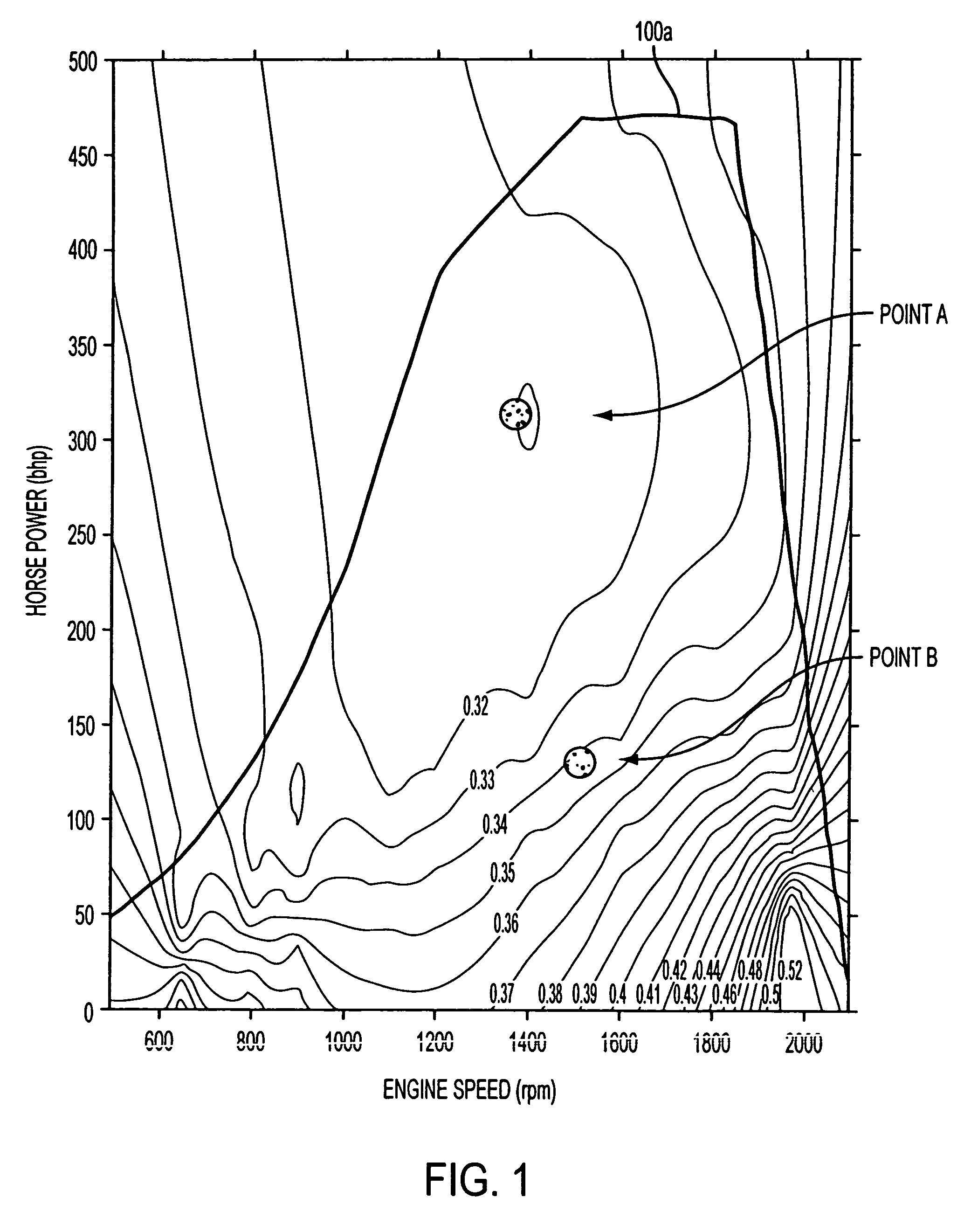
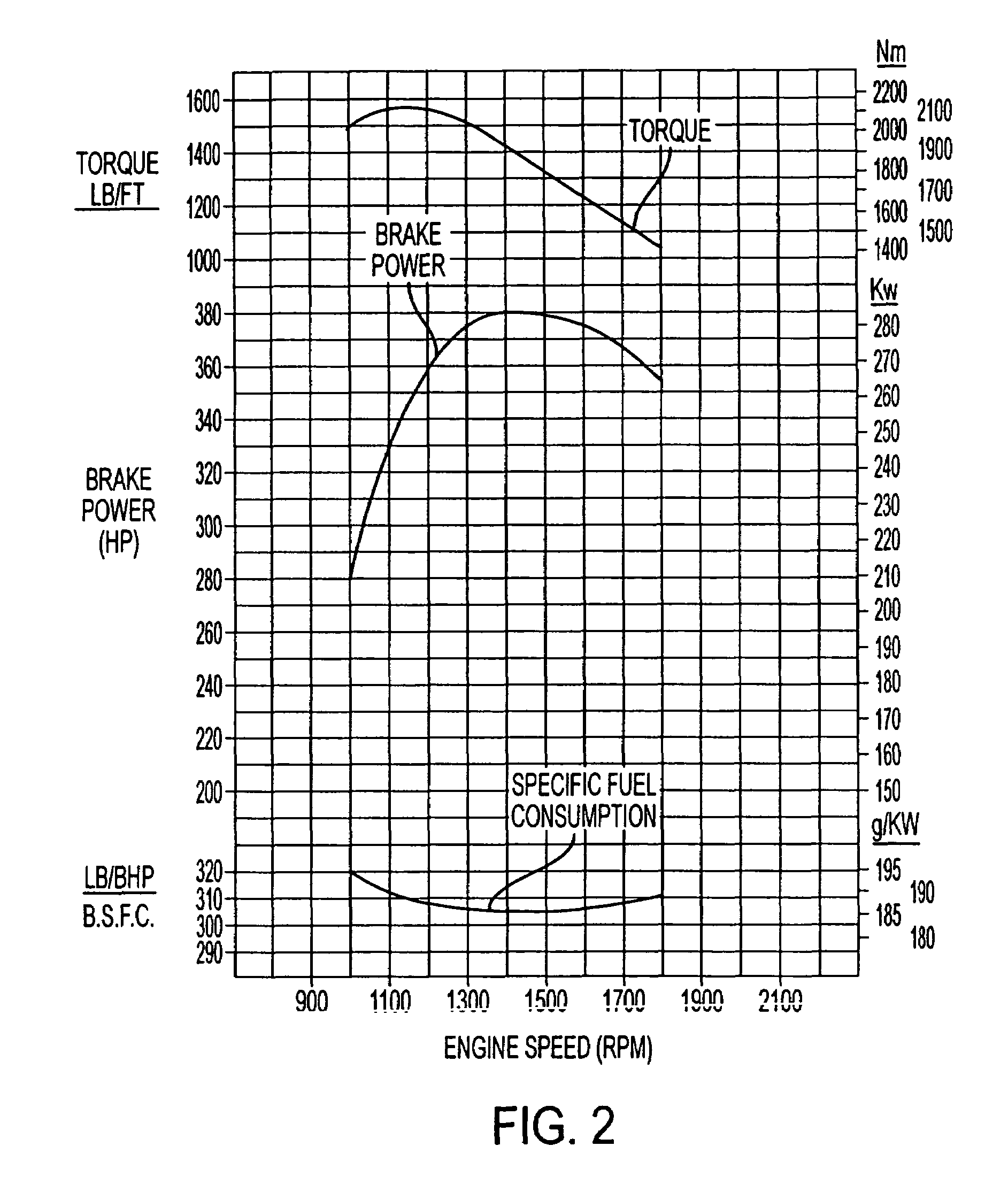
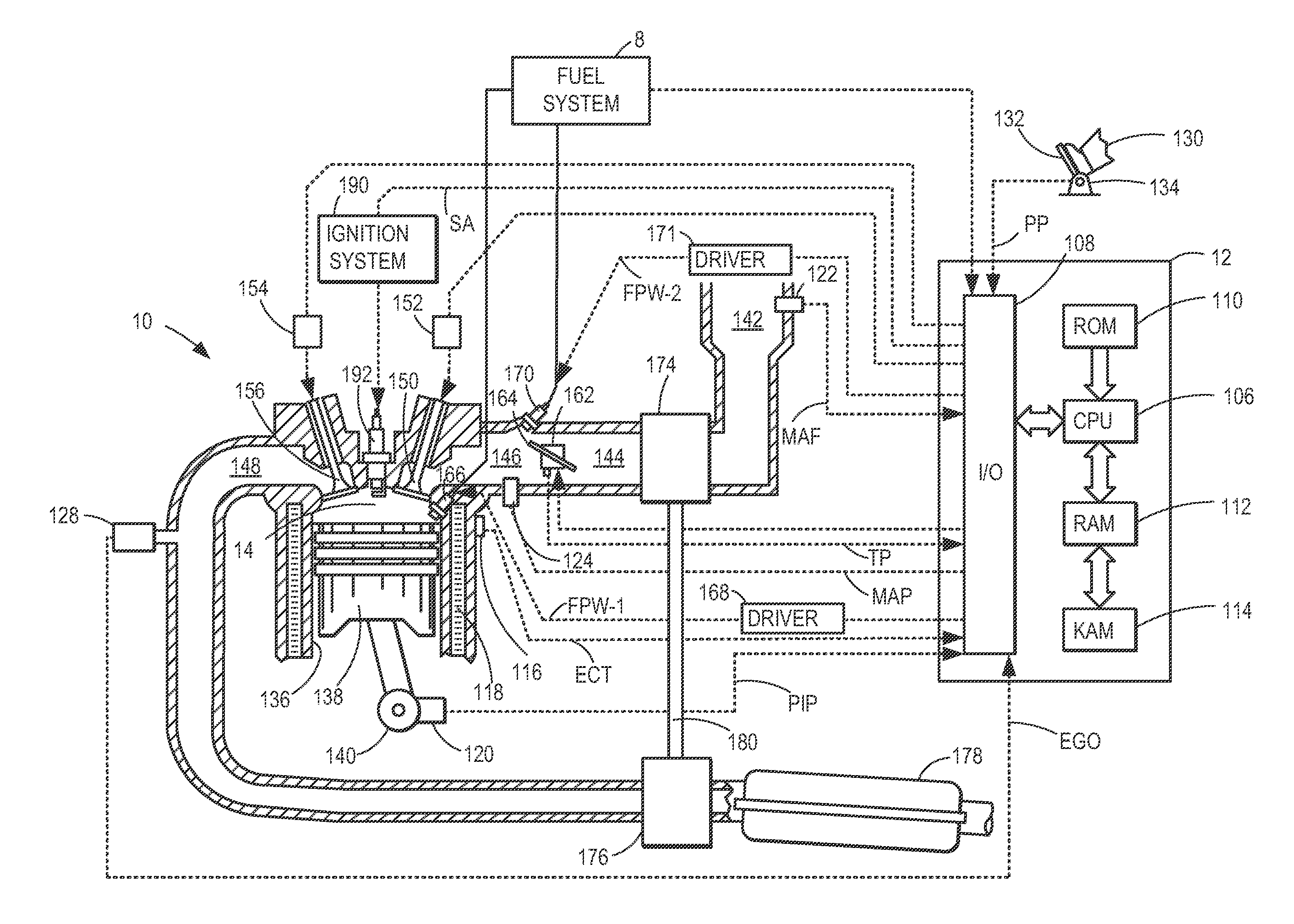
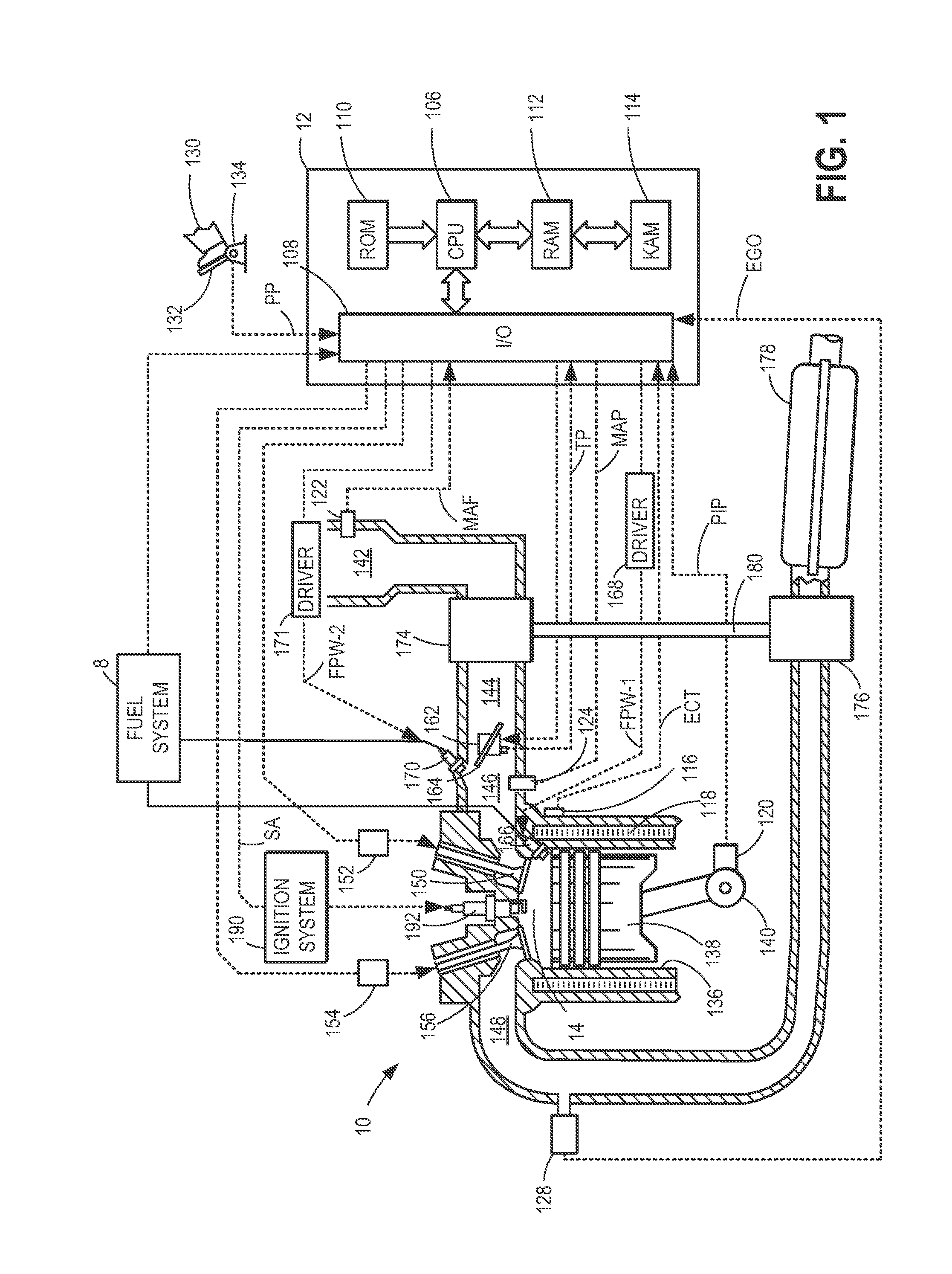
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1004 results about "Motor fuel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A motor fuel is a fuel that is used to provide power to motor vehicles. Currently, the majority of motor vehicles worldwide are powered by gasoline or diesel. Other energy sources include ethanol, biodiesel, propane, compressed natural gas (CNG), electric batteries charged from an external source, and hydrogen. The use of alternative fuels is increasing, especially in Europe.
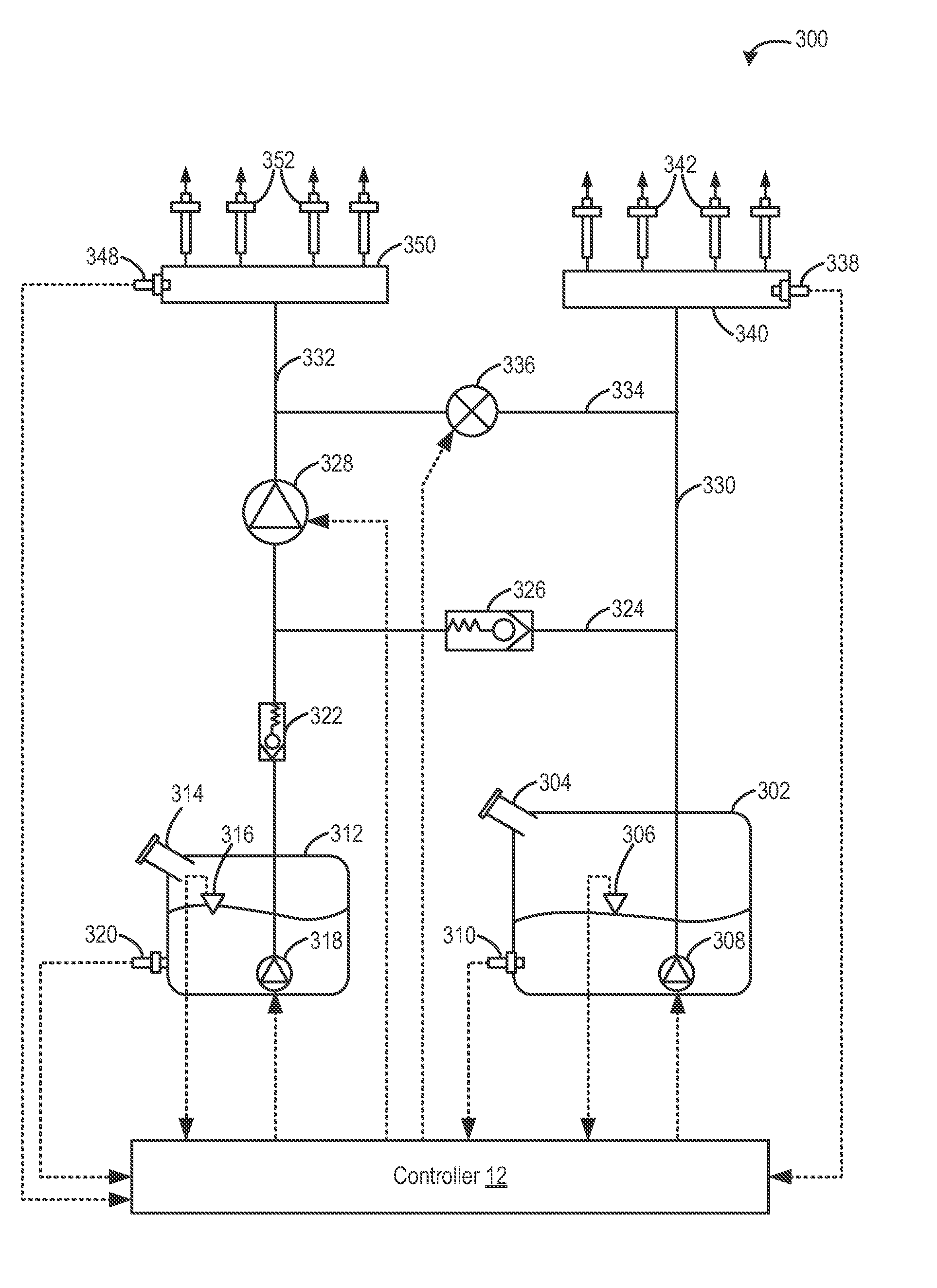
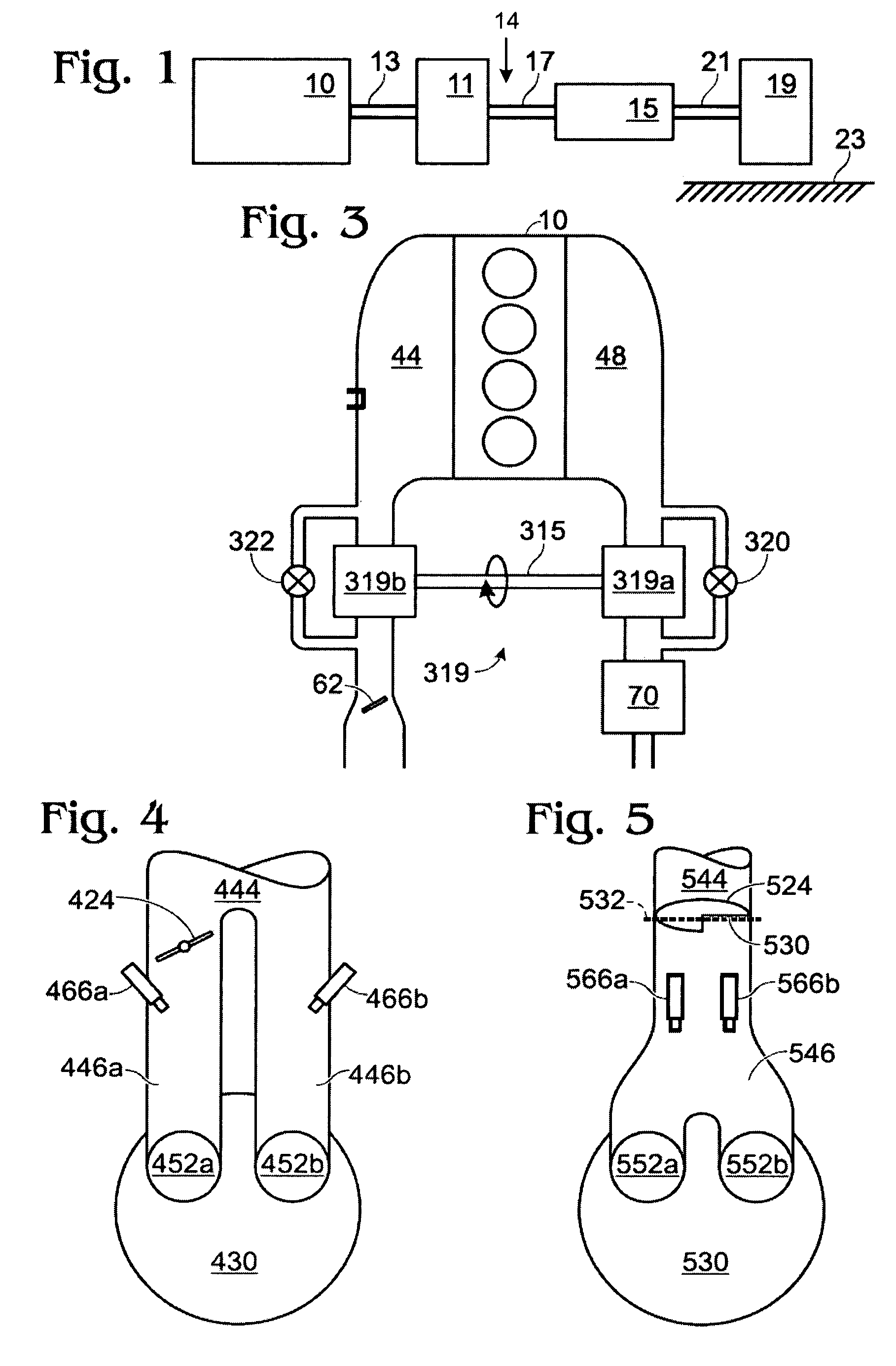
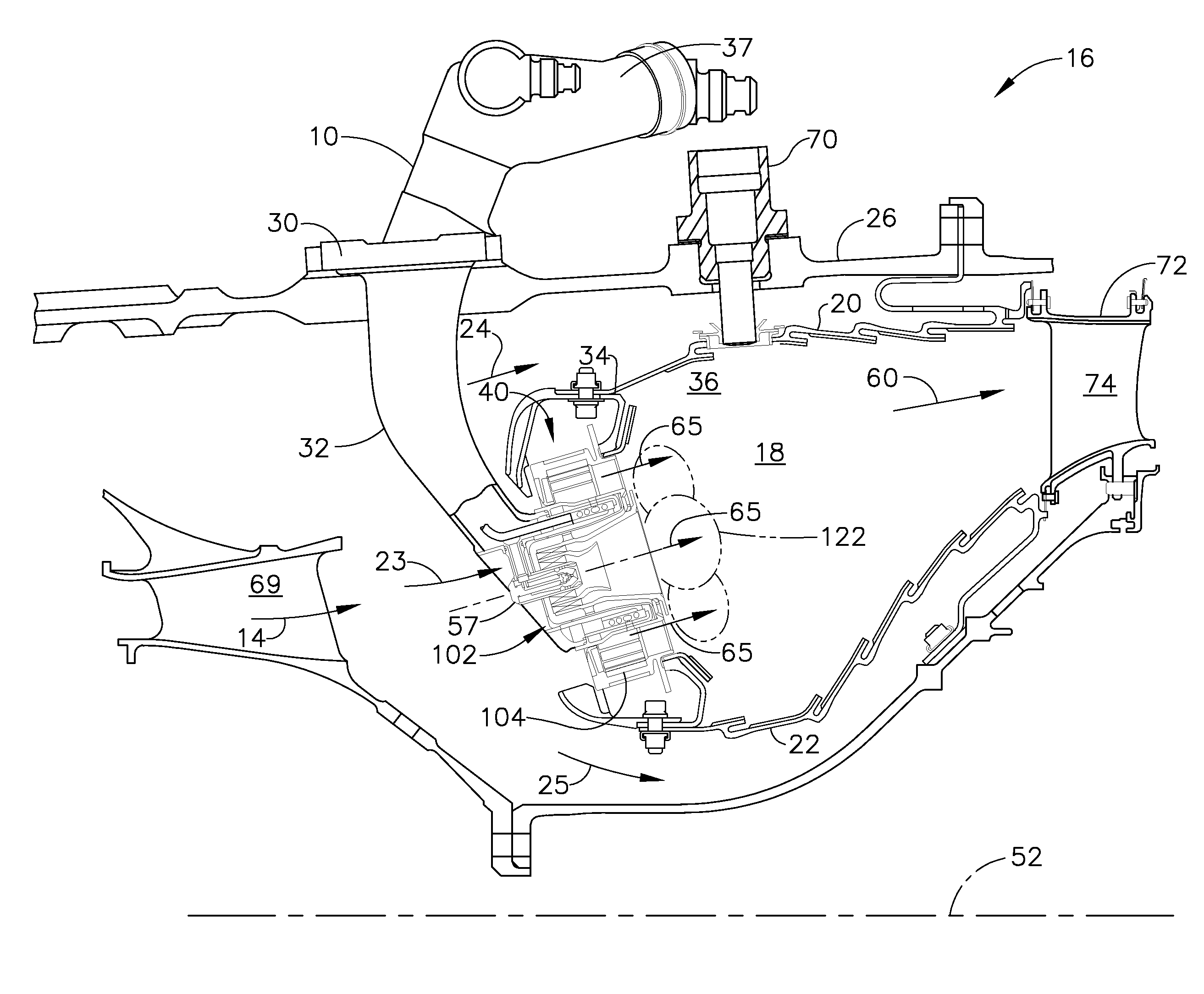
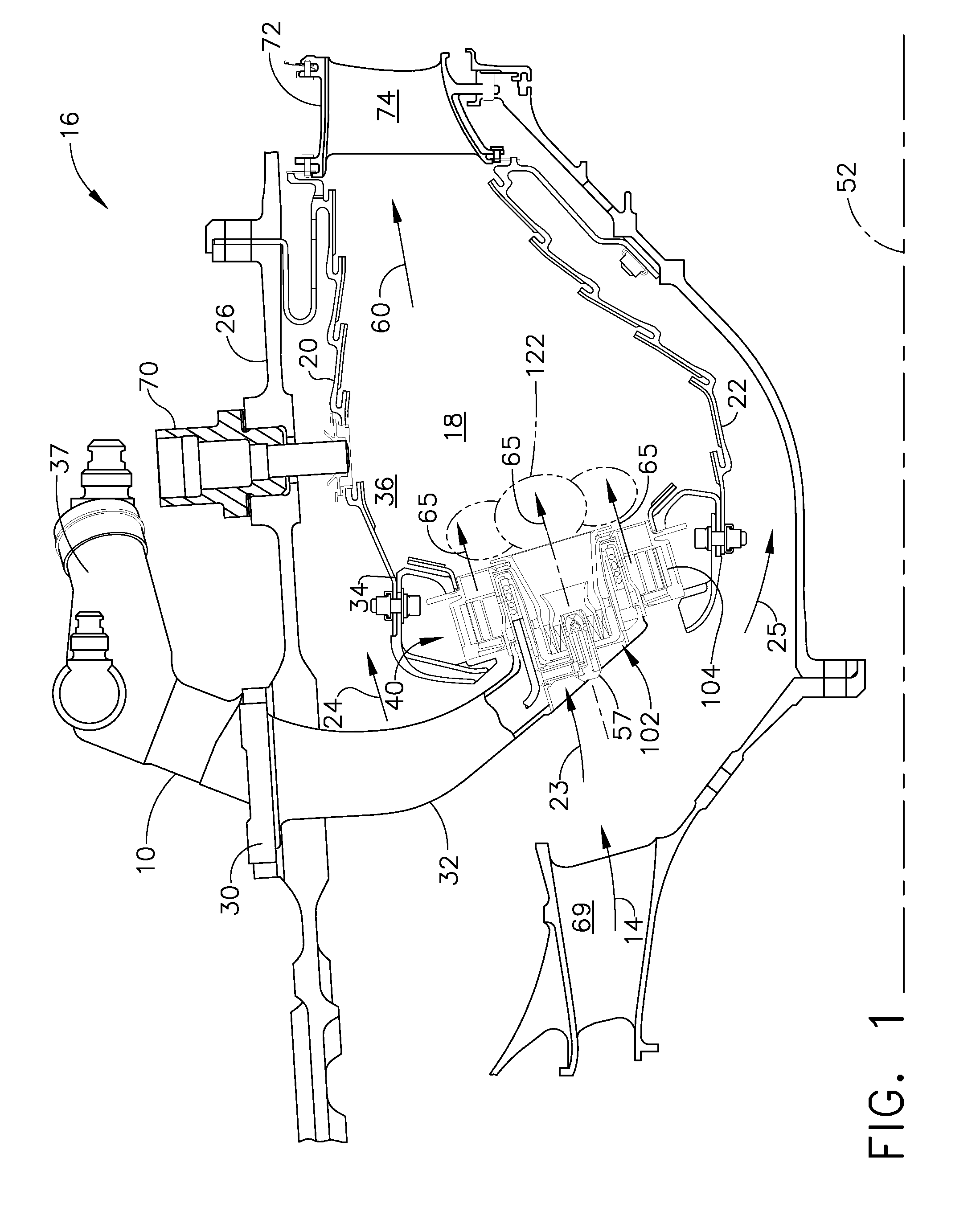
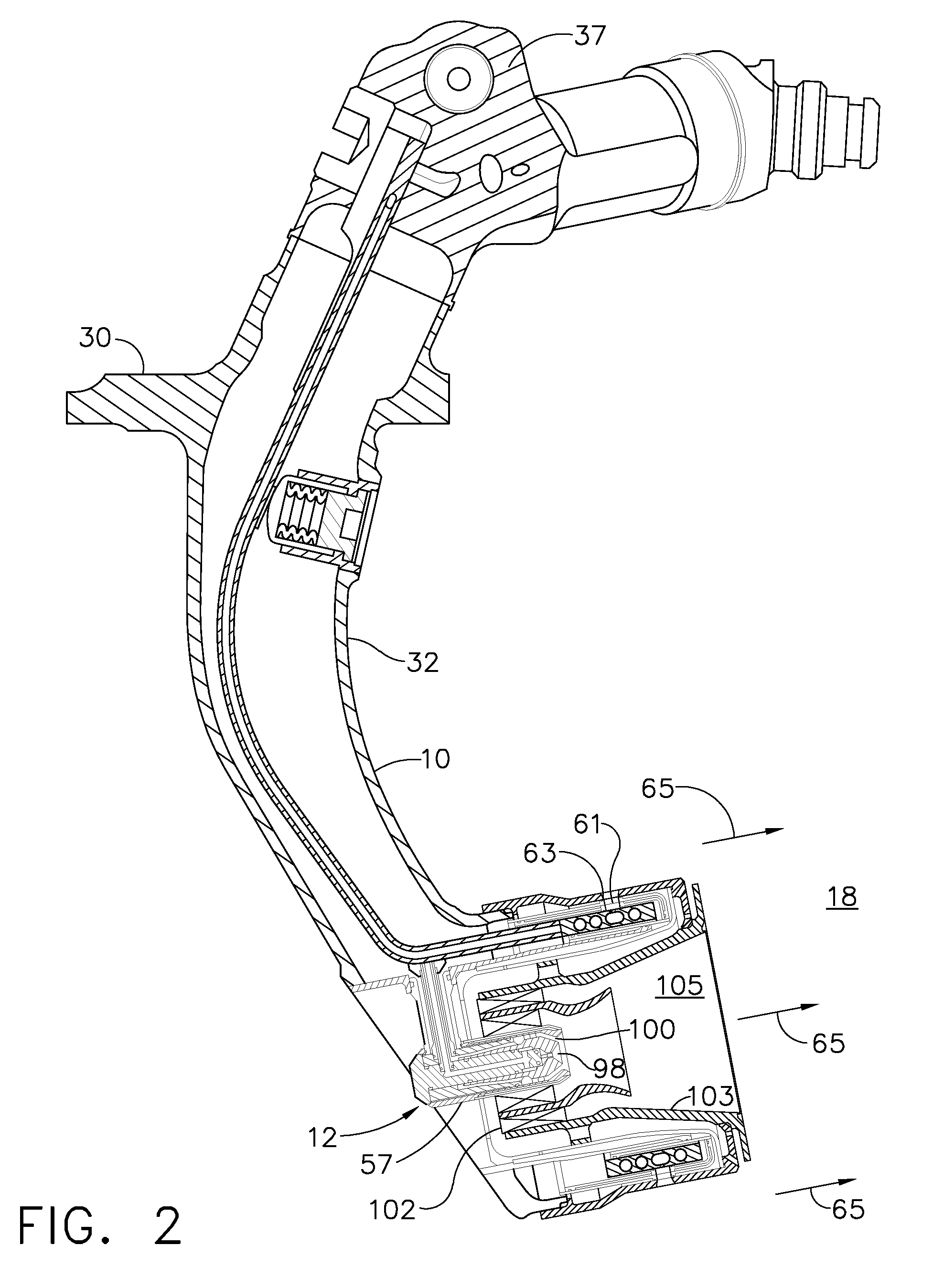
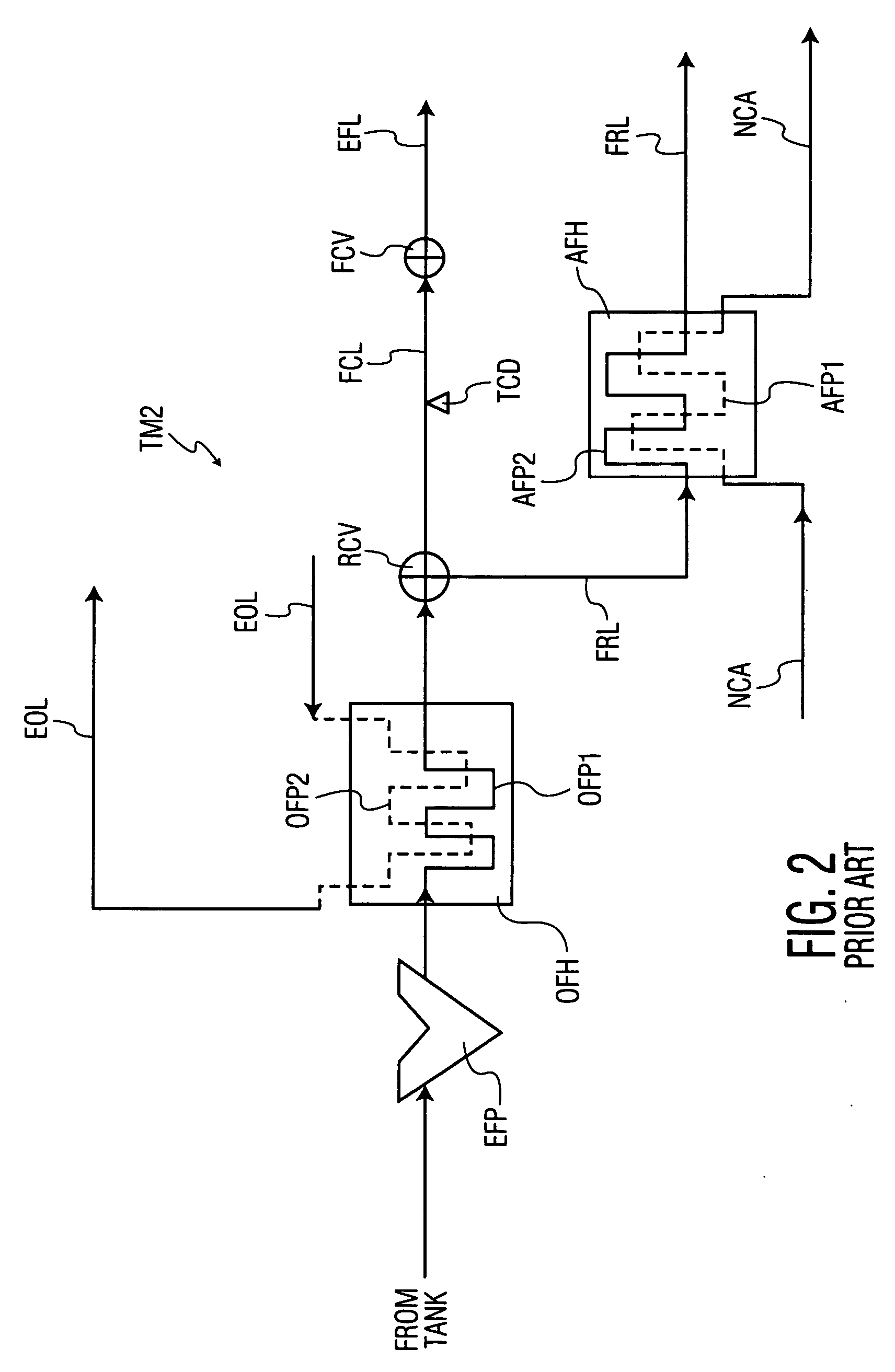
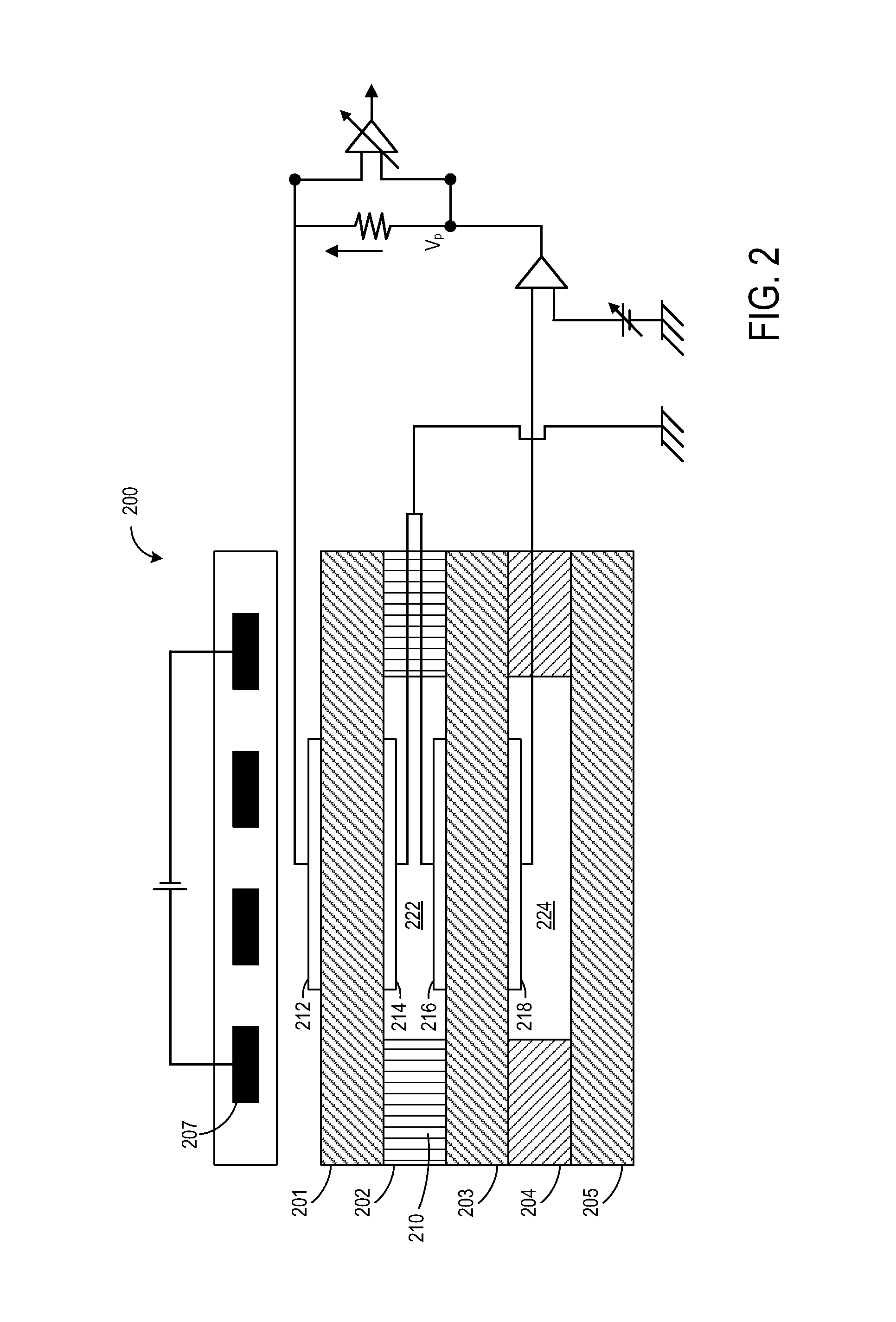
Fuel system for a multi-fuel engine
InactiveUS20120048242A1Reducing high pressure pump degradationReduce degradationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFuel typeHigh pressure
Methods and systems are provided for operating an engine fuel system including fuels of different fuel types. A first fuel type is delivered for port injection upon circulation through a high pressure pump when direct injection of a fuel is not requested to cool and / or lubricate the high pressure pump.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System and method for engine fuel blend control
