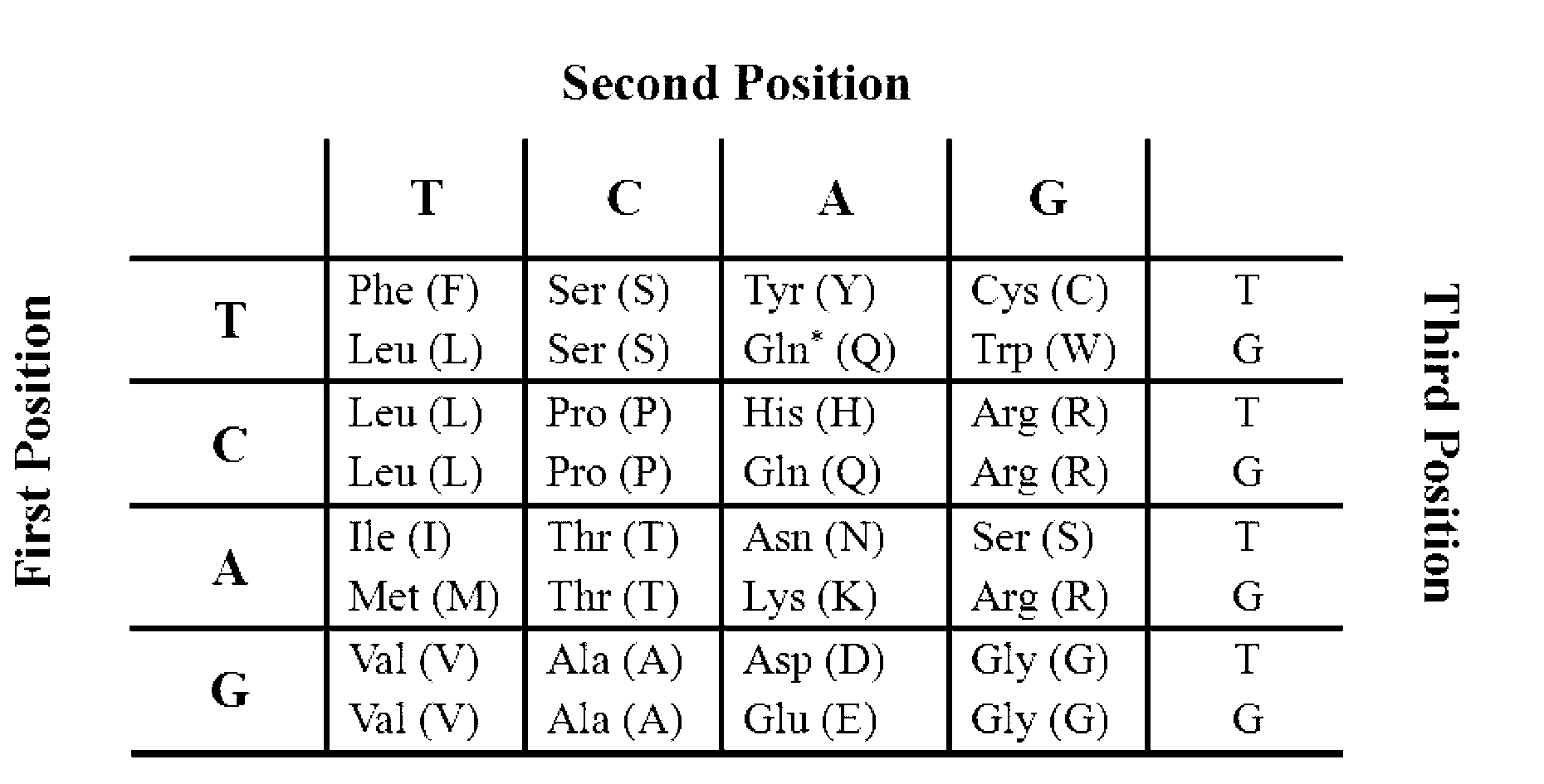
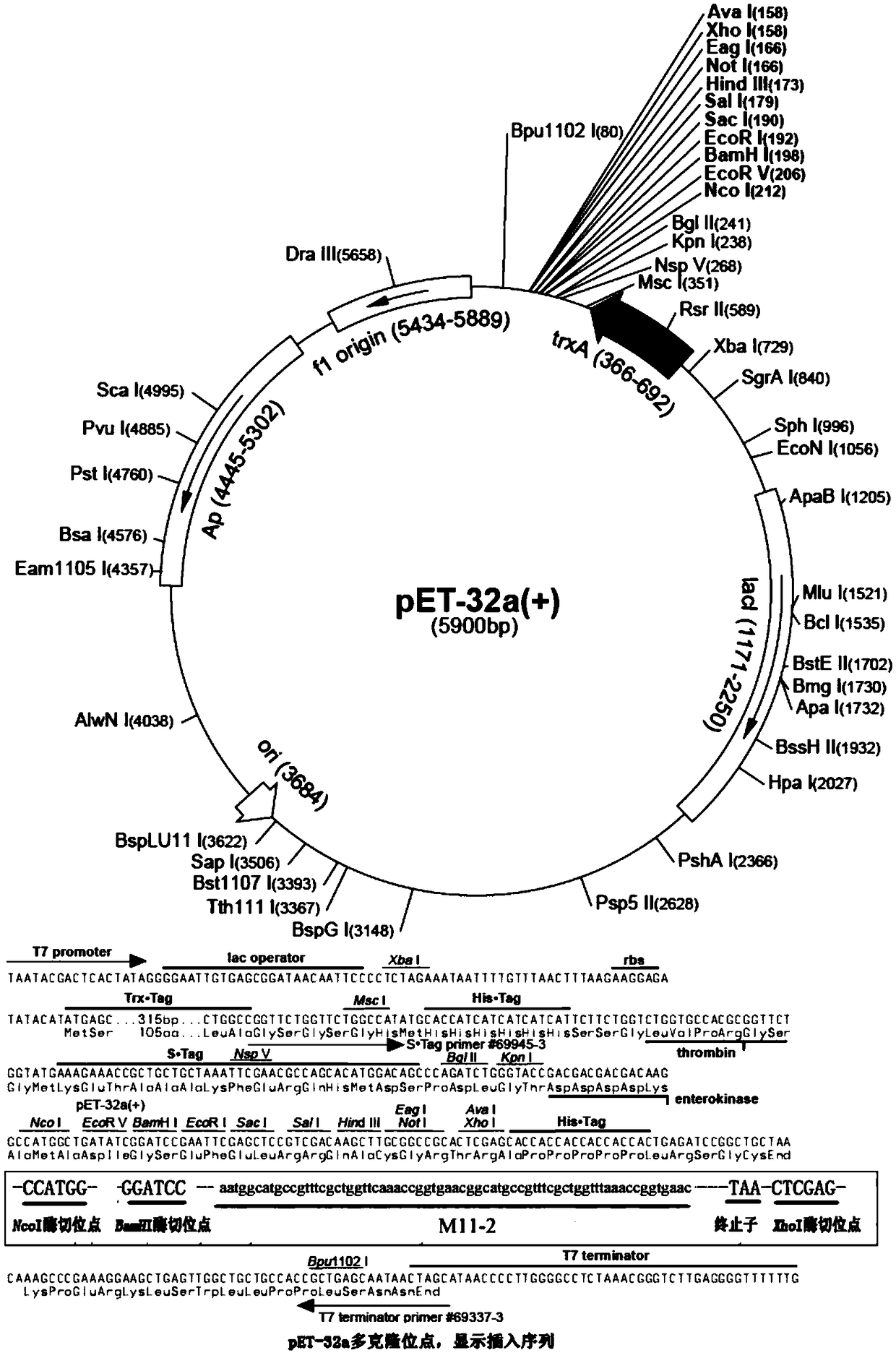
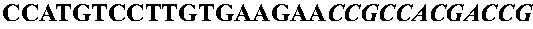Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Peptide display" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
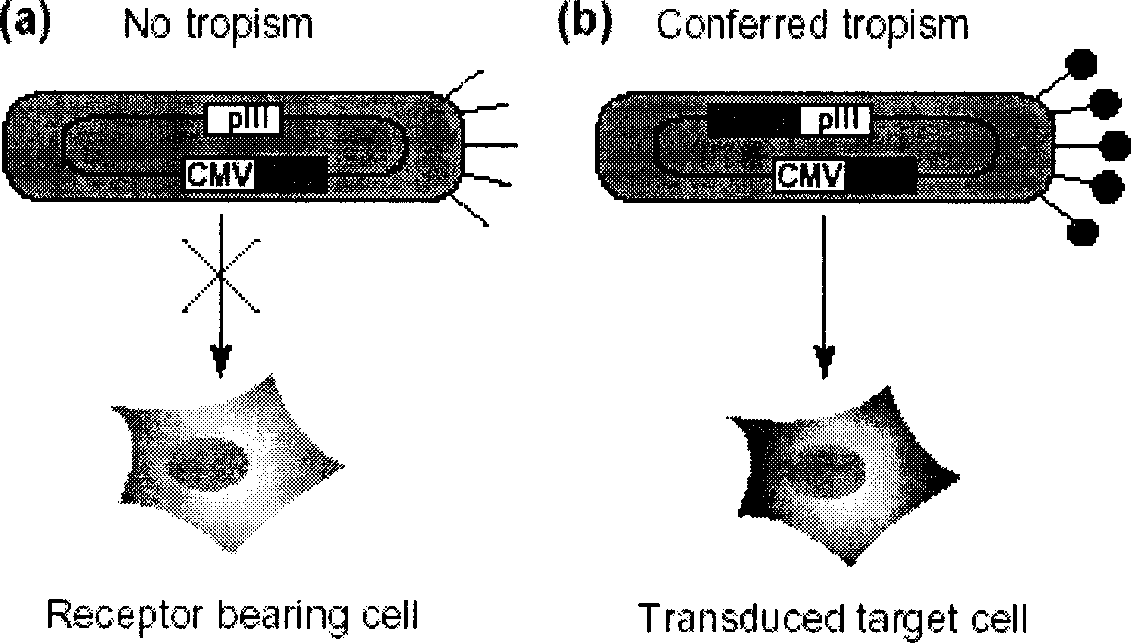
Identification of peptides that facilitate uptake and cytoplasmic and/or nuclear transport of proteins, DNA and viruses
The present invention relates to internalizing peptides which facilitate the uptake and transport of cargo into the cytoplasm and nuclei of cells as well as methods for the identification of such peptides. The internalizing peptides of the present invention are selected for their ability to efficiently internalize cargo into a wide variety of cell types both in vivo and in vitro. The method for identification of the internalizing peptides of the present invention comprises incubating a target cell with a peptide display library, isolating peptides with internalization characteristics and determining the ability of said peptide to internalize cargo into a cell.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Cellular libraries of peptide sequences (CLiPS) and methods of using the same
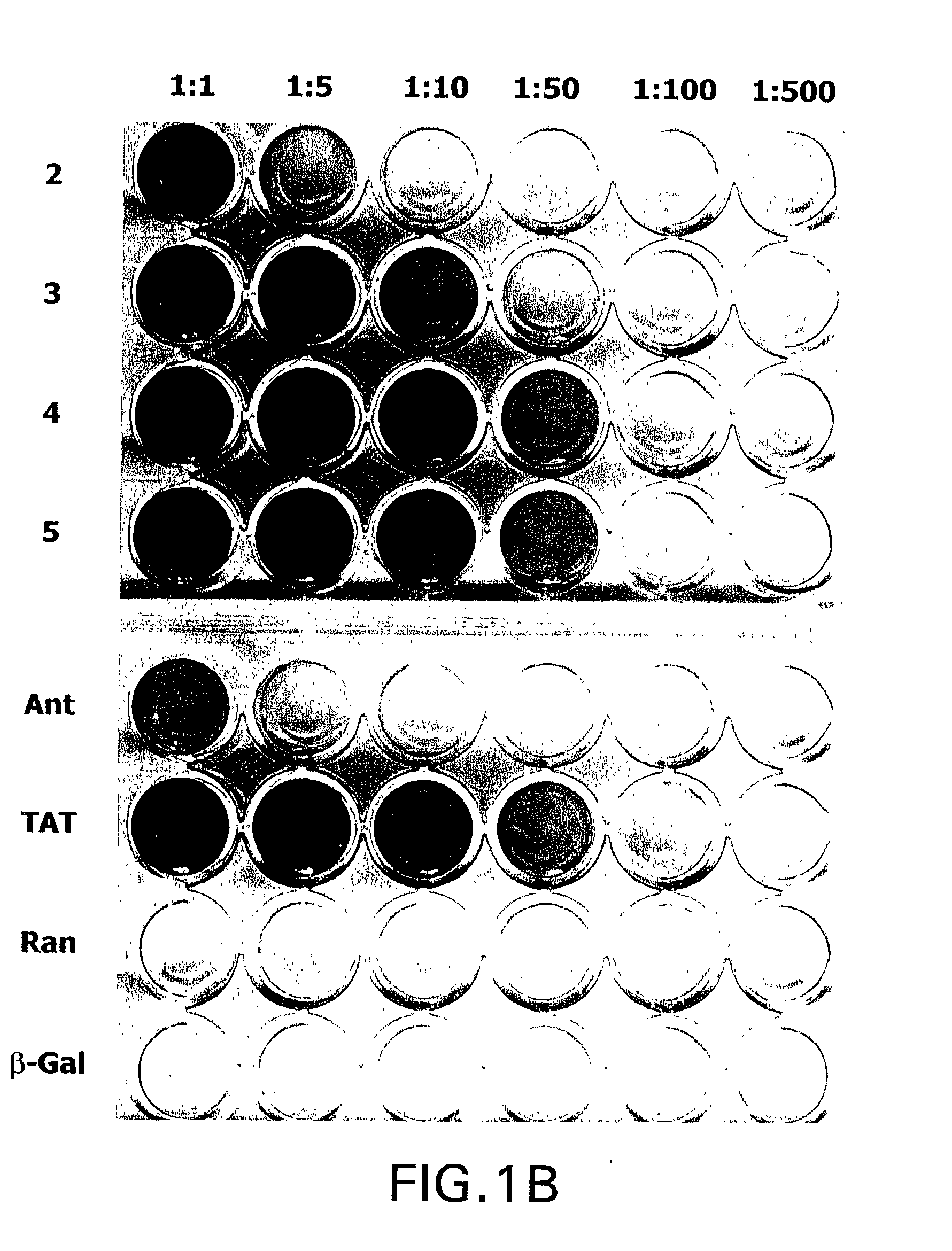
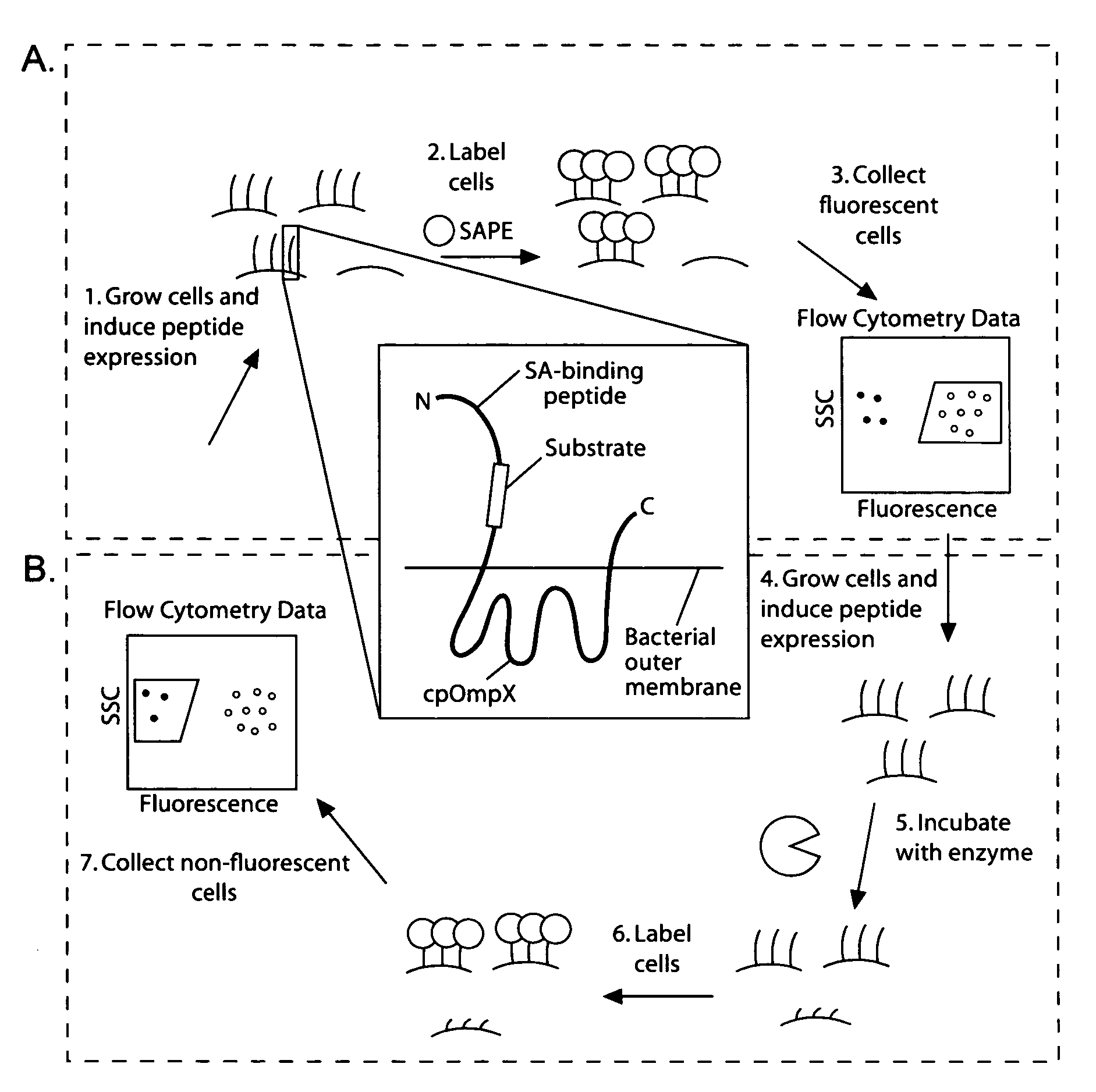
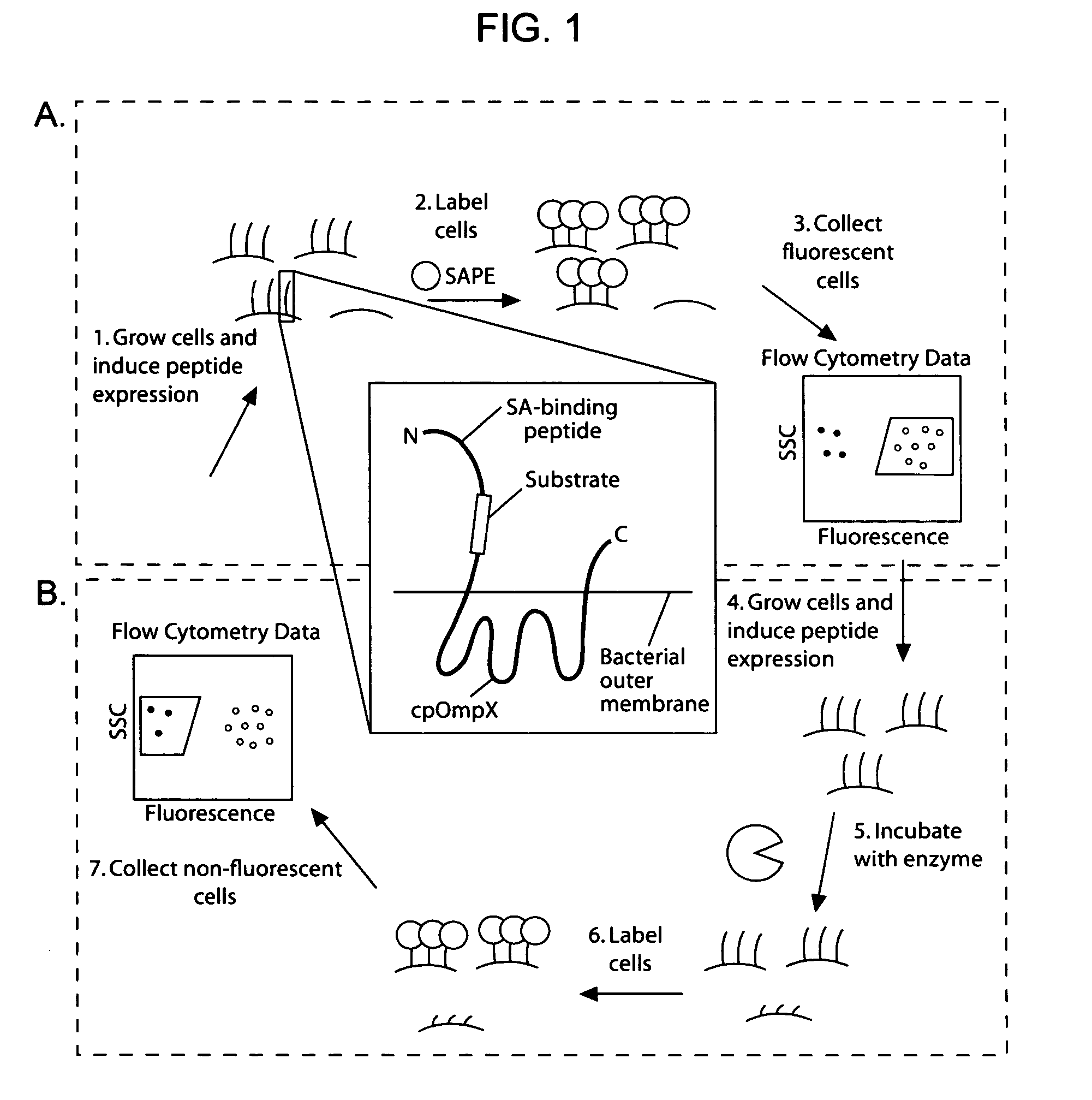
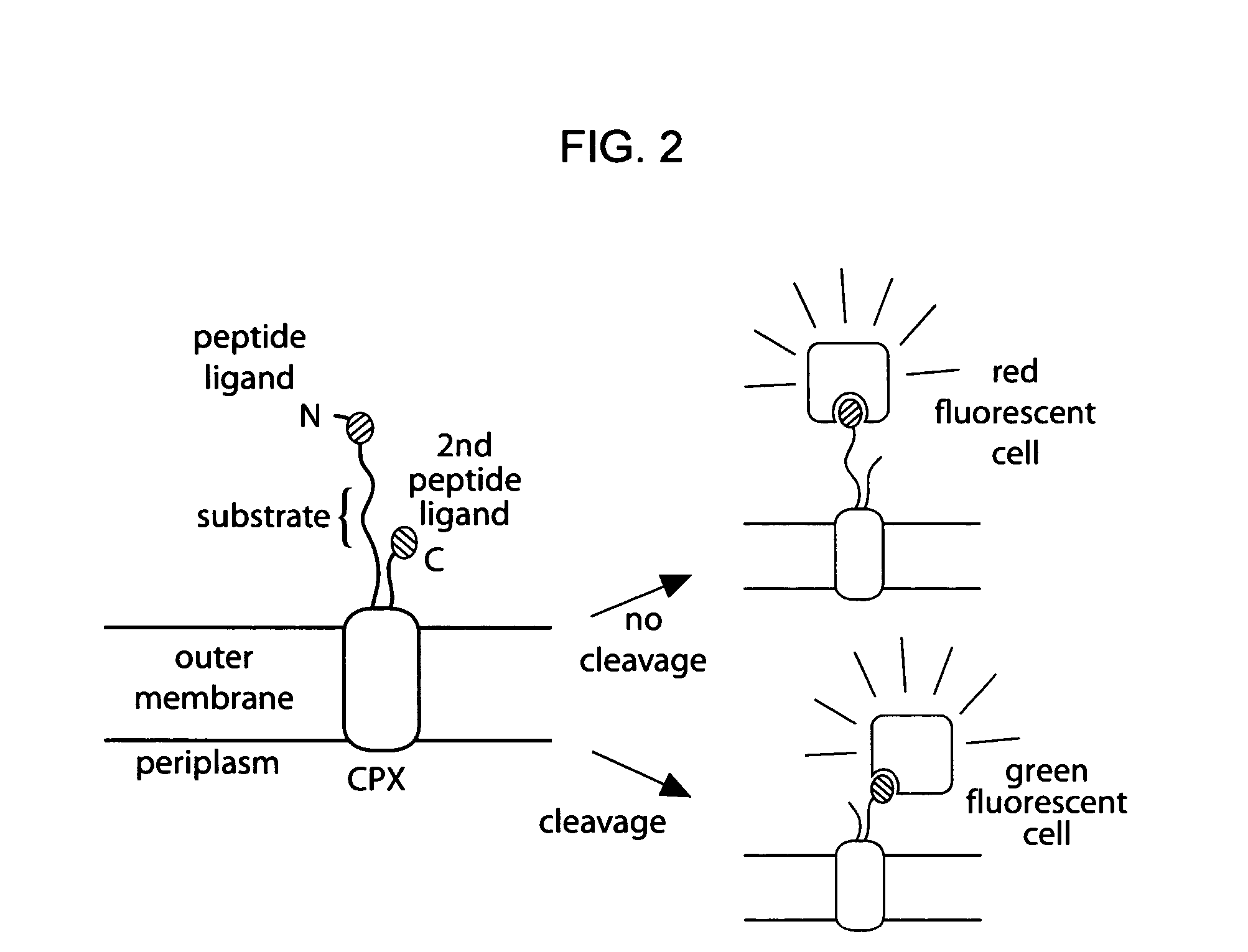
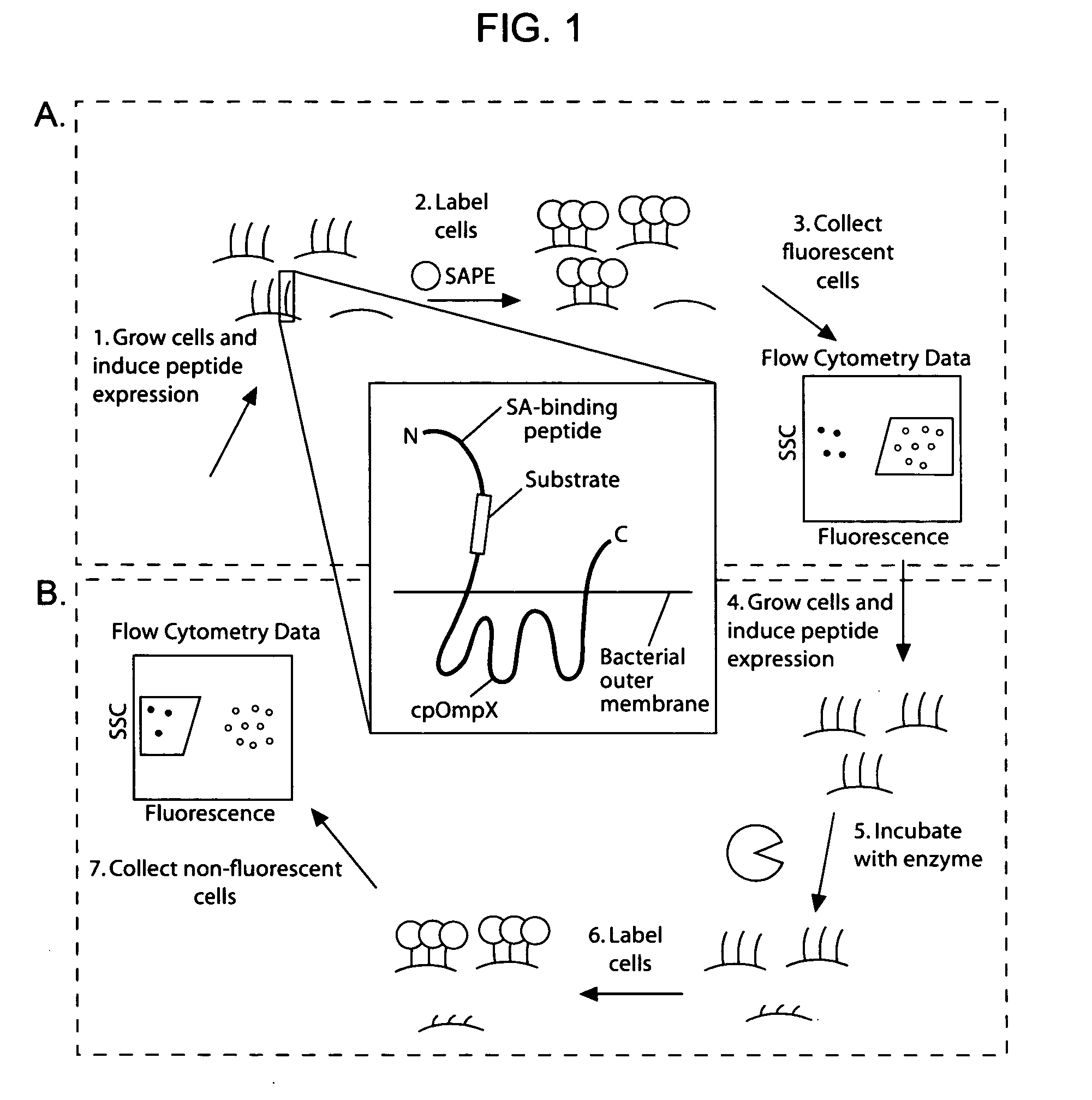
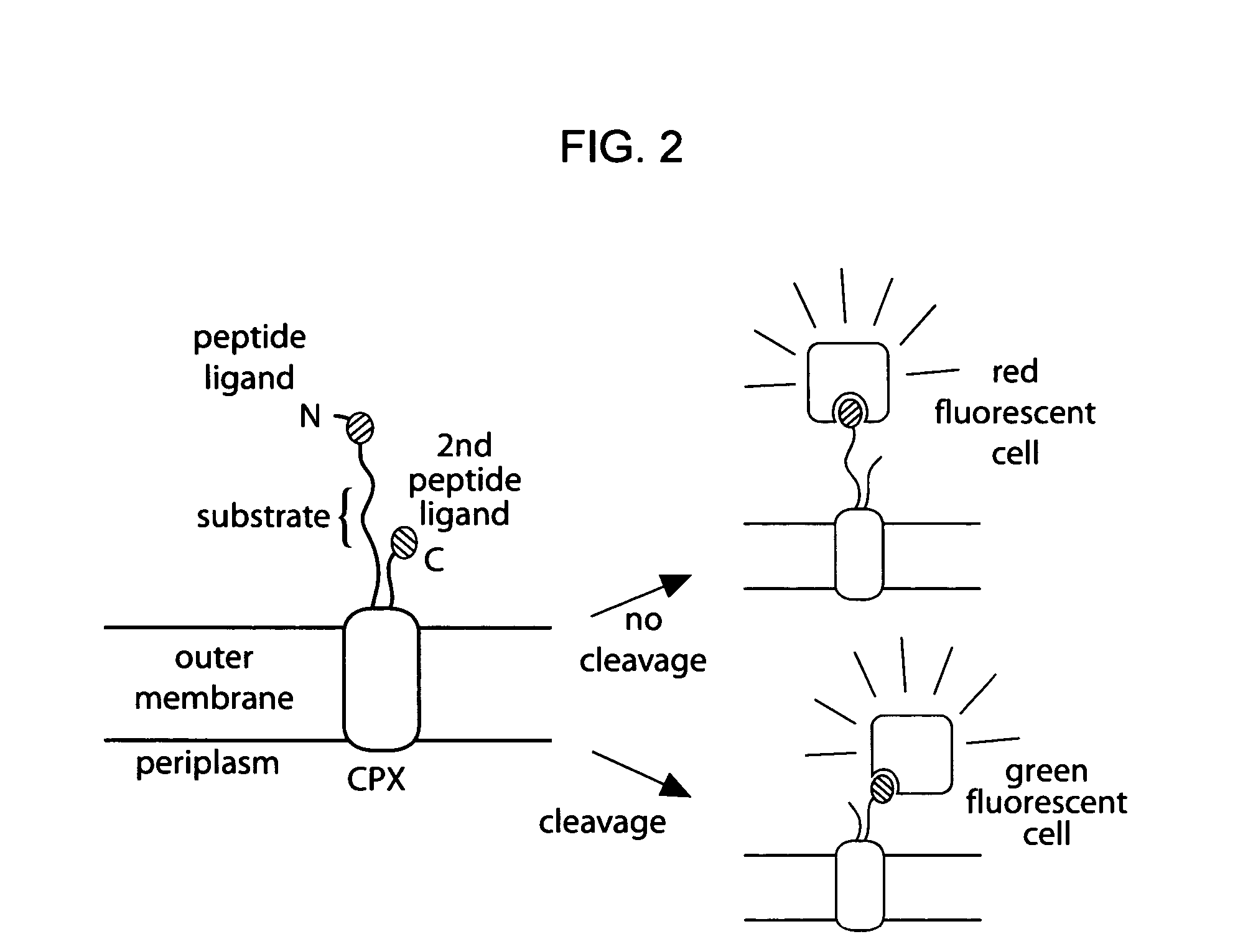
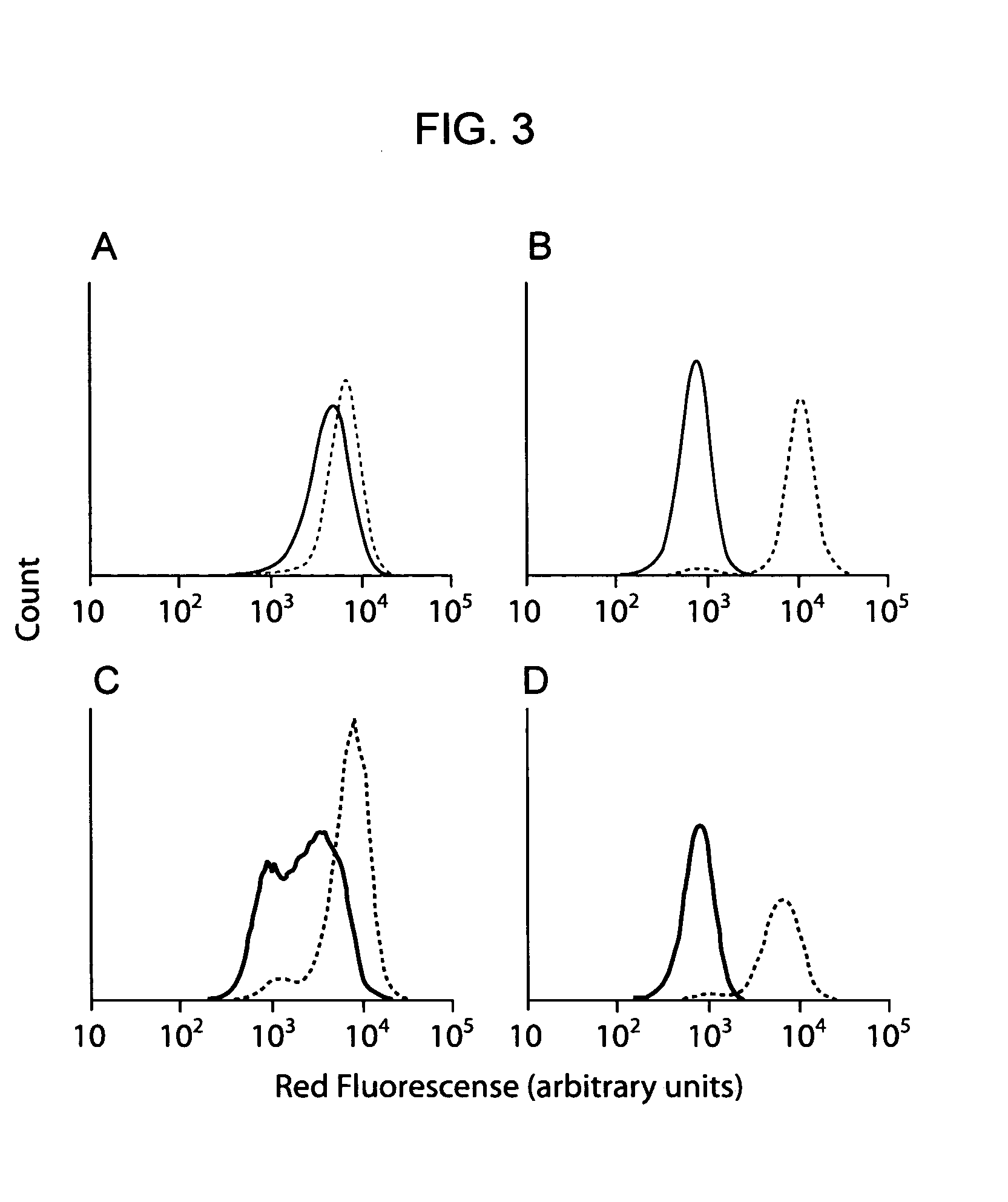
