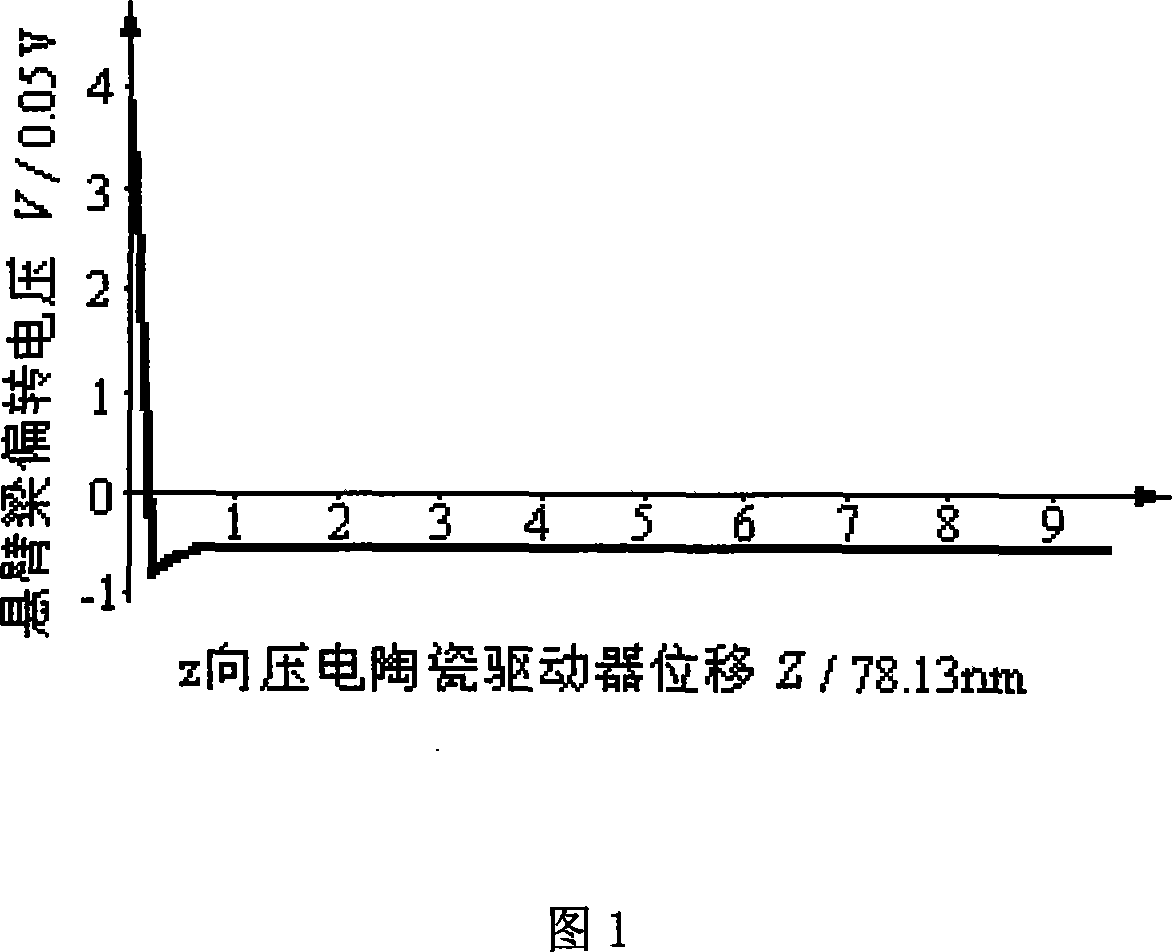
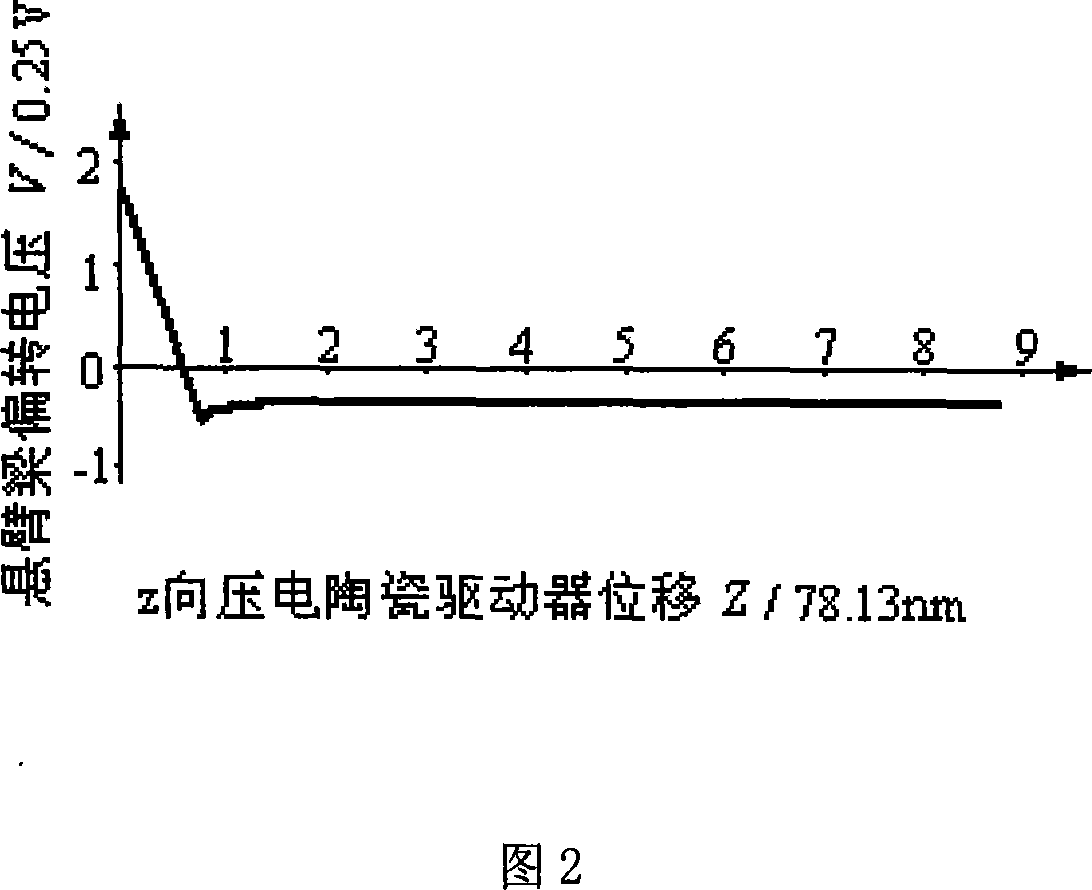
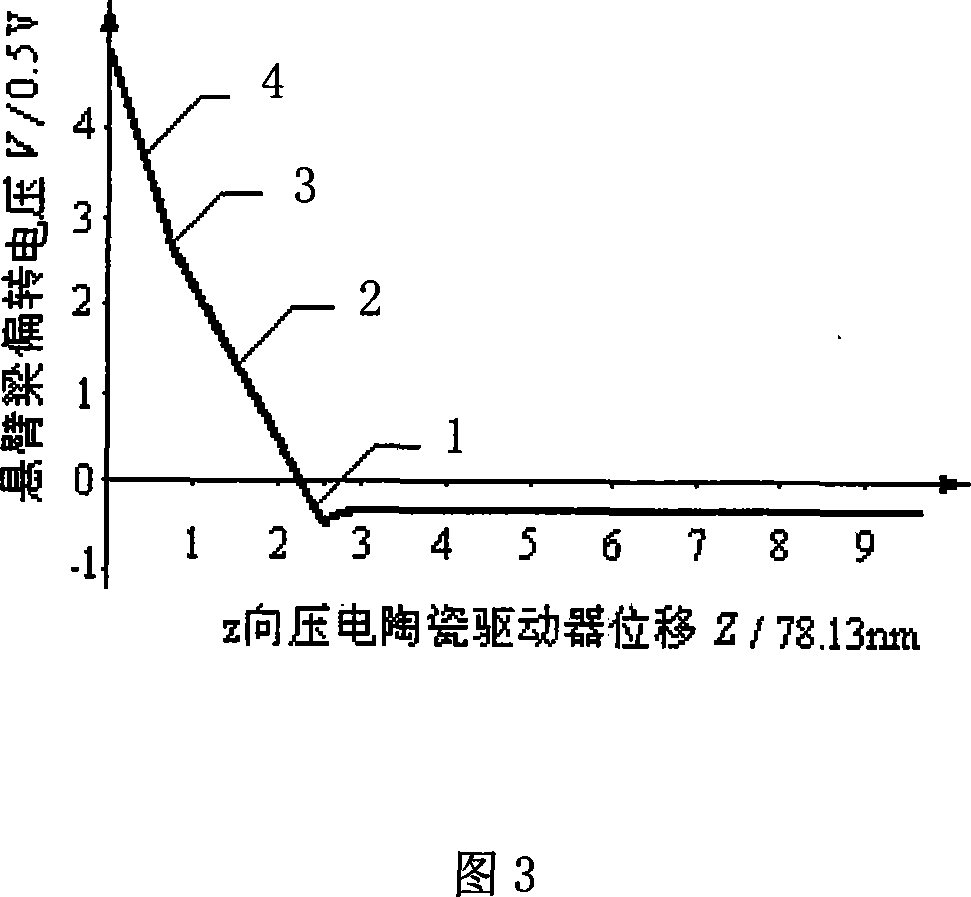
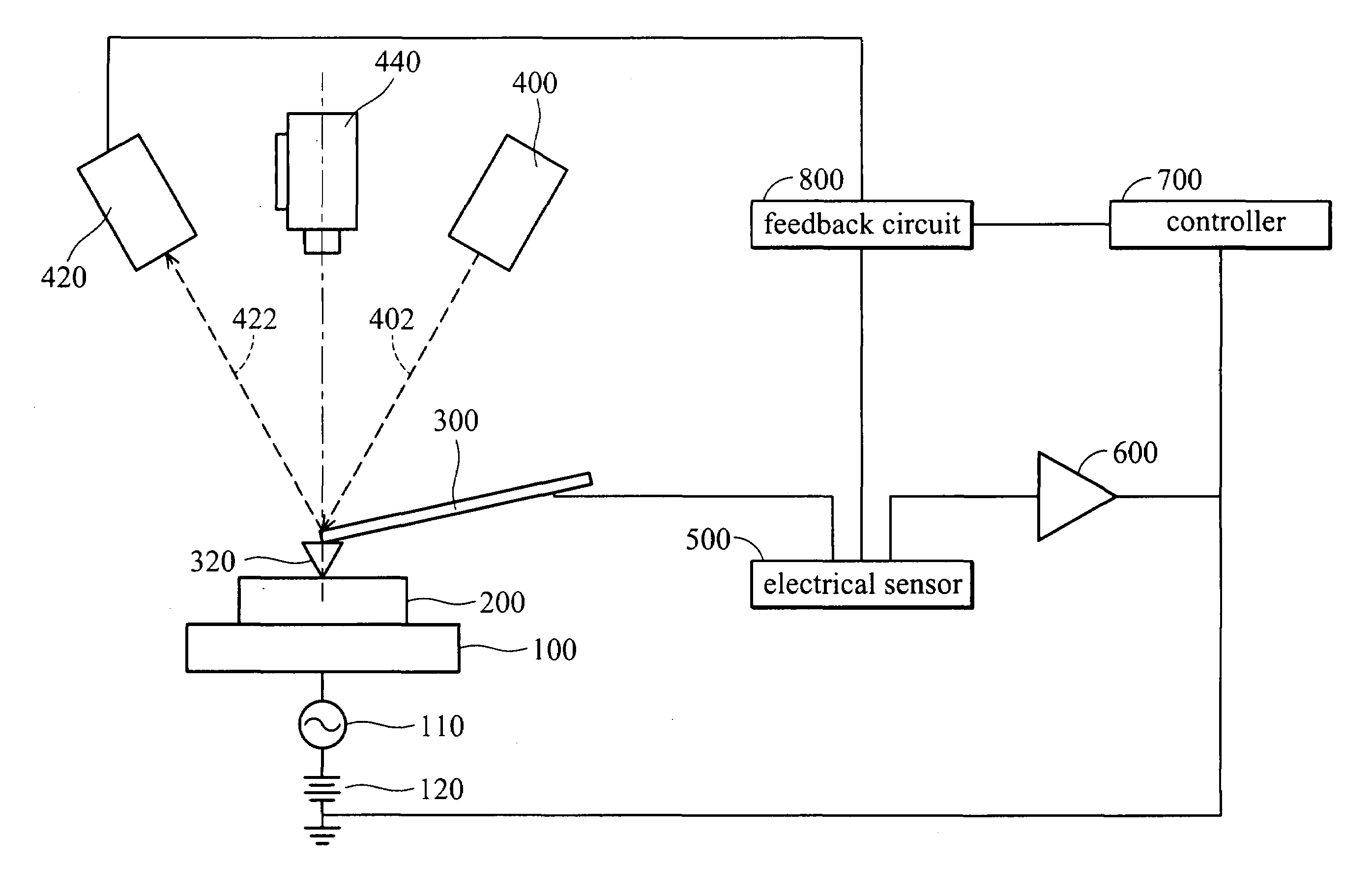
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Atomic force acoustic microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
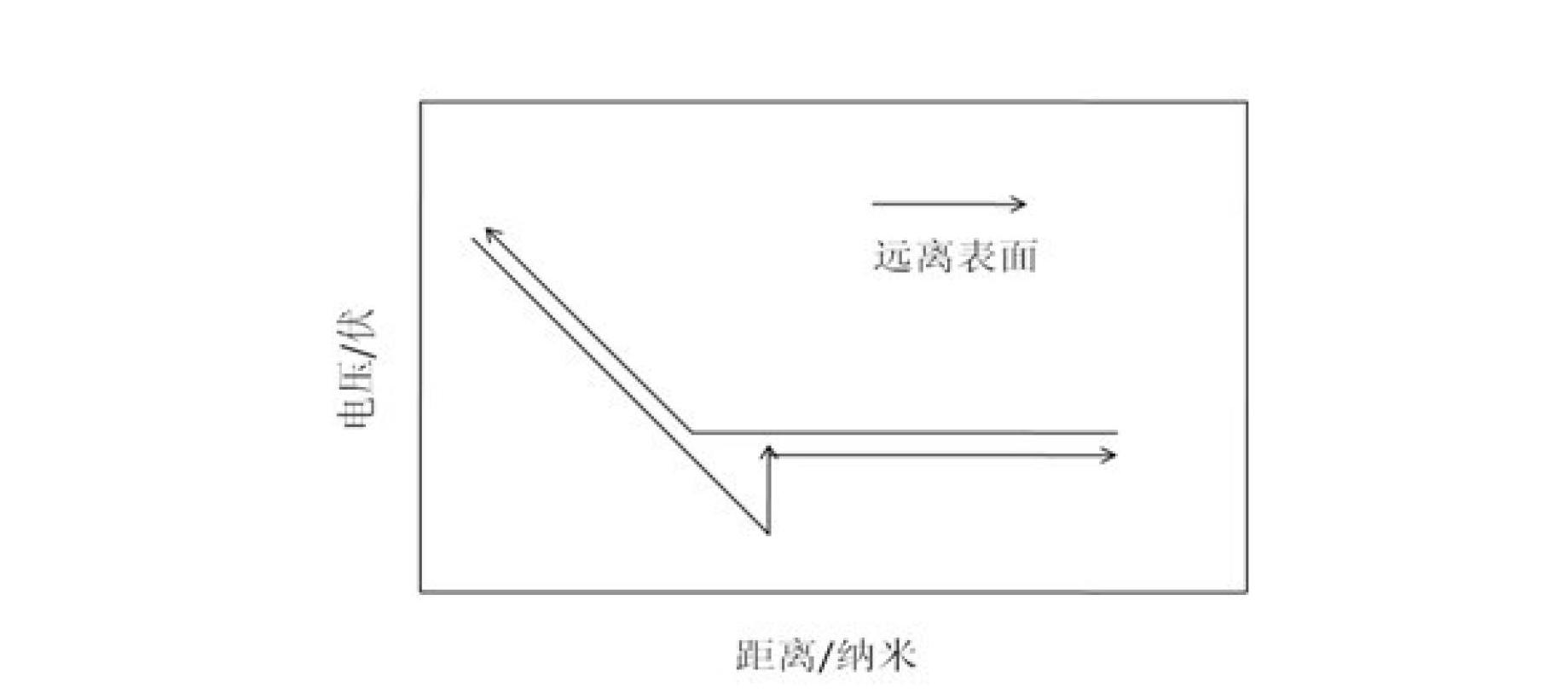
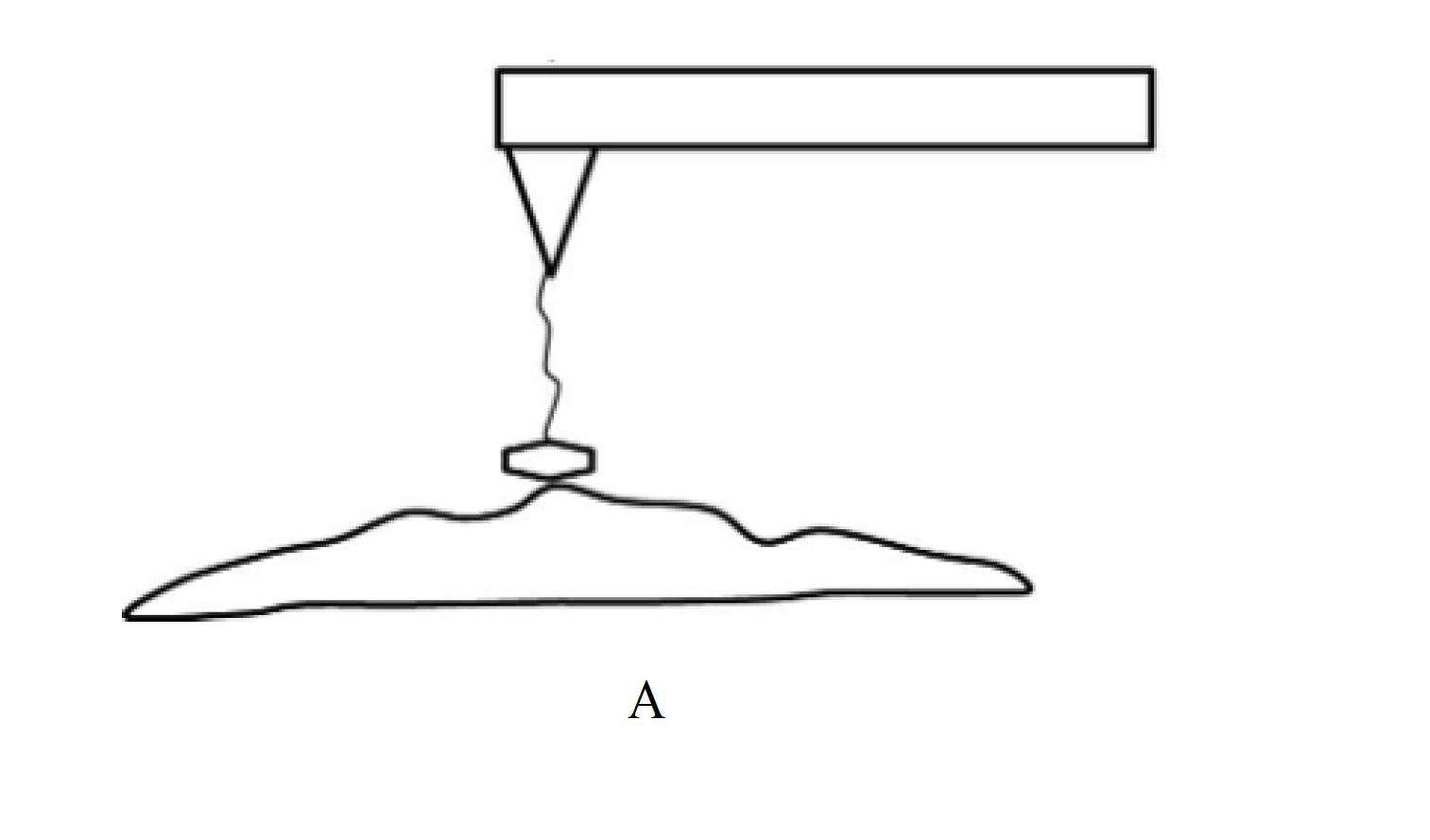
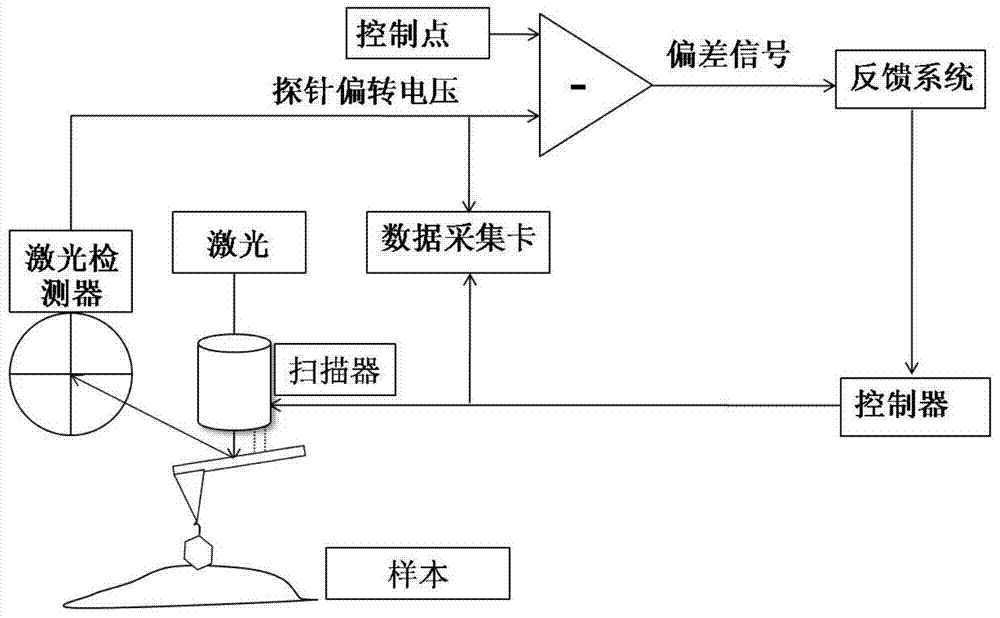
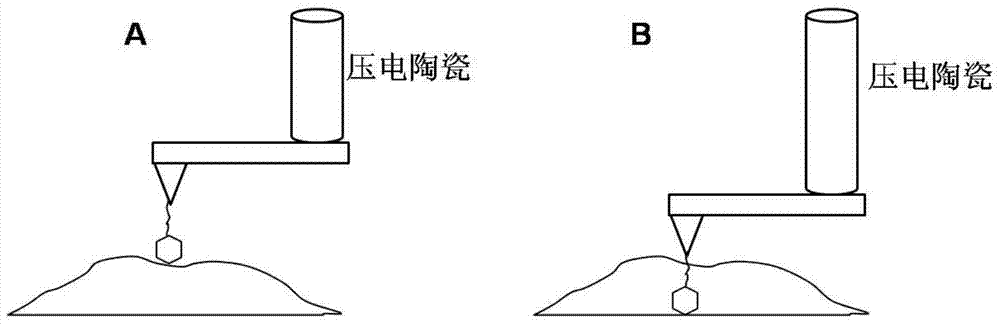
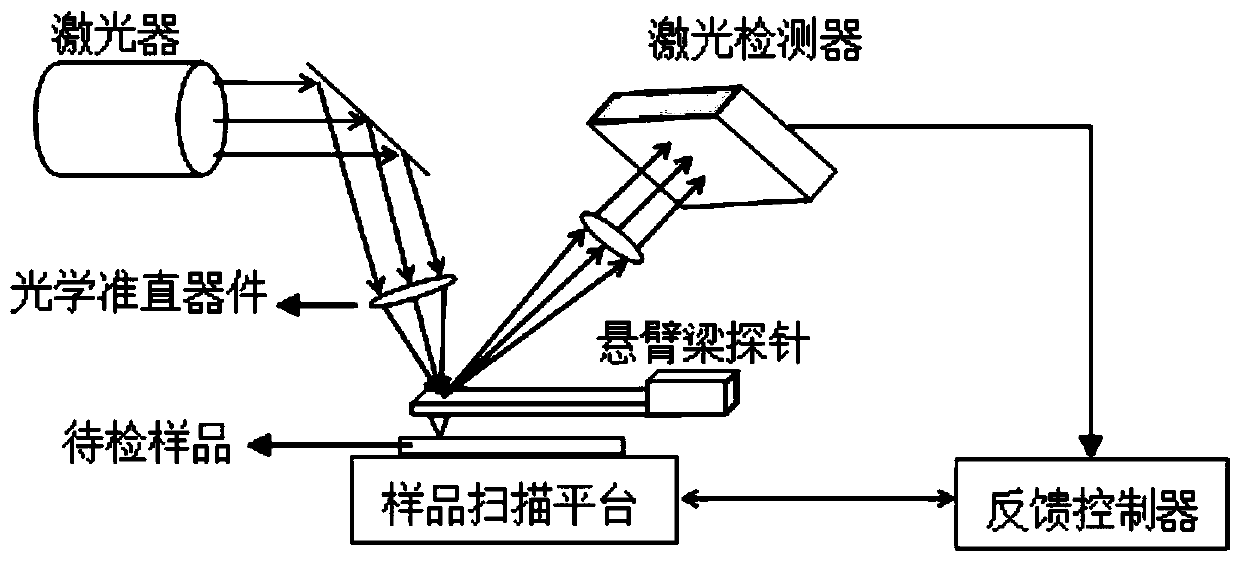
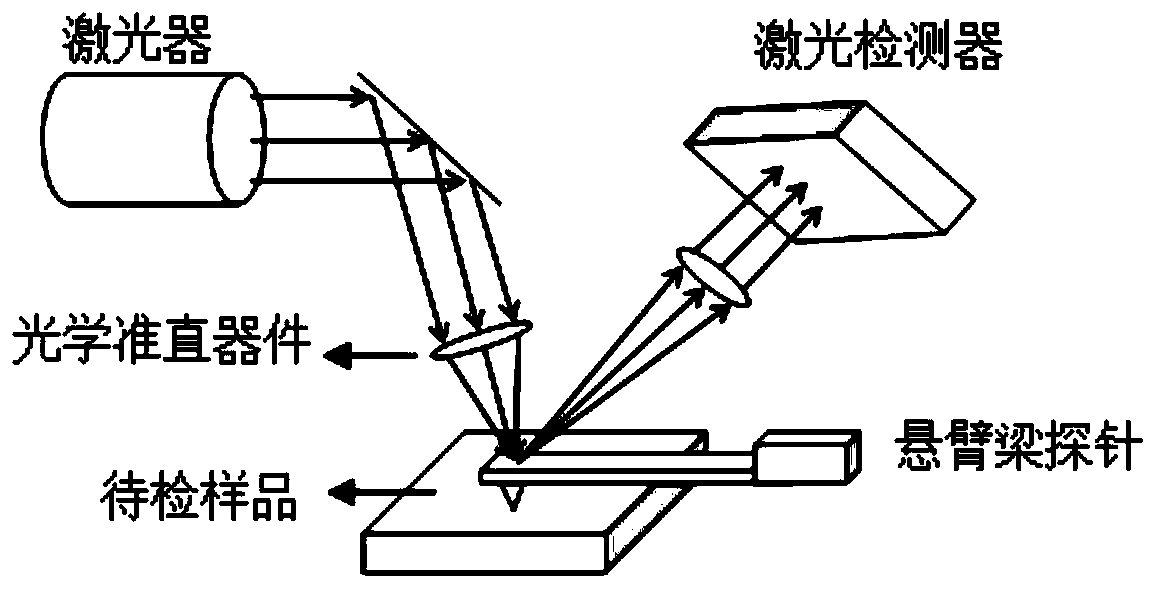
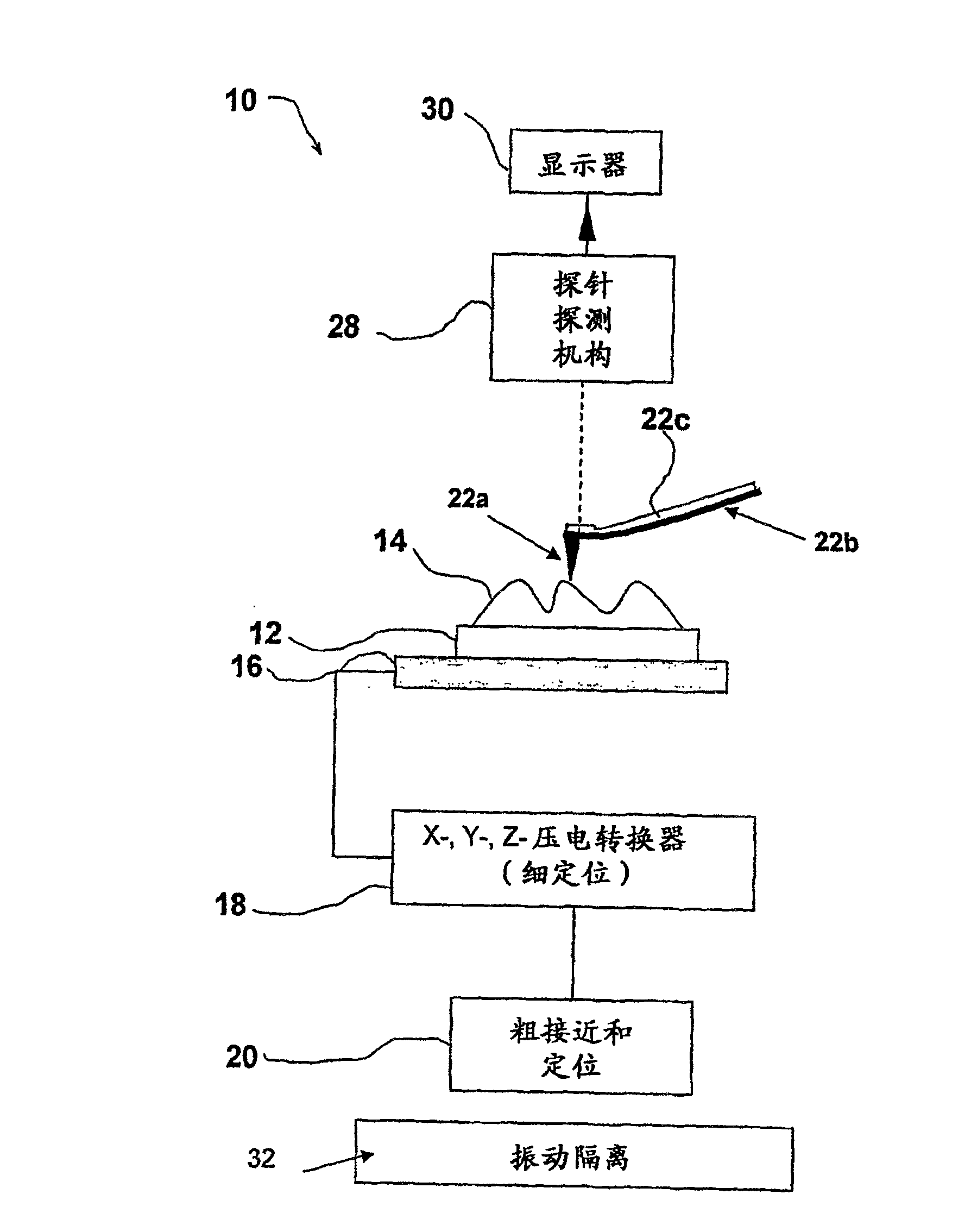
Atomic force acoustic microscopy (AFAM) is a type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM). It is a combination of acoustics and atomic force microscopy. The principal difference between AFAM and other forms of SPM is the addition of a transducer at the bottom of the sample which induces longitudinal out-of-plane vibrations in the specimen. These vibrations are sensed by a cantilever and tip called a probe. The figure shown here is the clear schematic of AFAM principle here B is the magnified version of the tip and sample placed on the transducer and tip having some optical coating generally gold coating to reflect the laser light on to the photodiode.
