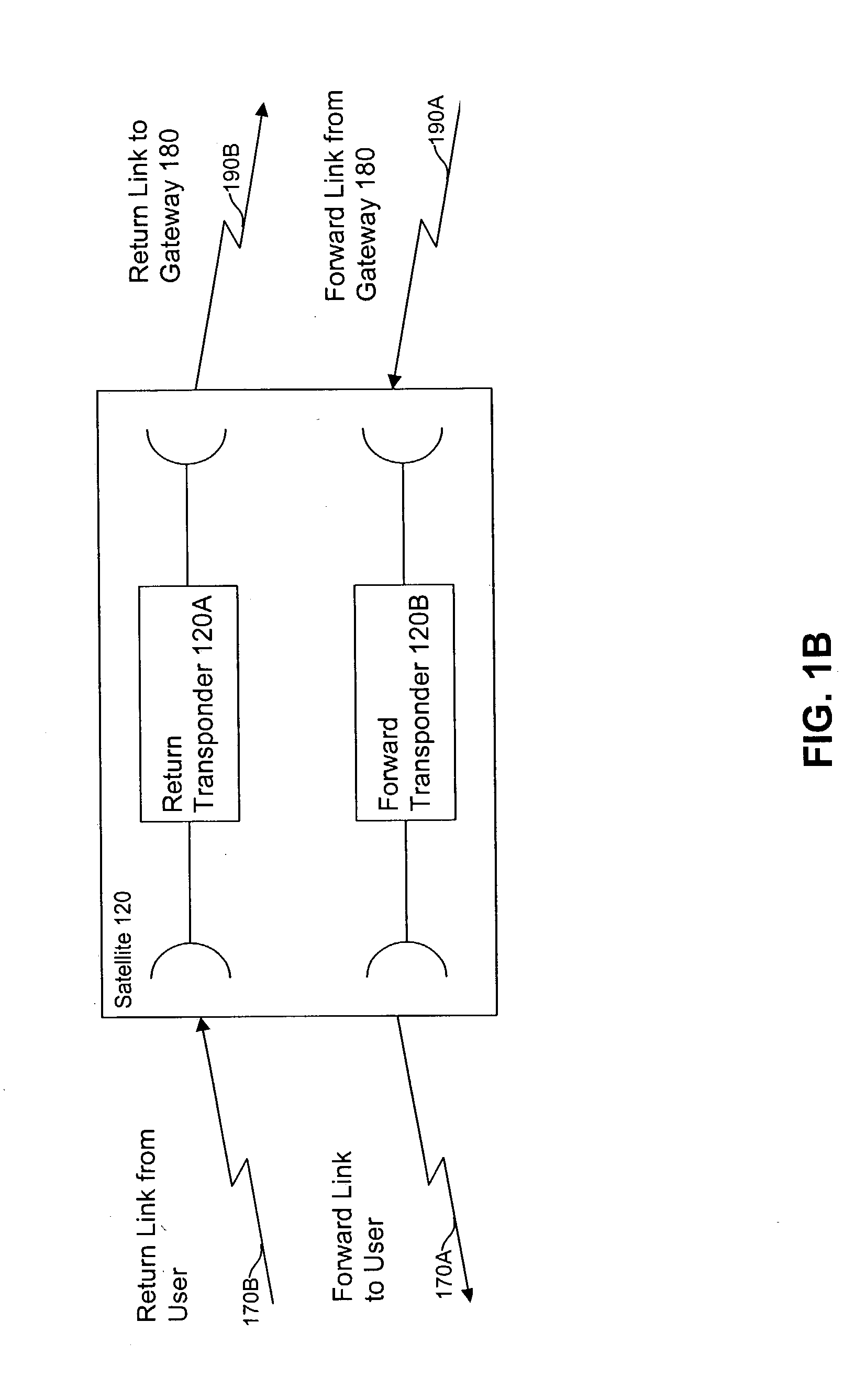
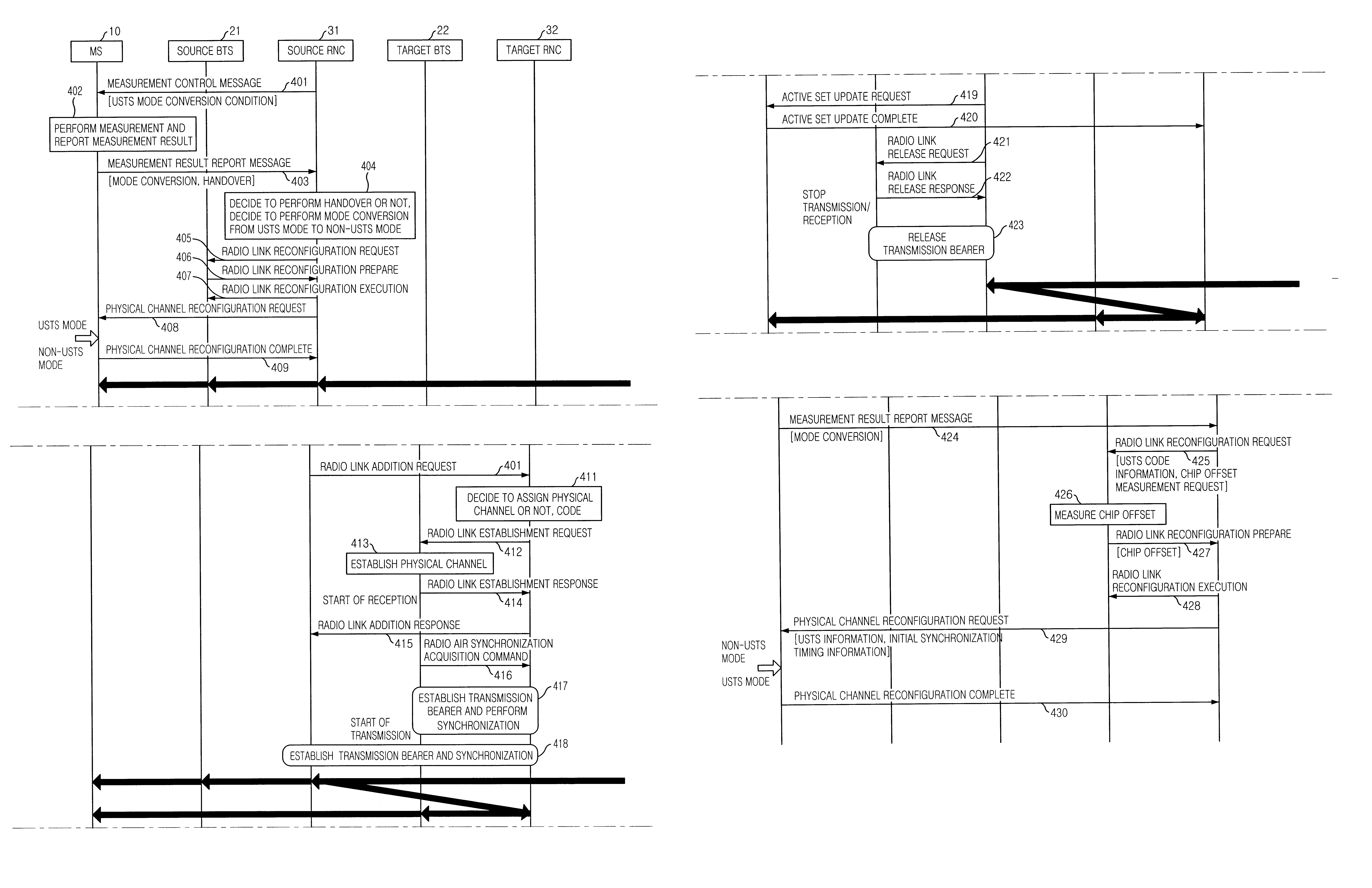
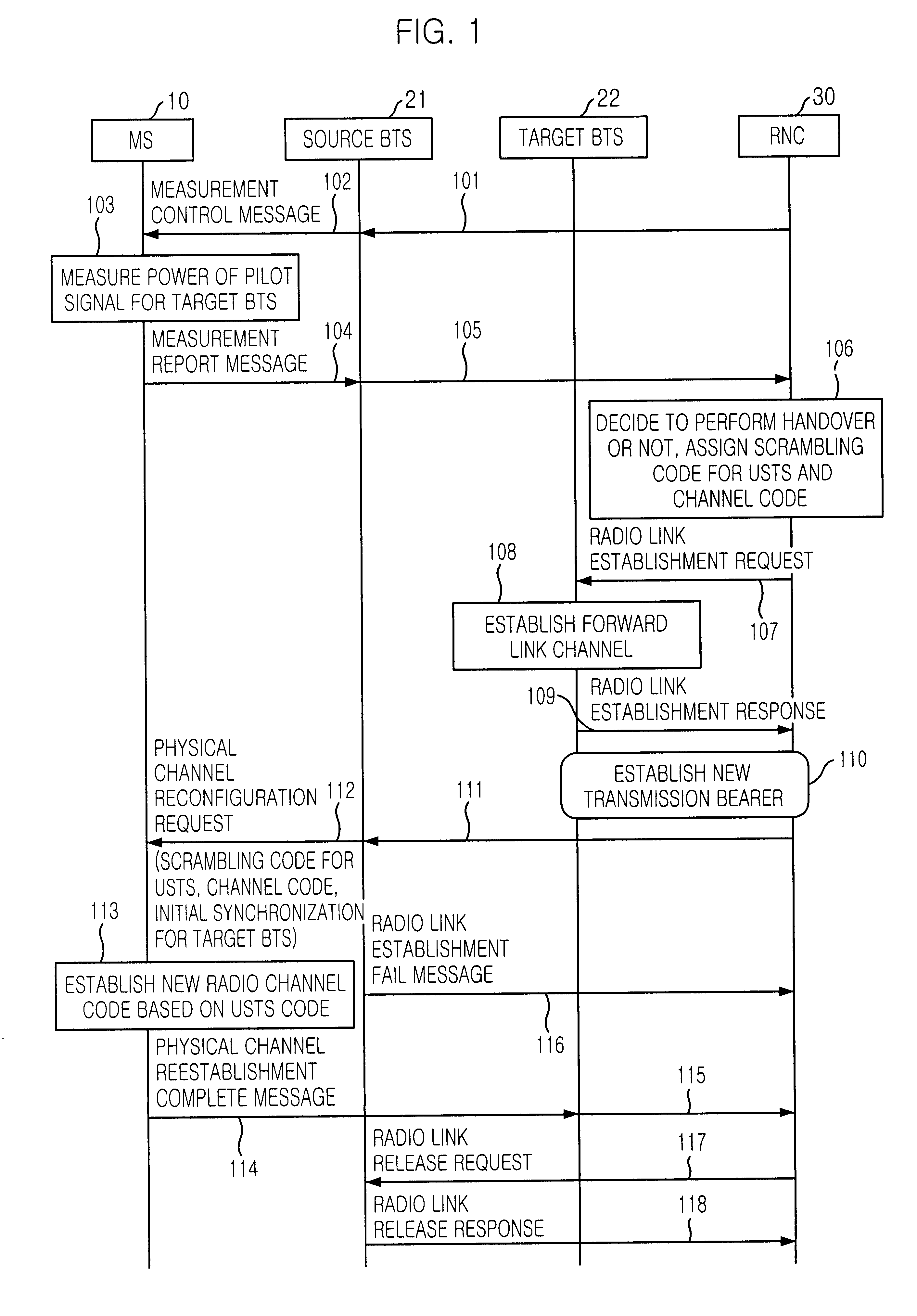
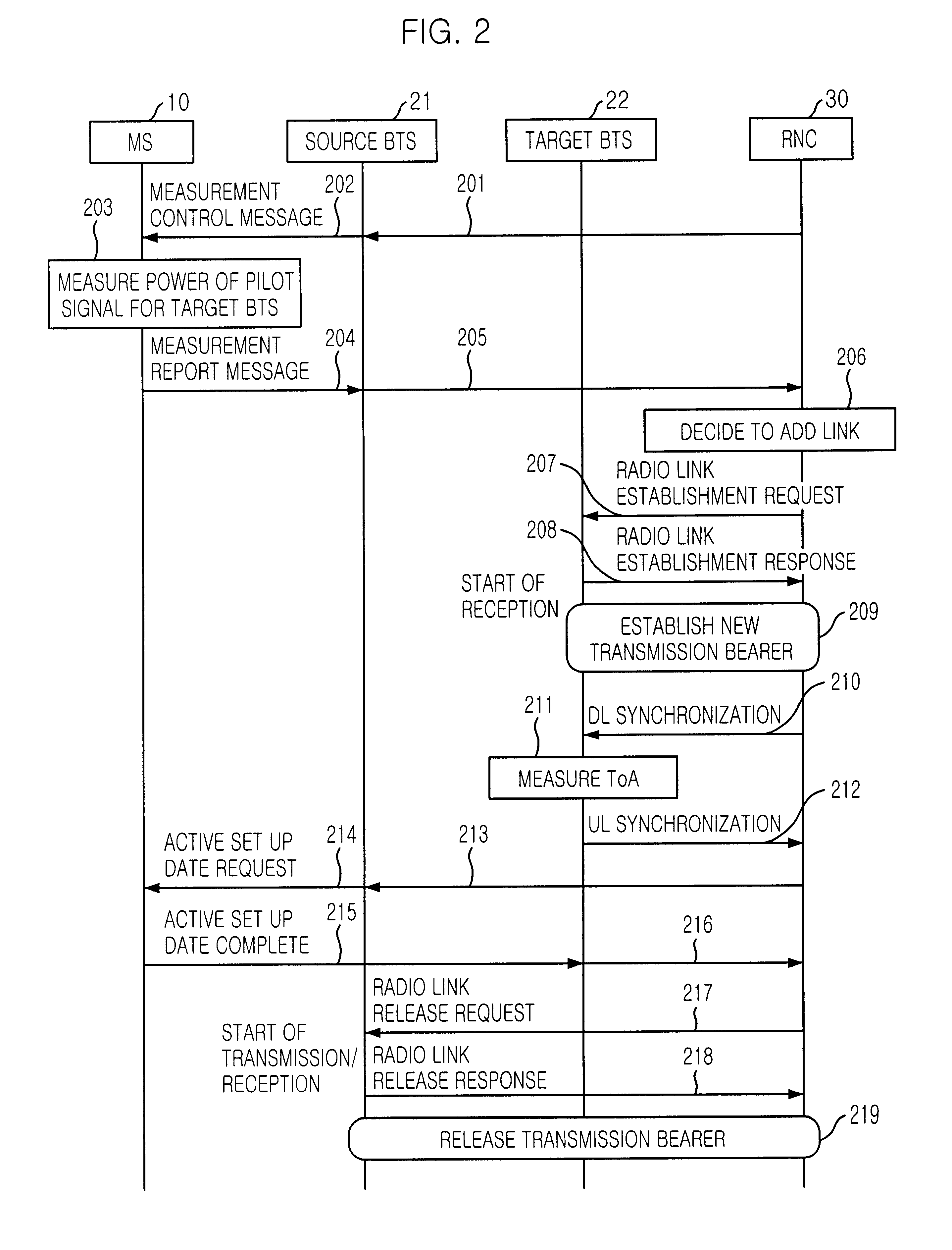
Handover method in wireless telecommunication system supporting USTS
InactiveUS20020045448A1Provide mobilitySynchronisation arrangementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile stationHandover
A handover method in wireless telecommunication system supporting USTS is disclosed. The method for performing a handover of a mobile station in an asynchronous wireless telecommunication system supporting an uplink synchronous transmission scheme (USTS) mode, includes the steps of: a) performing a mode conversion of the mobile station from the USTS mode to a non-USTS mode based on a first signal measurement result from the mobile station; and b) performing a handover for the mobile station. In another embodiment of the present invention, the method further includes the step of: c) performing a mode conversion from the non-USTS mode to the USTS mode based on a second signal measurement result from the mobile station.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
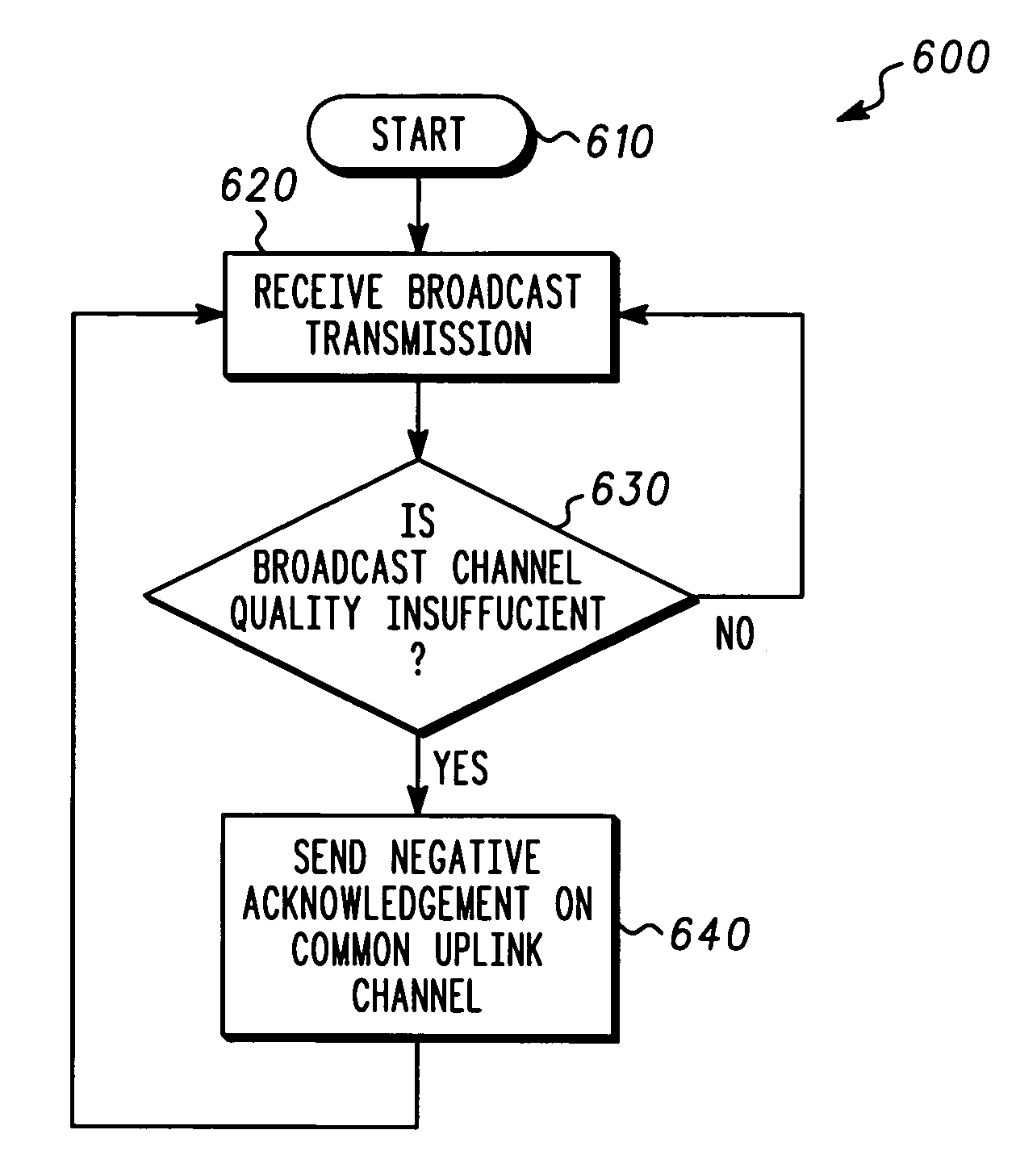
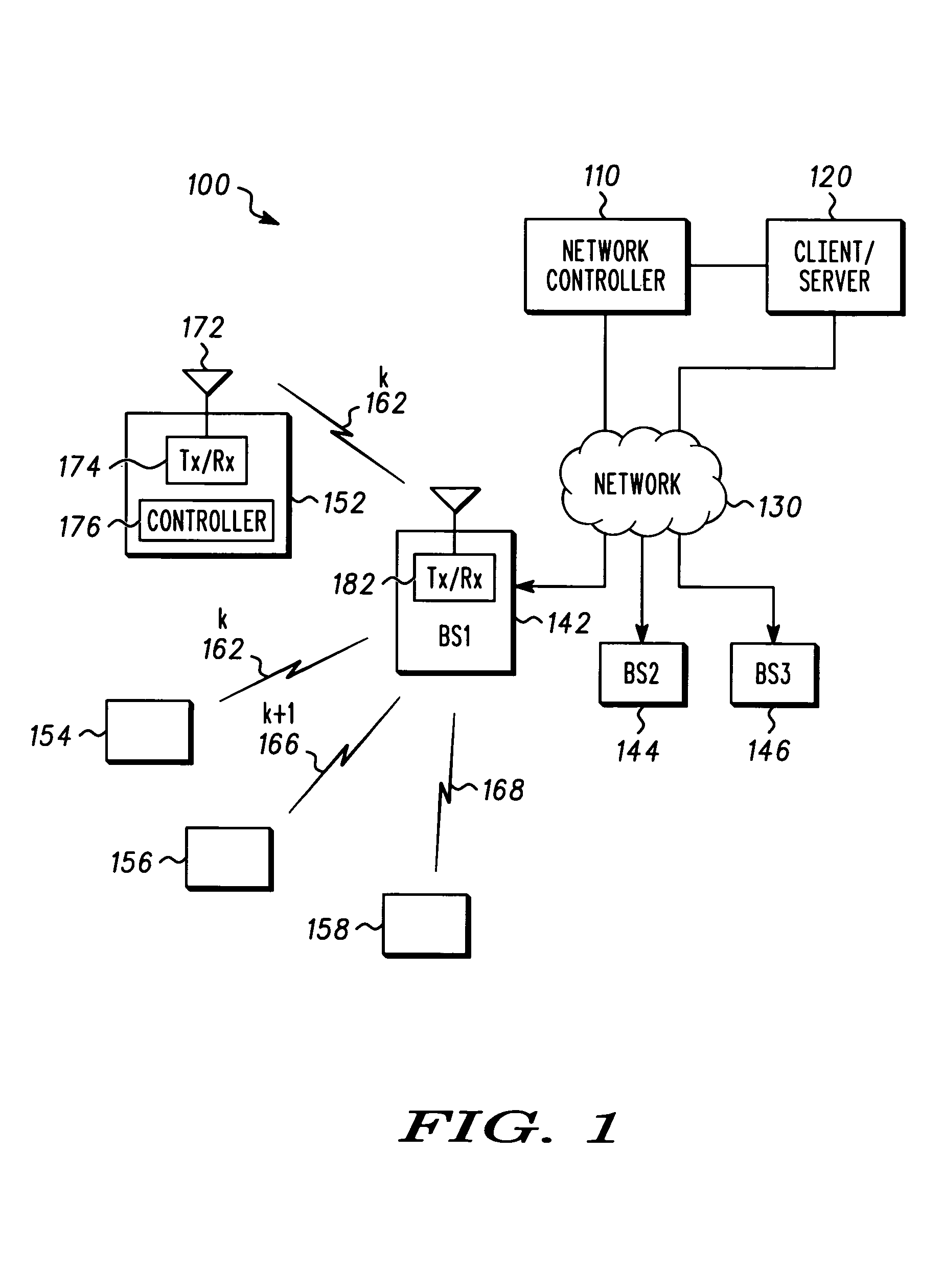
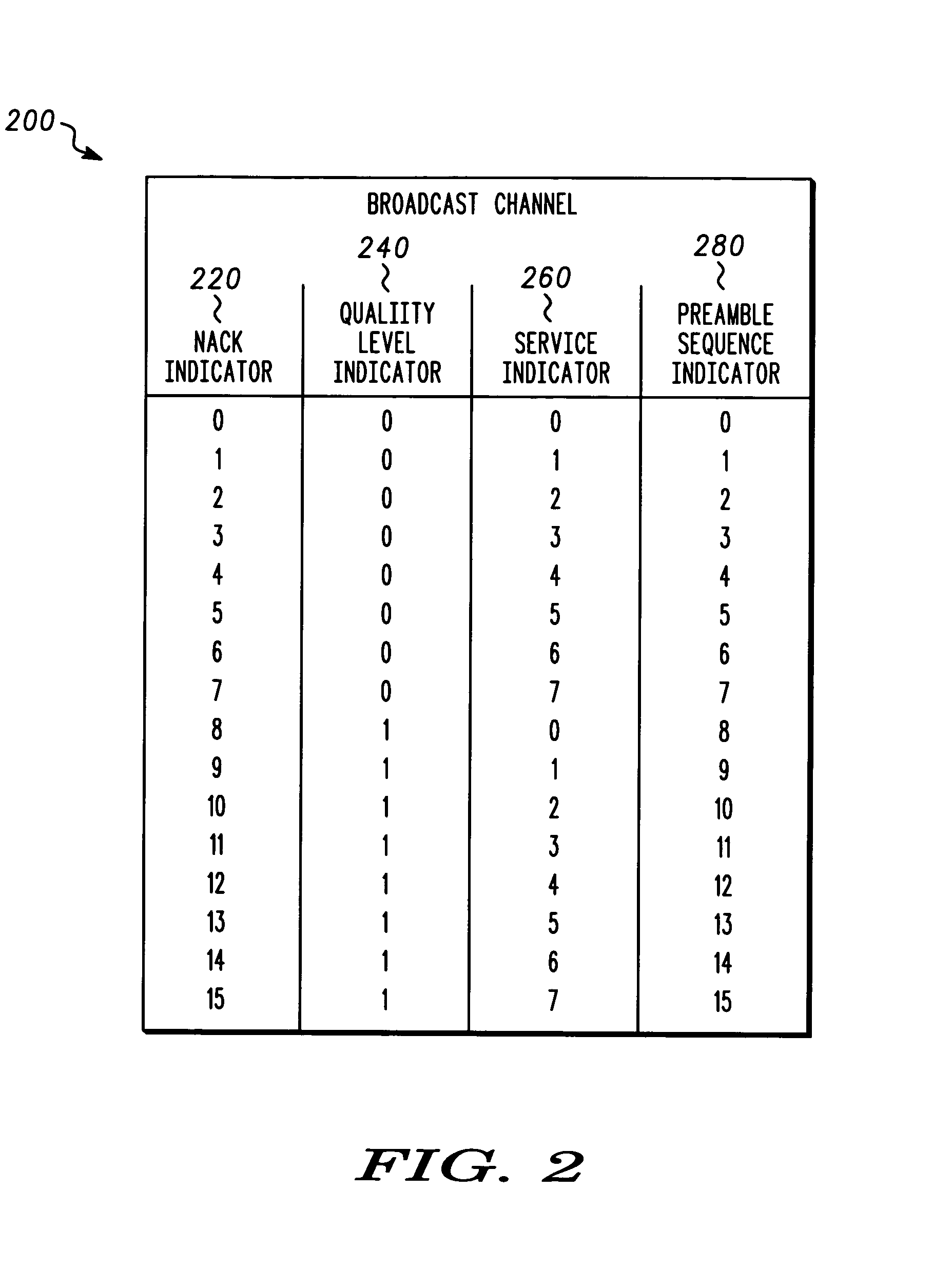
Apparatus and method for adaptive broadcast transmission
An apparatus and method for adaptive broadcast transmission. A broadcast transmission can be received. Insufficiency of a broadcast channel quality can be determined. A negative acknowledgement signal can be sent on a common uplink channel in response to determining the broadcast channel quality is insufficient. The negative acknowledgement signal can be received on the common uplink channel at another location, the negative acknowledgement signal indicating broadcast channel quality is insufficient. The broadcast channel quality can be adjusted in response to receiving the negative acknowledgement signal.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
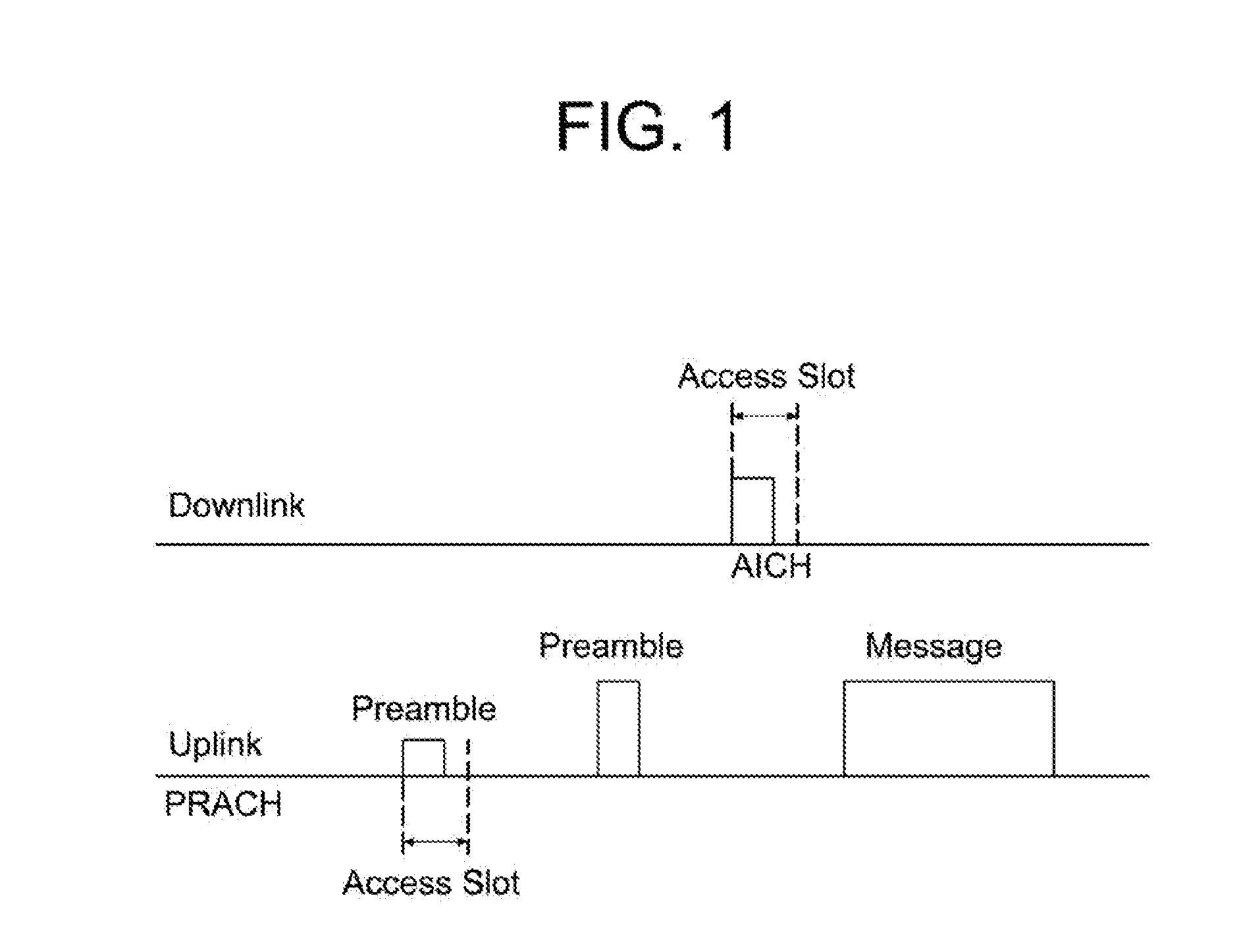
Channel assignment apparatus and method for a common packet channel in a WCDMA mobile communication system
InactiveUS6859445B1Improve reliabilityReduce complexityPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemCollision detection
A common packet channel assignment method and device in a CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) communication system is disclosed. The method comprises transmitting an access preamble signal having channel information which is used to access a base station, and then receiving an; access preamble acquisition indicator signal from the base station in response to the access preamble signal. A collision detection preamble for detecting a collision is transmitted in response to the received access preamble acquisition indicator signal. A first signal indicating acquisition of the collision detection preamble and a second signal indicating channel assignment are received, both of which the base station has transmitted in response to the collision acquisition signal. Upon receipt of the first signal, a common packet channel is assigned according to information designated by the second signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Code sequence generator in a CDMA modem
