Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3086results about "Gaseous engine fuels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Internal combustion engine
ActiveUS6990956B2Accurate calculationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMultifuelEngineering
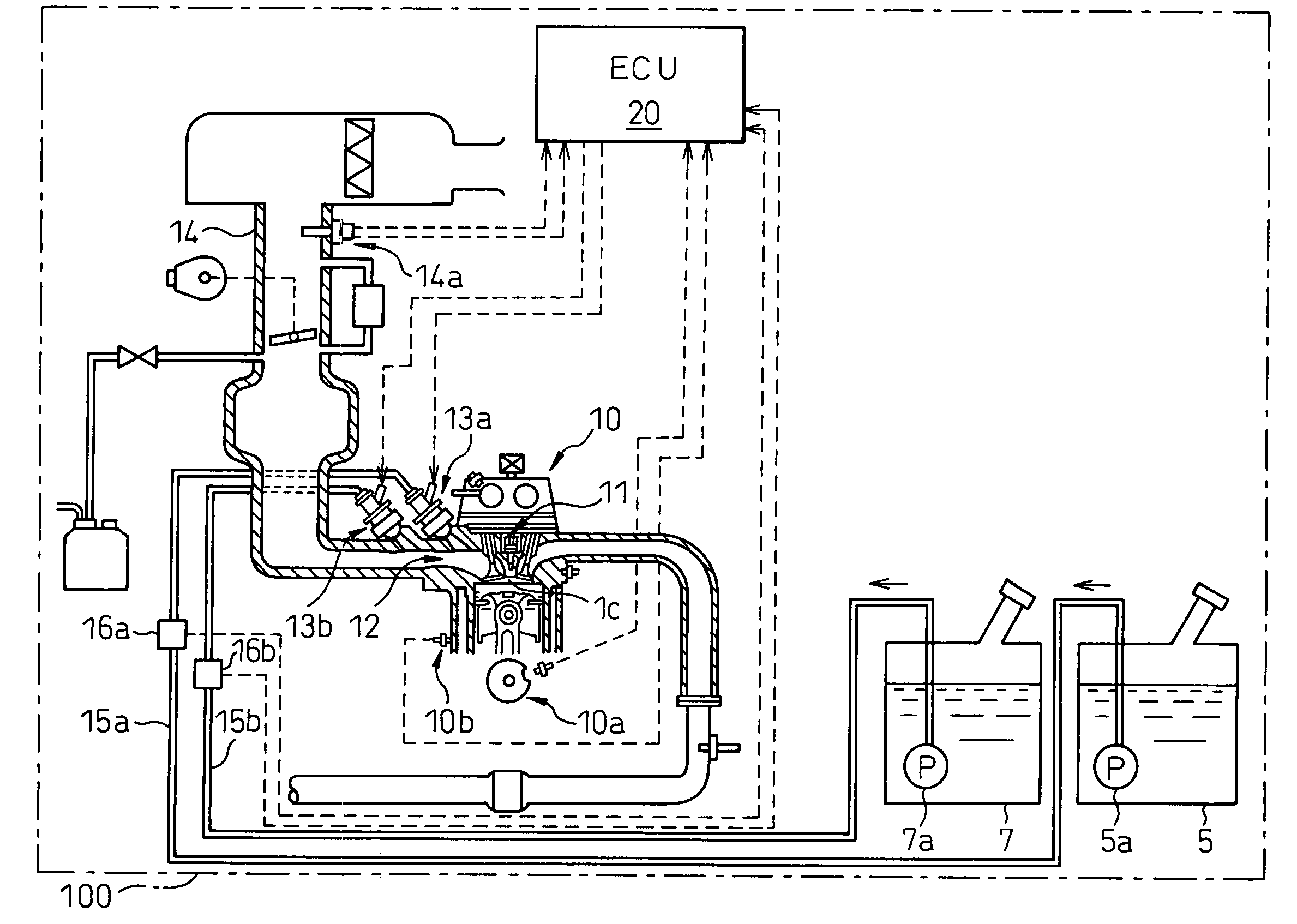
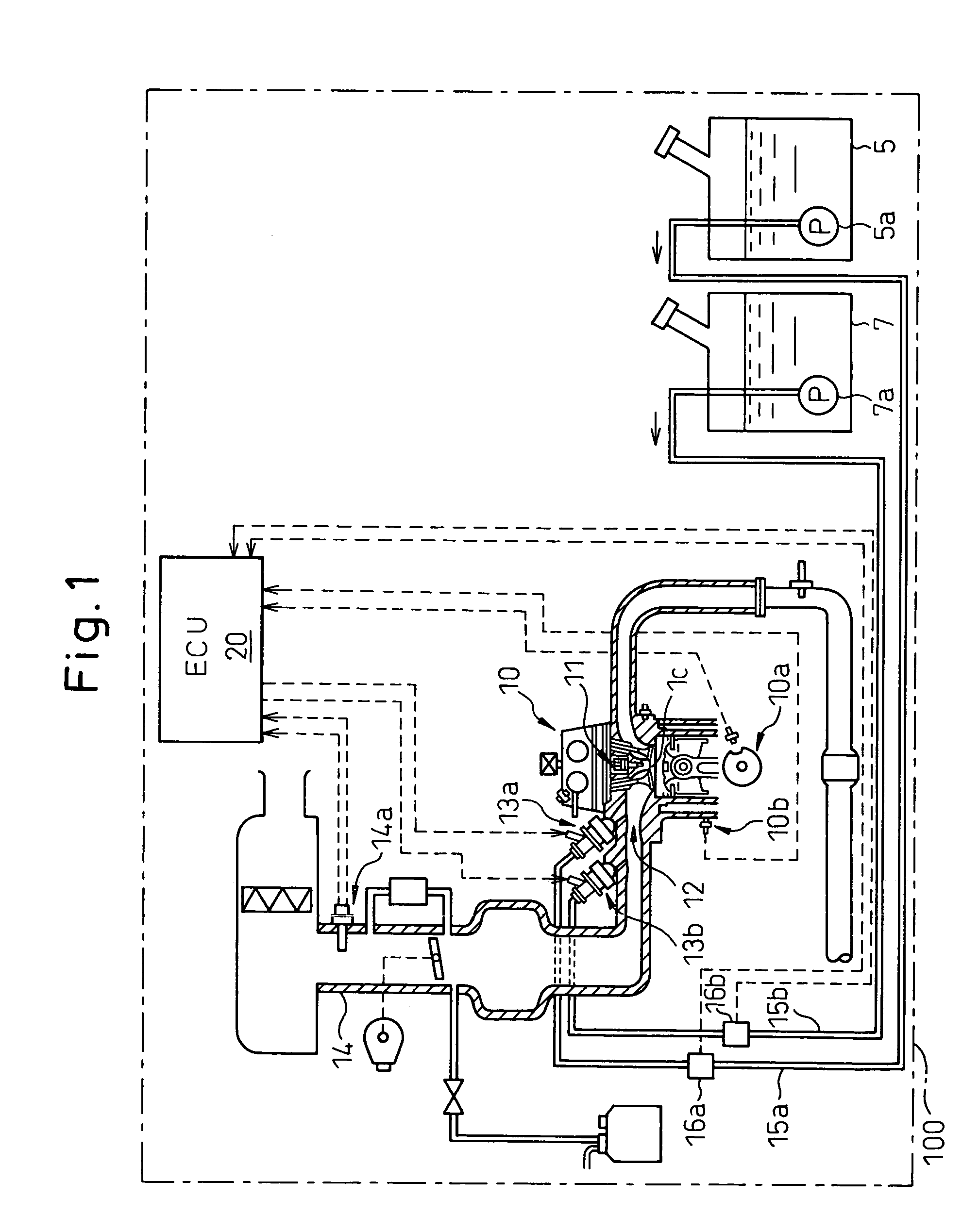
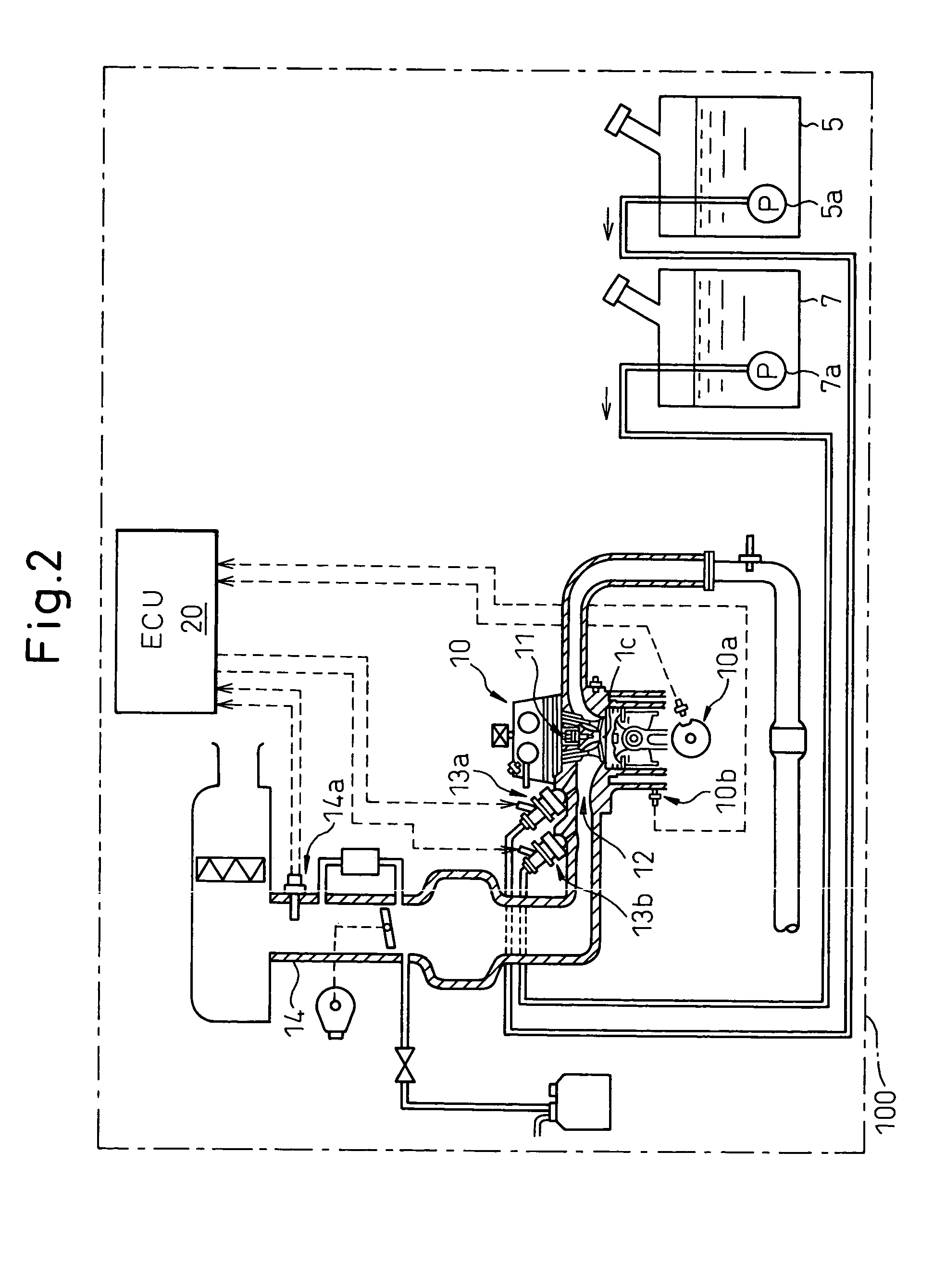
An internal combustion engine, in which multiple kinds of fuels are fed to a cylinder from multiple fuel injectors each corresponding to each of multiple kinds of fuels at a target mixing ratio determined according to a running condition, includes an actual fuel mixing ratio calculator calculating an actual fuel mixing ratio of fuel fed to cylinder. The actual fuel mixing ratio calculator at first calculates actual fuel injection quantity of each fuel injection by adding or subtracting predetermined stuck-on-wall fuel to or from each quantity of fuel injected from each fuel injector, and then calculates an actual fuel mixing ratio of fuel fed to cylinder on the basis of the calculated actual fuel injection quantity of each fuel injector.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
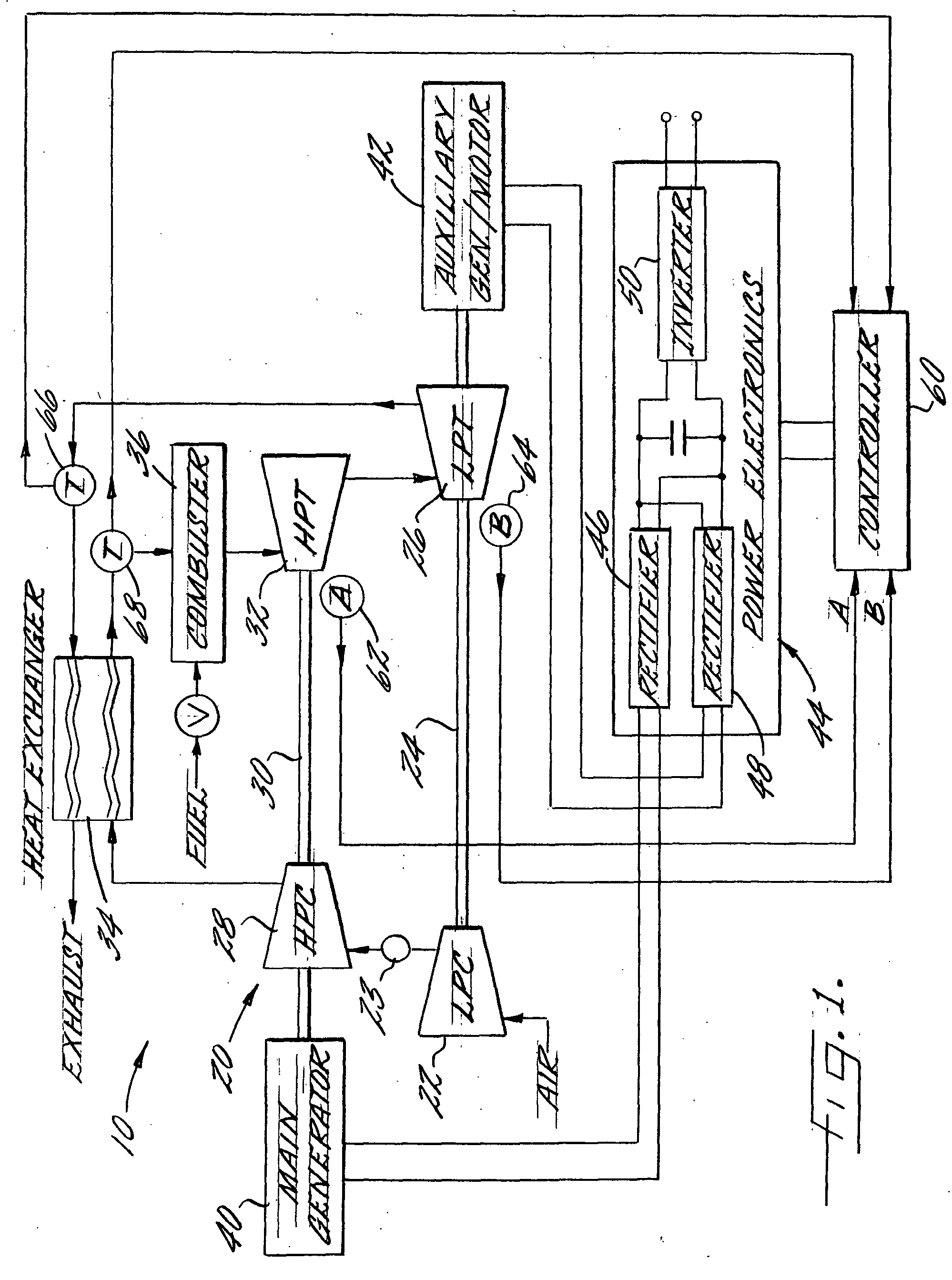
Multi-spool turbogenerator system and control method
ActiveUS20050056021A1Eliminate needMinimize and eliminate needCombustion enginesGas turbine plantsTurbineGas turbines
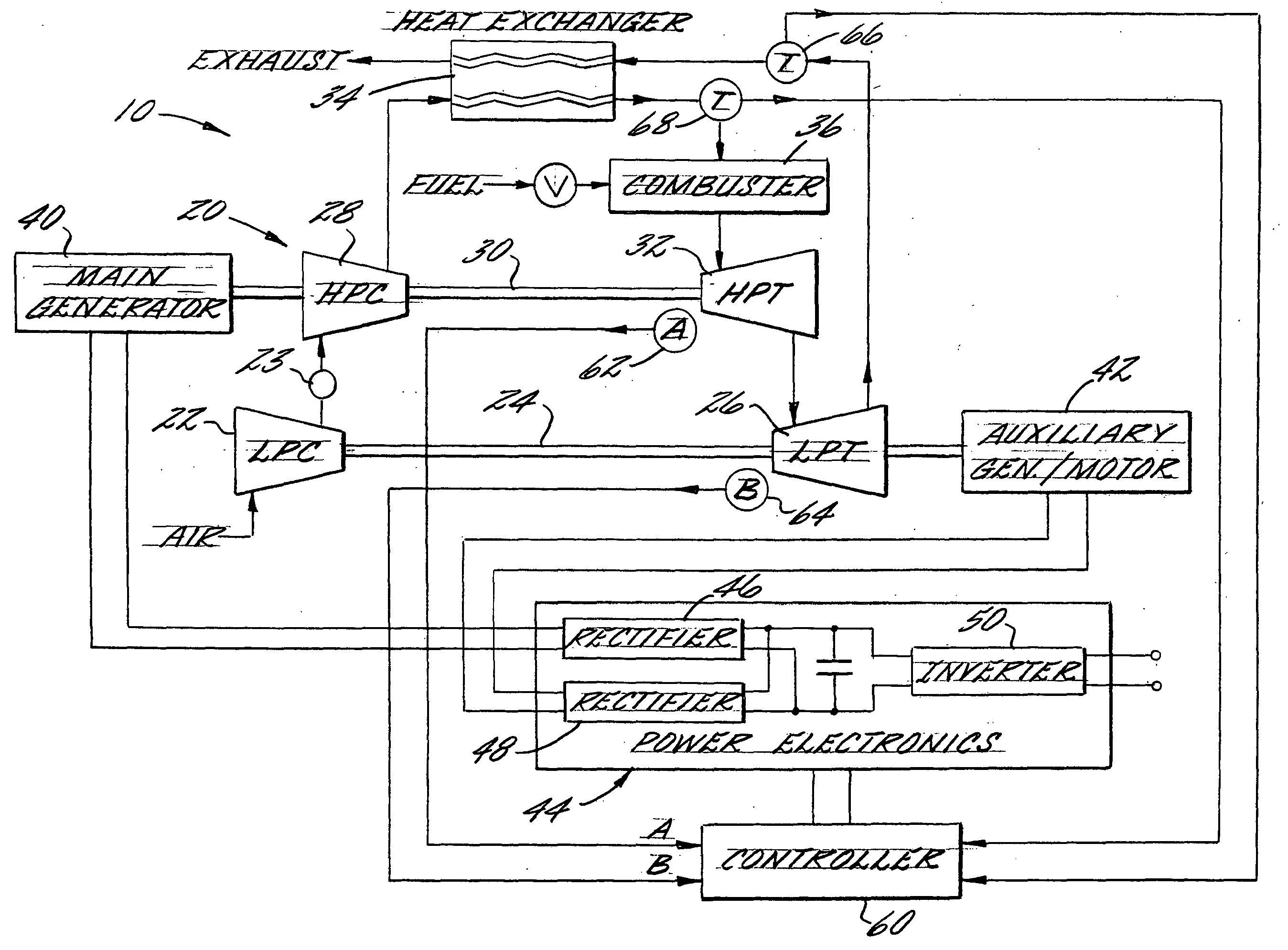
An electrical power generating system is driven by a multi-spool gas turbine engine including at least first and second spools. The first spool comprises a turbine and a compressor mounted on a first shaft; the second spool has at least a turbine mounted on a second shaft that is not mechanically coupled to the first shaft. A main generator is coupled with one of the spools, and an auxiliary generator / motor is also coupled with one of the spools. Speed control of each of the generators is employed for controlling operation of the engine. The auxiliary generator / motor can operate in either a generation mode to extract power from its spool or a motor mode to inject power into its spool.
Owner:MES INT INC
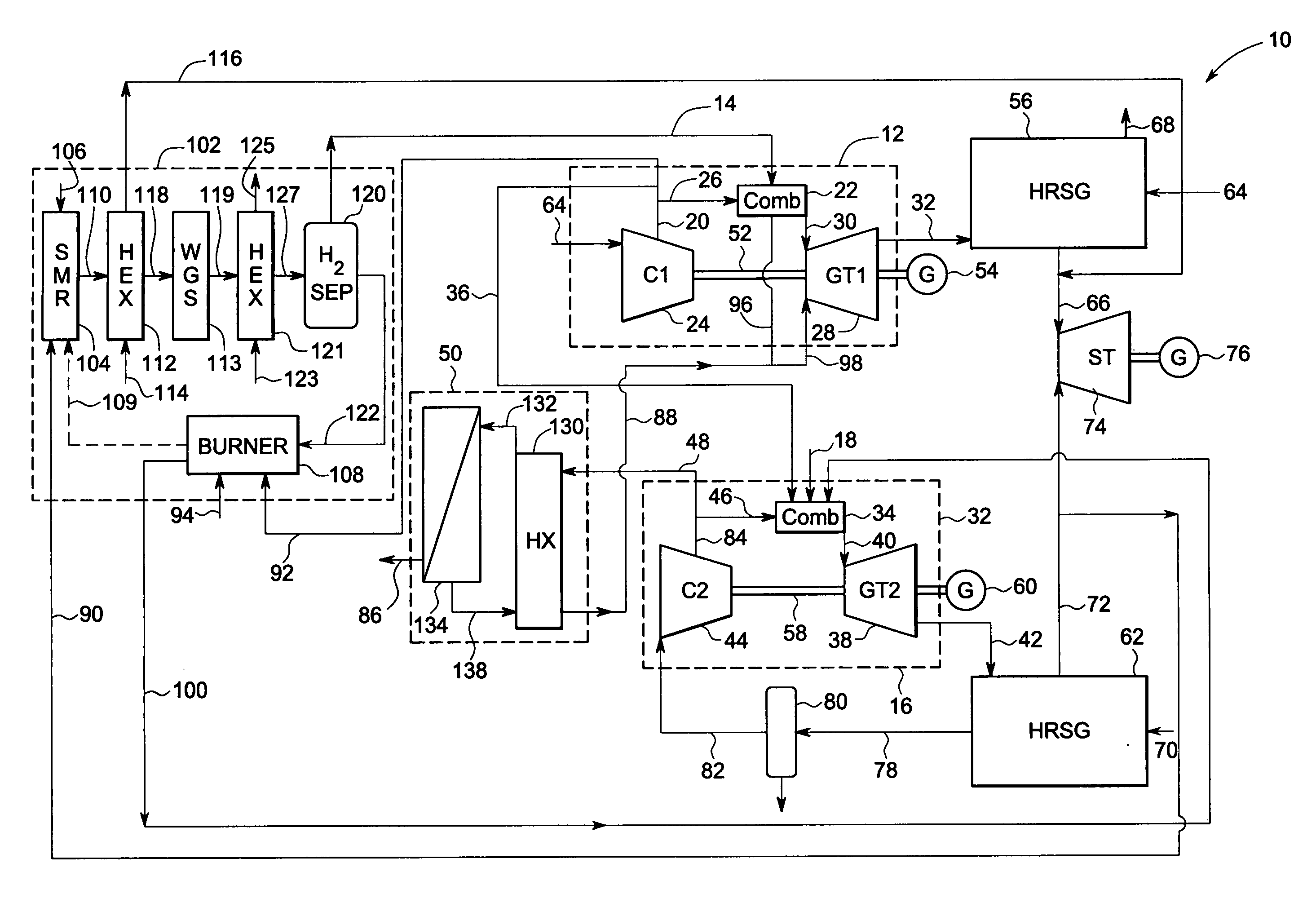
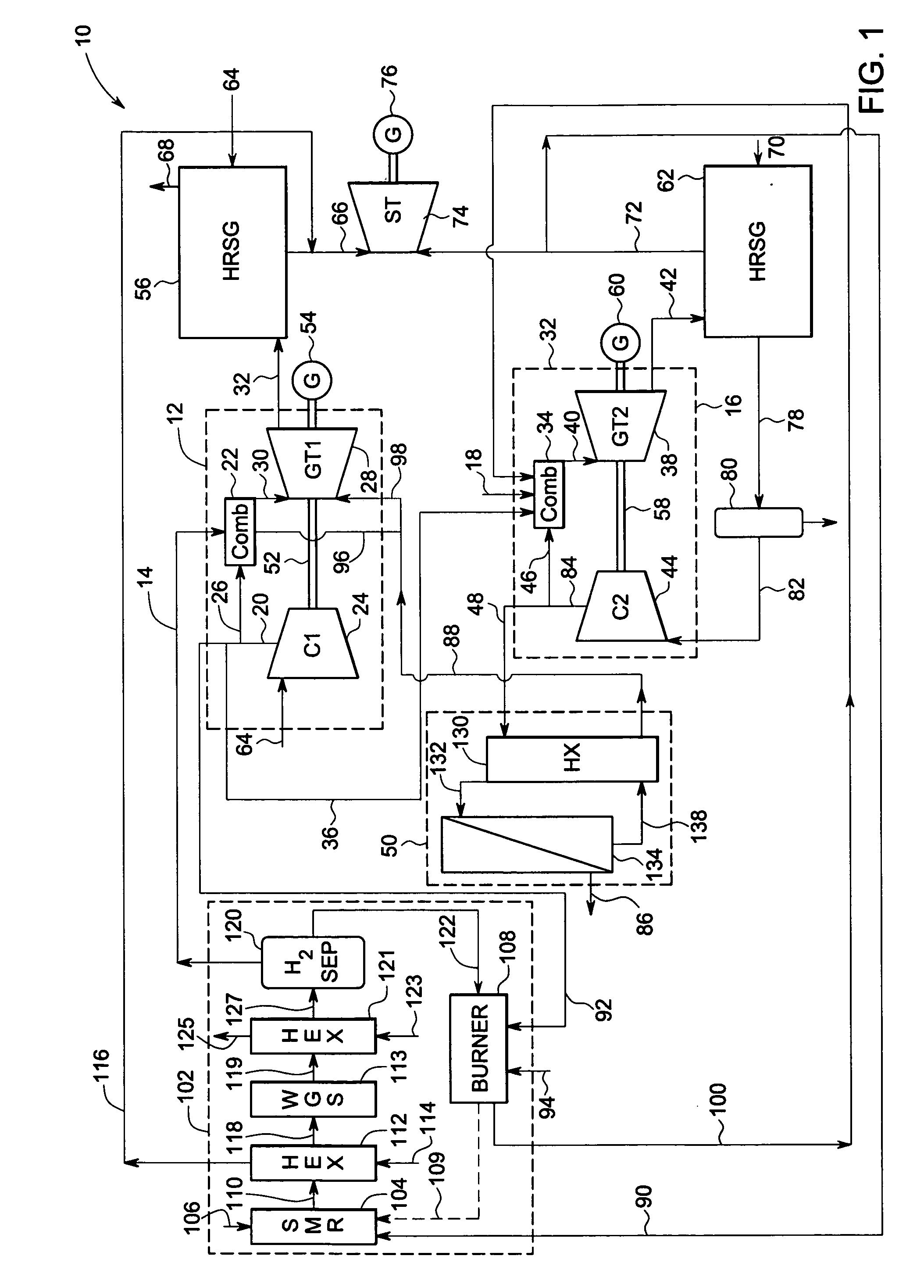
Reforming system for combined cycle plant with partial CO2 capture
A combined cycle system includes, a pre-steam-methane-reformer operating at a temperature of less than about 800 degrees Celsius to reform a mixed fuel stream to generate a first reformate stream, a water-gas-shift reactor to convert carbon monoxide in the first reformate stream to carbon dioxide and form a second reformate stream, a carbon dioxide removal unit for removing carbon dioxide from the second reformate stream and form a carbon dioxide stream and a third reformate stream; wherein less than about 50 percent of the carbon contained in the mixed fuel stream is recovered as carbon dioxide by the removal unit, a gas turbine unit for generating power and an exhaust stream, and a steam generator unit configured to receive the exhaust stream, wherein the heat of the exhaust stream is transferred to a water stream to generate the steam for the mixed fuel stream and for a steam turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
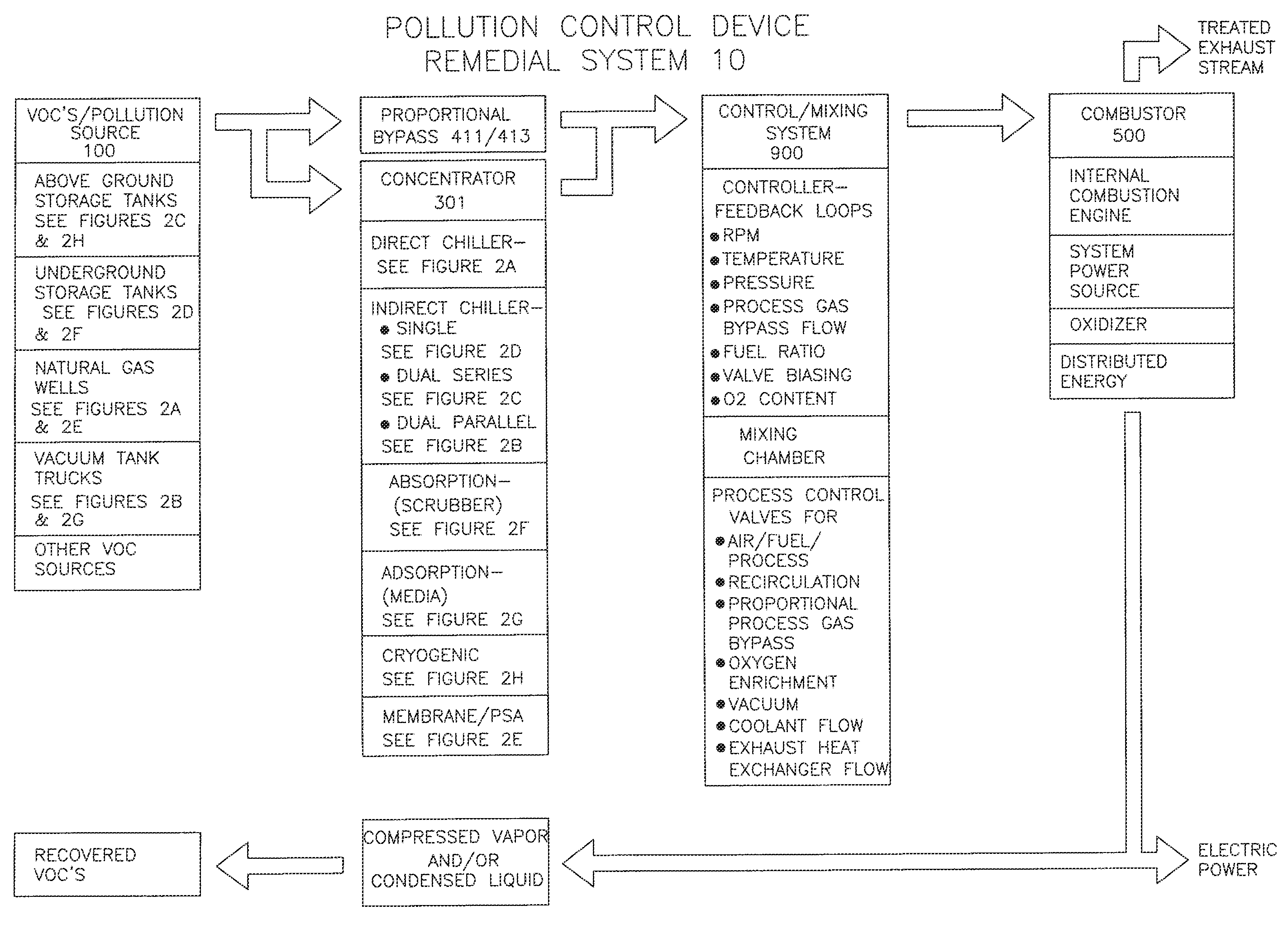
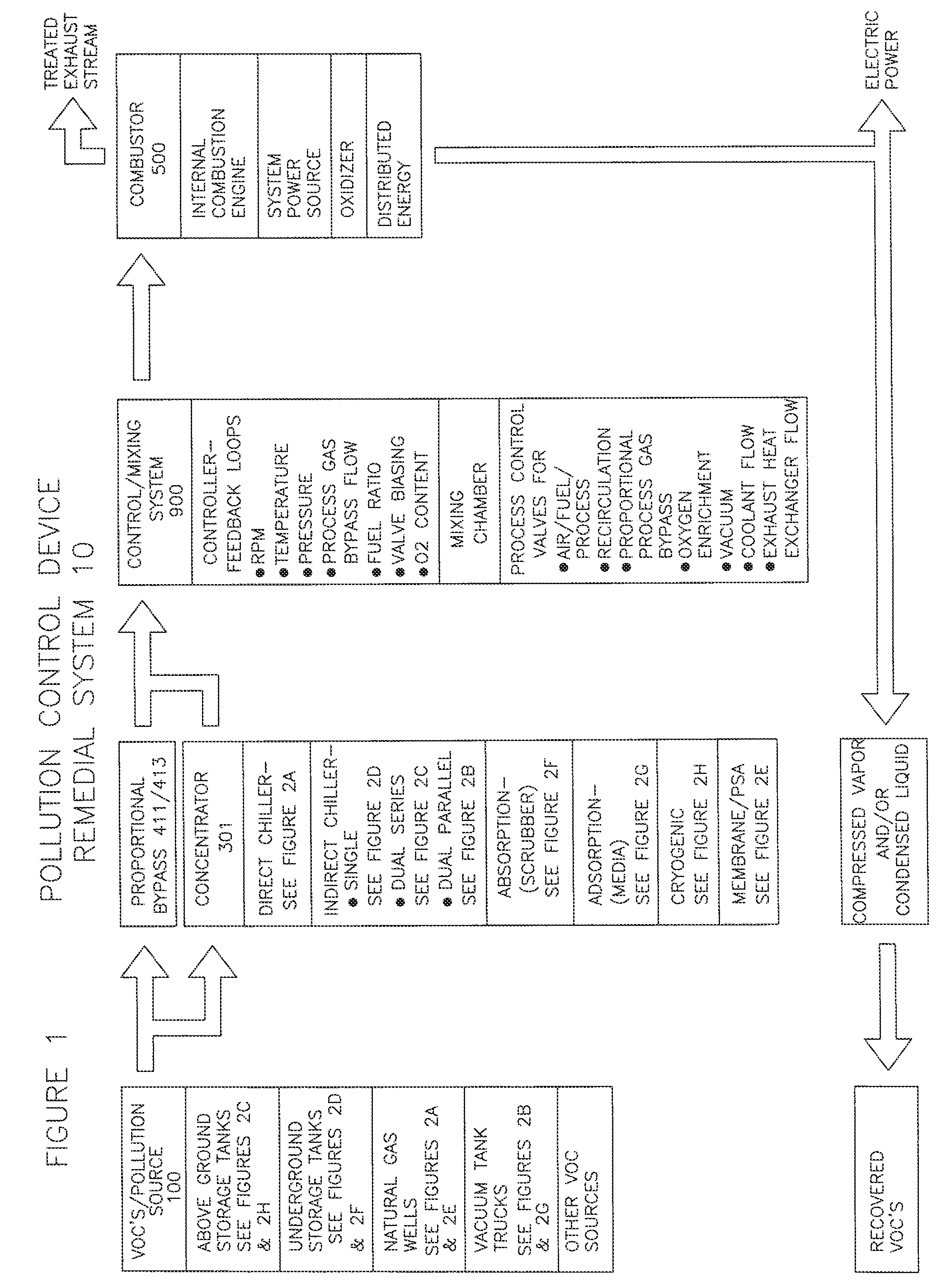
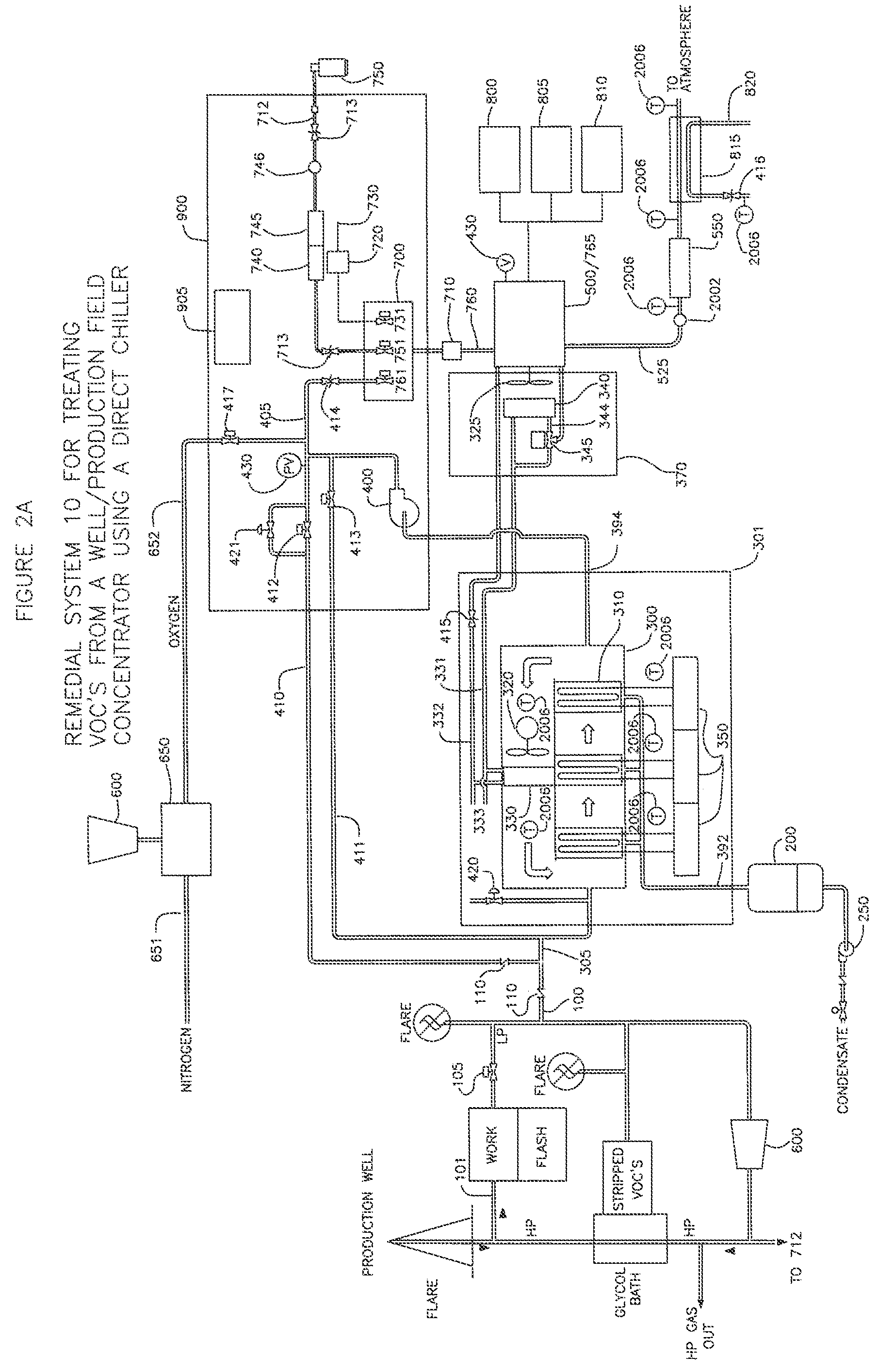
Remedial system: a pollution control device for utilizing and abating volatile organic compounds
ActiveUS8776734B1Easy to useTreatment safetyGas treatmentNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHybrid systemControl system