A system for an engine, comprising of a cylinder located in the engine, a fuel delivery system for varying relative delivery amounts of a first and second injection type into said cylinder, and a controller configured to adjust a parameter affecting flow through the engine in response to said relative delivery amounts of said first and second injection type.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
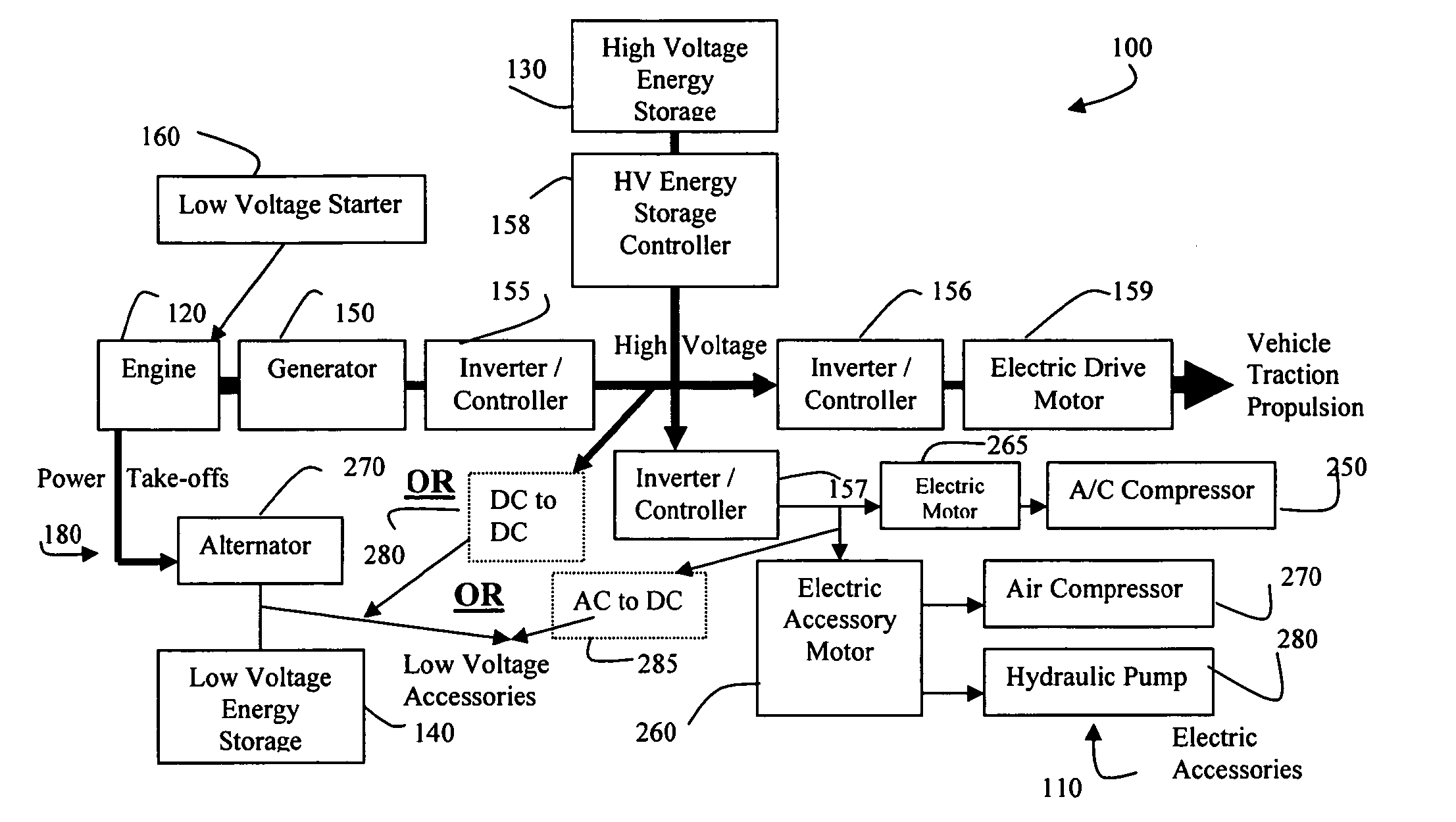
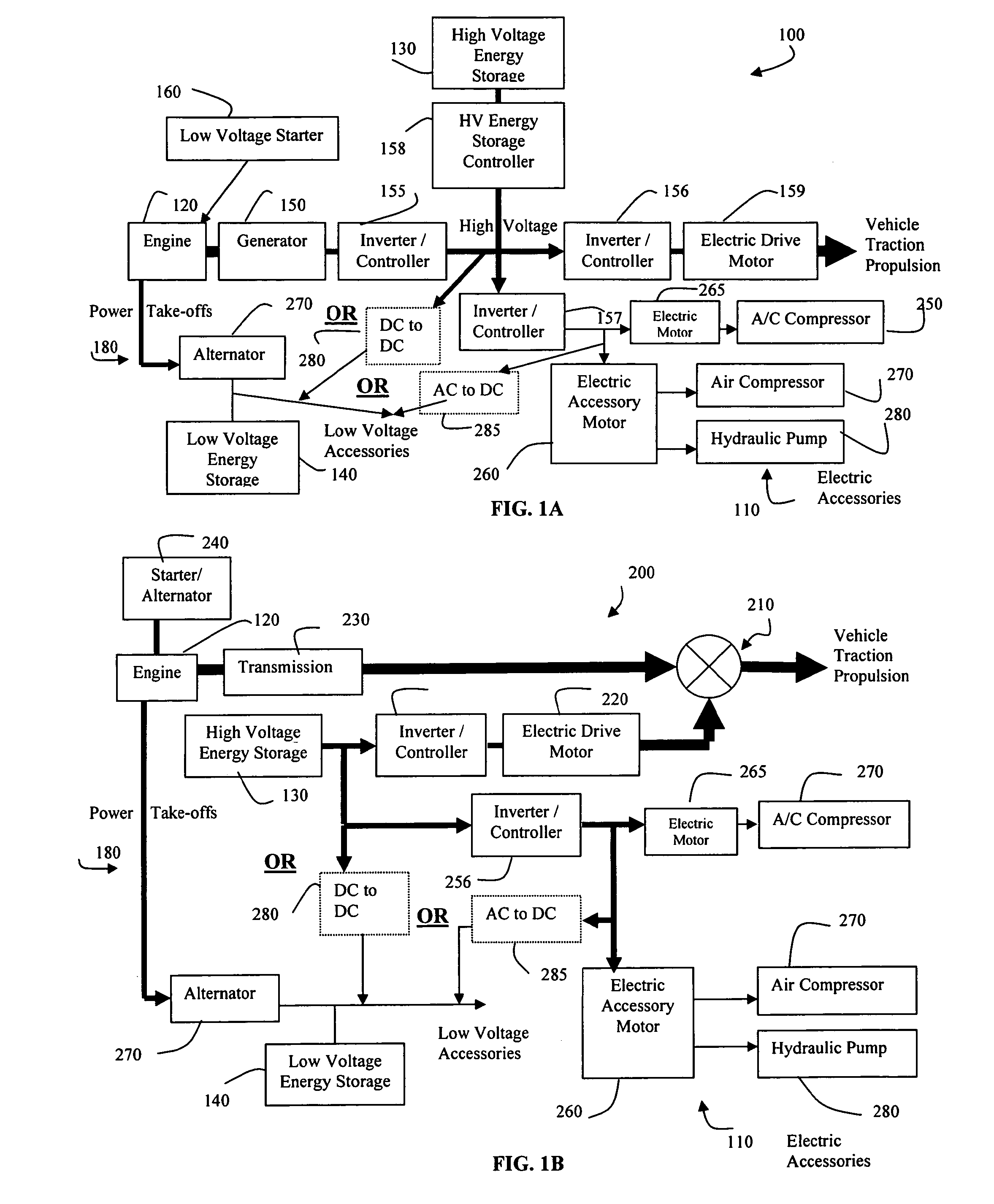
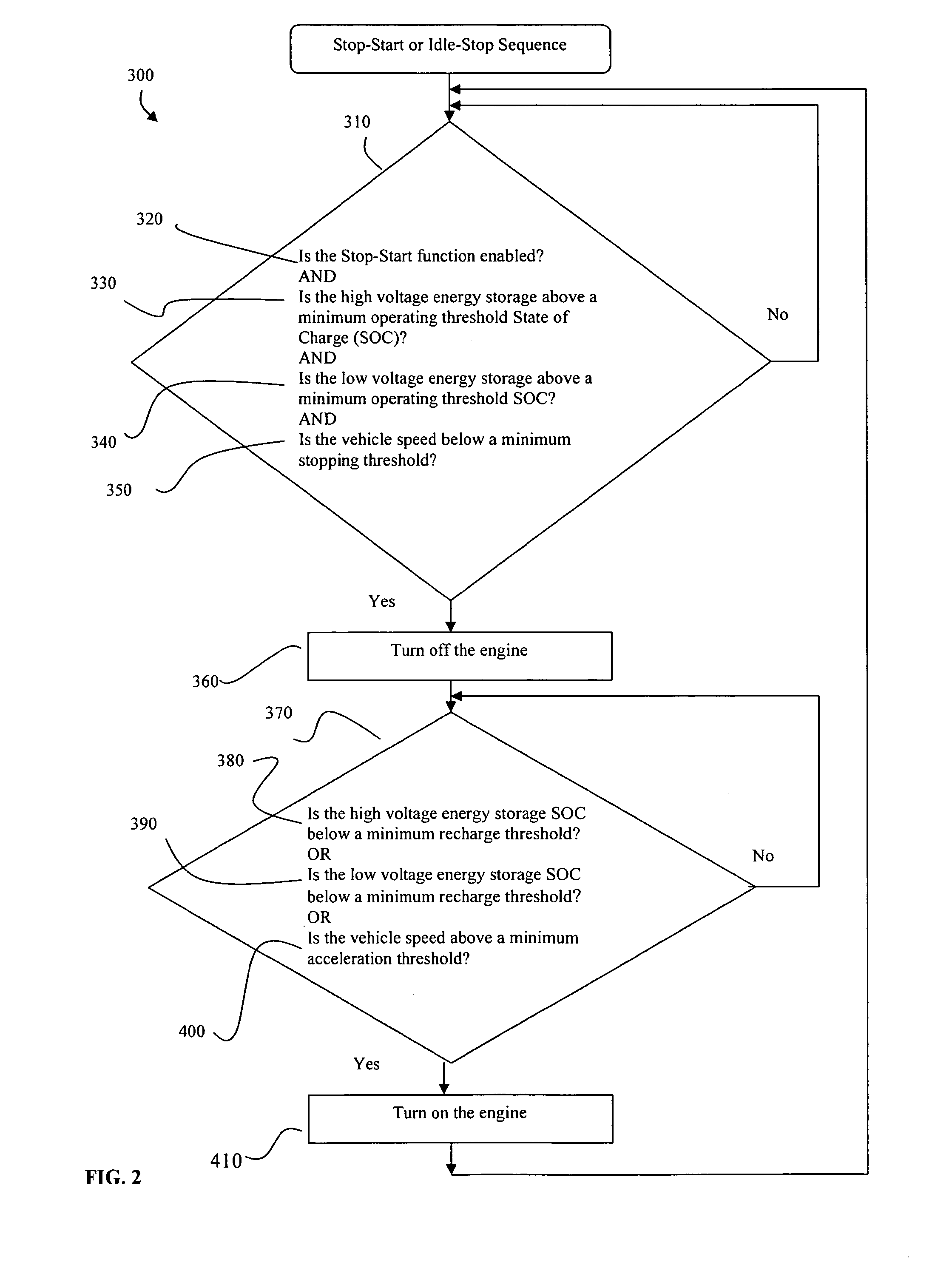
Method of Controlling Engine Stop-Start Operation for Heavy-Duty Hybrid-Electric Vehicles
InactiveUS20100145562A1Noise minimizationHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesElectric vehicleInternal combustion engine
A start-stop or idle-stop method for a heavy-duty hybrid vehicle that turns off the fuel supply while maintaining the crankshaft rotation of the internal combustion engine when the vehicle stops or, optionally, when the vehicle travels downhill, travels in a noise sensitive location, travels in an exhaust emissions sensitive location, or operates in an emergency situation. The stop-start or idle-stop method automatically turns on the engine fuel supply to restart combustion when the vehicle starts accelerating, is no longer traveling downhill, is no longer traveling in a noise sensitive or exhaust sensitive location, is no longer in an emergency situation, or has dropped below the minimum energy storage restart level. The stop-start or idle-stop may be inhibited upon certain override conditions.