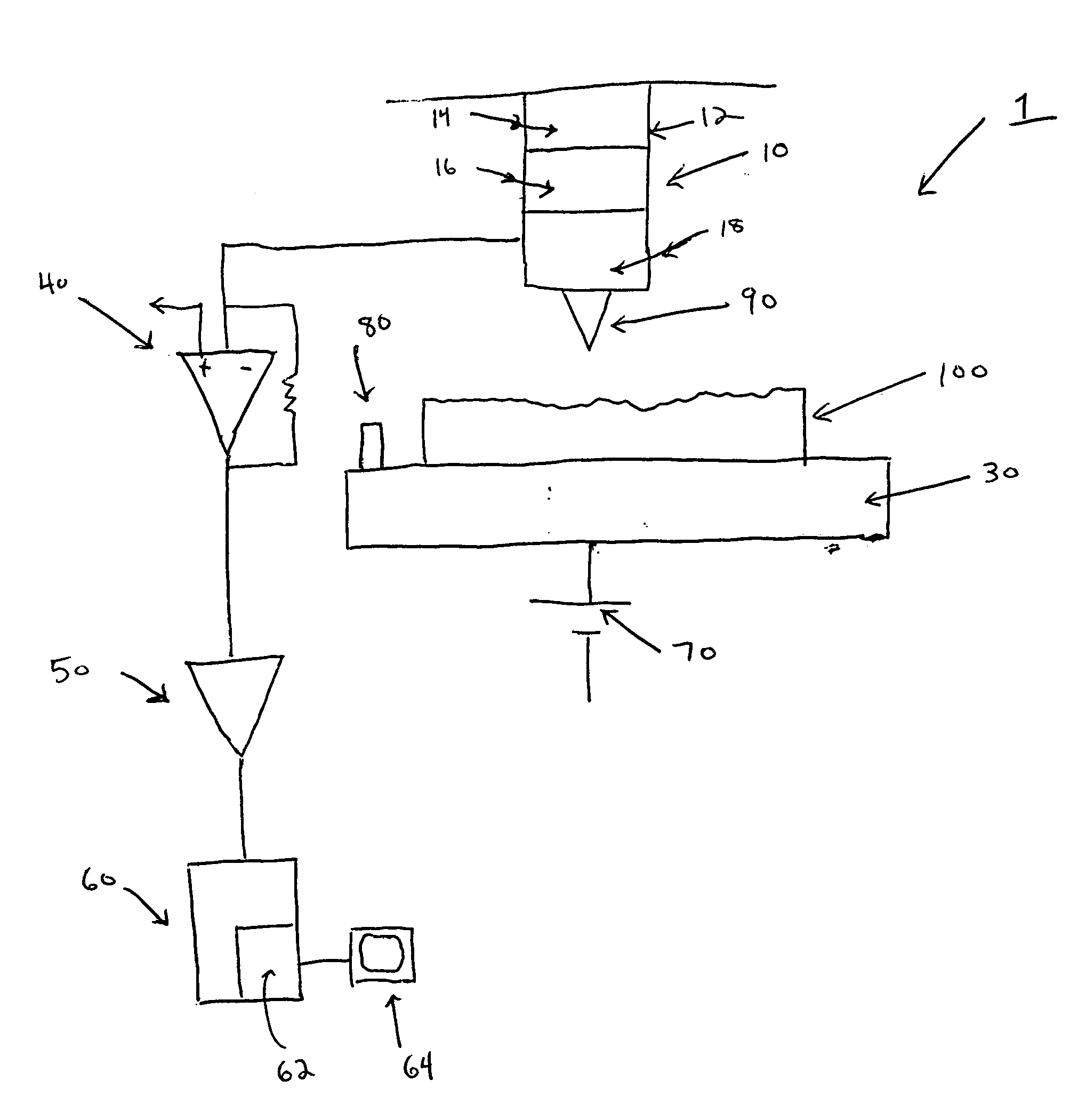
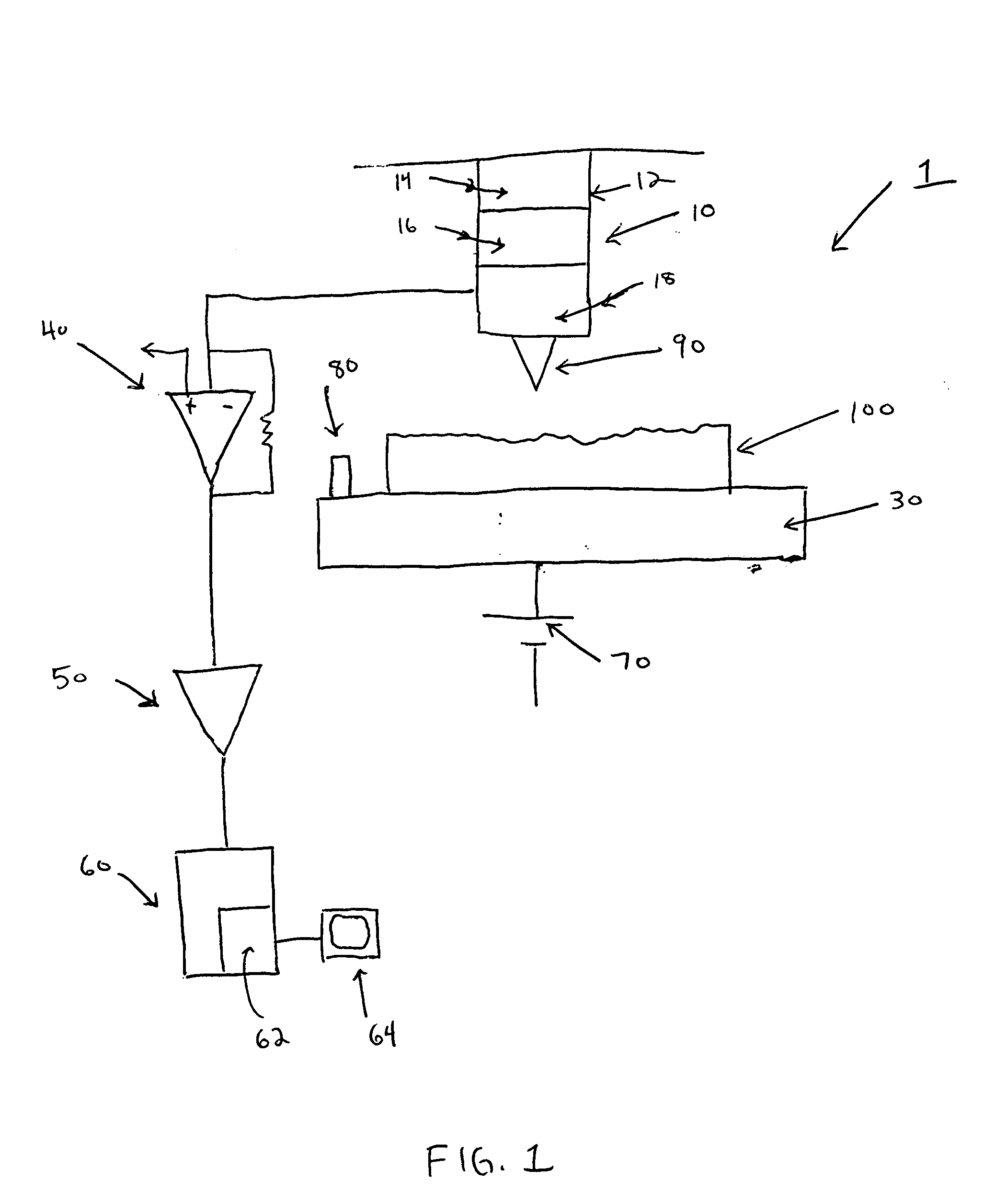
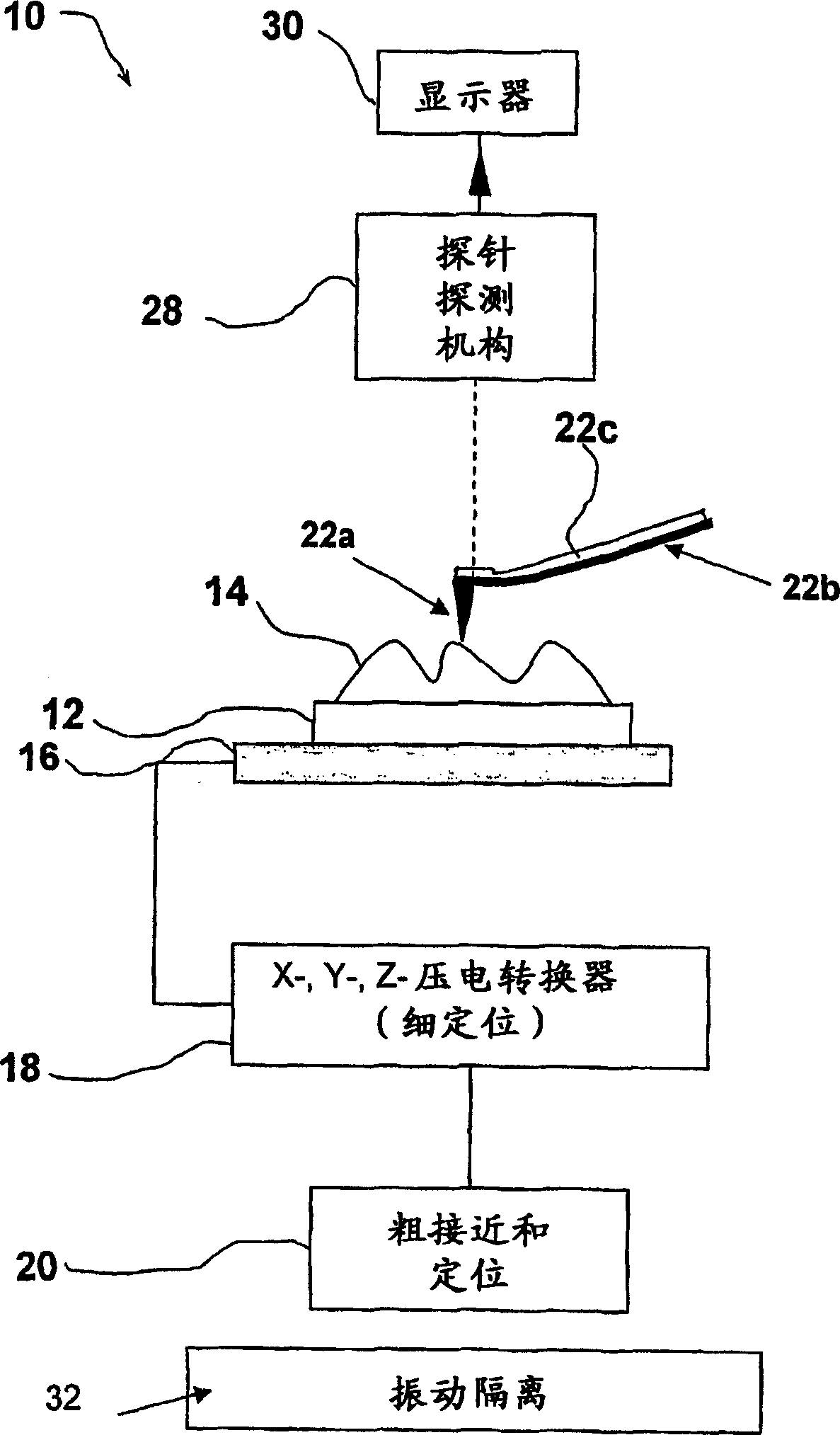
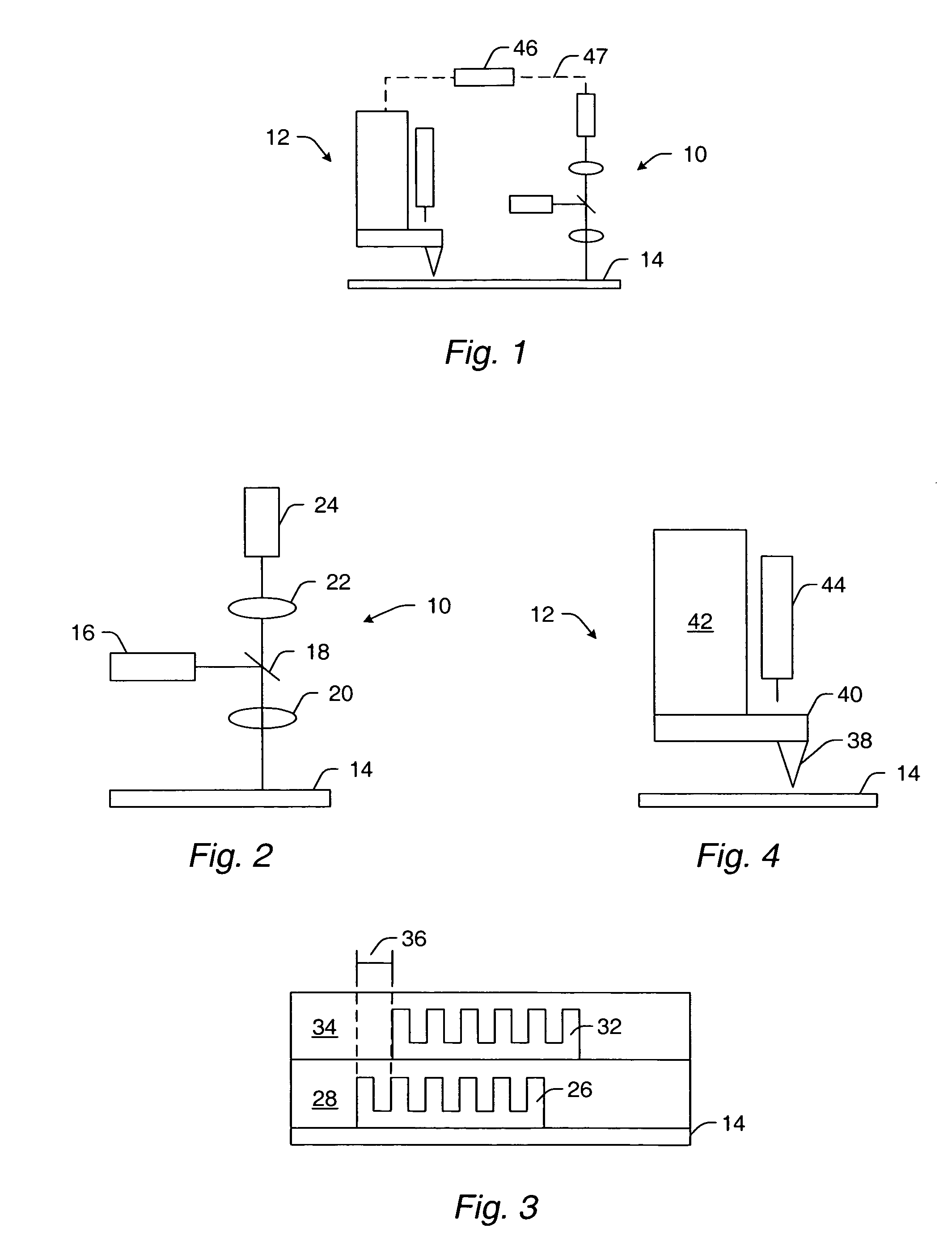
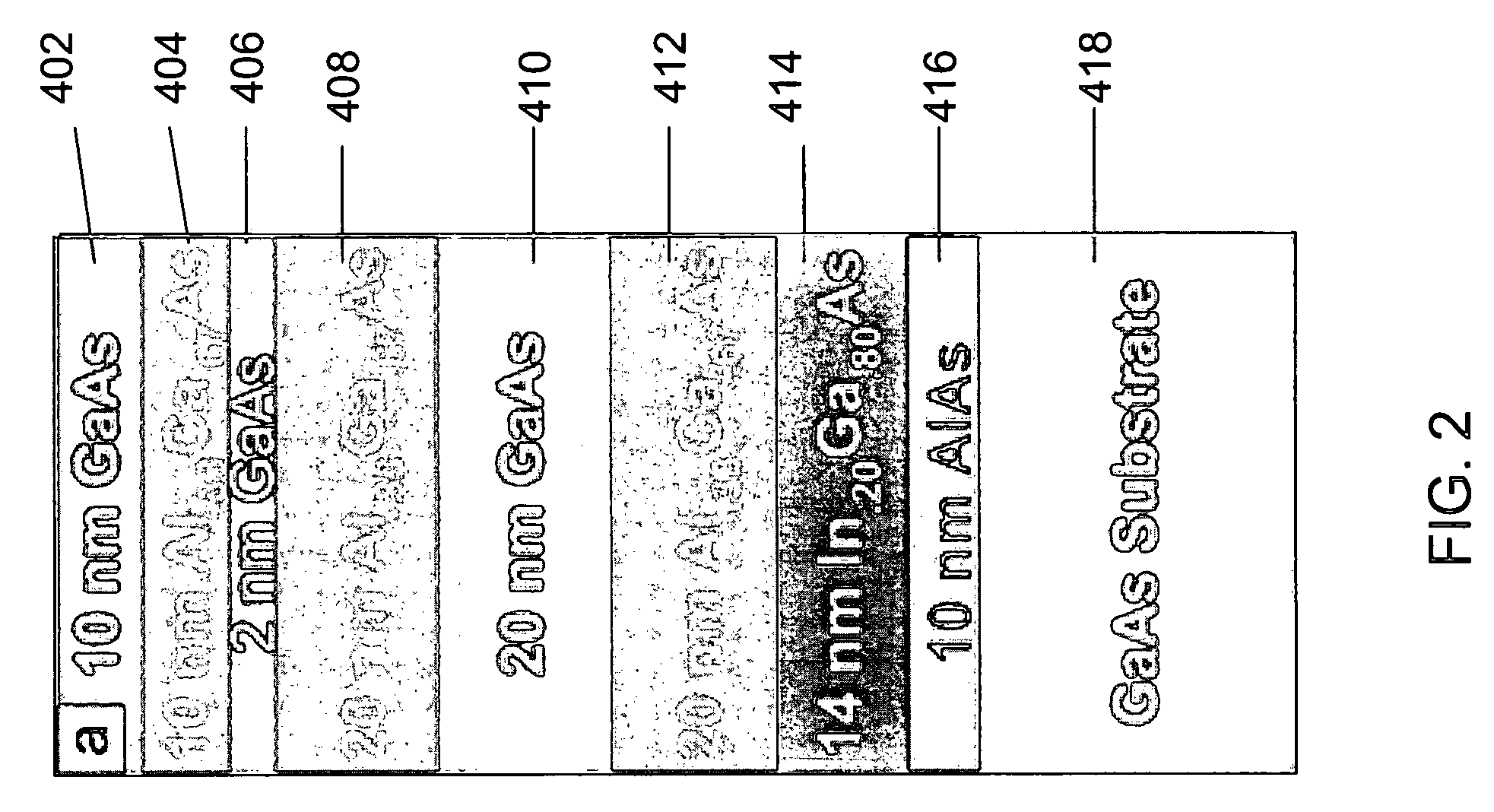
Atomic force microscope and method for determining properties of a sample surface using an atomic force microscope
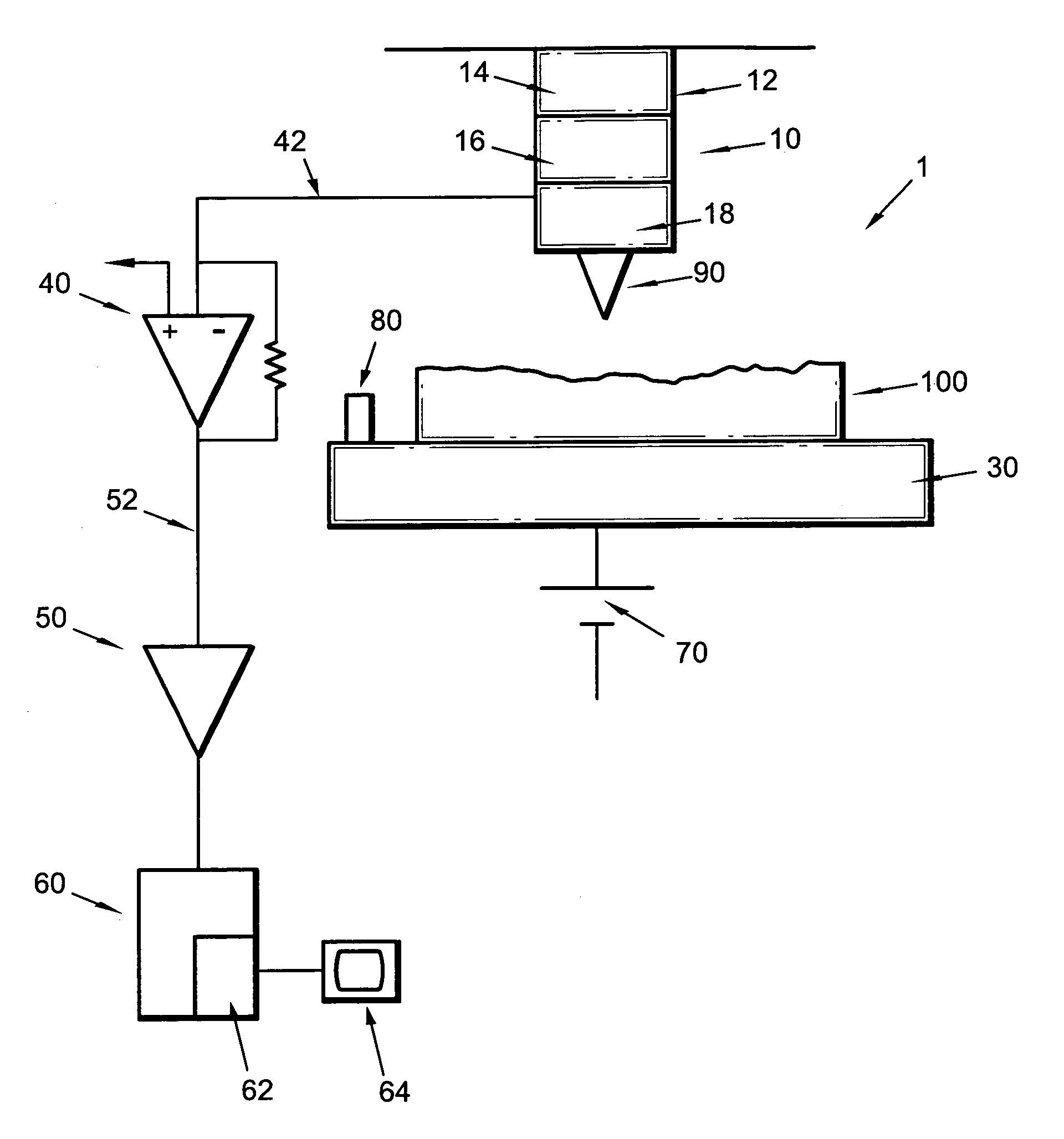
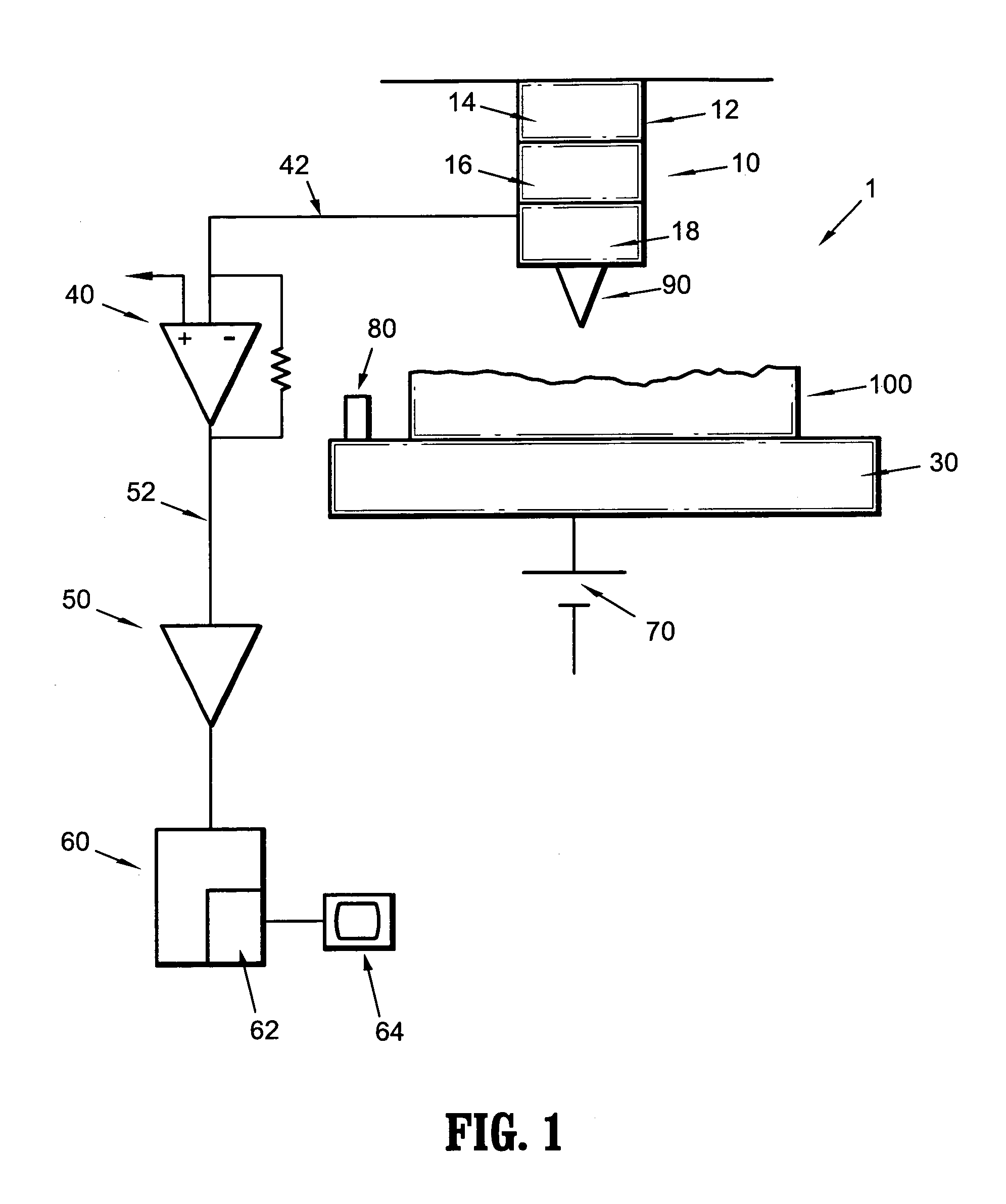
ActiveUS20050081609A1Reduced tip wearReduce wearNanotechnologyMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsAtomic force microscopyAtomic force acoustic microscopy
A method for determining properties of a sample surface using an atomic force microscope includes applying a first voltage between the sample and a probe, moving the probe towards the surface of the sample, and stopping movement of the probe towards the surface of the sample when current in the probe is initially detected. An oscillating magnetic field is applied to the probe such that the probe obtains stable contact with the surface of the sample.