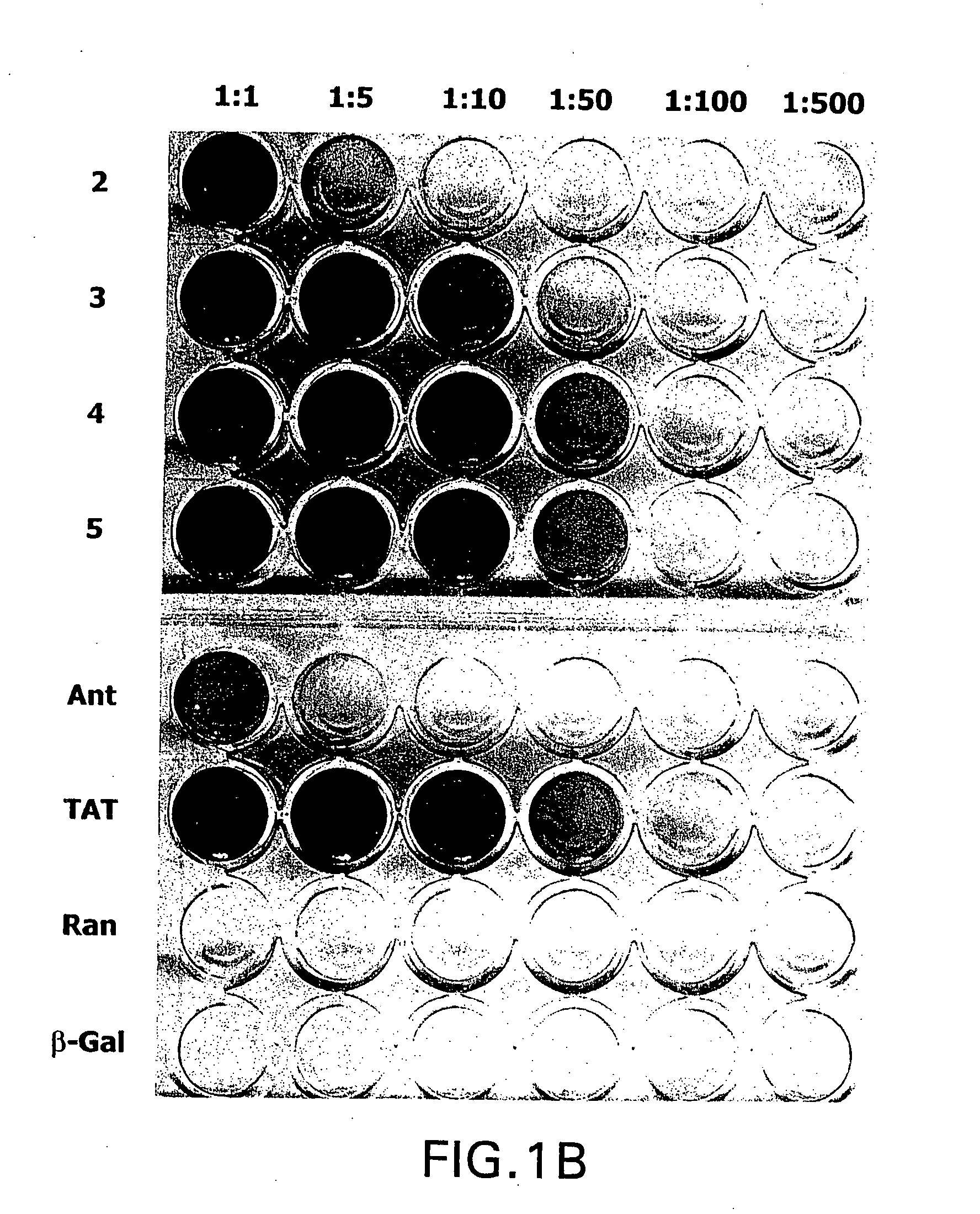
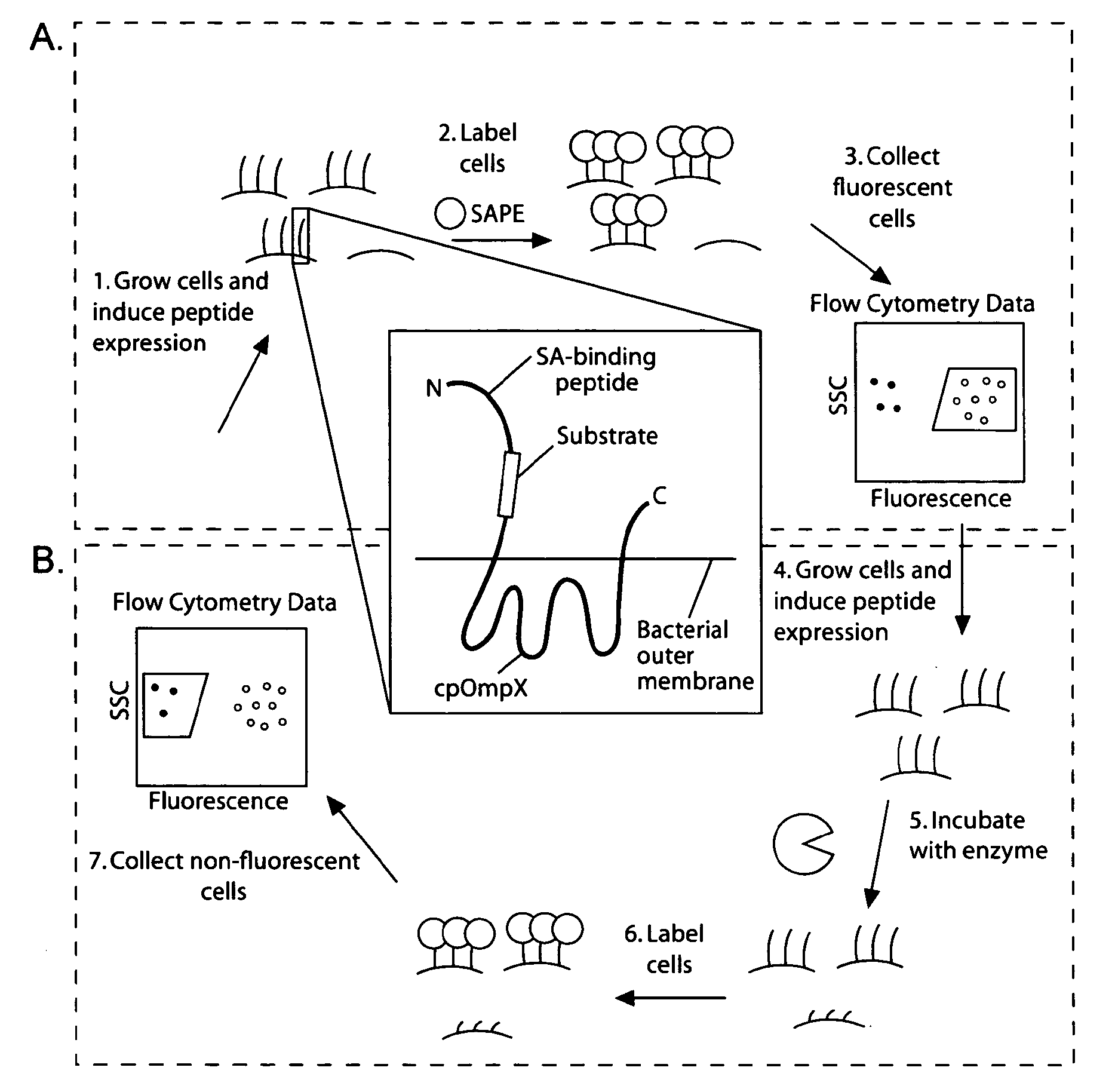
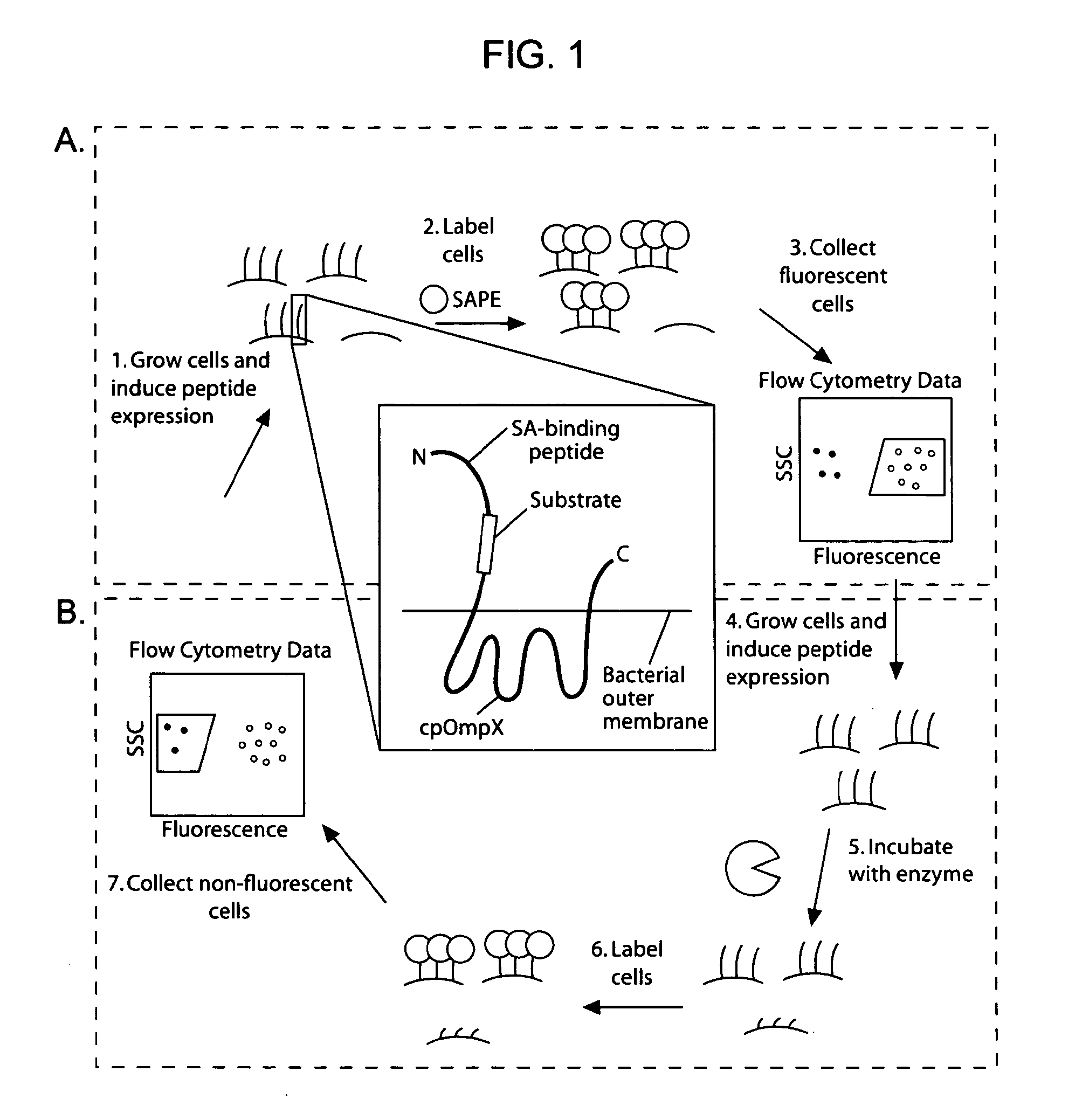
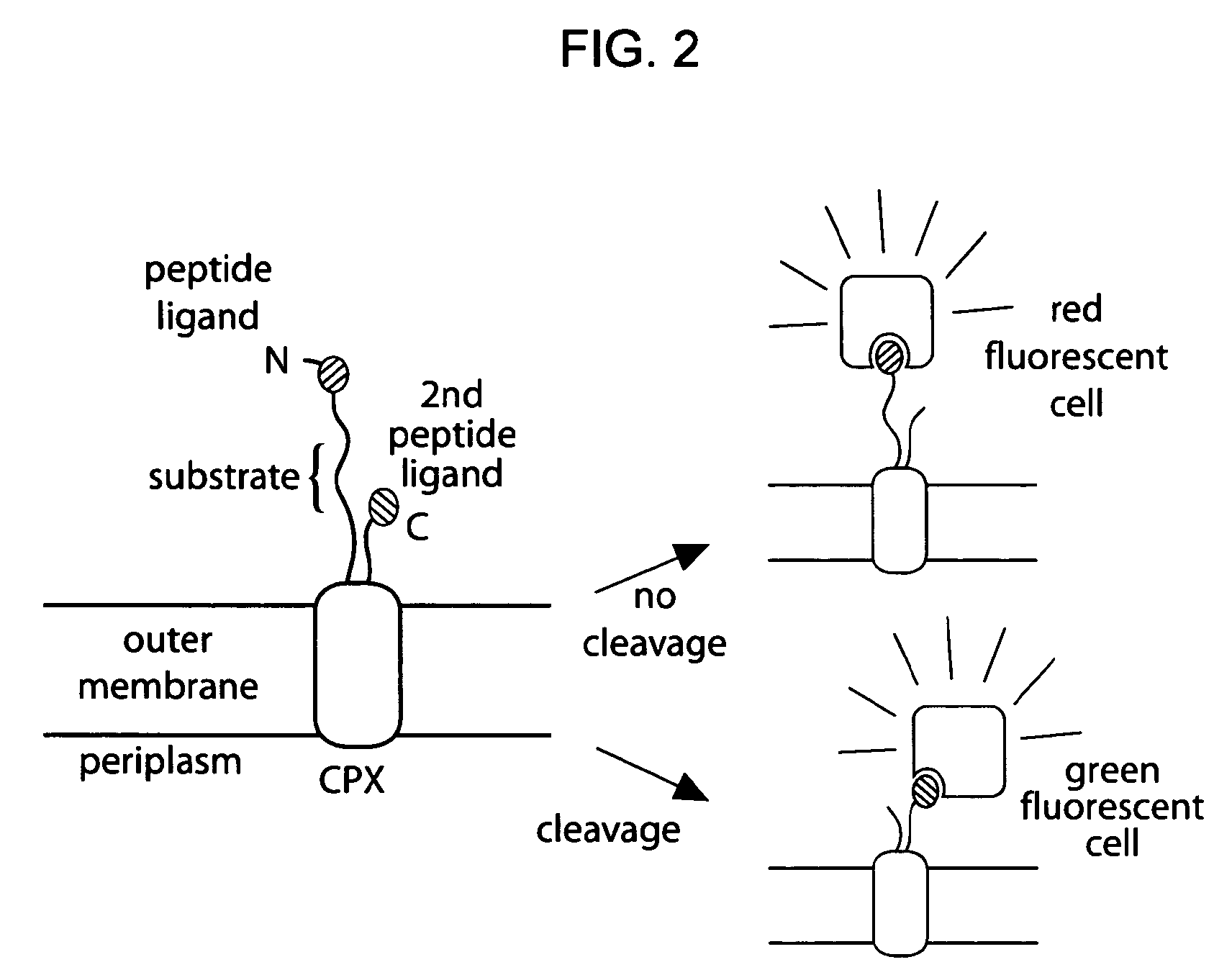
The present invention provides compositions including peptide display scaffolds that present at least one candidate peptide and at least one detectable moiety in at least one of the N-terminal and C-terminal candidate peptide presenting domains that when expressed in a cell are accessible at a surface of the cell outermembrane. In addition, the present invention also provides kits and methods for screening a library of cells presenting the candidate peptides in peptide display scaffolds to identify a ligand for an enzyme.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Peptide display arrays
InactiveUS20120270748A1Improve throughputDone relatively cheaplyNucleotide librariesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptide displayDiscrete set
The present invention provides arrays, methods of constructing arrays, and methods of use of such arrays. The arrays of the invention comprise a substrate with two or more discrete constructs or discrete sets of constructs associated on the surface of the substrate, optionally via a linker molecule. The constructs include an oligonucleotide comprising a region encoding a peptide of interest and an affinity tag and an untranslated region, a fusion peptide comprising both the peptide of interest and the affinity tag and a capture agent that forms a binding pair with the affinity tag.