Owner:SHEPPARD MULLIN RICHTER & HAMPTON
Dual orifice pilot fuel injector
A gas turbine engine fuel nozzle assembly has concentric primary and secondary pilot fuel nozzles with circular primary and annular secondary exits respectively and a main fuel nozzle spaced radially outwardly of the pilot fuel nozzles. The primary and secondary pilot fuel nozzles include conical primary and secondary exit holes respectively. The secondary pilot fuel nozzle is located directly adjacent to and surrounding the primary pilot fuel nozzle. Alternatively the secondary pilot fuel nozzle may be radially spaced apart from the primary pilot fuel nozzle. A fuel injector having a hollow stem may be used to support the fuel nozzle assembly. A first pilot swirler may be located radially outwardly of and adjacent to the dual orifice pilot fuel injector tip, a second pilot swirler located radially outwardly of the first swirler, and a splitter radially positioned between the first and second pilot swirlers.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
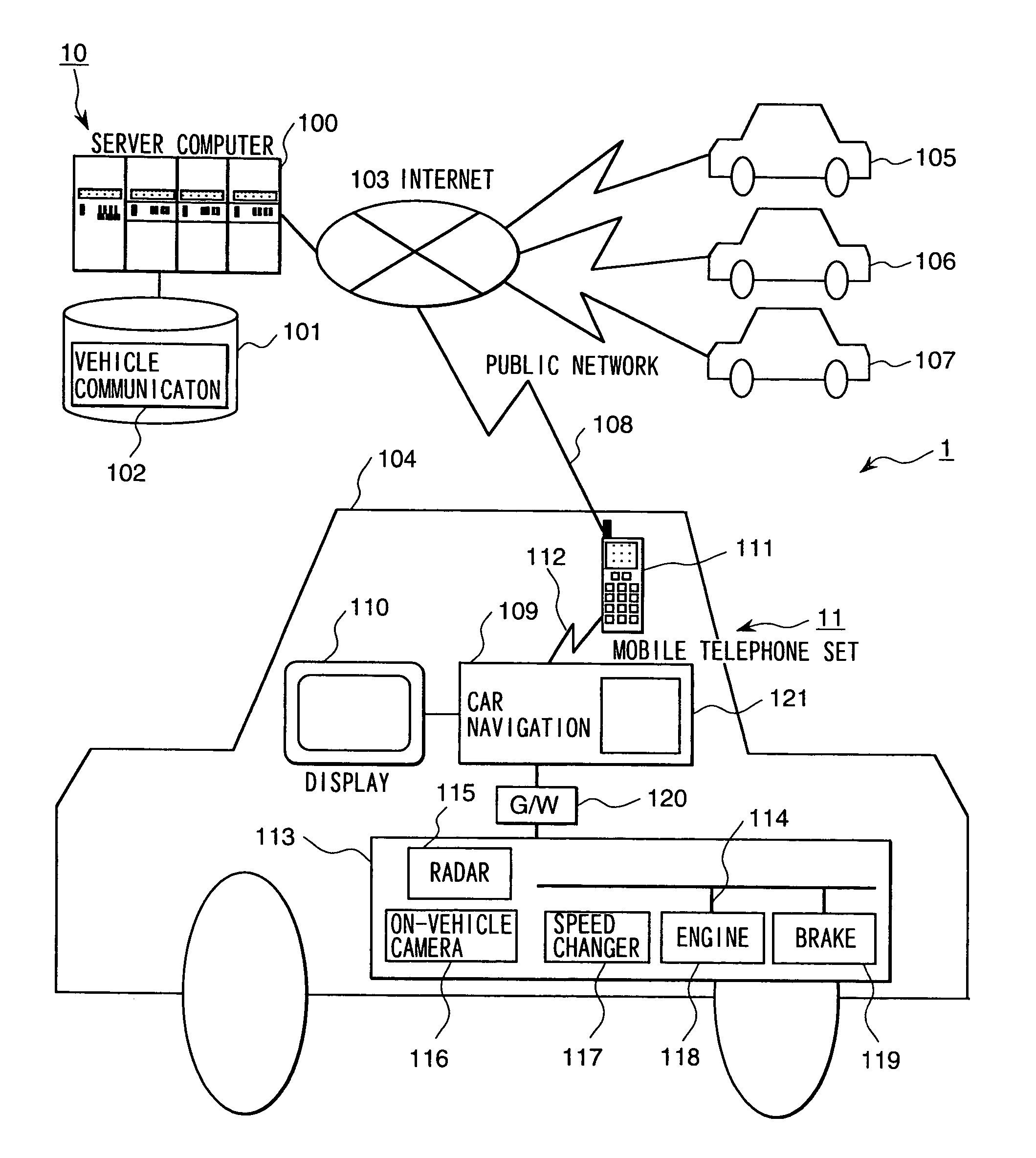
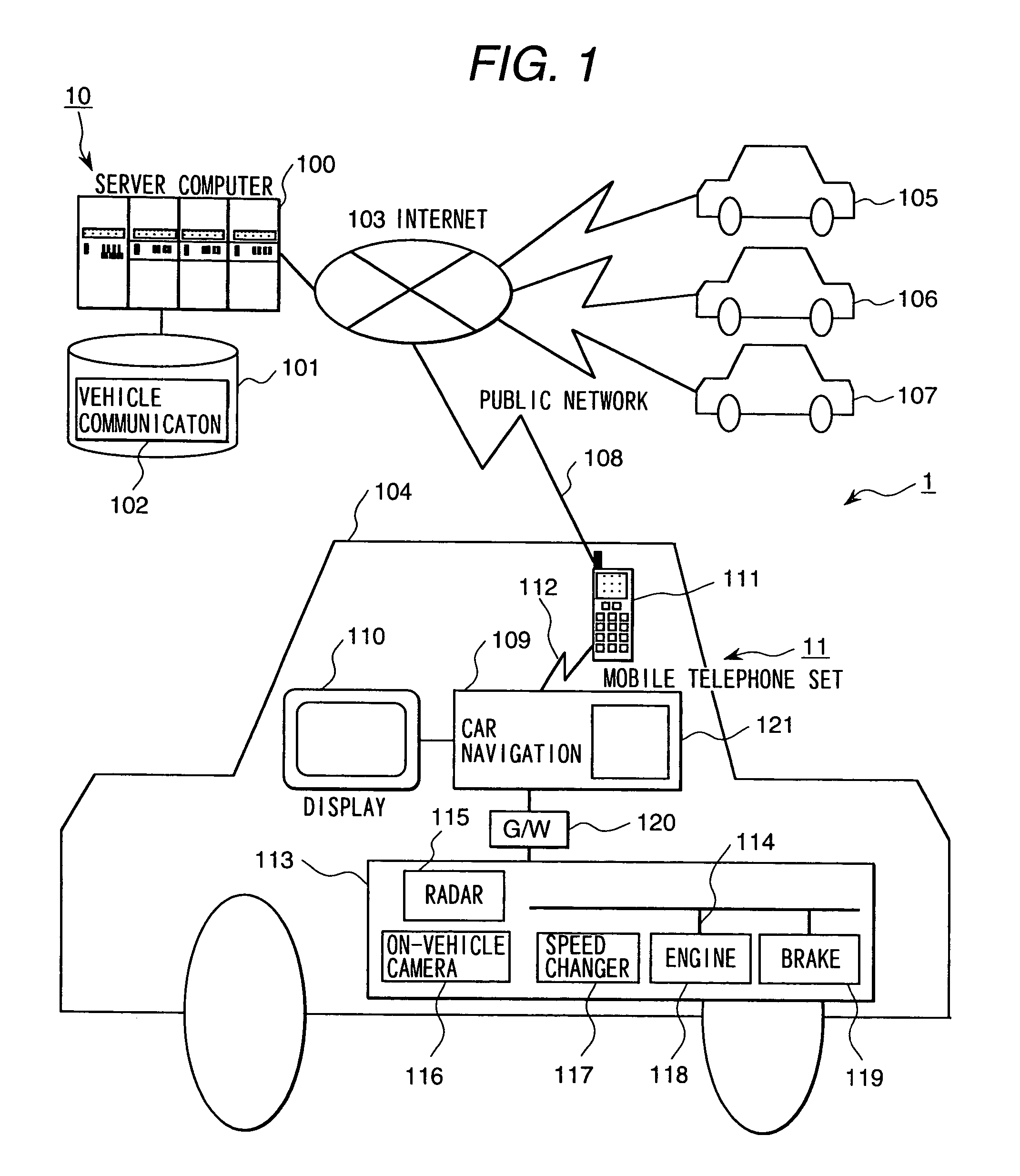
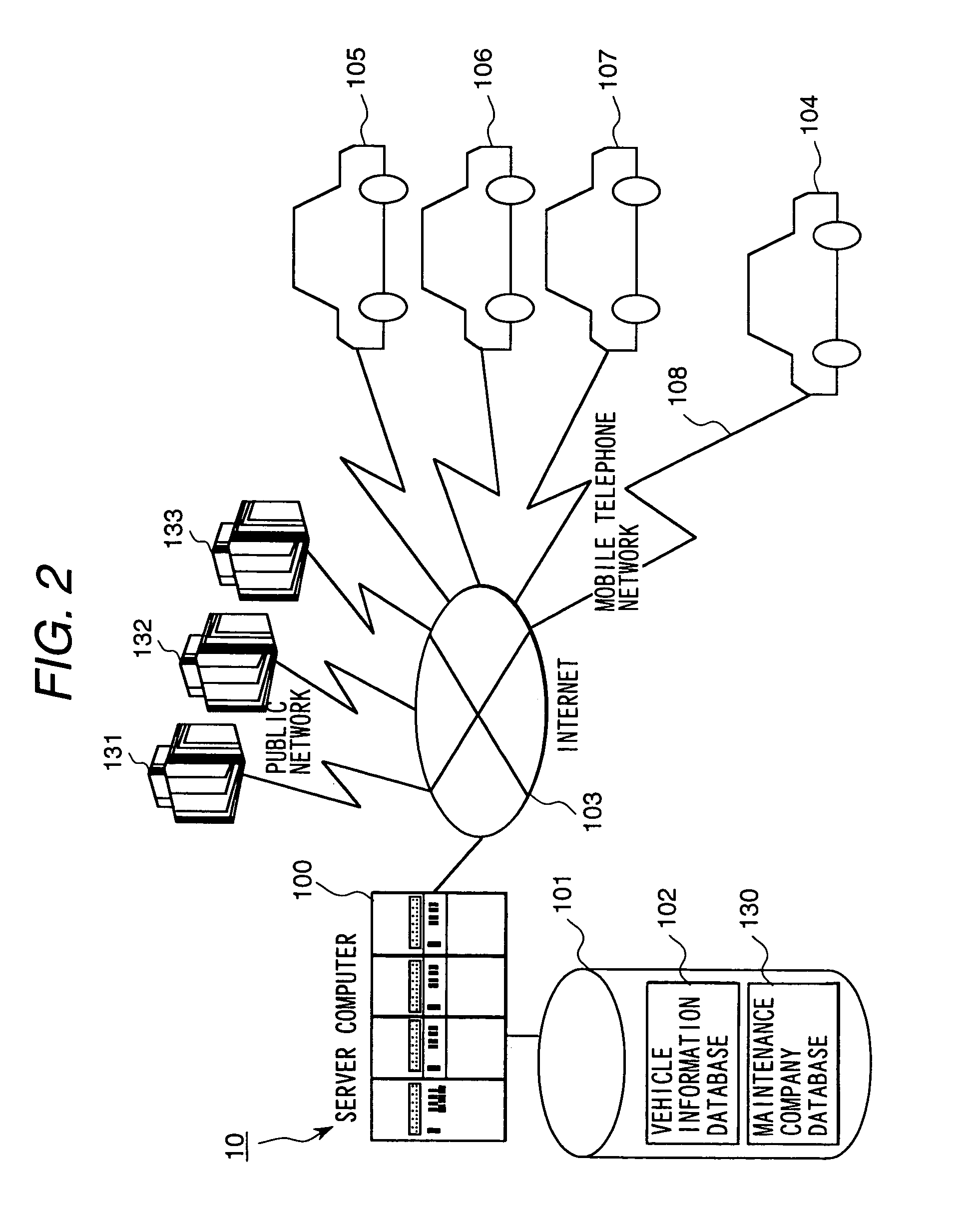
On-vehicle breakdown-warning report system
InactiveUS6972669B2Easy selectionShorten the timeVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDrivetrainCommunication device
An on-vehicle breakdown-warning report system is disclosed. an occurrence of break-down is detected and judged based on a signal in an electronic control system installed on a control apparatus for an engine ignition system, a charging system, an engine fuel system, a engine cooling system, a power transmission system, and an oil lubricating system of an automobile or a diagnosis display system; and a diagnostic data is sent to an information terminal device of a diagnosis and maintenance agency or a service company having a diagnosis and maintenance agency as a contents information by using an on-vehicle mobile communication apparatus, and an action for an emergency measures and a maintenance schedule is asked.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for producing hydrocarbons and oxygen-containing compounds from biomass
InactiveUS20050112739A1Improve direct utilizationImprove utilizationOrganic compound preparationHydrocarbon by hydrogenationChemical industryChemical reaction
The present invention generally relates to biochemical and chemical industry, and more particularly to a method which can be used in fermenting carbohydrate substrates of plant origin for producing C1-C5 alcohols, and for synthesis of higher alcohols, other oxygen-containing compounds and hydrocarbons as well as for the production of motor fuel components from biomass. Since C6 and higher alcohols, ethers, acetals, and higher hydrocarbons are not obtainable by a direct biochemical route, it is proposed to synthesize these using known chemical reactions, wherein by-products of fermentation are as raw materials for said synthesis.