Owner:IBM CORP
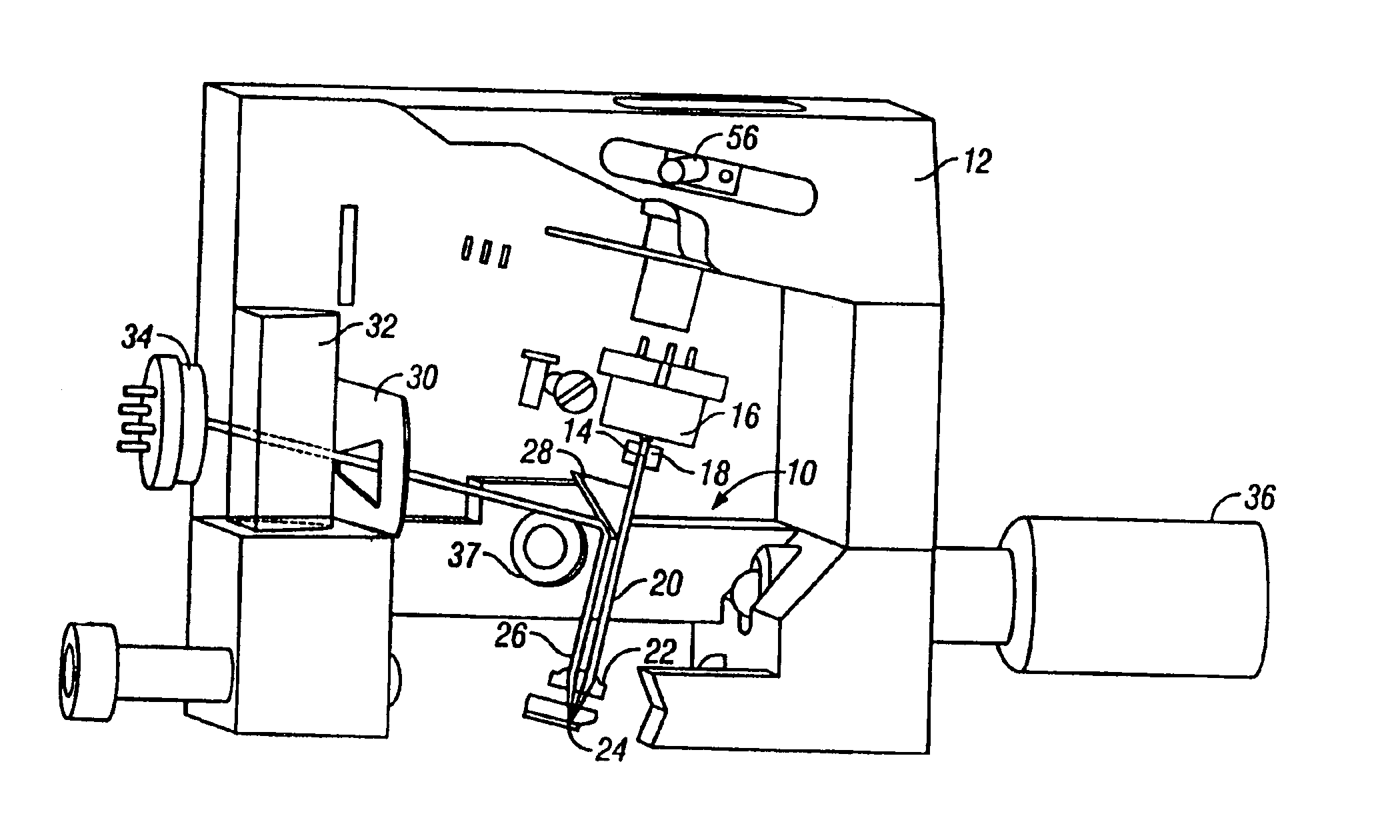
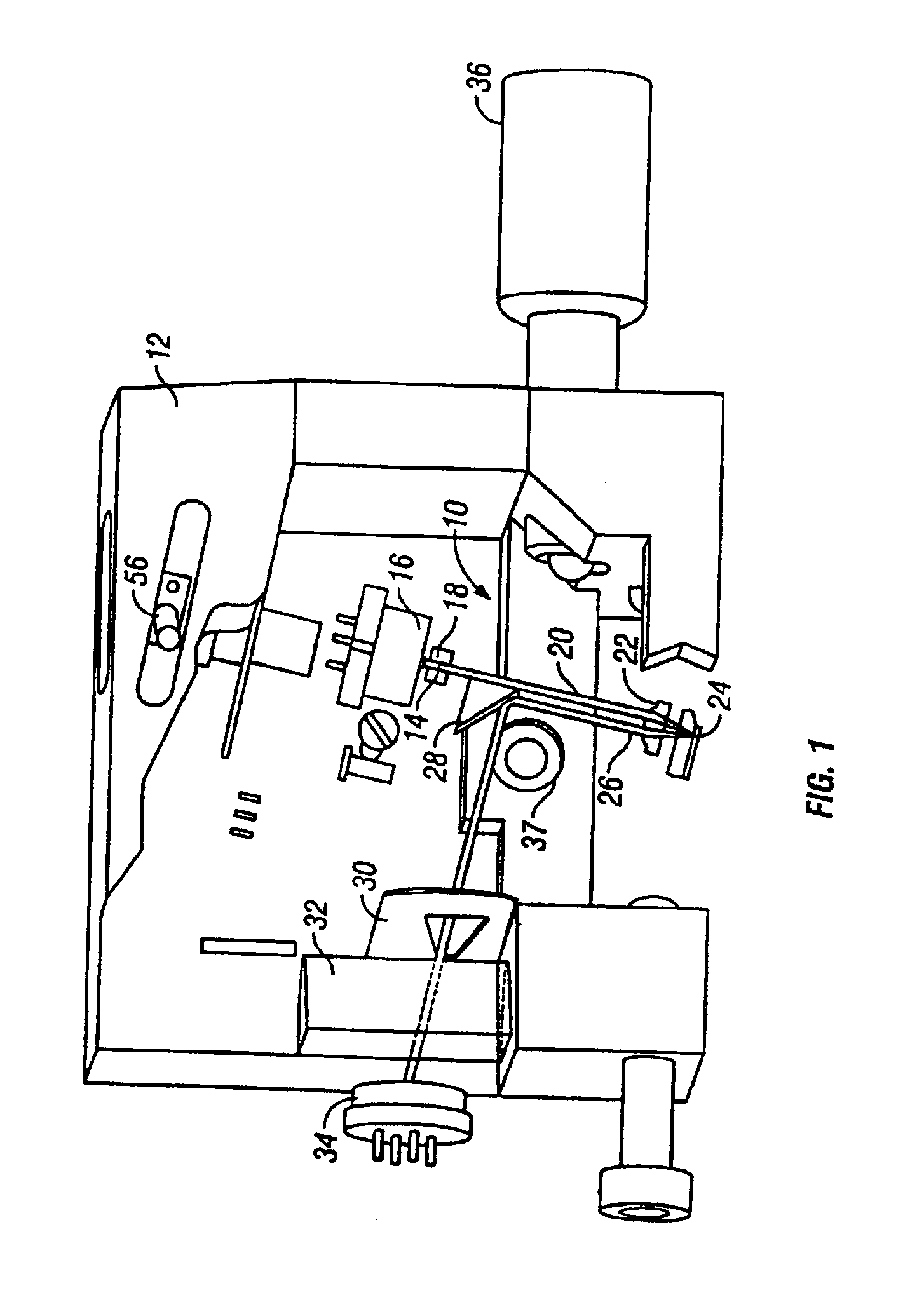
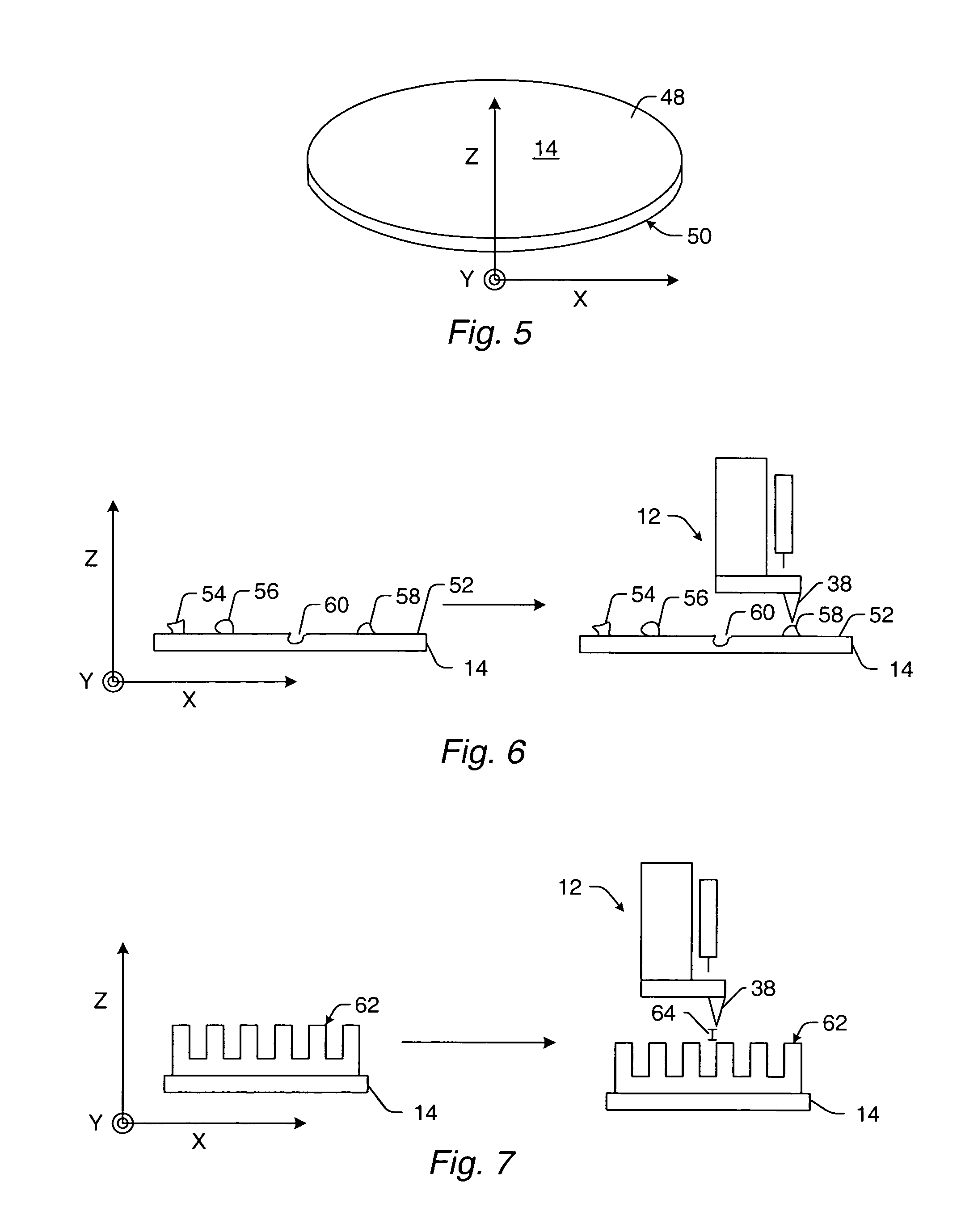
Measurement head for atomic force microscopy and other applications
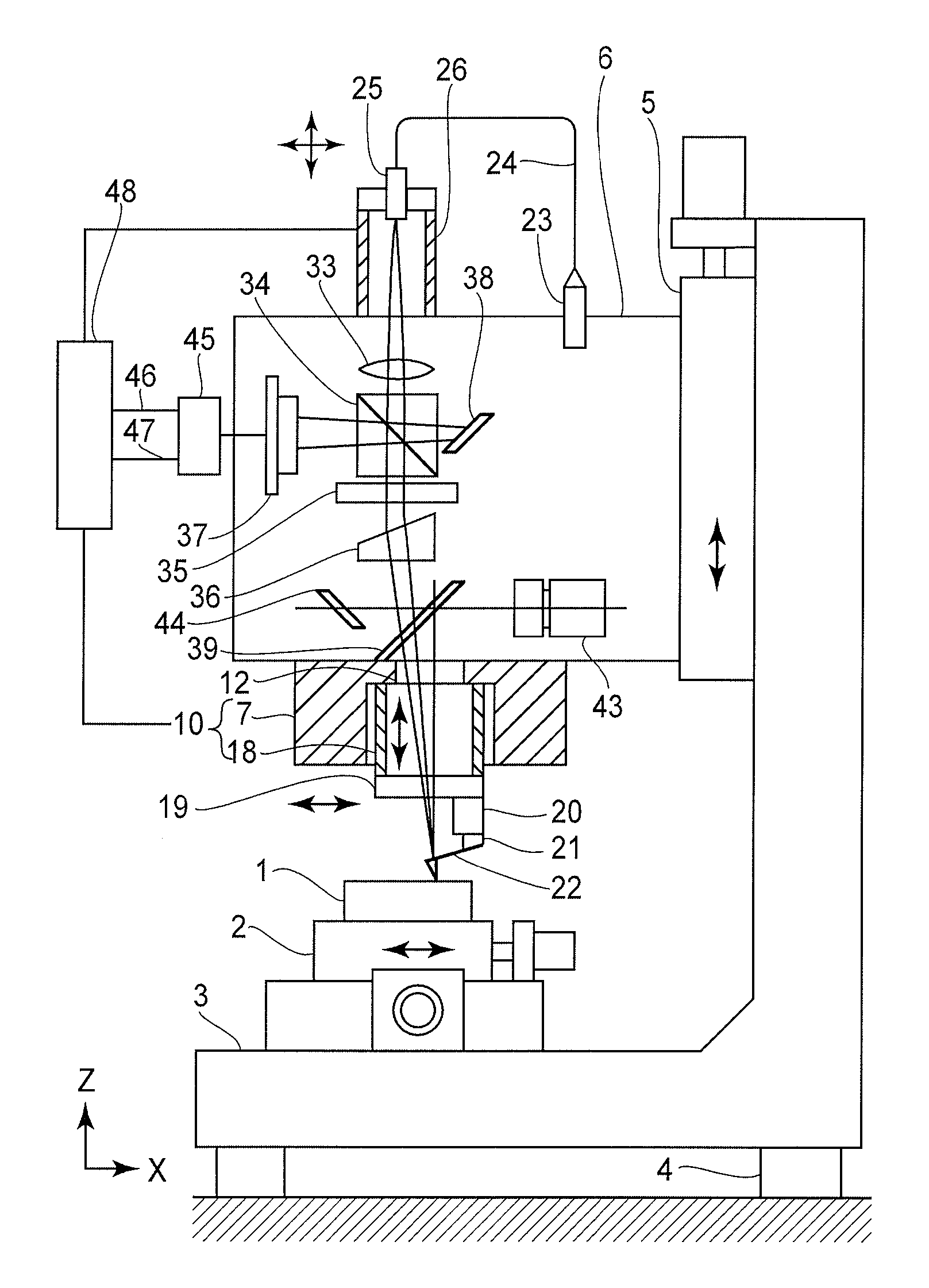
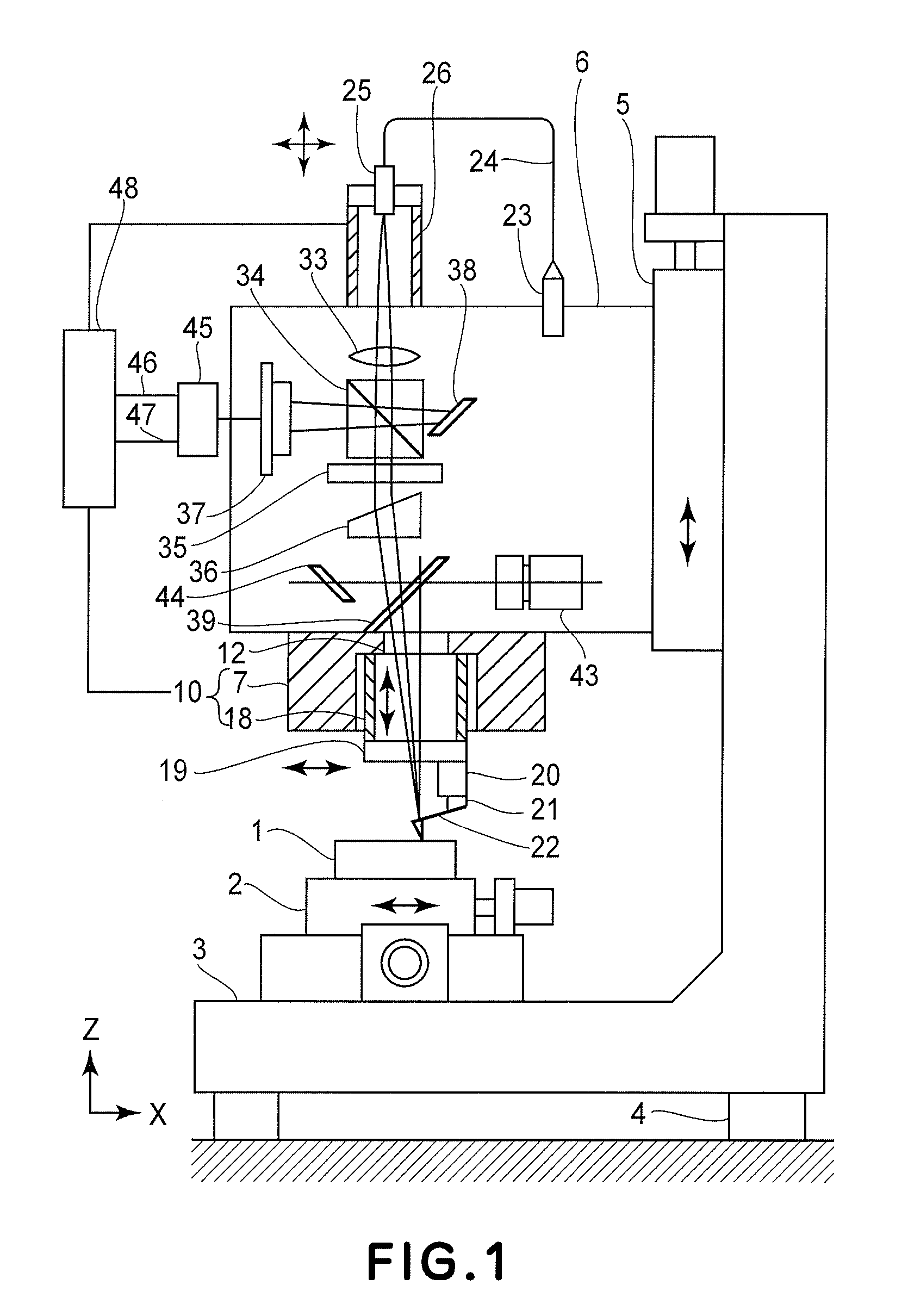
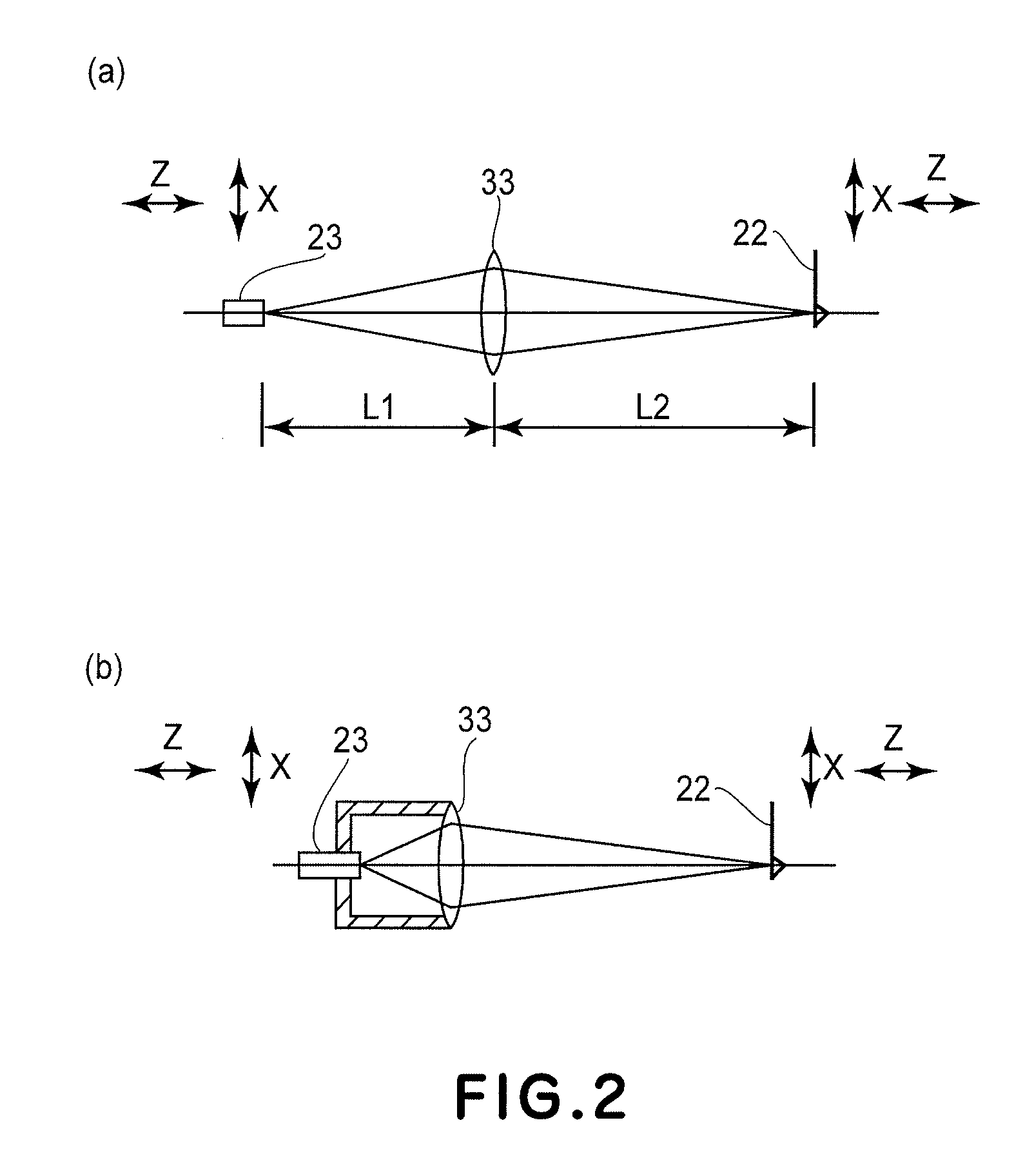
InactiveUS6871527B2Small and rigid packageIncrease stiffnessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsAtomic force microscopyLight beam
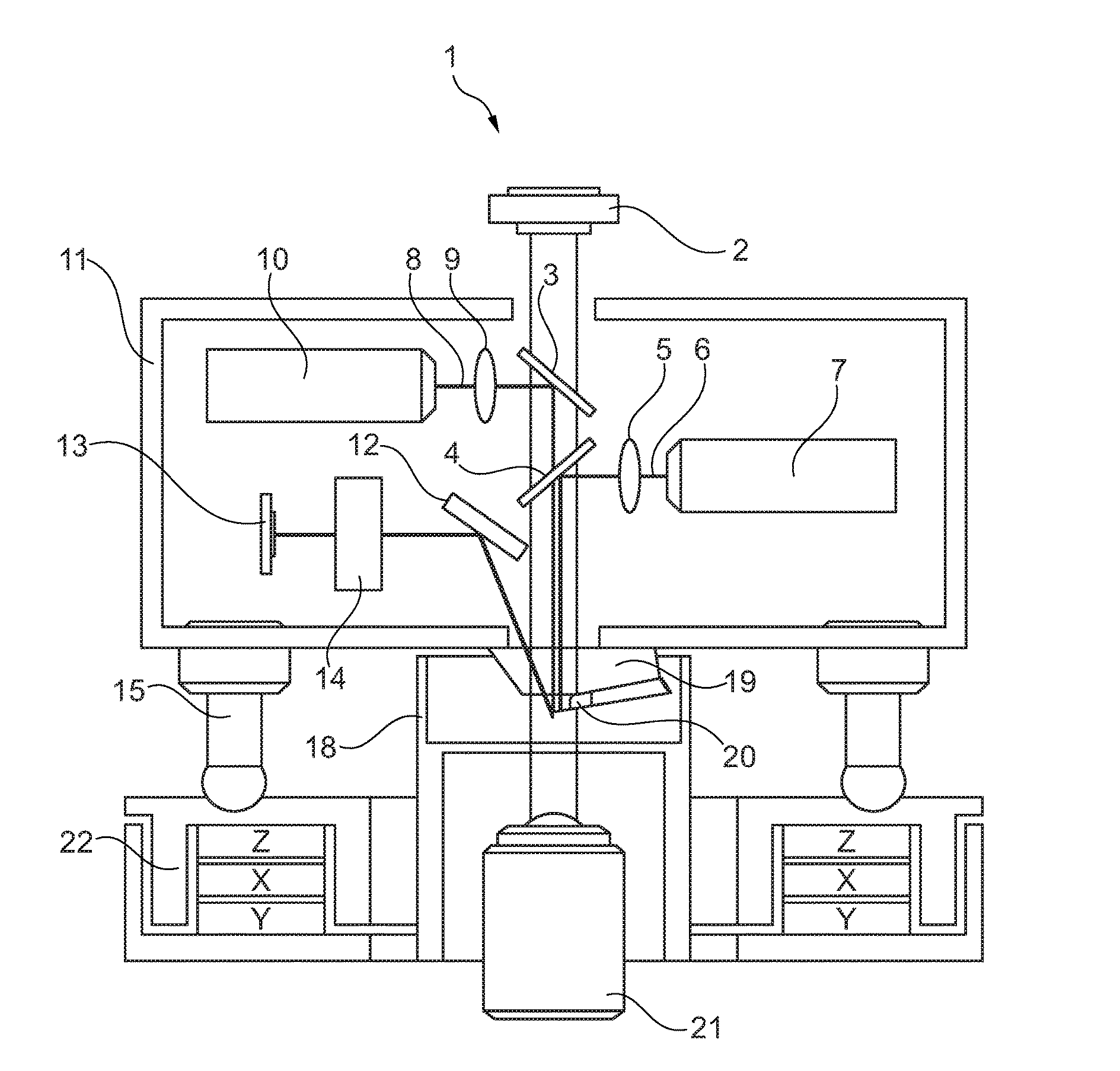
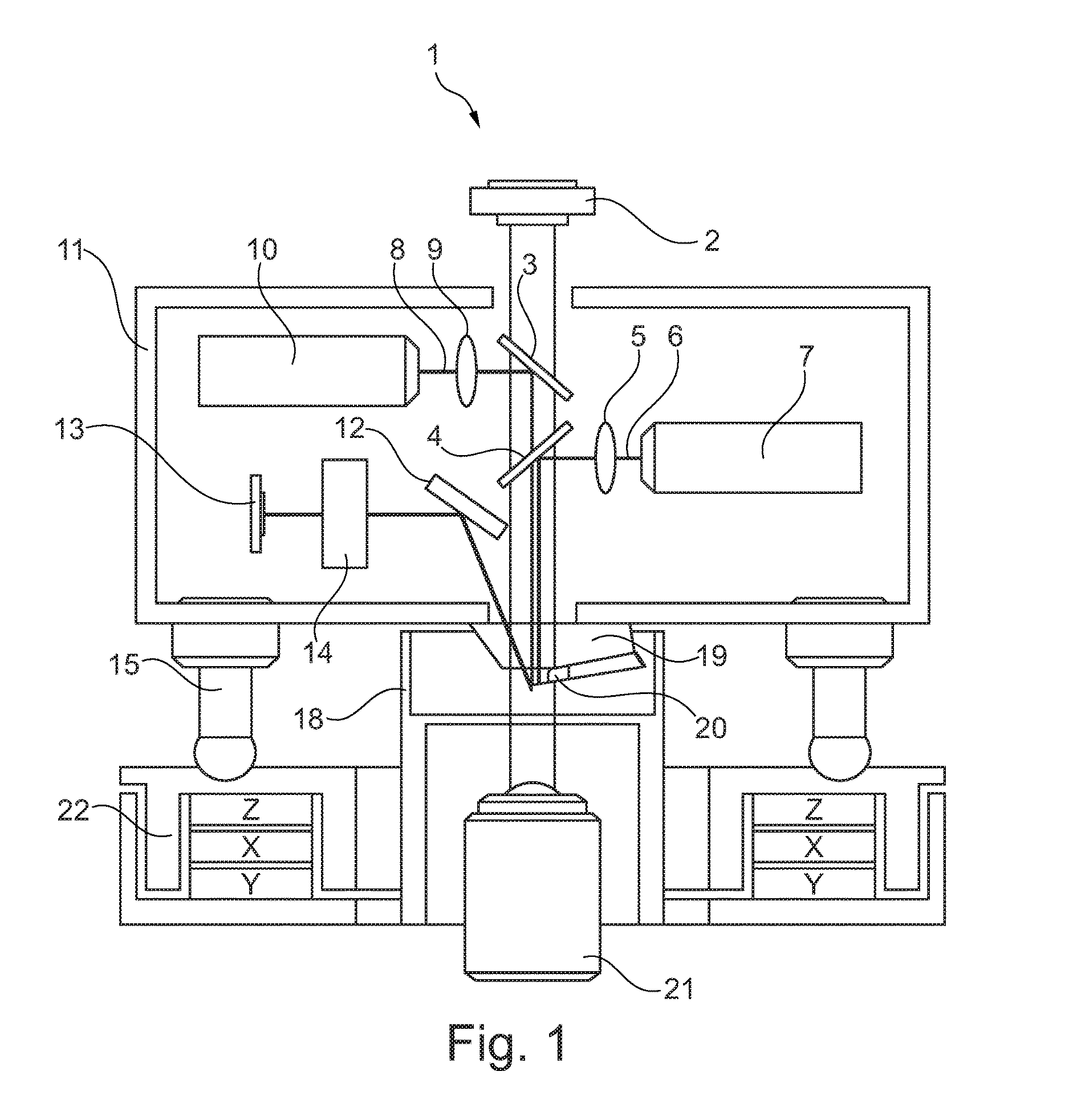
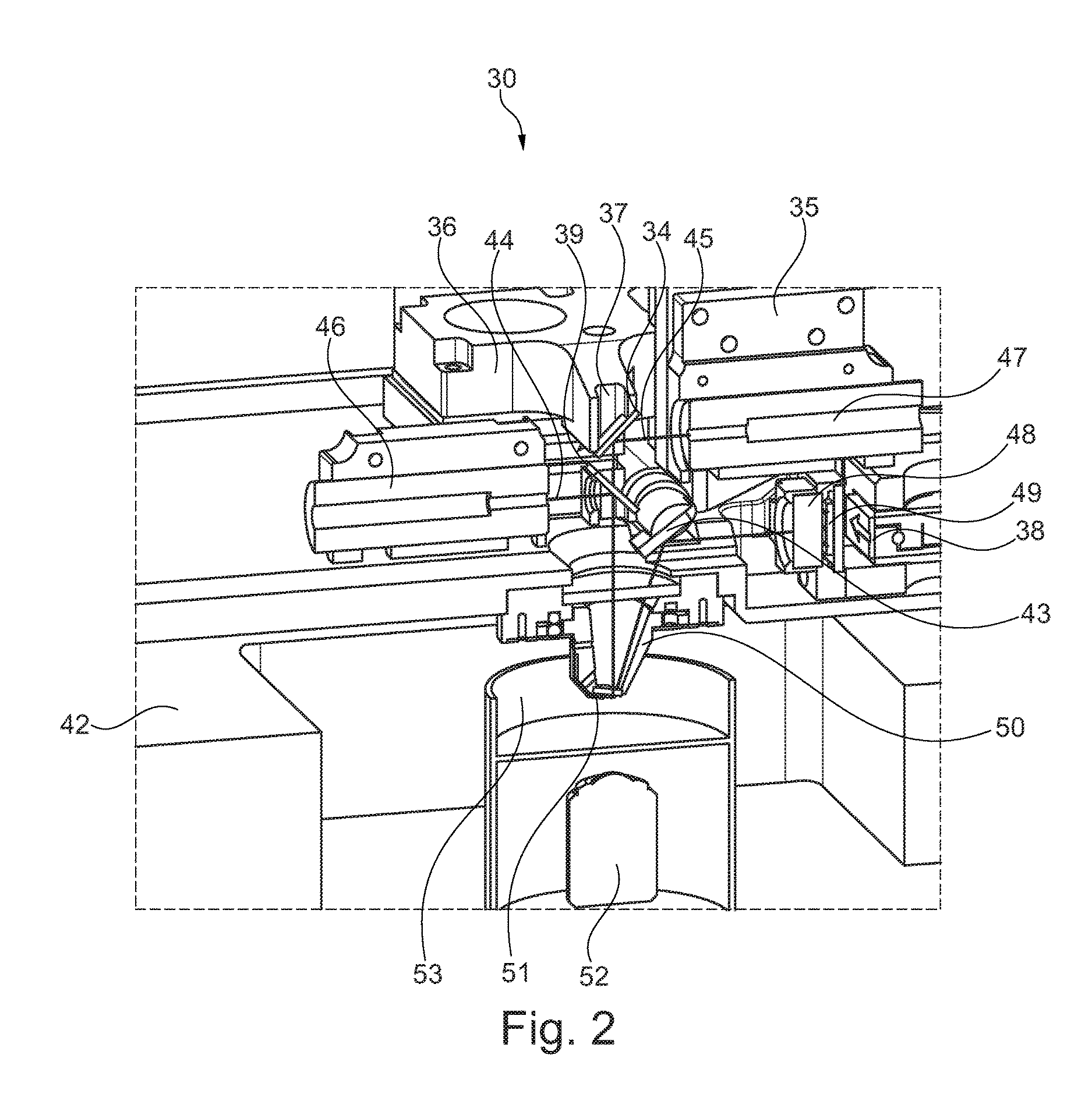
An improvement for atomic force microscopes, more generally for light beam detecting systems, but also in part applicable to scanning probe microscopes, providing significant novel features and advantages. Particular features include using different objective lens regions for incident and reflected light, a flexure that allows three dimensional motion of the optics block, forming the housing and optics block of a composite material or ceramic, arranging the components so that the beam never hits a flat surface at normal incidence, and providing a resonant frequency of cantilever vibration greater than 850 HZ between the cantilever and sample and the cantilever and focusing lens.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
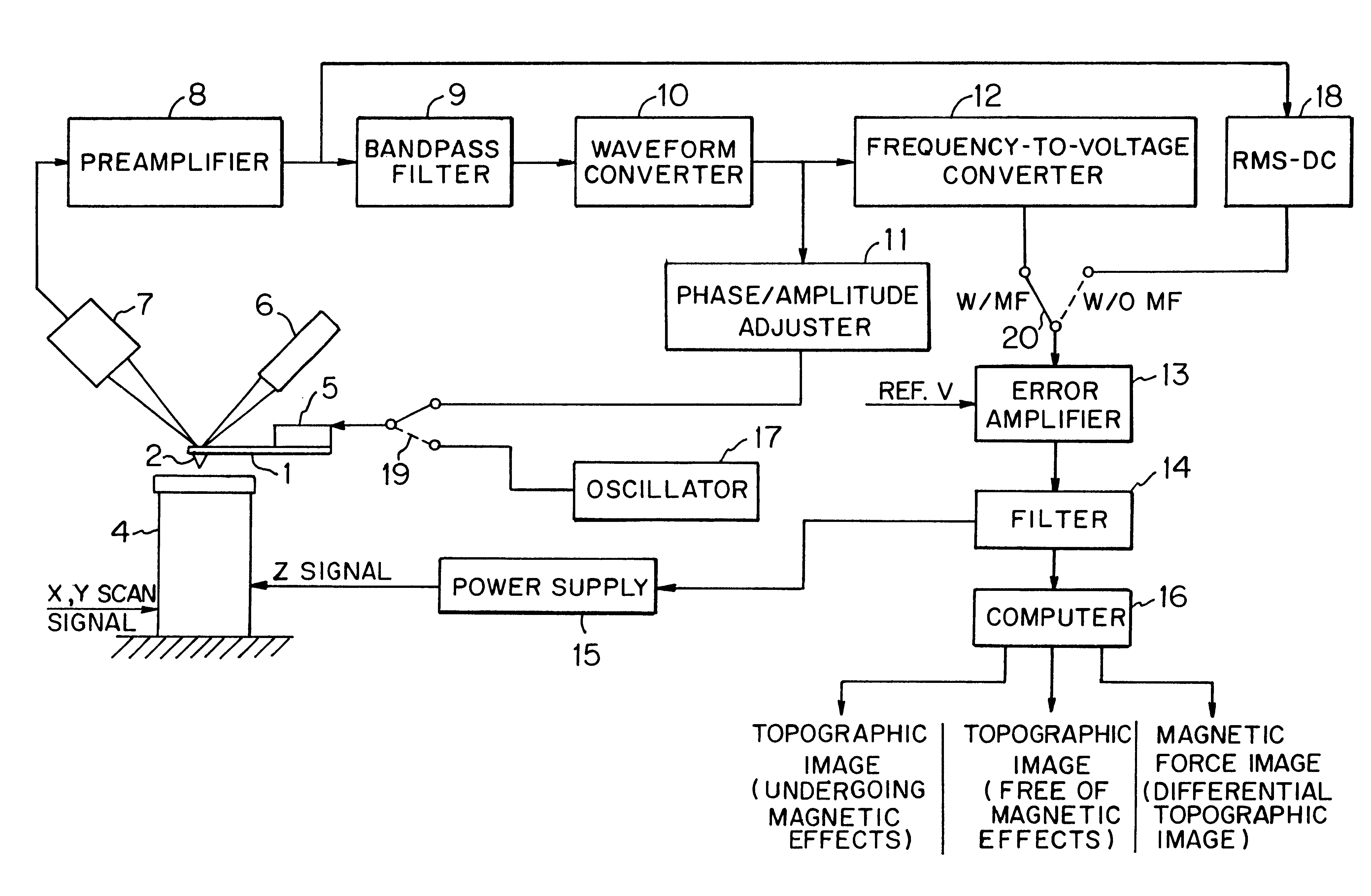
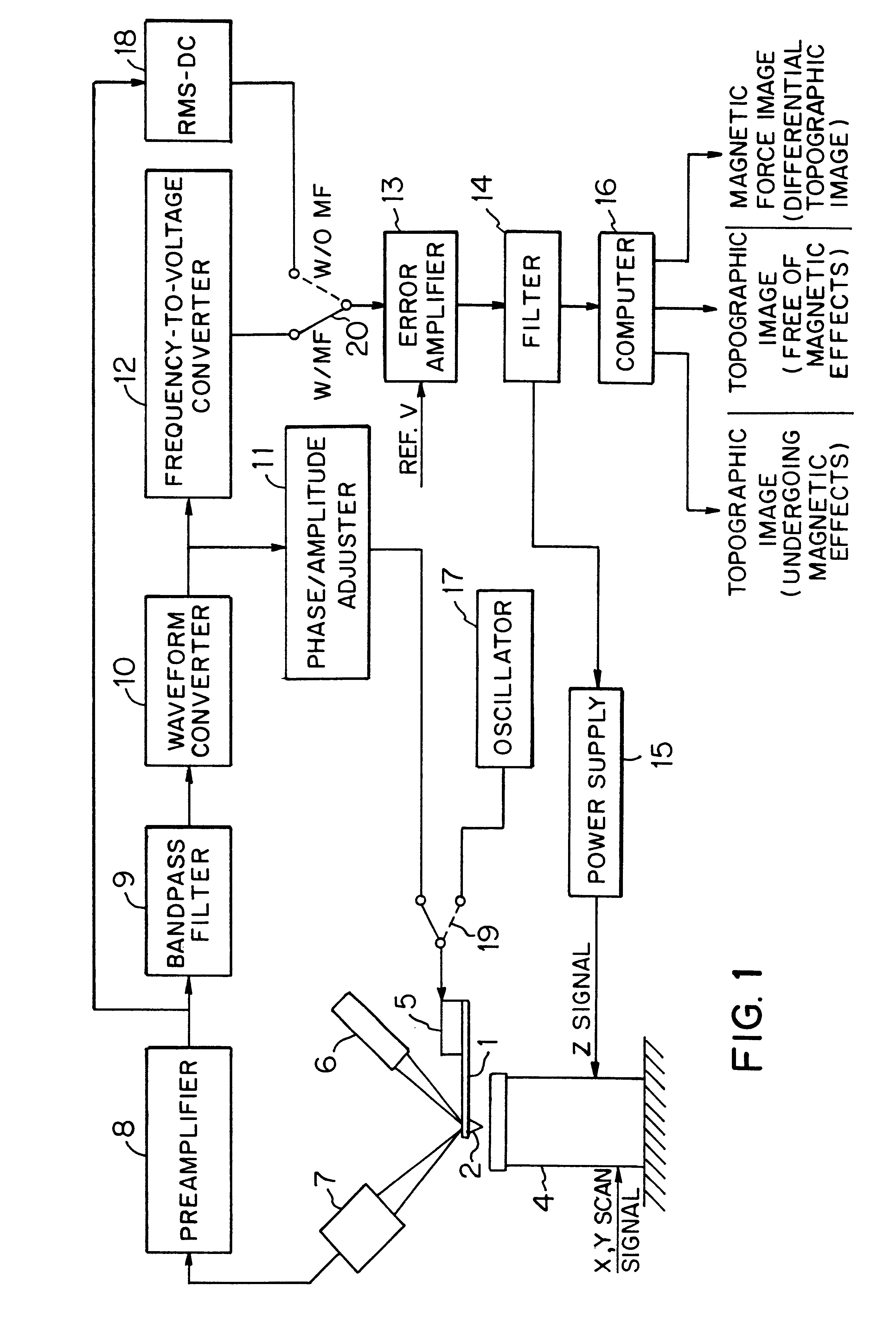
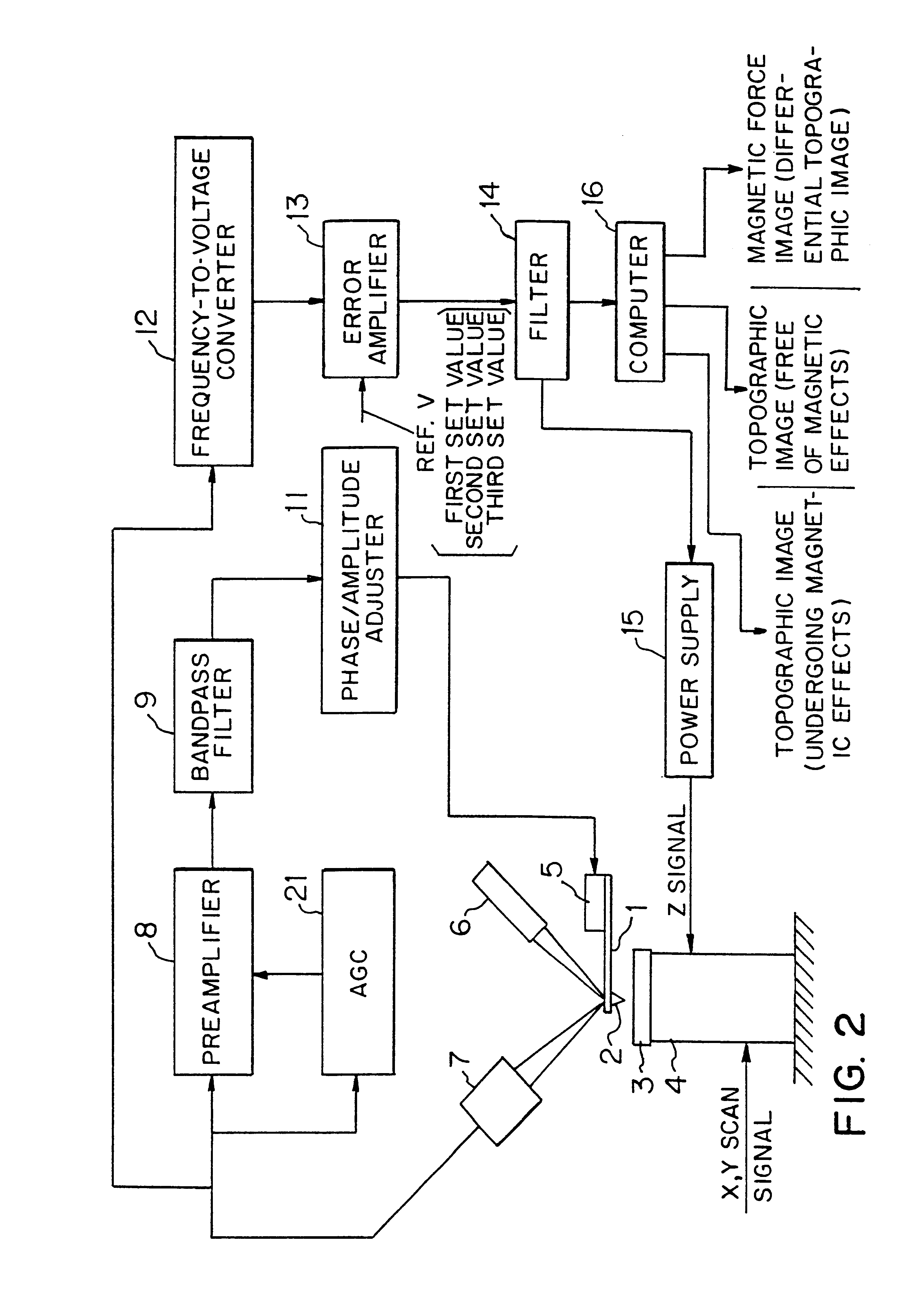
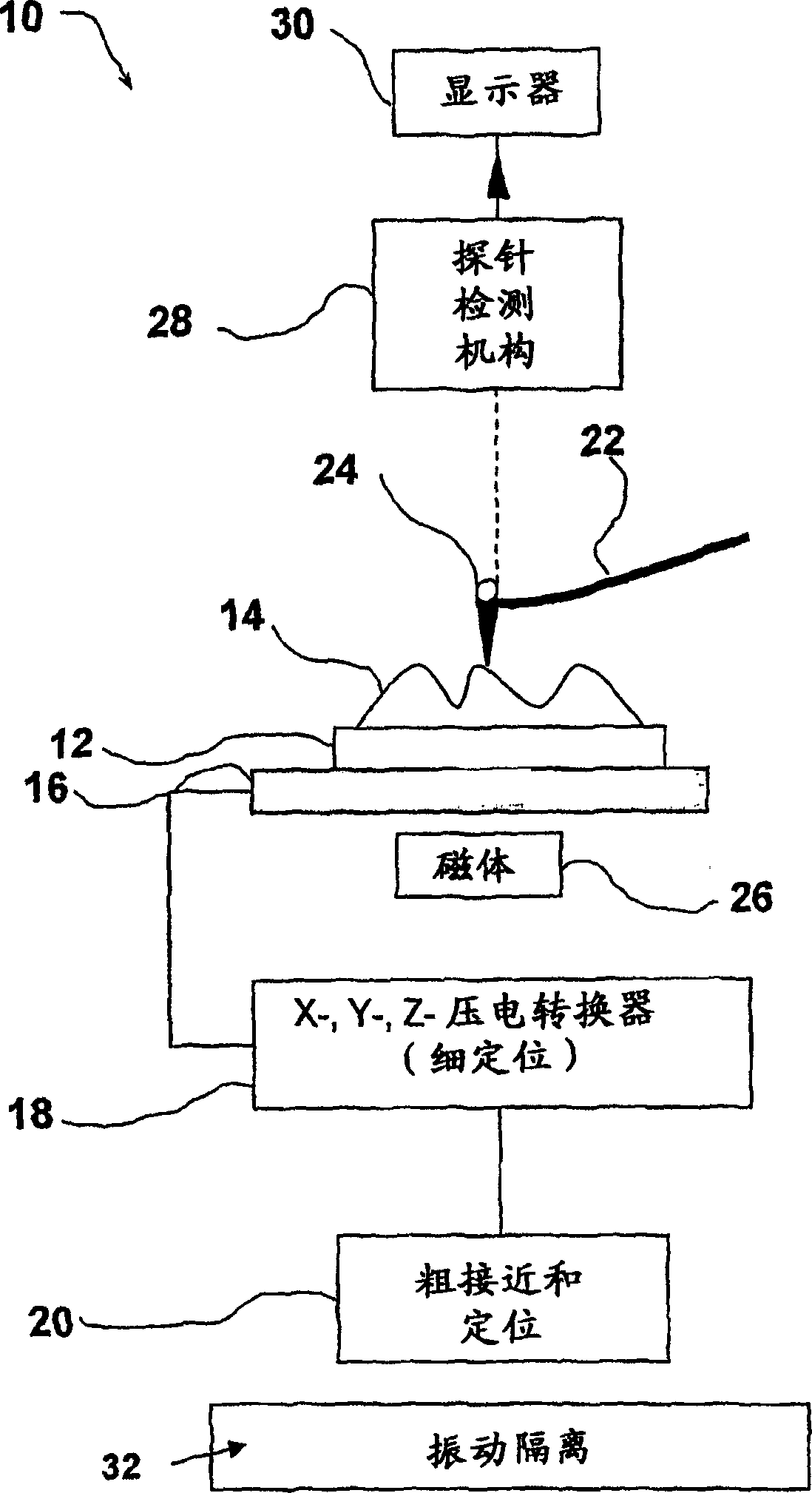
Method of producing magnetic force image and scanning probe microscope
InactiveUS6281495B1High resolutionNanomagnetismMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic tension forceAtomic force microscopy