Owner:PROGNOSYS BIOSCI
Cellular libraries of peptide sequences (CLiPS) and methods of using the same
The present invention provides compositions including peptide display scaffolds that present at least one candidate peptide and at least one detectable moiety in at least one of the N-terminal and C-terminal candidate peptide presenting domains that when expressed in a cell are accessible at a surface of the cell outermembrane. In addition, the present invention also provides kits and methods for screening a library of cells presenting the candidate peptides in peptide display scaffolds to identify a ligand for an enzyme.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
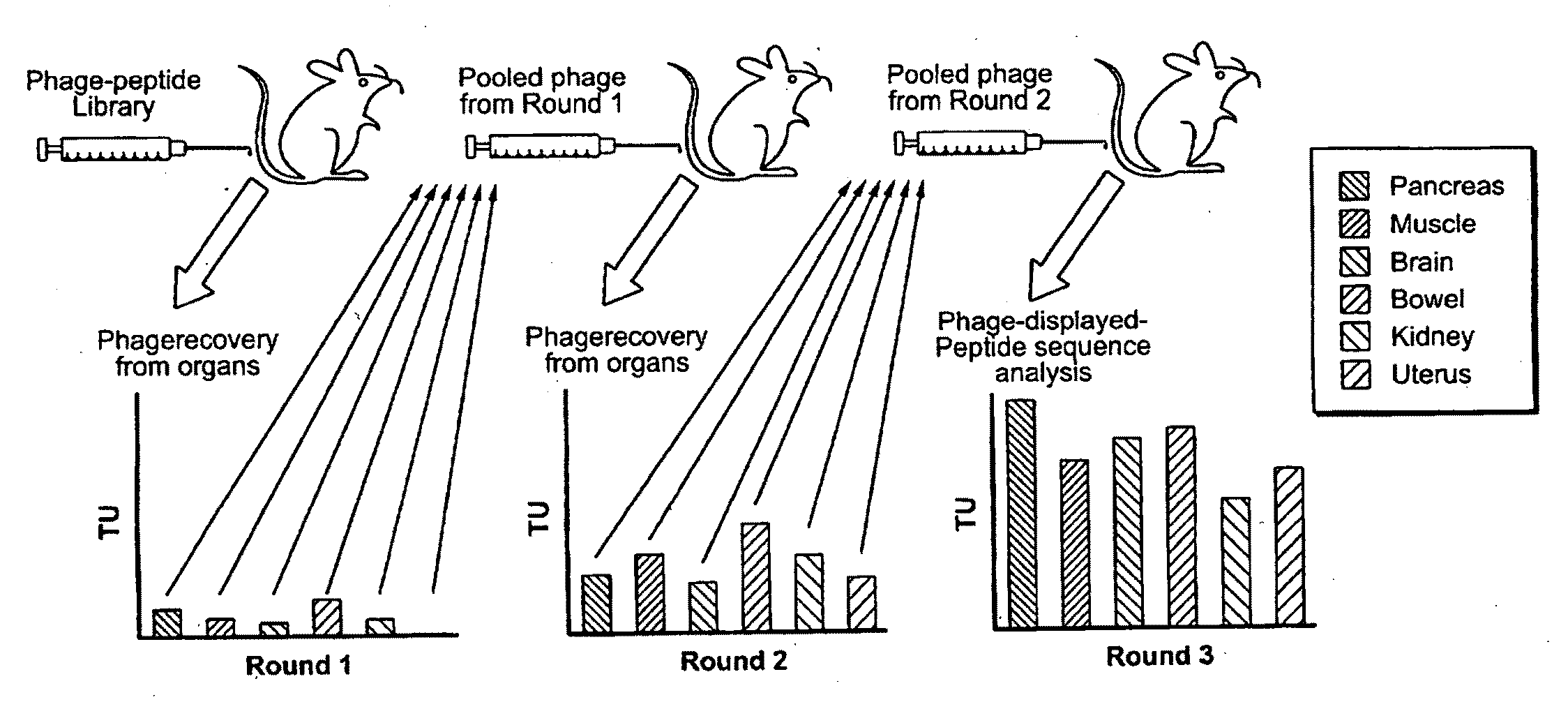
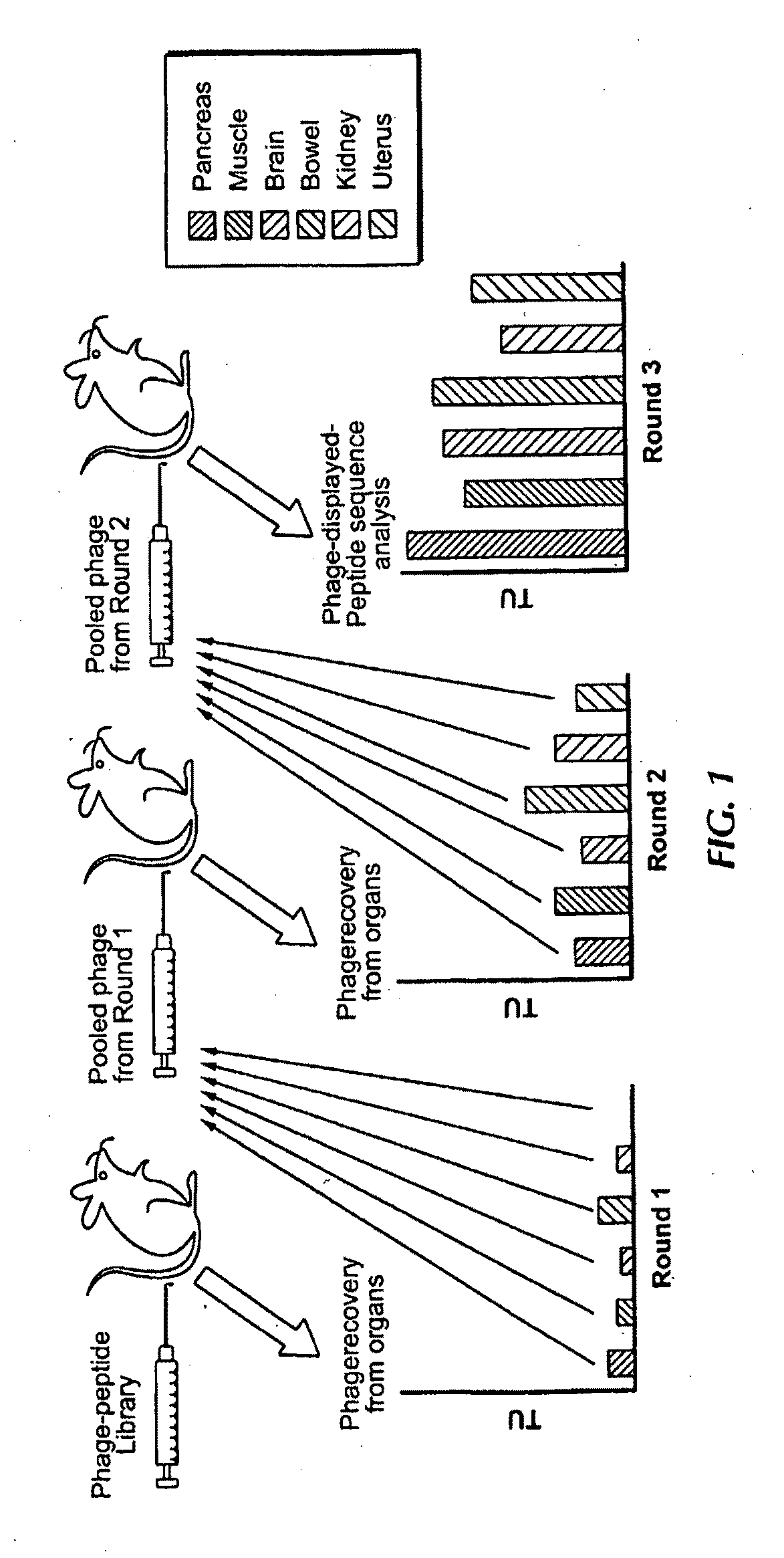
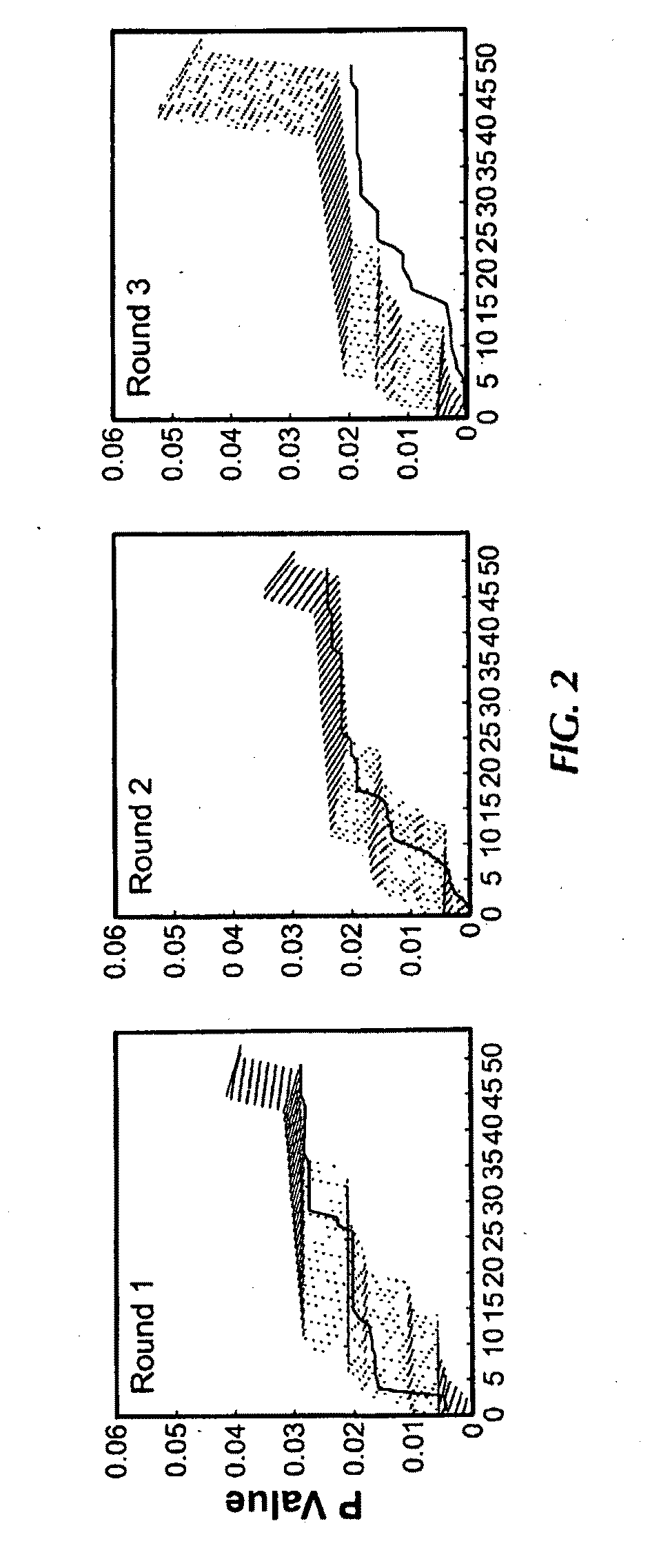
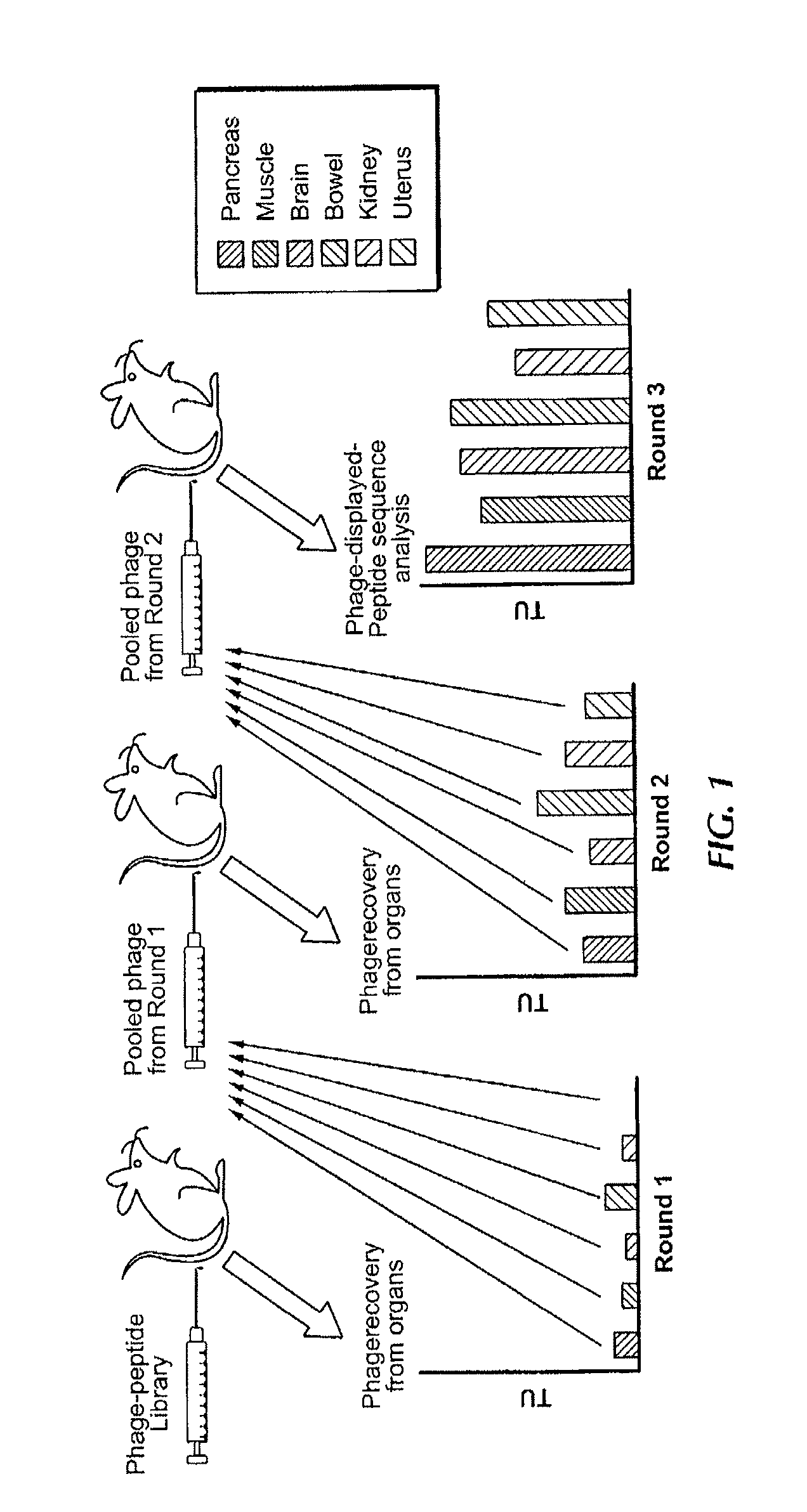
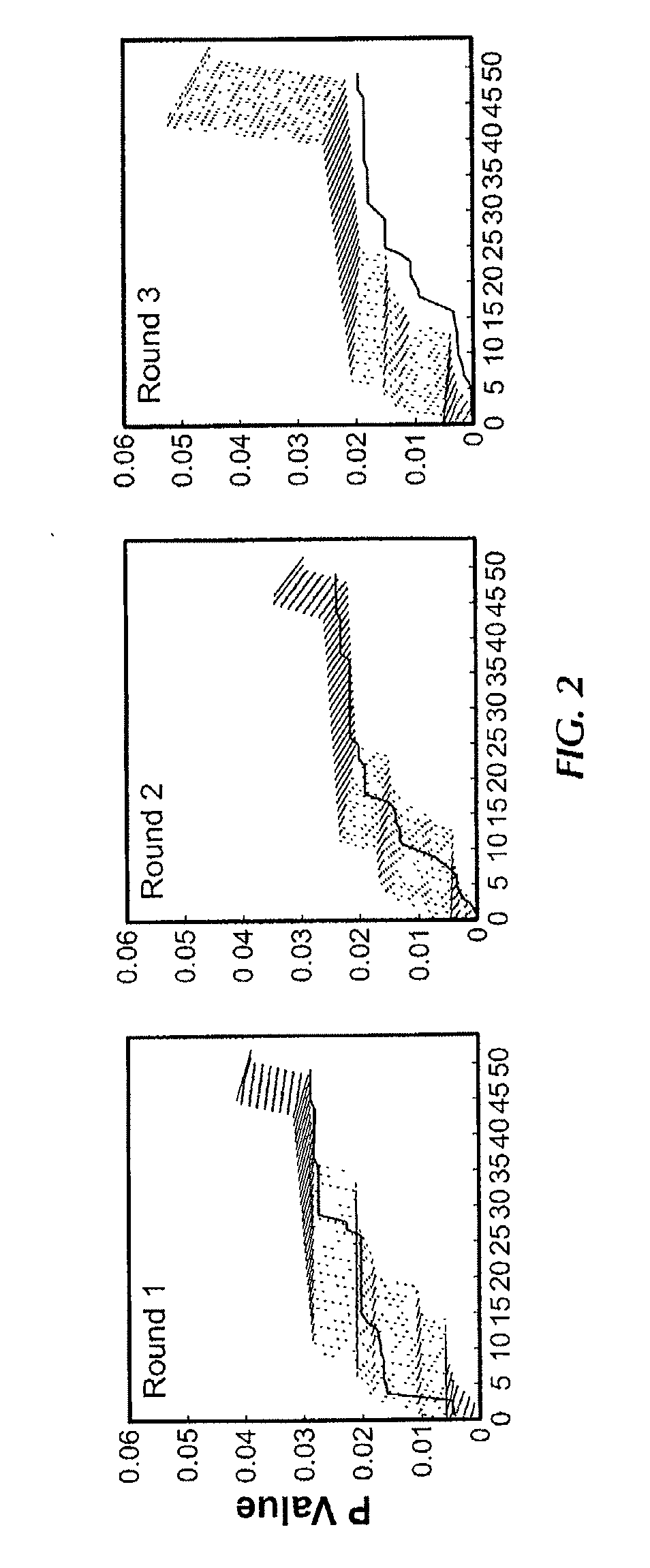
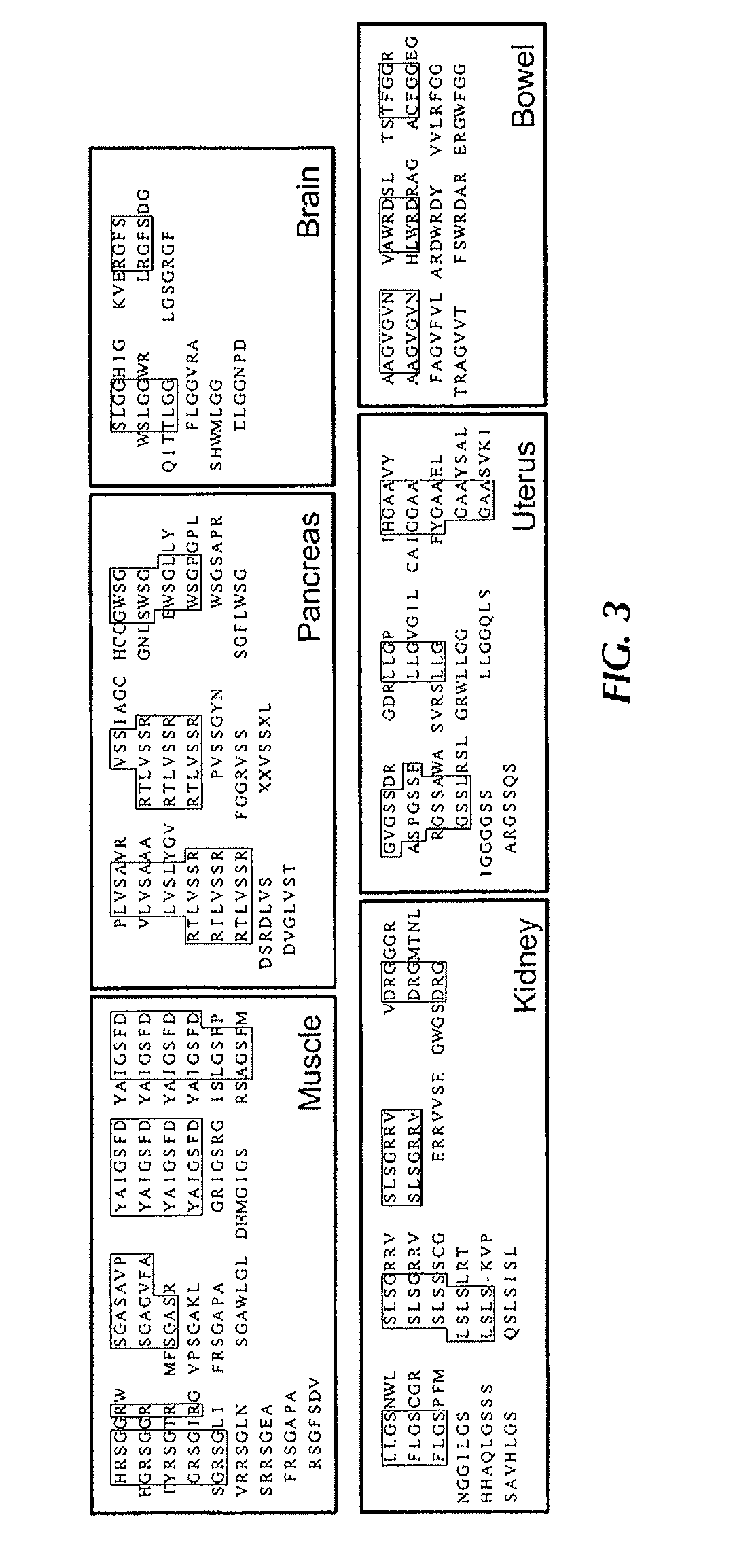
Compositions and methods related to synchronous selection of homing peptides for multiple tissues by in vivo phage display
Embodiments of the invention include methods for selecting in parallel (i.e., synchronously or simultaneously) peptides that target a number of organs, in which each peptide targets distinct tissues or organs. Typically, the methods of the invention provide for peptide selection in a Minimal number of subjects and still provides a selectively binding peptide. In certain aspects, methods of identifying peptides that bind to multiple selected tissues or organs of an organism may comprise the steps of administering a phage display library to a first subject; obtaining a sample of two or more selected tissues; obtaining phage displaying peptides that bind to the samples from the first subject; enriching for peptides by administering phage isolated from the samples of the first subject to a second subject; obtaining a sample of two or more selected tissues from the second subject; and identifying the peptides displayed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
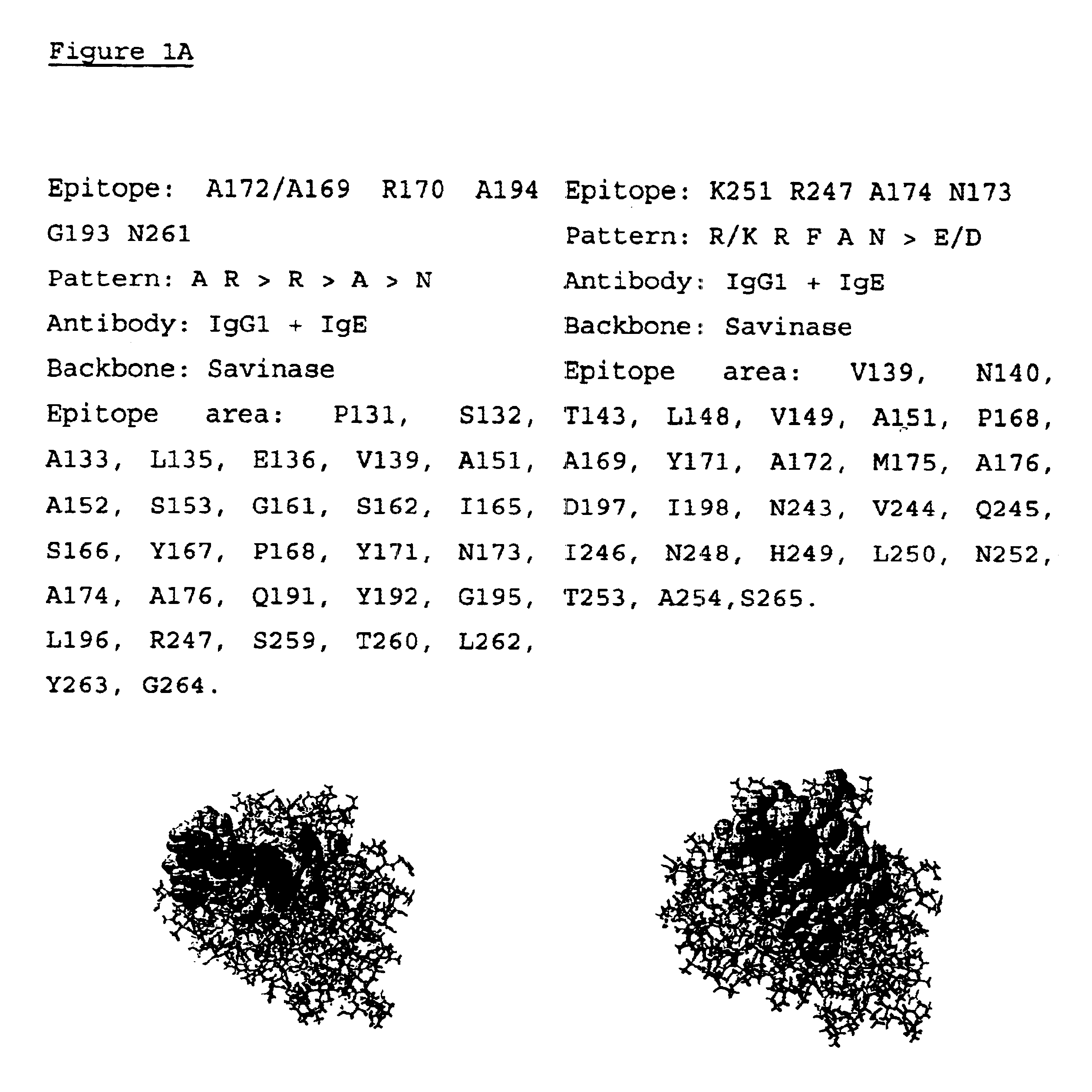
Low allergenic protein variants
The present invention relates to a method of selecting a protein variant having reduced immunogenicity as compared with the parent protein. This method includes the steps of screening a random peptide display package library with antibodies raised against any protein of interest, sequencing the amino acid sequence of the antibody binding peptides, or the DNA sequence encoding the antibody binding peptides, identifying epitope patterns of a protein by sequence alignment of the reactive peptide sequence, localization of epitope patterns on the primary 3-dimensional structure of the parent protein, defining an epitope area including amino acids situated within 5 Å from the epitope amino acids, and affecting antibody binding to the epitope, changing the localized epitope patterns, or amino acids defining the epitope area of the parent protein by genetic engineering mutations of a DNA sequence encoding the parent protein without impairing functionality of the protein using the emerging epitode database for eliminating amino acid substitutions creating new or duplicating existing epitope patterns, introducing the mutated DNA sequence into a suitable host, culturing the host and expressing the protein variant, and evaluating the immunogenicity of the protein variant using the parent protein as reference. The invention further relates to the protein variant and its use, as well as to a method for producing said protein variant.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Antibodies as t cell receptor mimics, methods of production and uses thereof
InactiveUS20120121577A1Less timeEfficient at generating a specific responseImmunoglobulin superfamilyImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPeptide displayMethods of production
Antibodies are produced that recognize peptides displayed in the context of MHC molecules and thus mimic the specificity of a T cell receptor (TCR). The antibodies are produced by immunizing a host with at least one peptide / MHC complex to elicit an immune response thereto. The desired antibodies can differentiate the peptide / MHC complex from the MHC molecule alone, the peptide alone, and a complex of MHC and irrelevant peptide. Finally, the desired antibodies are isolated.