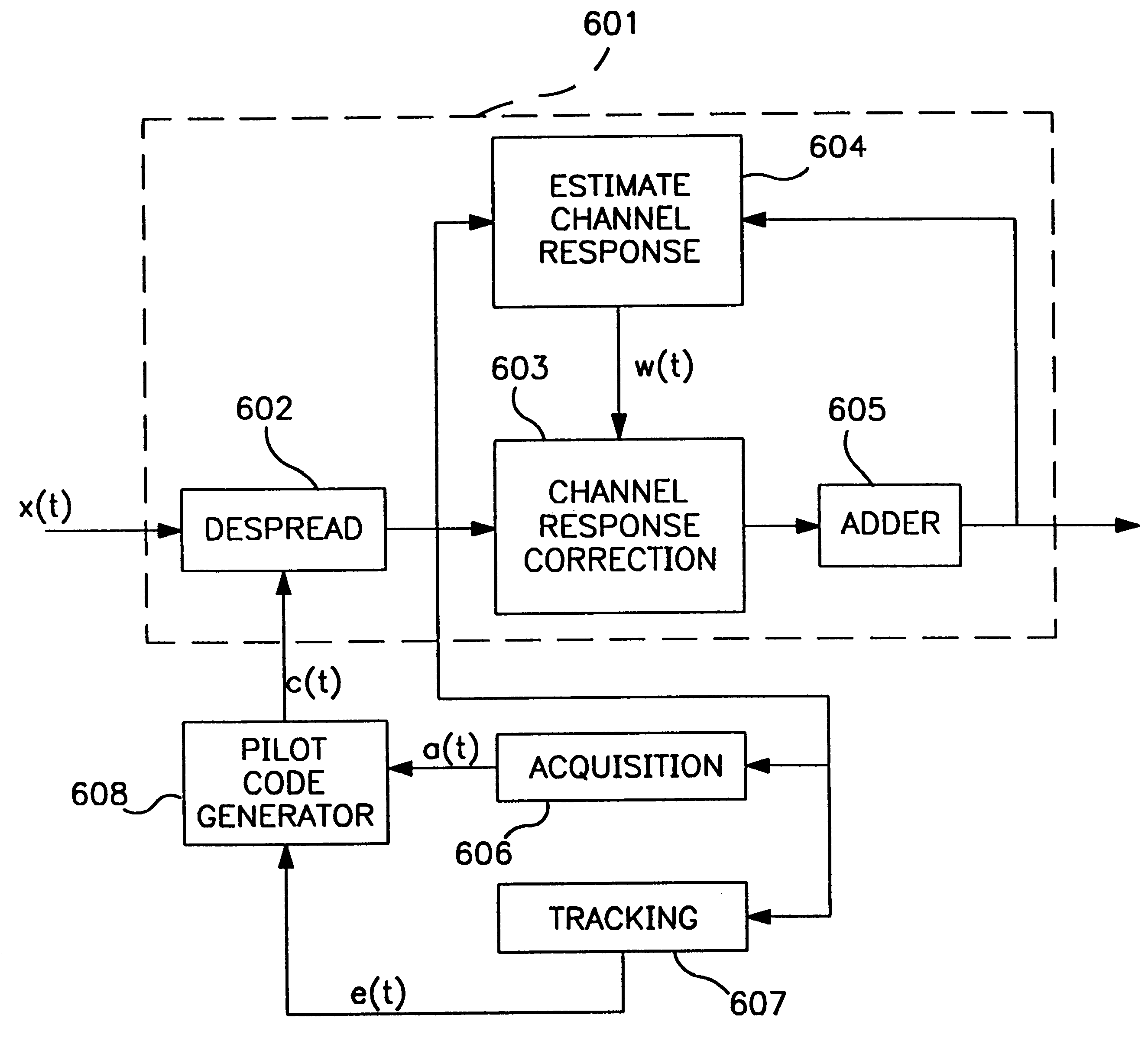
A CDMA modem includes a modem transmitter having: a code generator which provides an associated pilot code signal and which generates a plurality of message code signals: a spreading circuit which produces a spread-spectrum message signal by combining each of the information signals with a respective one of the message code signals; and a global pilot code generator that provides a global pilot code signal to which the message code signals are synchronized. The CDMA modem also includes a modem receiver having an associated pilot code generator and a group of associated pilot code correlators for correlating code-phase delayed versions of the associated pilot signal with a receive CDM signal to produce a despread associated pilot signal. The code phase of the associated pilot signal is changed responsive to an acquisition signal value until a pilot signal is received. The associated pilot code tracking logic adjusts the associated pilot code signal in phase responsive to the acquisition signal so that the signal power level of the despread associated pilot code signal is maximized. Finally, the CDMA modem receiver includes a group of message signal acquisition circuits, each including a plurality of receive message signal correlators which correlate respective local received message code signal to the CDM signal to produce a respective despread received message signal.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
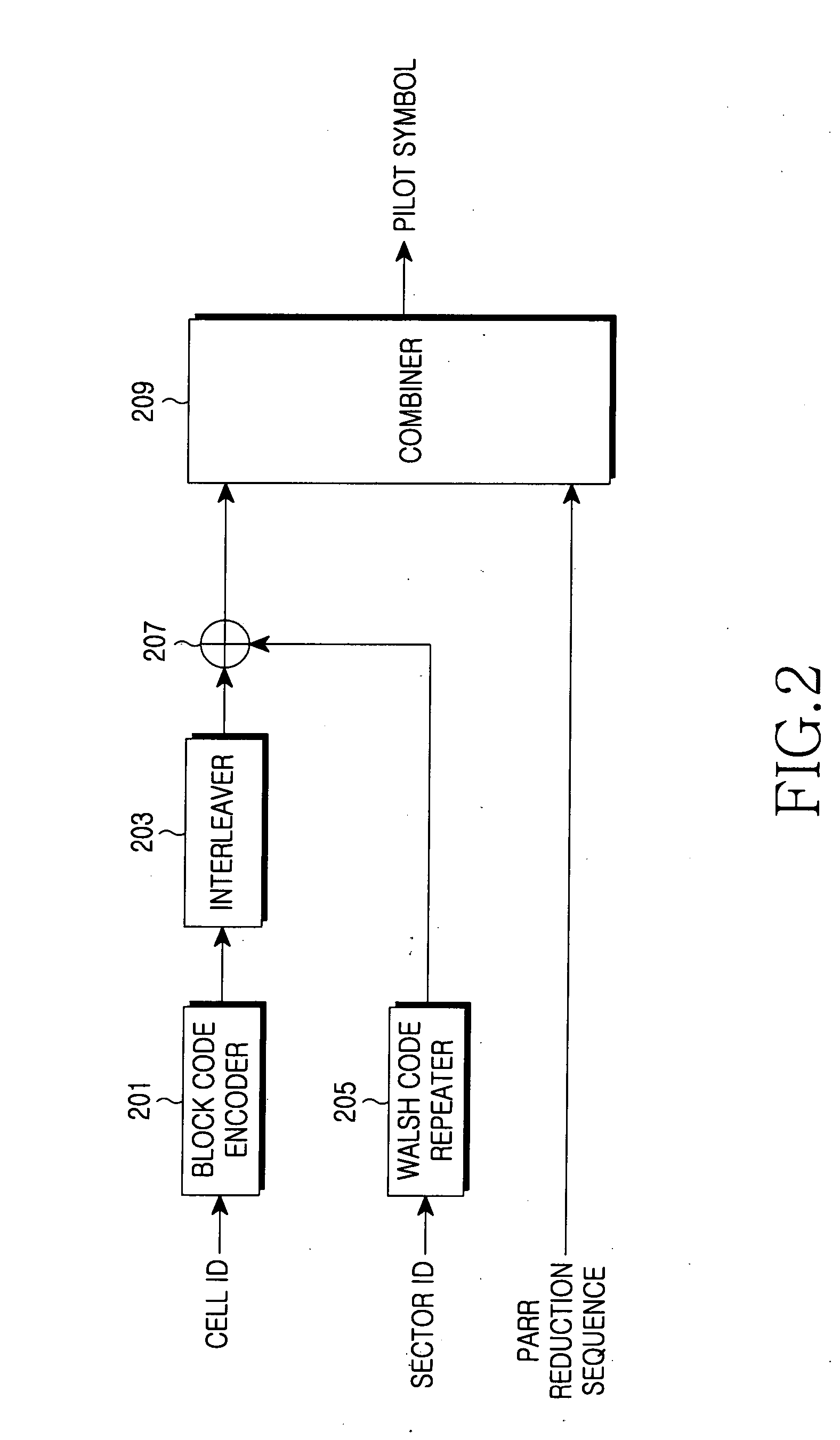
Radio communication apparatus and pilot symbol transmission method
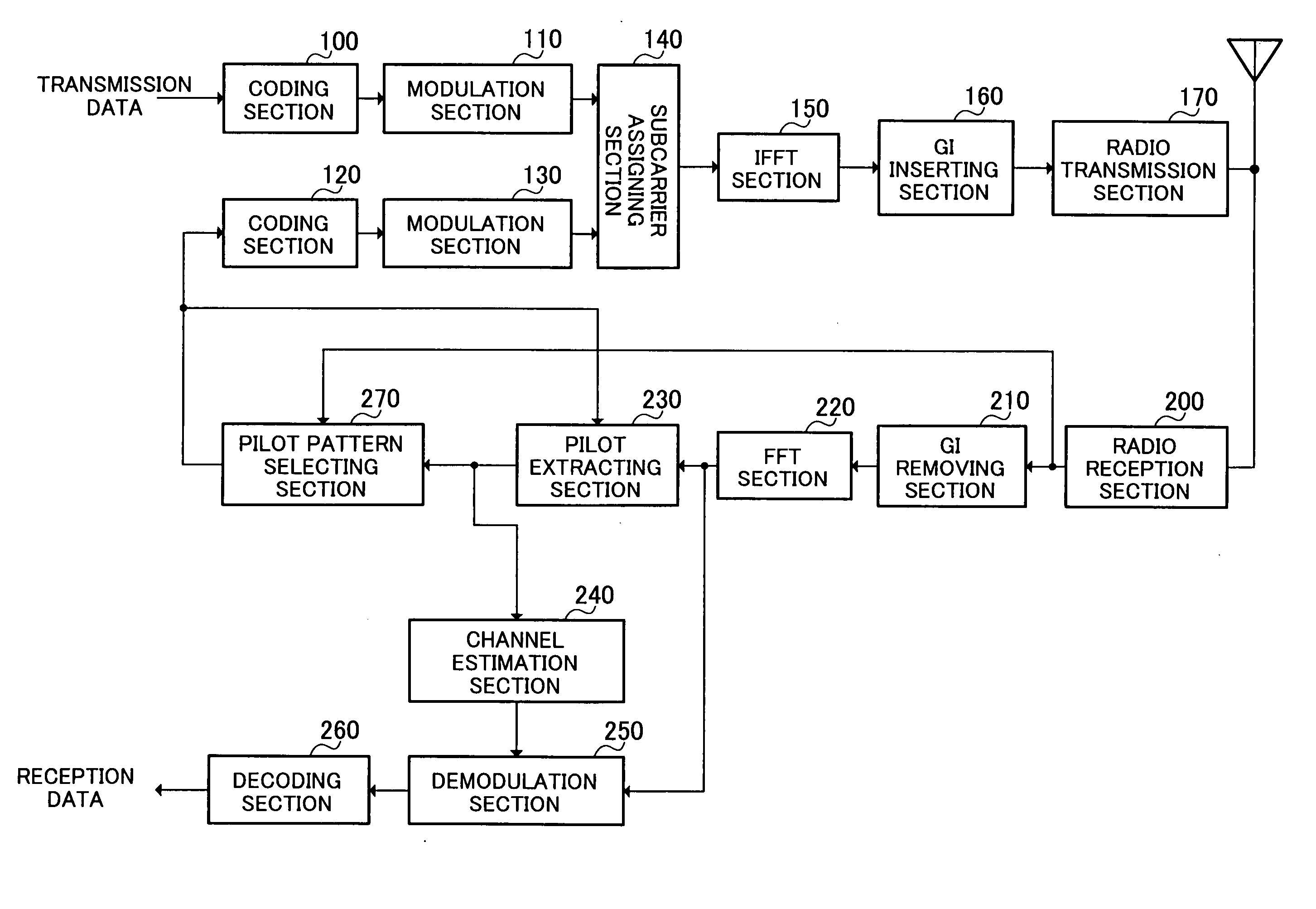
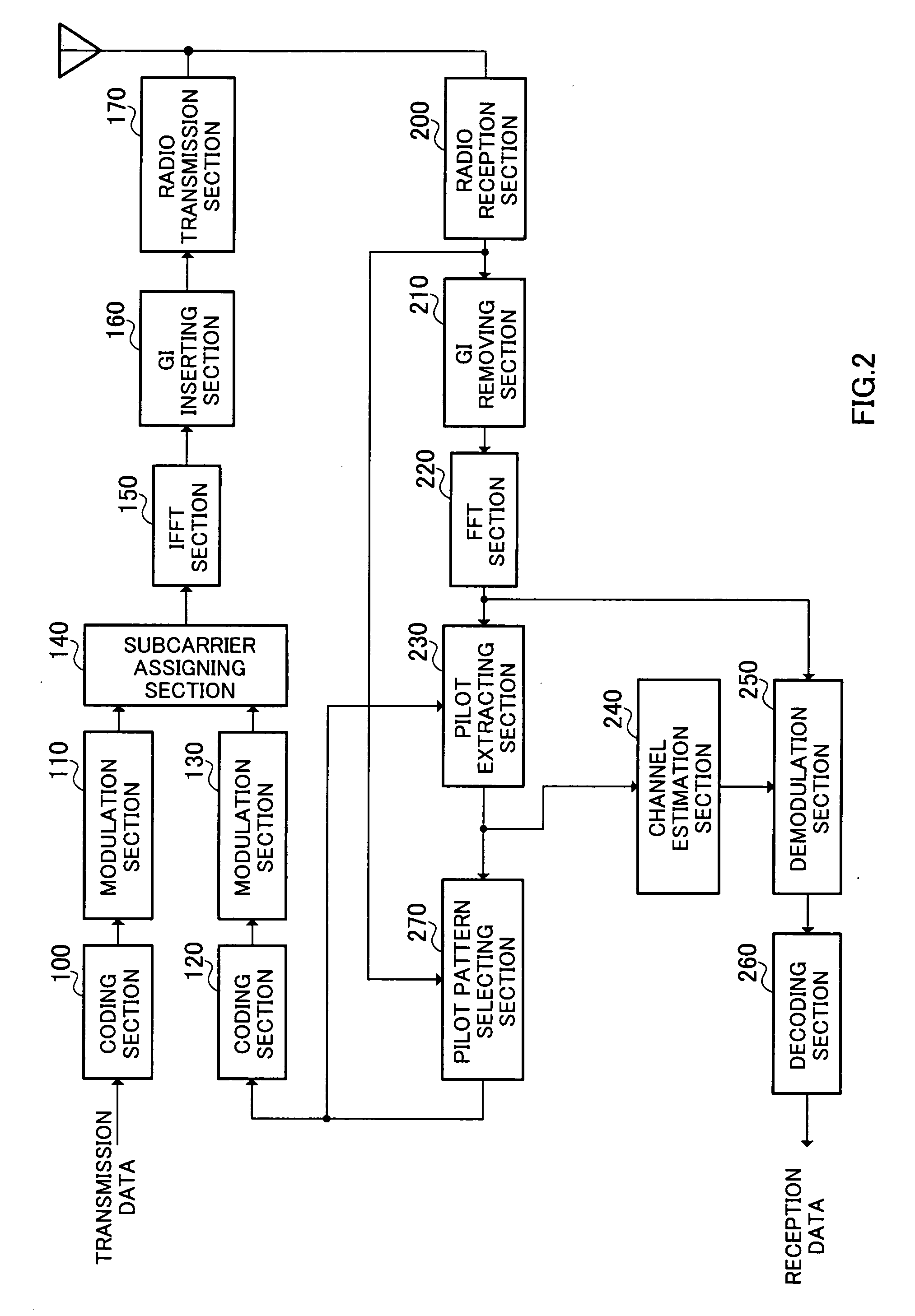
ActiveUS20060172704A1Channel capacity can be to minimumGuaranteed normal transmissionTransmission path divisionRadio transmissionEngineeringMobile station
A radio communication apparatus is disclosed that enables the influence of the feedback information on the channel capacity to be kept to the minimum without reducing the transmission efficiency of information by transmission of pilot symbol. In the apparatus, a delay dispersion measuring section (272) generates a delay profile using the received signal, and measures delay dispersion indicative of dispersion of delayed versions. A moving speed estimating section (274) estimates moving speed of a mobile station apparatus that transmits a pilot symbol based on the variation in reception power of the pilot symbol. An other-cell interference measuring section (276) measures other-cell interference caused by signals transmitted in cells except the cell to which the apparatus belongs. Corresponding to the delay dispersion, moving speed and other-cell interference, a pilot pattern information generating section (278) selects a pilot pattern such that placement of pilot symbol is optimal in a frame, and generates the pilot pattern information.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
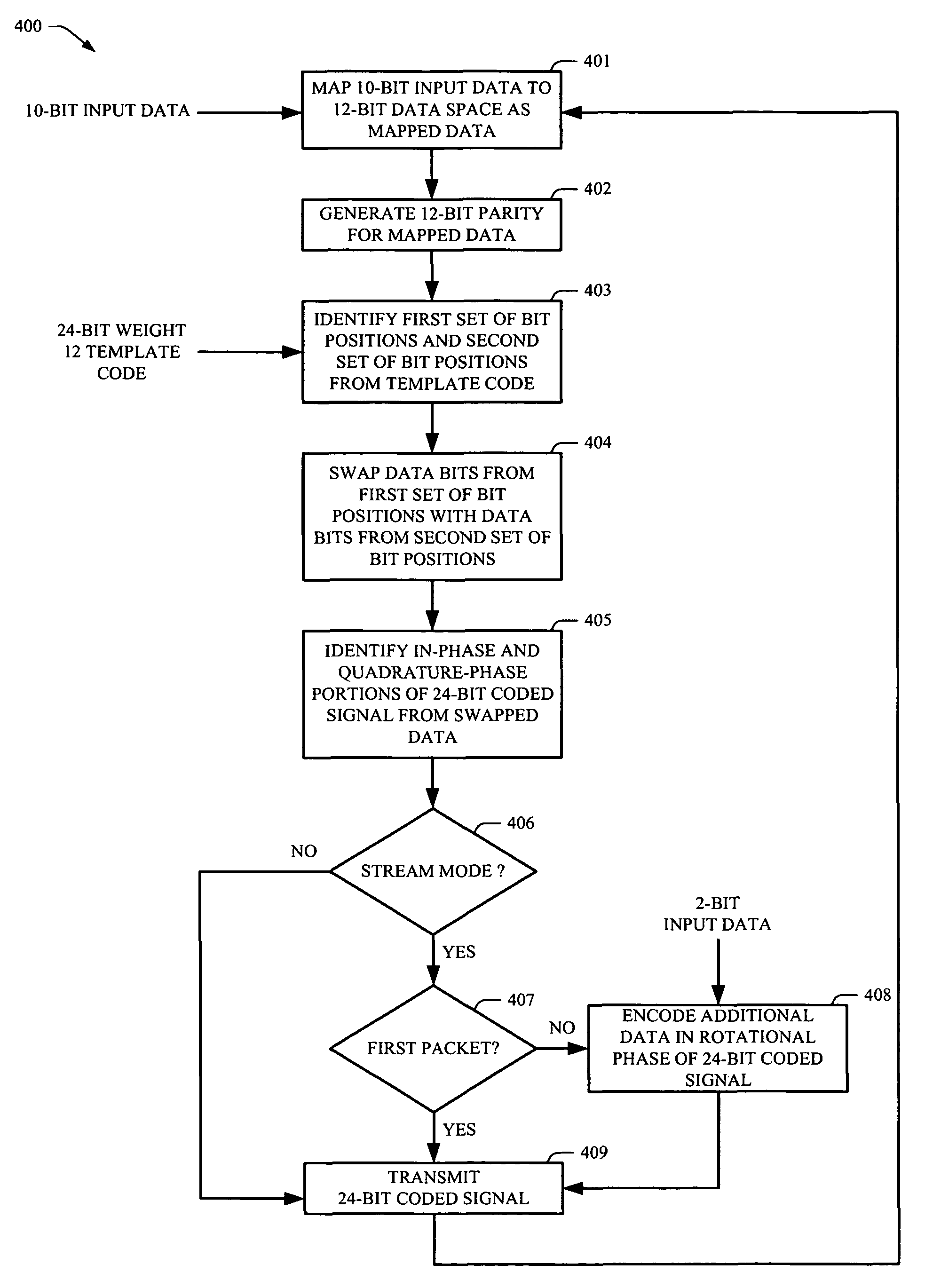