There is disclosed a scanning probe microscope for producing a topographic image of a surface of a sample by noncontact AFM (atomic force microscopy). First, a first topographic image of the sample undergoing magnetic effects is produced from the resonance frequency of a cantilever by FM detection. Then, a second topographic image of the sample free of magnetic effects is produced from the amplitude of the cantilever by slope detection. The difference between these two topographic images is taken. Thus, a magnetic force image is produced.
Owner:JEOL LTD
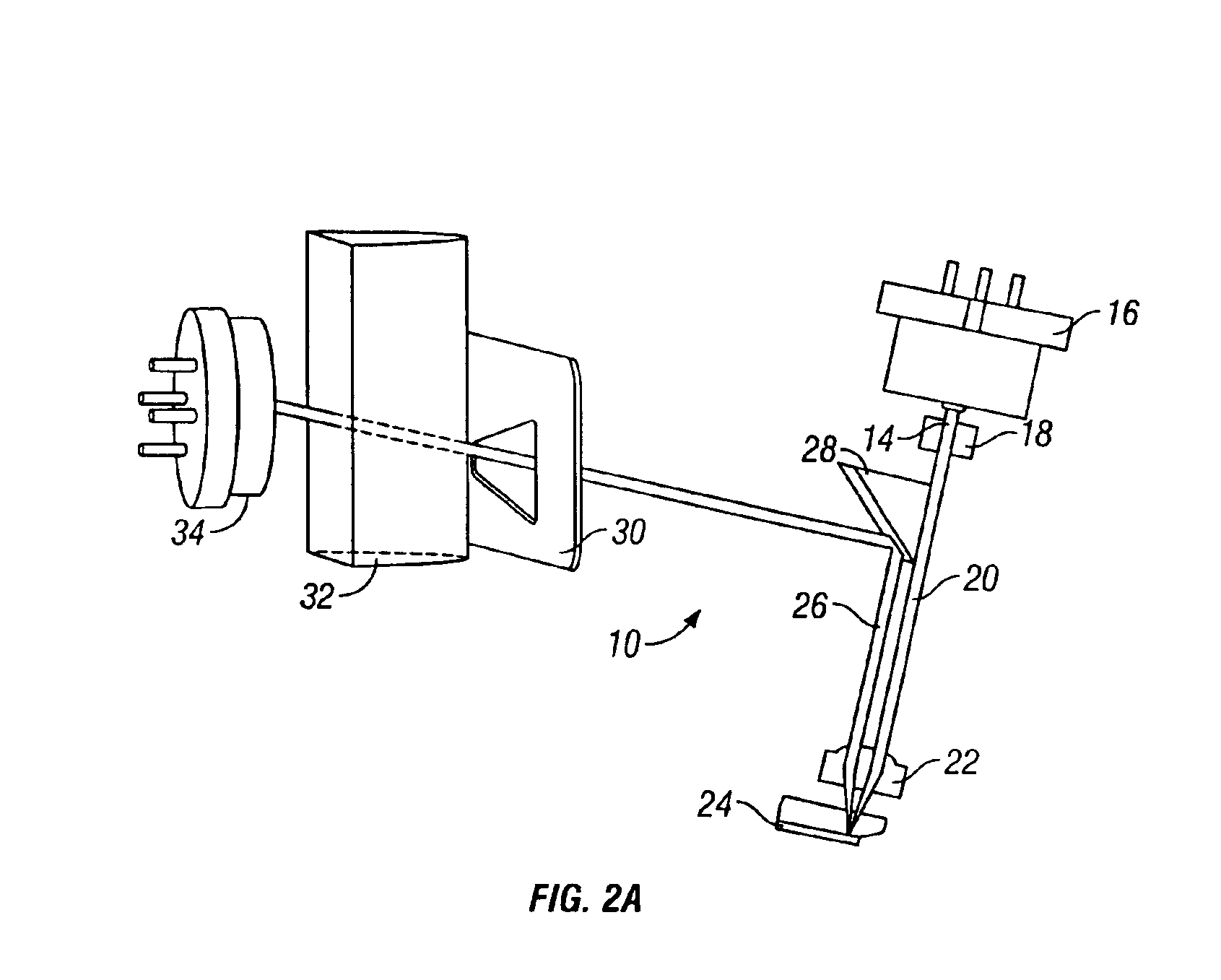
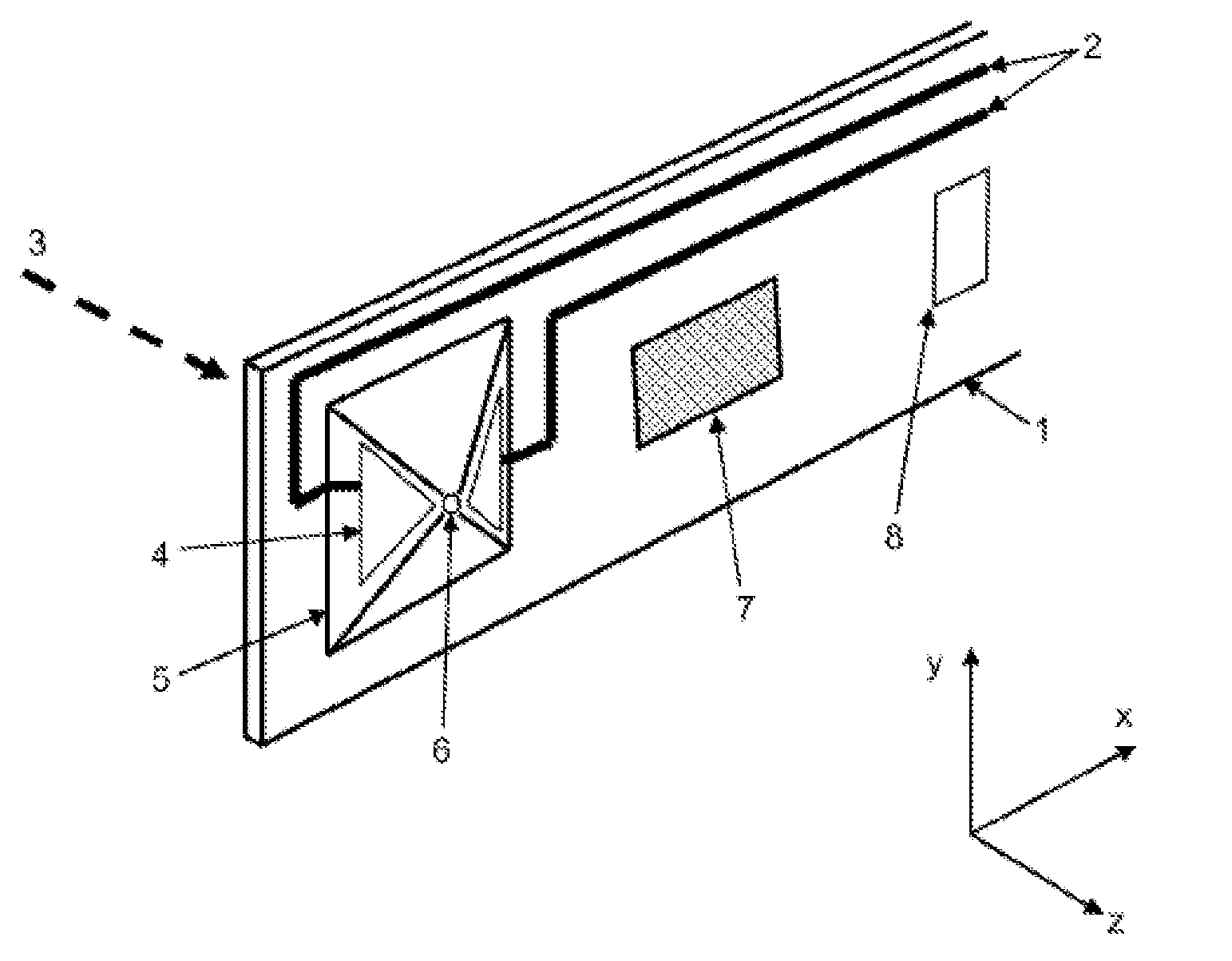
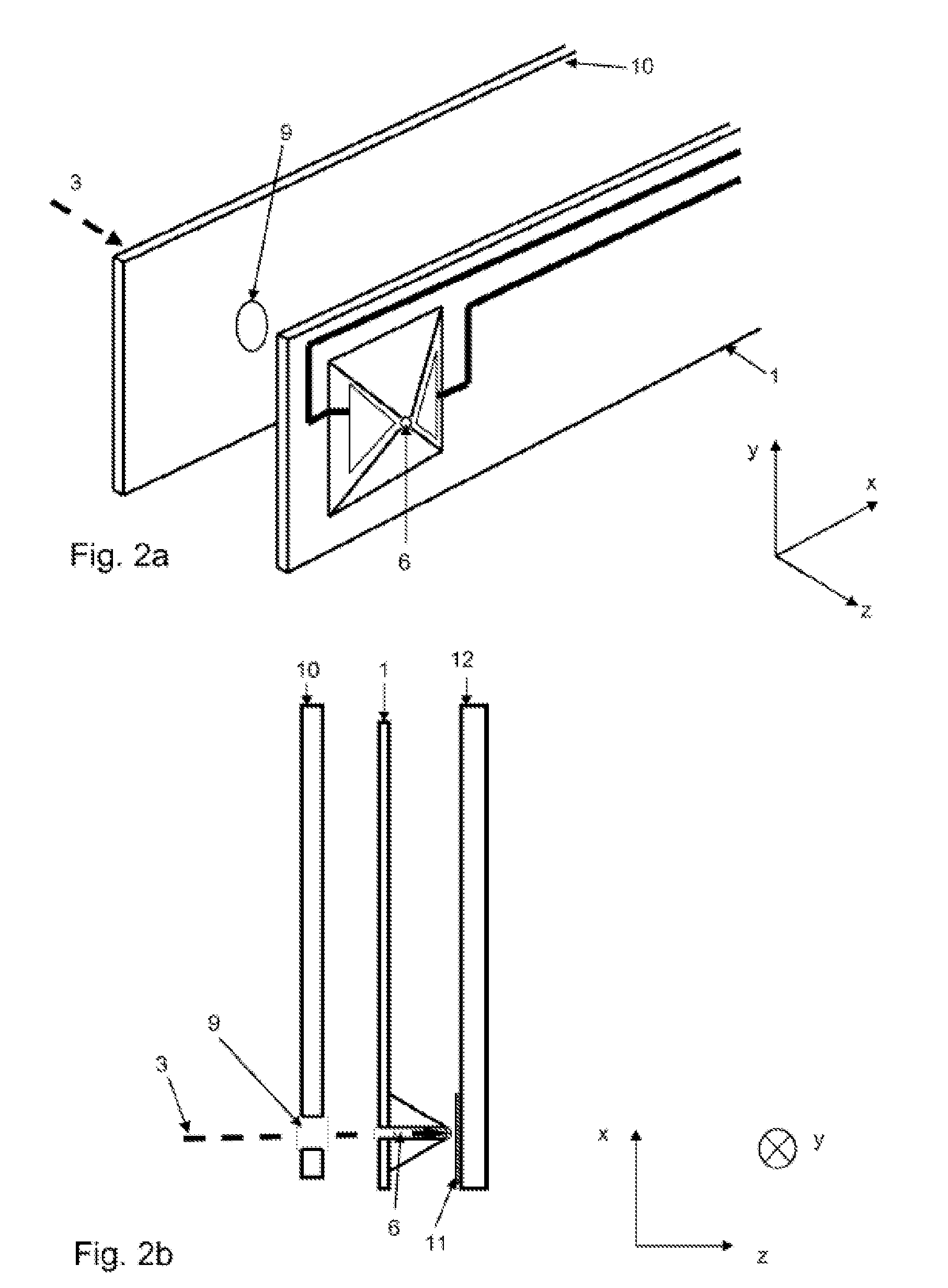
Probe for an atomic force microscope
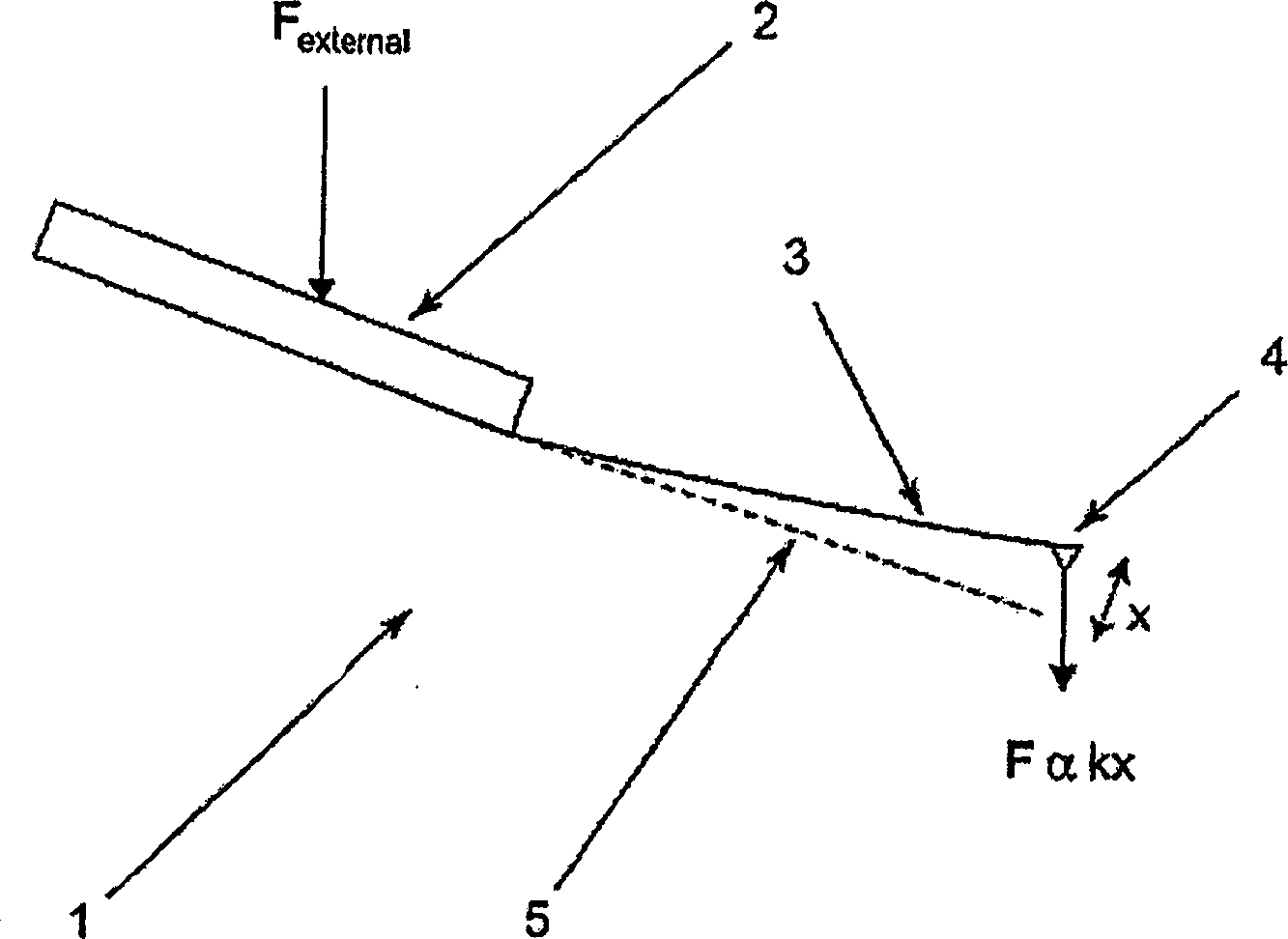
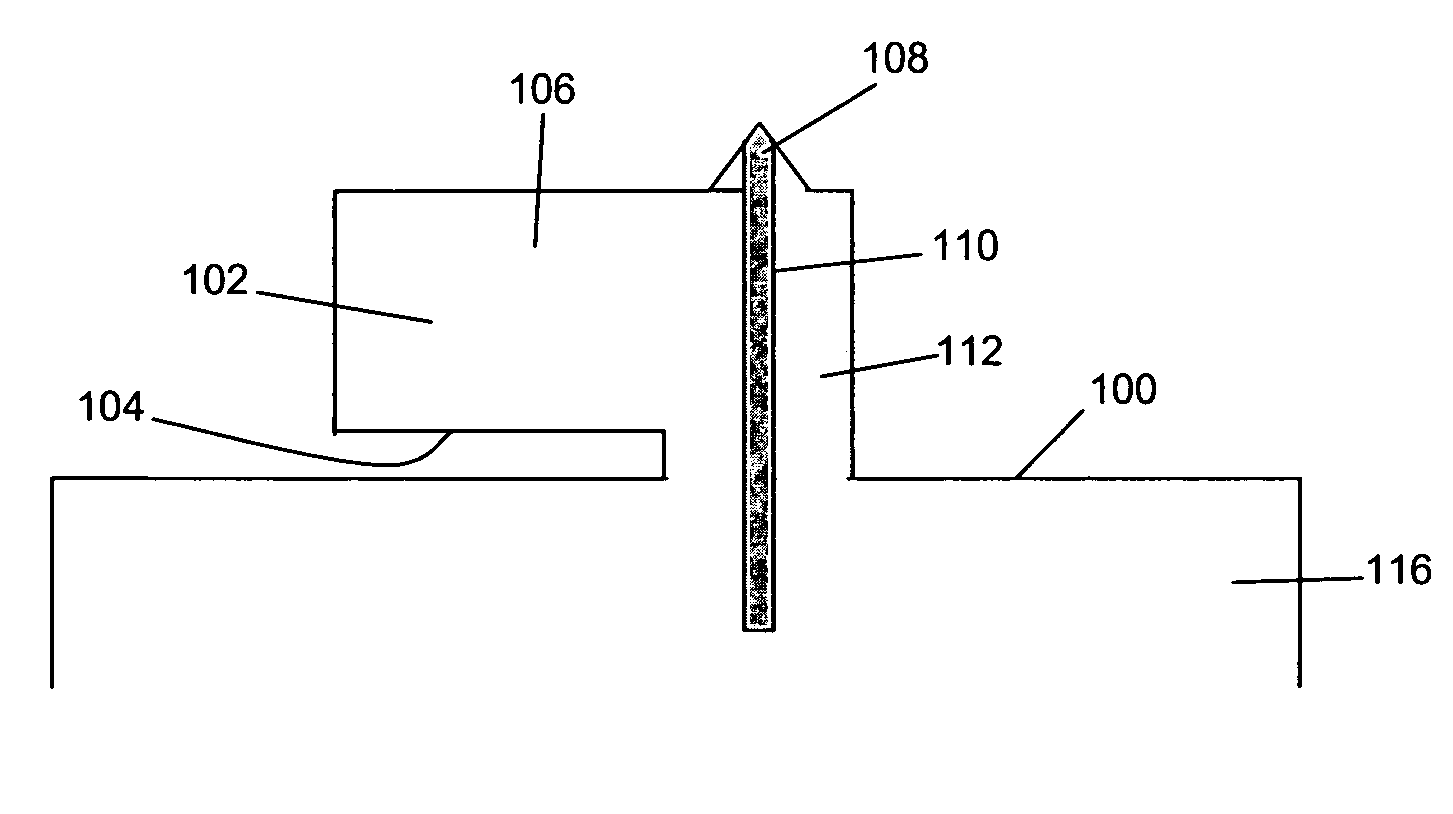
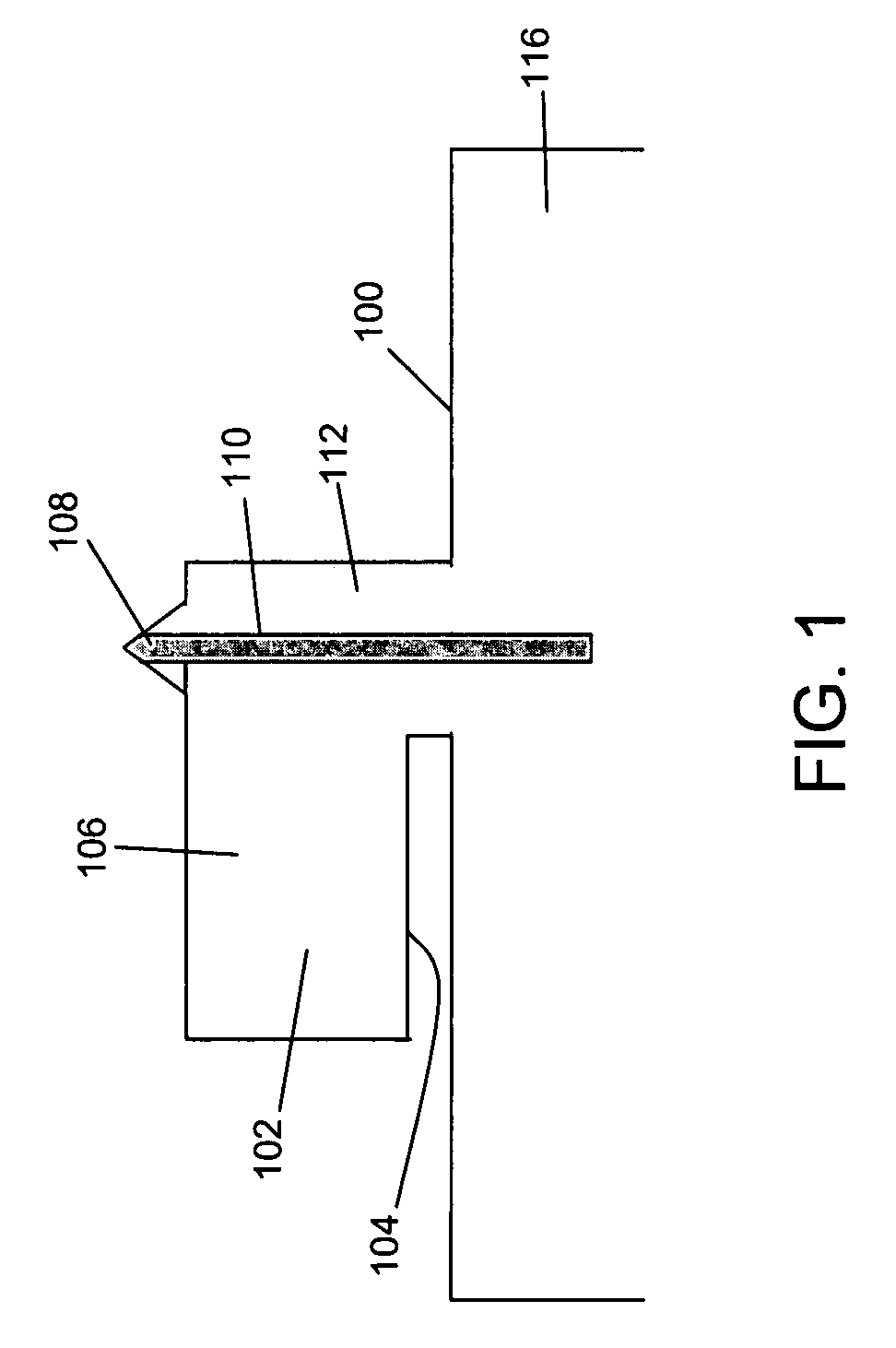
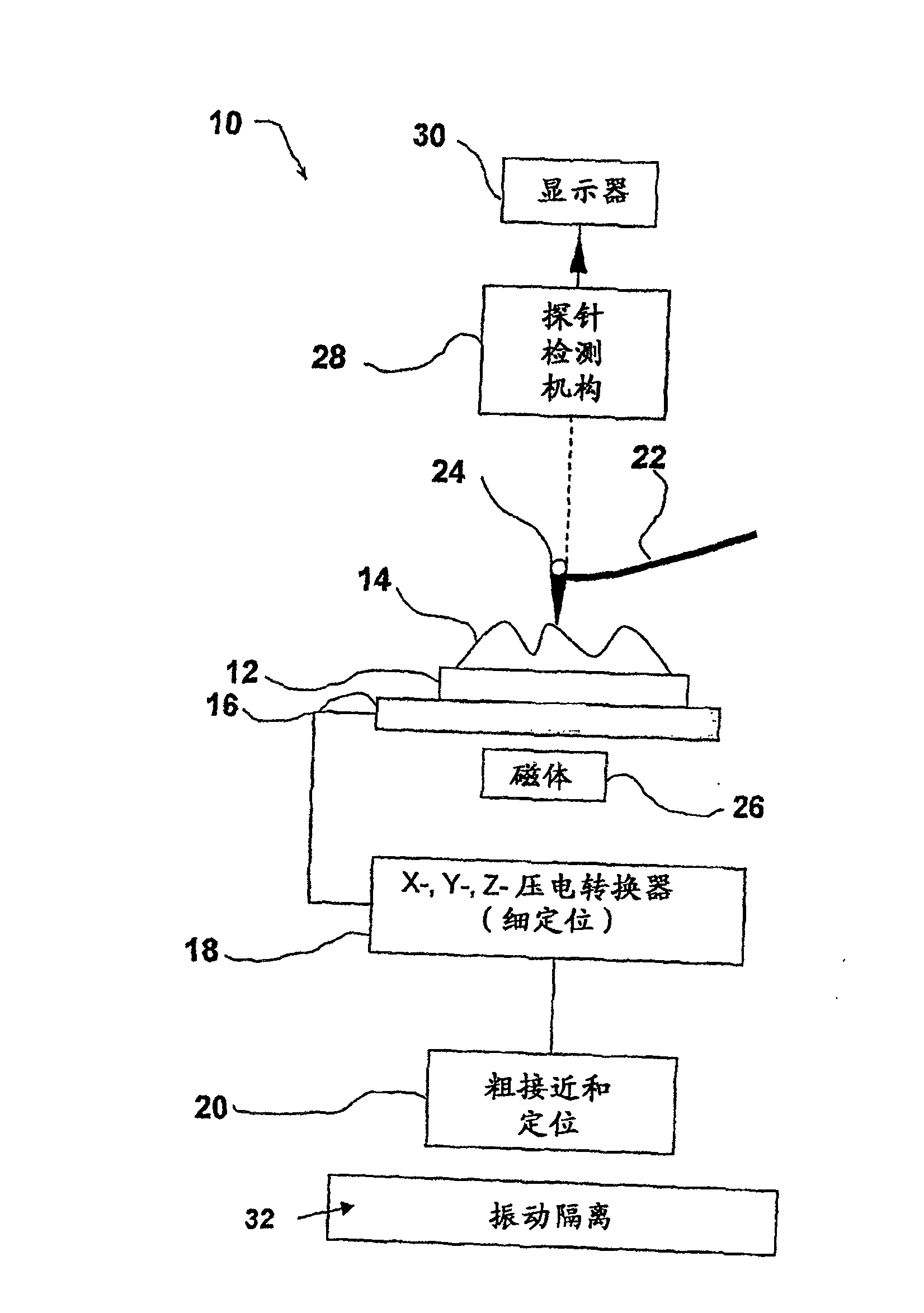
InactiveCN1836290AInstrumental componentsScanning probe techniquesMechanical energyAtomic force acoustic microscopy
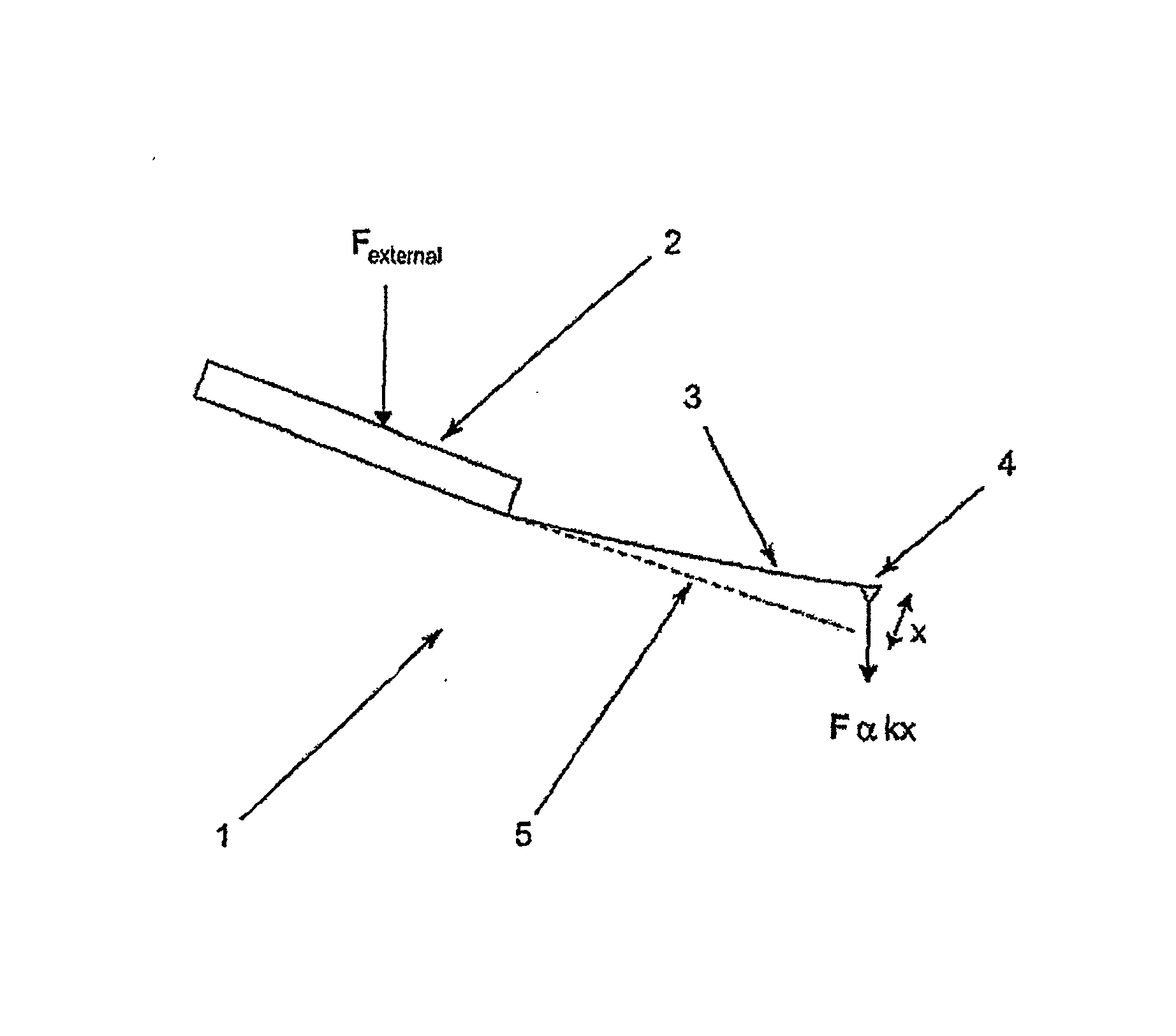
A probe (22) for an atomic force microscope is adapted such that, as a sample (14) is scanned, it experiences a biasing force Fdirect urging the probe towards the sample. This improves probe trackingof the sample surface and faster scans are possible. This is achieved by either including a biasing element (24, 50), which is responsive to an externally applied force, on the probe (22) and / or reducing the quality factor of a supporting beam. The biasing element may, for example, be a magnet (24) or an electrically-conducting element (50). The quality factor may be reduced by coating the beamwith a mechanical-energy dissipating material.