Owner:WEIDANZ JON A +1
Identification of peptides that facilitate uptake and cytoplasmic and/or nuclear transport of proteins, DNA and viruses
The present invention relates to internalizing peptides which facilitate the uptake and transport of cargo into the cytoplasm and nuclei of cells as well as methods for the identification of such peptides. The internalizing peptides of the present invention are selected for their ability to efficiently internalize cargo into a wide variety of cell types both in vivo and in vitro. The method for identification of the internalizing peptides of the present invention comprises incubating a target cell with a peptide display library, isolating peptides with internalization characteristics and determining the ability of said peptide to internalize cargo into a cell.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH +1
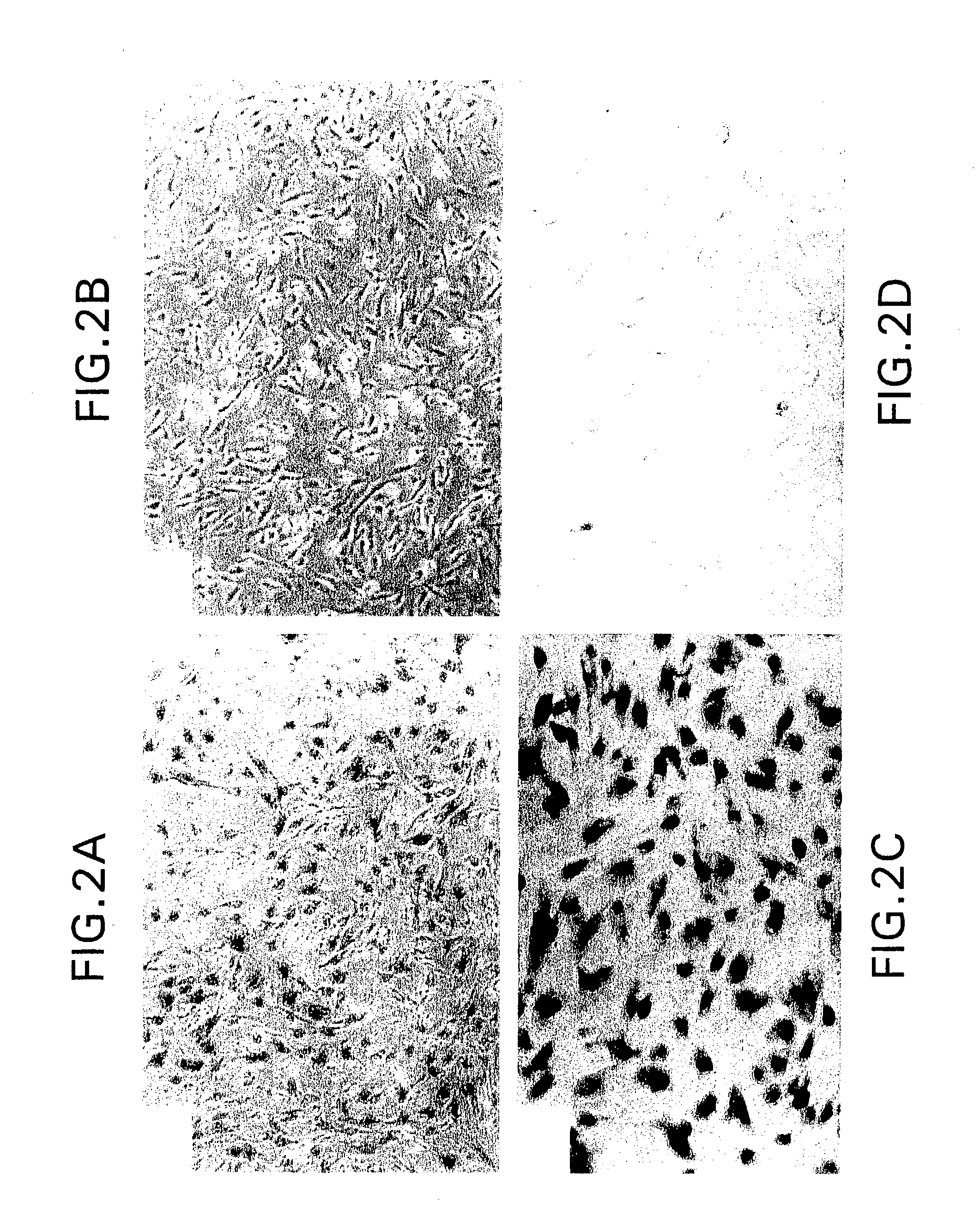
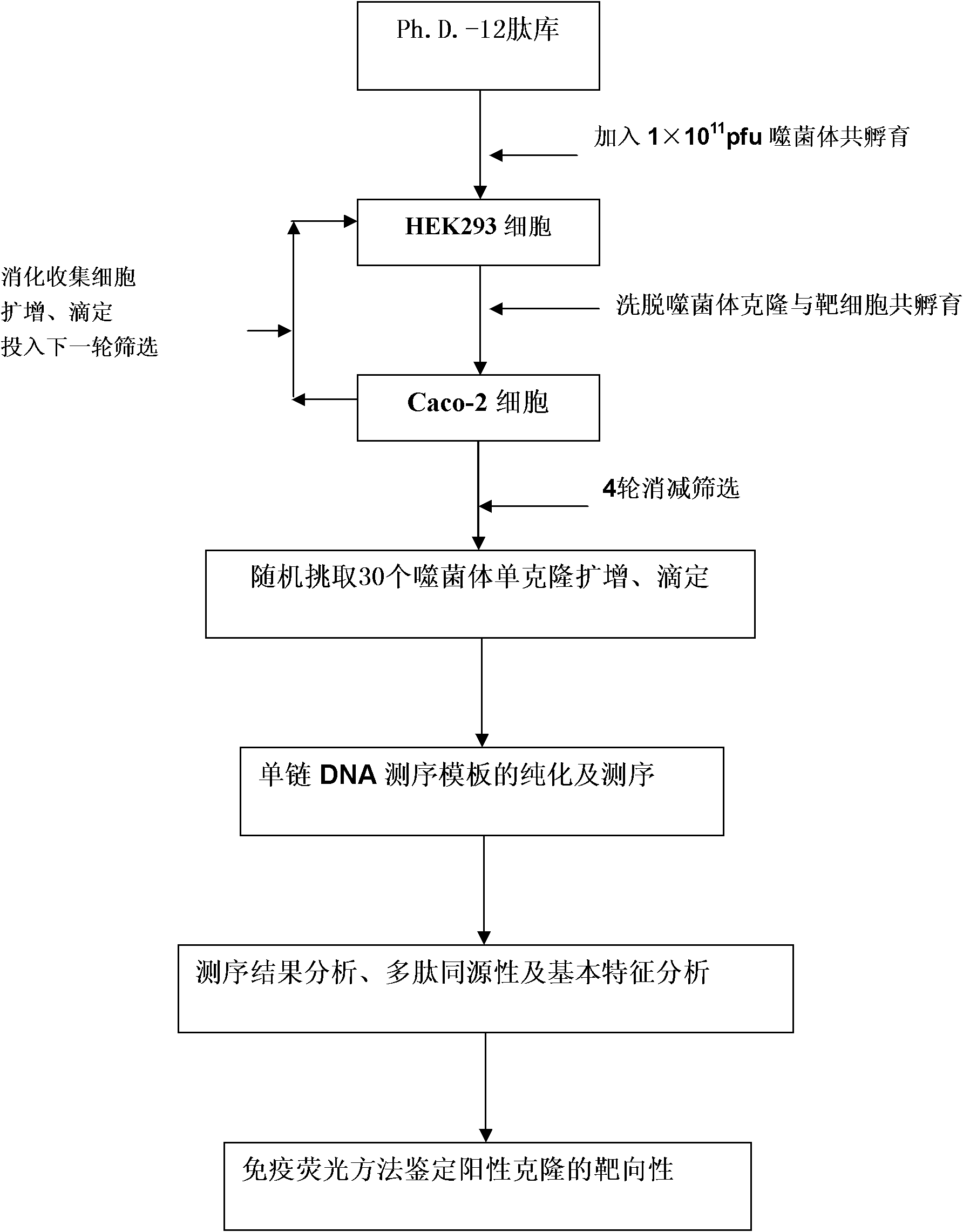
Caco-2 cell surface specific binding polypeptide and screening method thereof
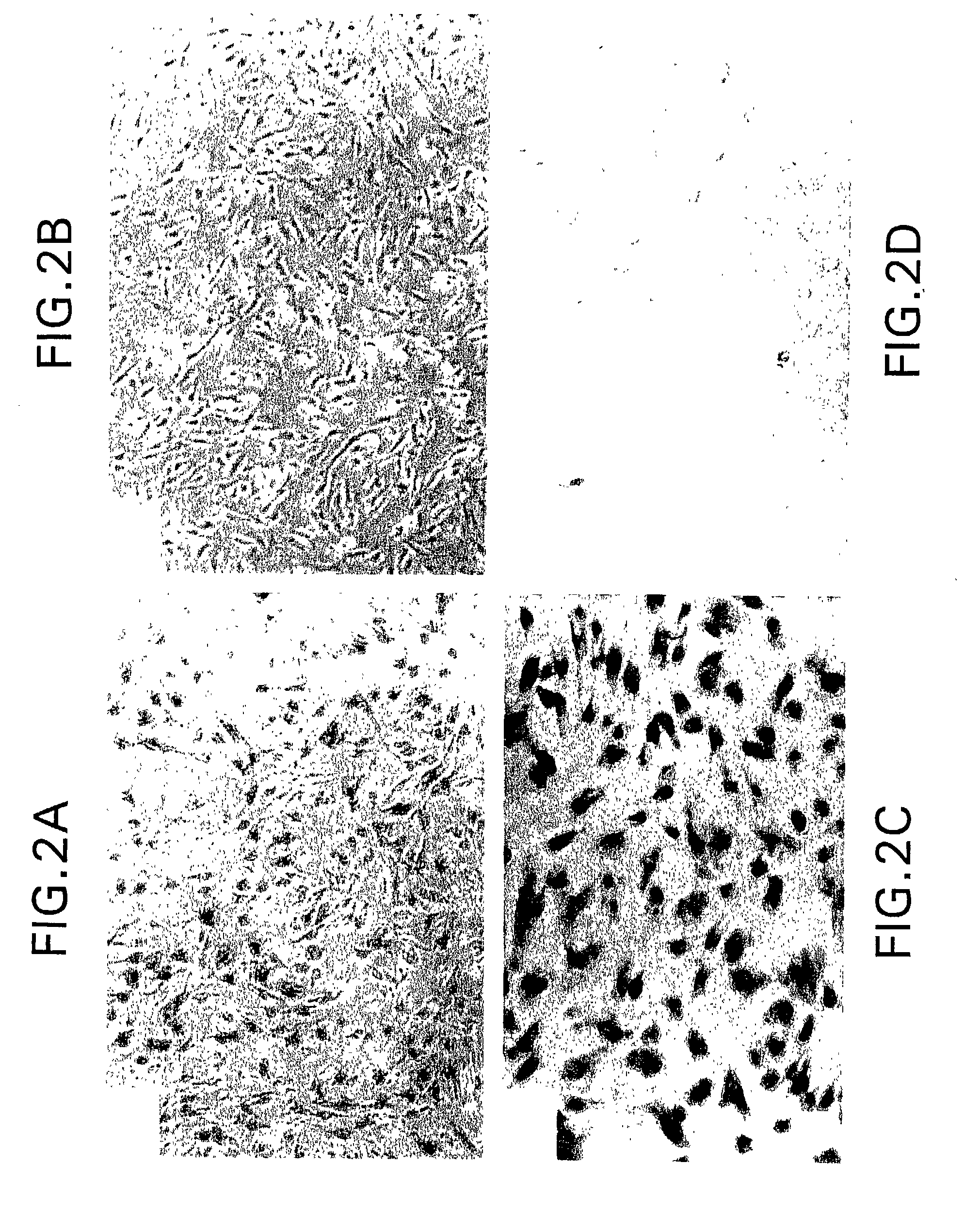
The invention discloses a Caco-2 cell surface specific binding polypeptide. Four polypeptide fragments are screened by phage display of a random dodecapeptide library, and the amino acid sequences of the four polypeptide fragments are respectively as follows: SPSIDTRYSRLG, CVSVGMKPSPRP, SVSVGMKPSPRP and MVSMDSSPRDRL. According to the screening method disclosed by the invention, colorectal carcinoma Caco-2 cell binding polypeptide sequences are screened by a phage polypeptide display technology, the affinity of phage clones with colorectal carcinoma cells is judged by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), ten phage clones are obtained, and four polypeptide sequences are obtained by sequencing. The consensus amino acid sequence is XXSXXXXXXXRXX; homology analysis indicates that the polypeptide motif is likely to be the amino acid determinant on the tumor cell surface receptor binding ligand protein; by further judgment of cell immunofluorescence, the targeting result of the phage positive clones implicates that the phage positive clones can be specifically bound with Caco-2 cells; and the colorectal carcinoma Caco-2 cell specific polypeptide acquired by screening provides a preliminary experiment basis for early diagnosis of colorectal carcinoma, targeted delivery of antitumor drugs and development of targeted small peptide drugs.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Identification of peptides that facilitate uptake and cytoplasmic and /or nuclear transport of proteins, DNA and viruses
InactiveUS20050074884A1Efficiently internalize and deliver cargoEasy to transportCompound screeningApoptosis detectionPeptide displayIn vivo
The present invention relates to internalizing peptides which facilitate the uptake and transport of cargo into the cytoplasm and nuclei of cells as well as methods for the identification of such peptides. The internalizing peptides of the present invention are selected for their ability to efficiently internalize cargo into a wide variety of cell types both in vivo and in vitro. The method for identification of the internalizing peptides of the present invention comprises incubating a target cell with a peptide display library, isolating peptides with internalization characteristics and determining the ability of said peptide to internalize cargo into a cell.