Rotationally invariant non-coherent burst coding
ActiveUS7779332B2Error correction/detection using block single space codingError preventionBit field24-bit
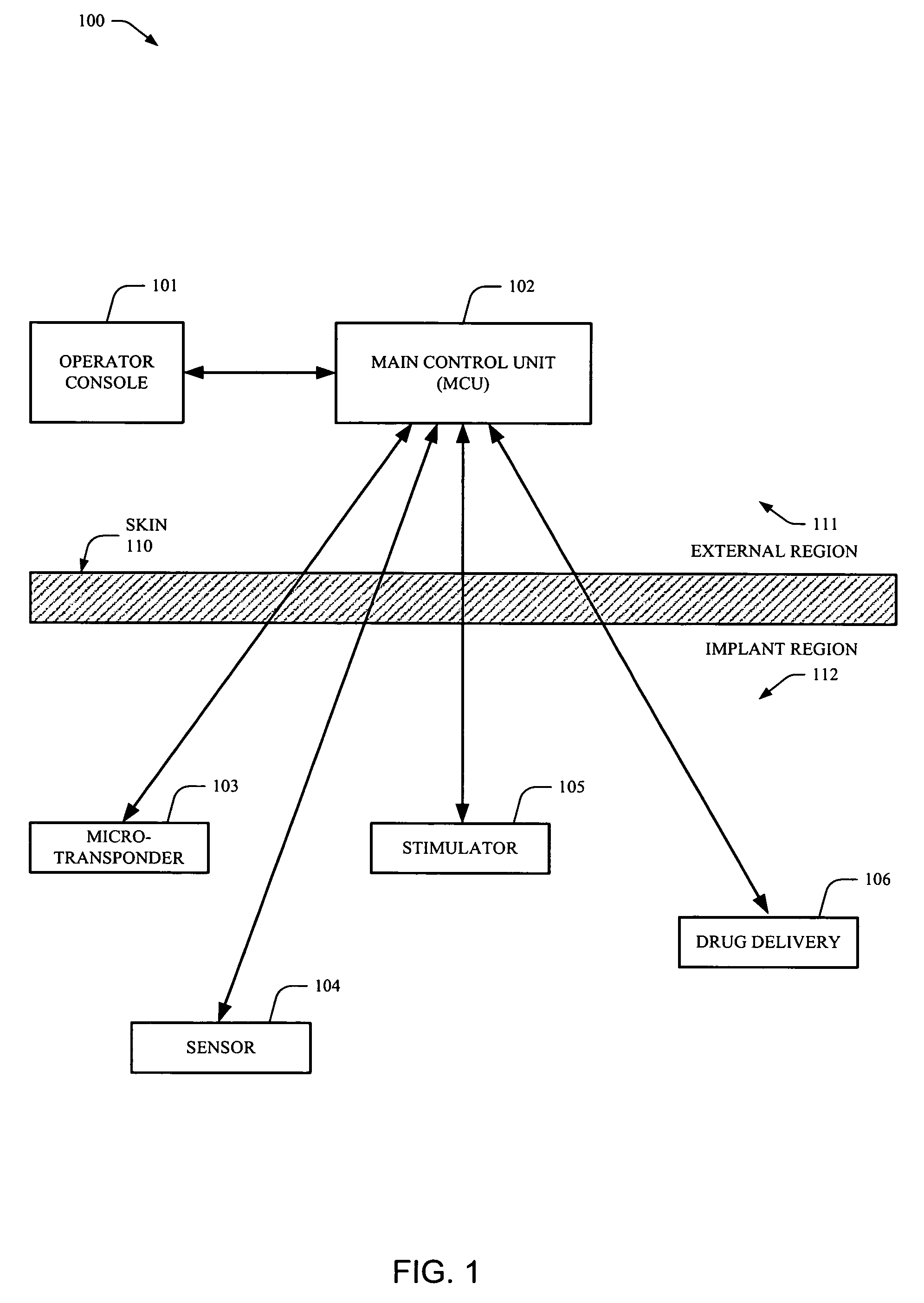
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
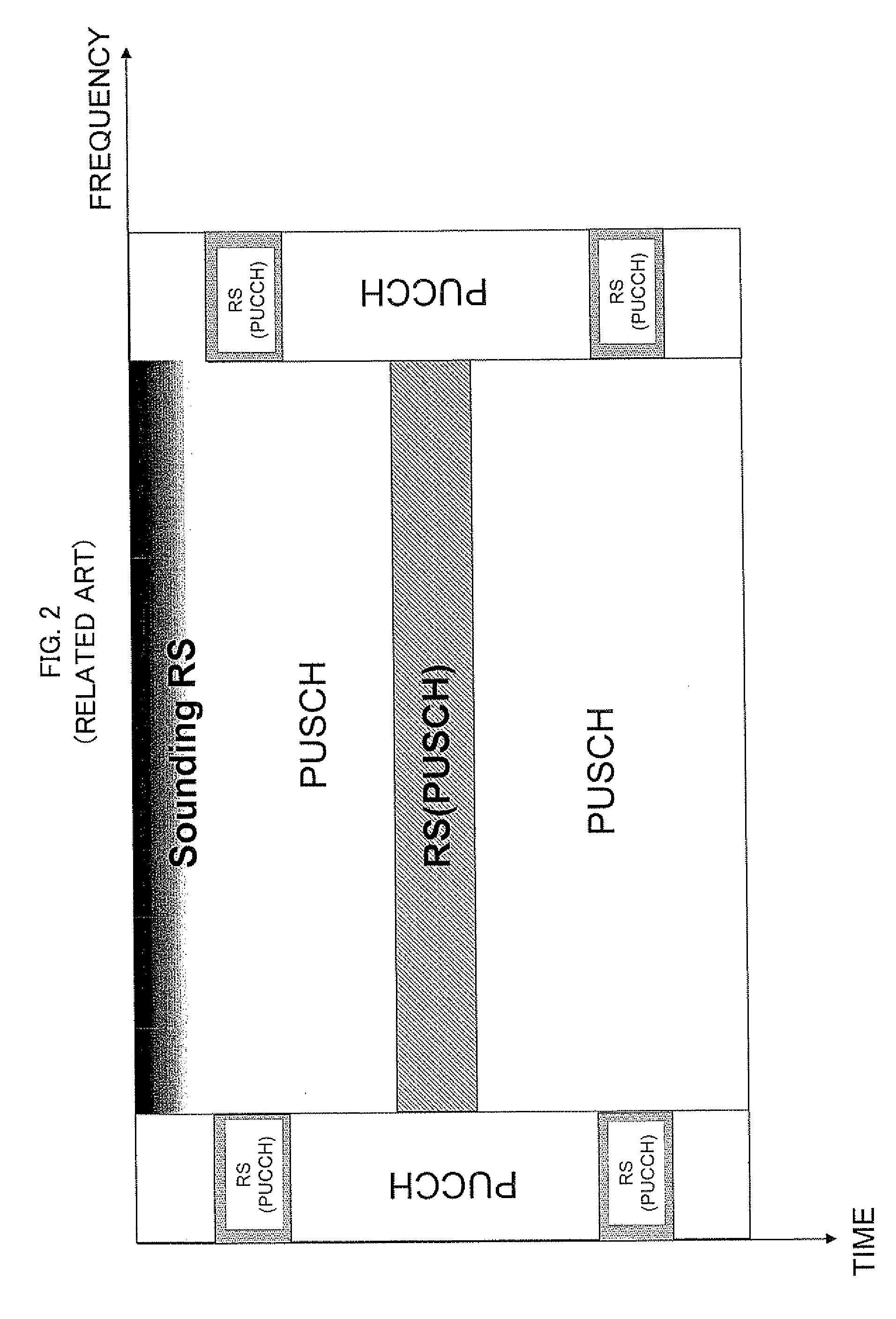
Method of transmitting sounding reference signal in wireless communication system
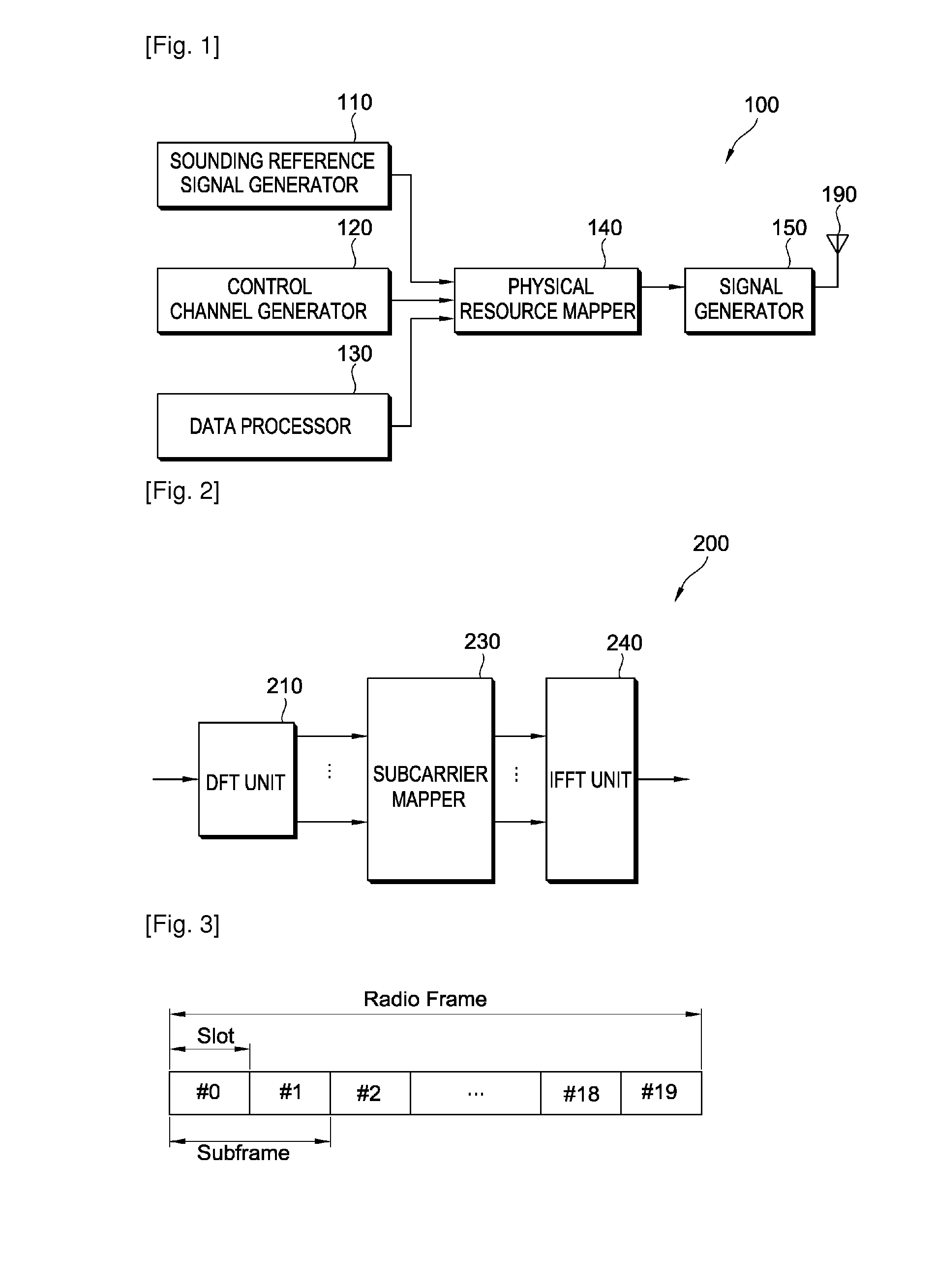
ActiveUS20100135273A1Reduce battery consumptionImprove spectral efficiencyError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemSounding reference signal
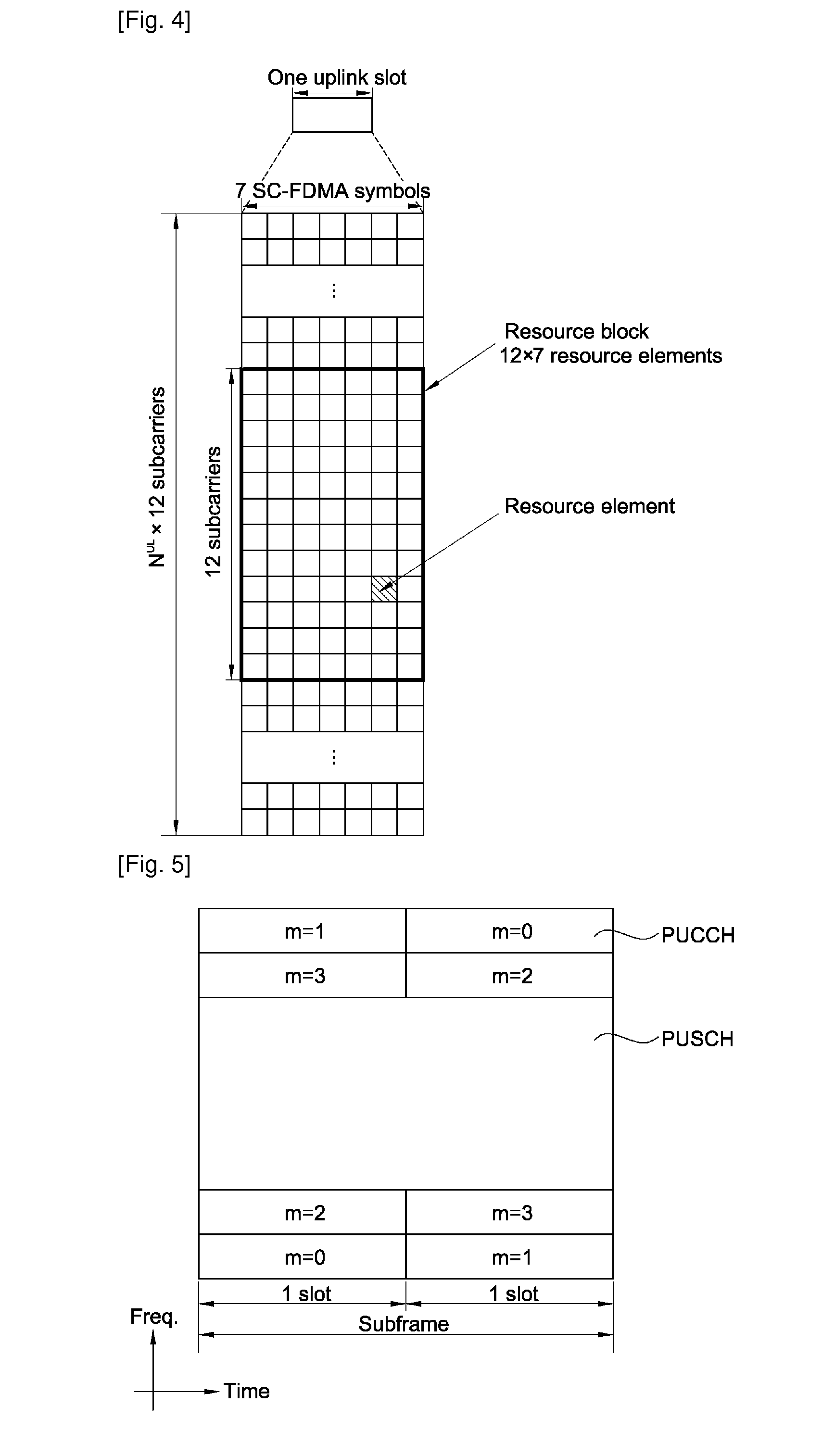
A method of transmitting a sounding reference signal includes generating a physical uplink control channel (PUCCH) carrying uplink control information on a subframe, the subframe comprising a plurality of SC-FDMA(single carrier-frequency division multiple access) symbols, wherein the uplink control information is punctured on one SC-FDMA symbol in the subframe, and transmitting simultaneously the uplink control information on the PUCCH and a sounding reference signal on the punctured SC-FDMA symbol. The uplink control information and the sounding reference signal can be simultaneously transmitted without affecting a single carrier characteristic.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Multicarrier transfer system and multicarrier modulation method
InactiveUS6870826B1Increase the number ofNetwork traffic/resource managementModulated-carrier systemsSoftware engineeringCarrier signal
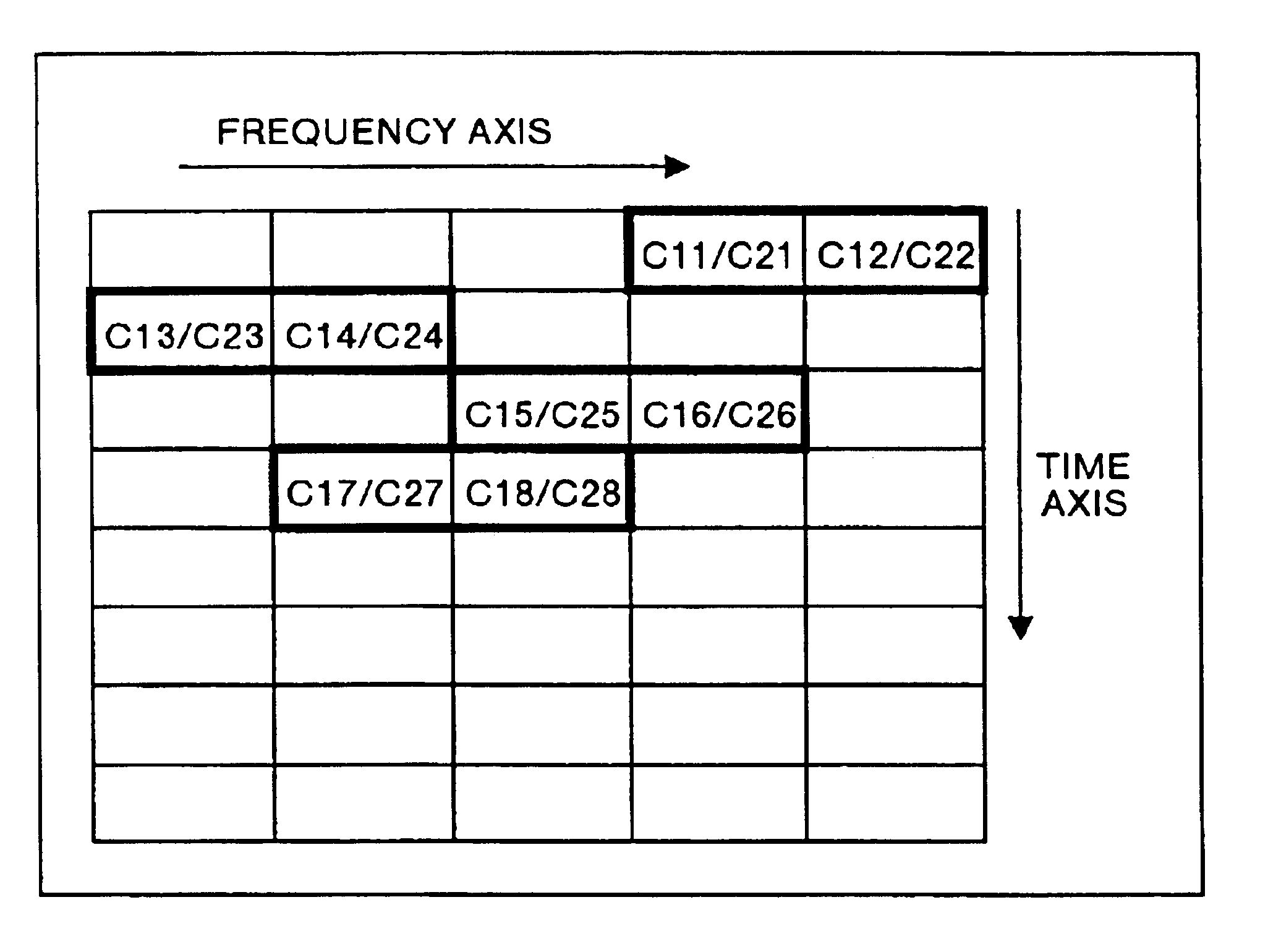
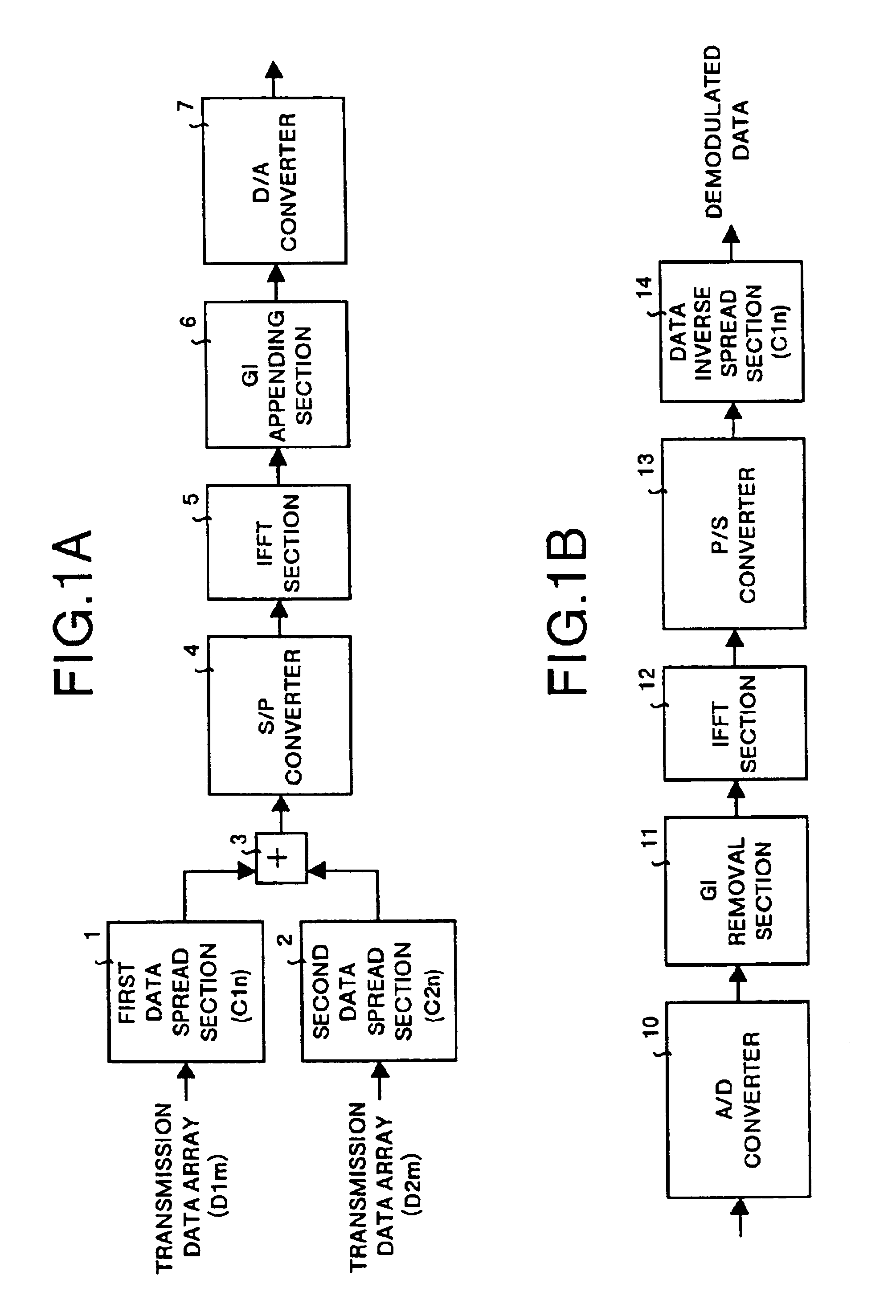
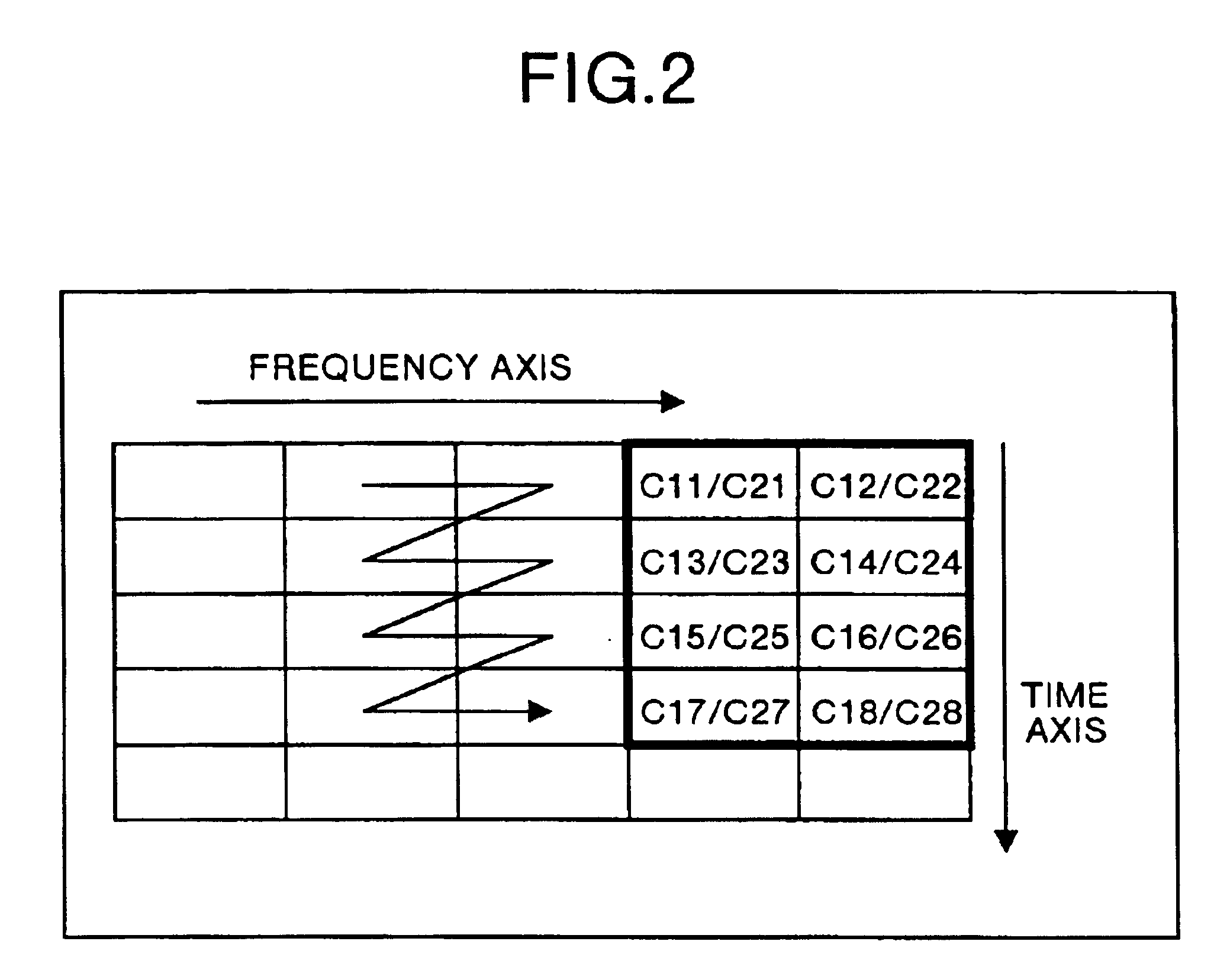
The multicarrier transfer system employing the OFDM / CDMA modulation system comprises a transmitter having an S / P converter which two-dimensionally arranges spread signals for a transmission data array on a frequency and time axes system and then rearrange the spread signals for one transmission data array arranged two-dimensionally. The transmitter transmits the signals generated in the S / P converter. A receiver receives the signals transmitted by the transmitter and demodulates the signal to reconstruct the transmission data array.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
Apparatus and method for modulating ranging signals in a broadband wireless access communication system
InactiveUS20050030931A1Avoid signal interferenceEasy searchTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionCommunications systemCell region
An method and apparatus for transmitting ranging information from at least one base station to subscriber stations and generating a ranging signal by the subscriber station using received ranging information in a Broadband Wireless Access (BWA) communication system including a plurality of neighbor cells and a plurality of the subscriber stations located in each cell region. A first code generator generates a first code using different first code information received from the base stations in the neighbor cells allocated the first code information. A second code generator generates a second code using second code information received by each of the subscriber stations existing in cell regions of the neighbor cells. A ranging signal generator generates a new ranging signal by combining the first code with the second code.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving pilot signal in communication system using OFDM scheme