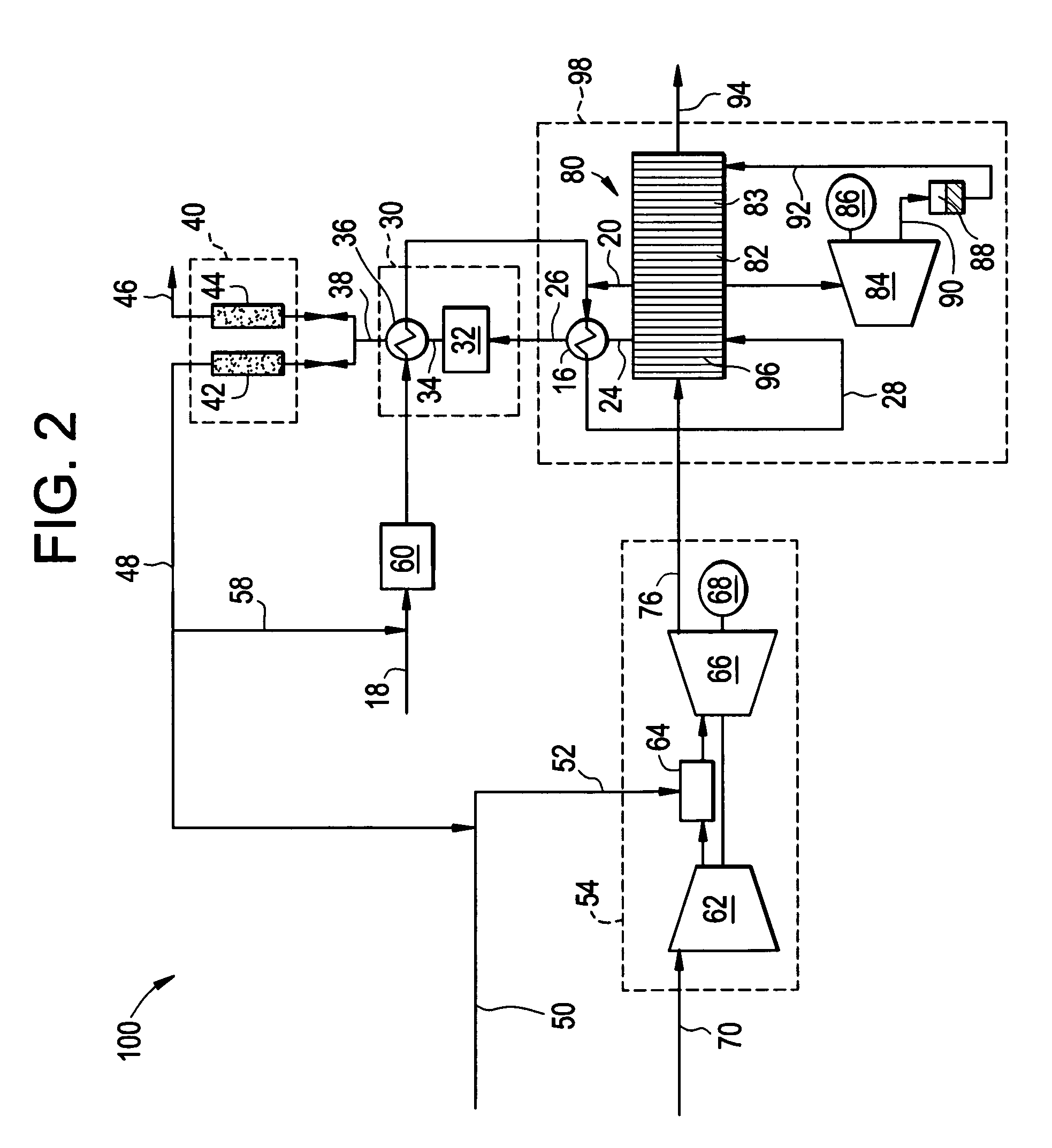
A remedial pollution control system for treating volatile organic compounds that may include a vapor concentrator connected to a line that is laden with volatile organic compounds, the concentrator has an organic condensate output line and a vapor output line; a mixing chamber adapted to receive air provided from an air supply line, combustible fuel from an alternate fuel supply line, and a vapor stream from the vapor output line to produce a mixed fuel supplied to an internal combustion engine, a control mixing system with a controller for producing a proper air to fuel ratio in the mixed fuel supply, and power generated to operate other devices used to more efficiently abate volatile organic compounds and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENVIRONMENTAL SOLUTIONS LLC DBA REMEDIATION SERVICE INTL
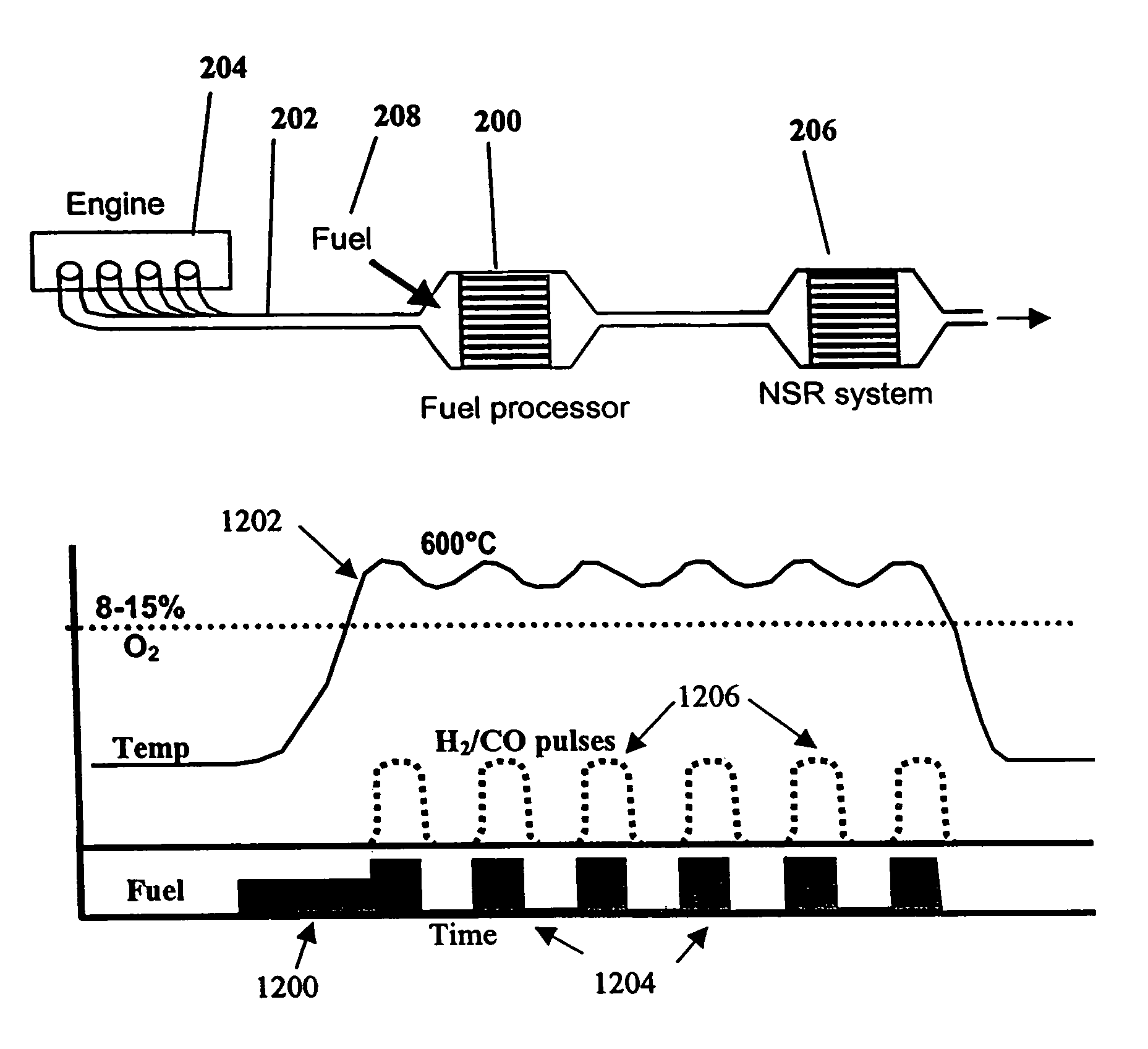
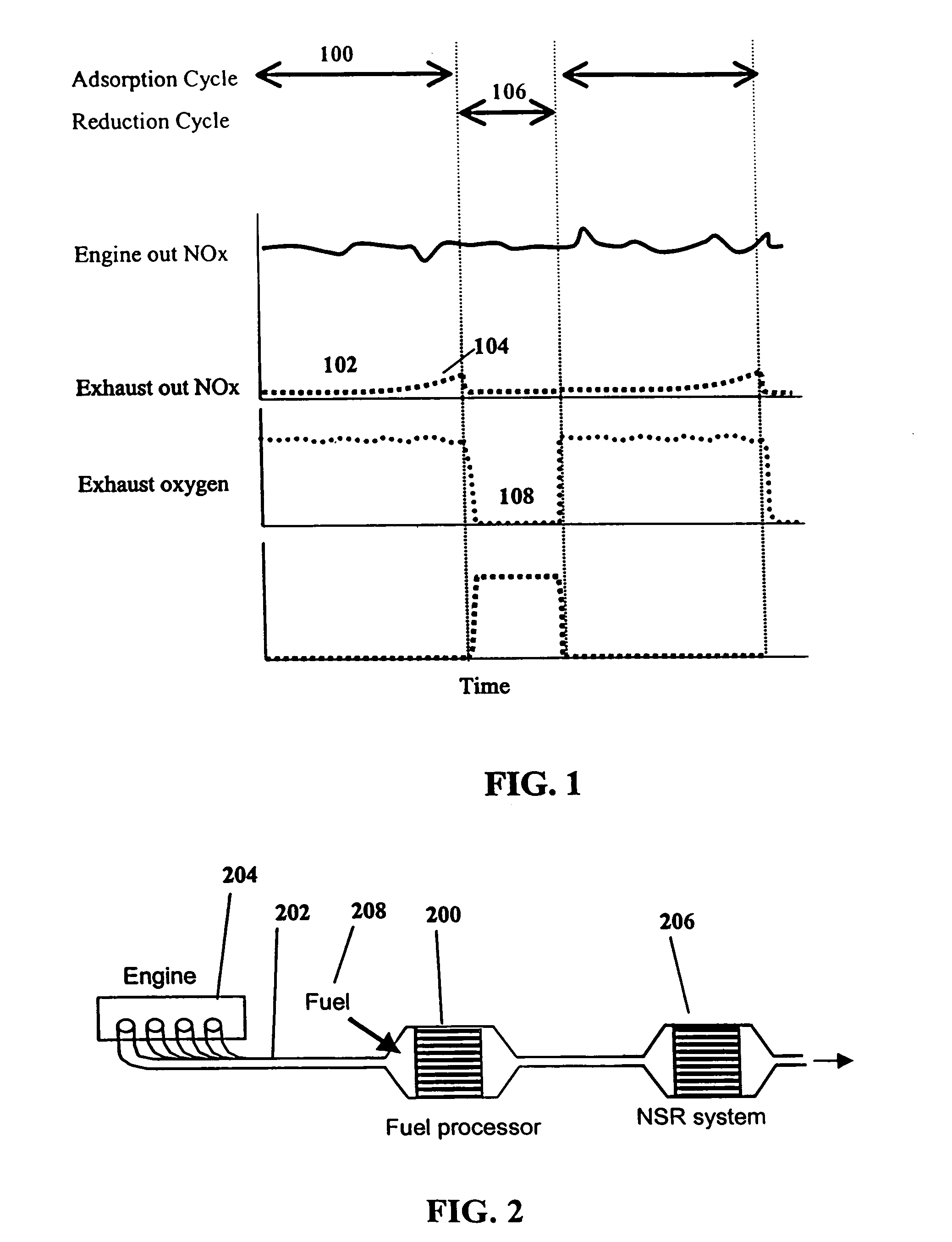
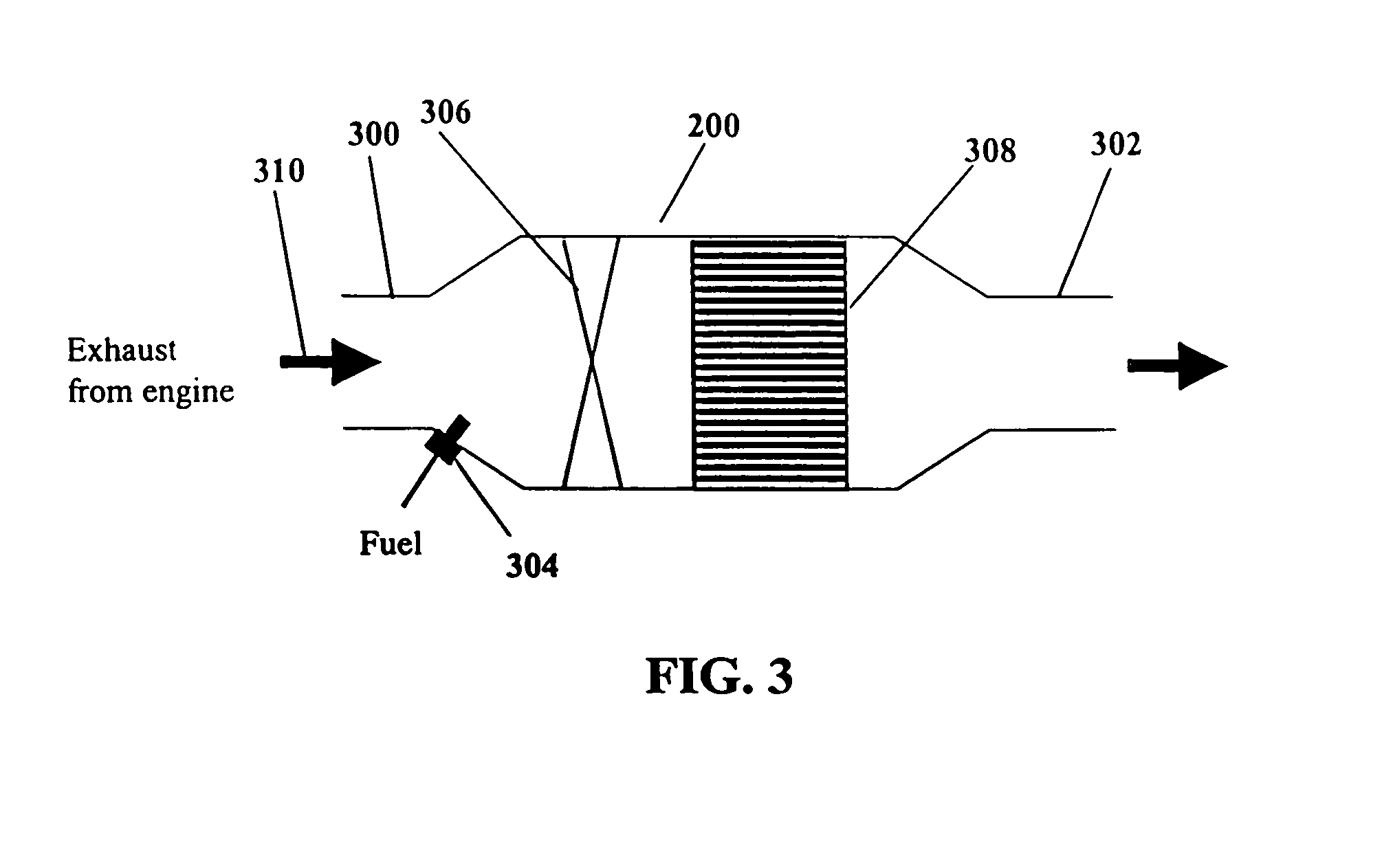
System and methods for improved emission control of internal combustion engines using pulsed fuel flow
InactiveUS7082753B2Save oilReducing greenhouse gas emissionExhaust apparatusCombustion enginesPartial oxidationExternal combustion engine
The present invention provides systems and methods to improve the performance and emission control of internal combustion engines equipped with nitrogen oxides storage-reduction (“NSR”) emission control systems. The system generally includes a NSR catalyst, a fuel processor located upstream of the NSR catalyst, and at least one fuel injection port. The fuel processor converts a fuel into a reducing gas mixture comprising CO and H2. The reducing gas mixture is then fed into the NSR catalyst, where it regenerates the NSR adsorbent, reduces the NOx to nitrogen, and optionally periodically desulfates the NSR catalyst. The fuel processor generally includes one or more catalysts, which facilitate reactions such as combustion, partial oxidation, and / or reforming and help consume excess oxygen present in an engine exhaust stream. The methods of the present invention provide for NSR catalyst adsorbent regeneration using pulsed fuel flow. Control strategies are also provided.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
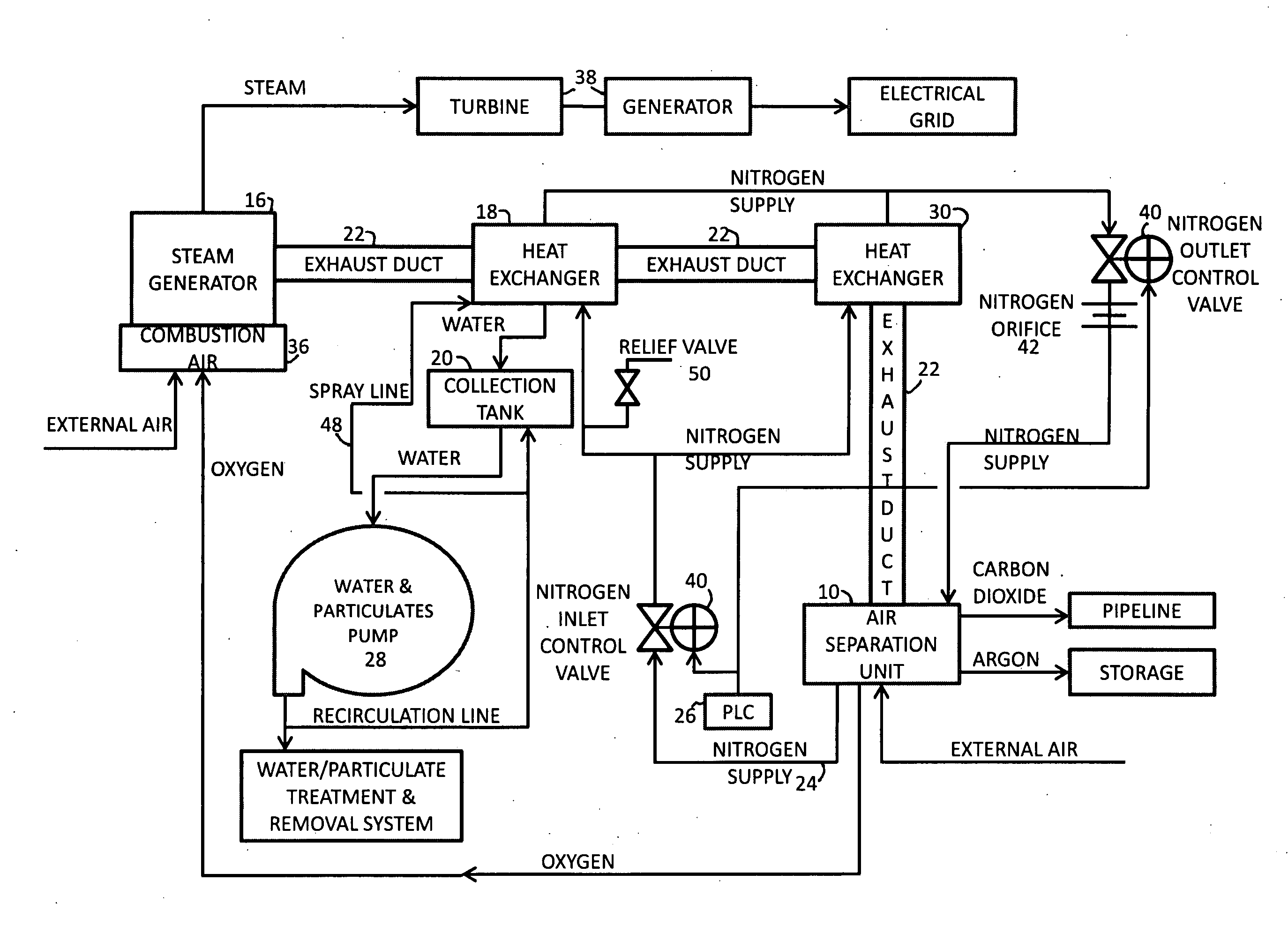
Power plant with emissions recovery
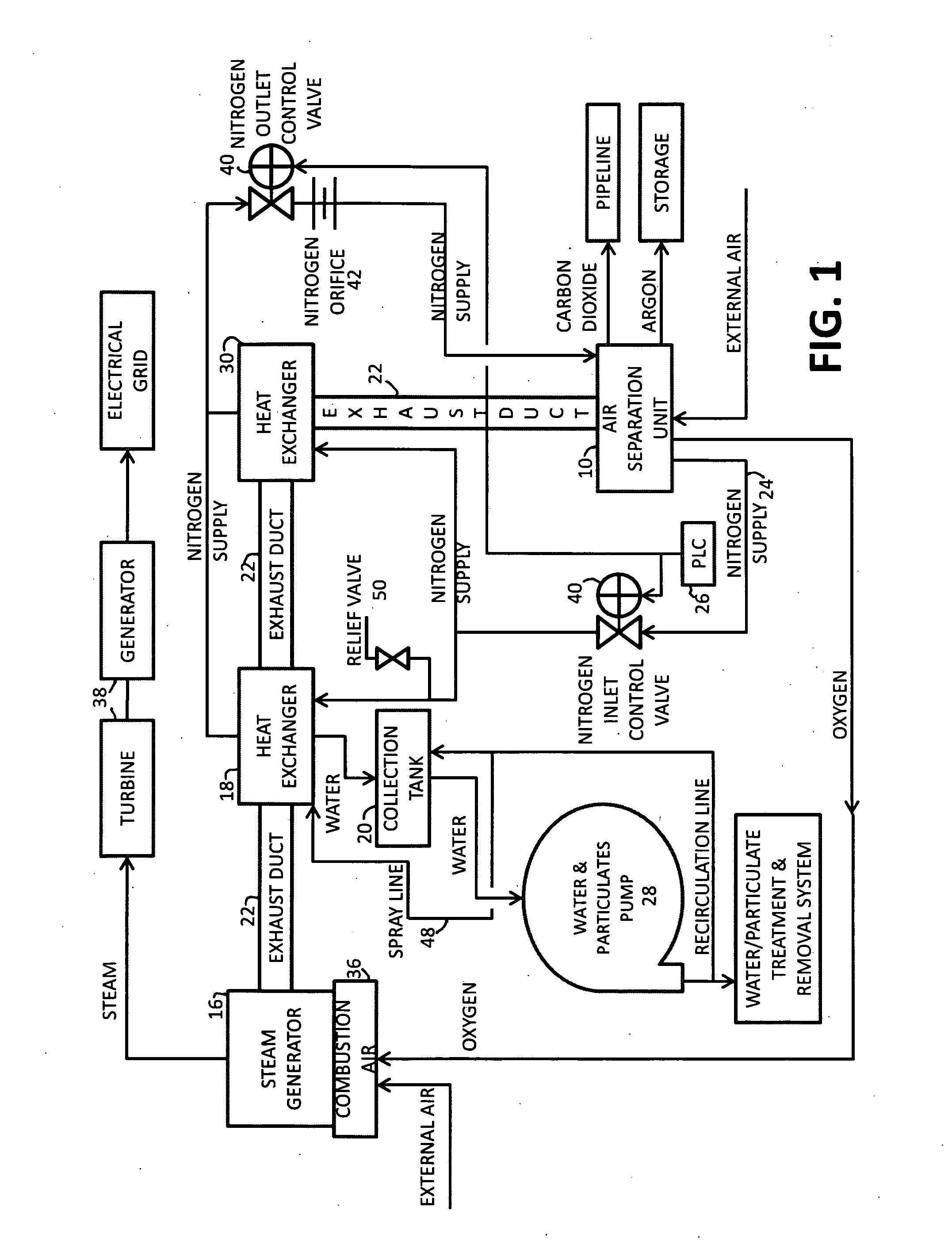
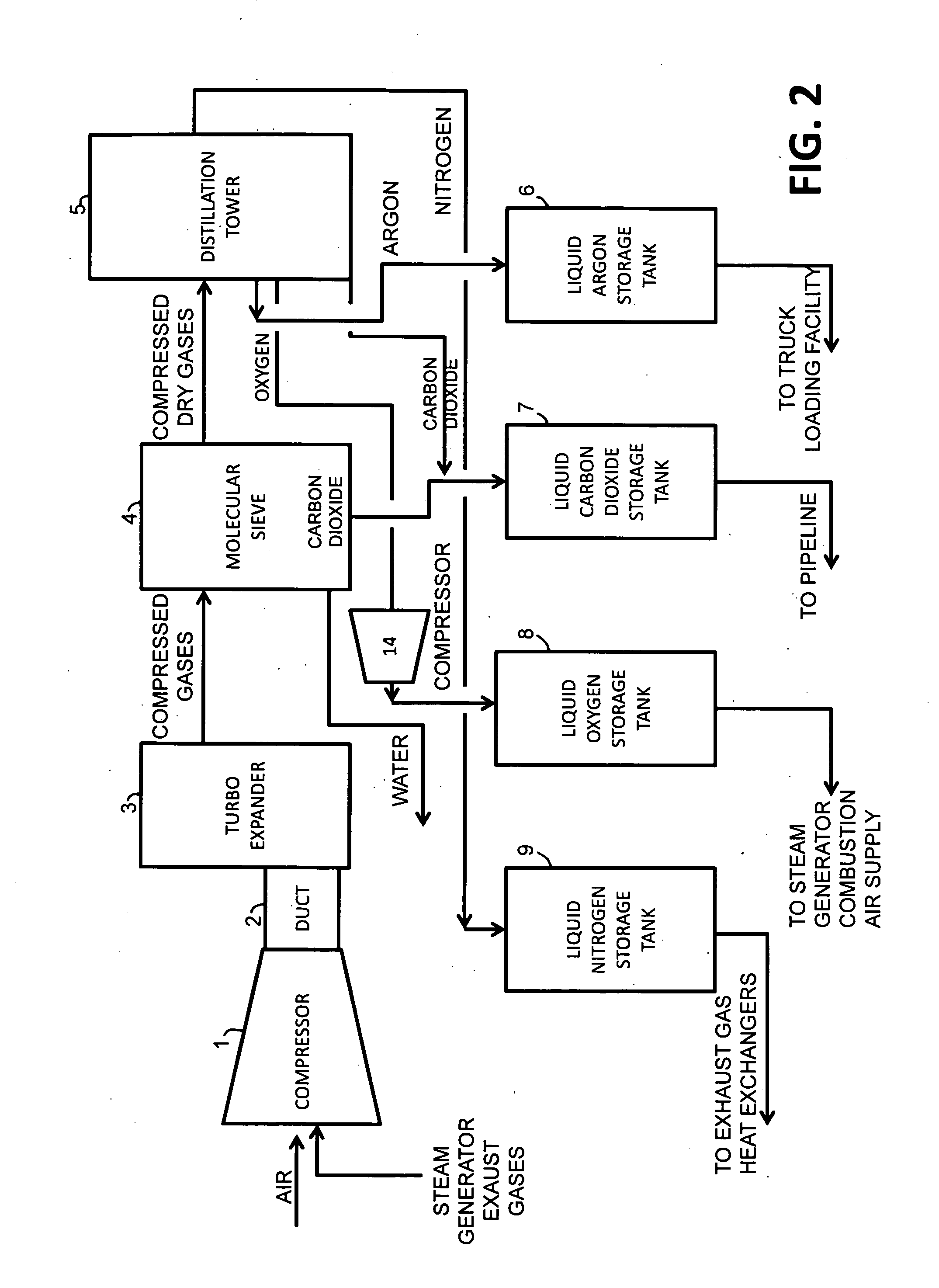
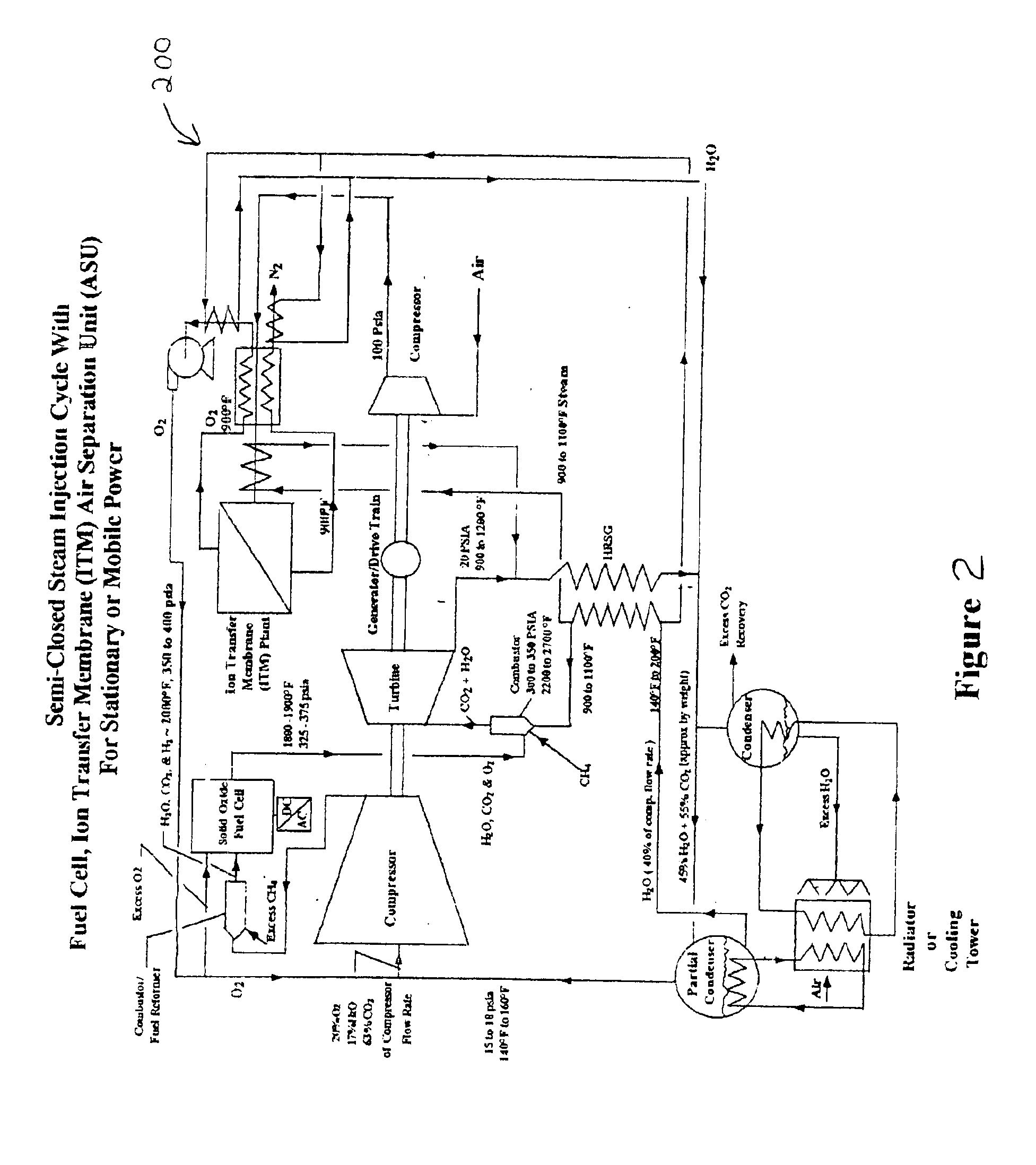
InactiveUS20100018218A1Reduce deliveryEnvironment safetySolidificationLiquefactionParticulatesNitrogen gas
A power plant including an air separation unit (ASU) arranged to separate nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and argon from air and produce a stream of substantially pure liquid oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and argon; a steam generator, fired or unfired, arranged to combust a fuel, e.g., natural gas, liquefied natural gas, synthesis gas, coal, petroleum coke, biomass, municipal solid waste or any other gaseous, liquid or solid fuel in the presence of air and a quantity of substantially pure oxygen gas to produce an exhaust gas comprising water, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, nitrogen, sulfur oxides and other trace gases, and a steam-turbine-generator to produce electricity, a primary gas heat exchanger unit for particulate / acid gas / moisture removal and a secondary heat exchanger arranged to cool the remainder of the exhaust gases from the steam generator. Exhaust gases are liquefied in the ASU thereby recovering carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, nitrogen, sulfur oxides, oxygen, and all other trace gases from the steam generator exhaust gas stream. The cooled gases are liquefied in the ASU and separated for sale or re-use in the power plant. Carbon dioxide liquid is transported from the plant for use in enhanced oil recovery or for other commercial use. Carbon dioxide removal is accomplished in the ASU by cryogenic separation of the gases, after directing the stream of liquid nitrogen from the air separation unit to the exhaust gas heat exchanger units to cool all of the exhaust gases including carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur oxides, and other trace gases.
Owner:TRIENCON SERVICES
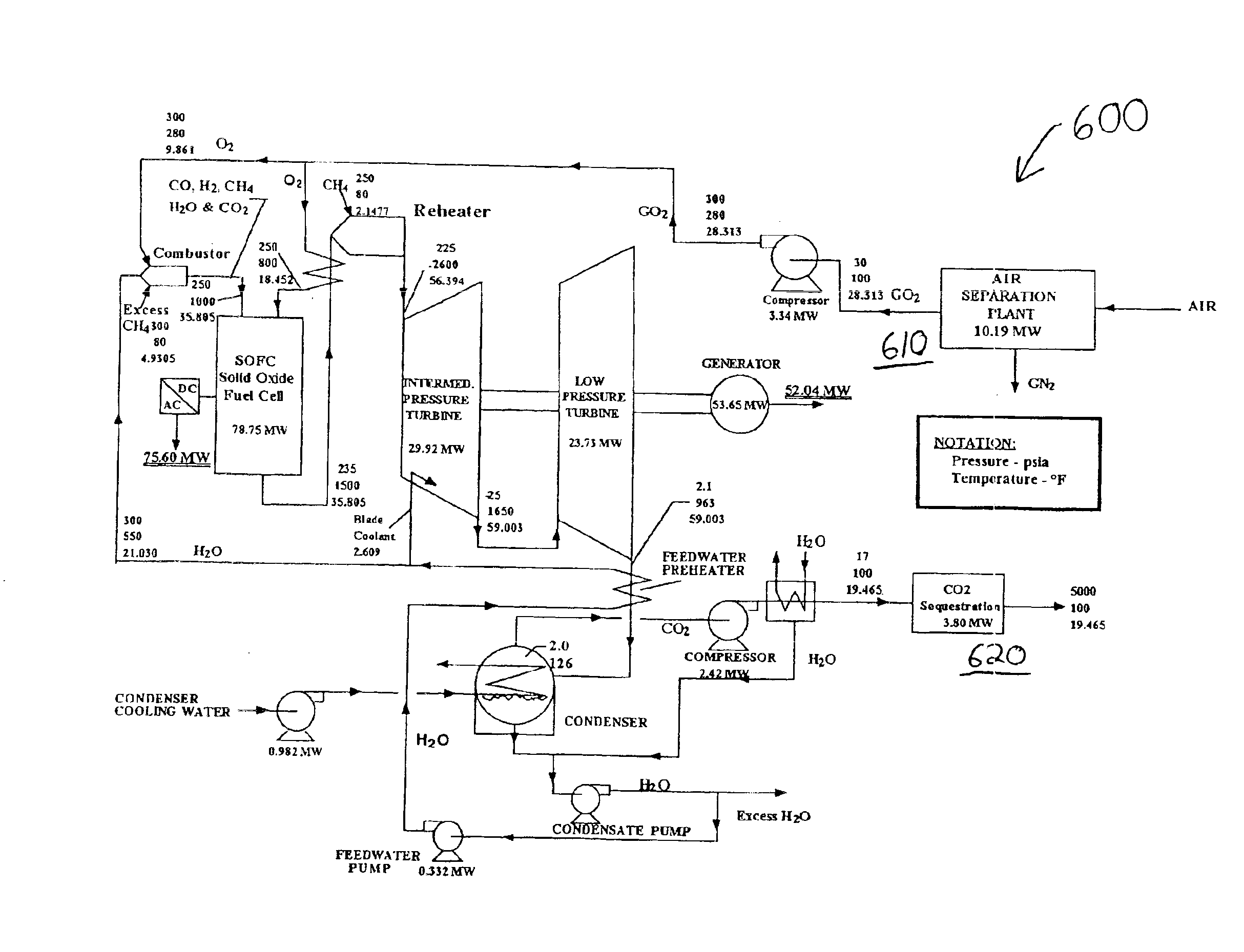
Combined fuel cell and fuel combustion power generation systems
A power generation system is provided which converts chemical energy in one or more fuels into electrical and / or mechanical power. The system includes both fuel cells to directly convert electrical energy in a fuel into electrical power and at lest one combustor and expander to generate mechanical power, optionally than converted to electrical power in a generator. Fuel cell products disclosed from the fuel cell are entered into the combustor to be heated along with products of combustion created in the combustor and expanded in the expander along with the products of combustion.
Owner:CLEAN ENERGY SYST
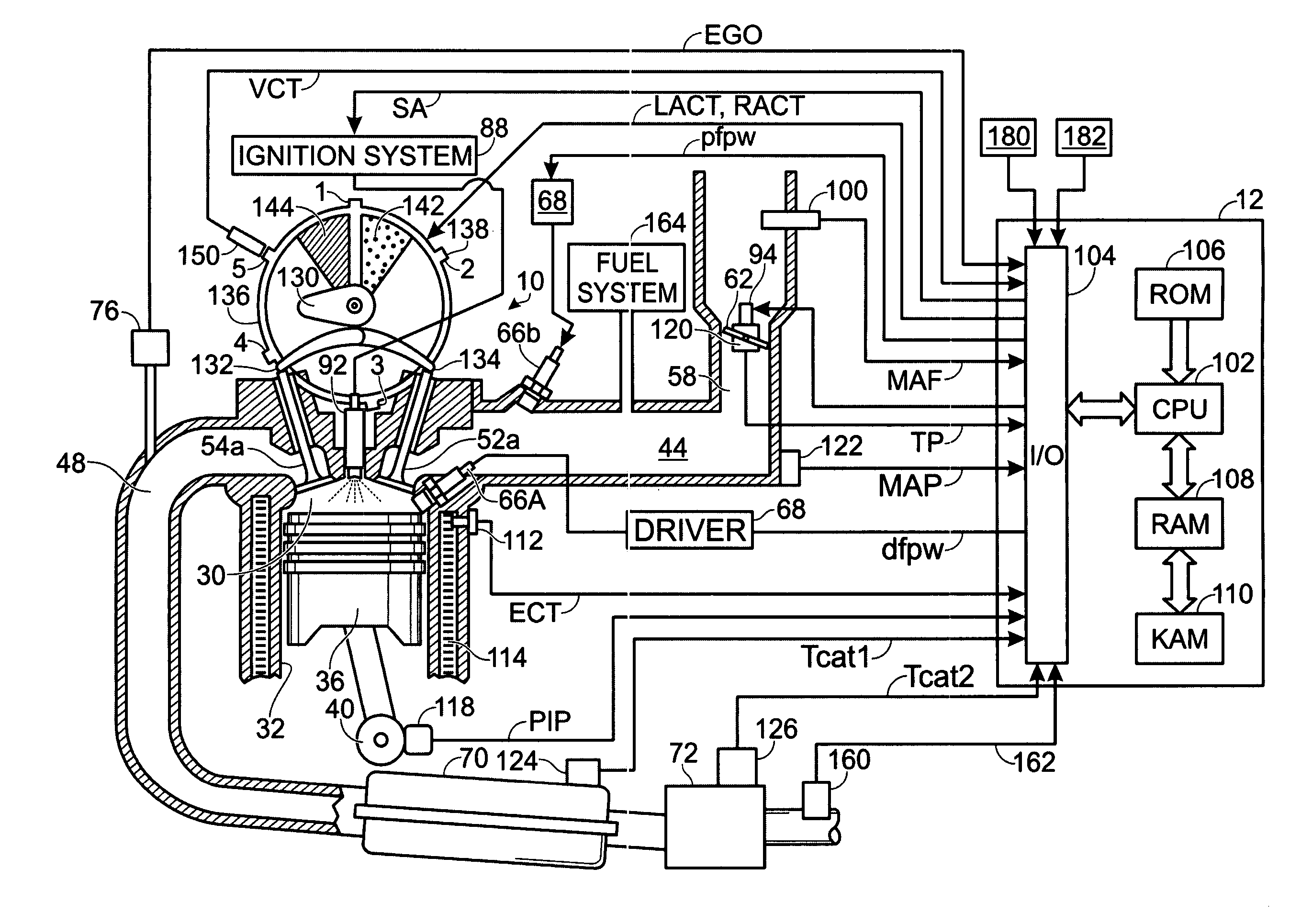
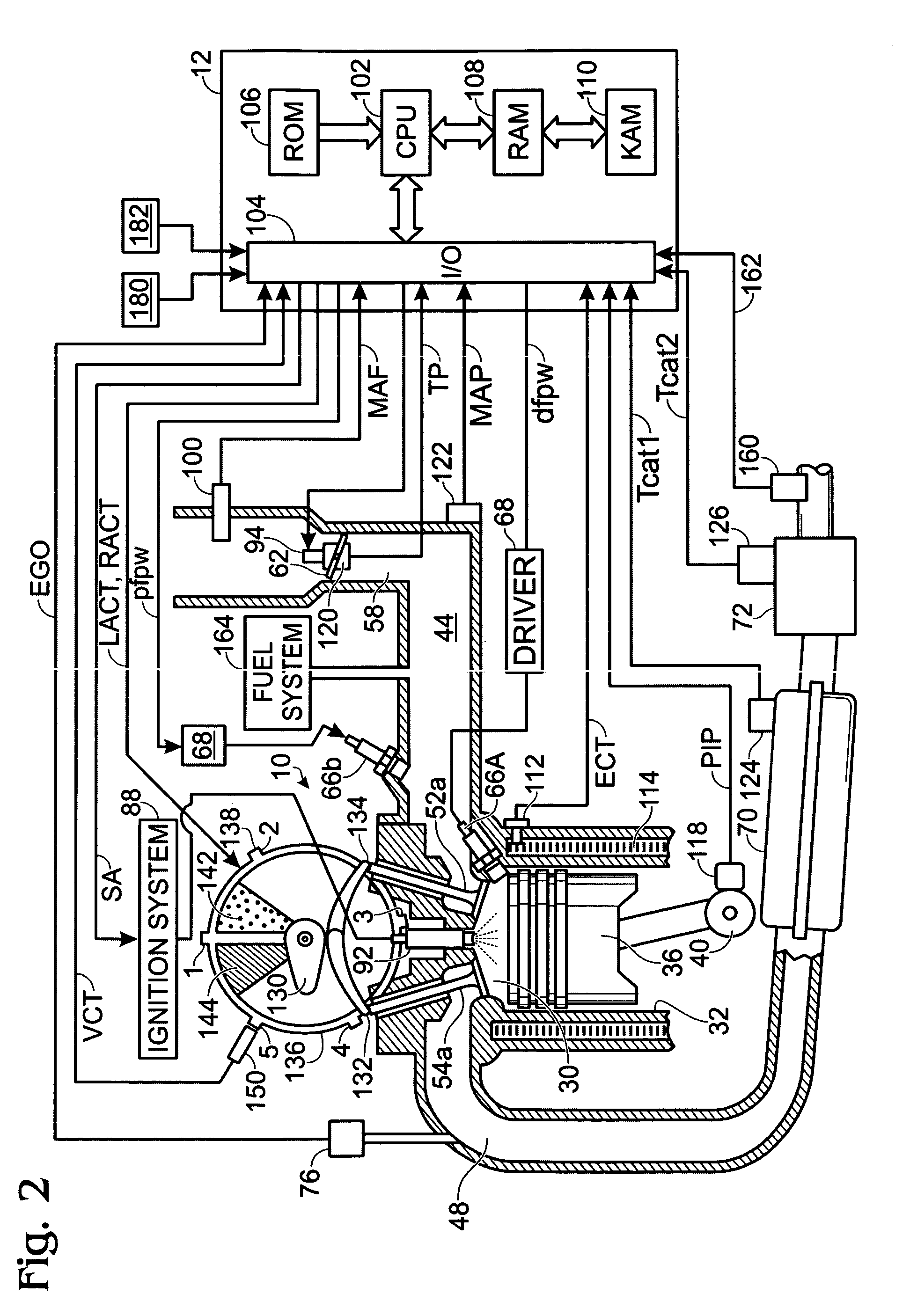
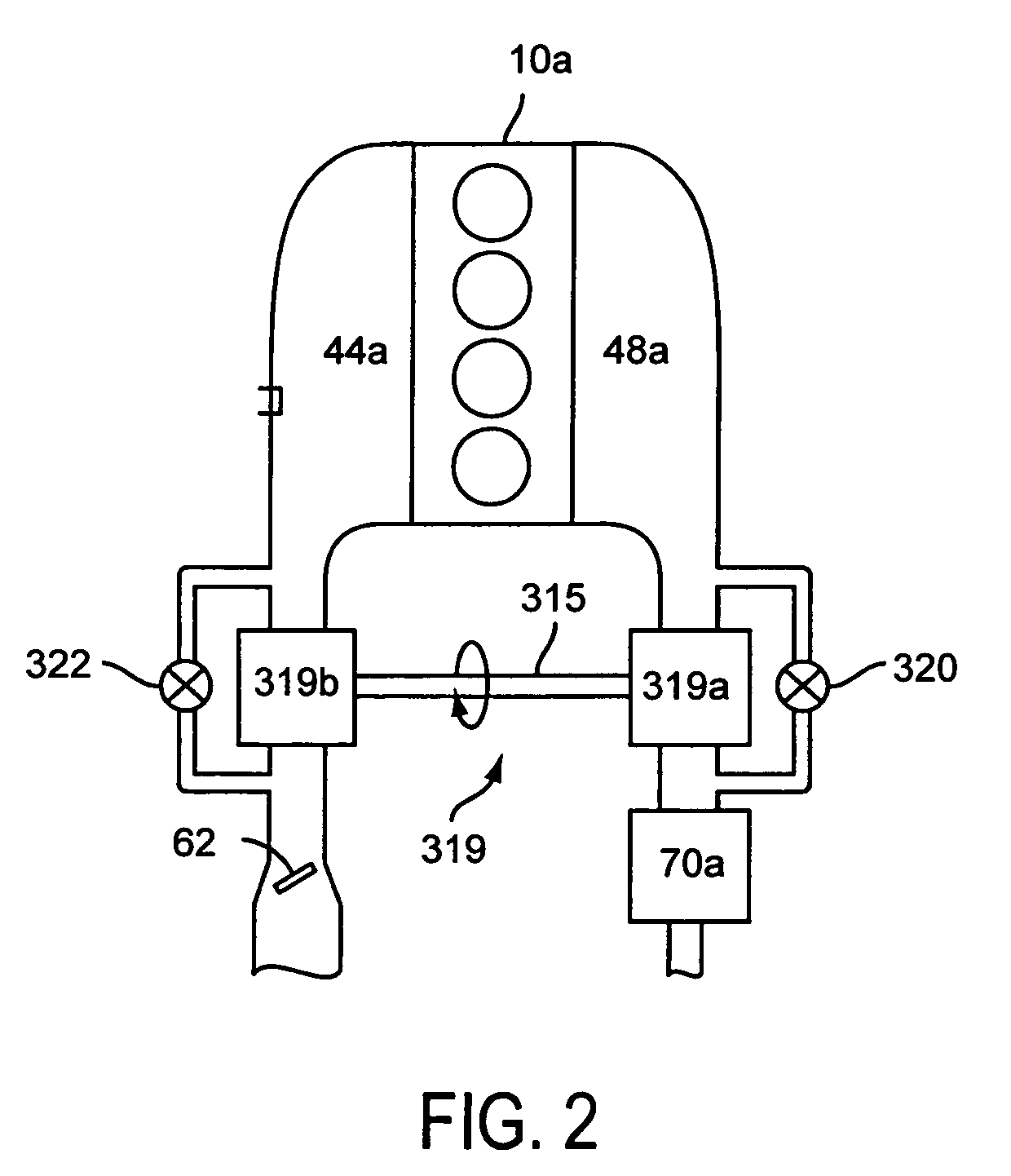
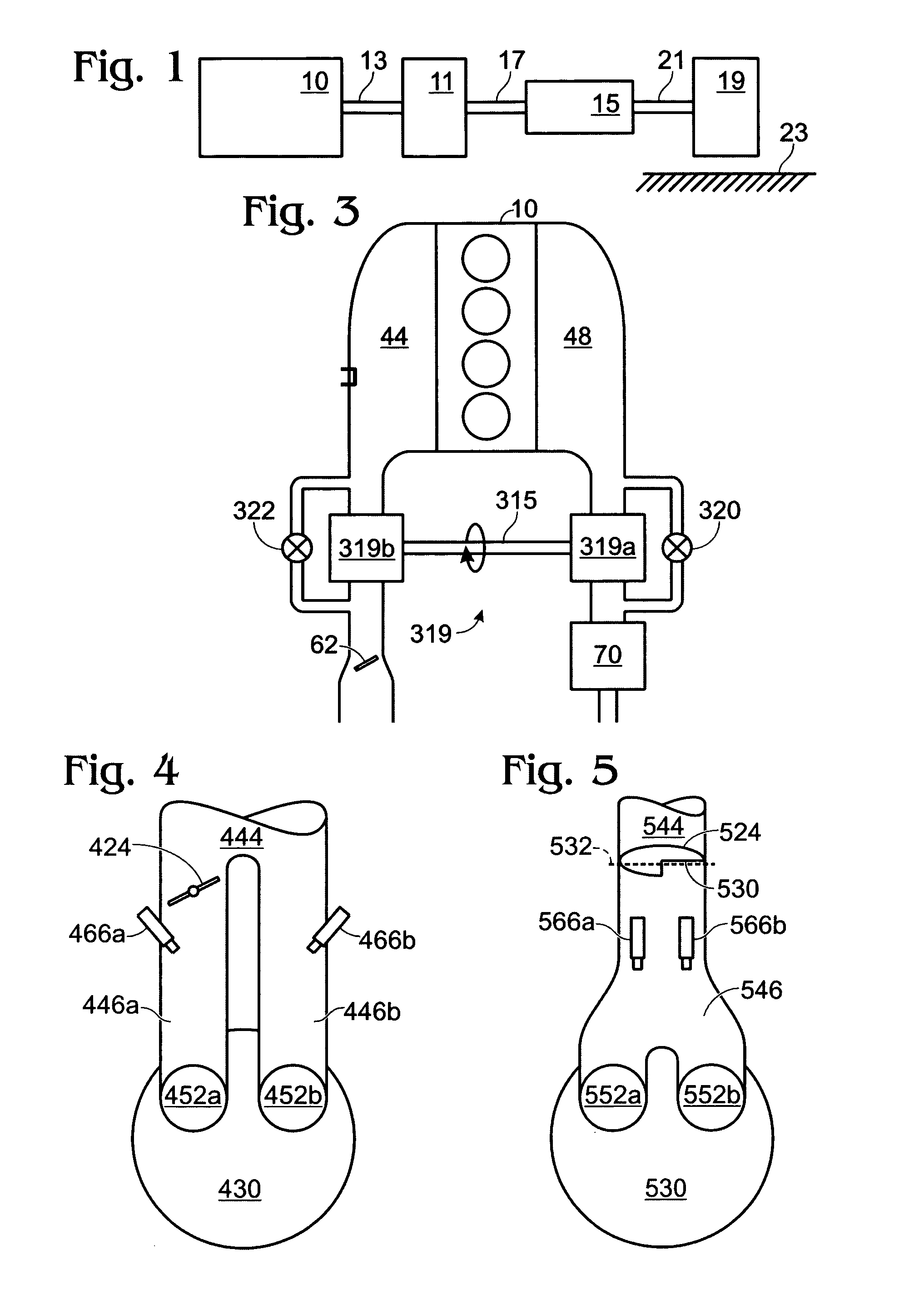
System and method for engine fuel blend control
A system for an engine, comprising of a cylinder located in the engine, a fuel delivery system for varying relative delivery amounts of a first and second injection type into said cylinder, and a controller configured to adjust a parameter affecting flow through the engine in response to said relative delivery amounts of said first and second injection type.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System for recirculating the exhaust of a turbomachine
ActiveUS20090107141A1HydrogenNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust fumesEnvironmental engineering
A portion of the exhaust generated by a turbomachine is recirculated through an inlet portion by an exhaust gas recirculation system. The system reduces the level of harmful constituents within the exhaust before the exhaust is recirculated.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Dual fuel supply system for a direct-injection system of a diesel engine with on-board mixing
InactiveUS8973560B2Non-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesOn boardEngineering
The present invention is directed to a dual fuel supply system for supplying fuel to a direct-injection system of a diesel engine. The dual fuel supply system includes a diesel supply system to supply diesel to the direct-injection system; and a mixed fuel supply system that is operatively able to supply a liquid fuel premixture of diesel and liquefied gaseous fuel to the direct-injection system at a supply pressure within a fuel demand pressure range of the direct-injection system and at a corresponding temperature range that retains the fuel premixture below its vapor temperature as it flows through the fuel path of the direct-injection system and the diesel engine. The dual fuel supply system is configured to permit selective change over between the diesel supply system and the mixed fuel system to supply the direct-injection system selectively with either diesel or liquid fuel premixture respectively.