Owner:ROBBINS PAUL +4
Cellular Libraries of Peptide Sequences (CLiPS) and Methods of Using the Same
The present invention provides compositions including peptide display scaffolds that present at least one candidate peptide and at least one detectable moiety in at least one of the N-terminal and C-terminal candidate peptide presenting domains that when expressed in a cell are accessible at a surface of the cell outermembrane. In addition, the present invention also provides kits and methods for screening a library of cells presenting the candidate peptides in peptide display scaffolds to identify a ligand for an enzyme.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Scaffold polypeptides for heterologous peptide display
The present invention relates to the use of Stefin A as a scaffold protein for the display of inserted peptides, particularly wherein the Stefin A is a human Stefin A. Several mutations are advantageously made in the wild type stefin A sequence to improve it as a scaffold; preferably the Stefin A comprises a heterologous peptide insertion at the Leu 73 site. Furthermore, preferably the scaffold protein comprises a V48D mutation; preferably the scaffold protein comprises a G4W mutation. Preferably the scaffold comprises Leu73, V48D and G4W mutations. The invention also relates to the scaffold proteins themselves, in particular a stefin A polypeptide having the Leu73, V48D and G4W mutations, such as shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also relates to a method for identifying binding proteins and to peptide A (RLNKPLPSLPV) and its use in treating yeast infections.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Modification of polypeptides
ActiveUS9932367B2Increase infectivityExtended stayPeptide preparation methodsBiological testingPeptide displayIon-exchange resin
Owner:BICYCLE THERAPEUTICS
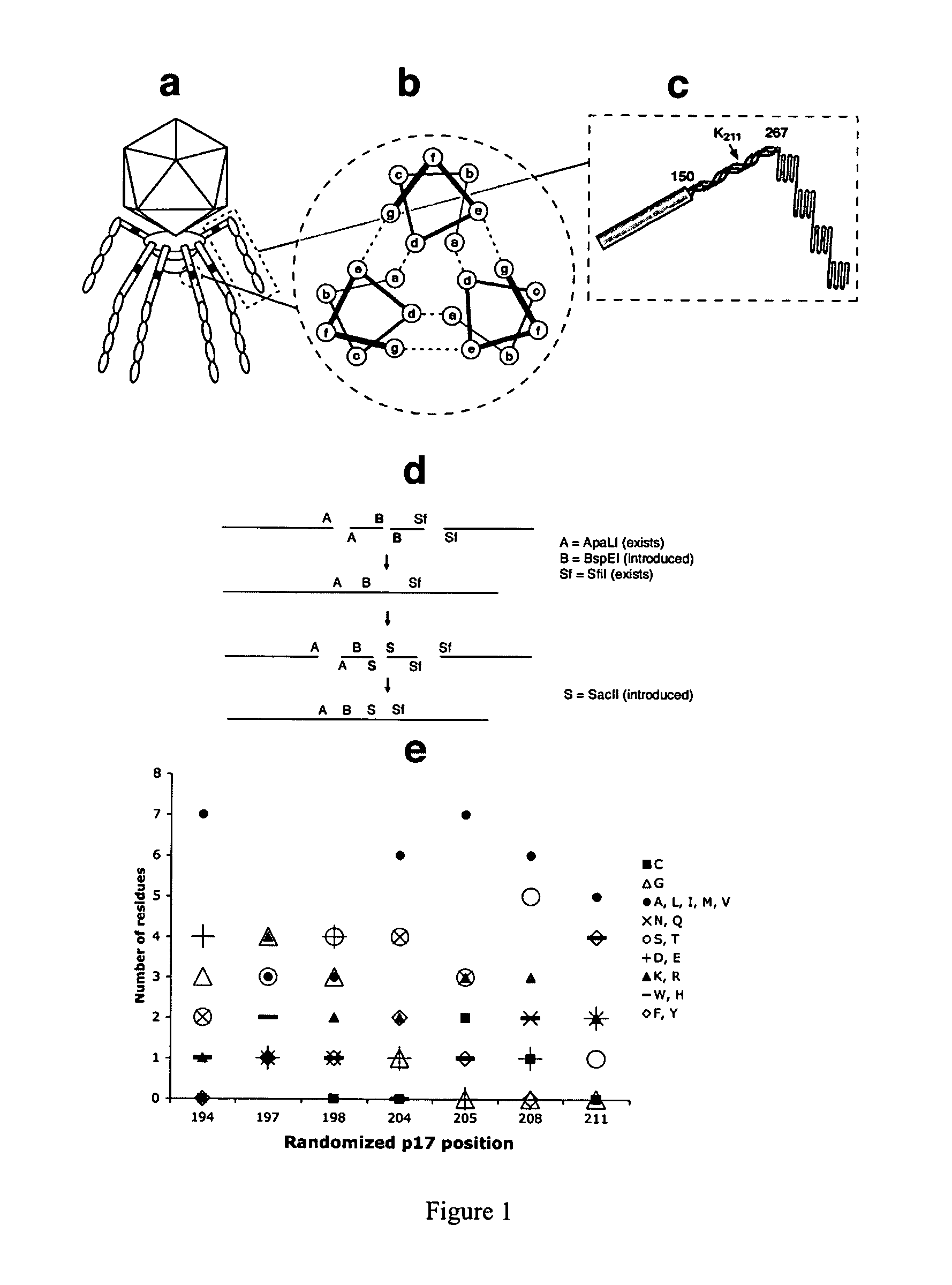
Novel T7 Phage Peptide Display System and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20090113562A1Strong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesFiberPeptide display
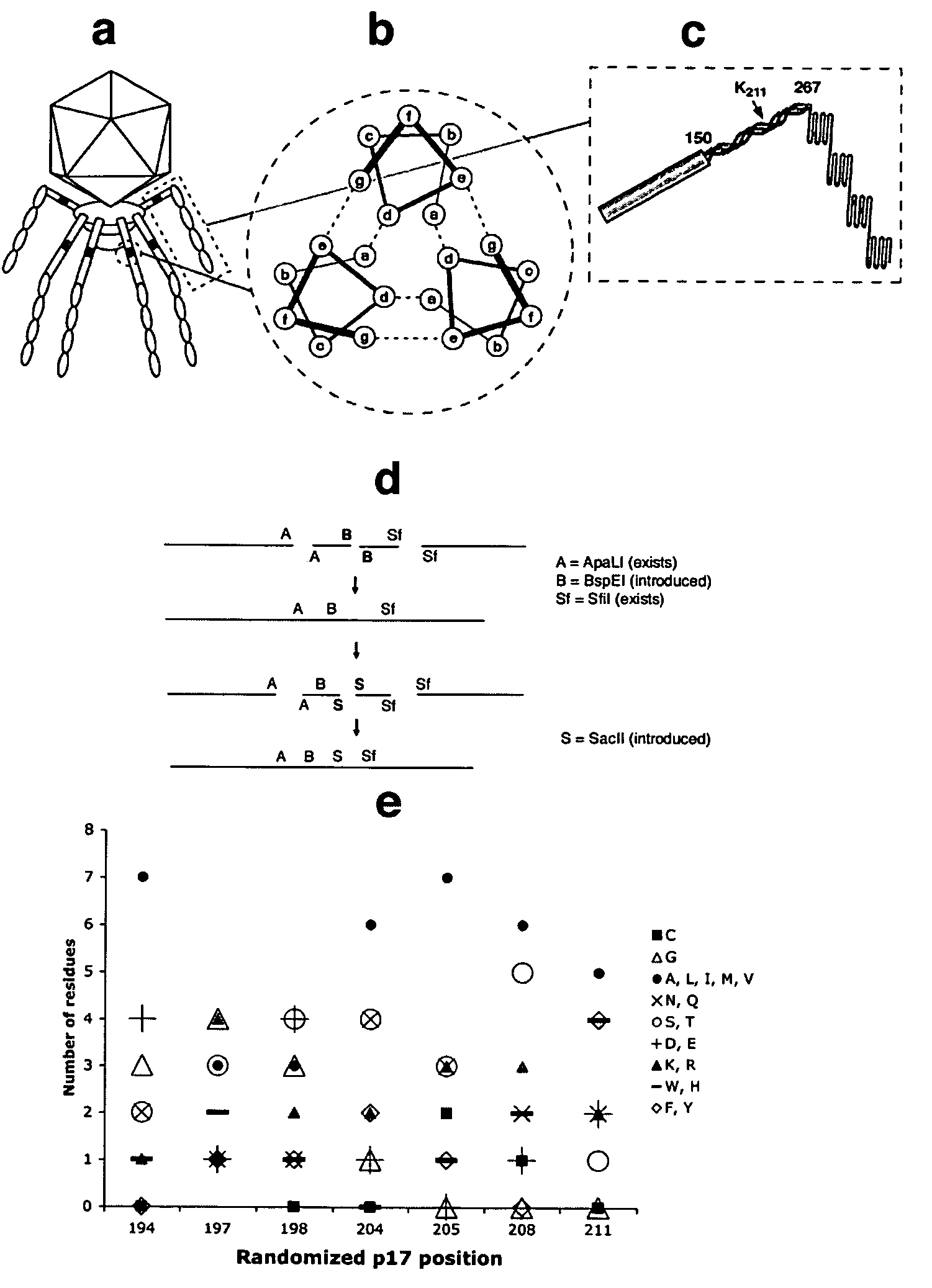
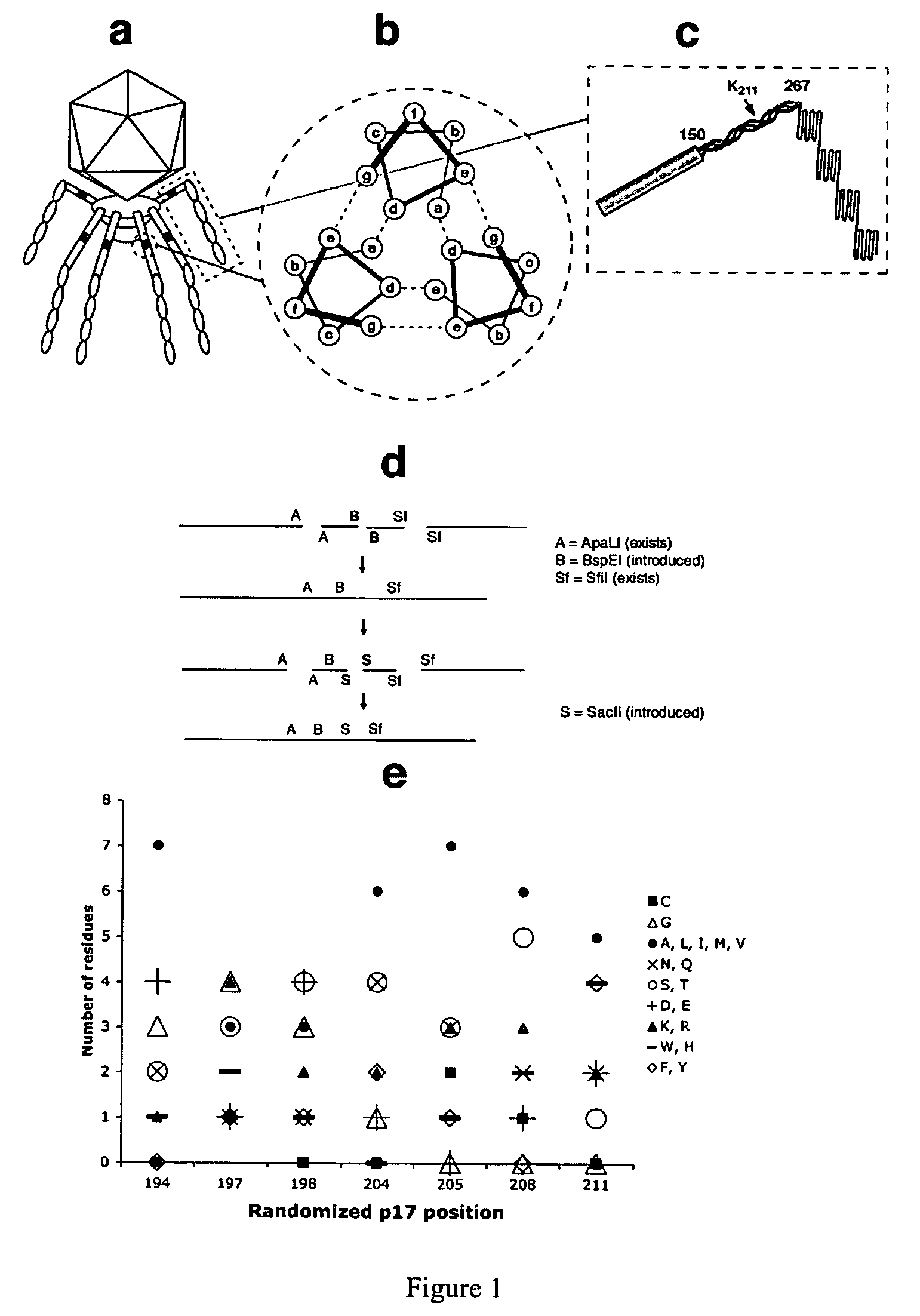
A bacteriophage T7 display vector for expressing and displaying an exogenous peptide, wherein the display vector comprises a polynucleotide encoding a bacteriophage T7 tail fiber protein p17 in which a hepatocyte-targeting determinant sequence is inactivated, and wherein a cloning site is contained in a coding sequence for the tail fiber protein p17 or in a coding sequence for a capsid protein p10B. Also provided are a host cell containing the display vector as described above, a bacteriophage T7 particle comprising at least one copy of a p17 protein which comprises an exogenous peptide displayed thereon, or at least one copy of a p10 protein with an exogenous peptide displayed thereon, wherein a hepatocyte-targeting determinant sequence on the bacteriophage T7 tail fiber protein p17 is inactivated. The present invention further provides a viral lysate containing assembled bacteriophage T7 particle described above, and a method for determining if a candidate peptide is a liver-targeting peptide, or for screening for liver targeting peptides.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Phage display vector, phages encoded thereby, and methods of use thereof
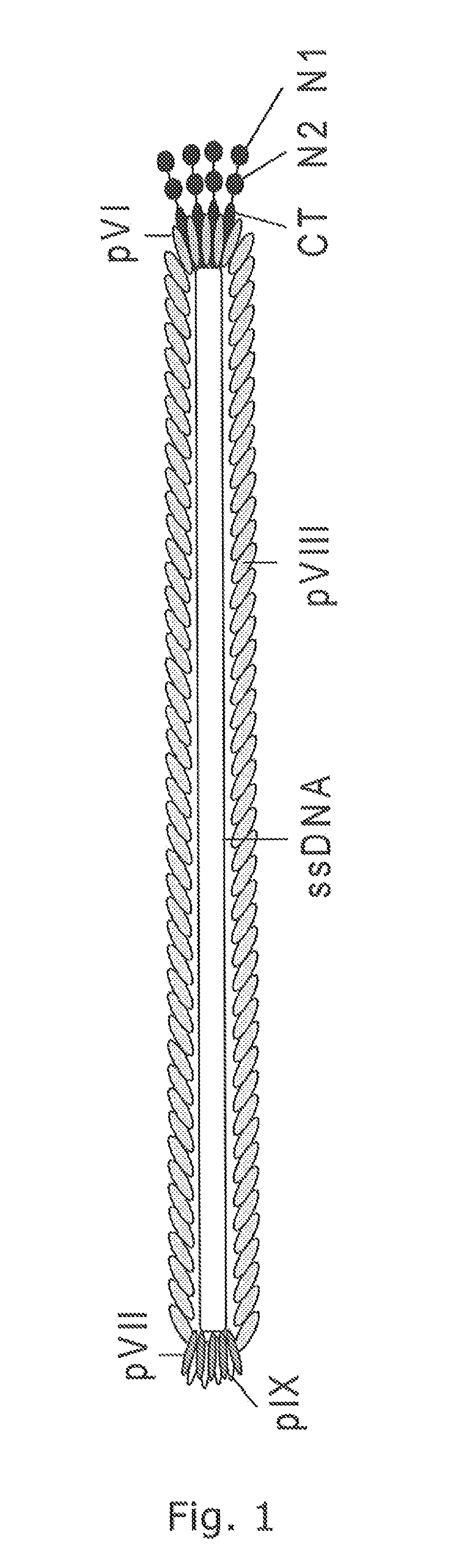
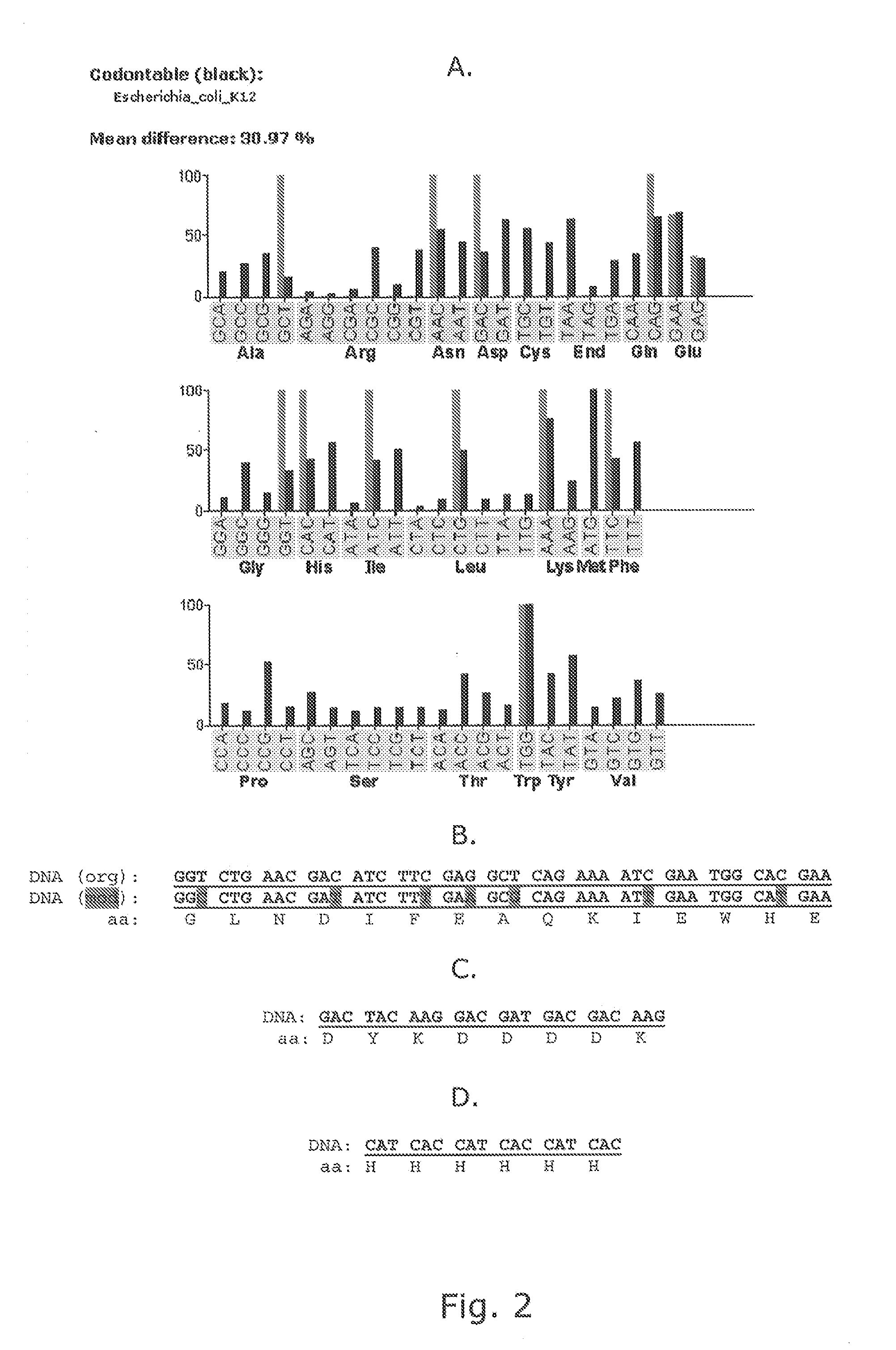
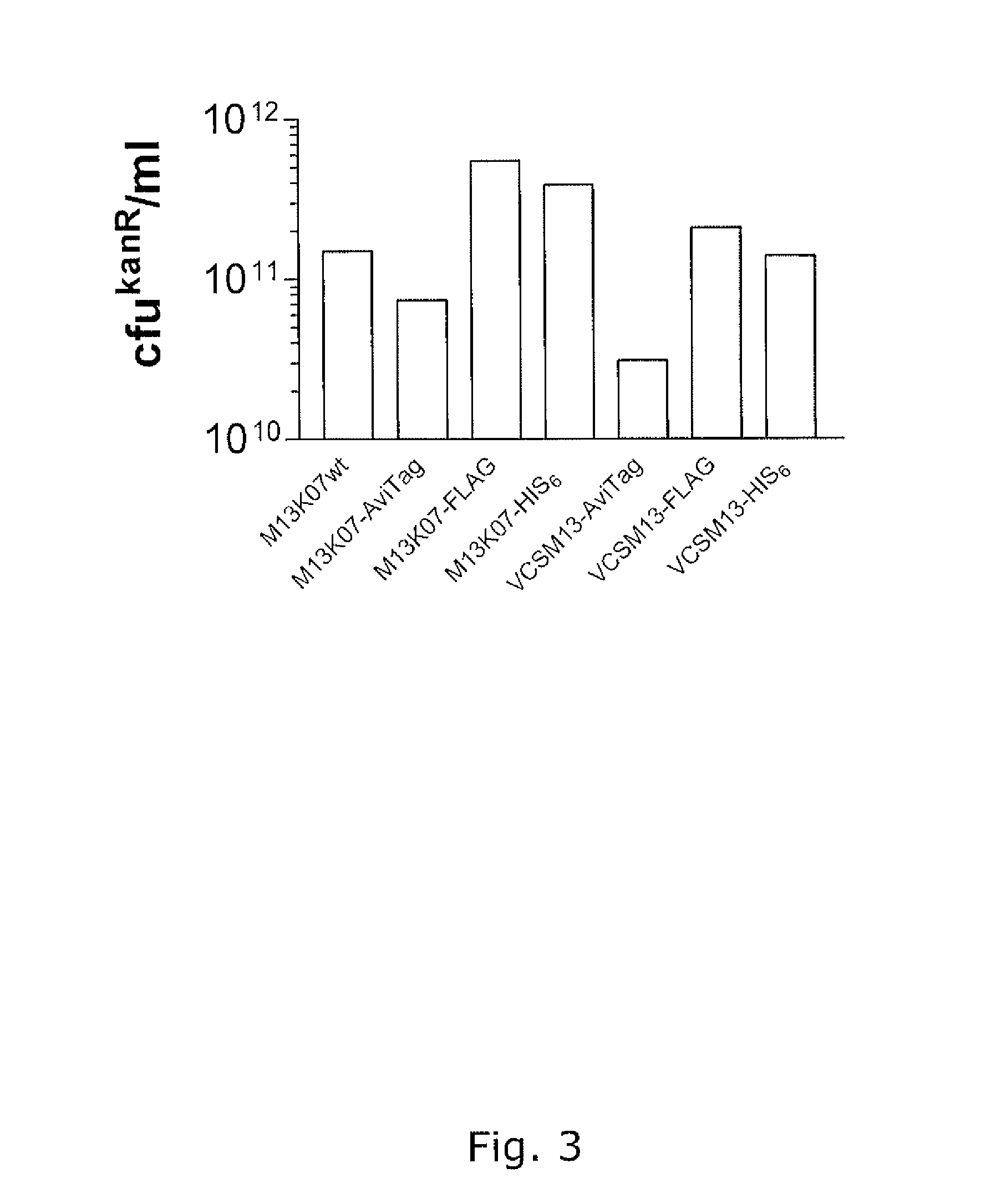
Filamentous bacteriophages are particularly efficient for the expression and display of combinatorial random peptides. Two phage proteins are often employed for peptide display: the infectivity protein, pIII and the major coat protein, pVIII. The use of pVIII typically requires the expression of two pVIII genes: the wild type and the recombinant pVIII genes to generate mosaic phages. “Type 88” vectors contain two pVIII genes in one phage genome. A novel “type 88” expression vector has been rationally designed and constructed, which can be used to express recombinant peptides as pVIII chimeric proteins in mosaic bacteriophages. This vector is not only genetically stable but also of high copy number and produces high titers of recombinant phages.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Method for preparing phase granule for displaying polypeptide
InactiveCN1884555AHigh level of presentationViruses/bacteriophagesHybrid peptidesPeptide displayCoat protein
This invention involves the phagemid in molecule biology field and medicine field. It is a preparation method of display peptide's phagemid. This method adopts the gene group plasmid of assistant phage fusion protein of coding foreign peptide and pIII coat protein, to co-transformation or successive-transformation F factor positive Isolates together with phagemid, so to obtain phagemid that display foreign peptide. The phagemid prepared by this method has high foreign peptide display level, and it is not necessarily prepare assistant phage so to simplified the process of preparation of assistant phage.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
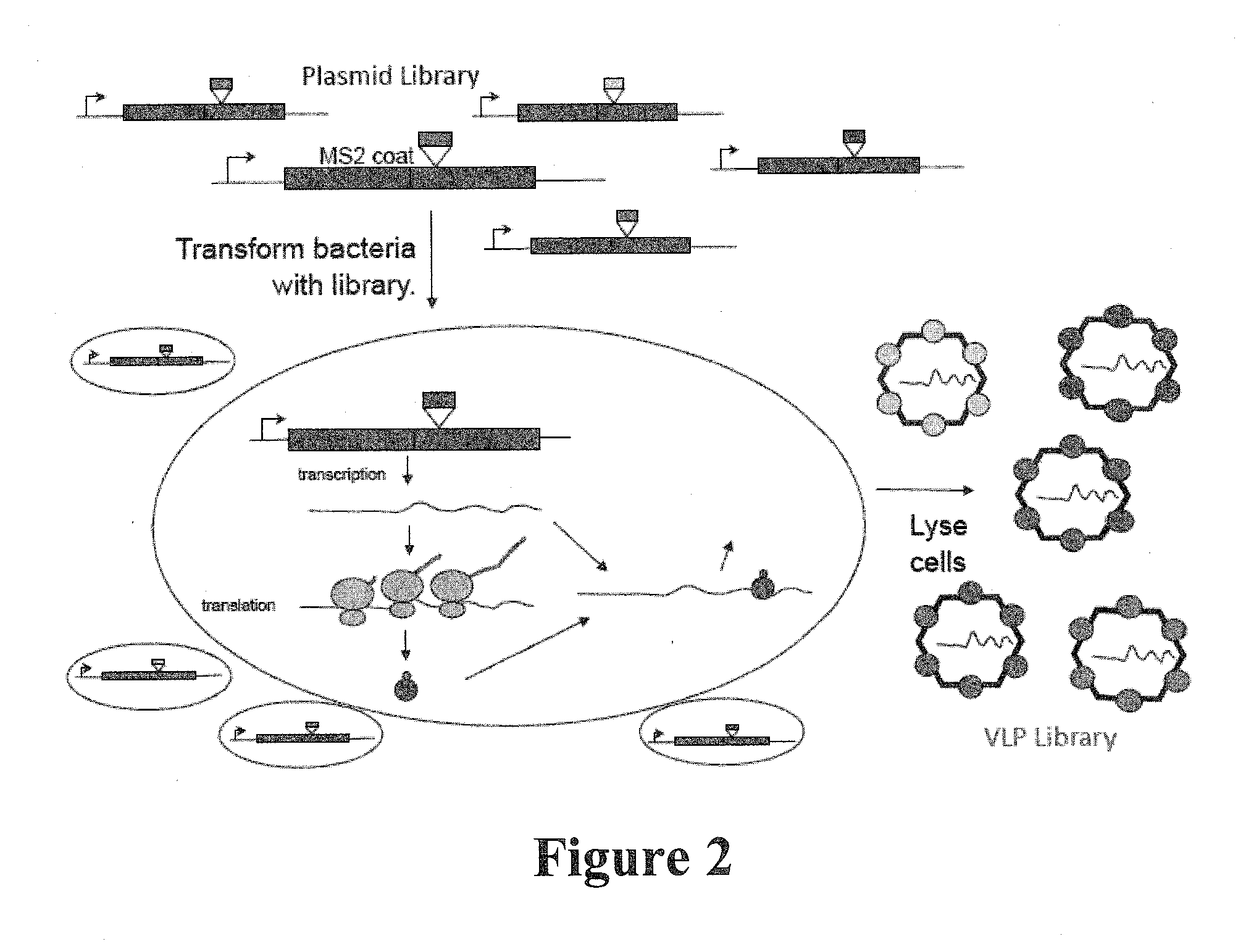
Plasmids and methods for peptide display and affinity-selection on virus-like particles of RNA bacteriophages
InactiveUS20140106982A1Eliminate side effectsHigh affinitySugar derivativesLibrary screeningHeterologousPeptide display
The present invention relates to a system and method for controlling peptide display valency on virus-like particles (VLPs), especially including MS2 or PP7 VLPs. In this method, large amounts of wild-type and low quantities of single-chain dimer coat proteins may be produced from a single RNA. Valency is controlled in immunogen (vaccine) production by providing a system that allows the production of large amounts of wild-type and low quantities of single-chain dimer coating proteins from a single RNA, allowing facile adjustment of display valency levels on bacteriophage VLPs, especially MS2 or PP7 VLPs over a wide range, from few than one—on average—to as many as ninety per particle. This facilitates the production of immunogens and vaccines, including VLPs exhibiting low valency. Nucleic acid constructs useful in the expression of virus-like particles are disclosed, comprised of a coat polypeptide of bacteriophage such as MS2 or PP7 modified by insertion of a heterologous peptide, optionally comprising a carbohydrate mimotope, wherein the heterologous peptide is displayed on the virus-like particle and encapsidates bacteriphage mRNA.