ActiveUS20060028976A1Interference minimizationMinimize interferenceModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionComputer hardwareFast Fourier transform
Disclosed is a method for transmitting a reference signal for identification of each cell in a communication system including a plurality of cells each of which is identified by a cell identifier. The method includes receiving a cell identifier, and generating a block code corresponding to the cell identifier using a predetermined block code generator matrix, and generating a first part sequence using the block code; selecting a second part sequence in accordance with the cell identifier; generating a reference signal of a frequency domain using the first part sequence and the second part sequence; converting the reference signal of the frequency domain to a reference signal of a time domain through an Inverse Fast Fourier Transform operation and transmitting the reference signal of the time domain in a predetermined reference signal transmission interval.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
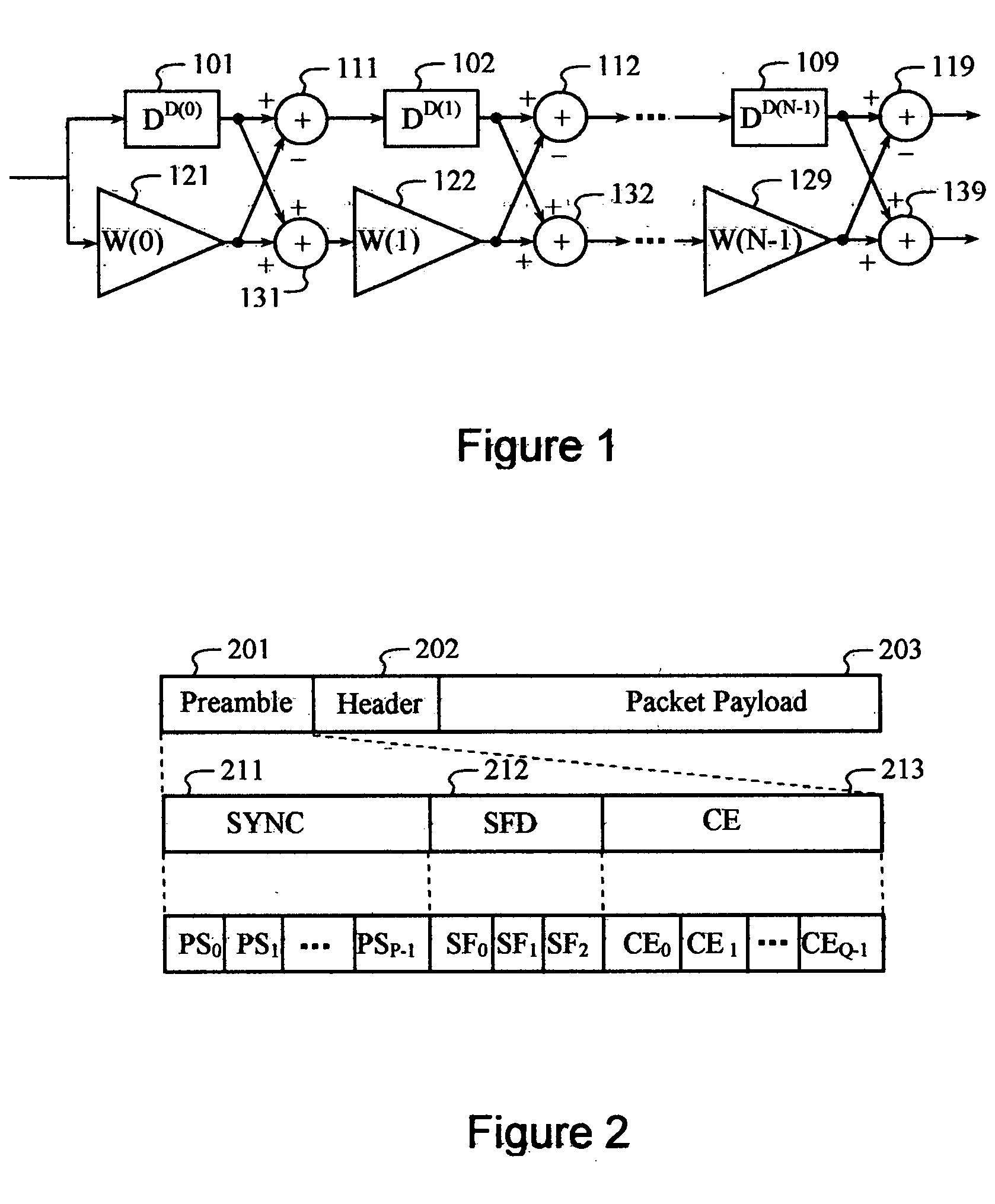
Frame format for millimeter-wave systems
ActiveUS20070168841A1Transmission path divisionCode conversionMillimeter wave communication systemsMultipath channels
A single frame format is employed by a millimeter wave communication system for single-carrier and OFDM signaling. A Golay-coded sequence in the start frame delimiter (SFD) field identifies the data transmission as single carrier or OFDM. Complementary Golay codes are employed in a channel estimation field to allow a perfect estimate of the multipath channel to be made. Marker codes generated from Golay codes are inserted periodically between slots for tracking and / or for reacquiring timing, frequency, and multipath channel estimates. The length of the marker codes may be adapted relative to the multipath delay spread.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
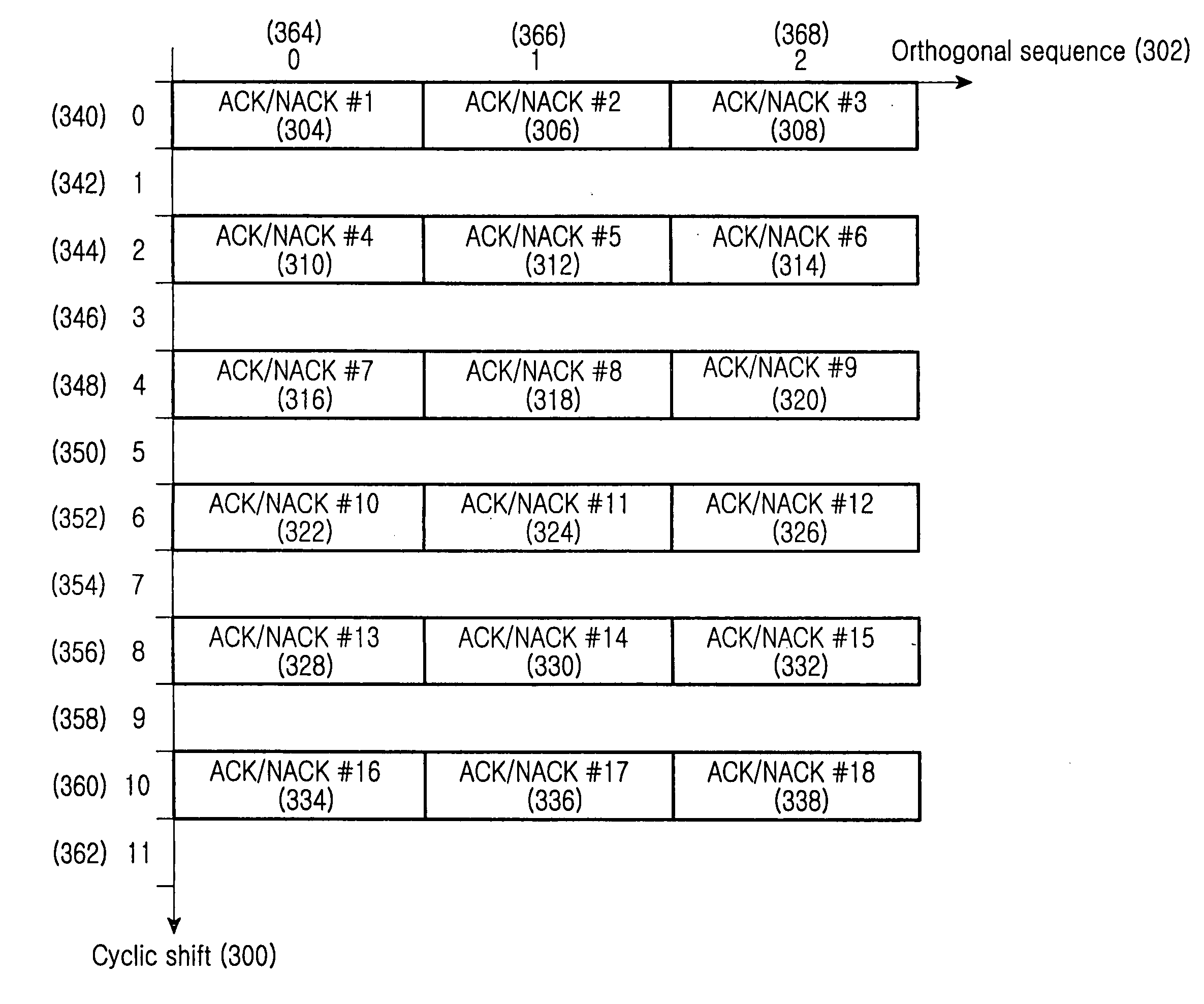
Apparatus and method for allocating code resources to uplink ack/nack channels in a cellular wireless communication system
ActiveUS20090046646A1Interference minimizationMinimize impactModulated-carrier systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemResource allocation
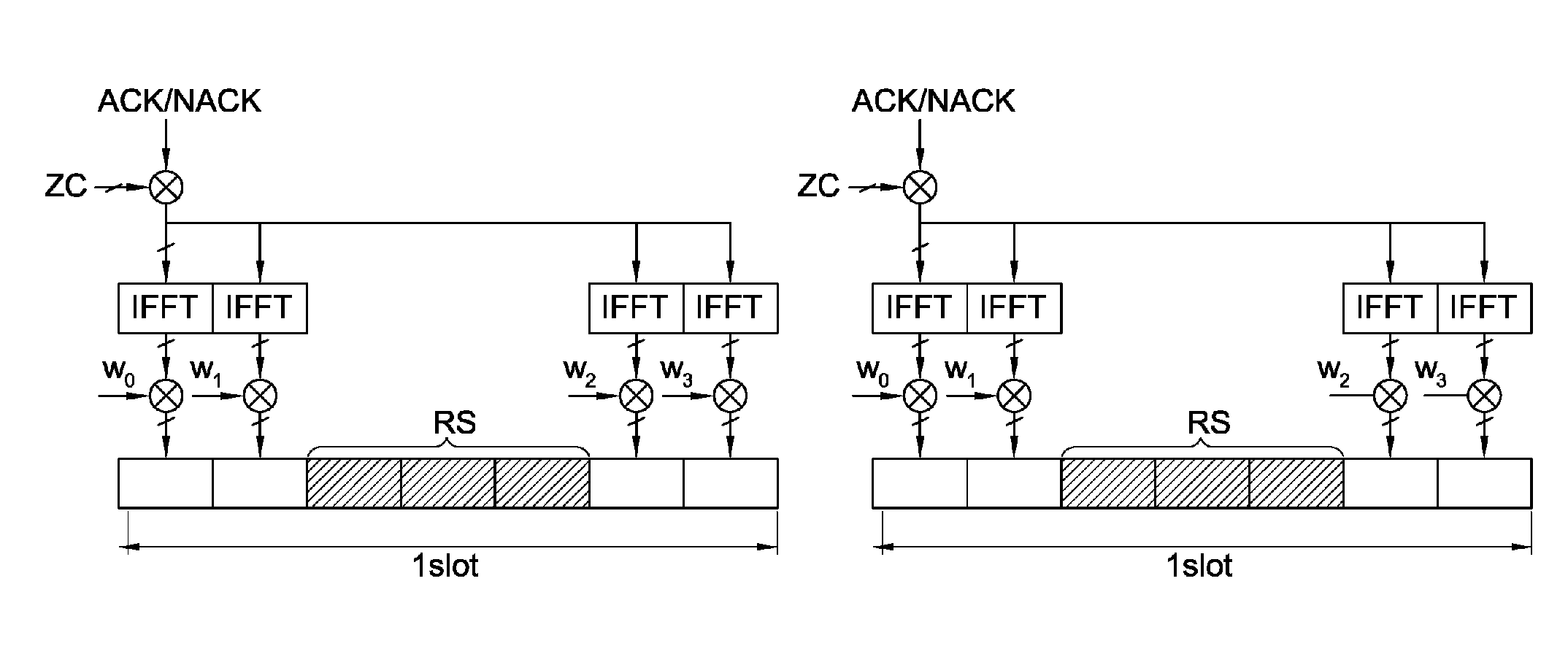
A method and apparatus are provided for allocating code resources to ACK / NACK channel indexes, when UEs need ACK / NACK transmission in a wireless communication system in which a predetermined number of orthogonal cover Walsh codes is selected from among available orthogonal cover Walsh codes, at least one subset is formed, having the selected orthogonal cover Walsh codes arranged in an ascending order of cross interference, subsets are selected for use in first and second slots of a subframe, and the orthogonal cover Walsh codes of the subset selected for each slot and ZC sequence cyclic shift values are allocated to the ACK / NACK channel indexes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of transmitting control signal in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20090290538A1Guaranteed normal transmissionImprove system performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemResource block