Owner:DGC IND
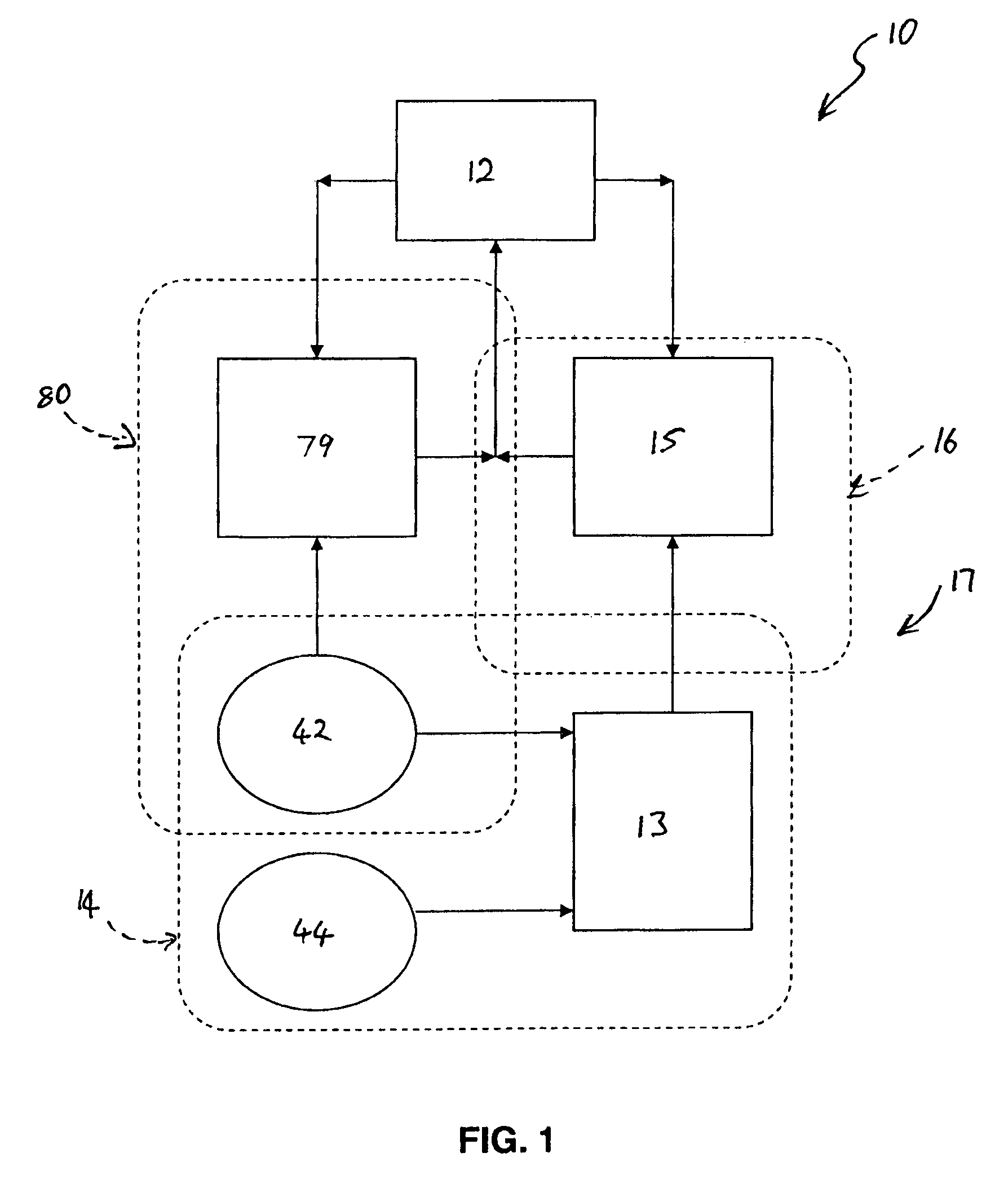
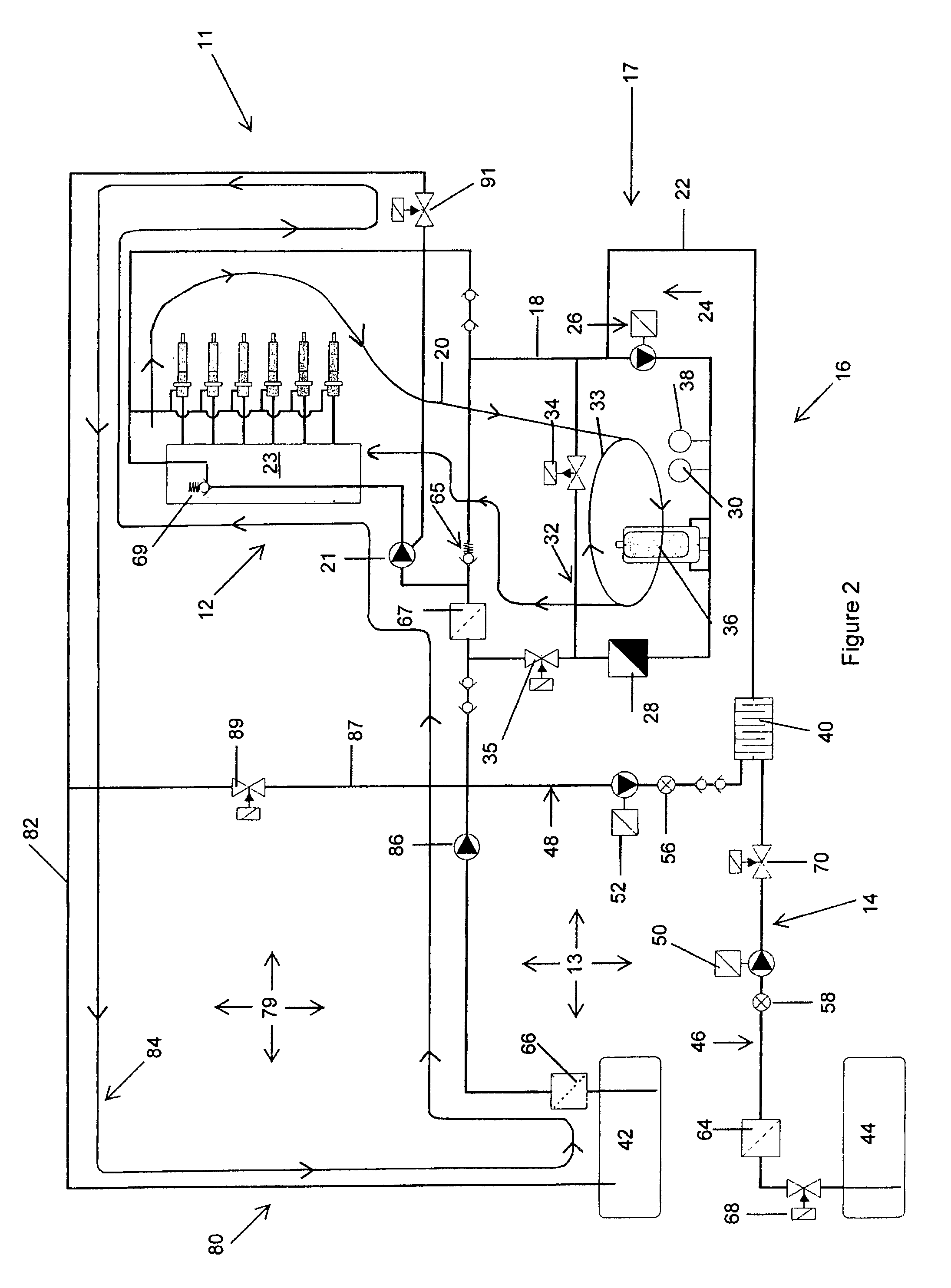
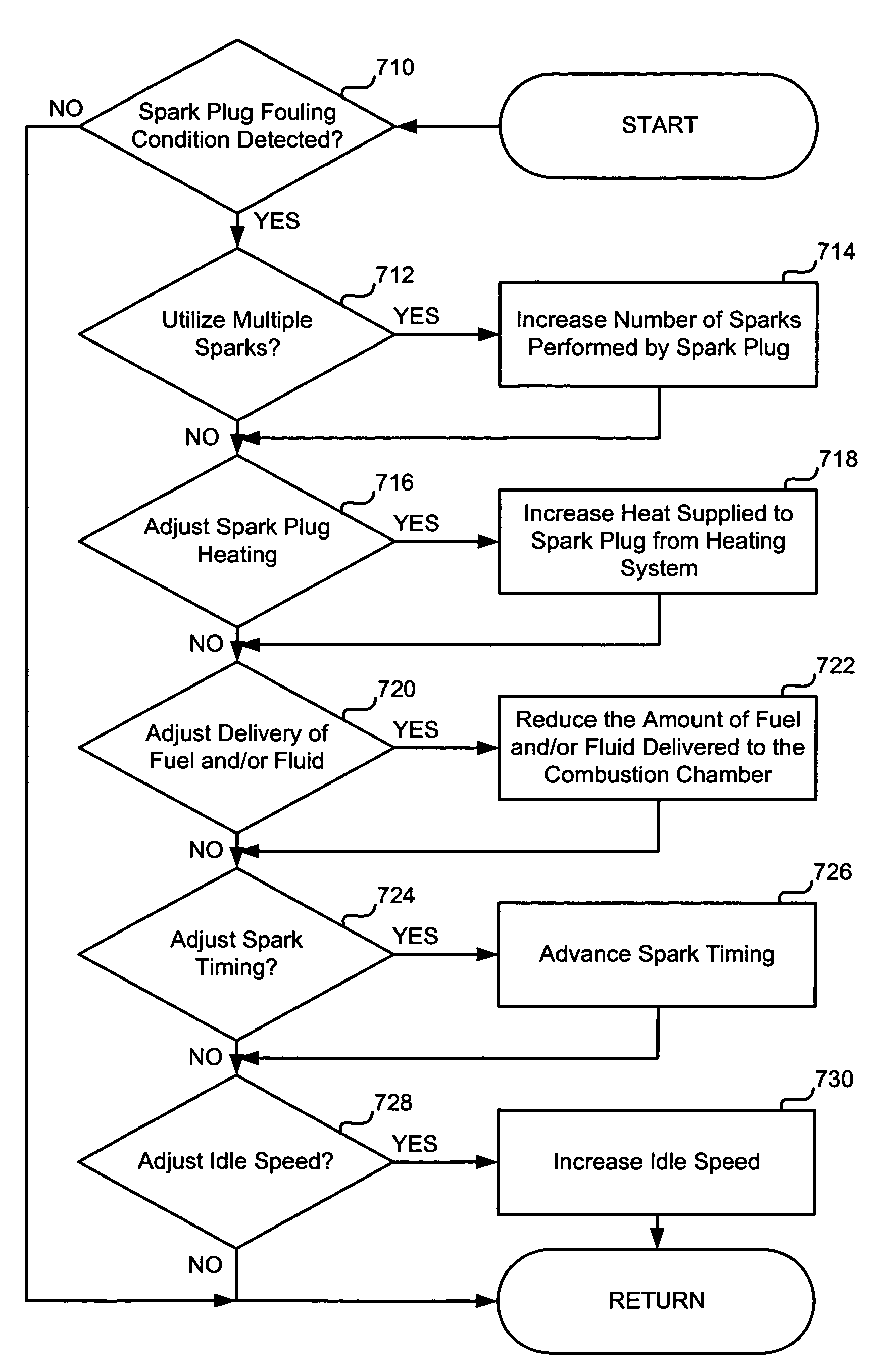
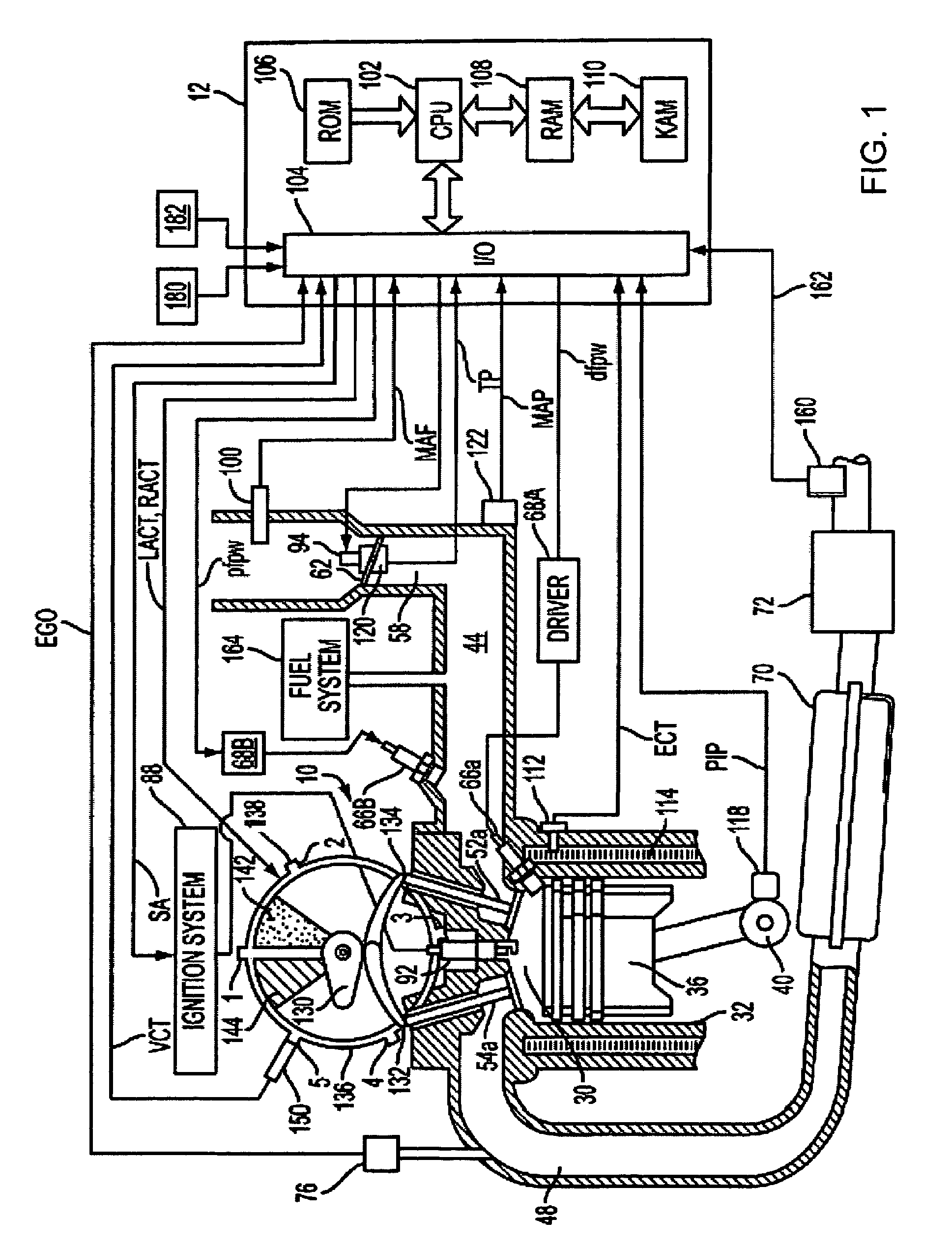
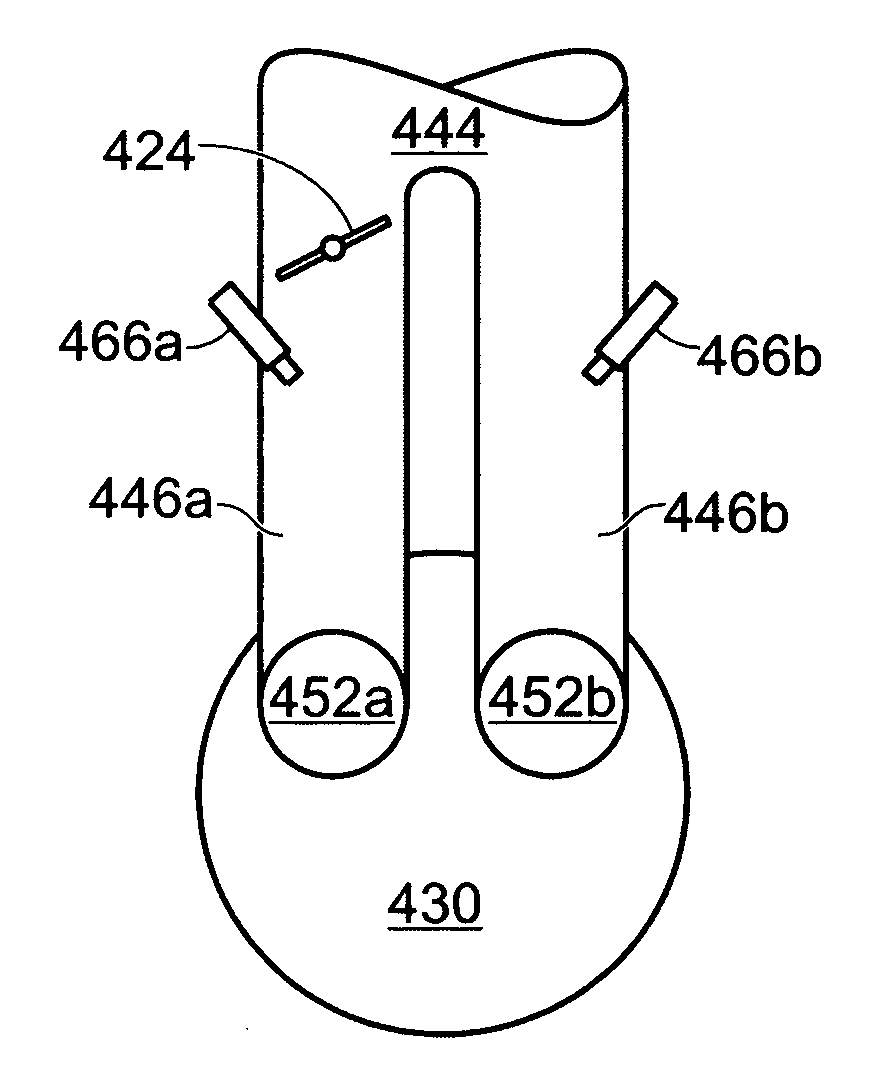
Spark plug heating for a spark ignited engine
A system for an engine of a vehicle, comprising of at least one combustion chamber located in the engine, a delivery system configured to deliver a fuel and a fluid to the combustion chamber, an ignition system including a spark plug configured to ignite the fuel within the combustion chamber, a spark plug heating system configured to supply heat to the spark plug, and a control system configured to vary an amount of heat supplied to the spark plug by the spark plug heating system responsive to a condition of the ignition system.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
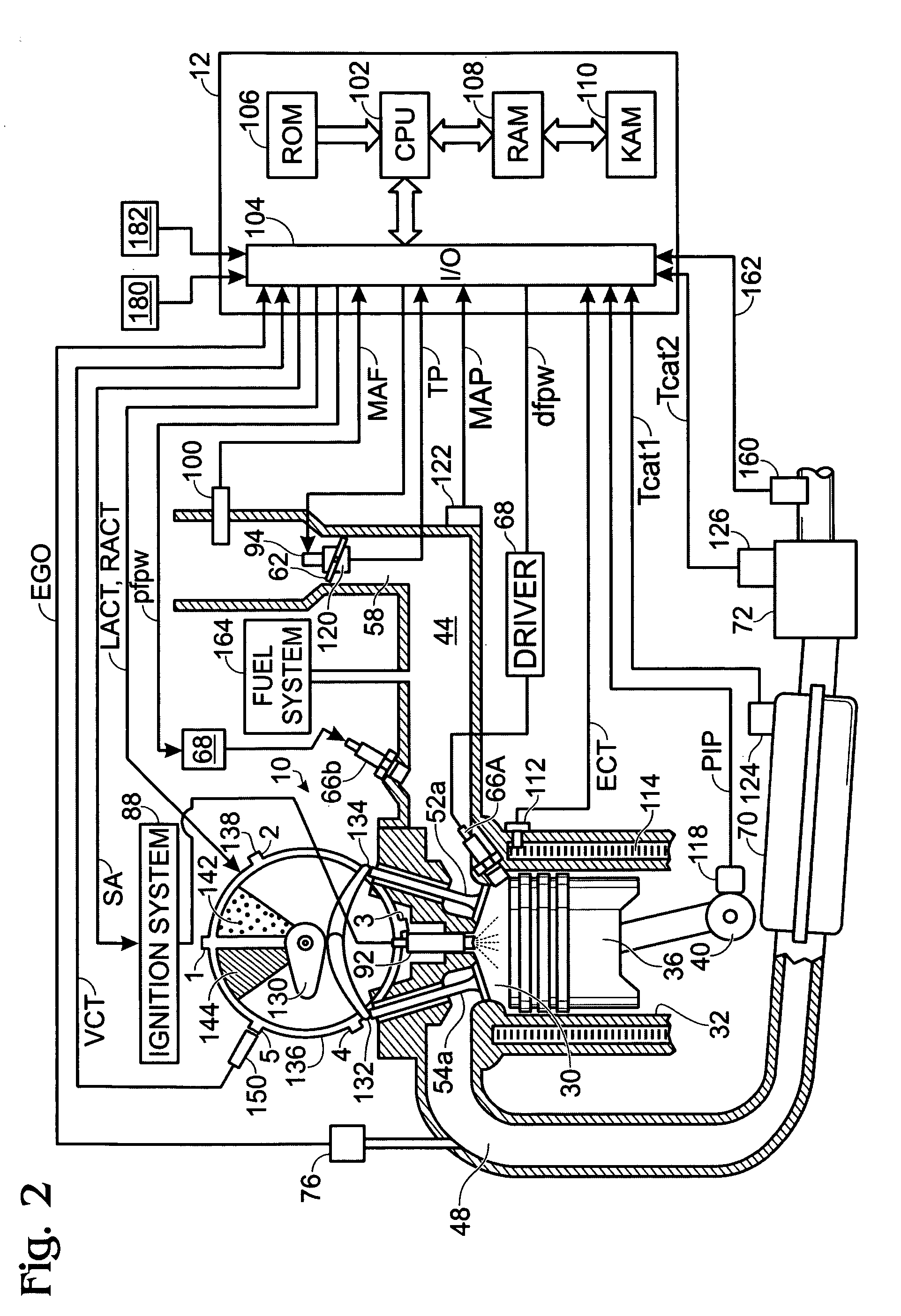
System and method for tip-in knock compensation
ActiveUS20070119425A1Improve the heating effectTrend downElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHeat capacityOperant conditioning
A method of controlling an engine, the method comprising of providing fuel having a blend to a cylinder of the engine, actively varying said fuel blend in response to at least an operating condition, and where during a transient operating condition, said blend is adjusted to increase a heat capacity of said fuel to reduce a tendency for knock.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
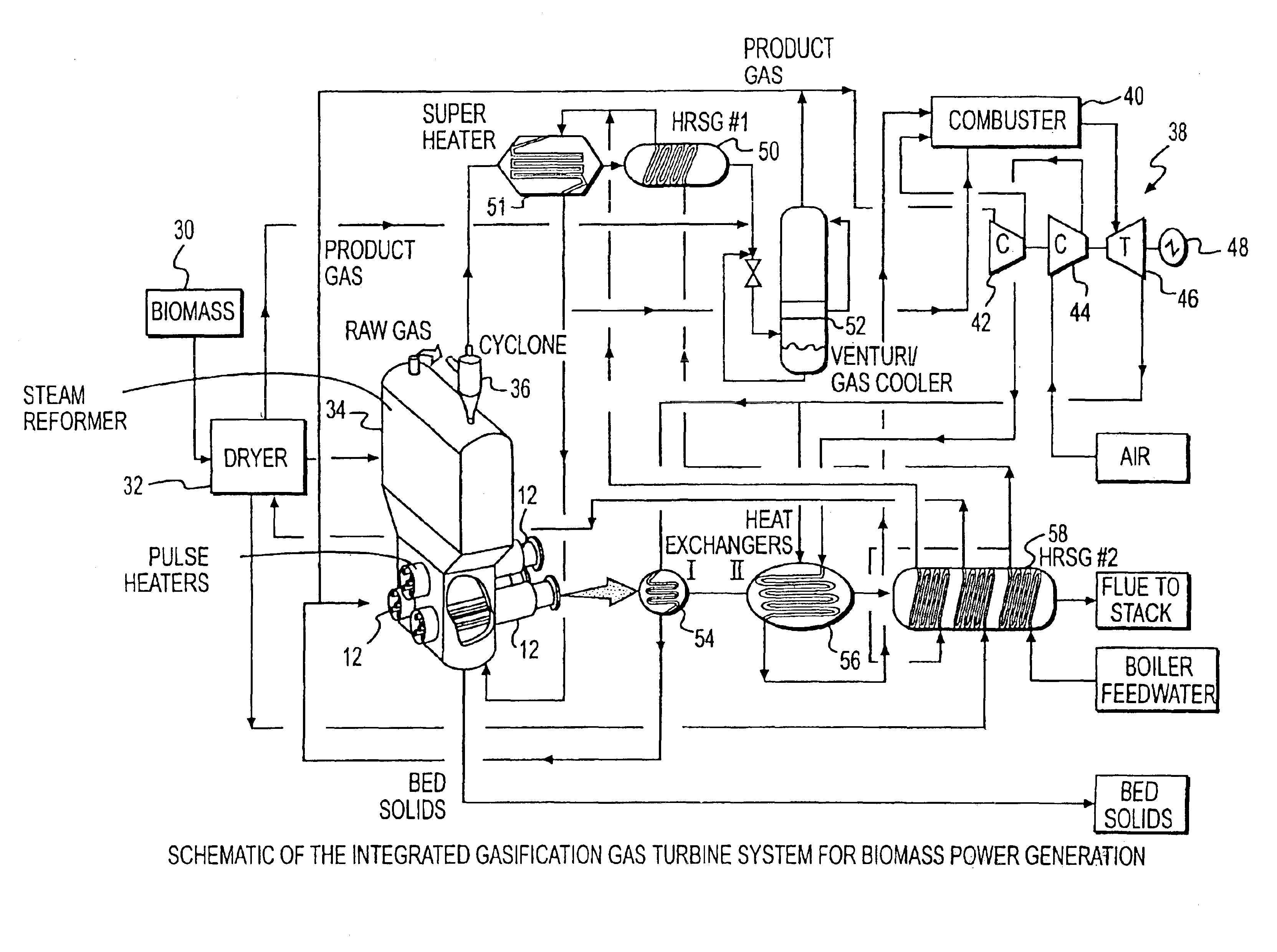
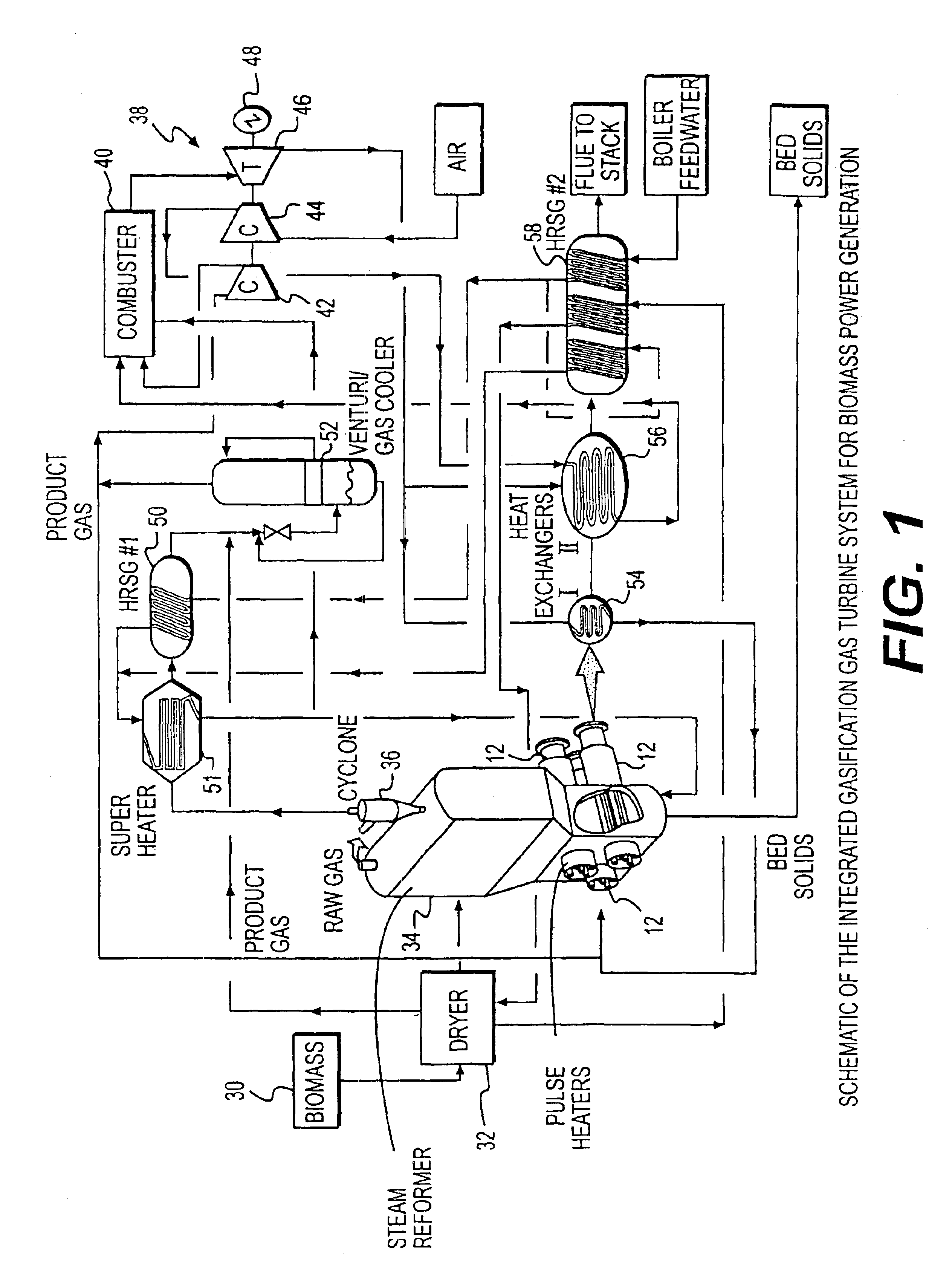
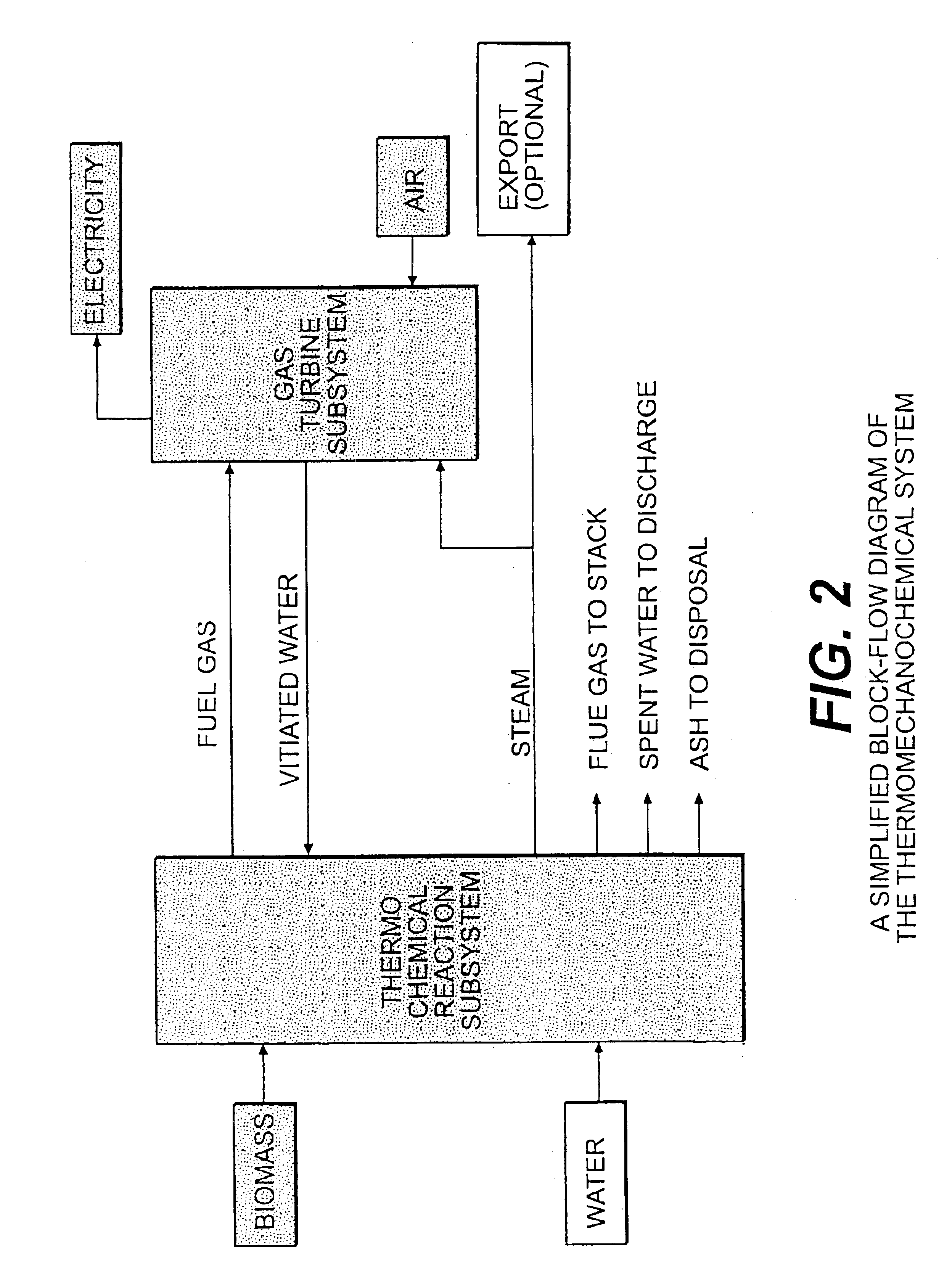
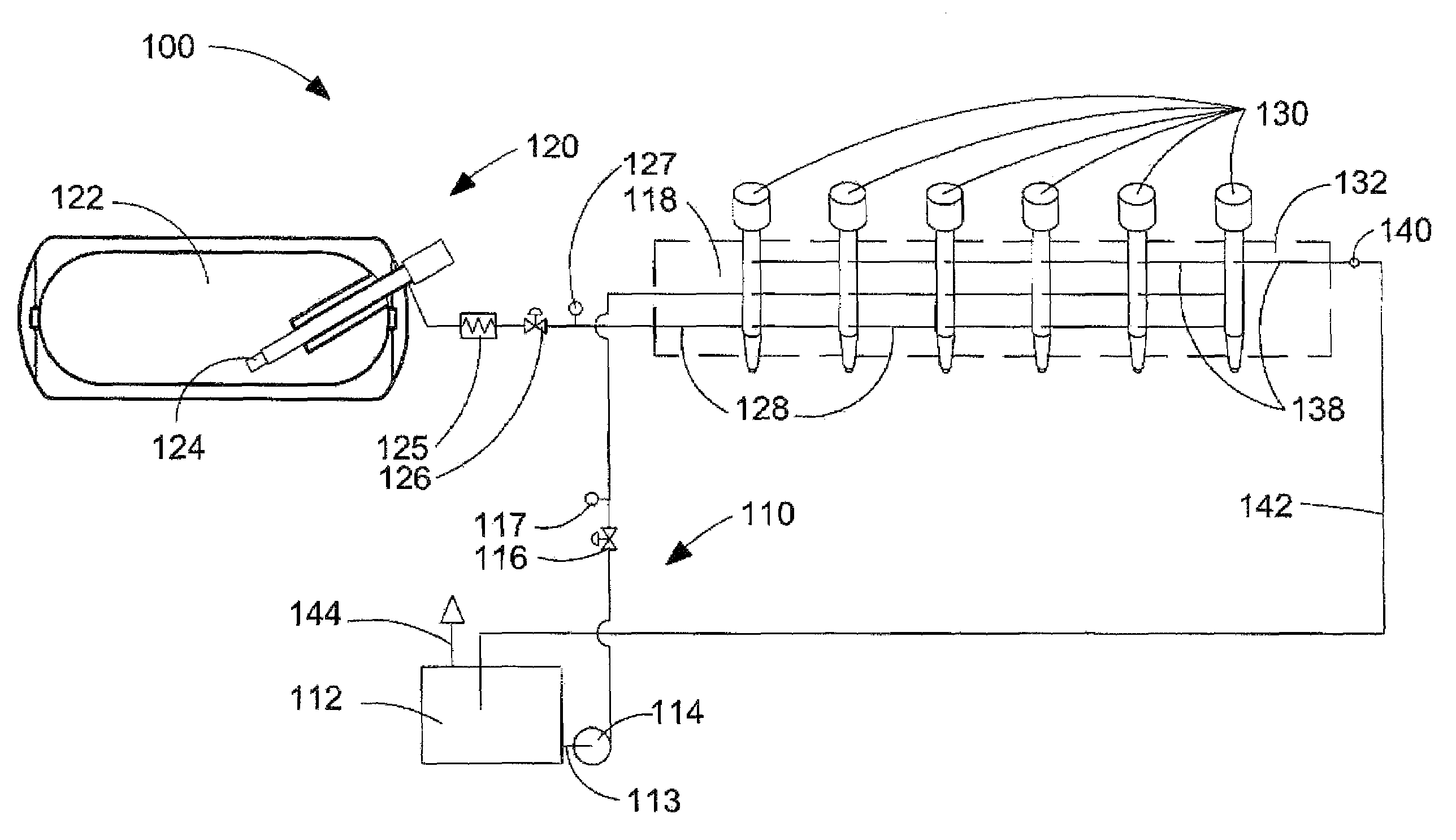
System integration of a steam reformer and gas turbine
A novel process and apparatus for power generation from biomass and other carbonaceous feedstocks are provided. The process integrates a pulse combustor steam reformer with a gas turbine to generate electricity such that (i) efficiency is higher than those of conventional and current advanced power systems, (ii) emissions are lower than those proposed in the new environmental regulations, and (iii) performance is comparable to that of combined cycle, even though a bottoming cycle is not included here. The pulse combustor steam reformer generates a hydrogen-rich, medium-Btu fuel gas that is fired in a gas turbine to generate electricity. The apparatus may be configured to produce only power or combined heat and power.
Owner:THERMOCHEM RECOVERY INT
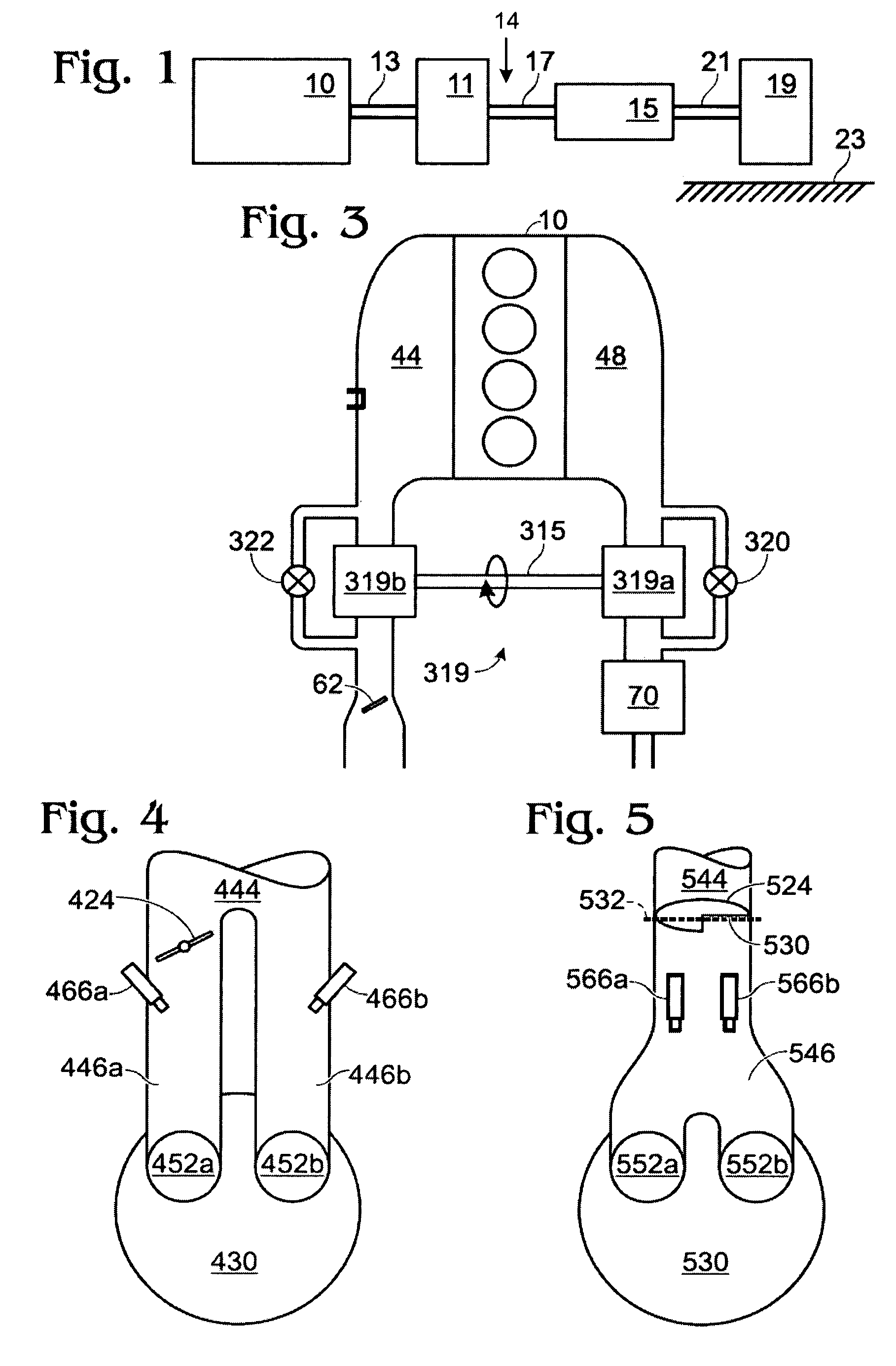
Method and apparatus for delivering two fuels to a direct injection internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7373931B2Increase energy densityReadily availableInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusInjection pressureCombustion chamber
An apparatus for delivering two fuels to a direct injection internal combustion engine comprises a liquid-fuel supply rail, a gaseous-fuel supply rail, a drain system with a shared drain rail for collecting both liquid fuel and gaseous fuel, and a venting device for venting gaseous fuel collected by the drain rail. The method comprises separately delivering a liquid fuel at injection pressure to an injection valve through a liquid-fuel rail, and actuating the liquid-fuel injection valve to introduce liquid fuel directly into the combustion chamber. The method further comprises delivering a gaseous fuel at injection pressure to an injection valve through a gaseous-fuel rail and actuating the gaseous-fuel injection valve to introduce gaseous fuel directly into the combustion chamber. The method further comprises collecting in a drain rail liquid fuel and gaseous fuel from the liquid-fuel injection valve and the gaseous-fuel injection valve, directing liquid fuel to a storage vessel, and directing gaseous fuel to a vent pipe.