Owner:PEABODY DAVID S +1
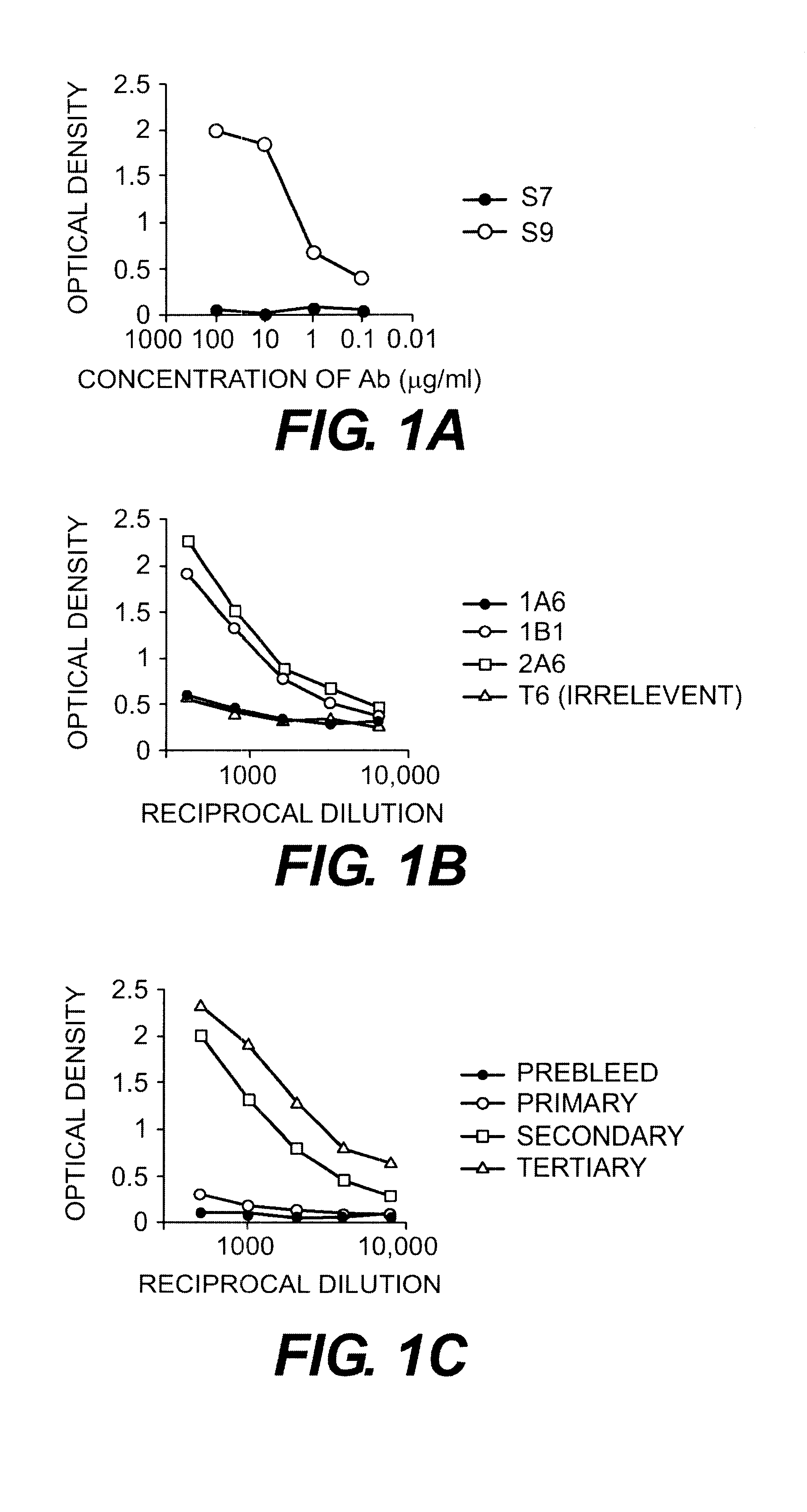
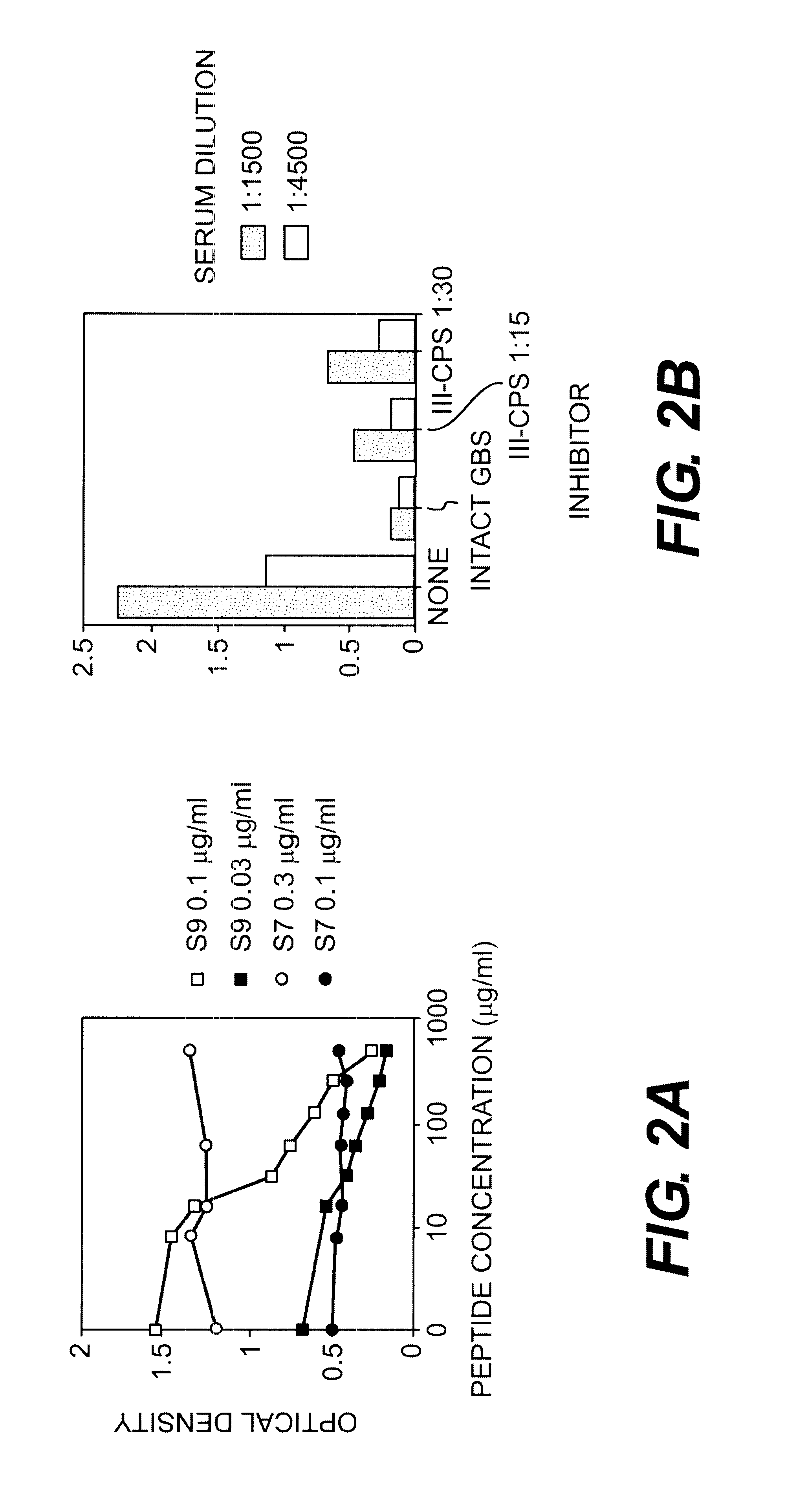
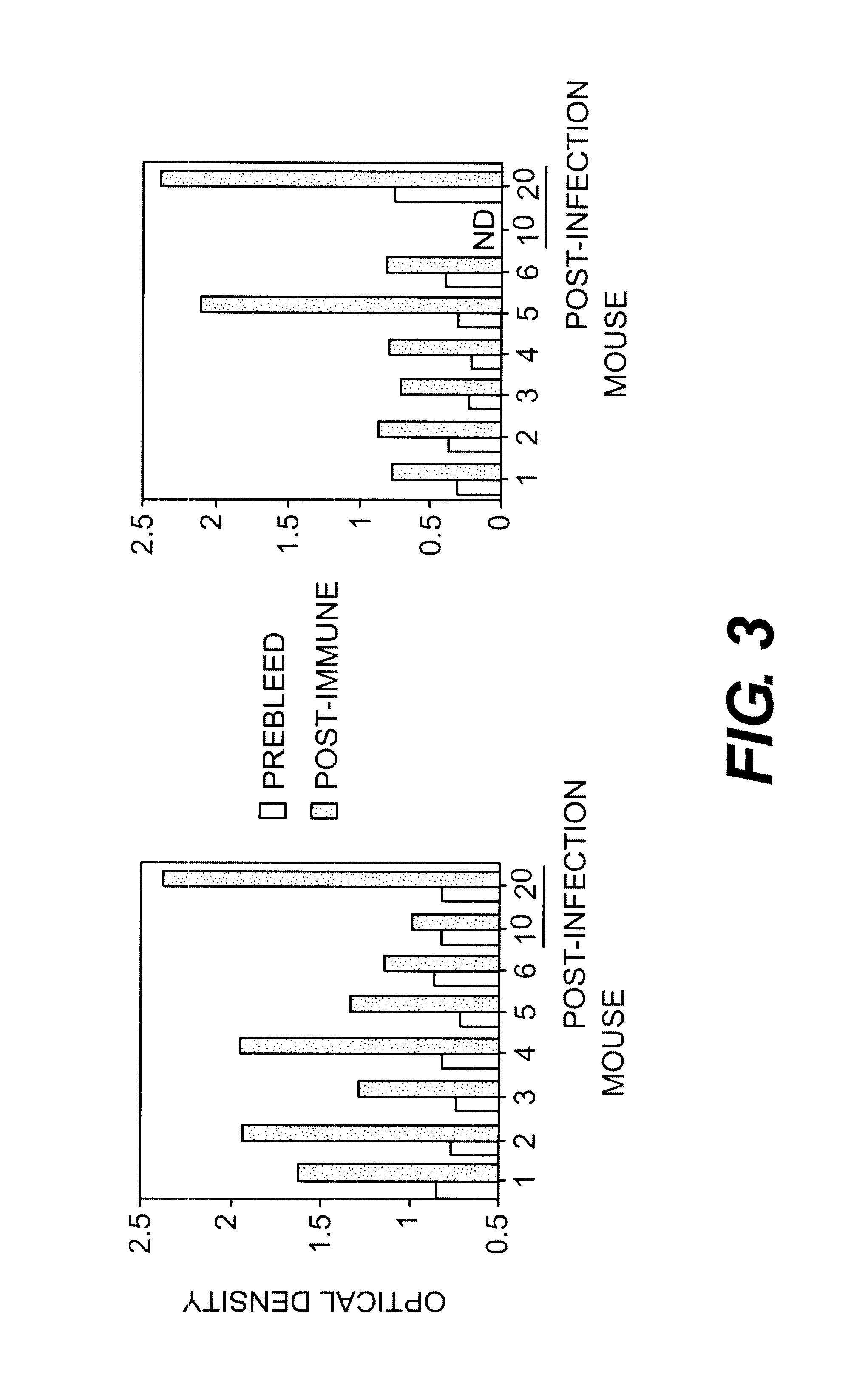
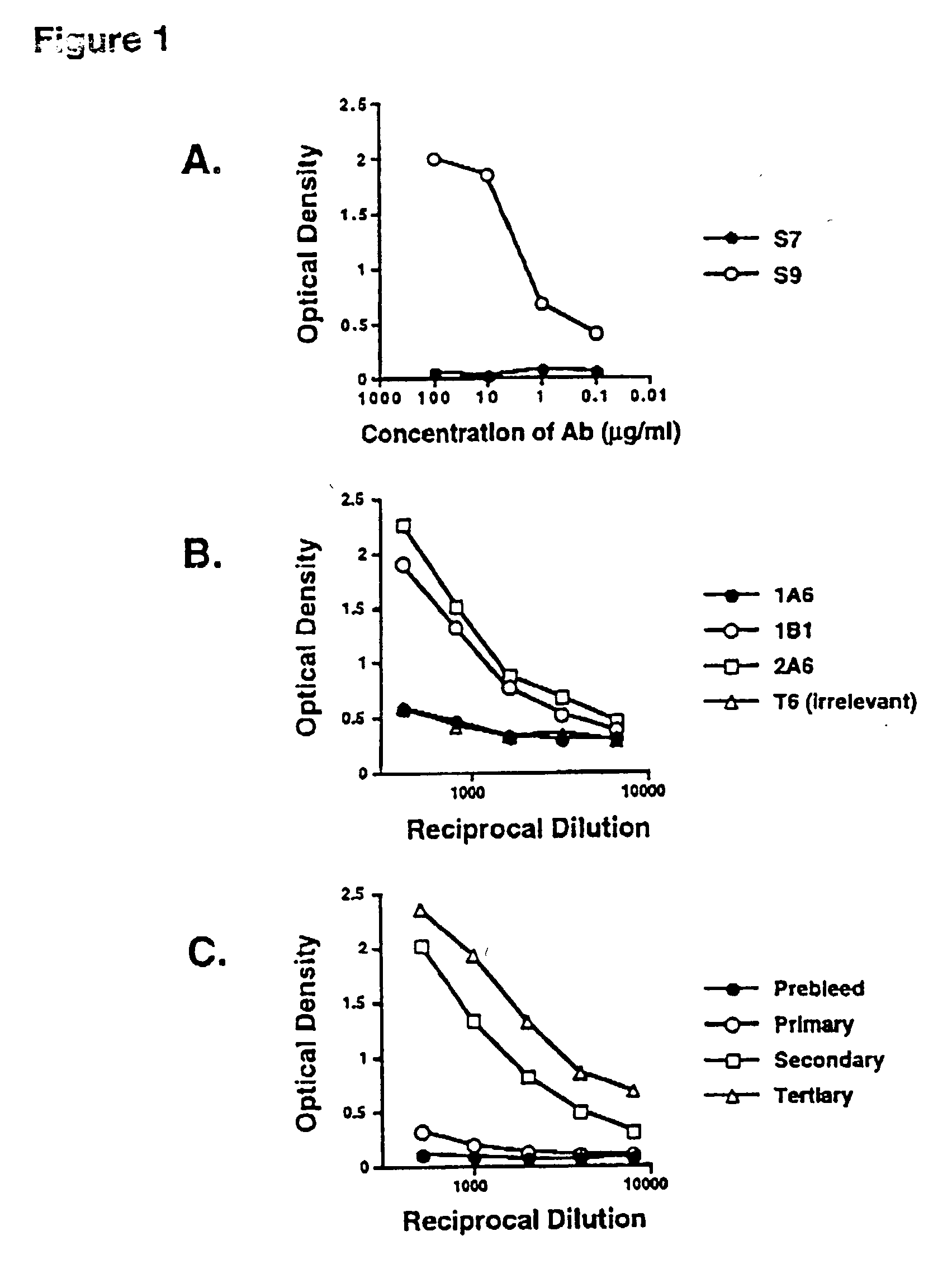
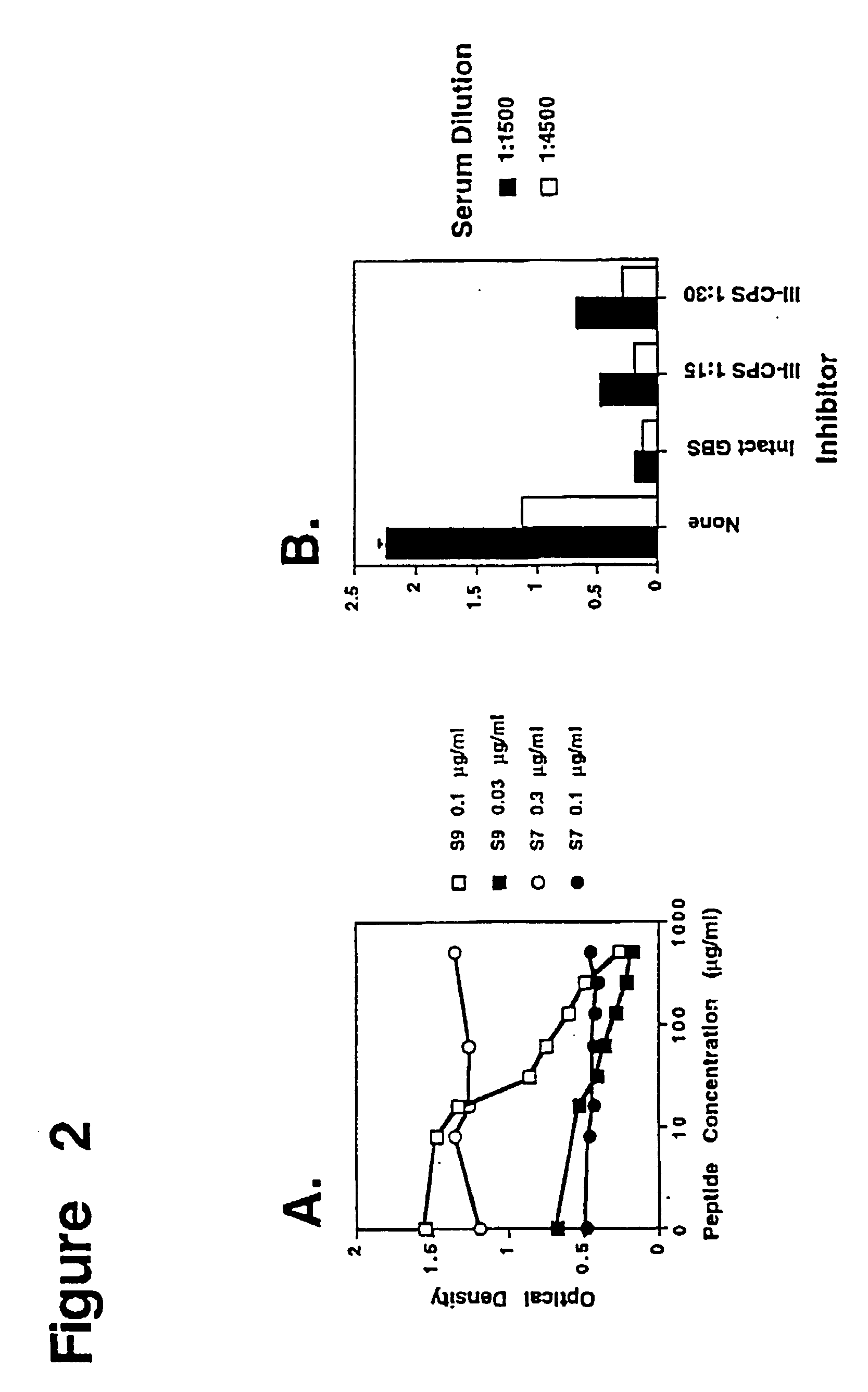
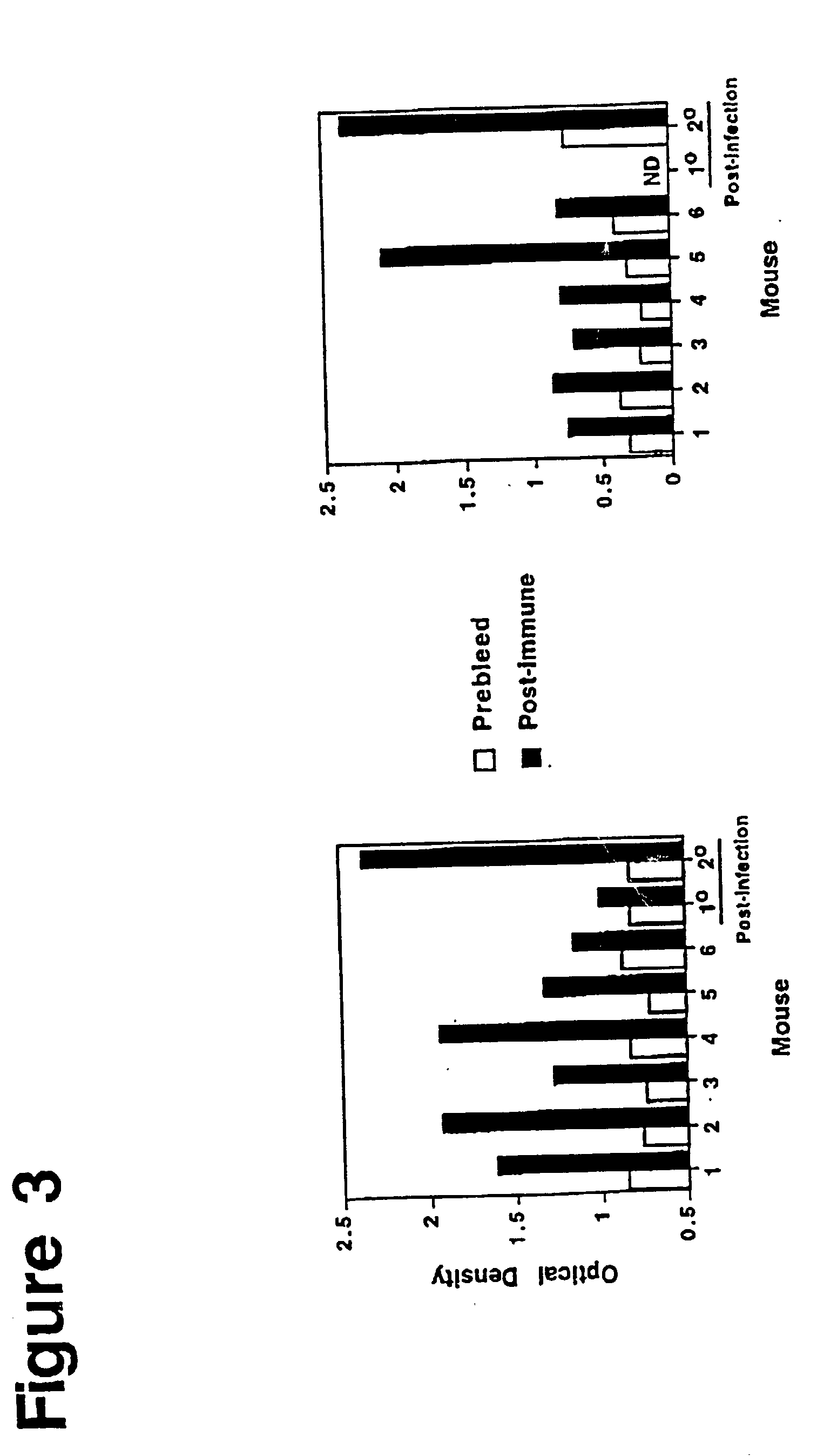
Method of isolating a peptide which immunologically mimics microbial carbohydrates including group B streptococcal carbohydrates and the use thereof in a vaccine
This invention relates to new vaccines against microorganisms based on antigenically mimetic peptides. The invention also relates to methods of discovering such mimetic peptides by first screening peptide-display phage libraries with antibodies against the microbial carbohydrates(s) of interest to locate antigenically mimetic peptides. Vaccines against Group B Streptococcus, or Streptococcus Agalactiae, are preferably produced using this method.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method of isolating a peptide which immunologically mimics microbial carbohydrates including group B streptococcal carbohydrates and the use thereof in a vaccine
InactiveUS20030082524A1Bacterial antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismStreptococcus agalactiae
This invention relates to new vaccines against microorganisms based on antigenically mimetic peptides. The invention also relates to methods of discovering such mimetic peptides by first screening peptide-display phage libraries with antibodies against the microbial carbohydrates(s) of interest to locate antigenically mimetic peptides. Vaccines against Group B Streptococcus, or Streptococcus Agalactiae, are preferably produced using this method.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
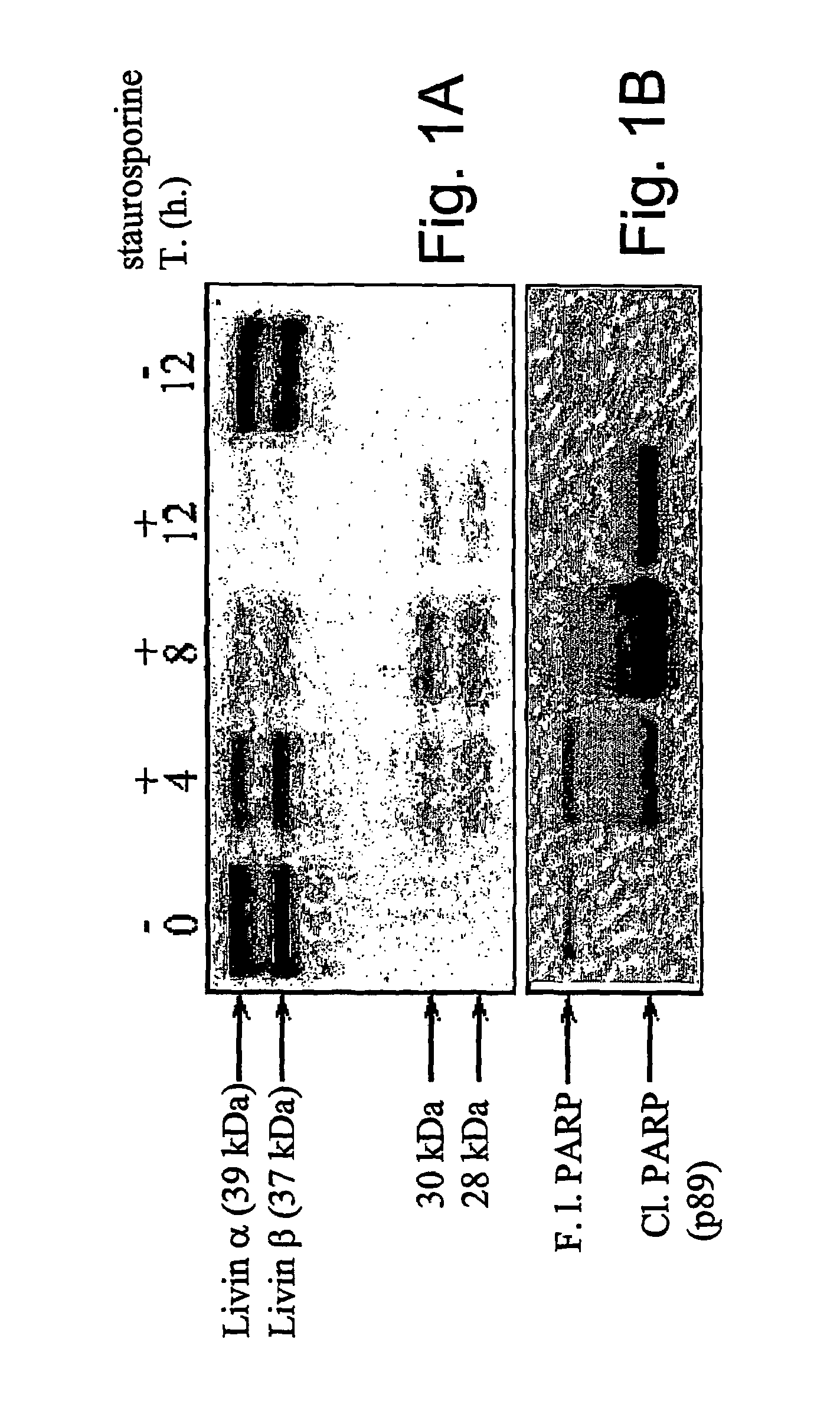
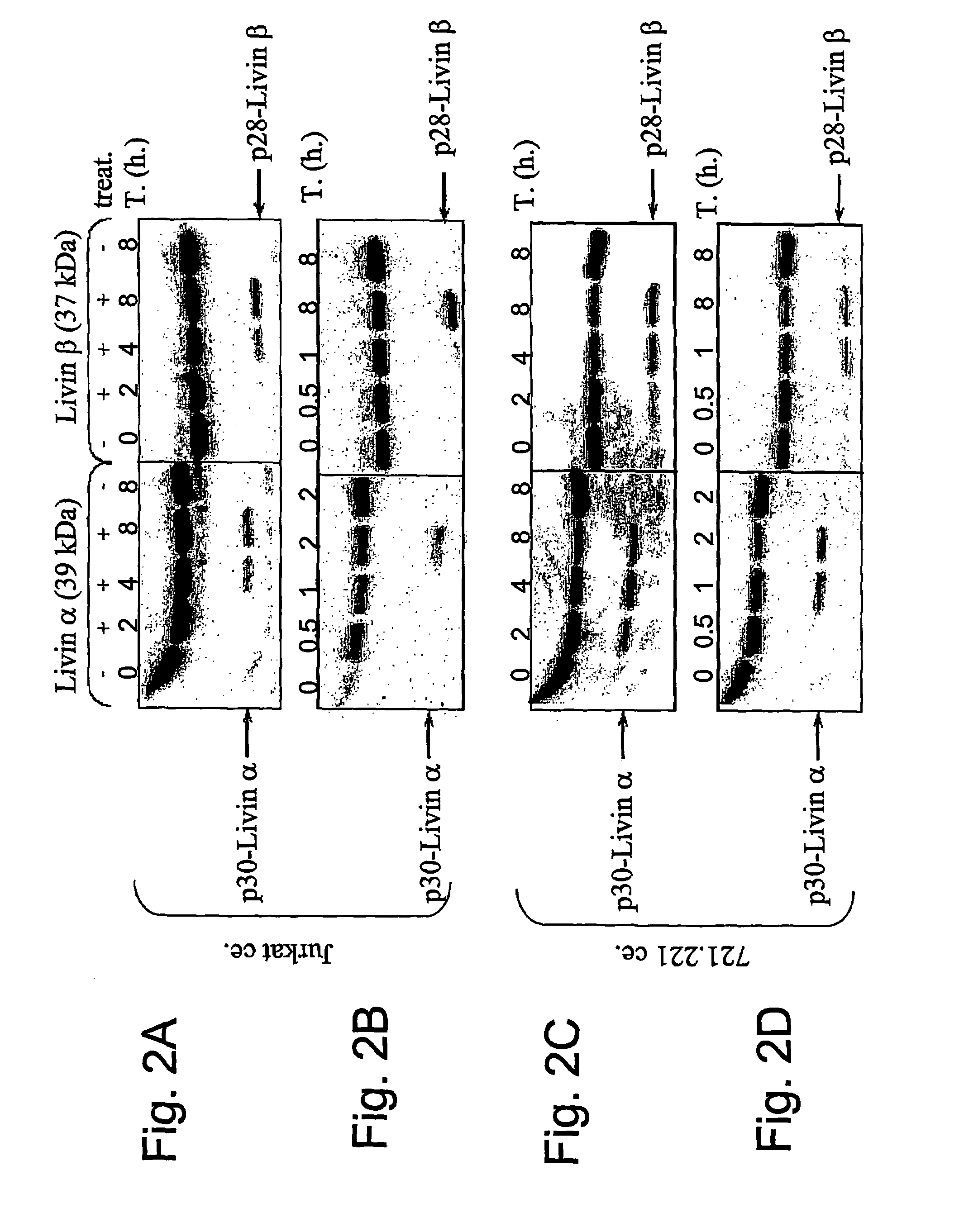
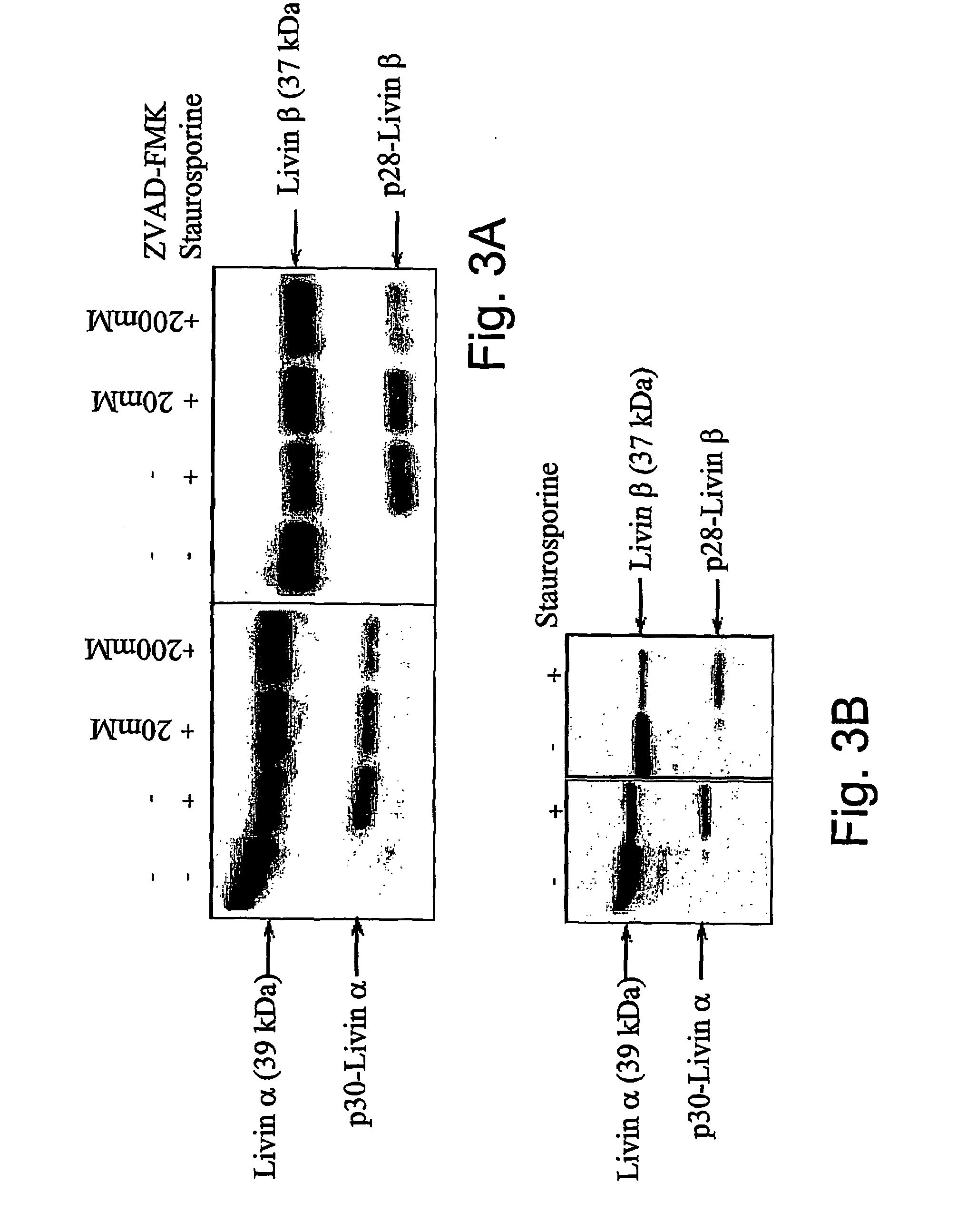
Livin-derived peptides, compositions and uses thereof
The present invention relates to livin-derived peptides with pro-apoptotic activity. More specifically, the present invention provides peptides p30-Livin α and p28-Livin β, derived from Livin α and β, respectively, as well as compositions thereof. These herein described peptides display pro-apoptotic activity. Thus, another object of the present invention is the use of the peptides or compositions thereof for the enhancement and / or induction of apoptosis, as well as for the treatment of cancer. Finally, the invention also provides a method of enhancing the sensitivity of cells to death-inducing treatments or agents through the use of the peptides of the invention.
Owner:HADASIT MEDICAL RES SERVICES & DEVMENT
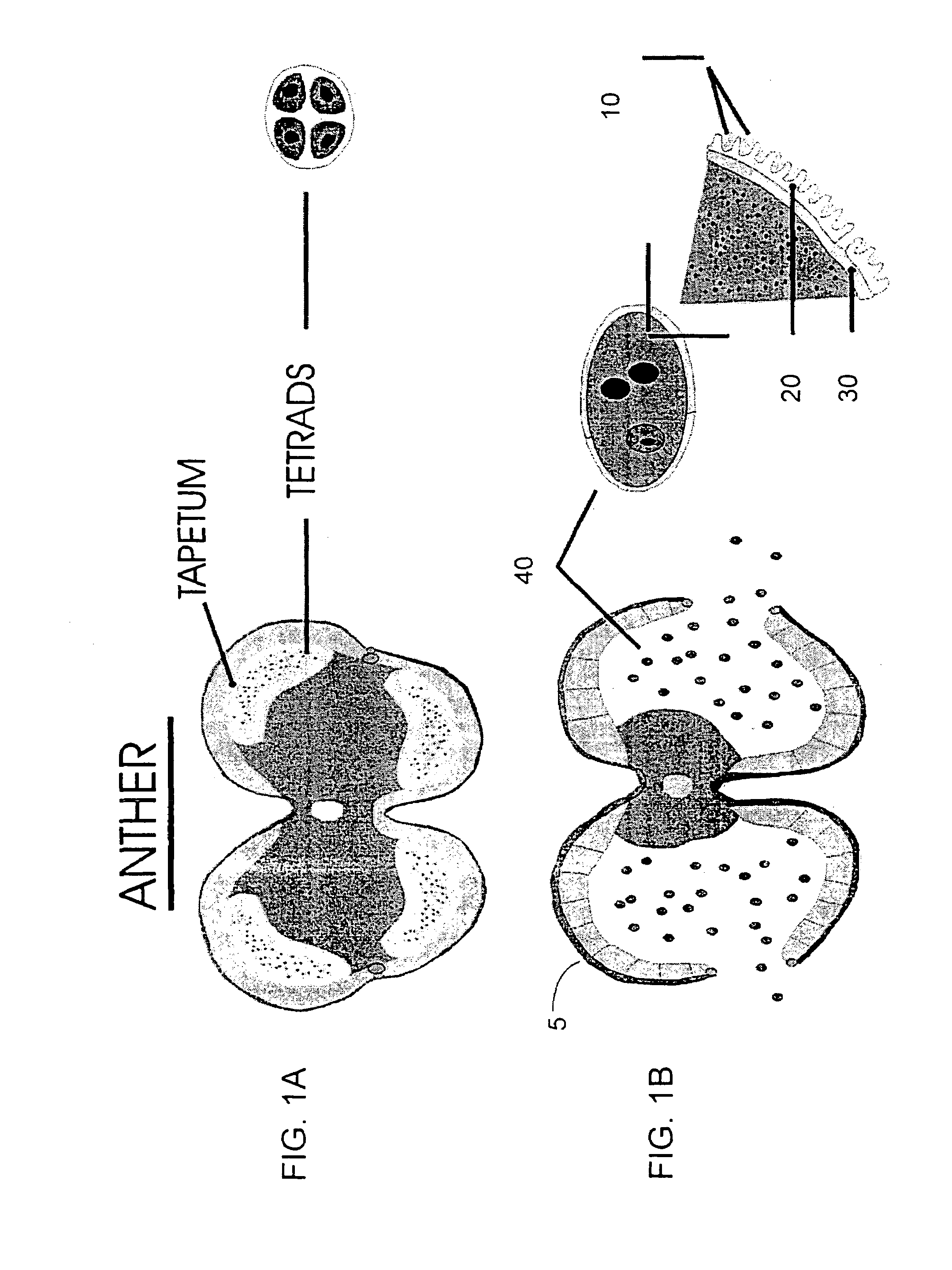
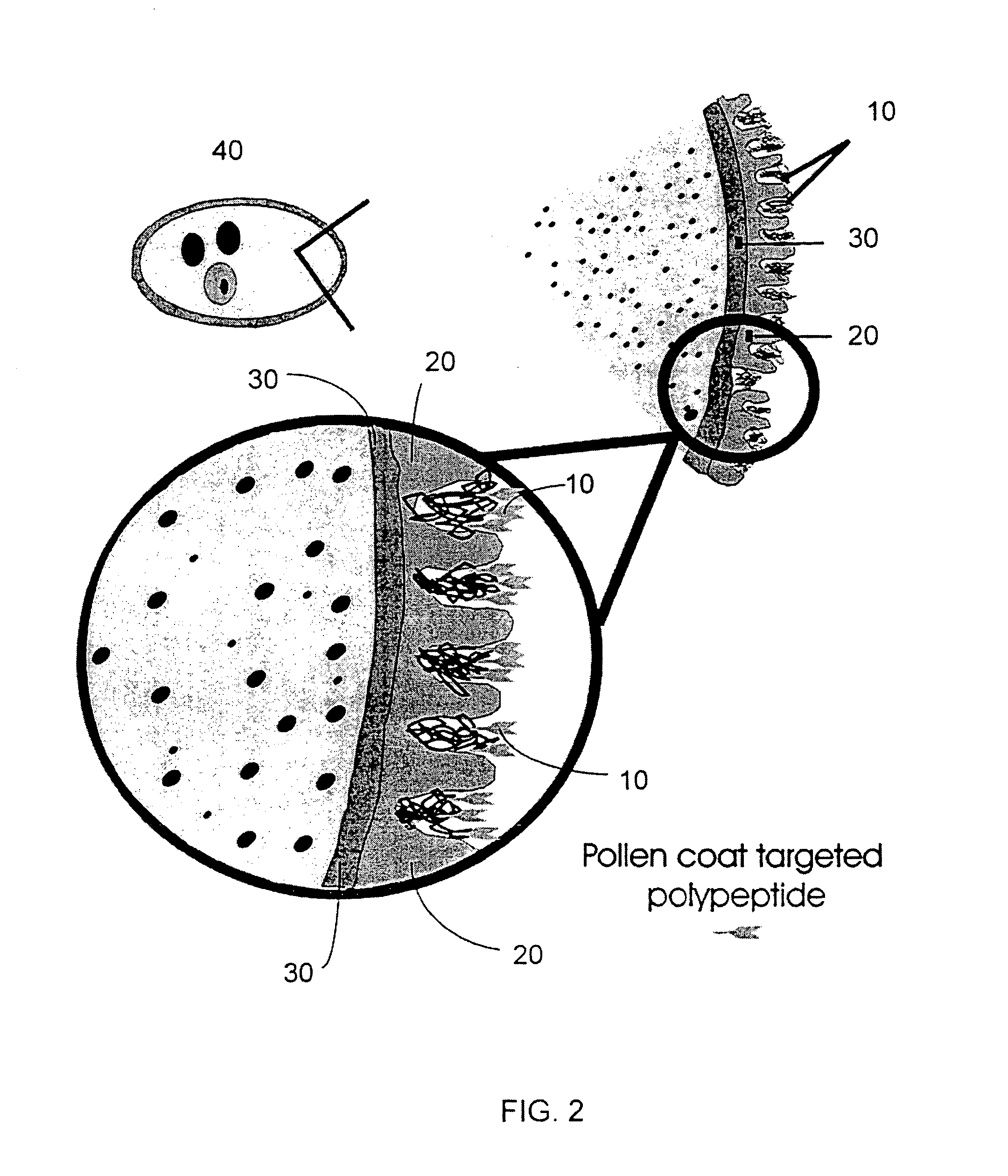
Modification of pollen coat protein composition
InactiveUS7303917B2Modification to compositionHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProtein compositionPeptide display
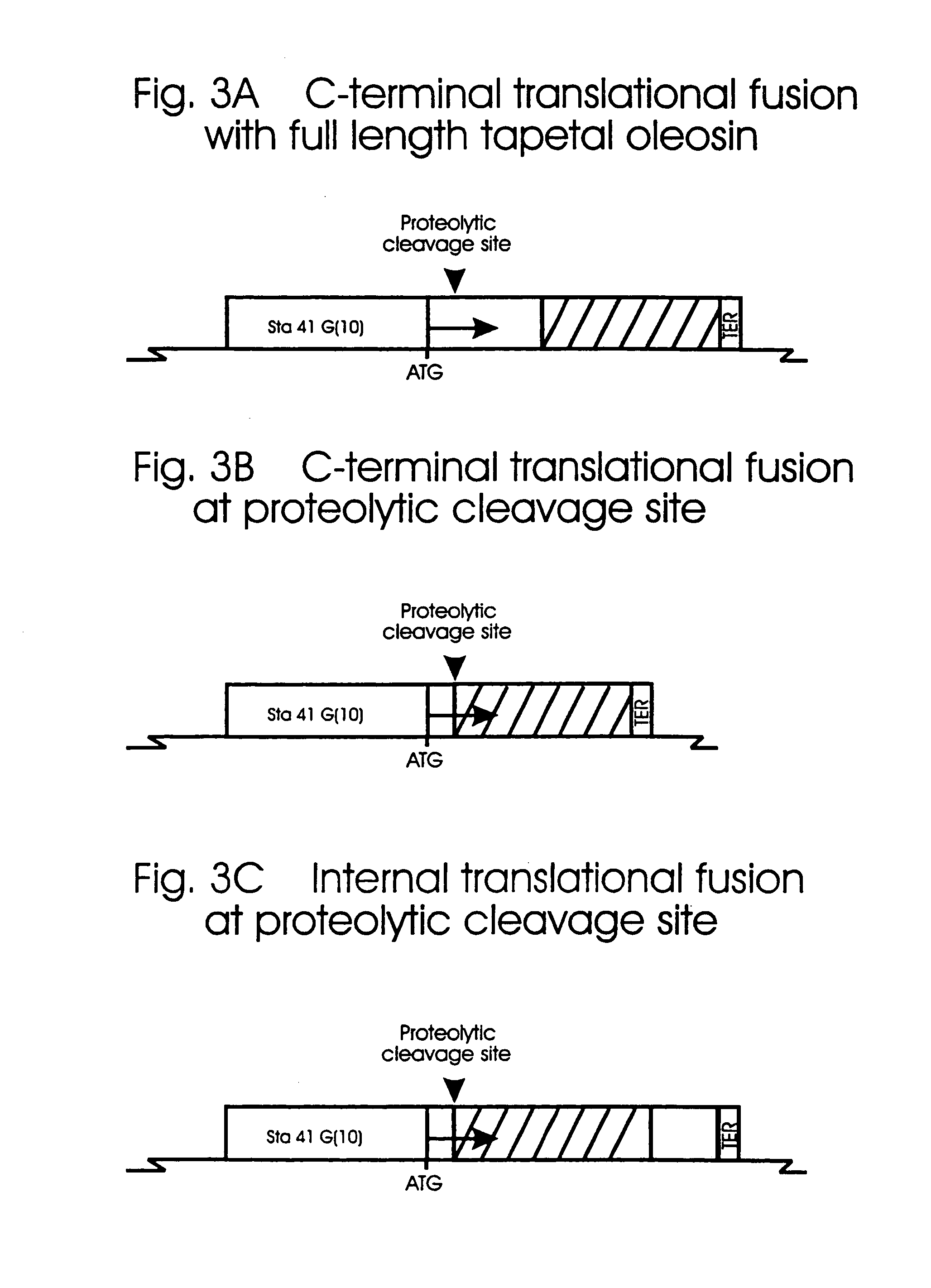