A method of transmitting a control signal in a wireless communication system is provided. The method includes acquiring a resource index, the number of cyclic shifts (CSs) and a CS interval, wherein the number of CSs is an integer multiple of the CS interval, determining a CS index based on the number of CSs and the CS interval, generating a cyclically shifted sequence by cyclically shifting a base sequence by a CS amount obtained from the CS index, generating a modulated sequence based on the cyclically shifted sequence and a symbol for a control signal and transmitting the modulated sequence after mapping the modulated sequence to a resource block obtained from the resource index.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Aggregating multiple wireless communication channels for high data rate transfers
InactiveUS20030081582A1Appropriate performancePulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision system scanning detailsNetwork connectionComputer terminal
A mobile wireless terminal (MWT) receives IP packets destined for a ground network in a predetermined sequence order. The MWT fragments each of the IP packets into many smaller packet fragments, appends identifying information to each of the packet fragments, and transmits the packet fragments in parallel with one another over concurrently operating satellite channels. A receiving station receives the packet fragments transmitted by the MWT. The receiving station forwards the received packet fragments to a ground controller over a network connection, based on the identifying information appended to the packet fragments. The ground controller combines the packet fragments into reconstructed IP packets based on the identifying information appended to the fragments. The ground controller also sequences the reconstructed IP packets in the predetermined sequence order based on the identifying information. The ground controller forwards the reconstructed IP packets in the correct sequence order to the destination ground network. The same sequence of events occur in the opposite direction as well i.e., from the ground controller to the MWT.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Handover method in wireless telecommunication system supporting USTS
InactiveUS6892071B2Synchronisation arrangementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile stationHandover