Owner:INFINITESIMA
Methods and systems for analyzing a specimen using atomic force microscopy profiling in combination with an optical technique
ActiveUS7430898B1NanotechSurface/boundary effectAtomic force microscopyAtomic force acoustic microscopy
A system that includes an optical subsystem and an atomic force microscope probe is provided. The optical subsystem is configured to generate positional information about a location on a surface of the specimen. The system is configured to position the probe proximate the location based on the positional information. One method includes generating positional information about a location on a surface of a specimen with an optical subsystem. The method also includes positioning an atomic force microscopy probe proximate the location based on the positional information. Another system includes an optical subsystem configured to measure overlay of a wafer using scatterometry. The system also includes an atomic force microscope configured to measure a characteristic of a feature on the wafer. An additional method includes measuring overlay of a wafer using scatterometry. The method also includes measuring a characteristic of a feature on the wafer using atomic force microscopy.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Specimen observation method in atomic force microscopy and atomic force microscope
A method and apparatus for observing a specimen in atomic force microscopy with a vibrating cantilever maintained in resonance while a probe attached to the cantilever is maintained in contact with the specimen. The Q factor of the cantilever is determined based upon the detected amplitude.
Owner:JEOL LTD
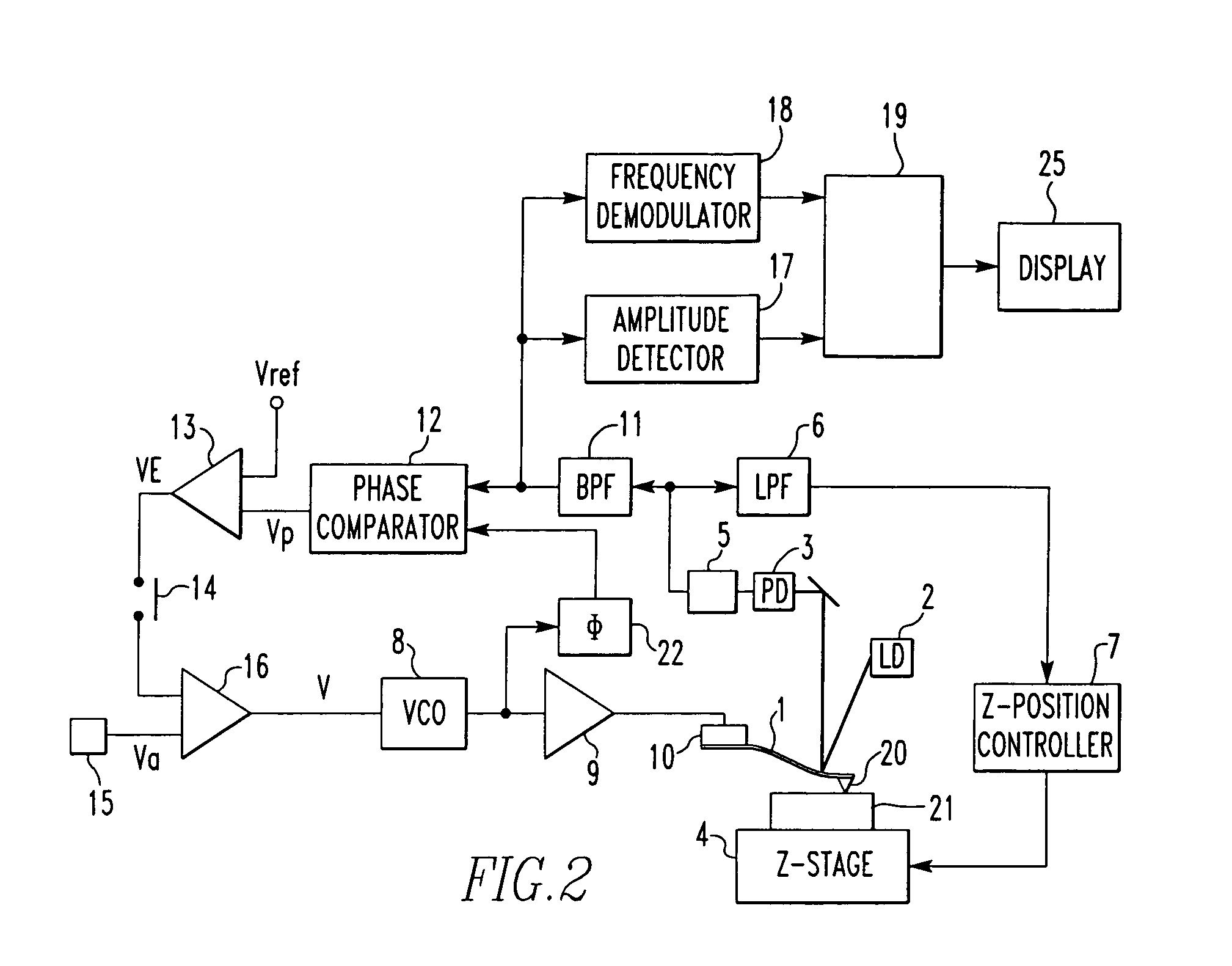
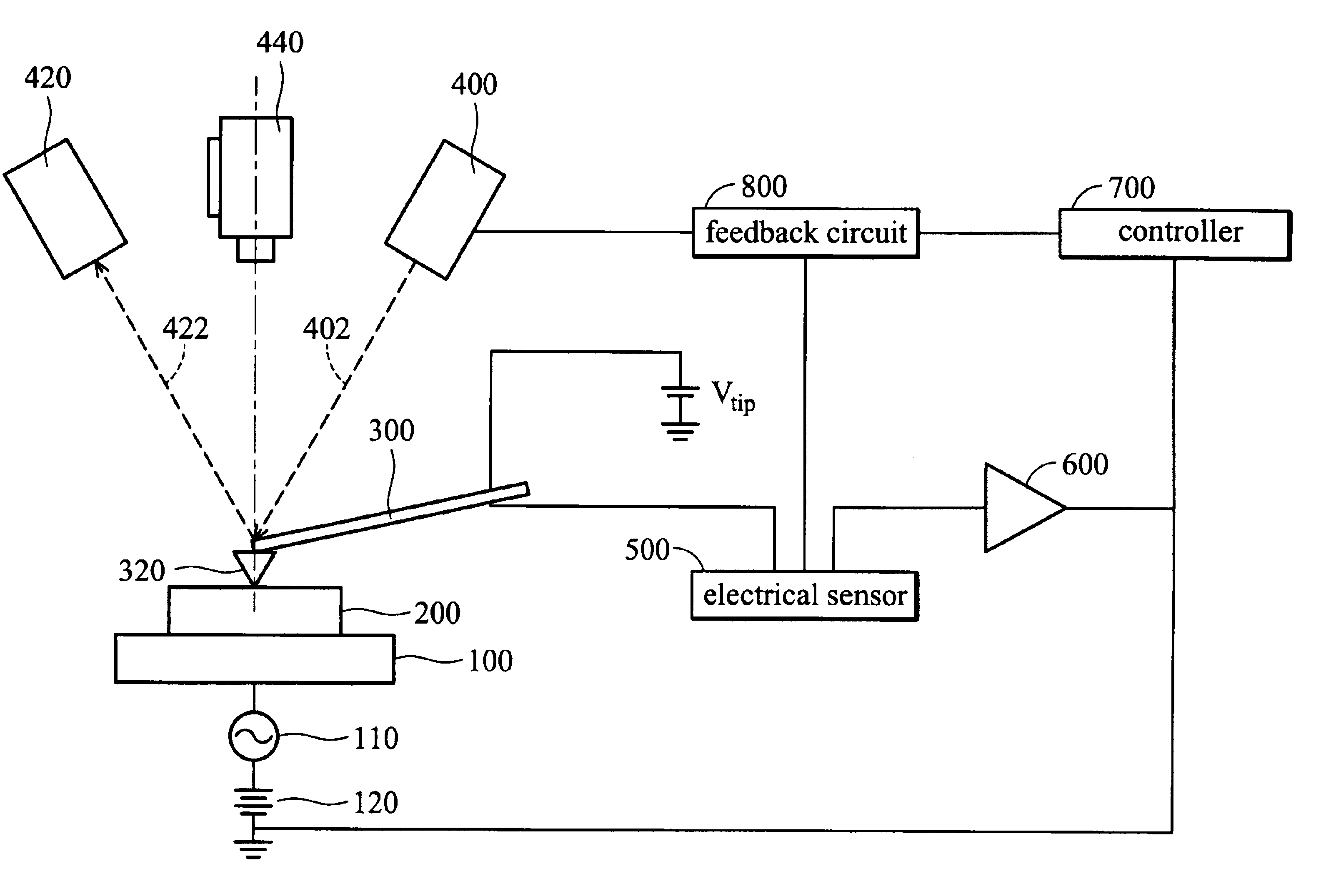
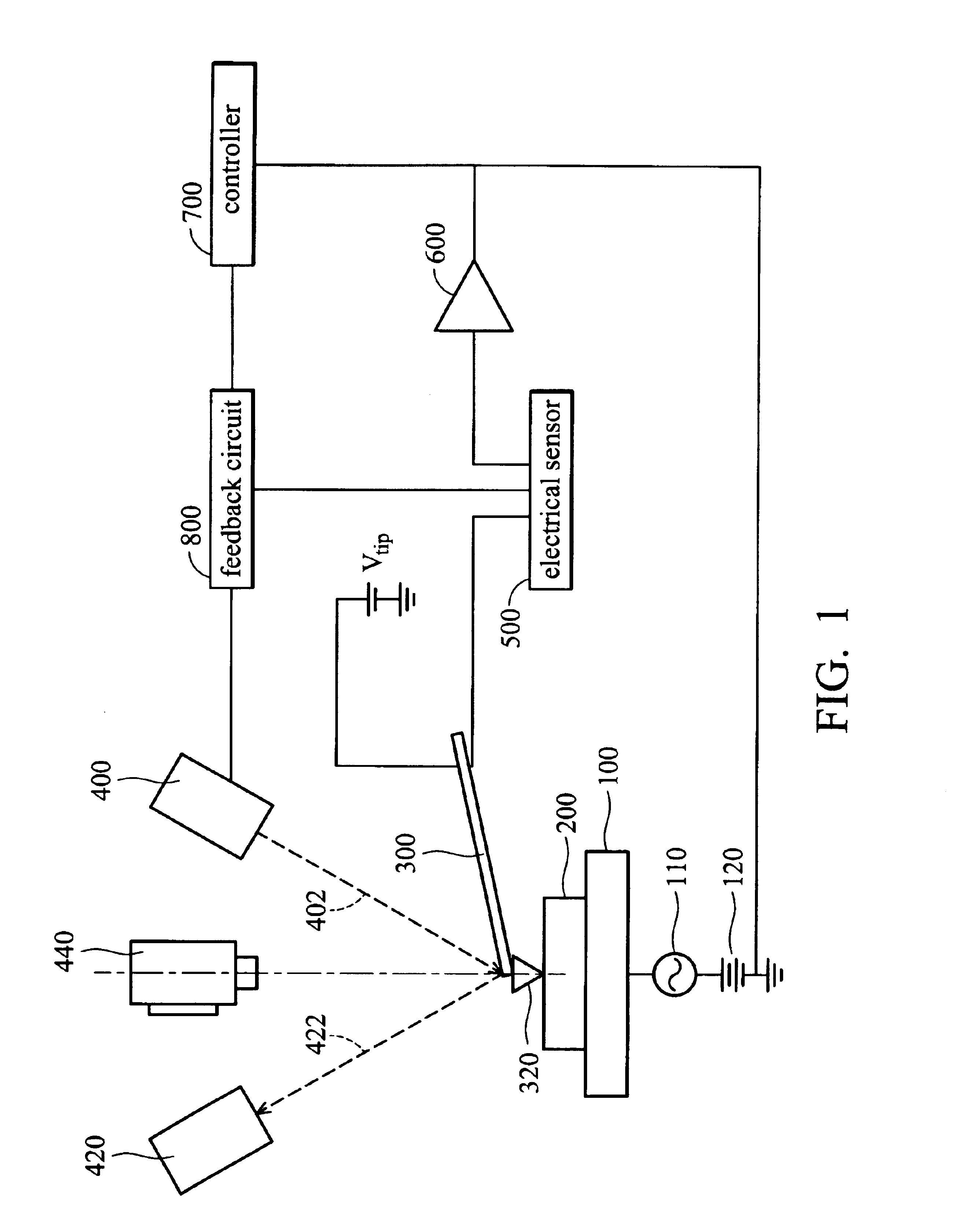
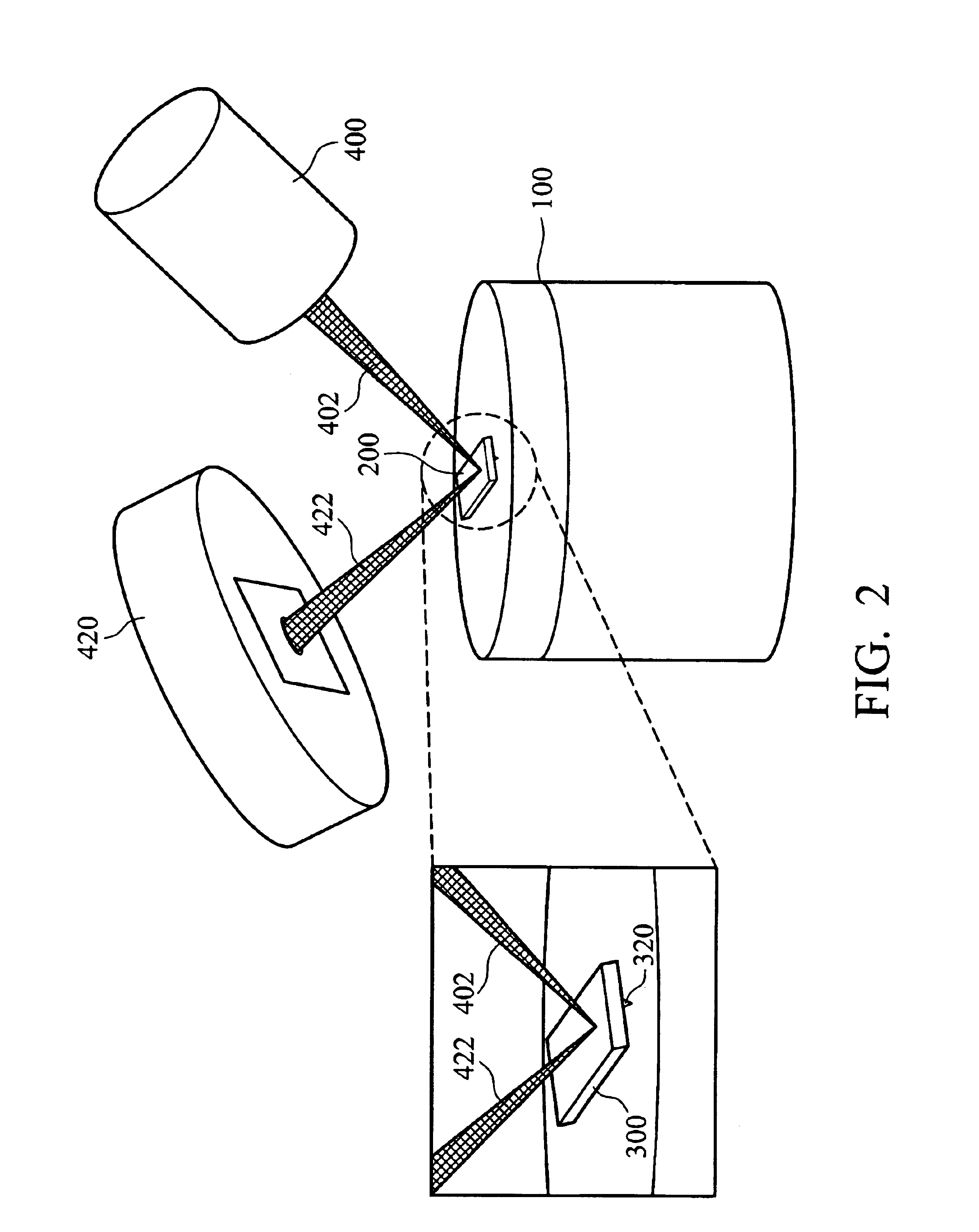
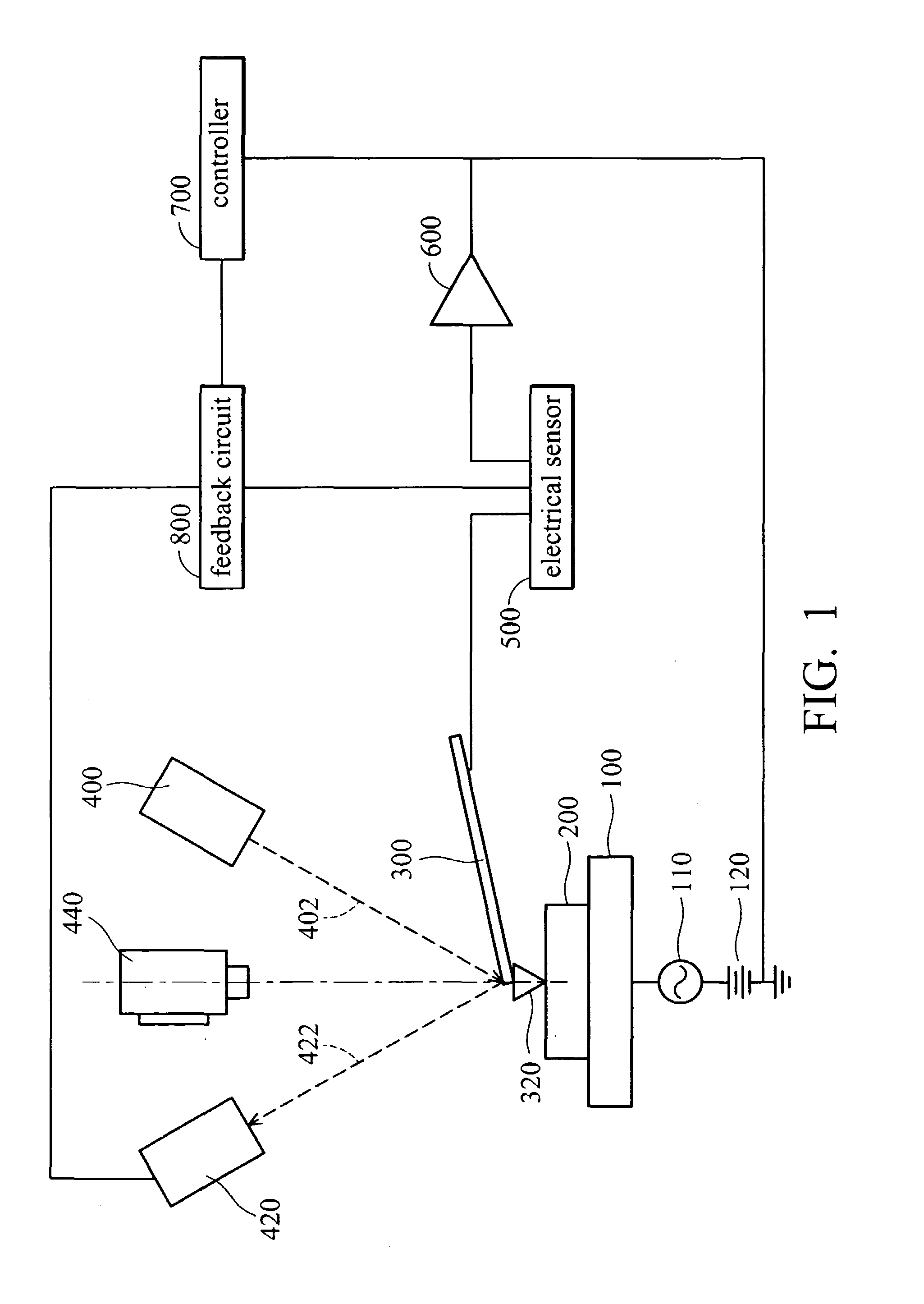
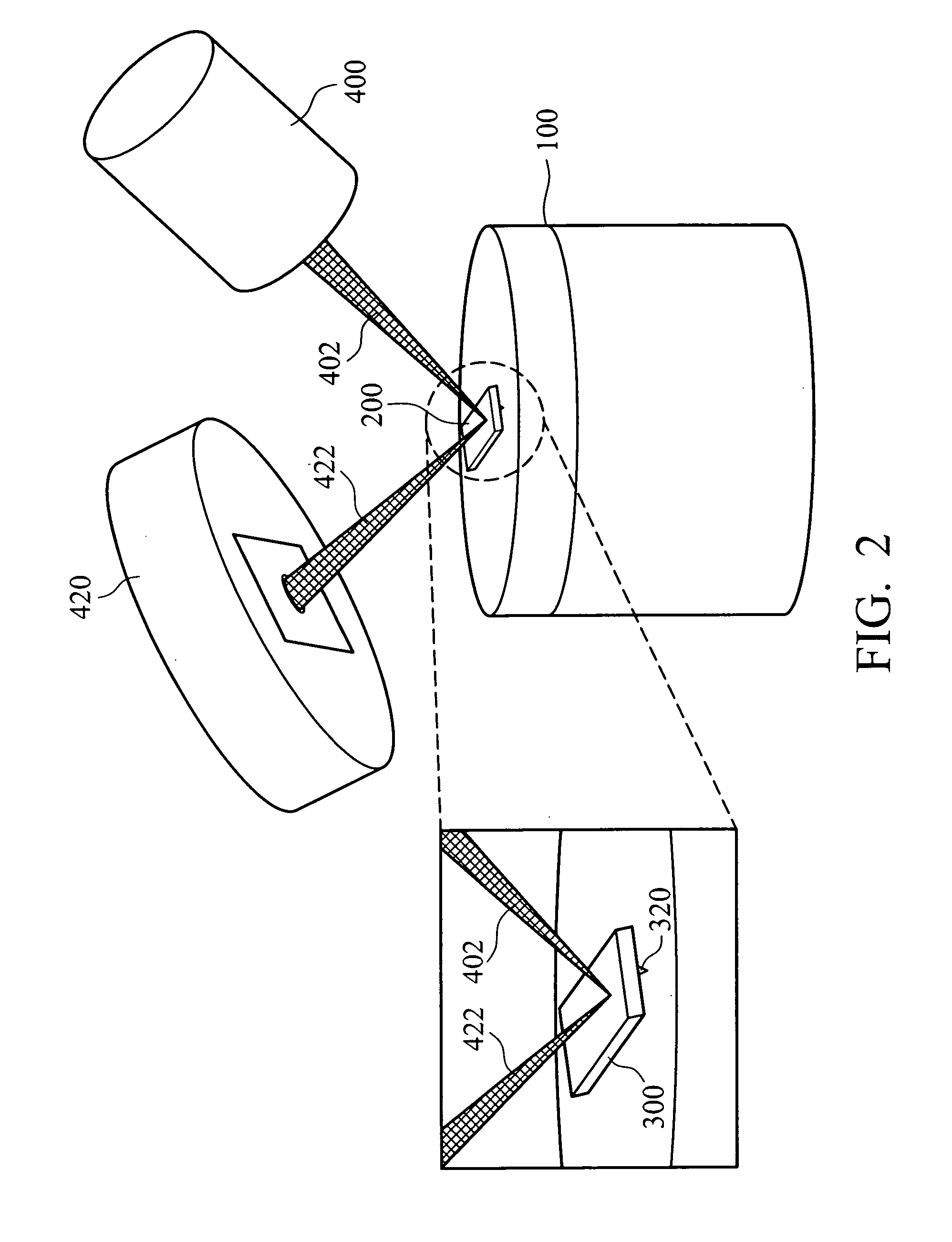
Electrical scanning probe microscope apparatus
An electrical scanning probe microscope (SPM) apparatus. The SPM apparatus is equipped with an atomic force microscope with long-wavelength laser source to acquire topographic images and an electrical scanning sensor operatively coupled to the atomic force microscope to acquire synchronous two-dimensional electrical images. The photoperturbation effects induced by stray light and perturbation of the contrast of SCM images can be ameliorated.