Owner:SWEDISH BIOFUELS AB
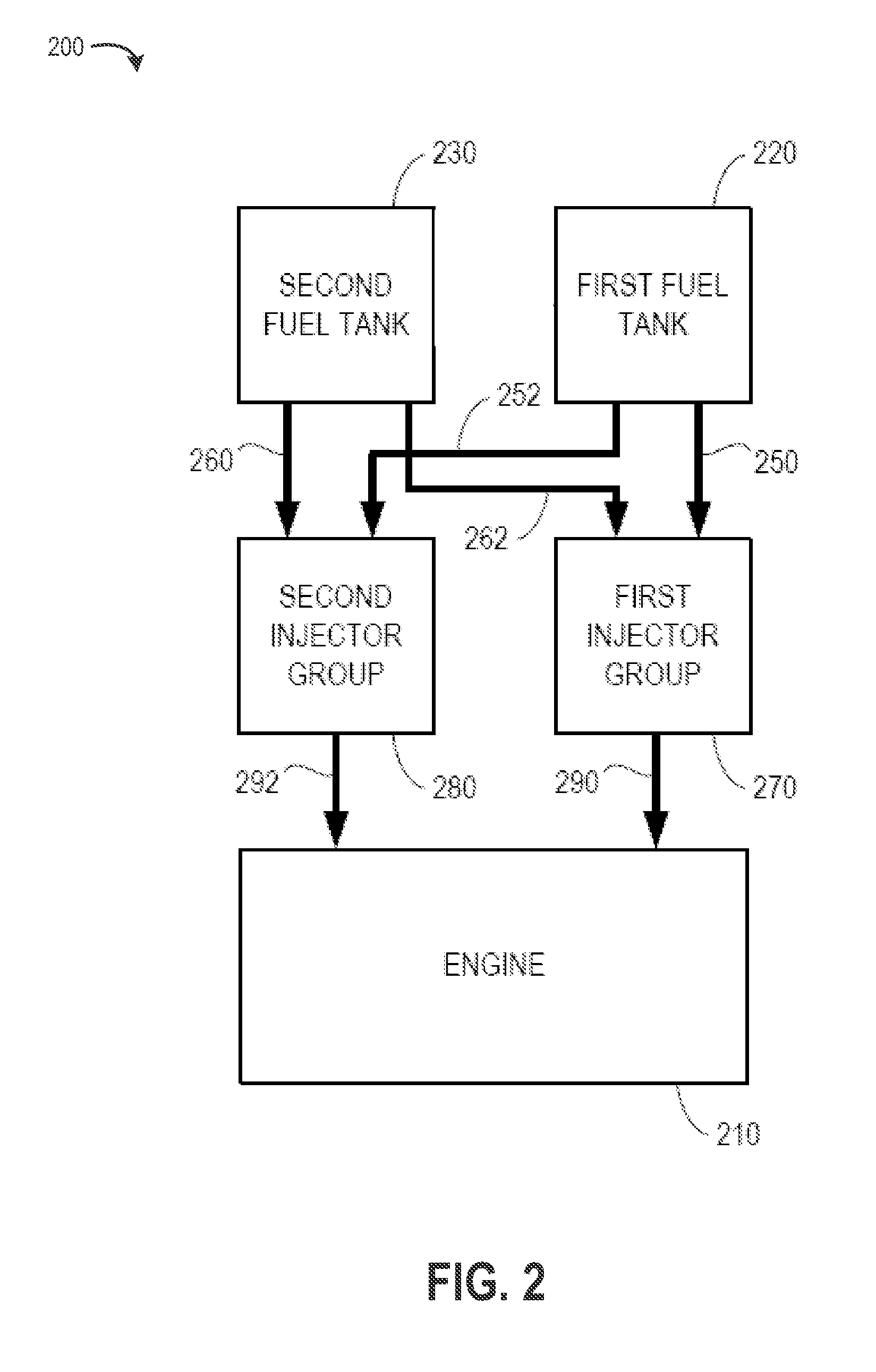
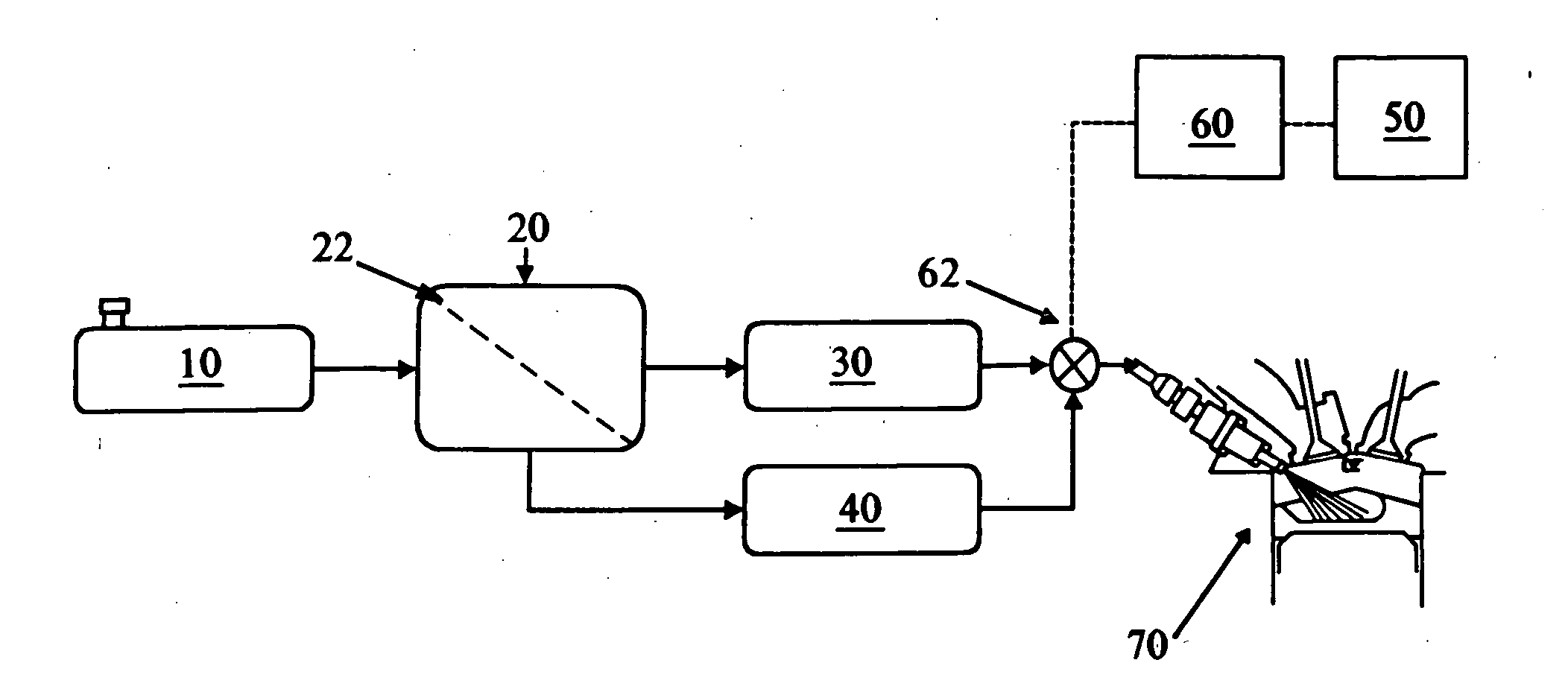
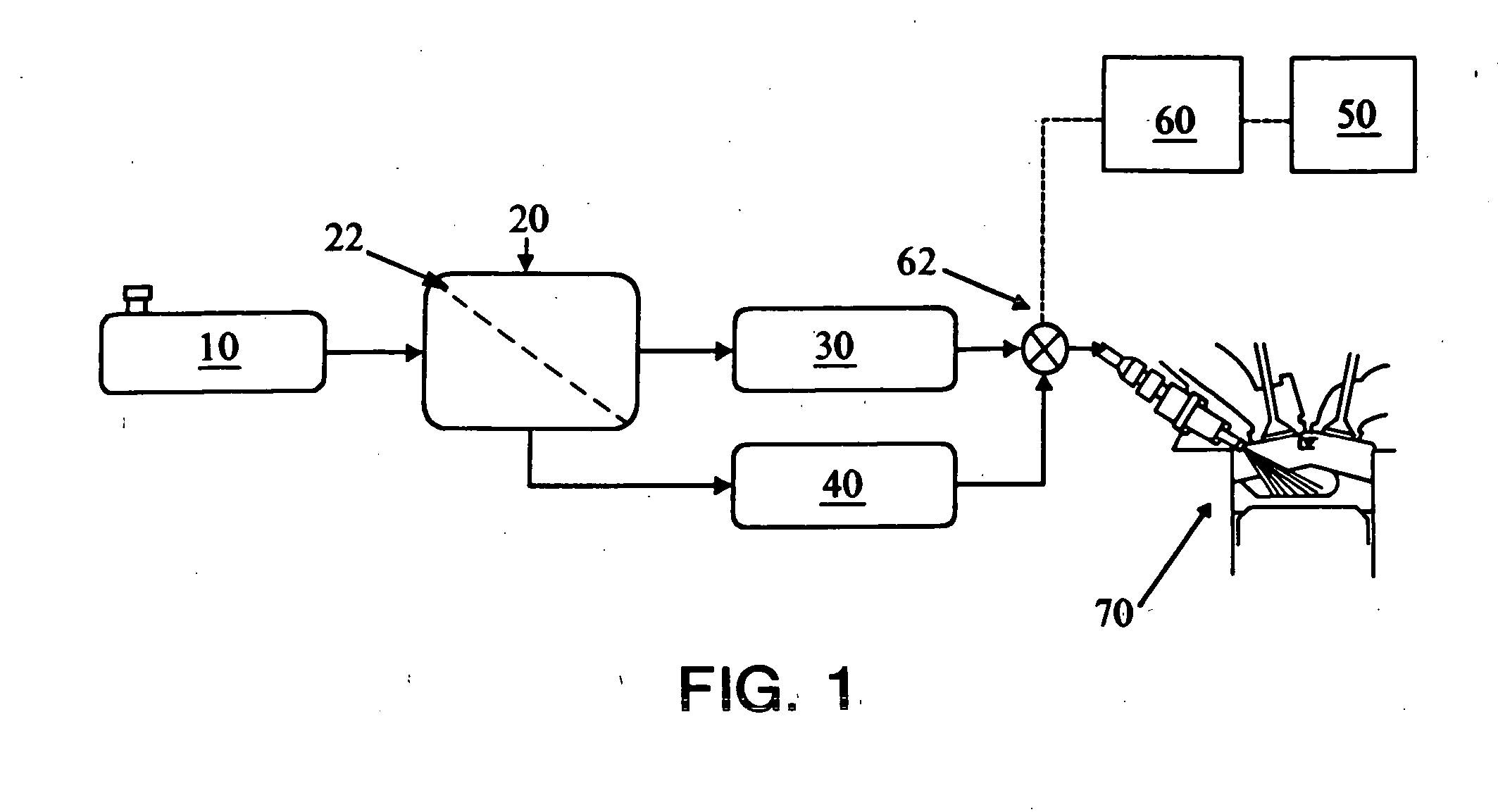
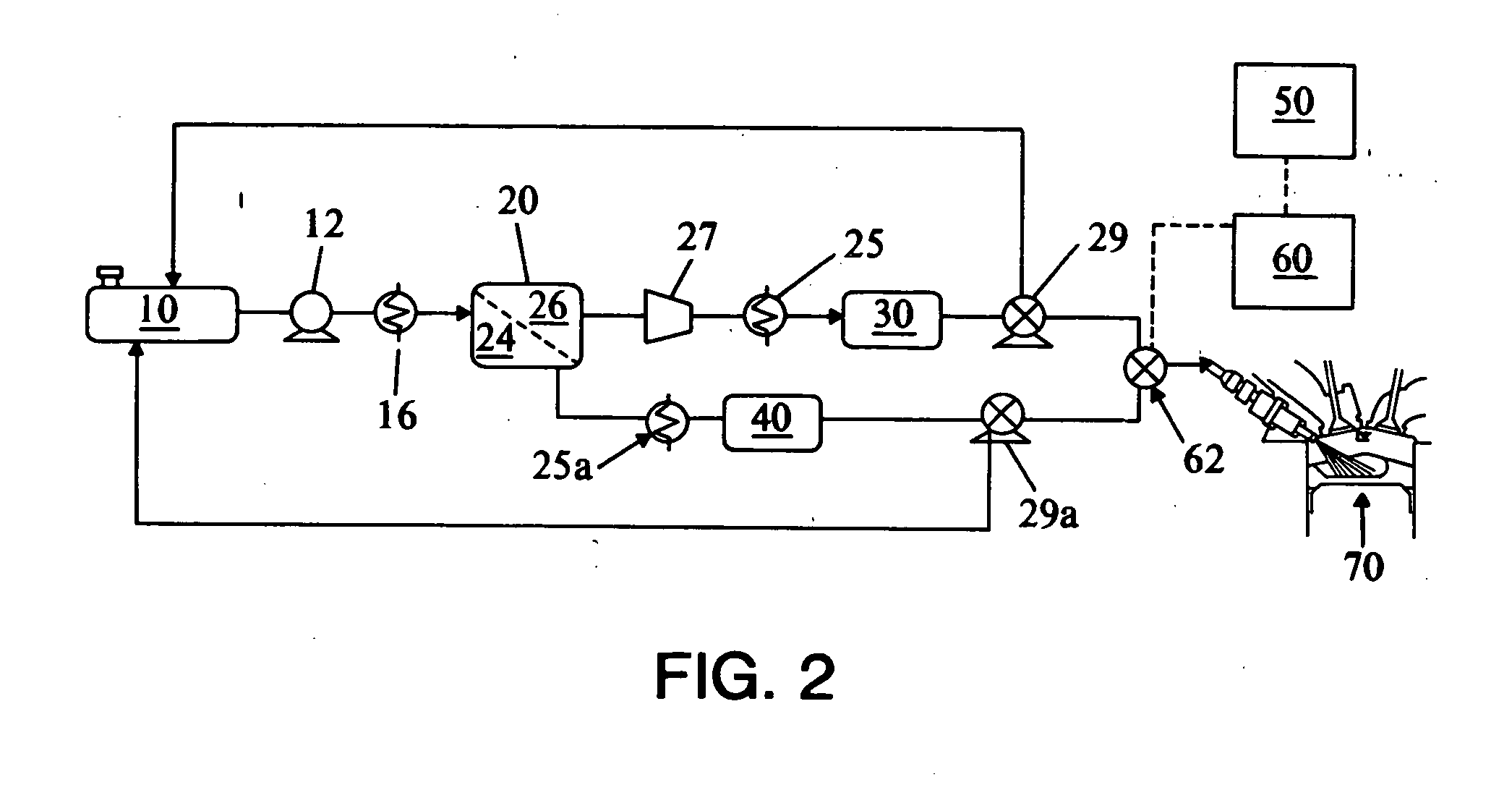
Fuel composition supply means for spark ignition engines
ActiveUS7107942B2More of efficiencyMore of emissionsNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesMotor fuelDriving cycle
A fuel system for on-board vehicle fuel separation to supply engine fuel compositions formulated as a function of driving cycle conditions. The invention results in improvements in one or more of feed efficiency and combustion emissions.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Cooling systems
InactiveUS6931834B2Sufficient heat exchanging capacityTurbine/propulsion engine coolingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsWorking temperatureEngineering
Apparatus for maintaining the temperature of a component of a gas turbine engine below a predetermined maximum working temperature comprises a reservoir for a cooling fluid having a boiling point below the working temperature and in which the component is immersed or with which it is in contact. At least two heat exchangers are associated with the reservoir and operable to effect condensation of vaporized cooling fluid and return of same to the reservoir. Preferably the apparatus is a closed system incorporating three heat exchangers respectively adapted to effect heat exchange with engine fuel, compressed air derived from a fan or low pressure compressor of the engine and ambient air. Means may advantageously be provided to ensure return of condensed cooling fluid to the reservoir when the attitude of the reservoir is altered as a result of aircraft maneuvers.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
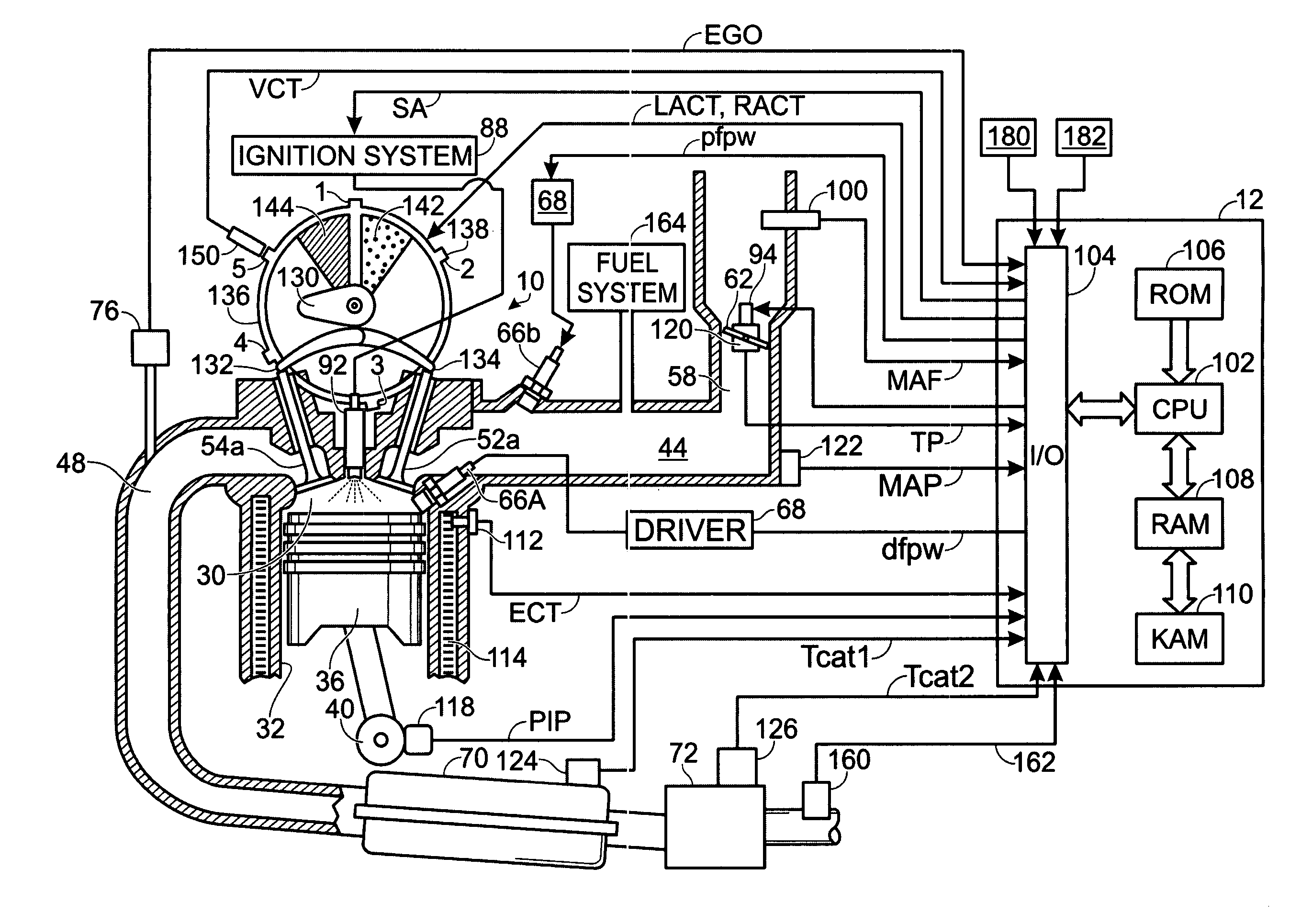
Method for load transient control between lean and stoichiometric combustion modes of direct-injection engines with controlled auto-ignition combustion
InactiveUS20060196469A1Electrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelStable stateHomogeneous charge compression ignition
A method is provided for control of a direct-injection engine operated with controlled auto-ignition (HCCI) during load transient operations between modes of lean combustion low load (HCCI / Lean) and stiochiometric combustion medium load (HCCI / Stoich.). The method includes 1) operating the engine at steady state, within a homogeneous charge compression-ignition (HCCI) load range, with fuel-air-exhaust gas mixtures at predetermined conditions, for each speed and load, and controlling the engine during changes of operating mode between one to another of the HCCI / Stoich. medium load mode and the HCCI / Lean lower load mode by synchronizing change rates of predetermined controlled inputs to the current engine fueling change rate.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Fuel composition supply means for driving cycle conditions in spark ignition engines
InactiveUS6622663B2More of efficiencyMore of emissionsInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelOn boardMotor fuel
A fuel system for on-board vehicle fuel separation to supply engine fuel compositions formulated as a function of driving cycle conditions. The invention results in improvements in one or more of feed efficiency and combustion emissions.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Fuel injection control method for diesel engine and regenerative control method for exhaust gas after treatment device
InactiveUS6901747B2Accumulate moreFilter meltingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesAfter treatmentCombustion
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
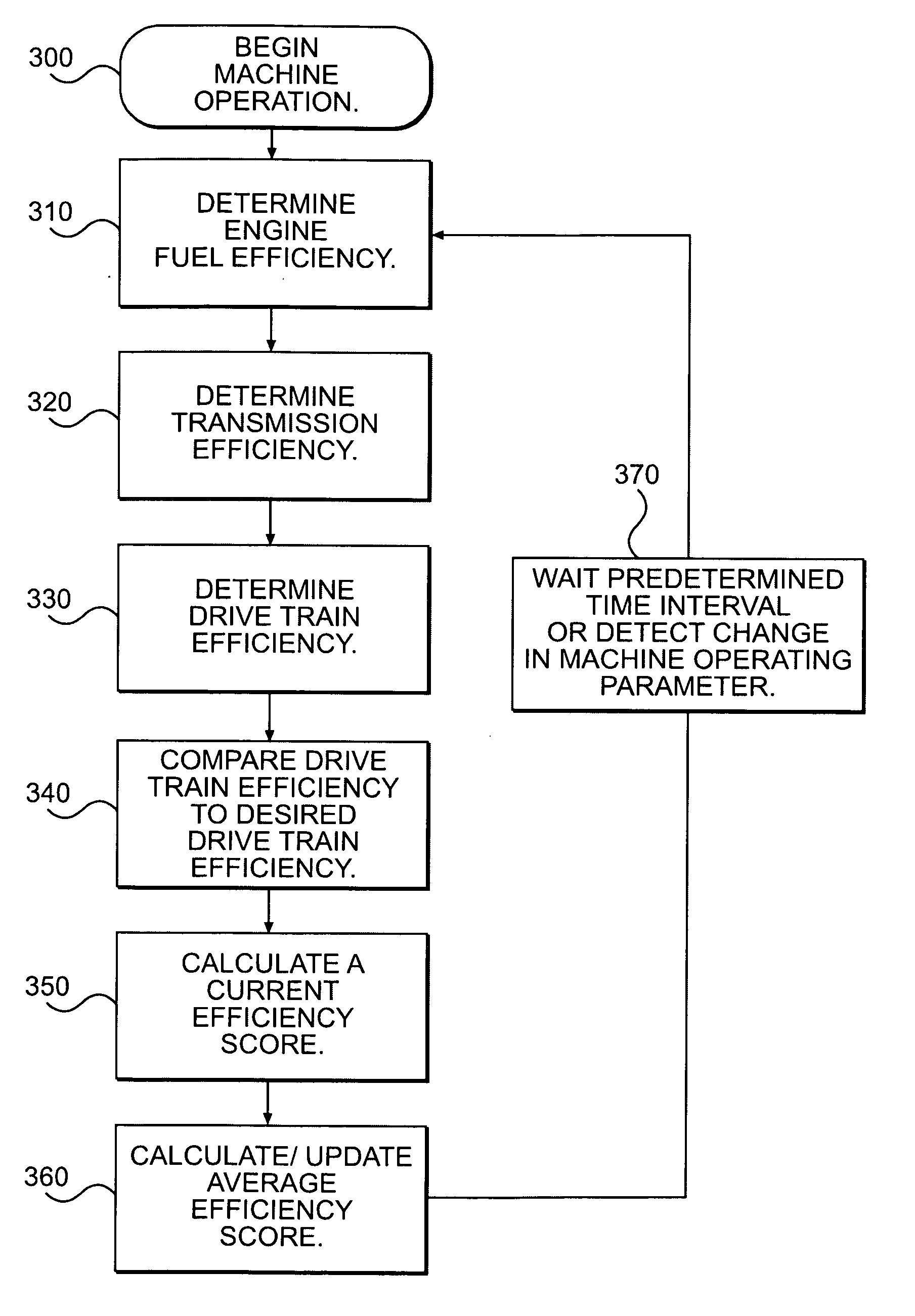
System for evaluating and improving driving performance and fuel efficiency