A handover method in wireless telecommunication system supporting USTS is disclosed. The method for performing a handover of a mobile station in an asynchronous wireless telecommunication system supporting an uplink synchronous transmission scheme (USTS) mode, includes the steps of: a) performing a mode conversion of the mobile station from the USTS mode to a non-USTS mode based on a first signal measurement result from the mobile station; and b) performing a handover for the mobile station. In another embodiment of the present invention, the method further includes the step of: c) performing a mode conversion from the non-USTS mode to the USTS mode based on a second signal measurement result from the mobile station.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
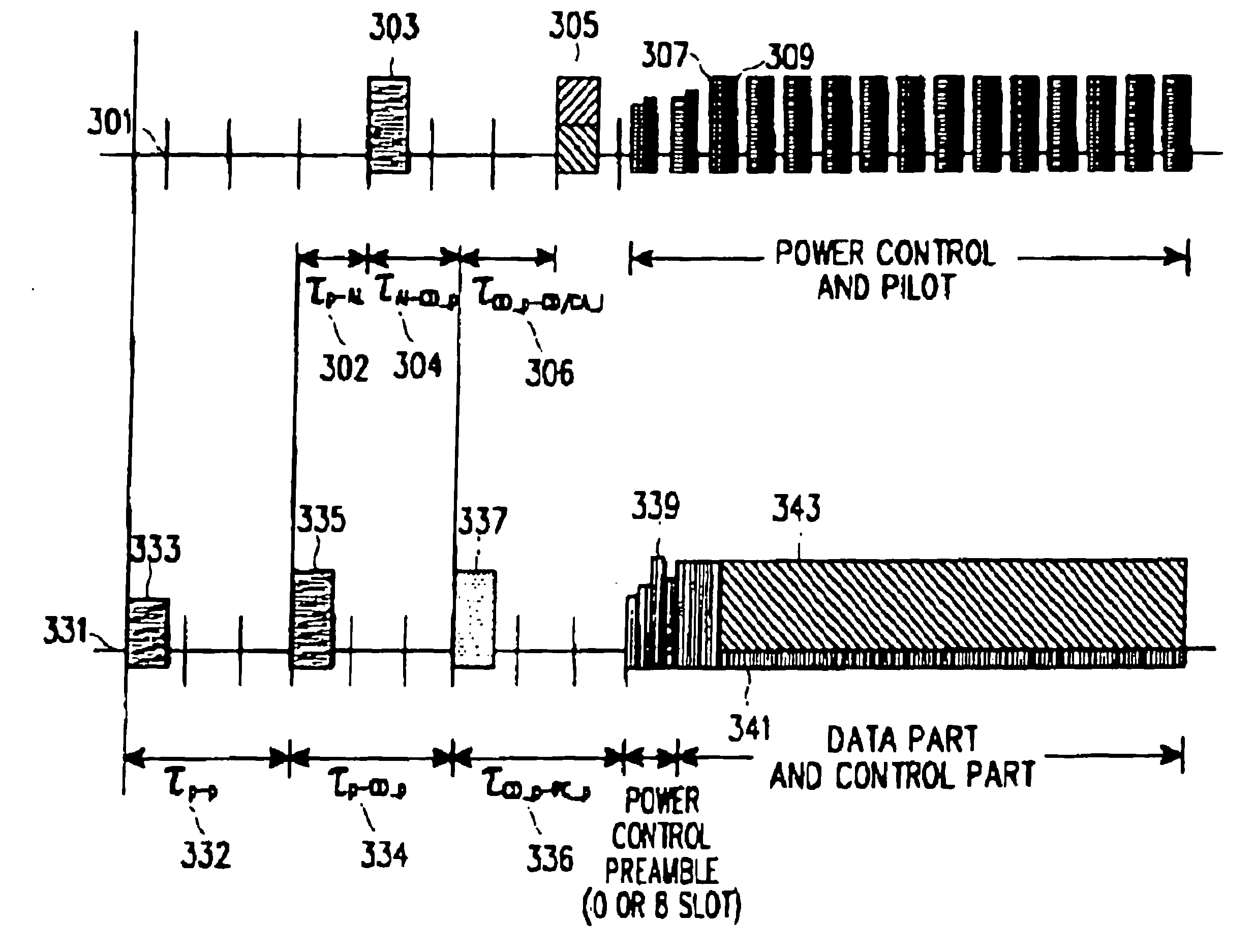
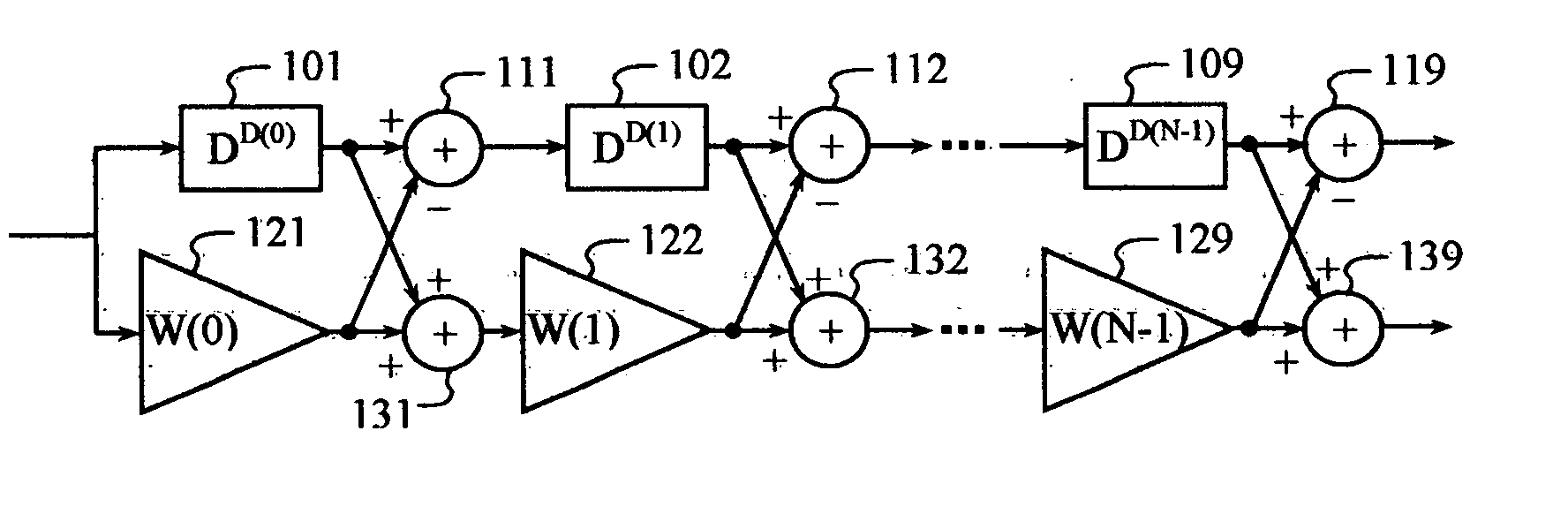
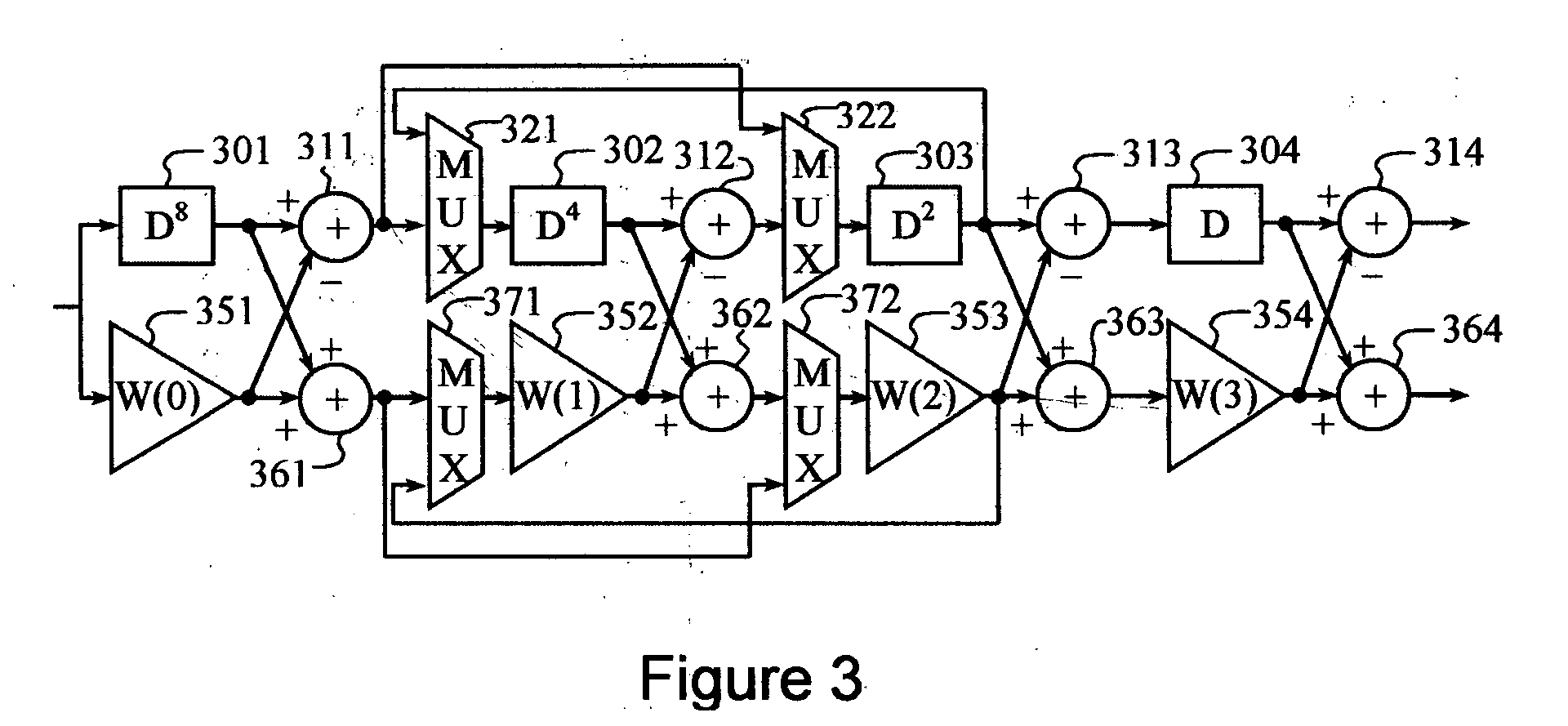
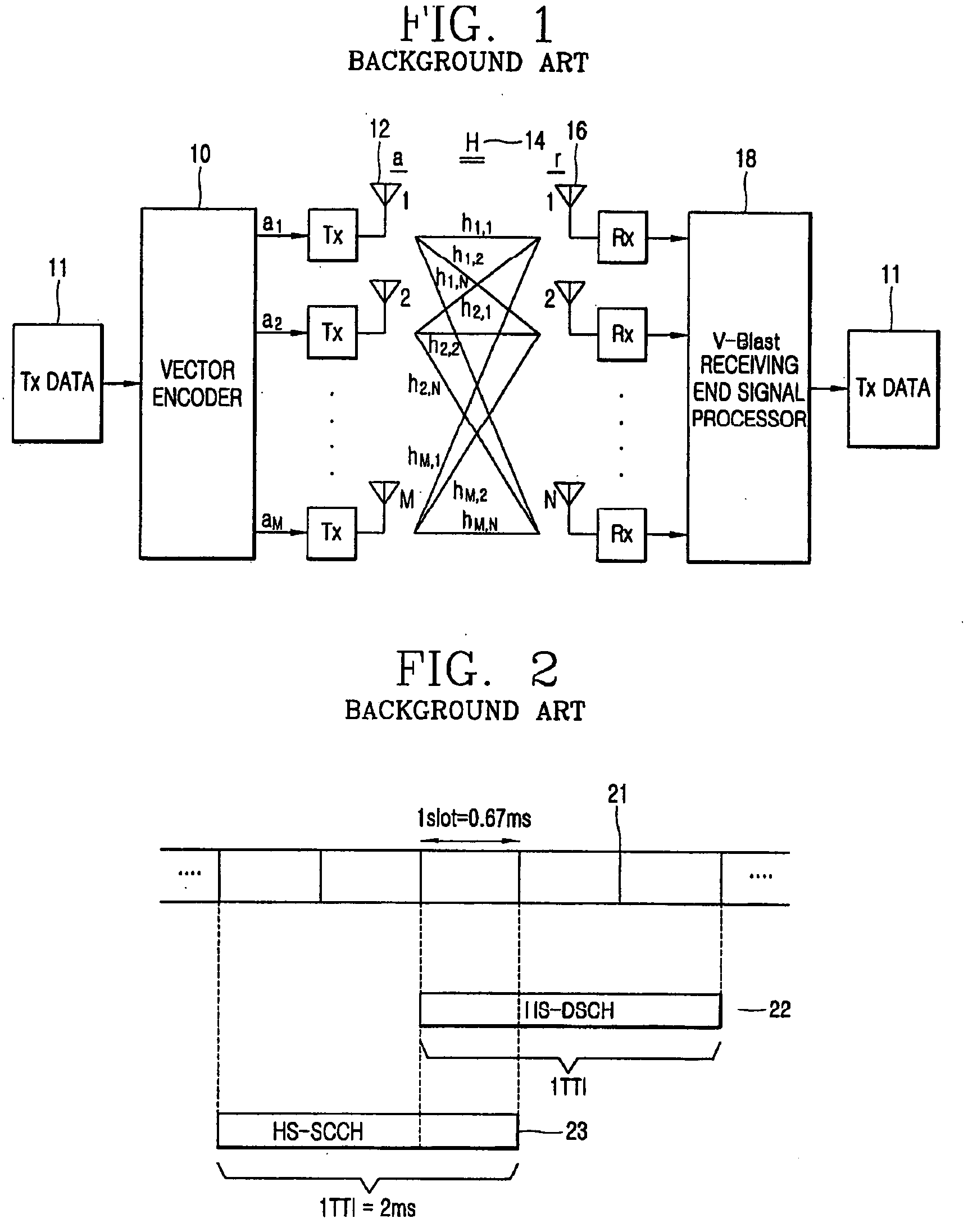
Transceiver apparatus and method for efficient high-speed data retransmission and decoding in a CDMA mobile communication system
ActiveUS7027782B2Improve radio communication performanceEfficiently transmitting and receivingError preventionBroadcast transmission systemsTransceiverSymbol mapping
A method for retransmitting coded bits by a transmitter in response to a retransmission request from a receiver in a mobile communication system which separates coded bits output from an encoder into coded bits with higher priority and coded bits with lower priority, and transmits from the transmitter to the receiver a stream of symbols obtained by symbol mapping the coded bits by a specific modulation technique. The method comprises determining orthogonal codes available for retransmission; separating the coded bits with higher priority and the coded bits with lower priority into a plurality of sub-packets with a given size, and selecting a part of the sub-packets or sub-packets to be repeatedly transmitted, depending on the determined number of available orthogonal codes; and transmitting a stream of symbols obtained by symbol-mapping coded bits of the selected sub-packets by the specific modulation technique, with the determined available orthogonal codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
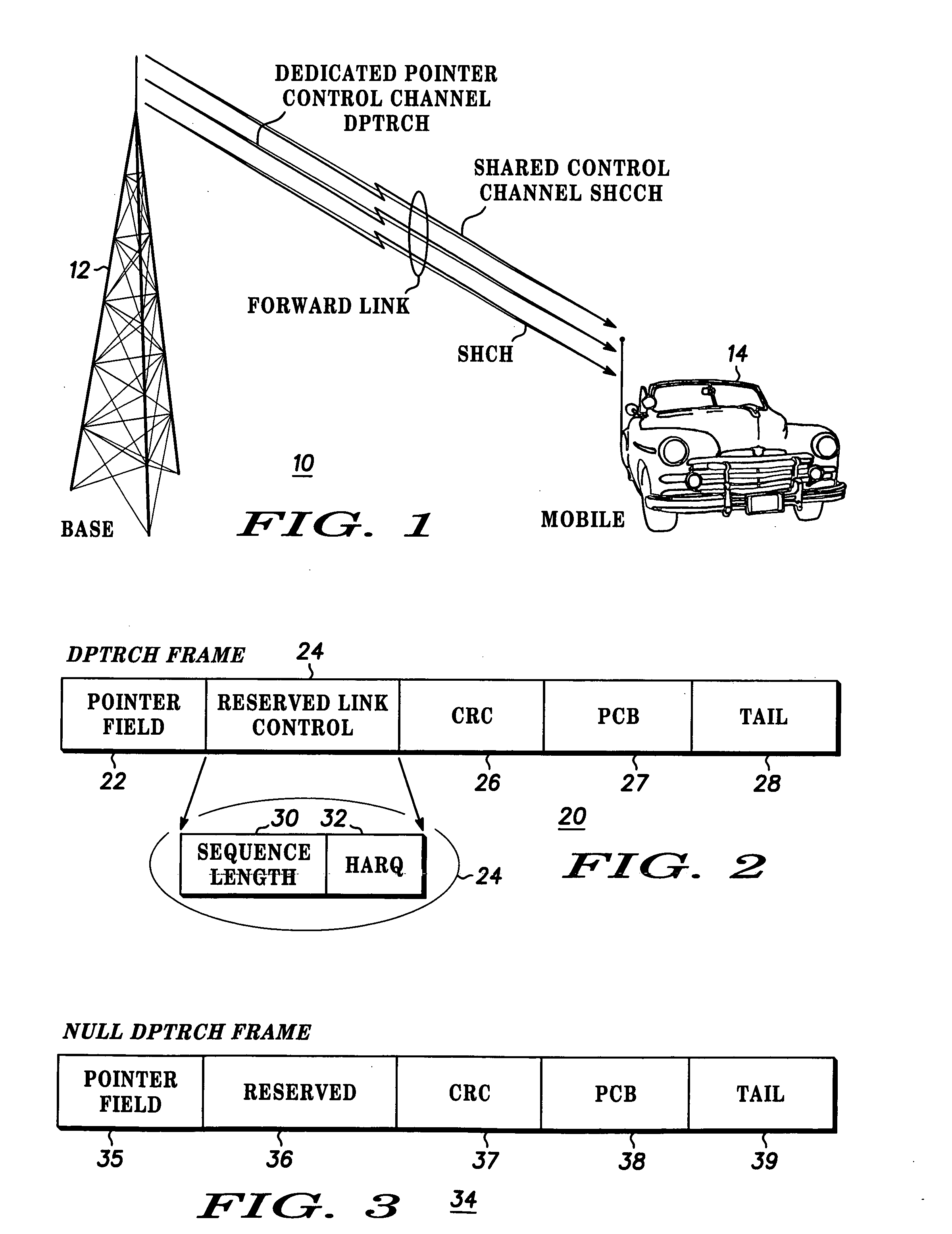
Apparatus and method for providing separate forward dedicated and shared control channels in a communications system
InactiveUS6934275B1Assess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemIntermittent control
Separate forward dedicated and shared control channels are provided in a spread-spectrum communication. The forward dedicated control channel is used to communicate persistent control information and point to the shared control channel when further intermittent control information concerning transmission of data to a mobile station needs to be communicated. The use of a dedicated control channel for only necessary persistent control information, while only pointing to a shared control channel when it is needed, affords more efficient utilization of system resources.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
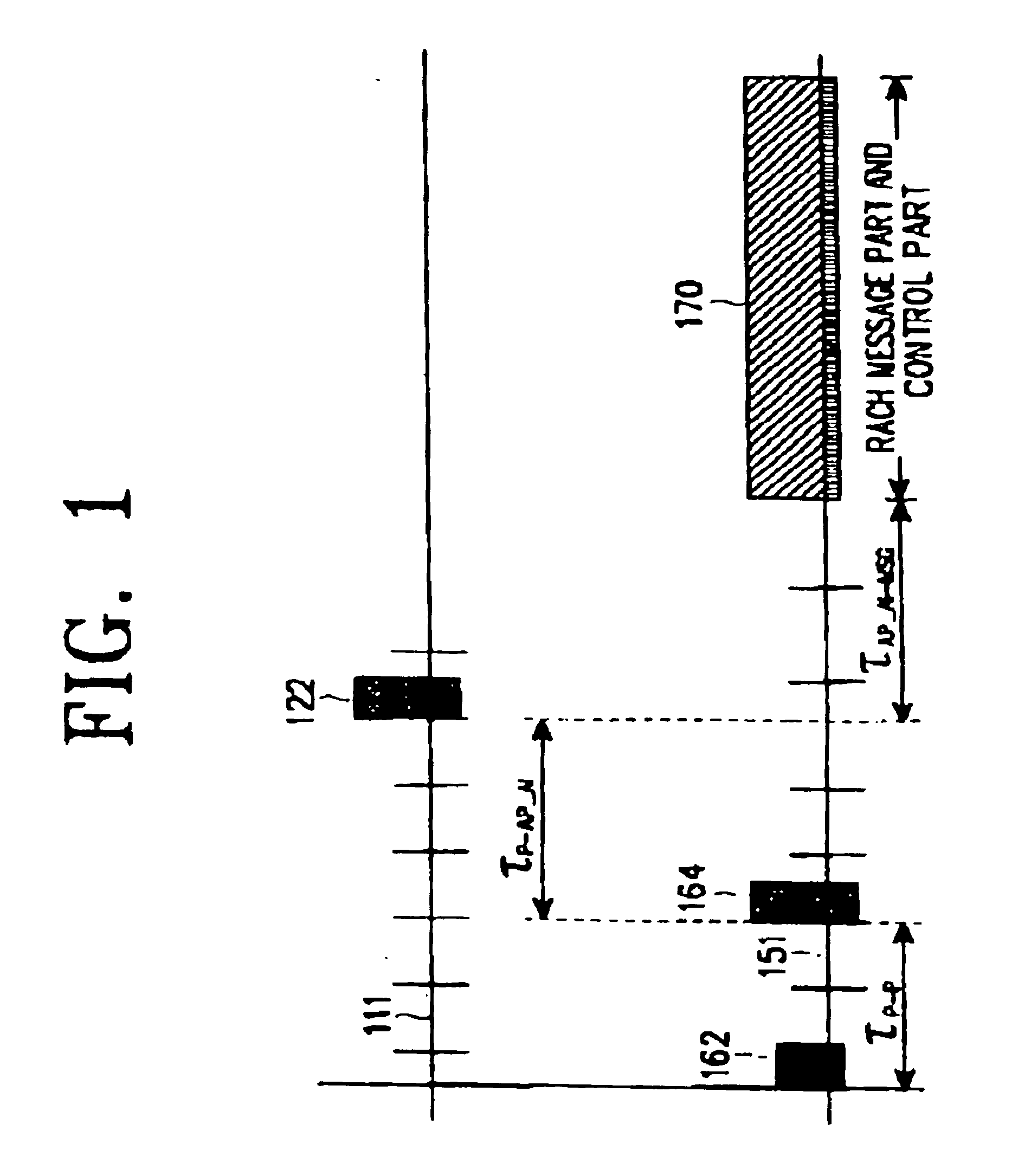
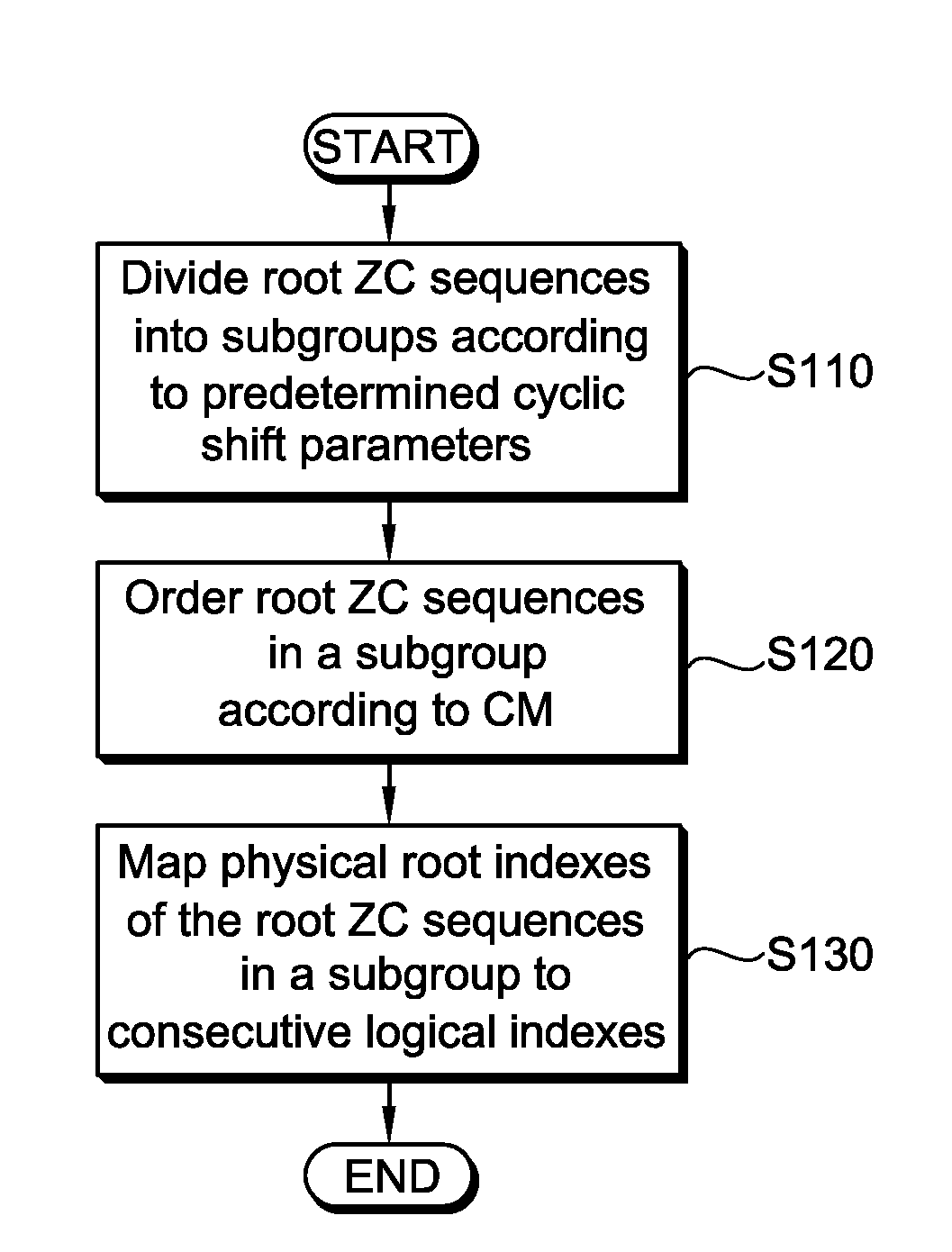
Method of generating random access preambles in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20080235314A1Modulated-carrier systemsMultiplex code generationCommunications systemTheoretical computer science