Owner:WESTPORT FUEL SYST CANADA INC
Method And Apparatus For Delivering Two Fuels To A Direct Injection Internal Combustion Engine
ActiveUS20070199539A1Saving operating costIncrease energy densityInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusCombustion chamberLiquid fuel
An apparatus for delivering two fuels to a direct injection internal combustion engine comprises a liquid-fuel supply rail, a gaseous-fuel supply rail, a drain system with a shared drain rail for collecting both liquid fuel and gaseous fuel, and a venting device for venting gaseous fuel collected by the drain rail. The method comprises separately delivering a liquid fuel at injection pressure to an injection valve through a liquid-fuel rail, and actuating the liquid-fuel injection valve to introduce liquid fuel directly into the combustion chamber. The method further comprises delivering a gaseous fuel at injection pressure to an injection valve through a gaseous-fuel rail and actuating the gaseous-fuel injection valve to introduce gaseous fuel directly into the combustion chamber. The method further comprises collecting in a drain rail liquid fuel and gaseous fuel from the liquid-fuel injection valve and the gaseous-fuel injection valve, directing liquid fuel to a storage vessel, and directing gaseous fuel to a vent pipe.
Owner:WESTPORT FUEL SYST CANADA INC
Low Emission Triple-Cycle Power Generation Systems and Methods
Methods and systems for low emission power generation in combined cycle power plants are provided. One system includes a gas turbine system that stoichiometrically combusts a fuel and an oxidant in the presence of a compressed recycle stream to provide mechanical power and a gaseous exhaust. The compressed recycle stream acts as a diluent to moderate the temperature of the combustion process. A boost compressor can boost the pressure of the gaseous exhaust before being compressed into the compressed recycle stream. A purge stream is tapped off from the compressed recycle stream and directed to a C02 separator which discharges C02 and a nitrogen-rich gas which can be expanded in a gas expander to generate additional mechanical power.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Optimized combustion control of an internal combustion engine equipped with exhaust gas recirculation
InactiveUS6948475B1Avoid condensationImprove concentrationElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust fumesExhaust gas recirculation
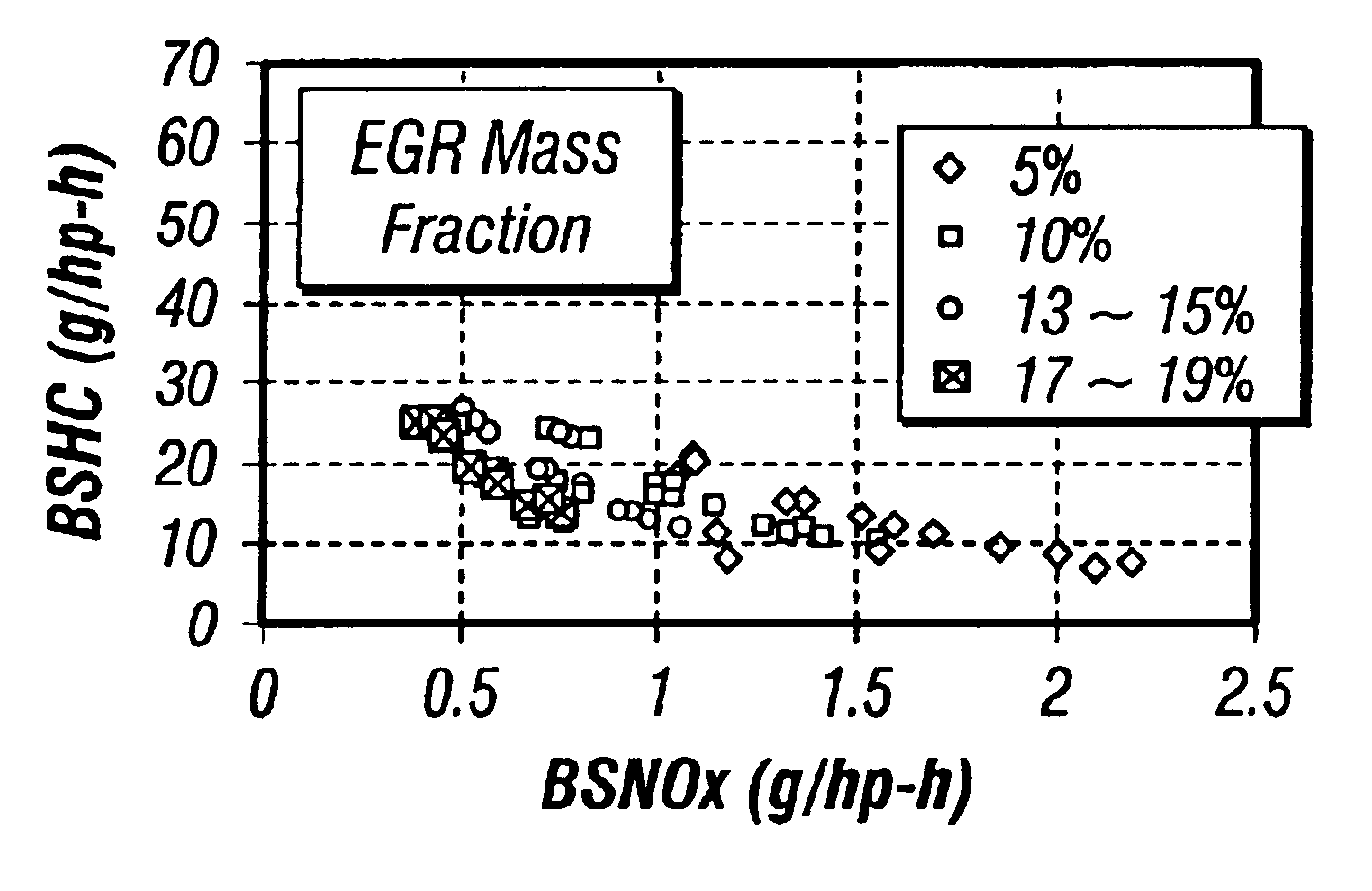
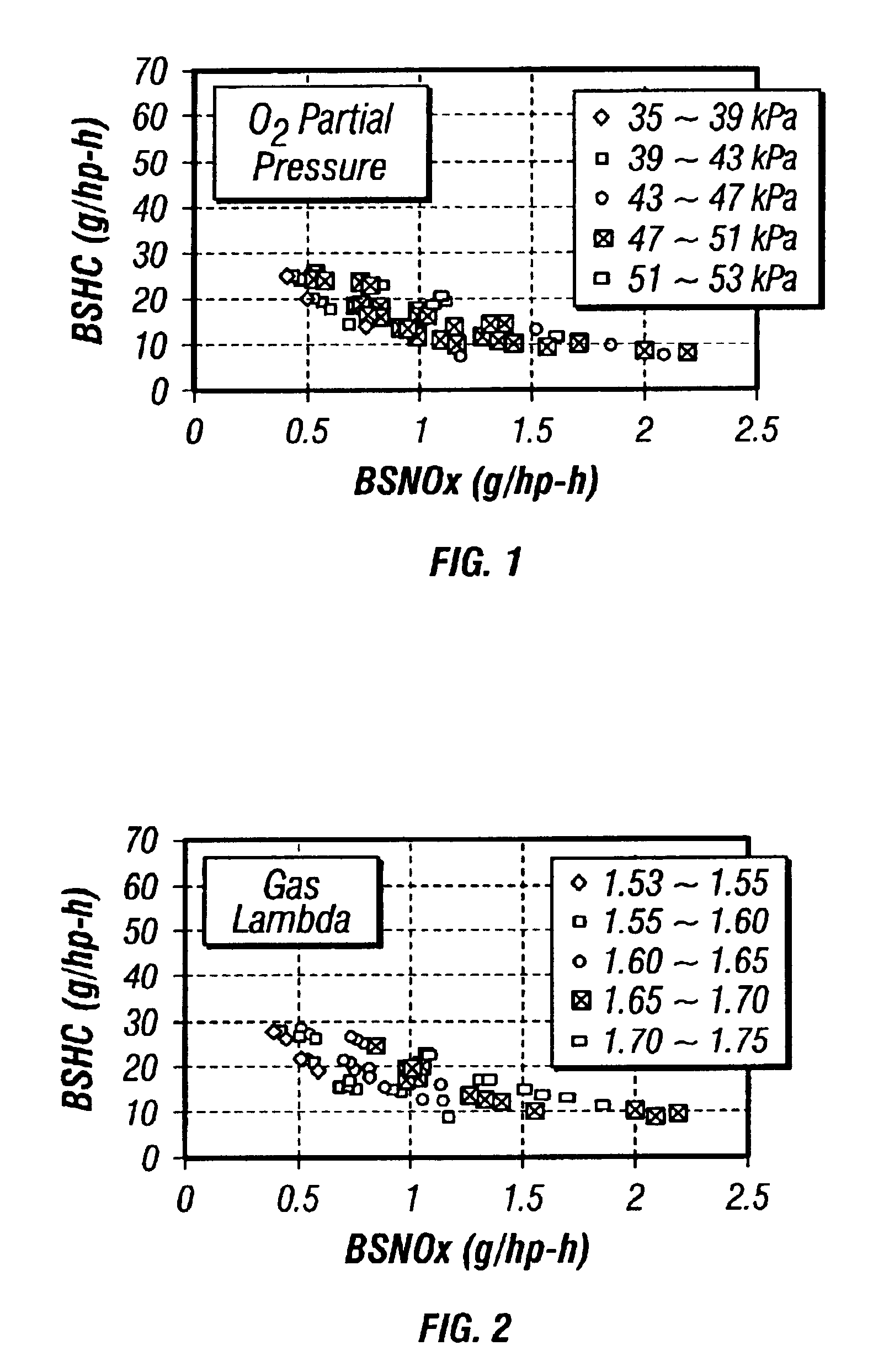
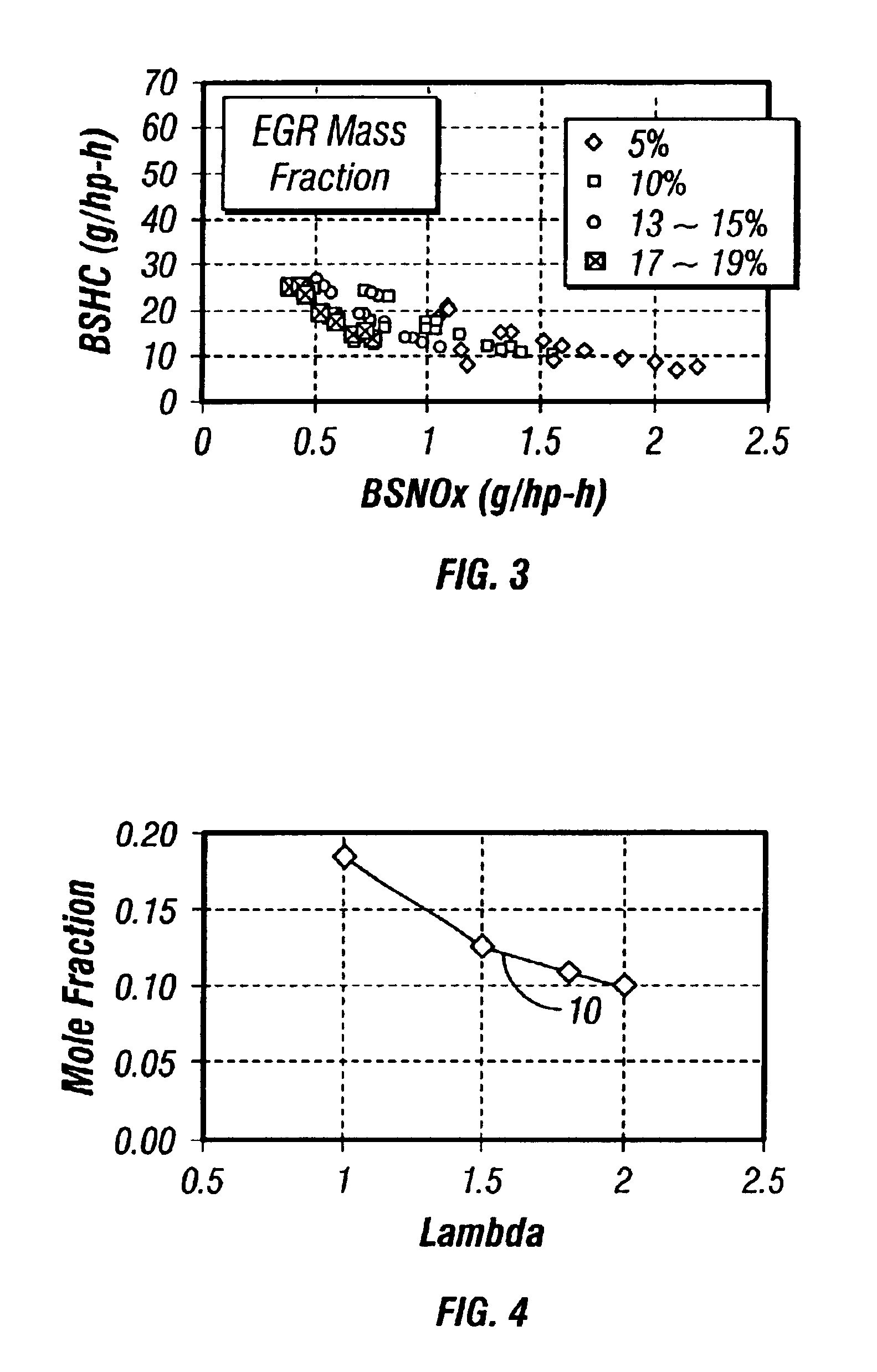
An EGR equipped internal combustion engine is controlled to maximize the beneficial effects and minimize the detrimental effects of EGR on engine operation. Specifically, at least one parameter indicative of the O2 concentration in the intake mixture and / or at least one parameter indicative of the H2O concentration in the intake mixture is monitored, and the monitored parameter is relied on to control one or more aspects of engine operation by open loop adjustment of other control strategies and / or by a separate closed loop control strategy. These controls are applicable to virtually any engine, and are particularly beneficial to lean burn engines such as diesel (compression ignition) engines, spark ignited natural gas engines, and dual fuel or other compression ignited natural gas engines. The engine may be equipped with either actively controllable EGR or passive and uncontrolled EGR.