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB
Force tracing method for atomic force microscope (AFM)
ActiveCN102662087AAvoid the impact of dynamic process studiesScanning probe microscopyAtomic force microscopyData acquisition
The invention discloses a force tracing method for an atomic force microscope (AFM), which relates to the technical field of micro force measurement methods and solves the problem that force signals obtained by the traditional AFM single molecule force spectrum method are easily regarded as signals generated by motions of an AFM probe but not signals generated in a dynamic process on cell surfaces. The force tracing method for the AFM comprises the following steps of: after needle feed is finished under the control of a feedback regulation system, closing the feedback regulation system, and determining a position of the AFM probe in a Z direction when the AFM probe is contacted with the surface of a tested object through an obtained force-distance curve; gradually approaching the AFM probe to the surface of the tested object, and when the AFM probe is just contacted with the surface of the tested object, closing the feedback regulation system and stopping feeding the probe to ensure that a cantilever is deflected immediately; and acquiring a relation of the deflection of the cantilever along with time by utilizing a data acquisition card. According to the force tracing method, influences of the motions in the Z direction of the AFM probe driven by a piezoelectric ceramic scanner on dynamic process researches of the surface of the tested object are avoided.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Imaging system of atomic force microscope on the basis of quartz tuning fork probe
InactiveCN103808967AReduce complexityReduce volumeScanning probe microscopyDamping factorAtomic force microscopy
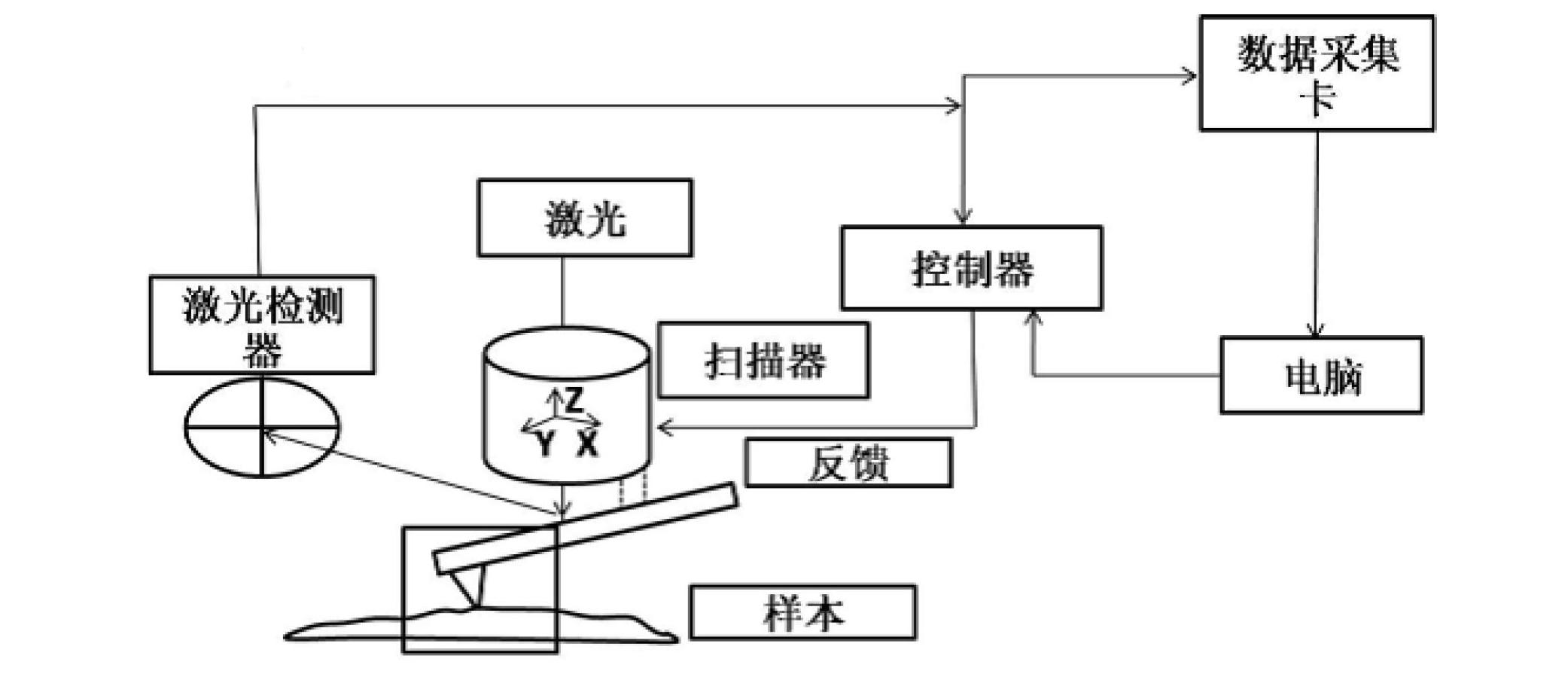
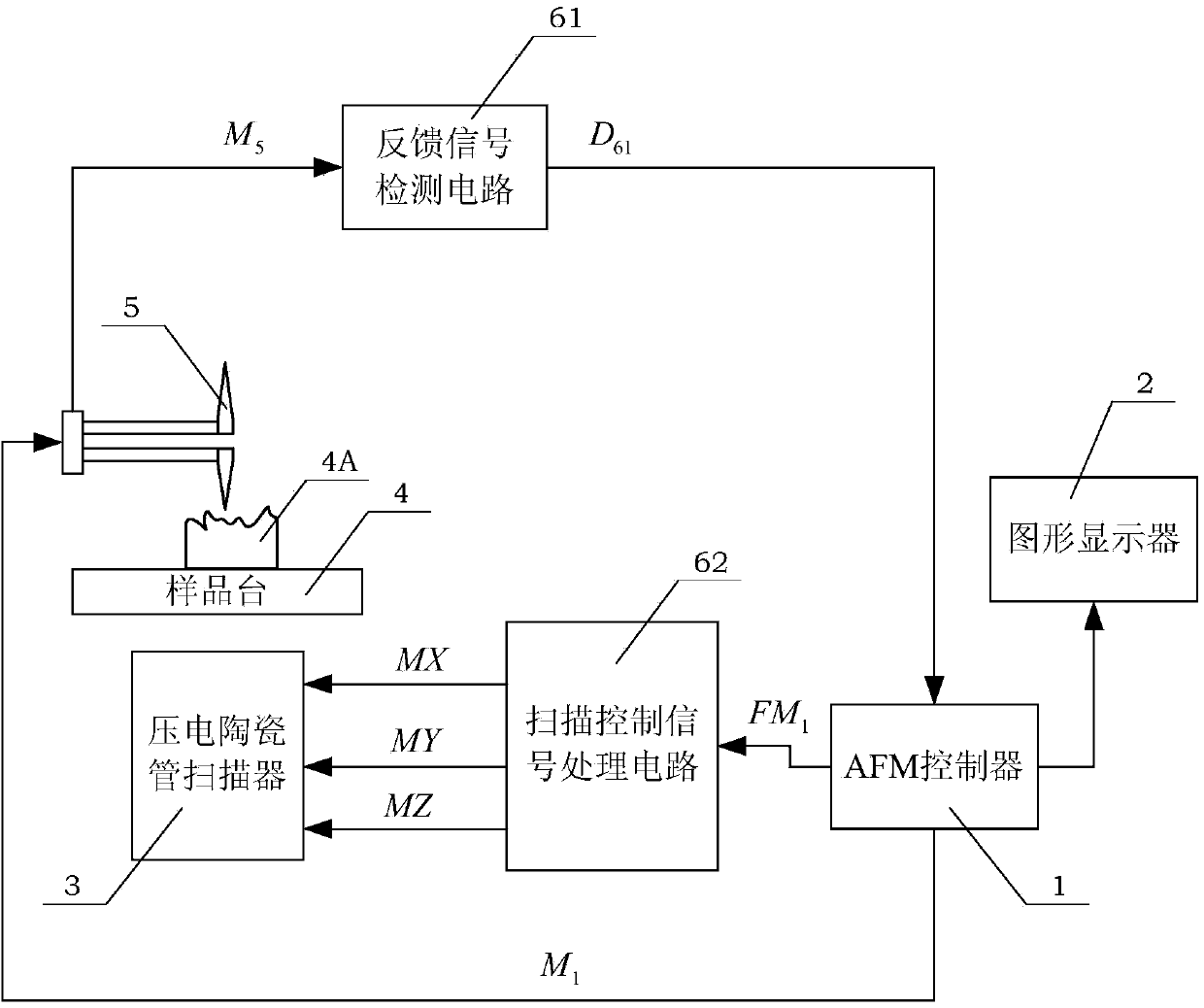
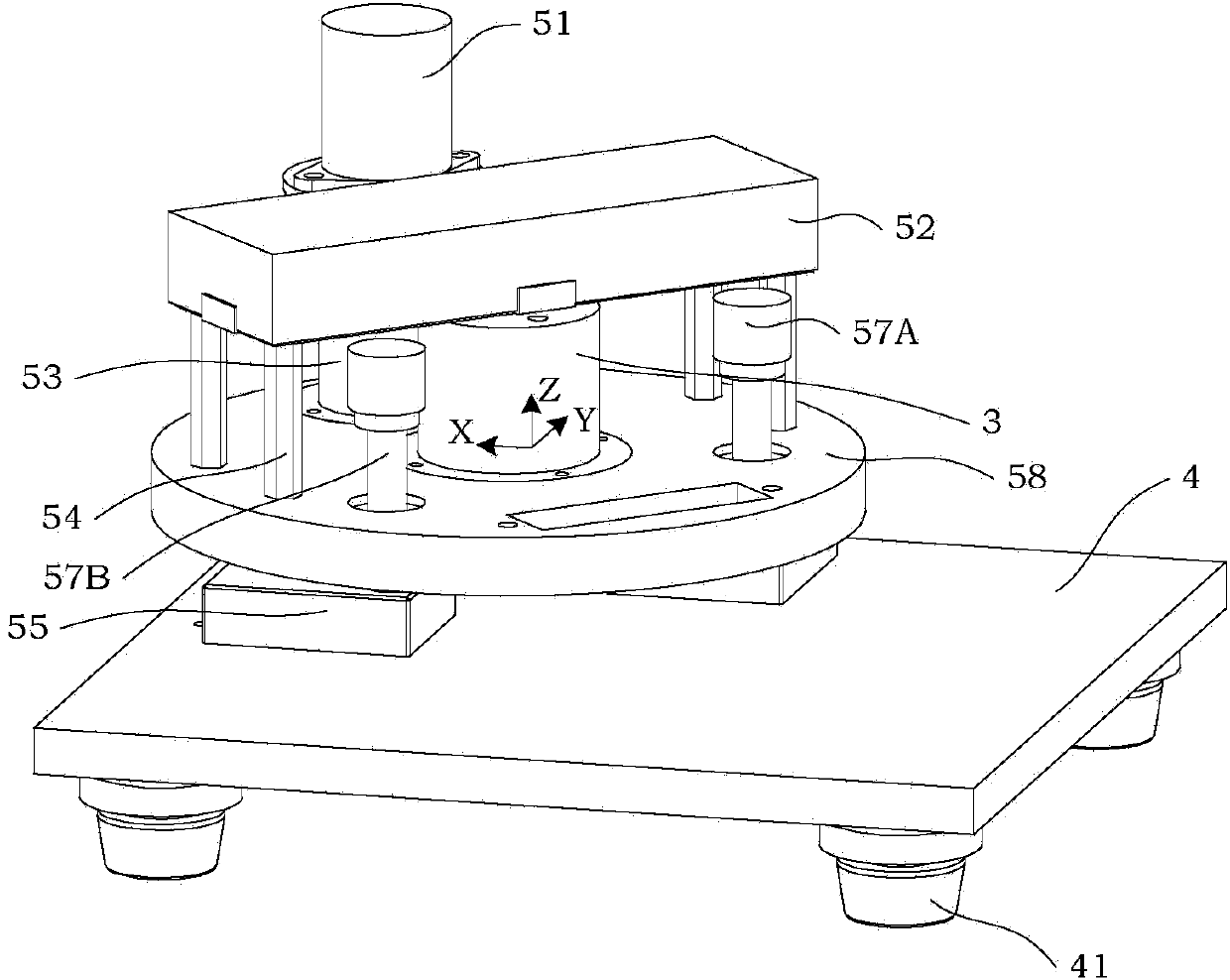
The invention discloses an imaging system of an atomic force microscope (AFM) on the basis of a quartz tuning fork probe. An AFM controller in the system is respectively connected with a graphic display, a piezoelectric ceramic tube scanner, a drive circuit of a stepping motor, a feedback signal detection circuit and a scanning control signal processing circuit through wire cables so as to achieve transmission of electrical signals, a probe limiting seat is installed on a sample table, a round mounting table is mounted above the probe limiting seat, and the piezoelectric ceramic tube scanner, a displacement adjusting component and a circuit mounting box which is supported by four supporting columns are installed on the round mounting table. By means of the imaging system of the AFM on the basis of the quartz tuning fork probe, a student can know basic working principles of the AFM and operating steps of the imaging system, and the imaging system can be used for observing a microstructure of a sample. During an experiment, the student can measure force sensor--quartz tuning fork probe damping coefficient of the imaging system and observe bistable state phenomena to further understand AFM force action mechanism and parameter setting.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Single particle or single molecule tracking device and method based on atomic force microscope
The invention relates to a single particle or single molecule tracking device and method based on an atomic force microscope. The tracking method comprises the following steps that before tracking measurement of a single particle or a single molecule is conducted, the point of a probe of the atomic force microscope is trimmed with a detection object; in the process of tracking measurement, the probe of the atomic force microscope makes contact with the surface of a detected object with constant force; when the detection object and the detected object act to each other, a micro cantilever deflects, and the telescopic distance of piezoelectric ceramics of a scanner is changed; a data acquisition card is used for collecting the changes over time of the deflection of the micro cantilever and the changes over time of the telescopic distance of the piezoelectric ceramics, so that the single particle or the single molecule is tracked. The single particle or single molecule tracking method based on the atomic force microscope can be applied to a study on the dynamic process of cell endocytosis viruses, nano particles and other particles, and is also suitable for a study on the transfer process of glucose, amino acid and other small biological molecules on cytomembrane.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Micro mirror box for scan probe microscope
InactiveCN1782692AIncrease vacuumReduce volumeWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationAtomic force microscopyMagnetic tension force
The micro mirror box for scanning probe microscope includes an electrostrictive stepped unit, an electrostrictive scanning tube, a box, a box cover, a sample seat, a probe, a probe rack, a communication interface and a pumping hole, as well as a sample cutting push rod and an auxiliary probe. The probe and the auxiliary probe may be available probe for scanning tunnel microscope, atomic force microscope and / or magnetic microscope. The present invention has the features of simple and reasonable structure, low cost, small size, etc. and is favorable to raising vacuum degree, lowering temperature, raising S / N ratio, raising signal stability, etc. It may be used for vacuum cutting, vacuum probe replacement and scanning with different kinds of probe, in scanning tunnel microscope, atomic force microscope, magnetic microscope and their combination.
Owner:陆轻锂
Atomic force microscopy
InactiveUSRE37299E1Convenient ArrangementMore compact designNanotechMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAtomic force microscopyImage resolution
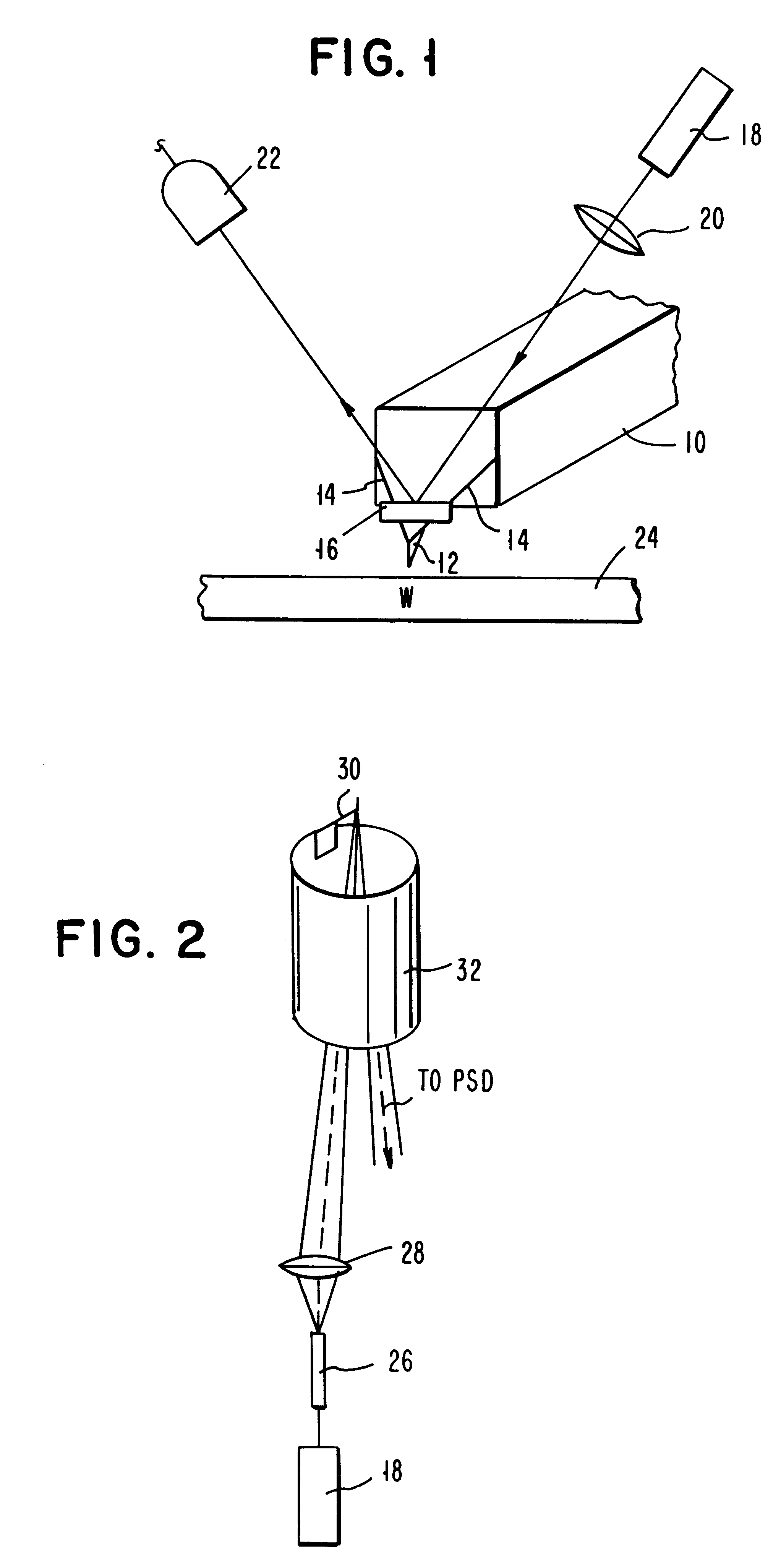