InactiveUS20070143002A1Analogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficFuel efficiencyMotor fuel
A method for monitoring driving performance is provided. The method may include determining an engine fuel efficiency based on an engine speed and power output and determining a transmission fuel efficiency based on a drive ratio. A drive-train fuel efficiency may be determined based on the engine fuel efficiency and transmission fuel efficiency, and the drive-train efficiency may be compared to a target drive-train efficiency.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
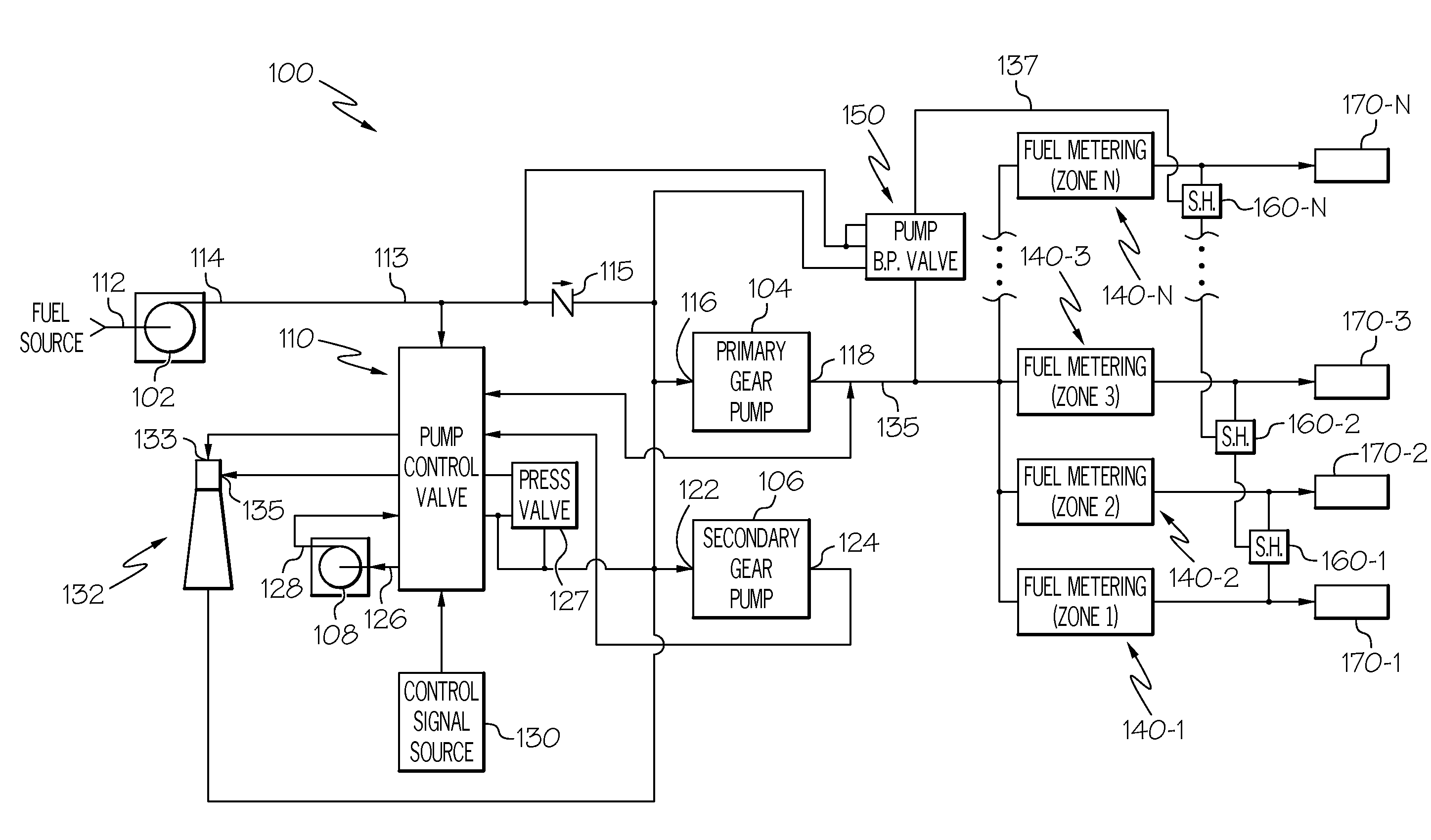
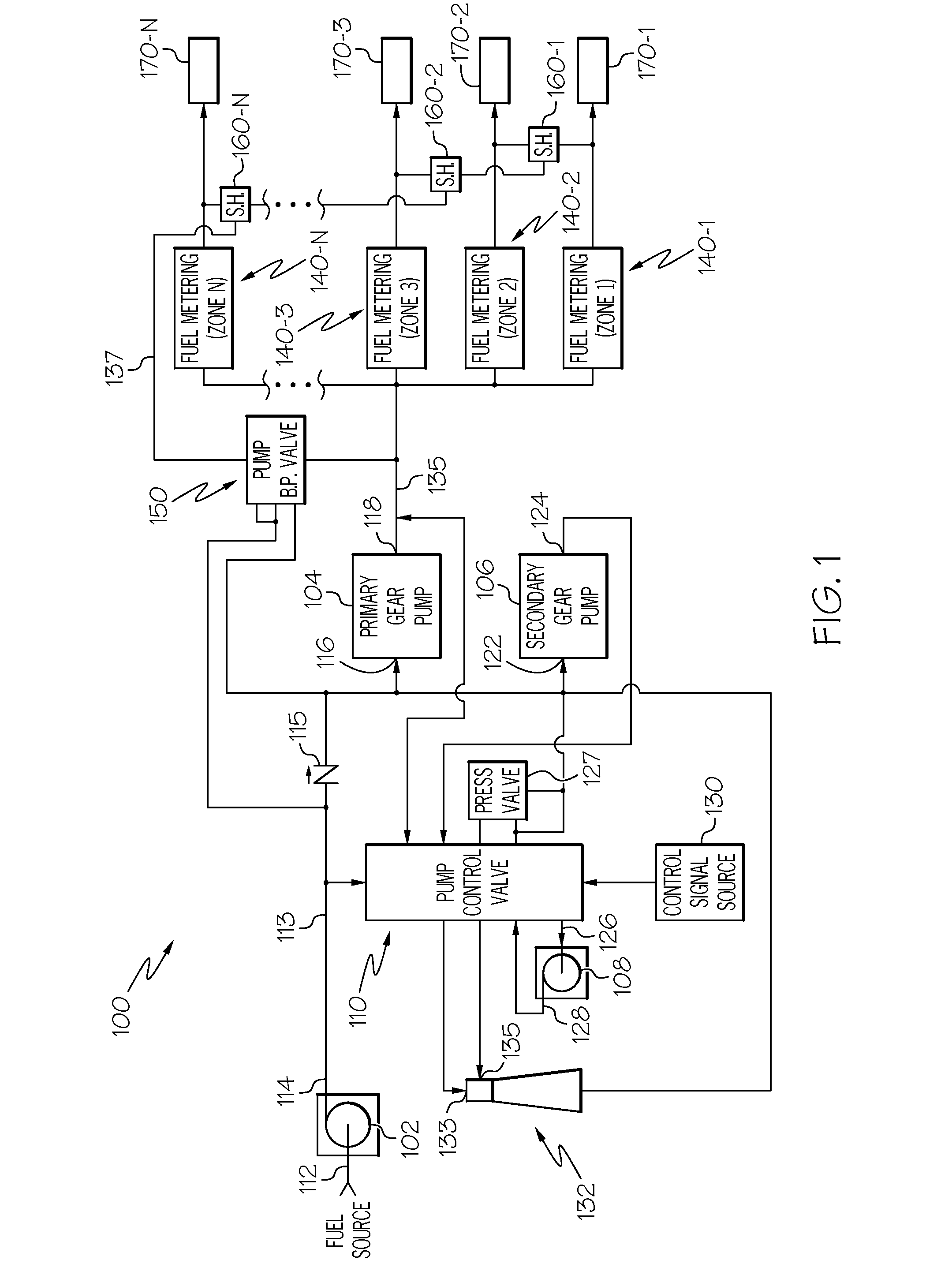
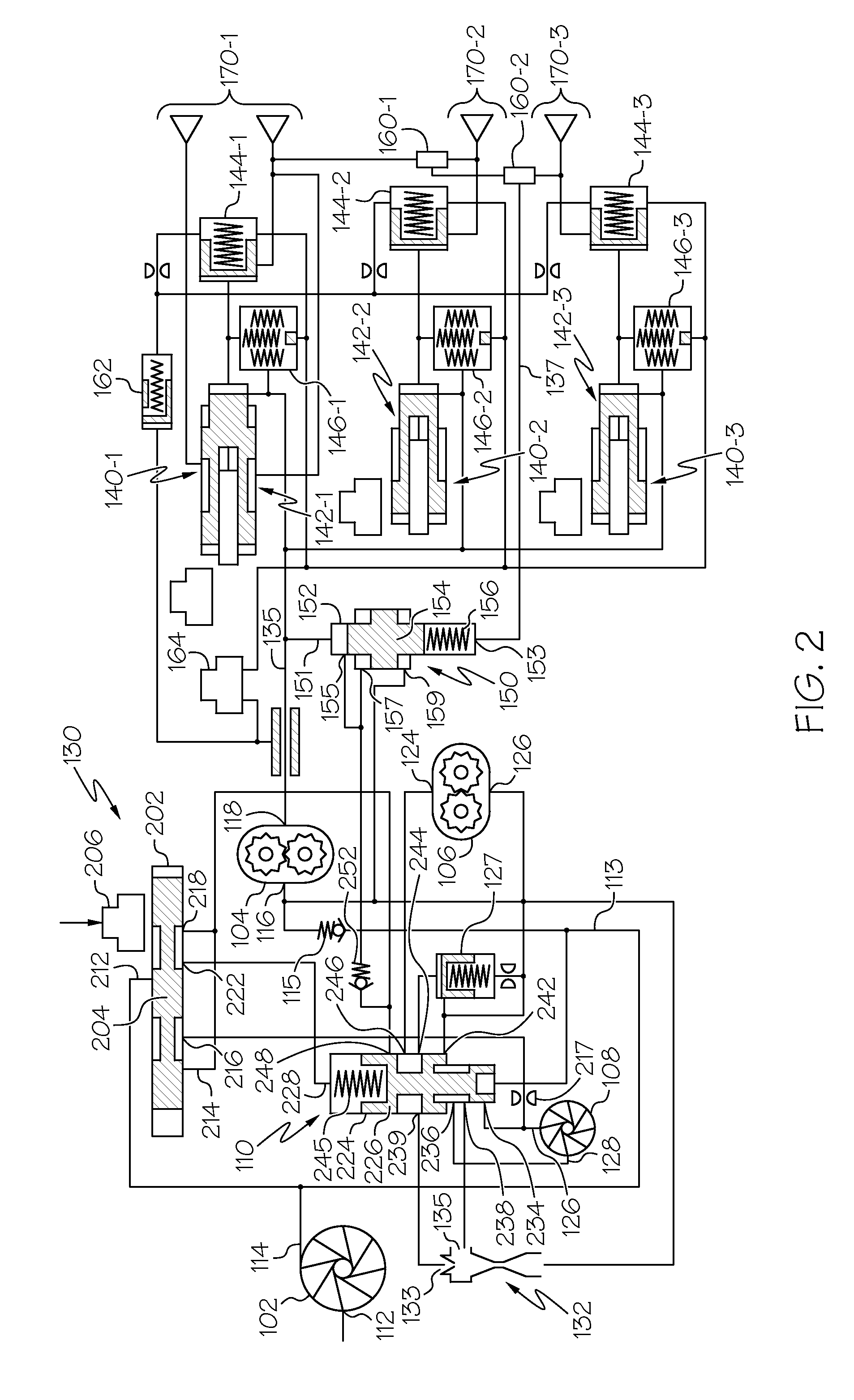
High pressure, multiple metering zone gas turbine engine fuel supply system and method
ActiveUS20140196459A1Heat generation is minimizedMinimizing power extractionTurbine/propulsion fuel deliveryGas turbine plantsDifferential pressureLow demand
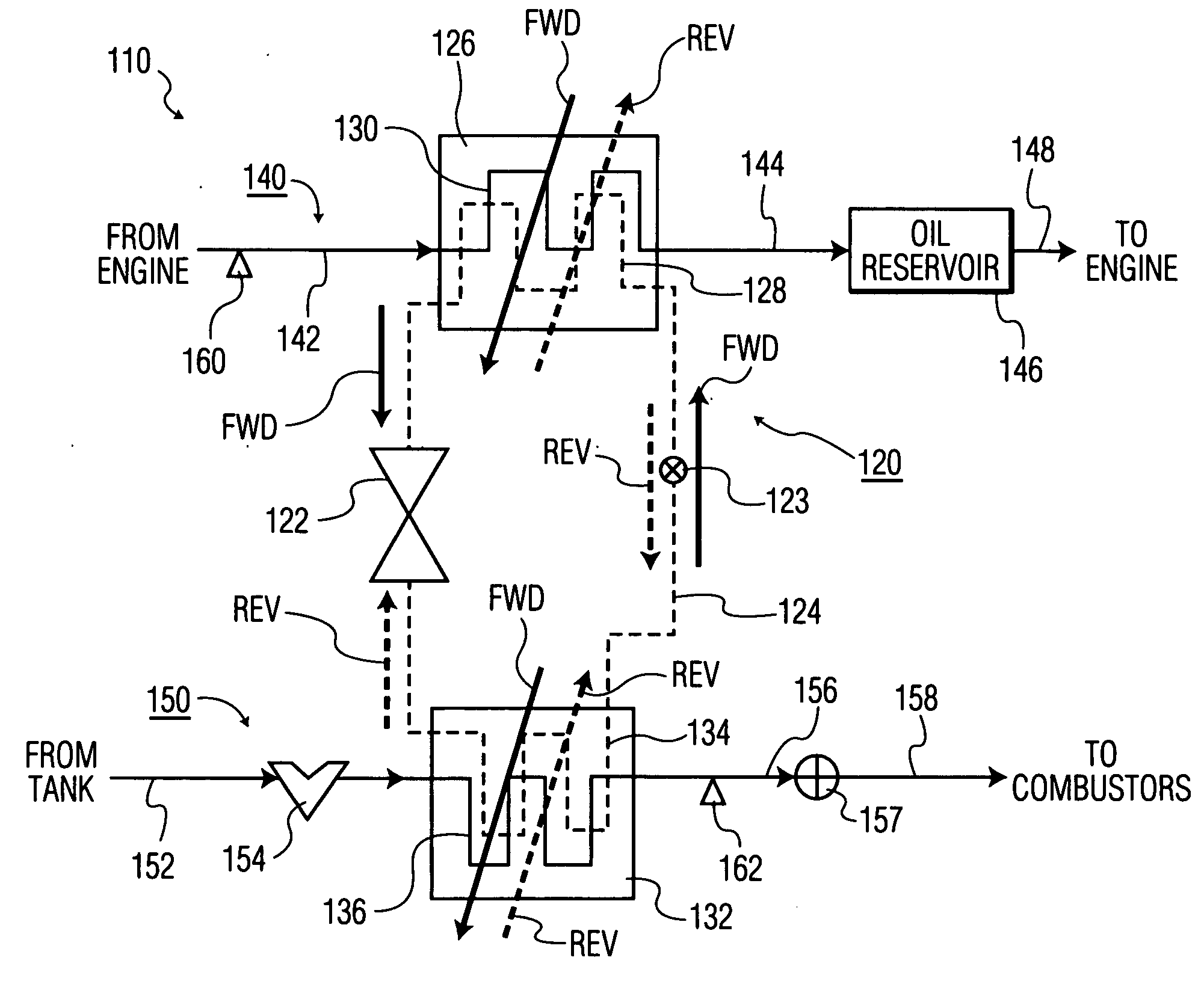
A gas turbine engine fuel supply system includes a primary gear pump, a secondary gear pump, and a pump bypass valve. The primary gear pump always actively delivers fuel to the downstream fuel system, and is sized to supply 100% of the burn flow needed at a select low demand condition. The secondary gear pump is sized to make up the remainder of the flow at high demand conditions, and actively delivers fuel to the downstream fuel system only during those conditions. To supply discharge fuel pressures in excess of gear pump capability, a supercharger pump is disposed upstream of the primary and secondary gear pumps. The pump bypass valve is configured to regulate fuel pressure at the primary gear pump outlet to one of a plurality of preset differential pressures above one of a plurality of fuel load pressures and prevents reverse pressurization of the gear pumps.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
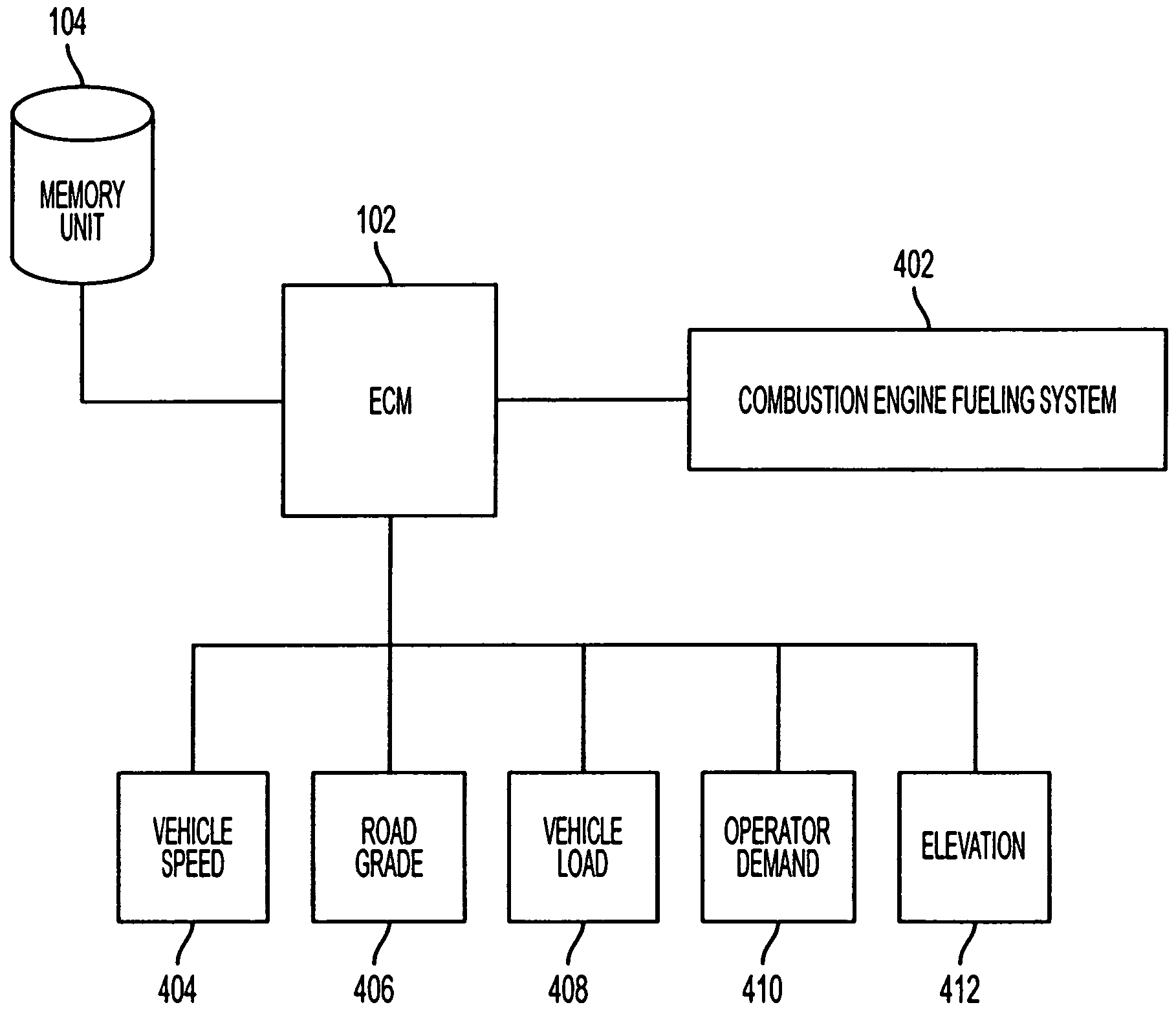
Control system and method for improving fuel economy
InactiveUS7497201B2Maximum efficiencyPower optimizationAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlCombustionControl system
A control system is provided for controlling the fueling system (402) of a combustion engine. The control system includes a sensing arrangement for measuring a plurality of engine and vehicle conditions (404, 406, 408, 410, 412) in real time. The control system also includes a fuel map that defines engine fueling parameters corresponding to engine operating conditions. The control system also includes a control module (102) that determines engine load from the sensed conditions, and controls the fueling parameters of the fueling system for optimized fuel consumption by selecting fueling parameters from the fuel map based on current engine load.
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
Fuel system for a multi-fuel engine
ActiveUS20120167859A1Reducing pump degradationFully filledInternal combustion piston enginesLow-pressure fuel injectionRail pressureFuel oil
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Engine fuel delivery systems, apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20100258099A1Avoid communicationAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlControl systemEngineering
A method of operating an engine is disclosed, which includes determining a peak power condition for the engine, measuring a temperature associated with the engine at said peak power condition, comparing the temperature measured with a previously determined temperature associated with a known peak power condition of the engine, determining an offset value based on the comparison made in step, controlling at least one of an air-fuel mixture delivered to the engine or ignition spark timing based on said offset value. Various engine fuel delivery systems, carburetors, fuel injection and control systems also are disclosed.