A method of generating random access preambles includes receiving information on a source logical index and generating random access preambles in the order of increasing cyclic shift from root ZC sequences with the consecutive logical indexes from the beginning of the source logical index until a predetermined number of the random access preambles are found, wherein the consecutive logical indexes are mapped to root indexes of the root ZC sequences.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Apparatus and method for adaptive broadcast transmission
ActiveUS20050138671A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelReceivers monitoringBroadcast channelsTelecommunications
An apparatus and method for adaptive broadcast transmission. A broadcast transmission can be received. Insufficiency of a broadcast channel quality can be determined. A negative acknowledgement signal can be sent on a common uplink channel in response to determining the broadcast channel quality is insufficient. The negative acknowledgement signal can be received on the common uplink channel at another location, the negative acknowledgement signal indicating broadcast channel quality is insufficient. The broadcast channel quality can be adjusted in response to receiving the negative acknowledgement signal.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
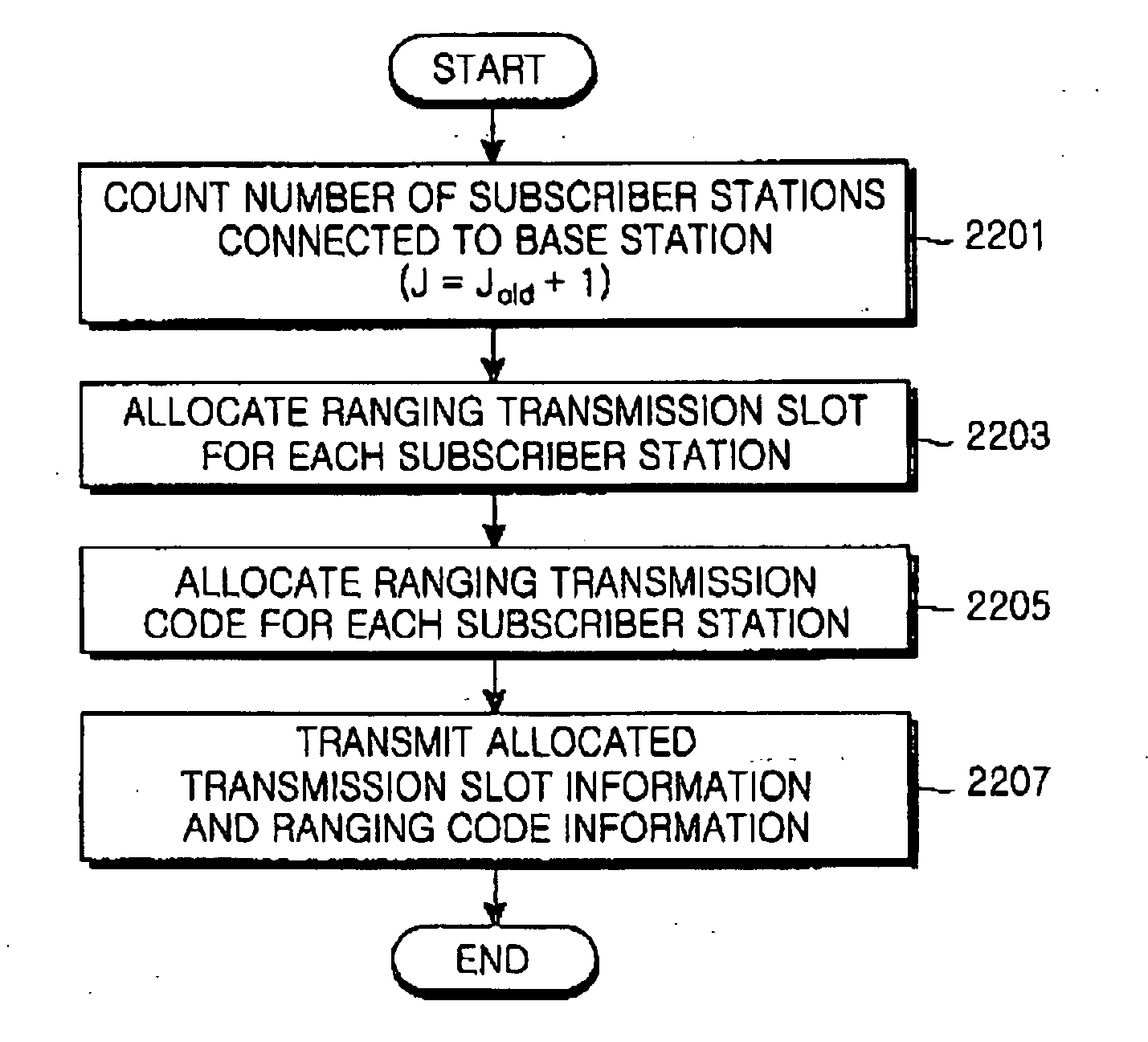
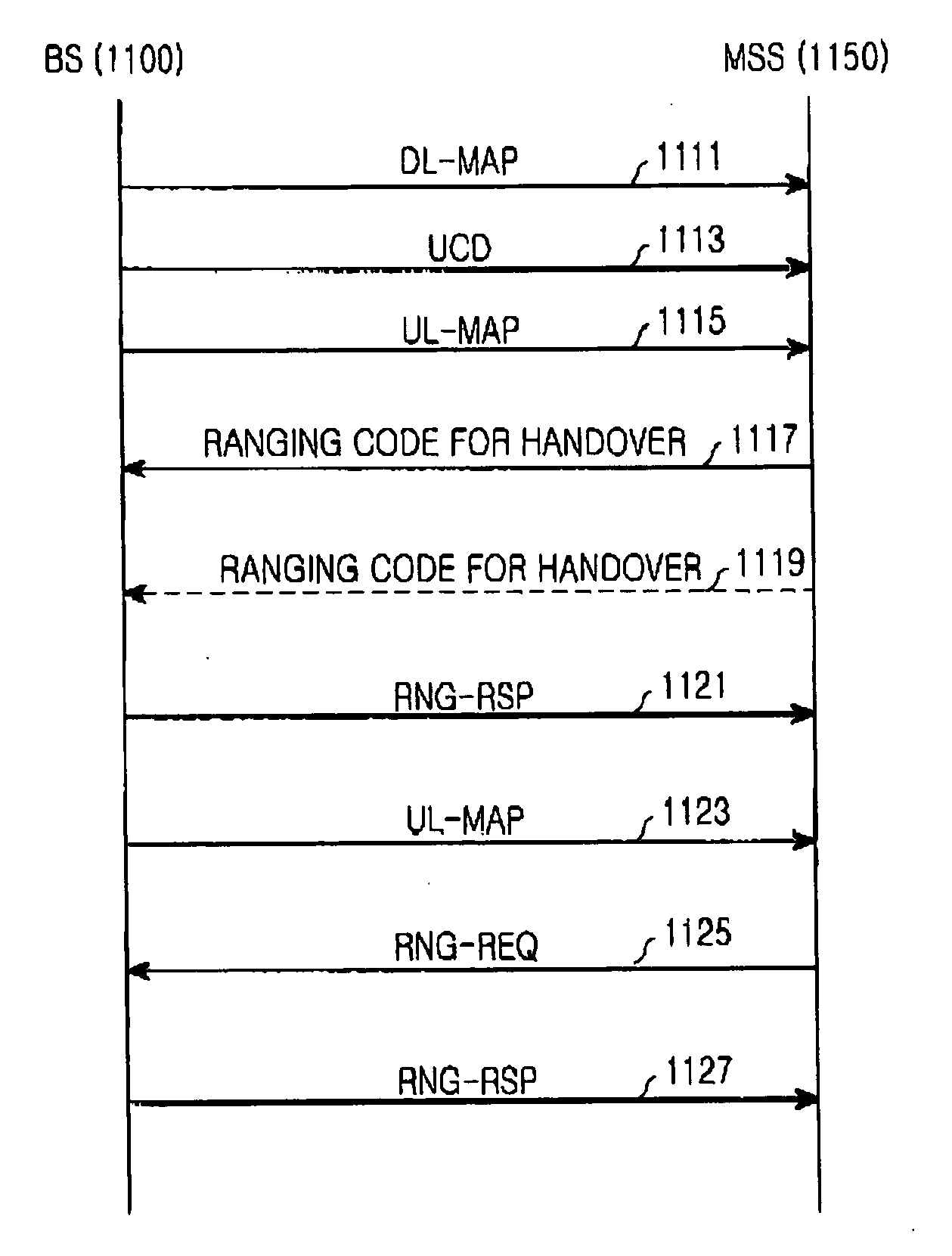
System and method for ranging for a fast handover in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050117539A1Reduce latencyData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemFrequency-division multiple access
A mobile communication system using an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) / orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) scheme. The method for assigning ranging codes in the OFDM / OFDMA communication system includes classifying rangings between a base station and a mobile subscriber station (MSS) of the OFDM / OFDMA communication system into an initial ranging, a periodic ranging, a bandwidth request ranging, and a handover ranging. A first number of ranging codes used for the rangings are created and a second number of ranging codes selected from the first number of ranging codes are assigned as handover ranging codes used for the handover ranging.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
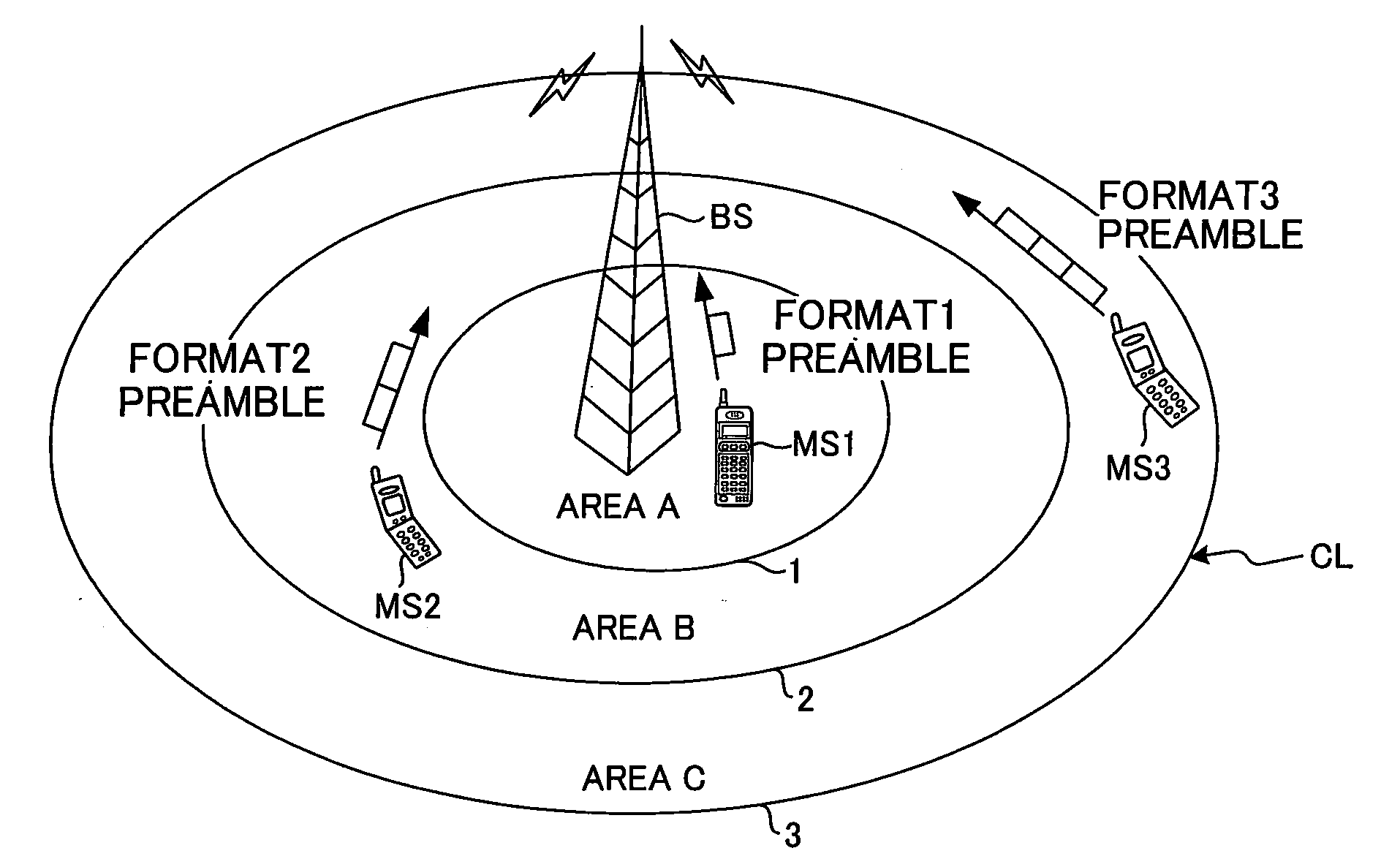
Radio communication system, base station and random access channel transmission method thereof
ActiveUS20090305693A1Reduce processing loadIncrease the number ofTransmission control/equlisationFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemEngineering
A random access channel transmission method in which a user terminal selects a preamble pattern from among a plurality of known preamble patterns and transmits that preamble pattern to a base station, where that transmission method comprises: a step of dividing a cell into a plurality of areas, and setting one or more preamble patterns and the number of repetitions for transmitting the preamble pattern for each area; and a step wherein a user terminal that exists in an are close to the base station transmits a specified preamble pattern one time, and a user terminal that exists in an area far from the base station transmits another specified preamble pattern a plurality of times.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Transmission method for downlink control signal in MIMO system
InactiveUS20050220000A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTime-division multiplexCommunications systemControl signal
Disclosed is a transmission method for a downlink control signal in a MIMO communication system where multiple transmit antennas and multiple receive antennas are used, in which each data transmitted from the multiple transmit antennas is transmitted with a different control signal through one downlink control signal transmission channel. The transmission method for a downlink control signal in a MIMO communication system efficiently transmits or receives data by transmitting control information such as a different modulation method and the number of OVSF codes of each transmit antenna to a mobile station. Also, a control channel is similar to that used in the conventional HSDPA system, thus allowing backward compatibility. Additionally, the transmission method can be applied not only for data transmitted to each antenna being composed of one packet but also for data transmitted to each antenna being composed of multiple packets.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Radio base station device, communication terminal device, and control information transmission method
ActiveUS20050238053A1Curb consumptionFully extractedPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiplexingInformation transmission
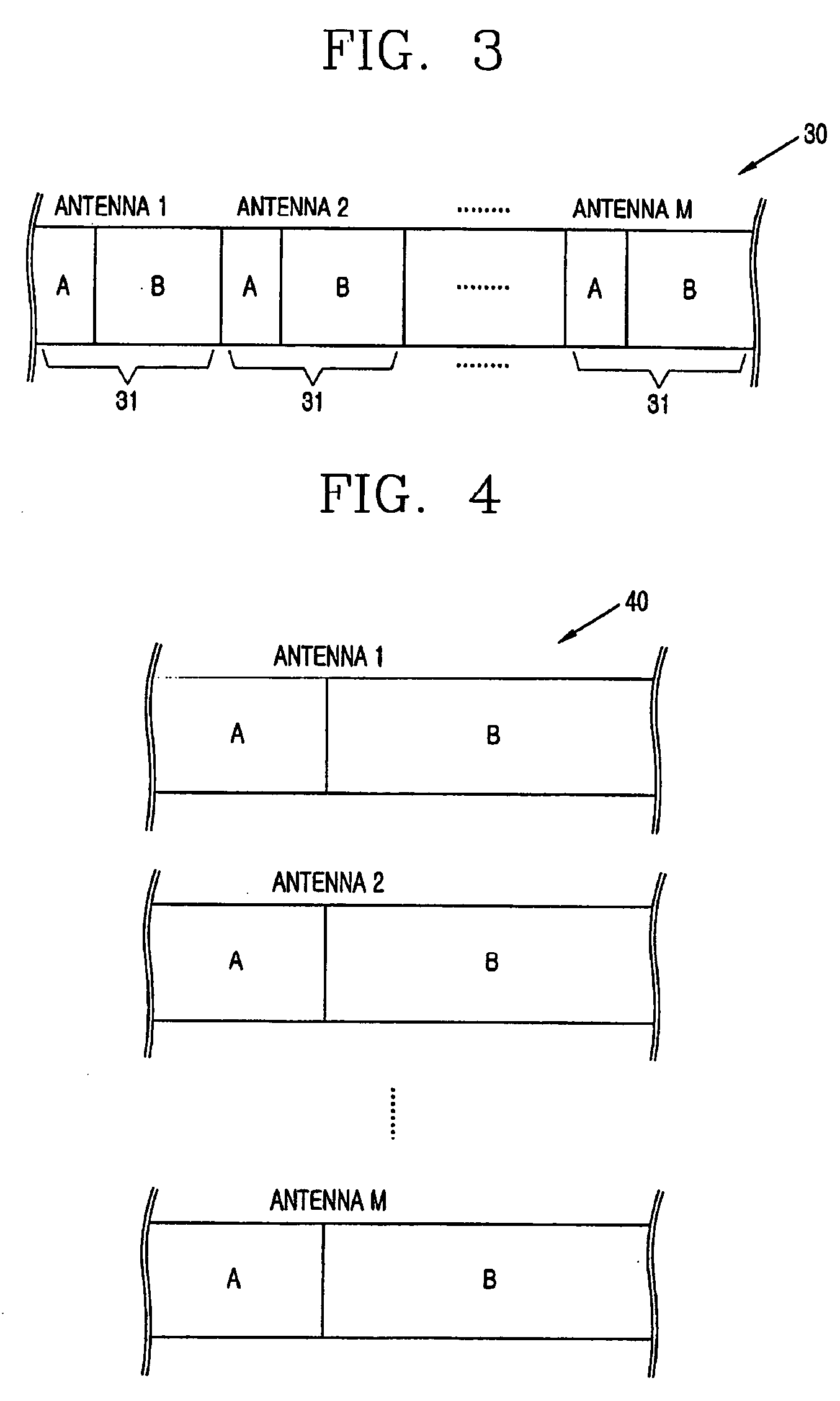
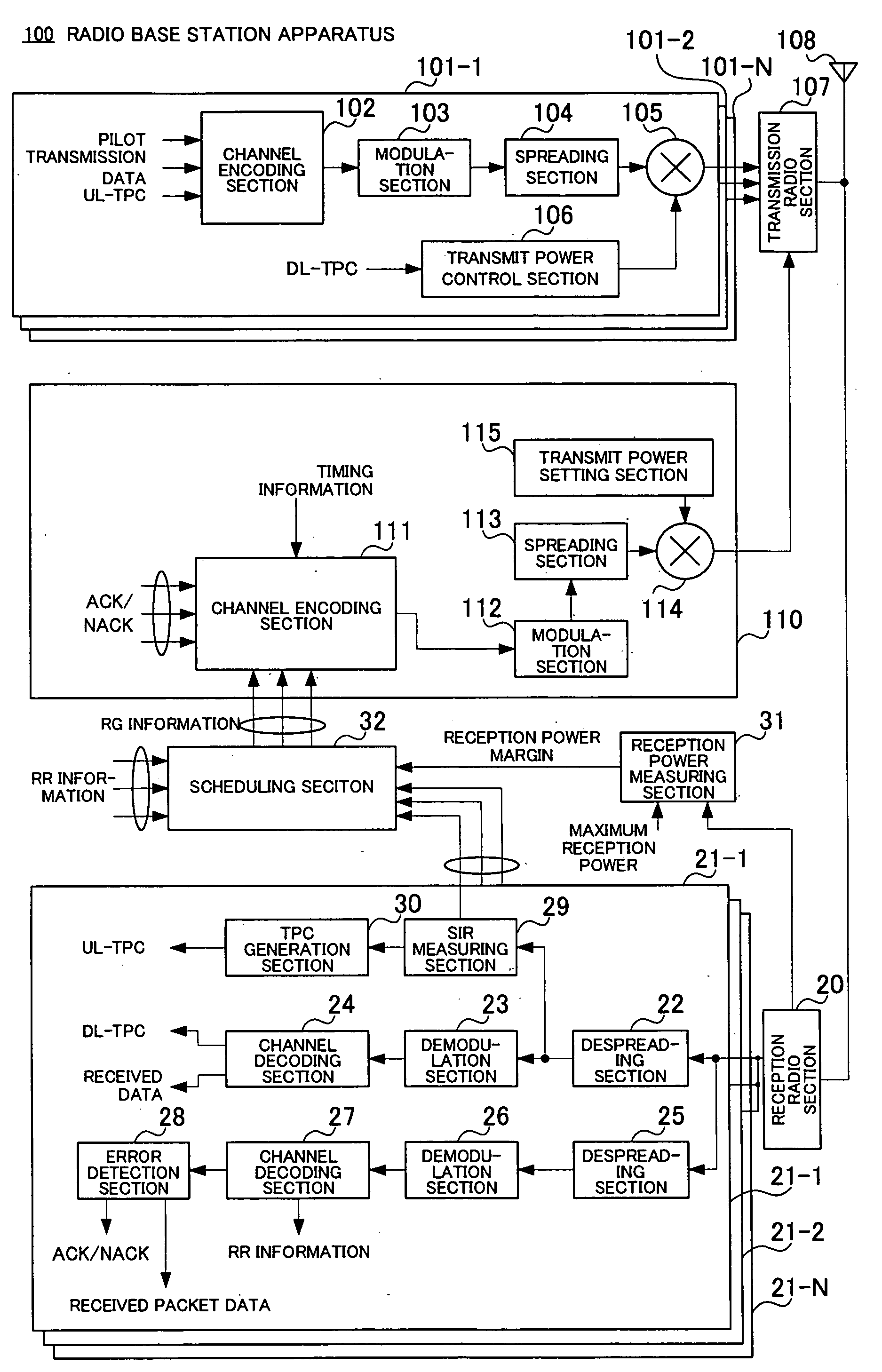
In addition to dedicated channel signal formation units 101-1 to 101-N, control information channel signal formation unit 110 is provided and this control information channel signal formation unit 110 forms control information for carrying out uplink packet transmission. The control information channel signal formation unit 110 multiplexes control information (RG information, ACK / NACK, etc.) directed to a plurality of communication terminals through a channel encoding section 111 according to a multiplexing rule preset between the base station apparatus and each communication terminal and spreads the control information using a spreading code common to the communication terminals through a spreading section 113 and thereby forms a control information channel signal for uplink packet transmission.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Popular searches
Channel estimation Multiplex code allocation Multi-frequency code systems Transmission path multiple use Radio wave reradiation/reflection Error prevention/detection by diversity reception Amplitude demodulation Transmission control/equalising Error detection/correction Radio transmission for post communication
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com