Owner:CLEAN AIR POWER
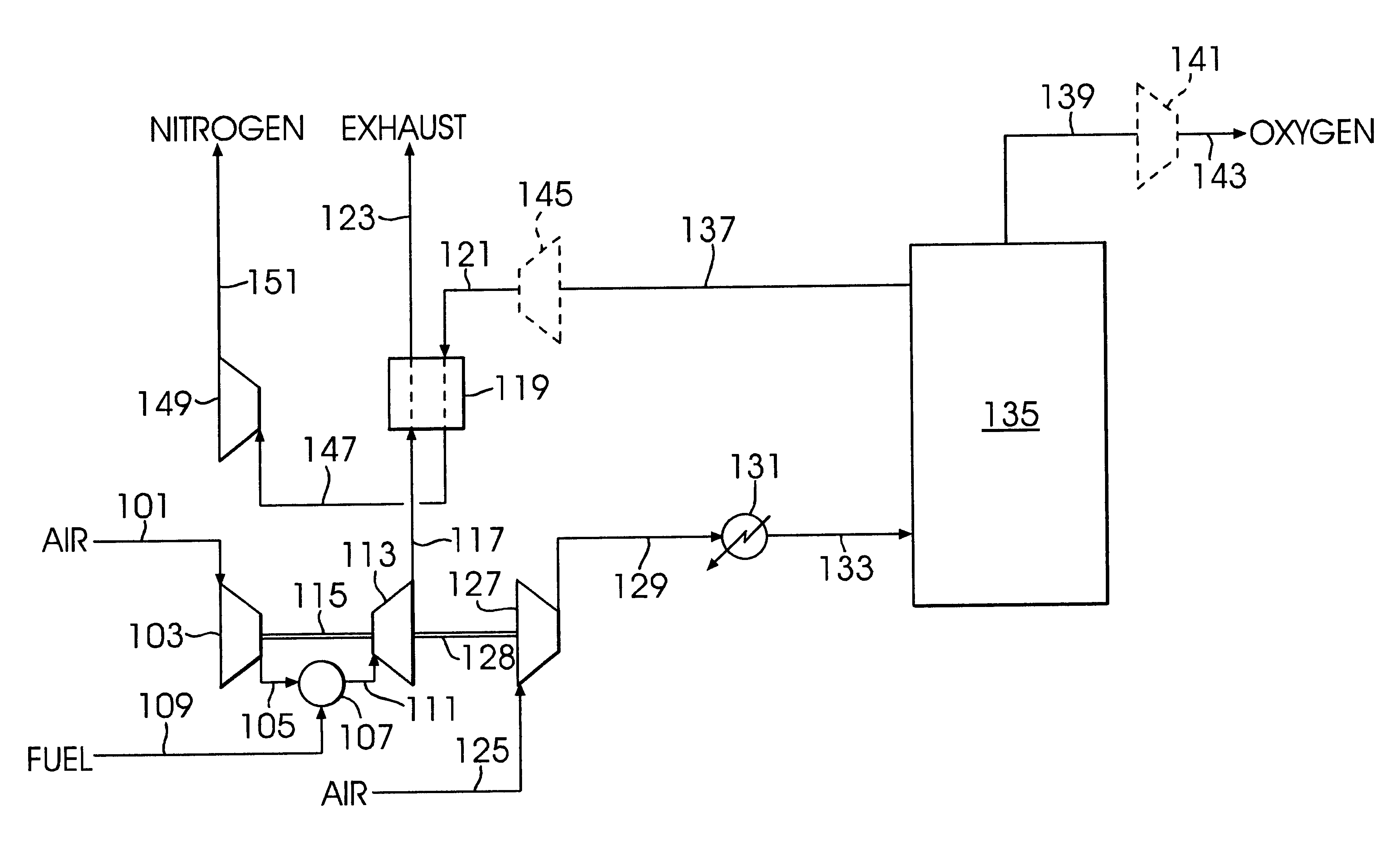
Air separation process integrated with gas turbine combustion engine driver
A method for the separation of a feed gas mixture comprising oxygen and nitrogen in which an oxidant gas and fuel are combusted in a combustion engine to generate shaft work and a hot exhaust gas, the feed gas mixture comprising oxygen and nitrogen is compressed, and the resulting compressed feed gas mixture is separated into two or more product gas streams with differing compositions. The shaft work of the combustion engine is utilized to provide at least a portion of the work required for compressing the feed gas mixture, one of the product gas streams by is heated by indirect heat exchange with the hot exhaust gas from the combustion engine, and the resulting heated product gas is work expanded to generate shaft work and yield an expanded product gas stream. The combustion engine may be a gas turbine combustion engine.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Systems and methods for power generation and hydrogen production with carbon dioxide isolation
A power generation system includes a first gas turbine system. The first turbine system includes a first combustion chamber configured to combust a first fuel stream of primarily hydrogen that is substantially free of carbon-based fuels, a first compressor configured to supply a first portion of compressed oxidant to the first combustion chamber and a first turbine configured to receive a first discharge from the first combustion chamber and generate a first exhaust and electrical energy. The power generation system further includes a second gas turbine system. The second turbine system includes a second combustion chamber configured to combust a second fuel stream to generate a second discharge, wherein the first compressor of the first gas turbine system is configured to supply a second portion of compressed oxidant to the second combustion chamber and a second turbine configured to receive the second discharge from the second combustion chamber to generate a second exhaust and electrical energy. A second compressor is configured to receive the second exhaust comprising carbon dioxide and to discharge a recycle stream to the second combustion chamber and a split stream to a separator system adapted to recover carbon dioxide. The power generation system also includes a hydrogen generation system configured to receive a third fuel and steam to generate the first fuel and a third exhaust gas, wherein the third exhaust gas is recycled into the second combustion chamber.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electrical power generation method
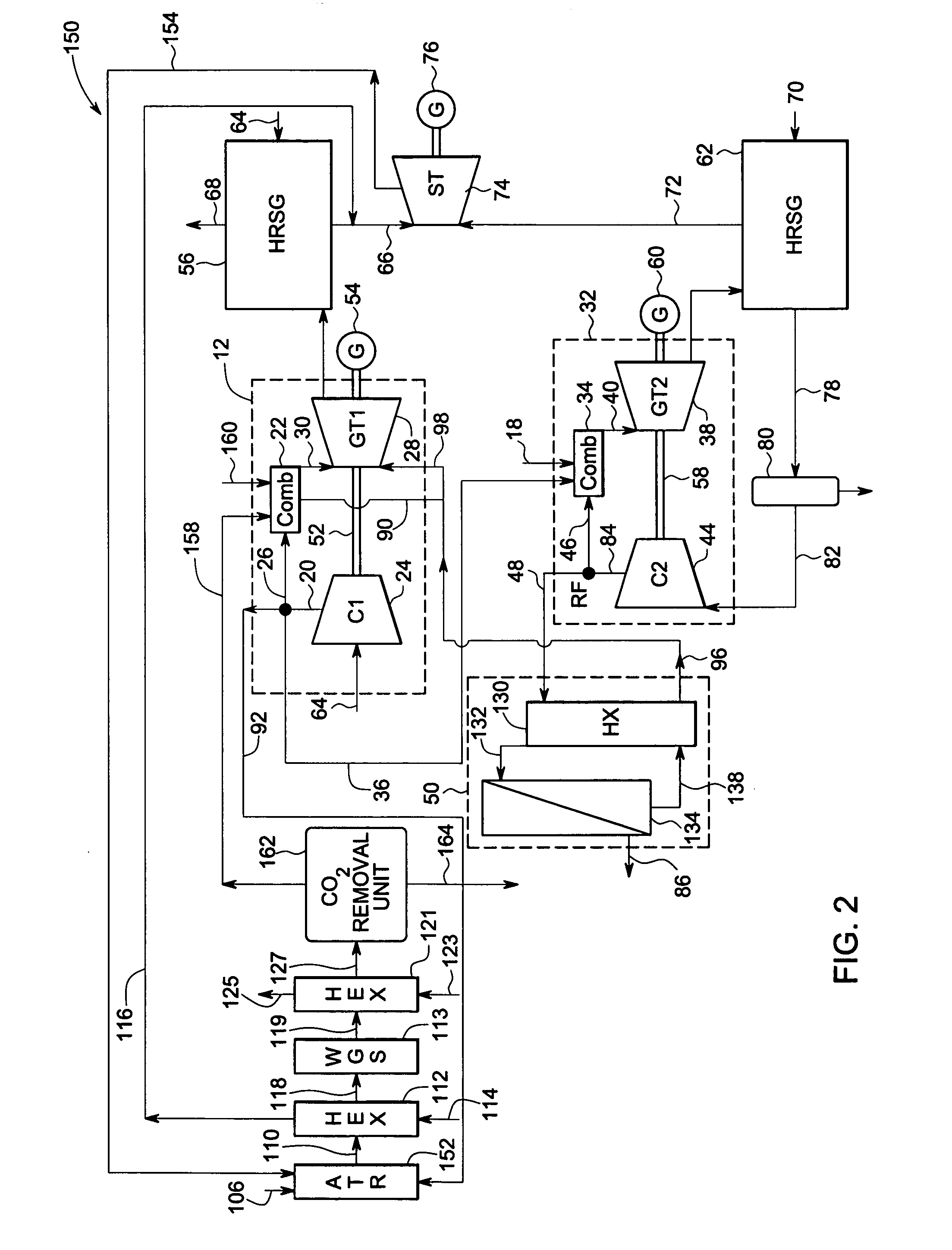
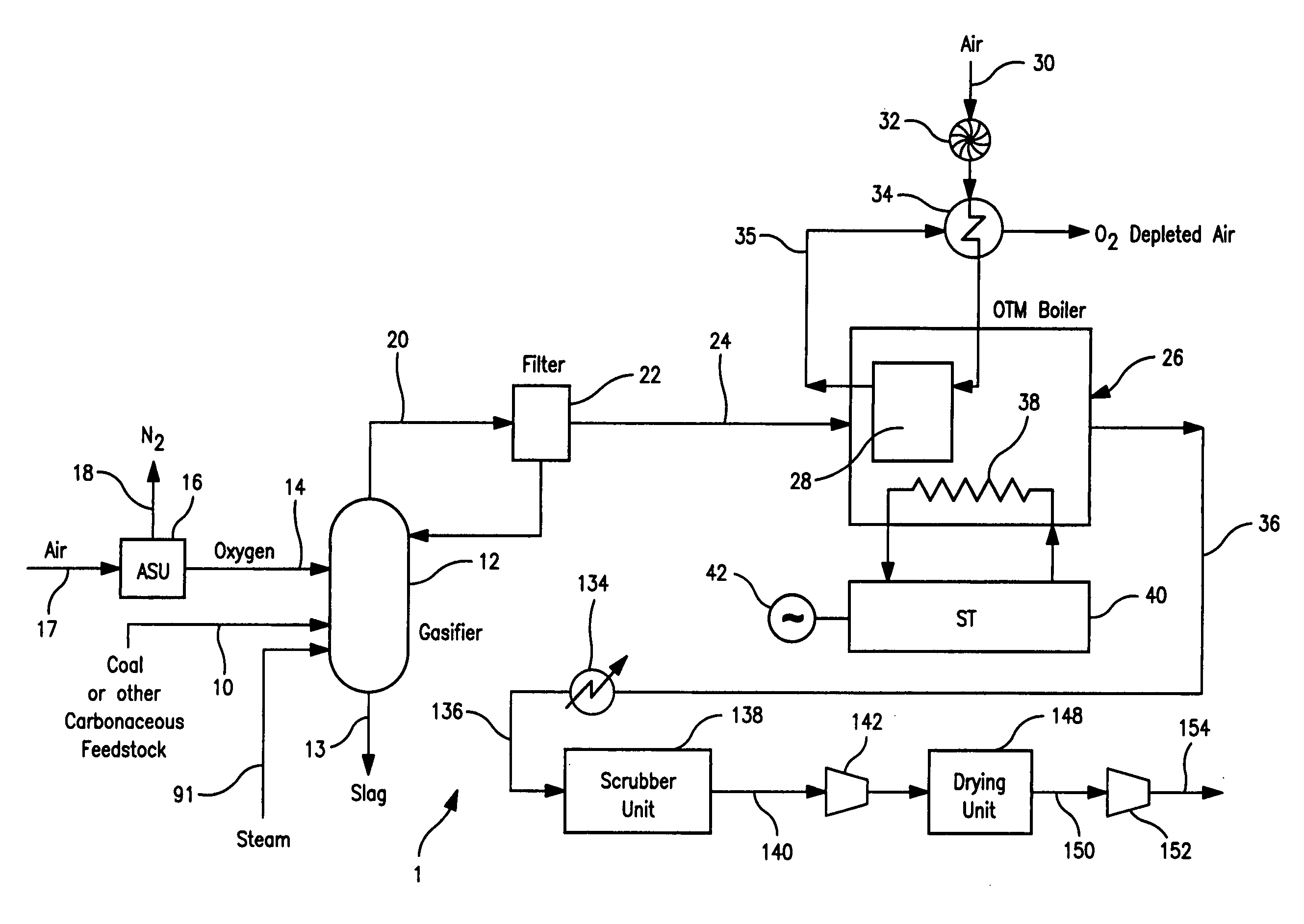
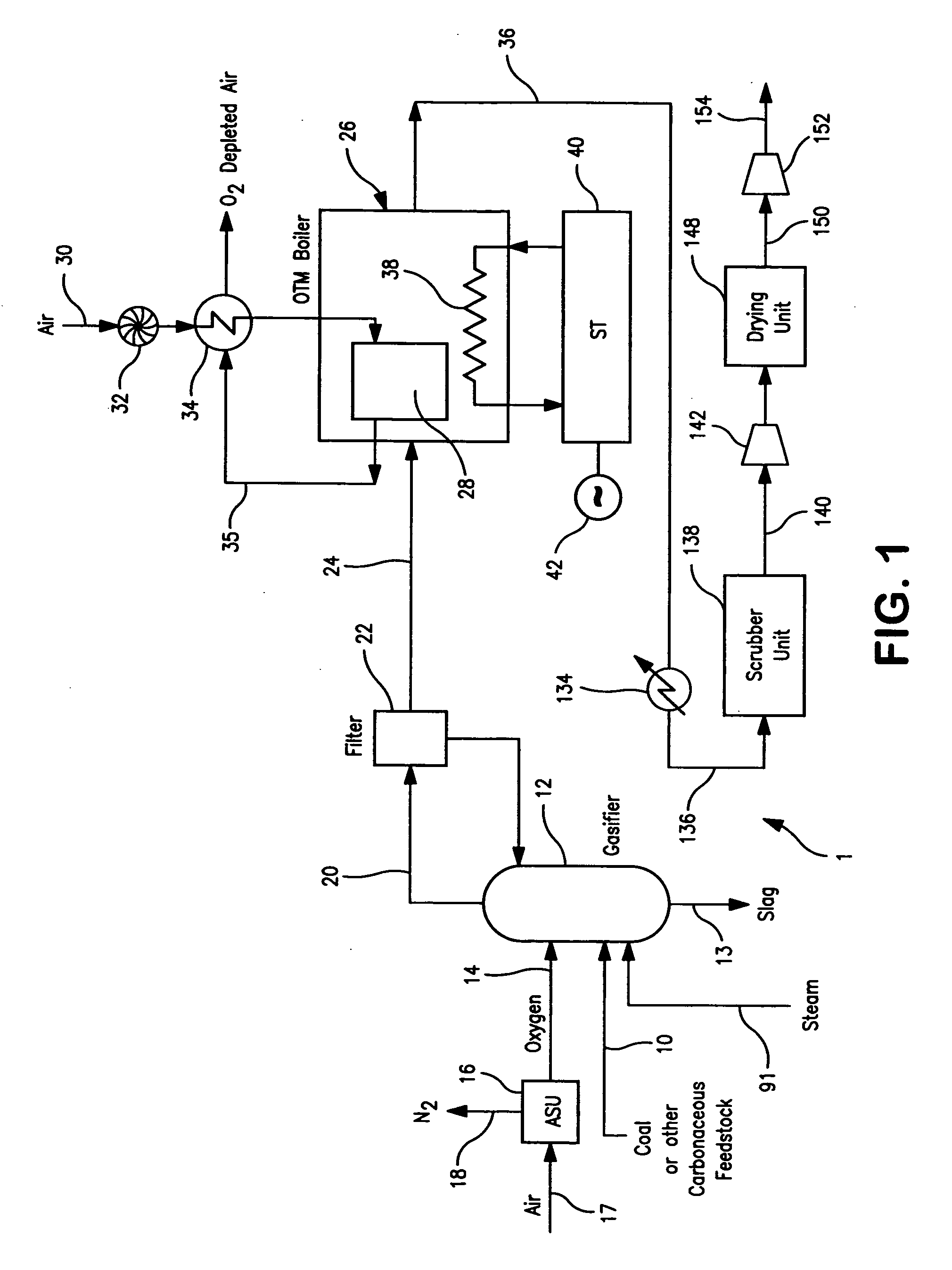
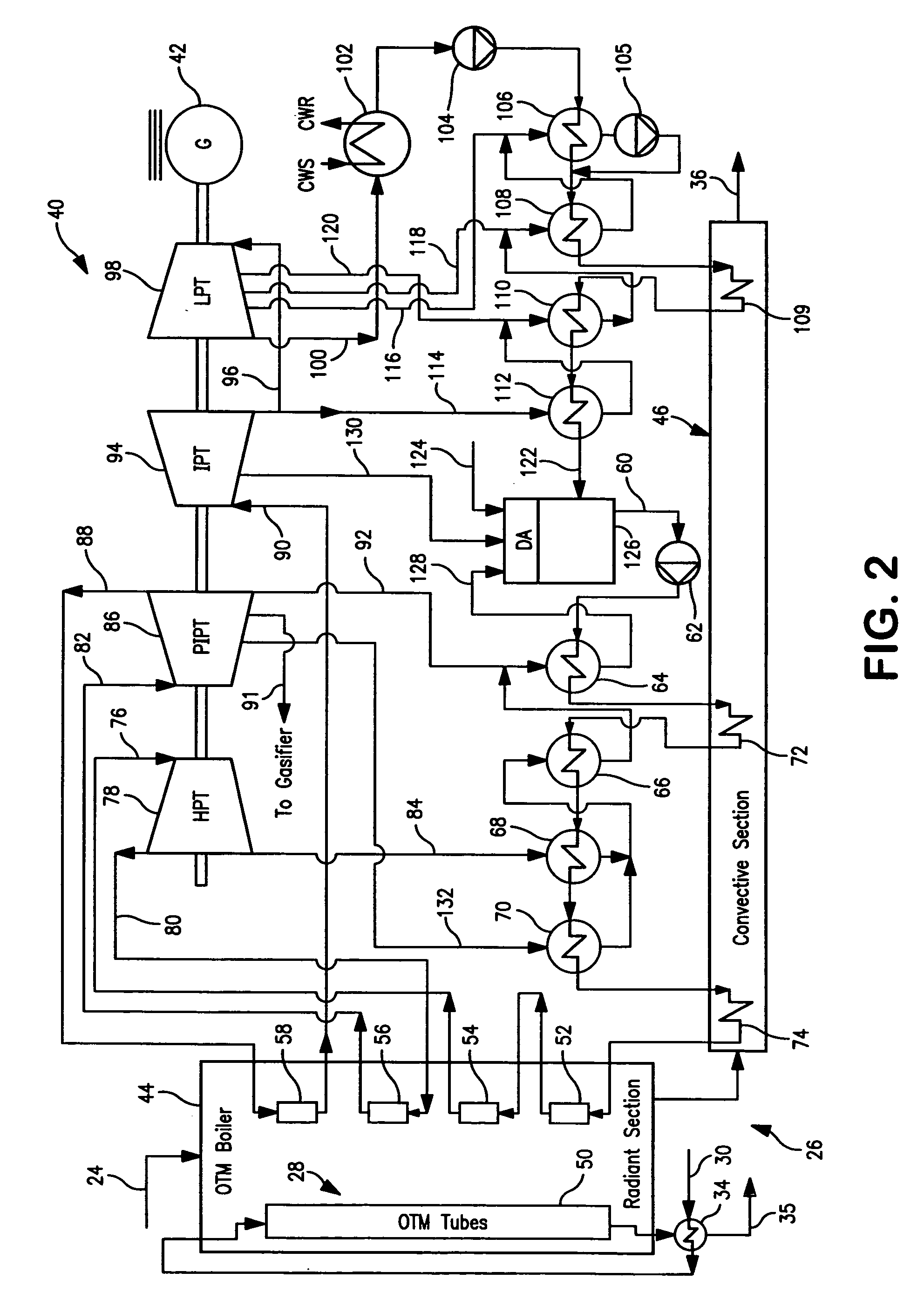
A method of generating electrical power in which a synthesis gas stream generated in a gasifier is combusted in an oxygen transport membrane system of a boiler. The combustion generates heat to raise steam to in turn generate electricity by a generator coupled to a steam turbine. The resultant flue gas can be purified to produce a carbon dioxide product.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
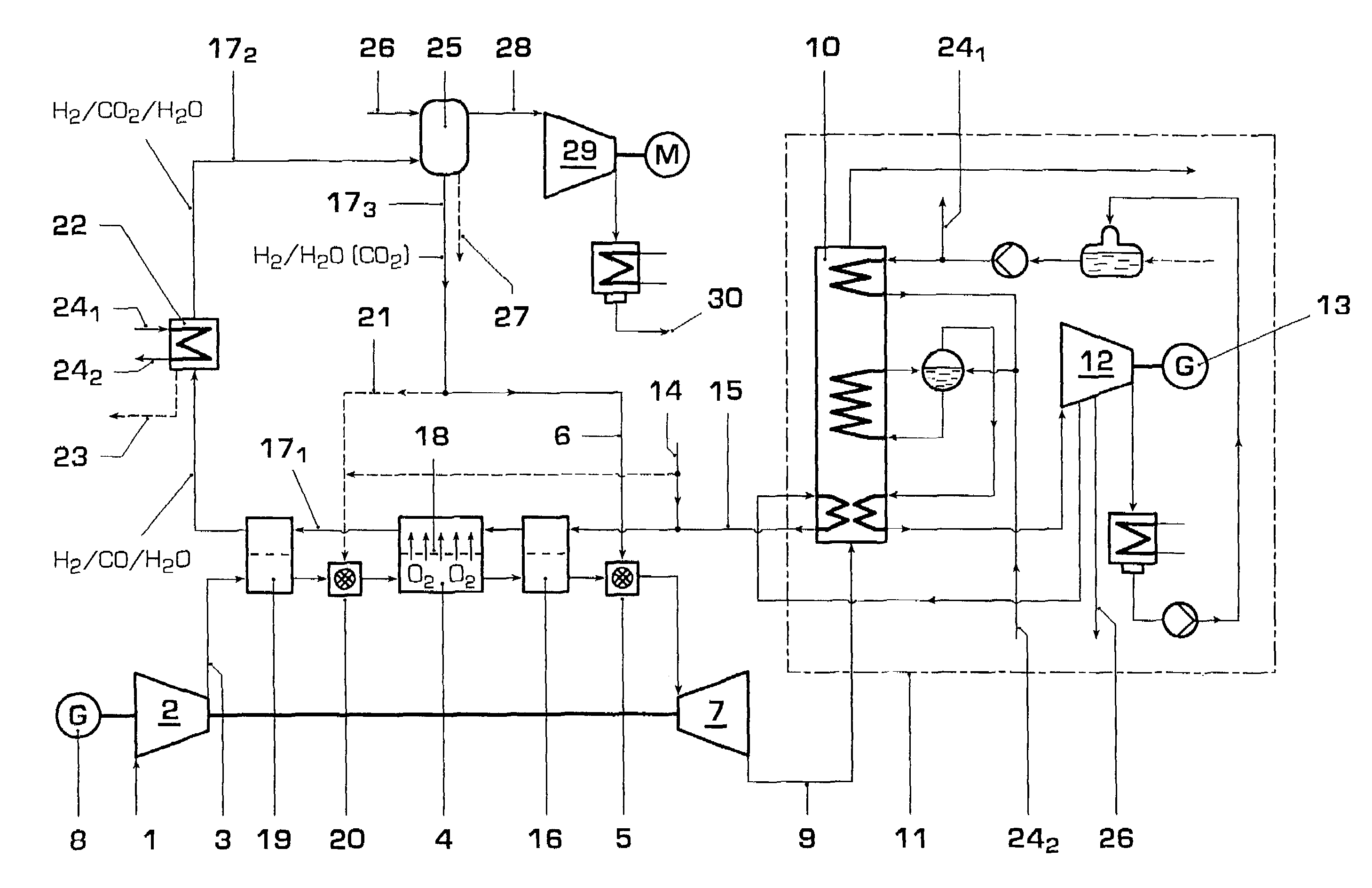
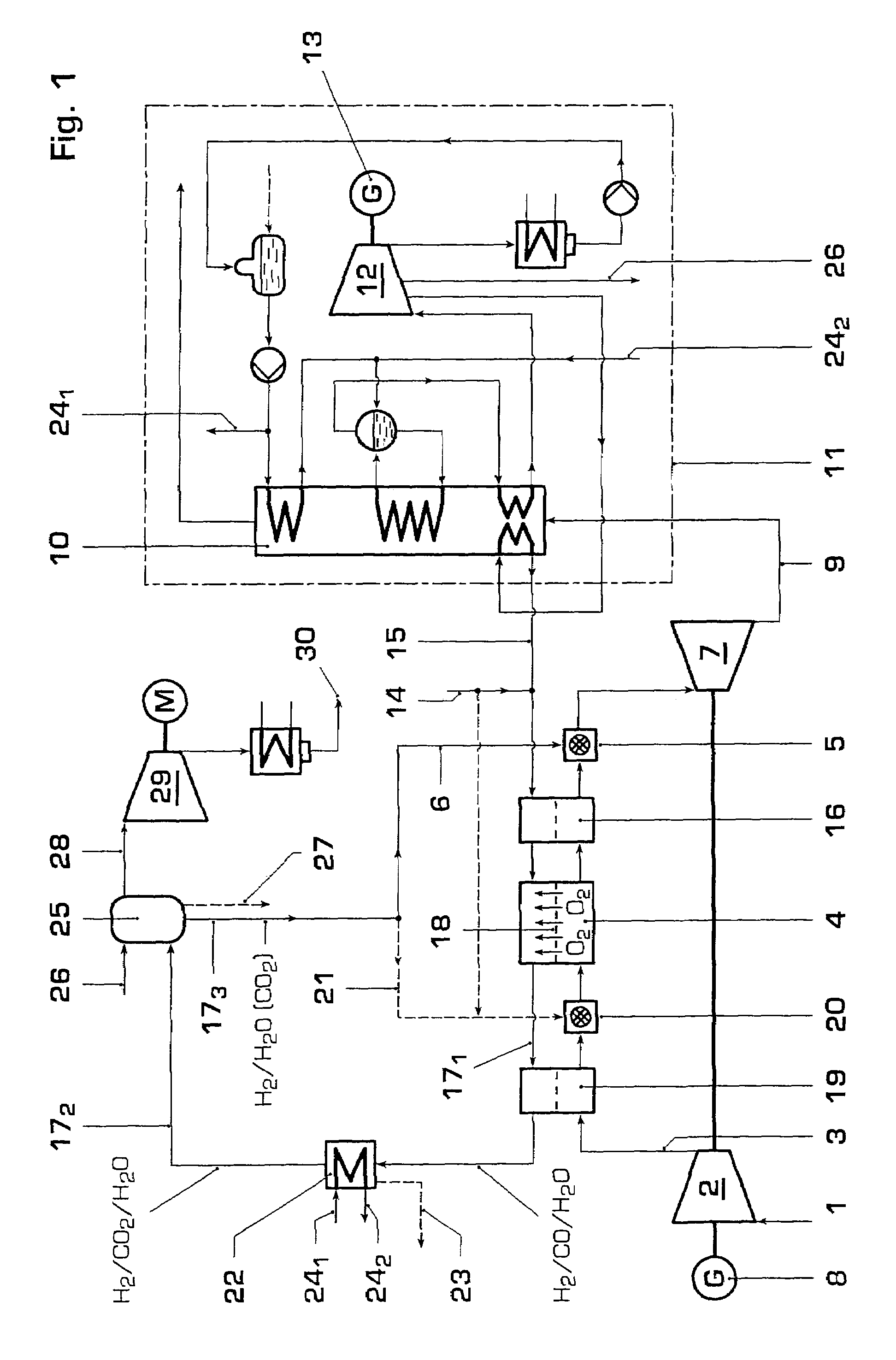
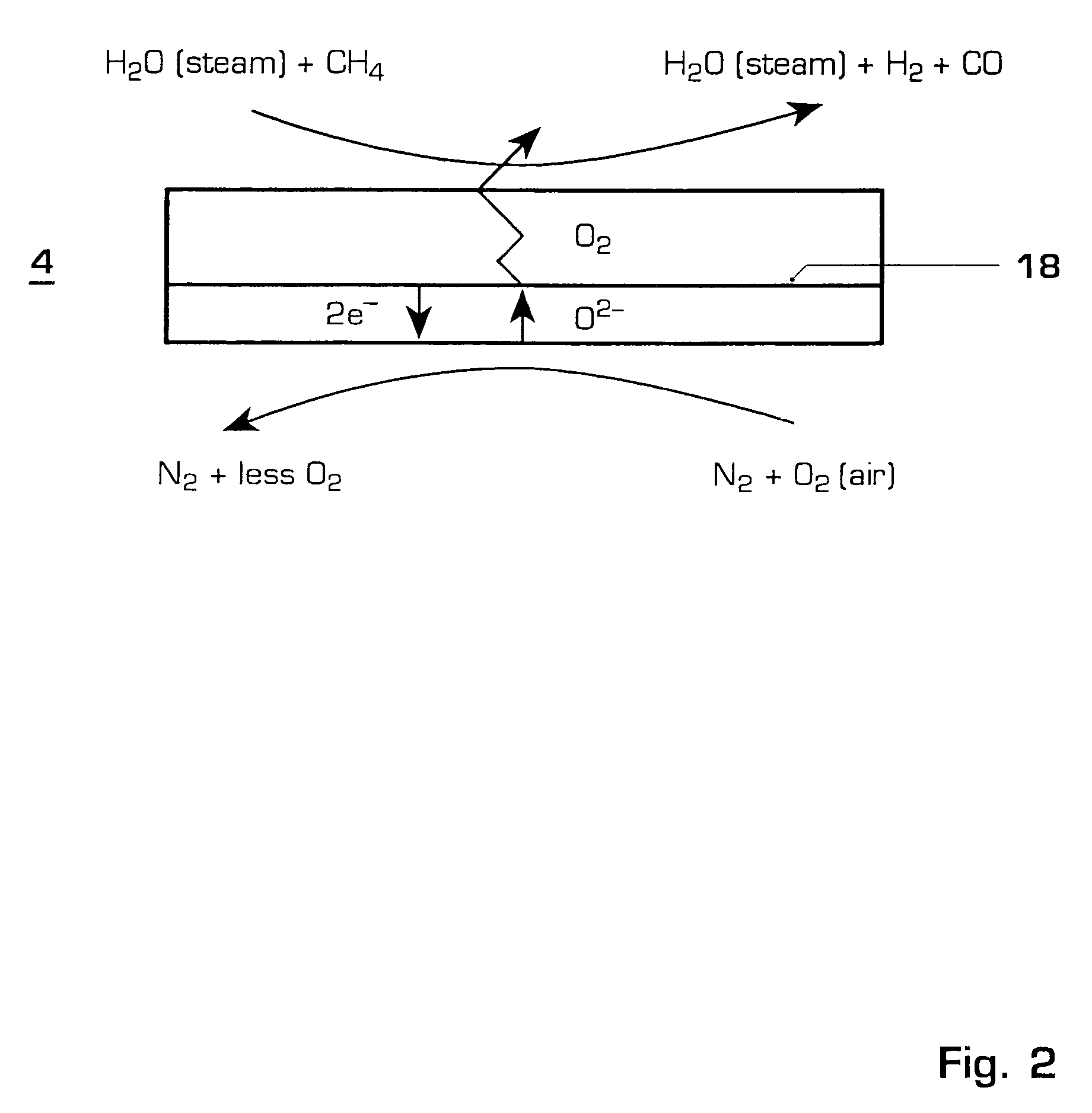
Gas turbine power plant and method of operating the same
InactiveUS7363764B2Improve efficiencyAvoid disadvantagesHydrogenOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideSyngasPartial oxidation
A method of operating a gas turbine power plant and gas turbine power plant are disclosed wherein hydrogen for the combusting process is produced by feeding natural gas mixed with steam through a membrane / partial oxidation reactor and converting the natural gas at least to H2 and CO. Thereby oxygen is transferred from the compressed air through the membrane of the membrane / partial oxidation reactor and the oxygen is used for the partial oxidation process of the natural gas. The process is followed by converting the syngas in a CO shift reactor and a CO shift reactor to a CO2 removal equipment to mainly hydrogen.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Fuel composition supply means for spark ignition engines
ActiveUS7107942B2More of efficiencyMore of emissionsNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesMotor fuelDriving cycle
A fuel system for on-board vehicle fuel separation to supply engine fuel compositions formulated as a function of driving cycle conditions. The invention results in improvements in one or more of feed efficiency and combustion emissions.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