Owner:WALBRO LLC
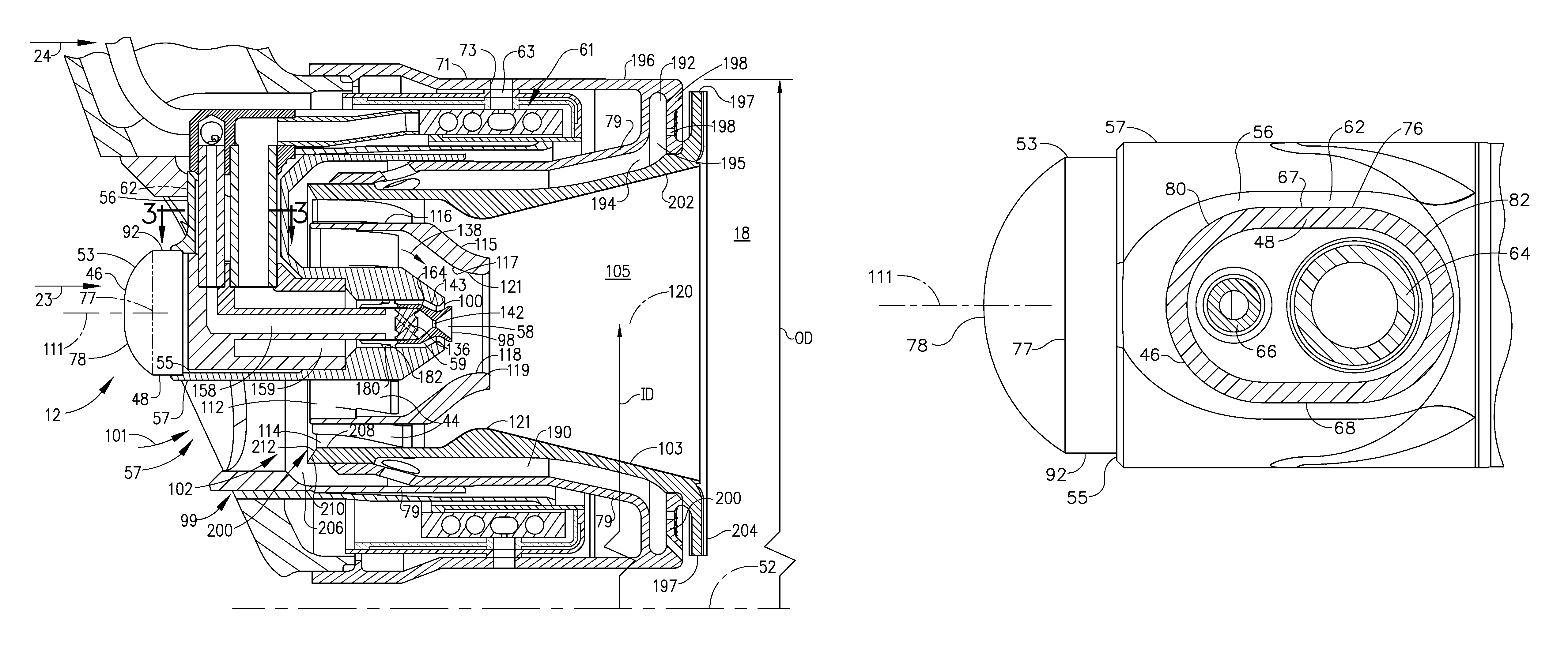
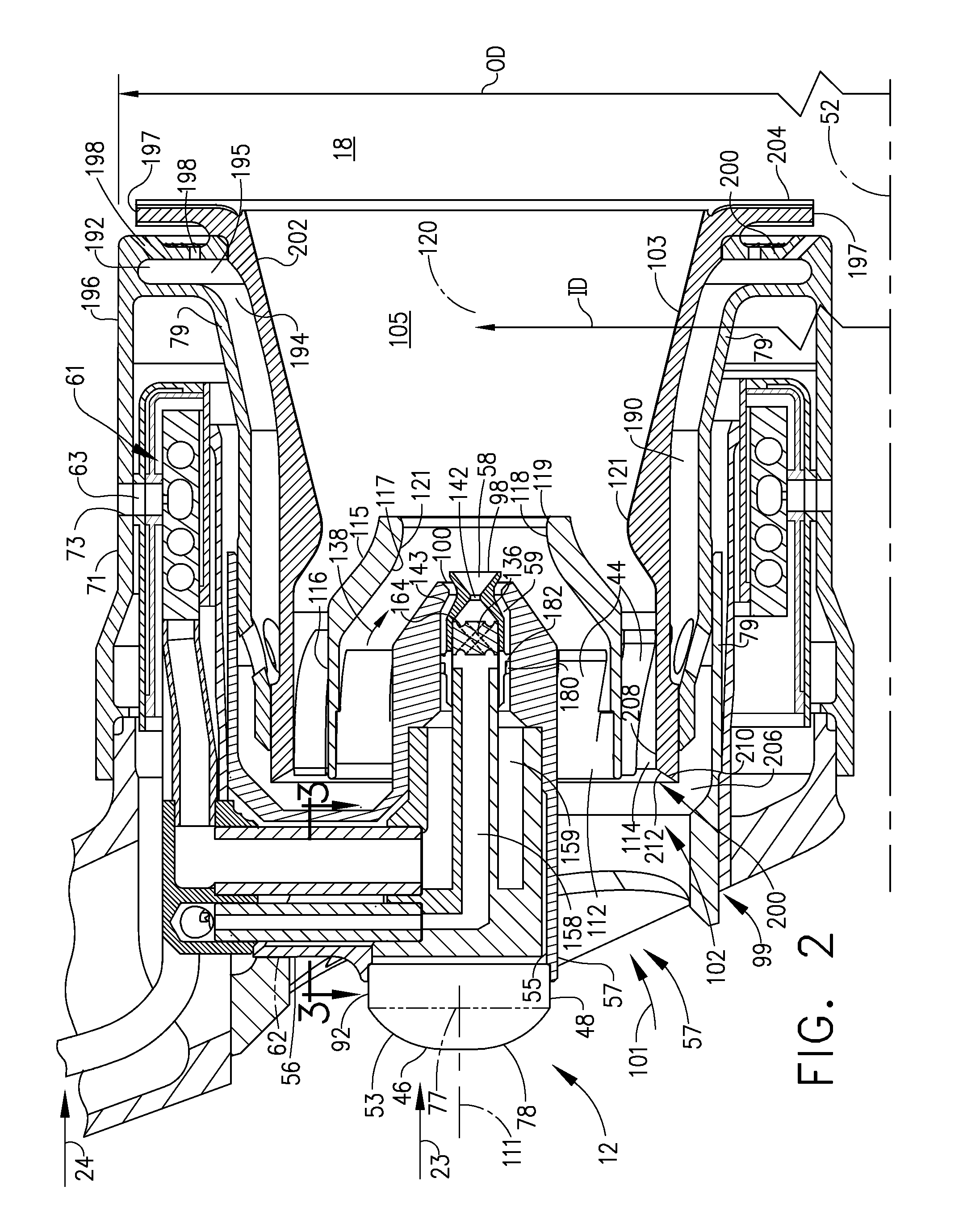
Method to transfer fuel in a fuel system for a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20050279079A1Eliminate needTurbine/propulsion fuel deliveryTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesFuel tankCheck valve
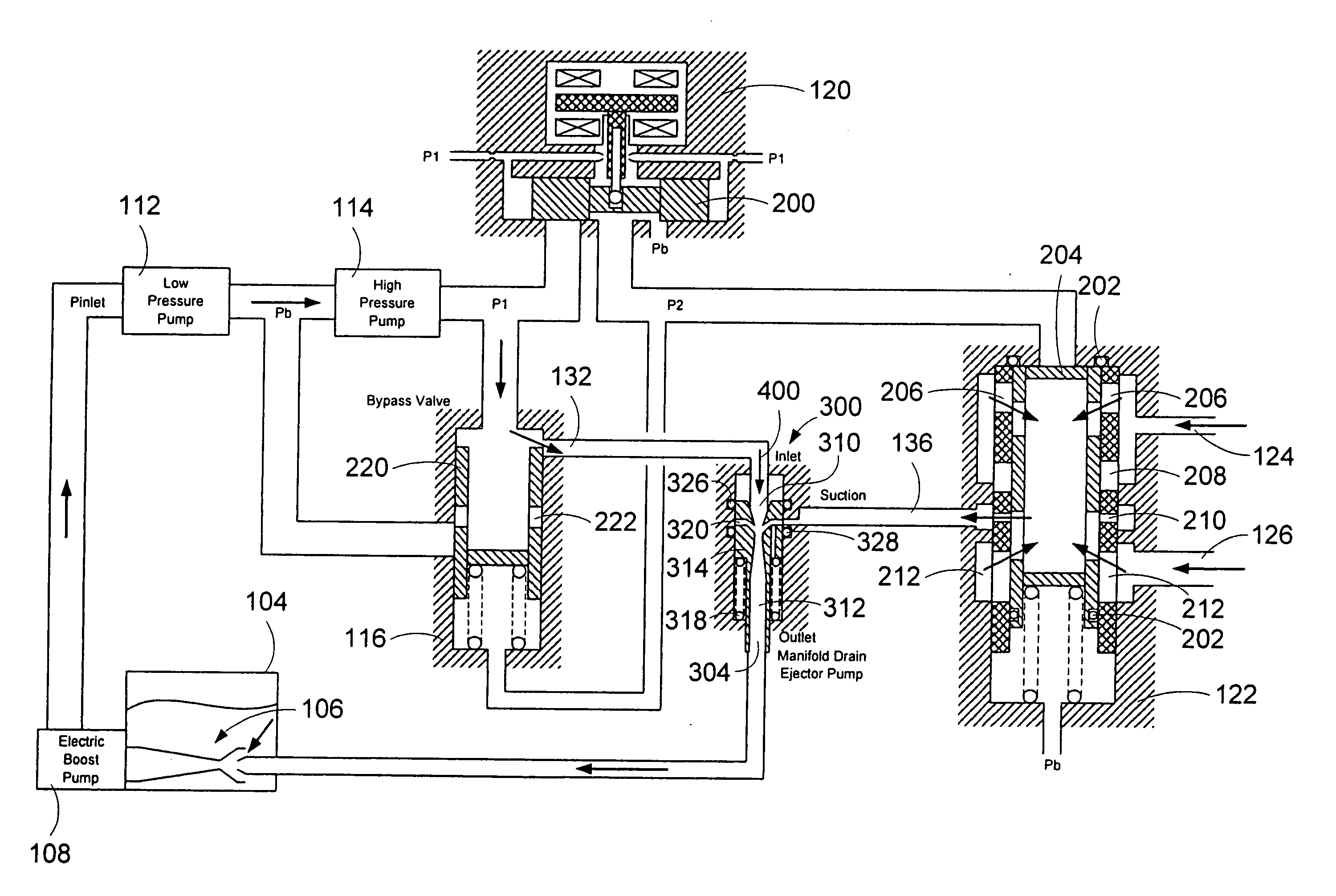
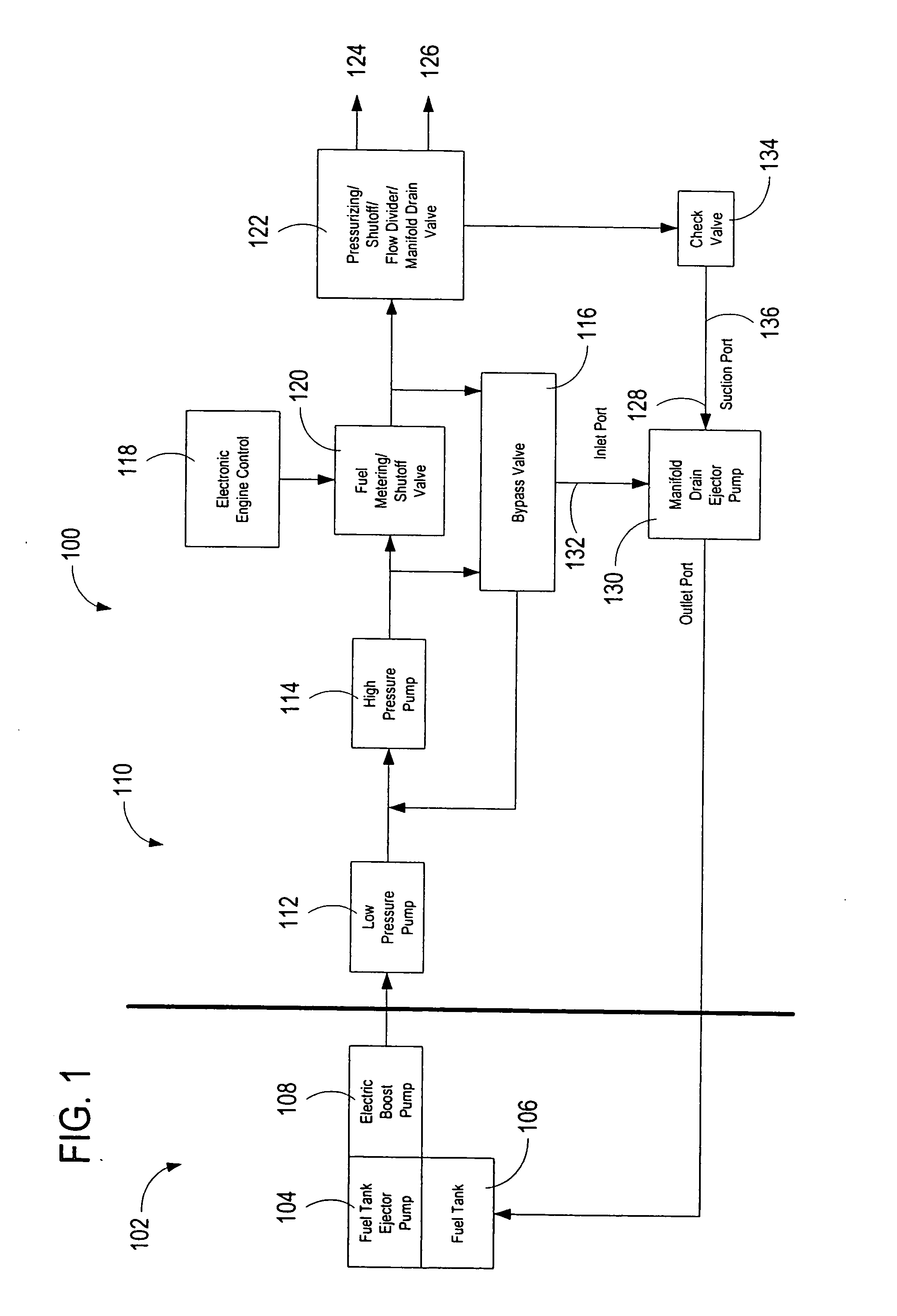
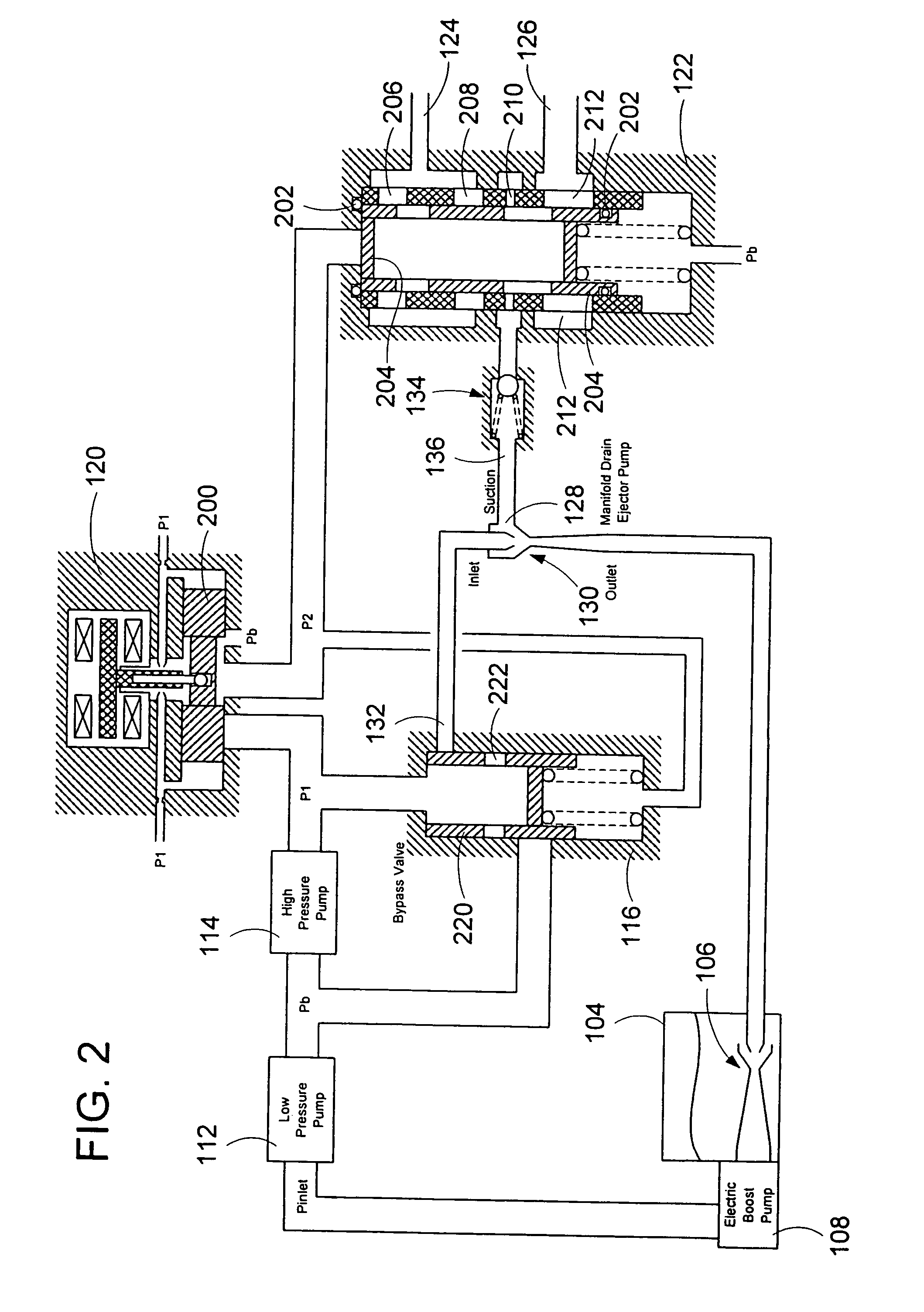
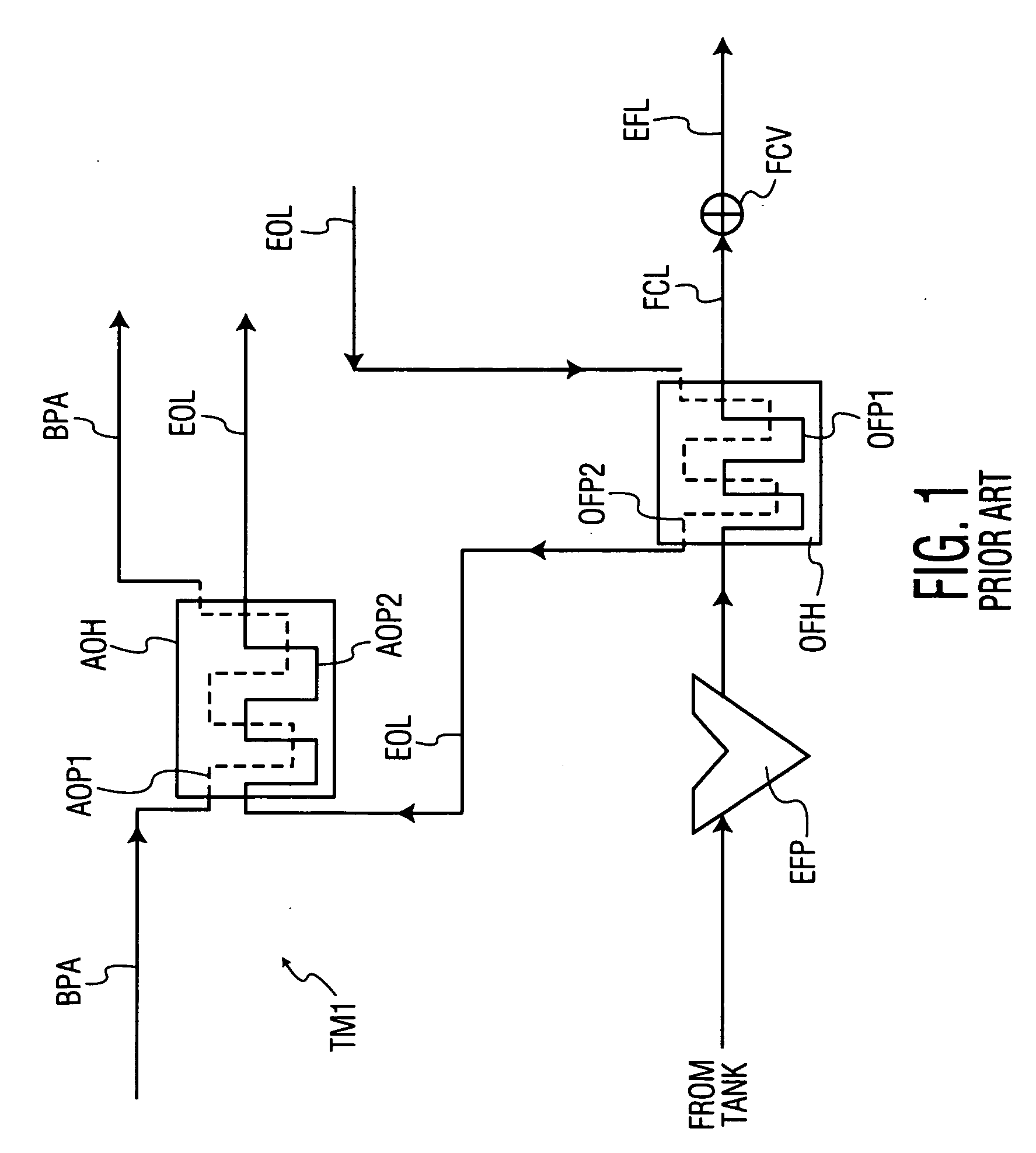
A system for automatically transferring the fuel from one or more engine fuel manifolds directly to the engine fuel tank(s) during engine shutdown using an ejector pump has been presented. A checkvalve, which may be integrated with the ejector pump, is also used. A metering valve initiates fuel flow shutoff and is used in the draining of the fuel manifolds, thereby eliminating the need for an additional solenoid dedicated mainly to the shutoff function. The shutoff and pressurizing valve provides flow division between manifolds and manifold drain for systems having multiple manifolds. The bypass valve is used to turn the motive flow and / or manifold drain functions on and off as a function of engine speed at start and shutdown.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
Cooling systems
InactiveUS7213391B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsAir-treatment apparatus arrangementsBoiling pointWorking temperature
Apparatus for maintaining the temperature of a component of a gas turbine engine below a predetermined maximum working temperature comprises a reservoir for a cooling fluid having a boiling point below the working temperature and in which the component is immersed or with which it is in contact. At least two heat exchangers are associated with the reservoir and operable to effect condensation of vaporised cooling fluid and return of same to the reservoir. Preferably the apparatus is a closed system incorporating three heat exchangers respectively adapted to effect heat exchange with engine fuel, compressed air derived from a fan or low pressure compressor of the engine and ambient air. Means may advantageously be provided to ensure return of condensed cooling fluid to the reservoir when the attitude of the reservoir is altered as a result of aircraft maneuvers.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Systems and methods for thermal management in a gas turbine powerplant
InactiveUS20100107603A1Minimize impactReduce coke depositionAnalogue computers for vehiclesTurbine/propulsion engine coolingWorking fluidThermal management system
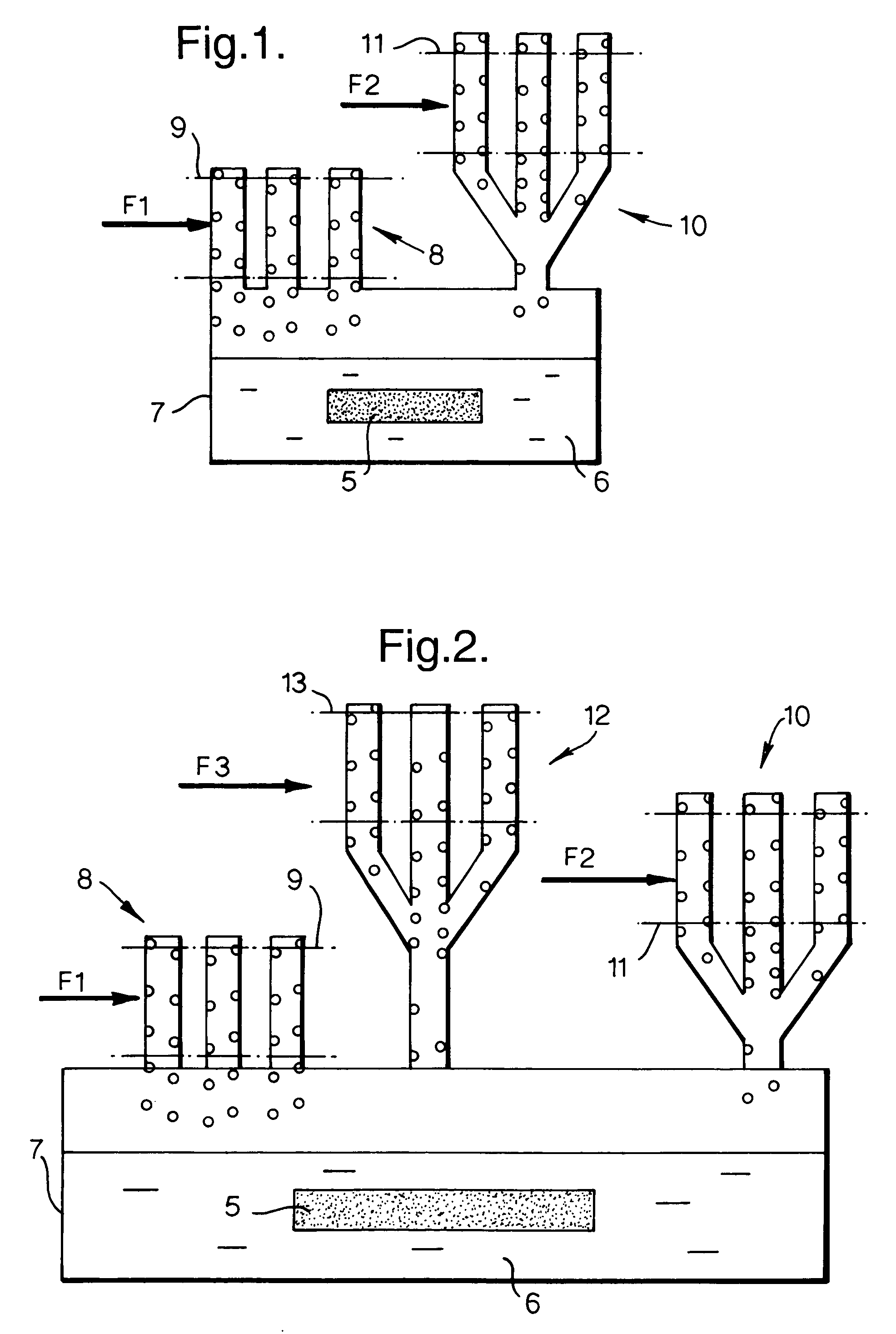
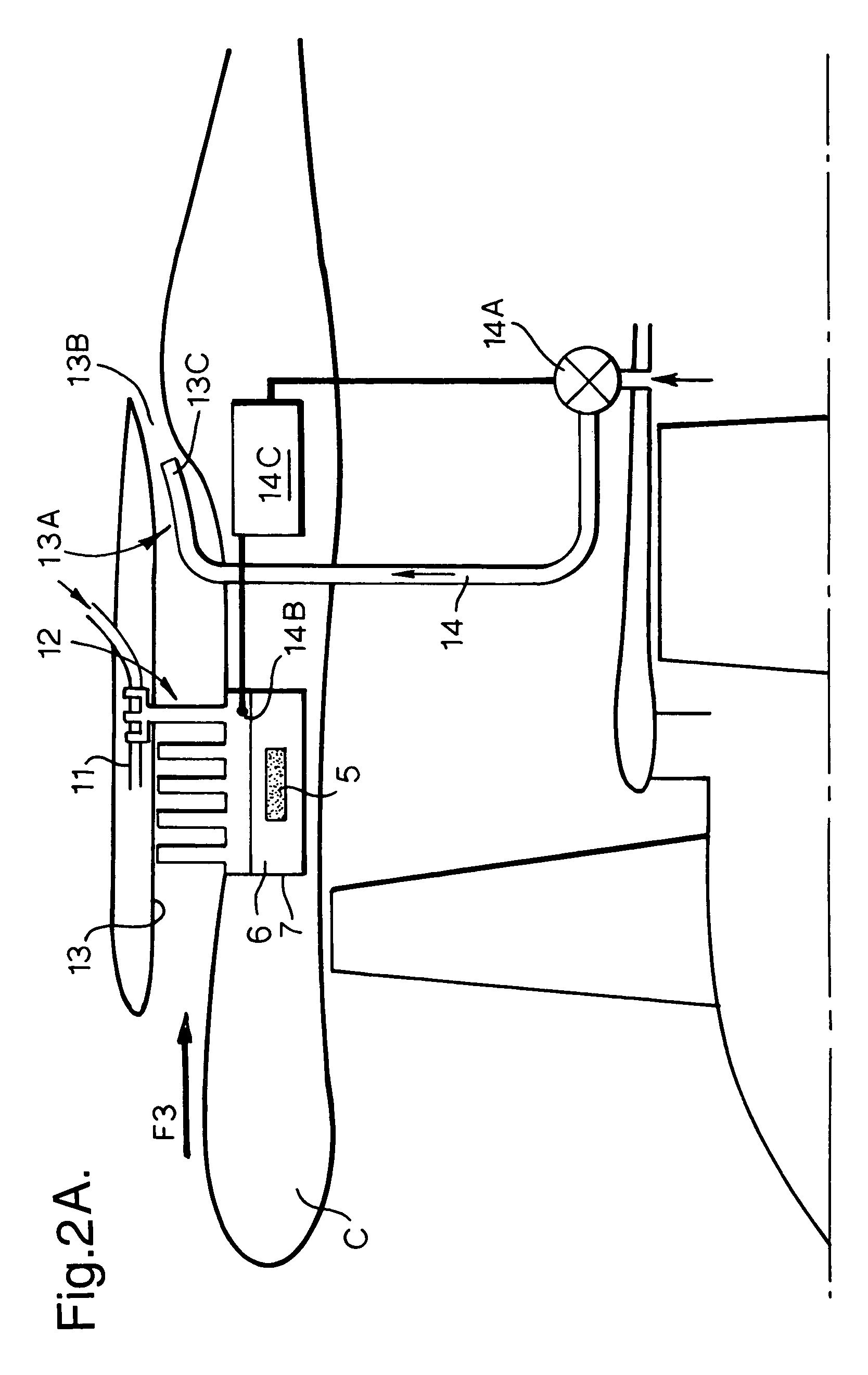
A thermal management system for a gas turbine powerplant with an engine oil line and an engine fuel line incorporates a heat transfer control module that includes a reversible heat pump with a heat pump compressor for circulating working fluid in forward and reverse directions through a working fluid line of the heat pump. The heat control module also includes a first heat exchanger having a heat exchange path for the working fluid between the compressor and a heat pump expansion valve and another heat exchange path for the engine oil. A second heat exchanger has a heat exchange path for the working fluid between the compressor and the expansion valve and another heat exchange path for the engine fuel. The heat pump can be operated in forward or reverse directions depending on whether heat is to be transferred from the engine oil or the fuel to the heat pump working fluid. In another embodiment an engine oil reservoir located between the first heat exchanger and the engine collects the oil before it is introduced to the engine and thus acts as a heat capacitor for the system.