An atomic force microscope includes a tip mounted on a micromachined cantilever. As the tip scans a surface to be investigated, interatomic forces between the tip and the surface induce displacement of the tip. A laser beam is transmitted to and reflected from the cantilever for measuring the cantilever orientation. In a preferred embodiment the laser beam has an elliptical shape. The reflected laser beam is detected with a position-sensitive detector, preferably a bicell. The output of the bicell is provided to a computer for processing of the data for providing a topographical image of the surface with atomic resolution.
Owner:IBM CORP
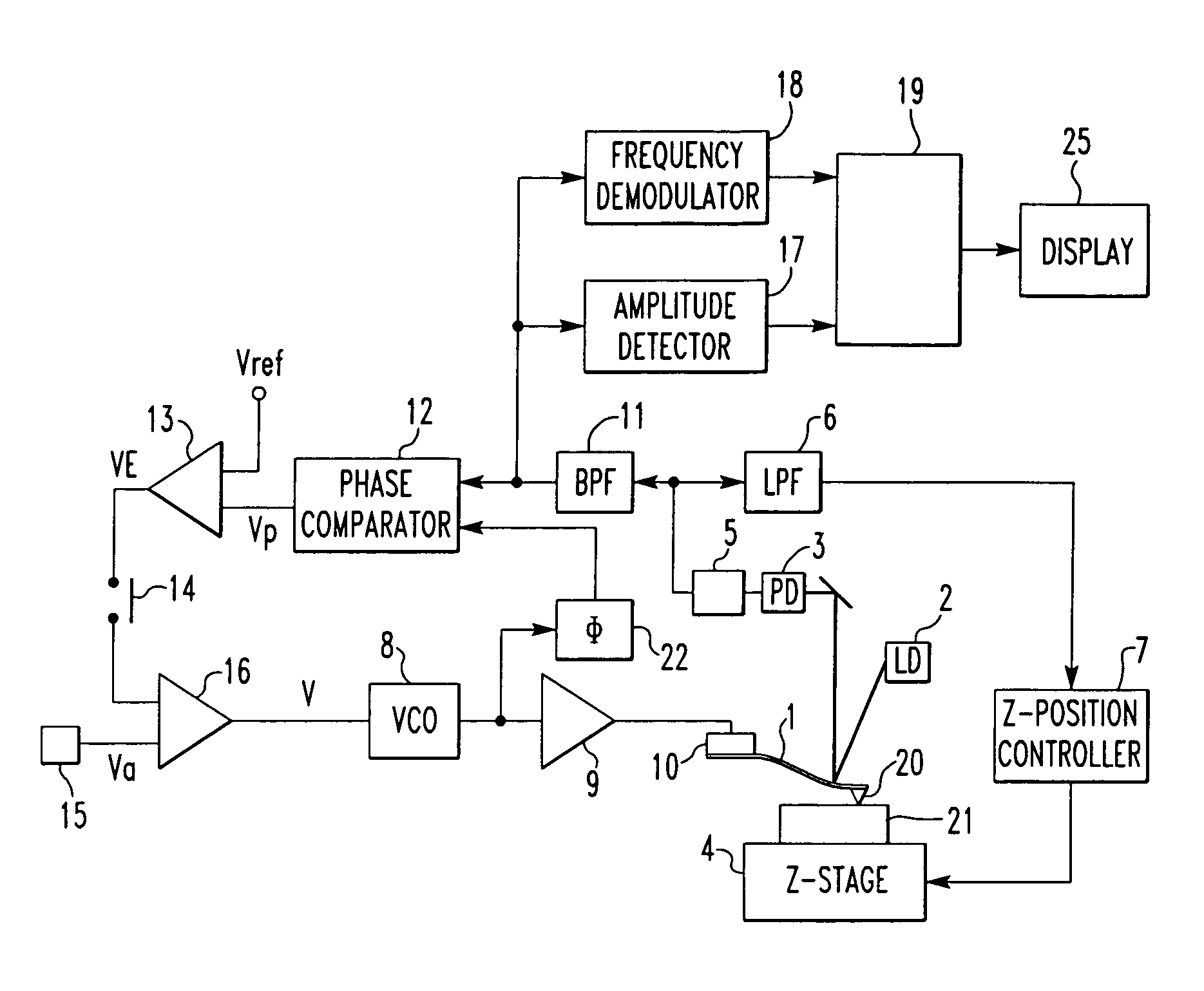
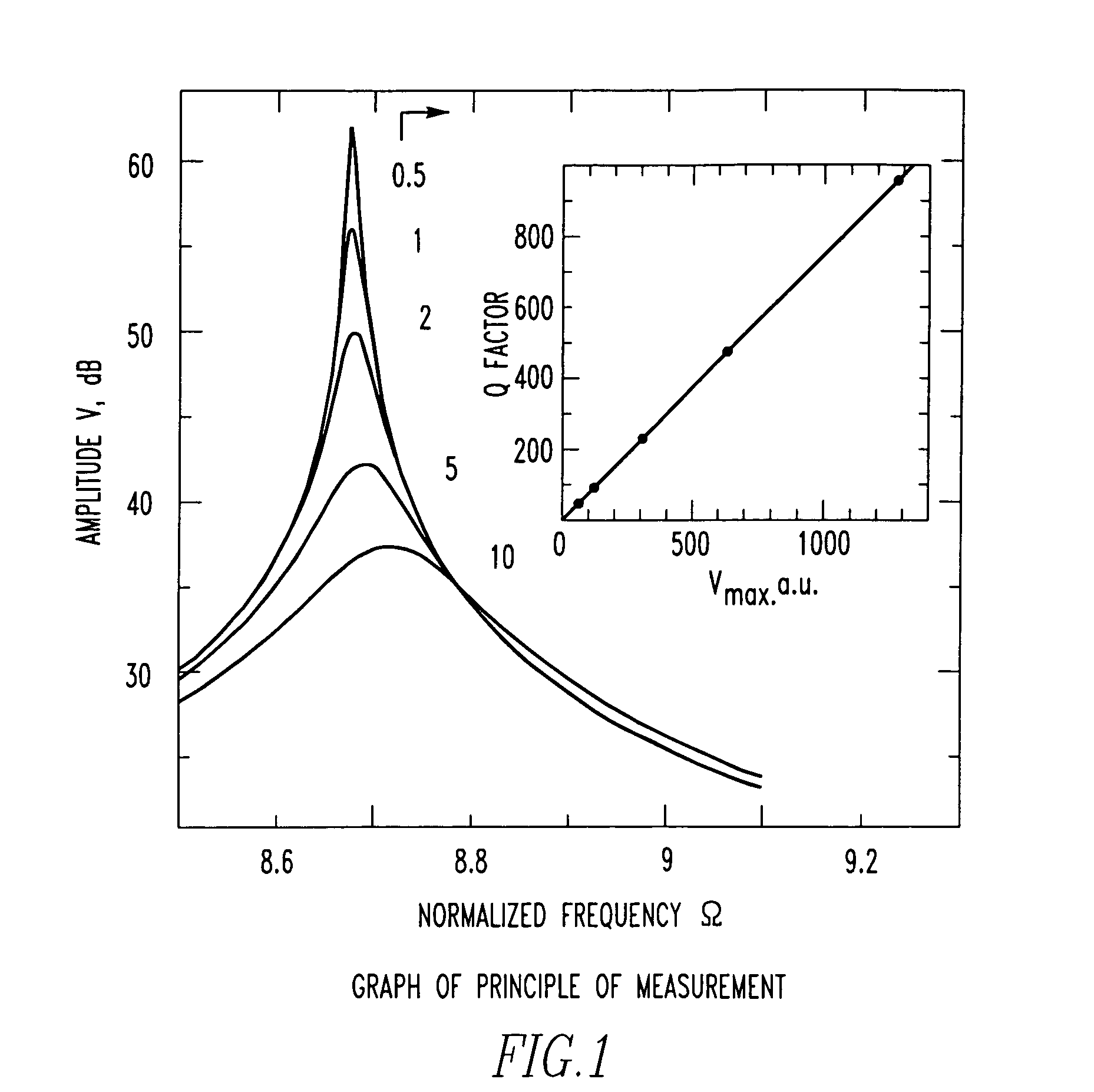
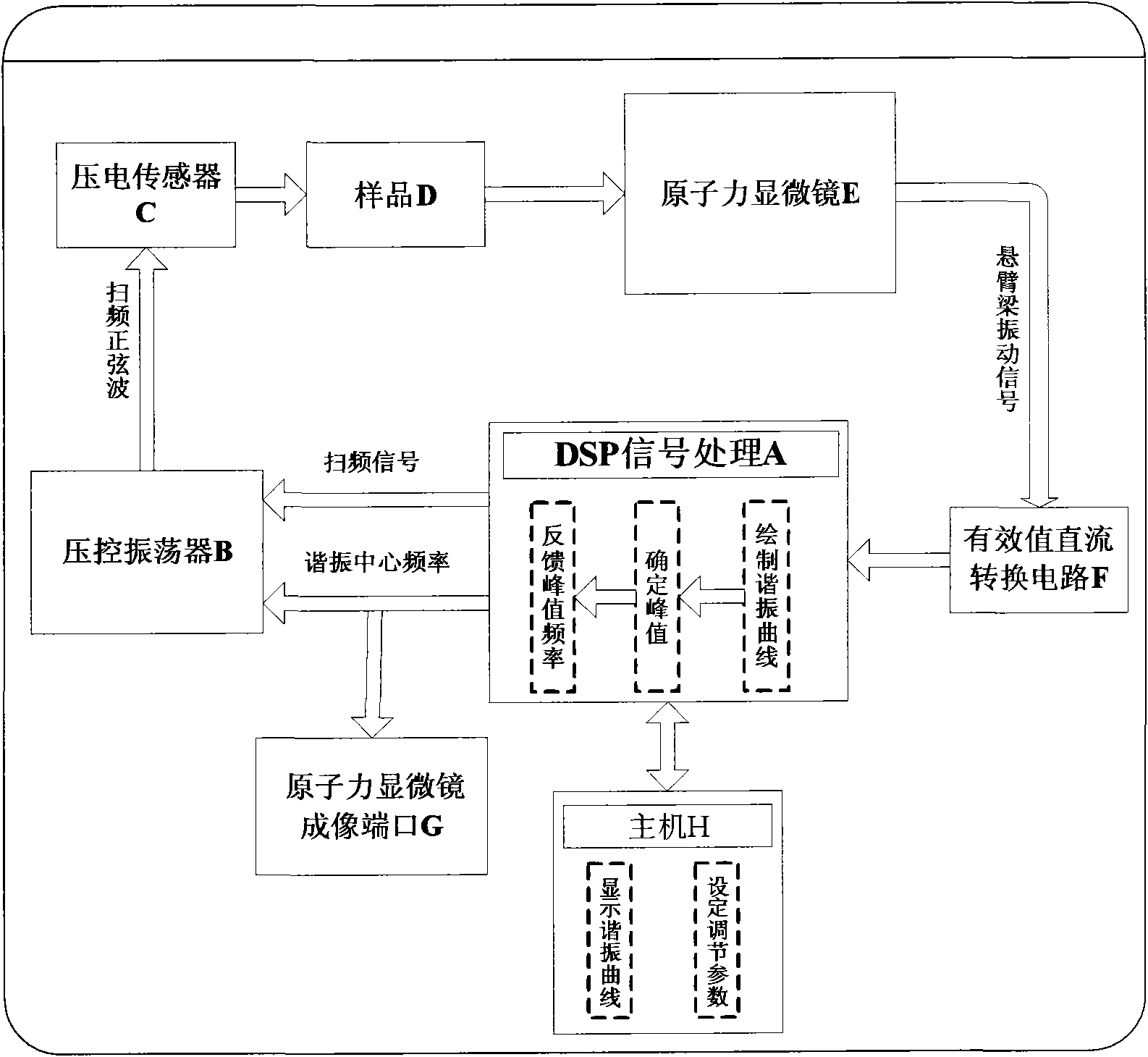
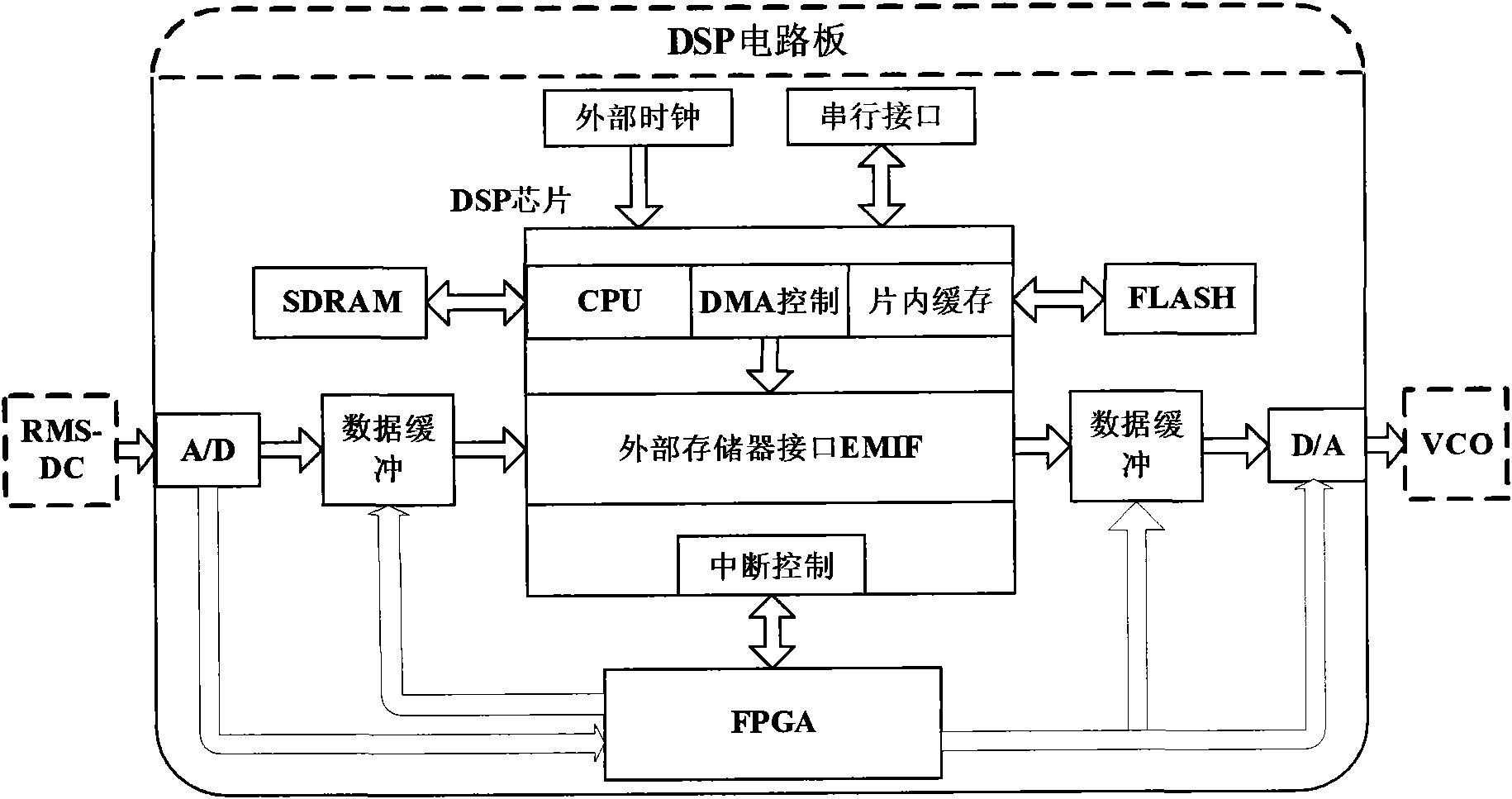
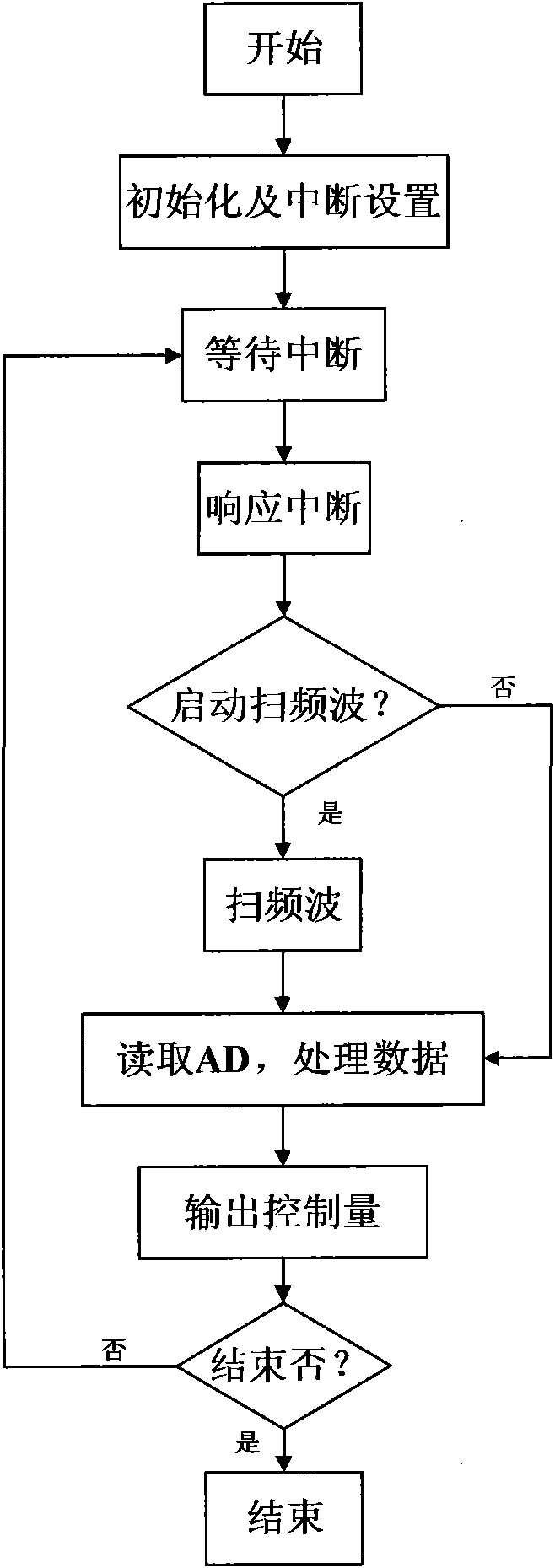
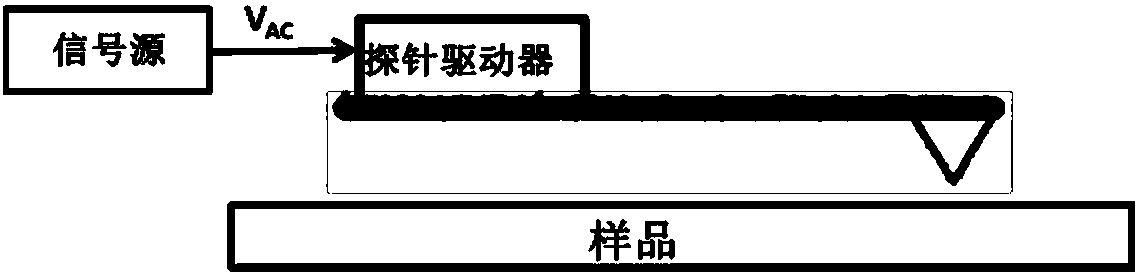
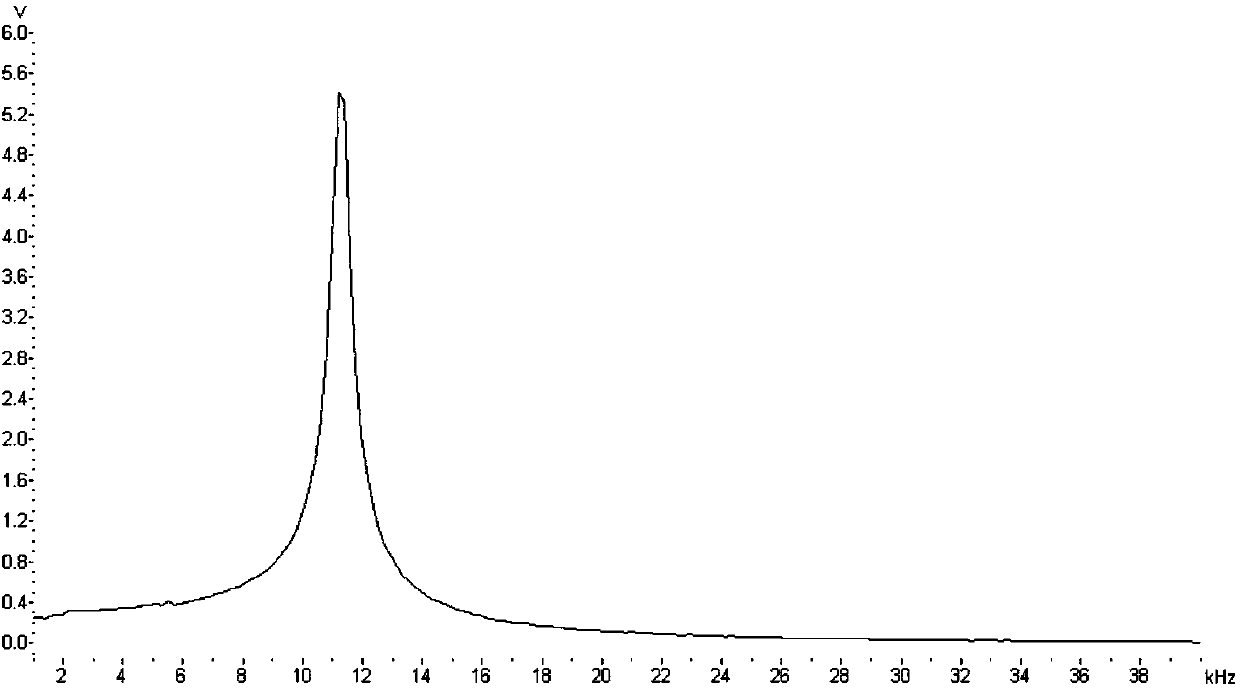
Atomic-force acoustic microscopy cantilever beam contact resonance frequency tracking system
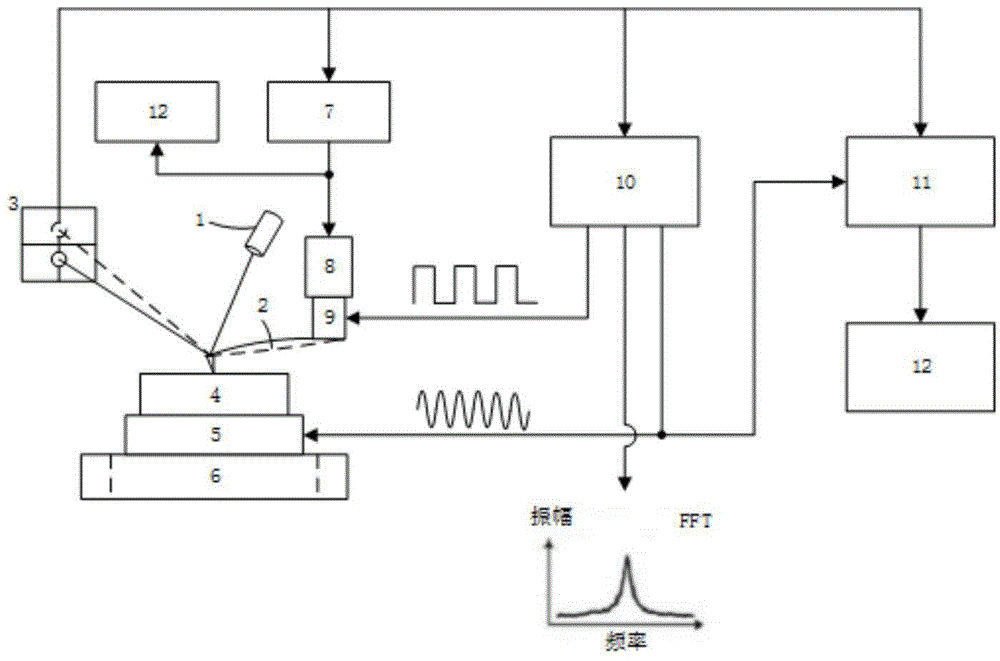
ActiveCN101839924ASubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing electrical meansCenter frequencyPiezoelectric sensor
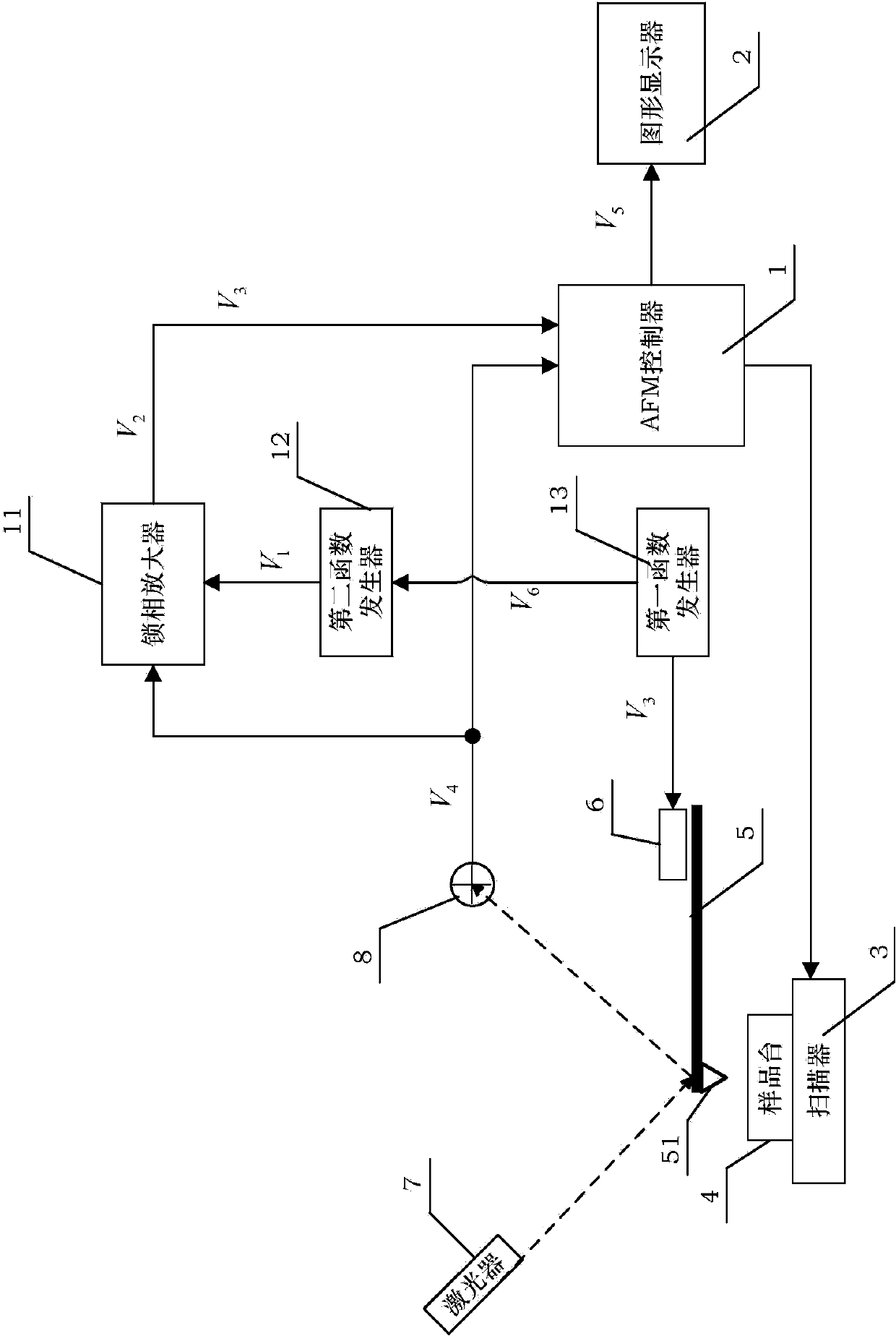
The invention discloses an atomic-force acoustic microscopy cantilever beam contact resonance frequency tracking system, which is mainly applied to rapidly acquiring the contact resonance frequency of an atomic-force acoustic microscopy cantilever beam so as to realize quick elastic modulus imaging of an atomic-force acoustic microscopy and belongs to the field of nondestructive testing. The system has the principle of controlling a voltage-controlled oscillator to output a sine voltage signal of the resonance center frequency so as to excite a piezoelectric sensor based on a voltage signal corresponding to the resonance peak of the atomic-force acoustic microscopy cantilever beam. The system mainly comprises an effective value DC conversion circuit (RMS-DC) which is connected with a photodiode detector of the atomic-force acoustic microscopy cantilever beam, a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) which is connected with the piezoelectric sensor of the atomic-force acoustic microscopy,and a DSP control panel for processing the frequency signals. The DSP control panel controls the VCO to output the sine voltage signal of the resonance center frequency so as to excite the piezoelectric sensor and obtain a resonance curve. Therefore, the center frequency of the resonance curve is obtained and a rapid automatic frequency tracking system is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Atomic force microscope
InactiveUS7591171B2Improve accuracySurface/boundary effectNanotechnologyAtomic force microscopyAtomic force acoustic microscopy
Owner:CANON KK
Method of tracking atomic force acoustical microscopy probe contact resonant frequency
InactiveCN104155477AAvoid Imaging Speed EffectsFast imagingScanning probe microscopyFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
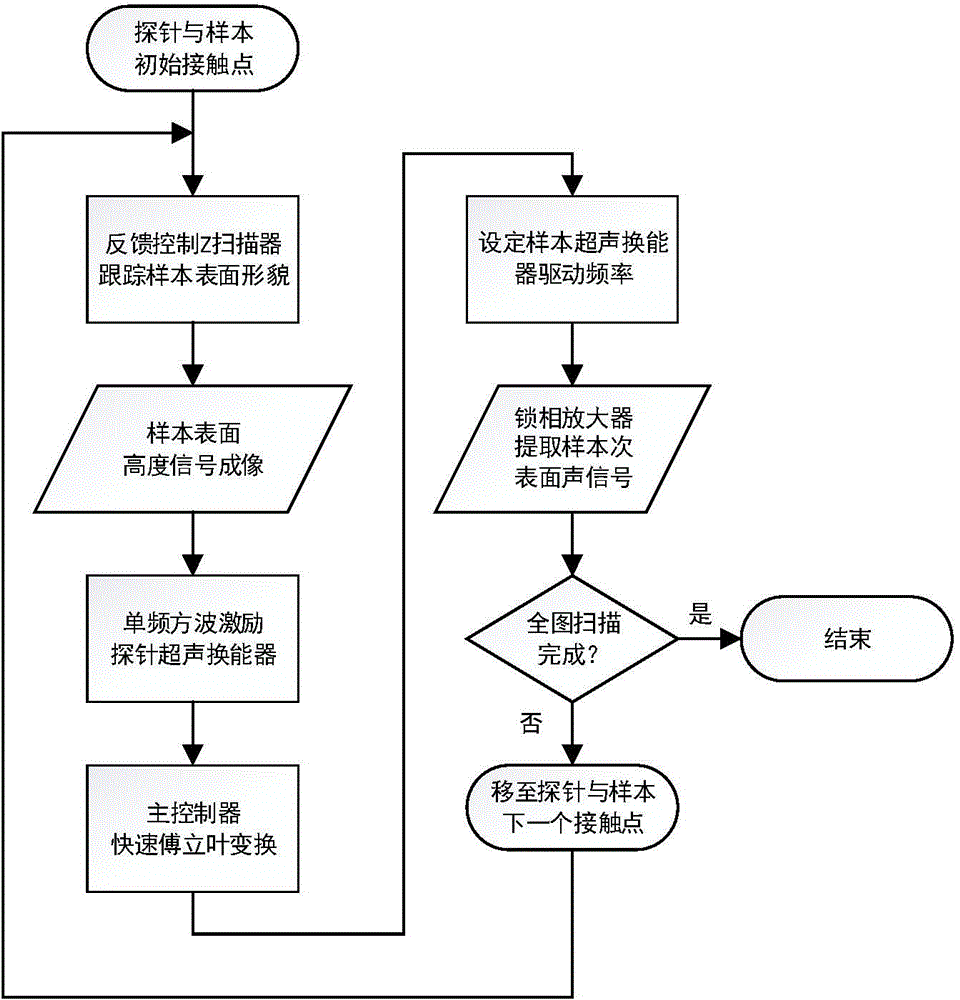
The present invention relates to a method of tracking an atomic force acoustical microscopy probe contact resonant frequency. The method enables the single frequency square wave excitation to substitute for the sine wave frequency sweep based on a spectrum analysis method and by the fast Fourier transform (FFT), thereby avoiding the influence of a frequency sweep process to the imaging speed of the atomic force acoustical microscopy, and realizing the fast tracking of the atomic force acoustical microscopy probe contact resonant frequency.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Atomic force microscope measuring device
InactiveUS20170023611A1Maximizes excitation efficiencyImprove efficiencyRaman scatteringScanning probe techniquesAtomic force microscopyMeasurement device
Atomic force microscope measuring device comprising a micro-cantilever and an intensity modulated laser exciting the cantilever, wherein the measuring device comprises an optical microscope, in particular a fluorescence microscope, a confocal microscope, a fluorescence energy transfer (FRET) microscope, a DIC and / or phase contrast microscope, all of those in particular construed as an inverted microscope.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH +1
Non-destructive measurement method of nanometer cantilever thickness based on force curve of atomic force microscope
InactiveCN101046374ARealize precise measurementAccurate measurementSemi-permeable membranesMeasurement devicesNon destructiveForce curves
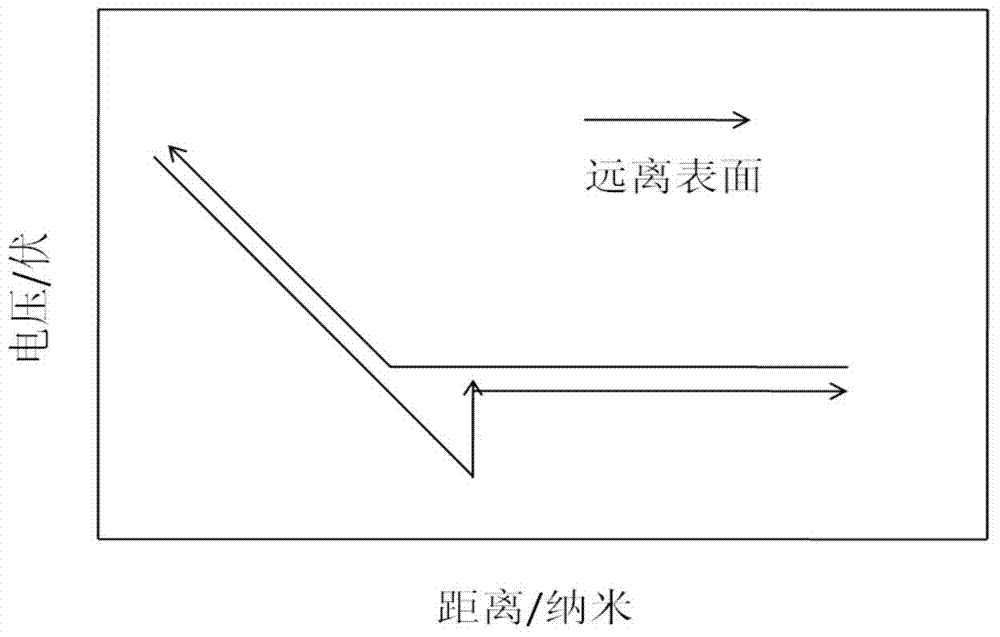
The non-destructive measurement method of nanometer cantilever thickness based on force curve of atomic force microscope includes the first scanning measurement to obtain the 3D topographic information of the nanometer cantilever area and the distance between the upper surface and the base of the nanometer cantilever; the subsequent reducing the scanning range to locate the probe of the atomic force microscope precisely and to load and unload vertically with the probe until the lower surface of the nanometer cantilever contacts with the base and the force curve exhibits turnover, and recording the real-time force curve of the atomic force microscope during loading and unloading to obtain the distance between the lower surface and the substrate of the nanometer cantilever; and finally subtracting the data obtained in the foregoing steps to calculate the nanometer cantilever thickness. The said method may be also used in measuring other dimensions of nanometer structure.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Electrical scanning probe microscope apparatus
InactiveUS7193424B2Improve accuracyElectrical measurement instrument detailsNanotechnologyAtomic force microscopyOpto electronic
An electrical scanning probe microscope (SPM) apparatus. The SPM apparatus is equipped with an atomic force microscope with an infrared laser source, a position-sensitive photo-detector (PSPD) to provide a topographic image, a charge-coupled device (CCD) monitor for optical alignment, and an electrical scanning sensor operatively coupled to the atomic force microscope to acquire synchronous two-dimensional electrical images. The photoperturbation effects induced by stray light and perturbation of the contrast of SCM images can thus be ameliorated.