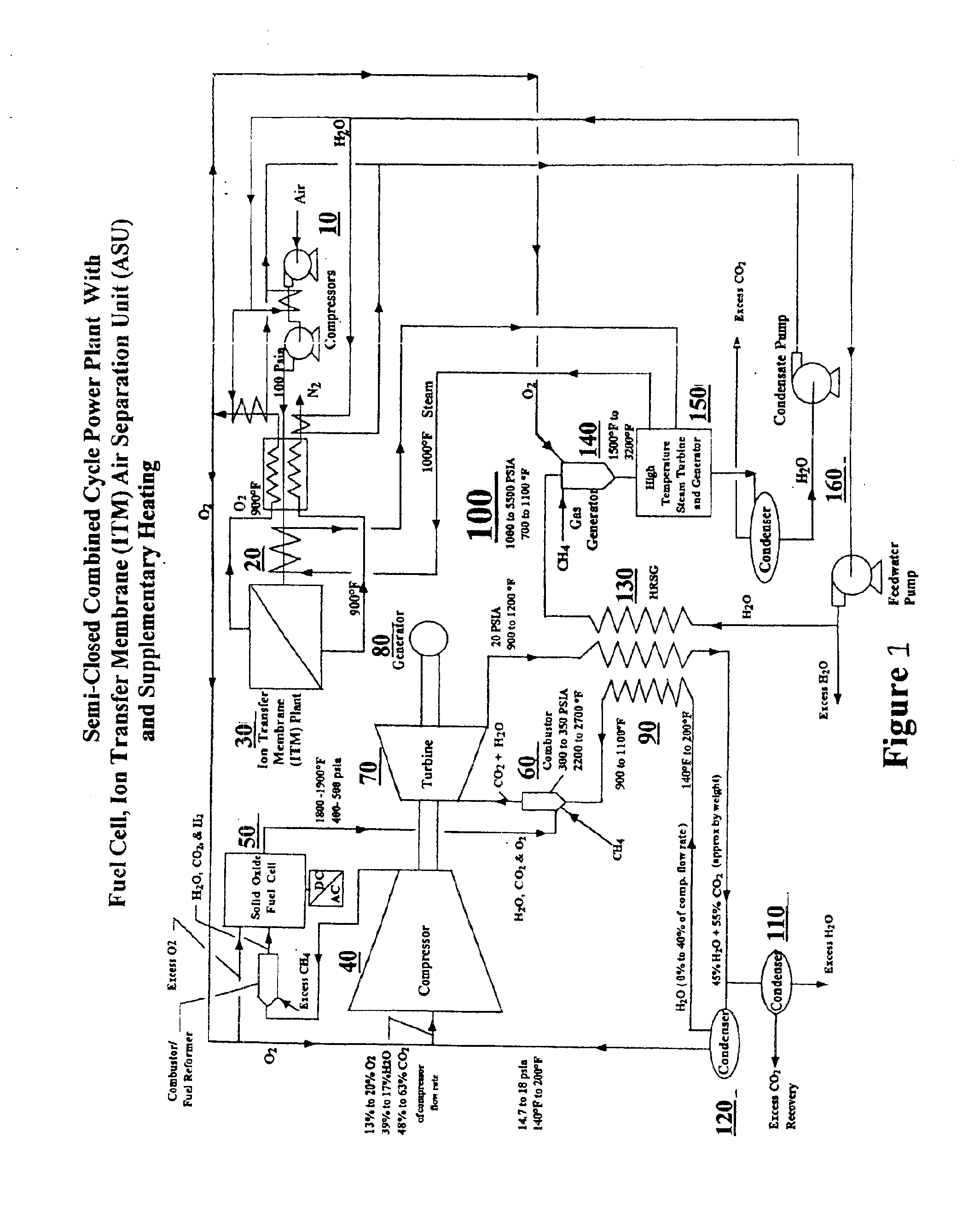
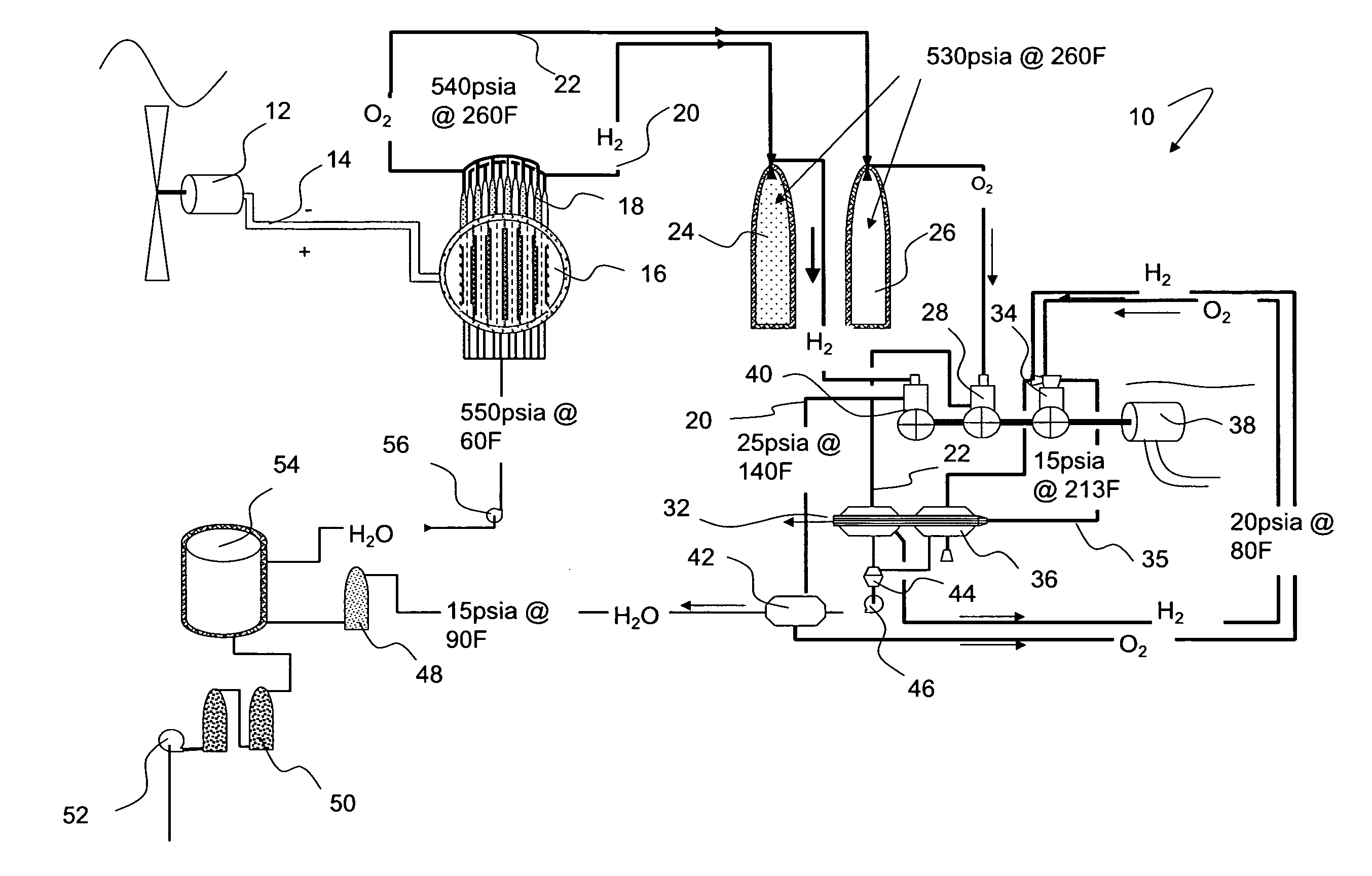
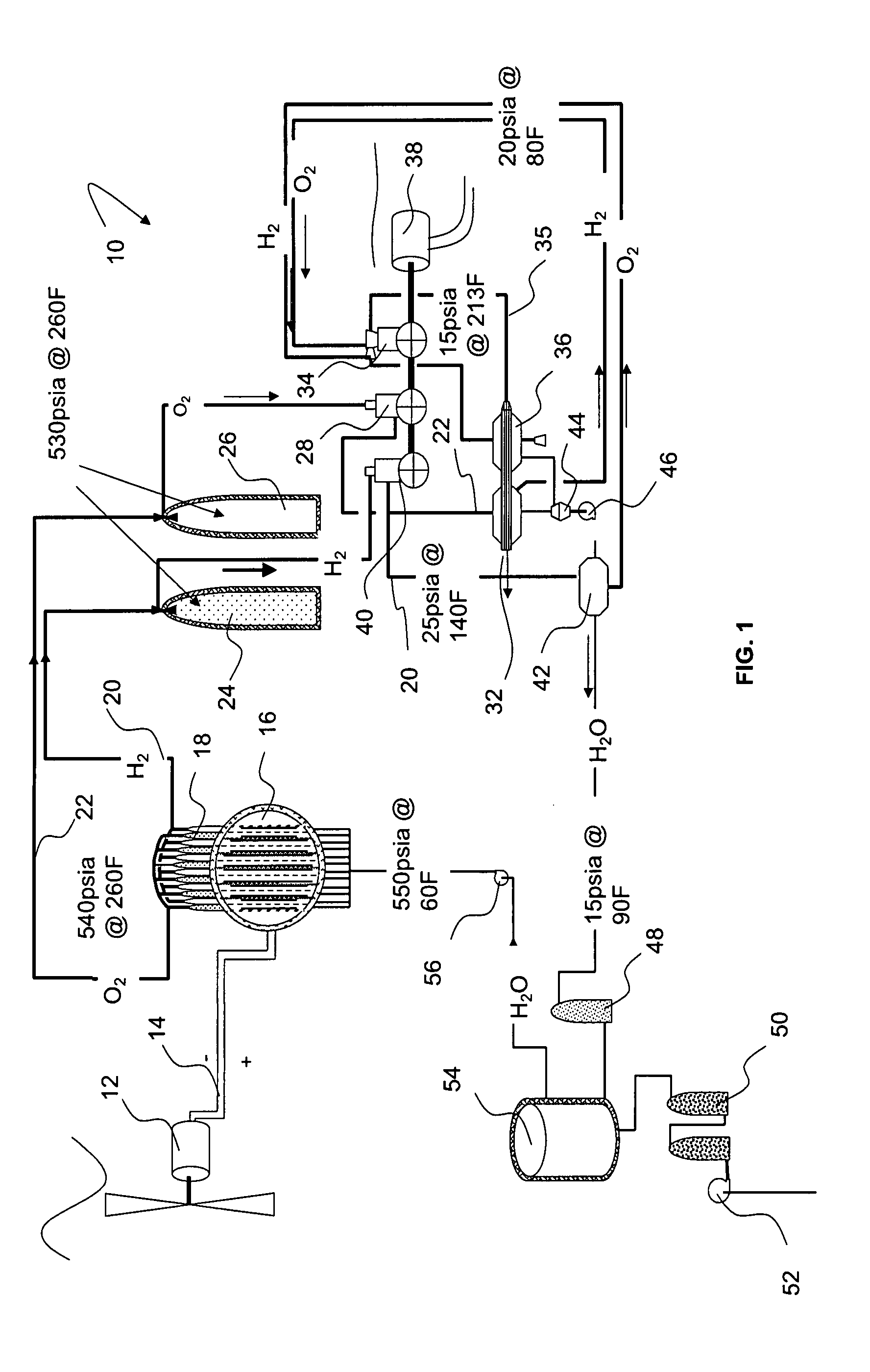
Hybrid Cycle Electrolysis Power System with Hydrogen & Oxygen Energy Storage
InactiveUS20080047502A1Increase fuel consumptionReduce operating costsPhotography auxillary processesInternal combustion piston enginesElectrolysisElectric power system
A method for generating power comprising the steps of feeding water into an electrolyzer, providing electricity to operate the electrolyzer to split at least some of the water into hydrogen and oxygen, and decompressing one or both of the hydrogen and oxygen to generate power. Water can be pressurized prior to being fed into the electrolyzer. The hydrogen and oxygen, which can be stored in insulated storage vessels, can be decompressed isentropically to yield energy, which can be used to power a generator. Heat can be extracted from the hydrogen and oxygen, such as through heat exchangers. Hydrogen and oxygen can combine in an internal combustion process to produce work and heat, which can be recycled into the thermodynamic process.
Owner:RUSSO MICHAEL
Onboard fuel separation apparatus for an automobile
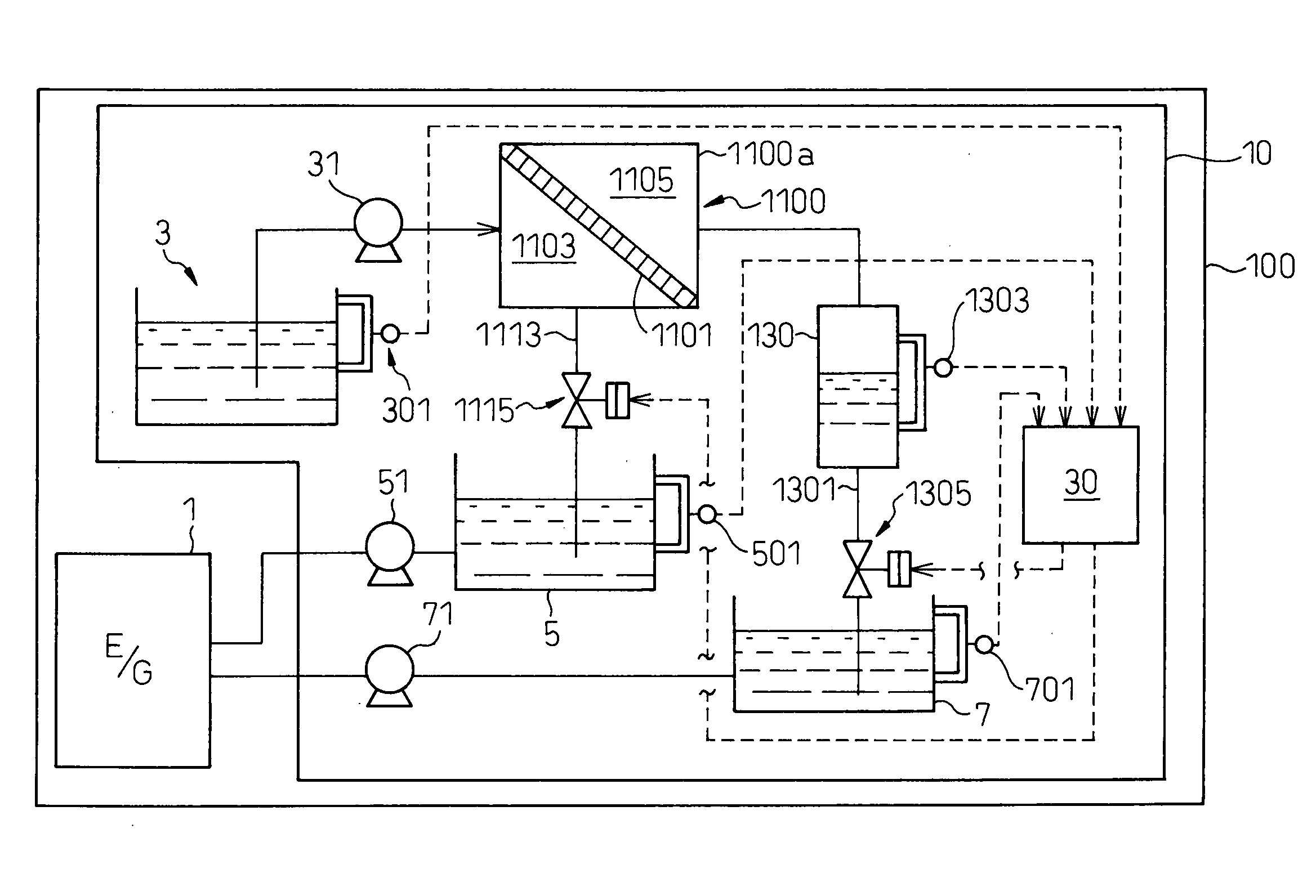
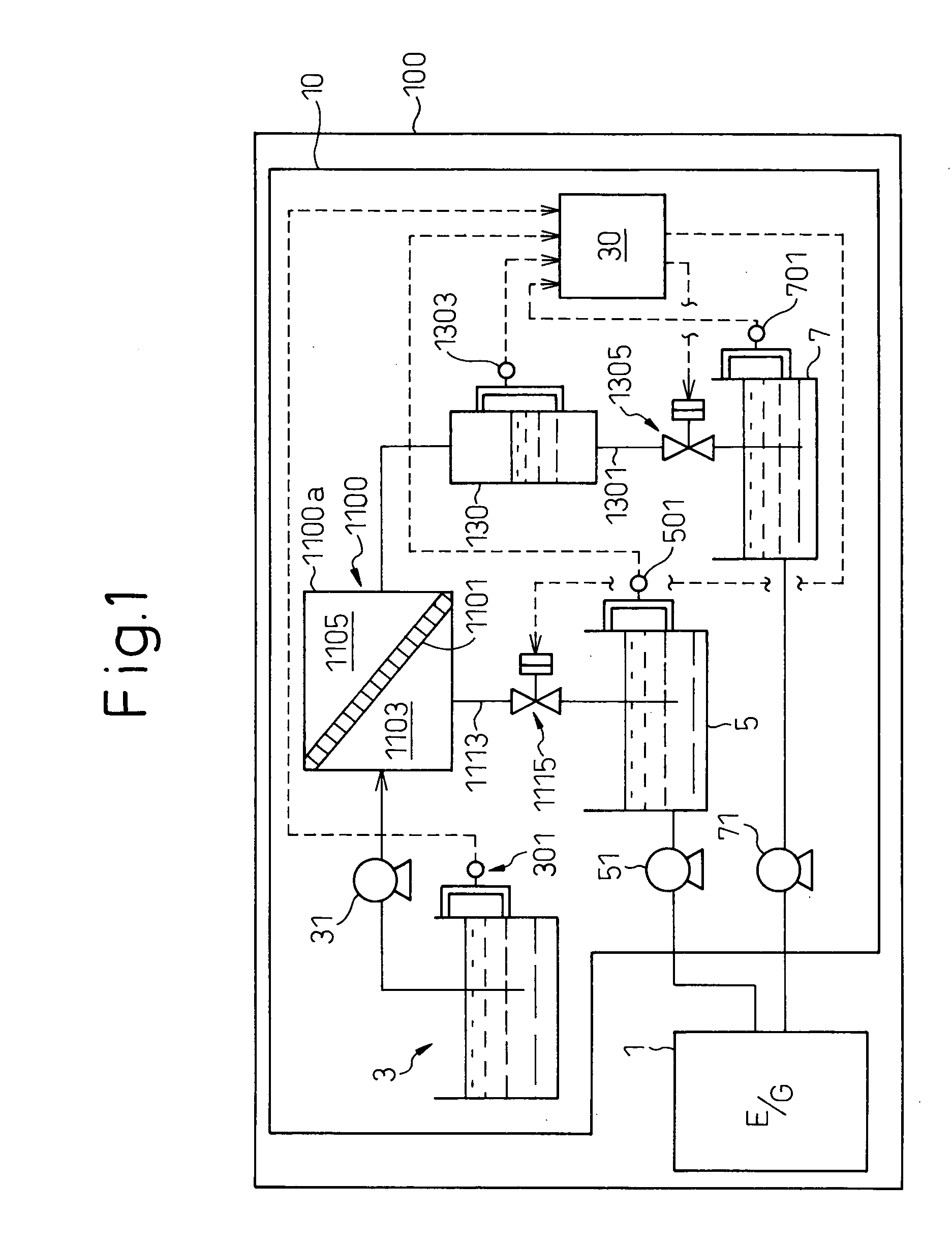
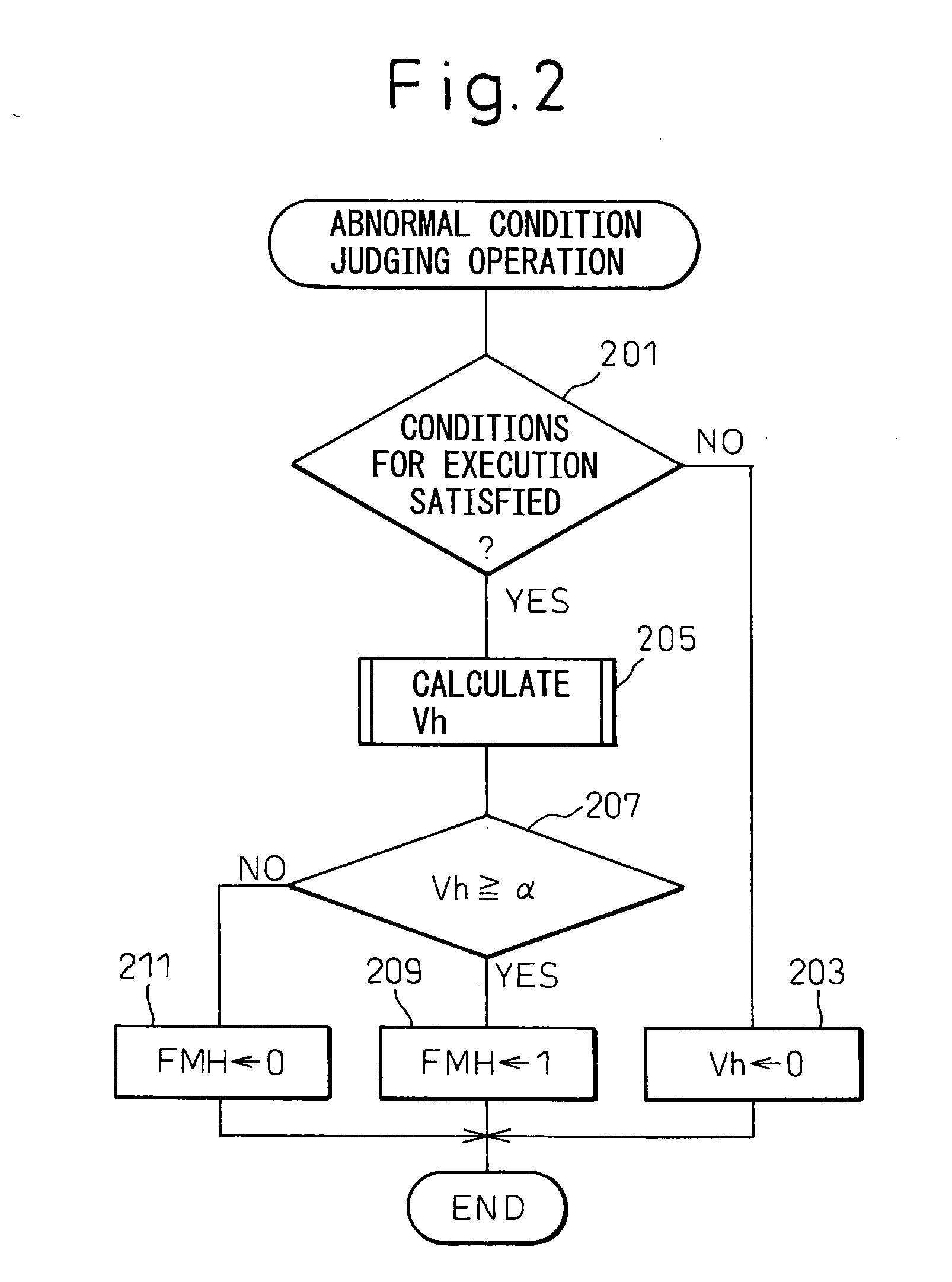
A fuel separation apparatus includes a fuel tank storing the material fuel fed to a separation membrane, a fuel tank storing a separated low-octane fuel, and a fuel tank storing a separated high-octane fuel. An electronic control unit of the separation apparatus calculates the flow rate (amount of formation) of the high-octane fuel flowing into the high-octane fuel tank based on a change in the liquid level in the tank and on the amount of fuel fed to an engine from the tank, and so judges that an abnormal condition is occurring due to the breakage of the separation membrane when the amount of forming the high-octane fuel is larger than a predetermined upper limit value and that an abnormal condition is occurring due to a drop in the function of the separation membrane when the amount of formation is smaller than a predetermined lower limit value.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method of treating a gaseous mixture comprising hydrogen and carbon dioxide
Hydrogen (H2) gas and crude carbon dioxide (CO2) gas are separated from a gaseous mixture thereof. Combustible gas(es) in the crude CO2 gas are combusted to produce heat, at least a portion of which is recovered by indirect heat exchange with at least a portion of the separated H2 gas or a gas derived therefrom. The invention may be integrated with coal-fired power stations to reduce or eliminate emission of harmful components into the atmosphere.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Power plant with energy recovery from fuel storage
InactiveUS20020112479A1Fuel cell heat exchangeInternal combustion piston enginesWorking fluidPower station
Power plant systems and processes are described that enable recovery of at least a portion of the fuel storage energy associated with a storage system for supplying fuel to the power plant systems. A first embodiment of an energy-recovery power plant system includes at least one fuel storage container and at least one expander that can receive fuel from the fuel storage container at a first pressure and provide the fuel to the power plant at a second pressure that is lower than the first pressure. A second embodiment of an energy-recovery power plant system includes a first conduit fluidly coupling the fuel storage container and the power plant for delivering fuel from the fuel storage container to the power plant and at least one regenerative thermodynamic cycle engine thermally coupled to the first conduit such that heat may be exchanged between the fuel and a working fluid for the regenerative thermodynamic cycle engine.
Owner:QUSIR TECH
Fuel filter including slow release additive
This invention relates to a fuel filter for use with internal combustion engines. The fuel filter includes a fuel additive that can be released into fuel. The rate of release for the fuel can be controlled. In one form the fuel additive can be mixed with a matrix material and released at a substantially constant rate to maintain a uniform level of fuel additive in the fuel. Use of the present invention provides a fuel filter having an extended life span that is longer than fuel filters typically used with combustion engines.