This invention is directed to a method for the expression of a gene of interest, or a chimeric or modified gene allowing the localization of a protein, protein fusion, peptide or fragment of interest within the extracellular domain of a floral cell. This method comprises preparing a construct comprising a promoter sequence capable of expressing a gene encoding the protein, protein fusion, peptide, or fragment of interest, within the floral cell; a translated sequence of the protein, protein fusion, peptide, or fragment of interest, which is localized within the extracellular domain of a floral cell; a gene that encodes the protein, protein fusion, peptide, or fragment of interest; and a terminator sequence, and transforming a plant. Plants transformed with such a construct are characterized as having a protein, fragment thereof, or peptide of interest on the surface of a floral cell. Such localized proteins or peptides may be used for the purposes of peptide display, mediating plant sterility, modifying pollen-pistil interactions, altering pollen for insect consumption etc.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD
T7 phage peptide display system and uses thereof
A bacteriophage T7 display vector for expressing and displaying an exogenous peptide, wherein the display vector comprises a polynucleotide encoding a bacteriophage T7 tail fiber protein p17 in which a hepatocyte-targeting determinant sequence is inactivated, and wherein a cloning site is contained in a coding sequence for the tail fiber protein p17 or in a coding sequence for a capsid protein p10B. Also provided are a host cell containing the display vector as described above, a bacteriophage T7 particle comprising at least one copy of a p17 protein which comprises an exogenous peptide displayed thereon, or at least one copy of a p10 protein with an exogenous peptide displayed thereon, wherein a hepatocyte-targeting determinant sequence on the bacteriophage T7 tail fiber protein p17 is inactivated. The present invention further provides a viral lysate containing assembled bacteriophage T7 particle described above, and a method for determining if a candidate peptide is a liver-targeting peptide, or for screening for liver targeting peptides.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Compositions and methods related to synchronous selection of homing peptides for multiple tissues by in vivo phage display
Embodiments of the invention include methods for selecting in parallel (i.e., synchronously or simultaneously) peptides that target a number of organs, in which each peptide targets distinct tissues or organs. Typically, the methods of the invention provide for peptide selection in a Minimal number of subjects and still provides a selectively binding peptide. In certain aspects, methods of identifying peptides that bind to multiple selected tissues or organs of an organism may comprise the steps of administering a phage display library to a first subject; obtaining a sample of two or more selected tissues; obtaining phage displaying peptides that bind to the samples from the first subject; enriching for peptides by administering phage isolated from the samples of the first subject to a second subject; obtaining a sample of two or more selected tissues from the second subject; and identifying the peptides displayed.