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB
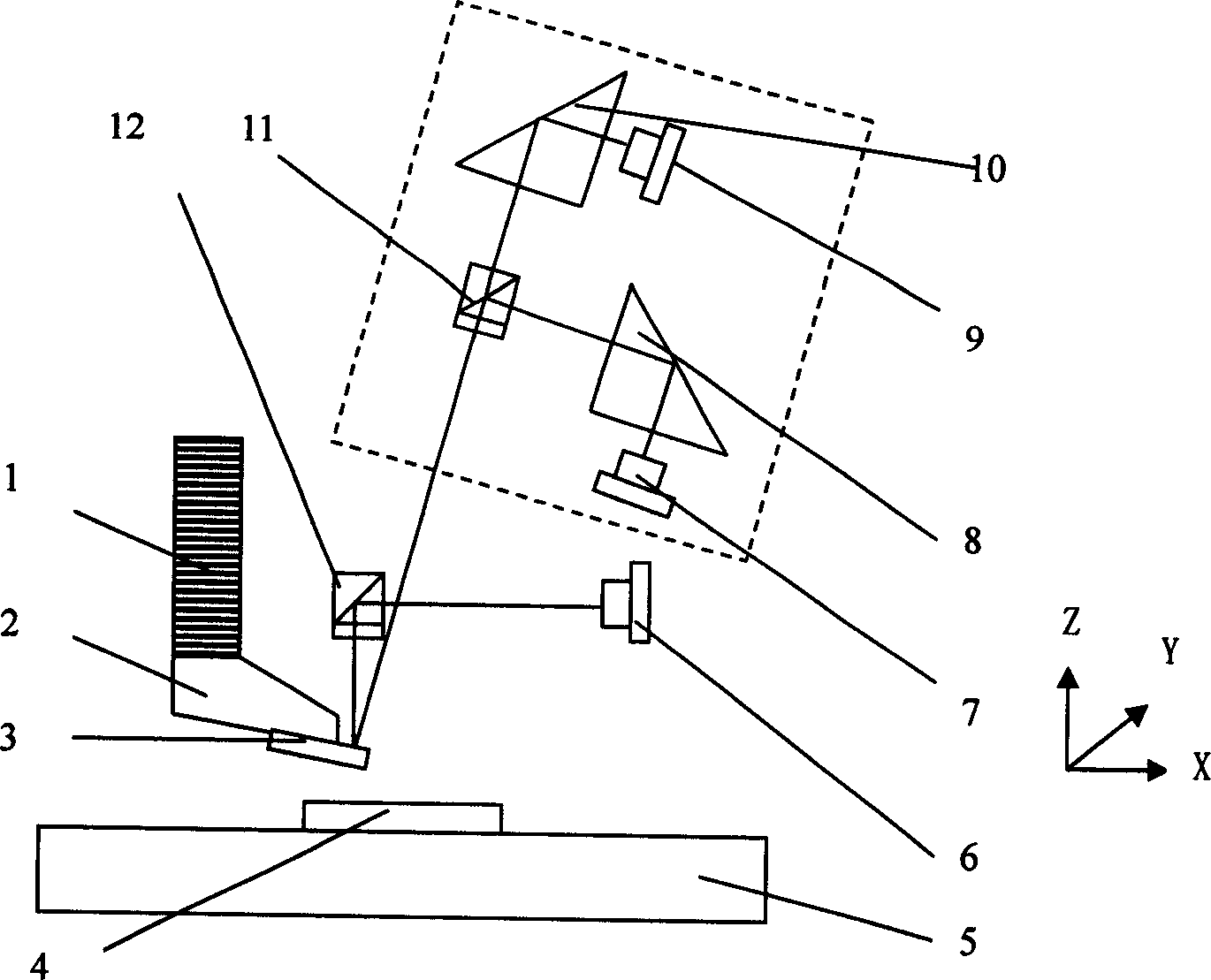
Atomic force microscope measuring device based on angular measurement
InactiveCN1632519AReduce sizeReduce weightSurface/boundary effectInstrumental componentsIn planeAtomic force microscopy
This invention discloses an atomic force microscope measurement method based on angle measurement, which belongs to the test system and device of the signals of atomic force microscope APM probe and cantilever. The said angle measurement device comprises calibration light source, focus lens, a quarter of wavelet, light splitter, two threshold prism, two photoelectricity diodes, Z-tracing micro-driver, two-dimensional micro-scanners in plane, probe clamper and APM probe. And the sample bench and the two-dimensional micro-scanner and APM probe and Z-tracing micro driver are separated with adjustable distance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Accurate positioning method based on atomic force microscope
InactiveCN101413865APrecise positioningPositioning is simple and fastSurface/boundary effectInstrumental componentsAtomic force microscopyAtomic force acoustic microscopy
The invention discloses a method for precise orientation by an atomic force microscope. The precise orientation method comprises steps of: firstly finding a sample to be measured by an optical microscope; putting a copper net Center_Marked Grids above the sample to be measured, the copper net being formed by ruled grids with the same size, recording the region of the grids corresponding to the sample to be measured under the optical microscope, scanning the Center_Marked Grids by using an atomic force microscope, reducing the scanning area stage by stage, locating a probe of the atomic force microscope above the corresponding grids of the sample to be measured; and finally, softly blowing the Center_Marked Grids from side by using a washing ear ball; thereby carrying out the precise observation of the atomic force microscope by knitting stitch. The method can precisely orientate the sample to be scanned.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
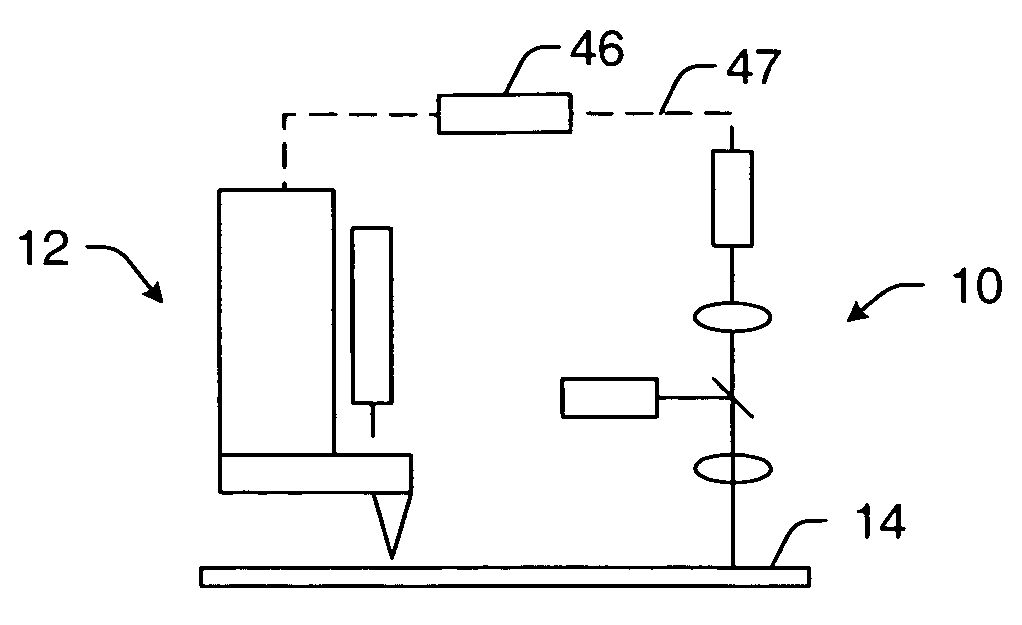
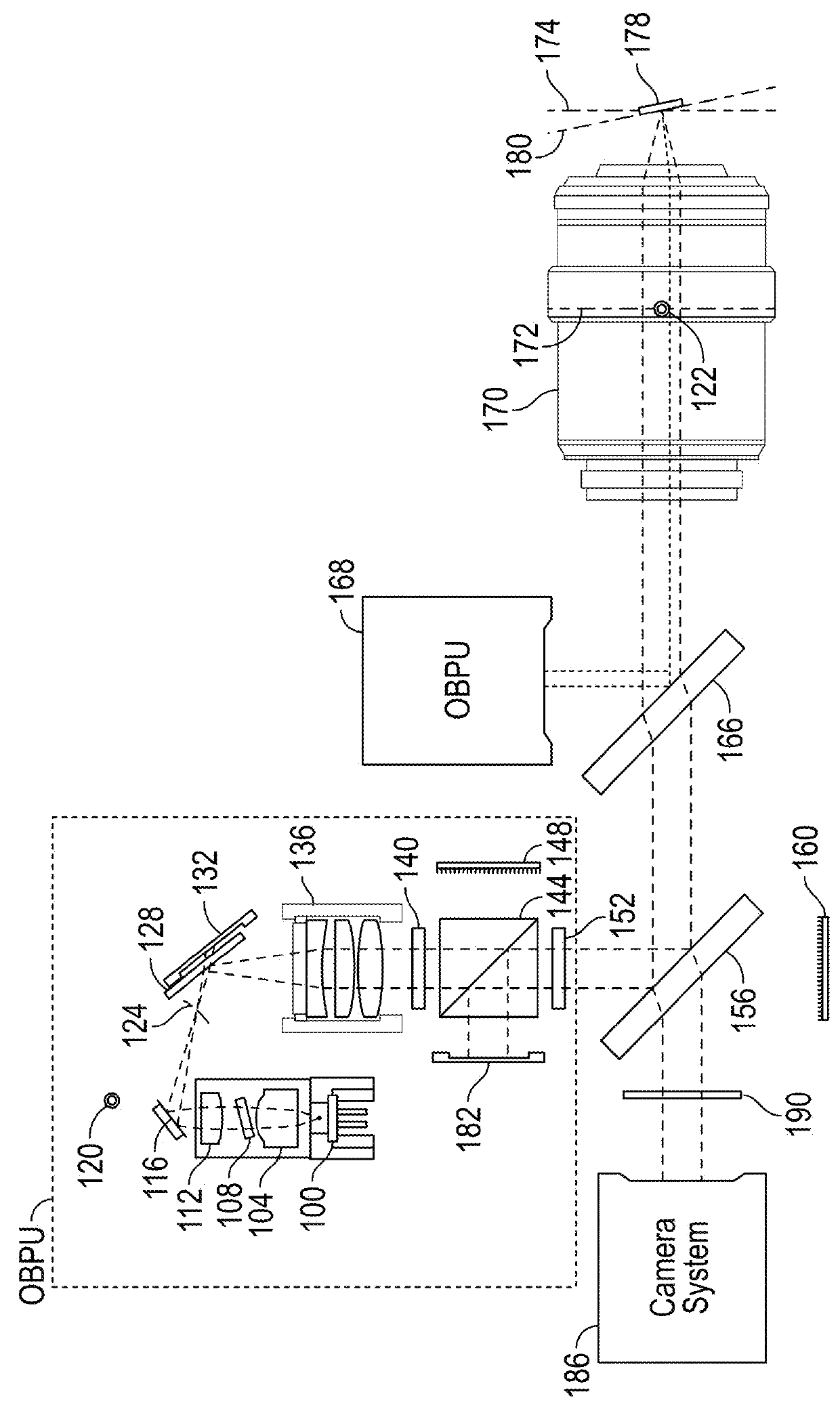
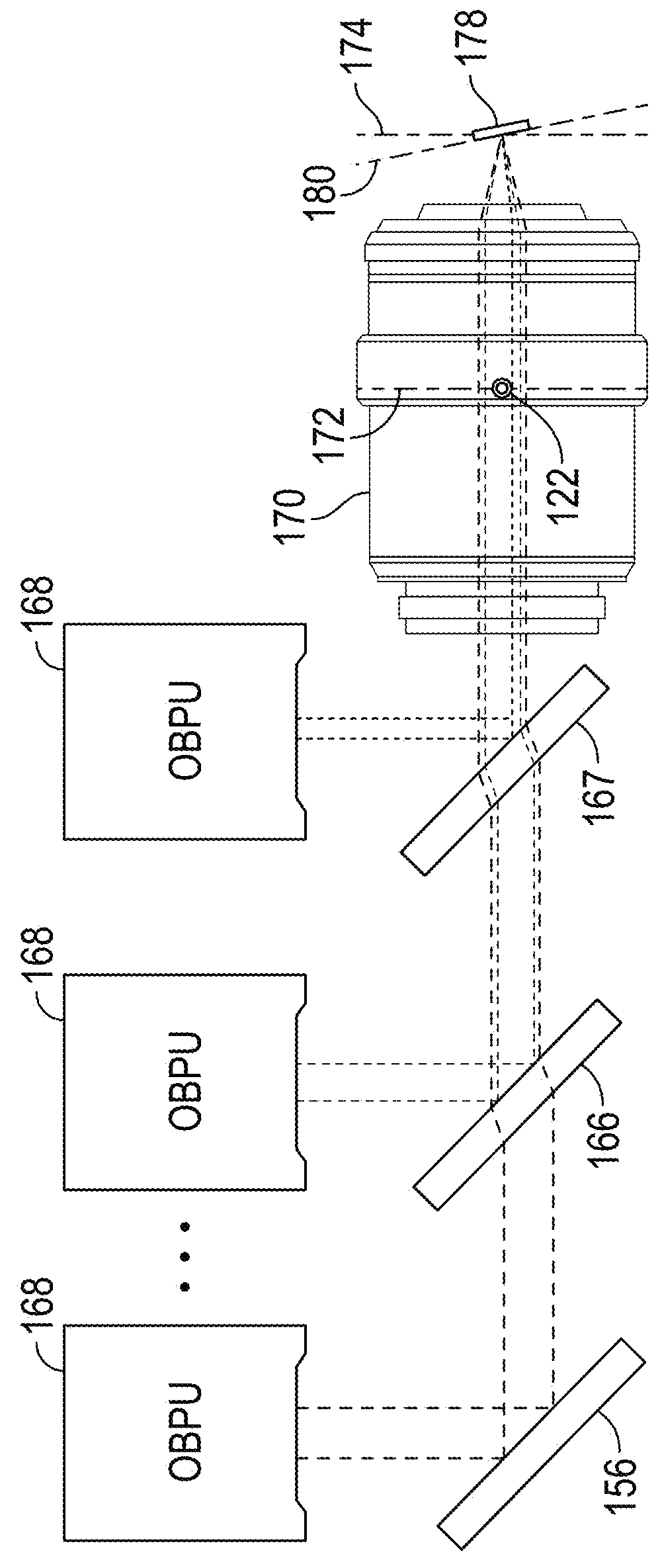
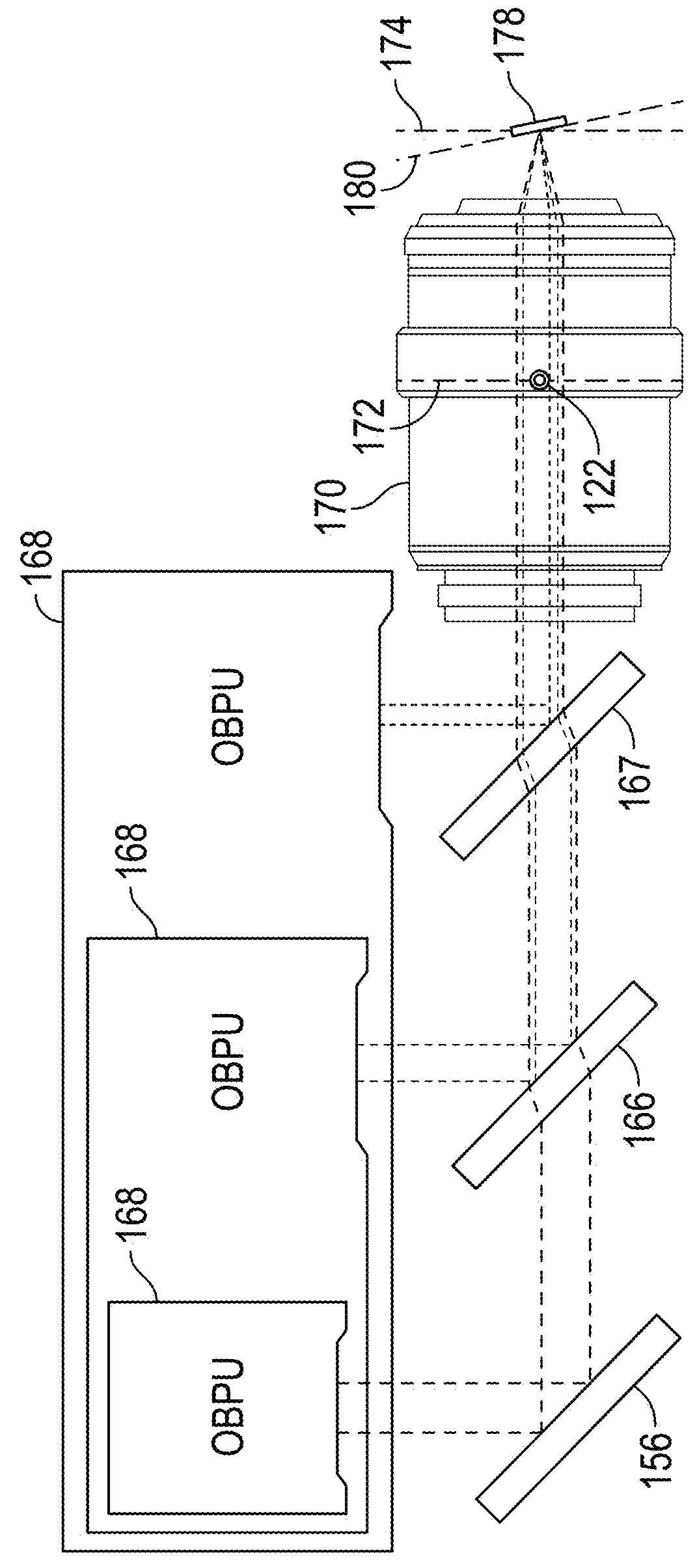
Optical beam positioning unit for atomic force microscope
This invention relates to an optical light beam positioning system that enables the combination of two or more light beams of different wavelengths to be focused onto a probe or sample of a scientific instrument, such as an atomic force microscope, for a number of specific uses typical to AFMs, like measuring the deflection or oscillation of the probe and illuminating an object for optical imaging, and less traditional ones like photothermal excitation of the probe, photothermal activated changes in the sample, photothermal cleaning of the probe and photochemical, photovoltaic, photothermal and other light beam induced changes in the sample. The focused light beams may be independently positioned relative to each other.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR ASYLUM RES INC
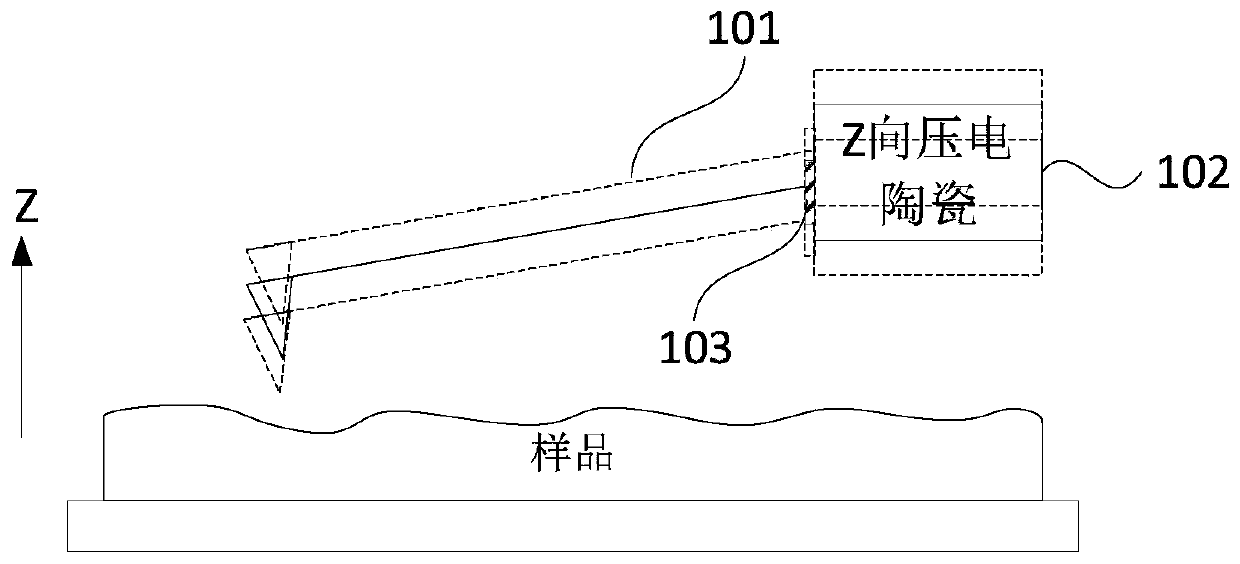
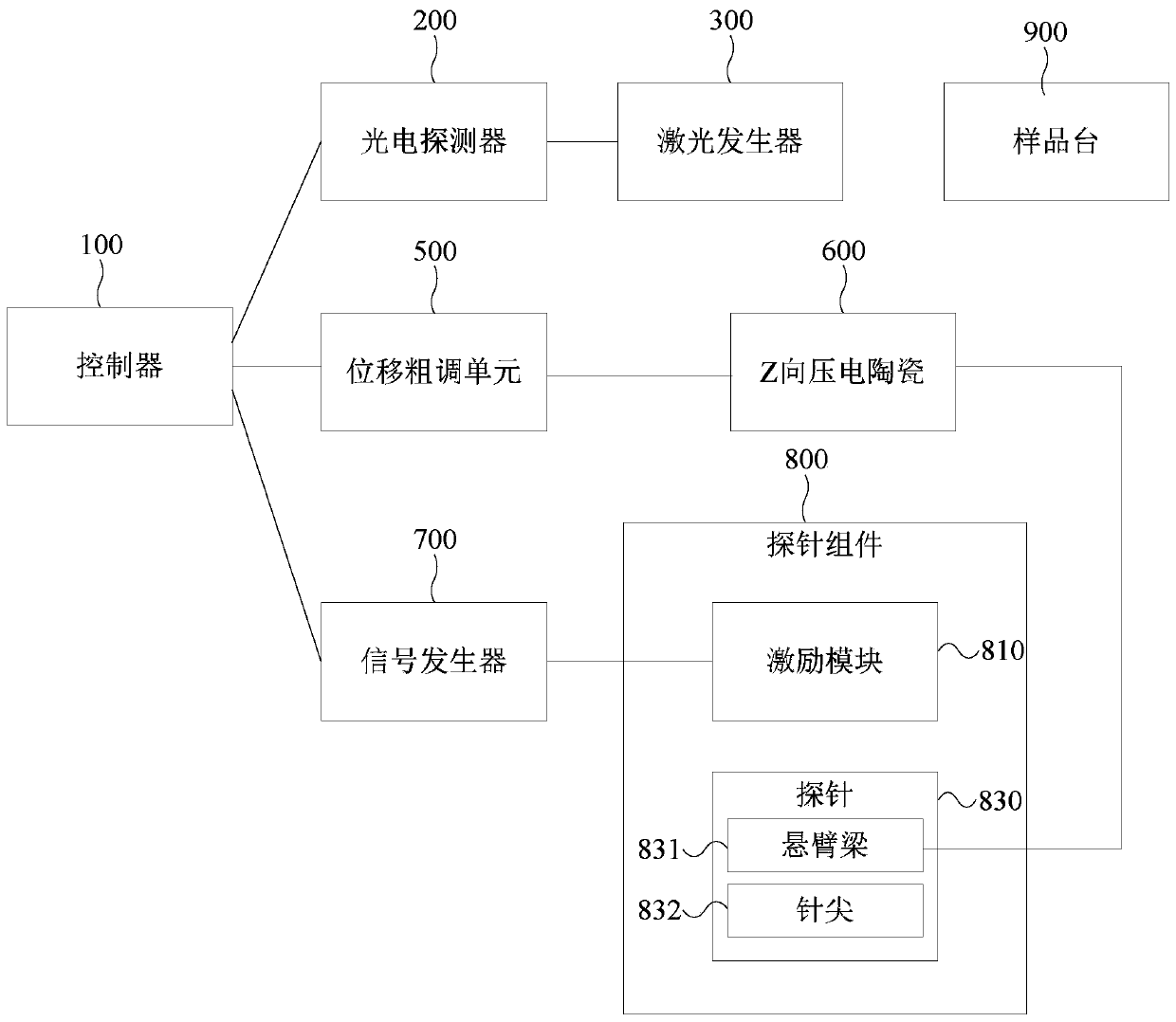
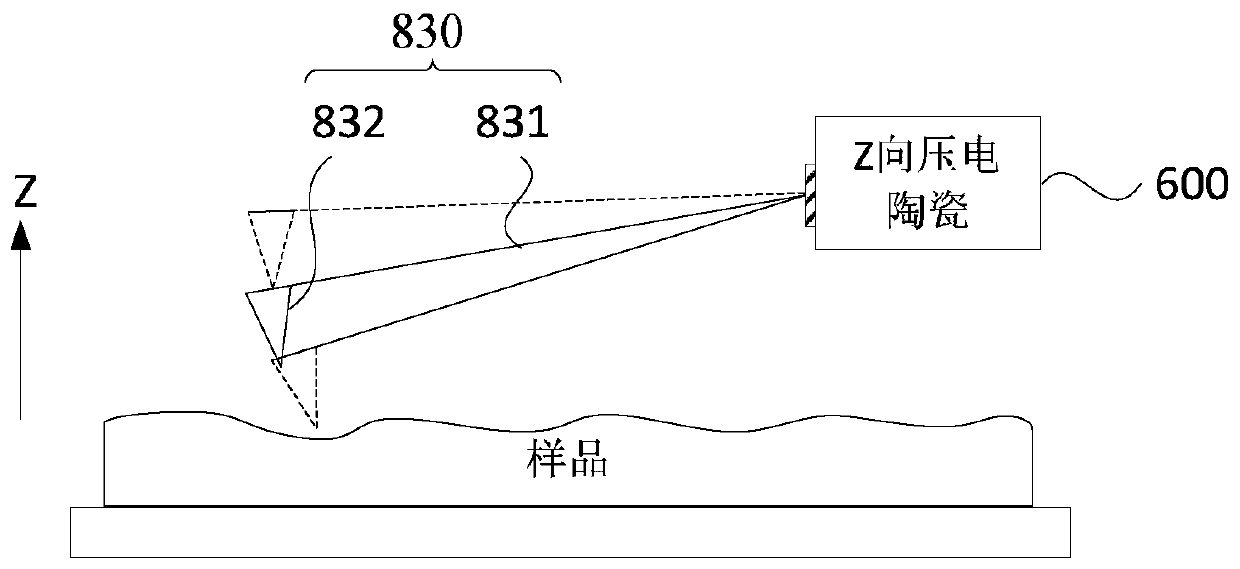
Atomic force microscope and test method of sample surface property
InactiveCN110095637AHigh vibration frequencyHigh speedScanning probe microscopyAtomic force microscopyPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses an atomic force microscope and a test method of a sample surface property. The atomic force microscope comprises a signal generator, a probe component, Z-direction piezoelectric ceramics, a laser generator, a photoelectric detector, a displacement coarse adjustment unit, a controller, and a sample stage. The probe component comprises a probe and an excitation module. The probe includes a cantilever beam and a needle tip located at a first end of the cantilever beam. The excitation module is connected to a signal generator, is used for receiving an excitation signal anddrives the probe to deflect at a first direction under the effect of the excitation signal. The excitation module is a non-laser photothermal excitation module. In the technical scheme of the invention, a vibration frequency of the probe is greatly increased so as to effectively speed up a speed when the surface property to be tested is tested by using a non-resonant tapping mode, and shorten testtime of the same surface to be tested.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Atomic force microscope and method for determining properties of a sample surface using an atomic force microscope
ActiveUS7009414B2Reduce wearReducing and eliminating damageNanotechnologyScanning probe microscopyAtomic force microscopyAtomic force acoustic microscopy
A method for determining properties of a sample surface using an atomic force microscope includes applying a first voltage between the sample and a probe, moving the probe towards the surface of the sample, and stopping movement of the probe towards the surface of the sample when current in the probe is initially detected. An oscillating magnetic field is applied to the probe such that the probe obtains stable contact with the surface of the sample.
Owner:IBM CORP
Microcoaxial probes made from strained semiconductor bilayers
ActiveUS7485857B2NanotechMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAtomic force microscopyMicrowave
The present invention provides microcoaxial probes fabricated from semiconductor heterostructures that include strained semiconductor bilayers. The microcoaxial probes are well suited for use as scanning probes in scanning probe microscopy, including scanning tunneling microscopy (STM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), scanning microwave microscopy, or a combination thereof.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Device and method for an atomic force microscope for the study and modification of surface properties
InactiveUS20110055985A1Active configurability of the contactsRadiation pyrometryPhotometrySpectroscopyLaser light
The invention relates to a device for an atomic force microscope (AFM) for the study and / or modification of surface properties. The device comprises a cantilever (flexible bar) having an integrated, piezoresistive sensor, an integrated bimorphic actuator, and a measuring tip. The measuring tip carries at least two metal electrodes, which can be activated via electrical terminals. The measuring tip and / or the cantilever have at least one nanoscopic hole through which synchrotron radiation or laser light is directed onto the material surface to be studied. Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for the study and modification of surface properties and surface-proximal properties, which can be executed using such a device. To this end, atomic force microscopy (AFM), surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), photo emission spectroscopy (XPS, XAS), and material modification by local exposure are executed in sequence or simultaneously using the same device.
Owner:SYNCHROTRON SOLEIL +2
Precision measurement method of nanometer clearance in nanostructure based on atomic force microscope
InactiveCN101303221AGet real heightEliminate measurement errorsUsing electrical meansObservational errorForce curves
The invention relates to a method of precision measurement of nanometer clearance of a nanometer structure based on an atomic force microscope, the method comprising: scanning the central region of a top surface of a target sample, and positioning the tip of a probe at the center of the sample; loading / unloading a vertical force with the probe of the atomic force microscope until the bottom surface of the sample contacts the substrate; and recording a force curve of the atomic force microscope during loading / unloading, so as to obtain a nanometer clearance between the bottom surface of the sample and the substrate. Specifically, the method comprises: calibrating the sensitivity of a micro cantilever of the atomic force microscope; positioning the tip of the probe of the atomic force microscope at the geometrical center of the top surface of the sample; obtaining a consistent force curve and a disjunctive force curve; comparing the slopes of the three curves including the sensitivity force curve, the consistent force curve, and the disjunctive force curve; and extracting the distance between the bottom surface of the sample and the substrate. According to the invention, measurement error due to offset of a target point from the center of a sample can be eliminated without damage on the structure of a target nanometer device, thus high-resolution measurement of nanometer clearance of nanometer structures is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
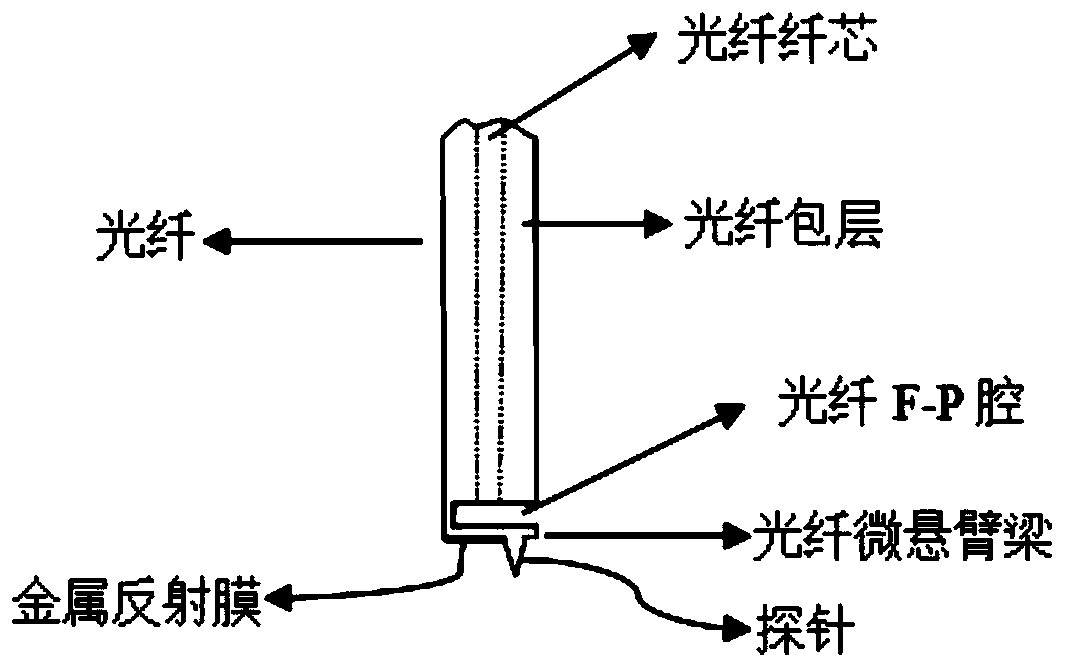
An optical fiber-based atomic force microscope probe and atomic force microscope system
ActiveCN106501551BHigh measurement accuracyHigh measurement sensitivityScanning probe microscopyFiberAtomic force microscopy
The invention relates to a fiber-based atomic force microscope probe and an atomic force microscope system. The fiber-based atomic force microscope probe comprises a probe pin and a micro cantilever beam; and the probe pin is arranged at one end of the micro cantilever beam arranged at one end of a fiber. A fiber F-P cavity is formed between the micro cantilever beam and one end surface of the fiber by a connecting arm. And the micro cantilever beam is used for sensing a change of a distance between the probe pin and a sample. When the length of the F-P cavity changes due to deformation of the micro cantilever beam, the reflected light intensity is modulated by the fiber F-P cavity.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for stimulating probe to vibrate in atomic force microscope
InactiveCN109870593AAchieve fine controlEasy to controlScanning probe microscopyAtomic force microscopyAdhesion force
The invention provides a method for stimulating a probe to vibrate in an atomic force microscope. A piezoelectric transducer is arranged below the probe; the piezoelectric transducer generates mechanical vibration in the vertical direction under the action of a signal source; and the probe is vibrated under the stimulation of mechanical vibration waves. Compared with an existing method for stimulating a cantilever to vibrate by adopting a probe driver so as to drive the probe to vibrate, the method has the advantages that the tip of the probe can more easily get rid of the action of adhesion force and capillary force on the surface of a sample to vibrate stably, so that stable scanning imaging is facilitated, a high-resolution scanning image is obtained, and the high-performance requirement on the cantilever is reduced.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Atomic force microscope (AFM) probe rapid positioning method for cell mechanical property detection
InactiveCN103123362BRealize programming controlImprove operational efficiencyScanning probe microscopyAtomic force microscopyHough transform
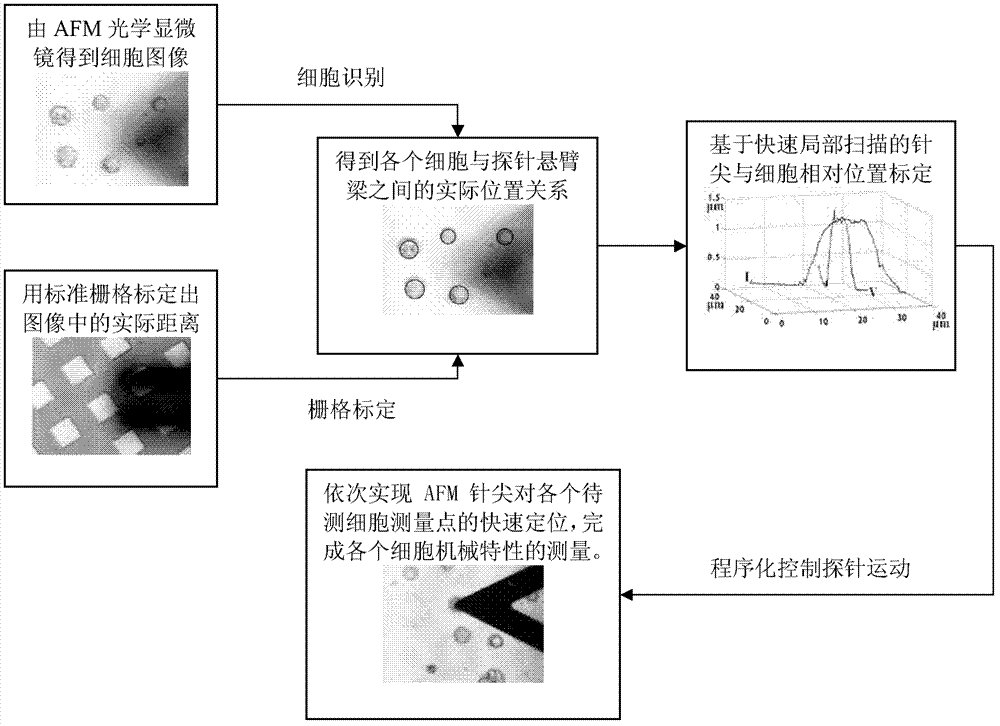
The invention relates to the technical field of nanometer operation, particularly to an AFM probe rapid positioning method for cell mechanical property detection. The method includes recognizing cells through carrying out a Hough transform round detection mode in cell edge images, obtaining radiuses and central position information of each cell to be detected simultaneously, and calculating the actual distance between each cell to be detected and a probe cantilever beam in working space; determining the relative position relation between the probe tip and cells to be detected through rapid local scanning of cells to be detected; and sequentially achieving rapid positioning of the AFM probe to measuring points of cells to be detected to complete measurement of the mechanical property of each cell. According to the rapid positioning method, a visual image processing technology is used for calibrating the relative position relation between the cells to be detected and the probe cantilever beam in the working space, programming control from probe motion to cells to be detected can be achieved, and the operating efficiency of the probe is improved; and the rapid local scanning method is used, so that accurate calibration of the AFM tip and the cell relative positions is achieved, and the accuracy of cell mechanical property measurement is improved.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
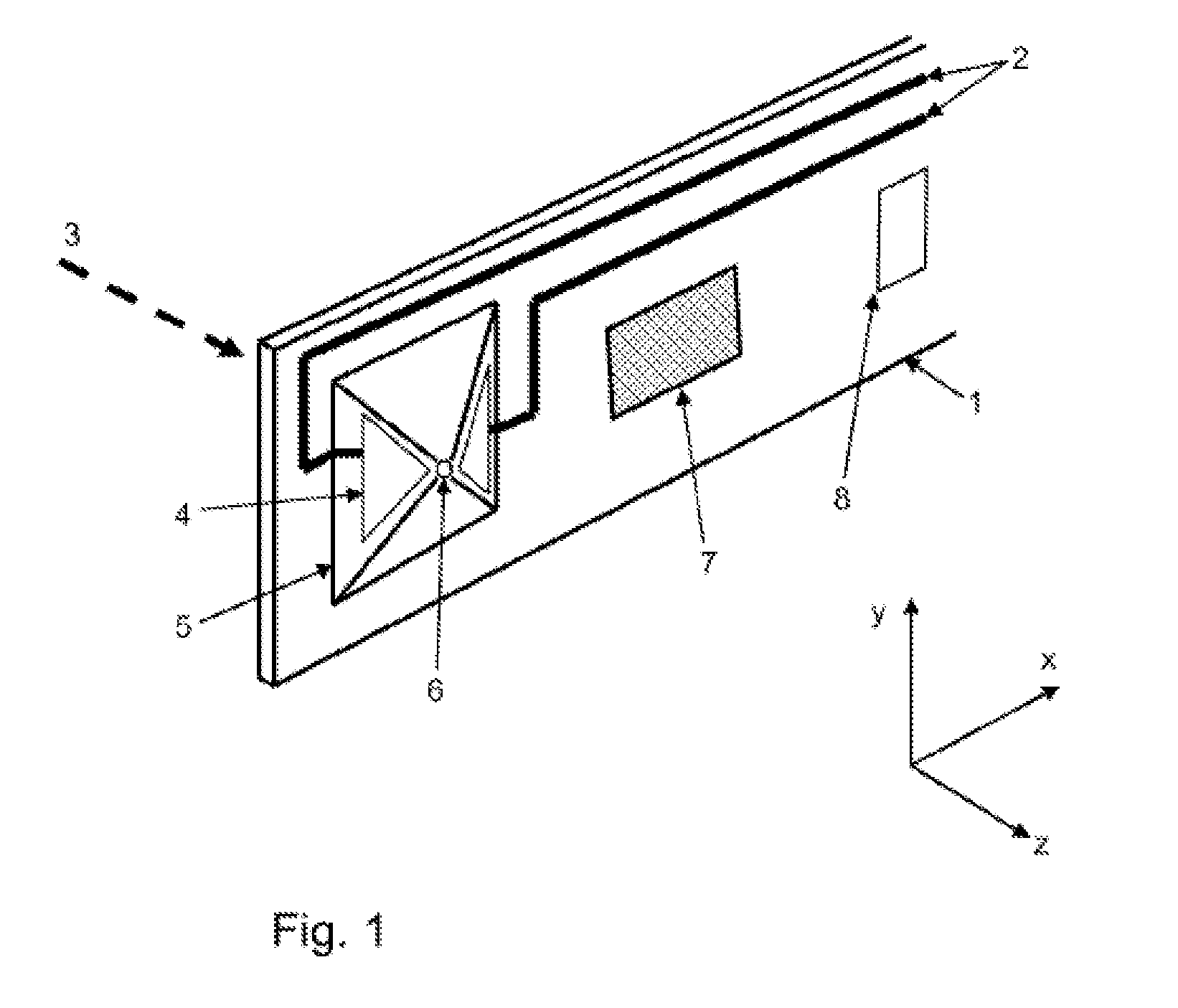
Probe for an atomic force microscope
A probe (22) for an atomic force microscope is adapted such that, as a sample (14) is scanned, it experiences a biasing force Fdirect urging the probe towards the sample. This improves probe trackingof the sample surface and faster scans are possible. This is achieved by either including a biasing element (24, 50), which is responsive to an externally applied force, on the probe (22) and / or reducing the quality factor of a supporting beam. The biasing element may, for example, be a magnet (24) or an electrically-conducting element (50). The quality factor may be reduced by coating the beamwith a mechanical-energy dissipating material.
Owner:INFINITESIMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com