Owner:PROPULSION GAS TURBINE & ENERGY EVALUATIONS
Fuel composition supply means for spark ignition engines
ActiveUS20050056264A1More of efficiencyMore of emissionsInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusMotor fuelDriving cycle
A fuel system for on-board vehicle fuel separation to supply engine fuel compositions formulated as a function of driving cycle conditions. The invention results in improvements in one or more of feed efficiency and combustion emissions.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
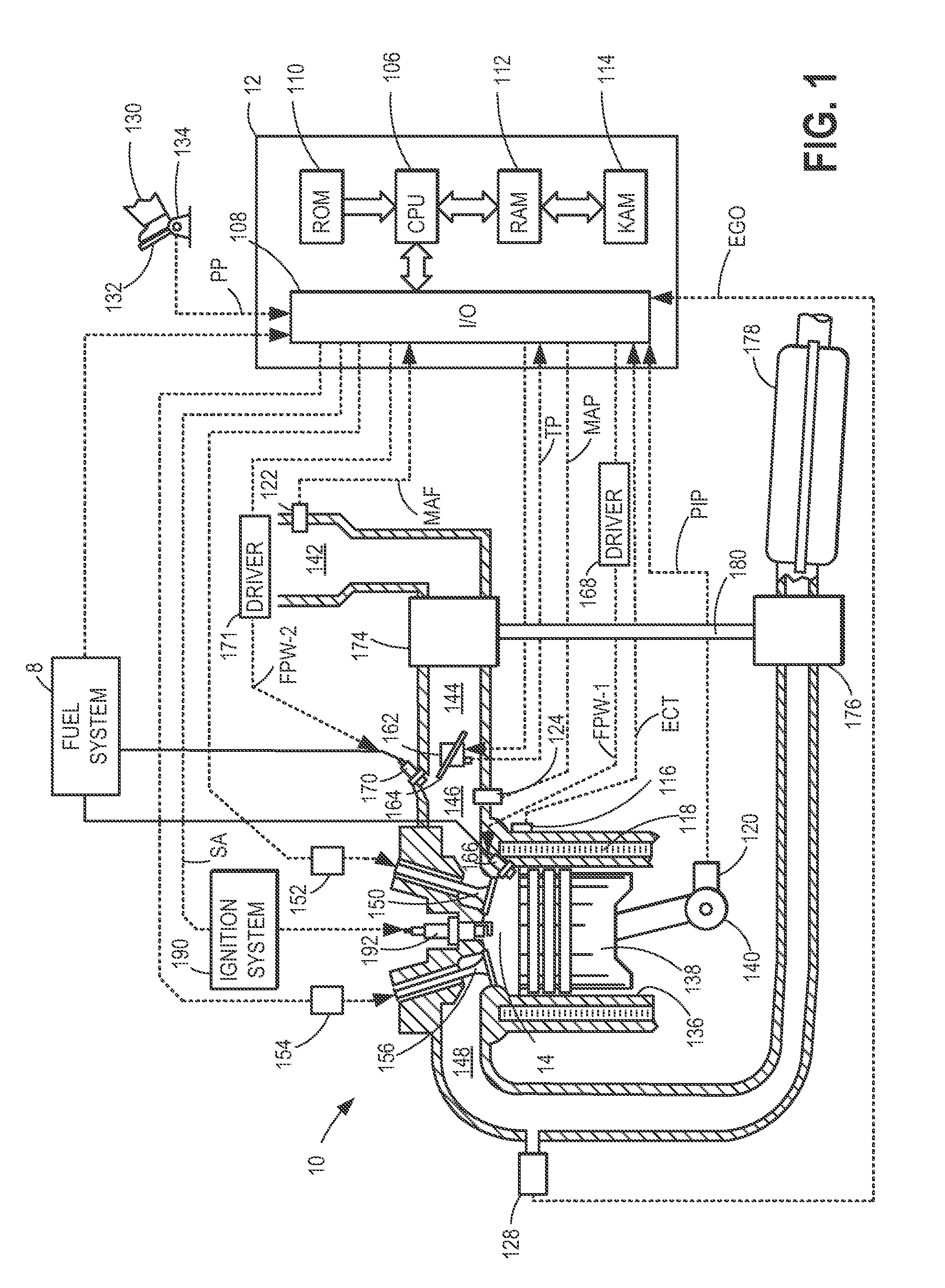
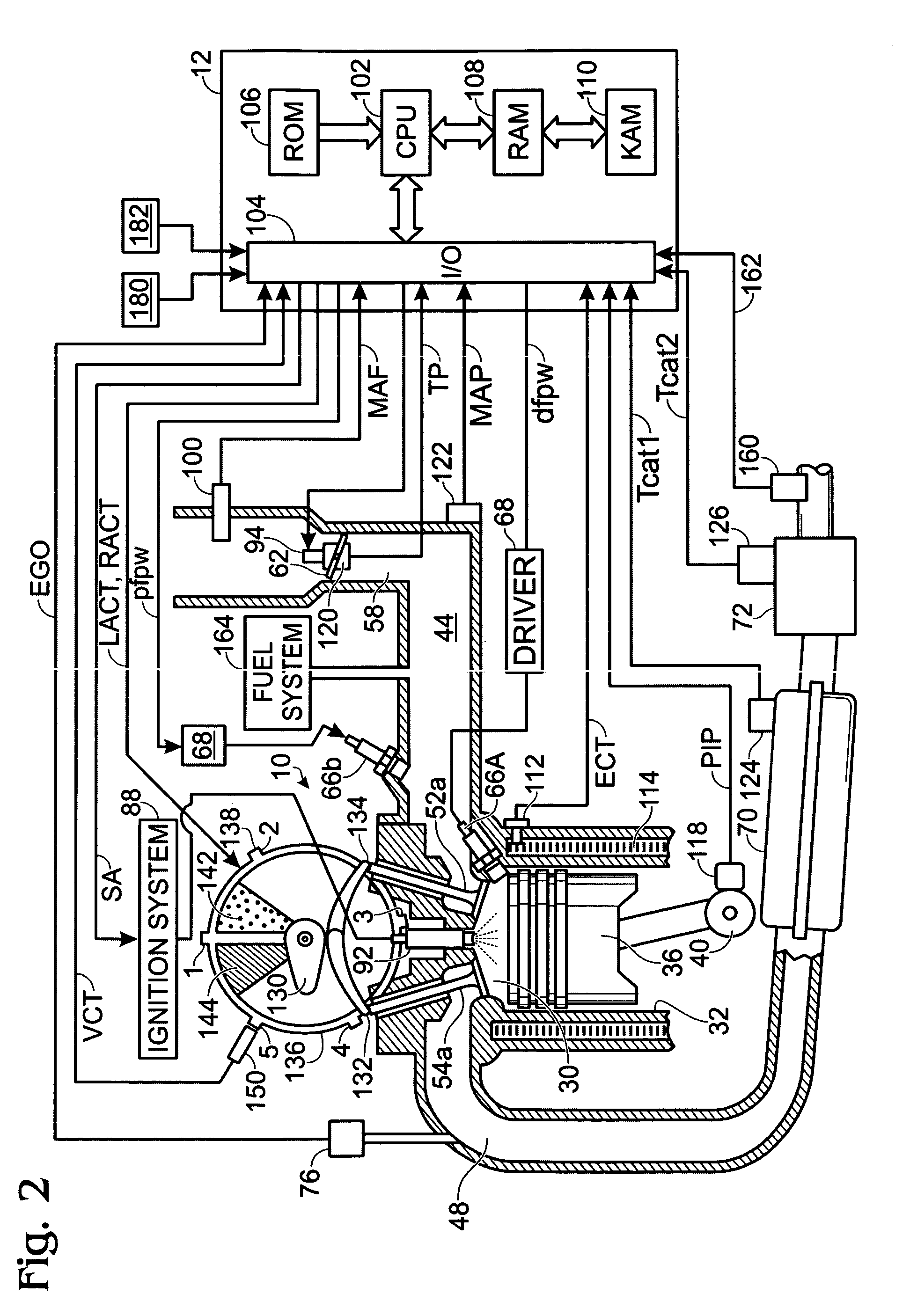
Fuel/air ratio feedback control with catalyst gain estimation for an internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7000379B2Low costSaving weightElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesIntegratorFeedback control
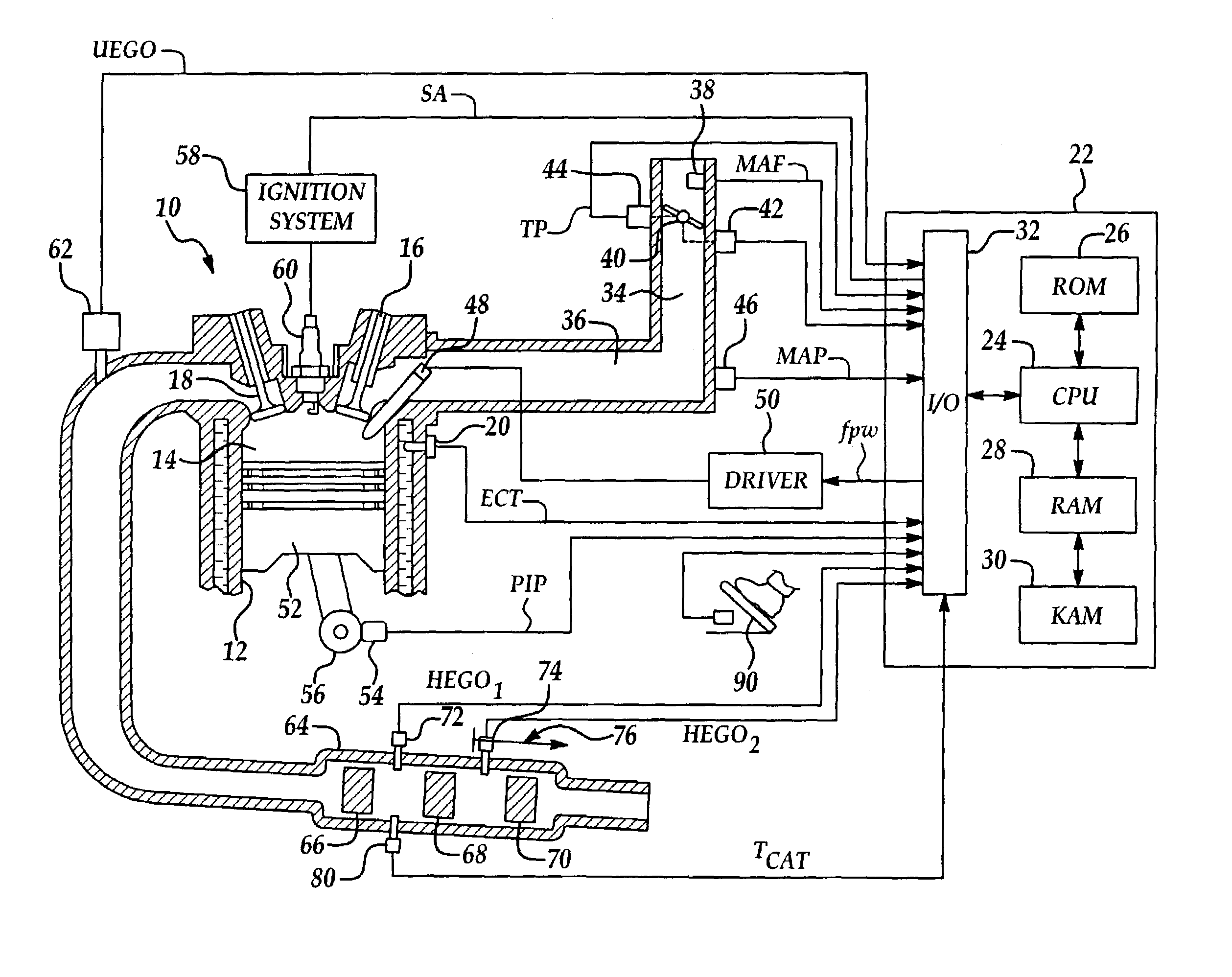
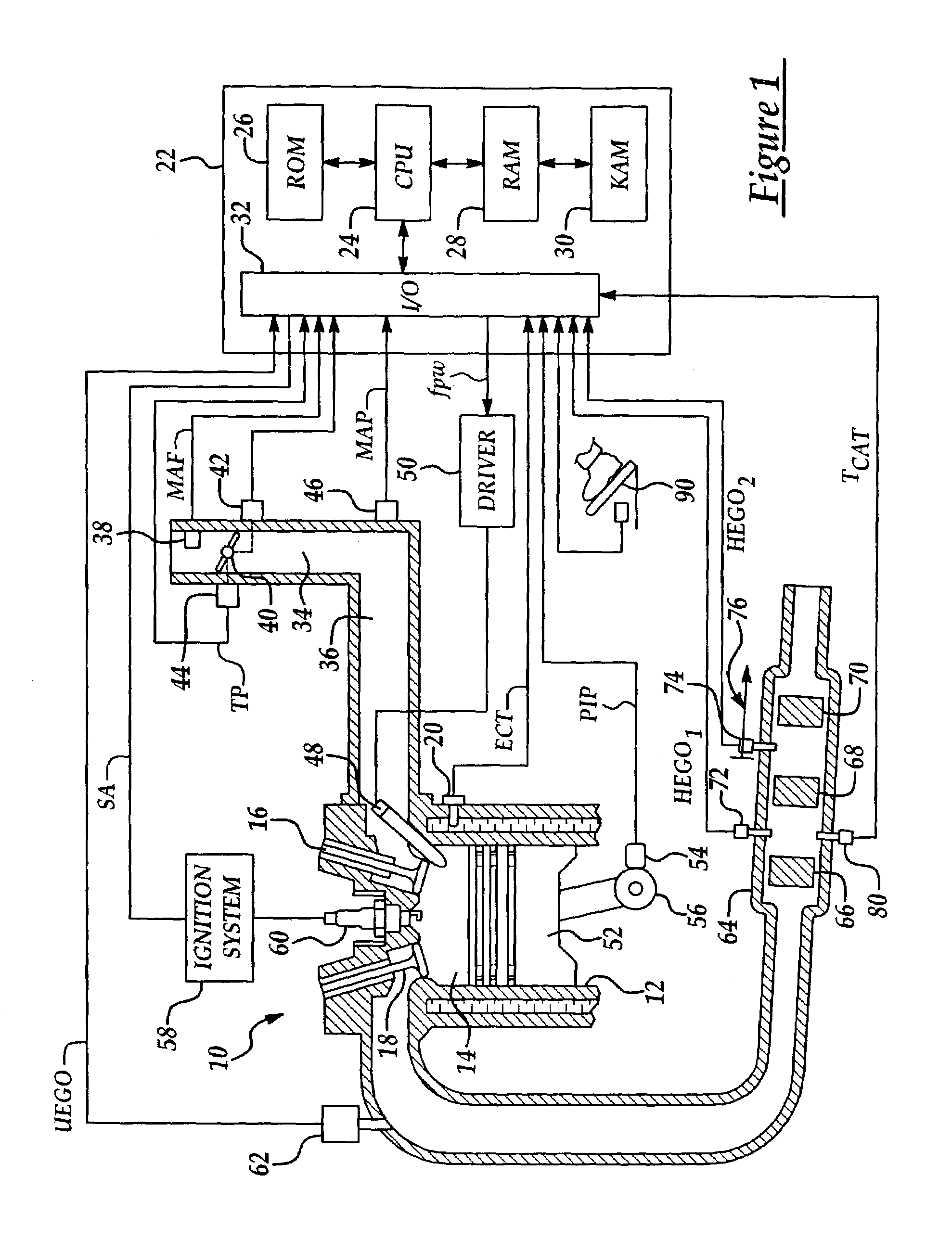
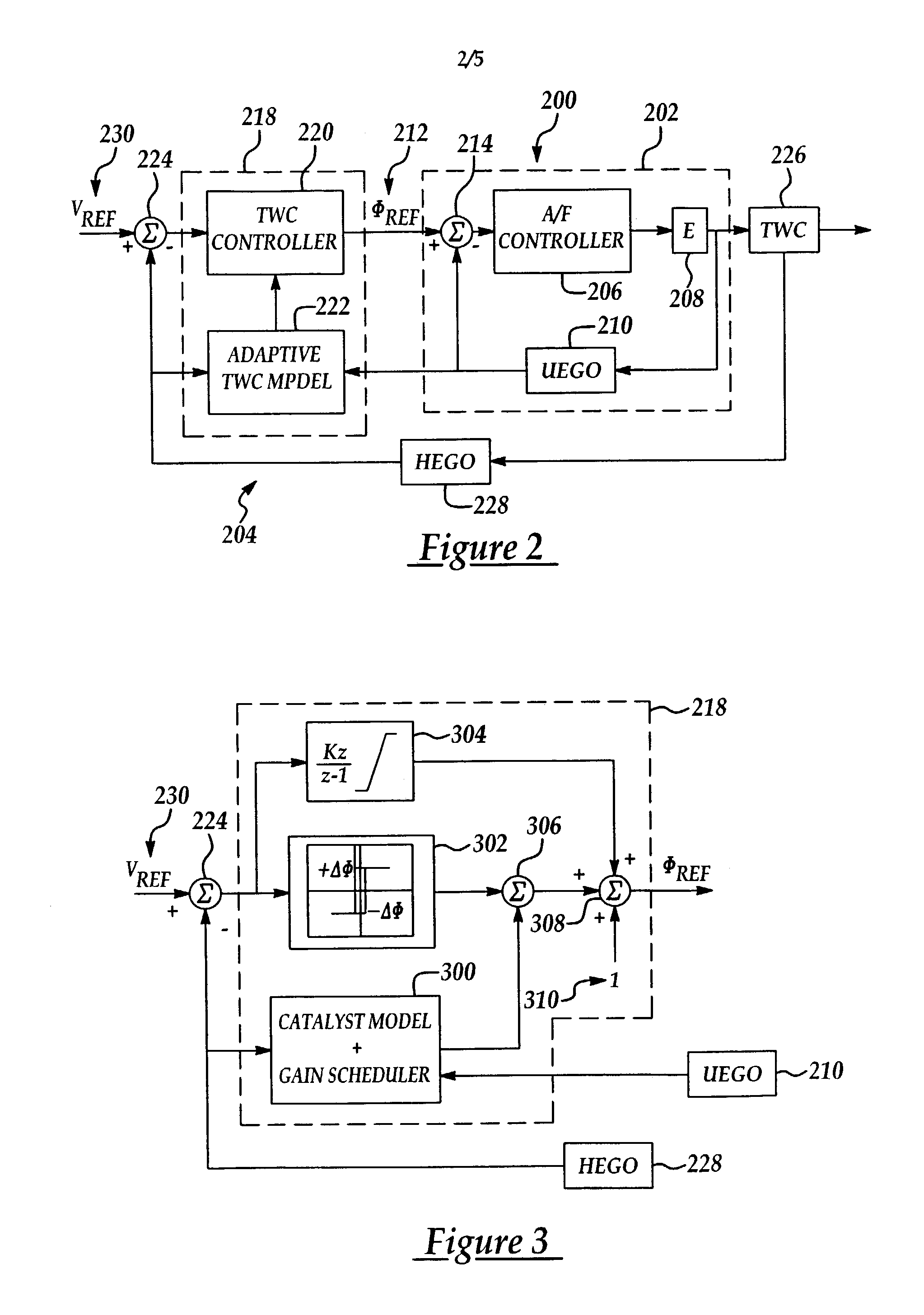
A system and method for controlling an internal combustion engine for low emissions include an inner feedback control loop to control the engine fuel / air ratio with feedback provided by a first exhaust gas sensor and an outer feedback control loop that modifies the fuel / air ratio reference provided to the inner feedback control loop based on feedback signals provided by the first exhaust gas sensor and a second exhaust gas sensor. The fuel / air ratio reference signal controller adapts to the oxygen storage capacity of the catalyst by modeling the catalyst as an integrator with an unknown gain and estimating the catalyst gain based on the first and second exhaust gas sensor signals. Using the estimated catalyst gain, an adaptive controller gain factor is determined and subsequently used to determine the fuel / air ratio reference signal provided to the fuel / air ratio controller of the inner feedback control loop.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and Apparatus to Selectively Reduce NOx in an Exhaust Gas Feedstream
ActiveUS20080066456A1Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsReduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelControl systemExhaust fumes
A method and apparatus are described to selectively reduce NOx emissions of an internal combustion engine. An exhaust aftertreatment system comprises an injection device operative to dispense a hydrocarbon reductant upstream of a silver-alumina catalytic reactor device. A control system determines a NOx concentration and hydrocarbon / NOx ratio based upon selected parameters of the exhaust gas feedstream and dispenses hydrocarbon reductant during lean engine operation. Included is a method to control elements of the feedstream during lean operation. The hydrocarbon reductant may comprise engine fuel.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Fuel alcohol content detection via an exhaust gas sensor
InactiveUS20110132342A1Degrade fuel alcohol content identificationReduce distractionsInternal-combustion engine testingElectrical controlAlcohol contentMotor fuel
Various systems and methods are described for an exhaust gas sensor coupled to an exhaust system of an engine. One example method comprises, during selected engine fueling conditions, alternating between applying different voltages to the sensor; and identifying an amount of alcohol in fuel injected to the engine based on sensor outputs at the different voltages.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Evaporative emissions control system including a charcoal canister for small internal combustion engines
InactiveUS20050178368A1Easy to collectEasy to trapNon-fuel substance addition to fuelLarge containersAtmospheric airControl system
Owner:TECUMSEH PROD CO +1
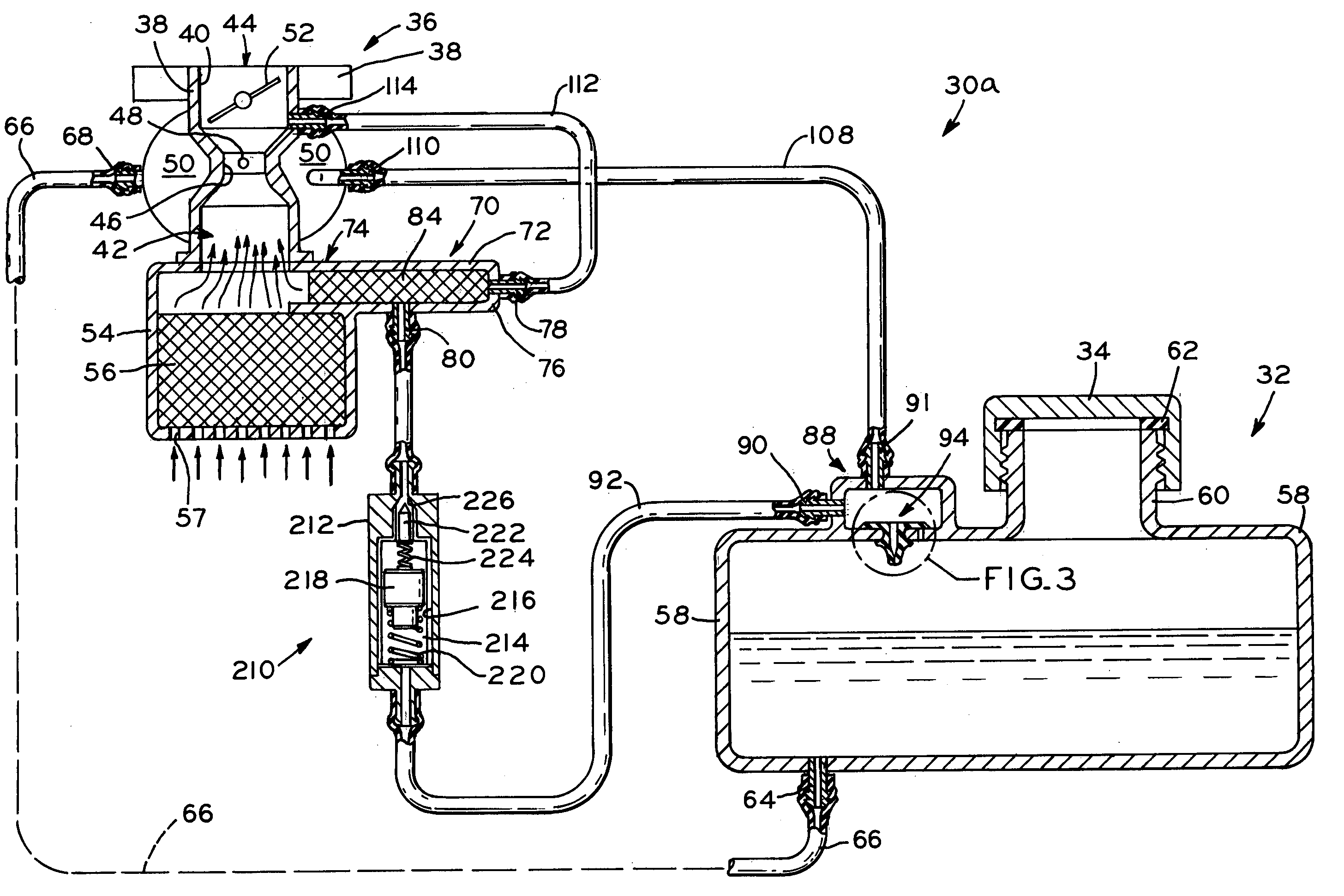
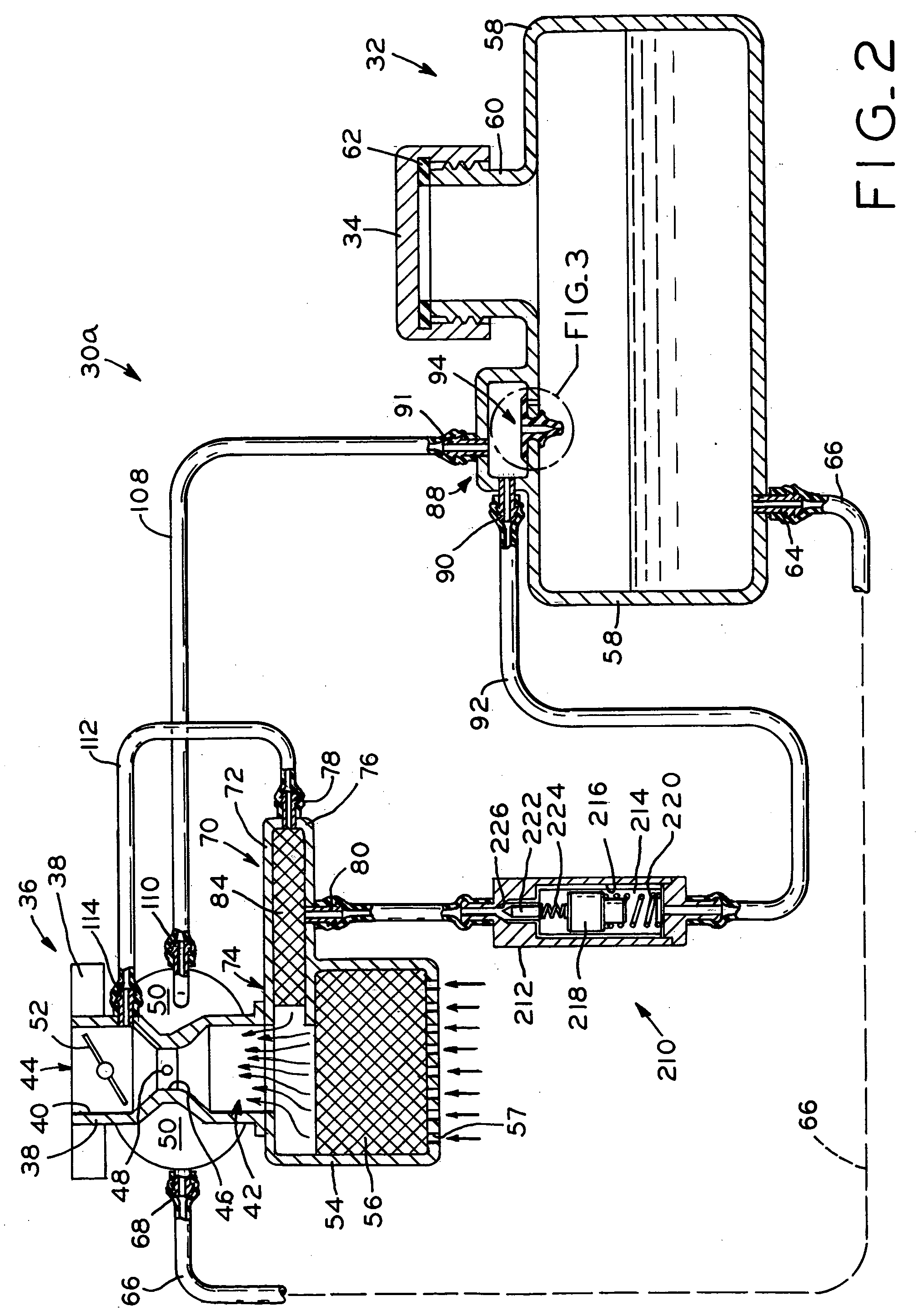
Thermal transfer internal combustion engine
A thermal transfer internal combustion engine with an air transfer cylinder located between a pair of power cylinders. The transfer cylinder has an intake valve and two transfer valves alternately feeding the two power cylinders. The power cylinders each contain a mono valve used for both intake and exhaust. Counter-flow manifolds connect the mono valves of the power cylinders to the transfer valves of the transfer cylinder. A regenerator with catalytic converter properties is located in each counter-flow manifold. The regenerator is heated by exhaust gases exiting the power cylinders, prior to exiting the engine through exhaust dump valves. Uncompressed intake air is pushed from the transfer cylinder through the regenerator where it is heated and delivered to the power cylinder for conventional processing. The heat recovery system provides high compression temperatures at low compression ratios, reducing engine fuel consumption.