Owner:DOBER CHEMICAL CORPORATION +1
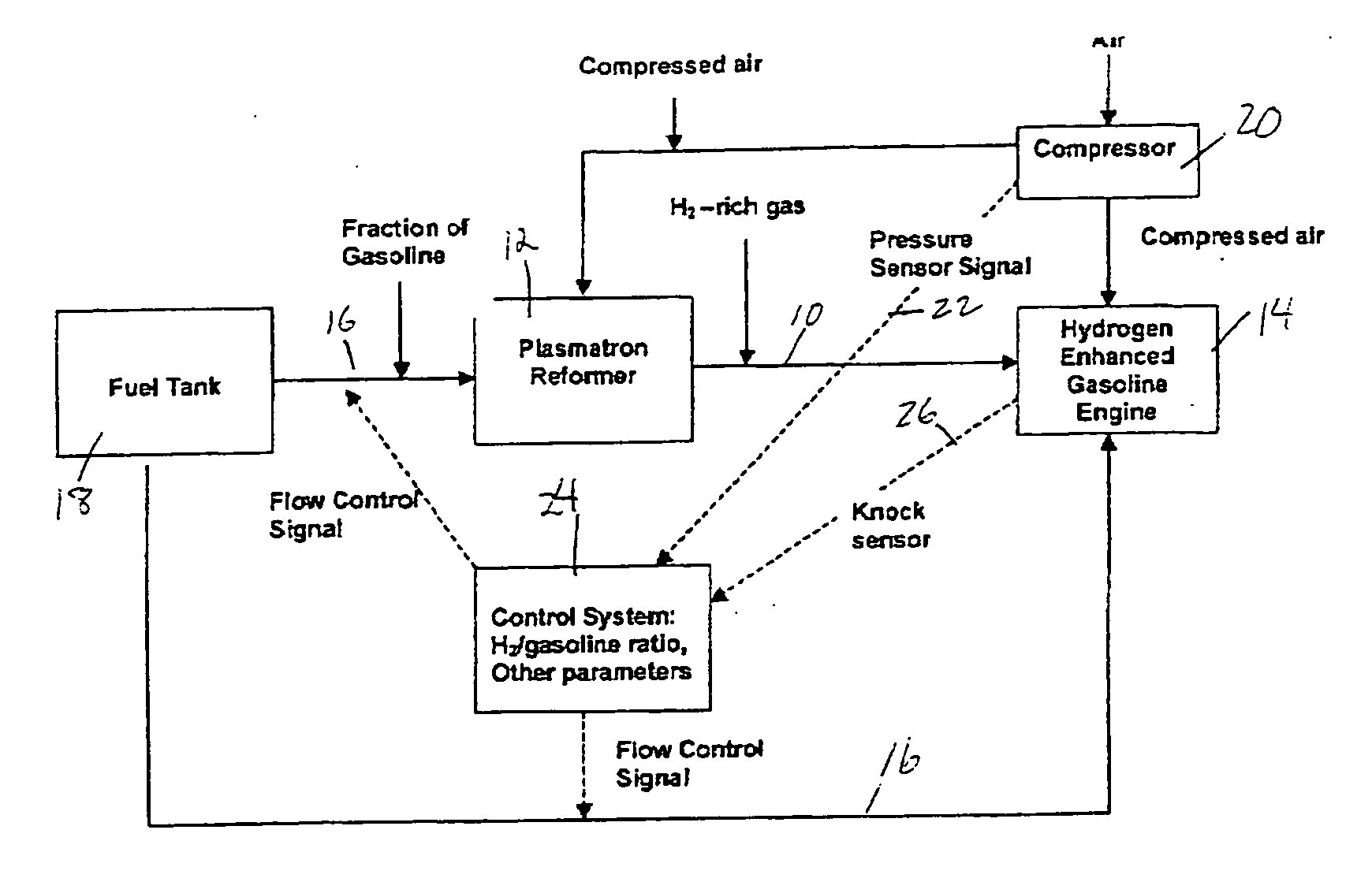
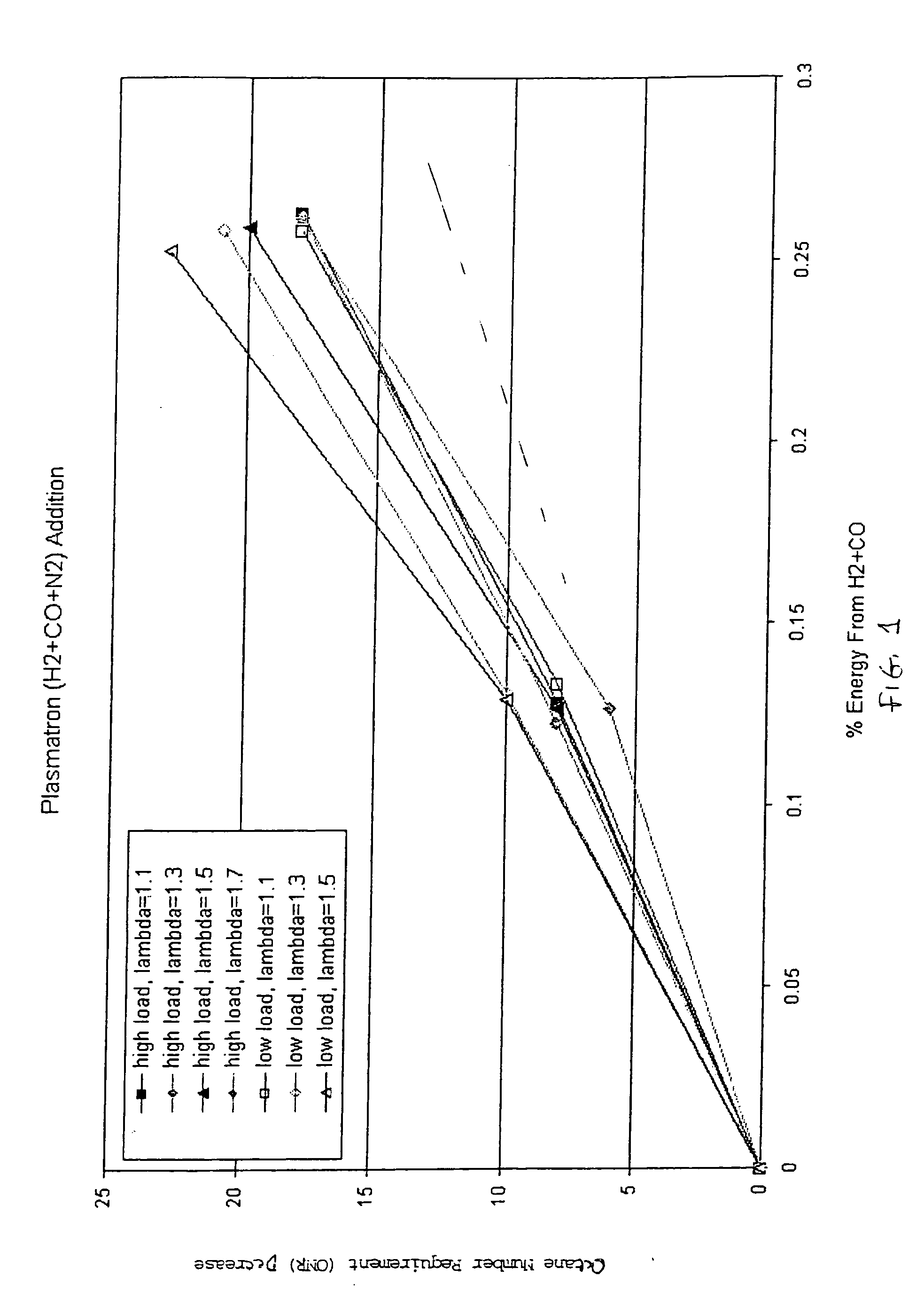
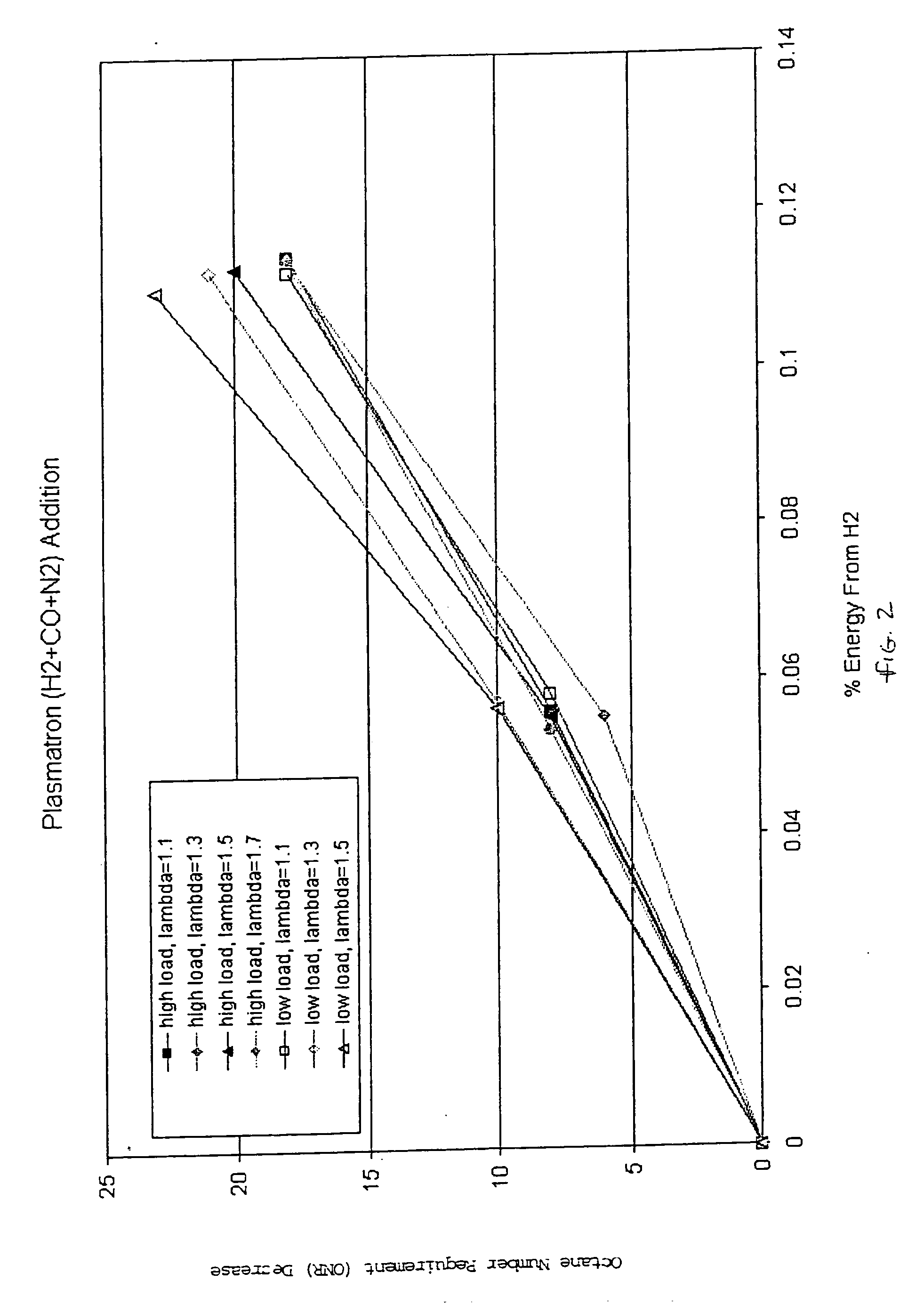
Hydrogen and carbon monoxide enhanced knock resistance in spark ignition gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060075991A1Good anti-knock performanceGreater spark retardElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHydrogenCombustion
A method for reducing required octane number and a spark ignition gasoline engine system with hydrogen-enhanced knock resistance. The method for reducing required octane number of gasoline needed to prevent knock includes the addition of hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas containing carbon monoxide to gasoline. Octane number can be improved by 5 or more for a hydrogen energy fraction of 10%. The spark ignition gasoline engine system includes a spark ignition gasoline engine and a source of gasoline and hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas. Apparatus is provided to supply the gasoline and the hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas to the engine at a varying hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas to gasoline ratio selected both to prevent knock and to ensure a desired level of combustion stability throughout a full range of engine operation. The engine system may be normally aspirated or boosted; the compression ratio may be high such as greater than 11 or below 11, and EGR may be added. The hydrogen or hydrogen-rich gas to gasoline ratio may be controlled as a function of boost pressure, torque, engine speed, or air / fuel mixture ratio.
Owner:HEYWOOD JOHN B +4
Internal combustion engine utilizing hydrogen
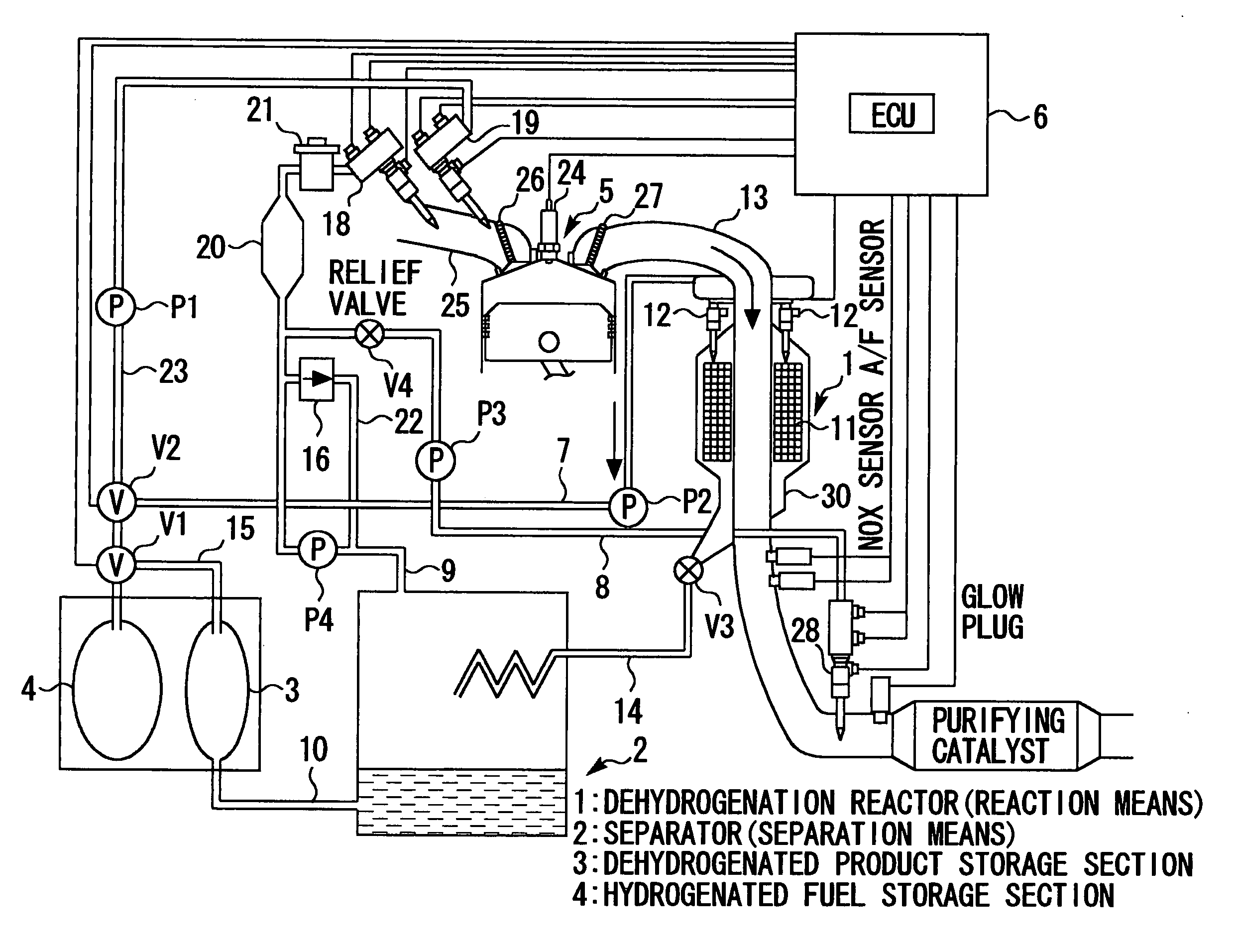
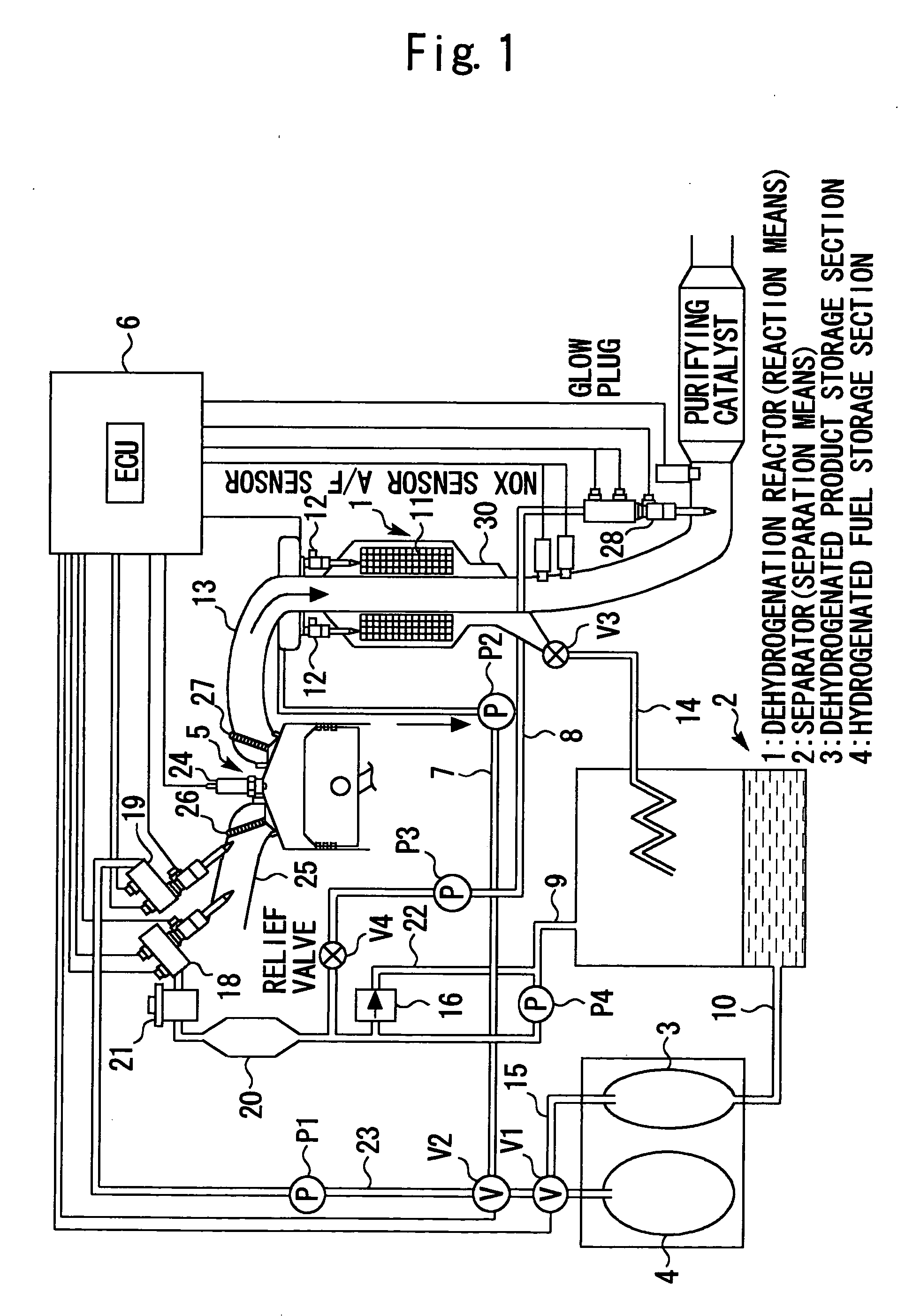
The present invention relates to a system that is capable of freely selecting one or two or more types of fuel and supplying the selected types of fuel to an internal combustion engine. Disclosed is a hydrogen-fueled internal combustion engine that operates upon receipt of one or more types of fuel that are selected from hydrogenated fuel and a dehydrogenated product and hydrogen, which are obtained by dehydrogenating the hydrogenated fuel. The hydrogen-fueled internal combustion engine comprises: a hydrogenated fuel storage section; reaction means for invoking a dehydrogenation reaction; separation means for separating hydrogen-rich gas and dehydrogenated product; and a dehydrogenated product storage section for storing the separated dehydrogenated product.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
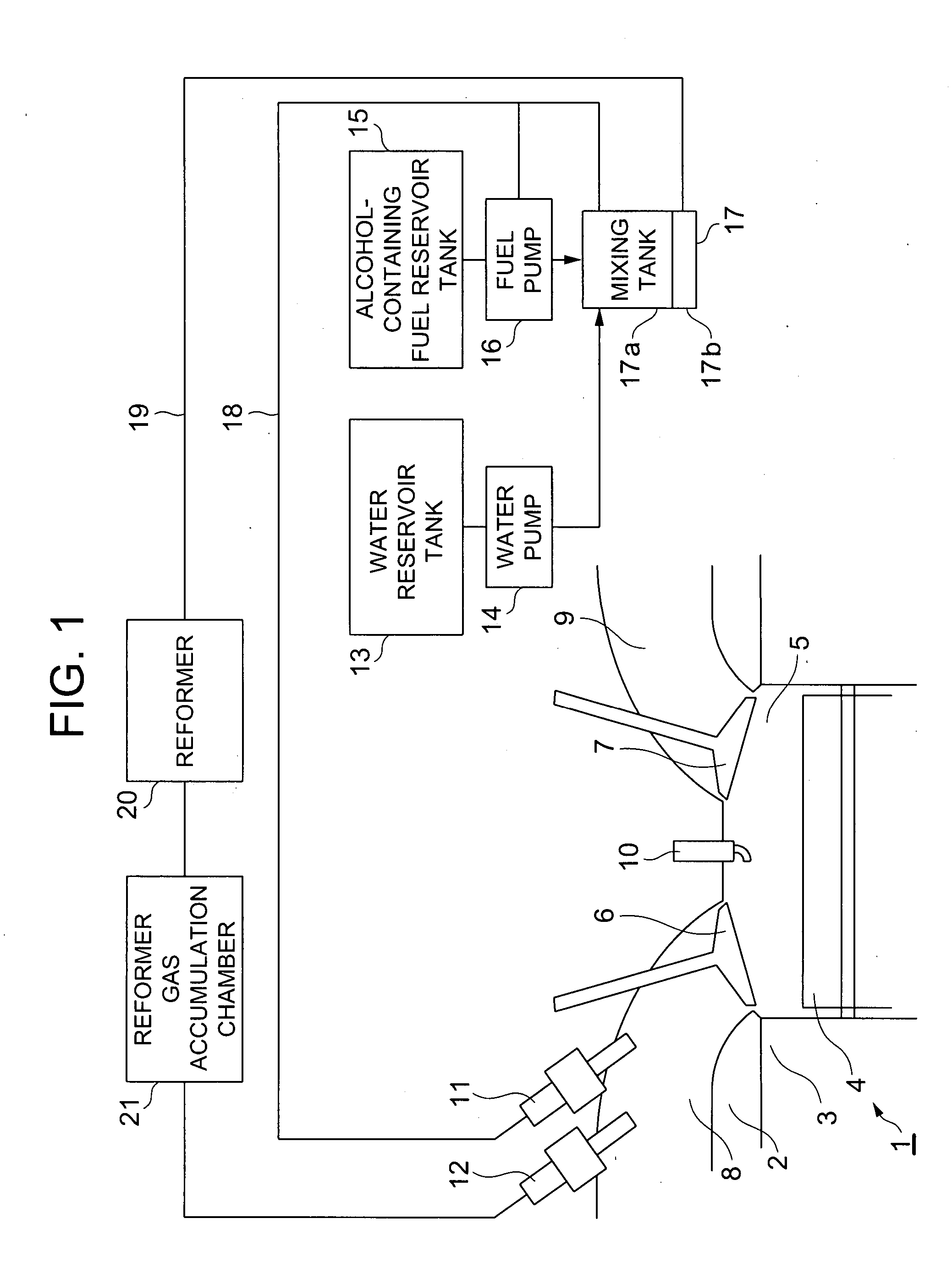
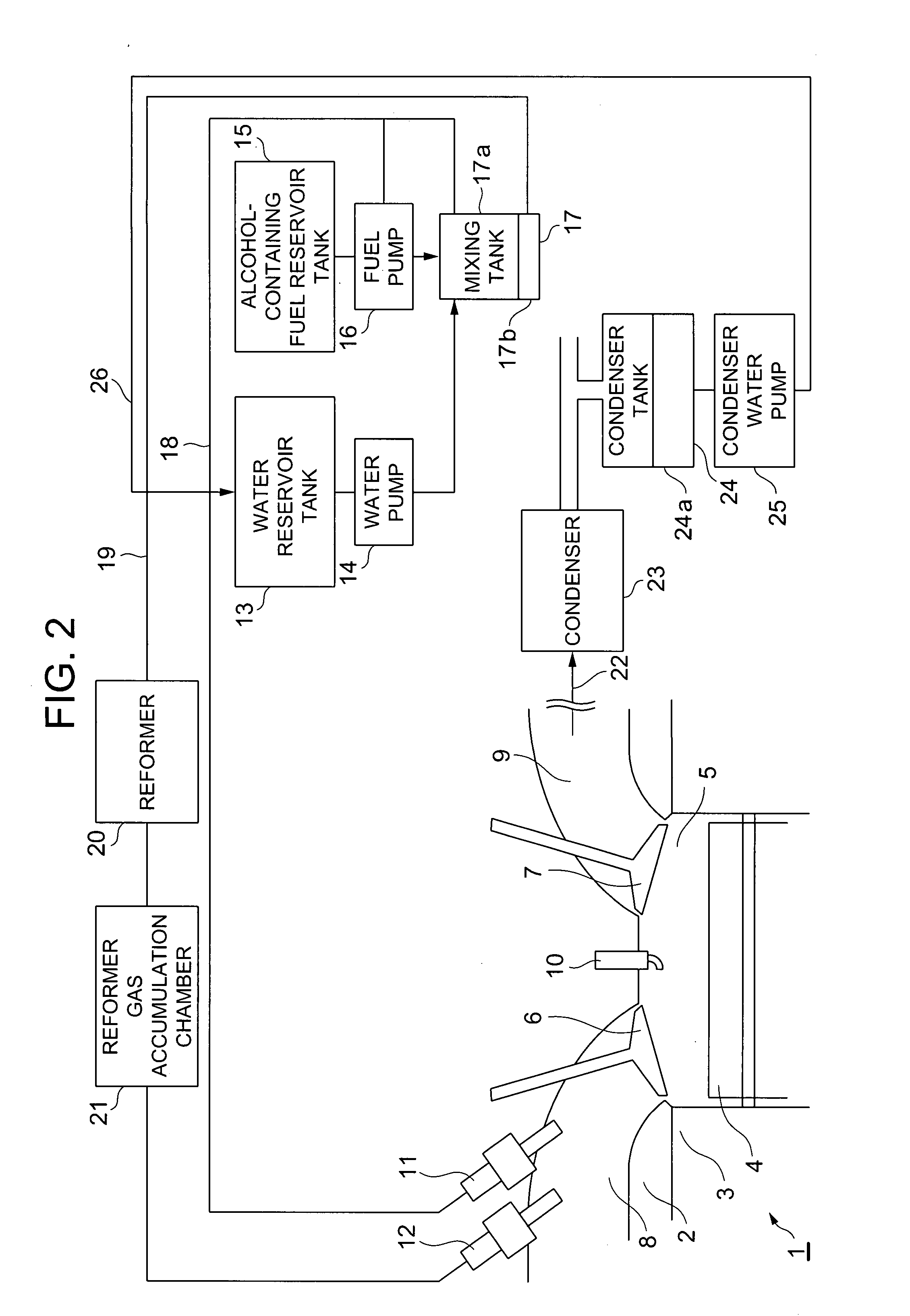
Reforming apparatus, internal combustion engine with reforming apparatus, and fuel cell system with reforming apparatus
InactiveUS20070204813A1Improve fuel consumption rateSimple and compactInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelElectricityFuel cells
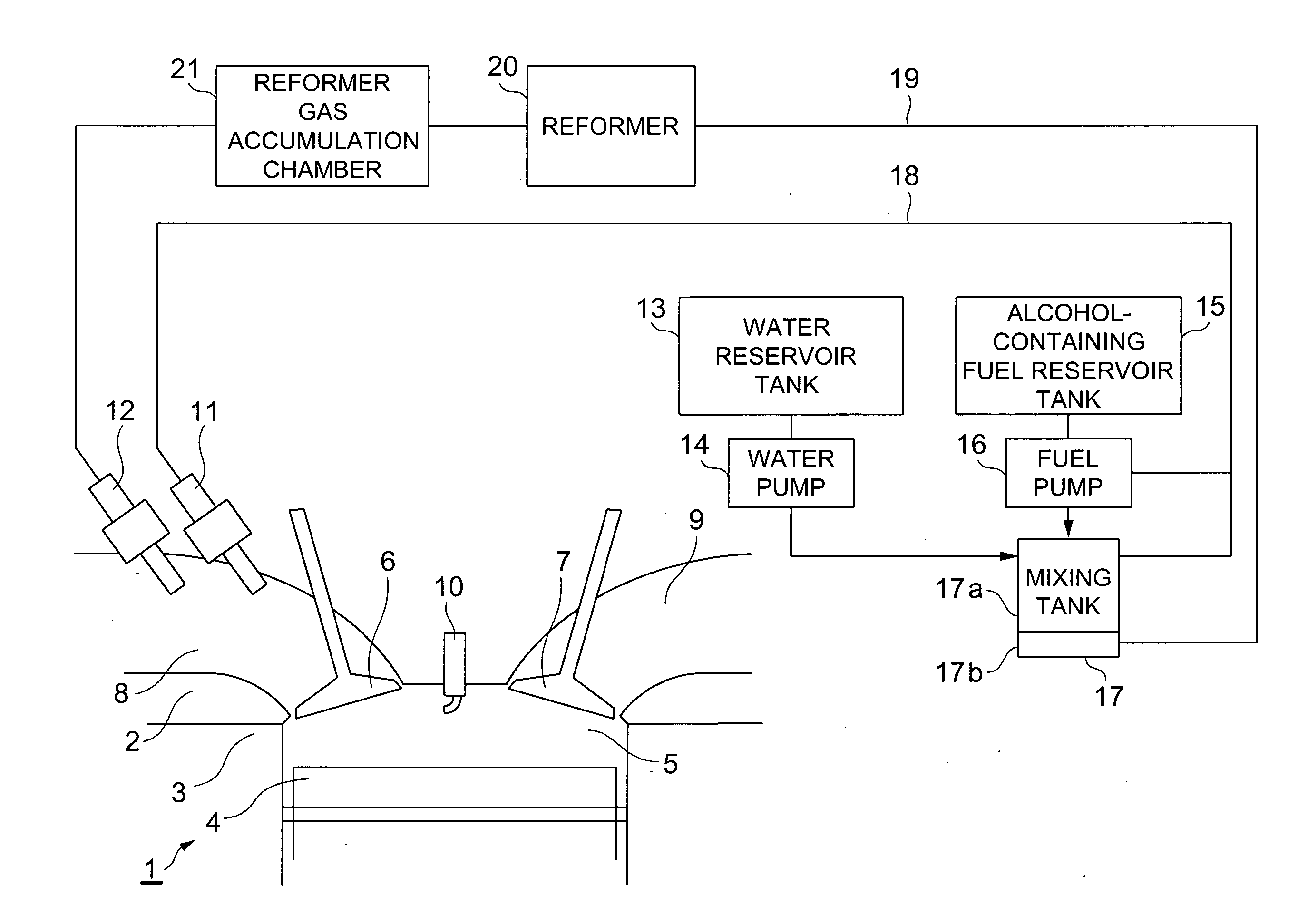
A heat engine system includes a fuel reforming system for supplying a reformed gas to be combusted in an internal combustion engine or used to generate electricity in a fuel cell. An alcohol-containing fuel and water are mixed in a tank and separated into a hydrocarbon based fuel and the fluid mixture of alcohol and water. A reformer uses an endothermic reaction, such as a water vapor reforming process, to obtain the reformed gas from the fluid mixture.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com