Owner:KOLONIN MIKHAIL +2
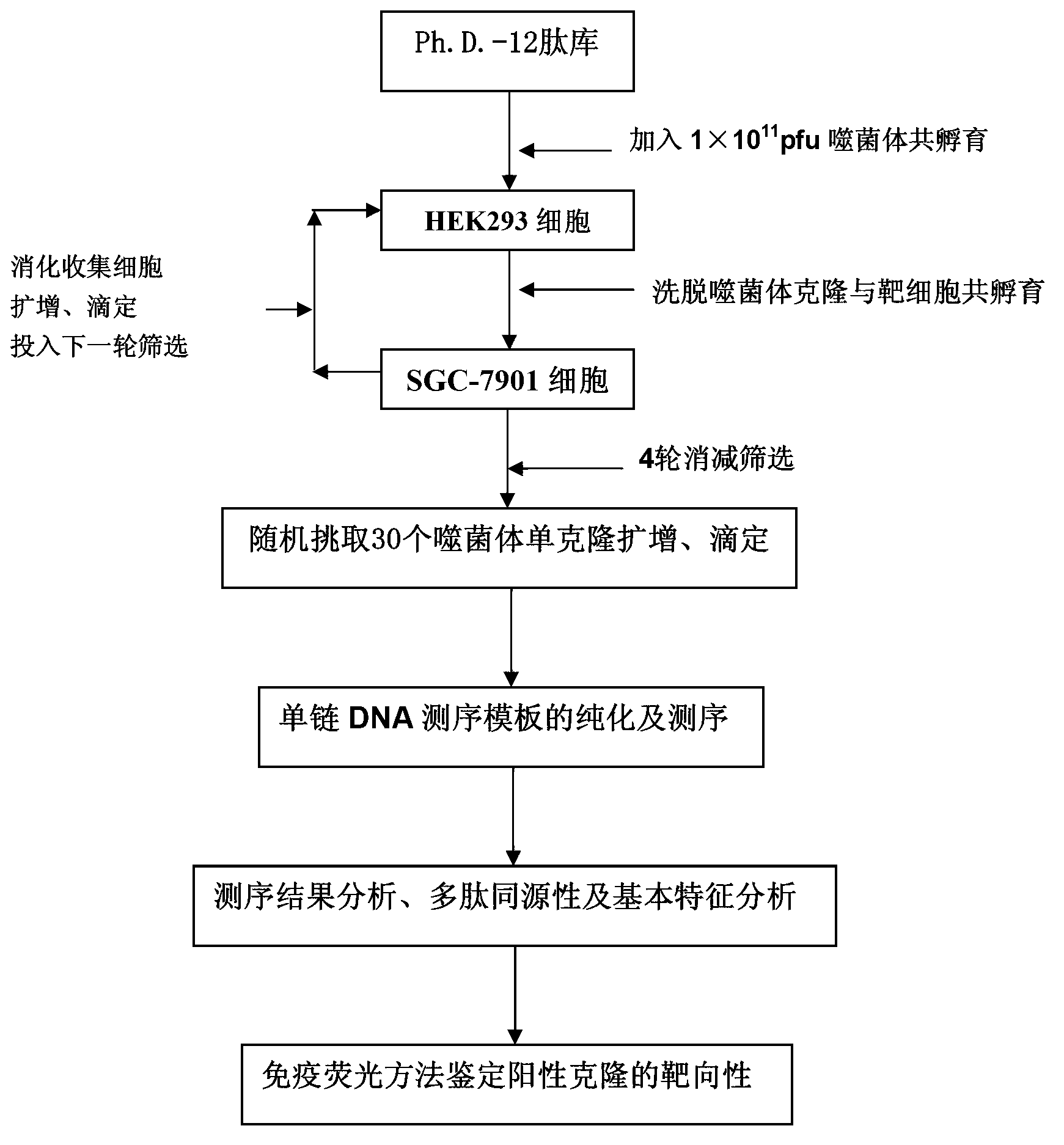
Polypeptide specifically bound to surface of SGC-7901 cell
The invention discloses polypeptide specifically bound to surface of an SGC-7901 cell. A random dodecapeptide library is displayed by bacteriophage to obtain five polypeptide segments in a screening manner; the amino acid sequences respectively are YTHNESSPKDTH, YTVPDYKHNSAH, THPWQITSVNFK, DVFPHSRPADEL and IHKDPANKSLVP. A polypeptide sequence bound to a gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell is screened by utilizing a phage peptide display technology; the affinity of phage clones and the gastric cancer is identified by enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA); 14 phage clones are obtained; five polypeptide sequences are obtained by sequencing. The homology analysis shows that the polypeptide sequence motif can be amino acid determinants bound to a tumor cell surface receptor on ligandin; the targeted results of positive phage clones are further identified by cell immunofluorescence to prompt the positive phage clones to be specifically bound to the SGC-7901 cell; an experimental evidence is provided for early diagnosis of the gastric cancer, targeted transportation of an antitumor medicament, and research and development of targeted short-peptide medicaments by the screened gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell specificity polypeptide.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Compound for Fab fragment of Rituximab and CD20 antigen epitope polypeptide
The invention discloses a compound of Fab segment of anti-cancer drug Rituximab and CD20 antigen epitope peptide, which also provides the preparing method of compound and three-dimensional crystal structure of compound and application, wherein the three-dimensional crystal structure of compound displays the key residue interacted between Rituximab and antigen epitope peptide, which provides theoretical base for higher affinity and specificity antibody; the CD20 antigen epitope peptide displays peculiar ring-shaped structure, which is fit for sieving new antibody of epitope.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
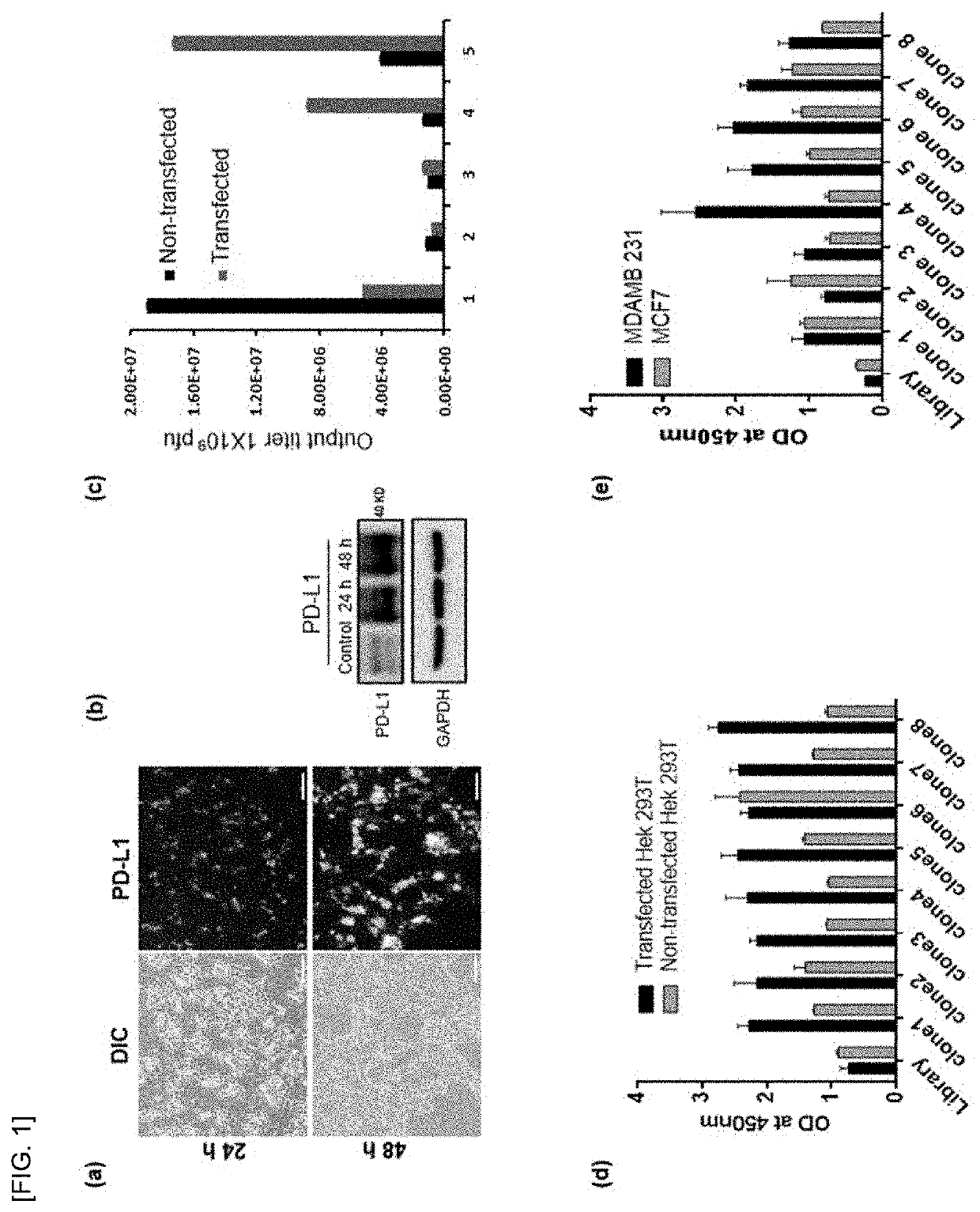
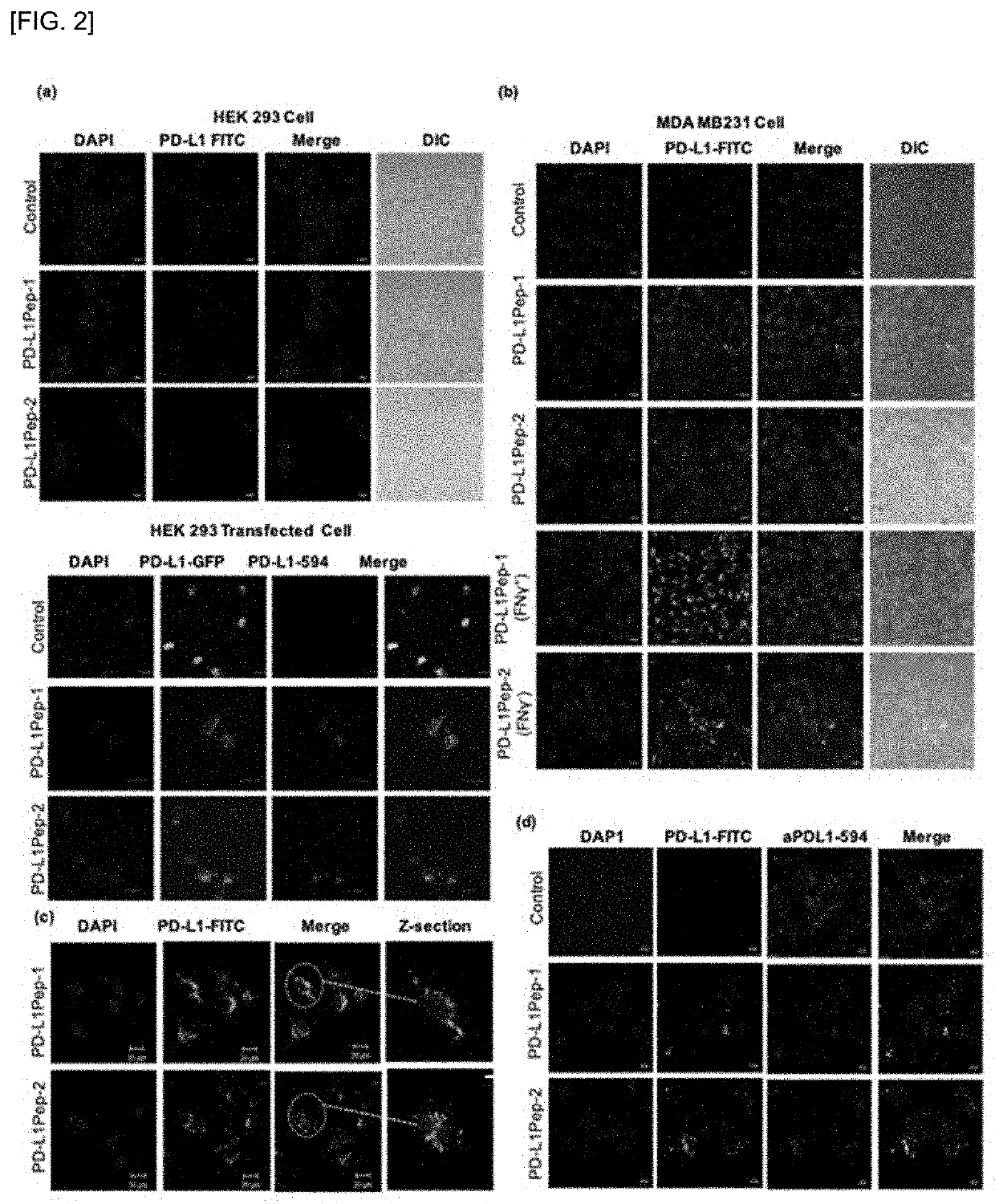
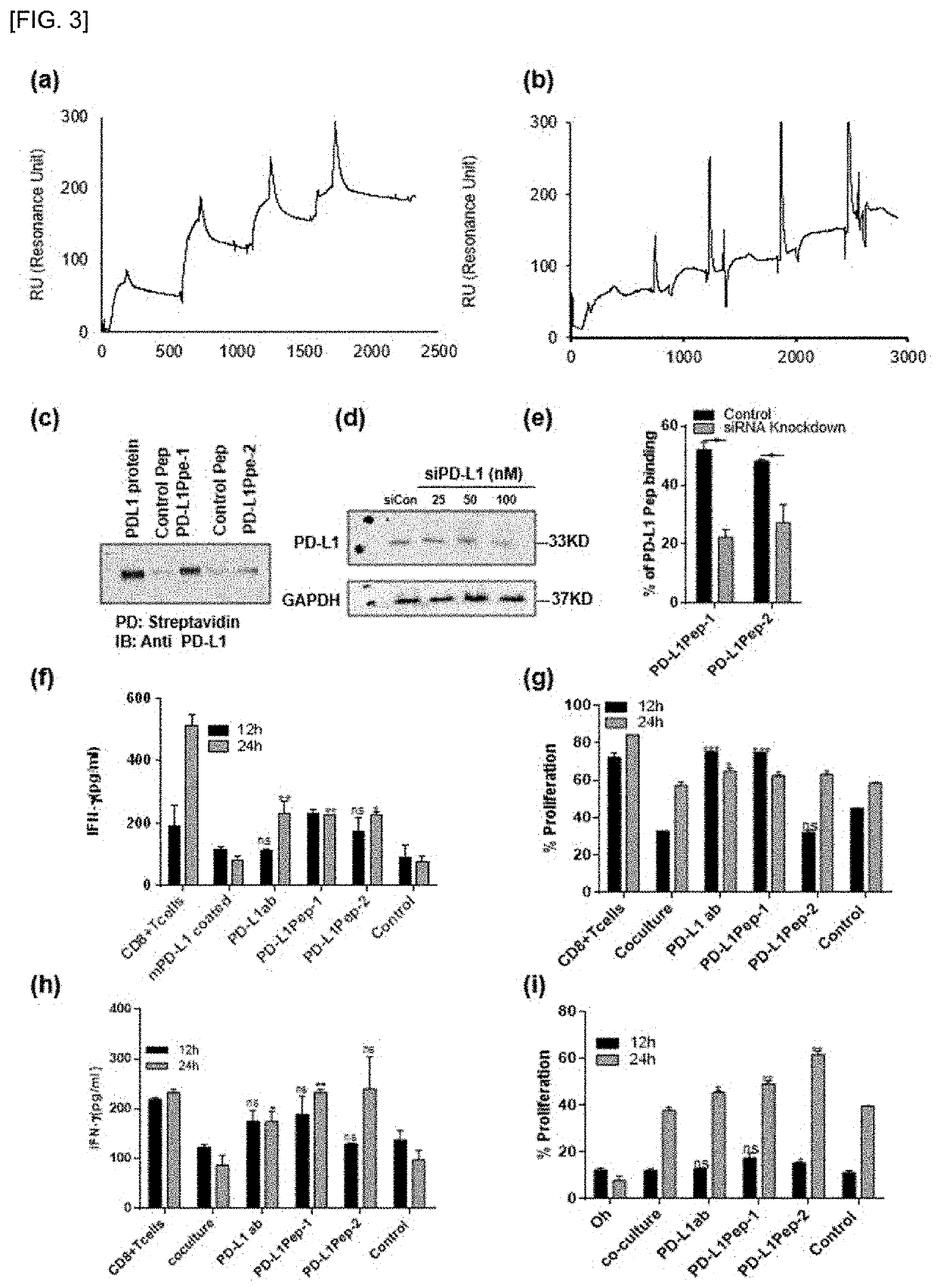
Peptide bound to pd-l1 and use thereof
ActiveUS20210163534A1Inhibit functioningRaise the potentialImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsAnticarcinogenic EffectPeptide display
The present invention relates to a peptide bound to PD-L1 and uses for cancer immunotherapy and anticancer using the same, and the peptide of the present invention specifically binds to PD-L1 and inhibits it, thereby activating the function of immune cells against cancer cells and exhibiting anticancer effects. The peptides of the present invention selected two peptides (PD-L1Pep-1 and PD-L1Pep-2) that bind well to cells with high expression of human PD-L1 protein using phage peptide display technology and it was confirmed that it inhibits its function by binding to PD-L1 in humans and mice. The peptide of the present invention showed an effect similar level to that of an antibody and is relatively stable in blood, indicating a high potential as a cancer immunotherapy in the future.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Modification of polypeptides
ActiveUS20160031939A1Increase infectivityExtended stayPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsPeptide displayIon-exchange resin
Owner:BICYCLE THERAPEUTICS
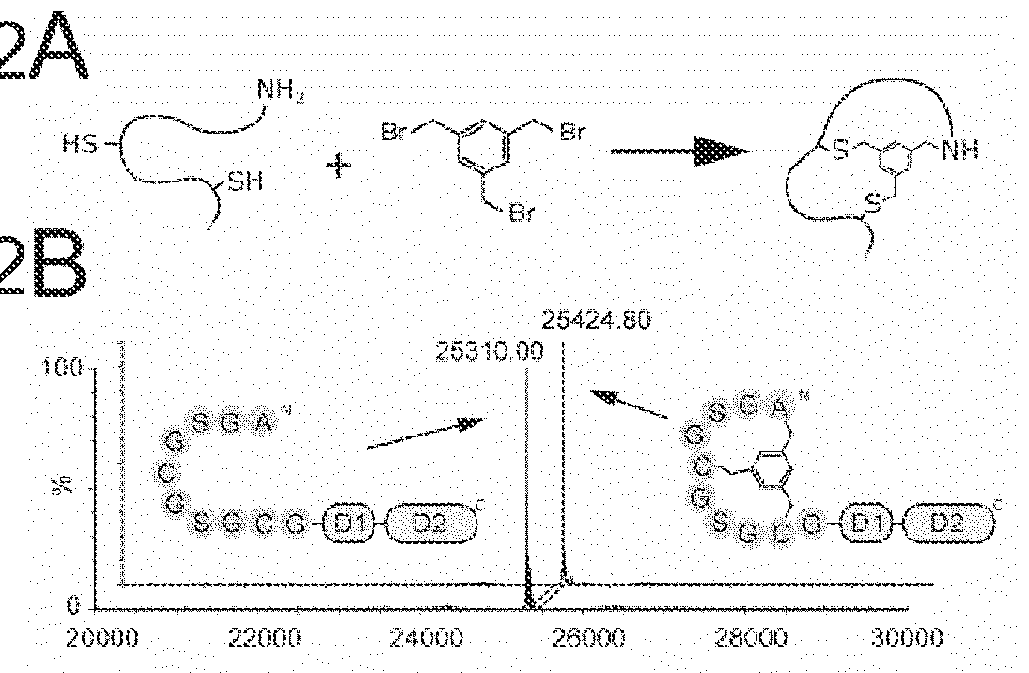
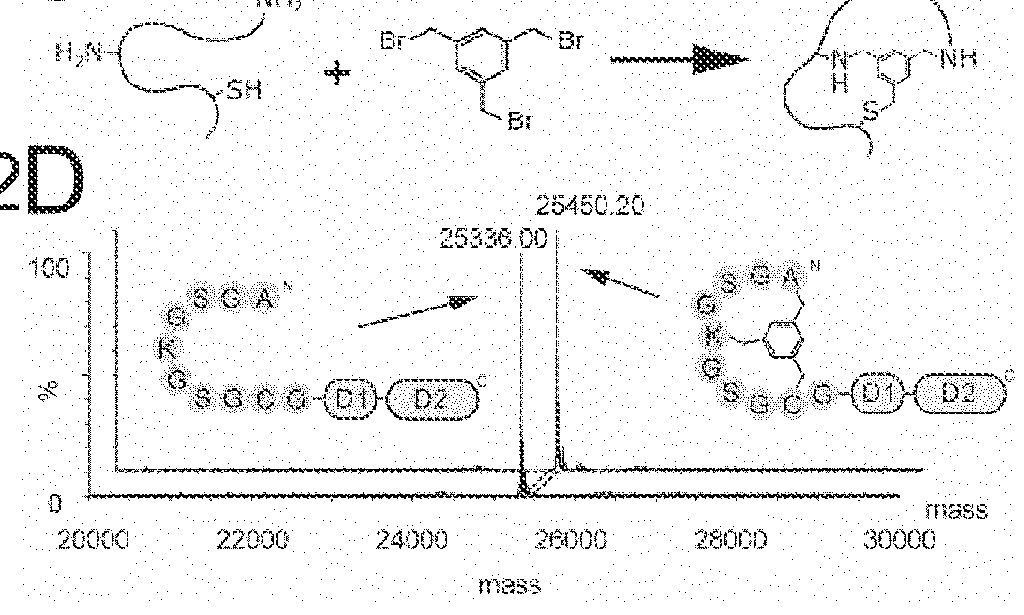
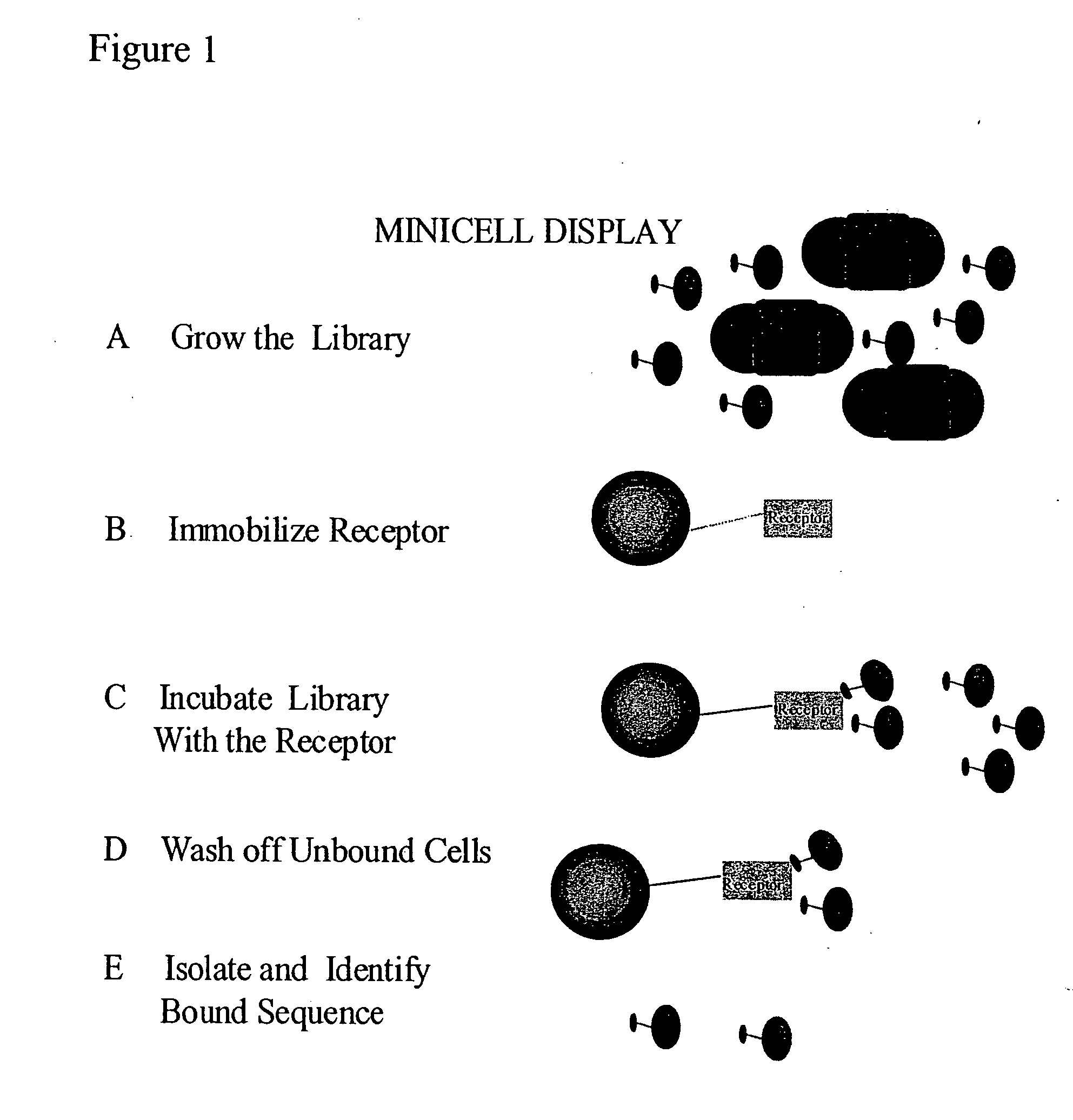
Methods to screen peptide display libraries using minicell display
InactiveUS20070072221A1Increase mutation frequencyEasy to identifyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaPeptide displayOrganismal Process
A minicell display method has been developed which has significant advantages for screening peptide libraries for candidates that can bind and effectively modulate a particular biological process. The method, based on the small, anucleate minicell, has increased versatility in generating unique sequences to screen as well as increasing the size of the peptides to be screened. In vivo mutagenesis, at the level of protein synthesis, as well as DNA replication, increases diversification of the library to be screened and therefore substantially increases the number of potential peptides that can modulate a particular biological response or mechanism.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Pvii phage display
The present invention provides an alternative scaffold for peptides displayed on filamentous phages through novel fusion proteins primarily originating from pVII. Libraries of filamentous phages can be created from fusion proteins, and a phage display system comprising a phagemid and a helper phage is a part of the invention. An aspect of the invention is a kit containing a phage display system comprising a phagemid and a helper phage that contains a nucleic acid encoding the fusion protein of the invention.
Owner:NEXTERA AS
Peptide and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108948151AGood water solubilityImprove stabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPeptide displayNucleotide
The invention relates to a peptide and a preparation method and application thereof. The peptide comprises a sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1 or a sequence, where one or more amino acids are substituted, deleted, inserted and / added in the sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1. The peptide displays activity of inhibiting melanoblast or melanogenesis or activity of whitening. The invention also providesa nucleotide sequence which encodes the peptide, a carrier containing the nucleotide sequence and a host comprising the vector. The peptide is similar to the amino acid sequence of MSH-alpha, and canbe prepared on a large scale by means of a biofermenting method, so that the peptide can be used for the whitening cosmetic industry.
Owner:SHANXI JINBO BIO PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com