Owner:WAIT IRVING S
Fuel injection method for dual-fuel engine
InactiveCN106870186ANot easy to knockIncrease concentrationElectrical controlMachines/enginesExhaust valveCombustion
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
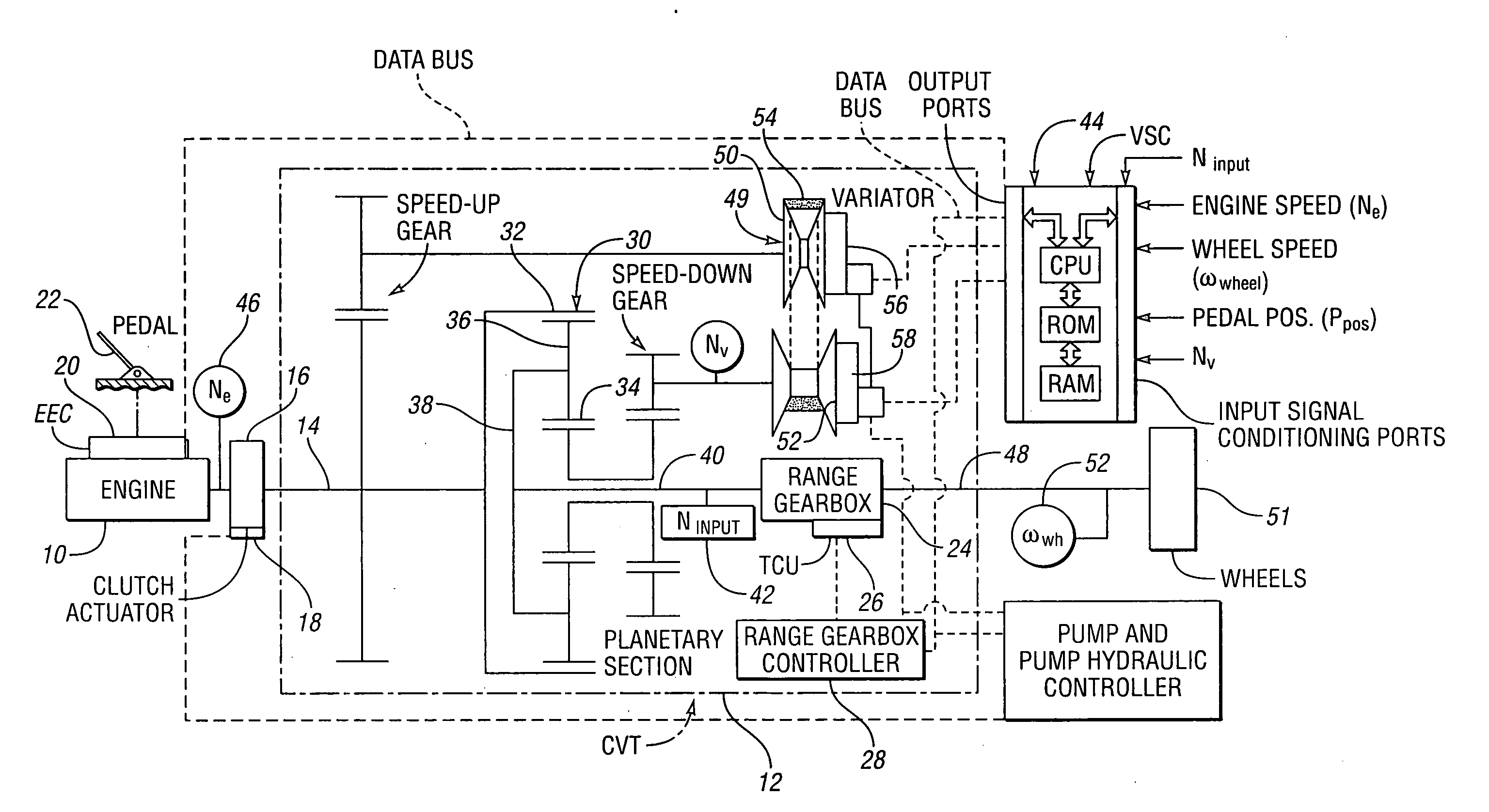
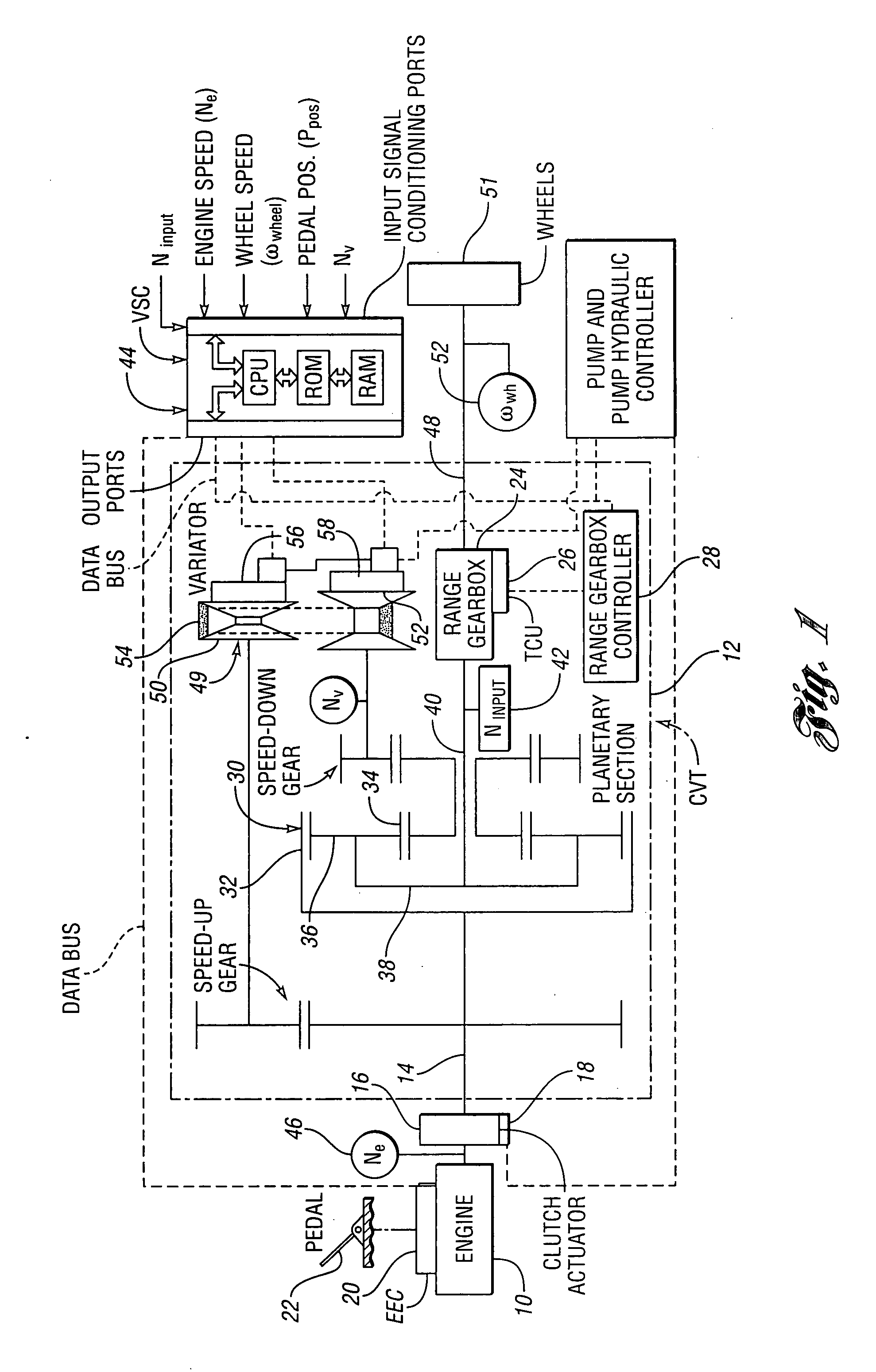
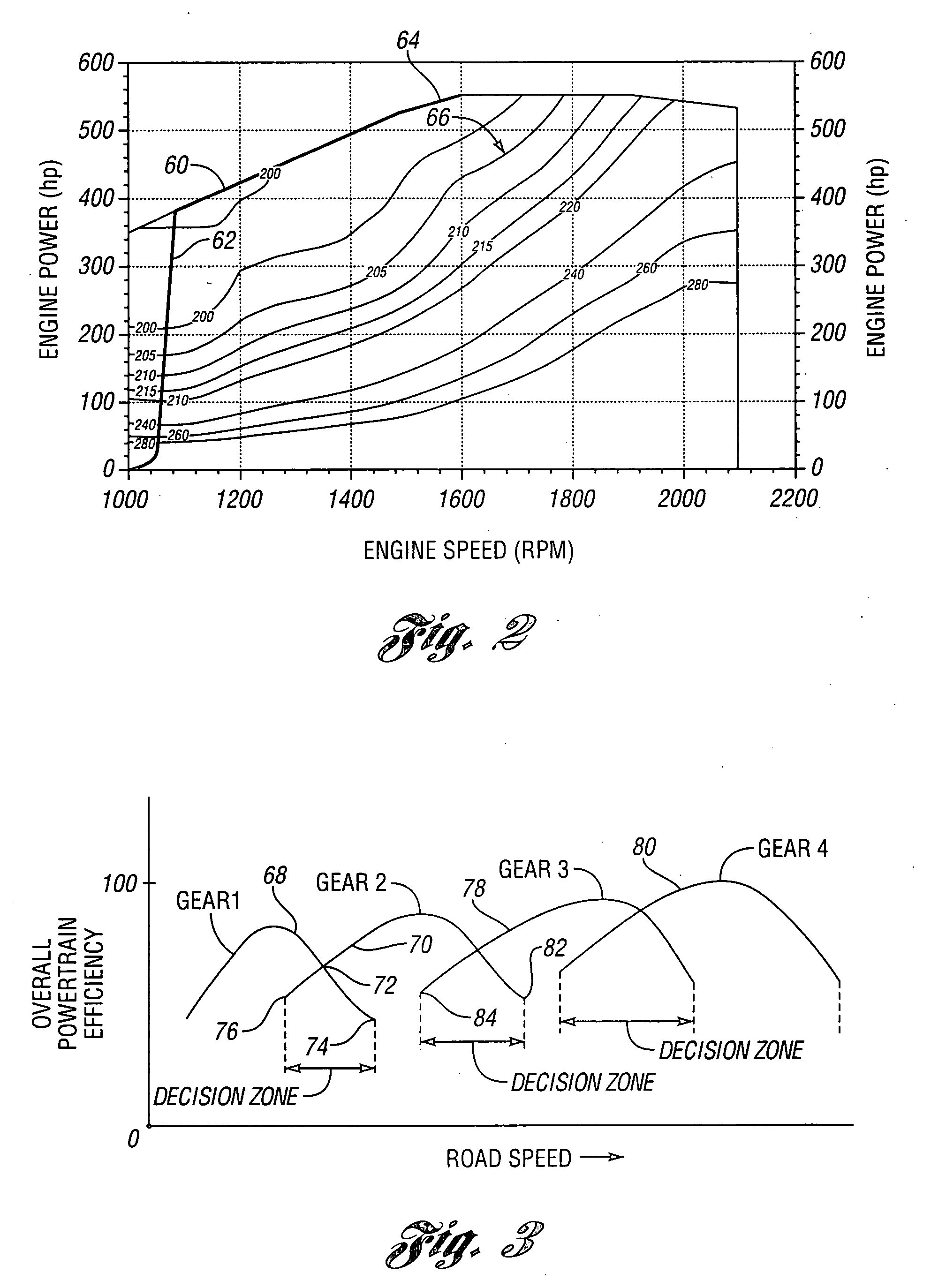
Method for controlling a vehicle powertrain having step ratio gearing and a continuously variable transmission to achieve optimum engine fuel economy
InactiveUS20090105041A1Ignores effectGuaranteed normal transmissionGearingRoad transportPowertrainMotor fuel
A method is disclosed for controlling overall transmission ratios in a vehicle powertrain with an engine, fixed multiple-ratio gearing and infinitely variable ratio components. For a given vehicle speed and for a given vehicle traction wheel horsepower, the fixed multiple-ratio gearing and the infinitely variable ratio components are controlled to operate with an overall ratio that will permit the engine to operate with optimum efficiency.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Renewable engine fuel
InactiveUS20080168706A1Efficient propulsion technologiesLiquid carbonaceous fuelsCarbon numberAlkane
The present invention provides fully renewable engine fuels derived completely from biomass sources. The fully renewable engine fuel is comprised of one or more low carbon number esters, one or more pentosan-derivable furans, one or more aromatic hydrocarbon, one or more C4-C10 straight chain alkanes derivable from polysaccharides, and one or more bio-oils. In addition, the fuel may contain triethanolamine. Such a lower octane renewable fuel may be utilized, for example, in automobile fuel, 100 LL aviation fuel applications, and turbine engine applications. These ethanol-based, fully renewable fuels may be formulated to have a wide range of octane values and energy, and may effectively be used to replace 100LL aviation fuel (known as AvGas), as well as high octane, rocket, diesel, and turbine engine fuels.
Owner:SWIFT ENTERPRISES
Aerodynamically enhanced fuel nozzle
A gas turbine engine fuel nozzle assembly includes a pilot fuel injector tip substantially centered about a centerline axis in an annular pilot inlet to a pilot mixer. A cross over arm extends across inlet to tip. Arm includes an arm fairing surrounding at least one fuel transfer tube to tip. A pilot nose cap is at an upstream end of tip. At least one of the cross over arm and the pilot nose cap includes a rounded forebody followed by a straight afterbody. Rounded forebody of pilot nose cap includes a substantially rounded dome extending forwardly from a rounded nose base and straight afterbody includes a substantially cylindrical nose afterbody parallel to a pilot nose centerline normal to nose base. An arm fairing surrounding fuel transfer tubes to tip includes rounded leading and trailing edges and a rectangular middle section therebetween having flat first and second sides.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
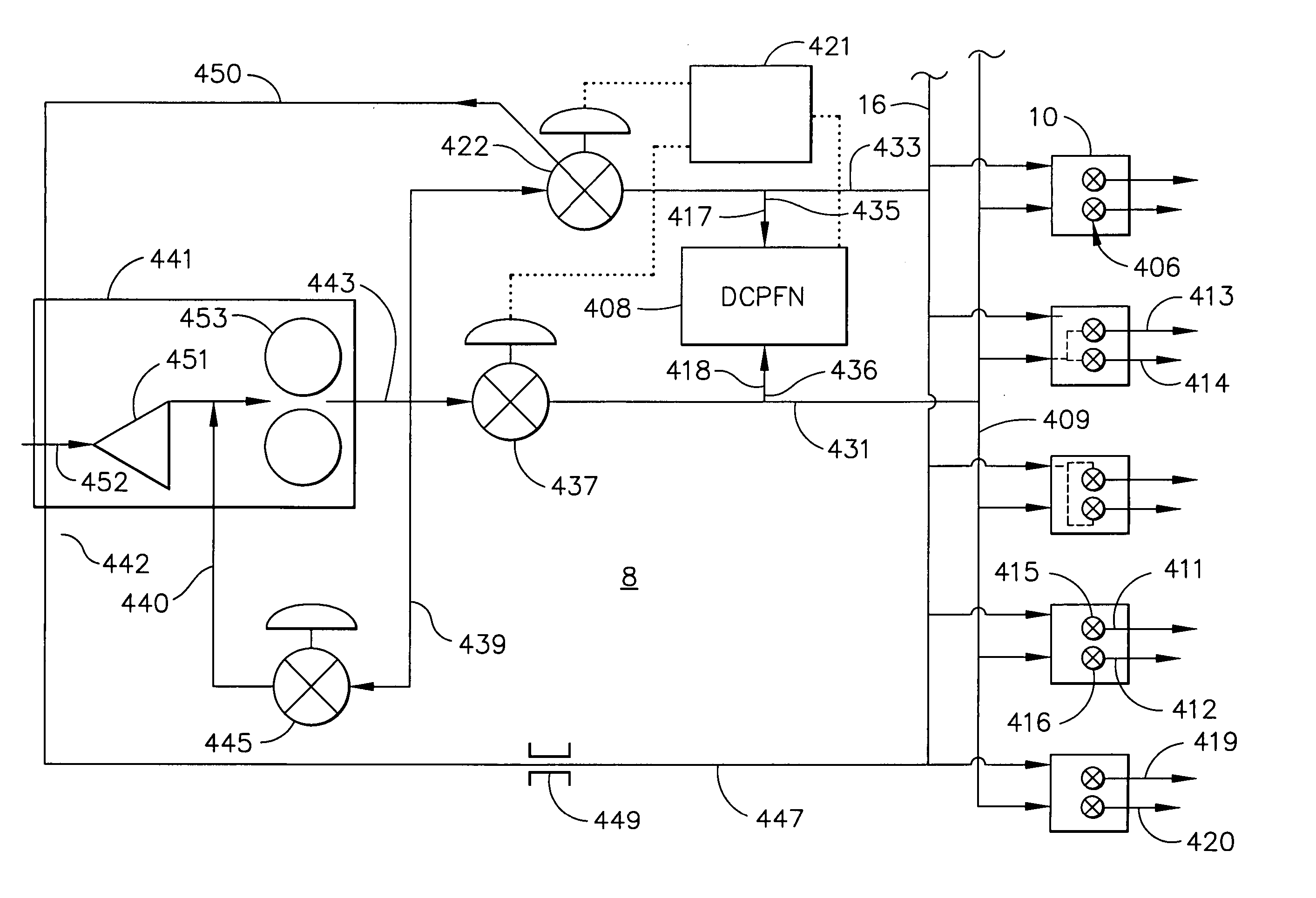
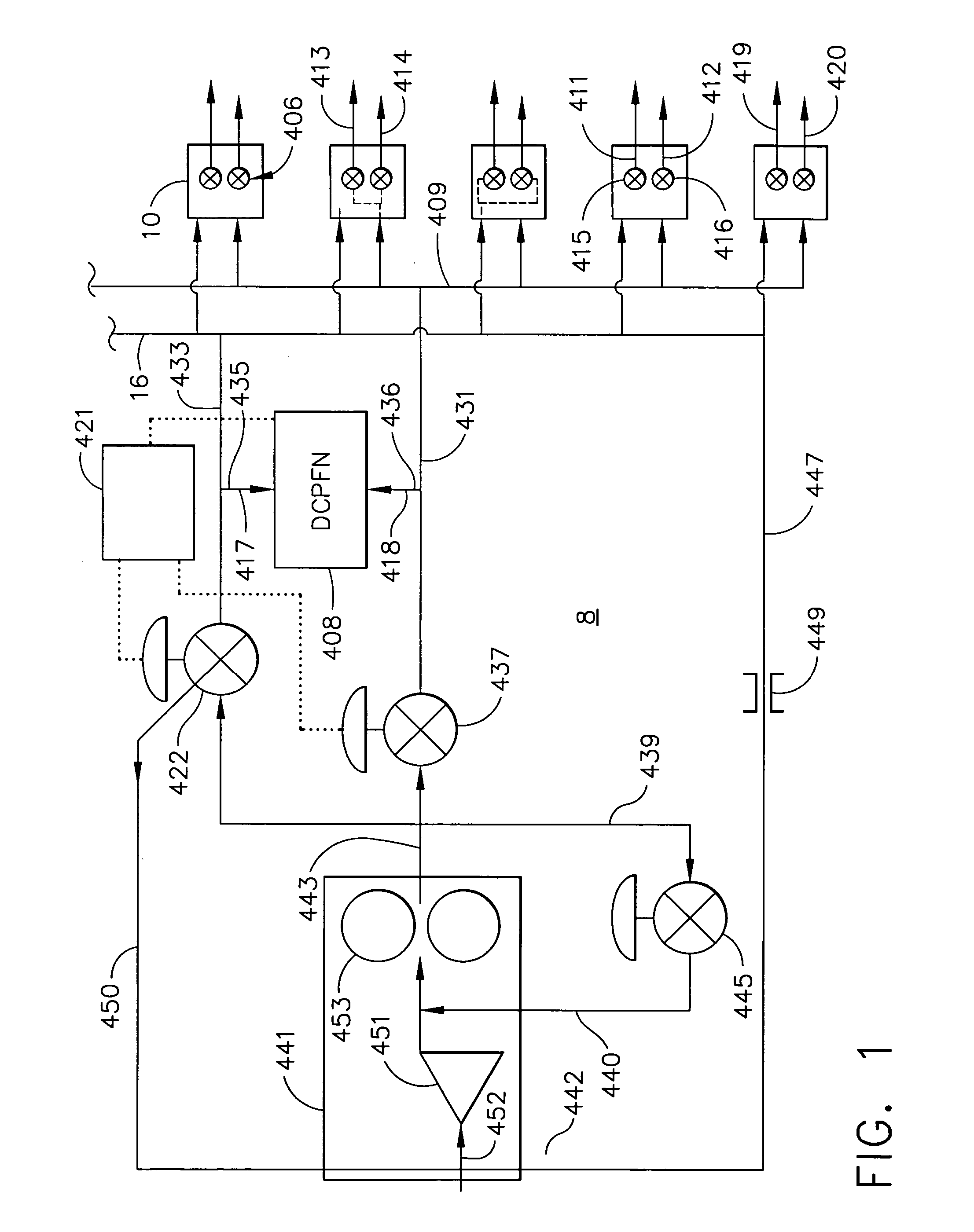
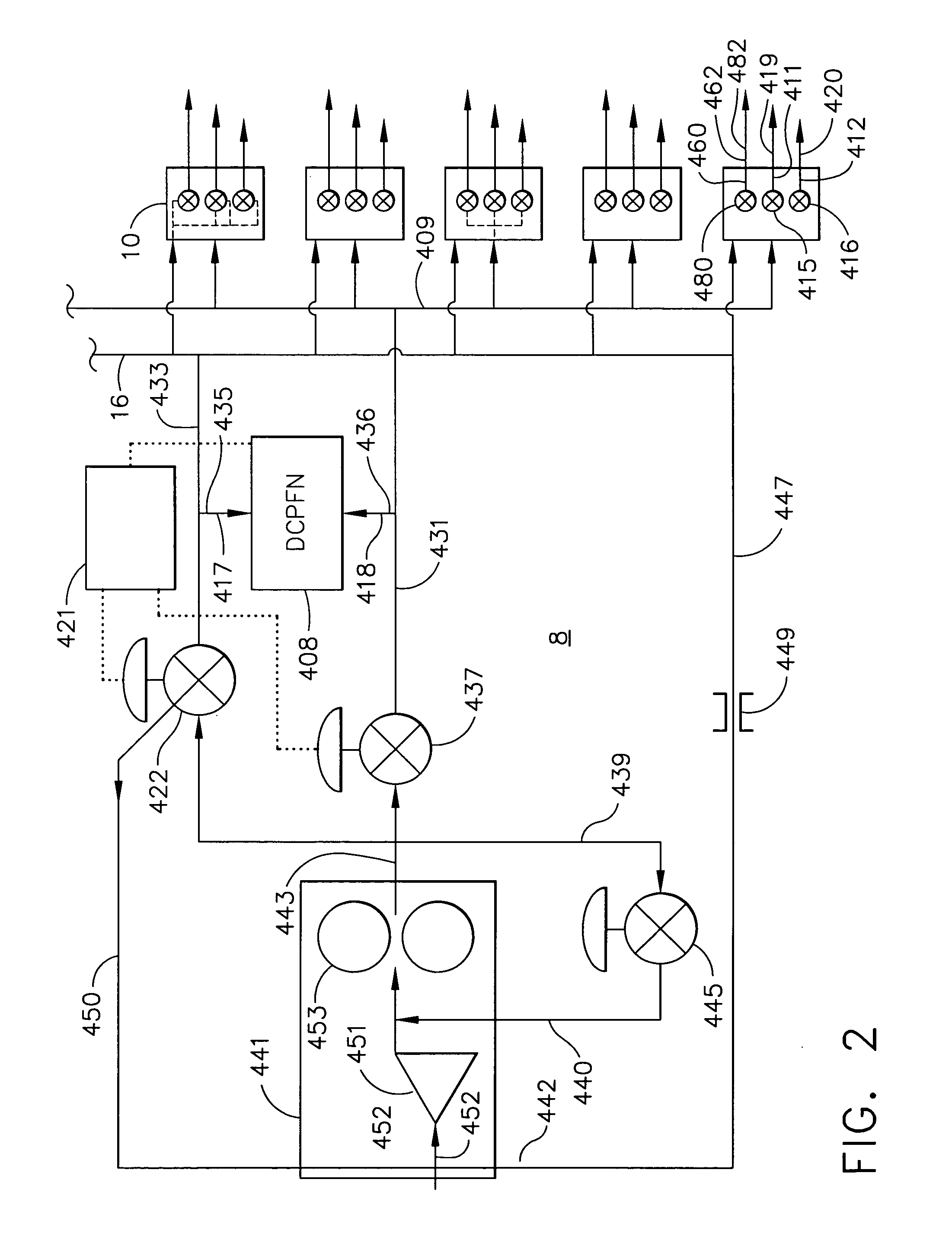
Controlled pressure fuel nozzle system
ActiveUS20050198964A1Continuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesEngineeringGas turbines
A multi-staged gas turbine engine fuel supply system includes a plurality of fuel injectors and at least first and second staged fuel injection circuits in each of the fuel injectors. Each of the first and second staged fuel injection circuits includes first and second fuel injection points and at least first and second fuel nozzle valves operable to open at different first and second crack open pressures and controllably connected to the first and second staged fuel injection circuits, respectively. A single fuel supply manifold is connected to all of the fuel nozzle valves. A single fuel signal manifold is controllably connected to all of the first and second fuel nozzle valves. The fuel injector may have a valve housing with one of the first fuel nozzle valves and one of the second fuel nozzle valves contained therein.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com